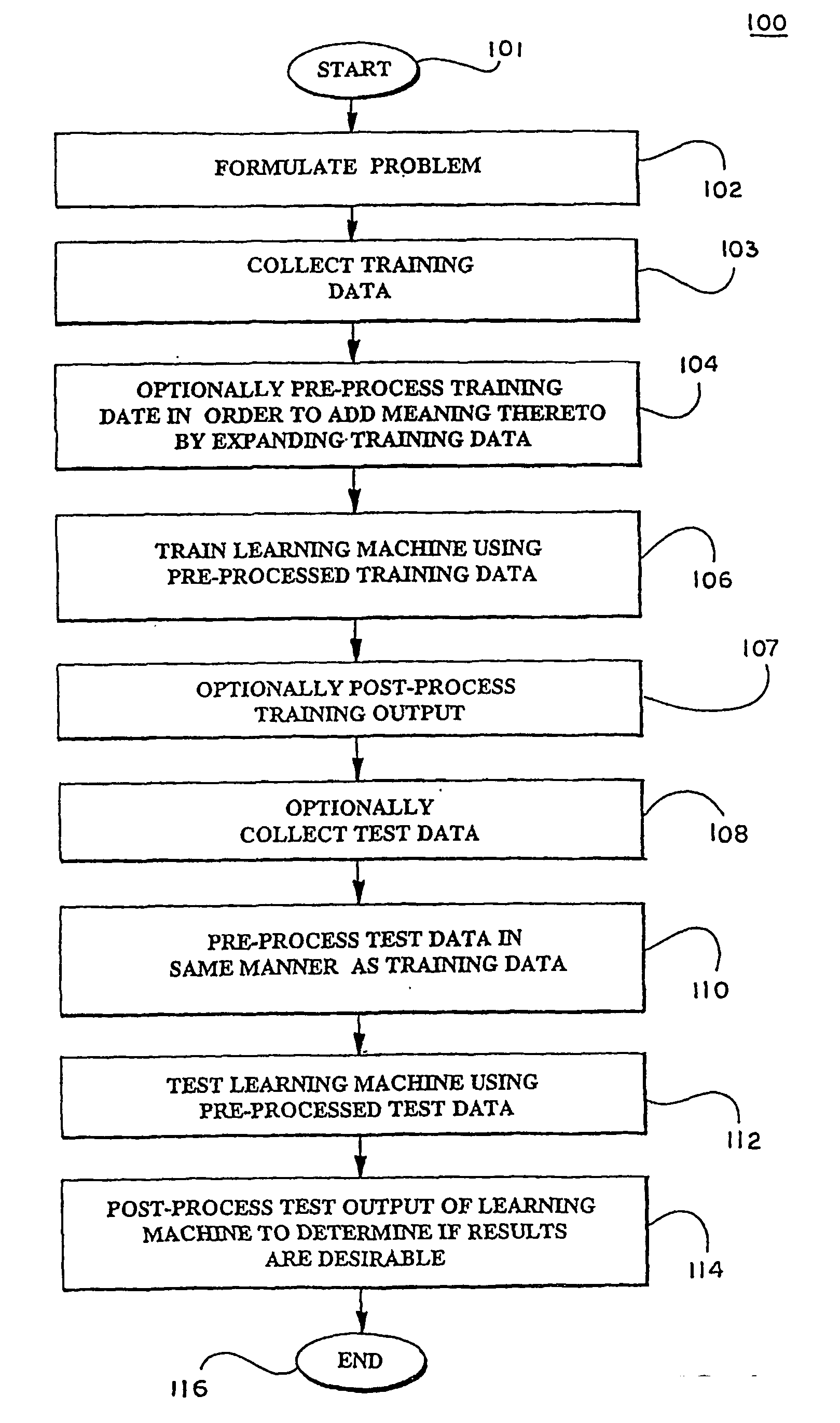
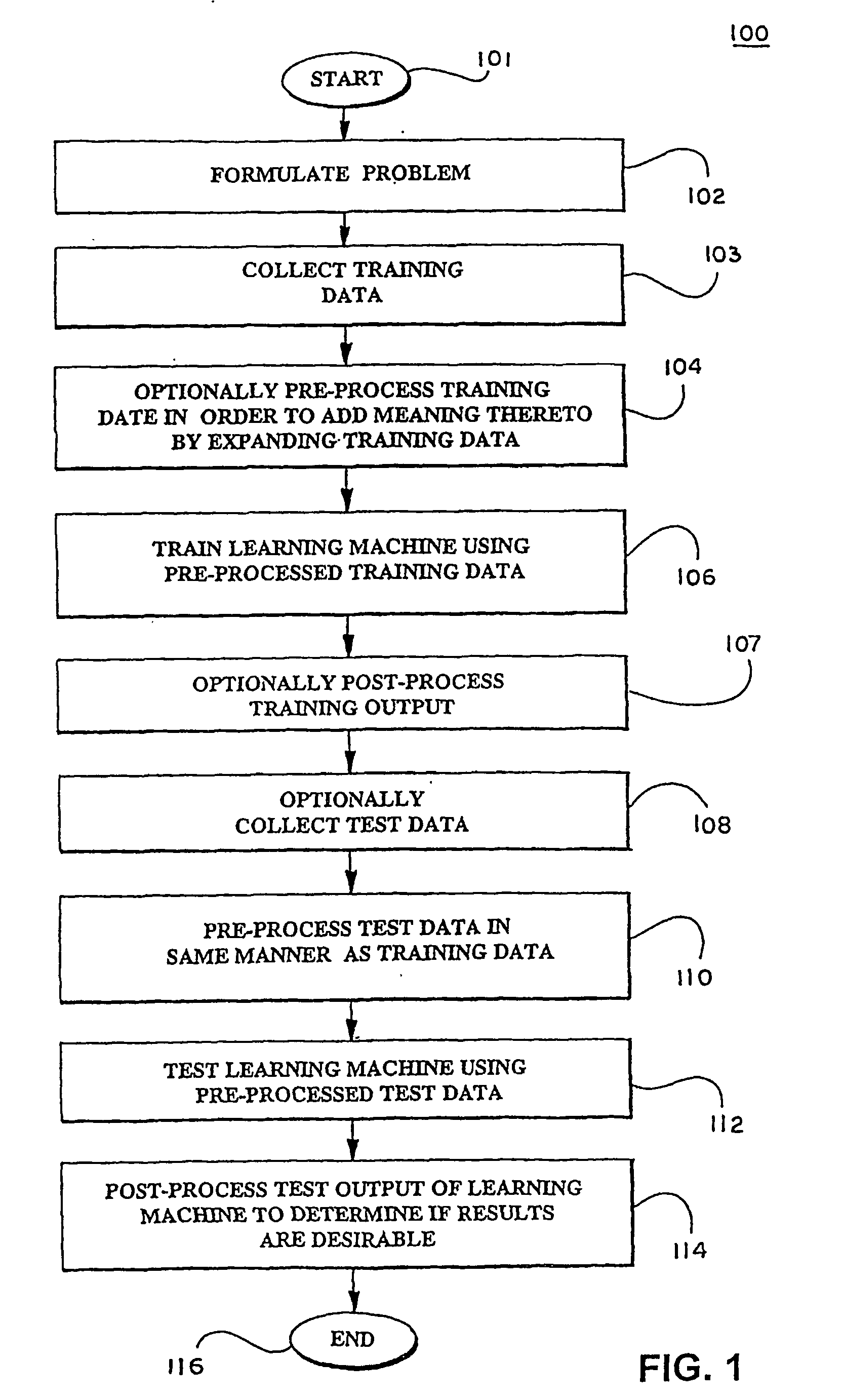
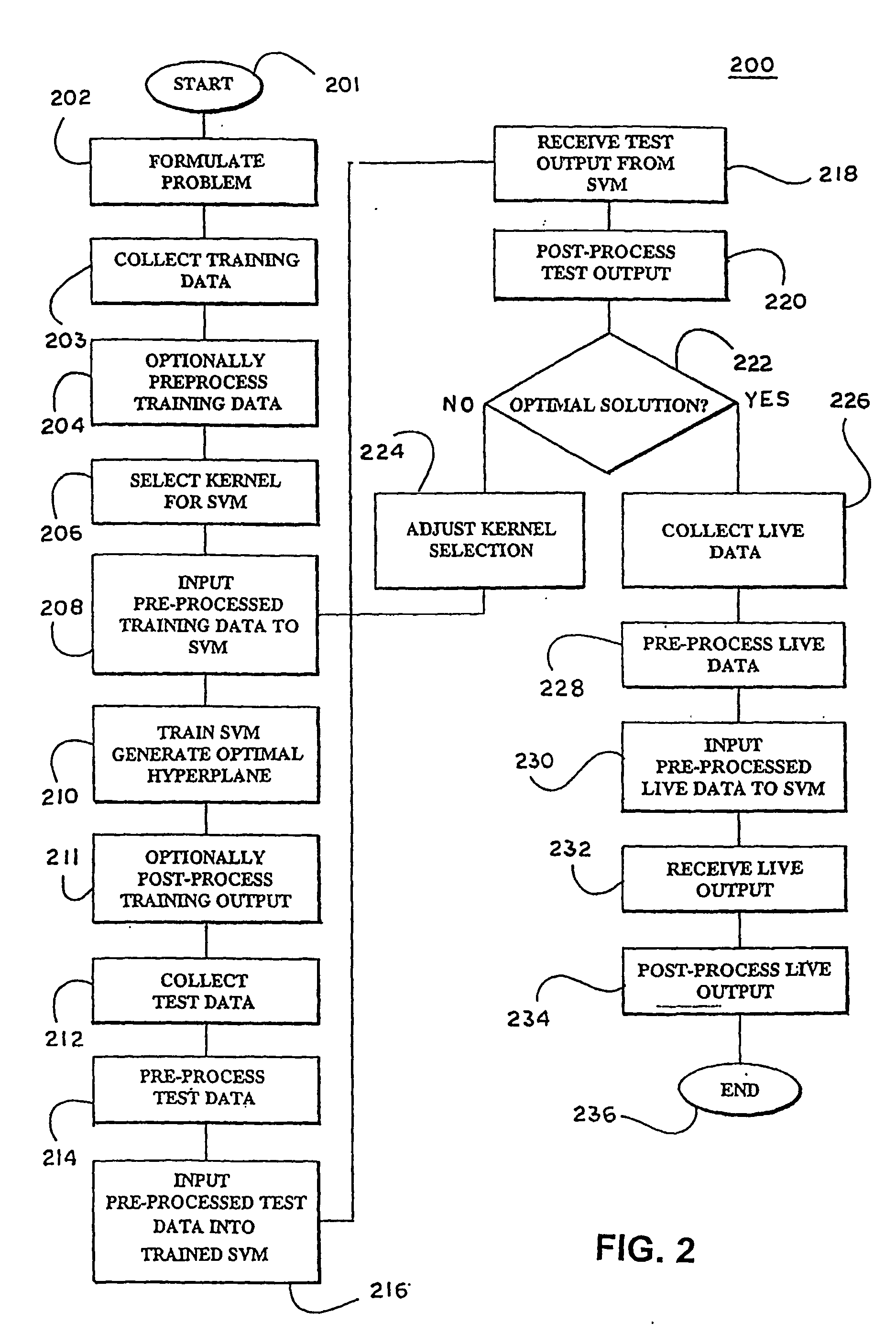
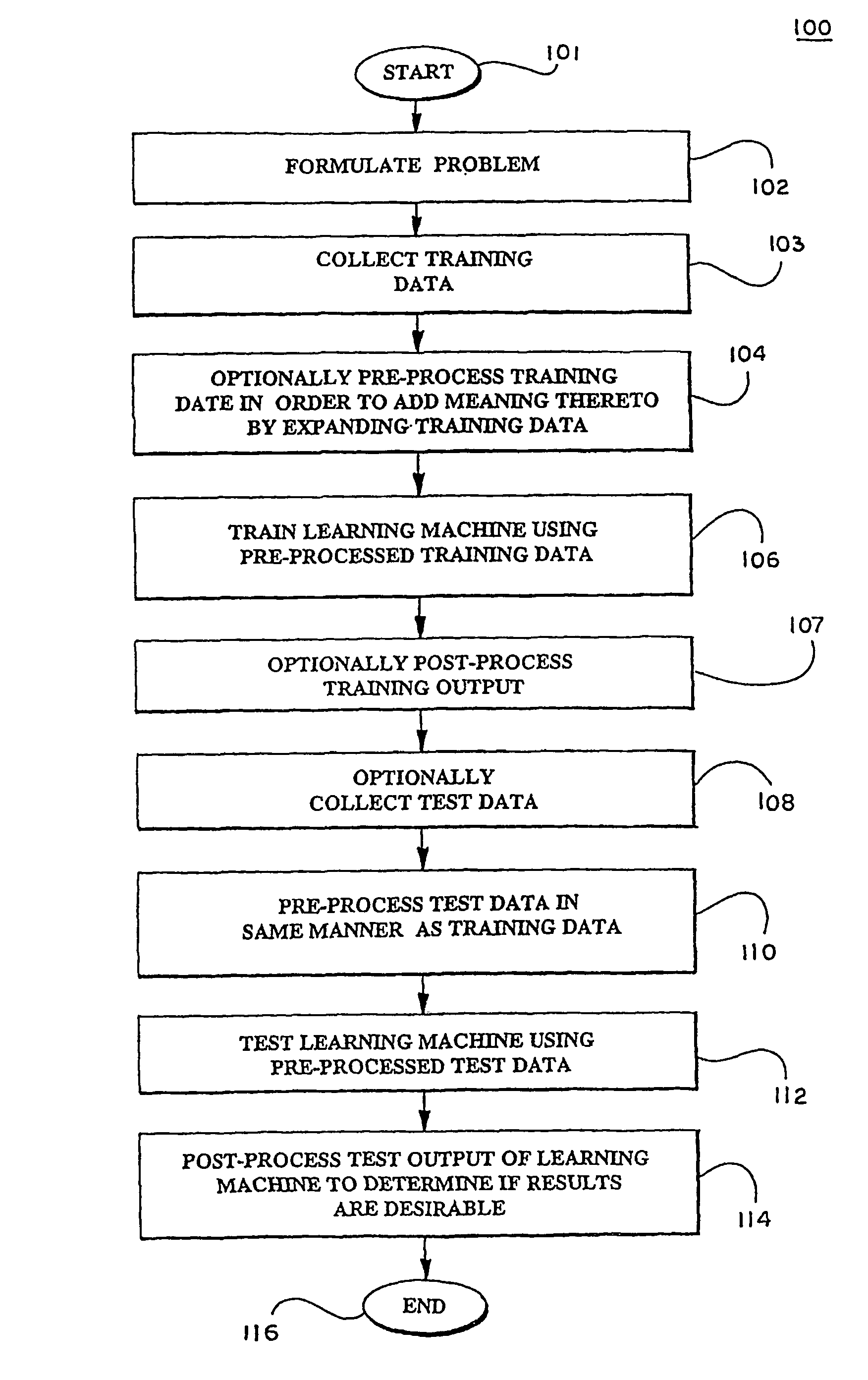
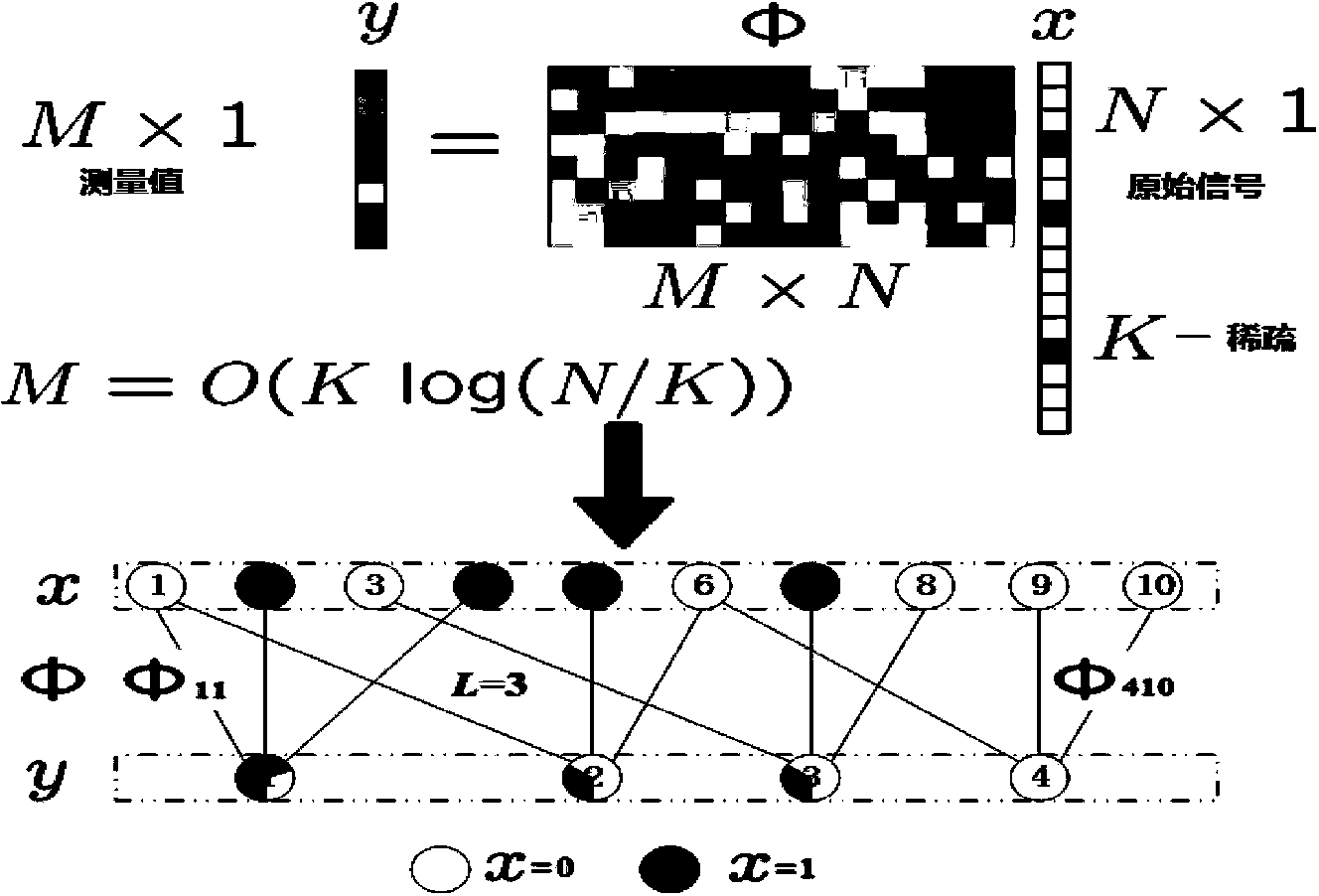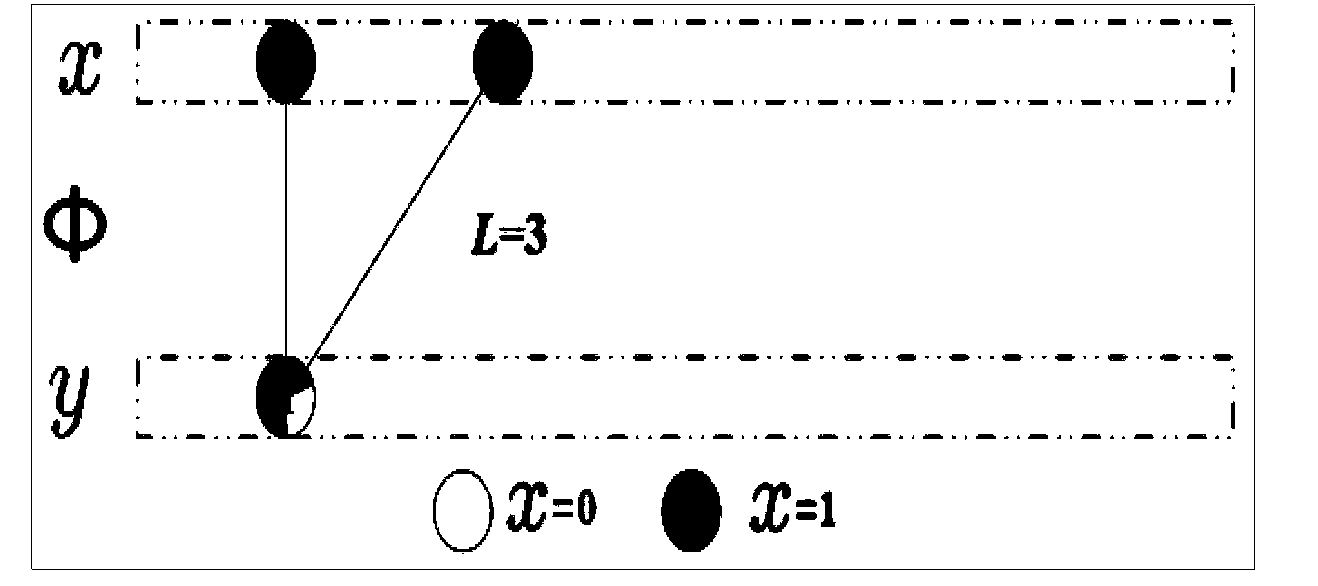Patents
Literature
63 results about "Norm minimization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Minimization of the ‘. 1 norm is a well-known heuristic for the cardinality minimization problem, and stunning results pioneered by Cand`es and Tao [10] and Donoho [17] have characterized a vast set of instances for which the ‘. 1 heuristic can be a priori guaranteed to yield the optimal solution.
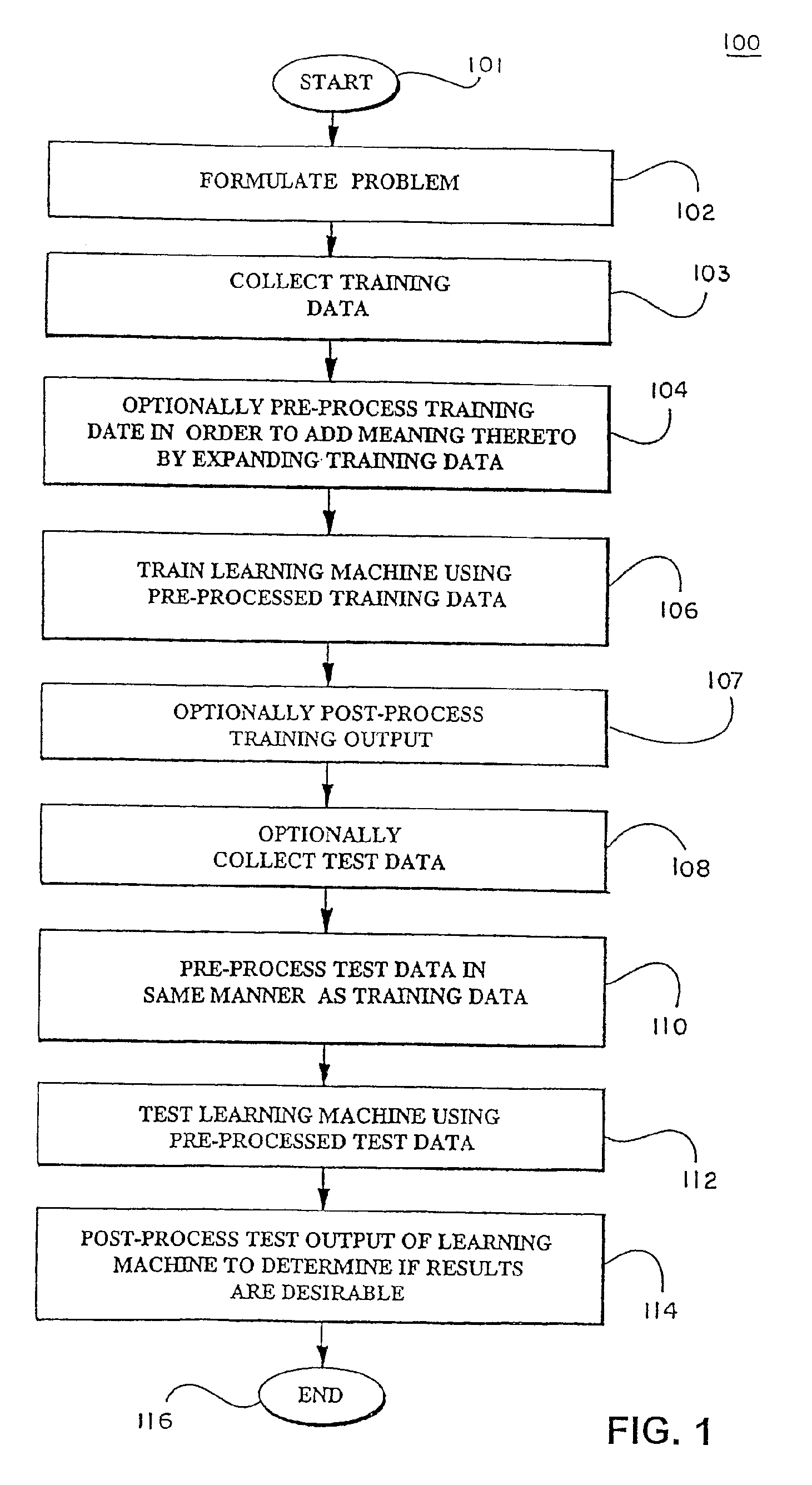
Methods for feature selection in a learning machine
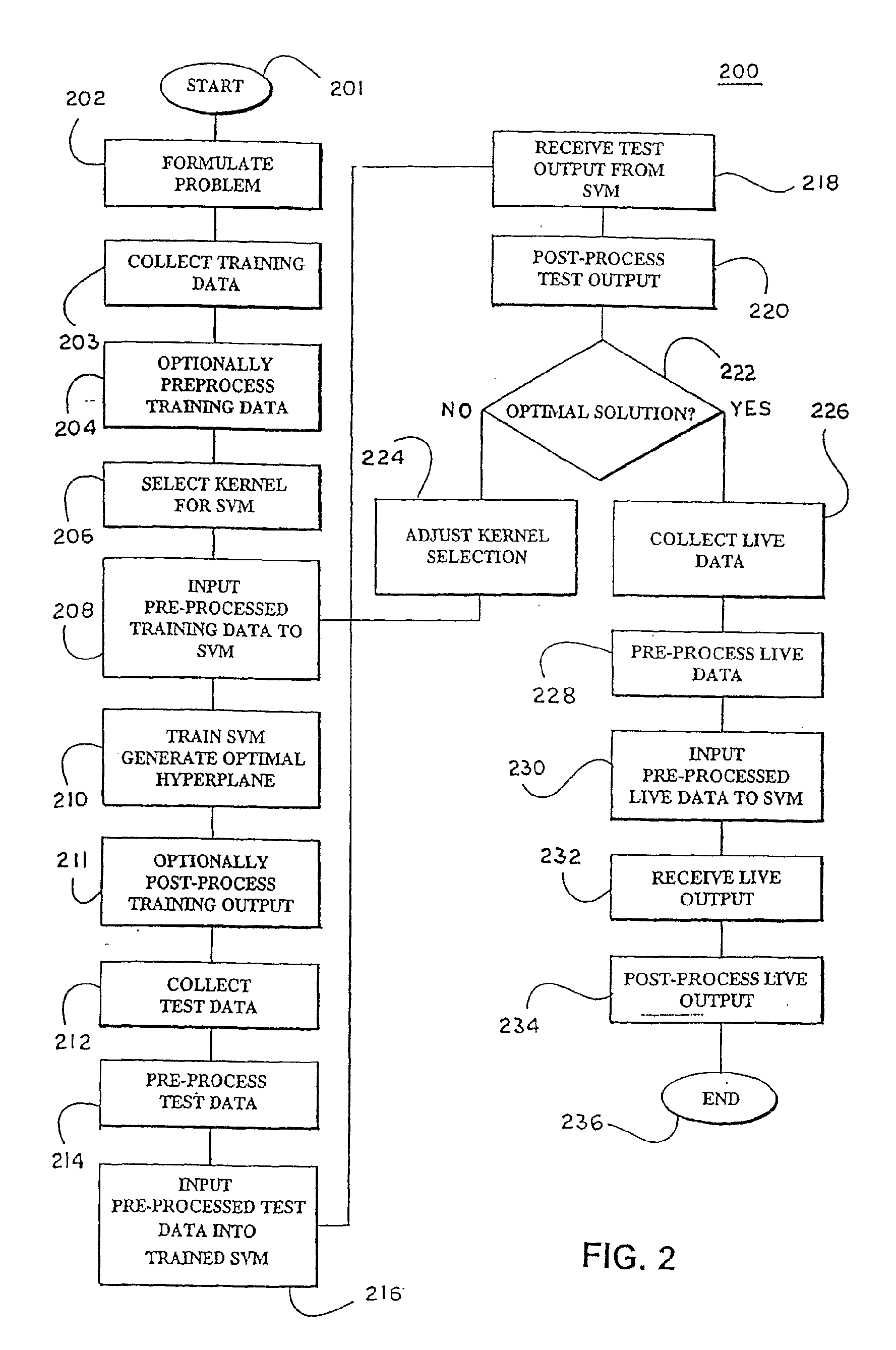
InactiveUS20050216426A1Reduce in quantityBroaden applicationKernel methodsDigital computer detailsLearning machineFeature selection
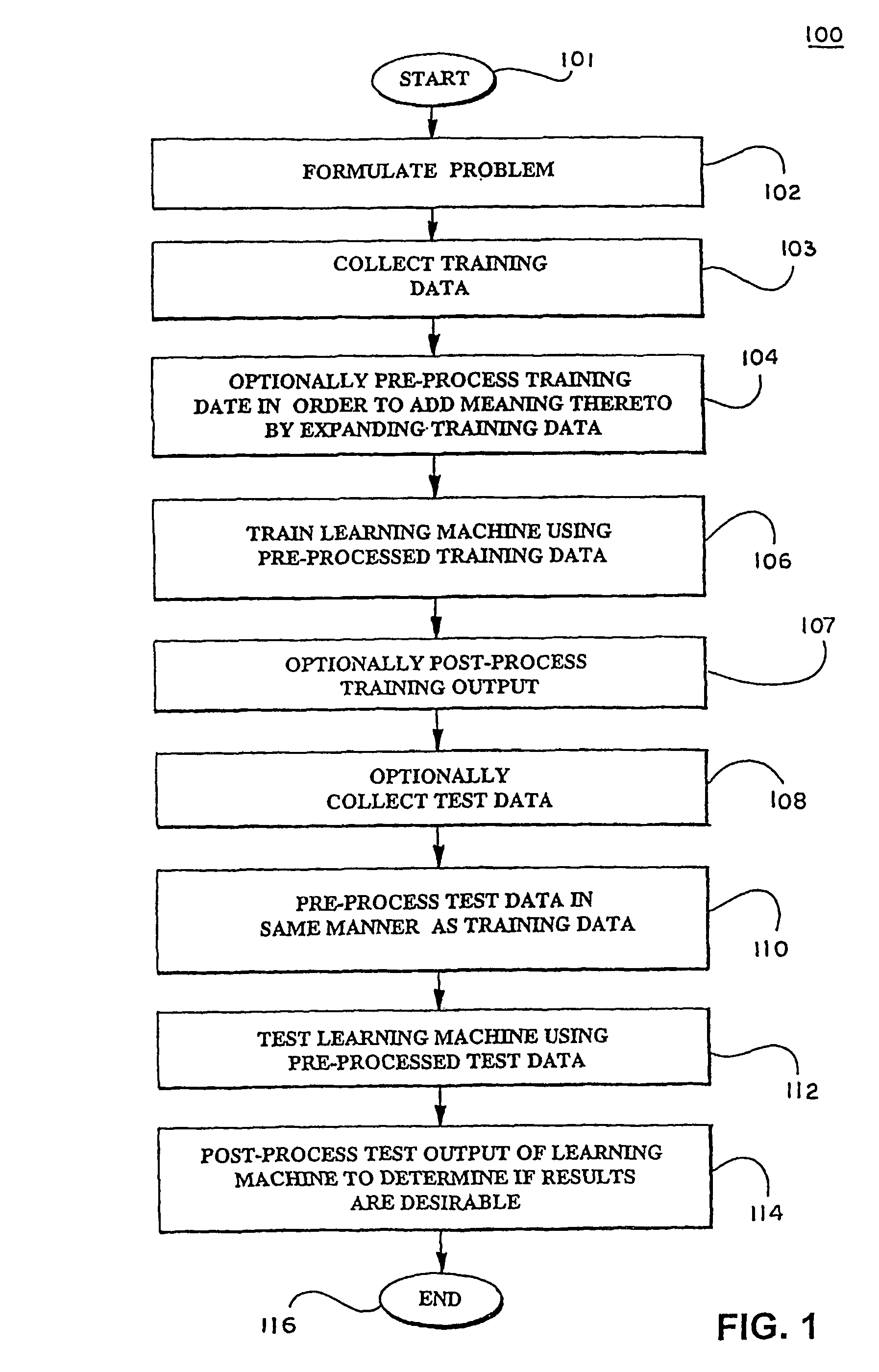
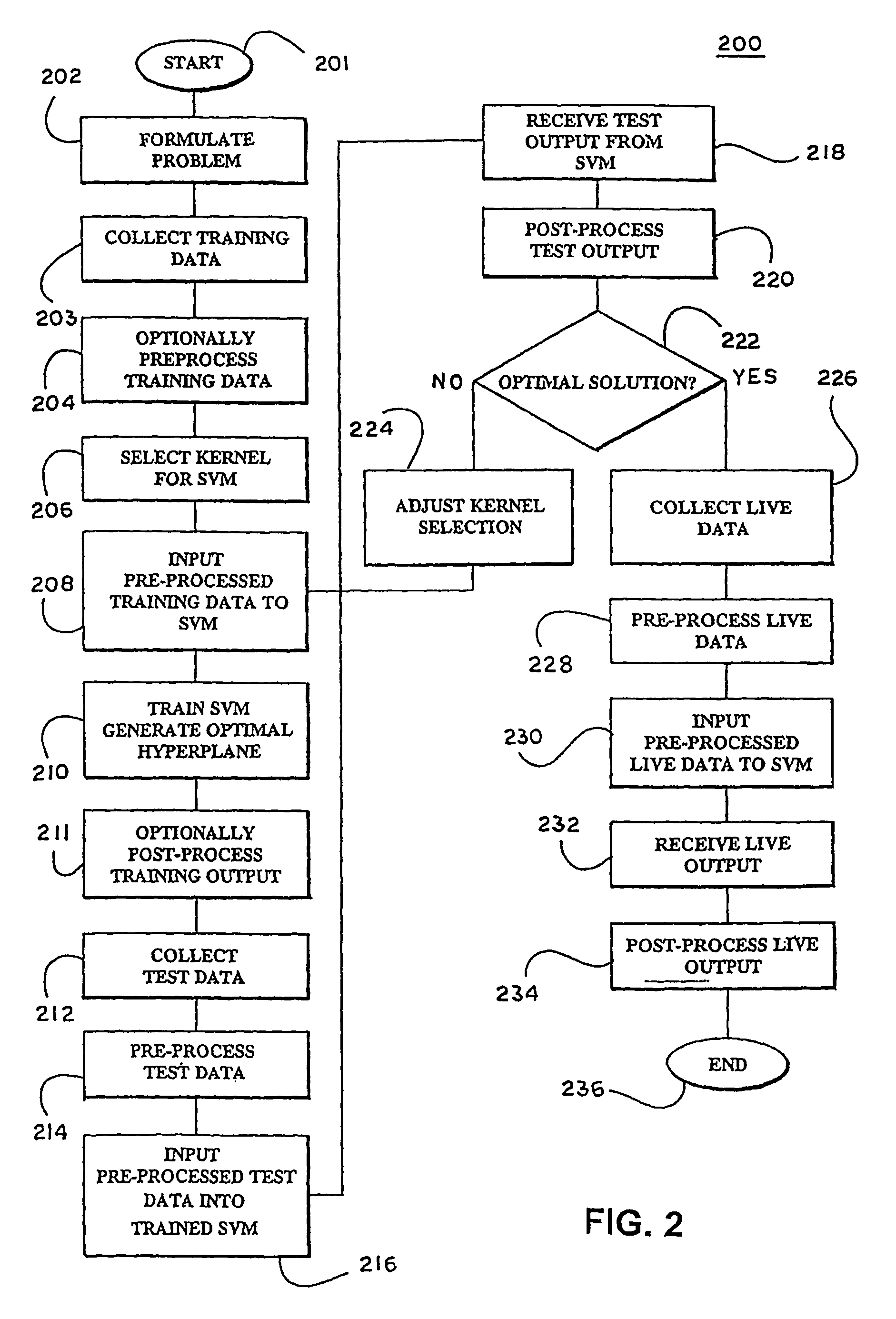
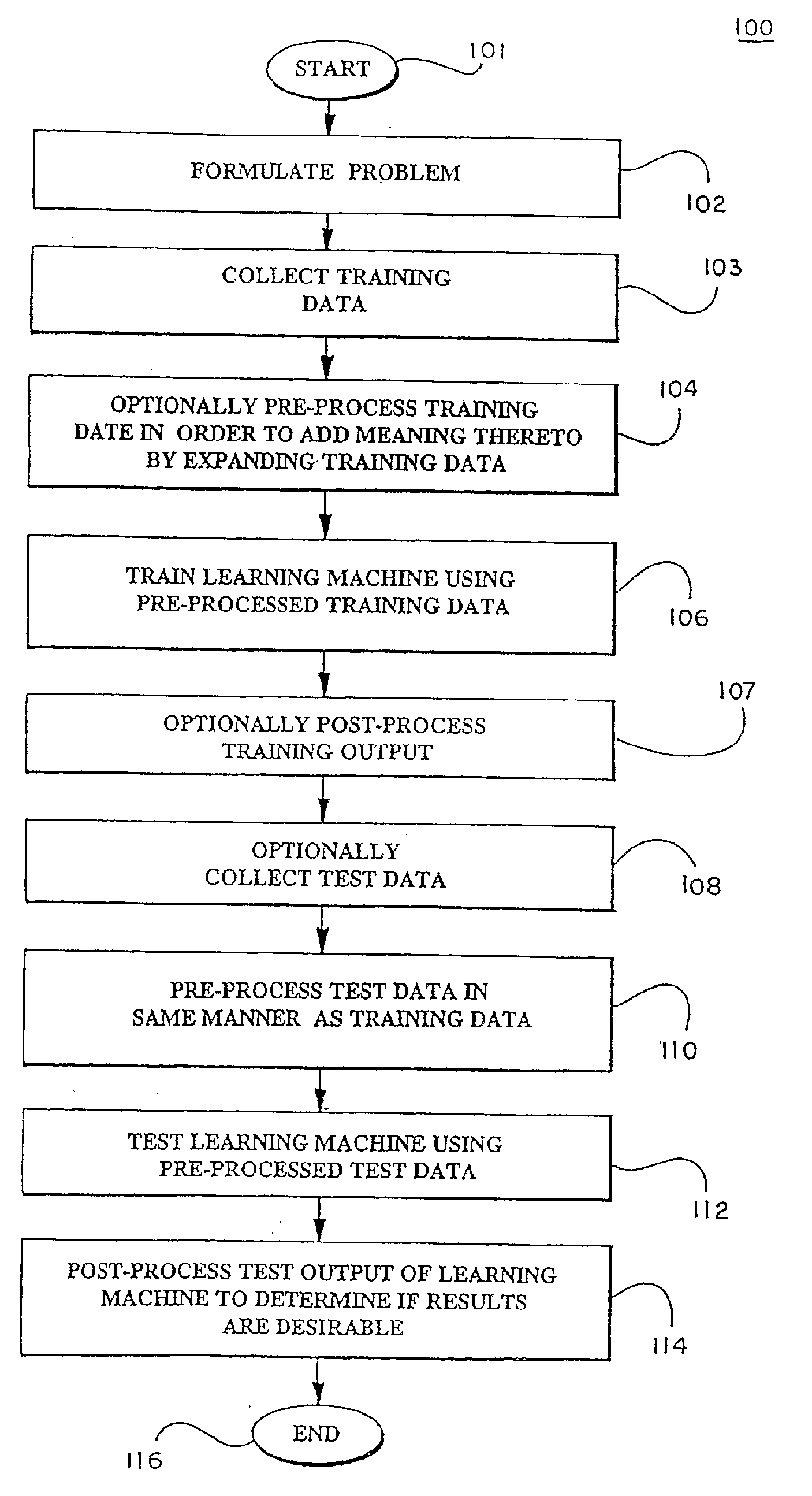
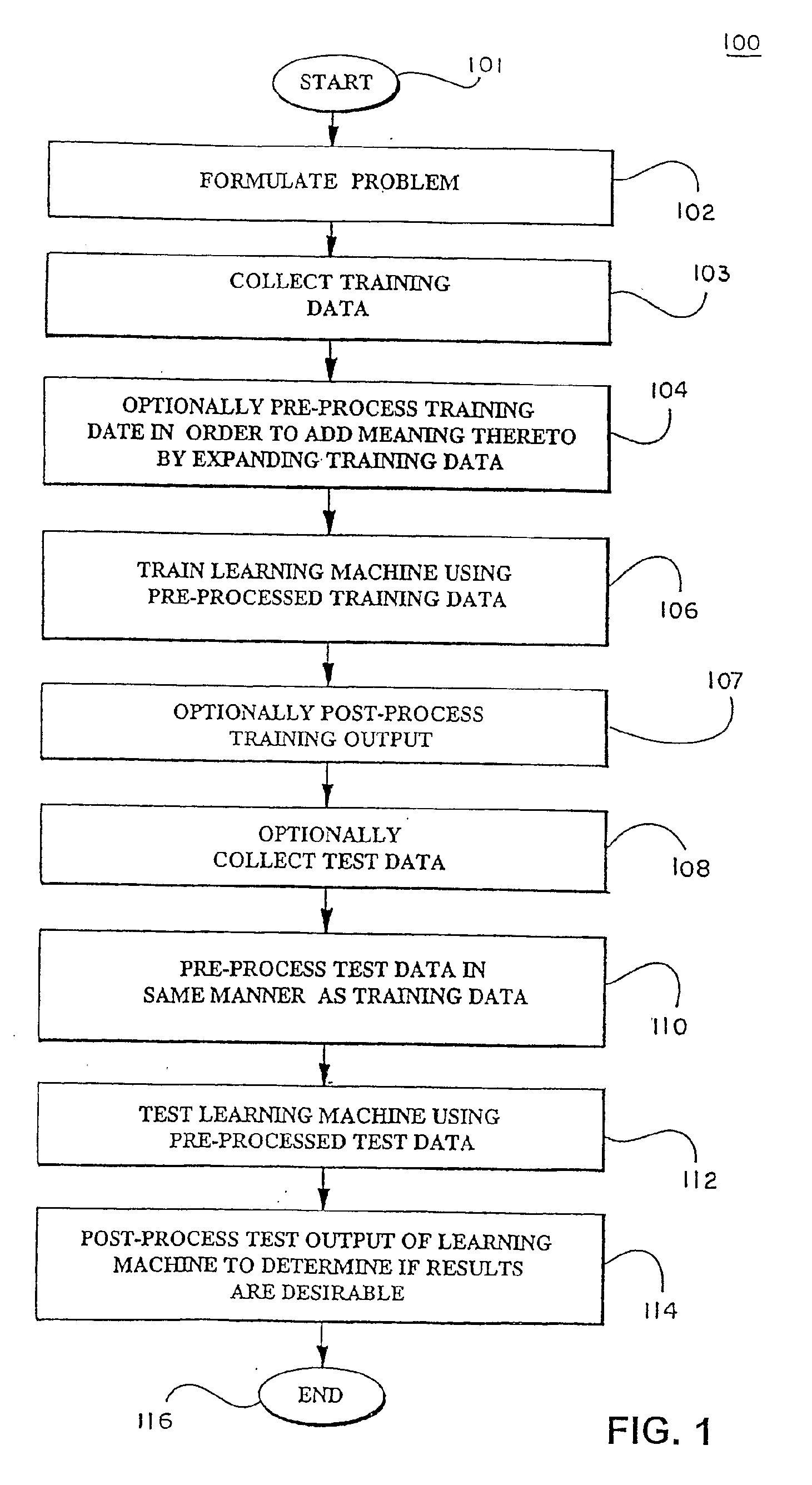
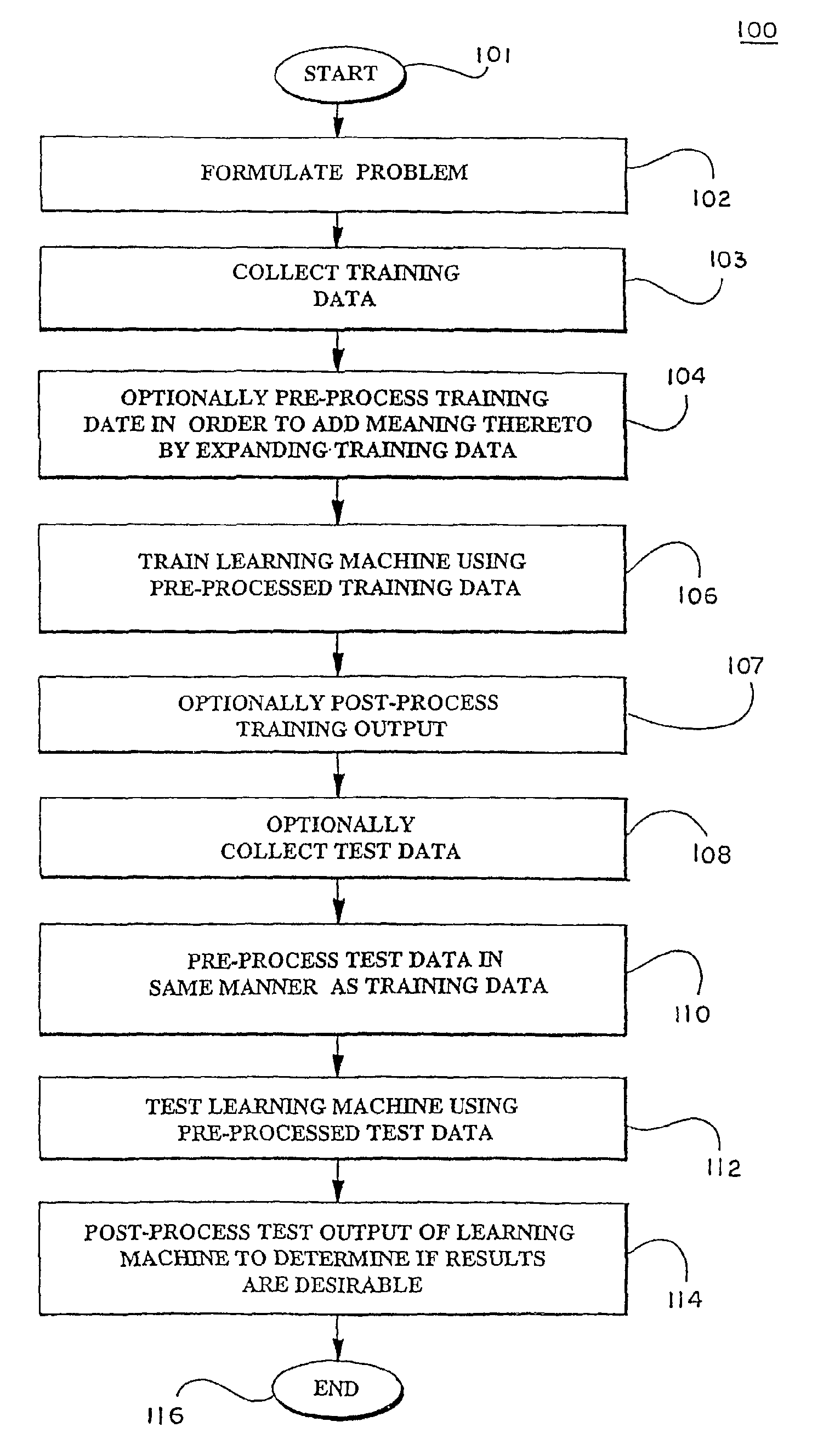
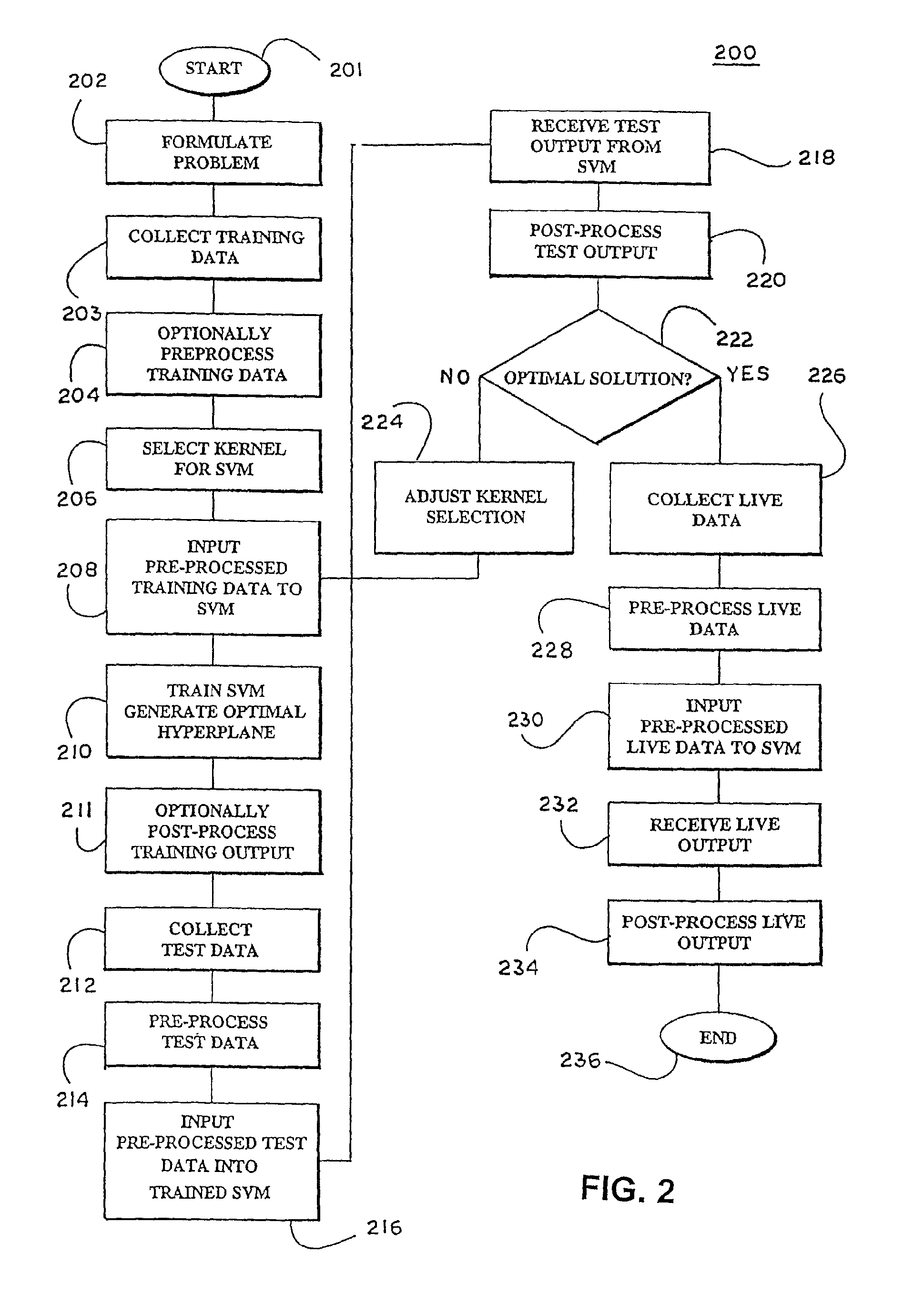
In a pre-processing step prior to training a learning machine, pre-processing includes reducing the quantity of features to be processed using feature selection methods selected from the group consisting of recursive feature elimination (RFE), minimizing the number of non-zero parameters of the system (lo-norm minimization), evaluation of cost function to identify a subset of features that are compatible with constraints imposed by the learning set, unbalanced correlation score and transductive feature selection. The features remaining after feature selection are then used to train a learning machine for purposes of pattern classification, regression, clustering and / or novelty detection.
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
Methods for feature selection in a learning machine
InactiveUS7318051B2Reduce in quantityMinimize the numberKernel methodsDigital computer detailsLearning machineFeature selection
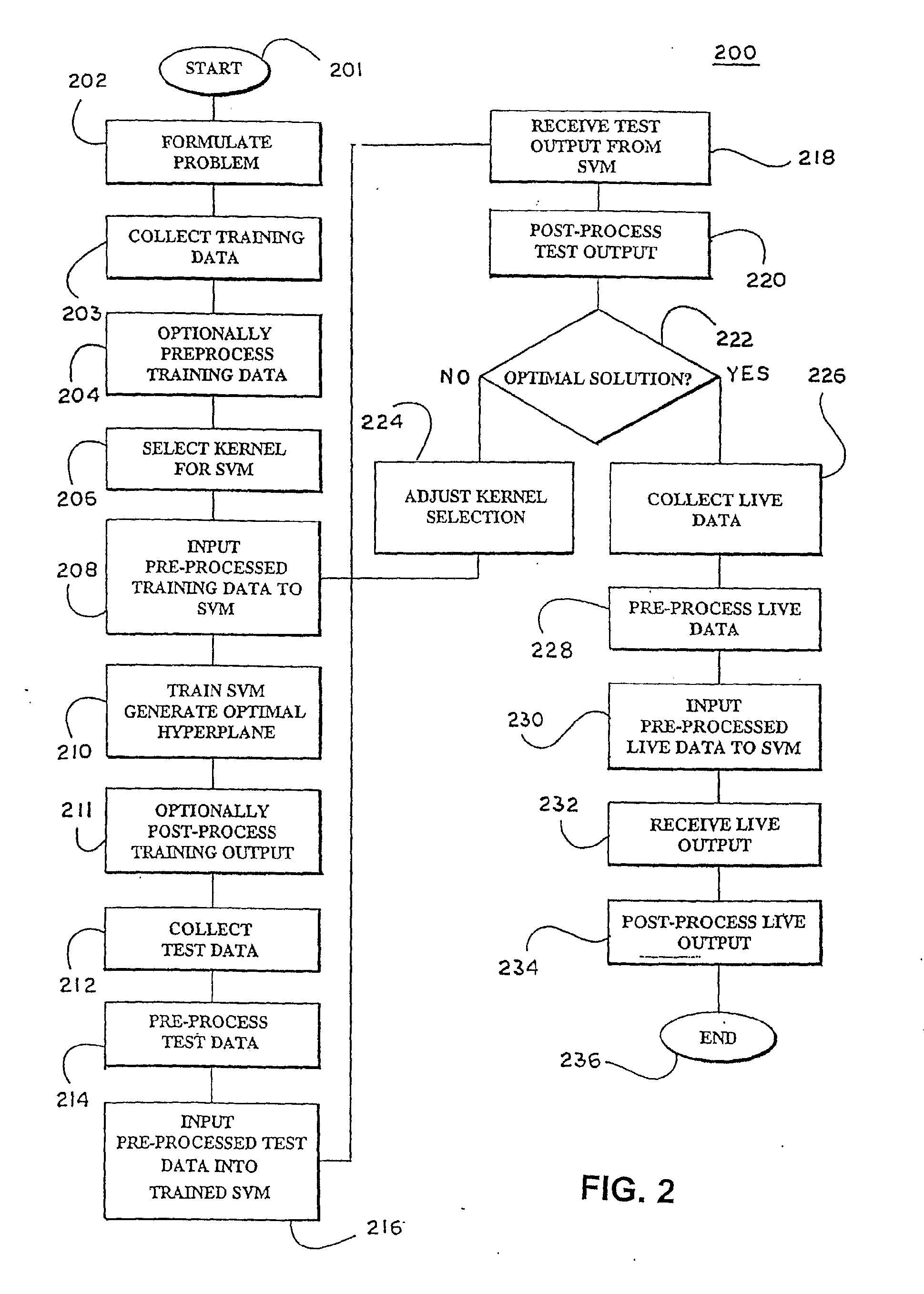
In a pre-processing step prior to training a learning machine, pre-processing includes reducing the quantity of features to be processed using feature selection methods selected from the group consisting of recursive feature elimination (RFE), minimizing the number of non-zero parameters of the system (lo-norm minimization), evaluation of cost function to identify a subset of features that are compatible with constraints imposed by the learning set, unbalanced correlation score and transductive feature selection. The features remaining after feature selection are then used to train a learning machine for purposes of pattern classification, regression, clustering and / or novelty detection. (FIG. 3, 300, 301, 302, 304, 306, 308, 309, 310, 311, 312, 314)
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
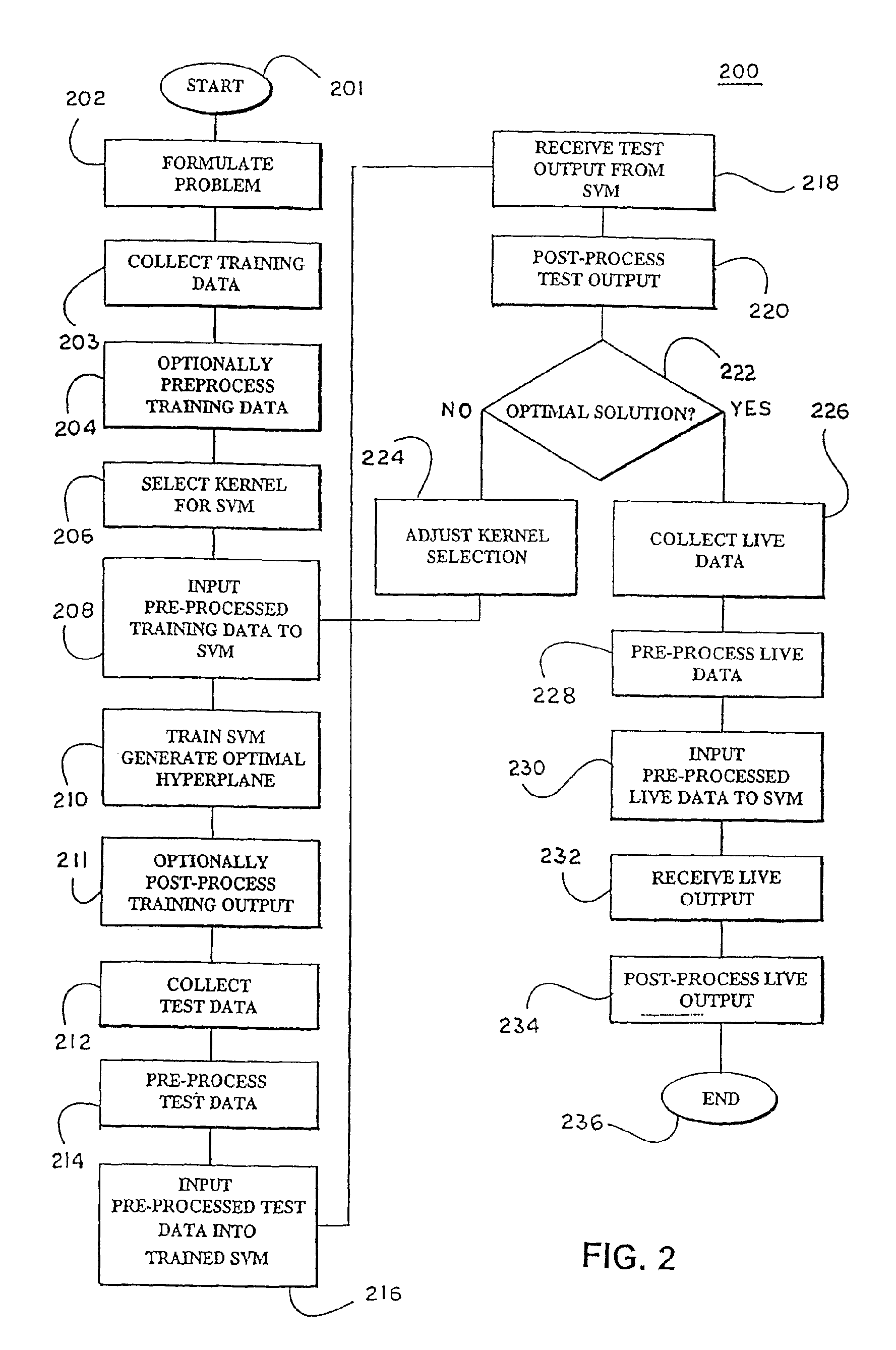
Method for feature selection in a support vector machine using feature ranking
InactiveUS20080233576A1Reduce in quantityMinimize the numberDigital data processing detailsMicrobiological testing/measurementLearning machineFeature ranking
In a pre-processing step prior to training a learning machine, pre-processing includes reducing the quantity of features to be processed using feature selection methods selected from the group consisting of recursive feature elimination (RFE), minimizing the number of non-zero parameters of the system (l0-norm minimization), evaluation of cost function to identify a subset of features that are compatible with constraints imposed by the learning set, unbalanced correlation score, transductive feature selection and single feature using margin-based ranking. The features remaining after feature selection are then used to train a learning machine for purposes of pattern classification, regression, clustering and / or novelty detection.
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
Methods for feature selection in a learning machine
InactiveUS20080215513A1Reduce in quantityBroaden applicationKernel methodsGenetic modelsLearning machineFeature selection
In a pre-processing step prior to training a learning machine, pre-processing includes reducing the quantity of features to be processed using feature selection methods selected from the group consisting of recursive feature elimination (RFE), minimizing the number of non-zero parameters of the system (l0-norm minimization), evaluation of cost function to identify a subset of features that are compatible with constraints imposed by the learning set, unbalanced correlation score and transductive feature selection. The features remaining after feature selection are then used to train a learning machine for purposes of pattern classification, regression, clustering and / or novelty detection.
Owner:BIOWULF TECH +1
Methods for feature selection in a learning machine
InactiveUS7624074B2Reduce in quantityMinimize the numberKernel methodsDigital computer detailsLearning machineFeature selection
In a pre-processing step prior to training a learning machine, pre-processing includes reducing the quantity of features to be processed using feature selection methods selected from the group consisting of recursive feature elimination (RFE), minimizing the number of non-zero parameters of the system (l0-norm minimization), evaluation of cost function to identify a subset of features that are compatible with constraints imposed by the learning set, unbalanced correlation score and transductive feature selection. The features remaining after feature selection are then used to train a learning machine for purposes of pattern classification, regression, clustering and / or novelty detection.
Owner:BIOWULF TECH +1
Method for feature selection in a support vector machine using feature ranking
InactiveUS7805388B2Reduce in quantityMinimize the numberKernel methodsBiological neural network modelsLearning machineFeature ranking
In a pre-processing step prior to training a learning machine, pre-processing includes reducing the quantity of features to be processed using feature selection methods selected from the group consisting of recursive feature elimination (RFE), minimizing the number of non-zero parameters of the system (l0-norm minimization), evaluation of cost function to identify a subset of features that are compatible with constraints imposed by the learning set, unbalanced correlation score, transductive feature selection and single feature using margin-based ranking. The features remaining after feature selection are then used to train a learning machine for purposes of pattern classification, regression, clustering and / or novelty detection.
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
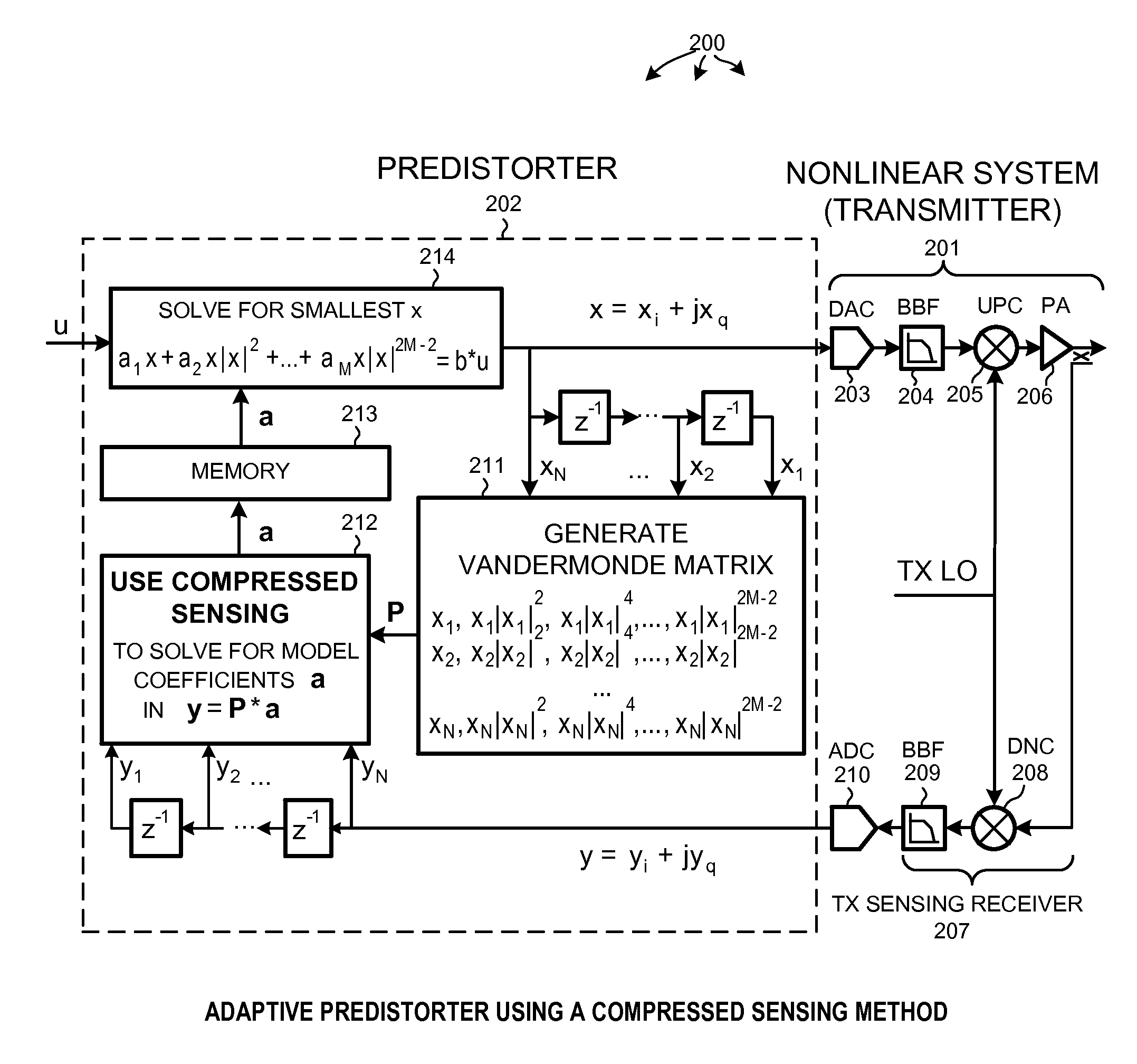
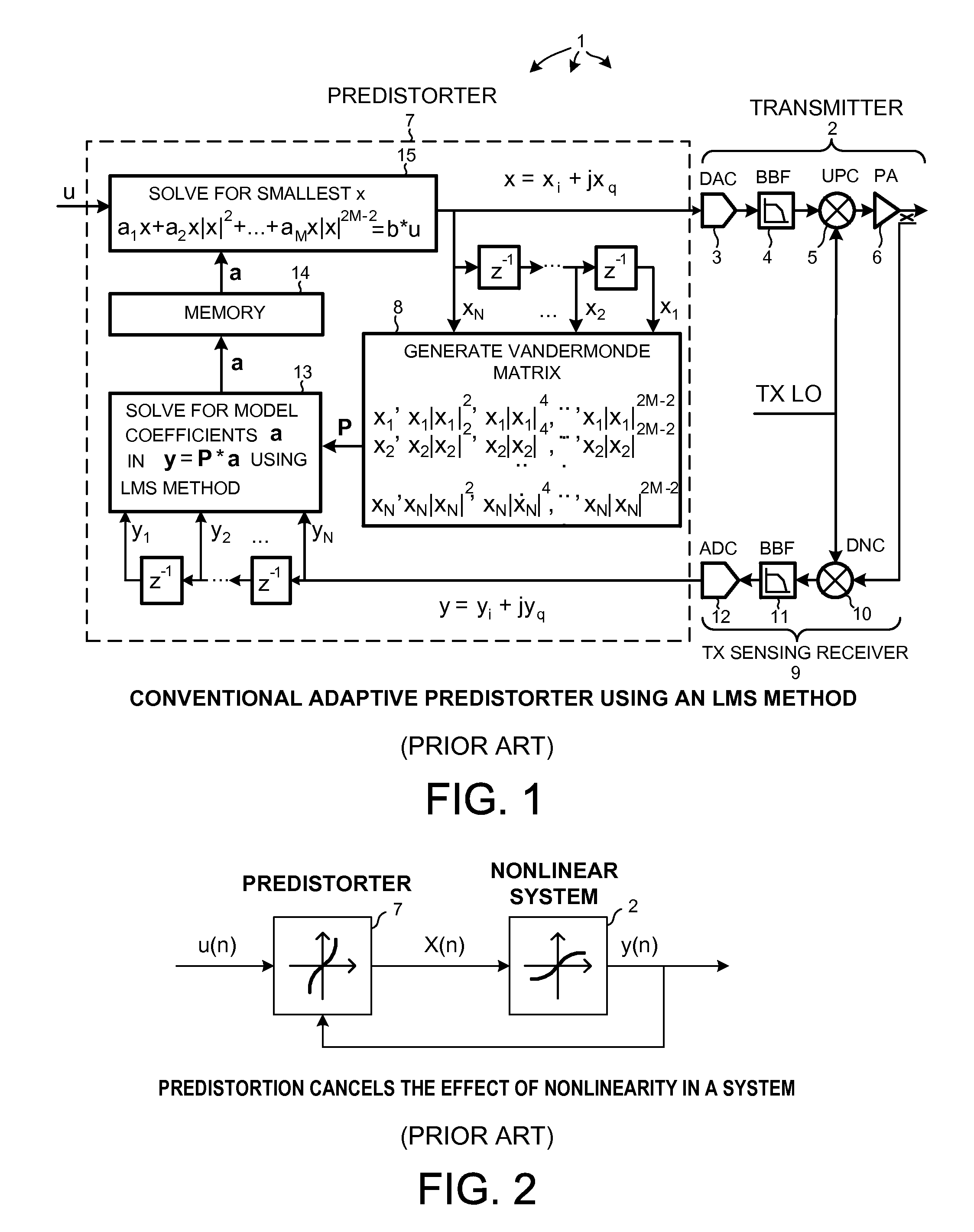
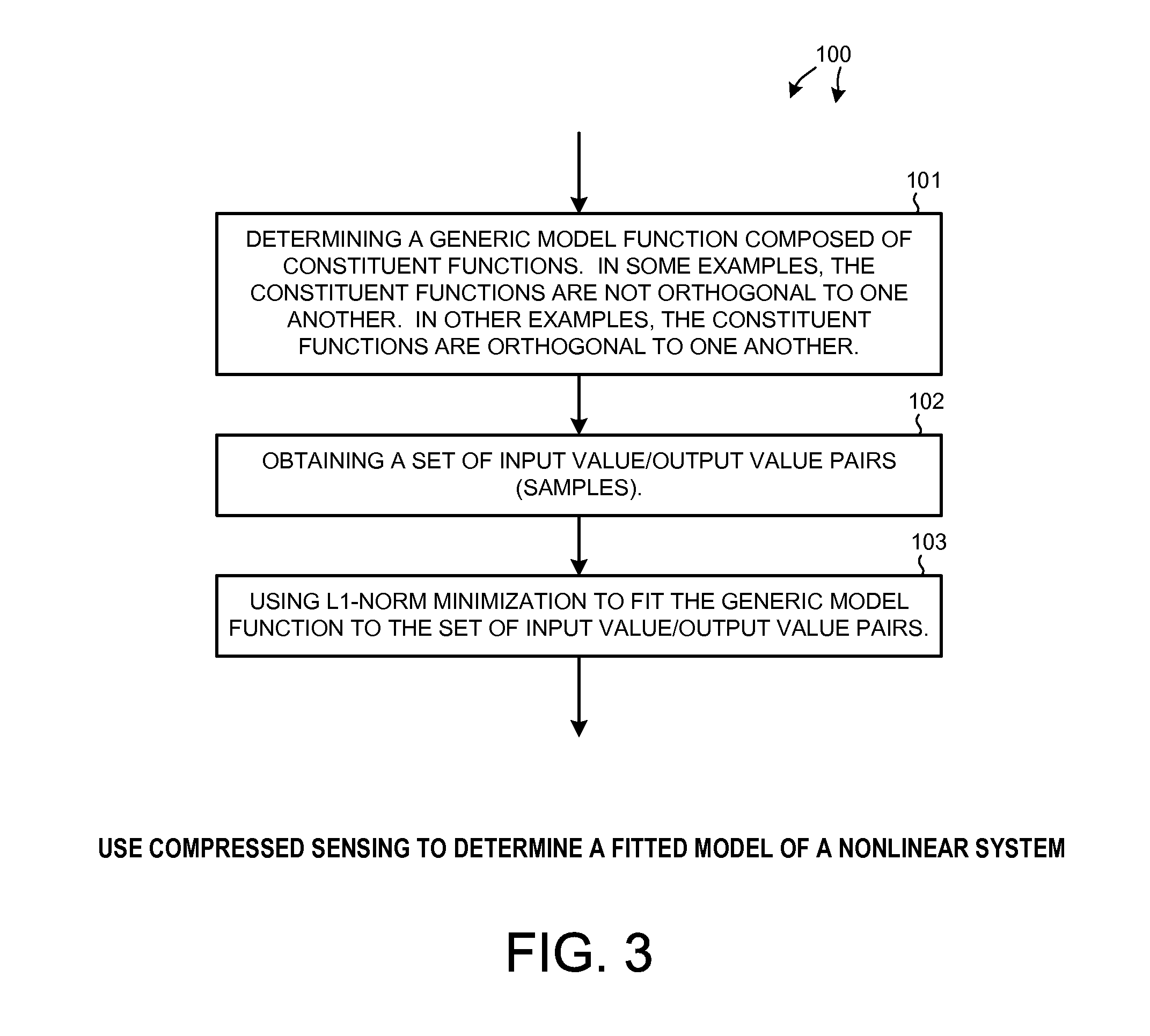
Nonlinear identification using compressed sensing and minimal system sampling
InactiveUS20110270590A1Minimize sumCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionModel systemPrediction system
Compressed sensing is used to determine a model of a nonlinear system. In one example, L1-norm minimization is used to fit a generic model function to a set of samples thereby obtaining a fitted model. Convex optimization can be used to determine model coefficients that minimize the L1-norm. In one application, the fitted model is used to calibrate a predistorter. In another application, the fitted model function is used to predict future actions of the system. The generic model is made of up of constituent functions that may or may not be orthogonal to one another. In one example, an initial model function of non-orthogonal constituent functions is orthogonalized to generate a generic model function of constituent orthogonal functions. Although the number of samples to which the generic model is fitted can be less than the number of model coefficients, the fitted model nevertheless accurately models system nonlinearities.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
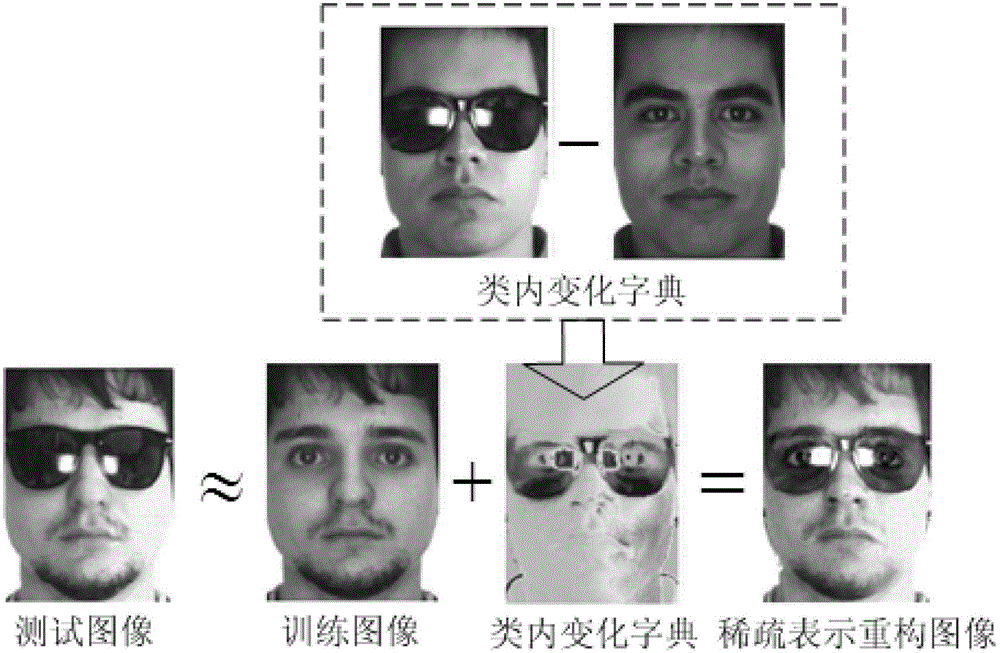
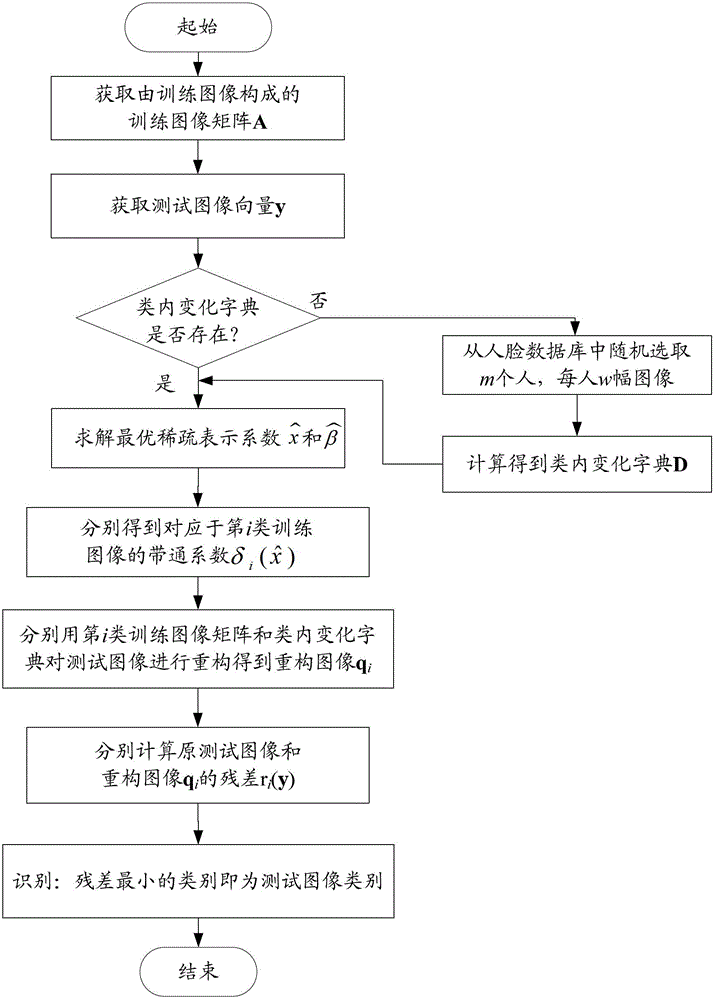
Sparse representation face recognition method based on intra-class variation dictionary and training image
InactiveCN102915436AImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSmall sampleEnvironment effect
The invention discloses a sparse representation face recognition method based on an intra-class variation dictionary and a training image, for solving the problems of limitation of the existing method in the aspects of small sample, uneven illumination, face shielded and expression variation and increasing the face recognition accuracy. The method comprises the following implementation steps of: (1) extracting image characteristics from a training image set and a test face image so as to form a training image matrix and a test image vector, and respectively normalizing the training image matrix and the test image vector; (2) collecting image texture differences of the same face in different external environments from a face database so as to form the intra-class variation dictionary of the face; (3) representing the test image as a linear combination of the training image matrix and the intra-class variation dictionary, and acquiring the optimal sparse representation coefficient through the L1 norm minimization criterion; and (4) acquiring a residual between the original test image and a recombination image recombined from each type of the training image and the intra-class variation dictionary, and substituting the residual into a type judgment formula so as to acquire a recognition result.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
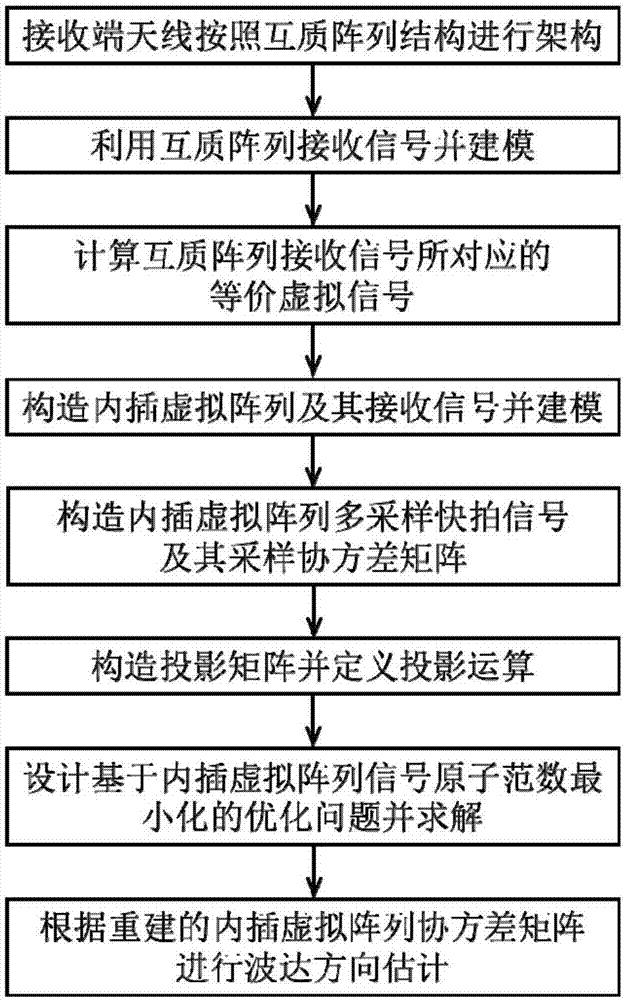
Co-prime array wave arrival direction estimation method based on interpolation virtual array signal atom norm minimization
ActiveCN107315160AGuaranteed Direction of Arrival EstimationGuaranteed resolutionRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsHat matrixImage resolution
The invention discloses a co-prime array wave arrival direction estimation method based on interpolation virtual array signal atom norm minimization. The objective of the invention is to solve the problem of an information loss caused by non-uniformity of a virtual array in the prior art. The method comprises following steps that a receiving end constructs a co-prime array; based on the co-prime array, an incidence signal is received and modeling is performed; an equivalence virtual signal corresponding to the a co-prime array receiving signal is calculated; an interpolation virtual array is constructed and modeling is performed; a multi-sampling snapshot signal of the interpolation virtual array and a sampling covariance matrix thereof are constructed; a projection matrix is constructed and projection calculation related to the projection matrix is defined; an optimization problem based on the interpolation virtual array signal atom norm minimization is designed and solved; and direction-of-arrival estimation is performed according to the reconstructed interpolation virtual array covariance matrix. According to the invention, the freedom degree and the resolution of the direction-of-arrival estimation are improved and the method can be used for passive positioning and target detection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Robust reconstruction of high resolution grayscale images from a sequence of low-resolution frames (robust gray super-resolution)
InactiveUS20060291751A1Solution stableRemove image artifactGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionCompression artifactImage resolution
A method for computing a high resolution gray-tone image from a sequence of low-resolution images uses an L1 norm minimization. In a preferred embodiment, the technique also uses a robust regularization based on a bilateral prior to deal with different data and noise models. This robust super-resolution technique uses the L1 norm both for the regularization and the data fusion terms. Whereas the former is responsible for edge preservation, the latter seeks robustness with respect to motion error, blur, outliers, and other kinds of errors not explicitly modeled in the fused images. This computationally inexpensive method is resilient against errors in motion and blur estimation, resulting in images with sharp edges. The method also reduces the effects of aliasing, noise and compression artifacts. The method's performance is superior to other super-resolution methods and has fast convergence.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
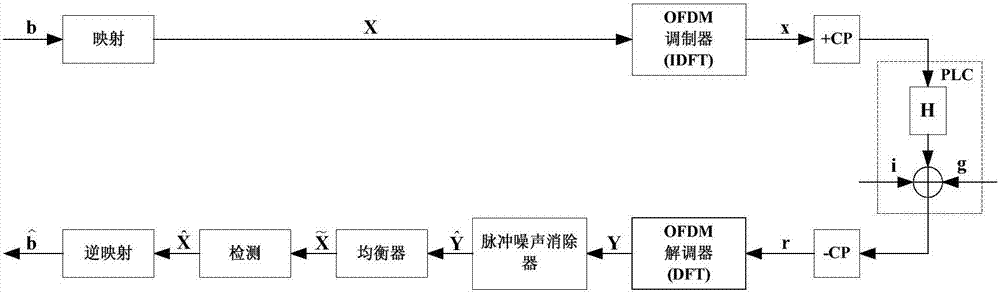
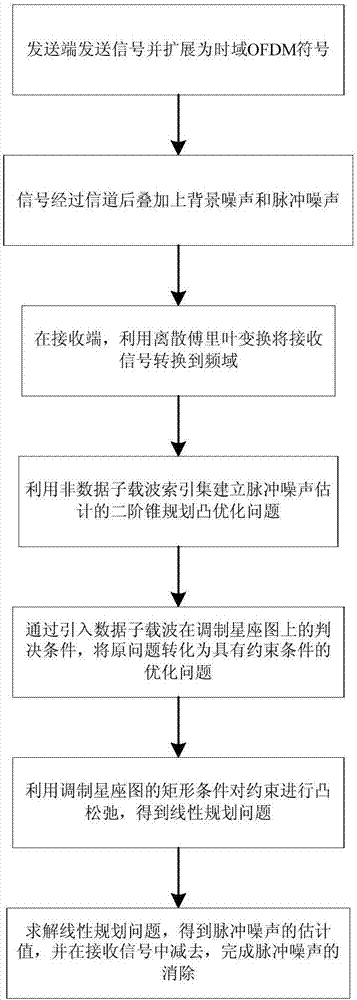
Method for eliminating pulse noise in power line communication based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN107360111AImprove accuracyImprove performancePower distribution line transmissionCross-talk reductionPhase noiseQam modulation
The invention discloses a method for eliminating pulse noise based on compressed sensing, which is characterized in that in allusion to serious interference imposed on data transmission by pulse noise in a PLC system, the pulse noise is projected to non-data subcarriers according to a CS (Compressed Sensing) algorithm utilizing all OFDM subcarrier information to estimate and eliminate the pulse noise, a compressed sensing problem is built firstly by using pulse noise l1-norm minimization according to an l1-norm minimization based compressed sensing technology, a judgment condition on OFDM symbol non-data subcarriers is introduced to act as a constraint condition, the range of a rectangle in a constellation diagram is modulated through introducing QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), convex relaxation is performed on the constraint condition, the original problem is simplified into a linear programming problem, the linear programming problem is solved by using the existing method, and a simulation result is displayed in channel coded and channel uncoded 4-QAM and 16-QAM modes. The method disclosed by the invention has better bit error rate performance than several conventional methods.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Point cloud data sparse representation method based on compressed sensing
InactiveCN103886625AImprove sparsityStrong sparse representation capabilityImage coding3D-image renderingData compressionPattern recognition
The invention provides a point cloud data sparse representation method based on compressed sensing. Under the premise of ensuring certain precision, massive point cloud data is compressed, thus the sparsity of the point cloud data is greatly raised, and a good foundation is laid for point cloud data compression and reconstruction based on compressed sensing. The method comprises the steps of (1) point cloud data normalization, (2) over-complete dictionary sparse representation based on a K-SVD algorithm, (3) normalized point cloud data observation, transmission and storage, (4) point cloud data reconstruction based on l1 norm minimization, and (5) normalized point cloud data recovery.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Fisher discriminant dictionary learning-based warehouse goods identification method
InactiveCN106778863ASmall within-class errorSmall between-class errorCharacter and pattern recognitionLogisticsGuidelineRapid identification
The invention relates to a Fisher discriminant dictionary learning-based warehouse goods identification method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly dividing warehouse goods images acquired under different conditions into two parts: a training sample set and a test sample set; respectively preprocessing the two sample sets, rearranging pixel values and carrying out PCA dimensionality reduction; learning the training sample set through a Fisher criterion method to obtain a discriminant dictionary, and representing a test sample by using linear weighting of the discriminant dictionary; solving an L2 norm minimization problem by adoption of a least square method, so as to obtain a sparse representation matrix of the test sample under the discriminant dictionary; and finally realizing warehouse goods identification via ei formed by various types of reconstruction errors and sparse encoding coefficients. According to the method provided by the invention, the problems that the traditional identification method is greatly influenced by selected features, the identification process is relatively complicated and plenty of classification information is lost in the construction processes of common dictionaries are solved; and the correct and rapid identification of different goods can be realized, so that foundation is laid for the realization of intelligent warehouses.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
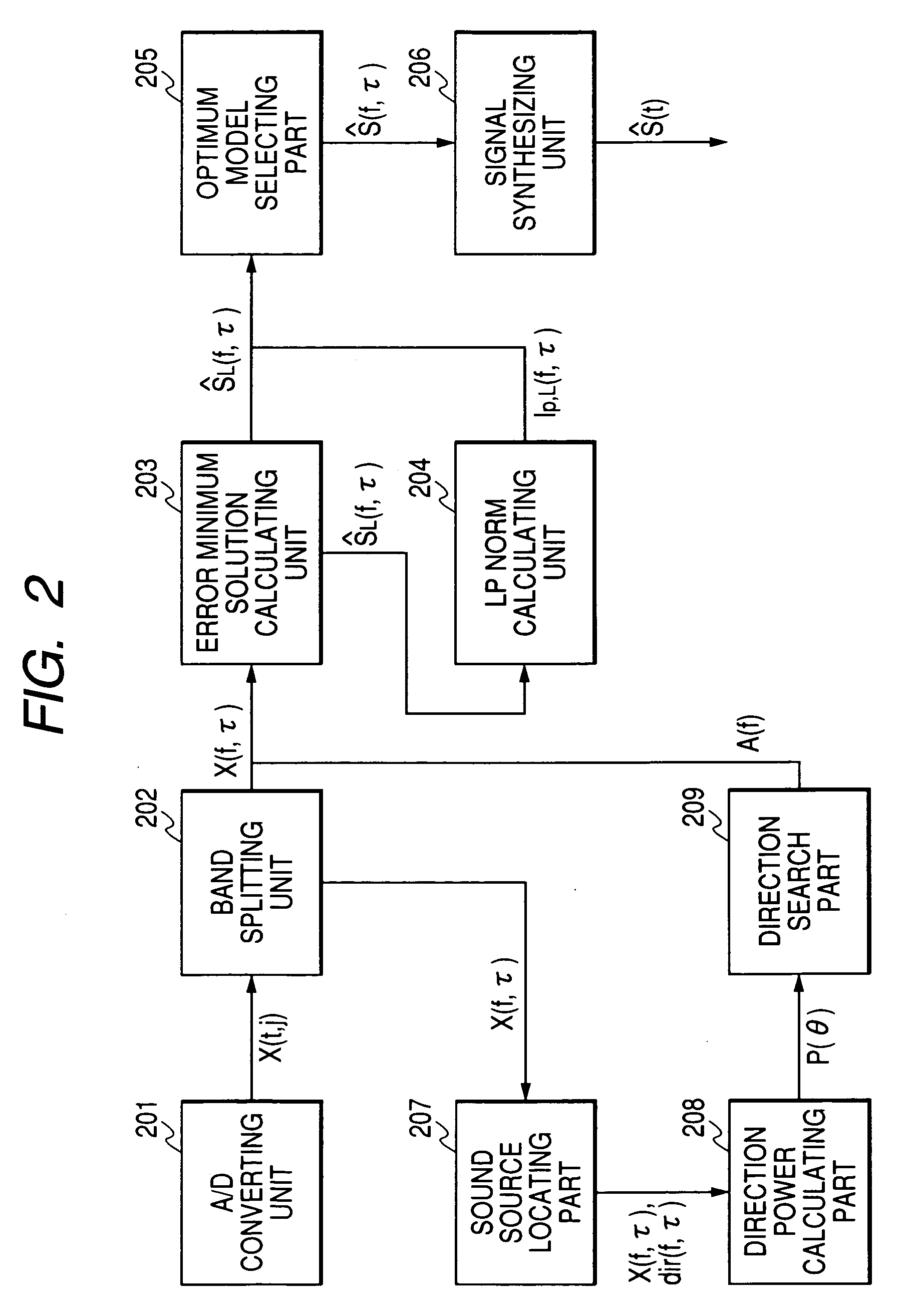
Sound source separating device, method, and program
InactiveUS20070223731A1Speech analysisMicrophones signal combinationSound source separationIndependent component analysis
Conventional independent component analysis has had a problem that performance deteriorates when the number of sound sources exceeds the number of microphones. Conventional l1 norm minimization method assumes that noises other than sound sources do not exist, and is problematic in that performance deteriorates in environments in which noises other than voices such as echoes and reverberations exist. The present invention considers the power of a noise component as a cost function in addition to an l1 norm used as a cost function when the l1 norm minimization method separates sounds. In the l1 norm minimization method, a cost function is defined on the assumption that voice has no relation to a time direction. However, in the present invention, a cost function is defined on the assumption that voice has a relation to a time direction, and because of its construction, a solution having a relation to a time direction is easily selected.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
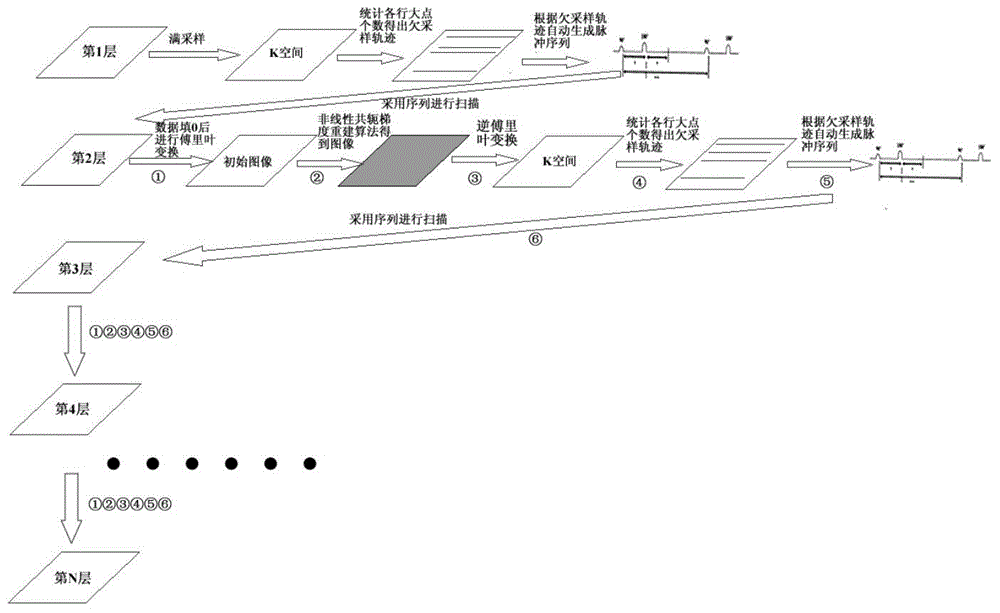
Multi-layer magnetic resonance fast imaging method based on adjacent layer information and undersampling
ActiveCN104434108AFast scanningImprove efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityResonance
The invention discloses a multi-layer magnetic resonance fast imaging method based on adjacent layer information and undersampling. The method includes: firstly, acquiring distribution positions of local large signal points and global large signal points of a K-space from a scanned layer adjacent to a to-be-scanned layer; secondly, planning an undersampling scan track of the to-be-scanned layer according to the distribution positions to complete scanning; finally, adopting a nonlinear conjugate gradient iterative method for image reconstruction by aiming at norm minimization for optimizing undersampling data in a sparse transform domain. The multi-layer magnetic resonance fast imaging method based on adjacent layer information and undersampling has the advantages that scanning time is shortened by reduction of sampling points, and imaging quality and stability are improved by guidance of information of the adjacent layer.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
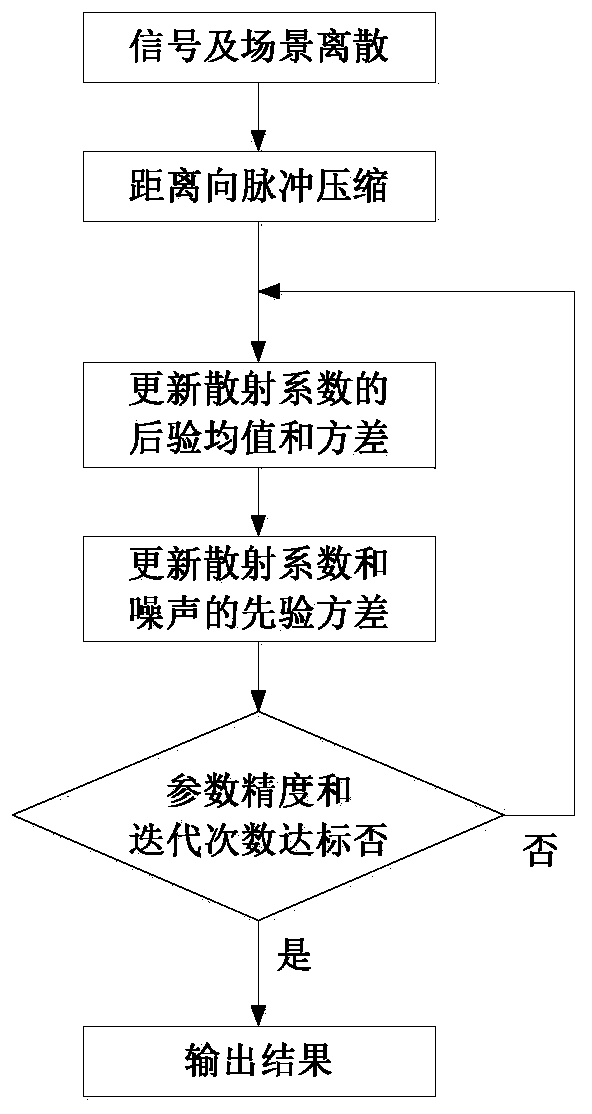
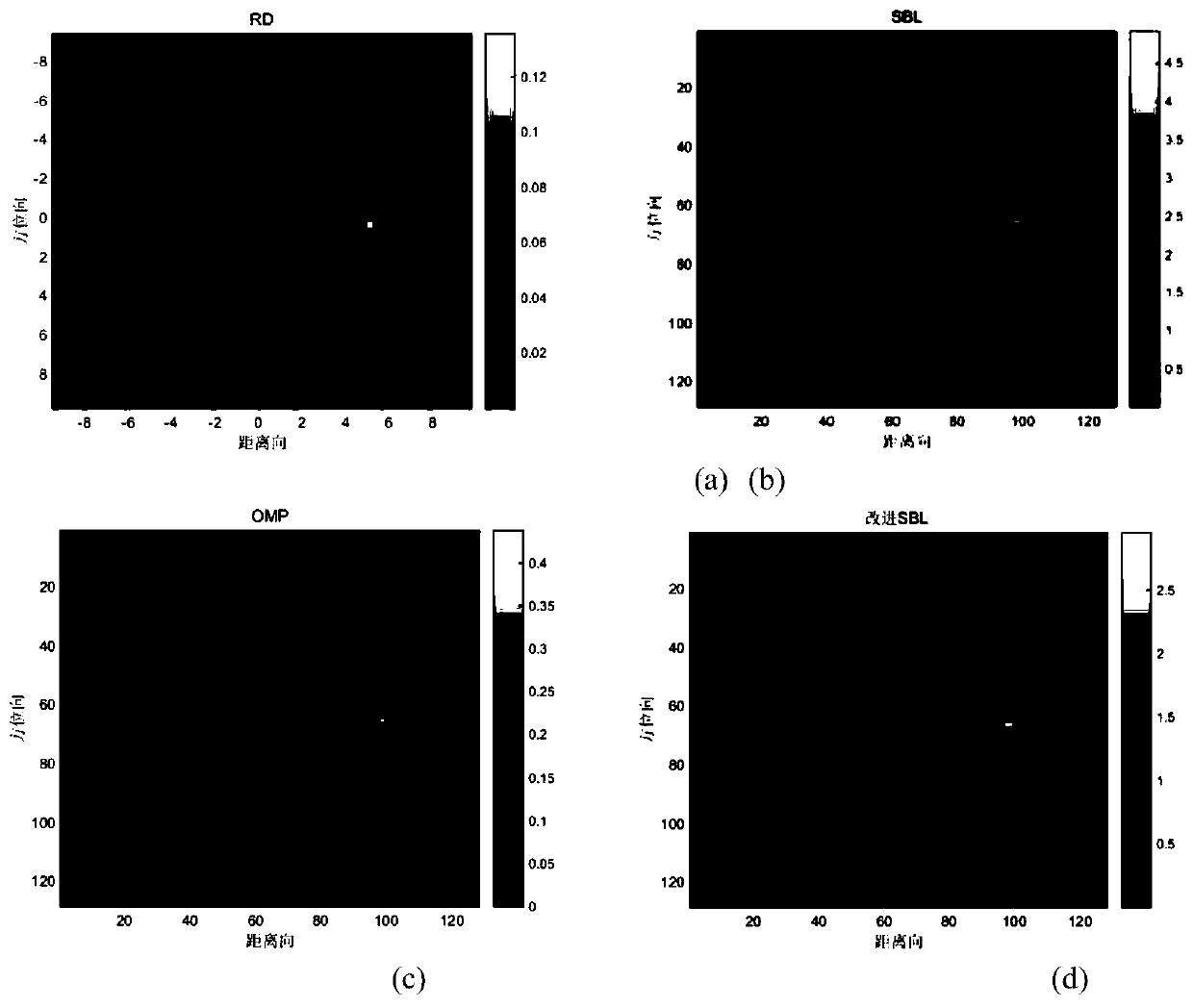
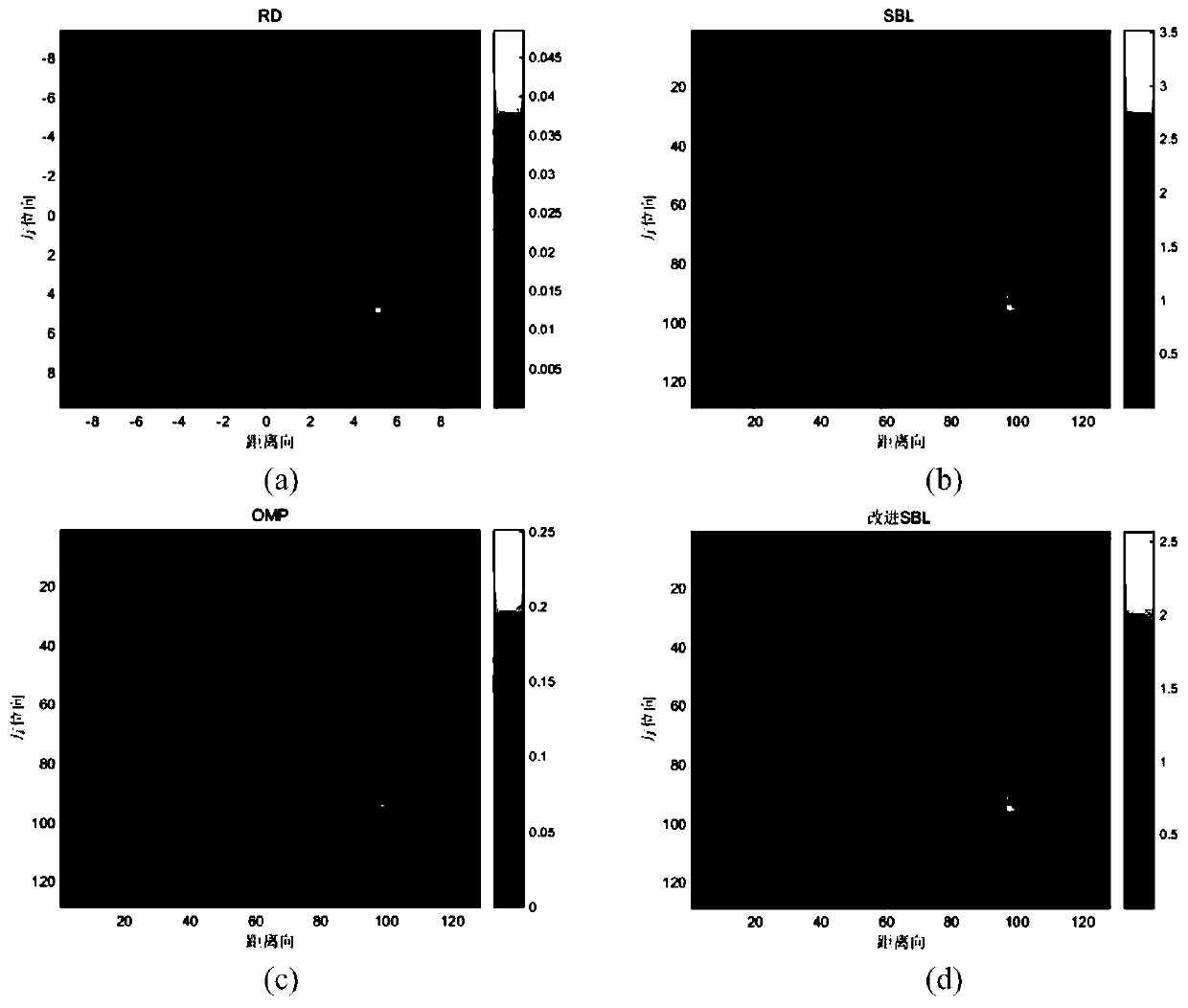
Improved sparse Bayesian learning ISAR imaging scattering coefficient estimation method
ActiveCN110161499AImprove the extraction effectReduce matrix sizeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionEstimation methods
The invention provides an improved sparse Bayesian learning ISAR imaging scattering coefficient estimation method. The method comprises the steps of: firstly discretizing an echo signal spectrum modeland a two-dimensional imaging scene, then performing distance dimension pulse compression processing on an echo signal spectrum, and establishing a sparse Bayesian learning model for the echo signalspectrum, initializing a scattering coefficient priori variance and a noise prior variance; estimating a posterior mean and a posterior variance of a scattering coefficient based on the scattering coefficient priori variance and the noise prior variance; changing the posterior mean of the scattering coefficient by using L0 norm minimization processing; reversely updating the scattering coefficientpriori variance and the noise prior variance based on the posterior mean and the posterior variance of the scattering coefficient; and performing repeated iteration to continuously optimize and update related parameters. After iteration convergence, a posterior mean matrix of the scattering coefficient is a desired imaging result. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the computational complexity is reduced, and the ISAR imaging effect is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
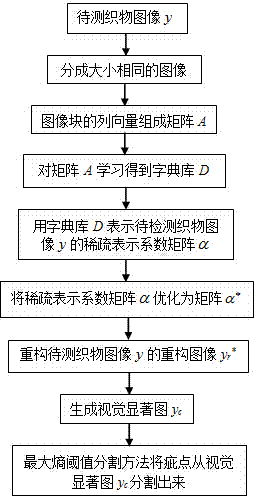
Fabric defect detection method based on sparse representation coefficient optimization
ActiveCN104778692AEffective positioningImprove detection accuracyImage analysisSaliency mapError processing
The invention discloses a fabric defect detection method based on sparse representation coefficient optimization. The detection method comprises self-adaptive dictionary database study, sparse coefficient matrix optimization and image reconstruction as well as generation and segmentation of a vision saliency map and specifically comprises steps as follows: an image is partitioned into blocks, self-adaptive dictionary database study is performed, and a dictionary database is obtained; a sparse representation coefficient matrix is solved with an L2-norm minimization method, and abnormal coefficient elements in the obtained matrix are optimized; a fabric image is reconstructed with adoption of the obtained dictionary database and the optimized sparse representation coefficient matrix, the fabric image and a to-be-detected image are subjected to residual error processing, and a residual error saliency map is obtained; the saliency map is segmented with a maximum entropy threshold segmentation method, and a fabric defect detection result is obtained. Randomness of fabric textural features and diversity of defect varieties are overall considered, the to-be-detected fabric image is taken as a detection reference for a dictionary database studying sample and a defect area, the method has higher detection accuracy, no defect information is required to be extracted, and the self-adaptive capability is high; the computation speed is higher, and the method is suitable for online detection.
Owner:ZHONGYUAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE
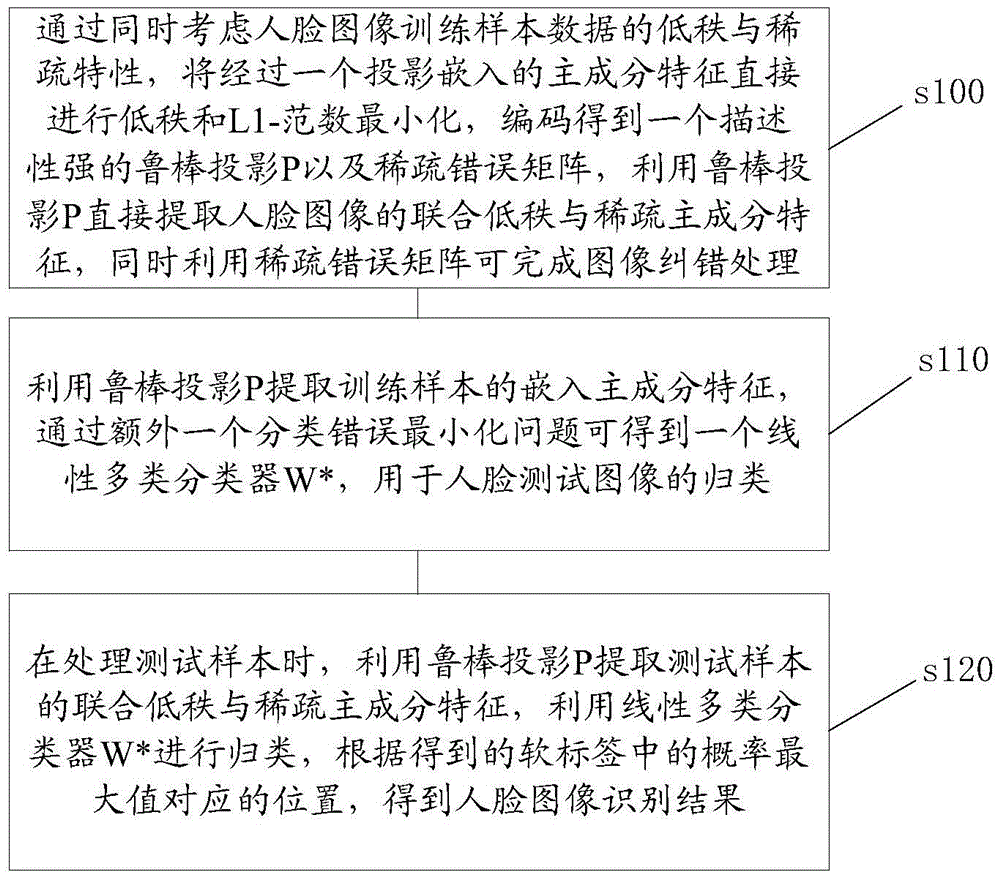
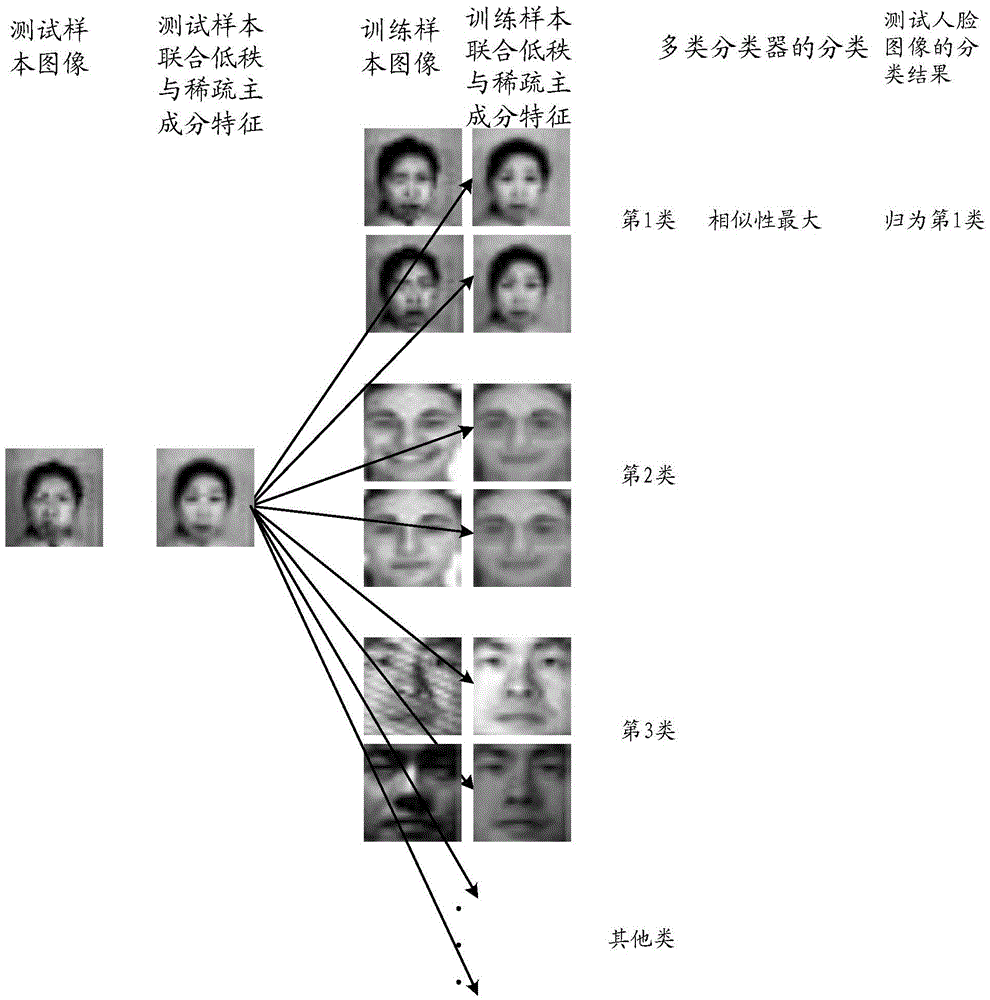
Robust human face image principal component feature extraction method and identification apparatus
ActiveCN105469063AStrong descriptive abilityCancel noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionTest sample
The invention discloses a robust human face image principal component feature extraction method and identification apparatus. The method comprises: by considering low-rank and sparse characteristics of training sample data of a human face image at the same time, directly performing low-rank and L1-norm minimization on a principal component feature embedded through projection, performing encoding to obtain robust projection P with good descriptiveness, directly extracting a low-rank and sparse principal component union feature of the human face image, and finishing image error correction processing; and by utilizing the embedded principal component feature of a training sample of a robust projection model, obtaining a linear multi-class classifier W* for classifying human face test images through an additional classification error minimization problem. When test samples are processed, a union feature of the test samples is extracted by utilizing a linear matrix P and then the test samples are classified by utilizing the classifier W*; and by introducing a thought of low-rank recovery and sparse description, the principal component feature, with better descriptiveness, of the human face image can be obtained by encoding, the noise can be eliminated, and the effect of human face identification is effectively improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
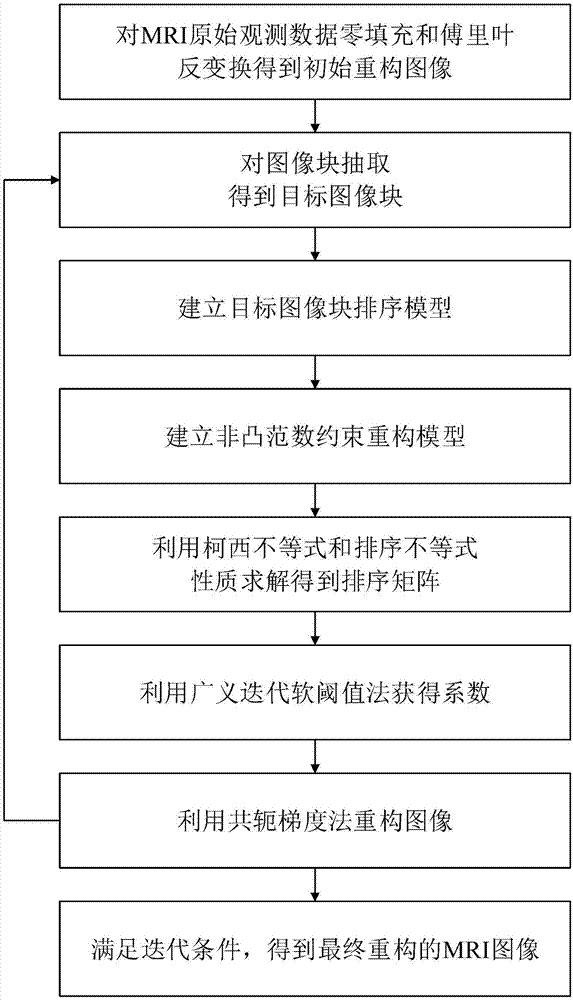
MRI image reconstruction method based on enhanced sparse representation of image blocks
ActiveCN107993204AImprove visual effectsImprove sparsityImage enhancementImage analysisDigital signal processingReconstruction method
The invention discloses an MRI image reconstruction method based on the enhanced sparse representation of image blocks, and belongs to the technical field of digital image processing. The method is used for improving the coefficient sparseness and the estimation performance by utilizing the pixel sequencing and the non-convex norm constraint in image blocks. According to the method, firstly, a target image block is extracted from an MRI image, and then a sequencing training model based on image blocks is built. Meanwhile, a reconstruction model of the MRI image is built according to the coefficient non-convex constraint. After that, an alternate direction method is adopted to iteratively solve a sequencing matrix and a sparse coefficient in the model. Based on the estimated sparse coefficient, a final MRI image is reconstructed. According to the method, through sequencing pixels in the image blocks, the performance of the sparse transformation is improved. Meanwhile, the non-convex norm minimization constraint is carried out on coefficients, so that estimated coefficients are closer to real coefficients. Based on the method of the invention, the overall effect of reconstructed images is better and the detail information is richer. Meanwhile, the reconstitution accuracy is higher. Therefore, the method can be used for reconstructing MRI images.
Owner:成都国一科技有限公司
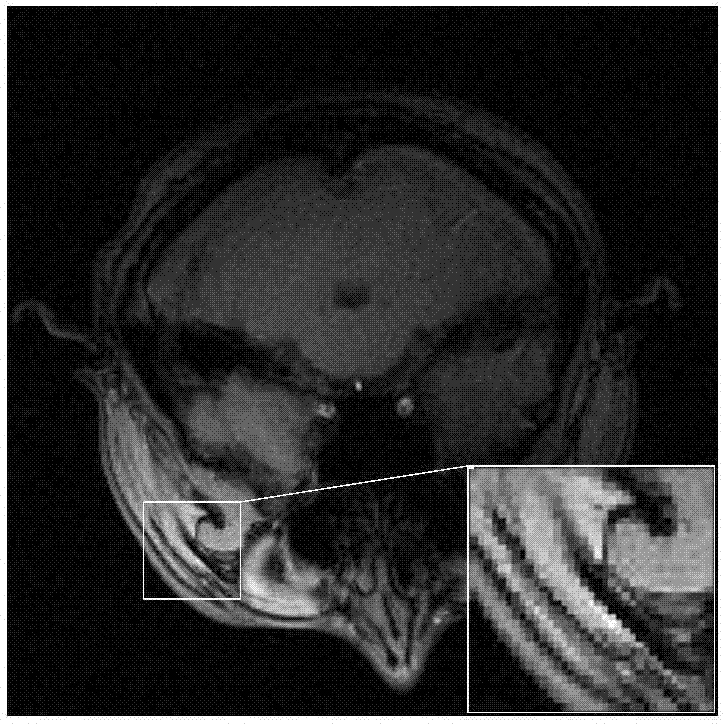
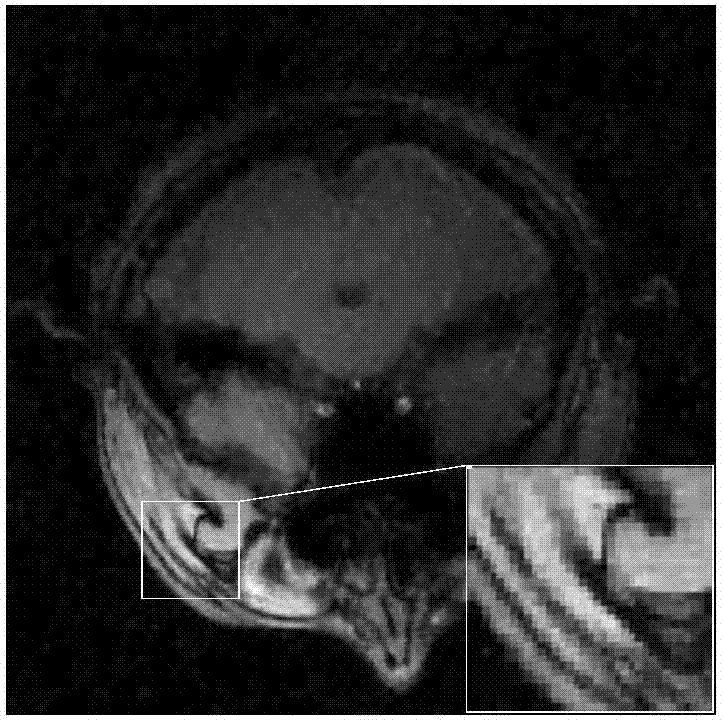
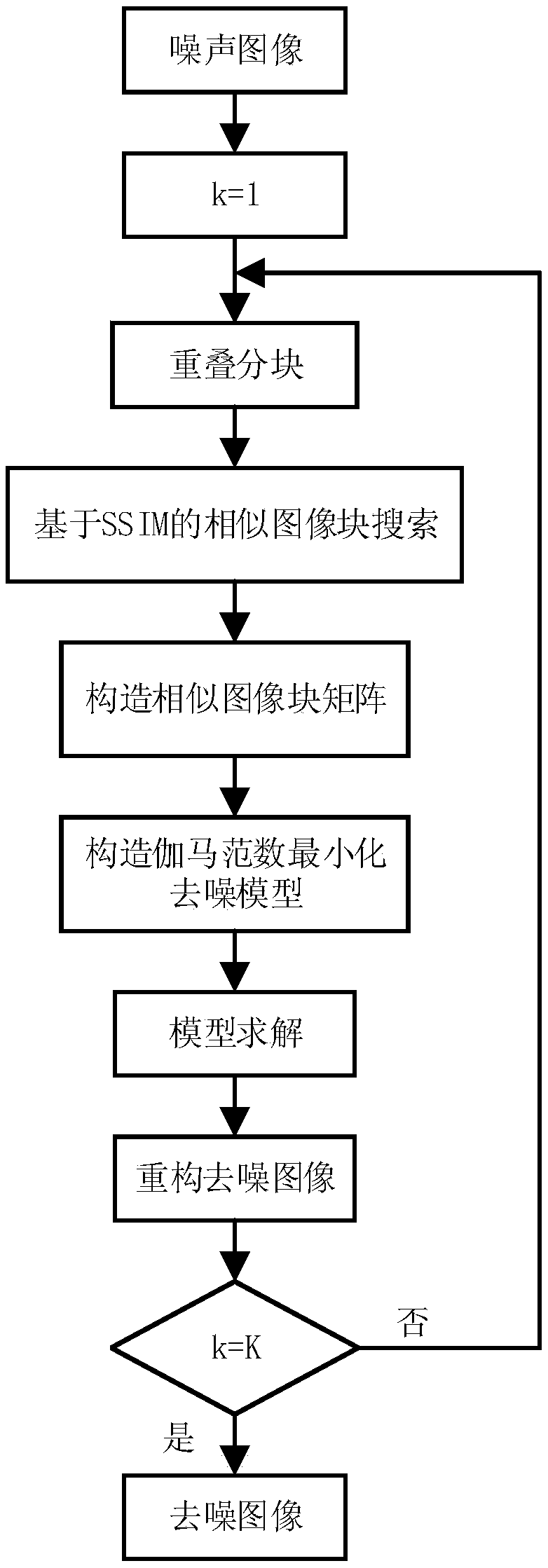
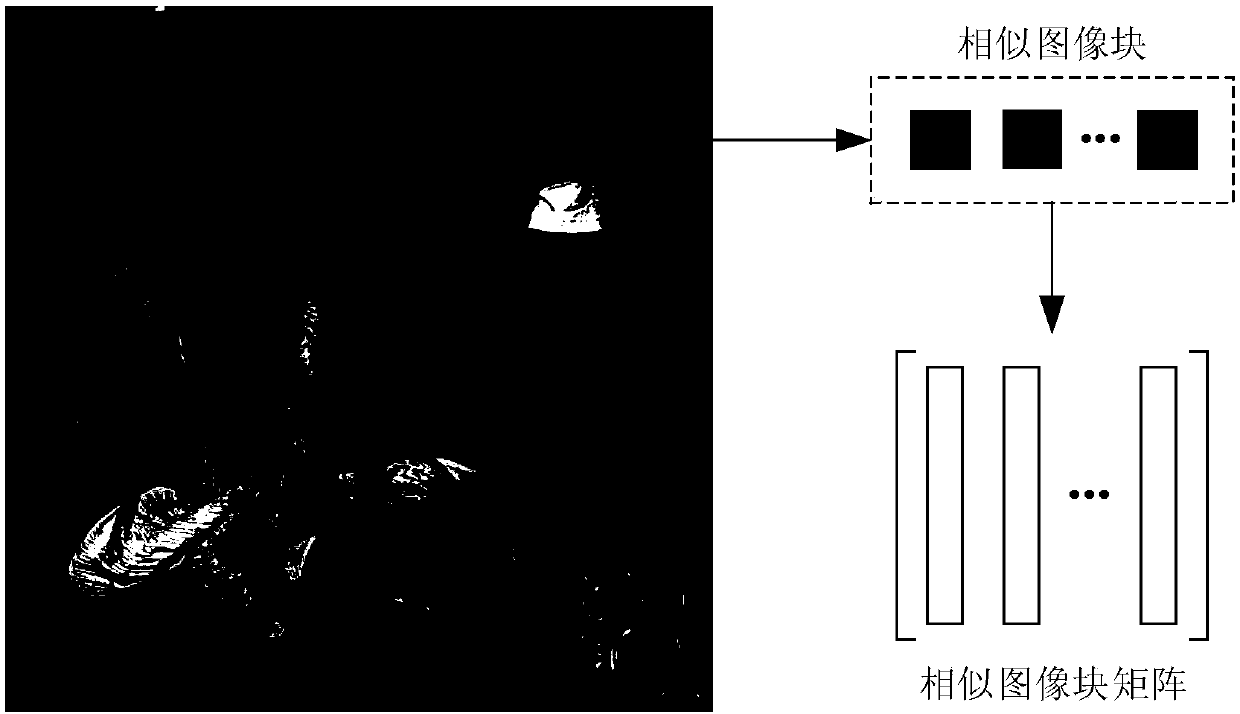
An image denoising algorithm based on gamma norm minimization
ActiveCN109671029AAvoid the downside of inaccurate searchesAvoid artifactsImage enhancementInternal combustion piston enginesSingular value decompositionPattern recognition
The invention belongs to the field of digital image processing, and relates to an image denoising algorithm based on gamma norm minimization. The algorithm comprises the following steps of overlappingand partitioning noise images; adaptively searching a plurality of non-local image blocks most similar to the current image block based on the structural similarity index to form a similar image block matrix; and then utilizing a non-convex gamma norm unbiased approximation matrix rank function to construct a low-rank denoising model, finally, solving the obtained low-rank denoising optimizationproblem based on singular value decomposition, and recombining the denoised image blocks into a denoised image. Simulation results show that compared with existing PID, NLM, BM3D and NNM algorithms, the algorithm provided by the invention can effectively eliminate the Gaussian noise, and can better recover the original image details.
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
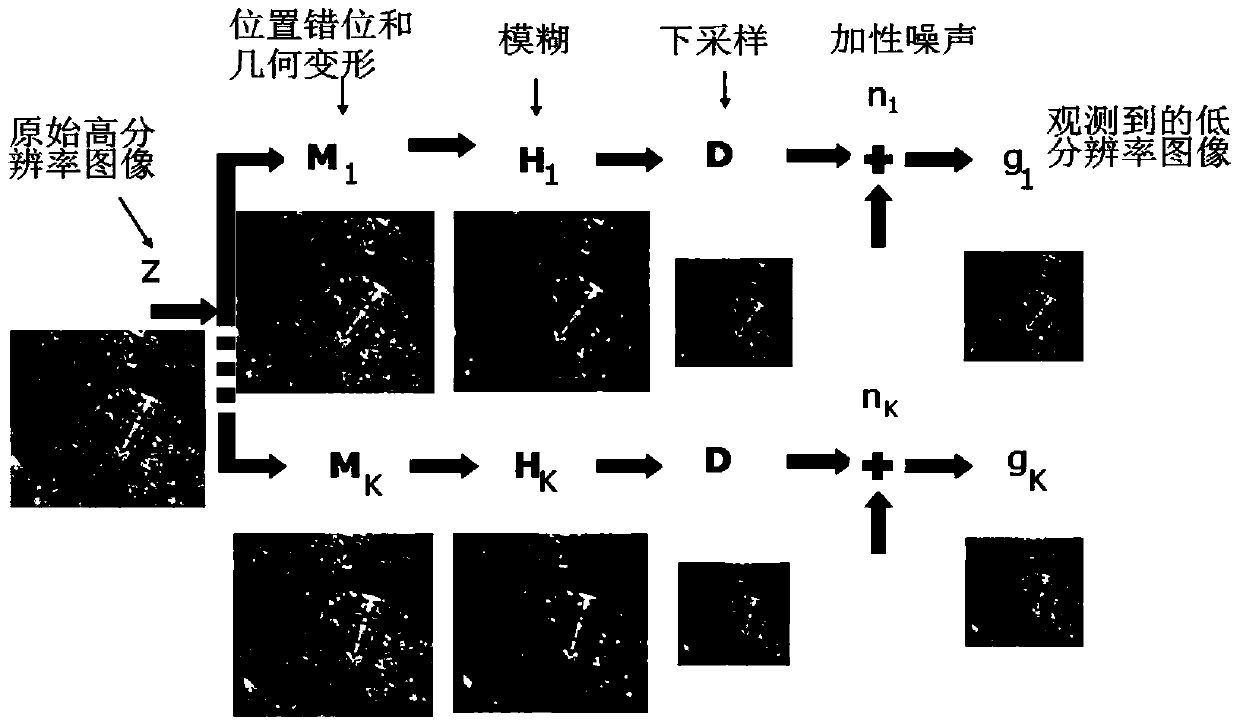
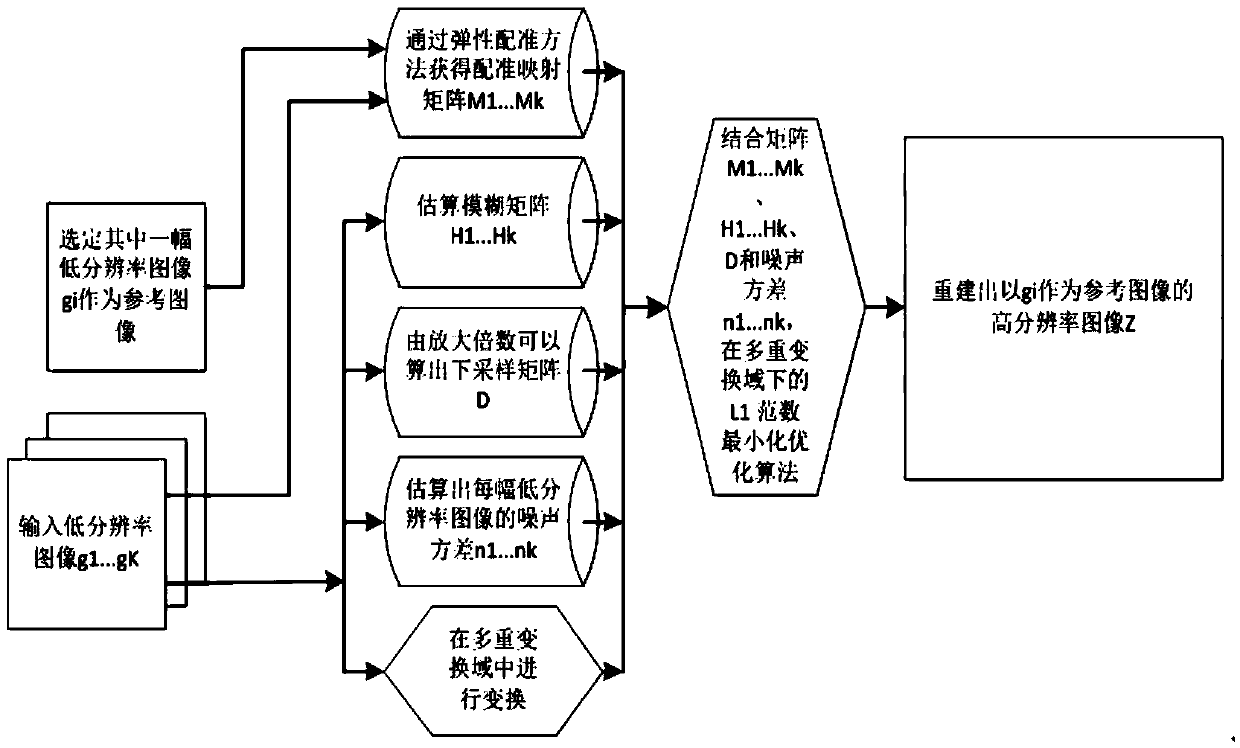
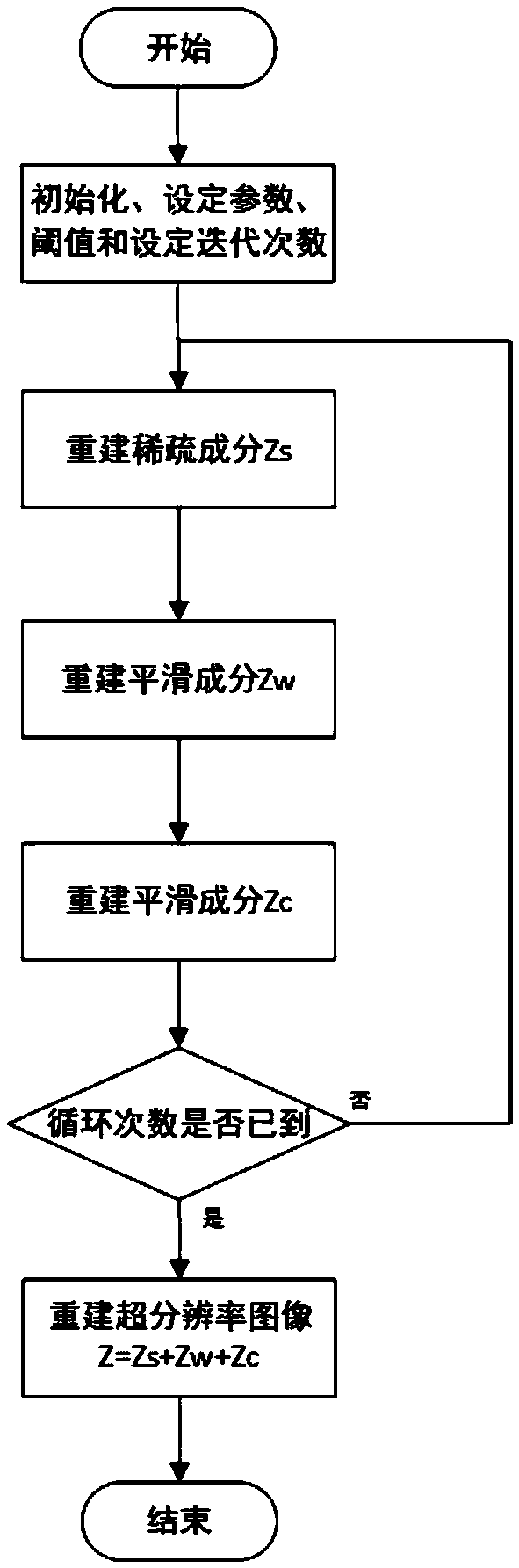
Multiple transform domain based super-resolution reconstruction method
The invention relates to a multiple transform domain based super-resolution reconstruction method and belongs to the technical field of image super-resolution. The method comprises the following steps: performing nonrelated transform domain analysis on K input low-resolution images separately; according to the sizes of a target super-resolution image and the input low-resolution images, determining a down-sampling matrix D; and reconstructing the super-resolution image by adopting an optimization algorithm for L1-norm minimization in multiple transform domains through the constraint of a cost function min lambda1||W1(z1)||1+lambda2||W2(z2)||2+......+lambdaj||Wj(zj)||1 by z=z1+z2+...+zj and ||DHiMiz-gi||2<=ni (i=1,2,...K). Compared with the prior art, the method solves the problem in selection of a priori probability model in super-resolution reconstruction, namely, multiple transform domain based remote sensing image sparsity expression; and meanwhile, the method solves the problems of irregular geometric distortion and dislocation of low-resolution remote sensing images caused by load platform shake and atmospheric disturbance, and reconstructs the super-resolution image with a good effect.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
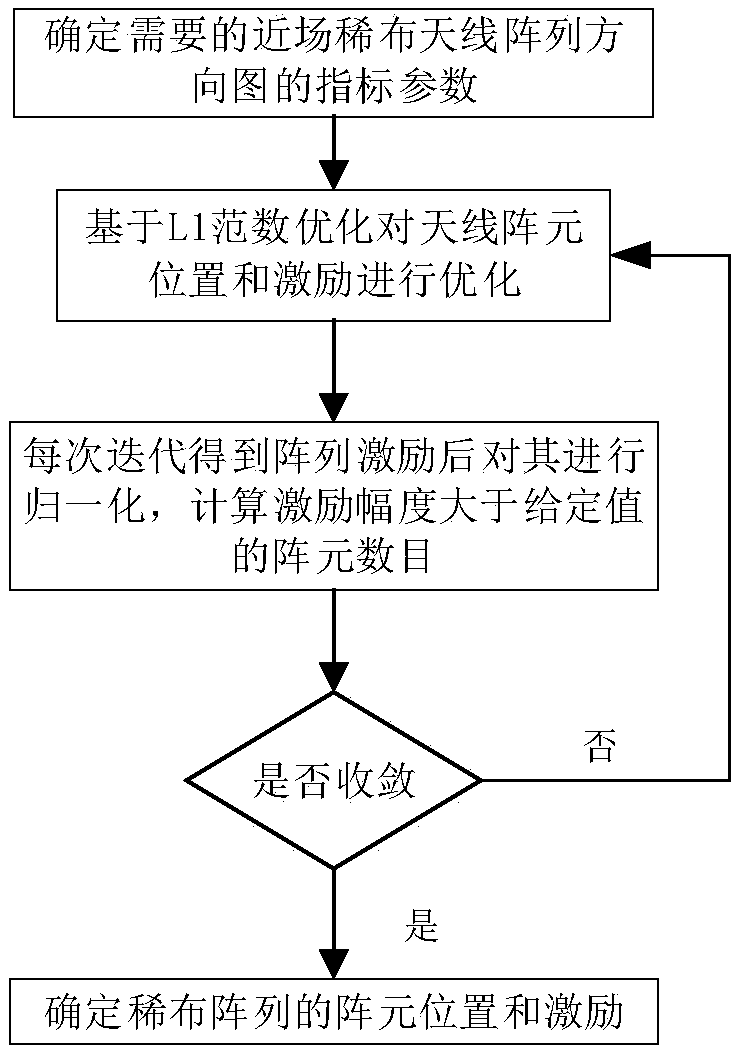
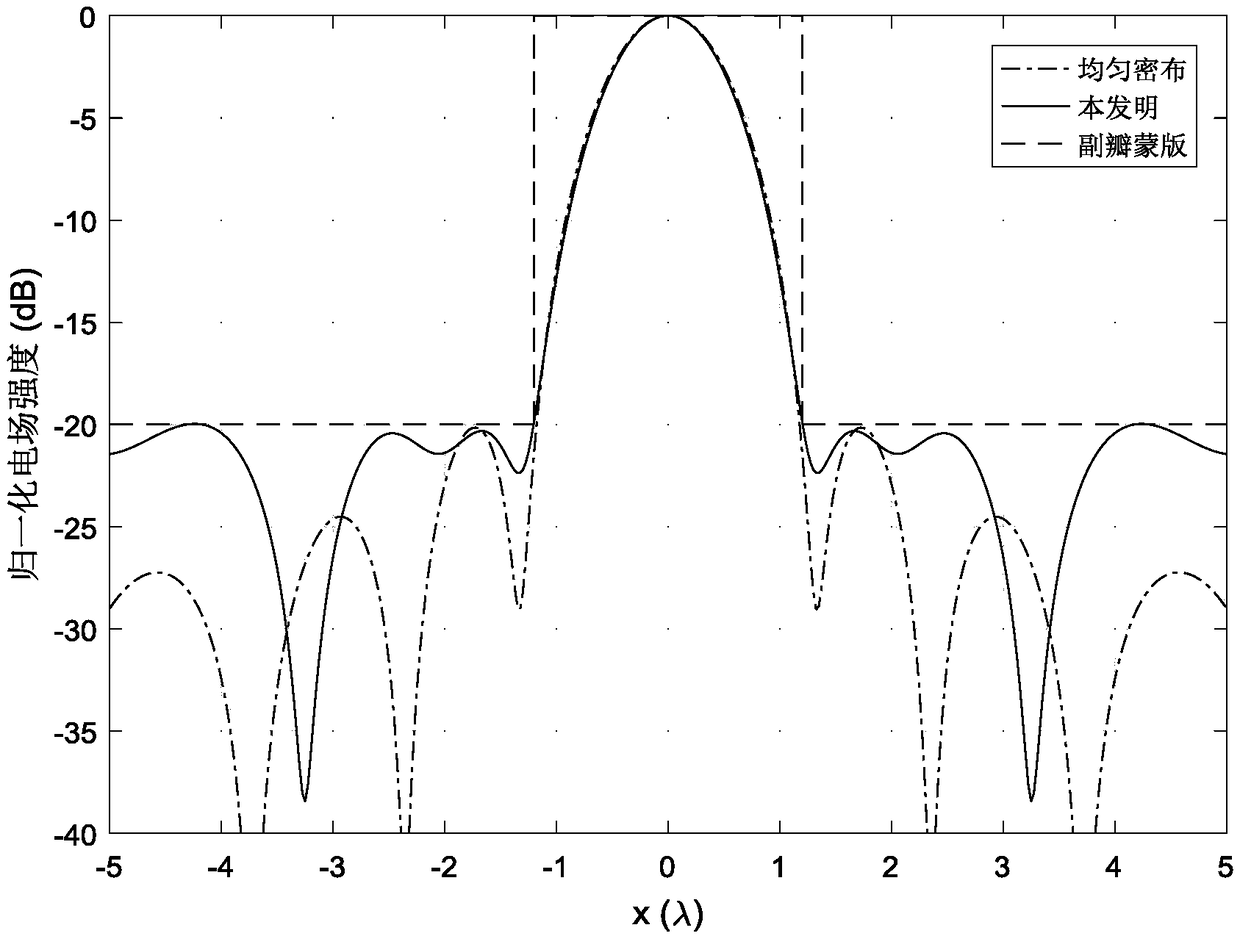
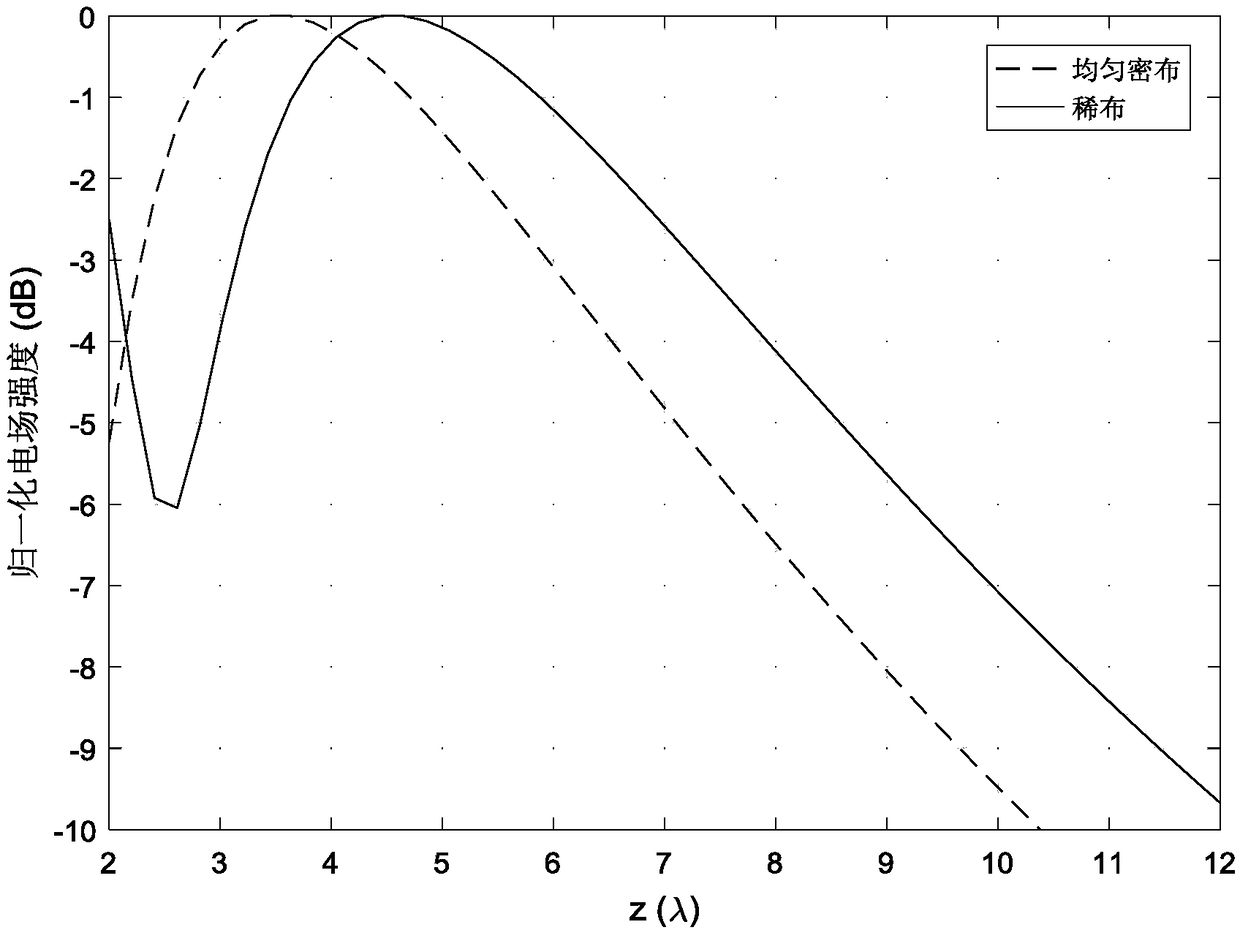
Near-field sparse antenna array optimization method based on L1 norm constraint
ActiveCN109033647ALevel controllableSolve the focus shift problemDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithm convergenceArray element
The invention provides a near-field sparse antenna array optimization method based on L1 norm constraint, which comprises the following steps: 1. determining the index parameters of the needed near-field sparse antenna array pattern; 2. determining the index parameters of the near-field sparse antenna array pattern. 2, using the L1 norm constraint theory to carry out iterative solution on the array element position and corresponding excitation; 3, normalizing the array excitation obtained by each iteration, and calculating the number of array elements whose excitation amplitude is greater thana given value; 4, judging whether that numb of units of three successive iterations is equal, if equal, the algorithm converges to obtain the final array topology and corresponding excitation. The invention obtains the sparse near-field antenna array topology and corresponding excitation based on the L1 norm minimization. Compared with the traditional method, the sidelobe level is controllable, and the problem of focus shift in the near-field focusing technology is solved at the same time.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
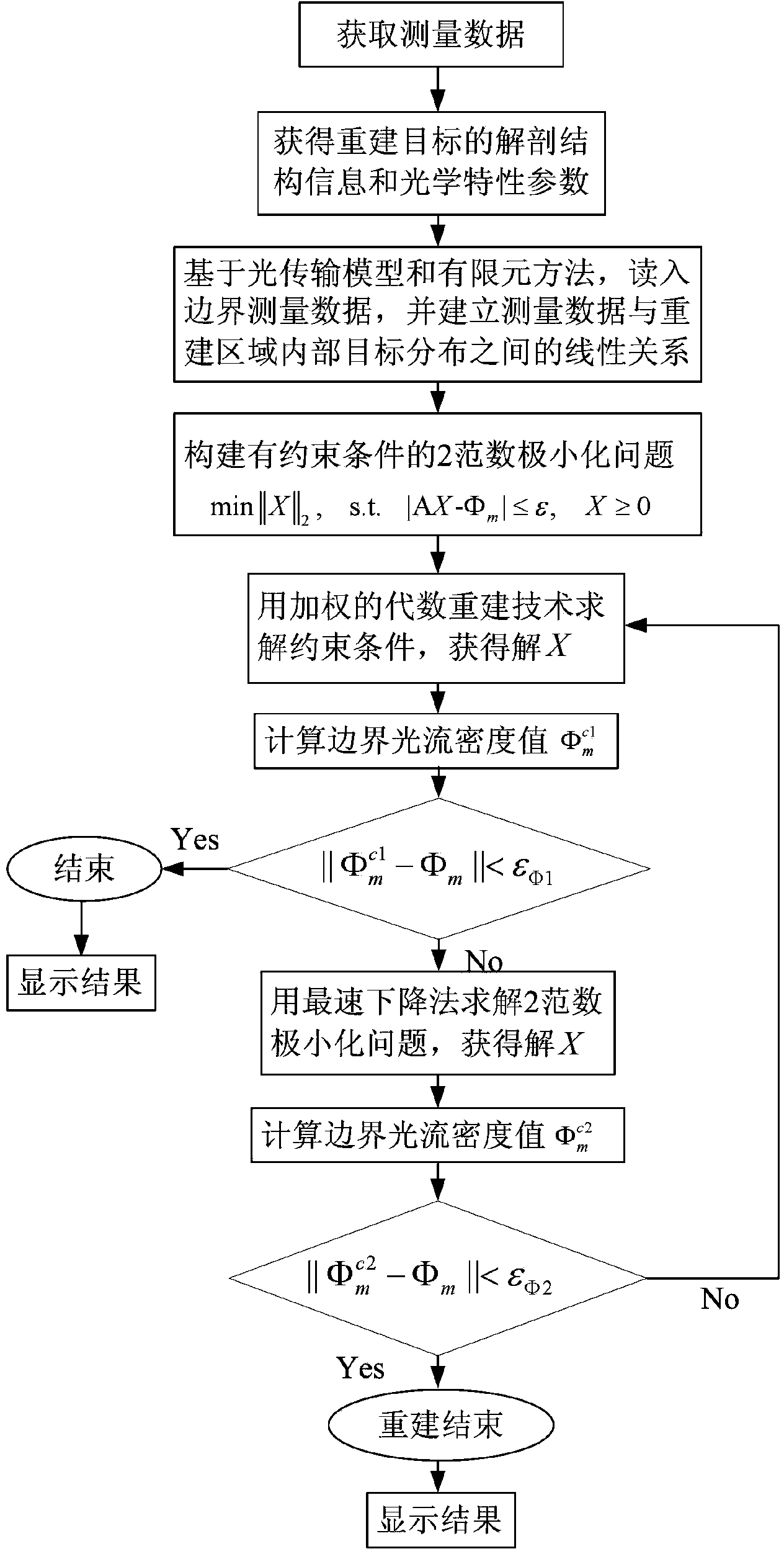
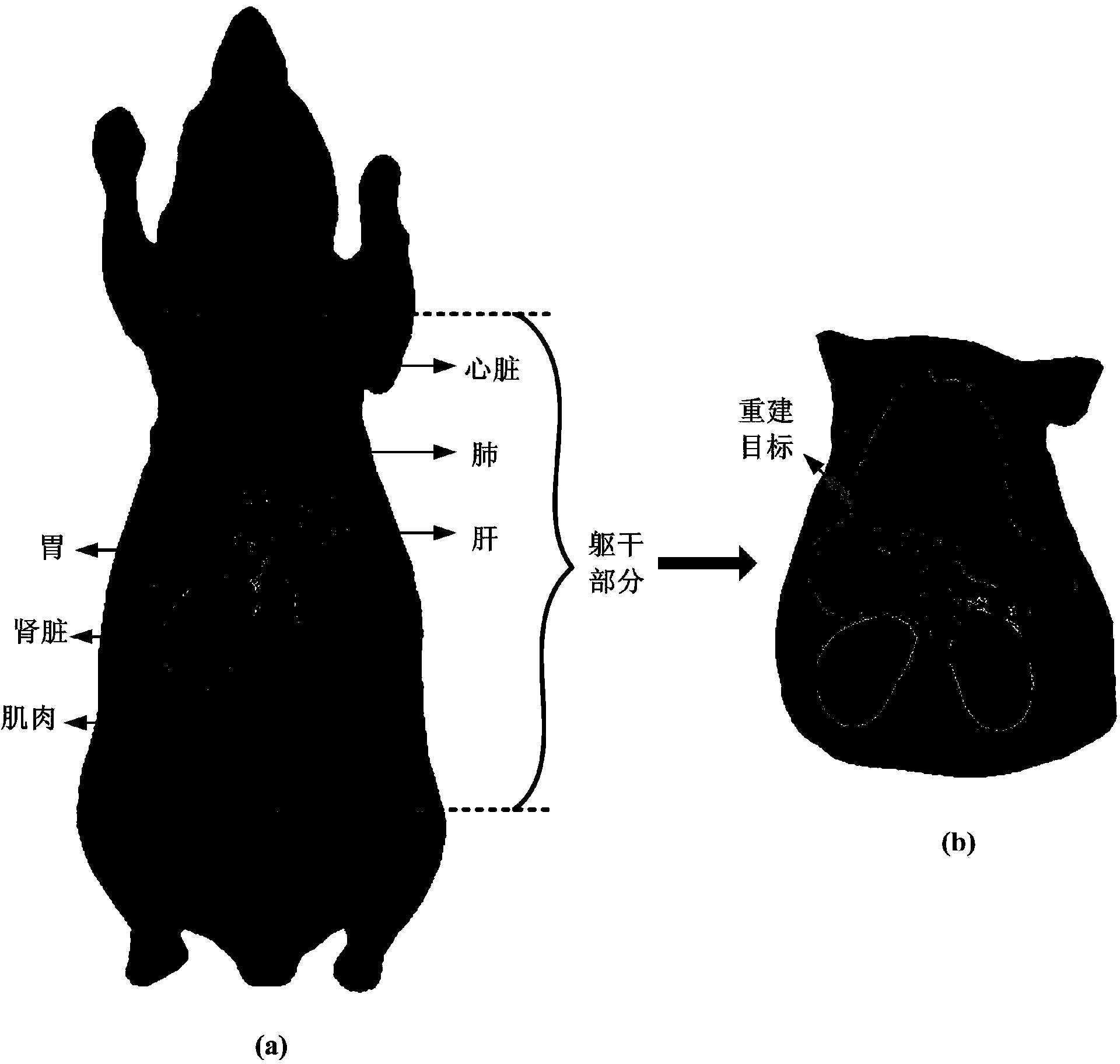
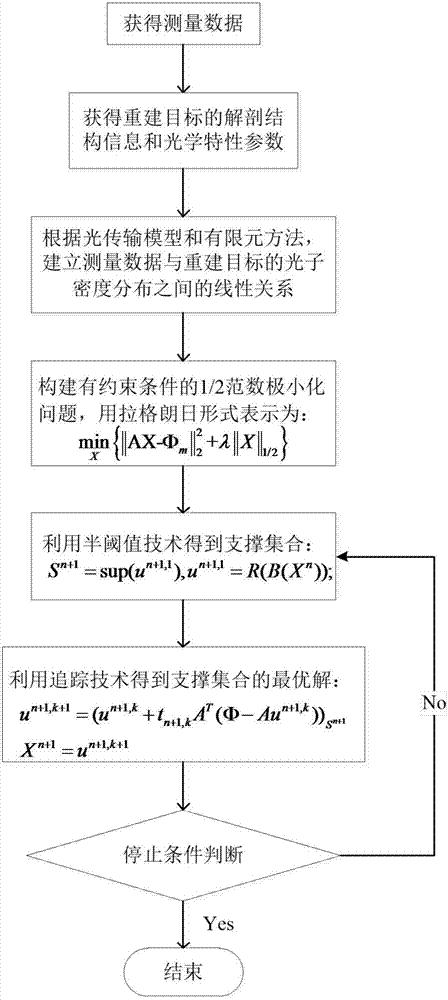
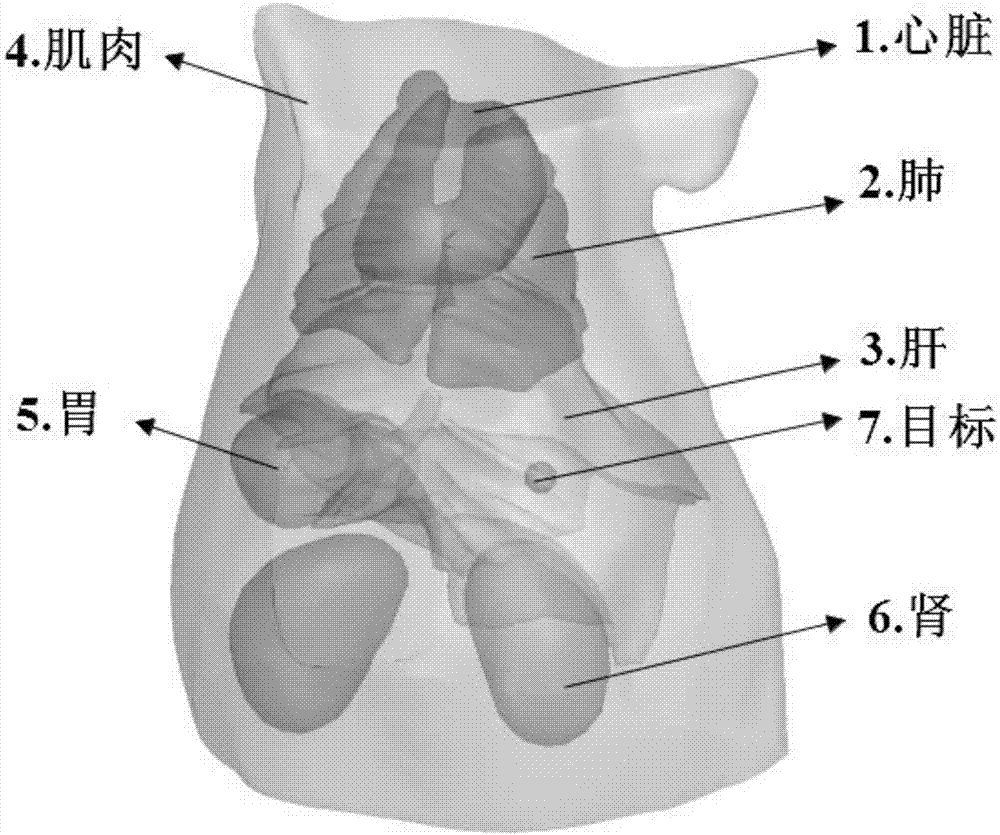
Fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction method based on alternative iterative operation
InactiveCN103393410AComprehensive measurement dataReduce morbidityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSteep descentAnatomical structures
The invention discloses a fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm based on an alternative iterative operation, which is characterized in that a weighted algebraic reconstruction technique and a steepest descent method are used alternately for solving. The fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm comprises the following steps that (1), measurement data is acquired; (2), a linear relationship between the measurement data and target distribution is established; (3), a 2 norm minimization problem with a constraint condition is constructed; and (4), the weighted algebraic reconstruction technique and the steepest descent method are used alternately for solving the minimization problem, and a target distribution diagram is obtained. According to the fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm, based on a light transmission theory and a finite element method, prior information such as an optical characteristic parameter and an anatomical structure is used, multipoint excitation and multipoint measurement are adopted, and the measurement data is obtained as far as possible, so that the pathosis of the problem is reduced; the weighted algebraic reconstruction technique and the steepest descent method are used alternately for solving the problem, so that a reconstruction result of fluorescence molecular tomography is improved effectively; and the fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm has an important application value in the fields of molecular imaging, reconstruction algorithms and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
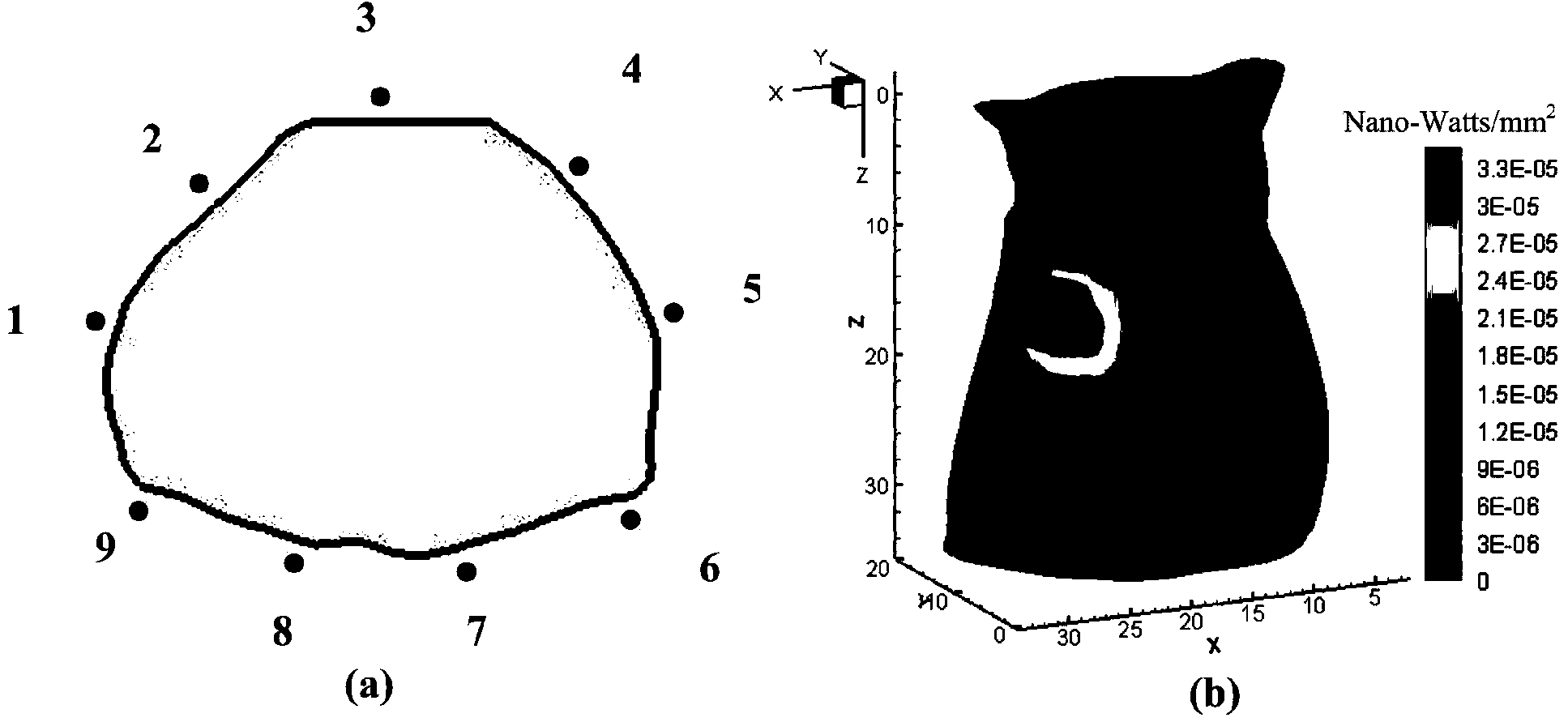
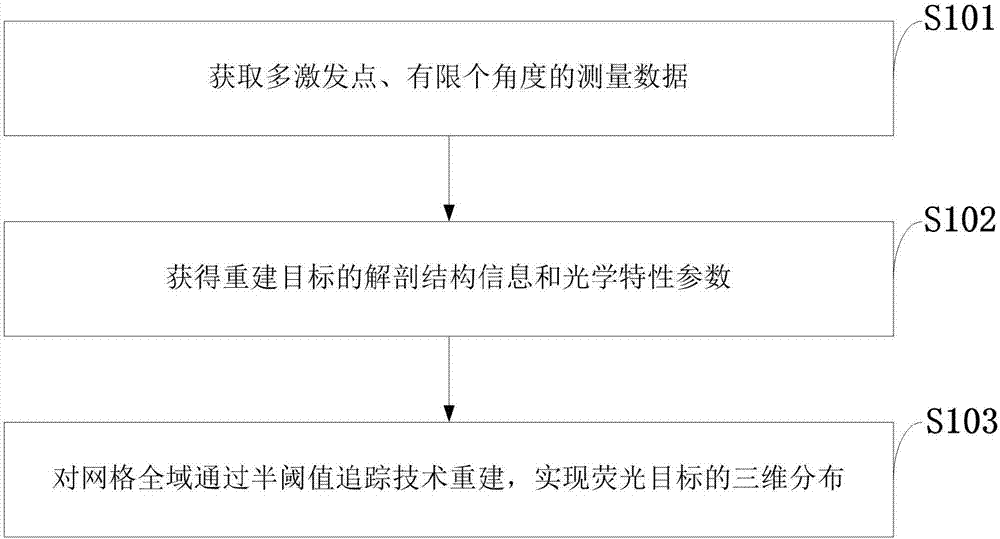
Method for reconstructing fluorescence molecular tomography based on semi-threshold tracking algorithm
InactiveCN107220961AImprove stabilityThe reconstruction results are accurateImage enhancementDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionAnatomical structuresCanonical model
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular imaging, and discloses a method for reconstructing fluorescence molecular tomography based on semi-threshold tracking algorithm. The multi-point excitation and finite angle measurement are used to construct a sparse canonical model of a non-convex problem, and the linear relationship between the surface measurement data and fluorescence target distribution is established. The linear relationship is transformed into the 1 / 2 norm minimization problem to solve and obtain the three-dimensional distribution and concentration of the fluorescent targets within a reconstructed target. The model is solved by threshold iteration and matching tracing algorithm. The method reduces the morbidity of the problem. Optical characteristic parameters and the anatomical structure information are used as a priori knowledge to improve the accuracy of the reconstruction result and the quality of a reconstructed image. The reconstruction problem is transformed into a 1 / 2-norm minimization problem with constraint conditions and is solved by using the semi-threshold tracing algorithm, which makes the solution satisfy the minimum of 1 / 2- norm and guarantees the robustness of the reconstruction problem to the parameters and the acceleration reconstruction time.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Effective '0,1' sparse signal compressed sensing reconstruction method
ActiveCN103825621AImplement refactoringNo reconstruction errorsCode conversionReconstruction methodReconstruction algorithm
The invention discloses an effective '0,1' sparse signal compressed sensing reconstruction method. The method mainly comprises a sparse and uniform measurement matrix construction part and an iteration reconstruction order part based on a bipartite graph. According to the method, a bipartite graph model in a graph theory is ingeniously introduced, the minimum cover characteristic of the bipartite graph is closely combined, a constraint condition is appropriately added, and the sparse, uniform and minimally-covered measurement matrix is constructed. Based on the special structure that the '0,1' sparse signals are fully utilized in an iteration reconstruction algorithm based on the bipartite, the connecting line phi ij of the bipartite graph is deleted and a measurement value y is updated through an iteration method, and an original signal reconstruction method is achieved finally. According to the method, the bipartite graph model in the graph theory is introduced in compressed sensing sampling and reconstruction, compared with an l1 norm minimization method, reconstruction errors do not exist, the method can be applied to compressive sampling of neutron pulse sequences, earthquake signals, wireless sensor networks, binary images and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for fast robustness tracking of infrared target based on sparse representation
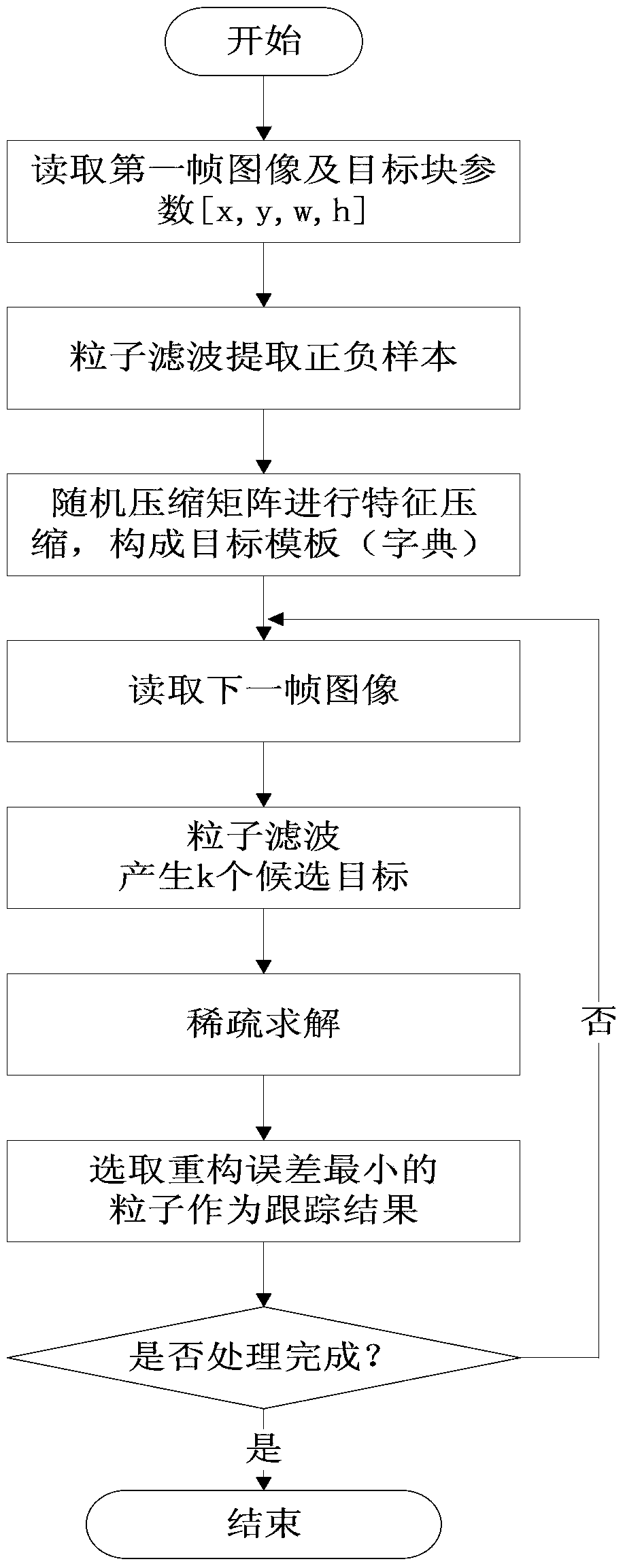
The invention discloses a method for fast robustness tracking of an infrared target based on sparse representation. Sparse solution is carried out by calculating L1 norm minimization, the reconstruction error is calculated to acquire the probability of each particle, and therefore target tracking is achieved. In view of the facts that in the method, because the number of dimensions of a dictionary is too large, considerably much time is consumed in the L1 minimization calculation process, real-time performance of an algorithm can not be met, and gray features can be easily disturbed by noise and illumination changes and similar objects, on the basis of compressive sensing, Harr-like characteristics are compressed based on a random measurement matrix, original image characteristics are well kept, and better expression ability is achieved. Because dictionary construction is carried out through characteristics based on compressive sensing, calculated amount is greatly reduced, the target can be more effectively expressed, problems like illumination changes, shielding, size changes and target deformation are solved, and fast robustness tracking of the infrared target can be achieved.
Owner:WUXI TONGCHUN NEW ENERGY TECH
Sparse dictionary-based wireless sensor network missing data reconstruction method
InactiveCN105743611AReduce reconstruction errorImprove reconstruction accuracyTransmitted data organisation to avoid errorsWireless mesh networkMissing data
The invention discloses a sparse dictionary-based wireless sensor network missing data reconstruction method. The method includes the following steps that: 1) the total number N of data frames requiring reconstruction are determined according to missing data; M data frames are selected from historical data and are adopted as training data, wherein M is an integer greater than K; 2) a K-SVD algorithm is called to obtain a dictionary D of which the size is K; 3) as for the dictionary D, an L1 norm minimization algorithm is adopted to sparse coefficients alpha i corresponding to each dictionary atoms di; 4) data frames of a current time point are reconstructed according to calculation results of the step 2) and the step 3); 5) whether dictionary update conditions are satisfied is judged, if the dictionary update conditions are satisfied, a dictionary update method is called to update data in the dictionary; 6) and data reconstruction is completed. According to the method of the invention, the influence of reconstructed data frames of the current time point on data frames to be reconstructed of a next time point is considered, the dictionary update conditions are set, and the sparse dictionary is updated adaptively, and therefore, the reconstruct data frames are closer to real data, and reconstruction precision is higher.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
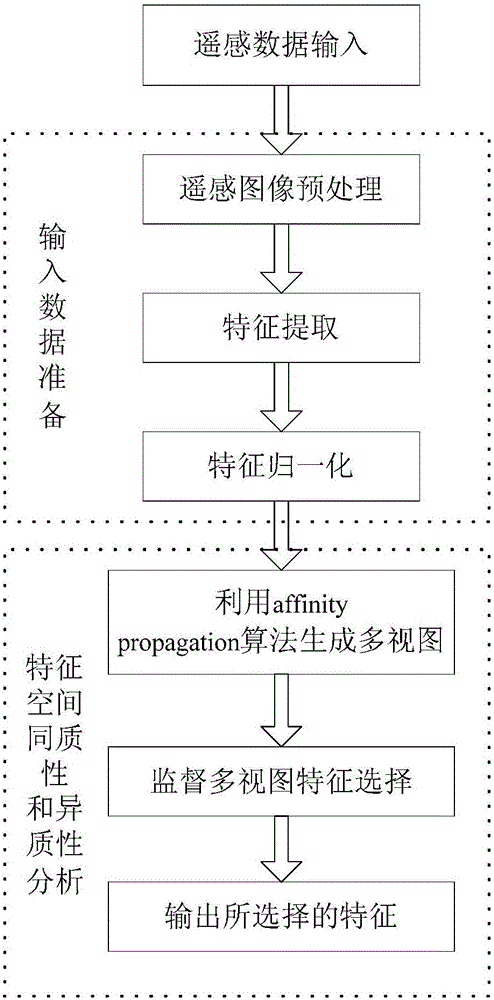
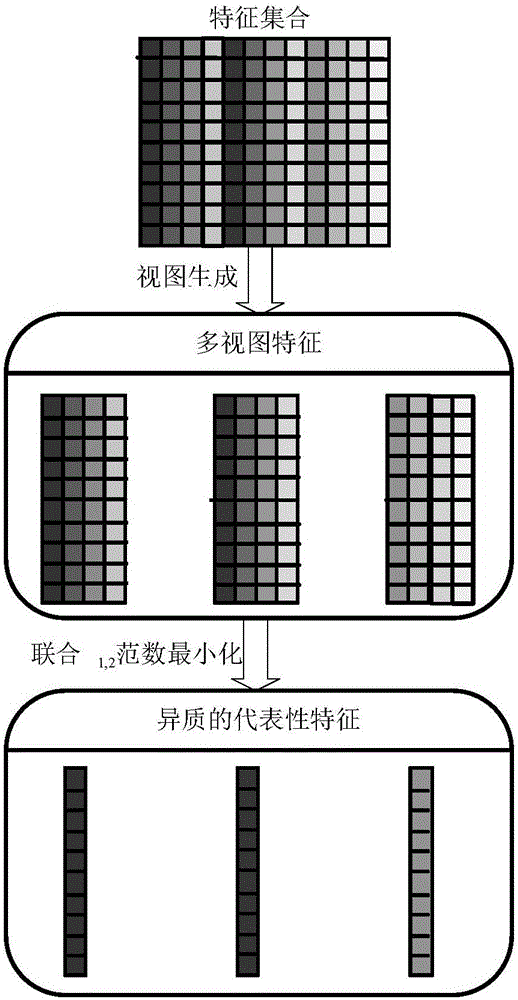
Supervision multi-view feature selection method based on automatic generation of view and unit with l1 and l2 norm minimization
ActiveCN105046286AOvercoming the disadvantages of lossStrong featuresCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorFeature extraction
A supervision multi-view feature selection method based on automatic generation of view and unit with l1 and l2 norm minimization belongs to the technical field of remote sensing image data processing. The method provided by the invention is to solve a problem of information loss of a high-resolution remote sensing image in the feature selection process. The method comprises three steps: 1. acquiring remote sensing image data and pre-processing the same; then carrying out feature extraction to obtain an feature vector set; and normalizing all feature vectors of the feature vector set to obtain an original feature vector set; 2. generating multiple views from the original feature vector set obtained in step 1 by adopting an affinity propagation algorithm; and and 3. carrying out supervision multi-view feature selection on the multiple views obtained in step 2 based on the l1 and l2 norms. The invention relates to the supervision multi-view feature selection method.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
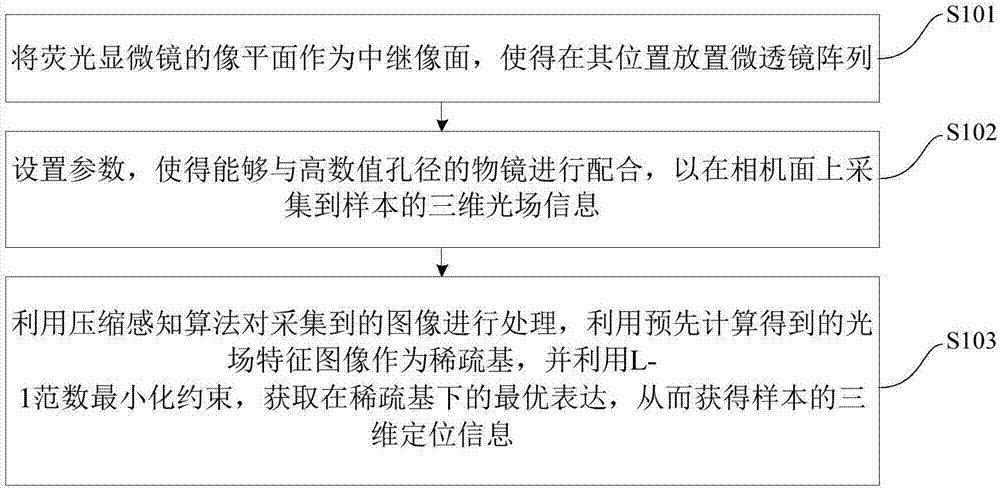
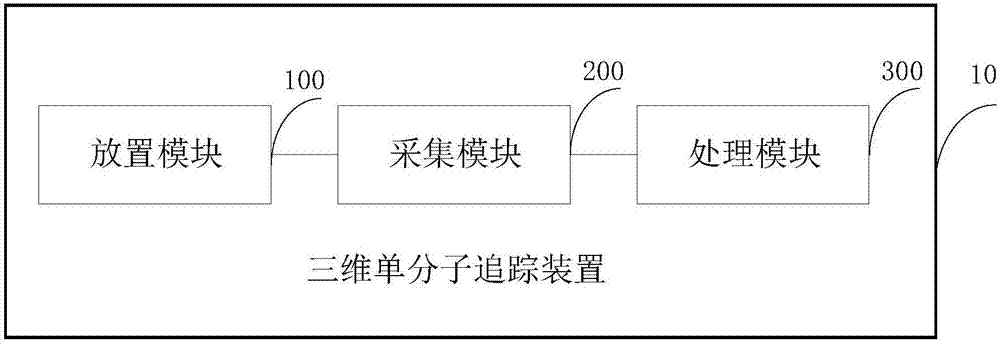
Three-dimensional single molecule tracking method and device
ActiveCN108010062AHigh precisionHigh speedImage enhancementImage analysisHigh numerical apertureFluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a three-dimensional single molecule tracking method and device, wherein the method comprises: taking the image plane of a fluorescence microscope as a relay image plane so as to place a micro lens array at the position of the relay image plane; setting parameters so as to enable cooperation with an objective lens with a high numerical aperture in order to acquire the three-dimensional light field information of a sample on a camera surface; processing the acquired image by using a compressed sensing algorithm, using a pre-calculated light field feature image as the sparse basis and using the L-1 norm minimization constraint to obtain the optimal expression under the sparse basis, and obtaining the three-dimensional location information of the sample. The method canachieve high-speed and high-precision three-dimensional single-molecule positioning, significantly improves the imaging accuracy, greatly improves the performance, and is low in transformation cost, simple in structure, and easy to implement.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
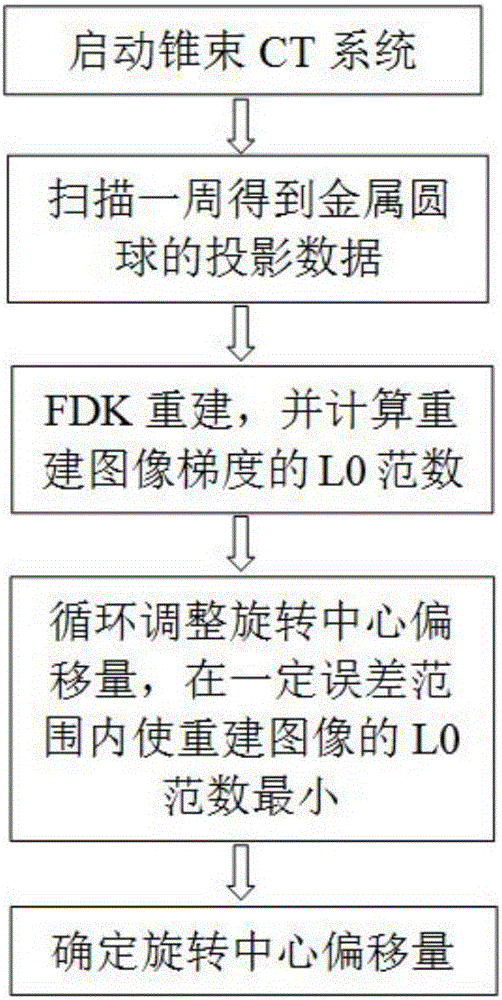
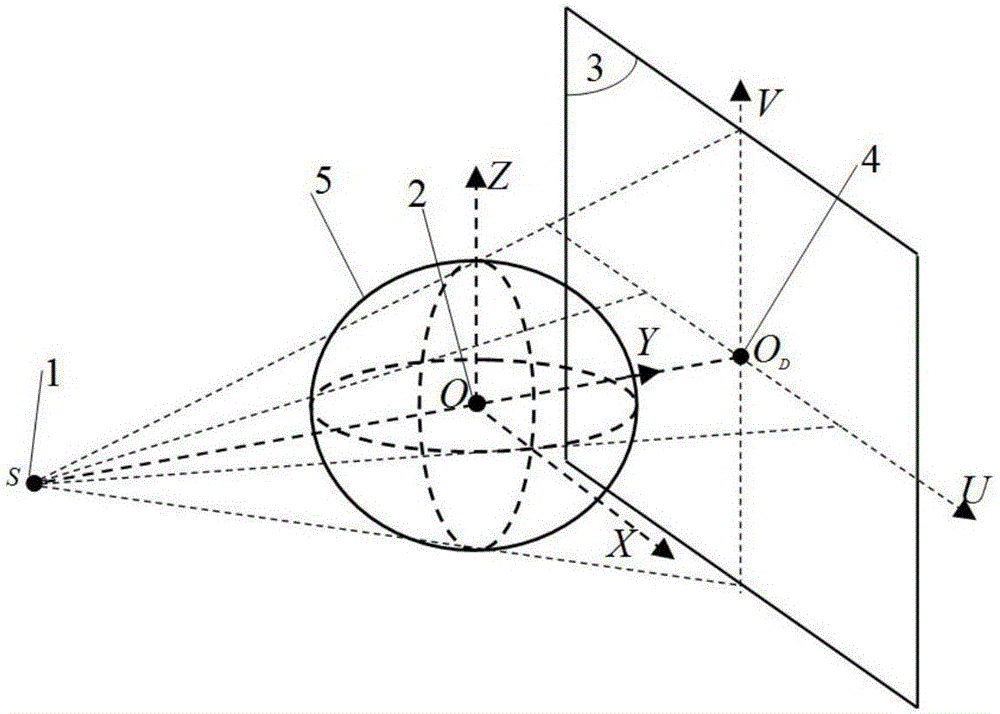
Cone-beam CT rotation center calibration method based on the L0 norm minimization of reconstructed image gradient
ActiveCN106651977AEasy to makeImprove image qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationImaging qualityReconstruction algorithm
The invention relates to a cone-beam CT rotation center calibration method based on the L0 norm minimization of reconstructed image gradient. The method comprises the following steps: S1) placing even metal round balls on a rotation station; arranging the ray source and the detector on the circular track around the rotation center; initiating the cone-beam CT system; and scanning to obtain the projection data of the metal round balls; S2) according to the projection data of the metal round balls and the initial rotation center position of the cone-beam CT, using the FDK reconstruction algorithm and reconstruction software to obtain the reconstruction images of the metal round balls; and calculating the L0 norm of the reconstructed image gradient; S3) adjusting the offset parameters of the rotation center in the reconstruction software and reconstructing again to obtain the updated reconstruction images and calculating the L0 norm of the reconstructed image gradient; and S4) circularly adjusting the offset parameters of step 3 until the L0 norm of the reconstructed image gradient becomes the smallest within a certain error scope; and calibrating the offset parameters of the rotation center at this time as the desired calibration ones. The mode that the method uses can be manufactured simply. With only one time of cone-beam CT scanning, the imaging quality of the cone-beam CT system is increased.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com