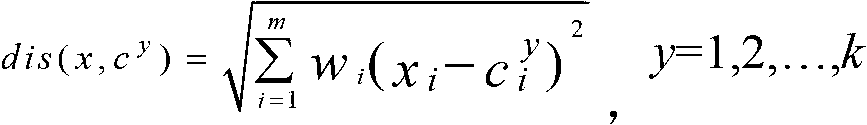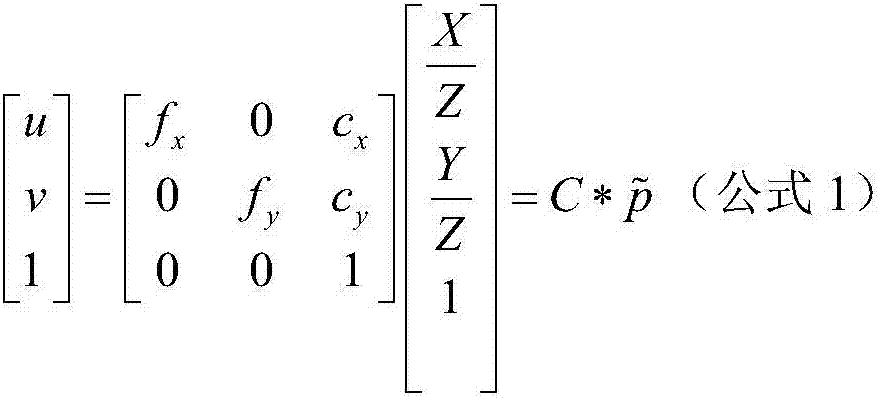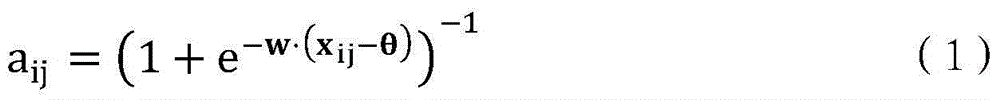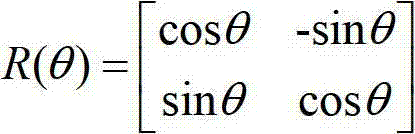Patents
Literature
517 results about "Algorithm convergence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
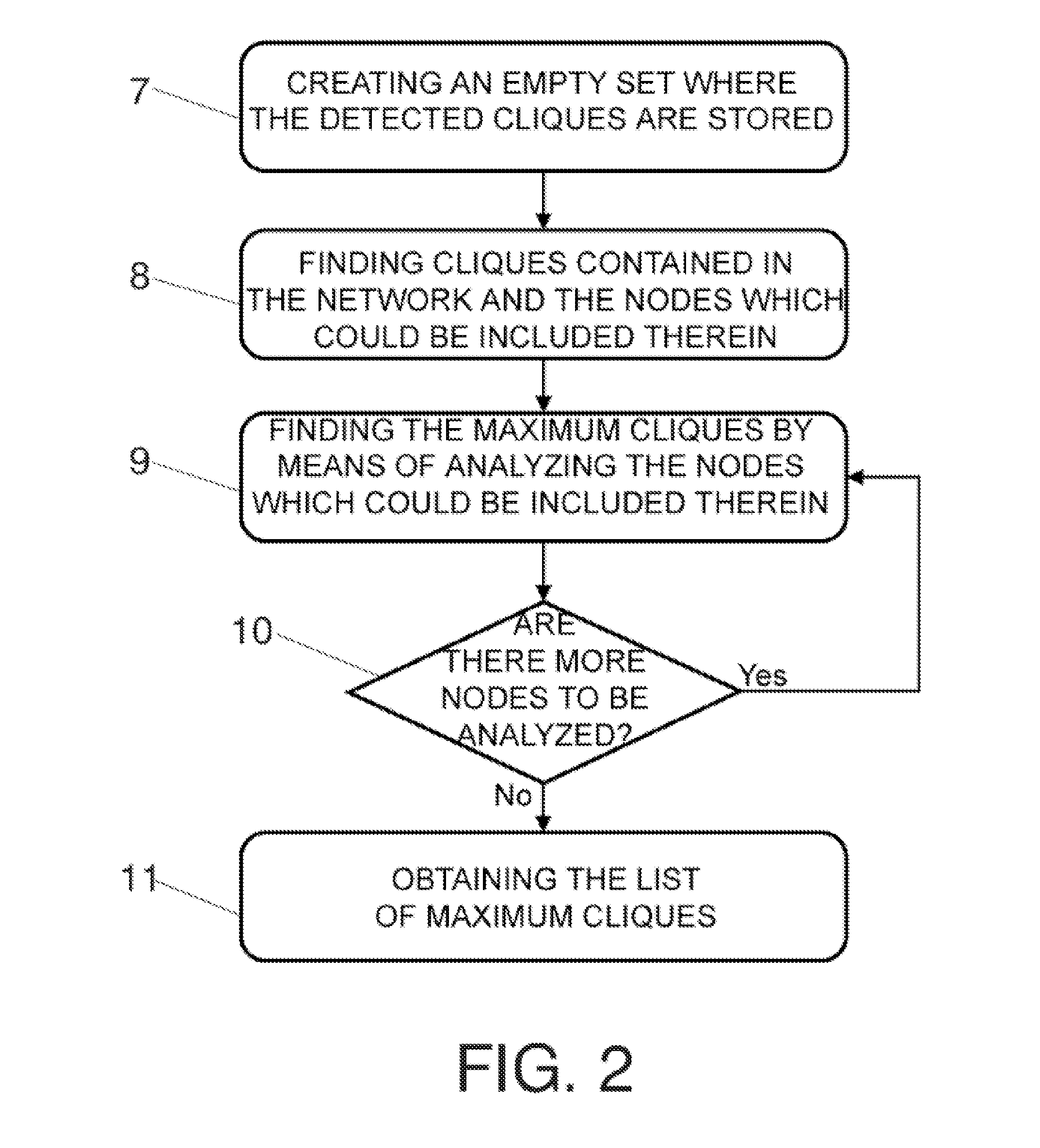
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Algorithms convergence assessment. Monolix includes a convergence assessment tool. It allows to execute a workflow of estimation tasks several times, with different, randomly generated, initial values of fixed effects, as well as different seeds.
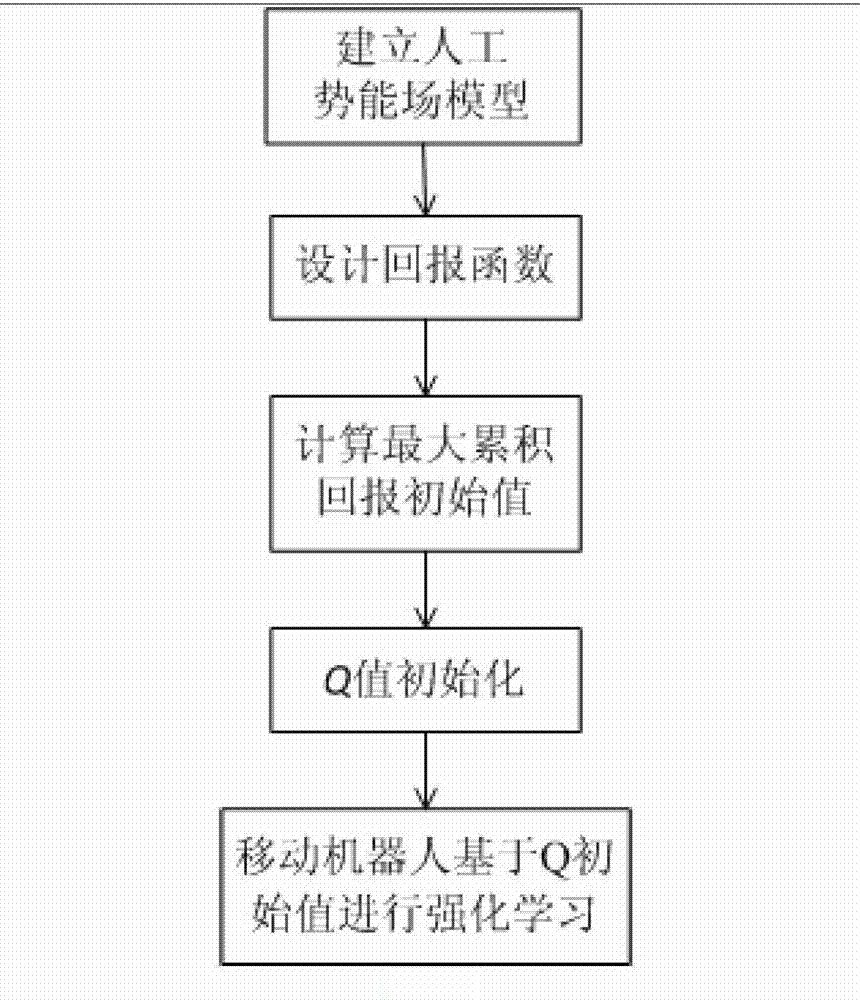
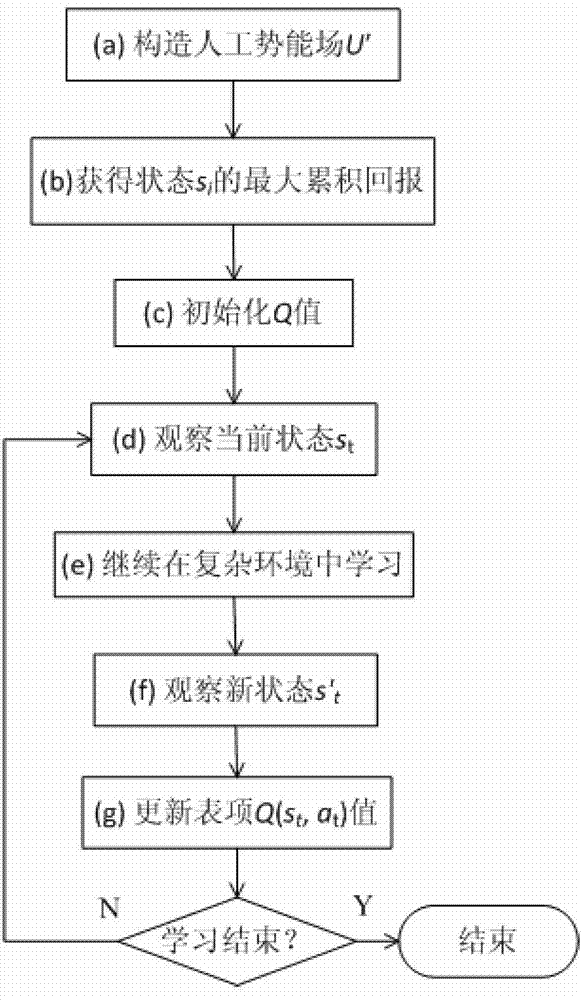
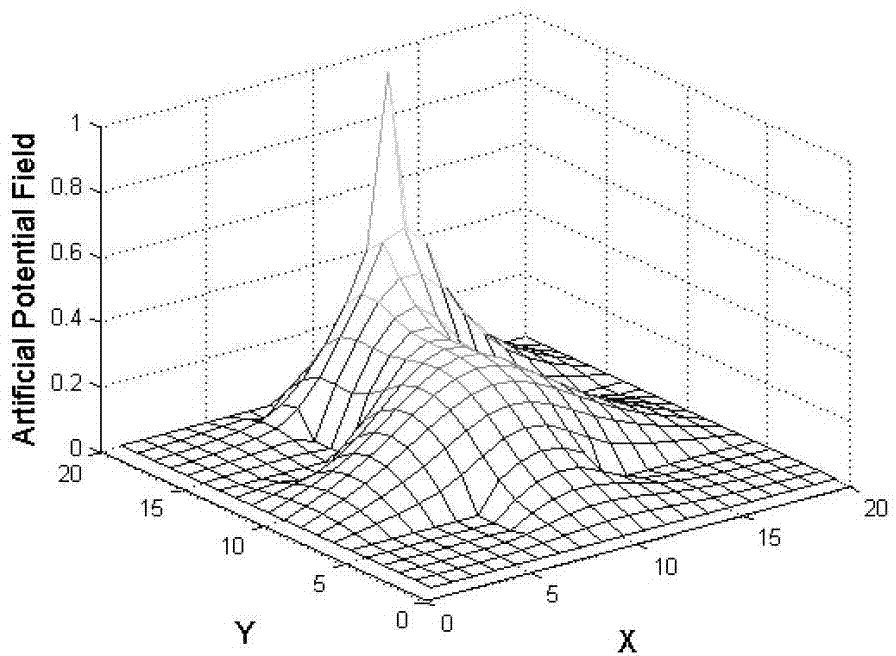
Path planning Q-learning initial method of mobile robot
InactiveCN102819264AImprove learning effectFast convergencePosition/course control in two dimensionsPotential fieldWorking environment
The invention discloses a reinforcing learning initial method of a mobile robot based on an artificial potential field and relates to a path planning Q-learning initial method of the mobile robot. The working environment of the robot is virtualized to an artificial potential field. The potential values of all the states are confirmed by utilizing priori knowledge, so that the potential value of an obstacle area is zero, and a target point has the biggest potential value of the whole field; and at the moment, the potential value of each state of the artificial potential field stands for the biggest cumulative return obtained by following the best strategy of the corresponding state. Then a Q initial value is defined to the sum of the instant return of the current state and the maximum equivalent cumulative return of the following state. Known environmental information is mapped to a Q function initial value by the artificial potential field so as to integrate the priori knowledge into a learning system of the robot, so that the learning ability of the robot is improved in the reinforcing learning initial stage. Compared with the traditional Q-learning algorithm, the reinforcing learning initial method can efficiently improve the learning efficiency in the initial stage and speed up the algorithm convergence speed, and the algorithm convergence process is more stable.
Owner:山东大学(威海)
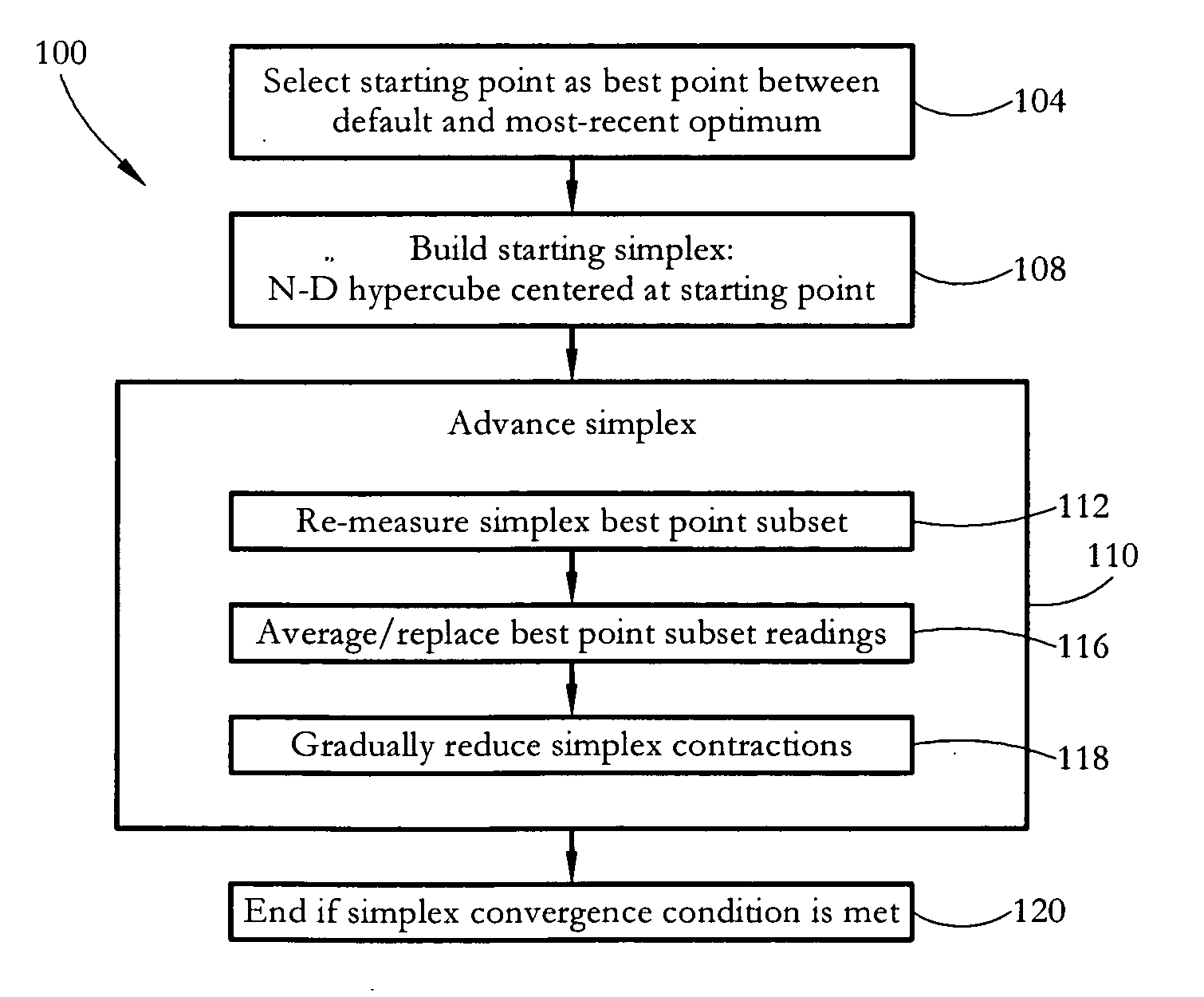
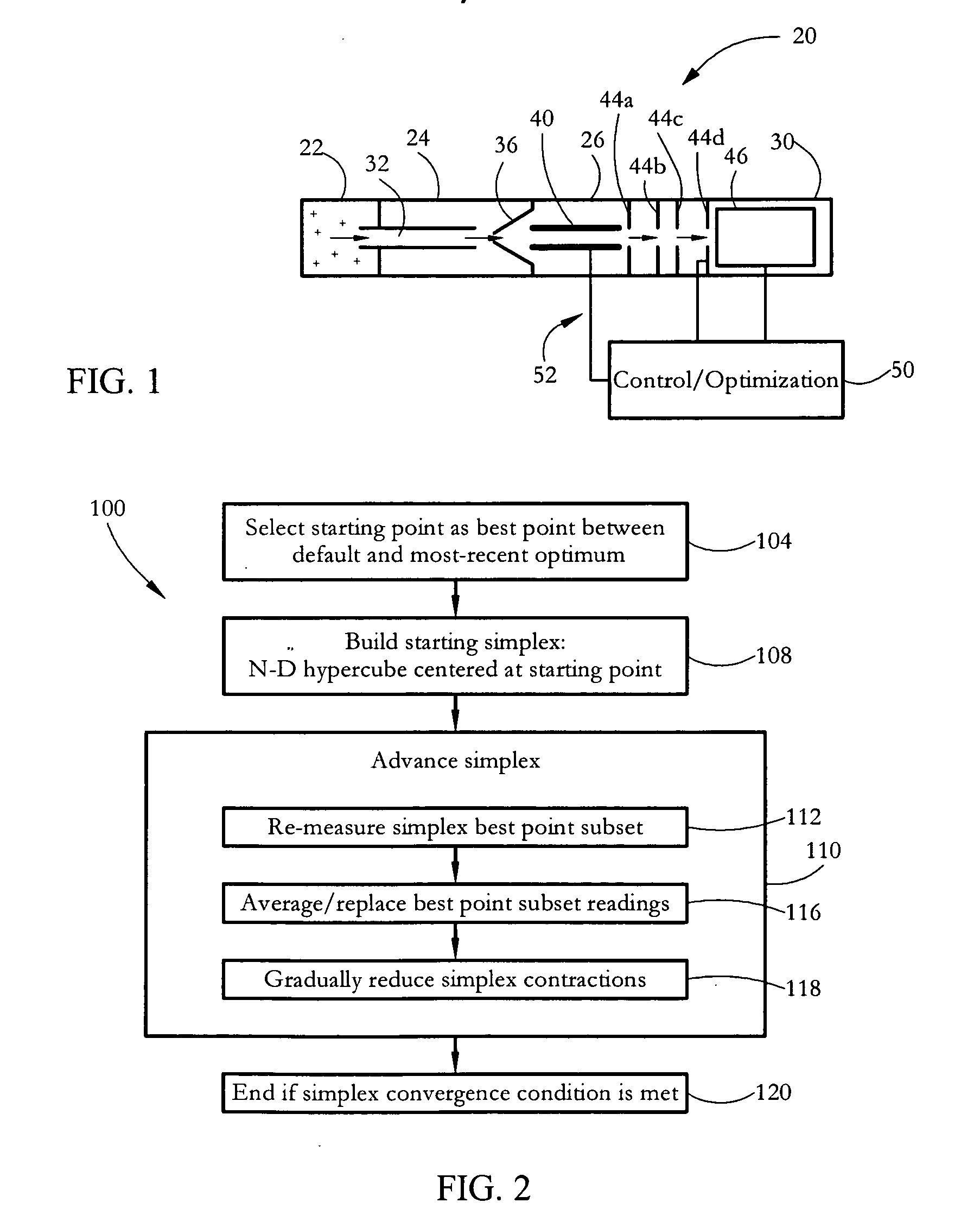
Simplex optimization methods for instrumentation tuning
InactiveUS20070084995A1Electron/ion optical arrangementsIsotope separationEngineeringAlgorithm convergence
In some embodiments, a method of optimizing operating parameters of an analytical instrument (e.g. lens voltages of a mass spectrometer) includes steps taken to minimize the method duration in the presence of substantial instrument noise and / or drift. Some methods include selecting a best point between a default instrument parameter set (vector) and a most-recent optimum parameter set; building a starting simplex at the selected best point location in parameter-space; and advancing the simplex to find an optimal parameter vector. The best simplex points are periodically re-measured, and the resulting readings are used to replace and / or average previous readings. The algorithm convergence speed may be adjusted by reducing simplex contractions gradually. The method may operate using all-integer parameter values, recognize parameter values that are out of an instrument range, and operate under the control of the instrument itself rather than an associated control computer.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
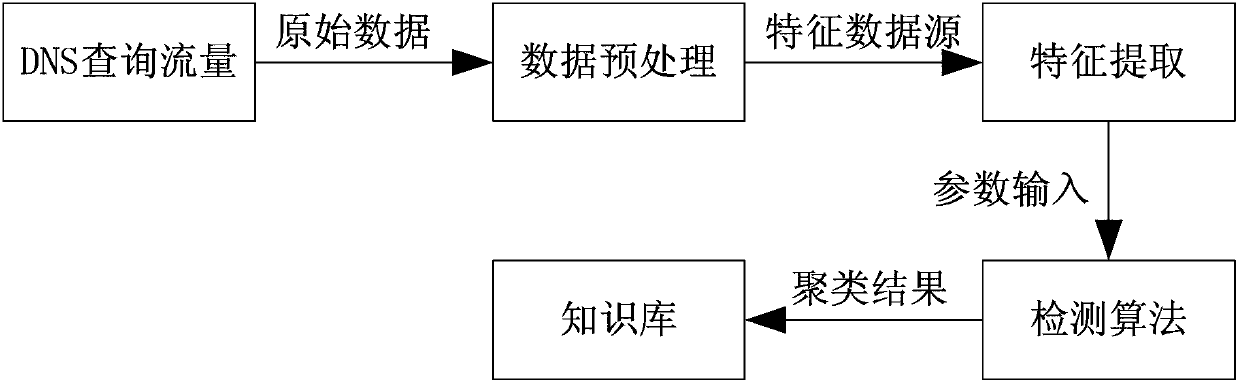
Method and system for detecting DNS (domain name system) traffic abnormality
ActiveCN103001825AAccurate detection rateReduce false alarm rateData switching networksAlgorithm convergenceDomain Name System
The invention provides a method and a system for detecting DNS (domain name system) traffic abnormality. The method includes: extracting corresponding characteristic values for DNS traffic data to be processed, giving different weights to each characteristic, and detecting an abnormality cluster marked in a training set by the aid of the W-Kmeans algorithm and the additional Euclidean distance threshold Dthreshold so that new unknown characteristic abnormality can be discovered. The method and the system have the advantages that the algorithm is high in convergence speed and small in calculation, new samples to be detected only need to be compared with a processed training clustering center, calculation of a great quantity of original training data is not needed, the method and the system are low in deployment cost, strong in generalization ability and capable of discovering DNS traffic abnormality rapidly and effectively, and the system is particularly suitable for being deployed on a large DNS server.
Owner:CHINA INTERNET NETWORK INFORMATION CENTER
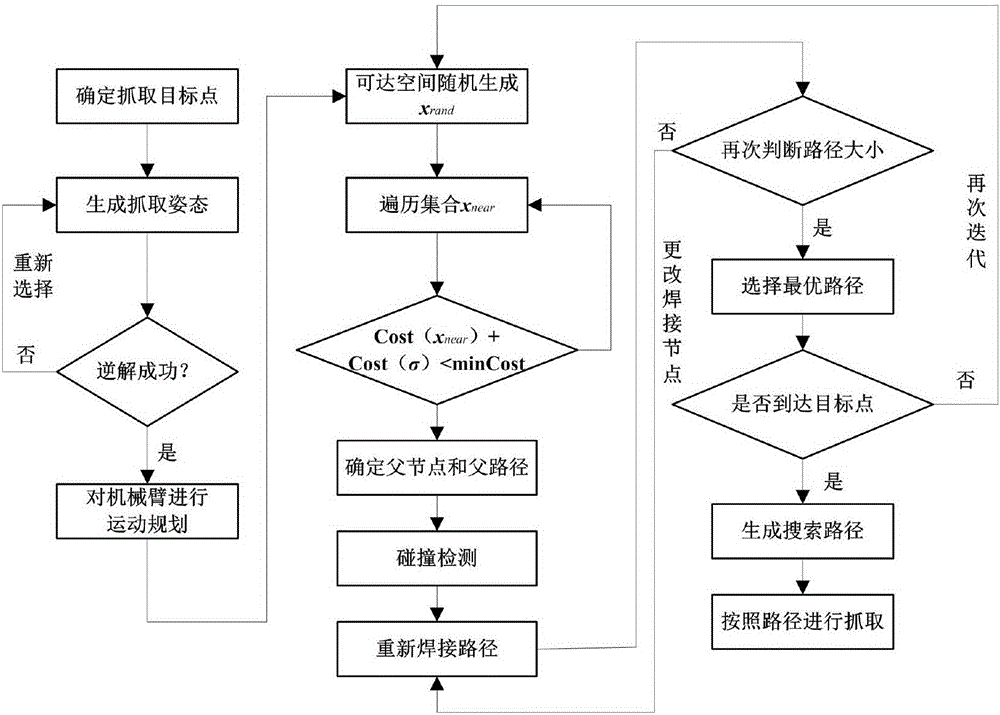
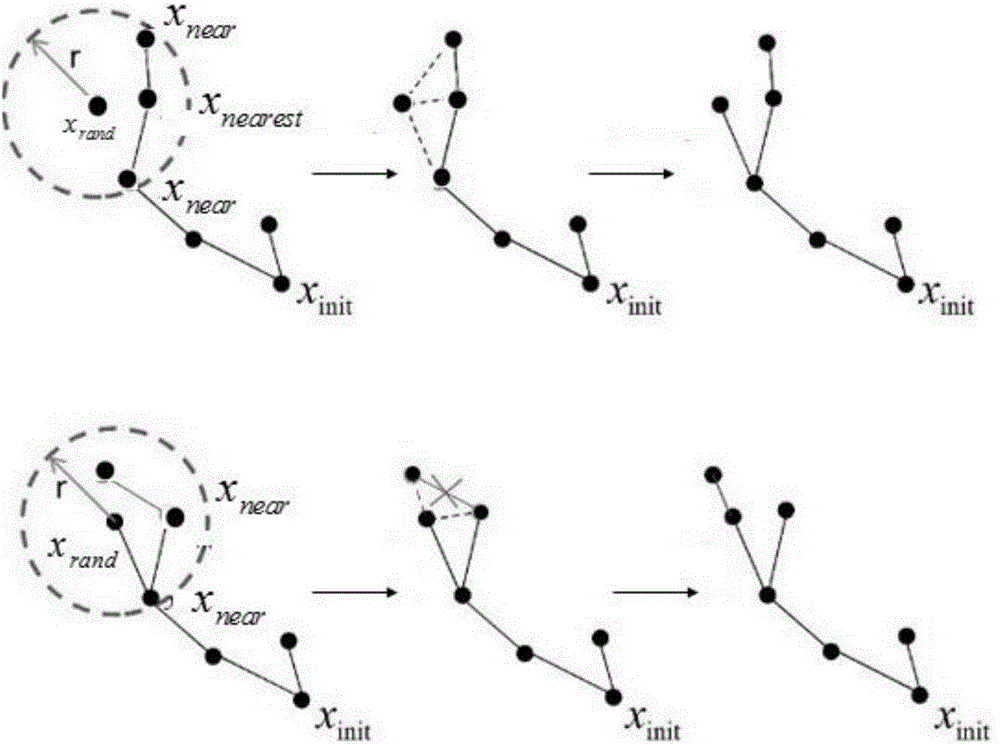
Improved RRT<*> obstacle avoidance motion planning method based on multi-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm
InactiveCN106695802AImprove convergence rateReduce search timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorRegular distributionNODAL
The invention discloses an improved RRT<*> obstacle avoidance motion planning method based on a multi-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm, and belongs to the field of mechanical arm motion planning. A six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm model with seven connecting rods and six rotary joints is built; parameters in a to-be-searched space are determined; if the distance is shorter than the distance of a path with lowest cost, the distances between a near node in a set to an initial point and the distance between the node to a random point are temporarily determined as the minimum path; a newly generated sigma is subjected to collision detection, and the node and the path are added if the newly generated path does not collide an obstacle interval; the steps are repeated until the optimal path is found; and the generated path is added into a path planning device. Compared with the prior art, the method has the following advantages that the random search characteristic is changed in a mode of adding normal distribution, the algorithm convergence rate can be increased through the heuristic search, the RRT<*> algorithm has the evolutionary optimization path, and a large number of calculations is not needed; and after Gaussian distribution of an inspiration point near a target point is added, the convergence rate is increased, and the search time is shortened.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Multi-machine collaborative air combat planning method and system based on deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN112861442ASolve hard-to-converge problemsMake up for the shortcomings of poor exploratoryDesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesEngineeringNetwork model
According to the multi-aircraft cooperative air combat planning method and system based on deep reinforcement learning provided by the invention, a combat aircraft is regarded as an intelligent agent, a reinforcement learning agent model is constructed, and a network model is trained through a centralized training-distributed execution architecture, so that the defect that the exploratory performance of a network model is not strong due to low action distinction degree among different entities during multi-aircraft cooperation is overcome; and by embedding expert experience in the reward value, the problem that a large amount of expert experience support is needed in the prior art is solved. Through an experience sharing mechanism, all agents share one set of network parameters and experience playback library, and the problem that the strategy of a single intelligent agent is not only dependent on the feedback of the own strategy and the environment, but also influenced by the behaviors and cooperation relationships of other agents is solved. By increasing the sampling probability of the samples with large absolute values of the advantage values, the samples with extremely large or extremely small reward values can influence the training of the neural network, and the convergence speed of the algorithm is accelerated. The exploration capability of the intelligent agent is improved by adding the strategy entropy.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method of path planning based on improved ant colony algorithm
ActiveCN107272679AReduce computing timeImprove operational efficiencyPosition/course control in two dimensionsNODALLocal optimum
The invention discloses a method for path planning based on an improved ant colony algorithm. Compared with the classical ant colony algorithm, the method has the following improvements: (1) a constant pheromone evaporation coefficient is adjusted to be an adaptive pheromone evaporation coefficient, and the size of the coefficient is changed adaptively along with increase in number of iterations of an ant colony method; a local optimum path is preferentially selected by adopting a rule that the number of inflection points is small on the basis that different paths are identical in length; (3) a path simplifying rule is adopted for the local optimum path, whether each passing node in the path and the starting node are neighboring nodes or not is judged, and redundant nodes on the path are eliminated; and (4) a pre-sorting rule is adopted when pheromone updating is performed on the path passing by an ant colony before, and only the top 1 / 3 of paths in path length sorting are updated. According to the above improvements, the method can effectively reduce the algorithm convergence time of the ant colony algorithm and improve the operating efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
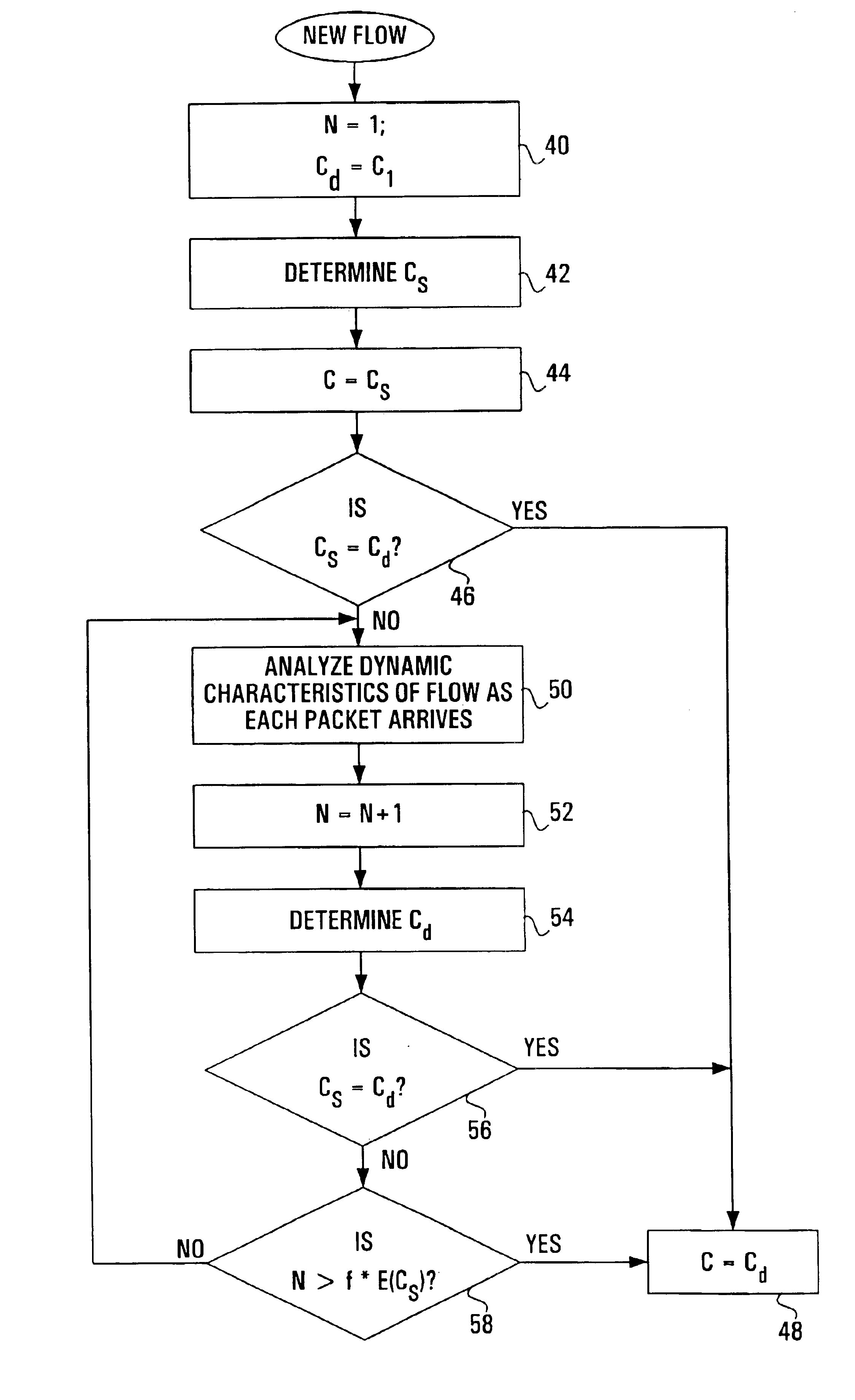
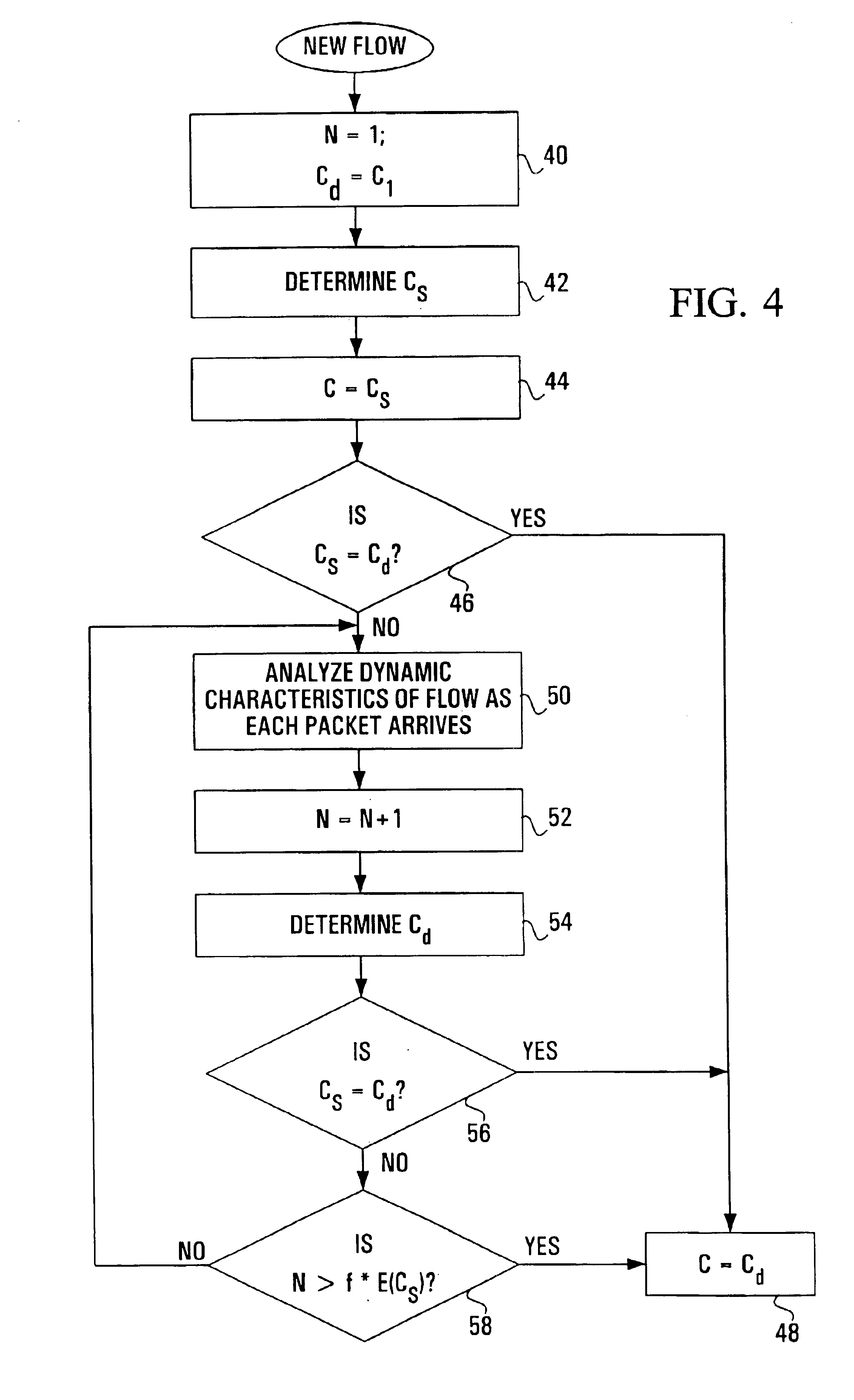
Three-dimensional measurement point cloud optimization registration method
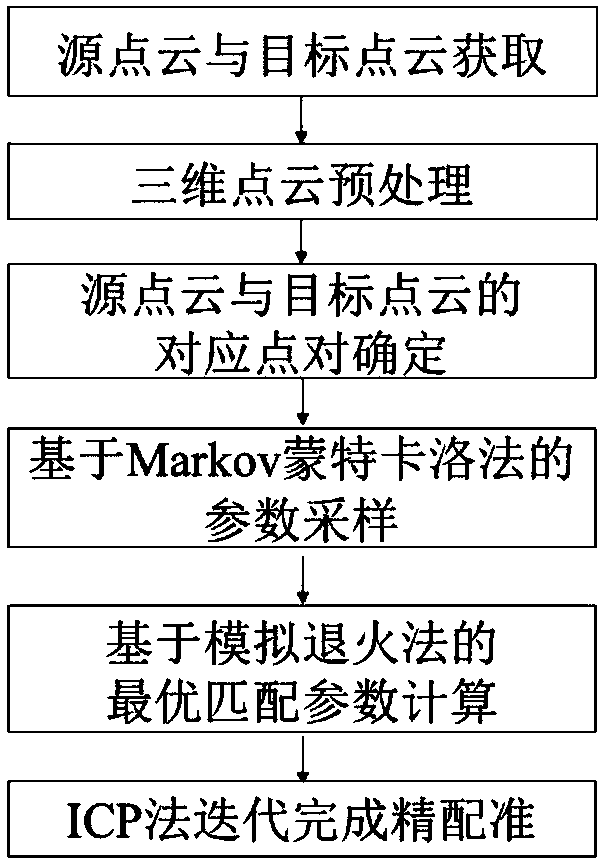
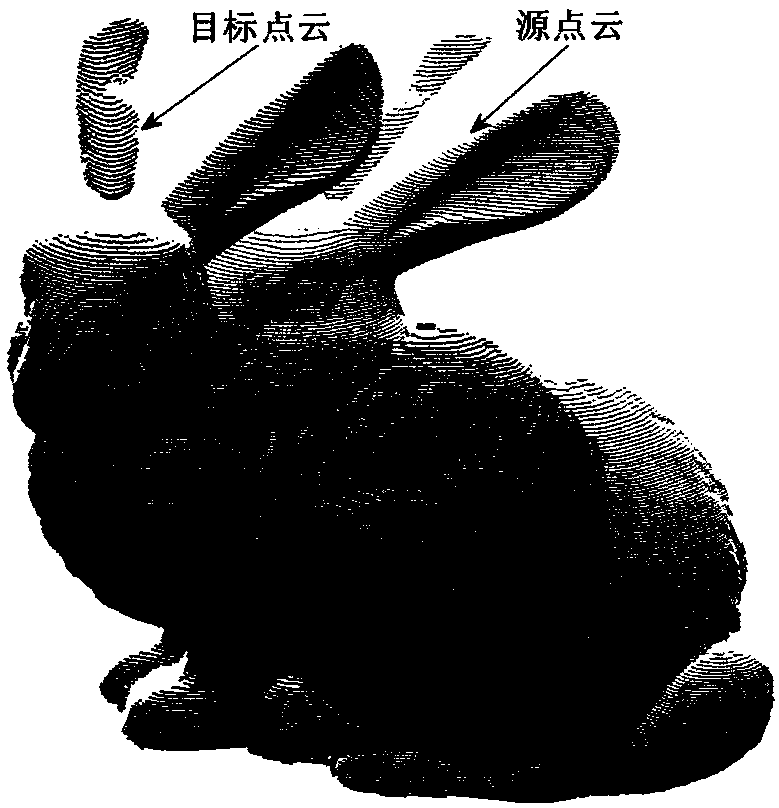
ActiveCN108564605AImprove registration accuracyHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisLocal optimumPoint cloud
The present invention belongs to the technical field of digital manufacturing, and particularly relates to a three-dimensional measurement point cloud optimization registration method. The method comprises: obtaining the source point cloud and the target point cloud; performing denoising preprocessing on the three-dimensional measurement point cloud; using the Markov Monte Carlo-based simulated annealing registration algorithm to solve the global optimal registration transformation matrix; and finally, using the ICP registration method to iteratively complete precise registration. According tothe method provided by the present invention, the problem of convergence to the local optimal solution in the ICP registration method is solved, the global optimization solution of the transformationmatrix in the process of three-dimensional point cloud registration is realized, falling into the local optimum is avoided, the precision of three-dimensional point cloud registration is improved, and the method is superior to the traditional ICP registration; and parameter sampling is realized based on the Markov Monte Carlo method, the convergence speed of the algorithm is accelerated, the accuracy of point cloud registration is improved, the method has strong adaptability to the point cloud, and the algorithm has good robustness.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
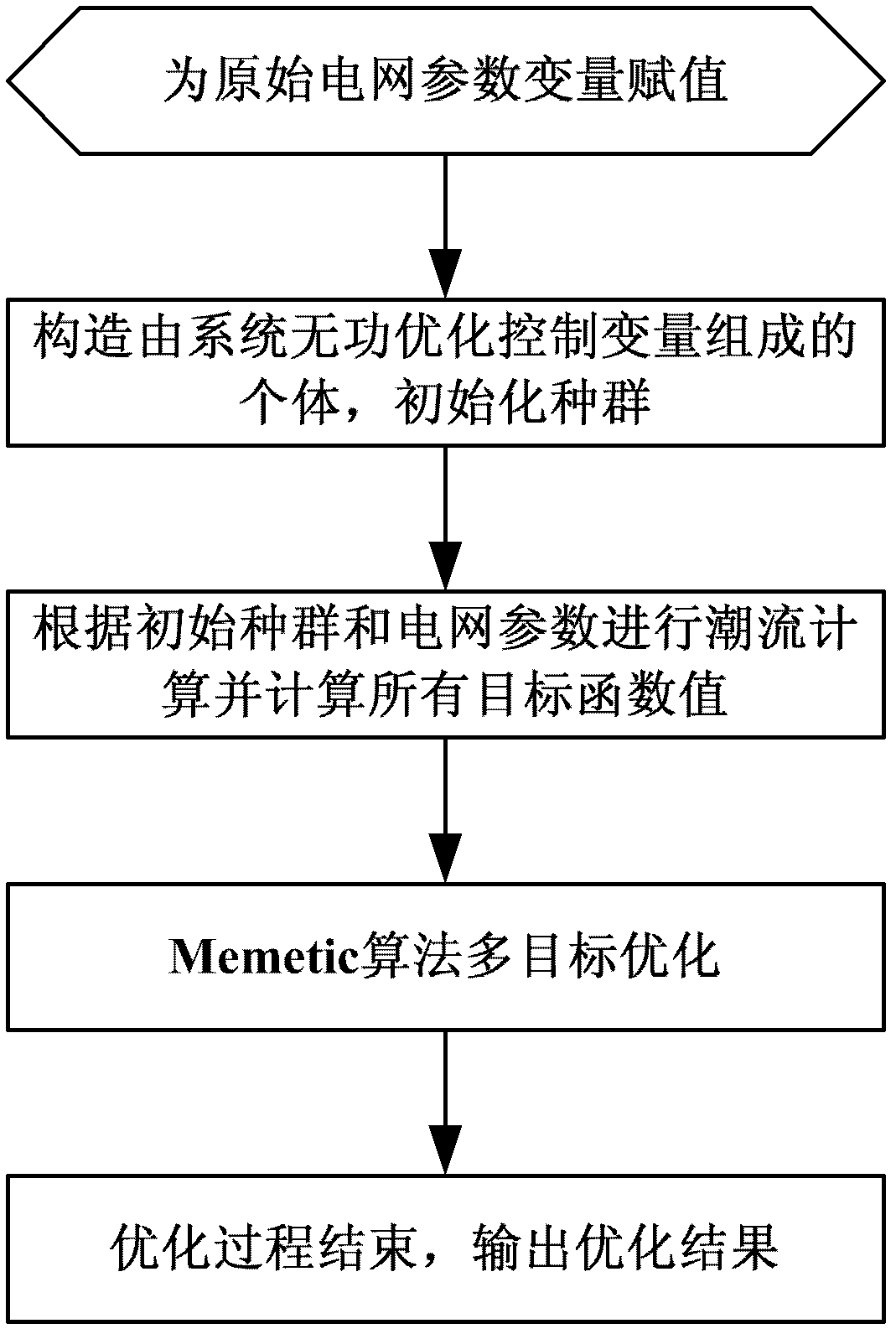
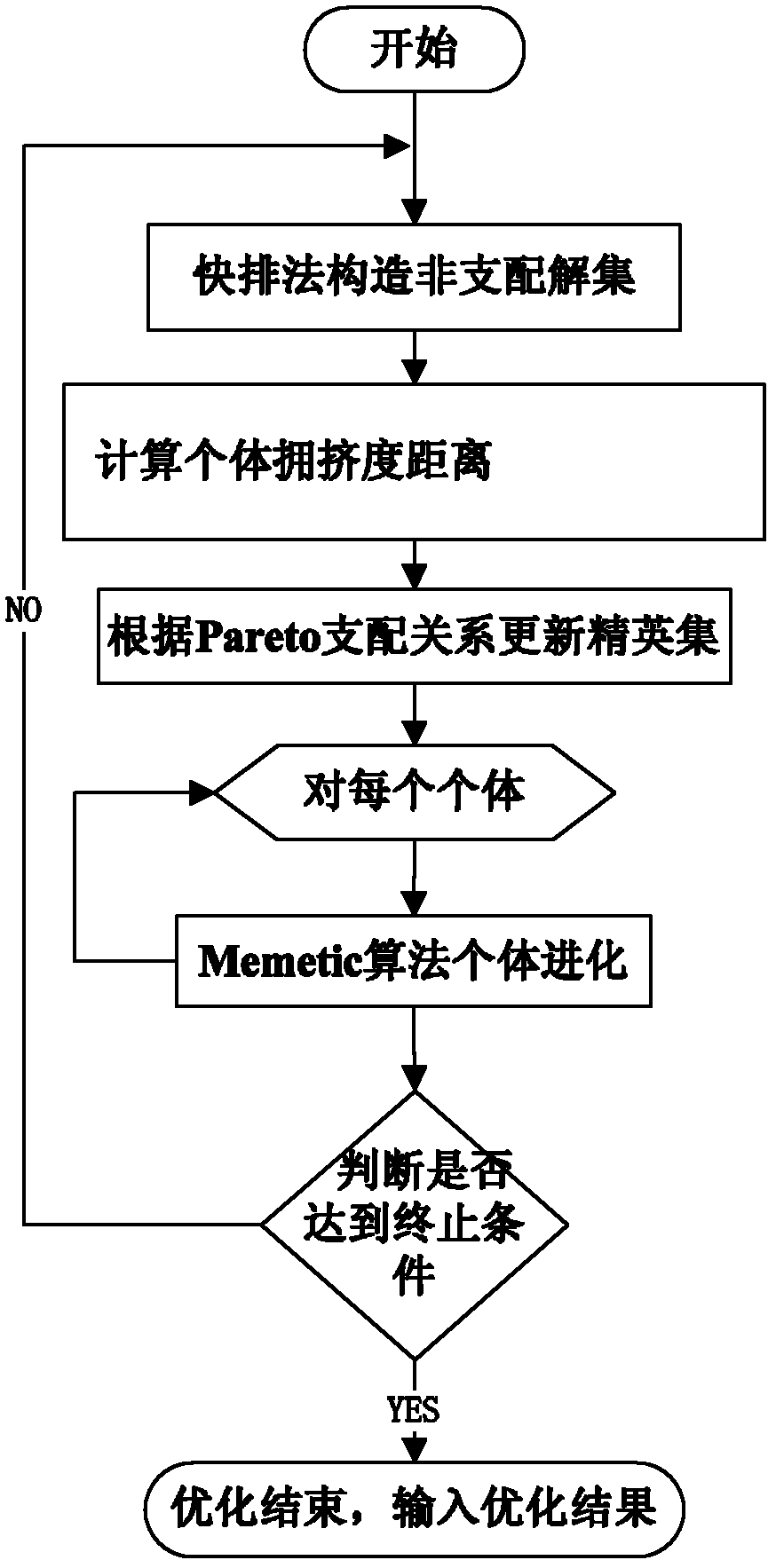
Multi-target reactive power optimization method for electric system
InactiveCN102611119AImprove robustnessEasy searchReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationReactive power compensationMemetic algorithmElectric power system
The invention discloses a multi-target reactive power optimization method for an electric system, which belongs to the field of reactive power optimization for electric systems. The method includes: modifying the Memetic algorithm to adapt to multi-target optimization, applying the modified Memetic algorithm to the problem of multi-target reactive power optimization for the electric system, and working out a Pareto optimal solution of the multi-target problem; and judging whether algorithm convergence conditions are met or not, and if yes, completing optimization and outputting optimization results. The multi-target reactive power optimization method has the advantages that the algorithm for solving the problem of multi-target reactive power optimization is provided, the method is more suitable for solving the multi-target problem while giving play to existing advantages of the Memetic algorithm which integrates local searching and evolutionary computation and has high global search capacity and the like, and searching efficiency is improved while algorithm robustness is improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for X-ray image
The invention provides a bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for an X-ray image. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) a selecting method of a fuzzy de-noising window; and 2) a bivariate fuzzy adaptive nonlocal average filtering algorithm. The method has the beneficial effects that in order to preferably remove the influence caused by the unknown quantum noise existing in an industrial X-ray scan image, the invention provides the bivariate nonlocal fuzzy adaptive non-linear average filtering de-noising method for the X-ray image, in the method, a quantum noise model which is hard to process is converted into a common white gaussian noise model, the size of a window of a filter is selected by virtue of fuzzy computation, and a relevant weight matrix enabling an error function to be minimum is searched. A particle swarm optimization filtering parameter is introduced in the method, so that the weight matrix can be locally rebuilt, the influence of the local relevancy on the sample data can be reduced, the algorithm convergence rate can be improved, and the de-noising speed and precision for the industrial X-ray scan image can be improved, so that the method is suitable for processing the X-ray scan image with an uncertain noise model.
Owner:YUN NAN ELECTRIC TEST & RES INST GRP CO LTD ELECTRIC INST +1
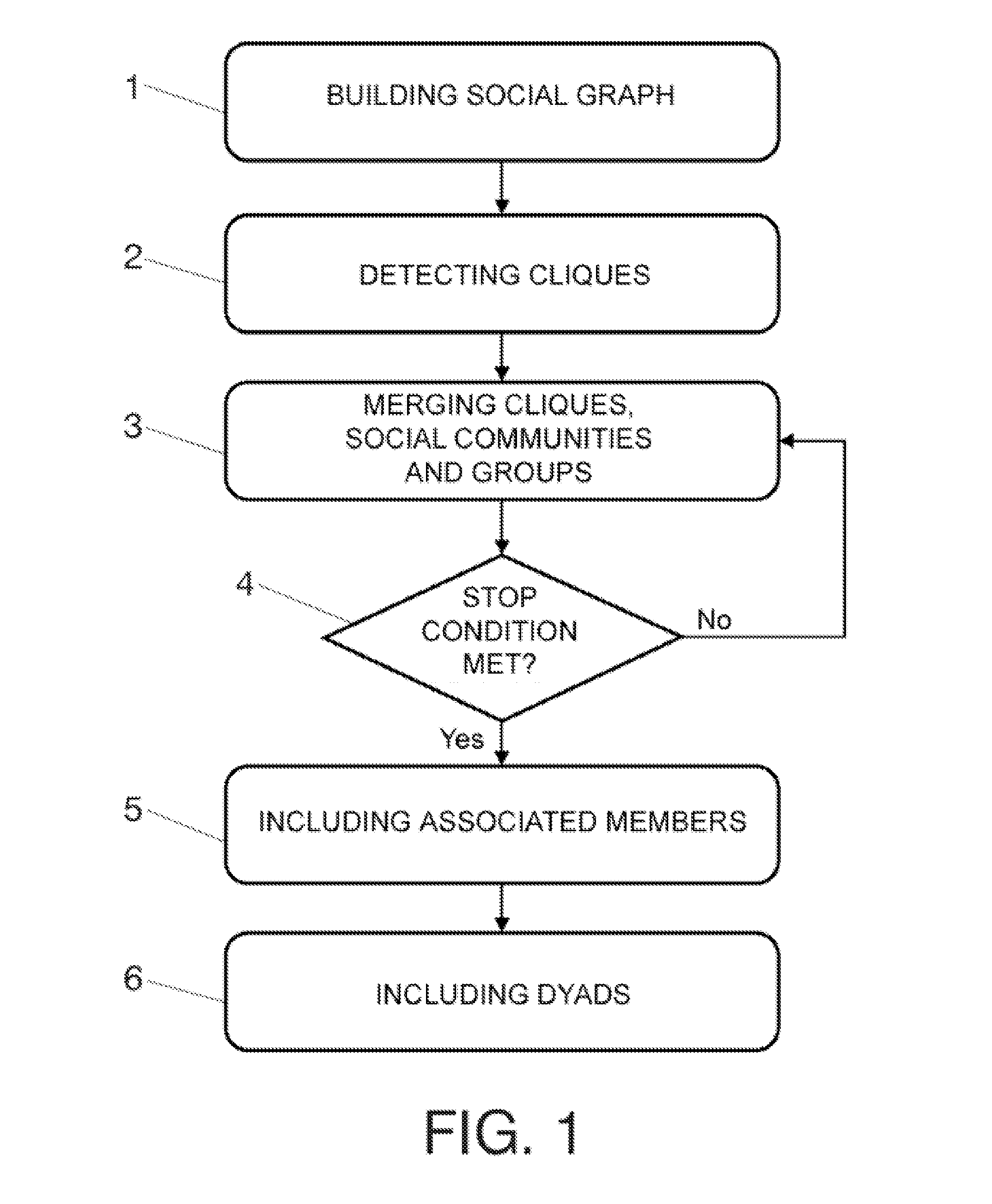
Method for detecting communities in massive social networks by means of an agglomerative approach
InactiveUS20130198191A1Facilitate communicationDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesSocial graphAlgorithm convergence
Disclosed is a method for detecting communities in massive social networks by means of an agglomerative approach in which core communities are built and gradually clustered in an iterative manner into higher level communities until the algorithm converges (a stop condition is met), whereby it becomes possible to easily trace how the communities are being formed, resulting in an easily explainable model that allows the detection of overlapping communities. The disclosed method starts from data representing social interactions between individuals, building a weighted social graph where the vertices represent individuals and the links represent social relationships between individuals.
Owner:TELEFONICA SA
Echo eliminator and echo cancellation method
InactiveCN101043560ASmall amount of calculationFast convergenceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingData stream
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
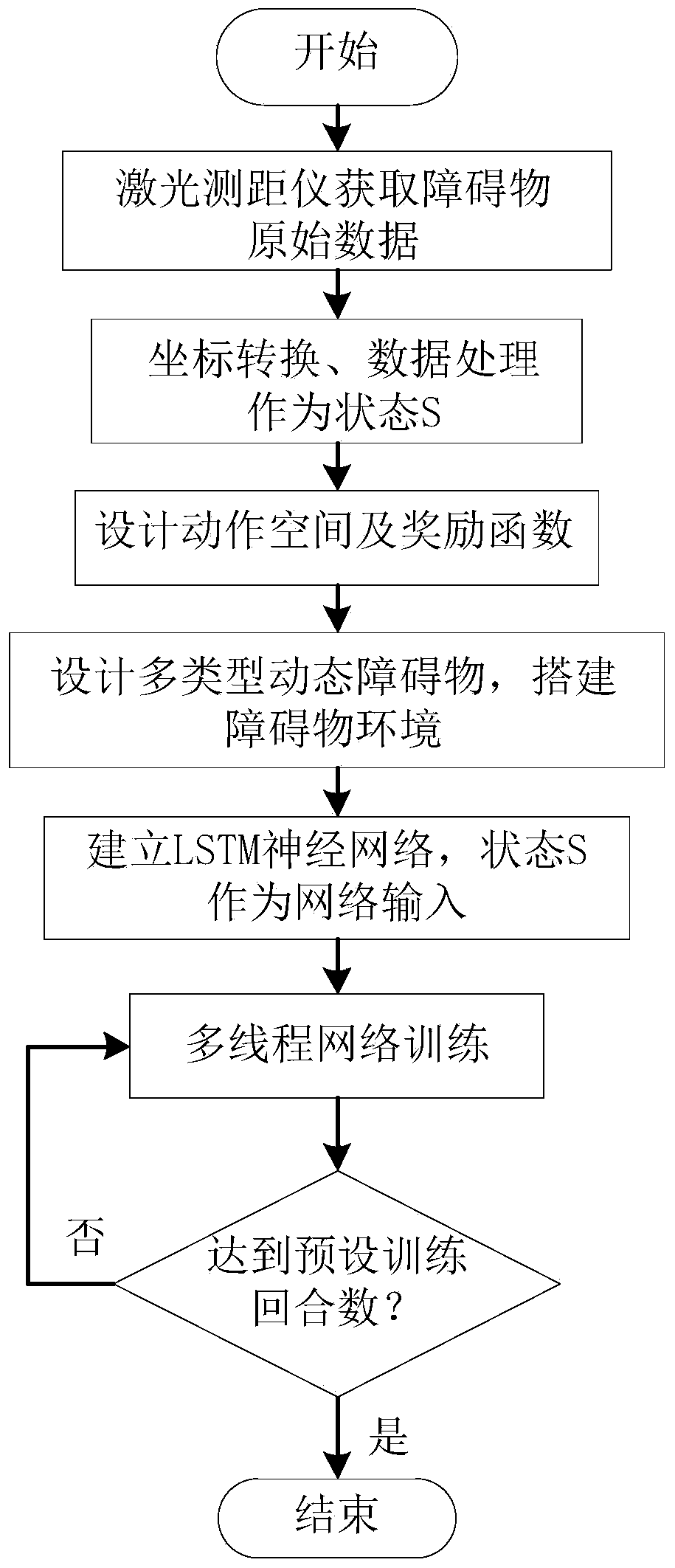
Collision avoidance planning method for mobile robots based on deep reinforcement learning in dynamic environment
ActiveCN110632931AAdaptableImprove smoothnessPosition/course control in two dimensionsAlgorithm convergenceStudy methods
The invention discloses a collision avoidance planning method for mobile robots based on deep reinforcement learning in a dynamic environment, and belongs to the technical field of mobile robot navigation. The method of the invention includes the following steps of: collecting raw data through a laser rangefinder, processing the raw data as input of a neural network, and building an LSTM neural network; through an A3C algorithm, outputting corresponding parameters by the neural network, and processing the corresponding parameters to obtain the action of each step of the robot. The scheme of the invention does not need to model the environment, is more suitable for an unknown obstacle environment, adopts an actor-critic framework and a temporal difference algorithm, is more suitable for a continuous motion space while realizing low variance, and realizes the effect of learning while training. The scheme of the invention designs the continuous motion space with a heading angle limitationand uses 4 threads for parallel learning and training, so that compared with general deep reinforcement learning methods, the learning and training time is greatly improved, the sample correlation isreduced, the high utilization of exploration spaces and the diversity of exploration strategies are guaranteed, and thus the algorithm convergence, stability and the success rate of obstacle avoidance can be improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
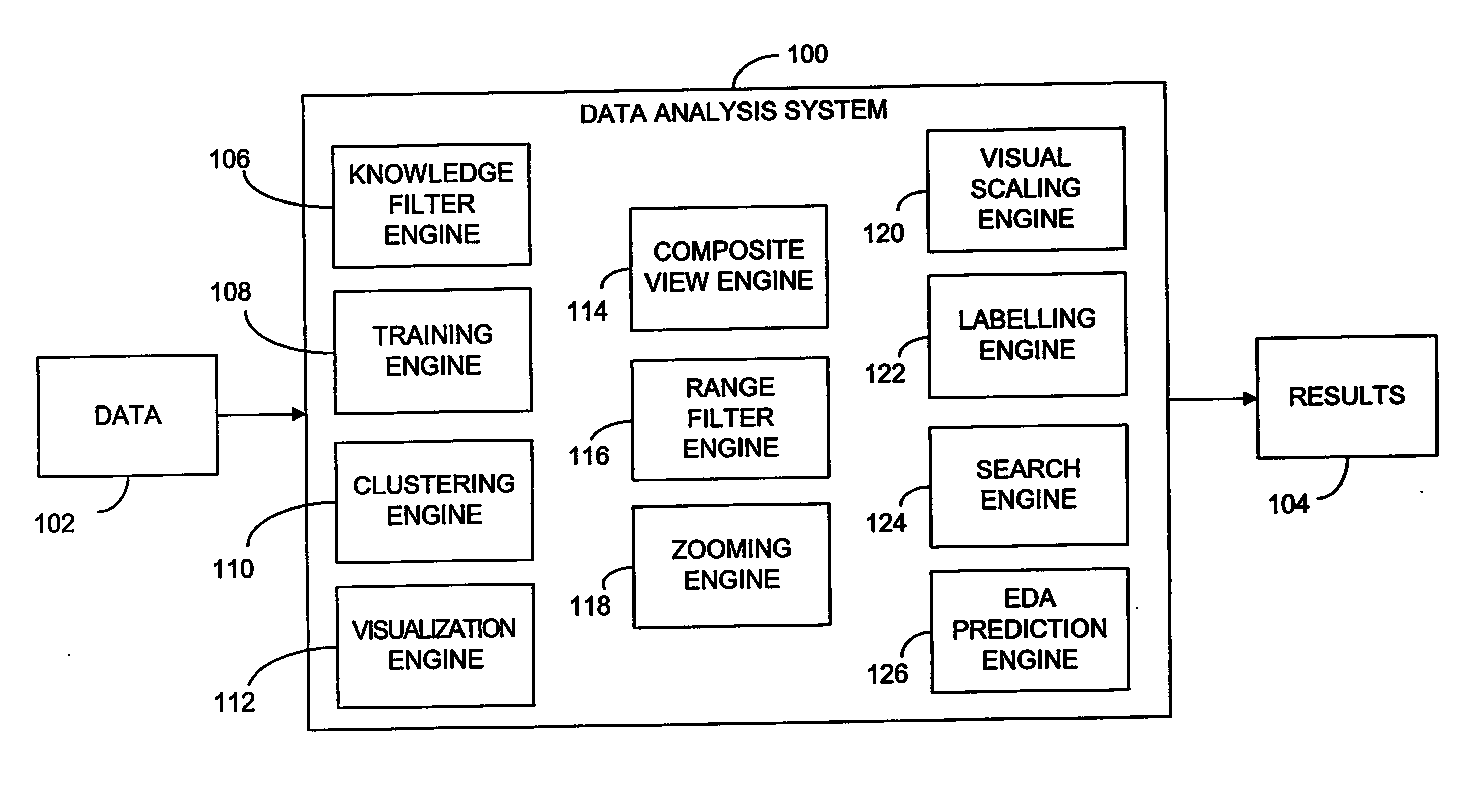
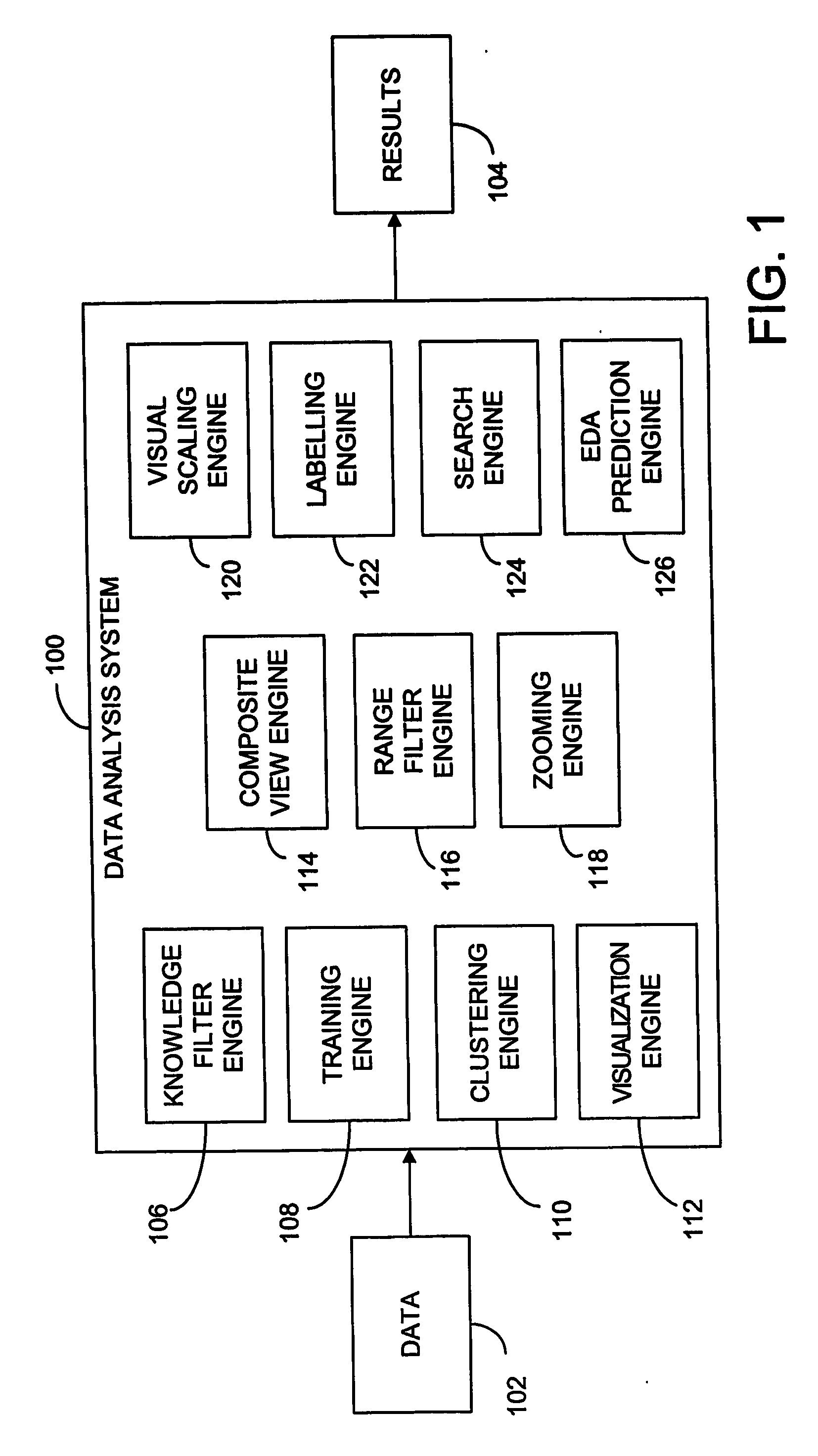
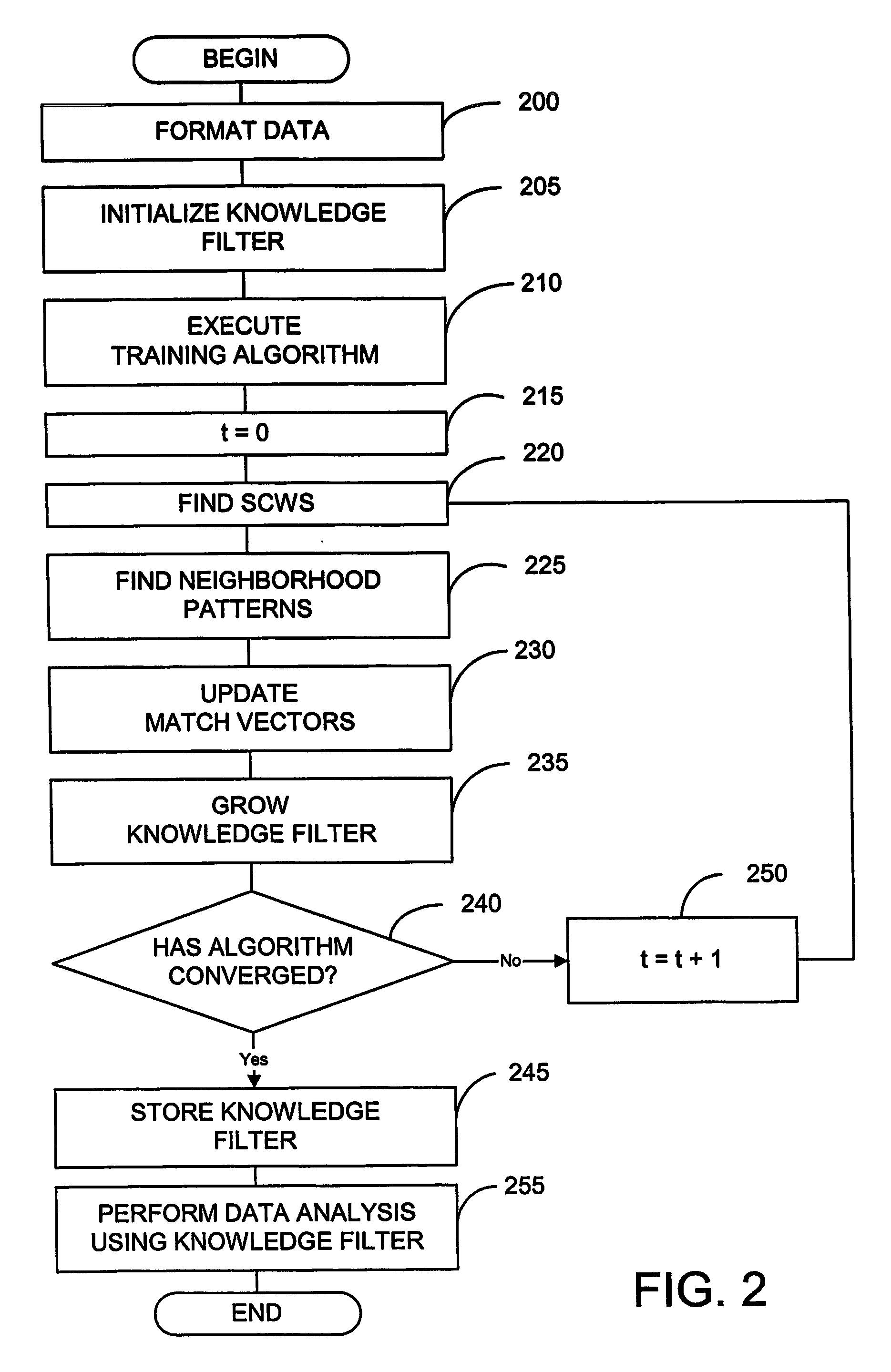
Method and system of data analysis using neural networks
A system and method of computer data analysis using neural networks. In one embodiment of the invention, the system and method includes generating a data representation using a data set, the data set including a plurality of attributes, wherein generating the data representation includes: modifying the data set using a training algorithm, wherein the training algorithm includes growing the data set; and performing convergence testing, wherein convergence testing checks for convergence of the training algorithm, and wherein the modifying of the data set is repeated until convergence of the training algorithm occurs; and displaying one or more subsets of the data set using the data representation. In one embodiment, the data representation is a knowledge filter that includes a representation of an input data set. The representation may be constructed during a training process. In one exemplary embodiment, the training process uses unsupervised neural networks to create the data representation. In general terms, the data representation may include a number of coupled, or connected, hexagons called nodes. Considering relevant attributes, two nodes that are closer together may be more similar than two nodes that are further apart.
Owner:RAPTOR INT
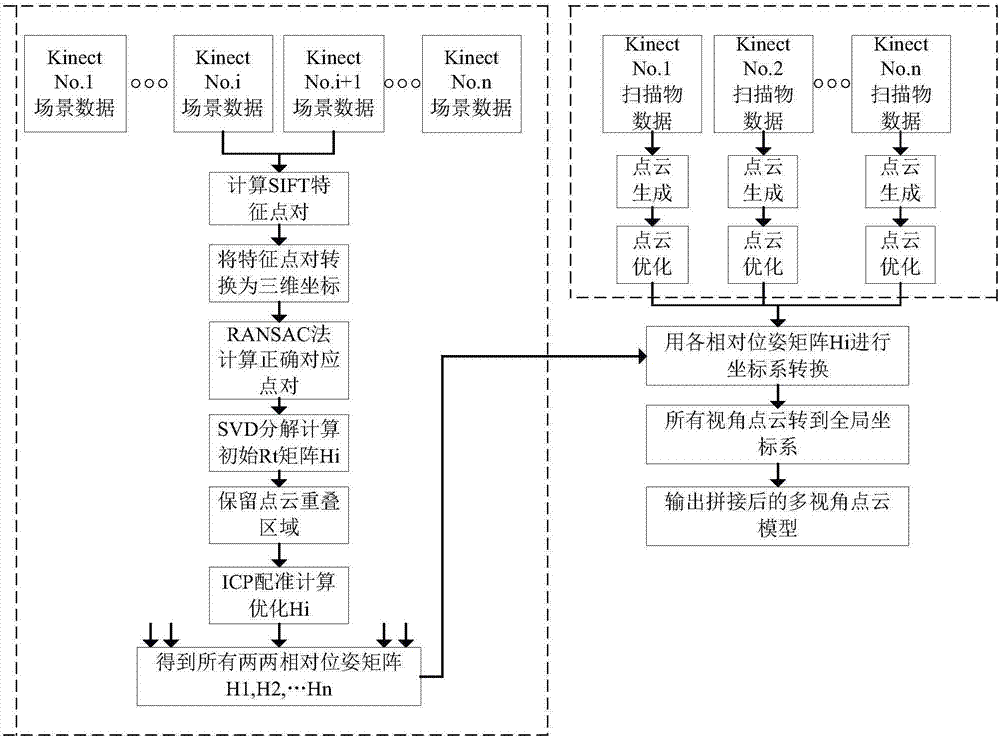
Fast three-dimensional reconstruction method based on Kinect camera
InactiveCN107292921AQuality improvementHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudOptical axis
The present invention belongs to the field of three-dimensional reconstruction technology and relates to a fast three-dimensional reconstruction method based on Kinect camera. Compared with the conventional technique, the method of the present invention uses the method of main optical axis constraints to remove the imaging error points in a single-view point cloud and improves the quality of the point cloud to a certain extent, making the three-dimensional reconstruction higher accuracy. In addition to that, considering that the point cloud has poor accuracy and less coincidence, the existing point cloud registration algorithm based on RGB-D data is improved. Although some computational time overhead is increased, the registration accuracy of the algorithm is greatly improved. This means the great possibility of the algorithm converging to a local minimum.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
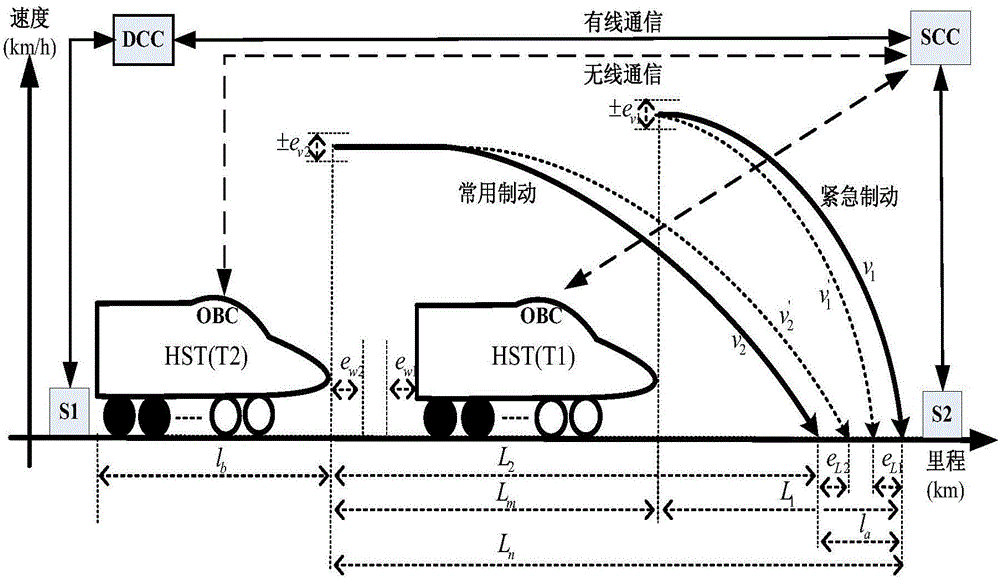
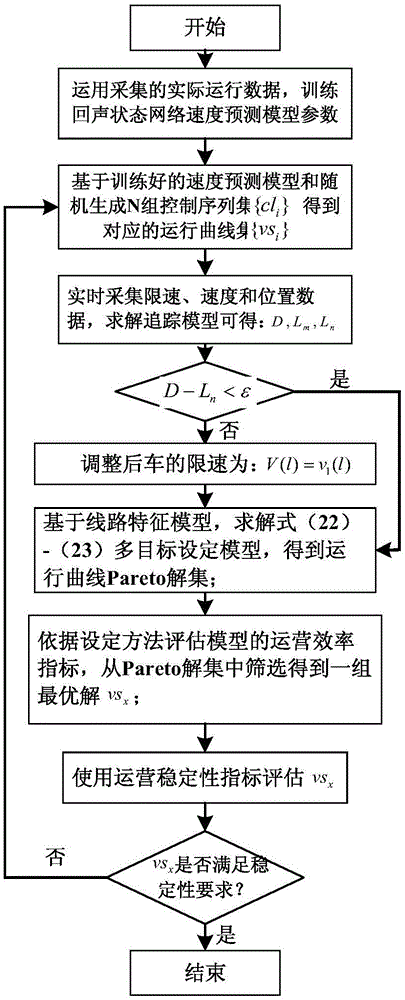
High-speed train tracking running curve optimization setting method
ActiveCN106777752AImprove efficiencySimplified Computational ComplexityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationReal-time dataEcho state network
The invention discloses a high-speed train tracking running curve optimization setting method. According to the characteristic of 'movable and dynamic length' of a tracking section of a high-speed train under movable blocking condition, the method establishes a high-speed train echo state network speed prediction model, a movable blocking based tracking running model, a line network and a tracking running curve multi-target setting model adopting innovative evaluation indexes based on line and high-speed train running data acquired in a site; an efficient multi-target particle swarm optimization is adopted to use an algorithm convergence condition as one of model setting constraints, and high-speed train tracking running curve optimization setting is performed based on the real-time data; finally, section operation efficiency and stability are used as the evaluation indexes of the setting method, and a group of optimal running curves are screened out, so that the high-speed train running process is safe and efficient, and meanwhile the high-speed train section operating efficiency and stability under the movable blocking condition are improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
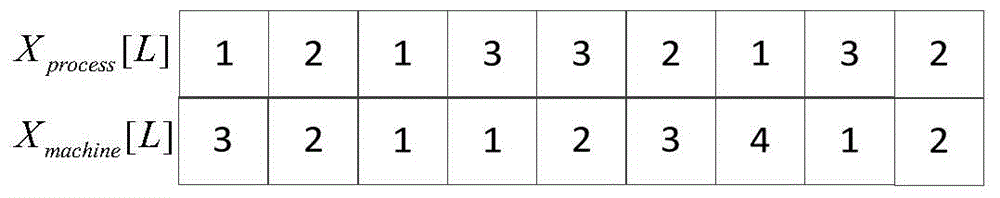
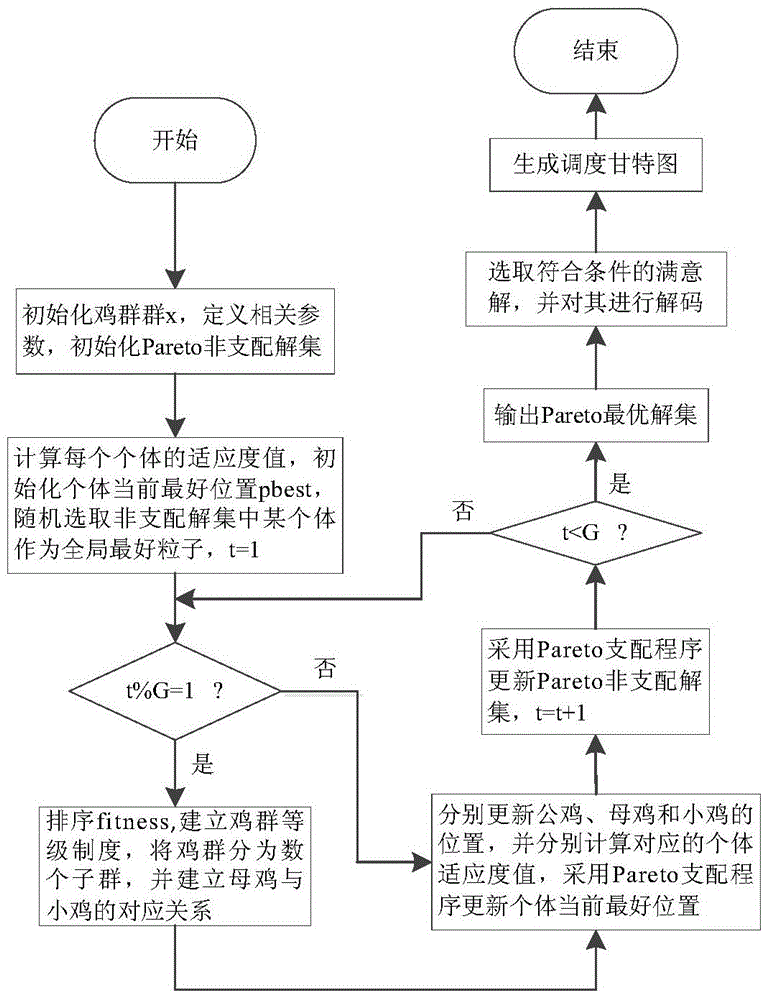
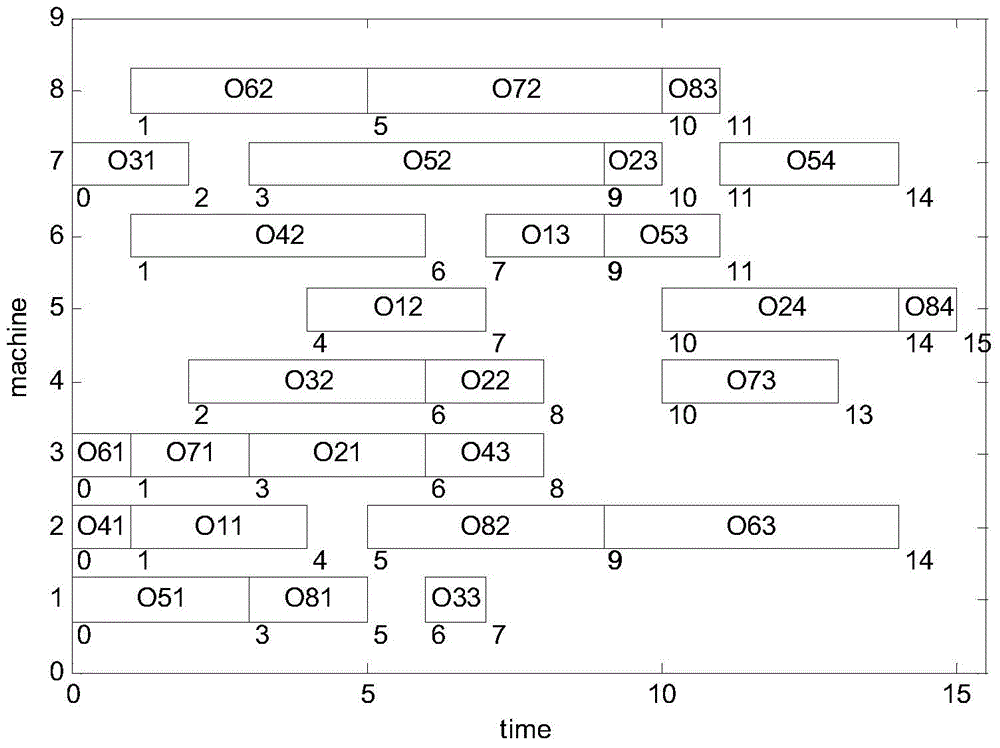
Method of acquiring workpiece-processing optimal scheduling based on improved chicken flock algorithm
ActiveCN104880949AQuality improvementFast convergenceTotal factory controlAdaptive controlAlgorithmOptimal scheduling
A method of acquiring a part-processing optimal scheduling scheme based on an improved chicken flock algorithm comprises the following steps: step 1, determining an evaluation index of an optimization object for a multi-objective flexible workshop scheduling problem; step 2, establishing an optimization object function; step 3, determining a constraint condition of a scheduling optimization process; step 4, designing Pareto improved chicken flock algorithm; step 5, carrying out iterative operation, outputting a Pareto non-dominated solution, selecting an optimal solution according with an enterprise need, carrying out decoding on the optimal solution and taking the solution as a final scheduling scheme. In the invention, under the condition of satisfying a resource constraint, an operation constraint and the like, time of completion, a maximum load of a single machine and a total load of all the machines are taken as an integration optimization object, the improved chicken flock algorithm is used so that an optimal scheduling scheme of part processing can be rapidly acquired. In a chicken position updating formula, a cock learning portion in the group where the chicken belongs is added. A algorithm convergence speed is guaranteed and simultaneously solution quality is greatly increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Water turbine parameter identification method based on self-adaptive chaotic and differential evolution particle swarm optimization
InactiveCN103853881AFast convergenceImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsWater turbineAlgorithm convergence
The invention discloses a water turbine parameter identification method based on self-adaptive chaotic and differential evolution particle swarm optimization. The water turbine parameter identification method is characterized by comprising the following steps of firstly, determining a nonlinear mode of a water turbine; secondly, acquiring frequency step test data; thirdly, determining a fitness function of the self-adaptive chaotic and differential evolution particle swarm optimization; fourthly, setting a basic parameter of an identification algorithm; fifthly, calculating a fitness function value of particles and an individual extreme value of the particles in a swarm as well as a global extreme value of the swarm and updating the speed and the position of the particles; sixthly, carrying out premature judgment, if the premature is judged, carrying out differential mutation, transposition, selection and other operations to avoid local optimization; seventhly, checking whether the algorithm meets end conditions or not, if so, outputting an optimal solution, and otherwise, self-adaptively changing an inertia factor and executing the fifth step to the seventh step again. According to the water turbine parameter identification method disclosed by the invention, a water hammer time constant of the water turbine is identified, and the algorithm is high in convergence speed and convergence precision; in addition, test data of the water turbine at any load level can be utilized, so that the test cost is effectively reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Unmanned aerial vehicle optimal path planning method based on adaptive ant colony algorithm
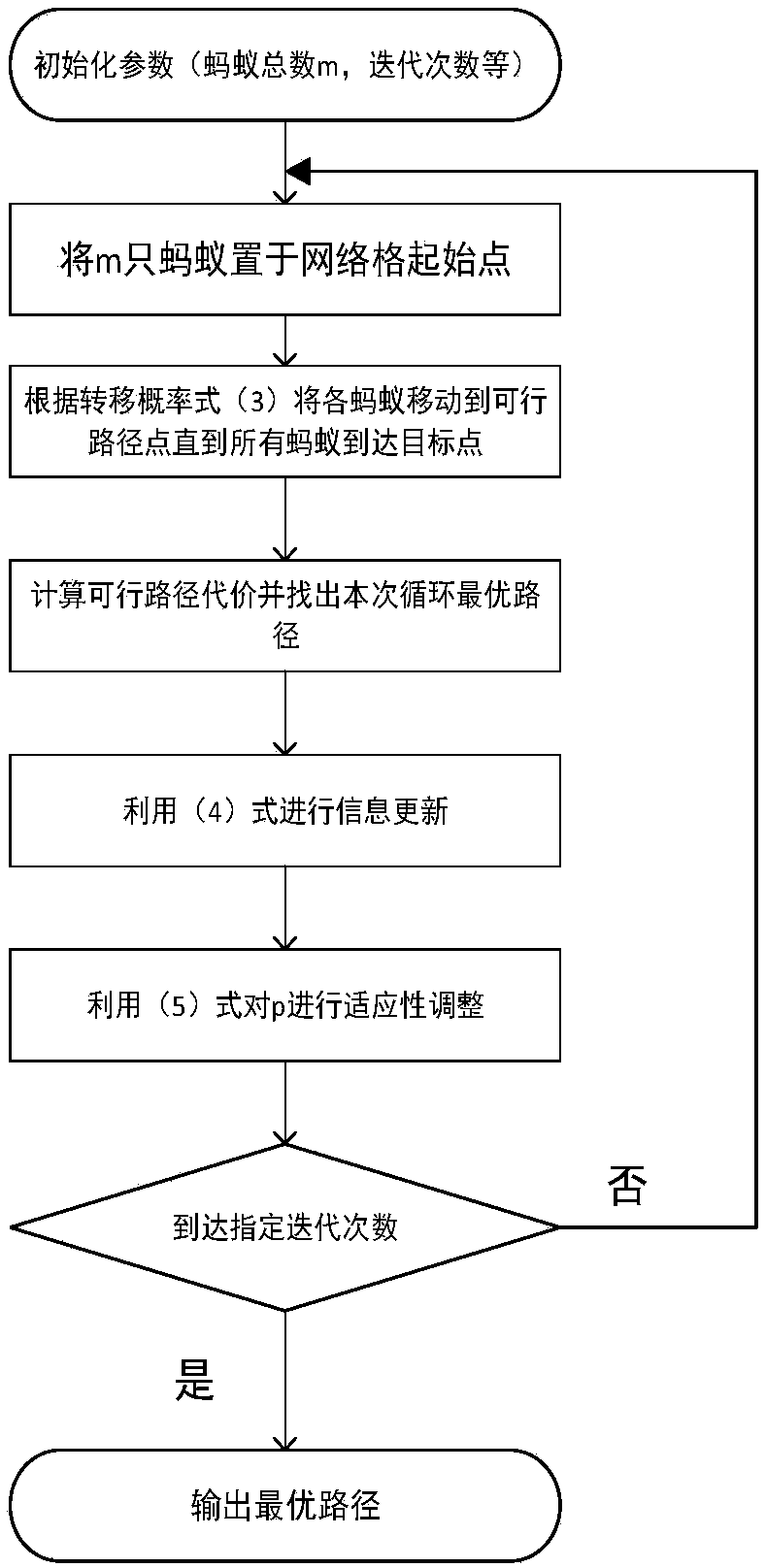
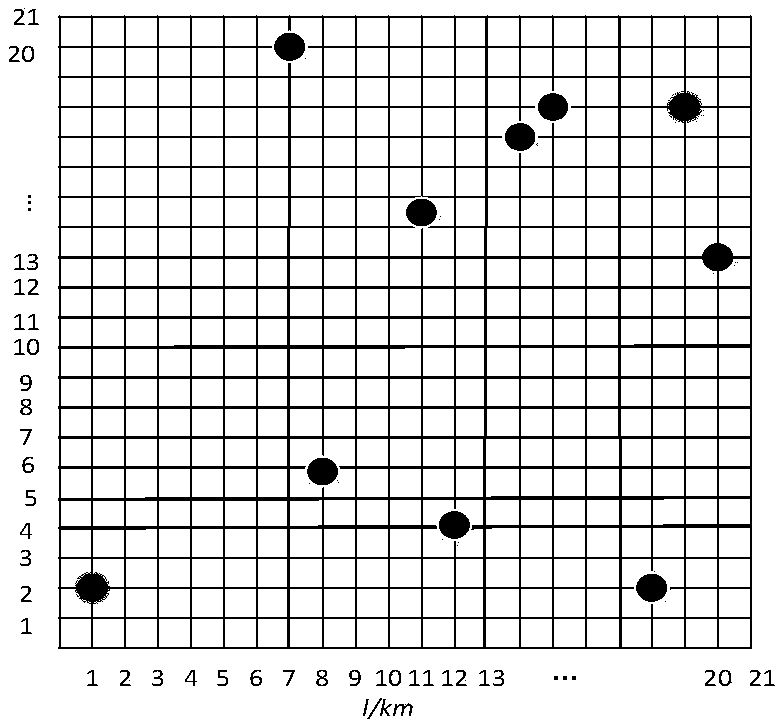
InactiveCN107562072AIncrease success rateShorten convergence timeAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsSimulationPlanning approach
The present invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle optimal path planning method based on an adaptive ant colony algorithm. The method comprises: performing meshing of a flight area, performingparameter initialization, and putting ants at a starting point of grids; moving each ant to a feasible path point until all ants reach target points, and calculating a feasible path cost and findingout a cycle optimal path; performing information updating, and performing adaptive regulation for [Rho]; and finally, outputting the optimal path. The unmanned aerial vehicle optimal path planning method based on an adaptive ant colony algorithm can effectively improve a success rate when an unmanned aerial vehicle executes a defense penetration reconnaissance mission, and an efficient unmanned aerial vehicle flight path must be planned and designed prior to execution of the reconnaissance mission in an enemy defense area, so that it is ensured that the unmanned aerial vehicle can reach a target point with the minimum detected probability and the optimal path. Sizes of pheromone volatilization factors are regulated according to the enemy defense area, and an adaptive ant colony algorithm suitable for path planning is used. The adaptive ant colony algorithm is employed to obtain an optimal path length, and an algorithm convergence time is obviously shortened compared to other methods.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Self-learning wheel chair control method based on change of gravity center of human body
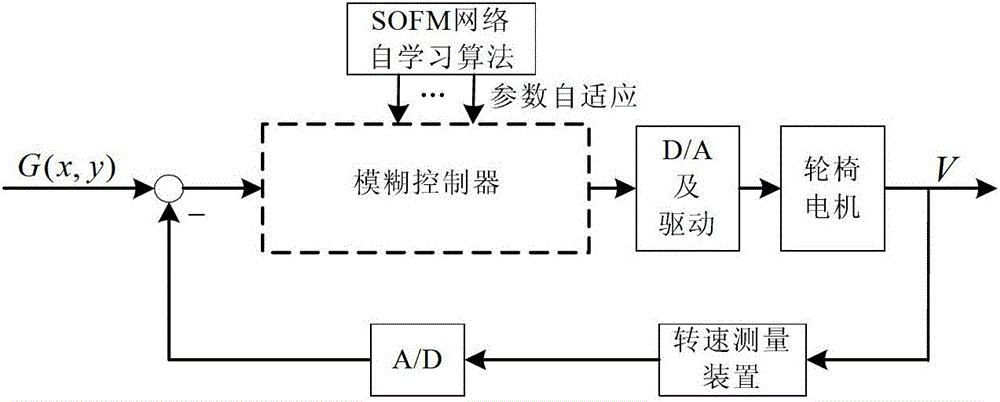
InactiveCN103064283AImprove real-time performanceFast convergenceWheelchairs/patient conveyanceAdaptive controlHuman bodyGravity center
The invention discloses a self-learning wheel chair control method based on change of a gravity center of a human body, and belongs to the field of pattern recognition and intelligent systems. According to the self-learning wheel chair control method, a pressure sensor is installed between a wheel chair seat and a framework so as to collect force distribution under a sitting position of the human body, two-dimensional areal coordinates are calculated, and real-time data of the center of the gravity are stored in an embedded type computer; and algorithm optimization is conducted to the number of neurons in an output layer, network initial weight value, a network neighborhood radius adjusting rule and the like according to a basic learning process of a normal self-organizing feature map (SOFM) algorithm, and therefore operating complexity is reduced, calculating instantaneity of the algorithm in application is improved, and the purpose that algorithms are controlled to be different according to difference of people is achieved. By utilizing the improved SOFM algorithm, and in the process of driving habit learning, rate of convergence of an SOFM clustering algorithm and learning efficiency are greatly improved, instantaneity of the algorithm and accuracy of cluster are improved, the requirement of wheel chair real-time learning and controlling is met, and the problem that manual parameter adjustment is fussy due to difference of driving habits of users is solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
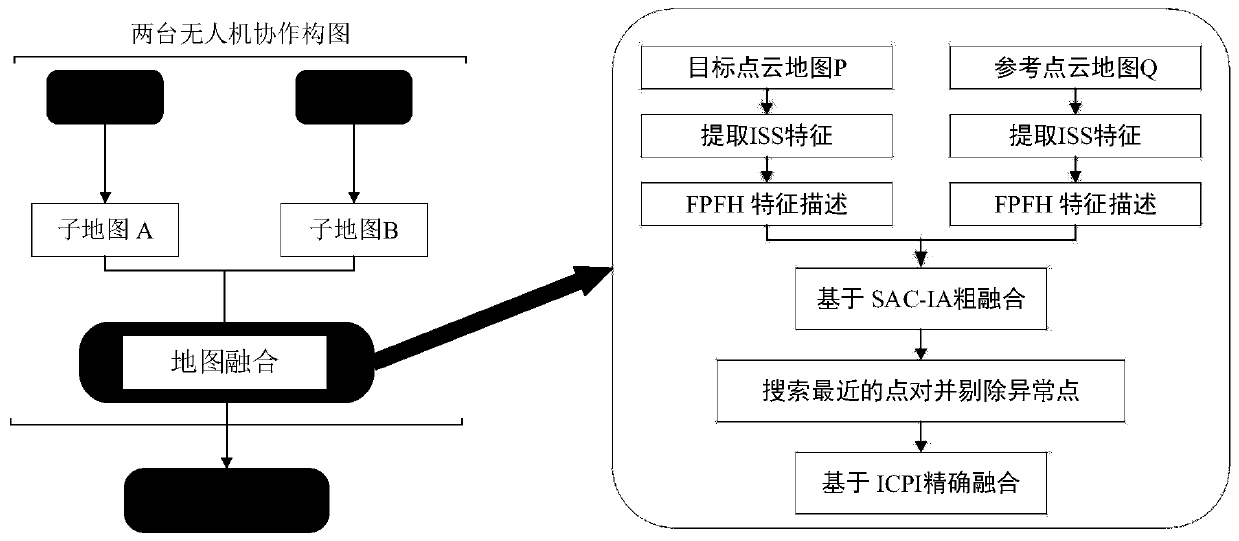
ICP point cloud map fusion method, system and device based on multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperation and storage medium
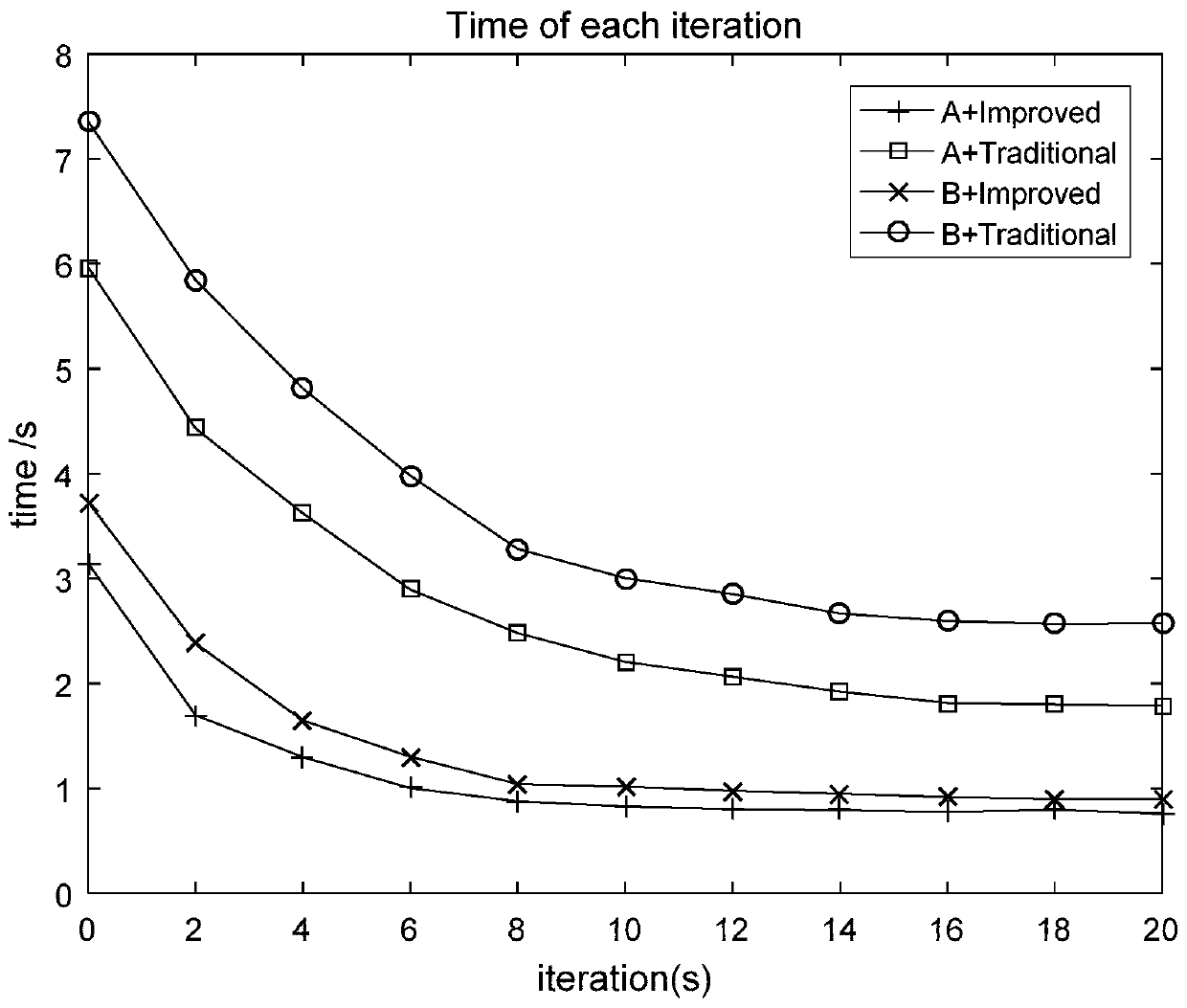
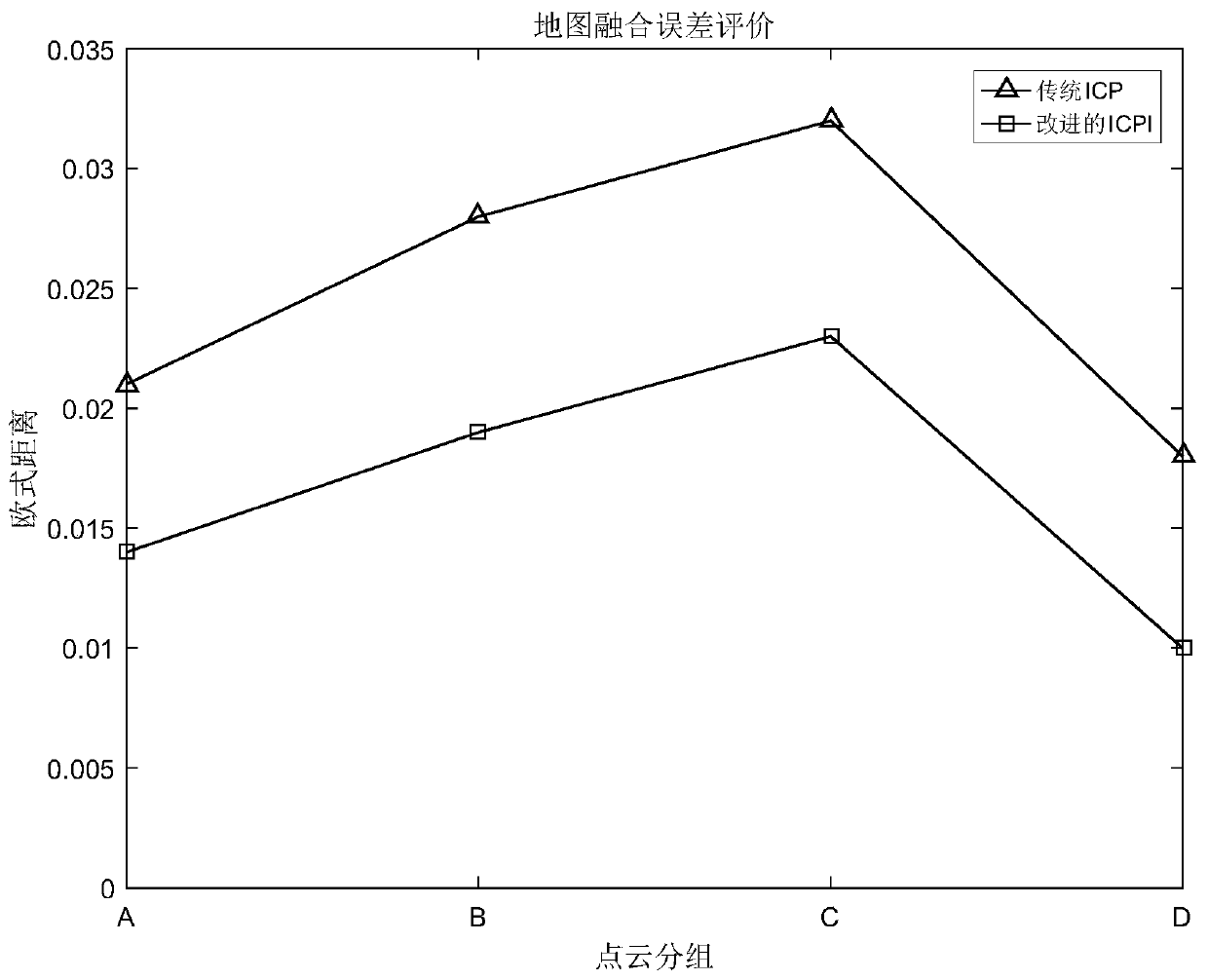
The invention provides an ICP point cloud map fusion method, system and device based on multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperation and a storage medium. The ICP point cloud map fusion method comprisesthe following steps: an extraction step: extracting key points from two data sets according to the same key point selection standard, the two data sets being two point cloud maps with overlapping regions and being respectively marked as a point cloud P and a point cloud Q, the point cloud P being a target point cloud, and the point cloud Q being a reference point cloud; in the calculation step, calculating feature descriptors of all the selected key points respectively; a processing step: combining the coordinate positions of the feature descriptors in the two data sets, taking the similarityof the features and the positions between the feature descriptors as the basis to estimate the corresponding relationship between the feature descriptors and the data sets, and estimating corresponding point pairs; and a registration step: estimating rigid body transformation by using the corresponding relationship, and performing complete registration. The method has the advantages that the convergence speed of the ICP algorithm can be increased while high precision is achieved, and a very good technical effect is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
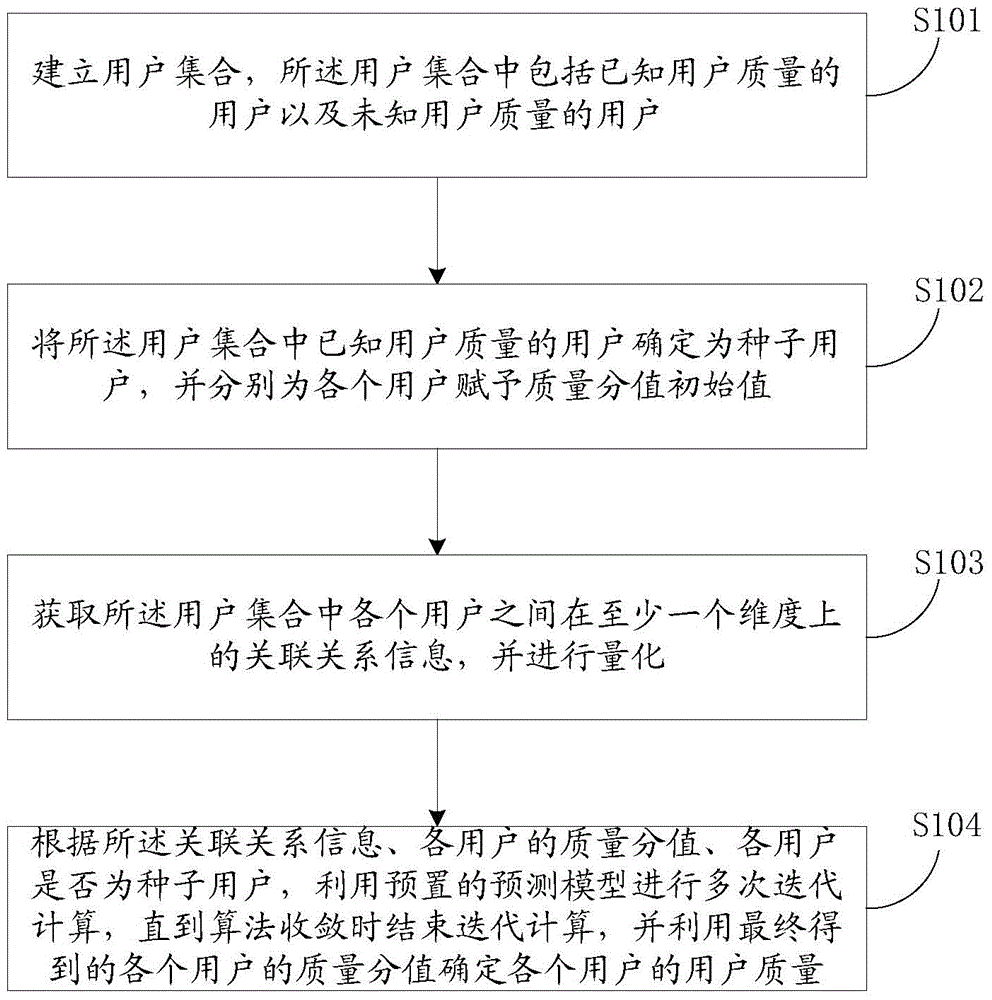
User quality detection method and device
InactiveCN105404947AImprove reliabilityReduce wasteBuying/selling/leasing transactionsResourcesAlgorithm convergenceDependability
The invention discloses a user quality detection method and device, and the method comprises the steps: building a user set which comprises a user with known user quality and a user with unknown user quality; determining the users with the known user quality in the user set as seed users, and respectively assigning quality score initial values for all users; obtaining correlation information of all users in the user set in at least one dimension, and carrying out quantification; employing a preset prediction model for multi-iteration calculation according to the correlation information, the quality scores of all users and the judgment whether all users are the seed users or not, ending the iteration calculation till an algorithm is convergent, and determining the user quality of all users according to the finally obtained quality scores of all users. According to the embodiment of the invention, the method and device can detect the user equality more accurately, improve the reliability of detection results, and reduce the waste of calculation resources.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
A cloud manufacturing resource configuration method based on an improved whale algorithm
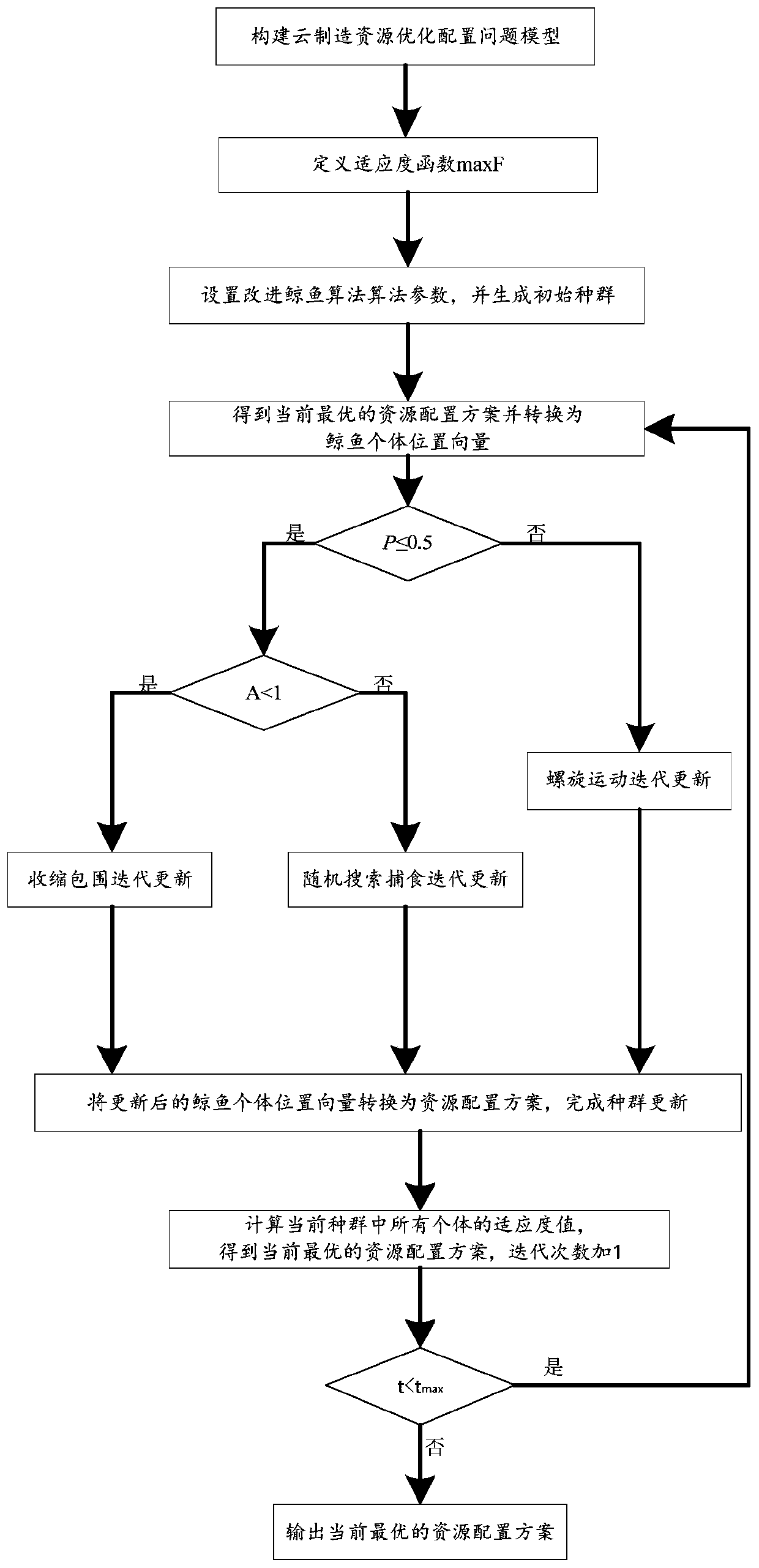
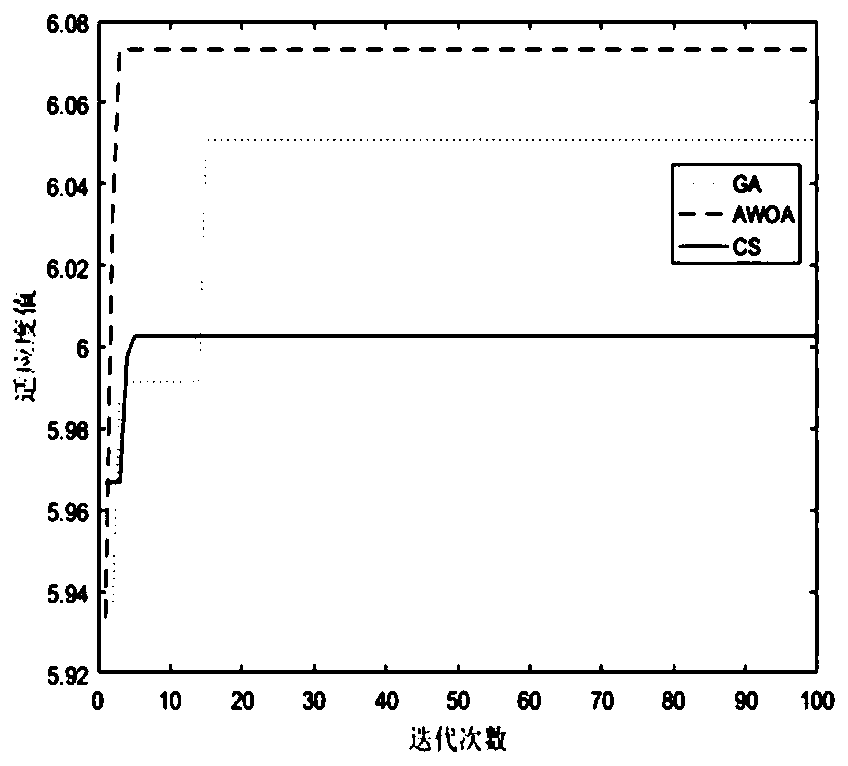
PendingCN109902873AImprove local search capabilitiesImprove convergence accuracyForecastingBiological modelsPredationAlgorithm convergence
The invention discloses a method for cloud manufacturing resource optimization configuration based on an improved whale algorithm, and the method comprises the steps: building a problem model, and defining a fitness function; setting improved whale algorithm parameters, and generating an initial population; Calculating fitness values of all individuals in the population, obtaining a current optimal resource allocation scheme and converting the current optimal resource allocation scheme into whale individual position vectors; Introducing a parameter p, and judging whether p is less than or equal to 0.5; If not, performing spiral motion iteration updating to complete population updating; If yes, whether the value A (1) of the coefficient vector of the improved whale algorithm is met or not is judged; If yes, performing shrinkage encircling iteration updating; If not, performing random search predation iteration updating; Obtaining a current optimal resource configuration scheme; Adding 1to the number of iterations, and judging whether the current number of iterations is smaller than the maximum number of iterations; If yes, repeating the operation; And if not, outputting the currentoptimal resource configuration scheme. The whale algorithm is improved, so that the algorithm convergence speed is higher, the optimal solution is easier to achieve, and a new method is provided forsolving the problem of resource allocation.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
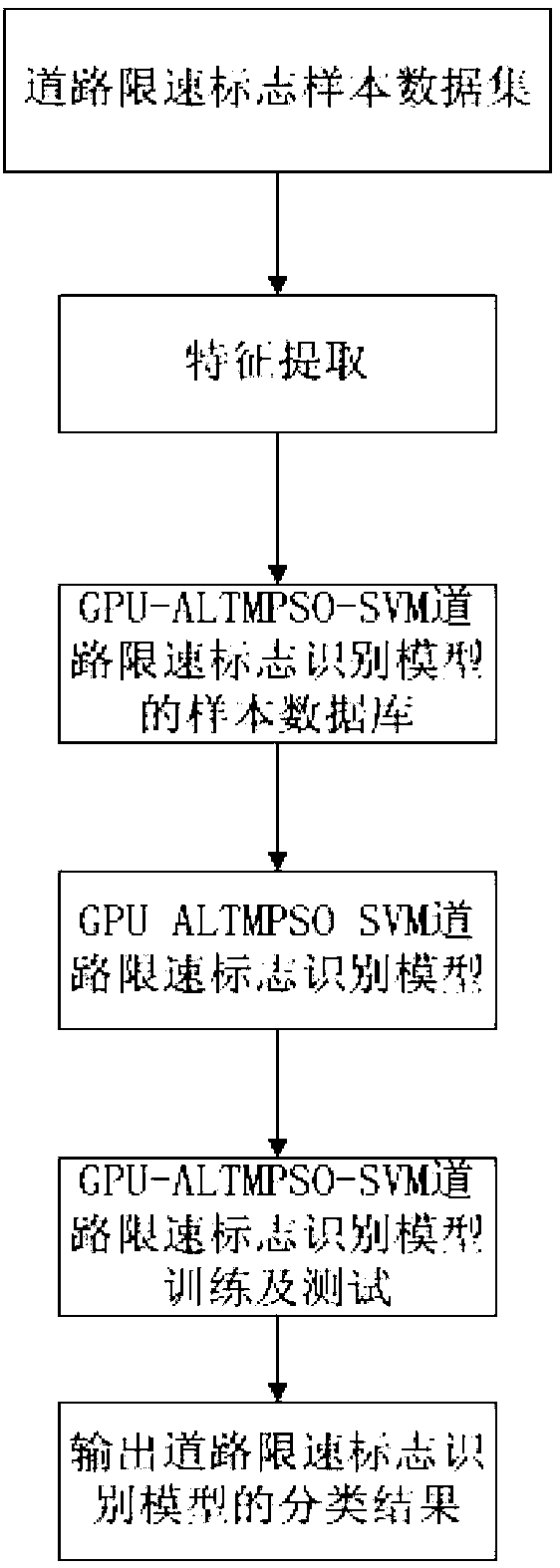
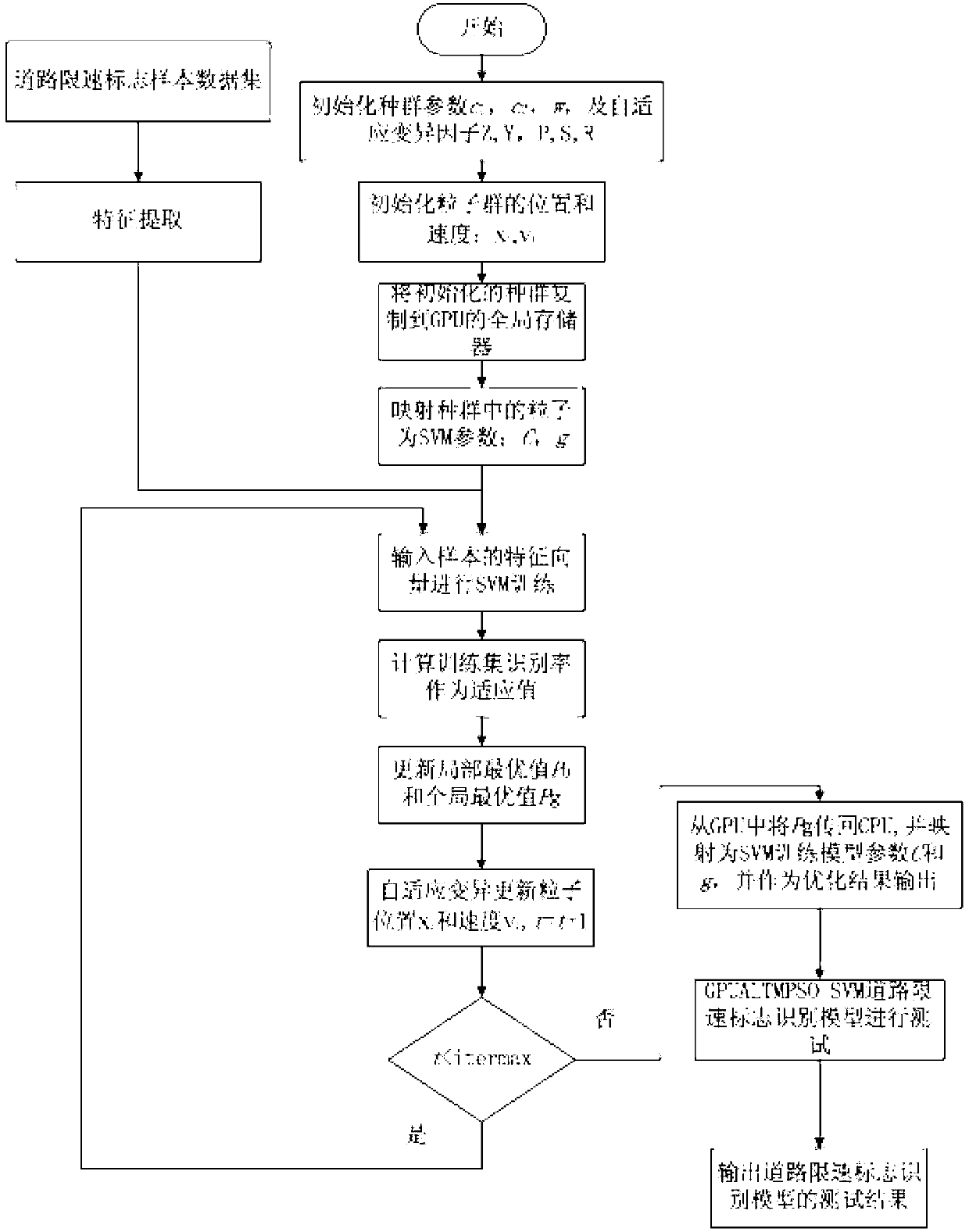
Method for recognizing road signs by PSO-SVM (particle swarm optimization-support vector machine) based on GPU (graphics processing unit)
ActiveCN102999756AAccurate identificationEfficient searchCharacter and pattern recognitionTone mappingSupport vector regression machine
The invention discloses a method for recognizing road speed limit signs by optimizing an SVM (support vector machine) by adaptive mutation particle swarm optimization based on a GPU (graphics processing unit). The category of the road speed limit signs is quickly and accurately recognized by using PSO (particle swarm optimization) to optimize parameters of an SVM. Based on the characteristics of particle swarm in optimizing parameters of the SVM, such as high data processing capacity and long computation time, the operating speed of PSO algorithm is increased by parallel computing of the GPU. The method has the advantages that the method of optimizing the support vector machine by GPU-accelerated ALTM PSO (adaptive local tone mapping-particle swarm optimization) is superior to the traditional SVM in accuracy of recognizing road speed limit signs and is superior to the standard PSO-SVM in algorithm convergence and operating speed.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Apparatus and method for classifying data packet flows
InactiveUS6917588B1Reduce disadvantagesQuick classificationError preventionTransmission systemsNetwork packetClassification methods
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Range-based wireless sensing network node positioning method
InactiveCN102883430AReduce measurement errorImprove node positioning accuracyNetwork topologiesWireless sensor networkingAlgorithm convergence
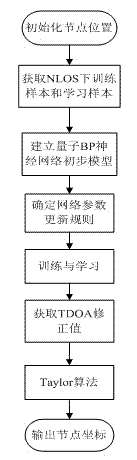
The invention discloses a range-based wireless sensing network node positioning method. Aiming at the conventional range-based wireless sensing network node positioning technology, the positioning precision is influenced because of relatively large wireless range data error such as a received signal strength indicator (RSSI), time of arrival (TOA), time difference of arrival (TDOA) and angle of arrival (AOA) caused by range-free transmission; and by the method, wireless range data are corrected by using a quantum BP neutral network, and positioning is performed by using the corrected range data. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the positioning precision of a wireless sensor network can be greatly improved, the training learning time is short, the algorithm convergence speed is high, and the robustness is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Weighting Voronoi diagram substation planning method based on chaotic and genetic strategy
InactiveCN103136585ASolve premature problemsPlanning results are excellentData processing applicationsGenetic modelsElectric power systemAlgorithm convergence
The invention relates to the field of electric systems and discloses a weighting Voronoi diagram substation planning method based on a chaotic and genetic strategy. The method aims at solving the problems that a prior algorithm is low in rate of convergence, poor in capacity of local optimization and sensitive in initial value, premature convergence exists, the unreasonable phenomenon caused by division of power-supply districts according to the principle of proximity exists, the load rate of a planned substation can not be controlled, and the like, and optimizing site selection of the substation and division of the power-supply districts by means of certain algorithms. The method comprises the steps of setting parameters; chaotic initialization and generating initial population including N individuals; carrying out the site selection of the substation and load distribution on the N individuals; judging whether end criterion is satisfied; calculating the fitness variance sigma 2 of the population; chaotic search; and executing and saving an optimized genetic algorithm and then returning to the fourth step. The weighting Voronoi diagram substation planning method based on the chaotic and genetic strategy is mainly applicable to the electric systems.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Fault diagnosis method based on adaptive manifold embedding dynamic distribution alignment
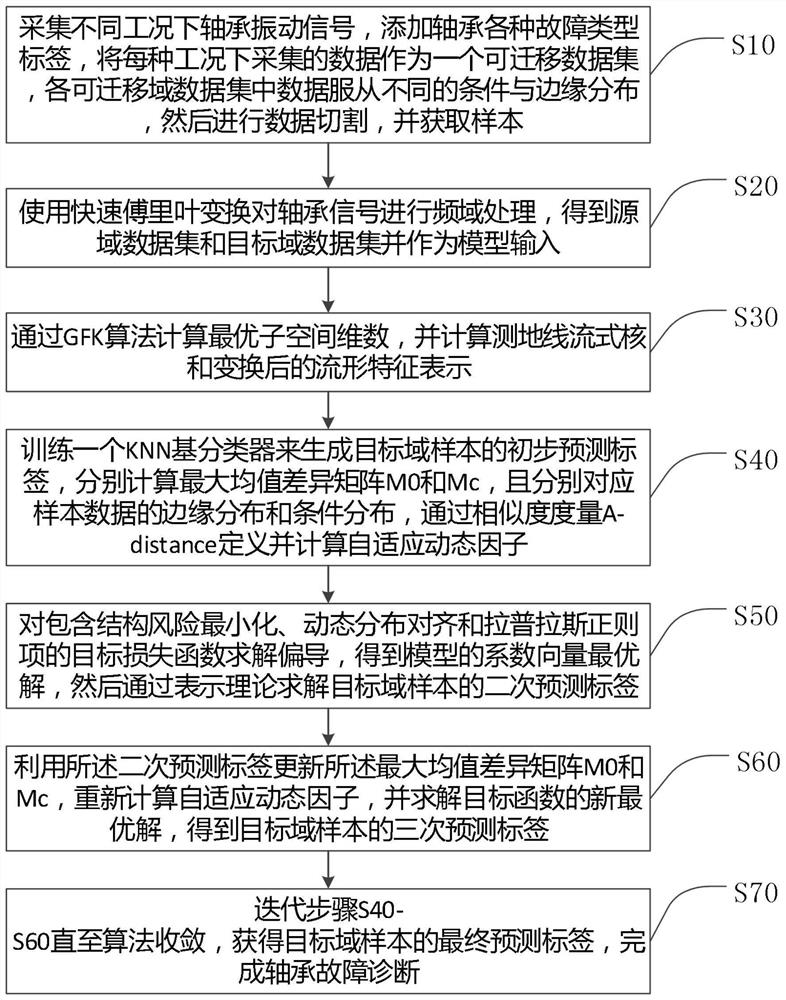
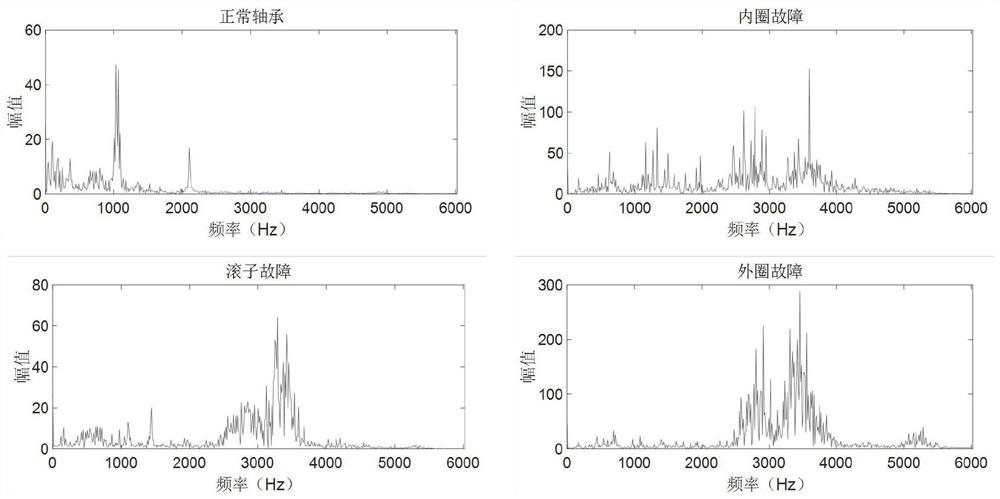
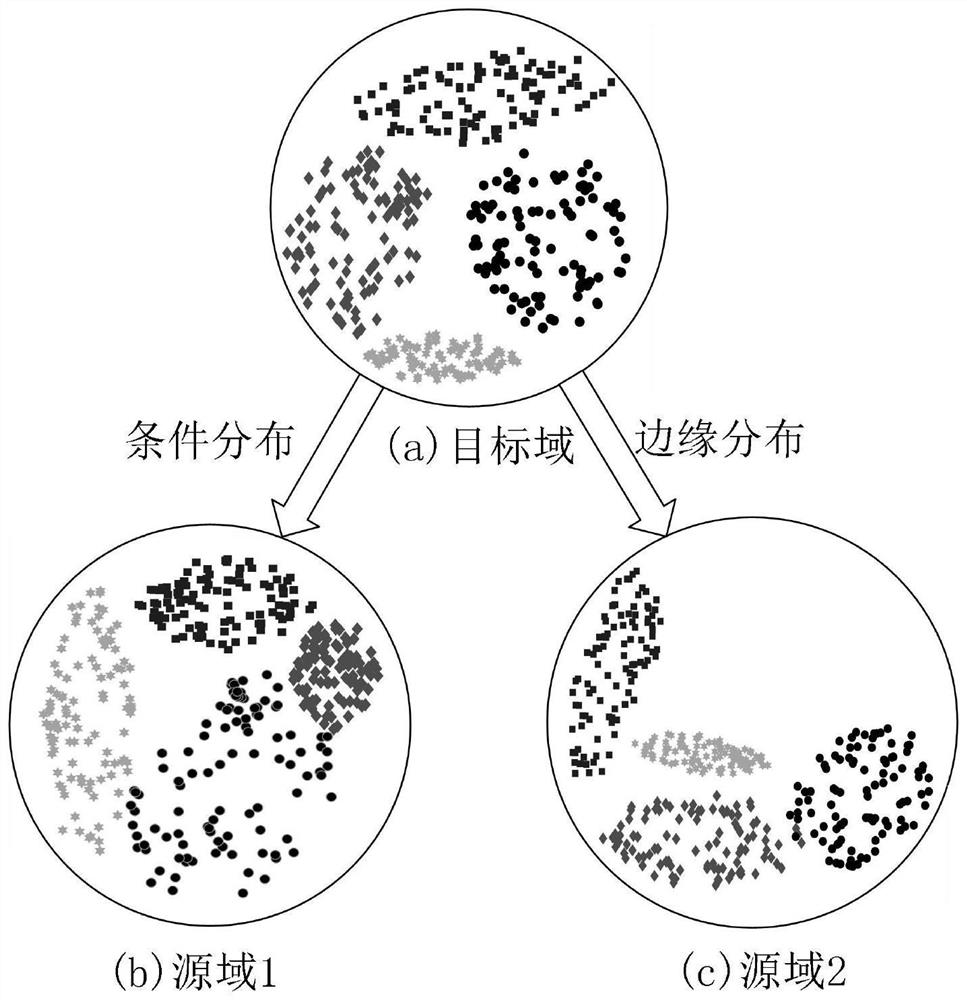
ActiveCN111829782AAvoid feature distortionReduce distribution varianceMachine part testingKernel methodsRobustificationAlgorithm
The invention discloses a fault diagnosis method based on adaptive manifold embedding dynamic distribution alignment. According to the method, the feature distortion of data in an original Euclidean space can be effectively avoided through the automatic calculation of the optimal subspace dimension and the calculation of the streaming kernel of a geodesic line and converted manifold feature representations; a similarity measure A-distance is introduced to define a self-adaptive factor; relative weights of condition distribution and edge distribution of sample data are dynamically adjusted, andtherefore, the distribution difference of source domain and target domain samples can be effectively reduced, the accuracy and effectiveness of rolling bearing fault diagnosis under variable workingconditions can be greatly improved. The method is high in interpretability, is lower in requirements for computer hardware resources, is higher in execution speed, and is excellent in diagnosis precision, algorithm convergence and parameter robustness. The method is especially suitable for multi-scene and multi-fault bearing fault diagnosis under variable working conditions, and can be widely applied to fault diagnosis tasks of complex systems such as machinery, electric power, chemical engineering and aviation under variable working conditions.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
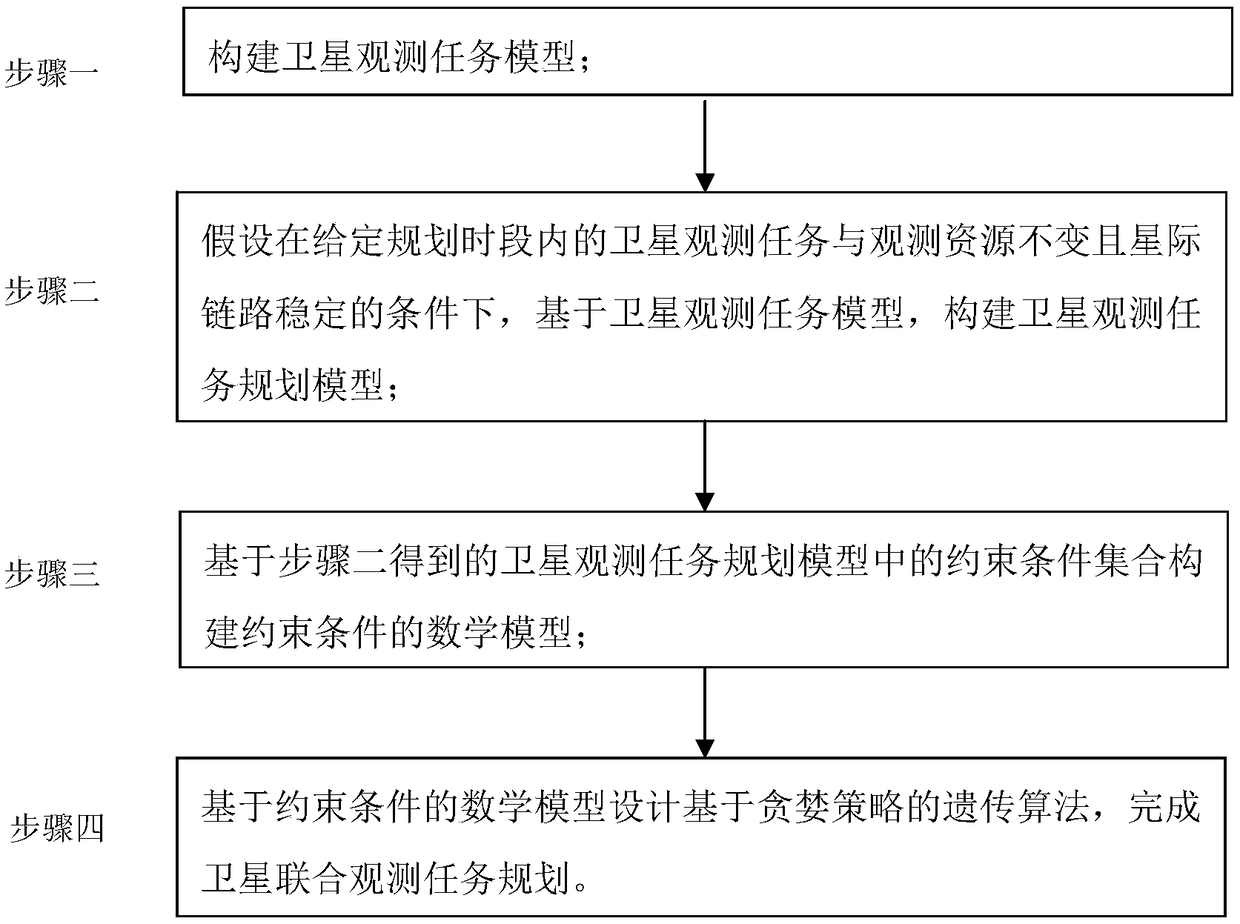
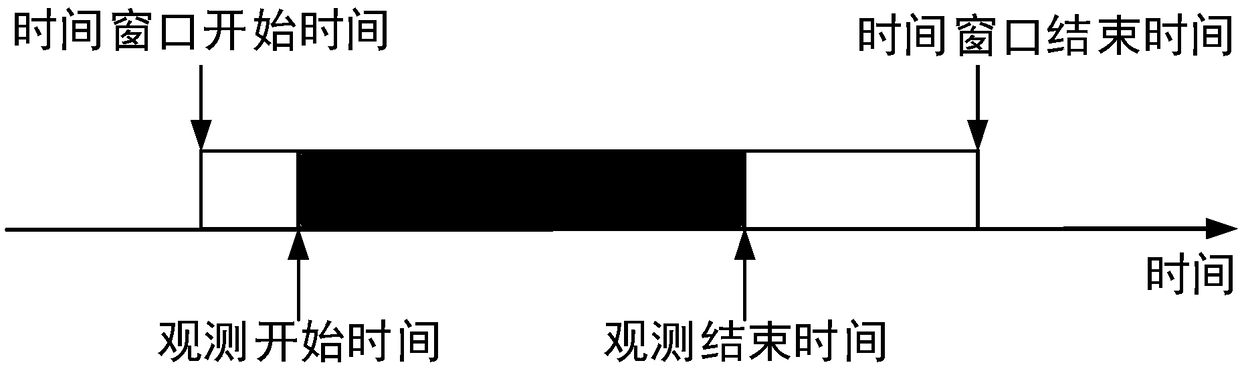
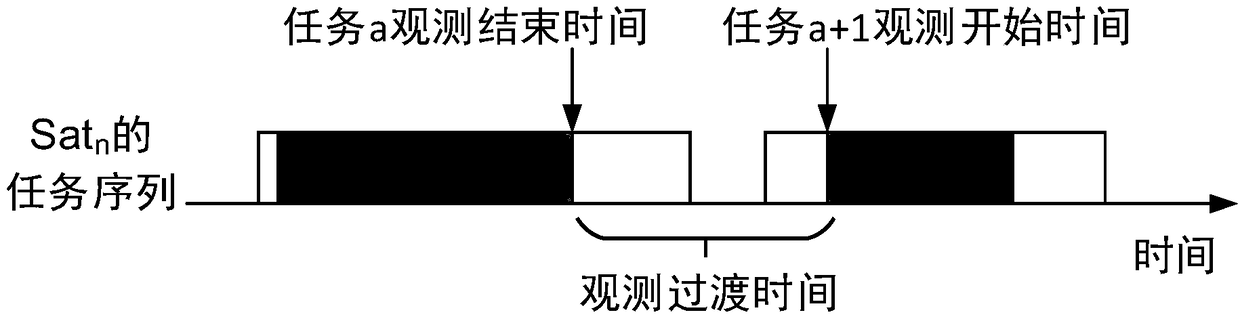
A satellite joint observation task planning method
ActiveCN109409775AGuaranteed solution accuracyFast convergenceResourcesGenetic algorithmsSatellite observationMathematical model
The invention discloses a satellite joint observation task planning method, and relates to a satellite joint observation task planning method. The objective of the invention is to solve the problems of insufficient modeling consideration constraint conditions, low algorithm convergence speed and long algorithm calculation time when a satellite joint observation task planning problem is solved in the prior art. The method comprises the steps of 1, constructing a satellite observation task model; 2, establishing a satellite observation task planning model on the basis of a satellite observationtask model under the conditions that satellite observation tasks and observation resources in a given planning time period are not changed and interstellar links are stable; Step 3, constructing a mathematical model of constraint conditions based on the constraint condition set in the satellite observation task planning model obtained in the step 2; and step 4, designing a genetic algorithm basedon a greedy strategy based on the mathematical model of the constraint condition to complete satellite joint observation task planning. The method is applied to the field of satellite joint observation task planning.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP +1
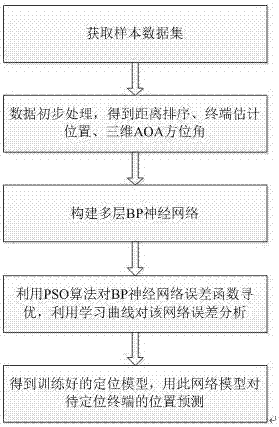
Three-dimensional positioning method based on PSO_BP neural network
InactiveCN106912105AFast convergenceHigh precisionWireless communicationObservational errorShortest distance
The invention provides a terminal three-dimensional positioning method based on a BP neural network optimized by a particle swarm optimizer (PSO), wherein the method can be widely used in a wireless positioning field. The method comprises the steps of measuring distance data between a plurality of base stations in an area and the terminal; sequencing actually measured distances from lowest to highest, selecting four base stations with shortest distances, and calculating a terminal position which comprises a non-sight-distance influence by means of the four base stations through a least square method; calculating all terminal positions which comprise the non-sight-distance, and calculating a three-dimensional direction angle of each base station to the terminal; and finally using the obtained terminal position coordinates, the distances between the base stations and the terminal, and the three-dimensional direction angle as a characteristic value input layer of the PSO_BP neural network, and using the corrected terminal position coordinates as an output layer. The terminal three-dimensional positioning method optimizes the BP neural network by means of a PSO algorithm, and an obtained result eliminates a terminal position measurement error caused by the non-sight-distance factor. The repented algorithm has advantages of stable performance, high algorithm convergence, high positioning precision, and high suitability for popularization, etc.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
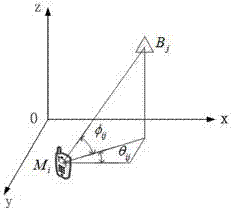
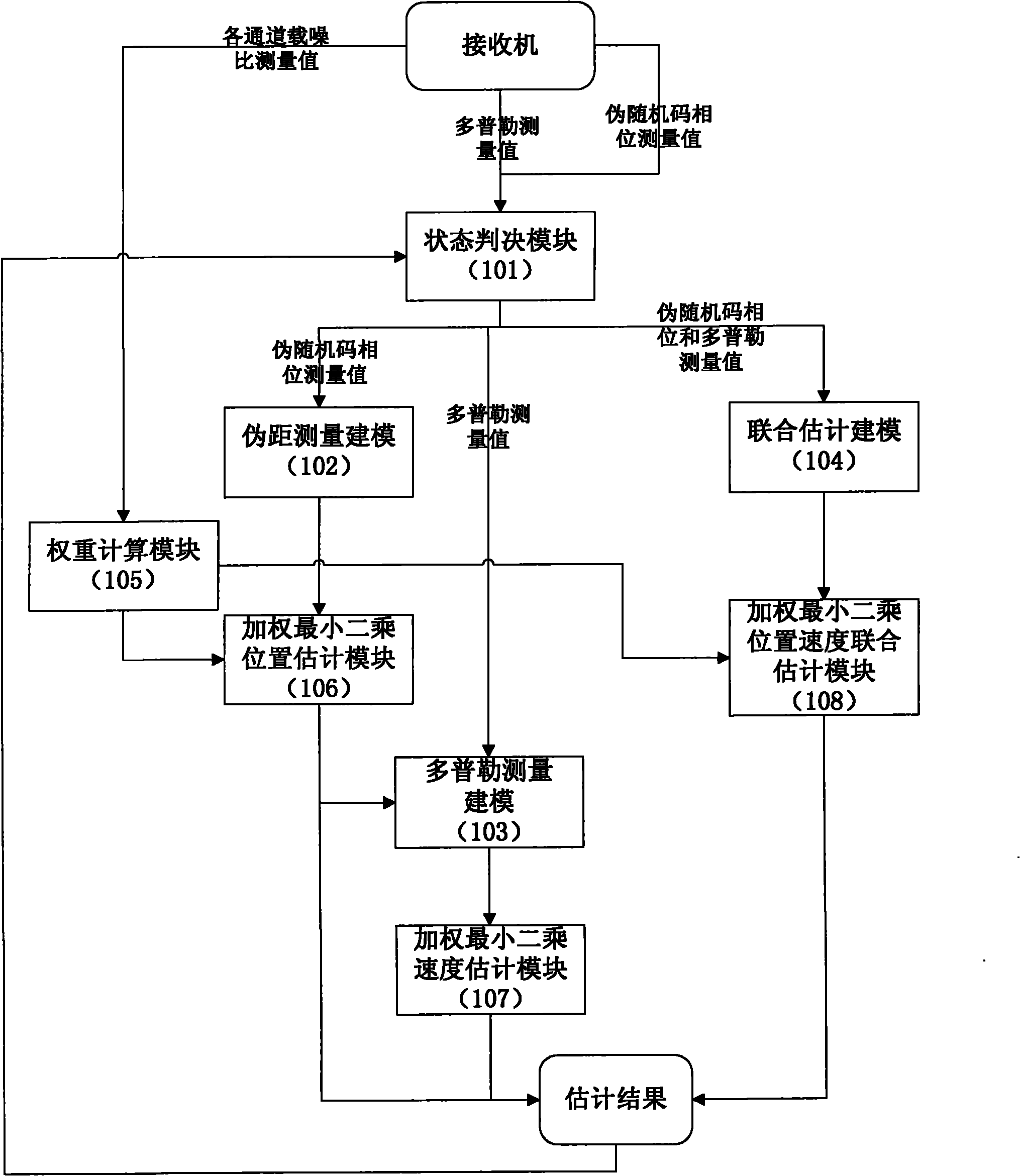
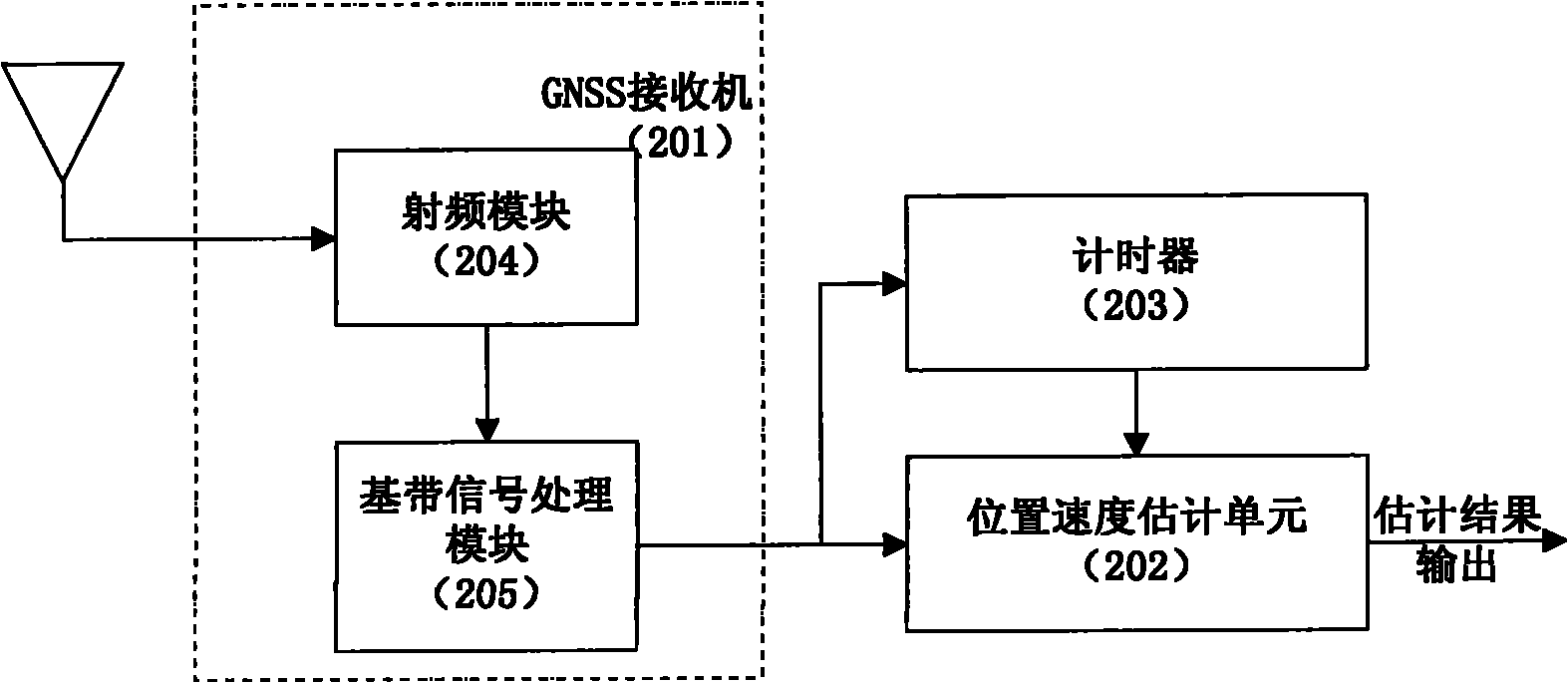
Position and speed combined estimation method for satellite navigation
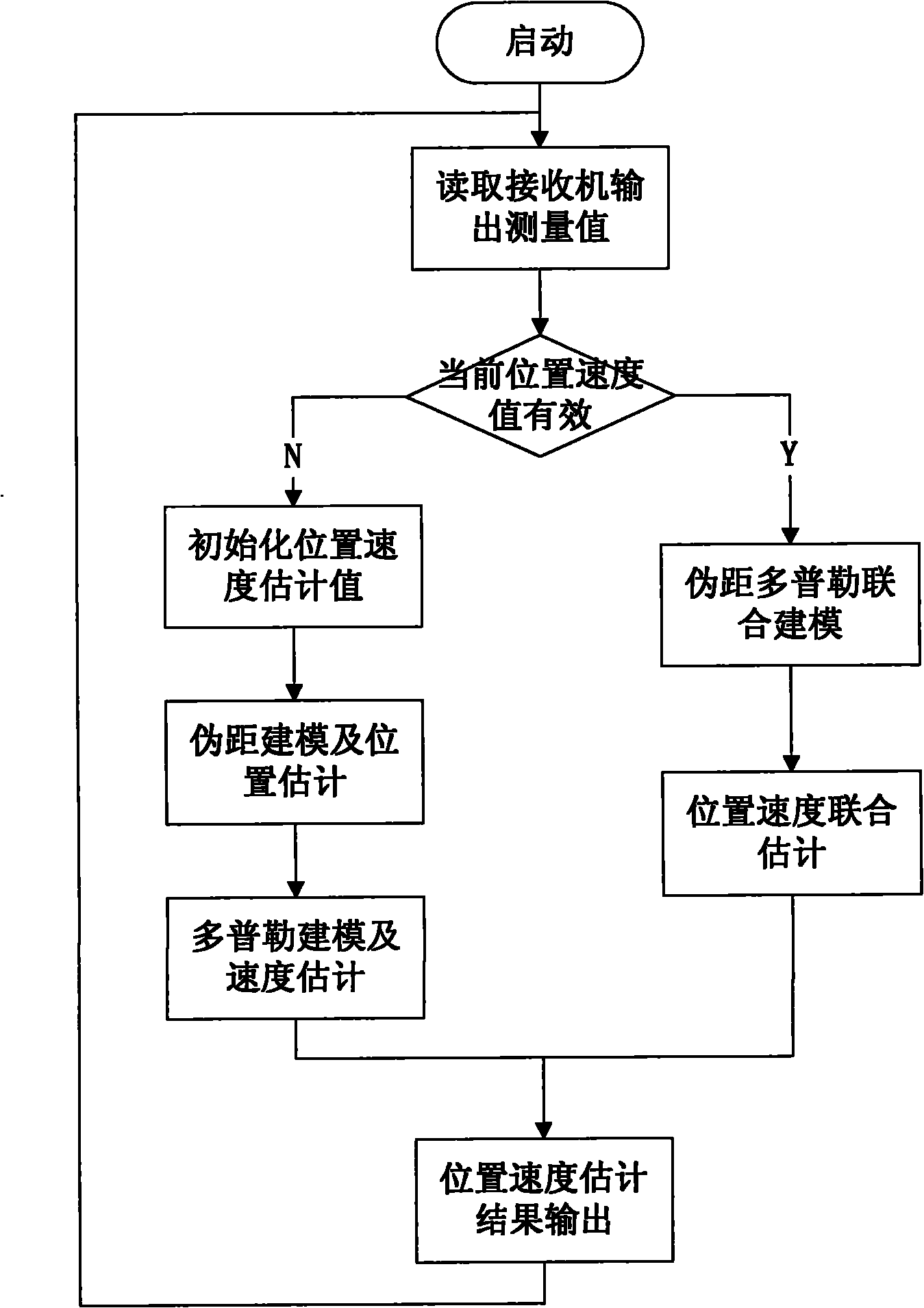
ActiveCN102033236AConvergence Judgment StrictSearch step downSatellite radio beaconingAlgorithm convergenceDoppler measurements
The invention discloses a position and speed combined estimation method for satellite navigation, which solves the problem of real-time estimation of the position and speed of a receiver when an accurate carrier phase measured value cannot be acquired by modeling a recurrent Doppler measured value of the receiver and performing coupled solution with a pseudo-range measurement model based on the correlation between the Doppler measured value and the position of the receiver. The method comprises the following steps of: performing combined estimation on positioning and speed measurement at each new epoch moment according to the current pseudo-range measured value and Doppler measured value; and weighting least square based on a nonlinear equation system to solve an estimated position in an iterative process to replace a pseudo-range positioning result to serve as a reference position for the speed estimation of the receiver, so that the speed estimated value is gradually converged along with the position estimation. Meanwhile, estimation error comprises speed error to ensure that the algorithm convergence judgment is stricter, and the search step of an algorithm around the actual position is reduced so as to acquire higher estimation accuracy. By the method, real-time positioning and speed measurement can be reliably realized, and the method is suitable for various satellite navigation systems such as a global positioning system (GPS), a global orbit navigation satellite system (GLONASS) and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com