Patents
Literature
896 results about "Motion planning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
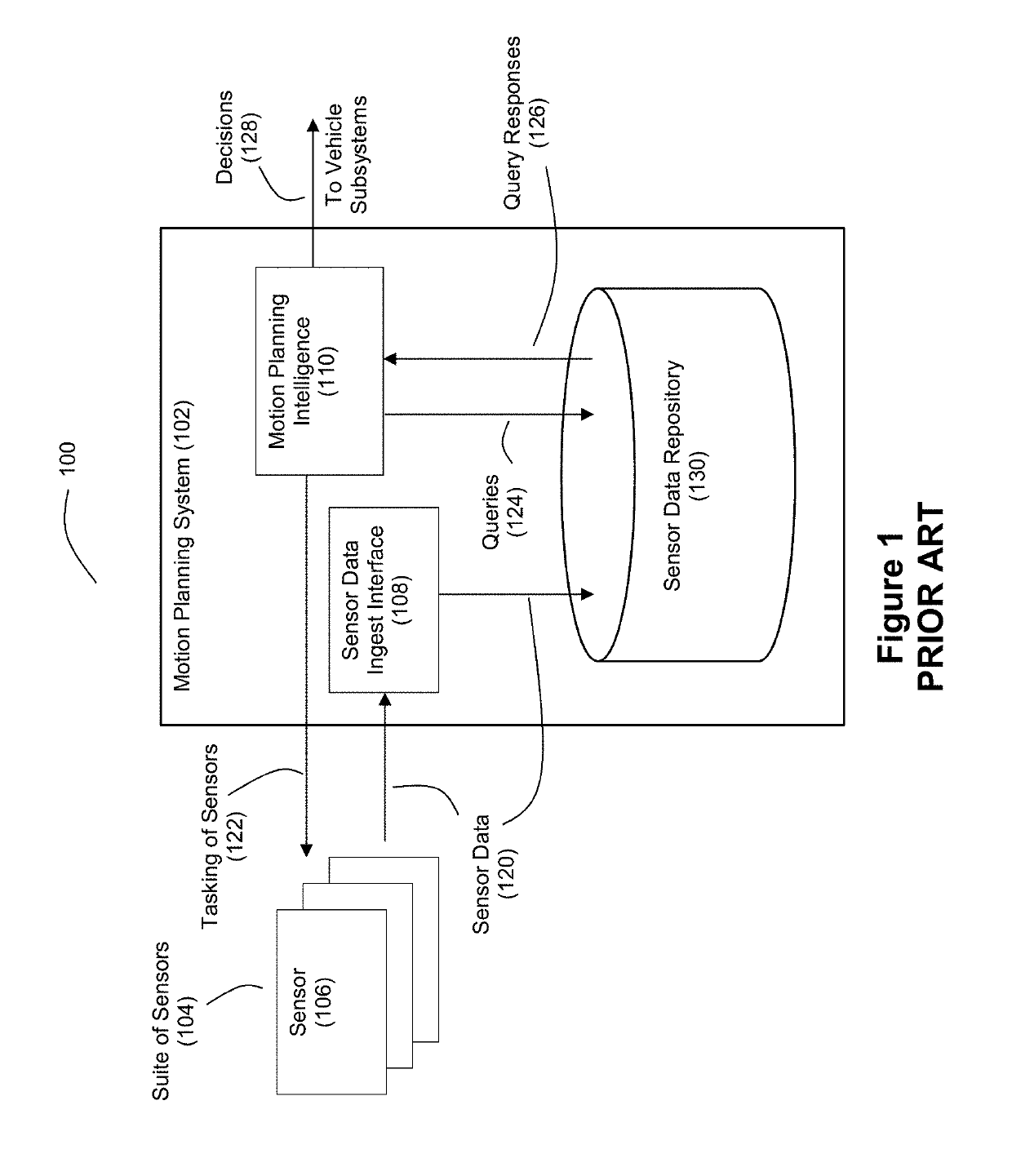
Motion planning (also known as the navigation problem or the piano mover's problem) is a term used in robotics is to find a sequence of valid configurations that moves the robot from the source to destination.
Unified motion planning algorithm for autonomous driving vehicle in obstacle avoidance maneuver
ActiveUS20150353082A1Reduces turning requirementReduced referenceSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringObstacle avoidance
A method for automated lane centering and / or lane changing purposes for a vehicle traveling on a roadway that employs roadway points from a map database to determine a reference vehicle path and sensors on the vehicle for detecting static and moving objects to adjust the reference path. The method includes reducing the curvature of the reference path to generate a reduced curvature reference path that reduces the turning requirements of the vehicle and setting the speed of the vehicle from posted roadway speeds from the map database. The method also includes providing multiple candidate vehicle paths and vehicle speeds to avoid the static and moving objects in front of the vehicle.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
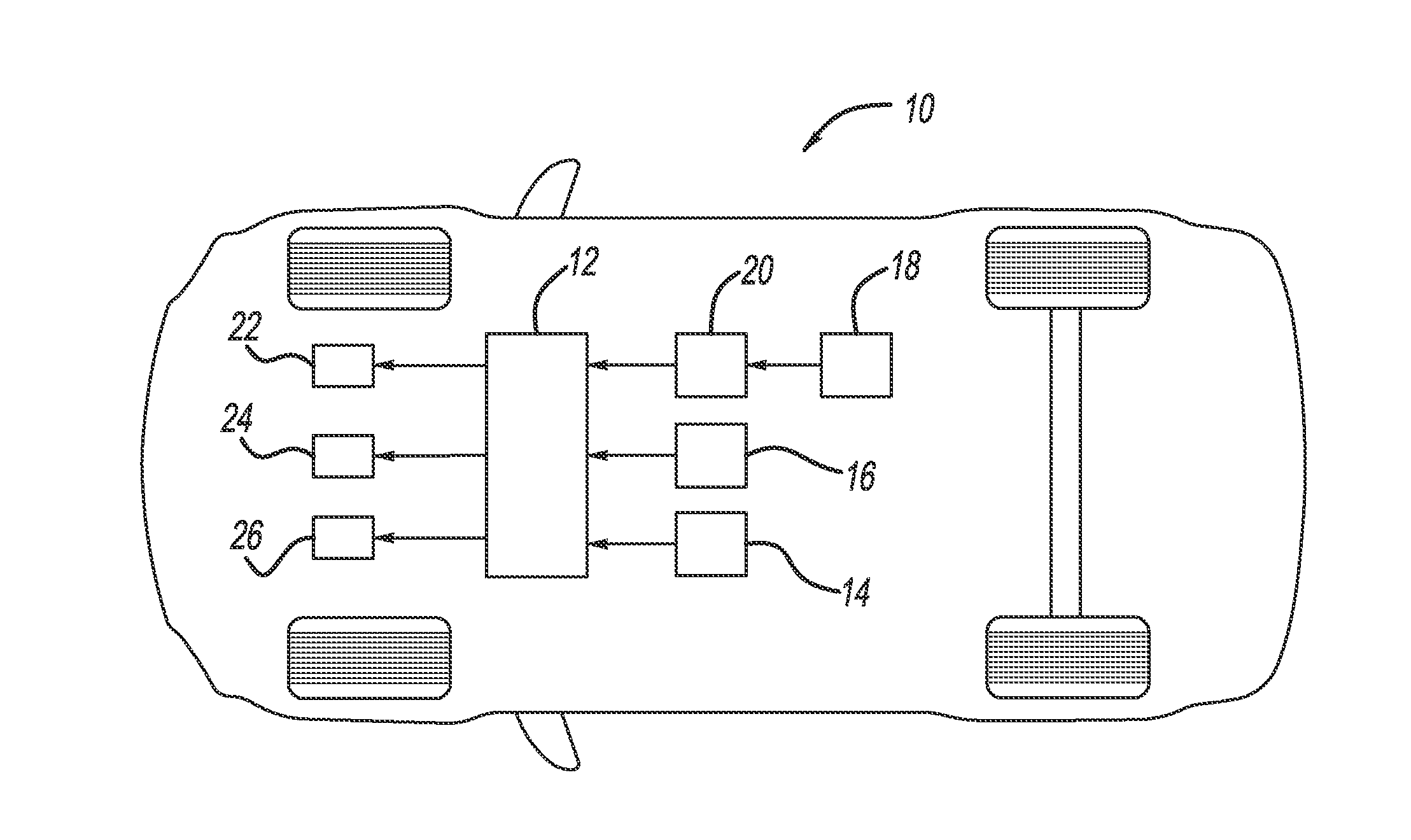
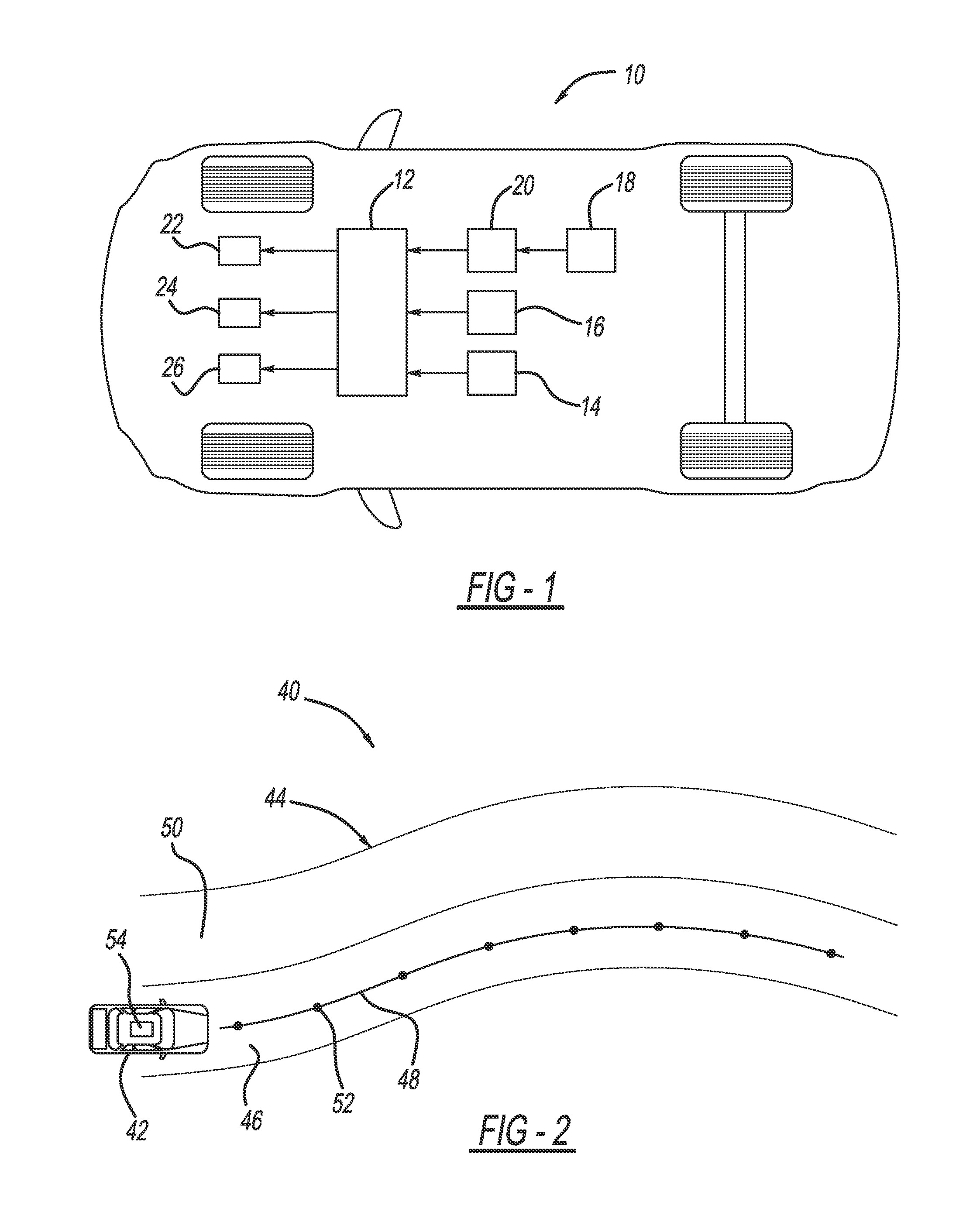
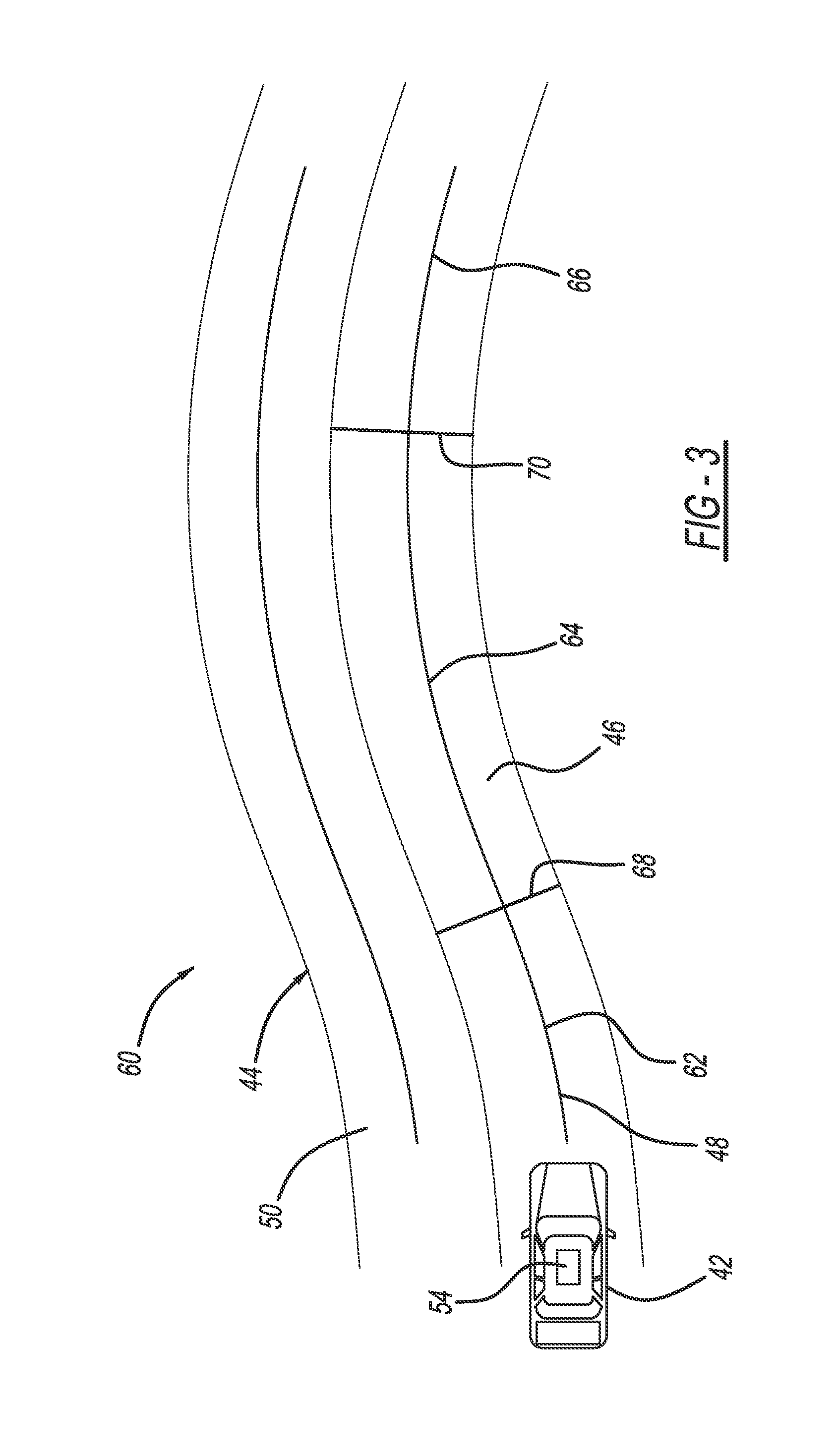
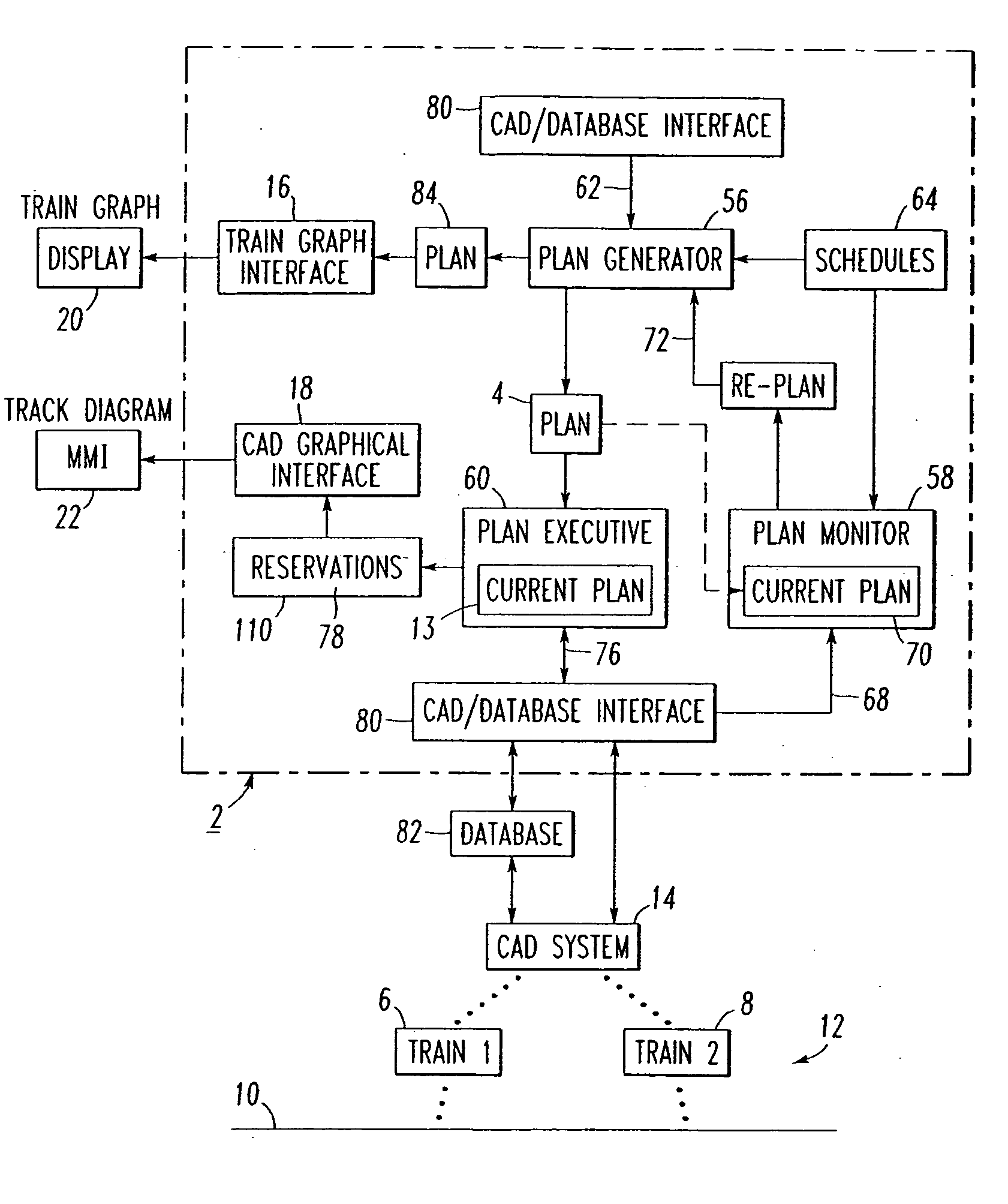
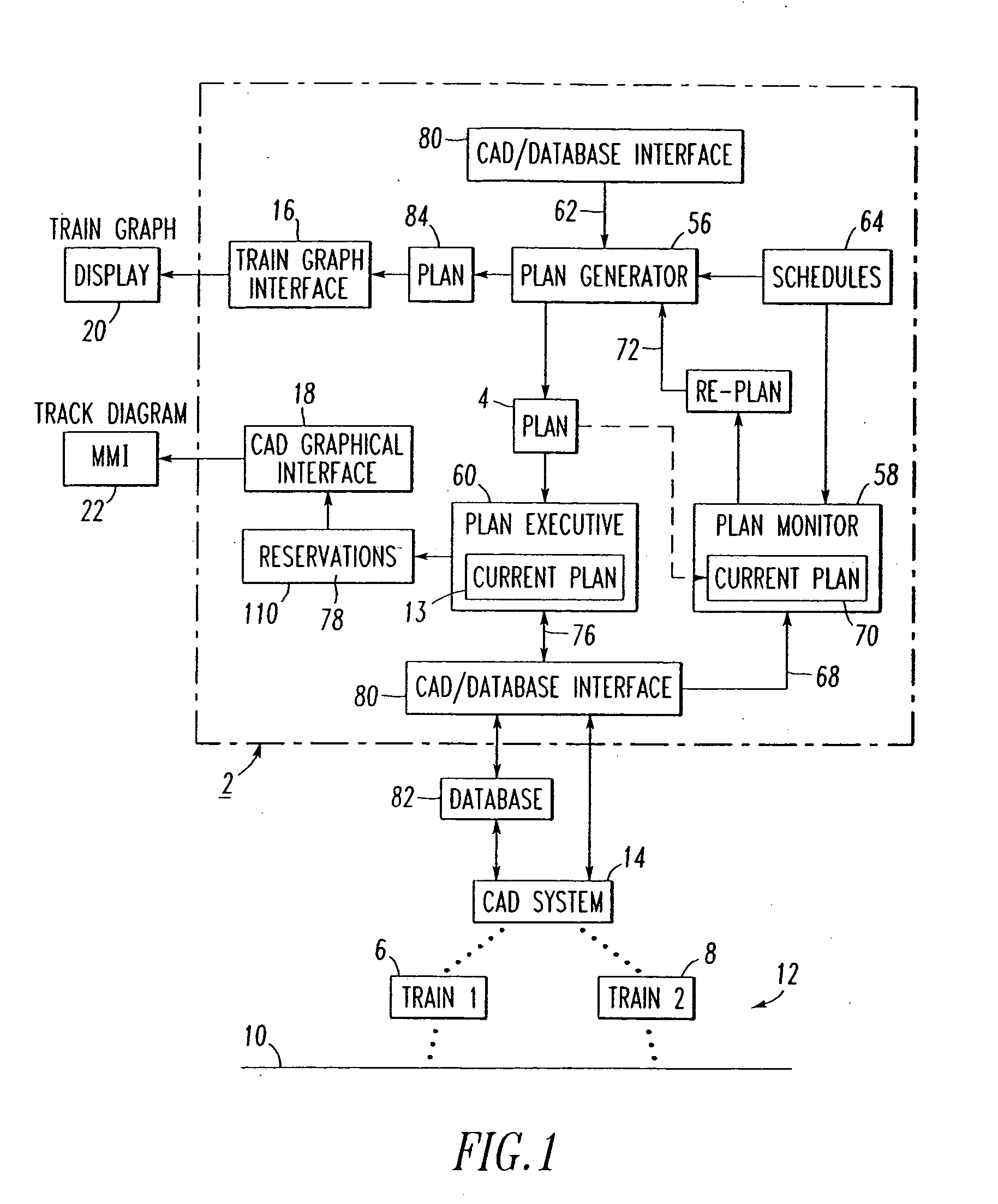
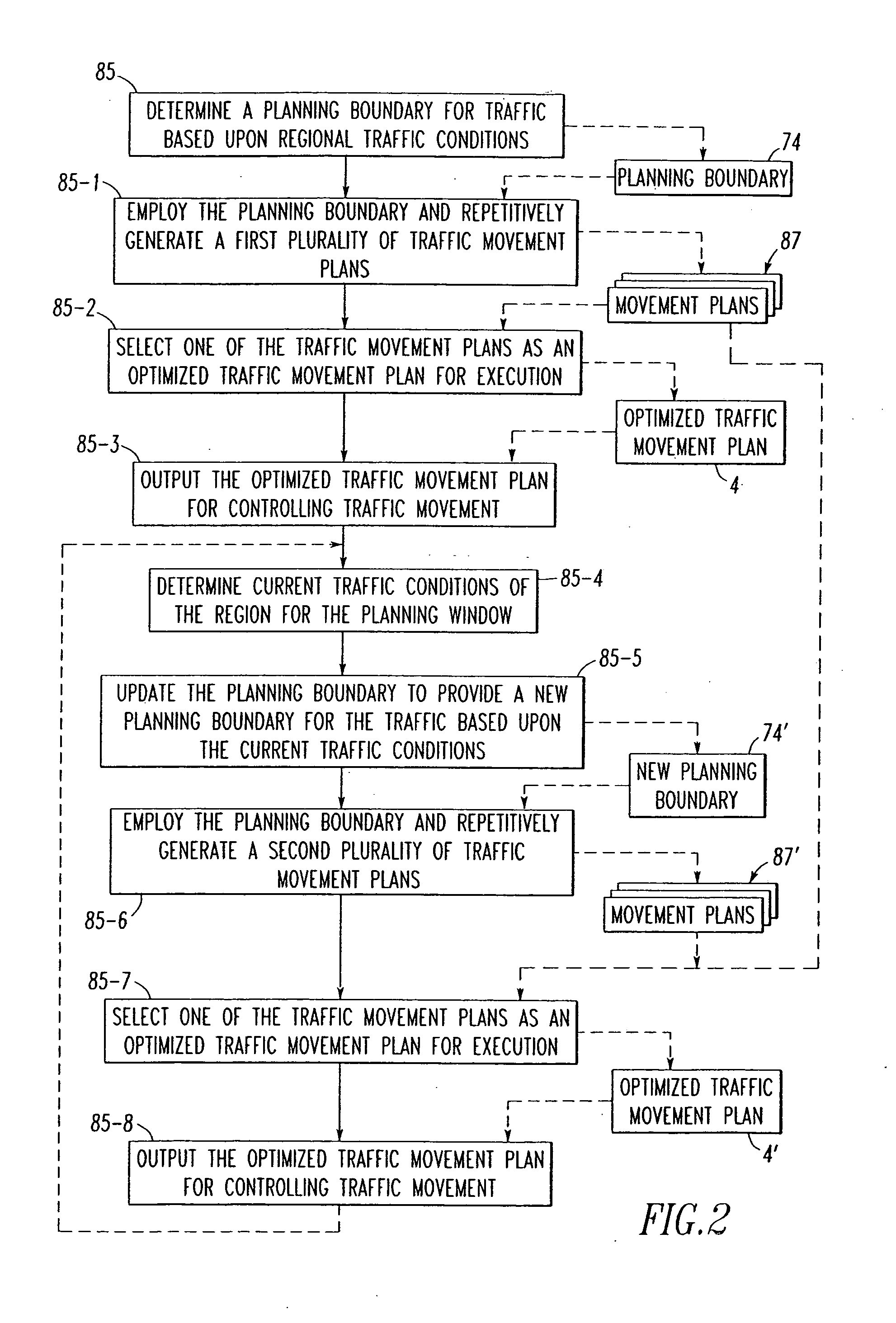
Dynamic optimizing traffic planning method and system
ActiveUS20060074544A1Analogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationProgram planningSimulation
A method generates optimized traffic movement plans. A plan monitor determines a first planning boundary for traffic based upon traffic conditions of a region. A plan generator employs the first planning boundary and repetitively generates first traffic movement plans for the traffic. The plan generator selects one of the first traffic movement plans as a first optimized traffic movement plan, and outputs the same for controlling traffic movement. The plan monitor determines current traffic conditions of the region for a planning window, and updates the first planning boundary to provide a second planning boundary for the traffic based upon the current traffic conditions. The plan generator employs the second planning boundary and repetitively generates second traffic movement plans for the traffic, selects one of the first and second traffic movement plans as a second optimized traffic movement plan, and outputs the same for controlling traffic movement.
Owner:ANSALDO STS USA INC
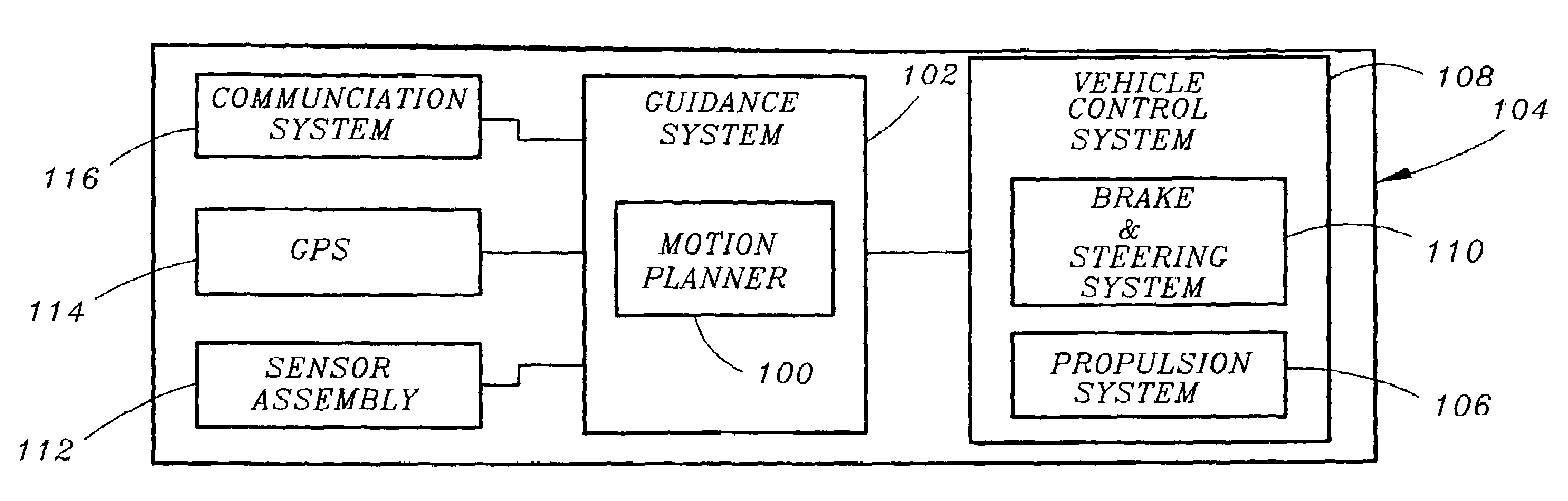
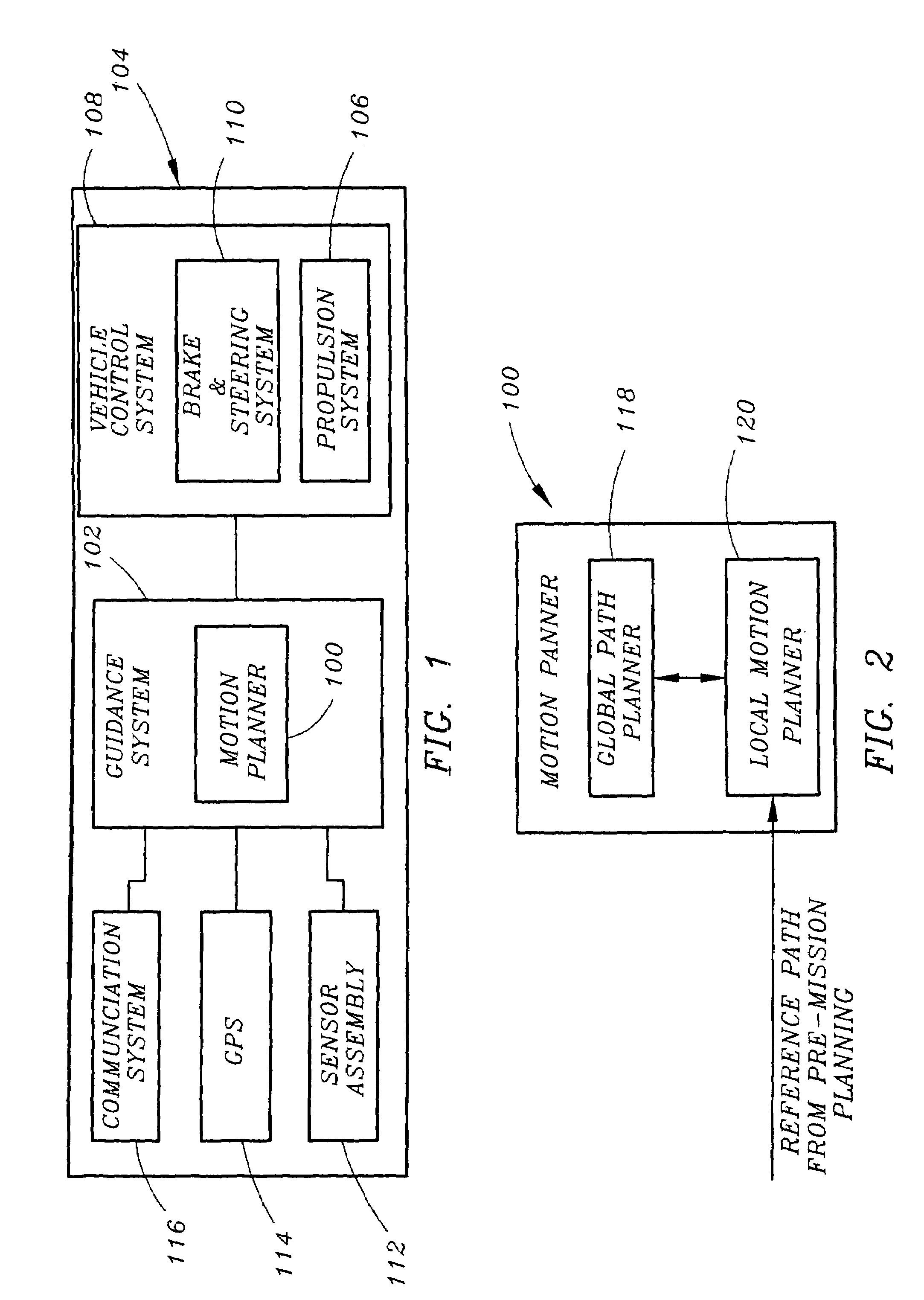
Motion planner for unmanned ground vehicles traversing at high speeds in partially known environments
InactiveUS7734387B1Low costIncrease speedInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsGround vehiclesMotion planning
A motion planner for unmanned ground vehicles capable of traversing at high speeds to reach remote locations in partially known environments. The motion planner comprises a global path planner and a local path planner in communication with the global path planner. The global path planner determines a path to reach a goal location. The local motion planner revises the path determined by the global path planner to generate a motion profile accounting for constraints on the maneuverability of the unmanned ground vehicle. The motion profile provides a revised path for being traversed by the unmanned ground vehicle to reach the goal location.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Syntactic inferential motion planning method for robotic systems
ActiveUS20070005179A1Programme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsRecovery methodRobotic systems
A method and system for planning and optimizing the movement of a robotic device comprises establishing a plurality of spatial locations where the device can possibly be positioned and establishing rule sets for constraining movement of the robotic device between the locations. Once a start and end point have been determined, the method of the invention calculates all possible routes for the device to move, via the established locations and following the constraints of the rule sets. The calculated routes are then compared to a criteria, such as minimizing time, and an optimum route, meeting the desired criteria is determined. The calculated routes may also be cached for future access. The invention also provides for an error recovery method for allowing a robotic device to recover should it encounter an error.
Owner:THERMO CRS
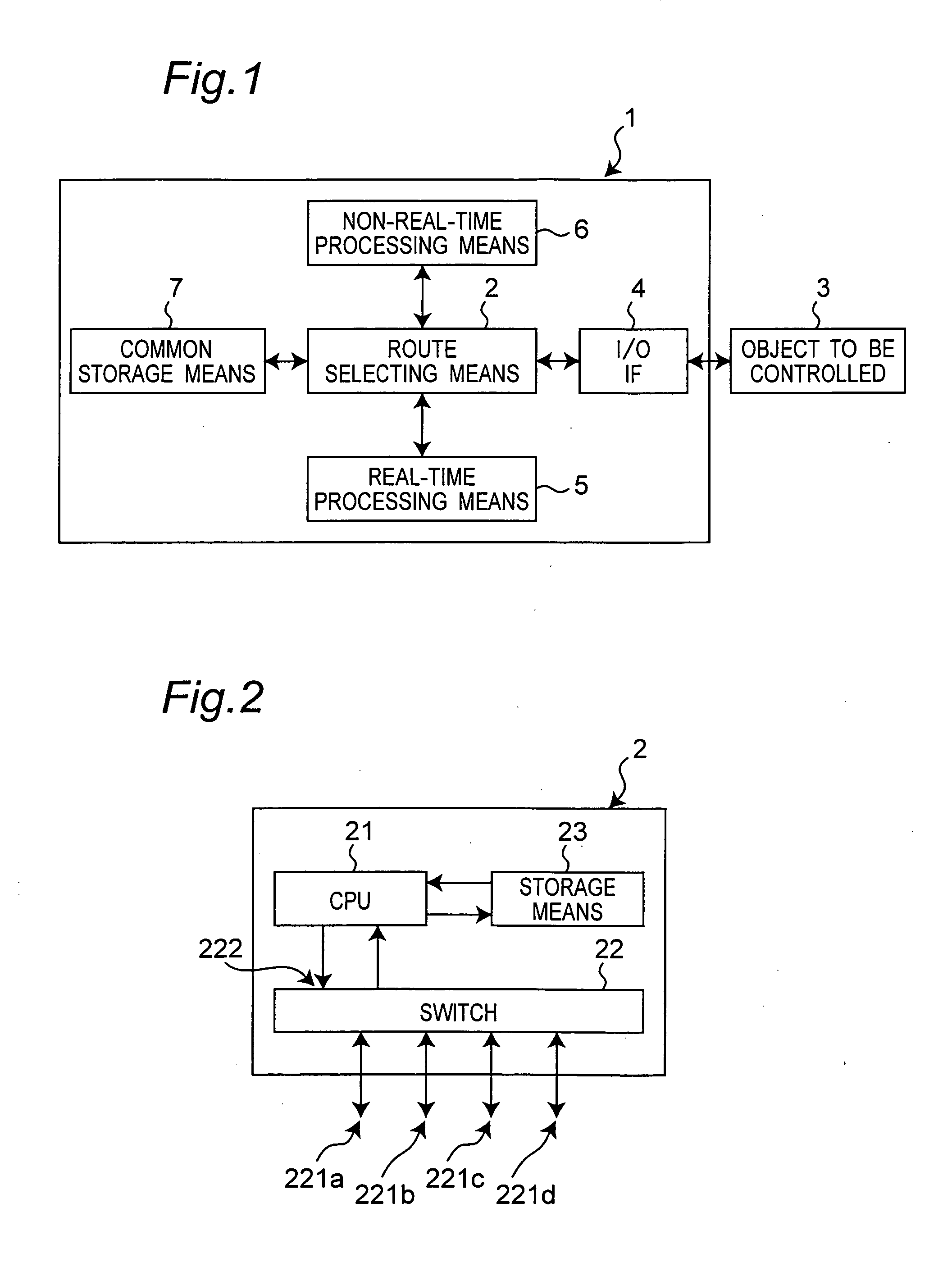
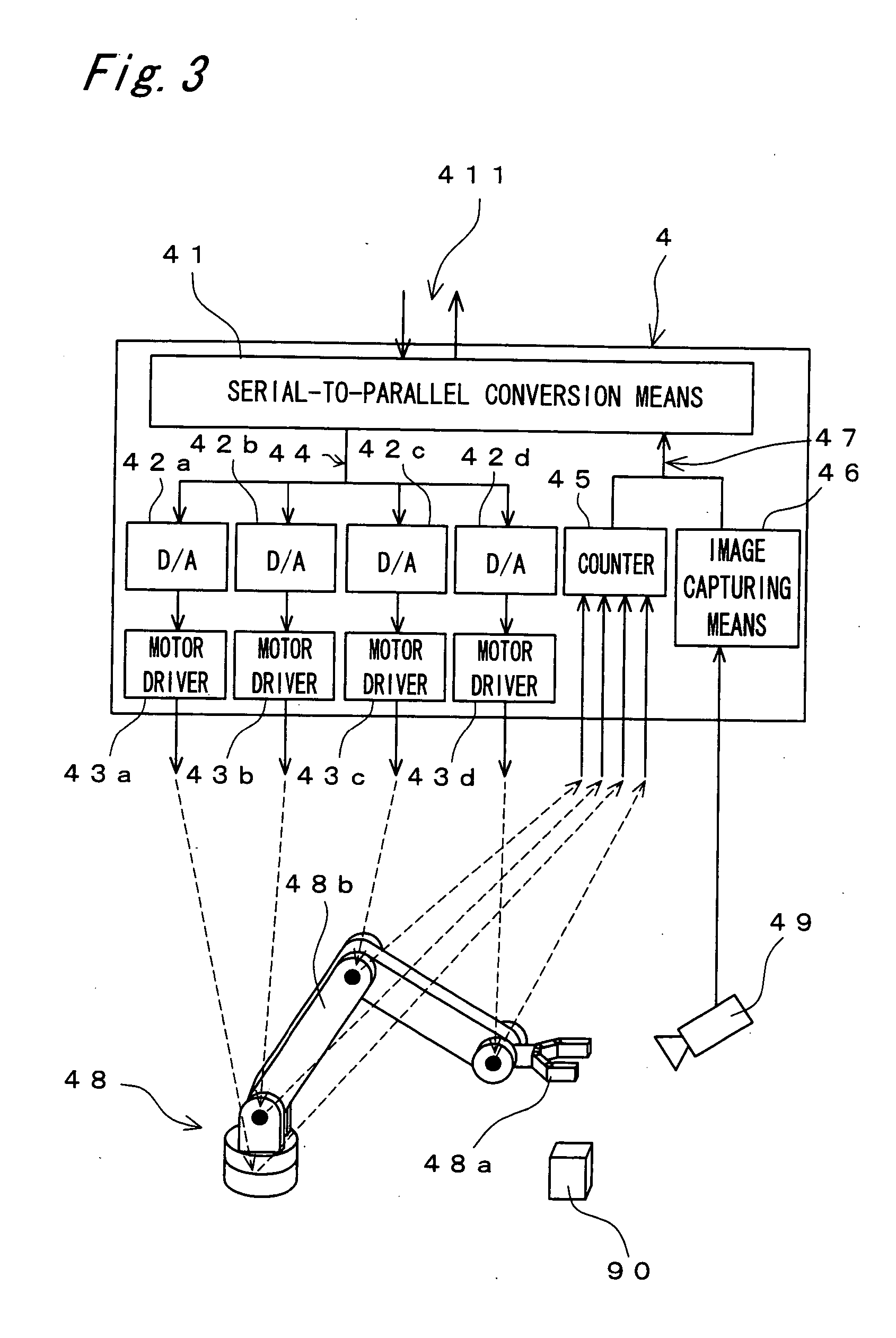
Robot controller
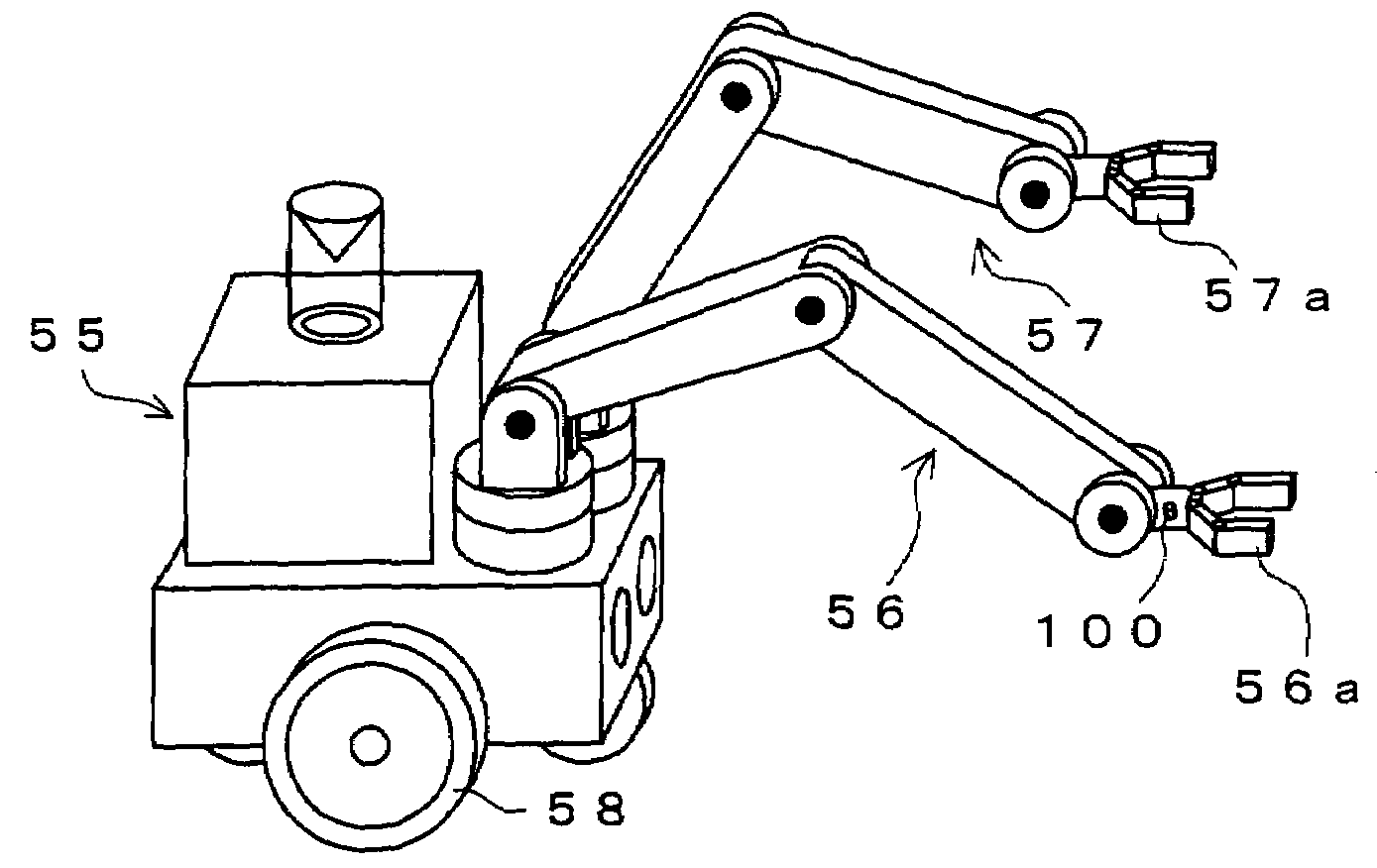
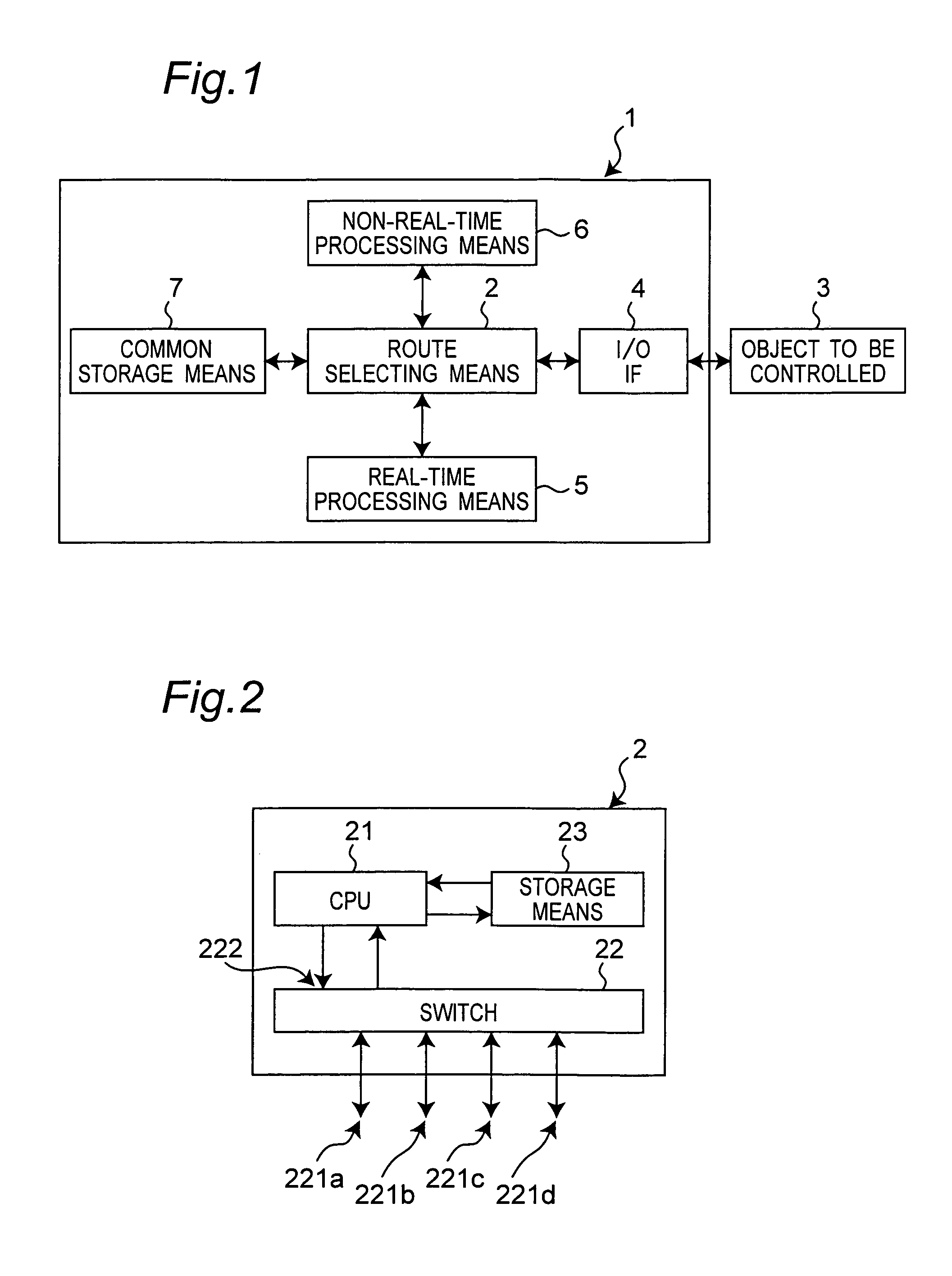
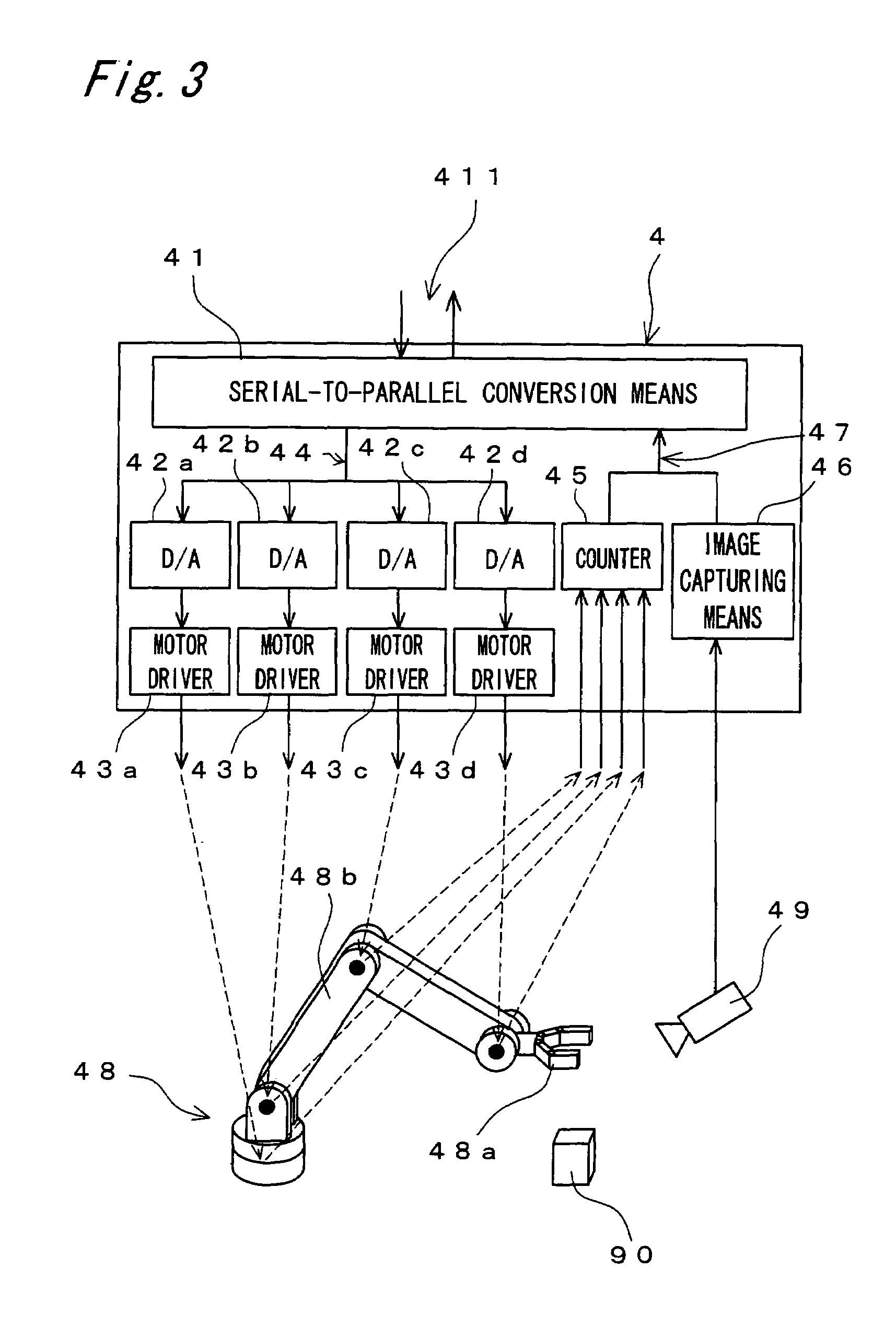
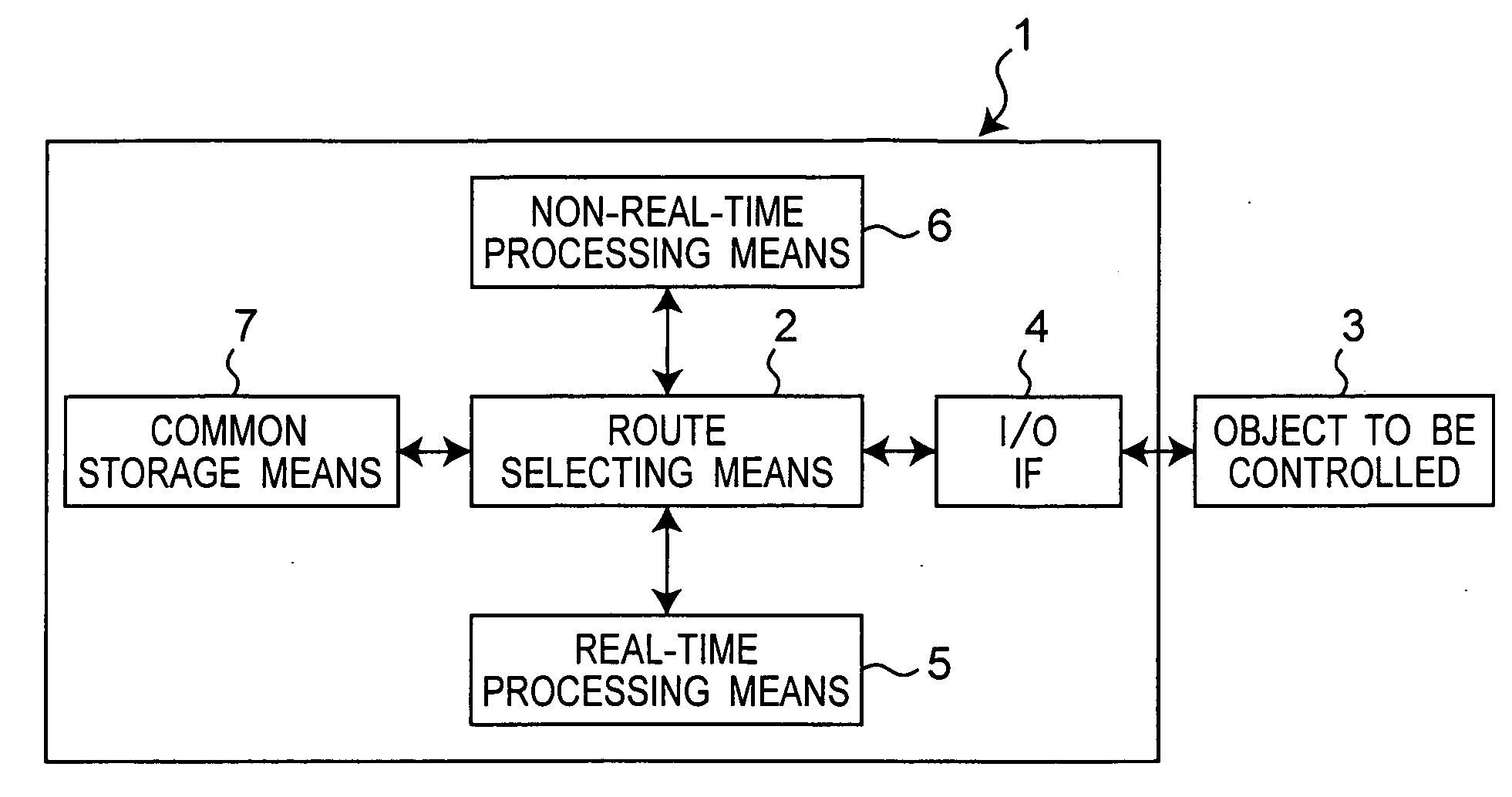
Realized is a robot controller capable of handling a large amount of data of images and so on necessary for advanced intelligence of control while securing a real-time performance with a simple structure. For this purpose, there are provided a motion control device for performing a calculation process for achieving motion control of an object to be controlled, a recognition and planning device for performing task and motion planning of the object to be controlled and recognition of outside world, an input / output interface for outputting a command to the object to be controlled and receiving as input, a state of the object to be controlled, and a route selecting device for controlling communications by switching connections among the motion control device the recognition and planning device, and the input / output interface. While controlling the communications by switching the connections among the motion control device, the recognition and planning device, and the input / output interface by the route selecting device, the motions of the robot of the object to be controlled are controlled on the basis of the results of the task and motion planning of the object to be controlled and the recognition of the outside world.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Robot controller
ActiveUS20060184272A1Programme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlControl communicationsMotor control
Realized is a robot controller capable of handling a large amount of data of images and so on necessary for advanced intelligence of control while securing a real-time performance with a simple structure. For this purpose, there are provided a motion control means for performing a calculation process for achieving motion control of an object to be controlled, a recognition and planning means for performing task and motion planning of the object to be controlled and recognition of outside world, an input / output interface for outputting a command to the object to be controlled and receiving as input, a state of the object to be controlled, and a route selecting means for controlling communications by switching connections among the motion control means, the recognition and planning means, and the input / output interface. While controlling the communications by switching the connections among the motion control means, the recognition and planning means, and the input / output interface by the route selecting means, the motions of the robot of the object to be controlled are controlled on the basis of the results of the task and motion planning of the object to be controlled and the recognition of the outside world.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
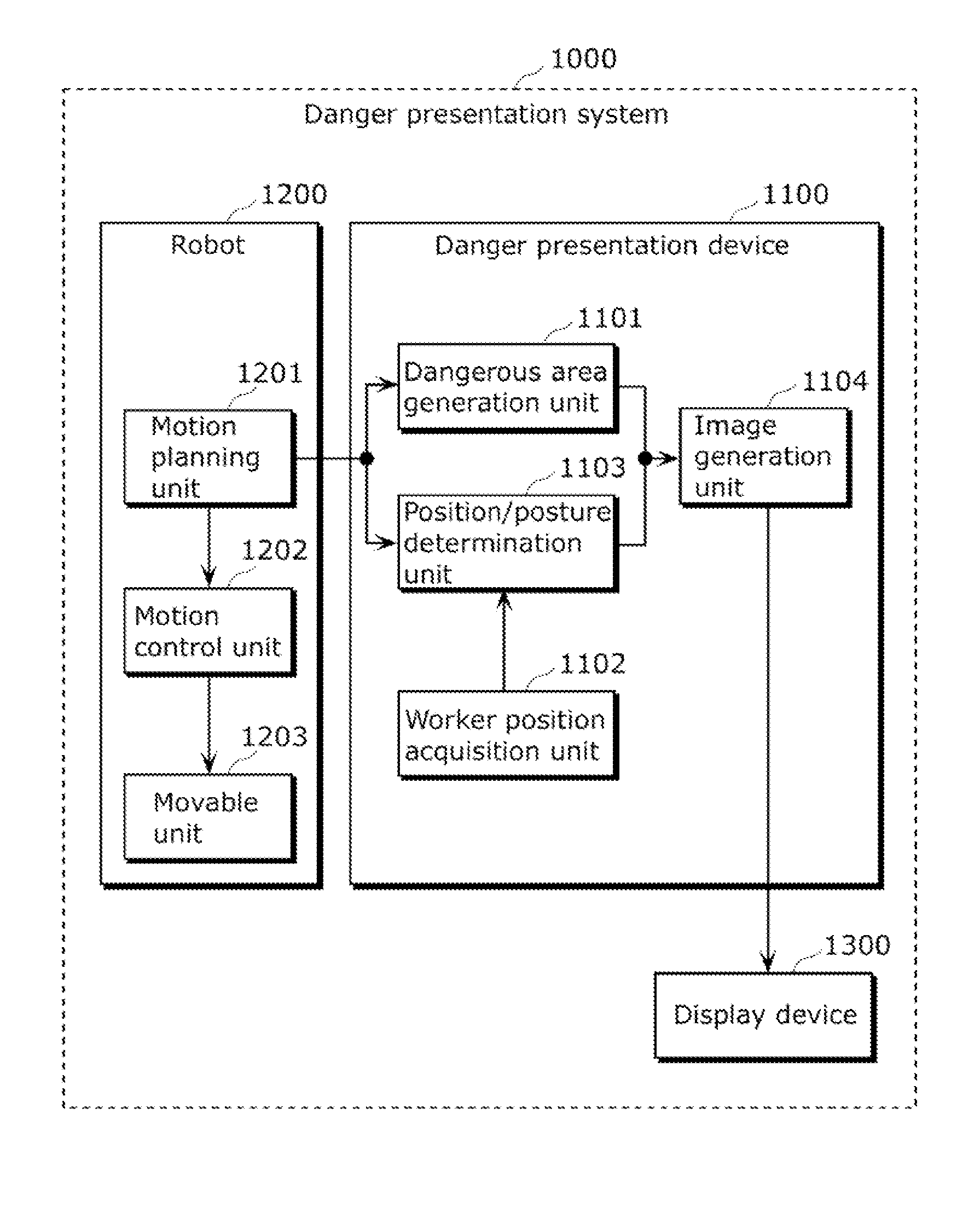
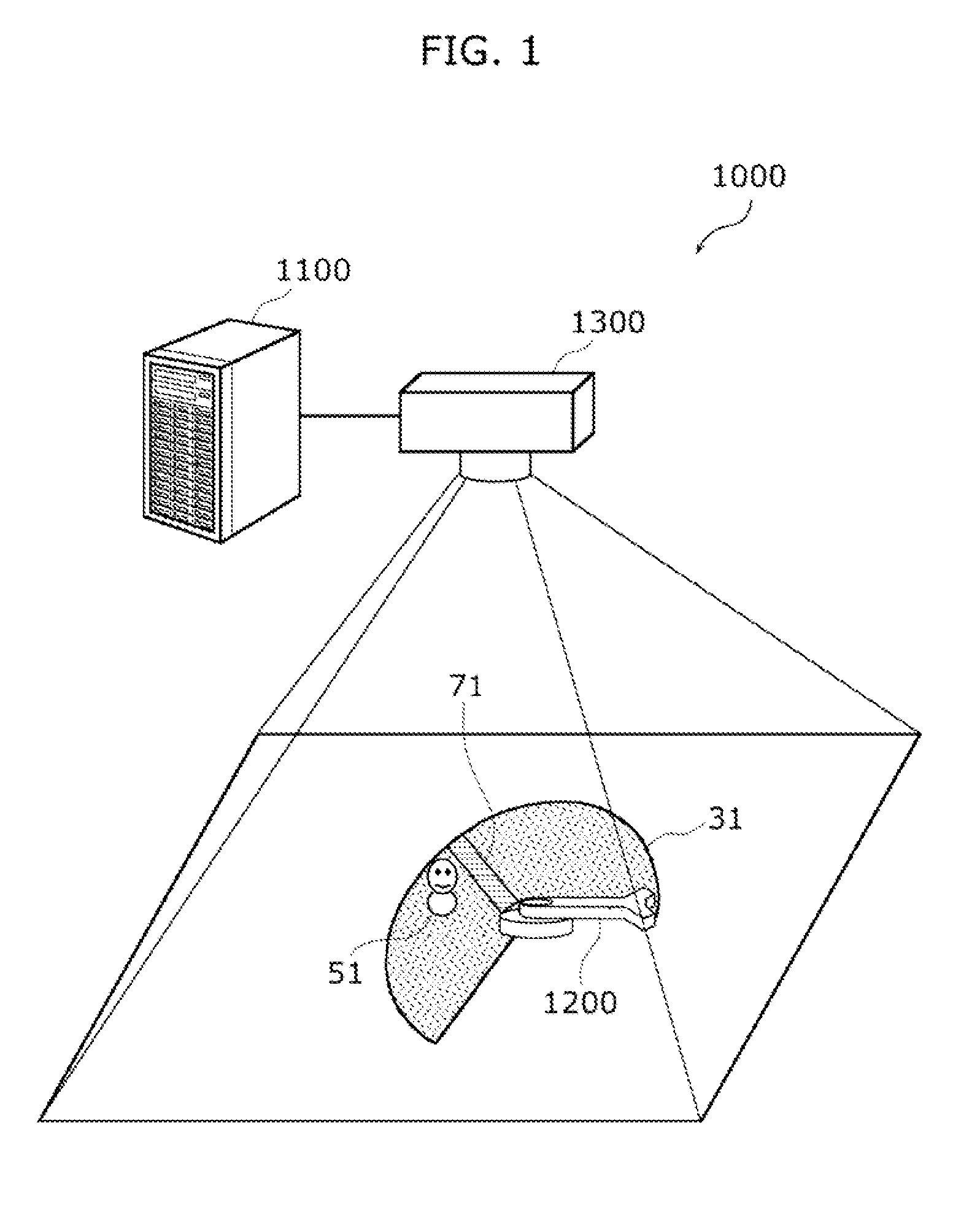
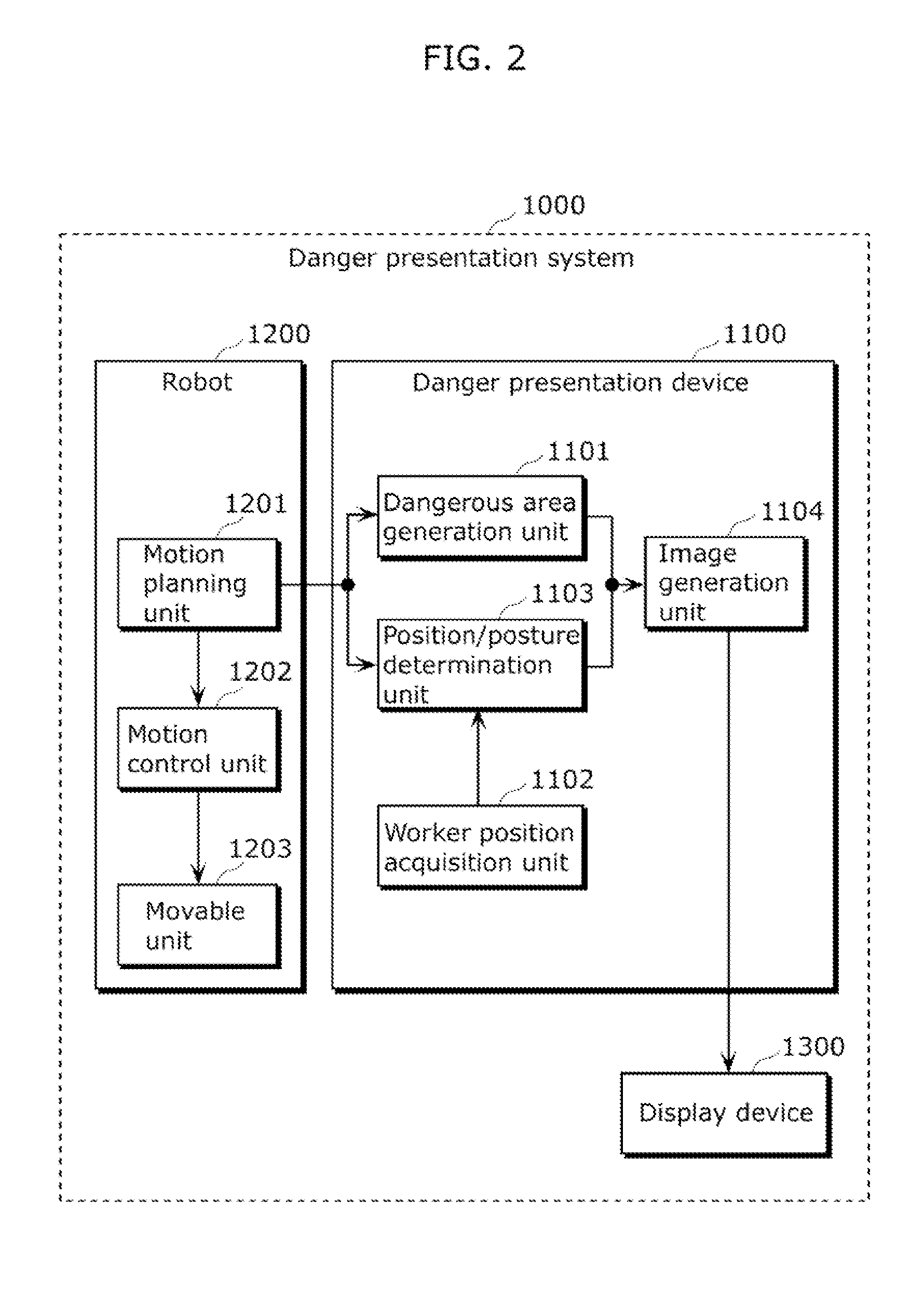
Danger presentation device, danger presentation system, danger presentation method and program
ActiveUS20120182155A1Dangerous situationSufficient distanceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringField of view
The danger presentation device includes: a worker position acquisition unit configured to acquire a worker position which is a position of a worker; a worker view range determination unit configured to determine a view range of the worker depending on the worker position acquired by the worker position acquisition unit; a position / posture determination unit configured to determine a position / posture which contains at least one of a position of a robot and a posture of the robot at a specific time in which at least a part of the robot which operates in accordance with a motion planning is included in the view range; and an image generation unit configured to generate image data for illustrating the position / posture determined by the position / posture determination unit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
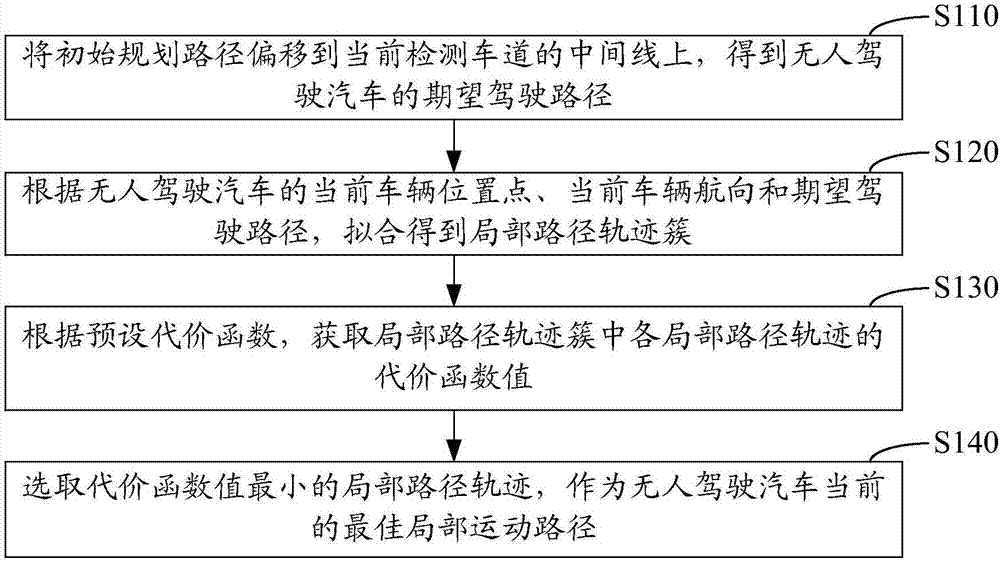
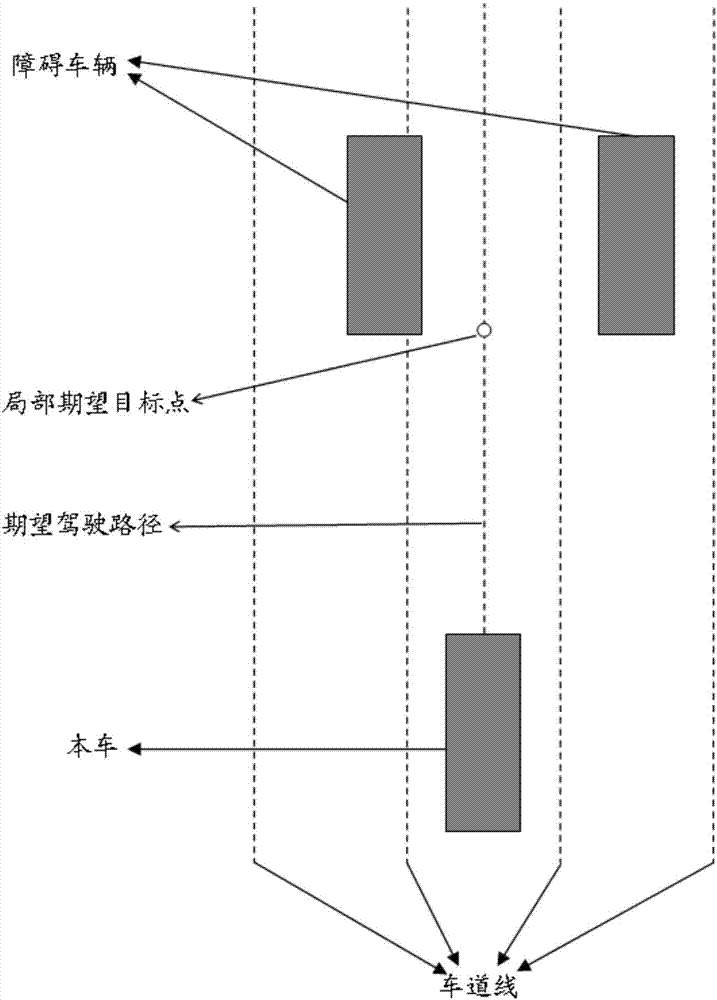
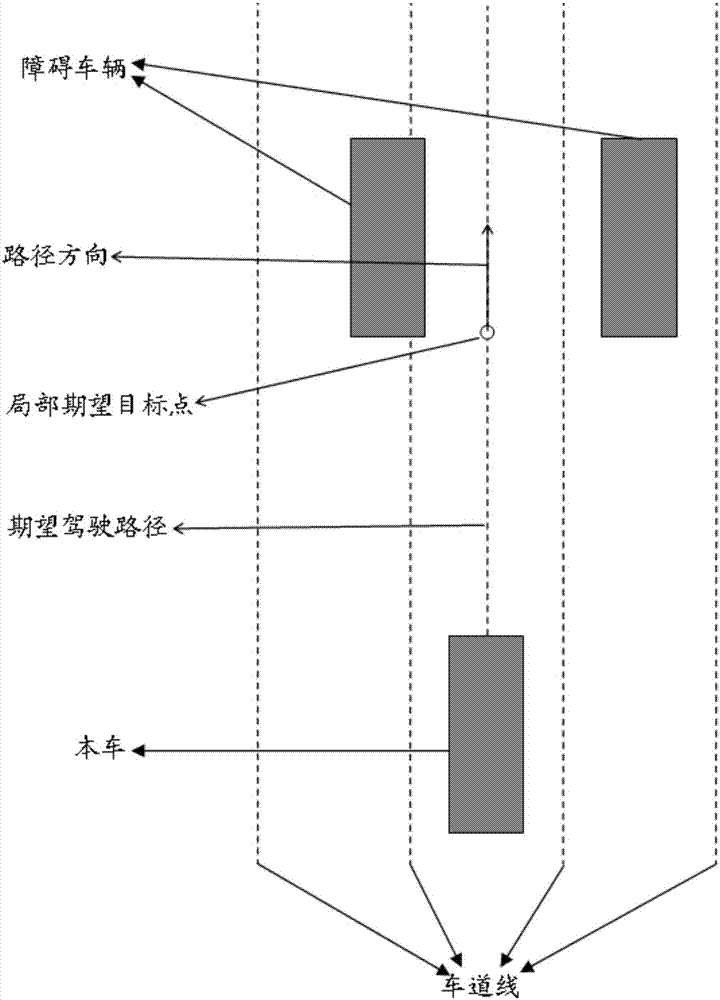
Method and device for local path motion planning of pilotless automobile
ActiveCN107992050AOptimal local motion pathPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesEngineeringMiddle line
The invention relates to a method and device for local path motion planning of a pilotless automobile. The method for local path motion planning of the pilotless automobile includes the steps of shifting an initial planning path to a middle line of a currently detected lane, to obtain a desired driving path of the pilotless automobile; according to a current vehicle position point of the pilotlessautomobile, the current vehicle heading and the desired driving path, fitting a local path trajectory cluster; according to a preset cost function, obtaining a cost function value of each local pathtrajectory in the local path trajectory cluster; and selecting a local path trajectory with the smallest cost function value as a current optimal local motion path for the pilotless automobile. According to the method and device for local path motion planning of the pilotless automobile, the optimal local motion path for driving is planned based on the desired driving path for the pilotless automobile and current vehicle peripheral obstacle information detected by a sensing system.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AUTOMOBILE GROUP CO LTD
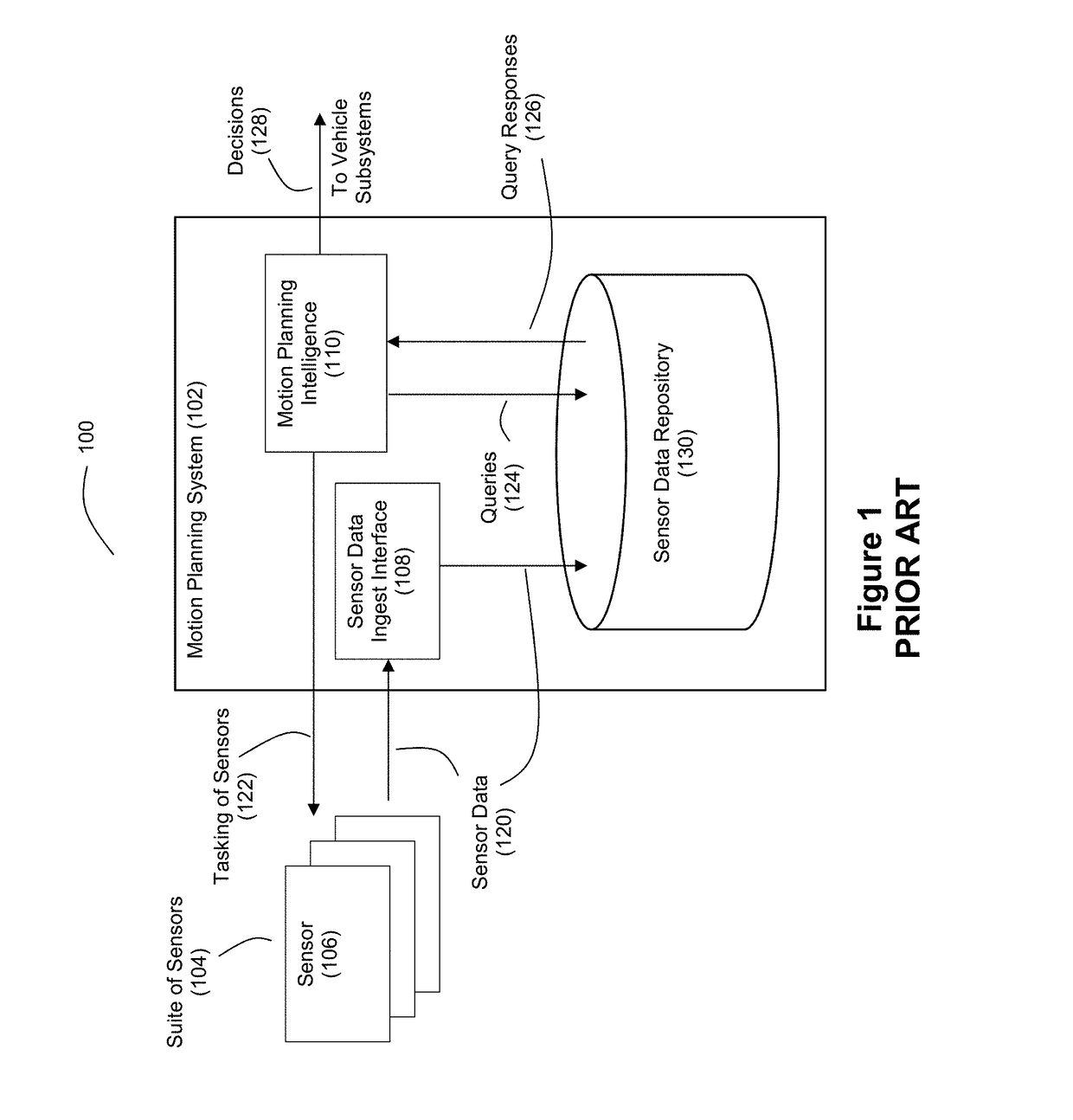
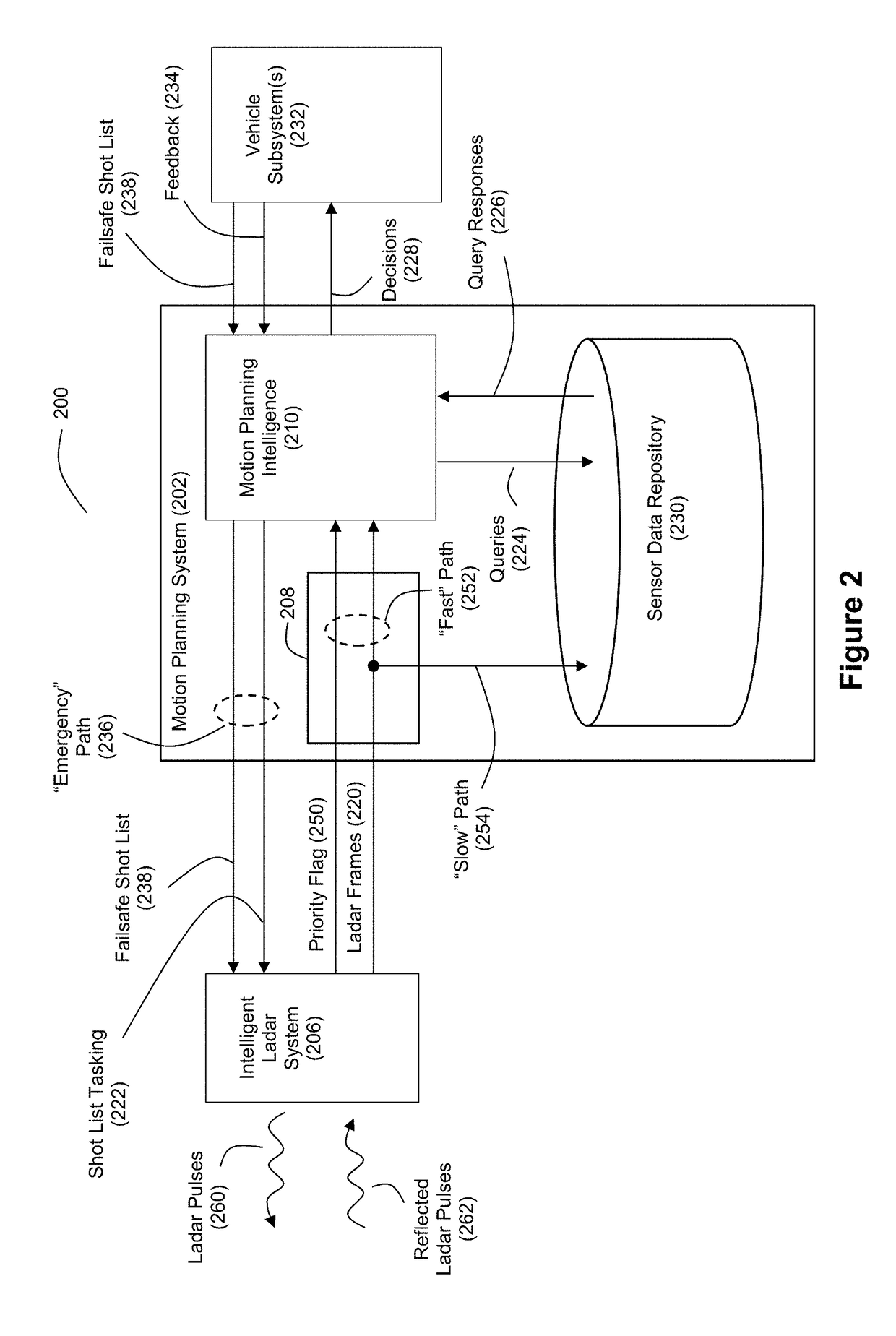
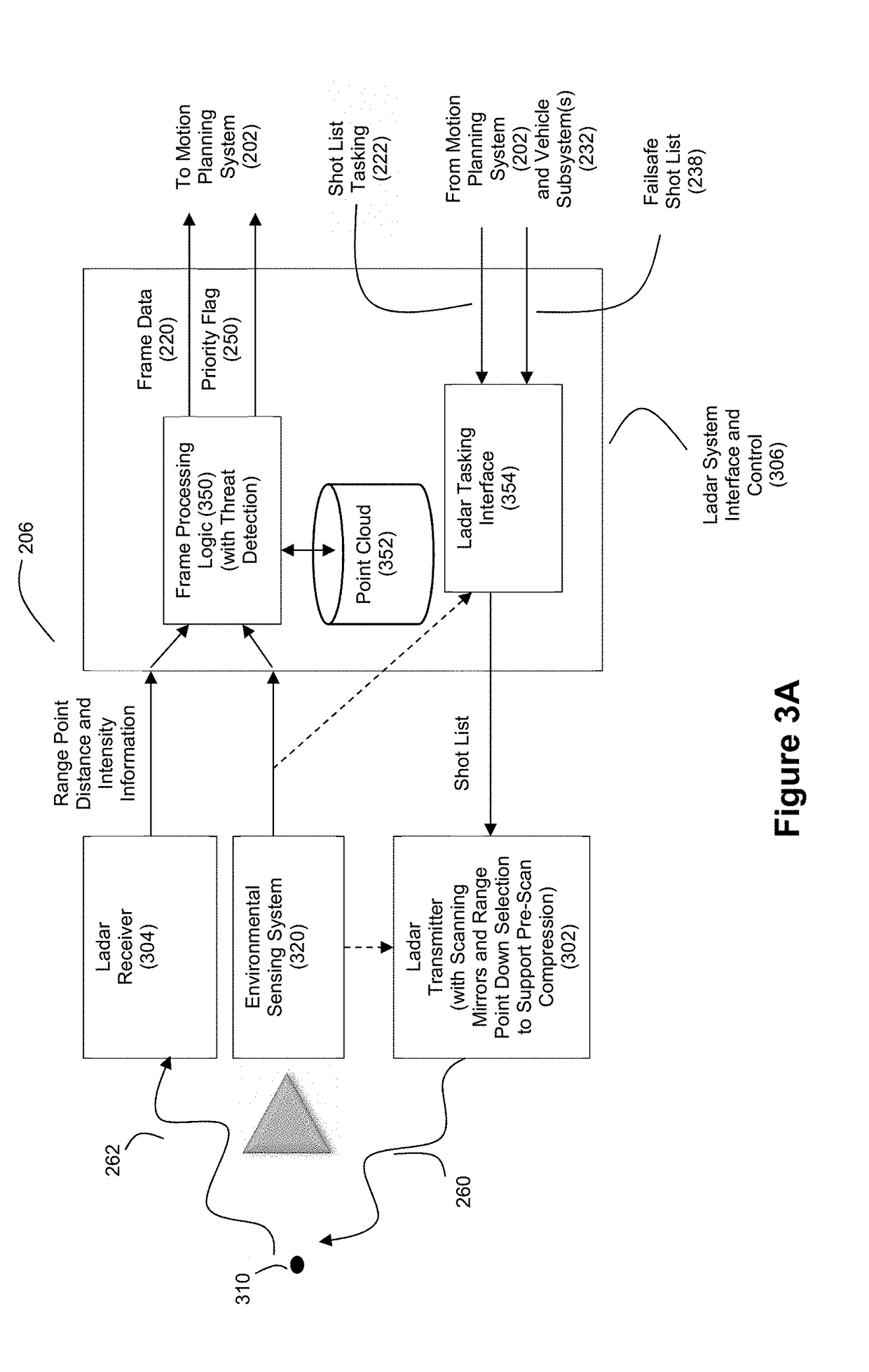
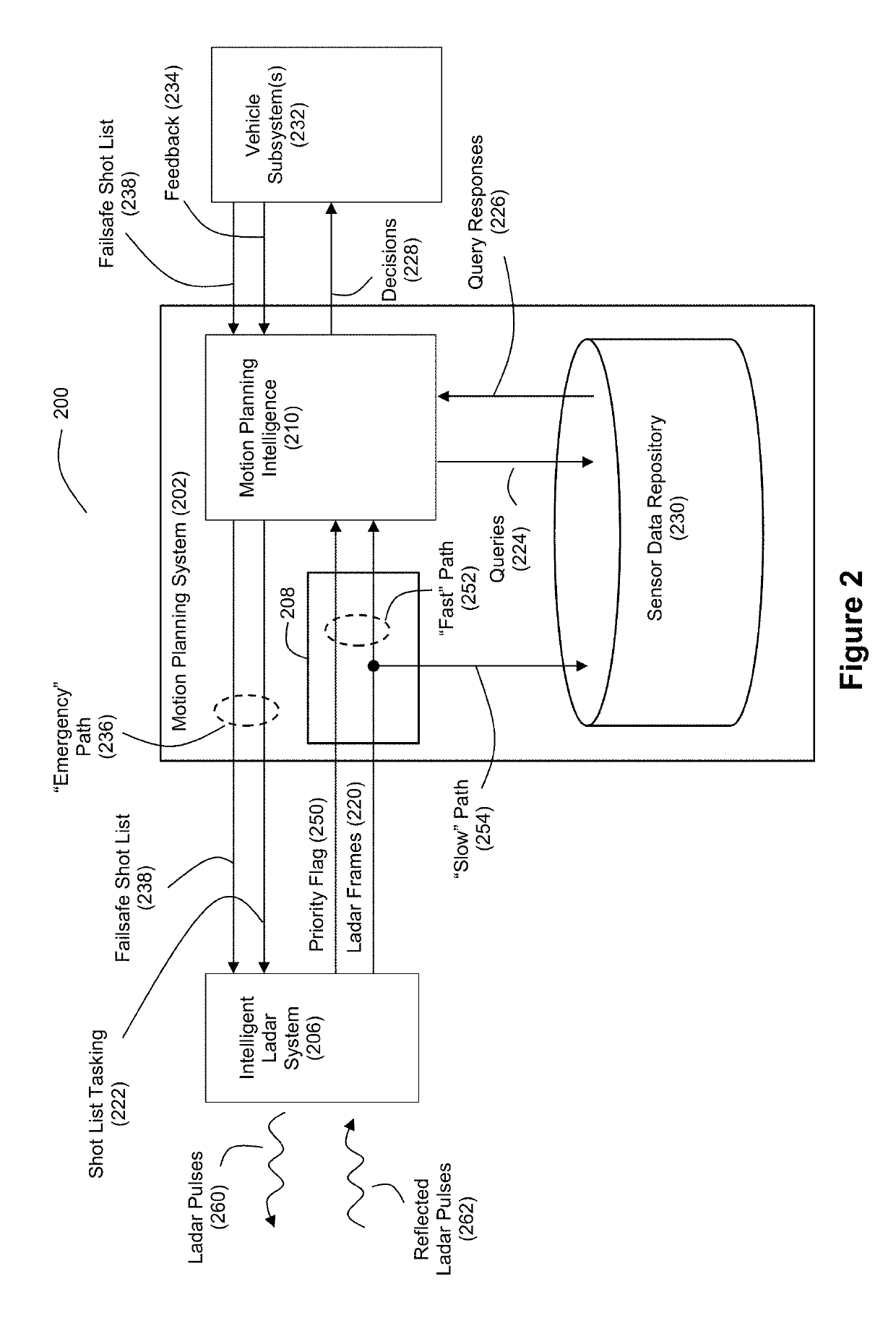
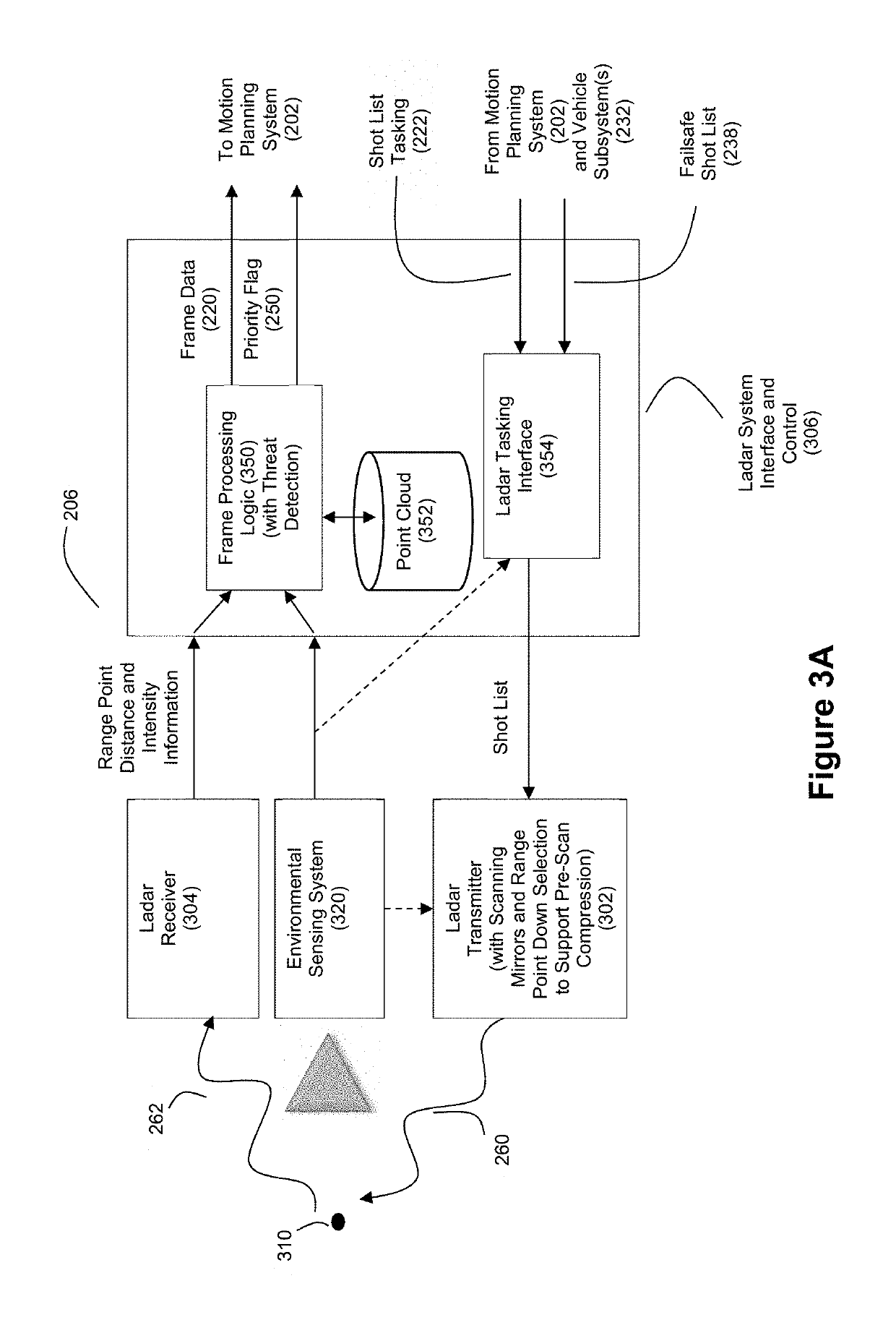
Intelligent Ladar System with Low Latency Motion Planning Updates
ActiveUS20190086550A1Rapid characterizationFast precisionCondensersElectromagnetic wave reradiationProgram planningRadar
Systems and methods are disclosed for vehicle motion planning where a sensor, such as a ladar system, is used to detect threatening or anomalous conditions within the sensor's field of view so that priority warning data about such conditions can be inserted at low latency into the motion planning loop of a motion planning computer system for the vehicle. The ladar system can perform compressive sensing to target the field of view with a plurality of ladar pulses.
Owner:AEYE INC
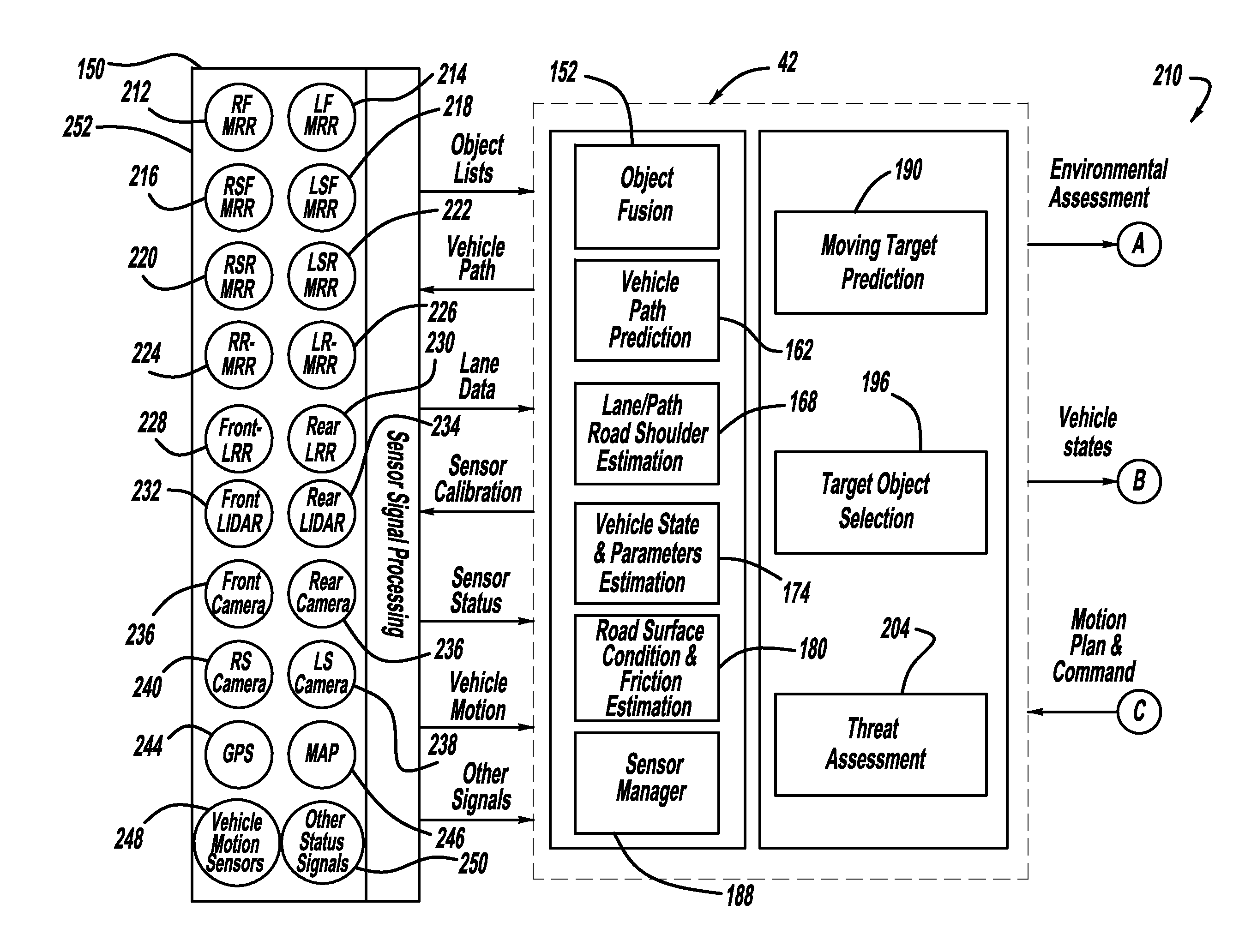
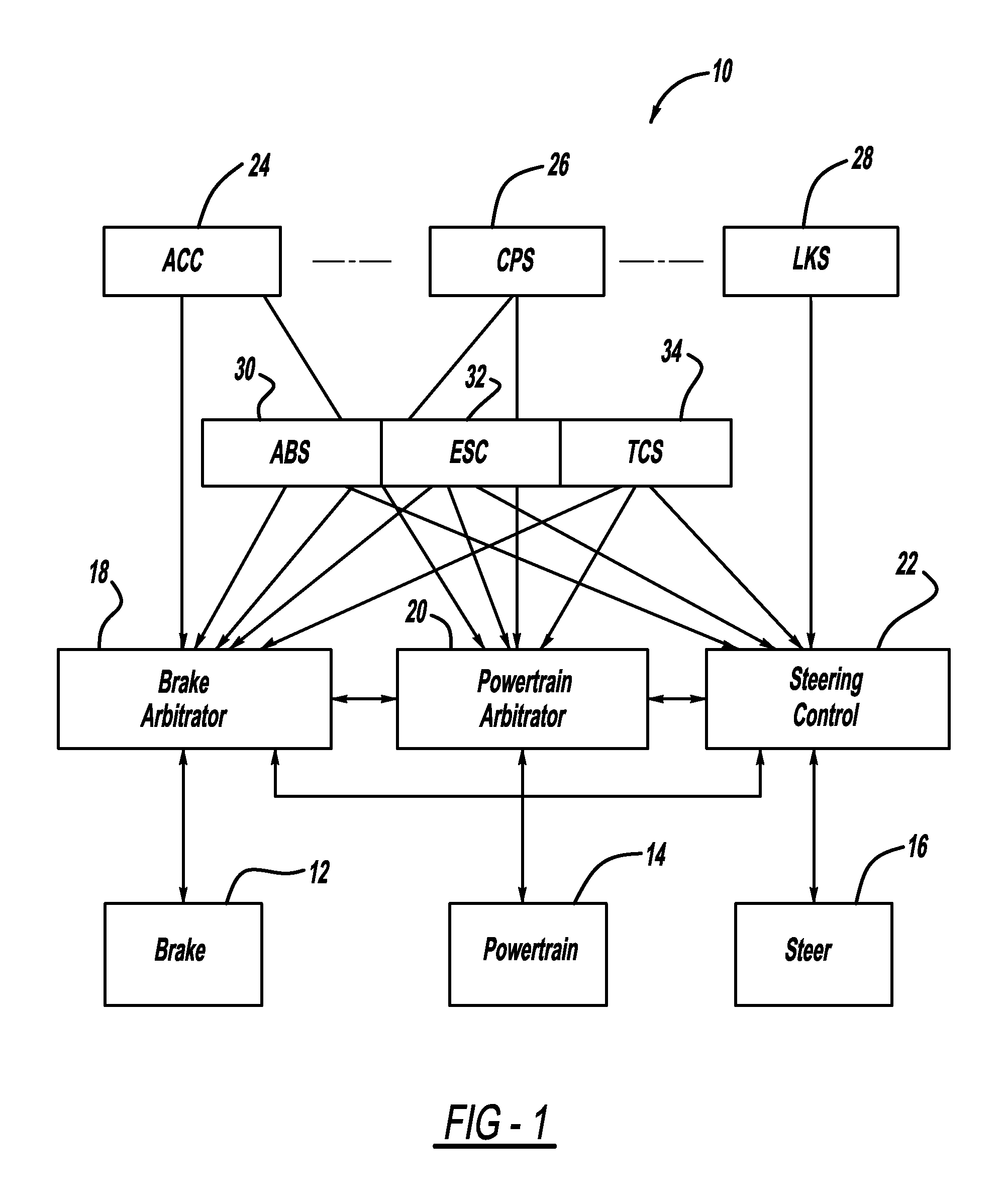
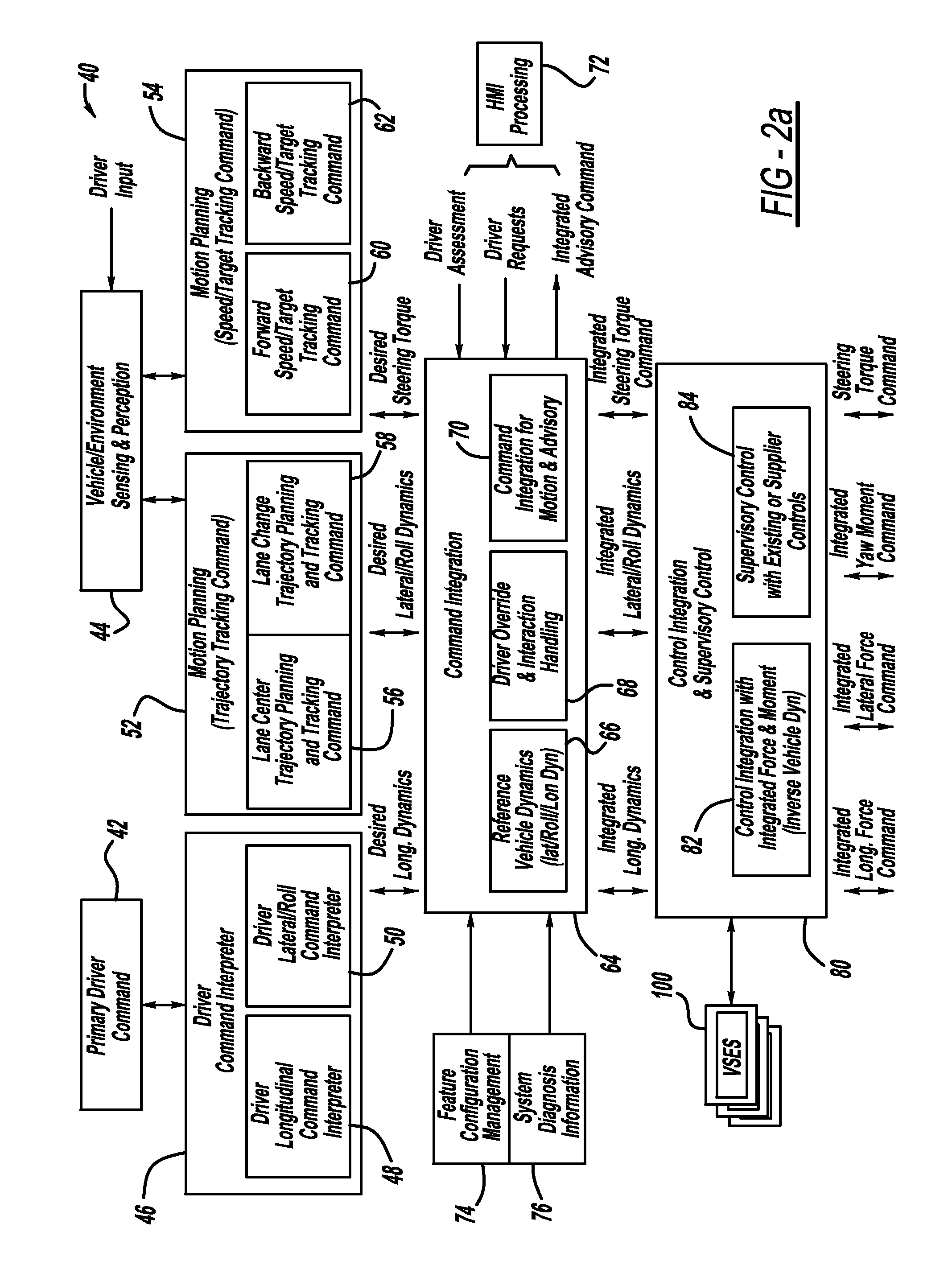
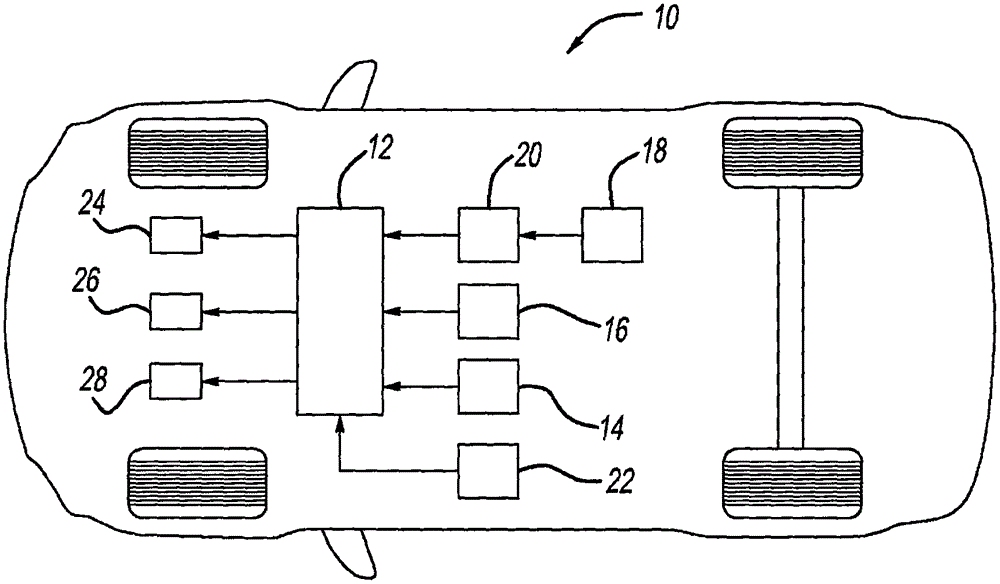
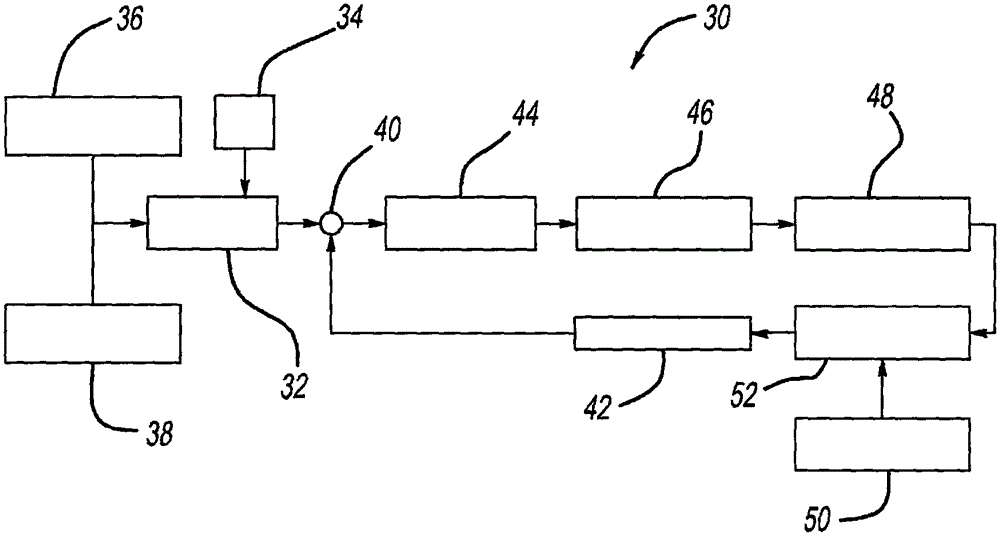
Function decomposition and control architecture for complex vehicle control system
InactiveUS20110098886A1Digital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsControl systemDecomposition
A vehicle control architecture designed based on a top-down approach with abstraction and modularity. The control architecture includes a vehicle / environment sensing and perception processor that processes sensor signals, and motion planning processors that provide lane center trajectory planning and tracking command, lane change trajectory planning and tracking command, and forward and backward speed and target tracking command. The architecture also includes a driver command interpreter that interprets driver commands and a command integration processor that provides reference dynamics for vehicle lateral, roll and longitudinal dynamics. The architecture also includes a control integration and supervisory controller that provides control integration and outputs integrated longitudinal force command signals, integrated lateral force command signals, integrated yaw moment command signals and steering torque command signals that are used by a vehicle longitudinal controller and a vehicle lateral controller.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
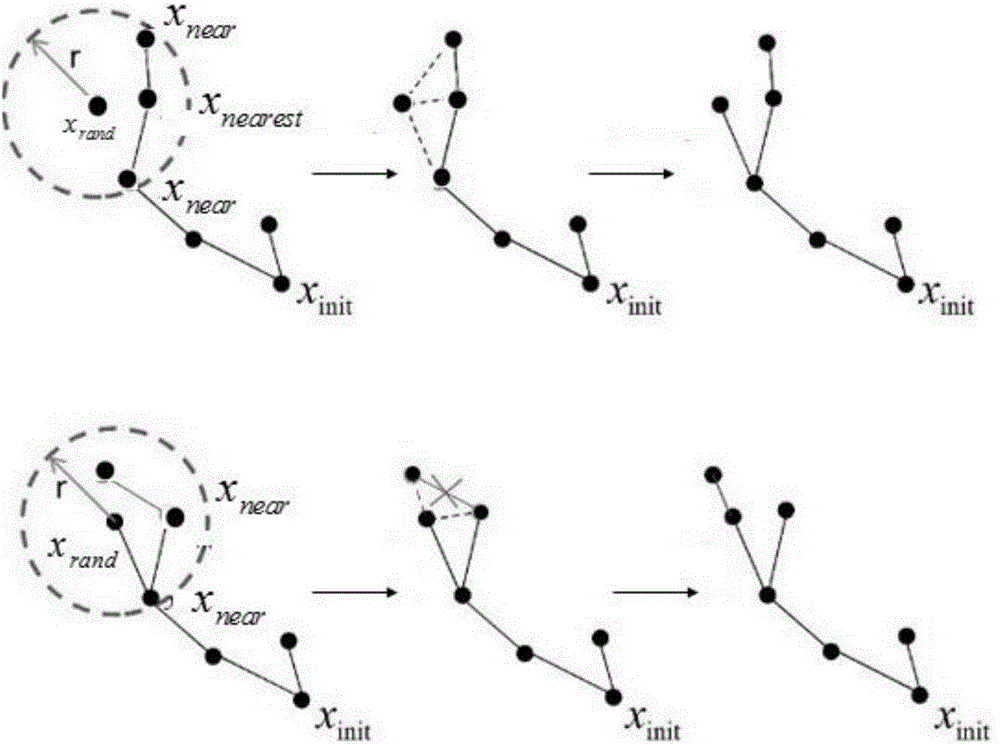
Improved RRT<*> obstacle avoidance motion planning method based on multi-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm
InactiveCN106695802AImprove convergence rateReduce search timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorRegular distributionNODAL
The invention discloses an improved RRT<*> obstacle avoidance motion planning method based on a multi-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm, and belongs to the field of mechanical arm motion planning. A six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm model with seven connecting rods and six rotary joints is built; parameters in a to-be-searched space are determined; if the distance is shorter than the distance of a path with lowest cost, the distances between a near node in a set to an initial point and the distance between the node to a random point are temporarily determined as the minimum path; a newly generated sigma is subjected to collision detection, and the node and the path are added if the newly generated path does not collide an obstacle interval; the steps are repeated until the optimal path is found; and the generated path is added into a path planning device. Compared with the prior art, the method has the following advantages that the random search characteristic is changed in a mode of adding normal distribution, the algorithm convergence rate can be increased through the heuristic search, the RRT<*> algorithm has the evolutionary optimization path, and a large number of calculations is not needed; and after Gaussian distribution of an inspiration point near a target point is added, the convergence rate is increased, and the search time is shortened.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
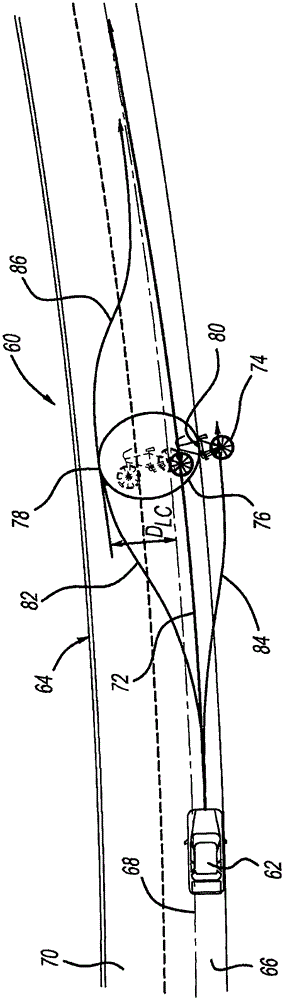
Unified motion planner for autonomous driving vehicle in avoiding the moving obstacle
ActiveCN105539586ANavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSteering partsMotion planningAutomotive engineering
A system and method for providing path planning and generation in a semi-autonomous or autonomously driven vehicle that provides a steering correction for collision avoidance purposes. The method includes detecting a lane center of a roadway lane that the vehicle is traveling along and determining a lane centering path that directs the vehicle from its current position to the lane center. The method also includes detecting a moving object in front of the vehicle and determining if a collision between the vehicle and the object will occur if the vehicle travels along the lane centering path at the current vehicle speed. The method solves a fifth-order polynomial equation to define a collision avoidance path from the current vehicle position to a waypoint a safe distance from the object and a return path from the waypoint to the lane center that the vehicle is automatically steered along.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
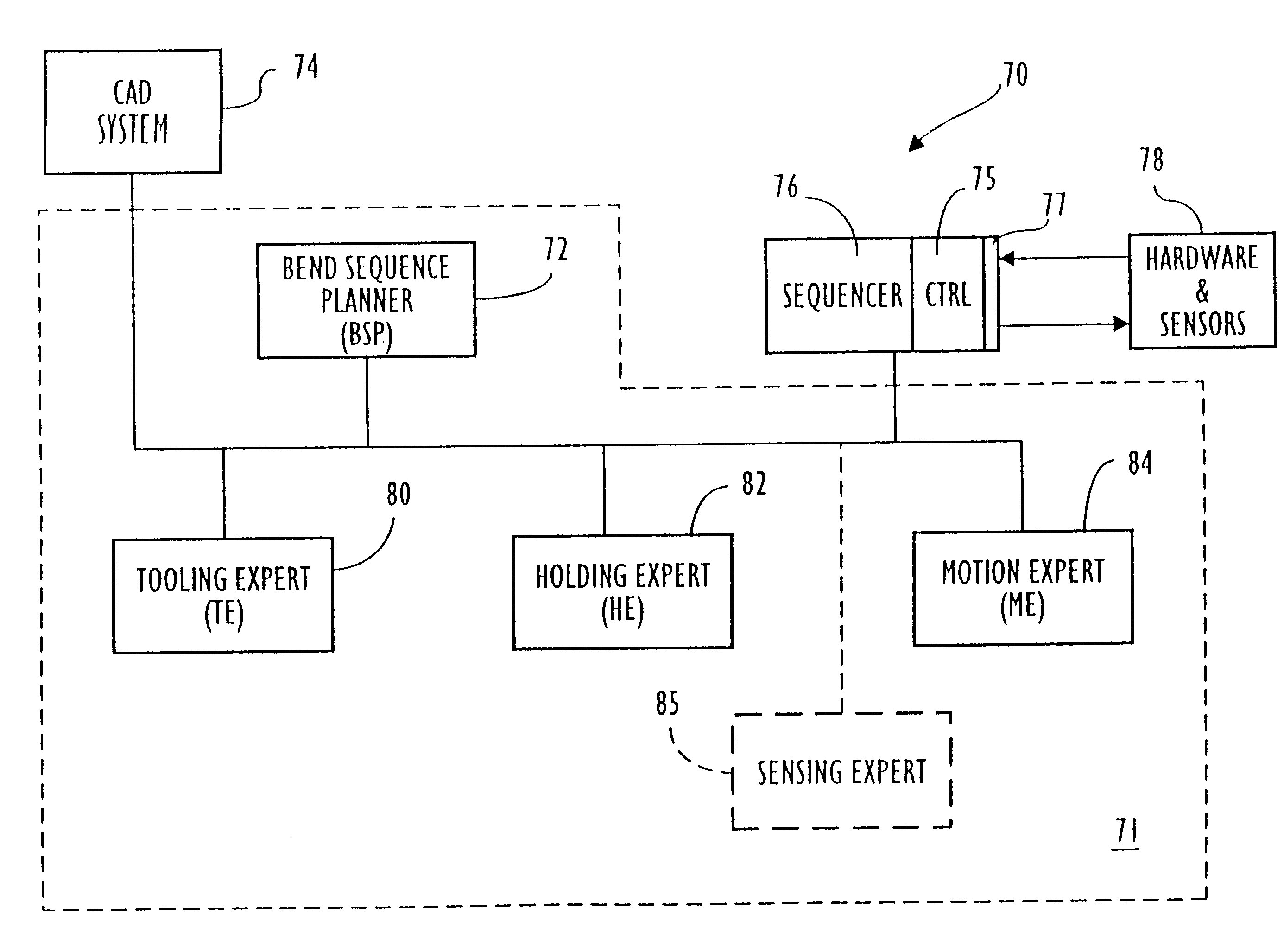
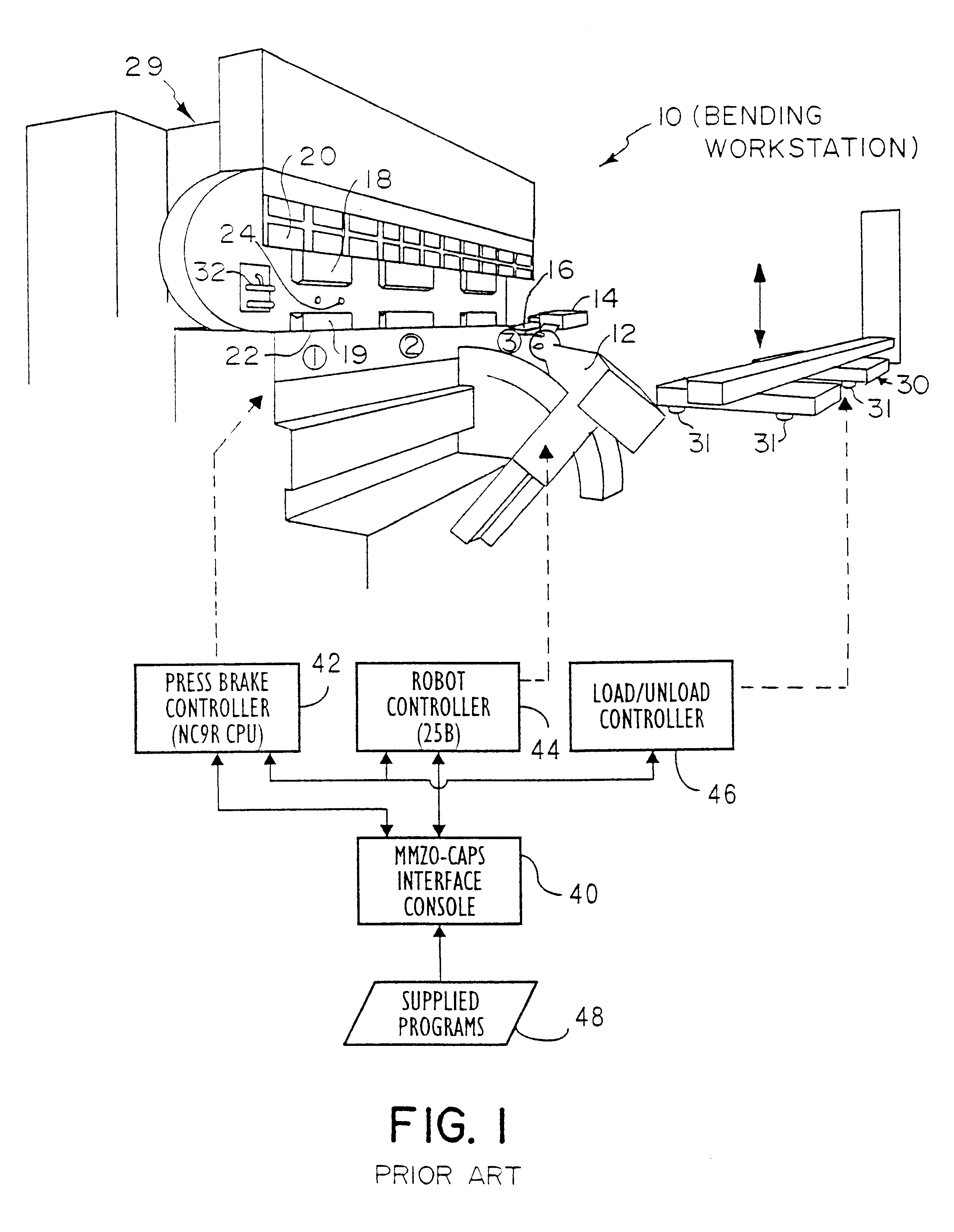
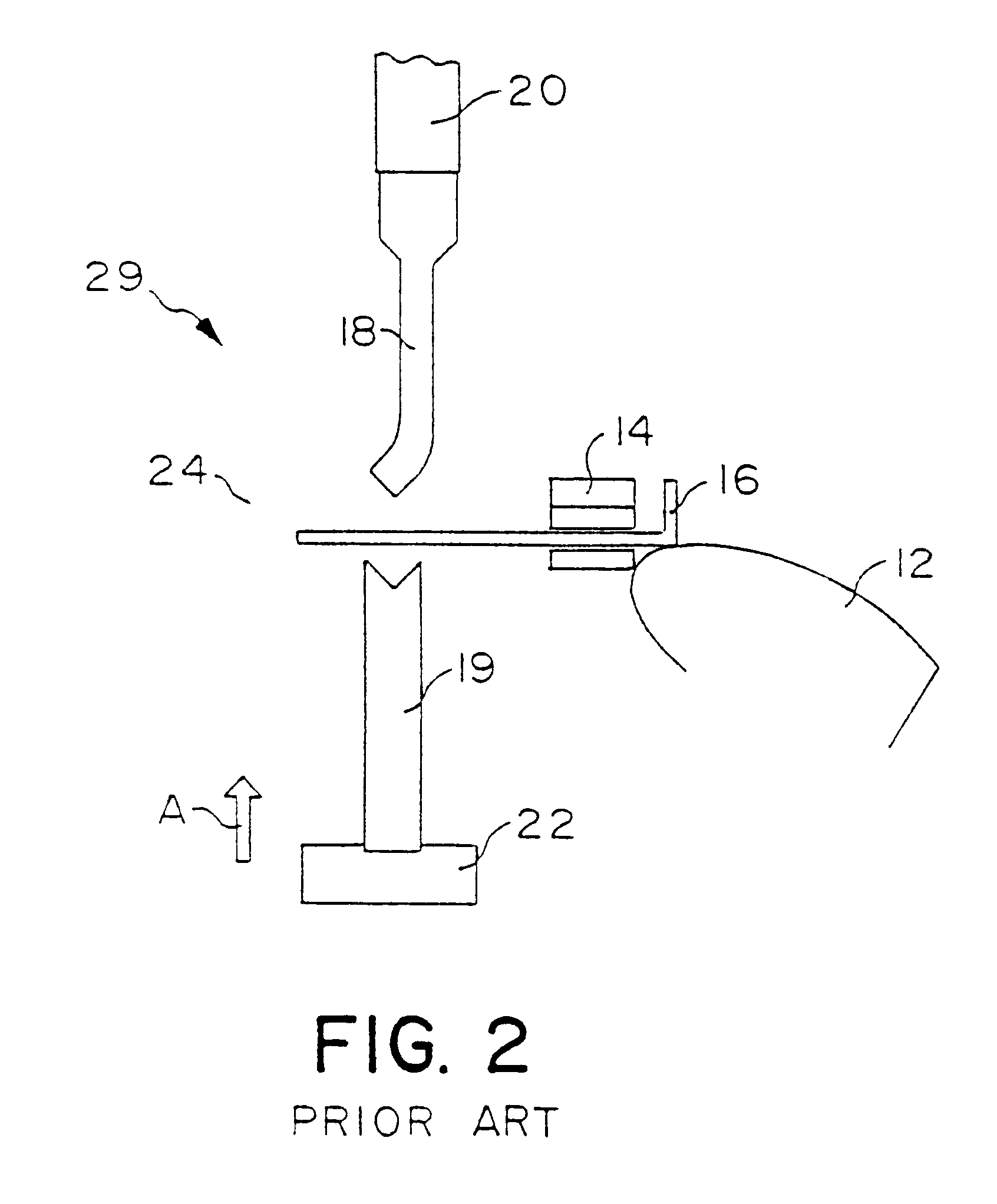
Intelligent system for generating and executing a sheet metal bending plan
An intelligent sheet metal bending system is disclosed, having a cooperative generative planning system. A planning module interacts with several expert modules to develop a bending plan. The planning module utilizes a state-space search algorithm. Computerized methods are provided for selecting a robot gripper and a repo gripper, and for determining the optimal placement of such grippers as they are holding a workpiece being formed by the bending apparatus. Computerized methods are provided for selecting tooling to be used by the bending apparatus, and for determining a tooling stage layout. An operations planning method is provided which allows the bending apparatus to be set up concurrently while time-consuming calculations, such as motion planning, are performed. An additional method or system is provided for positioning tooling stages by using a backgage guide member which guides placement of a tooling stage along the die rail the bending apparatus. A method is provided for learning motion control offset values, and for eliminating the need for superfluous sensor-based control operations once the motion control offset values are known. The planning system may be used for facilitating functions such as design and assembly system, which may perform designing, costing, scheduling and / or manufacture and assembly.
Owner:U S AMADA +1
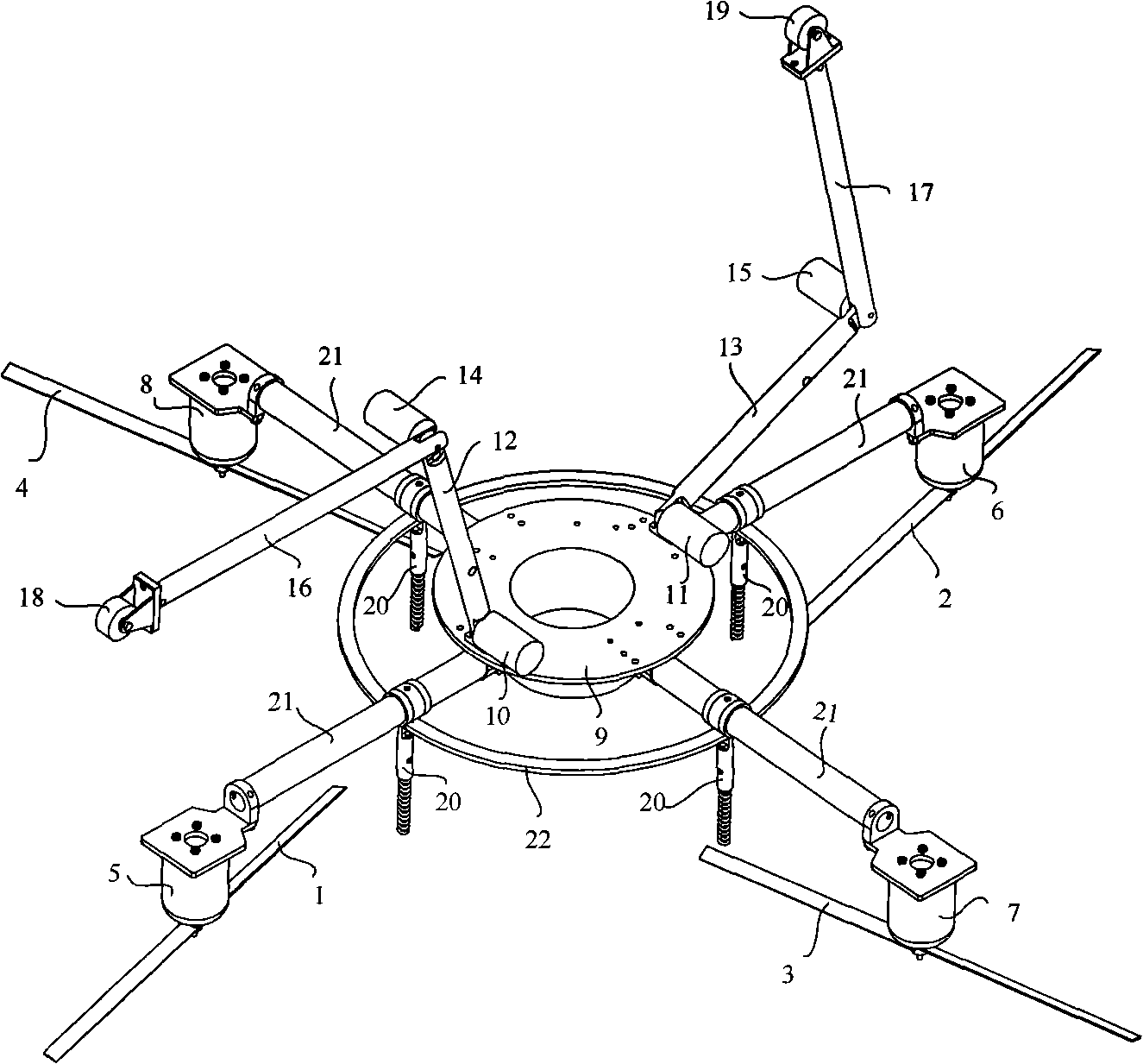
Multi-rotor wheel-leg type multifunctional air robot and sports programming method thereof
InactiveCN101491898AAchieve integrationSimple mechanical structureProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationKnee Joint
The invention discloses a multi-rotator leg-wheeled multifunctional aerial robot and a motion planning method thereof. The robot comprises rotators A, B, C and D, rotator driving motors A, B, C and D, wall-climbing thighs A and B, wall-climbing legs A and B, hip joint driving motors A and B, knee joint driving motors A and B, a robot main body, a wall-surface running wheels A and B, a ground supporting rod, rotating supporting rods and a rigidity-strengthened ring. The motion planning process comprises the motion planning of the robot in flight state, the motion planning of the robot undergoing a change from the flight state to a wall climbing state, the motion planning of the robot in a wall climbing state, the motion planning of the robot crossing an obstacle during wall climbing, and the motion planning of the robot undergoing a change from the wall climbing state to the flight state. The robot realizes the fusion of a rotator type aircraft and a leg-wheeled movement mechanism, is simple in mechanical structure and easy to realize, and has the advantages of high stability, small volume, strong adaptability to wall surfaces, large obstacle crossing capacity, wide application range and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
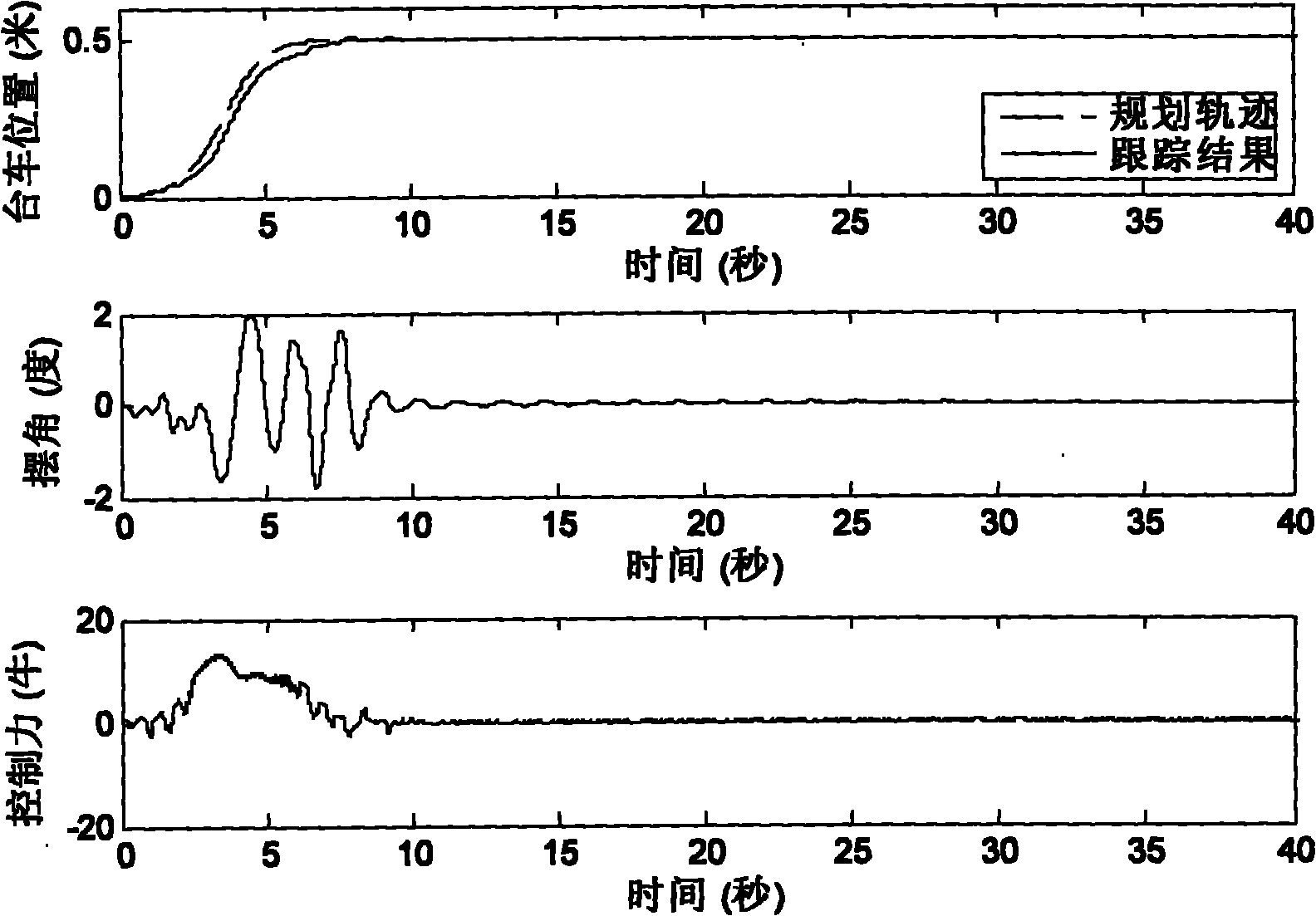
Motion planning-based adaptive control method for bridge crane
InactiveCN102030263AShow reliabilityImprove practicalityLoad-engaging elementsSelf adaptiveSmall range
The invention discloses a motion planning-based adaptive control method for a bridge crane. The method comprises the following steps of: formulating a motion planning, and designing an expected position-time curve for a crane trolley, wherein if the trolley moves along the curve, the trolley can reach a target position relatively quickly, and the load swing angle is in a small acceptable range; meanwhile, adjusting parameters of the trolley aiming at different conditions and requirements so that the maximum transport speed and the acceleration performance of the trolley meet the requirements and constraints of actual working conditions; and designing an adaptive tracking controller, and acquiring a control output by measuring trolley position, speed, load swing angle and angular speed on line in real time. When the resistance parameters such as load quality, sling length, friction and the like of the crane trolley are unknown, the controller can well track the set motion curve, and finally the error, swing angle and control force are fully kept in a small range and finally converged to 0. Therefore, the invention has the advantages of the locus planning and adaptive tracking control method.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
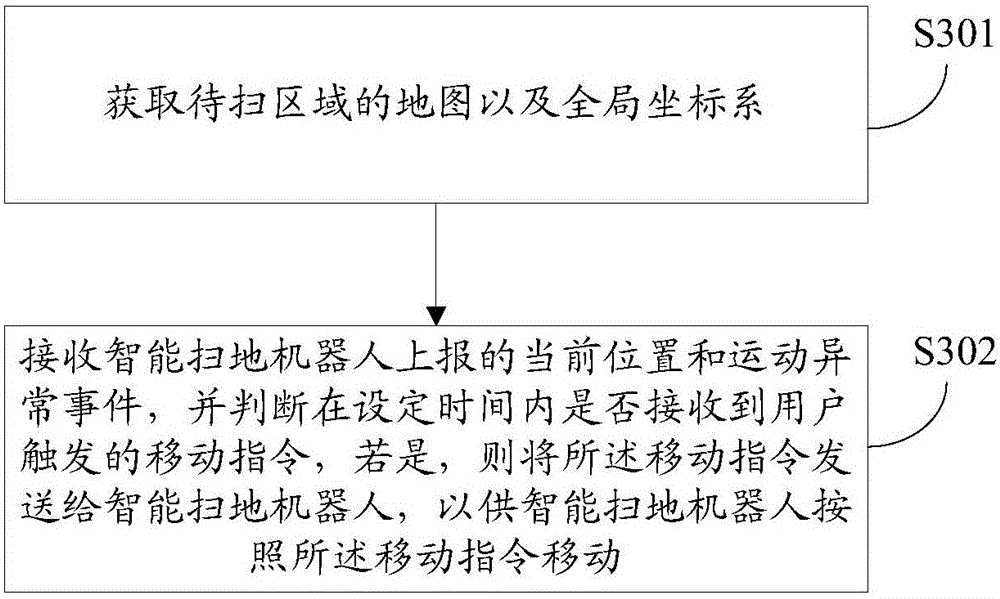
Interaction control method and device of intelligent sweeping robot
ActiveCN105739500ARealize intelligenceEmbody intelligencePosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesMotion planningInteraction control
The invention provides an interaction control method and device of an intelligent sweeping robot. The technical procedures, executed on an intelligent sweeping robot side, of the method comprise the following steps: in the moving process of the intelligent sweeping robot, when a motion abnormity occurs, a motion abnormity event of the intelligent sweeping robot is reported to a user terminal, and whether a moving instruction sent by the user terminal is received is determined; and, if the moving instruction sent by the user terminal is received, a movement is performed according to the moving instruction. Cleaning is efficiently completed on the basis of an accurate motion plan, and, through achievement of man-machine interactions, intelectualization and good experience of an intelligent household electrical appliance can be reflected well.
Owner:HAIER YOUJIA INTELLIGENT TECH BEIJING CO LTD +1
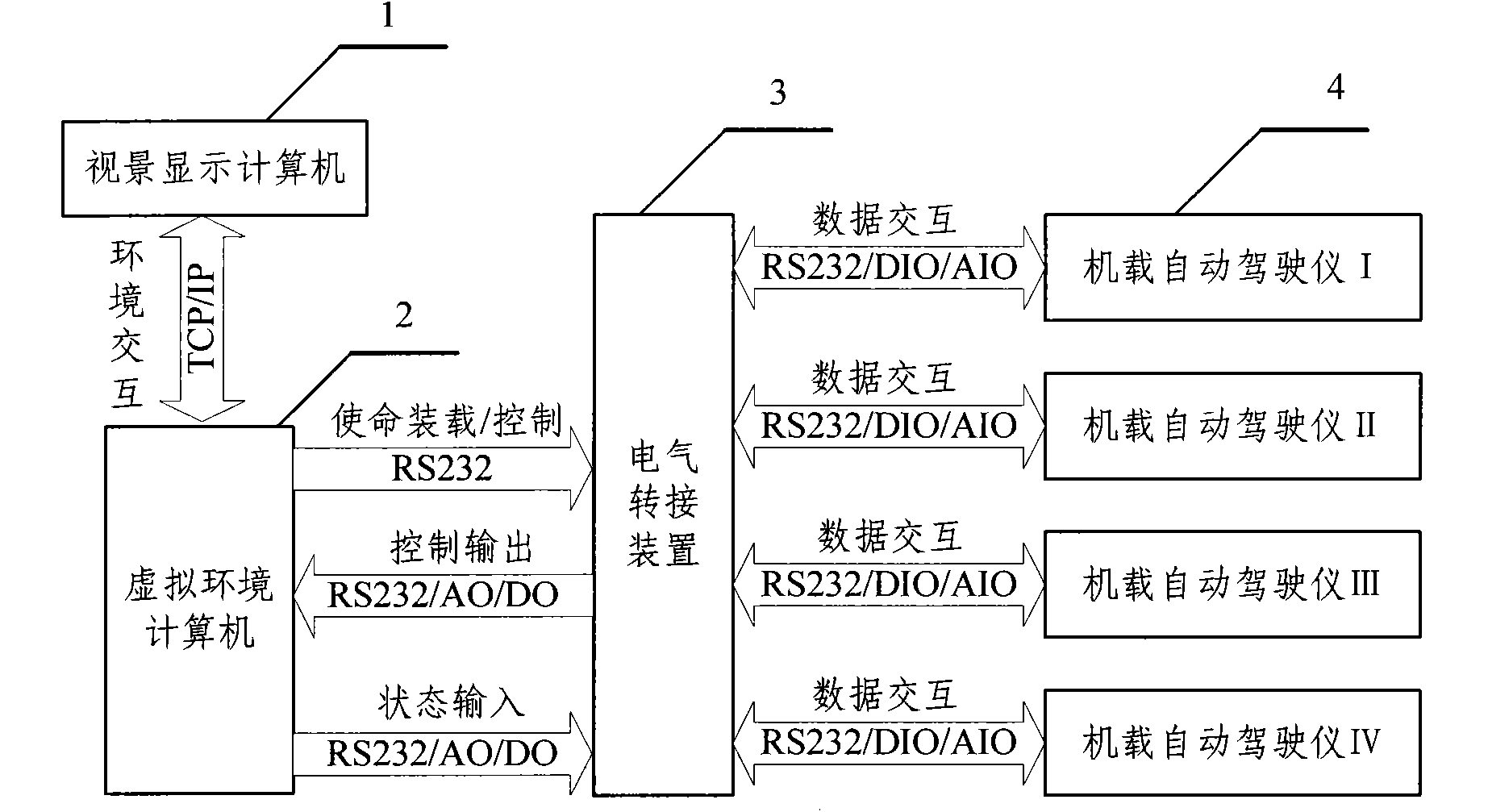
Multi-underwater robot semi-physical simulation system and control method thereof
ActiveCN102117071AImprove scalabilityImprove portabilityVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlDynamic modelsClosed loop
The invention relates to a multi-underwater robot semi-physical simulation system and a control method thereof. The system comprises a visual scene display computer, a virtual environment computer, an electric switching device and an airborne autopilot. The visual scene display computer is in network communication connection with the virtual environment computer; kinematics models and dynamics models of each robot are stored in the virtual environment computer, and various kinds of virtual sensor device information is generated through model computation; the electric switching device switchesa standard cable interface of an expansion card of the virtual environment computer to be an interface capable of conveniently connecting the multi-underwater robot airborne autopilot; the airborne autopilot is a real underwater robot soft hardware control system, and is used for generating the executor control quantity according to own motion planning and closed loop, transmitting the executor control quantity to the virtual environment computer through the electric switching device and transmitting cooperation information to other robots through the virtual environment computer according tomission requirements. The multi-underwater robot semi-physical simulation system and the control method thereof are convenient to expand sensors and device nodes, and the system is excellent in expandability, high in transportability and convenient to configure various kinds of underwater robots.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
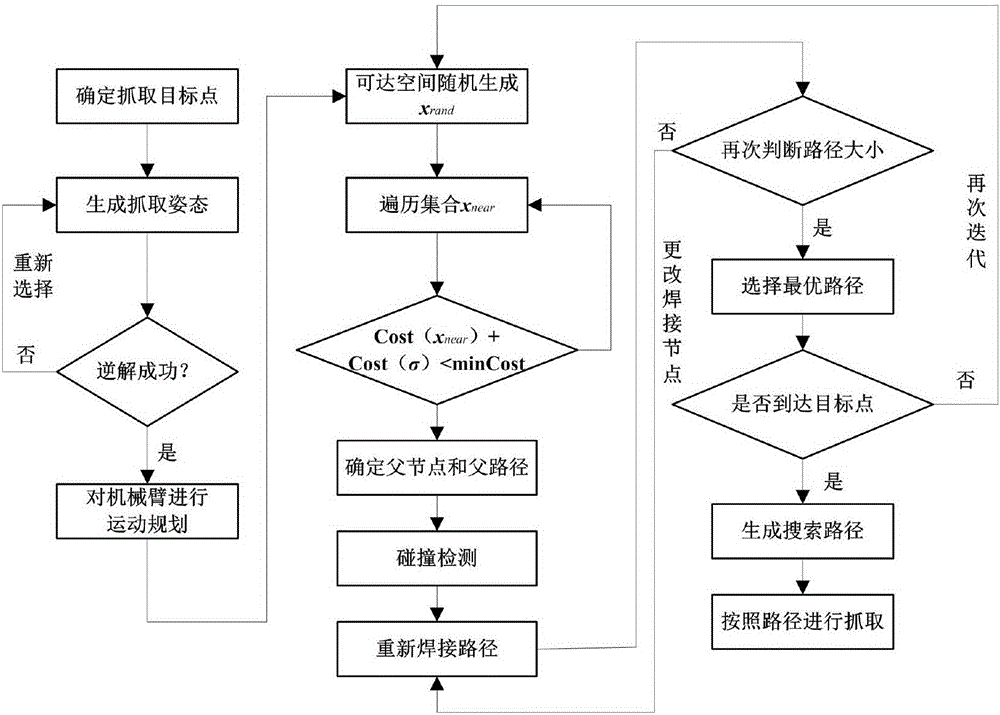
Mechanical arm on-line obstacle avoidance movement planning method
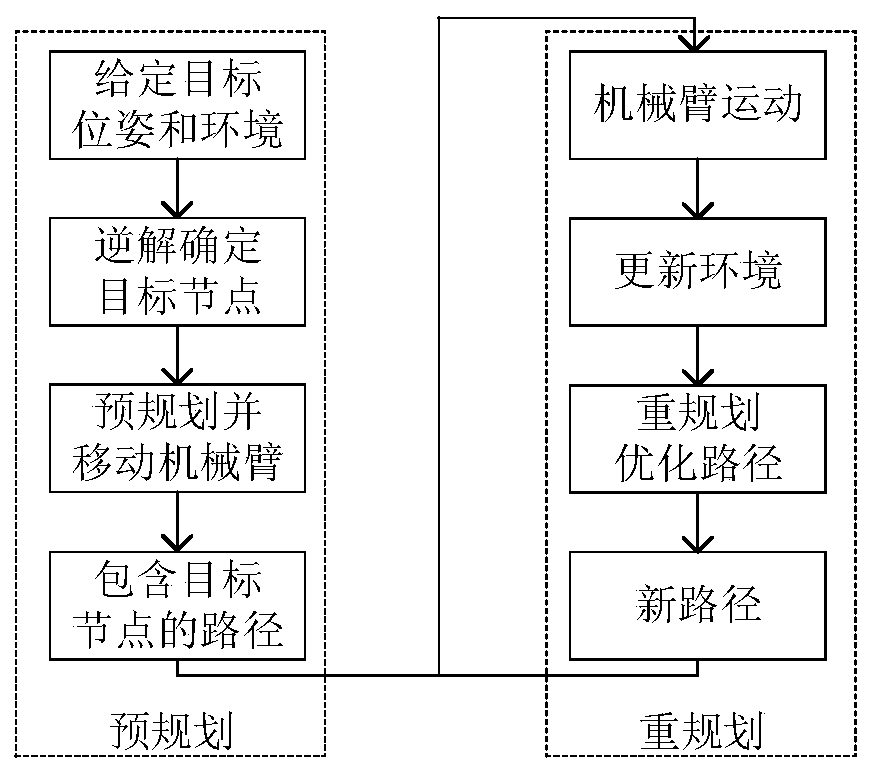
The invention provides a mechanical arm on-line obstacle avoidance movement planning method, and relates to the technical field of mechanical arm movement planning. The mechanical arm on-line obstacleavoidance movement planning method comprises the steps that modeling is conducted on a mechanical arm and an obstacle, and a target node is determined through the inverse solution; in the pre-planning stage, sampling is conducted in the joint space to generate a new node, collision detection is conducted on the new node to determine whether the new node is added to a search tree or not, and a node which enables the cost of the new node to be lowest and is located in the search tree serves as a parent node of the new node; first k nodes are planned from the search tree and sent to a track planning device until the situation that the target node enters the re-planning stage is searched out; and in the re-planning stage, sampling is conducted nearby path nodes to optimize a path, the path isplanned again when the obstacle movement and the path conflict, and planned nodes are sent to the track planning device at the same time until a mechanical arm moves to the target node. By the adoption of the mechanical arm on-line obstacle avoidance movement planning method, the path planning and the movement of the mechanical arm are synchronously conducted, the on-line obstacle avoidance movement is achieved, and even though the position of the target node changes, sampling can also be conducted again, and the mechanical arm can be connected with the path and arrive at the target node.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
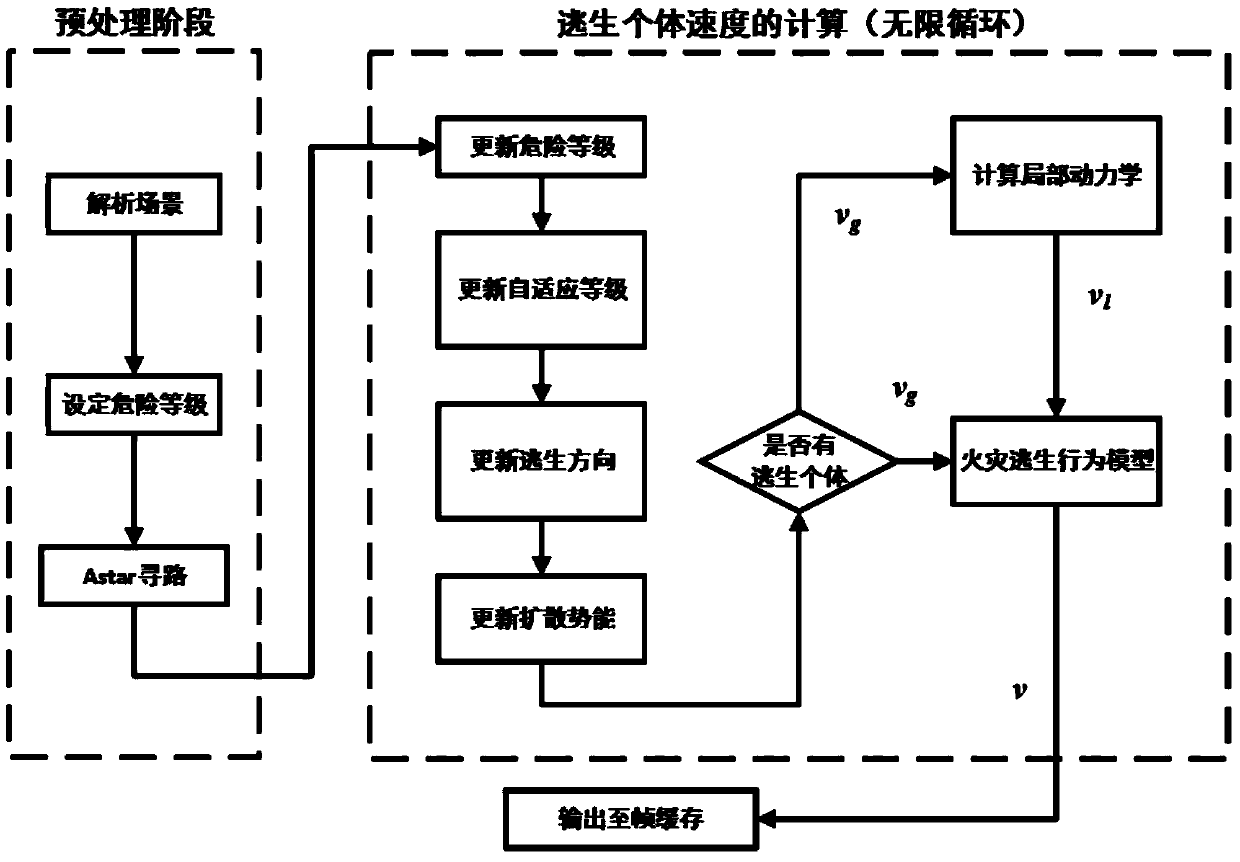
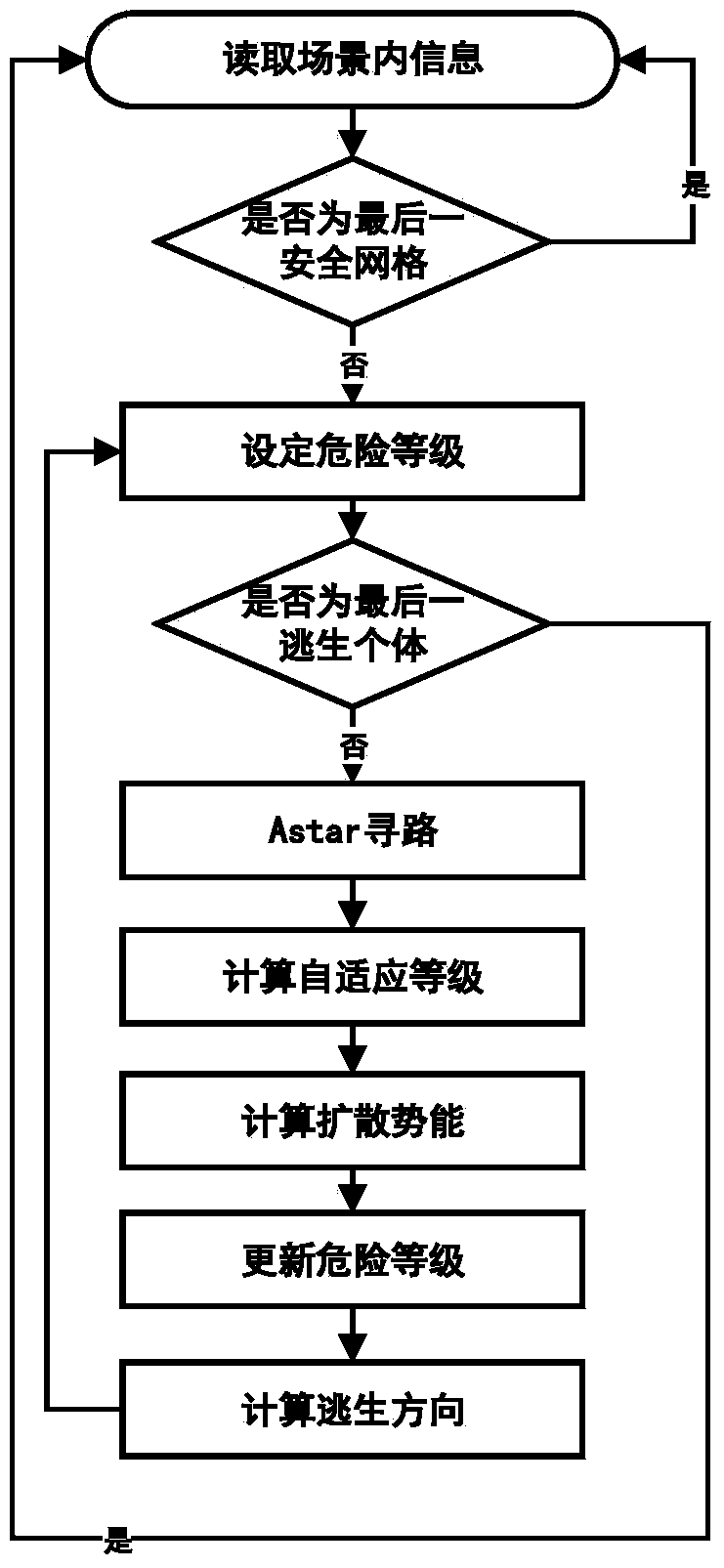
Fire emergency evacuation simulation method
ActiveCN104239636AAvoid Oscillating PhenomenaSmooth individual escape pathsSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexitySimulation
The invention provides a fire emergency evacuation simulation method. On the basis of establishing a real three-dimensional fire scene, researches are made around a vector-field-based global motion planning algorithm to navigate the escape of a plurality of individuals in the fire scene in real time. The method comprises the following steps of calculating a vector-field-based safety field in real time by virtue of the algorithm, constructing a fire-scene-based crowd behavior model in combination of a social force model-based local collision avoiding algorithm, and finally providing fire escape guidance for each escape individual in the scene according to the fire-scene-based crowd behavior model. According to the fire emergency evacuation simulation method, a theoretical basis is provided, the calculation accuracy can be ensured, and verification application is developed under various experimental conditions; the method has the characteristics of low calculation complexity, high simulation effect trueness and the like, and the real-time emergency evacuation of hundreds of escape individuals can be simulated during practical application.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Double-layer personification motion planning method for seven-freedom-degree simulated human mechanical arm
The invention discloses a double-layer personification motion planning method for a seven-freedom-degree simulated human mechanical arm, and belongs to the technical field of the mechanical arm control. The problems that the current seven-freedom-degree simulated human mechanical arm path planning method based on a Bi-RRTX algorithm is not suitable for the task space planning of the simulated human mechanical arm, and the path of an end effector and the mechanical arm configuration of the simulated human mechanical arm cannot be optimized at the same time can be solved. The method comprises the steps of planning a collisionless path for the end effector, executing the smoothing treatment to the collisionless path, calculating all usable mechanical arm configurations, selecting an optimal mechanical arm configuration set according to the kinematics characteristic of a human arm and controlling the simulated human mechanical arm to successively complete all arm configurations in the optimal mechanical arm configuration set. In the step of planning the collisionless path, an end new growth path point validity judgment method based on arm configuration description is used for replacing the collision detection method in the current Bi-RRTX algorithm. The method is suitable for the double-layer personification motion planning of the seven-freedom-degree simulated human mechanical arm.
Owner:HEFEI HEBIN INTELLIGENT ROBOTS CO LTD
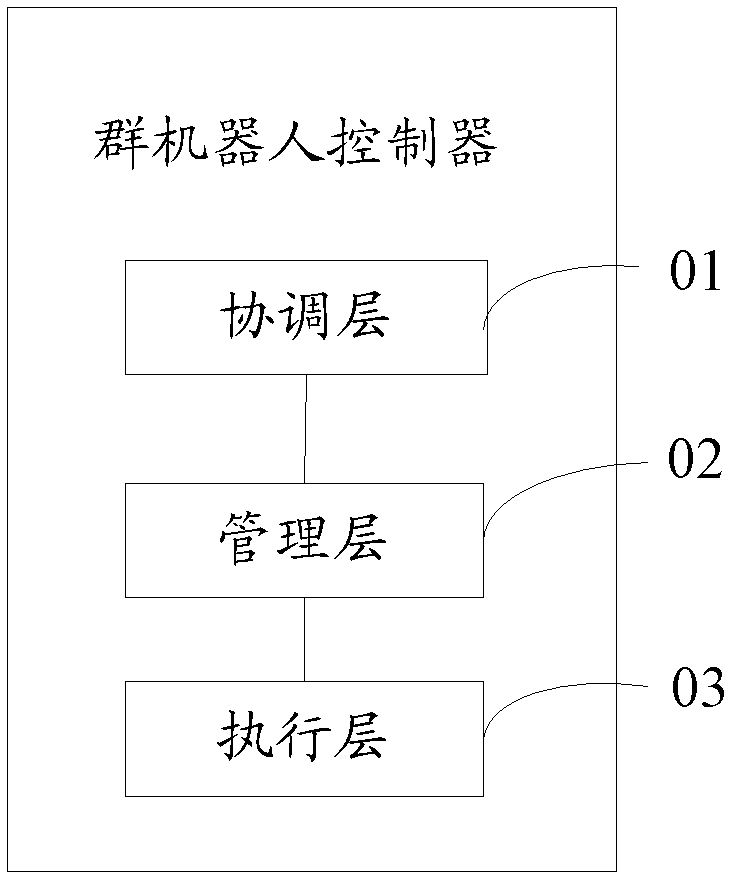
Swarm-robot controller, swarm-robot control method and controller terminal
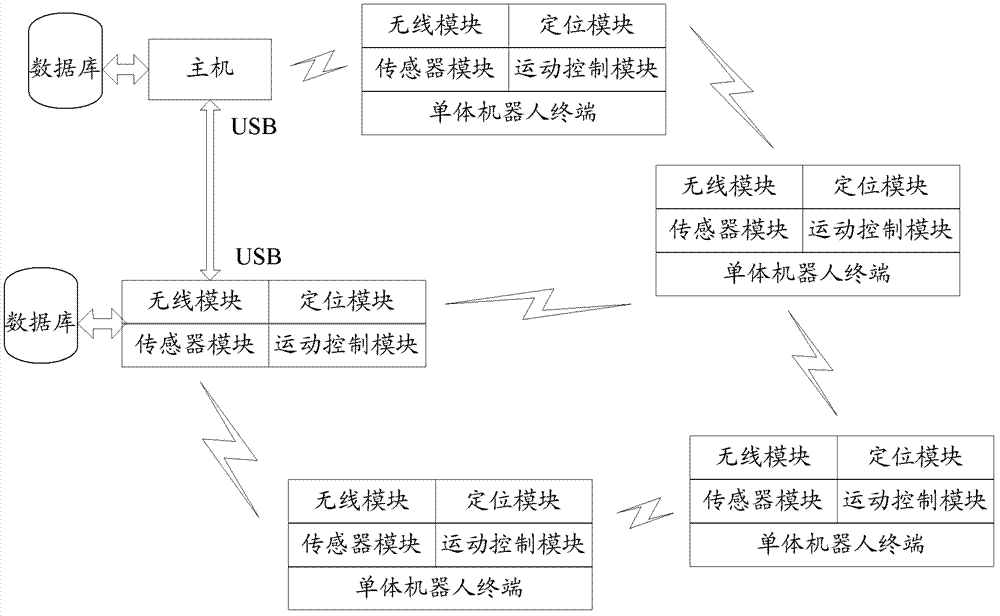
ActiveCN102707675AImprove work efficiencyShorten the timeTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlControl systemRobot control
The invention discloses a swarm-robot control method. The swarm-robot control method includes acquiring information of single robot terminals; planing and navigating movement of the single robot terminals according to the information of the single robot terminals; and transmitting movement planning and navigating information to the single robot terminals and controlling the single robot terminals to cooperatively move. The invention further discloses a swarm-robot controller and a controller terminal. The swarm-robot controller comprises a coordination layer, a management layer and an execution layer. The forecast weighted layering information technology is adopted, Mesh networking is carried out via a wireless communication module, by the aid of the method, a control system of swarm robots and individual characteristics of the robots are organically combined, the single robot terminals are controlled to cooperate, accordingly, the advantage that the swarm robots interact and cooperate with each other without manual intervention is realized, work efficiency of collective cooperation of the swarm robots and accuracy and stability of operation in special environments are improved, and collective task execution time of the swarm robots is shortened.
Owner:全童科教(东莞)有限公司 +1
Intelligent ladar system with low latency motion planning updates
ActiveUS10495757B2Rapid characterizationFast precisionAnti-collision systemsCondensersProgram planningRadar
Owner:AEYE INC
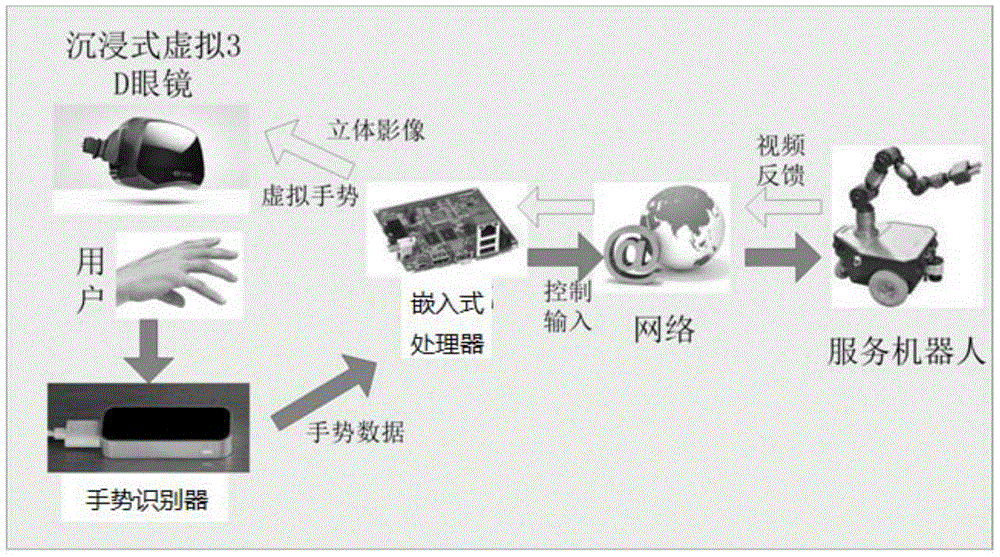
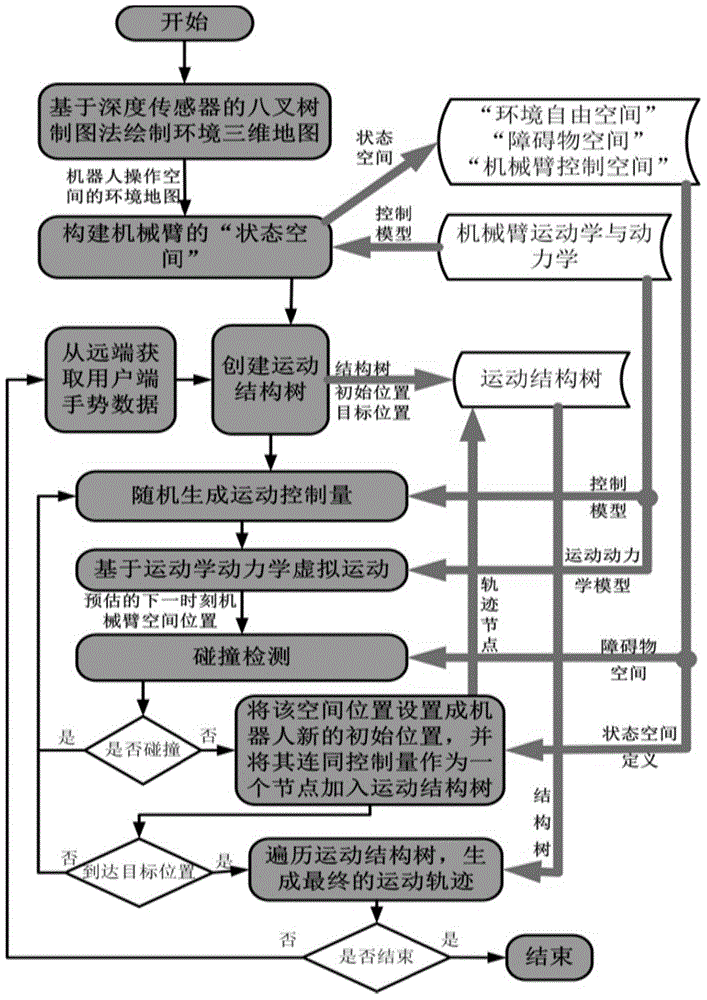
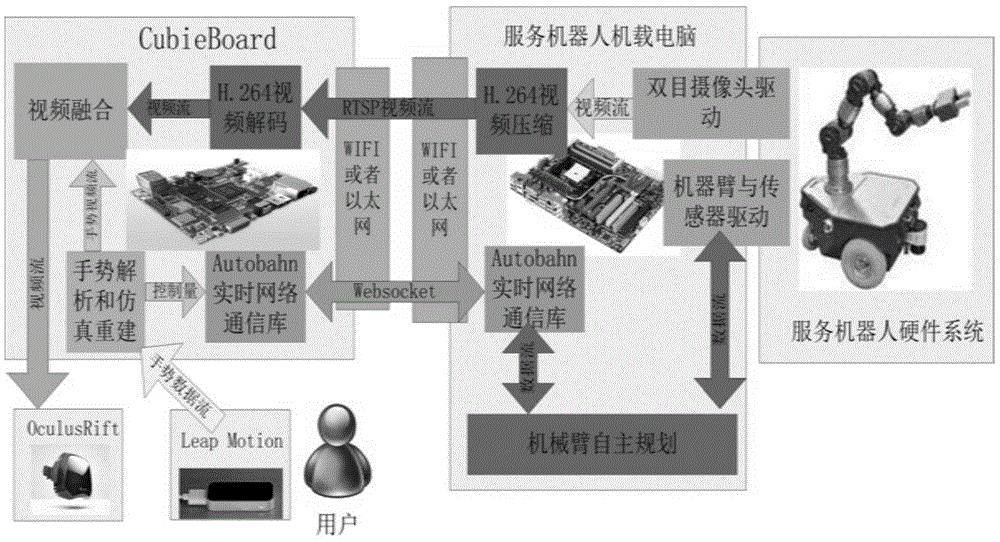
Teleoperation method of high-dimensional motion arm aiming at service robot
ActiveCN104057450ALow costReal-time controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorTotal factory controlIndependent motionSimulation
The invention provides a teleoperation method of a high-dimensional motion arm aiming at a service robot. The high-dimensional motion arm comprises a gesture recognizer, a pair of immersive virtual 3D glasses, an embedded processor with a router and the service robot; an independent motion planning method is adopted for a mechanical arm, the planning method is independently operated by a remote service robot, and the independent planning method is a path planning method based on sampling. By using the teleoperation method, the motion of arms of the remote service robot can be controlled in real time and can be experienced in a first visual angle, and the robot can independently plan a feasible motion path according to true environment. The teleoperation method can be applied to home service robots and has wide application values in the fields of industrial robots and industrial virtual manufacturing industries.
Owner:深圳市摩仑科技有限公司
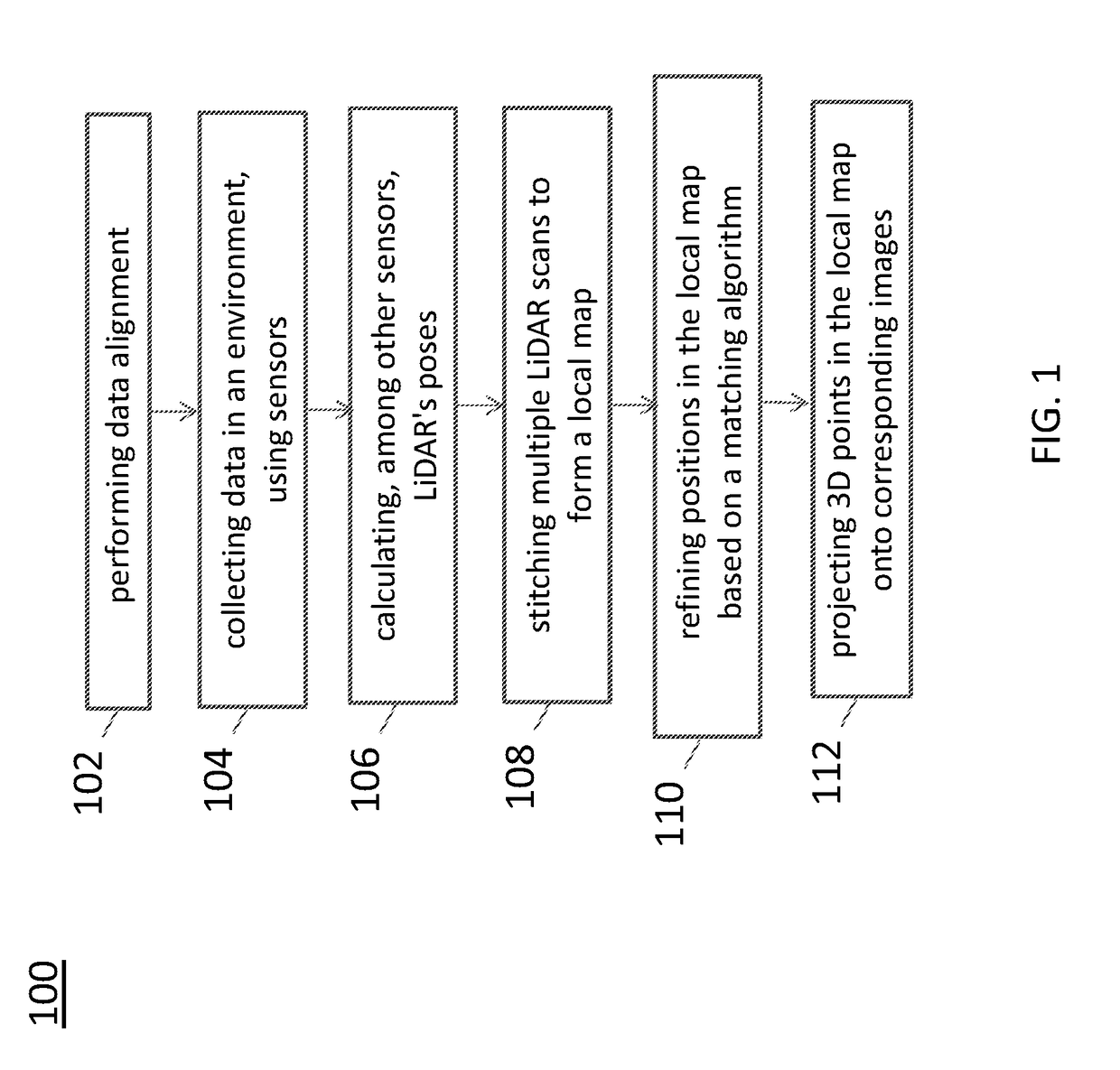
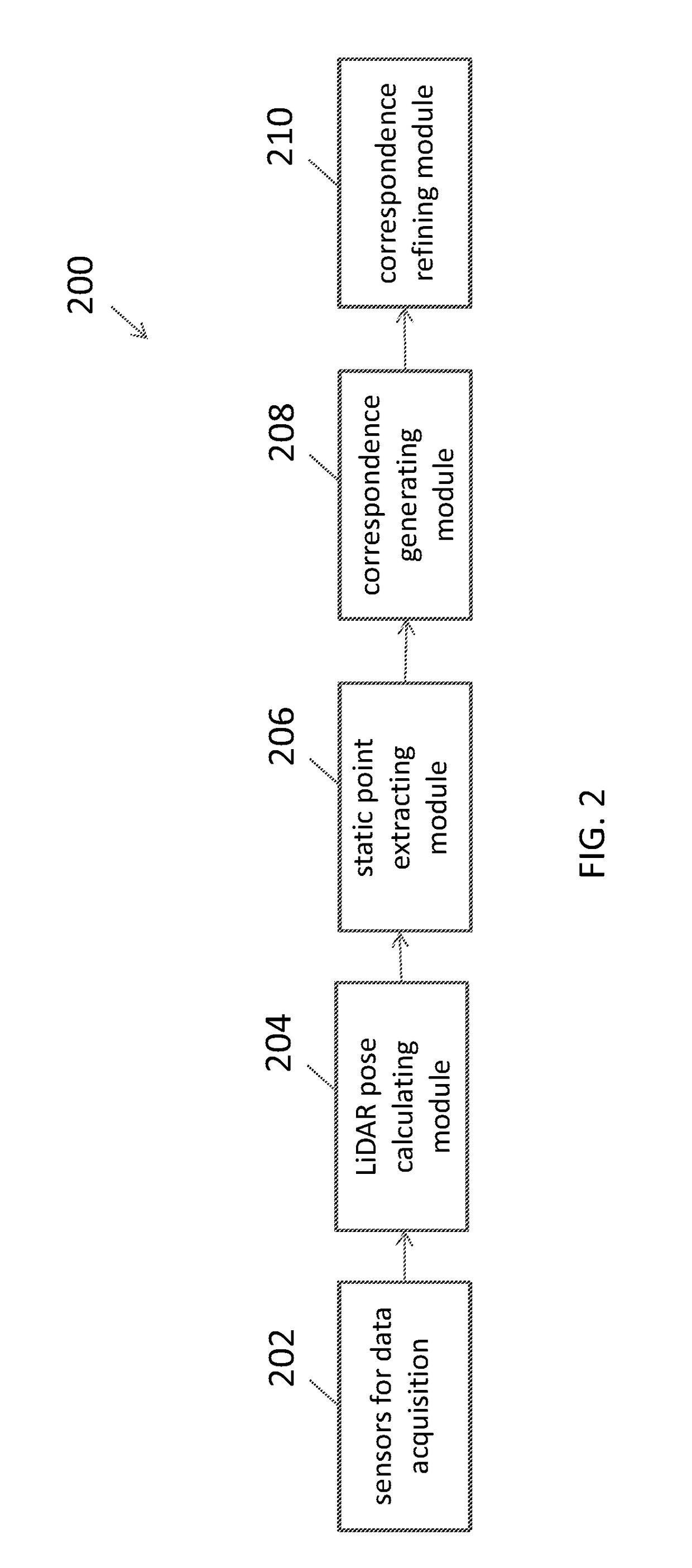
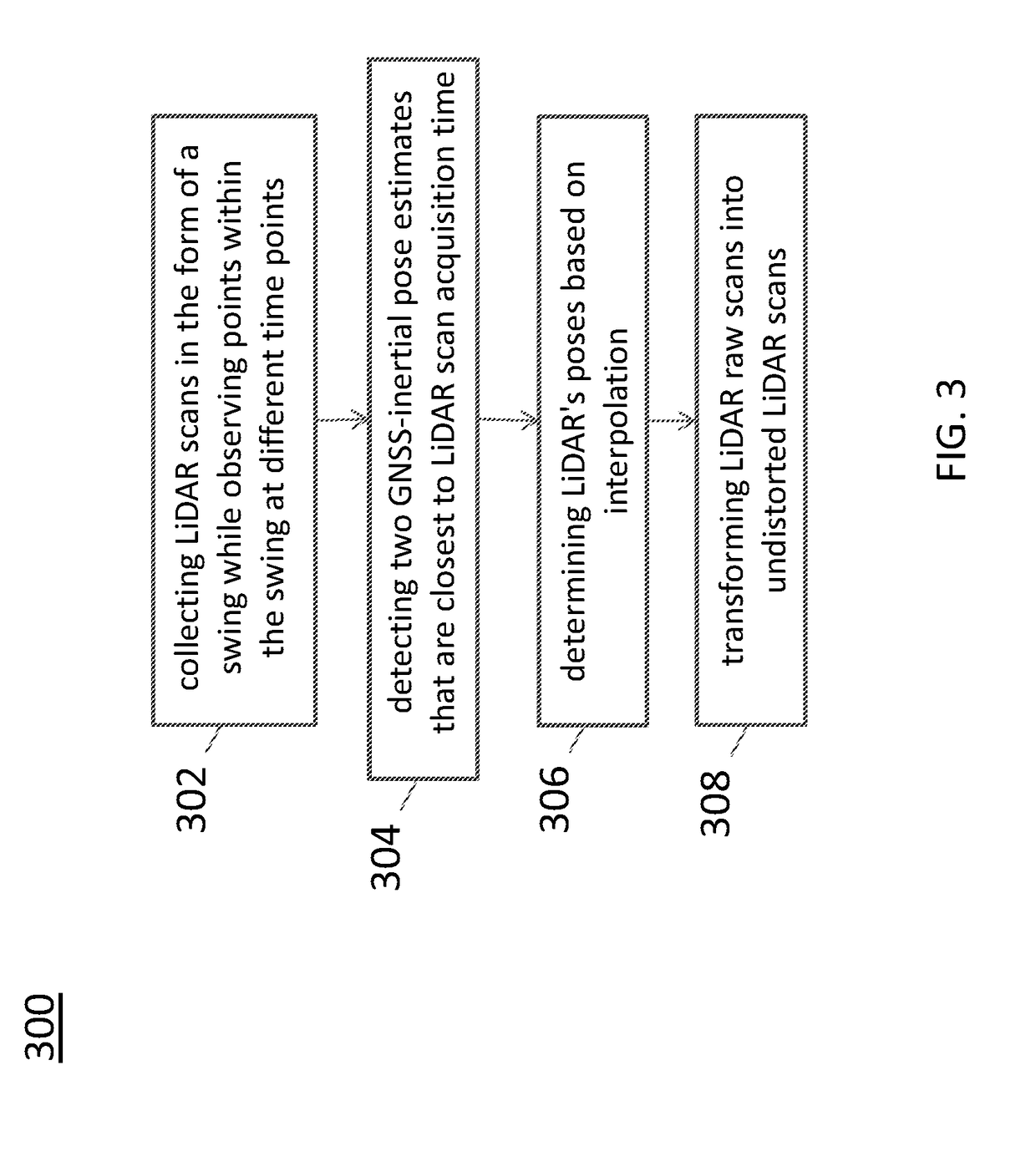
Sensor calibration and time system for ground truth static scene sparse flow generation
A system for generating a ground truth dataset for motion planning is disclosed. The system includes sensors for data acquisition for motion planning of a vehicle, the sensors including a LiDAR; a calculating module configured to calculate LiDAR poses in response to data from the sensors and generate undistorted LiDAR scans; an extracting module configured to extract static points from a target undistorted LiDAR scan and generate a LiDAR static-scene point cloud; and a generating module configured to generate sparse image point correspondences for each pair of images, using the LiDAR static-scene point cloud.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
Map data acquisition method
InactiveCN108958266APrecise positioningAccurate decisionSpecial data processing applicationsPosition/course control in two dimensionsPoint cloudRadar
The embodiment of the invention relates to a map data acquisition method, comprising the following steps: an intelligent vehicle acquiring first position information detected by a vehicle-mounted GPS;the intelligent vehicle loading map data according to the first position information; acquiring laser point cloud data detected by vehicle-mounted radar, matching the laser point cloud data with laser point cloud data in the map data to obtain second position information; acquiring inertial measurement data detected by a vehicle-mounted inertial measurement unit and wheel speed gauge data detected by a vehicle-mounted wheel speed gauge; conducting processing and fusion on the detected data through an algorithm, and obtaining accurate position information; correcting the loaded map data according to the accurate position information. A vehicle can be accurately positioned through fusion of detection data of a plurality of sensors, and the accuracy of positioning of the vehicle is guaranteed. Moreover, the map information is loaded in real time according to the accurate position of the vehicle, so that the vehicle can accurately make decision and make motion planning. In this way, the safety of the vehicle during automatic driving is guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIXINGZHE TECH CO LTD
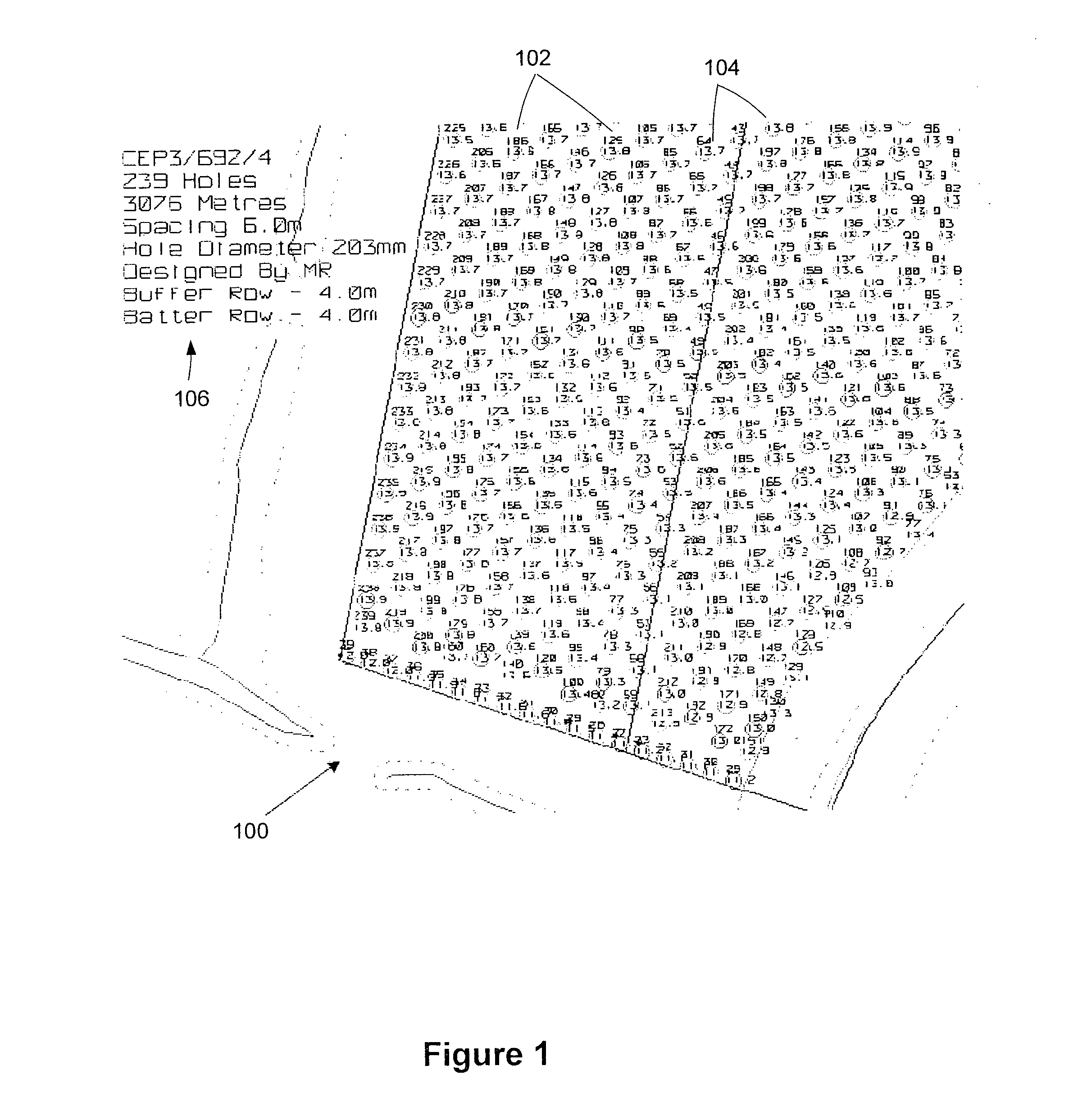
Drill hole planning
InactiveUS20120024605A1Cost of drillingGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsEngineeringMotion planning
Forming a sequence plan for a machine to travel to a series of specified locations is described. An initial cost table (414) and a pattern of locations (412) is inputted to a Sequential Ordering Problem (SOP) solver (402). The resulting sequence (410) is processed by a motion planner (404) to derive by a motion planning procedure a plan of machine motions through the sequence. A cost table update (408) is performed based on the motion plan, which is then used for another iteration of the SOP solver (402).
Owner:THE UNIV OF SYDNEY
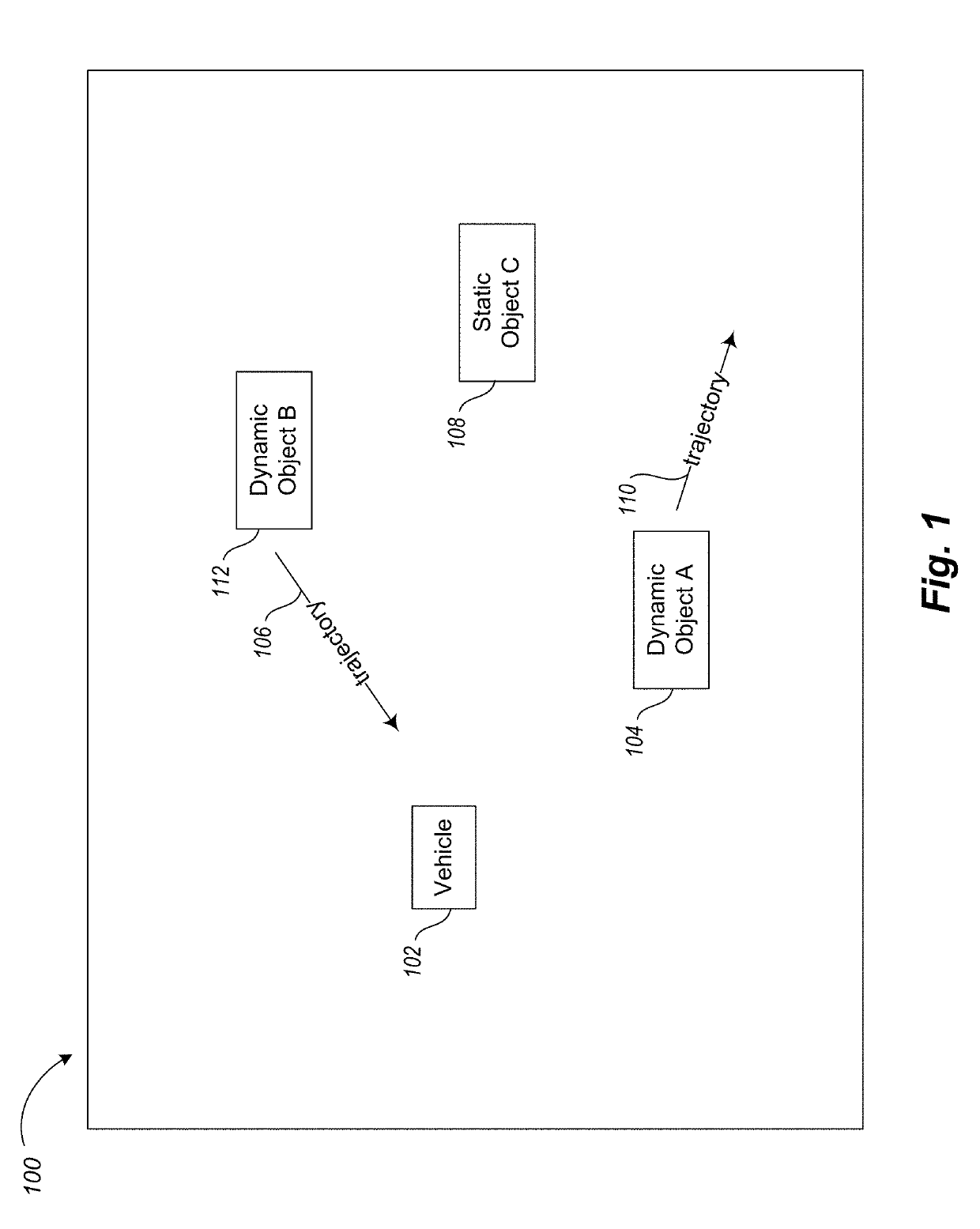
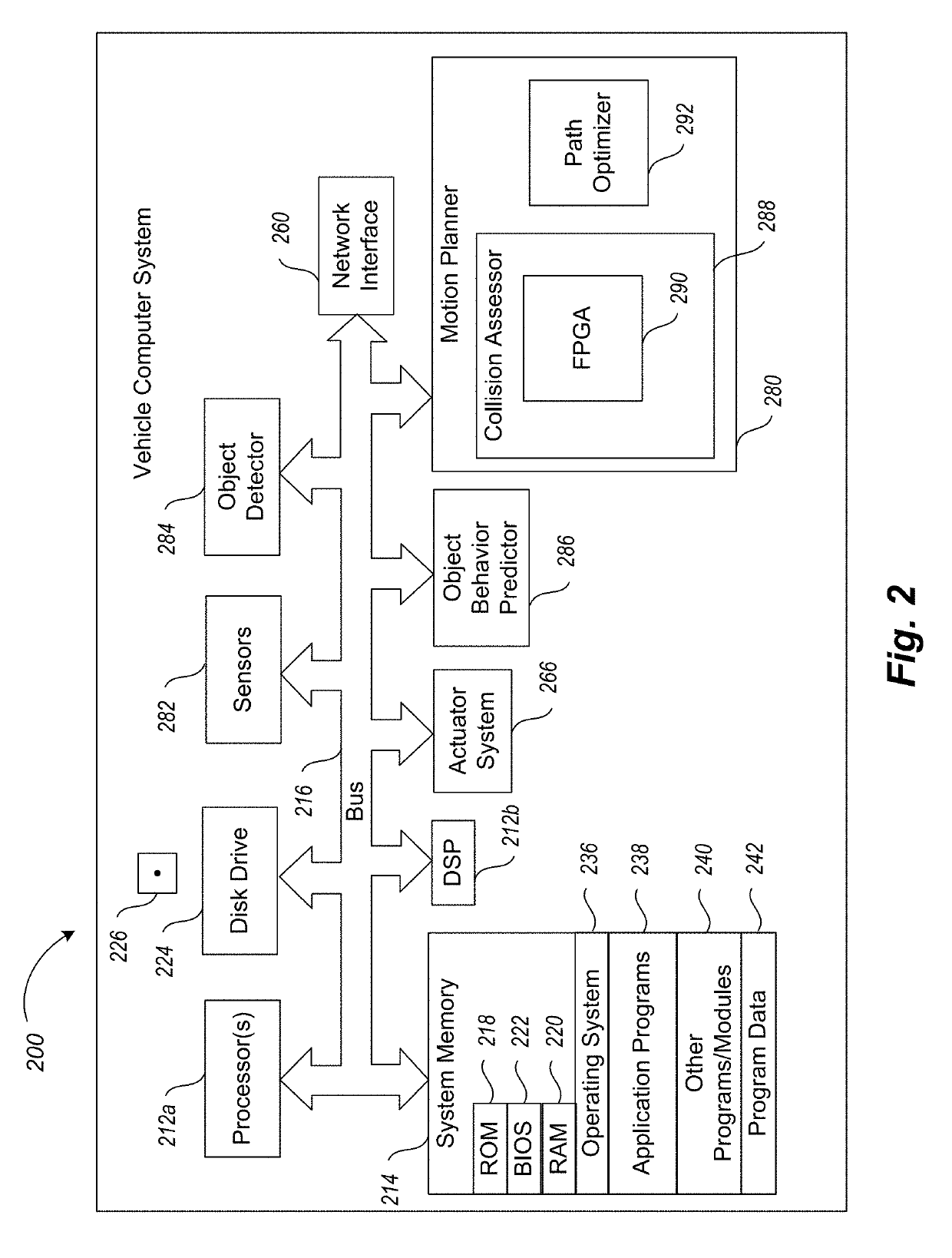
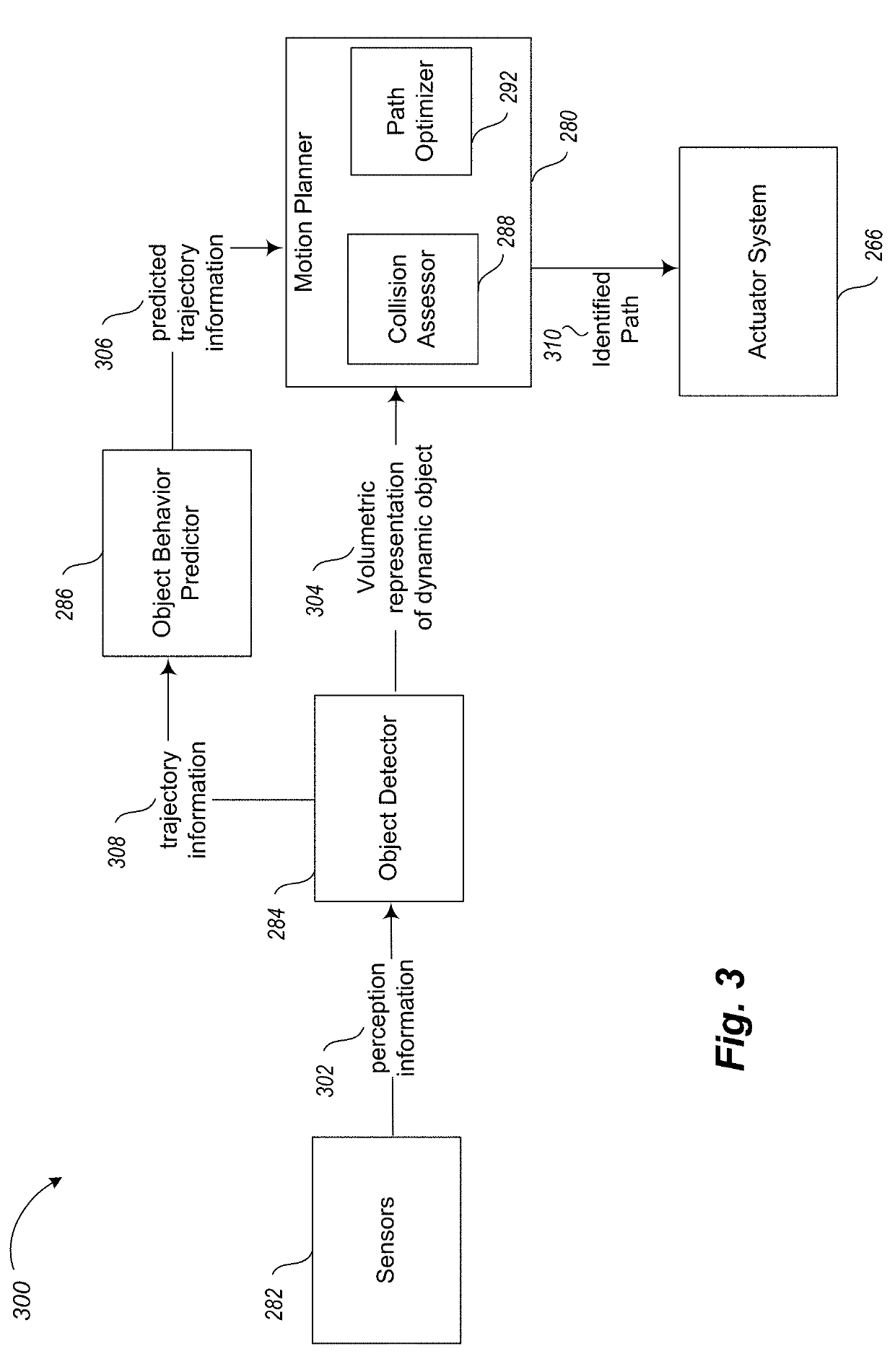
Apparatus, method and article to facilitate motion planning of an autonomous vehicle in an environment having dynamic objects
ActiveUS20190217857A1Autonomous decision making processScene recognitionProgram planningCollision detection
A motion planner of an autonomous vehicle's computer system uses reconfigurable collision detection architecture hardware to perform a collision assessment on a planning graph for the vehicle prior to execution of a motion plan. For edges on the planning graph, which represent transitions in states of the vehicle, the system sets a probability of collision with a dynamic object in the environment based at least in part on the collision assessment. Depending on whether the goal of the vehicle is to avoid or collide with a particular dynamic object in the environment, the system then performs an optimization to identify a path in the resulting planning graph with either a relatively high or relatively low potential of a collision with the particular dynamic object. The system then causes the actuator system of the vehicle to implement a motion plan with the applicable identified path based at least in part on the optimization.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY +1
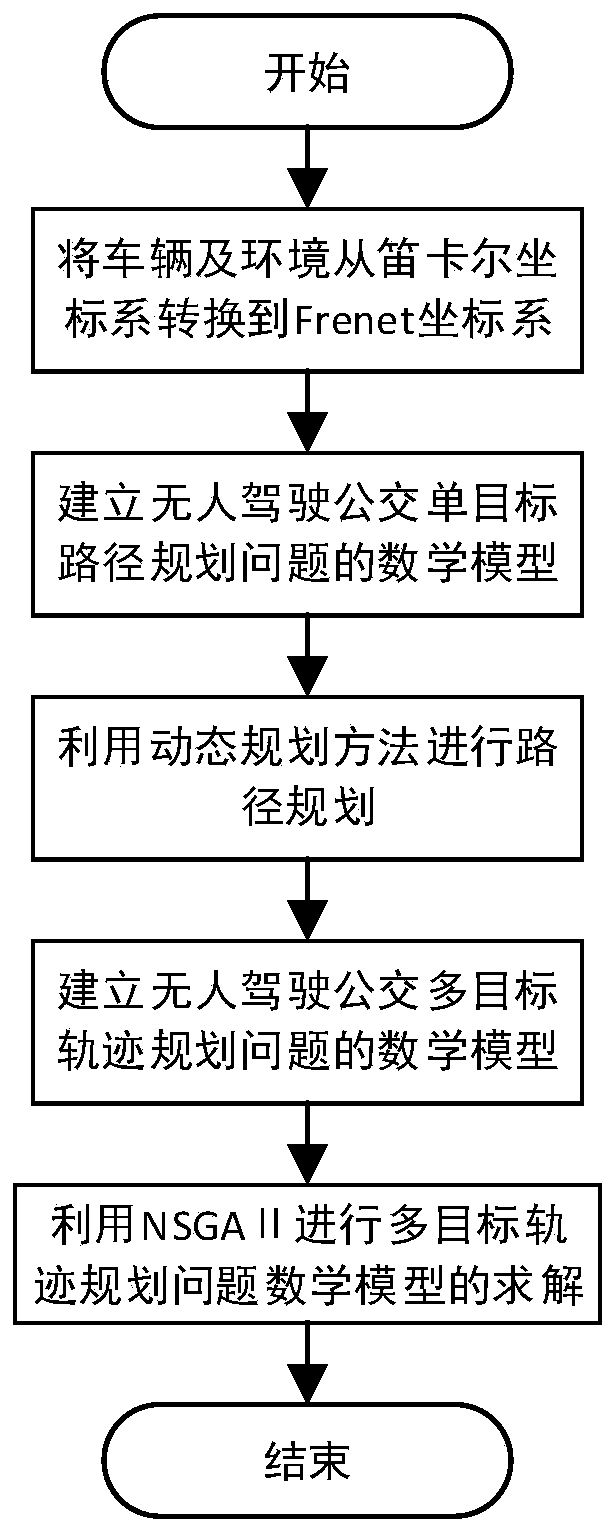
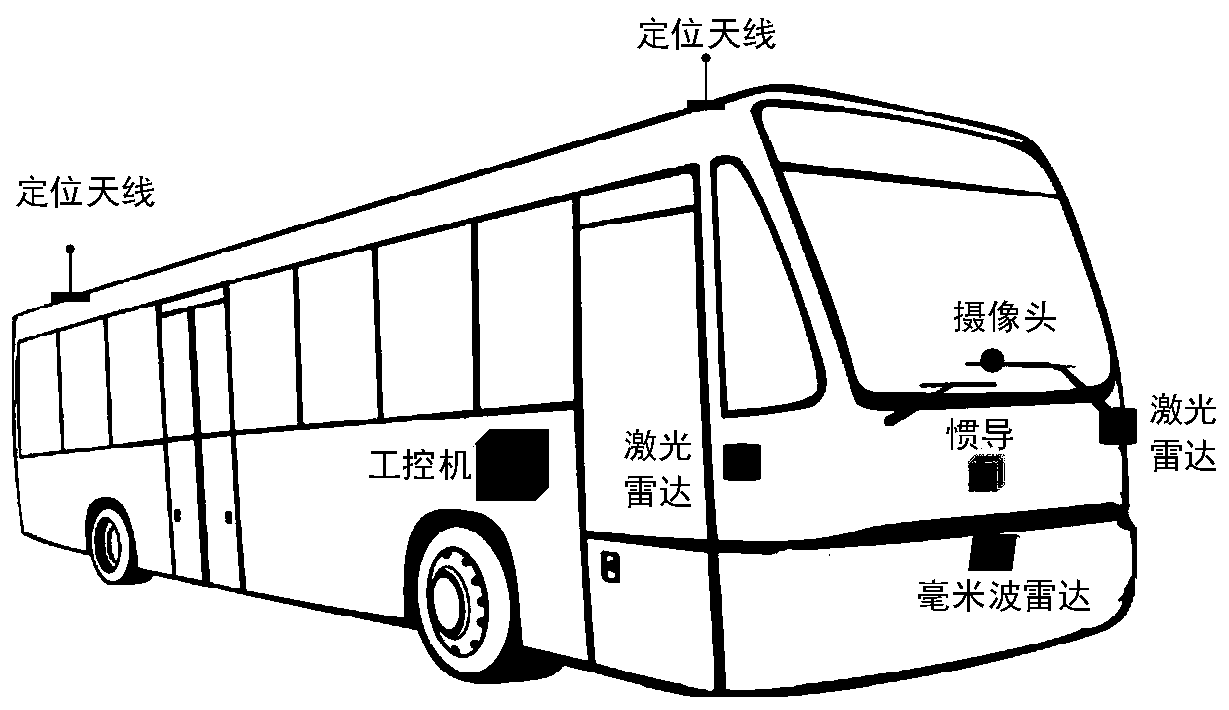
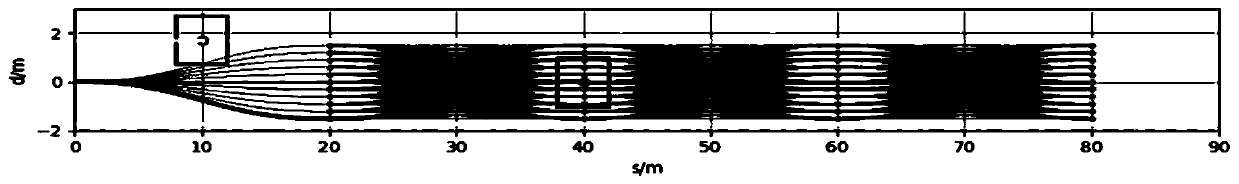
Multi-objective optimization-based unmanned vehicle motion planning method
ActiveCN110749333AComply with actual road constraintsAvoid the problem that the weight is difficult to determineInstruments for road network navigationDynamic planningSimulation
The invention discloses a multi-objective optimization-based unmanned vehicle motion planning method. A vehicle and an environment are mapped from a Cartesian coordinate system to a Frenet coordinatesystem. A mathematical model for an unmanned vehicle multi-objective path planning problem is established. Path planning is performed by using a linear dynamic planning method. A track is described byusing a piecewise quintic polynomial, and a mathematical model for an unmanned vehicle multi-objective track generation problem is established by using a minimum track slope, minimum curvature, comfortable riding experience, and a closest distance to a path obtained from linear dynamic planning respectively as optimization objectives, using a location of a piecewise quintic polynomial connectionpoint, a first order derivative, a second order derivative, and a third order derivative as equality constraints, and using a road natural boundary constraint and an obstacle boundary constraint as inequality constraints. An optimal solution of the unmanned vehicle multi-objective track generation problem is obtained. The invention solves a problem that a path obtained by using a random point scatter-based path planning method is difficult to meet a vehicle kinematics constraint.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Electric driven biomimetic four-leg robot with environment sensing ability and control method
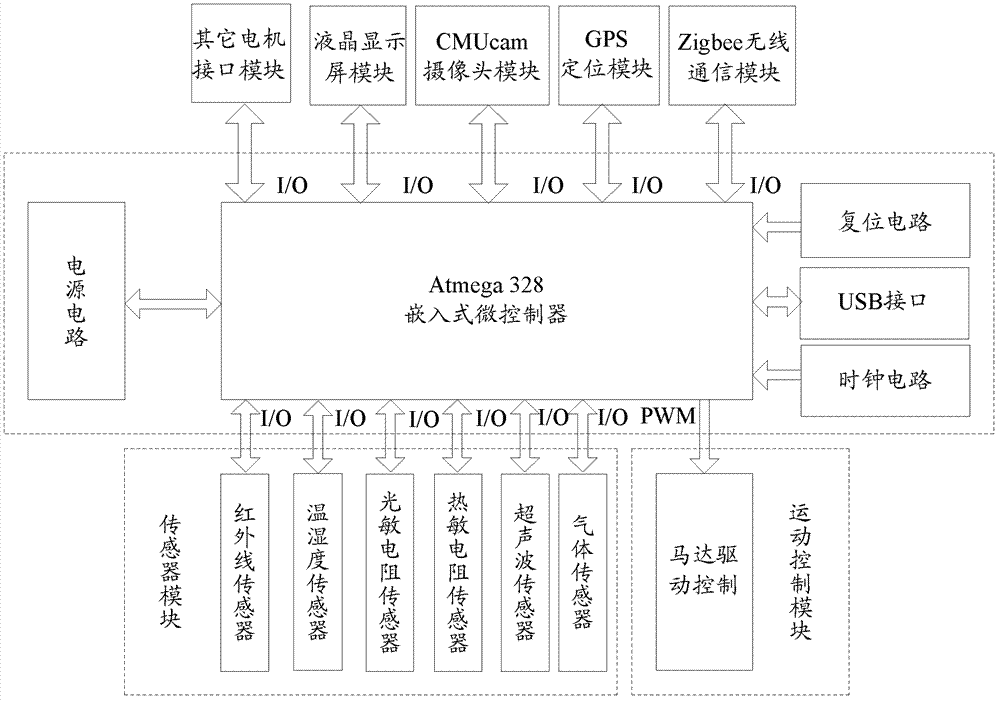
ActiveCN105599821AWide time rangeSolve the problem of inconsistent detection distanceProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersVehiclesElectricityComputer module
The invention discloses an electric driven biomimetic four-leg robot with the environment sensing ability and a control method. A head is hinged to a front body through a neck and a head connecting rod, the head is linked with the neck, and the front body is hinged to a back body; a tail is arranged at the back part of the back body, and is also hinged to the front body through a tail connecting rod; front legs are respectively arranged on the two sides of the front body; back legs are respectively arranged on the two sides of the back body; the length of the back legs are larger than that of the front legs; the widest part of the front body is wider than the widest part of the back body; the electric driven biomimetic four-leg robot further comprises an environment sensing sensor group and a camera; the environment sensing sensor group and the camera are connected with a central processing unit; the output end of the central processing unit is connected with an electric driven execution system; a power management module supplies power for the environment sensing sensor group, the central processing unit and the electric driven execution system. Through the adoption of the electric driven control mode, the biomimetic four-leg robot can realize dynamic sensing, autonomous navigation and real-time following on environment, and can adapt to biomimetic gait motion planning with topographical changes and random disturbance.
Owner:SHANDONG YOUBAOTE INTELLIGENT ROBOTICS CO LTD
Unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory smoothing method based on Bessel curve transition
ActiveCN106325294AGuaranteed flight performanceImprove flight performanceForecastingPosition/course control in three dimensionsKinematicsTransition function
The invention provides an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) trajectory smoothing method based on Bessel curve transition, comprising the following steps: constructing a Bessel transition function according to known linear route segments, and quickly establishing flight trajectory geometrical characteristics satisfying curvature continuity; with the length of the linear route segments and the allowed maximum trajectory smoothing error as constraints, establishing and solving an optimization problem of the smoothing transition length of each Bessel curve; determining maximum speed, acceleration and jerk constraints, and determining the maximum flight speed of transition segments based on the nature of the Bessel function; performing S-shaped motion planning for all linear segments, and determining the acceleration and deceleration time of each linear segment; iteratively searching and planning the flight speed of each segment to ensure the kinematic compatibility; and performing real-time interpolation to complete flight path generation. The flight performance of UAV can be improved greatly under the premise of guaranteeing the calculation efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com