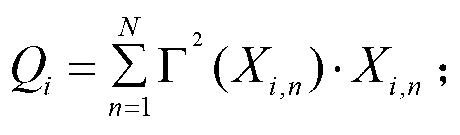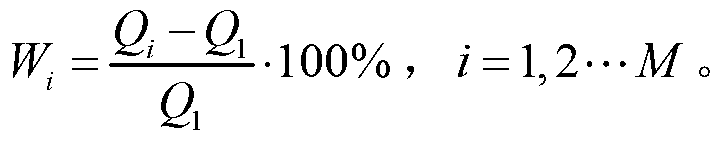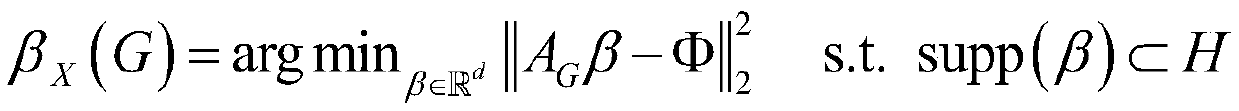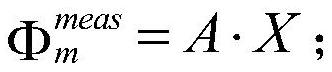Patents
Literature
55 results about "Fluorescence molecular tomography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
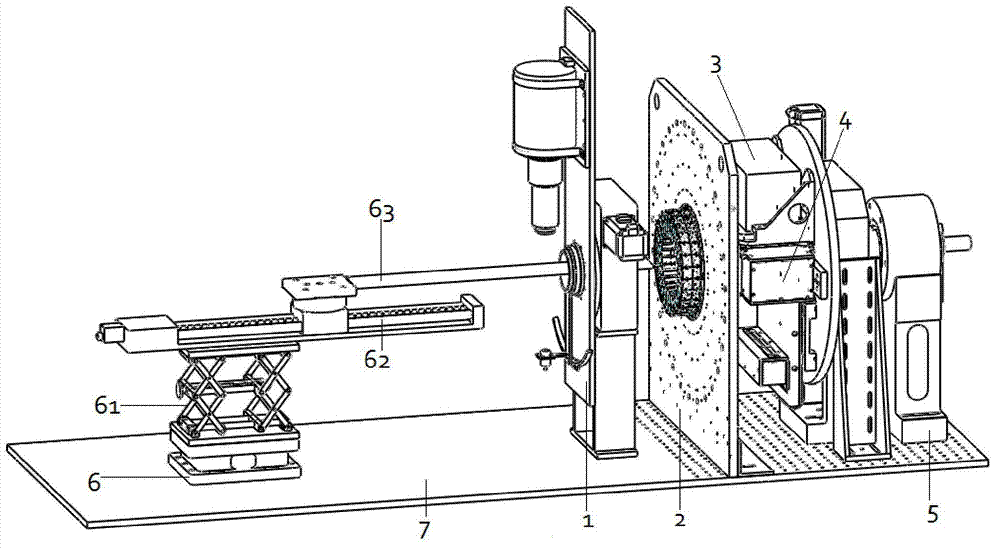
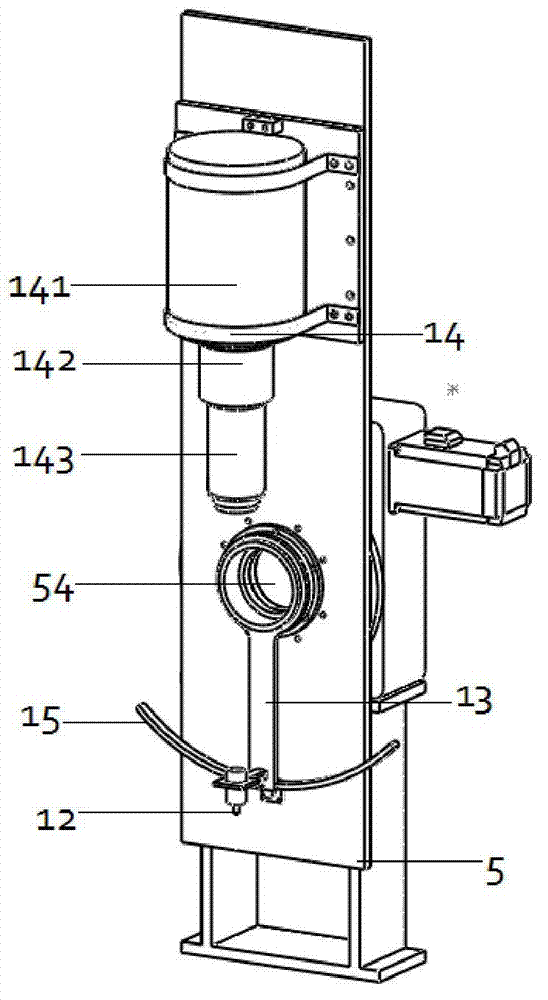
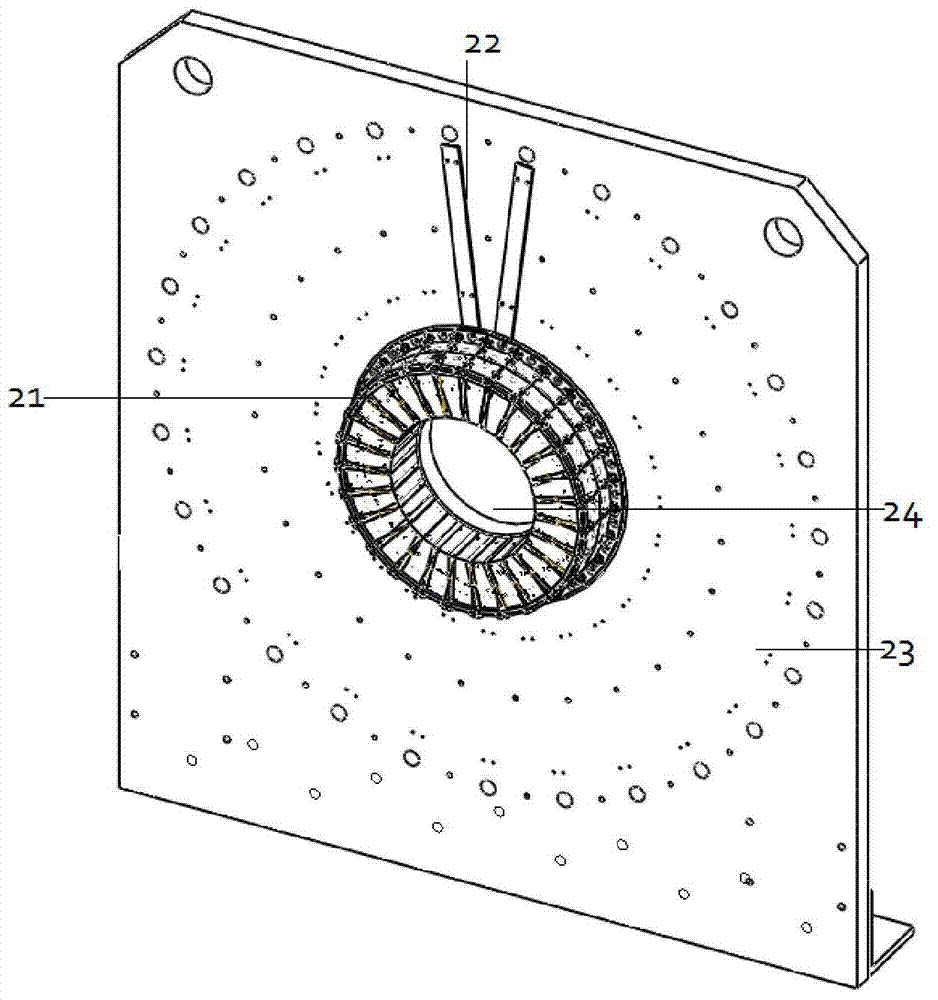
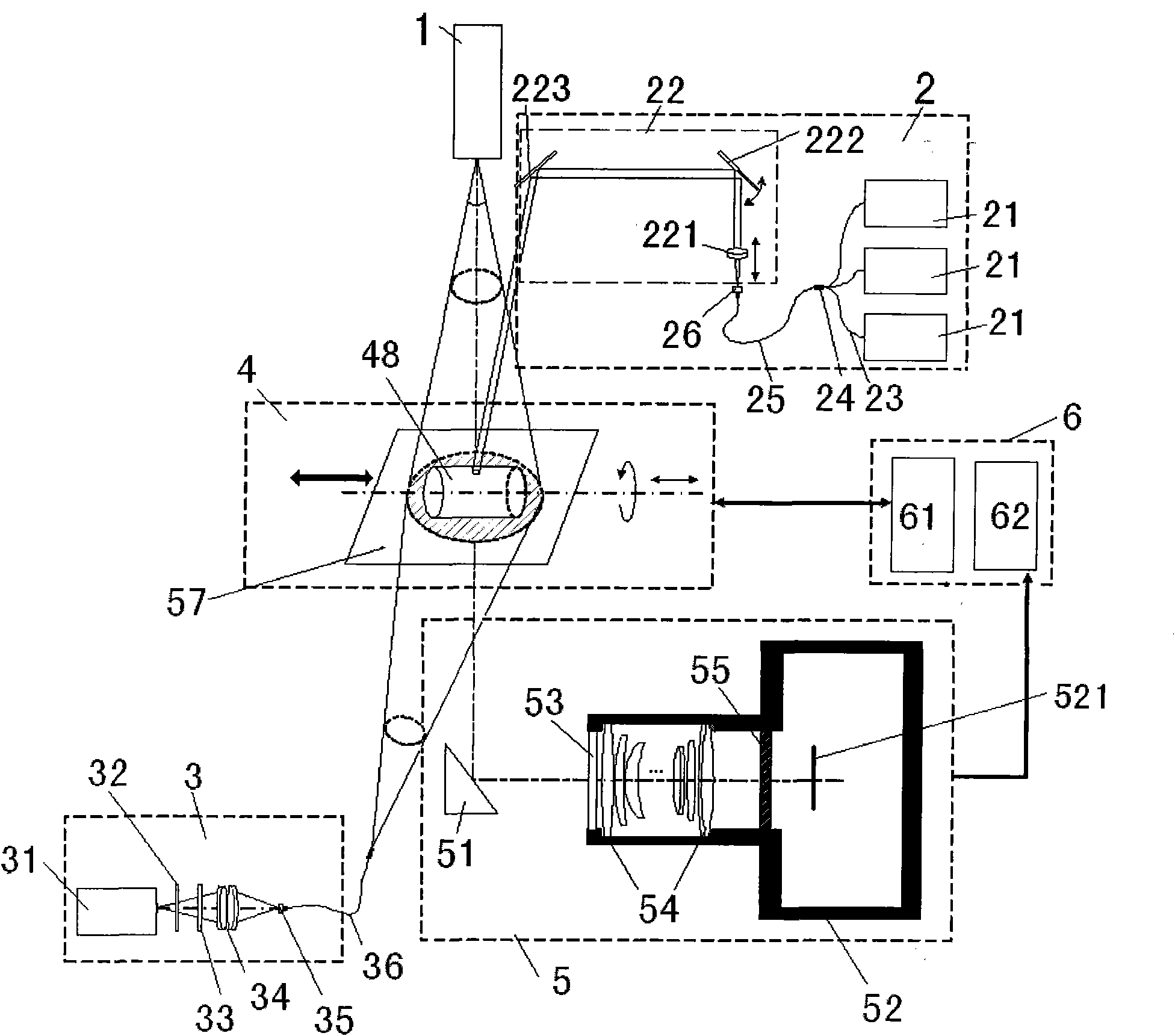
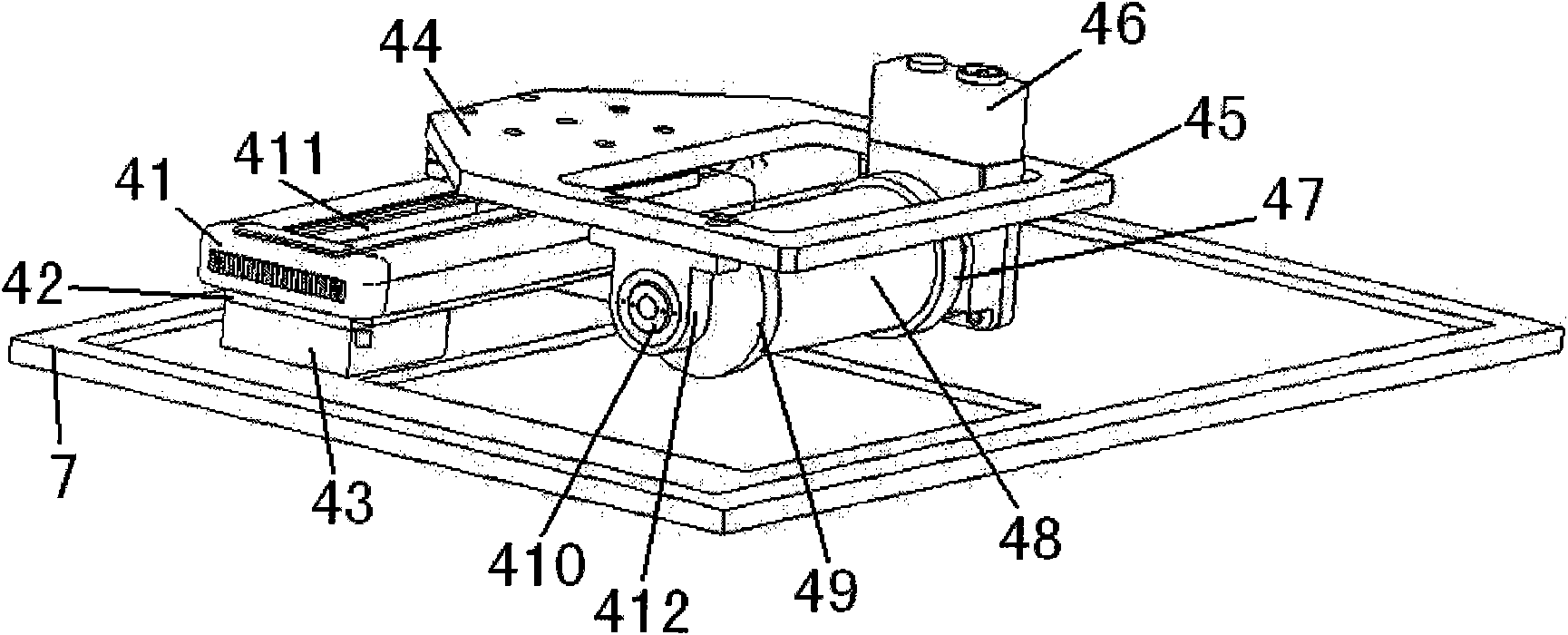
Multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and imaging method
ActiveCN102764138AImage results are accurateImage results are reliableComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityData acquisition
The invention discloses a multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and an imaging method thereof. The device comprises an X-ray computer tomography (CT) system, a positron emission tomography (PET) system, a single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) system, a fluorescence molecular tomography (FMT) system, a rotating rack system, a little animal bed system, a data acquisition system and a computer, various imaging systems are sampled and stored by the data acquisition system through a data line into the computer, and various imaging systems share one little animal bed system and the same inspection shaft. According to the multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and the imaging method, various imaging systems share one little animal bed system and the same inspection shaft, an installing fusion molecular medicine image of four modes of X-ray CT, PET, SPECT and FMT can achieve complementary advantages of different image devices, and the obtained image result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
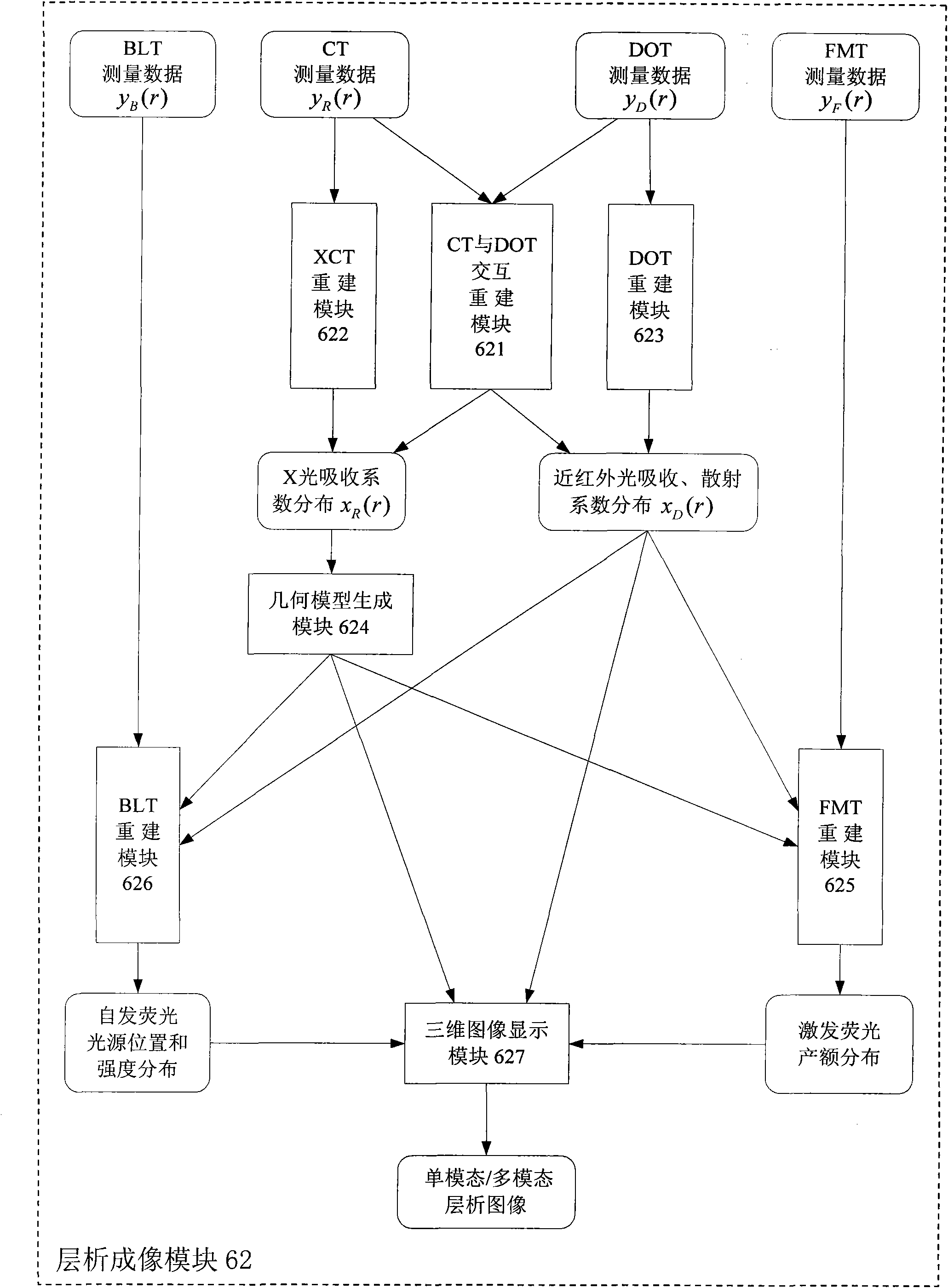
Multi-mode molecular tomography system
InactiveCN101984928ADoes not involve spatial registration issuesConsistent geometric coordinatesSurgeryComputerised tomographsSoft x rayOptical tomography
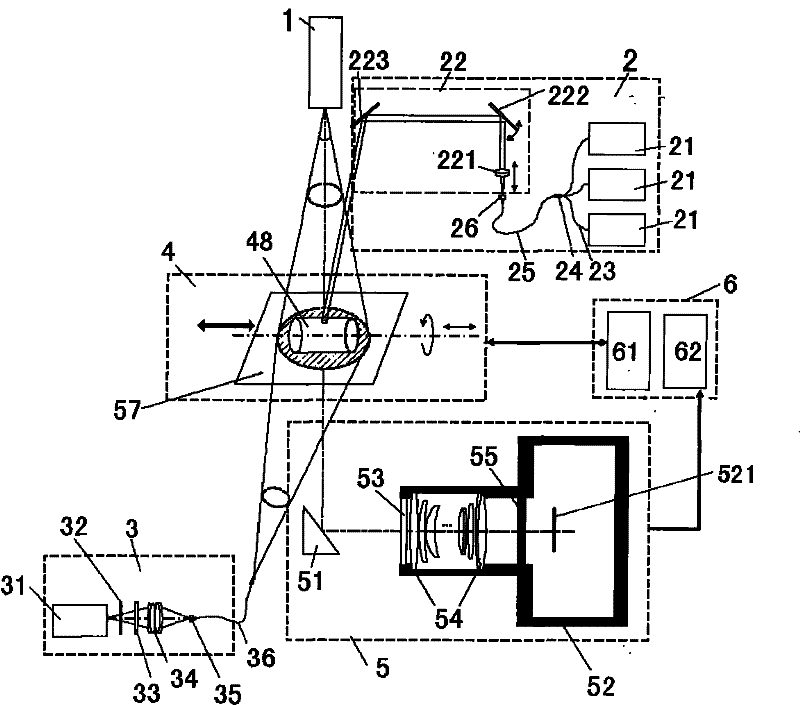
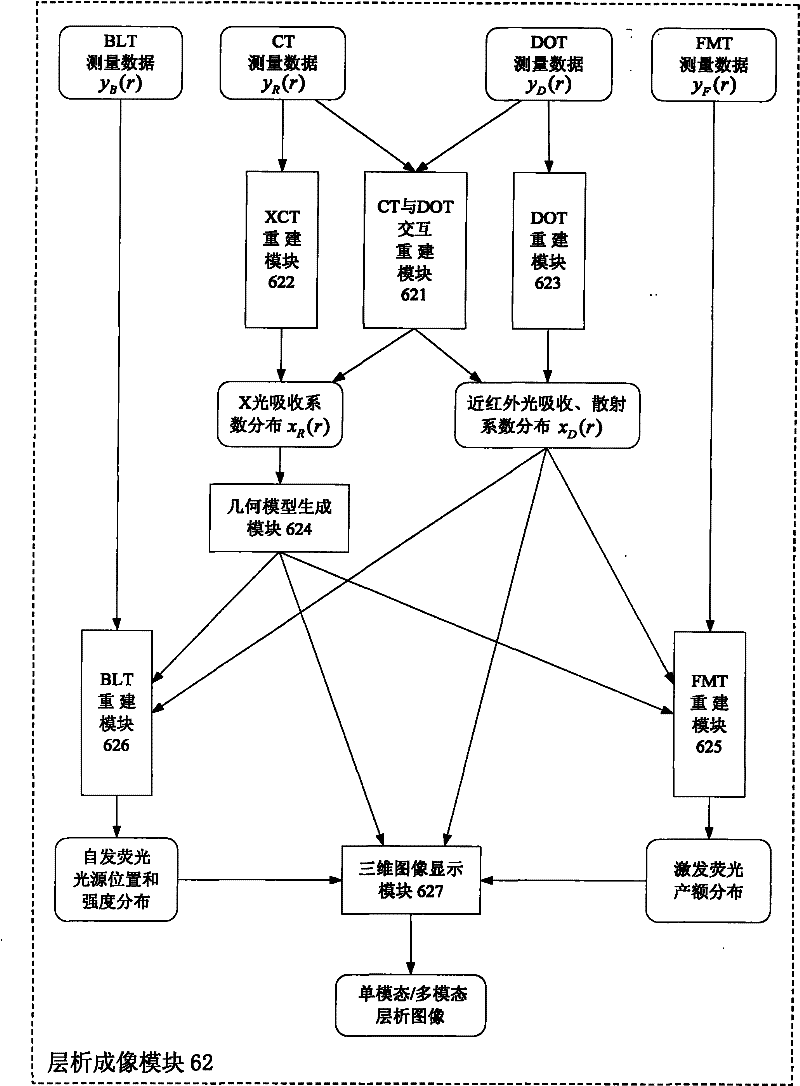
The invention relates to a multi-mode molecular tomography system which is characterized by comprising one or more light sources of an X-ray source, a near infrared laser light source and a finite spectral width light source for projecting scanning light to an object to be scanned, an electric loading device, an imaging device and a control and processing device, wherein the imaging device is used for obtaining intensity distribution data of x-rays, visible light or near infrared light emerging from the surface of the object to be scanned after scanning, and inputting the intensity distribution data into the control and processing device; the control and processing device is used for controlling the actions of the object to be scanned through the electric loading device; and the control and processing device comprises a tomography module, the tomography module is used for receiving the data of the imaging device, utilizing XCT (X-ray computed tomography) and DOT (diffuse optical tomography) modes to reconstruct an outer boundary and similar information of all internal organizations during marginalization, fusing and reconstructing XCT, DOT, FMT (fluorescence molecular tomography) and BLT (bioluminescence tomography) single-mode or multi-mode tomography image after fusion and outputting. The multi-mode molecular tomography system is applicable to the field of x-ray and optical biomedical imaging.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
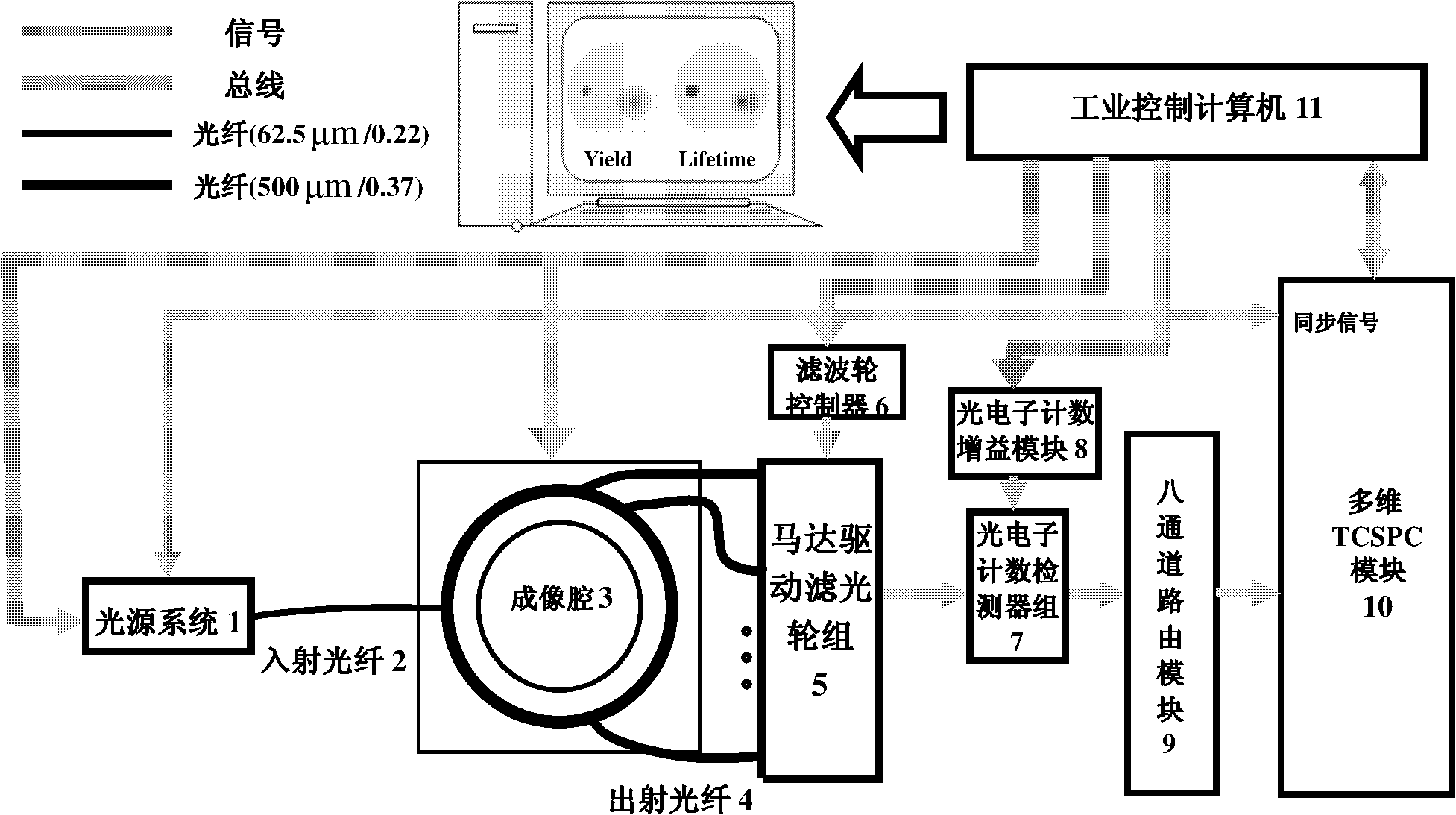
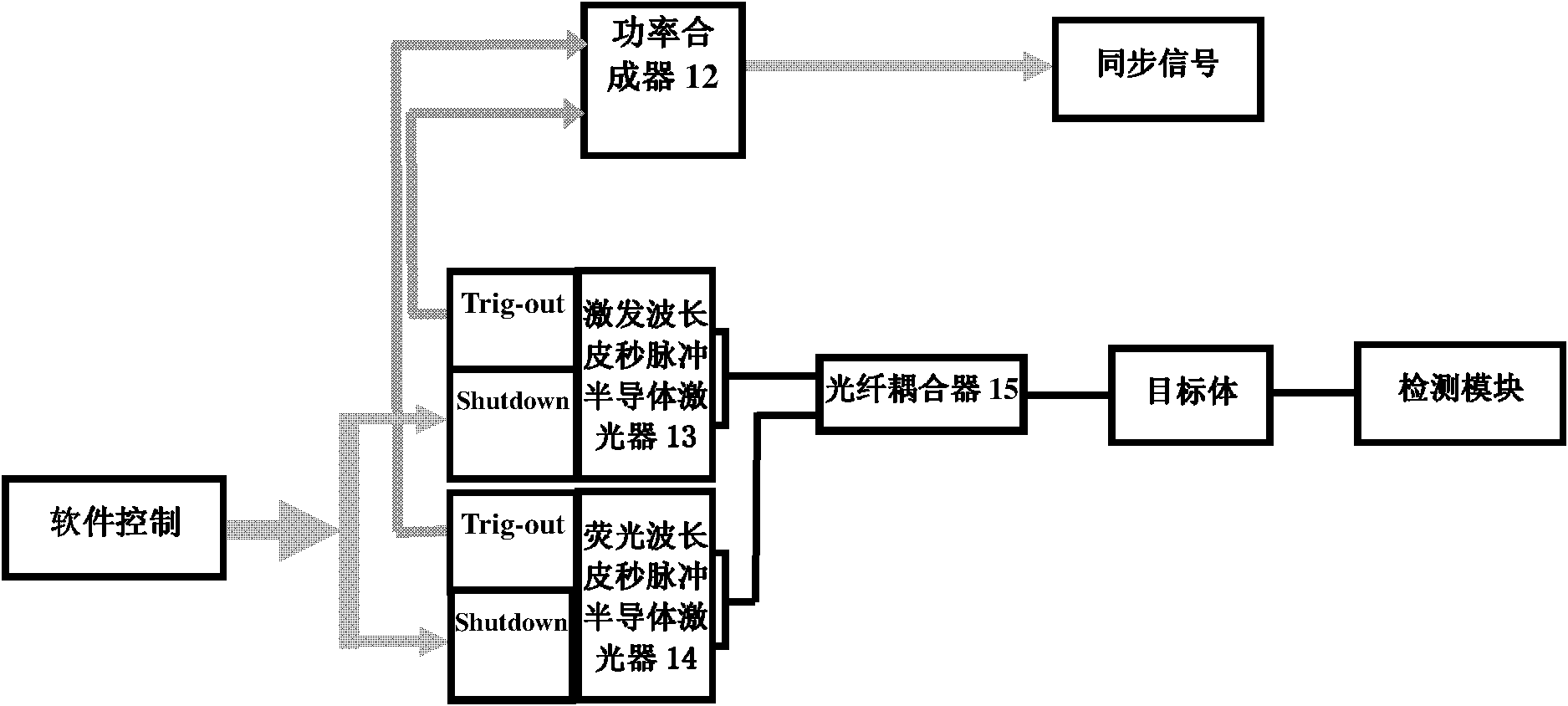
Imitating CT scanning mode multispectral time domain fluorescence molecular tomography measuring system
InactiveCN101816552AEnable time-resolved measurementsHigh resolutionDiagnostics using lightSensorsUltrashort laserPicosecond
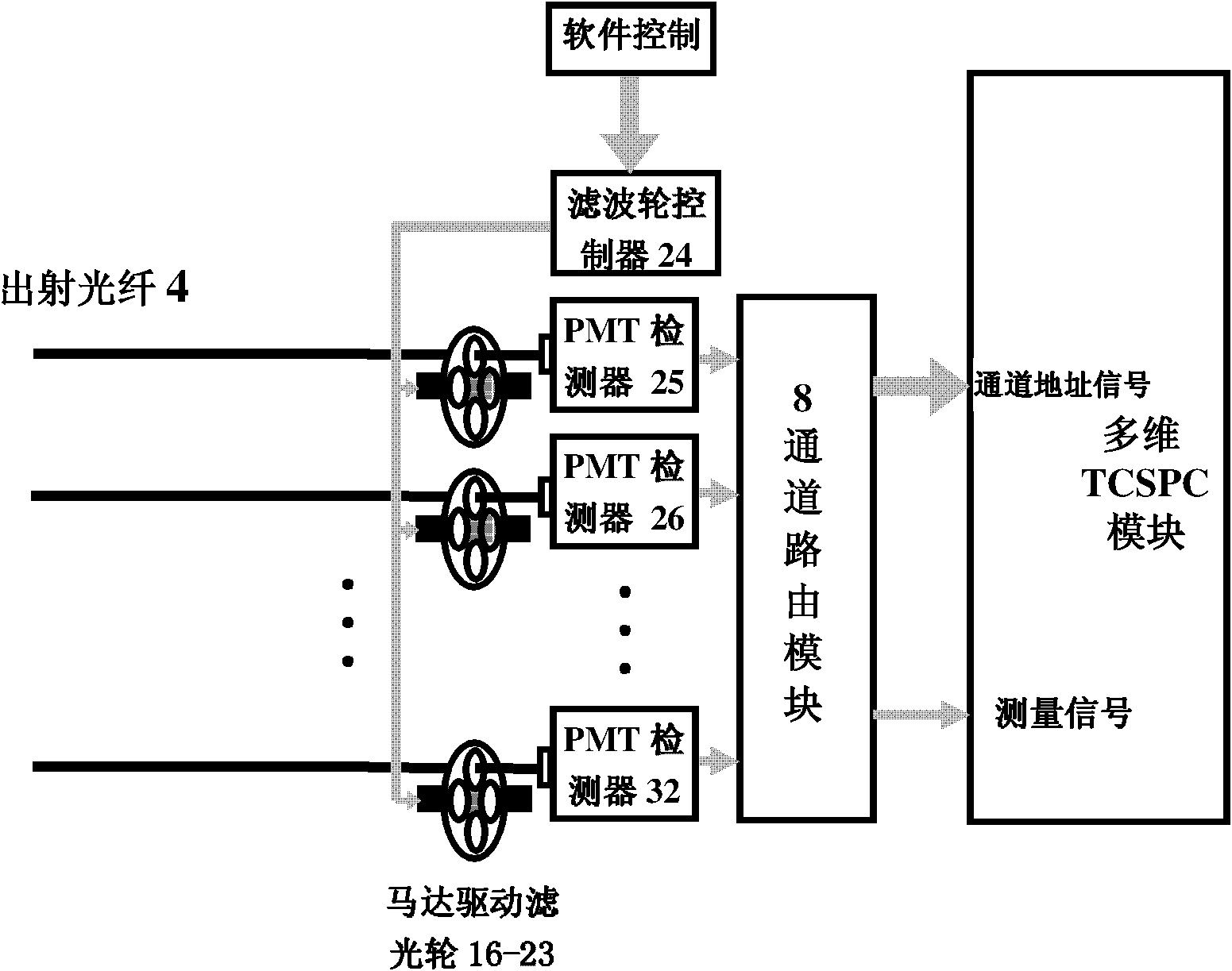
The invention relates to the field of small animal molecular imaging, and provides an imitating CT scanning mode multispectral time domain fluorescence molecular tomography measuring system with ultrasensitive and high time-space resolution measurement performances so as to realize the high-quality multi-component multi-parameter imaging function. The imitating CT scanning mode multispectral time domain fluorescence molecular tomography measuring system comprises two picosecond semiconductor lasers, an optical fiber coupler, an incident optical fiber, an imaging cavity, a rotating platform, a receiving optical fiber, a motor driving filter wheel and a detection module, wherein the two picosecond semiconductor lasers and the optical fiber coupler are used for providing wavelength ultrashort laser required, the optical fiber coupler is used for coupling two same-frequency ultrashort laser pulses of different wavelengths into a bundle of laser according to fixed time interval, the incident optical fiber is used for projecting emergent laser of two or one of both picosecond semiconductor lasers onto an object, the imaging cavity and the rotating platform are used for realizing the imitating CT scanning mode, the receiving optical fiber is used for receiving reflective or transmitted laser from the object, and the detection module is used for receiving emergent light passing through corresponding filter pieces. The invention is mainly applied to the molecular imaging of small animals.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Multi-modal in-vivo imaging system for small animals and small animal imaging method
InactiveCN104000617AUnlimited distanceHigh sensitivityComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityX-ray
The invention discloses a multi-modal in-vivo imaging system for small animals and a small animal imaging method. The multi-modal in-vivo imaging system for small animals comprises a bracket, the bracket comprises a carrying bed system and a bracket system, the bracket system is provided with a rotary disc, and the carrying bed system is located in the axial direction of the rotary disc; the rotary disc is provided with reflector devices of an X-ray computer tomography subsystem, a positron emission tomography subsystem and an optical subsystem; the optical subsystem comprises a bio-luminescence tomography optical subsystem, a fluorescence molecular tomography optical subsystem and an optical camera, and the optical camera is mounted on the carrying bed system; the imaging view of the X-ray computer tomography subsystem, the imaging view of the positron emission tomography subsystem and the imaging view of the optical camera are at least overlapped partially; the carrying bed system further comprises an animal carrying bed, and the animal carrying bed is used for moving small animals to the overlapped region of the views.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Reconstruction method and imaging device of three-dimensional profiles of object surfaces
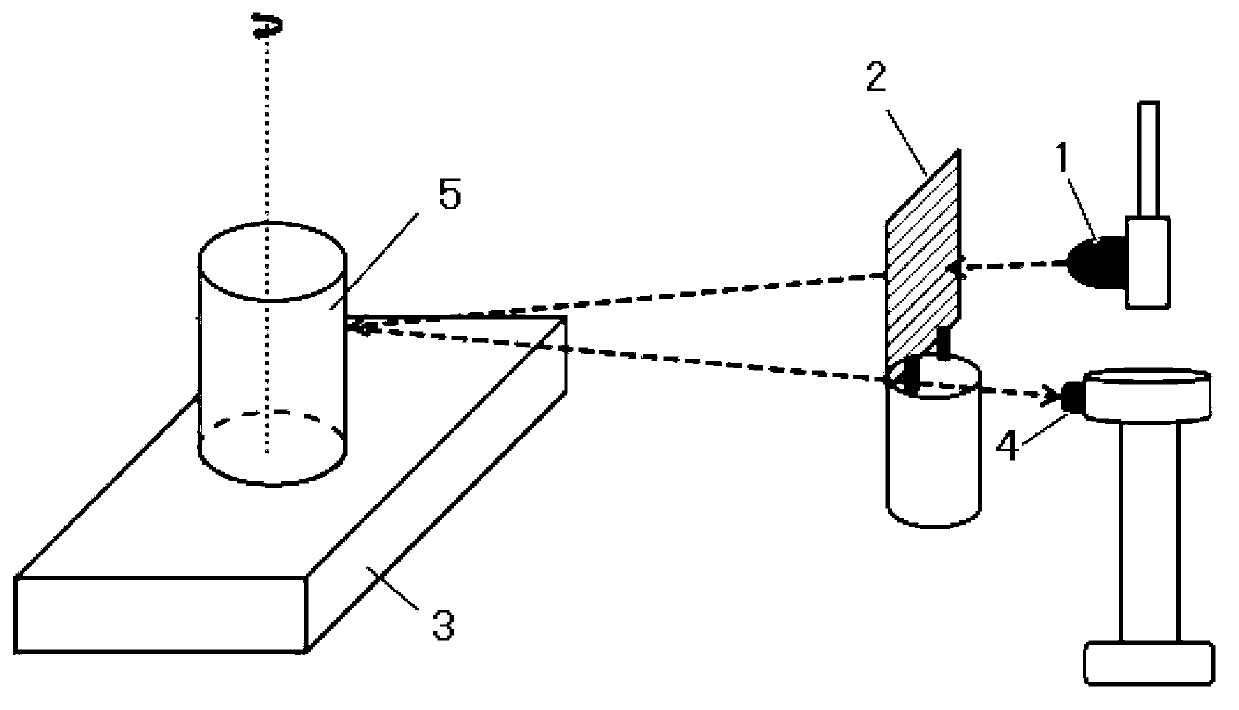
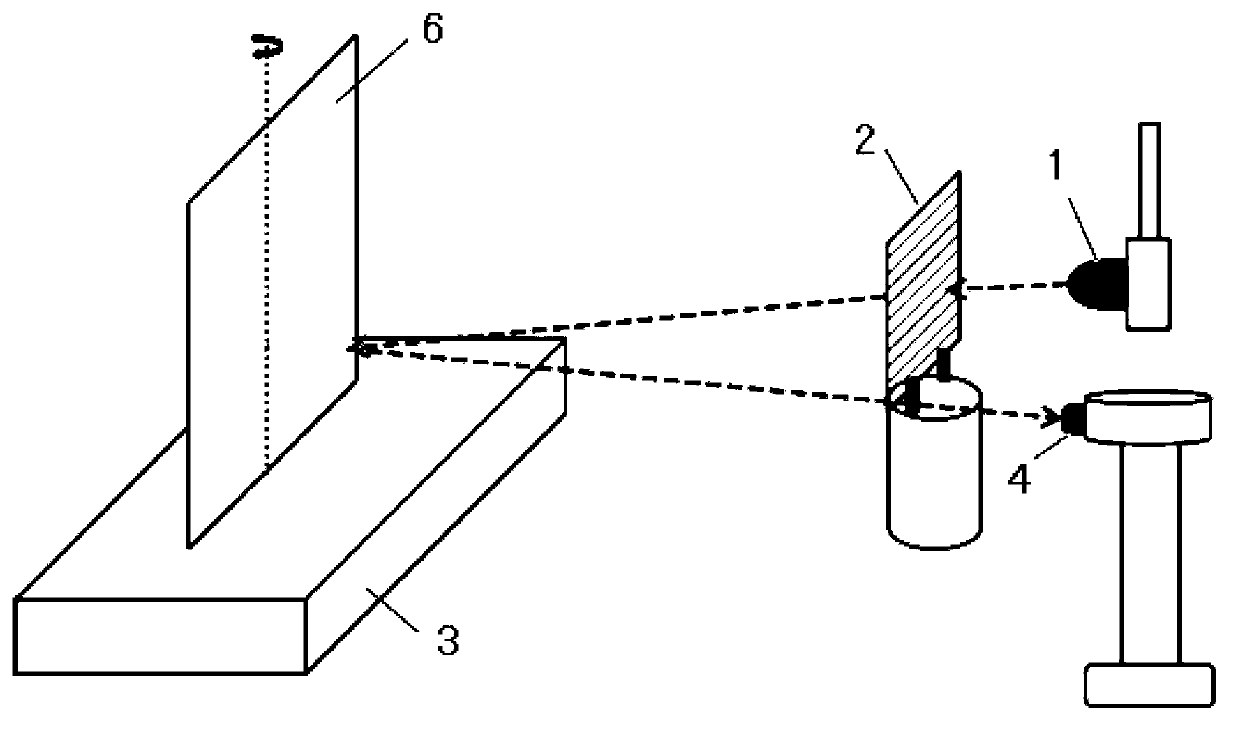
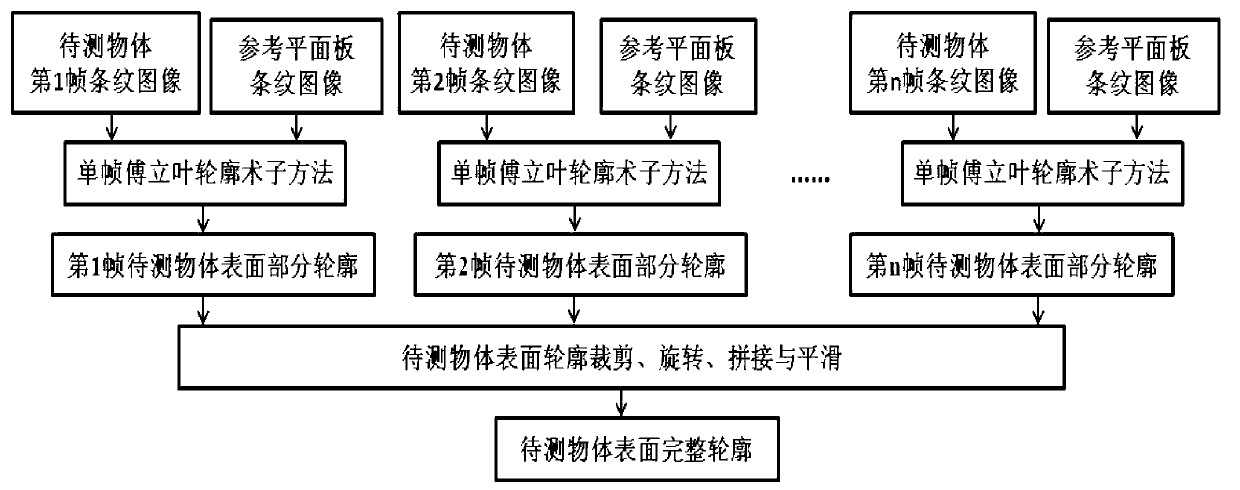
InactiveCN102997866AAdapt to the requirements of three-dimensional surface contoursImaging operation is simpleUsing optical meansRotary stageGrating
The invention relates to a reconstruction method and an imaging device of three-dimensional profiles of object surfaces. The reconstruction method includes that a reference plane plate is placed on a rotary table, light emitted by a luminous diode is projected to the surface of the reference plane plate to form a plurality of stripes through gratings, and a camera shoots the stripes of the reference plane plate and sends the stripes to a computer; an object to be tested is placed on the rotary table, the light emitted by the luminous diode is projected to the surface of the reference plane plate to form the plurality of the stripes through gratings, the camera shoots the stripes of the reference plane plate and sends the stripes to the computer; a controller controls the rotary table to rotate, and the camera shoots n frames of stripe images of the object to be tested in a range of 360 degrees; the computer obtains partial profiles of the surface of the object to be tested at n different angles through a single frame Fourier transform profilometry method; and a complete profile of the object to be tested is obtained by synthesizing the partial profiles of the surface of the object to be tested at all angles. The reconstruction method and the imaging device of three-dimensional profiles of object surfaces can be widely applied to three-dimensional profile reconstruction of object surfaces of fluorescence molecular tomography.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction method
InactiveCN104586366AFast convergenceAdd prior informationDiagnostic signal processingDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionAnatomical structuresMinimization problem
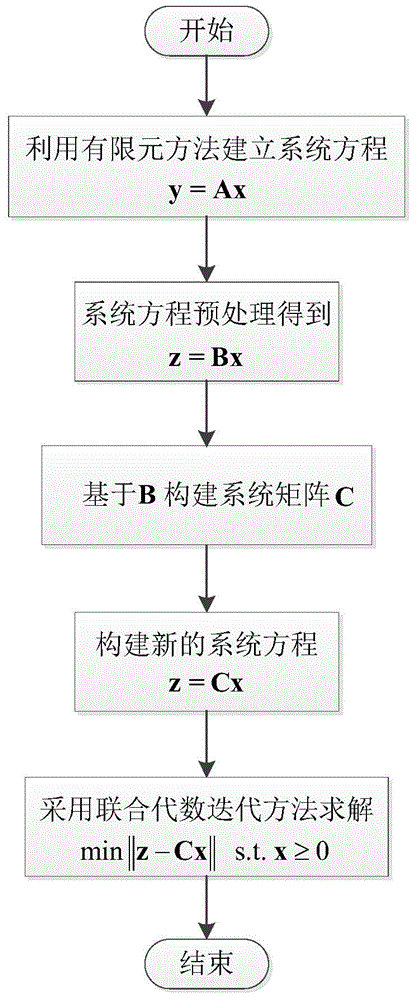
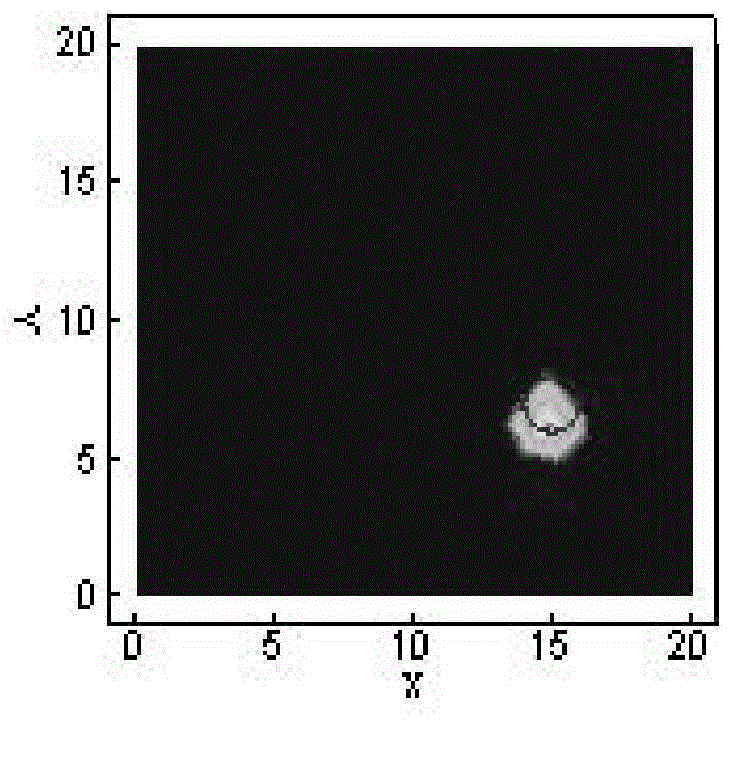
The invention discloses a fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a system equation for the measured data of a surface and the distribution of a fluorescent target inside an imaging object by taking the optical feature parameter and anatomical structure information of the imaging object as prior information based on an optical transmission model and a finite element theory; S2, preprocessing the system equation established in the step S1 in order that rows of a sparse matrix in the preprocessed system equation are orthogonal to each other; S3, fusing the sparse property of light source spatial distribution, selecting a plurality of rows from the system equation established in the step S1, and establishing a new coefficient matrix and a new system equation; S4, converting the new system equation established in the step S3 into a minimization problem with a constraint condition, and solving the new system equation by adopting a simultaneous algebraic reconstruction technique to obtain the three-dimensional distribution and concentration of the fluorescent target inside the imaging object. The method has the beneficial effects that the sparse property of the fluorescent target spatial distribution is fused, the prior information is increased, and the reconstruction accuracy can be increased; the system equation is preprocessed, and the rows of the coefficient matrix of the system equation are orthogonal to each other, so that the algorithm convergence can be accelerated, and the reconstruction speed is increased.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction method based on alternative iterative operation
InactiveCN103393410AComprehensive measurement dataReduce morbidityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSteep descentAnatomical structures
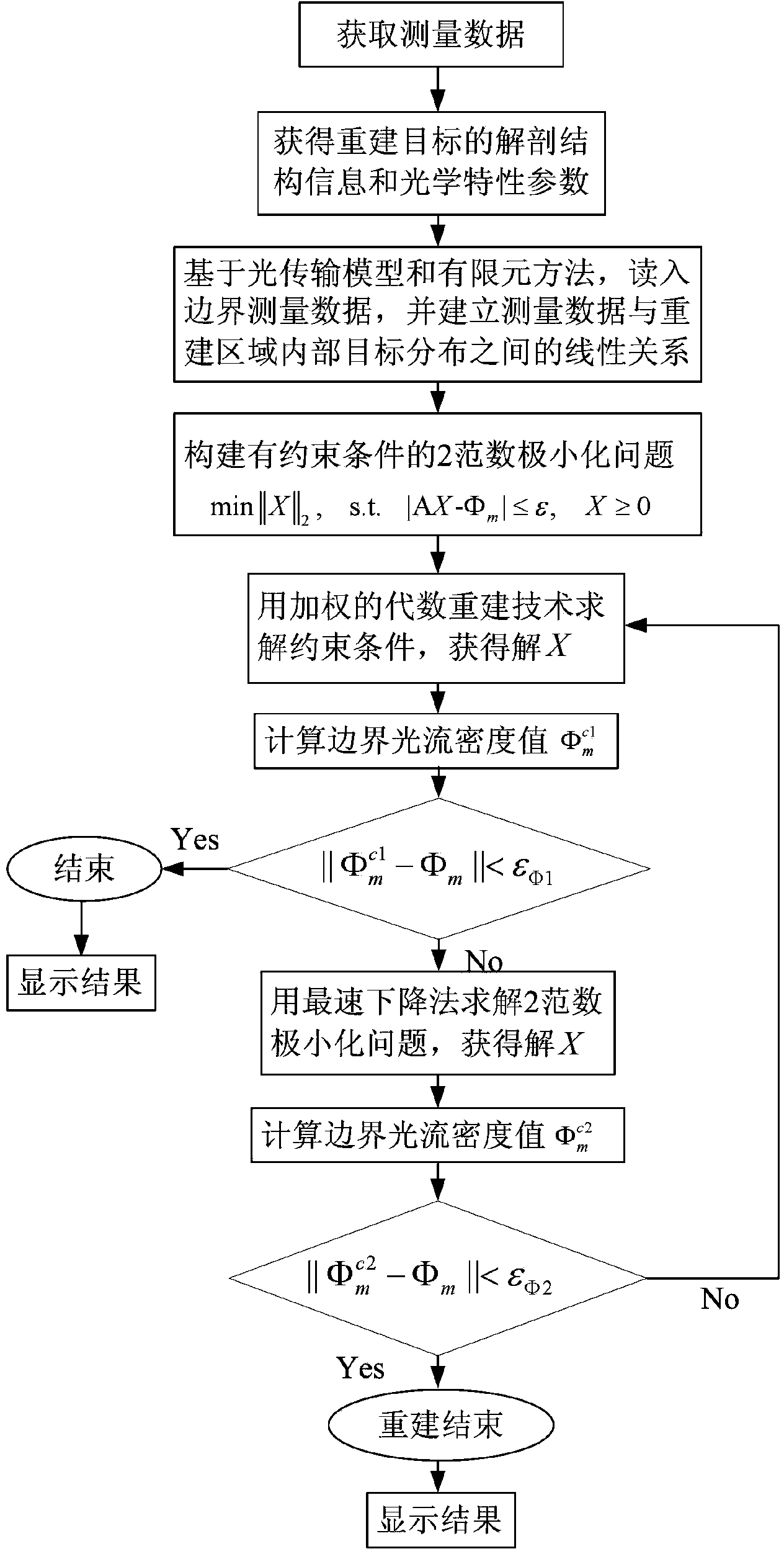
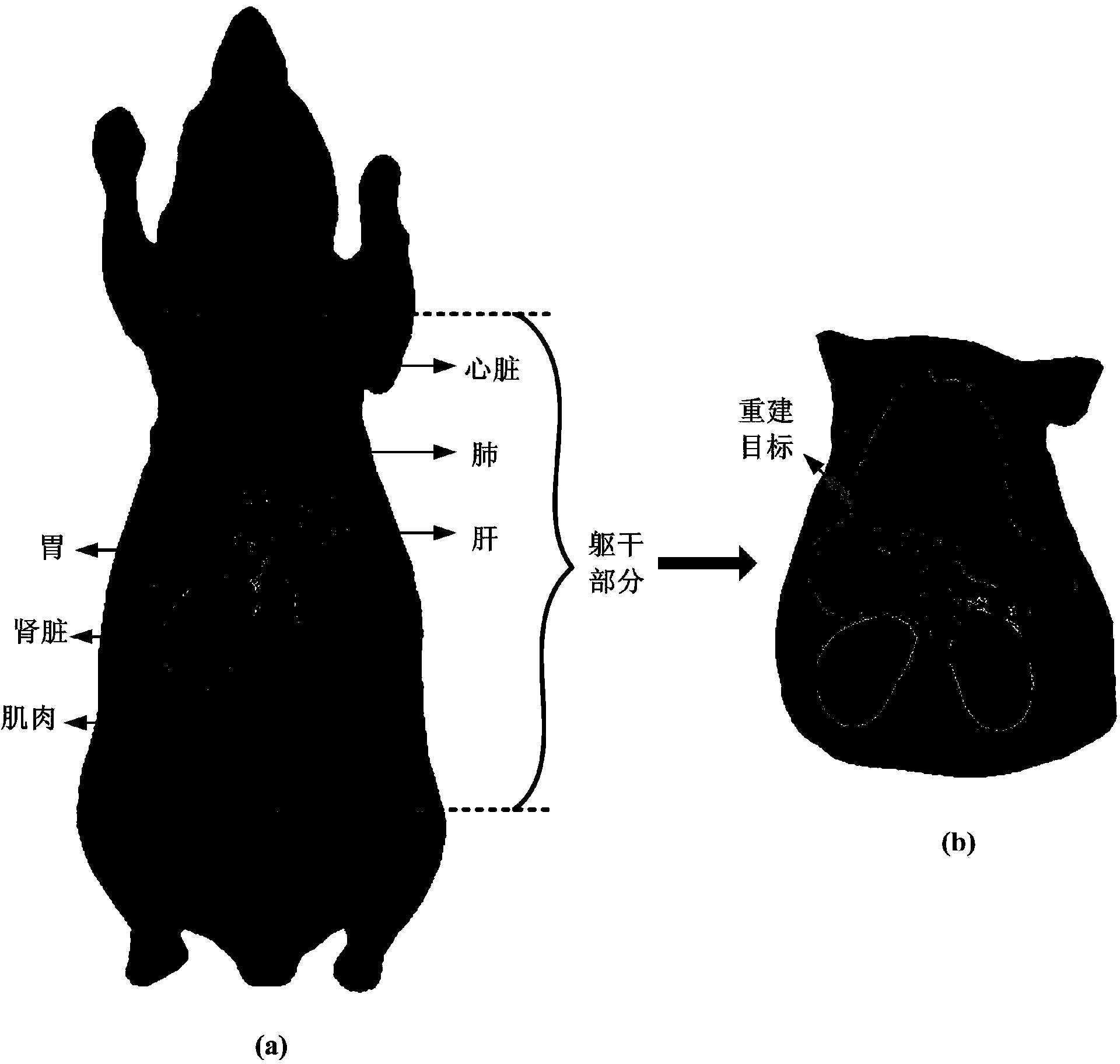
The invention discloses a fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm based on an alternative iterative operation, which is characterized in that a weighted algebraic reconstruction technique and a steepest descent method are used alternately for solving. The fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm comprises the following steps that (1), measurement data is acquired; (2), a linear relationship between the measurement data and target distribution is established; (3), a 2 norm minimization problem with a constraint condition is constructed; and (4), the weighted algebraic reconstruction technique and the steepest descent method are used alternately for solving the minimization problem, and a target distribution diagram is obtained. According to the fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm, based on a light transmission theory and a finite element method, prior information such as an optical characteristic parameter and an anatomical structure is used, multipoint excitation and multipoint measurement are adopted, and the measurement data is obtained as far as possible, so that the pathosis of the problem is reduced; the weighted algebraic reconstruction technique and the steepest descent method are used alternately for solving the problem, so that a reconstruction result of fluorescence molecular tomography is improved effectively; and the fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm has an important application value in the fields of molecular imaging, reconstruction algorithms and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
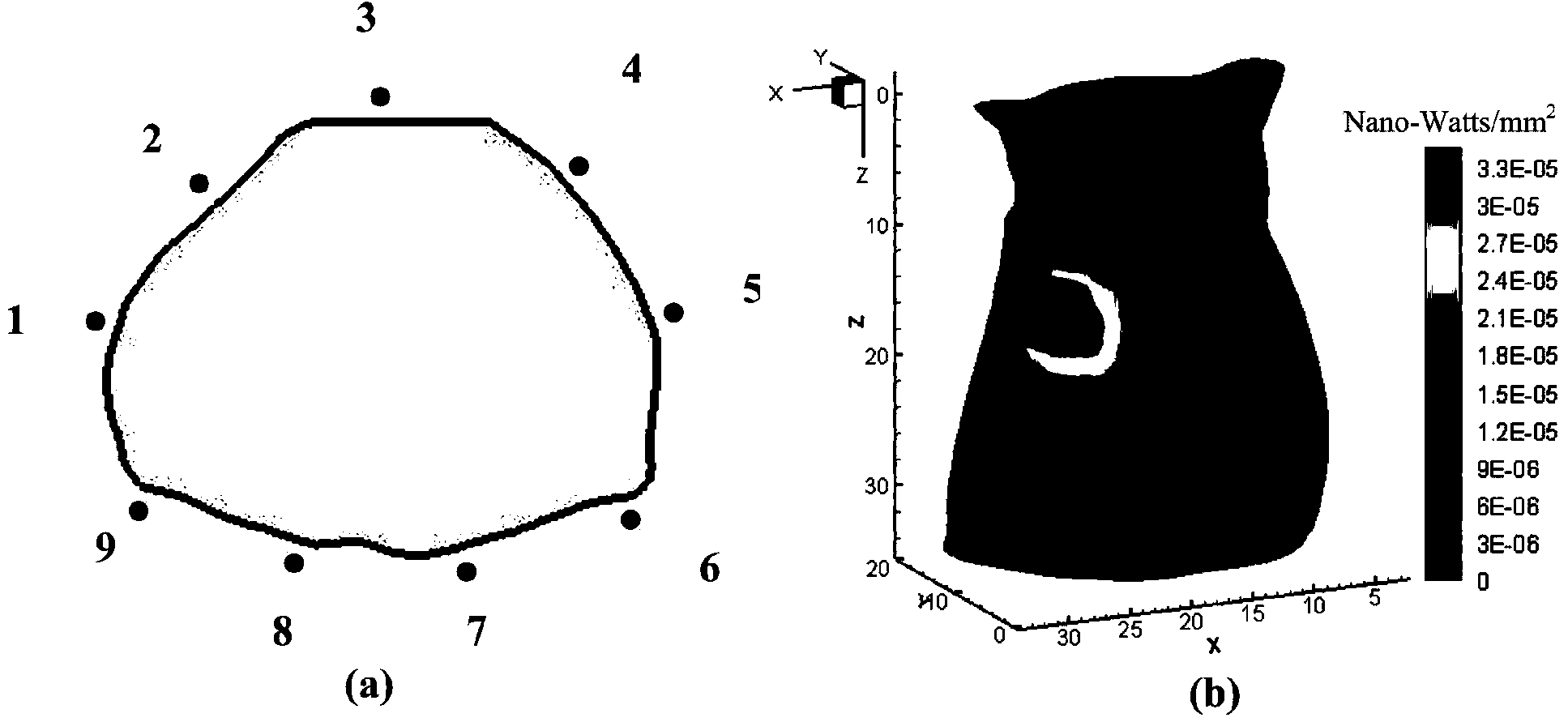
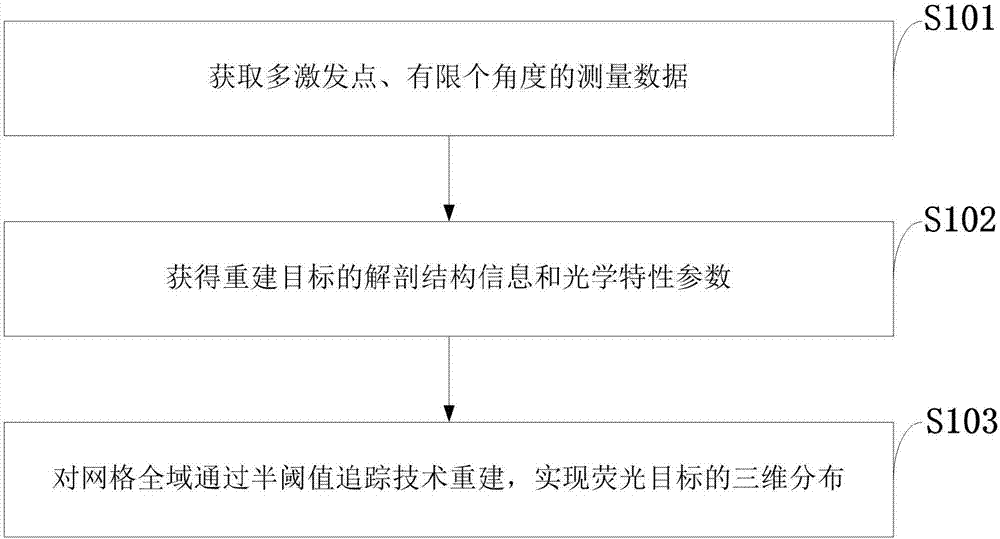
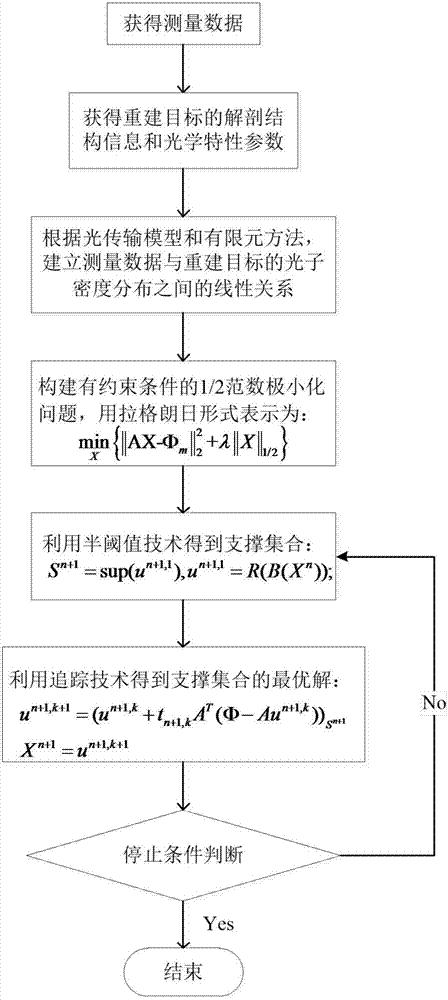
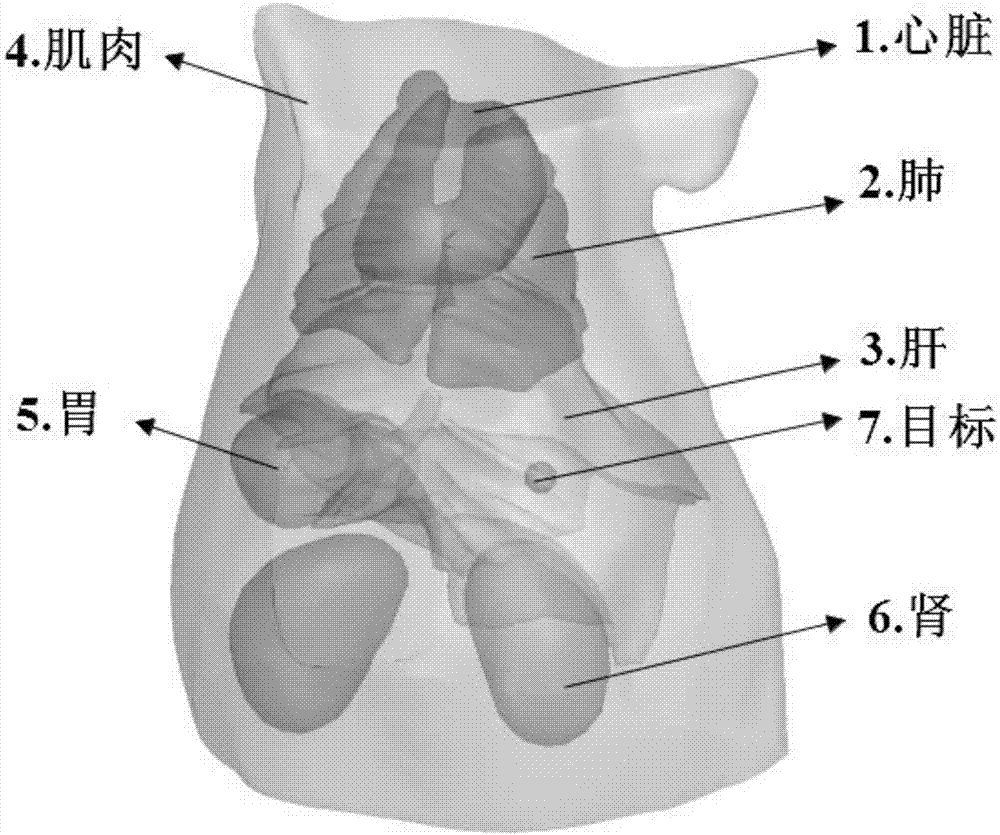
Method for reconstructing fluorescence molecular tomography based on semi-threshold tracking algorithm
InactiveCN107220961AImprove stabilityThe reconstruction results are accurateImage enhancementDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionAnatomical structuresCanonical model
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular imaging, and discloses a method for reconstructing fluorescence molecular tomography based on semi-threshold tracking algorithm. The multi-point excitation and finite angle measurement are used to construct a sparse canonical model of a non-convex problem, and the linear relationship between the surface measurement data and fluorescence target distribution is established. The linear relationship is transformed into the 1 / 2 norm minimization problem to solve and obtain the three-dimensional distribution and concentration of the fluorescent targets within a reconstructed target. The model is solved by threshold iteration and matching tracing algorithm. The method reduces the morbidity of the problem. Optical characteristic parameters and the anatomical structure information are used as a priori knowledge to improve the accuracy of the reconstruction result and the quality of a reconstructed image. The reconstruction problem is transformed into a 1 / 2-norm minimization problem with constraint conditions and is solved by using the semi-threshold tracing algorithm, which makes the solution satisfy the minimum of 1 / 2- norm and guarantees the robustness of the reconstruction problem to the parameters and the acceleration reconstruction time.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Method for reconstructing dynamic fluorescence molecular tomography
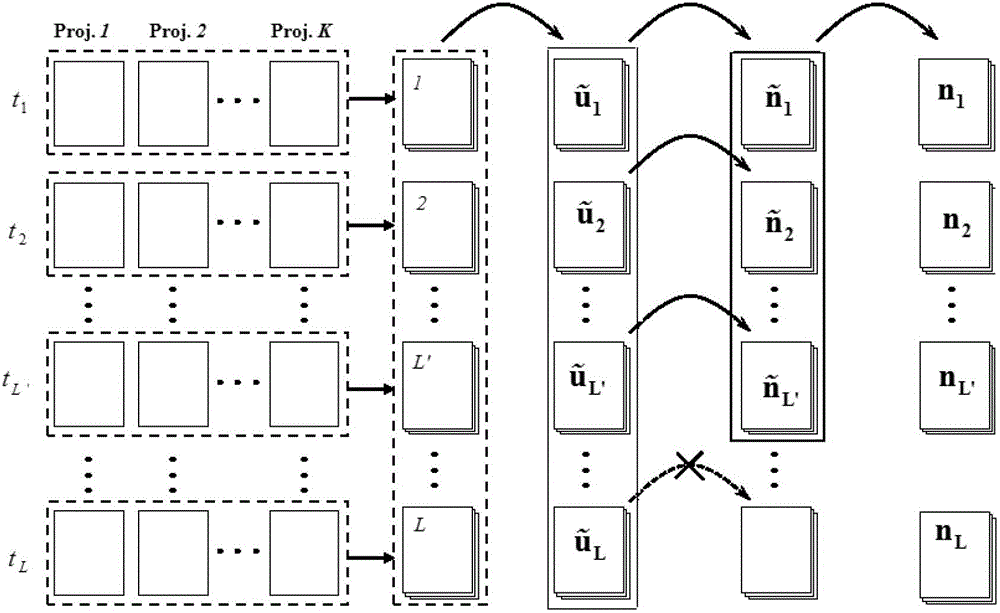
InactiveCN103188989AHigh speedReduce computing scaleReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSmall animalReconstruction method
The invention relates to a method for reconstructing a dynamic fluorescence molecular tomography. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) arranging a small animal-induced fluorescence molecular tomography system; 2) adopting the system to collect fluorescence projected image which reflects the metabolic distribution of a fluorescence probe in an imaging target in a full-angle and equal-interval manner at different time points and storing an acquired image as an input matrix u; 3) generating a KL transformational matrix A based on u; 4) calculating data after the input matrix u is transformed through KL; 5) obtaining L' KL components for 3D reconstruction after KL transformation; 6) generating a weight matrix W1 according to an optical field distribution function Phi x and a green function G; 7) performing 3D reconstruction on each KL component by adopting a 3D FMT reconstruction method according to a formula shown in the description; 8) and performing inverse KL transformation to reconstruction results of the KL components to obtain 4D fluorescence fault sequence. The invention can be widely applied to the reconstruction process of the dynamic fluorescence molecular tomography.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fluorescent molecular tomography method suitable for small animals
InactiveCN101509871AThe concentration is precisely determinedPrecise determination of concentratioFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiffusionSmall animal
The invention relates to the application of spectroscopic techniques in the field of biomedical engineering, in particular to a fluorescence molecule tomographic imaging method which is applicable to small animals, which describes a fluorescence propagation process in tissues in a approximately precise degree by utilizing the diffusion of a radioactive transfer equation, computes fluorescence distribution in the tissues by adopting a finite element method, back-deduces the concentration and position of a fluorescent marker by combining a nonlinear optimizing algorithm, and finally implements the display of fluorescence molecule tomographic imaging through computer graphic processing. The fluorescence molecule tomographic imaging method can locate the position and concentration of the fluorescent marker deep inside the tissues of small animals based on corresponding instrument measured data, and realize tomographic imaging; and specially for deep fluorescent signals, the fluorescence molecule tomographic imaging method can accurately and quickly recover the depth and intensity information that is carried by the deep fluorescent signals, thus achieving the accurate locating effect of the fluorescent marker position and intensity and providing reference means to medicine development and tumor treatment.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
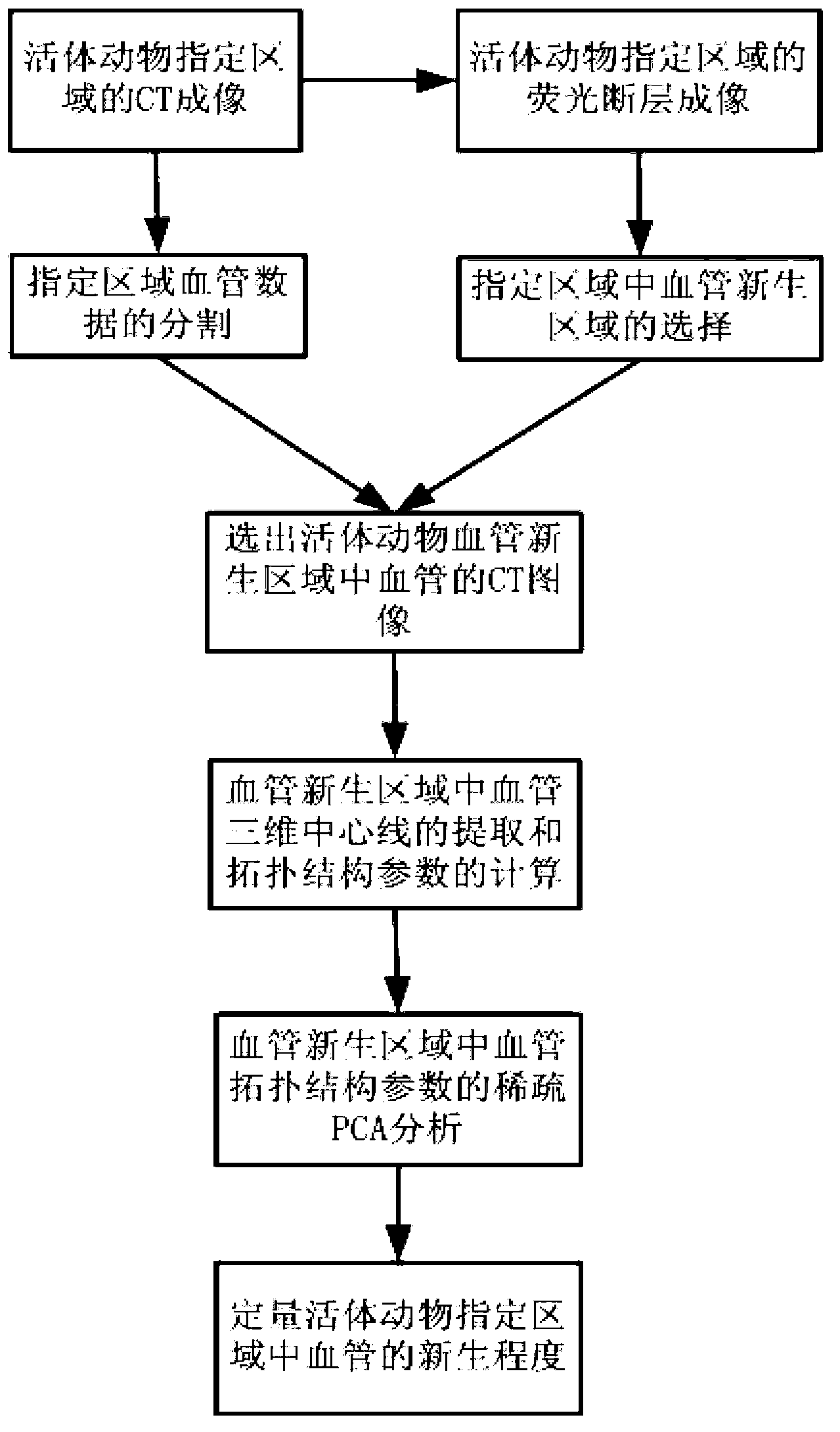
Method for quantitative analysis for angiogenesis of living animals
InactiveCN103284694AEffective Quantitative Evaluation MethodAddressing the inability to select angiogenesis regionsComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringComputed tomographyMedicine
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Systems for fusion of fluorescence molecular tomography and magnetic resonance images
ActiveUS20140031669A1Dianostics using fluorescence emissionSensorsNuclear magnetic resonanceFluorescence molecular tomography
An imaging cassette. The cassette includes a top frame, a bottom frame, and one or more of a front wall, back wall, or plurality of posts, and defines a chamber for holding an animal in a desired position for analysis in a fluorescence molecular tomography imager and a vertical bore magnetic resonance imager.
Owner:INST FOR CANCER RES
Non-contact stationary type fluorescent molecular tomography method and device
InactiveCN101485560AQuality improvementReduce quality problemsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCamera lensSignal on
The invention relates to a noncontact fixed fluorescence molecular tomography method and device, and is characterized in that an imaging device comprising an excitation light source, an optical switch part, a plurality of light transmitting optical fibers, a plurality of optical lenses, an image transmitting optical fiber and a detector is arranged; the plurality of the light transmitting optical fibers and the plurality of the optical lenses are respectively arranged around an object to be detected; the optical switch part is controlled by a computer; excitated light emitted by the excitation light source irradiates on the object to be detected through any light transmitting optical fiber; fluorescence excitated by the object to be detected is imaged on each forky end of the image transmitting optical fiber through each optical lens and then is transmitted to the detector arranged on the light outlet of the image transmitting optical fiber through the composite end of the image transmitting optical fiber; the excitated light is switched to the light transmitting optical fibers at different positions through the optical switch part in turn; the fluorescence signal acquisition process is repeated to realize 360-degree full-angle fluorescence signal on the boundary of the object to be detected. The noncontact fixed fluorescence molecular tomography method and device can realize 360-degree full-angle and noncontact fixed acquisition of the fluorescence signal of the object to be detected, and has high imaging efficiency and quality.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Microscopical hyperspectral chromatography three-dimensional imaging device
InactiveCN102661919AHas the effectInformativeScattering properties measurementsTransmissivity measurementsEcological environmentBeam splitting
The invention discloses a microscopical hyperspectral chromatography three-dimensional imaging device, which comprises a light source unit, a three-dimensional scanning platform, a front microscopical light path unit, a beam-splitting imaging unit, a signal pretreatment unit, a signal acquisition unit and a control unit. The device integrates a hyperspectral imaging technology, a microtechnique, a fluorescence molecular tomography and a three-dimensional imaging technology. The device can obtain the two-dimensional hyperspectral chromatography images under conditions of multiple wavelengths and angles of an object and can obtain the light spectrum under wavelength corresponding to each pixel; meanwhile, based on a three-dimensional image reconstruction technology, the device can obtain the three-dimensional microscopical hyperspectral image of the object; and combining with the microtechnique, the device can obtain the micro three-dimensional hyperspectral chromatography images of the surface and internal structures of micro objects. Compared with other spectrographs, the device has the advantages of more information, higher precision, more powerful functions and higher stability. The device is suitable for biomedical test, food safety test and ecological environment monitoring.
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
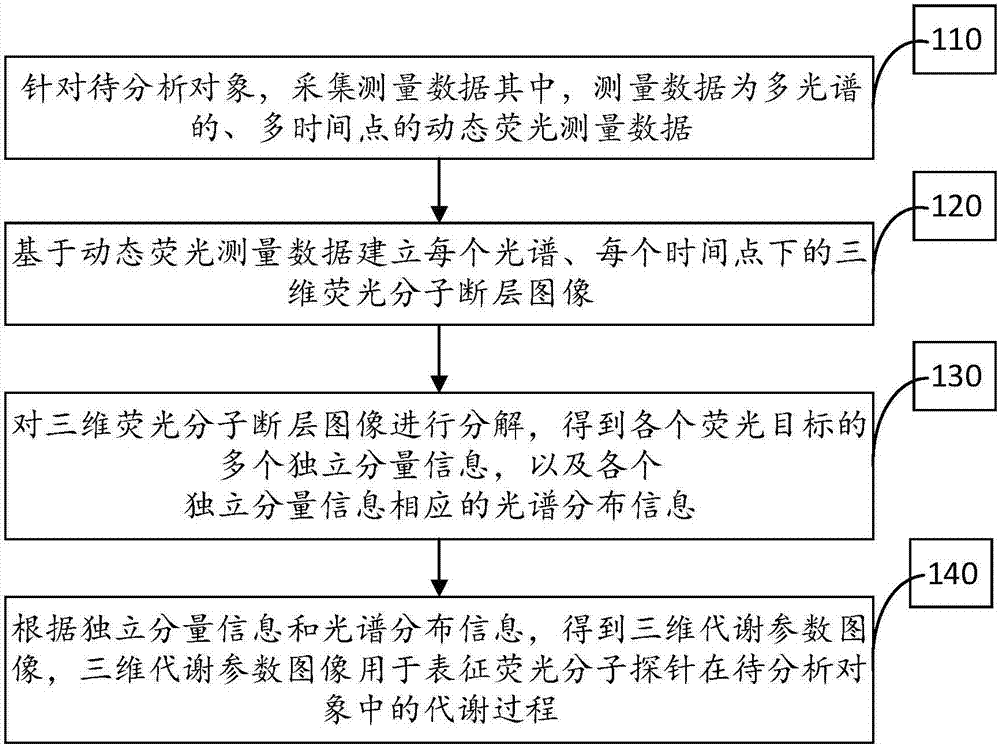
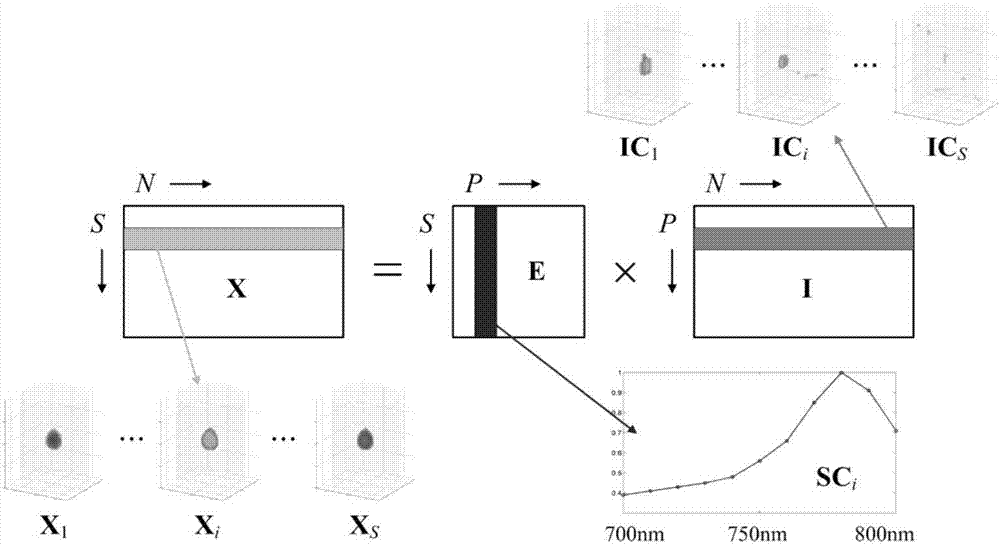
Processing method and system for dynamic fluorescence molecular tomography
InactiveCN107184181AReduce morbidityImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMolecular probeMultivariate analysis
The invention relates to a processing method and system for dynamic fluorescence molecular tomography. The method includes the steps of aiming at a to-be-analyzed object, collecting measurement data which is multi-spectrum and multi-time point dynamic fluorescence measurement data; based on the dynamic fluorescence measurement data, establishing three-dimensional fluorescence molecular tomography images under each spectrum and each time point; decomposing the three-dimensional fluorescence molecular tomography images to obtain the independent component information of each fluorescent target and spectral distribution information corresponding to the independent component information; according to the independent component information and the spectral distribution information, obtaining the three-dimensional metabolic parameter images used for representing the metabolic process of fluorescent molecular probes in the to-be-analyzed object. The processing method and system for the dynamic fluorescence molecular tomography contribute to reducing the morbidity of DFMT problems; in addition, on the basis of obtaining FMT images through reconstruction, multivariable analysis is carried out, and then metabolic parameter results are obtained aiming at each fluorescent target, so that the interference of other fluorescent targets and noise can be eliminated, and the accuracy of the reconstruction results can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
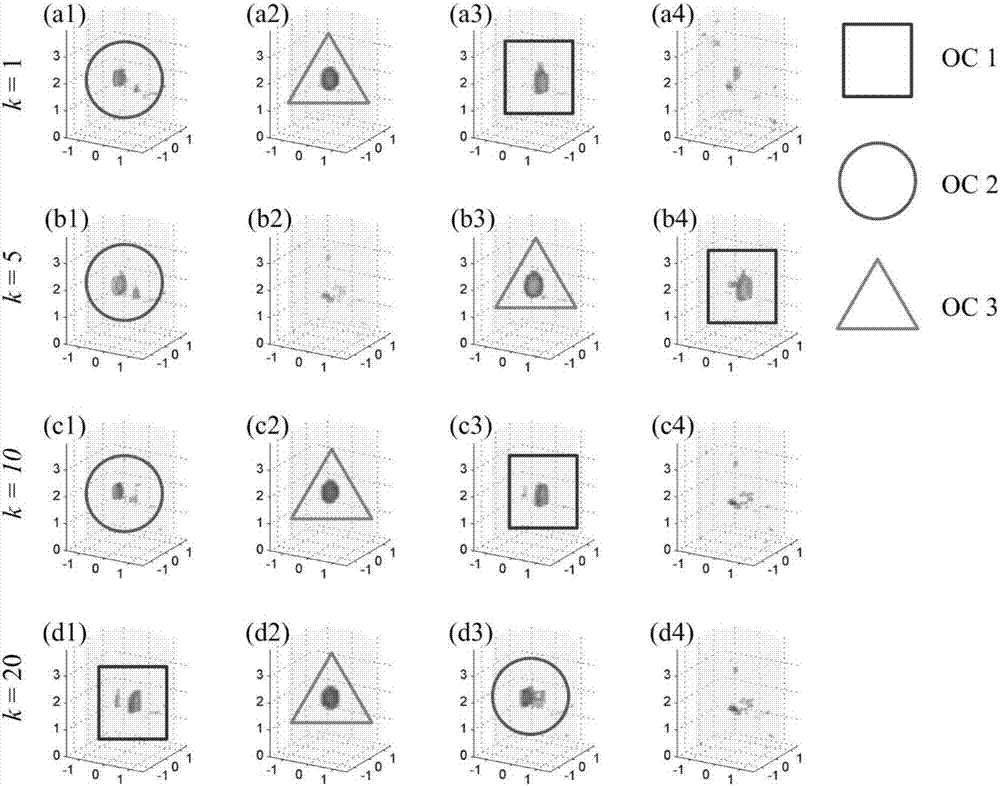
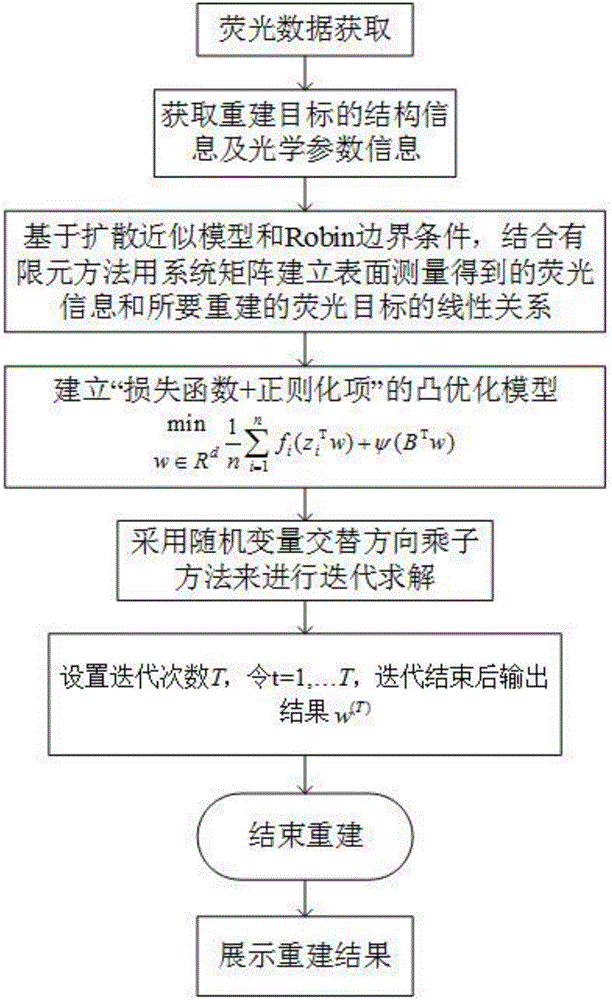
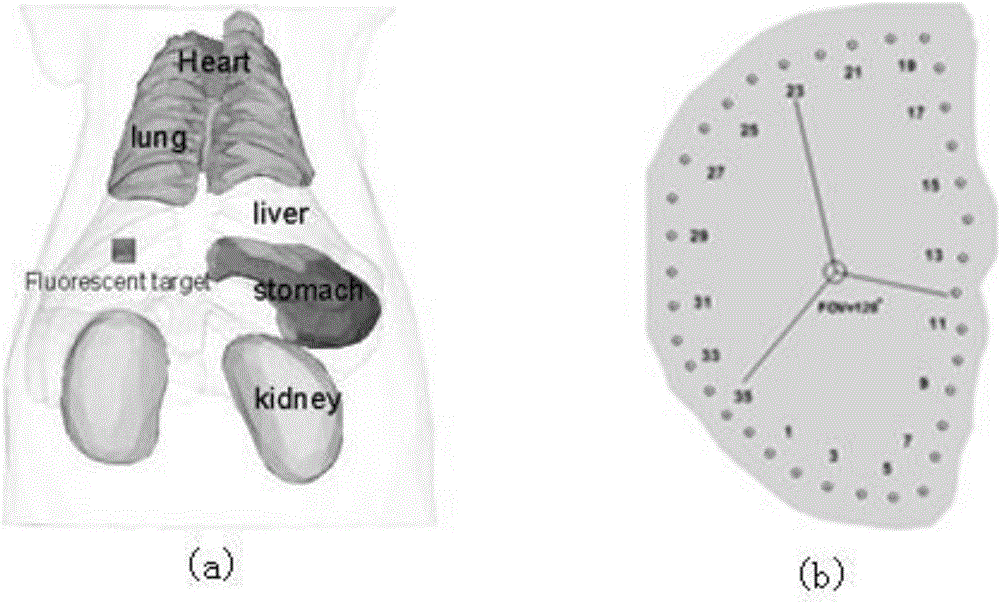
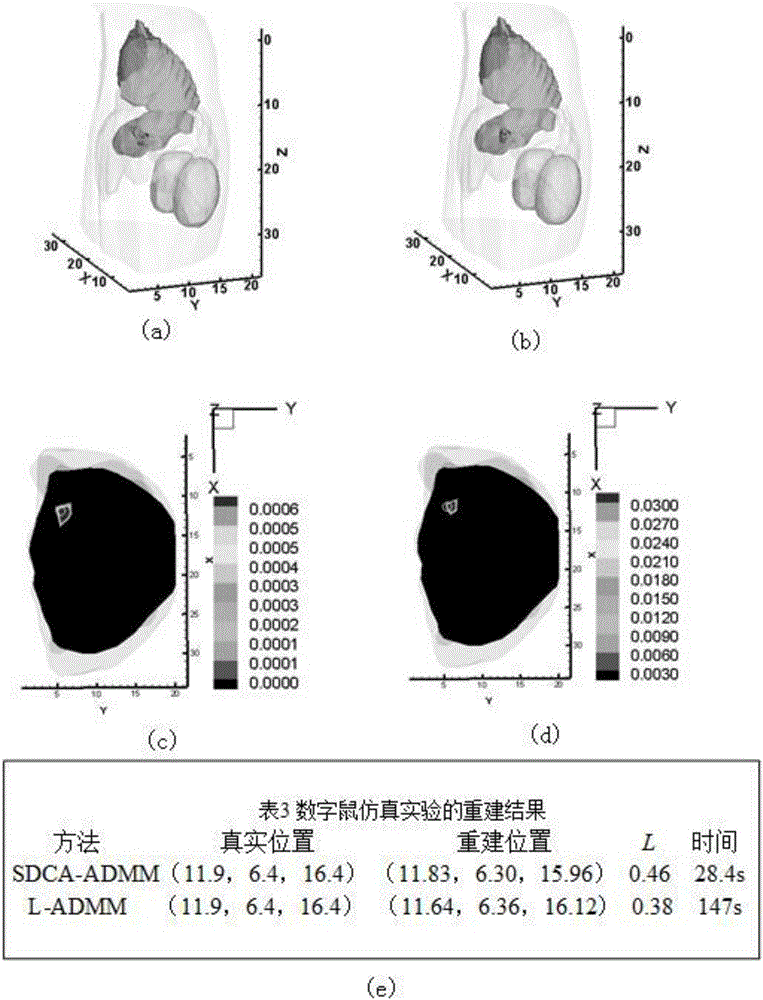
Fluorescence-molecular-tomography rebuilding method based on random-variable alternating direction multiplier method
InactiveCN106725347AReduce morbidityHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisCoordinate descent methodLinear relationship
The invention discloses a fluorescence-molecular-tomography rebuilding method based on a random-variable alternating direction multiplier method. The mode of the alternating direction multiplier method is converted into a random parameter mode with the randomness and the decomposability of the random dual coordinate descent method, and then solving is carried out through parameter alternating updating of the random-parameter alternating direction multiplier method; the fluorescence-molecular-tomography rebuilding method includes the following achieving steps that (1) large-scale fluorescence data is collected; (2) the linear relationship between measurement data and target distribution is built; (3) the linear relationship is converted into the convex optimization problem; (4) the convex optimization problem is solved in an alternated mode with the random-parameter dual coordinate descent method and the random-parameter alternating direction multiplier method, and a target distribution diagram and rebuilding time are obtained. The rebuilding efficiency of fluorescence molecular tomography is effectively improved while the quality of rebuilt images is guaranteed, and the fluorescence-molecular-tomography rebuilding method has the important application value in the field of medical molecular images, the field of rebuilding methods and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction method based on sparsity self-adaptive group orthogonal matching pursuit
ActiveCN110327018APrecise positioningPromote reconstructionDianostics using fluorescence emissionDiagnostics using tomographyAlgorithmReconstruction method
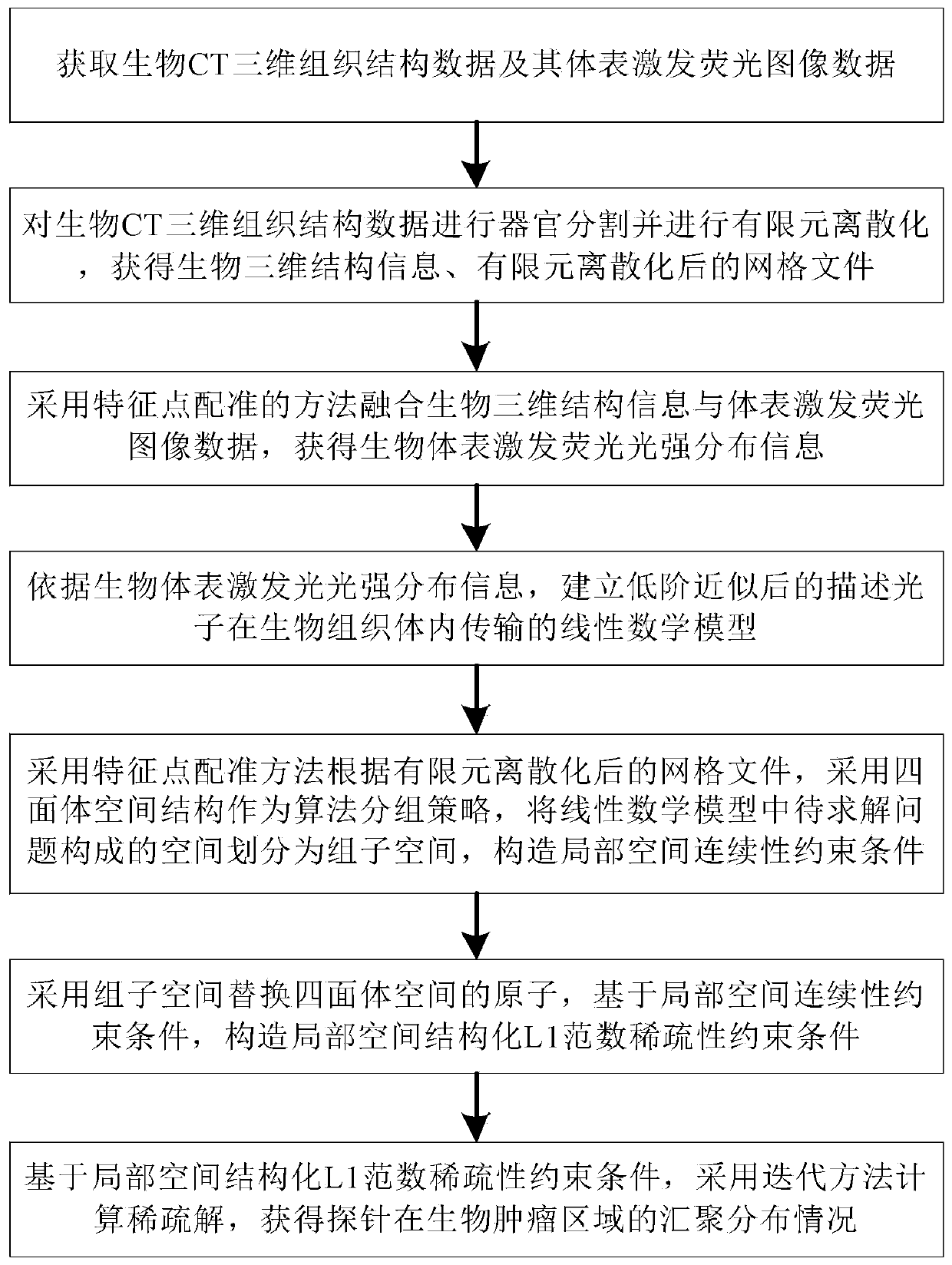
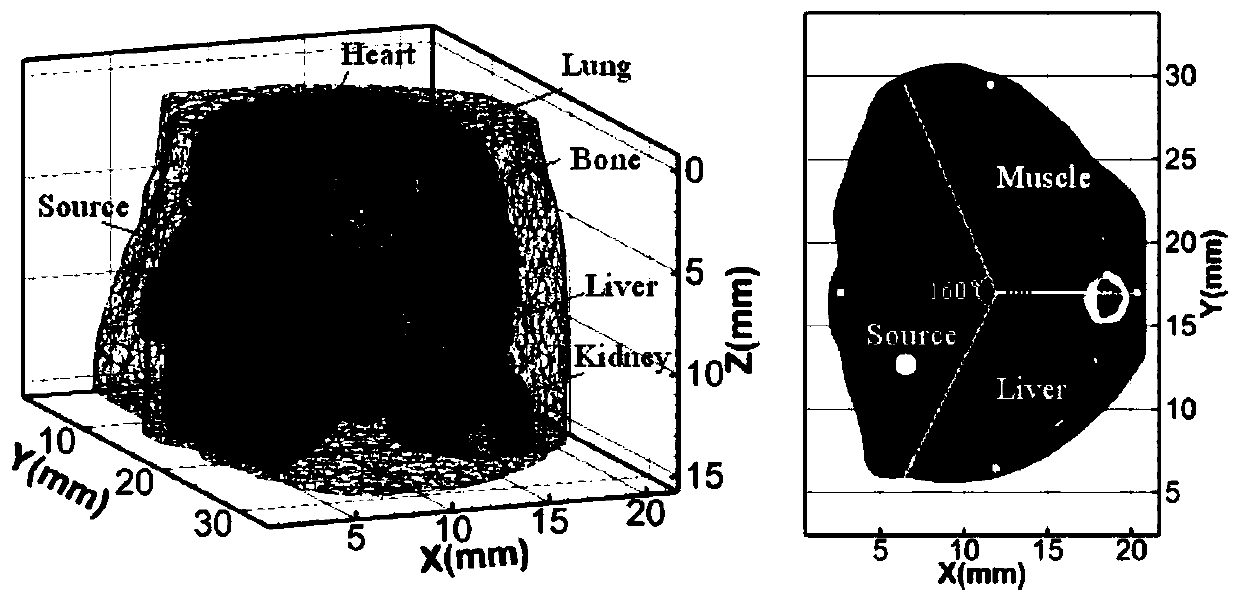
The invention belongs to the field of optical molecular imaging, and particularly relates to a fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction method based on sparsity self-adaptive group orthogonalmatching pursuit, in order to solve problems of excessive-sparse zones, spatial discontinuity and poor process robust performance in tumor distribution solving utilizing sparse constraint optimizationin the prior art. The method includes subjecting biological CT three-dimensional data to partitioning and finite element discretization, and performing fusion of the data with biology body surface excited fluorescence image data; building a model according to light intensity distribution information of the body surface excited fluorescence after fusion; dividing the model and constructing a localspatial continuity constraint condition; integrating L1 norm sparsity and performing iterative solution to obtain aggregation distribution of probes in a biological tumor zone. Through fusion of thespatial structure constraint and the sparse constraint, a novel spatial structure sparse regularization term is constructed, and problems of excessive-sparse zones, spatial discontinuity and poor process robust performance, which are caused by a manner that tumor distribution is solved only based on a sparse constraint, can be solved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
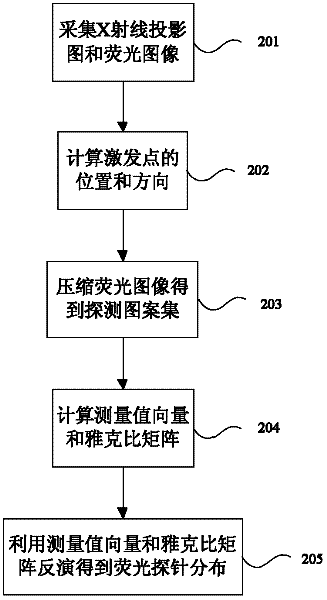
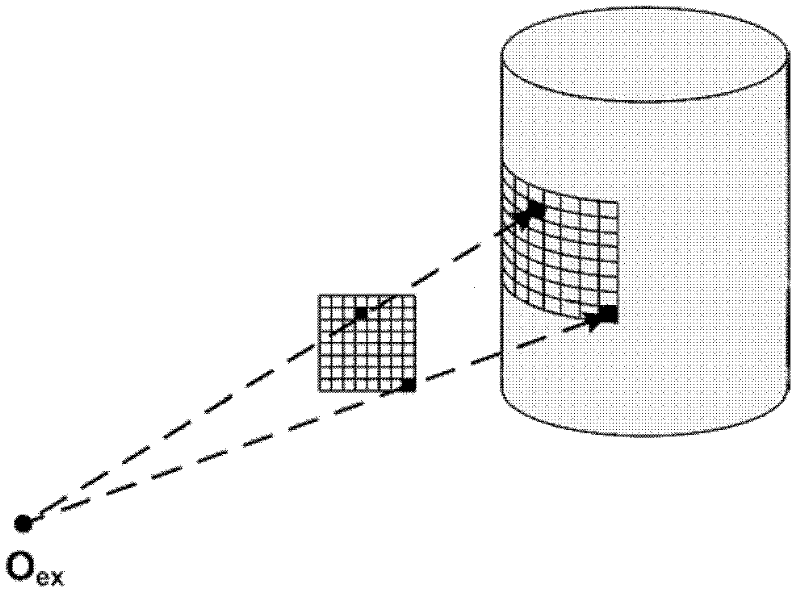
Double-mode in-vivo imaging system and method based on wavelet data compression
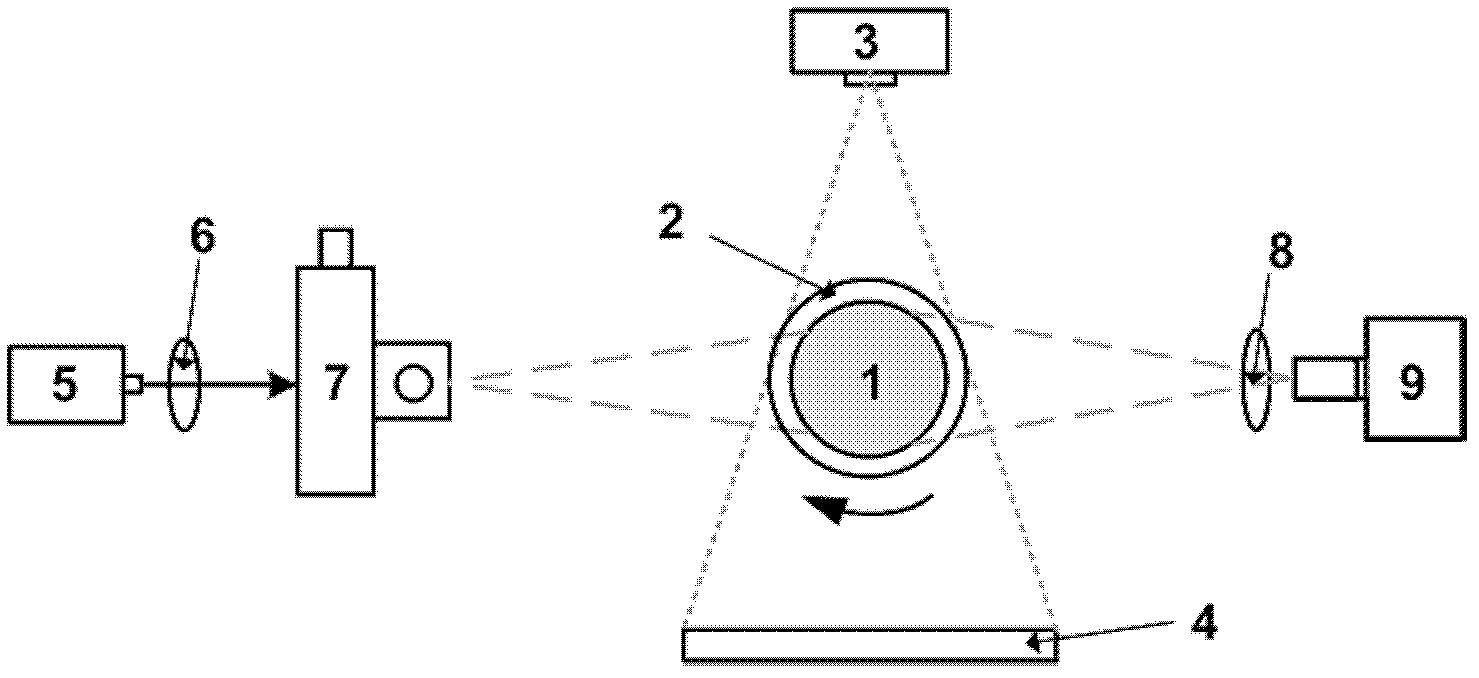
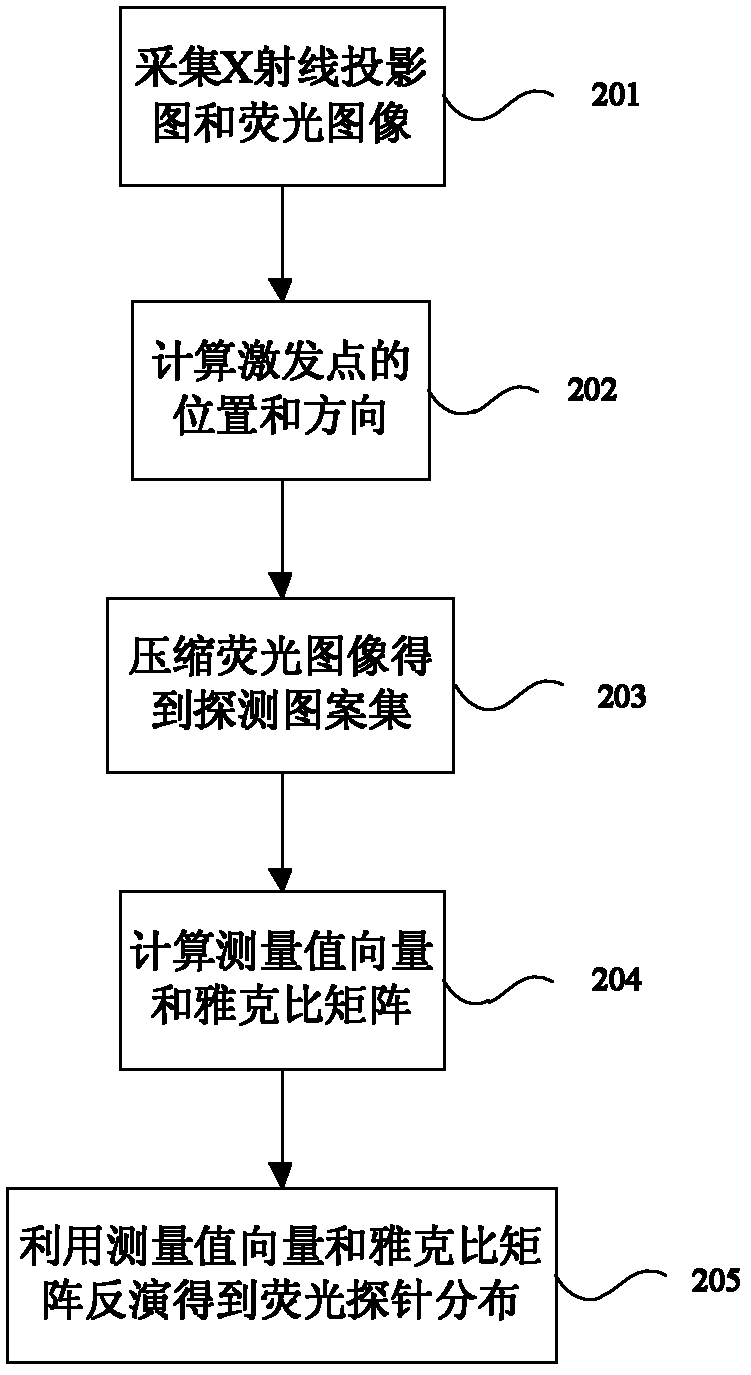
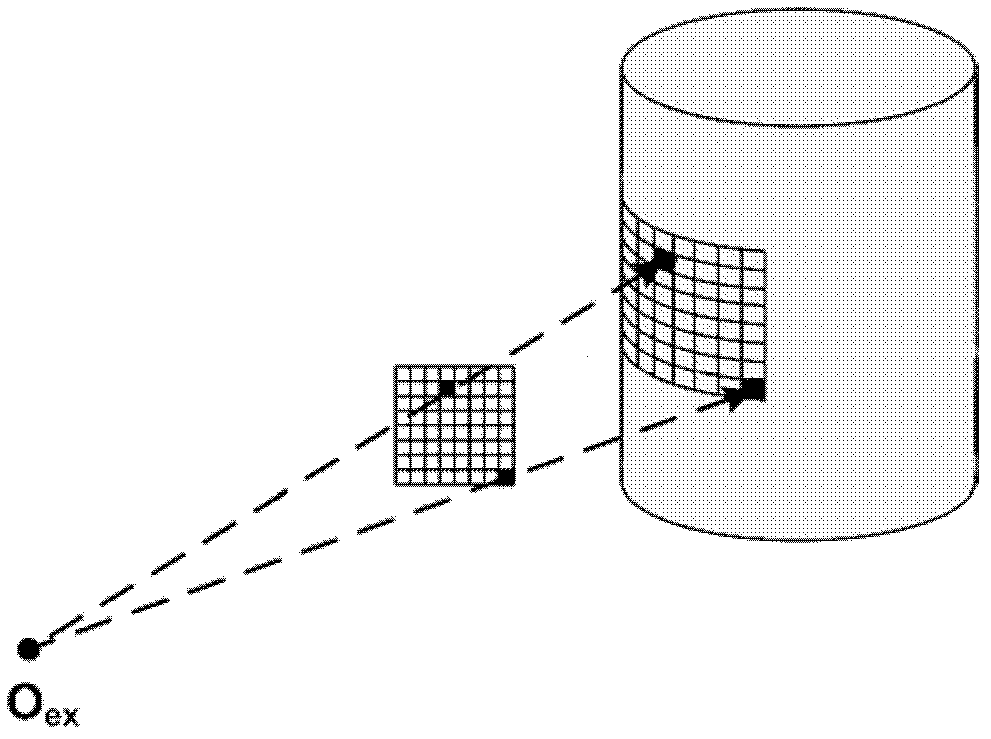
ActiveCN102512193AReduce acquisition timeReduce dimensionalityComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringData compressionData set
The invention discloses a double-mode in-vivo imaging system and method based on wavelet data compression, belonging to the technical field of molecule images. The double-mode in-vivo imaging system comprises a micro CT (Computed Tomography) subsystem and a fluorescence molecular tomography subsystem. Two subsystems are arranged in an orthogonal manner. The fluorescence molecular tomography subsystem is provided with a two-dimensional acousto-optic deflector. The double-mode in-vivo imaging method comprises the following steps of: collecting an X-ray projection image and a fluorescence image; using the two-dimensional acousto-optic deflector to control exciting light to scan in a process of collecting the fluorescence image; obtaining a position and a direction of an exciting point; obtaining a detection pattern set by compressing the fluorescence image; obtaining a measurement value vector and a Jacobian matrix according to the position and the direction of the exciting point and the detection pattern set; carrying out matrix inversion to obtain a fluorescence probe distribution according to the measurement value vector and the Jacobian matrix. According to the double-mode in-vivo imaging system and method provided by the invention, the faster collection of original data is realized, and the rapid reestablishment can be carried out by using a collected oversized data set.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
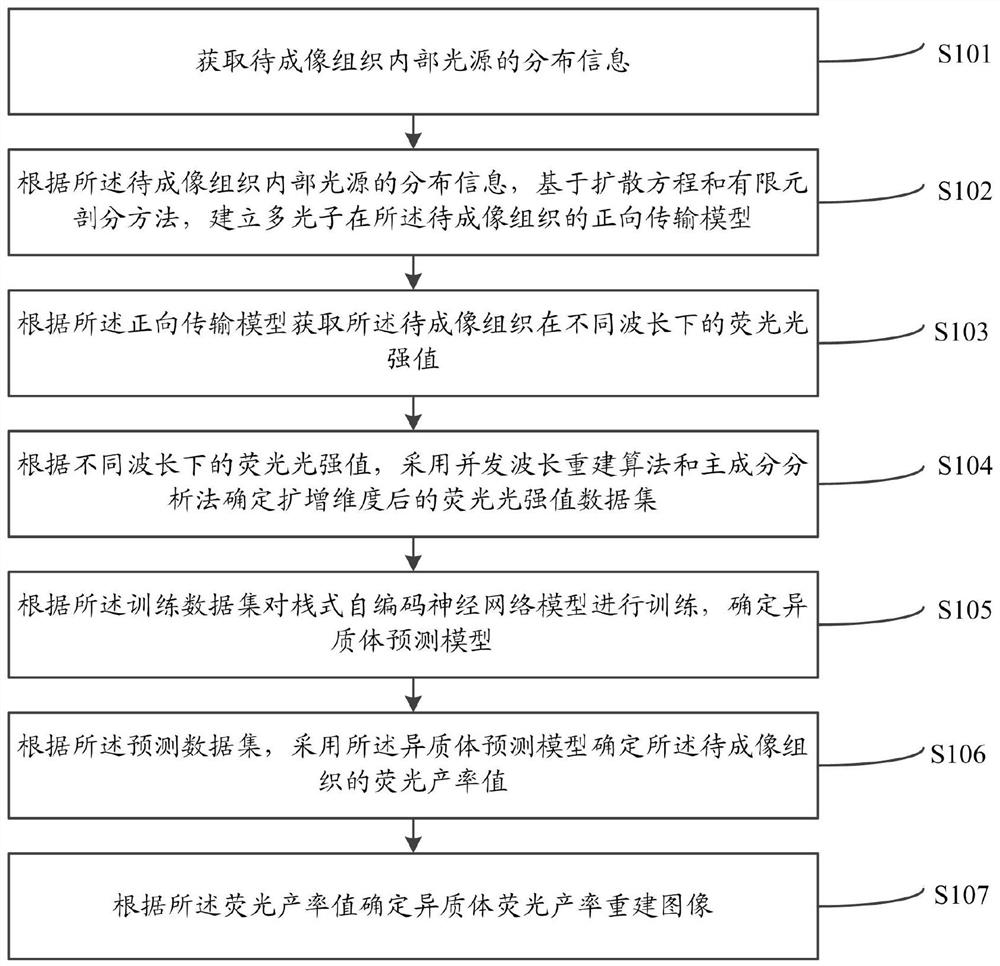
Fluorescence molecular tomography method and system based on multi-wavelength concurrent reconstruction
ActiveCN112734872AImproving Image Reconstruction AccuracyAchieve dimensionality reductionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setPrincipal component analysis
The invention relates to a fluorescence molecular tomography method and system based on multi-wavelength concurrent reconstruction. The method comprises the following steps: collecting distribution information of light sources in a to-be-imaged tissue; establishing a forward transmission model of the multiple photons in the tissue to be imaged based on a diffusion equation and a finite element subdivision method according to the distribution information; collecting fluorescence light intensity values of the to-be-imaged tissue under different wavelengths according to the forward transmission model; determining a fluorescence intensity value data set after dimension amplification by adopting a concurrent wavelength reconstruction algorithm and a principal component analysis method according to the fluorescence intensity values under different wavelengths; dividing the fluorescence intensity value data set into a training data set and a prediction data set; training the stack type self-encoding neural network model, and determining a heteroplasmon prediction model; determining a fluorescence yield value by adopting a heteroplasmon prediction model; and determining a heteroplasmon fluorescence yield reconstruction image according to the fluorescence yield value. According to the invention, the problem of ill-conditioned inverse in the FMT imaging process is effectively solved, and the imaging precision is greatly improved.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Mesoscopic fluorescence molecular tomography method and system based on bottleneck residual GAN
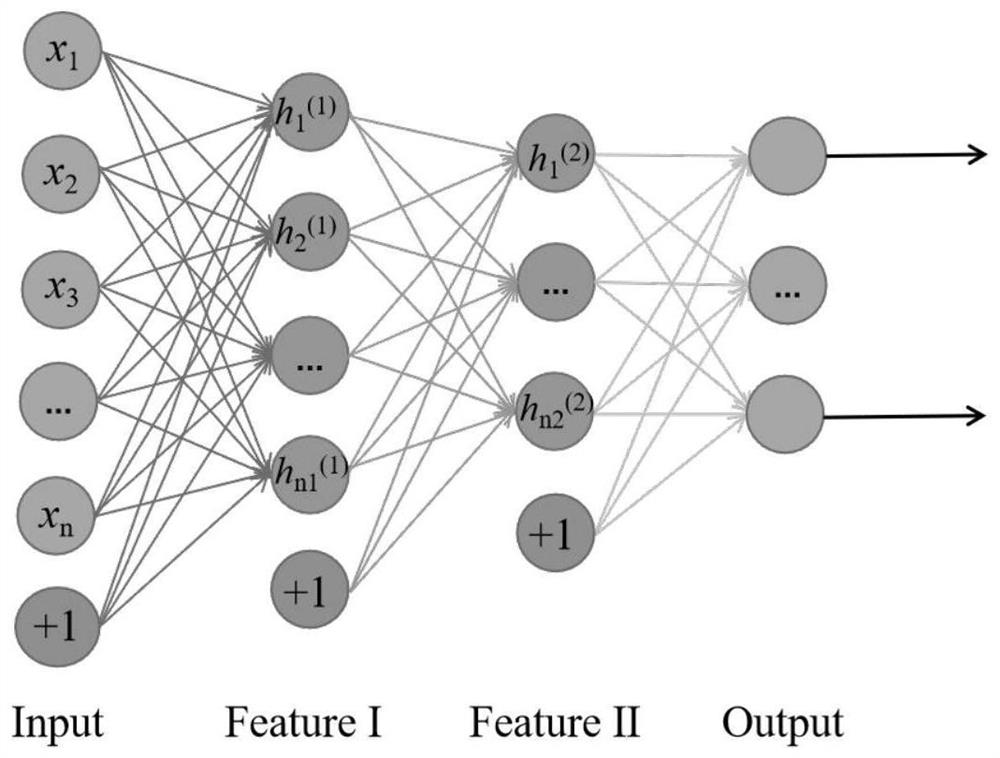
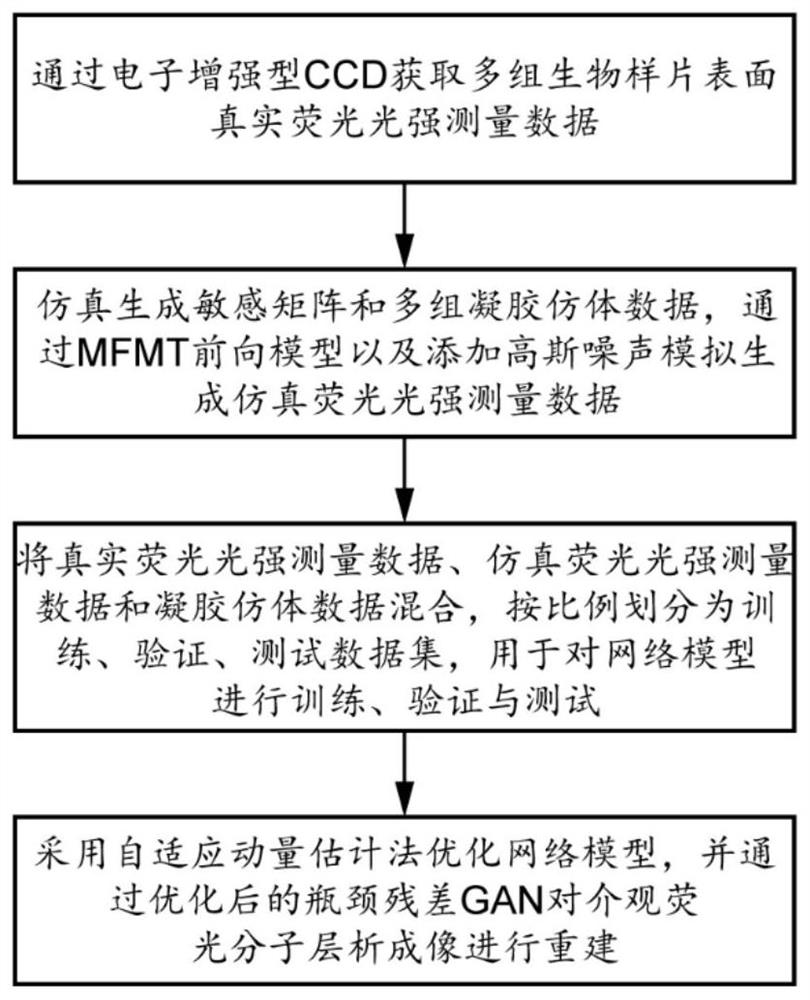
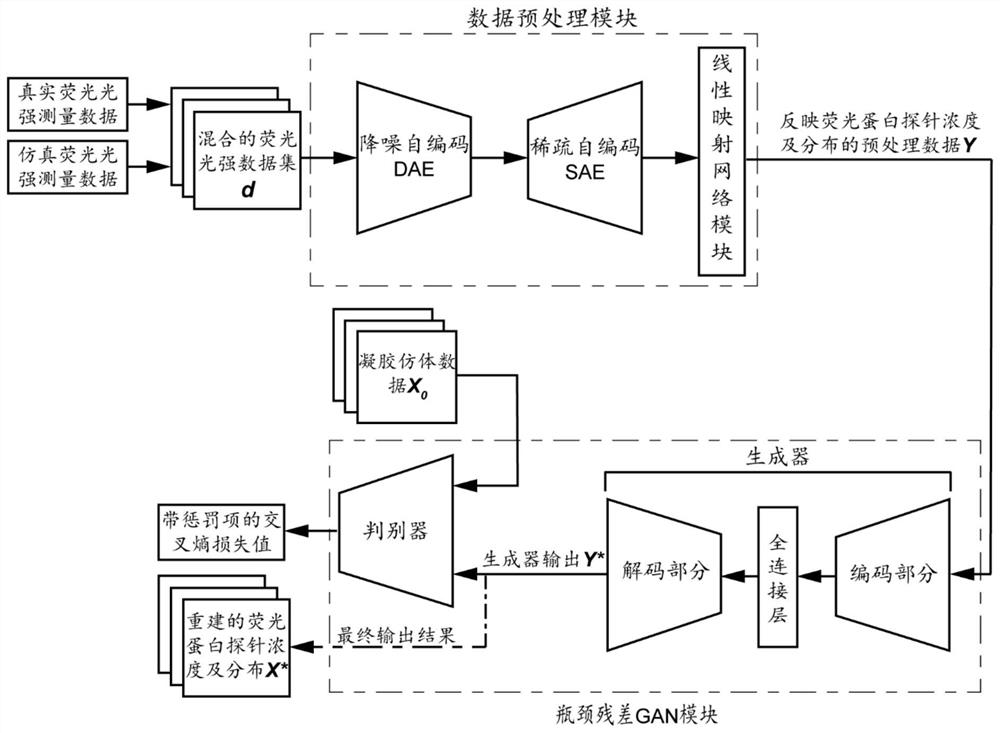
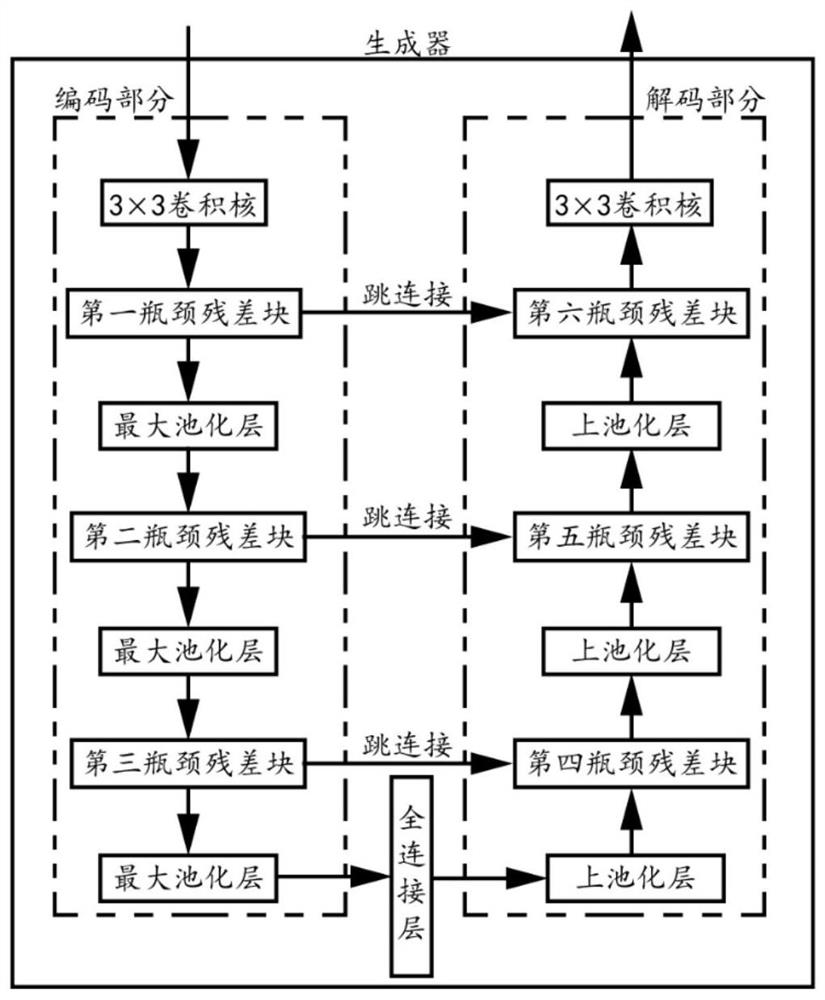
InactiveCN111751343AAvoid vanishing gradientsAvoiding the Cons of ExplosionsGeometric image transformationFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiologyFluorescence molecular tomography
The invention discloses a mesoscopic fluorescence molecular tomography method and system based on a bottleneck residual GAN. The method comprises the steps of: inputting the obtained fluorescence intensity data of the surface of a to-be-imaged biological sample into a pre-trained bottleneck residual GAN; firstly carryings out noise reduction, sparseness and mapping processing on the input data insequence by the bottleneck residual GAN; then, reconstructing the mapped data to obtain data reflecting the fluorescent protein probe concentration and distribution; and acquiring a mesoscopic fluorescence molecular tomography result based on the data reflecting the fluorescent protein probe concentration and distribution.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF BUSINESS & TECH
Fluorescent molecular tomography reconstruction method based on magnetic particle imaging prior guidance
ActiveCN114581553AOvercome the disadvantage of limited depthImprove reconstruction qualityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionAnatomical structuresMagnetic particle imaging
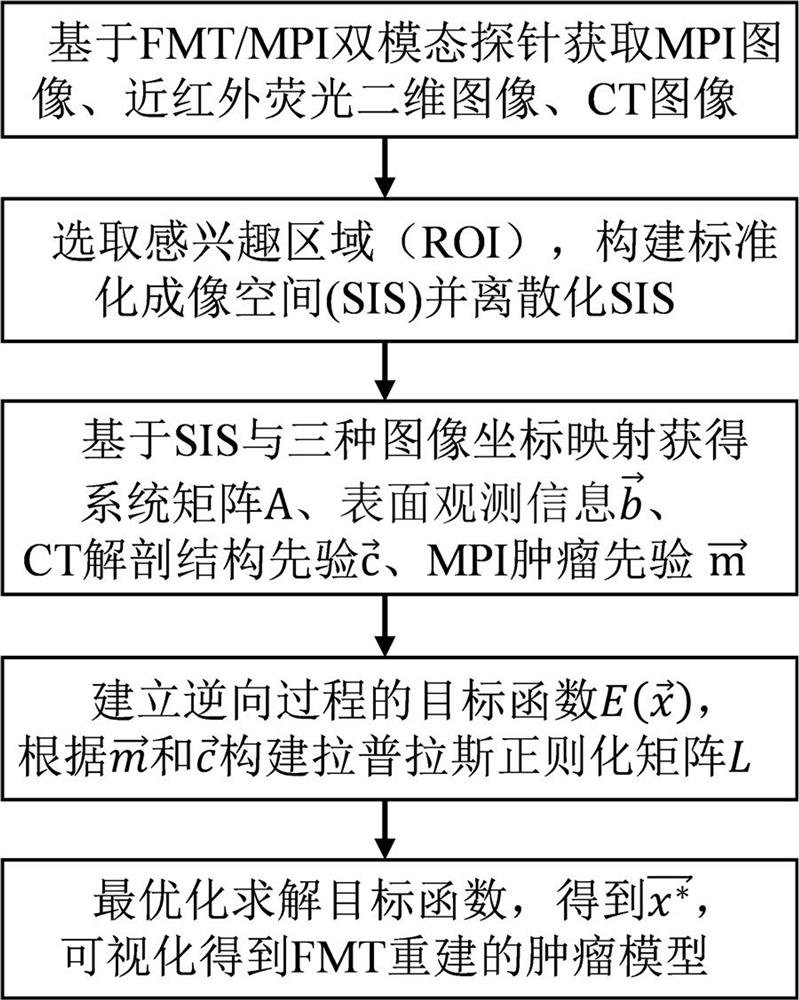
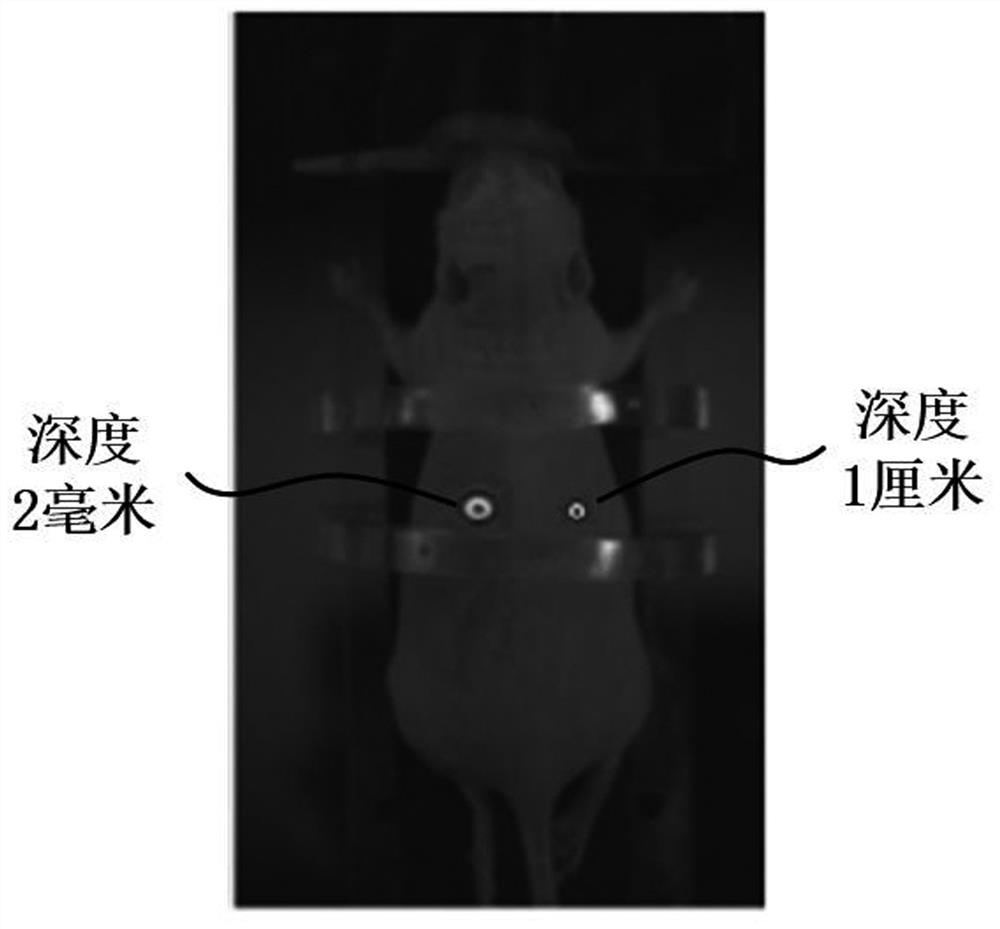
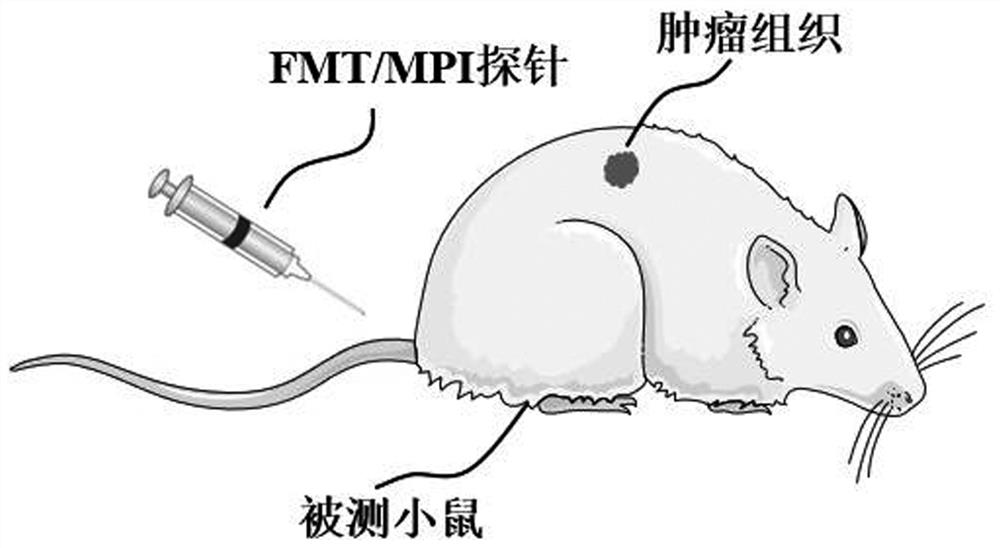
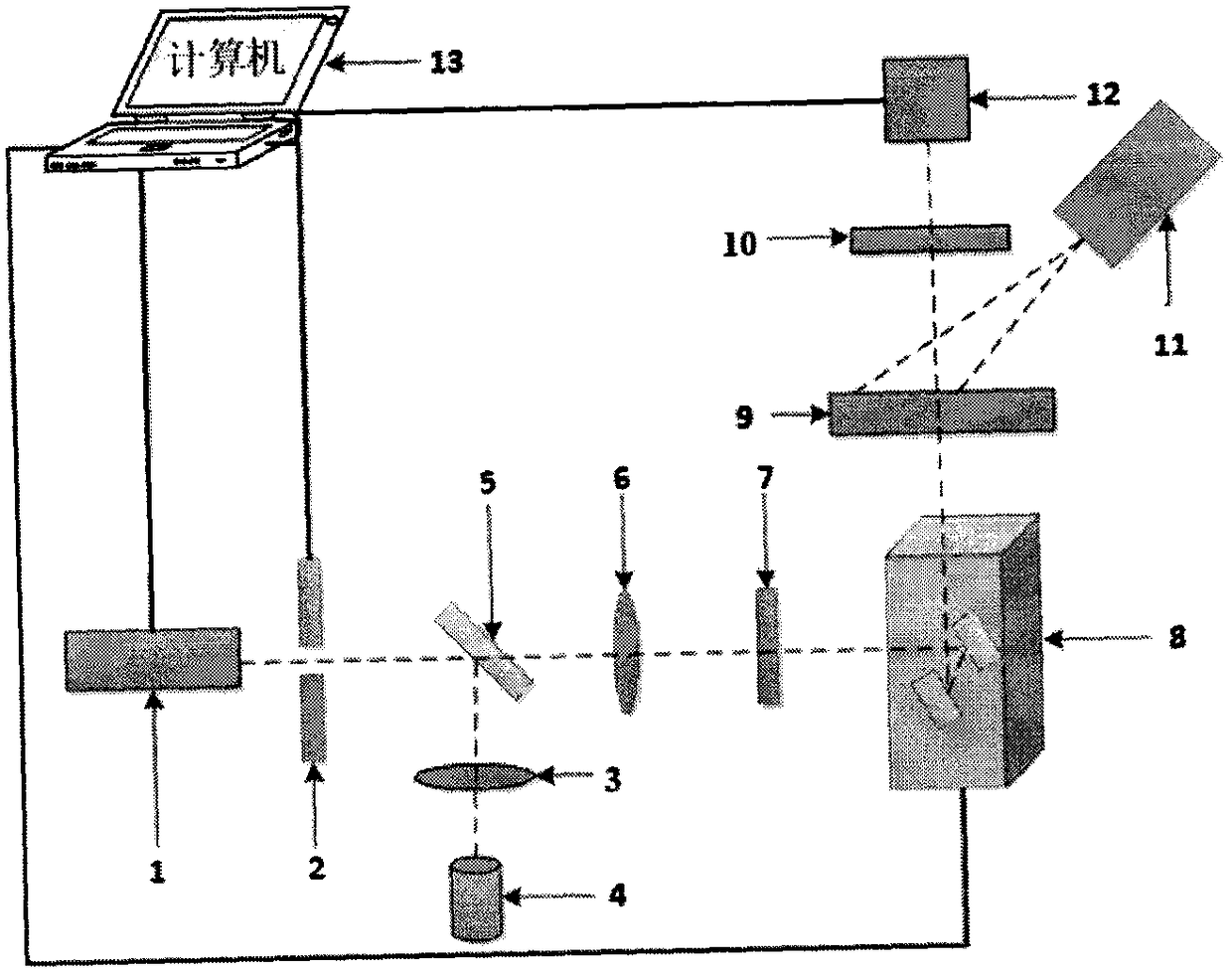
The invention belongs to the field of fluorescence molecular tomography, particularly relates to a fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction method based on magnetic particle imaging prior guidance, and aims to solve the problems that a guidance mode has no specificity for tumors, is low in accuracy and precision, and cannot overcome the defect that the depth of an FMT is limited, so that the FMT reconstruction quality is low when a light source moves deep. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an MPI-dimensional cross-sectional image, a near-infrared fluorescence two-dimensional image and a CT image; constructing an SIS capable of accommodating the ROI region, and discretizing the SIS by using a finite element method; performing data mapping to obtain a surface detected fluorescence signal, anatomical structure priori and tumor priori of tissues and organs around the tumor; a system matrix is obtained through forward model calculation, and a target function is constructed; and solving the objective function through Laplacian regularization matrix constraint iteration to obtain a fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction result. According to the method, the MPI is used for guiding the FMT to reconstruct the targeted tumor model which is complete in morphological structure, clear in tissue edge and accurate in spatial position.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Fluorescent molecular tomography system used in free space
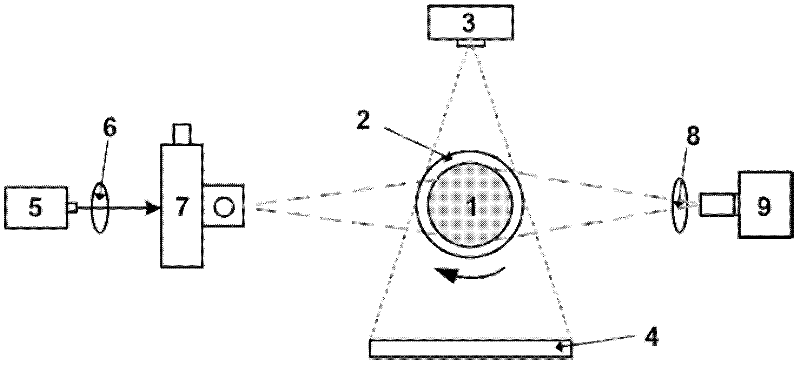
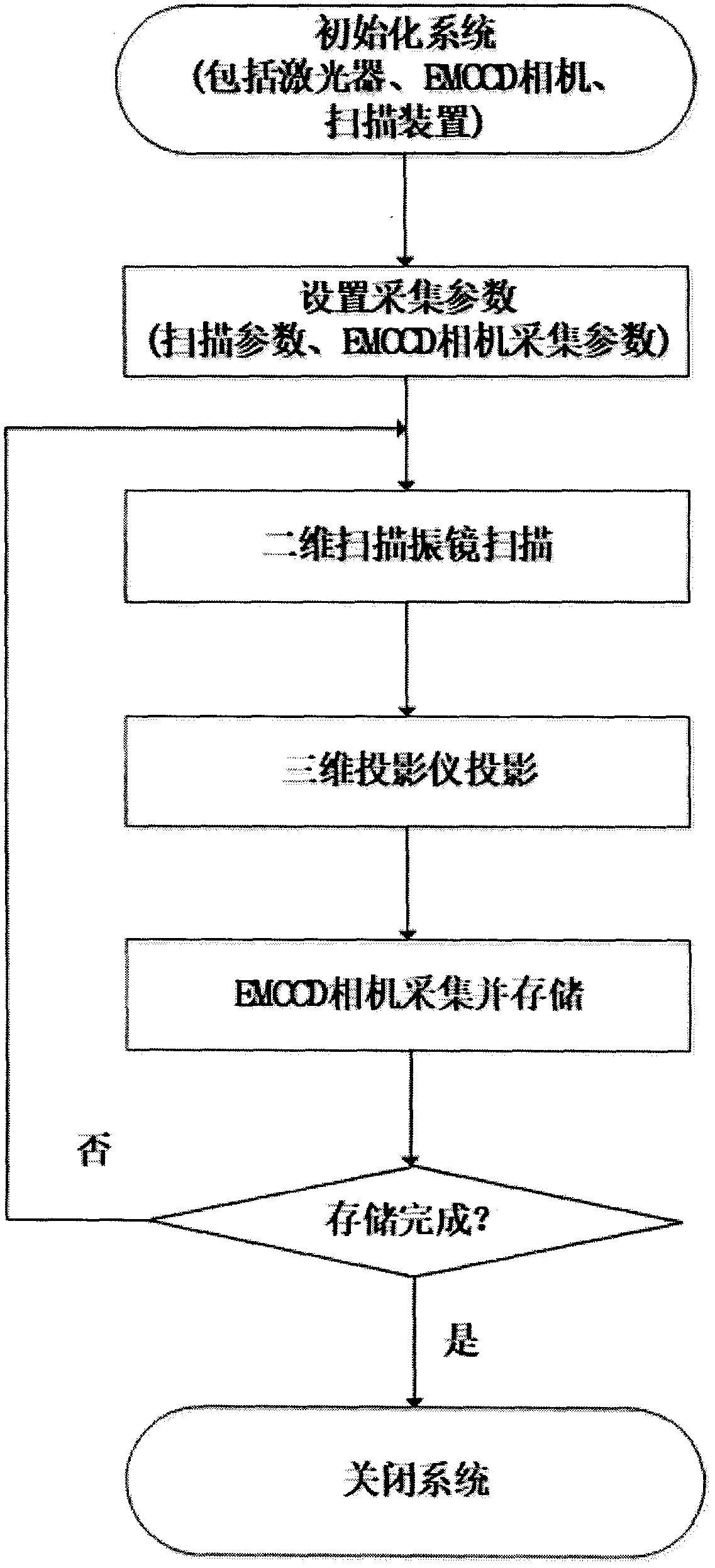
PendingCN108836275ACollaborative workComprehensive collection of dataDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionSensorsLaser scanningThree dimensional tomography
The invention provides a fluorescent molecular tomography system used in a free space. The fluorescent molecular tomography system comprises a laser device, an electric shutter, a semi-transparent semi-reflective mirror BS, a lens L1, a lens L2, a photodiode, a light filter F1, a light filter F2, a two-dimensional laser scanning galvanometer, a bearing table, a three-dimensional imaging projector,an EMCCD camera and a computer. The fluorescent molecular tomography system has the advantages of being compact, convenient to use and the like. The fluorescent molecular tomography system can achieve three-dimensional tomography of an examined body by controlling acquired data quantity and utilizing a reconstruction algorithm and accurately determine positions and strength fluorescence indicators.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
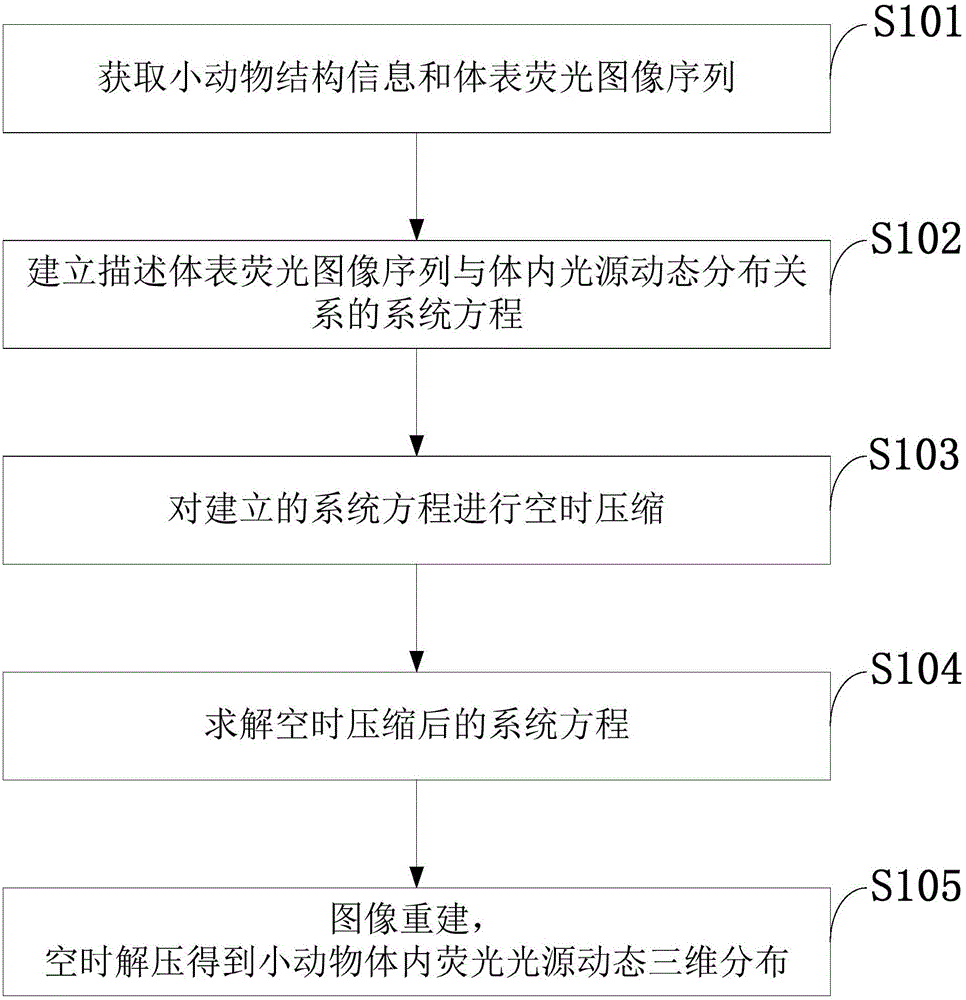
Space-time-compression-based dynamic fluorescence molecular tomography method for small animal
ActiveCN106562770AFast imagingImproving Imaging AccuracyDiagnostic signal processingDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionSingular value decompositionTime domain
The invention discloses a space-time-compression-based dynamic fluorescence molecular tomography method for a small animal. With a singular value decomposition technology, time-domain compression is carried out on a collected fluorescence image sequence; with matching filtering technology, space domain compression is carried out the fluorescence image sequence after time-domain compression; a small-animal dynamic fluorescence molecular tomography model after space domain compression is constructed; and with a least squares method, an inverse problem after the space-time compression is solved, image reconstruction is carried out, and then space-time decompression is carried out to obtain fluorescence source distribution sequences in the small animal at all collection time points. Because of the time-domain compression, the number of equations needing to be solved can be reduced; and with the space domain compression, the number of unknown numbers needing to be solved can be reduced. The reconstruction accuracy and reconstruction speed can be improved. The method has the great application value in dynamic fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction for small animals.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Noninvasive imaging of focal atherosclerotic lesions using fluorescence molecular tomography
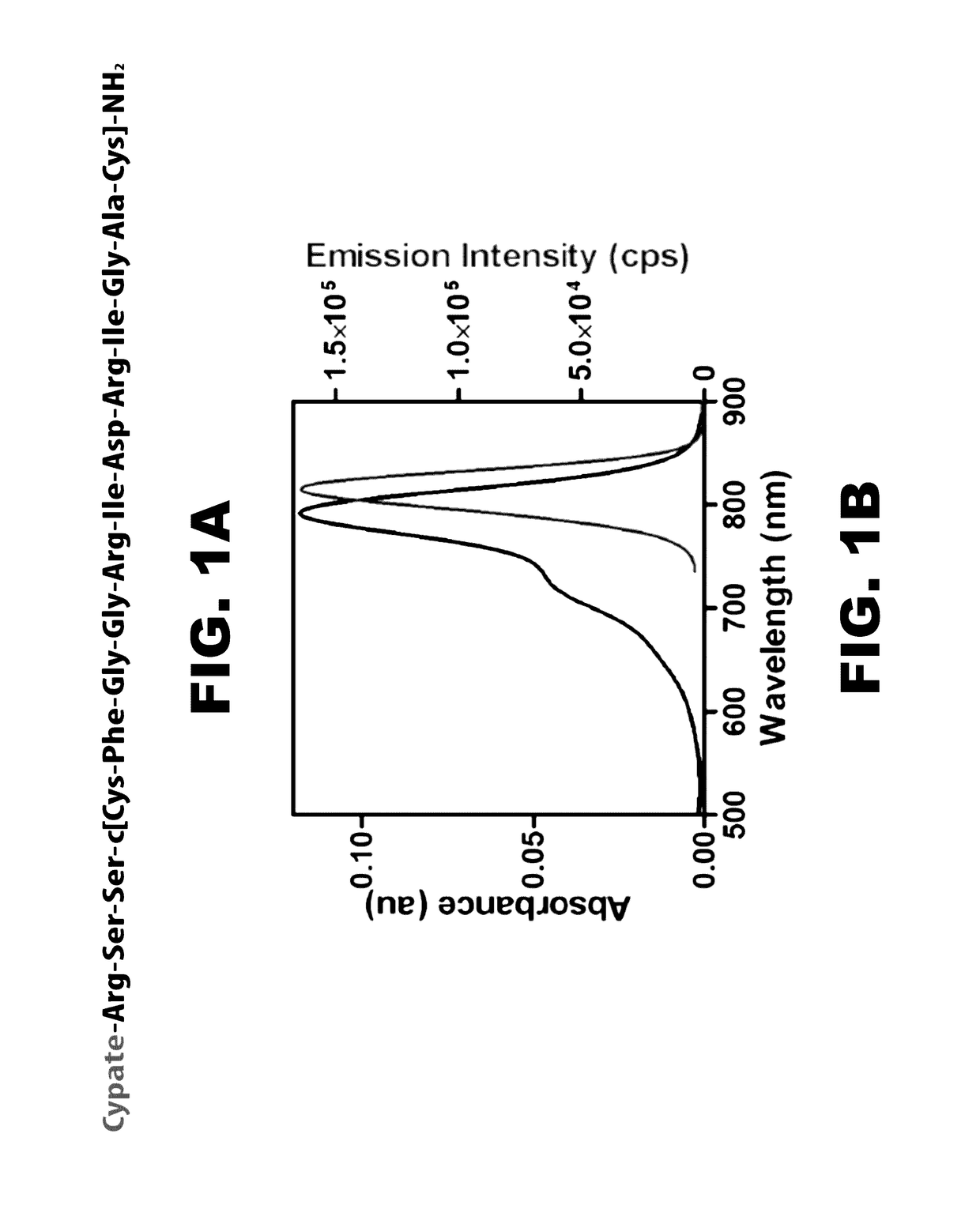
InactiveUS20170095577A1Pharmaceutical non-active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsNoninvasive imagingMedicine
The present disclosure provides compositions comprising an oligopeptide comprising a fragment of a natriuretic peptide, wherein the fragment comprises the sequence Arg-Ile-Asp-Arg-Ile (SEQ ID NO:1), and a detectable label. Further disclosed are methods of imaging atherosclerotic plaque by optical imaging using a peptide composition.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Multi-mode molecular tomography system
InactiveCN101984928BDoes not involve spatial registration issuesConsistent geometric coordinatesSurgeryComputerised tomographsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityOptical tomography
The invention relates to a multi-mode molecular tomography system which is characterized by comprising one or more light sources of an X-ray source, a near infrared laser light source and a finite spectral width light source for projecting scanning light to an object to be scanned, an electric loading device, an imaging device and a control and processing device, wherein the imaging device is used for obtaining intensity distribution data of x-rays, visible light or near infrared light emerging from the surface of the object to be scanned after scanning, and inputting the intensity distribution data into the control and processing device; the control and processing device is used for controlling the actions of the object to be scanned through the electric loading device; and the control and processing device comprises a tomography module, the tomography module is used for receiving the data of the imaging device, utilizing XCT (X-ray computed tomography) and DOT (diffuse optical tomography) modes to reconstruct an outer boundary and similar information of all internal organizations during marginalization, fusing and reconstructing XCT, DOT, FMT (fluorescence molecular tomography) and BLT (bioluminescence tomography) single-mode or multi-mode tomography image after fusion and outputting. The multi-mode molecular tomography system is applicable to the field of x-ray and optical biomedical imaging.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Novel target feasible region extraction method and system, medium, equipment and application
PendingCN112699581ADiagnostics using fluorescence emissionDiagnostics using tomographyLinear relationshipEngineering
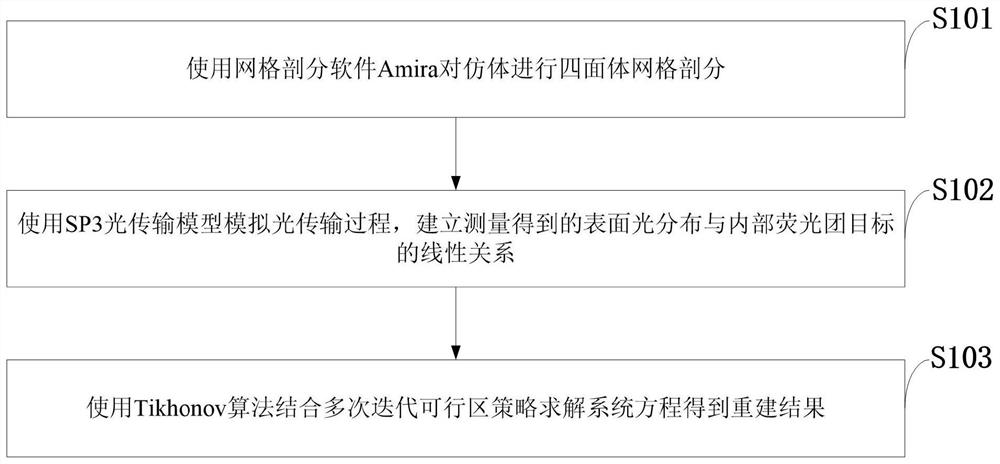
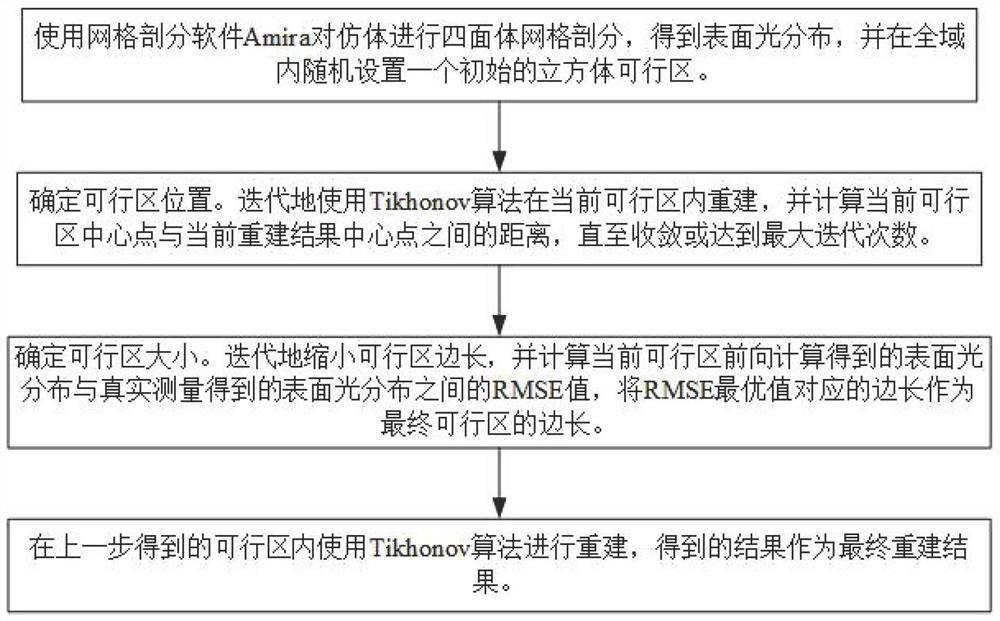
The invention belongs to the technical field of fluorescence molecular tomography, and discloses a novel target feasible region extraction method and system, a medium, equipment and an application, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out tetrahedral mesh generation of a research object through mesh generation software Amira; simulating a light transmission process by using an SP3 light transmission model, and establishing a linear relationship between measured surface light distribution and an internal fluorescence target; extracting a target feasible region in a self-adaptive manner through a multi-iteration technology; and solving the system equation by using a Tikhonov algorithm in combination with a feasible region strategy to obtain a reconstruction result. The technology can be used for fluorescent molecular tomography reconstruction, X-ray excitation tomography imaging, biological self-luminous tomography imaging and the like. Simulation experiments show that the position error is reduced to 0.71 mm, the accurate position of a fluorescent target can be obtained, the root-mean-square error value between calculated surface light distribution and measured surface light distribution can be minimum while the accurate result is obtained, and then the purpose of optimizing the reconstruction result is achieved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Non-contact stationary type fluorescent molecular tomography method and device
InactiveCN101485560BQuality improvementReduce quality problemsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCamera lensSignal on
The invention relates to a noncontact fixed fluorescence molecular tomography method and device, and is characterized in that an imaging device comprising an excitation light source, an optical switch part, a plurality of light transmitting optical fibers, a plurality of optical lenses, an image transmitting optical fiber and a detector is arranged; the plurality of the light transmitting opticalfibers and the plurality of the optical lenses are respectively arranged around an object to be detected; the optical switch part is controlled by a computer; excitated light emitted by the excitation light source irradiates on the object to be detected through any light transmitting optical fiber; fluorescence excitated by the object to be detected is imaged on each forky end of the image transmitting optical fiber through each optical lens and then is transmitted to the detector arranged on the light outlet of the image transmitting optical fiber through the composite end of the image transmitting optical fiber; the excitated light is switched to the light transmitting optical fibers at different positions through the optical switch part in turn; the fluorescence signal acquisition process is repeated to realize 360-degree full-angle fluorescence signal on the boundary of the object to be detected. The noncontact fixed fluorescence molecular tomography method and device can realize 360-degree full-angle and noncontact fixed acquisition of the fluorescence signal of the object to be detected, and has high imaging efficiency and quality.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
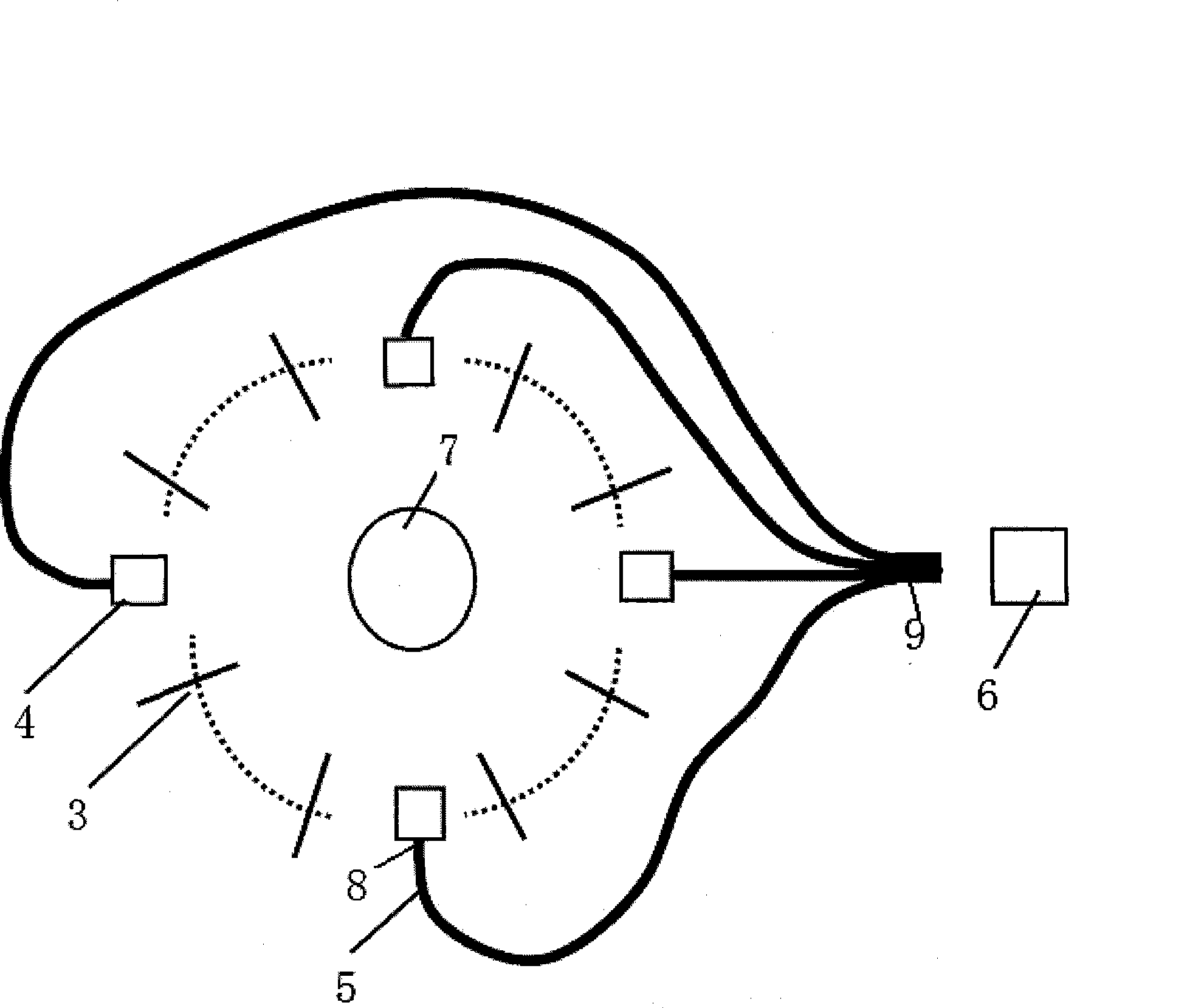
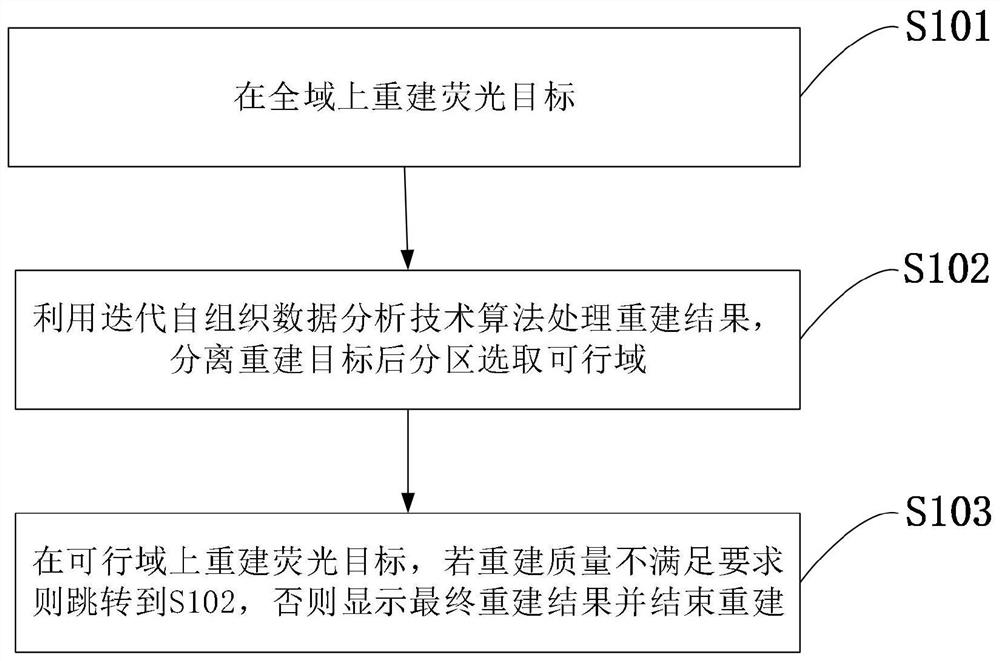
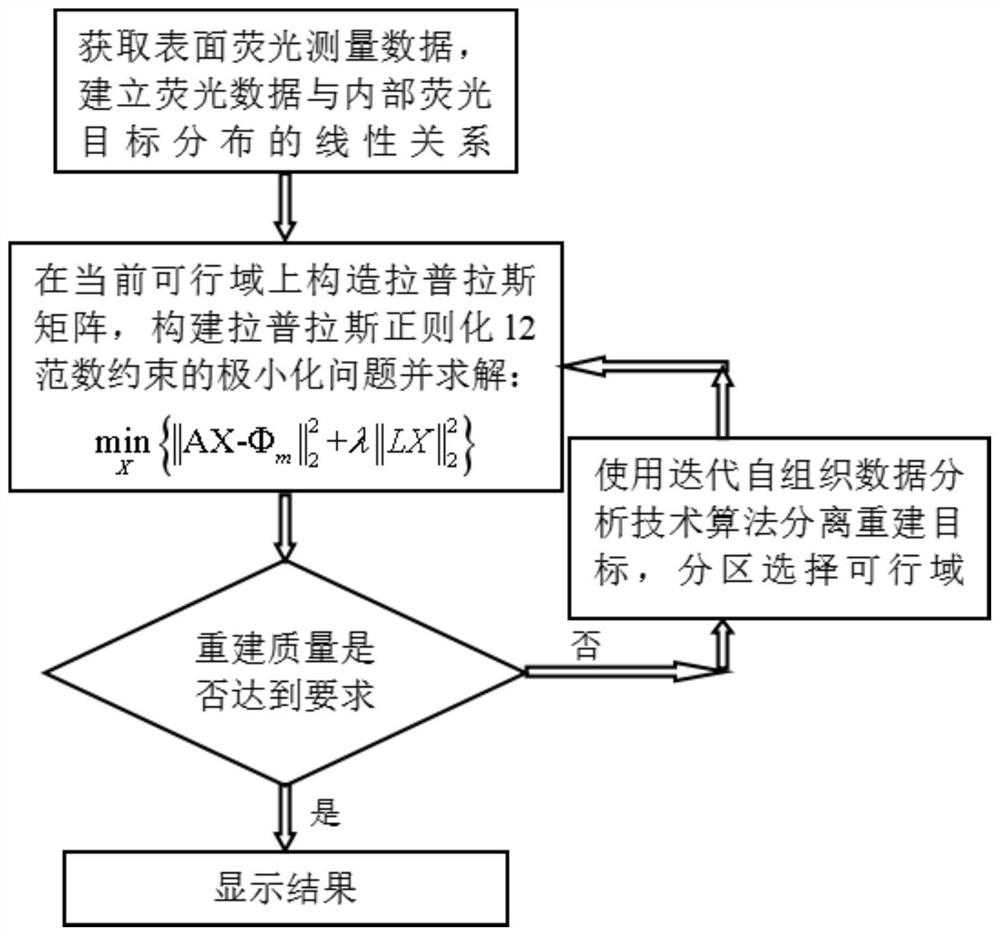
A Method for Selecting Feasible Regions of Targets in Fluorescence Molecular Tomography
ActiveCN108095686BReduce data collection timeFast rebuildDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionDiagnostics using tomographyOptical tomographyMolecular imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular imaging, and discloses a method for selecting a feasible region of a fluorescent molecular tomographic imaging target. If the reconstruction quality does not meet the requirements, jump to the iterative self-organizing data analysis technology algorithm to select the feasible region, otherwise display the final reconstruction result and end the reconstruction. The invention is suitable for reconstructing an optical molecular tomography system of multi-target fluorescence sources, requires less fluorescence measurement data, adopts an iterative self-organizing data analysis technique algorithm to partition and select feasible regions, and improves the accuracy of selecting feasible regions in multi-target reconstruction. The present invention reduces the morbidity of the reconstruction problem through multi-stage reconstruction, effectively improves the reconstruction quality of fluorescence molecular tomography, and has important application value in the fields of optical tomography three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
A Feasible Region Optimization Method for Fluorescence Molecular Tomography
ActiveCN109820479BTo achieve the purpose of optimizationQuality improvementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityLinear relationship
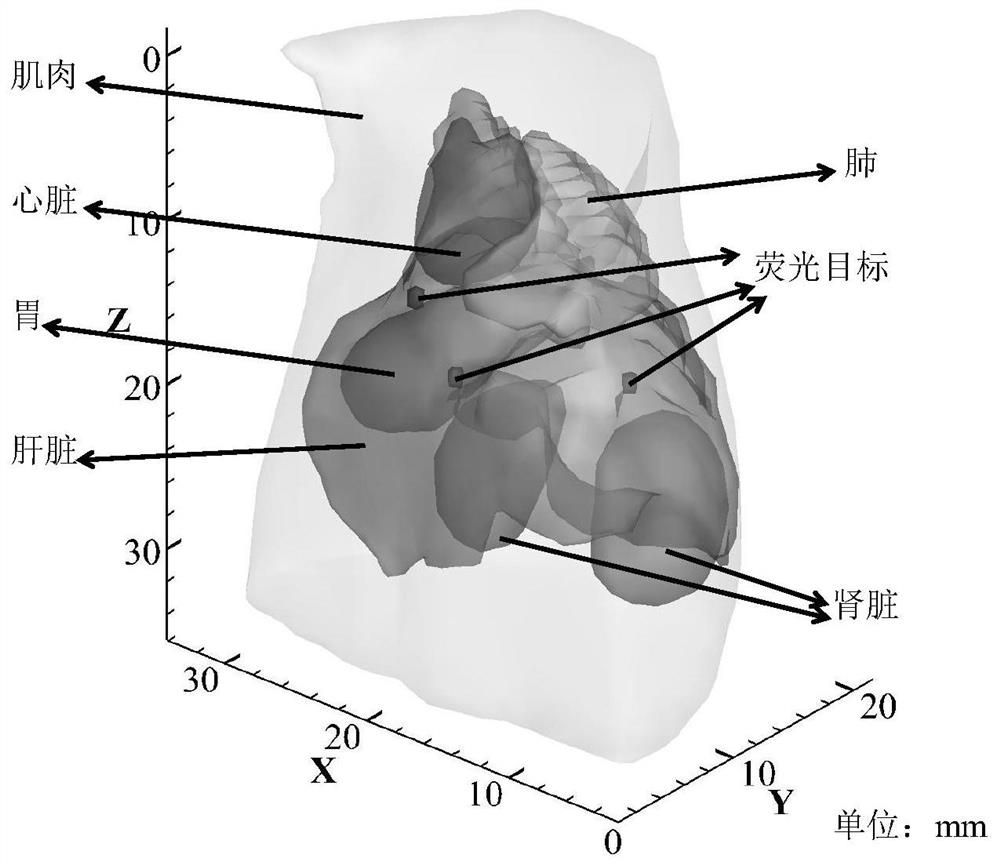
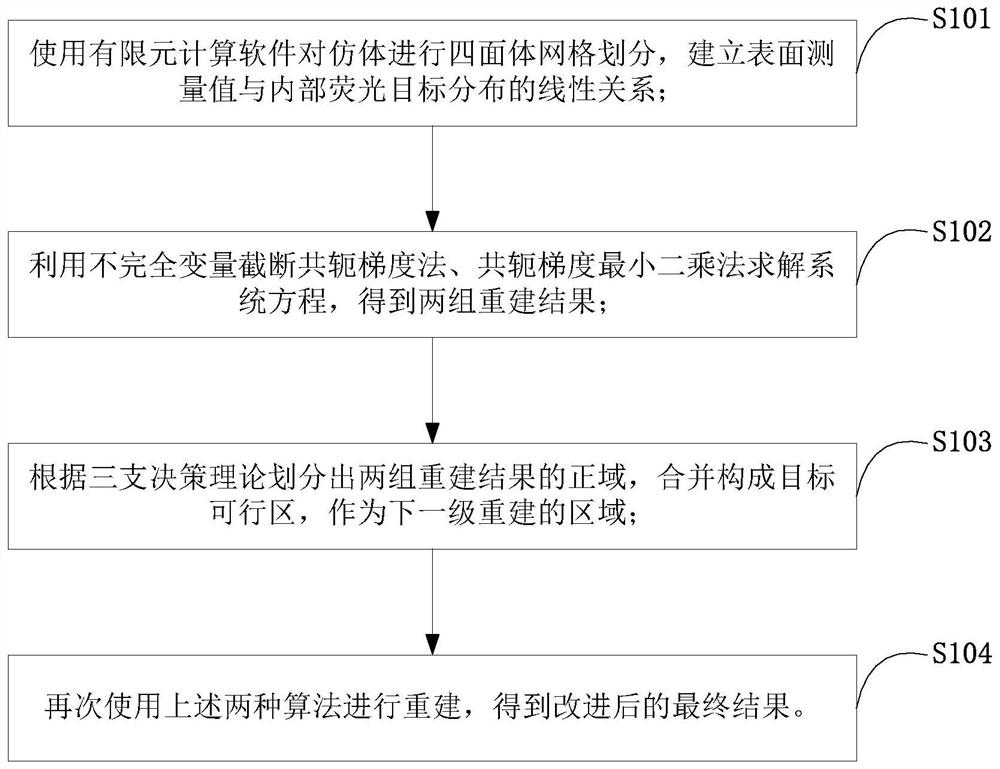
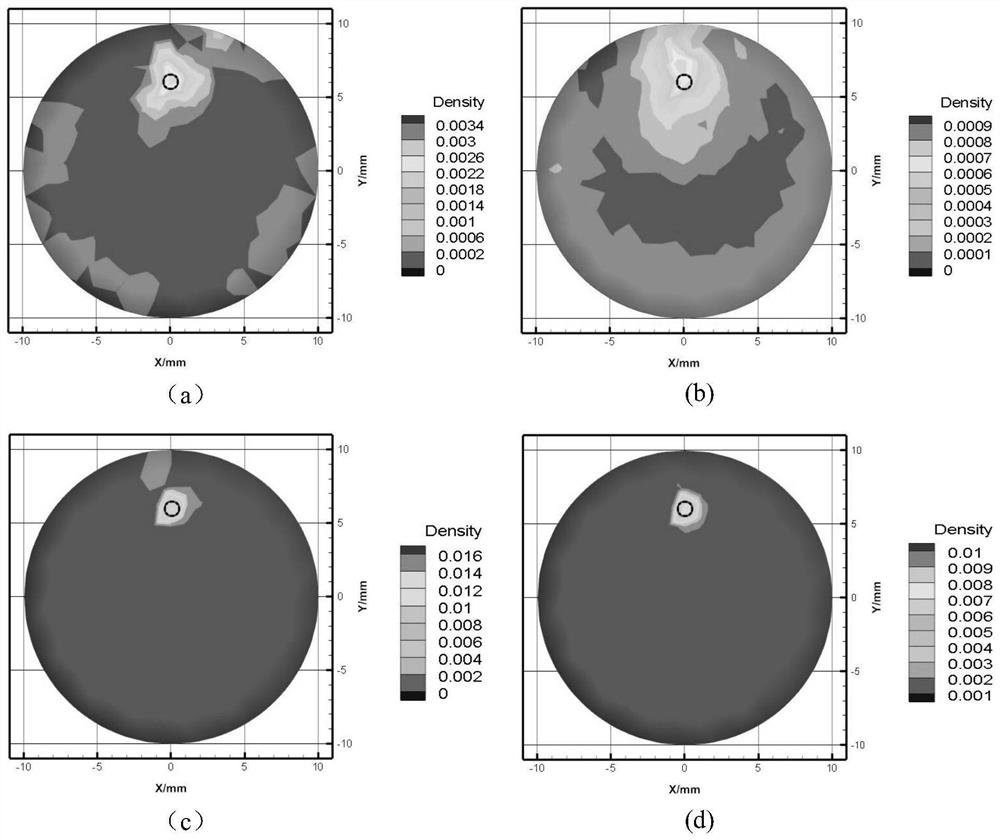
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical molecular imaging, and discloses a method for optimizing the feasible region of fluorescent molecular tomographic imaging; using finite element calculation software to divide the phantom into tetrahedral grids, and establish a linear relationship between surface measurement values and internal fluorescent target distribution; Using the incomplete variable truncated conjugate gradient method and the conjugate gradient least squares method to solve the system equations, two sets of reconstruction results are obtained; according to the three-way decision theory, the positive domains of the two sets of reconstruction results are divided, and combined to form the target feasible area, as the next step The area reconstructed at the level; the incomplete variable truncated conjugate gradient method and the conjugate gradient least squares method are used again for reconstruction, and the improved final result is obtained. The invention adopts two different reconstruction algorithms for reconstruction; extracts the positive domain in the two groups of results; and completes the final reconstruction in this area. The present invention can obtain accurate target range area, effectively alleviates the morbidity of the problem, and the image quality of the above two reconstruction methods is obviously improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Dual-mode in vivo imaging system and method based on wavelet data compression
ActiveCN102512193BReduce acquisition timeReduce dimensionalityComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringData compressionData set
The invention discloses a double-mode in-vivo imaging system and method based on wavelet data compression, belonging to the technical field of molecule images. The double-mode in-vivo imaging system comprises a micro CT (Computed Tomography) subsystem and a fluorescence molecular tomography subsystem. Two subsystems are arranged in an orthogonal manner. The fluorescence molecular tomography subsystem is provided with a two-dimensional acousto-optic deflector. The double-mode in-vivo imaging method comprises the following steps of: collecting an X-ray projection image and a fluorescence image; using the two-dimensional acousto-optic deflector to control exciting light to scan in a process of collecting the fluorescence image; obtaining a position and a direction of an exciting point; obtaining a detection pattern set by compressing the fluorescence image; obtaining a measurement value vector and a Jacobian matrix according to the position and the direction of the exciting point and the detection pattern set; carrying out matrix inversion to obtain a fluorescence probe distribution according to the measurement value vector and the Jacobian matrix. According to the double-mode in-vivo imaging system and method provided by the invention, the faster collection of original data is realized, and the rapid reestablishment can be carried out by using a collected oversized data set.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com