Method for reconstructing dynamic fluorescence molecular tomography
A technology of fluorescent molecular tomography and fluorescent molecular imaging, which is applied in the field of reconstruction of fluorescent molecular tomographic images, can solve the problems of exceeding the computing power, exceeding the computing power of ordinary computers, occupying space-time weight matrix, etc., to reduce the calculation scale and make up for Time dependency considerations, effects of high data compression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0019] For FMT imaging, based on the first-order Born approximation, the fluorescence projection image acquired at the detection point r can be expressed by the following formula:
[0020] Φ m (r)=∫ r′∈V G(r,r')n(r')Φ x (r')dr' (1)
[0021] In the formula, V is the reconstruction area; Φ x is the light field distribution function, which describes the photon density corresponding to the excitation light wavelength, Φ m is the photon density of the emission (fluorescence) wavelength; n(r′) is the fluorescence yield to be reconstructed at the point r′ in the reconstruction area V, usually n(r′) is proportional to the concentration of the fluorescent probe; Green’s function G( r, r') describe the propagation of photons in the imaging object in the fluorescence band.
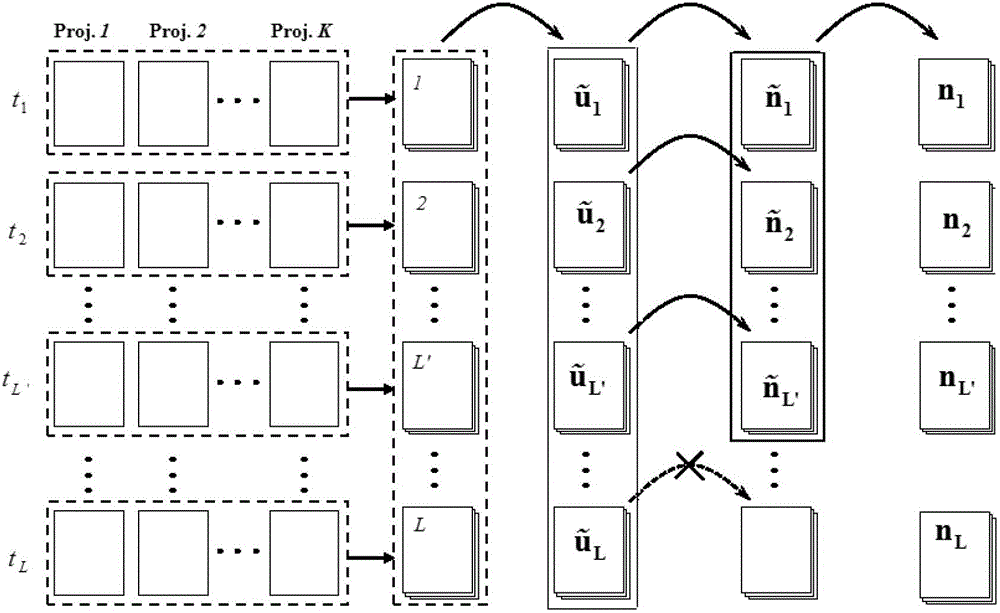
[0022] For dynamic FMT, after the reconstruction area V is discretized into a smal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com