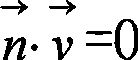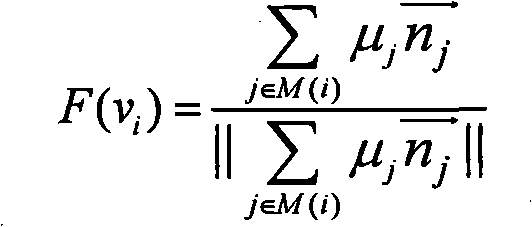Patents
Literature
48 results about "Vertex normal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
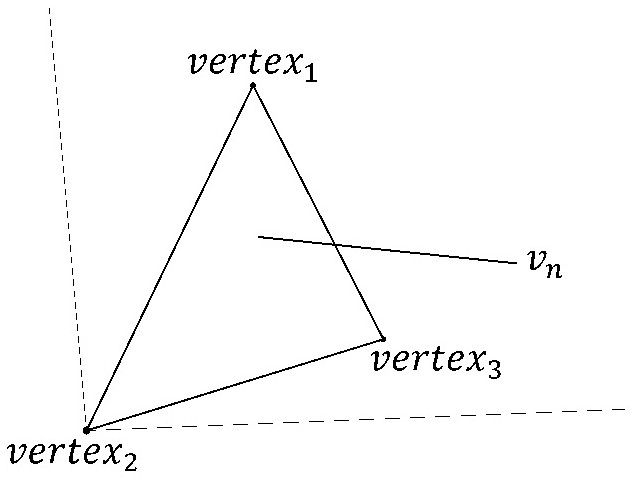
In the geometry of computer graphics, a vertex normal at a vertex of a polyhedron is a directional vector associated with a vertex, intended as a replacement to the true geometric normal of the surface. Commonly, it is computed as the normalized average of the surface normals of the faces that contain that vertex. The average can be weighted for example by the area of the face or it can be unweighted. Vertex normals can also be computed for polygonal approximations to surfaces such as NURBS, or specified explicitly for artistic purposes. Vertex normals are used in Gouraud shading, Phong shading and other lighting models. Using vertex normals, much smoother shading than flat shading can be achieved; however, without some modifications, it cannot produce a sharp edge.
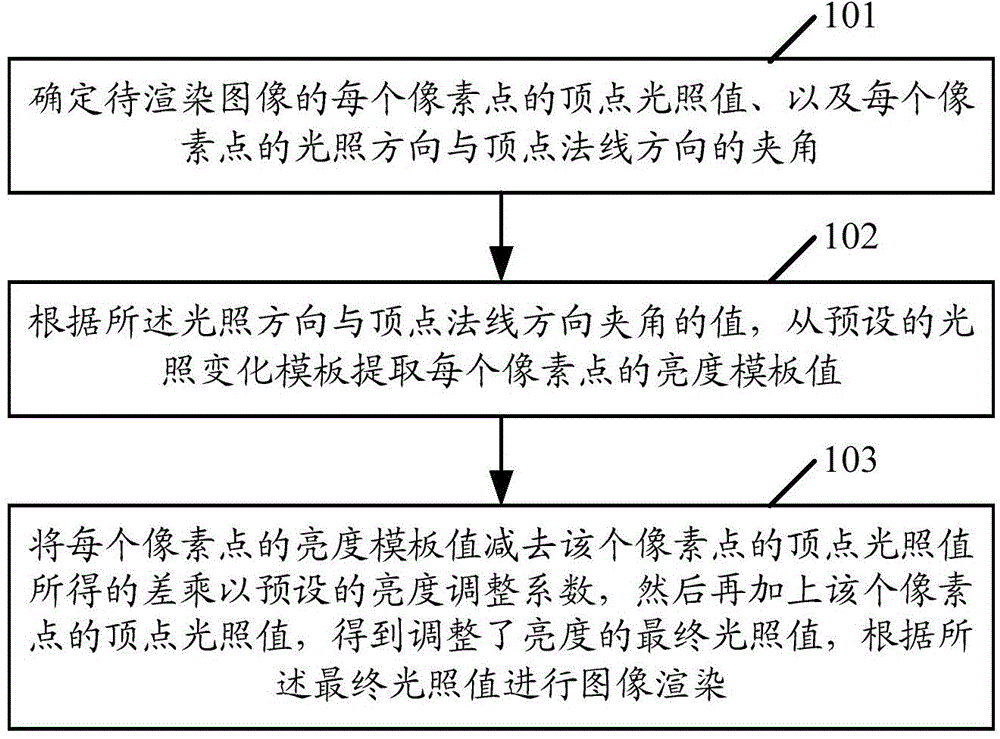
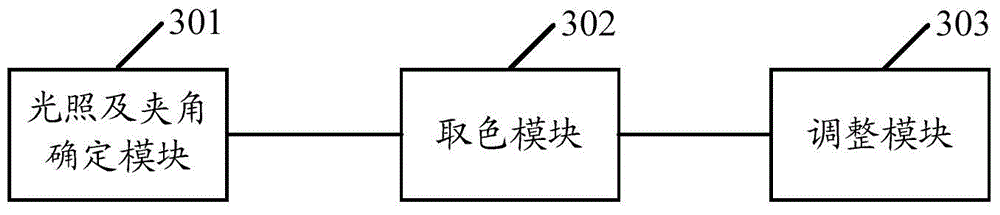
Method and device for rendering image
ActiveCN104574495AThree-dimensional display effect3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Vertex normal
The invention discloses a method and device for rendering an image. The method comprises the following steps: determining a vertex lighting value of each pixel point of an image to be rendered, and an included angle between the lighting direction of each pixel point and the vertex normal direction; extracting a brightness template value of each pixel point from a preset lighting change template according to the value of the included angle between the lighting direction of each pixel point and the vertex normal direction; multiplying the difference, which is obtained by subtracting the vertex lighting value of each pixel point from the brightness template value of each pixel point, by a preset brightness adjustment coefficient, and then adding the vertex lighting value of the pixel point to obtain a final lighting value after the brightness is adjusted, and rendering the image according to the final lighting value. Through the method and the device for rendering the image, the image is more real, and the display effect is more three-dimensional.
Owner:BEIJING PIXEL SOFTWARE TECH
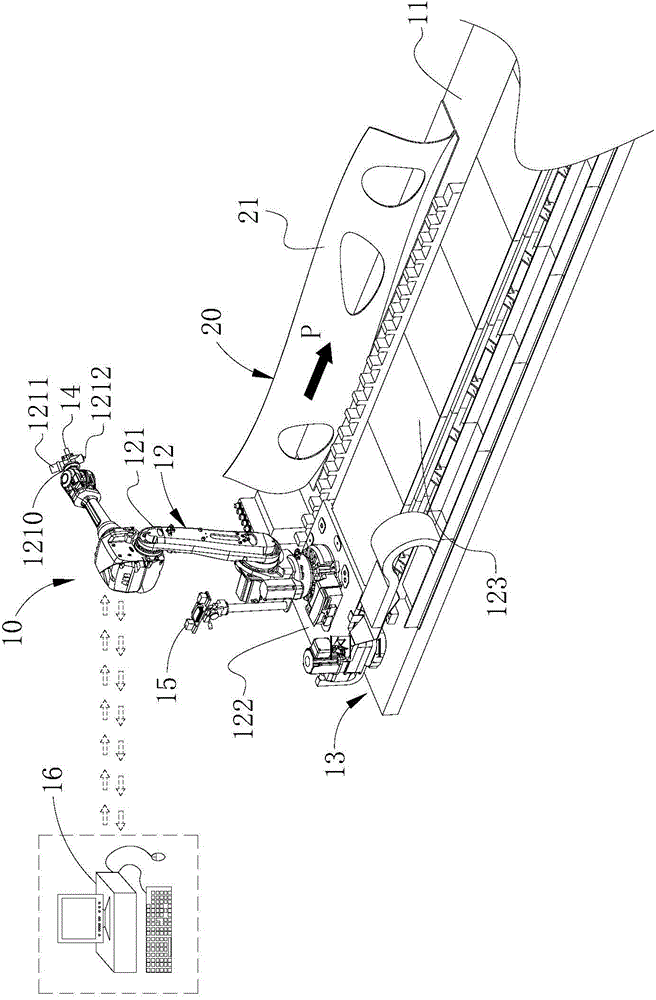
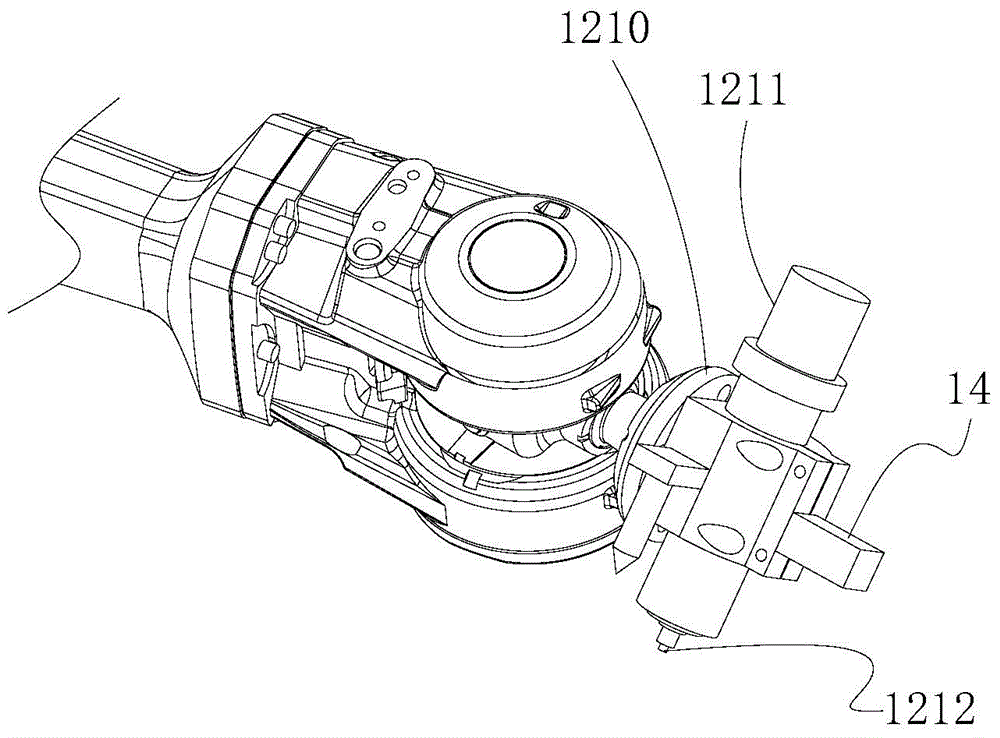
Curved part processing method and curved part processing equipment
ActiveCN104865897AImprove pose positioning accuracyHigh precisionProgramme controlComputer controlActuatorPosition error
The invention provides a curved part processing method which concretely comprises the steps that the vertex normal vectors of a curved part are confirmed before processing and then converted into position coordinate theoretical values according to a robot algorithm model; the positional relation of position calibration blocks relative to the central point of a processing tool is calibrated before processing; then a robot is moved to a processing area, and the normal vectors of the processing cutter are adjusted according to the position coordinate theoretical values; then the position calibration blocks are scanned by a three-dimensional scanning device so that the practical position values of the position calibration blocks are obtained, and then a practical position error is obtained according to the difference value between the practical position values and the theoretical values; then compensation and correction are performed on the current position coordinate values of the actuator of the robot via a control unit according to the practical position error; then the robot is enabled to perform processing on the corresponding processing area on a processing surface; and then the aforementioned steps are repeated until processing of the processing area on the processing surface is completed. The invention also provides curved part processing equipment.
Owner:深圳市威雄精机有限公司 +1
Three-dimensional auxiliary two-dimensional pattern drafting method
InactiveCN101441772ASpeed up preparationAvoid manual matchingAnimation3D modellingGraphicsViewpoints
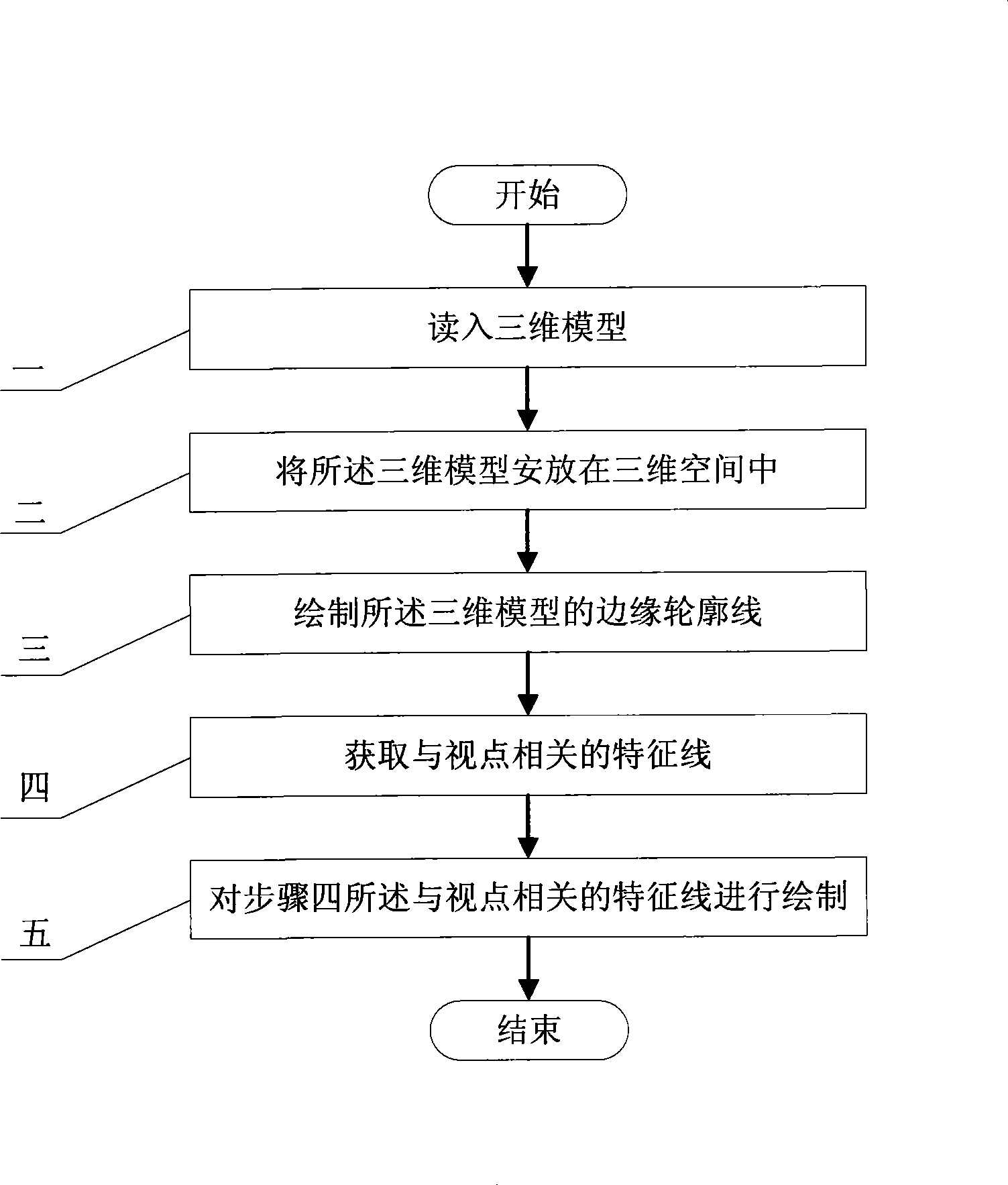
The invention relates to a method for drawing a three-dimensionally assisted two-dimensional graphic, which relates to a drawing method applying a three-dimensional model to a two-dimensional animation and belongs to the field of digital entertainment. The method aims at solving the problem that the prior software cannot automatically determine which parts of a role will be covered under a condition that the visual angle is changed. The method comprises the following steps: 1, reading in the three-dimensional model, and acquiring a vertex normal vector, a vertex principal curvature, a vertex Gaussian curvature and the direction of the vertex principal curvature of the three-dimensional model; 2, placing the three-dimensional model in a three-dimensional space; 3, drawing an edge contour line of the three-dimensional model; 4, acquiring a characteristic line related to a viewpoint; and 5, drawing the characteristic line related to the viewpoint in the step 4. Through the combination of the two-dimensional animation and a three-dimensional animation, the visual effect is enriched, and the source of animation raw data is expanded.
Owner:MUDANJIANG NEWS MEDIA GROUP
Vertex normal processing method and apparatus
ActiveCN107316337ASolve the problem of poor lighting rendering effect3D-image rendering3D modellingComputer graphics (images)Three-dimensional space
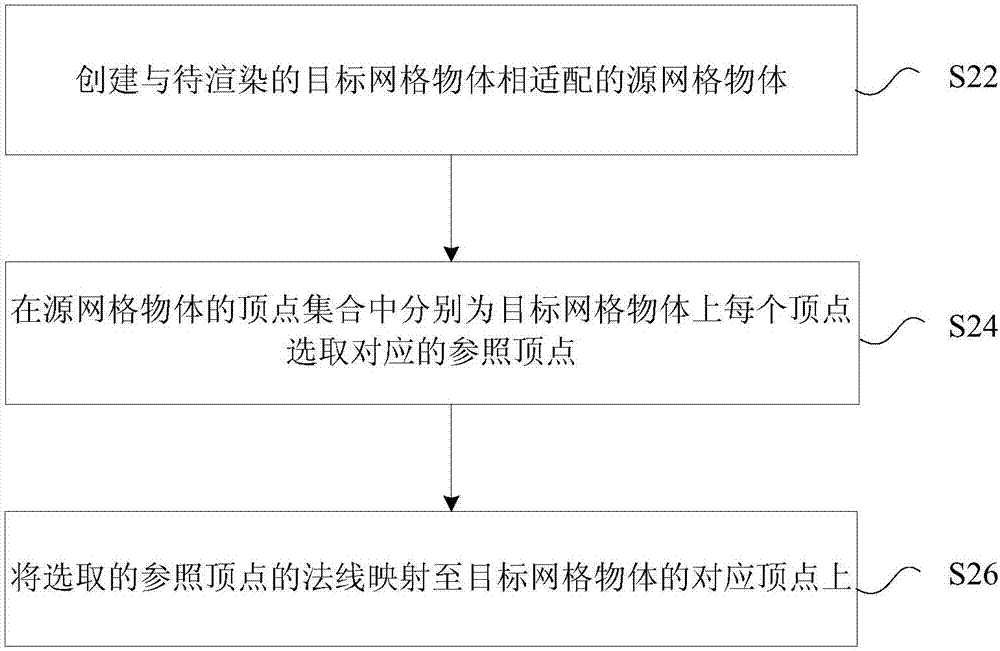
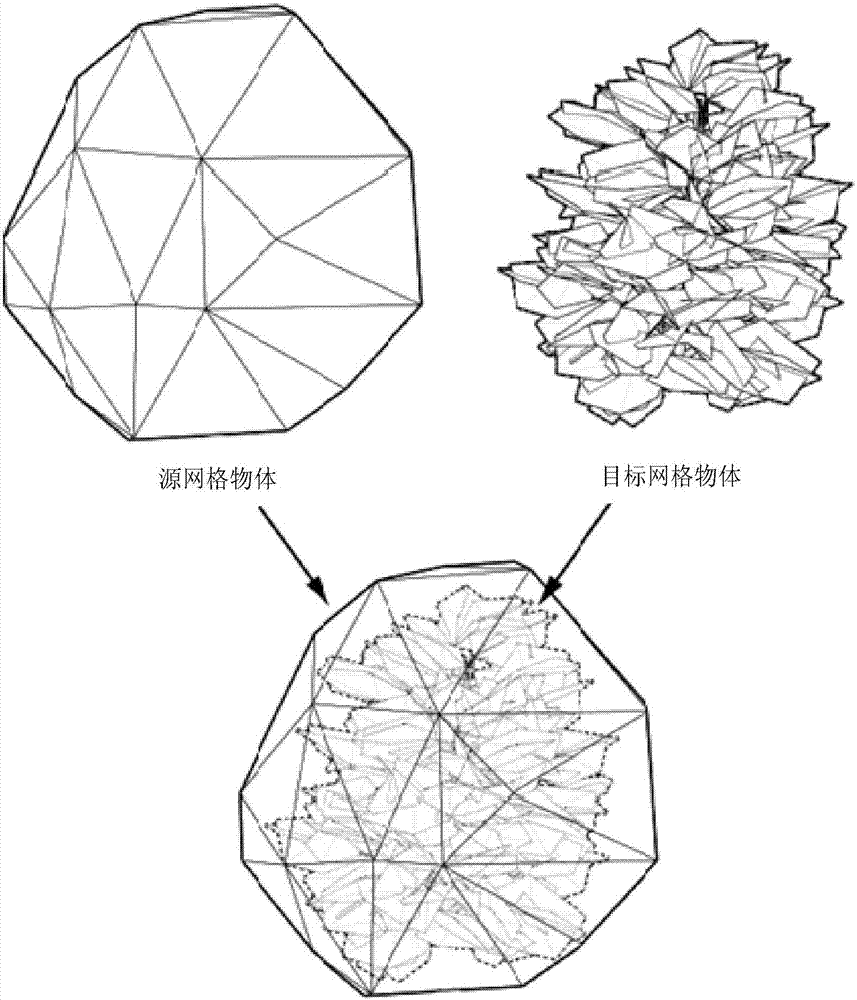
The present invention provides a vertex normal processing method and apparatus. According to the method provided by the present invention, a source mesh object that is adapted to a to-be-rendered target mesh object is created; in the vertex set of the source mesh object, a corresponding reference vertex is selected for each vertex of the target mesh object; and the normal of the selected reference vertex is mapped to the corresponding vertex of the target mesh object, so that the problem of the relatively poor light rendering effect obtained by using the vertex normal setting manner on the target mesh object in the related art is solved, and the overall light rendering effect with the volumetric feeling of the to-be-rendered target mesh object in the three-dimensional space can be achieved.
Owner:NETEASE (HANGZHOU) NETWORK CO LTD
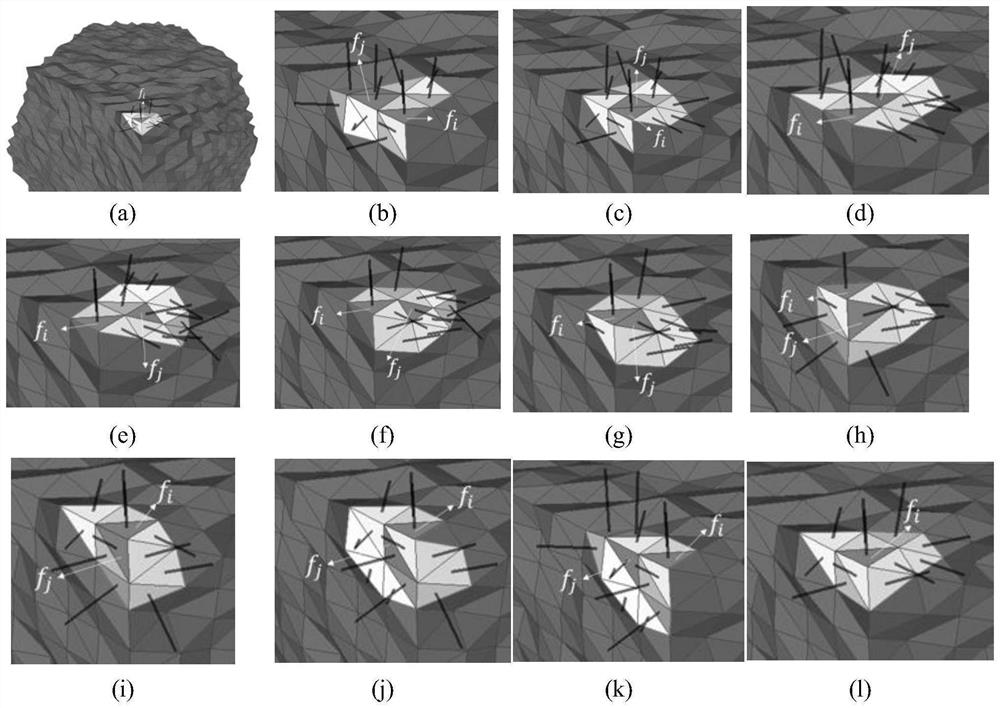
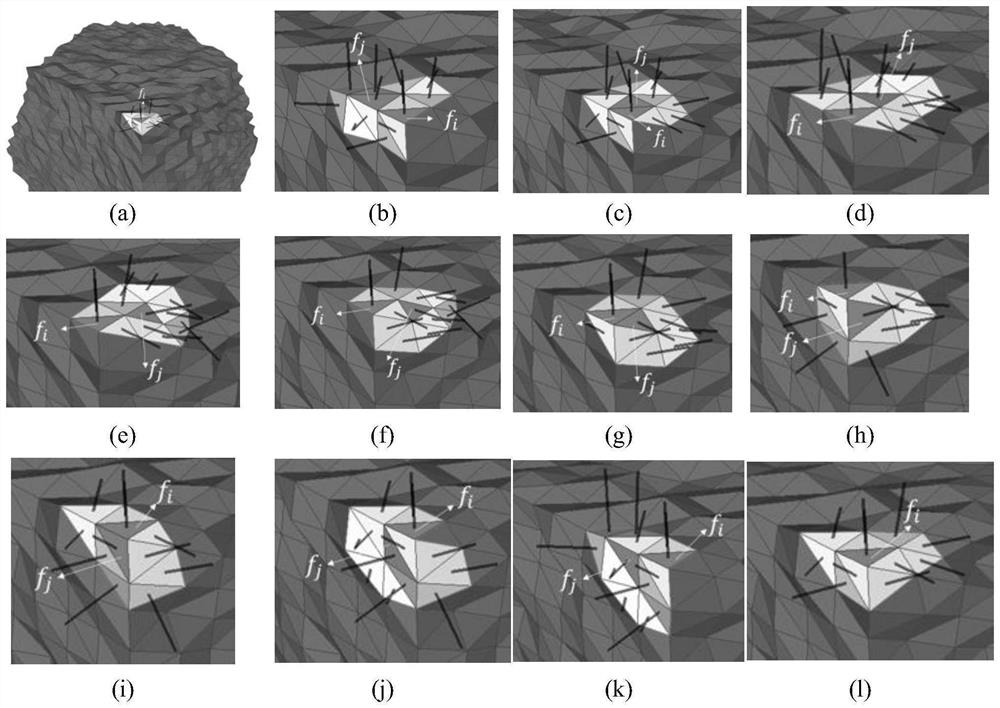
A dual-normal mesh model fairing method based on vertex characteristics
ActiveCN109242972APreserve detailed featuresReduce mistakes3D modellingComputer graphics (images)Vertex normal
The invention discloses a dual-normal mesh model fairing method based on vertex characteristics, which mainly comprises the following steps: 1) all vertices in the mesh model are divided into characteristic points and non- characteristic points. 2) the surface normal field is constructed by using guide filter. 3) The accurate surface normal field can be obtained by filtering the normal field of the surface opposite to each surface. 4) Computing the normal directions of the vertices of the characteristic points and the non-characteristic points in the triangular mesh model respectively, so as to construct the normal fields of the vertices. 5) updating the position of the non-characteristic vertices according to the surface normal direction; The characteristic vertex positions are updated iteratively according to the surface normal and vertex normal. 6) smoothing that mesh model. The invention can better retain the detail characteristic of the mesh model while removing the noise of the mesh model, and the error of the mesh model after smoothing is small, and the mesh model can more accurately approach the actual model.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
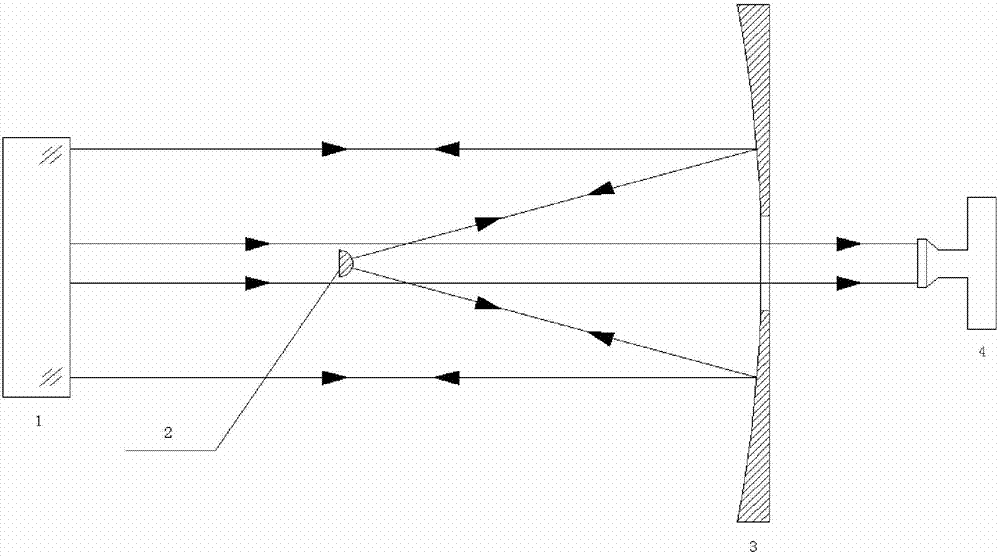
Optical lead-out method for vertex normal of large-caliber concave non-spherical reflector
The invention discloses an optical lead-out method for a vertex normal of a large-caliber concave non-spherical reflector. The method comprises the following steps: arranging a concave non-spherical surface in front of an optical interferometer which emits parallel light, and arranging a small-caliber standard spherical mirror at a position which is about 1 / 2 of vertex radius of the non-spherical surface away from the vertex of the non-spherical surface, the concave non-spherical surface, the optical interferometer and the small-caliber standard spherical mirror are coaxially arranged to be used for reflecting light rays reflected by the non-spherical mirror back to the interferometer; substituting beam wavefront data analyzed by the interferometer into optical design software for performing simulating calculation, and obtaining an included angle between the vertex normal of the non-spherical surface and parallel beams of the interferometer; aiming the parallel beams of the interferometer through a theodolite, and guiding the parallel beams to other devices which can characterize the direction; and continuously adjusting the concave non-spherical mirror and a small standard reflector thereof and analyzing and calculating through simulation software, and finally, precisely controlling an angle guided out of a vertex normal direction to be a second order. The method is simple and practicable, is high in precision and has very important application in adjustment and test aspects of spatial optical remote sensors.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
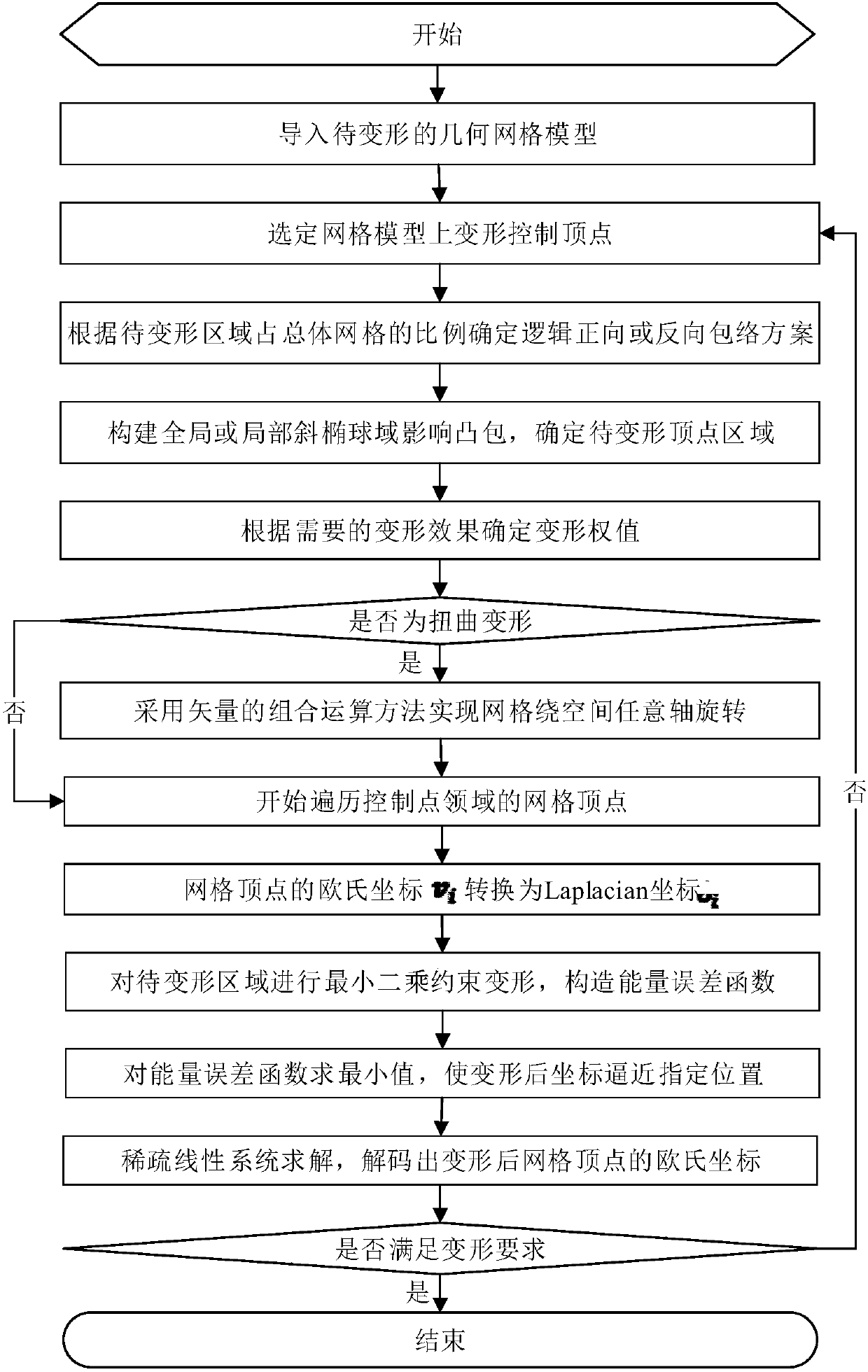
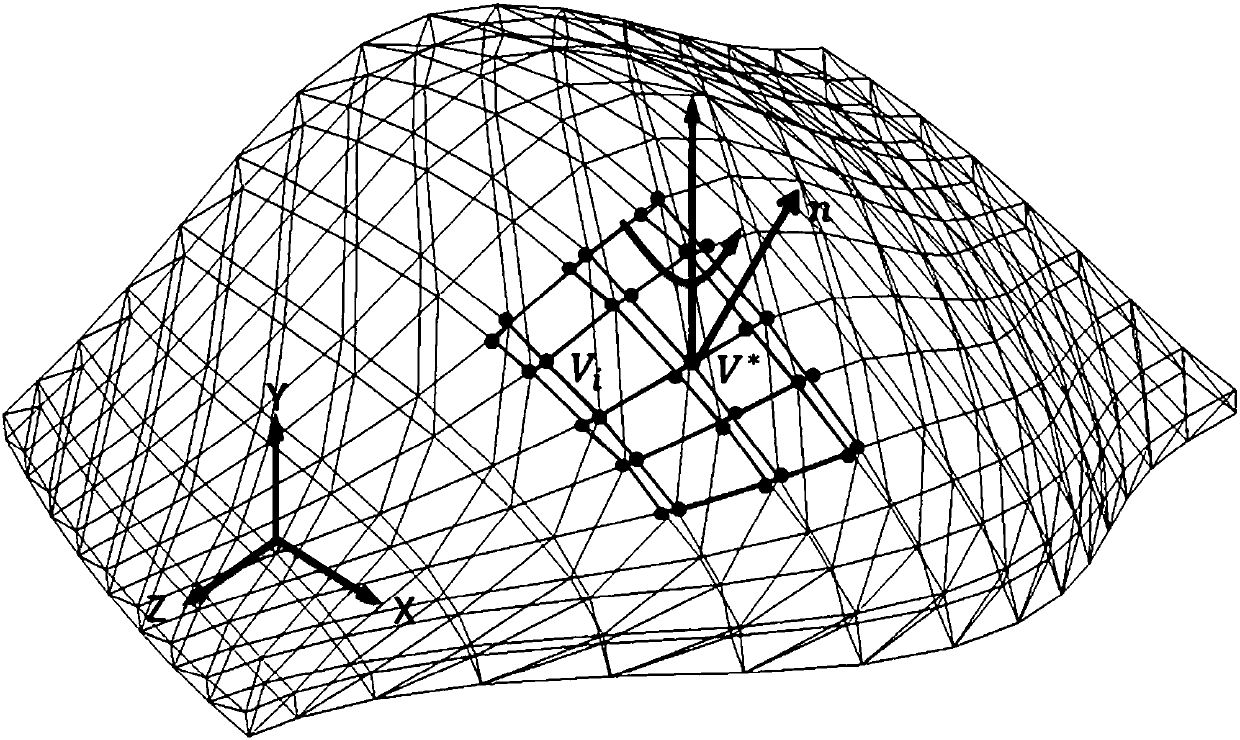
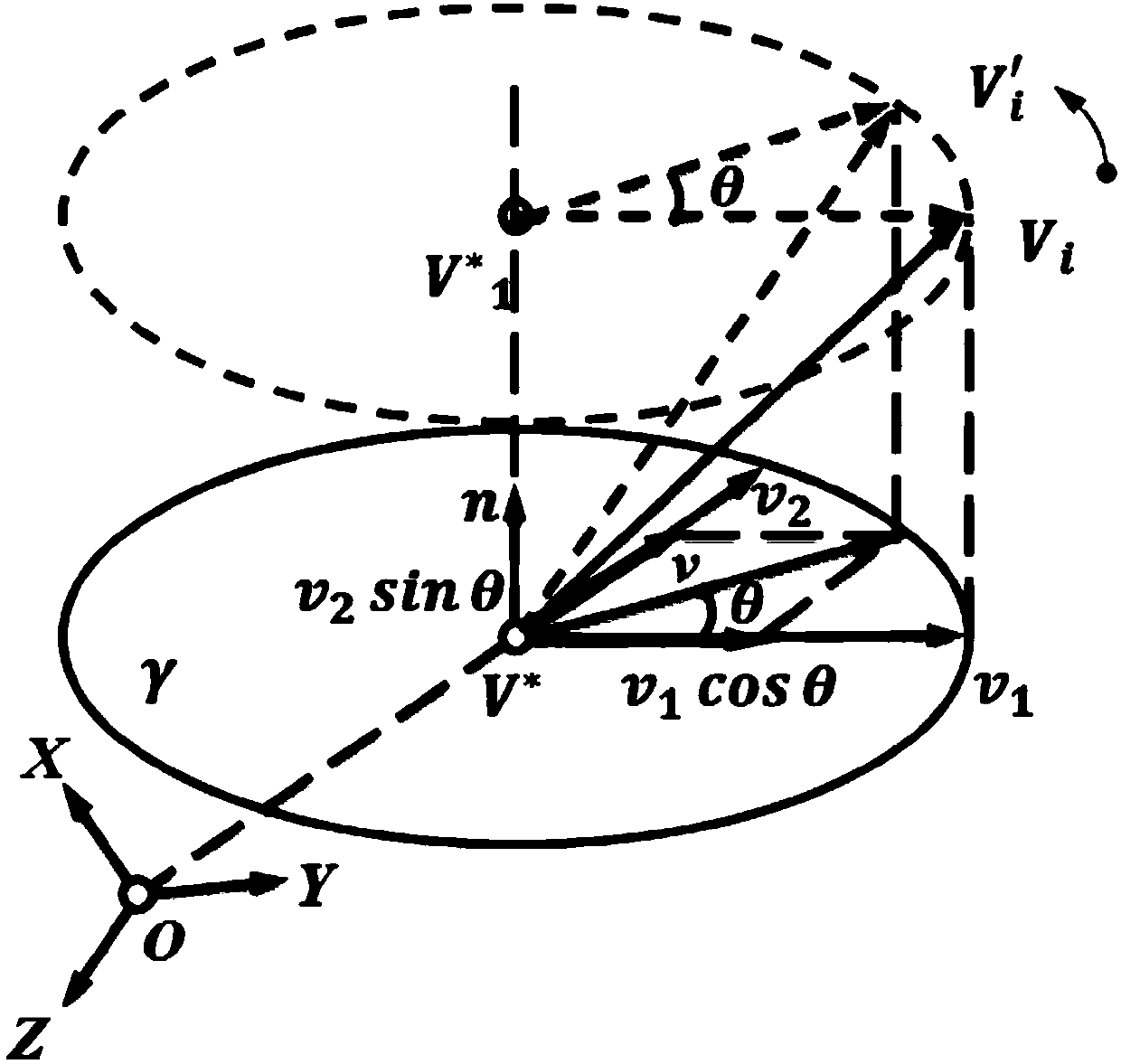
Geometric mesh model deformation method based on oblique ellipsoid domain influence convex hull
InactiveCN106991722ASolve the disadvantages of rotational distortionAchieving Multimodal MorphingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLaplacian coordinatesLeast squares
The invention discloses a geometric mesh model deformation method based on oblique ellipsoid domain influence convex hull. The method includes selecting a control vertex to be deformed according to regions of interest, deciding to select an influence region in a logically forward or backward direction from a global mesh vertex, establishing a global or local oblique ellipsoid domain influence convex hull, traversing an annular neighborhood of the control vertex to be deformed, calculating Laplacian coordinates at the mesh vertex, performing least squares restrained deformation for the region to be deformed, and overlapping the region to be deformed and a non-influence convex hull region to obtain a deformation model. According to the invention, the minimum volume enclosing oblique ellipsoid domain is used for representing the influence region of the control vertex, the influence range of the deformation vertex is enveloped precisely, the drawback of rotational distortion of a local vertex in the zooming and rotation transformation of the Laplacian differential coordinates can be overcome, the deformed mesh patch normal vector or vertex normal vector transitions smoothly and uniformly, better smoothness is gained, and the geometric mesh model deformation of a region of geometry adjacency with a non-connected topology is facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
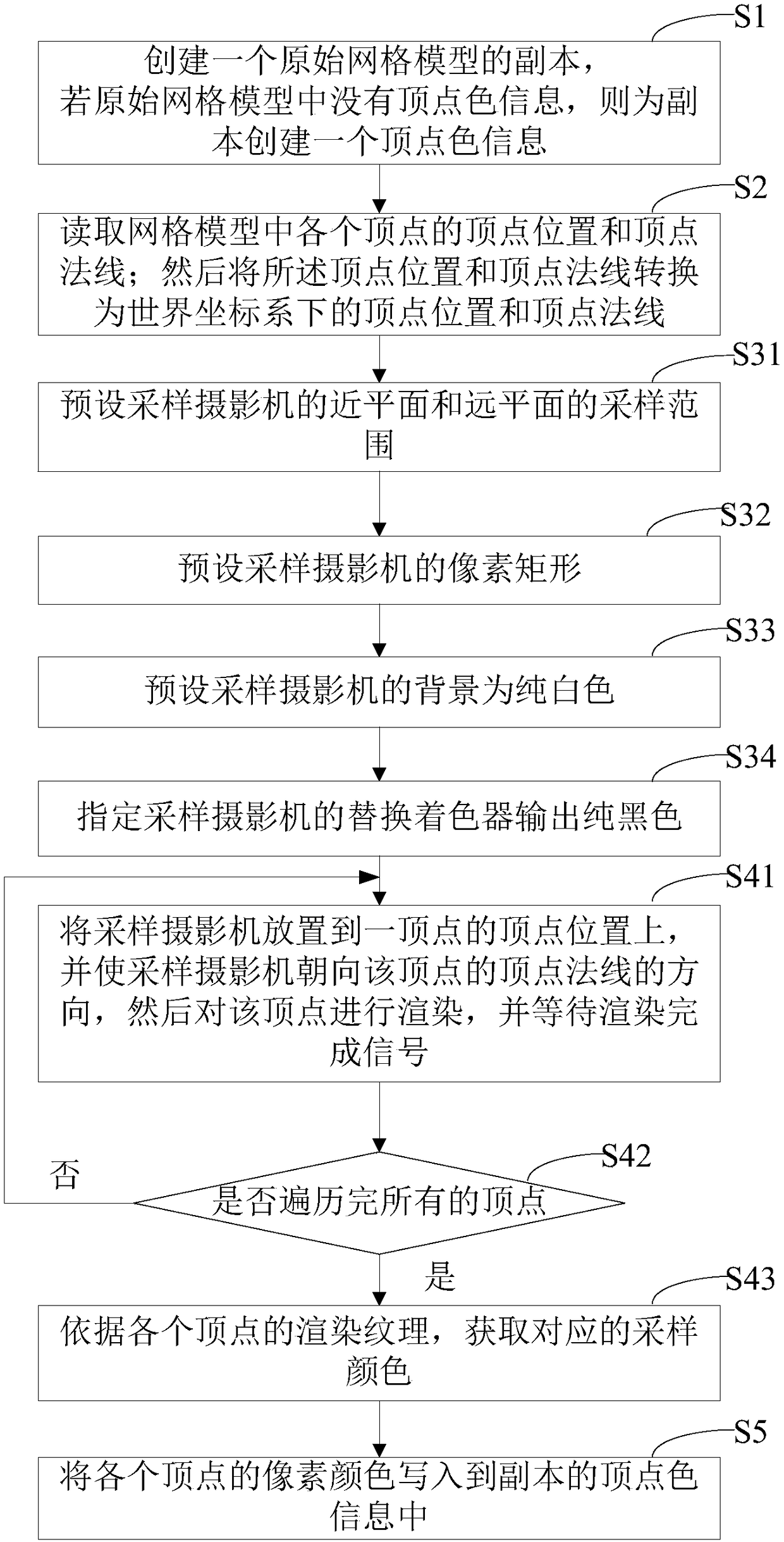
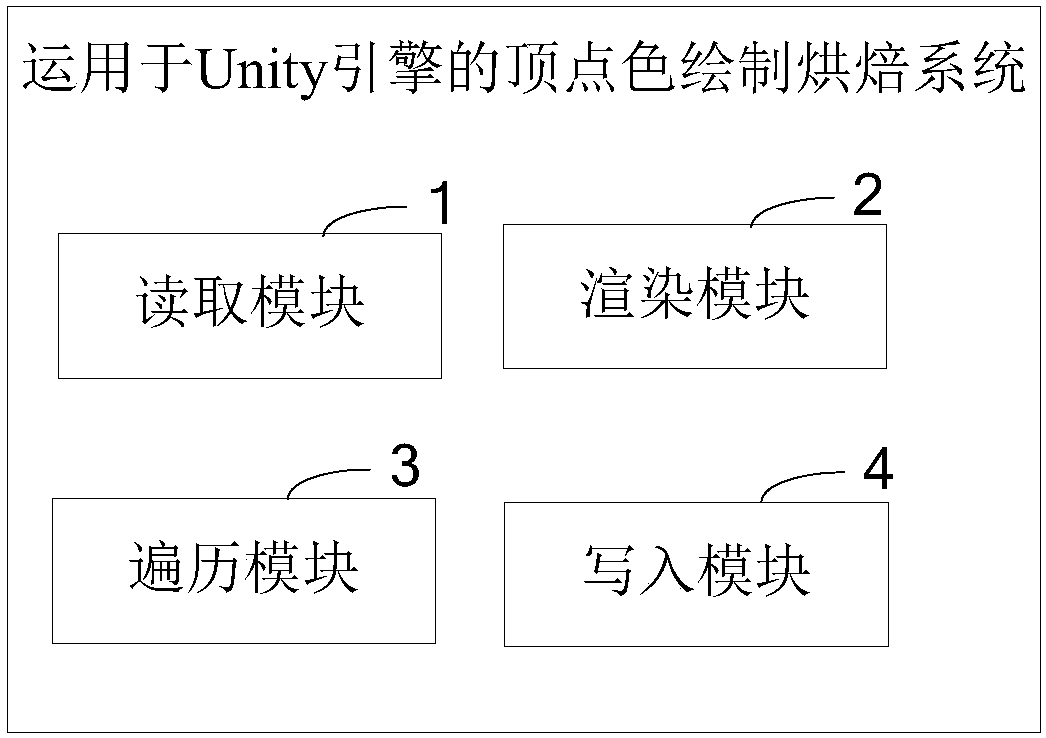
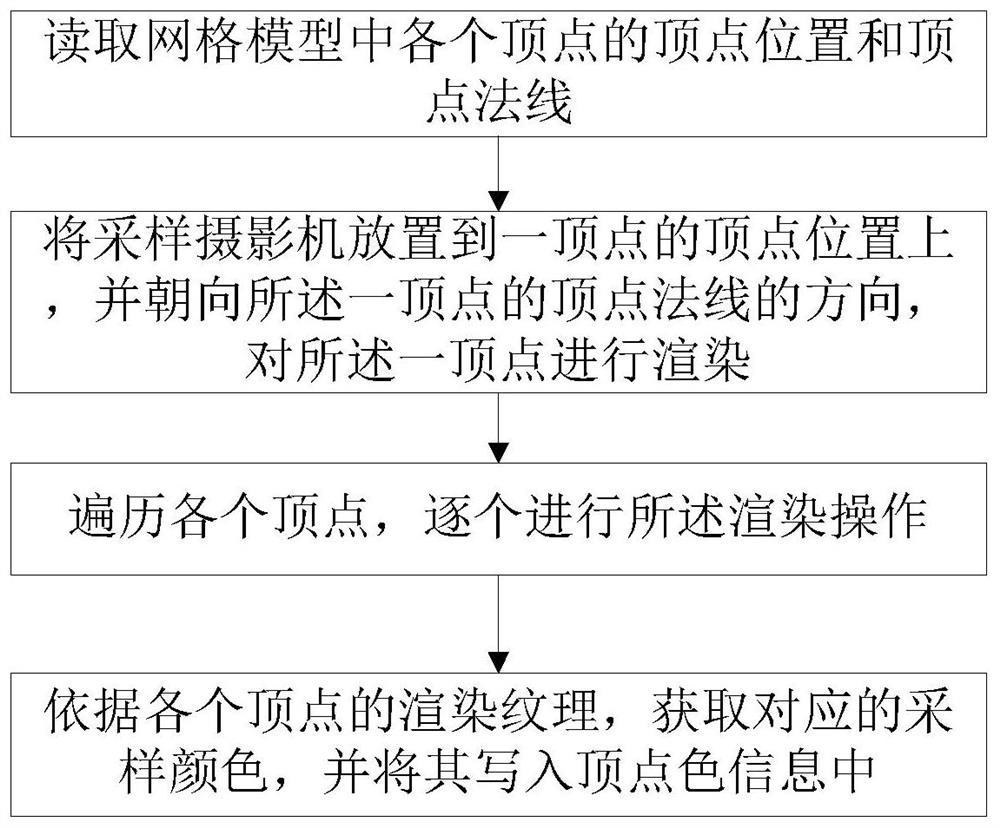
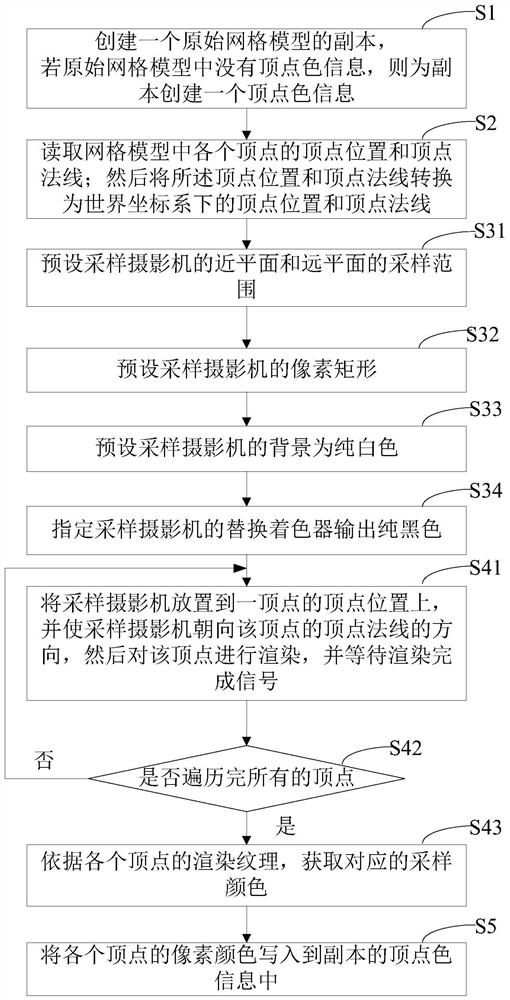
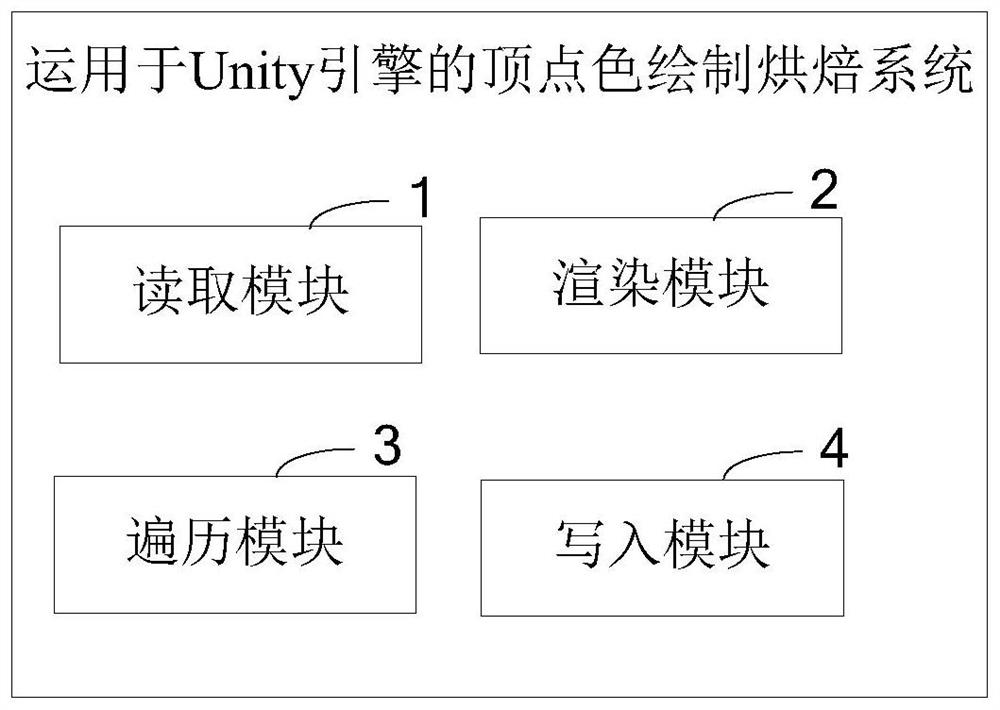
Method and system for vertex color drawing baking used for Unity engine
ActiveCN108257204ALess quantitySmall footprint3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Computer science
The present invention provides a method and a system for vertex color drawing baking used for a Unity engine. The method comprises the steps of: reading the vertex position and the vertex normal of each vertex in a mesh model; putting a sampling camera to the vertex position of one vertex, facing the direction of the vertex normal of the vertex, and performing rendering of the vertex; traversing each vertex, and performing rendering operation one by one; and according to rendering textures of each vertex, obtaining corresponding sampling colors, and writing the corresponding sampling colors into the vertex color information. The method and the system for vertex color drawing baking used for the Unity engine can reduce the storage capacity of AO information, can improve the baking efficiency, further, are high in model correlation to facilitate later-stage editing, and finally, can support customized fine tuning of the vertex colors after baking.
Owner:福建省天奕网络科技有限公司
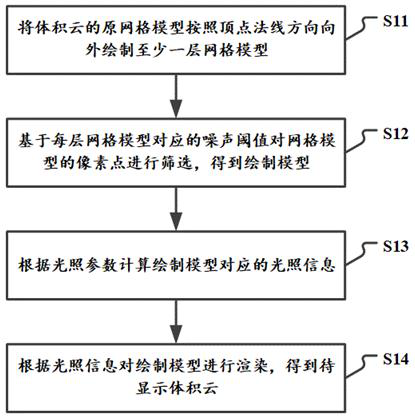
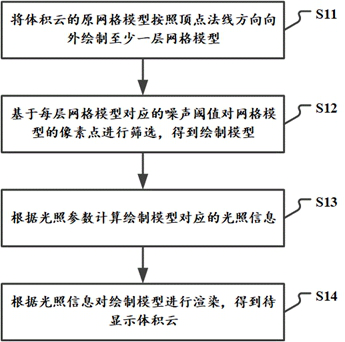
Volume cloud rendering method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN112200900AReduce the number of adoptionsReduce performance overhead3D-image renderingComputational scienceAlgorithm
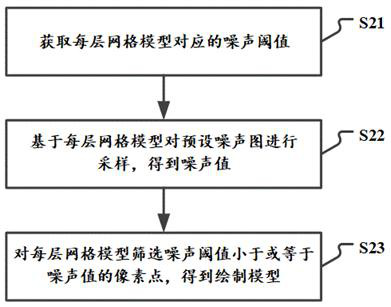
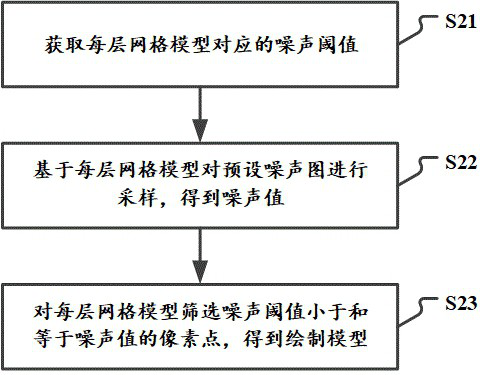
The invention relates to a volume cloud rendering method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: drawing at least one layer of grid model outwards from an original grid model of volume cloud according to a vertex normal vector; screening pixel points of the grid model based on the noise threshold corresponding to each layer of the grid model to obtaina drawing model; calculating illumination information corresponding to the drawing model according to the illumination parameters; and rendering the drawing model according to the illumination information to obtain a to-be-displayed volume cloud. According to the technical scheme, the shape of the volume cloud is determined based on the grid model instead of the shape of the noise map, and if theshape of the volume cloud needs to be changed, only the number of additionally drawn layers needs to be set and the noise threshold value of the pixel points needs to be screened, and the specific noise map does not need to be selected in advance; therefore, the number of times of adopting the noise map is reduced, the performance overhead of generating the volume cloud is further reduced, and the volume cloud can smoothly run on the mobile terminal equipment.
Owner:CHENGDU PERFECT WORLD NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Model rendering method, device and equipment and storage medium
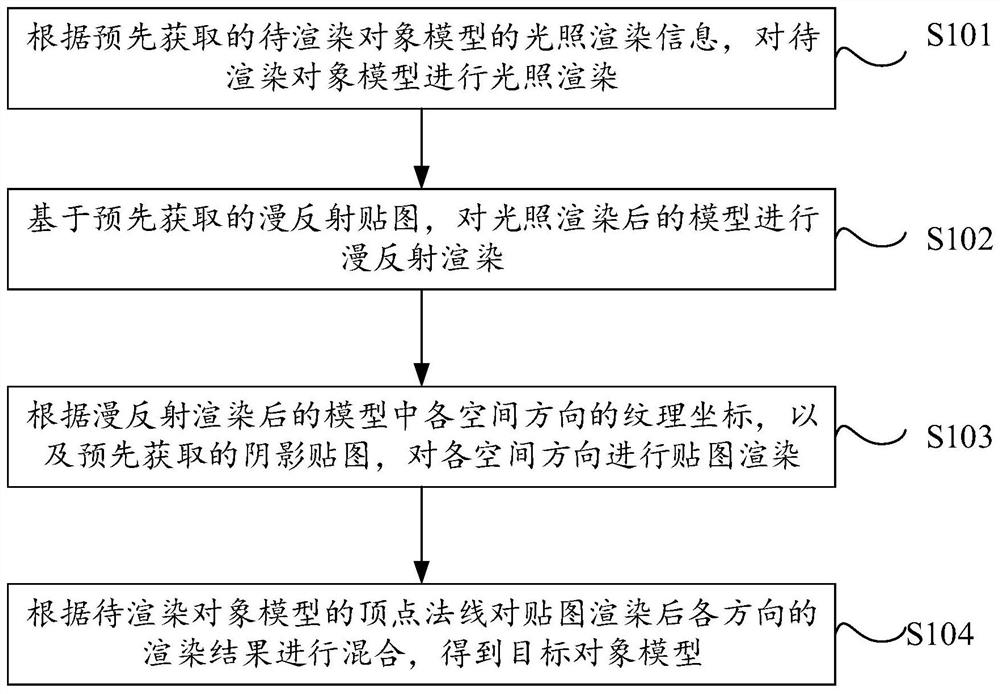
PendingCN112316420ASolve the problem of texture offsetIncrease authenticityVideo gamesPattern recognitionShadow mapping
The invention provides a model rendering method, device and equipment and a storage medium, and relates to the technical field of model rendering. The method comprises the steps: performing illumination rendering on a to-be-rendered object model according to pre-acquired illumination rendering information of the to-be-rendered object model; performing diffuse reflection rendering on the model after illumination rendering based on a pre-acquired diffuse reflection map; performing mapping rendering on each spatial direction according to the texture coordinates of each spatial direction in the model after diffuse reflection rendering and a shadow map acquired in advance; and according to the vertex normal of the to-be-rendered object model, mixing rendering results in all directions after maprendering to obtain a target object model. According to the target model obtained through the method, the problem of map offset caused by displacement of the model is well solved, so that the authenticity of a rendered picture is improved, and the visual perception of a user is improved.
Owner:NETEASE (HANGZHOU) NETWORK CO LTD
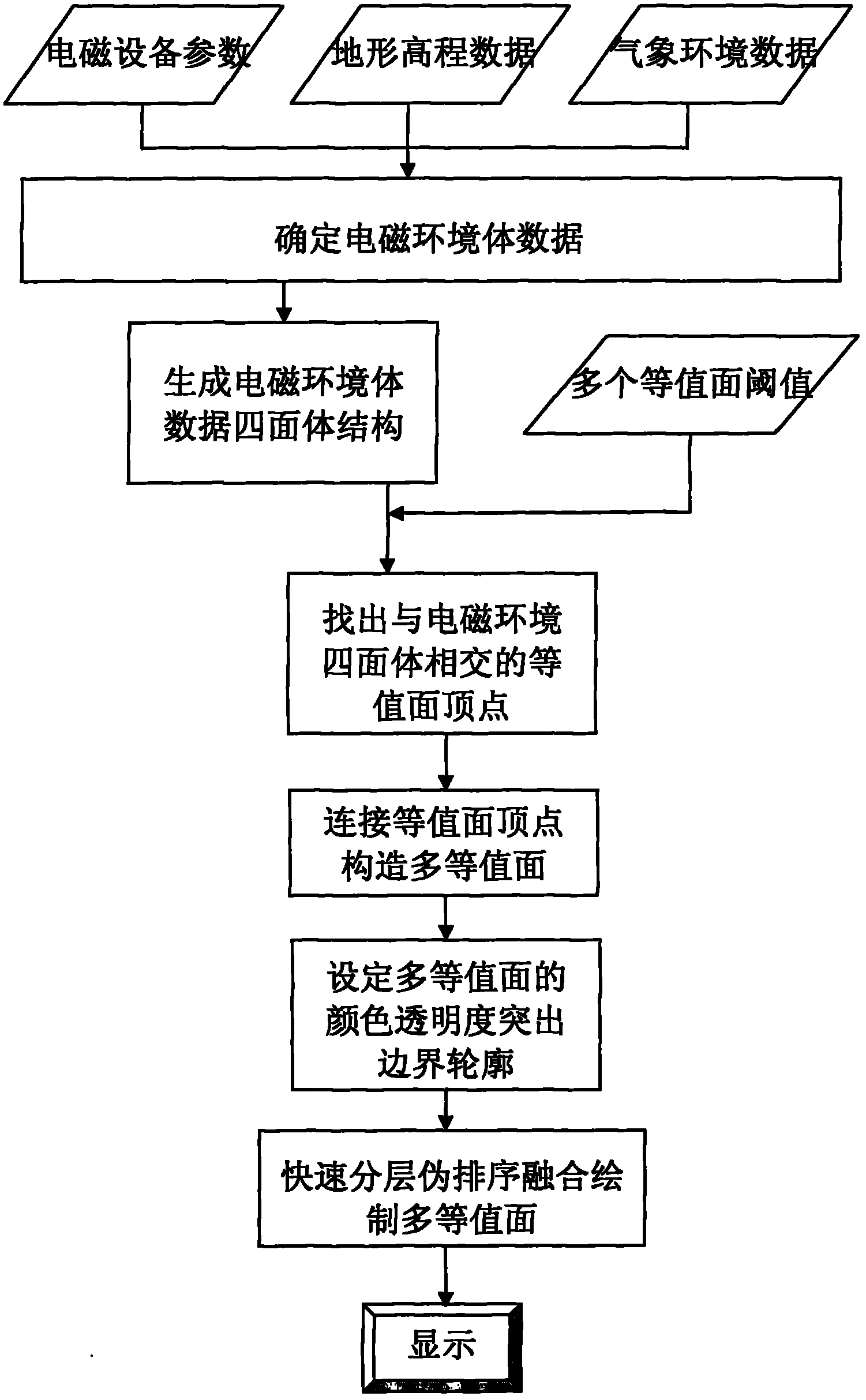
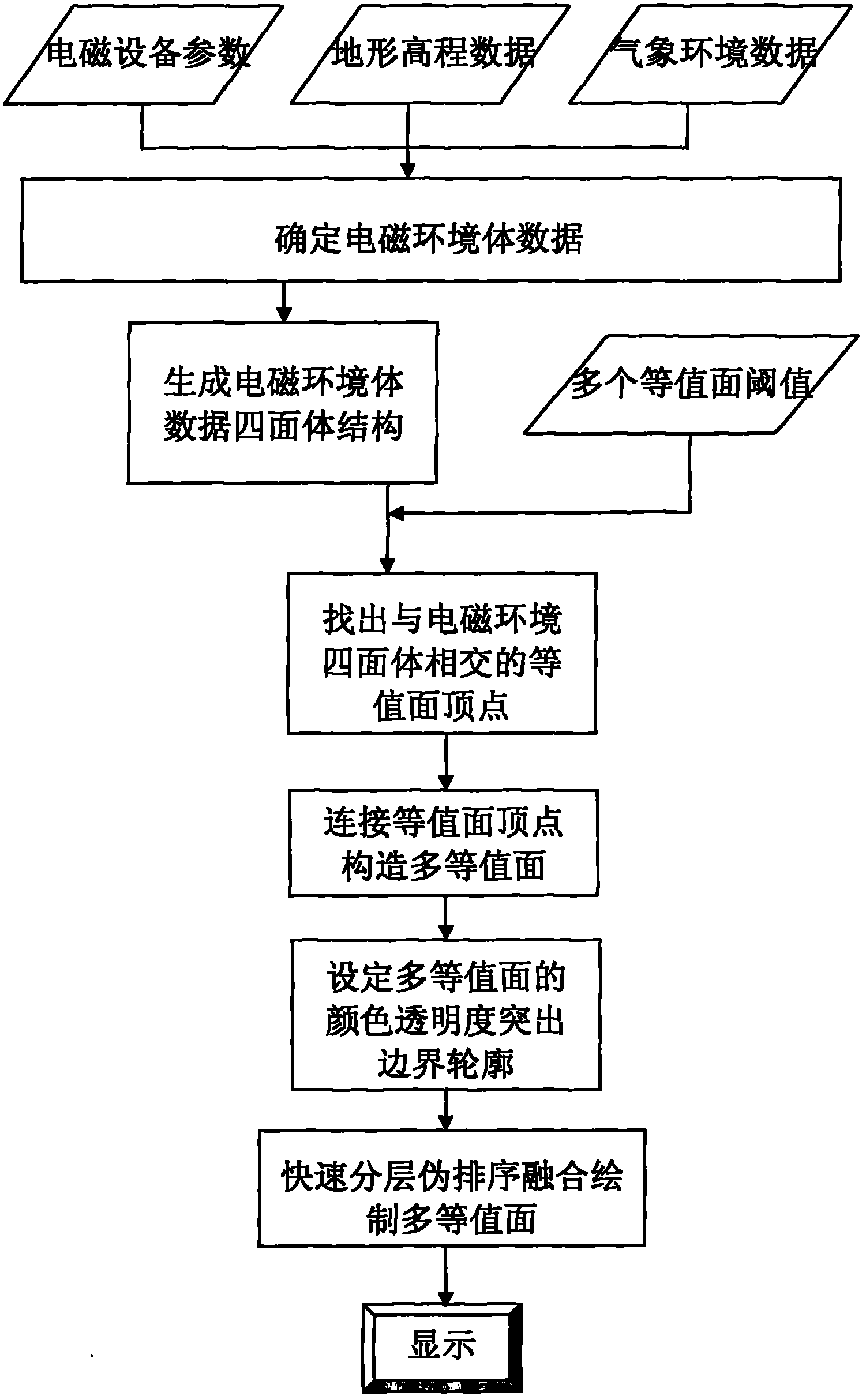
Three-dimensional visualization method for electromagnetic environment body data
InactiveCN102254347AFull internal detailsComplete representation internal details3D modellingBoundary contourGraphics
The invention belongs to the technical field of electromagnetic environment visualization, and discloses a three-dimensional visualization method for electromagnetic environment body data. The method comprises the following steps of: determining the electromagnetic environment body data by a radio wave propagation physical model; dividing the electromagnetic environment body data into a tetrahedron structure, forming a two-dimensional texture in a vertex index manner according to the vertexes of the tetrahedron, and inputting a tetrahedron vertex function value texture and a vertex index texture into a graphics processor; generating contour surface vertexes according to predetermined contour surface threshold judgment, connecting the contour surface vertexes of same threshold into a contour surface, and forming a plurality of contour surfaces of the electromagnetic environment; and displaying the edge of an electromagnetic environment model in a manner of extruding according to a relation between vertex normal vectors and view points, and fusing and embedding the plurality of contour surfaces into the three-dimensional environment in a semitransparent manner. With the method, the three-dimensional electromagnetic environment can be represented visually and intuitively, more internal information representation of the electromagnetic environment are provided, and the correctnessand the completeness of the electromagnetic environment representation and the definition of a boundary contour are all improved.
Owner:中国人民解放军装备指挥技术学院
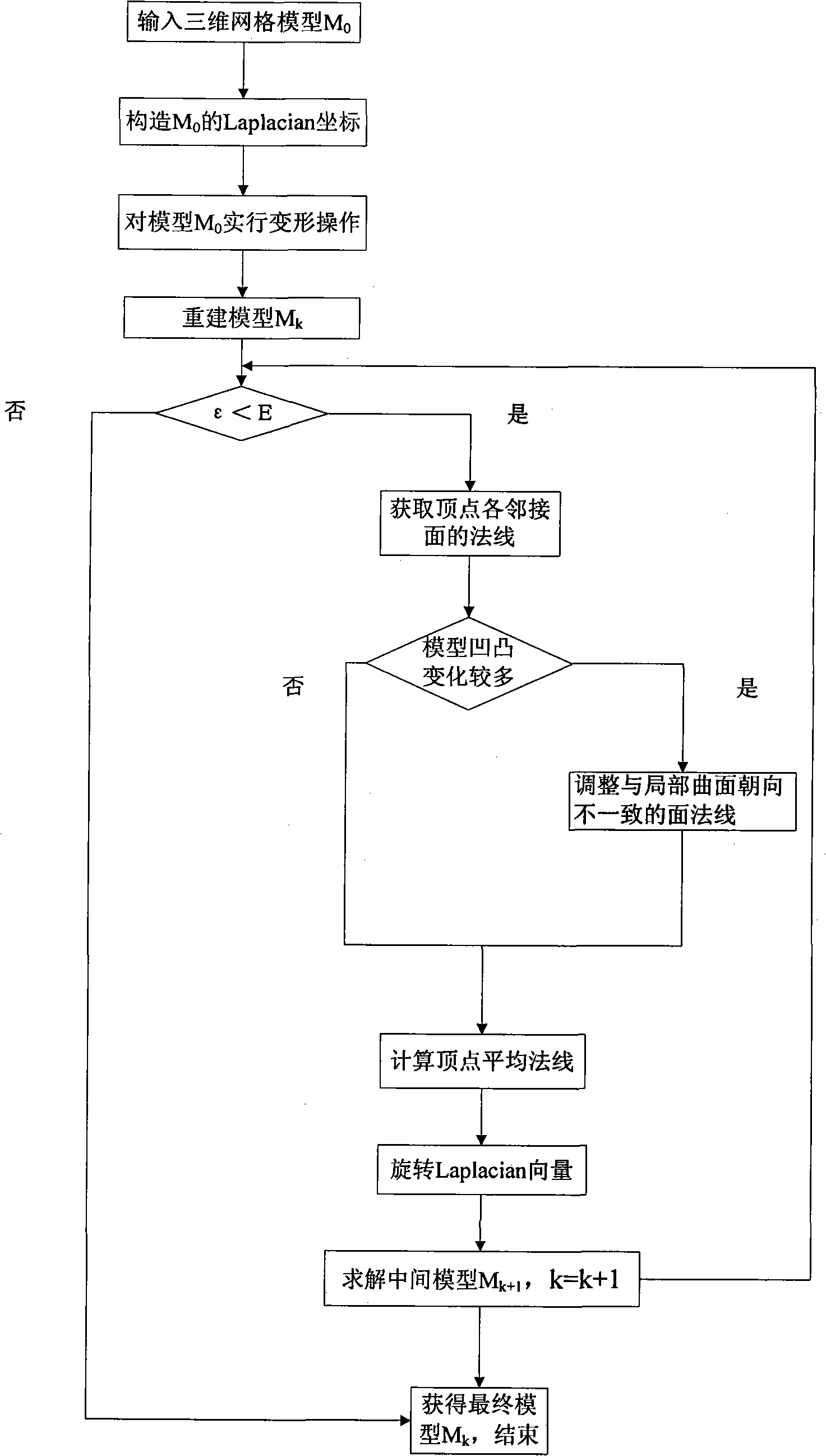
Method for implementing parallel moving hypersensitive Laplacian gridding edition
InactiveCN101276483ARealize the deformation effectAvoid the estimation process3D-image rendering3D modellingLaplacian coordinatesComputer animation
The invention provides a Laplacian grid editting method for realizing translation sensitivity. The method is usually used for model editting in computer cartoons and industrial modeling, but a Laplacian coordinate have no translation sensitivity, thereby geometrical detail characters of the model can not be held well. Thus, the invention proposes a method for rotating the Laplacian coordinate by a vertex normal, which comprises re-building a middle model based on the original Laplacian coordinate, calculating the vertex normal of the model, and rotating the original Laplacian coordinate to a parallel direction of the vertex normal, and rebuilding the model to obtain the result. According to the method of the invention, the Laplacian coordinate realizes the deformation effect of translation sensitivity, the vertex normal is automatically calculated, fussy Laplacian vector estimation is avoided, and the geometrical detail characters of the model can be held well.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
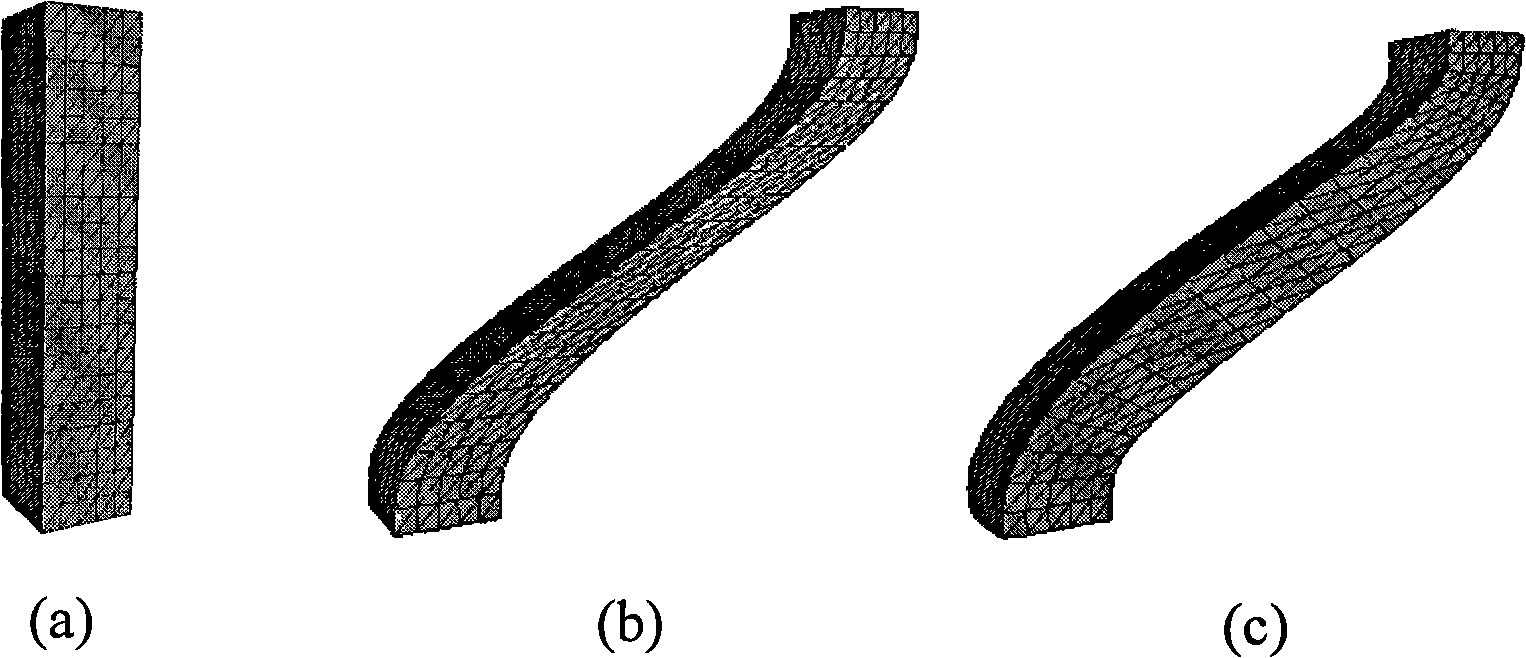
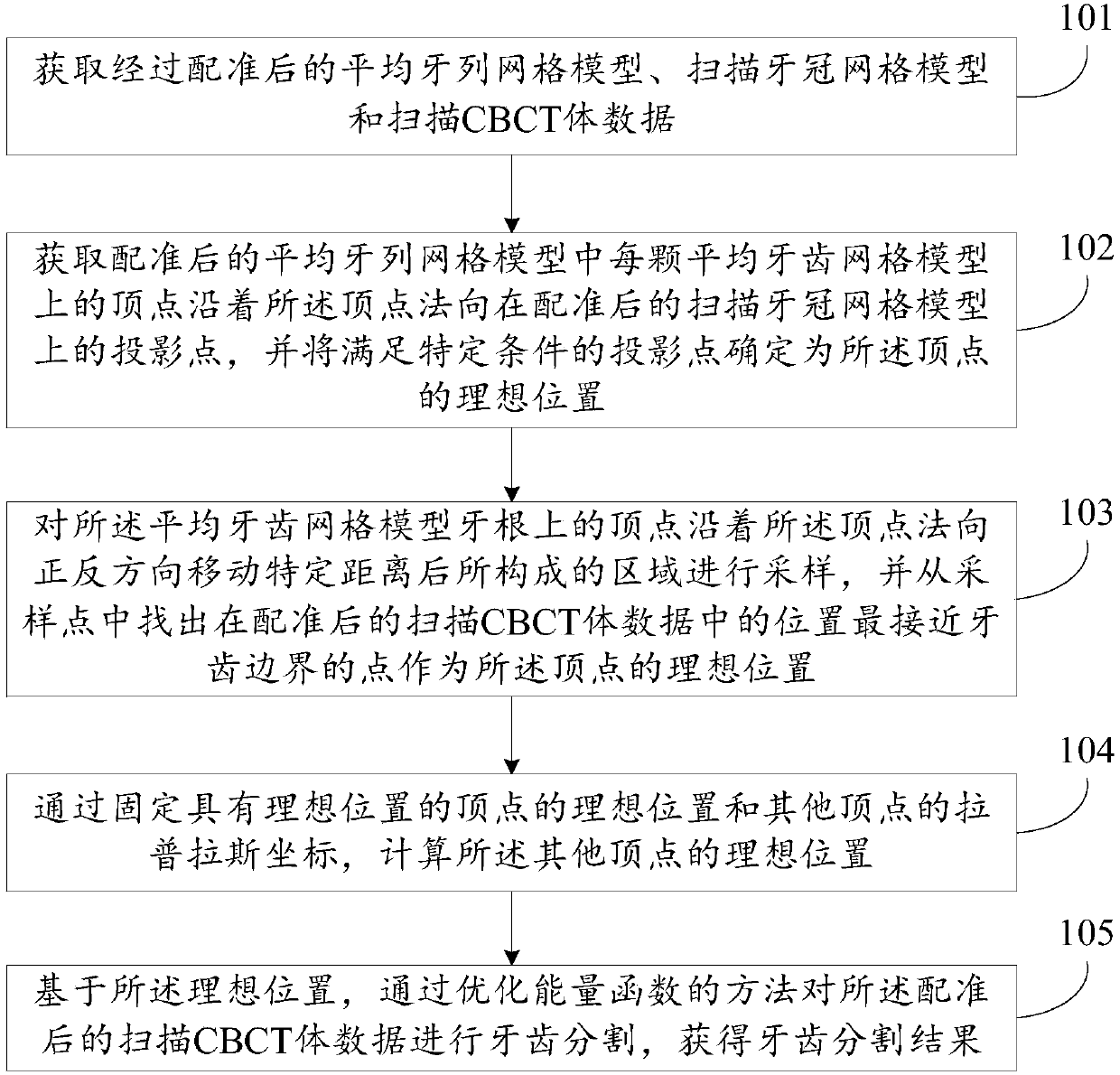
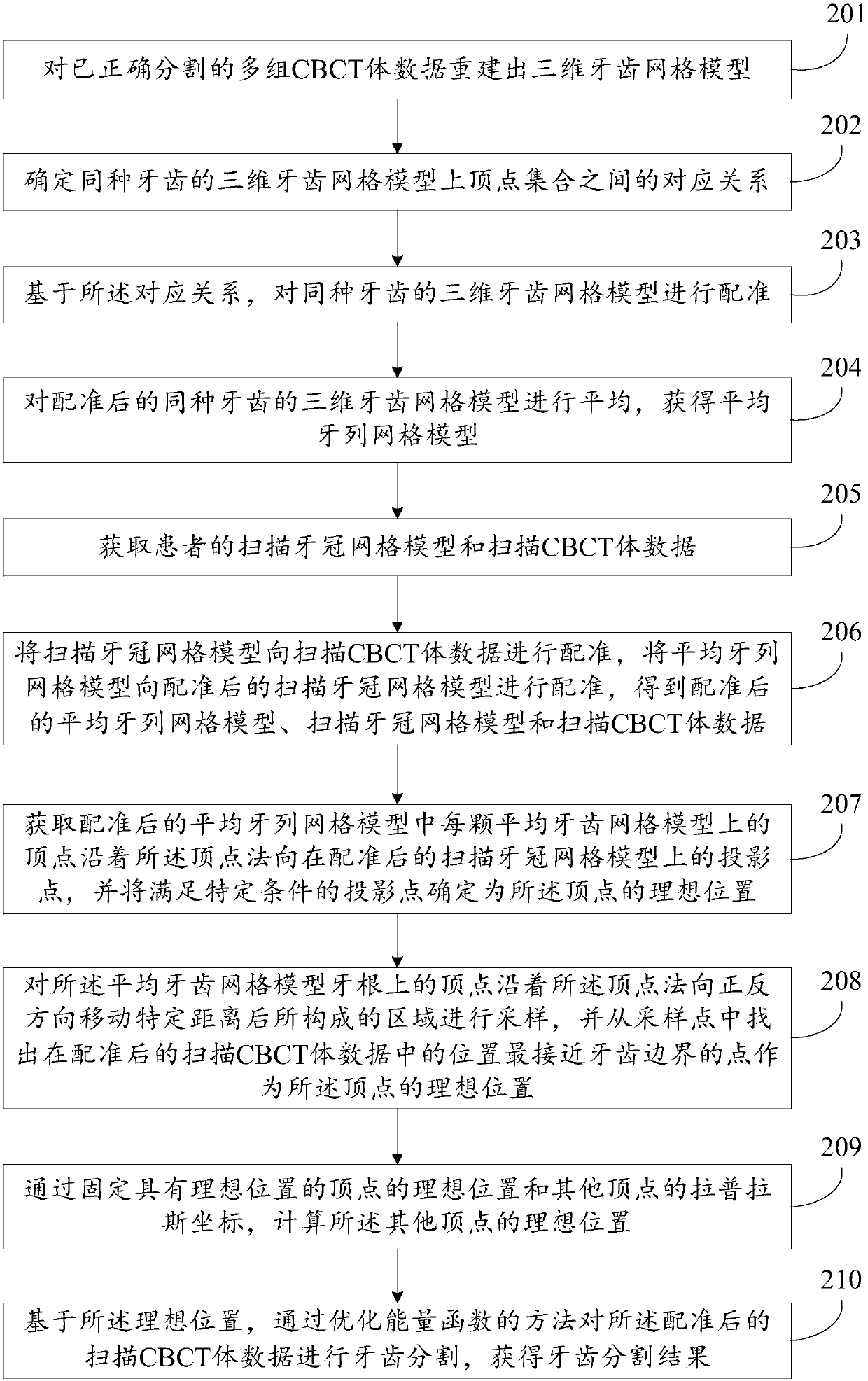
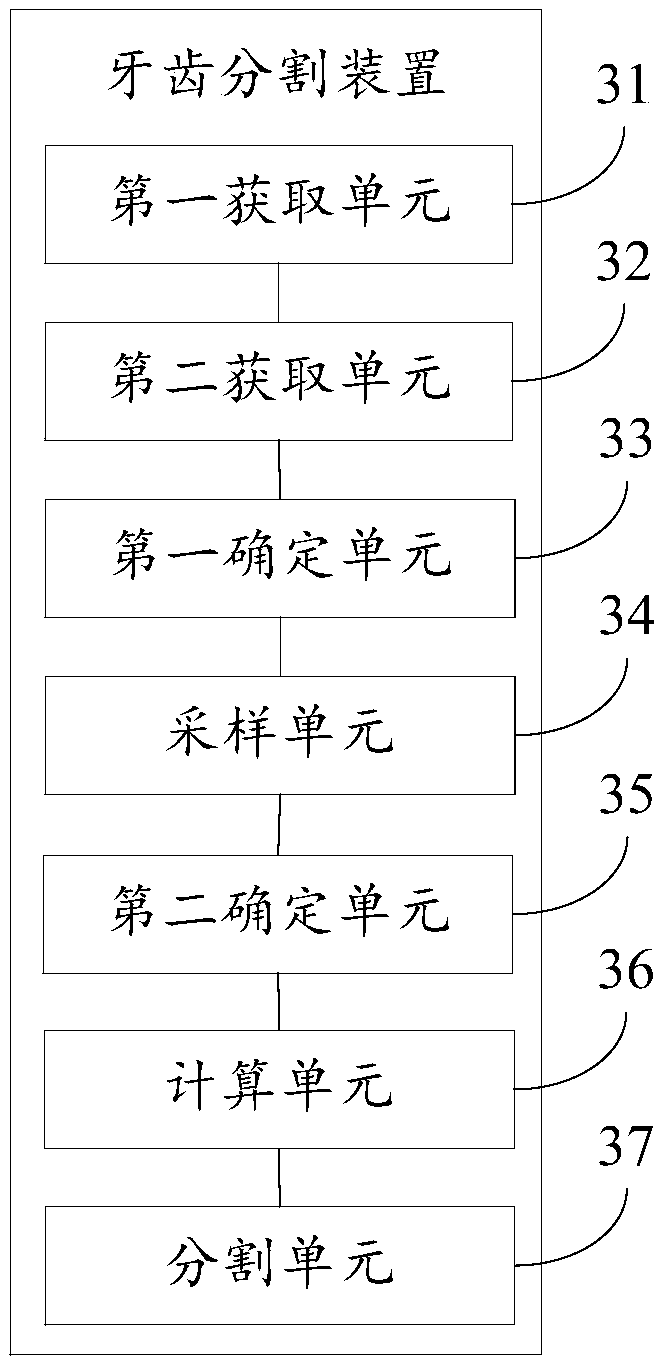
Tooth segmentation method and device
ActiveCN108648283AThe segmentation result is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisLaplacian coordinatesCbct imaging
The invention discloses a tooth segmentation method and a tooth segmentation device, relating to the oral field and capable of solving the problem of imprecise automatic teeth segmentation. The methodcomprises: obtaining the registered average dentition mesh model, the scanned crown mesh model and the scanned CBCT volume data; determining the projection point satisfying the specific condition inthe projection point of the vertices of the average tooth mesh model on the registered scanned crown mesh model along the vertex normal orientation as the ideal position of the vertex; sampling the region formed by moving the vertices on the root of the average tooth mesh model along forward and backward directions for specific distance, finding the point located closest to the tooth boundary in the volume data from the sampling points as the ideal position of the vertex; calculating the ideal positions of the other vertices by fixing the ideal position of the vertex with the ideal position and the Laplacian coordinates of the other vertices; and performing tooth segmentation on the volume data by the optimized energy function method based on the ideal position. The invention is suitable for scenes where automatic tooth segmentation is performed on CBCT images.
Owner:北京正齐口腔医疗技术有限公司
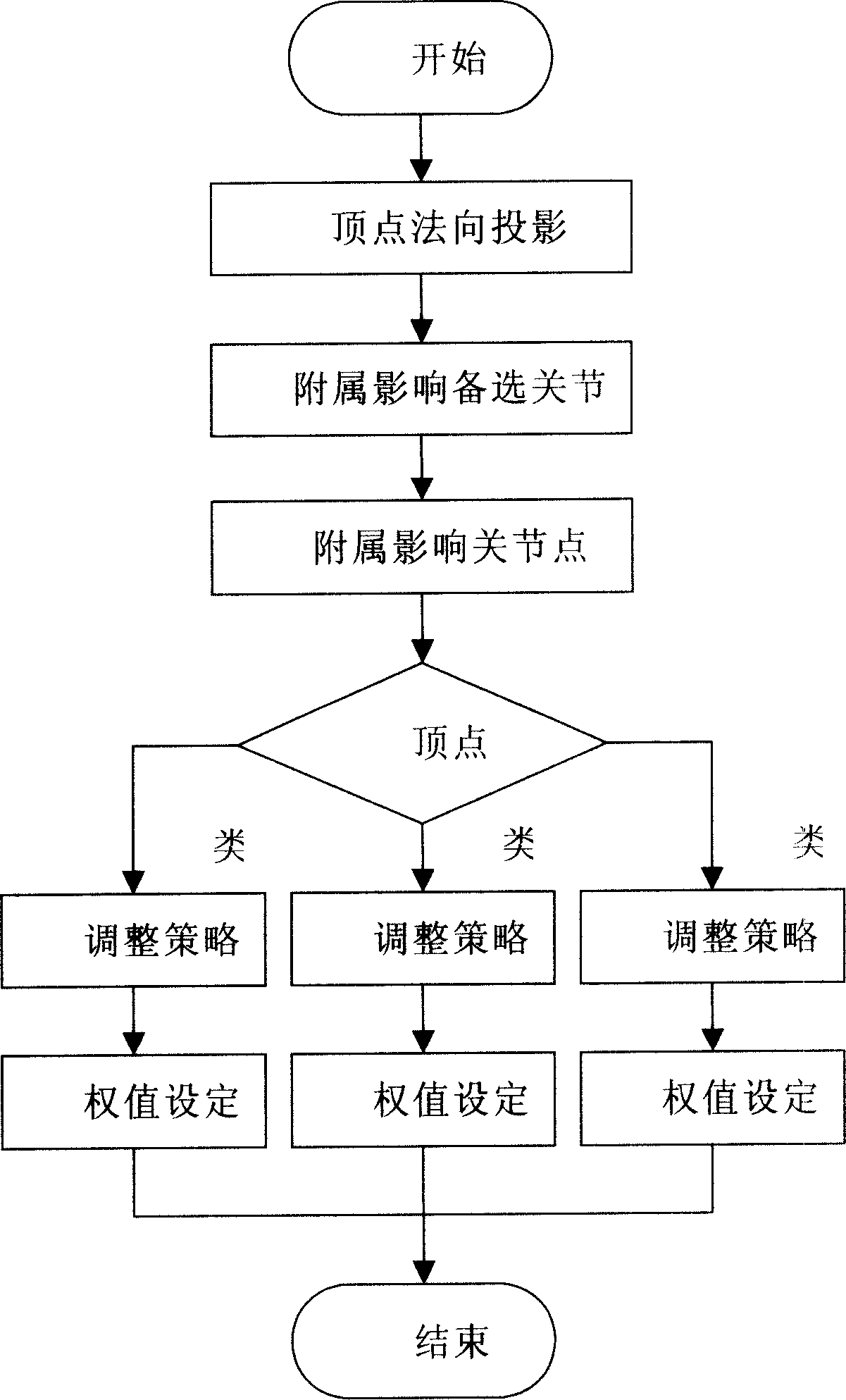
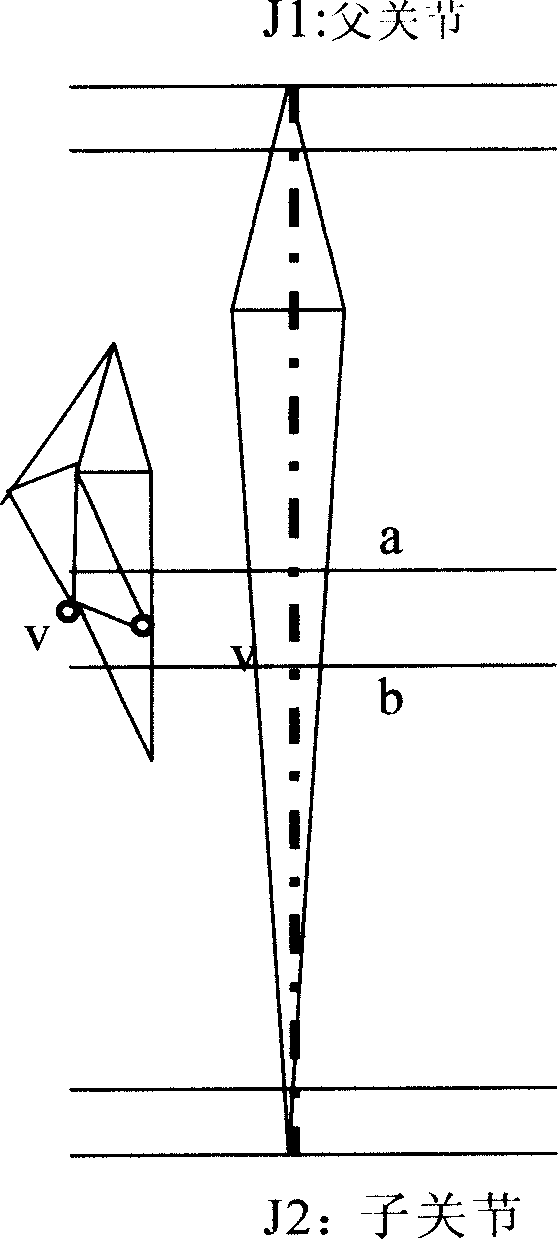
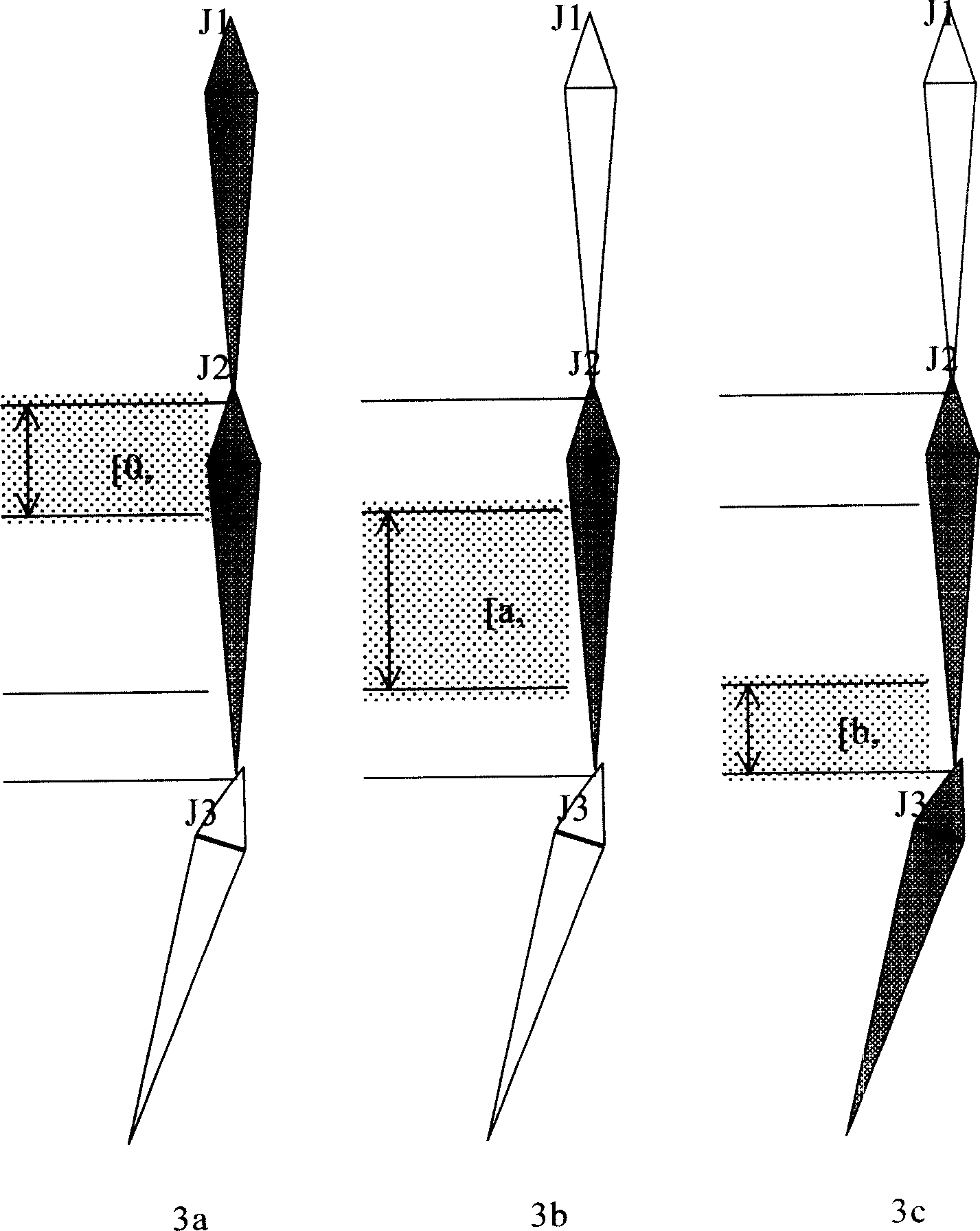
Skin-top affecting weight distribution method based on standby joint point collection
InactiveCN1710612AReduce laborHigh degree of automation3D-image renderingDistribution methodGeometric modeling
The method includes steps: (1) vertex normal projection, i.e. spot projecting all skin vertexes and prepared articulation points to be selected onto normal direction of parallel intercepted plane in concentration; (2) dividing the said articulation points, and attaching two adjacent articulation points to divided skin vertexes; (3) attaching determined articulation points to skin vertexes; (4) according to sorting rules, sorting skin vertexes; according to relation between skin vertexes and positions of two affected articulation points, setting up class attribute of vertex, and adjusting accessory affected articulation points according to adjusting strategy; (5) setting up weight value of affected articulation points on skin vertexes including three classes. The invention saves manual labor for modeling, as well as raises automatic degree in procedure for geometrical modeling virtual human and in matching procedure between geometrical model of virtual human and moving data framework.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
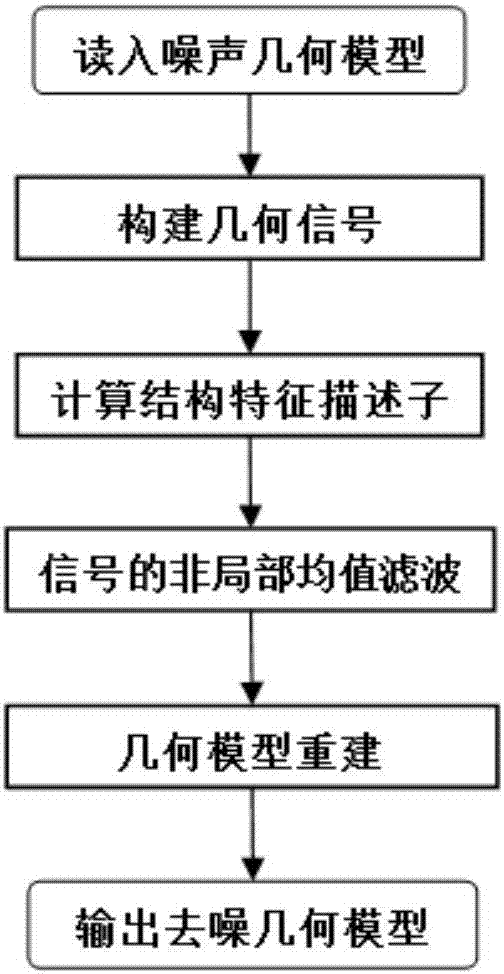
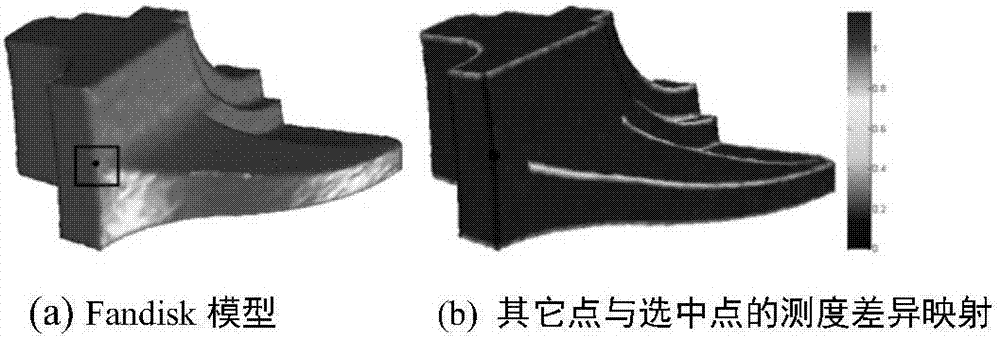
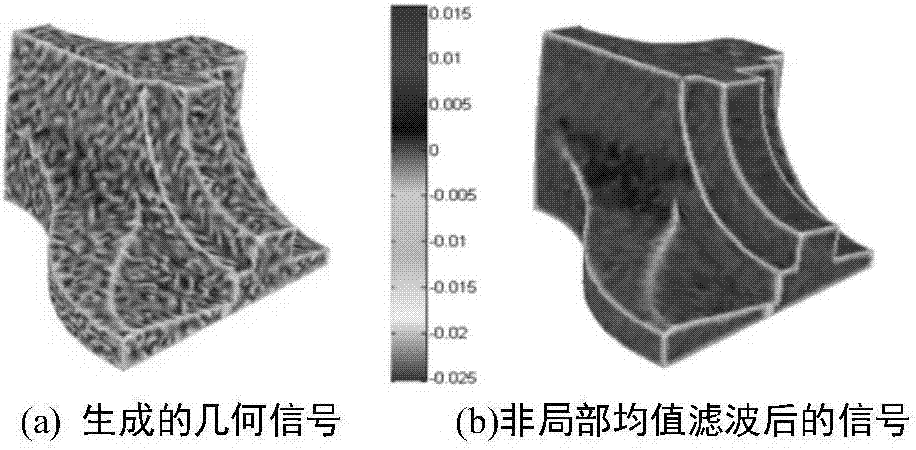
Denoising method for three-dimensional geometric model based on structural feature description
ActiveCN107274367AEasy to describeImprove robustnessImage enhancement3D modellingPattern recognitionFeature description
The invention relates to a denoising method for a three-dimensional geometric model based on structural feature description. The denoising method is characterized by comprising the steps of firstly constructing a vertex signal through performing inner product on a vertex Laplace vector and a vertex normal; then constructing a structural feature descriptor of each vertex based on a normal tensor of the vertex of the three-dimensional model so as to depict features of the geometric model, taking the structural feature descriptors as a basis for calculating a non-local mean filtering weight so as to perform smoothing on the vertex signal; and finally performing curve planar reconstruction on the smoothed signal so as to acquire a denoising model. The denoising method can well keep features of the geometric model while removing noise of the model, and acquires an excellent denoising effect.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
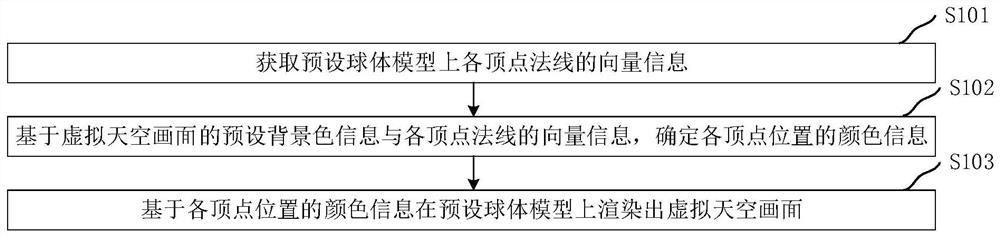
Virtual sky picture rendering method and related equipment
ActiveCN113077541AControl resolutionChange in control effectTexturing/coloring3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Vertex normal
The embodiment of the invention provides a virtual sky picture rendering method and related equipment and relates to the technical field of computers. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring the vector information of each vertex normal on a preset sphere model; based on the preset background color information of the virtual sky picture and the vector information of each vertex normal, determining the color information of each pixel point position on the preset sphere model; and rendering a virtual sky picture on a preset sphere model based on the color information of each pixel point position. According to the method, efficiency of rendering the virtual sky picture can be effectively improved.
Owner:广州益聚未来网络科技有限公司
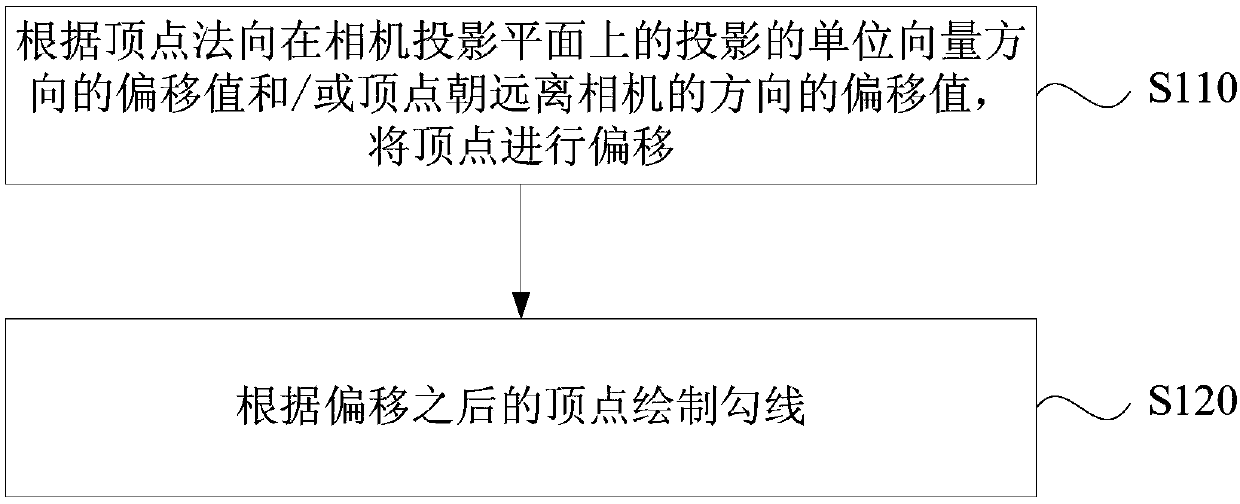
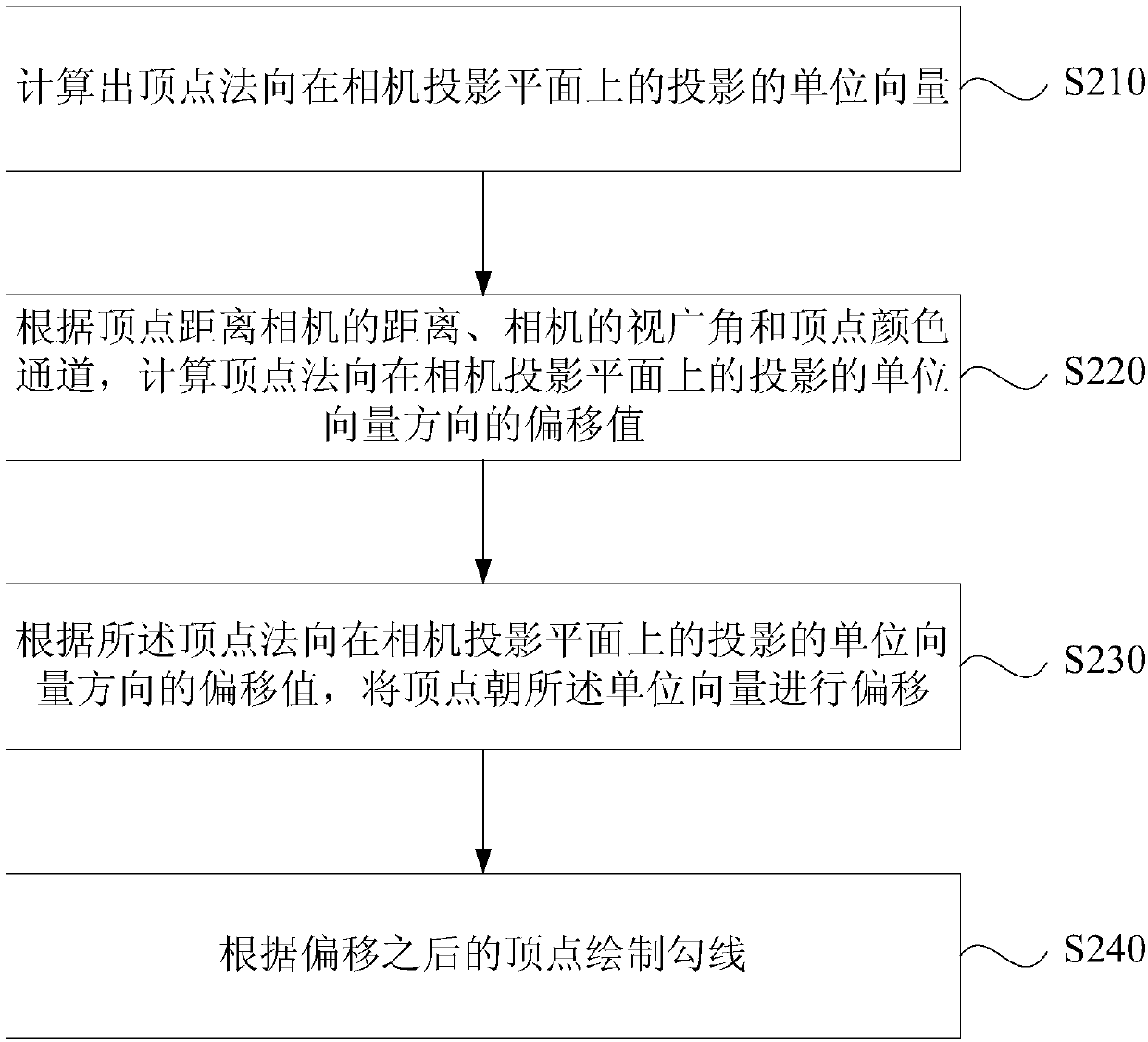
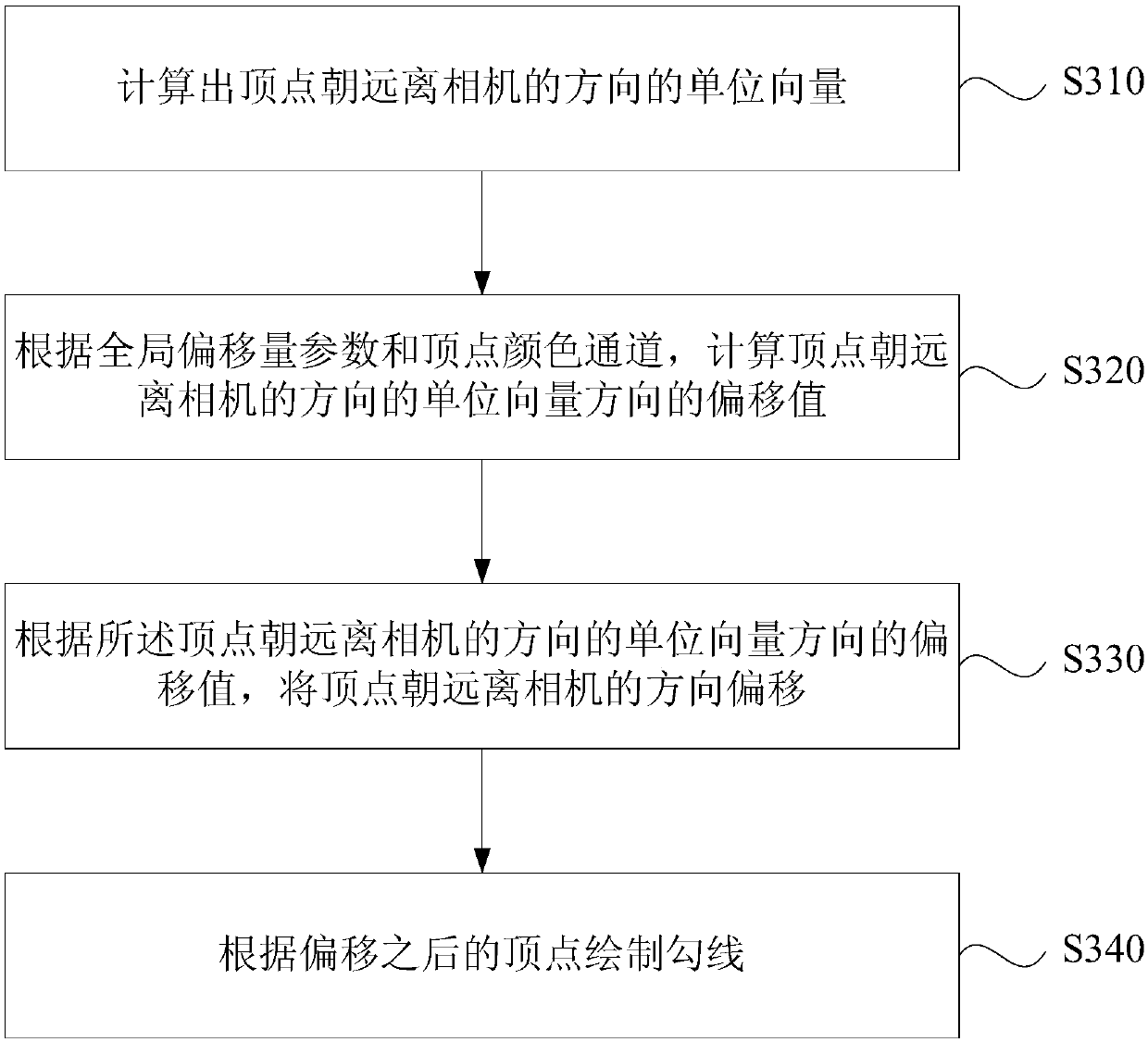
Outline rendering method, device, equipment and medium
The embodiment of the invention discloses an outline rendering method, an outline rendering device, equipment and a medium. The method comprises the steps of offsetting a vertex according to an offsetvalue of a vertex normal in a unit vector direction of projection on a camera projection plane and / or an offset value of a vertex towards to the direction away from a camera; and drawing an outline according to the offset vertex. According to the embodiment, the real-time adjustment for the outline is realized so that the rendered outline is more controllable and vivid and smooth.
Owner:米哈游科技(上海)有限公司
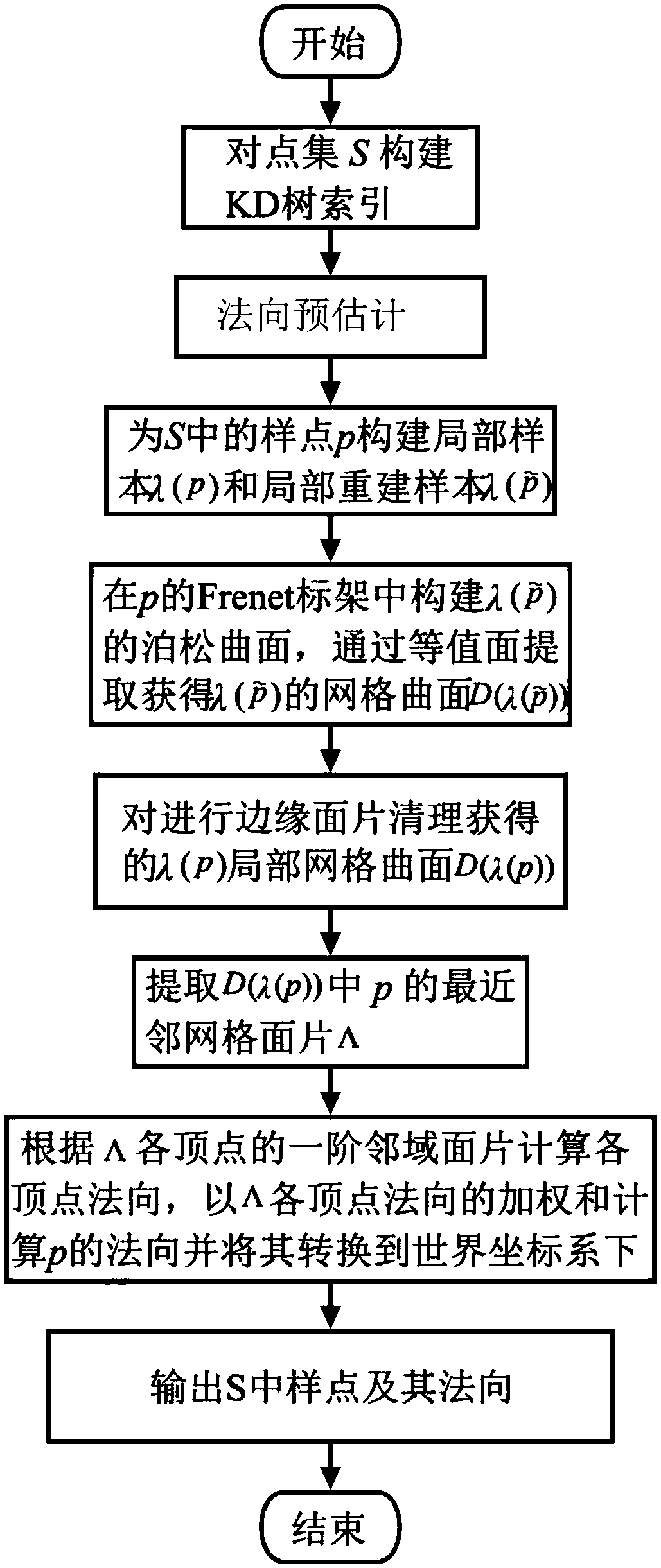
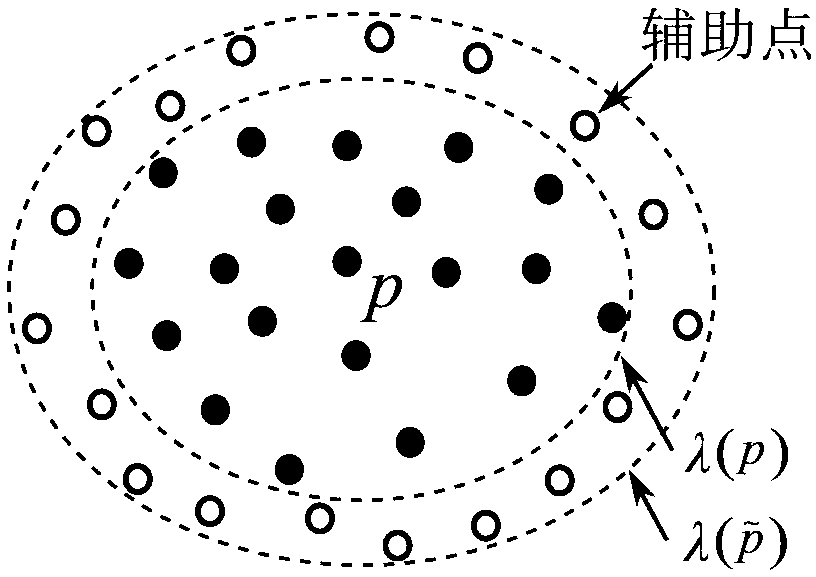
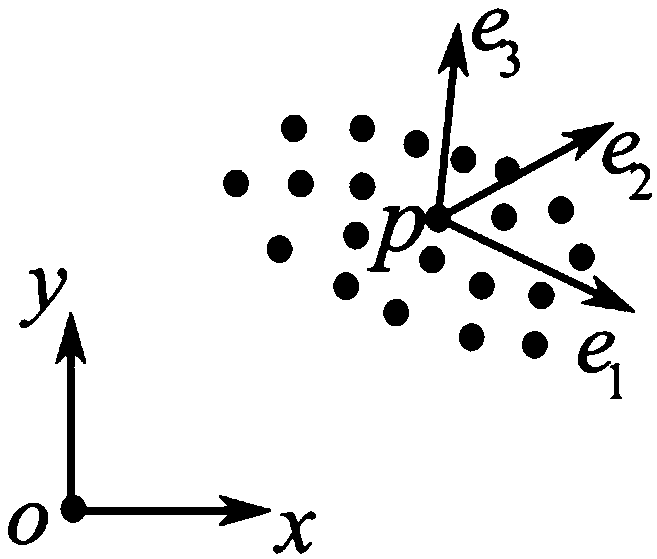
Real object surface sampling point set normal estimation method based on local Poisson curved surface constraint
PendingCN109636839AAvoid the effects of set sampling flawsImprove adaptabilityImage analysis3D modellingPattern recognitionSize determination
The invention provides a scattered point cloud normal estimation method based on local Poisson curved surface constraint. The method is characterized in that a spatial index structure is constructed for a sampling point set; based on the structure, a local sample of a target sample point and a local reconstruction sample containing an auxiliary point are rapidly obtained; then constructing a Frenet standard frame of a target sample point according to the local sample; a Poisson grid curved surface is constructed for a local sample in the Frenet standard frame; and querying the nearest neighborgrid surface patch of the target sample point from the Poisson grid curved surface, determining the weight value of the neighborhood surface normal direction according to the shape and size of the first-order neighborhood surface of the vertex of the grid surface patch, calculating the nearest neighbor grid surface patch vertex normal direction, and taking the weighted sum of the nearest neighborgrid surface patch vertex normal directions as a robust estimation result of the sample point normal direction. An example proves that the method is suitable for scattered point cloud data of a complex curved surface, has a good normal calculation result for point clouds with noise and non-uniform sampling, and realizes normal smooth transition of sample points.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
High-fidelity triangular mesh smoothing algorithm
PendingCN111145357APreserve Geometry InformationSmooth effectImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionTheoretical computer scienceVertex normal
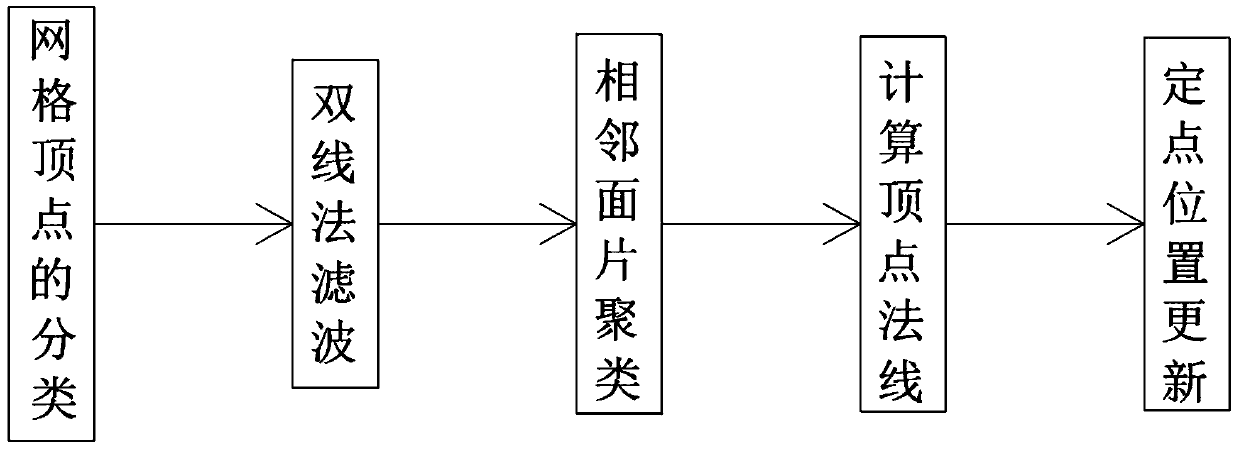
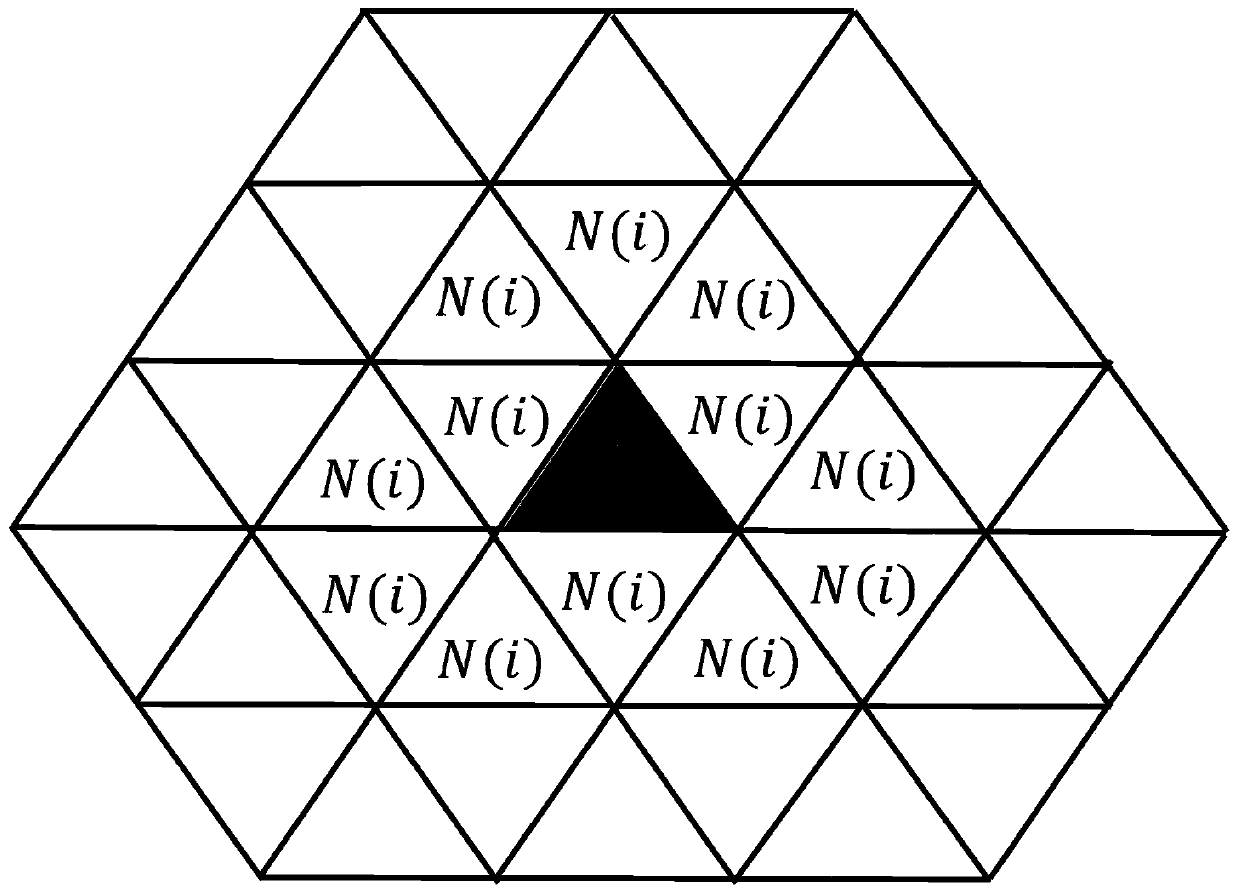
The invention discloses a high-fidelity triangular mesh smoothing algorithm which comprises the following steps: step 1, classifying mesh vertexes; step 2, filtering by a double-line method; step 3, clustering adjacent patches; step 4, calculating vertex normals; the invention belongs to the technical field of triangular mesh smoothing algorithms, and particularly relates to a high-fidelity triangular mesh smoothing algorithm, which not only can effectively protect geometrical characteristic information of an original mesh, but also can effectively smooth the original mesh, and is robust.
Owner:浙江影加医疗设备有限公司
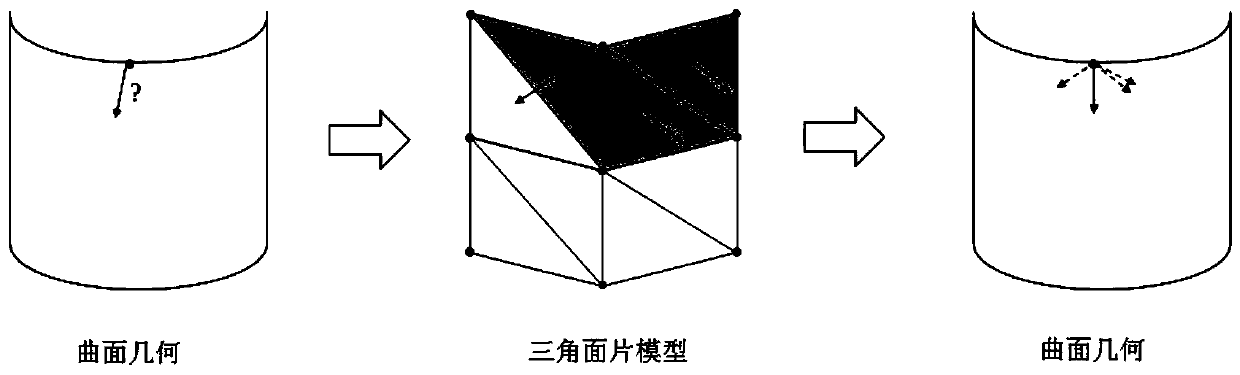
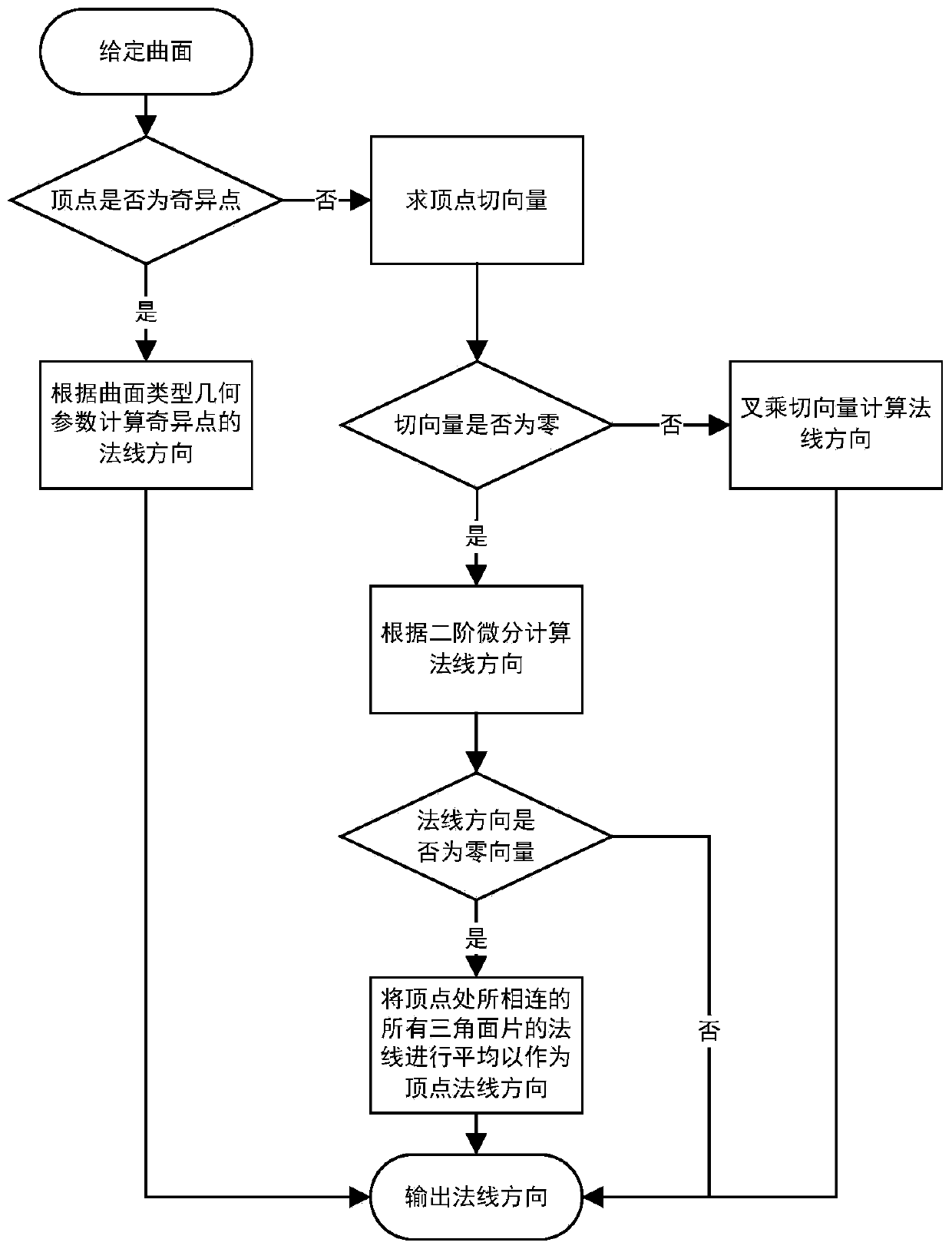
Improved method for calculating vertex normal of curved surface grid in grid division
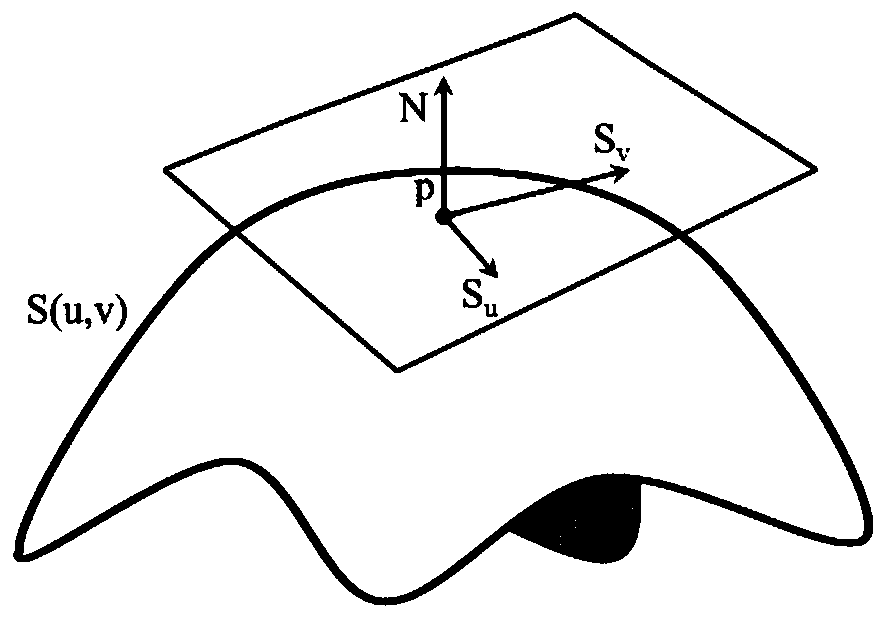
An improved method for curved surface grid vertex normal calculation in grid division comprises the steps: S1, judging whether the vertex of a given curved surface is a singular point or not: if yes,executing the step S2, and otherwise, executing the step S3; S2, based on the geometric parameters of the given curved surface, calculating the normal direction of the singular point, and entering S7;S3, solving a tangent vector in the UV direction at the vertex, judging whether the tangent vector is zero or not: if so, entering S4, and otherwise, entering S5; S4, calculating the normal directionof the vertex, judging whether the normal direction is a non-zero vector or not: if yes, entering S7, and otherwise, entering S6; S5, obtaining the normal direction through cross multiplication of the two tangent vectors, executing the step S7; S6, averaging the normal lines of all the triangular patches connected to the vertex to serve as a vertex normal line direction, and entering S7; S7, outputting a normal direction; S8, when a point set is generated based on the boundary of the triangular patch model, interpolating to generate the point set on the boundary according to the normal direction, and performing triangular mesh generation on a given curved surface.
Owner:上海索辰信息科技股份有限公司
A volume cloud rendering method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN112200900BReduce the number of adoptionsReduce performance overhead3D-image renderingComputational scienceAlgorithm
The present application relates to a volume cloud rendering method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium, the method comprising: drawing the original grid model of the volume cloud according to the vertex normal vector to draw at least one layer of grid model; The noise threshold corresponding to the grid model screens the pixels of the grid model to obtain a rendering model; calculates the illumination information corresponding to the rendering model according to the illumination parameters; renders the rendering model according to the illumination information to obtain Volumetric cloud to be displayed. The shape of the volumetric cloud in this technical solution is determined based on the grid model, rather than the shape of the noise map. If you want to change the shape of the volumetric cloud, you only need to set the number of additional layers drawn and the noise threshold for filtering pixels. , there is no need to pre-select a specific noise map; reducing the number of noise maps used further reduces the performance overhead of generating volumetric clouds, making volumetric clouds run smoothly on mobile devices.
Owner:CHENGDU PERFECT WORLD NETWORK TECH CO LTD
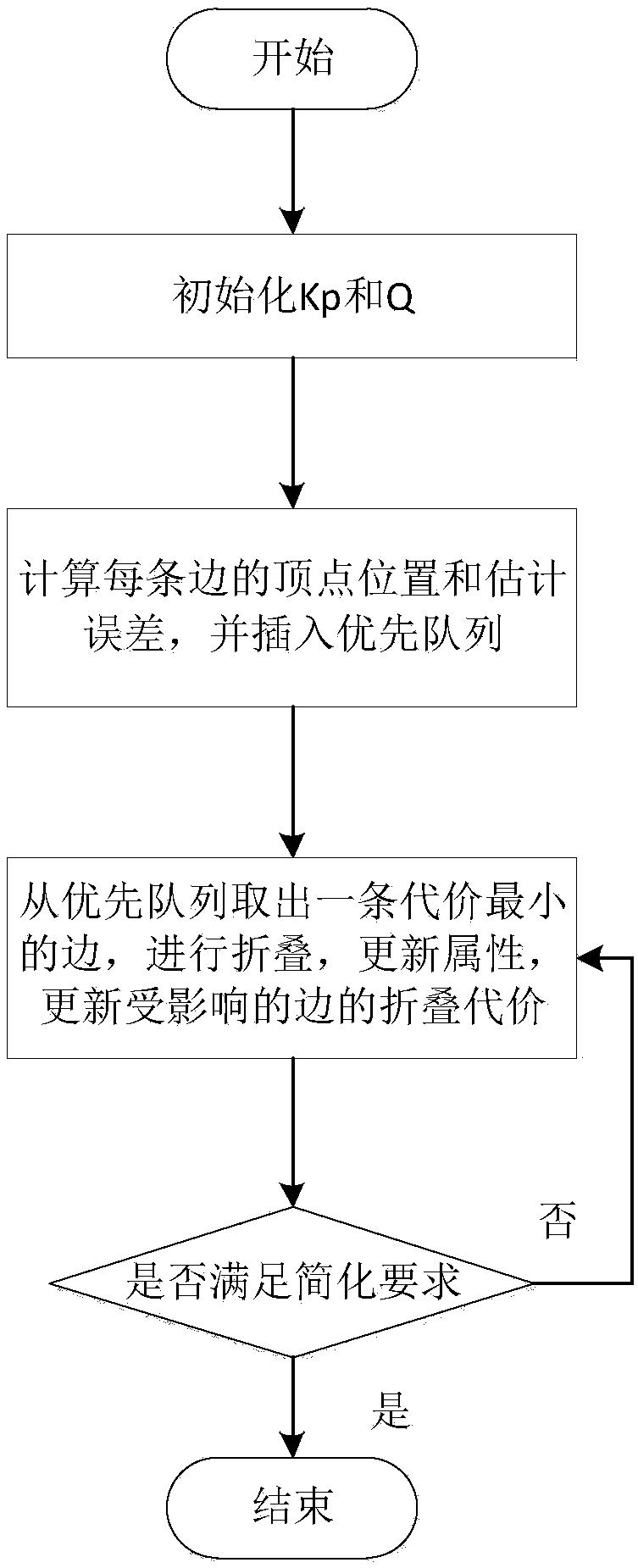
Area and normal vector-based grid simplification method for unsmooth surfaces
The invention discloses a grid simplification method considering the area and normal vector for the non-smooth surface. The estimated error of each edge folding and the position of the new vertex, the normal vector constraint is included in the cost of the new vertex after folding, the minimum folding cost and the corresponding position of the new vertex and the original vertex are stored in the vertex attribute, and the folding error Insert into the priority queue; take out the edge with the least folding cost from the queue, fold it, and update the relevant vertices and faces; until the set simplification conditions are satisfied. The present invention can keep the detail features of the original model as much as possible while quickly simplifying the grid. Especially for some non-fluid and non-smooth surfaces, compared with the traditional method, this method can better preserve the details and achieve a more prominent simplification effect, thereby improving the overall simplification effect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
MatCap algorithm for texture sampling based on line-of-sight direction
InactiveCN108665407ANo offsetAccurate Texture SamplingImage analysisGeometric image transformationPattern recognitionField of view
The invention relates to a MatCap algorithm for texture sampling based on a line-of-sight direction. A new transformation matrix is used for transforming the new Matcap algorithm of vertex normals, obtained results are equally accurate at any position in the field of view, there is no offset, and accurate texture sampling based on the line-of-sight direction is achieved.
Owner:武汉山骁科技有限公司
Radiation rendering method and device for finite element model
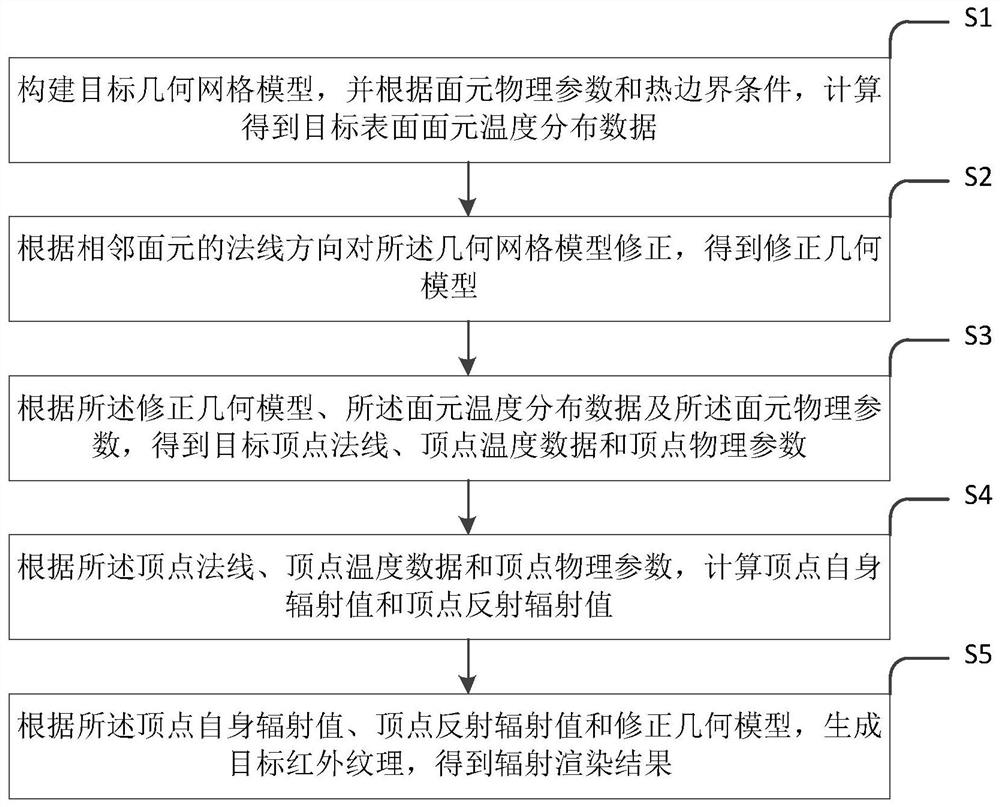
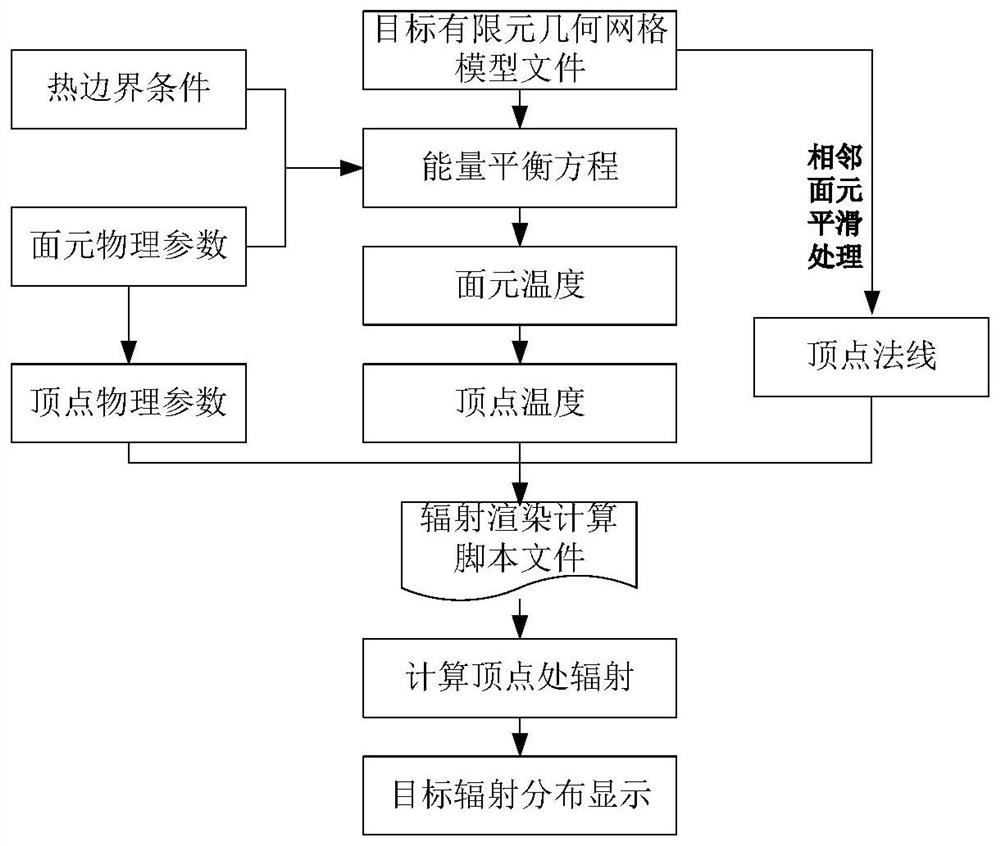
ActiveCN111881610AImprove simulation realismRealize real-time rendering calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTarget surfaceElement model
The invention relates to a radiation rendering method and device for a finite element model, and the method comprises the steps: building a target geometric grid model, and carrying out the calculation to obtain target surface element temperature distribution data according to surface element physical parameters and thermal boundary conditions; correcting the geometric grid model according to thenormal directions of the adjacent surface elements to obtain a corrected geometric model; obtaining a target vertex normal, vertex temperature data and vertex physical parameters according to the corrected geometric model, the surface element temperature distribution data and the surface element physical parameters, and then calculating a vertex self radiation value and a vertex reflection radiation value; and finally, generating a target infrared texture according to the vertex radiation value, the vertex reflection radiation value and the corrected geometric model to obtain a radiation rendering result. According to the method, excessive smoothing processing of adjacent surface elements at the edge of the target edge is avoided, and the simulation authenticity of a finite element model radiation rendering result is effectively improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
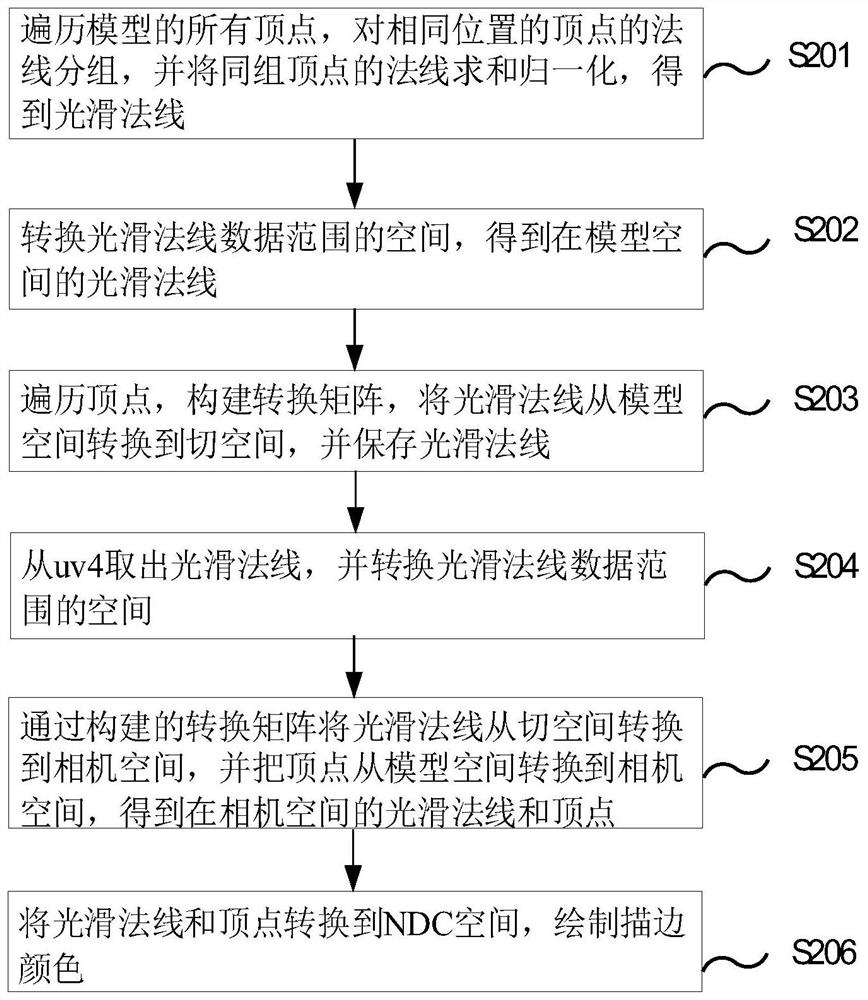
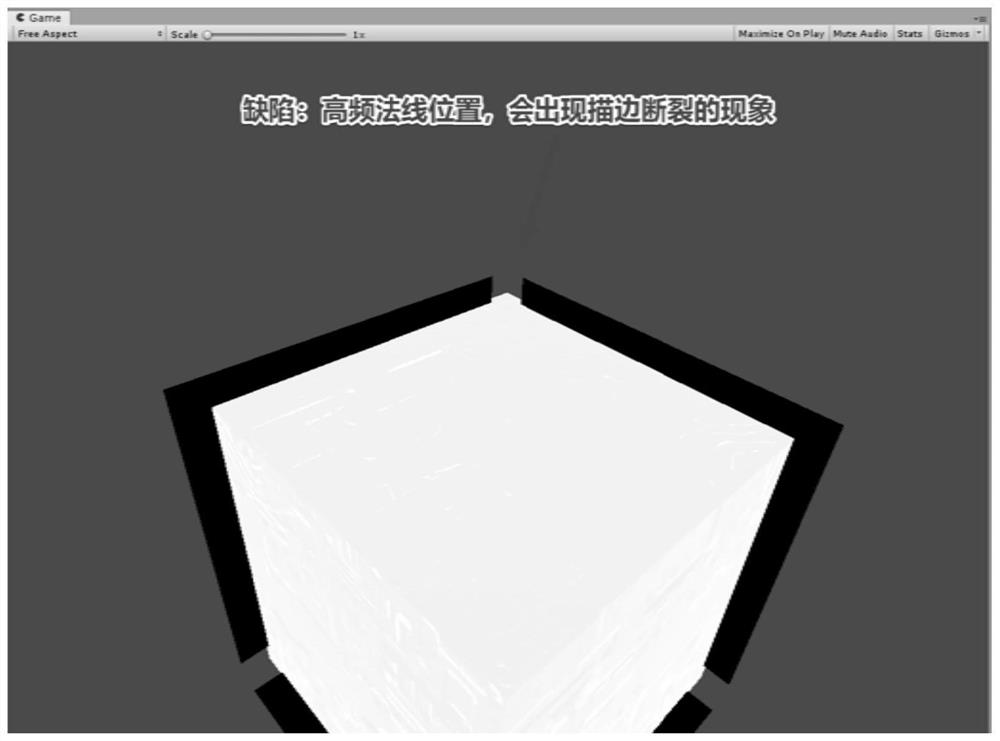
Rendering optimization method and system for stroking effect, electronic device and storage medium
PendingCN112270726ASolve the problem of broken strokesGuaranteed performanceImage analysisDrawing from basic elementsComputer graphics (images)Algorithm
The invention relates to a rendering optimization method and system for a stroking effect, an electronic device and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps of traversing all vertexes of amodel, carrying out the grouping of the normal lines of the vertexes at the same position, and carrying out the summation normalization of the normal lines of the vertexes in the same group, and obtaining a smooth normal line; converting the smooth normal data range space to obtain a smooth normal in the model space; traversing vertexes, constructing a conversion matrix, converting a smooth normal from a model space to a tangent space, and storing the smooth normal; taking out a smooth normal from uv4, and converting the space of the data range; converting the smooth normal from the tangent space to the camera space through the constructed conversion matrix, and converting the vertex from the model space to the camera space; and finally, converting the smooth normal and the vertex into anNDC space, and drawing a stroking color. The problem of stroking breakage during high-frequency normal stroking is solved, and an excellent stroking effect can be rendered in real time while the performance is ensured on a mobile platform.
Owner:HANGZHOU ELECTRONICS SOUL NETWORK TECH
Three-dimensional visualization method for electromagnetic environment body data
InactiveCN102254347BFull internal detailsComplete representation internal details3D modellingBoundary contourGraphics
The invention belongs to the technical field of electromagnetic environment visualization, and discloses a three-dimensional visualization method for electromagnetic environment body data. The method comprises the following steps of: determining the electromagnetic environment body data by a radio wave propagation physical model; dividing the electromagnetic environment body data into a tetrahedron structure, forming a two-dimensional texture in a vertex index manner according to the vertexes of the tetrahedron, and inputting a tetrahedron vertex function value texture and a vertex index texture into a graphics processor; generating contour surface vertexes according to predetermined contour surface threshold judgment, connecting the contour surface vertexes of same threshold into a contour surface, and forming a plurality of contour surfaces of the electromagnetic environment; and displaying the edge of an electromagnetic environment model in a manner of extruding according to a relation between vertex normal vectors and view points, and fusing and embedding the plurality of contour surfaces into the three-dimensional environment in a semitransparent manner. With the method, the three-dimensional electromagnetic environment can be represented visually and intuitively, more internal information representation of the electromagnetic environment are provided, and the correctnessand the completeness of the electromagnetic environment representation and the definition of a boundary contour are all improved.
Owner:中国人民解放军装备指挥技术学院
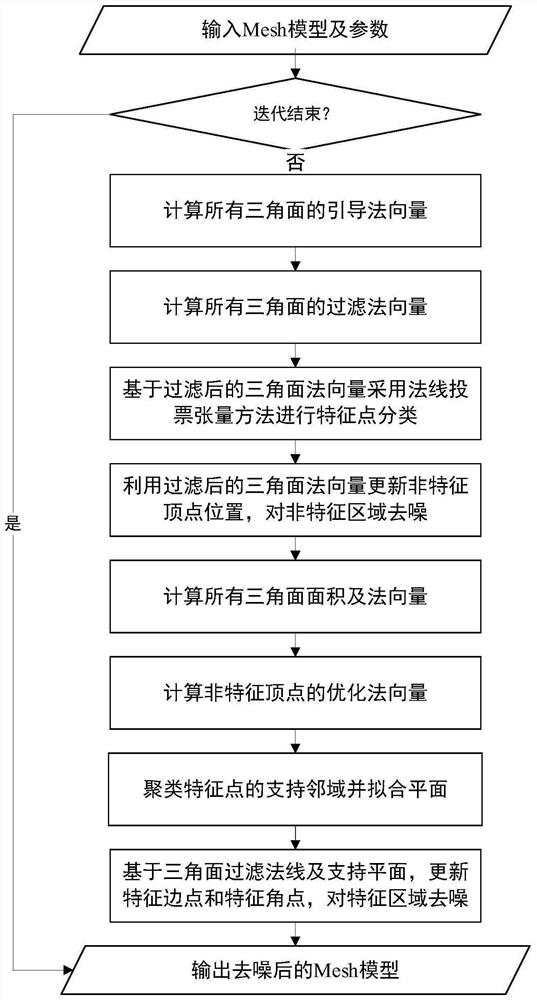
Three-dimensional Mesh model denoising method capable of reserving features
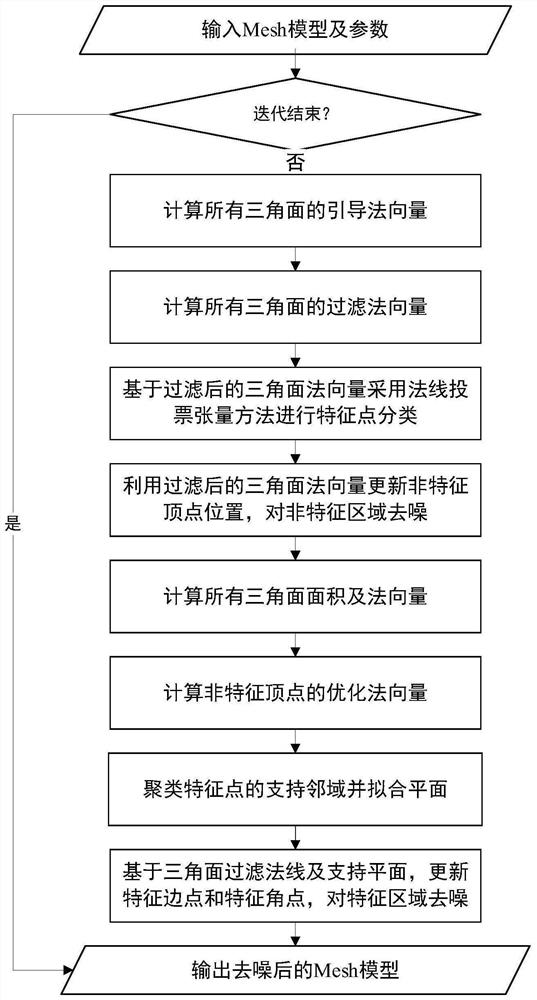
ActiveCN112529803AImprove fidelityEffective classificationImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorNoise removal
The invention relates to a three-dimensional Mesh model denoising method capable of reserving features. The method comprises steps of firstly, calculating guide normal vectors of all triangular surfaces, and using the guide normal vectors for filtering the normal vectors of all the triangular surfaces based on a joint bilateral filtering algorithm; secondly, classifying feature points by using thefiltered triangular surface normal vector based on a normal voting tensor method, enhancing weak features, and removing pseudo features; then, updating non-feature vertexes based on the normal vectorconstraint terms after neighbor triangular surface filtering, and denoising a non-feature region to obtain optimized normal vectors of non-feature points; clustering a support neighborhood point setof the feature points according to the similarity of the feature vectors of the tensor matrix and the vertex normal vectors, and fitting a support plane of the feature points; and finally, updating the feature points based on the normal vector constraint term of the neighbor triangular surface and the constraint term of the support plane, and denoising the feature region. According to the method,the problems of feature oversmoothness and feature loss in the denoising process of the three-dimensional Mesh model can be solved, so that the three-dimensional Mesh model with features reserved after noise removal is obtained.
Owner:深圳市数字城市工程研究中心 +1
A feature-preserving 3D mesh model denoising method
ActiveCN112529803BImprove fidelityEffective classificationImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorNoise removal
The invention relates to a feature-preserving three-dimensional Mesh model denoising method. First calculate the guide normal vectors of all triangle faces, and use the guide normal vectors to filter the normal vectors of all triangle faces based on the joint bilateral filtering algorithm; secondly, use the filtered triangle face normal vectors to classify feature points based on the normal voting tensor method, and enhance Weak features and false features are eliminated; then, the non-feature vertices are updated based on the normal vector constraint items filtered by the neighbor triangles, the non-feature areas are denoised and the optimized normal vectors of the non-feature points are obtained; then according to the eigenvectors of the tensor matrix and Vertex normal vector similarity clusters the support neighborhood point set of the feature point, and fits the support plane of the feature point; finally, the feature point is updated based on the normal vector constraint item of the neighbor triangle surface and the constraint item of the support plane, and the feature area is removed. noise. This method can solve the problem of feature over-smoothing and feature loss in the denoising process of the 3D Mesh model, so as to obtain a 3D Mesh model that retains features after noise removal.
Owner:深圳市数字城市工程研究中心 +1
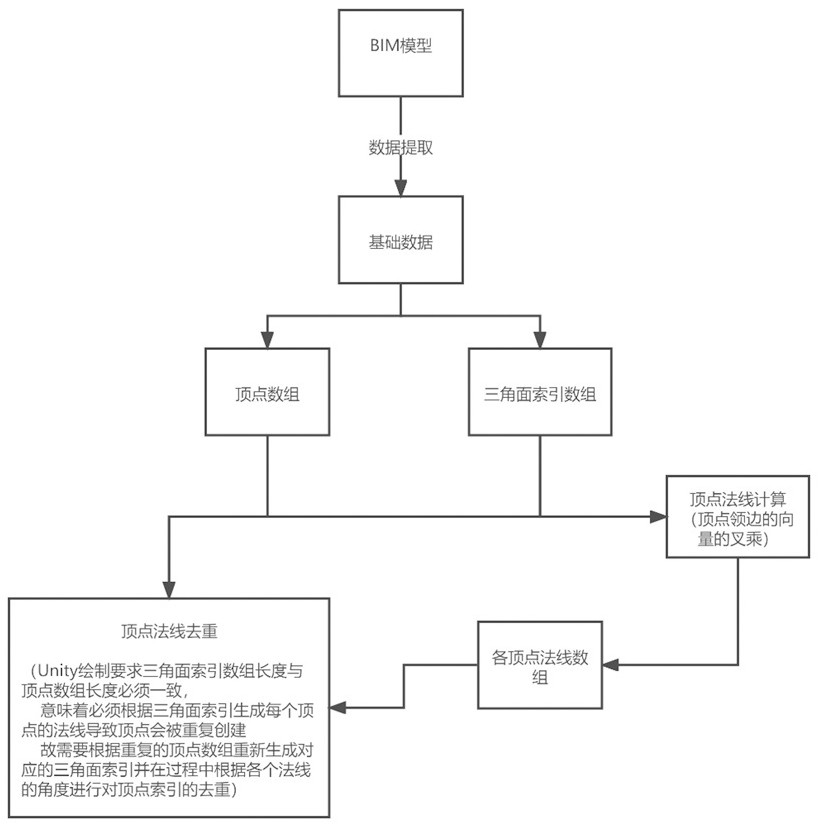
BIM model surface reduction method based on vertex normal angle calculation
PendingCN114565718AAchieve cullingReduce in quantity3D modellingAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a BIM (Building Information Modeling) surface reduction method based on vertex normal angle calculation, which is characterized in that triangular patch data and vertex data optimization is carried out on a large BIM through a mathematical algorithm, the number of triangular patches and the number of vertexes of the BIM are reduced fundamentally, and lightweight processing of BIM data is completed. The method has the advantages that effective and invalid surface patch and vertex data can be calculated and distinguished according to the original vertex and surface patch data of the BIM model and the lightweight level of the original vertex and surface patch data, and the effective and invalid surface patch and vertex data are automatically and reasonably processed, so that invalid model primitives are removed, the number of geometric elements of the model is reduced, and the efficiency is improved. The method has the advantages of high automation degree, difficulty in making mistakes, high processing speed and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI TUNNEL ENGINEERING RAILWAY TRANSPORTATION DESIGN INSTITUTE
Vertex color rendering and baking method and system applied to unity engine
ActiveCN108257204BLess quantitySmall footprint3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Engineering
The present invention provides a vertex color drawing and baking method and system applied to the Unity engine. The method includes reading the vertex position and vertex normal of each vertex in the grid model; According to the direction of the vertex normal of a vertex, render the vertex; traverse each vertex, and perform the rendering operation one by one; obtain the corresponding sampling color according to the rendering texture of each vertex, and write it into the vertex color information . The invention can not only reduce the storage capacity of AO information, but also improve the baking efficiency; further, the model has high correlation, which is convenient for post-editing; finally, it can also support custom fine-tuning of the baked vertex color.
Owner:福建省天奕网络科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com