Optical lead-out method for vertex normal of large-caliber concave non-spherical reflector
A spherical mirror and mirror technology, which is applied in the field of using optical interference technology, can solve problems such as the limitation of extraction precision, and achieve the effect of ensuring quality and increasing the precision of normal extraction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
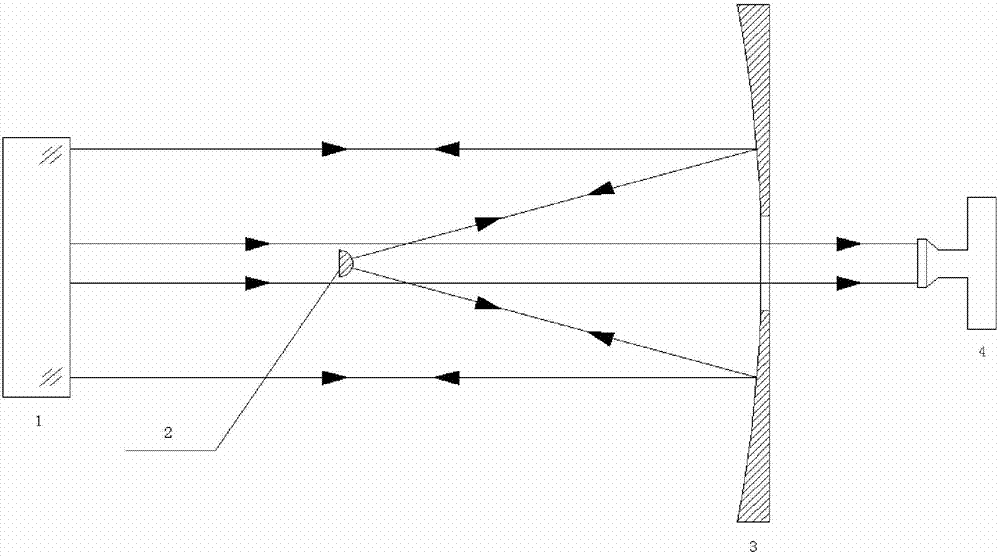
[0013] Such as figure 1 As shown, the hardware used in the present invention includes an optical interferometer 1 , a standard spherical mirror 2 , a measured concave aspheric mirror 3 , and a theodolite 4 .
[0014] (1) Place the optical interferometer 1, the measured concave aspheric mirror 3, the standard spherical mirror 2, and theodolite 4 coaxially, and the center of the standard spherical mirror 2 coincides with the focus of the measured concave aspheric mirror 3 . Use a paper ruler to measure the distance between the left edge of the light spot of the parallel light beam emitted by the optical interferometer 1 hitting the concave aspheric mirror 3 under test and the left edge of the concave aspheric mirror 3 under test. Use a paper ruler to measure the distance between the right edge of the light spot of the parallel light beam emitted by the optical interferometer 1 hitting the concave aspheric mirror 3 under test and the right edge of the concave aspheric mirror 3 u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com