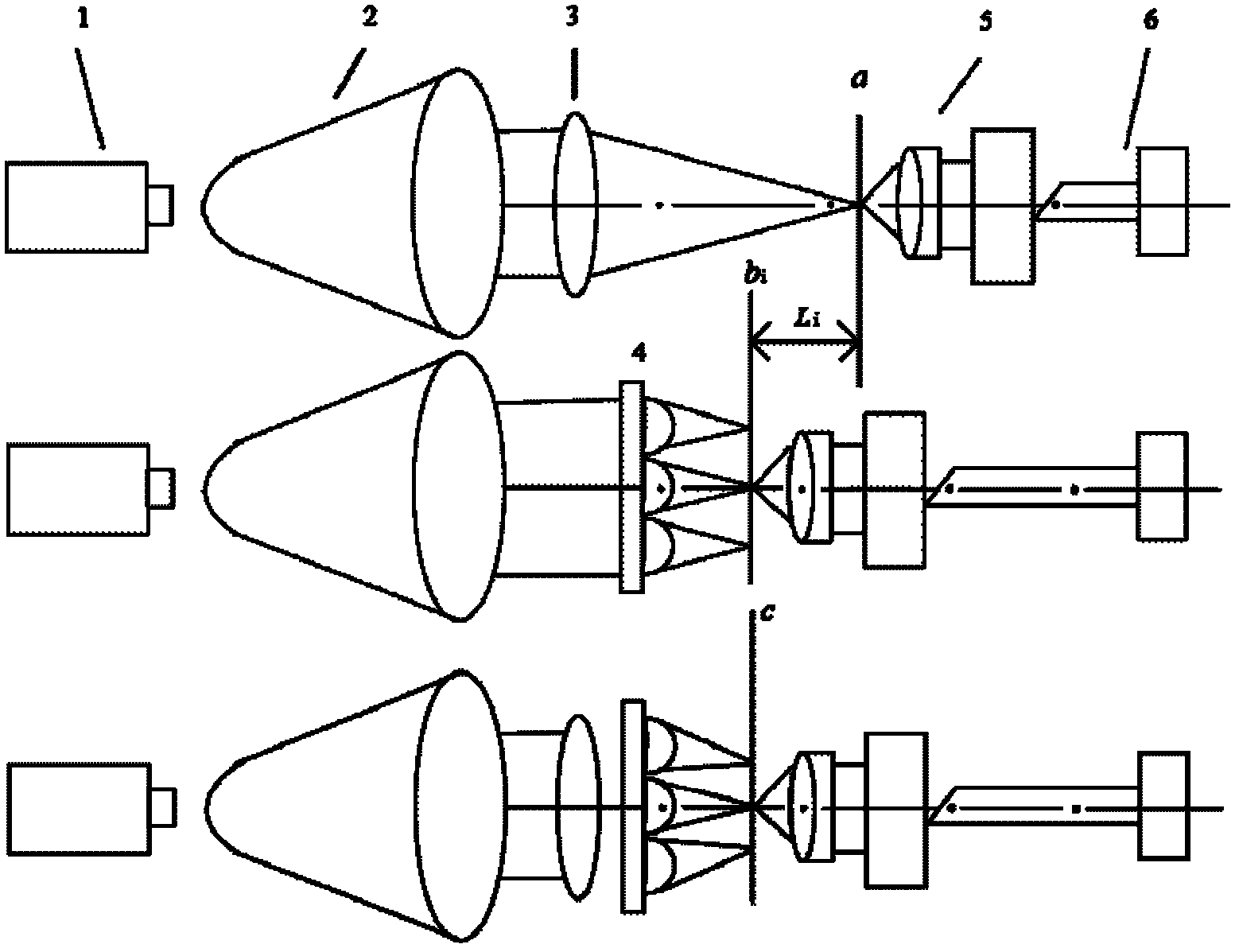
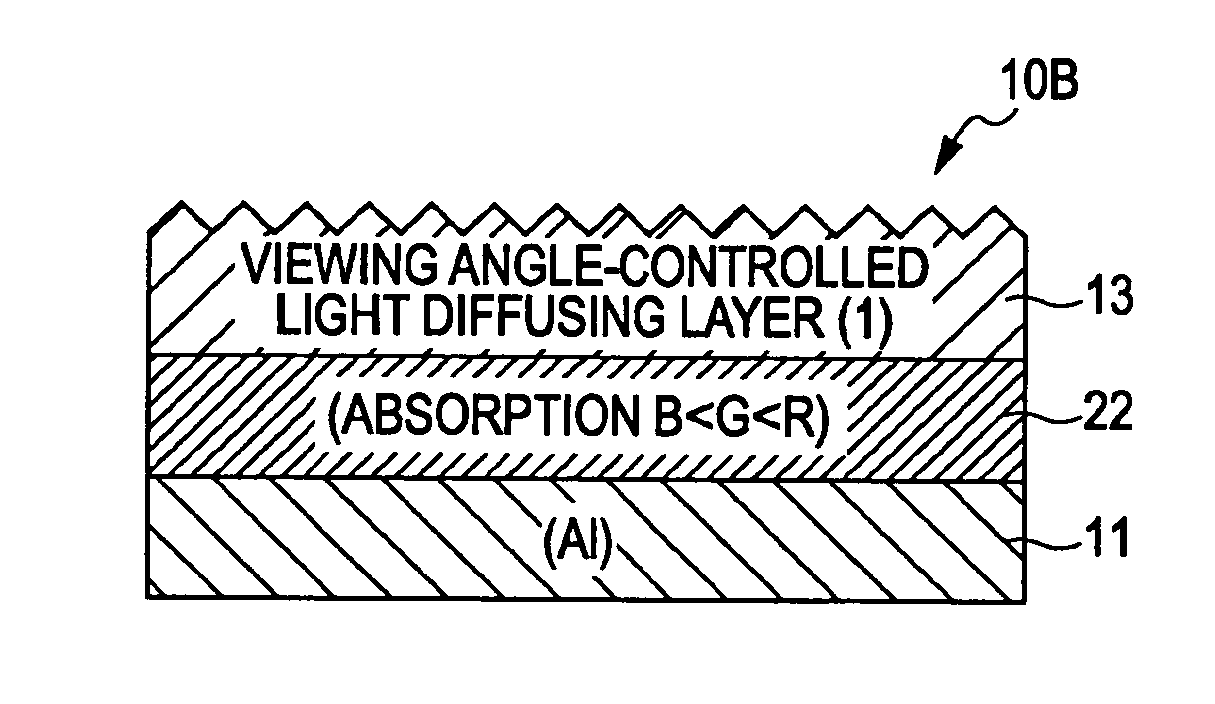
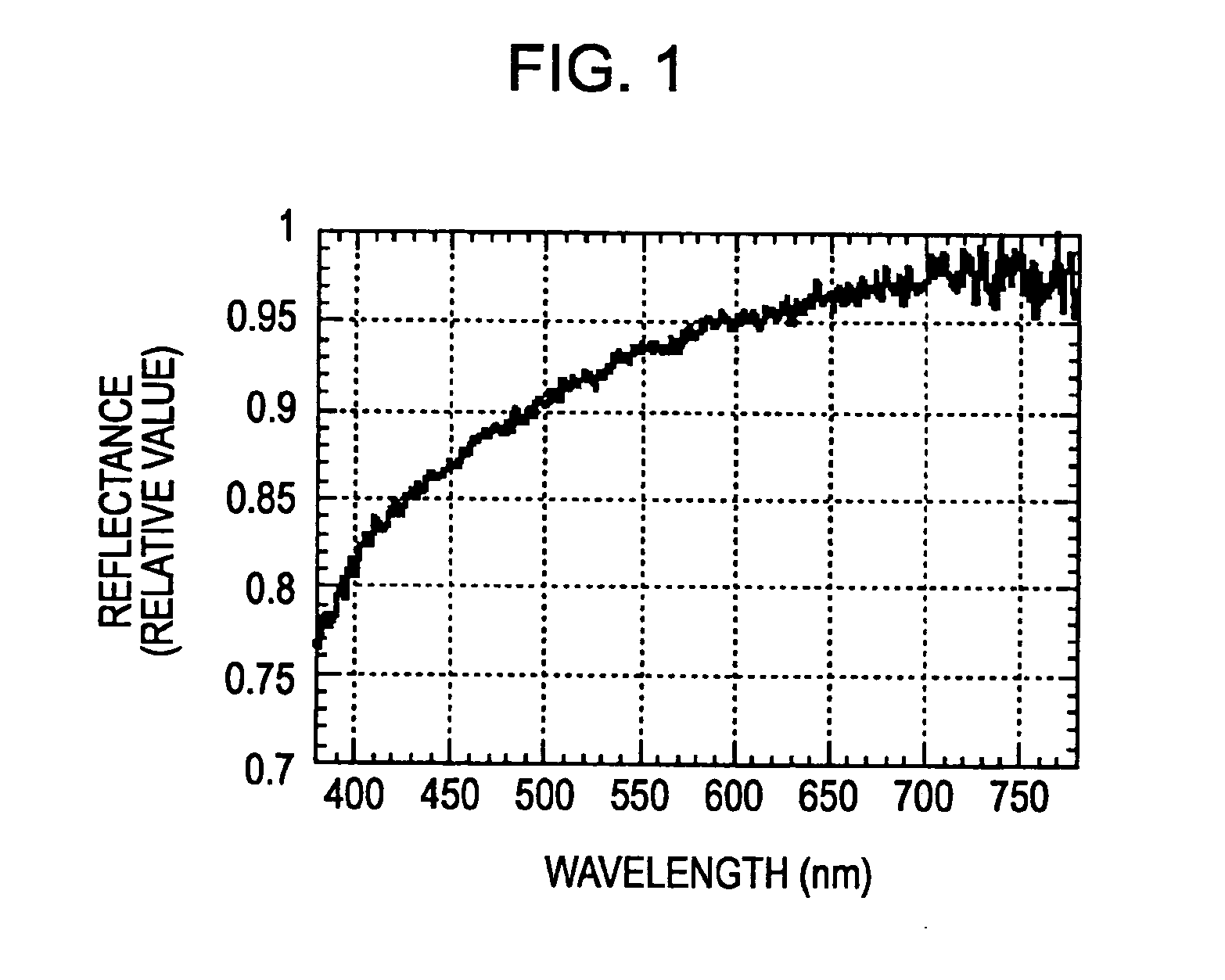
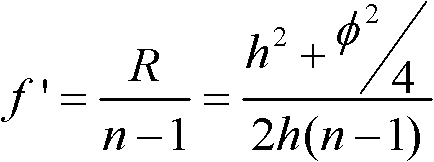Patents
Literature
272 results about "Normal waves" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Normal waves are of physical significance because any disturbance in a region free of sources may be represented as the superposition of normal waves, and the resultant elastic or electromagnetic energy flow is equal to the sum of the flows in all the normal waves.
Stacked waveguides having different diffraction gratings for combined field of view
ActiveUS20180275350A1Light source combinationsPicture reproducers using projection devicesWaveguideField of view
In one aspect, an optical device comprises a plurality of waveguides formed over one another and having formed thereon respective diffraction gratings, wherein the respective diffraction gratings are configured to diffract visible light incident thereon into respective waveguides, such that visible light diffracted into the respective waveguides propagates therewithin. The respective diffraction gratings are configured to diffract the visible light into the respective waveguides within respective field of views (FOVs) with respect to layer normal directions of the respective waveguides. The respective FOVs are such that the plurality of waveguides are configured to diffract the visible light within a combined FOV that is continuous and greater than each of the respective FOVs
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
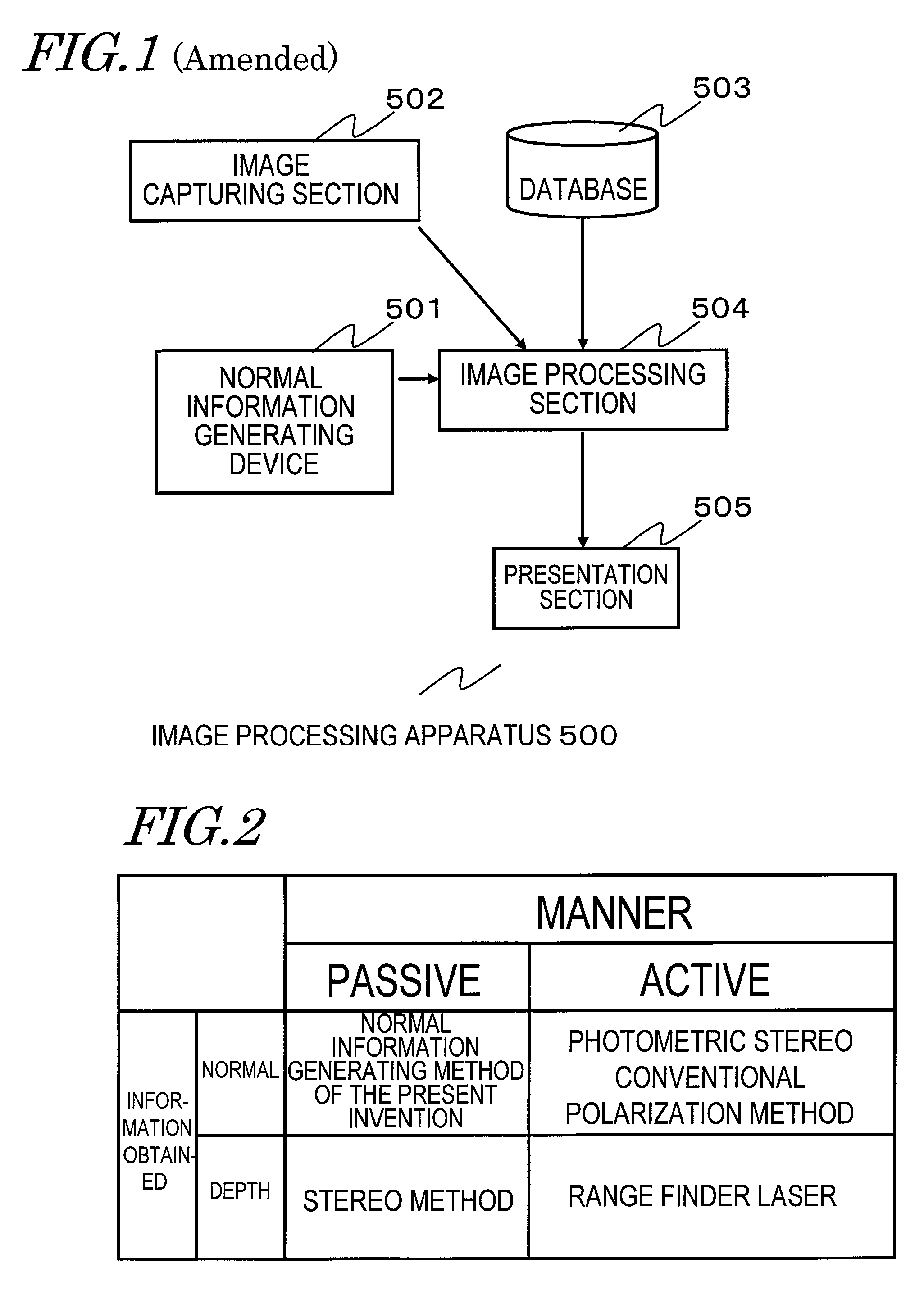
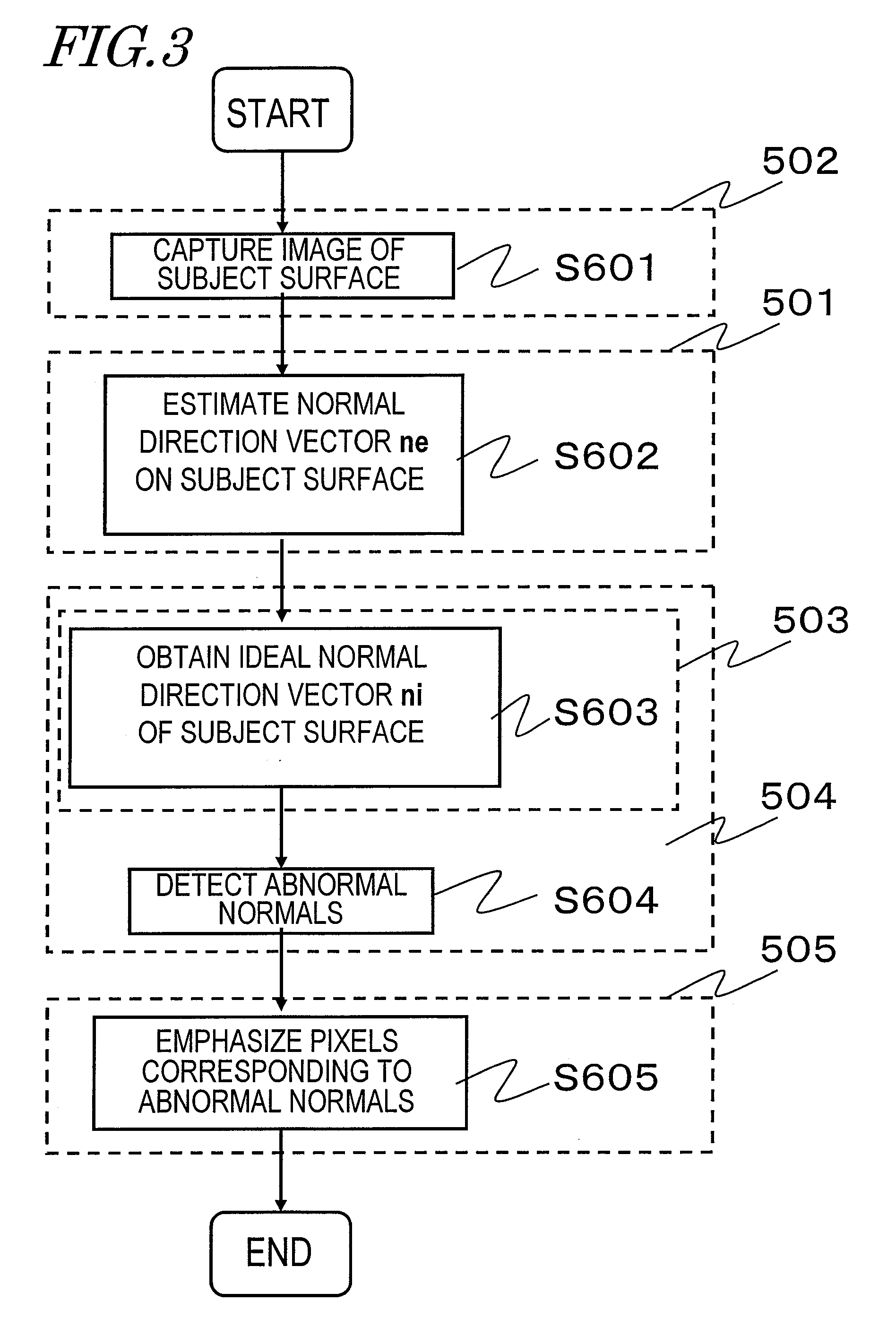
Image processing apparatus, method and computer program for generating normal information, and viewpoint-converted image generating apparatus
ActiveUS20100289878A1Improve accuracyReduce ambiguityImage analysisStereoscopic photographyImaging processingViewpoints
High-precision normal information on the surface of a subject is generated by capturing an image of the subject. A normal information generating device captures the image of the subject and thereby passively generates normal information on the surface of the subject. The normal information generating device includes: a stereo polarization image capturing section for receiving a plurality of polarized light beams of different polarization directions at different viewpoint positions and obtaining a plurality of polarization images of different viewpoint positions; and a normal information generating section for estimating a normal direction vector of the subject based on the plurality of polarization images of different viewpoint positions.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Collimating illumination systems employing a waveguide
ActiveUS20140098558A1Improve directionalityMechanical apparatusCoupling light guidesLighting systemSurface shape
Owner:VASYLYEV SERGIY
Multichannel array waveguide diffraction grating multiplexer/demultiplexer and method of connecting array waveguide and output waveguide
InactiveUS20060177180A1Reduce connection lossSmall lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideMultiplexerWaveguide
An array waveguide diffraction grating optical multiplexer / demultiplexer having an input waveguide, an input side slab waveguide, an output side slab waveguide, an output waveguide, an array waveguide provided between the input side slab waveguide and output side slab waveguide having a length different sequentially between the adjacent waveguides, wherein the output waveguide is arranged so that the angle formed between each output waveguide and the normal line of the Rowland circle of the output waveguide is sequentially increased from the central output waveguide to the output waveguide at both ends of the central output waveguide, and asymmetry of the passband of the output waveguide based on the form of field distribution at a light collecting point of the output side slab waveguide is decreased.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Series connection fault arc pre-warning system and detection method thereof
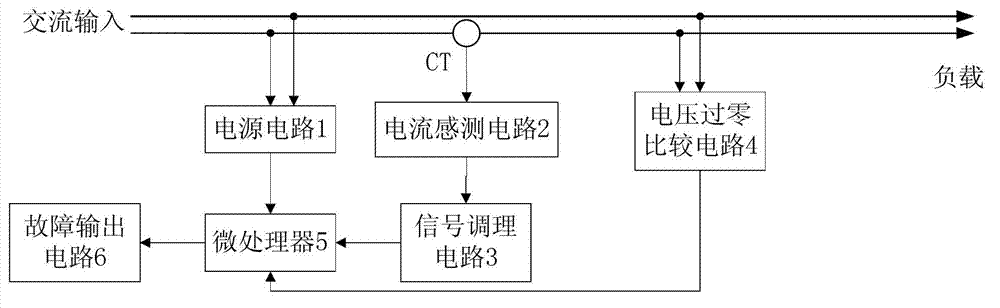
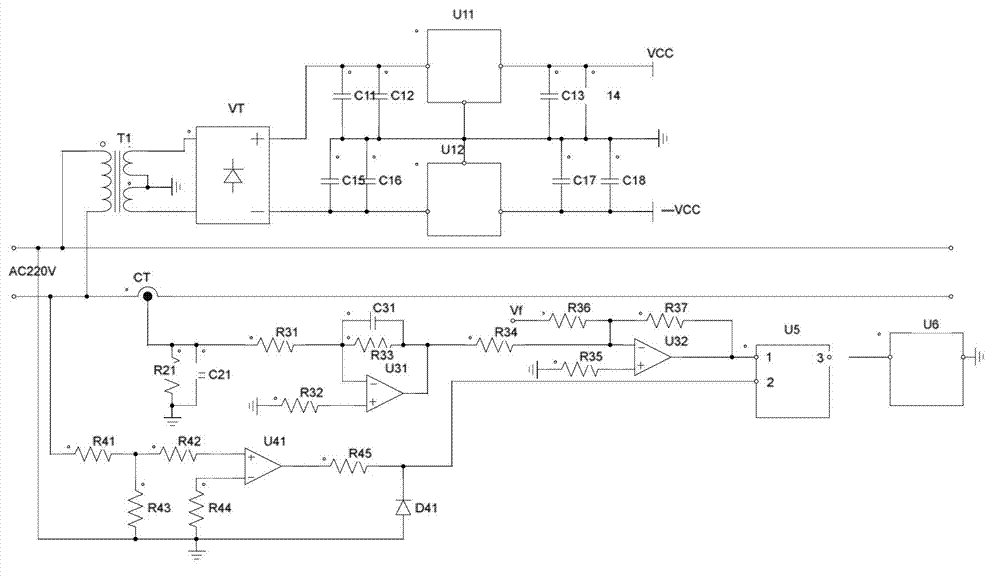
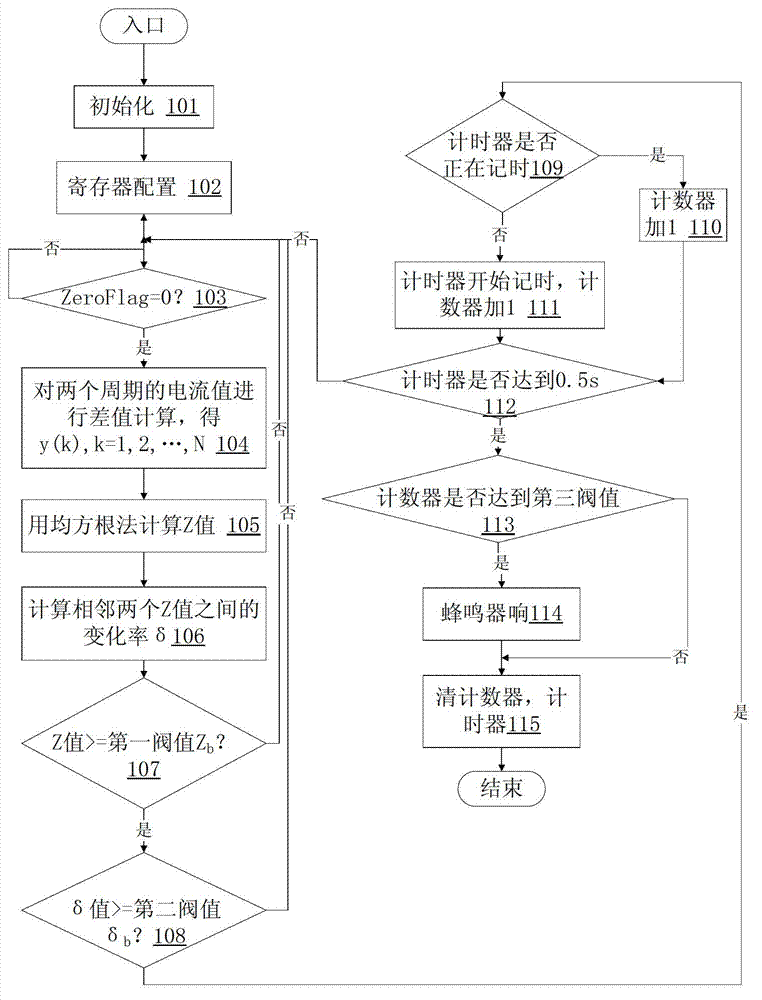
InactiveCN103116093AAccurately differentiate arc faultsAccurately distinguish normal waveformsElectrical testingSignal processing circuitsVIT signals
The invention provides a series connection fault arc pre-warning system. The series connection fault arc pre-warning system comprises a power circuit, a current transformer, a current sensing circuit, a signal processing circuit, a voltage zero balancing comparison circuit, a microprocessor and a fault output circuit. The current transformer, the current sensing circuit, the signal processing circuit and the microprocessor are successively connected. The voltage zero balancing comparison circuit and the fault output circuit are respectively connected with the microprocessor. The current transformer collects a current signal in a power network to transform the current signal into a voltage signal through the current sensing circuit to input to the microprocessor through the signal processing circuit, and the voltage zero balancing comparison circuit outputs a voltage zero balancing pulse signal to the microprocessor. The invention further provides a series connection arc fault detection method. The series connection fault arc pre-warning system and the series connection arc fault detection method have the advantages that due to the fact that a signal is directly processed in time domain after sampling, the complicated Fourier transform is saved, the fault arc and normal wave form can be distinguished accurately, and the computation time is saved. The series connection fault arc detection can be achieved by the more economical microprocessor. The detection is reliable and effective, and effective and timely pre-warning information can be supplied to workers.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Pipeline crack far-field vortex checking method
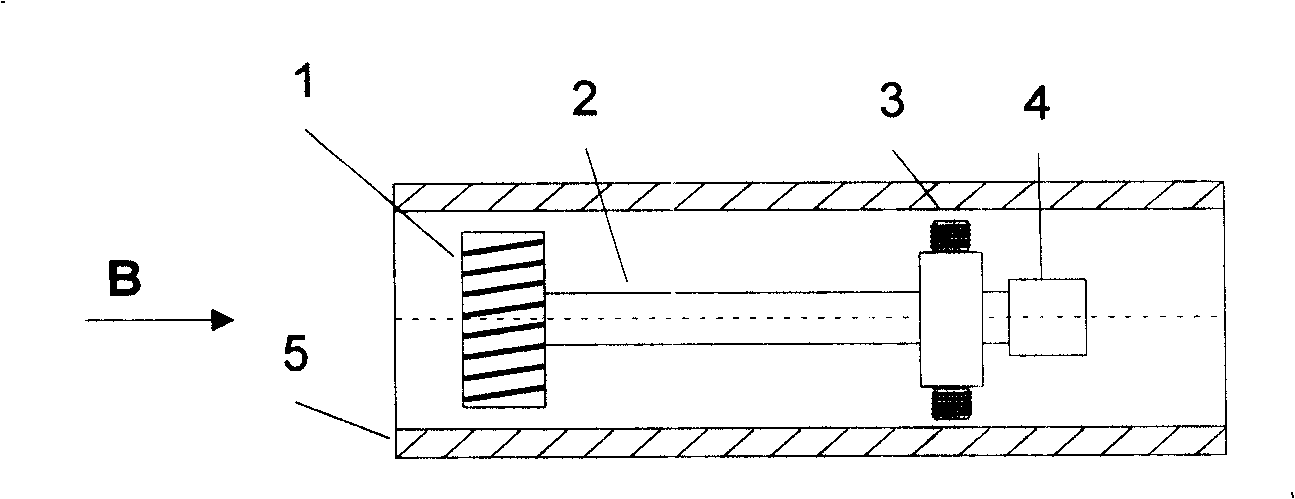
InactiveCN101261246ARealize detectionResponsivePipeline systemsMaterial magnetic variablesPhase differenceMagnetization
The invention discloses a pipeline crack far field vortex test method, belonging to the nondestructive testing technique field. The online test technique of the pipeline crack far field vortex in axial direction based on a circumferential magnetization principle is concretely realized in two different configuration methods of exciting coils: using a coil in radial direction with low frequency AC current as an exciting coil to produce a circumferential magnetic field, or using two coils which are placed crossly and the plane normals of which are vertical to each other as the exciting coil. The two coils are respectively electrified with low frequency AC current of the same amplitude but a phase difference of 90 degrees to produce a rotating magnetic field in a circumferential cross section of the pipeline, and the rotating magnetic field produces the circumferential magnetic field. The measurement of the test coils in circumferential layout in the far field area is indirectly coupled with magnetic field signals and the amplitude of signals and the change of signals relative to the phase difference of the exciting current show the existence of the defects of the cracks. The far field vortex technique based on the circumferential magnetization principle has the advantages of more intense function of the circumferential magnetic field and cracks of the pipeline wall in axial direction, which leading the test of cracks in axial direction to be easily realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
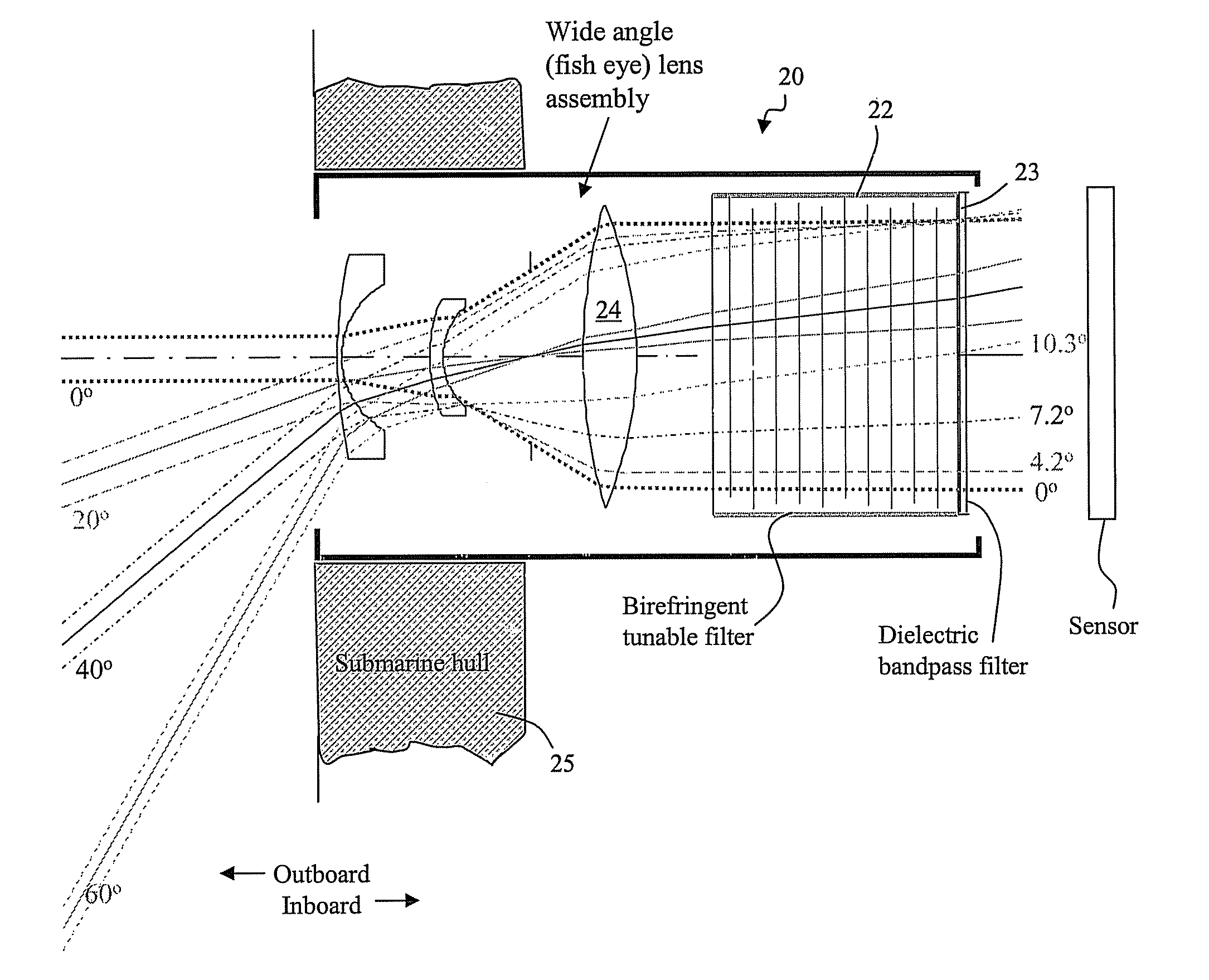
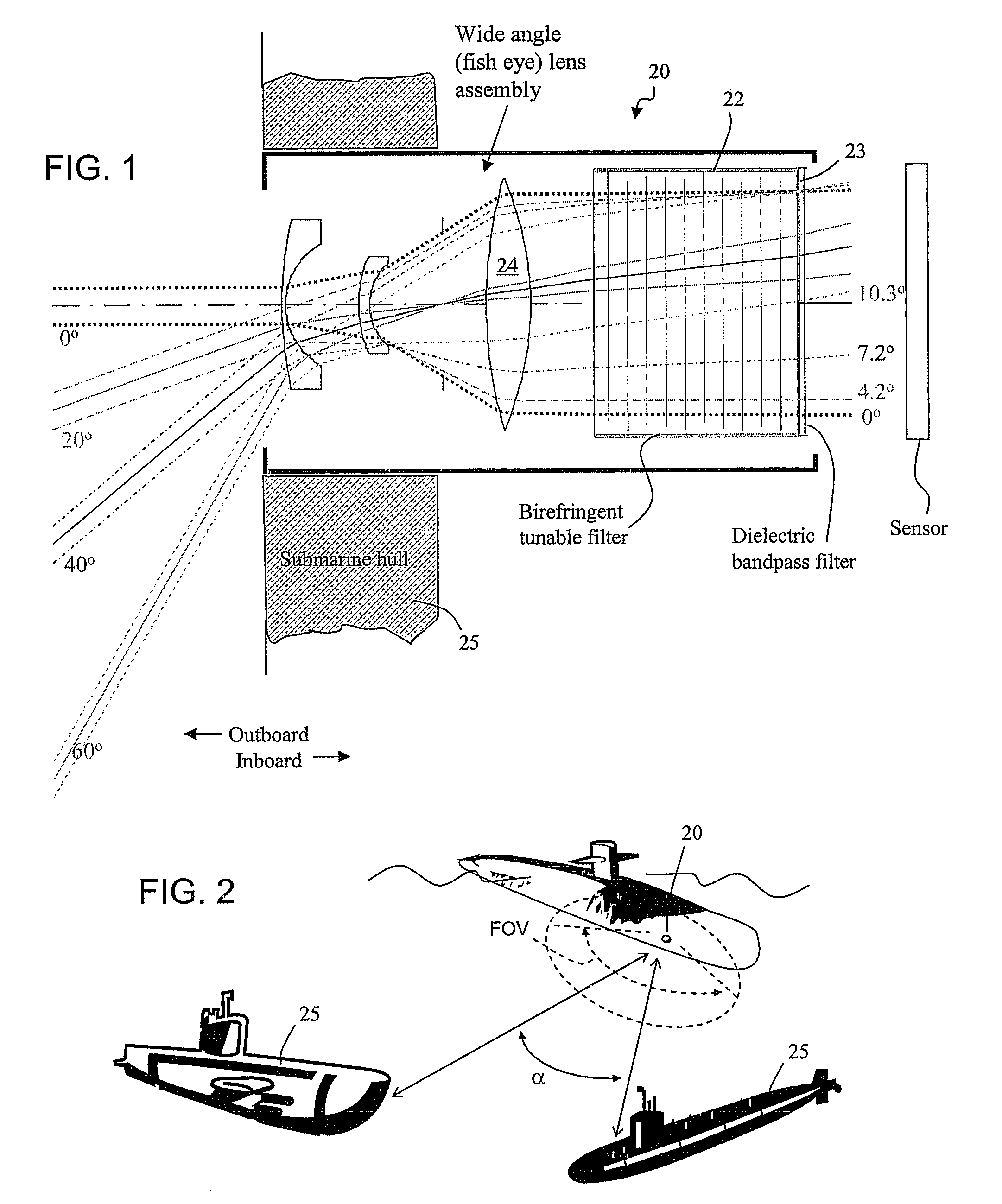
Birefringent spectral filter with wide field of view and associated communications method and apparatus
ActiveUS20070166045A1Wide field of viewPolarising elementsElectromagnetic transmissionOcean bottomPeak value
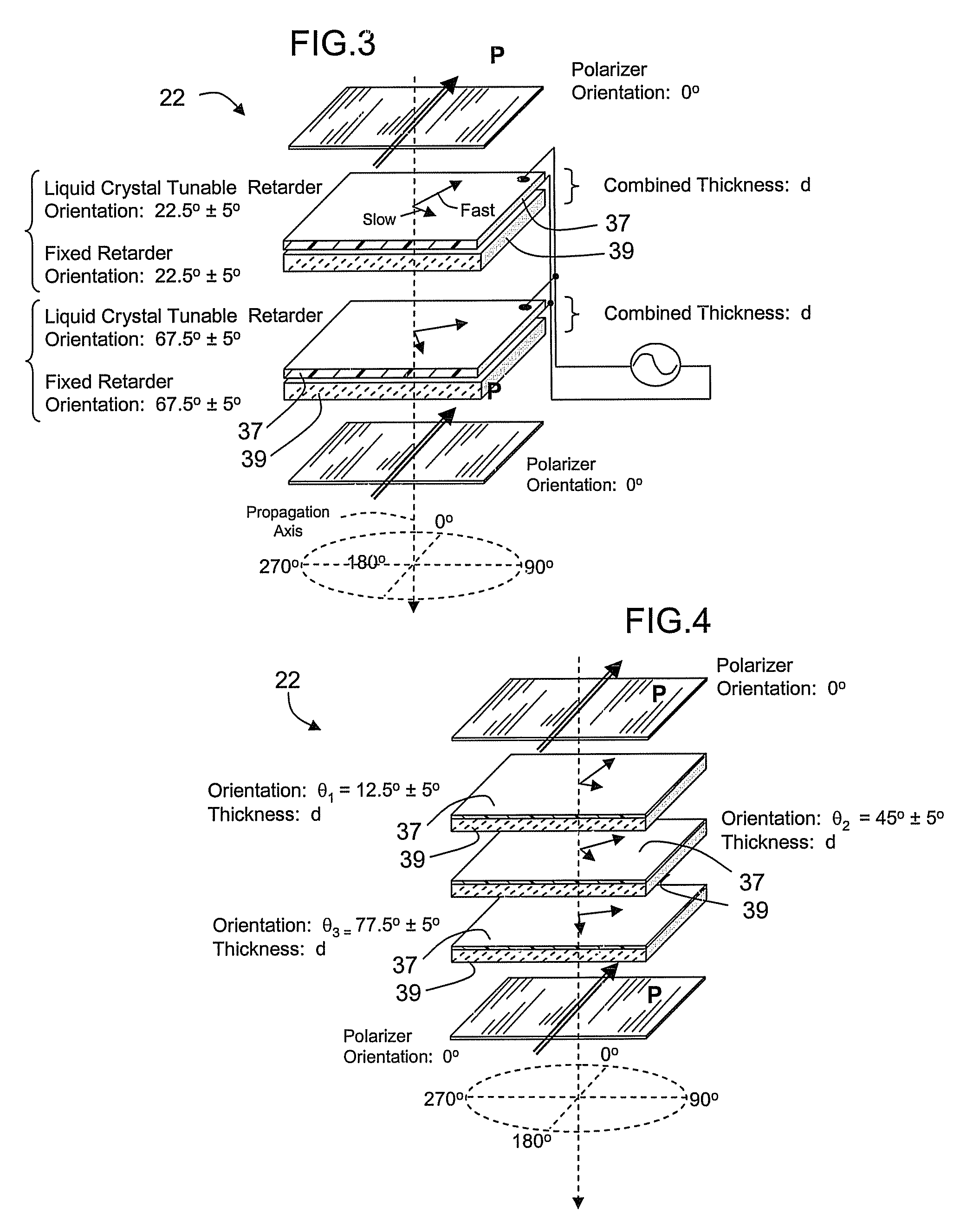
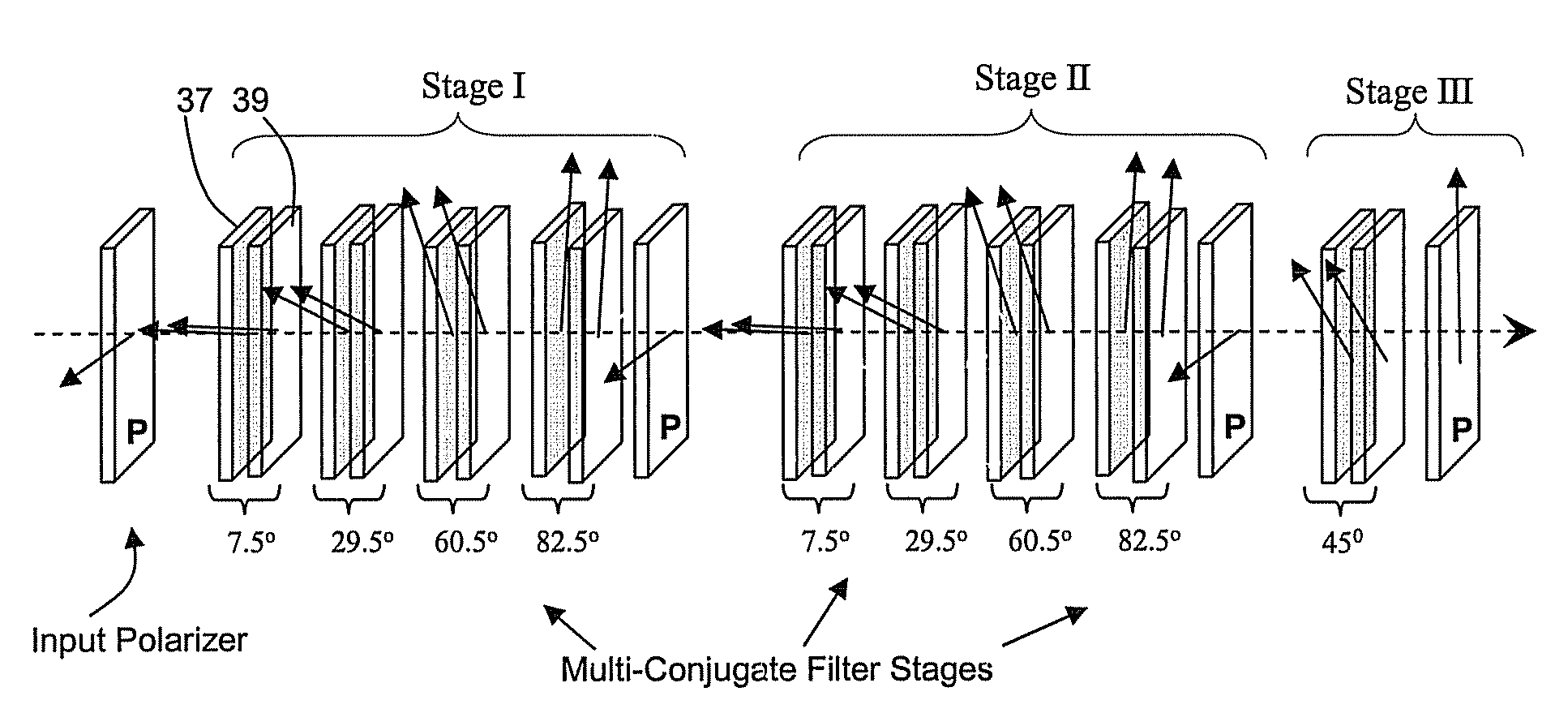
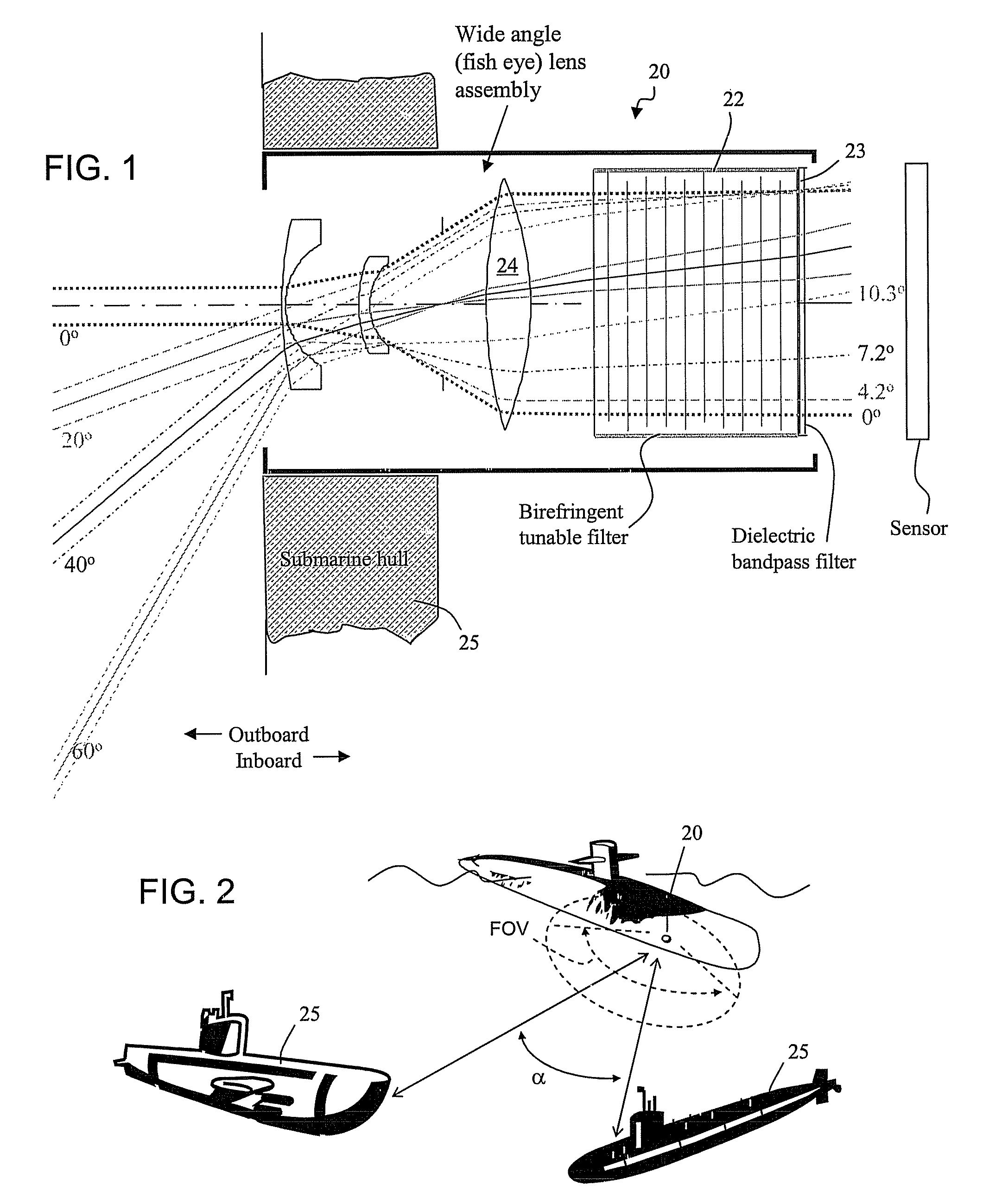
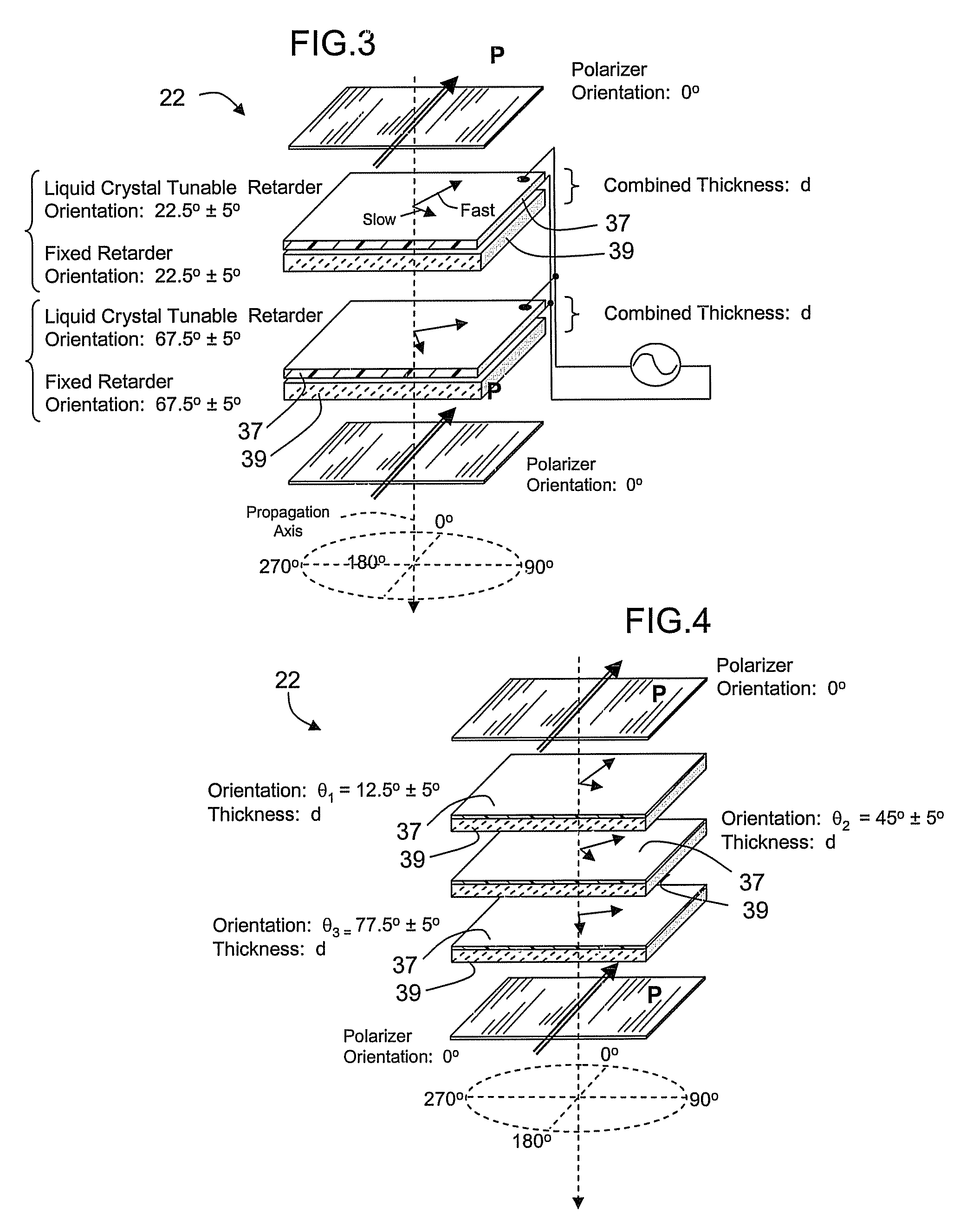
A spectral filter is adapted for use in a receiver, for example in a short range submarine laser signal path, wherein the relative orientations of the receiver is such that the signal may appear diffusely or at an unknown point in a wide external field of view around an optical axis of the receiver. A narrow band spectral filter in the receiver has cascaded stages of tunable retarders with includes multi-conjugate stages that tolerate light that is oblique to normal, up to a diverging internal field of view angle up to about 10°. A fisheye lens assembly refracts incoming light from a wider external field of 170° or more and directs the light into the filter over the narrow internal field of view. Calibration and feedback control can be provided to stabilize the discriminated wavelength peak, which remains at the same center wavelength over the span of the internal field of view notwithstanding the difference in retarder thicknesses traversed along paths that are normal to the retarders versus oblique to the optical axis.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
Surround sensing system with telecentric optics
ActiveUS20160200161A1Decrease the filling factorReduce lossesDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesBandpass filteringAngle of incidence
The invention pertains to a system comprising: a source to generate a pulsed radiation pattern; a detector; a processor to process data from the detector when radiation is reflected by an object; a synchronization means interfacing between the detector and the source; wherein: the detector is synchronized with the source so that radiation to be processed is detected only during the pulses, the processor determines a characteristic of the object by determining displacement of detected spots with reference to predetermined positions, the source emits monochromatic light and the detector is equipped with a bandpass filter and optics arranged so as to modify an angle of incidence onto said filter to confine light to a predetermined range around a normal of said filter, said optics comprising an image-space telecentric lens.
Owner:XENOMATIX NV
System and Method for Simulating Shallow Water Effects on Arbitrary Surfaces
ActiveUS20080177519A1Effective simulationFacilitate real-time fluid controlAnimationImage generationFluid controlWave equation
A system and method for shallow water simulation may provide a framework for solving General Shallow Wave Equations (GSWE) to efficiently simulate 3D fluid effects on arbitrary surfaces using a height field representation. The height field representation may include height columns constructed along surface normals, which may be dependent on a condition of boundary cells adjacent to fluid cells and / or artificial viscosity effects. The framework may provide implicit schemes for solving for the effects of external forces applied to the fluid, including gravity and surface tension, and explicit schemes for solving for advection effects. The system and method may be implemented on general-purpose CPU(s) and / or GPU(s) and may be capable of simulating a variety of fluid effects including: waves, rivulets and streams, drops, and capillary events. In some embodiments, the system and method may achieve real-time fluid control and fluid shape design through user-interaction (e.g., in a graphical painting application).
Owner:ADOBE INC
Arbitrary polarization dynamic control device and method based on metamaterial-surface-phase-change-material
ActiveCN106681026AAchieve separationSolve the problem that it is difficult to realize dynamic polarization controlNon-linear opticsMicro nanoPhase difference
The invention relates to an arbitrary polarization dynamic control device and method based on metamaterial surface-phase change material, and belongs to the technical field of micro-nano optical applications. A metamaterial surface based on a V type nano-antenna array is used for reacting with a light field to generate a surface phase gradient, which causes that the abnormally transmitted polarized light generated under the condition of line polarized light normal incidence, deflects from the normal direction of the surface. At the same time, with the introduction of an interval modulation layer comprising periodically arrayed germanium-antimony-tellurium, under external excitation, phase differences of orthogonal polarization state emitted by different units are modulated, and overlap in space to achieve random polarization state synthesis of an outgoing light field. The method is an all-solid-state modulation method with no necessity of any mechanical modulation measures such as drawing or rotating. The separation of random polarized light and background light beams can be achieved to avoid cross fire. The method provides a flexible regulation and control measure for on-chip polarization applications of integrated optics.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
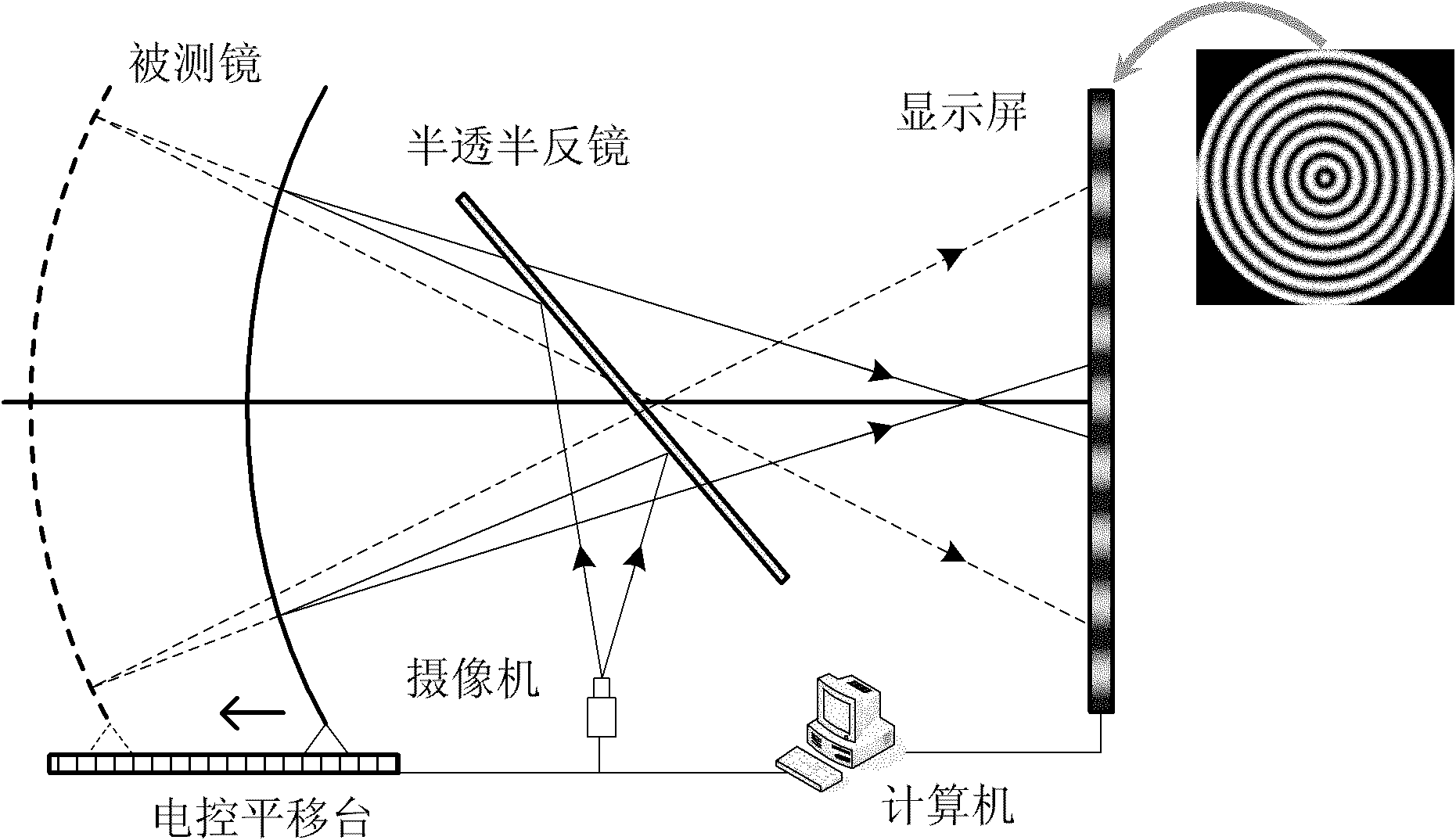
Aspherical mirror detection method based on phase measurement deflectometry
ActiveCN102183213ALarge measurement dynamic rangeSimple structureUsing optical meansOptical axisRectangular coordinates
The invention provides an aspheric mirror detection method based on phase measurement deflectometry. The detection system is composed of a display screen, a camera, an electronic control translation stage, a half transparent and half reflecting mirror and an electronic computer, wherein the optical centre of the camera is arranged on the optical axis of the mirror to be detected; a sine (cosine) fringe pattern is generated by the computer and is displayed on the display screen; then the fringe pattern on the display screen can be projected on the mirror to be detected and the camera can shoot the reflected image; during the process of measurement, the mirror to be detected is fixed on the electronic control translation stage and can precisely move along the optical axis under the control of the computer; the fringe pattern shot during the moving process of the mirror to be detected can be analyzed and processed to obtain a phase distribution, then the relationship between the normal line distance and the normal angle of the aspherical surface can be obtained by calculation, namely the surface shape can be described by the normal line congruence of the aspherical surface; and meanwhile, the normal line congruence can be converted to the rectangular coordinate system through geometry calculation for evaluation. The invention has a large dynamic measurement range and provides detection means for the accurate grinding and primary polishing processes of a non-spherical reflector with a larger wavefront variation range during processing.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spatial filter for sample inspection system
ActiveUS7184138B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansElevation angleForward scatter
Spatial filtering is disclosed that improves the signal to noise ration of a sample inspection system of the type having a detector and collection optics that receive radiation scattered from a point on a sample surface and direct the scattered radiation toward the detector. The spatial filtering may screen the detector from substantially all of the forward-scattered radiation from back-scattered radiation that is scattered in a at an elevation angle less than about 45° with respect to a normal to the surface. Forward scattered noise is screened from the detector while backscattered signal reaches the detector. Programmable spatial filters may be used to selectively block scattered noise due to surface roughness while transmitting scattered signal due to surface defects.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
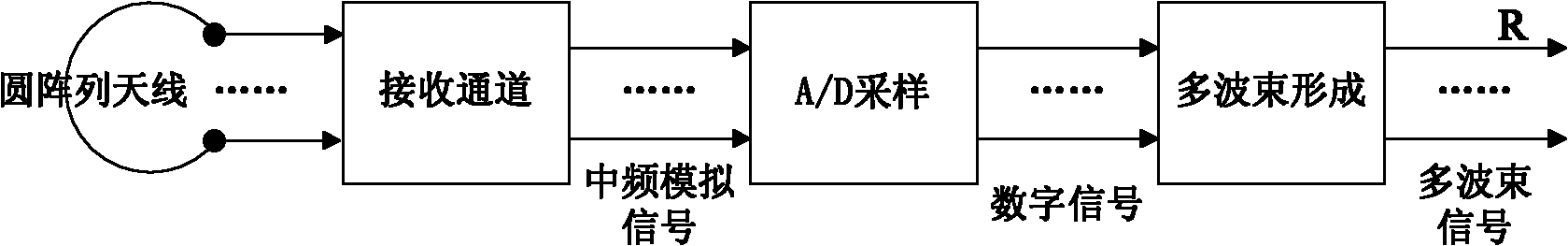
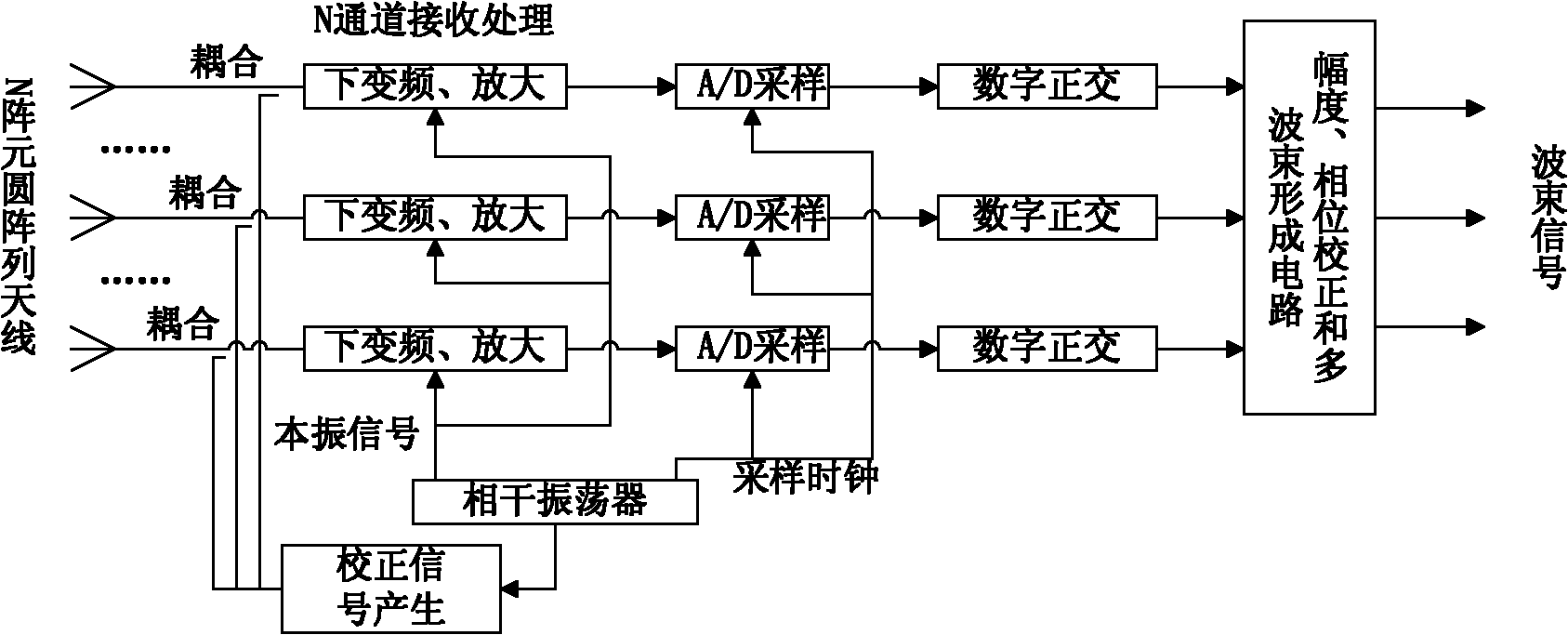
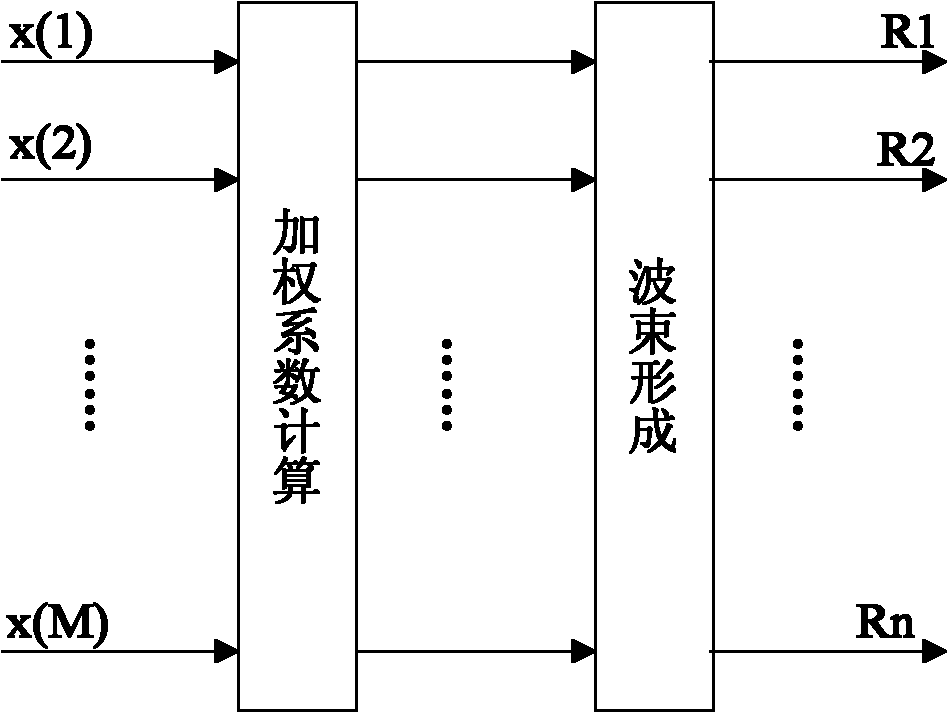
Method for forming circular array antenna digital wave beams
InactiveCN102082591ASolve the problem of not being able to cover 360° at the same timeResolution widthSpatial transmit diversityAntenna gainEngineering
The invention provides a method for forming circular array antenna digital wave beams. Part of adjacent arrays in a circular array consisting of a plurality of arrays form a small circular array, a main wave beam extending outward along the centre of a circle is formed in the normal direction of the arrays in the center of the circular array, so that a circular array can be constructed by taking every array as a center so as to form a wave beam extending outward along the center of the circle, and the whole circular array can form a plurality of wave beams at equal intervals, which cover the 360-degree space; thus the circular array antenna digital wave beams are formed. The method solves the problems of the prior art, and the problems that a planar array antenna cannot simultaneously cover the 360-degree space, and the antenna beamwidth is increased along with the increment of a scanning angle and the antenna gain and angle measurement accuracy are reduced along with the increment of the scanning angle.
Owner:WUHAN BINHU ELECTRONICS
Screens for RF magnetic flux
InactiveUS6768051B2Reducing and obviating needShielding materialsAntennasCapacitanceConductive materials
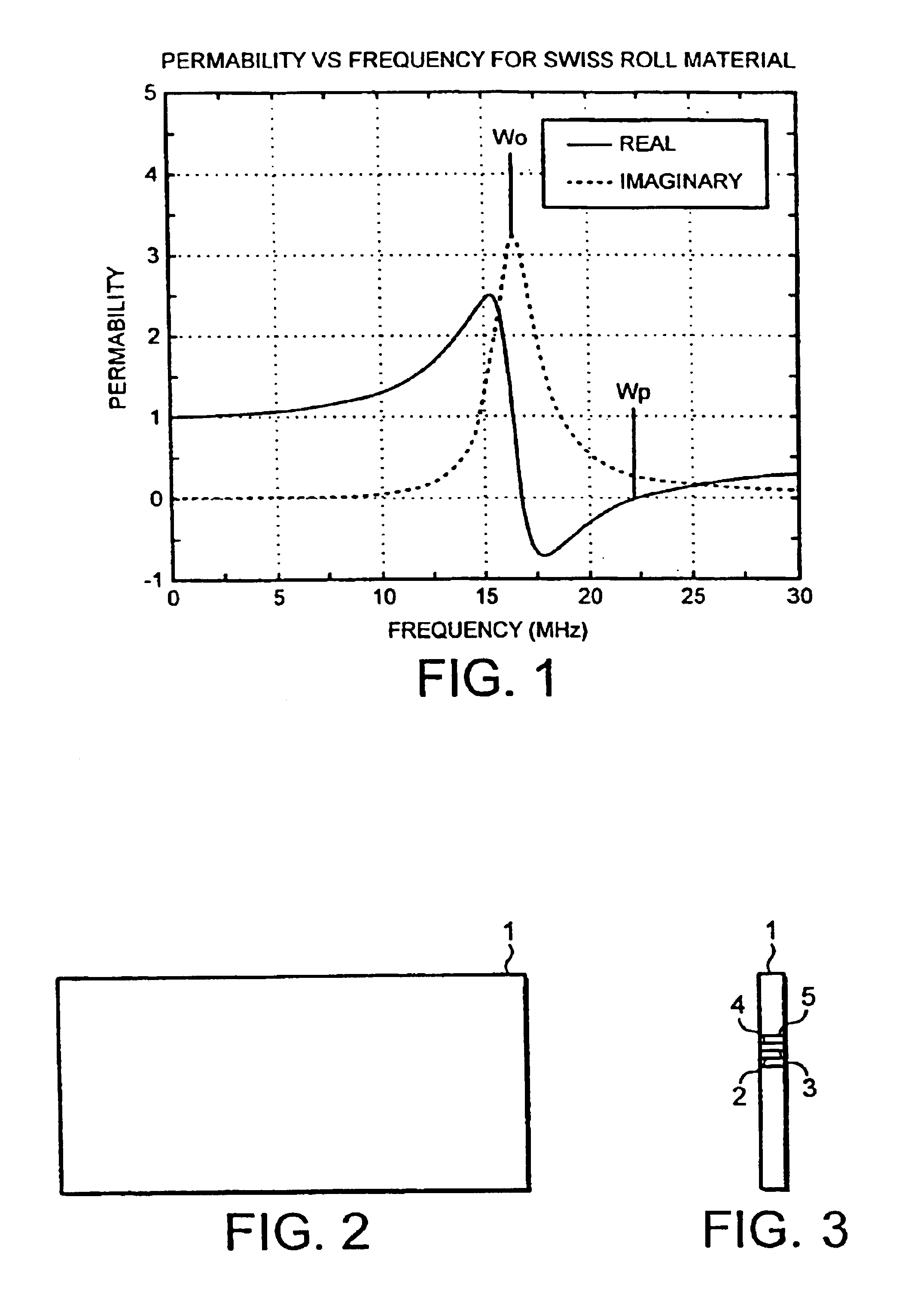
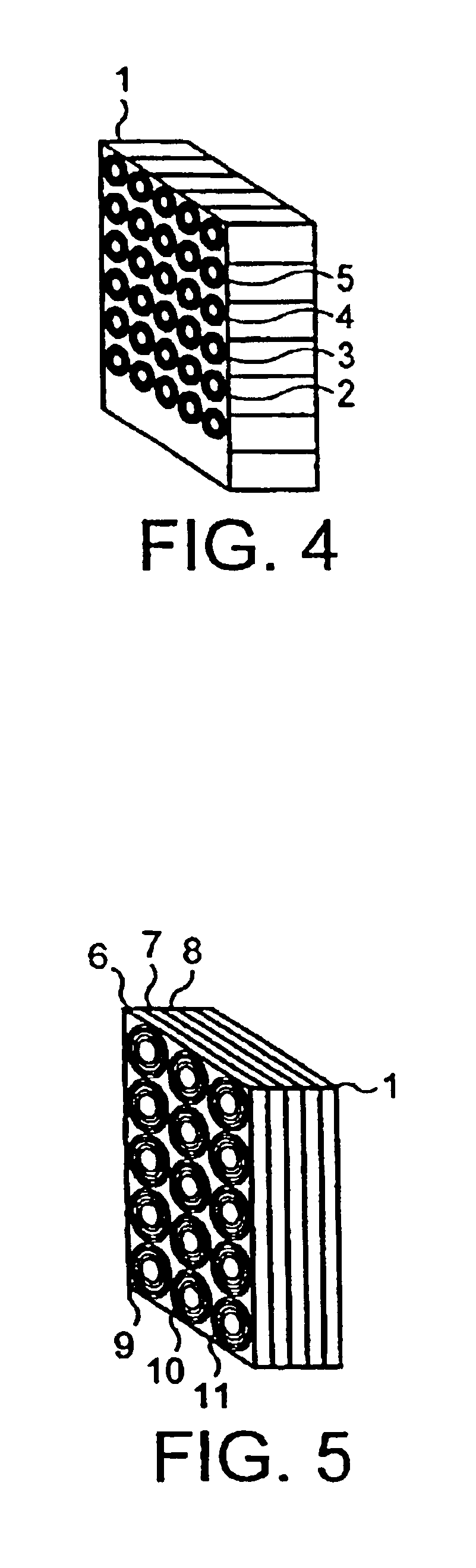
Microstructured materials which can be tuned to a particular range of r.f. frequencies to display particular magnetic permeabilities have been proposed. A typical material is made of an array of capacitive elements e.g. spirals or rolls of conducting material on a non-conducting substrate. These materials can be used as screening material which is effective for the particular band of frequencies to which it is tuned. In one example, the rolls 2 to 5 are orientated normal to the face of the screen 1, which reflects or absorbs the magnetic vector of electromagnetic radiation impinging normal onto the reflector face.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method for simulating shallow water effects on arbitrary surfaces
ActiveUS7921003B2Effective simulationEasy to controlAnimationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationFluid controlWave equation
A system and method for shallow water simulation may provide a framework for solving General Shallow Wave Equations (GSWE) to efficiently simulate 3D fluid effects on arbitrary surfaces using a height field representation. The height field representation may include height columns constructed along surface normals, which may be dependent on a condition of boundary cells adjacent to fluid cells and / or artificial viscosity effects. The framework may provide implicit schemes for solving for the effects of external forces applied to the fluid, including gravity and surface tension, and explicit schemes for solving for advection effects. The system and method may be implemented on general-purpose CPU(s) and / or GPU(s) and may be capable of simulating a variety of fluid effects including: waves, rivulets and streams, drops, and capillary events. In some embodiments, the system and method may achieve real-time fluid control and fluid shape design through user-interaction (e.g., in a graphical painting application).
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
High-precision sub-pixel extraction method for centers of light bars of structured light
ActiveCN105931232AImprove extraction accuracyAccurate extractionImage enhancementImage analysisMean squareMachine vision
The invention discloses a high-precision sub-pixel extraction method for the centers of light bars of structured light, and belongs to the technical field of computer vision. The method is characterized in that that the method employs a skeleton refining method to obtain the initial positions of the centers of stripes; solving the normal direction of each position on a skeleton through a mean square gray scale gradient; employing an adaptive threshold value to extract the normal width value of each column of stripes; carrying out Fourier fitting through gray scale data in the stripe normal width value; solving a peak value of a fitting curve, and obtaining the sub-pixel coordinates of the centers of the light bars, and connecting the centers of the light bars to form the center of the light bar. The extracted center of the light bar is higher in precision, and the method also can accurately extract the center of the light boars under the condition that the gray scale of the light bar and the width of the light bar are not uniform.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
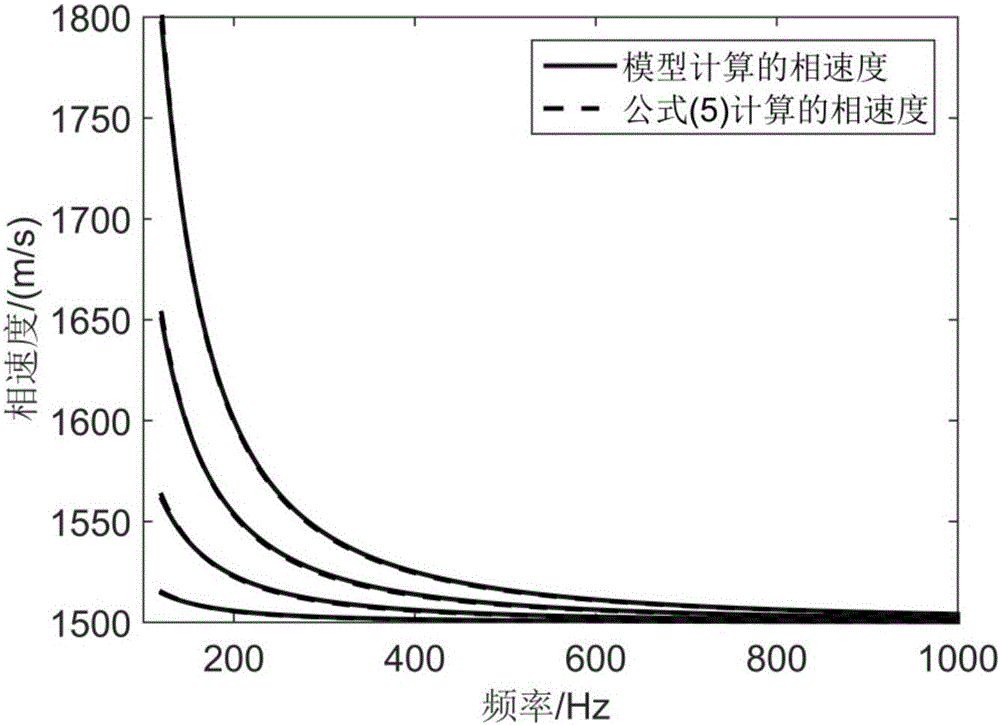
Normal wave modal frequency dispersion elimination transformation-based sound source distance and depth estimation method
ActiveCN106019288AEstimates are simple and reliableAccurate estimateAcoustic wave reradiationTime domainSound sources
The invention relates to a normal wave modal frequency dispersion elimination transformation-based sound source distance and depth estimation method. According to the method, based on a phenomenon that shallow sea received signals are subject to frequencydispersion elimination transformation and then realize sound pressure focusing on a distance-frequency dispersion parameter two-dimensional plane, only when the transmission distance parameter of the received signals is equal to the distance of a target sound source, the sound pressure amplitude of normal waves can be maximum, and therefore, the distance parameters of the target sound source can be estimated; after the received signals have been subjected to the frequency dispersion elimination transformation, modes of first few orders can be separated obviously in the time domain, and the energy of the modes of the first few orders can be accurately estimated; and a multi-modal energy matching mode is adopted, so that the depth of the target sound source can be determined.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Continuous two-dimensional corneal topography target
InactiveUS6926408B2Robust image processingFine surfaceAntibacterial agentsFibrinogenCorneal surfaceImaging processing
A means to generate a continuous two-dimensional reflection pattern suitable for corneal topography that uses sinusoidal profiles of both intensity and color values. The technique provides a more robust image processing due to the ability to apply digital band pass filters, continuous data for improved surface reconstruction, and the ability to directly measure the meridian of the reflection pattern source point when the corneal surface normal does not lie in the meridian of the measurement instrument.
Owner:Z OPTICS INC
Highly directive antenna based on grooved cross metal strip artificial medium structure
InactiveCN101527394AImprove directivitySmall sizeDifferential interacting antenna combinationsLeaky-waveguide antennasMetal stripsMicrostrip antenna array
The invention discloses a high-gain low-sidelobe highly directive antenna based on an artificial medium structure, comprising a microstrip antenna array and a radome composed of a plurality of grooved cross metal strip artificial medium structures; the grooved cross metal strip structure is printed on a tellite and is used as the radome of the microstrip antenna array; the structure can be equivalent to a homogeneous medium with plasma frequency by rationally designing the cycle and size of the metal structure; the equivalent index of refraction of the frequency of the electromagnetic wave is similar to zero when the frequency is in a certain frequency band. The energy of the electromagnetic wave radiated by the microstrip antenna array is collected in the normal direction of the radome when the electromagnetic wave passes through the radome to achieve the effect of gathering energy, thus improving the overall directivity and gain of the antenna and reducing the sidelobe of the antenna. The antenna not only has the advantages of high gain, good directivity, low sidelobe and the like, but also has the characteristics of good mechanical performance, convenient fixed mounting, simple processing, low cost, small structure size and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
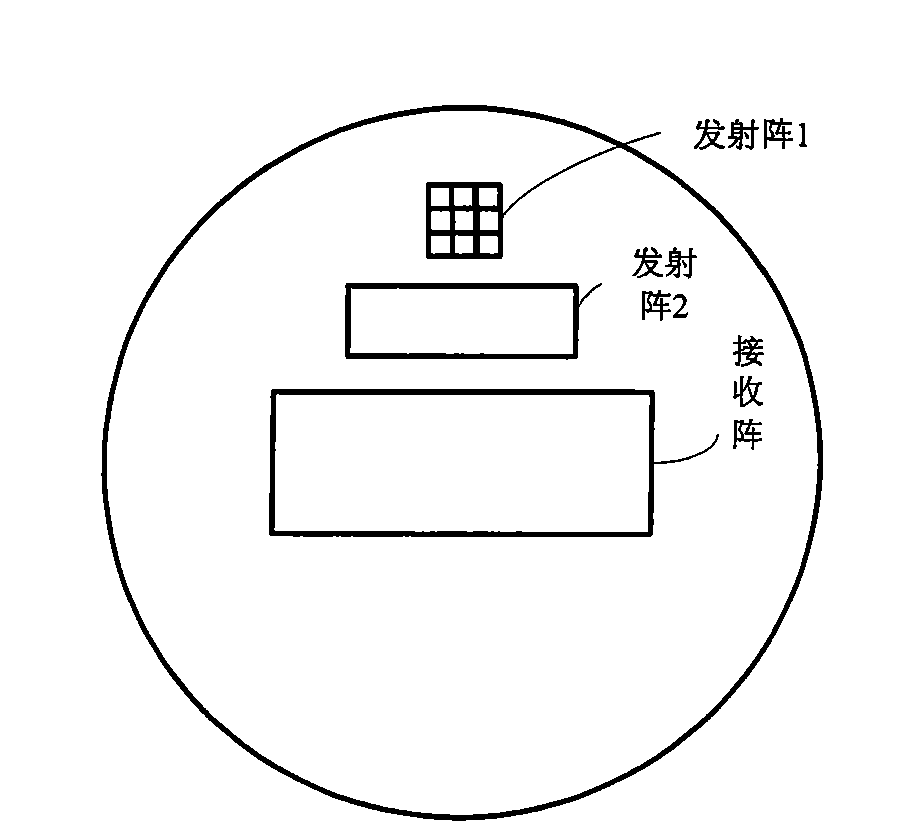
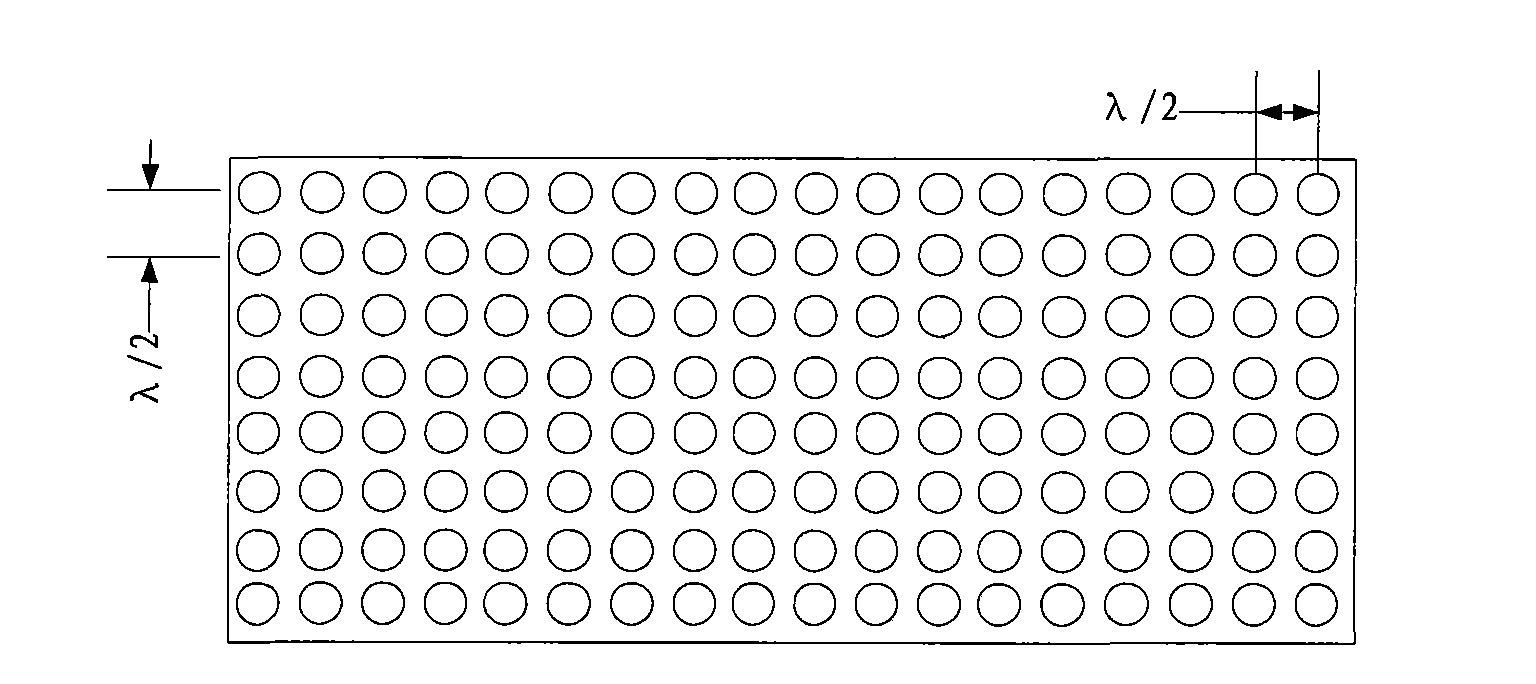
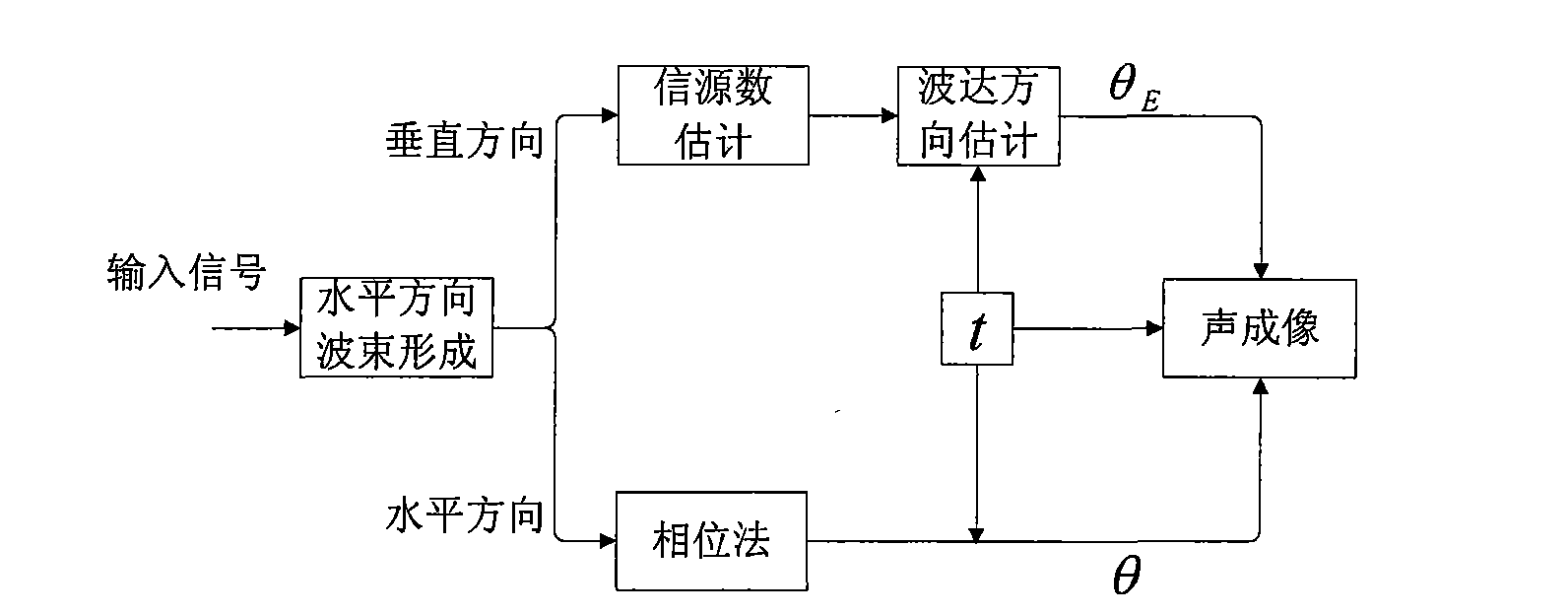
Three-dimensional looking forward sound imaging sonar system for underwater vehicle and using method thereof
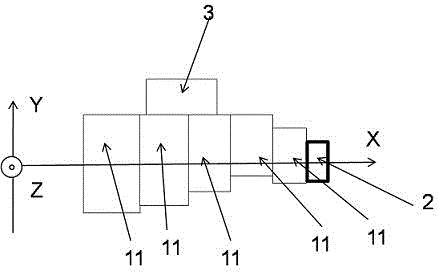
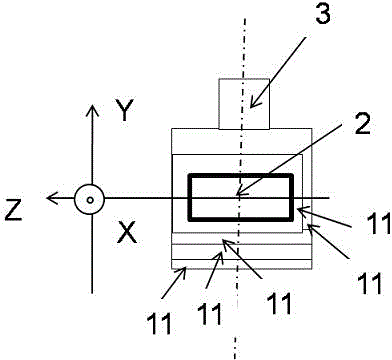
InactiveCN101581785ASmall front areaHigh resolutionAcoustic wave reradiationVertical planeSound image
The invention discloses a three-dimensional looking forward sound imaging sonar system for an underwater vehicle, which comprises a sonar transmitting array 1, a sonar transmitting array 2 and a sonar receiving array, wherein the sonar transmitting array 1 is used for short-distance detection and consists of a plurality of rows of primitives at half-wavelength intervals; the sonar transmitting array 2 is used for long-range detection and consists of a plurality of rows of sonar arrays which are arranged in a circular-arc shape horizontally and at half-wavelength intervals vertically; and the sonar receiving array is a planar array consisting of receiving transducer units at half-wavelength intervals, a central primitive is used for receiving sonar, and edge primitives are dummy primitives. The system forms a plurality of horizontal wave beams by using normal wave beam forming technology; in the wave beams, a phase method is used to work out a horizontal incidence angle; on a vertical plane, information source number estimation and direction-of-arrival estimation technology is used to work out a vertical incidence angle; and the three-dimension spatial position of a scattering point is worked out by using the time of arrival of back waves and a sound image is obtained. The system can realize small-front area, high-resolution, long-distance and wide-coverage detection of forward objects.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Focal length measurement method for micro-lens array
InactiveCN102607820AEasy to operateReduce cost of measurementTesting optical propertiesOptical axisMicro lens array
The invention relates to a focal length measurement method for a micro-lens array. All sub-units of the micro-lens array are used for dividing the front parts of spherical surface waves and are imaged on respective focal surfaces; the imaging principle is analyzed, and normal directions of all divided wave surfaces pass through the centers of all sub-hole diameters, the centers of light spots on the focal surfaces and the converging centers of the front parts of the spherical surface waves; and the offsets of the centers of the light spots of all the sub-units of the micro-lens array with an optical axis can be measured through determining the converging centers of the front parts of the spherical surface waves, so as to complete the measurement for the focal lengths of the all the sub-units. According to the method, the measurement for the focal lengths of a plurality of sub-units can be completed through one-time image acquisition and treatment, so that the measurement efficiency and the measurement accuracy are higher, and the method can be used for detecting the micro-lens array with more arrays.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reflective screen
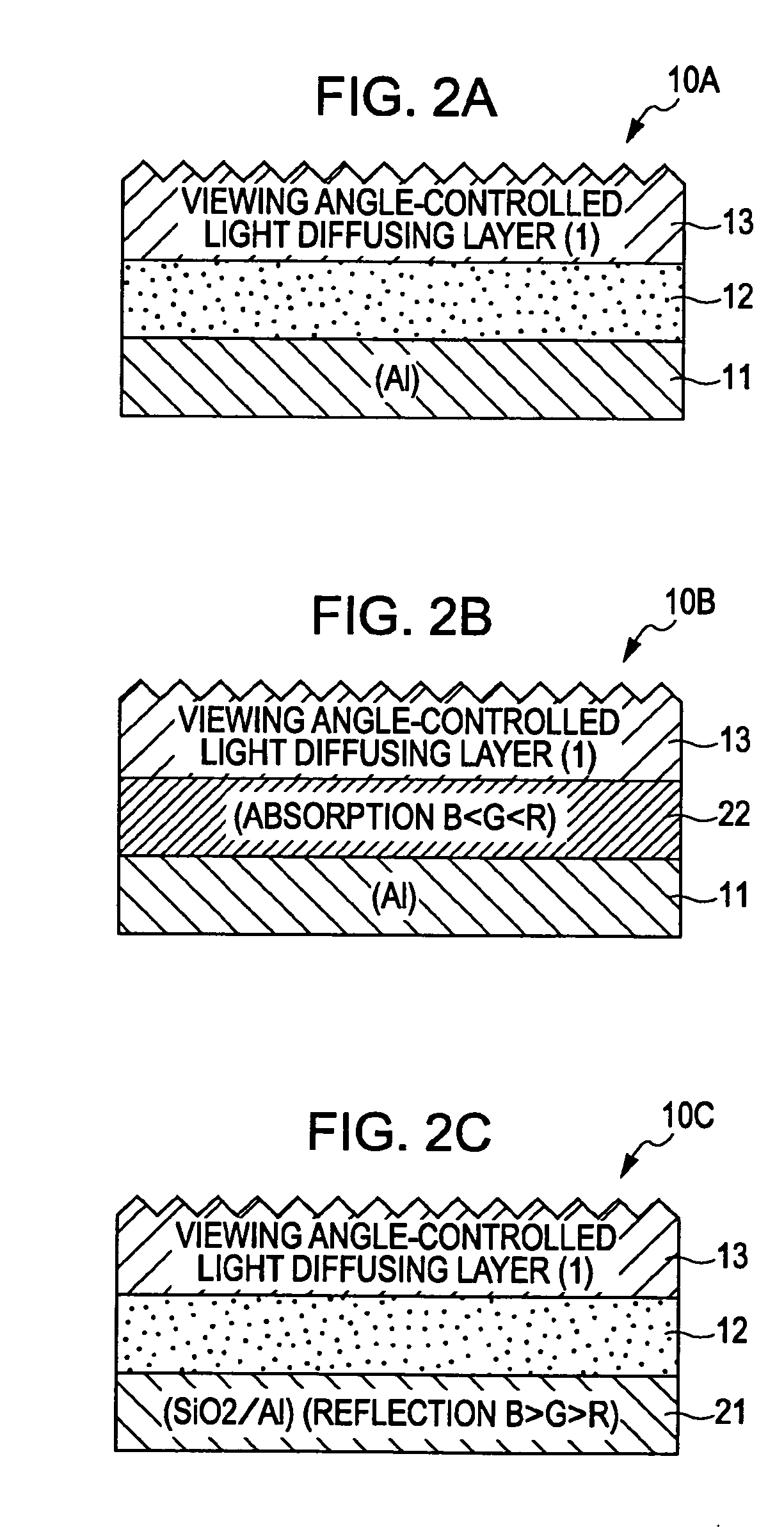
InactiveUS20070035827A1Increase contrastWell formedDiffusing elementsProjectorsLight reflectionLightness
A reflective screen includes a light reflecting layer, and a light diffusing layer provided on the light reflecting layer. The light diffusing layer has the diffusion property that in one (A axis) of two perpendicular axial directions on a light diffusion plane, a luminance distribution curve versus incidence angle is asymmetric with respect to the zero-incidence-angle axis, and the side on which the incidence angle (half-luminance incidence angle) with half of a peak luminance on the A axis in the normal direction to the screen plane is small faces in a direction in which external light has the highest strength.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical acoustic panel
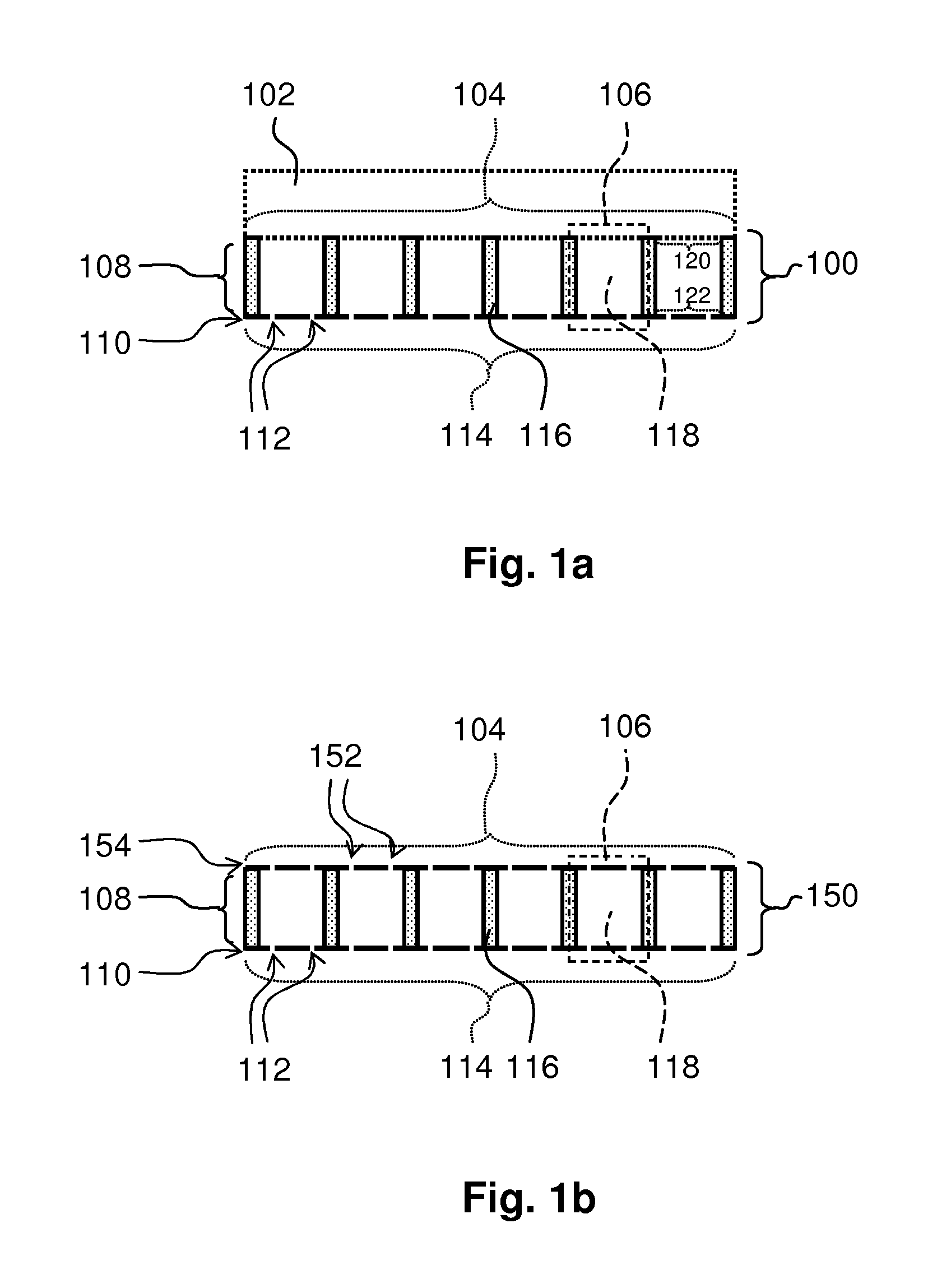
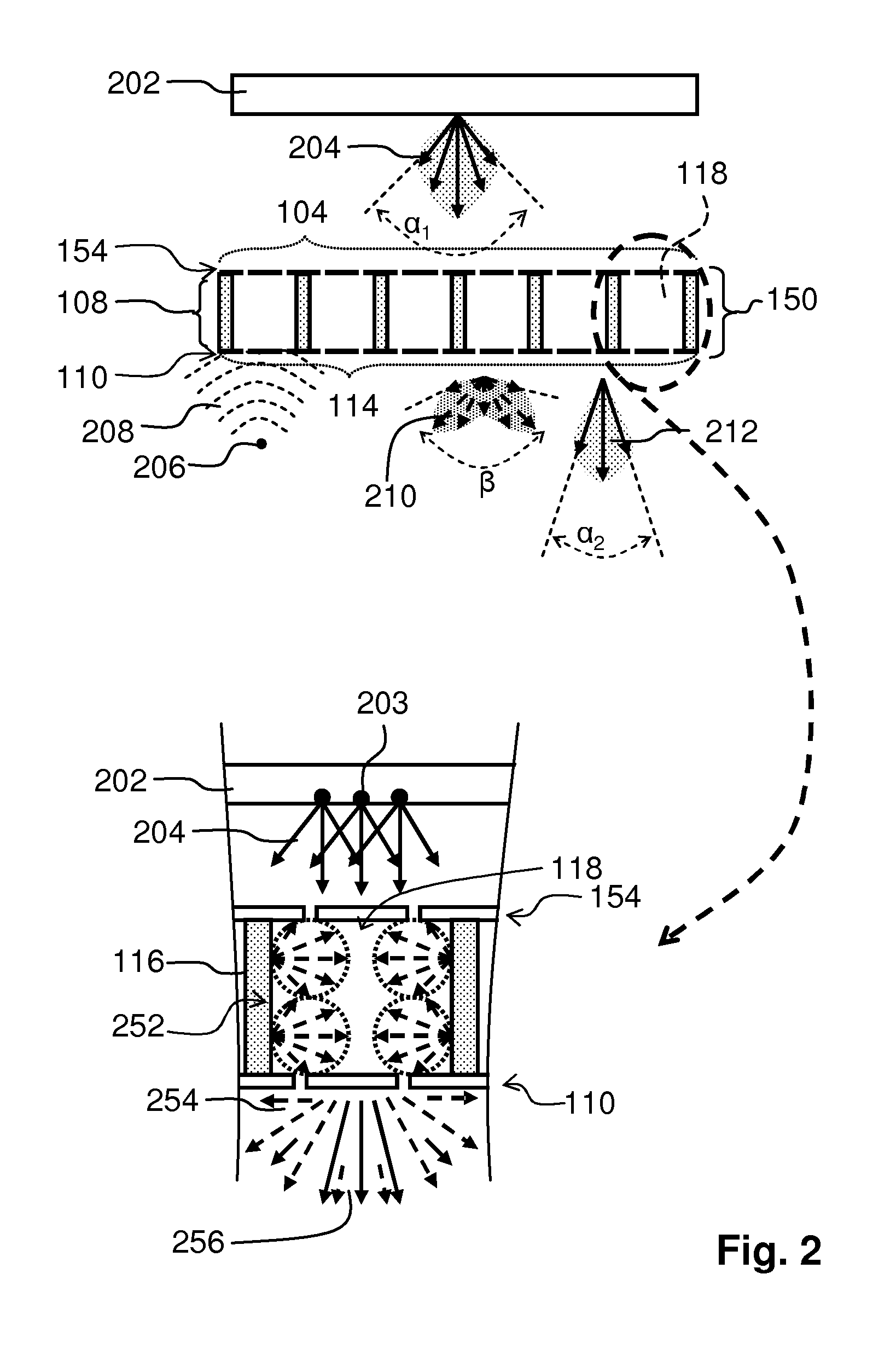
ActiveUS20140299408A1Efficient preparationSmall shapeCeilingsLighting elementsTransmission channelDaylight
An optical acoustic panel 100 for absorbing sound and providing a daylight appearance and a luminaire are provided. The optical acoustic panel 100 comprises a first side 114, a second side 104, a micro perforated foil 110 and a spacing structure 108. The first side 114 receives sound. The second side 104 is opposite the first side 114 and receives light. The micro perforated foil 110 comprises sub-millimeter holes 112, is light transmitting and is arranged at the first side 114. The sub-millimeter holes 112 are entrance holes of a cavity. The spacing structure 108 spaces the first side 114 at a predefined distance from the second side 104. The spacing structure 108 comprises a plurality of light transmitting cells 106. The light transmitting cells 106 comprise a light transmitting channel 118, a light exit window 122, a light input window 120 and a wall 116. The light transmitting channel 118 collimates a part of the light received at the second side 104 of the optical acoustic panel 100. The light transmitting channels 118 extend from the first side 114 towards the second side 104 and are filled with air. The light input window 120 is arranged at the second side 104. At least a part of the light exit window 122 being arranged at the first side 114. The wall 116 is interposed between the light input window 120 and the part of the light exit window 122. The wall 116 encloses the light transmitting channel 118. At least a part of the wall 116 being reflective or transmissive in a predefined spectral range for obtaining a blue light emission at relatively large light emission angles with respect to a normal to the first side 114.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Optical sensor and image forming device
InactiveUS20130235377A1Increasing costIncreasing sizePolarisation-affecting propertiesLight polarisation measurementPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An optical sensor includes: a light emission module to emit a linearly polarized light beam having a first polarizing direction to a surface of an object in an incident direction inclined relative to a direction of a normal to the surface; a first photodetector module including a first photodetector disposed within a plane of incidence of the surface in an optical path inclined relative to an optical path of a light beam emitted from the light emission module and regularly reflected on the surface; and a second photodetector module including an optical element disposed within the plane of incidence of the surface in an optical path of a diffused reflection light beam from the surface to separate a linearly polarized light beam having a second polarizing direction perpendicular to the first polarizing direction, and a second photodetector to receive the light beam separated by the optical element.
Owner:RICOH KK
Birefringent spectral filter with wide field of view and associated communications method and apparatus
ActiveUS7848000B2Wide field of viewPolarising elementsElectromagnetic transmissionOcean bottomFeedback control
A spectral filter is adapted for use in a receiver, for example in a short range submarine laser signal path, wherein the relative orientations of the receiver is such that the signal may appear diffusely or at an unknown point in a wide external field of view around an optical axis of the receiver. A narrow band spectral filter in the receiver has cascaded stages of tunable retarders with includes multi-conjugate stages that tolerate light that is oblique to normal, up to a diverging internal field of view angle up to about 10°. A fisheye lens assembly refracts incoming light from a wider external field of 170° or more and directs the light into the filter over the narrow internal field of view. Calibration and feedback control can be provided to stabilize the discriminated wavelength peak, which remains at the same center wavelength over the span of the internal field of view notwithstanding the difference in retarder thicknesses traversed along paths that are normal to the retarders versus oblique to the optical axis.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
Micro-structure surface global lighting drawing method based on direction light radiation intensity
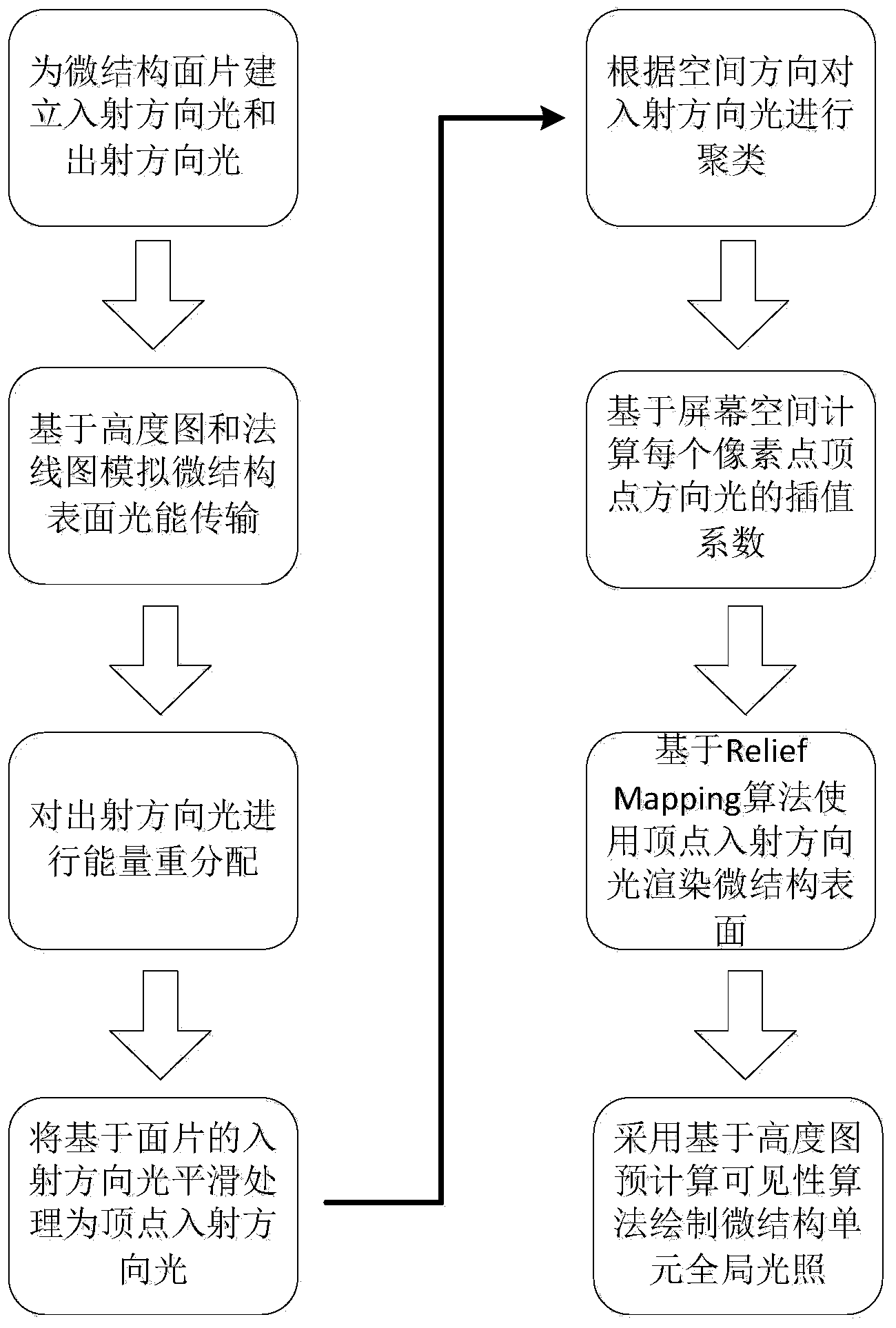
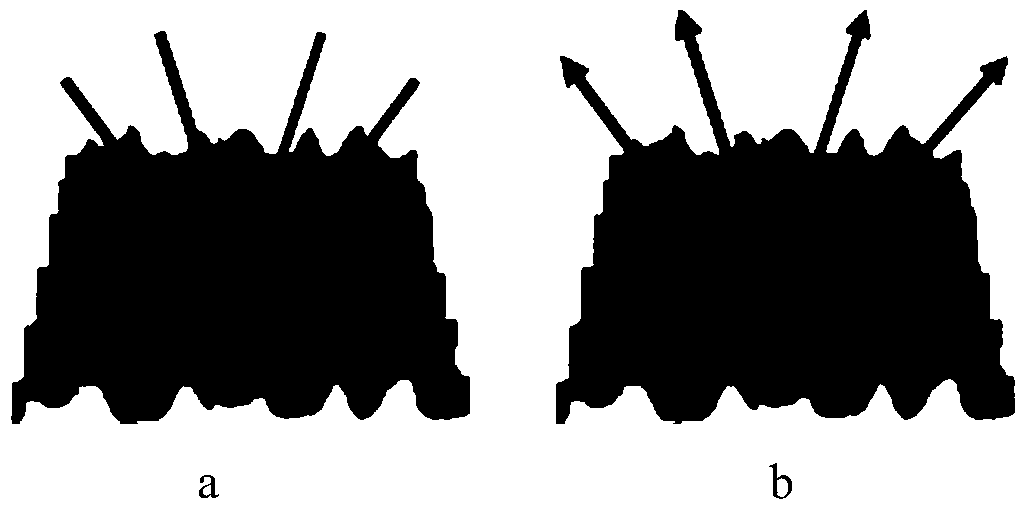
The invention discloses a micro-structure surface global lighting drawing method based on direction light radiation intensity. The method includes the following steps that a cluster of incidence direction light and exit direction light is established for a micro-structure surface, based on a height graph and a normal graph, a progressive radiation intensity algorithm is used for simulating the optical energy transmission of the scene of the micro-structure surface, energy redistribution is performed on the exit direction light, the incidence direction light is clustered after energy transmission is finished, smoothing processing from the facet incidence light to the top point incidence light is performed with the direction light roughly identical in space direction, based on screen space, the interpolation coefficient of the top point light in each pixel point is calculated, the scene is rendered through the clustered top point direction light via using the interpolation coefficient based on an Relief Mapping algorithm, and the global lighting effect among micro-structure units is drawn through a precomputation visibility algorithm based on the height graph.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Antenna module and communication device
ActiveUS20200119453A1Improve featuresReduce thicknessIndividually energised antenna arraysModular arraysMechanical engineeringCommunication device
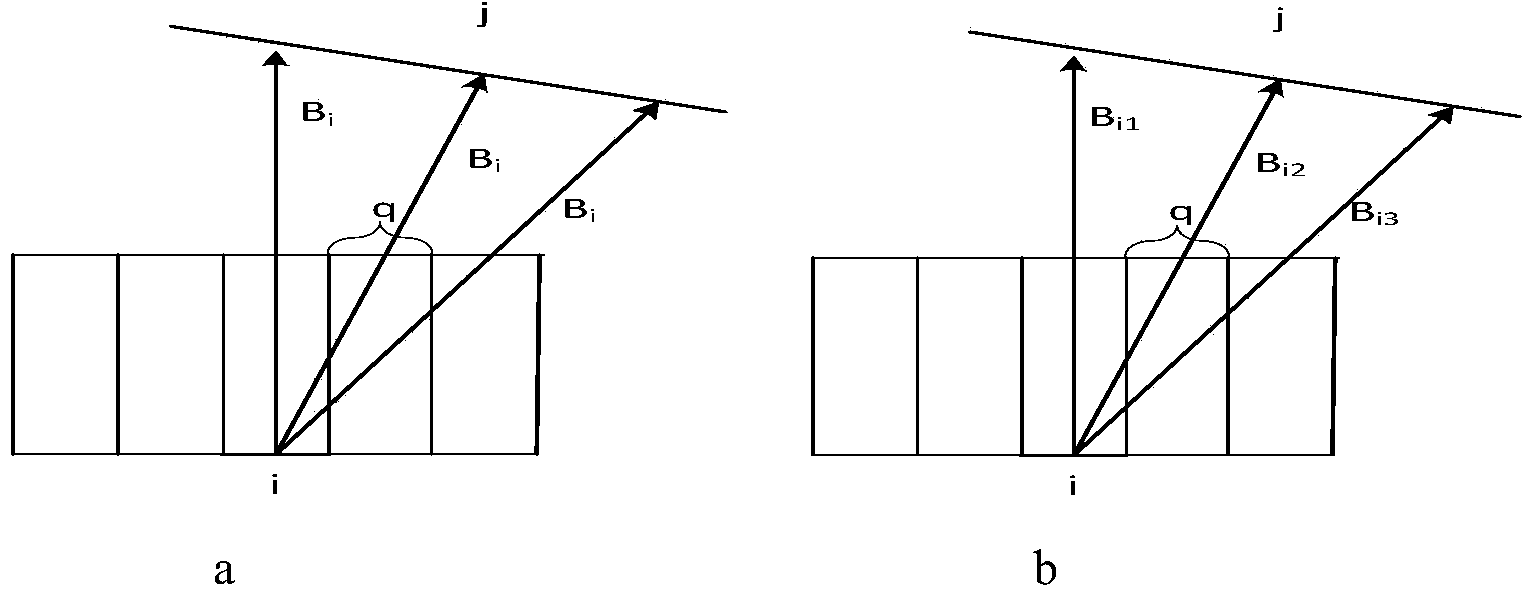
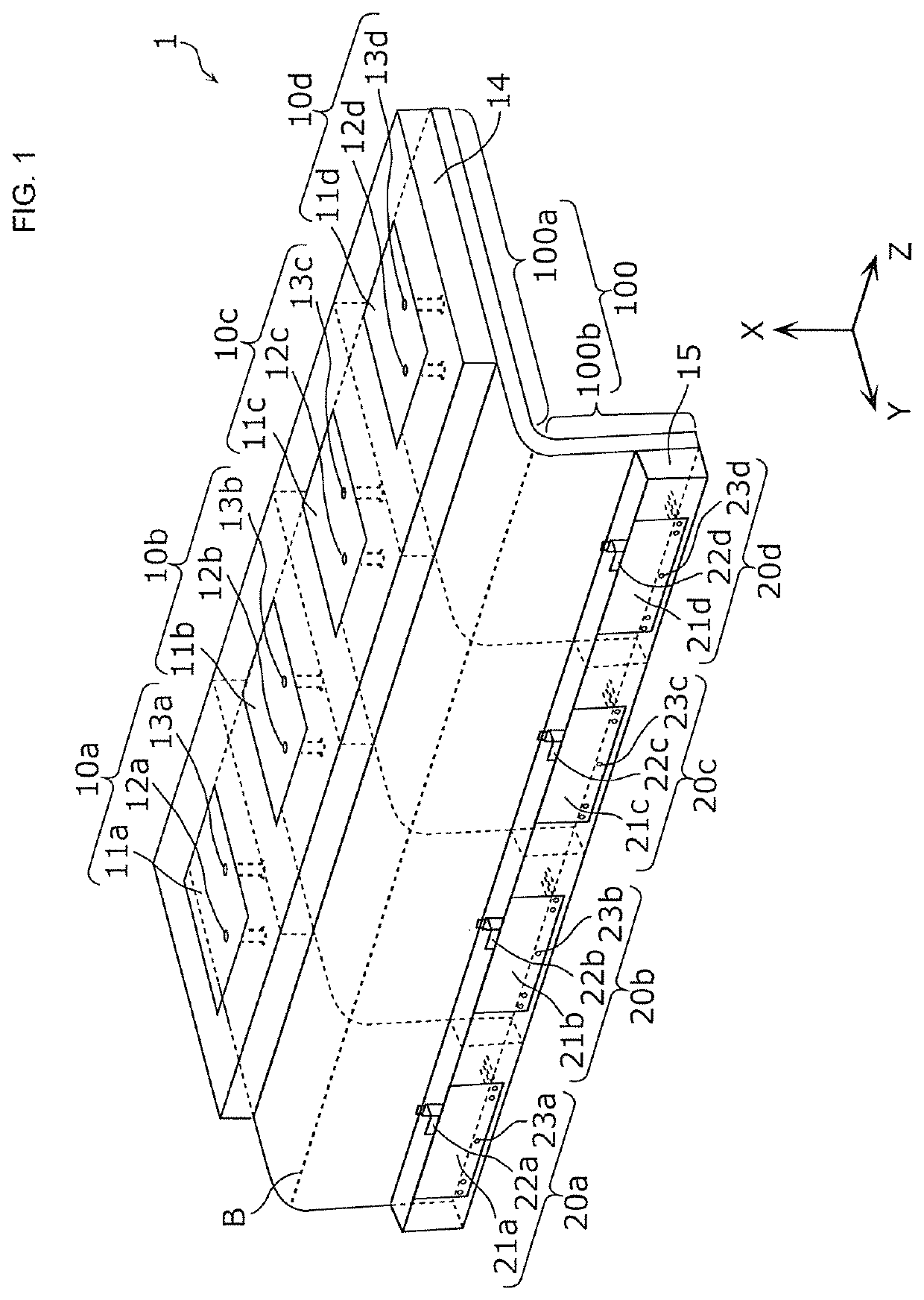
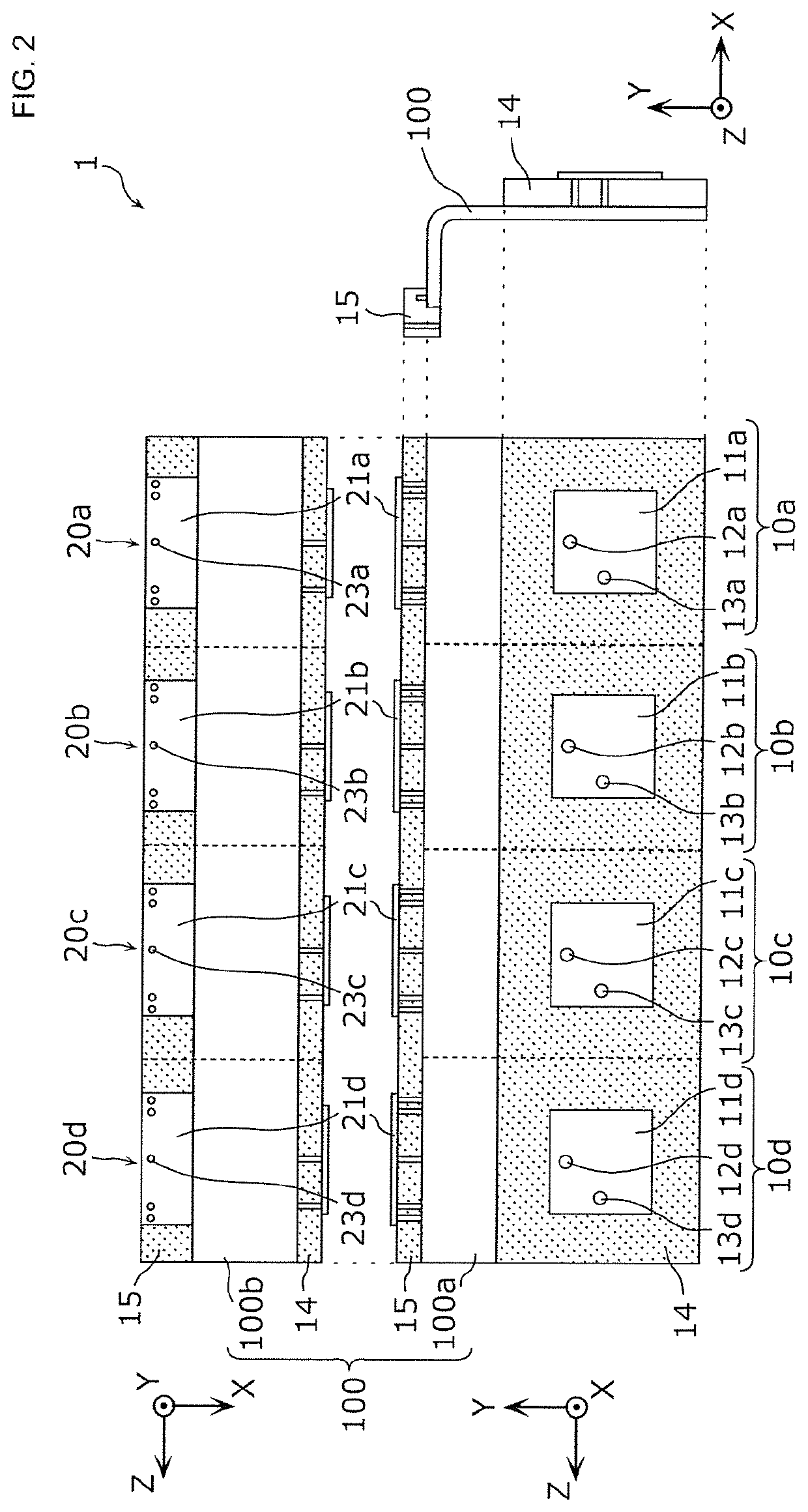
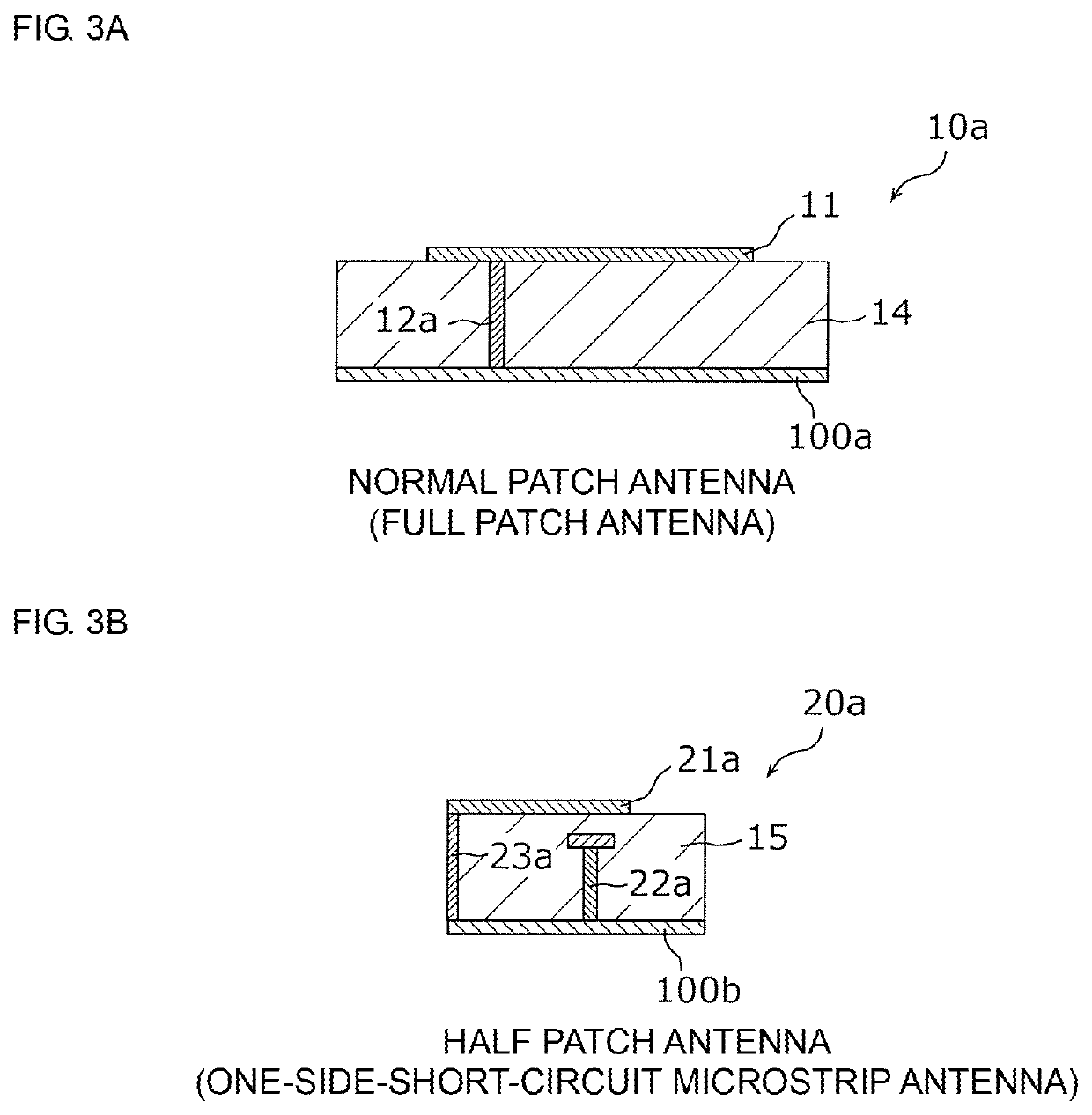
An antenna module (1) includes a substrate (100) including a first flat plate portion (100a) and a second flat plate portion (100b) that have respective normals intersecting with each other and that are continuous, first patch antennas (10a to 10d) that are formed on the first flat plate portion (100a) and second patch antennas (20a to 20d) that are formed on the second flat plate portion (100b). The first patch antennas (10a to 10d) are arranged in at least a column in a column direction parallel to a boundary line (B) between the first flat plate portion (100a) and the second flat plate portion (100b). The second patch antennas (20a to 20d) are arranged in at least a column in the column direction.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method for monitoring a high resistivity reservoir rock formation
ActiveUS20060255809A1Guaranteed normal transmissionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentEngineeringHigh resistivity
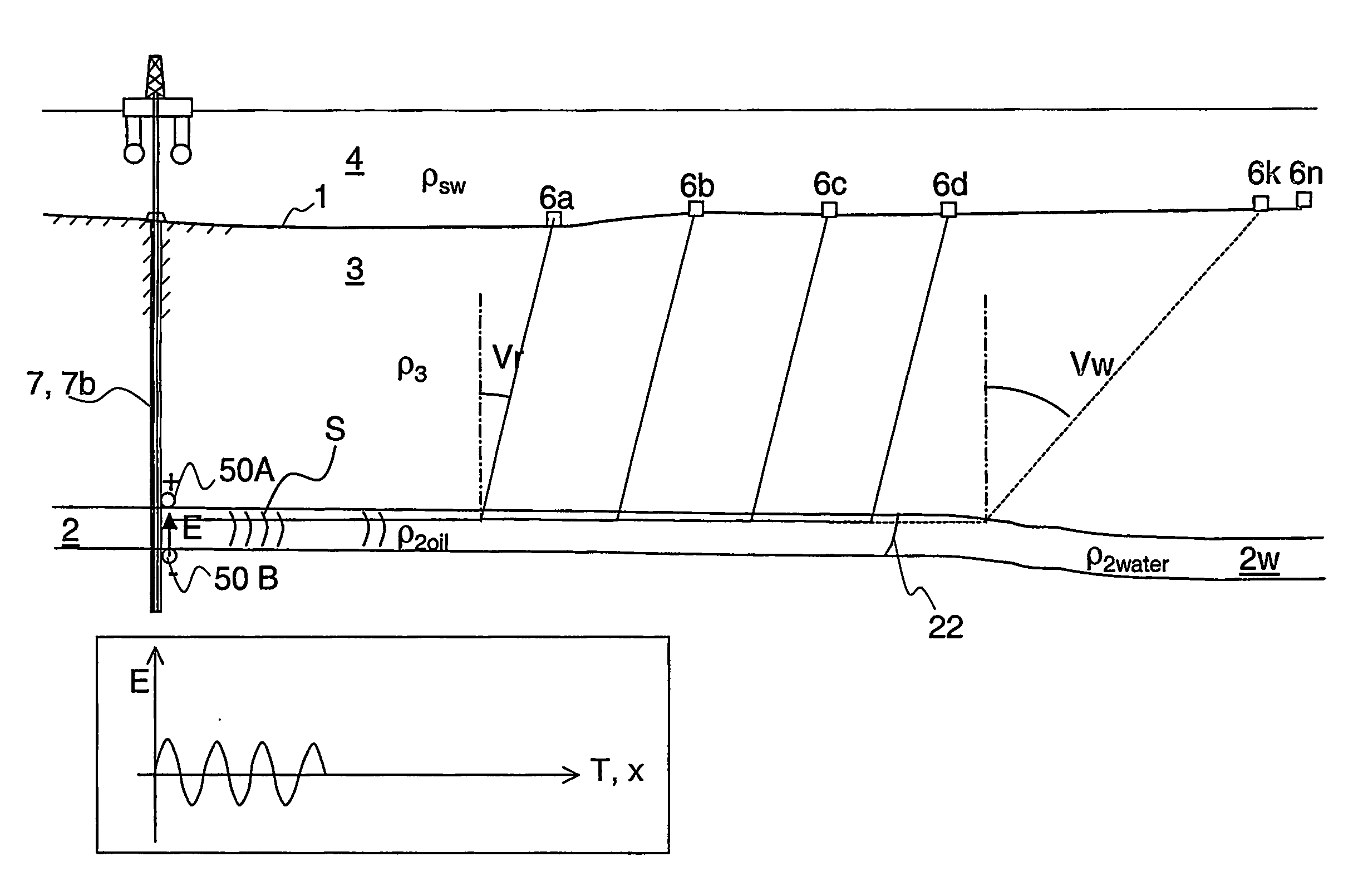
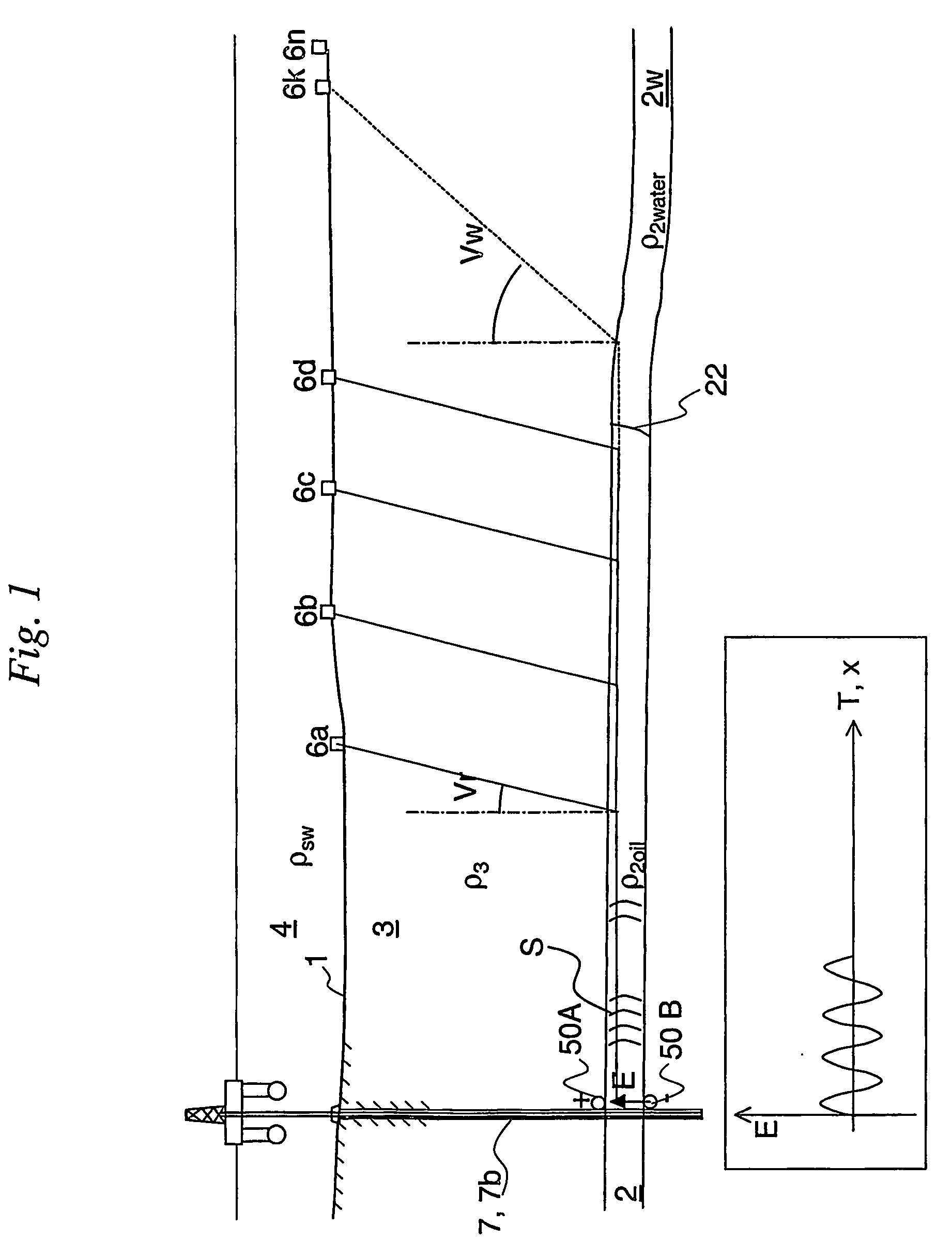
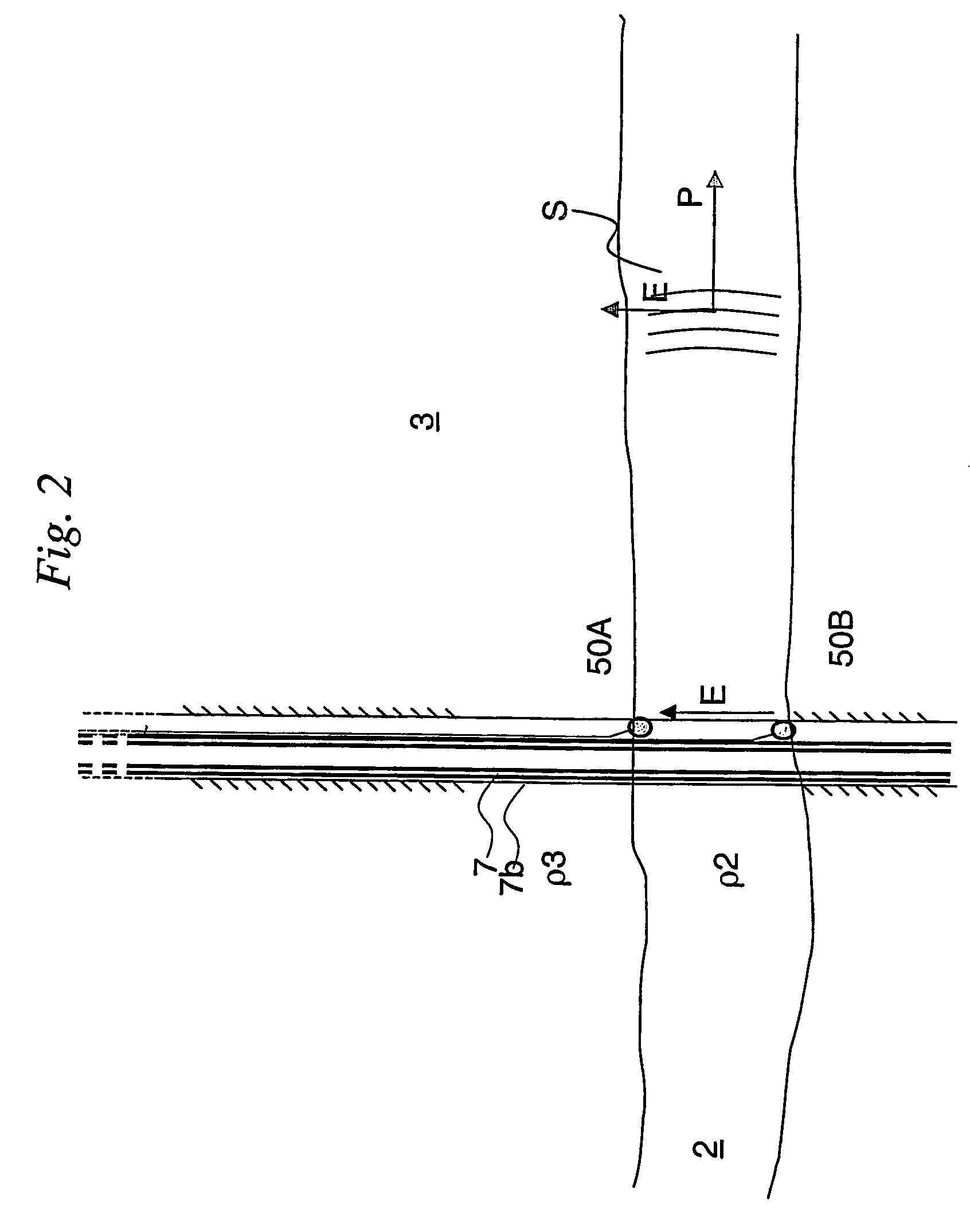
A method for monitoring a high-resistivity reservoir rock formation (2) below one or more less resistive formations (3), comprising the following steps: Transmitting an electromagnetic signal (S) propagating from near a seafloor or land surface (1) by means of an electromagnetic transmitter (5) powered by a voltage signal generator (G). The electromagnetic signal (S) propagates from the seafloor (1) and is guided along a conductive string (7) to the high-resistive formation (2), and propagates as a guided-wave electromagnetic signal (S2) at a relatively higher speed (V2) inside the high-resistivity formation (2) than a propagation speed (V3) in the less resistive formations (3). The guided-wave electromagnetic signal (S2) gives rise to an upward refracting electromagnetic signal (R3) having the relatively lower propagation speed (V3) in the less resistive formations (3) and having an exit angle nearer to the normal N to the interface between said high-resistivity formation (2) and the lower-resistivity formation (3), and gives rise to a steeply rising refraction wave front (F3). The refracted electromagnetic wave front (F3) comprising refracted electromagnetic signals (R3) is detected along an array of sensor antennas (6a, 6b, 6c, . . . , 6k, . . . , 6n) along the seafloor, the array having a direction away from the transmitter (5). In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the electromagnetic transmitter (5) comprises an antenna (50) transmitting the electromagnetic signal (S) to an upper end (70 U) of an electrically conductive string (7), e.g. a steel casing or liner, the upper end (70 U) being arranged near said seafloor (1).
Owner:DEN NORSKE STATS OLJESELSKAP AS
Single-vector hydrophone passive positioning method based on array invariants
ActiveCN105158734AReduce dependenceSolve problems that require prior knowledge of marine environmental informationPosition fixationHydrophoneShort time fourier transformation
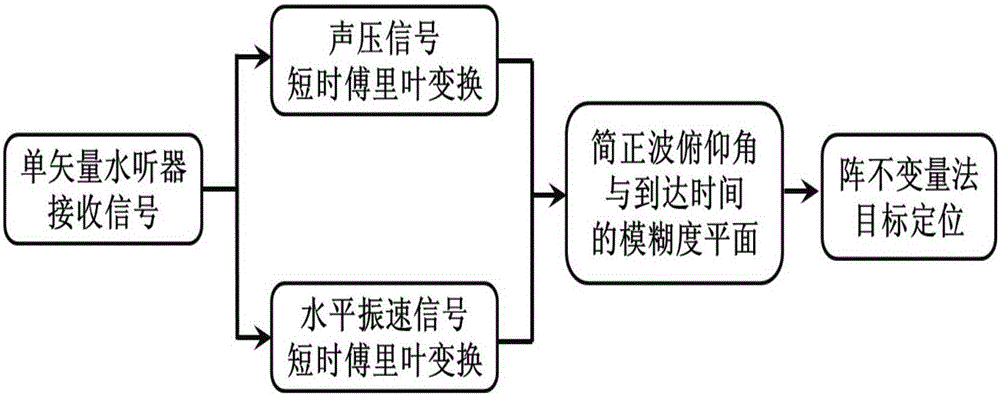
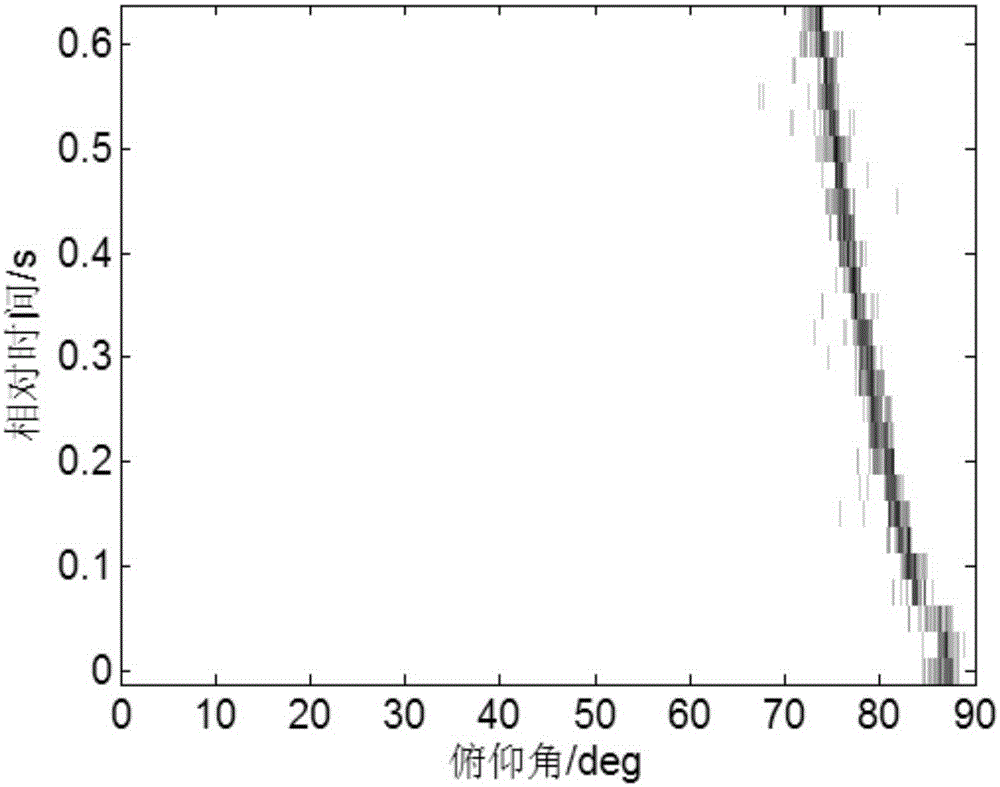
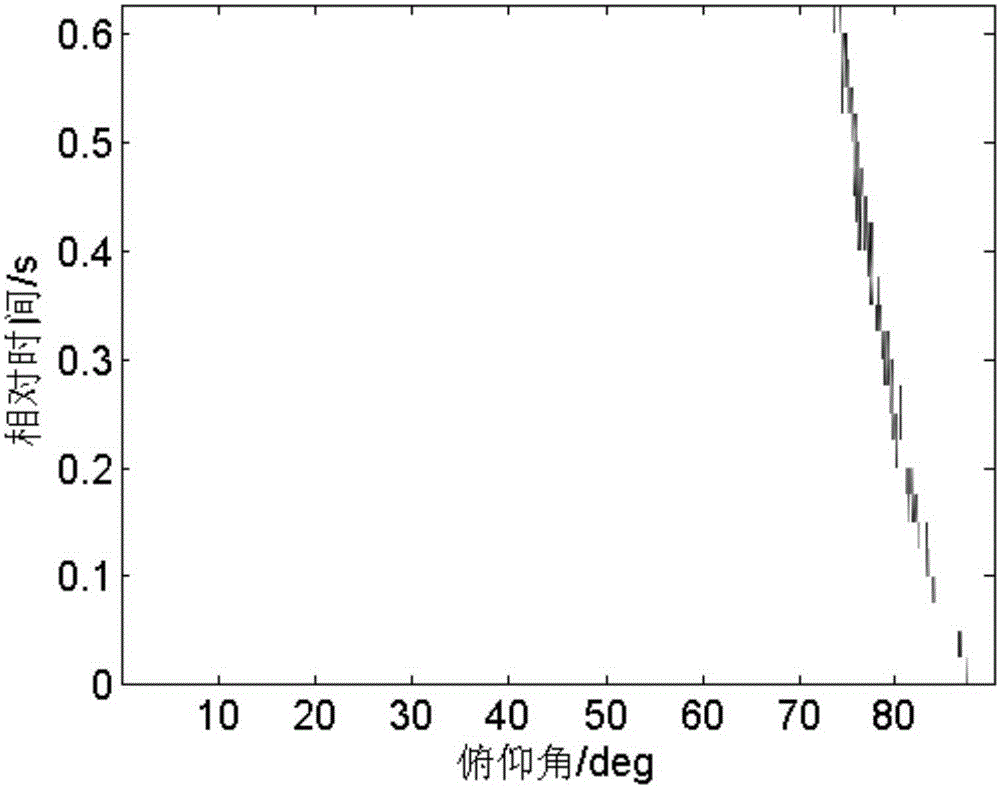
The invention discloses a single-vector hydrophone passive positioning method based on array invariants. The method comprises steps that, short-time Fourier transform of a sound pressure signal p(t) and a horizontal vibration velocity signal vr(t) is carried out to obtain sound pressure time frequency distribution P(tau, f) and horizontal vibration velocity time frequency distribution Vr(tau, f); the sound pressure time frequency distribution P(tau, f) and the horizontal vibration velocity time frequency distribution Vr(tau, f) acquired in the first step are utilized to acquire a fuzziness plane R(tau, phi) of a normal wave pitching angle phi and a normal wave arriving time tau; target positioning is realized by utilizing the array invariant method according to the fuzziness plane R(tau, phi) of the normal wave pitching angle phi and the normal wave arriving time tau in the second step. Through the method, dependence on prior sea environment knowledge is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Orthogonal mode adaptor
ActiveCN104617359AAccuracy is easy to guaranteeReduce processing costsWaveguide type devicesCommunications systemMicrowave
The invention discloses an orthogonal mode adaptor. The orthogonal mode adaptor comprises a coupled cavity and a transverse output end. The coupled cavity comprises at least two coupling sections which are communicated from left to right. The coupled cavity is communicated with the transverse output end in the back direction. In all the coupling sections from left to right, the first coupling section is a rectangular body with the axis in the direction from left to right, wherein the difference between the width and the height of the left end face of the first coupling section is smaller than 20%. The upper surfaces of all the coupling sections are flush. Meanwhile, a rectangular longitudinal output end is an external port, and the normal at the center of the external port coincides with the direction of the normal at the center of the cross section of the first coupling section from left to right. The orthogonal mode adaptor has the advantages that the orthogonal mode adaptor can be easily obtained by conducting milling and cutting through a machining center, and the influence of the assembly error of a cover plate and a base on the device performance is small, and the orthogonal mode adaptor can be widely applied to microwaves especially satellite communication systems of millimeter waves and terahertz frequency bands and other communication systems.
Owner:成都赛纳赛德科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com