Single-vector hydrophone passive positioning method based on array invariants
An array-invariant and passive positioning technology, applied in the field of single-vector hydrophone passive positioning based on array-invariant, can solve problems such as weak positioning method of dependence on prior knowledge of marine environment, and achieve the effect of reducing dependence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
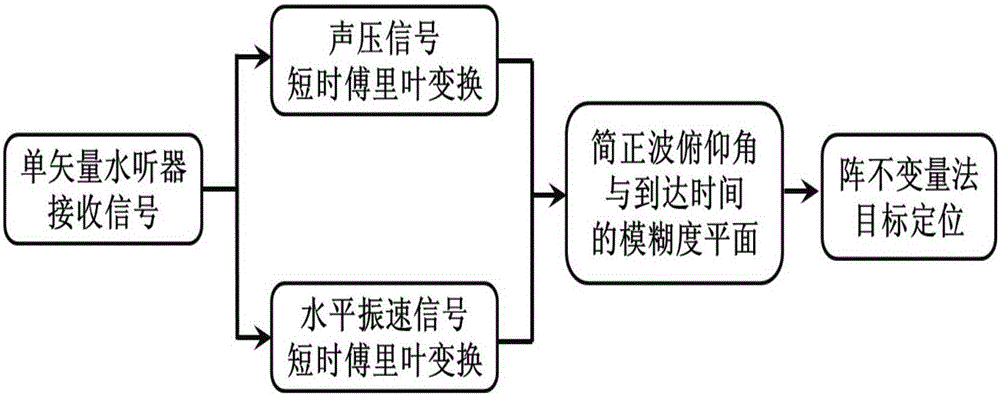
[0042] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Illustrate this embodiment, a kind of single-vector hydrophone passive positioning method based on array invariant is specifically carried out according to the following steps:
[0043] Step 1. The sound pressure signal p(t) and the horizontal vibration velocity signal v received by the vector hydrophone r (t) Perform short-time Fourier transform to obtain the time-frequency distribution of sound pressure P(τ,f) and the time-frequency distribution of horizontal vibration velocity V r (τ,f);
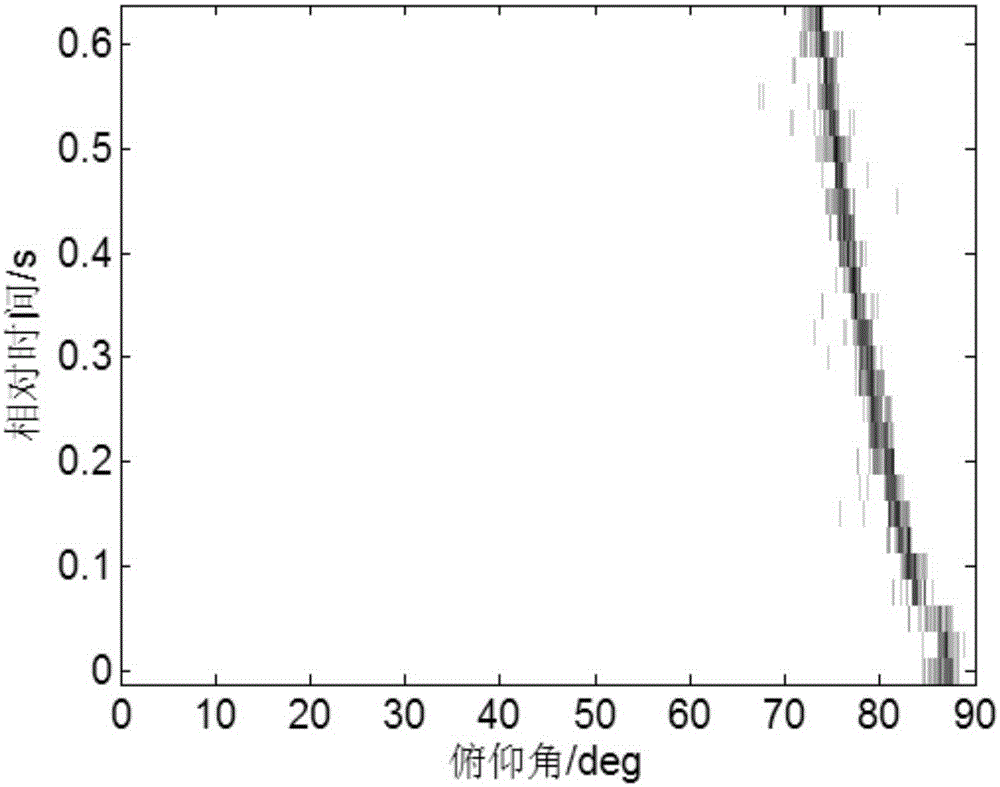
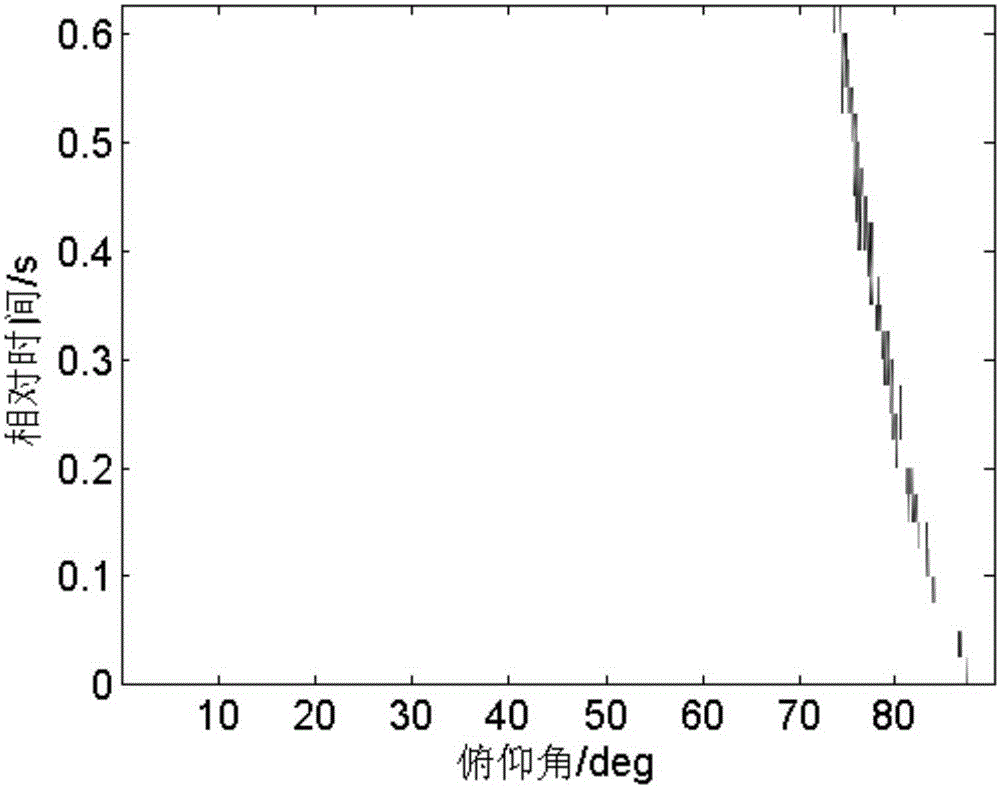
[0044] Step 2. Using the time-frequency distribution P(τ, f) of the sound pressure and the time-frequency distribution V of the horizontal vibration velocity in the step 1 r (τ,f) to get the normal wave elevation angle Ambiguity plane with normal wave arrival time τ
[0045] Step 3. According to the normal wave pitch angle in step 2 Ambiguity plane with normal wave arrival time τ The method of array invariant is used to ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0046] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the sound pressure signal p (t) and the horizontal vibration velocity signal v received by the vector hydrophone in the step one r (t) Perform short-time Fourier transform to obtain the time-frequency distribution of sound pressure P(τ,f) and the time-frequency distribution of horizontal vibration velocity V r (τ,f); the specific process is:
[0047] P ( τ , f ) = ∫ - ∞ + ∞ p ( t ) h ( t - τ ) e - j 2 π f t ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0053] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the time-frequency distribution P(τ, f) of the sound pressure in the step one and the time-frequency distribution V of the horizontal vibration velocity are used in the second step r (τ,f) to get the normal wave elevation angle Ambiguity plane with normal wave arrival time τ The specific process is:
[0054] According to the normal wave theory, the sound pressure P(r,z,f) and the horizontal vibration velocity V in the vector sound field in the shallow sea waveguide r (r,z,f) is expressed as follows:
[0055] P ( r , z , f ) = j 2 π r e - j π 4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com