Patents
Literature
278 results about "Plane of incidence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
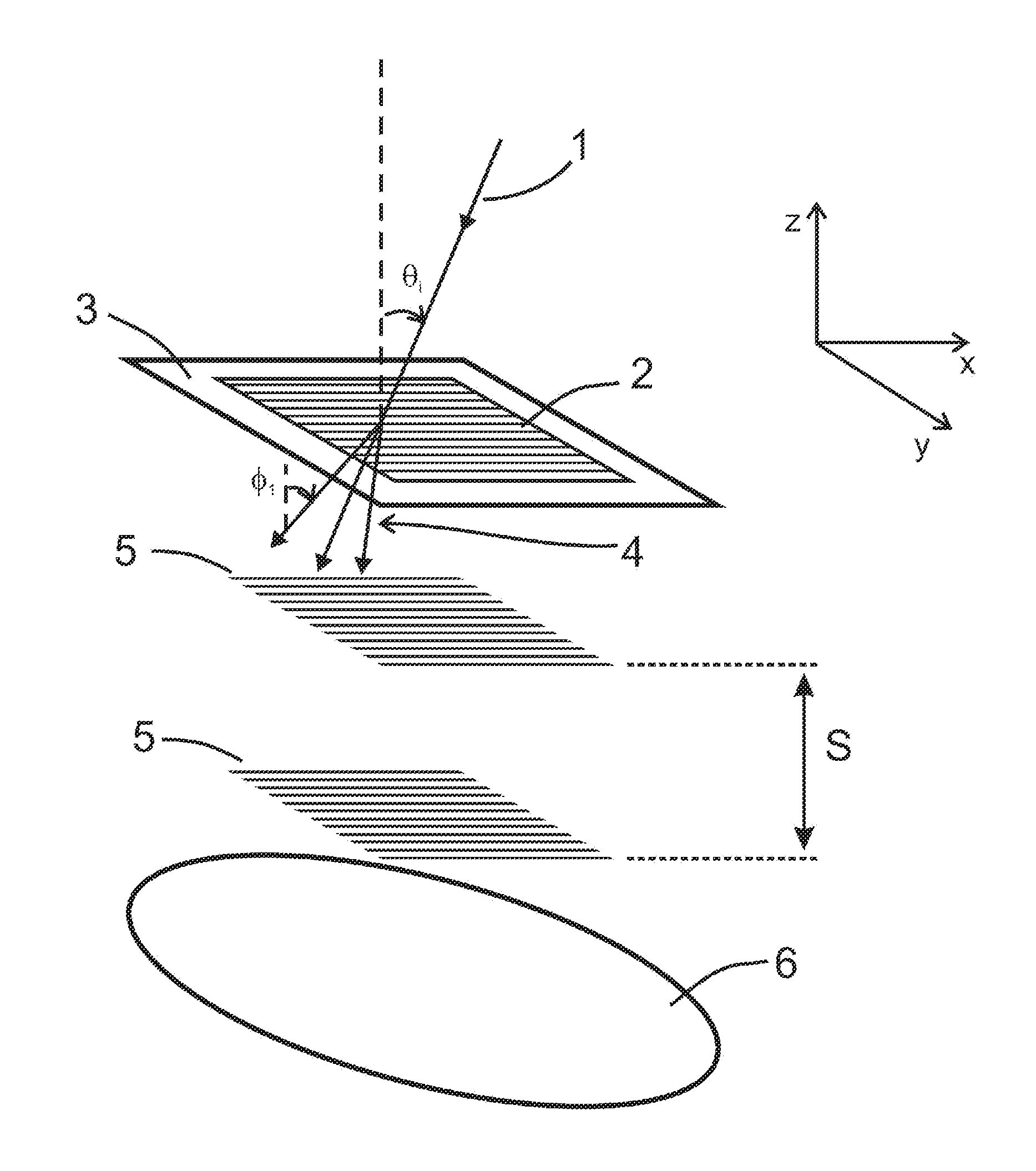
In describing reflection and refraction in optics, the plane of incidence (also called the incidence plane or the meridional plane) is the plane which contains the surface normal and the propagation vector of the incoming radiation. In wave optics, the latter is the k-vector, or wavevector, of the incoming wave. When reflection is specular, as it is for a mirror or other shiny surface, the reflected ray also lies in the plane of incidence; when refraction also occurs, the refracted ray lies in the same plane.
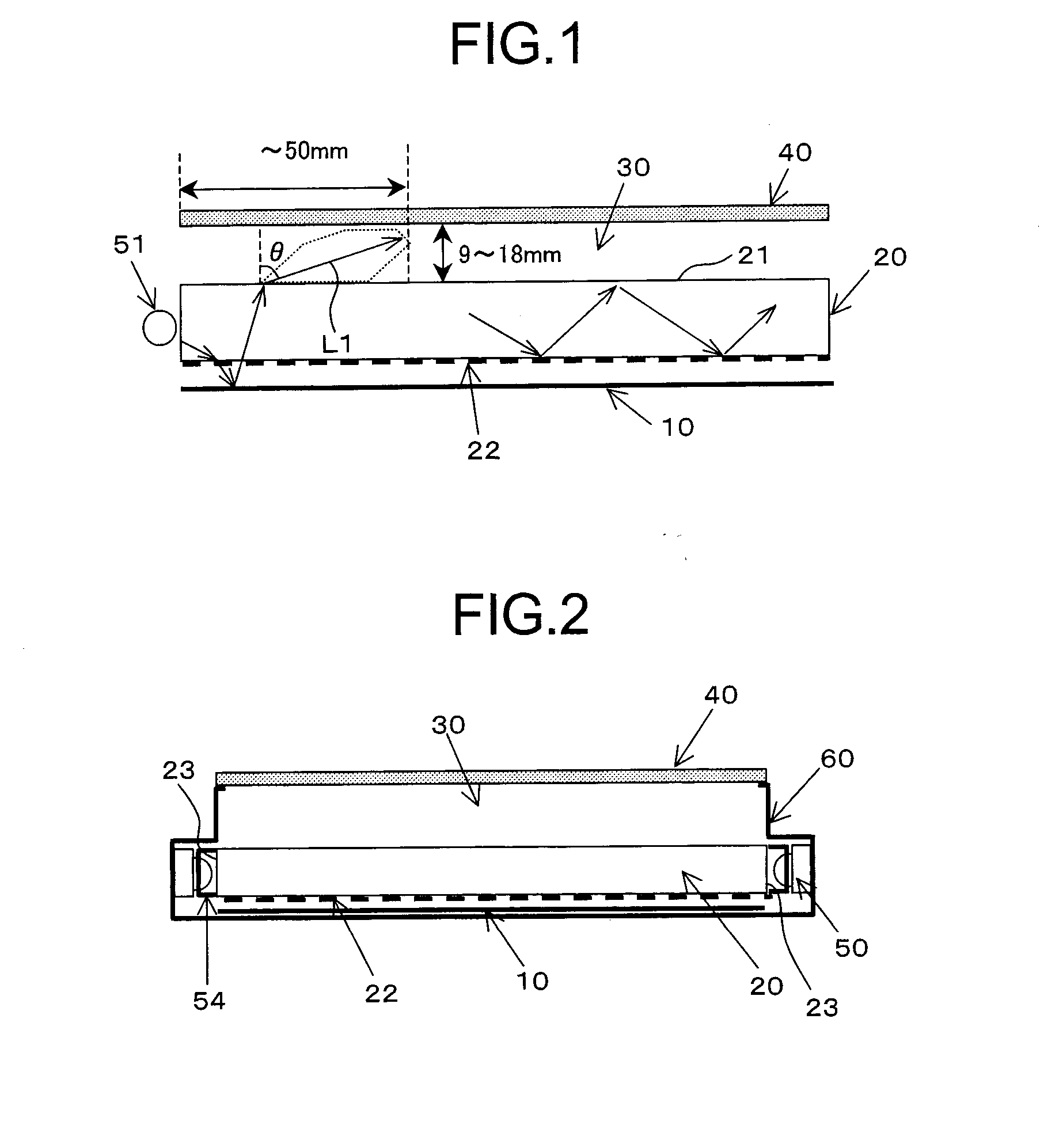
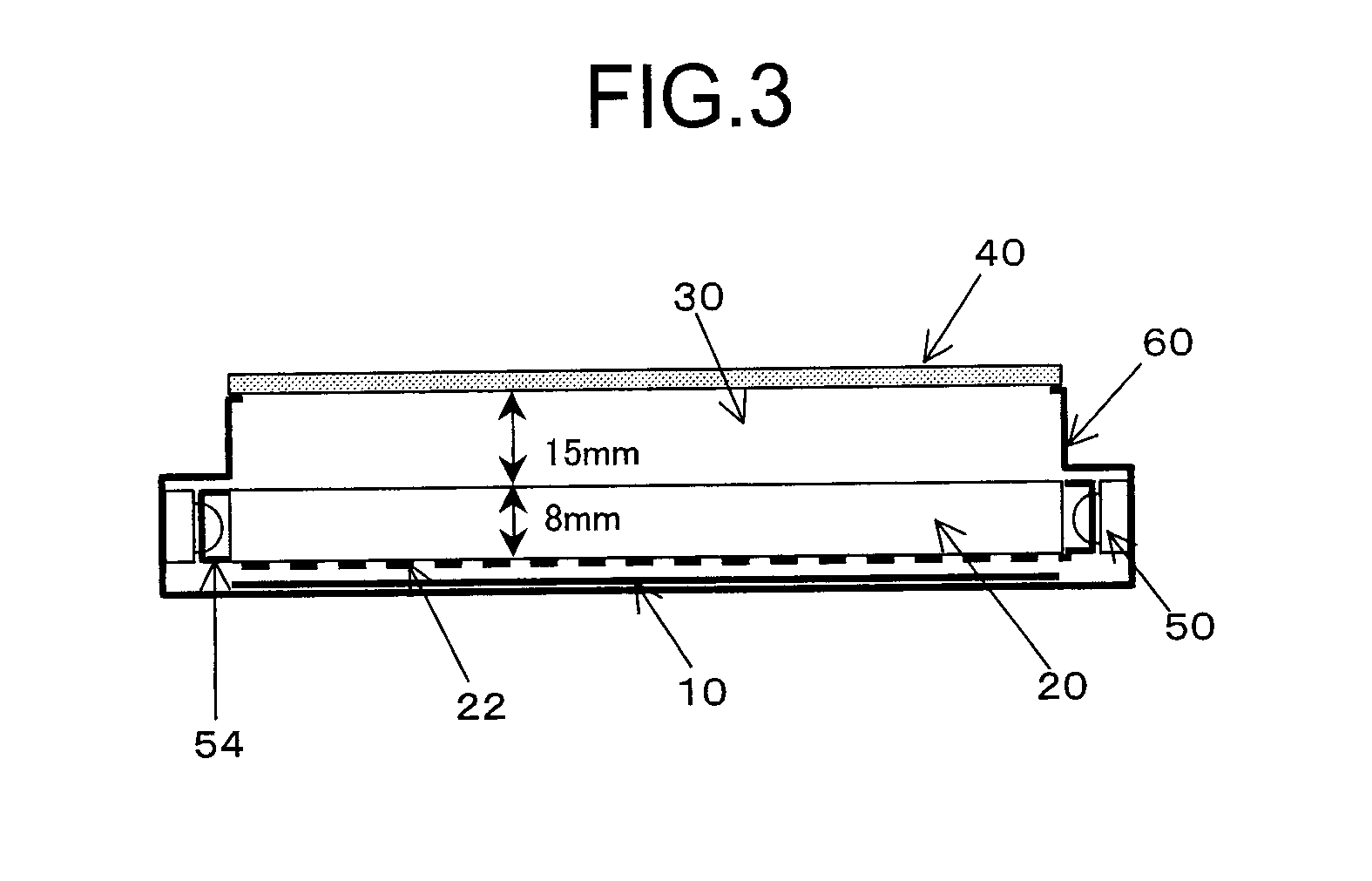
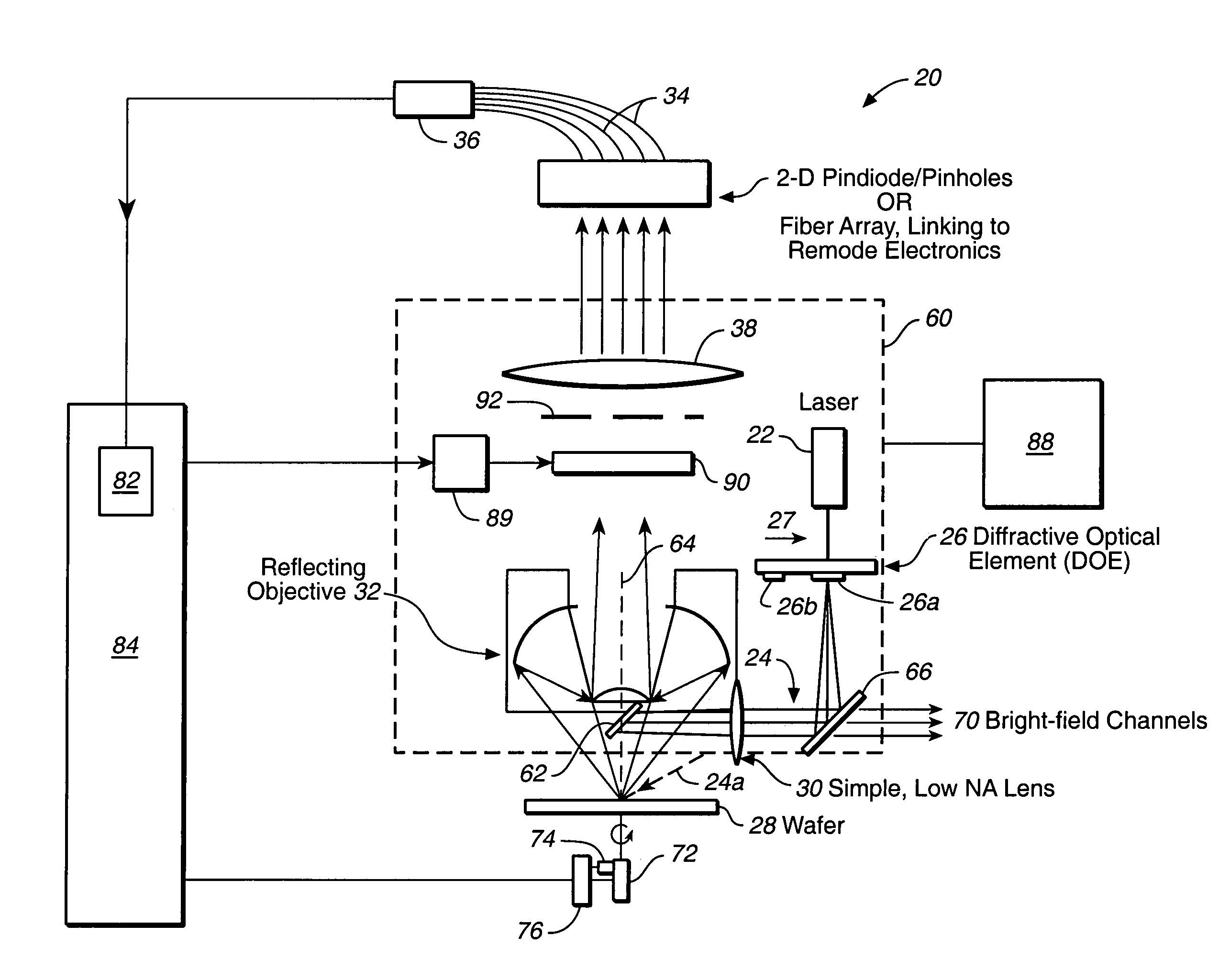
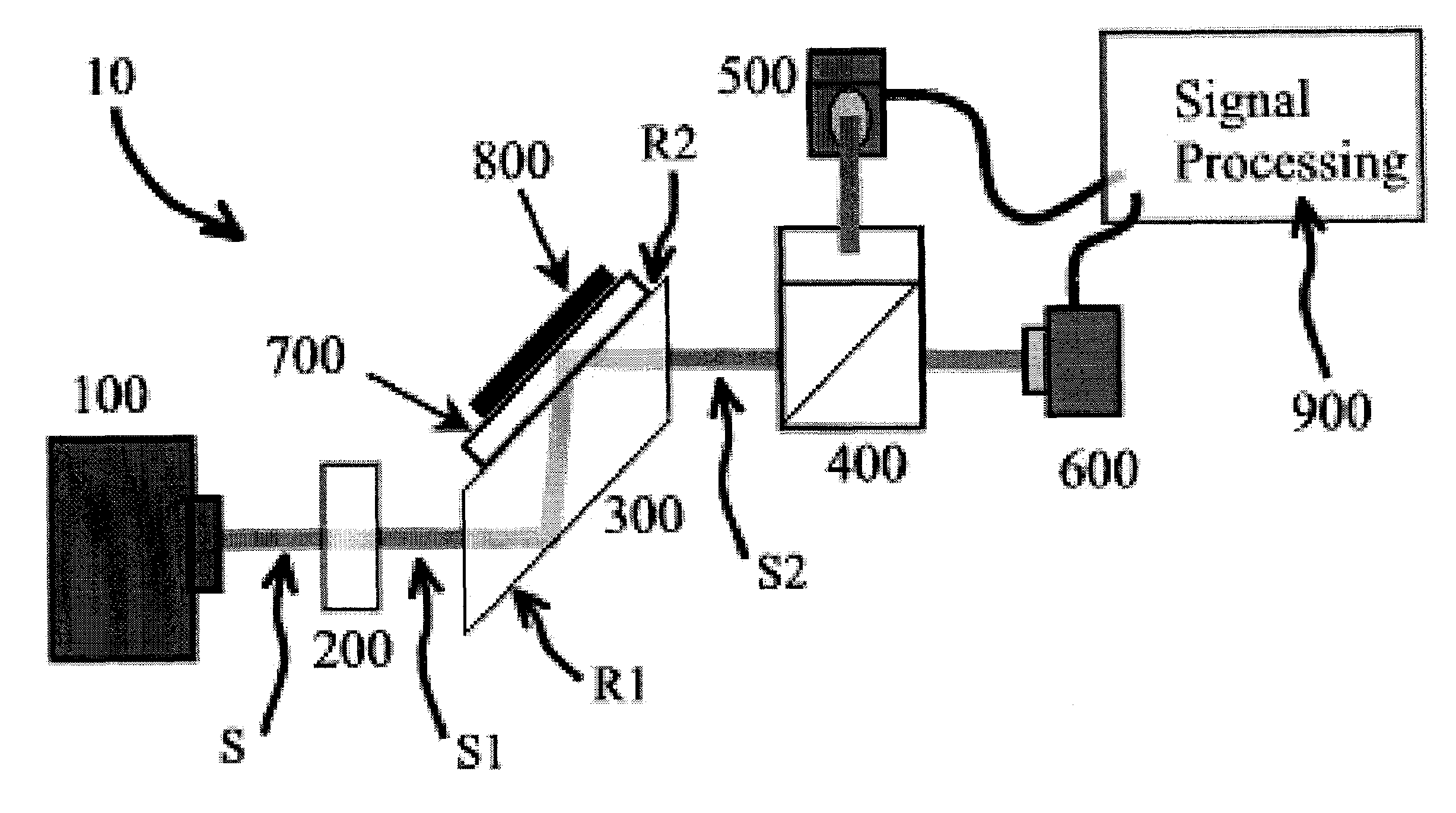
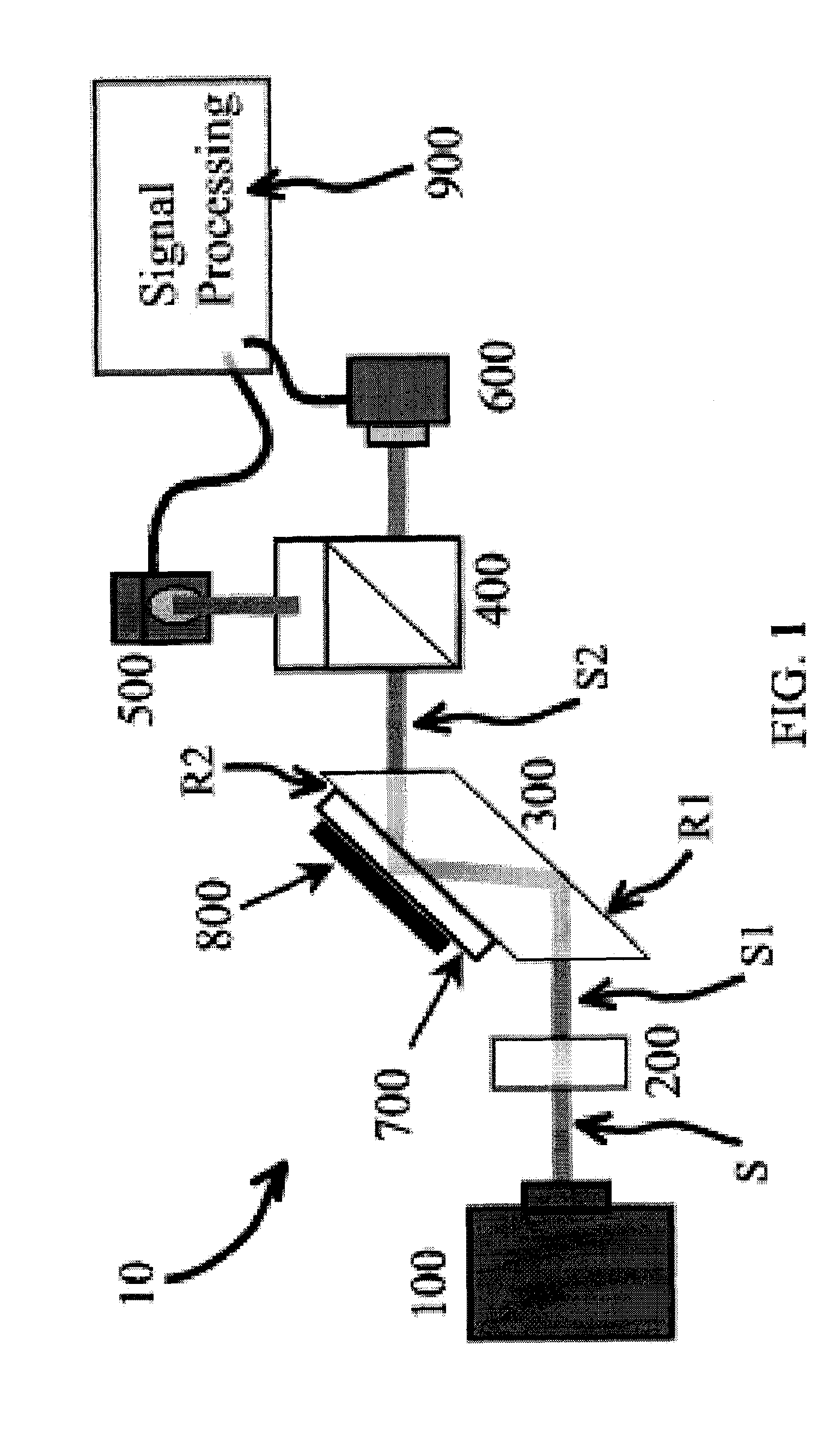
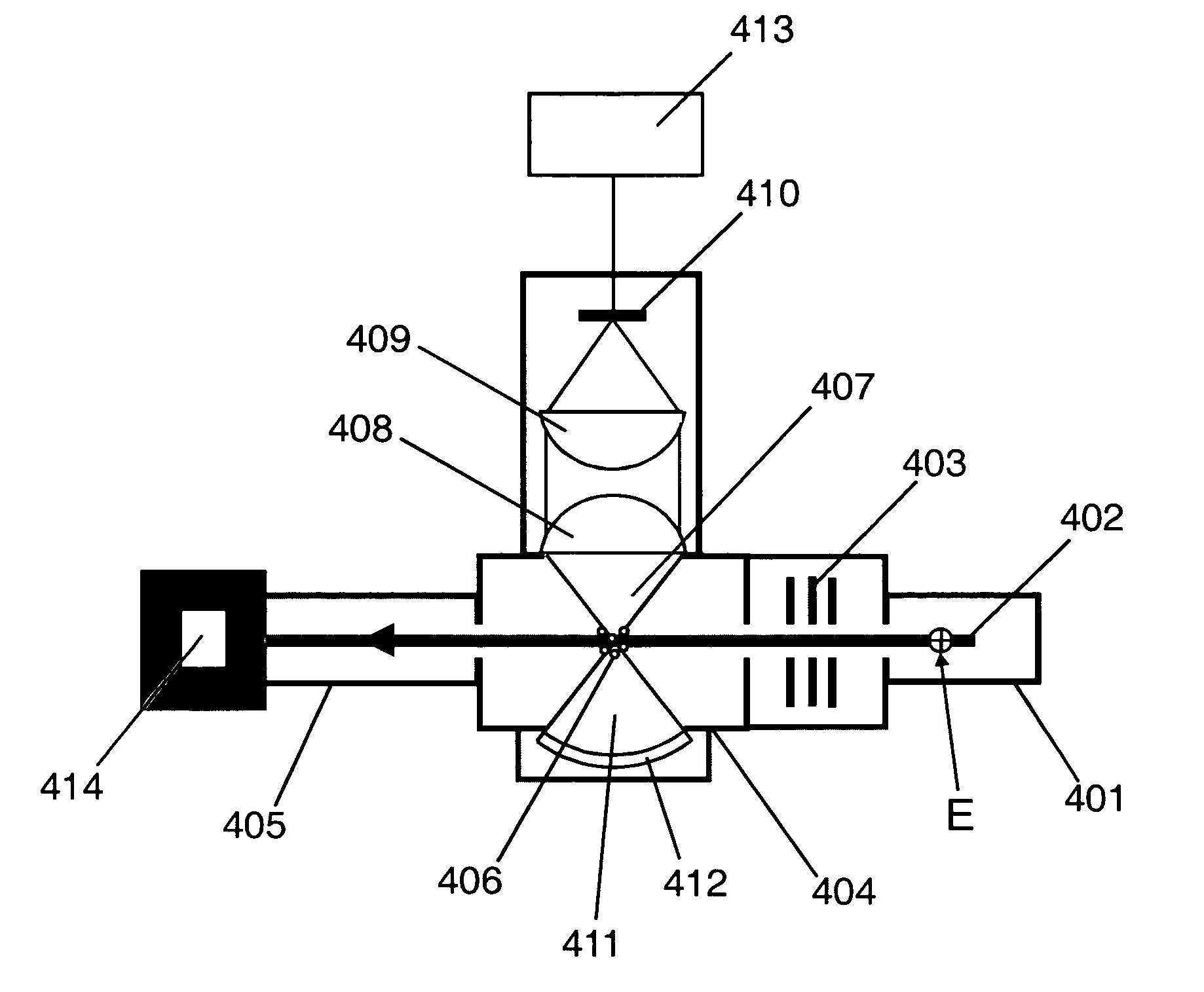
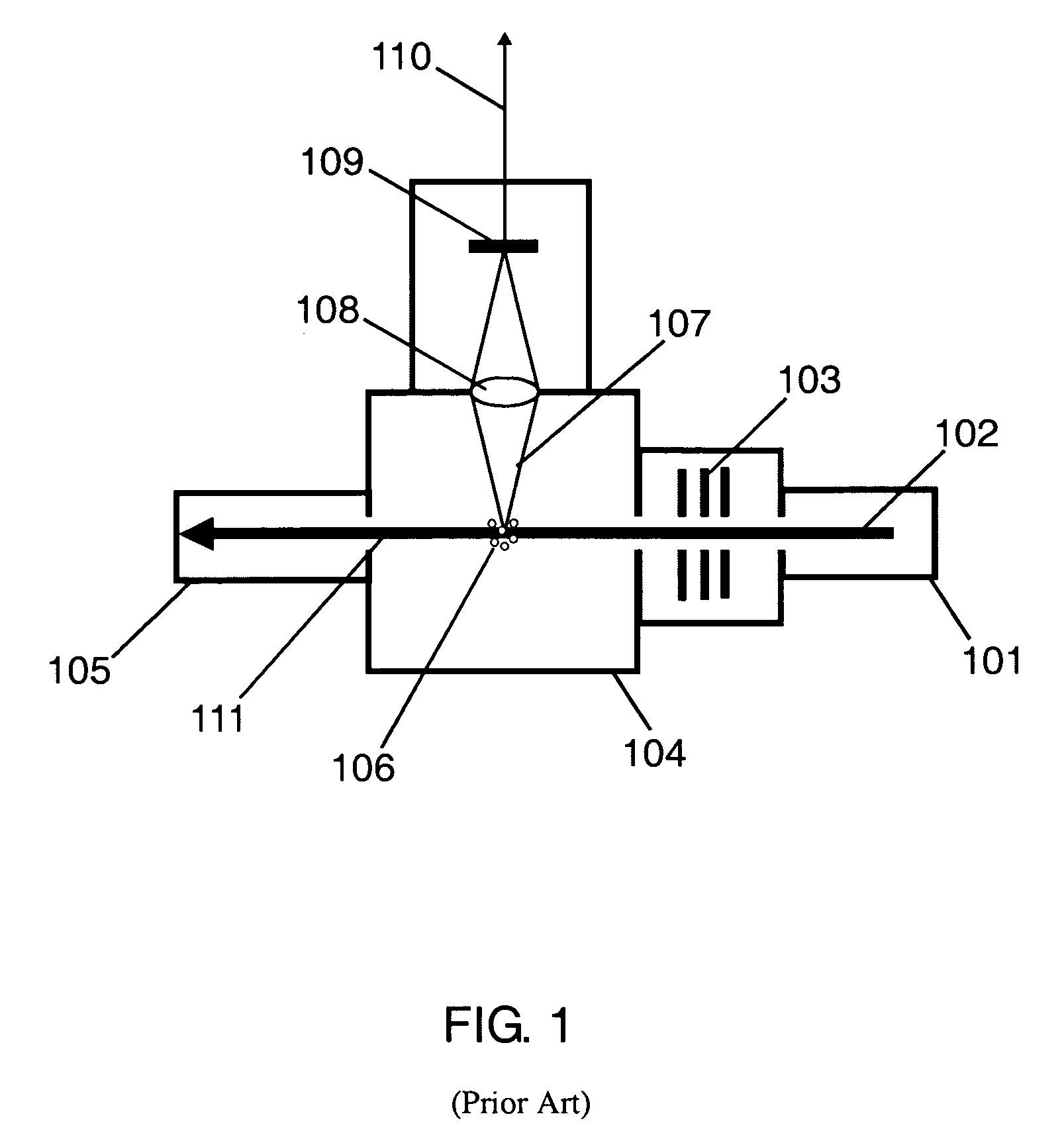
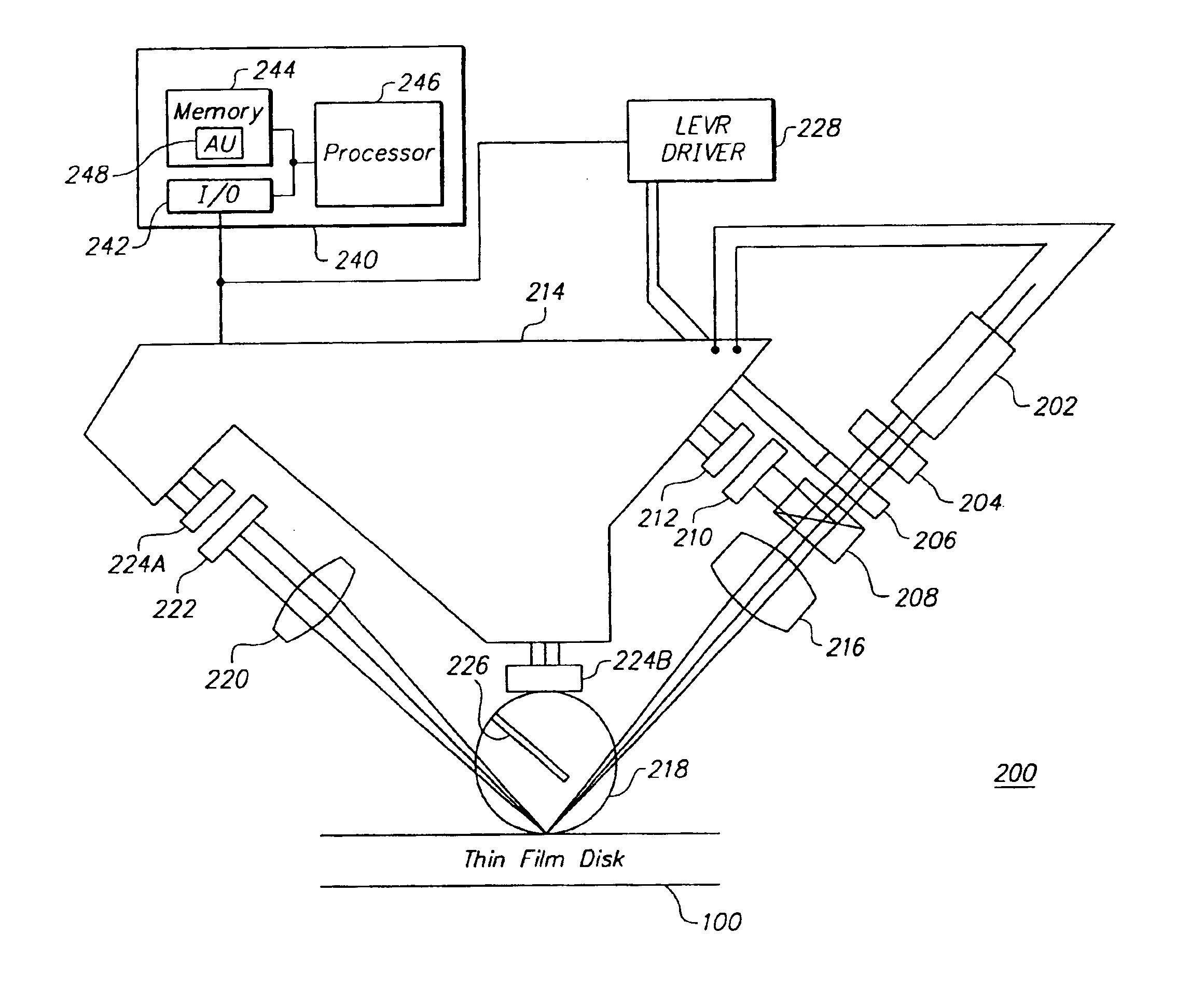
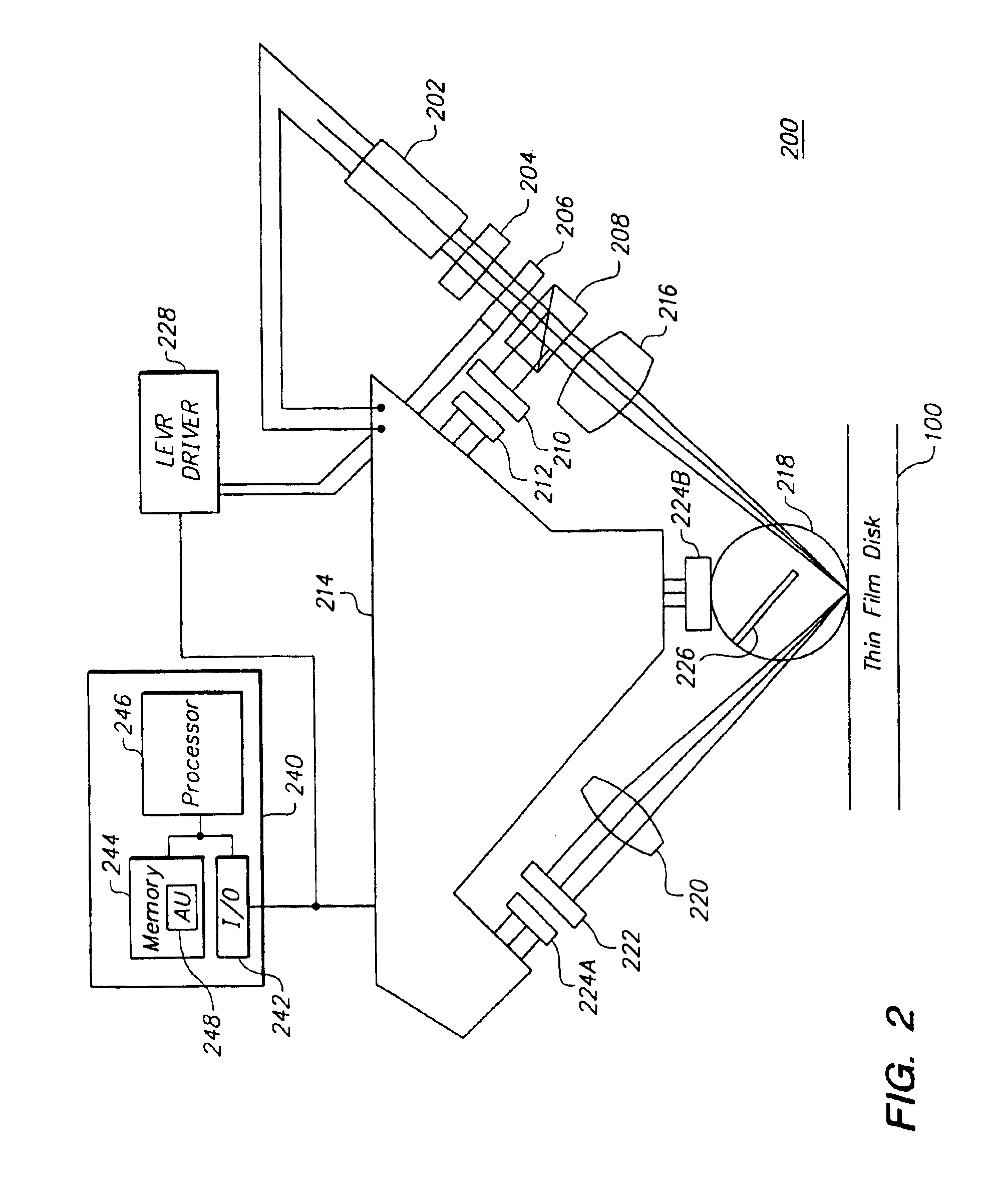
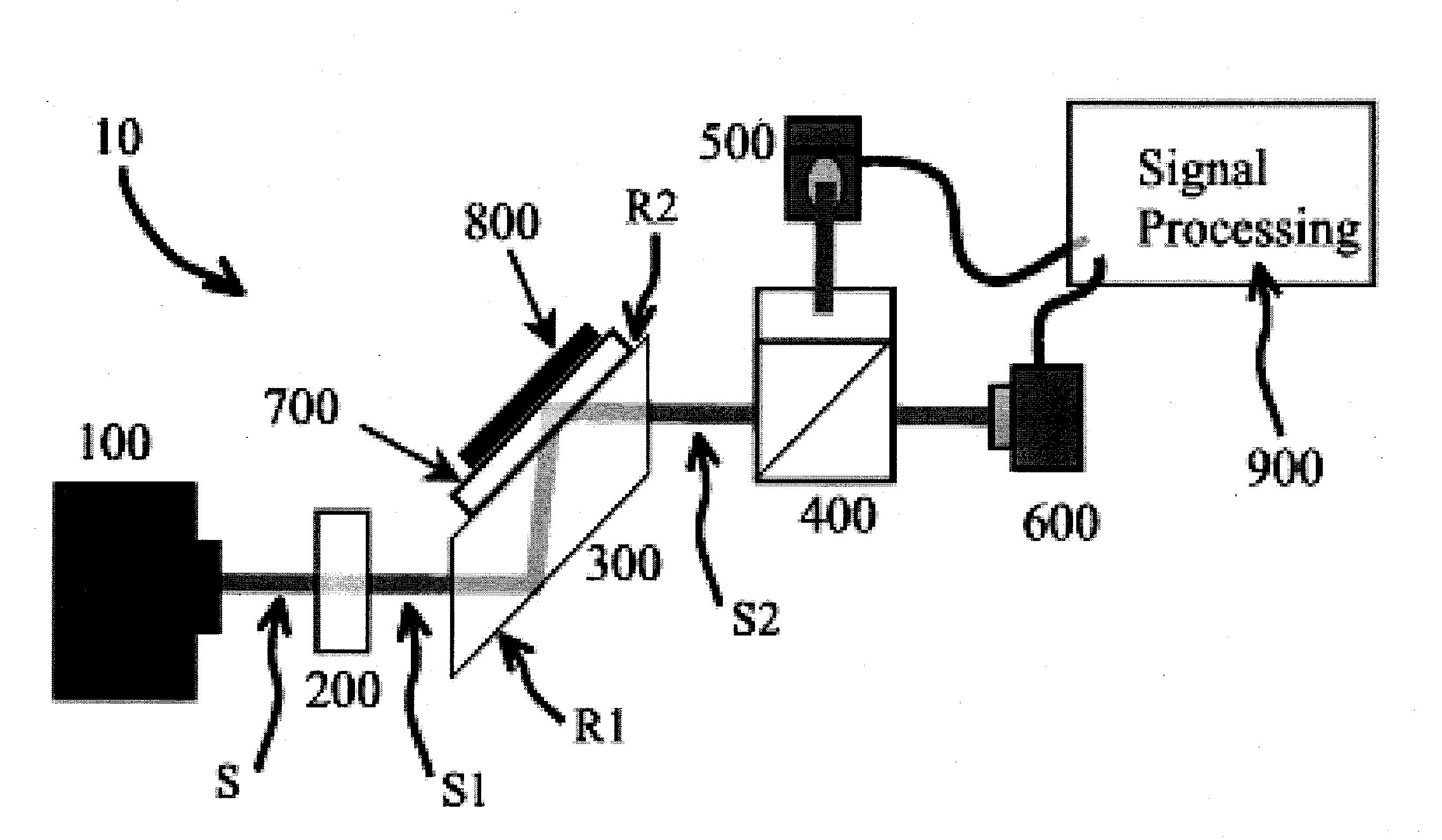
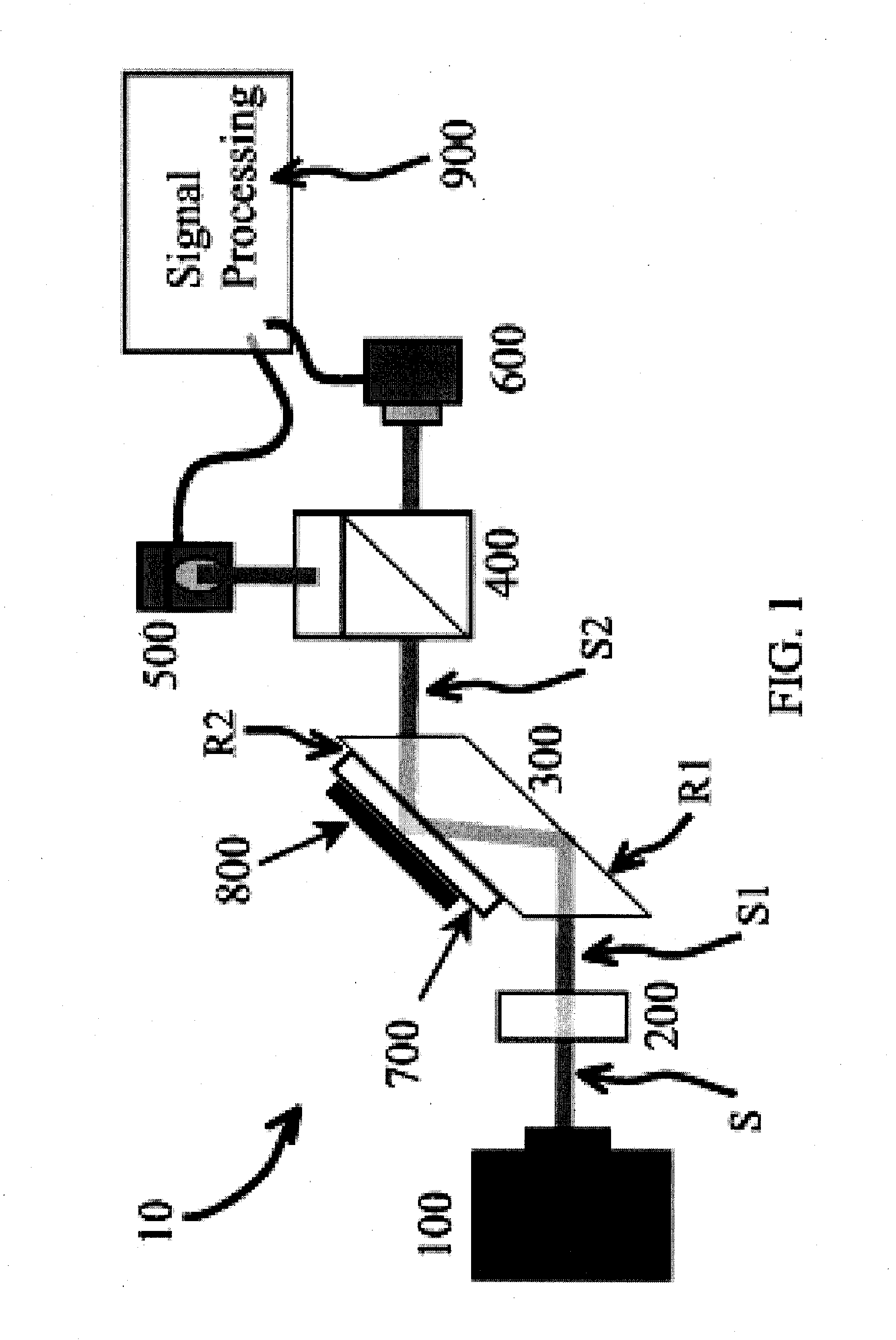
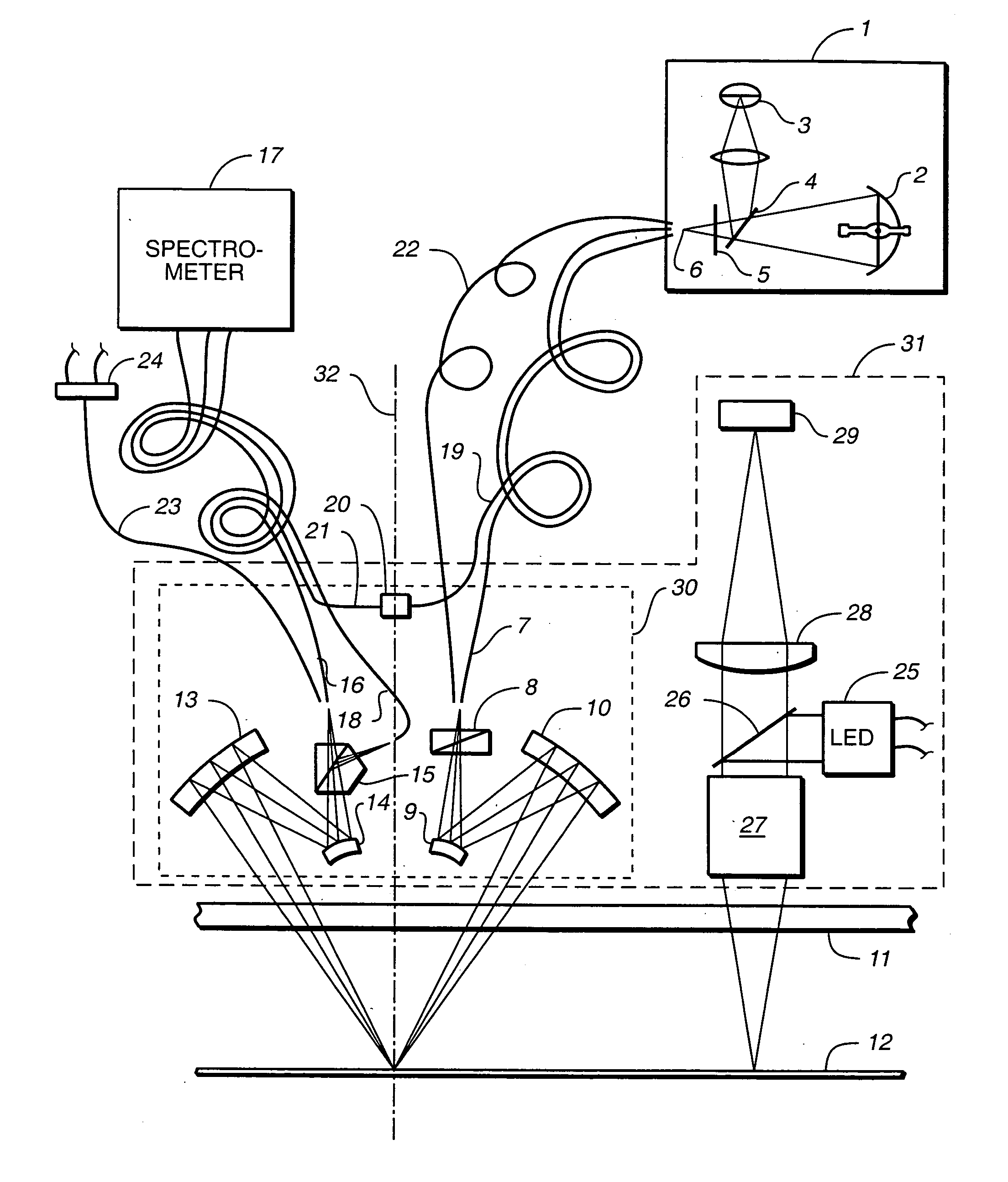
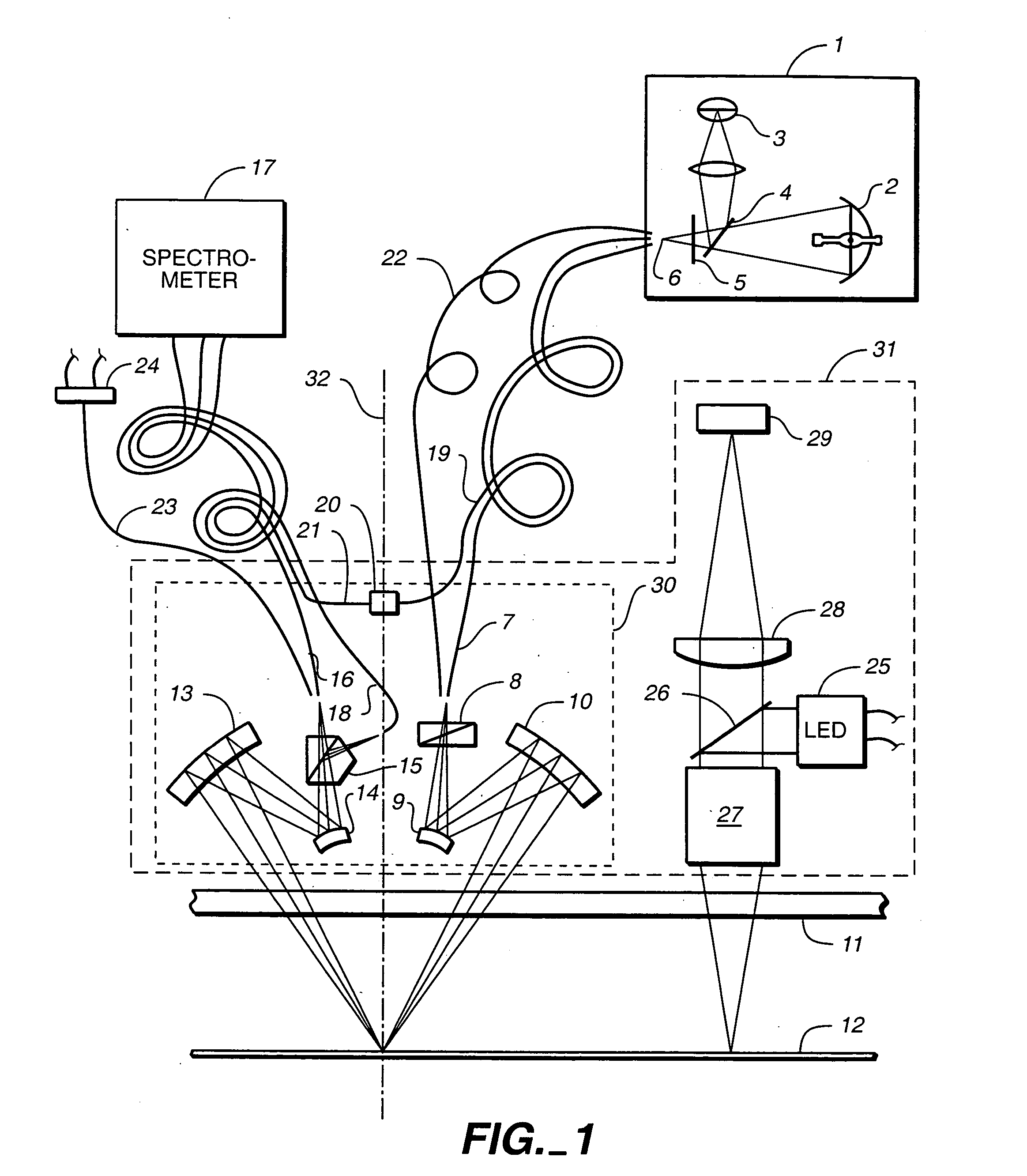
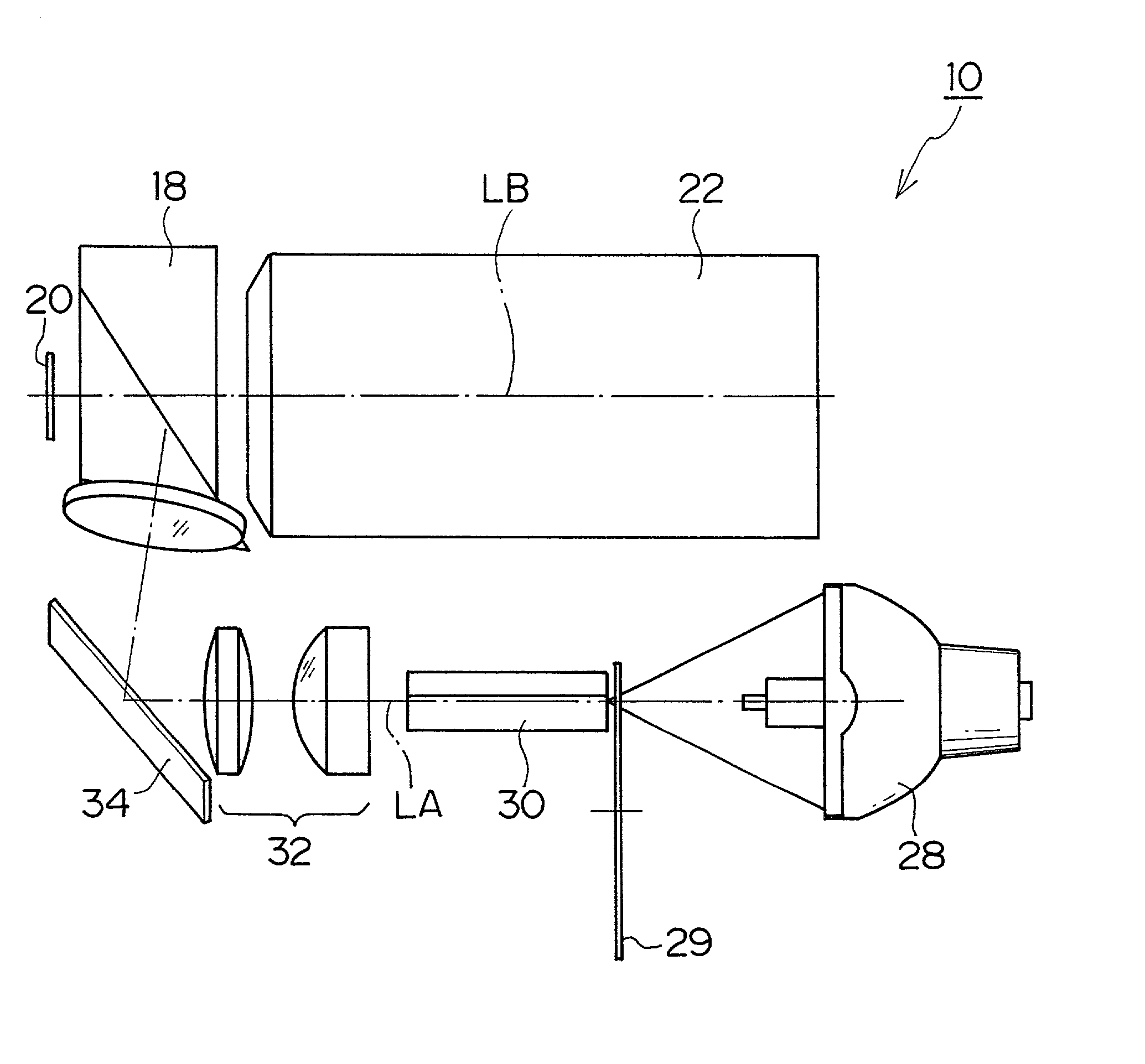
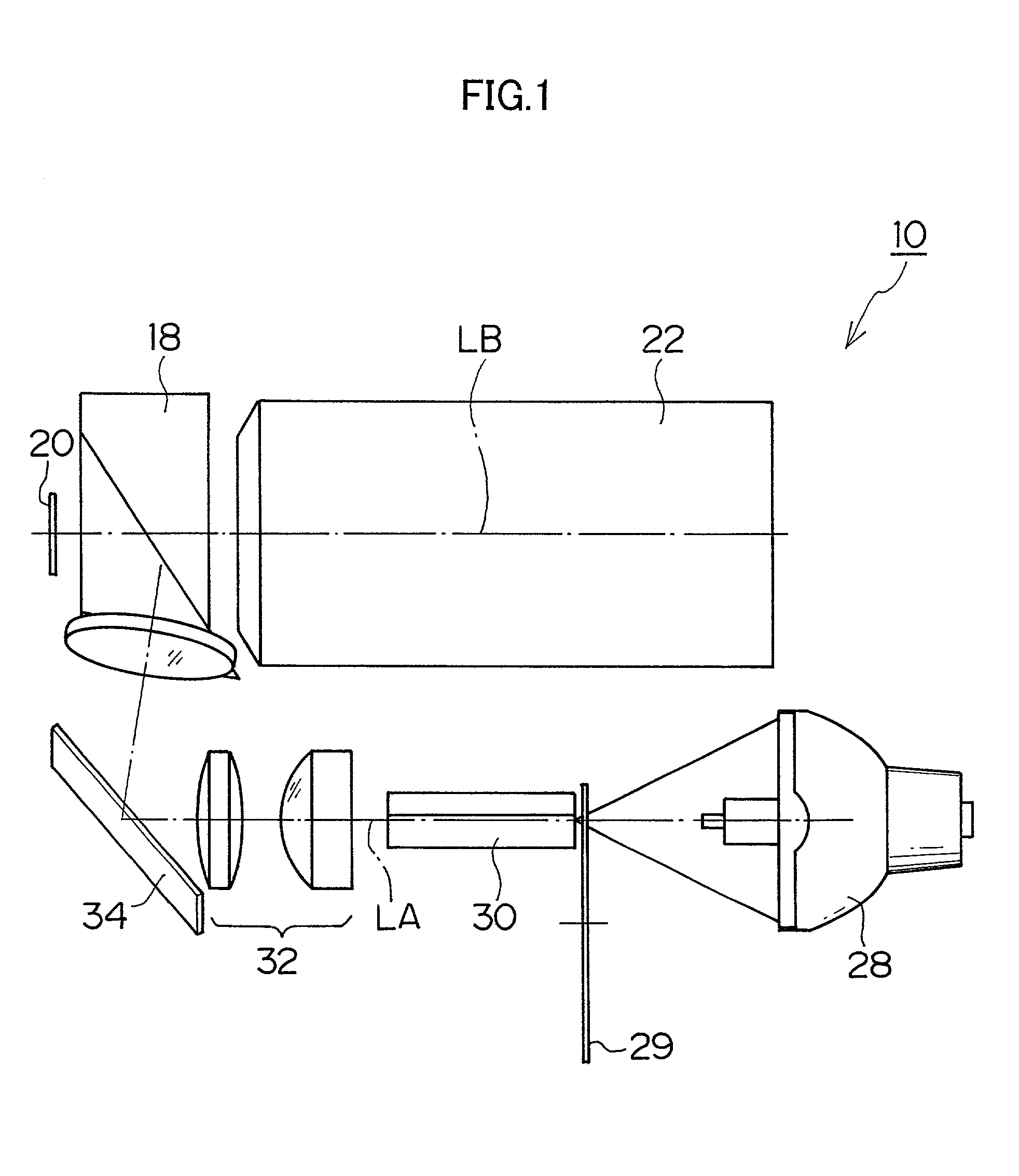
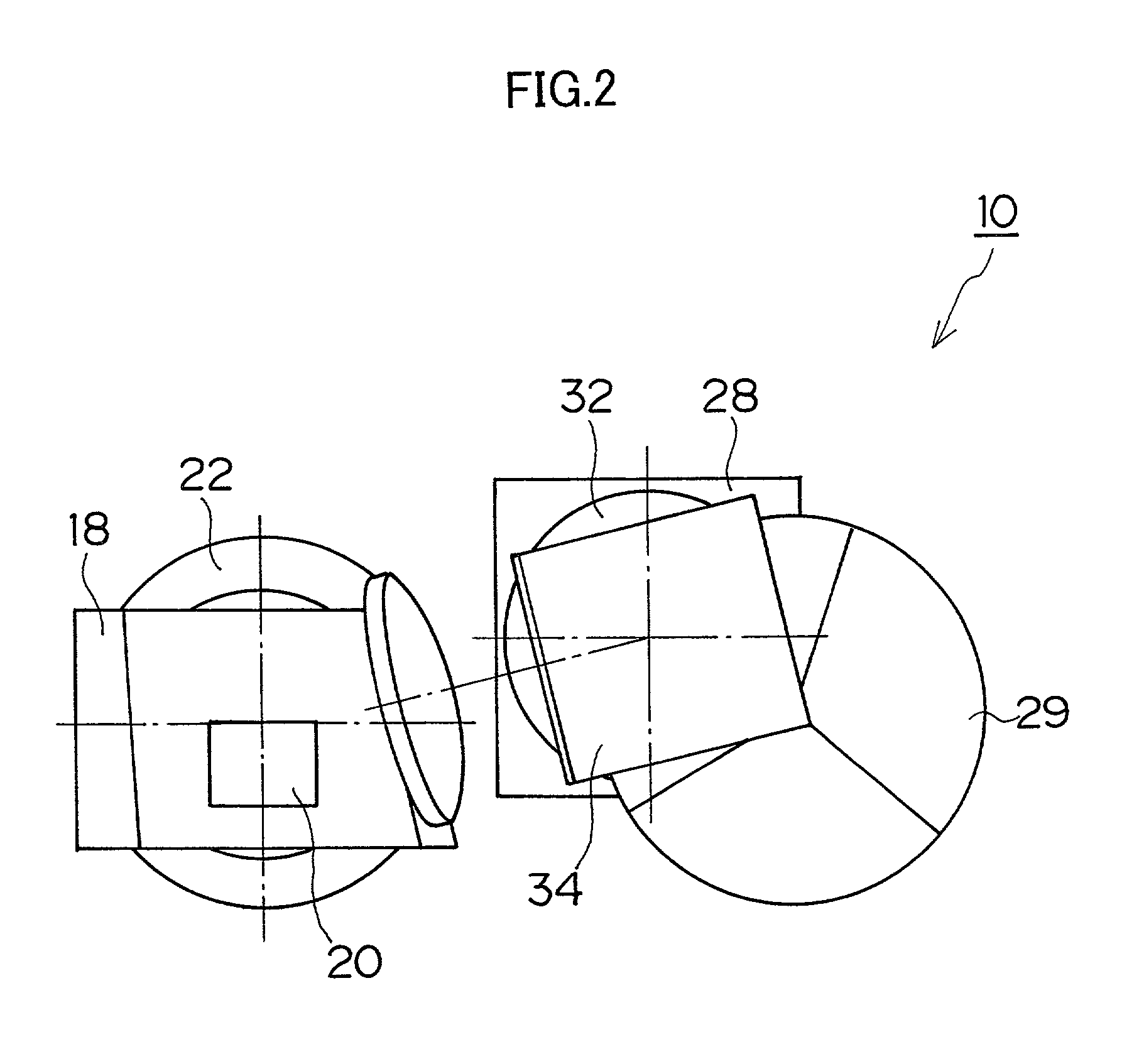
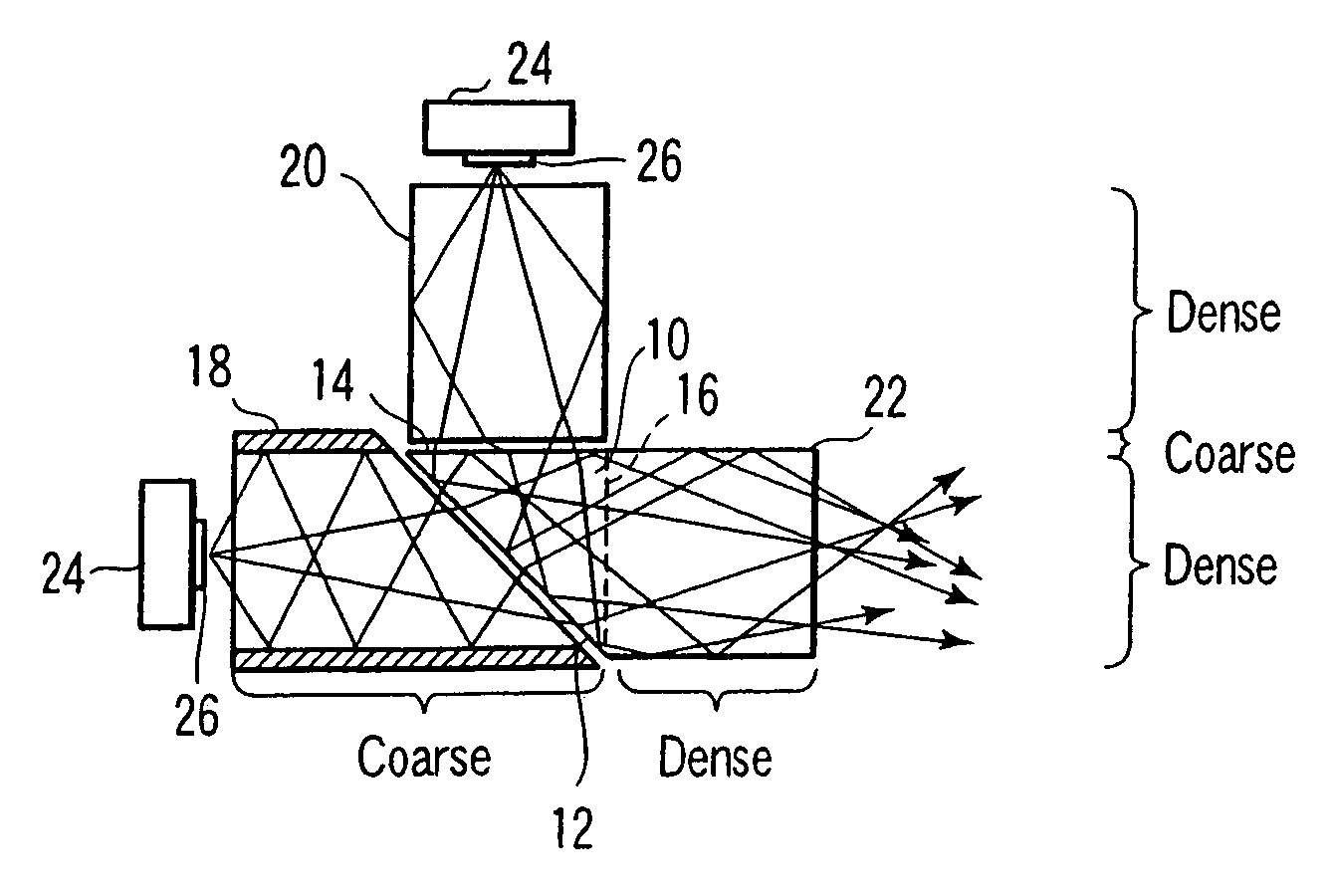
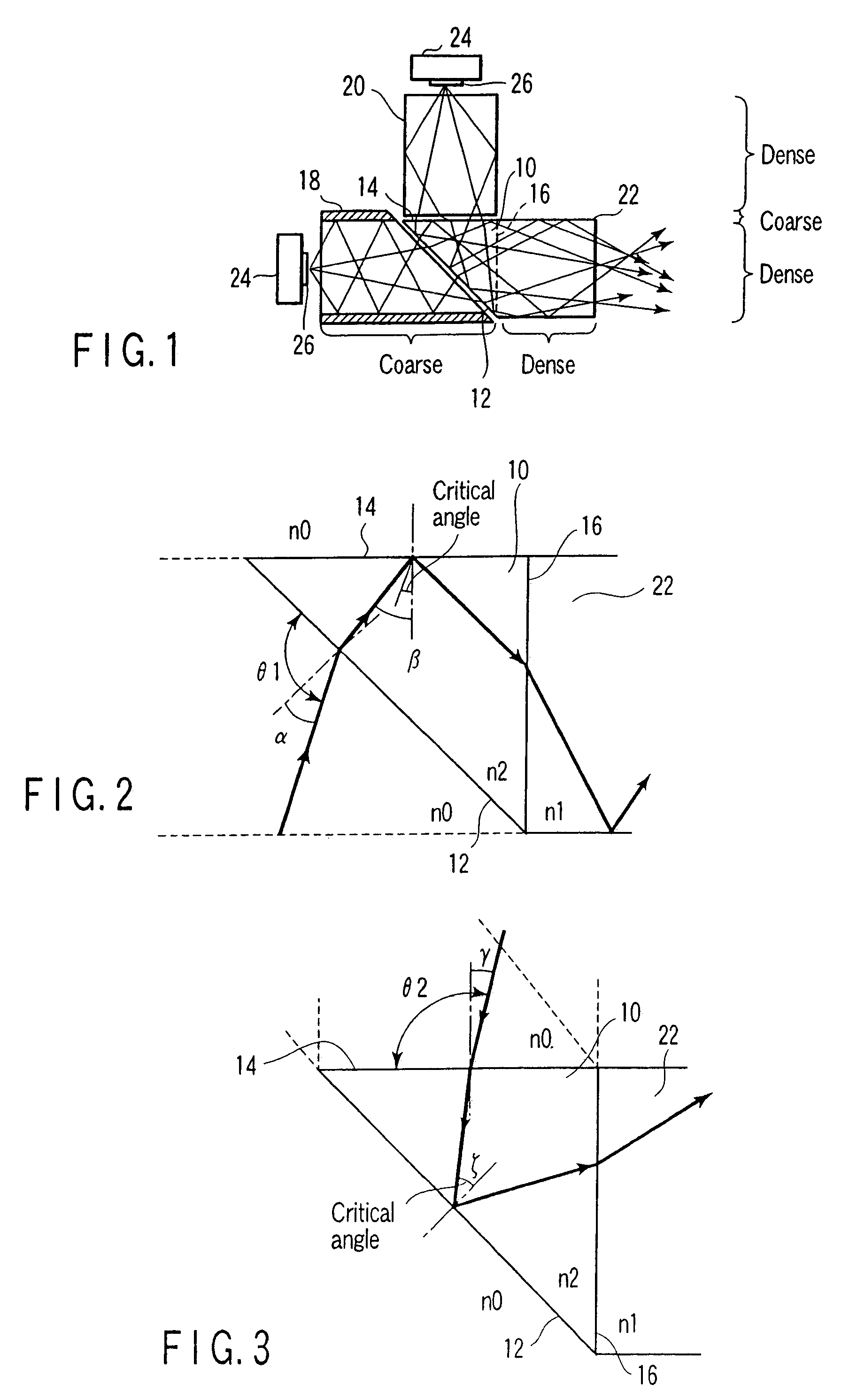
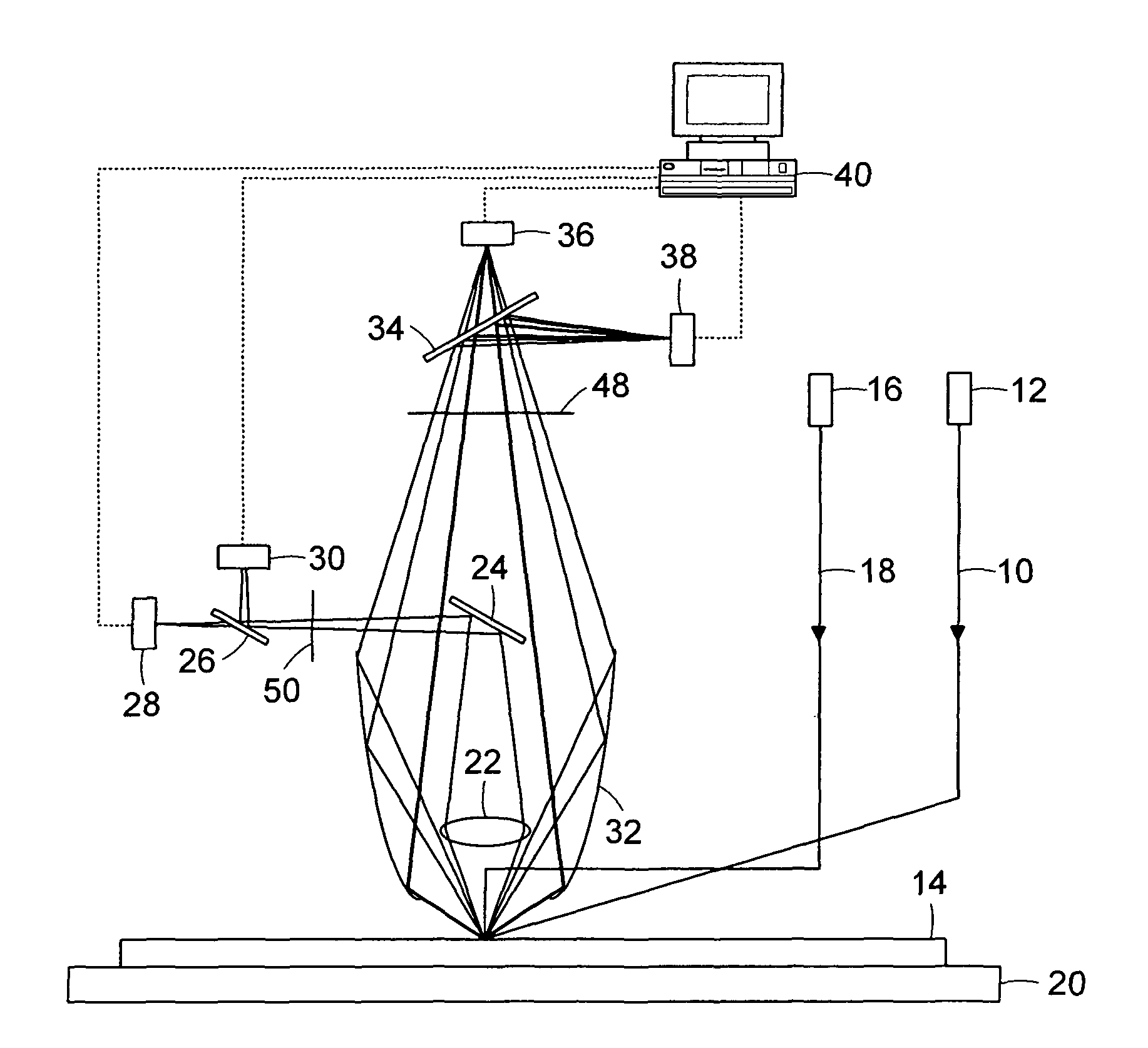
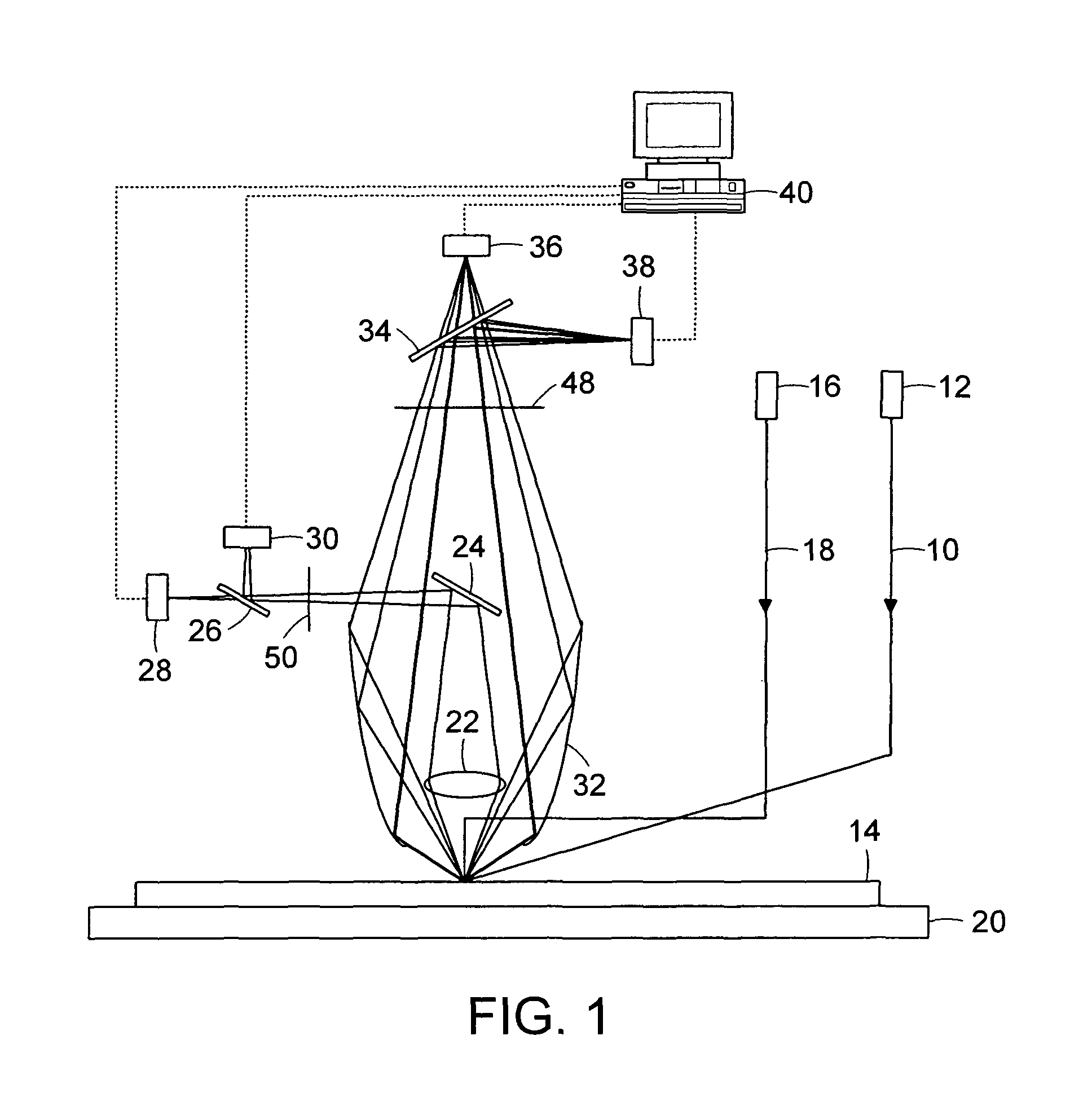
Surface inspection system using laser line illumination with two dimensional imaging
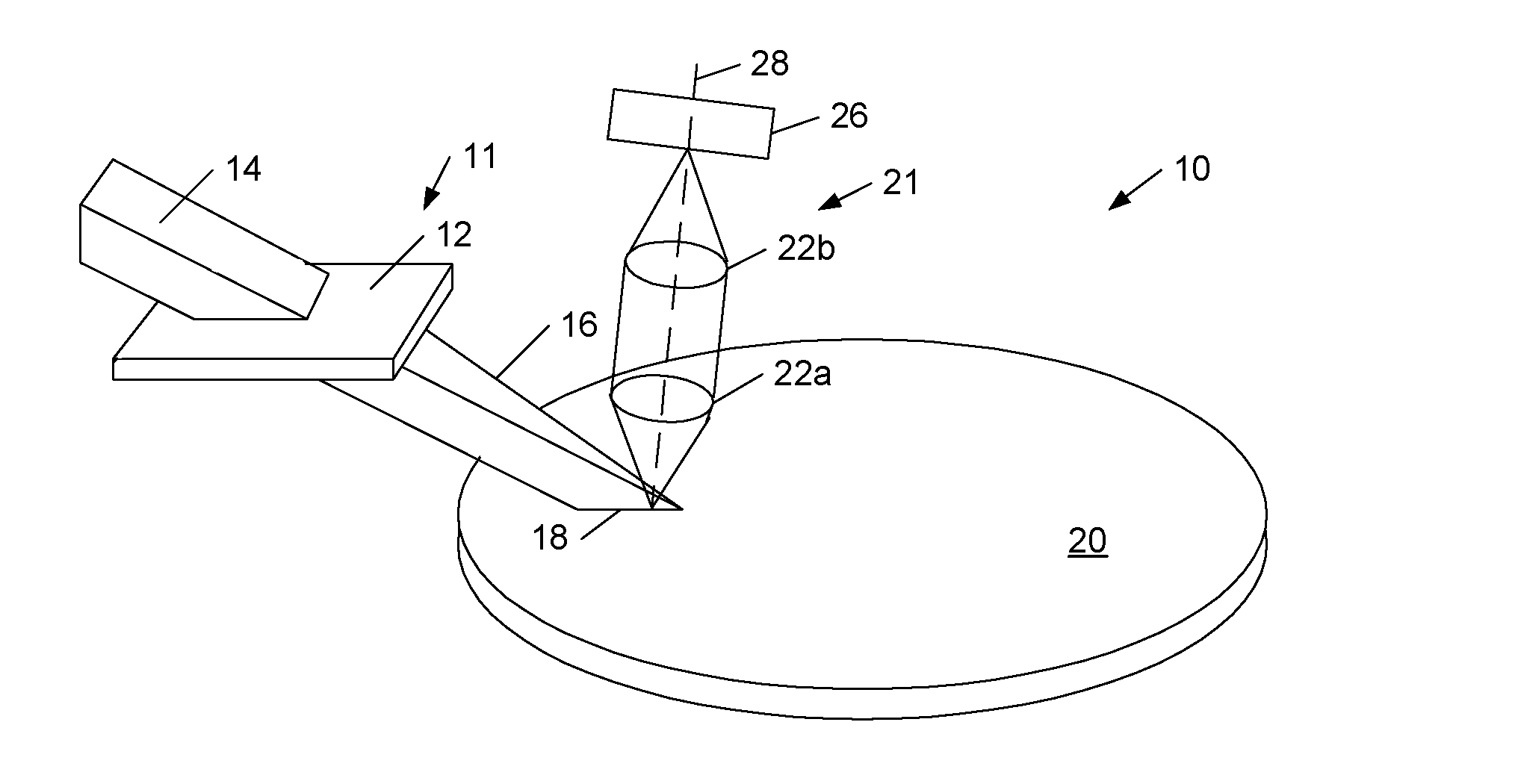
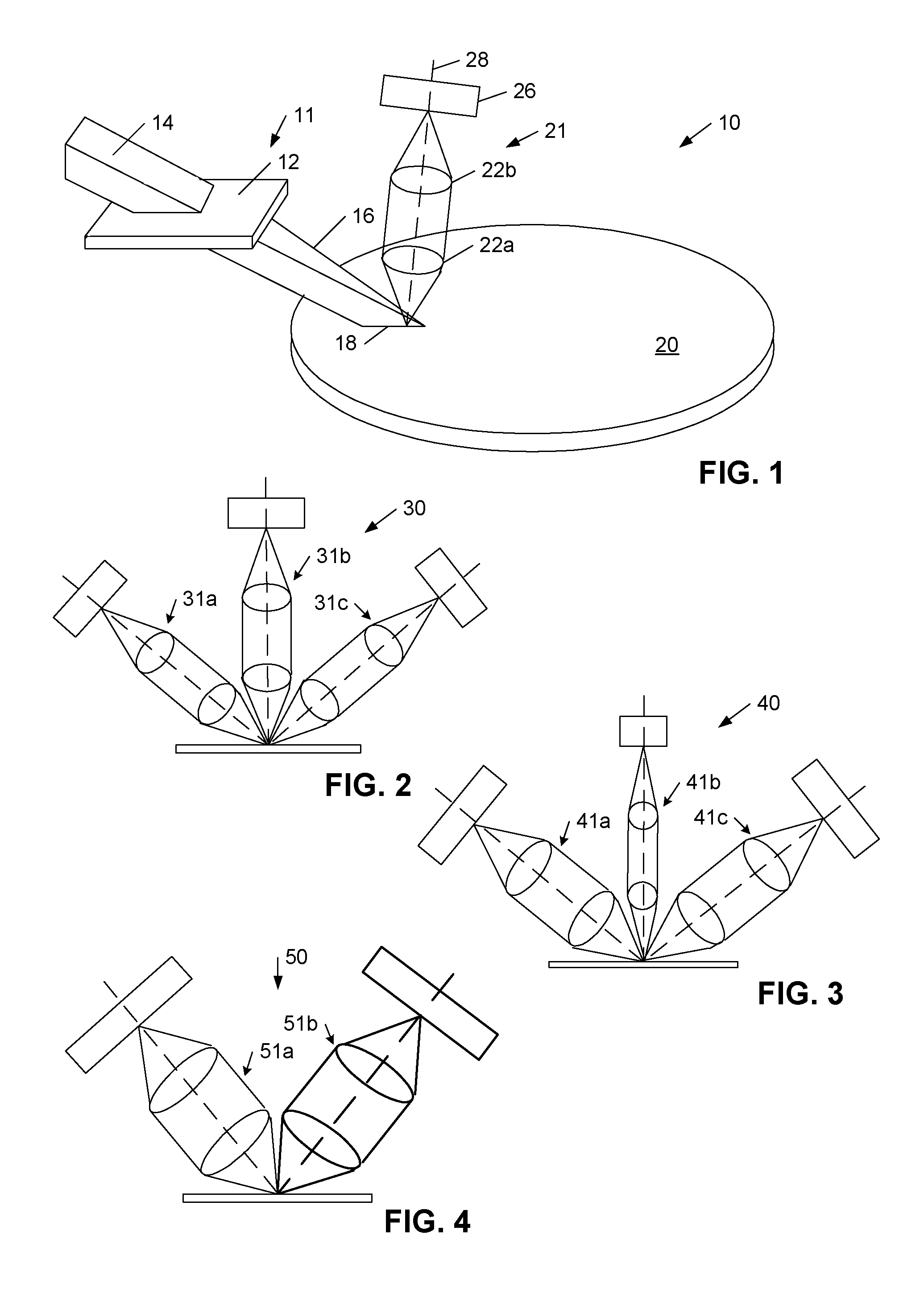
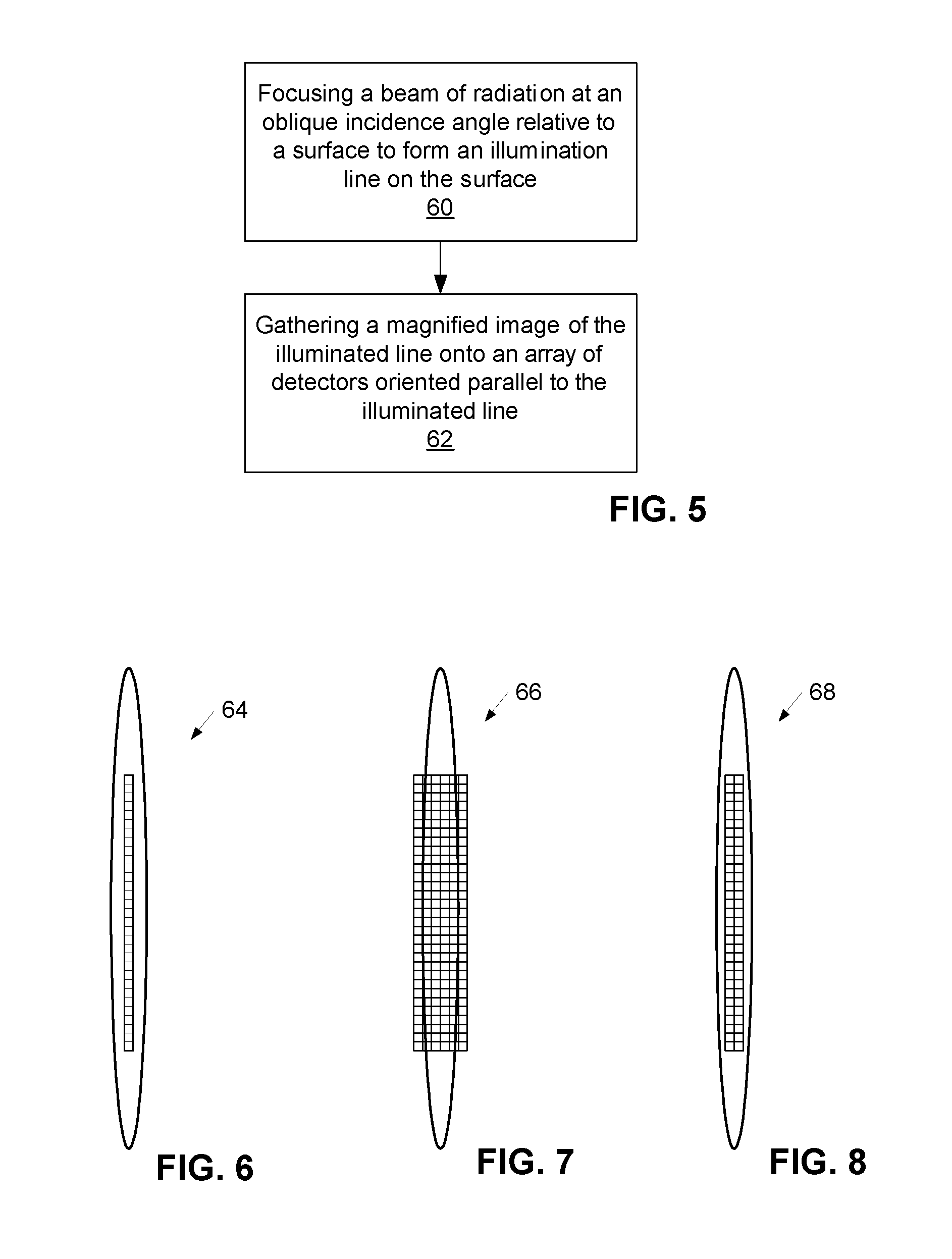
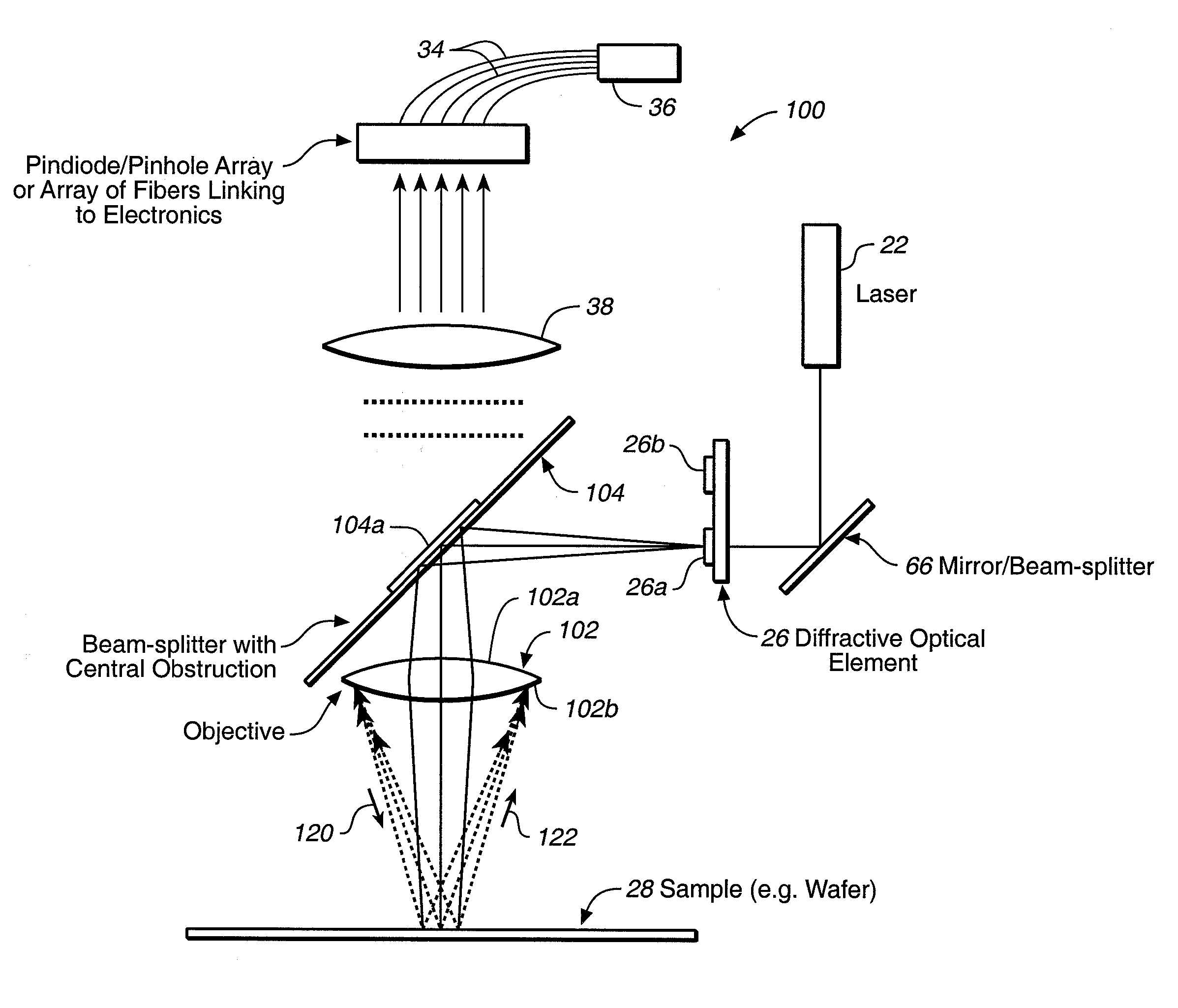
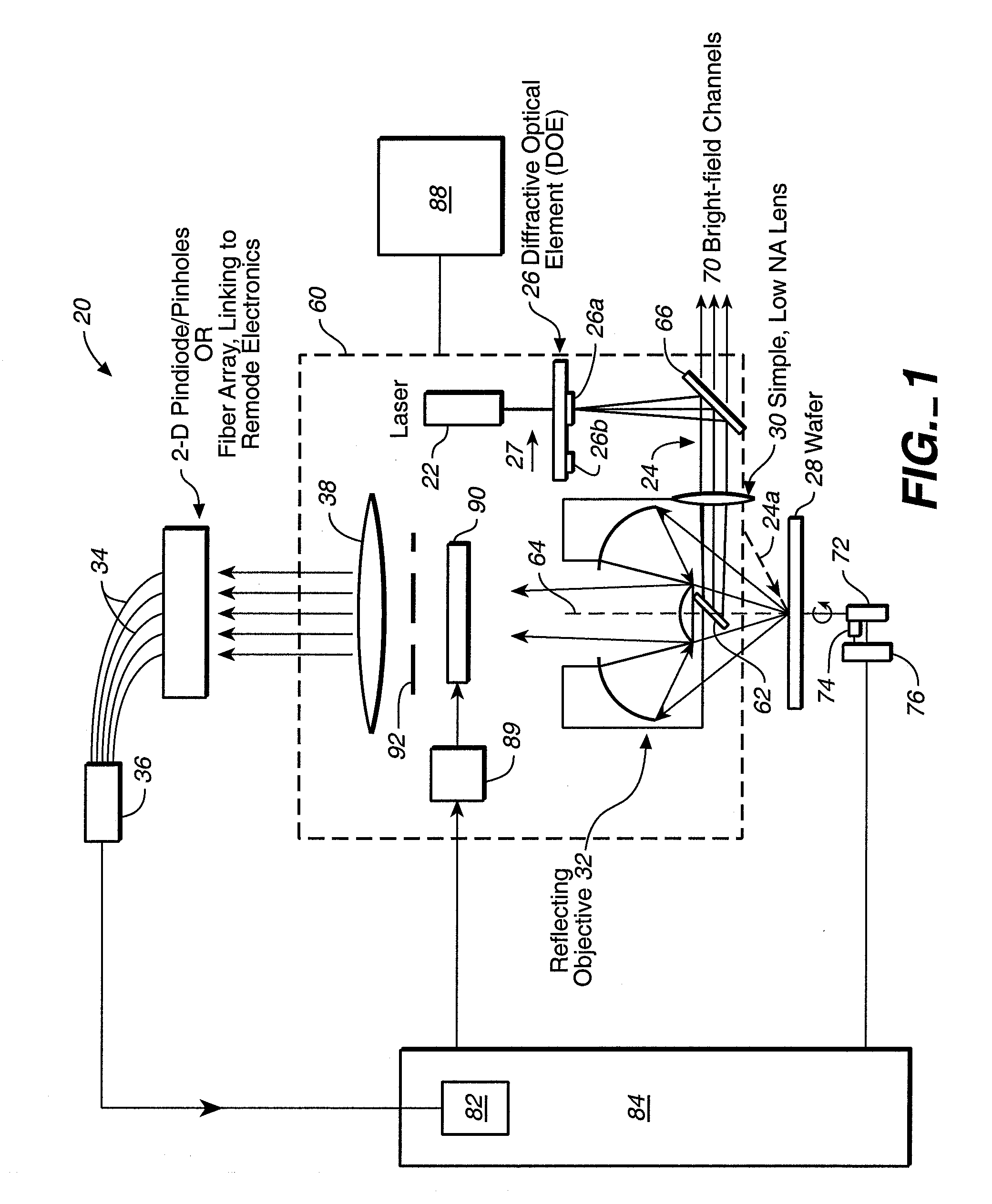
A surface inspection apparatus and a method are provided which include an illumination system configured to focus a beam of radiation at a non-orthogonal incidence angle to form an illumination line on a surface substantially in a plane of incidence of the focused beam. The apparatus and method further include a collection system configured to image the illumination line onto an array of detectors oriented parallel to the illumination line. The collection system includes an imaging lens for collecting light scattered from the illumination line, a focusing lens for focusing the collected light, and the array of detectors, each configured to detect a corresponding portion of the illumination line. The collection system may be configured to image the illumination line such that the width of the imaged illumination line on the array of detectors is larger than the pixel size of the detectors along the same direction.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
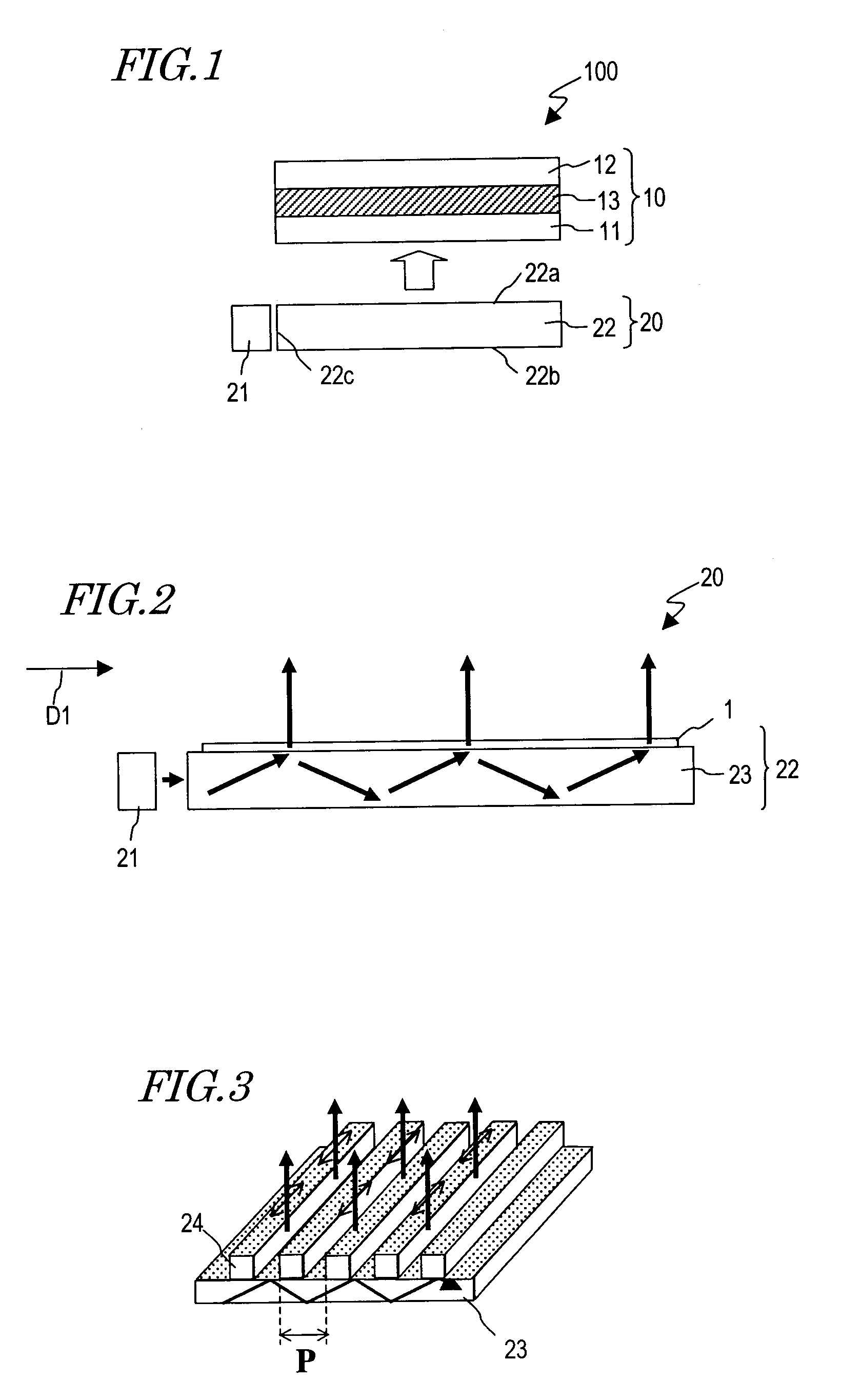
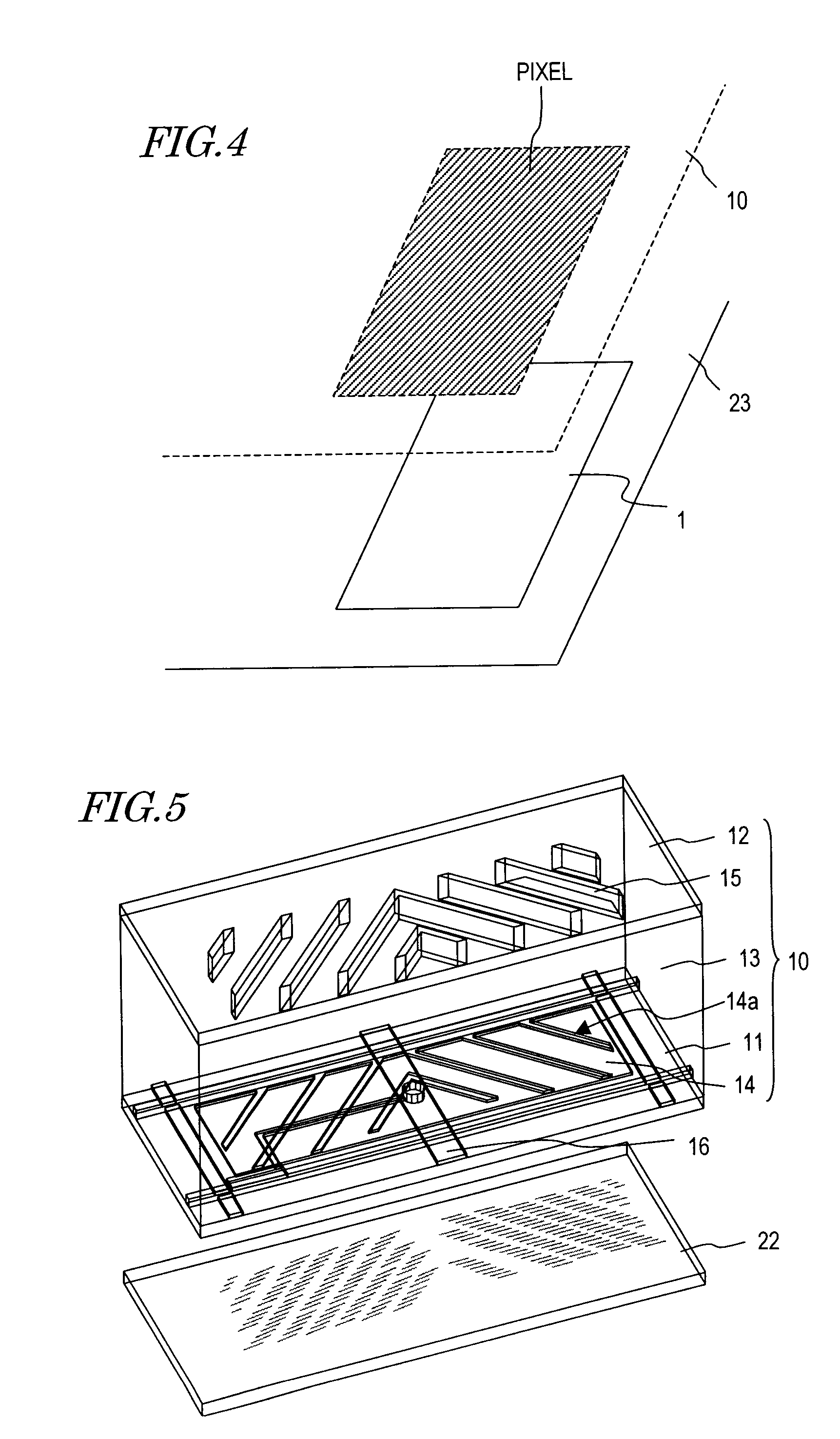
Backlight unit and liquid crystal display device having the same
ActiveUS20070153548A1Improve display qualityShow cabinetsMechanical apparatusLiquid-crystal displayLight guide
A backlight unit has a light source, a reflection sheet, a light guide plate, an air space, and a diffuser, wherein the reflection sheet, the light guide plate, the air space, and the diffuser are overlaid in this order. The light source is configured to arrange individual light sources having different spectra or different light emission quantities near an incident plane of the light guide plate, and on a plane facing the reflection sheet of the light guide plate, scatter dots are disposed which take light propagating through the light guide plate out of the reflection sheet side. The backlight unit and a liquid crystal display device including the same have excellent display quality.
Owner:SHARP KK
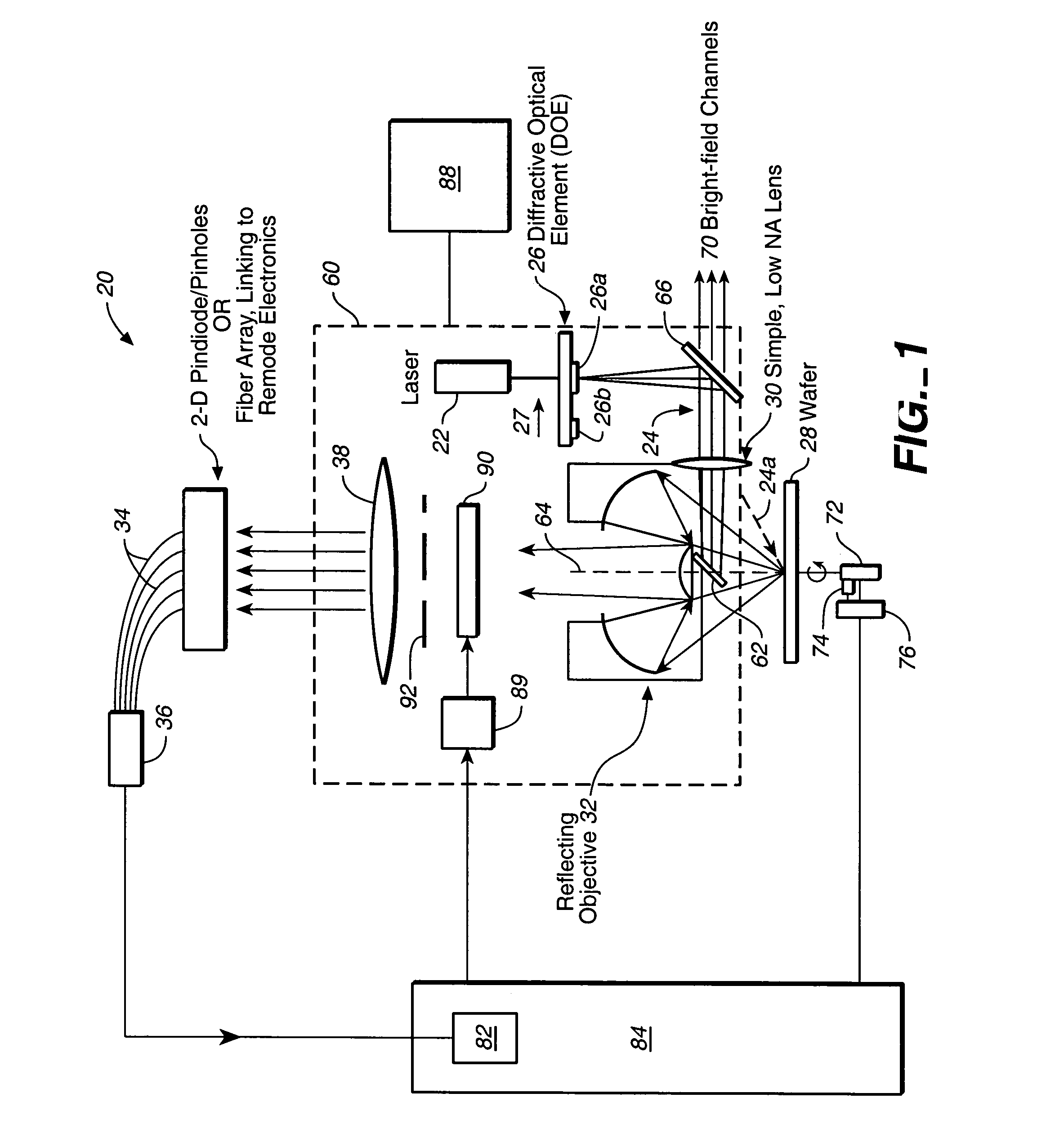
Simultaneous multi-spot inspection and imaging
InactiveUS7130039B2High detection sensitivityImprove performanceAnalysis by electrical excitationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDetector arrayAnnular aperture
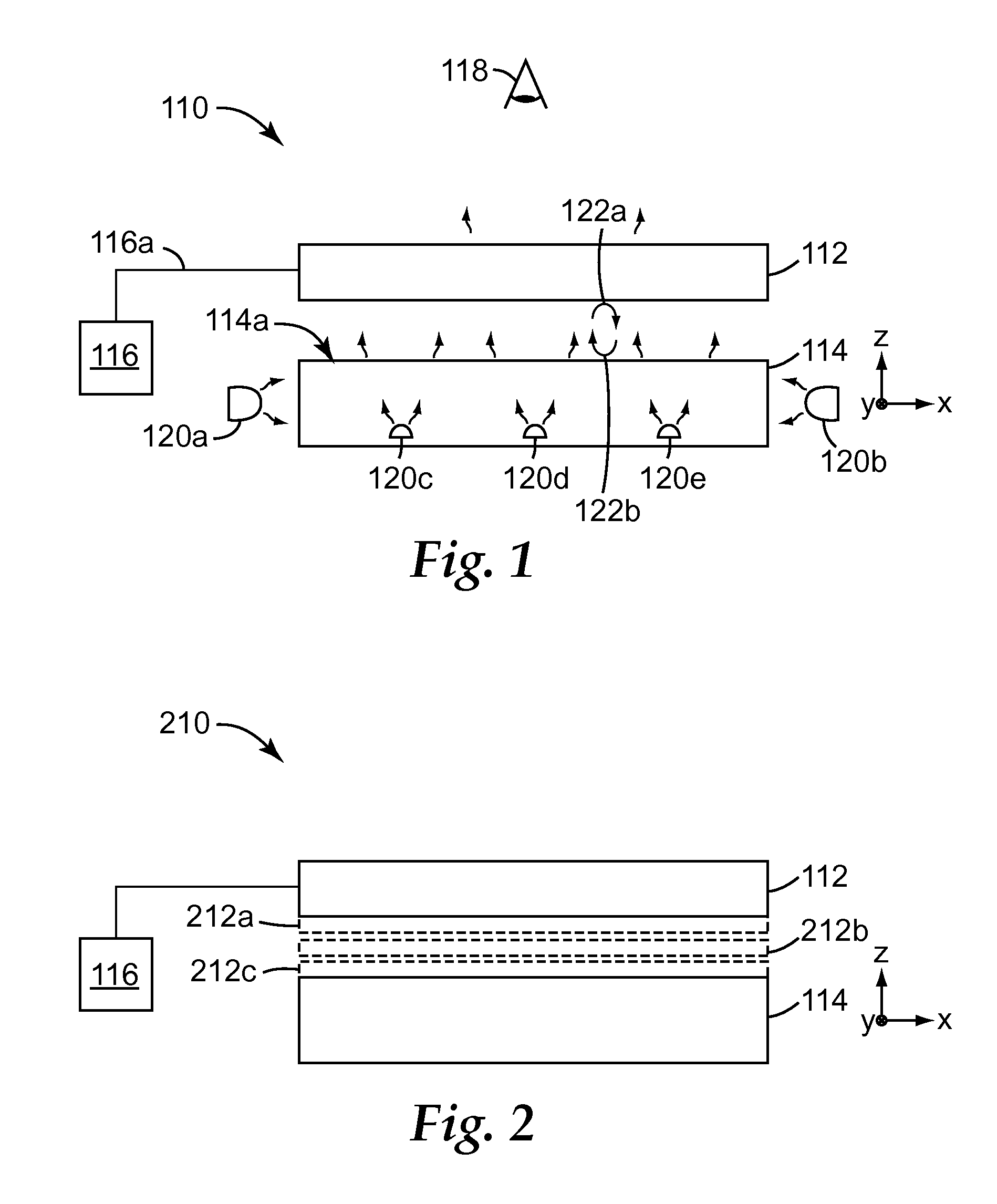
A compact and versatile multi-spot inspection imaging system employs an objective for focusing an array of radiation beams to a surface and a second reflective or refractive objective having a large numerical aperture for collecting scattered radiation from the array of illuminated spots. The scattered radiation from each illuminated spot is focused to a corresponding optical fiber channel so that information about a scattering may be conveyed to a corresponding detector in a remote detector array for processing. For patterned surface inspection, a cross-shaped filter is rotated along with the surface to reduce the effects of diffraction by Manhattan geometry. A spatial filter in the shape of an annular aperture may also be employed to reduce scattering from patterns such as arrays on the surface. In another embodiment, different portions of the same objective may be used for focusing the illumination beams onto the surface and for collecting the scattered radiation from the illuminated spots simultaneously. In another embodiment, a one-dimensional array of illumination beams are directed at an oblique angle to the surface to illuminate a line of illuminated spots at an angle to the plane of incidence. Radiation scattered from the spots are collected along directions perpendicular to the line of spots or in a double dark field configuration.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
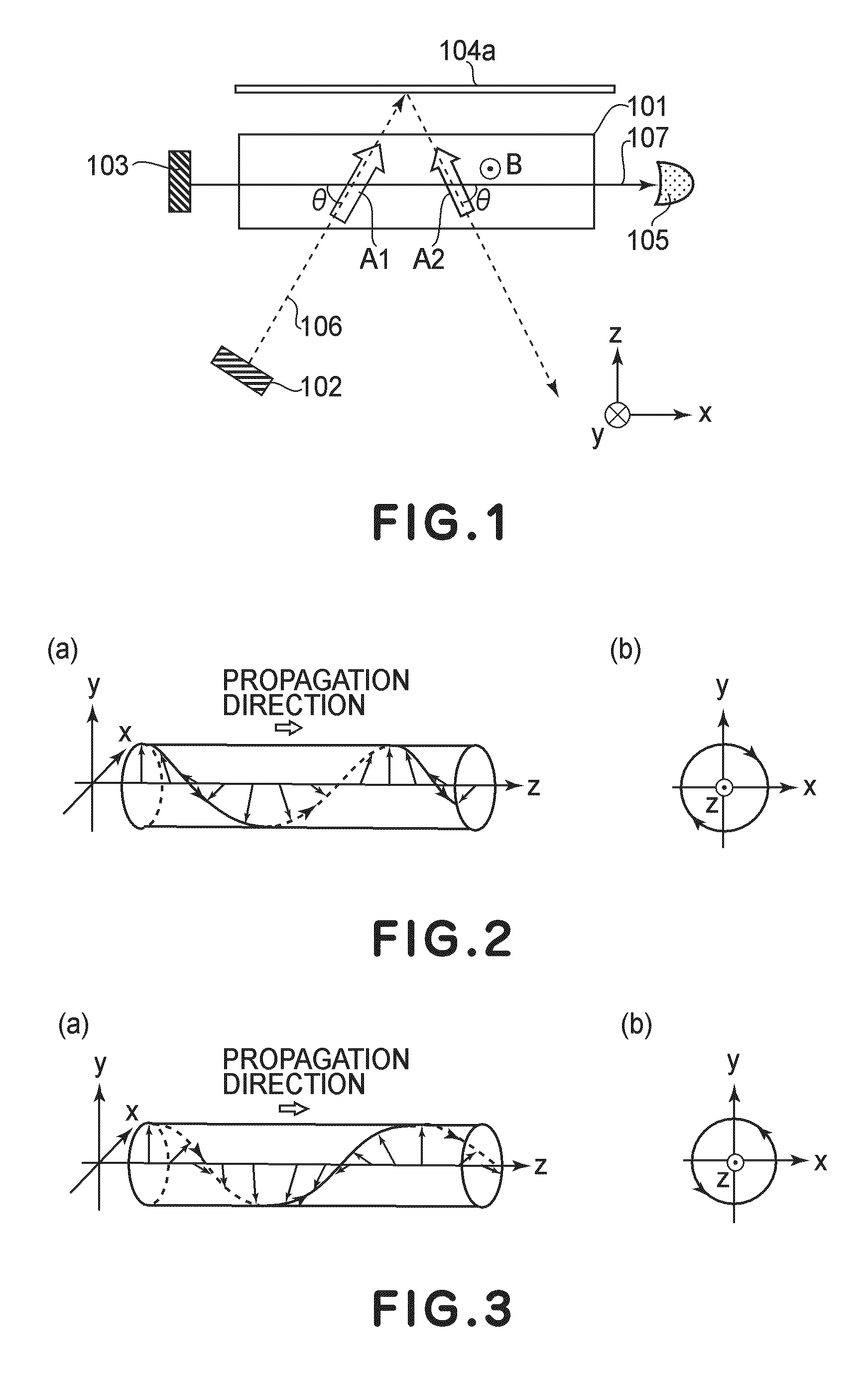
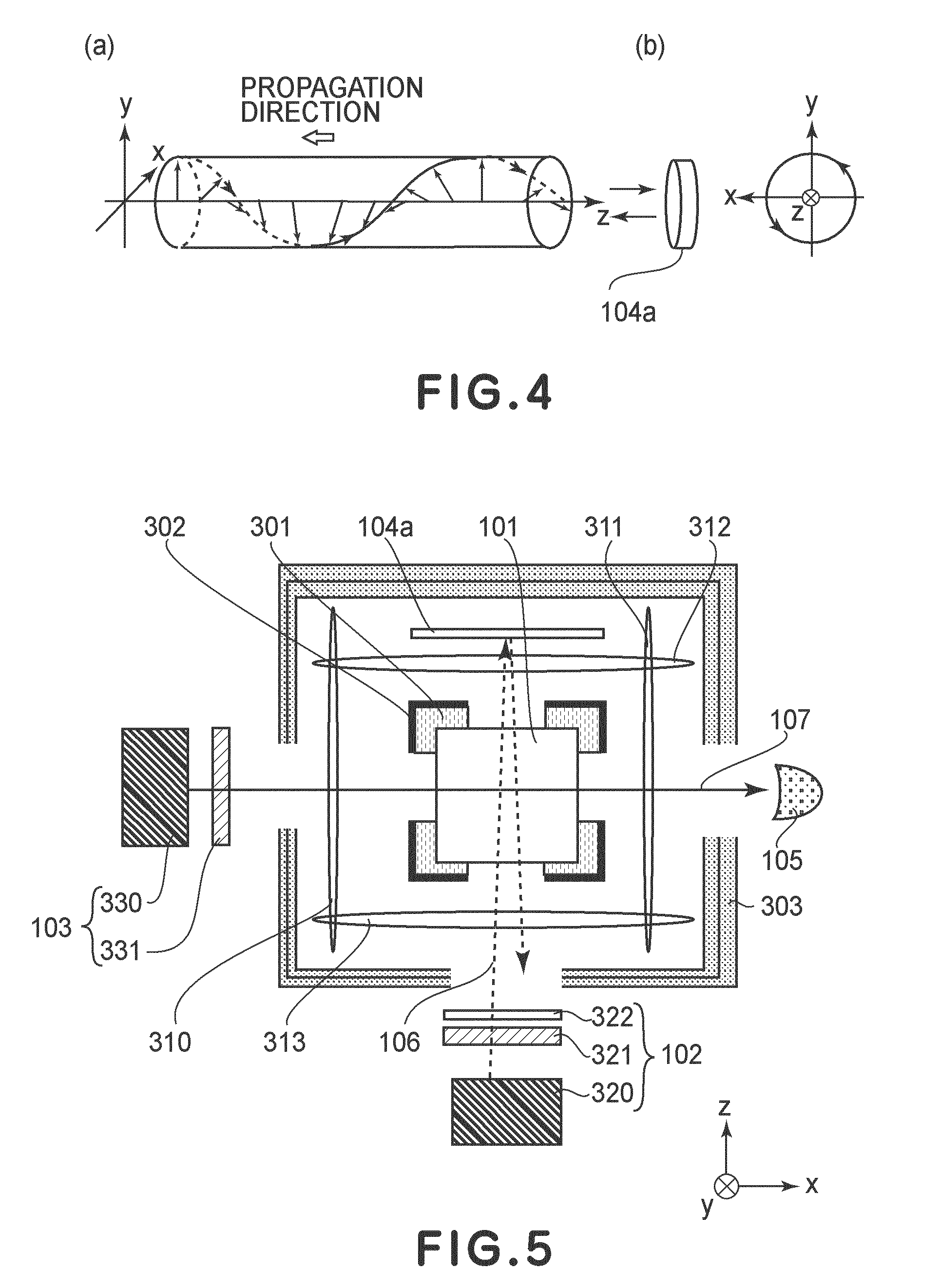
Atomic magnetometer and magnetic force measuring method
ActiveUS8054074B2High sensitivityNanomagnetismElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic tension forceAtomic group
An atomic magnetometer includes a cell containing an atomic group, a pump light source, a probe light source, a mirror, and a detector. The cell is disposed between the pump light source and the mirror and between the probe light source and the detector. A pump beam emitted from the pump light source is circularly polarized light. The pump beam passes through the cell and is reflected by the mirror and then passes through the cell again. The probe beam emitted from the probe light source is linearly polarized light. An optical path of the probe beam is parallel to the plane of incidence of the pump beam and is also parallel to the surface of the mirror. The optical path of the probe beam crosses the optical path of the pump beam in the cell. The probe beam which has passed through the cell enters the detector.
Owner:CANON KK
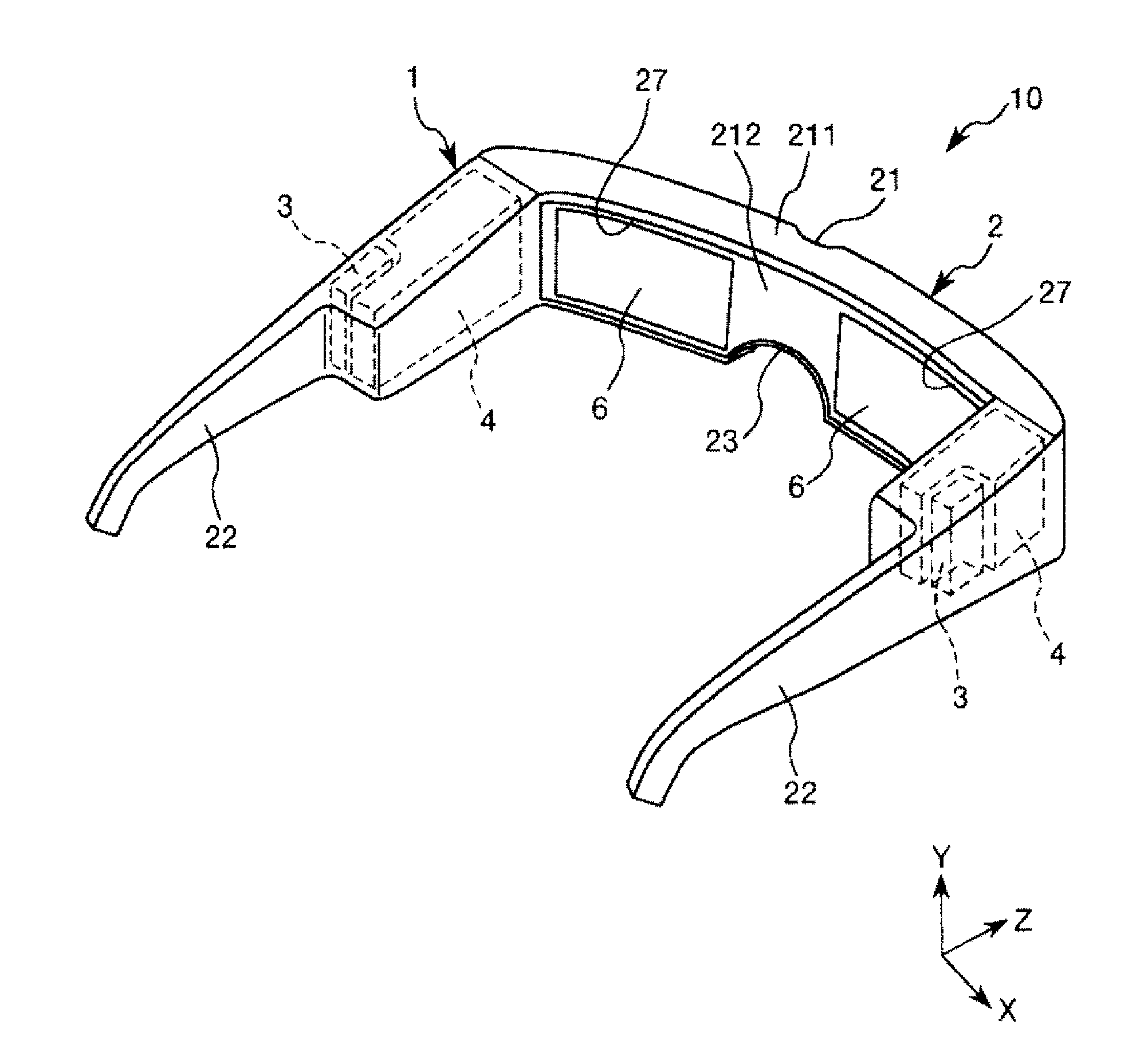
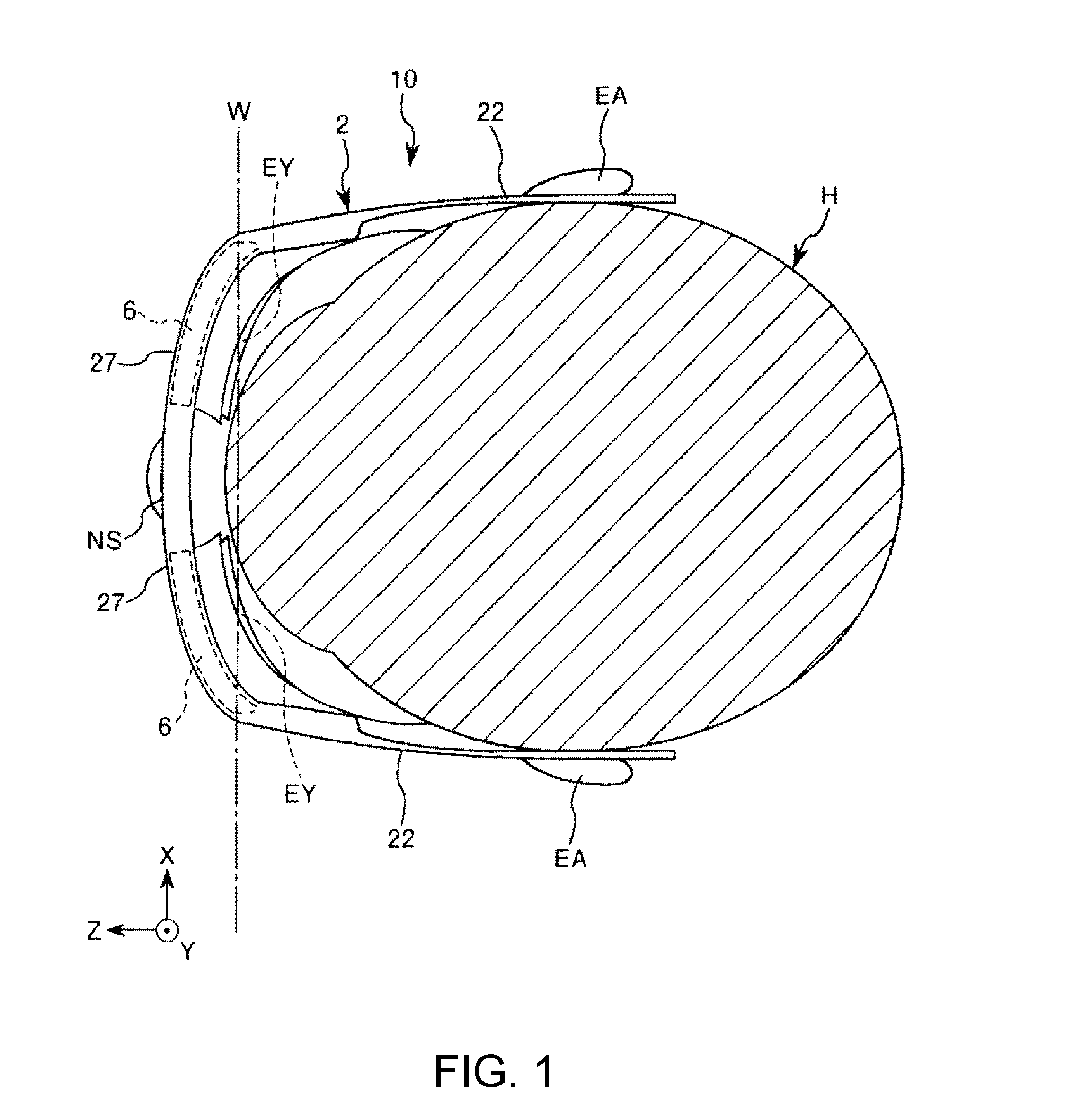
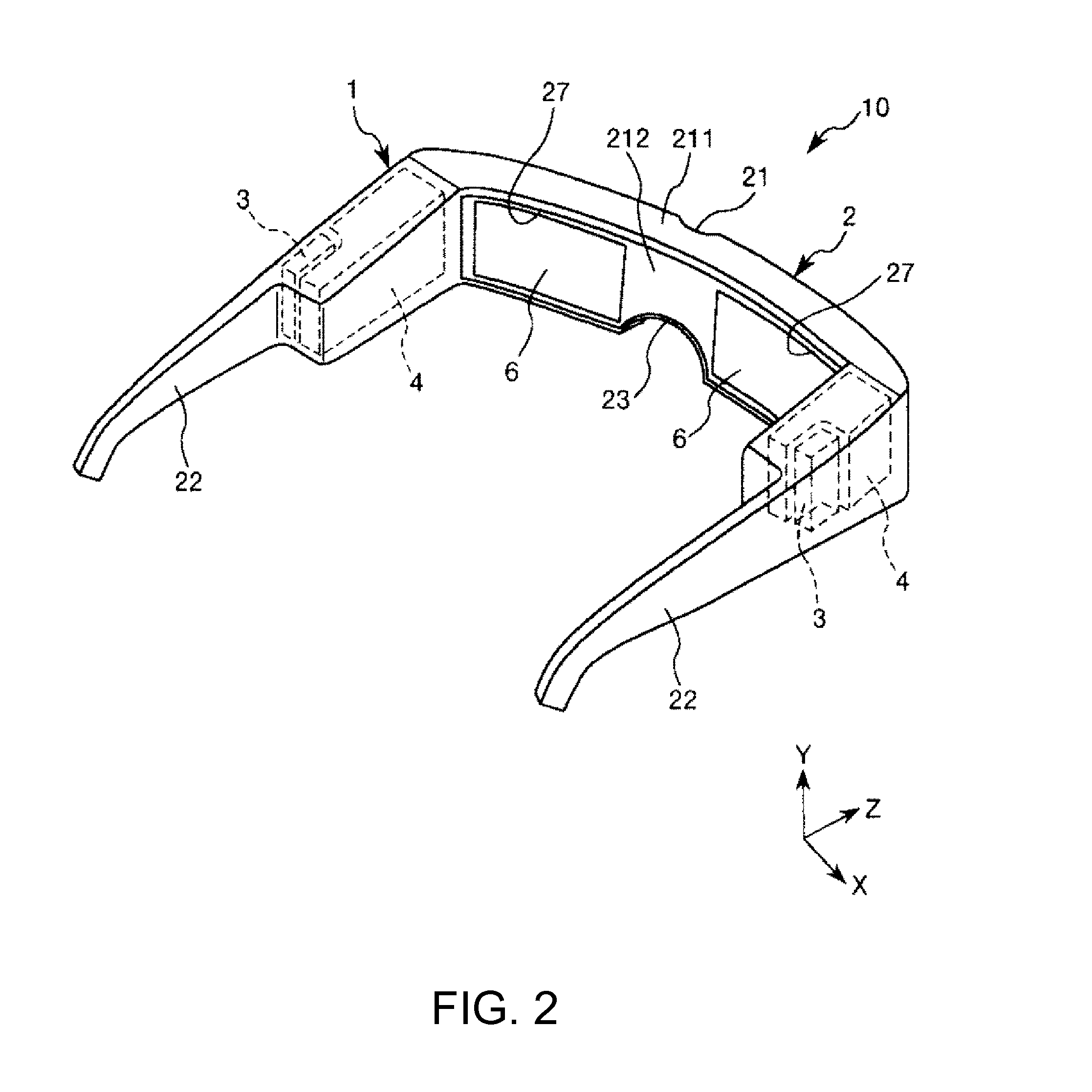
Virtual image display device and head-mounted display
ActiveUS20150279114A1Simple structureEasy to identifyMechanical apparatusCathode-ray tube indicatorsLight guideDisplay device
A virtual image display device includes: an image generator generating a picture light beam modulated based on a video signal; and an optical element including a plane of incidence to which the picture light beam emitted from the image generator is input, and an exit surface emitting the picture light beam after a cross-sectional area of the picture light beam input to the plane of incidence has been enlarged. The optical element includes a first light guide and a second light guide connecting the plane of incidence and the exit surface and guiding the picture light beam. A first light branching layer is disposed between the first and second light guides, and partially reflects and partially transmits the picture light beam. The picture light beam emitted from the image generator obliquely enters the first light branching layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Atomic magnetometer and magnetic force measuring method
ActiveUS20090243610A1High sensitivityNanomagnetismElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic tension forceAtomic group
An atomic magnetometer includes a cell containing an atomic group, a pump light source, a probe light source, a mirror, and a detector. The cell is disposed between the pump light source and the mirror and between the probe light source and the detector. A pump beam emitted from the pump light source is circularly polarized light. The pump beam passes through the cell and is reflected by the mirror and then passes through the cell again. The probe beam emitted from the probe light source is linearly polarized light. An optical path of the probe beam is parallel to a plane of incidence of the pump beam and is also parallel to a surface of the mirror. The optical path of the probe beam crosses an optical path of the pump beam in the cell. The probe beam which has passed through the cell enters the detector.
Owner:CANON KK
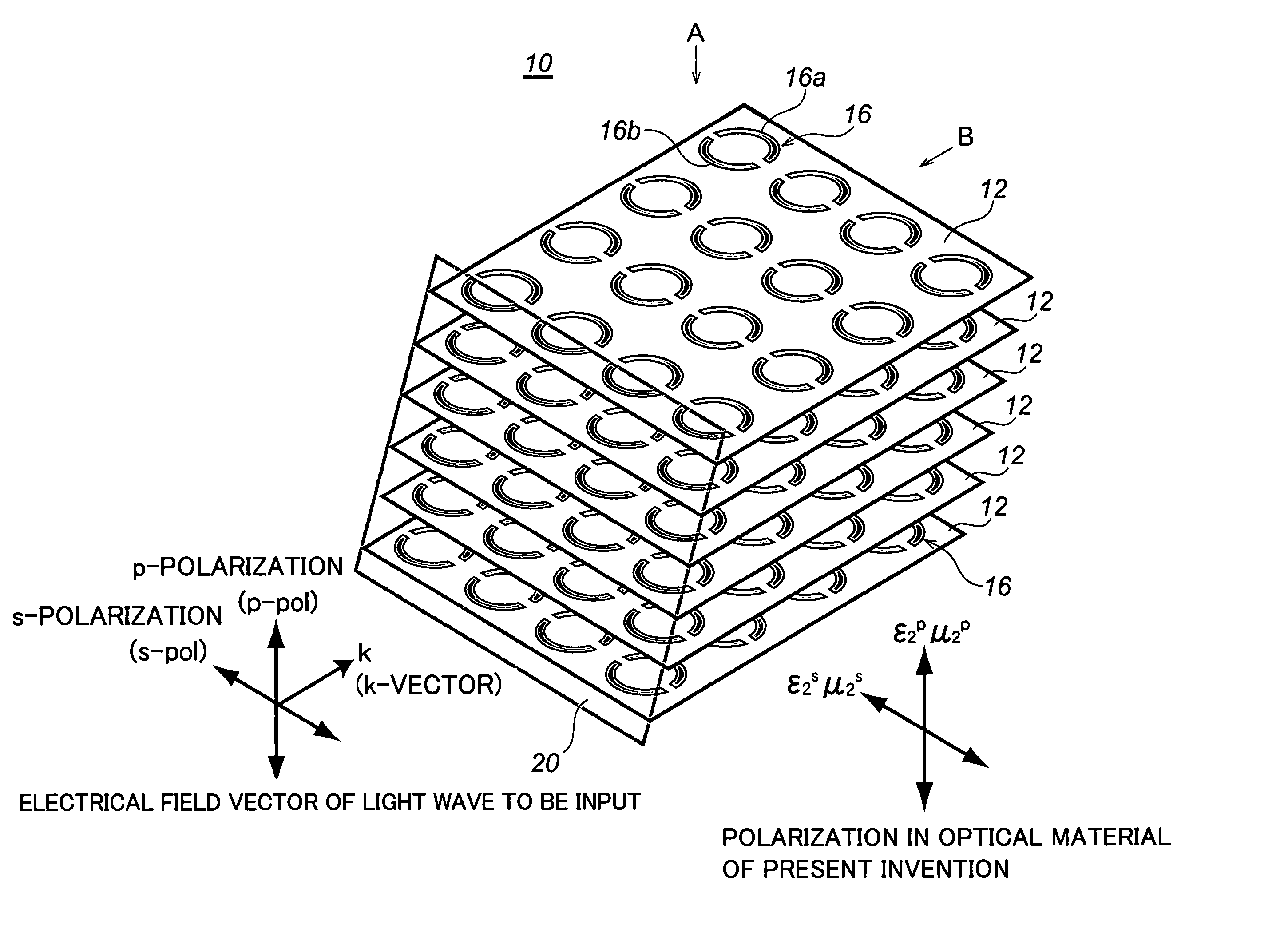
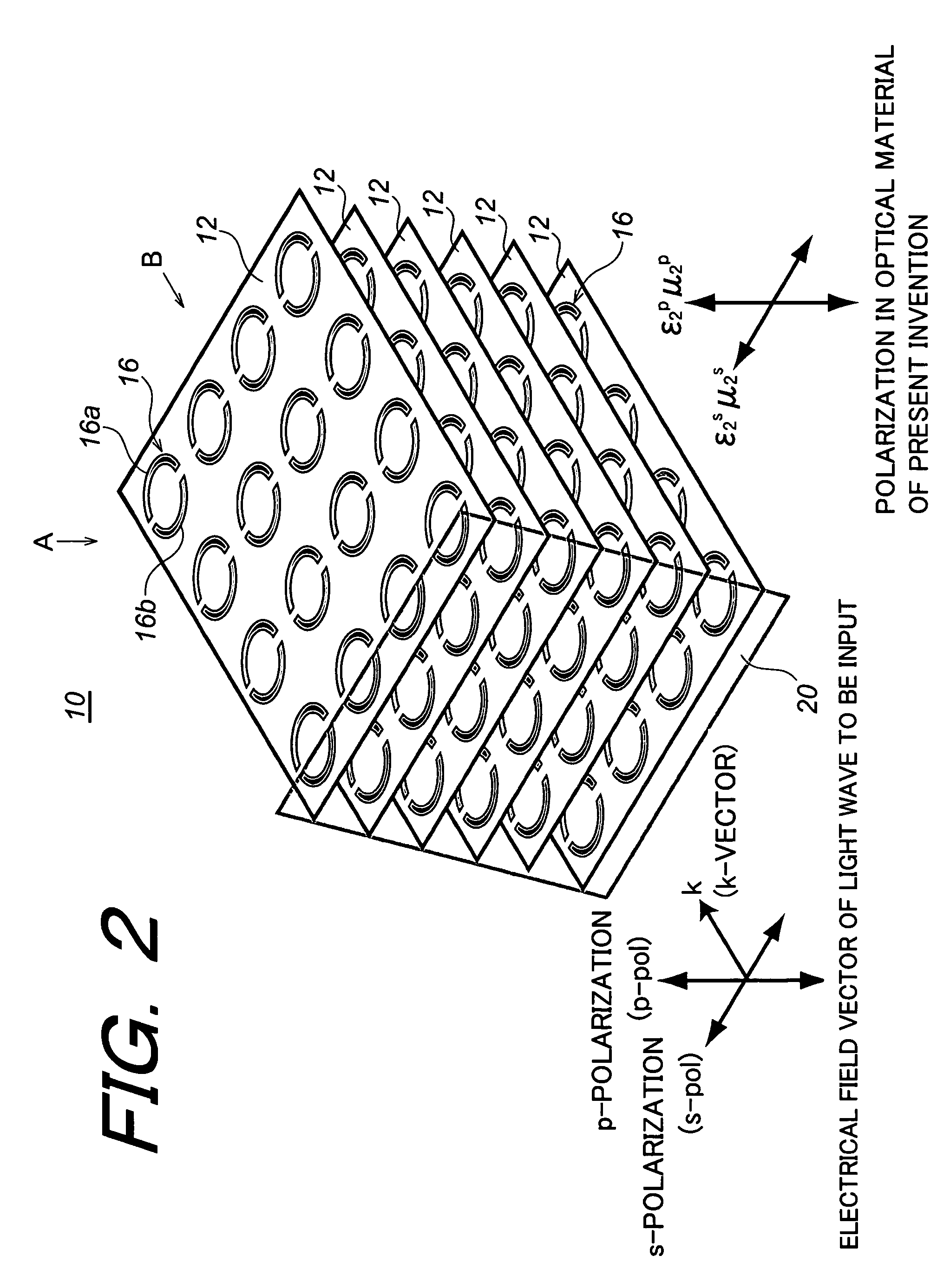
Optical material, optical device fabricated therefrom, and method for fabricating the same
In order to make a reflection coefficient in boundary surface between materials to be zero and permeate 100% of a light independent of a polarization direction, an optical device made of an optical material composed of a metamaterial prepared by arranging a plurality of at least either of electrical resonators or magnetic resonators each being smaller than a wavelength of a light wave in only a predetermined plane, and at least either of the electrical resonators and the magnetic resonators arranged functioning with respect to s-polarization, whereby at least either of the dielectric constant or the magnetic permeability is controlled in response to the function to induce a Brewster phenomenon in the s-polarization wherein the incident plane of a light wave being set out at a Brewster's angle with respect to the p-polarization and further at least either of the dielectric constant and the magnetic permeability of the optical material being controlled with respect to the s-polarization of the optical material, whereby the Brewster condition is independently satisfied in both the p-polarization and the s-polarization at the same time.
Owner:RIKEN
System for detecting anomalies and/or features of a surface
InactiveUS7088443B2Improved sensitivity and performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsRelative motionCharge couple device
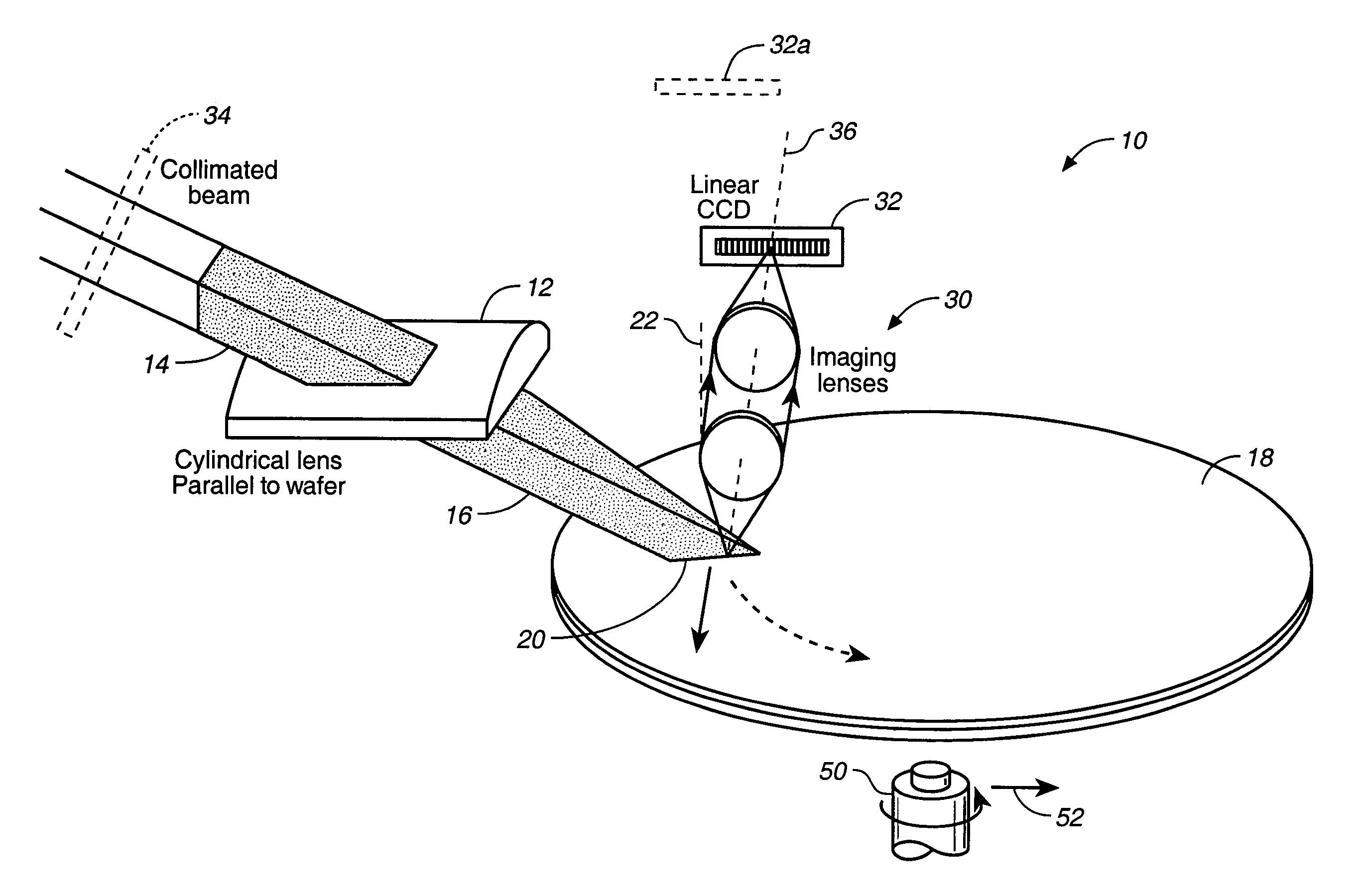
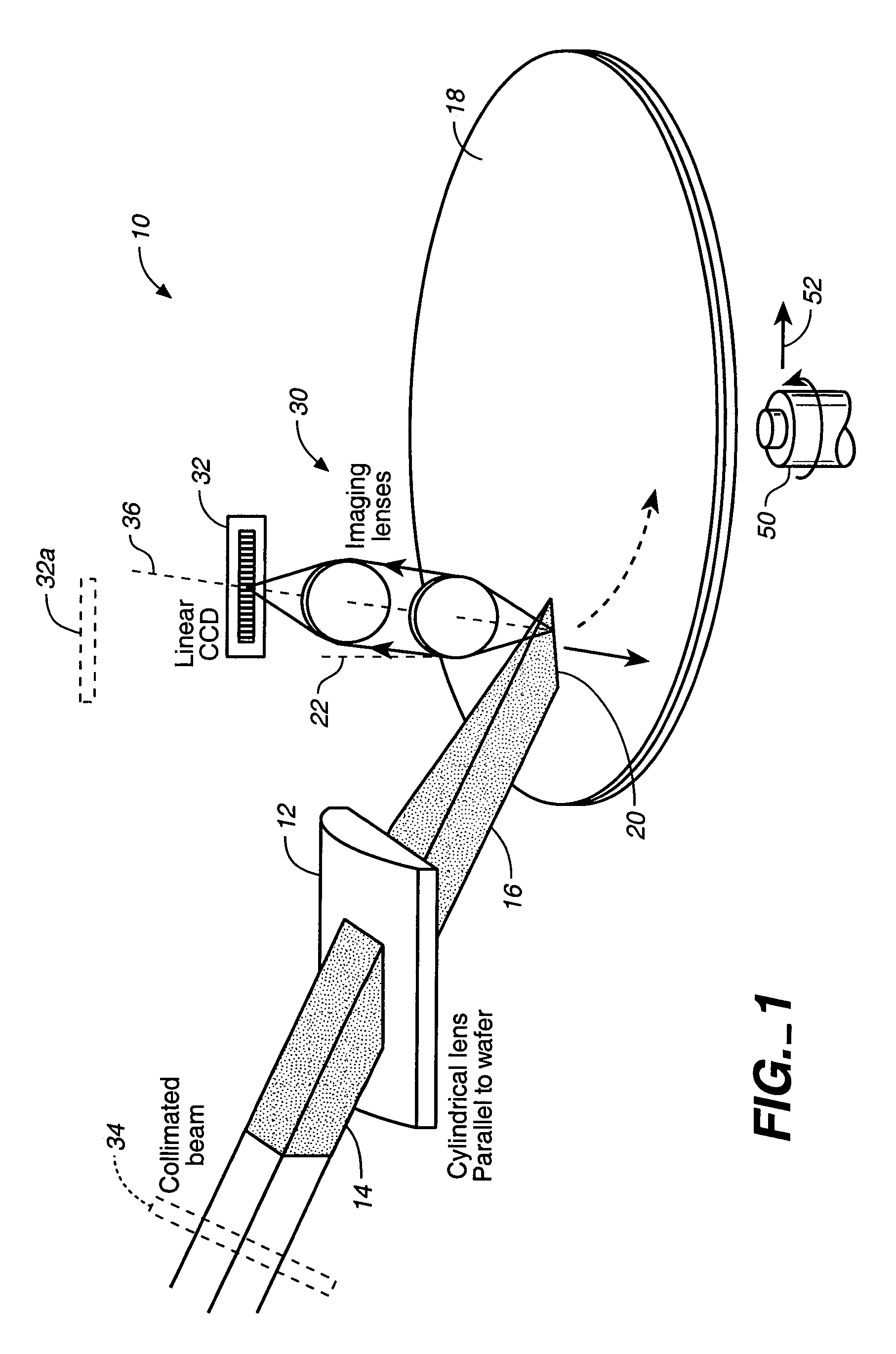
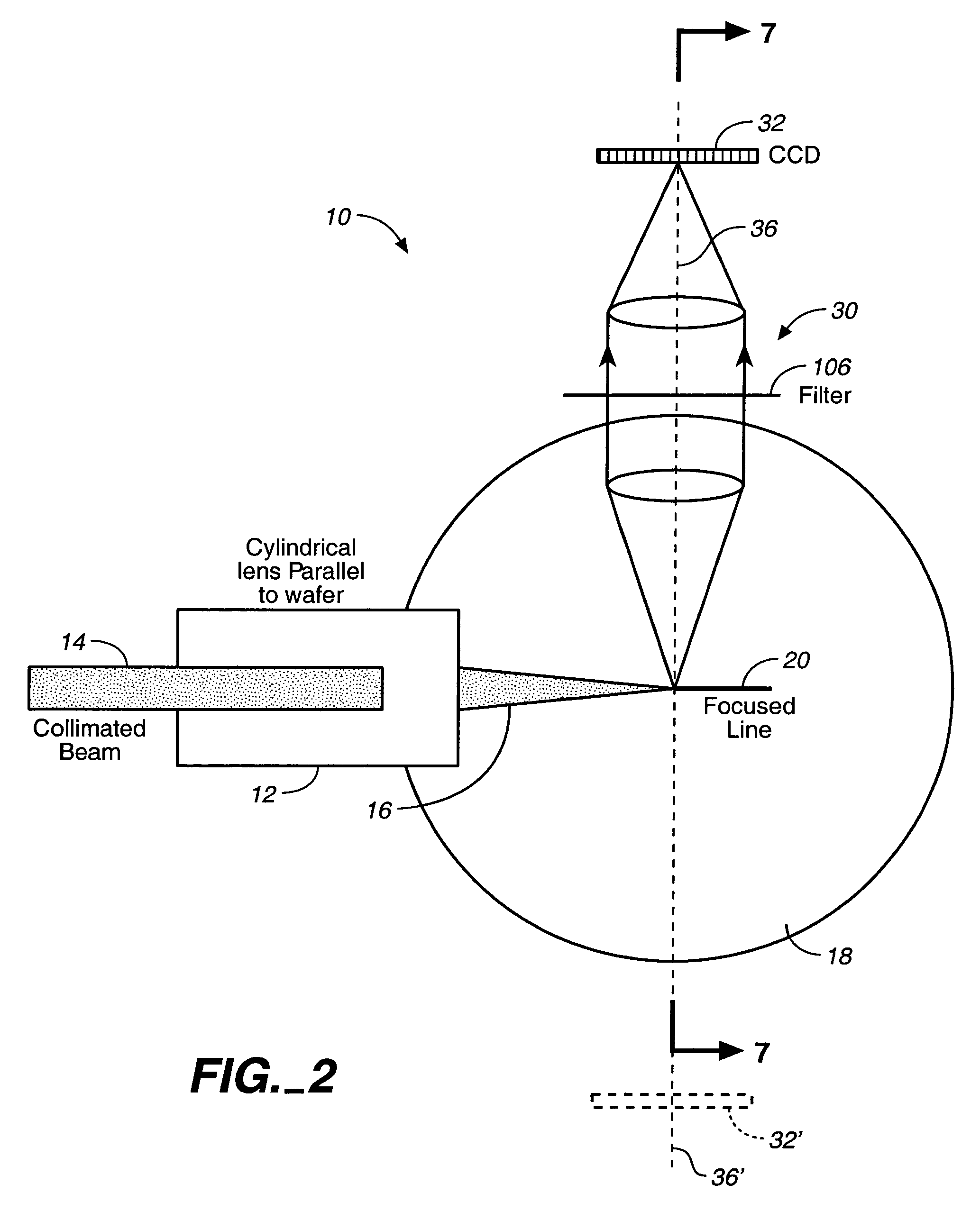
A cylindrical mirror or lens is used to focus an input collimated beam of light onto a line on the surface to be inspected, where the line is substantially in the plane of incidence of the focused beam. An image of the beam is projected onto an array of charge-coupled devices parallel to the line for detecting anomalies and / or features of the surface, where the array is outside the plane of incidence of the focused beam. For inspecting surface with a pattern thereon, the light from the surface is first passed through a spatial filter before it is imaged onto the charge-coupled devices. The spatial filter includes stripes of scattering regions that shift in synchronism with relative motion between the beam and the surface to block Fourier components from the pattern. The spatial filter may be replaced by reflective strips that selectively reflects scattered radiation to the detector, where the reflective strips also shifts in synchronism with the relative motion.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Polarization based interferometric detector
ActiveUS7233396B1Fast resultsReduce complexityPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhase-affecting property measurementsOptical propertyPhase difference
A sensor and method for determining the optical properties of a sample material is disclosed. The sensor comprises a light source that generates a linearly polarized light beam having a predetermined polarization orientation with respect to the plane of incidence. The linearly polarized light beam is reflected off the sample and is split into second and third light beams where the second and third light beam consist of the combined projections of mutually orthogonal components of the first light beam. A signal processor measures the intensity difference between the second and third light beams to calculate the phase difference induced by the sample material.
Owner:CARTERRA INC
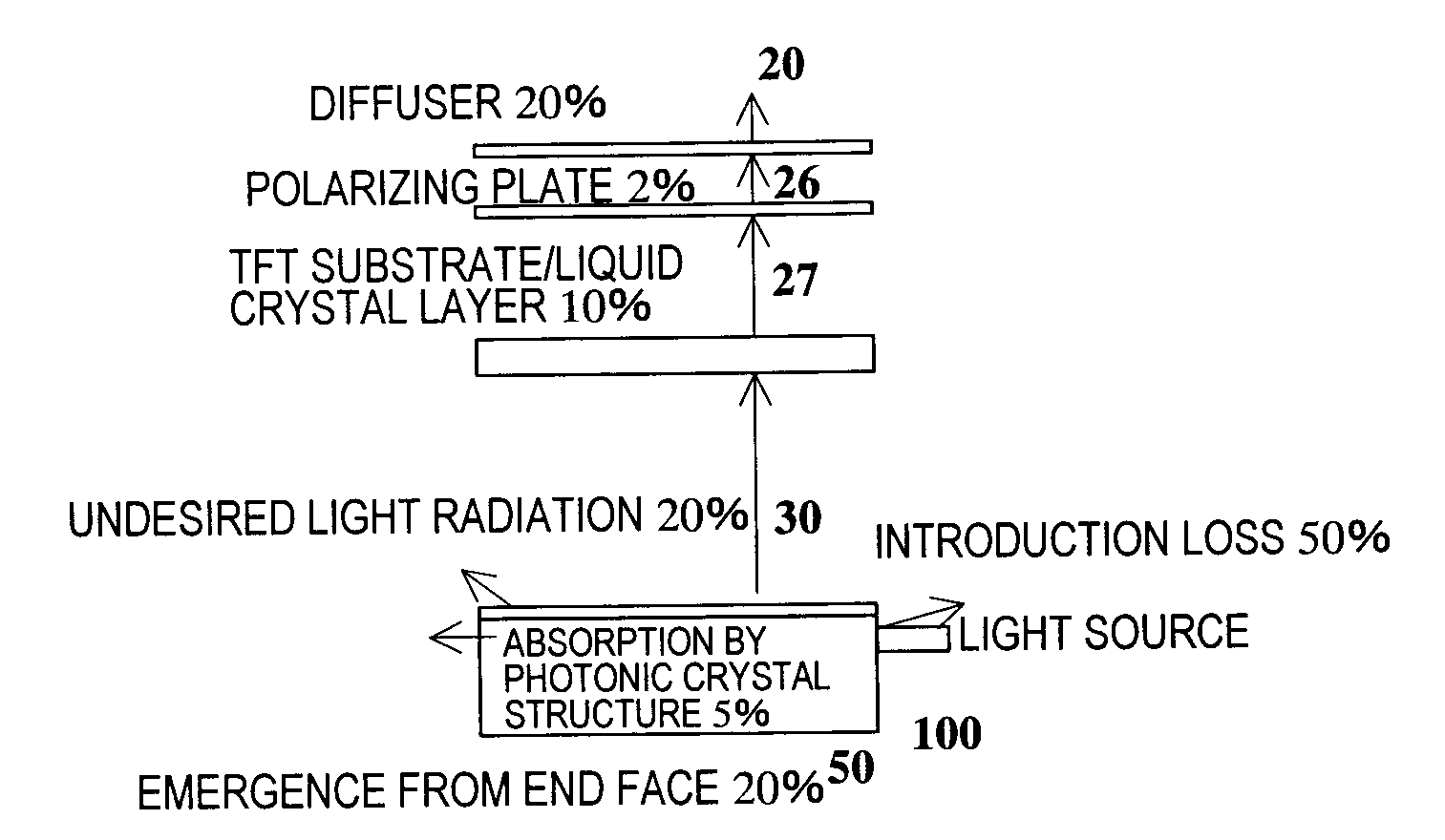
Light guiding body, substrate for display device, and display device
InactiveUS20090190068A1Improve light utilization efficiencyMechanical apparatusNanoopticsLight guideDisplay device
A display device higher in light use efficiency than conventional ones, a display device substrate suitably used for such a display device, and a light guide suitably used for an illuminator of such a display device are provided. The light guide has a plane of incidence on which light is incident and a plane of emergence from which light emerges, and has a first photonic crystal structure having a refractive index changing periodically along a direction substantially parallel to the plane of emergence.
Owner:SHARP KK
Light scattering detector
InactiveUS20050179904A1High sensitivityImprove light collectionComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesAngle of incidenceCurrent mode
The invention concerns high sensitivity light scattering detection and its application to evaporative light scattering detection in liquid chromatography. The exemplary embodiment includes a detection cell to accept particles suspended in a gas stream and permit a polarized light beam to pass through a trajectory of the particles and gas stream. A sample light detector is disposed to detect light scattered in the detection cell. A light trap accepts the polarized beam after it passes through the detection cell. The light trap includes an elongated housing through which the polarized beam passes, and light absorptive material within the elongated housing. An absorptive filter is aligned such that the angle of incidence of the light beam upon the filter approximates Brewster's angle and the electric field vector of the beam is aligned with the plane of incidence between the beam and the filter. Other embodiments of the invention provide increased light collection. Embodiments of the invention include temperature-controlled entrance and exit ports that control particle trajectory. Embodiments of the invention include a reference cell disposed between a detection cell and a light trap, and the reference cell includes lensing and a spherical mirror to direct light toward a reference light detector. The reference light detector provides a reference signal that may be used with noise cancellation circuitry, operating in either voltage or current mode, to reduce light source noise in the sample signal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
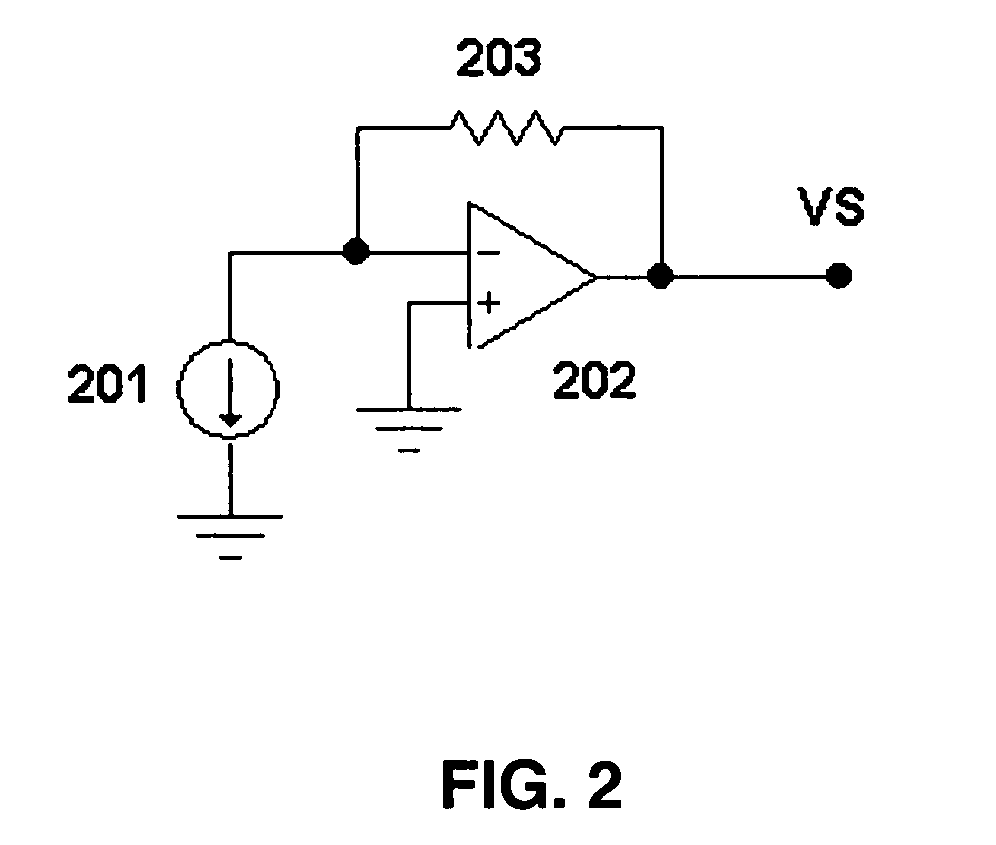
System and method for measuring properties of an object using a phase difference between two reflected light signals
A system and method for measuring a phase difference between first and second reflected polarized light signal components, including transmitting a first incident light signal toward a first object, wherein the first object is a magnetic disk and / or a glass substrate. Seperating from a reflected light signal, a first mixed reflected polarized light signal component having a first phase and a second mixed reflected polarized light signal component having a second phase that is different from said first phase, wherein said mixed reflected polarized light signal components comprises both P-polarized and S-polarized light relative to a plane of incidence of said reflected light signal. Detecting the intensities of said first and second mixed reflected polarized light signal components, and determining a difference in phase between said first and second mixed reflected polarized light signal component based upon said first and second intensities.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Polarization Based Interferometric Detector
ActiveUS20080002202A1Fast resultsReduce complexityPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhase-affecting property measurementsOptical propertyPhase difference
A sensor and method for determining the optical properties of a sample material is disclosed. The sensor comprises a light source that generates a linearly polarized light beam having a predetermined polarization orientation with respect to the plane of incidence. The linearly polarized light beam is reflected off the sample and is split into second and third light beams where the second and third light beam consist of the combined projections of mutually orthogonal components of the first light beam. A signal processor measures the intensity difference between the second and third light beams to calculate the phase difference induced by the sample material.
Owner:CARTERRA INC
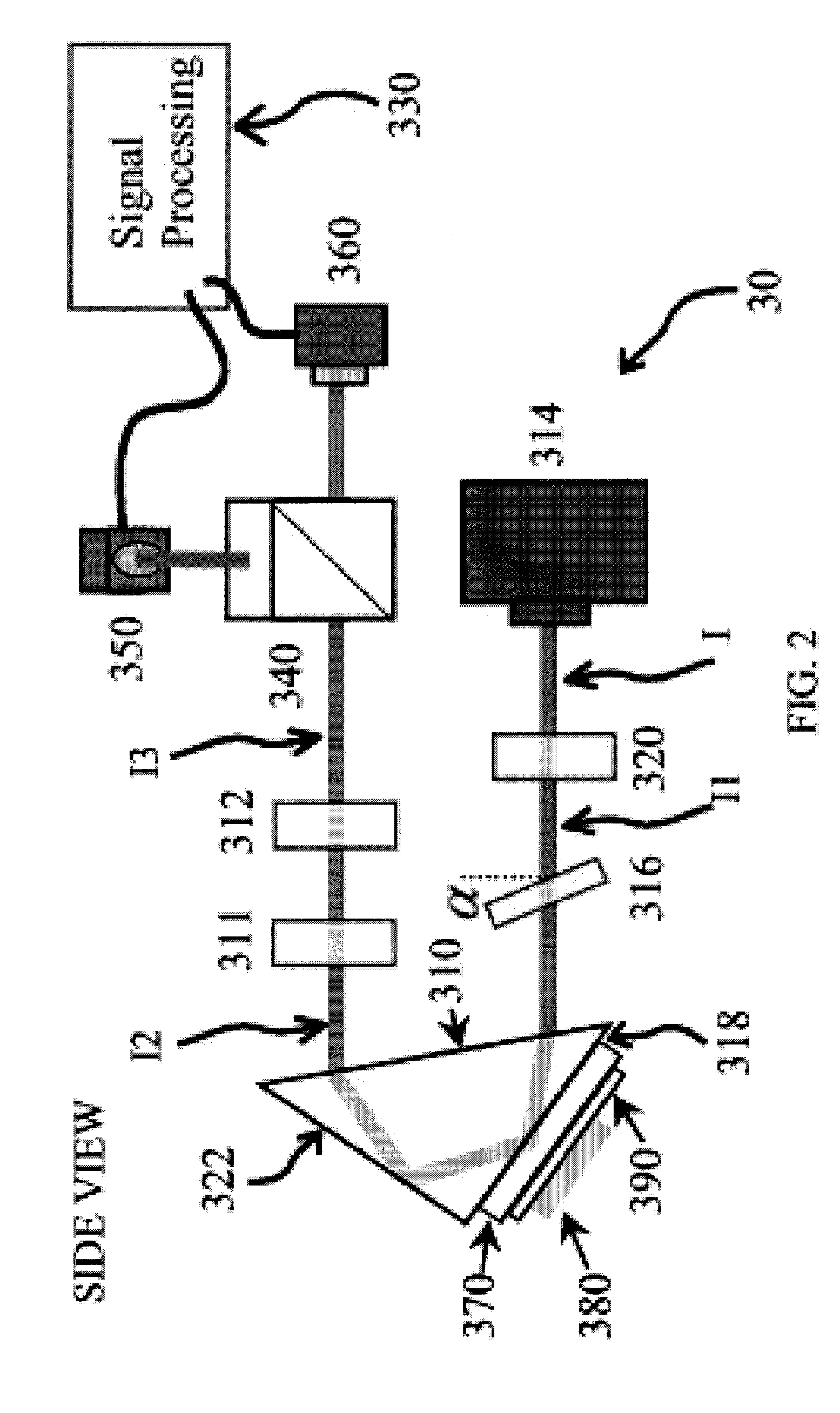
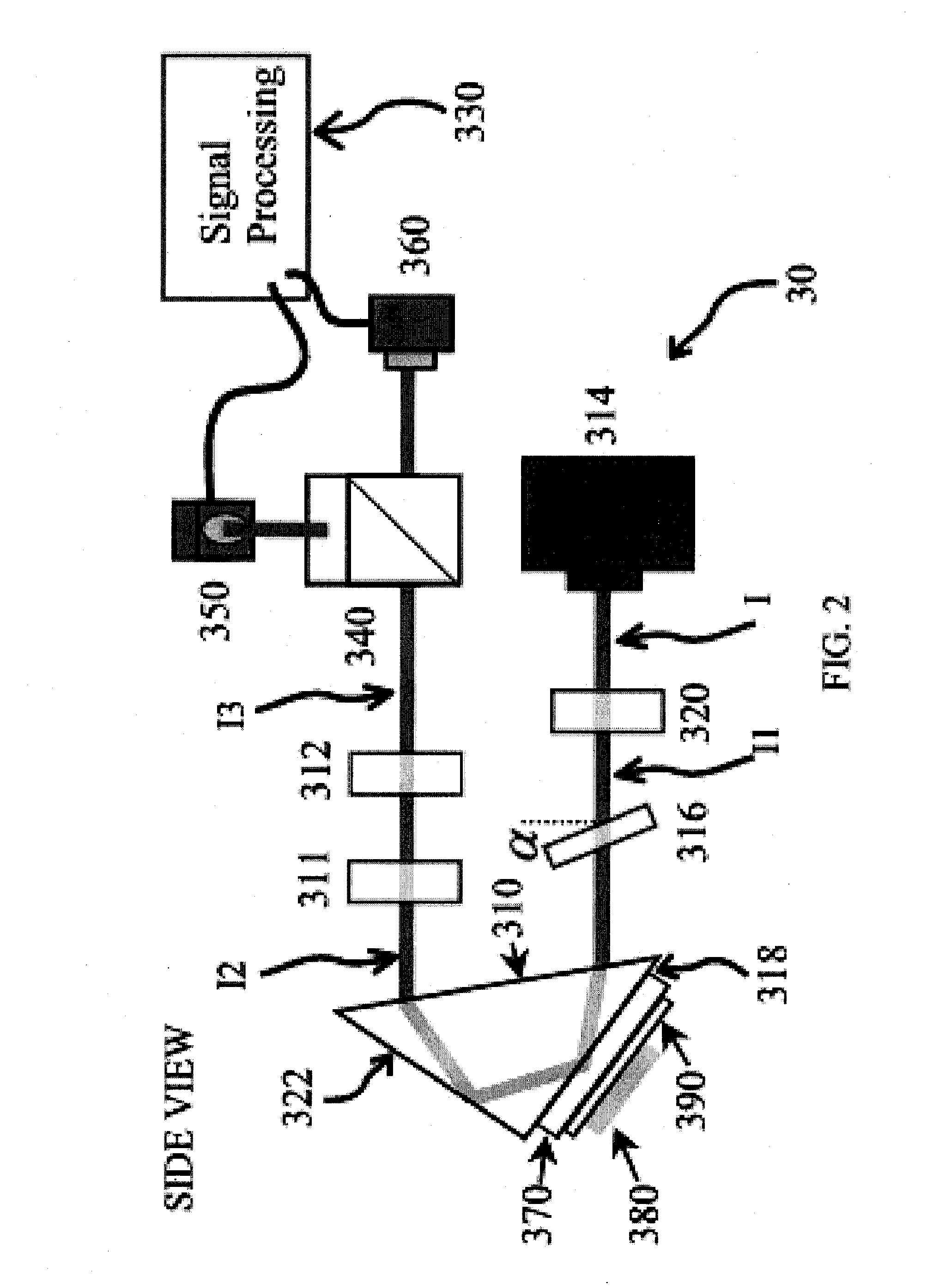
Wide spatial frequency topography and roughness measurement
InactiveUS7362425B2Material analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansLight beamPlane of incidence
In one embodiment, a system to inspect a surface comprises an assembly to direct a first radiation beam onto a surface in a first plane of incidence, a first detector to generate a first signal from a portion of the radiation reflected from the first radiation beam, a first spatial filter interposed between the surface and the first detector, a first ellipsoidal mirror to collect scattered light, a second detector to generate a second signal from the scattered portion of the beam, and a processor to generate, from the first and second signals, a data set representing one or more characteristics of the surface using the first and second signals.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
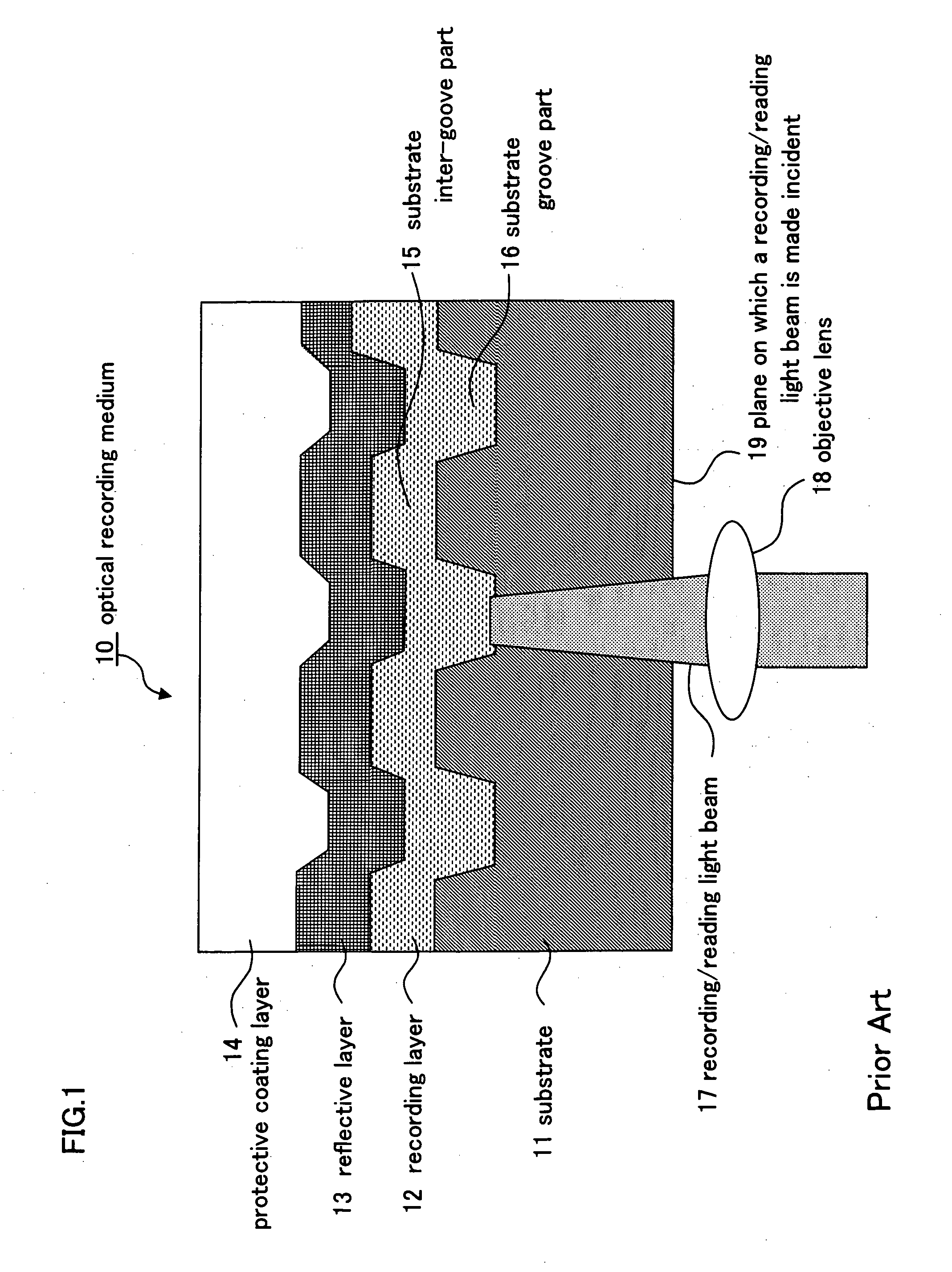
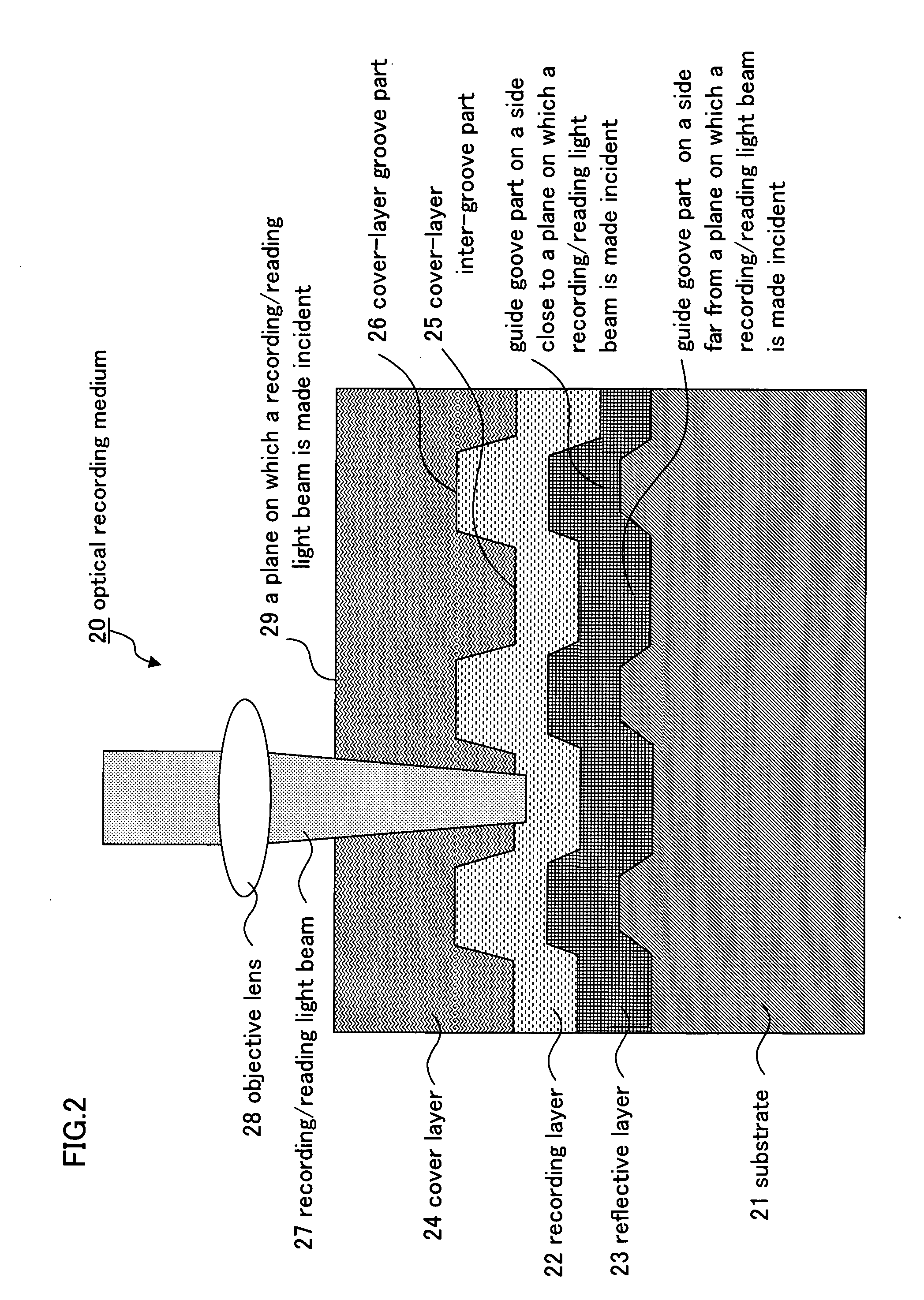
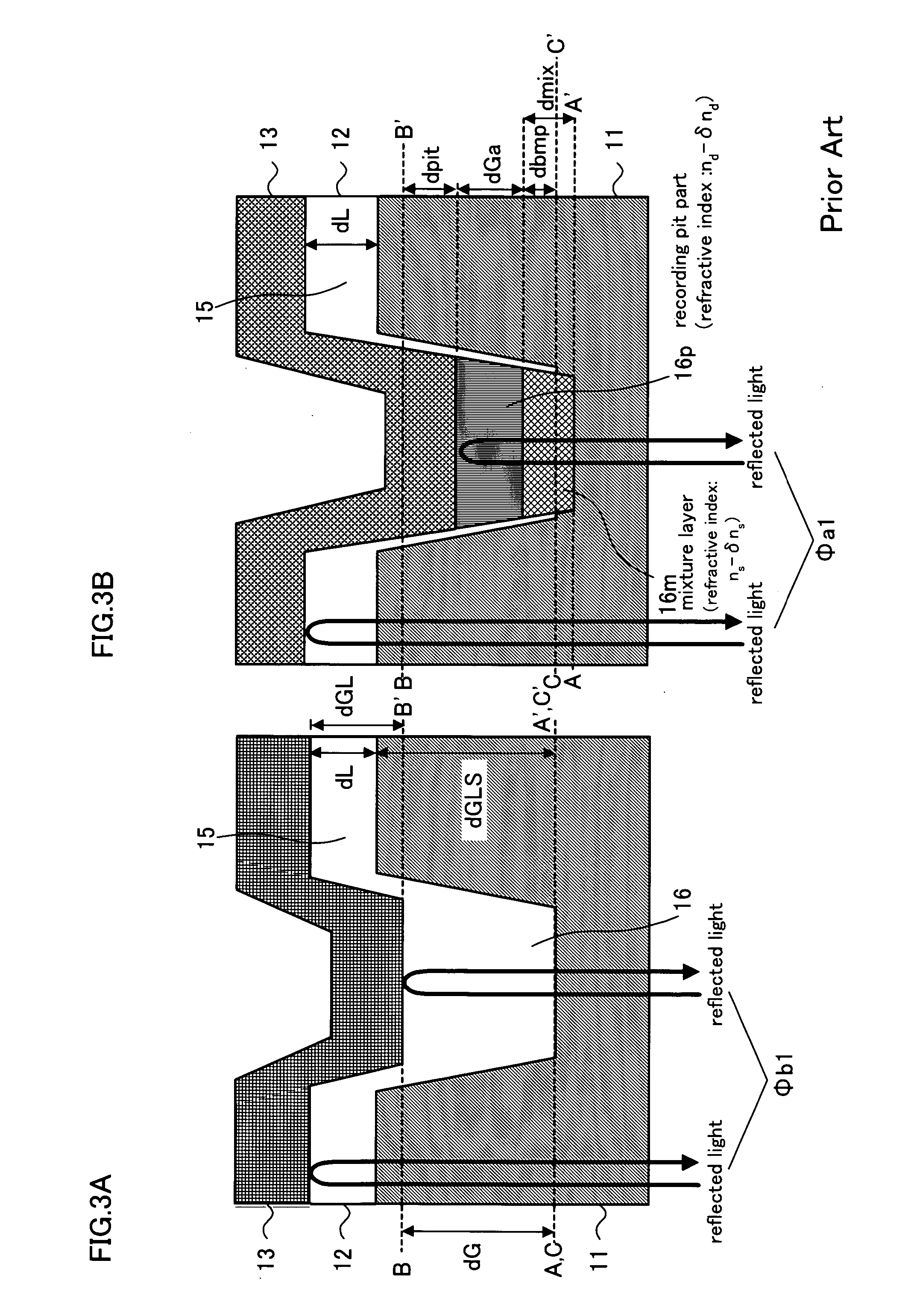
Optical recording medium and optical recording method of the same
InactiveUS20060204706A1Good recording/reading characteristicHigh-density opticalLayered productsMechanical record carriersPhase shiftedHigh density
By use of a substrate which can be stably formed and has a relatively small groove depth, a very high density optical recording medium having good recording / reading characteristics is provided. In an optical recording medium of a surface incidence type, in which a reflective layer, a recording layer containing a dye as a main component and a cover layer are sequentially formed on a substrate having guide grooves formed therein, a guide groove part on a far side from a plane of incidence of a recording / reading light beam on the cover layer is set as a recording groove part, and reflected light intensity in a recorded pit portion formed in the recording groove part is increased by a phase shift and is set higher than reflected light intensity in unrecorded.
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
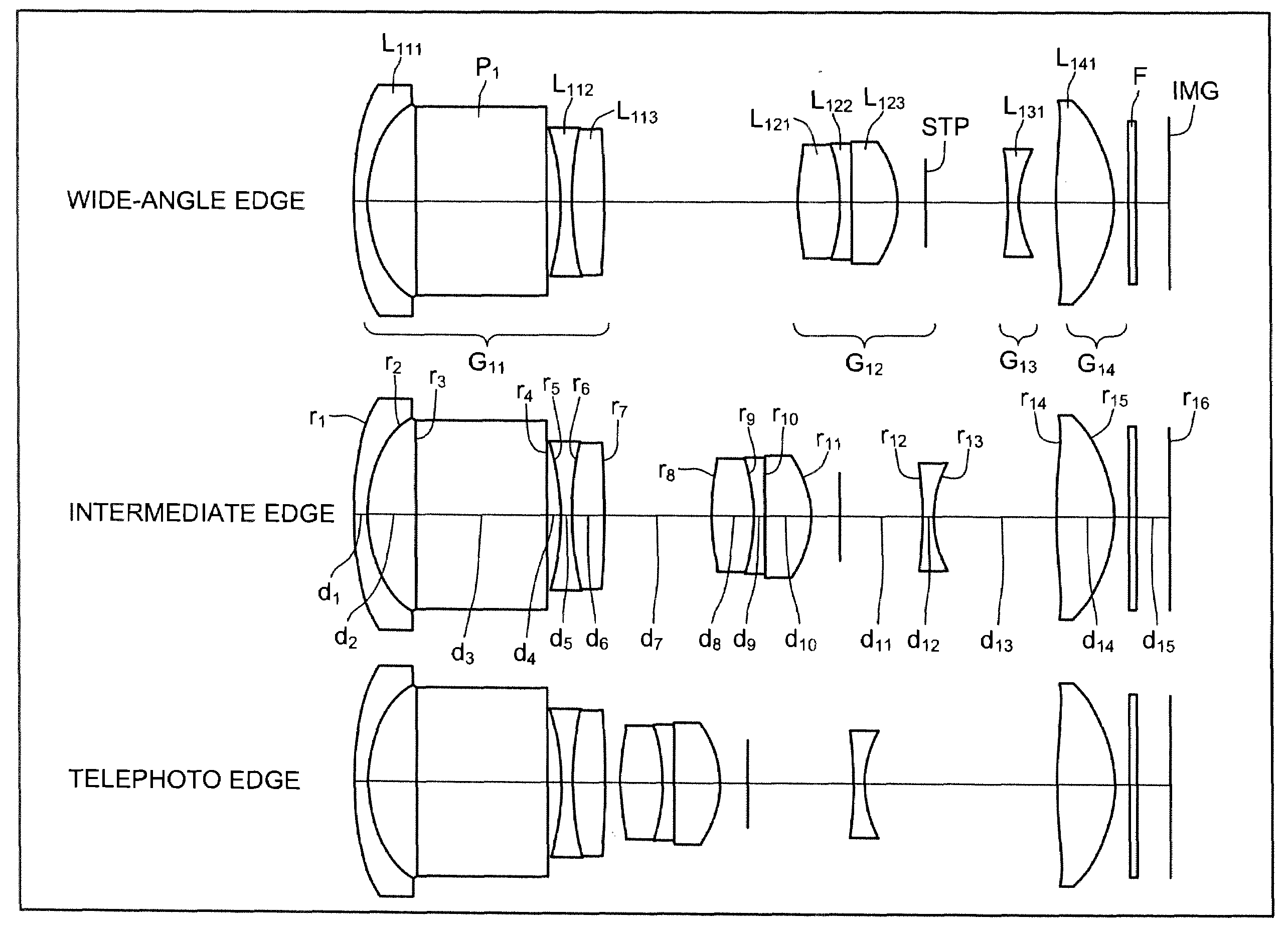
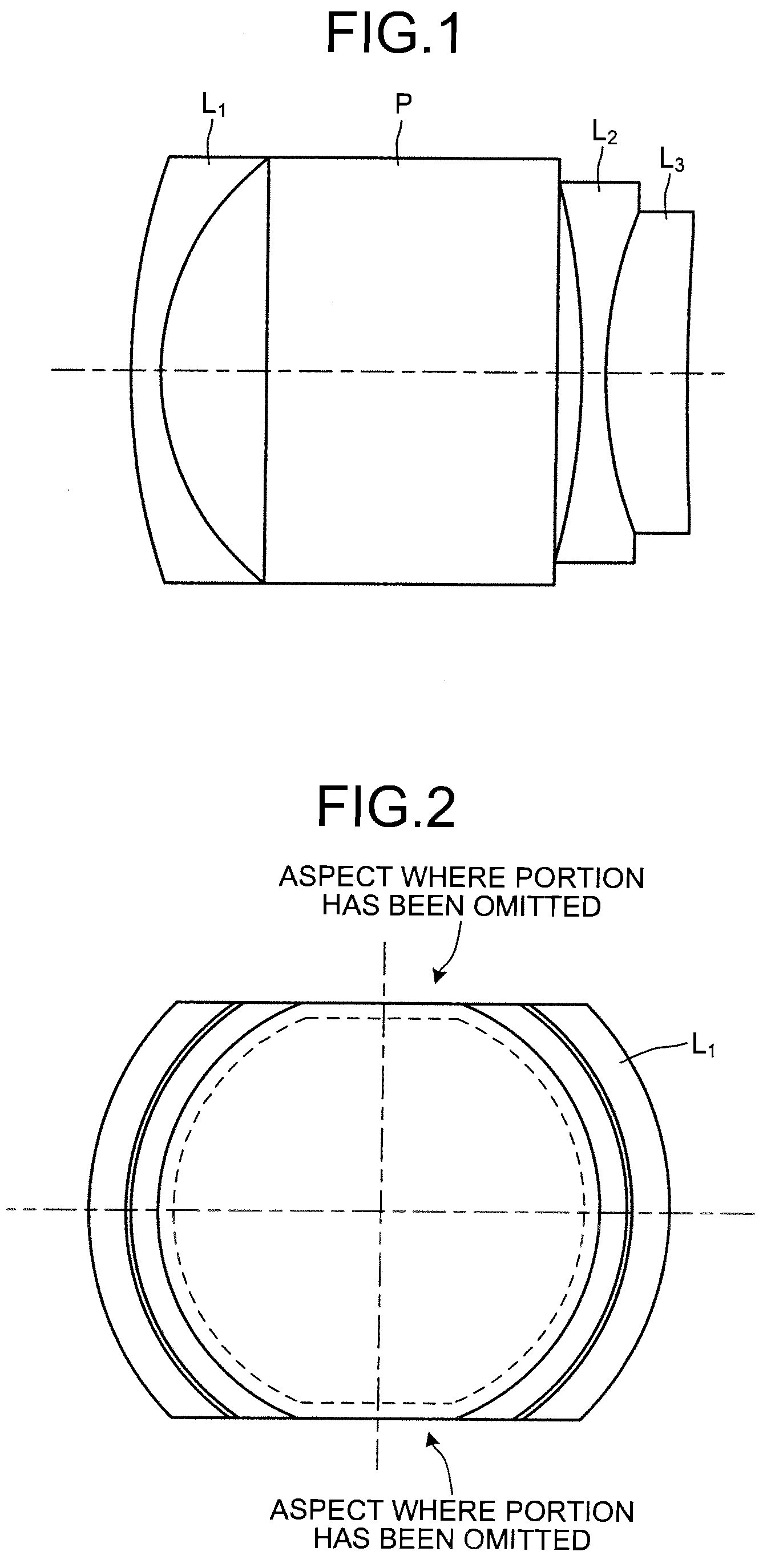
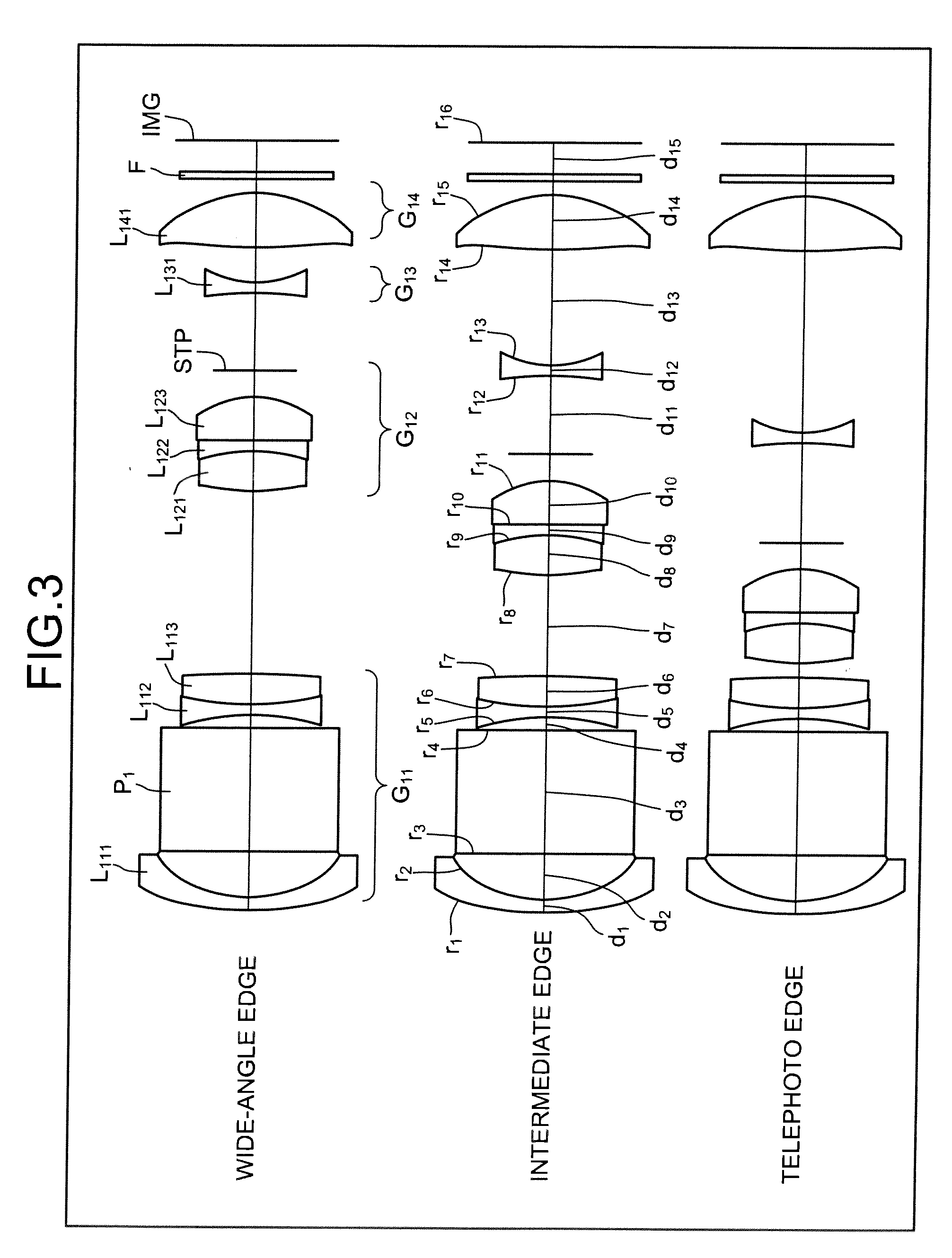
Reflex, magnifying optical system
InactiveUS20090225438A1Deterioration and variation is preventedReduce error sensitivityOptical elementsReflexPrism
A first lens group in a reflex, magnifying optical system includes sequentially from the side of an object, a first lens that has a negative refractive power and is a meniscus lens having a concave aspect facing toward an image, an optical element (prism) that refracts an optical path, a second lens having a negative refractive power and a concave aspect facing toward the object, and a third lens having a positive refractive power. A portion of an image-side aspect of the first lens abuts a plane of incidence of the optical element. A portion of an object-side aspect of the second lens abuts a plane of transmission of the optical element.
Owner:TAMRON
Projector device
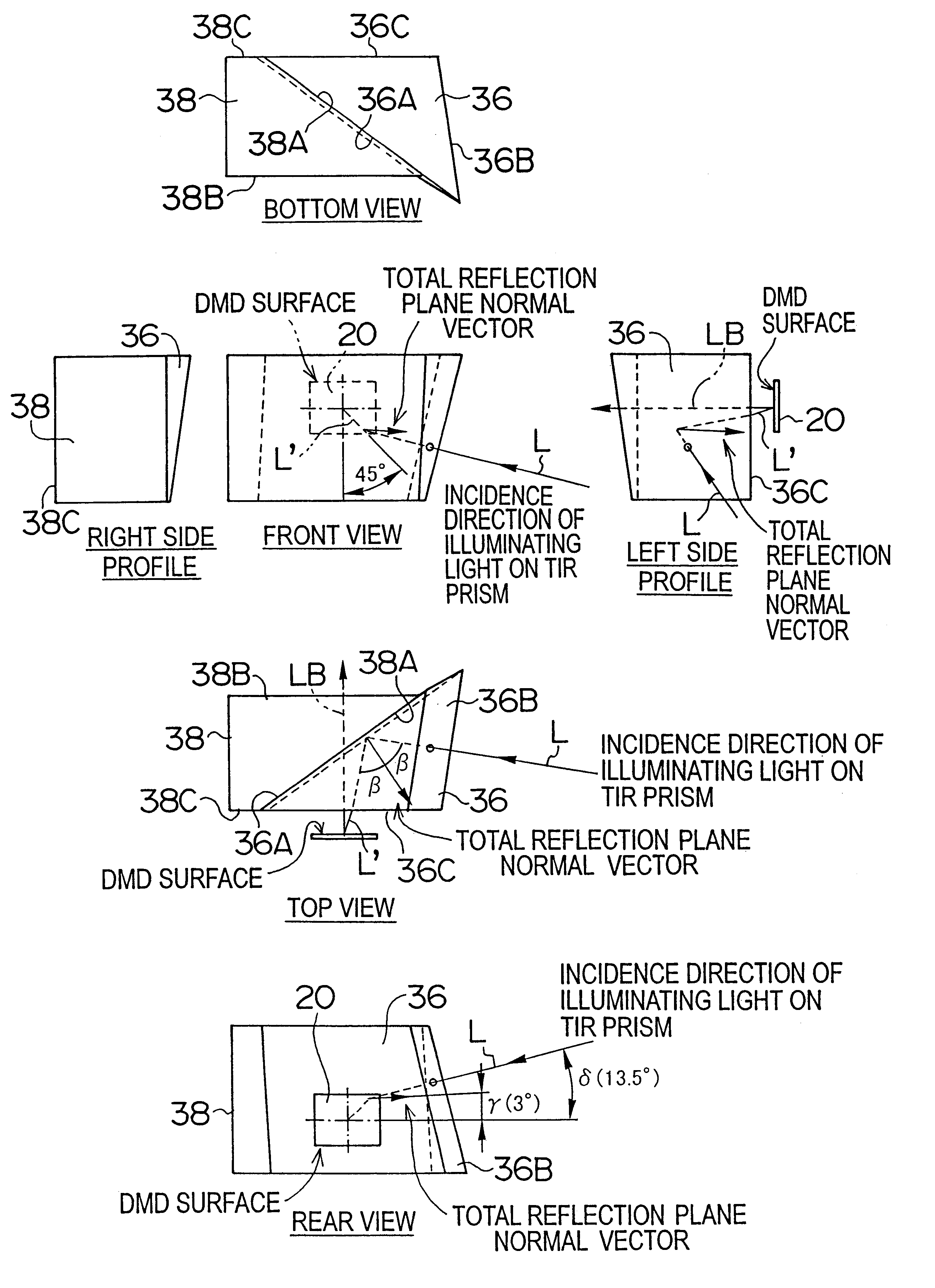
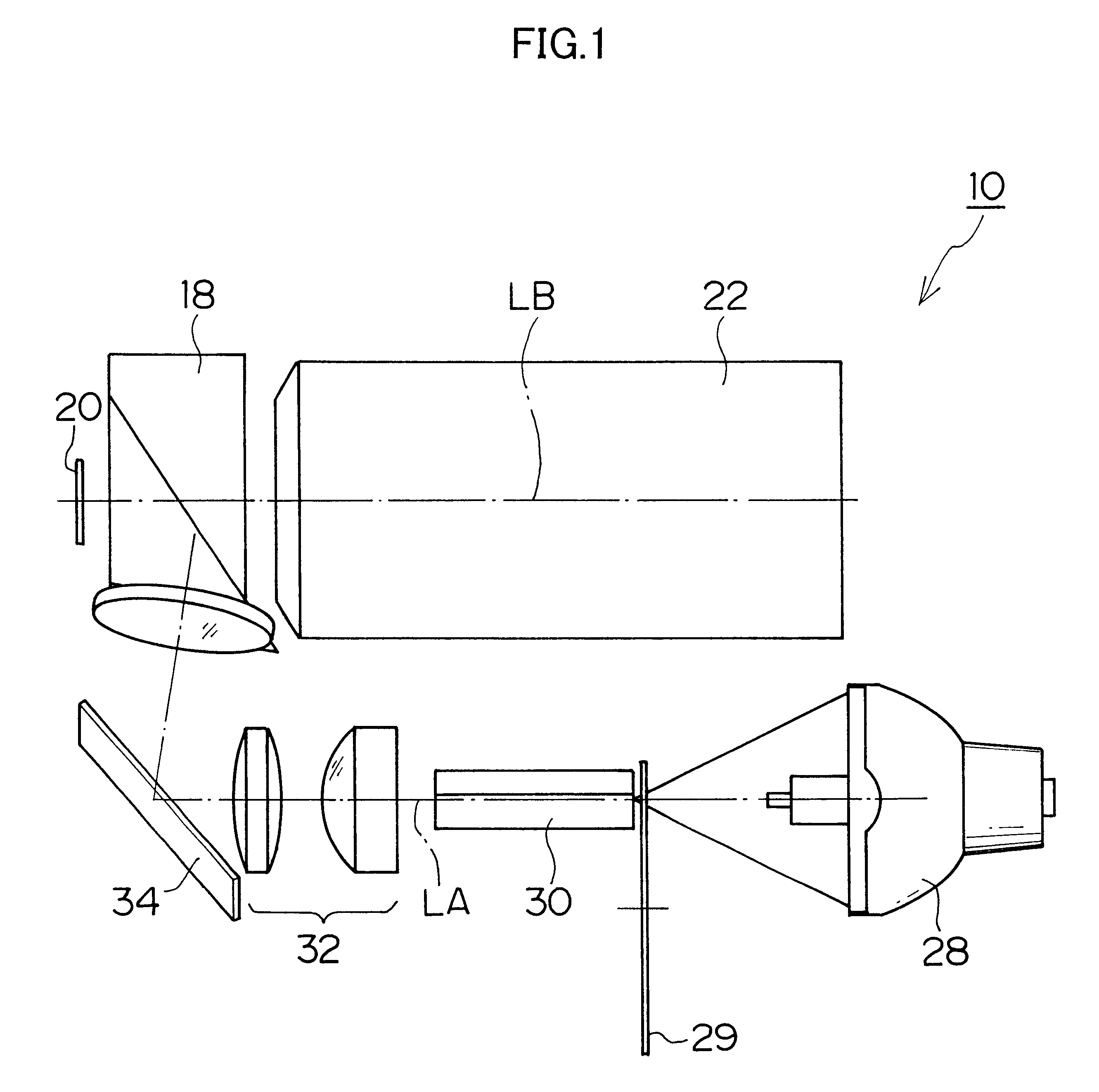
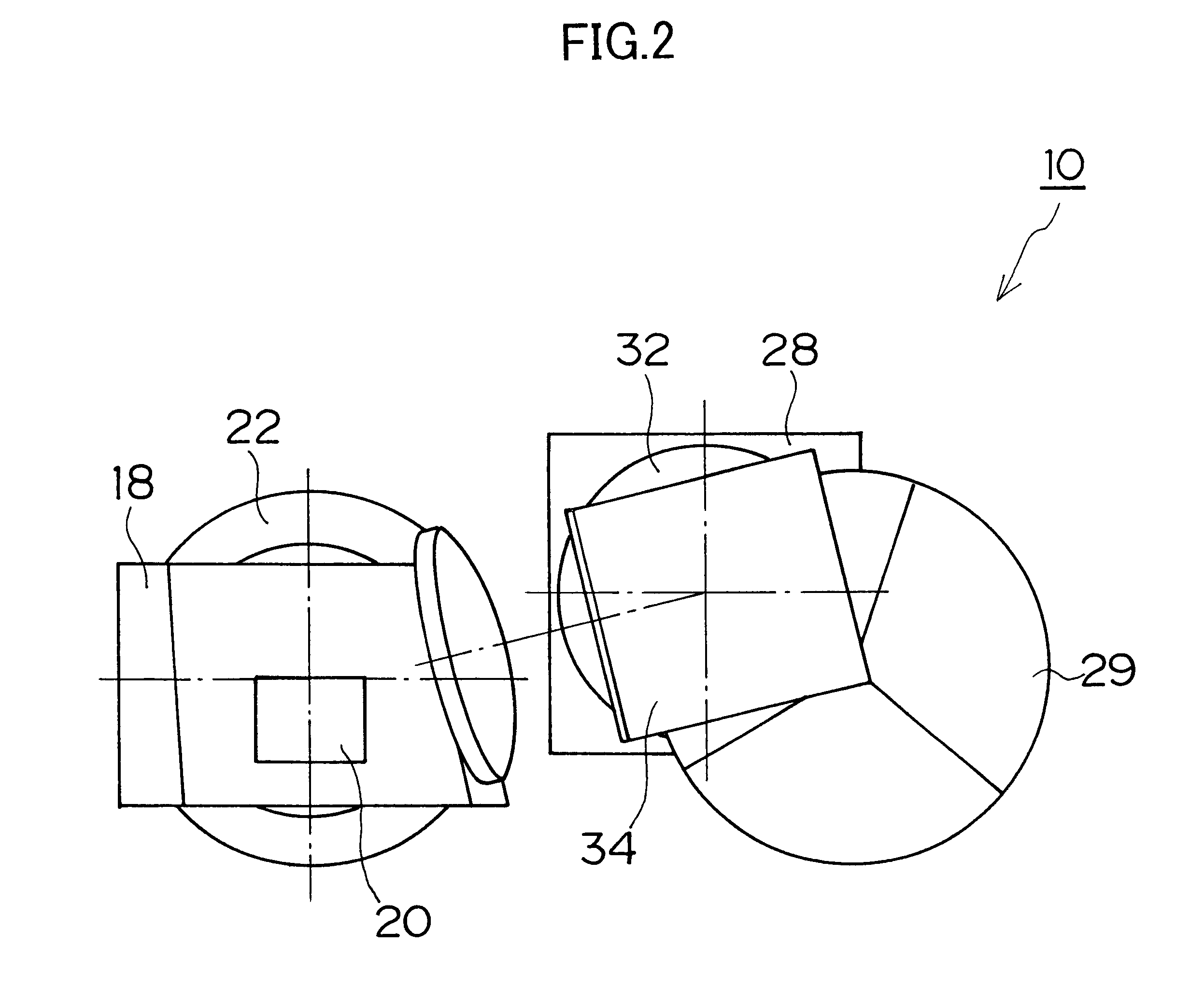
The projector device can be reduced in thickness by using a total internal reflection (TIR) prism wherein the angle formed between a line of projection of the normal vector of the total reflection plane on the surface of a digital micromirror device (DMD) and the long or short side of the DMD is set to be smaller than 45°. The TIR prism has a total reflection plane for totally reflecting illuminating light brought to incidence by an illuminating optical system to guide it to the DMD and totally transmit light optically modulated by the DMD to guide it to a projecting optical system, and this total reflection plane is so arranged relative to the DMD that the angle formed between a line of projection of its normal vector on the surface of the DMD and the long side of the DMD form an angle smaller than 45°. An incidence plane on which the illuminating light is brought to incidence by the illuminating optical system is so formed that the illuminating light brought to incidence vertically on its incidence plane, when totally reflected by the total reflection plane and emitted from an emission plane toward the DMD, be emitted at an incidence angle of 24° to the surface of the DMD in a direction at an angle of 45° to the long side of the DMD.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Polarimetric scatterometry methods for critical dimension measurements of periodic structures
InactiveUS20050174575A1Polarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsMotor driveOptical property
An optical measurement system for evaluating a sample has a motor-driven rotating mechanism coupled to an azimuthally rotatable measurement head, allowing the optics to rotate with respect to the sample. A polarimetric scatterometer, having optics directing a polarized illumination beam at non-normal incidence onto a periodic structure on a sample, can measure optical properties of the periodic structure. An E-O modulator in the illumination path can modulate the polarization. The head optics collect light reflected from the periodic structure and feed that light to a spectrometer for measurement. A beamsplitter in the collection path can ensure both S and P polarization from the sample are separately measured. The measurement head can be mounted for rotation of the plane of incidence to different azimuthal directions relative to the periodic structures. The instrument can be integrated within a wafer process tool in which wafers may be provided at arbitrary orientation.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Projector device
The projector device can be reduced in thickness by using a total internal reflection (TIR) prism wherein the angle formed between a line of projection of the normal vector of the total reflection plane on the surface of a digital micromirror device (DMD) and the long or short side of the DMD is set to be smaller than 45°. The TIR prism has a total reflection plane for totally reflecting illuminating light brought to incidence by an illuminating optical system to guide it to the DMD and totally transmit light optically modulated by the DMD to guide it to a projecting optical system, and this total reflection plane is so arranged relative to the DMD that the angle formed between a line of projection of its normal vector on the surface of the DMD and the long side of the DMD form an angle smaller than 45°. An incidence plane on which the illuminating light is brought to incidence by the illuminating optical system is so formed that the illuminating light brought to incidence vertically on its incidence plane, when totally reflected by the total reflection plane and emitted from an emission plane toward the DMD, be emitted at an incidence angle of 24° to the surface of the DMD in a direction at an angle of 45° to the long side of the DMD.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Optical Component and Backlight Unit Using the Optical Component
InactiveUS20070285941A1Wide viewing angleExcellent light diffusionPrismsMechanical apparatusHigh intensityPlane of incidence
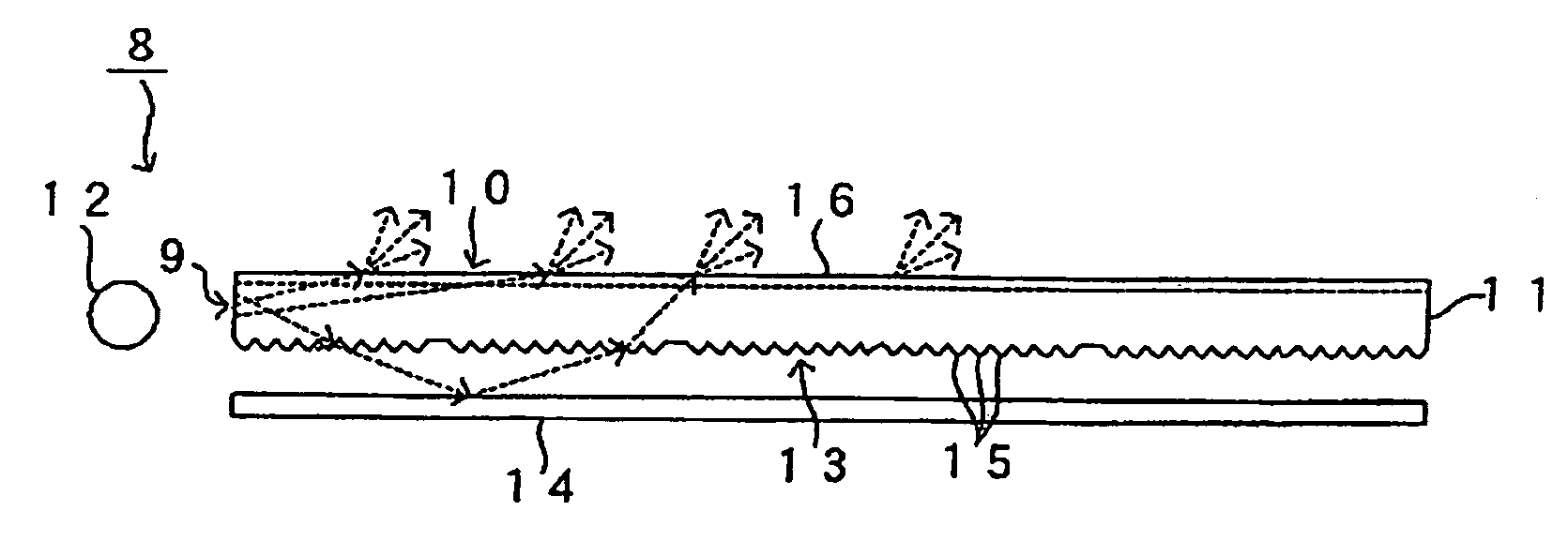
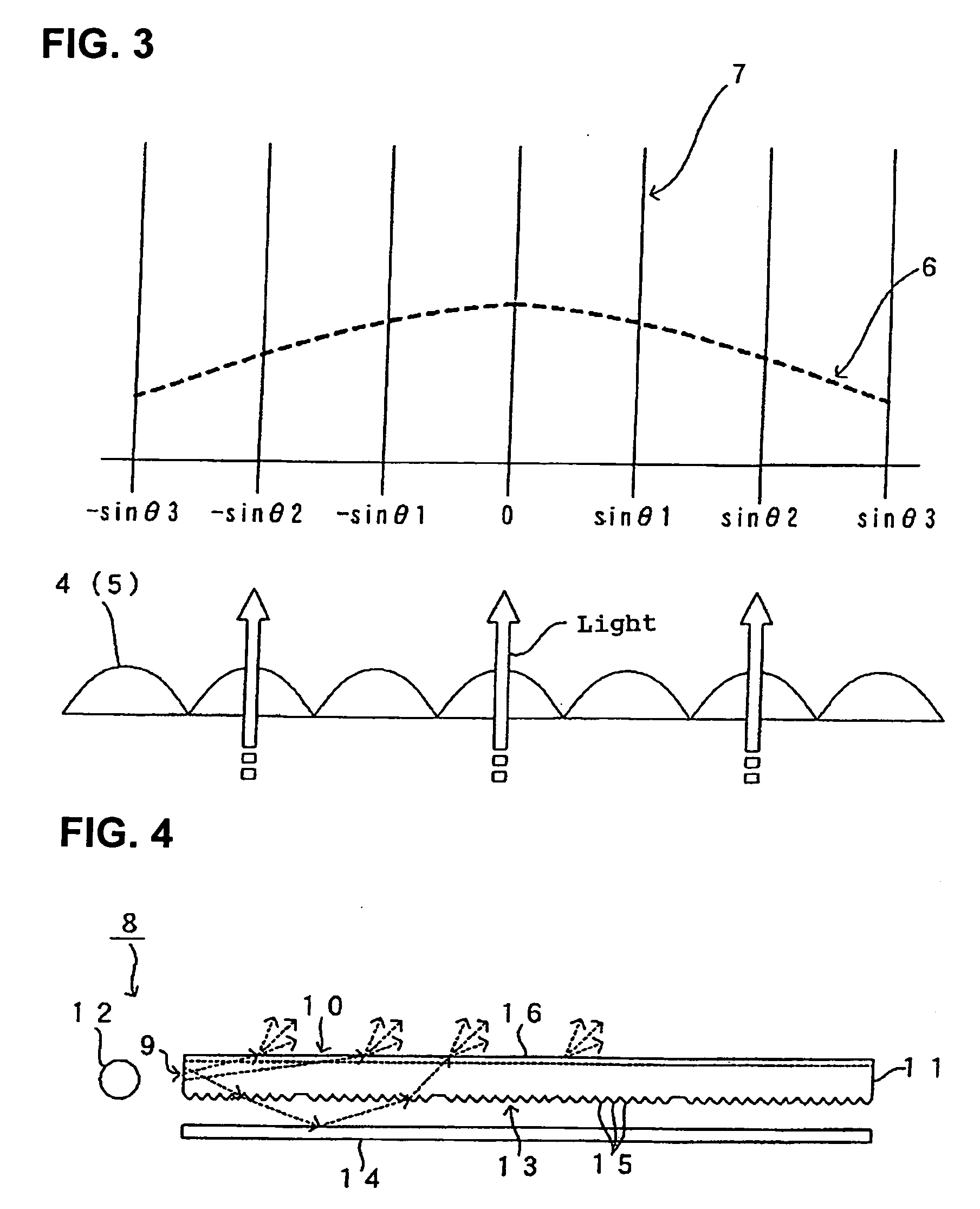
[PROBLEMS] An optical component in which the viewing angle can be widened while sustaining a high luminance and the defect of a display can be made inconspicuous, and a backlight employing the optical component. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] When a substantially collimated light impinges on the plane of incidence (9), an outgoing light from the outgoing plane (10) exhibits anisotropy in its intensity along an azimuth of 30° to normal to the outgoing plane (10), the anisotropy being such that the ratio between a highest intensity and a lowest intensity in the intensity distribution of outgoing light intensity along the azimuth of 30° is set to not smaller than 1.2.
Owner:SAKARI +1
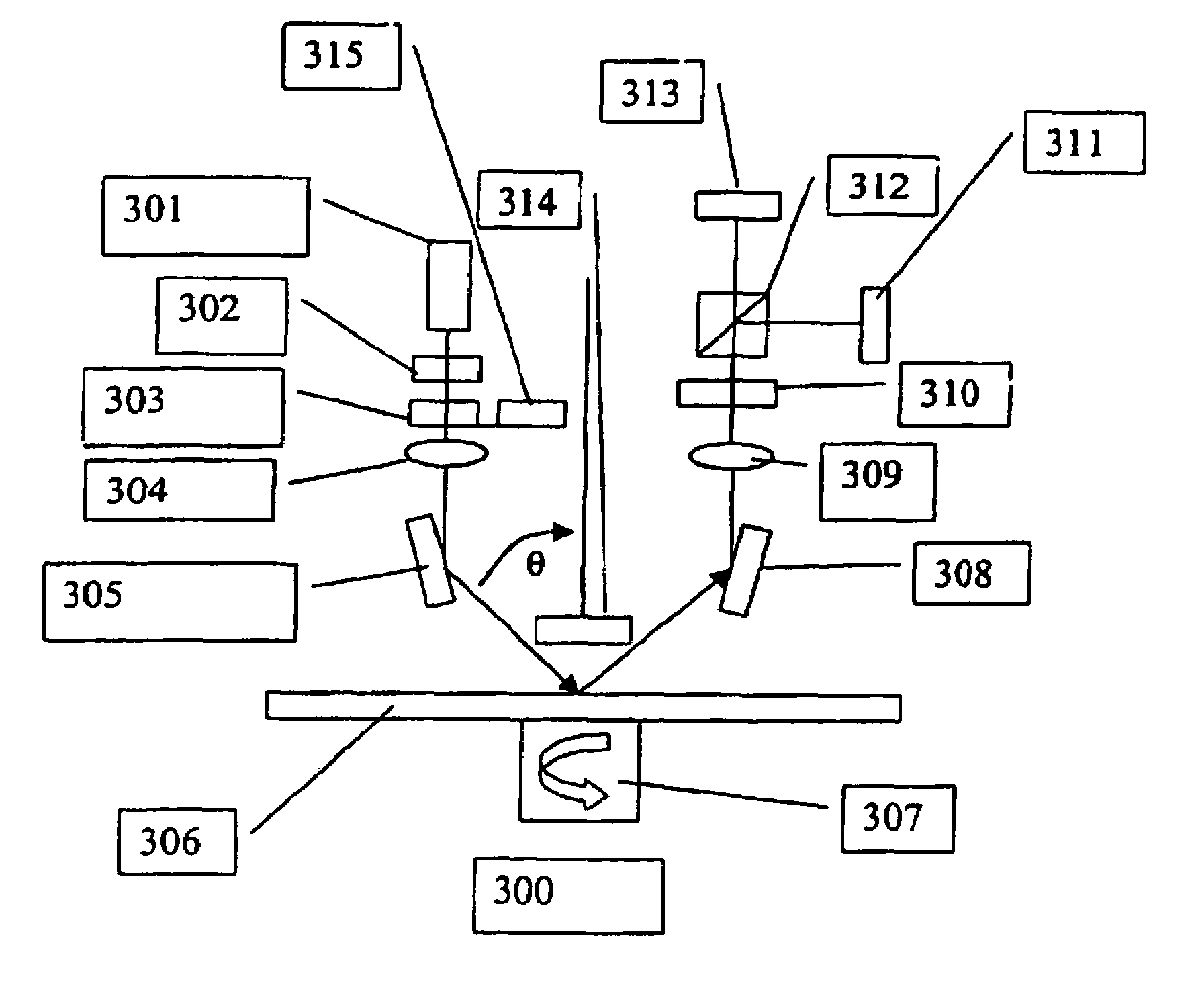
Microscope
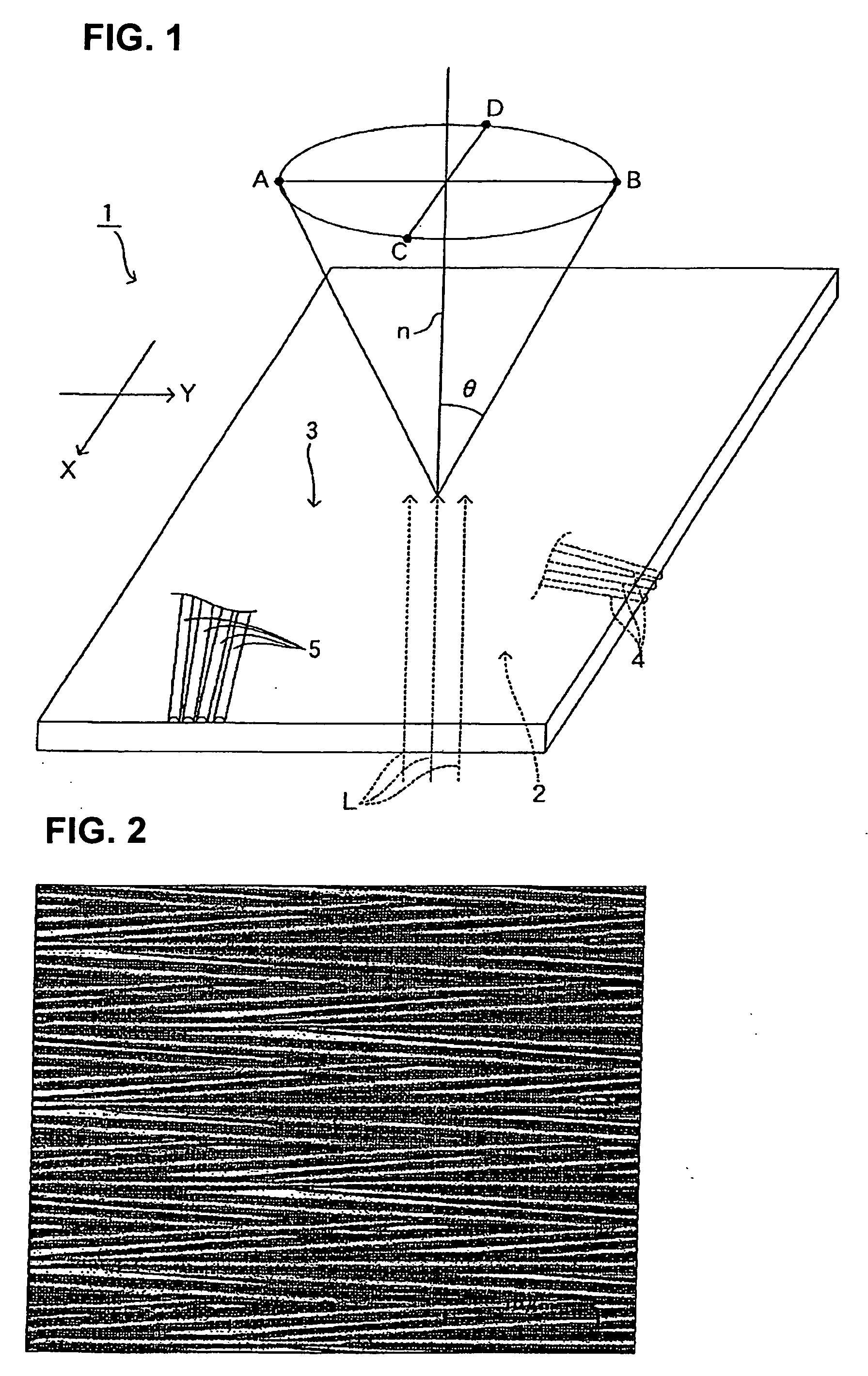
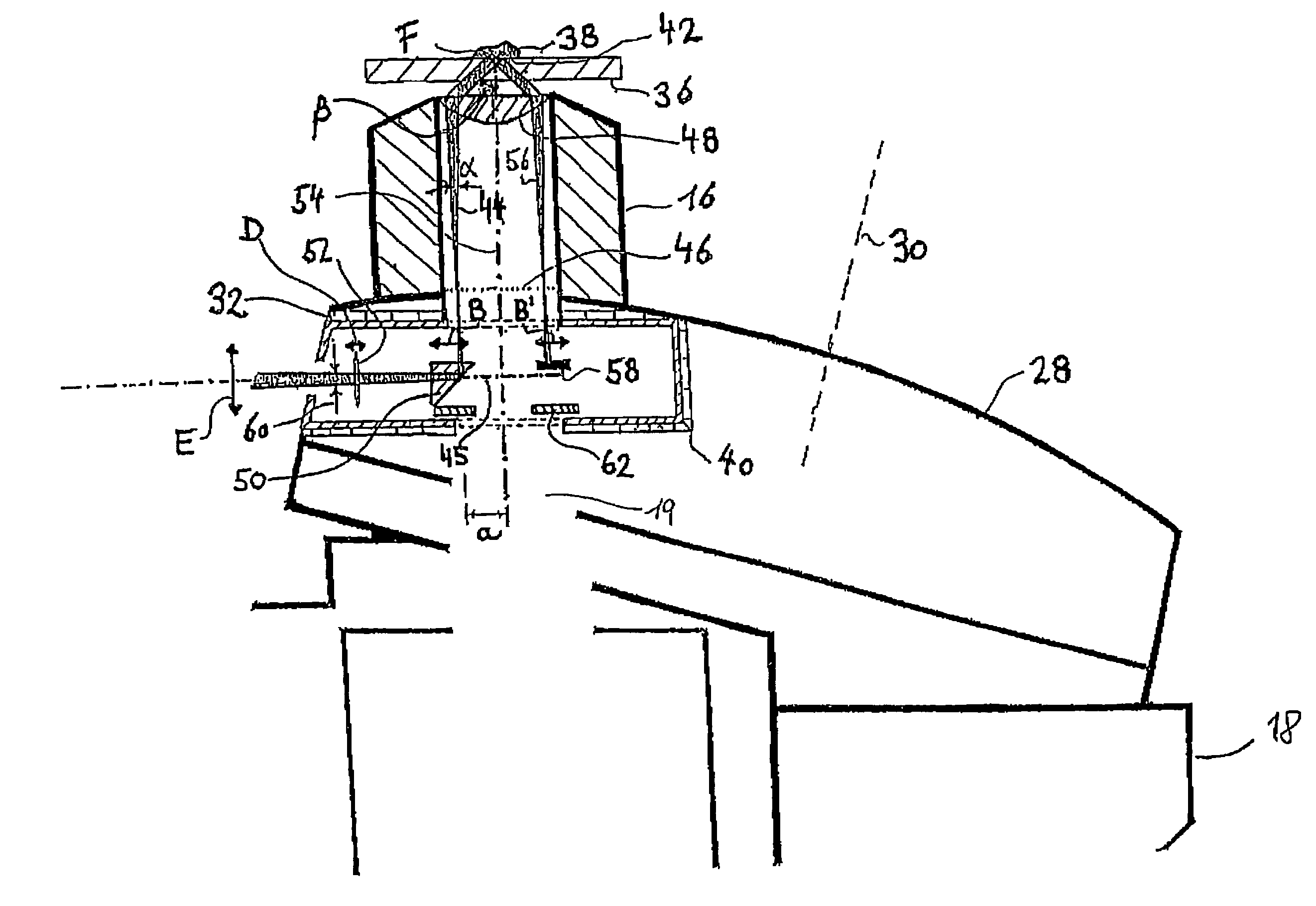
The invention relates to a microscope comprising a microscope housing (18), an optics system (16) consisting of at least one lens system that contains at least one respective lens (48) and is positioned at one end of a passage (19) of the microscope housing (18), at least one observation device, in particular an ocular, located at the other end of the passage (19), an illumination device, whose light forms at least one illumination beam (44), originating from a plane of incidence (45) that vertically intersects the passage (19), said beam traversing the lens system and striking an object carrier (36) at a predetermined angle (β). According to the invention, the illumination beam or beams (44) originating from the plane of incidence (45) is / are provided by an optical device, whose cross-section lying in the vicinity of the passage (19) is substantially smaller than the cross-section of said passage (19).
Owner:EURO LAB FUER MOLEKULARBIOLOGIE EMBL
Optical device, illumination apparatus, and color illumination apparatus
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP +1
Optical irradiation apparatus, image reading apparatus using the same, and image forming apparatus using the same
A novel optical irradiation apparatus includes a light source and a light guide. The light source is configured to radially irradiate a light beam. The light guide is configured to include a transparent material configured to lead the light beam irradiated from the light source in a specific direction and to emit the light beam. The light guide also includes an incidence plane, an exit plane, and plural connecting planes. The incidence plane is configured to receive the light beam. The exit plane is configured to emit the light beam to so as to irradiate an object. The plural connecting planes are configured to connect the incidence plane to the exit plane. A part of at least one of the plural connecting planes is inclined with respect to an axis of the light beam.
Owner:RICOH KK
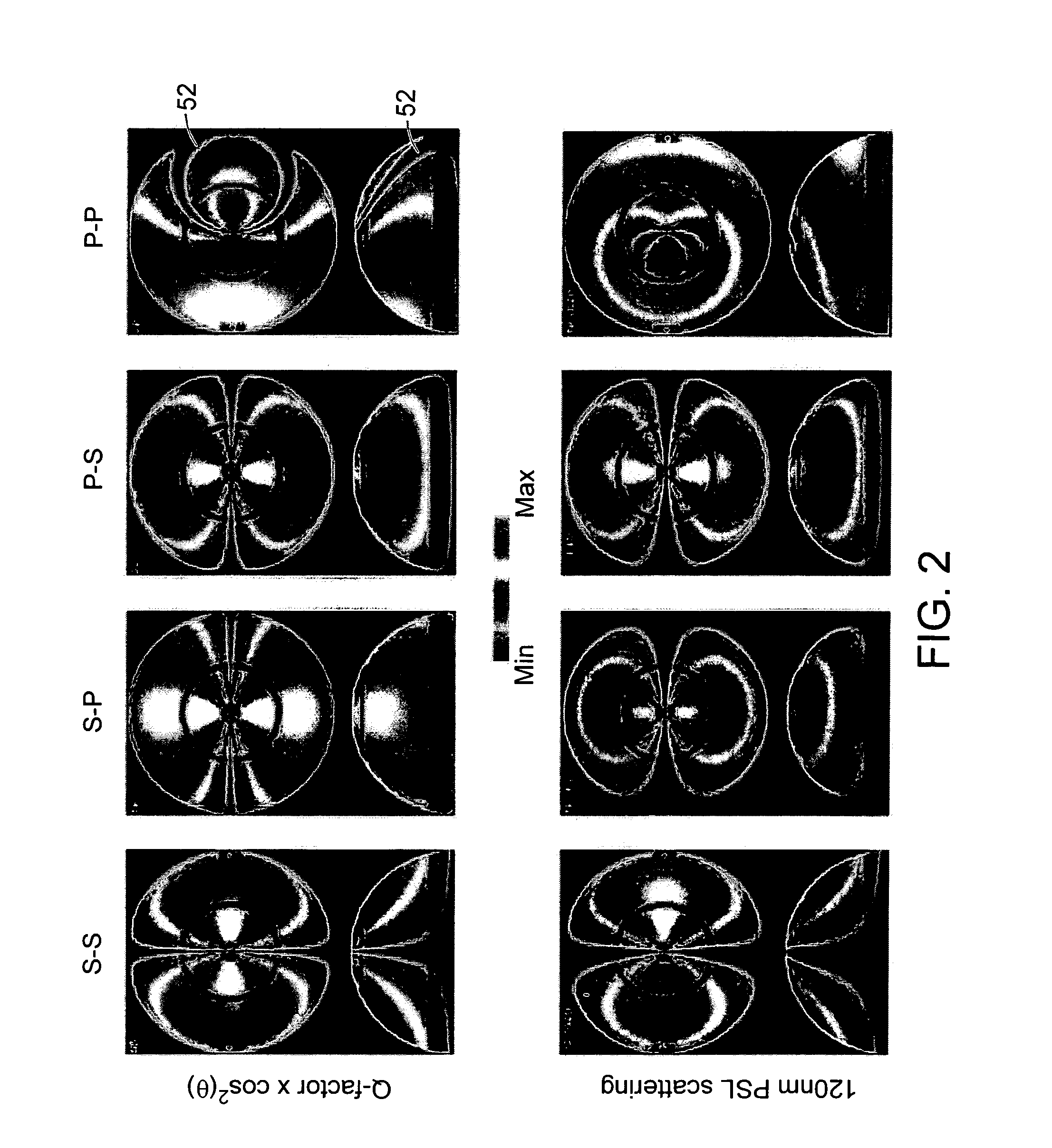
Systems and methods for inspecting specimens including specimens that have a substantially rough uppermost layer
ActiveUS8582094B1Material analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementOblique angleLength wave
Systems and methods for inspecting a specimen are provided. One system includes an illumination subsystem configured to direct light to the specimen at an oblique angle of incidence. The light is polarized in a plane that is substantially parallel to the plane of incidence. The system also includes a detection subsystem configured to detect light scattered from the specimen. The detected light is polarized in a plane that is substantially parallel to the plane of scattering. In addition, the system includes a processor configured to detect defects on the specimen using signals generated by the detection subsystem. In one embodiment, such a system may be configured to detect defects having a size that is less than half of a wavelength of the light directed to the specimen.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for printing a periodic pattern with a large depth of focus
ActiveUS20120009525A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusAngle of incidenceOptoelectronics
A method for printing a desired pattern into a photosensitive layer that includes providing a mask bearing a pattern of linear features that are parallel to a first direction, arranging the layer parallel to and separated from said mask, generating substantially monochromatic light, and illuminating the mask pattern with said light over a range of angles of incidence in a plane parallel to said first direction, at substantially a single angle in an orthogonal plane of incidence and so that the light of each angle of incidence transmitted by the mask forms a light-field component at the layer whereby the integration of said components prints the desired pattern, wherein the range of angles is selected so that the integration of said components is substantially equivalent to an average of the range of transversal intensity distributions formed between Talbot image planes by light at one of the angles of incidence.
Owner:EULITHA
Focusing lens for LED
InactiveCN101251611AReduce lossesEffective lightingPoint-like light sourceCondensersOptical axisAspheric lens
A focusing lens for an LED, which concentrates light emitted from the LED so as to have directionality parallel to an optic axis, comprises: a transparent body; a first lens part formed in the body; and a second lens part covering the first lens part, and wherein the first lens part comprises: a first and second aspheric lens surfaces which are convex with different sizes and form on plat surfaces symmetric with each other. The second lens comprises a plane of incidence formed to protrude from an outer circumference of the first aspheric lens surface, the plane of incidence into which the LED is inserted and which is configured to allow the light emitted from the LED to be incident and refracted; a plane of reflection formed to have a convex curved surface which extend and slopes to be progressive wider from the plane of incidence towards the second aspheric lens surface, the plane of reflection which is configured to allow the light emitted from the LED to be totally reflected; and a plane of emission formed to have a concave curved surface which extends and slopes from the plane of reflection towards the second aspheric lens surface, the plane of emission which is configured to allow the light emitted from the LED to be refracted and emitted as light being parallel to the optic axis.
Owner:SEKONIX
Systems and methods for inspecting an edge of a specimen
ActiveUS7728965B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansPlane of incidenceOblique angle
Systems and methods for inspecting an edge of a specimen are provided. One system includes an illumination subsystem configured to direct light to the edge of the specimen at an oblique angle of incidence. The plane of incidence of the light is substantially perpendicular to a plane substantially tangent to the edge of the specimen. The system also includes a detection subsystem configured to collect light scattered from the edge and to generate signals responsive to the scattered light. One method includes directing light to the edge of the specimen at an oblique angle of incidence. The plane of incidence is substantially perpendicular to a plane substantially tangent to the edge of the specimen. The method also includes collecting light scattered from the edge and generating signals responsive to the scattered light. The signals described above can be used to detect defects on the edge of the specimen.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
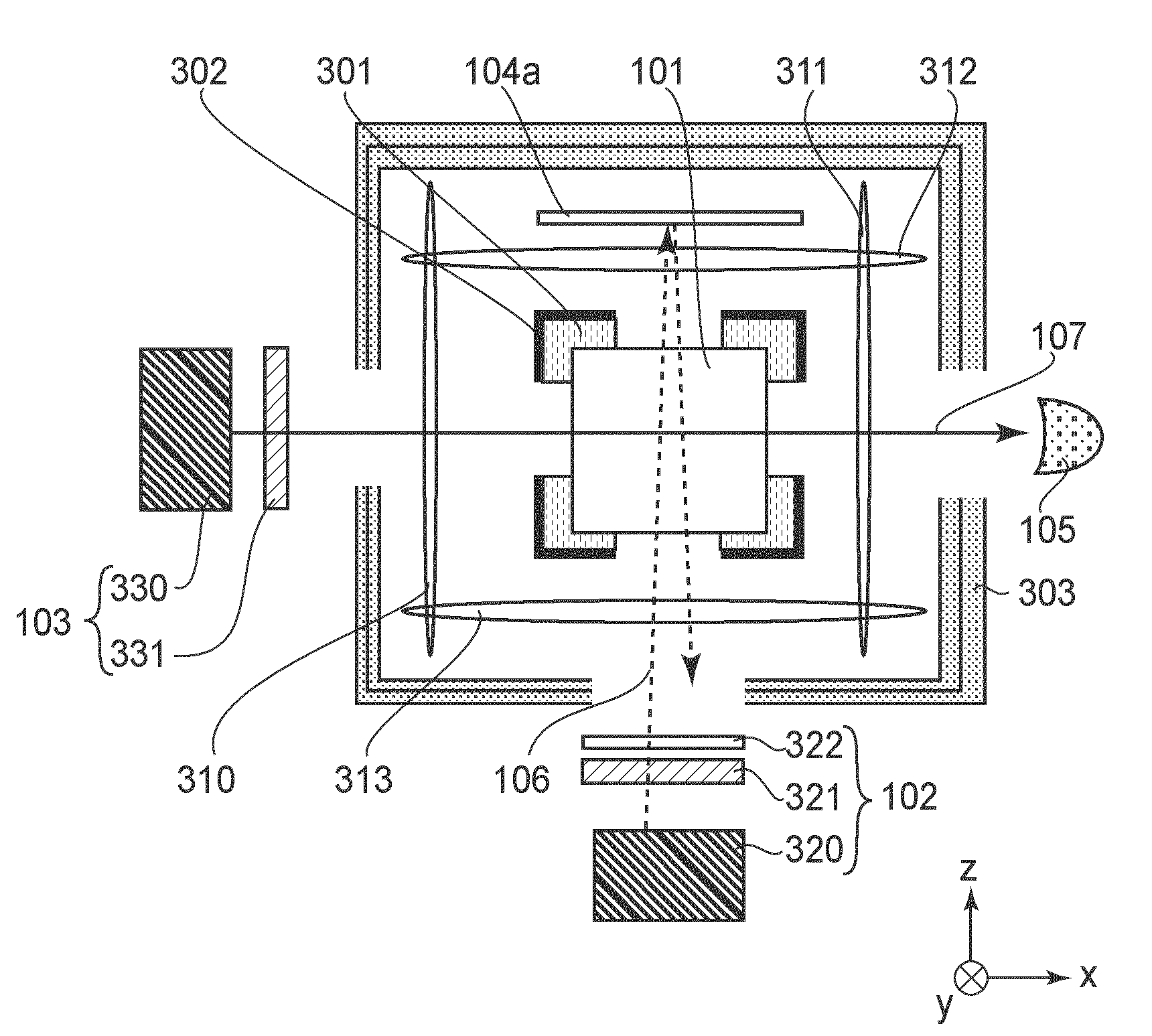
Systems And Methods For Extended Infrared Spectroscopic Ellipsometry
ActiveUS20170205342A1Accurate representationSmall featureRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Semiconductor structure
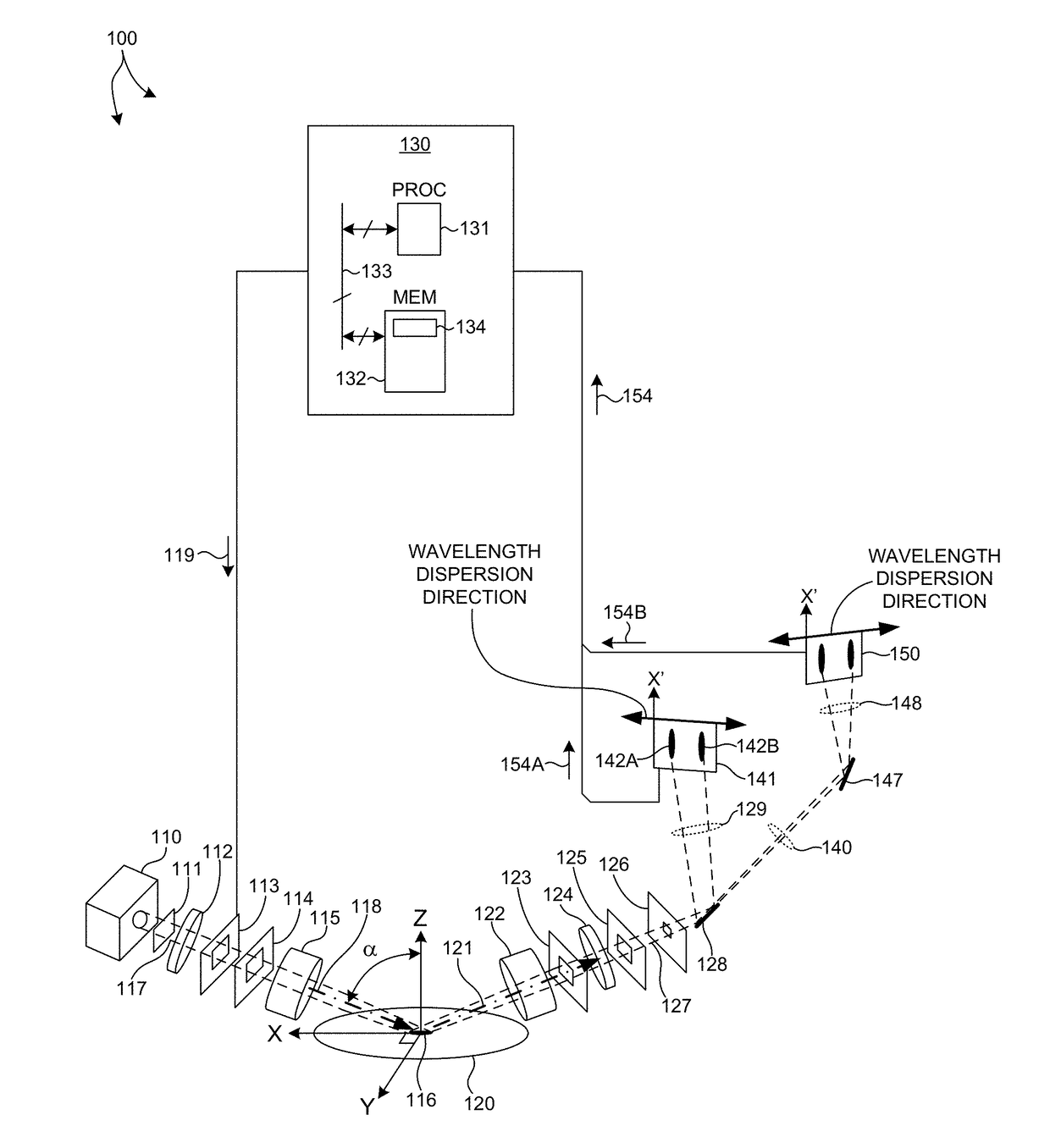
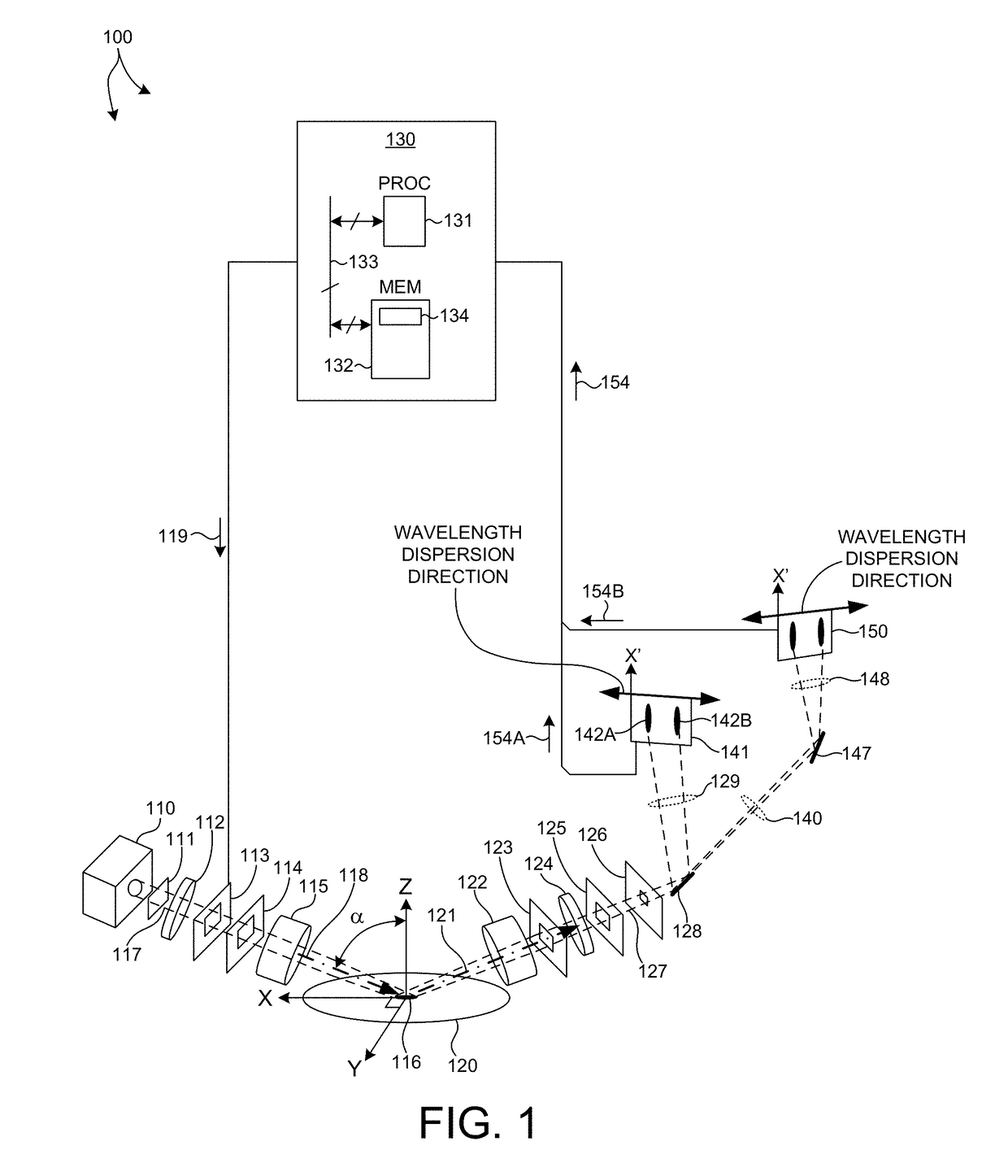
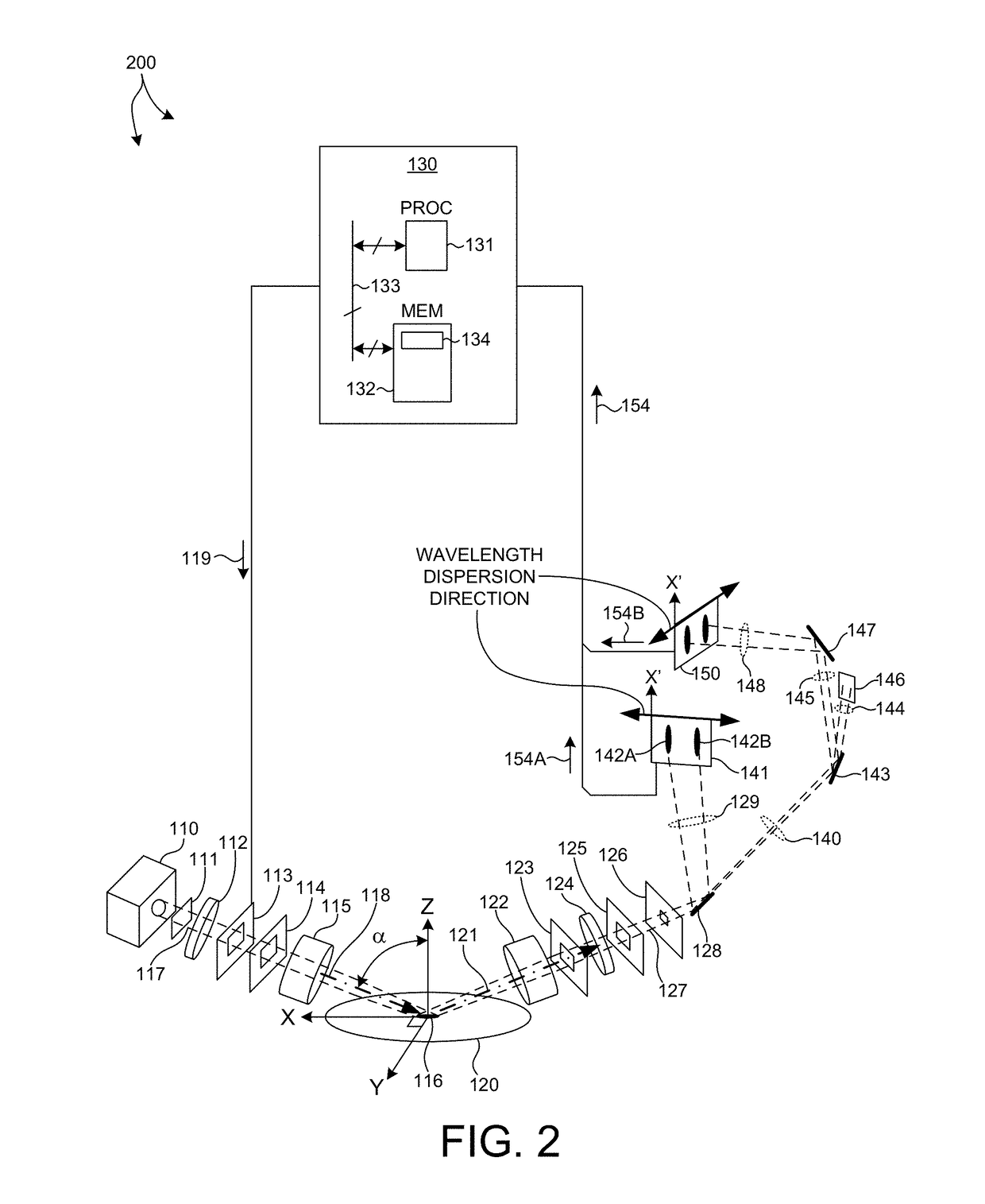
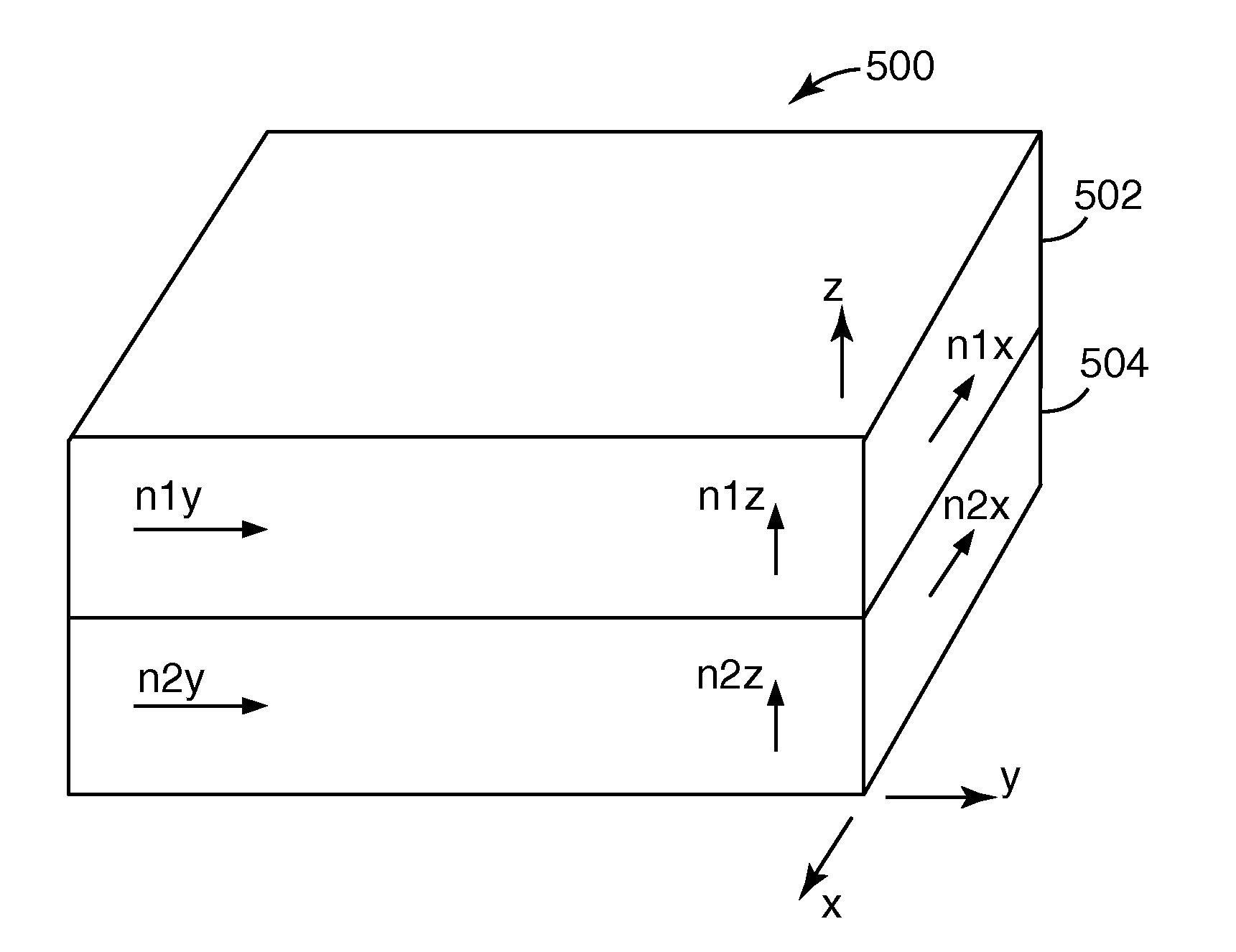
Methods and systems for performing simultaneous spectroscopic measurements of semiconductor structures at ultraviolet, visible, and infrared wavelengths are presented herein. In another aspect, wavelength errors are reduced by orienting the direction of wavelength dispersion on the detector surface perpendicular to the projection of the plane of incidence onto the detector surface. In another aspect, a broad range of infrared wavelengths are detected by a detector that includes multiple photosensitive areas having different sensitivity characteristics. Collected light is linearly dispersed across the surface of the detector according to wavelength. Each different photosensitive area is arranged on the detector to sense a different range of incident wavelengths. In this manner, a broad range of infrared wavelengths are detected with high signal to noise ratio by a single detector. These features enable high throughput measurements of high aspect ratio structures with high throughput, precision, and accuracy.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Immersed reflective polarizer with angular confinement in selected planes of incidence
ActiveUS20120275023A1Enhance axial brightness and contrast ratioSimple manufacturing processPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsAngle of incidenceRefractive index
A film construction (330) includes a broad band reflective polarizing film (312) that may be immersed in an ultra low refractive index medium (332, 334). The reflecting polarizing film is characterized by a pass axis and a block axis, and its reflectivity for white light of the pass state polarization increases with increasing incidence angle to provide a compressed or narrowed viewing cone selectively in one plane of incidence. In some embodiments, the plane of incidence associated with the compressed viewing cone is aligned with the pass axis. In other embodiments it is aligned with the block axis.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Simultaneous Multi-Spot Inspection and Imaging
InactiveUS20070153265A1Small footprintLarge numerical apertureOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDetector arrayOblique angle
A compact and versatile multi-spot inspection imaging system employs an objective for focusing an array of radiation beams to a surface and a second reflective or refractive objective having a large numerical aperture for collecting scattered radiation from the array of illuminated spots. The scattered radiation from each illuminated spot is focused to a corresponding optical fiber channel so that information about a scattering may be conveyed to a corresponding detector in a remote detector array for processing. For patterned surface inspection, a cross-shaped filter is rotated along with the surface to reduce the effects of diffraction by Manhattan geometry. A spatial filter in the shape of an annular aperture may also be employed to reduce scattering from patterns such as arrays on the surface. In another embodiment, different portions of the same objective may be used for focusing the illumination beams onto the surface and for collecting the scattered radiation from the illuminated spots simultaneously. In another embodiment, a one-dimensional array of illumination beams are directed at an oblique angle to the surface to illuminate a line of illuminated spots at an angle to the plane of incidence. Radiation scattered from the spots are collected along directions perpendicular to the line of spots or in a double dark field configuration.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com