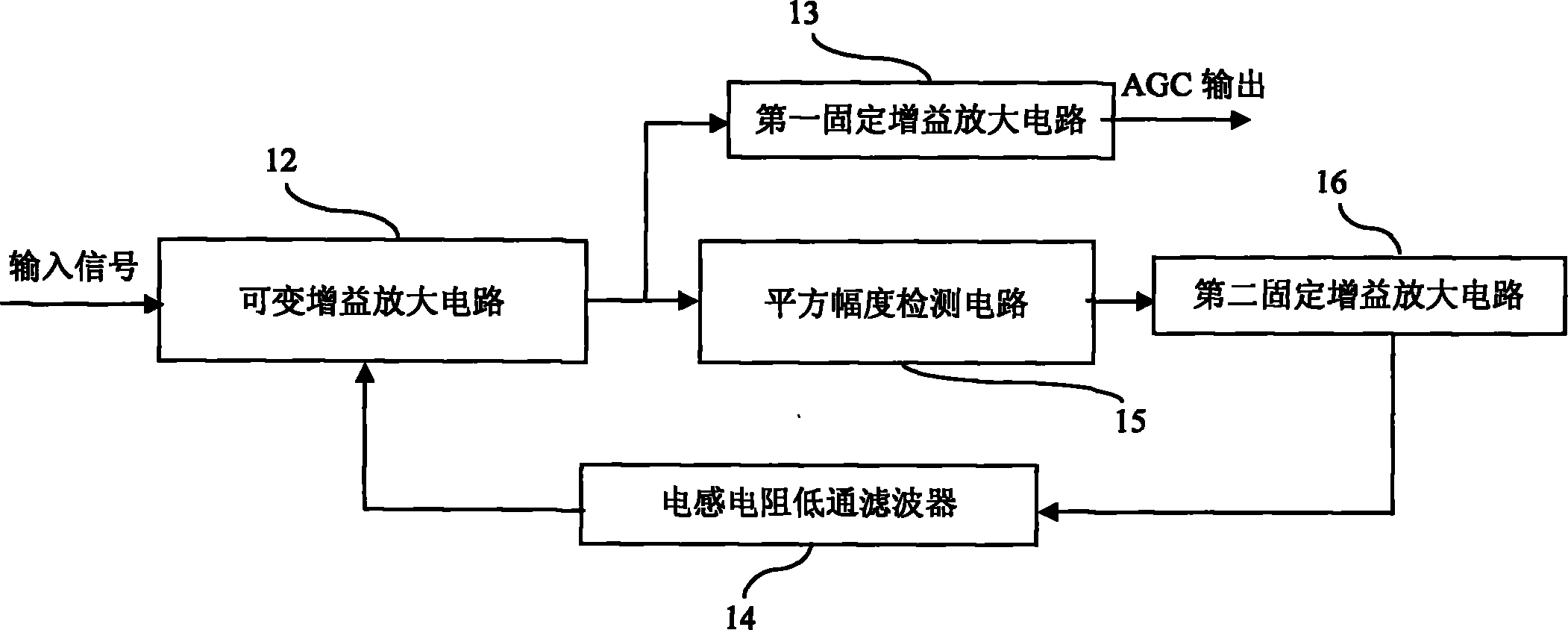
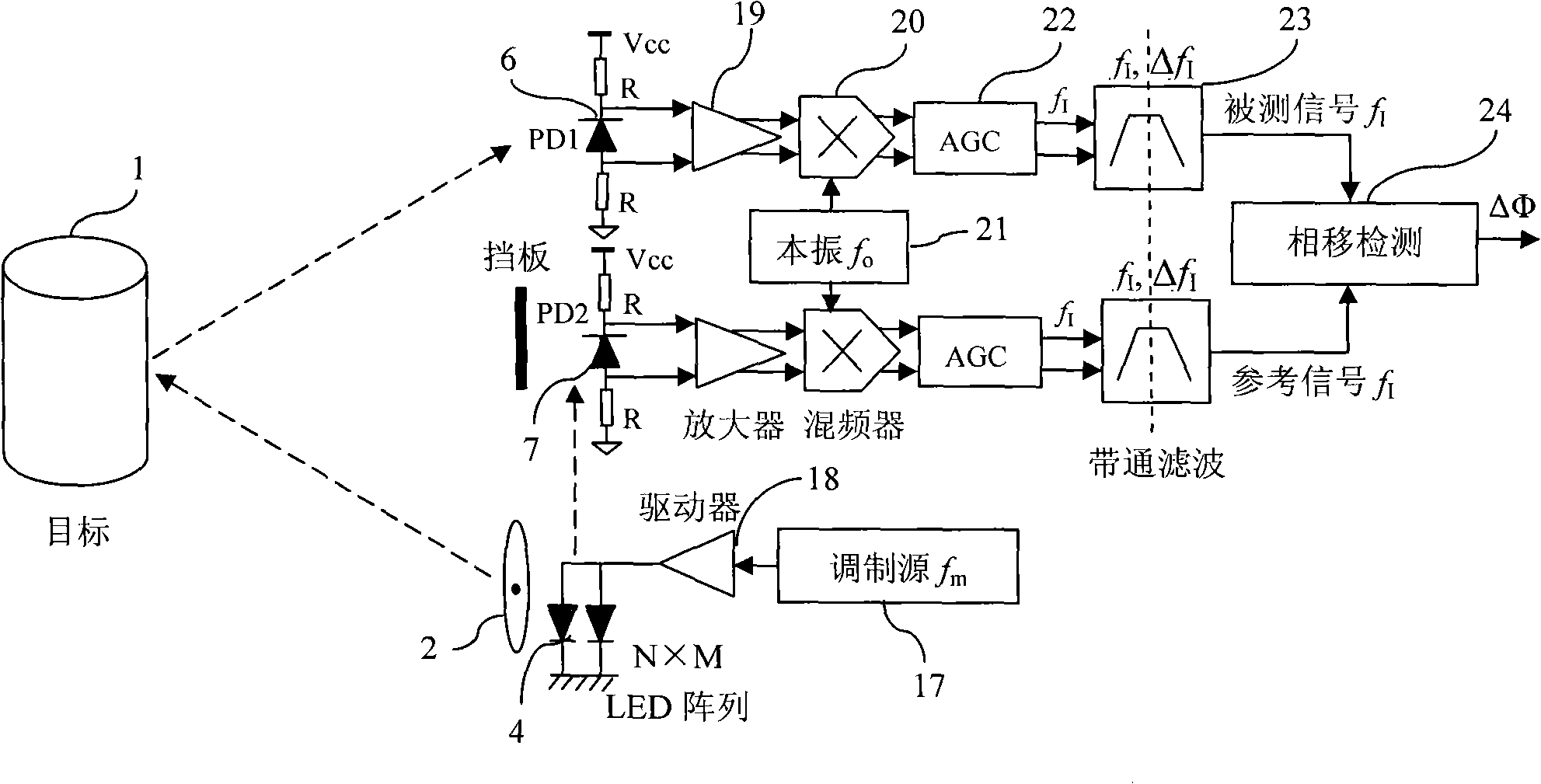
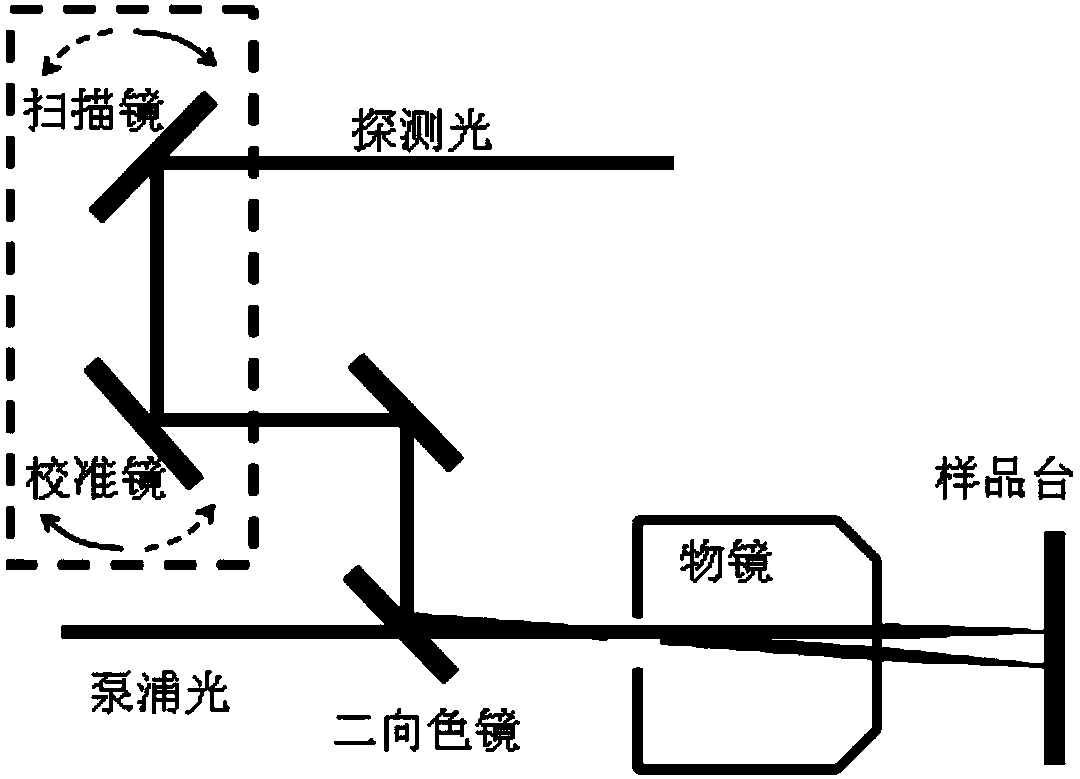
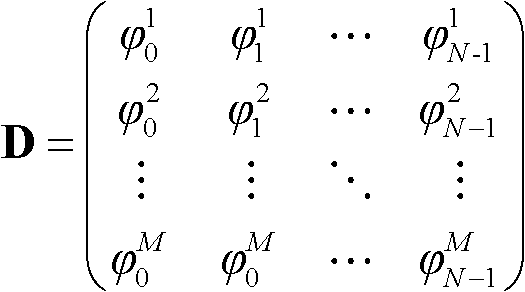Patents
Literature
476 results about "Two dimensional imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
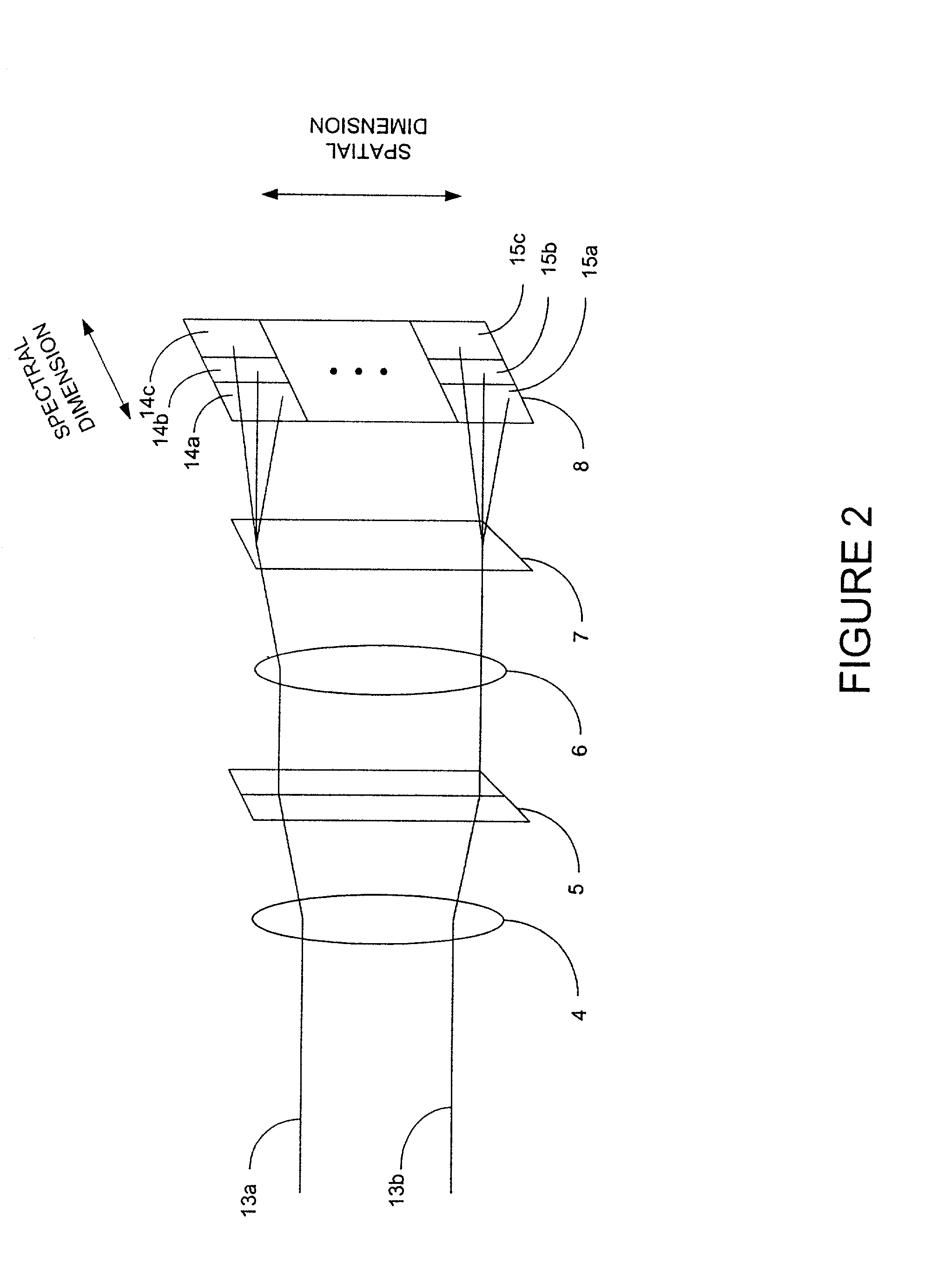
Two-dimensional imaging. An MRI term for the Fourier transformation process, which reconstructs the detected frequency and phase-encoded image information—which are rotated 90° from each other—into a usable image.
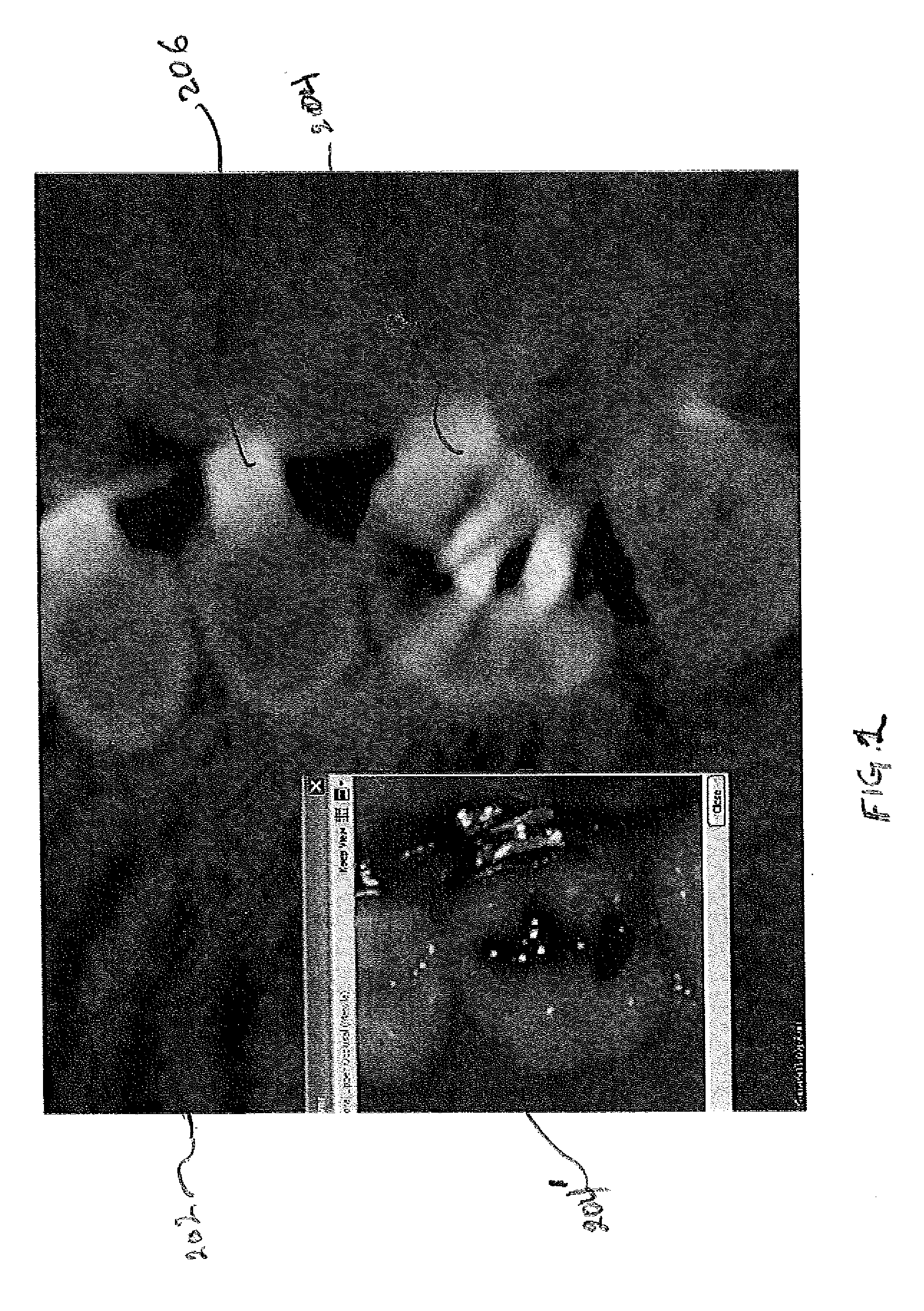
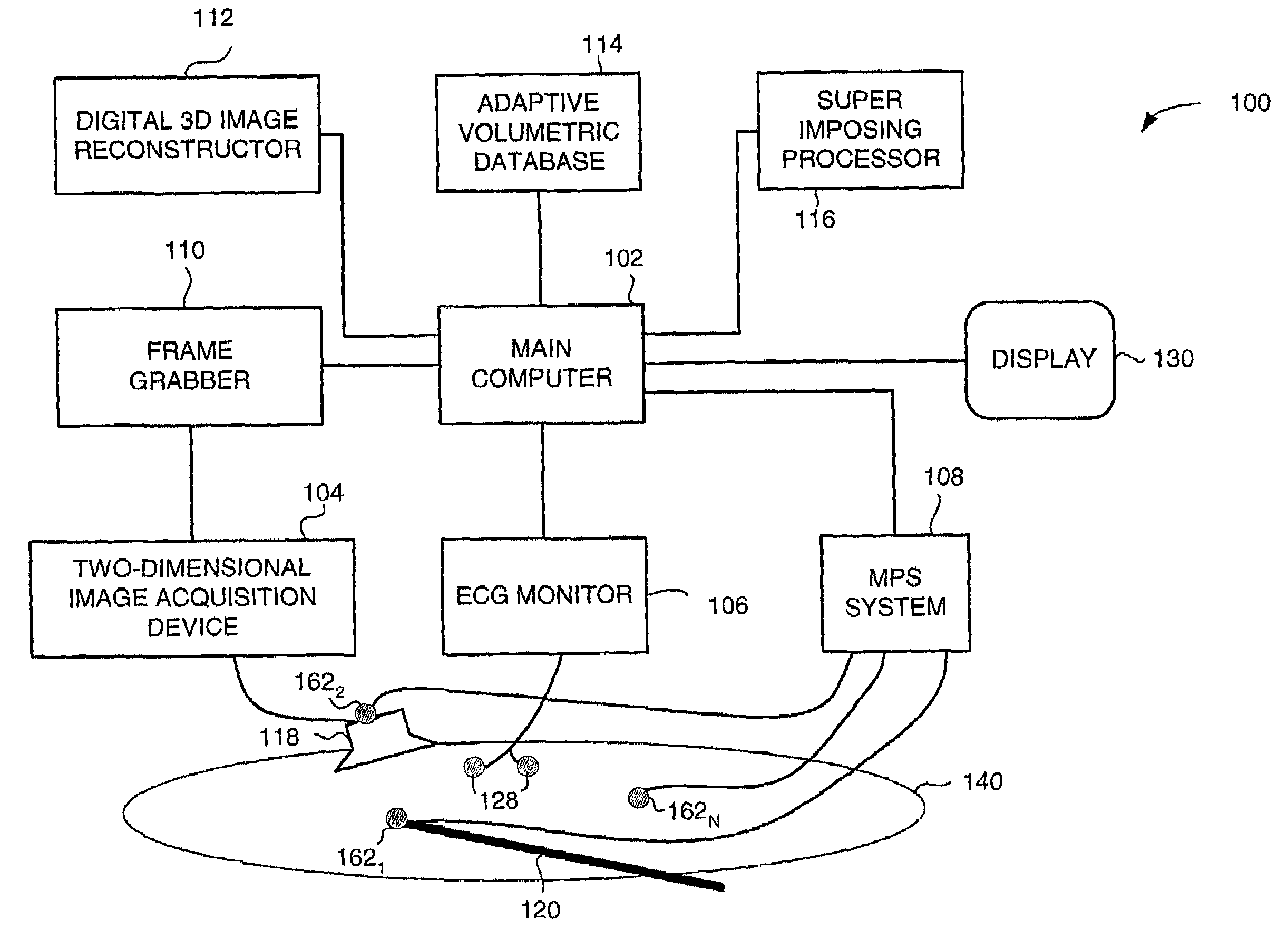
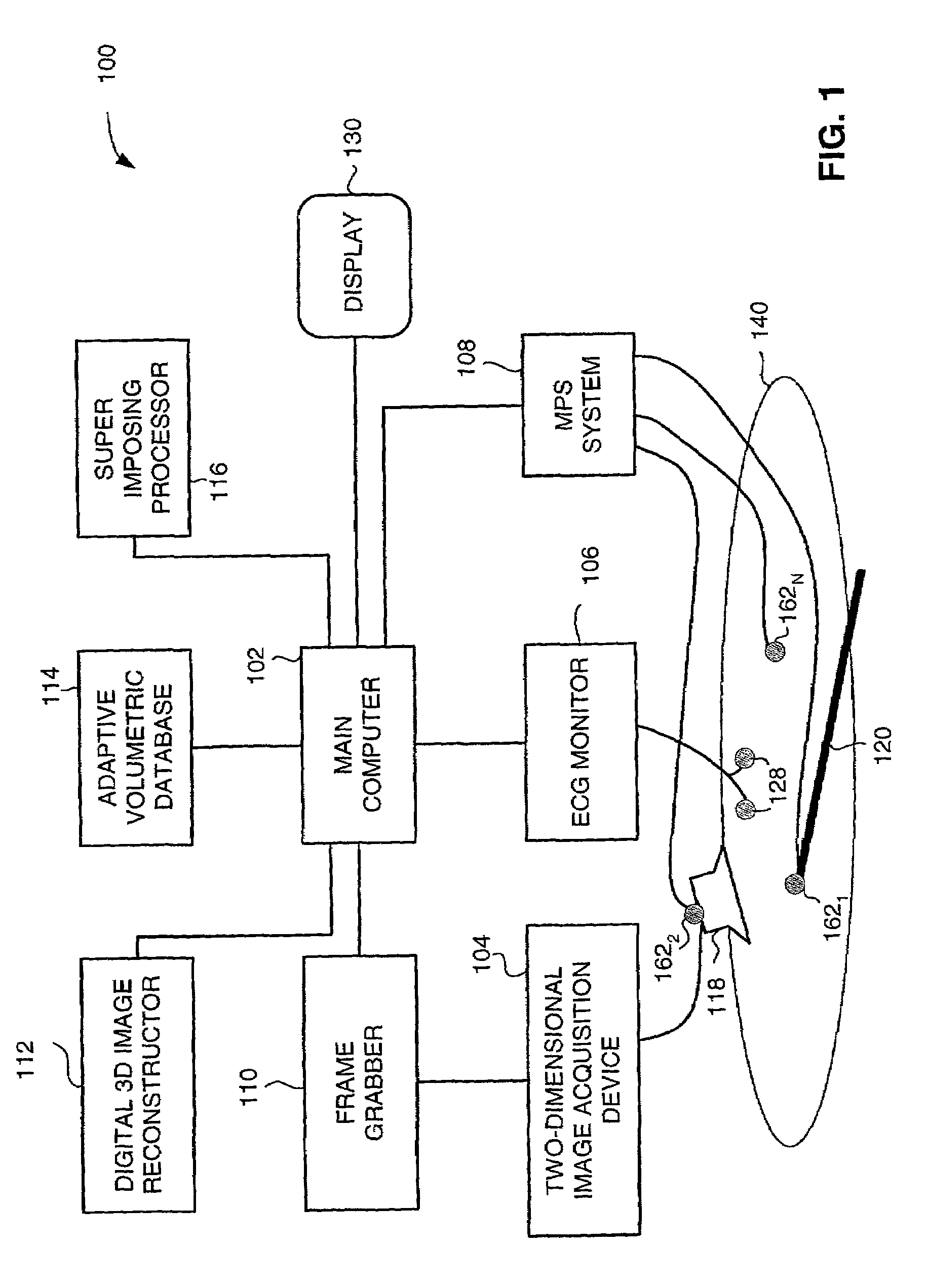
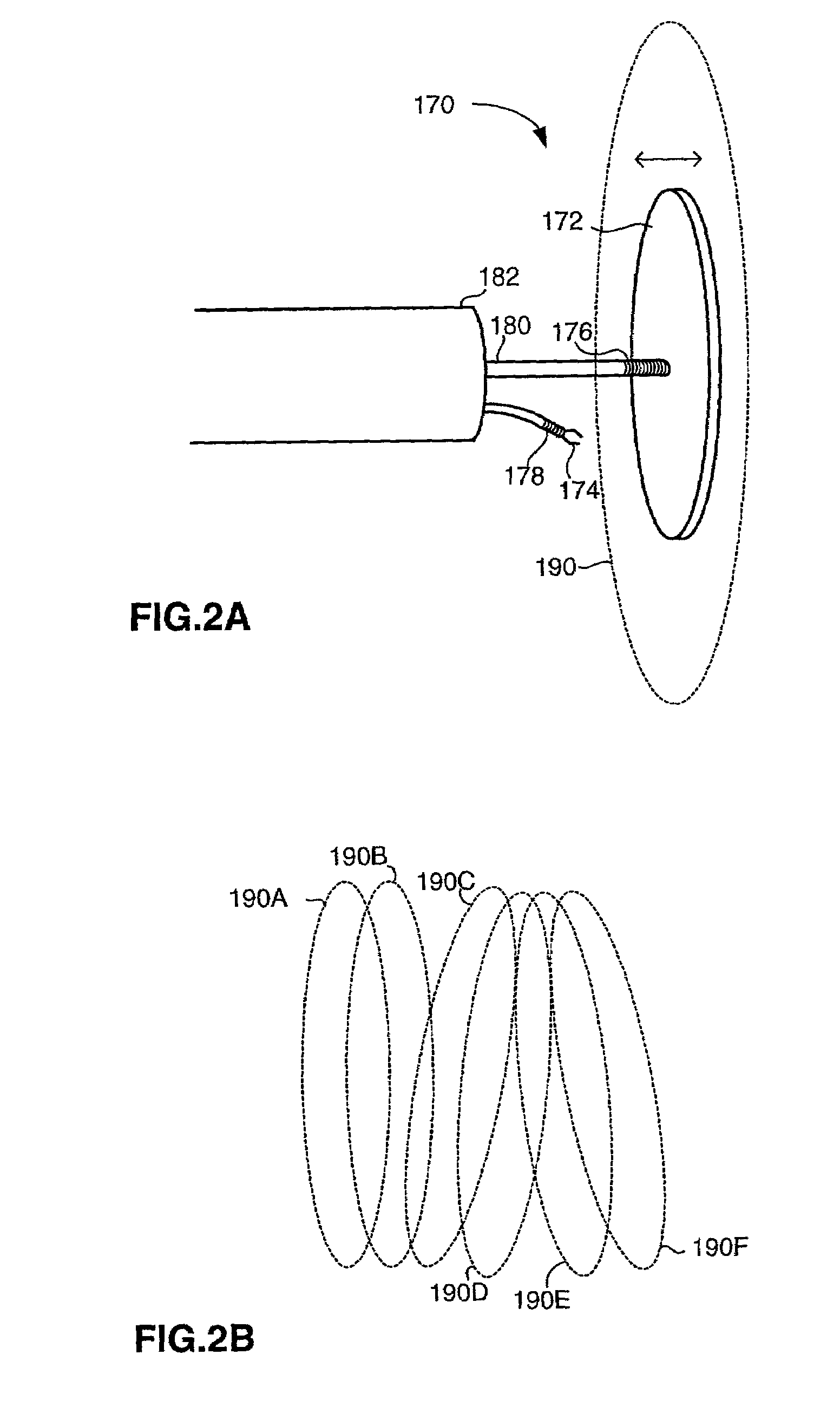
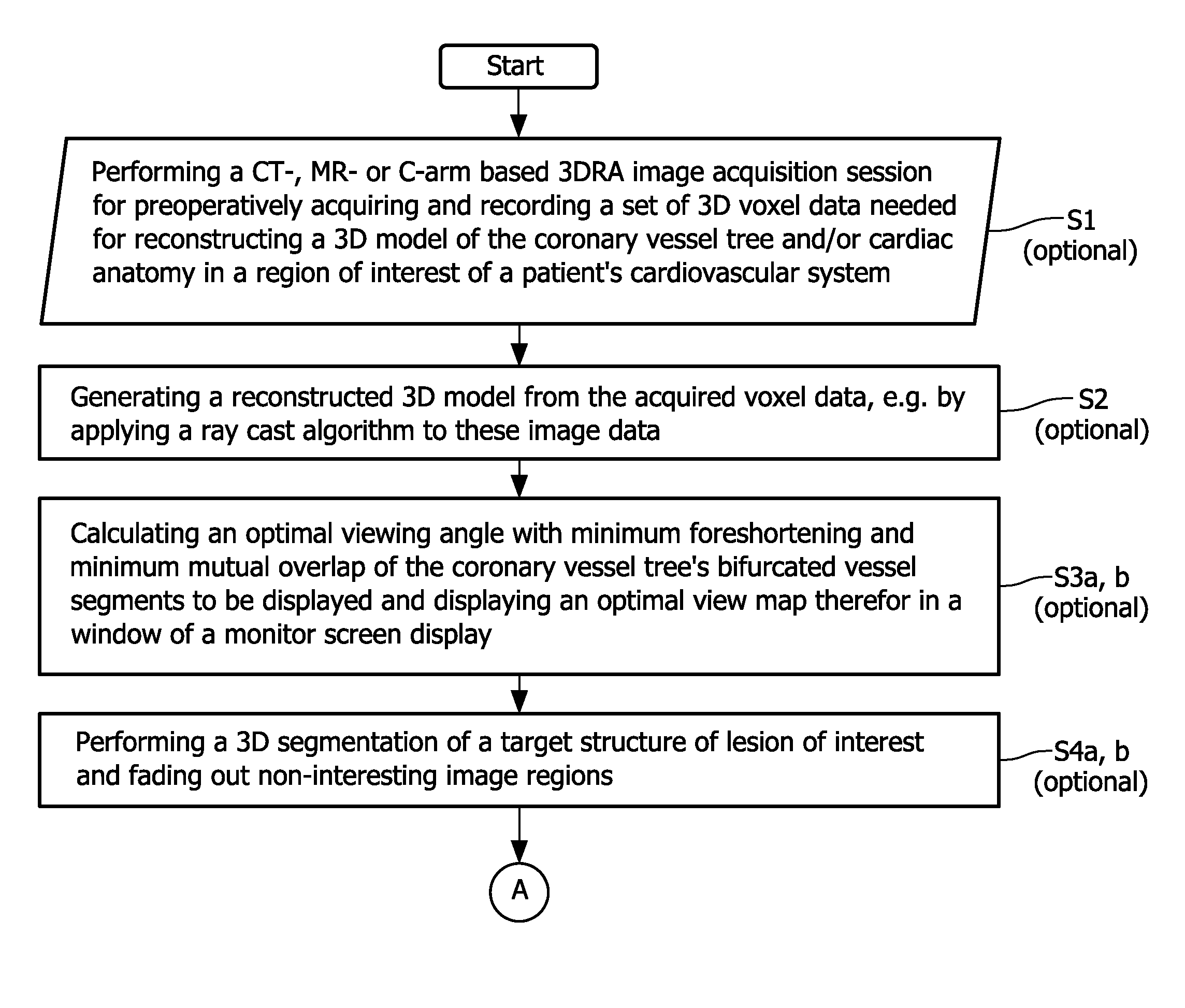
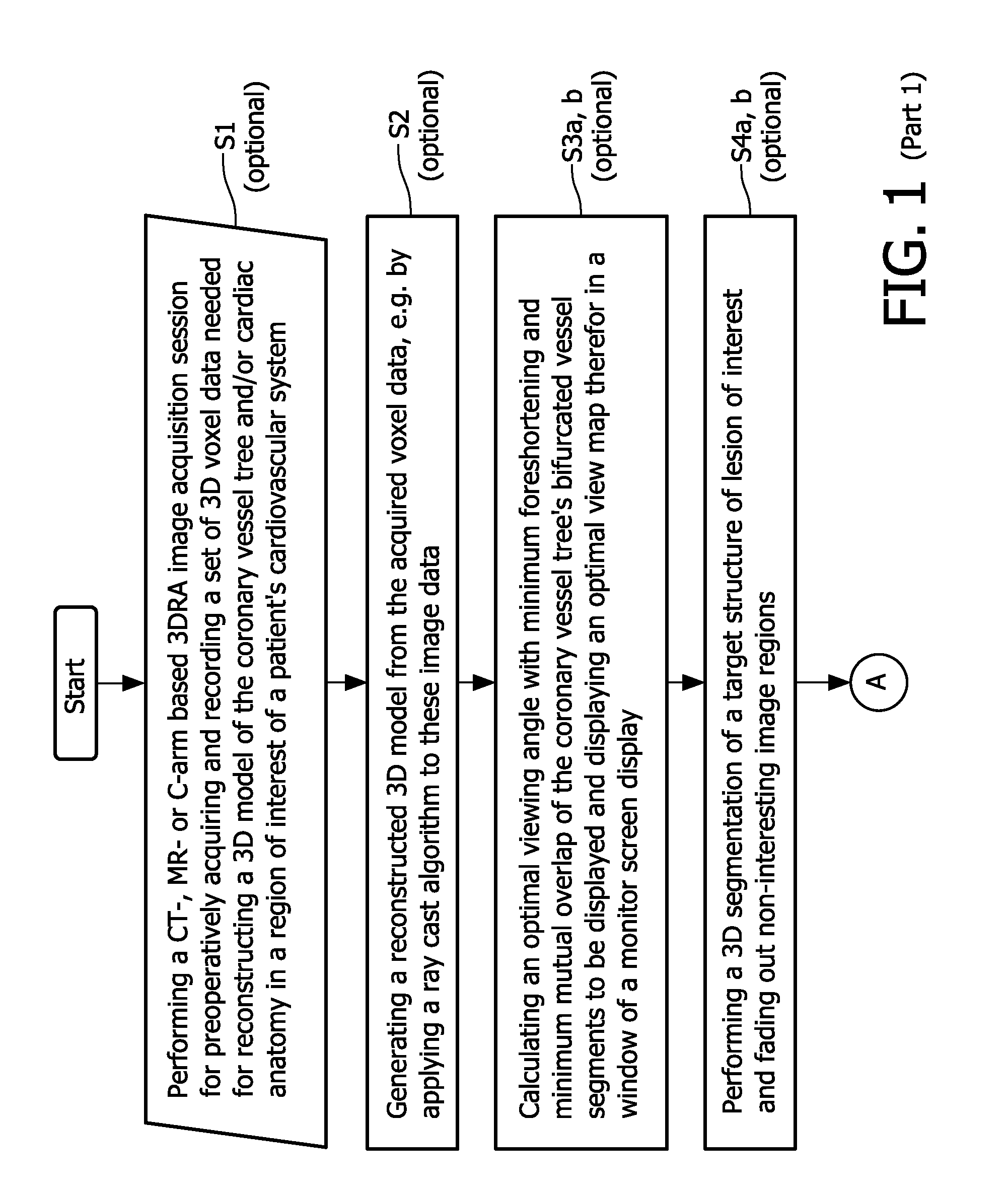
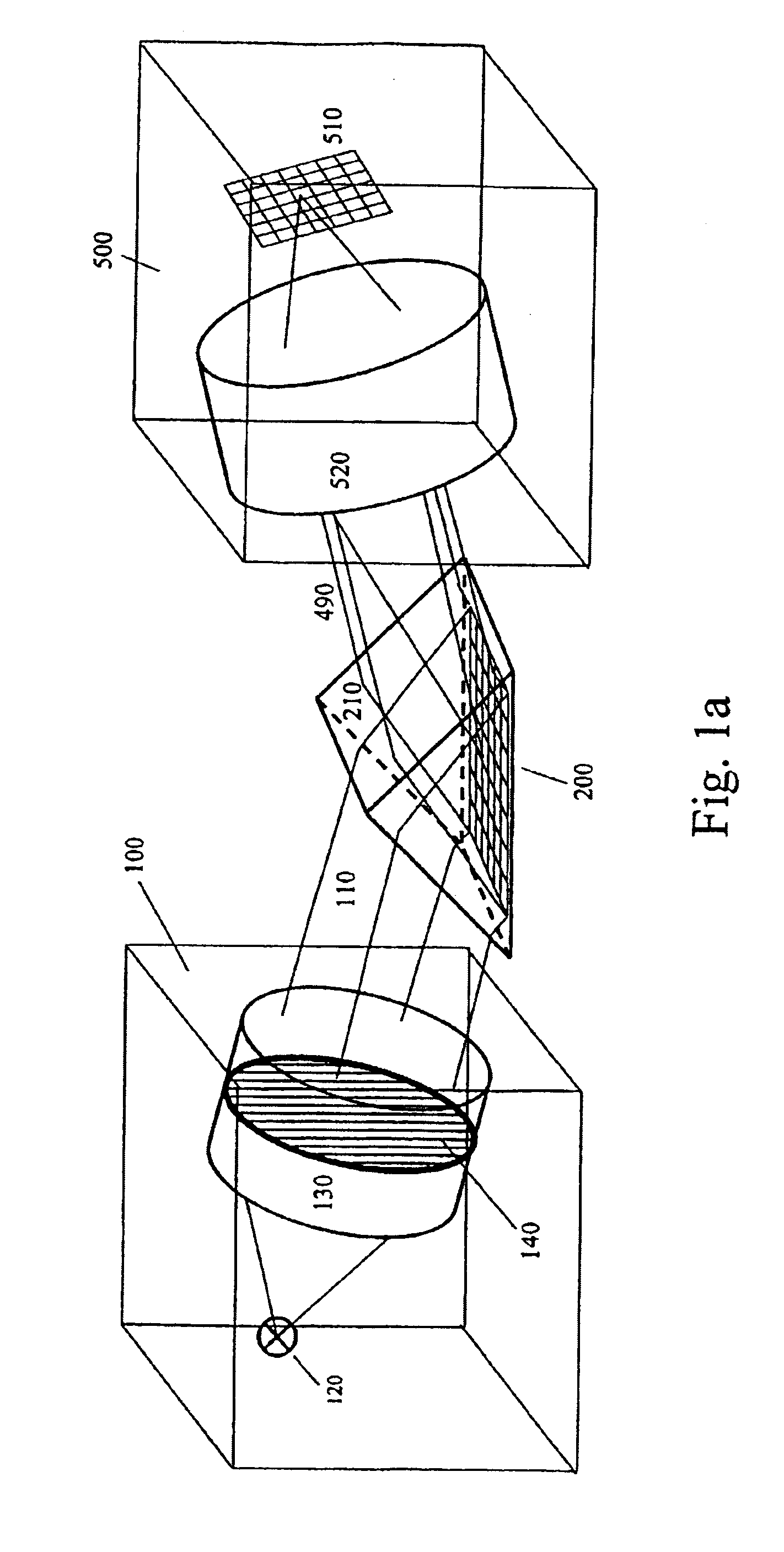
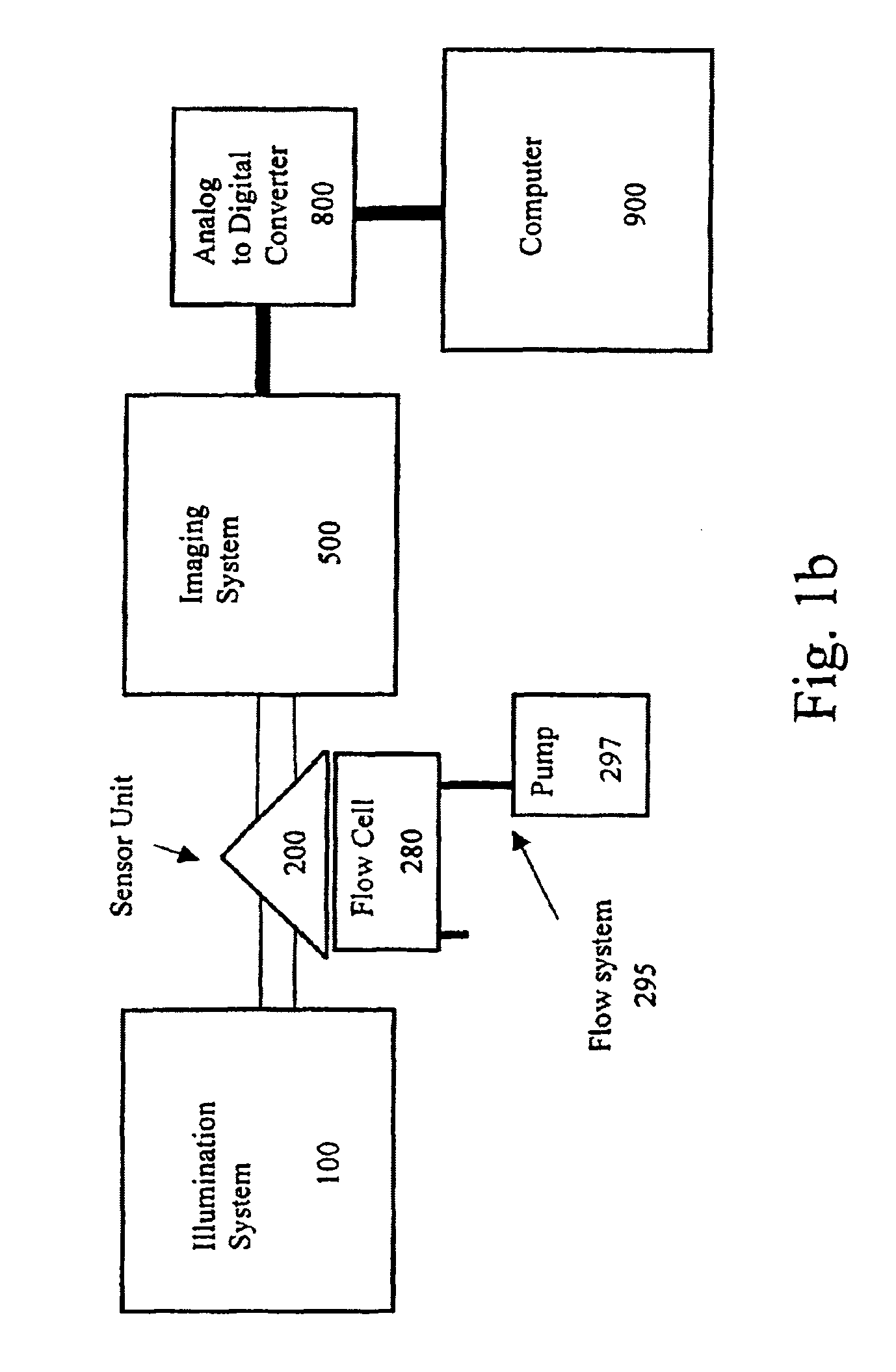
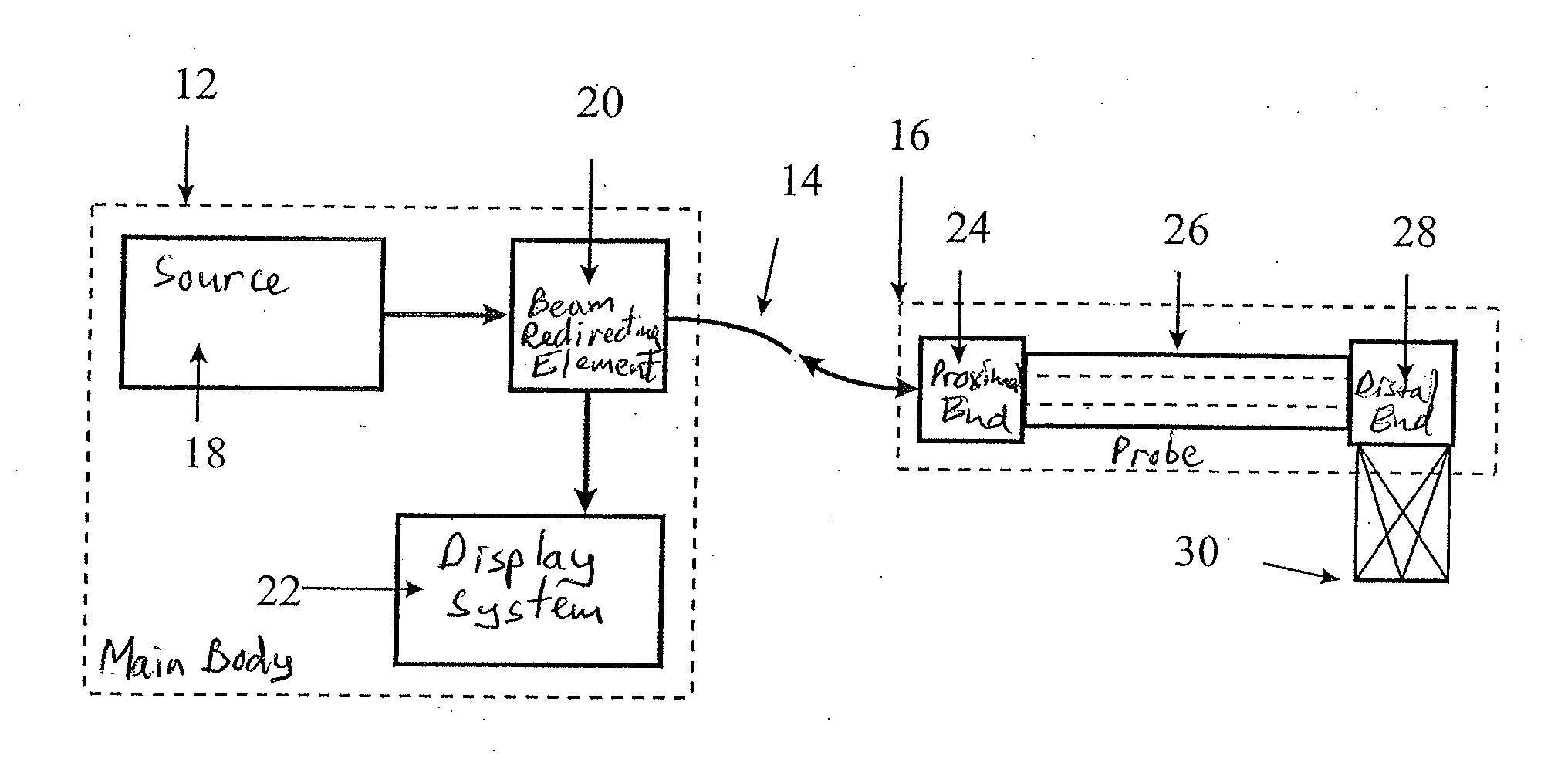
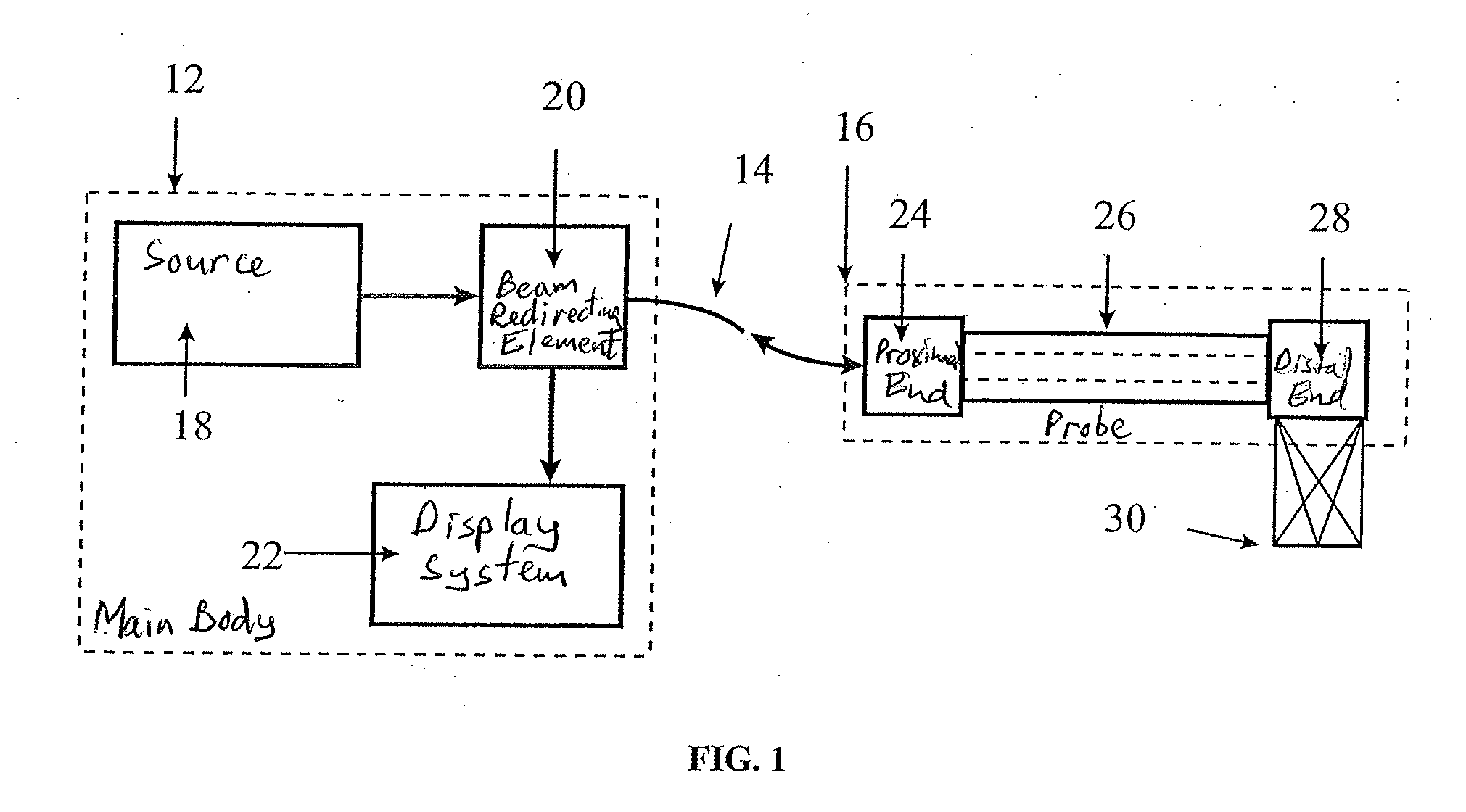
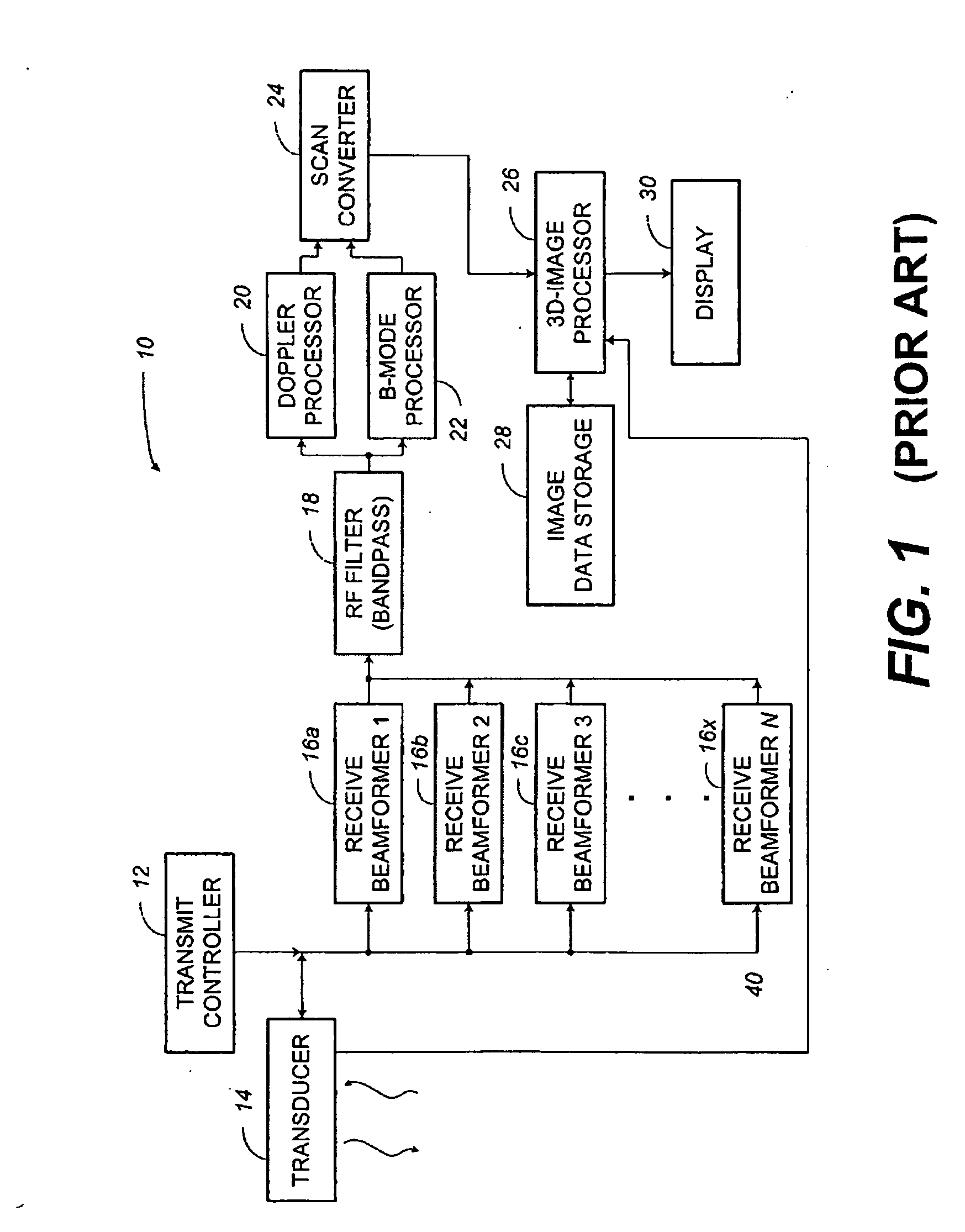
Method and apparatus for real time quantitative three-dimensional image reconstruction of a moving organ and intra-body navigation
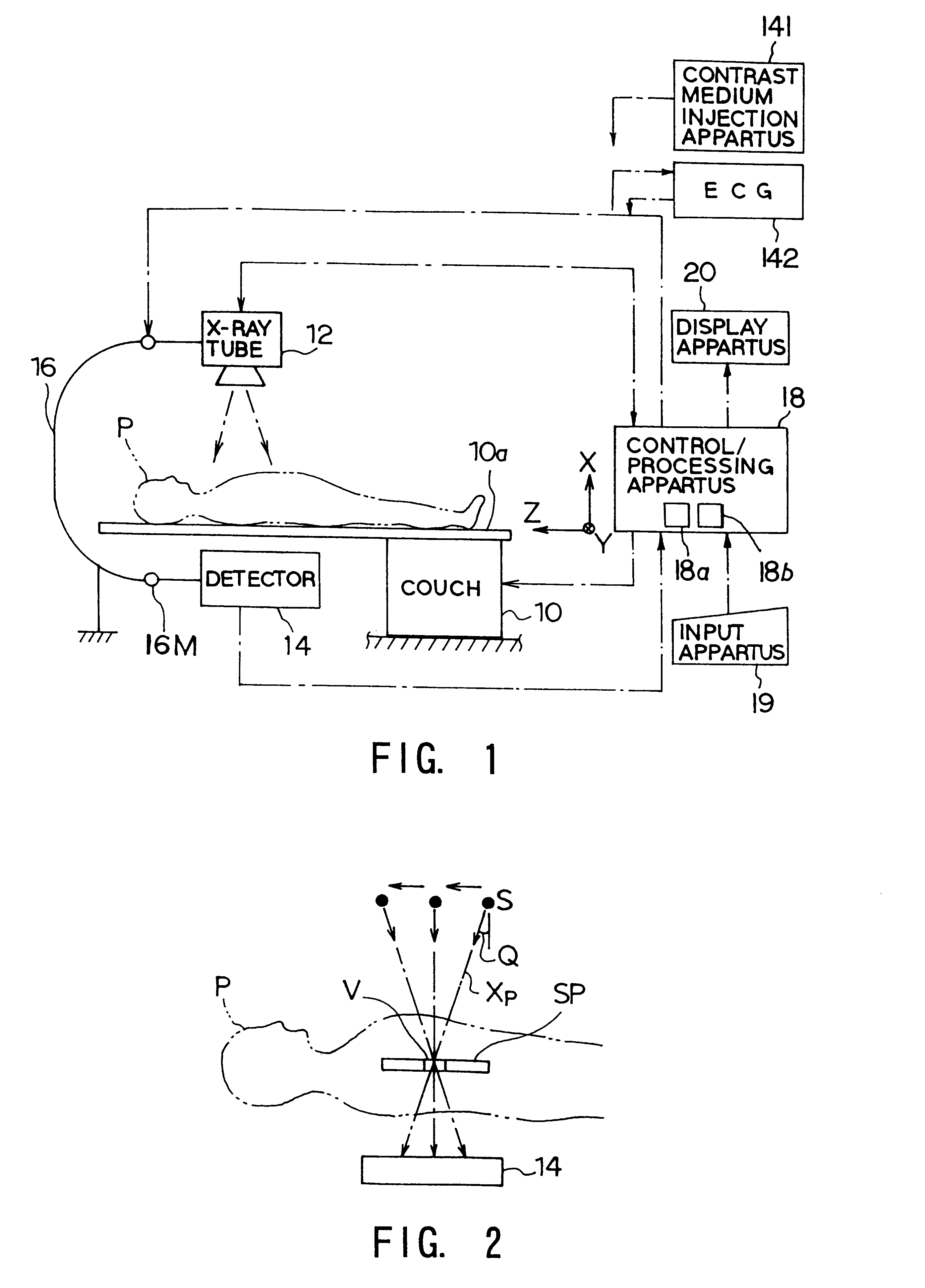
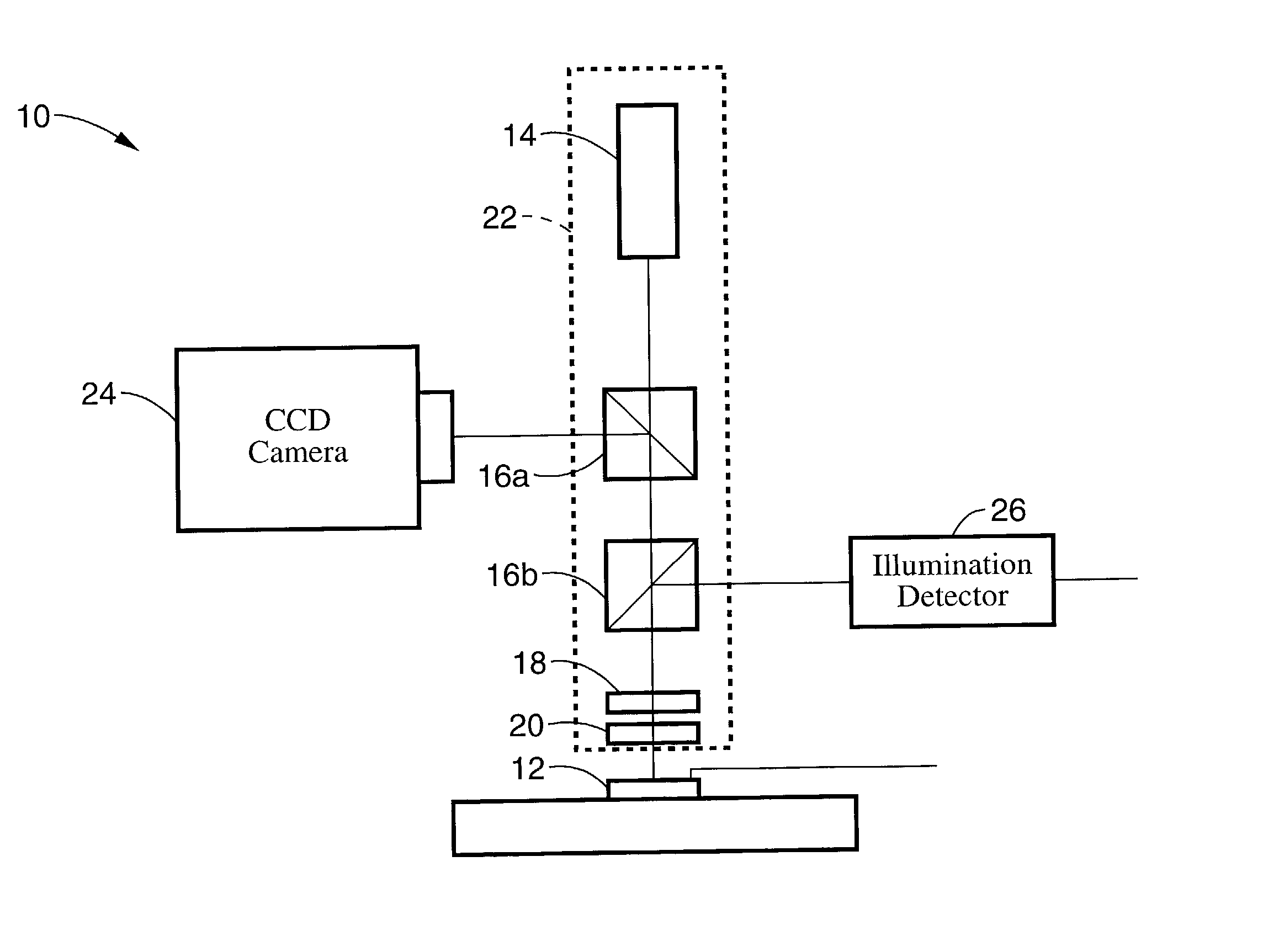
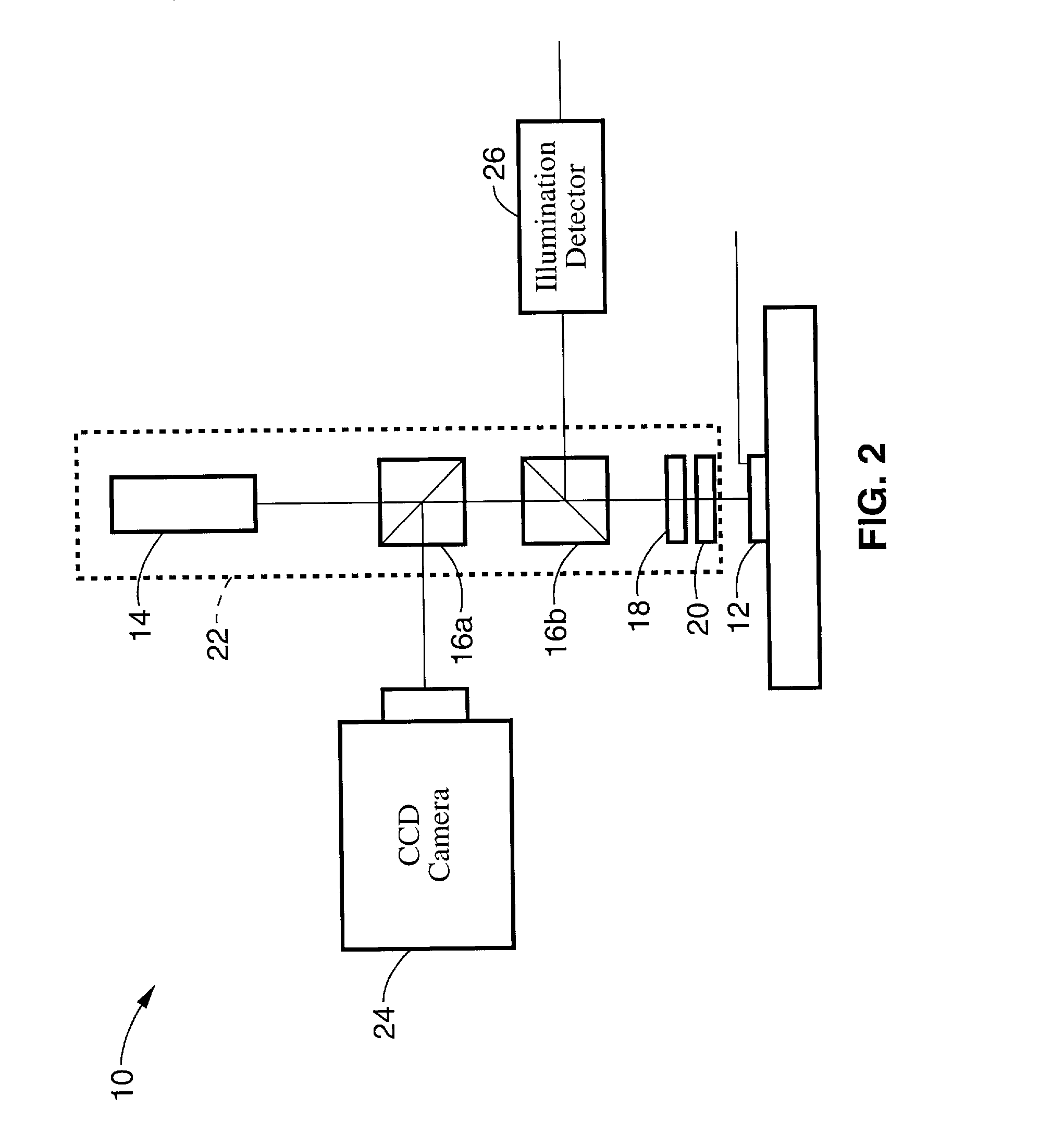
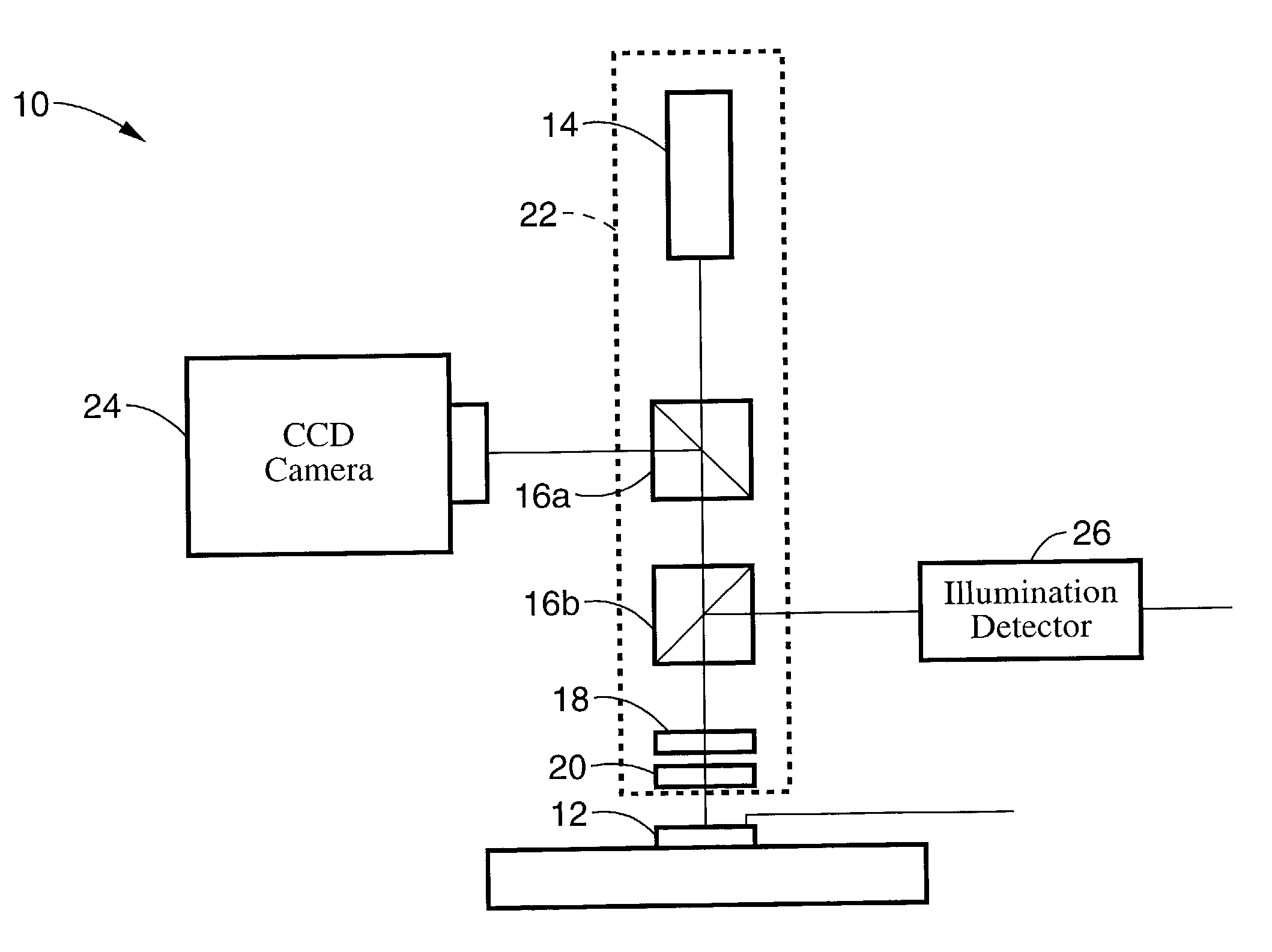
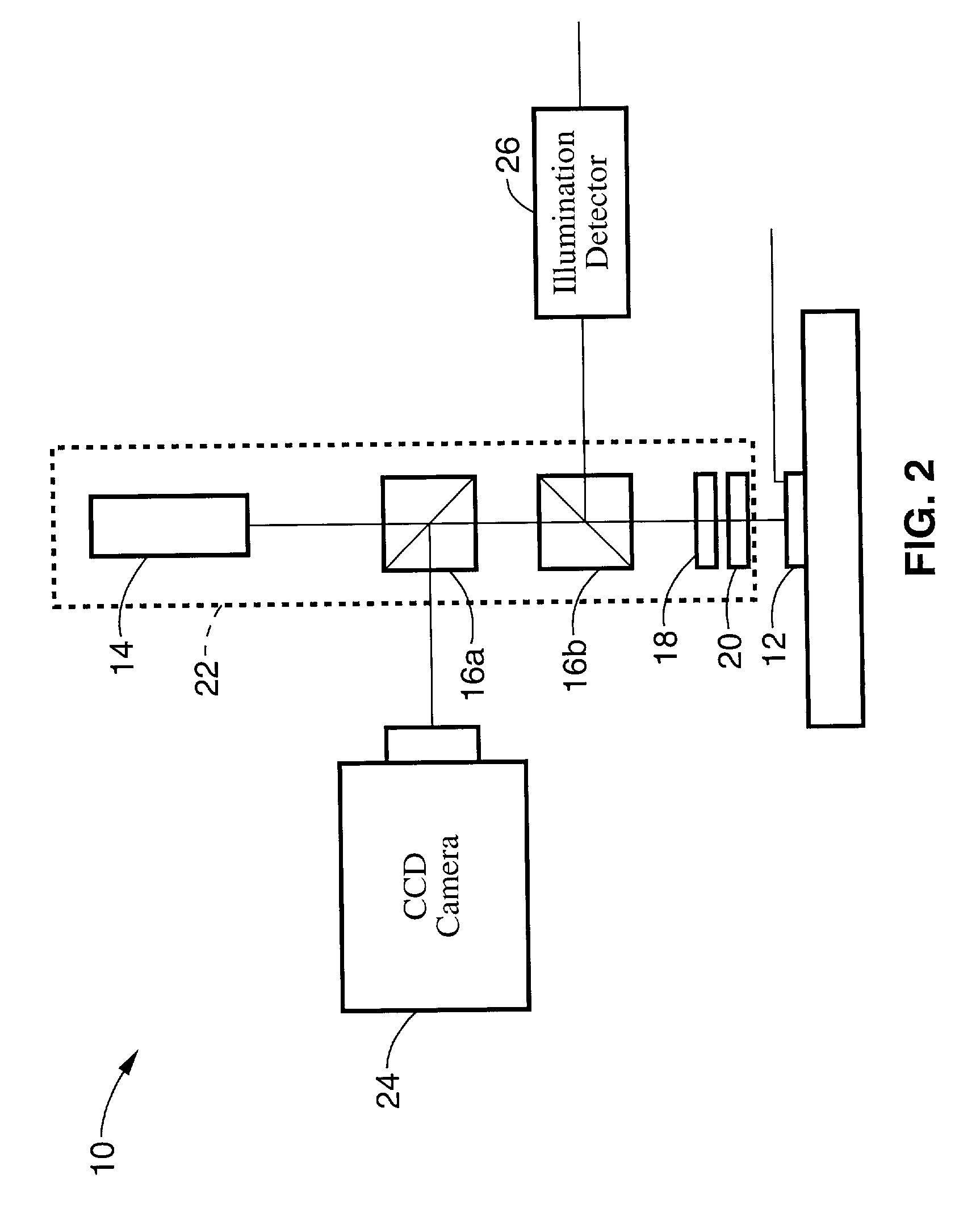
InactiveUS7343195B2Operating tablesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansImage detectionMedical imaging
Medical imaging and navigation system including a processor, a medical positioning system (MPS), a two-dimensional imaging system and an inspected organ monitor interface, the MPS including an imaging MPS sensor, the two-dimensional imaging system including an image detector, the processor being coupled to a display unit and to a database, the MPS being coupled to the processor, the imaging MPS sensor being firmly attached to the image detector, the two-dimensional imaging system being coupled to the processor, the image detector being firmly attached to an imaging catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
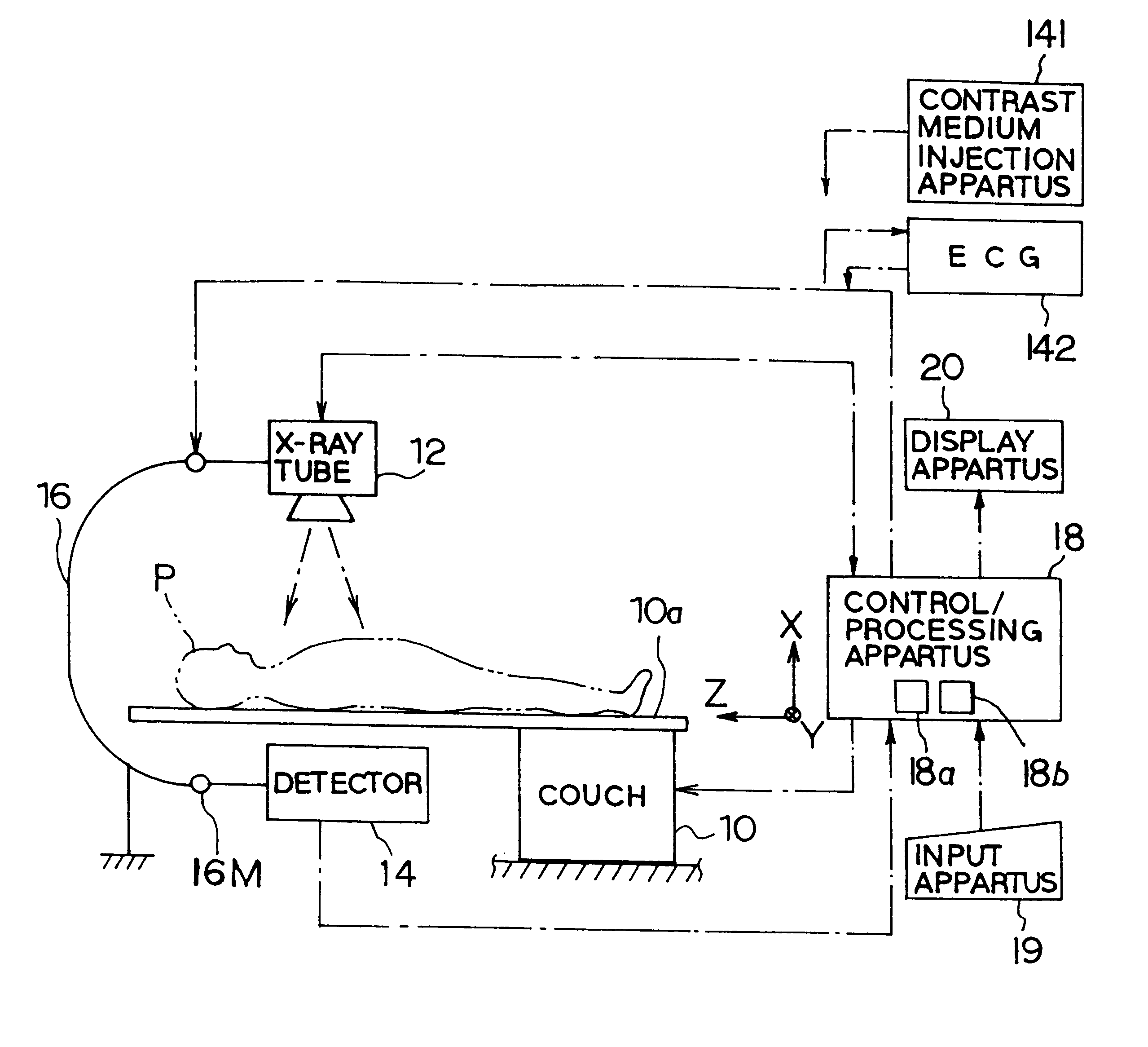
X-ray diagnostic system preferable to two dimensional x-ray detection
InactiveUS6196715B1Suppress and prevent generationImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisX-ray generator
An X-ray tomosynthesis system as an X-ray diagnostic system is provided. The system comprises an X-ray generator irradiating an X-ray toward a subject, and a planar-type X-ray detector detecting the X-ray passing through the subject and outputting two dimensional imaging signals based on the detected X-ray. The system comprises a supporting / moving mechanism supporting at least one of the X-ray generator and the X-ray detector so that the at least one is moved relatively to the subject. The system also comprises an element setting a ROI position of the subject, an element for obtaining a plurality of three dimensional coordinates of pixels included in the ROI, a calculating element obtaining two dimensional coordinates of data in the two dimensional imaging signals for each of the two dimensional imaging signals detected by the X-ray detector, the data being necessary for obtaining pixel values of the three dimensional coordinates; and an element for obtaining the pixel value of each of the three dimensional coordinates by extracting the corresponding data of the two dimensional coordinates from the detected two dimensional imaging signals and adding the extracting data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
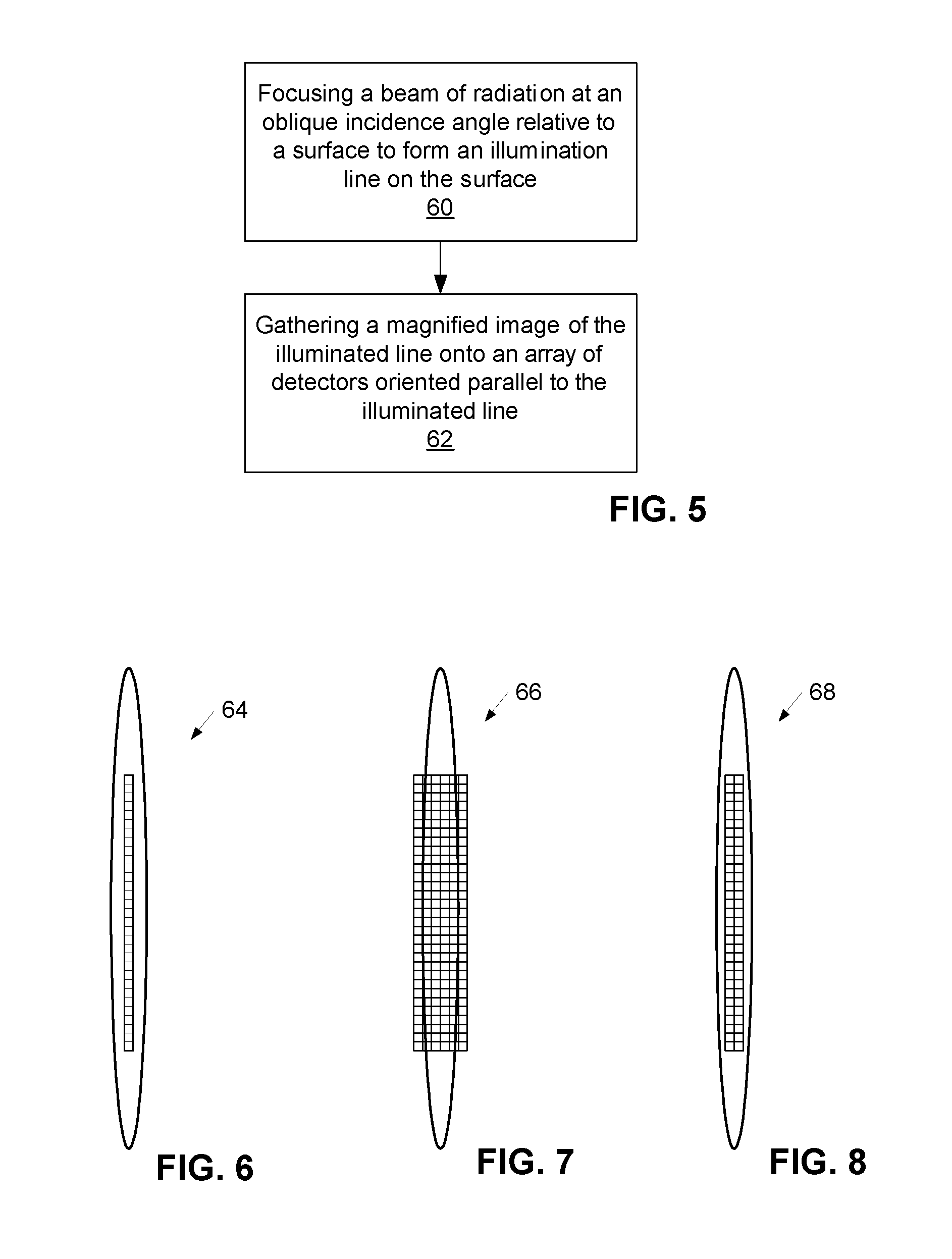
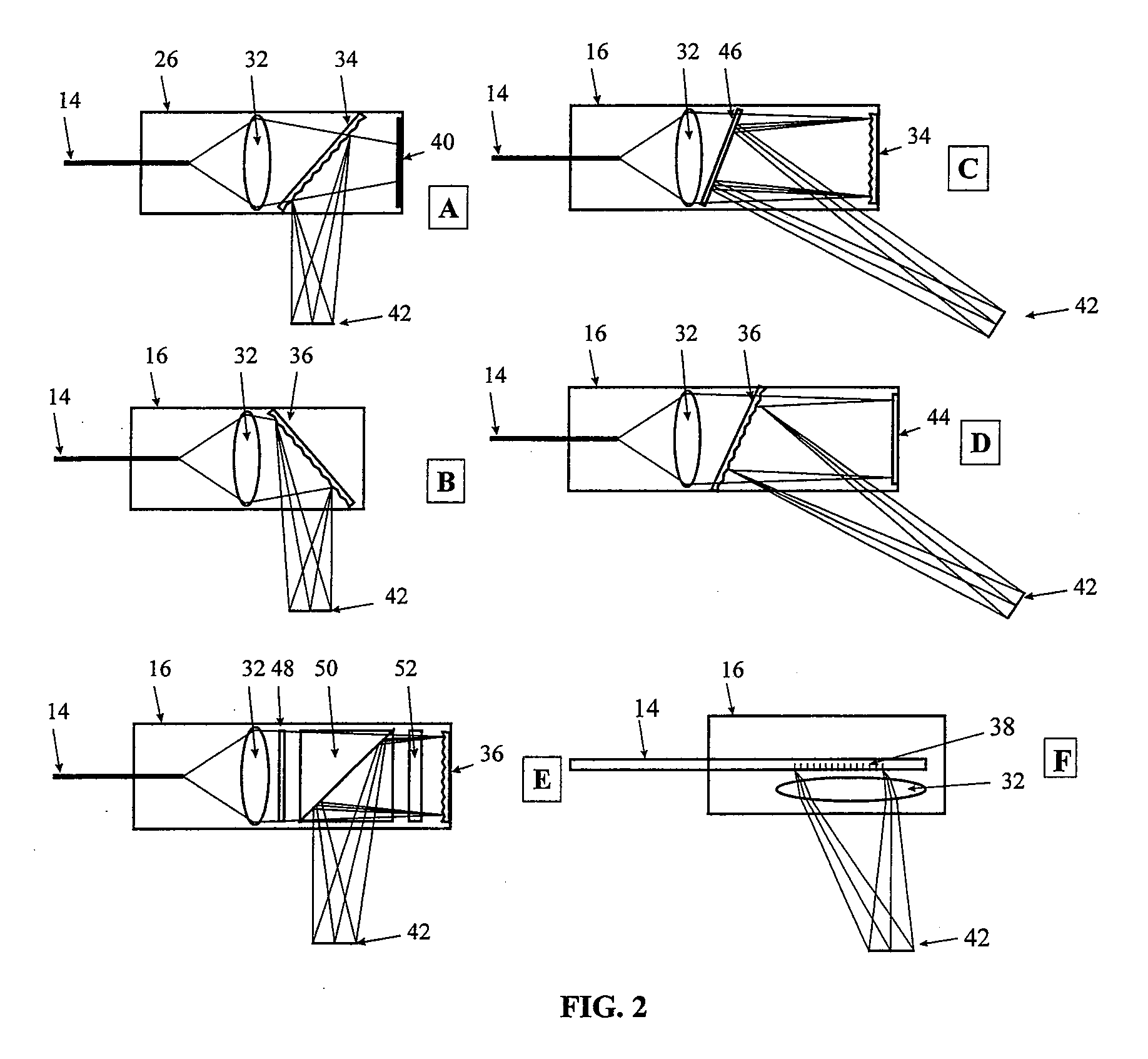
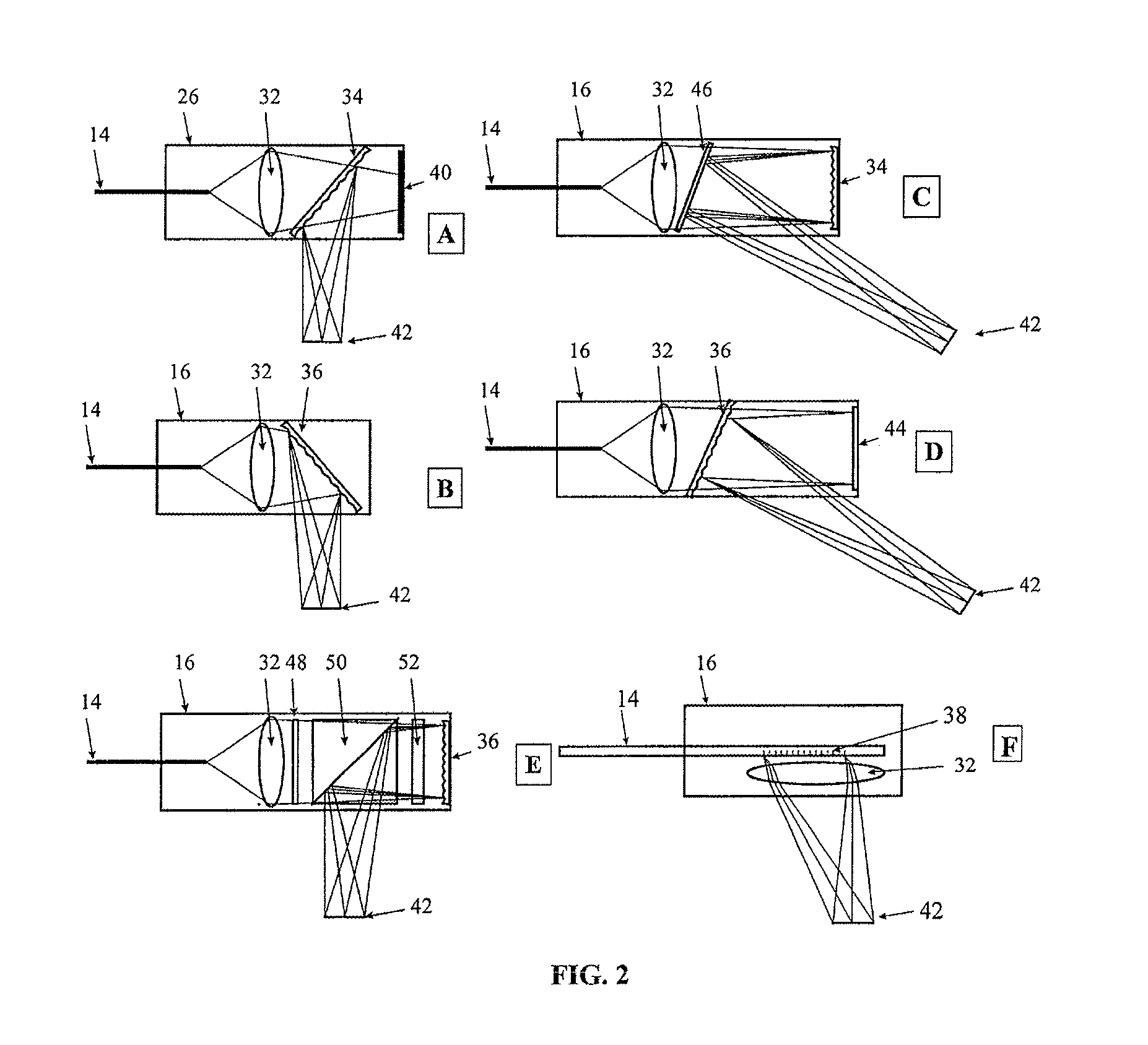
Surface inspection system using laser line illumination with two dimensional imaging
A surface inspection apparatus and a method are provided which include an illumination system configured to focus a beam of radiation at a non-orthogonal incidence angle to form an illumination line on a surface substantially in a plane of incidence of the focused beam. The apparatus and method further include a collection system configured to image the illumination line onto an array of detectors oriented parallel to the illumination line. The collection system includes an imaging lens for collecting light scattered from the illumination line, a focusing lens for focusing the collected light, and the array of detectors, each configured to detect a corresponding portion of the illumination line. The collection system may be configured to image the illumination line such that the width of the imaged illumination line on the array of detectors is larger than the pixel size of the detectors along the same direction.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Apparatus and method for providing information for at least one structure
A spectrally encoded endoscopic probe having high resolution and small diameter comprising at least one flexible optical fiber; an energy source; a grating through which said energy is transmitted such that the energy spectrum is dispersed; a lens for focusing the dispersed energy spectrum onto a sample such that the impingement spot for each wavelength is a separate position on the sample, the wavelength spectrum defining a wavelength encoded axis; means for mechanically scanning the sample with focused energy in a direction perpendicular to the wavelength encoded axis; a means for receiving energy reflected from the sample; and, a means for detecting the received reflected energy. The probe grating and lens delivers a beam of multi-spectral light having spectral components extending in one dimension across a target region and which is moved to scan in another direction. The reflected spectrum is measured to provide two dimensional imaging of the region.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
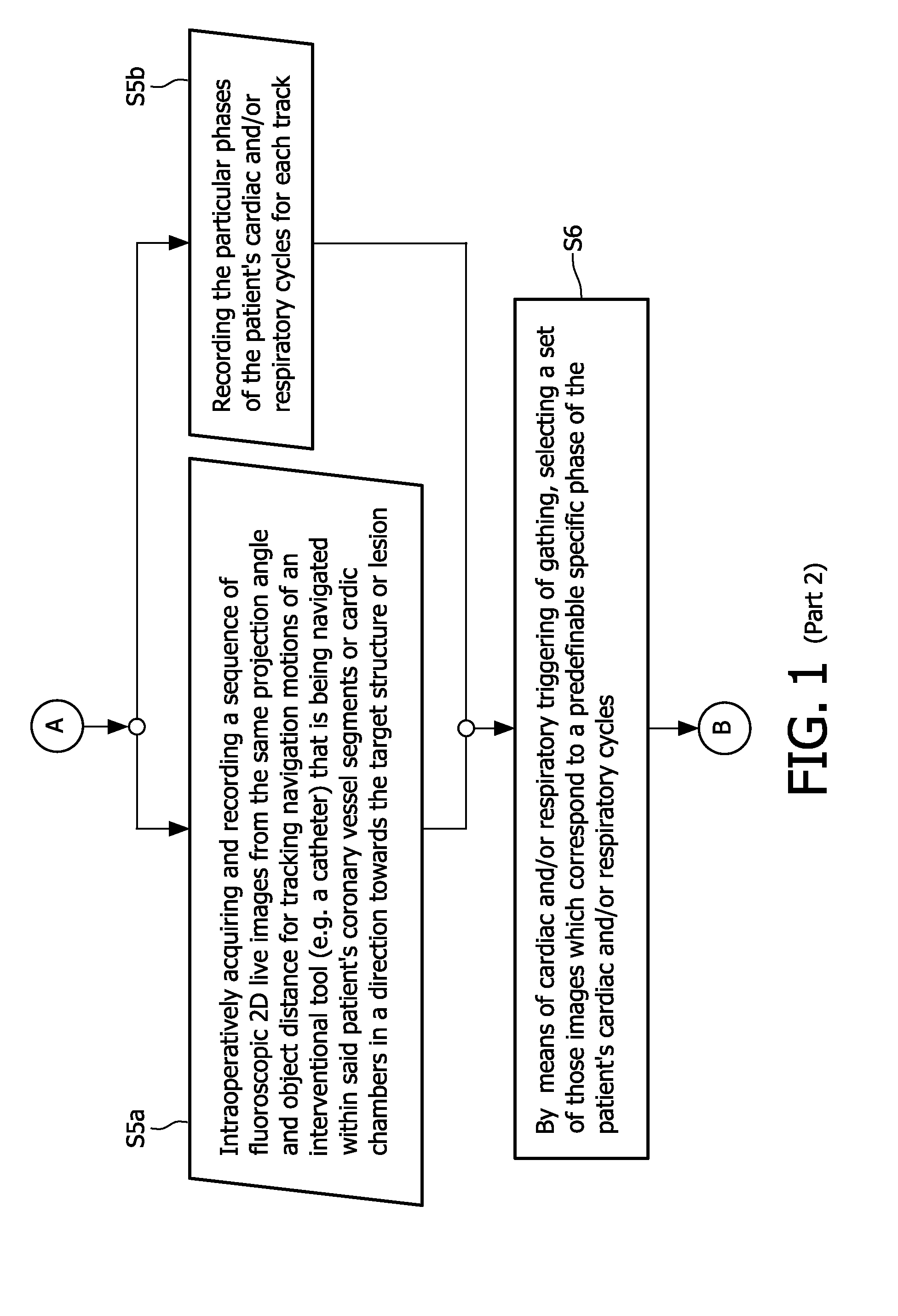
Cardiac and or respiratory gated image acquisition system and method for virtual anatomy enriched real time 2d imaging in interventional radiofrequency ablation or pace maker replacement procecure
ActiveUS20110201915A1Improve accuracyReduce inaccuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac pacemaker electrodePacemaker Placement
The present invention refers to the field of cardiac electrophysiology (EP) and, more specifically, to image-guided radio frequency ablation and pacemaker placement procedures. For those procedures, it is proposed to display the overlaid 2D navigation motions of an interventional tool intraoperatively obtained from the same projection angle for tracking navigation motions of an interventional tool during an image-guided intervention procedure while being navigated through a patient's bifurcated coronary vessel or cardiac chambers anatomy in order to guide e.g. a cardiovascular catheter to a target structure or lesion in a cardiac vessel segment of the patient's coronary venous tree or to a region of interest within the myocard. In such a way, a dynamically enriched 2D reconstruction of the patient's anatomy is obtained while moving the interventional instrument. By applying a cardiac and / or respiratory gating technique, it can be provided that the 2D live images are acquired during the same phases of the patient's cardiac and / or respiratory cycles. Compared to prior-art solutions which are based on a registration and fusion of image data independently acquired by two distinct imaging modalities, the accuracy of the two-dimensionally reconstructed anatomy is significantly enhanced.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
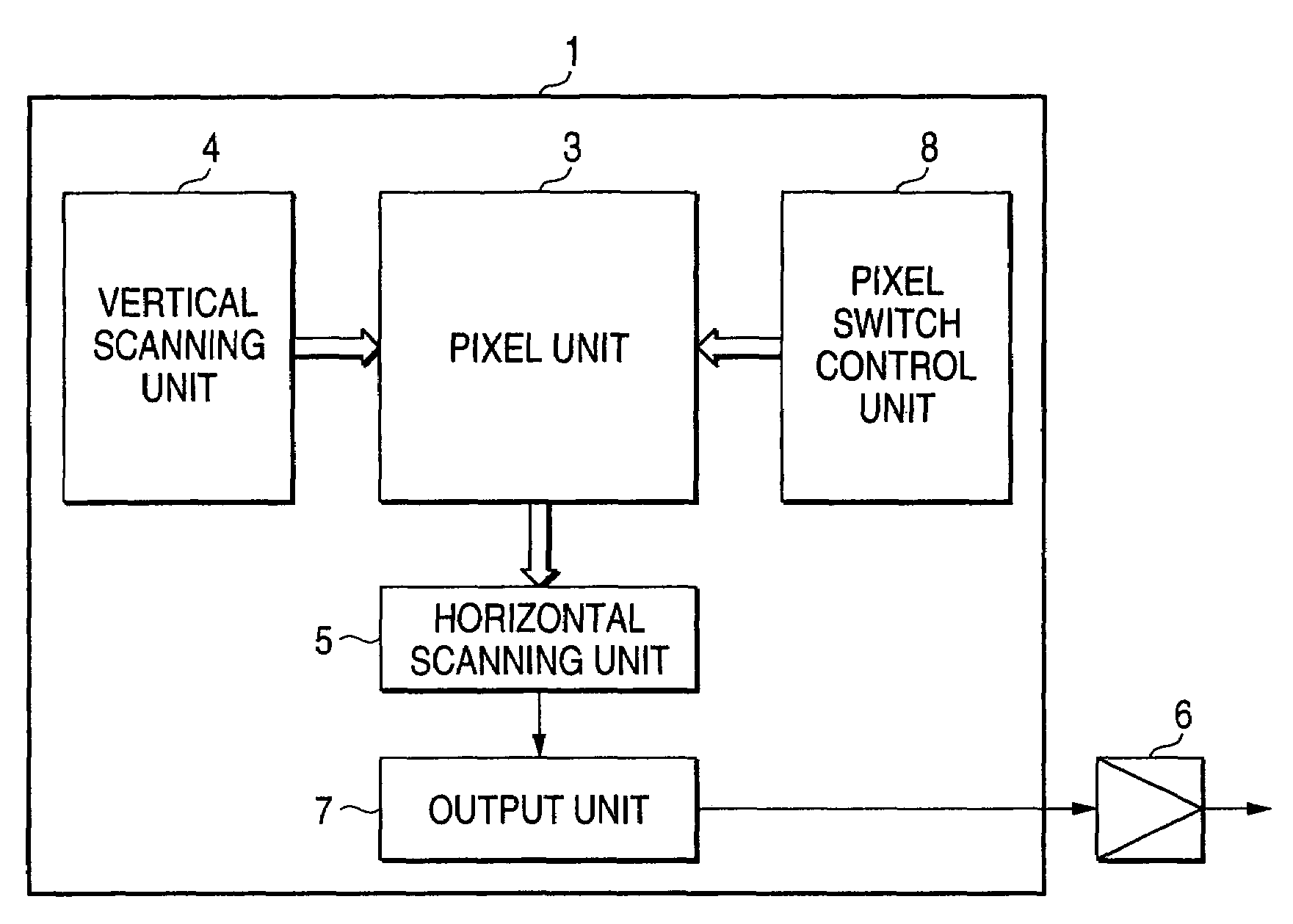
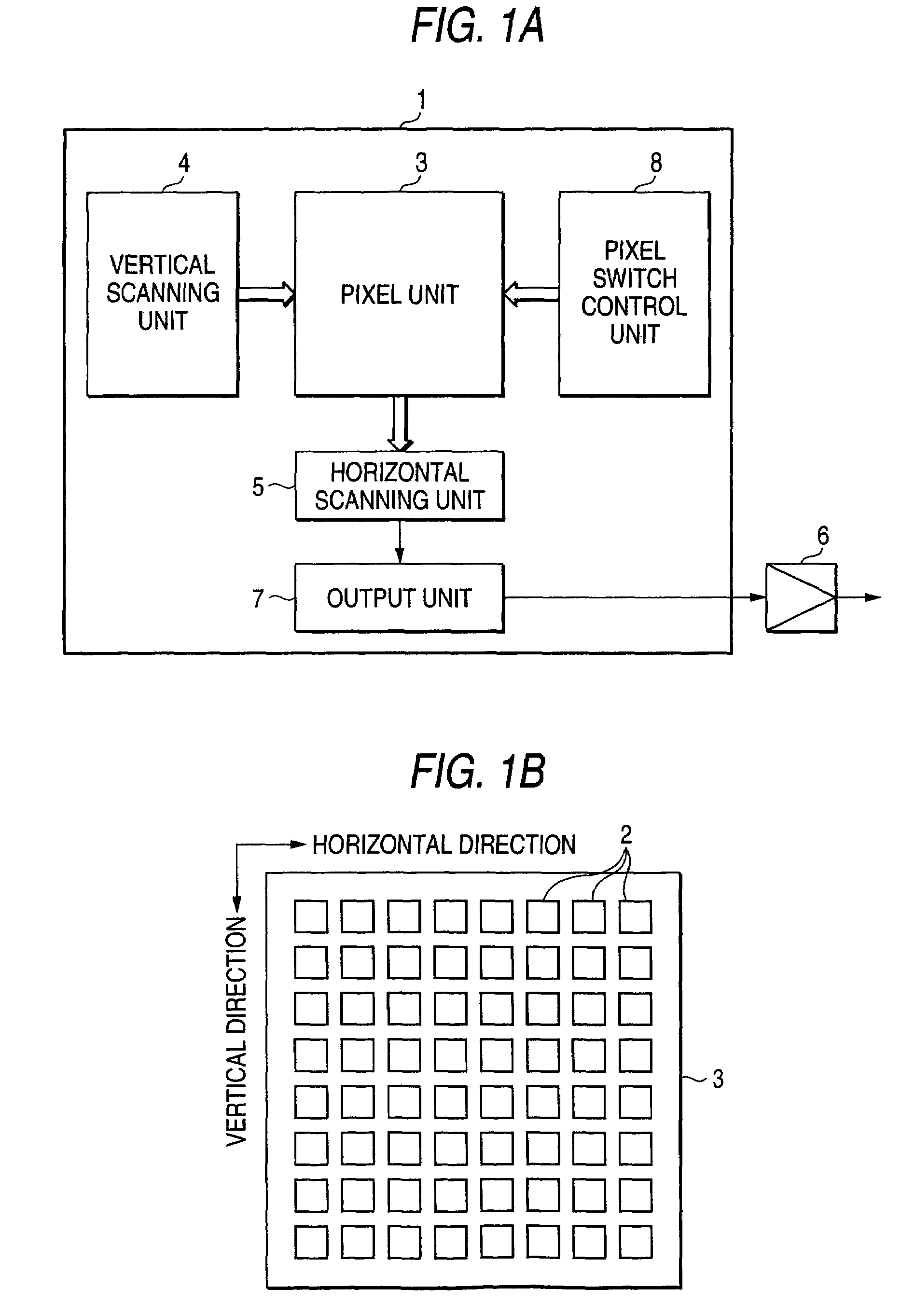
Car-mounted imaging apparatus and driving assistance apparatus for car using the imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7030738B2Sensitivity is deterioratedWithout losing informationTelevision system detailsAnti-theft devicesImaging qualityImaging equipment
The invention provides a car-mounted imaging apparatus that renders a frame rate variable and yet does not spoil image quality and does not either invite the drop of sensitivity and deterioration of an S / N ratio. The car-mounted imaging apparatus 1 has two-dimensional imaging means (pixel unit 3, vertical scanning unit 4, horizontal scanning unit 5, output unit 7) having a large number of pixels 2 arranged in a two-dimensional matrix, and pixel information addition means (pixel switch control unit 8) for combining a plurality of pixels 2 and adding and extracting their pixel information. When the number of combination of the pixels 2 is changed, a frame rate becomes variable.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Method and apparatus for high-speed thickness mapping of patterned thin films
InactiveUS20020030826A1Scattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMechanical engineeringImaging spectrometer
A system is described that permits high-speed, high-resolution mapping of thicknesses (or other properties) of layers on patterned semiconductor wafers. The system comprises one or more spectrometers that each simultaneously image a plurality of spatial locations. In one example, the spectrometer comprises a two-dimensional CCD imager with one axis of the imager measuring spectral data and the other axis measuring spatial data. Spectral reflectance or transmission of the patterned wafer under test is obtained by passing the wafer under (or over) the imaging spectrometer(s) and taking sequential reflectance or transmission images for successive pluralities of spatial locations. The resulting spectral reflectance or transmission map can then be analyzed at discrete locations to determine the thicknesses or other properties of the layers at those locations.
Owner:FILMETRICS
Submicron thermal imaging method and enhanced resolution (super-resolved) ac-coupled imaging for thermal inspection of integrated circuits
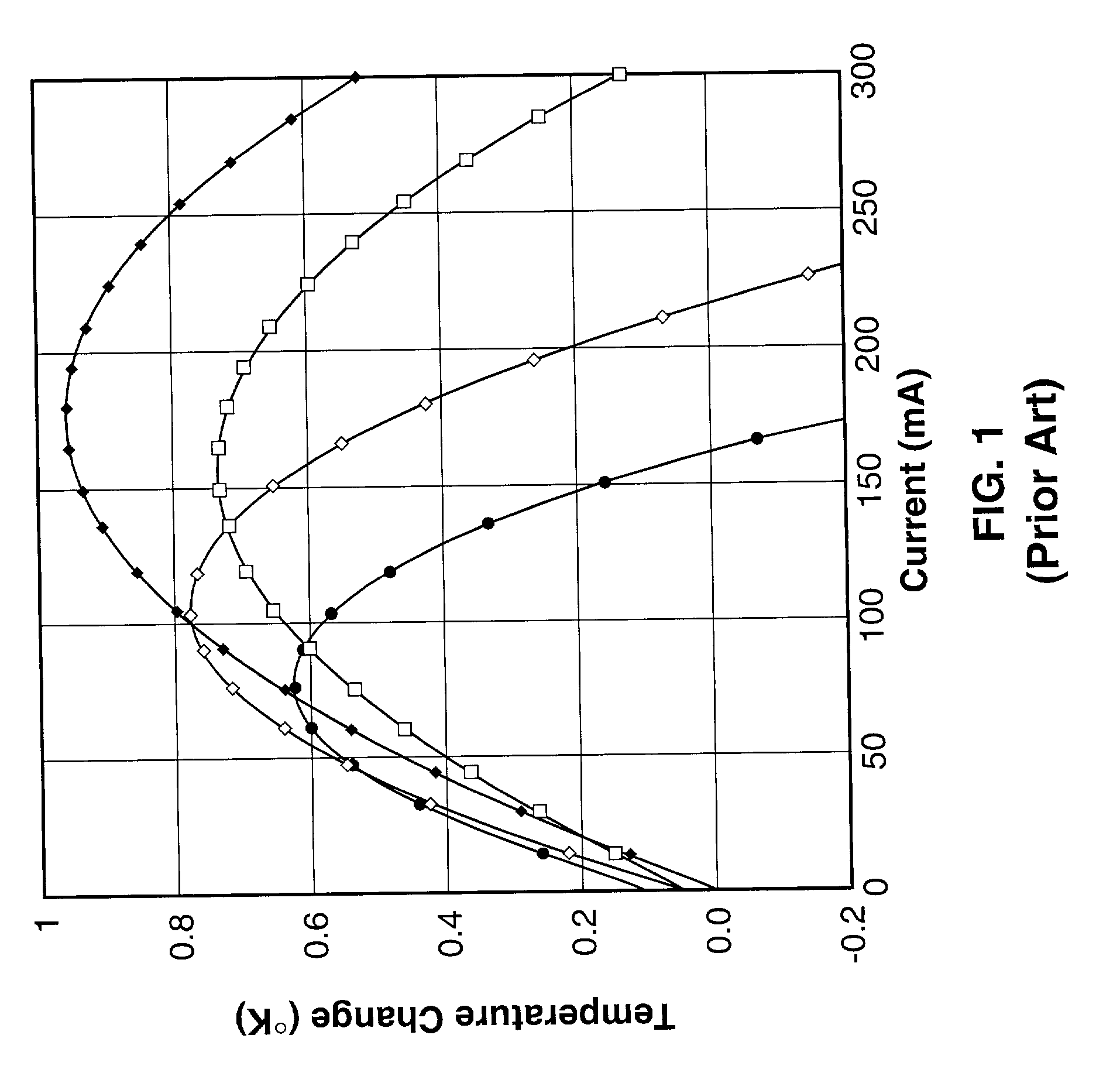
ActiveUS20020126732A1Simple and inexpensive temperature measurementImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionImage detection
Methods and apparatus for non-contact thermal measurement which are capable of providing sub micron surface thermal characterization of samples, such as active semiconductor devices. The method obtains thermal image information by reflecting a light from a surface of a device in synchronous with the modulation of the thermal excitation and then acquiring and processing an AC-coupled thermoreflective image. The method may be utilized for making measurements using different positioning techniques, such as point measurements, surface scanning, two-dimensional imaging, and combinations thereof. A superresolution method is also described for increasing the resultant image resolution, based on multiple images with fractional pixel offsets, without the need to increase the resolution of the image detectors being utilized. The thermoreflective method provides a spatial resolution better than current infrared cameras, operates within a wide temperature range, and is capable of a thermal resolution on the order of 10 mK.degree..
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
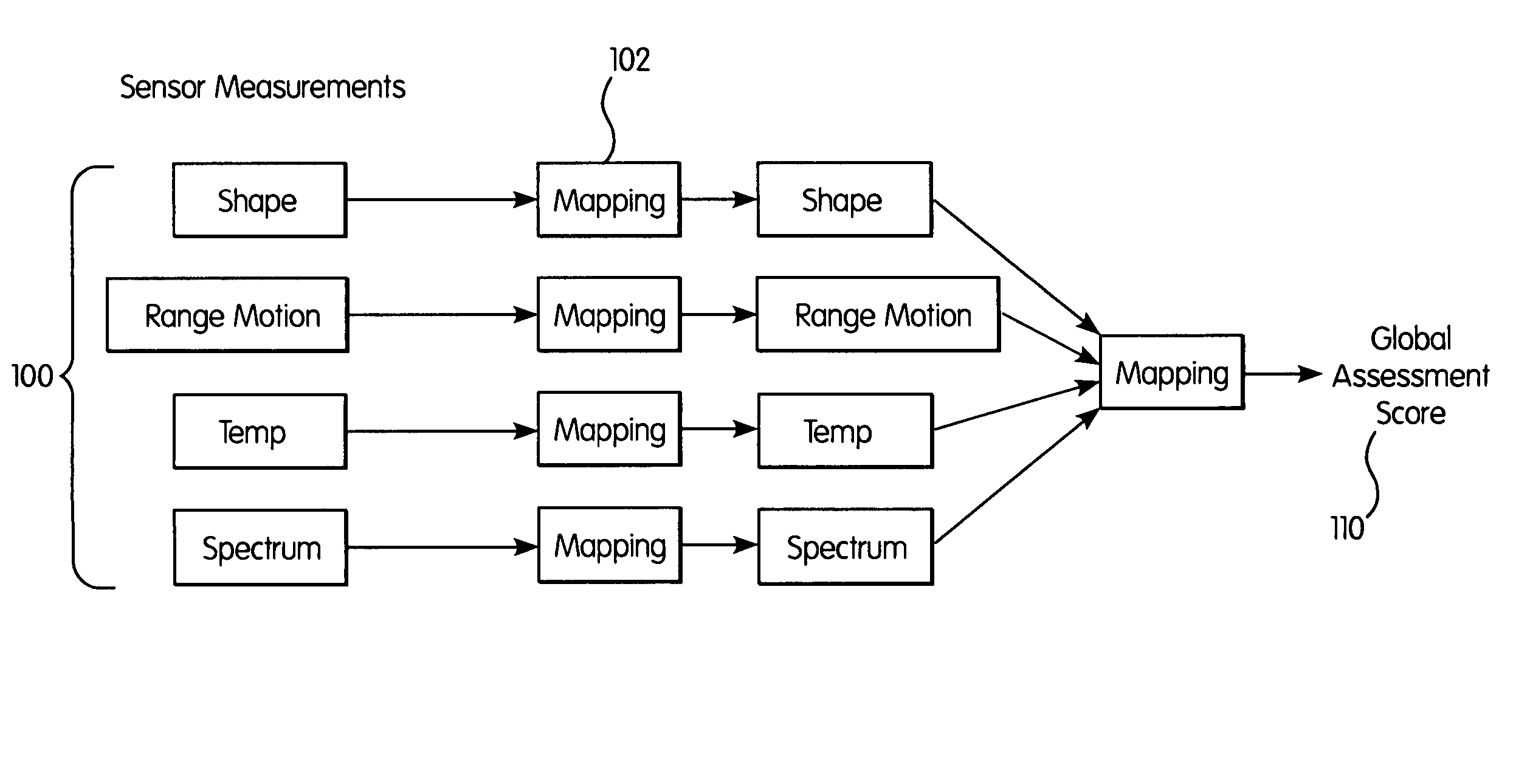
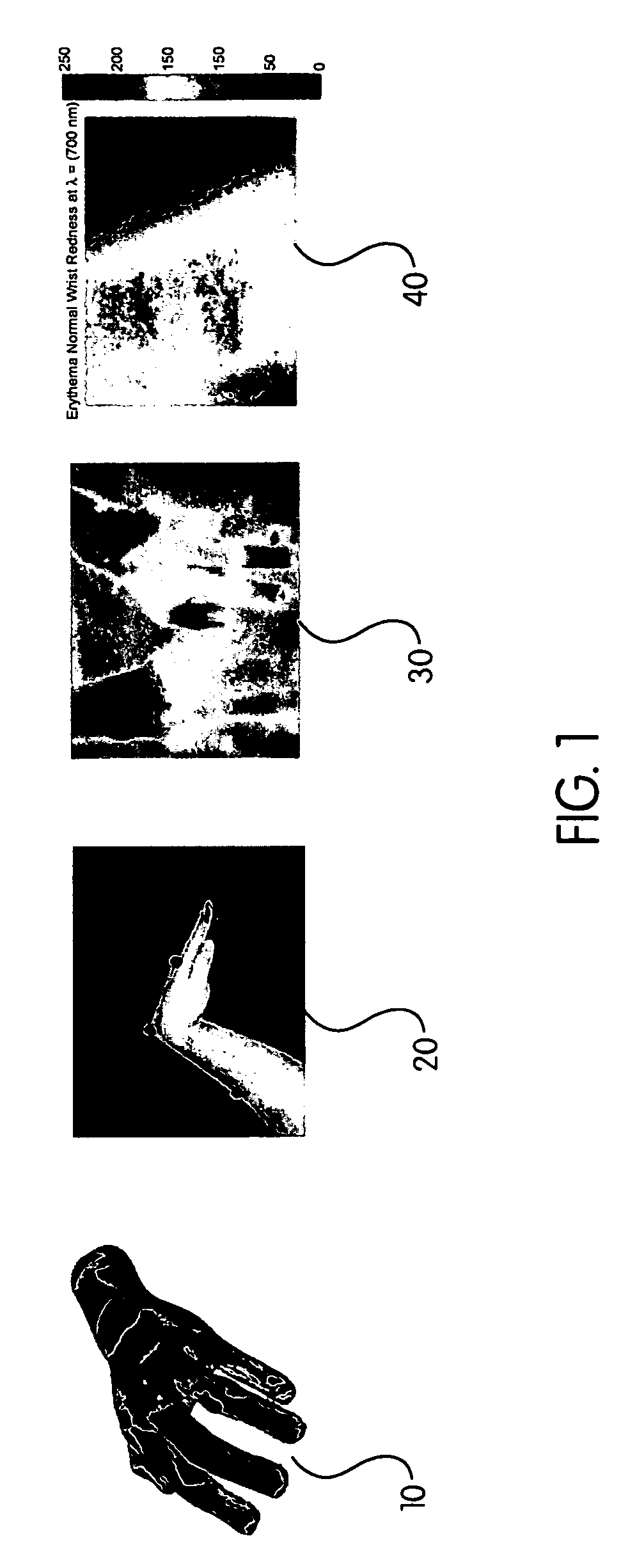
Method of assessing localized shape and temperature of the human body
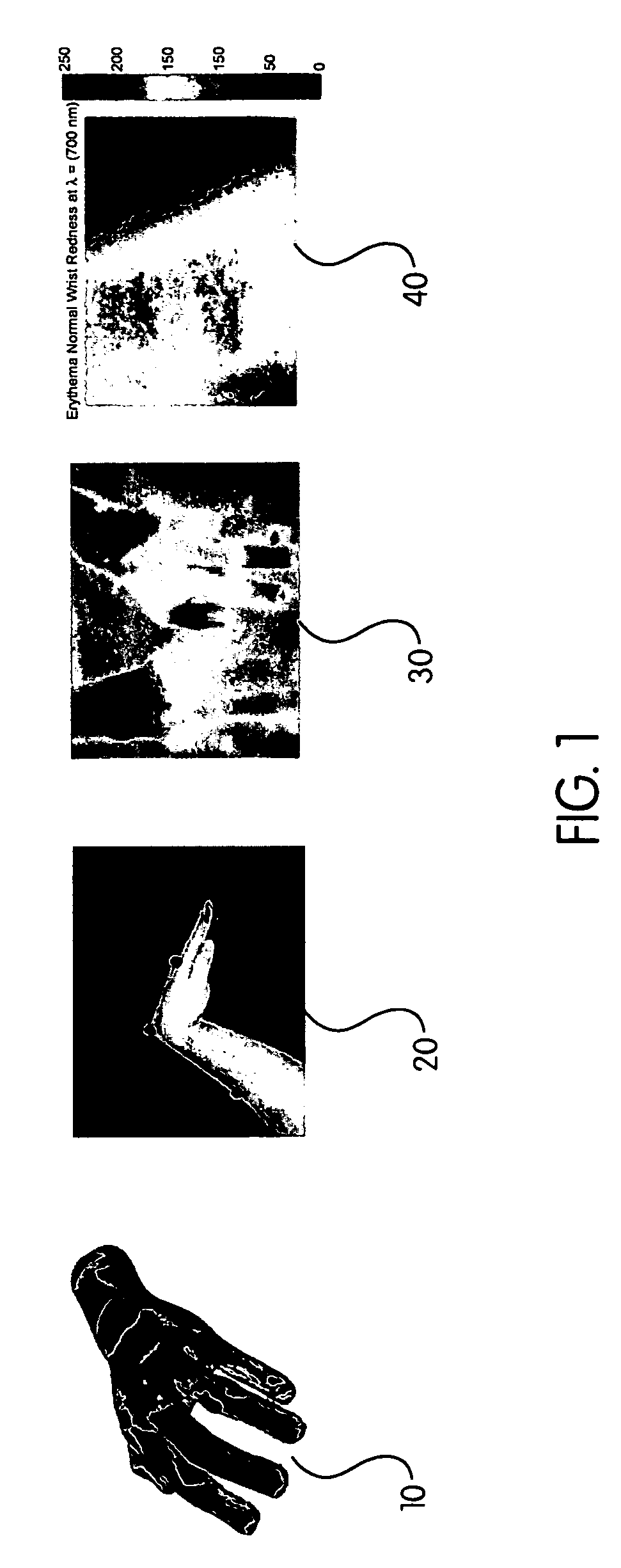
InactiveUS20060062448A1Improve clinical trial outcome measureImprove accuracyImage enhancementX-ray/infra-red processesDiagnostic Radiology ModalityHuman body
A method of objectively quantifying assessments of joints having arthritis for purposes of assessment, diagnosis and treatment. The objective measurements utilize known imaging modalities including 3D scanning, thermal imaging, visible and near-infrared imaging and two-dimensional imaging to quantify swelling, heat distribution, erythema, and range or motion. The objective measurements can be combined in various ways to assess the extent of the disease and can be used to adjust treatment protocols.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
Generating three dimensional digital dention models from surface and volume scan data
A method and apparatus are disclosed enabling an orthodontist or a user to create an integrated three dimensional digital model of dentition and surrounding anatomy of an orthodontic patient from a three-dimensional digital model obtained using a scanner with a three-dimensional digital model obtained using a Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) or Magnetic Resonance Tomography (MRT) imaging devices. The digital data obtained from scanning as well as from CBCT imaging are downloaded into a computer workstation, and registered together in order to create a comprehensive 3-D model of the patient's teeth with roots, bones and soft tissues. The invention provides substantial improvement over the traditional two dimensional imaging modalities such as x-rays, photographs, cephalometric tracing for diagnosis and treatment planning
Owner:ORAMETRIX
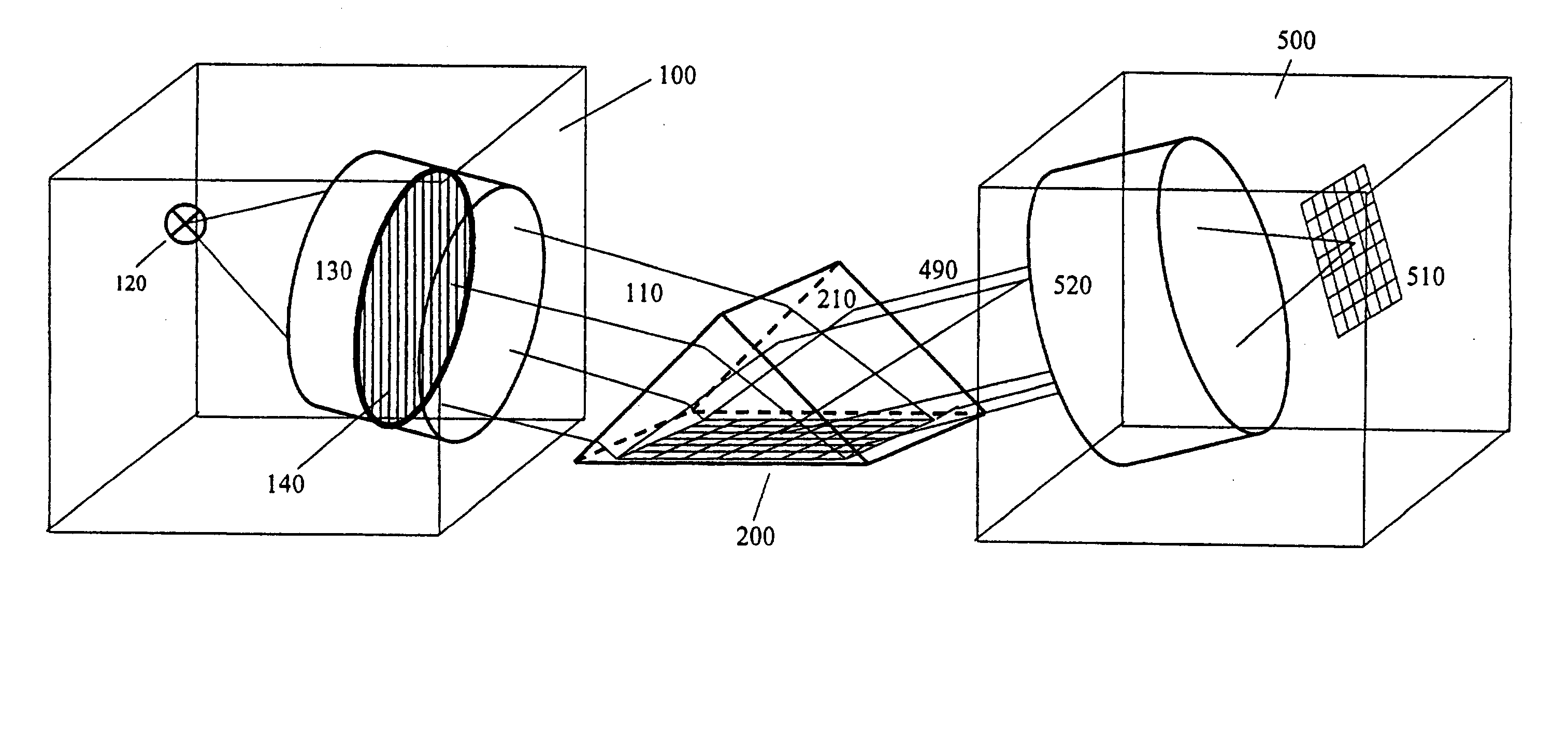
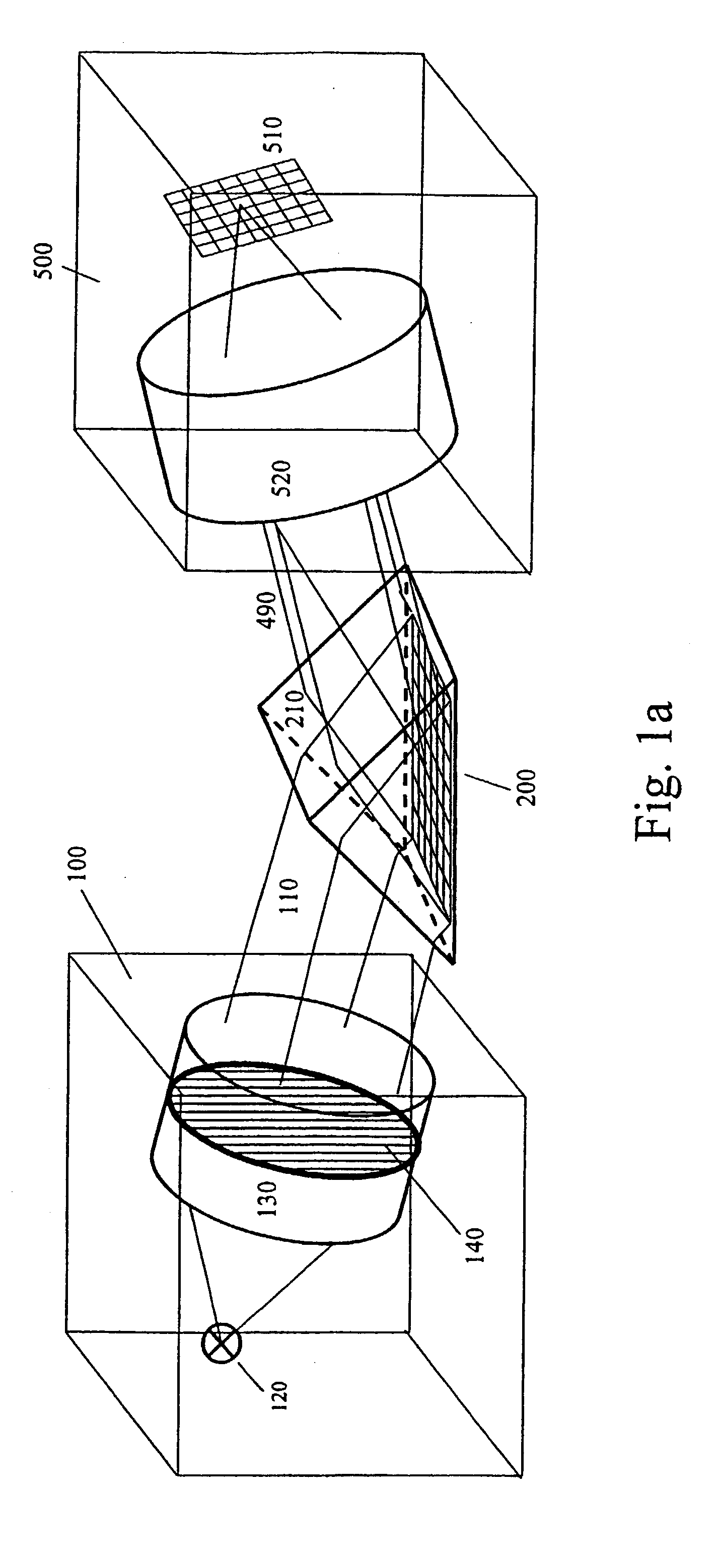
Imaging SPR apparatus
InactiveUS6862094B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsColor imageConductive materials
Owner:SPRING SYST
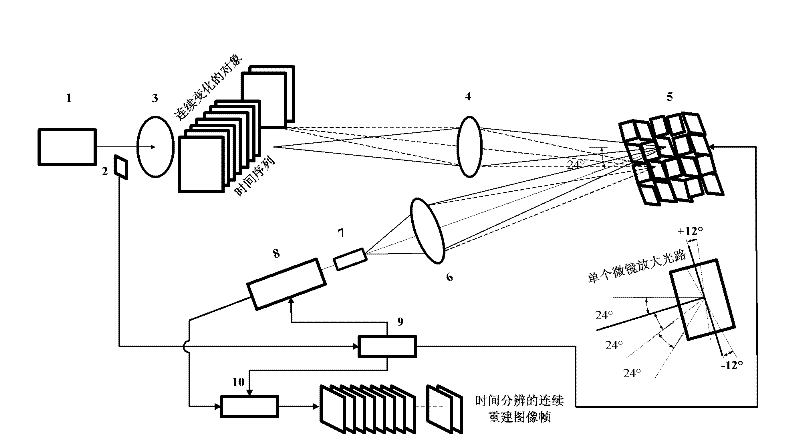
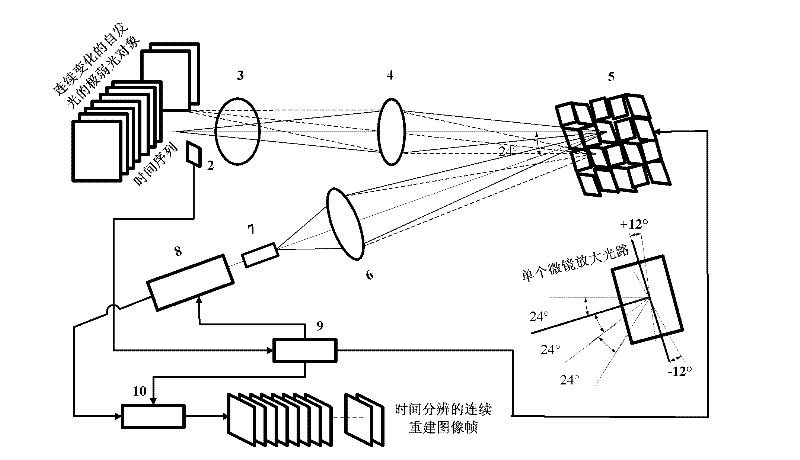
Time-resolved single-photon counting two-dimensional imaging system and method
ActiveCN102510282AResolve SensitivitySolve the small size of the arrayPulse techniqueDigital micro mirror deviceData acquisition
The invention provides a time-resolved single-photon counting two-dimensional imaging system and a time-resolved single-photon counting two-dimensional imaging method and belongs to the technical field of extremely-weak light detection. A trigger 2 is triggered to start sampling, centralized sampling is performed at t time intervals, and measurement and counting are performed if light comes at the intervals, so that time resolving of an extremely-weak light object is realized, and a time sequence image is generated. Imaging is performed on the basis of a compressive sensing (CS) theory, a digital micro-mirror device (DMD5) performs linear random projection on a compressible two-dimensional image, the compressible two-dimensional image is optically modulated and then synchronously detected by using a single-photon counter, and a high-resolution extremely-weak light image can be reconstructed by a small amount of sampling operation. The measurement process is linear and non-adaptive, the reconstruction process is non-linear, and the invention has the advantages of high generality, robustness, expandability, superposition and computation asymmetry, and can be widely applied to the fields of life science, medical imaging, data acquisition, communication, astronomy, military affairs, hyper-spectral imaging and quantum measurement.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Machine for detecting sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) leaks using a carbon dioxide laser and the differential absorption lidar ( DIAL) technique and process for making same
InactiveUS20070018104A1Minimal manipulationQuantify distanceRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsSulfur hexafluorideRechargeable battery pack
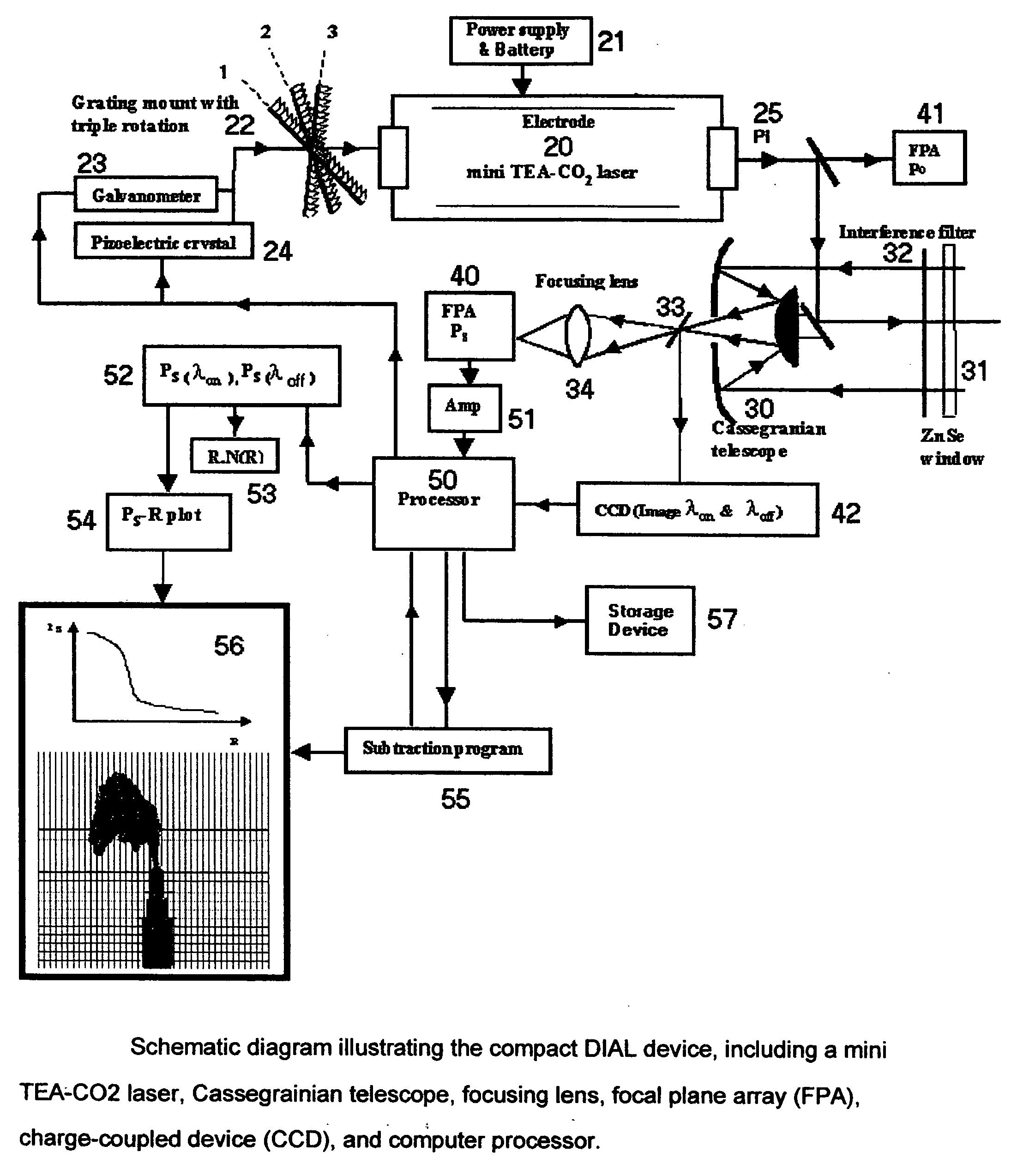
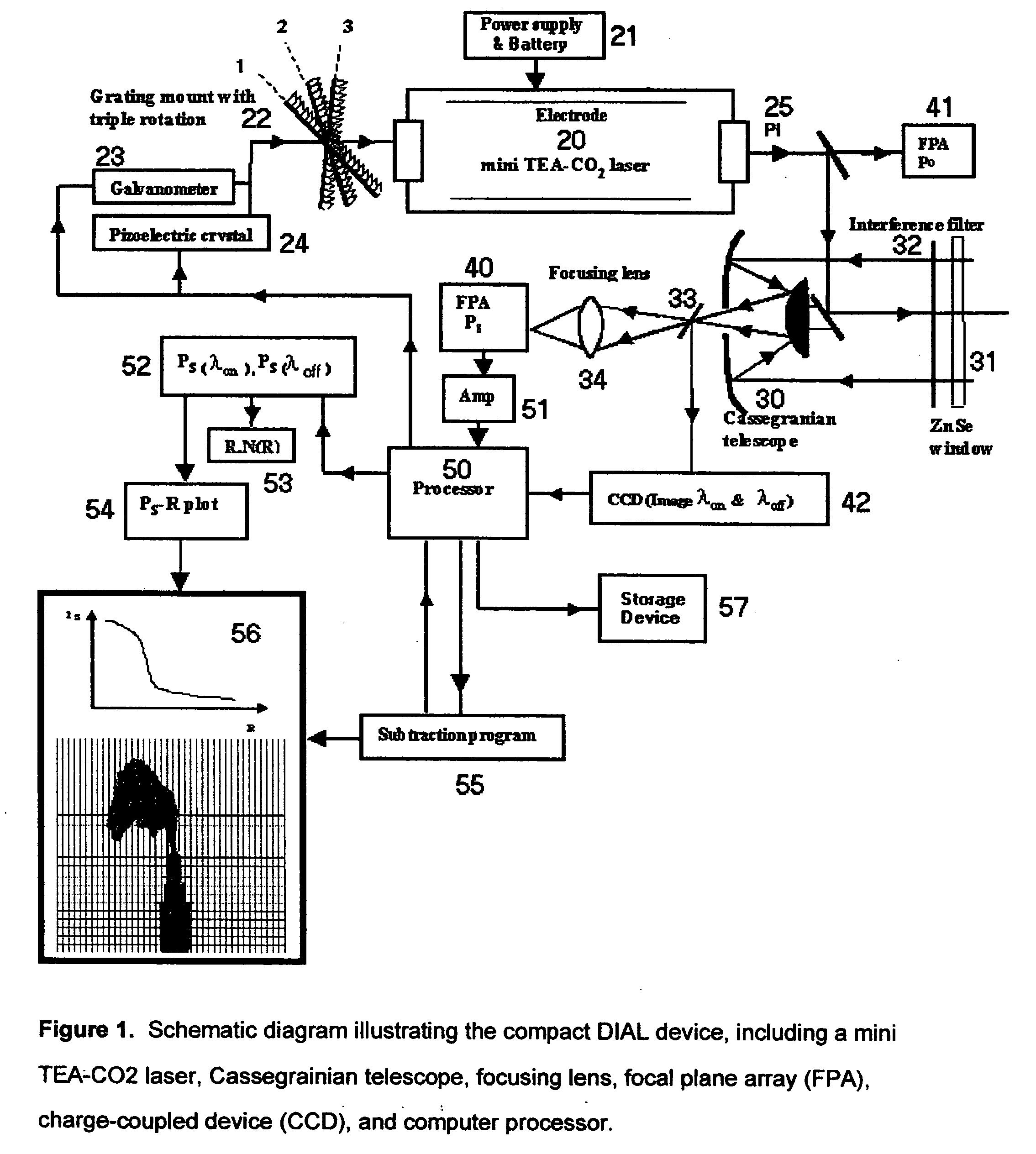
A machine for detecting sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) leaks using the mid-infrared differential absorption lidar (DIAL) technique with a commercically available, air-cooled, compact, pulsed transversely-excited-atmospheric (TEA) carbon dioxide (CO.sub.2) laser, a Cassegranian optical telescope for focusing both the laser emission and returning reflected signal, a user-operated focusing mechanism, a two-dimensional, thermoelectrically-cooled focal plane array (FPA) sensitive in the mid-infrared wavelength range (10.2-10.6 micrometers), a charge-coupled device (CCD) for 2-D imaging, a computer-based control system to rapidly switch the laser wavelength between 10.2470 micrometers, 10.7415 micrometers, and 10.5518 micrometers to utilize the Differential Absorption Lidar (DIAL) chemical detection technique, a rechargeable battery pack and power supply, and an image and data storage device using a solid-state memory stick.
Owner:PARVIN PARVIZ +1
3D imaging method and system based on LED array common lens TOF depth measurement
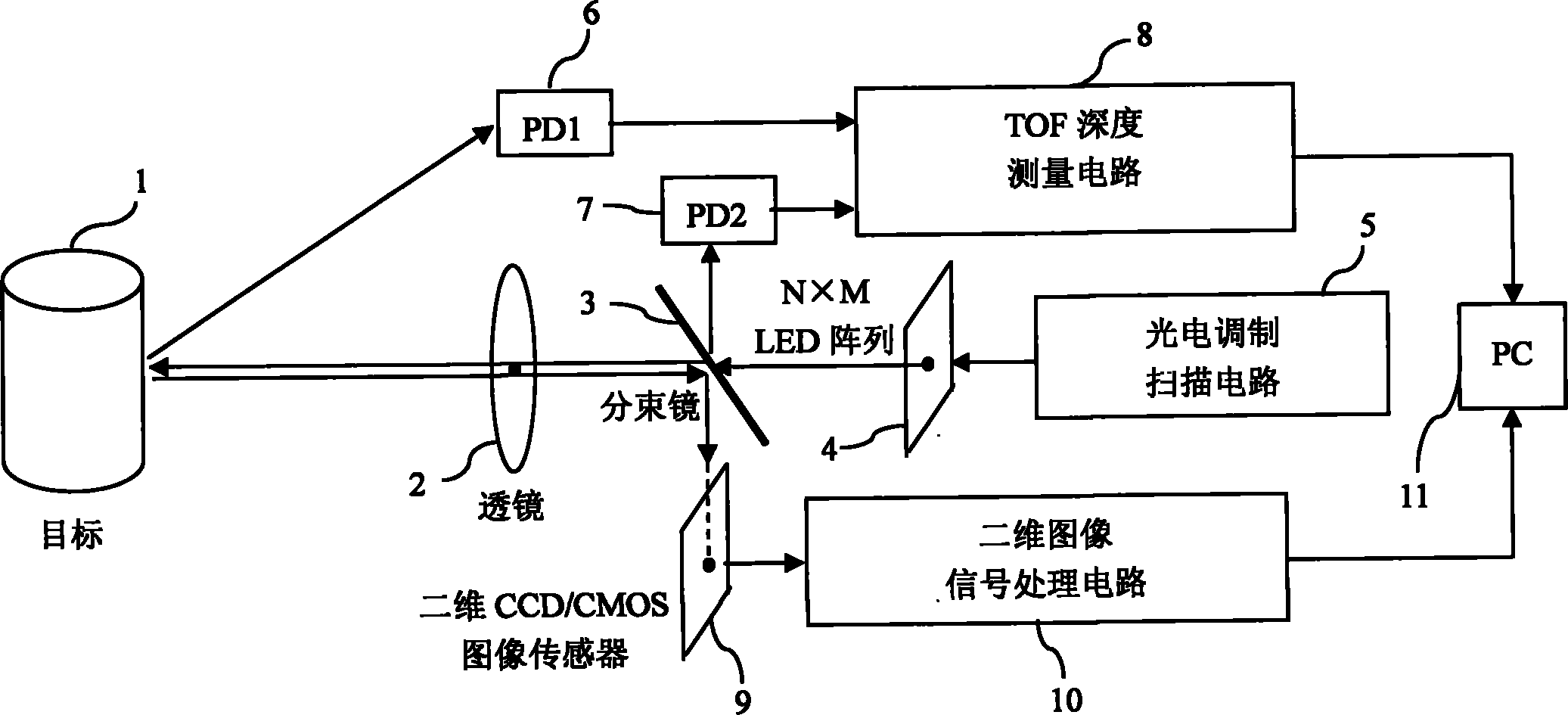
The invention discloses a 3D imaging method and system based on LED array common lens TOF depth measurement, which is characterized in that a 2D LED array is used as the lighting source, only one LED is in the lightened state every time, the modulated light emitted by the LED is projected onto the surface of the target by a projecting lens, a photoelectric receiver receives the scattered light on the surface of the target, measures the round-trip time of flight (TOF) from the light source to the target, acquires the LED depth pixel value in the lightened state according to the round-trip TOF and completes measurement of the single LED depth pixel value; time division scanning is carried out on the whole 2D LED array, the measurement process of the single LED depth pixel value is repeated and all the LED depth pixel values are acquired and are combined to generate the depth image of the target; a 2D image sensor acquires the 2D image of the target after the scattered light on the surface of the target passes through a 2D imaging lens; the projecting lens and the 2D imaging lens are the same; and the 2D image and the depth image are fused to generate the 3D image of the target. The depth image is fast in acquisition and the depth measurement resolution is high.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
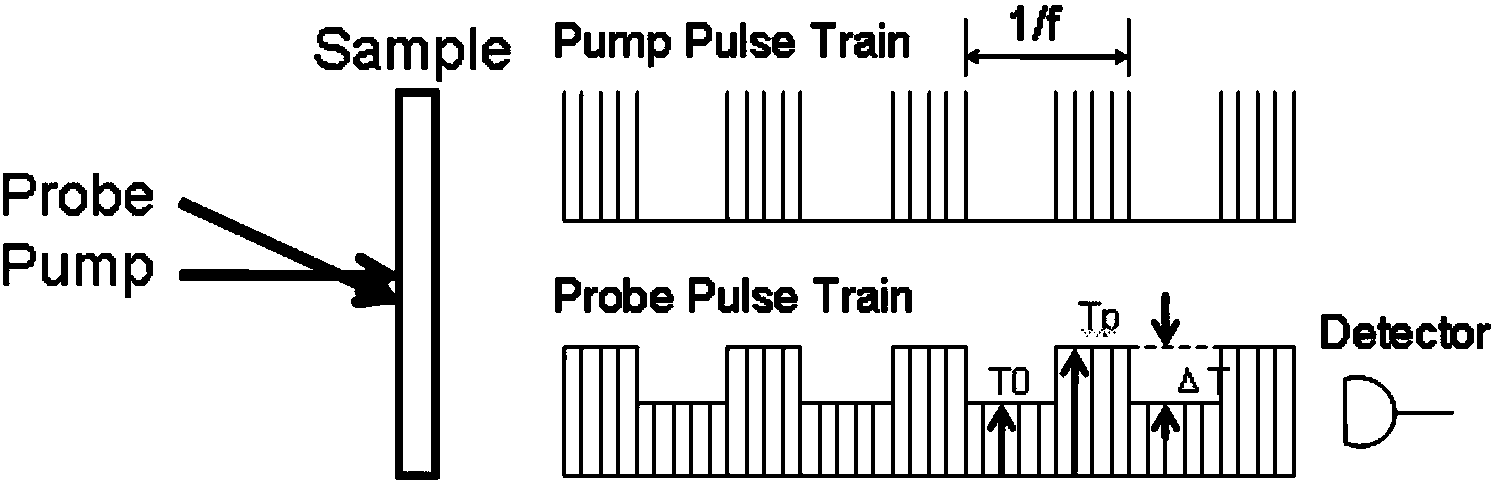
Spatially-separated pump-probe transient absorption spectrograph and realization method
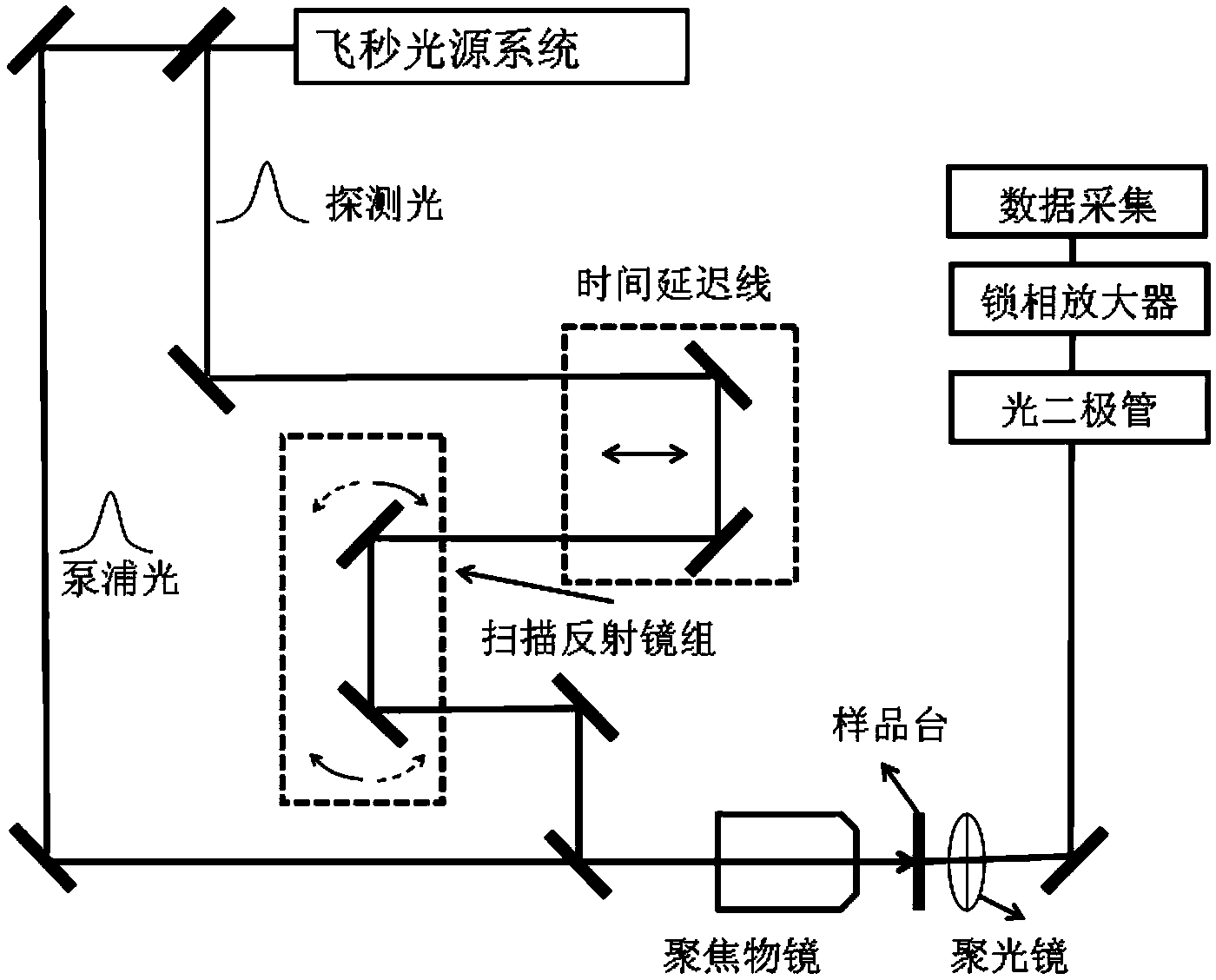
ActiveCN103868595AMotivating realizationImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyBeam splitterVertical plane
The invention discloses a spatially-separated pump-probe transient absorption spectrograph and a realization method. The realization method is characterized by generating a light source through a femtosecond light source system; realizing the beam splitting of pump light and probe light through a beam splitter; realizing the different time delay of the probe light through a time delay line; realizing the two-dimensional rotation and the calibration of the probe light within a horizontal plane and a vertical plane through a sweep reflector group; calibrating which means guaranteeing the incidence of the rotated probe light into a aperture within the front section of an objective lens; finally, obtaining a two-dimensional image formed on a sample under the combined action of the probe light and the pump light by a data collection system. According to the spatially-separated pump-probe transient absorption spectrograph and the realization method, the extremely high spatial discrimination can be realized, and moreover, the visual probe of carriers, excitors or plasmons can be realized.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method of assessing localized shape and temperature of the human body
InactiveUS7519210B2Improve accuracyImprove effectivenessImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseDiagnostic Radiology Modality
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
Spectrally encoded miniature endoscopic imaging probe
A spectrally encoded endoscopic probe having high resolution and small diameter comprising at least one flexible optical fiber; an energy source; a grating through which said energy is transmitted such that the energy spectrum is dispersed; a lens for focusing the dispersed energy spectrum onto a sample such that the impingement spot for each wavelength is a separate position on the sample, the wavelength spectrum defining a wavelength encoded axis; means for mechanically scanning the sample with focused energy in a direction perpendicular to the wavelength encoded axis; a means for receiving energy reflected from the sample; and, a means for detecting the received reflected energy. The probe grating and lens delivers a beam of multi-spectral light having spectral components extending in one dimension across a target region and which is moved to scan in another direction. The reflected spectrum is measured to provide two dimensional imaging of the region.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Imaging spr apparatus
InactiveUS20030048452A1Improve imaging effectImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsColor imageConductive materials
A two-dimensional imaging surface plasmon resonance (SPR) apparatus for optical surface analysis of a sample area on a sensor surface is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a sensor surface layer of a conductive material that can support a surface plasmon, such as a free electron metal, e.g. gold, silver or aluminum, a source of electromagnetic beams of two or more wavelengths that illuminate a two-dimensional surface area from either the front or the backside of the sensor surface layer, and a detector for simultaneous, or pseudo simultaneous, detection of two or more wavelengths of reflected intensities from the two-dimensional surface area, providing two or more two-dimensional images of the surface area, the two-dimensional images being a function of the effective refractive index at each point on the surface area. The two-dimensional images put together result in a color image. The apparatus is suitable for use in biological, biochemical, chemical and physical testing.
Owner:SPRING SYST
High Intensity Focused Ultrasound Therapeutic System Guided by an Imaging Device
InactiveUS20100174188A1Low production costGood treatment effectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound imagingTreatment effect
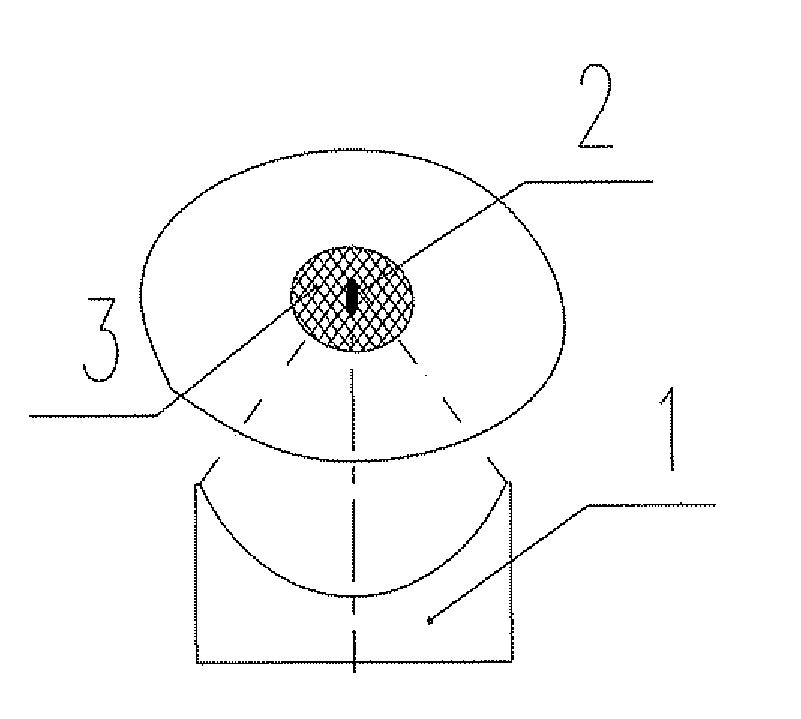
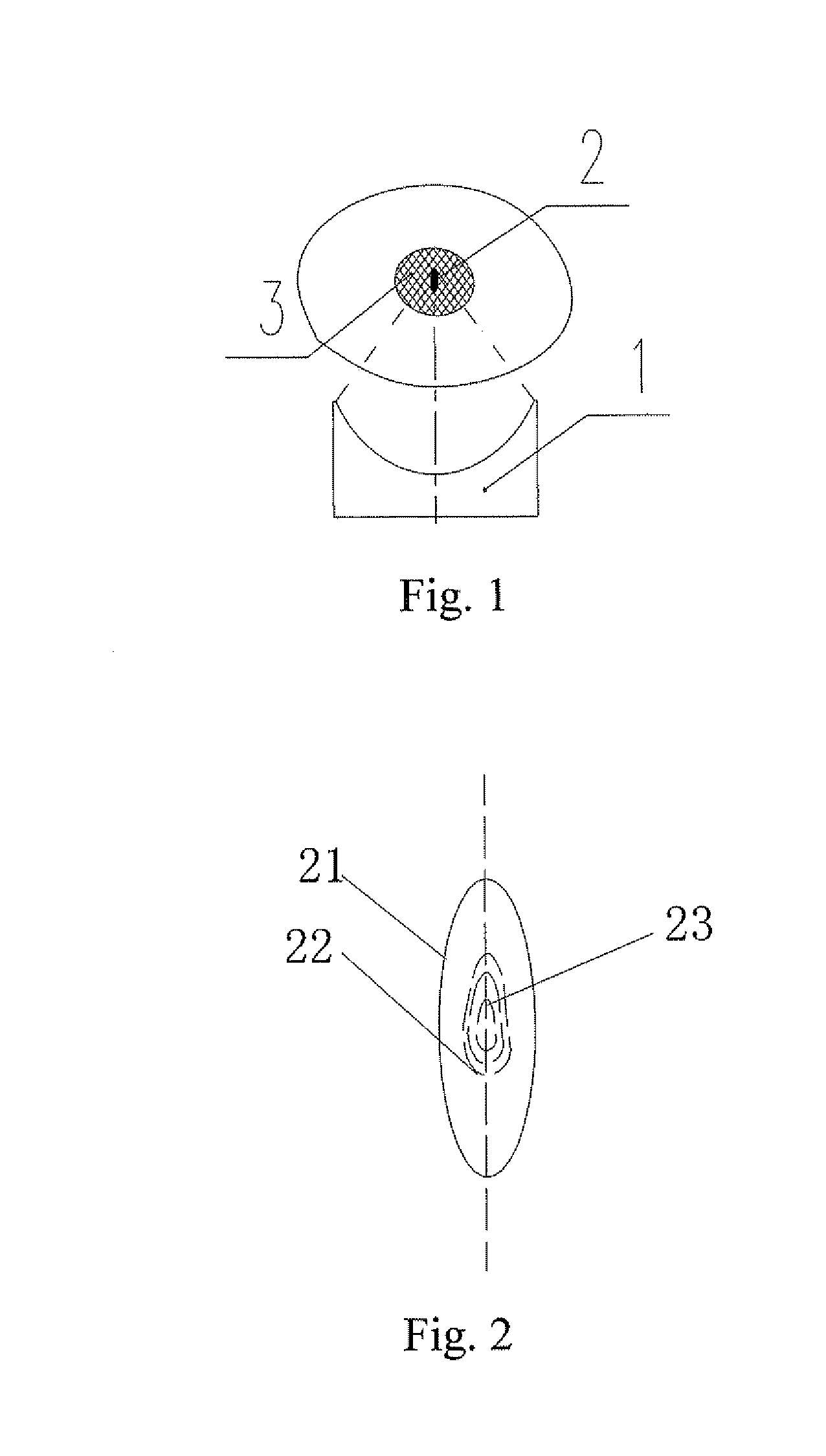
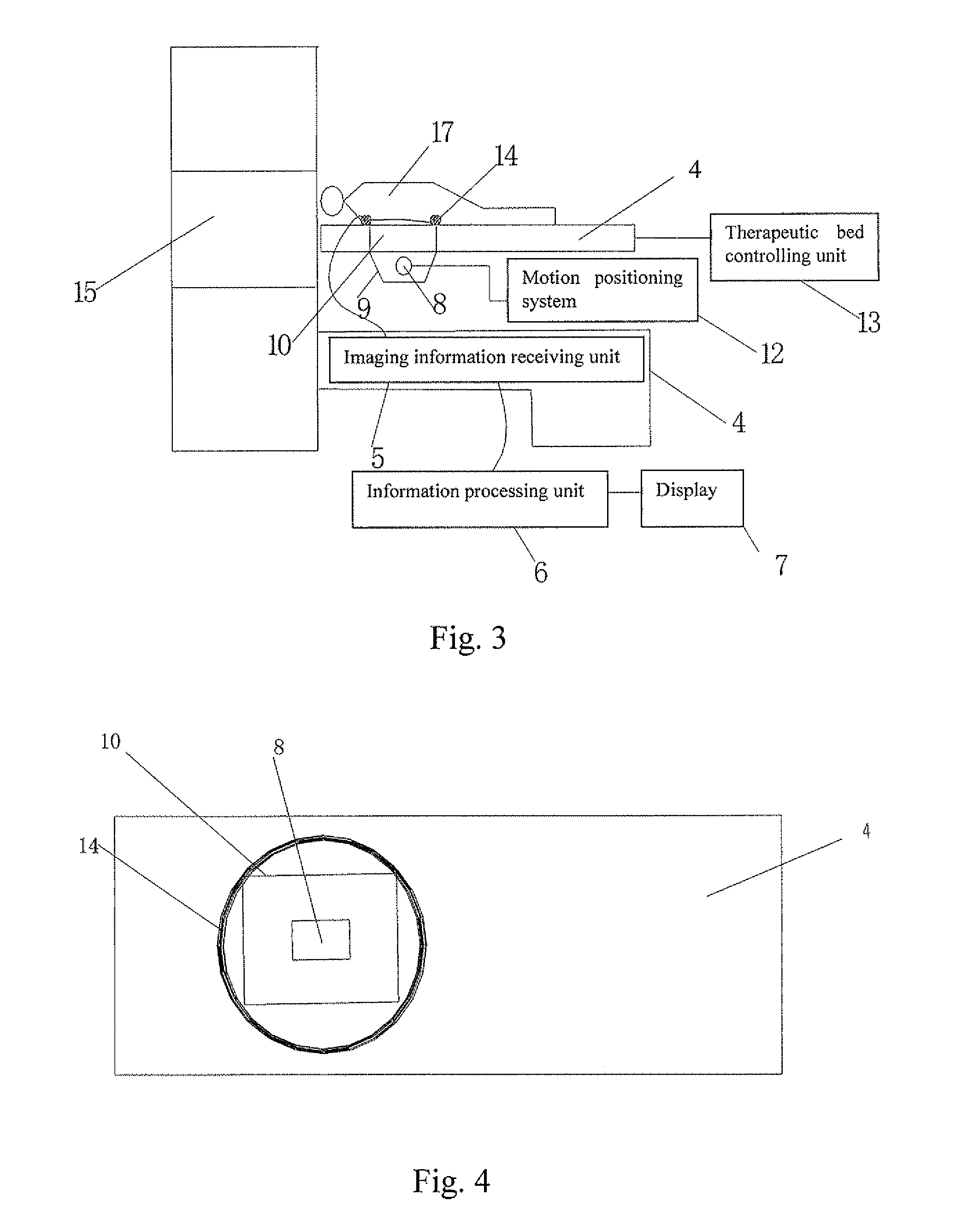
A high intensity focused ultrasound therapeutic system guided by an imaging device is provided and includes an ultrasound therapeutic applicator which contains an ultrasound transducer (8), a therapeutic bed (11), on which a patient (17) lies, and an imaging device used for imaging a diseased tissue (3). Wherein, the imaging device is a non-ultrasound imaging device with two-dimensional imaging function. The ultrasound transducer (8) with the diameter of focal core (23) ranging from 0.1 mm to 5 mm, preferably, ranging from 0.2 mm to 2 mm, in a biological focal region (2) located in the diseased tissue (3) is adopted. The non-ultrasound imaging device is a CT or an MRI device with two-dimensional imaging function. The present invention can image the target accurately, so it can be applied to all kinds of complicated surgeries and has good therapeutic effects.
Owner:RONGHAI SUPERSONIC MEDICINE EN
Imaging system and imaging optical system
ActiveUS20130050405A1Uniform qualityIncrease ratingsTelevision system detailsPrismsMagnificationOptic system
An imaging system includes n or more photographing optical system having an imaging optical system having a full angle of view A (degree) larger than 360 / n where n is a natural number of 2 or more and a two-dimensional imaging element configured to convert light condensed by the imaging optical system into an image signal, wherein in the imaging optical system of each of the imaging optical systems, a magnification per unit angle of view monotonically increases from 0 to 360 / n-degree angle of view, and an increase rate of the magnification monotonically decreases to the full angle of view A (degree) after the 360 / n-degree angle of view.
Owner:RICOH KK
Telescopic array type portable MIMO-SAR (multiple-input multiple-output synthetic aperture radar) measurement radar system and imaging method thereof
ActiveCN104614726AQuick checkRapid positioningRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a telescopic array type portable MIMO-SAR (multiple-input multiple-output synthetic aperture radar) measurement radar system and an imaging method thereof. The system comprises a telescopic MIMO antenna array, a radar transmitting / receiving machine, a control and processing computer, a liftable antenna frame and the like. The system has the advantages in an aspect of meeting field diagnosis and measurement of scattering properties in using and maintenance processes of a low detectable target that firstly, quick detection, positioning and imaging diagnosis of an abnormal scattering part of the low detectable target can be realized, that is, an MIMO-SAR different from a linear guiderail SAR in mechanical scanning imaging can finish high-resolution two-dimensional imaging of a measured target through one-time or two-time 'snapshot' electric scanning imaging; secondly, the requirement on a target test site environment is lowered, that is, guide rails for precision mechanical screening measurement do not need to be mounted in a target test site, so that the requirement on the site test environment in imaging diagnosis and measurement operation processes is greatly lowered; thirdly, the antenna array is telescopic, so that miniaturization, quick unfolding and folding as well as portability of the measurement radar system can be easily realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
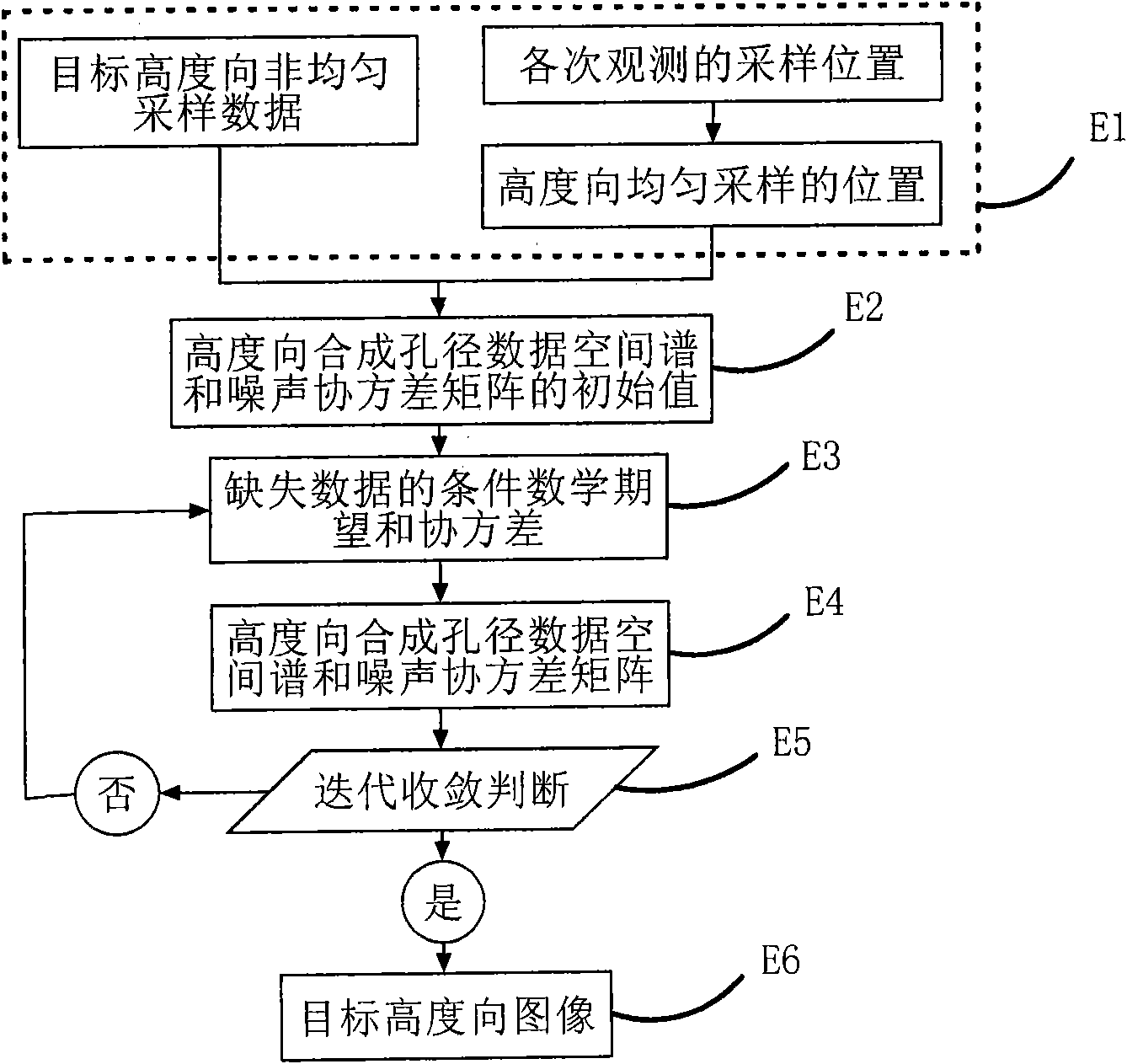
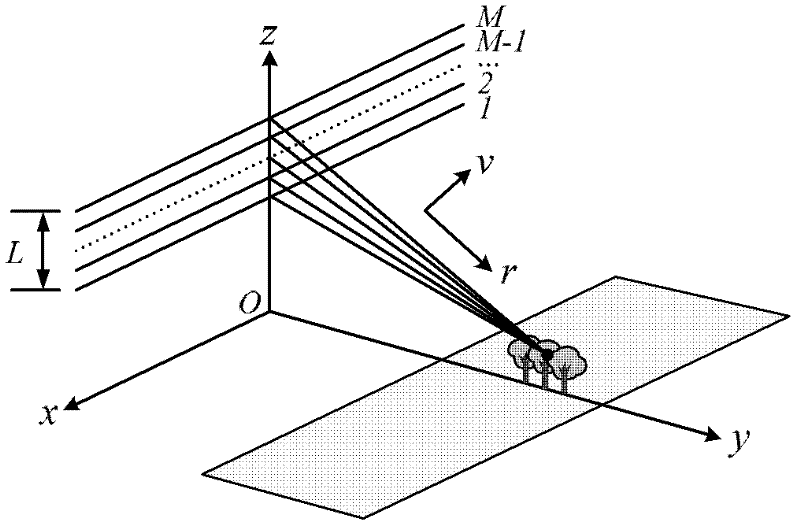
Non-uniform distributed multi-baseline synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging method
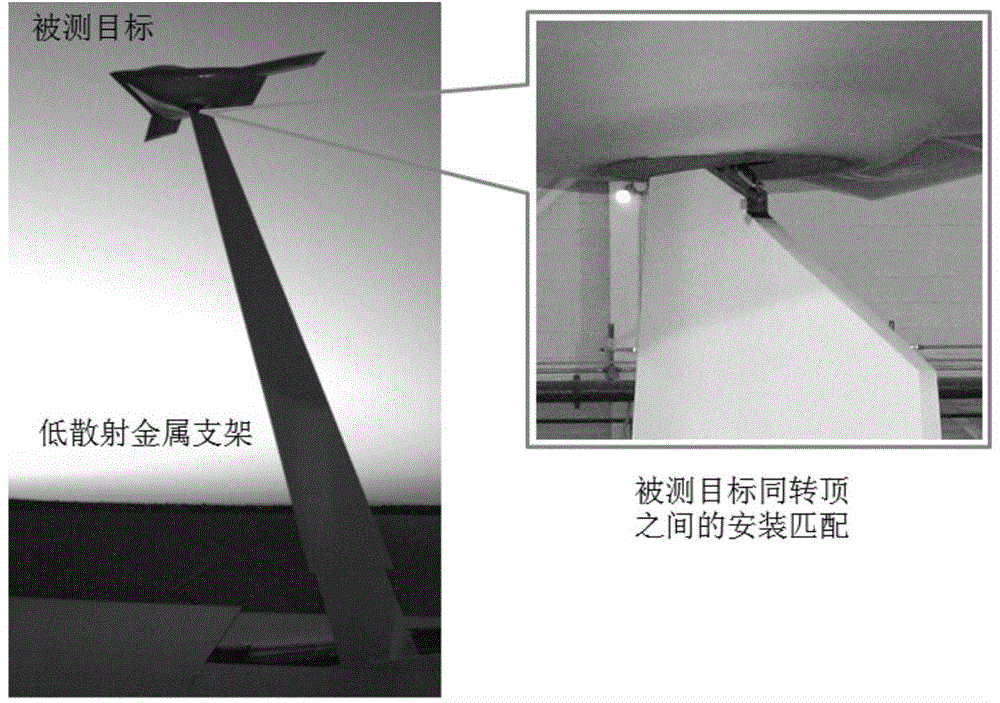
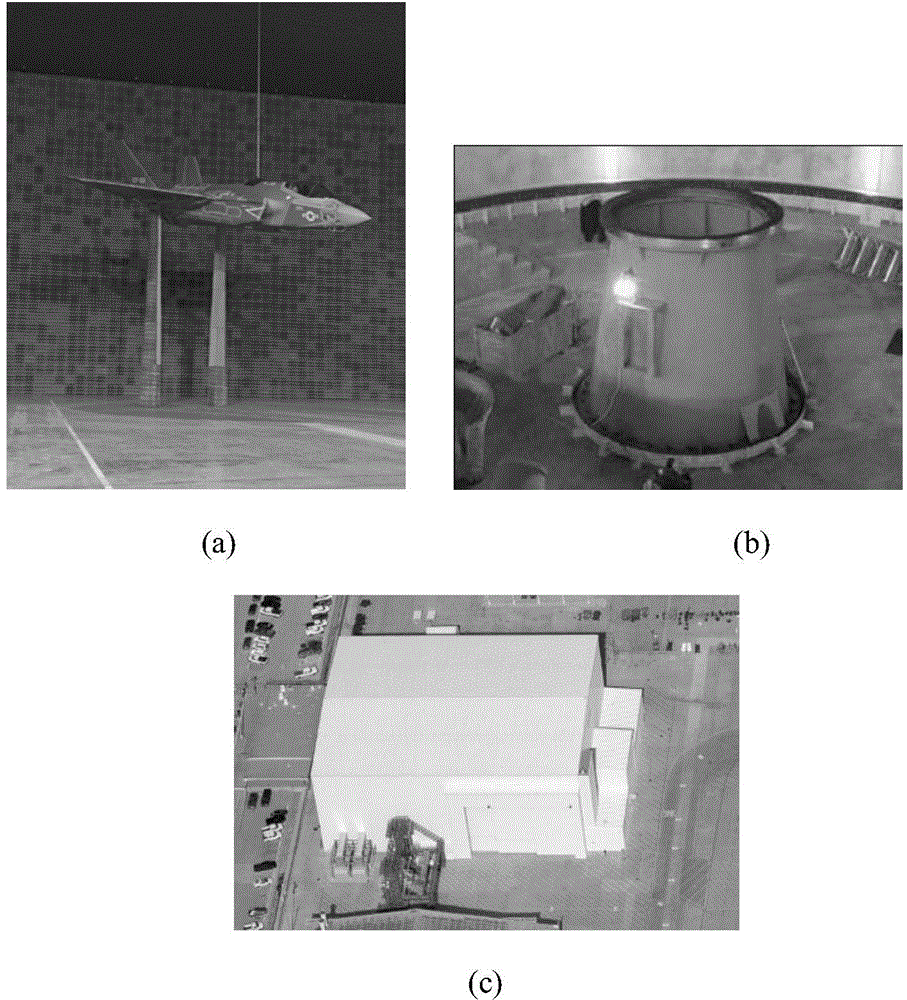
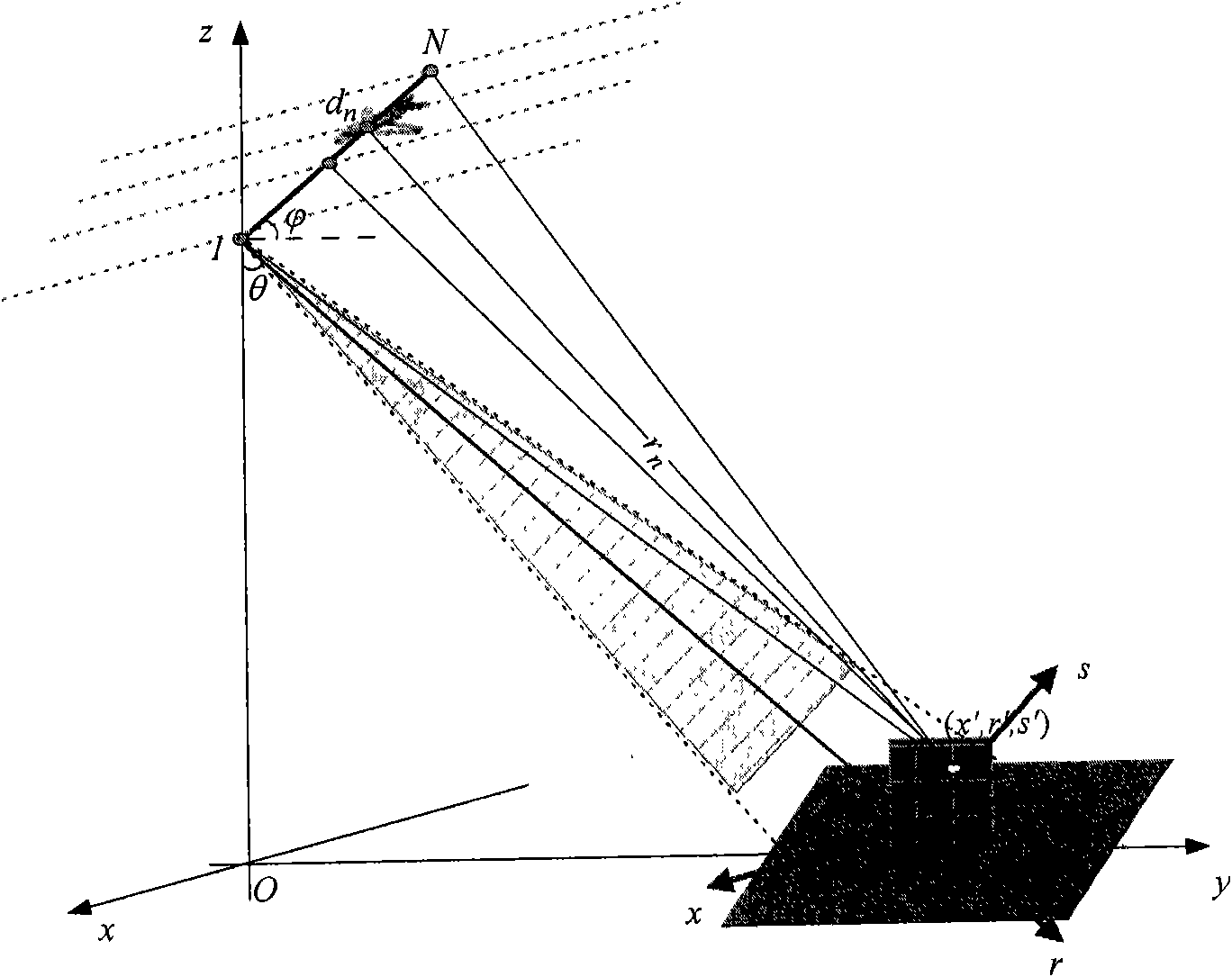
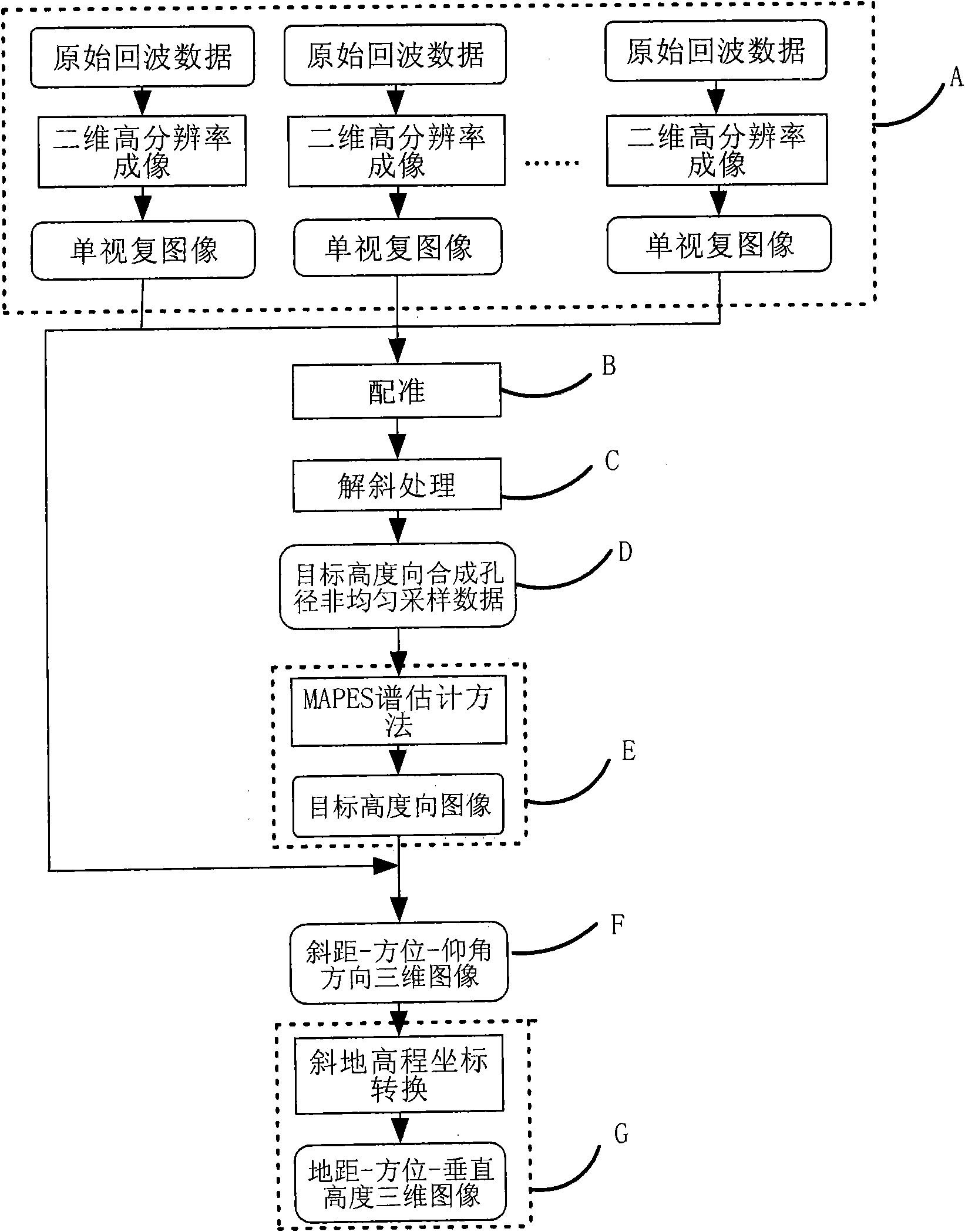
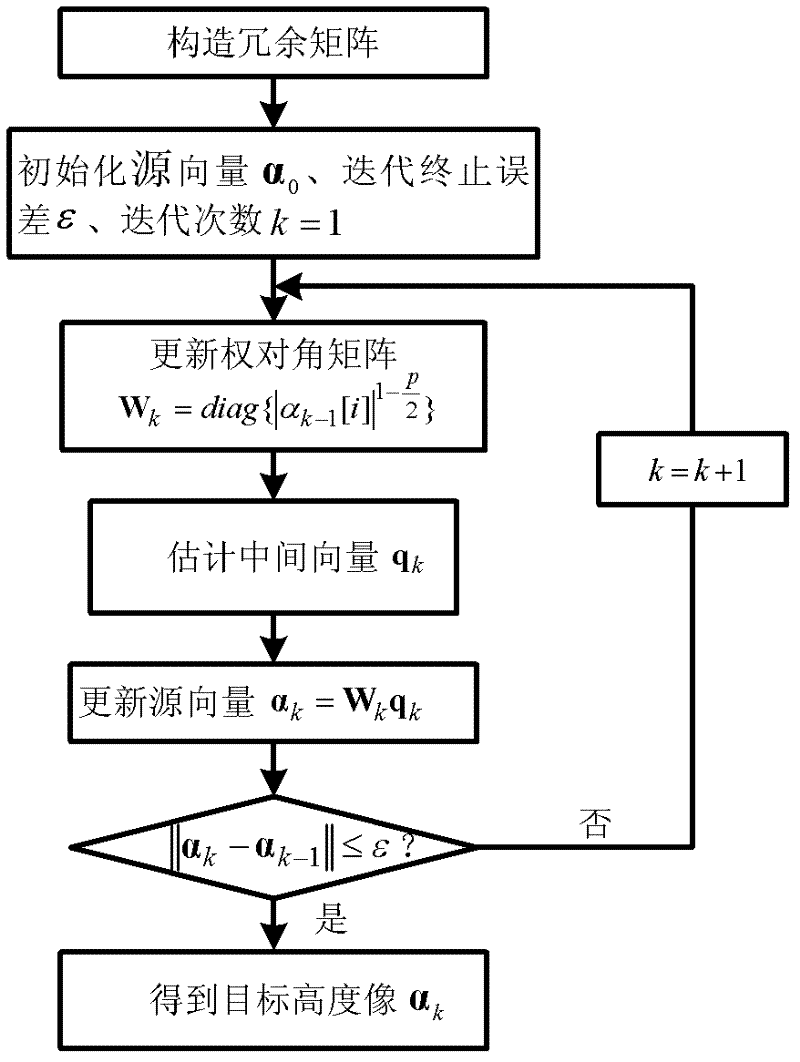
The invention discloses a non-uniform distributed multi-baseline synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging method, and relates to the three-dimensional imaging technology. The method comprises the following steps of: performing two-dimensional focusing on primary echo data obtained by flying observation at each time to obtain single-look complex images; registering sequences of the single-look complex images to acquire non-uniform sampling data of an observation target under different visual angles; removing inclination aiming at the non-uniform sampling data to perform phase modulation; then estimating a spatial spectrum of the primary uniform sampling data by using a missing data-based amplitude phase estimation method and maximizing mathematically expected iterative operation of observation data so as to implement imaging of a target height direction; and finishing three-dimensional imaging of the target by combining a two-dimensional target image obtained in two-dimensional imaging of each track. The method for performing the imaging of the height direction based on the amplitude phase estimation method reduces elevation blur caused by multi-baseline non-uniform distribution and acquires clear high-resolution target three-dimensional imaging results.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for comprehensively measuring reflectivity
InactiveCN102169050AAchieving Arbitrary ReflectivityEasy to switchScattering properties measurementsReflective surface testingReflectivity measurementLaser beams
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively measuring reflectivity, which comprises the following steps: dividing continuous incident laser beams into a reference beam and a detection beam, wherein the reference beam is focused on a photoelectric detector for direct detection and the detection beam is injected into an optical resonant cavity; using a cavity ring-down technology to measure an optical element with reflectivity more than 99%, respectively measuring a ring-down time tau 0 of an original optical resonant cavity output signal and a ring-down time tau 1 of the measured optical resonant cavity output signal after an optical element to be measured is added, and calculating the reflectivity R of the optical element to be measured; using the spectrophotometry to measure the reflectivity of the optical element to be measured when the R value is less than 99%; moving away an output cavity mirror; focusing detecting light reflected by a measuring mirror on the photoelectric detector for detecting while recording a light intensity signal ratio of the detection beam to the reference beam; and calibrating to further obtain the reflectivity R of the optical element to be measured. The device for measuring reflectivity can be used for measuring optical elements with any reflectivity and also can be used for realizing the high-resolution two-dimensional imaging of the reflectivity distribution of a large-aperture optical element.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
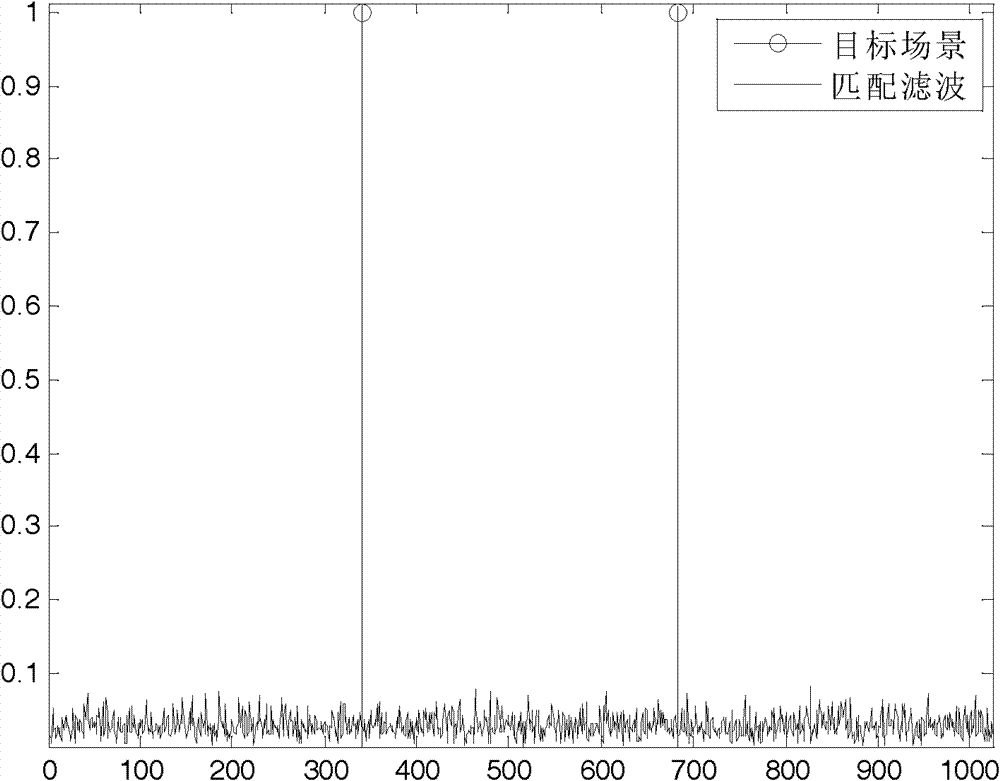
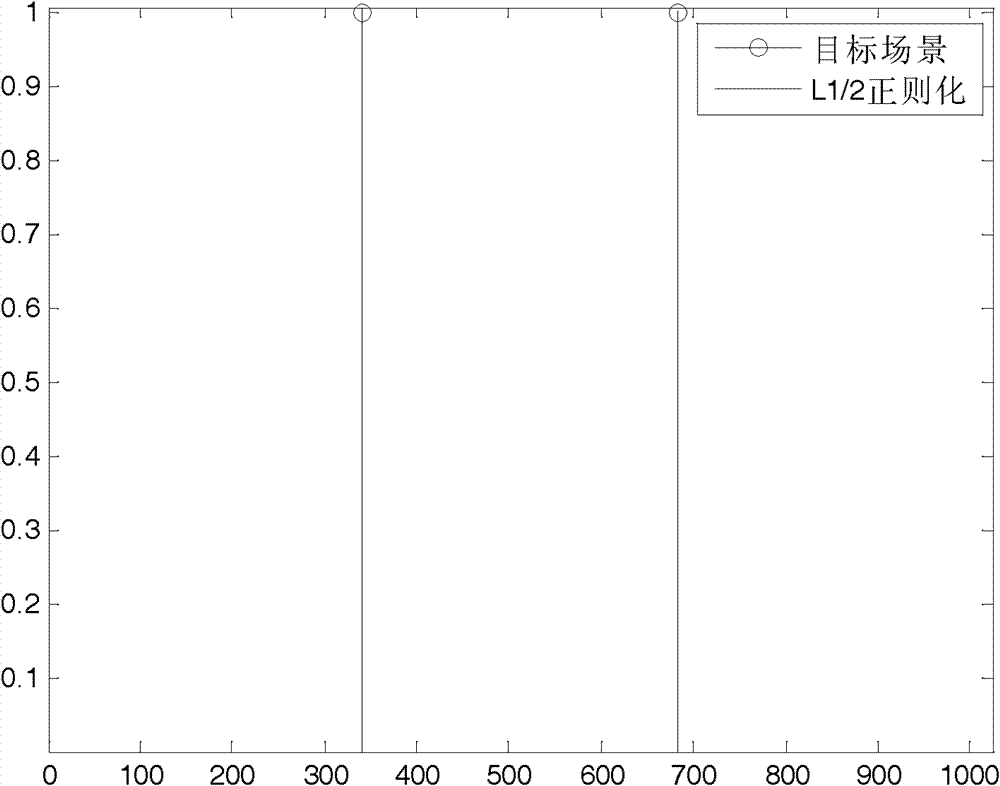
Synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on L<1/2> regularization
ActiveCN102788977AEffective imagingFew samplesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on L<1 / 2> regularization and relates to a radar two-dimension imaging technology. The synthetic aperture radar imaging method includes the steps of a, establishing a synthetic aperture radar imaging model based on the L<1 / 2> regularization according to a synthetic aperture radar observation model; and b, using an iteration half threshold value algorithm to reconstruct an observation scene backscattering coefficient. Compared with traditional synthetic aperture radar imaging methods, the synthetic aperture radar imaging method is capable of reducing a sampling quantity required by the correct reconstruction of an objective scene and achieving effective imaging of synthetic aperture radar data.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single photon counting formatter
InactiveCN101387548AStitching is not requiredHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMicro imagingPhotocathode
The invention relates to a single photon counting and imaging detection device. A high-voltage power supply of the device is connected with a micro-imaging reinforced tube through a high tension lead; a display, an image processing device and a printer are connected with a computer respectively; an anode collector is arranged between the micro-imaging reinforced tube and a preamplifier; the anode collector comprises a substrate, an electrode plated on the substrate and a signal lead; an anode is connected with the preamplifier through the signal lead; and the micro-imaging reinforced tube comprises a photocathode and a microchannel plate connected with the photocathode which are arranged sequentially along a light path. The device has the characteristics that the device can read out a time mark for arriving time and a general image of integral in a period, realize the single photon counting and two-dimensional imaging detection of an extremely-weak object, has the function of single photon counting, and can perform two-dimensional imaging on the extremely-weak luminous object. The device has the advantages of large area array, high sensitivity, low dark count, high resolution factor, good imaging linearity and the real-time measurement and processing.
Owner:陕西光电子先导院科技有限公司
Device for two-dimensional imaging of scenes by microwave scanning
InactiveUS8009116B2Acceptable image qualityHigh processing expenditure and expenditureAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionContinuous scanningEarth observation
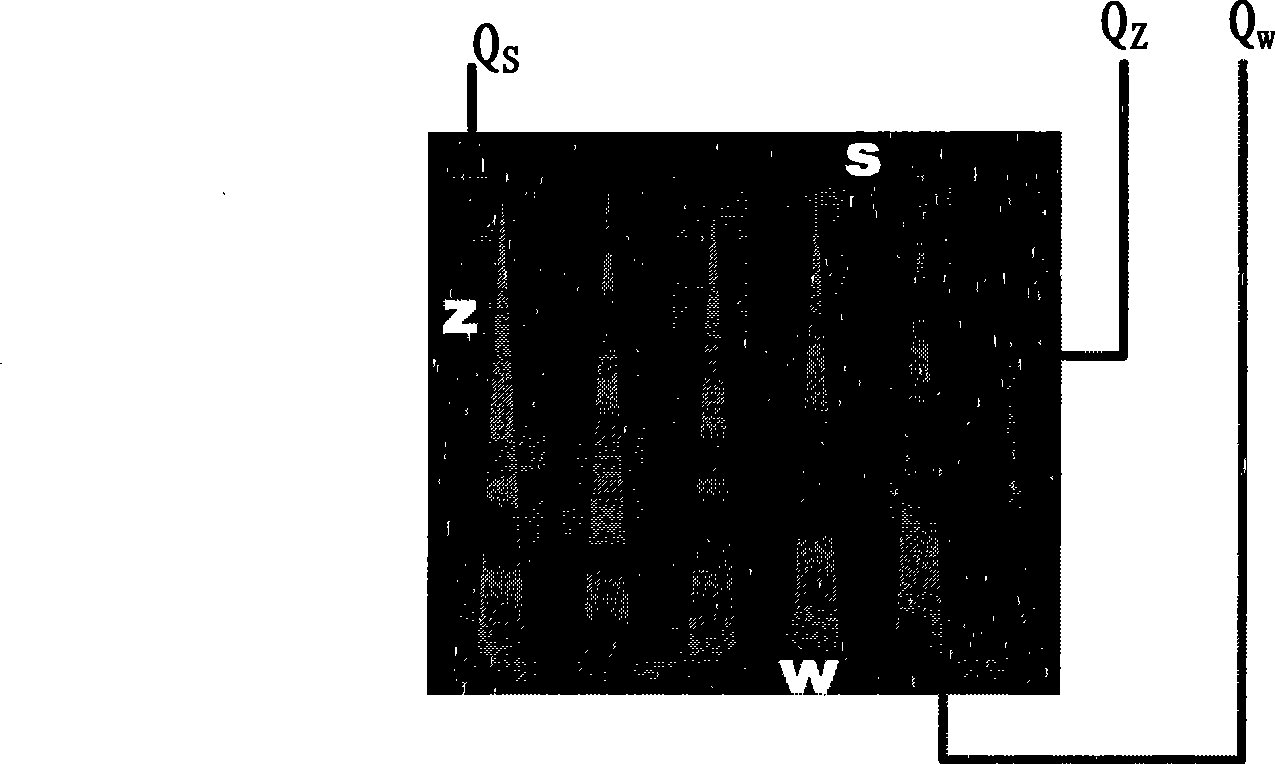
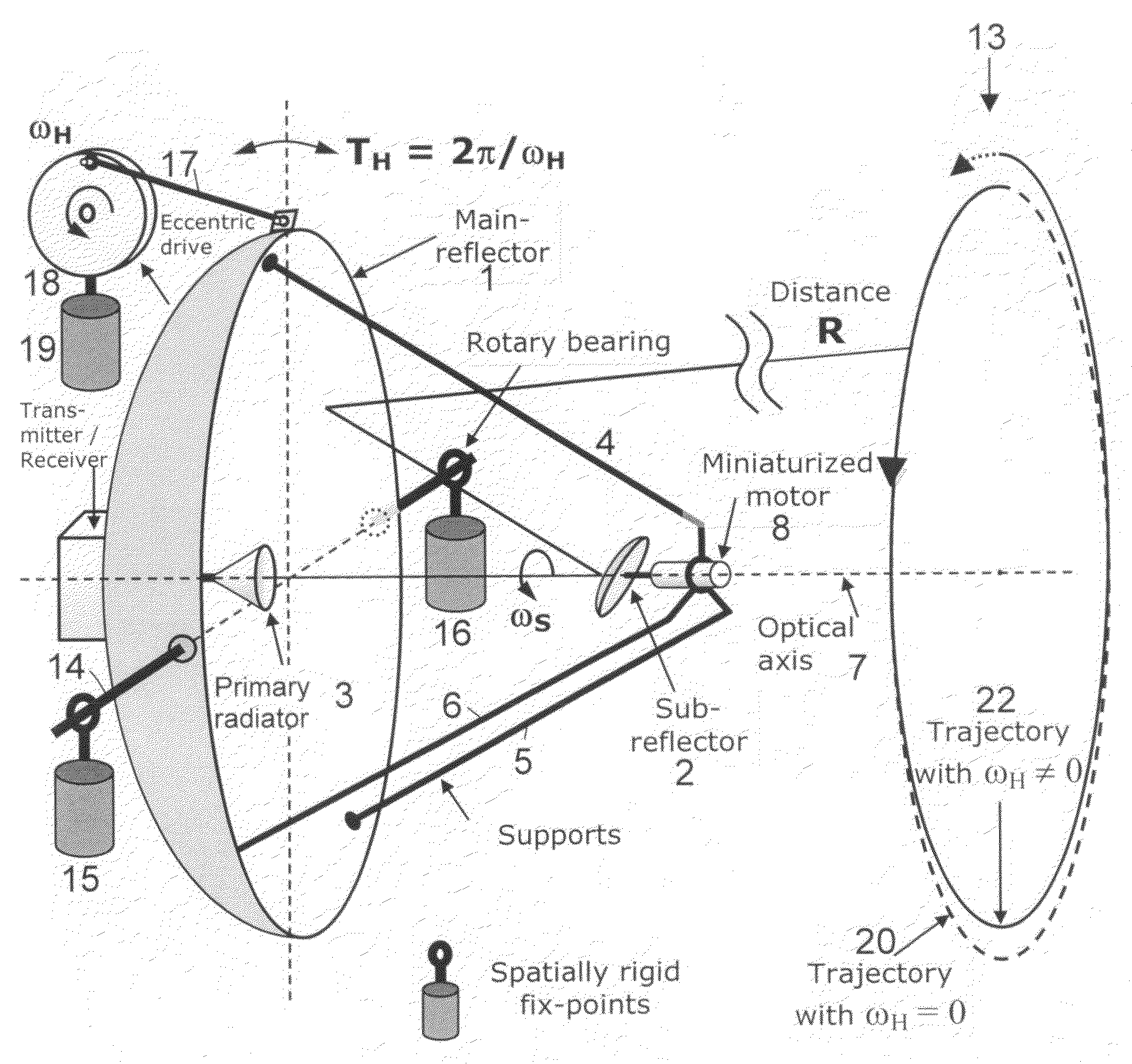
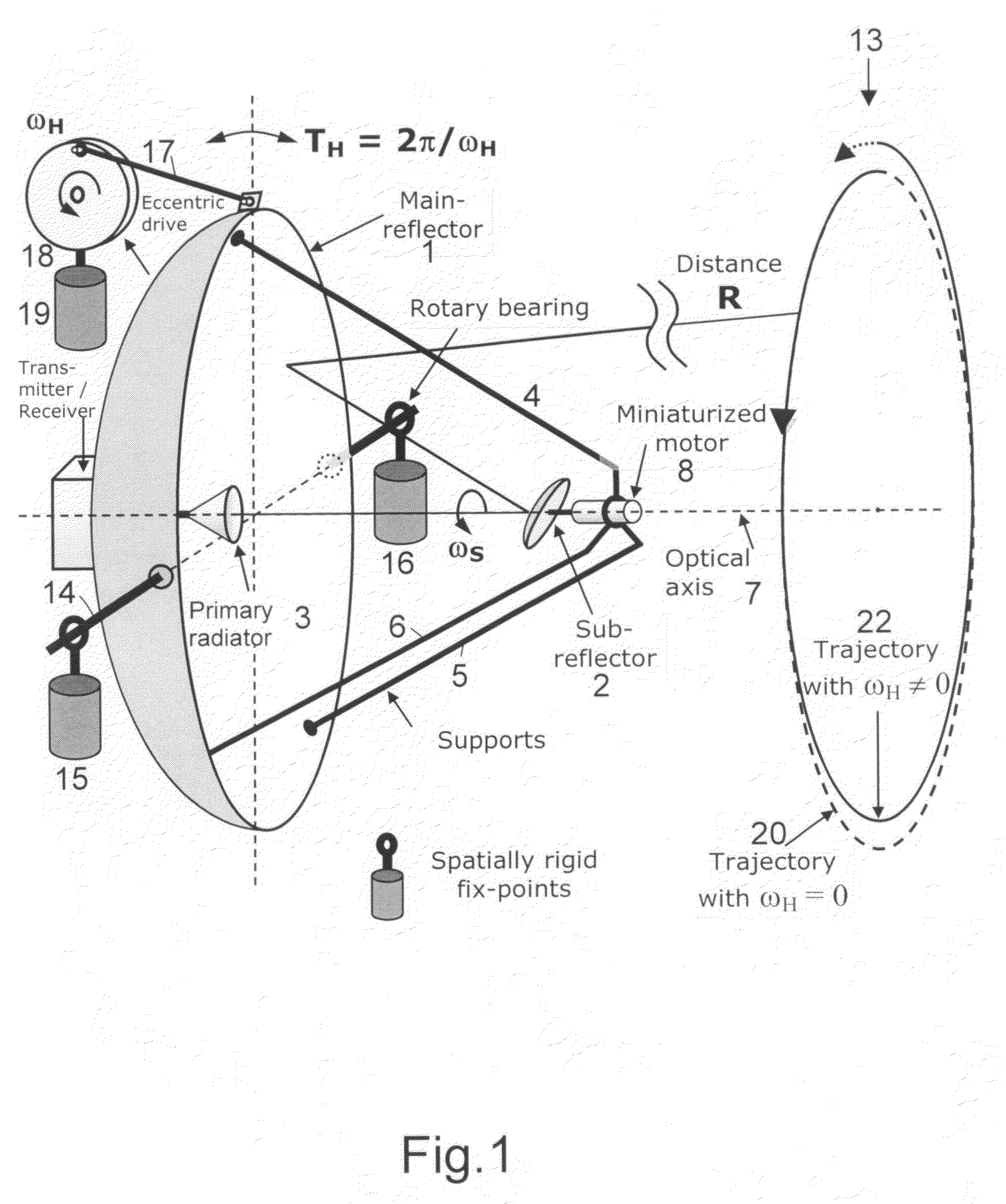
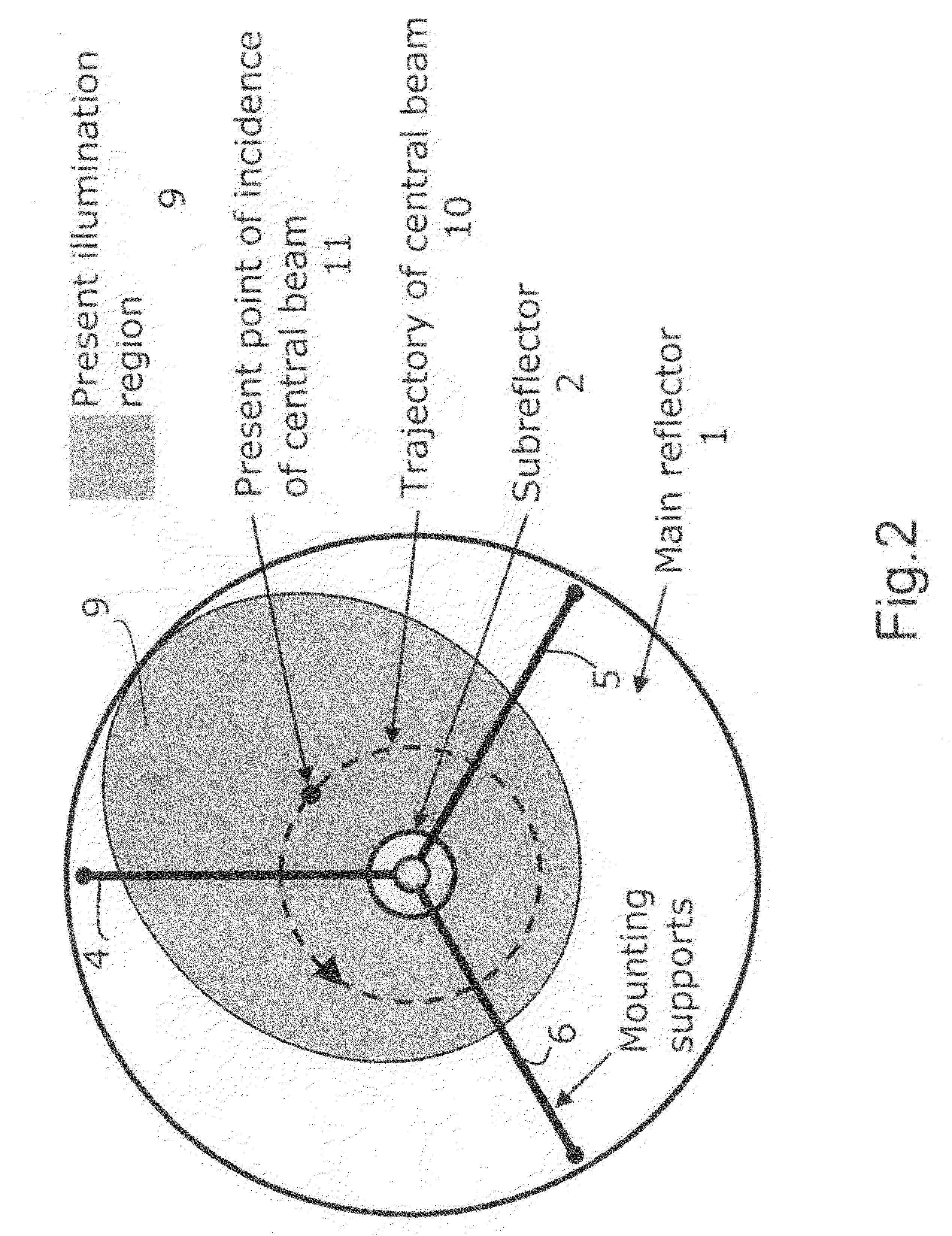
For two-dimensional imaging of scenes through continuous passive or active microwave scanning, use is made of a fully mechanized directional antenna array comprising a main reflector (1), a primary radiator array (3) and a subreflector (2) having a small size in comparison to the main reflector and being tilted relative to the optical axis (7) of the directional antenna array. First drive means (8) are operative to rotate the subreflector (2) about the optical axis (7), and second drive means (17,18) are operative to move the total directional antenna array in a direction approximately vertical to the optical axis (7). The moving speed of the subreflector (2) is very high in comparison to that of the total directional antenna array. The shape of the main reflector (1), the shape of the subreflector (2), the primary radiator (3), the distance between primary radiator and subreflector and the distance between subreflector and main reflector as focusing parameters are attuned to each other in such a manner that, for a given scene distance, an optimum focusing and an optimum size of the field of view are achieved. The focusing parameters and the moving speeds of the two drive means are set in a manner allowing for a gapless, continuous scanning of the scene with the aid of the focusing spot (12) moving at the scene distance. Applicability in remote investigation, particularly in earth observation and in safety technology.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Submicron thermal imaging method and enhanced resolution (super-resolved) AC-coupled imaging for thermal inspection of integrated circuits
ActiveUS7173245B2Simple and inexpensive temperature measurementImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionImage detection
Methods and apparatus for non-contact thermal measurement which are capable of providing sub micron surface thermal characterization of samples, such as active semiconductor devices. The method obtains thermal image information by reflecting a light from a surface of a device in synchronous with the modulation of the thermal excitation and then acquiring and processing an AC-coupled thermoreflective image. The method may be utilized for making measurements using different positioning techniques, such as point measurements, surface scanning, two-dimensional imaging, and combinations thereof. A superresolution method is also described for increasing the resultant image resolution, based on multiple images with fractional pixel offsets, without the need to increase the resolution of the image detectors being utilized. The thermoreflective method provides a spatial resolution better than current infrared cameras, operates within a wide temperature range, and is capable of a thermal resolution on the order of 10 mK°.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Ultrasound-imaging systems and methods for a user-guided three-dimensional volume-scan sequence
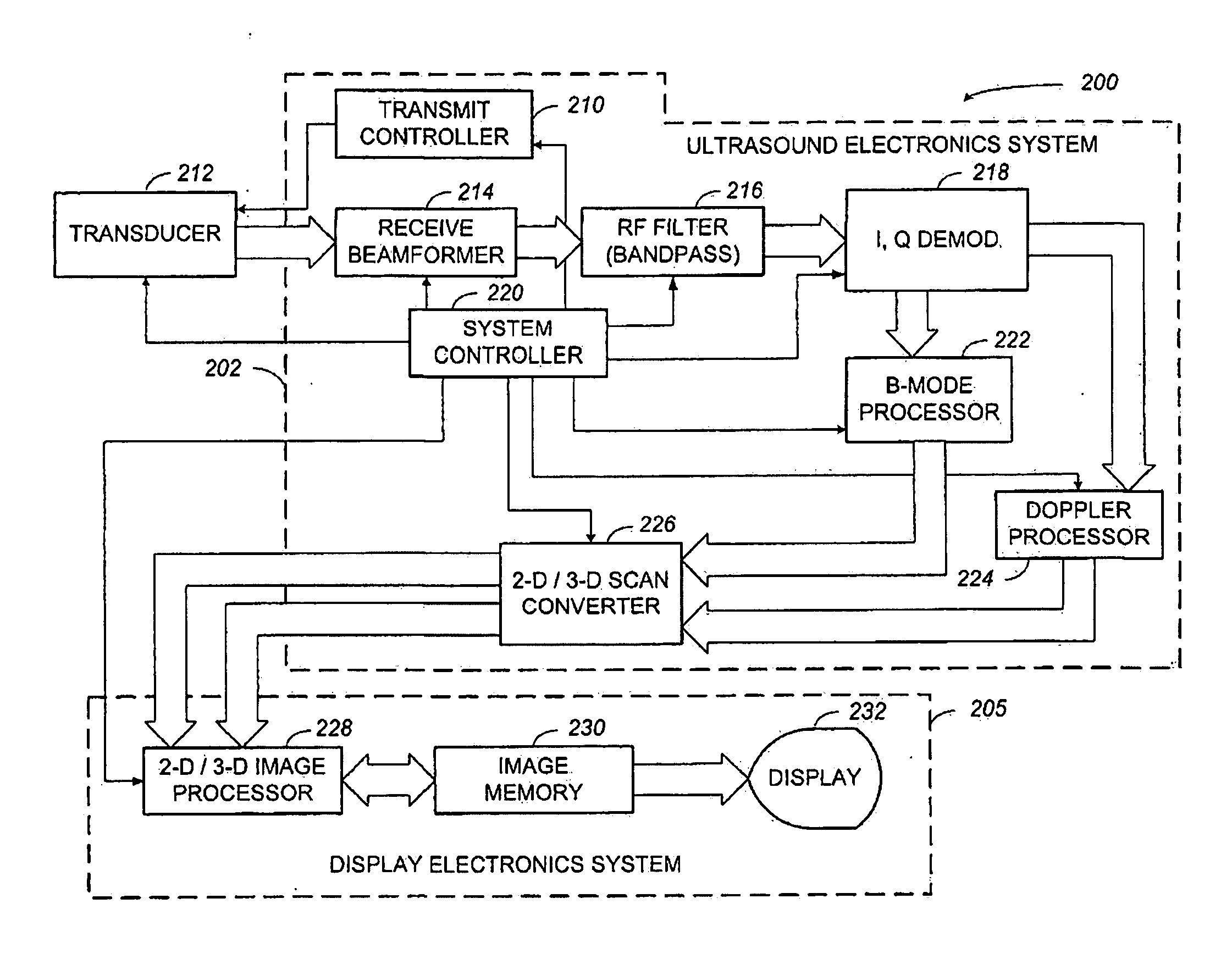
InactiveUS20090203996A1Frame rate can be optimizedInfluence the rate of target-volume acquisitionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingSonification
An ultrasound-imaging system and method is provided that permits an operator to acquire an image of a volume-of-interest in a time critical fashion, that is capable of referencing the volume rendering to a standard two-dimensional imaging mode, and permits the operator to selectively choose a number of display-mode parameters that result in an operator directed view of the volume-of-interest. The ultrasound-imaging system comprises an input device configured to receive a plurality of imaging parameters and a controller in communication with the input device. The ultrasound-imaging system generates an operator-directed transmit-beam scan sequence in response to the imaging parameters and transmits a spatially modified transmit-beam scan sequence over a portion of the volume-scan range of the ultrasound-imaging system. Moreover, the ultrasound-imaging system provides the flexibility for an operator to direct a plurality of operator-configurable multi-dimensional views.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
SAR (synthetic aperture radar) tomography super-resolution imaging method
InactiveCN102645651ASolve the problem of fewLow number of solutionsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarImage resolution
The invention discloses an SAR (synthetic aperture radar) tomography super-resolution imaging method. The SAR tomography super-resolution imaging method includes registering obtained two-dimensional imaging results of various SAR tomography baselines, creating height-direction signals pixel by pixel according to the sequence of the baselines, realizing frequency modulation correction and constructing a redundancy matrix; and modeling a height-direction imaging problem into a sparse signal reconstruction problem according to the characteristic of sparsity of height-direction scattering coefficients, computing a sparse solution of the spares signal reconstruction problem by means of iteration by the aid of the constraint condition of the minimum weighted norm, and realizing height-dimensional imaging of an object. The method is applied to SAR tomography height-dimensional imaging, and problems that the quantity of two-dimensional SAR images in the same area and ( / or) trajectory distribution is uneven, and only a few parts of trajectory intervals (baselines) meet the Nyquist sampling theory are solved. In addition, by the aid of the method, energy of the object is more concentrated, namely, the resolution is improved, and the problem that the quantity of baselines is small is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Radar target two-dimensional imaging method based on vortex electromagnetic wave
ActiveCN106526589AImaging RealizationHigh angular imaging resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal classificationMultiple signal classification
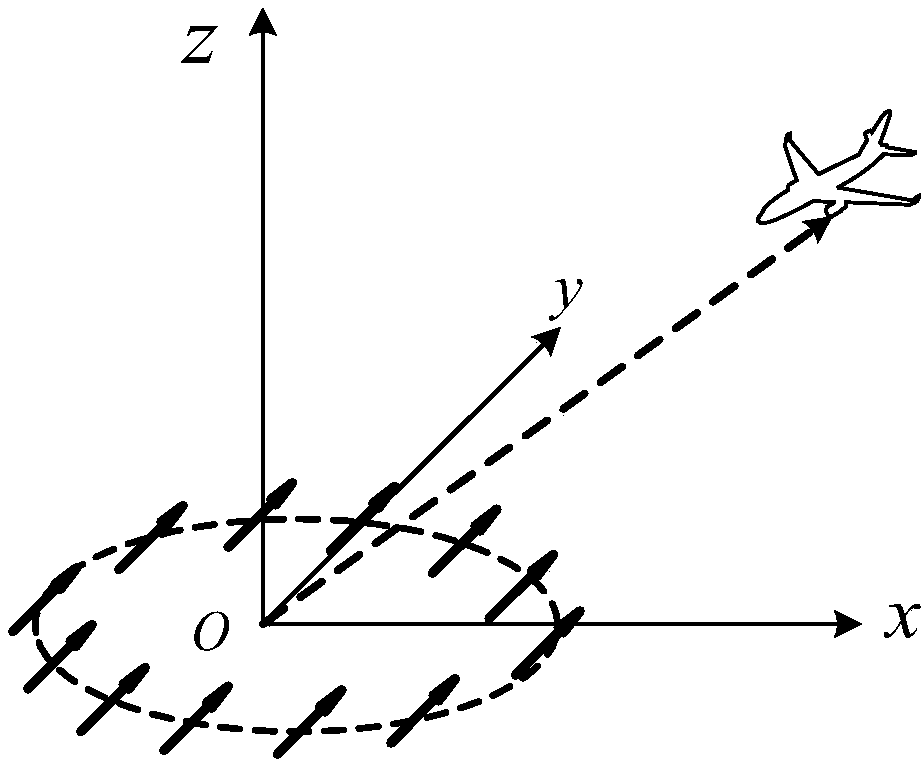
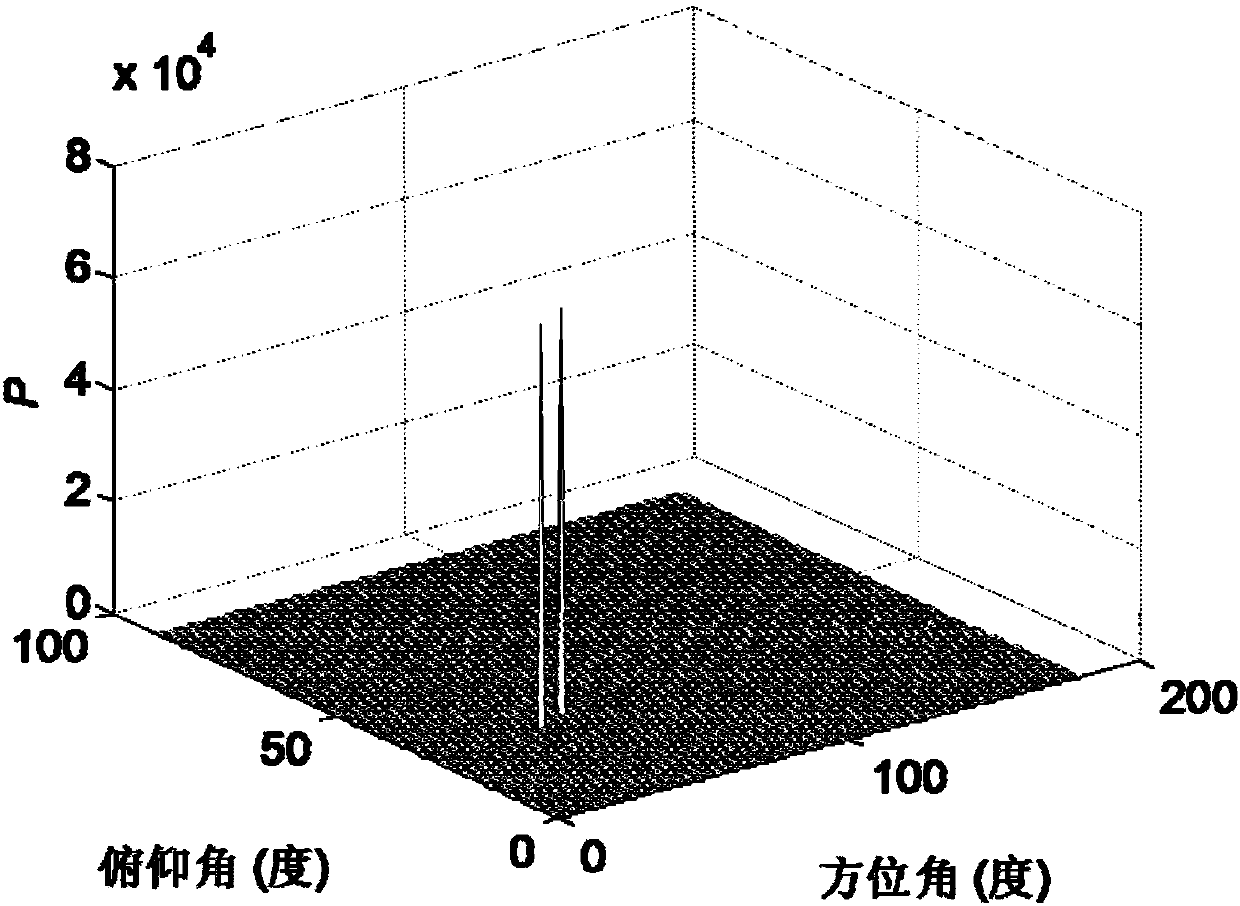
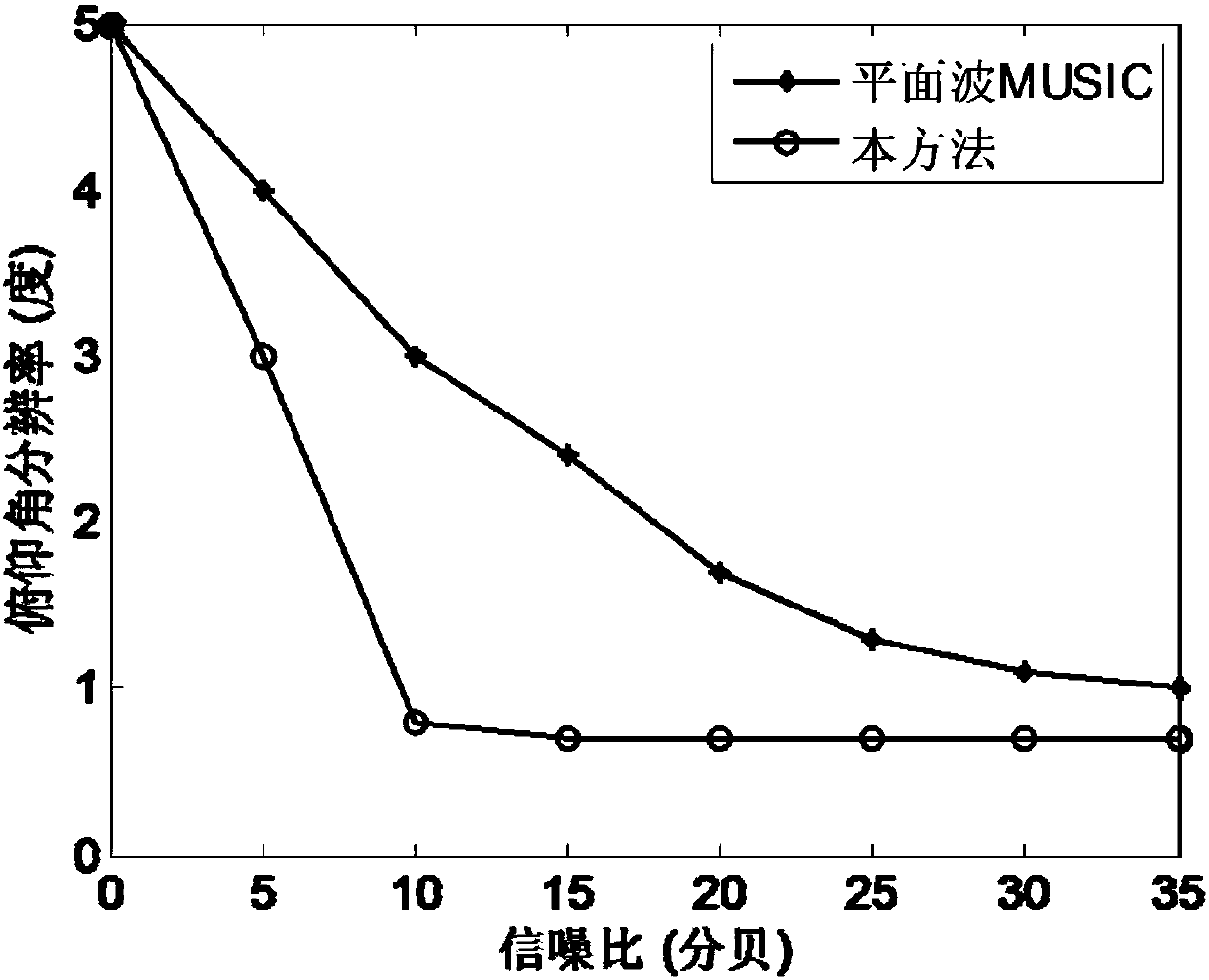
The invention discloses a radar target two-dimensional imaging method based on vortex electromagnetic waves. The radar target two-dimensional imaging method is based on an echo model of ideal scattering points under projection of the vortex electromagnetic waves generated by a uniform loop antenna array, performs orbital angular momentum (OAM) mode sampling on radar target echo signals and calculates a related function, adopts a multiple signal classification (MUSIC) algorithm to obtain a spatial spectrum function, and carries out two-dimensional spectrum peak searching to realize two-dimensional joint detection of a pitch angle and an azimuth angle of a radar target. Compared with a traditional direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation scheme based on a plane wave MUSIC algorithm, the radar target two-dimensional imaging method provided by the invention can realize higher angular resolution; and compared with an existing radar target azimuth angle imaging scheme based on vortex electromagnetic waves, the radar target two-dimensional imaging method can realize the imaging of the target pitch angle without increasing hardware cost, and is of great reference significance to the modern radar design of the new system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com