Patents
Literature
60 results about "Cardiac electrophysiology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cardiac electrophysiology is the science of elucidating, diagnosing, and treating the electrical activities of the heart. The term is usually used in a clinical context to describe studies of such phenomena by invasive (intracardiac) catheter recording of spontaneous activity as well as of cardiac responses to programmed electrical stimulation (PES), see Clinical cardiac electrophysiology. Cardiac electrophysiology also encompasses basic research and translational research components. Someone who studies cardiac electrophysiology, either clinically or solely through research, is known as a cardiac electrophysiologist.
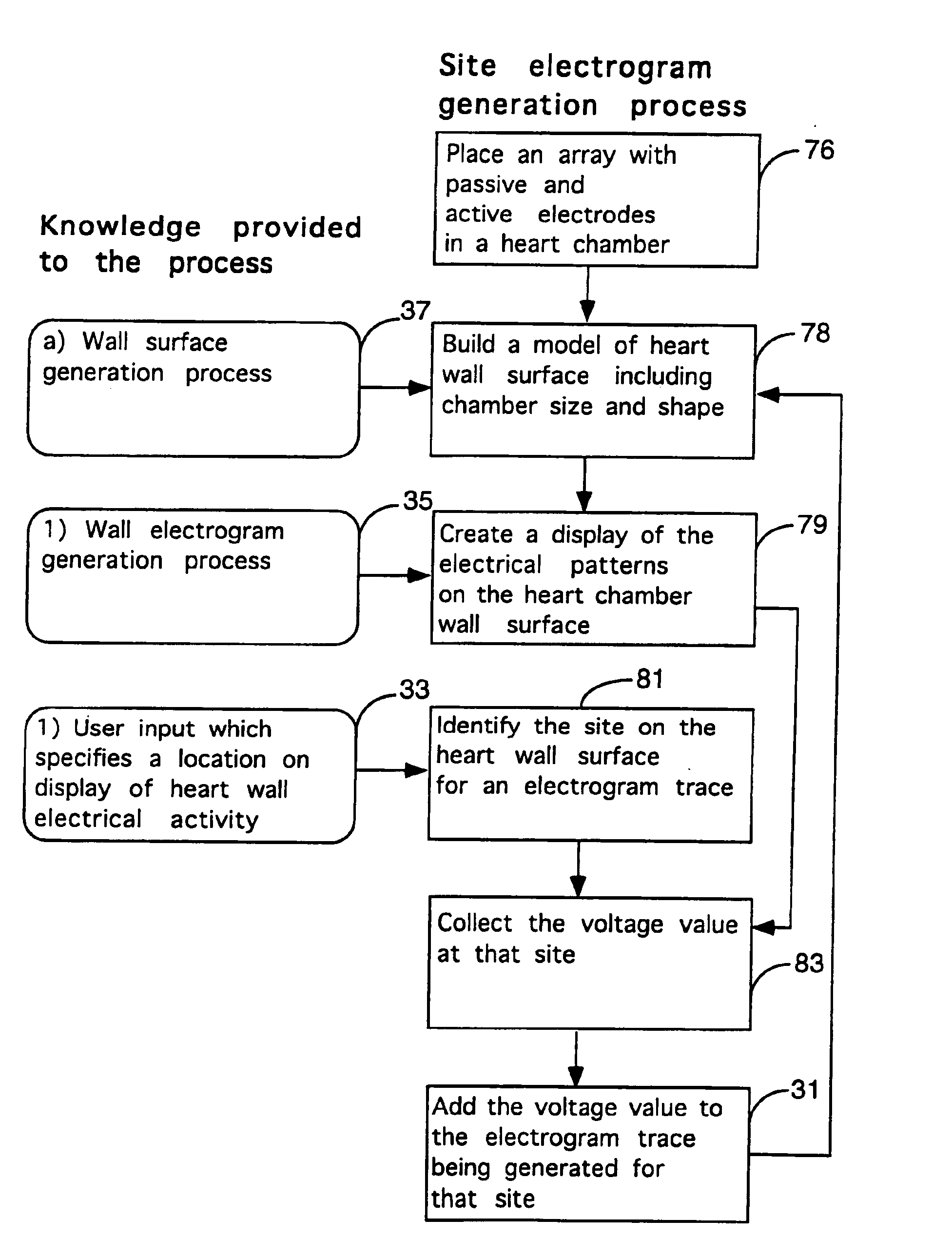
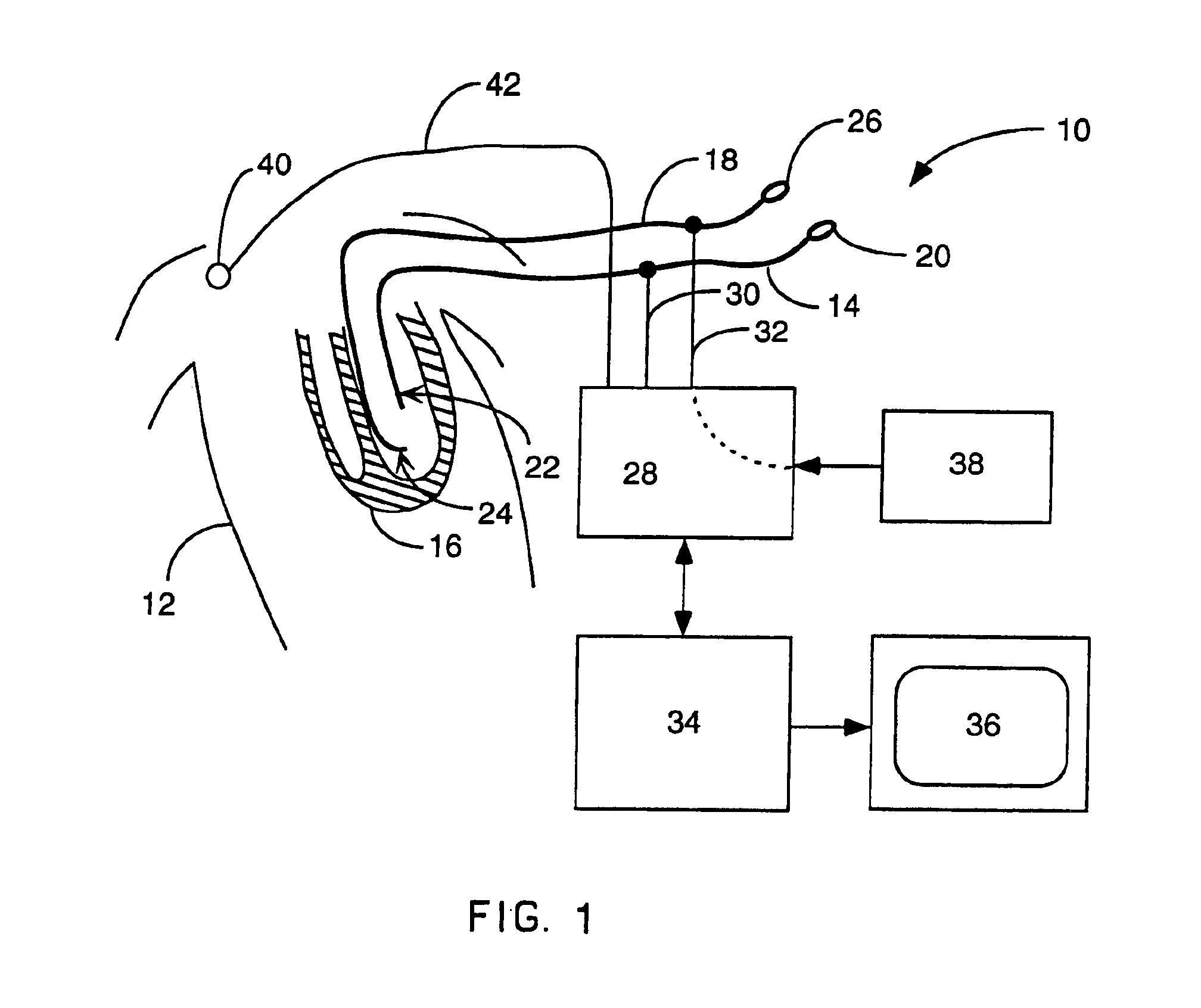
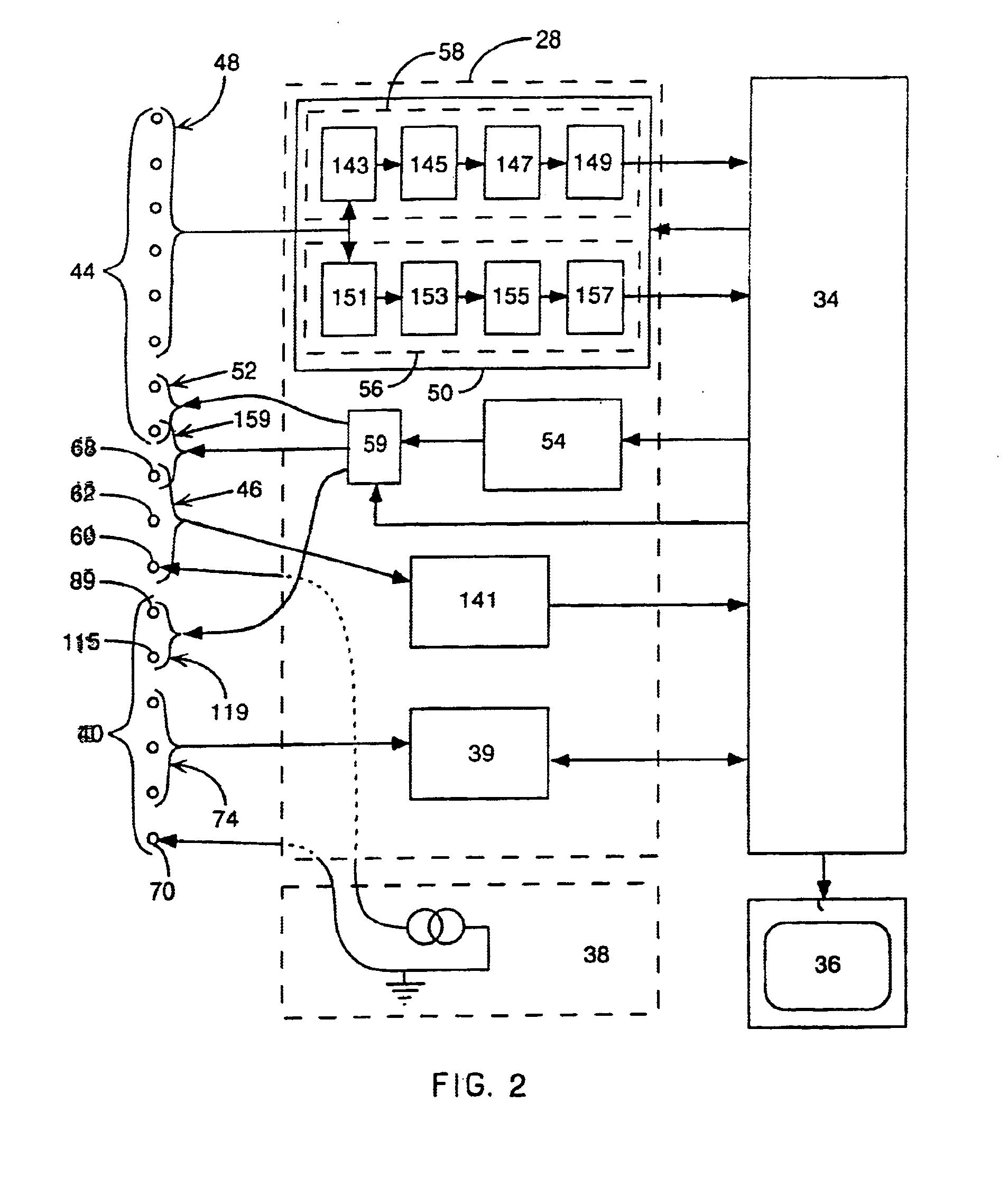
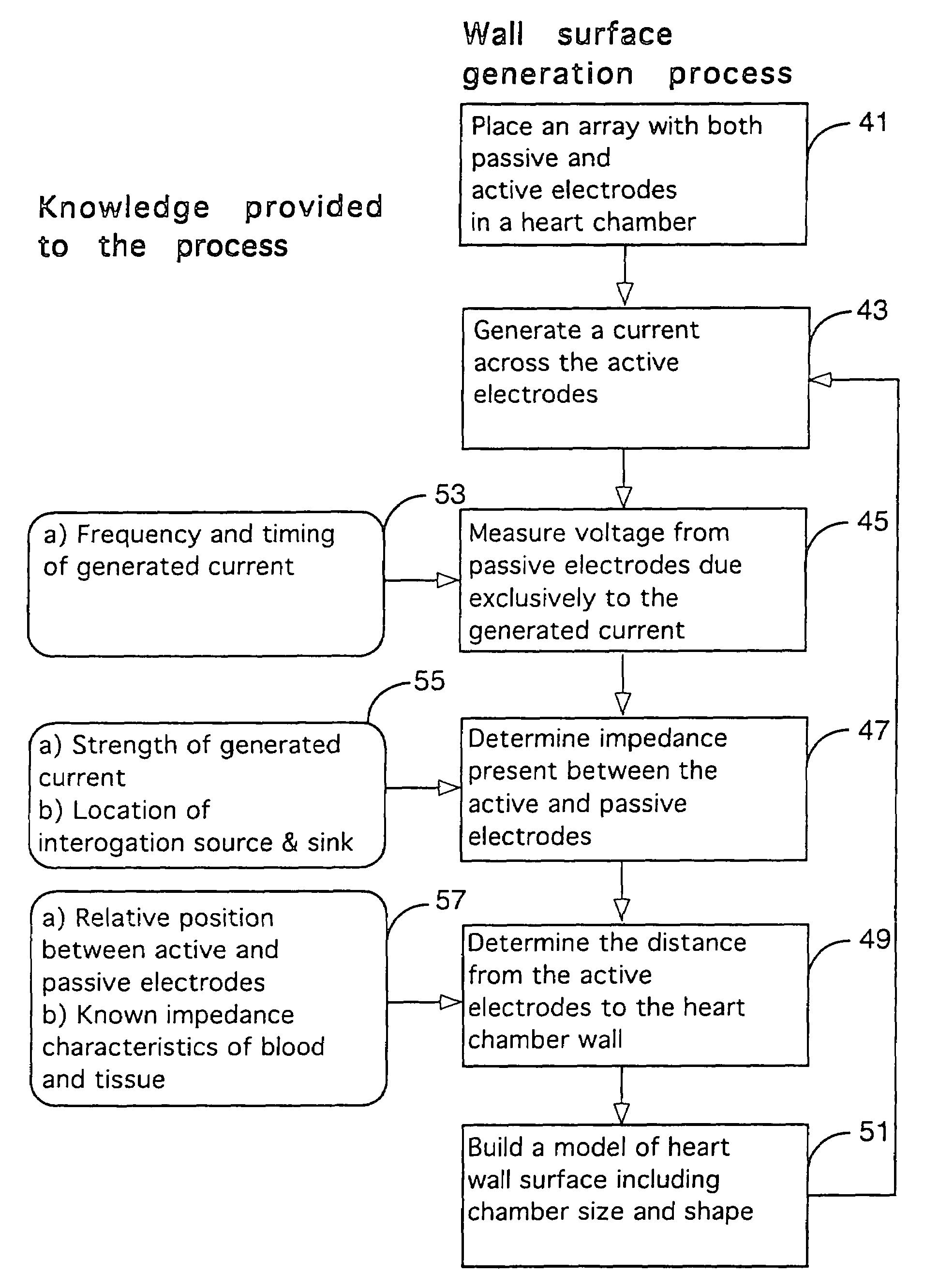
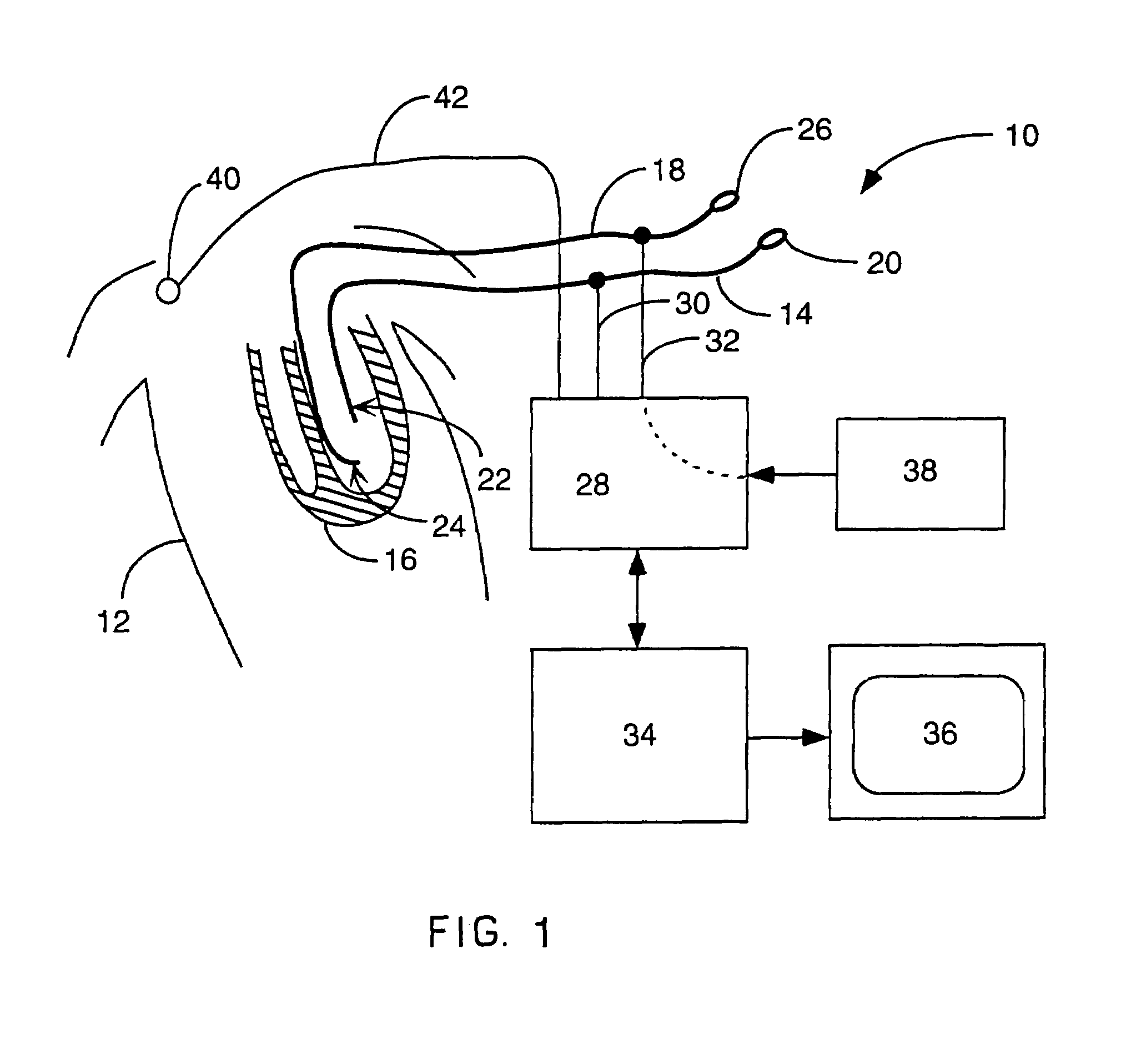
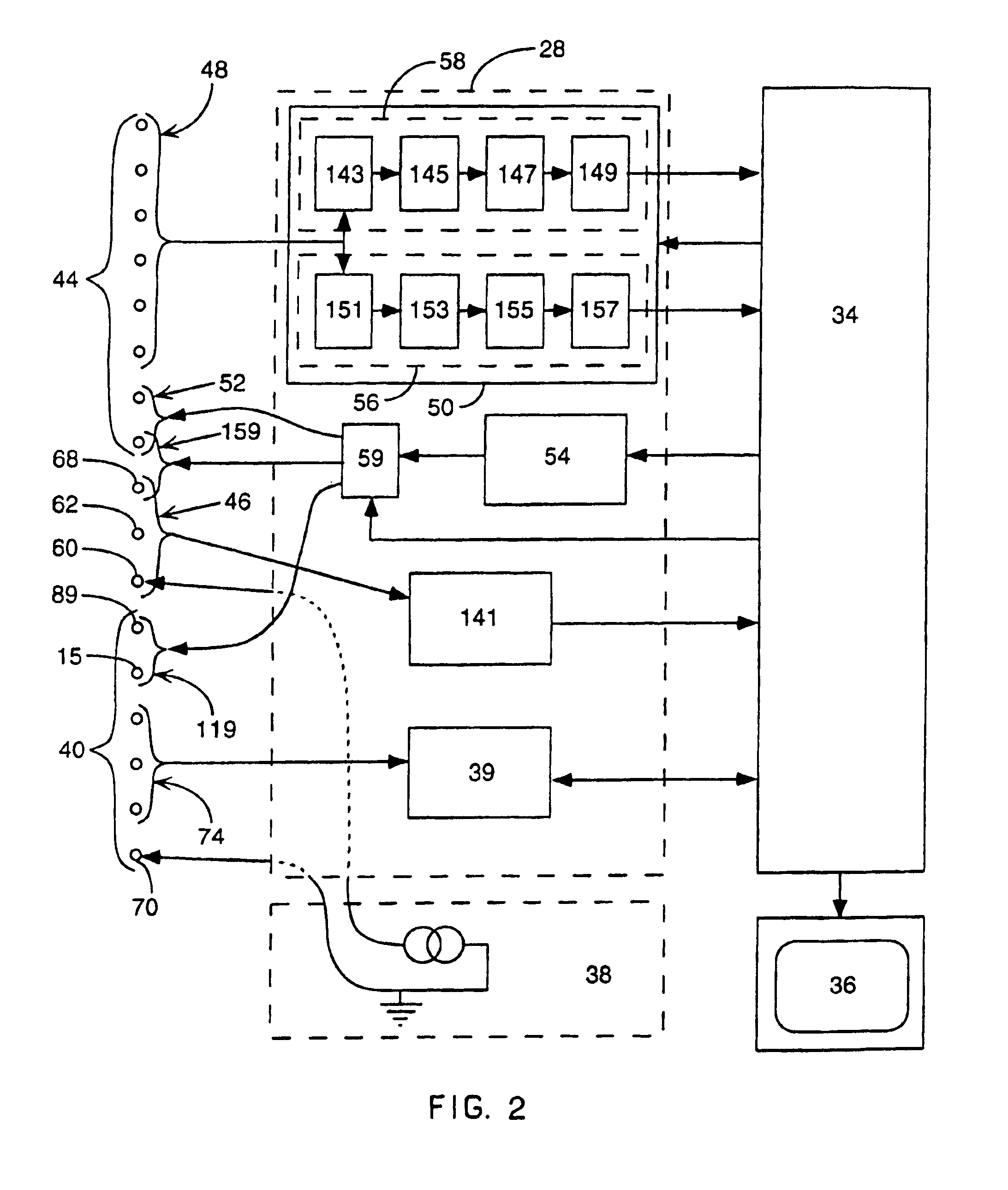
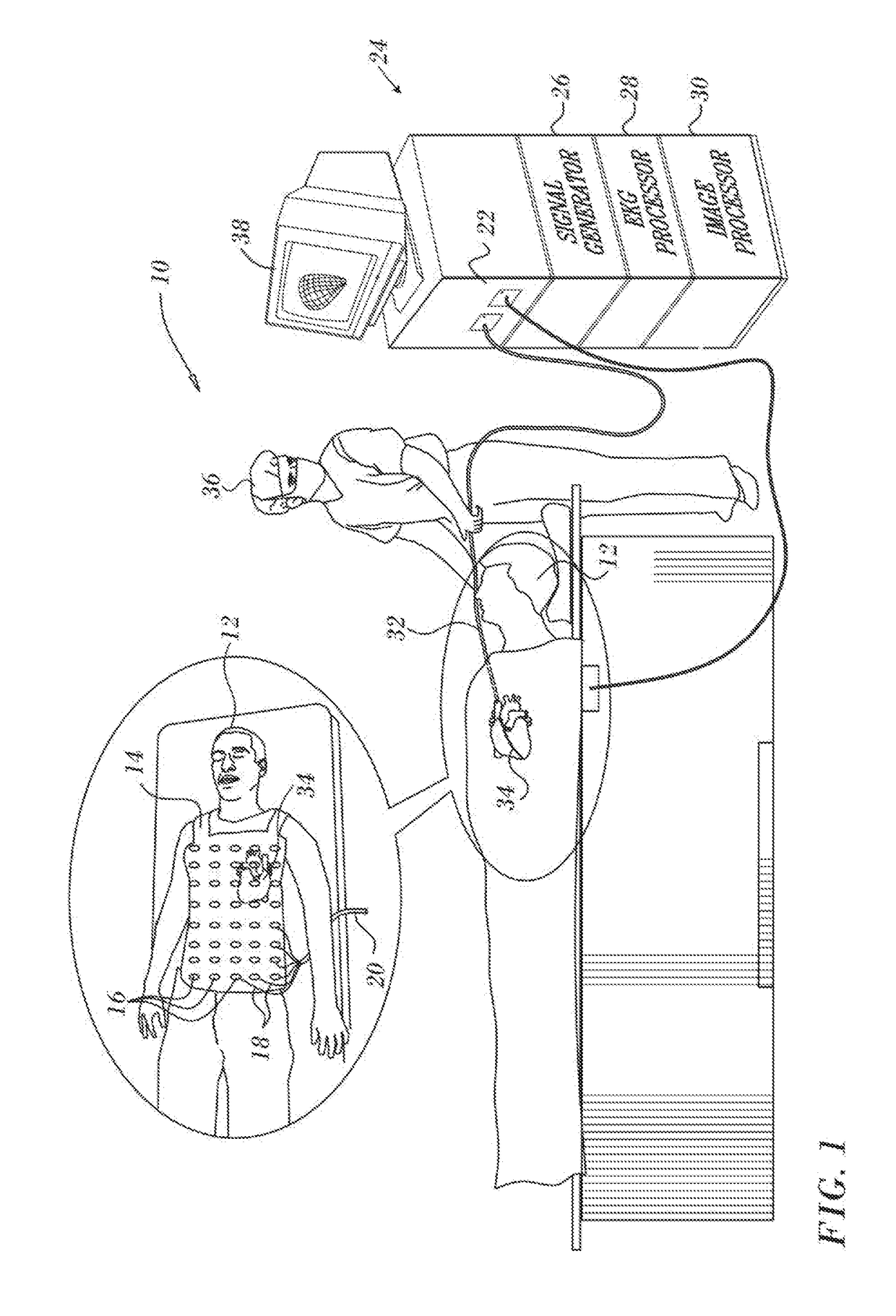
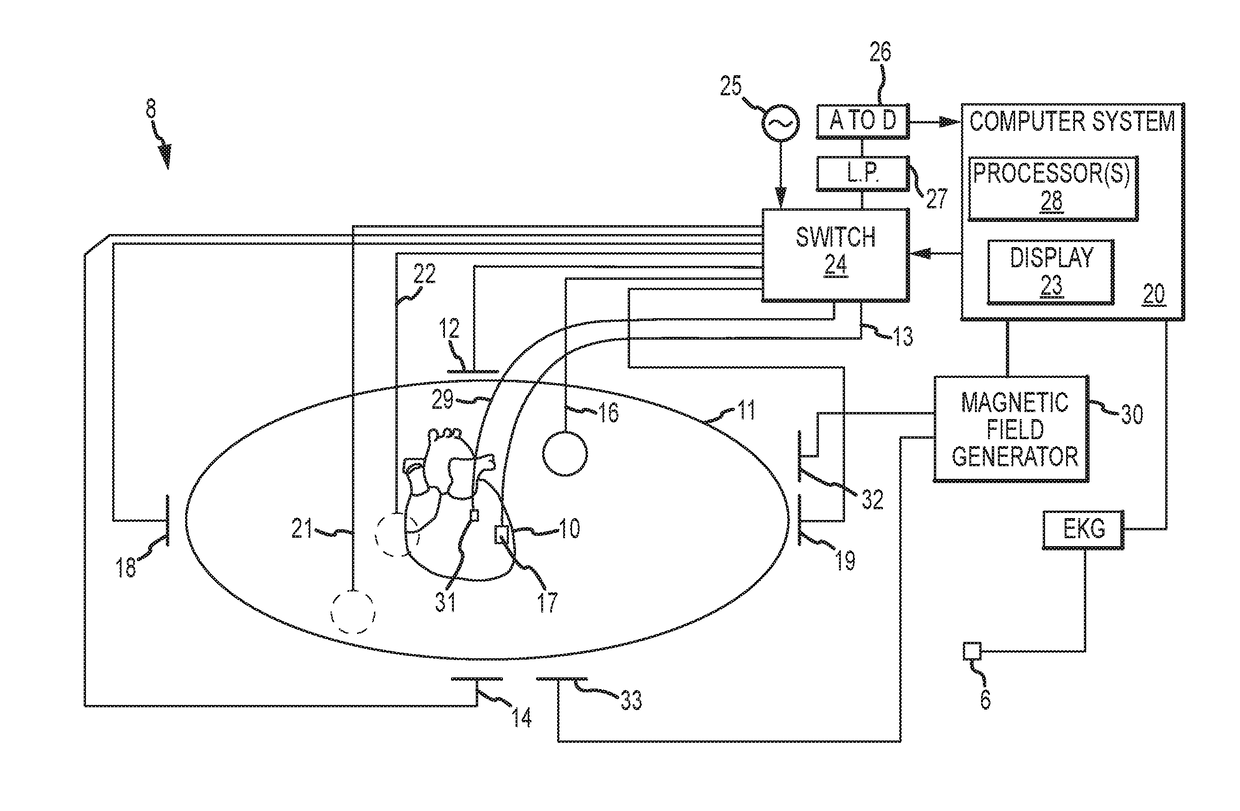
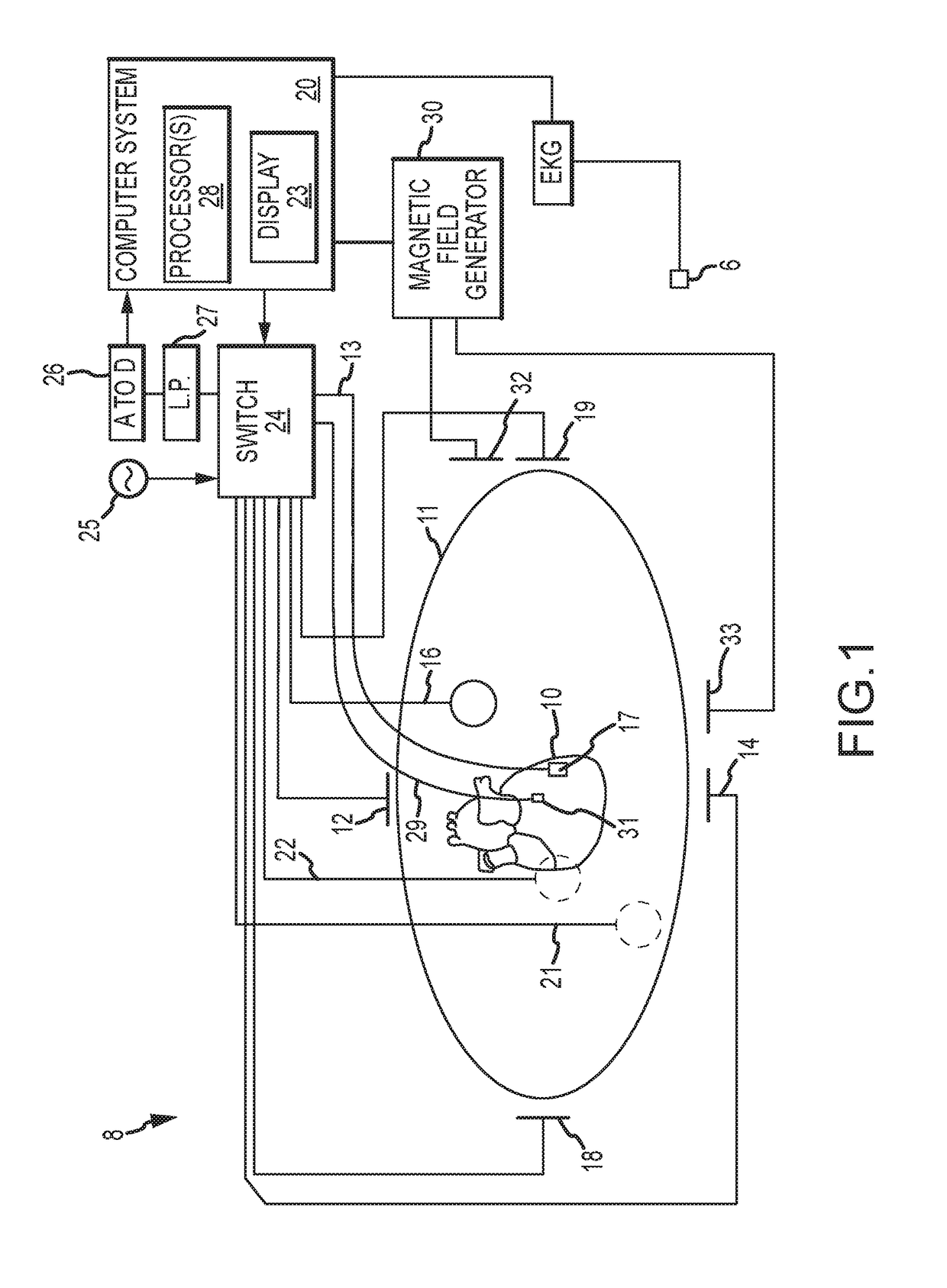
Method for mapping heart electrophysiology
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
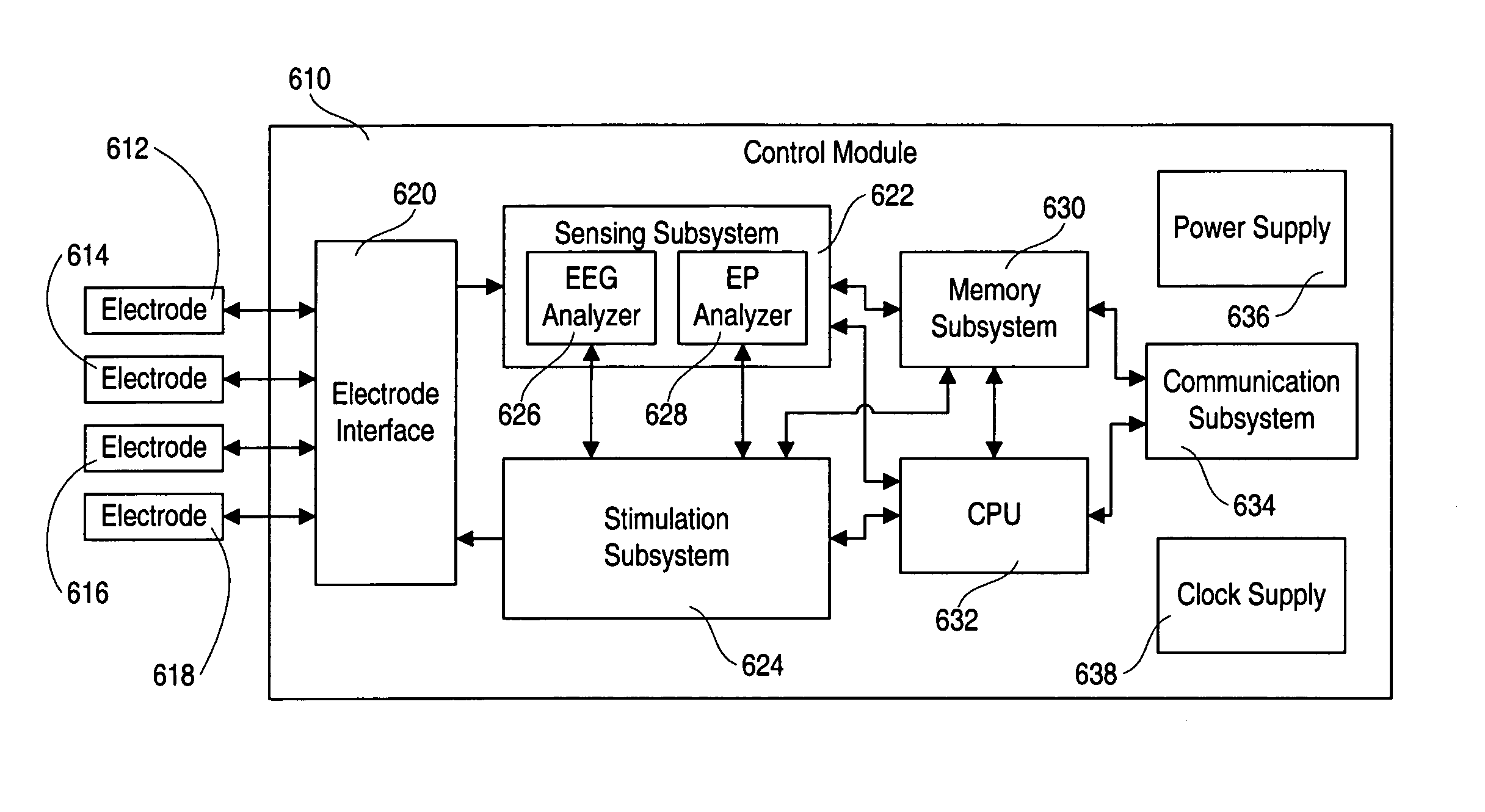
Predicting susceptibility to neurological dysfunction based on measured neural electrophysiology
InactiveUS7089059B1Improve rendering capabilitiesEasy to detectElectroencephalographyElectrotherapySeizure clustersMedicine
A system and method for determining and predicting a patient's susceptibility to neurological dysfunction based on measured electrophysiological parameters employs a self-contained implantable device with depth electrodes implanted in desired locations in the patient's brain. The patient's neurological tissue is stimulated to determine excitability and refractoriness (or inhibition period) parameters, which are employed to identify susceptibility to abnormal neurological activity, particularly epileptic seizures.
Owner:NEUROPACE
Method for measuring heart electrophysiology
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
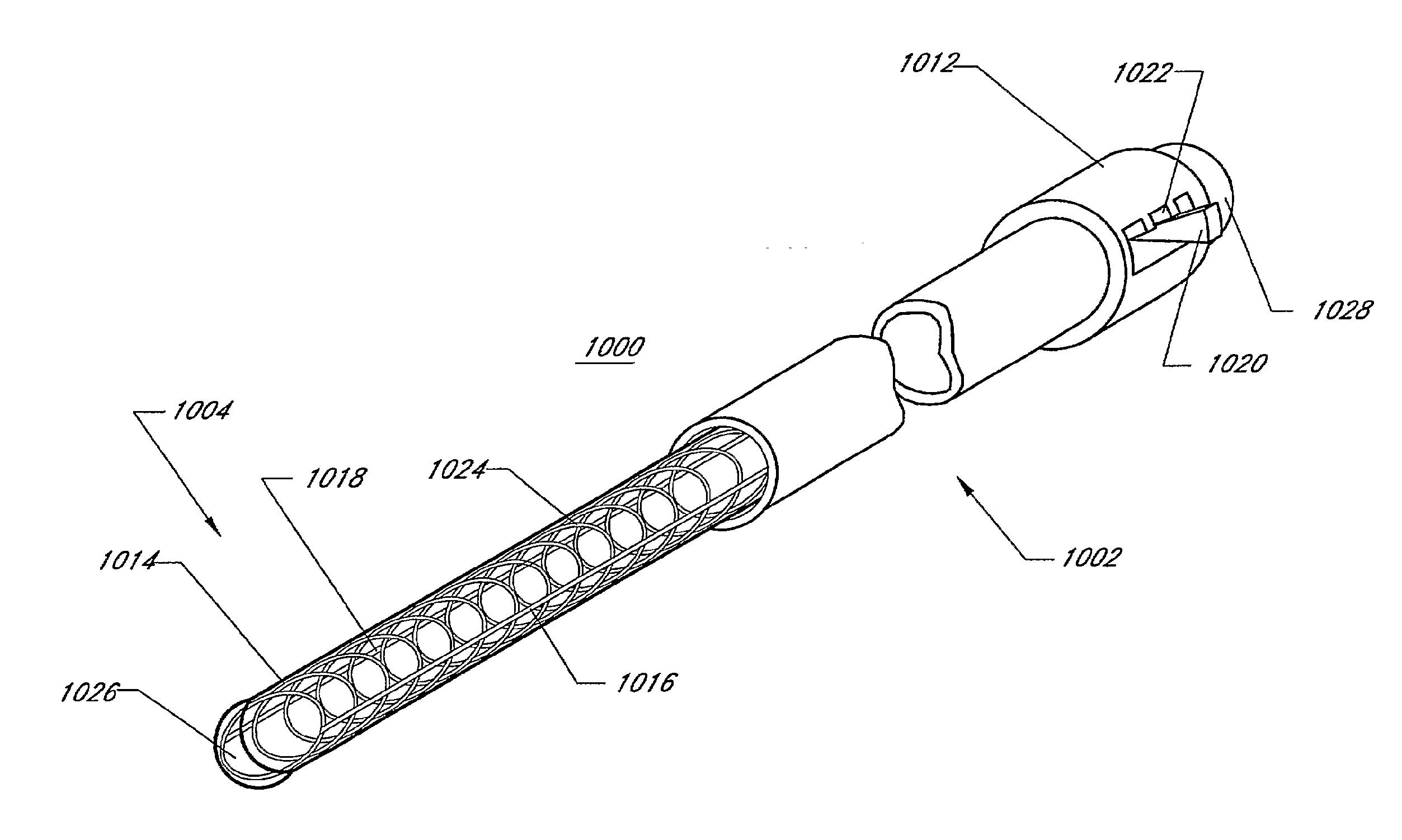
Expandable transluminal sheath
InactiveUS20060135981A1Minimize strain and catchingPrevent shrinkageGuide needlesBalloon catheterBiomedical engineeringCardiac electrophysiology
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, low cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration and expanded using a radial dilatation device. In an exemplary application, the sheath is utilized to provide access for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures such as ureteroscopy, cardiac electrophysiology, gastroenterology, and spinal access.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
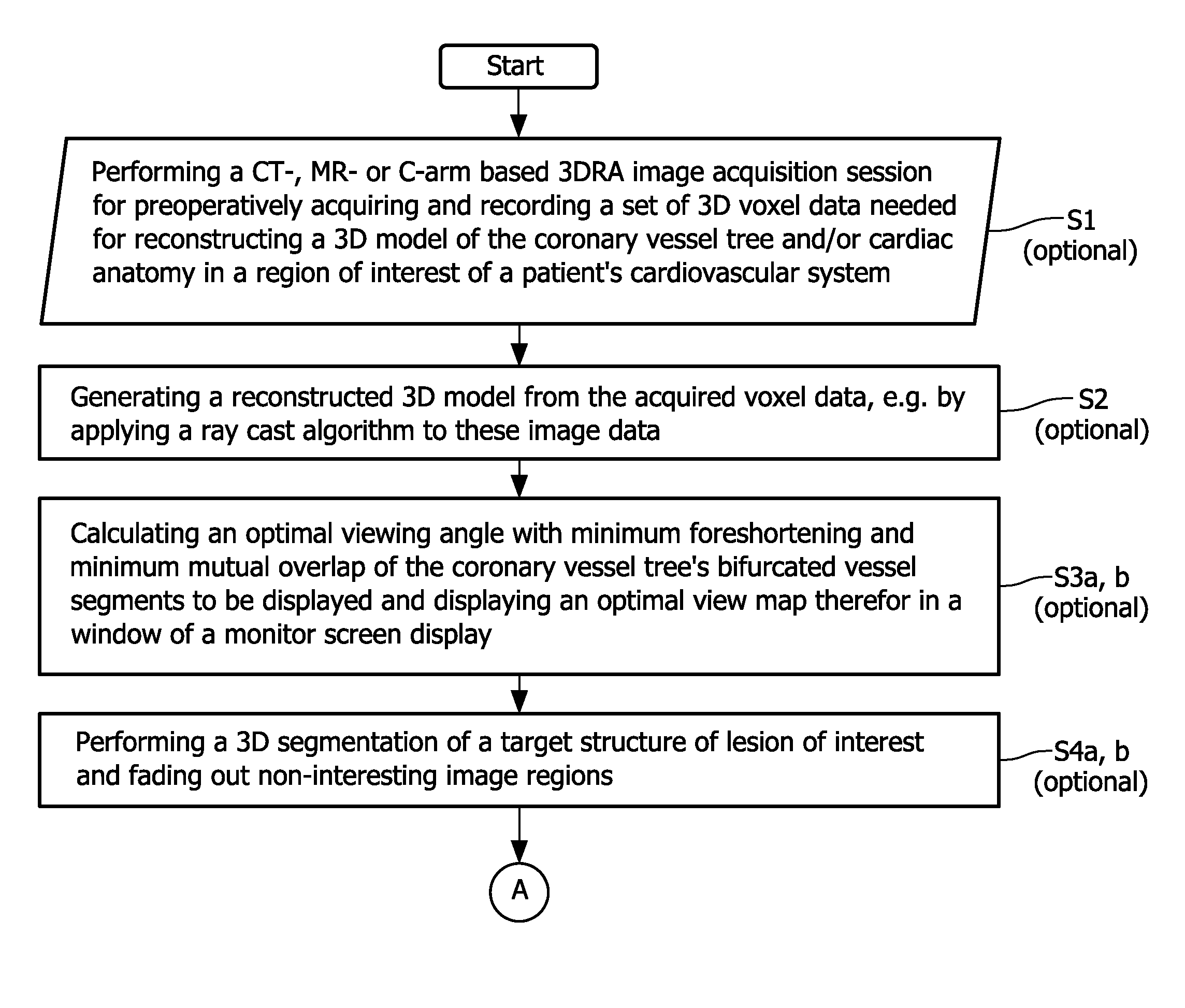
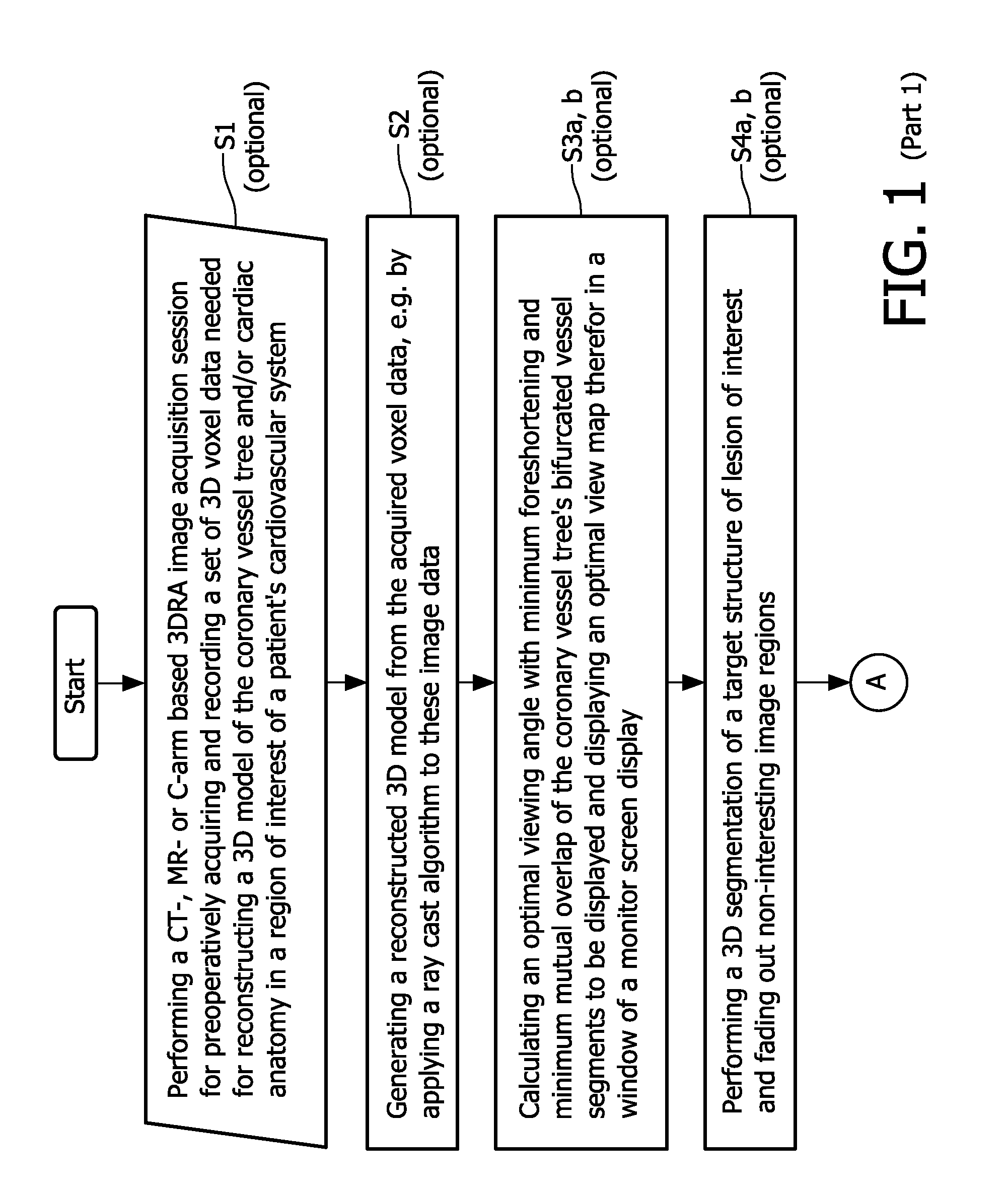
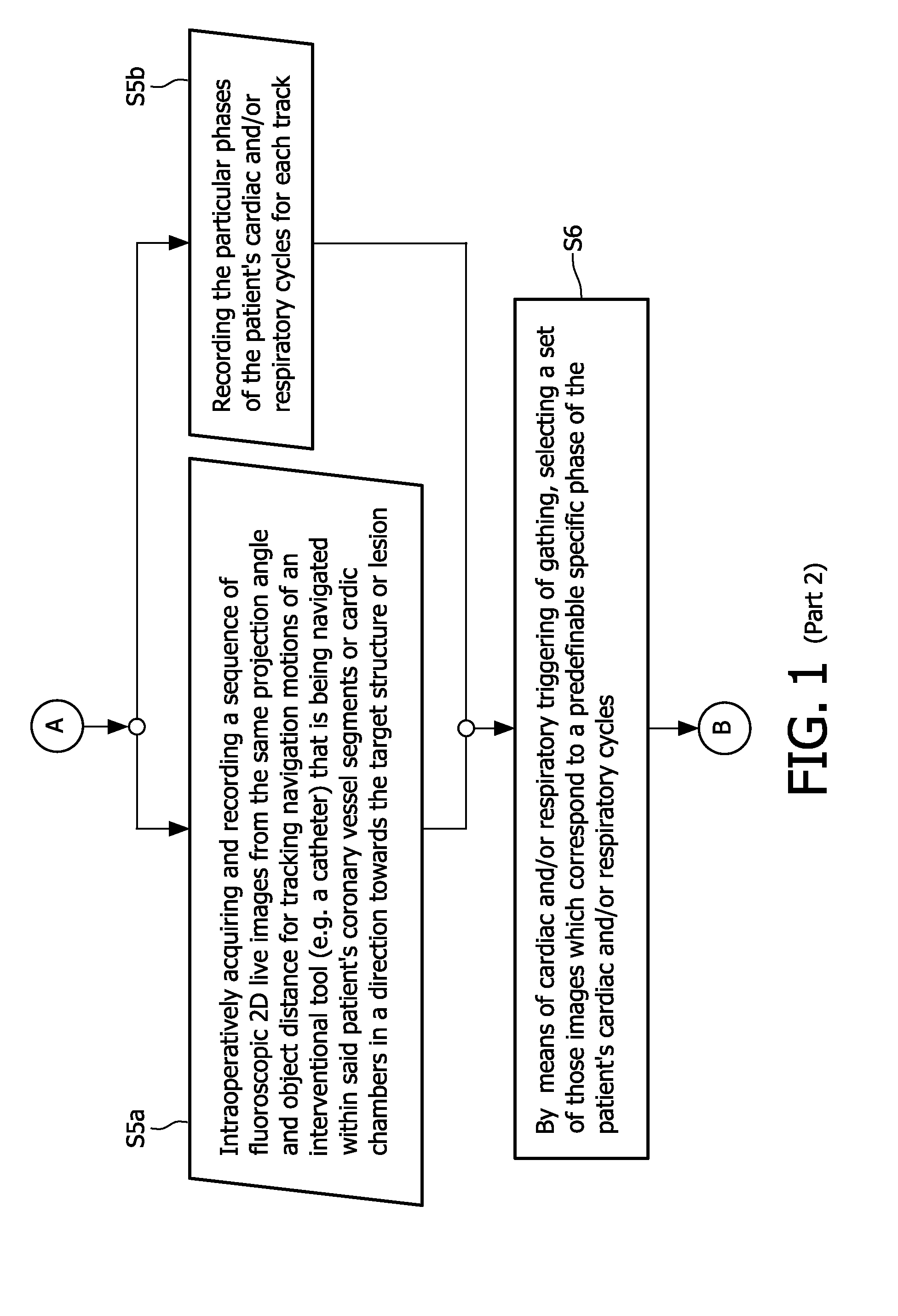
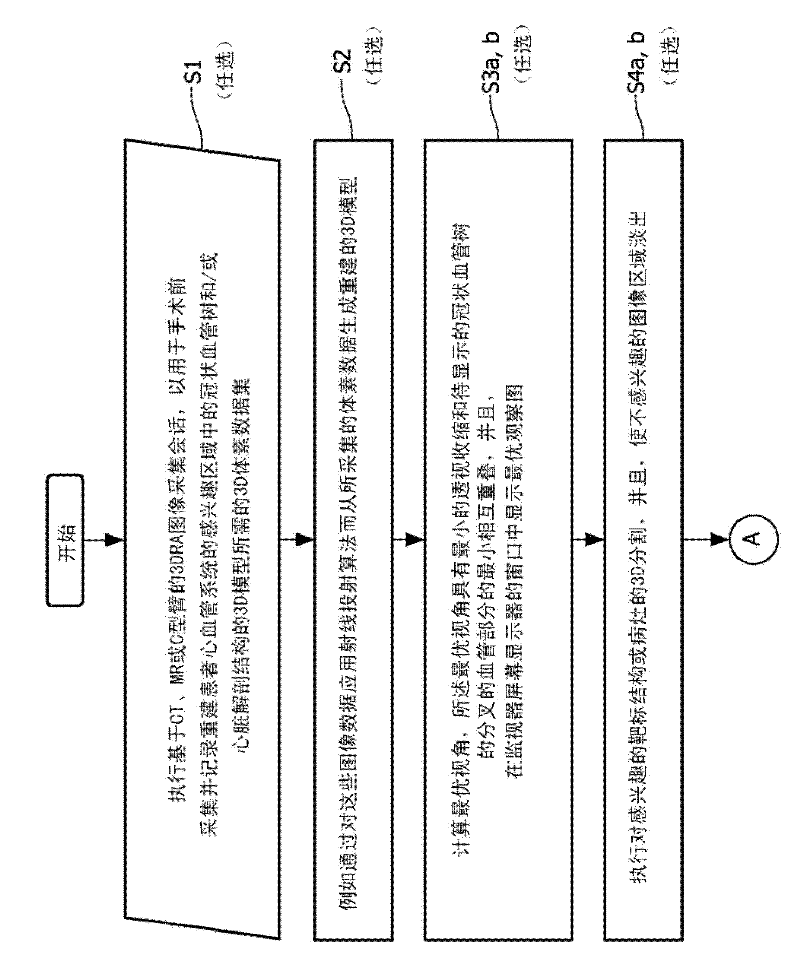
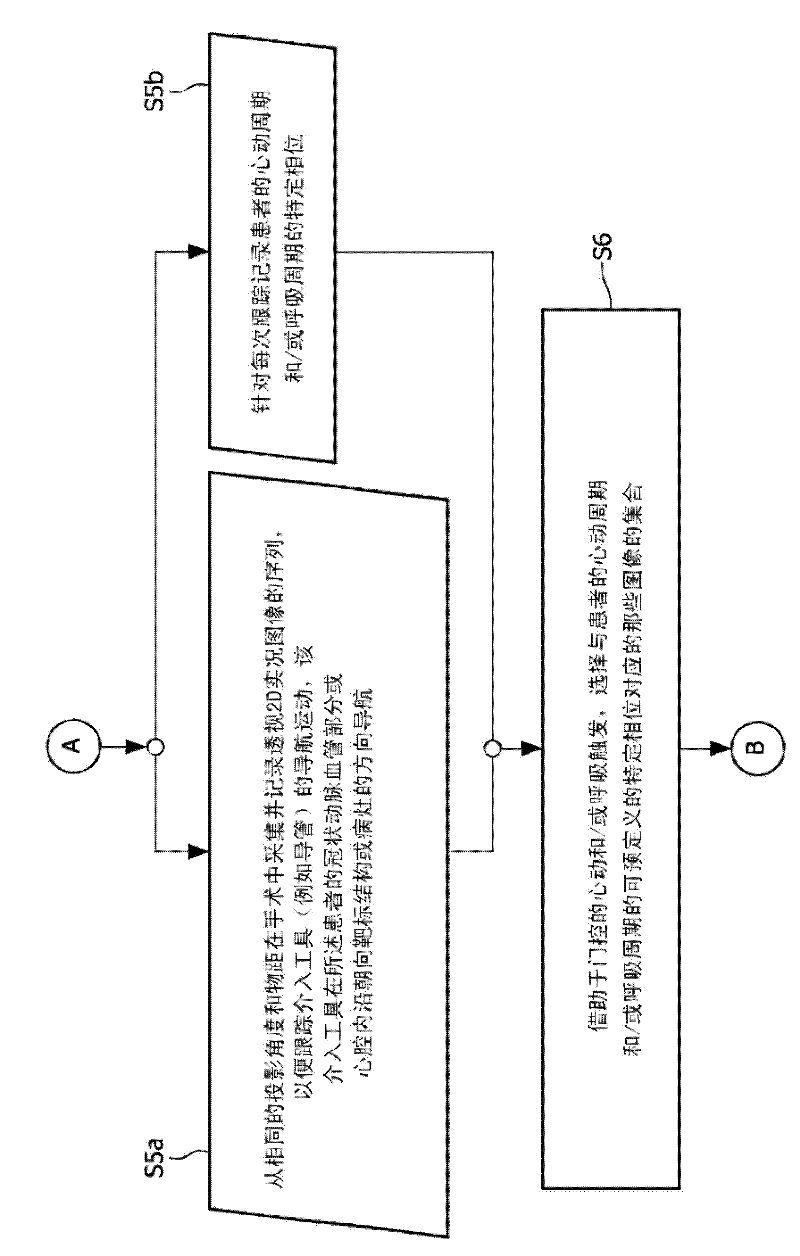
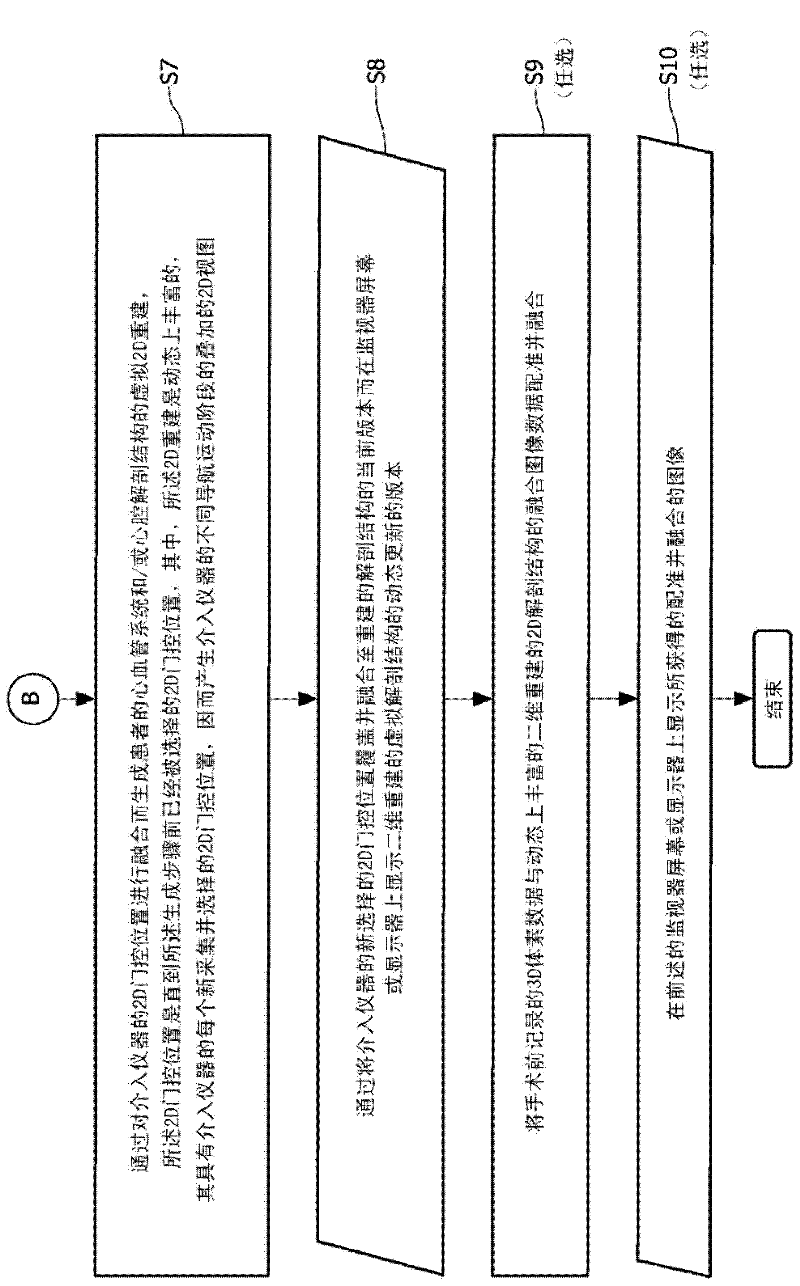
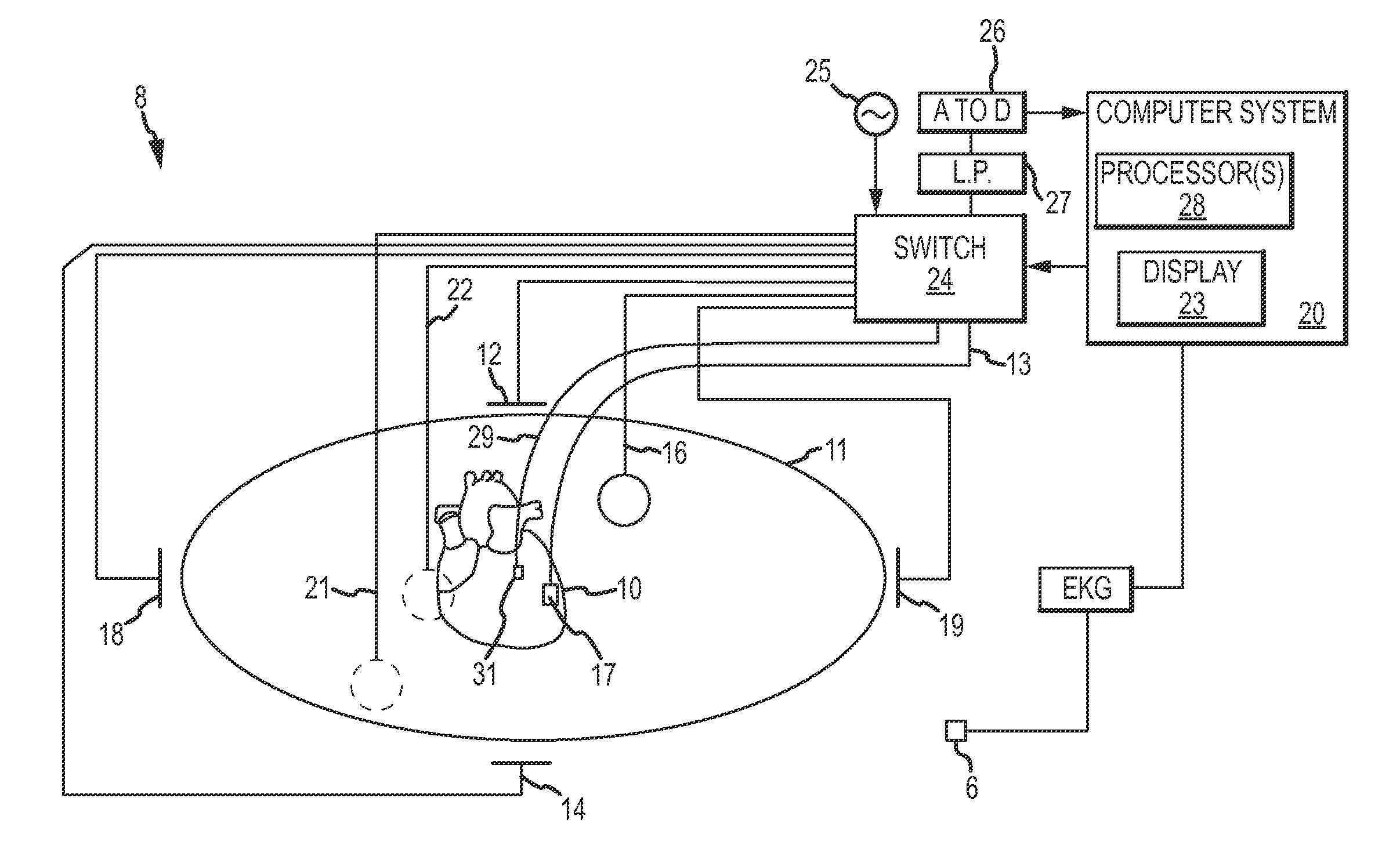
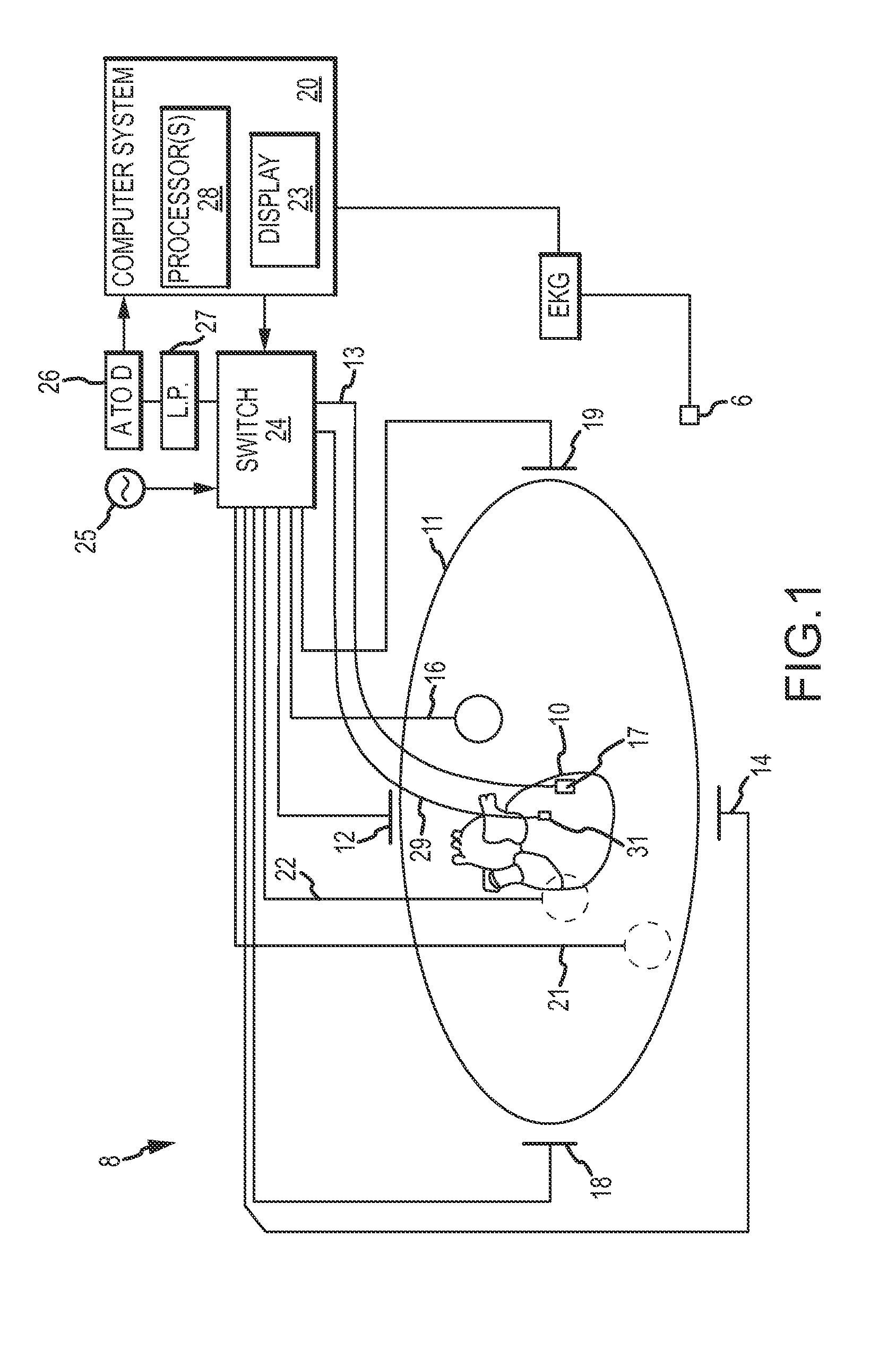
Cardiac and or respiratory gated image acquisition system and method for virtual anatomy enriched real time 2d imaging in interventional radiofrequency ablation or pace maker replacement procecure
ActiveUS20110201915A1Improve accuracyReduce inaccuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac pacemaker electrodePacemaker Placement
The present invention refers to the field of cardiac electrophysiology (EP) and, more specifically, to image-guided radio frequency ablation and pacemaker placement procedures. For those procedures, it is proposed to display the overlaid 2D navigation motions of an interventional tool intraoperatively obtained from the same projection angle for tracking navigation motions of an interventional tool during an image-guided intervention procedure while being navigated through a patient's bifurcated coronary vessel or cardiac chambers anatomy in order to guide e.g. a cardiovascular catheter to a target structure or lesion in a cardiac vessel segment of the patient's coronary venous tree or to a region of interest within the myocard. In such a way, a dynamically enriched 2D reconstruction of the patient's anatomy is obtained while moving the interventional instrument. By applying a cardiac and / or respiratory gating technique, it can be provided that the 2D live images are acquired during the same phases of the patient's cardiac and / or respiratory cycles. Compared to prior-art solutions which are based on a registration and fusion of image data independently acquired by two distinct imaging modalities, the accuracy of the two-dimensionally reconstructed anatomy is significantly enhanced.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
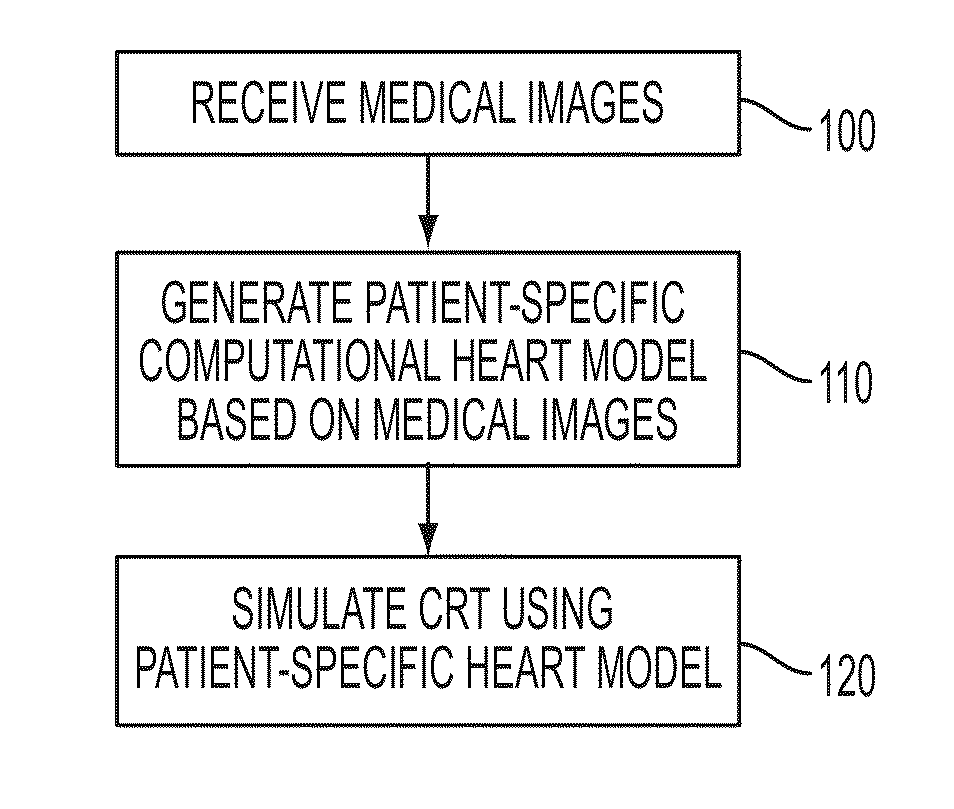
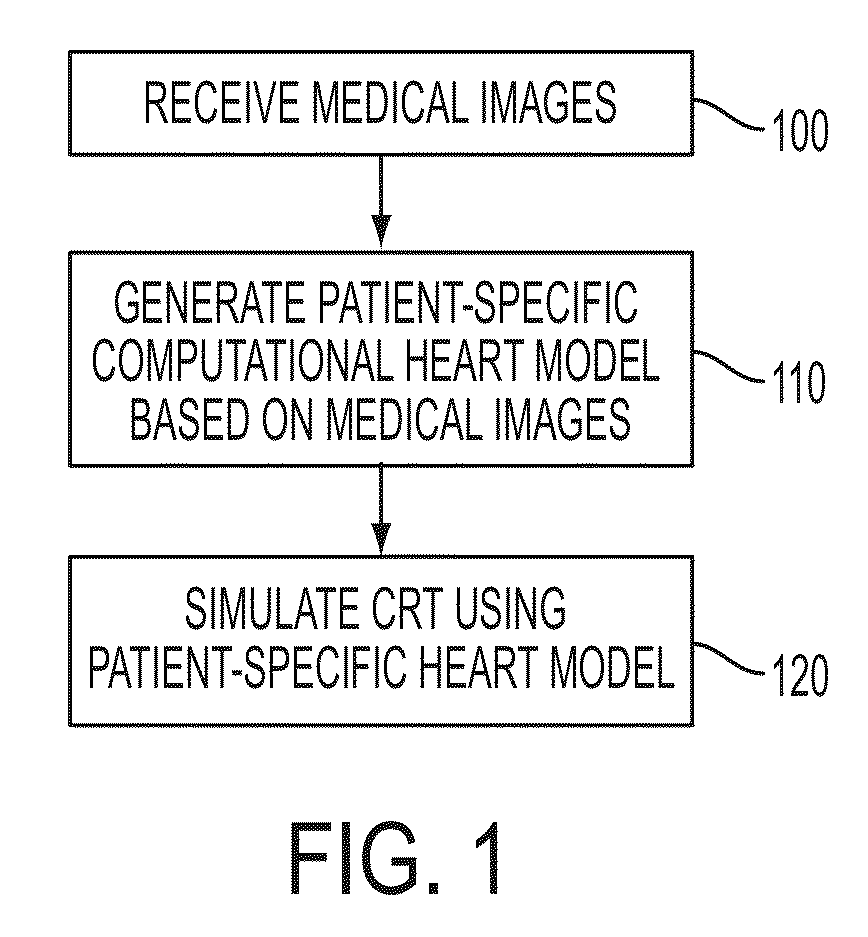
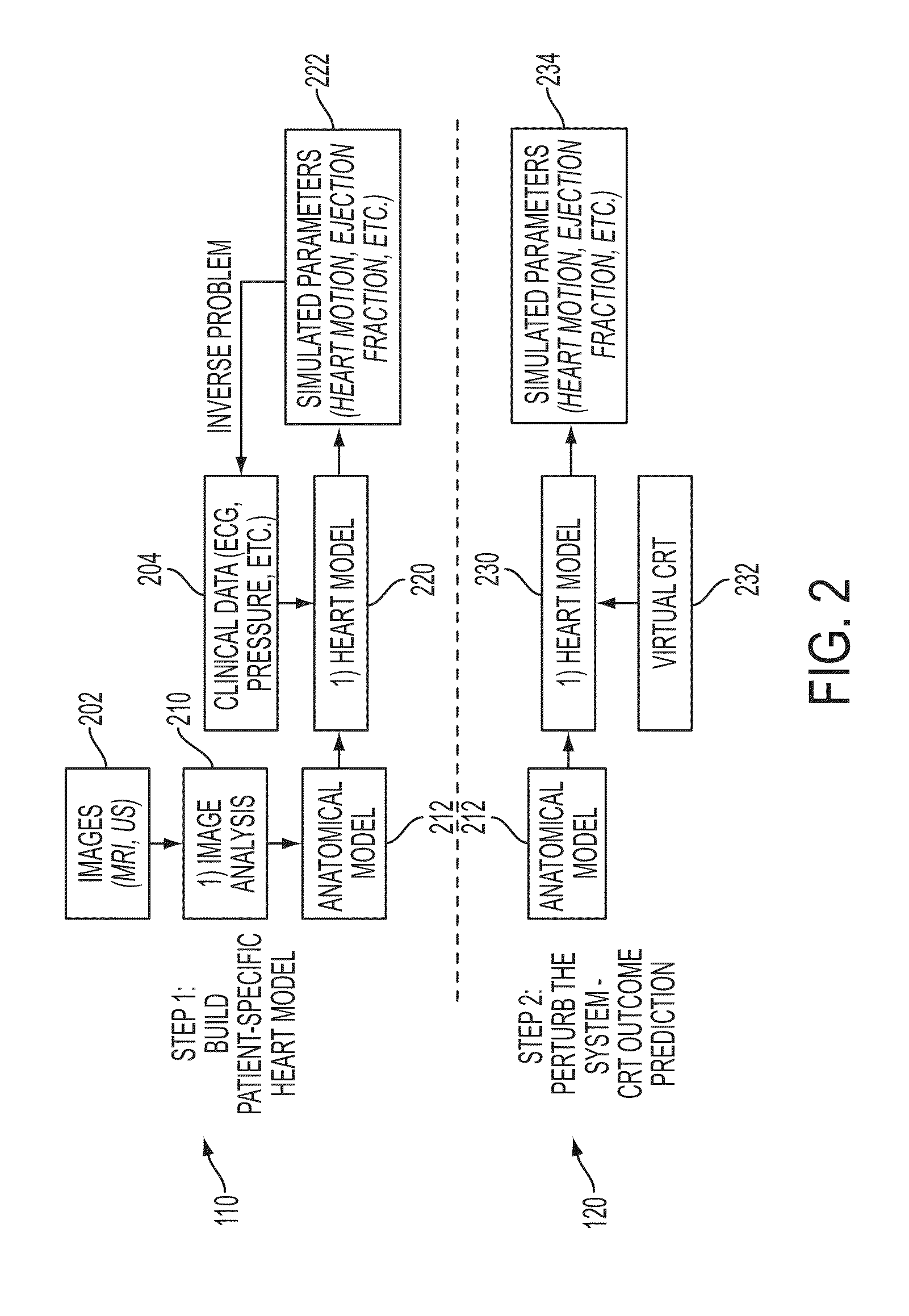
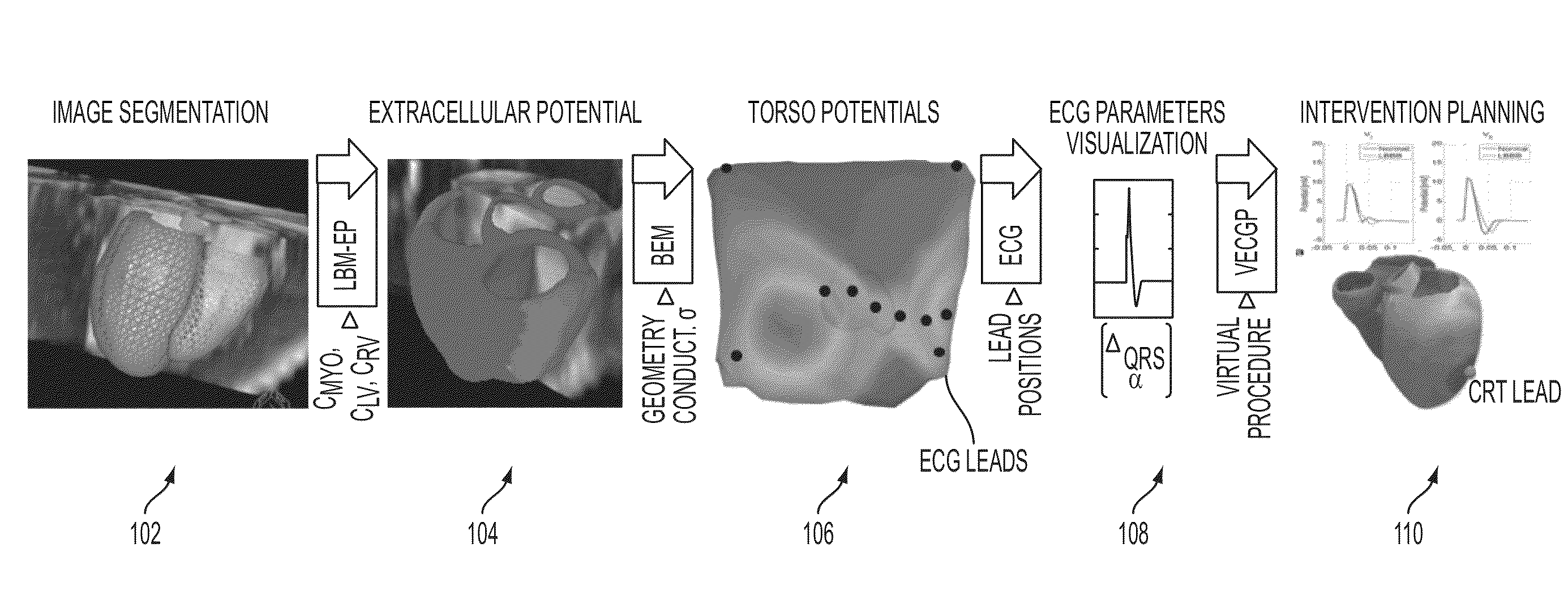
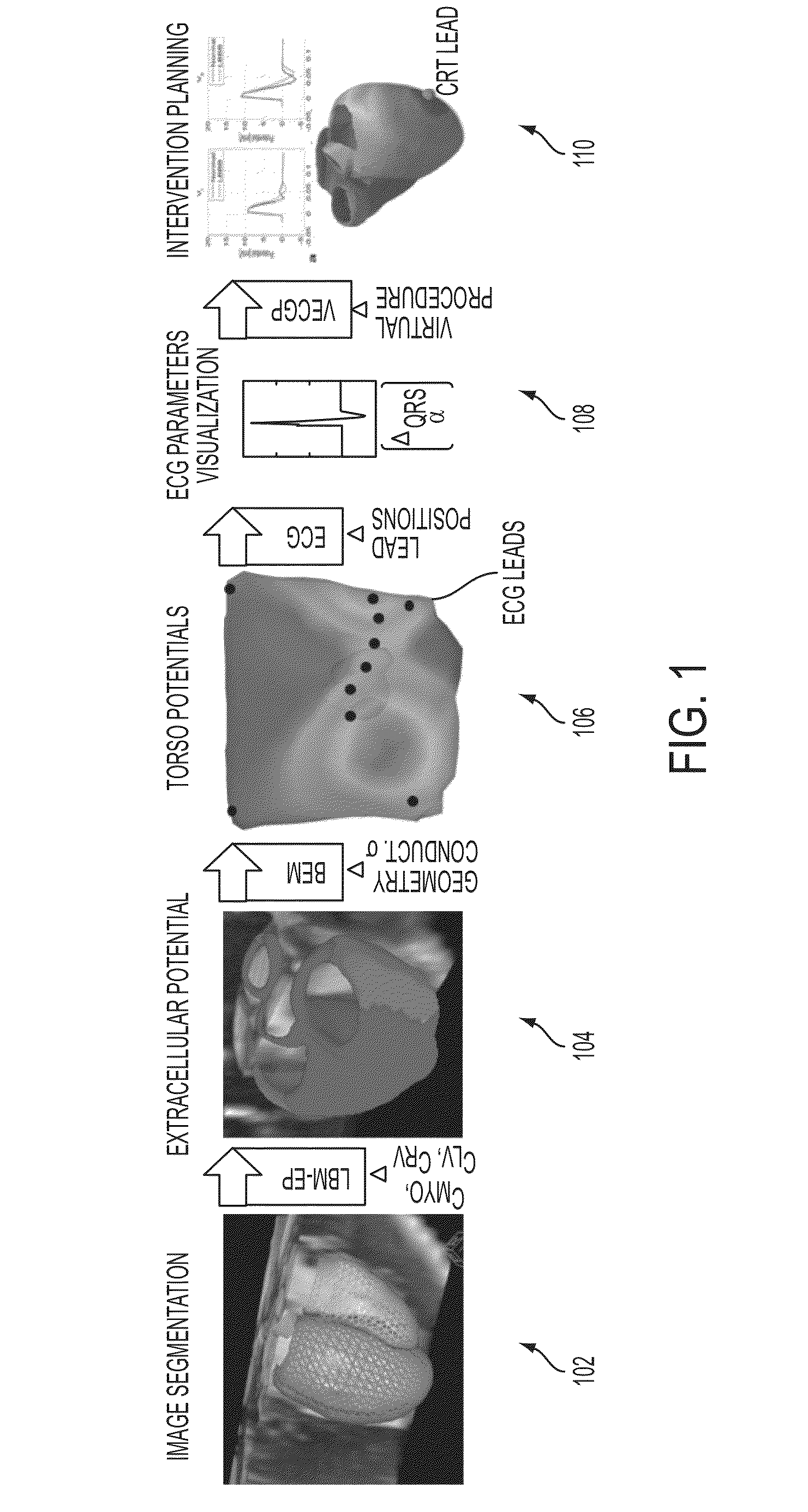
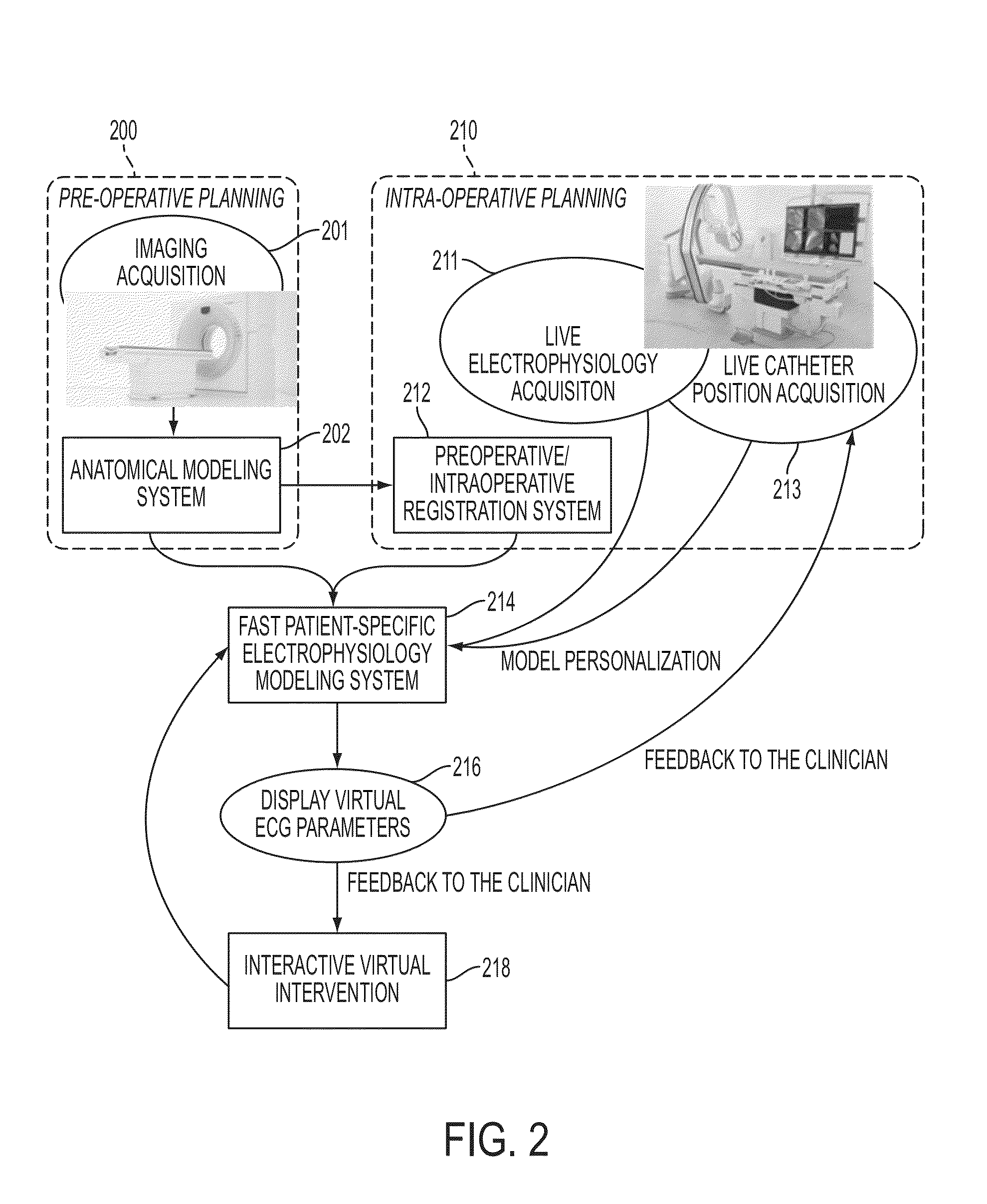
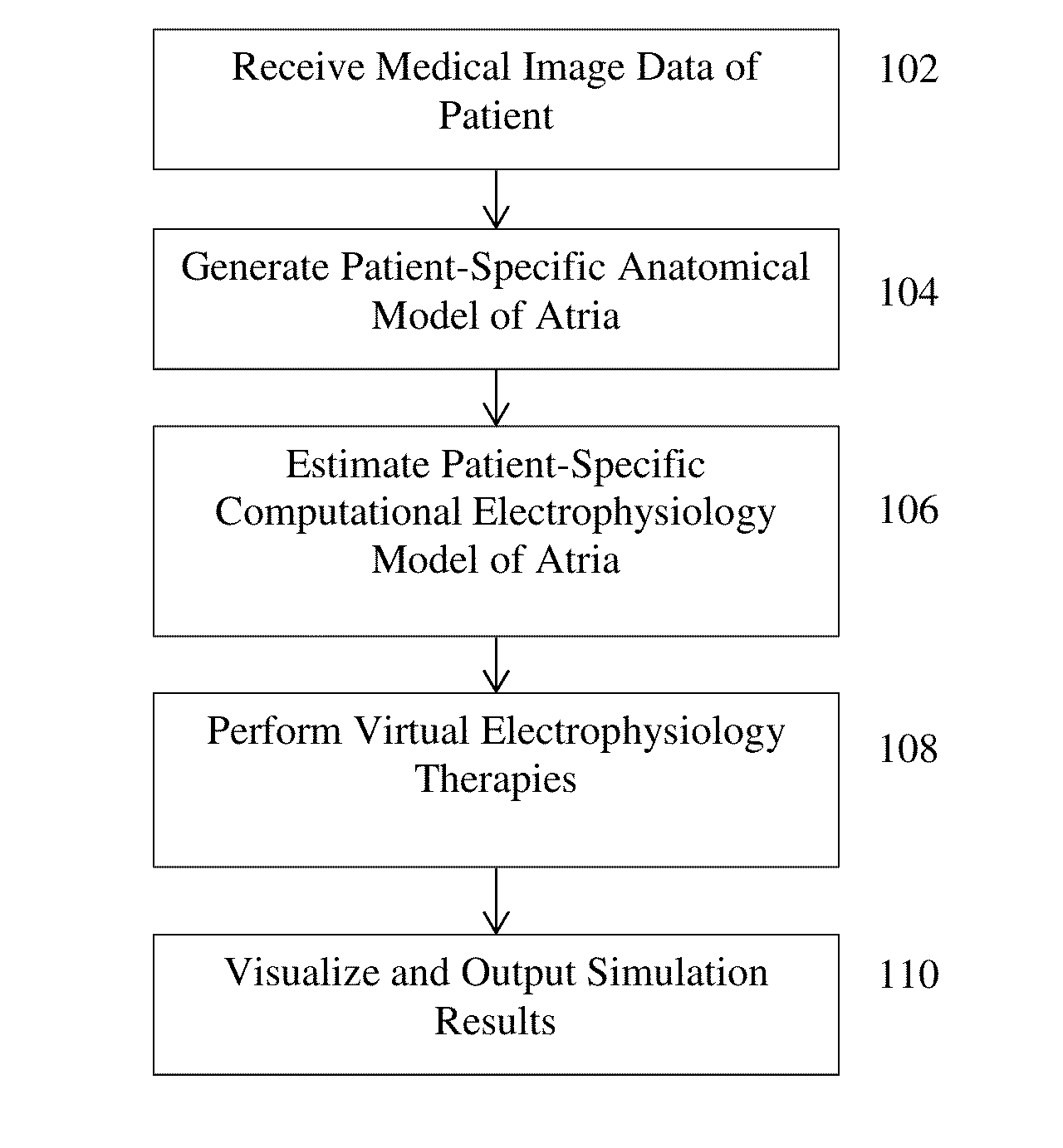
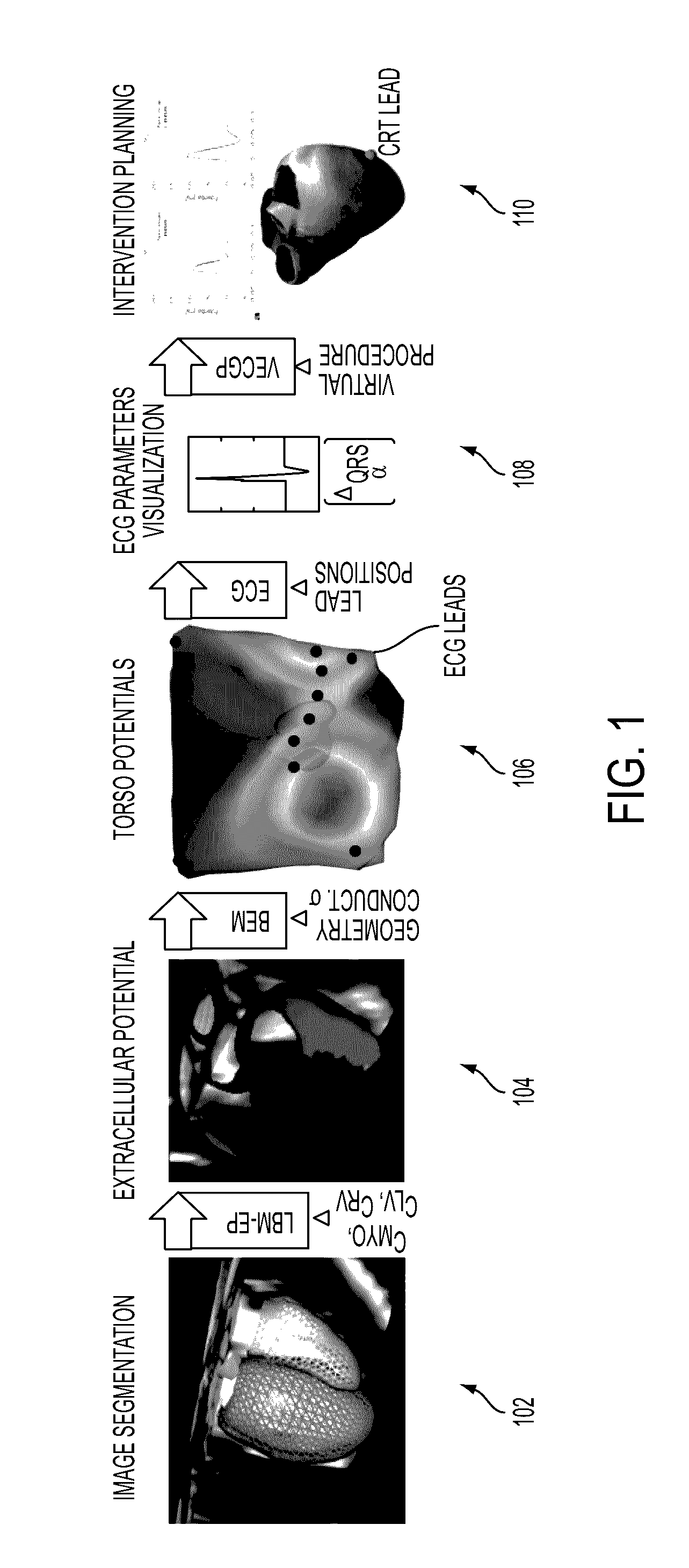
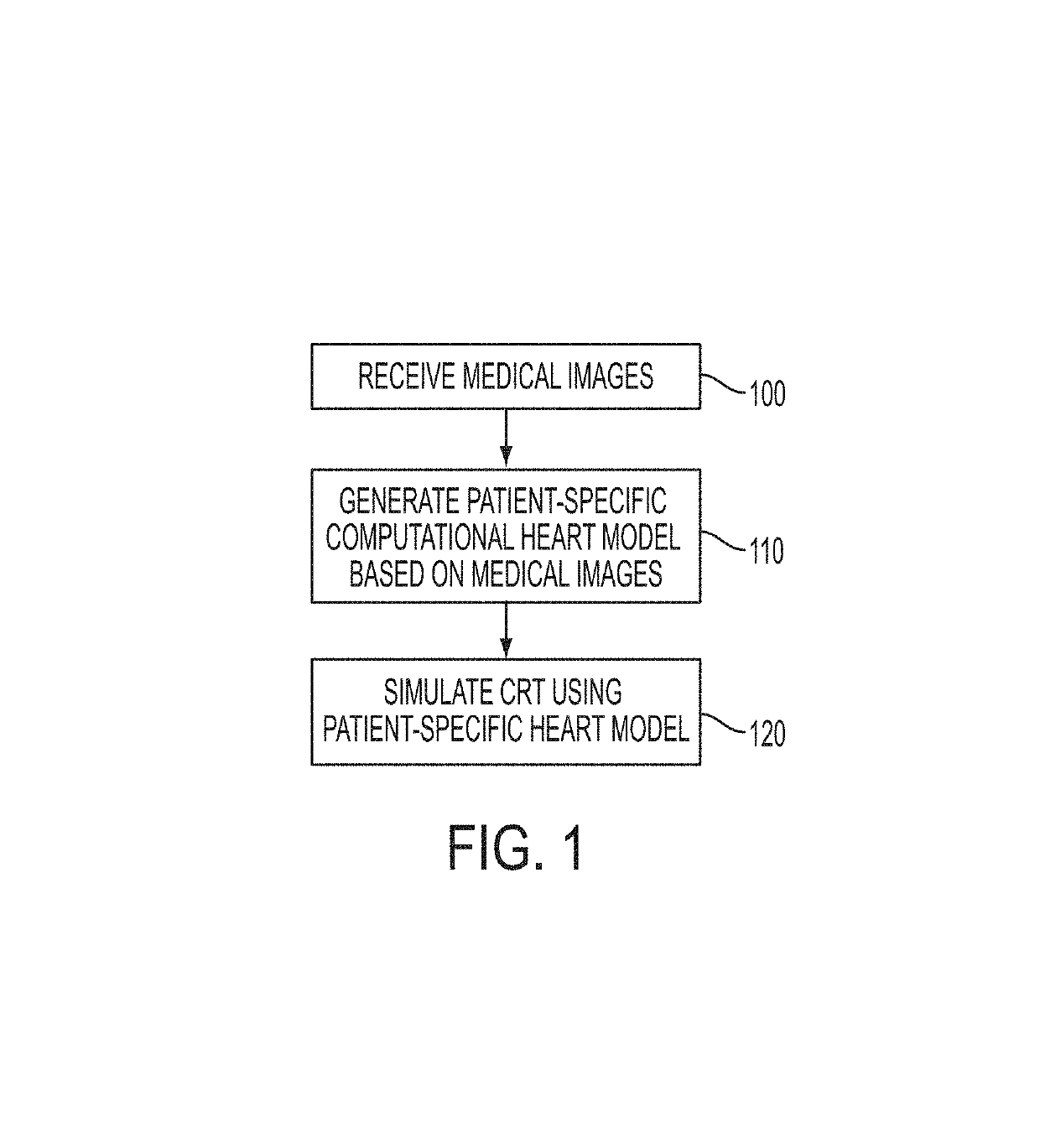
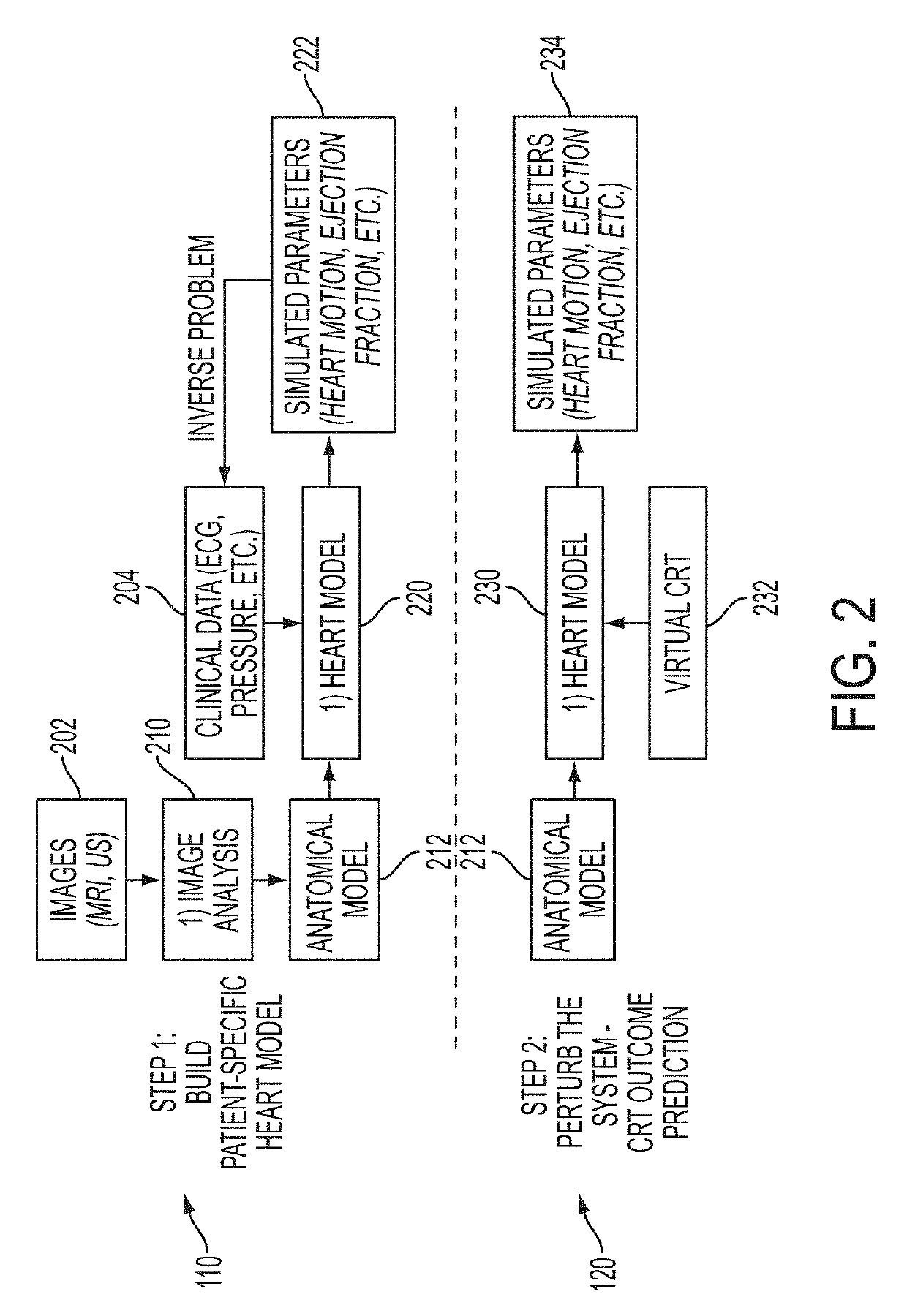
Method and System for Patient Specific Planning of Cardiac Therapies on Preoperative Clinical Data and Medical Images
ActiveUS20130197881A1Increase the number ofEasy to placeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingSonificationBiomechanics
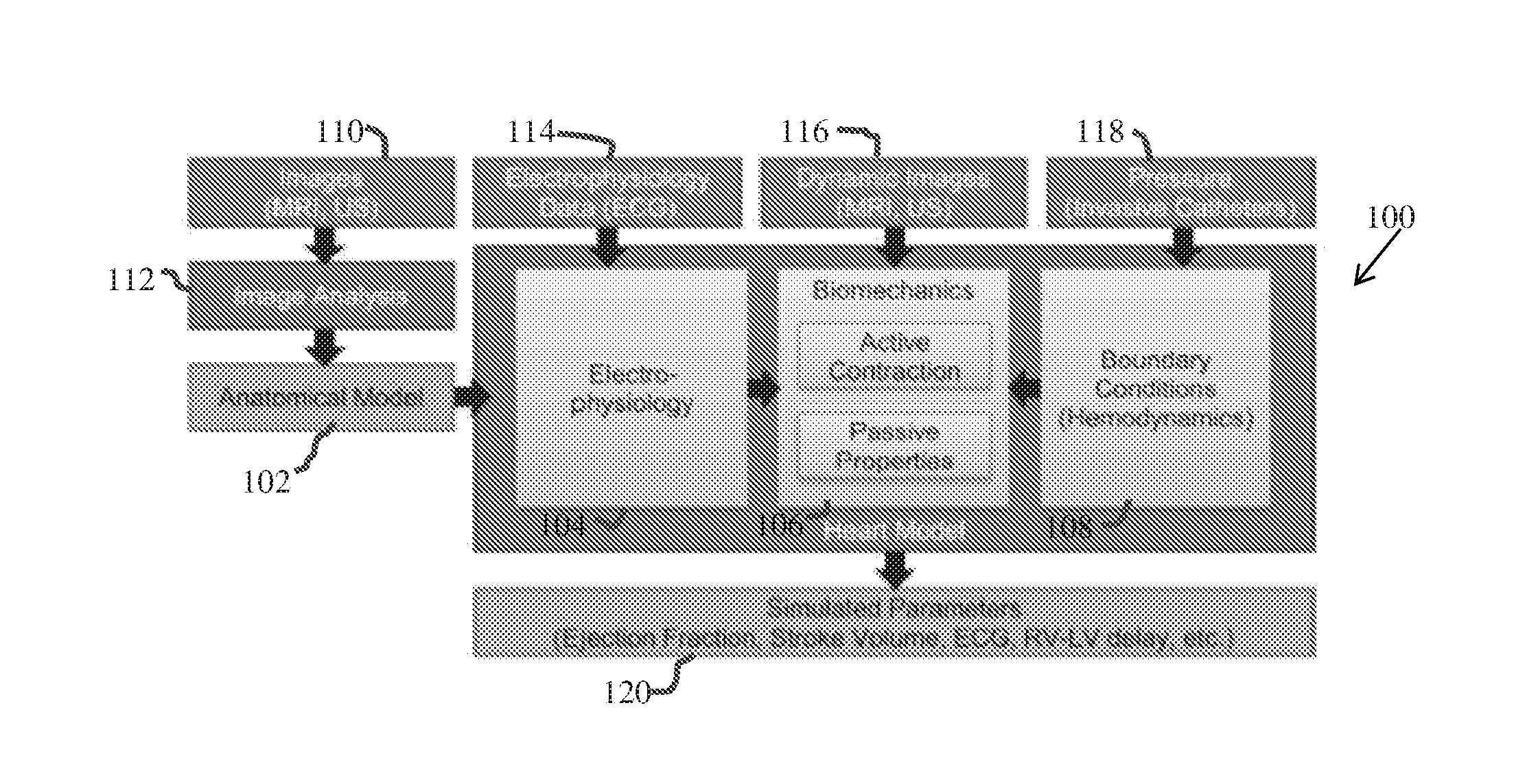
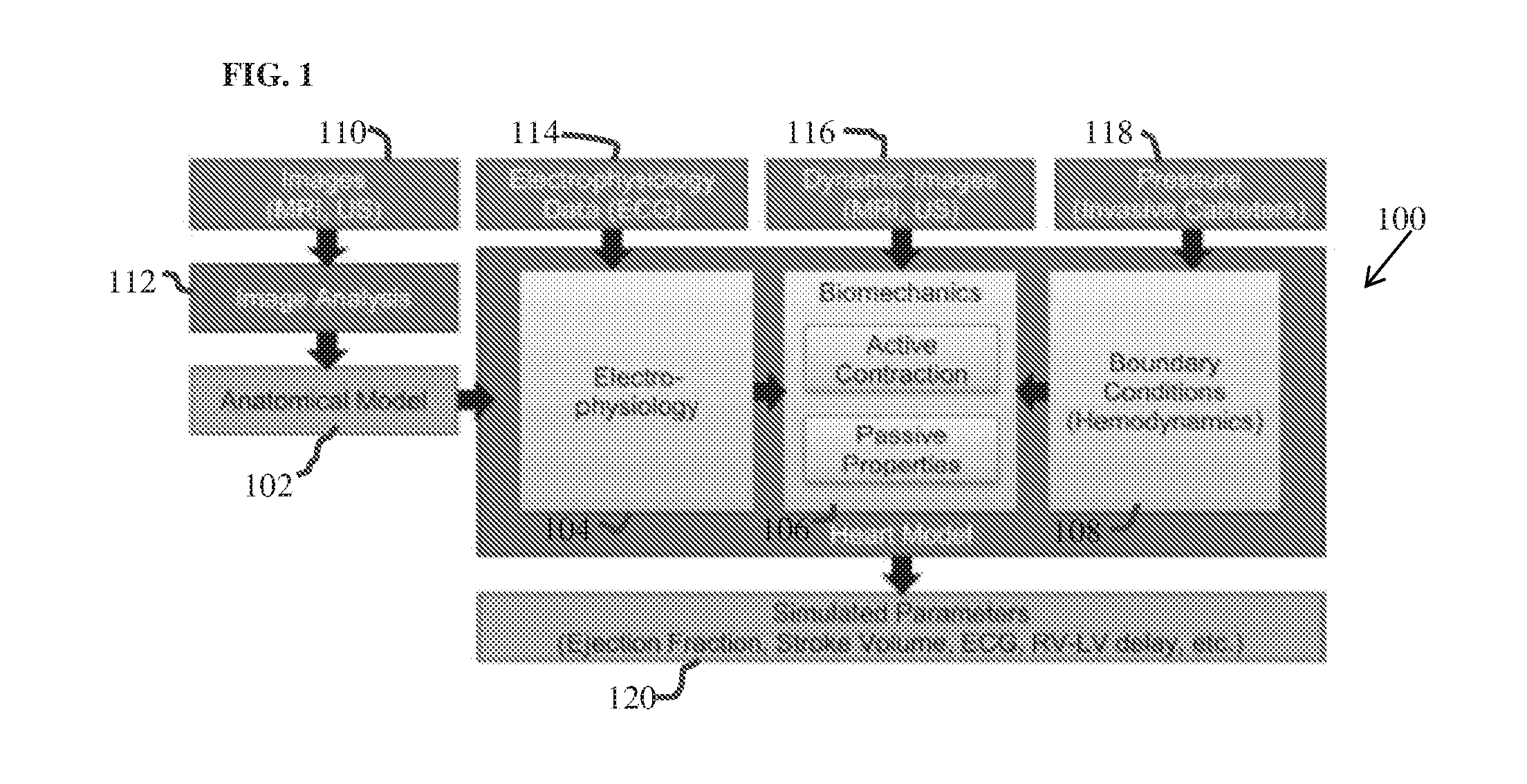
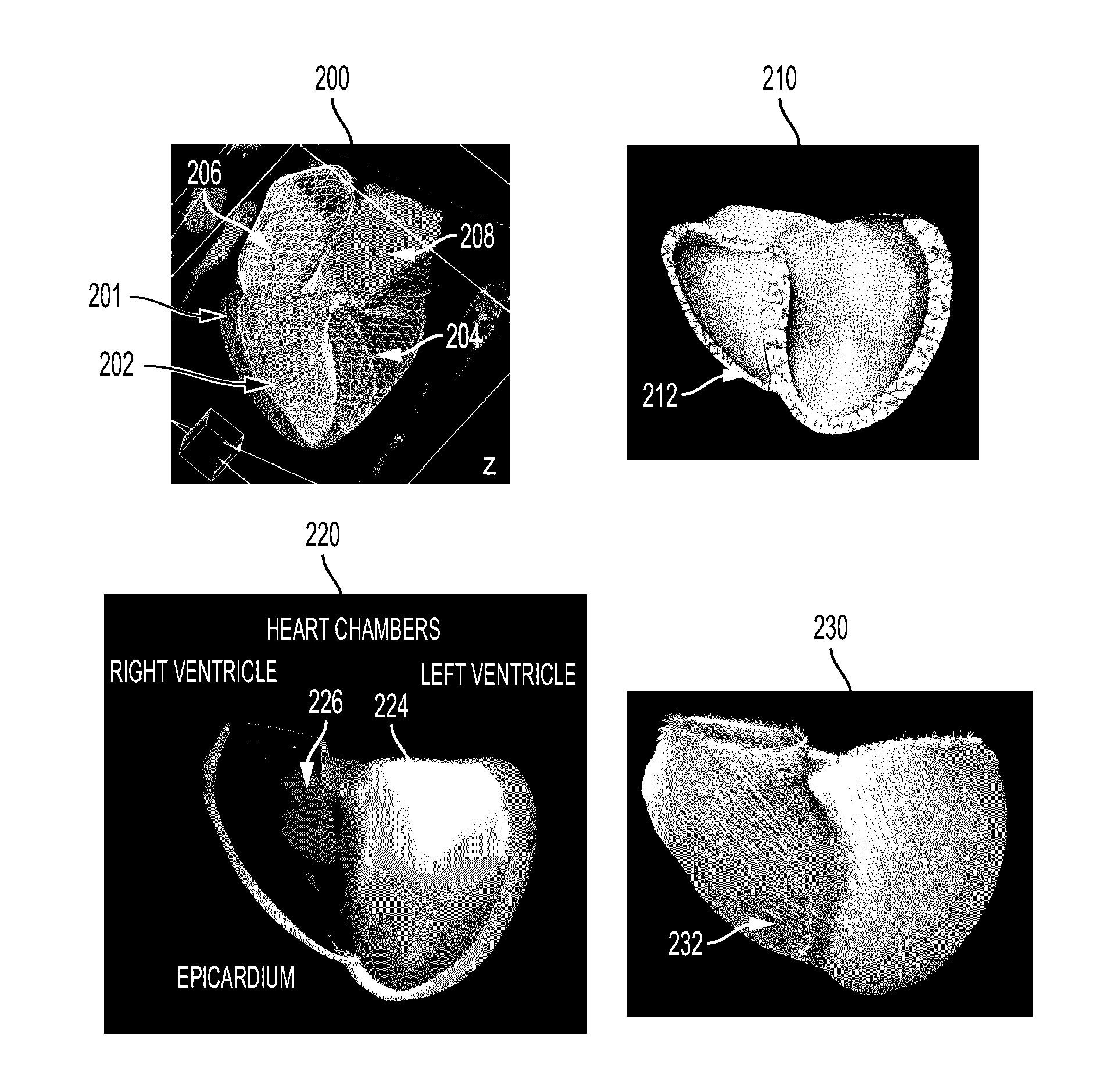
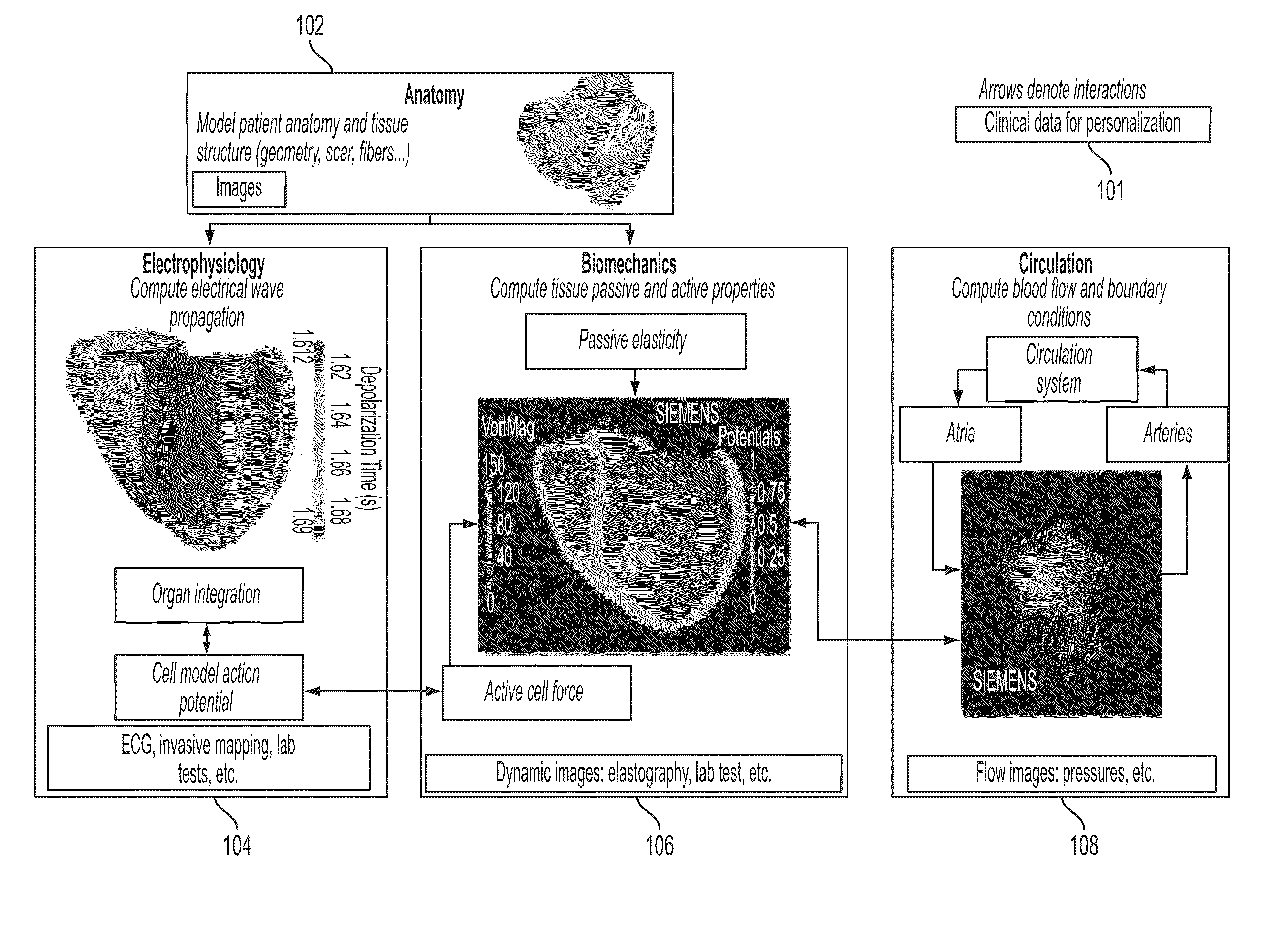
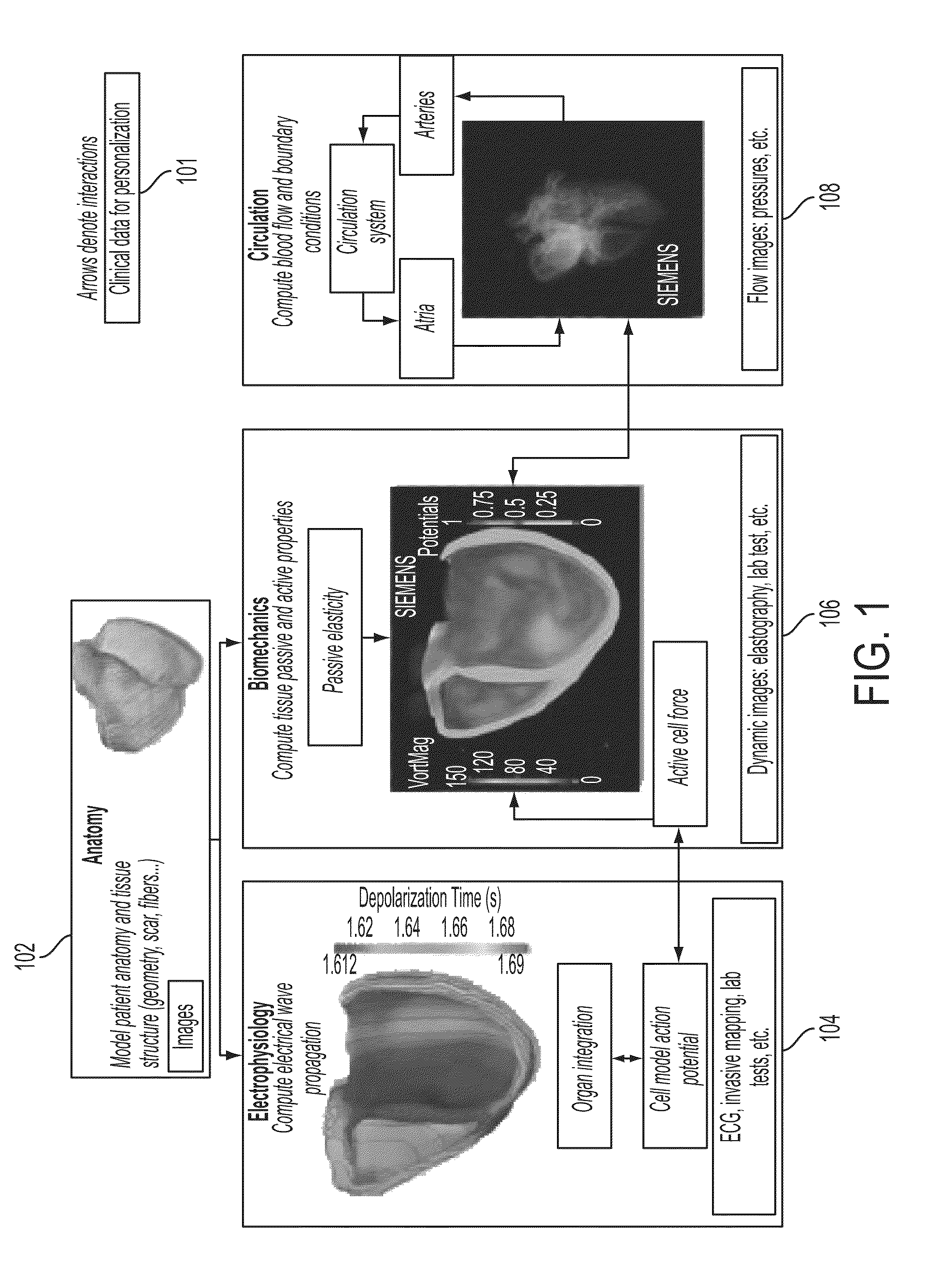
A method and system for patient-specific planning of cardiac therapy, such as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), based on preoperative clinical data and medical images, such as ECG data, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, and ultrasound data, is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles is generated from medical image data of a patient. A patient-specific computational heart model, which comprises cardiac electrophysiology, biomechanics and hemodynamics, is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles and clinical data. Simulations of cardiac therapies, such as CRT at one or more anatomical locations are performed using the patient-specific computational heart model. Changes in clinical cardiac parameters are then computed from the patient-specific model, constituting predictors of therapy outcome useful for therapy planning and optimization.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
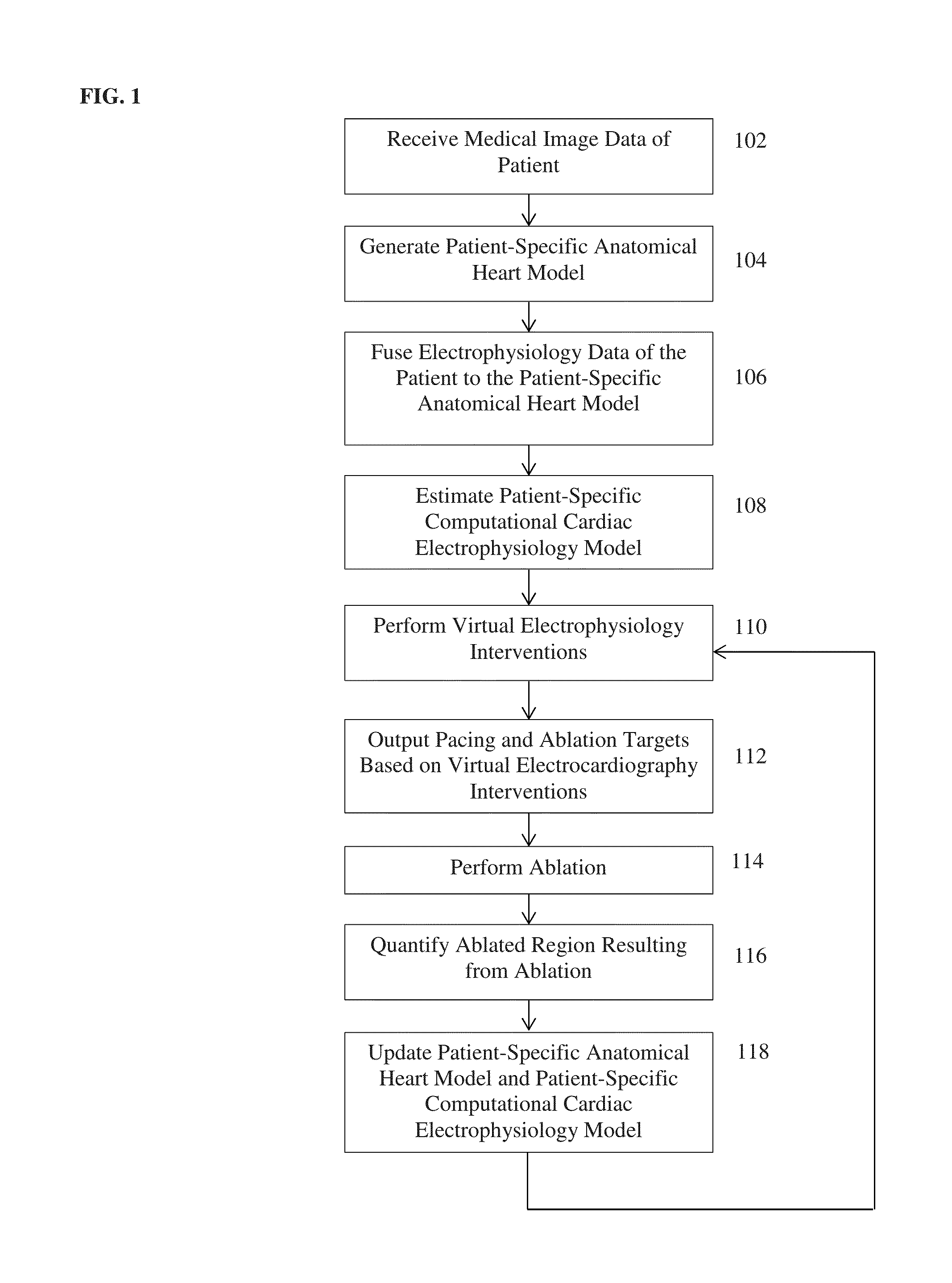
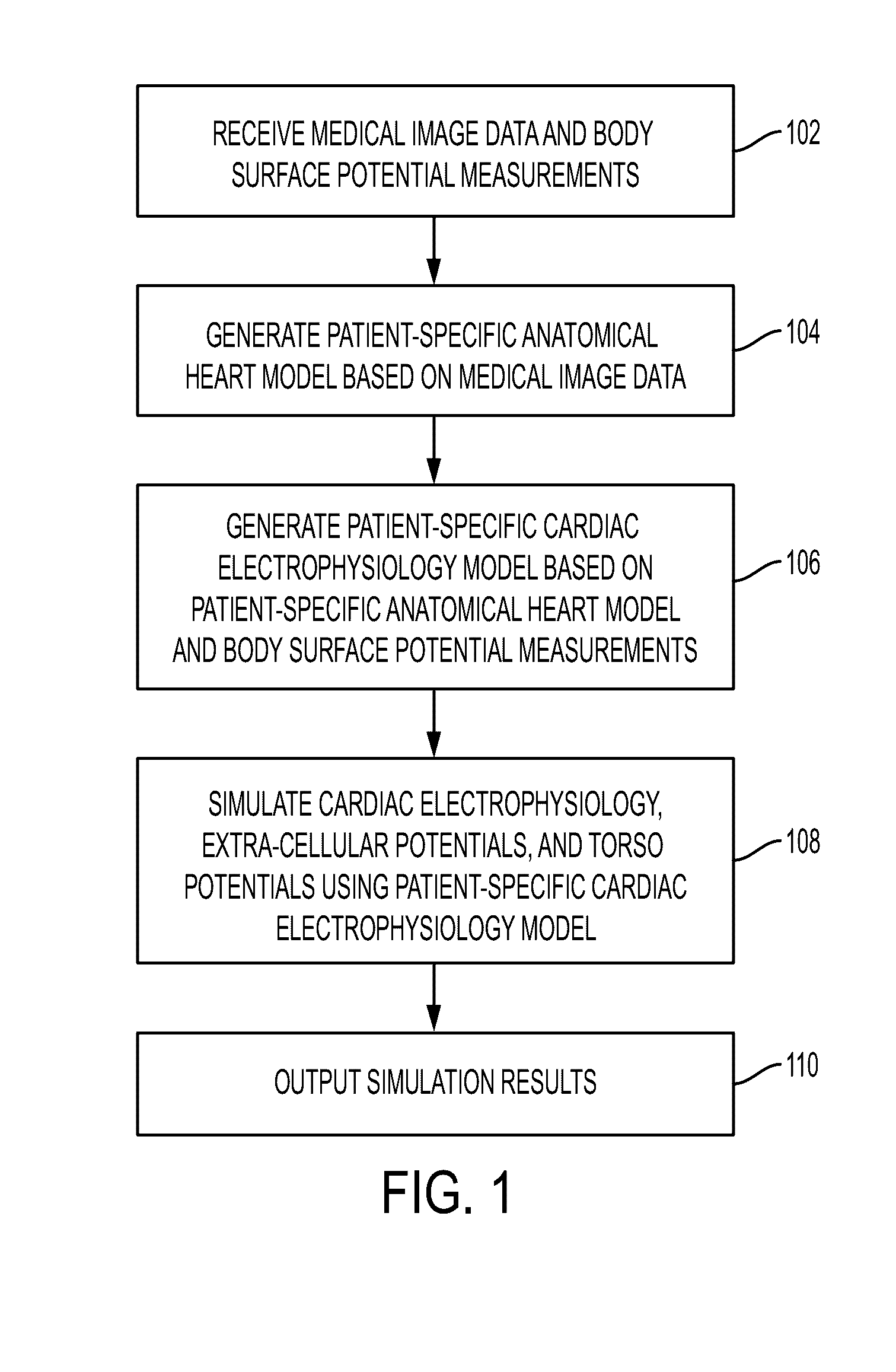
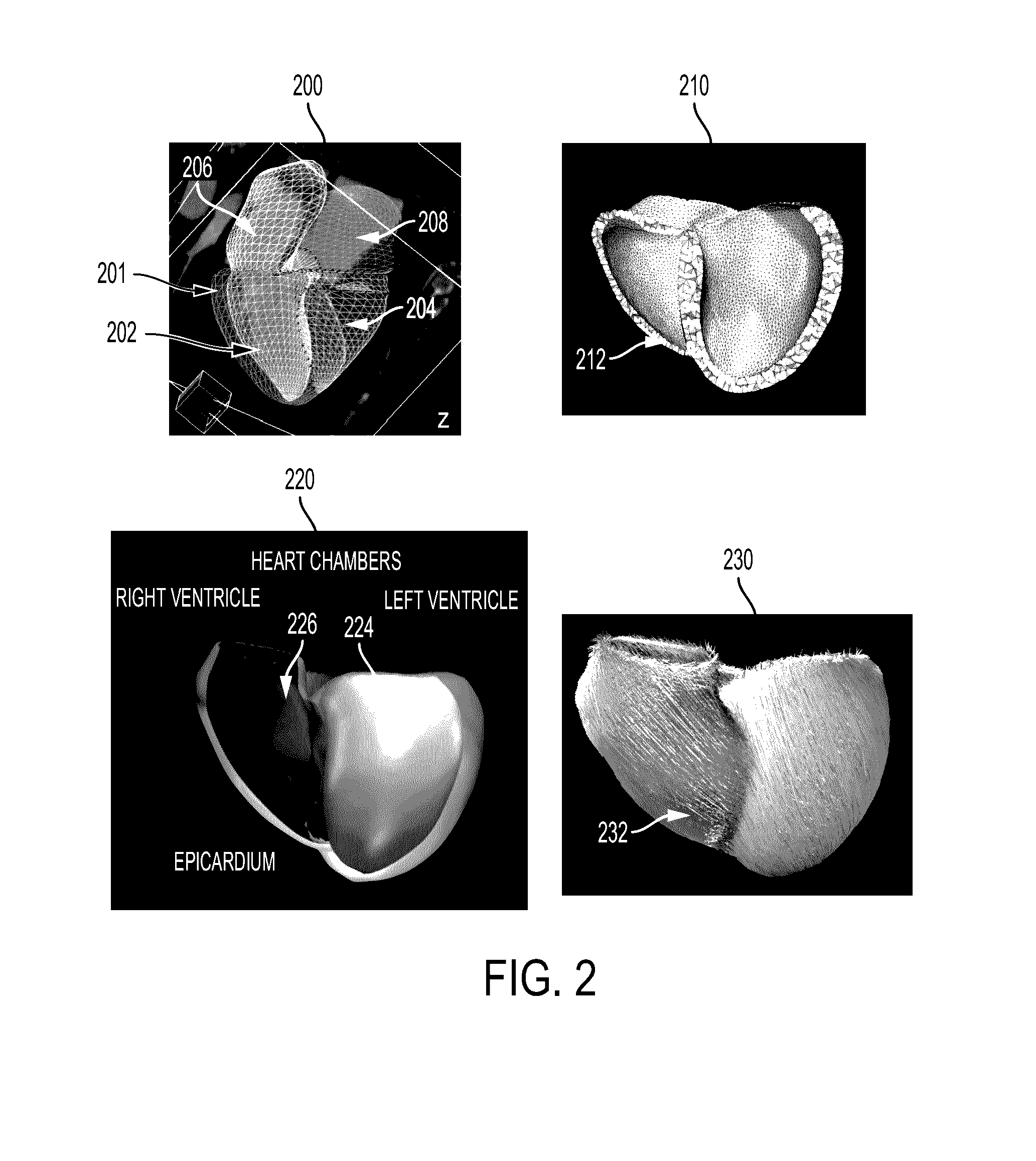
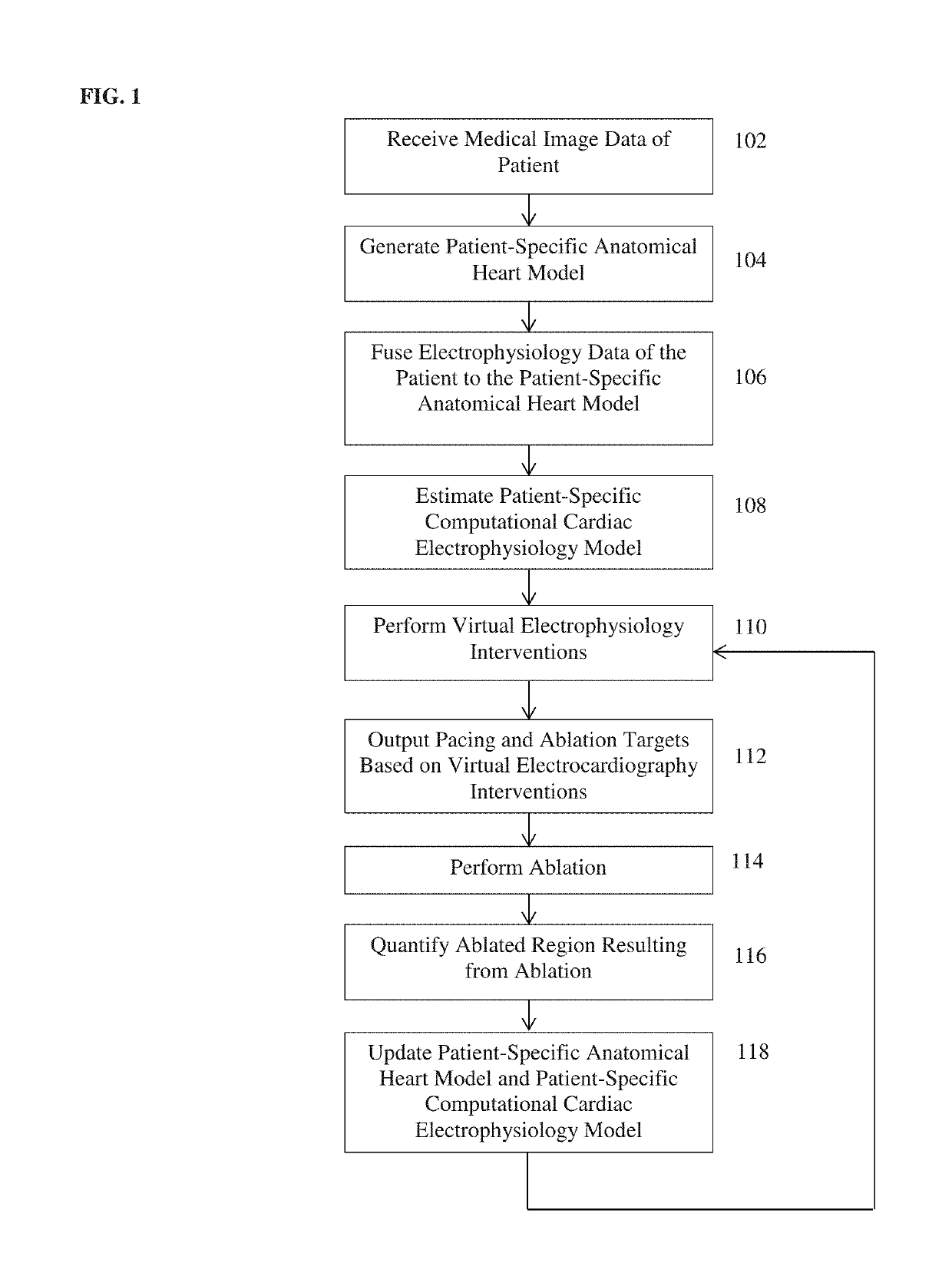
System and method for patient-specific image-based guidance of cardiac arrhythmia therapies
ActiveUS20150294082A1Reduce intervention timeMaximize therapeutic outcomeMedical simulationElectrotherapyRadiologyCardiac arrhythmia
A method and system for image-based patient-specific guidance of cardiac arrhythmia therapies is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical heart model is generated from medical image data of a patient. A patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical heart model and electrophysiology measurements of the patient. One or more virtual electrophysiological interventions are performed using the patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model. One or more pacing targets or ablation targets based on the one or more virtual electrophysiological interventions are displayed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for real-time simulation of patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology including the effect of the electrical conduction system of the heart
ActiveUS20170068796A1Increase speedAccuracy of modelMedical simulationComputer-aided planning/modellingElectricityReal-time simulation
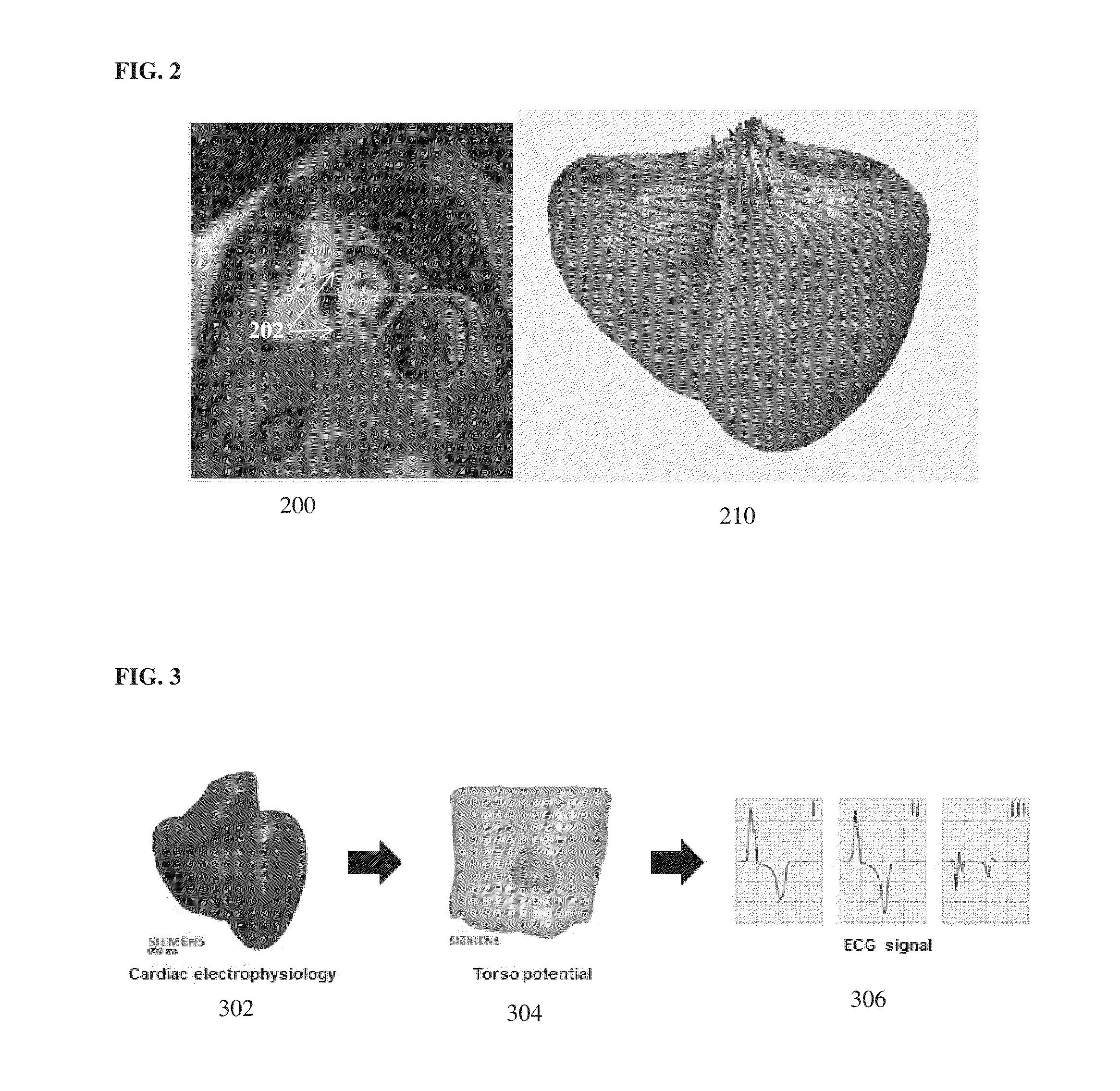
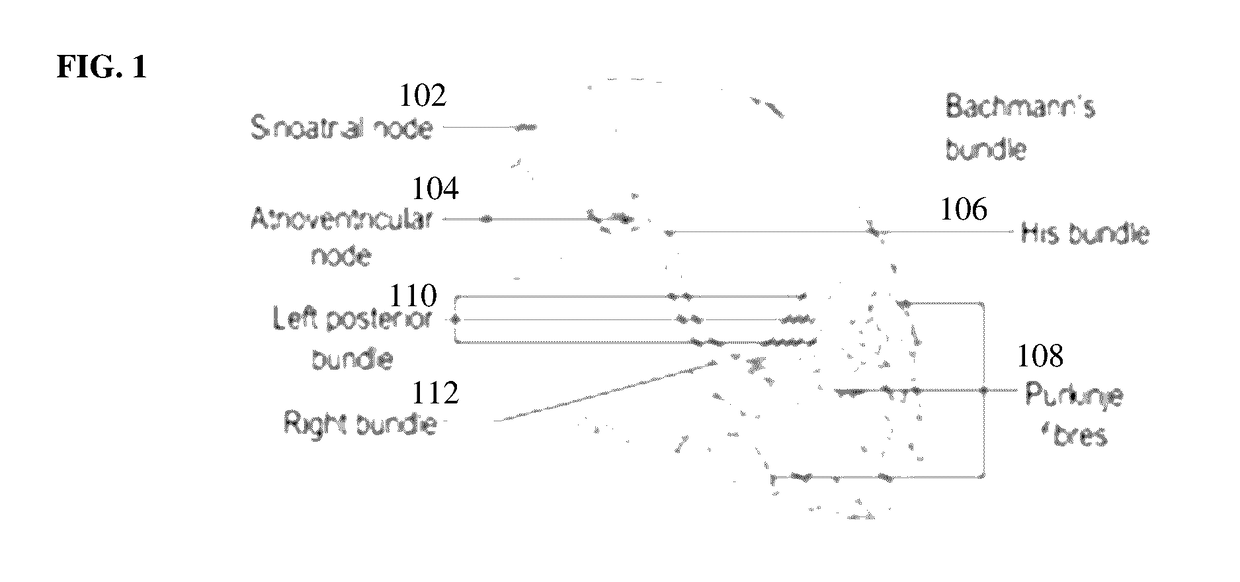
A method and system for simulating patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology including the effect of the electrical conduction system of the heart is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical heart model is generated from cardiac image data of a patient. The electrical conduction system of the heart of the patient is modeled by determining electrical diffusivity values of cardiac tissue based on a distance of the cardiac tissue from the endocardium. A distance field from the endocardium surface is calculated with sub-grid accuracy using a nested-level set approach. Cardiac electrophysiology for the patient is simulated using a cardiac electrophysiology model with the electrical diffusivity values determined to model the Purkinje network of the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and Method for Patient Specific Planning and Guidance of Electrophysiology Interventions
ActiveUS20150042646A1Physical therapies and activitiesDetails involving processing stepsRadiologyCell electrophysiology
A method and system for patient-specific planning and guidance of electrophysiological interventions is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical heart model is generated from cardiac image data of a patient. A patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical heart model and patient-specific electrophysiology measurements. Virtual electrophysiological interventions are performed using the patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model. A simulated electrocardiogram (ECG) signal is calculated in response to each virtual electrophysiological intervention.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for characterization of electrical properties of the heart from medical images and body surface potentials
ActiveUS20170185740A1Improved patient selectionEasy to planMedical imagingComputerised tomographsElectricityBody surface point
Methods and systems for estimating patient-specific cardiac electrical properties from medical image data and non-invasive electrocardiography measurements of a patient are disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical heart model is generated from medical image data of a patient. Patient-specific cardiac electrical properties are estimated by simulating cardiac electrophysiology over time in the patient-specific anatomical heart model using a computational cardiac electrophysiology model and adjusting cardiac electrical parameters based on the simulation results and the non-invasive electrocardiography measurements. A patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model with the patient-specific cardiac electrical parameters can then be used to perform virtual cardiac electrophysiology interventions for planning and guidance of cardiac electrophysiology interventions.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
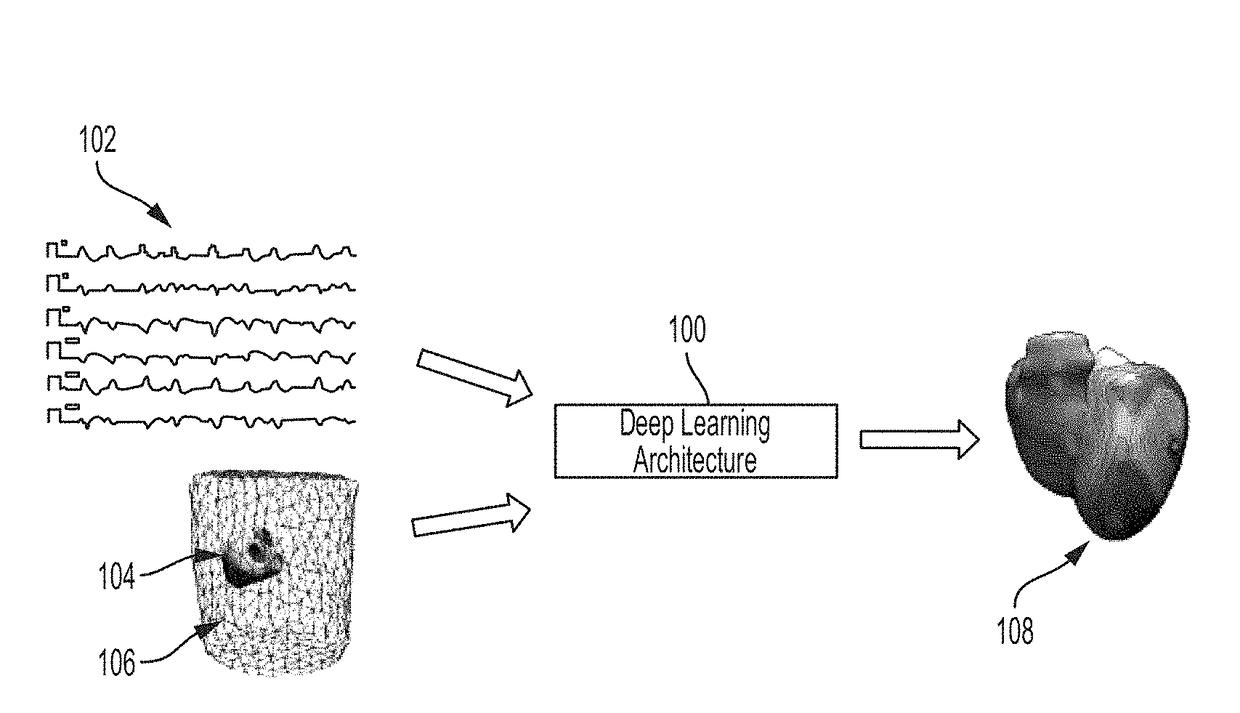
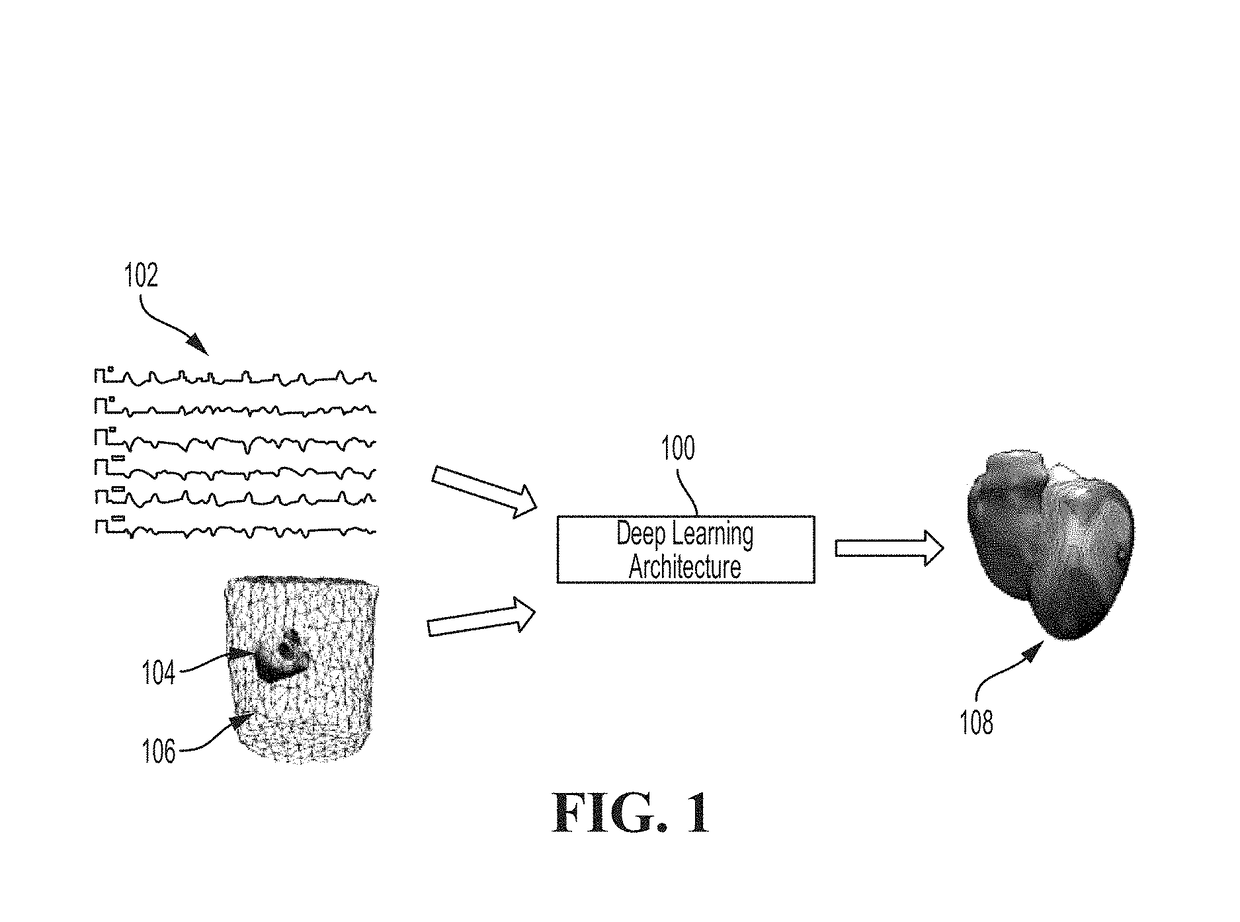
System and method for deep learning based cardiac electrophysiology model personalization
A method and system for deep learning based cardiac electrophysiological model personalization is disclosed. Electrophysiological measurements of a patient, such as an ECG trace, are received. A computational cardiac electrophysiology model is personalized by calculating patient-specific values for a parameter of the computational cardiac electrophysiology model based at least on the electrophysiological measurements of the patient using a trained deep neural network (DNN). The parameter of the computational cardiac electrophysiology model corresponds to a spatially varying electrical cardiac tissue property.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
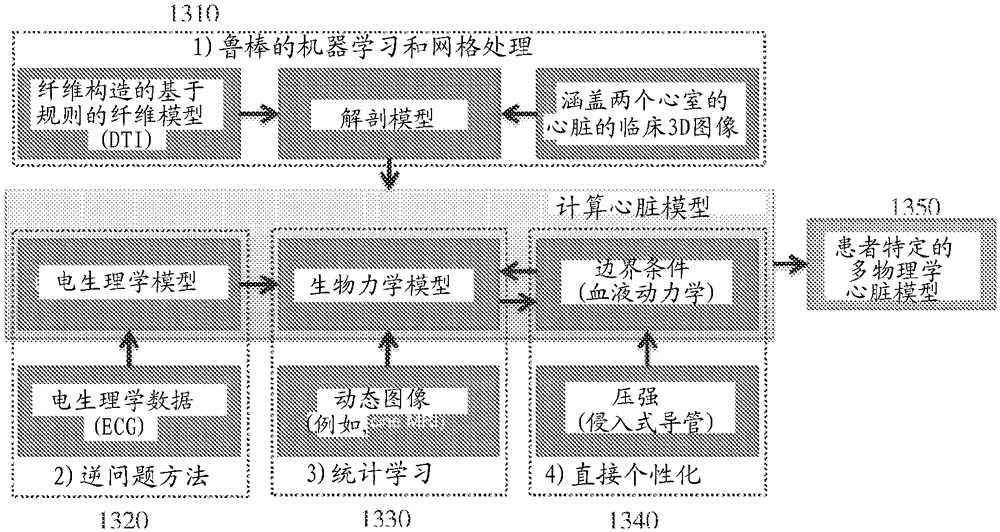
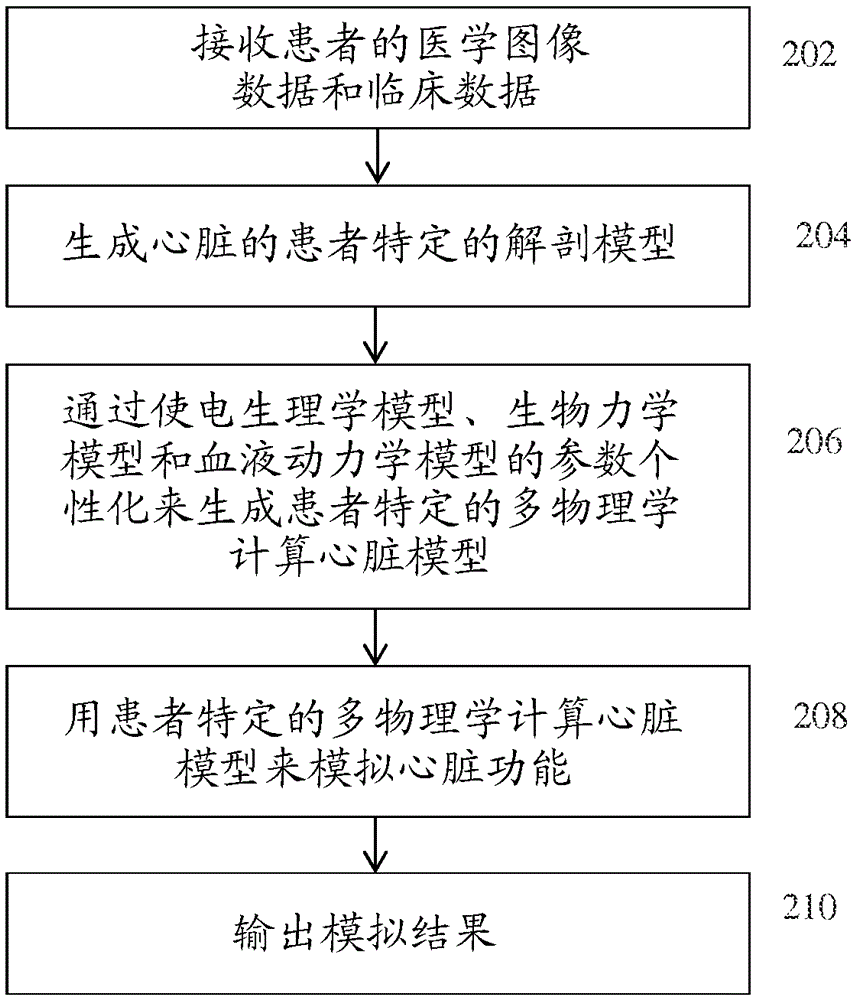
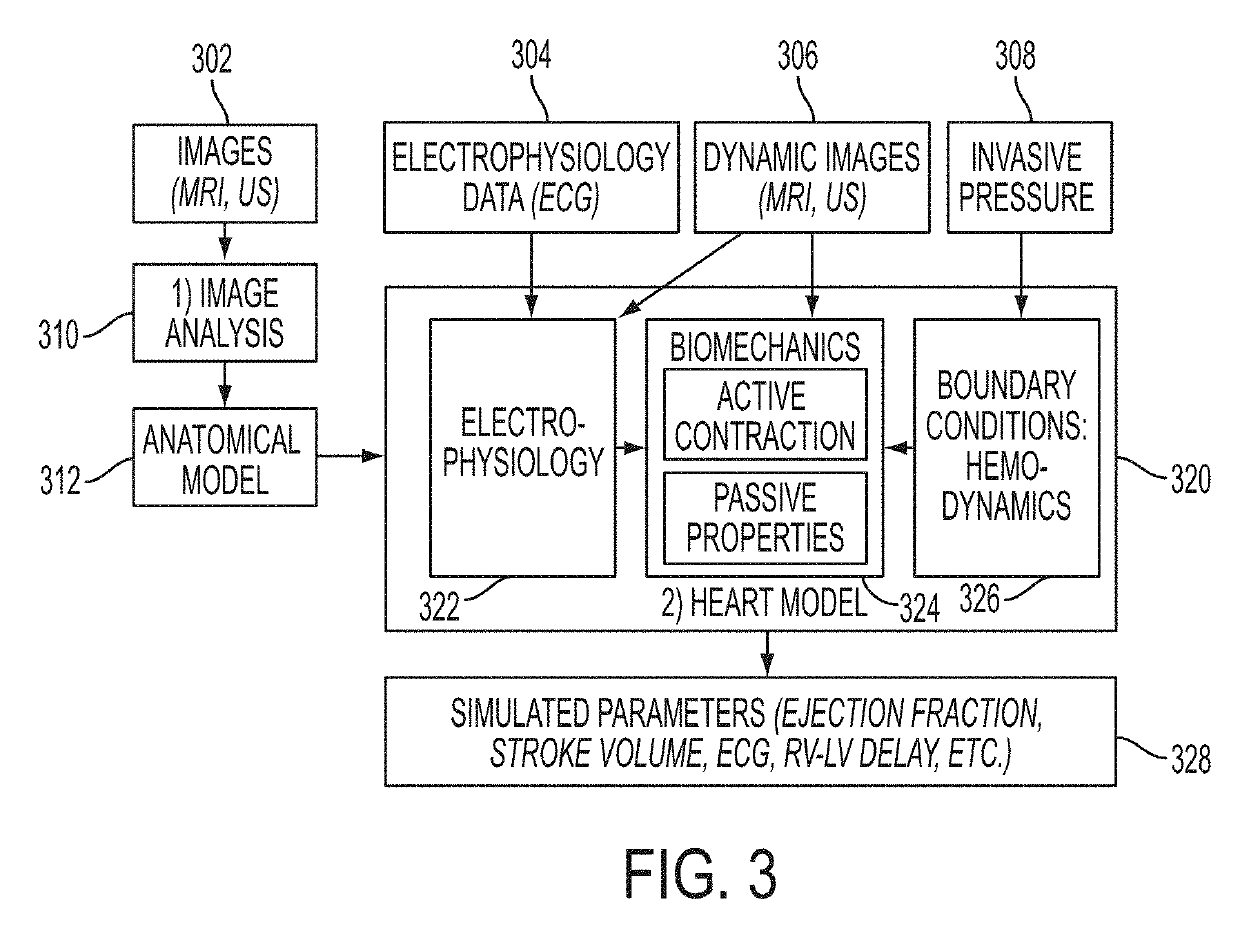
Systems and methods for estimating physiological heart measurements from medical images and clinical data
ActiveUS20160210435A1Quick buildUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingLearning basedBiomechanics
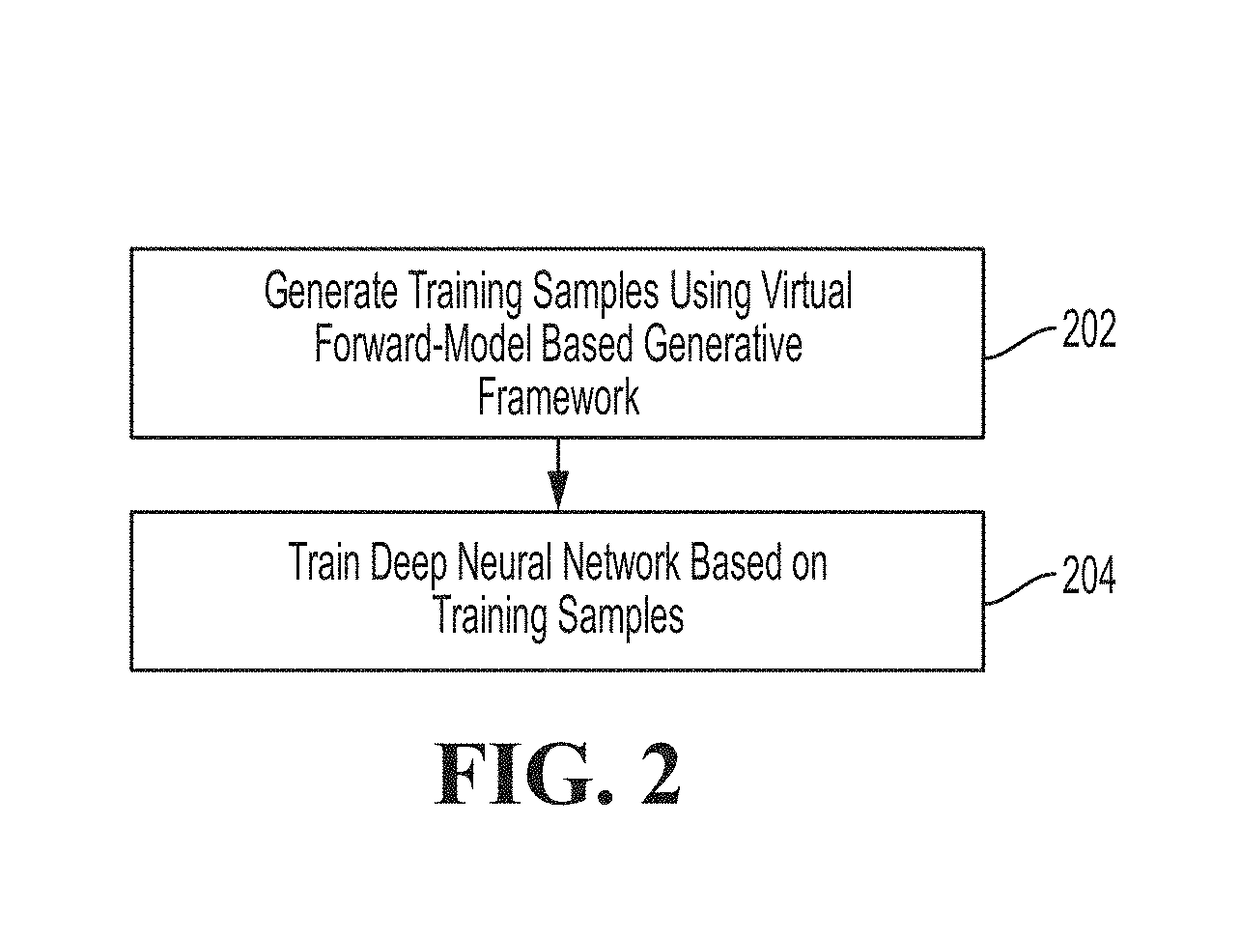
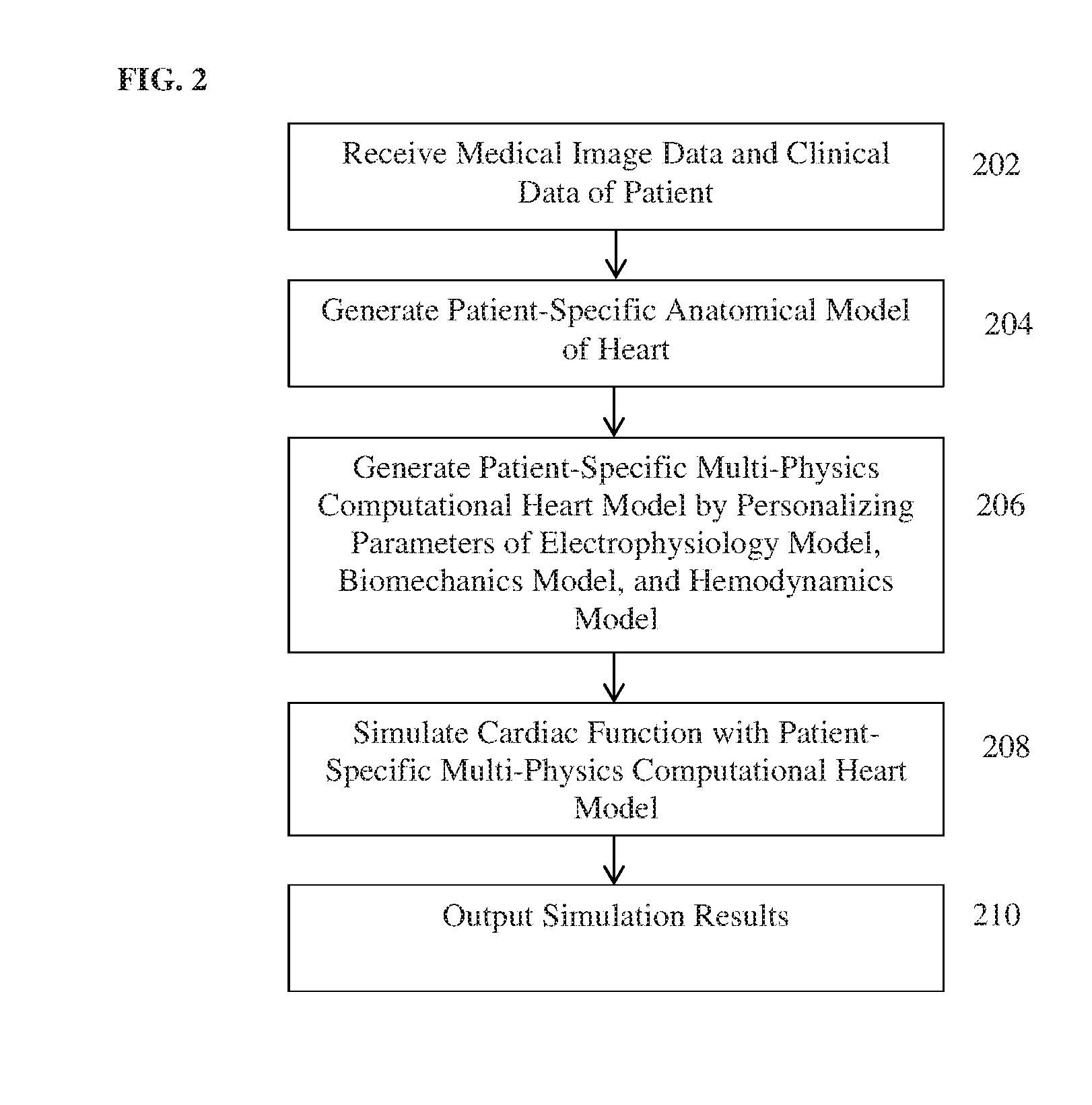
A method and system for estimating physiological heart measurements from medical images and clinical data disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the heart is generated from medical image data of the patient. A patient-specific multi-physics computational heart model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model by personalizing parameters of a cardiac electrophysiology model, a cardiac biomechanics model, and a cardiac hemodynamics model based on medical image data and clinical measurements of the patient. Cardiac function of the patient is simulated using the patient-specific multi-physics computational heart model. The parameters can be personalized by inverse problem algorithms based on forward model simulations or the parameters can be personalized using a machine-learning based statistical model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and Method for Patient-Specific Image-Based Simulation of Artial Electrophysiology
A method and system for simulating patient-specific atrial electrophysiology is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical atria model is generated from medical image data of a patient. A patient-specific atria electrophysiology model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical atria model and electrophysiology measurements of the patient. One or more virtual electrophysiological therapies are performed by performing atrial electrophysiology simulations using the patient-specific atria electrophysiology model. Atrial electrophysiology simulation results resulting from the one or more virtual electrophysiological therapies are displayed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
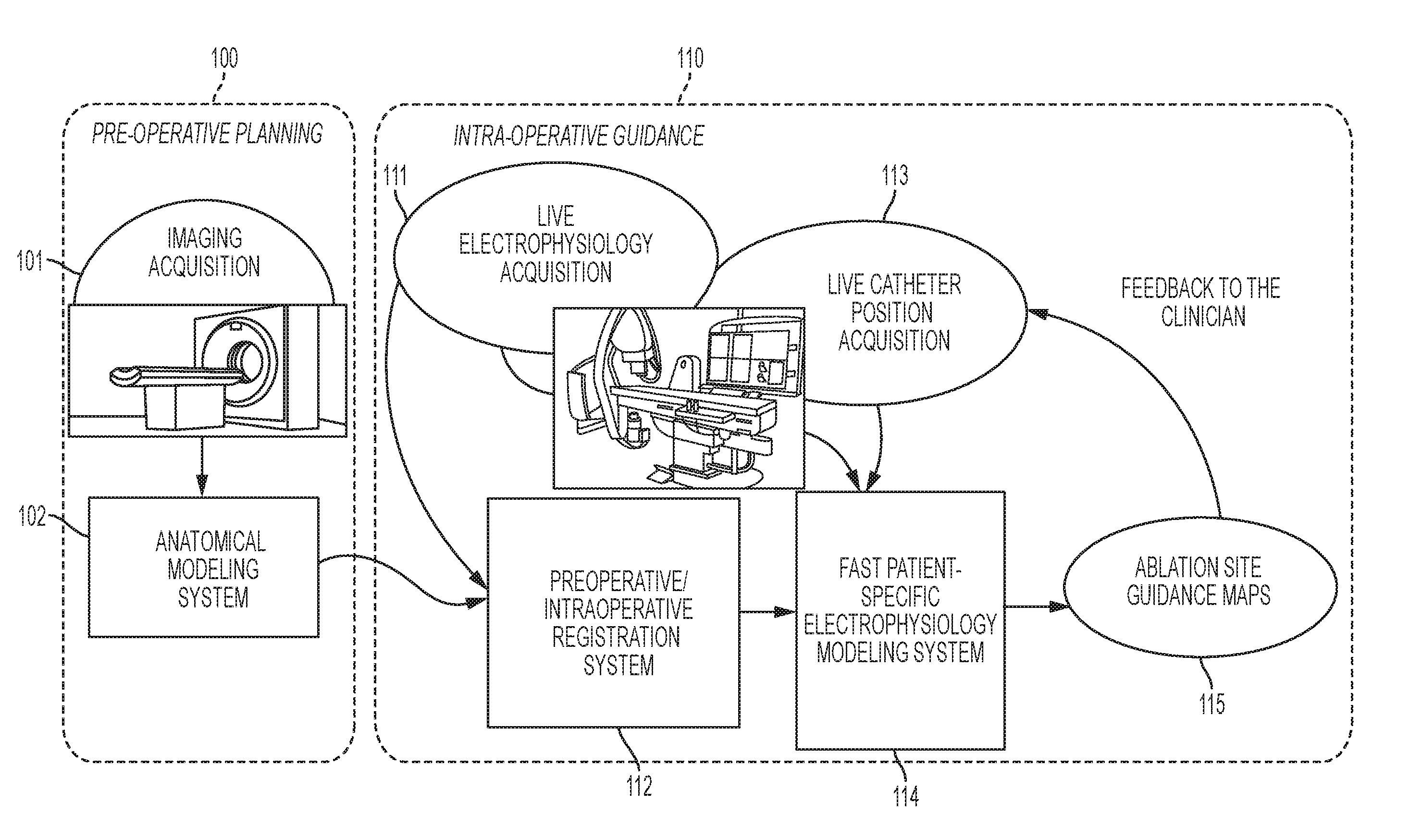
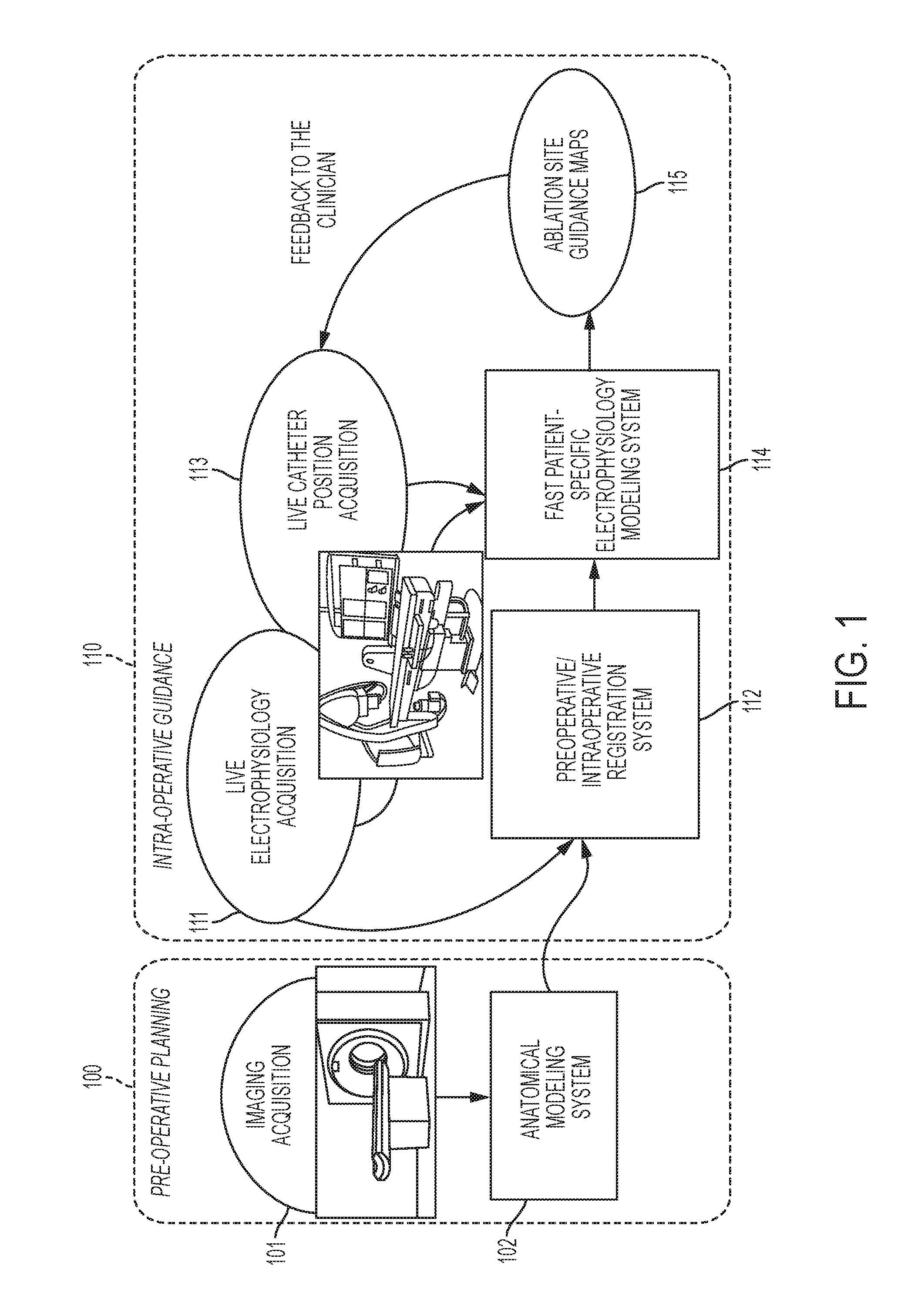
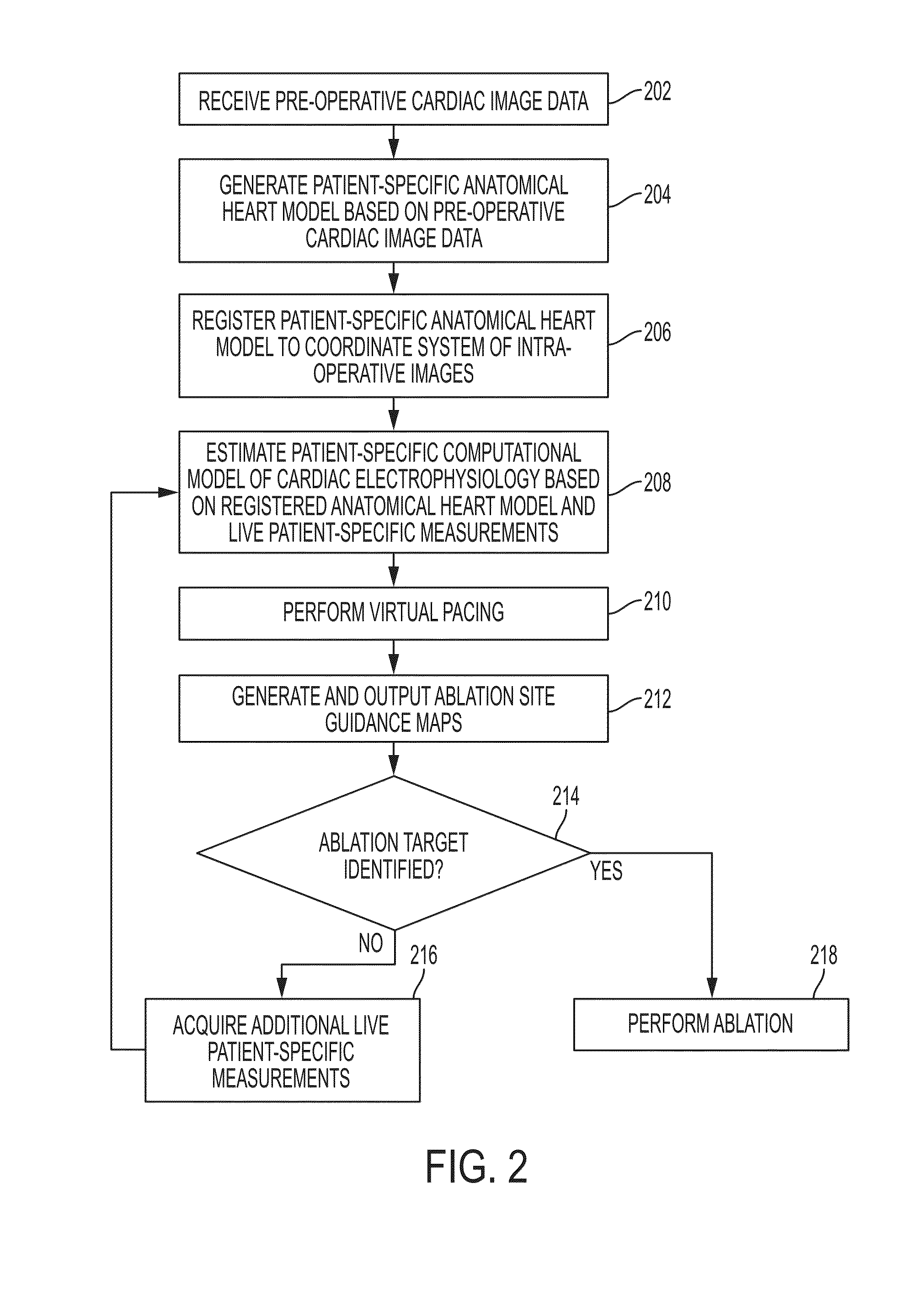
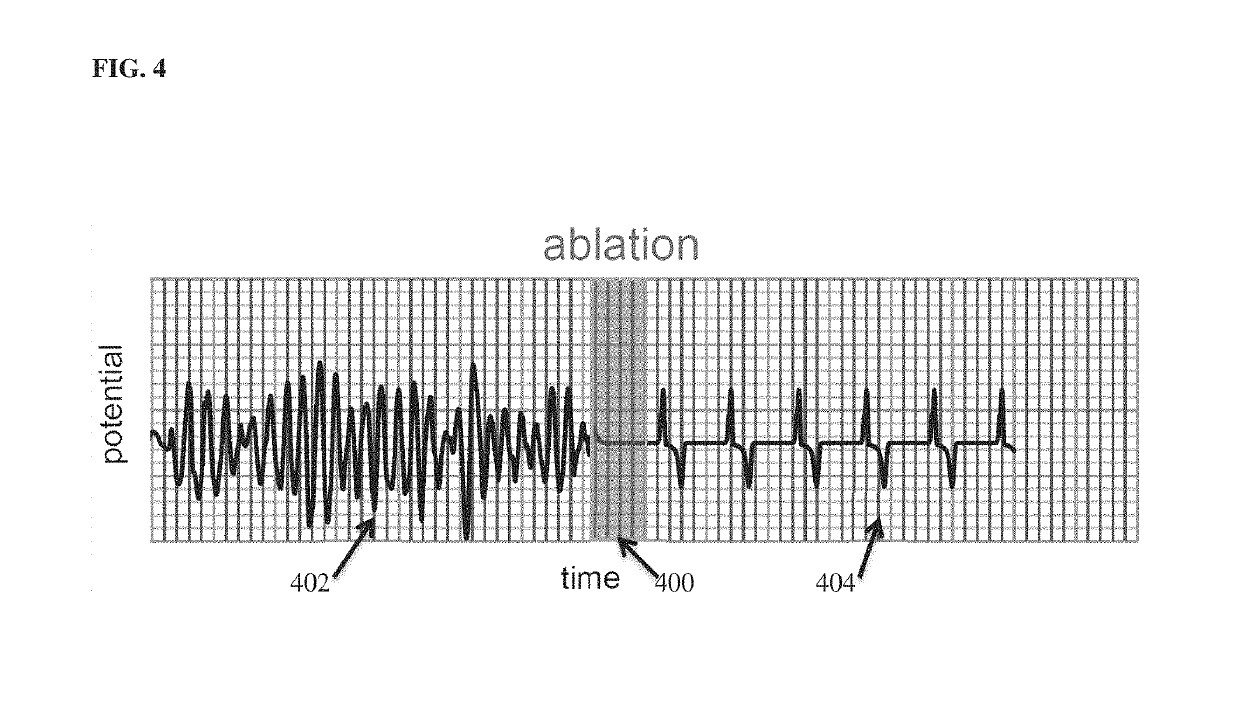
System and method for patient specific planning and guidance of ablative procedures for cardiac arrhythmias
ActiveUS9277970B2Minimizing life-threatening riskBetter target ablation sitesImage enhancementImage analysisPersonalizationDisplay device
A method and system for patient-specific planning and guidance of an ablation procedure for cardiac arrhythmia is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical heart model is generated based on pre-operative cardiac image data. The patient-specific anatomical heart model is registered to a coordinate system of intra-operative images acquired during the ablation procedure. One or more ablation site guidance maps are generated based on the registered patient-specific anatomical heart model and intra-operative patient-specific measurements acquired during the ablation procedure. The ablation site guidance maps may include myocardium diffusion and action potential duration maps. The ablation site guidance maps are generated using a computational model of cardiac electrophysiology which is personalized by fitting parameters of the cardiac electrophysiology model using the intra-operative patient-specific measurements. The ablation site guidance maps are displayed by a display device during the ablation procedure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Systems and methods for estimating physiological heart measurements from medical images and clinical data
A method and system for estimating physiological heart measurements from medical images and clinical data disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the heart is generated from medical image data of the patient. A patient-specific multi-physics computational heart model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model by personalizing parameters of a cardiac electrophysiology model, a cardiac biomechanics model, and a cardiac hemodynamics model based on medical image data and clinical measurements of the patient. Cardiac function of the patient is simulated using the patient-specific multi-physics computational heart model. The parameters can be personalized by inverse problem algorithms based on forward model simulations or the parameters can be personalized using a machine-learning based statistical model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
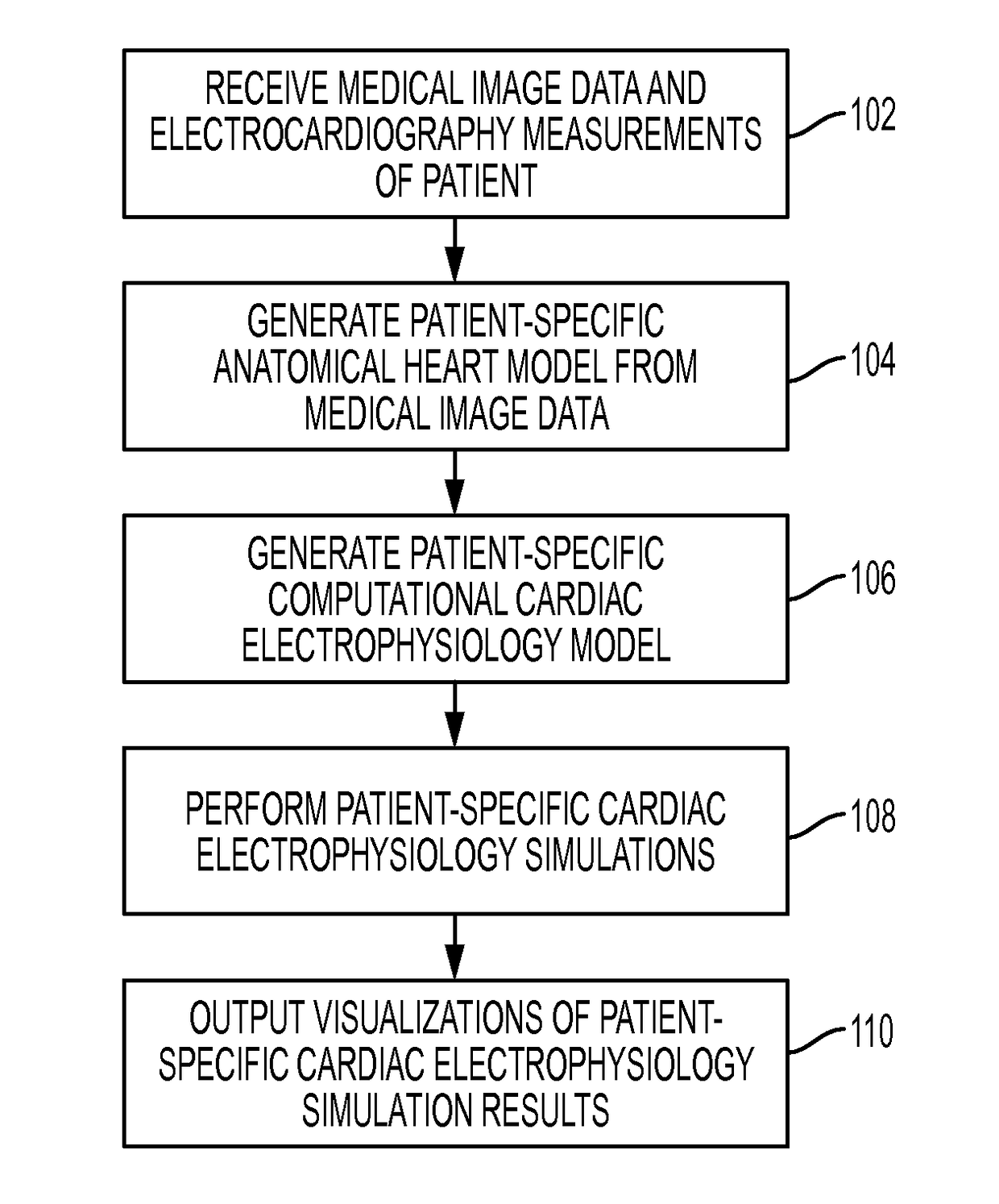
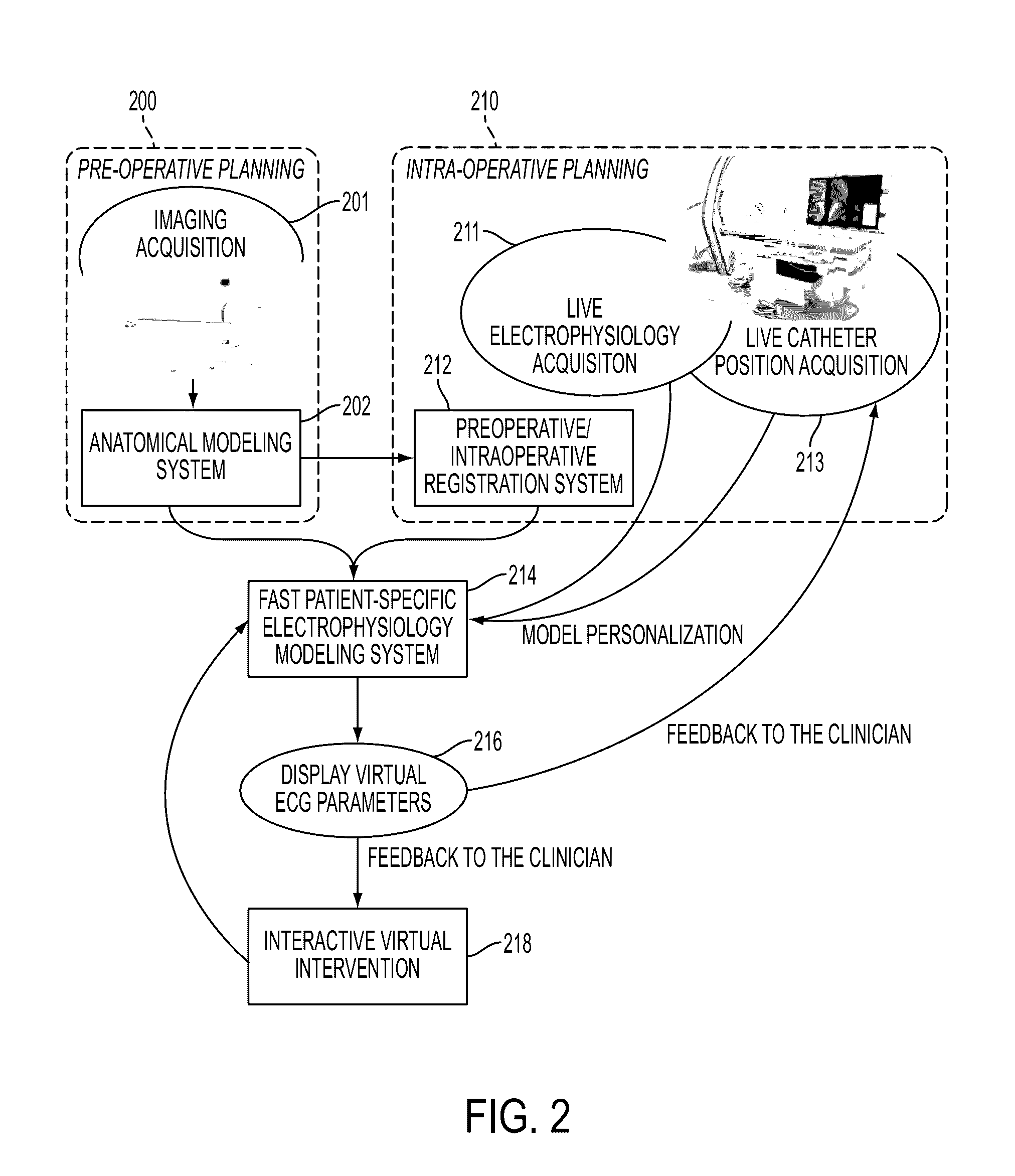
Method and System for Fast Patient-Specific Cardiac Electrophysiology Simulations for Therapy Planning and Guidance
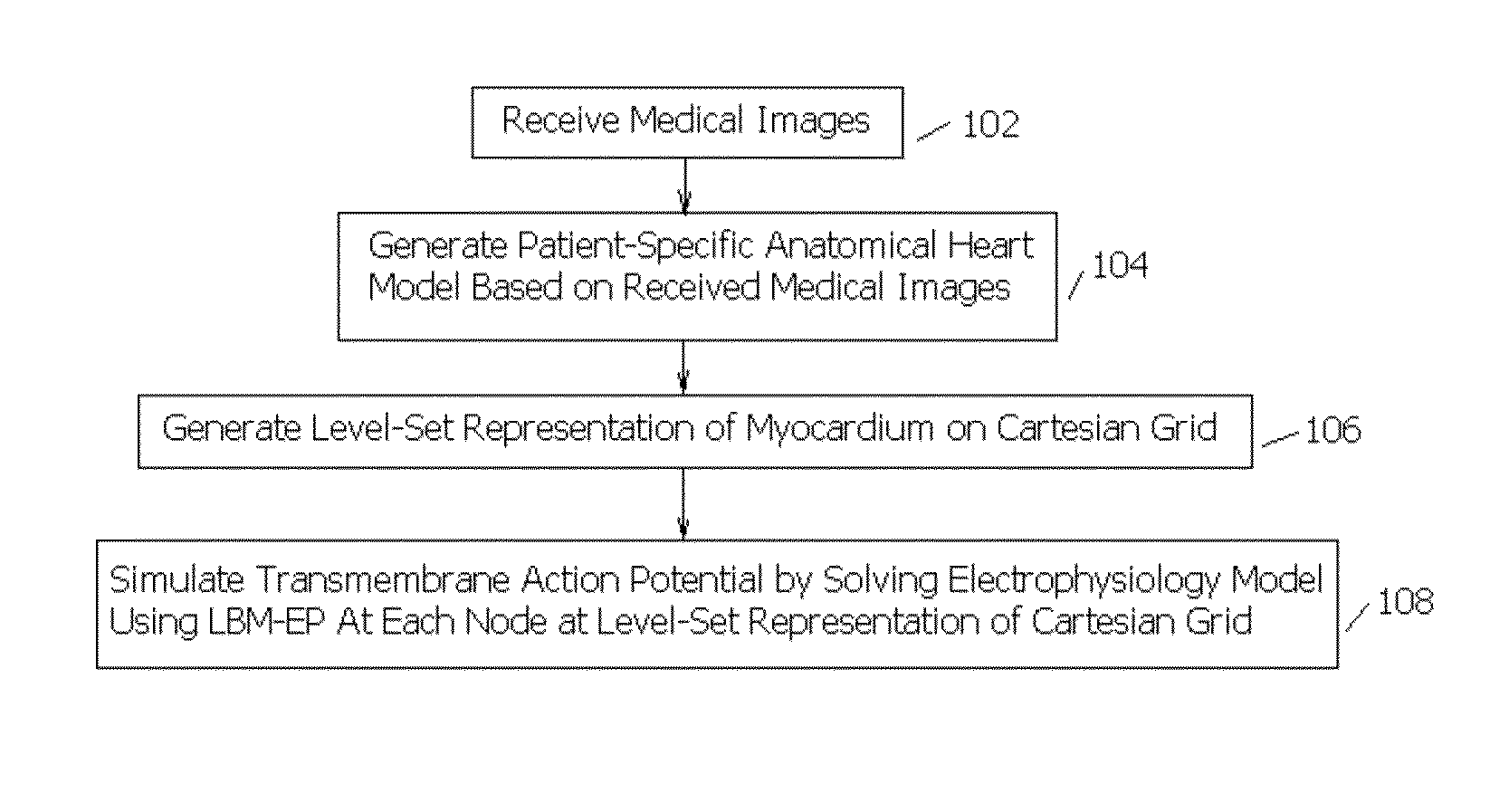
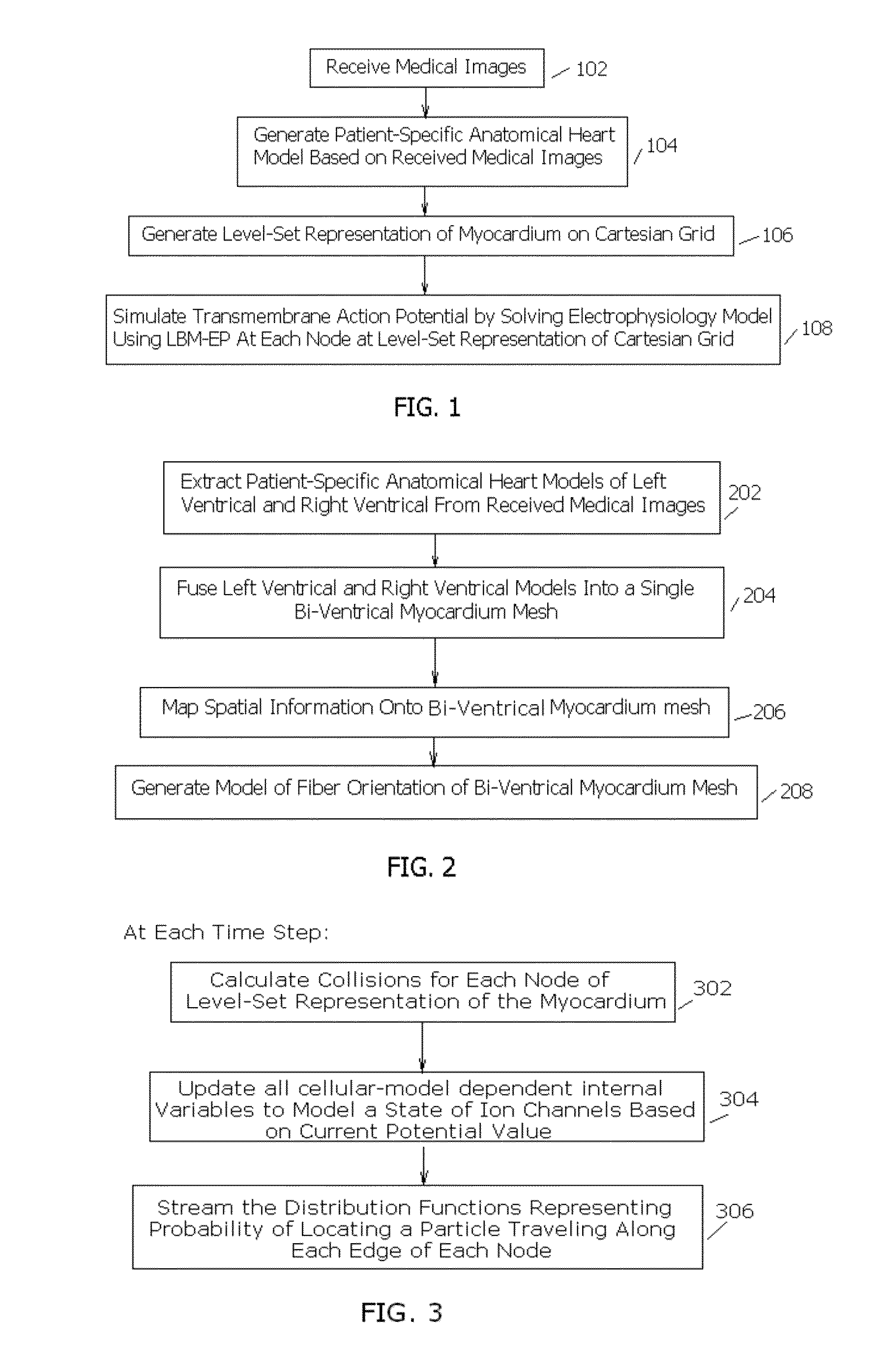
A method and system for patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology is disclosed. Particularly, a patient-specific anatomical model of a heart is generated from medical image data of a patient, a level-set representation of the patient-specific anatomical model is generated of the heart on a Cartesian grid; and a transmembrane action potential at each node of the level-set representation of the of the patient-specific anatomical model of the heart is computed on a Cartesian grid.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for patient specific planning and guidance of electrophysiology interventions
A method and system for patient-specific planning and guidance of electrophysiological interventions is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical heart model is generated from cardiac image data of a patient. A patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical heart model and patient-specific electrophysiology measurements. Virtual electrophysiological interventions are performed using the patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model. A simulated electrocardiogram (ECG) signal is calculated in response to each virtual electrophysiological intervention.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Cardiac- and/or respiratory-gated image acquisition system and method for virtual anatomy enriched real-time 2D imaging in interventional radiofrequency ablation or pacemaker placement procedures
ActiveCN102196768AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac cyclePacemaker Placement
The present invention refers to the field of cardiac electrophysiology (EP) and, more specifically, to image-guided radio frequency ablation and pacemaker placement procedures. For those procedures, it is proposed to display the overlaid 2D navigation motions of an interventional tool intraoperatively obtained from the same projection angle for tracking navigation motions of an interventional tool during an image-guided intervention procedure while being navigated through a patient's bifurcated coronary vessel or cardiac chambers anatomy in order to guide e.g. a cardiovascular catheter to a target structure or lesion in a cardiac vessel segment of the patient's coronary venous tree or to a region of interest within the myocard. In such a way, a dynamically enriched 2D reconstruction of the patient's anatomy is obtained while moving the interventional instrument. By applying a cardiac and / or respiratory gating technique, it can be provided that the 2D live images are acquired during the same phases of the patient's cardiac and / or respiratory cycles. Compared to prior-art solutions which are based on a registration and fusion of image data independently acquired by two distinct imaging modalities, the accuracy of the two-dimensionally reconstructed anatomy is significantly enhanced.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and Method for Analyzing Biological Signals and Generating Electrophyisology Maps
A method of generating a cardiac electrophysiology map includes receiving a reference biological signal and an electrical signal indicative of electrical activity at a location on a patient's heart. Using a graphical user interface, a practitioner designates at least two trigger point icons, one upward-pointing and one downward-pointing, on a graphical representation of the reference biological signal (e.g., a waveform). By pairing one upward-pointing icon with one downward-pointing icon, a plurality of triggering criteria are defined. Electrophysiology data points are captured and / or added to the electrophysiology map when the triggering criteria are satisfied.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Expandable transluminal sheath
ActiveUS20110282156A1Minimize strain and catchingPrevent shrinkageCannulasPretreated surfacesBiomedical engineeringCardiac electrophysiology
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Method and system for patient specific planning of cardiac therapies on preoperative clinical data and medical images
A method and system for patient-specific planning of cardiac therapy, such as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), based on preoperative clinical data and medical images, such as ECG data, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, and ultrasound data, is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles is generated from medical image data of a patient. A patient-specific computational heart model, which comprises cardiac electrophysiology, biomechanics and hemodynamics, is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles and clinical data. Simulations of cardiac therapies, such as CRT at one or more anatomical locations are performed using the patient-specific computational heart model. Changes in clinical cardiac parameters are then computed from the patient-specific model, constituting predictors of therapy outcome useful for therapy planning and optimization.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and Method for Analyzing Biological Signals and Generating Electrophysiology Maps
A method of generating a cardiac electrophysiology map includes receiving a reference biological signal and an electrical signal indicative of electrical activity at a location on a patient's heart. Using a graphical user interface, a practitioner designates at least two trigger point icons, one upward-pointing and one downward-pointing, on a graphical representation of the reference biological signal (e.g., a waveform). By pairing one upward-pointing icon with one downward-pointing icon, a plurality of triggering criteria are defined. Electrophysiology data points are captured and / or added to the electrophysiology map when the triggering criteria are satisfied.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
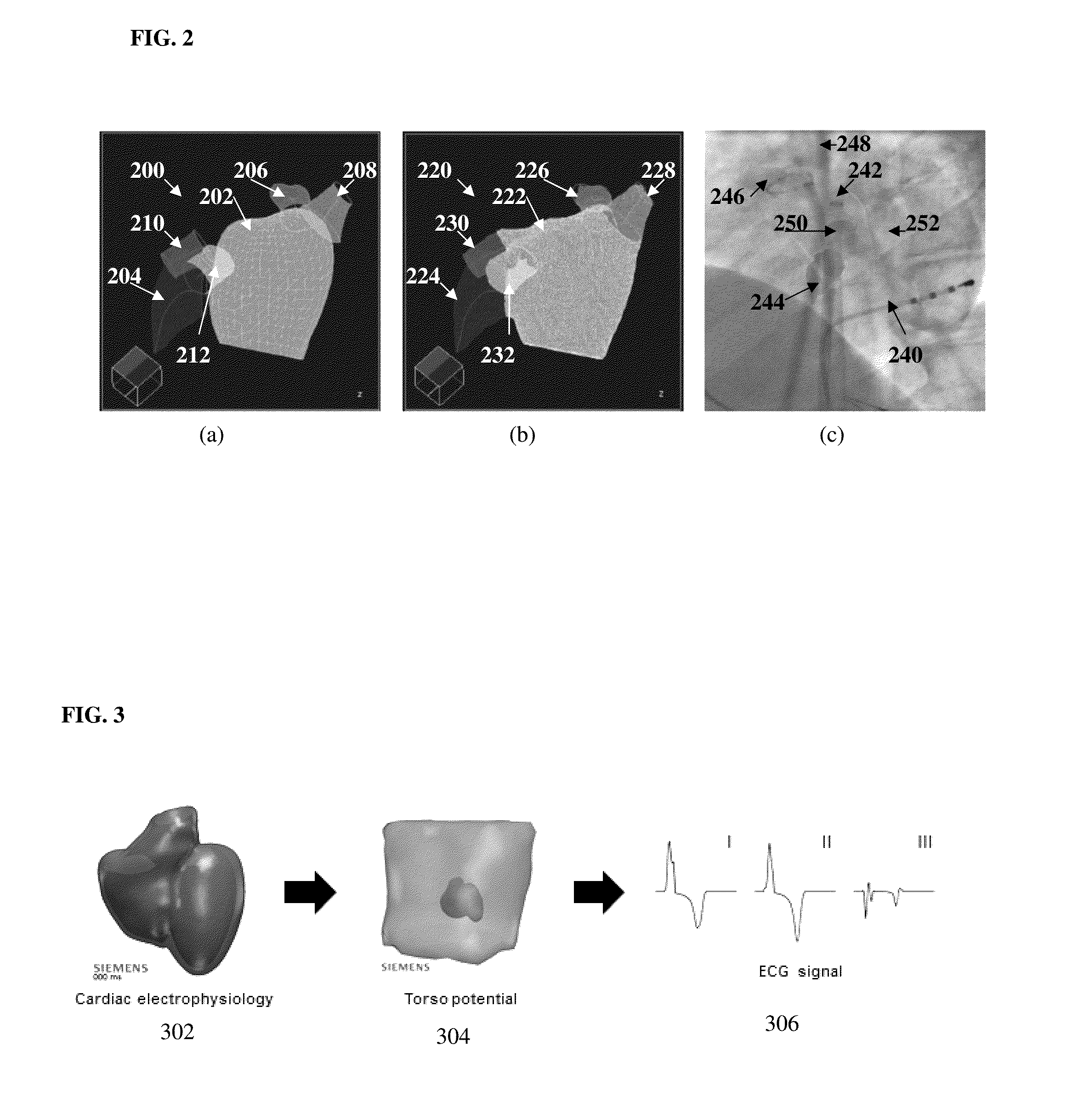
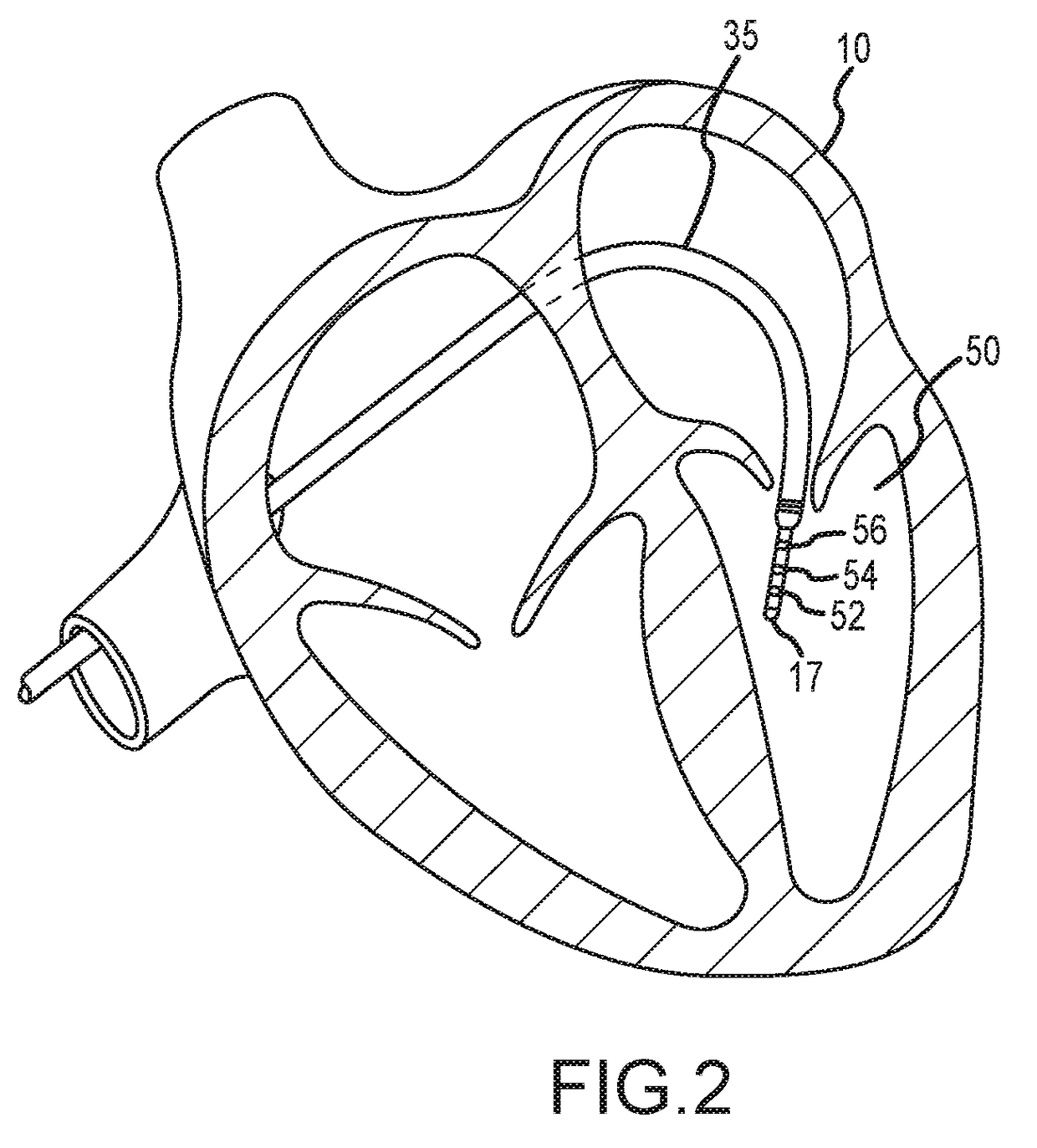
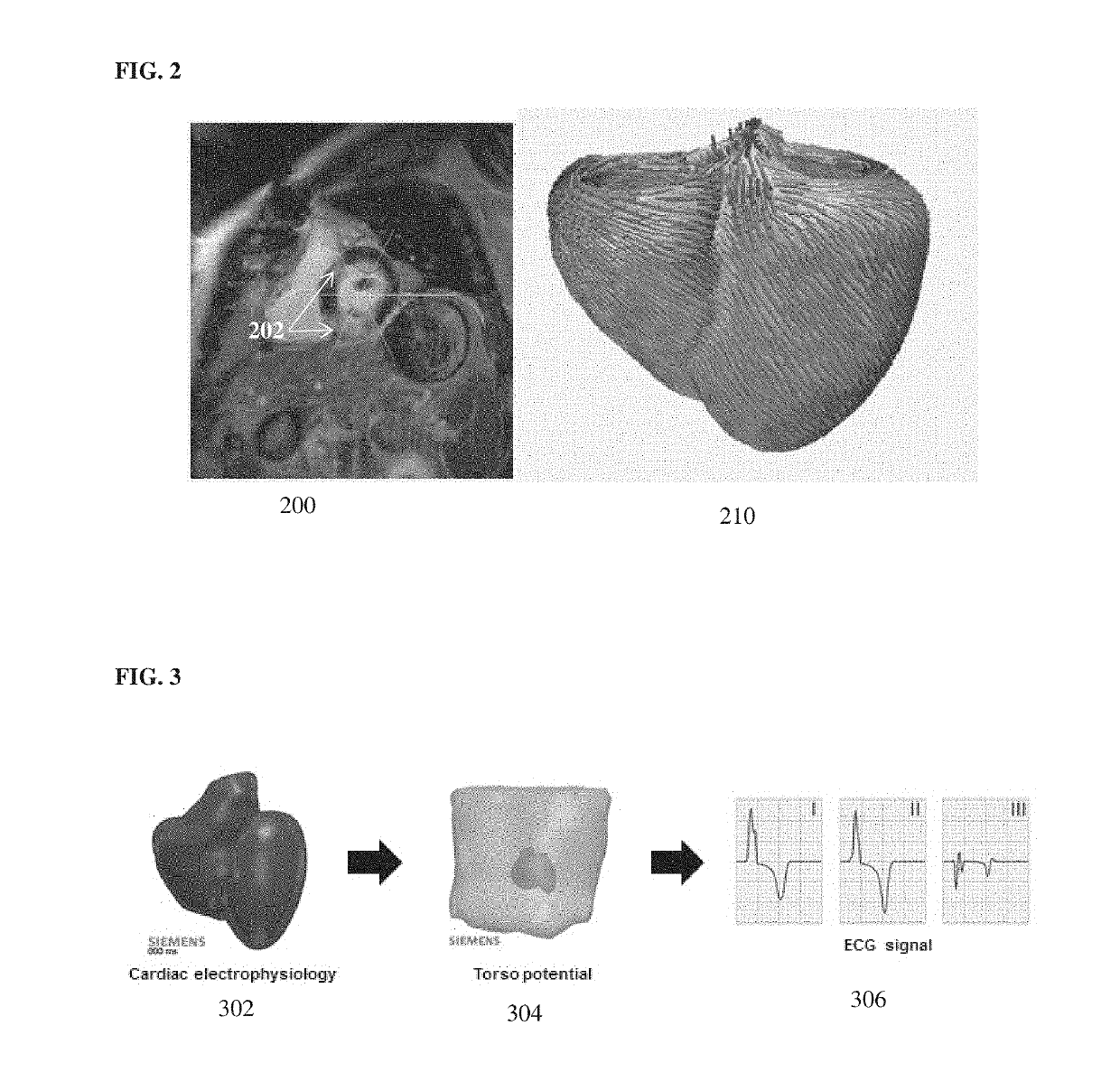
System and Method for Non-Invasively Estimating Electrophysiological Maps and Measurements from Cardio-Thoracic 3D Images and Electrocardiography Data
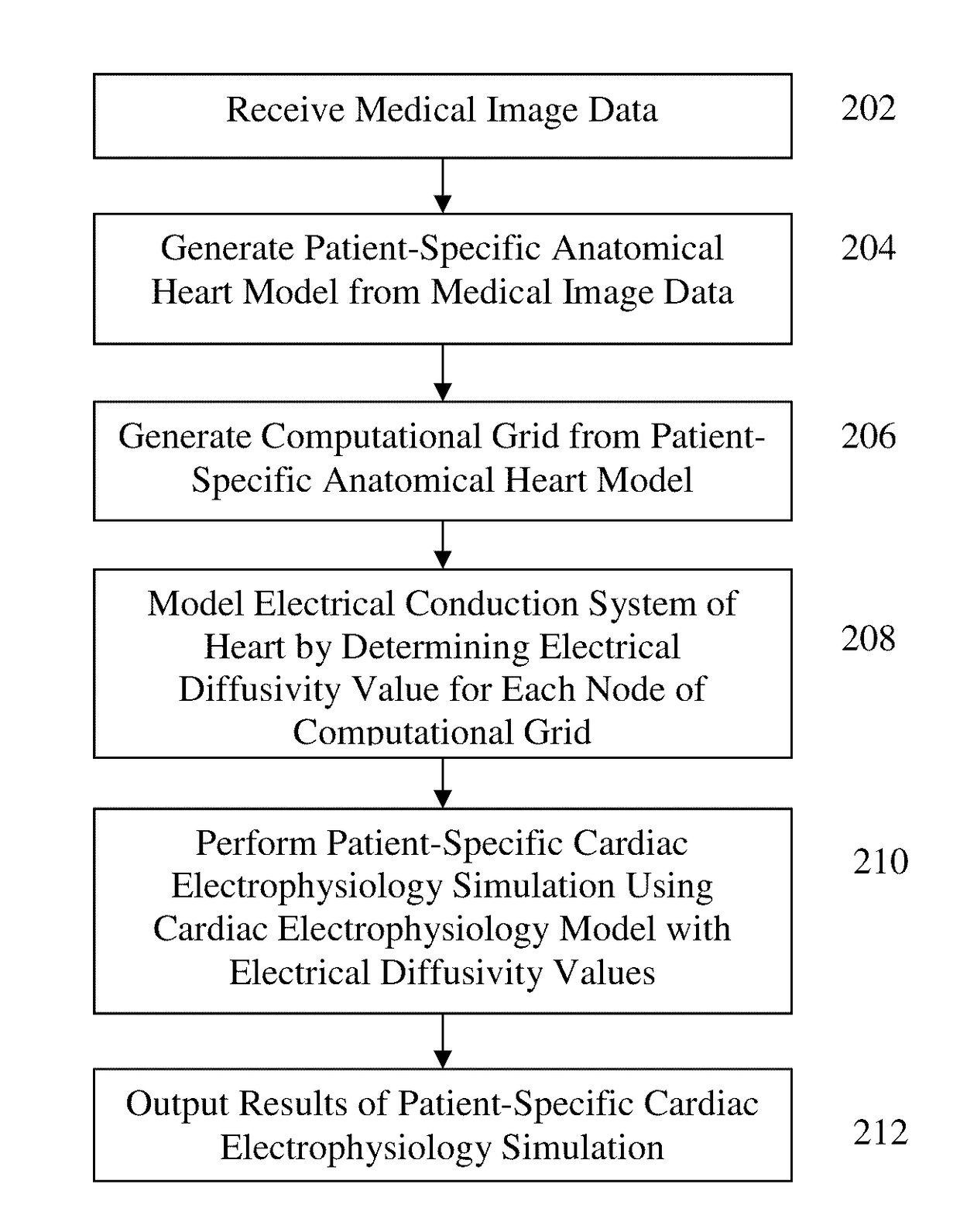
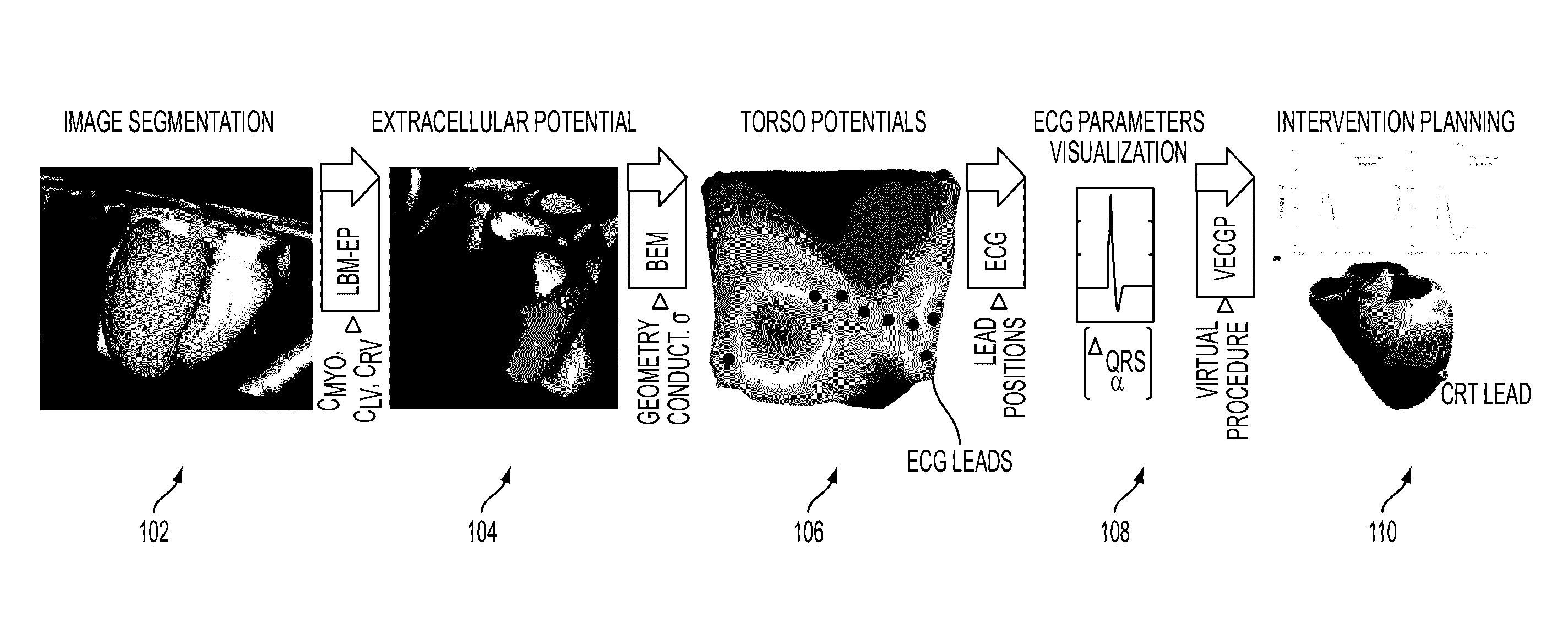
A method and system for patient-specific simulation of cardiac electrophysiology is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical heart model is generated from medical image data of a patient. A patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model is generated based on simulated torso potentials and body surface potential measurements of the patient. Cardiac electrophysiology of the patient is simulated over time for the patient-specific anatomical heart model using the patient-specific electrophysiology model. One or more electrophysiology maps are generated based on the cardiac electrophysiology simulated using the patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
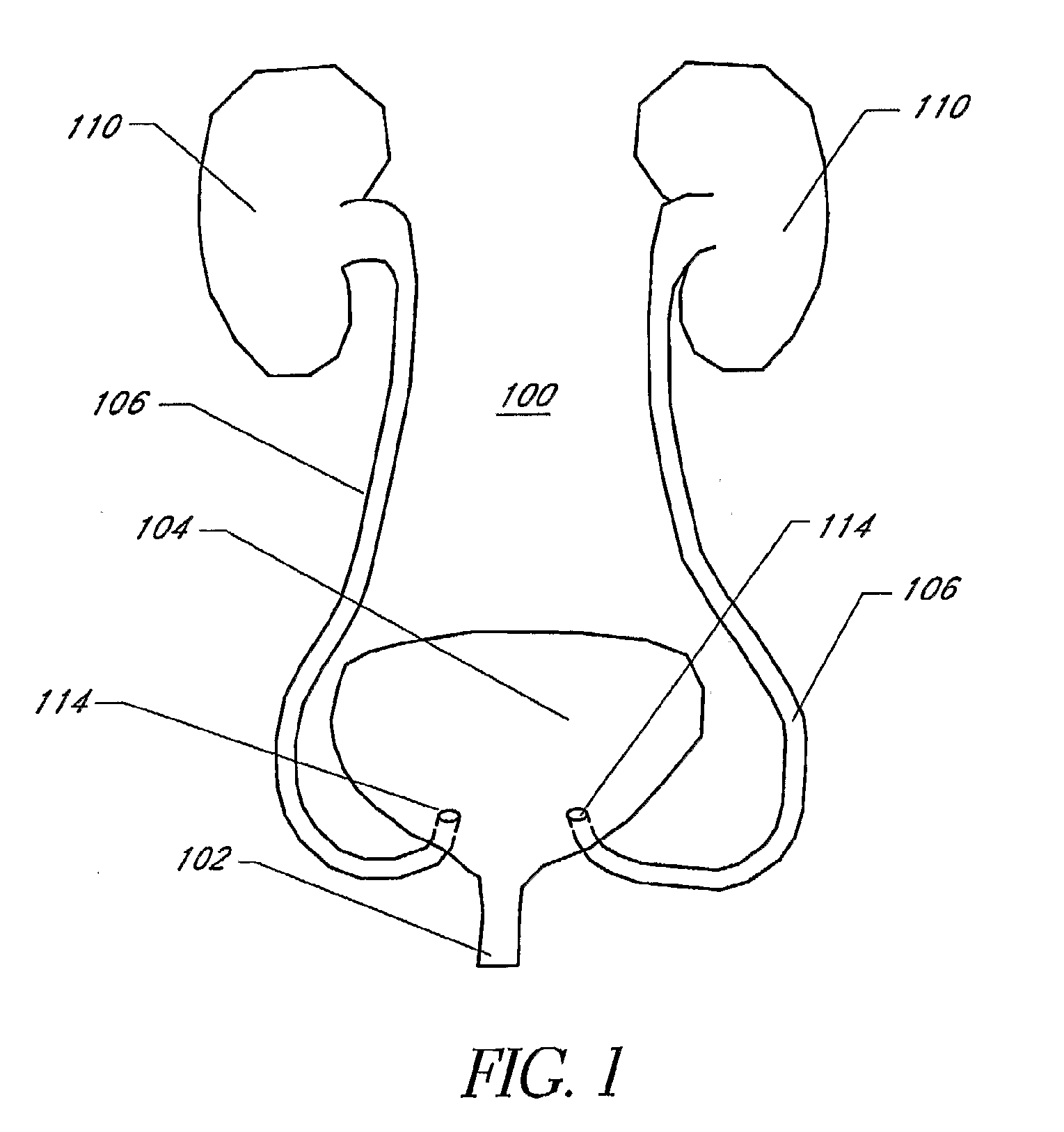
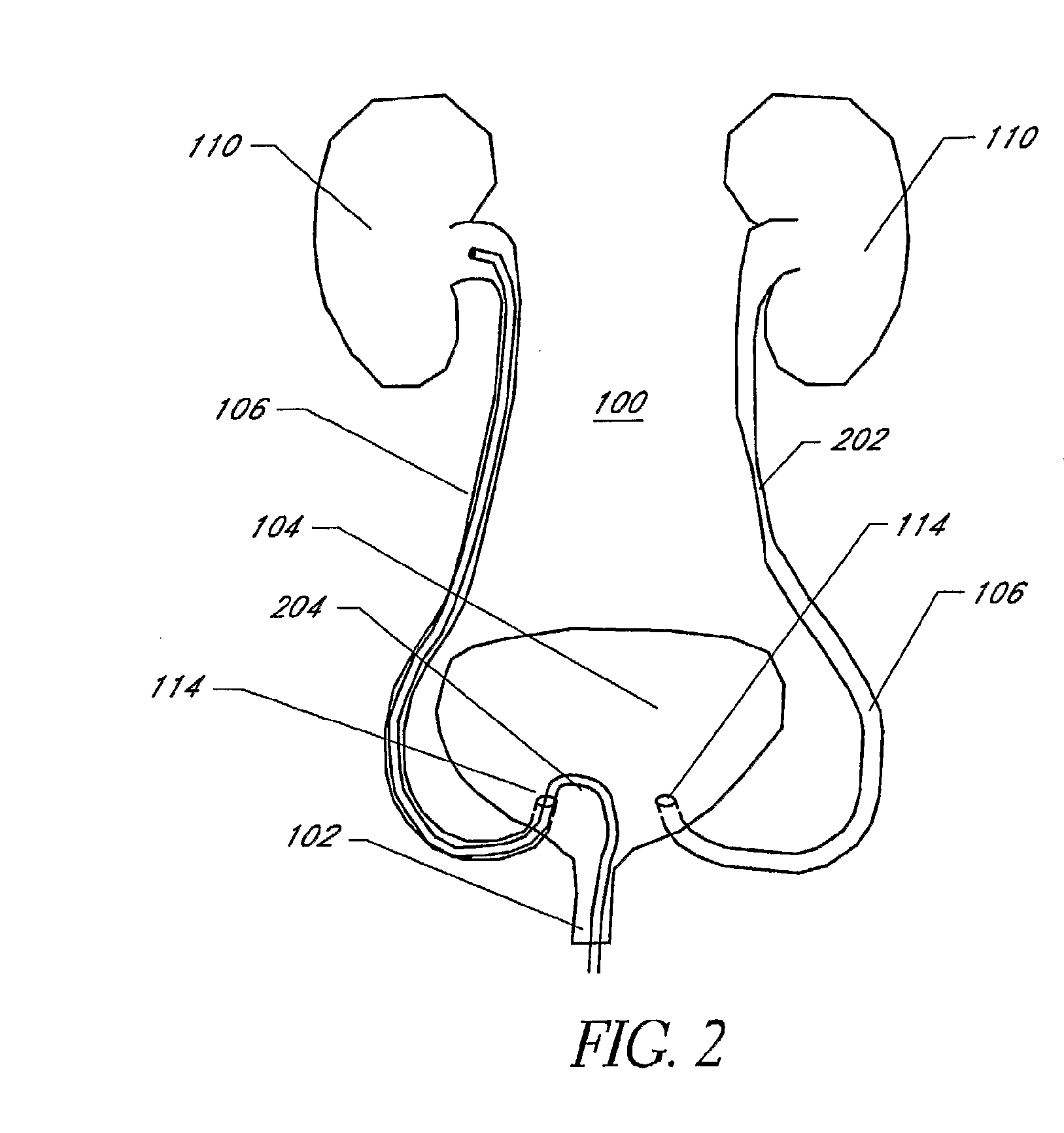
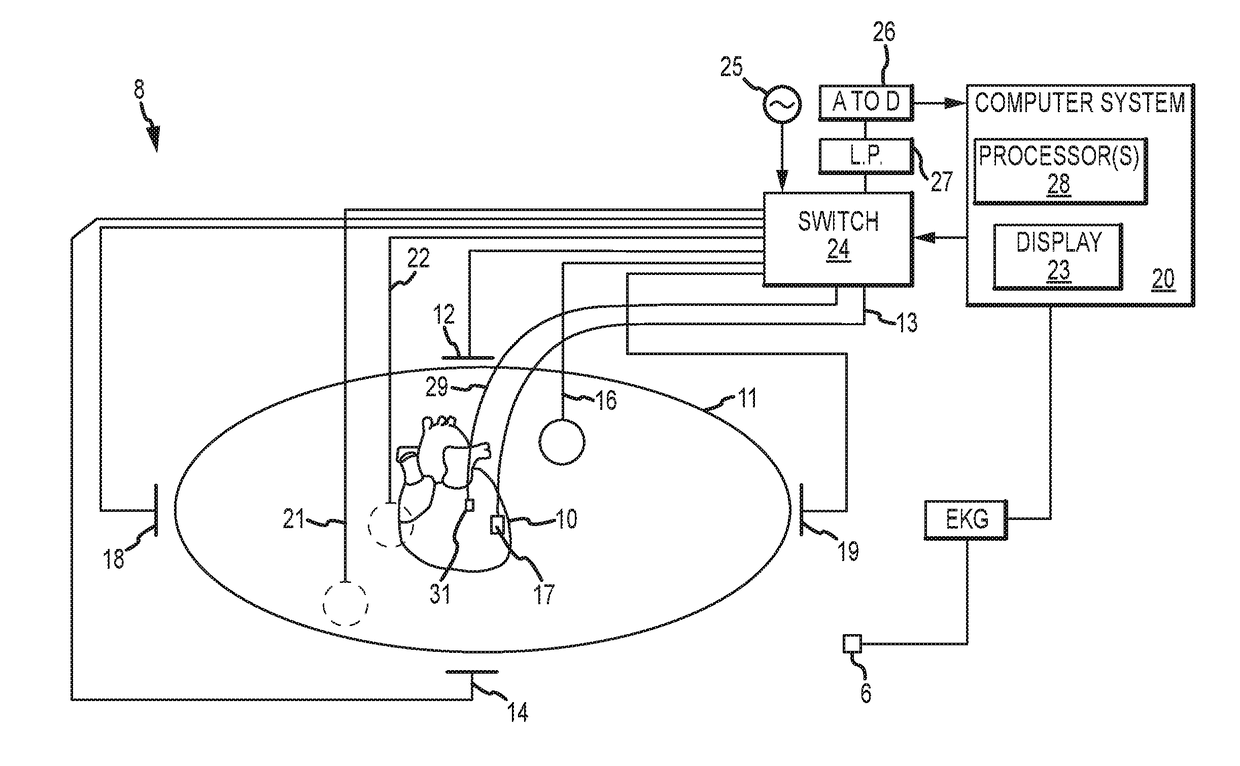
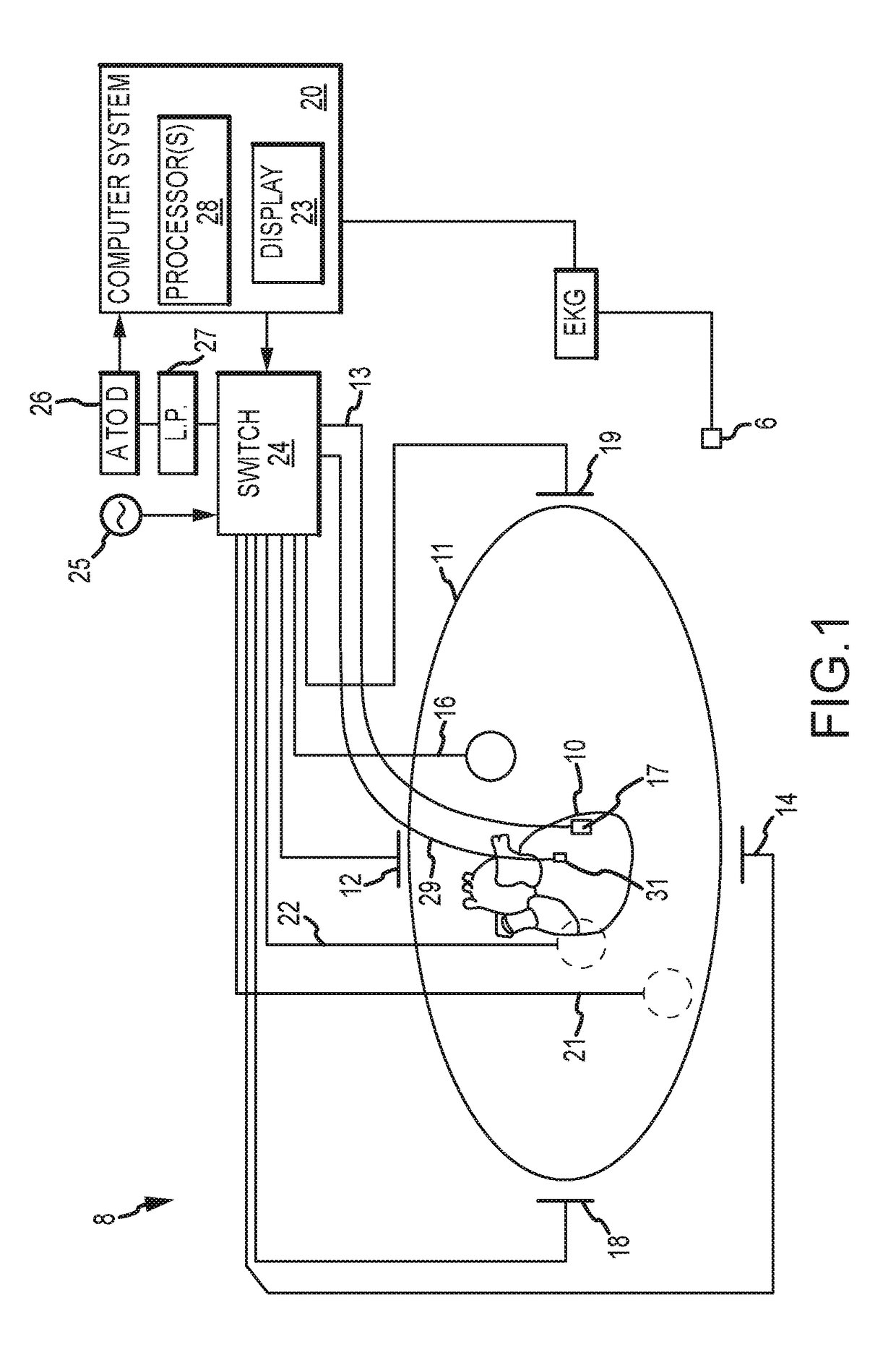
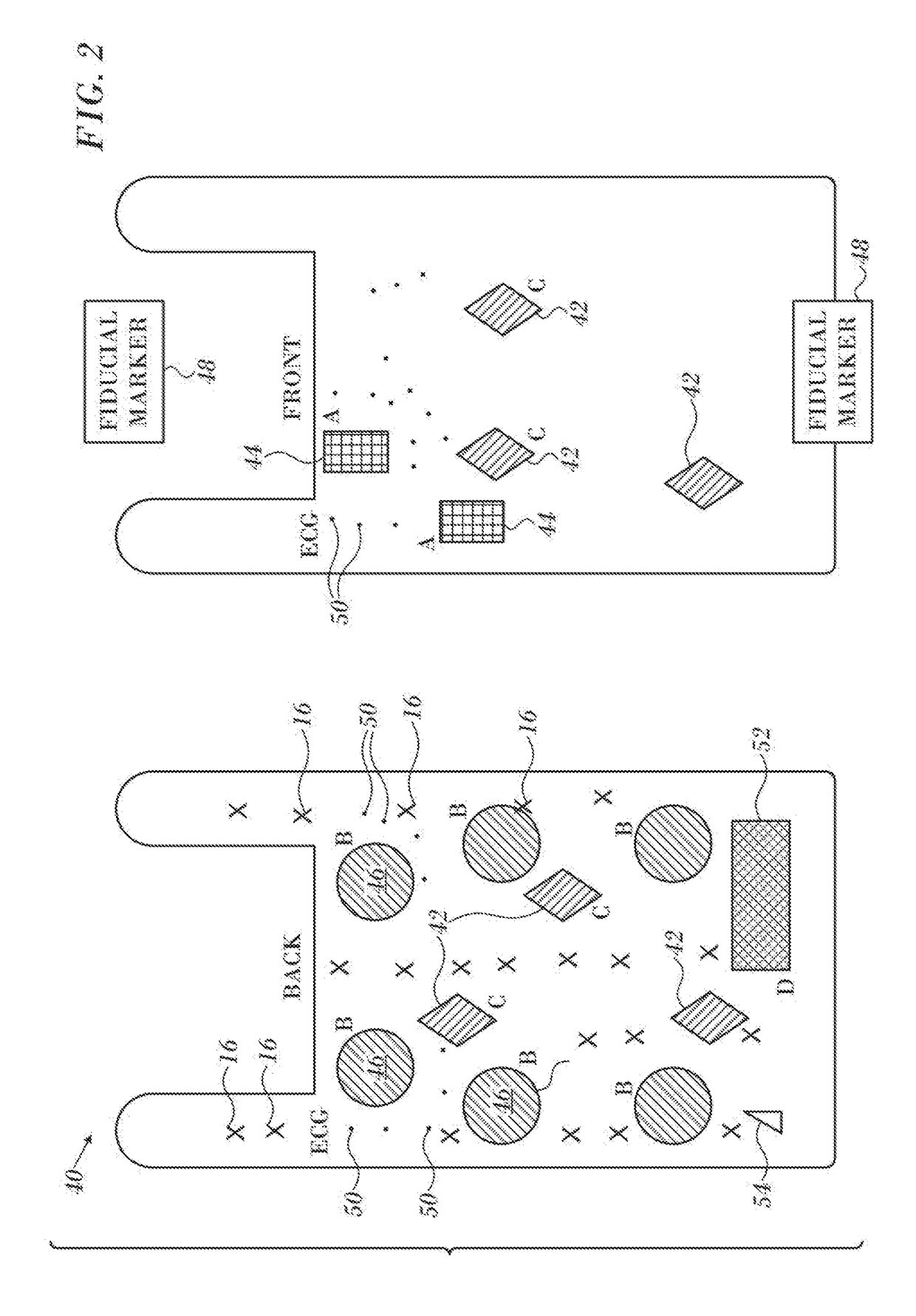
Combination torso vest to map cardiac electrophysiology
Cardiac catheterization is carried out by clothing a subject in a torso vest having a plurality of sensing electrodes, magnetic location sensors, active current location sensors and patches for establishing galvanic contact with the skin. A multi-electrode probe is inserted into a cardiac chamber such that a plurality of intracardiac electrodes are disposed at respective locations in the heart. Respective locations are determined using the active current location sensors, Electrical calibration signals are emitted from the intracardiac electrodes, and received in the sensing electrodes of the torso vest. Relationships between the emitted calibration signals and the received calibration signals in the intracardiac electrodes are established to map a correspondence between the received calibration signals and the respective locations.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
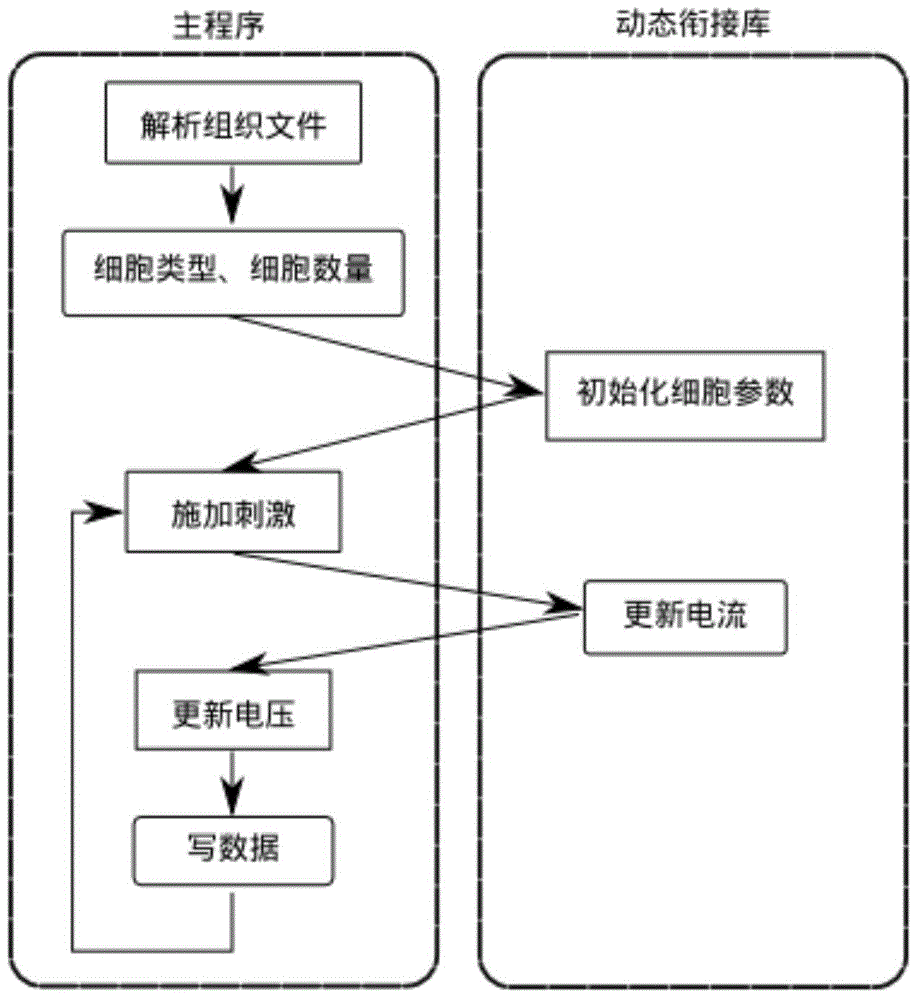
Steering type virtual heart simulation method
ActiveCN104537187ARealize simulationAchieve the purpose of simulationSpecial data processing applicationsOrganizational documentComputation process
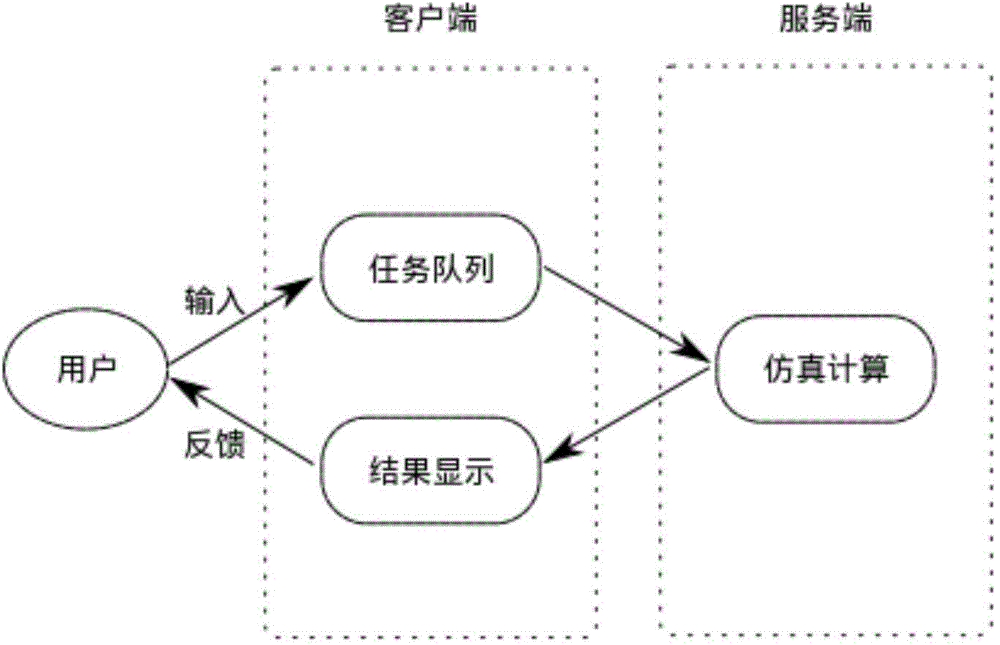
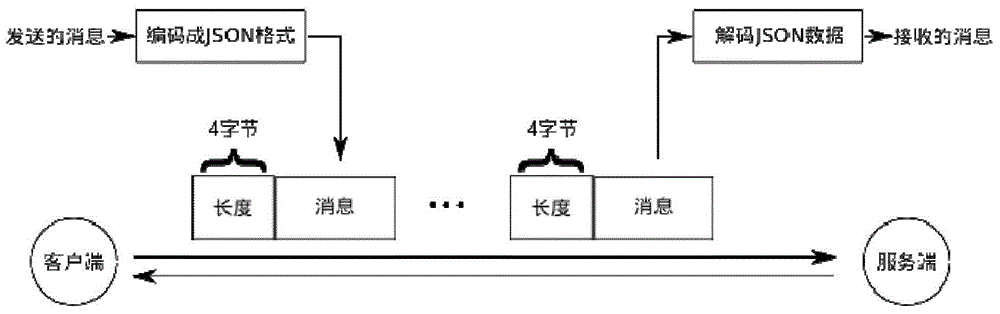
The invention provides a steering type virtual heart simulation method, and relates to a method for cardiac electrophysiology simulation based on steering computation. The steering type virtual heart simulation method aims at solving the problems that traditional heart modeling computation is complex and unreasonable or fails, the whole process needs to be re-conducted after correction is finished, and therefore a large number of human and material resources are wasted. The steering type virtual heart simulation method includes the steps that firstly, the virtual heart model electrophysiology simulation computation process includes the three parts of organizational document analysis, boundary initialization and simulation iterative computation, and a virtual cardiac electrophysiology simulation framework is designed; secondly, a steering type control simulation client side state machine is designed; thirdly, a client side and service side program communication mode and a message format are designed, wherein the C / S mode is adopted, and a client side program and a service side program communicate with each other based on a TCP. The method is applied to the field of computer simulation.
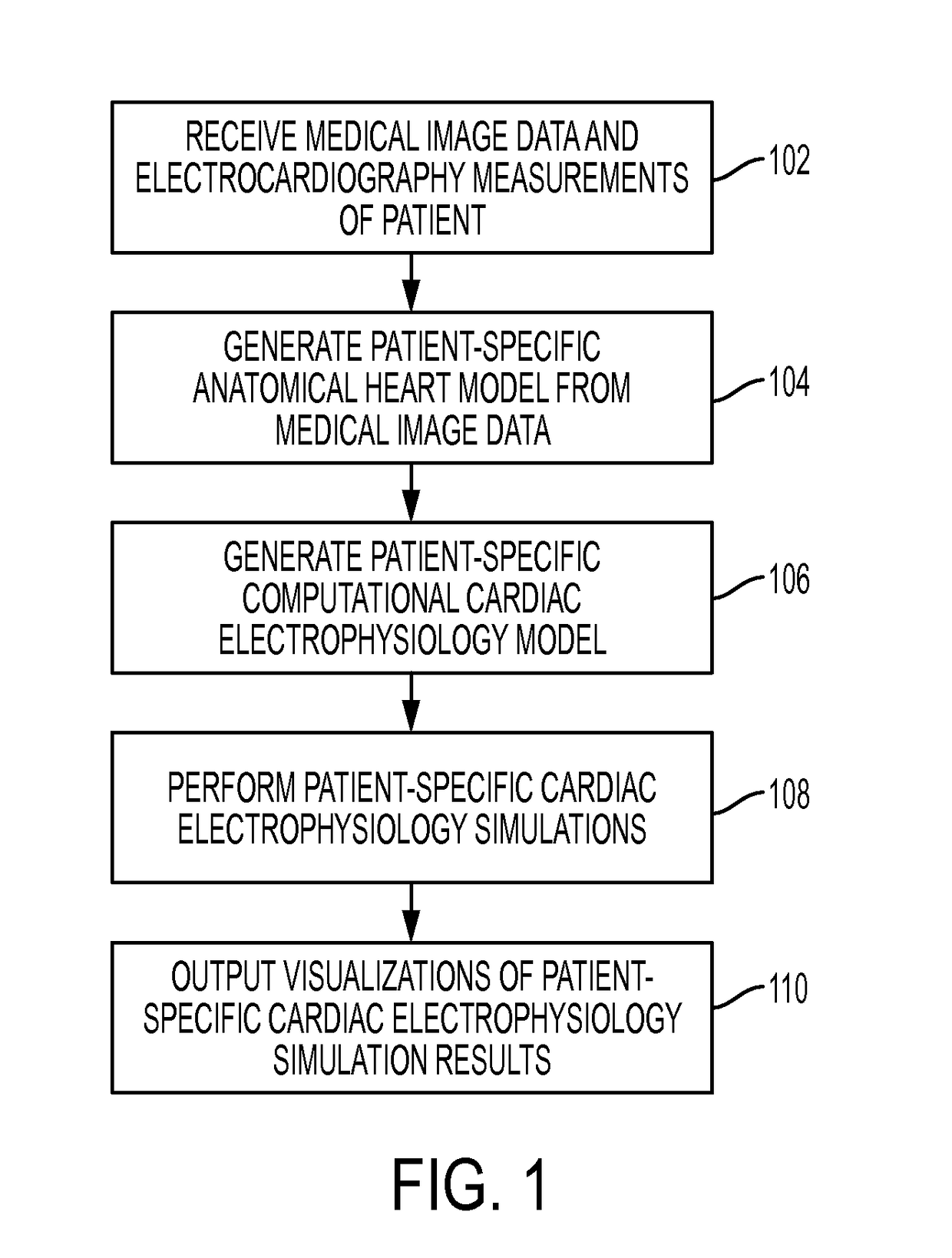
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
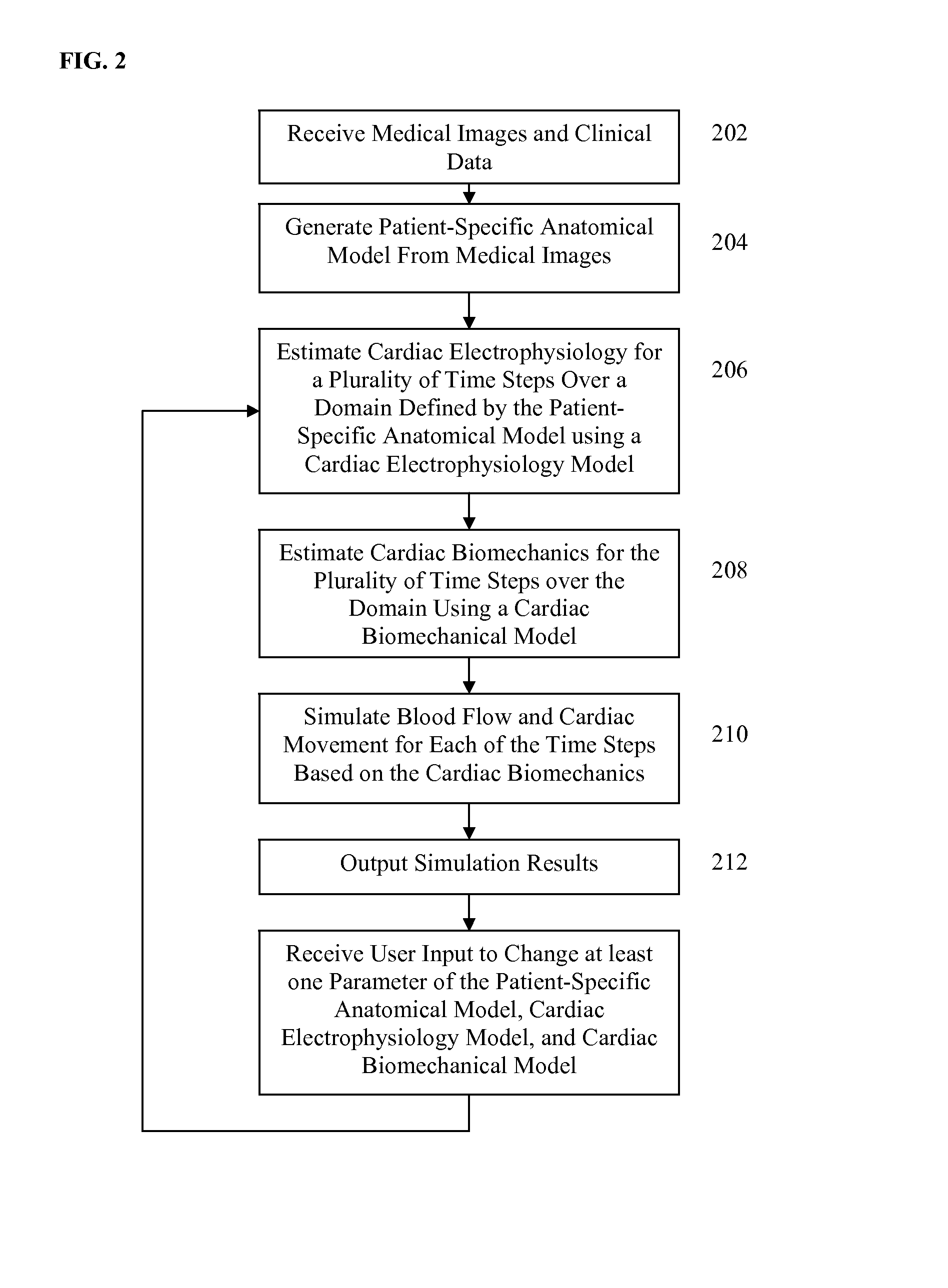
Method and system for interactive computation of cardiac electromechanics
A method and system for simulating cardiac function of a patient is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of at least a portion of the patient's heart is generated from medical image data of the patient. Cardiac electrophysiology potentials are calculated over a computational domain defined by the patient-specific anatomical model for each of a plurality of time steps using a patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model. The electrophysiology potentials acting on a plurality of nodes of the computational domain are calculated in parallel for each time step. Biomechanical forces over the computational domain for each of the plurality of time steps using a cardiac biomechanical model coupled to the cardiac electrophysiology model. The biomechanical forces acting on a plurality of nodes of the mesh domain are estimated in parallel for each time step. Blood flow and cardiac movement are computed at each of the plurality of time steps based on the calculated biomechanical forces. Computed electrophysiology potentials, biomechanical forces and cardiac parameters are displayed, user input is interactively received to change at least one of the parameters of the patient-specific models, and the electrophysiology potentials, the biomechanical forces, and the blood flow and cardiac movement are recalculated.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Three-dimensional modeling method
The invention discloses a three-dimensional modeling method. The method comprises the following steps: generating a topological surface morphology of medicinal three-dimensional marking data through a convex hull algorithm; initially generating a deformable sealed cambered surface which envelops all the acquired three-dimensional marking data points; iteratively approaching the deformable sealed cambered surface to the topological surface morphology by using a level set reconstruction method; and partially adjusting the deformable sealed cambered surface near each medicinal three-dimensional marking data, so that part of the deformable sealed cambered surface can be superposed with each three-dimensional marking data, thereby establishing a sealed smooth superpose model of which the accuracy approaches to the topological surface morphology of the medicinal three-dimensional marking data. By acquiring the medicinal three-dimensional marking data with medicinal ducts in the cardiac chamber, the medicinal three-dimensional mark data is performed three-dimensional surface reconstruction ao as to establish a three-dimensional surface model of which the accuracy approaches to the surface morphology of the endomembrane in the cardiac chamber; and the three-dimensional surface model can be used for supervising and assisting doctors to do researches of cardiac electrophysiology or arrhythmia.
Owner:李楚雅
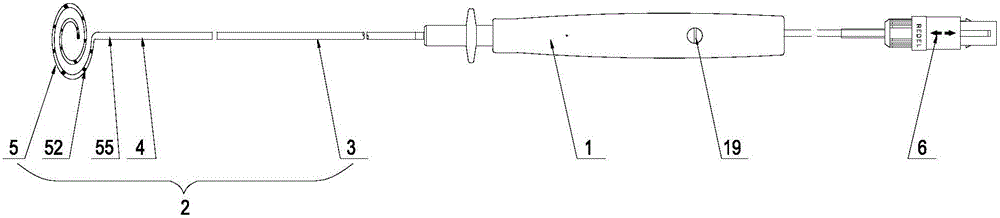
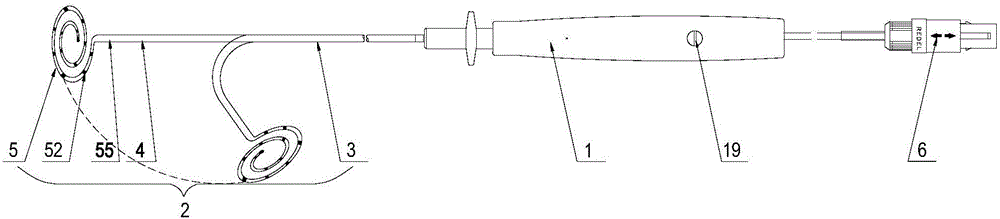
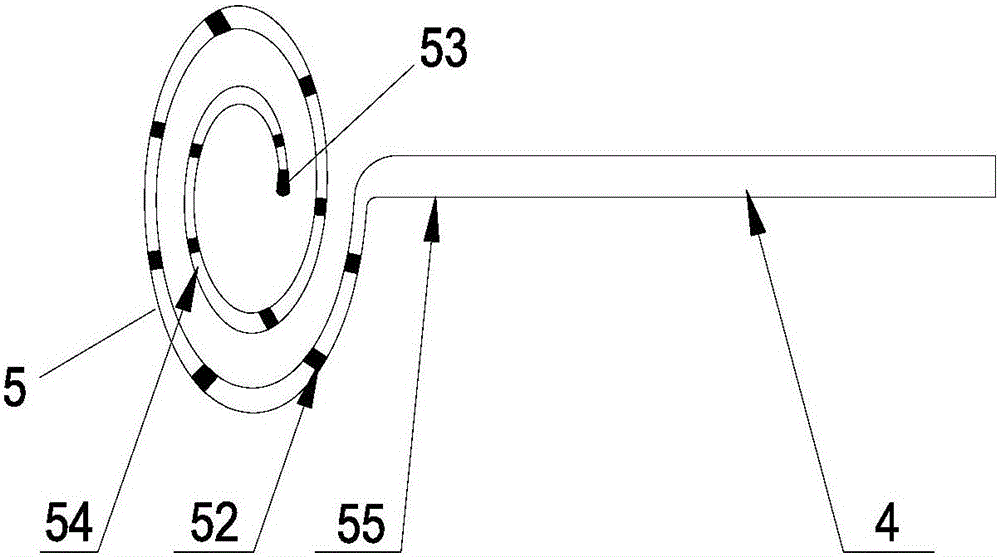
Magnetic-positioning ring mapping electrode catheter provided with sensor and disc-like spiral structure at head end
ActiveCN105919589AAchieve positioningIncrease contactCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityX-ray
The invention discloses a magnetic-positioning ring mapping electrode catheter provided with a sensor and a disc-like spiral structure at the head end and aims to shorten exposure time of X-rays generated through traditional cardiac electrophysiology mapping, reduce use of a contrast medium and reduce identification difficulty of a doctor. A controllable ring is fixedly connected onto a far end head of a catheter and comprises a controllable ring shaped steel wire, the controllable ring shaped steel wire adopts a spiral structure spirally encircled by at least one loop in a plane, the spiral structure is disc-like, the controllable ring shaped steel wire and an axis of the catheter are arranged in the same plane, the controllable ring shaped steel wire is covered with a controllable ring shaped steel wire outer sleeve and an electrode end tube sequentially, at least one ring electrode is arranged on the surface of a ring body of the electrode end tube, the sensor is arranged in a near end of the controllable ring, and a bracing wire is arranged in the catheter. Compared with the prior art, the magnetic-positioning ring mapping electrode catheter has the advantages that the collecting capability of signals is improved, effectiveness and operability of an operation are greatly improved clinically, and the operation time is saved.
Owner:APT MEDICAL INC
System and method for patient-specific image-based guidance of cardiac arrhythmia therapies
ActiveUS10296707B2Maximize therapeutic outcomeReduce intervention timeMedical simulationHeart stimulatorsRadiologyCardiac arrhythmia
A method and system for image-based patient-specific guidance of cardiac arrhythmia therapies is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical heart model is generated from medical image data of a patient. A patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical heart model and electrophysiology measurements of the patient. One or more virtual electrophysiological interventions are performed using the patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model. One or more pacing targets or ablation targets based on the one or more virtual electrophysiological interventions are displayed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and Method for Electrophysiology Procedures
A method of performing a cardiac electrophysiology procedure includes using a magnetically-localizable catheter to generate a cardiac model and then removing the catheter from the patient's heart. An electrophysiology catheter, such as a multi-electrode, non-contact mapping catheter, is then inserted into the heart. The electrophysiology catheter is also magnetically-localizable, and therefore can be localized within the model. The electrophysiology catheter is used to perform the electrophysiology procedure, such as electrophysiological mapping or ablation. Advantageously, because the electrophysiology catheter is magnetically-localizable, it can move during the electrophysiology procedure, either deliberately or inadvertently, without invalidating any previously-collected data or requiring recreation of the cardiac model.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com