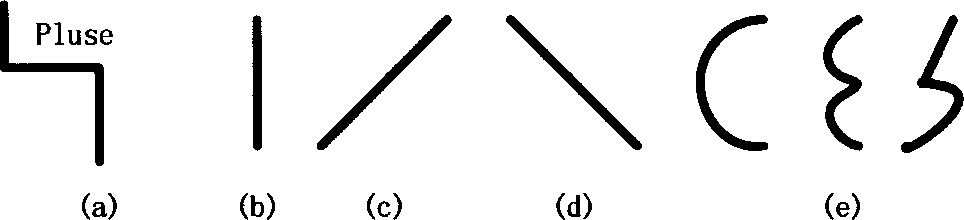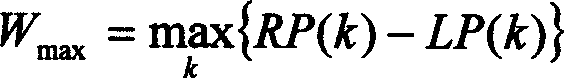Patents
Literature
44 results about "Set representation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
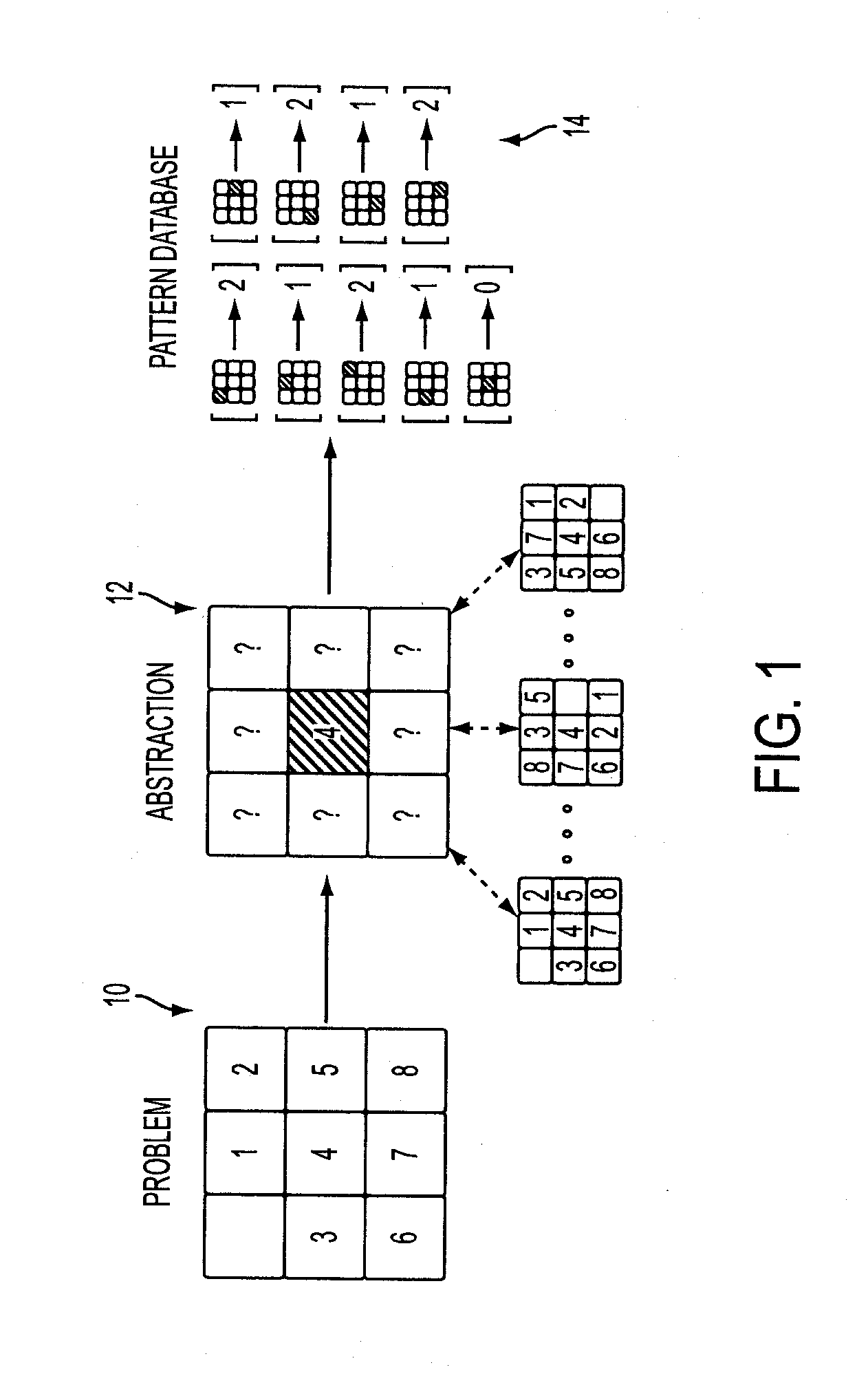
In representation of set there are three ways : Representation of set. 1) A set is denoted by a capital letter. Example : set A, set B, set N etc. 2) The elements of a set are denoted by small letters.All elements are written in { } (curly) brackets separated by , (comma).
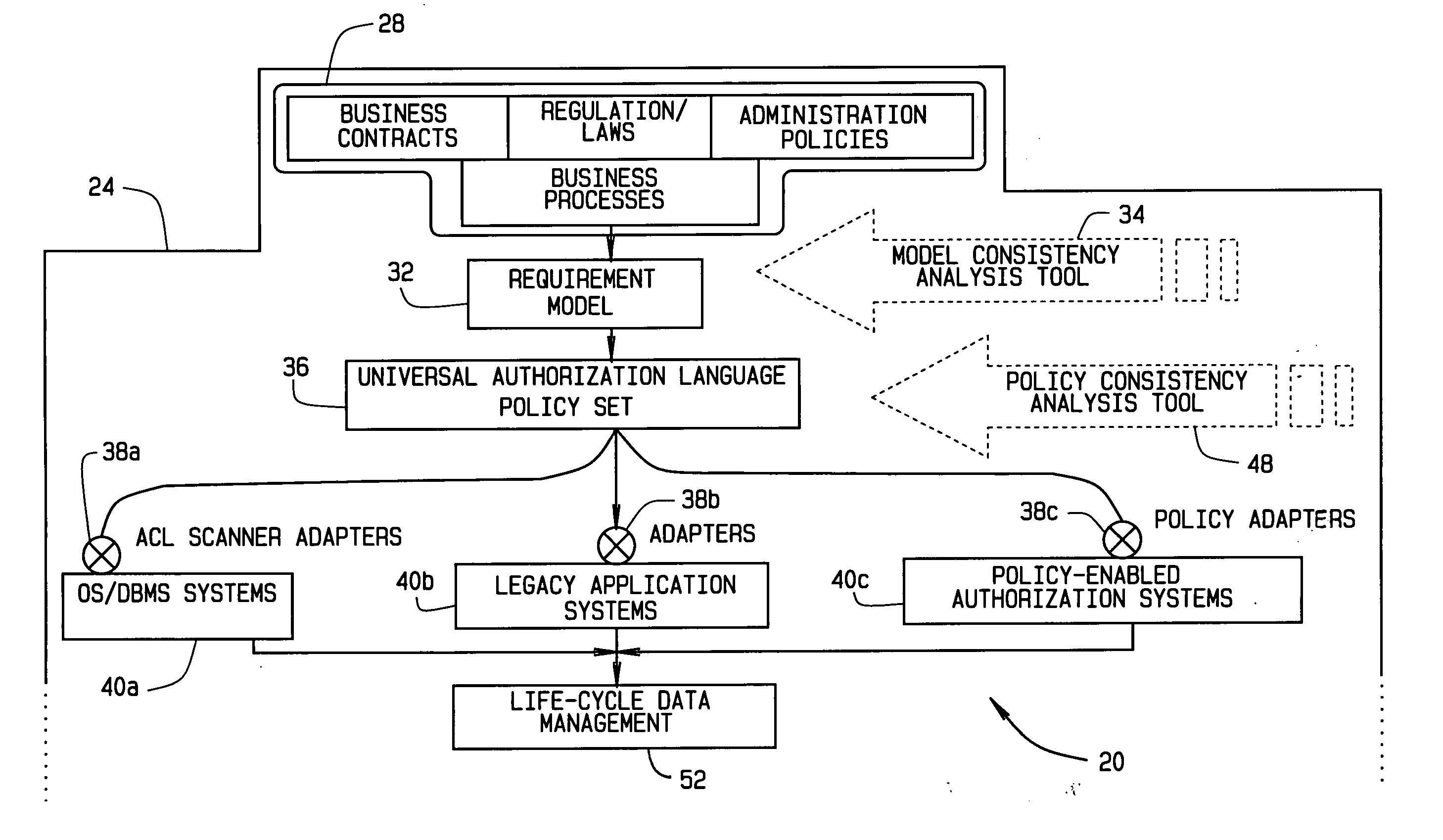
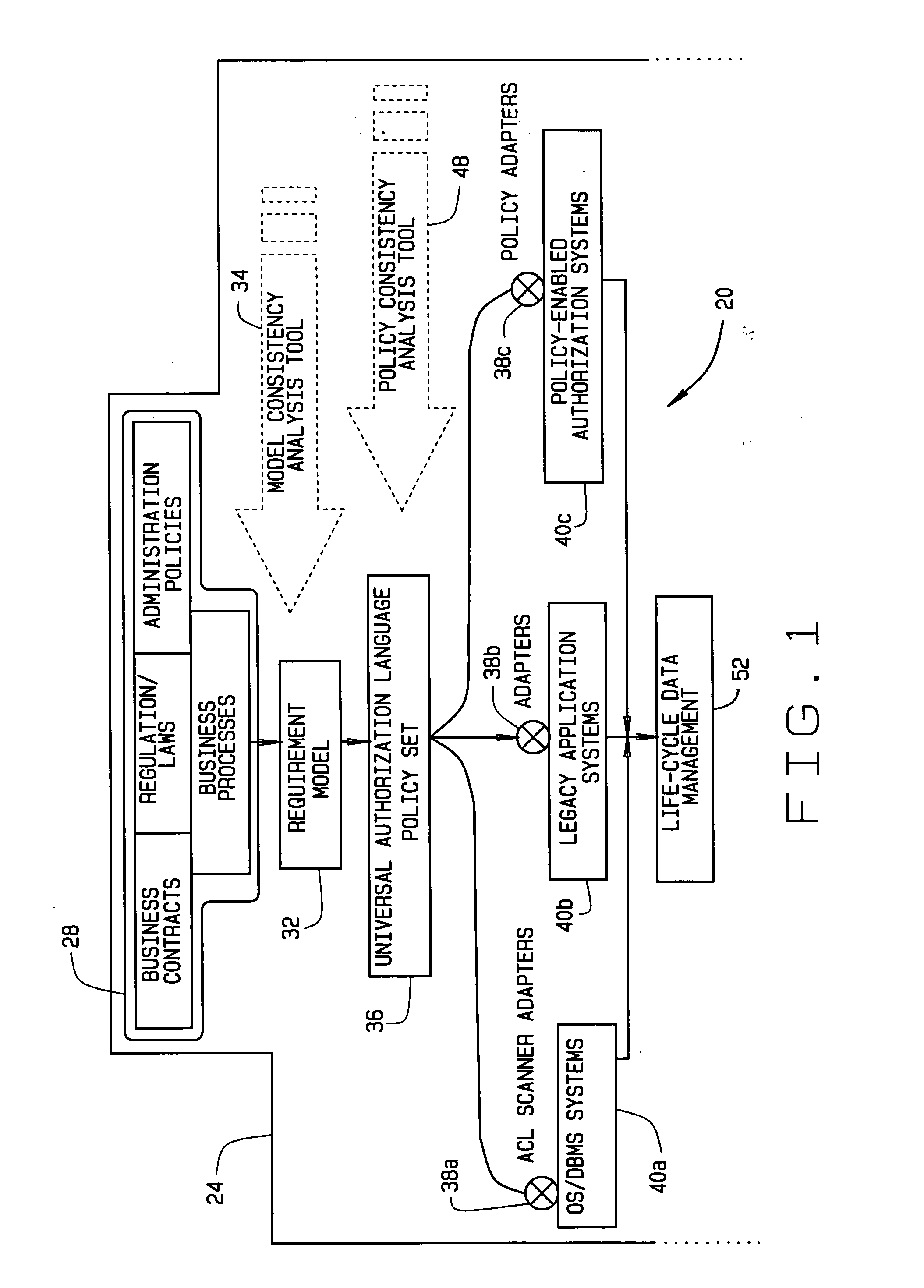
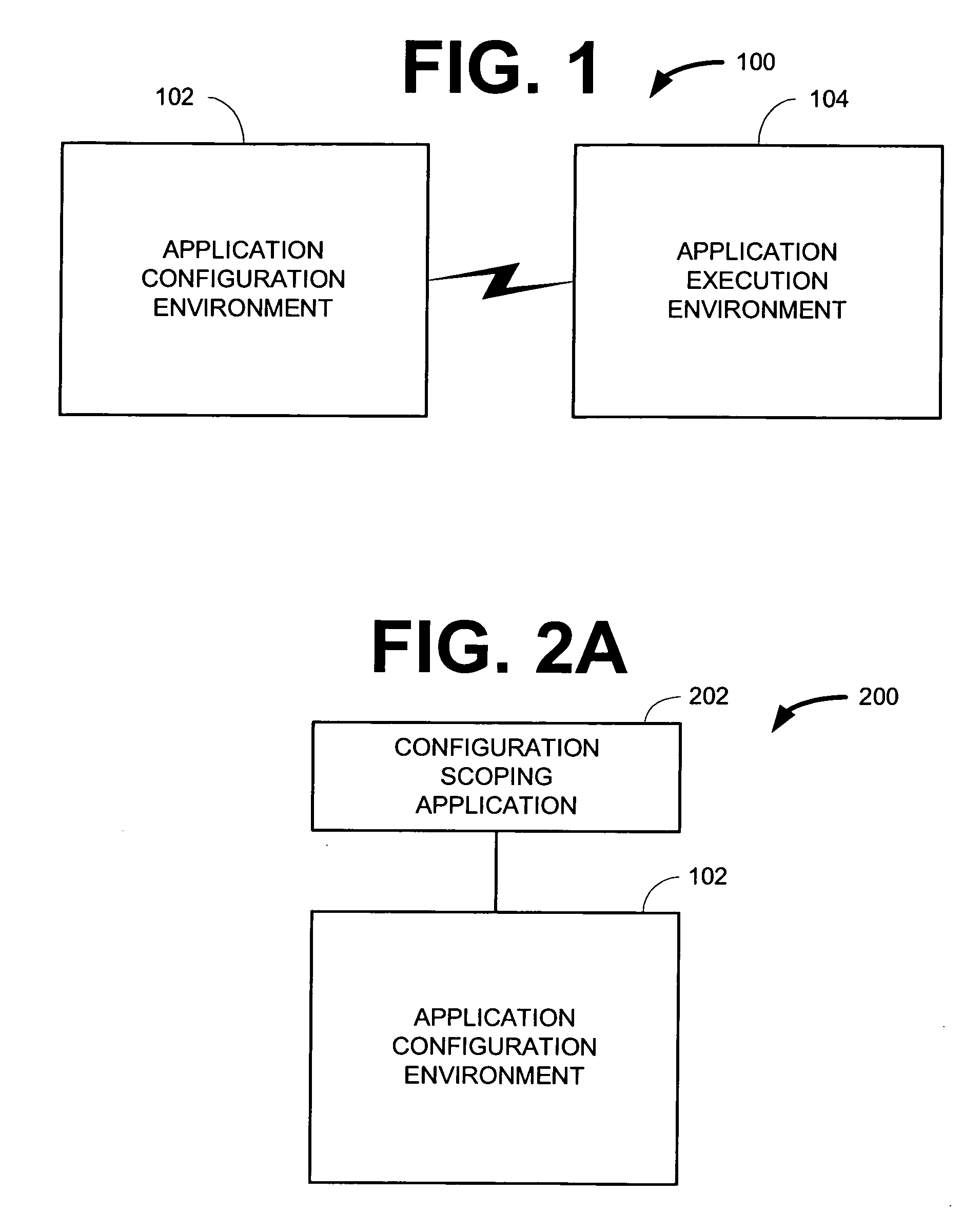
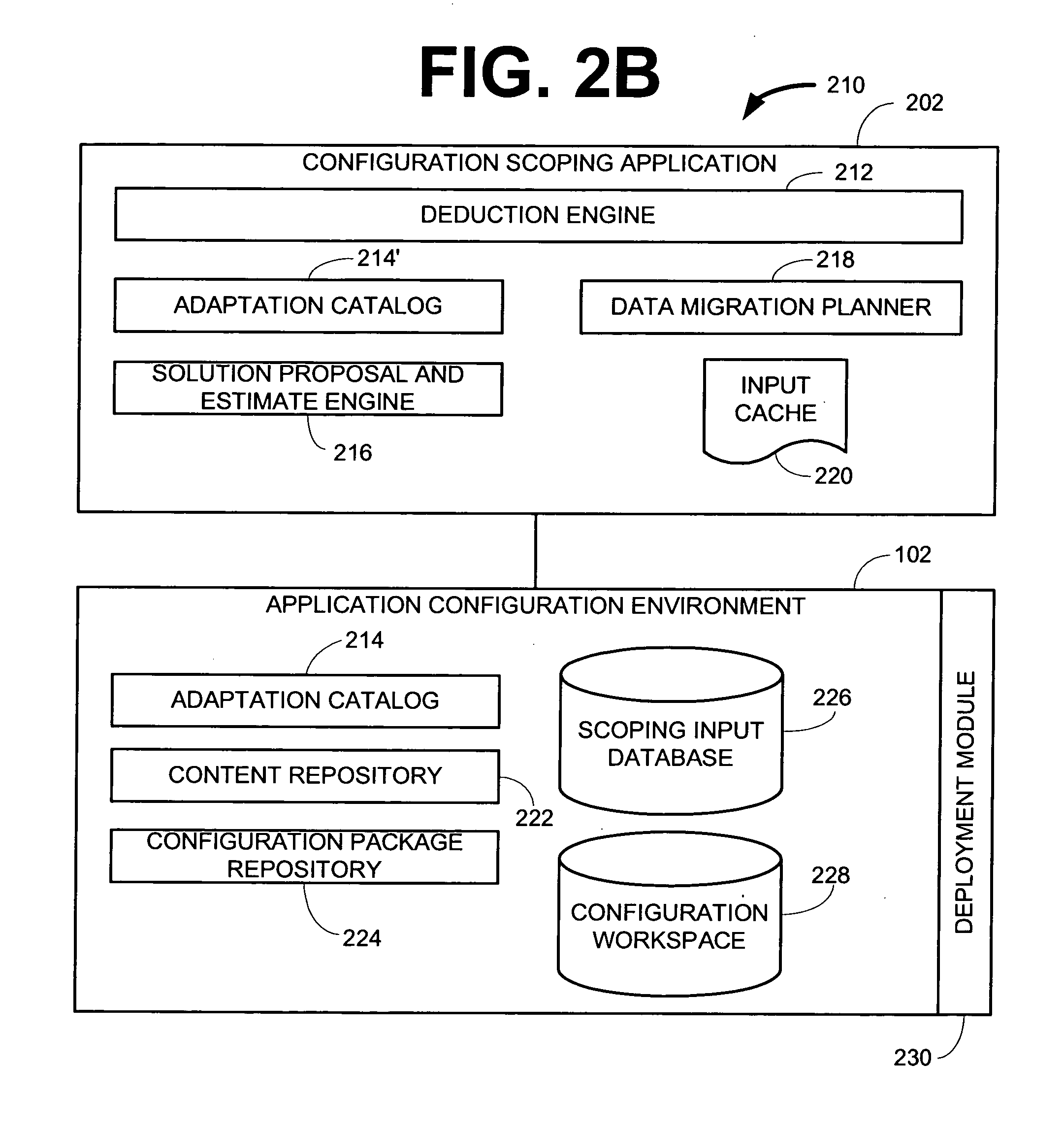
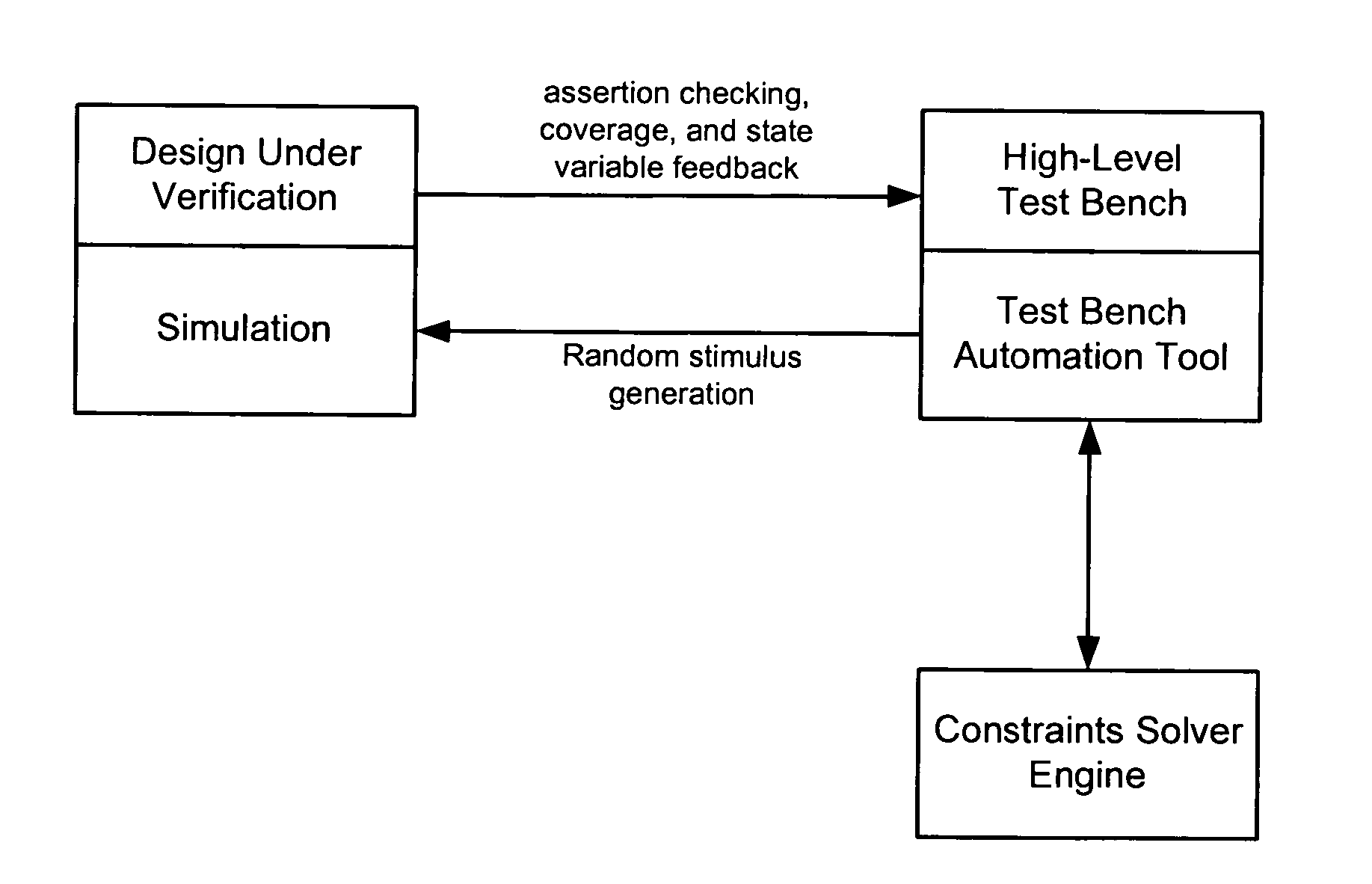
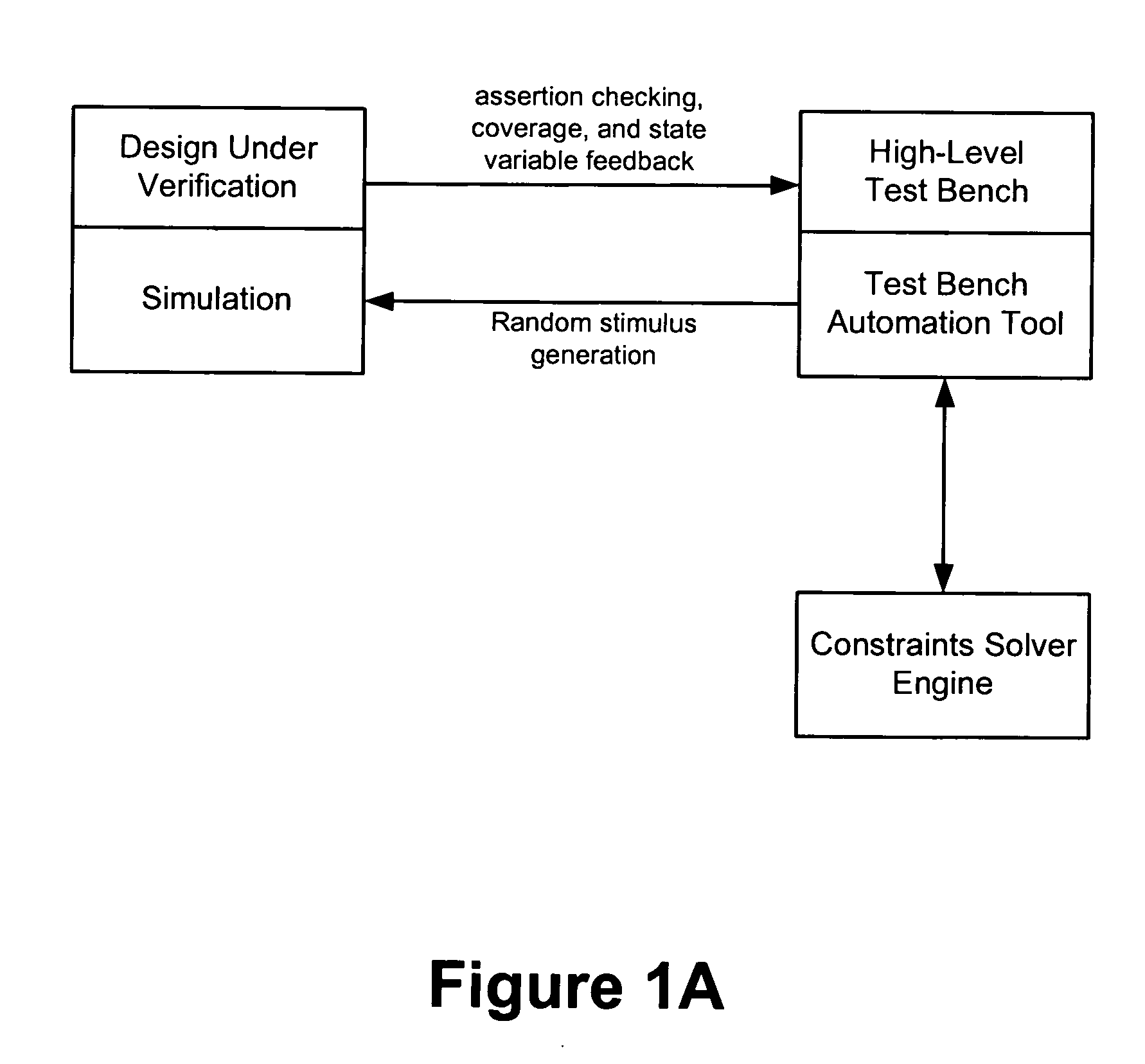
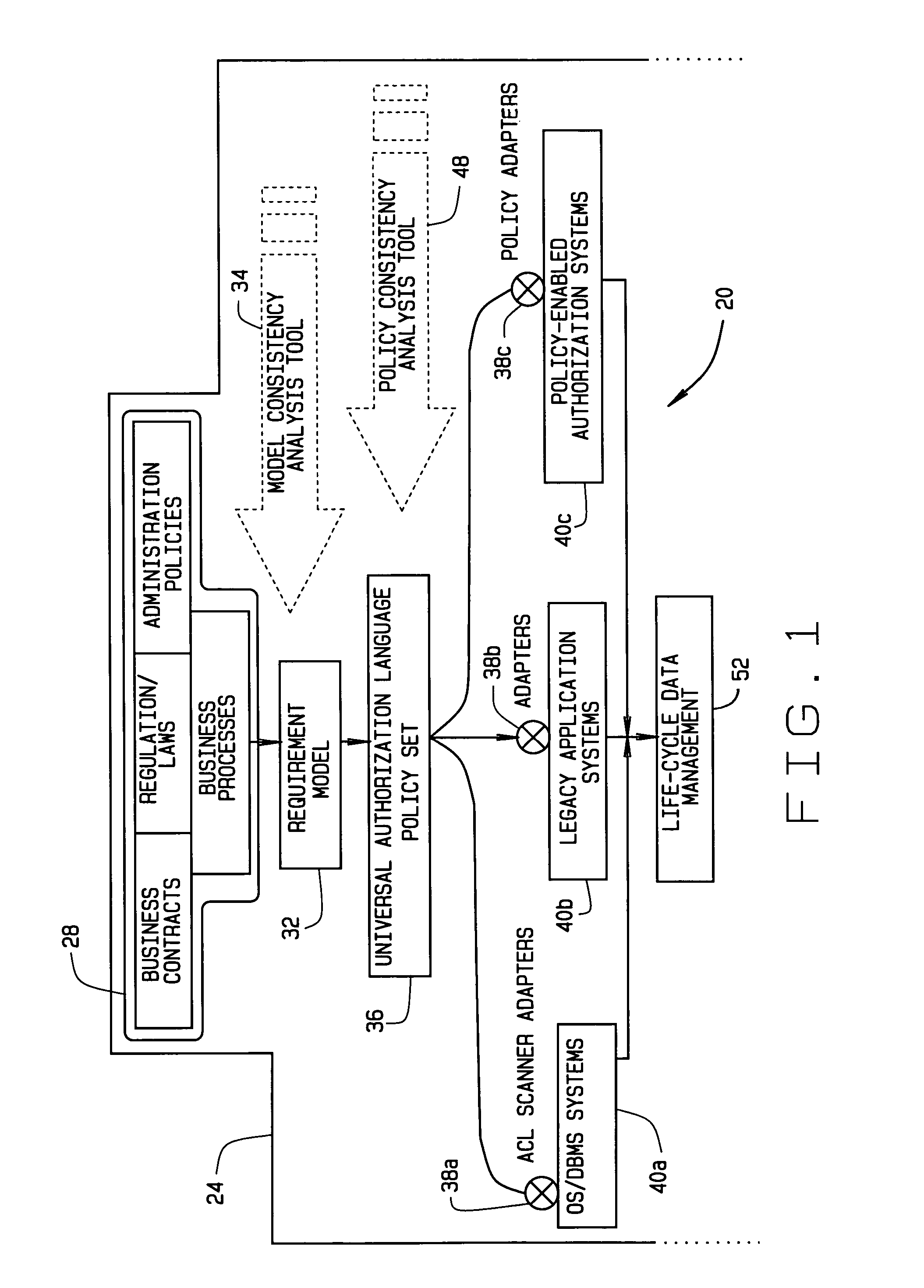
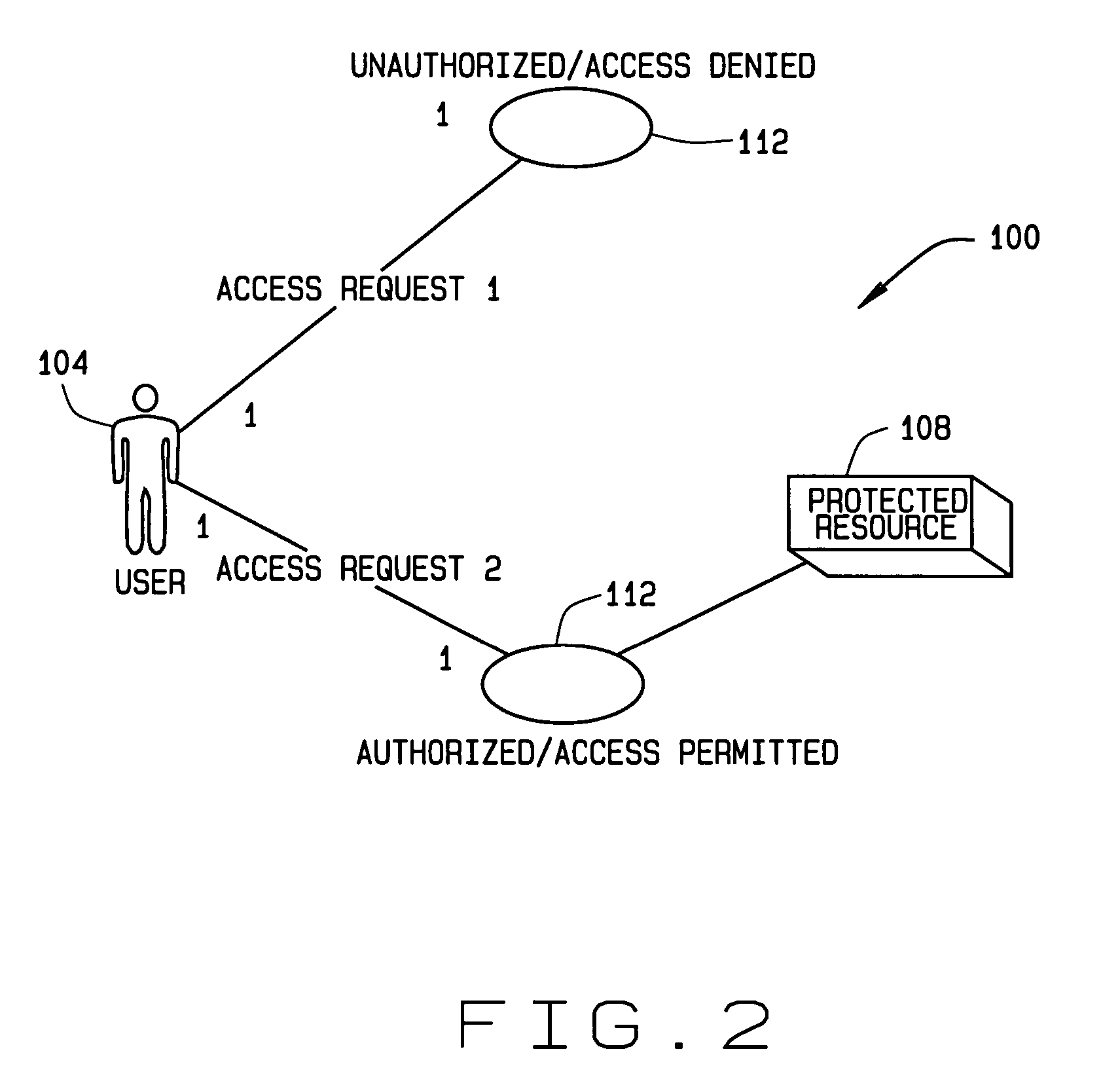
Implementing access control policies across dissimilar access control platforms
ActiveUS20070056019A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSet representationGoal system
A method of implementing access control requirements to control access to a plurality of system resources. The requirements are modeled as contents of security policies. The security policy contents are integrated into a policy set. Representations of the integrated policy set are generated, each representation corresponding to a target system that controls access to the resources. The policy set representation(s) are integrated with the corresponding target system(s) to implement the policy set. This method makes it possible to implement high-level security requirements correctly and consistently across systems of a system-of-systems (SoS) and / or distributed system.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
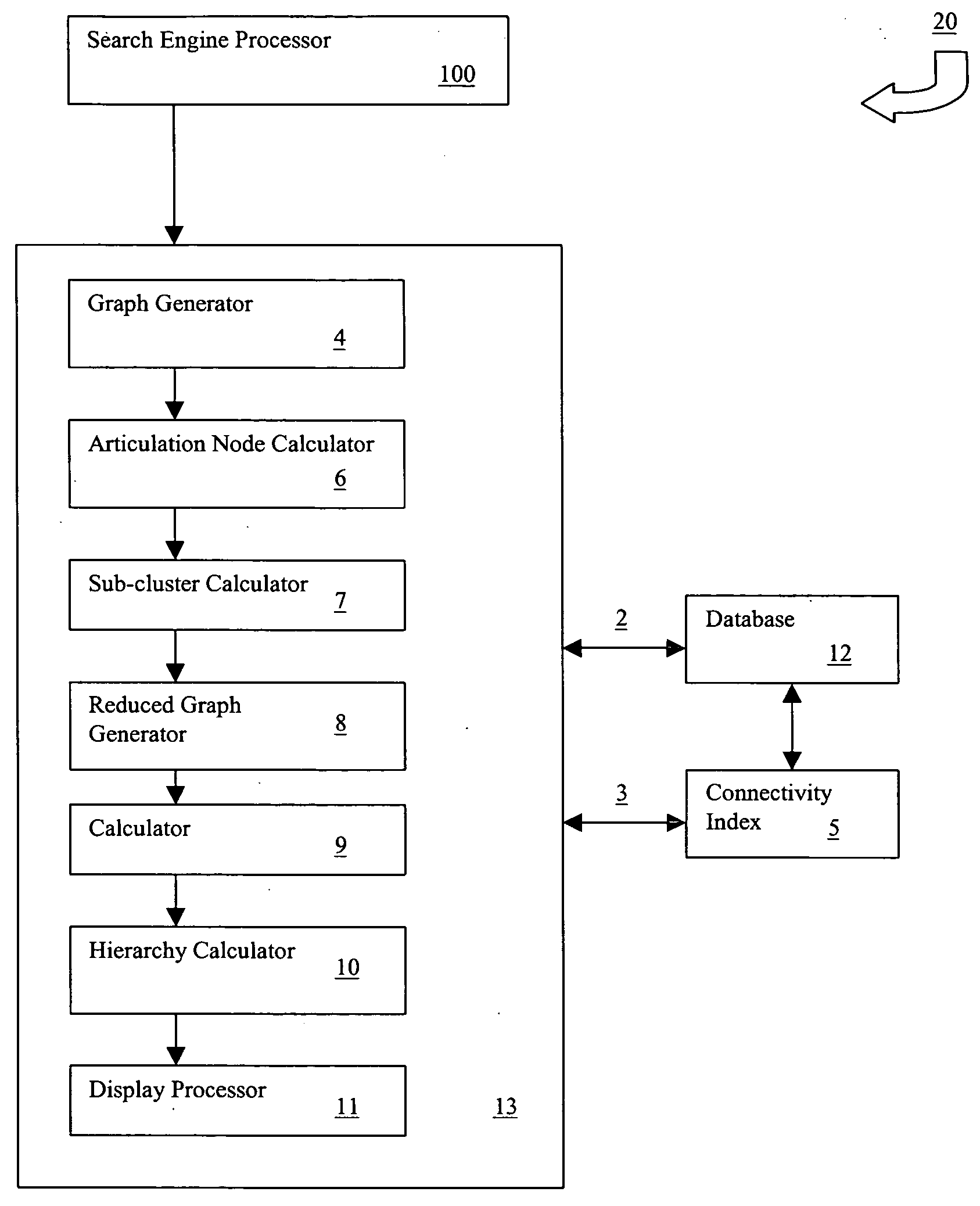
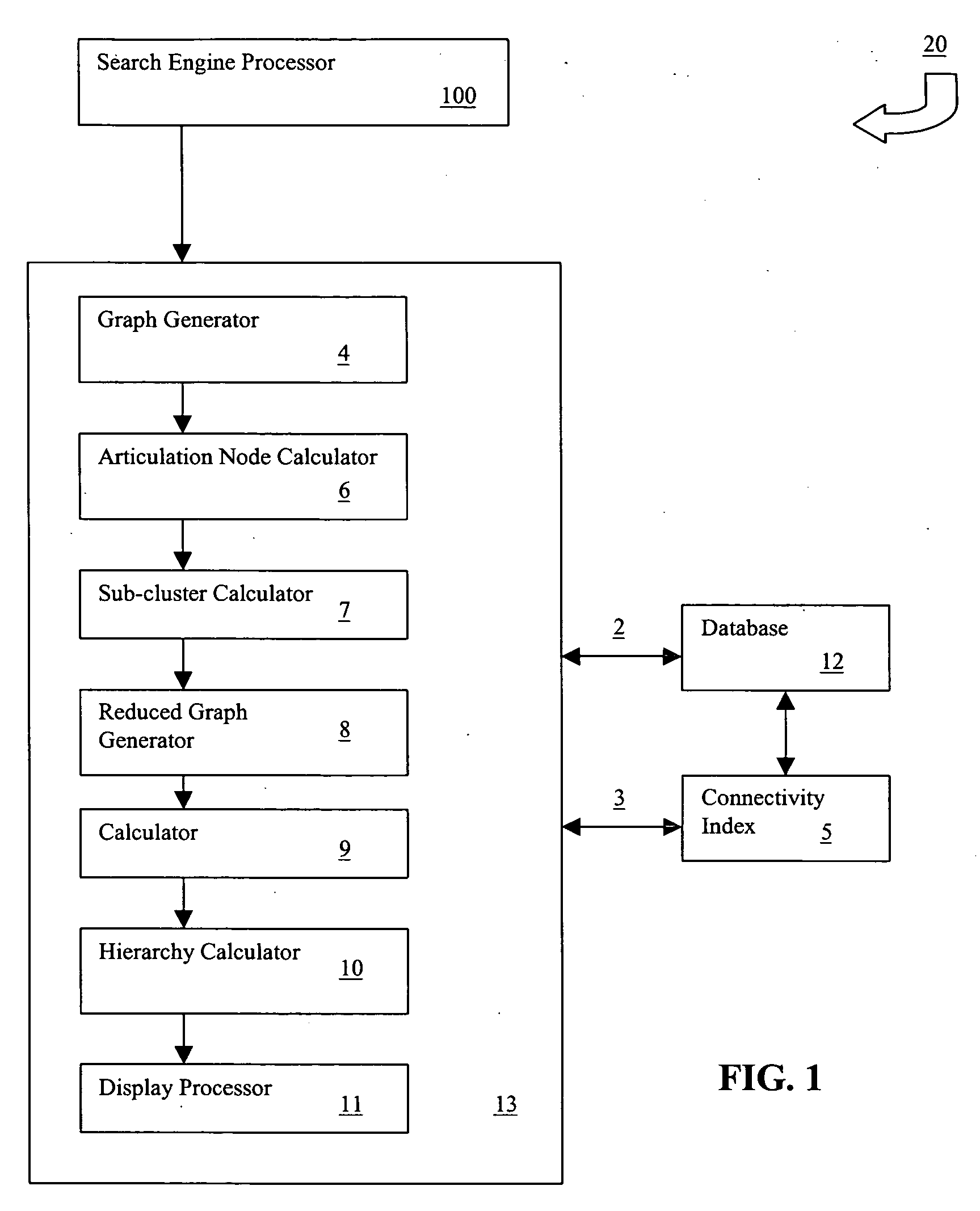
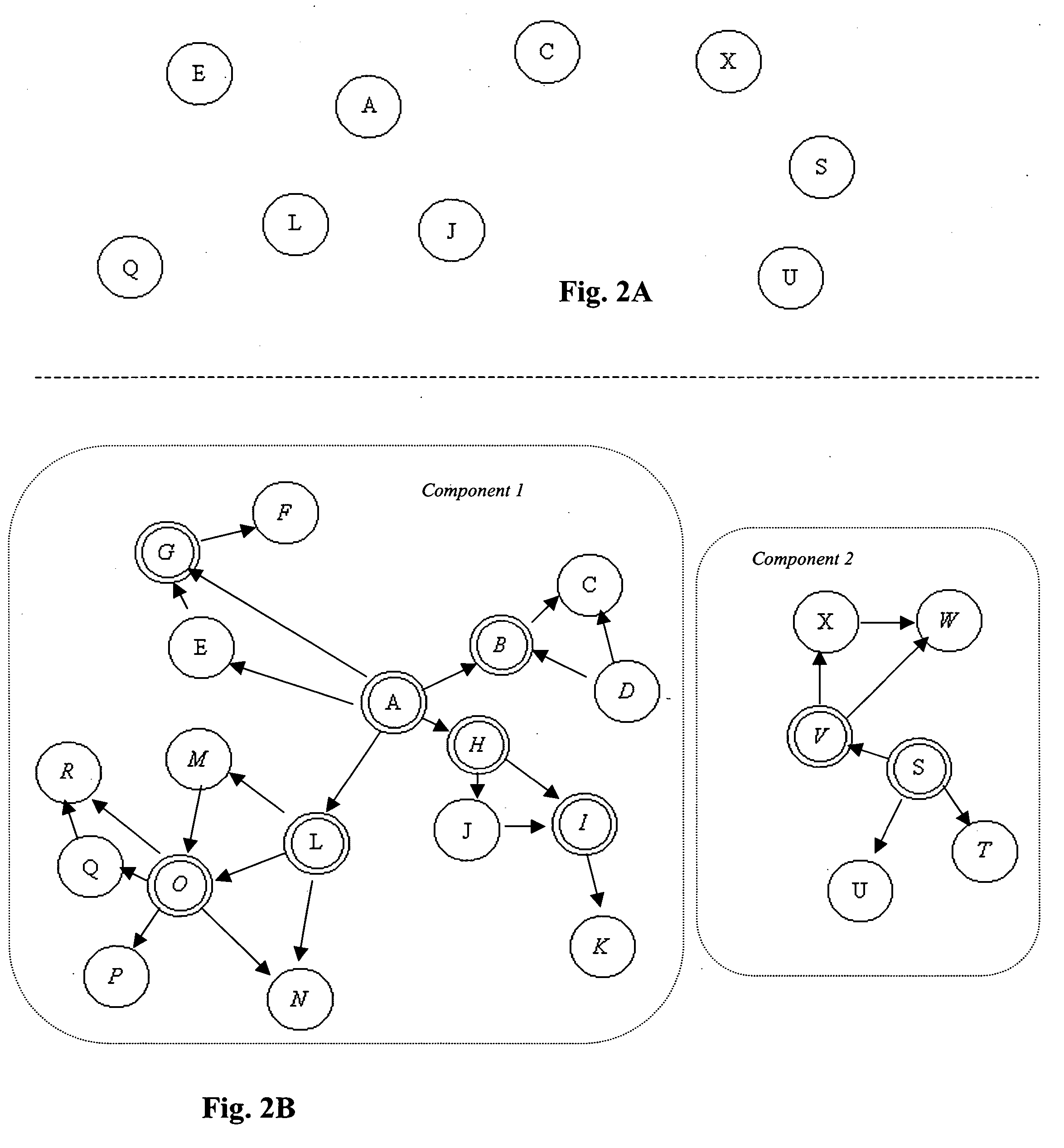
System and method for automatic clustering, sub-clustering and cluster hierarchization of search results in cross-referenced databases using articulation nodes
InactiveUS20050060287A1Easily and rapidly zero-inEasy to browseWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsNODALGraphics
Within the context of a cross-referenced data-base, an initial “base-set” of results to a query is generated using any conventional search engine tool. The base-set is then expanded by adding to it entries referencing entries in the original set or referenced by those entries, in a possibly iterative manner. The resulting collection of entries and references is represented as a mathematical graph or network, amendable to graph theoretic analysis. Connected components within the graph form top-level clusters, and articulation nodes within these clusters are calculated. These articulation nodes serve as both navigational “gateways” and anchors for sub-clusters. Sub-clusters, consisting of the transitive descendants of the articulation nodes, are associated with each articulation node. The articulation nodes themselves then form a graph, which is analyzed further for prominence, and a hierarchy of articulation nodes is calculated. The resulting hierarchy consisting of the top-level clusters and the sub-clusters associated with the articulation nodes is then presented visually to users in a manner enabling them to easily navigate through the space of expanded search results.
Owner:HELLMAN ZIV Z +1
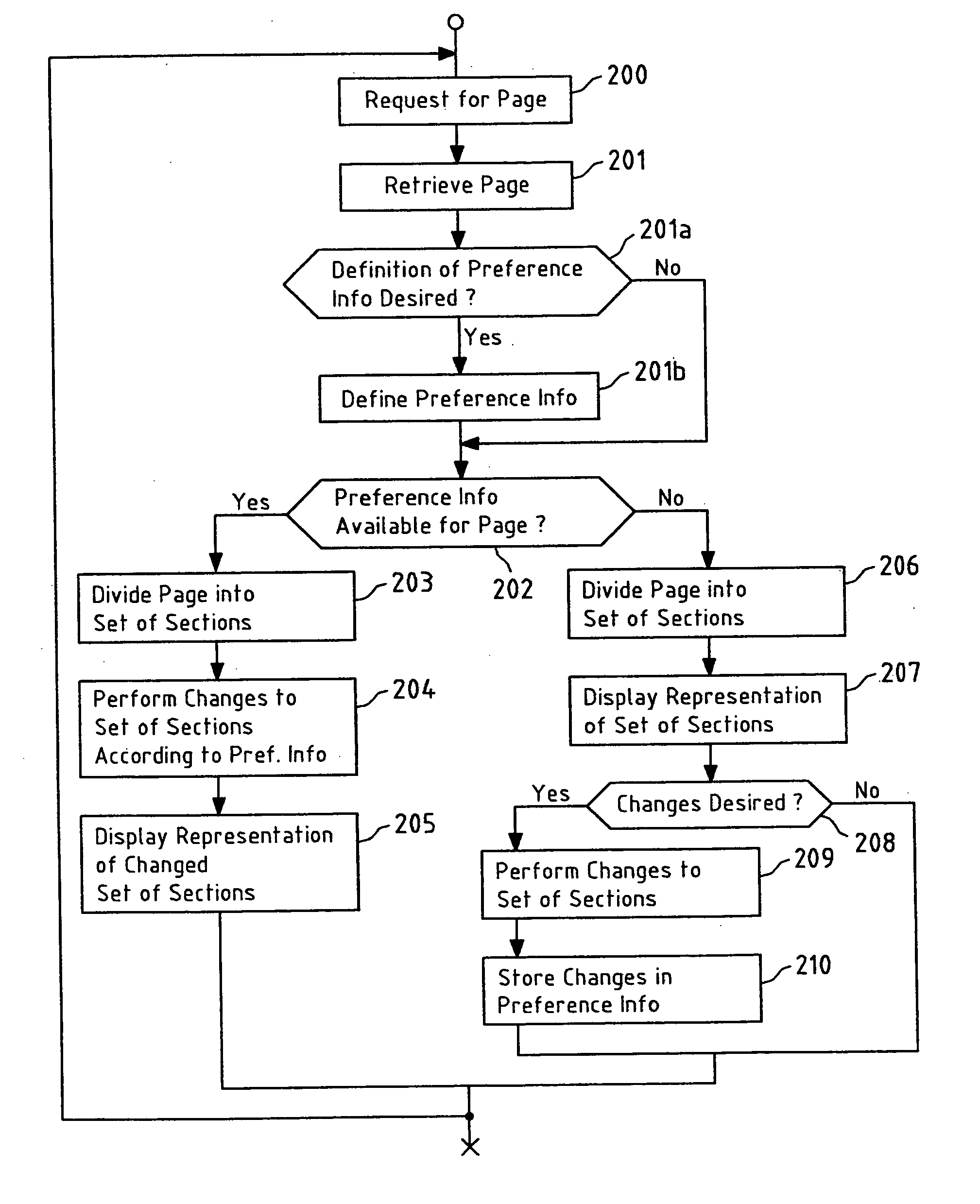
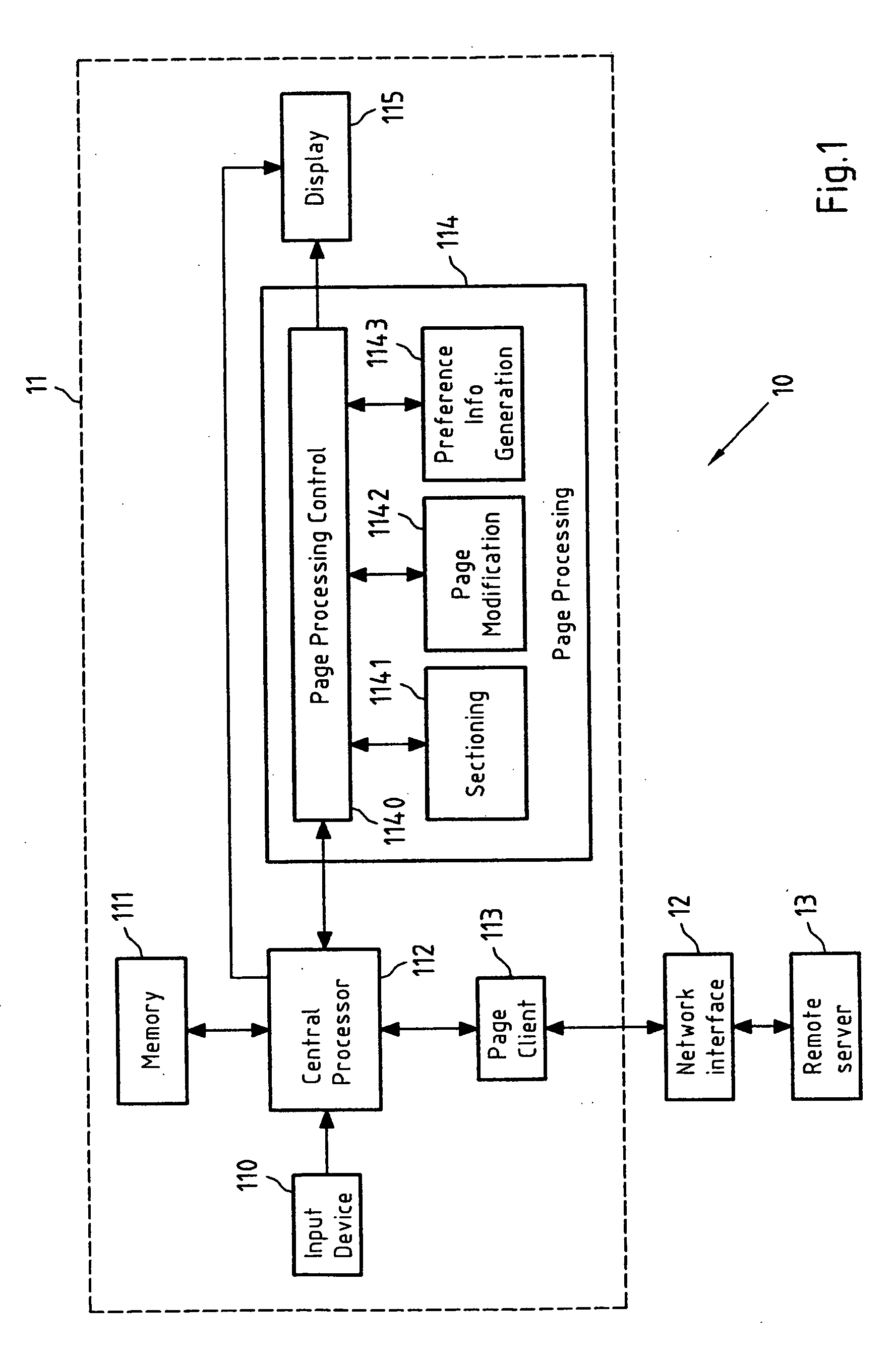
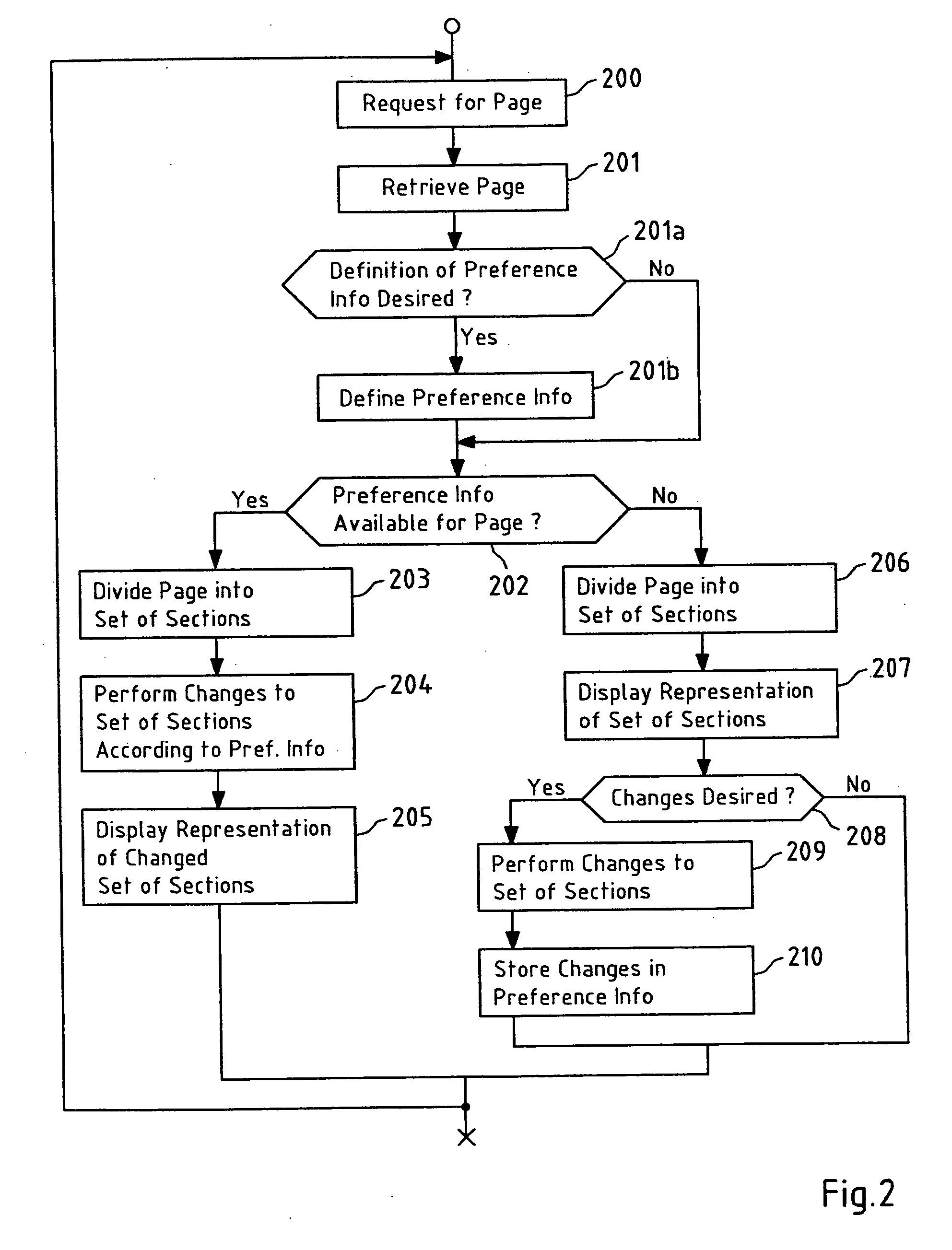
User-defined changing of page representations
InactiveUS20060288280A1Improve readabilityReduce the amount requiredNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsSet representationDatabase
This invention relates to a method for generating a changed representation of a page object, wherein the page object is one of a page and a part of the page, the method comprising retrieving (201; 301) the page object in response to a request (200; 300) for the page; dividing (203; 303) the page object into a set (4a) of sections; and performing (204; 304) changes to the set (4a) of sections according to preference information to obtain a changed set (4b) of sections representing the changed representation of the page object. This invention further relates to a device, a system, a computer program and a computer program product for generating a changed representation of a page object.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Statistical signatures used with multivariate statistical analysis for fault detection and isolation and abnormal condition prevention in a process
InactiveUS7526405B2Testing/monitoring control systemsNuclear monitoringSet representationMultivariate statistics
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
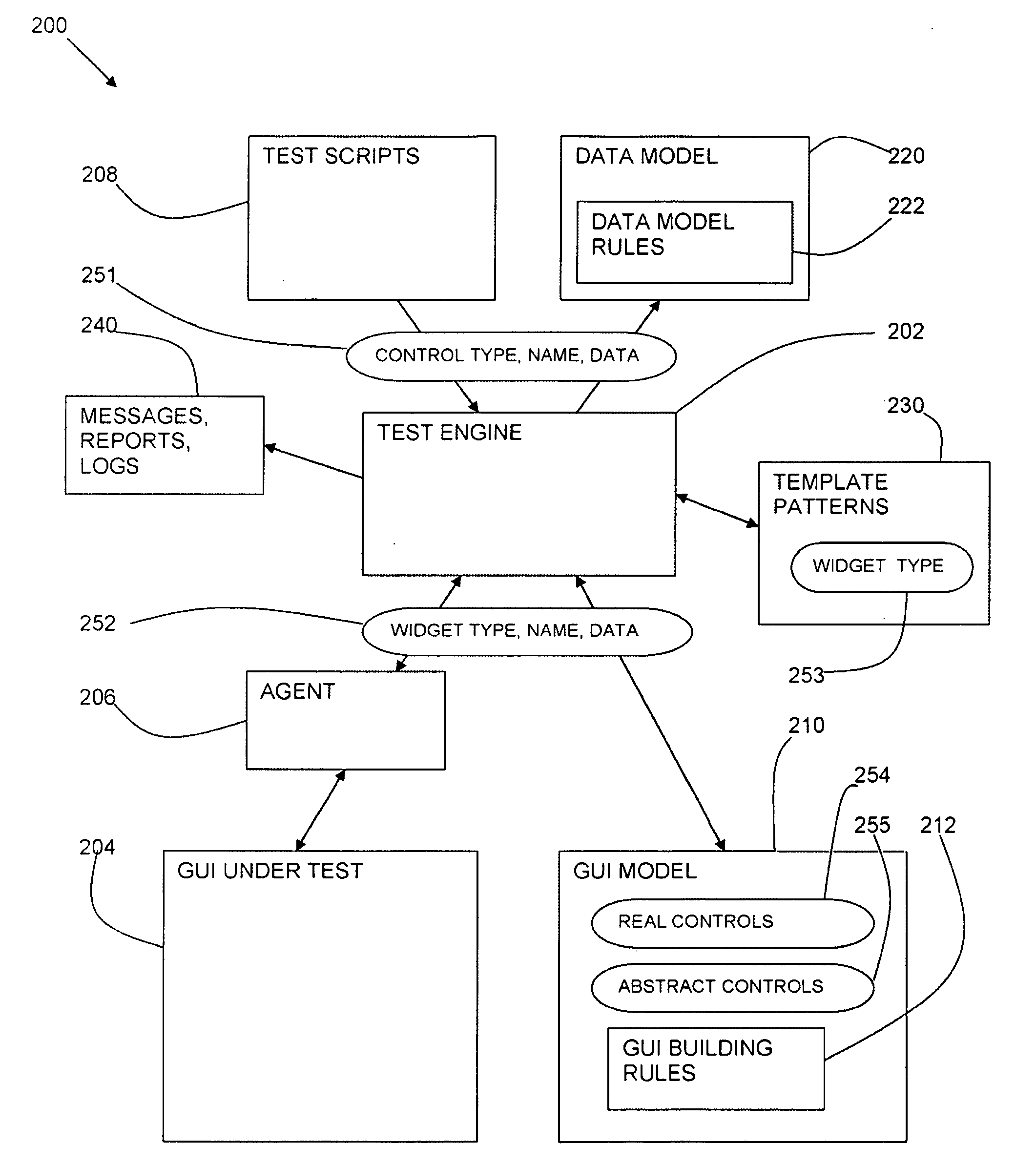
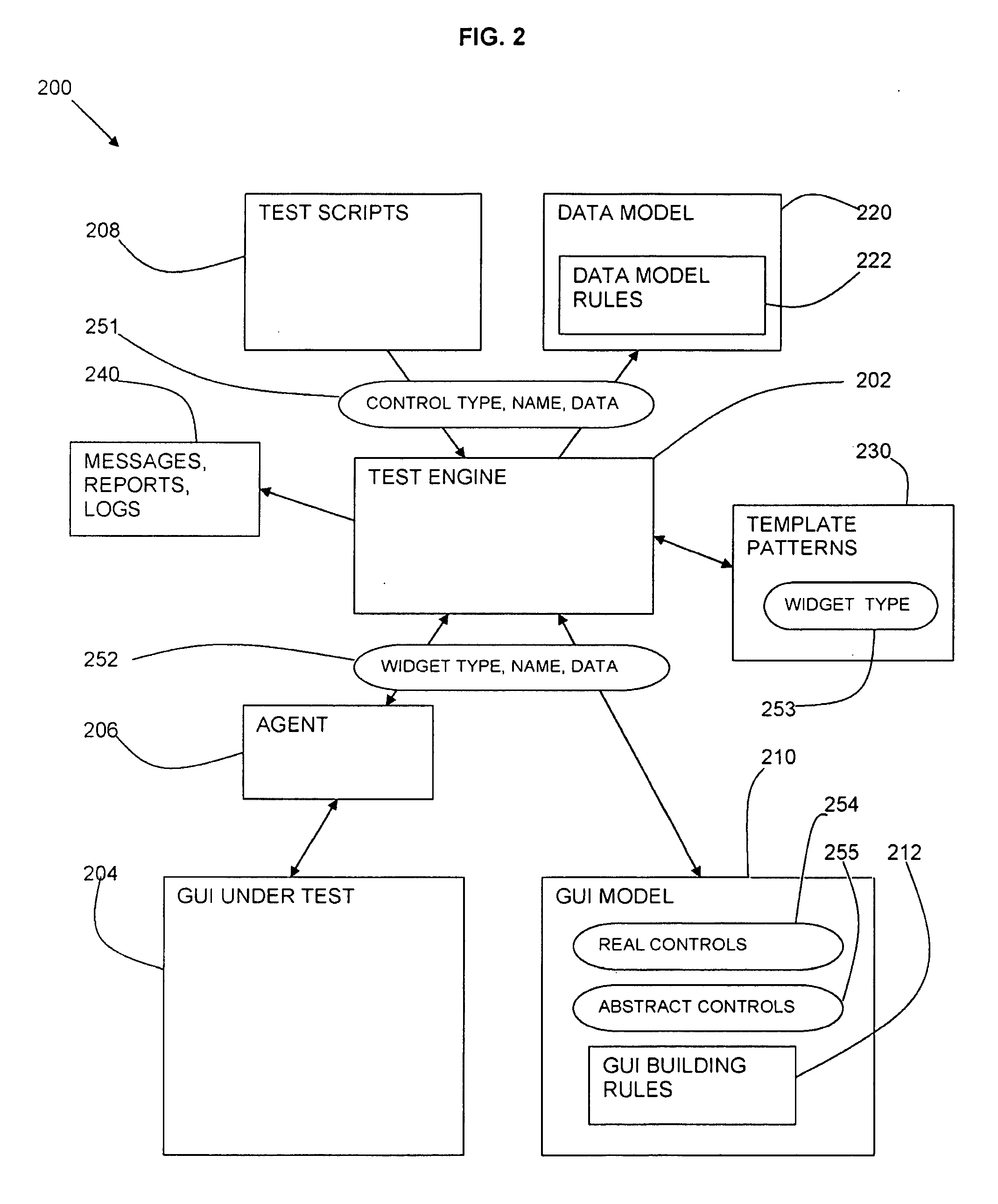
Method and System for Graphical User Interface Testing
InactiveUS20080155515A1Software testing/debuggingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationGraphicsSet representation
A method and system are provided for testing a graphical user (GUI) (204). The method includes providing a pattern (230) of a collection of generalised interface object types and searching an interface (204) or a model (210) of an interface for instances of collections of interface objects matching the pattern (230). Identifying a control provided by the interface (204) represented by the collection of interface object types and its location in the interface hierarchy. A pattern (230) includes a first generalised object type and a second generalised object type with a specified relative position in the interface (204) to the first object type.
Owner:IBM CORP
Test engine
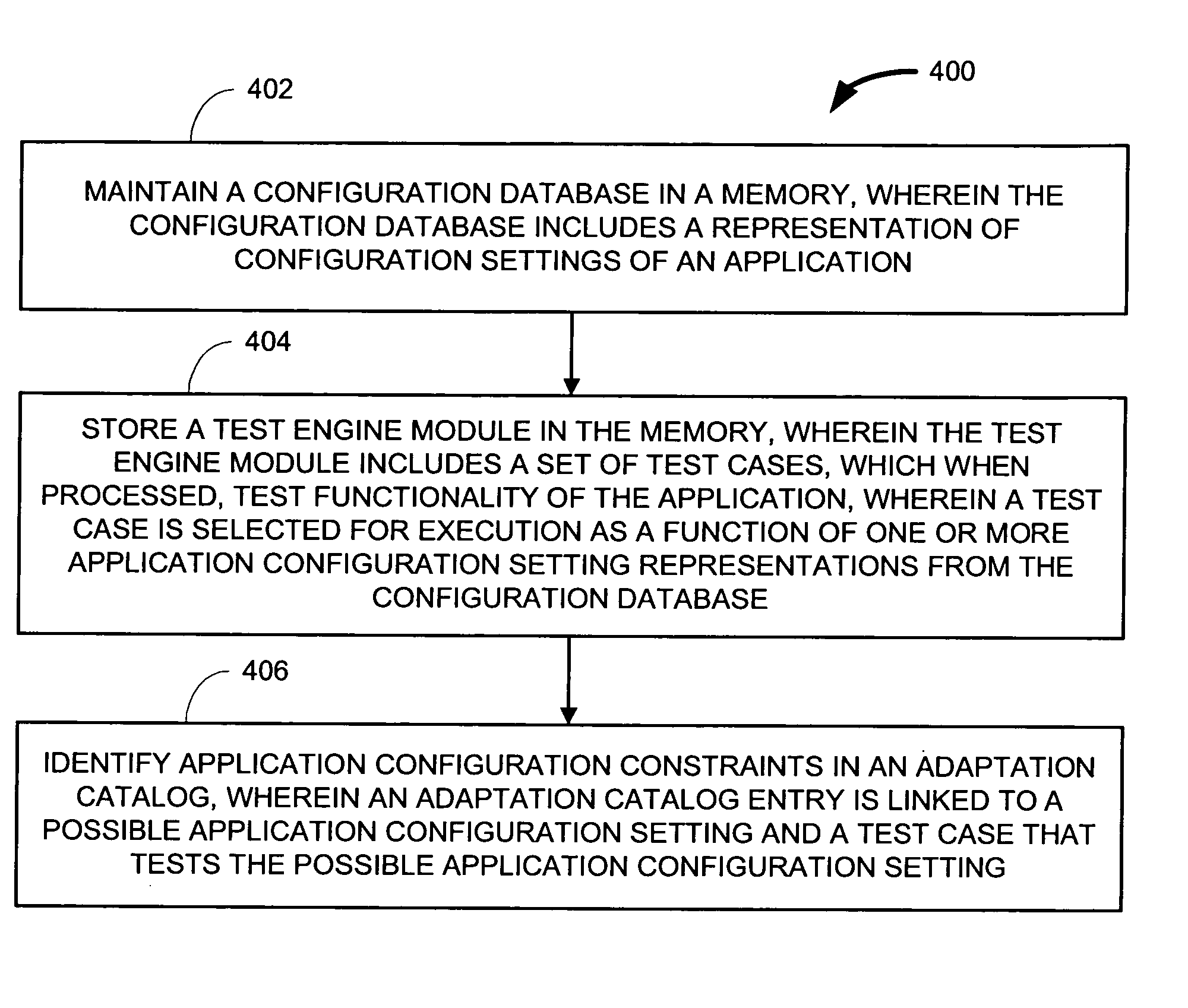
ActiveUS20080126448A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsComputer hardwareSet representation
The present subject mater relates to testing software application configurations and, more particularly, to a test engine. The various embodiments described and illustrated herein provide systems, methods, and software that maintain a configuration database in a memory, wherein the configuration database includes a representation of configuration settings of an application. Some such embodiments may further store a test engine module in the memory, wherein the test engine module includes a set of test cases, which when processed, test functionality of the application, wherein a test case is selected for execution as a function of one or more application configuration setting representations from the configuration database.
Owner:SAP AG
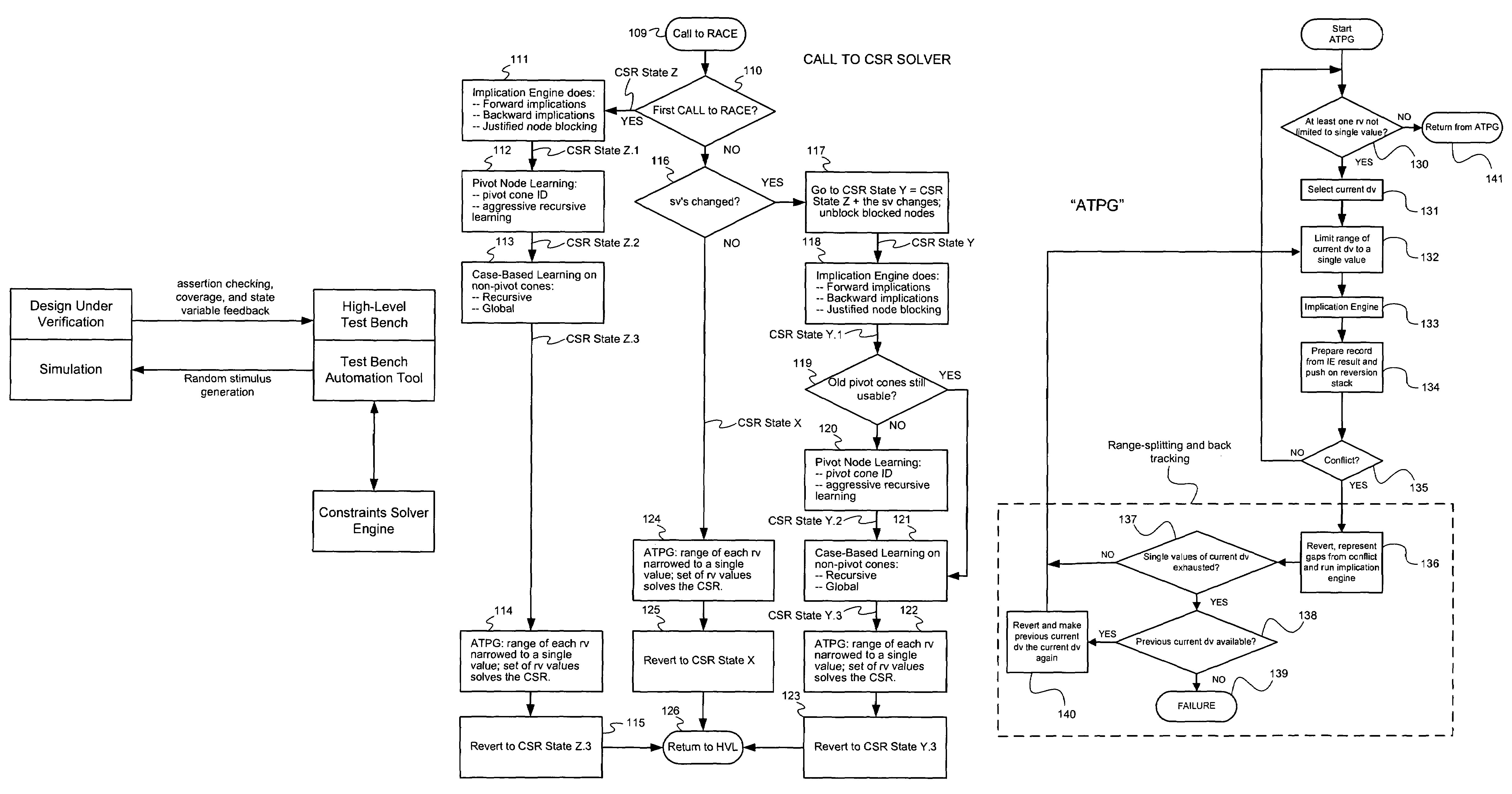
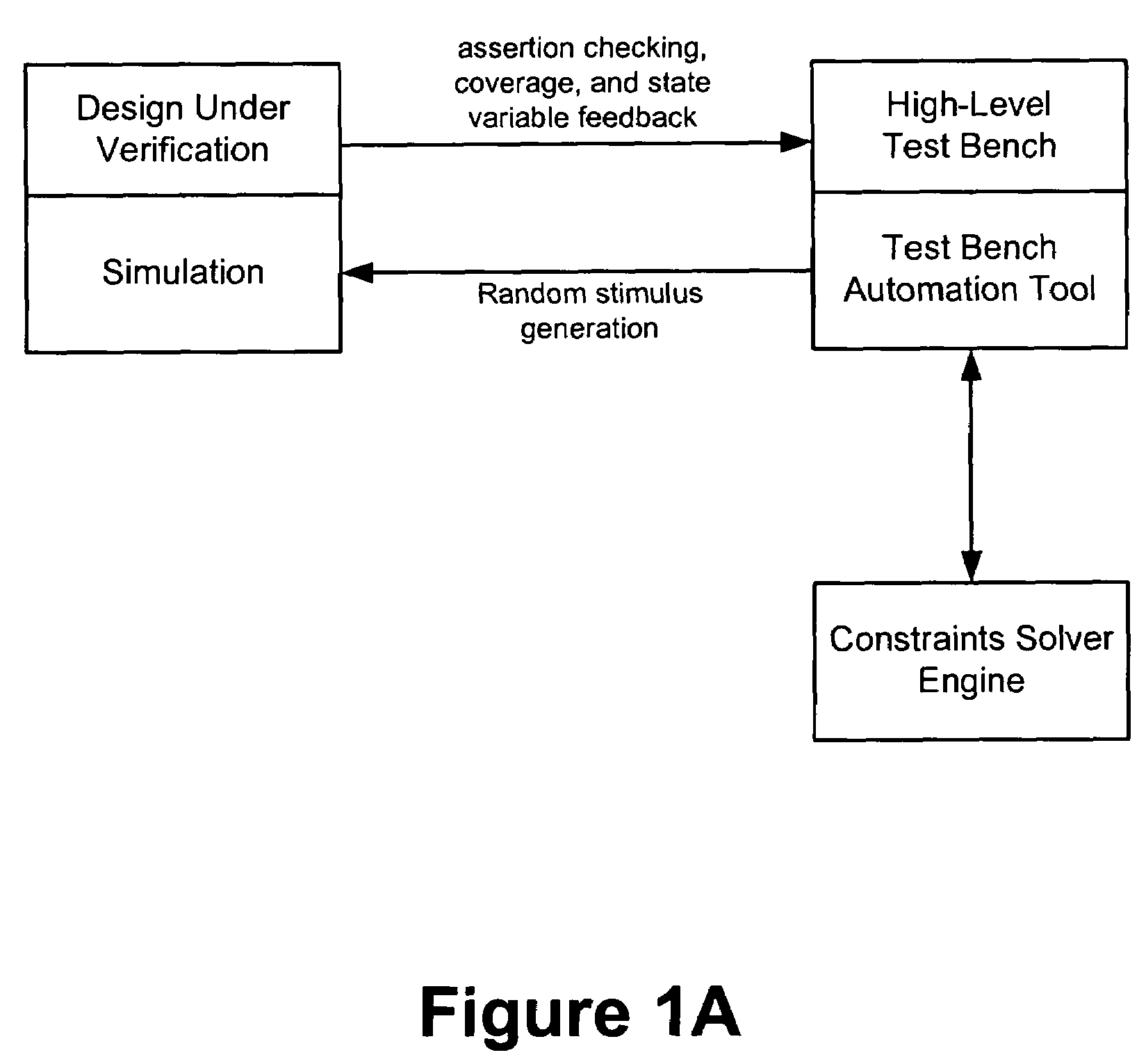
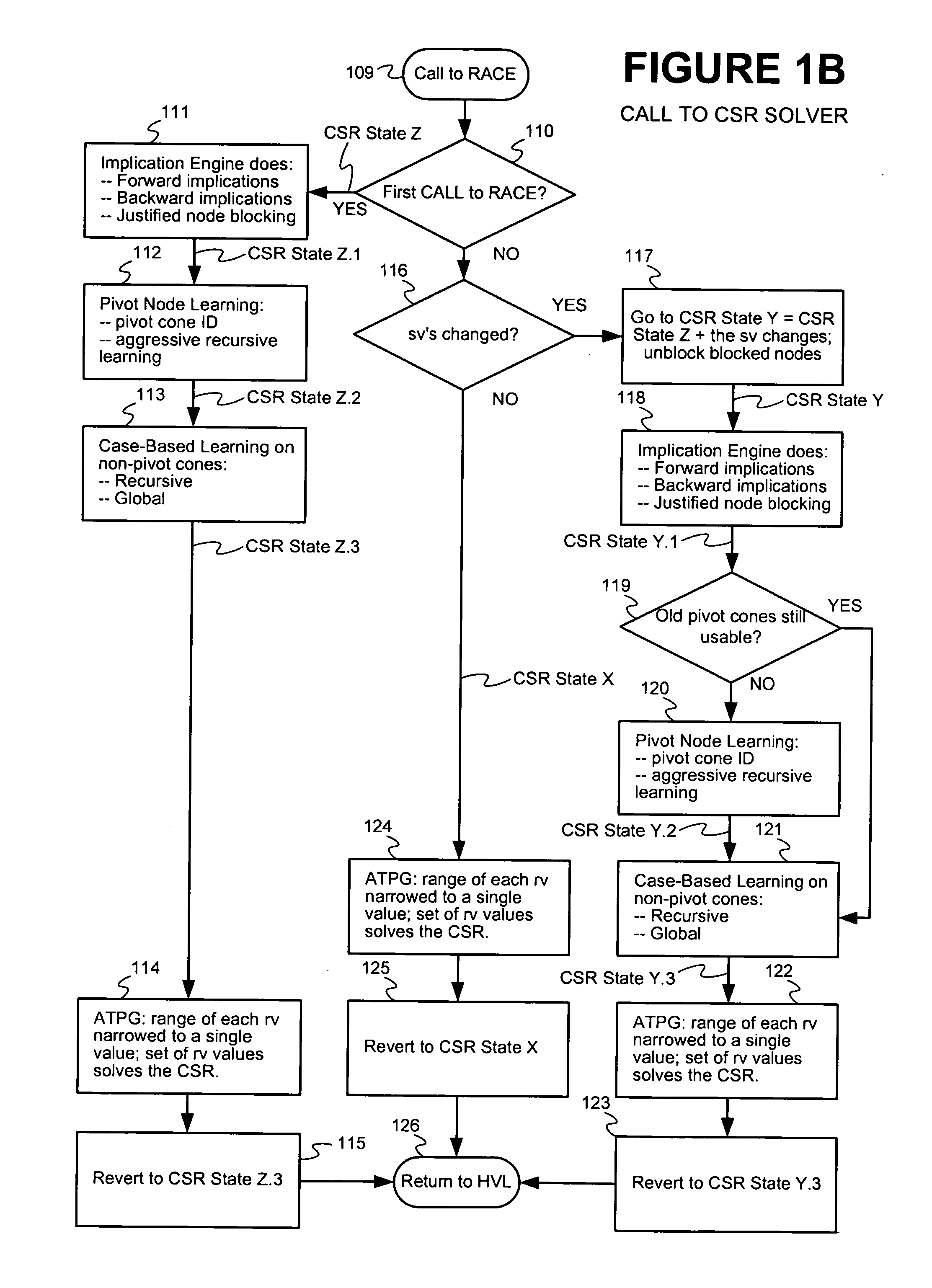
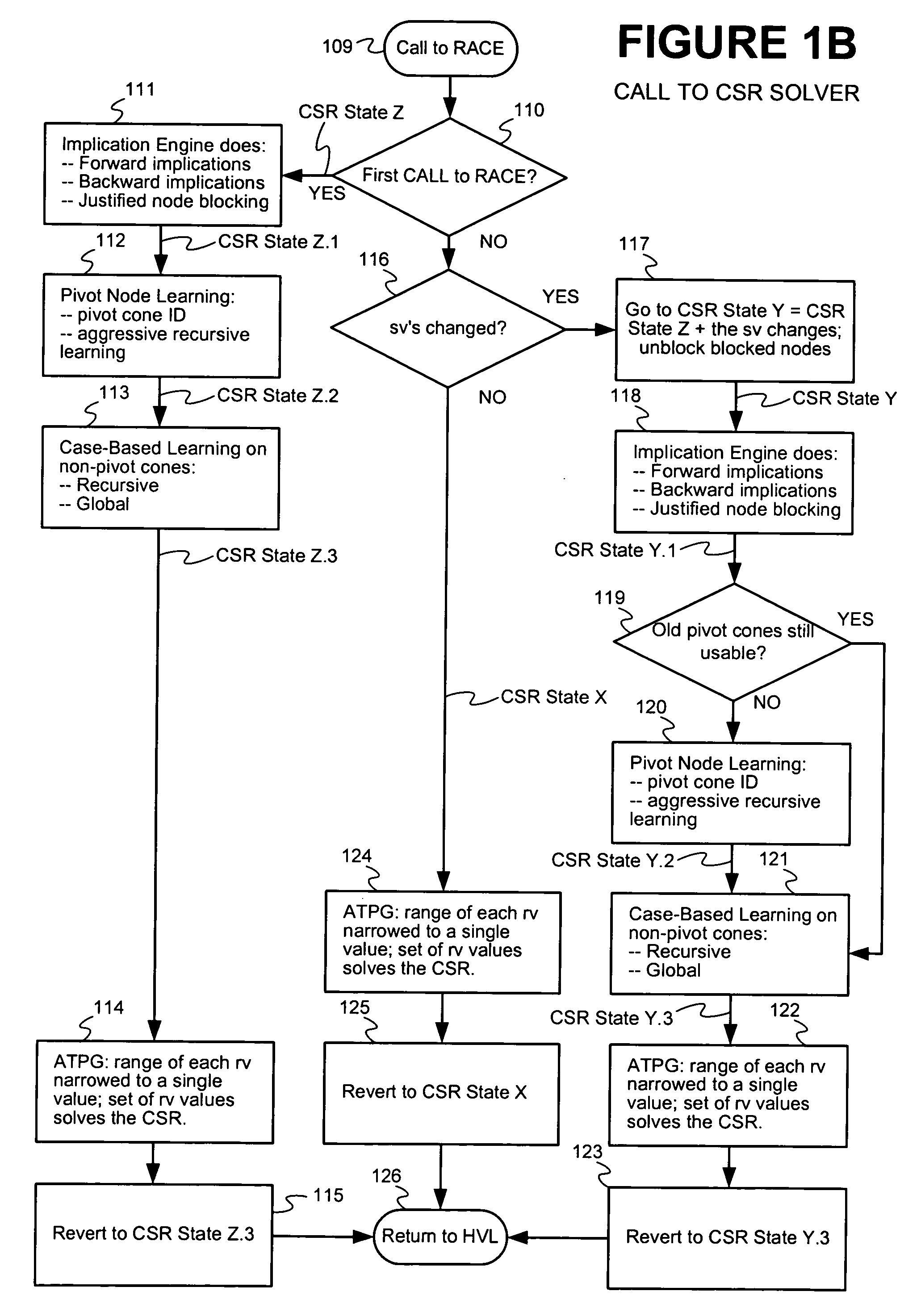
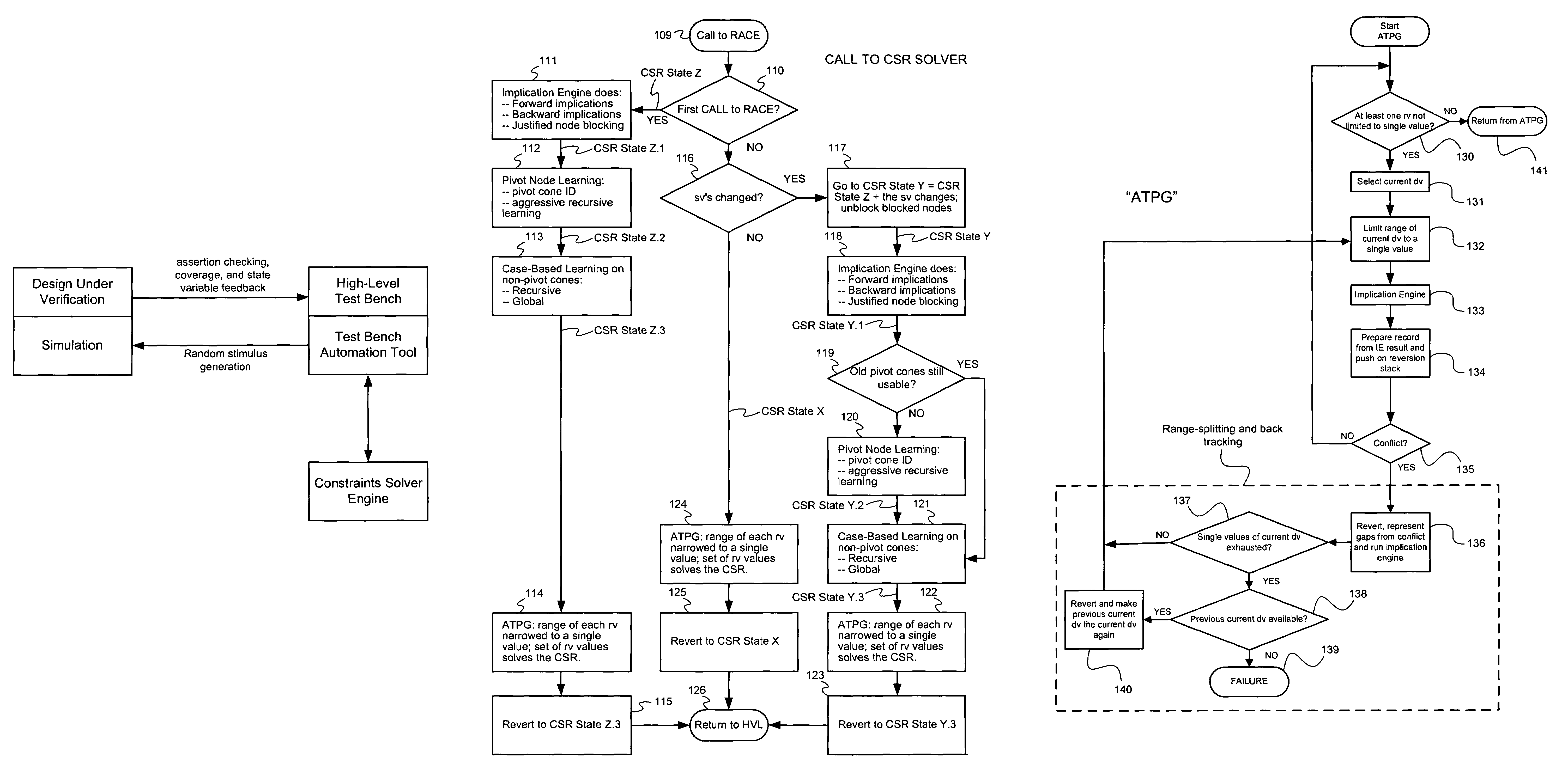
Method and apparatus for improving efficiency of constraint solving
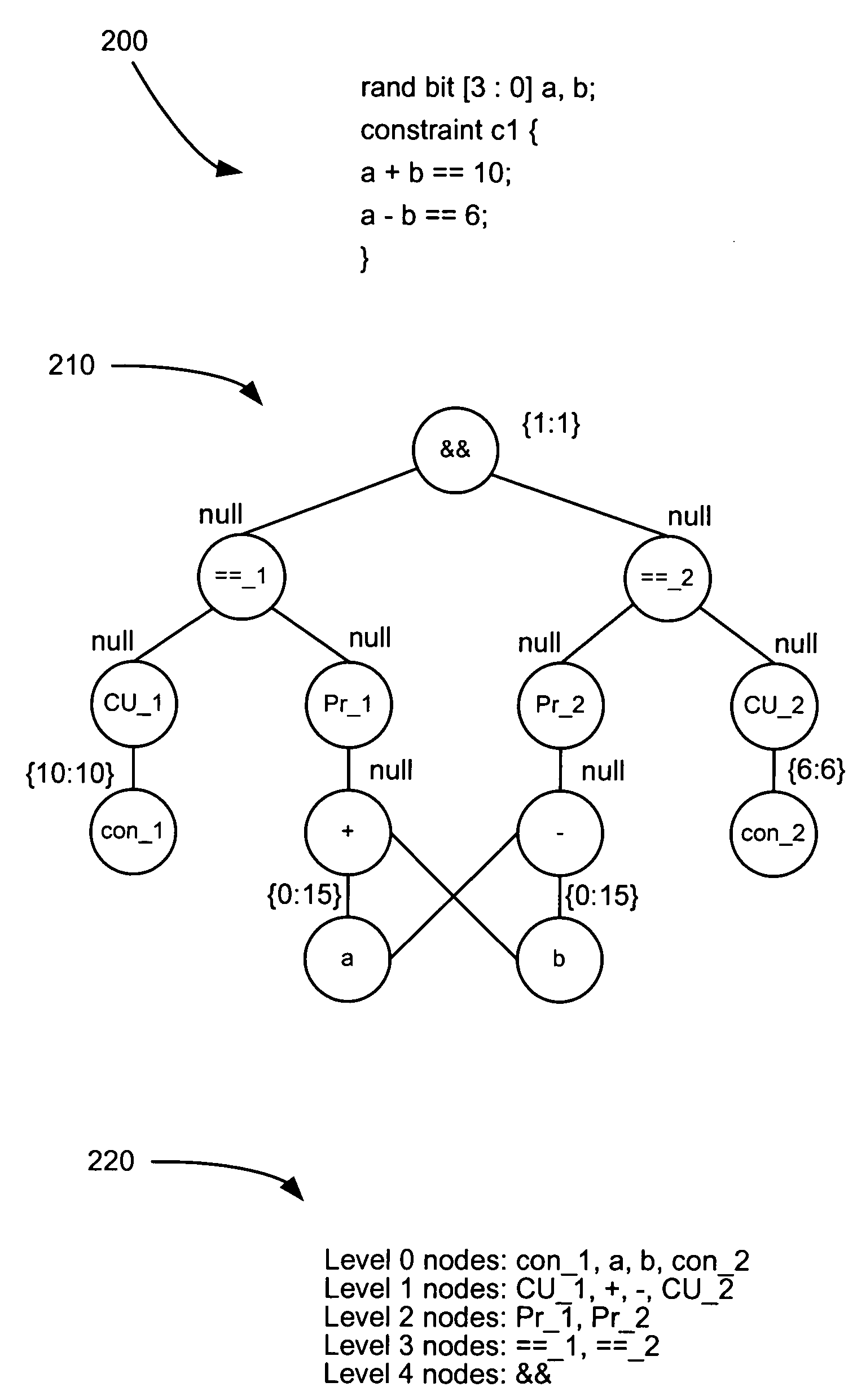
ActiveUS7302417B2Less timeReduce processDigital computer detailsDigital dataSet representationTheoretical computer science
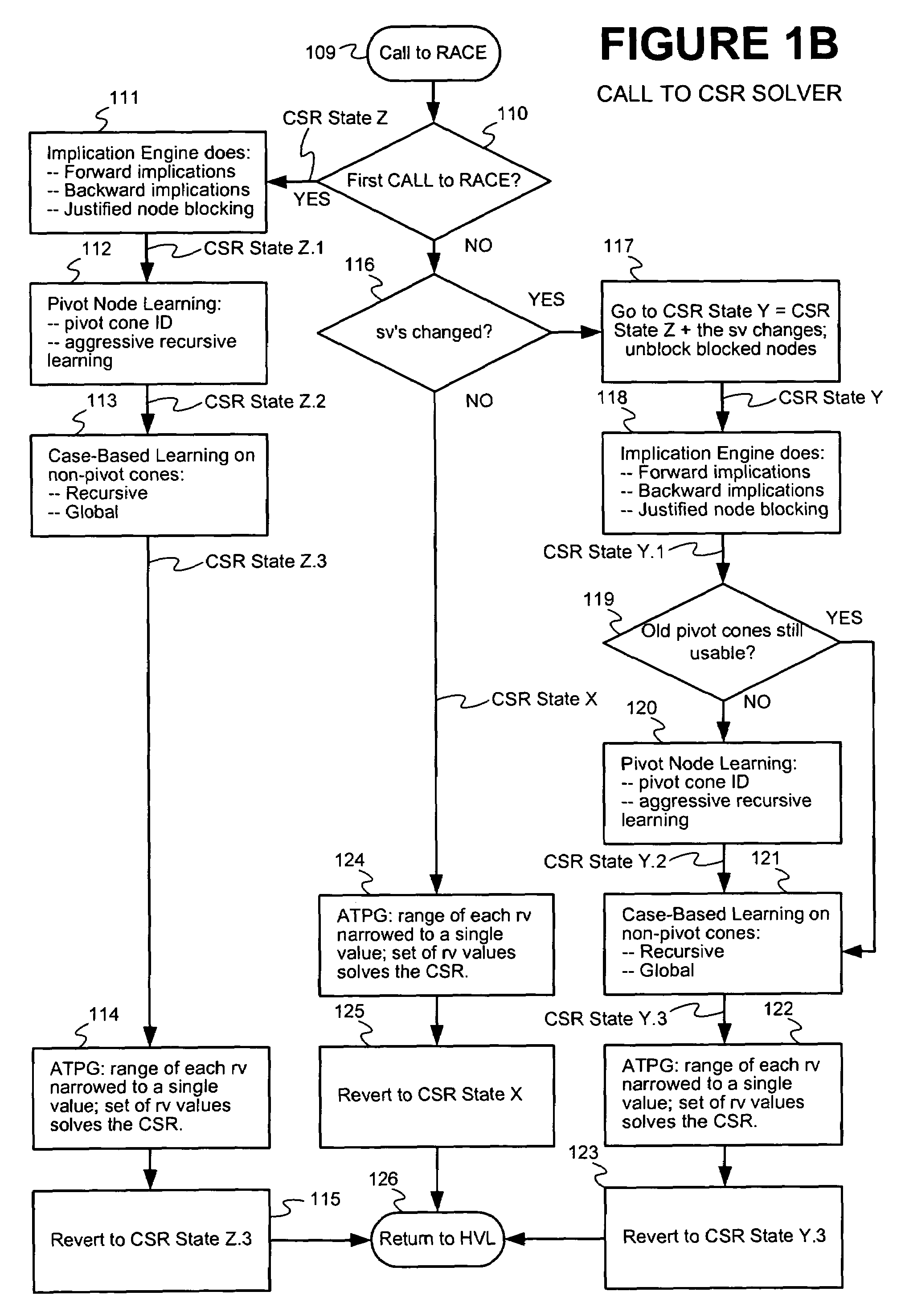
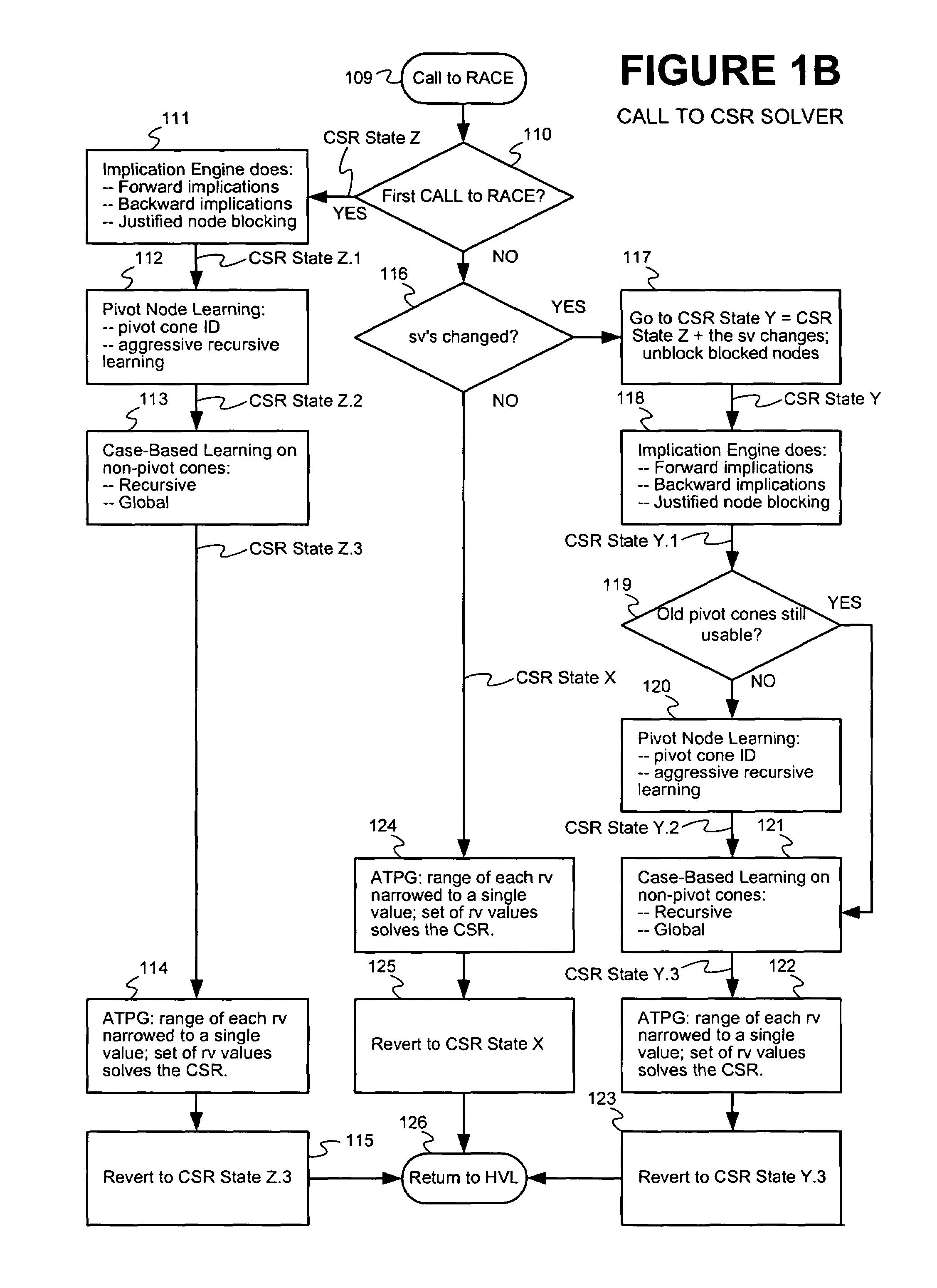
Techniques are presented for identifying blockable subsets. Blockable subsets can increase the efficiency by which solutions to a constraint set representation (CSR) can be found. Nodes of a blockable subset can be marked as “blocked” and learning or implication procedures, used as part of a CSR solving process, can be designed to skip nodes marked as blocked. The identification of a particular blockable subset is typically associated with certain conditions being true. If and when the conditions no longer hold, the nodes of the blockable subset need to be unblocked. One type of blockable subset can be identified during the operation of an implication engine (IE) by a technique called justified node blocking (JNB). Another type of blockable subset can be identified by a technique called pivot node learning (PNL). PNL can be applied in-between application of an IE and application of case-based learning.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
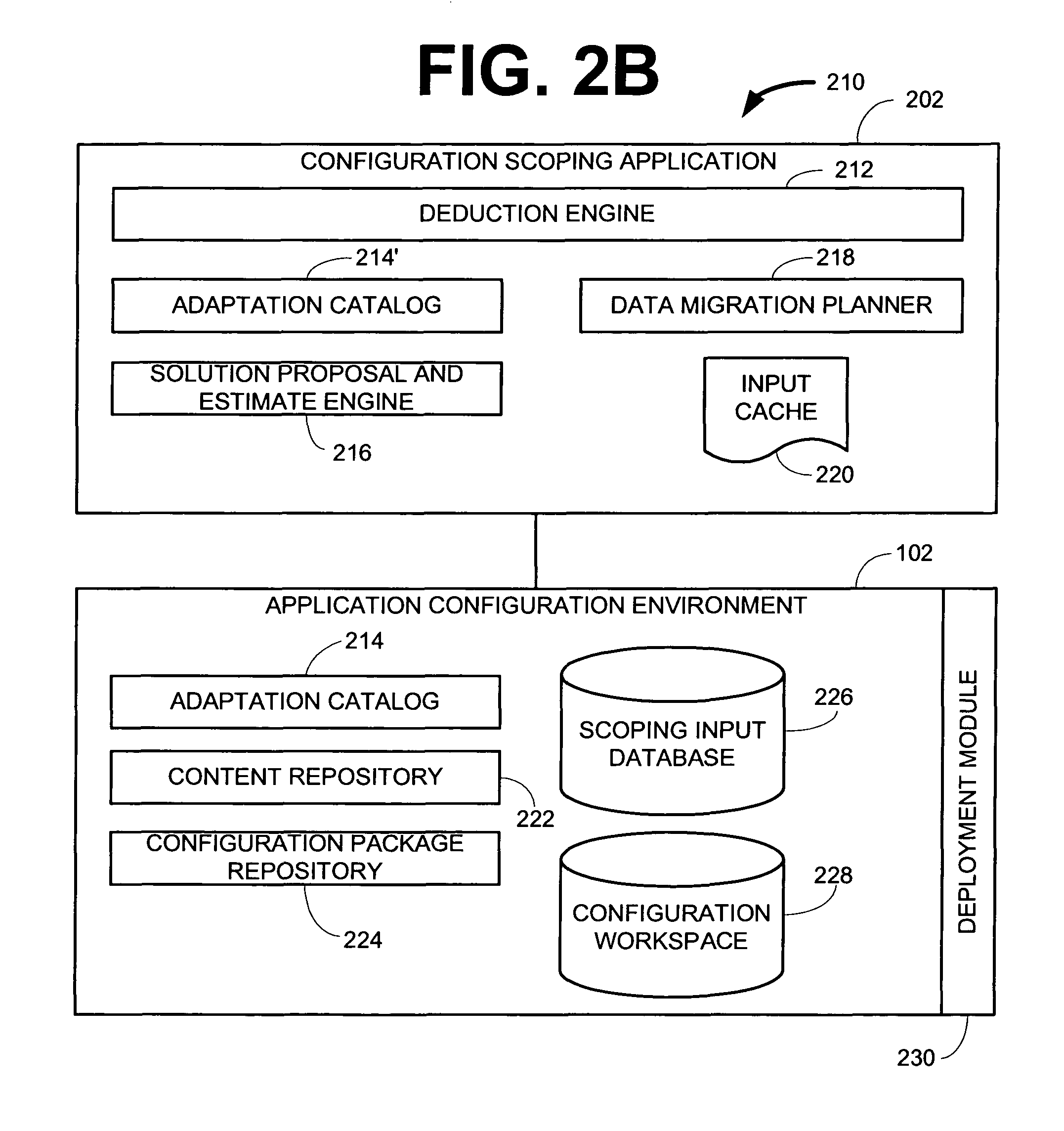
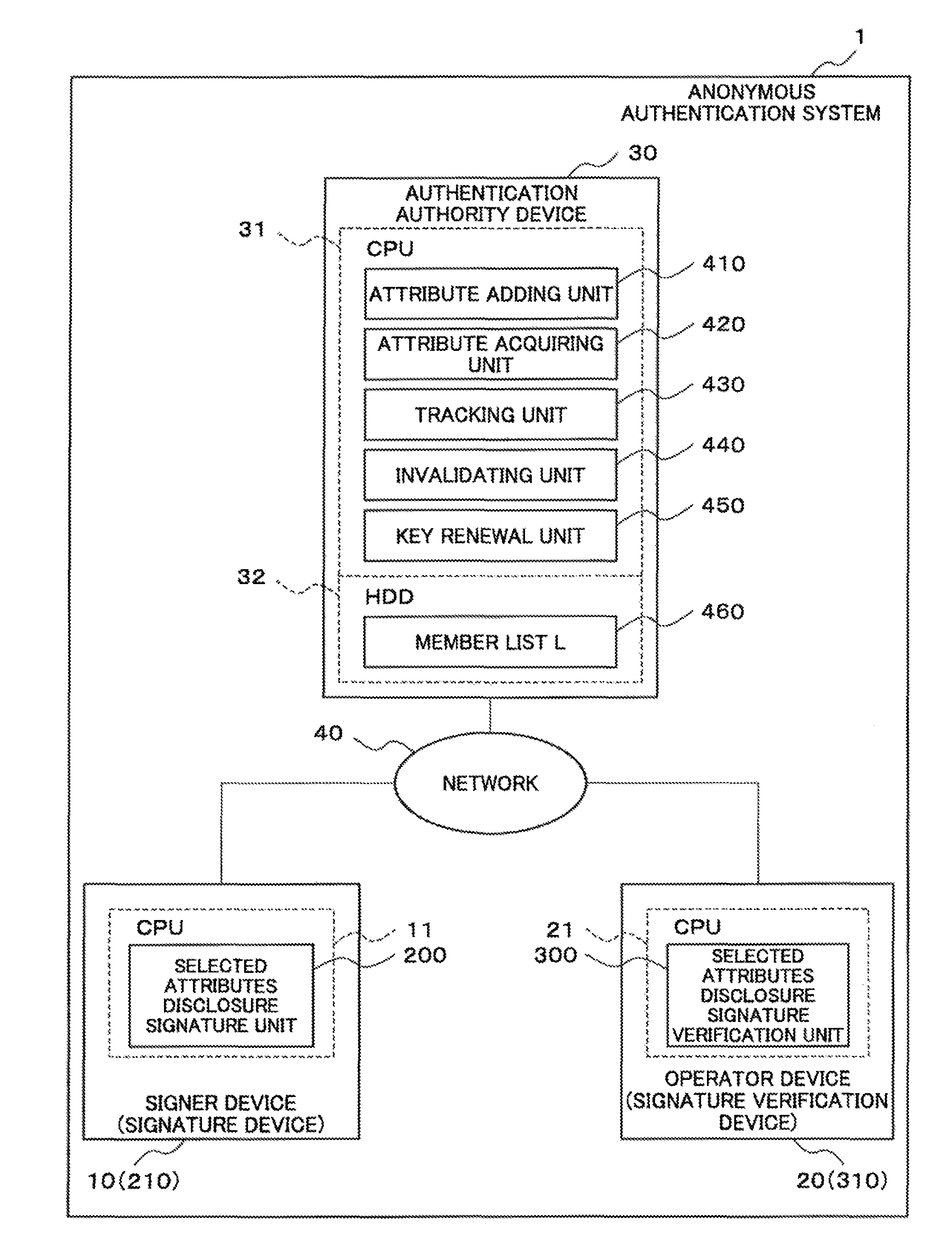
Signature device, signature verification device, anonymous authetication system, signing method, signature authentication method, and programs therefor
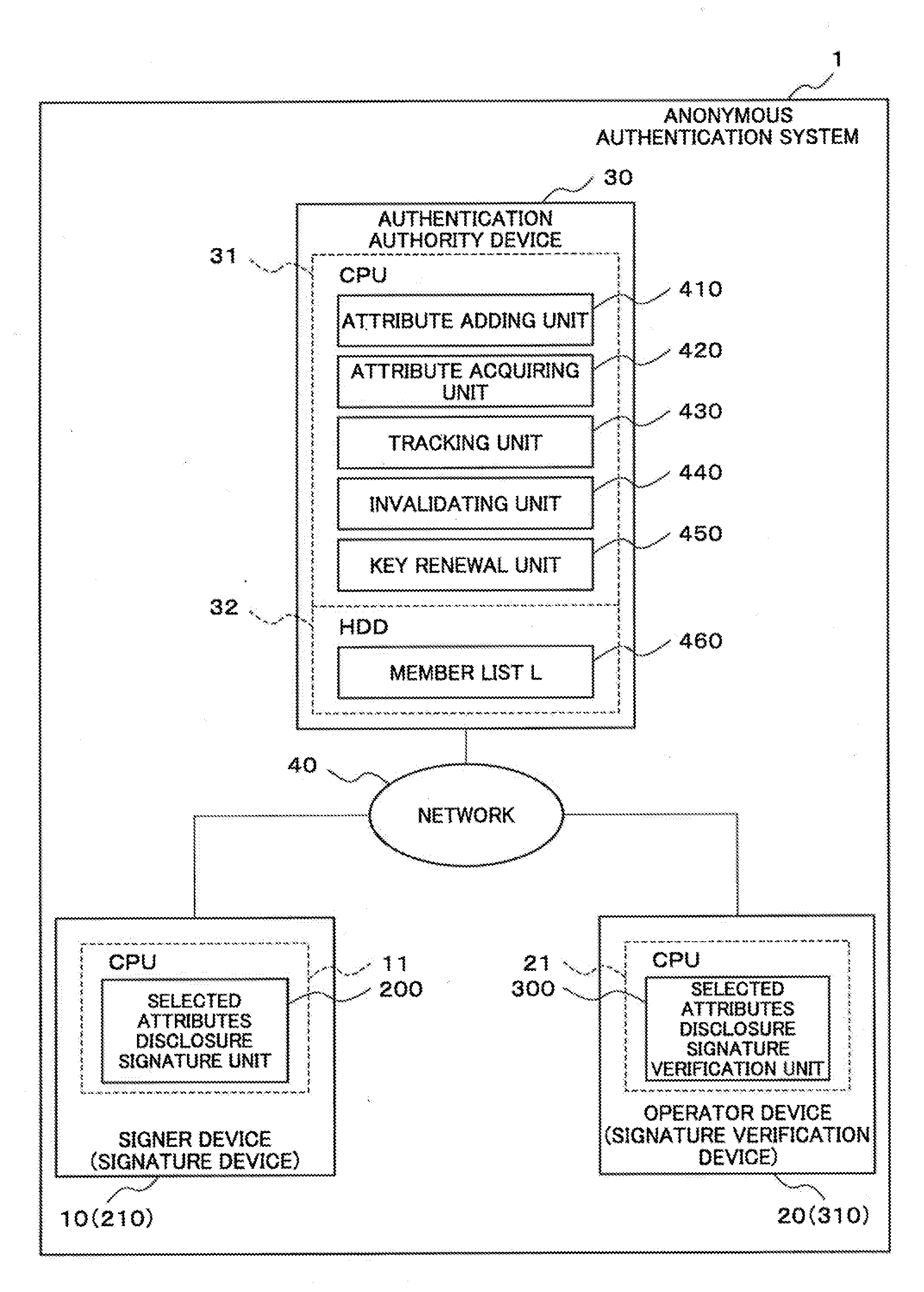
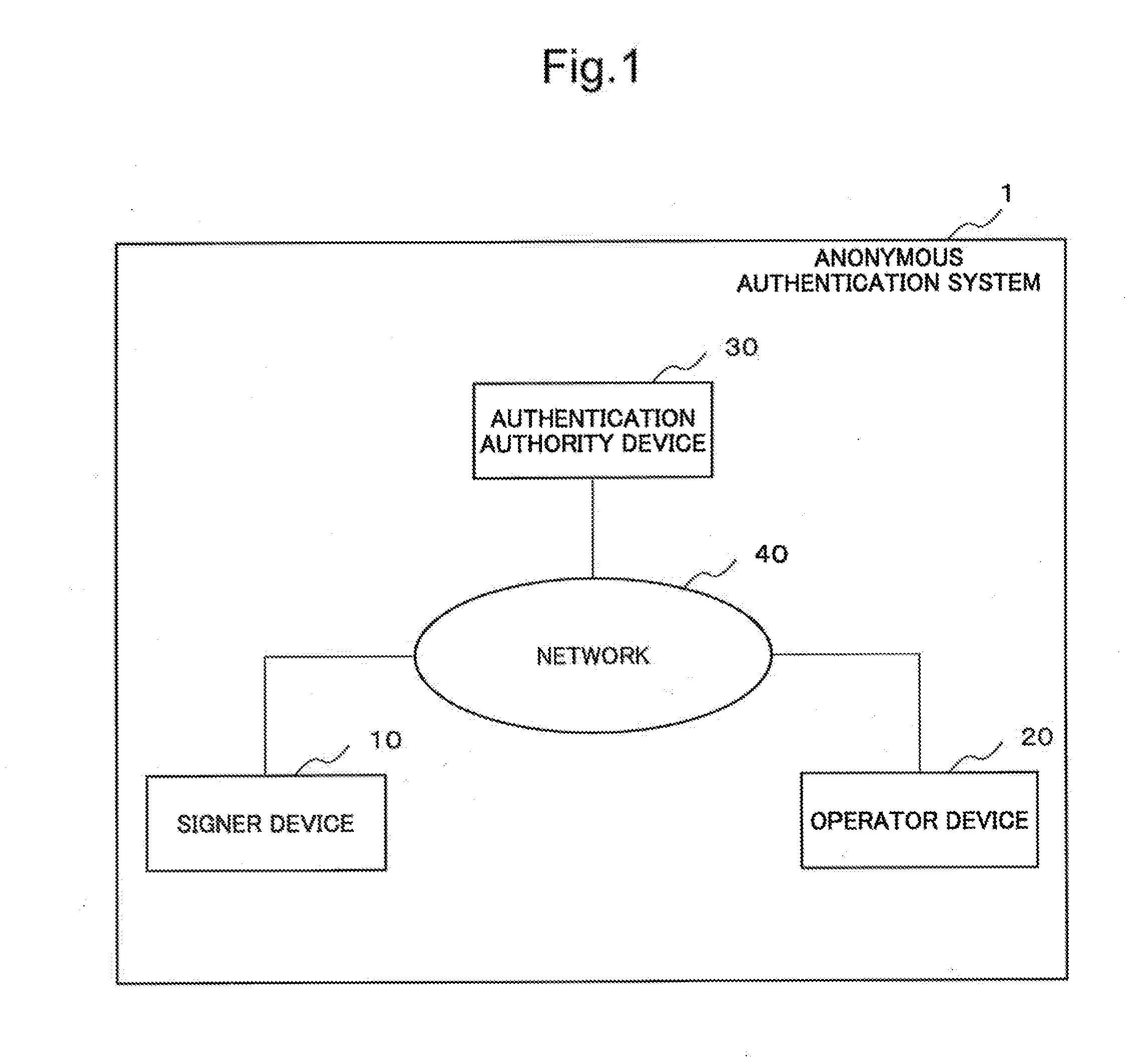
ActiveUS20120060028A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationSet representationNon-interactive zero-knowledge proof
[Problem]Provided is an anonymous authentication system which can issue an anonymous authentication certificate that can hold any number of attributes.[Means for Solving the Problem]A signature device of the invention has a means for receiving the input from an authentication authority public key, an anonymous authentication certificate, a signature key, a text, an attribute proof set, and an attribute public key; a means for generating an attribute set representation value which generates an attribute set representation value from the attribute proof set and attribute public key which were input; a means for generating an attribute set representation key which generates an attribute set representation key from the attribute proof set; a means for generating non-interactive zero-knowledge proof which generates non-interactive zero-knowledge proof from the authentication authority public key, anonymous authentication certificate, signature key, and text which were input, and the attribute set representation value generated by the means for generating an attribute set representation value and the attribute set representation key generated by the means for generating an attribute set representation key; and a signature output means which outputs the non-interactive zero-knowledge proof as signature data.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus for improving efficiency of constraint solving
ActiveUS20070005533A1Aggressive learningEasy to operateDigital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsSet representationTheoretical computer science
Techniques are presented for identifying blockable subsets. Blockable subsets can increase the efficiency by which solutions to a constraint set representation (CSR) can be found. Nodes of a blockable subset can be marked as “blocked” and learning or implication procedures, used as part of a CSR solving process, can be designed to skip nodes marked as blocked. The identification of a particular blockable subset is typically associated with certain conditions being true. If and when the conditions no longer hold, the nodes of the blockable subset need to be unblocked. One type of blockable subset can be identified during the operation of an implication engine (IE) by a technique called justified node blocking (JNB). Another type of blockable subset can be identified by a technique called pivot node learning (PNL). PNL can be applied in-between application of an IE and application of case-based learning.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Implementing access control policies across dissimilar access control platforms
ActiveUS8056114B2Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSet representationGoal system
A method of implementing access control requirements to control access to a plurality of system resources. The requirements are modeled as contents of security policies. The security policy contents are integrated into a policy set. Representations of the integrated policy set are generated, each representation corresponding to a target system that controls access to the resources. The policy set representation(s) are integrated with the corresponding target system(s) to implement the policy set. This method makes it possible to implement high-level security requirements correctly and consistently across systems of a system-of-systems (SoS) and / or distributed system.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Comparing patterns
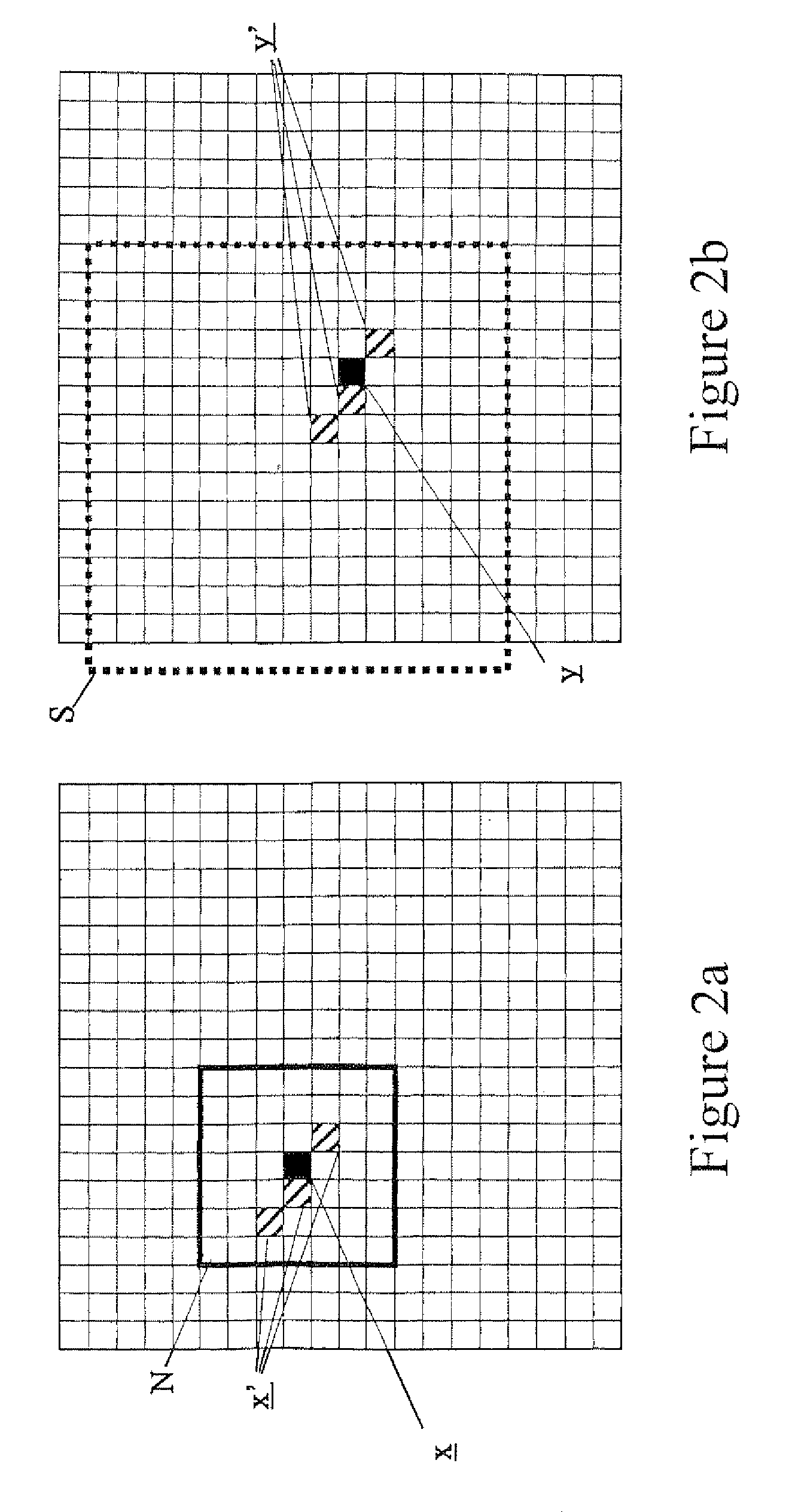
A first image (or other pattern) is represented by a first ordered set of elements A each having a value and a second pattern is represented by a second such set. A comparison of the two involves performing, for each of a plurality of elements x of the first ordered set the steps of selecting from the first ordered set a plurality of elements x′ in the vicinity of the element x under consideration, selecting an element y of the second ordered set and comparing the elements x′ of the first ordered set with elements y′ of the second ordered set (each of which has the same position relative to the selected element y′ of the second ordered set as a respective one x′ of the selected plurality of elements of the first ordered set has relative to the element x under consideration). The comparison itself comprises comparing the value of each of the selected plurality of elements x′ of the first set with the value of the correspondingly positioned element y′ of the like plurality of elements of the second set in accordance with a predetermined match criterion to produce a decision that the plurality of elements of the first ordered set matches the plurality of elements of the second ordered set. The comparison is them repeated with a fresh selection of the plurality of elements x′ of the first set and / or a fresh selection of an element y of the second ordered set generating a similarity measure V as a function of the number of matches. Preferably, following a comparison resulting in a match decision, the next comparison is performed with a fresh selection of the plurality of elements x′ of the first set and the same selection of an element y of the second set.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Adaptive process dispatch in a computer system having a plurality of processors
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and apparatus for improving efficiency of constraint solving
ActiveUS20060247930A1Less timeReduce processDigital computer detailsDigital dataSet representationTheoretical computer science
Techniques are presented for identifying blockable subsets. Blockable subsets can increase the efficiency by which solutions to a constraint set representation (CSR) can be found. Nodes of a blockable subset can be marked as “blocked” and learning or implication procedures, used as part of a CSR solving process, can be designed to skip nodes marked as blocked. The identification of a particular blockable subset is typically associated with certain conditions being true. If and when the conditions no longer hold, the nodes of the blockable subset need to be unblocked. One type of blockable subset can be identified during the operation of an implication engine (IE) by a technique called justified node blocking (JNB). Another type of blockable subset can be identified by a technique called pivot node learning (PNL). PNL can be applied in-between application of an IE and application of case-based learning.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
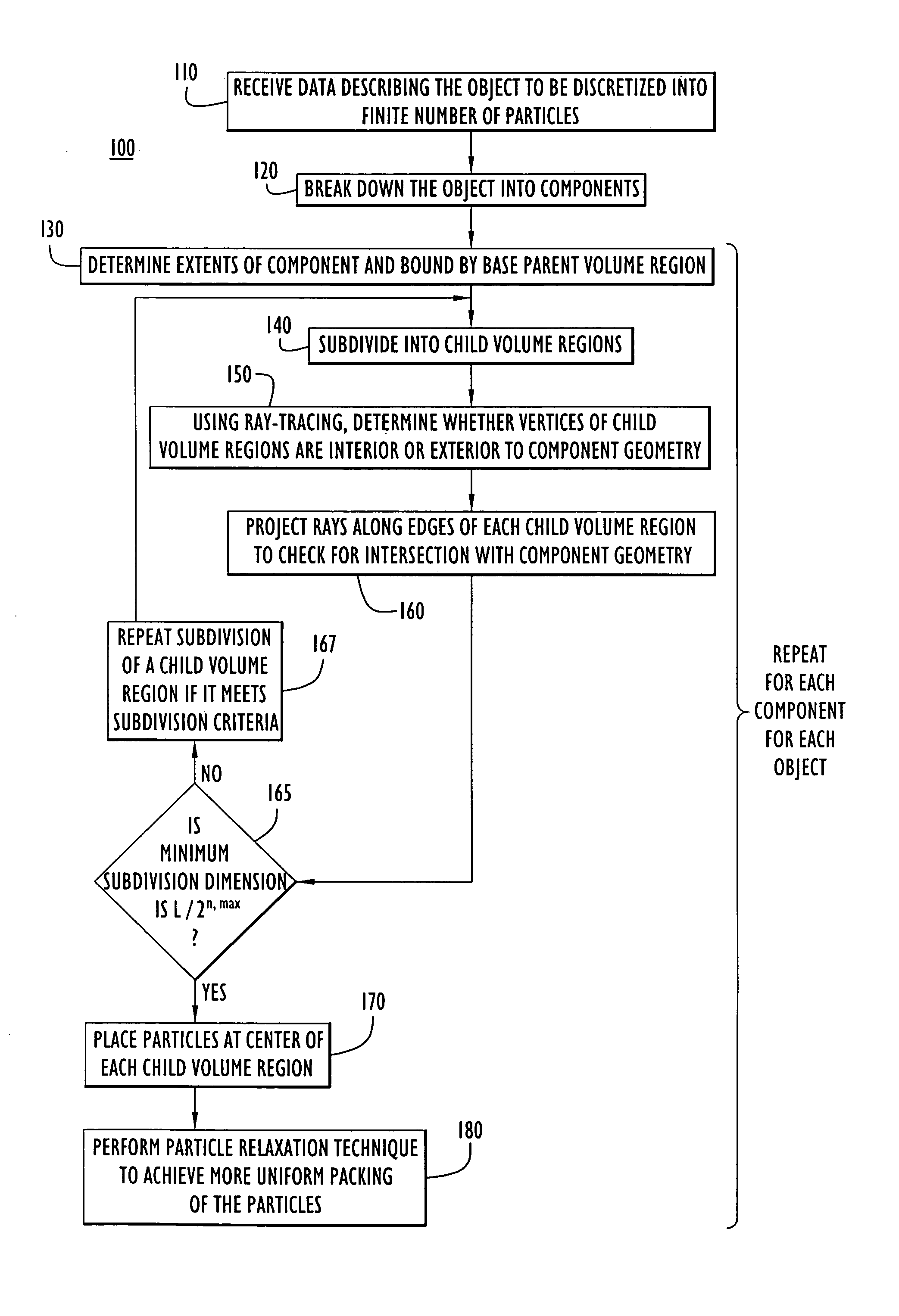
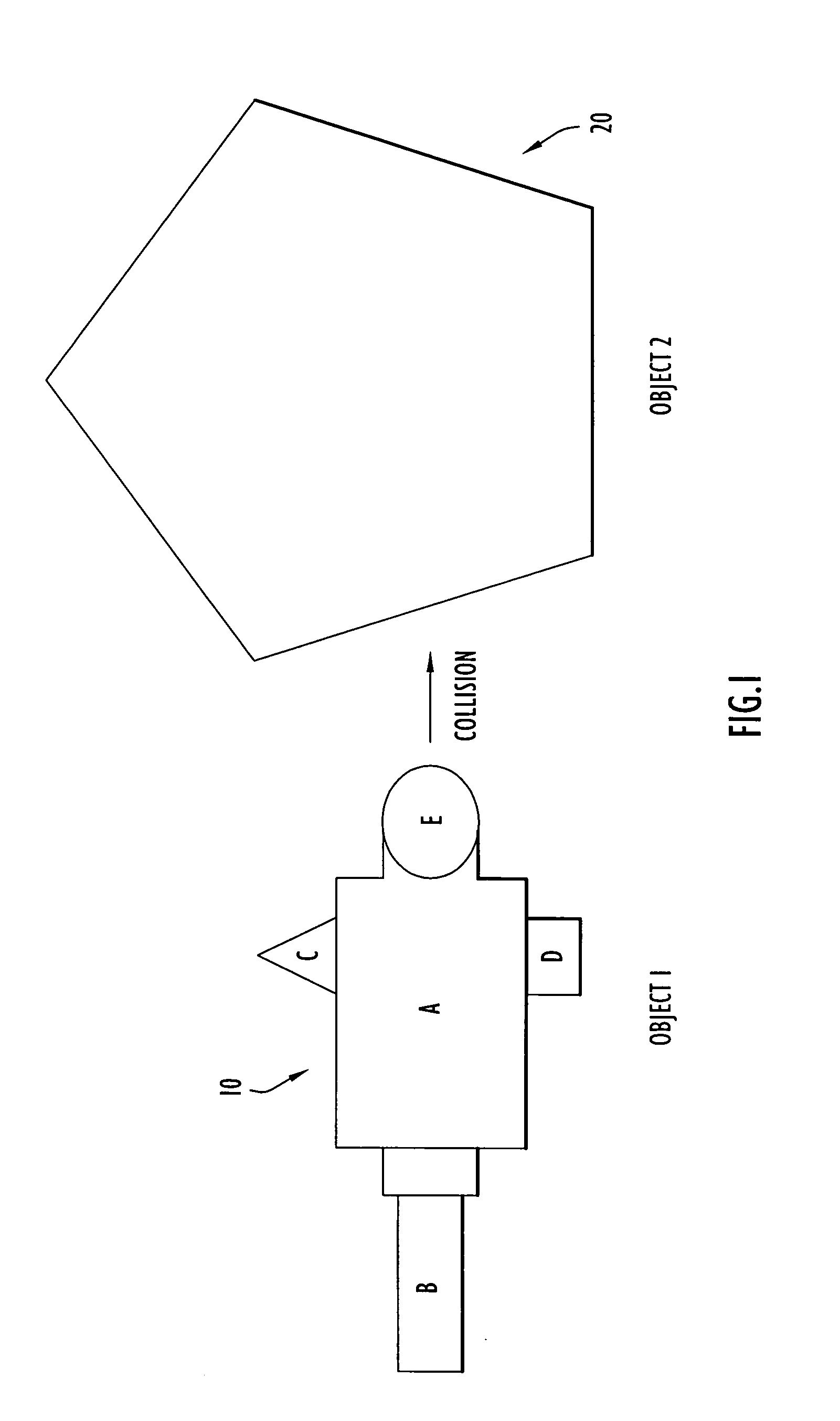
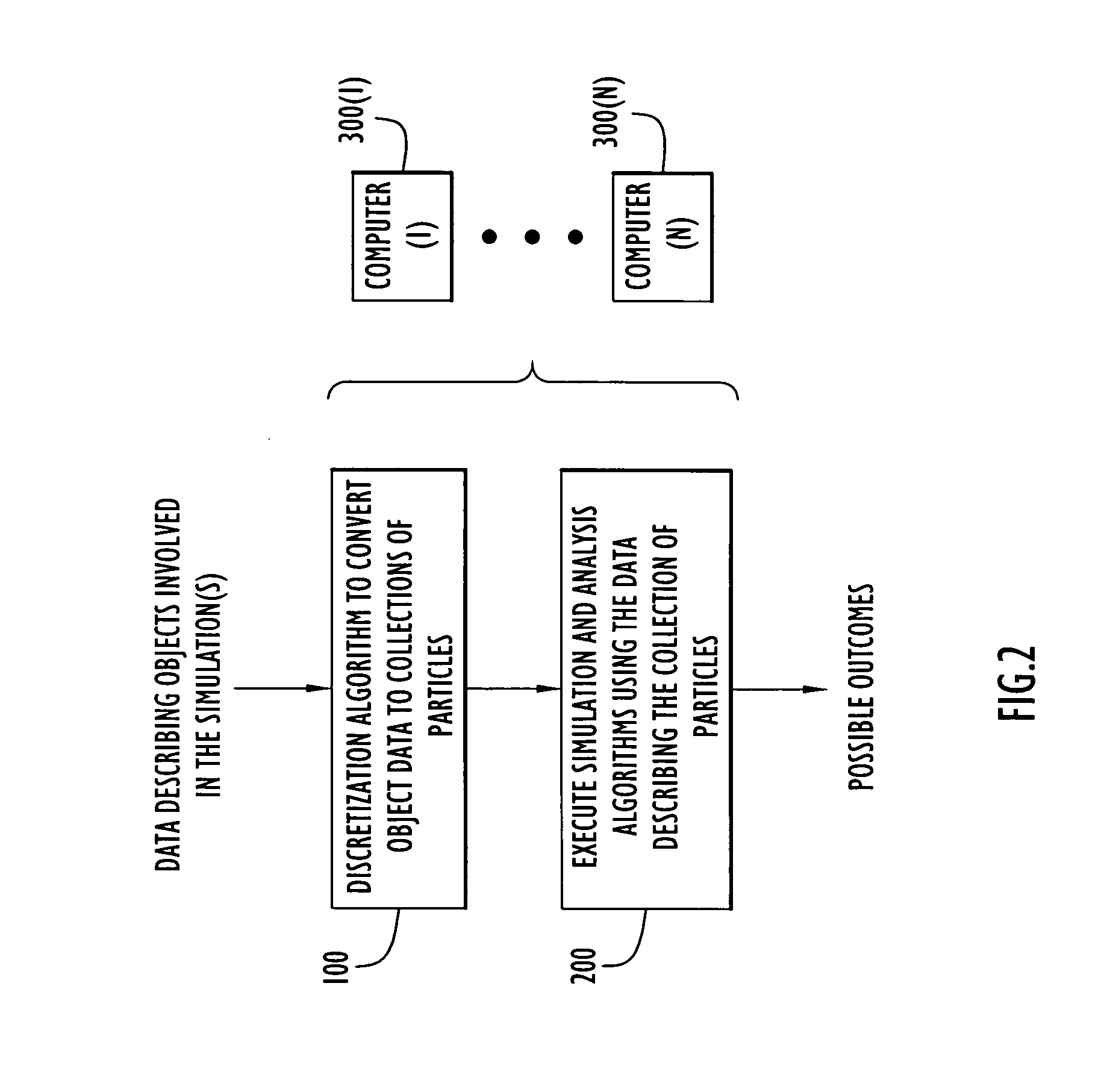
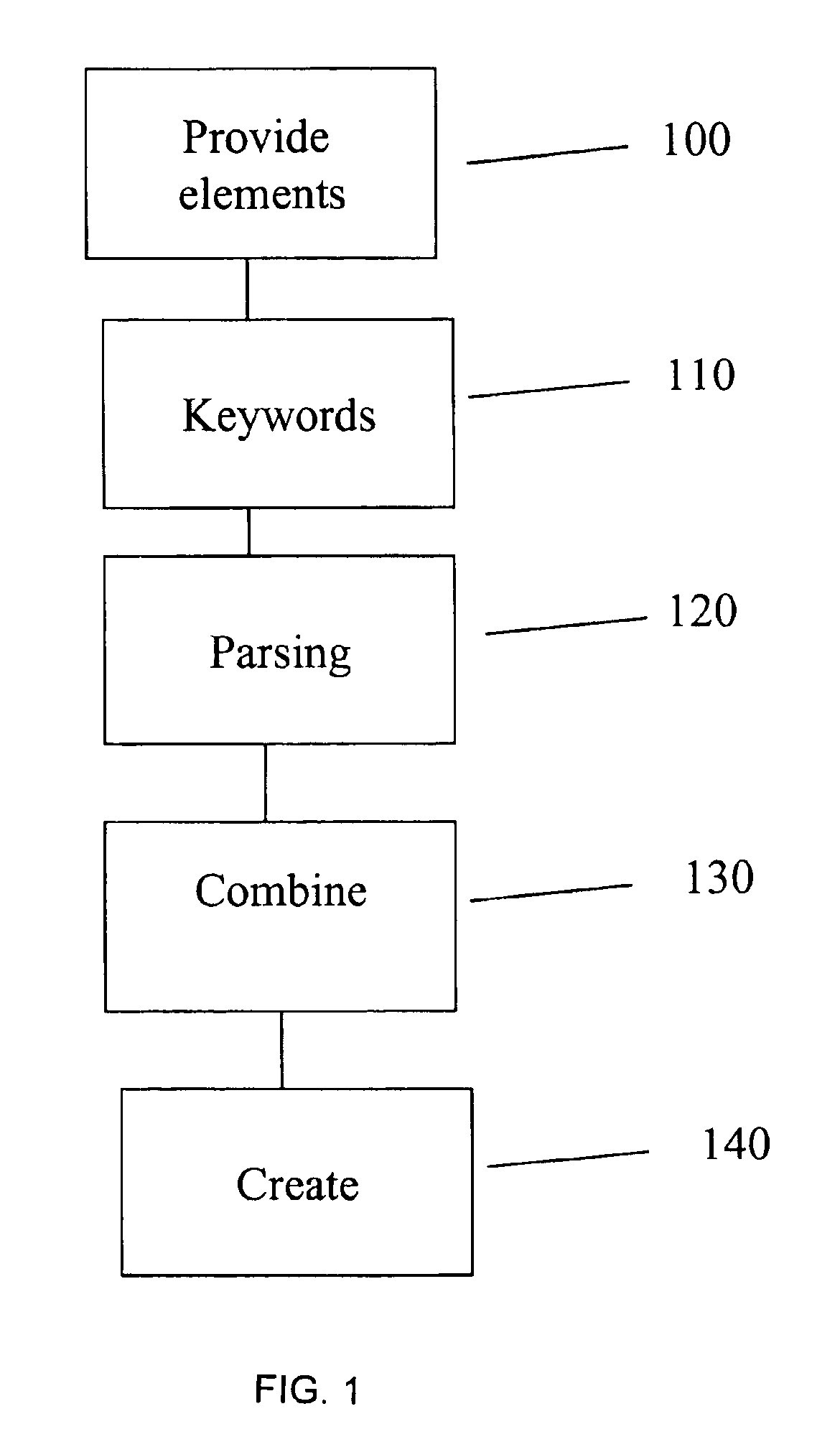
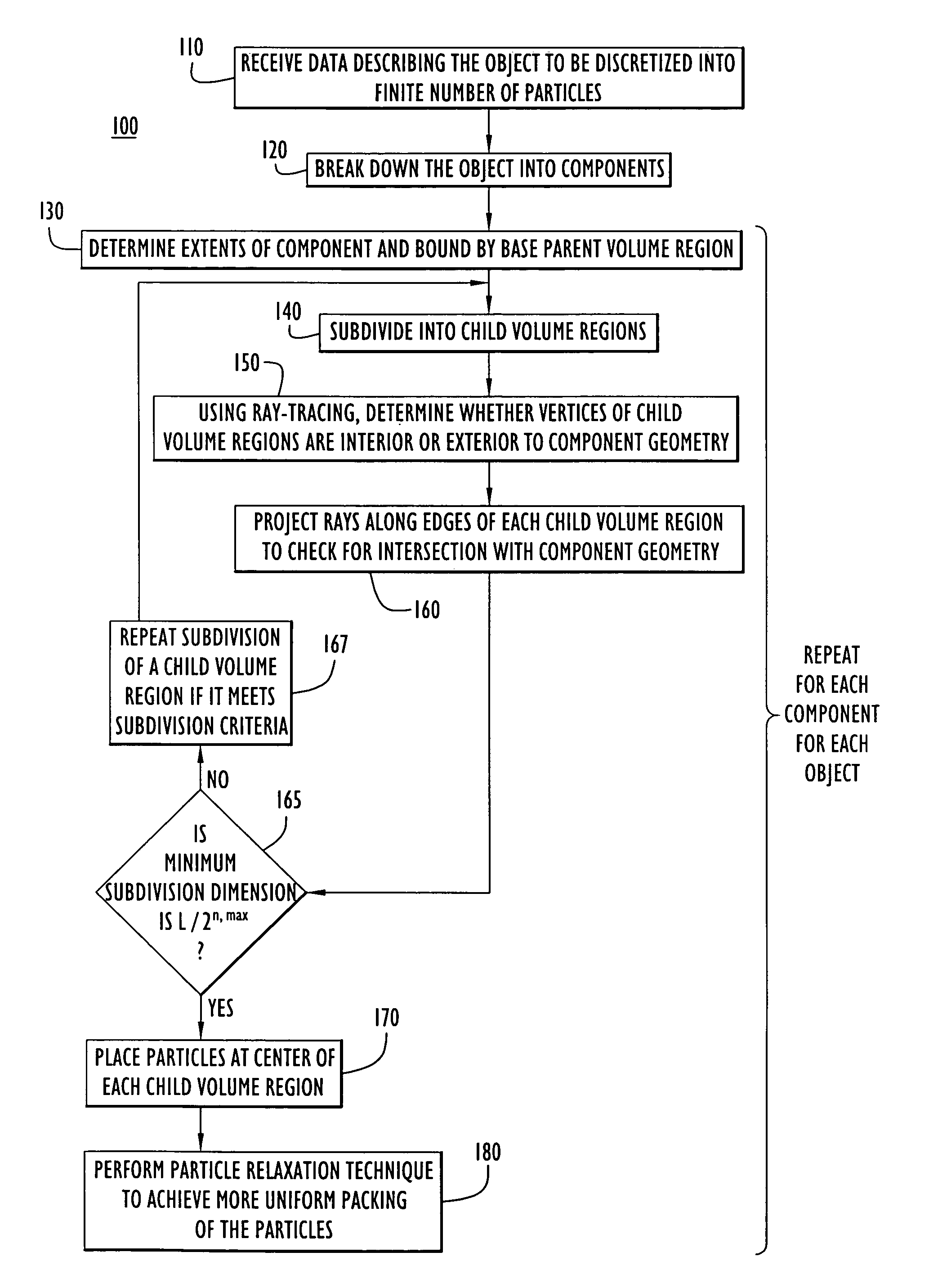
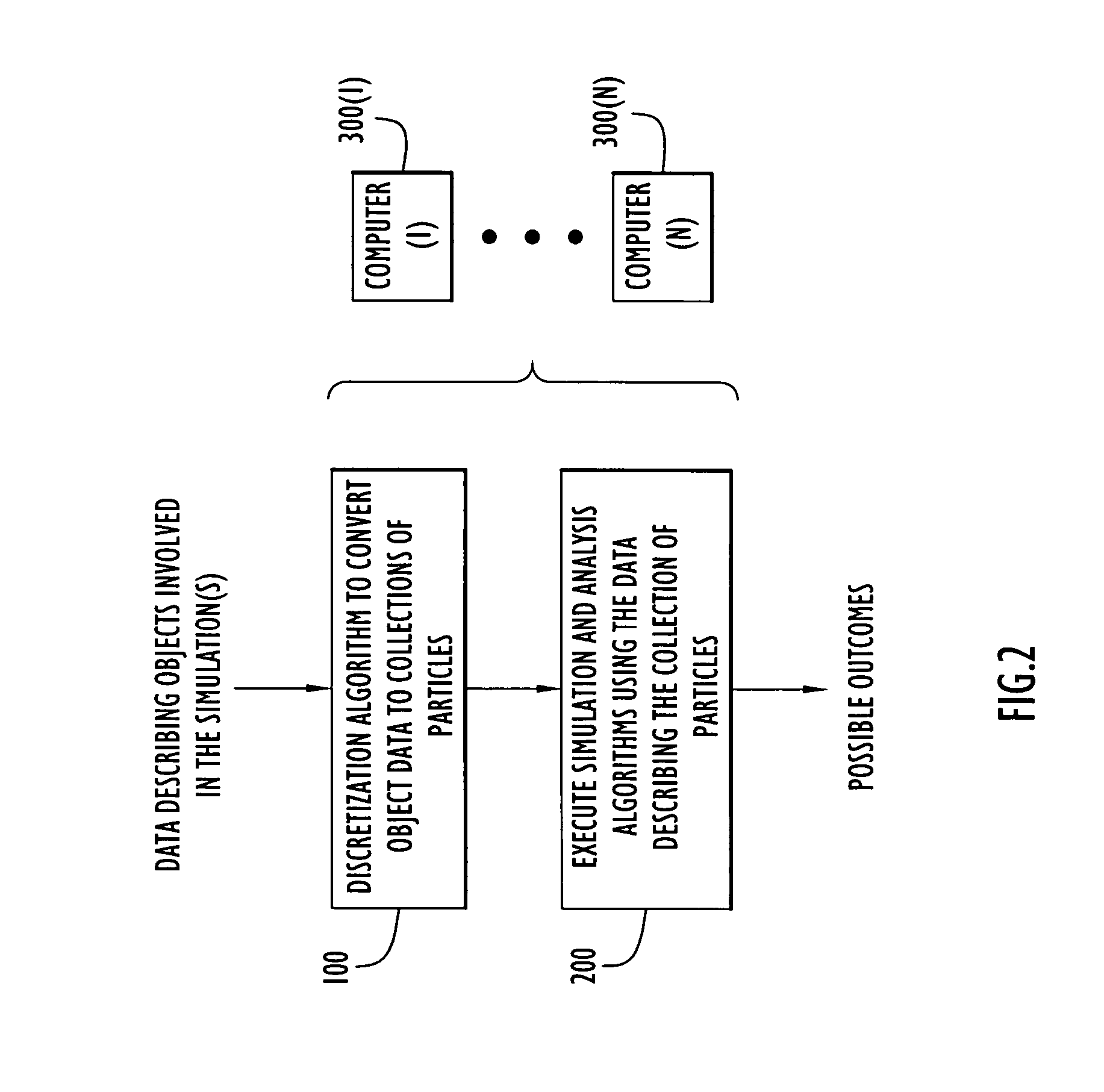
Object discretization to particles for computer simulation and analysis
ActiveUS20070174028A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsObject basedSet representation
A computer-implemented method is provided for generating data representing an object involved in a computer-implemented simulation of a physical experiment. Data describing geometric dimensions and material for the object is received as input. The data may be broken down into data representing distinct components of the object. Data is generated that describes a base parent volume region that extends at least beyond extents of the geometric dimensions of a portion of the object. Next, data is generated that describes child volume regions produced by subdividing the base parent volume region into the child volume regions each having dimensions that are a fraction of the dimensions of the base parent volume region. The data describing each child volume region is examined to determine whether vertices of each of the child volume regions are in the interior or exterior of the portion. The subdivision and examining process is repeated for each child volume region that is not entirely in the interior or entirely in the exterior of the portion to further subdivide each such child volume region to produce data describing a set of child volume regions that do not satisfy the criteria for further subdivision. Data is generated that uniformly distributes particles at positions of the portion of the object based on dimensions of the child volume region in the set, wherein the data for each particle describes a mass density, velocity, pressure, stress and energy at a position and a collection of the particles represent the object portion for use in the computer-implemented simulation.
Owner:PERATON INC
Identifying method for fragmentary printed digits
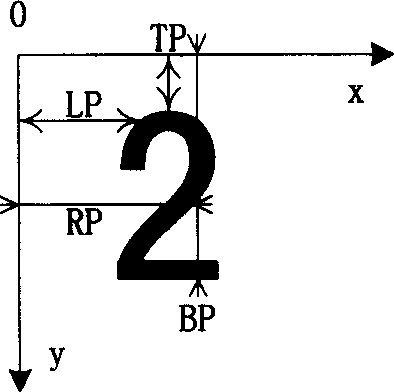
InactiveCN1584921AAccurate identificationOvercome unrecognized problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionSet representationImage identification
A method for identifying incomplete print hand of digital character includes dividing complete character to be four local contours of left, right, top and bottom, using coordinate set to present contour and carrying out discrete differentiation to position coordinate of counter picture element, integrating stroke number, contour structural features for setting up digital character model, applying structural statement method to identify incomplete digital character.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
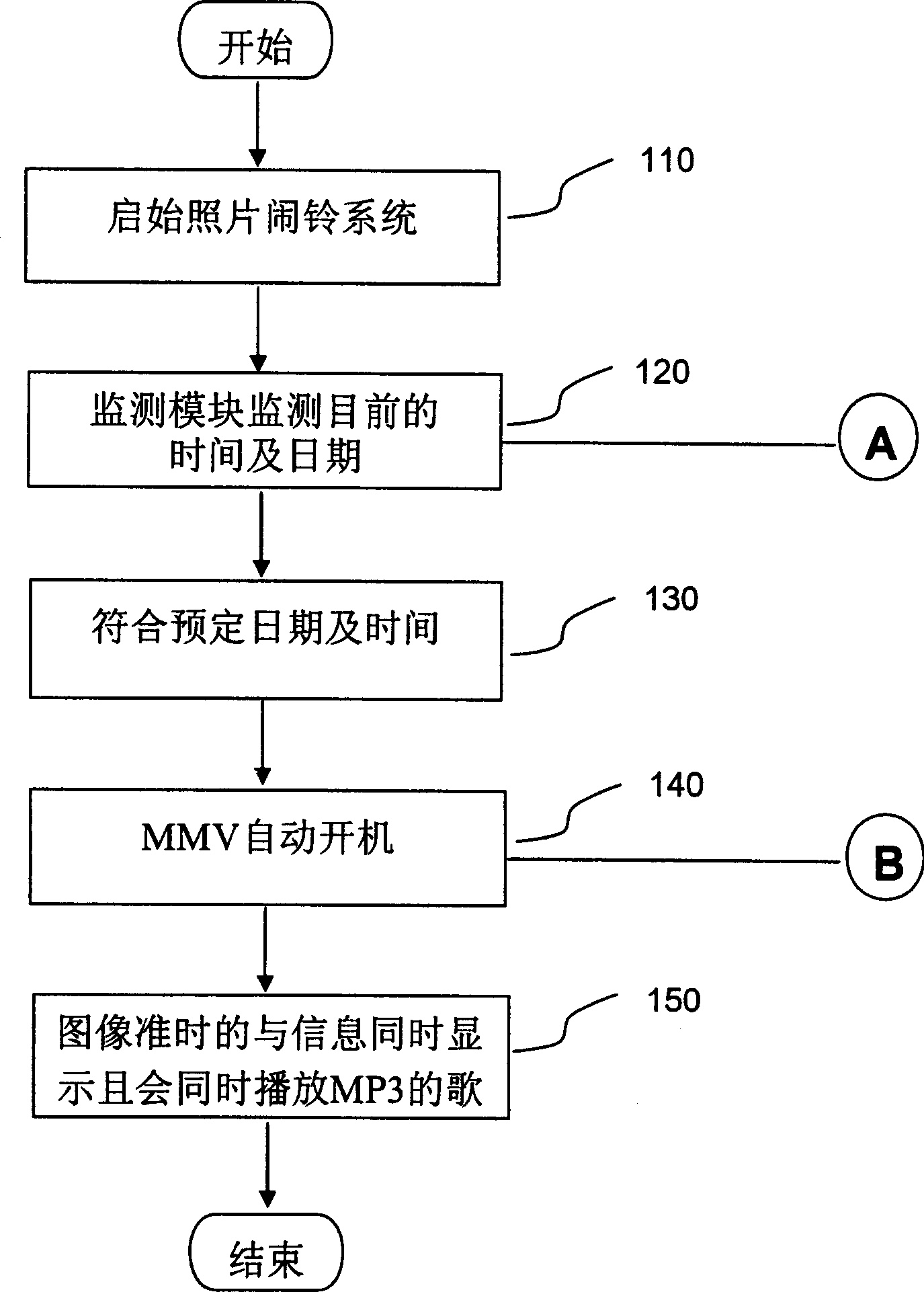
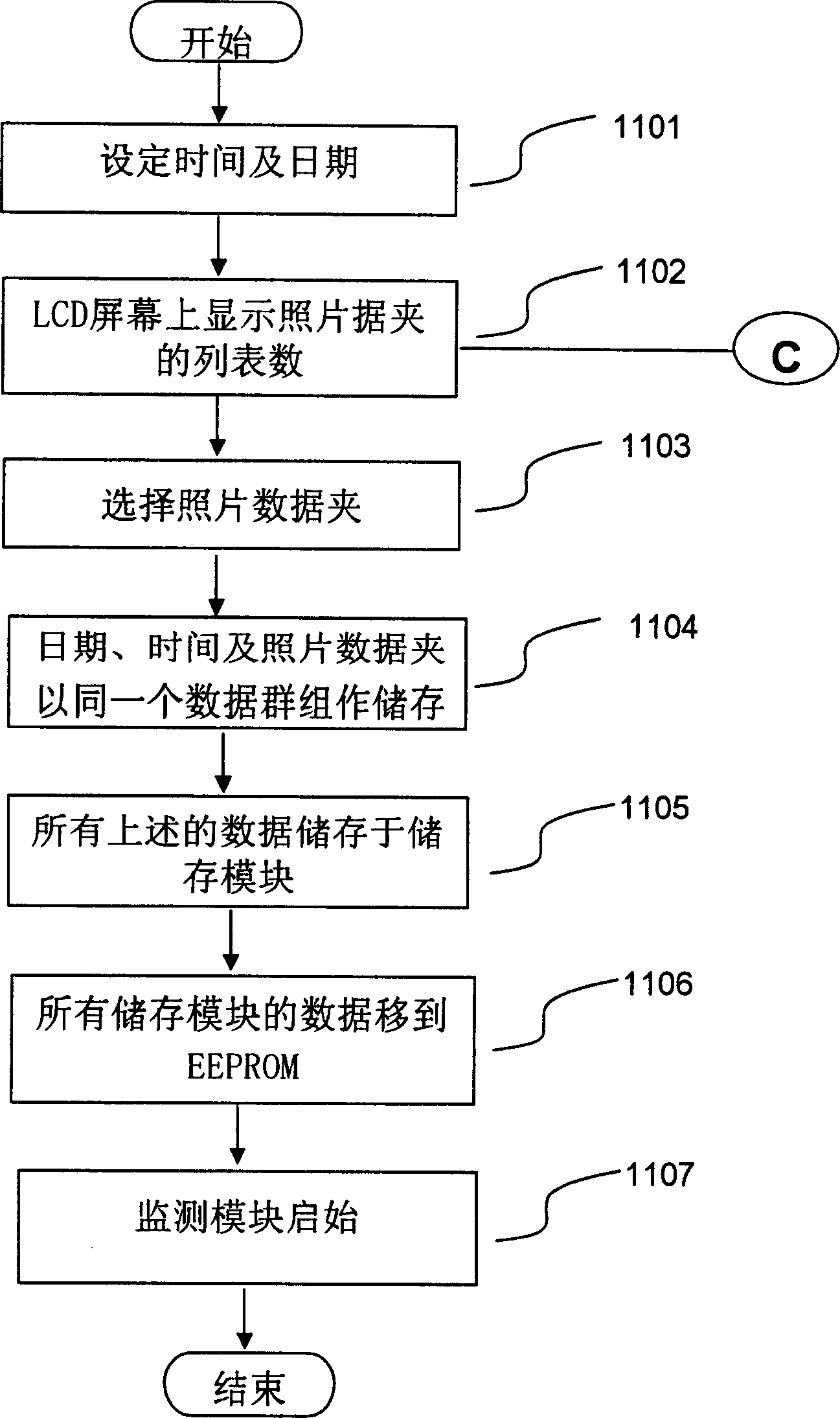
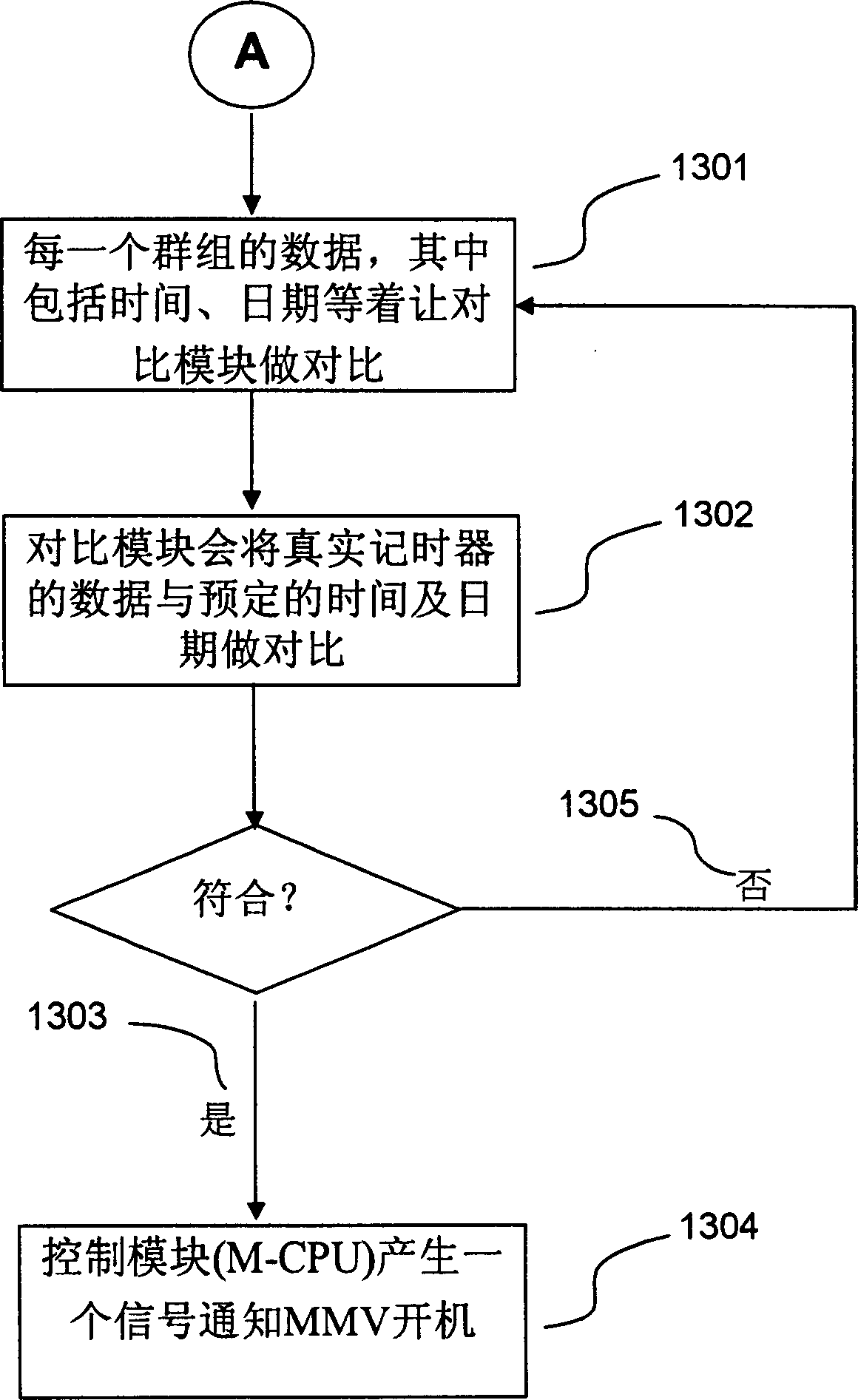
A multimedia alarm bell presenting method and apparatus thereof
The present invention discloses a representation method of multimedia alarm clock, it is applicable to multimedia monitoring device with storage module. Its storage module also includes at least a data group, every data group includes a multimedia data folder and set representation time and date data correspondent to said multimedia data folder. Its representation method at least includes the following steps: continuously receiving current time and date information, comparing the current time and date information with set representation time and date of every multimedia data folder in current erasable and programmable read-only memory, when confirming that current time and date are identical to set representation date and time correspondent to some multimedia data folder in said storage module, extracting said multimedia data folder data from the current erasable and programmable read-only memory module and utilizing display module and sonification module to represent image and voice data of said multimedia data folder. Said image and voice data includes image, voice and characters.
Owner:INVENTEC MULTIMEDIA & TELECOM
Producing method capable of global indexing coding sequence and uses thereof
InactiveCN101042295AImprove efficiencyImprove rebuild efficiencyImage codingUsing optical meansTheoretical computer scienceValue code
This invention relates to one generation method for whole index codes sequence, which comprises the following steps: giving codes set as P={c1, c2, c3, ...cp}, p>=3 with cp for special physical values codes with k for code length; generating k element set w ranking as sizes to form set V and to select p-1 code as initial codes and to delete p-1 code; using the last k-1 unit code as initial one in set V and selecting maximum codes into S for connection and adding the last unit code into S and to delete this code; repeating above steps till all codes in set V into S sequence to form one longest whole index codes sequence.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Test engine
ActiveUS8065661B2Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsSet representationComputer module
The present subject mater relates to testing software application configurations and, more particularly, to a test engine. The various embodiments described and illustrated herein provide systems, methods, and software that maintain a configuration database in a memory, wherein the configuration database includes a representation of configuration settings of an application. Some such embodiments may further store a test engine module in the memory, wherein the test engine module includes a set of test cases, which when processed, test functionality of the application, wherein a test case is selected for execution as a function of one or more application configuration setting representations from the configuration database.
Owner:SAP AG
Signature device, signature verification device, anonymous authetication system, signing method, signature authentication method, and programs therefor
ActiveUS8583932B2User identity/authority verificationSet representationNon-interactive zero-knowledge proof
[Problem]Provided is an anonymous authentication system which can issue an anonymous authentication certificate that can hold any number of attributes.[Means for Solving the Problem]A signature device of the invention has a means for receiving the input from an authentication authority public key, an anonymous authentication certificate, a signature key, a text, an attribute proof set, and an attribute public key; a means for generating an attribute set representation value which generates an attribute set representation value from the attribute proof set and attribute public key which were input; a means for generating an attribute set representation key which generates an attribute set representation key from the attribute proof set; a means for generating non-interactive zero-knowledge proof which generates non-interactive zero-knowledge proof from the authentication authority public key, anonymous authentication certificate, signature key, and text which were input, and the attribute set representation value generated by the means for generating an attribute set representation value and the attribute set representation key generated by the means for generating an attribute set representation key; and a signature output means which outputs the non-interactive zero-knowledge proof as signature data.
Owner:NEC CORP
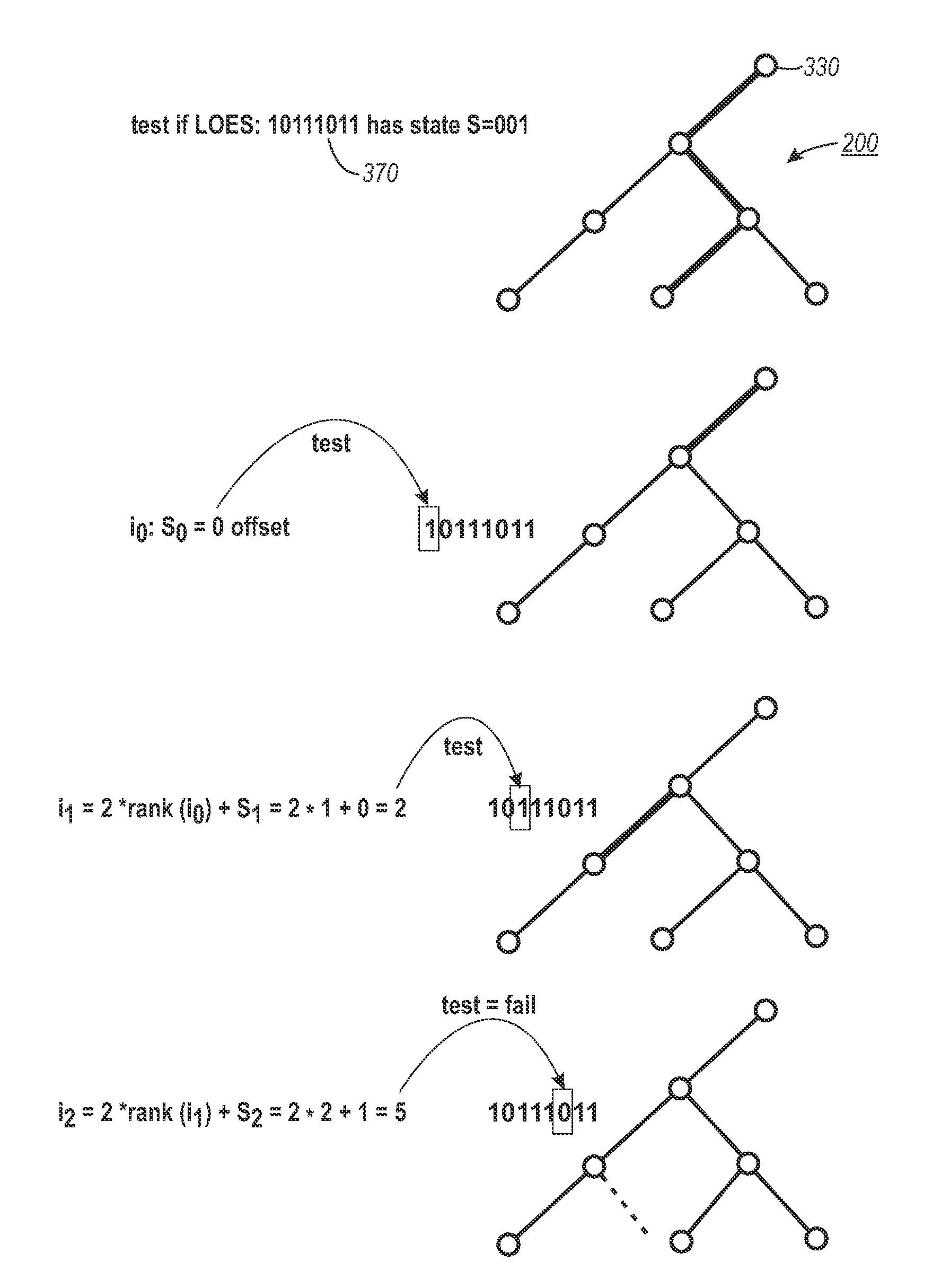
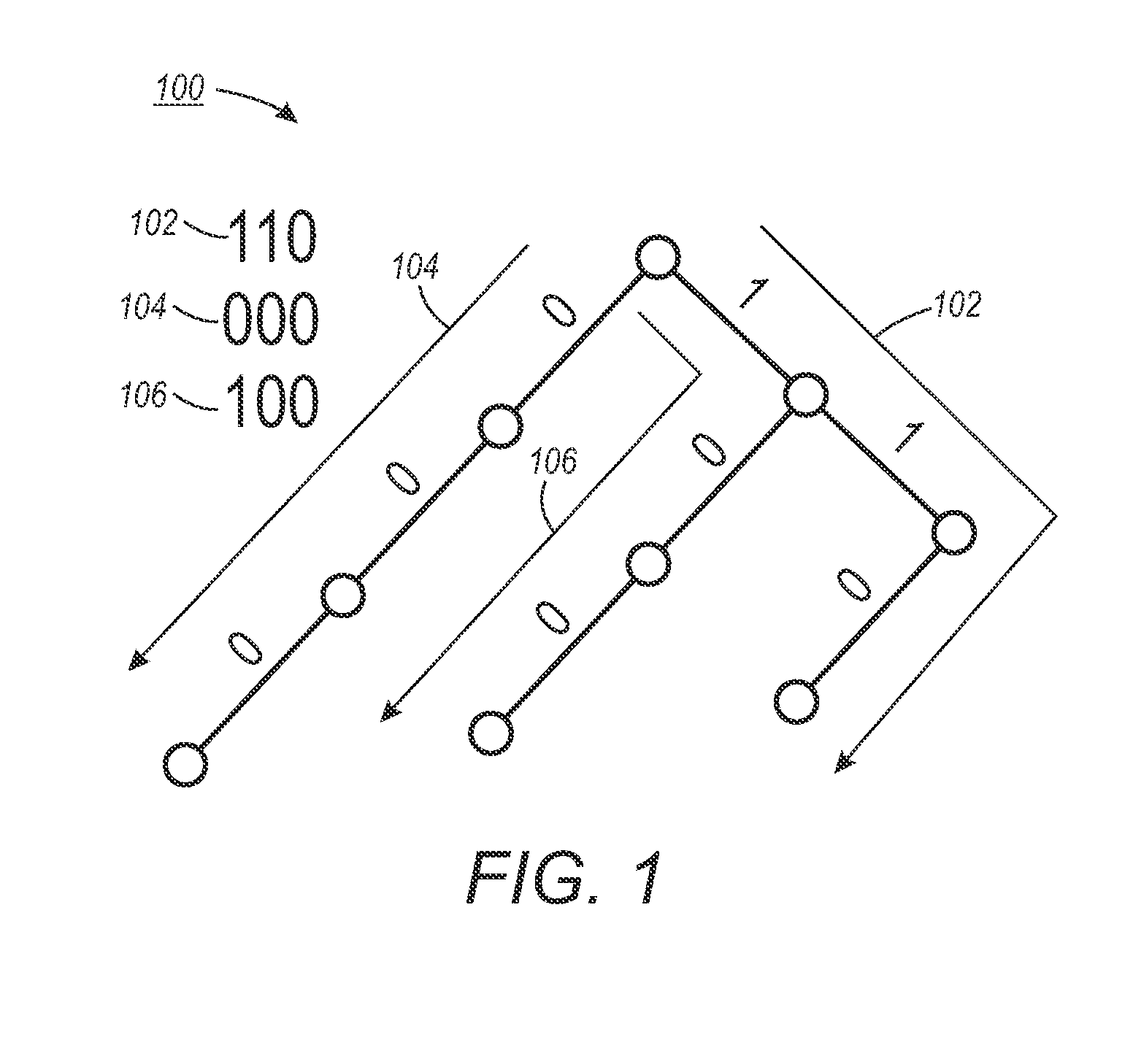
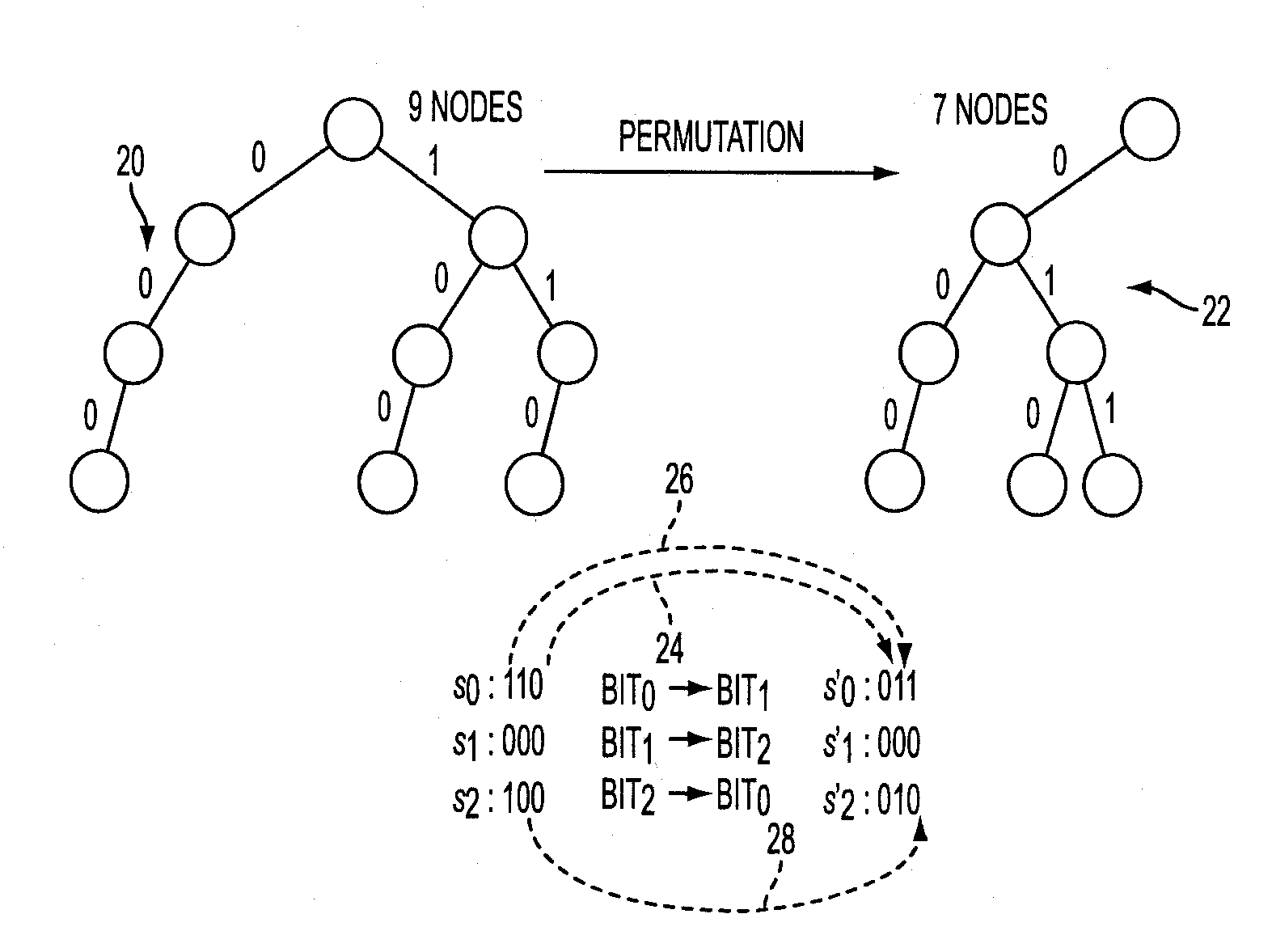
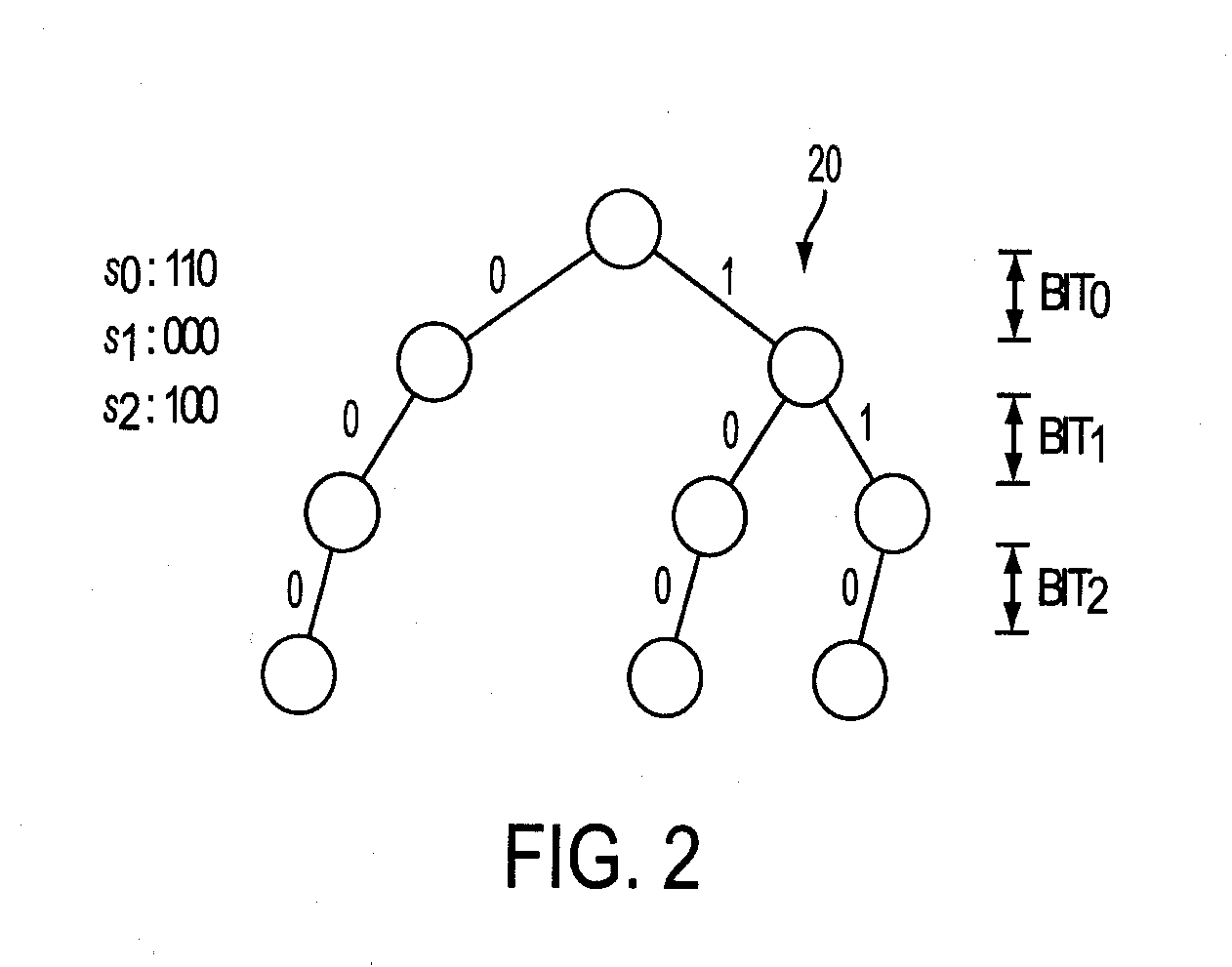
Memory efficient state-set representation for planning
A method for encoding state sets which encodes a binary prefix tree representation as a level ordered edge sequence (LOES) where the inner tree nodes are ordered from left to right, and top to bottom order and coded as bit pairs which represent the presence of leaf nodes.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and system of design verification
InactiveUS7711534B2Small sizeReduce complexityError detection/correctionAnalogue computers for electric apparatusSpecific functionProgram planning
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Object discretization to particles for computer simulation and analysis
ActiveUS7620532B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTransfer mechanismsObject basedSet representation
A computer-implemented method is provided for generating data representing an object involved in a computer-implemented simulation of a physical experiment. Data describing geometric dimensions and material for the object is received as input. The data may be broken down into data representing distinct components of the object. Data is generated that describes a base parent volume region that extends at least beyond extents of the geometric dimensions of a portion of the object. Next, data is generated that describes child volume regions produced by subdividing the base parent volume region into the child volume regions each having dimensions that are a fraction of the dimensions of the base parent volume region. The data describing each child volume region is examined to determine whether vertices of each of the child volume regions are in the interior or exterior of the portion. The subdivision and examining process is repeated for each child volume region that is not entirely in the interior or entirely in the exterior of the portion to further subdivide each such child volume region to produce data describing a set of child volume regions that do not satisfy the criteria for further subdivision. Data is generated that uniformly distributes particles at positions of the portion of the object based on dimensions of the child volume region in the set, wherein the data for each particle describes a mass density, velocity, pressure, stress and energy at a position and a collection of the particles represent the object portion for use in the computer-implemented simulation.
Owner:PERATON INC
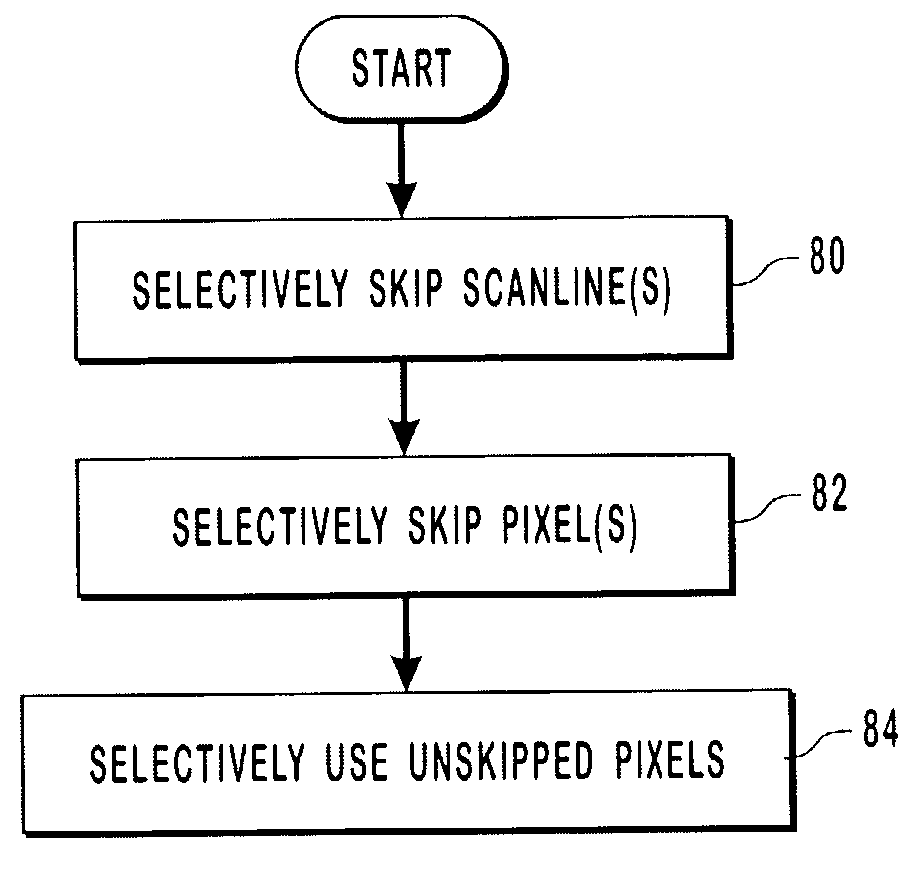
Systems and methods for downscaling an image
InactiveUS7154514B2Efficiently downscaleDownscaling imageGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsRight shiftSet representation
Systems and methods for downscaling an image. An original image, represented by a collection of individual pixels, is provided so as to be downscaled. One or more of the scan lines of the original image are selectively skipped. One or more of the pixels of non-skipped scan lines are selectively skipped. The remaining pixels are then used to provide the pixels of the downscaled image. In a further implementation, the remaining pixels are used by selectively being averaged to downscale the image. Accordingly, a reduced number of pixels are averaged in order to create a new pixel of the downscaled image. Implementation of the present invention may also avoid a division process by using a right shift instead of division in the averaging process. Accordingly, implementation of the present invention reduces the time required to downscale an image and is also device independent.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and system of design verification
InactiveUS20060064296A1Small sizeReduce complexityError detection/correctionAnalogue computers for electric apparatusProgram planningSet representation
A method and system comprises extracting resources required to run a discrete test case or set of associated test cases on a design. The method and system further includes building a simulation model based on the extracted resources and executing the simulation model using only the extracted resources, exclusive of an entire design, to test a specific function or group of interrelated functions represented by the discrete test case or set of associated test cases for design verification, and correlating the simulation results with the test plan.
Owner:IBM CORP
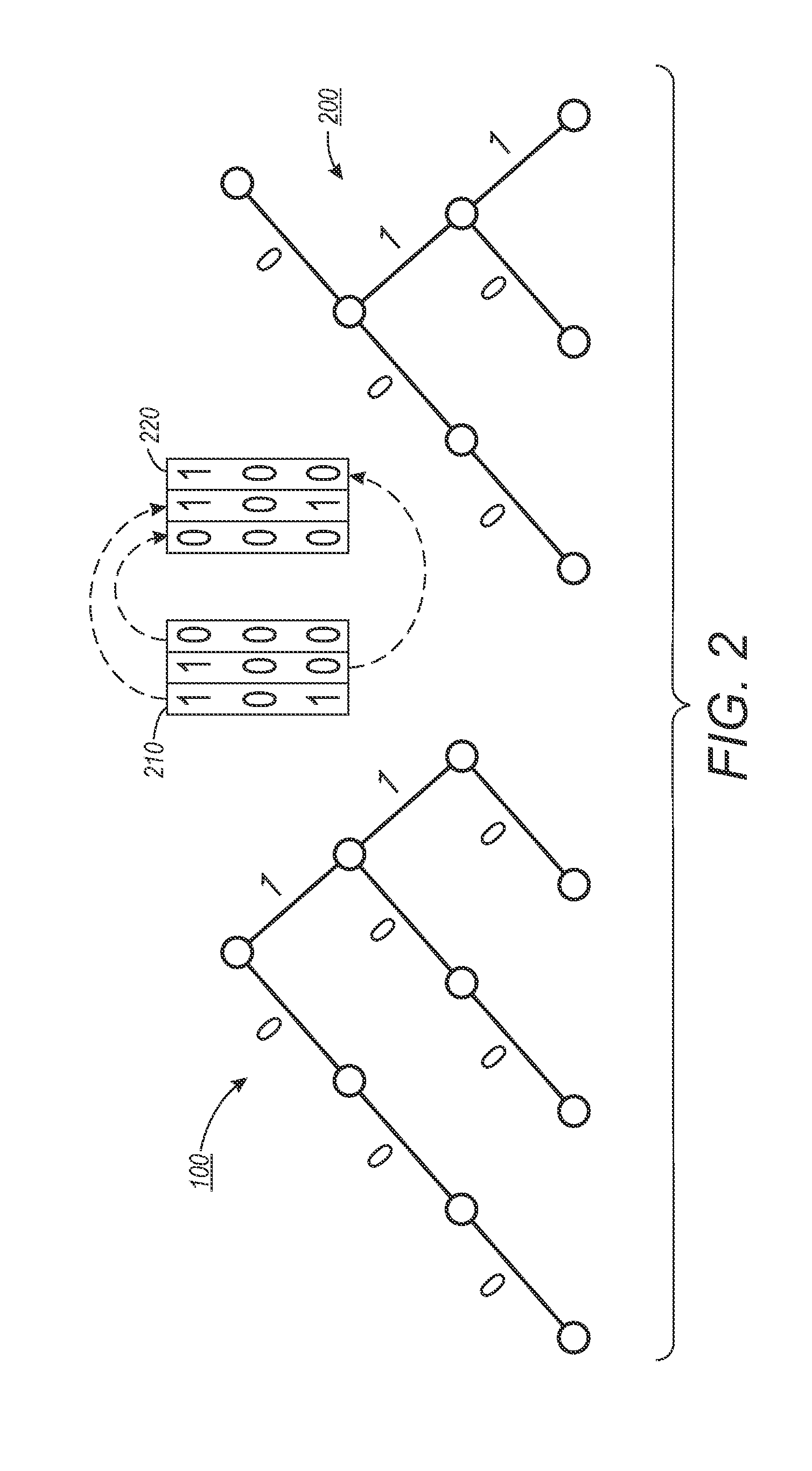
System and method for compressed level-ordered edge sequence encoding
Compressed Level-Ordered Edge Sequence (CLOES) encodings are described. These techniques enable more aggressive compression of a state-set representation.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and apparatus for improving efficiency of constraint solving
ActiveUS7353216B2Less timeReduce processDigital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsNODALSet representation
Techniques are presented for identifying blockable subsets. Blockable subsets can increase the efficiency by which solutions to a constraint set representation (CSR) can be found. Nodes of a blockable subset can be marked as “blocked” and learning or implication procedures, used as part of a CSR solving process, can be designed to skip nodes marked as blocked. The identification of a particular blockable subset is typically associated with certain conditions being true. If and when the conditions no longer hold, the nodes of the blockable subset need to be unblocked. One type of blockable subset can be identified during the operation of an implication engine (IE) by a technique called justified node blocking (JNB). Another type of blockable subset can be identified by a technique called pivot node learning (PNL). PNL can be applied in-between application of an IE and application of case-based learning.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Graphene thin film reel-to-reel production device and method
PendingCN110629191ACharacterization parameters as expectedGrapheneChemical vapor deposition coatingSet representationEngineering
The invention provides a graphene thin film reel-to-reel production device and method. The device comprises a vacuum cavity, a vacuum pump assembly and a process gas introducing assembly, and furthercomprises at least one monitoring assembly and a parameter control assembly. The vacuum cavity comprises an unreeling cavity, a growing cavity and a reeling cavity which sequentially communicate. Onemonitoring assembly is connected to the growing cavity and used for obtaining first representation parameters of a graphene thin film located in the growing cavity and comparing the first representation parameters with a first set representation parameter to obtain a first comparison result. The parameter control assembly is connected to the monitoring assemblies and used for responding to the first comparison result and adjusting all process gas introduction amounts and ratio and / or the temperature of the growing cavity and / or the movement speed of a growing substrate and / or the pressure intensity in the growing cavity so that the first representation parameters are equal to the first set representation parameter.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Active fault diagnosis method
ActiveCN110597230AEnable proactive fault diagnosisImplement collection separationProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringActive faultControl objective
The present invention discloses an active fault diagnosis method. The method comprises the following steps: S1 aiming at a linear discrete time-invariant system (LDIT) with multiple faults, obtainingan invariant set representation form of an output estimation set; S2 transferring the output estimation set obtained from step S1 into the equivalent form of a polyhedral set via set form change; S3 realizing set separation by maximizing the distance among output estimation sets represented by invariant set(s), and thus obtaining an input sequence capable of realizing the active fault diagnosis (AFD) and realizing the control objective(s) of the system. The input sequence obtained by the method is capable of achieving the AFD objectives in a limited time and has the potential of applying in the control objective(s), and thus the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Representation method for topological structure of pentabasic area
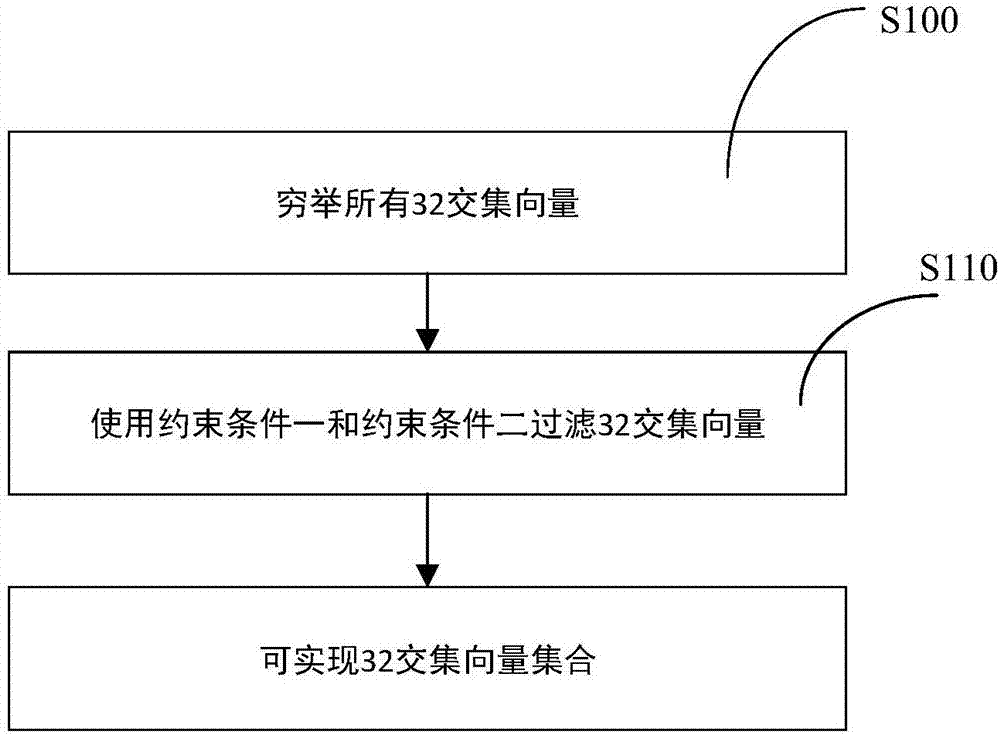
InactiveCN108009641AInsensitivityComplete characterizationInference methodsSet representationEuclidean vector
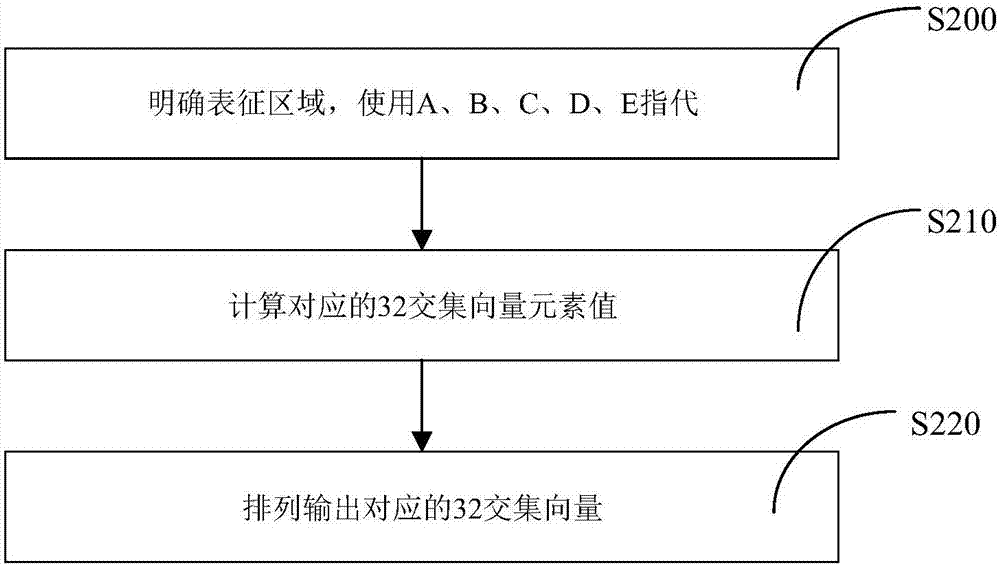
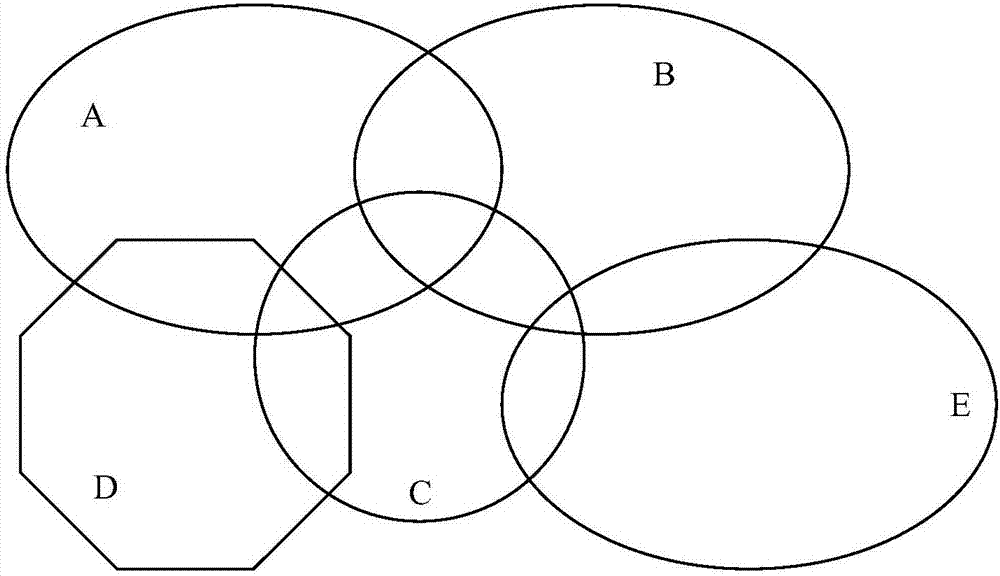
The invention puts forward a complete set representation method for the topological structure of a pentabasic simple area. The method gives a complete set which contains S100 and S110 and is used forcalculating 32 intersection vectors, and provides a calculation step which contains S200, S210 and S220 and is used for calculating the 32 intersection vectors of a given pentabasic area. The method exhibits completeness for the representation method of a pentabasic intersection vector, and is insensitive for boundaries.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
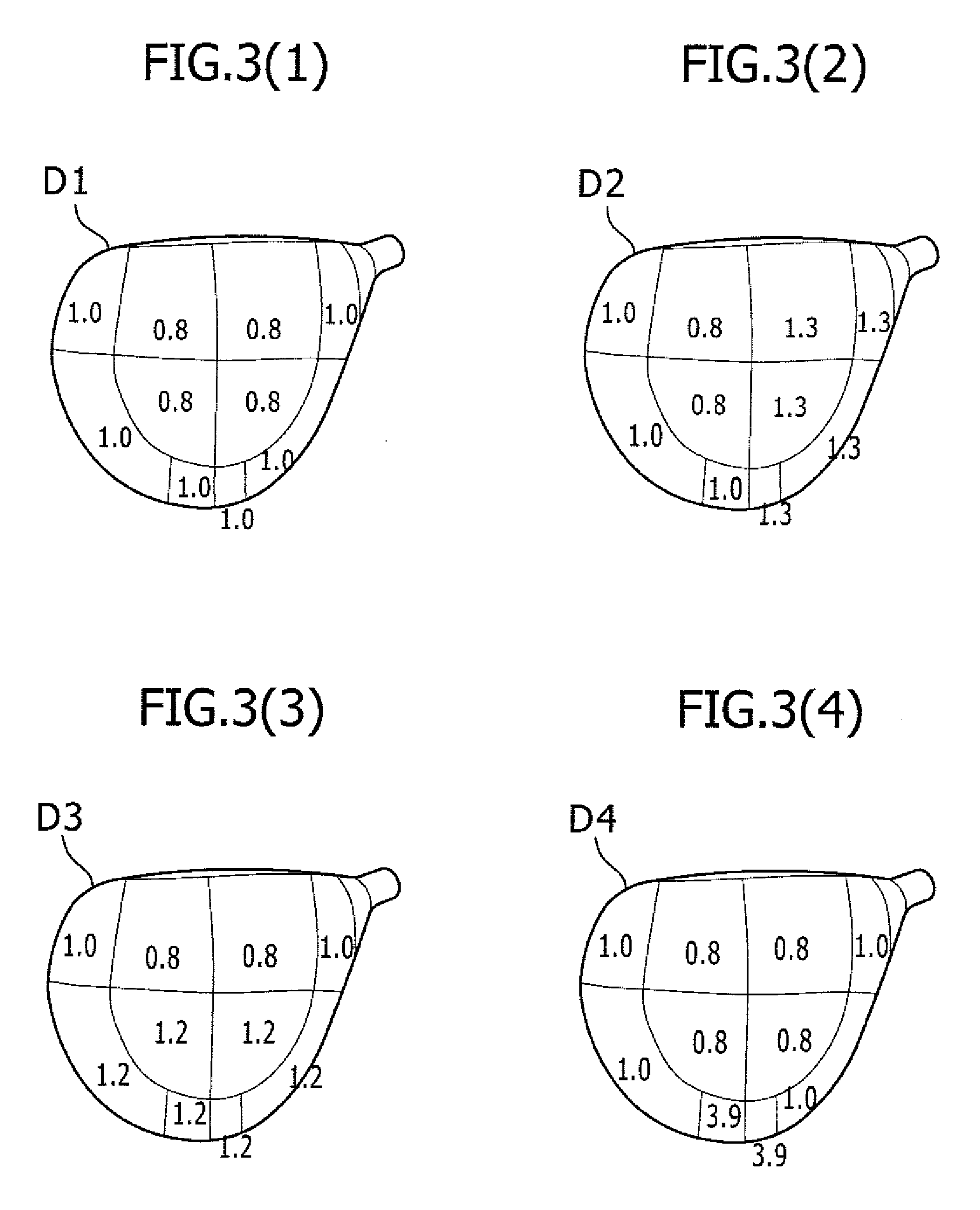
Method of analysis for kinetic properties of golf club head and golf club therefor
InactiveUS20100161294A1Suppressing significant increase of computation timeImprove calculation accuracyComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationSet representationEngineering
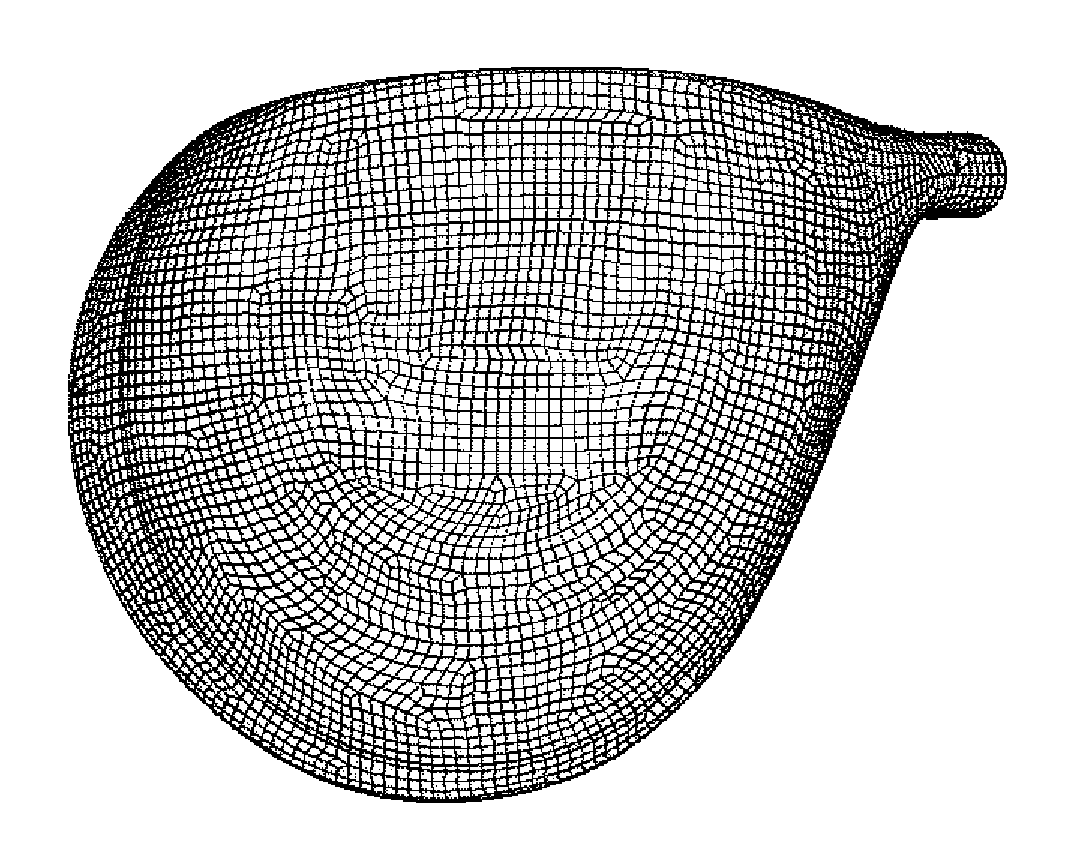
The accuracy or computation speed of analysis of a club head using the finite element method is increased. In a method of analysis of a golf club head, a model of a golf club head represented by the collection of elements including polygonal shell elements 30 each having three or four vertexes is prepared on a computer, six or more nodes 32 are provided at the vertexes and on at least one side of the element, and the kinetic properties of the golf club head are computed by the finite element method in which the elements and nodes of the model are used and the nodes are made output points of computation.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com