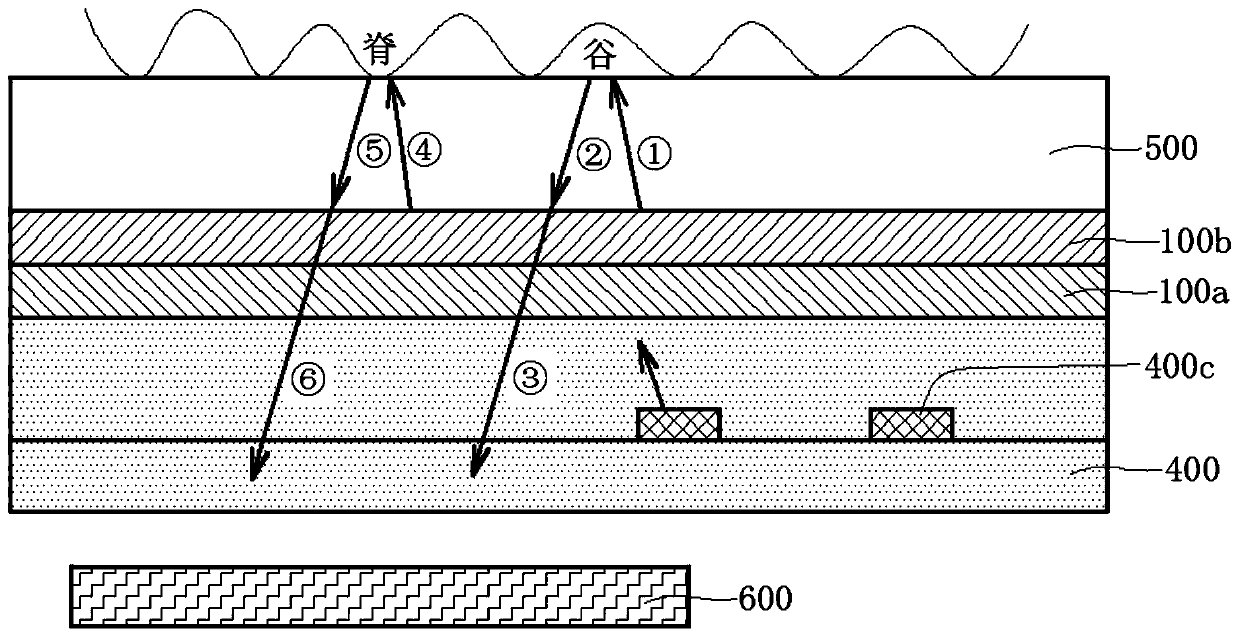
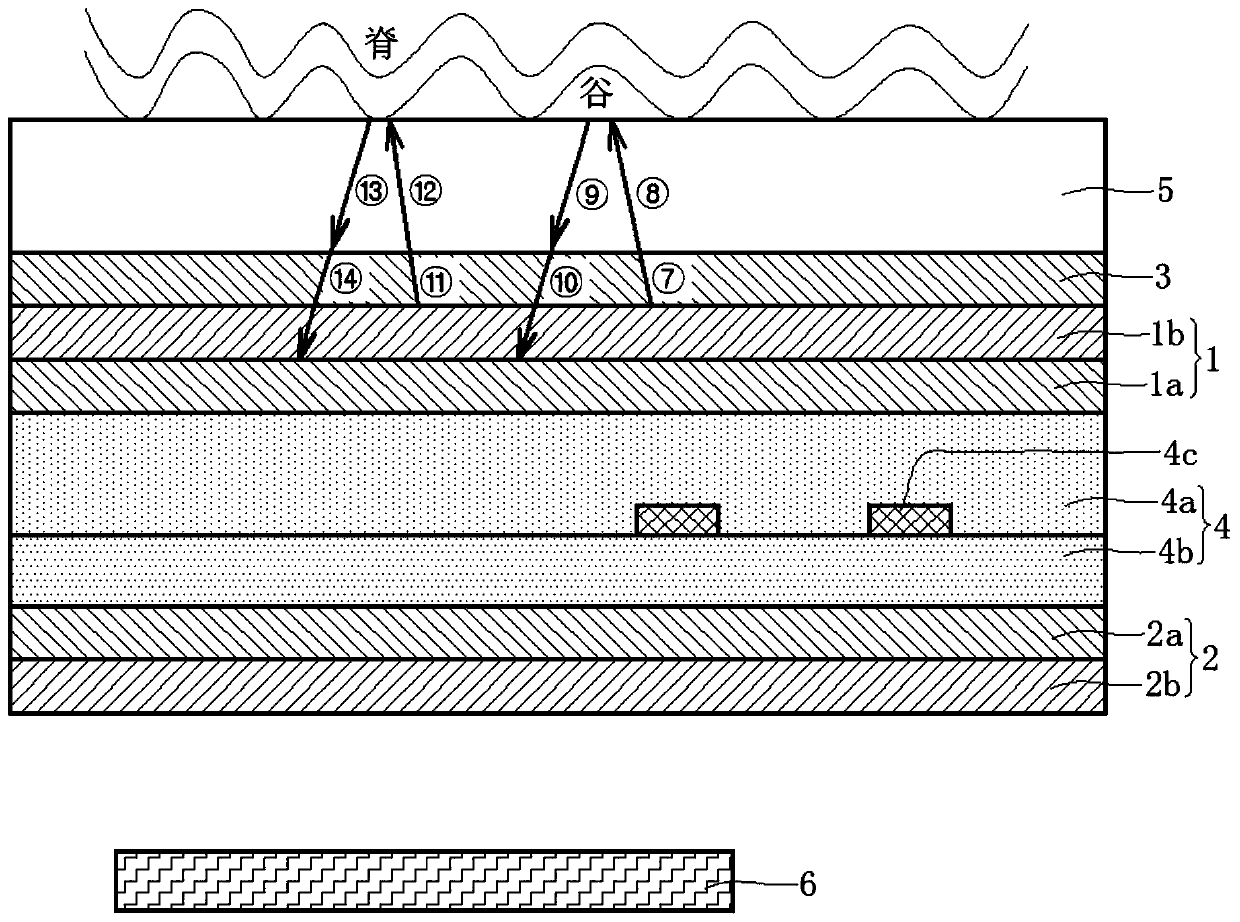
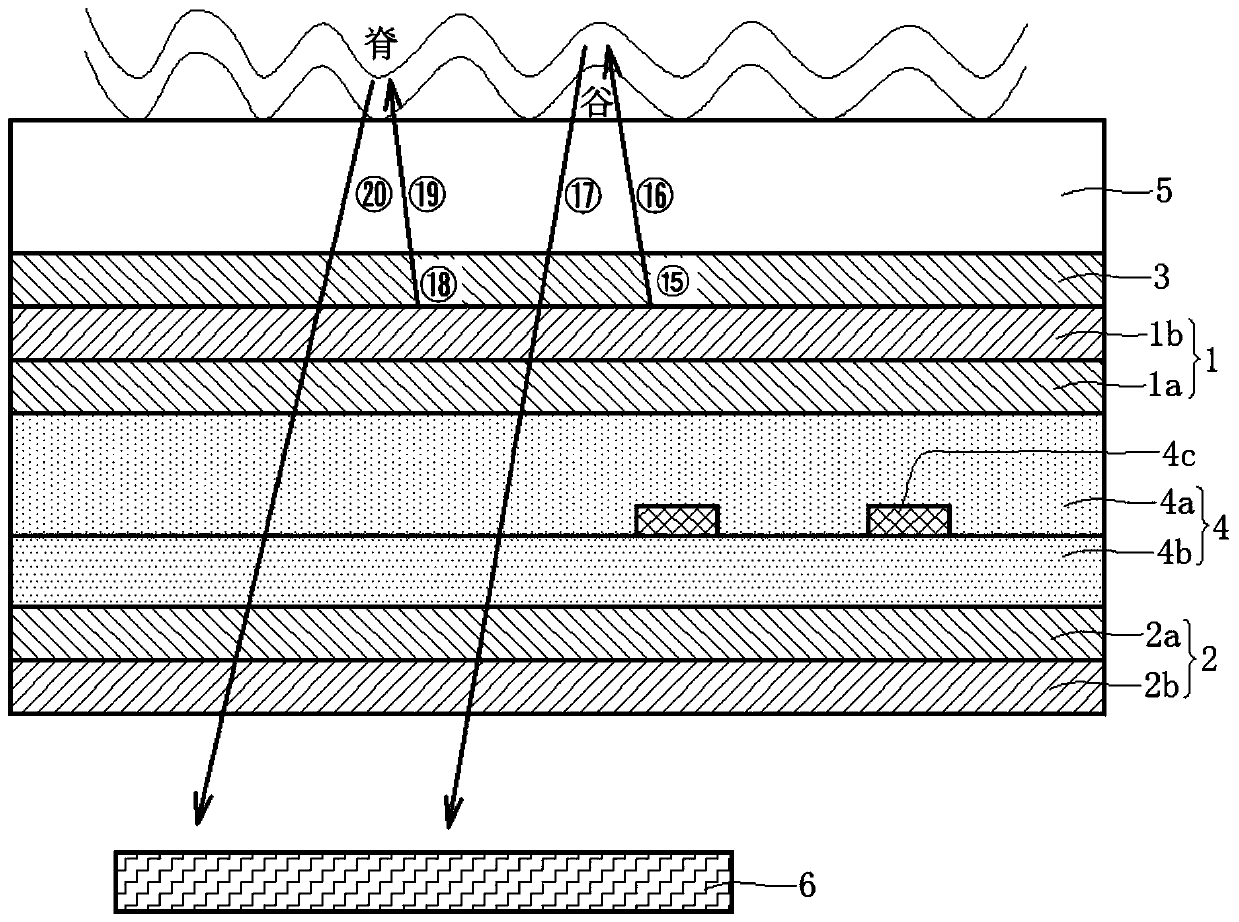
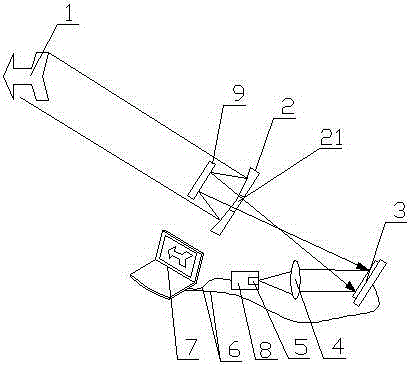
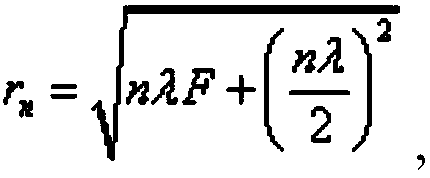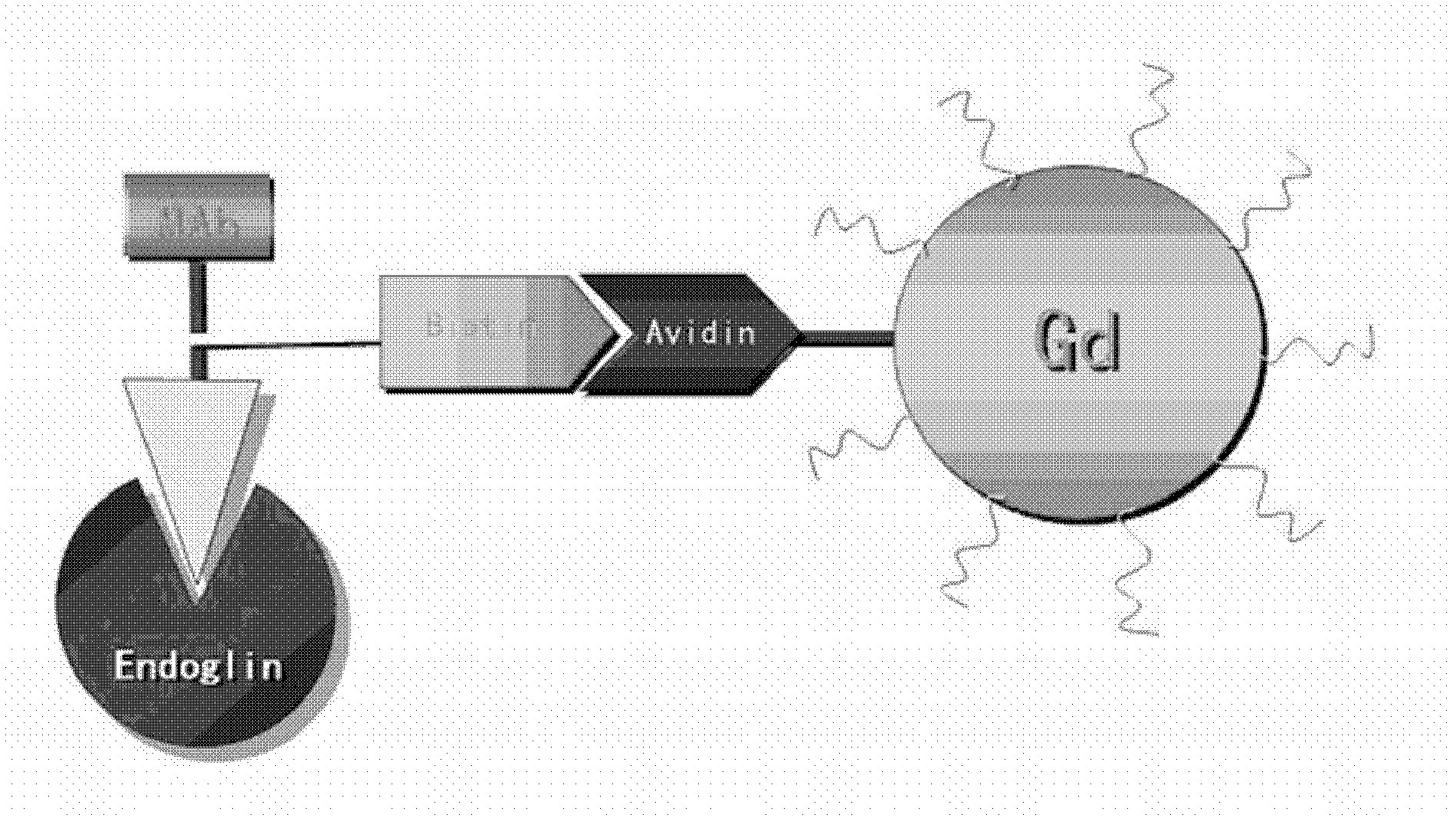Patents
Literature
137results about How to "Imaging Realization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
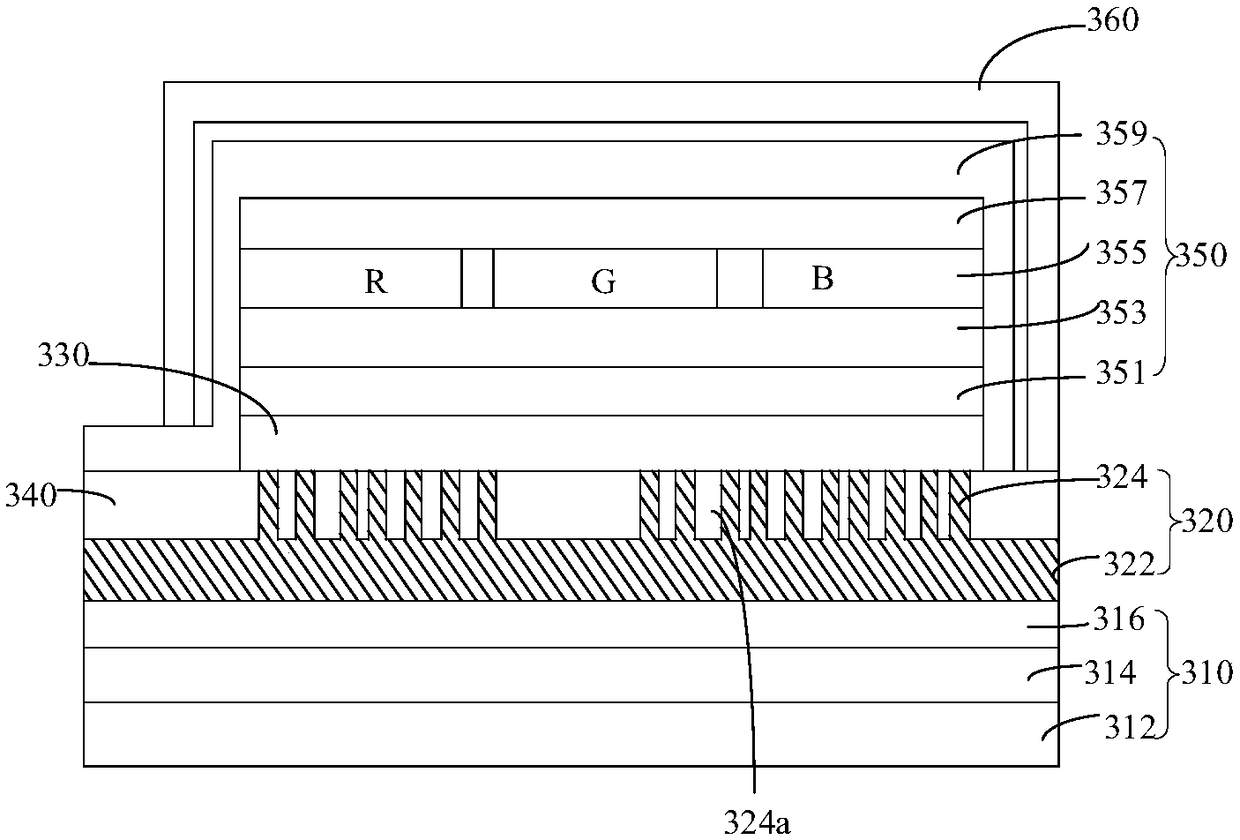
Display screen and electronic equipment
ActiveCN108389879AIncrease the proportionGood light transmissionSolid-state devicesIdentification meansComputer graphics (images)Transmittance
The invention relates to a display screen and electronic equipment. The display screen is provided with a first display region and a second display region, wherein a pixel driving array in the seconddisplay region deviates from the second display region. In the display screen, pixels in the second display region can be driven to emit light by the pixel driving array in the second display region when an image is needed to be displayed, so that the second display region and the first display region simultaneously and normally display the image; and when imaging is needed, the transmittance of the second display region is improved due to the pixel driving array, deviating from the second display region, in the second display region, so that ambient light can smoothly irradiate and pass through the second display region of the display screen to achieve imaging. With the display screen provided by the invention, the non-display region of the display screen in the prior art can be omitted,the duty ratio of the screen is expanded, and the application feeling is optimized.
Owner:YUNGU GUAN TECH CO LTD
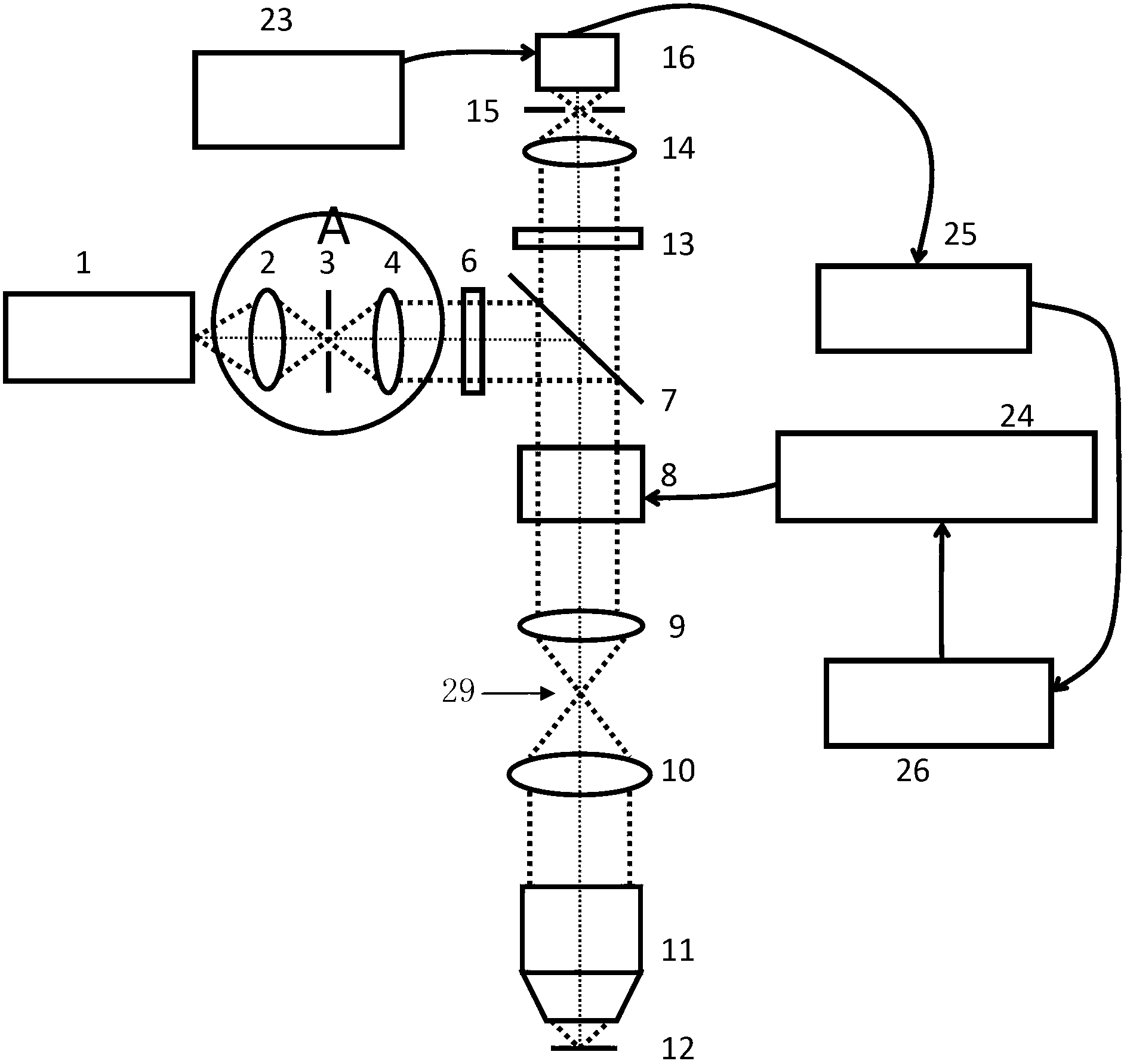
Near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system
ActiveCN102706846AImaging RealizationReduce absorptionFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLaser scanning
The invention discloses a near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system, which comprises a light path scanning unit and a control unit which adopt a confocal structure, wherein the light path scanning unit comprises a near-infrared laser source, a collimation and extension module, a laser optical filter, a dichroic reflector, a scanning galvanometer, an f-theta lens, a tube lens, an imaging objective lens, a fluorescent optical filter, a convergent lens, a pinhole, a detector and the like, the control unit comprises a motion control module used for controlling the scanning galvanometer, a data acquisition module used for acquiring an output signal of the detector, a data processing module connected with the motion control module and the data acquisition module, and the like. The method matched with the system is characterized in that a sample is marked with near-infrared quantum dots with the fluorescence emission spectrums between 932nm and 1250nm, and then the sample is detected by the near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system. According to the system disclosed by the invention, deep-level imaging of samples such as biological tissues can be accurately and efficiently realized, and the system has a simple structure and is easy to operate.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
High dynamic equipment for reconstructing image in high resolution
InactiveCN1874499AImprove super-resolutionImprove performance2D-image generationClosed circuit television systemsHigh resolution imageImage quality
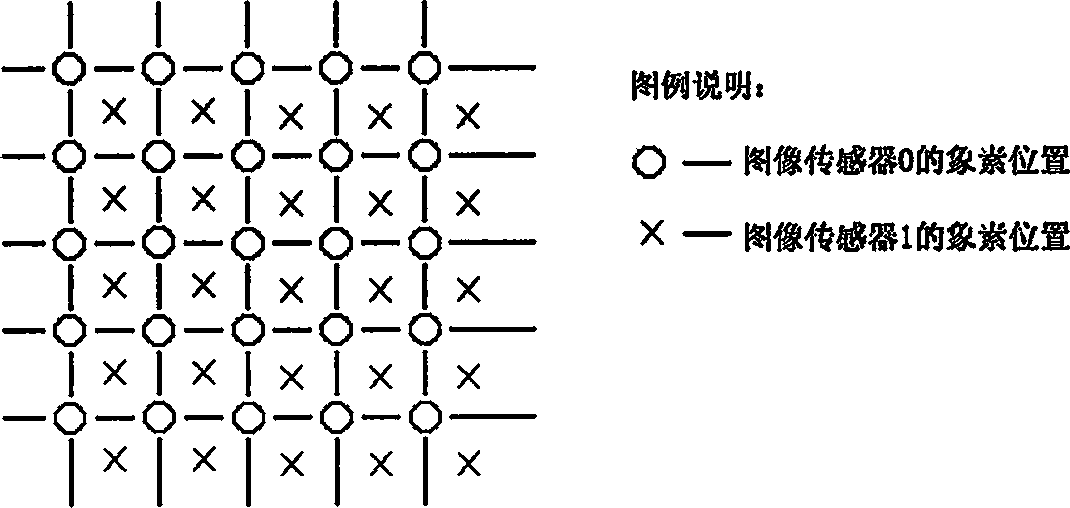
The method uses multi low resolution and low dynamic imagers to incorporates the sub-pixel dynamical image formation technology with the technology of multi image reconstructing high dynamical image, and uses a special site distribution of image sensor to implement the reconstructing of ultra-high resolution image, and uses image gray level interpolation to reconstruct image gray level so as to get a high dynamic range and high resolution image.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Three-dimensional printer, printing method of three-dimensional printer and printing device of printing method
ActiveCN104085107ASimple structureLower imaging costsTypewritersComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
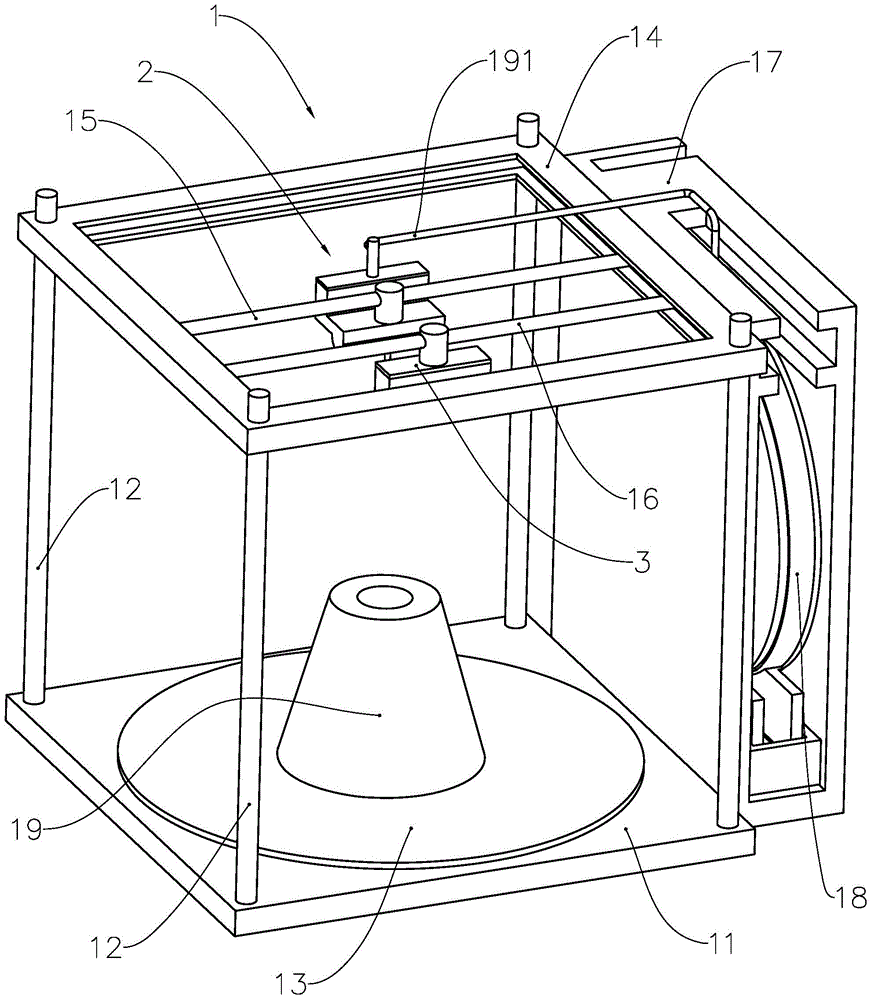
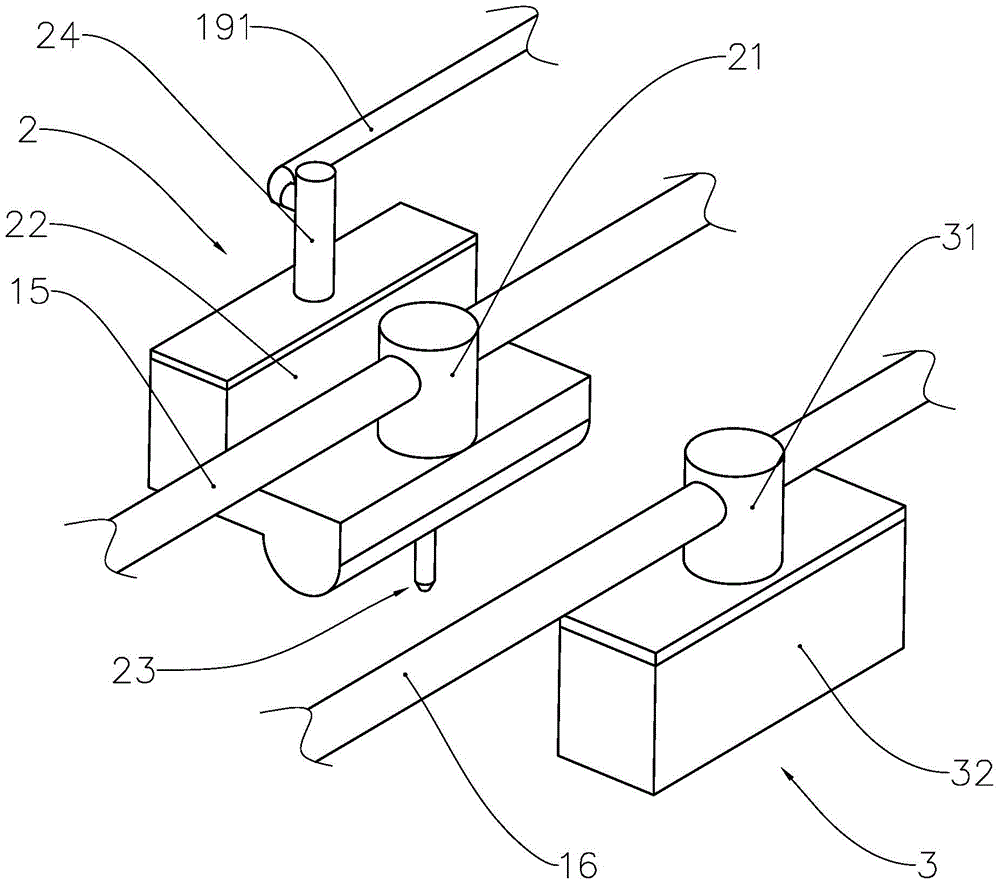
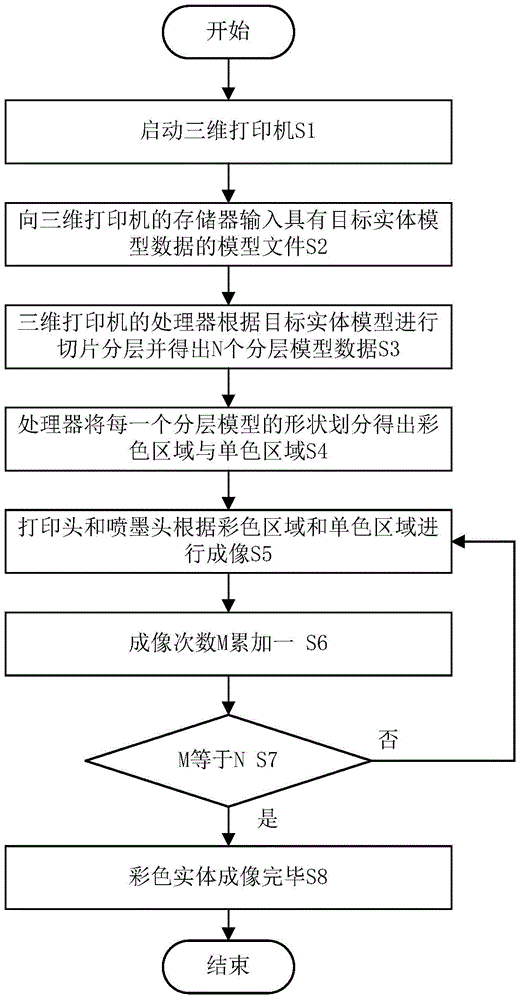
The invention provides a three-dimensional printer, a printing method of the three-dimensional printer and a printing device of the printing method. The printing method of the three-dimensional printer comprises the following steps: starting the three-dimensional printer which comprises a printing head for entity imaging and an ink jet head for color imaging; inputting a model file with target entity model data into a memorizer; slicing and layering according to the target entity model data through a processor, processing and obtaining a plurality of layering model data; performing entity imaging according to each layering model data through the printing head; performing color imaging on the layering model according to the layering model data in the same layer through the ink jet head. The invention provides the printing device and the three-dimensional printer using the method. By performing color imaging on each layering model, the colorful printing of the overall three-dimensional entity is achieved finally, then the structure of the three-dimensional printer is simplified, and the three-dimensional printer has the advanstages of low imaging cost, high color reproduction accuracy, high image resolution ratio, simple imaging method and the like.
Owner:PRINT RITE UNICORN IMAGE PROD CO LTD
Sound wave focusing lens and ultrasonic imaging device and method
PendingCN109431543ASimple structureEasy to processUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingAcoustic wave
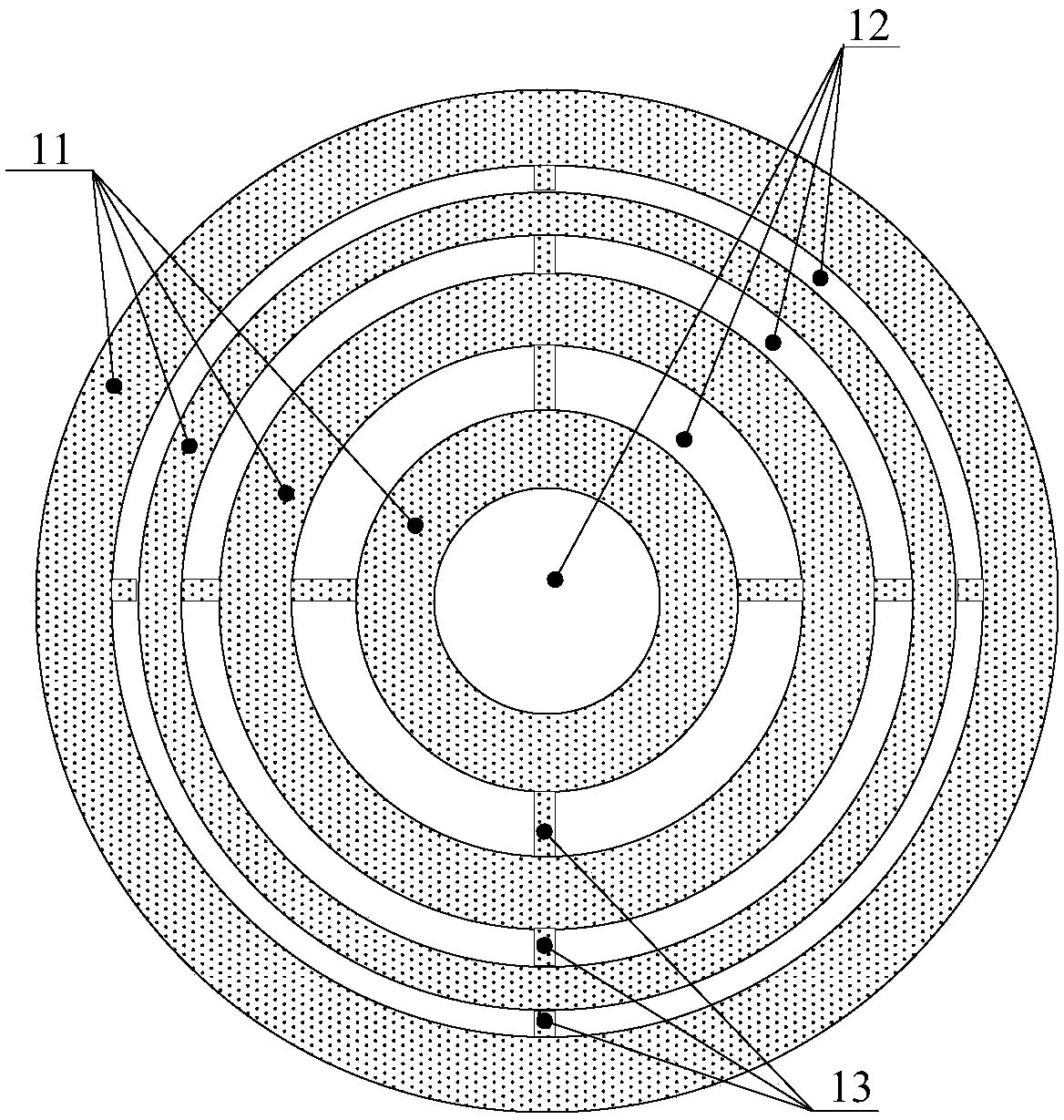
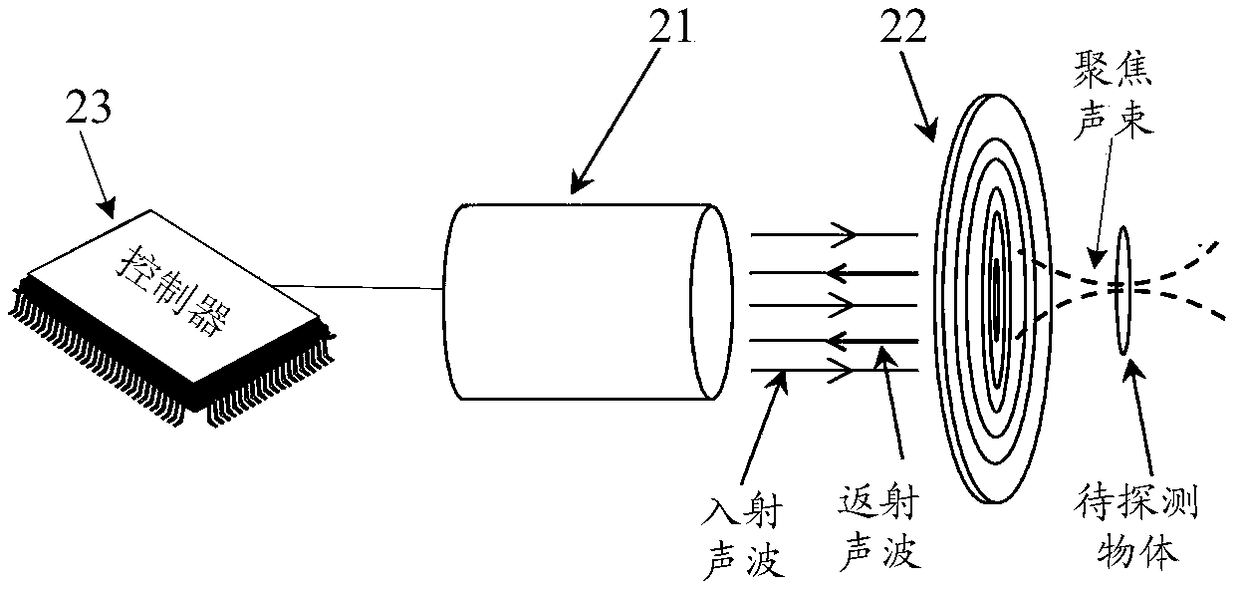
An embodiment of the invention discloses a sound wave focusing lens and an ultrasonic imaging device and method. The sound wave focusing lens is simple in structure and comprises a plurality of concentric rings, wherein a slit is formed between each two adjacent rings; the rings are made from rigid materials; the thicknesses of the rings are the same; and the slits in the sound wave focusing lensare successively narrows from inside to outside. The structure is easy to process and low in cost, is matched with a planar ultrasonic transducer, and is flexible to use, and imaging of objects at different depths can be realized by changing the frequency of transmitting sound wave of the ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Double helix electrode capacitance tomography sensor for measuring annular space
InactiveCN105353004ARealize 3D ImagingReduce in quantityMaterial capacitanceElectricityProcess tomography
The invention discloses a double helix electrode capacitance tomography sensor for measuring an annular space that belongs to the field of an electrical process tomography device. The sensor comprises a main structure part and a capacitance measurement part. The main structure part is composed of concentric inner and outer tubes and a connection bracket used for fixing position. An annular space between the inner and outer tubes is a measured space. The capacitance measurement part comprises detection electrodes, electrode end shields, shielding cases, a signal transmission cable, ECT signal acquisition equipment and connection wires. By the utilization of electrode sensor parts which are respectively spirally arranged on the inner and outer tube walls, three-dimensional imaging of the measured annular space is truly realized. Due to the sensor structure with electrodes uniformly distributed on the two tube walls, imaging of the annular space is realized, and the problem of weak capacitance signal is also improved. The invention is a big breakthrough of the ECT technology.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
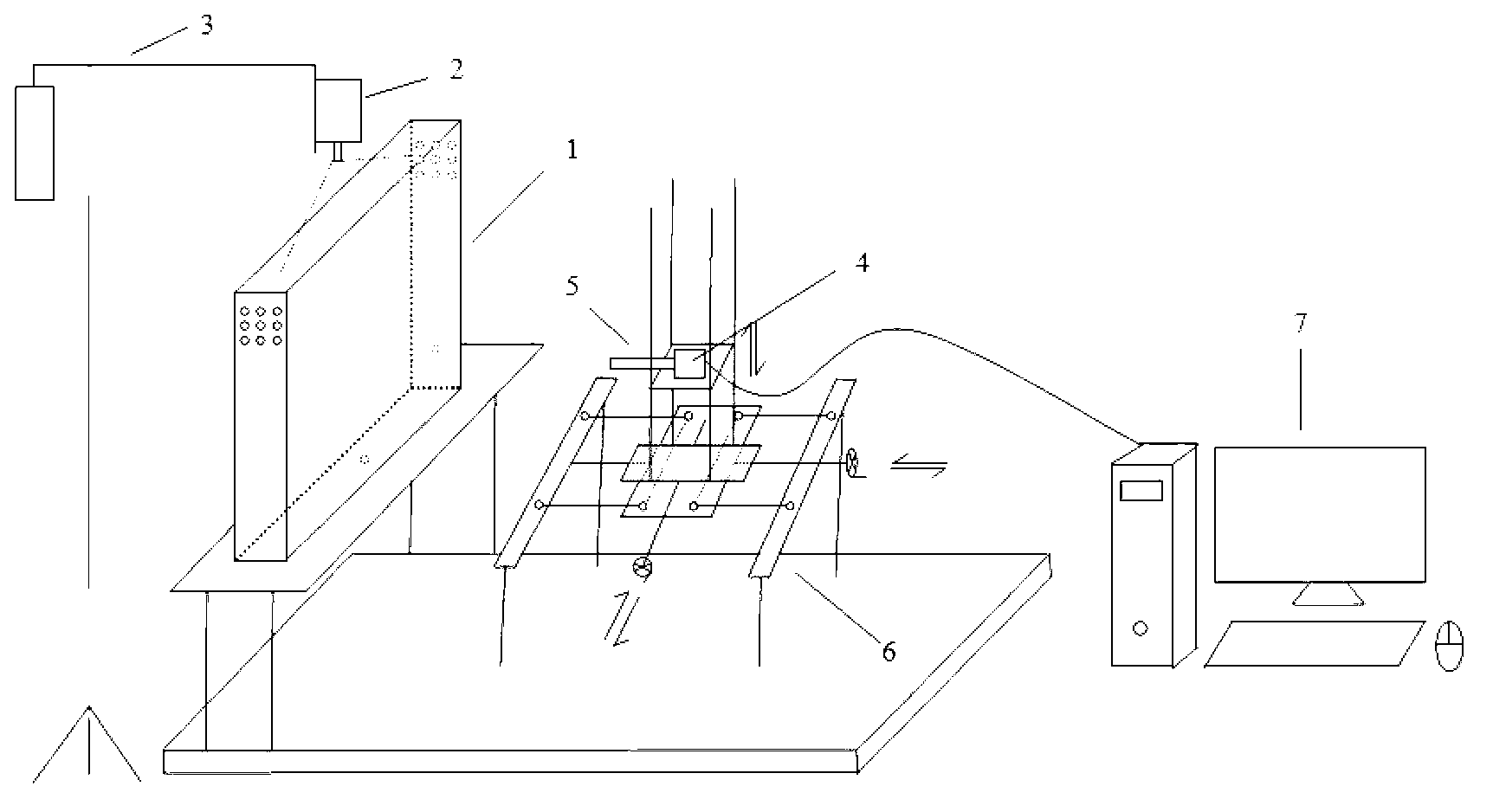
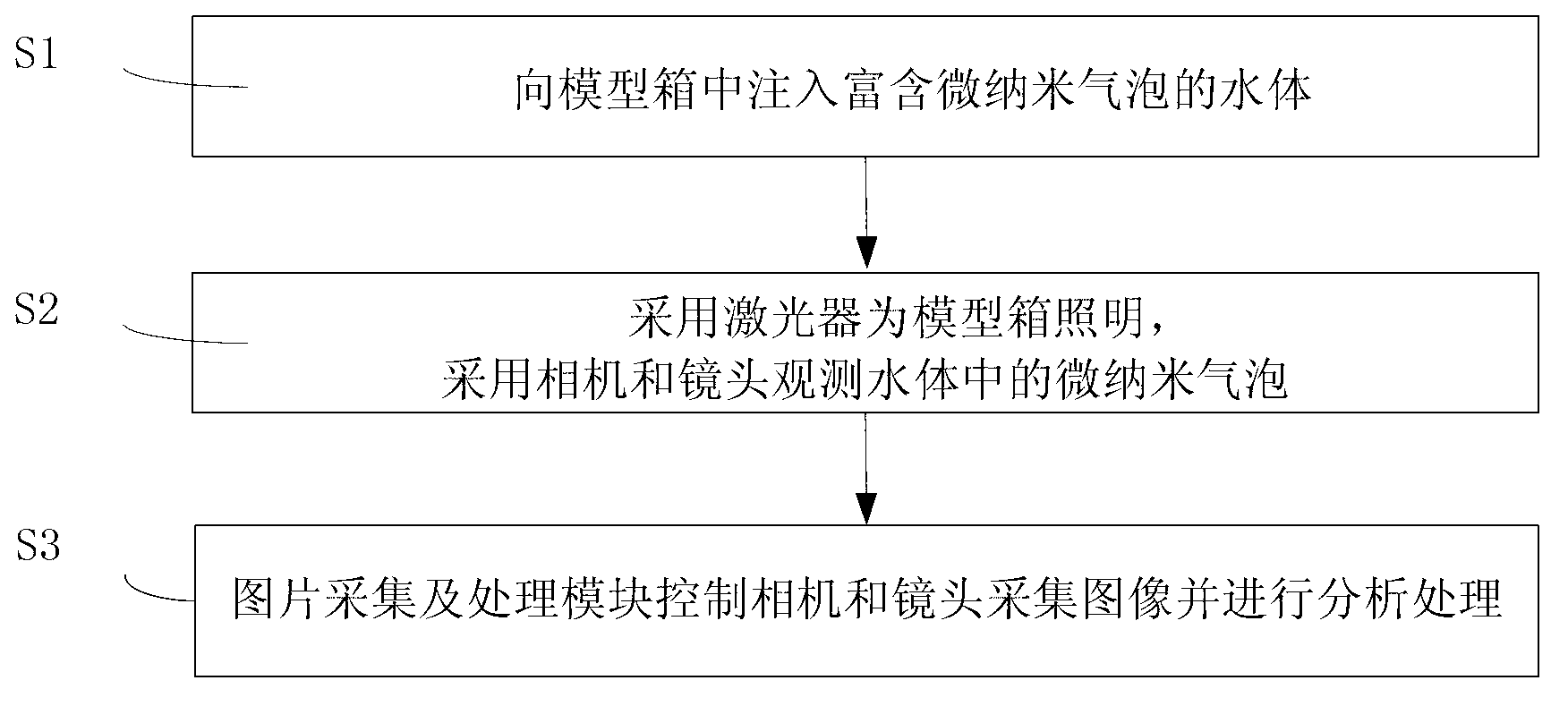
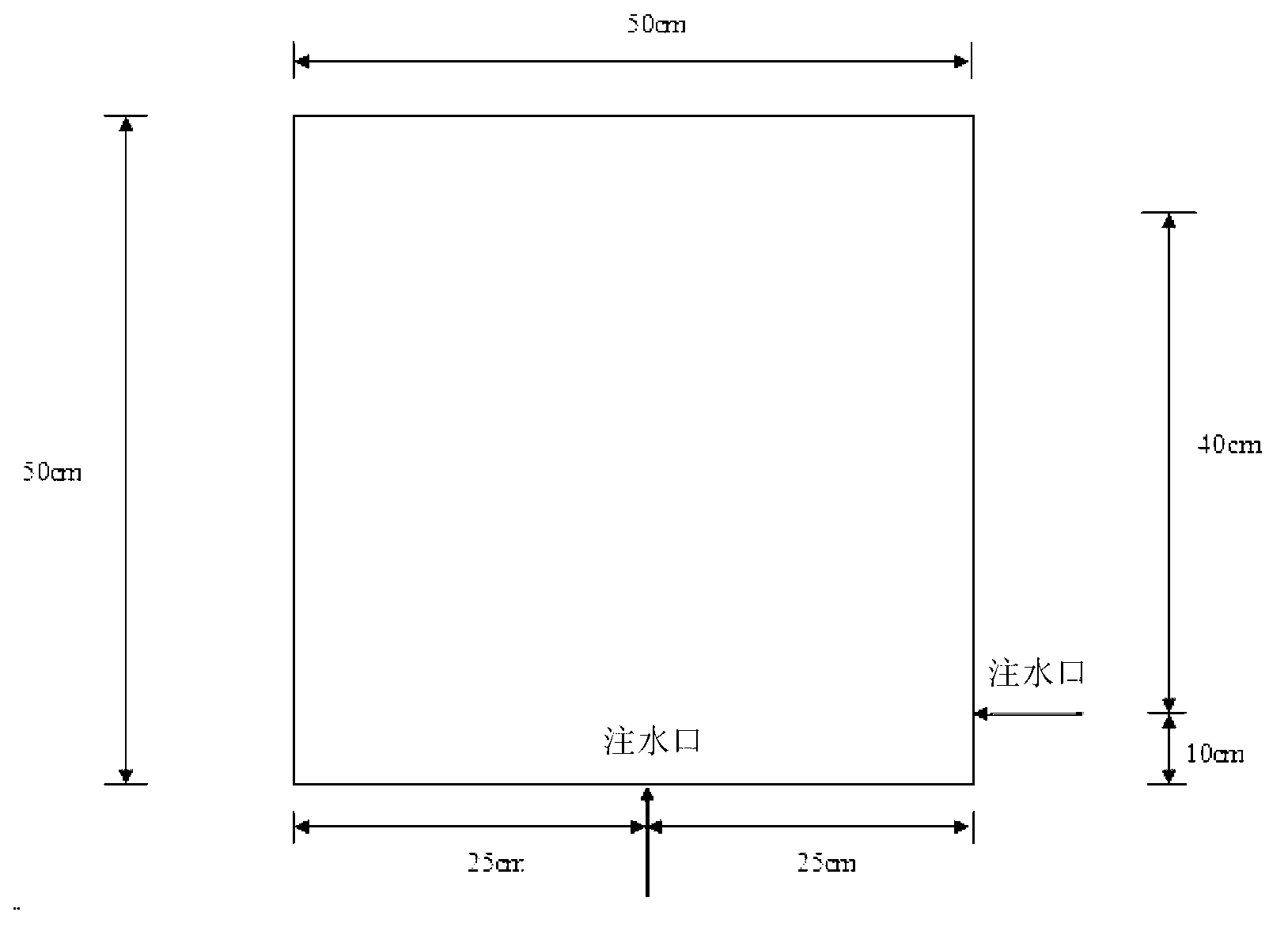
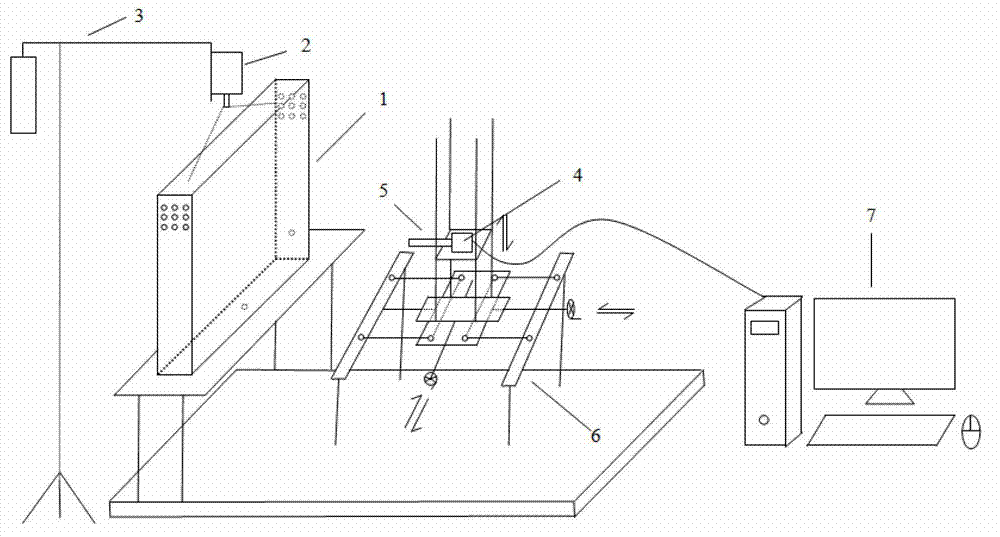
System and method for observing micro-nano air bubbles in water body
ActiveCN103175760AAchieve particle sizeAchieve speedParticle size analysisDevices using optical meansCamera lensMicro nano
The invention provides a system and a method for observing micro-nano air bubbles in water body. The system comprises a model box, a laser device, a camera, a lens and a picture acquiring and processing module, wherein the model box is provided with a water filling nozzle, and can be filled with and contain the water body which is rich in micro-nano air bubbles, moreover, each face of the model box adopts different materials and colors, and the imaging definition of the micro-nano air bubbles in the water body is improved to the greatest extent; the laser device is located at the top of the model box, and is used for providing a light source needed for observation; the camera and the lens are arranged on one side of the model box, and are used for observing the micro-nano air bubbles in the water body; and the picture acquiring and processing module is connected with the camera, and is used for acquiring and processing pictures. The system and the method provided by the invention are simple, convenient, practical and high in observation accuracy.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
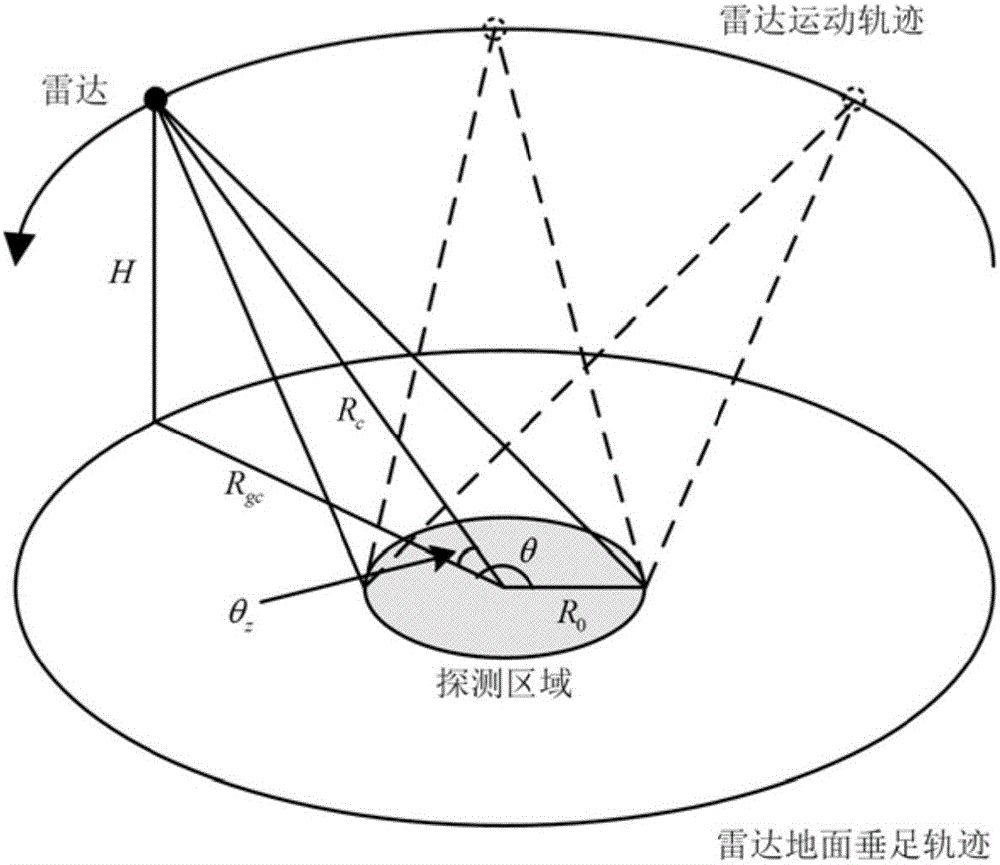
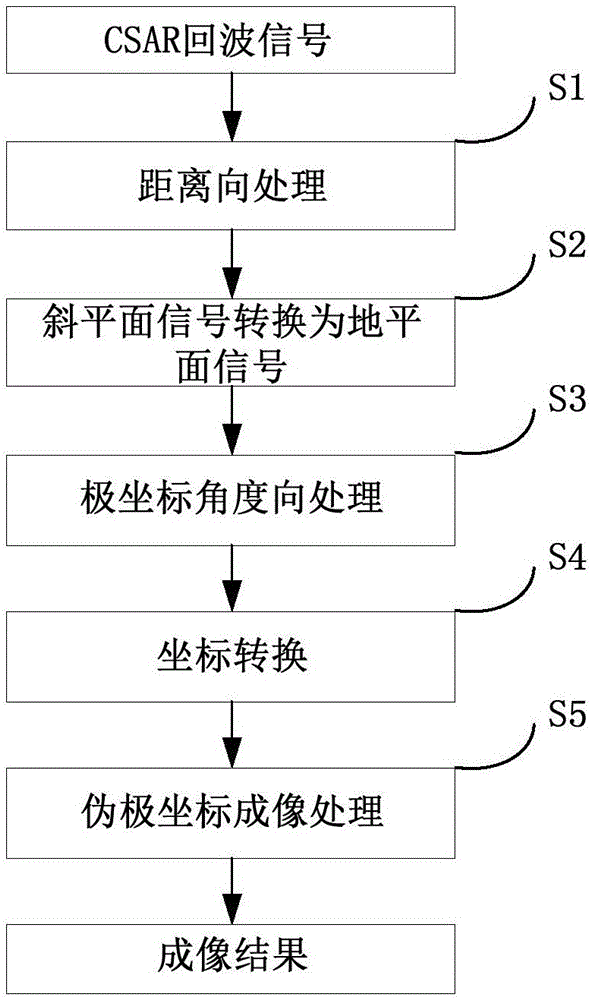
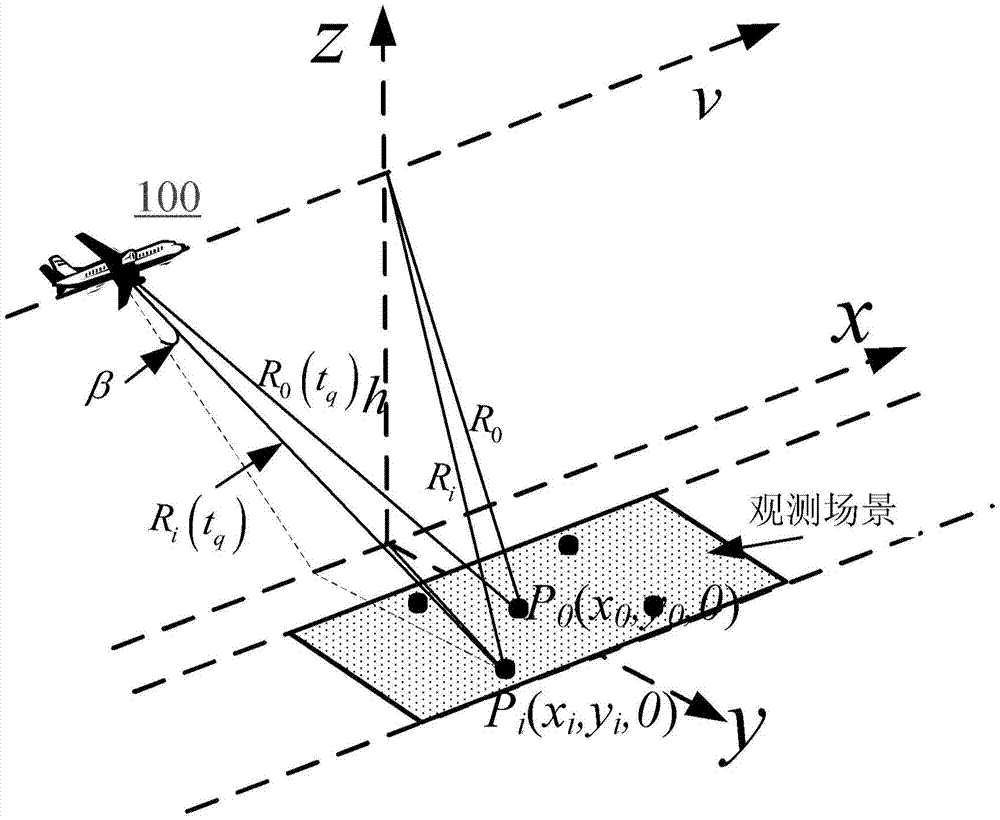
Circular synthetic aperture radar imaging method
InactiveCN106772380AHigh resolutionHigh resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInformation processingRapid imaging
The invention discloses a circular synthetic aperture radar imaging method, belonging to the technical field of electronic signal processing. The invention relates to a spatial remote sensing and air-to-ground observation information processing technology, in particular to an onboard circular synthetic aperture radar imaging technology. According to the imaging method, an original oblique plane echo is mapped to the ground plane by solving the inverse of a system kernel function, and the distribution of signals in a wave number domain is obtained by multiplying an azimuth frequency domain with a reference function, so that plane wave approximation is avoided, the problem that the size of an imaging area of the traditional polar format algorithm is limited can be solved, and the imaging of a large imaging scene can be realized; pseudo-polar coordinates are used for replacing rectangular coordinates as an intermediate interpolation transition matrix, and the distribution density characteristic of the signals in the wave number domain is considered, so that the interpolation precision is higher, the obtained image resolution is higher, and the high resolution imaging can be realized; the imaging process only involves one-dimensional interpolation, and fast algorithms such as chirp z transform (CZT) and inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) are adopted, so that the method has very high computational efficiency and can realize rapid imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
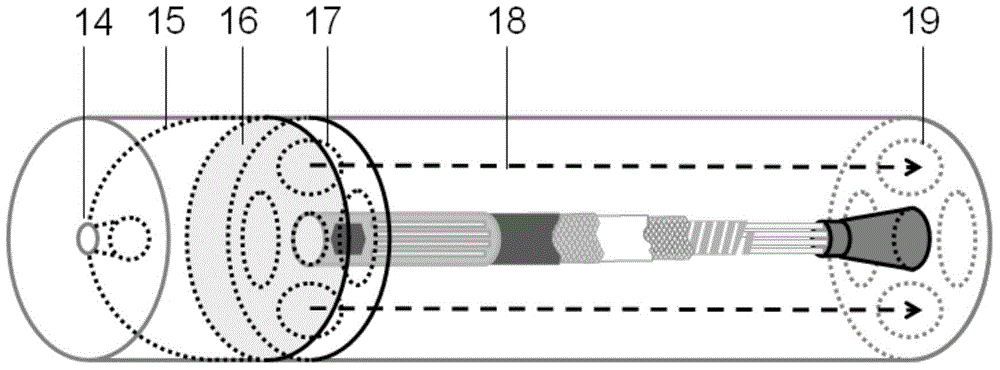
Under-screen optical fingerprint imaging device
ActiveCN109858417AEliminate reflectionsImaging RealizationCharacter and pattern recognitionPolarizerFingerprint
The invention provides an under-screen optical fingerprint imaging device. The under-screen optical fingerprint imaging device comprises a substrate provided with a light-emitting unit; a light sensing element which is arranged on one side of the substrate and is used for converting the light signal into an electric signal for imaging; a first diaphragm unit which is arranged on the side, deviating from the light sensing element, of the substrate and comprises a first 1 / 4 wave plate and a first linear polarizing film, and the first 1 / 4 wave plate is located between the first linear polarizingfilm and the substrate; a third 1 / 4 wave plate is arranged on one side, deviating from the substrate, of the first diaphragm unit, a third angle is formed between the optical axis of the third 1 / 4 wave plate and the polarization direction of the first linear polaroid, and the value of the third angle is 45 + / -5 degrees; a cover plate which is arranged on the side, deviating from the substrate, ofthe third 1 / 4 wave plate and provided with a light-transmitting area, and the light-transmitting area is used for being pressed by fingers of a user or getting close to the light-transmitting area. The under-screen optical fingerprint imaging device provided by the embodiment of the invention can effectively improve the imaging stability and quality.
Owner:SILEAD
Passive single pixel telescope imaging system and imaging method
InactiveCN105227815ASimple structureLow environmental requirementsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSpatial light modulatorMacroscopic scale
The invention discloses a passive single pixel telescope imaging system, and belongs to an optical imaging field. The passive single pixel telescope imaging system comprises an imaging lens, a spatial light modulator, a light beam convergent lens and a data acquisition card, which are orderly arranged on a light path; the spatial light modulator is arranged at an imaging position of the imaging lens; the light beam convergent lens is located on a light path of an output beam of the spatial light modulator; the data acquisition card is provided with a photovoltaic conversion chip; the data acquisition card and the spatial light modulator are connected with a processor through a data line. The imaging system is simple in structure and low in environmental requirement; besides, the acquisition time can be effectively reduced and the recovery of target images under a low sampling rate can be realized. The invention further discloses a passive single pixel telescope imaging method. The imaging method is simple in recovery algorithm and fast in image reconstruction speed, and can shoot and reconstruct the images of large sizes, so that the imaging method has a higher application value in the macro fields like military, remote sensing satellite, astronomy and engineering detection, etc.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Design method of multi-layer metal dielectric film capable of implementing imaging function
A design method for multi-layer metal dielectric film capable of realizing the imaging function is characterized by selecting incident wave; selecting two sets of metallic material and dielectric material with a certain thickness, alternatively arranging the metal and medium in two sets to form two kinds of multi-layer metal dielectric film structures, respectively computing the equivalent dielectric constant of the two kinds of multi-layer metal dielectric film structures based on equivalent dielectric constant of each material and the thickness of each film layer; realizing the variation of the value and plusminus of the dielectric constant in respective direction by designing the thickness of each film layer so as to make the optical wave diverge through the first set of multi-layer metal dielectric film structure and converge through the second set of multi-layer metal dielectric film structure; binding the divergent structure multilayer film and the convergent structure multilayer film together according to a specific thickness ratio to the multi-layer metal dielectric film structure device which can make the fine structure far less than the operating wavelength image so as to achieve the super resolution.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
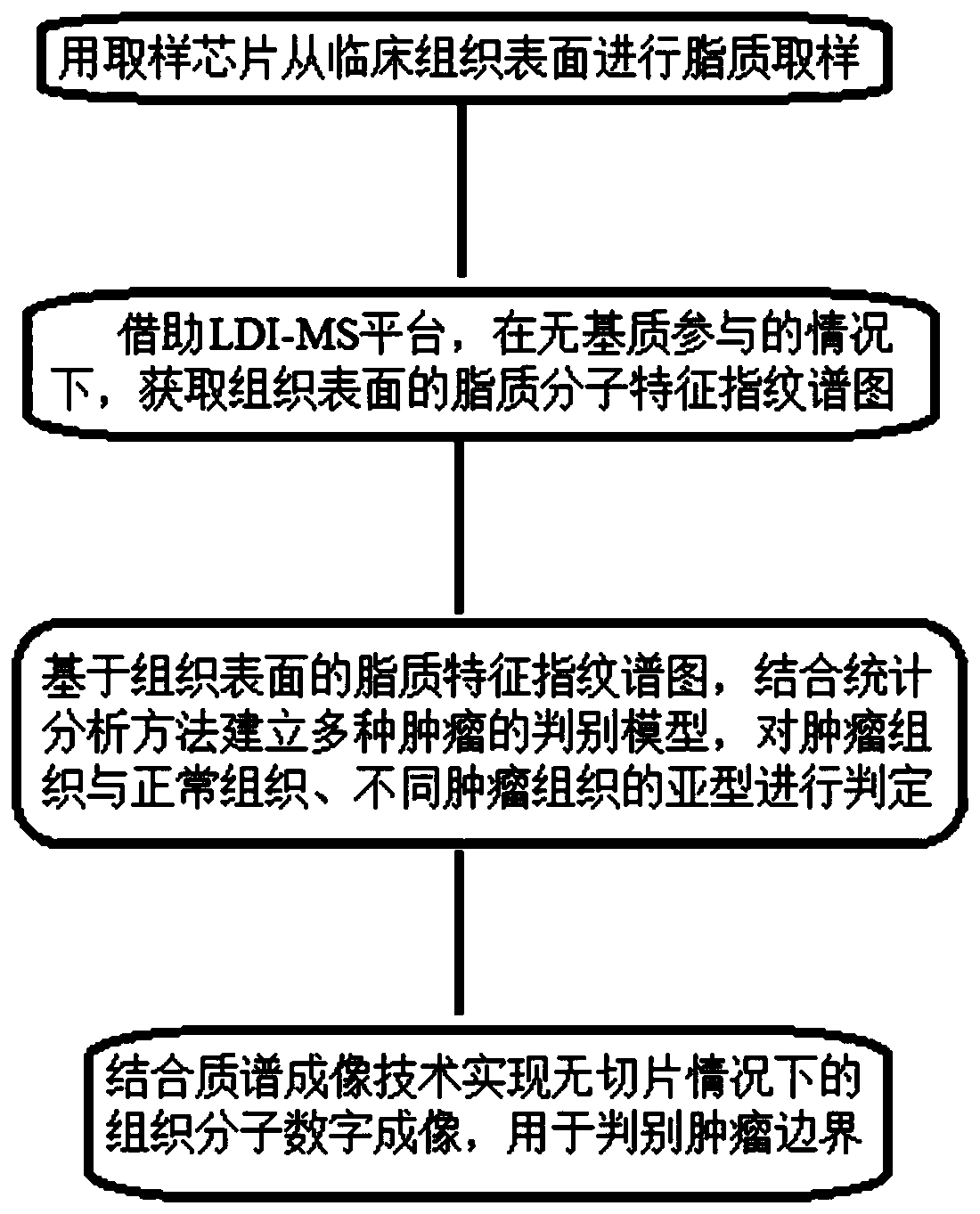
Rapid tumor tissue discrimination method based on tissue surface lipid fingerprint spectrogram
ActiveCN110243921AImaging RealizationImprove stabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDigital imagingStatistical analysis
The invention discloses a rapid tumor tissue discrimination method based on a tissue surface lipid fingerprint spectrogram, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting lipid molecules on the surface of a tissue and keeping in-situ information of the lipid molecules; then, acquiring a lipid molecular characteristic fingerprint spectrum of the surface of the tissue by means of a laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry platform under the condition of no matrix participation; then, establishing a discrimination model of various tumors based on a lipid characteristic fingerprint spectrogram of the surface of the tissue by combining a statistical analysis method, and judging subtypes of tumor tissues, normal tissues and various tumor tissues; finally, realizing the tissue molecular digital imaging without the slice by combining the mass spectrum imaging technology, and using the tissue molecular digital imaging to distinguish the tumor boundary; and the rapid tumor tissue discrimination method realizes rapid, efficient and high-accuracy clinical tissue identification, tumor subtype discrimination and tumor boundary imaging, improves the detection flux, and increases the stability of lipid molecule information on the surface of the tissue and the difference dimension in tumor tissue identification.
Owner:HANGZHOU WELL HEALTHCARE TECH CO LTD
Parallel low-light-loss high-temperature backlight industrial endoscope
The invention belongs to the field of instrument detection, and provides a parallel low-light-loss backlight high-temperature industrial endoscope. The parallel low-light-loss high-temperature backlight industrial endoscope comprises an optical eyepiece used for obtaining an image in a furnace, a light source luminous part, a light source drive circuit, a communication circuit, an image guide fiber bundle, a light guide structure, an imaging chip, an imaging drive circuit, a cooling system and a shell. The shell comprises a circular tube and a square shell body. The light guide structure comprises an ellipsoidal concave mirror, a round convex lens and a light guide light path, wherein the ellipsoidal concave mirror is arranged on the rear portion of the light source luminous part, and the round convex lens is opposite to the light source luminous part. The front end of the circular tube is provided with the optical eyepiece and a backlight hole, and an image obtaining probe is connected with the imaging chip through the image guide fiber bundle. A novel backlight technology is provided, an original light-guide fiber backlight mode is converted into a parallel light direct backlight mode, the structure of the light path is simplified, the utilization rate of light energy is improved, the backlight area and brightness are increased, constrains to backlight light sources are eliminated, and the parallel low-light-loss high-temperature backlight industrial endoscope is suitable for various light sources, improves stability of equipment and reduces equipment cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
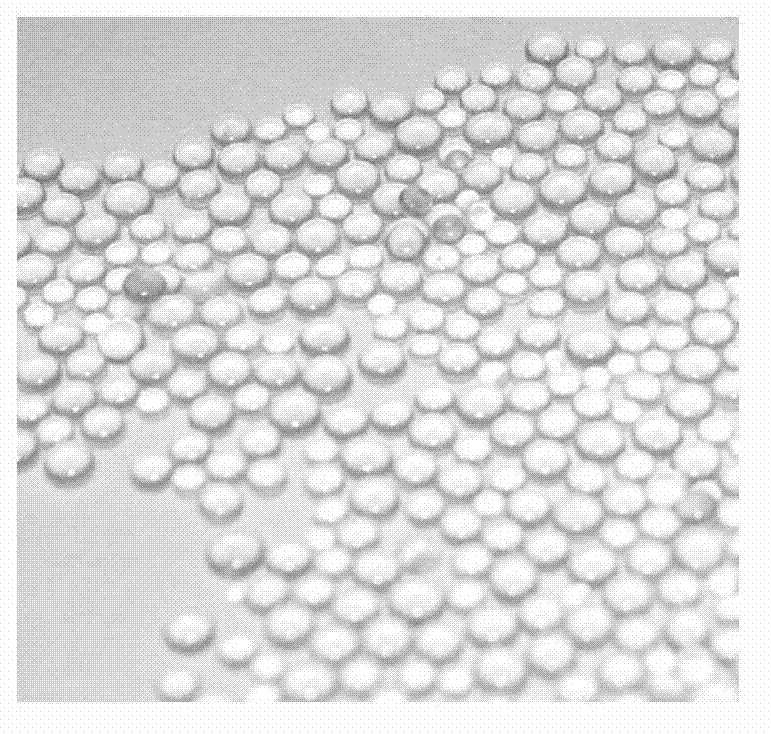
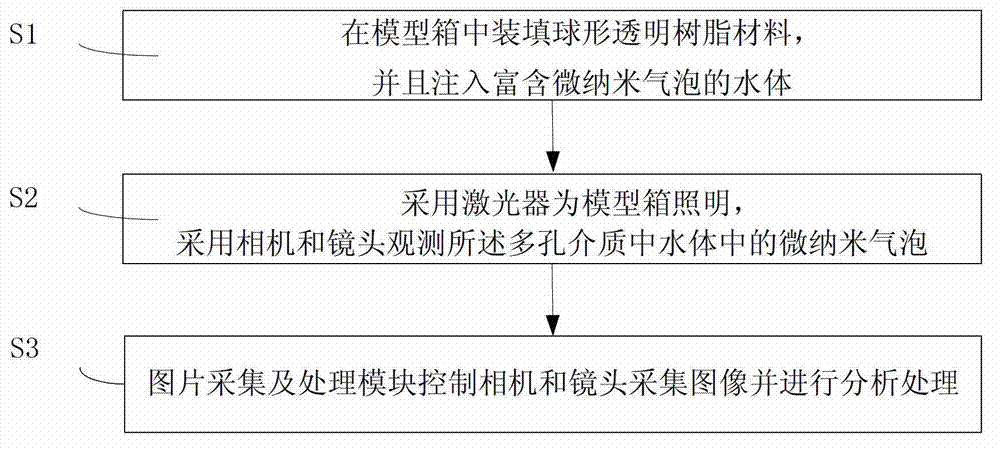
System and method for observing micro-nano bubbles in porous medium
ActiveCN103115860AGet adsorption propertiesAchieve adsorptionIndividual particle analysisMicro nanoProcess module
The invention provides a system and method for observing micro-nano bubbles in a porous medium. The system comprises a model box, a laser, a camera, a lens and an image acquiring and processing module, wherein a spherical transparent resin material for simulating the porous medium is filled in the model box, the model box is provided with a water filling port for filling and containing a water body which is used for simulating underground water and is rich in micro-nano bubbles, and the surfaces of the model box are different in material and color so as to improve the imaging definition of the micro-nano bubbles in pore water of the porous medium to the maximum extent; the laser is positioned on the top of the model box and used for providing a light sheet required for observation; the camera and the lens are positioned on one side of the model box and used for observing the micro-nano bubbles in the porous medium; and the image acquiring and processing module is connected with the camera and used for acquiring and processing images. The system has the advantages of easiness, practicability, high simulation degree and high observation precision.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation of super paramagnetic nano particles dispersible in water
InactiveCN1583575AImprove stabilityGood dispersionIron oxides/hydroxidesInorganic material magnetismParamagnetic nanoparticlesSuperparamagnetism
A process for preparing the super-paramagnetic nanoparticles dispersed in water easily includes such steps as mixing the polymer chelating agent with Fe ions, dripping alkali while reacting to generate inn oxide and continuously dripping alkali until pH=9-10.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Spatial self-focusing laser differential confocal Raman spectroscopy imaging detection method and device thereof
InactiveCN108169207AEnhanced Raman Scattered Light Collection CapabilityIncrease detectable distanceRaman scatteringScattered lightZero crossing
The invention relates to a spatial self-focusing laser differential confocal Raman spectroscopy imaging detection method and a device thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of spatial optical imaging and spectral measurement. The spatial self-focusing laser differential confocal Raman spectroscopy imaging detection method comprises the following steps: performing nondestructive separation onRayleigh scattered lights and Raman scattered lights, accurately controlling a telescope system to automatically adjust a focus point through searching a response zero crossing point by using the characteristic of the zero crossing point of the differential confocal response curve of detector, accurately corresponding to the focus position, in order to make an excitation beam automatically focused on a measured object and obtain the spectral information of the focal point position of laser spots, and acquiring the image and pattern information of a target through the image detector; and the device realizes spatial automatic focusing spectral detection and image acquisition, so the method and the device can realize the spatial self-focusing spectrum and image detection of a sample. The method and the device have the advantages of automatic focusing, accuracy in positioning, large spatial range, high spectral detection sensitivity, and acquisition of the target image.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Iterative ultrasonic tomography method for axial flow field imaging in pipeline
InactiveCN106199064AImaging RealizationOvercome limitationsFluid speed measurementSonificationChannel network
The invention provides an iterative ultrasonic tomography method for the axial flow field imaging in a pipeline. The method comprises the steps of constructing a dense sound channel network by ultrasonic sensors large in emission angle and arranged on the upstream and downstream cross sections of a pipeline, exciting to receive an ultrasonic signal, acquiring the average flow velocity of the axial flow field of the pipeline along each sound channel through calculating the time for the ultrasonic wave to spread in the clockwise direction of each sound channel so as to obtain a plurality of original projection data, grouping the projection data into parallel sound channel groups for interpolation and subdivision, expanding the number of projection data, discretizing a to-be-constructed pipeline axial flow velocity field image, and reconstructing a pipeline axial flow velocity field through the iterative tomography of projection data in the prior constraint condition. According to the technical scheme of the invention, on the condition that the original fluid state is not disturbed, the distribution of the axial flow field in the pipeline can be detected. Furthermore, the high-precision reconstruction of the axial flow field of the pipeline is realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
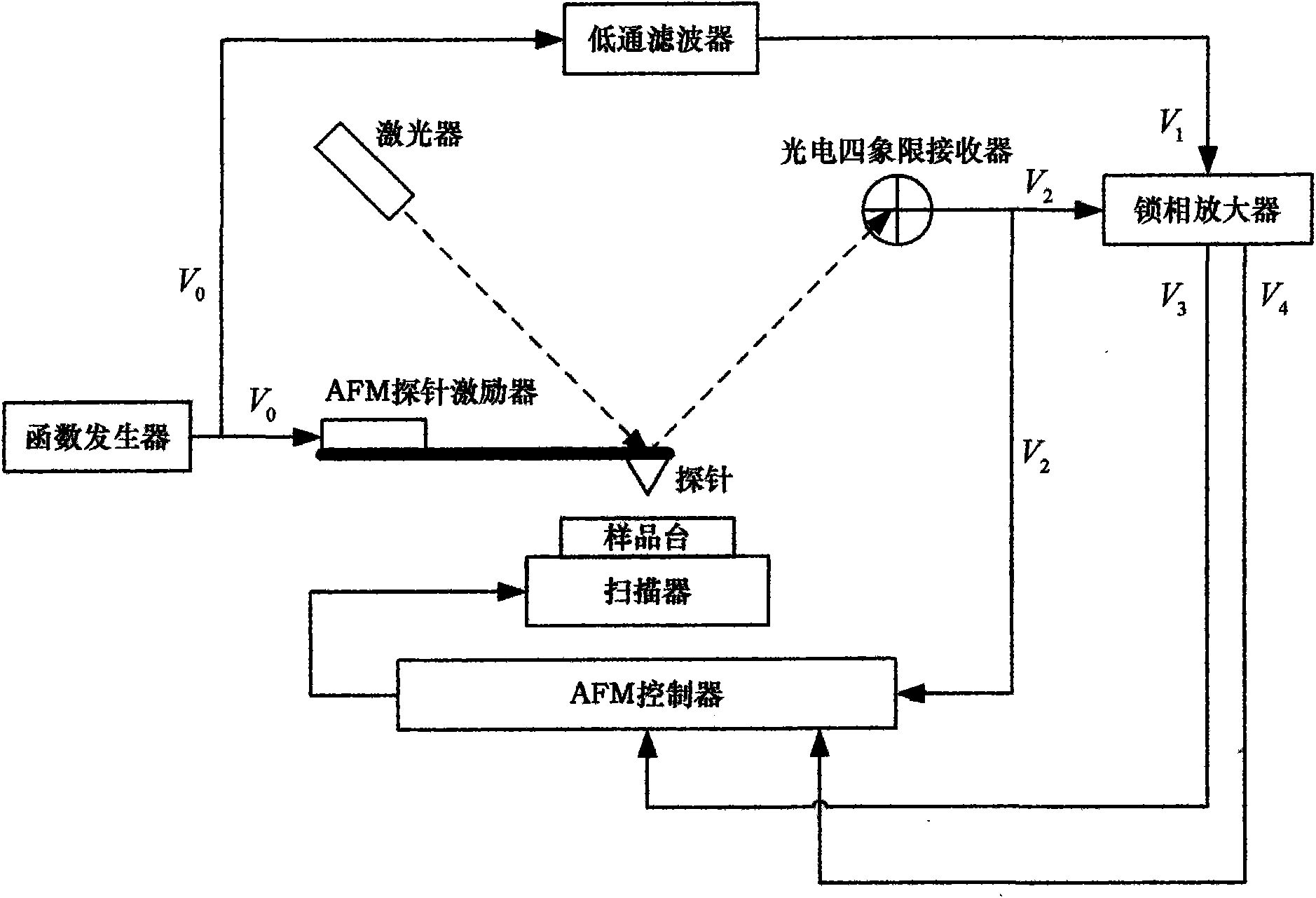
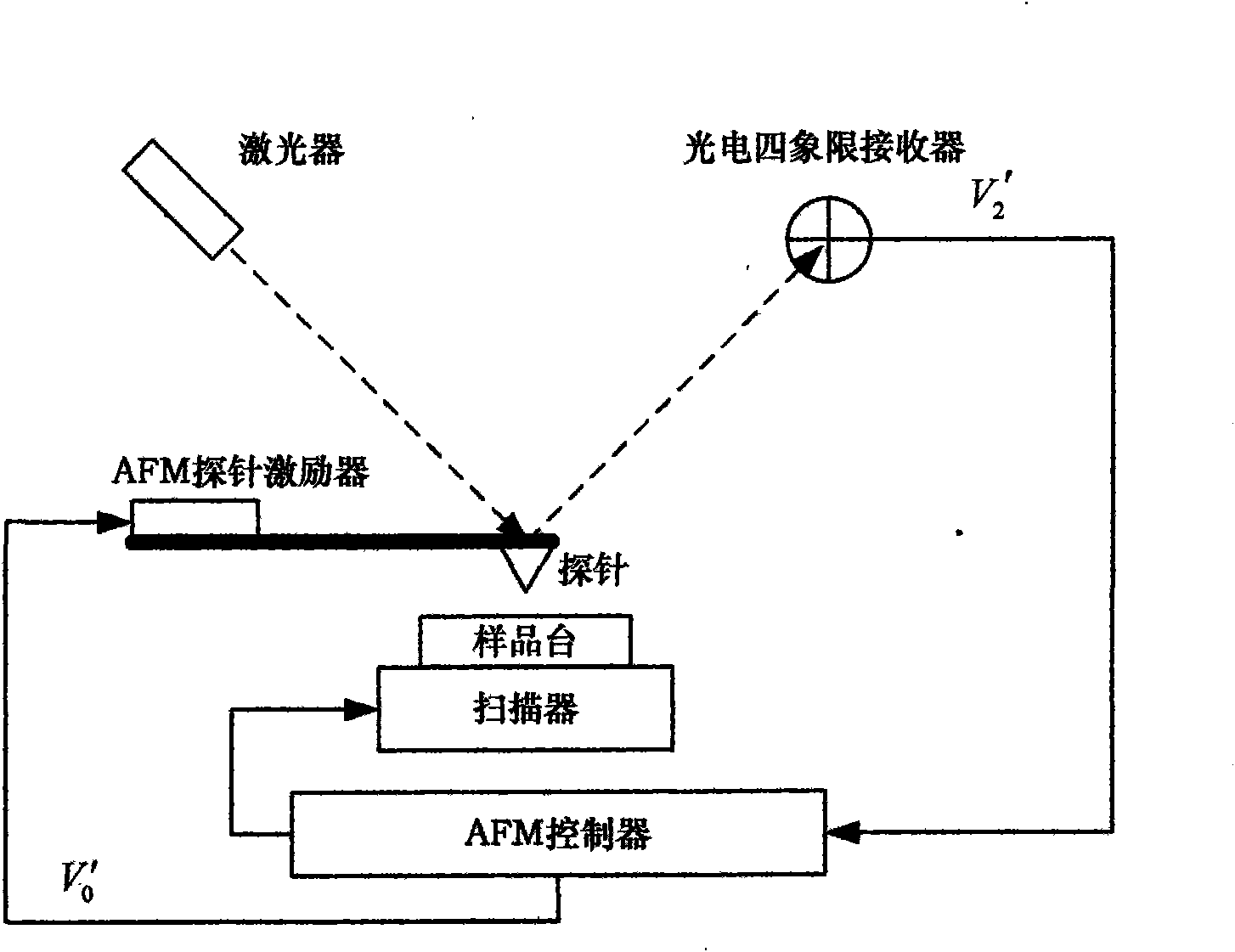
Harmonic excitation imaging system for tapping-mode atomic force microscopy
InactiveCN101592583AHigh sensitivityAdded component imaging functionSurface/boundary effectAtomic force microscopyHigher order harmonics
The invention discloses a harmonic excitation imaging system for a tapping-mode atomic force microscopy. The harmonic excitation imaging system comprises a function generator, a low-pass filter and a phase lock amplifier added to the prior tapping-mode atomic force microscopy, wherein the function generator is connected with the excitation signal input end of an AFM probe exciter; the phase lock amplifier is connected between a photoelectric four quadrant receiver and an AFM controller; and the low-pass filter is connected in series between the function generator and the phase lock amplifier. The harmonic excitation imaging system is imaging technology which adopts a harmonic superposed signal as an excitation source in a tapping mode and the phase lock amplifier to obtain the high-order harmonic components of probe motion and makes use of the amplitudes and phases of the high-order harmonic components to acquire more information and higher resolution.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Short-wave, long-wave and infrared dual-band focal plane-shared large-relative aperture optical system
The present invention provides a large-relative aperture optical system. The large-relative aperture optical system has the advantages of few consumed materials, small size and compact structure, and can effectively eliminate inter-band and intra-band chromatic aberration in a dual-band system. The optical system includes a front fixed lens assembly, an diaphragm, an intermediate fixed lens assembly, a rear fixed lens assembly and a detector which are sequentially distributed from an object side to a focal plane and are fixedly connected with one another; the front fixed lens assembly, the diaphragm, the intermediate fixed lens assembly and the rear fixed lens assembly share the same central axis; the front fixed lens assembly has positive focal power and comprises a first positive lens, a first negative lens and a second negative lens which are distributed sequentially along the central axis from the object side to the focal plane coaxially; the intermediate fixed lens assembly has negative focal power and comprises a second positive lens and a third negative lens which are distributed sequentially along the central axis from the object side to the focal plane coaxially; the diaphragm is located between the third negative lens and the second positive lens; and the rear fixed lens assembly is a third positive lens.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
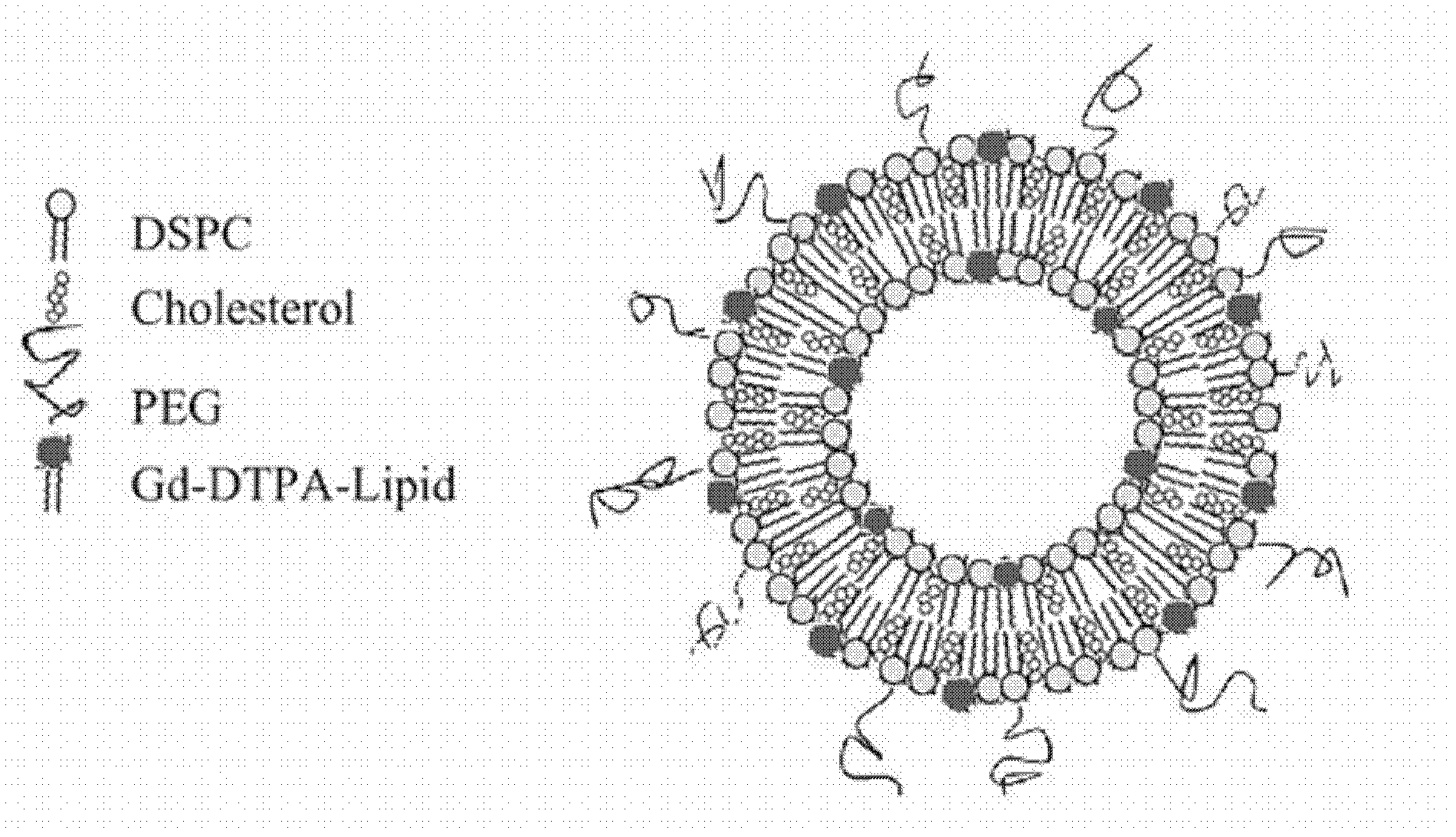
Glioma-targeting molecule magnetic resonance contrast agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102350002AWeighted imaging effect close toSmall particle sizeEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsChemistryBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecule imaging, and relates to a glioma-targeting molecule magnetic resonance contrast agent as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The contrast agent comprises two complexes, namely a biotinylated monoclonal antibody and a streptavidin Gd-coated spatial stable immune liposome; and the two complexes are reacted and combined toform MAb-X-Y-Z-Gd. The experiment results show that: the molecular probe can combine with glioma neogenesis blood capillaries without passing through the blood-brain barrier while actively targeting the tumor neogenesis blood vessels, and an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) signal is amplified by a biotin-avidin system, thereby achieving high-resolution glioma-specific targeting imaging; and the biotin-avidin-mediated two-step imaging method has effectivity, thereby proving a new nondestructive method for glioma early-stage diagnosis, the research of biological behavior, and anti-vessel survival treatment targeting and treatment effect evaluation.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Sparse stepped-frequency SAR imaging method under spatial-frequency-domain two-dimensional condition
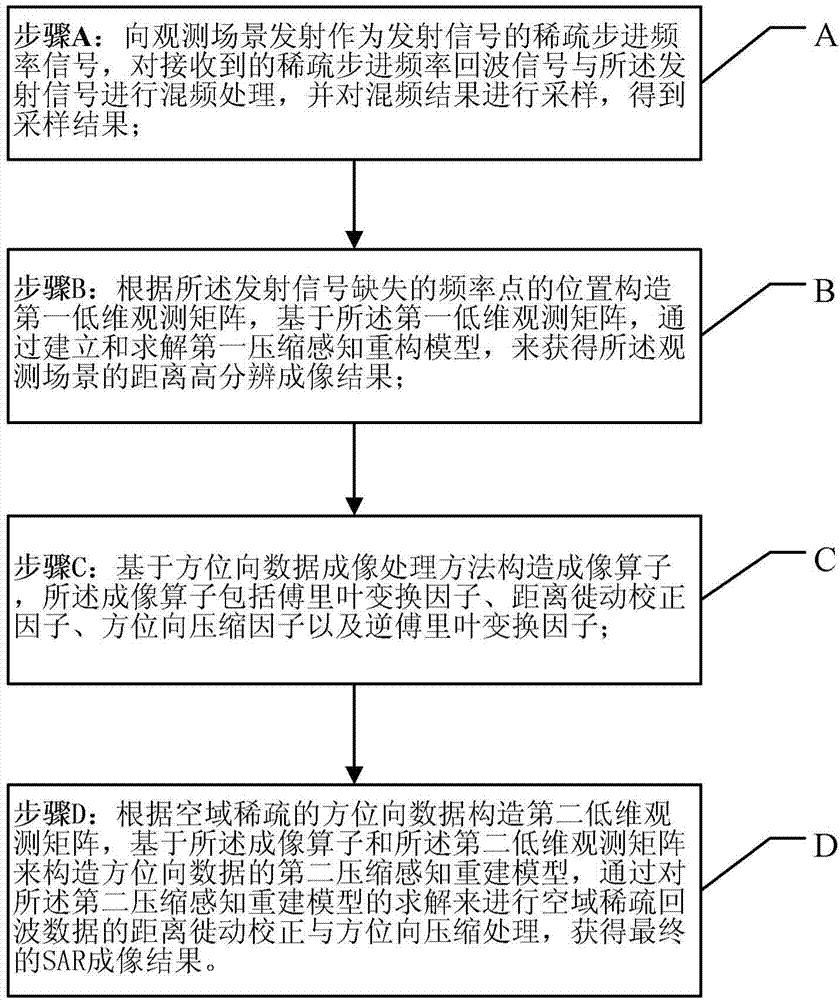
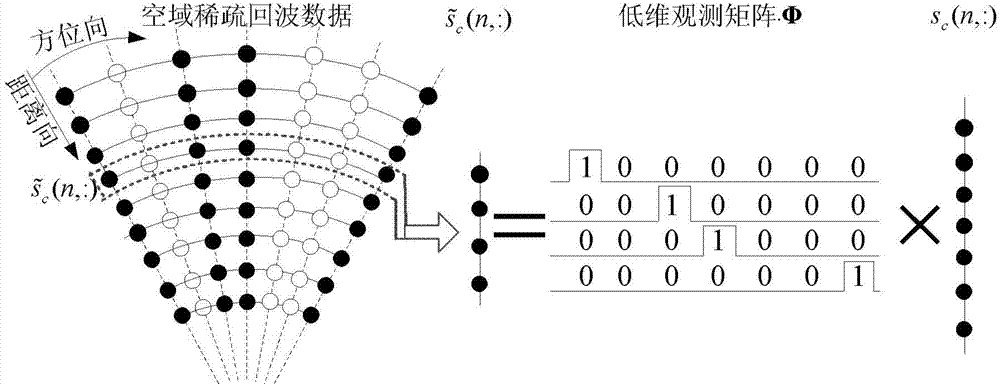
ActiveCN104749573AImaging RealizationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRange migrationCompressed sensing
The invention provides a sparse stepped-frequency signal SAR imaging method under the spatial-frequency-domain two-dimensional condition. The sparse stepped-frequency signal SAR imaging method is technically characterized in that a sparse stepped-frequency signal echo model is analyzed, a compressed sensing theory is combined and sparse stepped-frequency points are utilized to obtain a high-resolution distance imaging result; under the situation of SAR space domain data missing, range migration correction and orientation compression processing of echo data are achieved by establishing an imaging operator and a compression sensing reconstruction model, and further a final SAR imaging result is obtained. Compared with traditional even sparse stepped-frequency signal SAR imaging, the method can achieve SAR imaging only by needing few frequency resources and small radar echo numbers, interfered frequency points can be jumped over and the anti-interference capacity can be improved by utilizing the sparse stepped-frequency signals, meanwhile signal transmitting duration is shortened, equivalent repeating frequency is improved, and azimuth Doppler fuzzy is avoided.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Variable PRI squint bunching SAR imaging method, device and equipment and storage medium
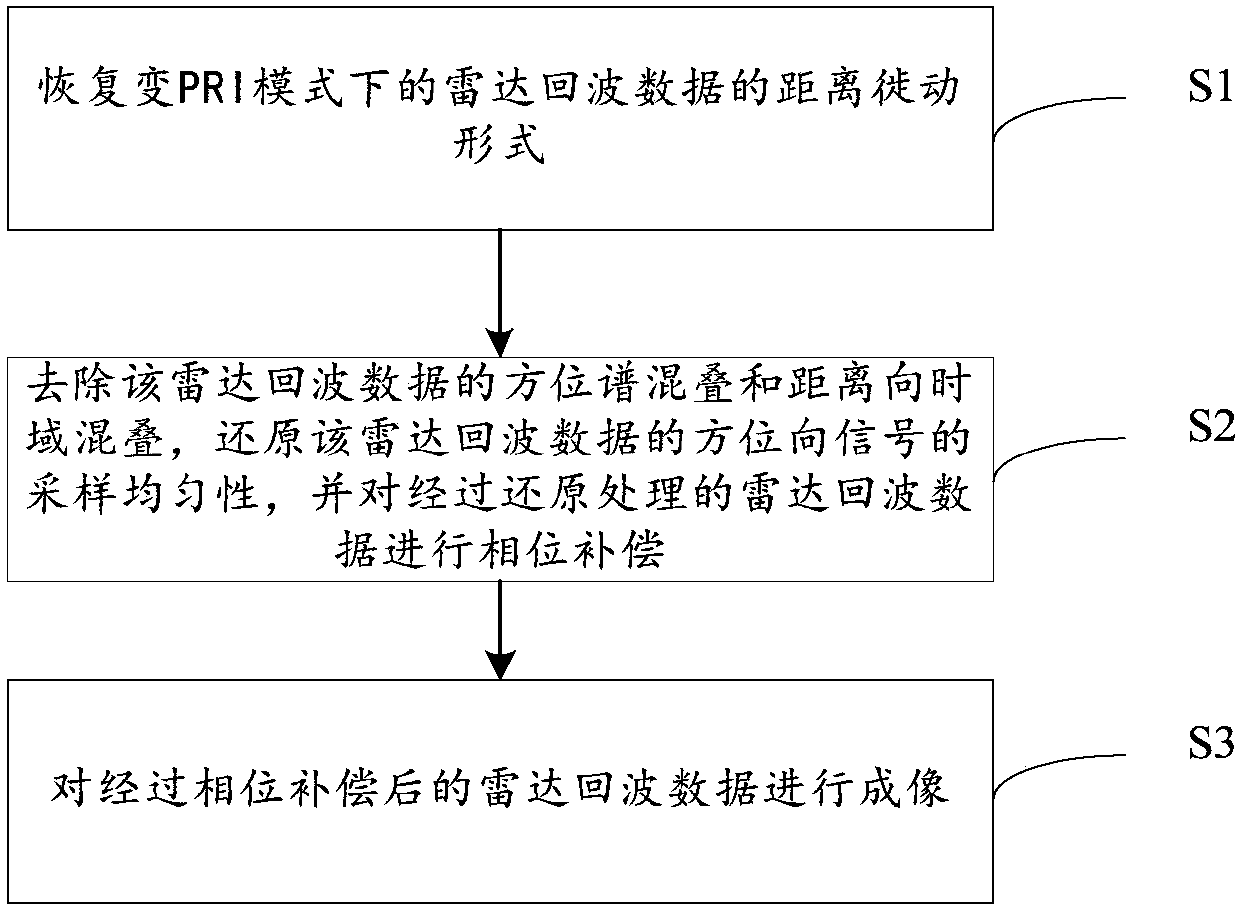
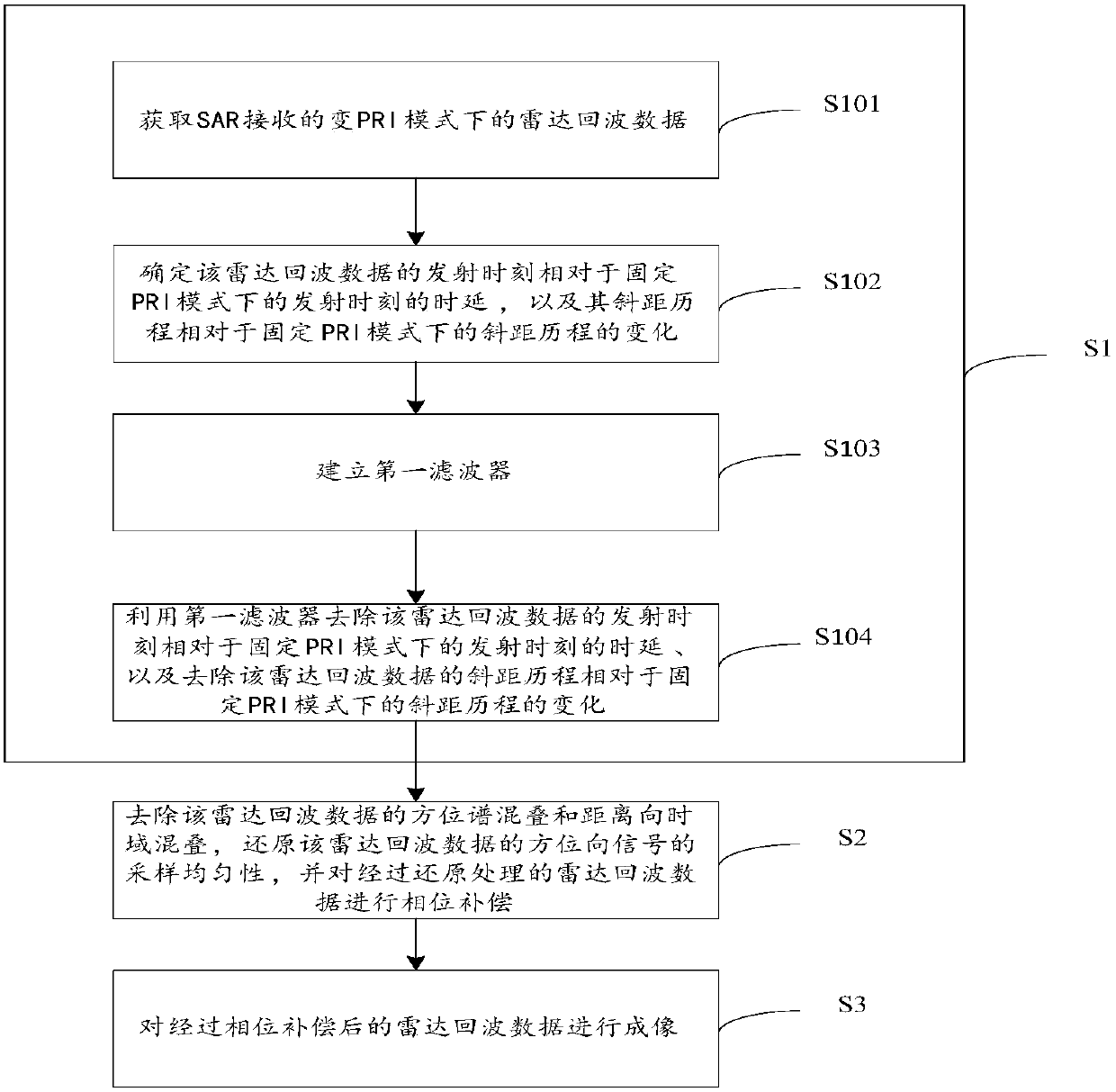
ActiveCN109782277AImaging RealizationAchieve restorationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRange migrationEnvironmental geology
The invention discloses a variable PRI squint bunching SAR imaging method and device, equipment and a storage medium. The invention relates to the technical field of synthetic aperture radars. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the steps of recovering a range migration form of radar echo data in a variable PRI mode; removing azimuth spectrum aliasing and range direction time domain aliasing of the radar echo data; restoring the sampling uniformity of azimuth signals of the radar echo data; performing phase compensation on the restored radar echo data; and carrying out imaging on the radar echo data subjected to phase compensation. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, under-sampling under the condition that the azimuth signal ofthe radar echo data under the variable PRI mode is non-uniform can be restored under the condition that the calculation efficiency is ensured, so that the processing efficiency of the frequency domain imaging algorithm is improved.
Owner:CETC OCEAN INFORMATION CO LTD
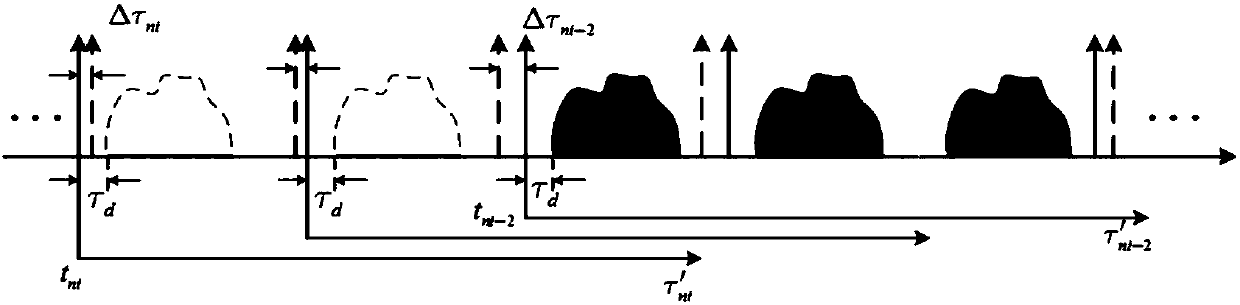
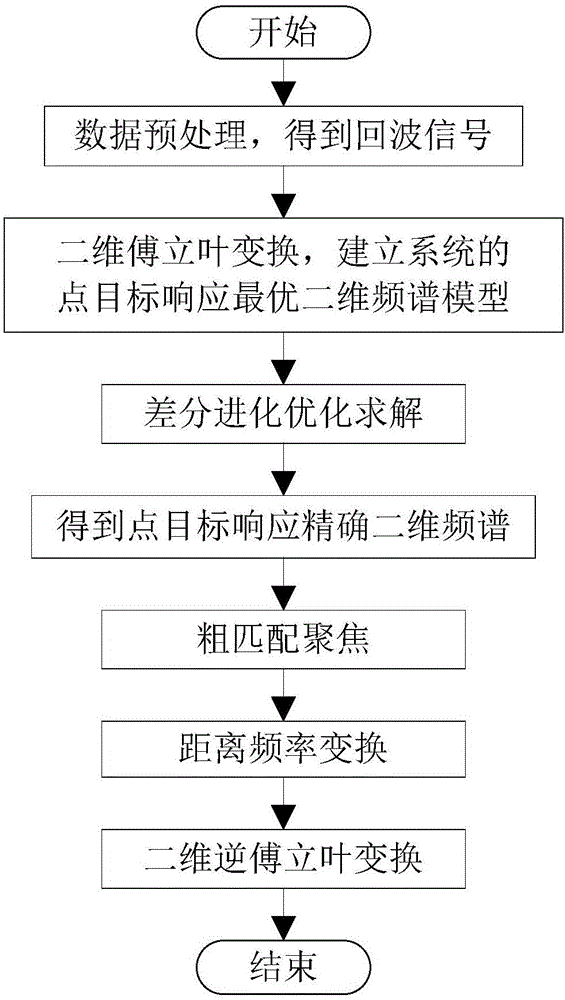
Bistatic foresight SAR frequency domain imaging method based on frequency spectrum optimization modeling
ActiveCN106054190AAccurate imagingImaging RealizationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumImaging algorithm
The present invention discloses a bistatic foresight SAR frequency domain imaging method based on frequency spectrum optimization modeling. The method comprises the following steps: S1, performing data preprocessing, and obtaining echo signals; S2, performing two-dimensional Fourier transform of the echo signals, establishing the point target response optimal two-dimensional frequency spectrum mode of the system, and solving the point target response two-dimensional frequency spectrum through adoption of a difference evolution optimization method; S3, performing rough matching focusing of the point target response accurate two-dimensional frequency spectrum; S4, performing distance frequency transformation of the two-dimensional frequency spectrum; and S5, performing two-dimensional inverse Fourier transform of the two-dimensional frequency spectrum after the distance frequency transformation, and obtaining final complex images. The problem is overcome that the current imaging algorithm cannot process the space variation of the bistatic foresight SAR distance to the nonlinearity, an accurate bistatic foresight SAR two-dimensional frequency spectrum is obtained through the difference evolution optimization method, and the echo signals are subjected to imaging process on the two-dimensional frequency domain according to the point target response accurate two-dimensional frequency spectrum to realize the accurate focusing of the bistatic foresight SAR original data.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Device and method for sliding type multi-layer magnetic induction tomography
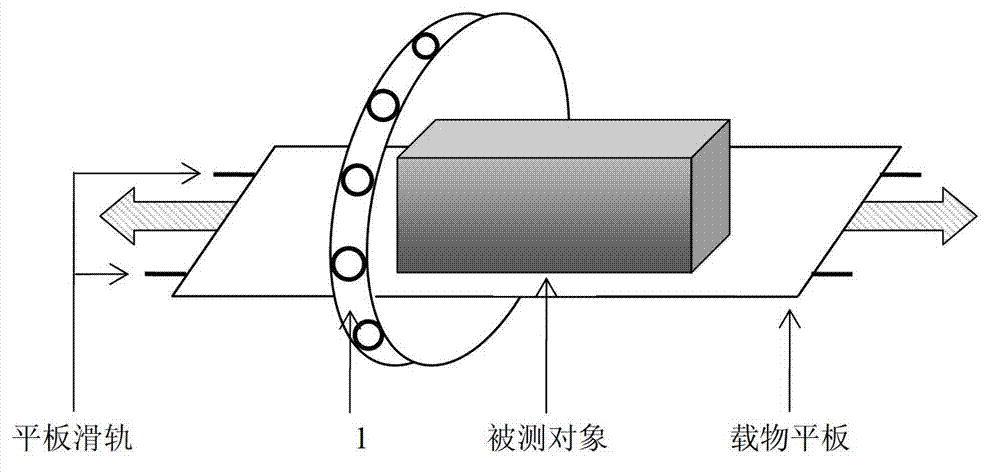
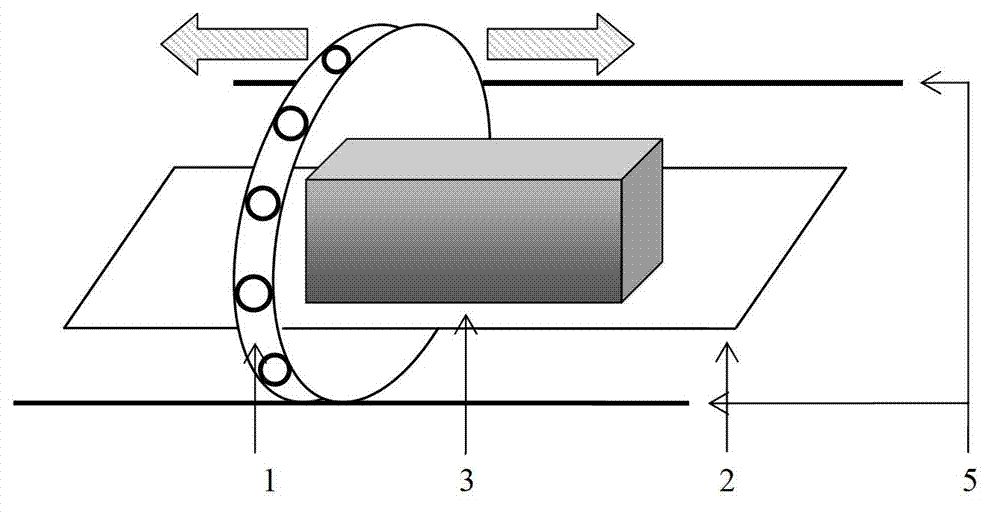
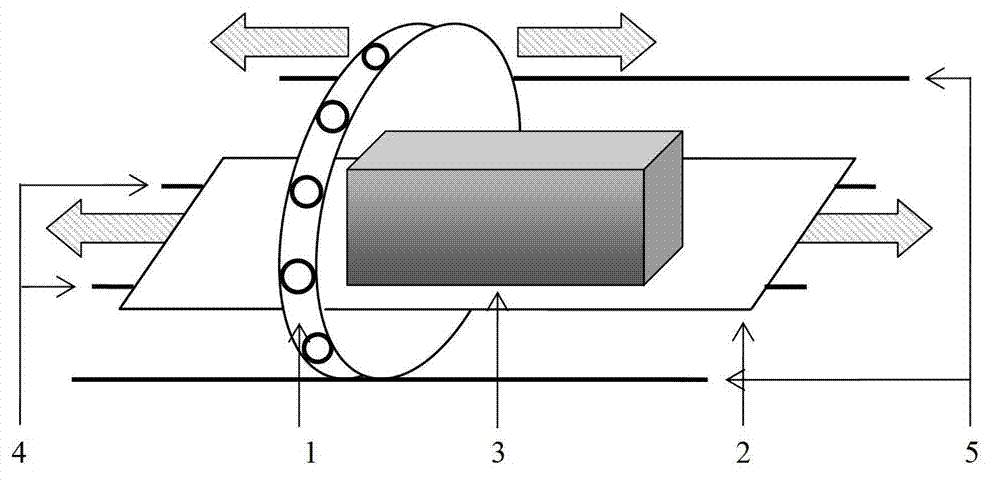
ActiveCN103033847AImaging RealizationElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationPhysicsCollections data
The invention discloses a device and a method for sliding type multi-layer magnetic induction tomography. According to the method of sliding type multi-layer magnetic induction tomography, a measured object is put on a plate, a measuring coil array is driven to surround the measured object and the plate, the coil array can slide on the plate so that the central surface of the coil array is corresponding with different faults of the object, one magnetic induction tomography data collection is carried out when the coil array is corresponding with one fault of the object, the conductivity distribution map of the object at the fault is rebuilt through imaging algorithm, data collection can be carried out for a plurality of times by sliding the coil array or plate and a conductivity distribution map at the fault is rebuild each time, a plurality of conductivity distribution maps of the object at adjacent faults are obtained though a plurality of times of data collection and maps rebuilding, and the overall conductivity distribution condition of the object is obtained. The device and the method for sliding type multiple layer magnetic induction tomography has the advantages that conductivity distribution maps of the measured object at different faults are obtained conveniently, and multiple layer non-contact electrical impedance tomography is achieved.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Multi-mode cholangiopancreatography system
PendingCN109349982AImaging RealizationEffective mutationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryElectricityImaging processing
The invention discloses a multi-mode cholangiopancreatography system which comprises an image processing system, a first optical imaging system, an ultrasonic imaging system, an endoscope probe, a photoelectric slip ring component, a first optical fiber, a second optical fiber, a first electric signal line and a second electric signal line. The endoscope probe is provided with an optical probe component and an ultrasonic transducer, the photoelectric slip ring component drives the endoscope probe to rotate and comprises a rotary photoelectric coupling unit and a rotation driving device for driving the rotary photoelectric coupling unit to rotate, a photoelectric slip ring is arranged in the rotary photoelectric coupling unit, the first optical imaging system is connected with one end of the photoelectric slip ring through the first optical fiber, the other end of the photoelectric slip ring is connected with the optical probe component through the second optical fiber, the ultrasonic imaging system is connected with one end of the photoelectric slip ring through the first electric signal line, and the other end of the photoelectric slip ring is connected with the optical probe component through the second electric signal line. According to the multi-mode cholangiopancreatography system, by the aid of multi-mode (optical and ultrasonic) cooperative imaging, imaging resolution ratio and imaging depth are increased, and the system is applicable to cholangiopancreatography.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method for improving linearity of microwave imaging by using compressed sensing
InactiveCN109283530ALower equivalent dielectric constantImproving Imaging LinearityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging algorithmLinearity
The invention discloses a method for improving the linearity of microwave imaging by using compressed sensing, which comprises the steps of setting up a microwave imaging system, wherein a plurality of transmitting and receiving antennas are uniformly distributed at intervals in a circle around a target to be measured with a large dielectric constant, one of the transmitting and receiving antennasserves as a transmitting antenna to emit electromagnetic waves to the target to be measured so as to form an incident field, the incident field forms a scattering field around the target to be measured, the rest of the transmitting and receiving antennas serve as receiving antennas to uniformly receive the scattering field; establishing a preliminary imaging area according to the approximate position range of the target to be measured, enabling the target to be measured to be located in the preliminary imaging area, increasing the space sparsity characteristics between the target to be measured and the imaging area, and carrying out processing and imaging on received scattering field signals by adopting a compressed sensing method, wherein the imaging effect is ideal along the increase inlinearity of an imaging algorithm. The method disclosed by the invention can effectively improve the nonlinearity of the traditional microwave imaging algorithm when imaging a target with a large dielectric constant, and has the characteristics of simple and convenient implementation, fast calculation and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Near space circular synthetic aperture radar rapid back-direction projection imaging method
ActiveCN103869315AReduce the numberReduce computational complexityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRapid imagingSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a near space circular synthetic aperture radar rapid back-direction projection imaging method. In view of the problem of near space circular synthetic aperture radar rapid imaging, the method replaces a phase error in coherent imaging method with a pixel amplitude error as the evaluation criterion of imaging precision, approximately expands through low order of Green function which is based on chebyshev nodes and lagrange interpolation according to the principle of minimum mean square error, switches the problem of calculation of sub aperture projection to the problem of calculation of limited number of approximate expansion coefficients, and reduces as much as possible the number of expansion coefficients under the condition of meeting the focusing accuracy so that algorithm computational complexity is reduced, and then accomplishes the imaging from coarse focusing to fine focusing by applying recursive computation. Compared with the existing circular SAR back-direction projection imaging method, the near space circular synthetic aperture radar rapid back-direction projection imaging method has the advantages that computing speed is greatly improved, big scene imaging is achieved and imaging accuracy is much higher.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Ultrasonic transducer array, ultrasonic intervention treatment system and ultrasonic ablation catheter
ActiveCN106037803AReduce volumeIncrease useUltrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic imagingExAblate
The invention discloses an ultrasonic transducer array, an ultrasonic intervention treatment system and an ultrasonic ablation catheter, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The ultrasonic transducer array comprises a first ultrasonic transducer set including a first ultrasonic transducer for ultrasound ablation, a second ultrasonic transducer set including a second ultrasonic transducer for ultrasonic imaging, a metallic conductive support, wherein the first ultrasonic transducer and the second ultrasonic transducer are jointly installed, and which is respectively connected with the grounding ends of the first ultrasonic transducer and the second ultrasonic transducer, an ablation electrode leading-out wire set respectively connecting with the electrode end of the first ultrasonic transducer, an imaging electrode leading-out wire set respectively connecting with the electrode end of the second ultrasonic transducer, and a common-ground electrode leading-out wire connecting with the metallic conductive support. The ultrasonic transducer array has the advantages of good positioning and ablation effects, and realizes mixing frequencies work. The ultrasonic transducer array can be used for ultrasound ablation and internal lumen imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Single-pixel imaging method and system based on image frequency domain splicing
ActiveCN106791355ARealize mode acquisitionChange frequency componentsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPhase retrievalSingle pixel
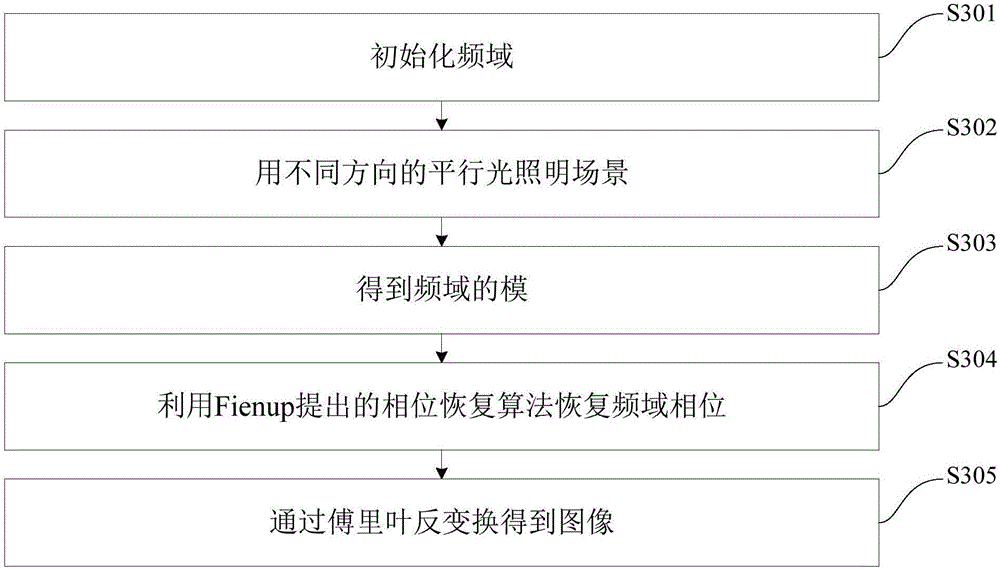
The invention discloses a single-pixel imaging method and system based on image frequency domain splicing. The single-pixel imaging method comprises the steps of acquiring a transfer function according to a parallel incident light source; determining corresponding information between offsets of the parallel incident light angle and the frequency domain according to the transfer function; illuminating a scene through different directions of parallel light, receiving the illumination intensity at the very center of the frequency domain through a single-pixel sensor, and thus the mode of the frequency domain according to the corresponding information between the offsets; retrieving the phase of the frequency domain by adopting a phase retrieval algorithm according to the mode of the frequency domain; and acquiring a scene image by adopting Fourier inverse transform according to the retrieved phase of the frequency domain. According to the imaging method, the characteristic of high sensitivity of the single-pixel sensor for light can be utilized, so that image can be realized by only requiring low illumination intensity and short exposure time, and the imaging speed is improved. In addition, the reliability of imaging is improved, and the imaging cost is reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Quantum imaging method and quantum imaging system
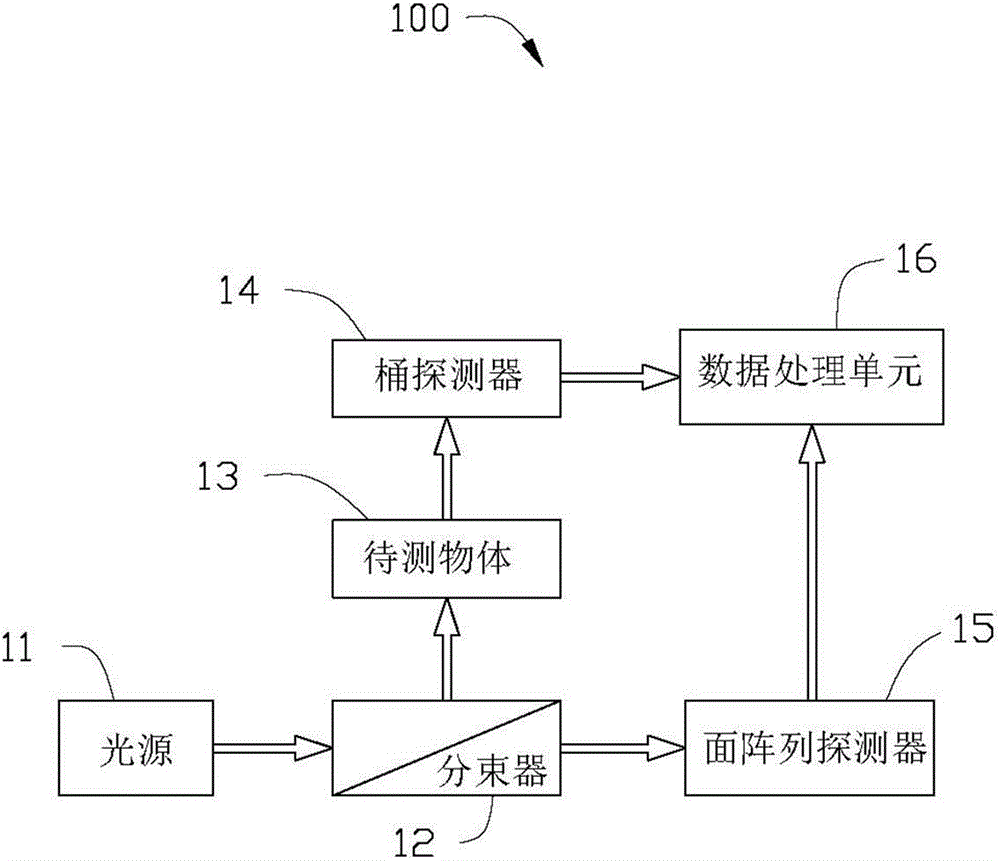
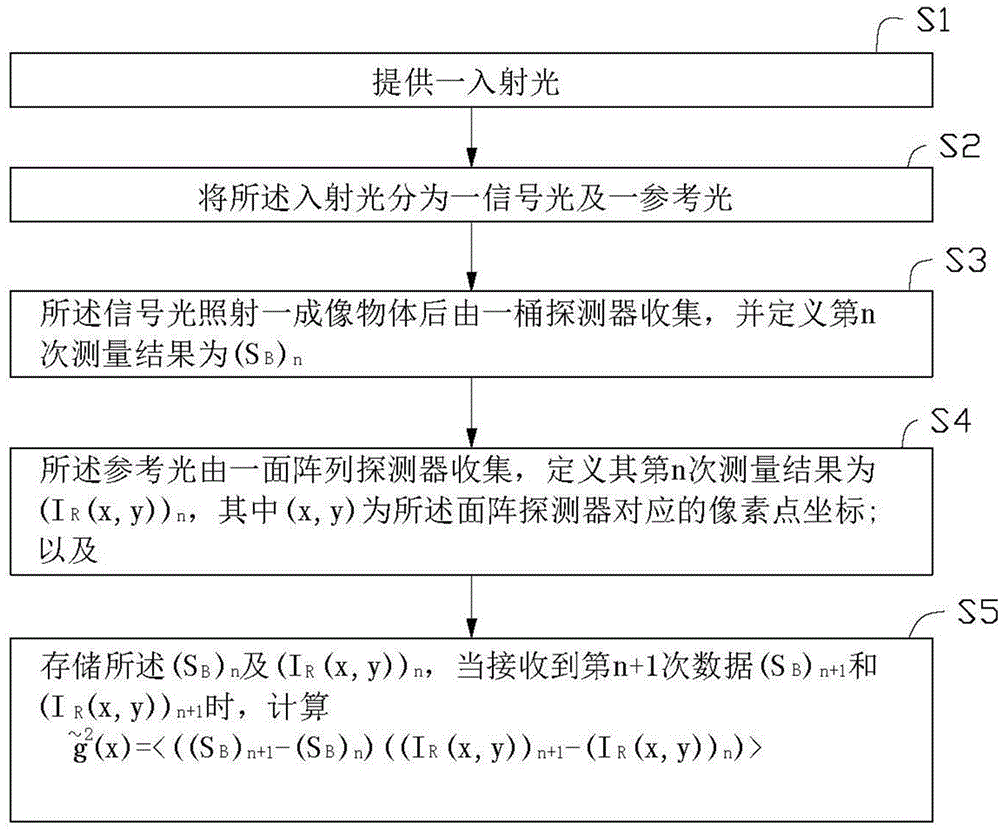
The invention discloses a quantum imaging method and a quantum imaging system. The method comprises the following steps: S1) providing incident light; S2) splitting the incident light into signal light and reference light; S3) after the signal light irradiates an imaging object, collecting the light by a bucket detector and defining the nth measuring result as (SB)n; S4) collecting the reference light by a planar array detector, and defining the nth measuring result as (IR(x,y))n, wherein the (x,y) is pixel point coordinates corresponding to the planar array detector; and S5) storing the (SB)n and the (IR(x,y))n, and when receiving (n+1) data (SB)n+1 and the (IR(x,y))n+1, calculating g<~><2>(x)=<((SB)n+1- (SB)n)((IR(x,y))n+1-(IR(x,y))n)>.
Owner:北京坤煜量子科技有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com