Near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system
A laser scanning and imaging system technology, applied in the optical field, can solve the problems of difficult to observe tissue, difficult to meet multi-dimensional, deep-level observation, inconvenient operation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
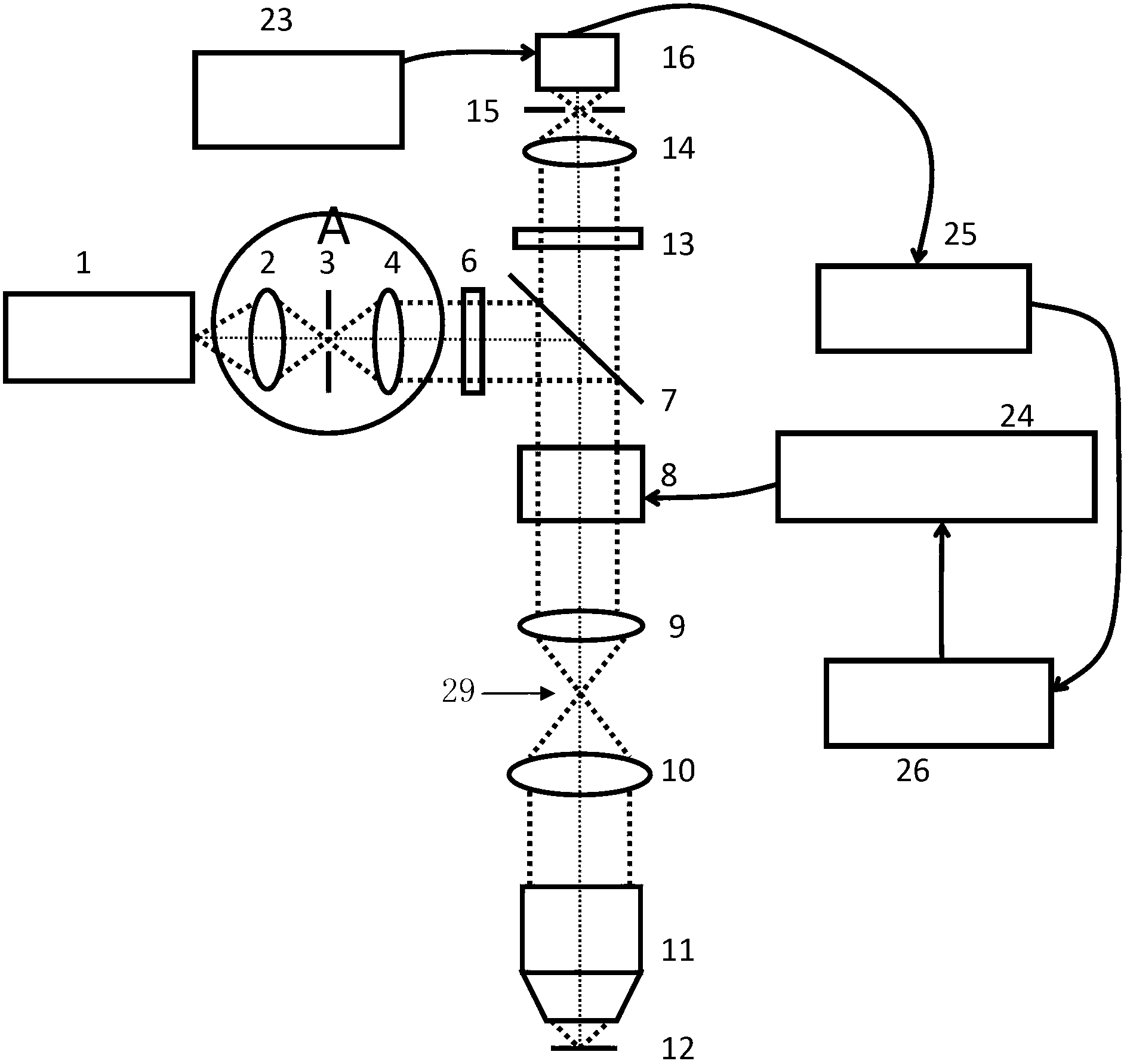
[0064] refer to figure 2 , the main structure of this embodiment is the same as figure 1 It is similar, but the Kohler illumination system B is added. The function of the Koehler illumination system is to assist the near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system to find the focal plane position of the imaging objective lens, that is, to place the biological sample on the infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system through the Kohler illumination system. Focus position of the imaging system.
[0065] The Koehler illumination system B is composed of a white light source 17 , an imaging lens 18 , a half mirror 19 , a mirror 20 , an imaging objective lens 11 , a barrel lens 21 and a CCD 22 . The white light source 17 is imaged by the imaging lens 18, and reflected by the half-reflective mirror 19 and the reflector 20, the image of the white light source is reflected to the rear focus position of the imaging objective lens 11, so that uniform illumination is formed on t...
Embodiment 2
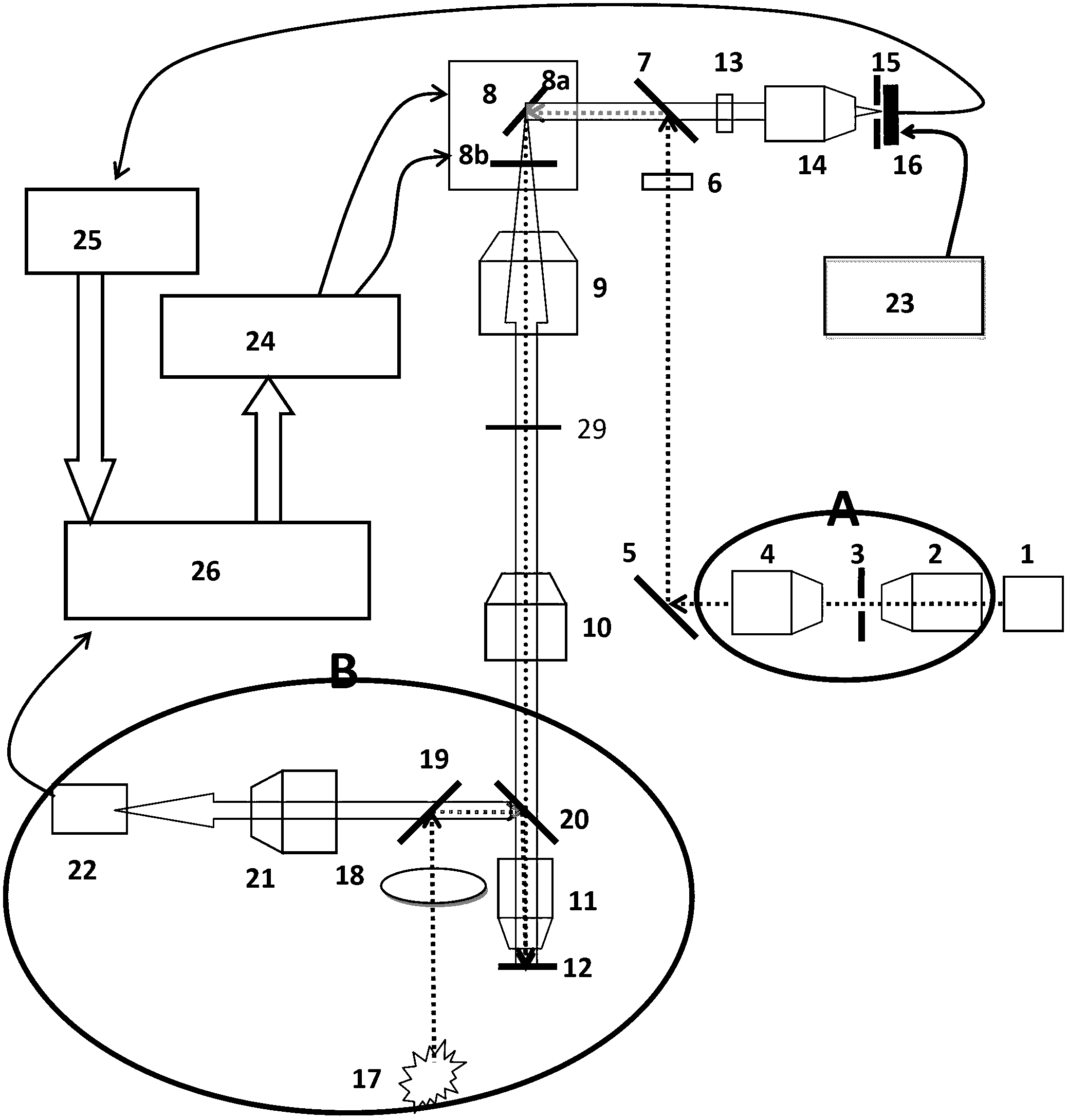
[0070] refer to image 3 , the working principle of this embodiment is similar to that of Embodiment 1, the only difference is that the Kohler lighting method adopts transmissive lighting, and its specific implementation process is as follows:
[0071] The white light source 17 forms an image at the focal point of the lens 27 through the lens 18, and the light emitted by the white light source image becomes parallel light through the lens 27, and uniformly illuminates the biological sample 12 from below the biological sample. The light emitted by the sample is formed by the imaging objective lens 11, reflected by the mirror 20, and finally imaged by the lens tube lens 21 on the CCD22.
[0072] After the position of the biological sample is determined by the Kohler illumination system, the reflector 20 is moved away from the optical path between the lens tube lens 10 and the imaging objective lens 11, and the white light source is turned off at the same time. Then, near-infrar...
Embodiment 3
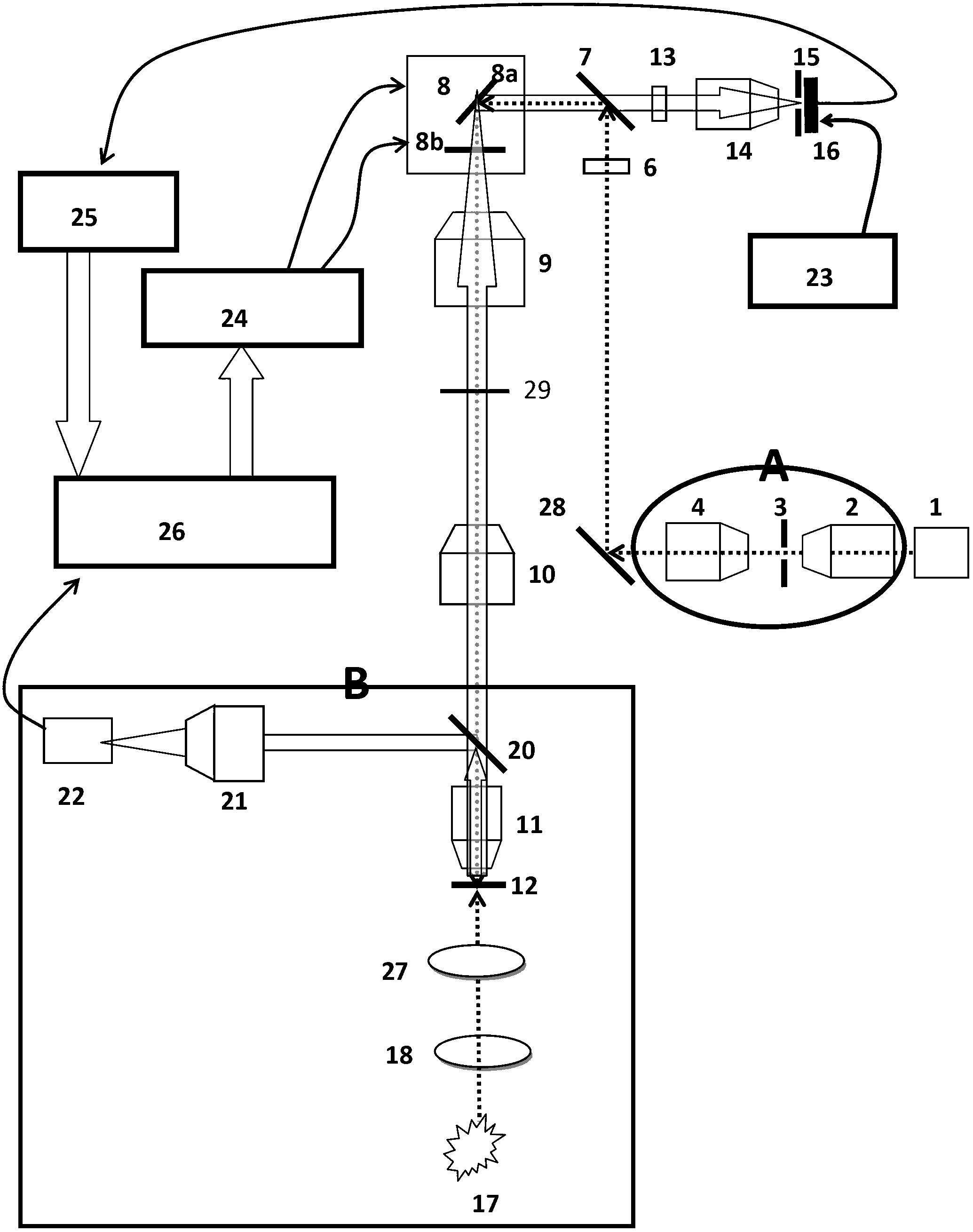
[0075] refer to Figure 4, this embodiment adopts the transmissive Kohler illumination method as in Embodiment 2, and the difference is that the detection light path of the Kohler illumination system is modified. The specific implementation process is:
[0076] The biological sample 12 is uniformly illuminated from below the biological sample using the white light illumination optical path in Embodiment 2, and the embodiment 1 (see figure 2 ) and Example 2 (see image 3 The filter 6 in ) is placed between the reflector 5 and the collimating lens 4, and the reflector 5 is replaced by a half-reflective mirror 28, and the reflector 20 is removed. Place the tube lens 21 and CCD22 into the Figure 4 location shown. In this way, the Koehler illumination biological imaging detection optical path and the laser excitation biological fluorescence detection optical path share the imaging objective lens 11 , lens tube lens 10 , f-theta lens 9 and scanning galvanometer 8 .
[0077] A...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com