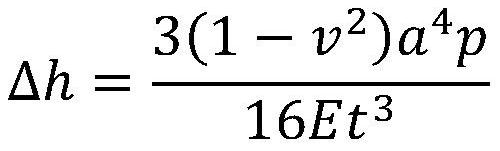Patents
Literature
69results about How to "Realize 3D Imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
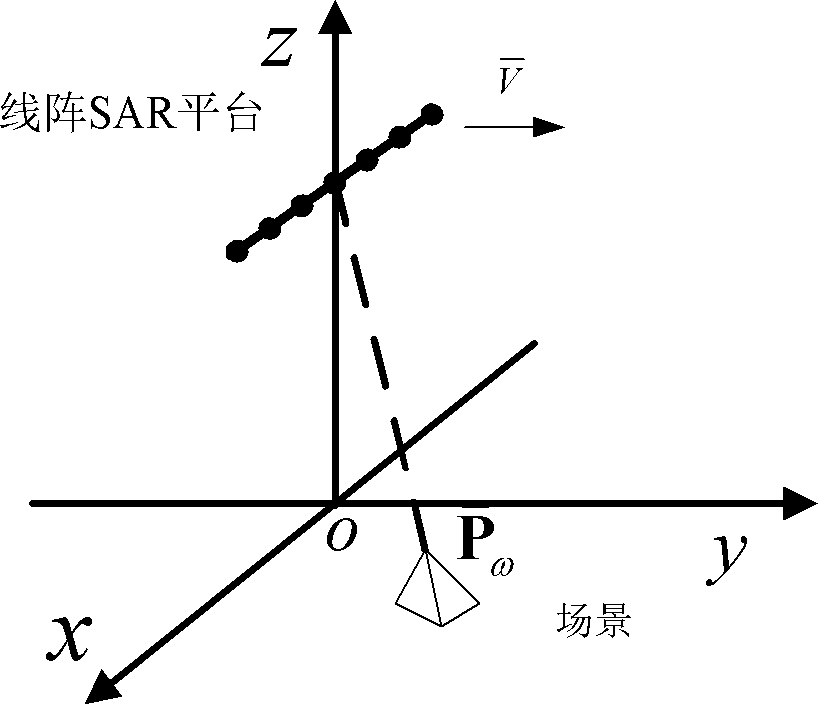
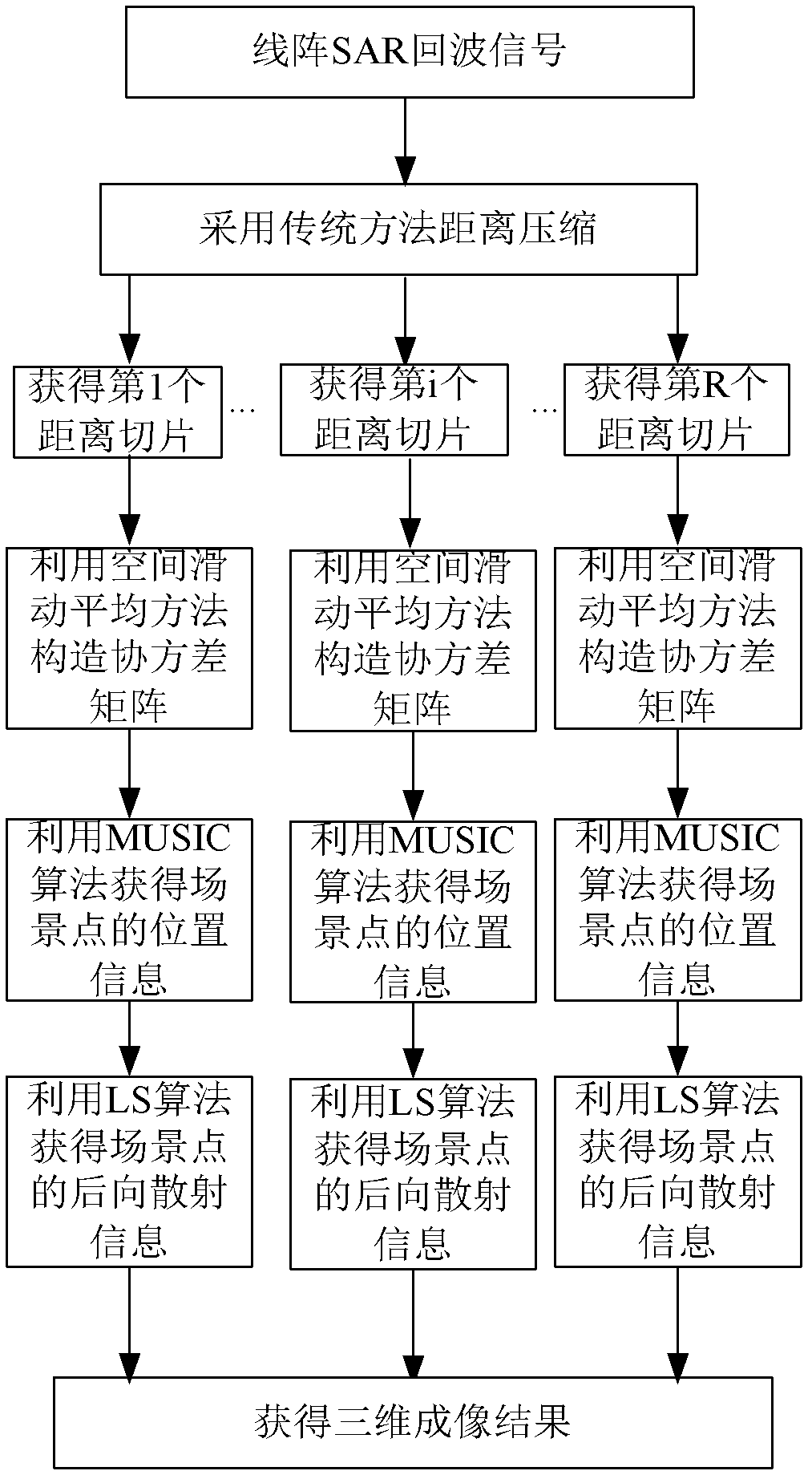
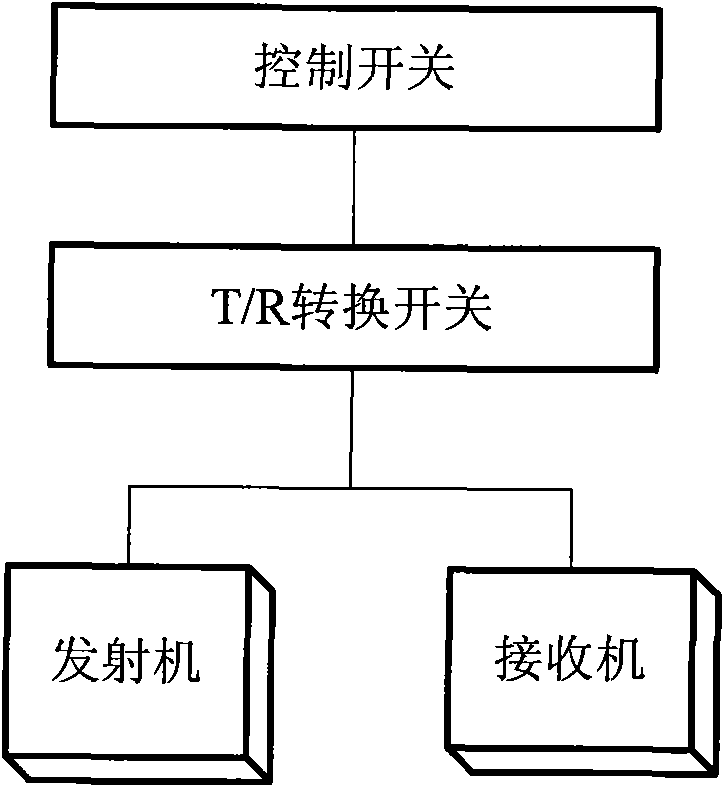
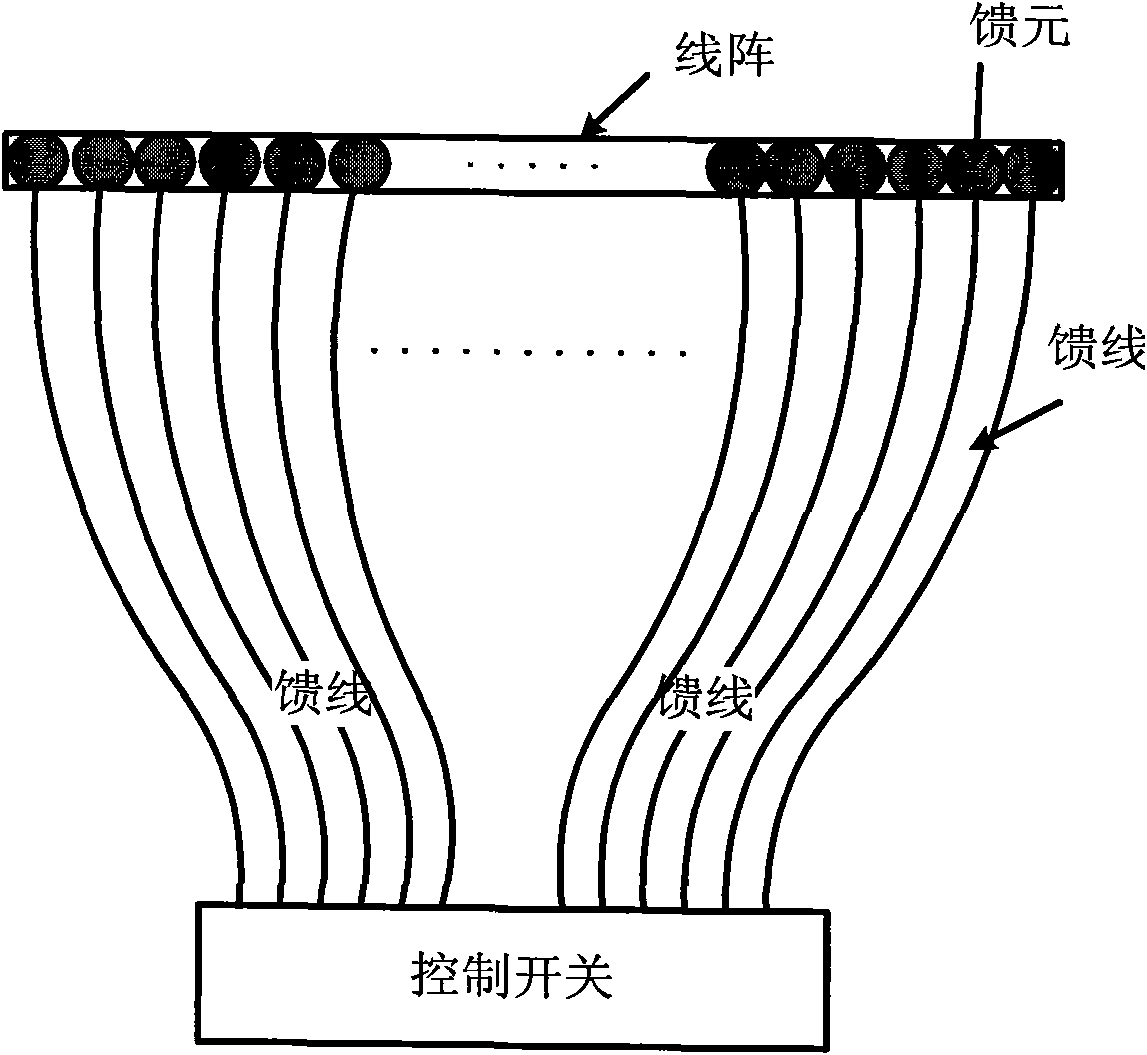
Super-resolution linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging method
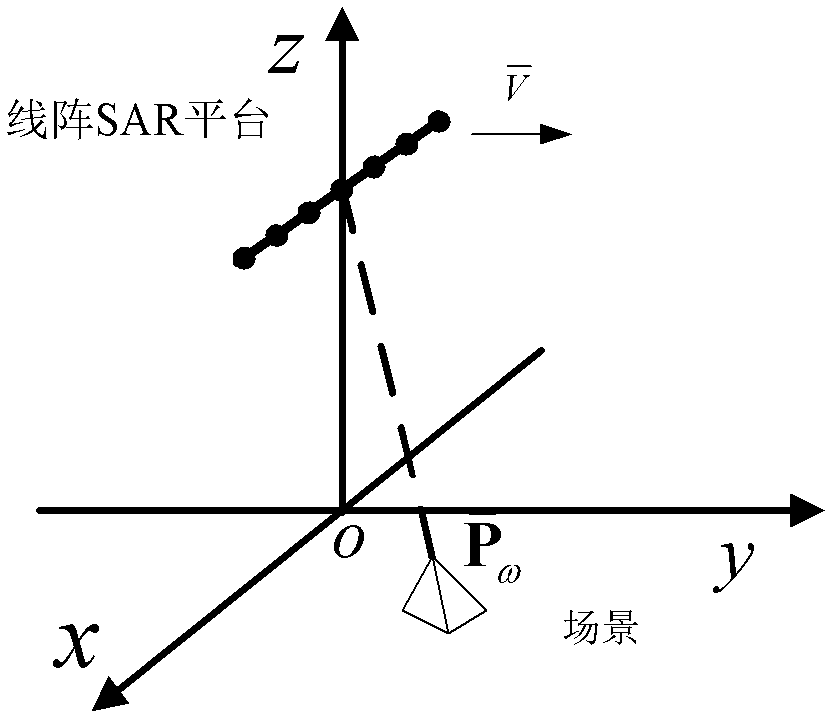
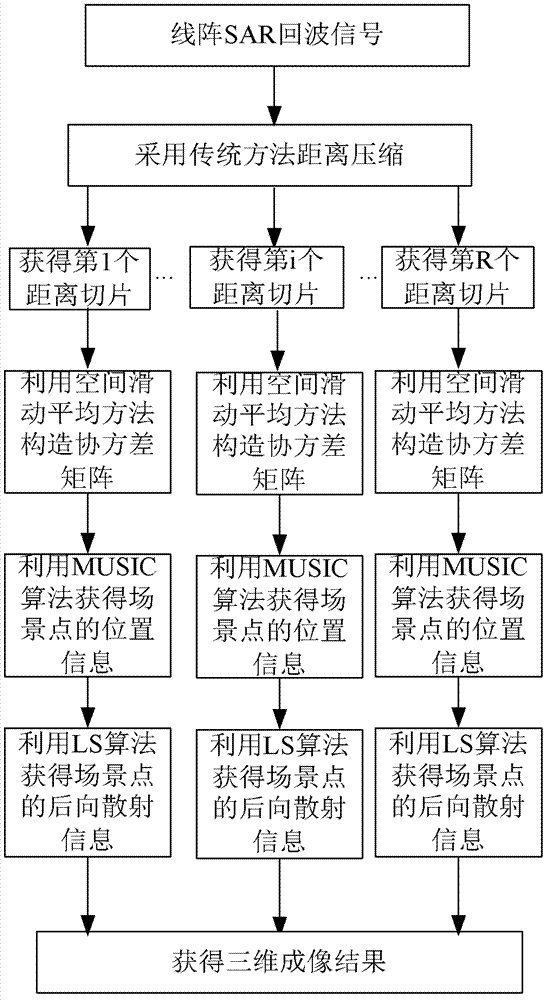
InactiveCN102323583AImprove imaging effectOvercome the problem of limited lengthRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLeast squaresImage resolution
The invention discloses a super-resolution linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on an MUSIC (MUltiple SIgnal Classification) algorithm, which comprises the steps of: firstly, compressing distance data by adopting pulse; secondly, focusing scene information by adopting the MUSIC algorithm for each distance section, obtaining reverse scattering information ofa scene point by adopting an LS (Least Square) algorithm; and finally, integrating processed distance sections and displaying to obtain a three-dimensional reconstruction graph. Compared with the traditional imaging methods, such as a BP algorithm and an MF algorithm, the super-resolution linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging method has the advantages of overcoming the problem of Rayleigh limit and limited antenna length, realizing sidelobe weakening by using an MUSIC method while the length of an antenna is not increased, reducing the influence of sidelobe crosstalkto imaging quality, increasing resolution, realizing three-dimensional imaging and improving imaging quality.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
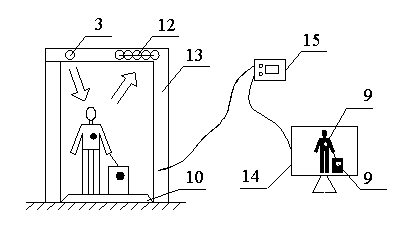
Terahertz imaging passenger luggage rapid security inspection system and dangerous goods detection method thereof
The invention relates to a passenger luggage security inspection system, in particular to a terahertz imaging passenger luggage rapid security inspection system and a dangerous goods detection method of the terahertz imaging passenger luggage rapid security inspection system. Terahertz rays are focused on passenger luggage by controlling a two-dimensional transversely-moving platform through a computer, and are received by a detector after being reflected by passenger luggage and focused by a lens, terahertz signals are converted into voltage signals, and images are output through the computer after noise reduction and amplification are conducted on the voltage signals. The problems that during X-ray detection, hurts are great, formed images are not clear, luggage simultaneous detection signals interfere with one another, and a detection device is complex in structure, large in occupied area, low in detection efficiency and high in cost are solved. The terahertz imaging passenger luggage rapid security inspection system and the dangerous goods detection method are wide in application range, accurate in detection, small and exquisite in structure, and capable of simultaneously conducting security inspection on passenger luggage, and the potential safety hazards of public places are reduced on the premise of efficient security inspection.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
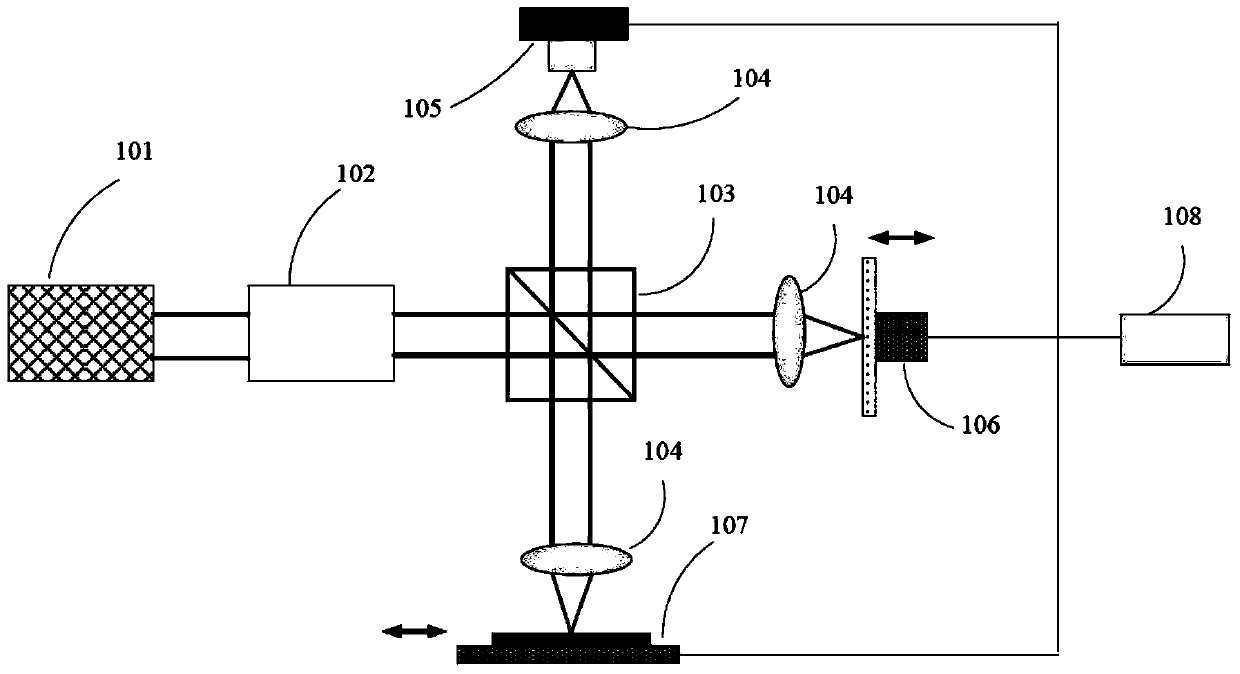
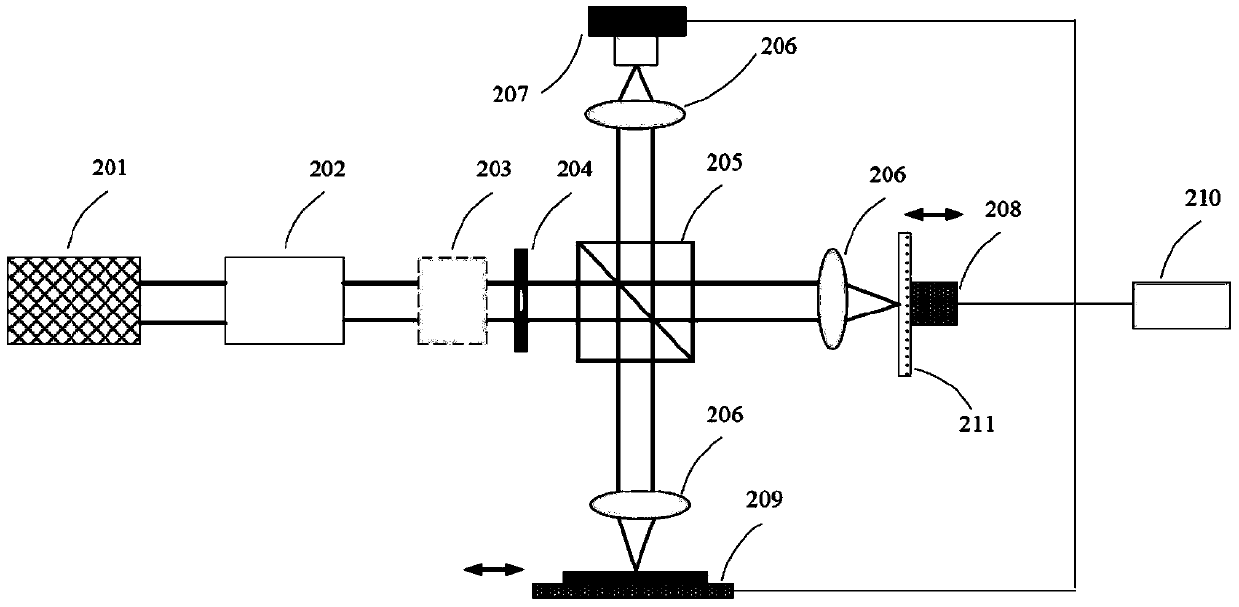
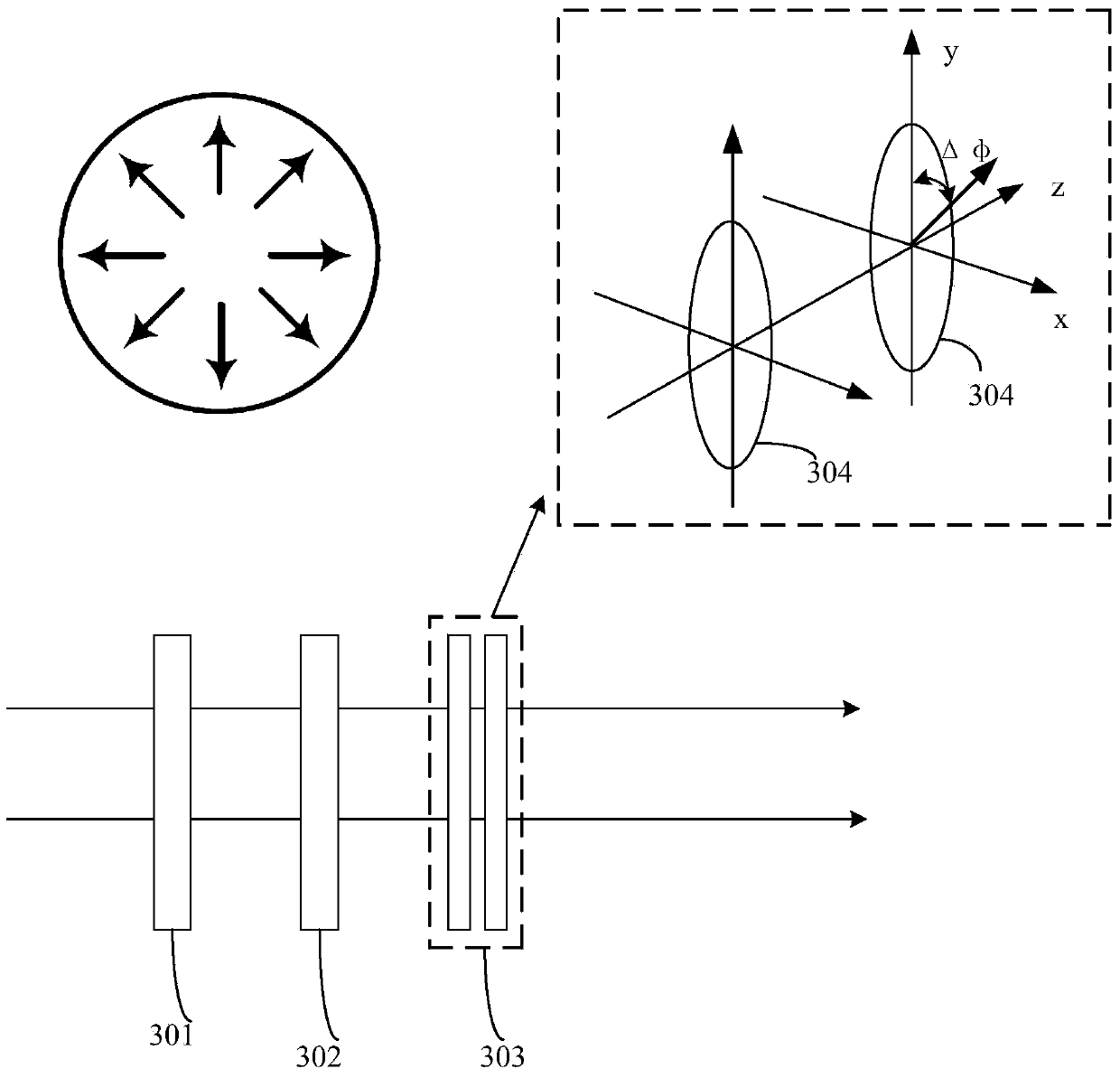
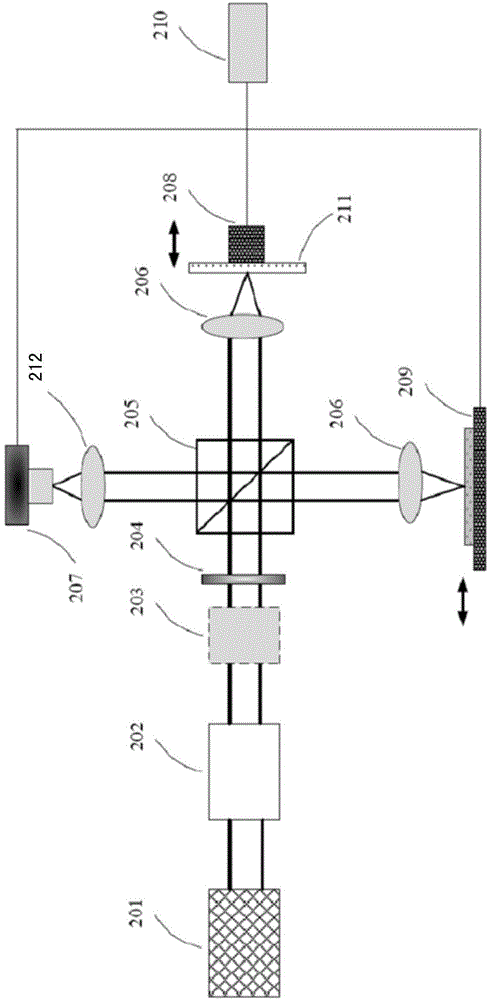
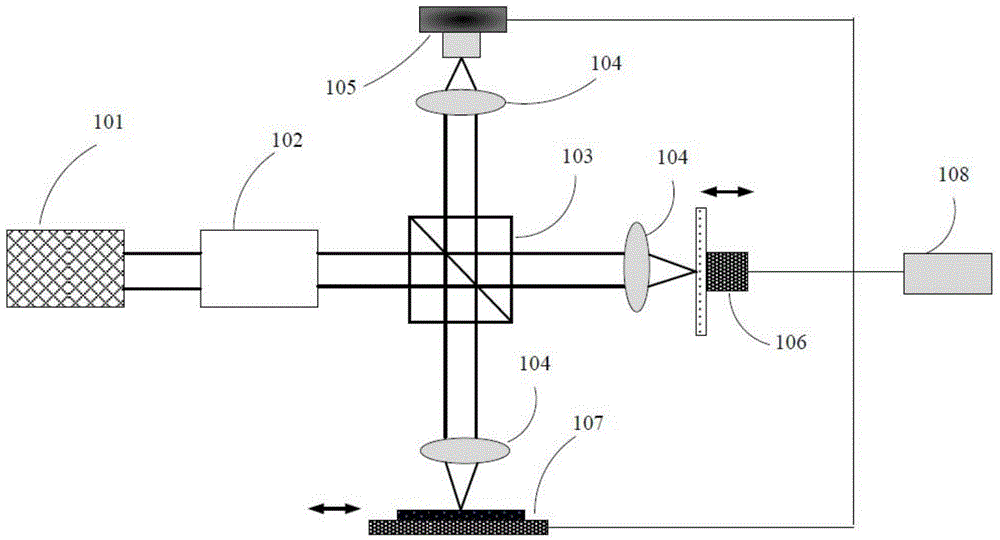
Optical coherence tomography method and device based on radial-direction polarized beams
ActiveCN103431845AImprove imaging resolutionFix horizontal resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBeam splitterOptoelectronics
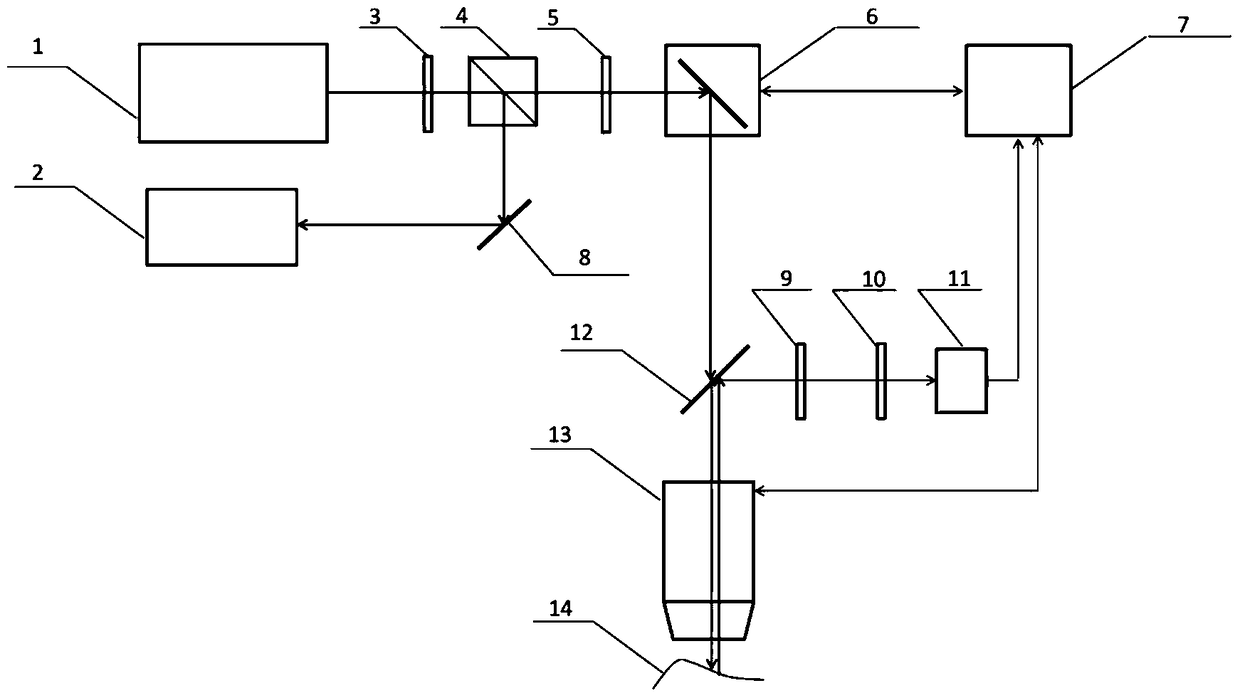
The invention provides an optical coherence tomography method and device based on radial-direction polarized beams. The method comprises the following steps that after light beams emitted by a low-coherence light source are processed through a Kohler illumination system, the polarization state of the light beams is adjusted and controlled through a polarization transformation system, the amplitude and phase distribution of the light beams are adjusted and controlled through a pupil filter, and accordingly the radial-direction light beams are formed; the radial-direction polarized beams enter a beam splitter prism in an incident mode, are divided into two paths, and enter a sample arm and a reference arm respectively; the two-path light beams are focused on a sample to be measured and a reference plane mirror through microscope objectives of the two-path light beams respectively; returned light after being reflected by the sample to be measured and the reference plane mirror joins in the position of the beam splitter prism, is focused through a focusing lens, is imaged in a probe and is then transmitted to a computer to be post-processed; the reference plane mirror transversely moves to achieve transverse scanning; the sample to be measured is placed on a three-dimensional horizontal-moving table capable of moving in space to achieve three-dimensional imaging of the sample.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Double helix electrode capacitance tomography sensor for measuring annular space
InactiveCN105353004ARealize 3D ImagingReduce in quantityMaterial capacitanceElectricityProcess tomography
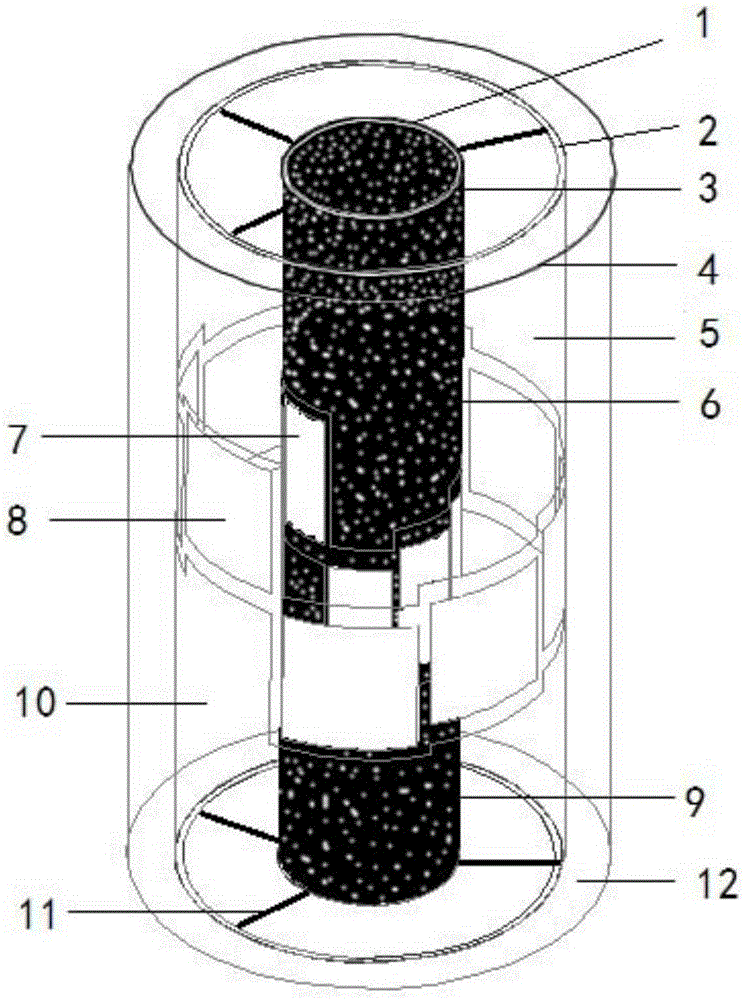
The invention discloses a double helix electrode capacitance tomography sensor for measuring an annular space that belongs to the field of an electrical process tomography device. The sensor comprises a main structure part and a capacitance measurement part. The main structure part is composed of concentric inner and outer tubes and a connection bracket used for fixing position. An annular space between the inner and outer tubes is a measured space. The capacitance measurement part comprises detection electrodes, electrode end shields, shielding cases, a signal transmission cable, ECT signal acquisition equipment and connection wires. By the utilization of electrode sensor parts which are respectively spirally arranged on the inner and outer tube walls, three-dimensional imaging of the measured annular space is truly realized. Due to the sensor structure with electrodes uniformly distributed on the two tube walls, imaging of the annular space is realized, and the problem of weak capacitance signal is also improved. The invention is a big breakthrough of the ECT technology.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
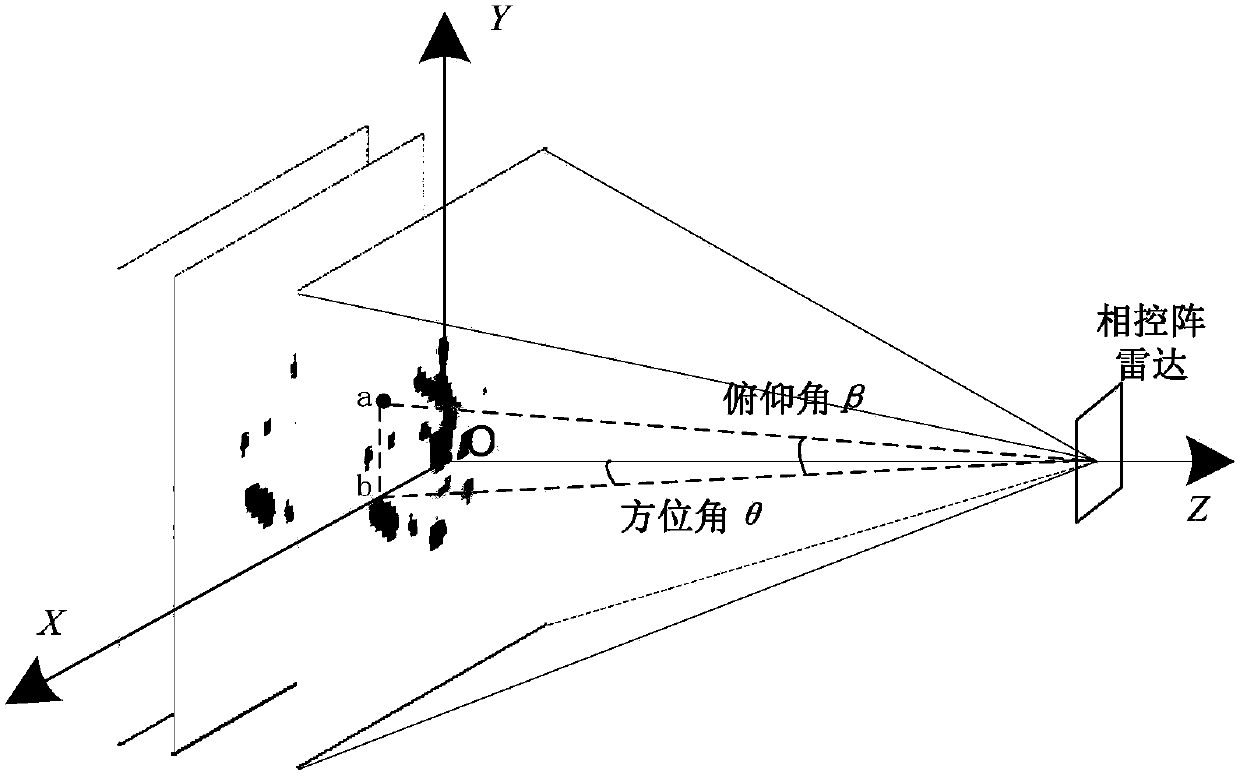
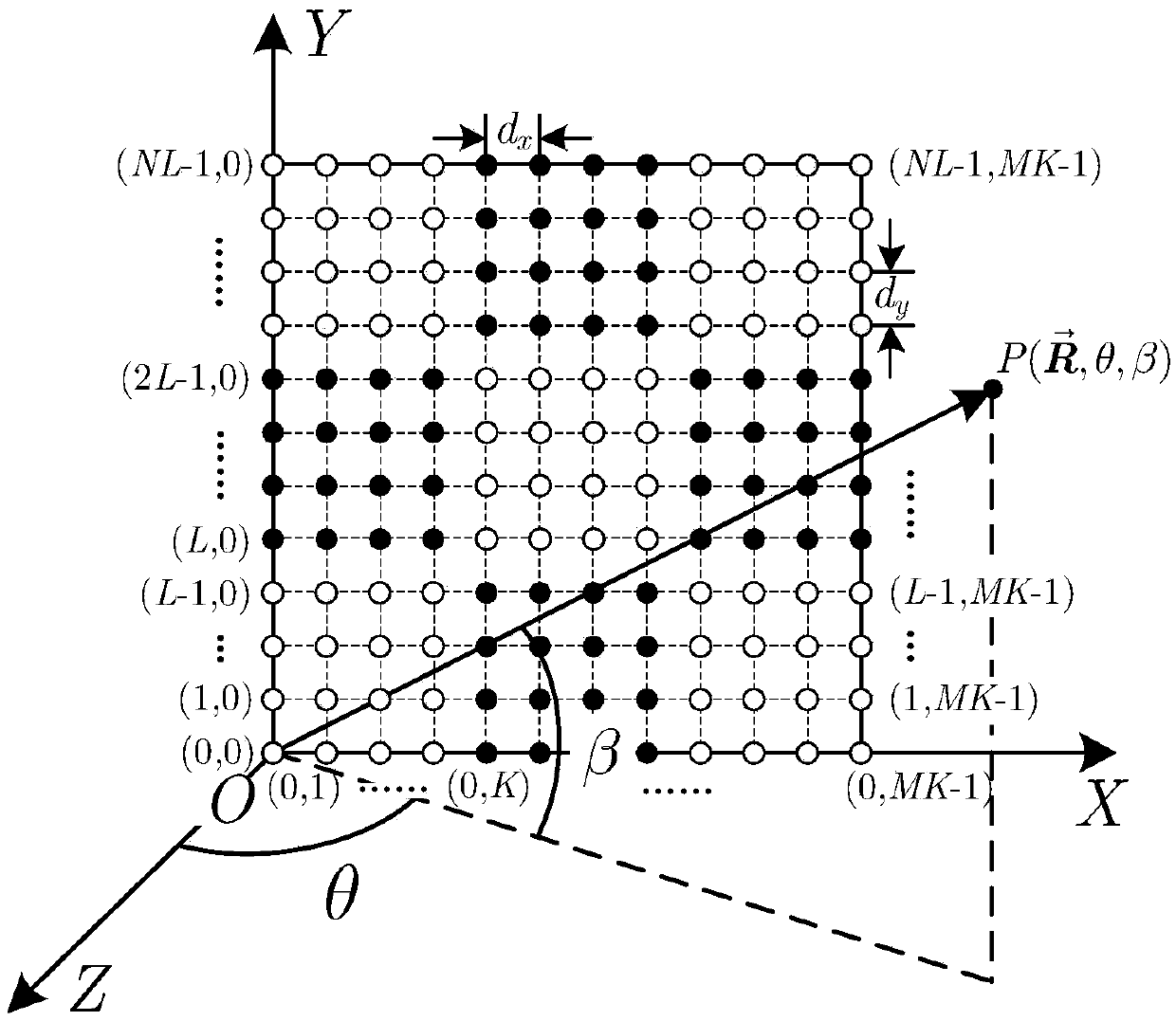
Three-dimensional correlated imaging method based on phased array radar
ActiveCN104181531AHigh resolutionRealize 3D ImagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar antennas3d image
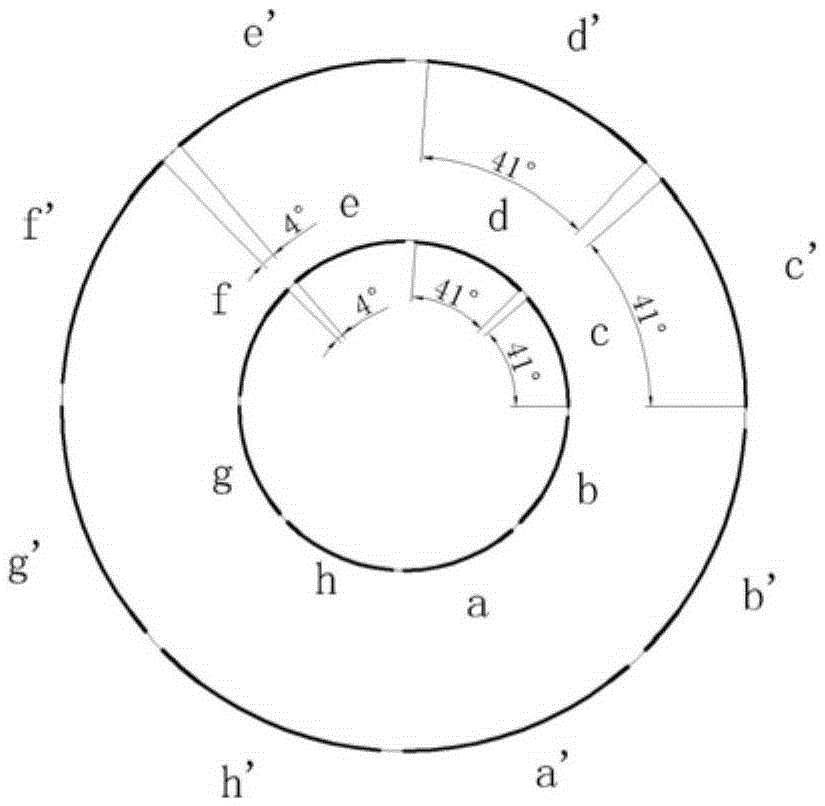
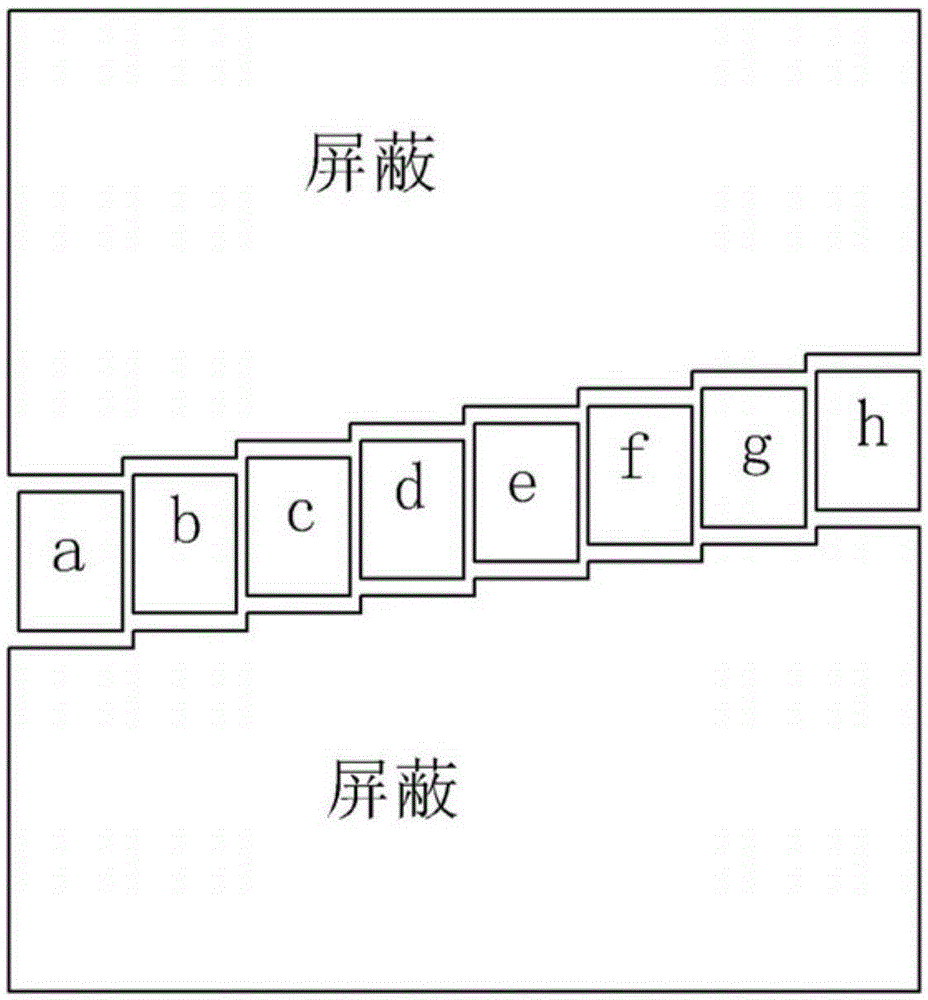
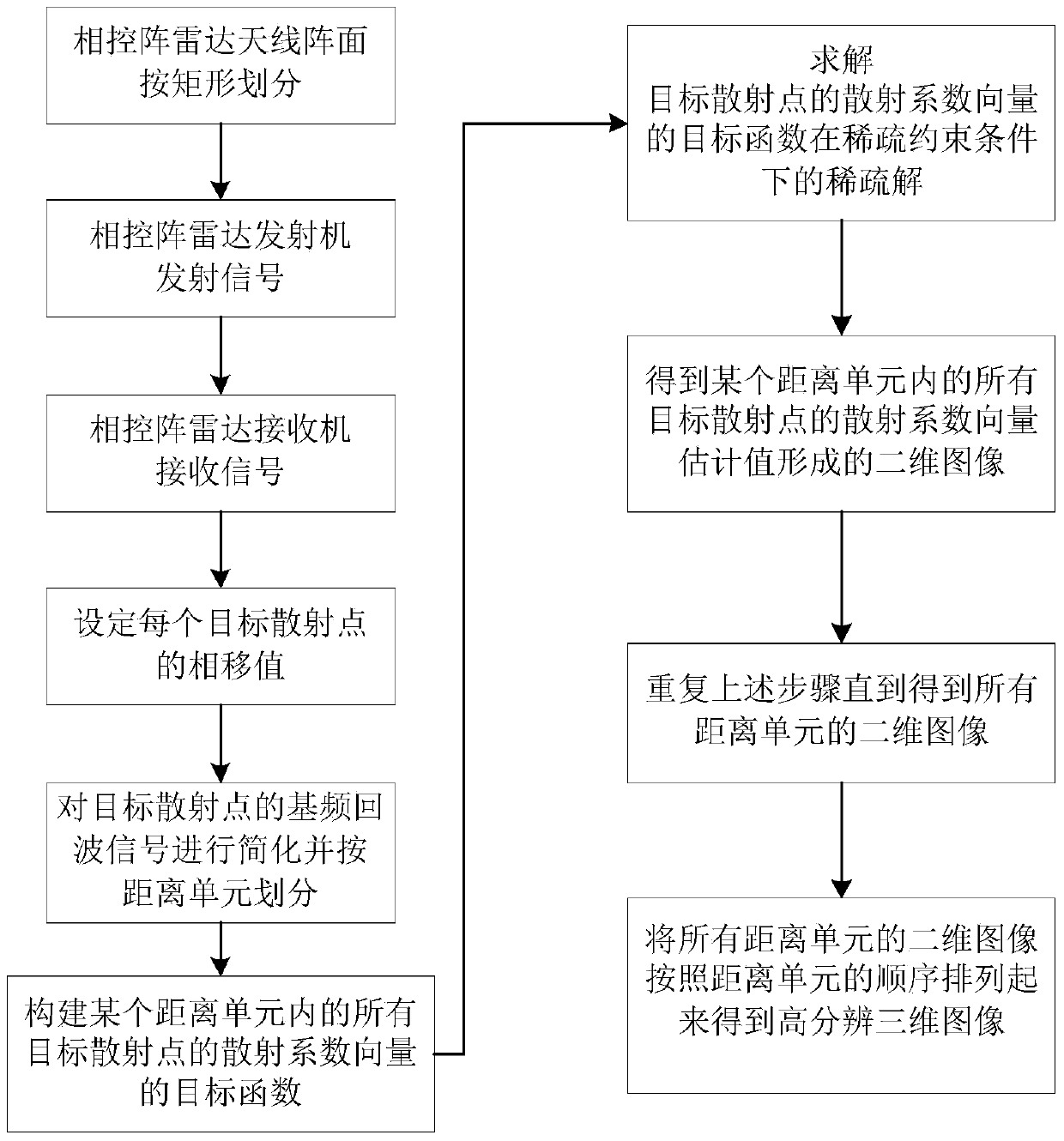
The invention discloses a three-dimensional correlated imaging method based on phased array radar and relates to the field of radar imaging. The three-dimensional correlated imaging method based on the phased array radar comprises the steps that firstly, the antenna array surface of the phased array radar is divided, a linear frequency modulation signal is sent by a phased array radar transmitter, echo signals of target scattering points are received, and the phase shifting values of the target scattering points are set; secondly, base frequency echo signals obtained after distance pulse pressing are divided according to the distance unit; thirdly, an objective function for the scattering coefficient vectors of the target scattering points is constructed, and the objective function is solved under the sparse constraint condition, so that the estimated value of the scattering coefficient vector of the target scattering point in the u distance unit is obtained; fourthly, a two-dimensional image is formed through the estimated value of the scattering coefficient vector of the target scattering point in the u distance unit, and then a three-dimensional image is obtained by ranking the two-dimensional images of all the distance units in the sequence the same as that of the distance units. By the adoption of the three-dimensional correlated imaging method based on the phased array radar, high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of a target is achieved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Double-frequency interference-based THz radar target three-dimensional imaging method
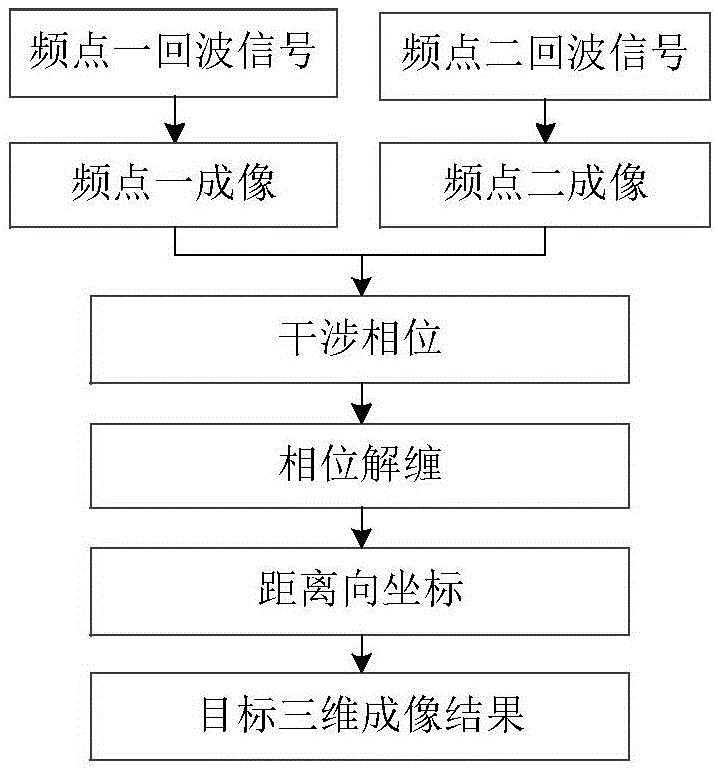
ActiveCN105676218AAvoid measurement errorsAvoid nonlinear effectsRadio wave reradiation/reflection3d imageRadar
The present invention provides a double-frequency interference-based THz radar target three-dimensional imaging method, wherein the coordinates of a target in three dimensions of distance, azimuth and pitch can be obtained. Meanwhile, the azimuth-pitch 2D image of the target, including the 2D coordinates of the target and the 2D scattering intensity distribution of the target, is obtained through the azimuth-pitch imaging process. The distance-dimension coordinates of the target are obtained through the interference treatment on two azimuth-pitch images of two adjacent frequency points. During the double-frequency interference-based azimuth-pitch imaging process, the small-angle two-dimensional rotation of a target is utilized to obtain the high resolution in the dimensions of both azimuth and pitch. Meanwhile, the double-frequency imaging mode avoids the usage of wideband signals during the 3D imaging process and the non-linear influence of signals. The above method is simple in imaging process and high in efficiency, which realizes the 3D imaging of a radar target.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
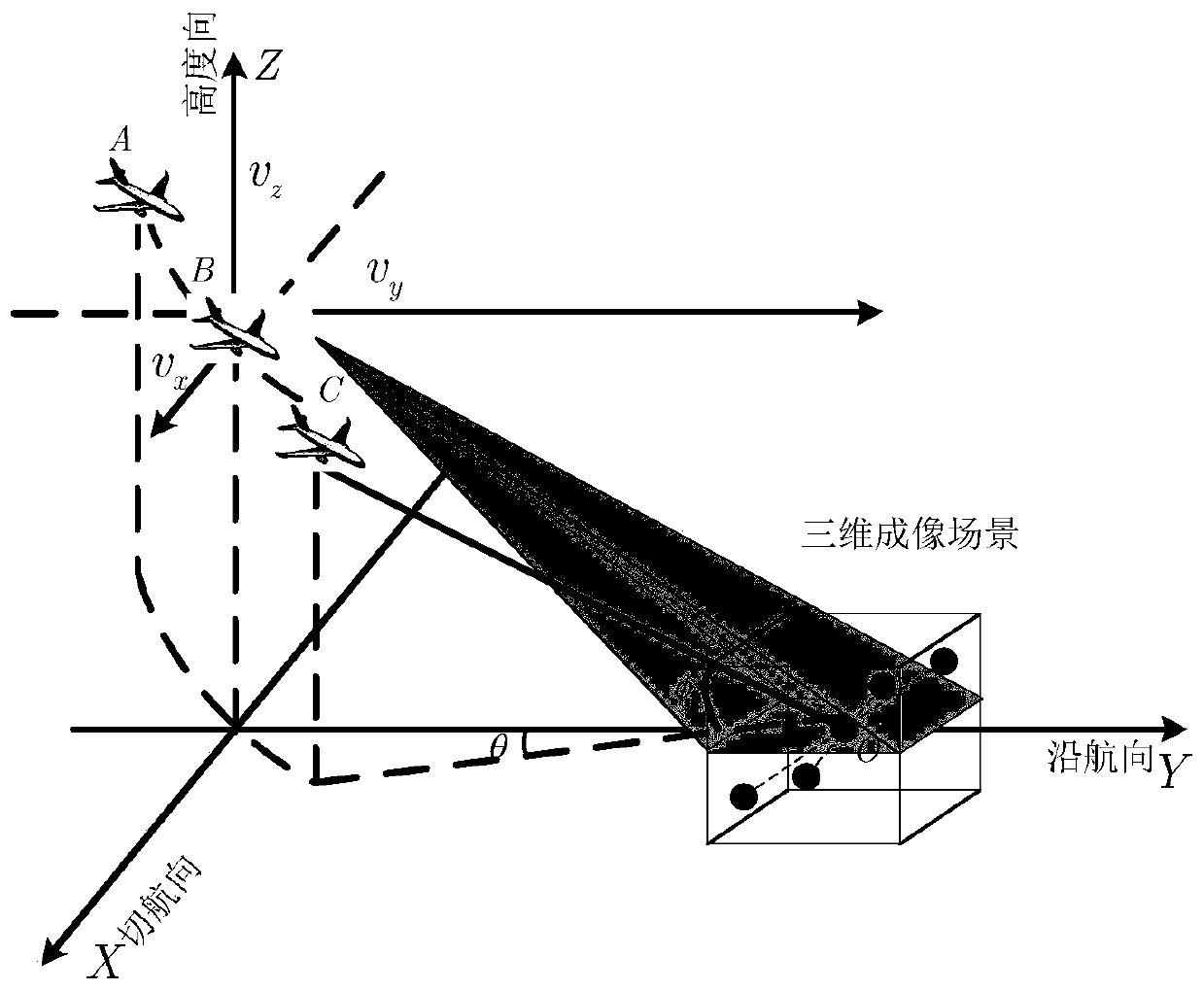
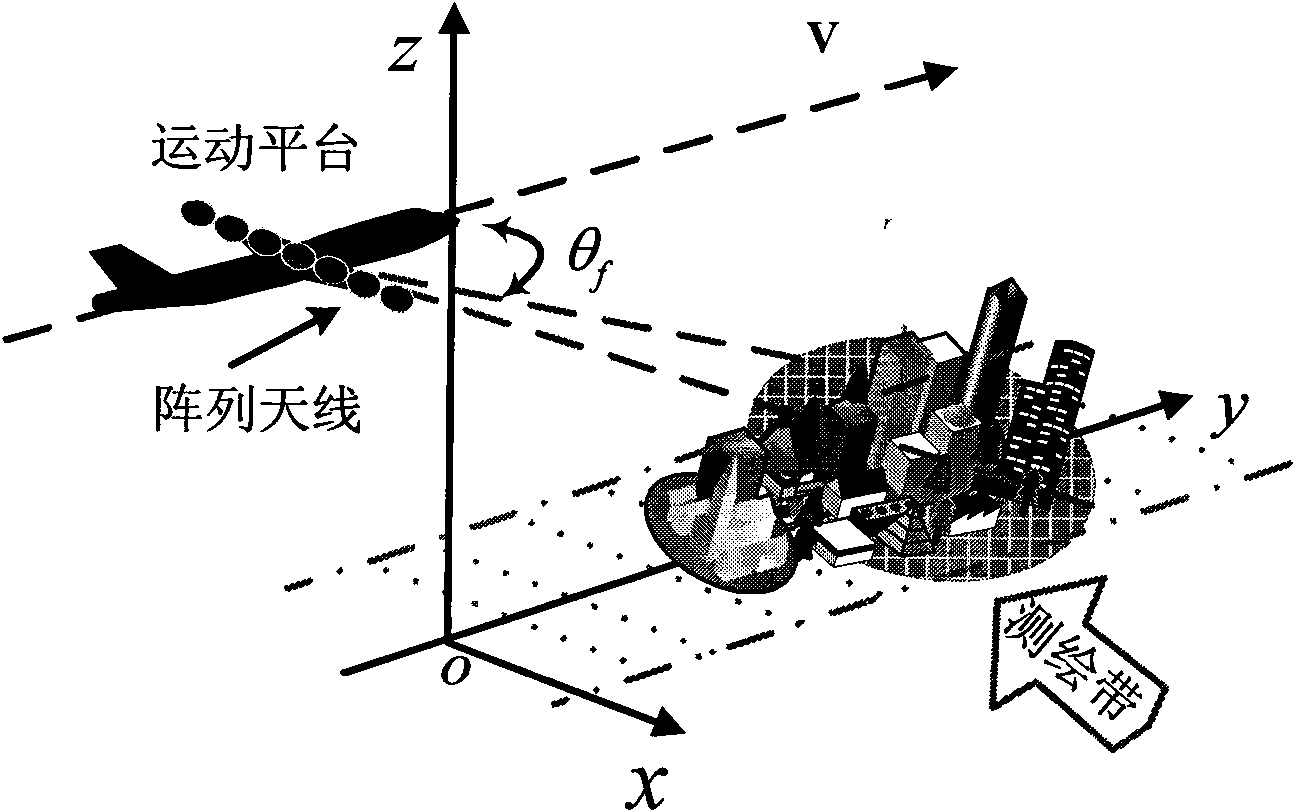
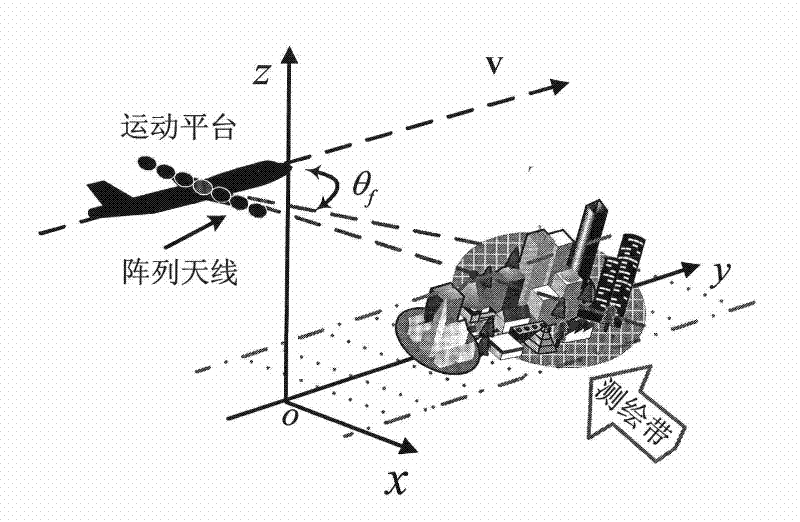
Radar foresight three-dimensional imaging method based on descending segment curve trajectory
ActiveCN109959932ASave energyRealize continuous observationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarMathematical model
The invention discloses a radar foresight three-dimensional imaging method based on a descending segment curve trajectory. The problem that a descending segment curve trajectory radar can only form atwo-dimensional image for a target is solved. The method comprises the steps that an echo signal mathematical model is established; a mathematical model of SAR configuration is vectorized to acquire athree-dimensional wavenumber spectrum of SAR configuration; the coordinate information of the target and a target scattering coefficient are acquired; and radar foresight three-dimensional imagingof the descending segment curve trajectory is realized. According to the invention, the influence of a one-dimensional weakly coupled wavenumber spectrum is ignored in the three-dimensional wavenumber spectrum; the two-dimensional coordinate information of the scene target corresponding to another two-dimensional wavenumber spectrum is extracted; an optimal processing algorithm based on l1 optimization is used to acquire the target scattering coefficient; the unique tangential flight characteristics of a missile are used to add spatial freedom to achieve a synthetic aperture in the tangentialdirection; three-dimensional imaging is carried out on the target to solve the problem that a traditional missile-borne SAR model has a certain angle with the target spacing to achieve azimuth high-resolution; and the method is suitable for a missile-borne high-resolution radar guidance technology.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
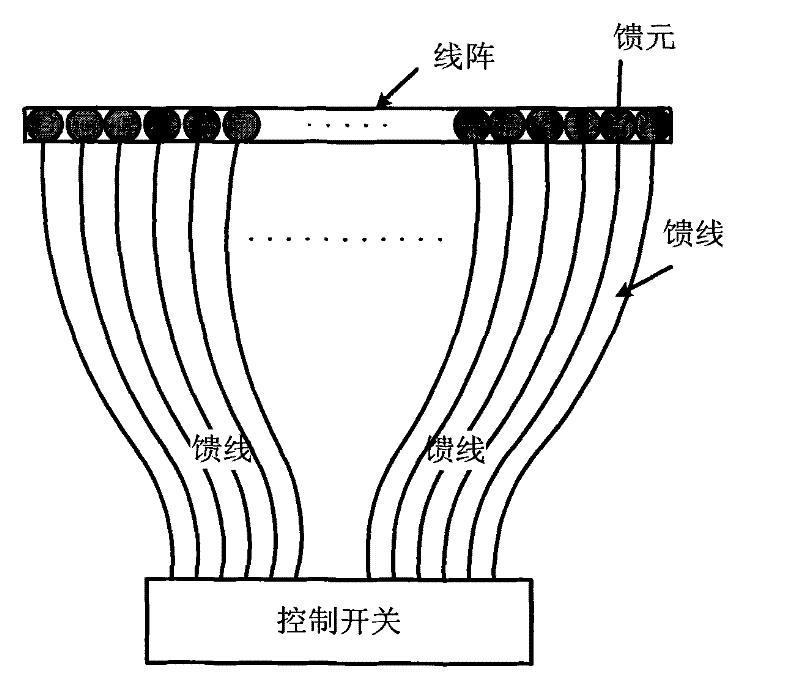
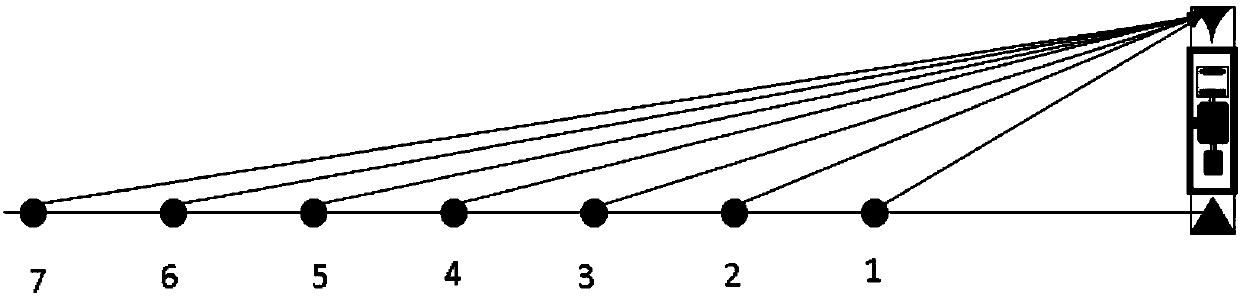
A construction method of forward looking linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar system
ActiveCN101551457AGet it in advance and in real timeRealize 3D ImagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a construction method of forward looking linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar system, which takes advantage that: the antenna phase centre control precision of the single stimulation linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar is high; the forward looking synthetic aperture radar system can acquire the ahead topographical information; the method causes the beam of the single stimulation linear array three-dimensional SAR to irradiate in a forward looking manner by using the mode of combining the single stimulation linear array three-dimensional SAR system and forward looking SAR system, then processes the received echo data by back-projection algorithm of the standard in real time to acquire the three-dimensional imaging result of ahead surveying area; the method can acquire the information of the three-dimensional topographical ahead the aircraft in advance and at real time; the invention provides a new method for the precise guide, and navigation, approaching and landing and blind landing of the aircraft.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
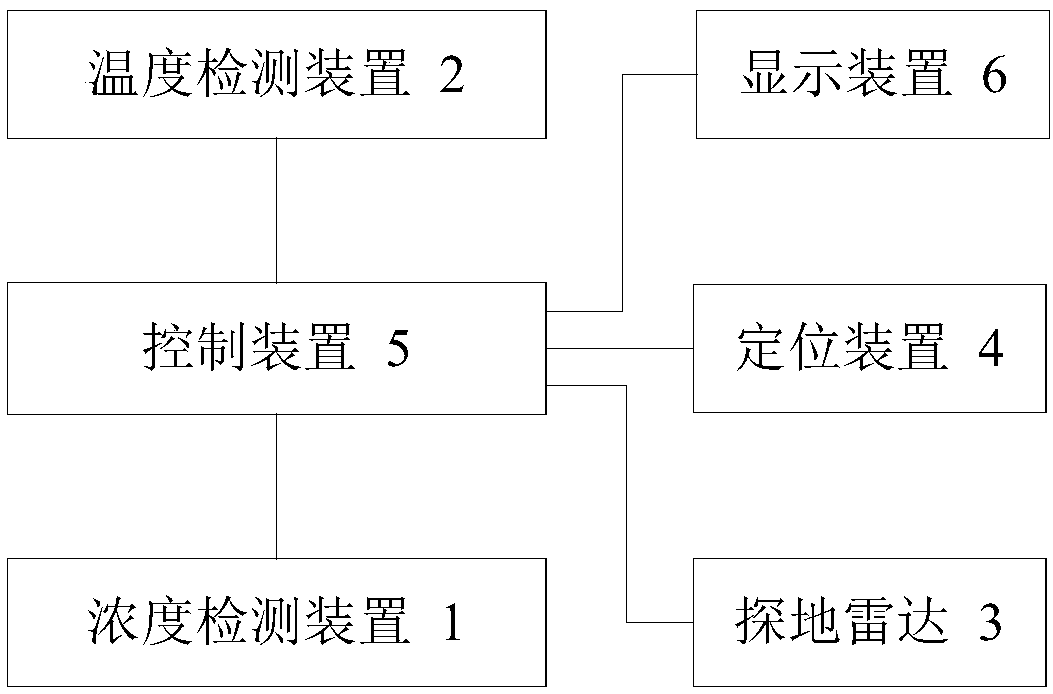
Pipeline inspection device and method
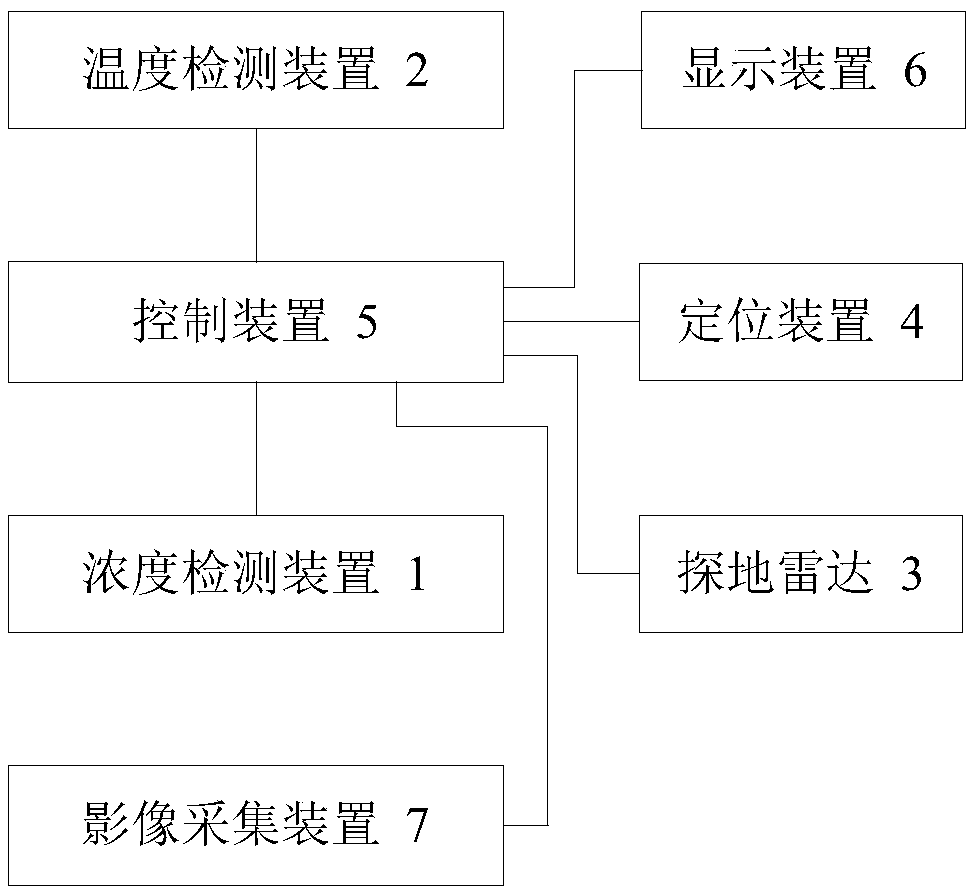
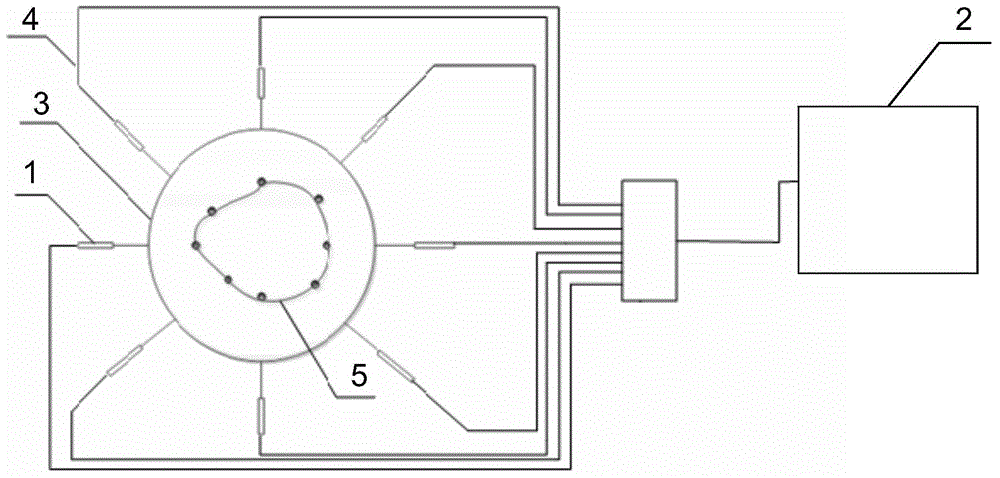
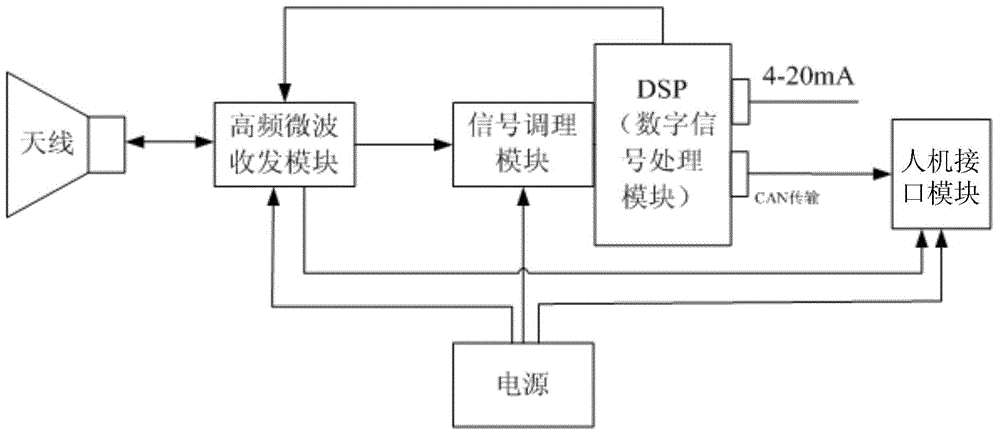
ActiveCN108286654AHigh positioning accuracyRealize 3D ImagingMeasurement devicesPipeline systemsCombustible gasDisplay device
The invention relates to a pipeline inspection device and method. The pipeline inspection device comprises a moving carrier, a concentration detecting device, a temperature detecting device, a groundpenetrating radar, a positioning device, a control device and a display device, wherein the concentration detecting device, the temperature detecting device, the ground penetrating radar, the positioning device, the control device and the display device are installed on the moving carrier. The concentration detecting device is used for detecting the concentration of combustible gas on an inspection route; the temperature detecting device is used for detecting the temperature on the inspection route; the control device is used for receiving echo signals of the ground penetrating radar, performing three-dimensional imaging of soil according to the echo signals, determining a leakage point of a gas pipeline according to the concentration and determining a leakage point of a heat pipeline according to the temperature, and marking the leakage points on a three-dimensional image; and the display device is used for displaying the three-dimensional image and the leakage points. According to the pipeline inspection device and method, the leakage points can be marked in the three-dimensional image, and the leakage points of various pipelines can be comprehensively displayed; and the processof data combination after the independent detection of the various pipelines is avoided effectively, so that the working efficiency is enhanced greatly.
Owner:BEIJING HUAHANG RADIO MEASUREMENT & RES INST
Blast furnace raceway imaging system and imaging method
InactiveCN104457606ARealize 3D ImagingEfficient measurementUsing optical meansPhysicsThree dimensional imaging
The invention discloses a blast furnace raceway imaging system and imaging method. The system comprises a microwave measuring instrument for depth measurement of a blast furnace raceway and a three-dimensional imaging computer of a zone dead stock. High-frequency microwaves are emitted to the detected blast furnace raceway, reflection echo waves are received, after the echo waves are converted into zero intermediate frequency signals through frequency-mixing filtering processing, the zero intermediate frequency signals are adjusted then, after signal processing, distance data measured by the microwave measuring instrument is converted into coordinate data through the three-dimensional imaging computer, and a three-dimensional image of the zone dead stock is fitted according to the coordinate data. By using the imaging system and the imaging method, the depth of the blast furnace raceway can be measured effectively, such that 3D imaging of the dead stock at the bottom of a furnace is realized.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
Non-coherent telescoping digital holographic imaging method and assorted device
InactiveCN104793475ARealize 3D ImagingSimple structureInstrumentsSpatial light modulatorMacroscopic scale
The invention provides a non-coherent telescoping digital holographic imaging method, and belongs to the technical field of non-coherent holographic three-dimensional imaging. Light which is transmitted or reflected through a target object can be outputted into parallel light beams via a convergence / collimation system, after the parallel light beams are processed by a polarizing film, an interference filter and a phase type spatial light modulator sequentially, an obtained hologram is received by an image sensor; the image sensor outputs signals to a central processing unit; and an image of the target object is reestablished by the central processing unit through a phase shift technology and a diffraction reappearance algorithm. The non-coherent telescoping digital holographic imaging method has characteristics of simple structure, small data volume, high imaging speed, low requirements on an environment of an imaging system and the like, and is suitable for industrial and commercial application of a holographic technique, and has high application value in the macroscopic fields of military affairs, remote sensing satellites, astronomy, engineering detection and the like.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Rapid frequency-domain backward projection three-dimensional imaging method based on GPU
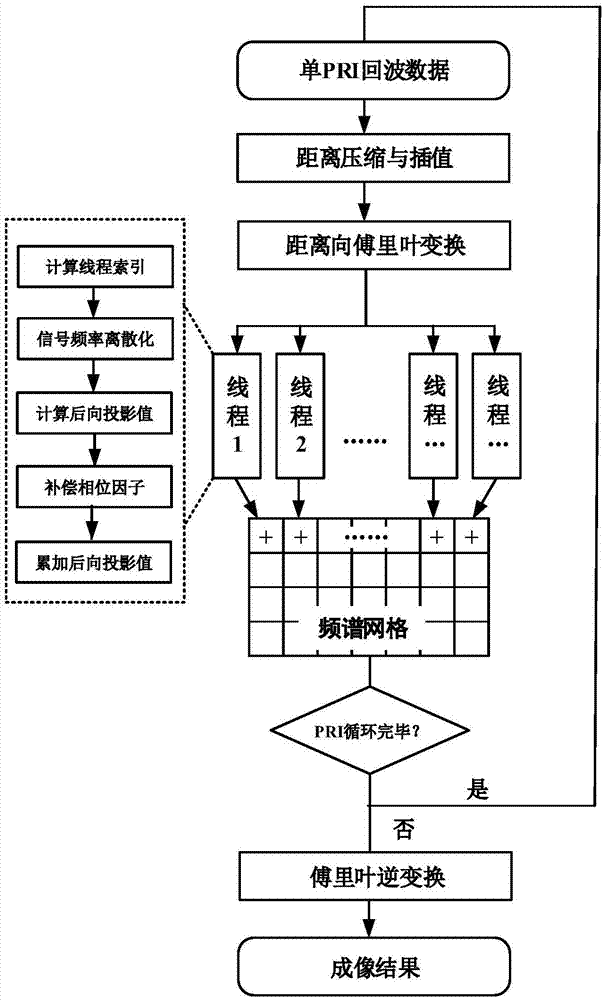
ActiveCN108008389AImprove operational efficiencyRealize 3D ImagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionGraphicsFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a rapid frequency-domain backward projection three-dimensional imaging method based on a GPU. The method is characterized by based on a parallel processing ability of the GPU,using a three-dimensional frequency-domain backward projection algorithm, using a graphic processing unit GPU and adopting a single-program multi-data instruction mode to schedule abundant hardware resources so that one thread in the graphic processing unit GPU is responsible for one frequency spectrum grid point; in each thread, calculating backward projection values of current frequency domain grid points in all array directions in parallel and accumulating; and finally, through three-dimensional inverse Fourier transform, acquiring a three-dimensional SAR image. Operation efficiency of a backward projection algorithm is greatly increased. Compared with the prior art, the method possesses high operation efficiency and a three-dimensional imaging characteristic of a linear array SAR is realized. The method is suitable for synthetic aperture radar imaging, earth remote sensing and other fields.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Endoscopic OCT-Raman dual-mode imaging device and imaging method
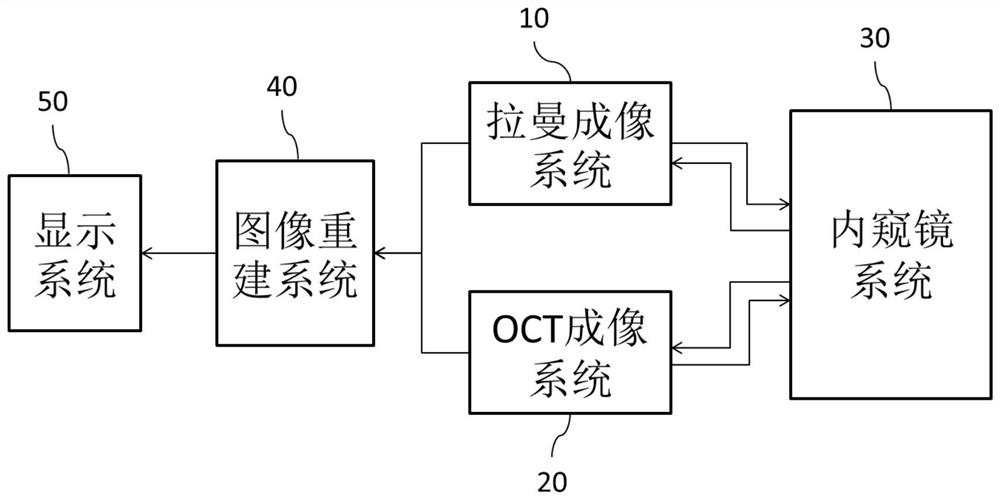
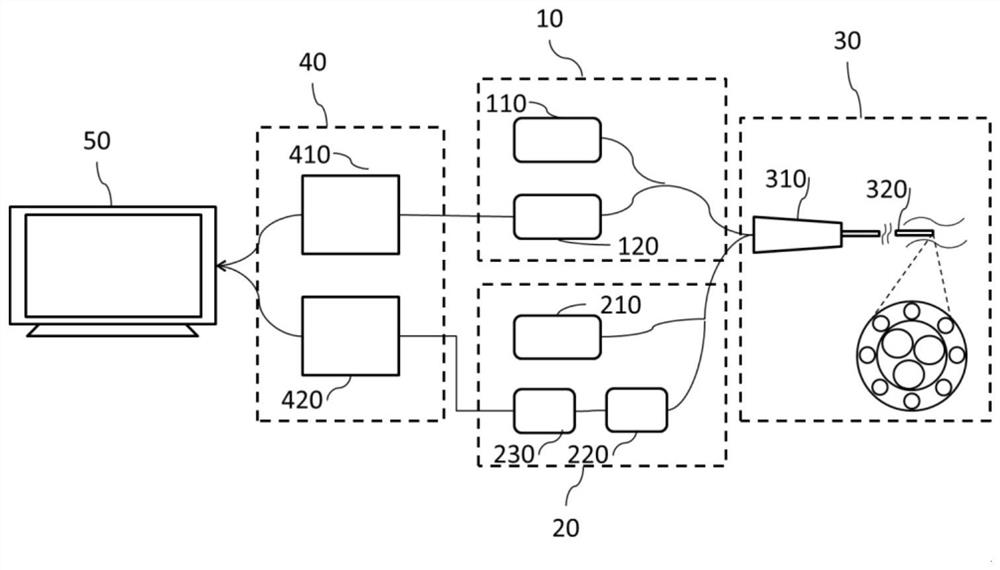
ActiveCN112089404AThe location of the lesion corresponds clearlyHigh degree of visualizationDiagnostics using spectroscopyEndoscopesRaman imagingOptical resolution
The invention discloses an endoscopic OCT-Raman dual-mode imaging device and an imaging method. The endoscopic OCT-Raman dual-mode imaging device comprises a Raman imaging system, an OCT imaging system, an endoscope system, an image reconstruction system and a display system, wherein the endoscope system is connected with the Raman imaging system and the OCT imaging system respectively, the Ramanimaging system and the OCT imaging system are both connected with the image reconstruction system, and the image reconstruction system is connected with the display system. According to the OCT-Ramandual-mode imaging device disclosed by the invention, a three-dimensional image with high optical resolution can be obtained, the spectral line form existence mode of a Raman spectrum is changed, the Raman spectrum is associated with OCT three-dimensional imaging, reconstruction of an OCT cavity tiled three-dimensional image and the corresponding Raman three-dimensional image is realized, lesion position correspondence is more obvious, the imaging visualization degree is improved, and accurate and rapid acquisition of OCT imaging data and Raman signals is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Multiband fluorescence loss method, multicolor super-resolution imaging method and device
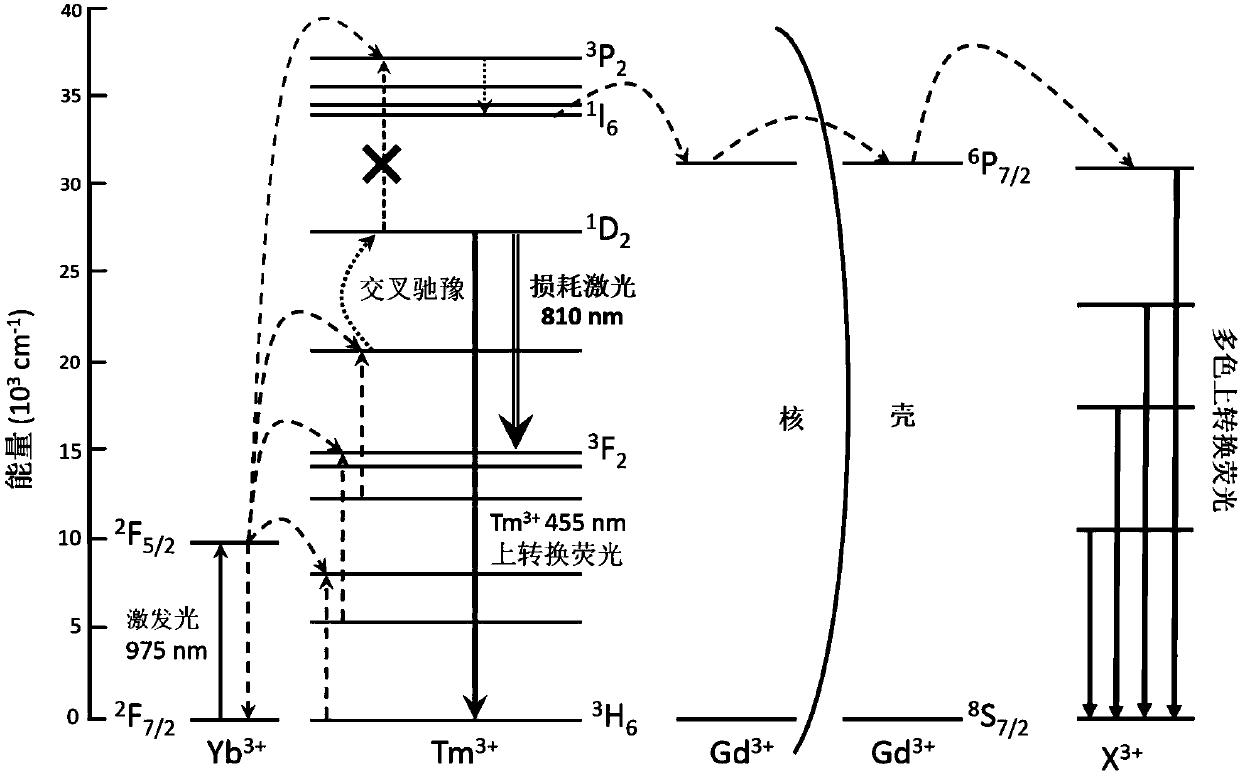
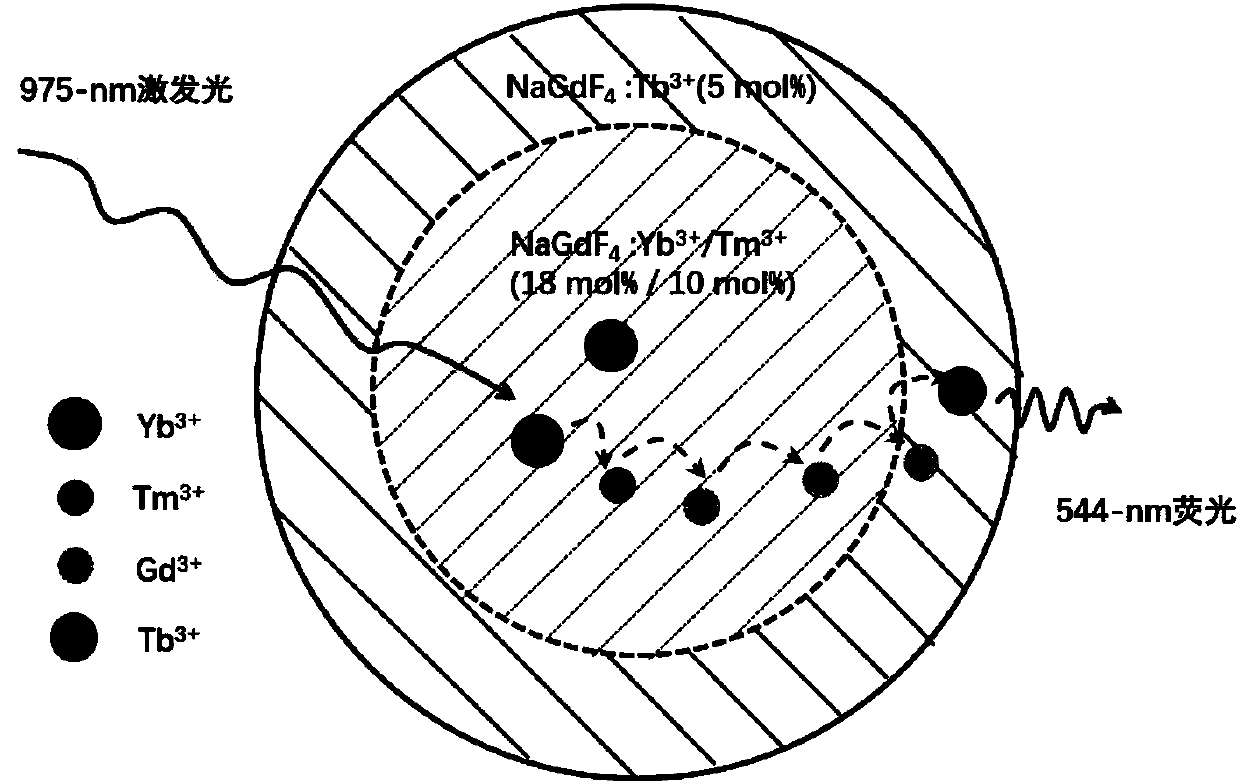
ActiveCN107831147ALow costHigh efficiency light control lossMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnergy migrationHigh energy
The invention discloses a multiband fluorescence loss method, a multicolor super-resolution imaging method and a device. Multiband fluorescence refers to up-conversion fluorescence emitted in the process of electrons reaching a Tm<3+> high energy level and then sequentially migrating energy to the Gd<3+> ions and shell activated ions X<3+> in the Yb<3+> / Tm<3+> sensitization and up-conversion process of an other activated ions-doped shell wrapping a NaGdF4:Yb<3+> / Tm<3+> core. The up-conversion fluorescence can be different by changing the activated ions by means of the same sensitization, up-conversion and energy migration process. The fluorescence loss process is the process of loss of electrons of the Tm<3+> high energy level and the loss of multiband fluorescence emitted during the transfer of the Tm<3+> high energy level from Gd<3+> to X<3+>, caused by the stimulated emission transition of intermediate energy level electrons to a low energy level in the up-conversion process by using the stimulated emission of laser with the wavelength nearby 810 nm between the Tm<3+> matching energy levels. Nano-particles of different activated ions are synthesized based on the fluorescence loss method, and multicolor super-resolution microscopy imaging is realized using the same pair of excitation light and hollow loss light. An optical system is greatly simplified, and the cost of the system is reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Panoramic three-dimensional display device based on single projection machine and transmission-type scattering screen
InactiveCN103616769ASimple structureRealize 3D ImagingProjectorsOptical elementsGratingVertical plane
The invention relates to a panoramic three-dimensional display device based on a single projection machine and a transmission-type scattering screen and belongs to the field of three-dimensional display. The panoramic three-dimensional display device comprises a transmission-type scattering screen and a projection device, wherein the projection device is projected to the transmission-type scattering screen; the projection device needs to be arranged on a vertical plane of the transmission-type scattering screen; the transmission-type scattering screen comprises a convex lens set and a cylindrical surface optical grating set; the convex lens set and the cylindrical surface optical grating set can be arrayed and combined randomly and a strip-shaped exit pupil is formed by an exit pupil of the high-speed projection device. According to the device, the rotation of the transmission-type scattering screen and the high-speed refreshing of a high-speed projection image are utilized so that images of left and right eyes of a person are from a zonal observation region formed by different image sources and the left and right eyes can see the different images, and furthermore, a three-dimensional image is synthesized by a human brain.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Three-dimensional imaging photon counting system using N-fold pulse coding and counting method
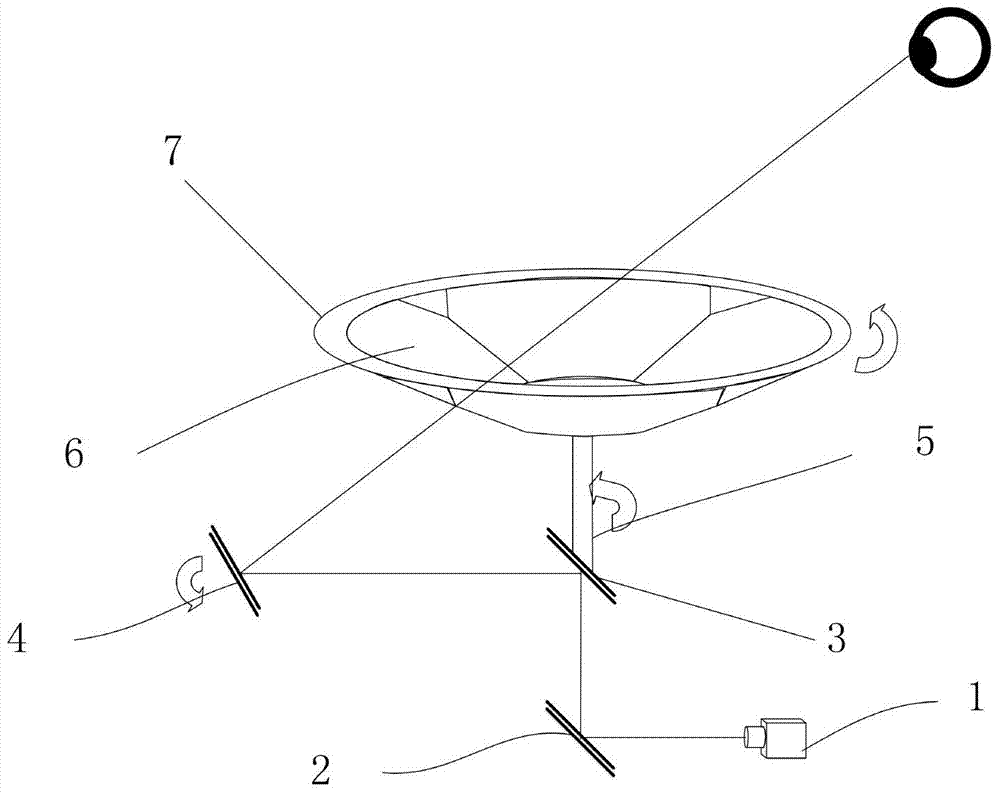
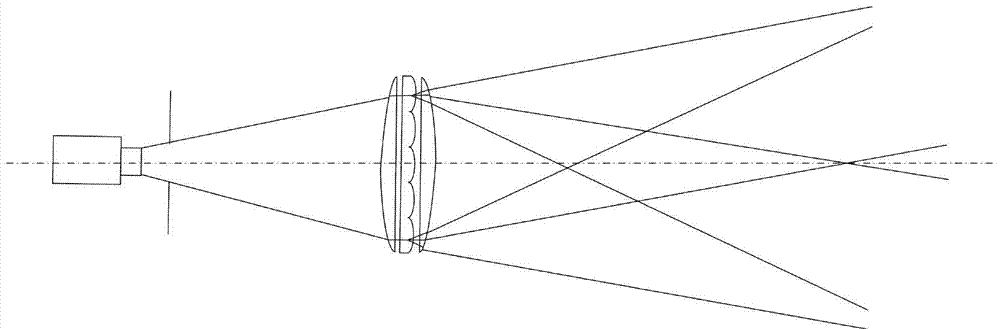
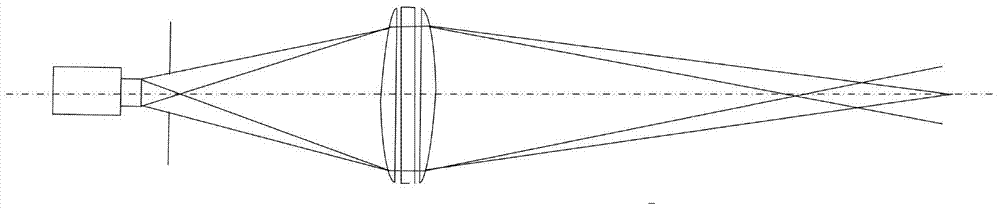
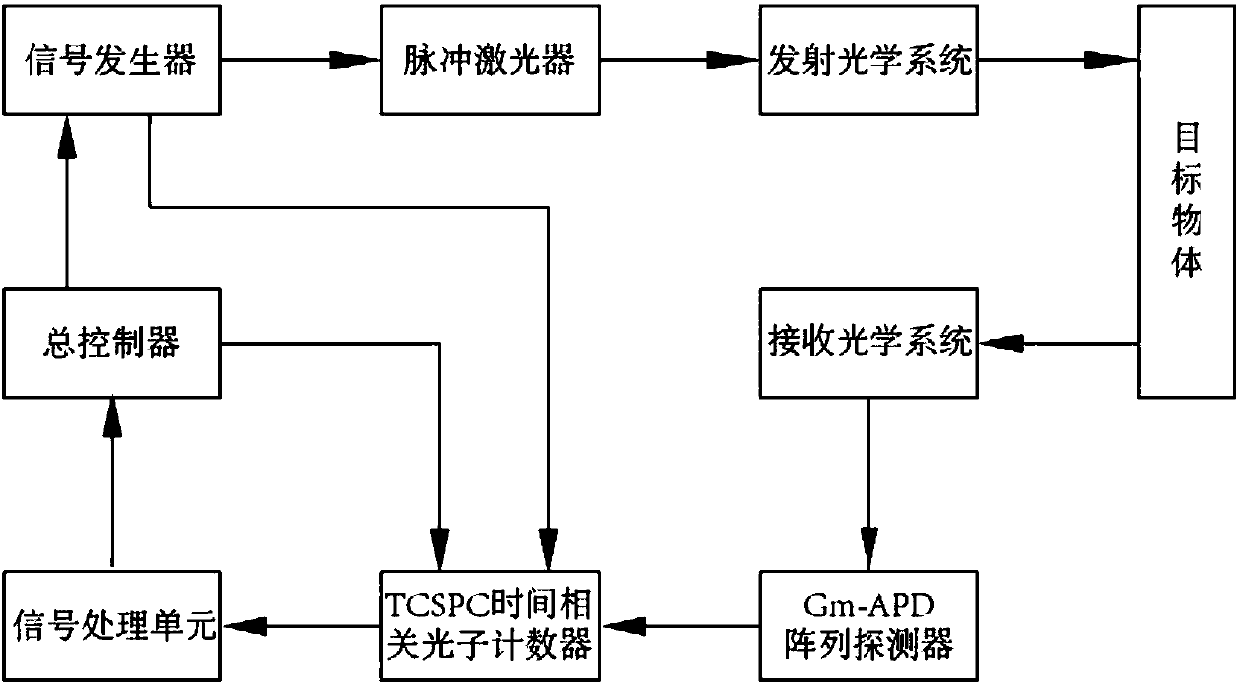
ActiveCN107807353AReduced Power RequirementsRealize 3D ImagingWave based measurement systemsTime correlationControl signal
The present invention relates to a three-dimensional imaging photon counting system using N-fold pulse coding and a counting method. The system includes a total controller, a signal generator, a pulselaser, a transmission optical system, a receiving optical system, a Gm-APD array detector, and a TCSPC (time-correlated single photon counter) and a signal processing unit. According to the method ofthe present invention, the total controller controls the signal generator to generate N-fold pulse signals; the N-fold pulse signals are converted into pulse optical signals through the pulsed laser;thee pulse optical signals hit a target object through the transmission optical system; the energy of echo pulse signals reflected by the target object is collected by the receiving optical system; the echo pulse signals irradiate the Gm-APD array detector; signals generated by the detector pass through the TCSPC (time-correlated single photon counter); counted signals are transmitted to the signal processing unit for time correlation and solution; and a counting result is transmitted to the total control module, and the total control module outputs a result. With the counting method of the invention adopted, the problems of strength information loss and incapability of resisting environmental interference in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
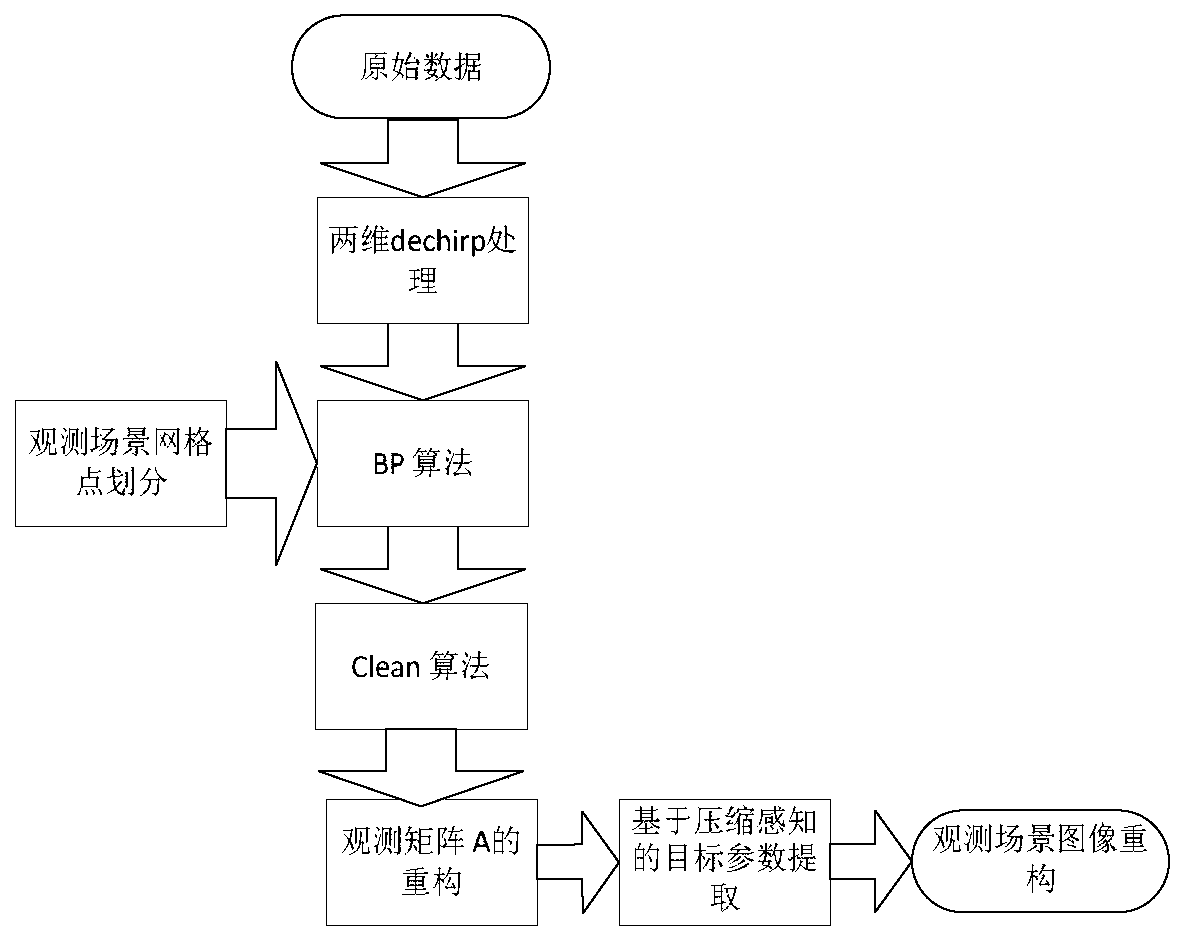
Sliding spotlight SAR three-dimensional imaging method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN104062659AHigh-resolutionRealize 3D ImagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarDevice form
The invention relates to the field of three-dimensional imaging, in particular to a sliding spotlight SAR three-dimensional imaging method based on compressed sensing. The sliding spotlight SAR three-dimensional imaging method based on compressed sensing aims to solve the problems that the imaging area is small and the imaging precision is low in the prior art. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a sliding spotlight SAR echo model is established for airborne radar devices according to original echo signals received by a scene irradiation area; secondly, SAR imaging is carried out on a two-dimensional sliding spotlight of each radar device in the model; thirdly, SAR images, obtained in the second step, of the radar devices form a three-dimensional matrix; fourthly, compressed sensing is carried out on slices of the three-dimensional matrix, and then the process of sliding spotlight SAR three-dimensional imaging based on compressed sensing is completed.
Owner:哈尔滨工大雷信科技有限公司
360-degree three-dimensional imaging projection device
InactiveCN104457616AImprove accuracyRealize 3D ImagingUsing optical meansInformation processingSpeckle pattern
The invention discloses a 360-degree three-dimensional imaging projection device. The 360-degree three-dimensional imaging projection device comprises a rotating platform for placing an object to be measured, a surface projector for projecting coordinate fixed points, a left camera, a right camera and an information processing control module; the left camera and the right camera are used for obtaining image information, and the information processing control module receives information of the surface projector, the left camera and the right camera to solve three-dimensional information of a unit view angle; the surface projector is arranged between the left camera and the right camera. Through speckle patterns and a mark point array with ruleless projection, the accuracy degree of binocular matching is improved, meanwhile, a rotating platform is additionally arranged, and 360-degree three-dimensional imaging is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU JIANGAO OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Scanner and coaxial and non-coaxial radar systems using same
ActiveCN111856481ALess intrusiveRealize 3D ImagingElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationOptical switchOptical amplifier
A scanner and coaxial and non-coaxial radar systems using the same belong to the technical field of laser radars, and the scanner comprises a wafer substrate, a plurality of optical switches and a plurality of grating antenna groups; the plurality of optical switches and the plurality of grating antenna groups are fixedly arranged on the upper end surface of the wafer substrate; the plurality of optical switches are in one-to-one correspondence with the plurality of grating antenna groups. Namely, one grating antenna group is electrically connected with one optical switch. The plurality of grating antenna groups are distributed in an array to form a grating part; a lens module is movably arranged on the upper side of the grating part; secondly, two-dimensional scanning is carried out through the scanner; three-dimensional imaging is realized and the detection precision is improved by combining the distance information calculated by the system in the third dimension, noise is removed through joint participation of the optical amplifier and the grating antennas, the interference of the outside to a detection result is reduced, the detection distance is improved, and in addition, thesystem is integrated on the chip, the size is small, installation is simple and easy, and the cost reduction and the mass production are convenient.
Owner:HANGZHOU XIGHT SEMICON CO LTD
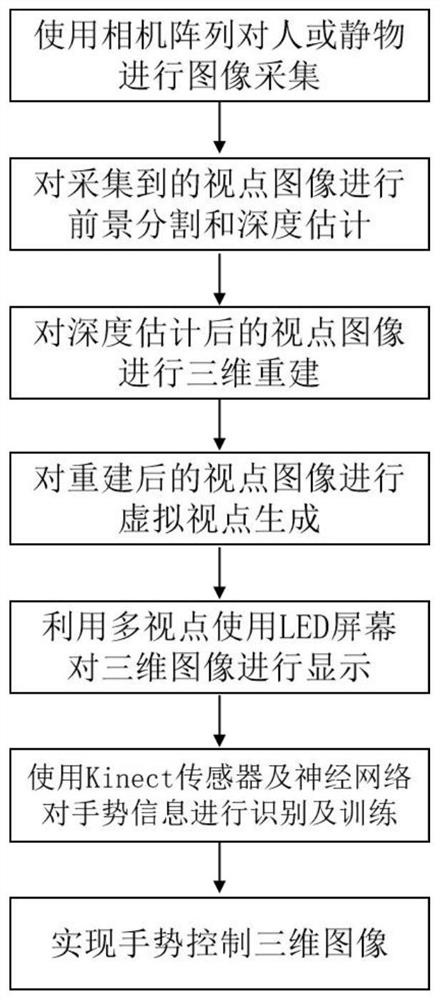
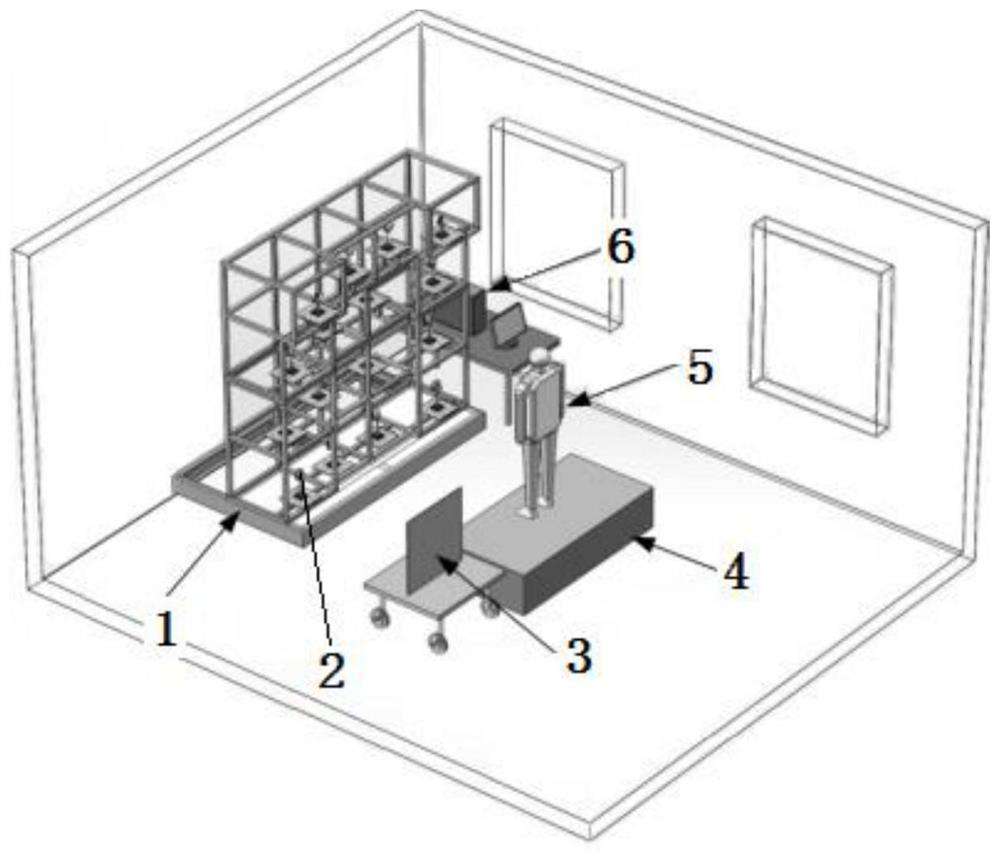
Method for realizing dynamic gesture recognition and control in integrated imaging display system
InactiveCN111897433ARealize 3D displayRealize 3D ImagingInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancement3d imageImage segmentation
The invention discloses a method for realizing dynamic gesture recognition and control in an integrated imaging display system and belongs to the technical field of image processing. According to theinvention, an image acquisition system of a light field camera, an image acquisition server side, a display system of a three-dimensional image, a server side of the display system and a dynamic gesture recognition system are utilized. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a light field image, then carrying out image segmentation and virtual trial point generation on a shot viewpoint, displaying a three-dimensional image after three-dimensional reconstruction, and finally identifying and training a gesture of a control image. According to the invention, the problems of visual fatigue caused by wearing 3D glasses and the like for watching a three-dimensional scene, image movement control with the help of equipment and the like can be solved, and the effects of realizing dynamic gesture recognition and controlling a three-dimensional image in an integrated imaging display system are achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
C-arm breast machine with 3 degrees of freedom of movement
ActiveCN102283661AAccurate diagnosisPrecise positioningRadiation diagnosticsThree degrees of freedomLight beam
The invention discloses a mammary machine with a three-degree-of-freedom-of-motion C-shaped arm. The mammary machine comprises a frame, a C-shaped arm, a bulb tube and a detector, wherein one end of the C-shaped arm is connected with the bulb tube, and the other end of the C-shaped arm is connected with the detector; and the C-shaped arm is connected to the frame through a rotating shaft. By the mammary machine, the technical problems of difficulty in imaging by using the most uniform part of an X light beam of the bulb tube to the maximum extent in a low dose and difficulty in front-and-back inclined three-dimensional motion of the C-shaped arm can be solved. The mammary machine can be used as a medical instrument.
Owner:杭州美诺瓦医疗科技股份有限公司
Improved coal cutter
InactiveCN106089196ALower working temperatureExtended service lifeFluid-pressure actuator testingSlitting machinesHydraulic cylinderControl signal
The invention discloses an improved coal cutter. The improved coal cutter comprises rollers and a machine body. The rollers are located at the front end and the rear end of the machine body and connected to the machine body through supporting arms. The machine body is provided with hydraulic cylinders to control the lifting heights of the supporting arms. Force sensors are arranged in oil ways of the hydraulic cylinders and located in the machine body. Baffles are arranged between the rollers and the supporting arms. Blowholes are formed in the baffles. The baffles can swing in a certain angle range, and power is provided by gears located at the tail ends of stepping motors on the supporting arms. Driving motors at the tail ends of the supporting arms drive gearboxes to provide power for the rollers. A control cabinet and an air pump are arranged in the middle of the machine body. The control cabinet controls the operation process of the whole coal cutter and outputs control signals to motor achieving advancing and retracting. The coal cutter is reasonable in improvement.
Owner:南京同歌网络科技有限公司
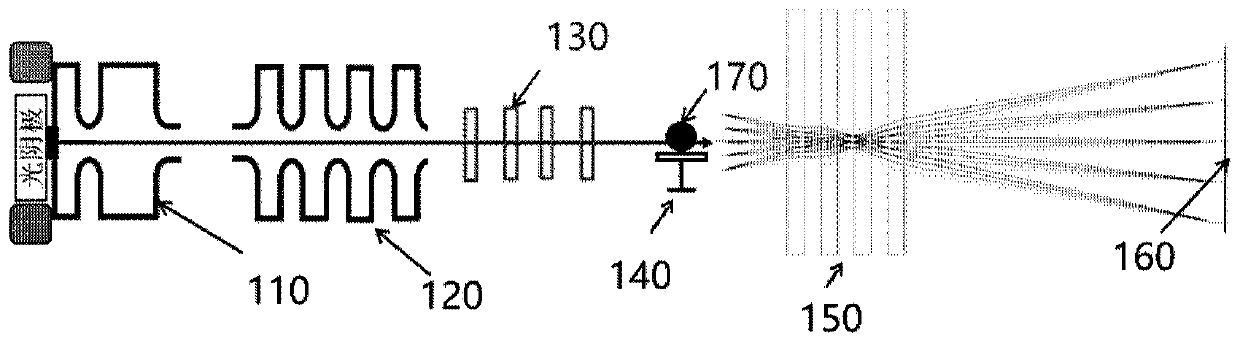
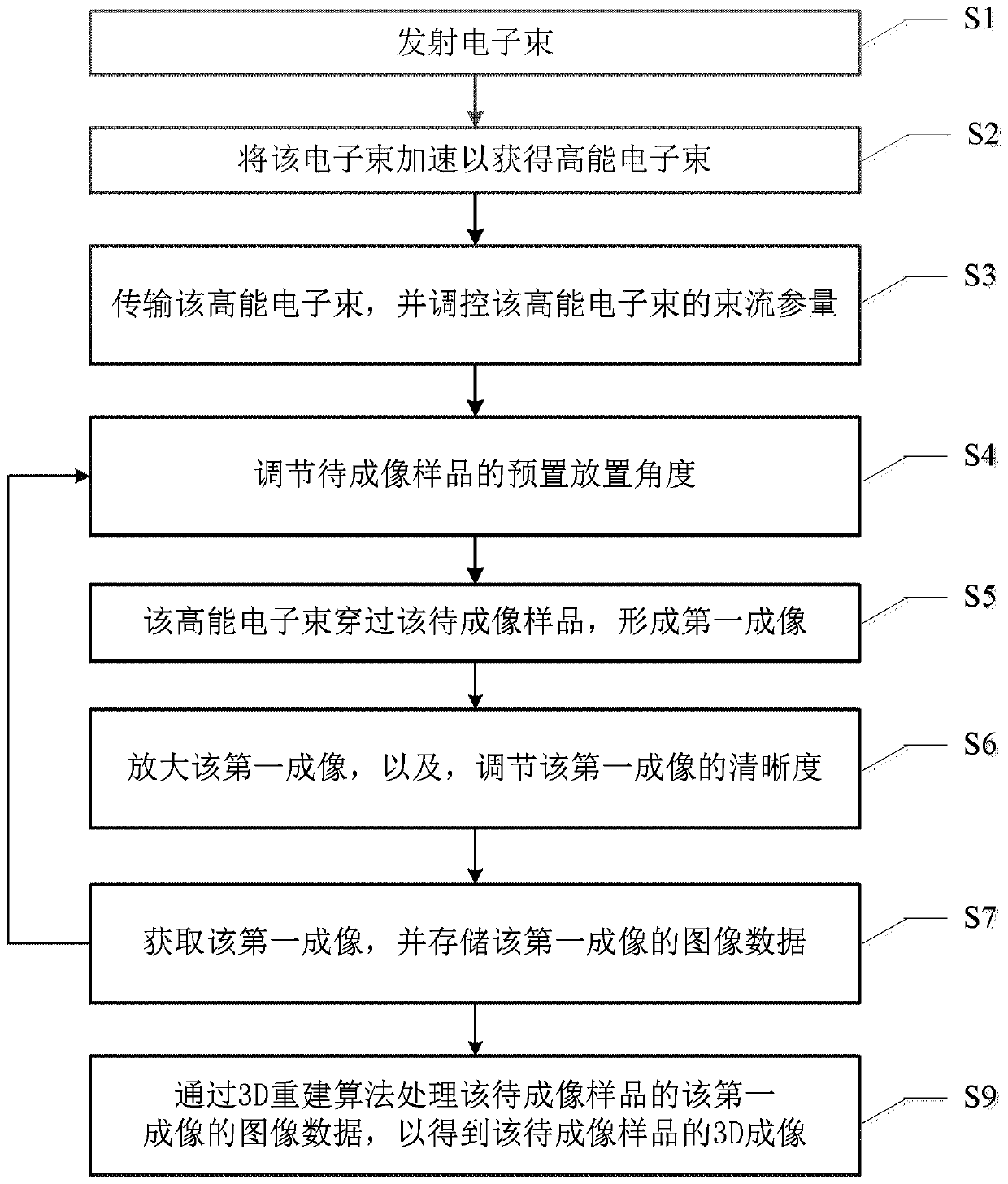
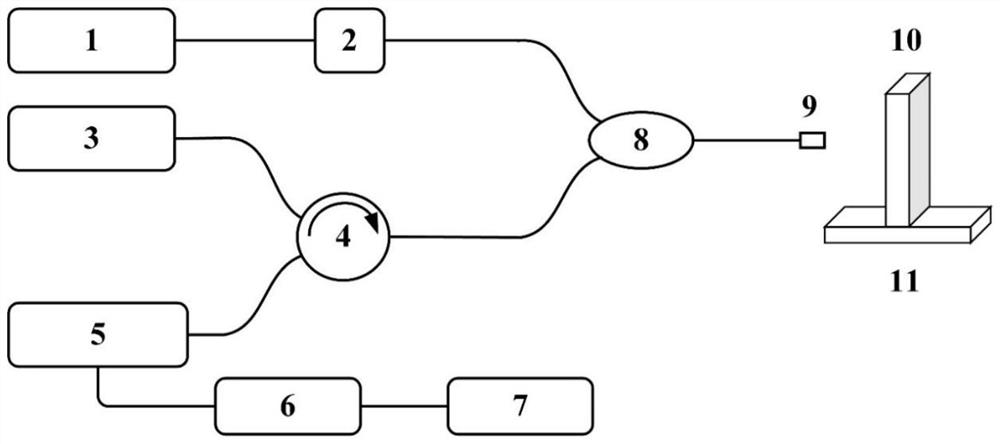
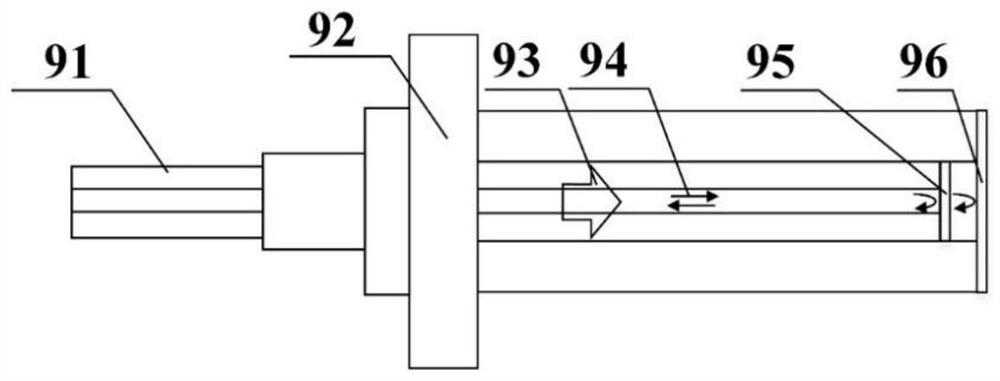
High-energy electron 3D imaging device and method
ActiveCN109872937AImproving High Energy Electron Imaging CapabilitiesRealize 3D ImagingElectric discharge tubesSteroscopic systemsHigh energyImage system
The invention discloses a high-energy electron 3D imaging device and method, applied to the technical field of high-energy electron imaging. The high-energy electron 3D imaging device comprises an electron gun used for transmitting an electron beam; an accelerator used for accelerating the electron beam to acquire a high-energy electron beam; a beam transportation component used for transmitting the high-energy electron beam and controlling the beam quality of the high-energy electron beam; a rotary support used for holding a sample to be imaged and regulating a preset placement angle of the sample to be imaged; a detector system used for receiving the high-energy electron beam, acquiring a first image formed by receiving the high-energy electron beam, and storing the image data of the first image; a point-to-point magnetic lens imaging system used for amplifying the first image and regulating the definition of the first image; and a 3D rebuilding system used for processing the image data of the first image via a 3D rebuilding algorithm to acquire a 3D image of the sample to be imaged. According to the high-energy electron 3D imaging device and method provided by the invention, the3D imaging can be achieved, and the problem that at the present stage, the imaging technology only can achieve two-dimensional imaging can be effectively solved.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Photoacoustic lithium battery detection system based on optical fiber
PendingCN114486748ASmall sizeReduce volumeMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringOptical fiber coupler
The invention discloses a photoacoustic lithium battery detection system based on optical fibers, and belongs to the field of battery structure health monitoring. Comprising an excitation module, a signal demodulation module, a detection module and an optical fiber coupler. Excitation light enters the surface of the battery through the beam shaping unit, the optical fiber coupler and the optical fiber ultrasonic probe to generate an ultrasonic signal. The detection light is reflected to form a detection signal after passing through the optical fiber circulator, the optical fiber coupler and the optical fiber ultrasonic probe. The lithium battery is moved through the displacement control platform, ultrasonic signals of different parts of the lithium battery can be obtained, accordingly, corresponding detection signals are generated, structural information of the different parts of the lithium battery is obtained through analysis, and imaging of the battery structure is achieved. According to the method, an optical and ultrasonic combined method is adopted, internal structure data of the lithium battery can be measured in practical application, and analysis and prediction of internal damage of the battery are achieved. The device has the advantages of being small in size and high in resolution ratio, can conduct nondestructive testing on the lithium battery and has the high-precision imaging capacity.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Non-destructive 3D imaging and component identification method for cultural relics based on two-photon excited fluorescence
InactiveCN105548099BRealize analysisRealize 3D ImagingFluorescence/phosphorescenceFemto second laser3d image
The invention discloses a method for non-destructive three-dimensional imaging and component identification of cultural relics based on two-photon excited fluorescence: Step 1: Reflect a beam of femtosecond laser through a laser scanner, and further focus it on the target position of the cultural relic to be measured by a variable focus microscope objective. ; Step 2, detect the reflected two-photon excited fluorescence; Step 3, scan the target point by point with the laser scanner to obtain a two-dimensional image of the two-photon excited fluorescence; Step 4, change the focal length of the microscope objective lens to obtain double-photon excited fluorescence at different depths. Photon-excited fluorescence two-dimensional image; Step 5, reconstruct a series of two-photon excited fluorescence two-dimensional images obtained at different depths to obtain a three-dimensional image; Step 6, the components of the cultural relics can be identified according to the wavelength range of the fluorescence. The characteristic fluorescence images of components can determine the distribution of different components in mineral materials. The invention can realize cultural relic composition analysis and three-dimensional imaging at the same time; it can realize intrusive, non-contact and non-destructive detection.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Super-resolution linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging method
InactiveCN102323583BImprove imaging effectOvercome the problem of limited lengthRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging qualityImage resolution
The invention discloses a super-resolution linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on an MUSIC (MUltiple SIgnal Classification) algorithm, which comprises the steps of: firstly, compressing distance data by adopting pulse; secondly, focusing scene information by adopting the MUSIC algorithm for each distance section, obtaining reverse scattering information ofa scene point by adopting an LS (Least Square) algorithm; and finally, integrating processed distance sections and displaying to obtain a three-dimensional reconstruction graph. Compared with the traditional imaging methods, such as a BP algorithm and an MF algorithm, the super-resolution linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging method has the advantages of overcoming the problem of Rayleigh limit and limited antenna length, realizing sidelobe weakening by using an MUSIC method while the length of an antenna is not increased, reducing the influence of sidelobe crosstalkto imaging quality, increasing resolution, realizing three-dimensional imaging and improving imaging quality.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Neutron ghost imager
ActiveCN109342462ASimple structureReduce volumeMaterial analysis using neutronsSensor arrayIrradiation
The invention discloses a neutron ghost imager. The ghost imager comprises a neutron source, a magnet structure, least one neutron sensor, and imaging devices. The neutron source is used for generating a neutron beam. The magnet structure is arranged towards the emission direction of the neutron beam, and is used for spatially modulating the neutron beam and irradiating the modulated neutron beamto the surface of a to-be-imaged object. The neutron sensor is arranged in parallel with the to-be-imaged object, and is used for receiving a neutron beam passing through the to-be-imaged object. Theimaging devices are respectively connected with the magnet structure and the neutron sensor, and are used for reconstructing the to-be-imaged object according to the received neutron beam and a magnetic polarization direction distribution function at irradiation of the received neutron beam in the magnet structure, or reconstructing the to-be-imaged object according to the received neutron beam and the magnetic polarization direction distribution function of the neutron beam after spatial modulation. According to the neutron ghost imager, the purpose of the invention can be achieved with onlyone or more neutron sensors and without focusing imaging on the neutron beam and a neutron sensor array; and the structure is simple, the size is small, and the cost is low.
Owner:GUIZHOU MINZU UNIV
A construction method of forward looking linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar system
ActiveCN101551457BGet it in advance and in real timeRealize 3D ImagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarFlight vehicle
The invention discloses a construction method of forward looking linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar system, which takes advantage that: the antenna phase centre control precision of the single stimulation linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar is high; the forward looking synthetic aperture radar system can acquire the ahead topographical information; the method causes the beam of the single stimulation linear array three-dimensional SAR to irradiate in a forward looking manner by using the mode of combining the single stimulation linear array three-dimensional SAR system and forward looking SAR system, then processes the received echo data by back-projection algorithm of the standard in real time to acquire the three-dimensional imaging result of ahead surveying area; the method can acquire the information of the three-dimensional topographical ahead the aircraft in advance and at real time; the invention provides a new method for the precise guide, and navigation, approaching and landing and blind landing of the aircraft.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Solid-state annular three-dimensional imaging device
PendingCN110345863ARealize 3D ImagingSimple structureOptical rangefindersUsing optical meansCamera moduleOptoelectronics
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of photoelectricity, in particular relates to a solid-state annular three-dimensional imaging device comprising a frame supporting module, a light emitting module and an electronic circuit module. The light emitting module and the electronic circuit module are arranged in the frame supporting module. The electronic circuit module is configured tocontrol the light emitting module to emit light. A light cone reflection module that is used for converting light into annular structural light and reflecting the light to a surrounding target area is arranged at one end of the frame supporting module; and an array light receiving module and an inverted cone reflection module that are arranged at the inner side and the outer side of the frame supporting module are arranged at the other end of the frame supporting module, or a camera module is arranged at the other end of the frame supporting module. The inverted cone reflection module is usedfor reflecting reflected light of an object in the target area to the array light receiving module; and the array light receiving module is used for receiving reflected light reflected by the inverted cone reflection module and converting the light into a photoelectric signal for outputting. Compared with the conventional single-point scanning structure, the solid-state annular three-dimensionalimaging device has characteristics of simple structure, small size, and long service life.
Owner:深圳慎始科技有限公司
Optical coherence tomography method and device based on radially polarized beams
ActiveCN103431845BRealize 3D ImagingEnable horizontal scanningDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBeam splitterPlane mirror
The invention provides an optical coherence tomography method and device based on radial-direction polarized beams. The method comprises the following steps that after light beams emitted by a low-coherence light source are processed through a Kohler illumination system, the polarization state of the light beams is adjusted and controlled through a polarization transformation system, the amplitude and phase distribution of the light beams are adjusted and controlled through a pupil filter, and accordingly the radial-direction light beams are formed; the radial-direction polarized beams enter a beam splitter prism in an incident mode, are divided into two paths, and enter a sample arm and a reference arm respectively; the two-path light beams are focused on a sample to be measured and a reference plane mirror through microscope objectives of the two-path light beams respectively; returned light after being reflected by the sample to be measured and the reference plane mirror joins in the position of the beam splitter prism, is focused through a focusing lens, is imaged in a probe and is then transmitted to a computer to be post-processed; the reference plane mirror transversely moves to achieve transverse scanning; the sample to be measured is placed on a three-dimensional horizontal-moving table capable of moving in space to achieve three-dimensional imaging of the sample.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com