Non-destructive 3D imaging and component identification method for cultural relics based on two-photon excited fluorescence
A technology of two-photon excitation and identification method is applied in the field of three-dimensional imaging and component identification of cultural relics by two-photon excitation fluorescence, which can solve the problems of inability to identify substances, inability to obtain information on mineral composition and other components, and achieve the effect of deep imaging.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
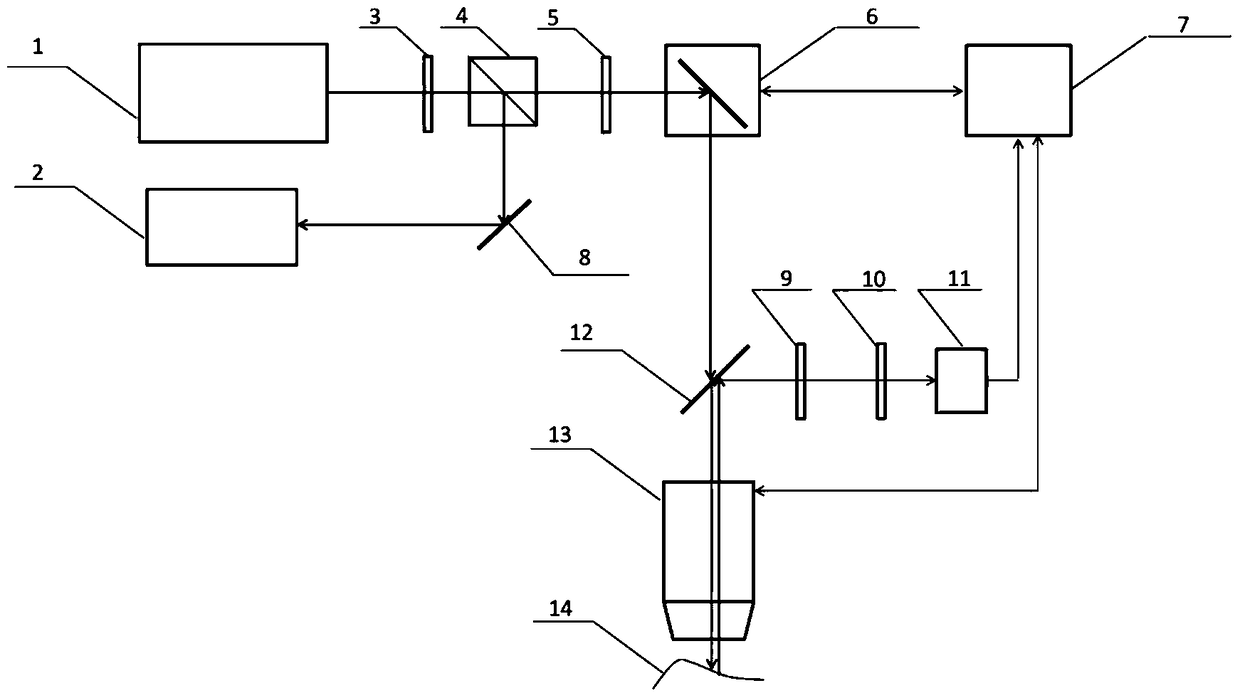
[0026] Comply with the above technical solutions, such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a method for non-destructive three-dimensional imaging and component identification of cultural relics based on two-photon excited fluorescence. The method includes the following steps:
[0027] Step 1: Reflect a beam of femtosecond laser through the laser scanner, and focus it on the target position of the cultural relic to be measured by the variable-focus microscope objective lens;
[0028] More specifically, the femtosecond laser is emitted by a femtosecond laser, and a half-wave plate, a polarization beam splitter cube, and a quarter-wave plate are sequentially arranged between the femtosecond laser and the laser scanner;
[0029] In step 1, the femtosecond laser output by the femtosecond laser passes through a half-wave plate, and the half-wave plate is rotated to change the polarization direction of the femtosecond laser, so that the femtosecond laser passes throu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com