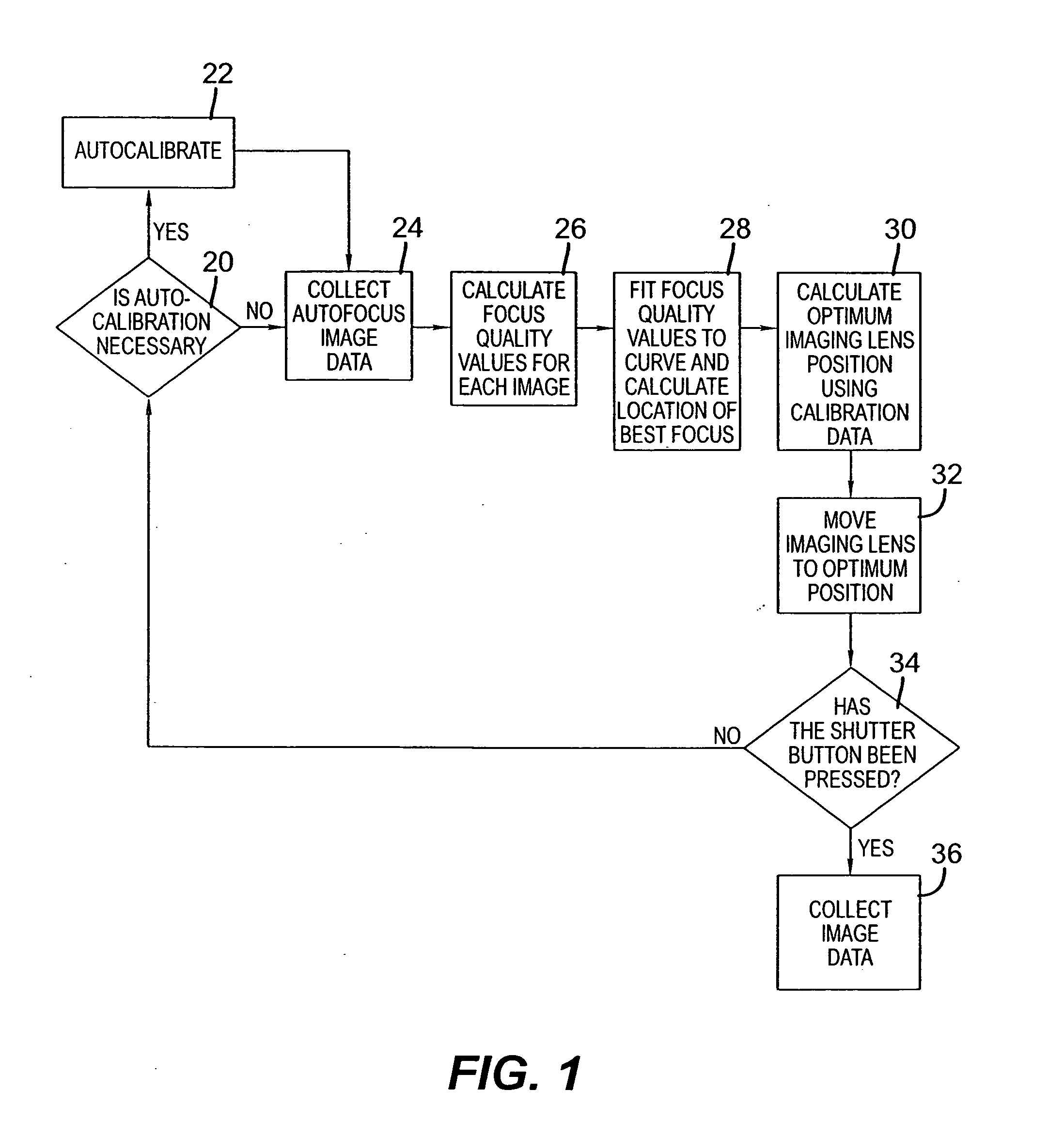
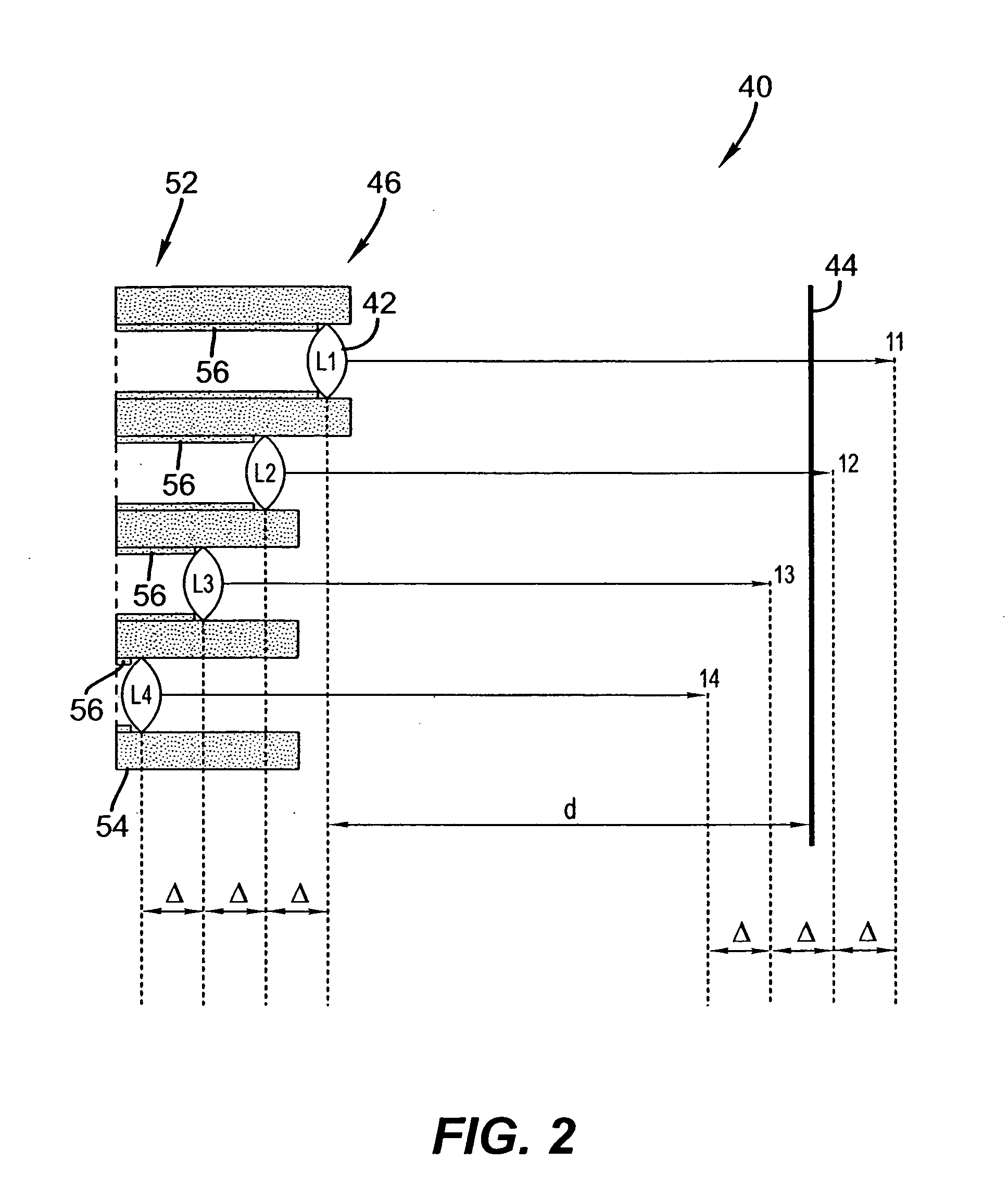
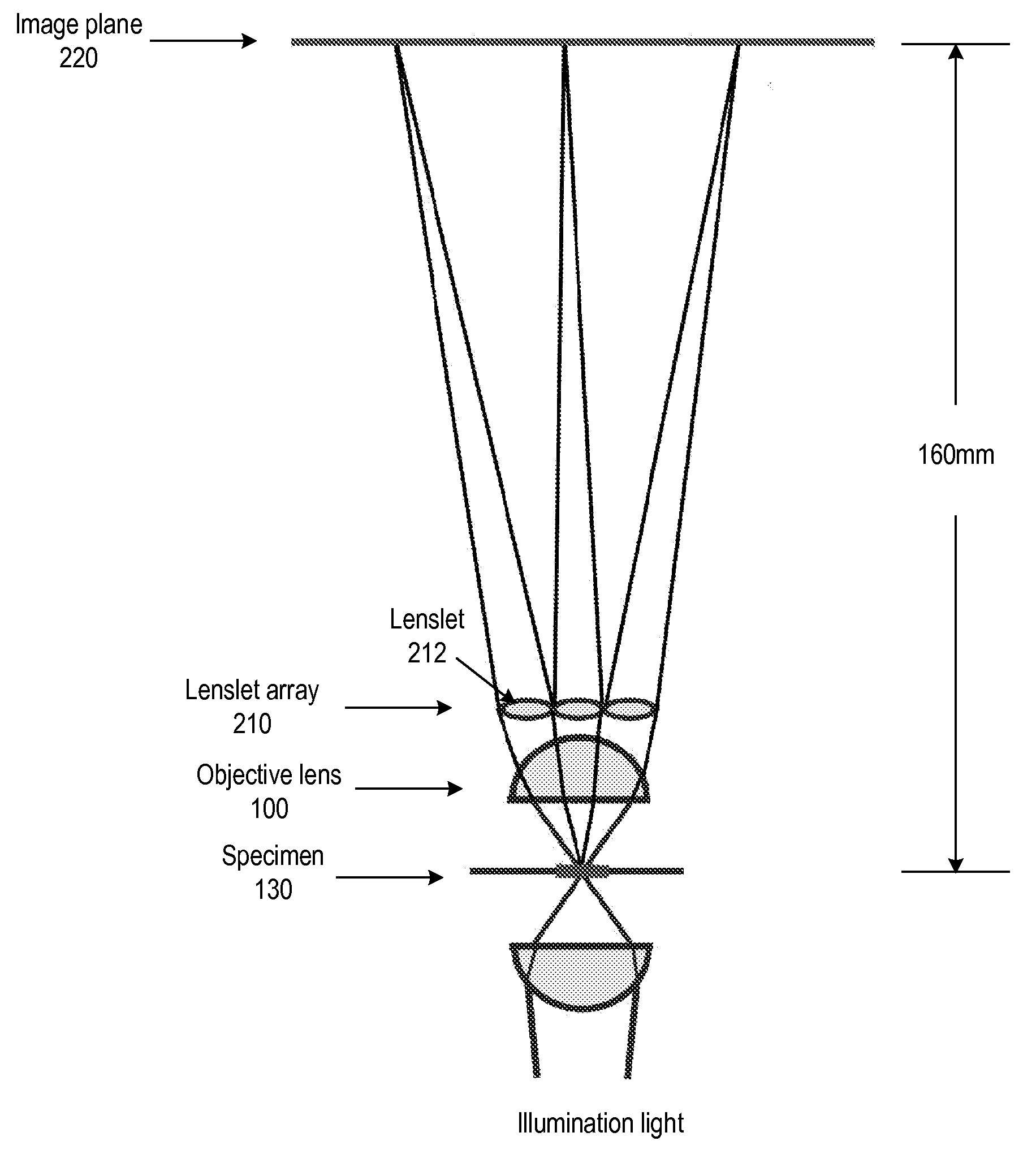
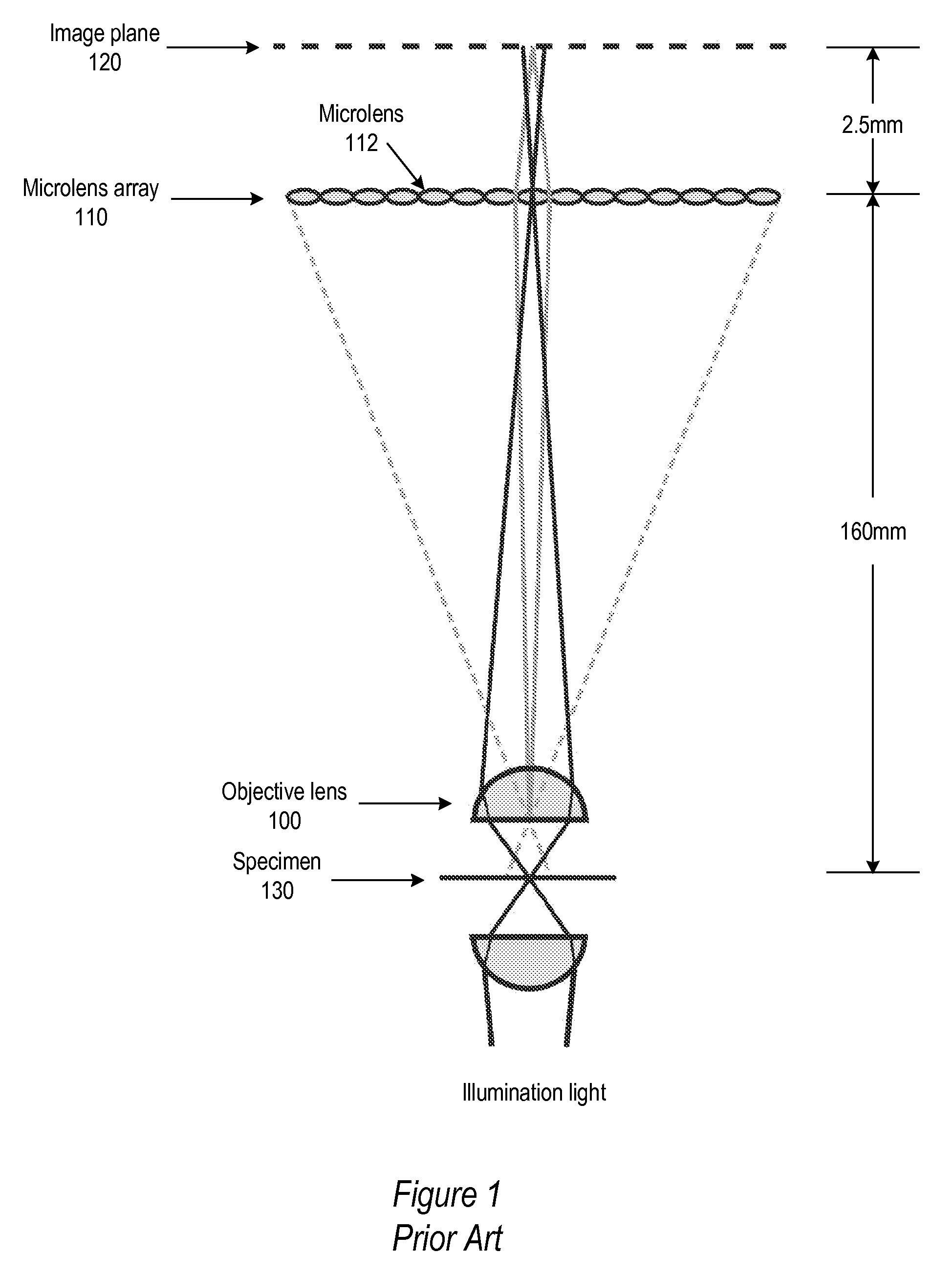
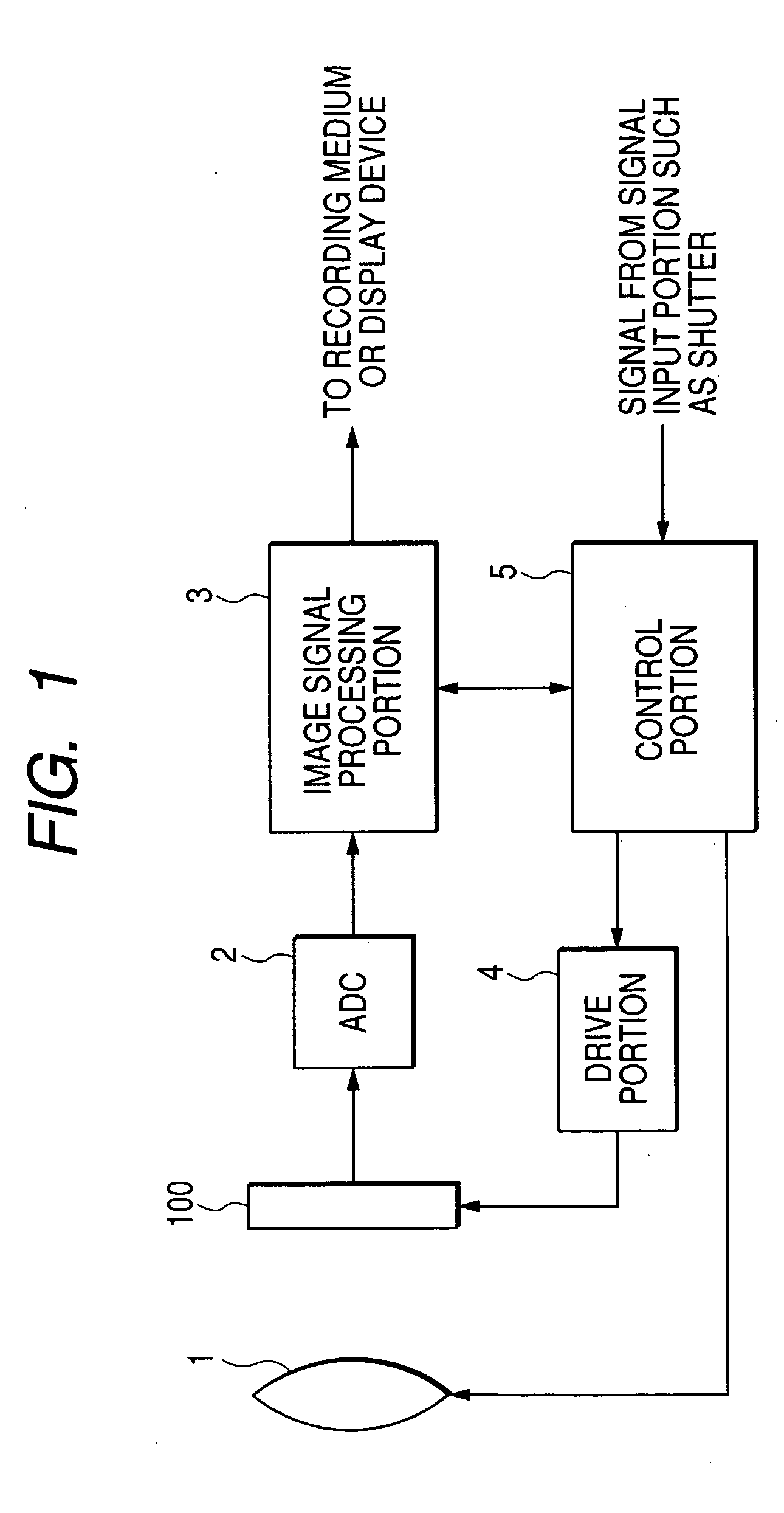
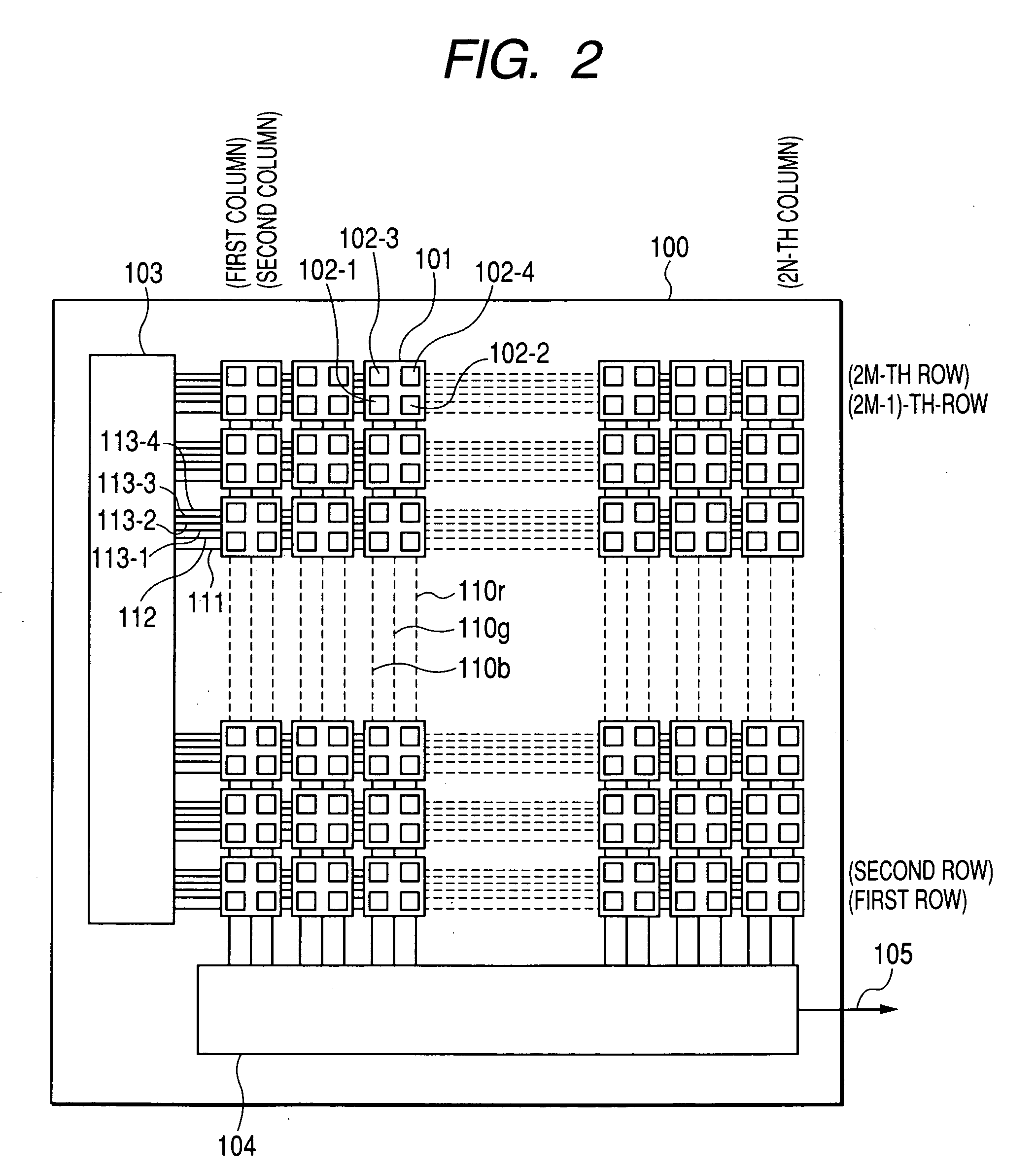
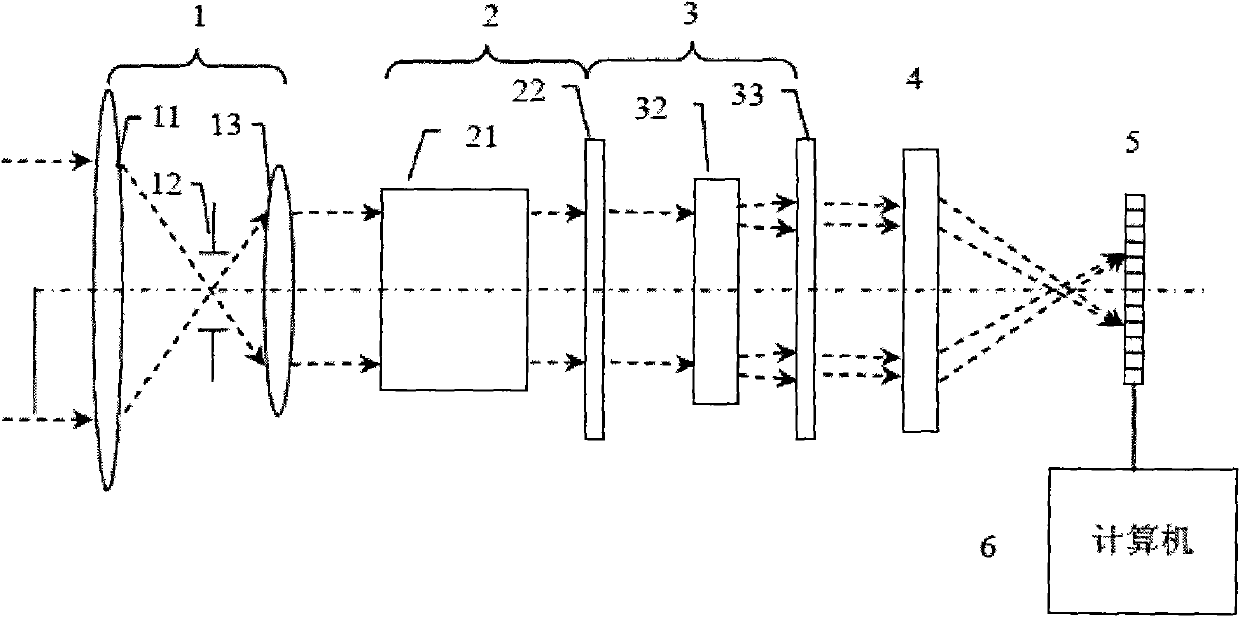
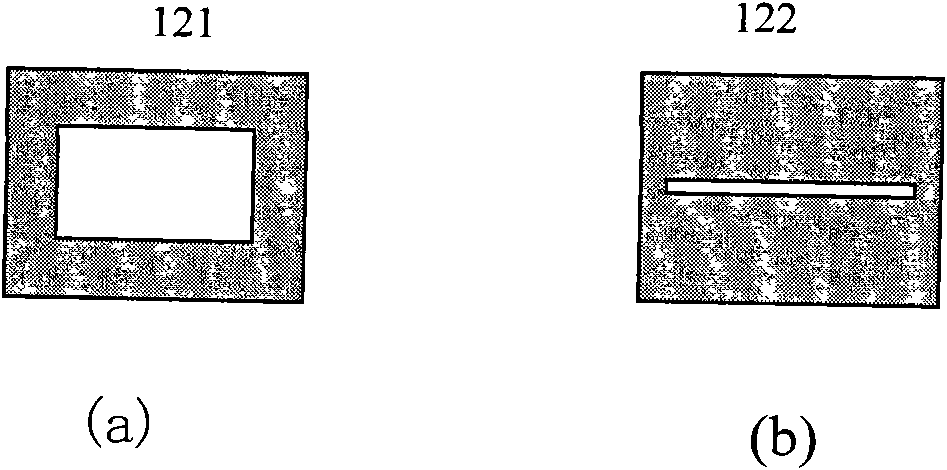
Patents
Literature
119results about How to "High resolution imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
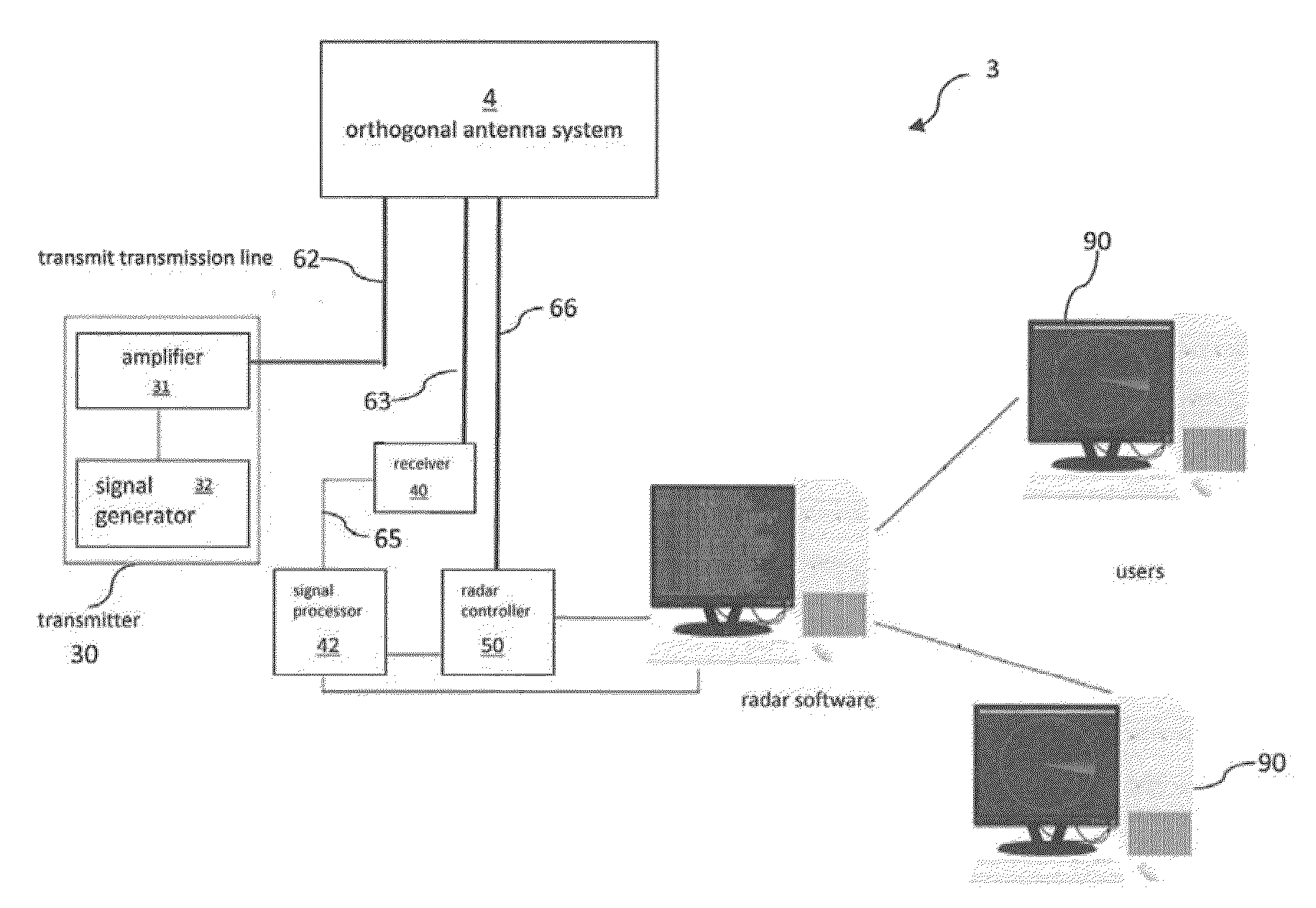
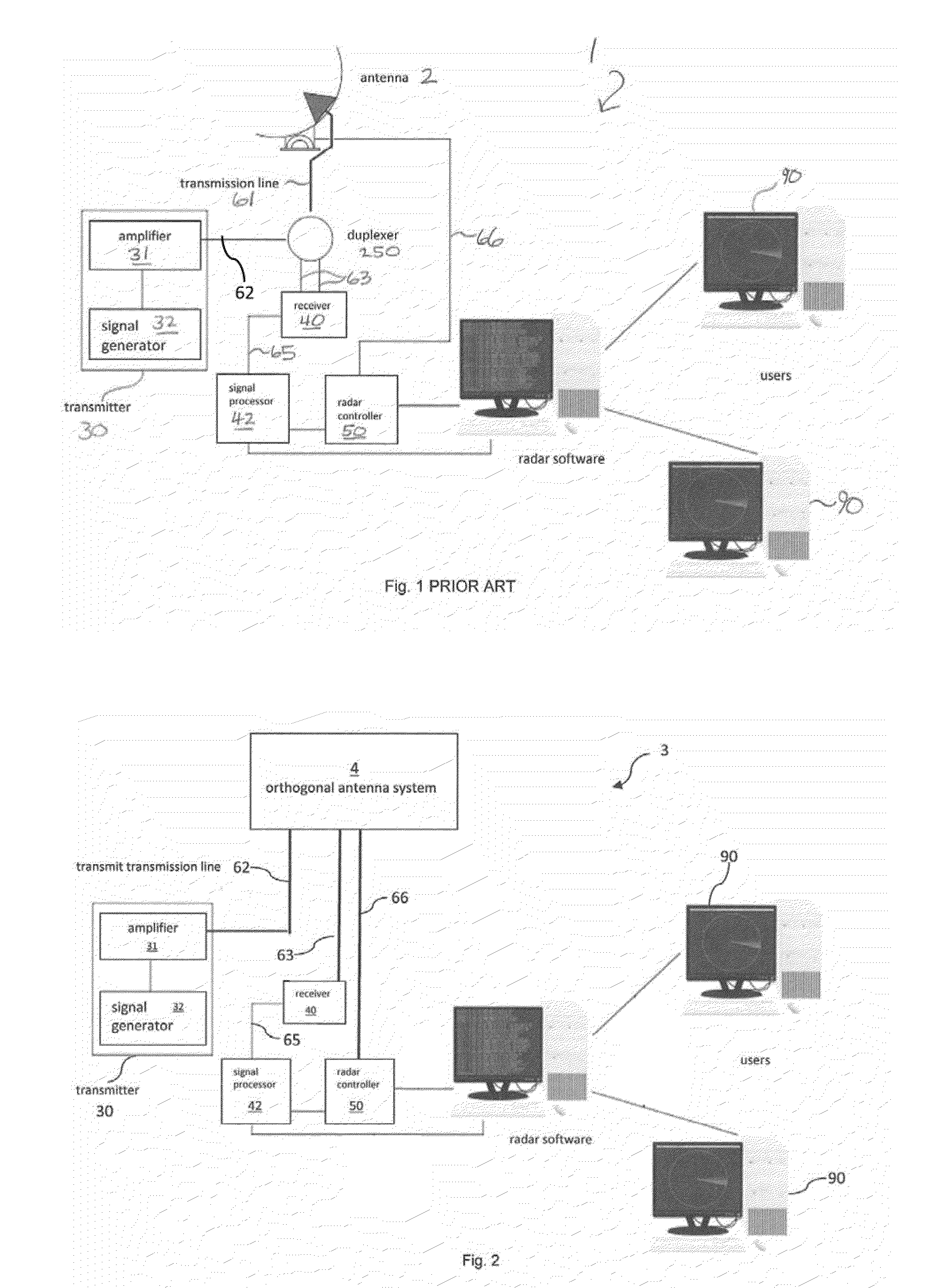
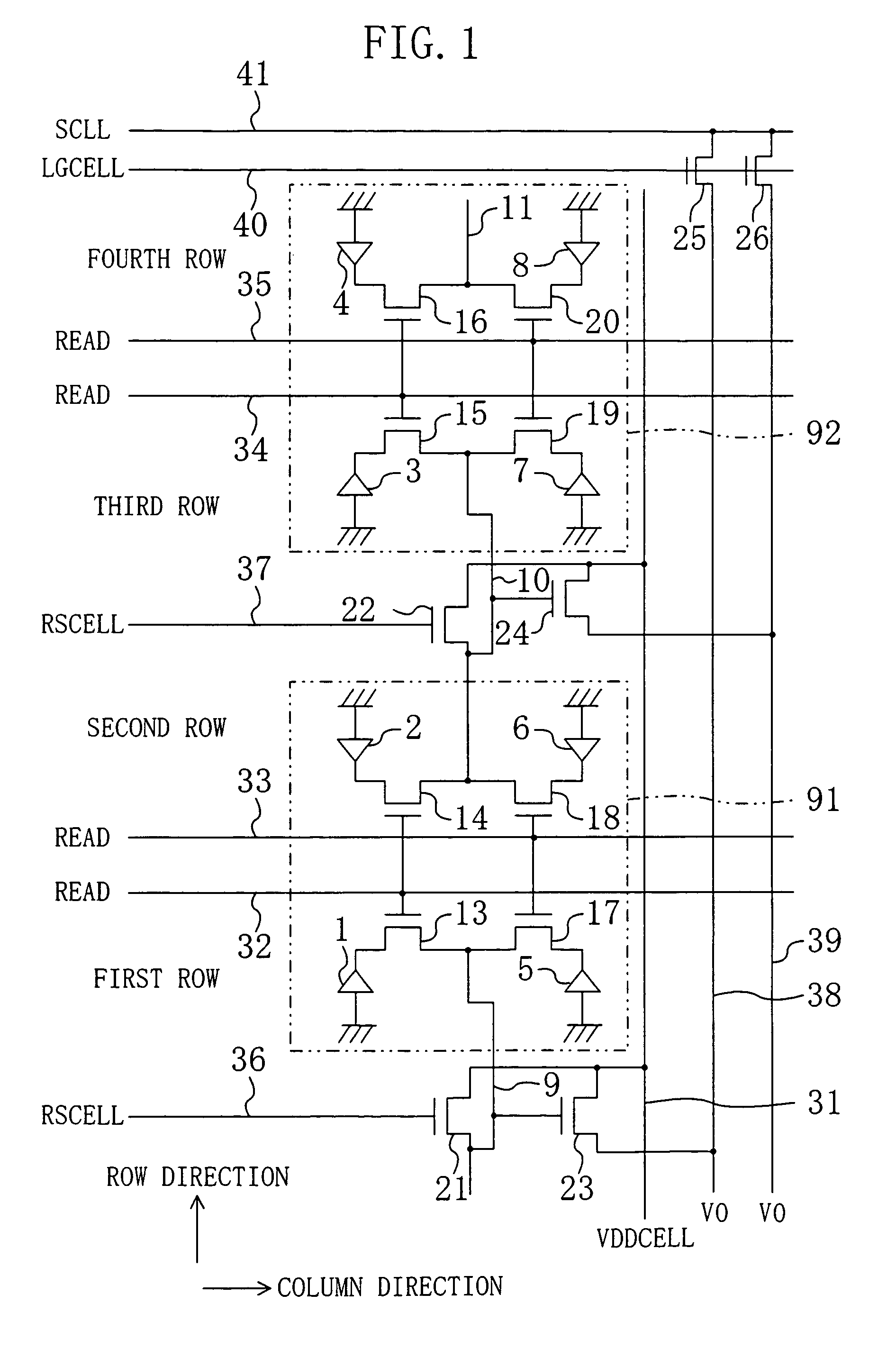
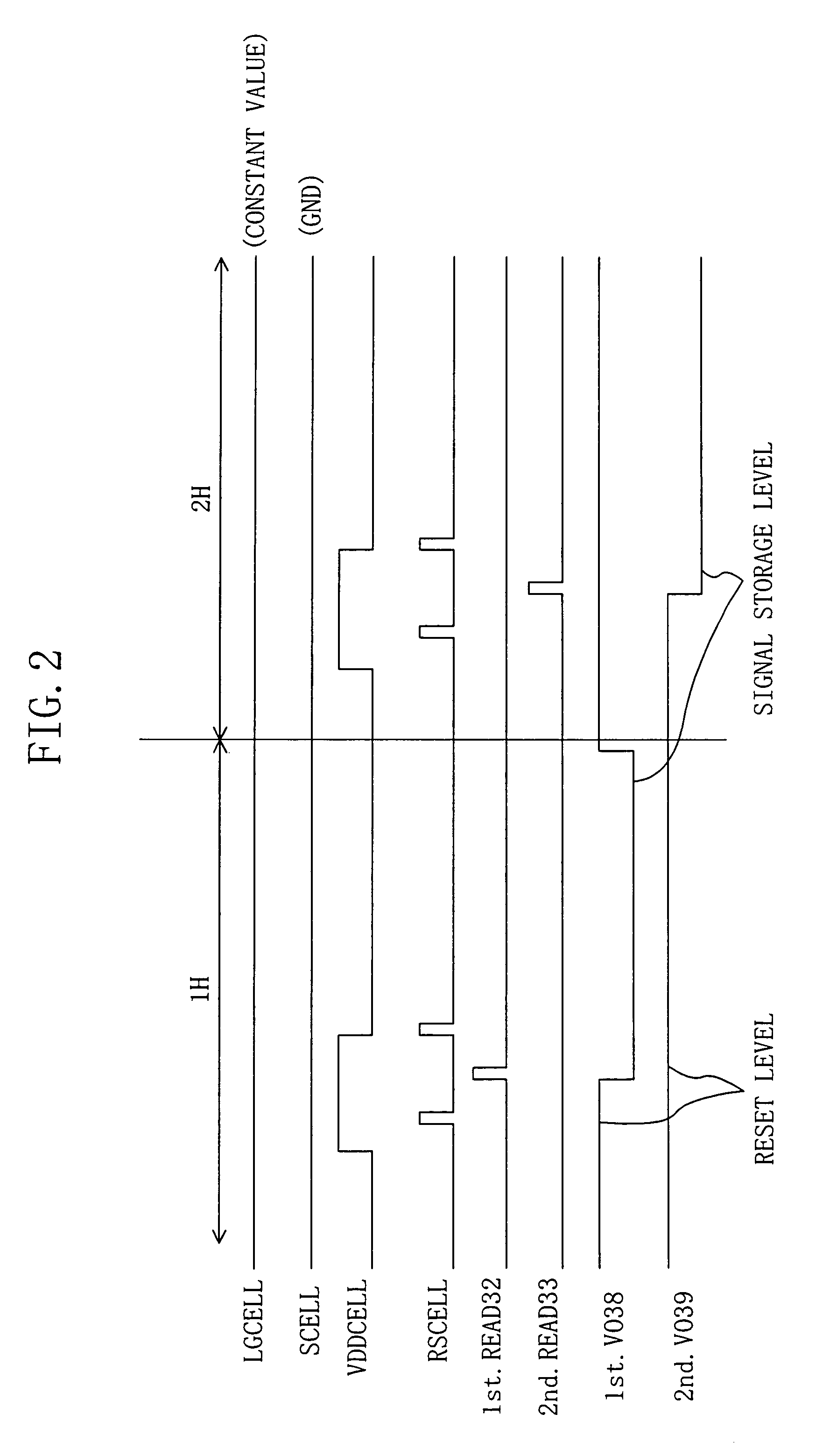
Orthogonal linear transmit receive array radar
ActiveUS20100141527A1High resolution imagingHigh resolution imageIndividually energised antenna arraysPolarised antenna unit combinationsRadar systemsLight beam
A radar system having orthogonal antenna apertures is disclosed. The invention further relates to an antenna system wherein the orthogonal apertures comprise at least one transmit aperture and at least one receive aperture. The cross-product of the transmit and receive apertures provides a narrow spot beam and resulting high resolution image. An embodiment of the invention discloses orthogonal linear arrays, comprising at least one electronically scanned transmit linear array and at least one electronically scanned receive linear array. The design of this orthogonal linear array system produces comparable performance, clutter and sidelobe structure at a fraction of the cost of conventional 2D filled array antenna systems.
Owner:FIRST RF CORP
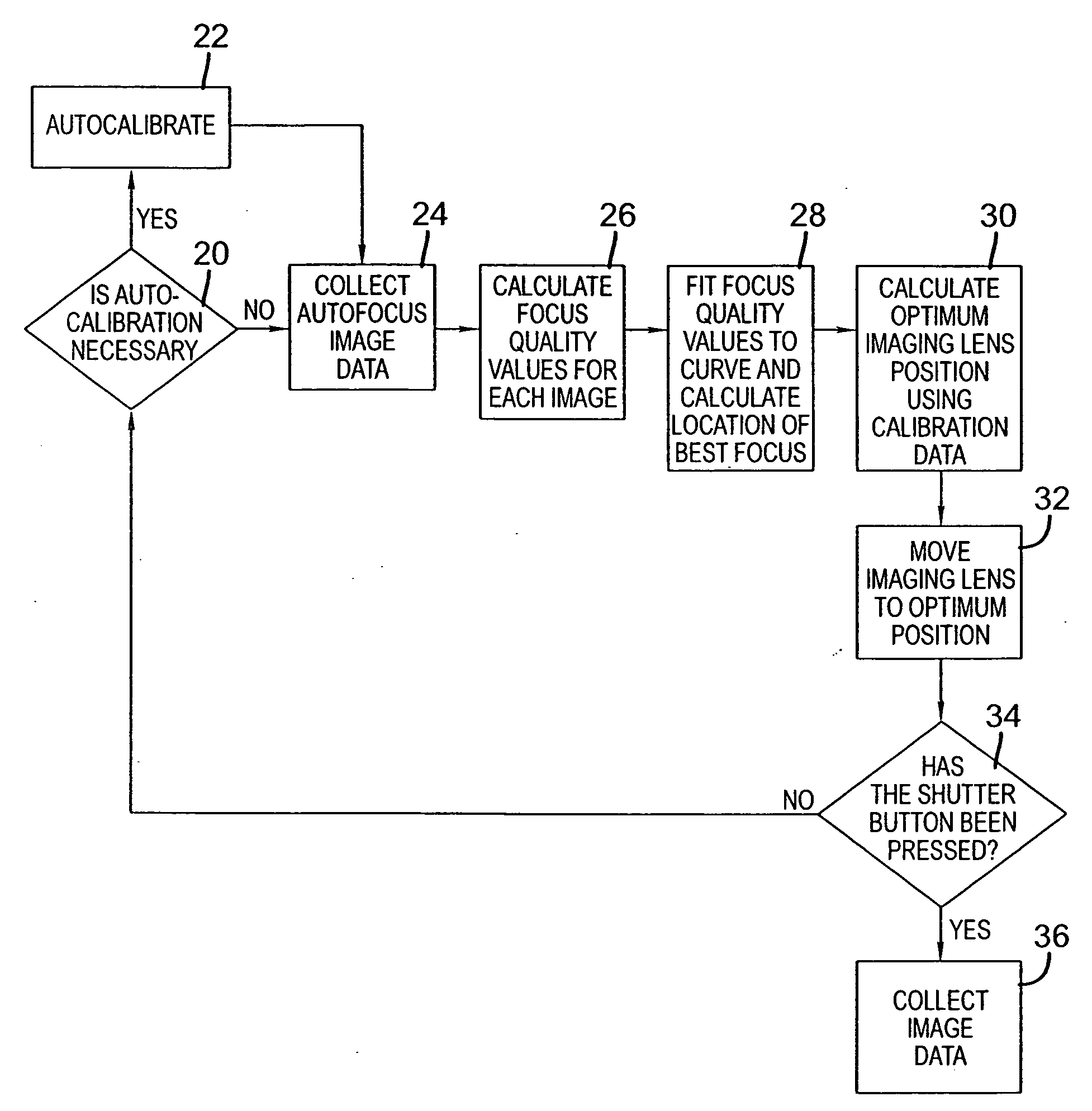
Lens array assisted focus detection
InactiveUS20080095523A1Fast analysisQuick captureTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCamera lensComputer science
A focus detection device includes an image sensor and a plurality of lenslets. Each of the plurality of lenslets has a distinct conjugate length and is associated with a distinct portion of the image sensor.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
Light Field Microscope With Lenslet Array
ActiveUS20080180792A1Avoids mechanical complicationAberration correctionMicroscopesLensViewpointsImage plane
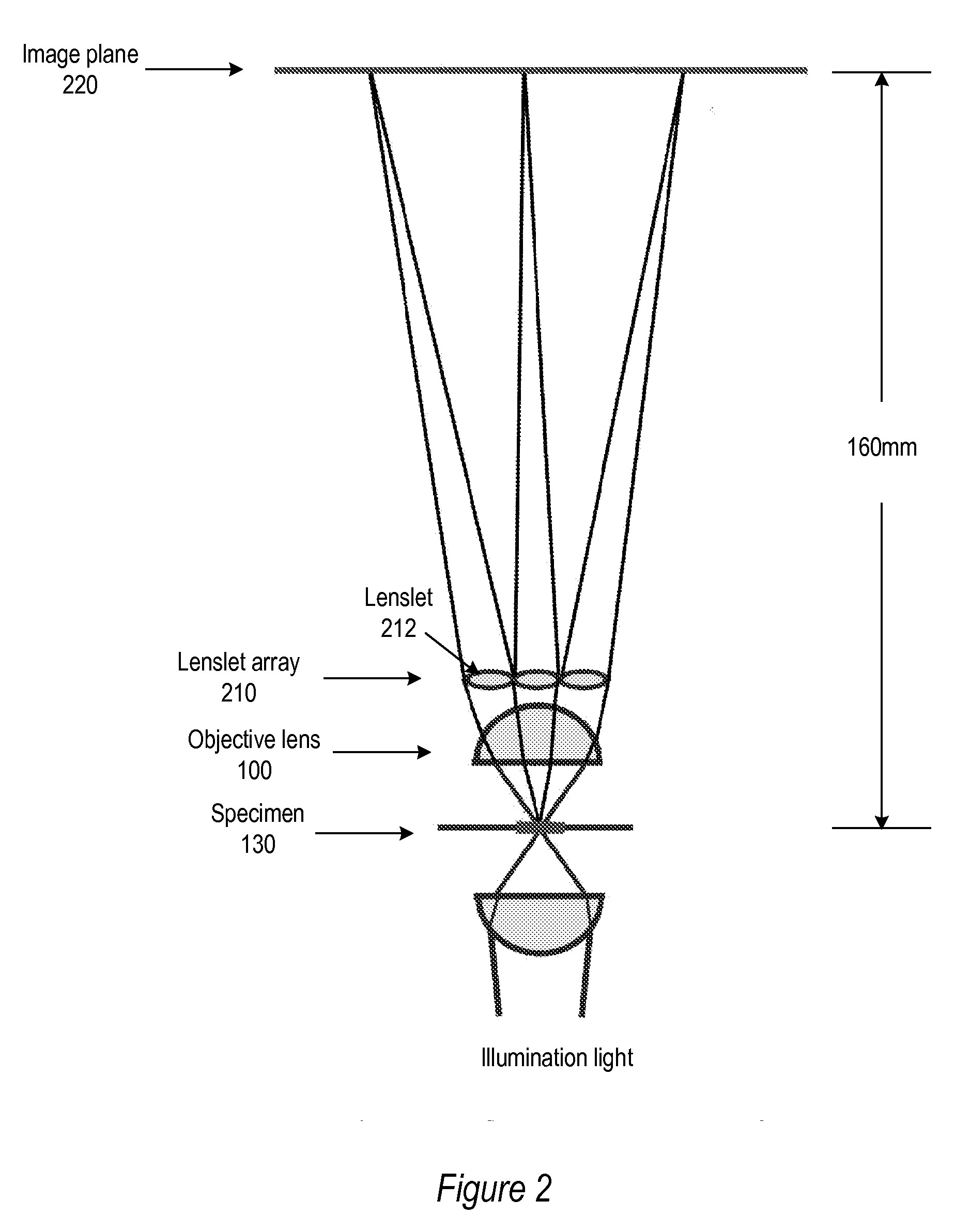
A light field microscope incorporating a lenslet array at or near the rear aperture of the objective lens. The microscope objective lens may be supplemented with an array of low power lenslets which may be located at or near the rear aperture of the objective lens, and which slightly modify the objective lens. The result is a new type of objective lens, or an addition to existing objective lenses. The lenslet array may include, for example, 9 to 100 lenslets (small, low-power lenses with long focal lengths) that generate a corresponding number of real images. Each lenslet creates a real image on the image plane, and each image corresponds to a different viewpoint or direction of the specimen. Angular information is recorded in relations or differences among the captured real images. To retrieve this angular information, one or more of various dense correspondence techniques may be used.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Super resolution optofluidic microscopes for 2d and 3D imaging
ActiveUS20110234757A1High resolutionHigh resolution imagingTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationSurface layerElectronic communication
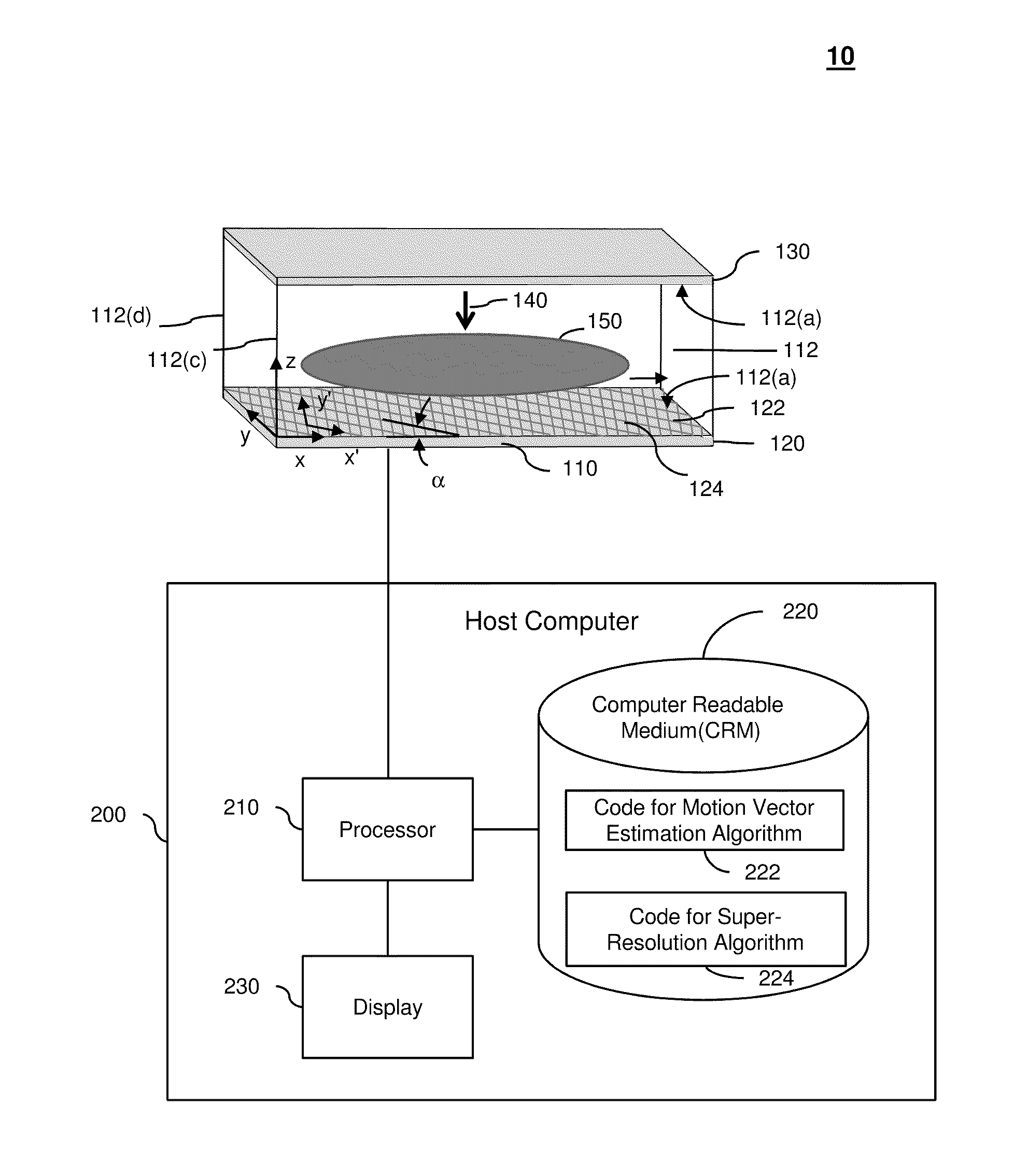
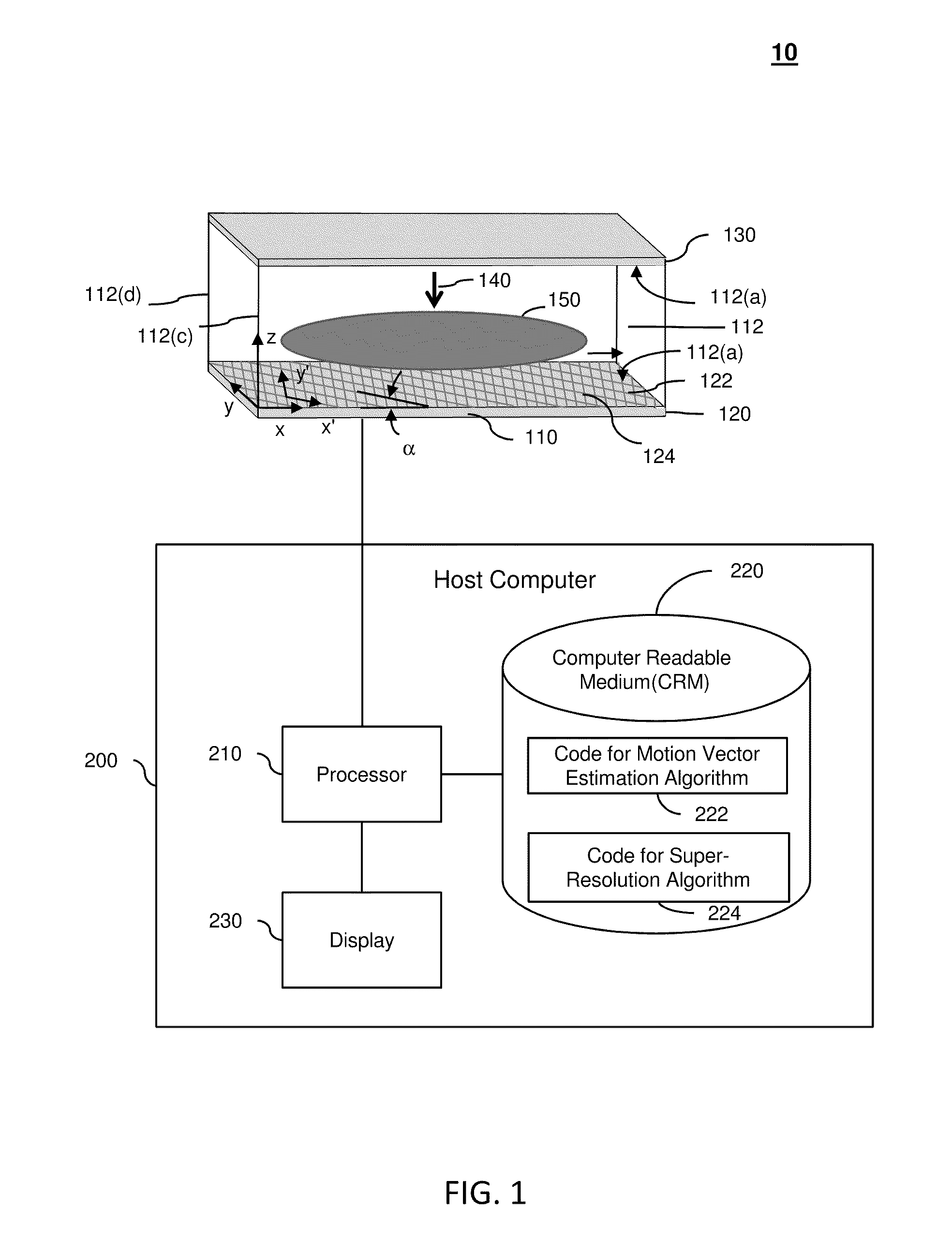
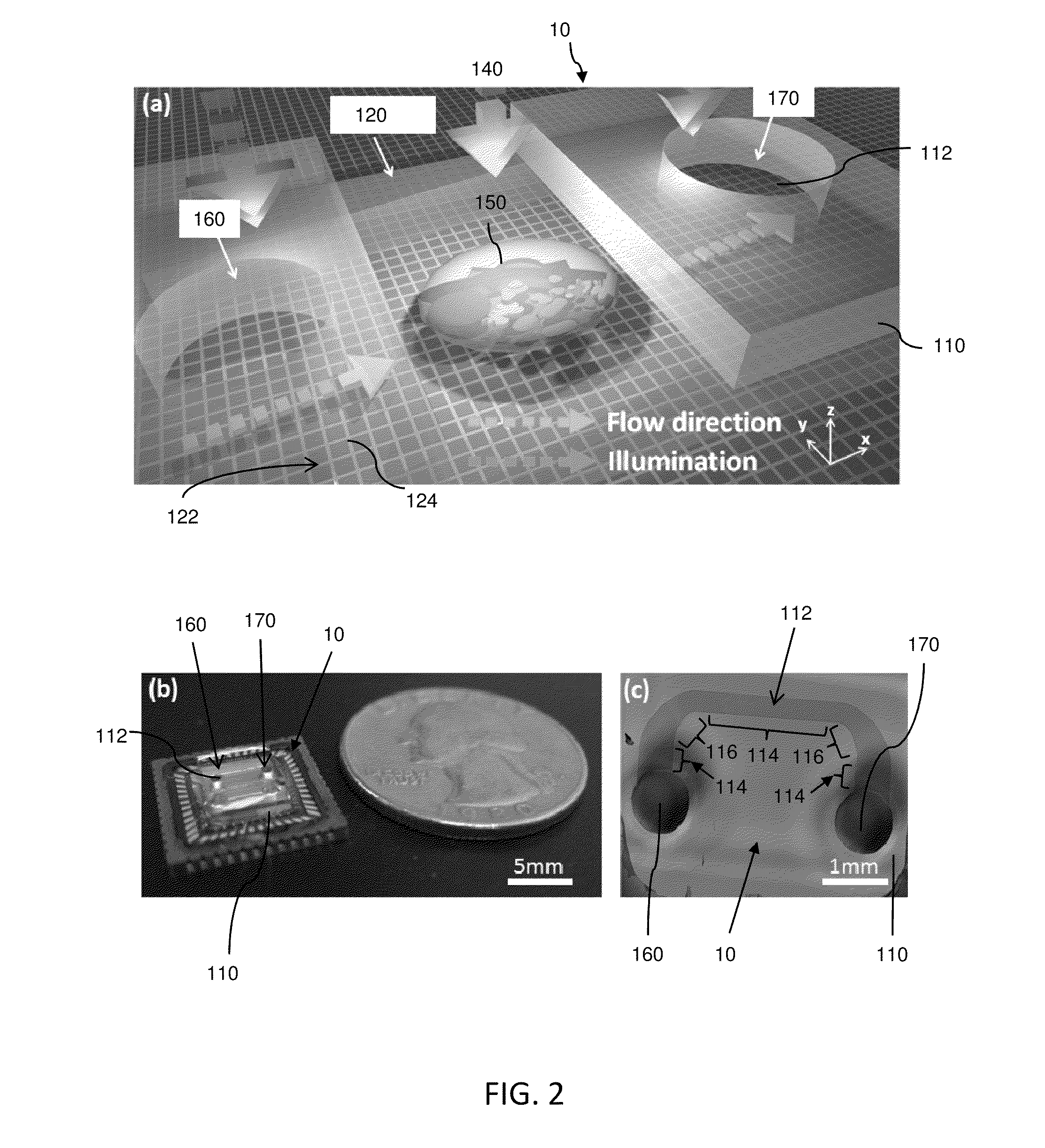
A super resolution optofluidic microscope device comprises a body defining a fluid channel having a longitudinal axis and includes a surface layer proximal the fluid channel. The surface layer has a two-dimensional light detector array configured to receive light passing through the fluid channel and sample a sequence of subpixel shifted projection frames as an object moves through the fluid channel. The super resolution optofluidic microscope device further comprises a processor in electronic communication with the two-dimensional light detector array. The processor is configured to generate a high resolution image of the object using a super resolution algorithm, and based on the sequence of subpixel shifted projection frames and a motion vector of the object.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Three-dimensional image projection employing retro-reflective screens
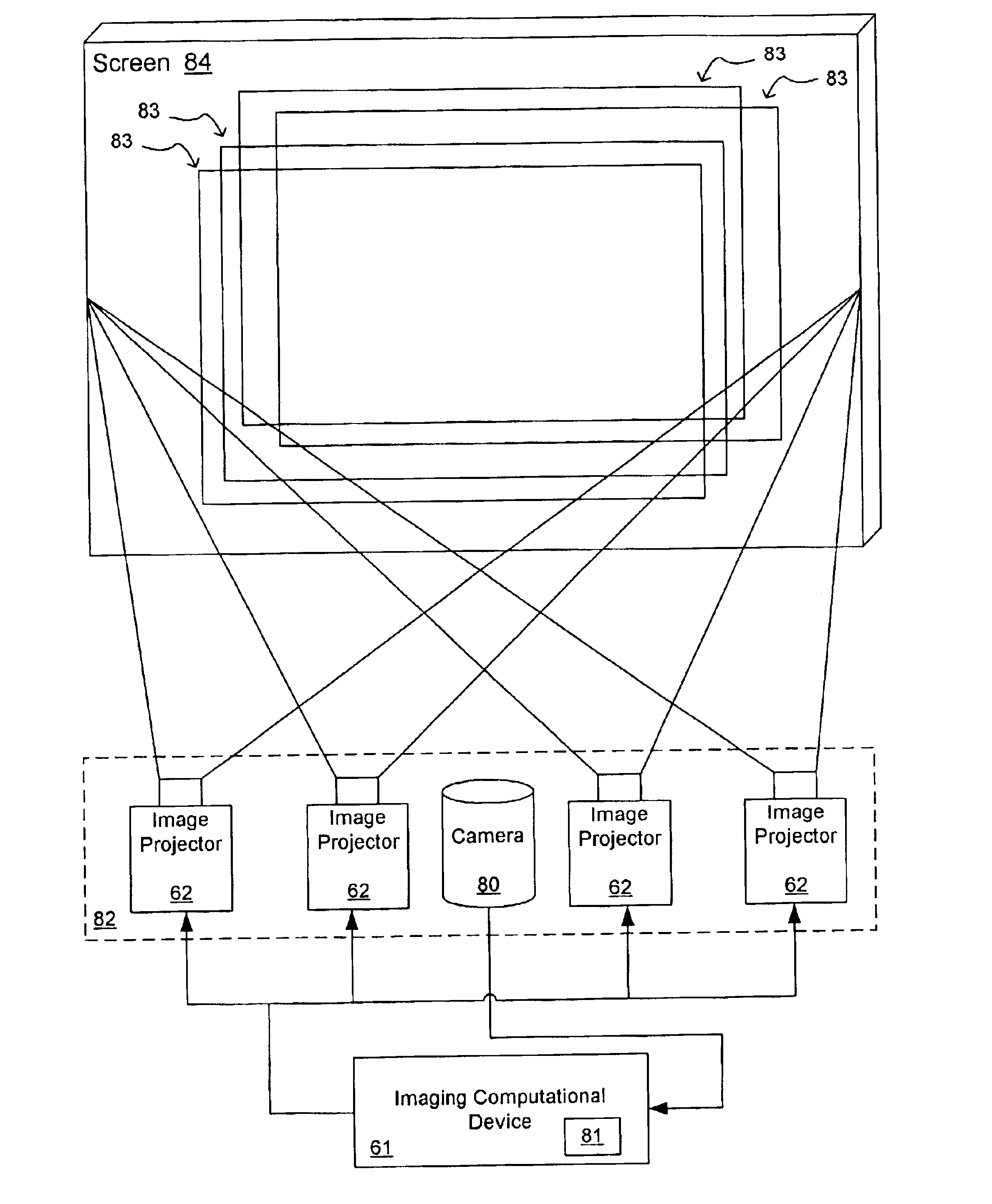
InactiveUS6843564B2High resolution imagingHigh resolution imageBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsStereoscopic photographyLight reflectionProjection system
Disclosed herein are three-dimensional projection systems and related methods employing two electronically controlled projectors and a retro-reflective screen. The retro-reflective screen produces a known non-linear light reflection pattern when images are projected thereon. Image computational means are used to calculating flat image information for each projector based upon inputted stereopair images and information regarding the projectors and screen. In preferred embodiments of the present invention, the projection system uses an image computational device that employs a neural network feedback calculation to calculate the appropriate flat image information and appropriate images to be projected on the screen by the projectors at any given time. More than two projectors can be employed to produce multiple aspect views, to support multiple viewers, and the like. In another embodiment, the projection system includes a digital camera that provides feedback data to the image computational device.
Owner:VIRRILLI JAMES
Systems and methods for remote access media production
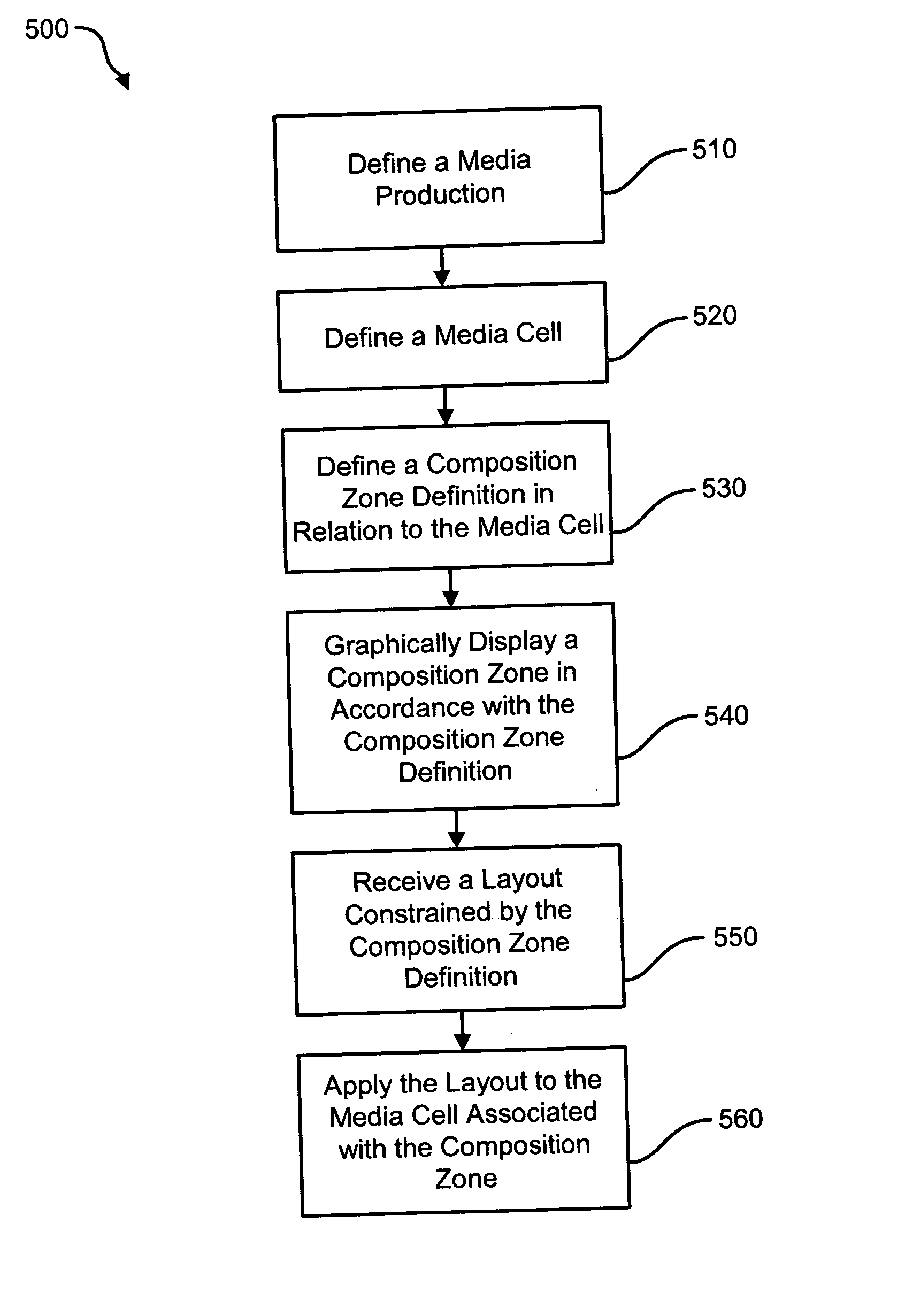
InactiveUS20060212805A1High resolution imagingEasy to produceDigital data information retrievalNatural language data processingPaper documentDocument preparation
Systems and methods for remote access document production are disclosed herein. As an example, one such method includes providing a first computer executing a document production suite. The first computer is communicably coupled to a computer network, and provides a layout space to a second computer via the communication network. Commands are received from the second computer in relation to the layout space, and based on the commands, a document is constructed.
Owner:QUARK INC
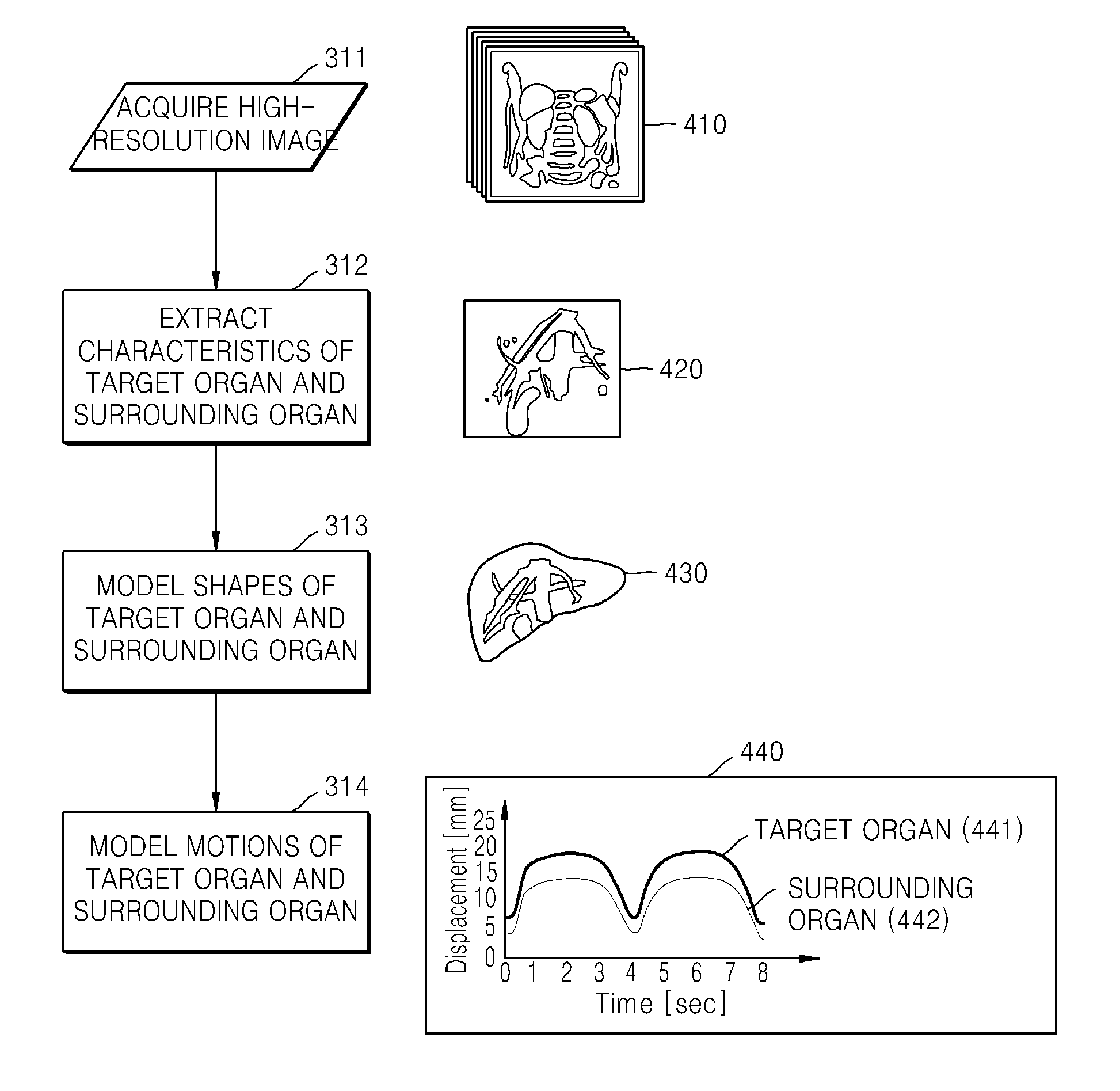
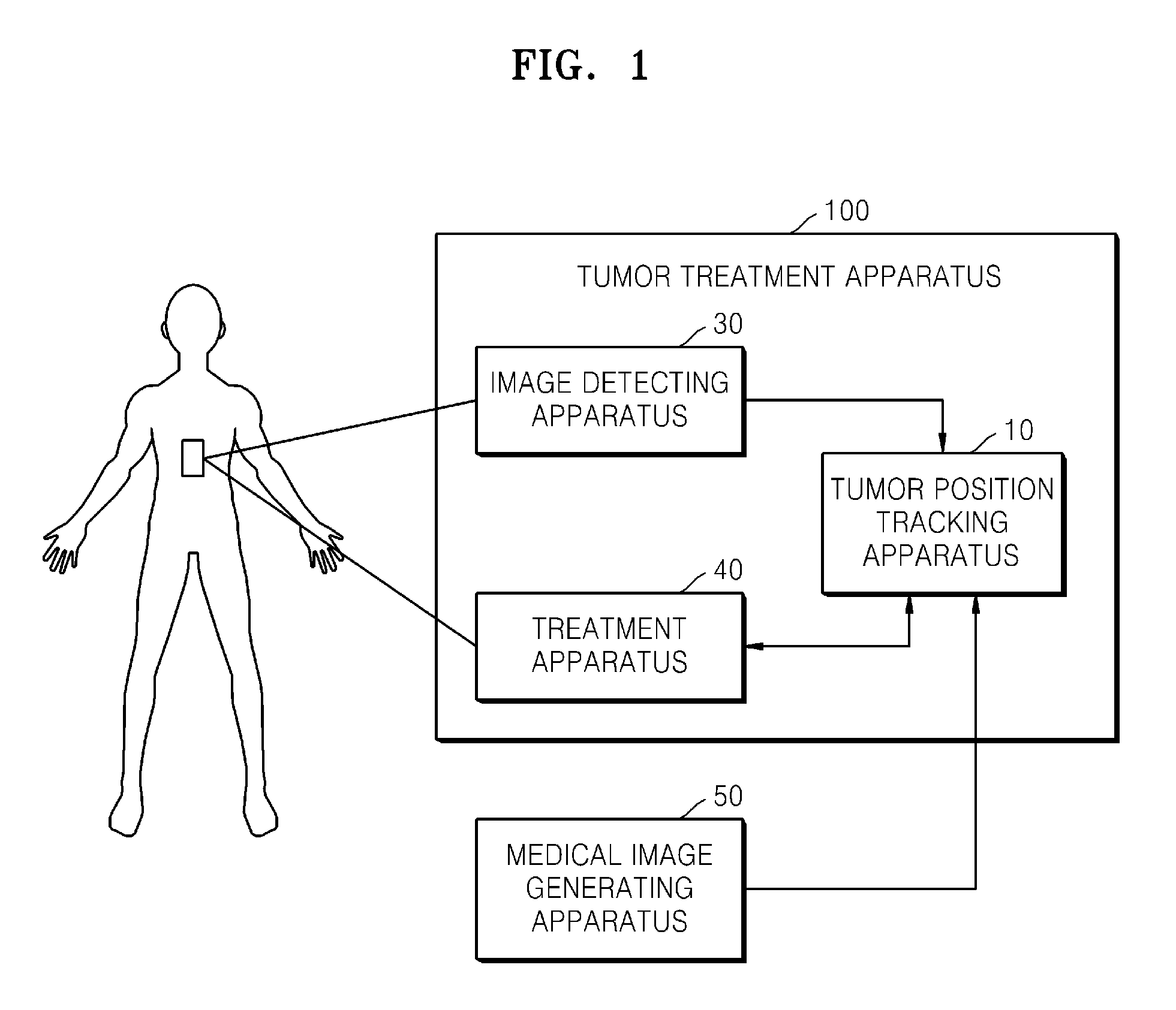
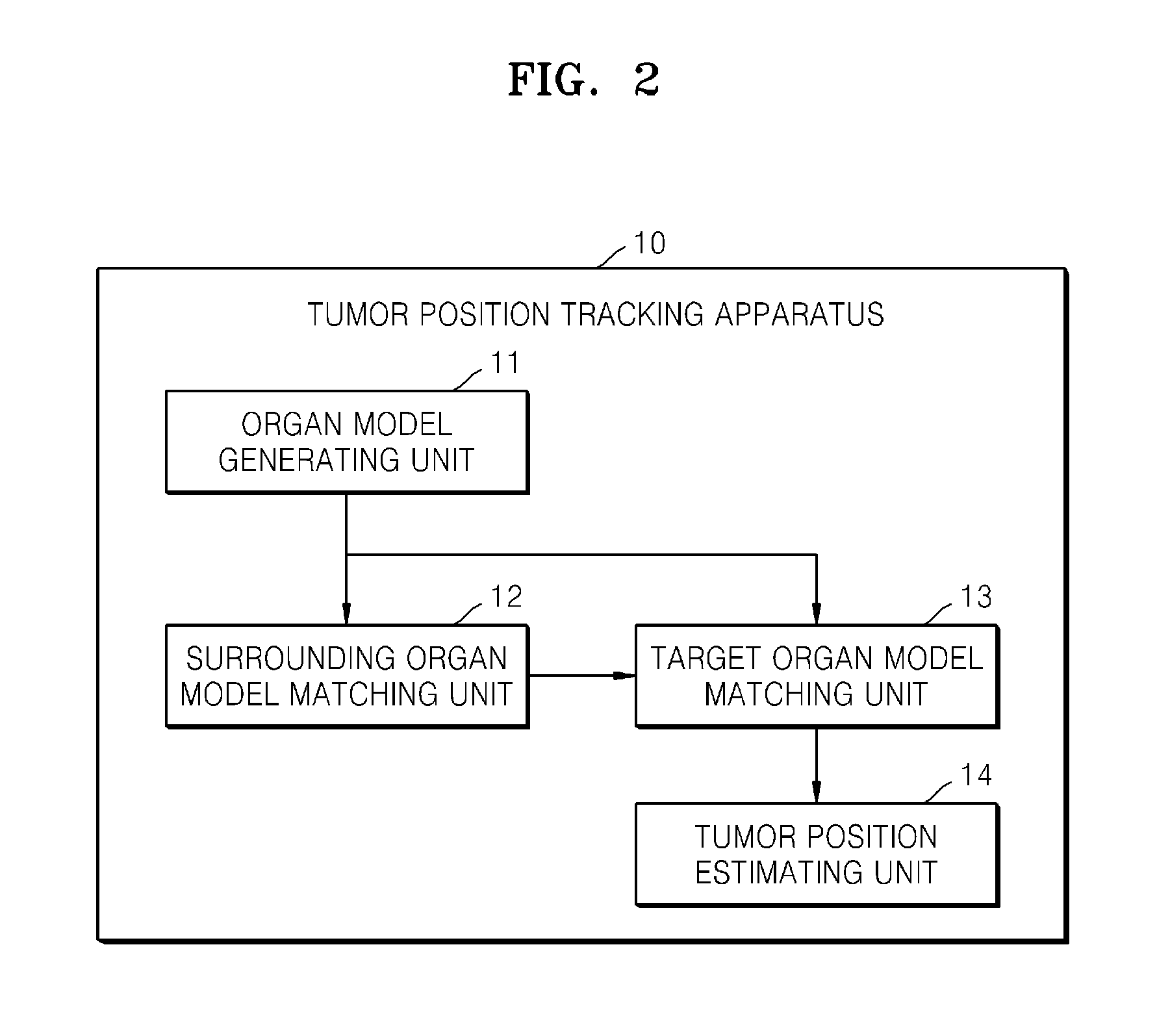
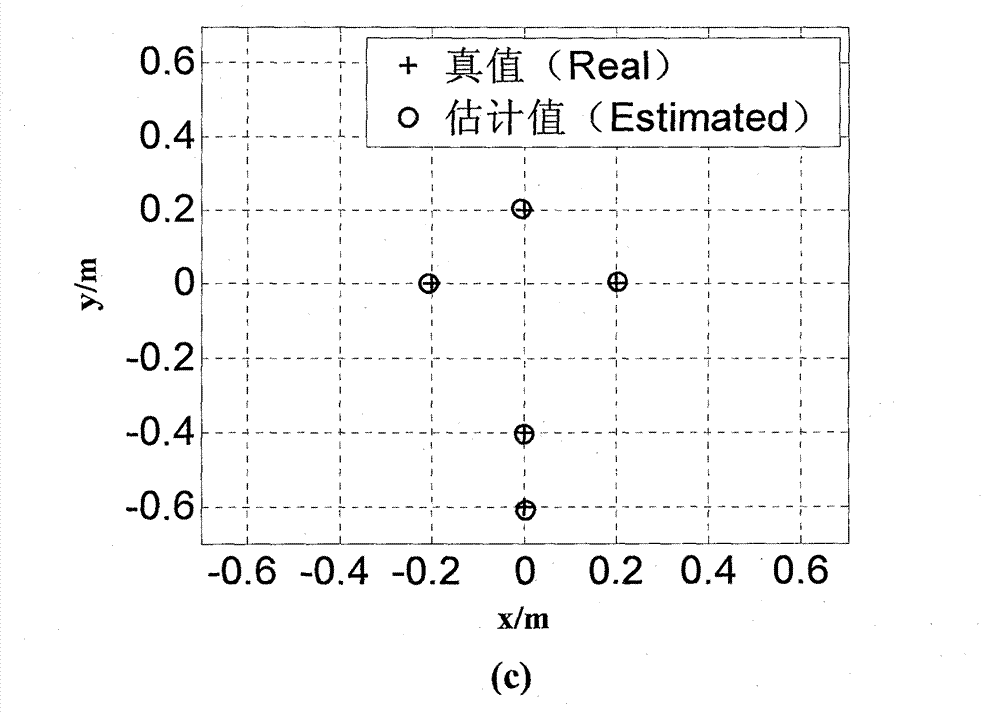
Method and apparatus for tracking a position of a tumor
ActiveUS20140046172A1High resolution imagingHigh resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementComputer visionTarget organ
Provided is a method and apparatus for tracking a tumor position, which changes by the movement of a body. According to various aspects, a location of a tumor position of a target organ may be estimated using images of one or more surrounding organs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
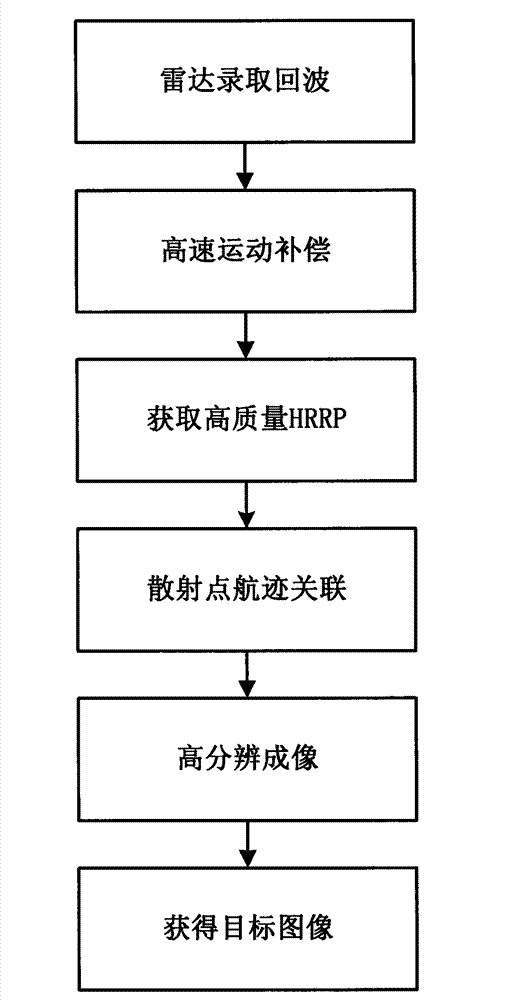
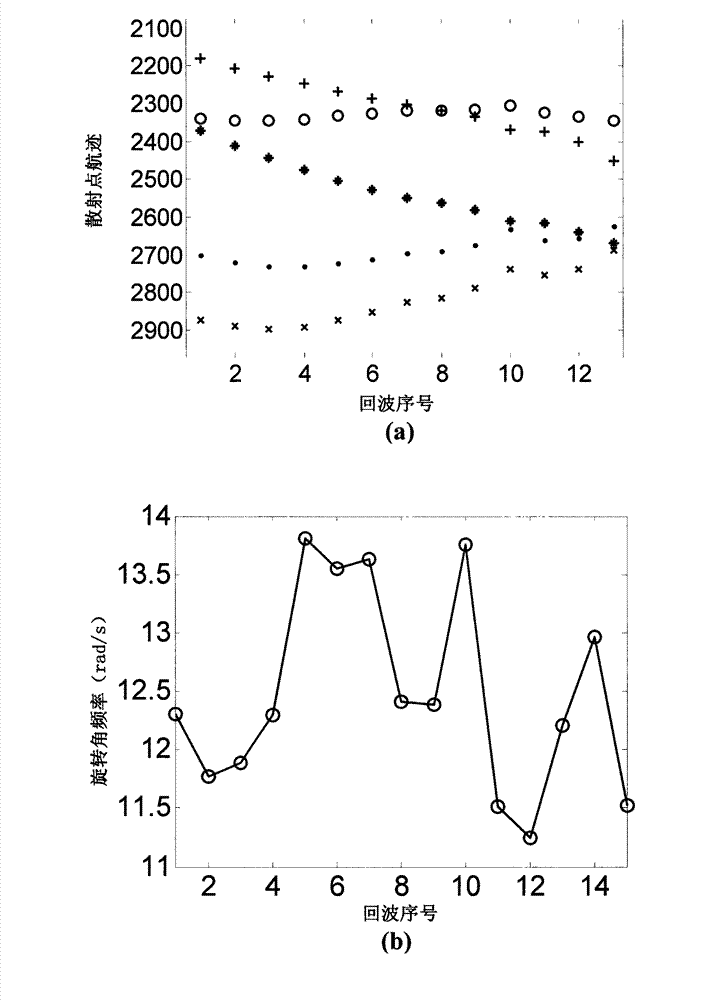
Space target high resolution imaging method based on high resolution range profile (HRRP) sequence
ActiveCN103091674AHigh resolution imagingWell focusedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMatrix decompositionPhase correction
The invention discloses a space target high resolution imaging method based on a high resolution range profile (HRRP) sequence. The space target high resolution imaging method includes a first step of recording inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) echo through a radar, a second step of obtaining high-speed motion compensation, a third step of obtaining high quality HRRP, a fourth step of carrying out scattering point flight path correlation, and a fifth step of achieving high resolution imaging. Firstly, through sparse signal reconstruction, the high quality HRRP sequence can be obtained, then an effective flight path correlation method is adopted to generate a scattering point flight path matrix in the HRRP sequence, and further, through matrix decomposition with a constraint condition, the high resolution imaging can be achieved. The method overcomes the defects that a transforming method based on subsection false Keystone is high in requirements for pulse repetition frequency (PRF), strict in requirements for a target motion model, big in difficulty in accurate translation compensation and phase correction to a high-speed rotating target in the imaging process, big in the amount of calculation and the like, and has the advantages of being capable of carrying out high resolution imaging on the conditions of low PRF and even direction Doppler blur, and having universality to the target motion model, being free from translation compensation, high in efficiency, good in image focusing, and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
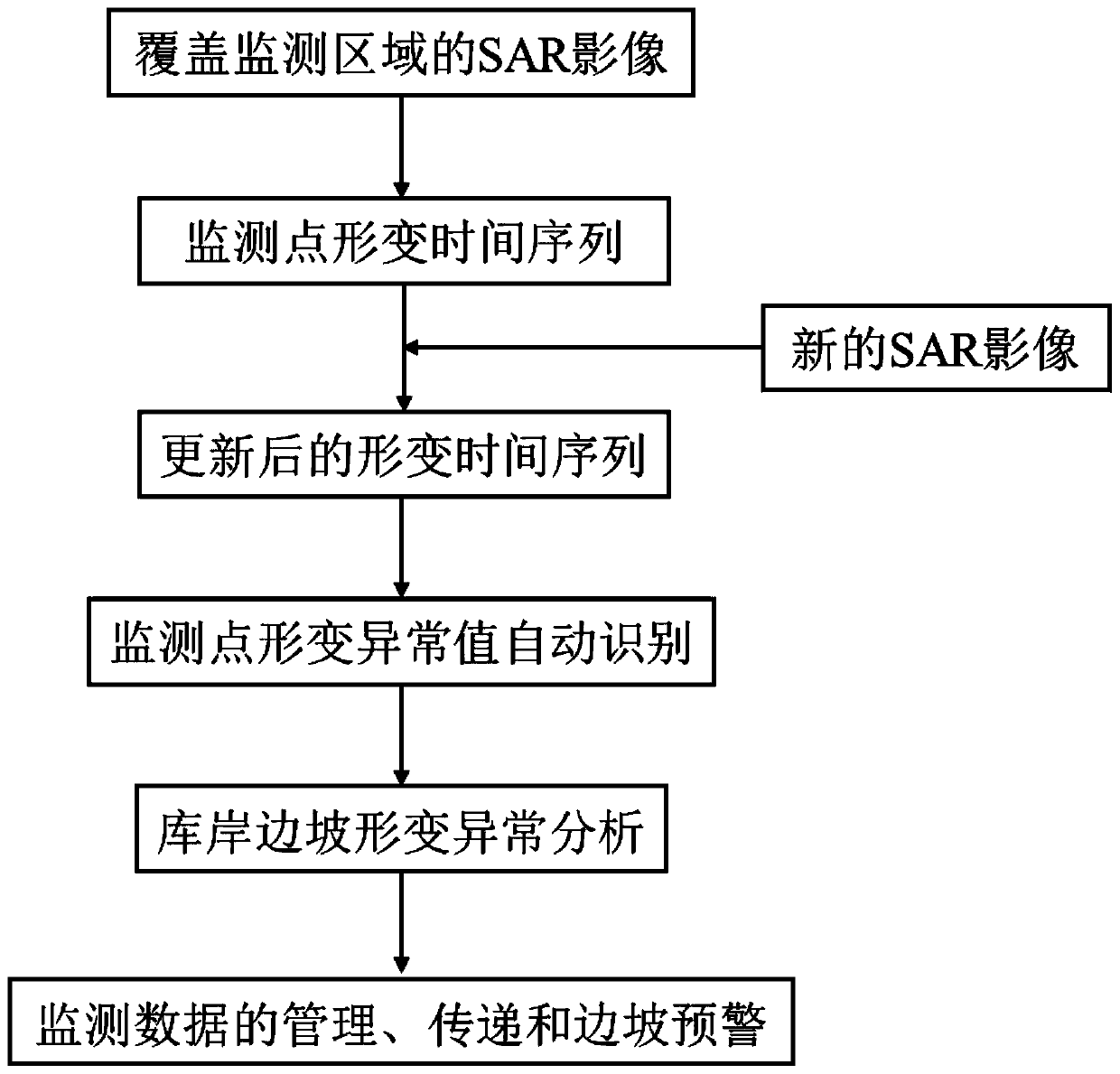
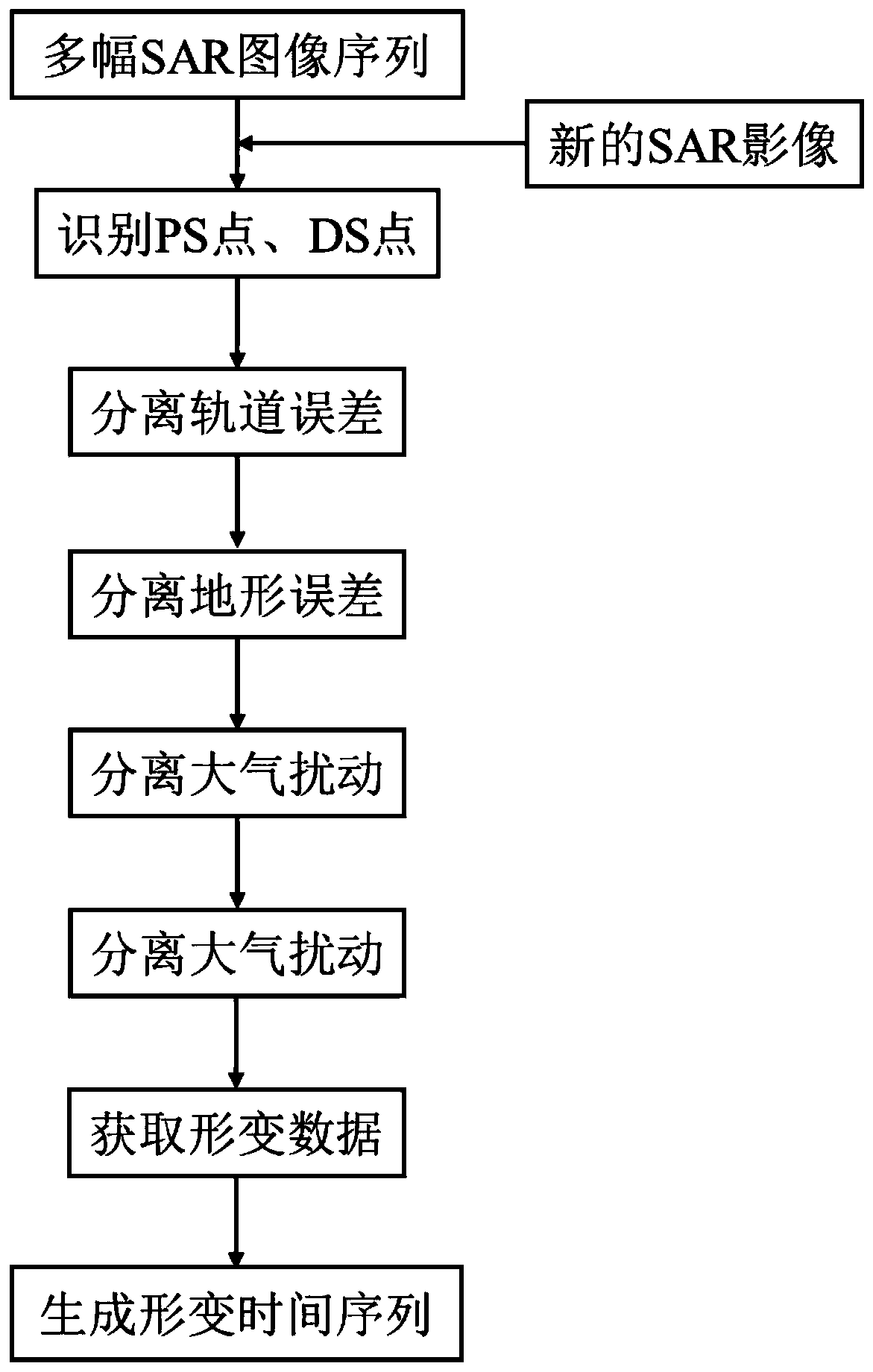
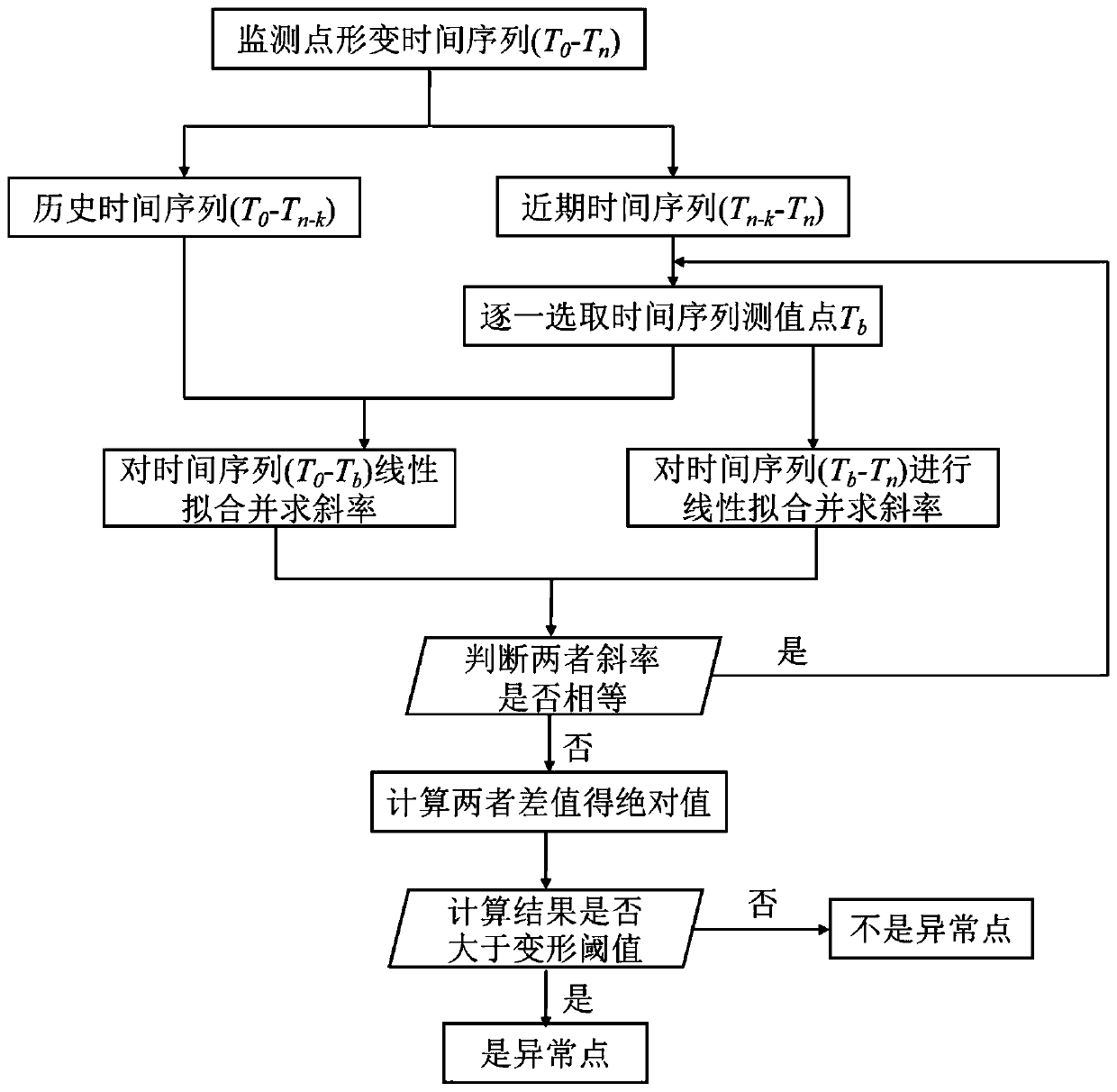
Method for monitoring and processing reservoir bank slope deformation based on InSAR image data
ActiveCN109709550AHigh resolution imagingImprove spatial resolutionClimate change adaptationElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementReservoir waterDrainage basin
The invention discloses a method for monitoring and processing the reservoir bank slope deformation based on InSAR image data. The method is characterized in that on the basis of acquiring the InSAR data of a reservoir bank slope of a drainage basin, the deformation information of a monitoring area is extracted by means of the SqueeSAR technology and differential interference processing, abnormalvalue identification is performed for the acquired deformation time sequence to define unstable regions appearing within the monitoring range; secondly, two factors of a reservoir water level and therainfall are considered, in combination with relevant geological conditions, through the correlation analysis method, causes of deformation abnormality of the slope are determined and explained; and lastly, the monitoring data and related analysis are reflected in a monitoring report through graphs, tables and the like. Compared with the prior art, the method is advantaged in that continuous and semi-automatic monitoring of the large-scale and high-precision reservoir bank slope of the drainage basin can be realized, and deformation abnormality of the slope can be more reasonably predicted.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
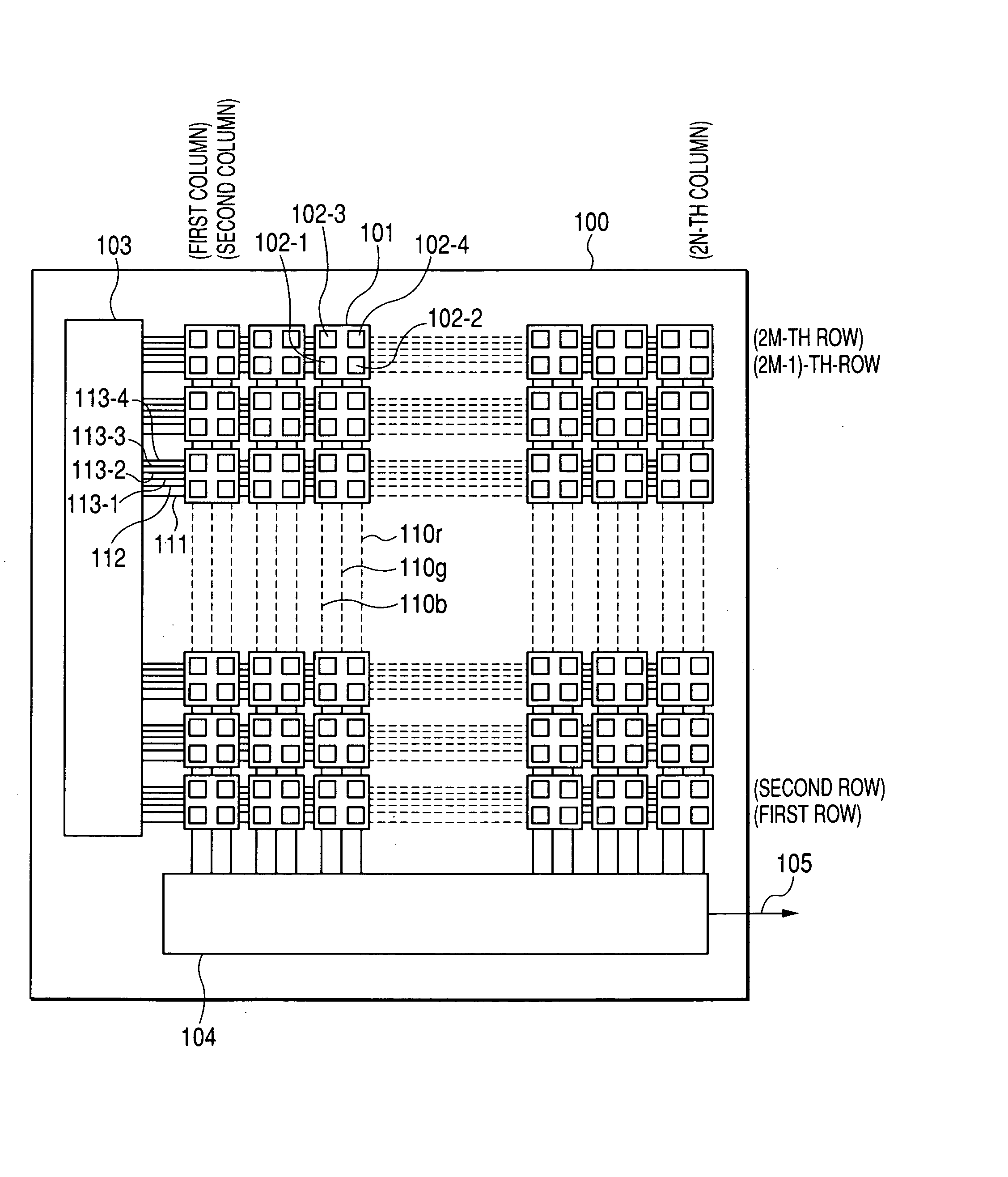
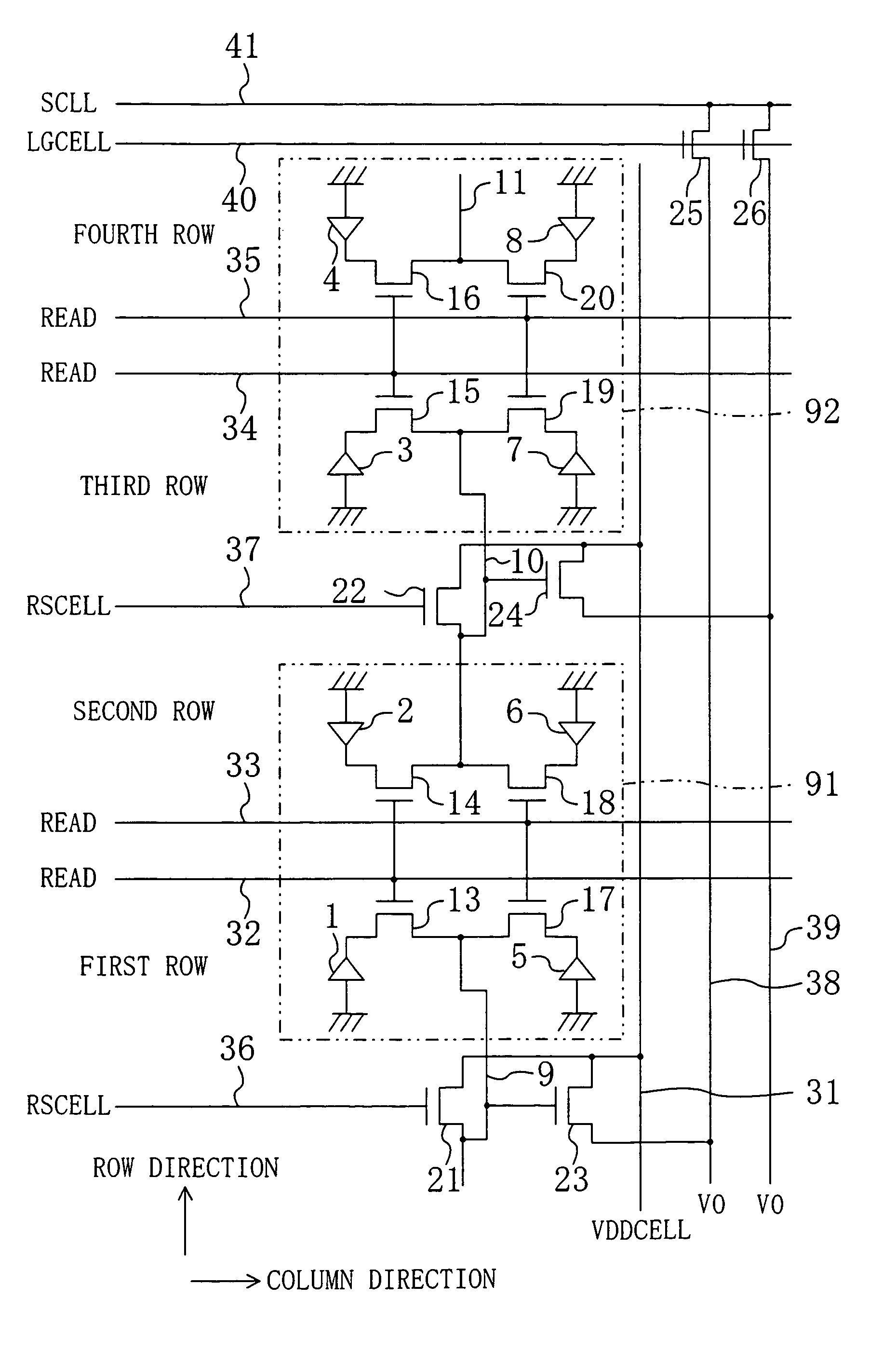
Photoelectric conversion film-stacked type solid-state imaging device, method for driving the same and digital camera
InactiveUS20050219392A1High resolutionHigh imagingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionOpto electronic
To obtain high sensitivity image data in a dark scene, a solid-state imaging device includes: a semiconductor substrate; photoelectric conversion films stacked in a direction perpendicular to the semiconductor substrate, each converting an incident light to a signal charge; pixel electrode films on the photoelectric conversion films, each receiving the signal charge, the pixel electrode films being partitioned and arranged in an array in accordance with pixels, the array comprising units each comprising the pixel electrode films adjacent to one another; and a signal readout circuit in the semiconductor substrate in accordance with one of the units, the signal readout circuit comprising: pixel selection transistors each independently reading out the signal charge from one of the pixel electrode films; and an output transistor connecting to output portions in the pixel selection transistors, so that the signal readout circuit outputs an signal in accordance with the signal charge.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Light and small interference imaging spectrum full-polarized detection device
ActiveCN101793559AHigh resolution imagingStrong vibration resistanceInterferometric spectrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesBirefringent crystalLuminous flux
The invention discloses a light and small interference imaging spectrum full-polarized detection device comprising a preposed optics looking-out system, a static full-light modulation module, an angle shearing static interference imaging spectrometer, an imaging mirror set and a detector which are coaxially and successively arranged in sequence, wherein the detector is connected with a signal obtaining and processing system; after being collected, collimated and performed with stray light elimination by the preposed optics looking-out system, irradiation light emitted by a target source enters the static full-light modulation module; after passing through an angle shearing birefringent crystal set, one beam of modulation line polarized light is sheared into polarization light at an angle; after passing through an analyzer, the polarization light is divided into two beams of line polarized lights; the two beams of the line polarized lights are gathered in the detector after passing through the imaging mirror set; and the received signal is processed by the signal obtaining and processing system to obtain a target image, hyperspectral information and full-polarized information. The invention has the characteristics of compact and simple structure, no moving components and large luminous flux, can obtain a target two-dimensional space image, one-dimensional hyperspectral information and integral polarization information in one time.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Ghost imaging method and ghost imaging system based on bionic vision mechanism
ActiveCN106646512AHigh resolution imagingFast imagingElectromagnetic wave reradiationHigh resolution imagingDetector array
The invention relates to a ghost imaging method and a ghost imaging system based on a bionic vision mechanism, and belongs to the photoelectric imaging field. A laser source, a collimating lens, a rotary frosted glass, and a spectroscope are respectively disposed on the same optical path sequentially. The laser source, the collimating lens, and the rotary frosted glass are used to generate parallel pseu-dothermal light required by the ghost imaging. The spectroscope is used to divide the pseu-dothermal light into two optical paths, and reflection light is a reference arm optical path, and transmission light is a detection arm optical path. The light intensity distribution of the reference arm optical path is received by a bionic detector array, and pseu-dothermal light source two-dimensional light intensity distribution information is completed. After the light of the detection arm is irradiated on a target, the light is reflected, and then the light is reflected by the spectroscope, and the reflection light total light intensity is received by a barrel detector, and the target reflection light total light intensity information acquisition is completed. A related arithmetic unit is used for the operation of the information acquired by the bionic detector array and the barrel detector. The bionic variable resolution detector array is adopted, and large visual field, high resolution imaging and fast imaging are realized at the same time.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Image processing apparatus, image processnig method, and program
InactiveUS20110211765A1High resolution imagingHigh-quality high resolution imageImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingImage resolution
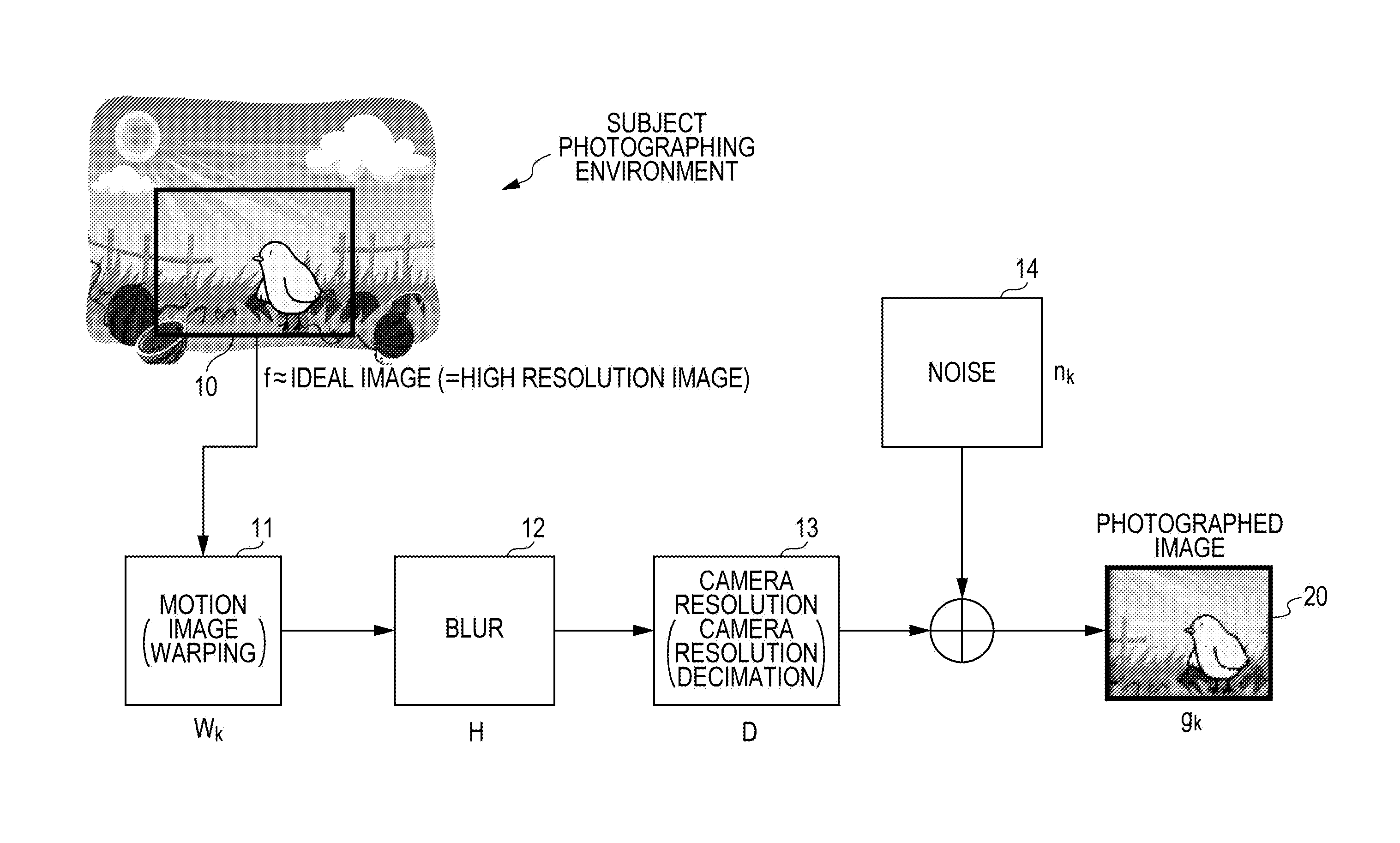
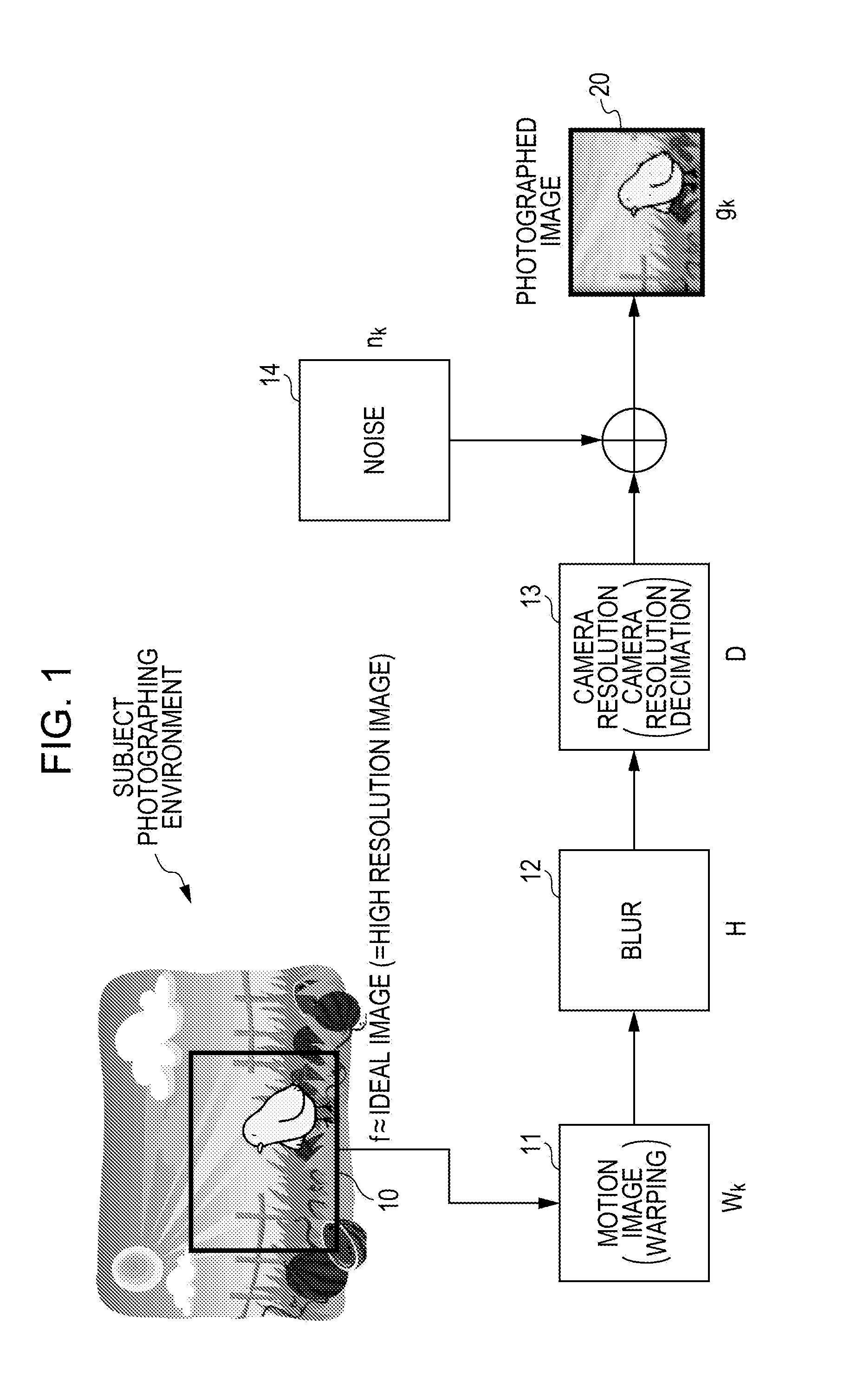
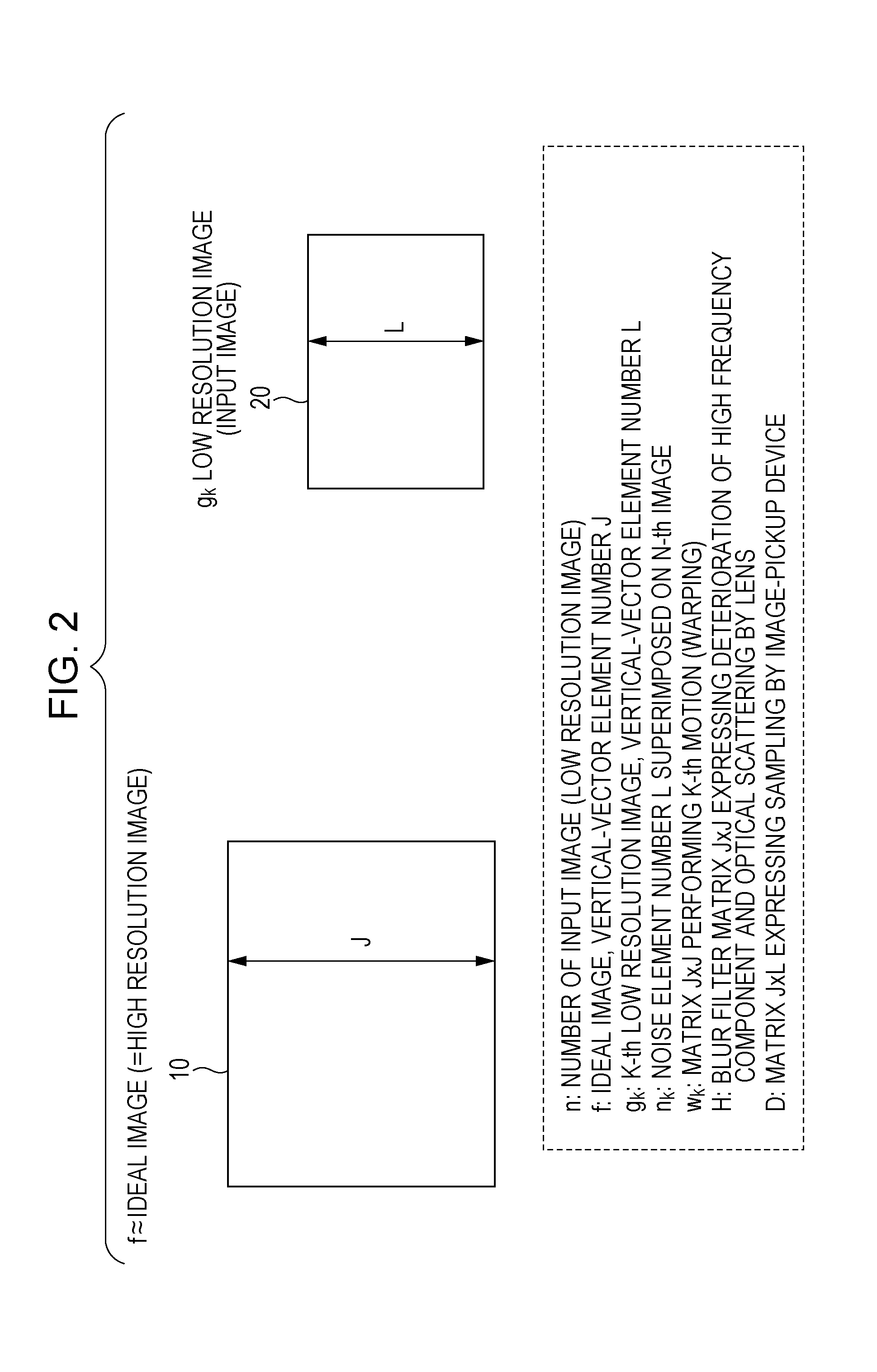
Provided is an image processing apparatus including a super resolving processor including: a high frequency estimator which generates difference image information between a low resolution image input as a processing object image of a super resolving process and a mid-processing image of the super resolving process or a processed image, that is, an initial image; and a calculator which performs a process of updating the processed image through a process of calculation between the difference image information output from the high frequency estimator and the processed image, wherein the high frequency estimator performs a learning type data process using learned data in the difference image information generating process.
Owner:SONY CORP
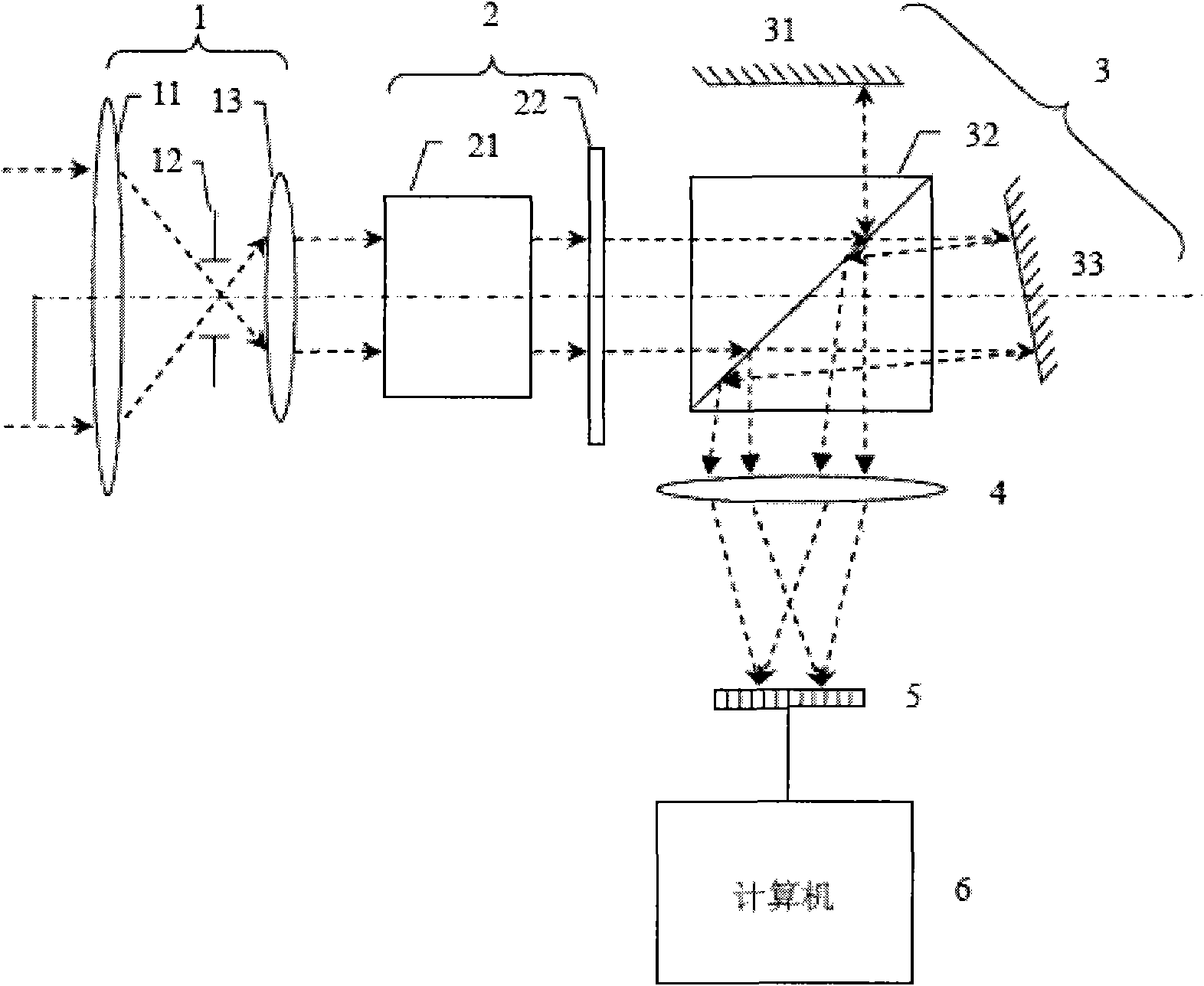
Static Fourier transform interference imaging spectrum full-polarization detector
ActiveCN101806625AHigh resolution imagingReal-time detectionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryImaging lensLuminous flux
The invention discloses a static Fourier transform interference imaging spectrum full-polarization detector, which comprises a fronting optical telescope system, a static all-optical modulation module, a static Fourier transform interference imaging spectrometer, an imaging lens group, an area-array detector which are arranged in sequence along the light transmission direction, wherein the area-array detector is connected with a signal acquiring and processing system; light emitted by a target source is collimated by the fronting optical system, and then is modulated by the static all-optical modulation module; after the modulated transmission light passes through the static Fourier transform interference imaging spectrometer, emergent light is changed into two beams of coherent light; the two beams of light pass through the imaging lens group and then are convergent on the area-array detector for imaging and interference; and a signal received by the area-array detector is sent to the signal acquiring and processing system for processing. The static Fourier transform interference imaging spectrum full-polarization detector has the characteristics of simple and compact structure, no moving parts, high luminous flux, and acquisition of target two-dimensional spacial images, one-dimensional spectral information and complete polarization information at one time.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Compression perception radar high resolution imaging equipment under low signal to noise ratio and imaging method thereof
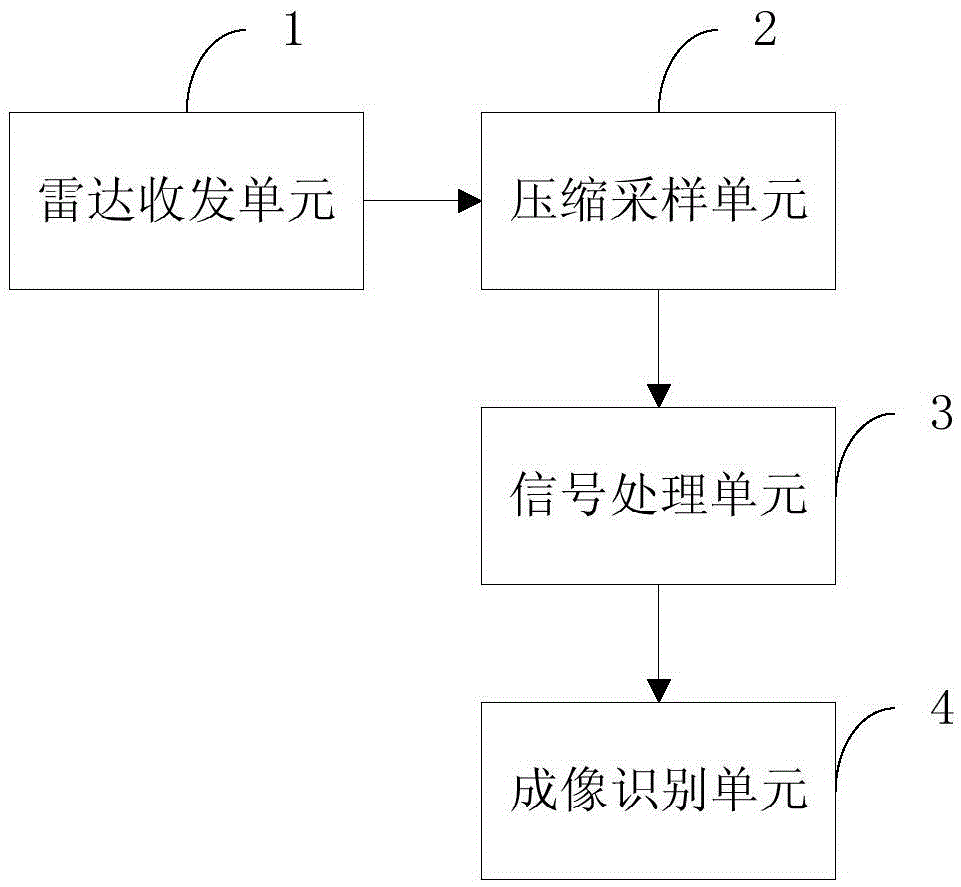
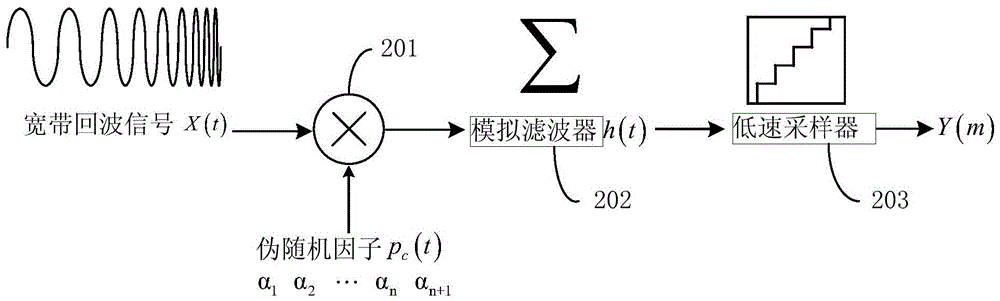
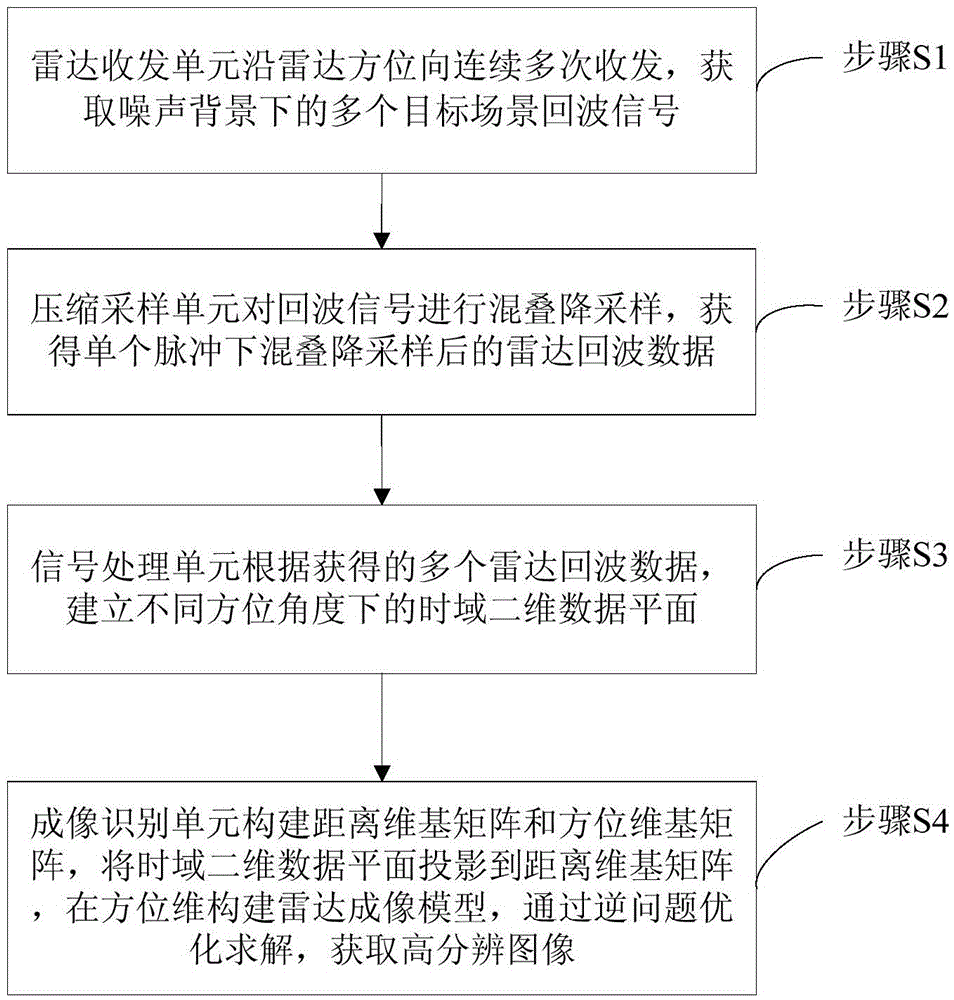
InactiveCN105467388AHigh resolution imagingSuppress noiseRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingTransceiver
Compression perception radar high resolution imaging equipment under a low signal to noise ratio and an imaging method thereof are disclosed. A radar transceiver unit carries out continuous multi-time transmitting and receiving along a radar azimuth and acquires a plurality of target scene echo signals under a noise background. A compression sampling unit carries out aliasing downsampling on the acquired echo signals and acquires radar echo data after aliasing downsampling under a single pulse. A signal processing unit establishes time-domain two-dimensional data planes under different orientation angles according to the plurality of radar echo data. An imaging identification unit constructs a distance dimension basis matrix and an orientation dimension basis matrix. The time-domain two-dimensional data planes are projected to the distance dimension basis matrix. A radar imaging model is constructed on the orientation dimension. Through an inverse optimization method, a high resolution image is acquired. In the invention, a small aperture radar effectively restrains a noise interference and a side lobe through a small echo data volume and simultaneously realizes high resolution imaging, and a performance index of a small aperture radar system is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
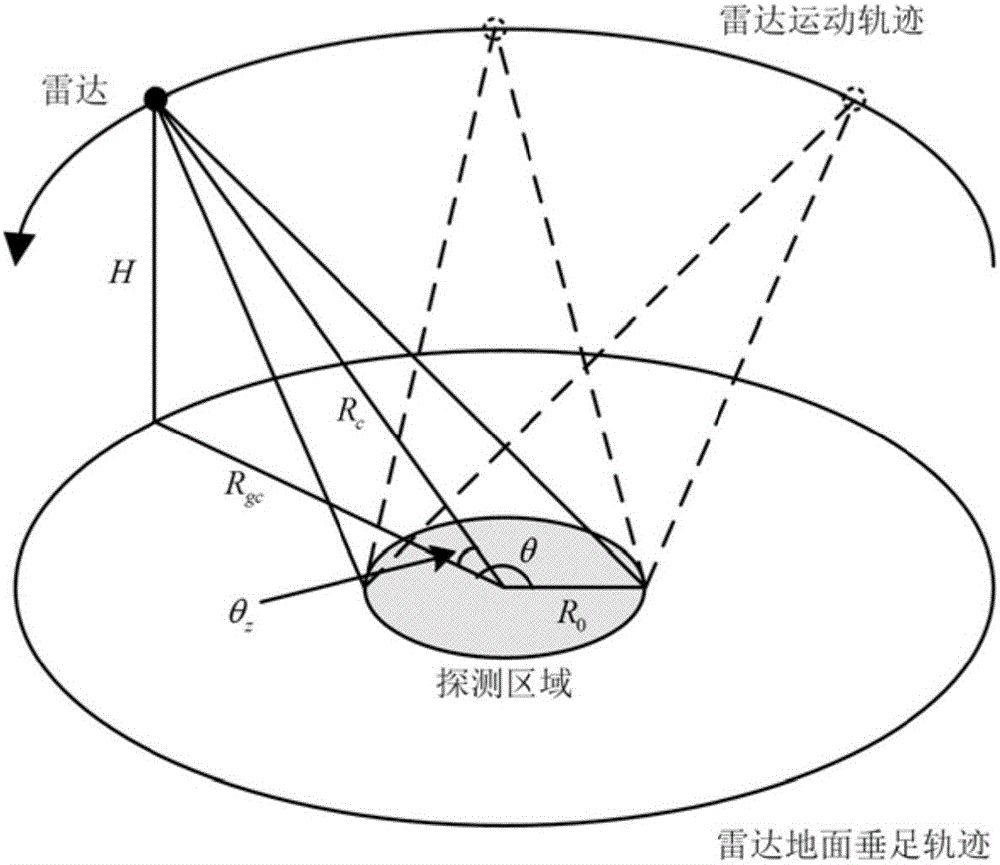
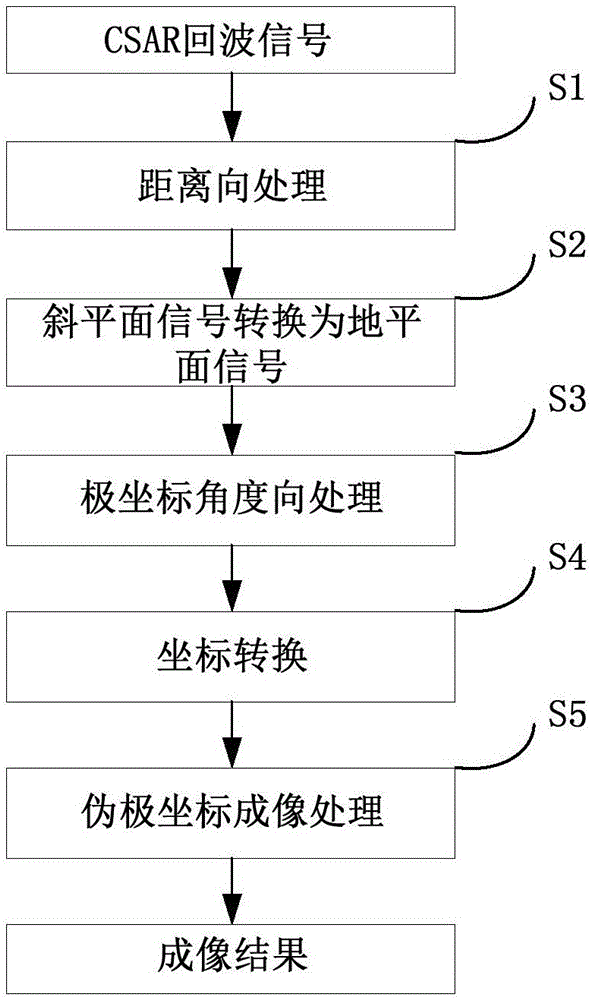
Circular synthetic aperture radar imaging method
InactiveCN106772380AHigh resolutionHigh resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInformation processingRapid imaging
The invention discloses a circular synthetic aperture radar imaging method, belonging to the technical field of electronic signal processing. The invention relates to a spatial remote sensing and air-to-ground observation information processing technology, in particular to an onboard circular synthetic aperture radar imaging technology. According to the imaging method, an original oblique plane echo is mapped to the ground plane by solving the inverse of a system kernel function, and the distribution of signals in a wave number domain is obtained by multiplying an azimuth frequency domain with a reference function, so that plane wave approximation is avoided, the problem that the size of an imaging area of the traditional polar format algorithm is limited can be solved, and the imaging of a large imaging scene can be realized; pseudo-polar coordinates are used for replacing rectangular coordinates as an intermediate interpolation transition matrix, and the distribution density characteristic of the signals in the wave number domain is considered, so that the interpolation precision is higher, the obtained image resolution is higher, and the high resolution imaging can be realized; the imaging process only involves one-dimensional interpolation, and fast algorithms such as chirp z transform (CZT) and inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) are adopted, so that the method has very high computational efficiency and can realize rapid imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Solid state imaging apparatus, method for driving the same and camera using the same
ActiveUS7436010B2High resolution imagingIncrease the aperture ratioTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierPhotoelectric conversion
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Two-dimensional MIMO (multi-input multi-output) array implementation method
InactiveCN104808201ASimple and versatileSave resource costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti inputHigh resolution imaging
The invention provides a two-dimensional MIMO (multi-input multi-output) array implementation method. The method includes the steps: determining intervals and quantity of array elements of a to-be-imaged equivalent virtual array; designing an initial one-dimensional linear transmitting array and a one-dimensional linear receiving array; enabling the transmitting array and the receiving array to move relatively; when a distance between each two adjacent transmitting antennas and a distance between each two adjacent receiving antennas are both / 2 / 2 times of a wavelength, stopping moving; judging whether the designed array meets requirements or not according to index requirements, and if not, continuing to execute until an antenna array meeting the design requirements is obtained; starting image testing after array design is finished. The two-dimensional MIMO array implementation method is simple, flexible and uniform and is highly advantageous in terms of array optimization selection, high-resolution imaging, saving of hardware resource cost and the like. Furthermore, two-dimensional or three-dimensional imaging of a target can be realized effectively by the aid of the antenna array designed according to the method.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
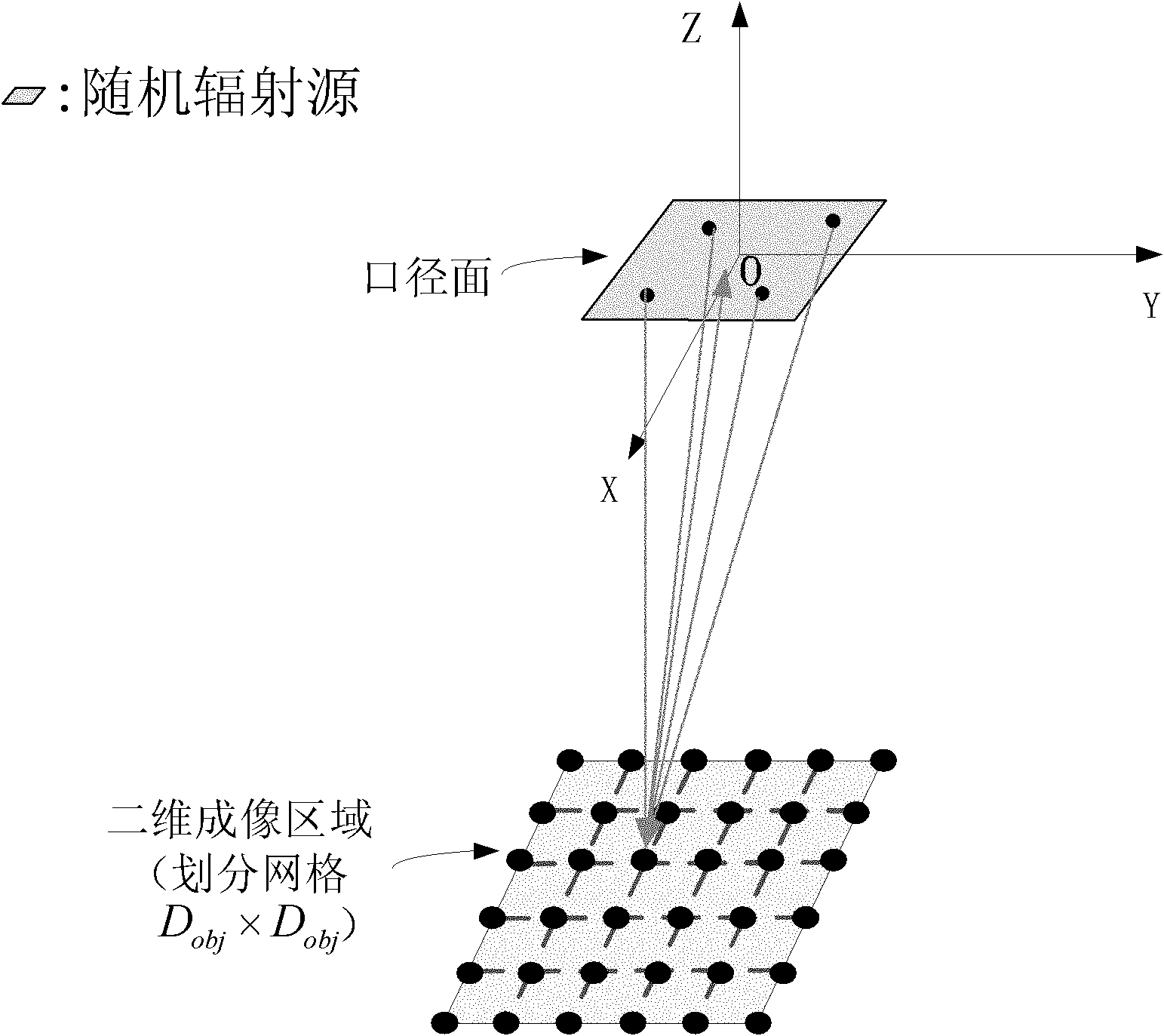
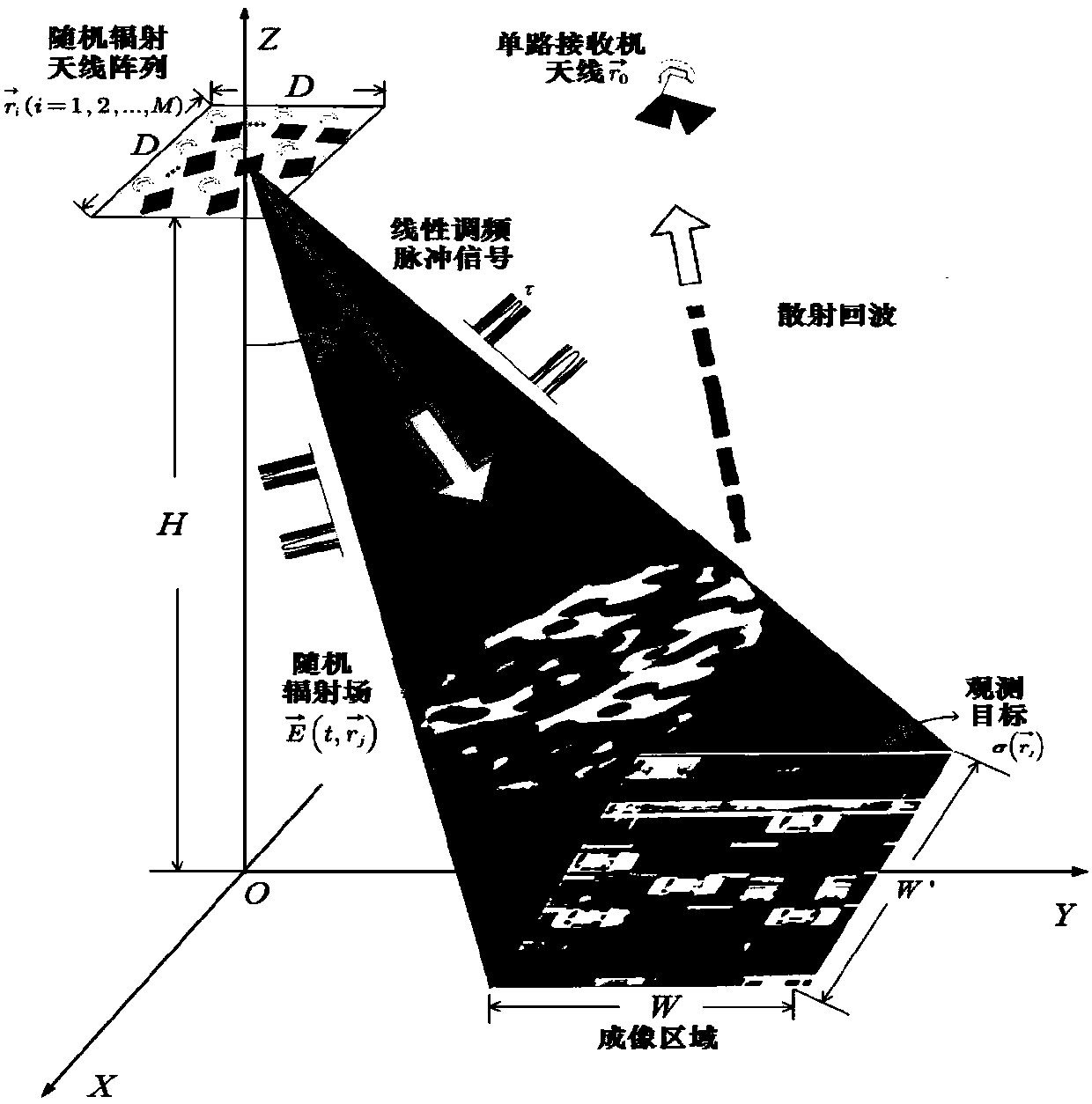
Microwave staring imaging correlation method
InactiveCN102141617AHigh resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMicrowaveElectromagnetic field
The invention discloses a microwave staring imaging correlation method which comprises the following stepsof irradiating a target area object through a random radiation field and forming the distribution of the radiation field on an object surface; receiving a scattering field through a multi-channel or a single channel and carrying out electromagnetic field analysis to the imaging physical process of the target area object to obtain a time and space two-dimensional radiation field function corresponding to the object surface within the whole imaging area scope; counting the relevant characteristics of a time and space two-dimensional radiation field according to the time and space two-dimensional radiation field function; and carrying out correlated processing on the scattering field and the random radiation field according to the statistic characteristics to obtain the imaging of the target area object through inversion. The microwave staring imaging correlation method can be combined with the scattering field and the time and space two-dimensional radiation field to realize the high-resolution target imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
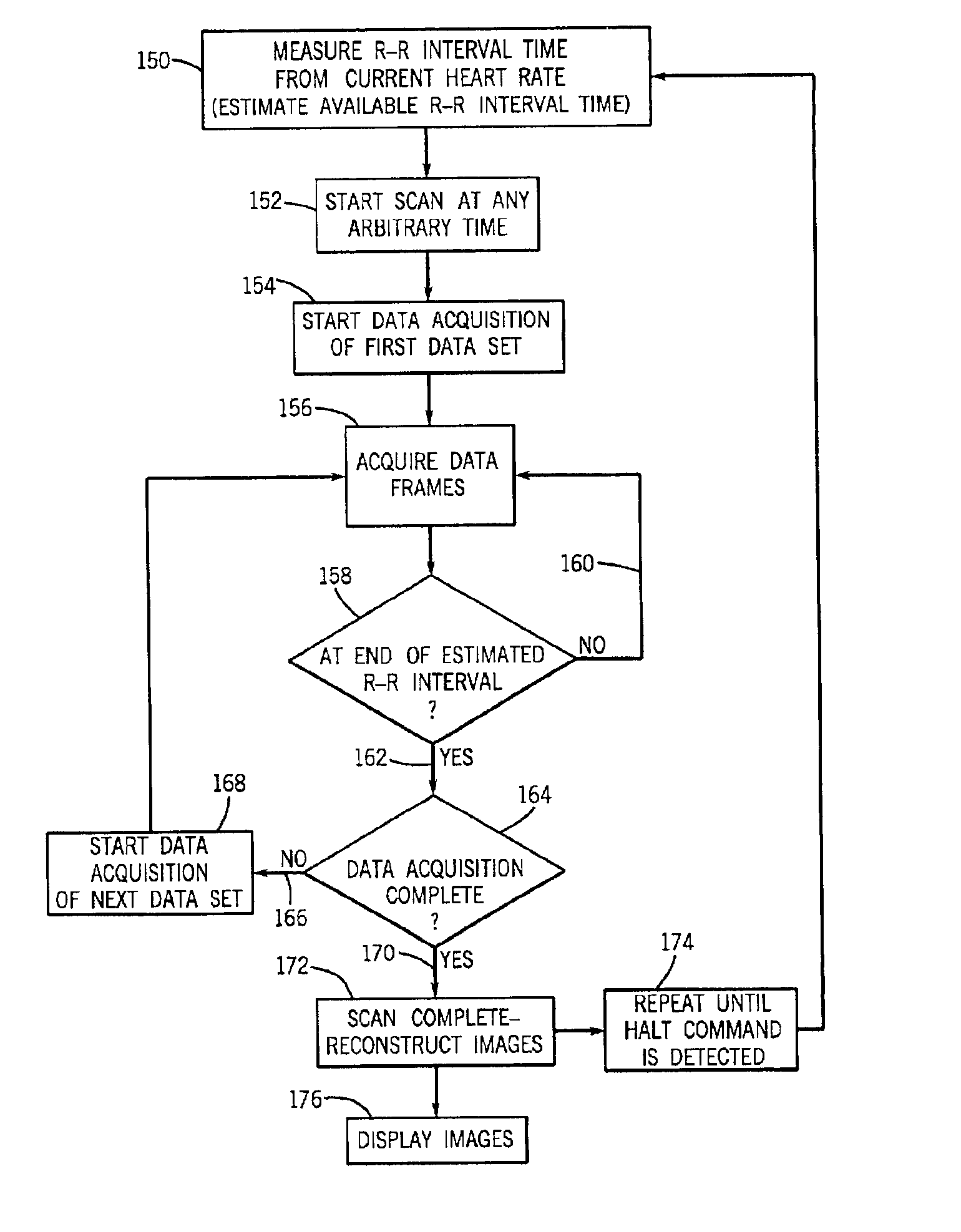
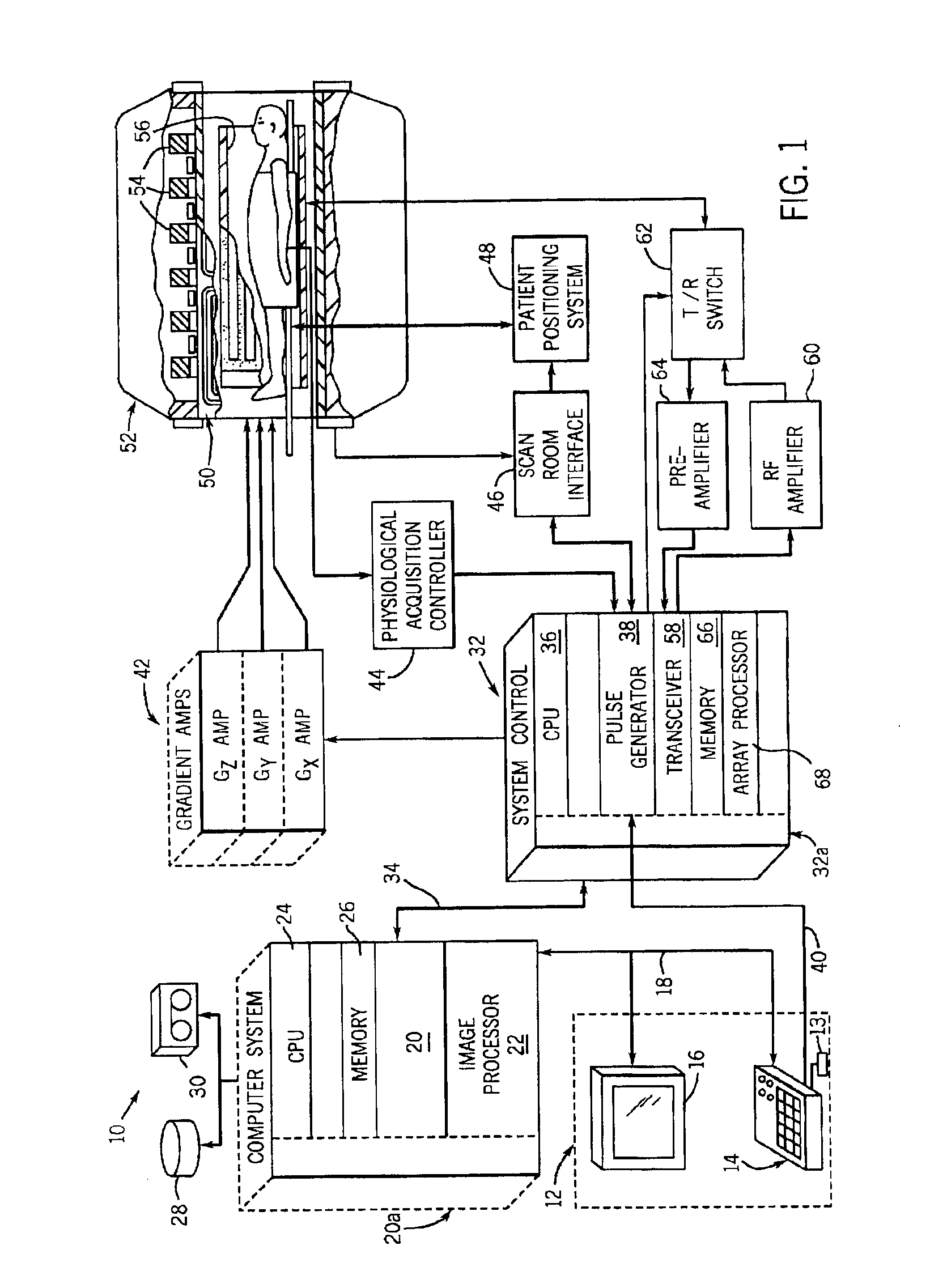
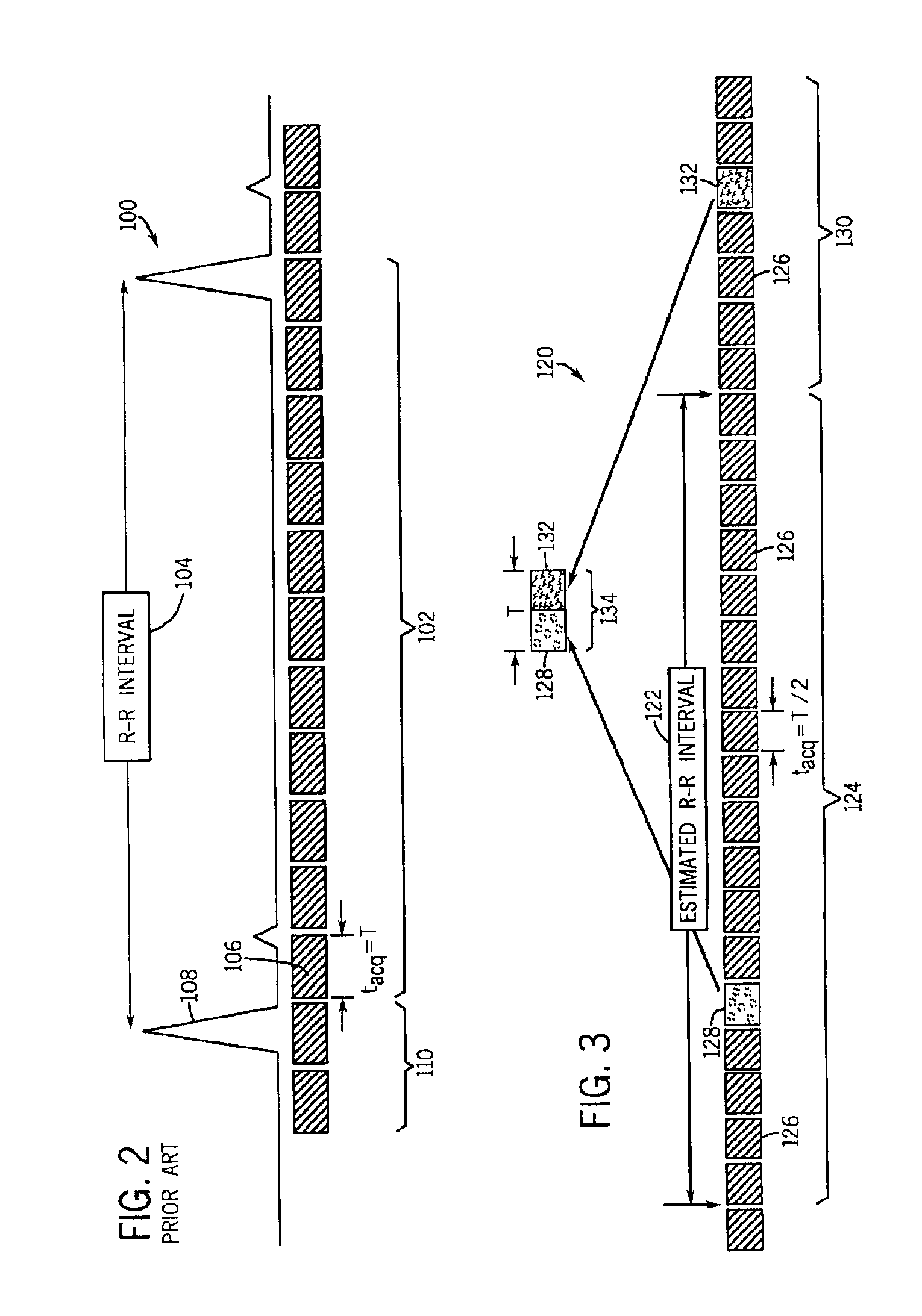
Acquisition of high-temporal free-breathing MR images
InactiveUS6889071B2Short acquisition timeHigh resolution imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImage resolutionTime segment
A system and method are disclosed to acquire high temporal resolution free-breathing cardiac MR images. The technique includes monitoring heart rate of a patient just prior to image acquisition to acquire a time period of an R—R interval, and using this time period from the heart rate monitoring to prospectively estimate future R—R intervals. The acquisition of MR data can then commence at any point in an R—R interval and extend for the time period recorded. The data acquisition can be segmented and acquired in successive R—R intervals, then combined to create high temporal resolution images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
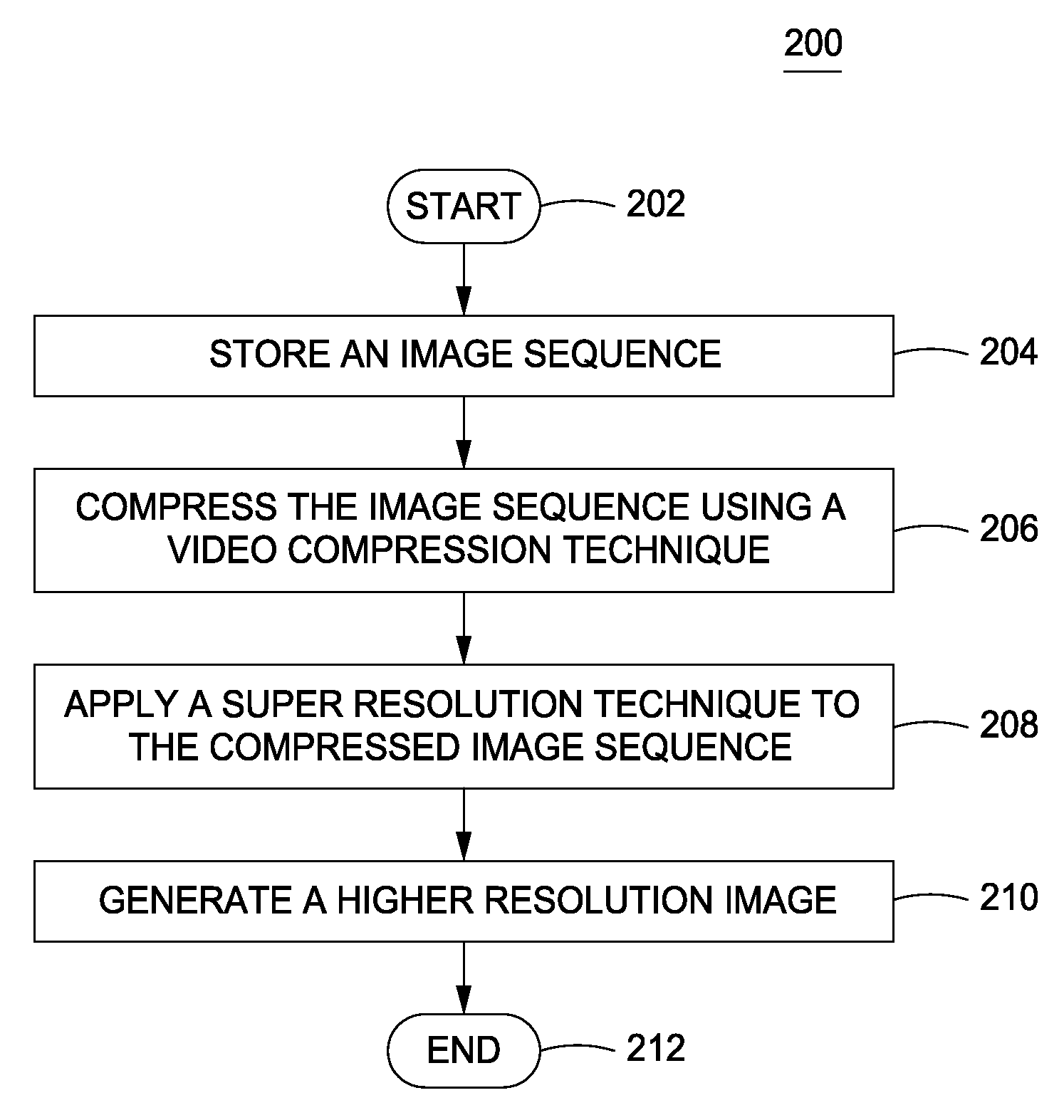
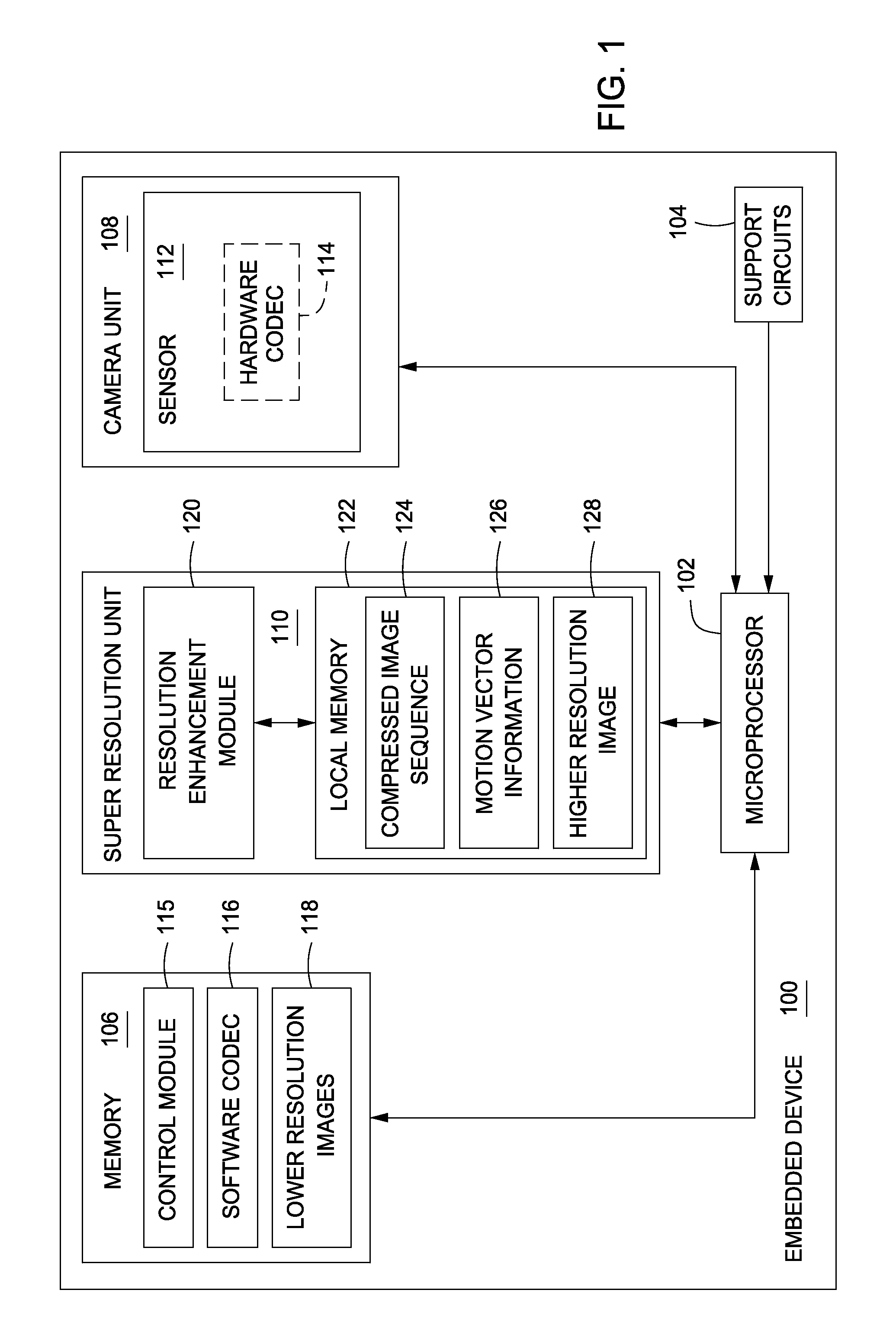
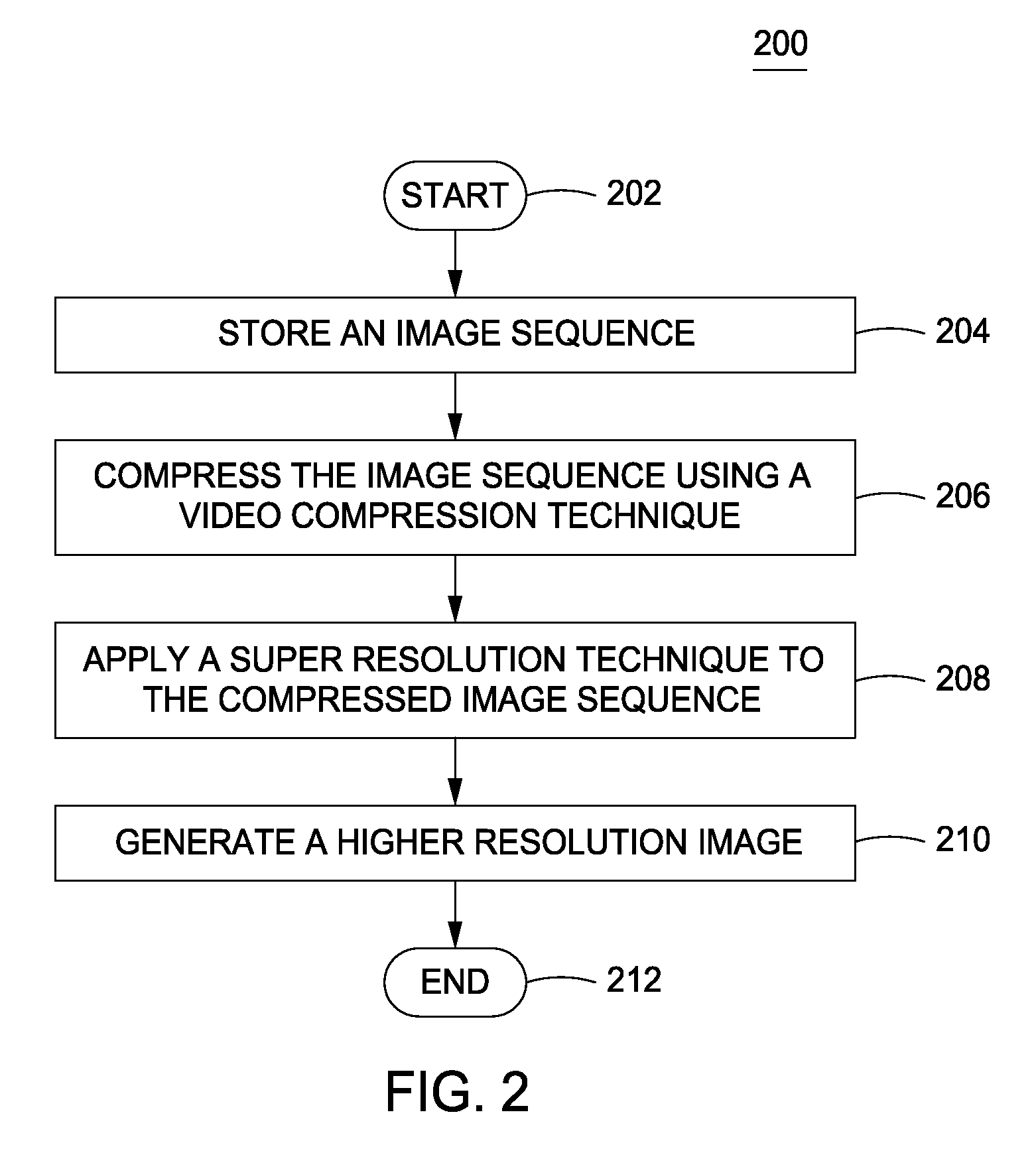
Method and apparatus for providing higher resolution images in an embedded device
ActiveUS20100034477A1High resolutionHigh resolution imagingGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
A method and apparatus to providing higher resolution images on an embedded device by performing a super resolution technique on a compressed image sequence and one or more motion vectors are described. In one example, the method includes compressing an image sequence using a video compression technique, wherein the image sequence comprises a plurality of lower resolution images and applying a super resolution technique to the compressed image sequence to generate a higher resolution image.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
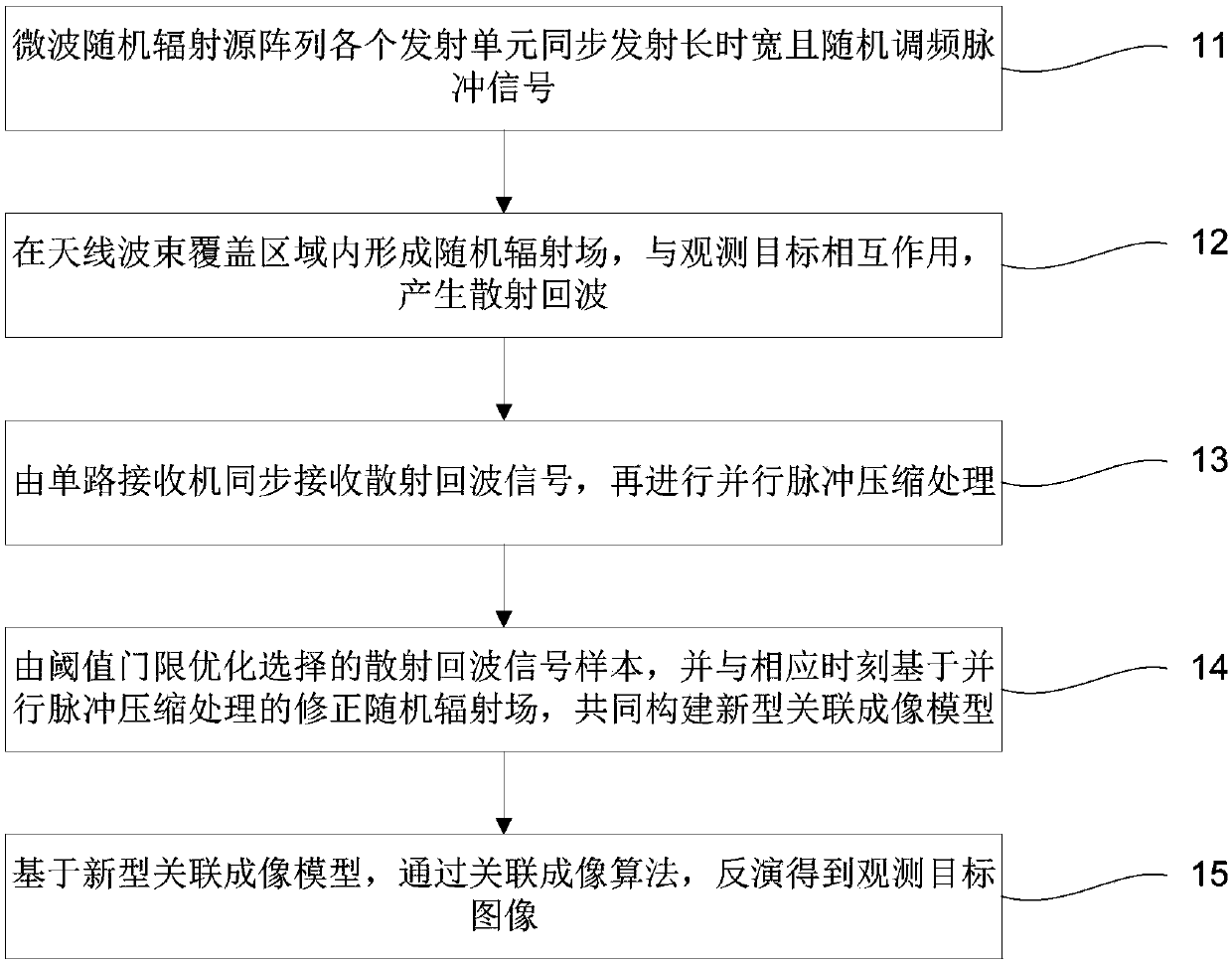
Microwave stare correlated imaging method under condition of low signal to noise ratio
ActiveCN107678028AHigh resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Physics
The invention discloses a microwave stare correlated imaging method under the condition of a low signal to noise ratio, and the method comprises the steps: enabling all transmitting units of a microwave random radiation source array to transmit random frequency modulation pulse signals with the long time widths synchronously; forming a random radiation field in an antenna wave beam coverage area,enabling the random radiation field to interact with an observation object, and generating echo waves; synchronously receiving scattered echo signals through single-way receivers, and carrying out theparallel pulse compression processing; optimizing a selected scattered echo signal sample through a threshold, and constructing a new correlated imaging model with a corrected random radiation fieldat a corresponding moment based on parallel pulse compression processing; and obtaining an observation target image through inversion and a correlated imaging algorithm based on the novel correlated imaging model. The method can achieve the high-resolution imaging of the target under the condition of the low signal to noise ratio.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
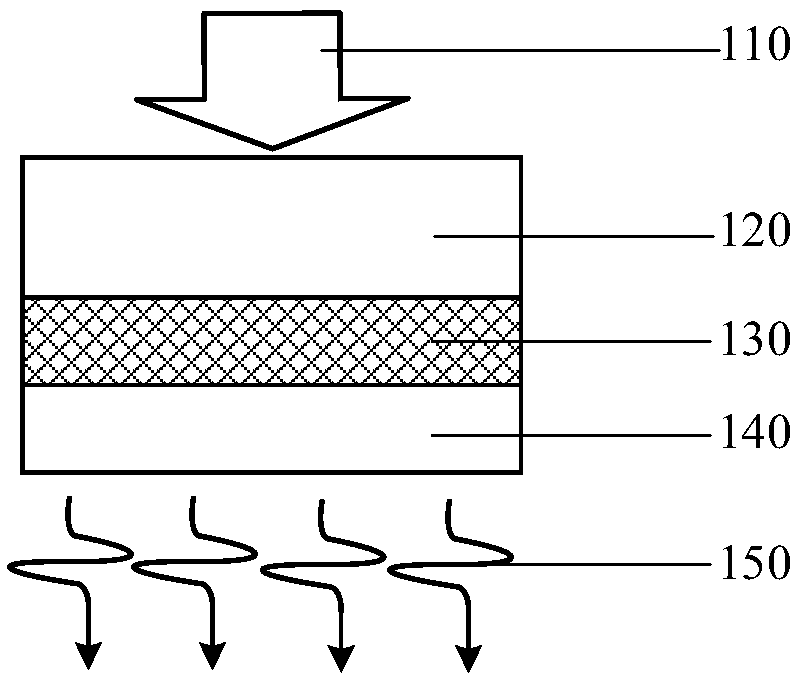
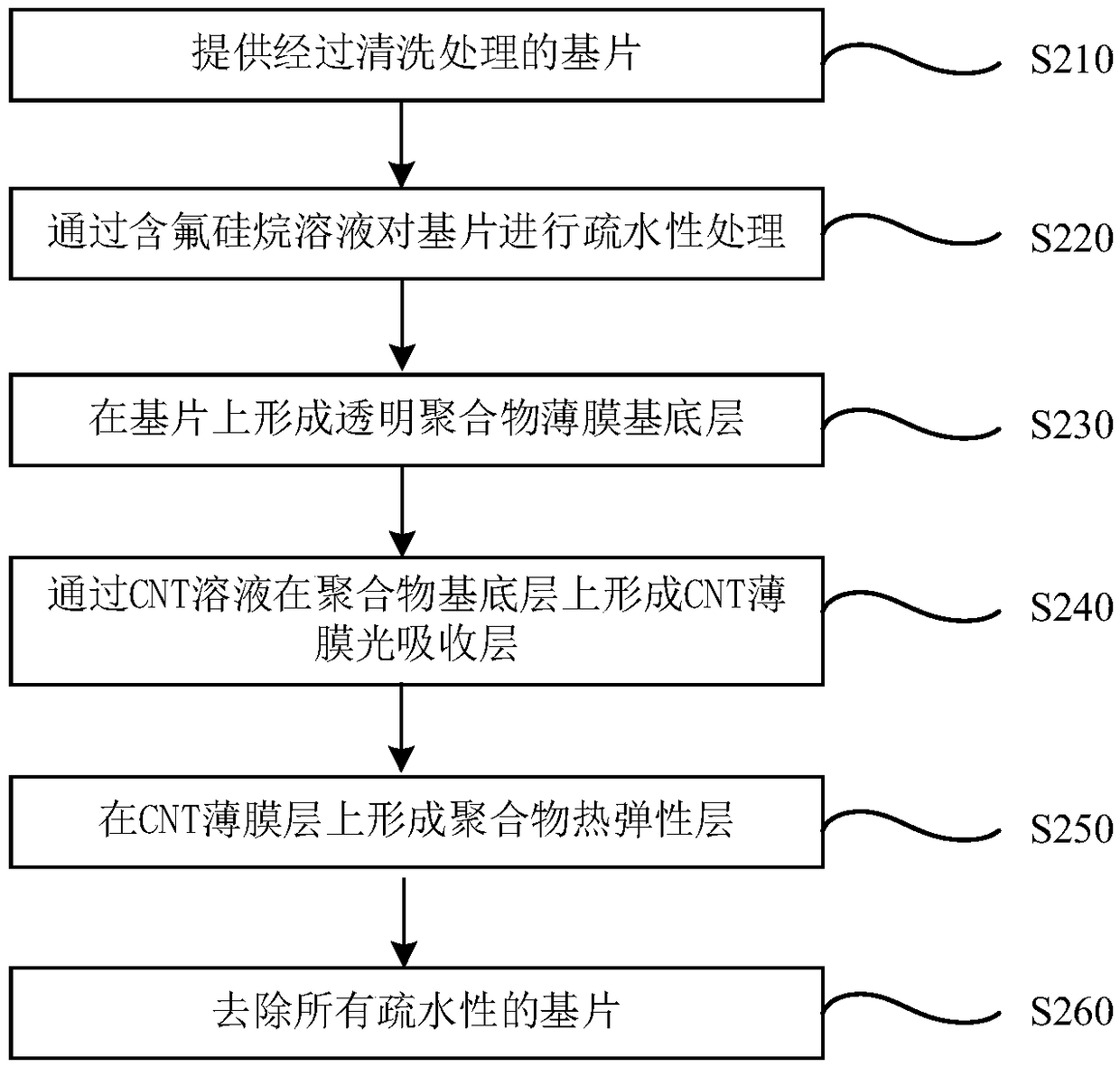
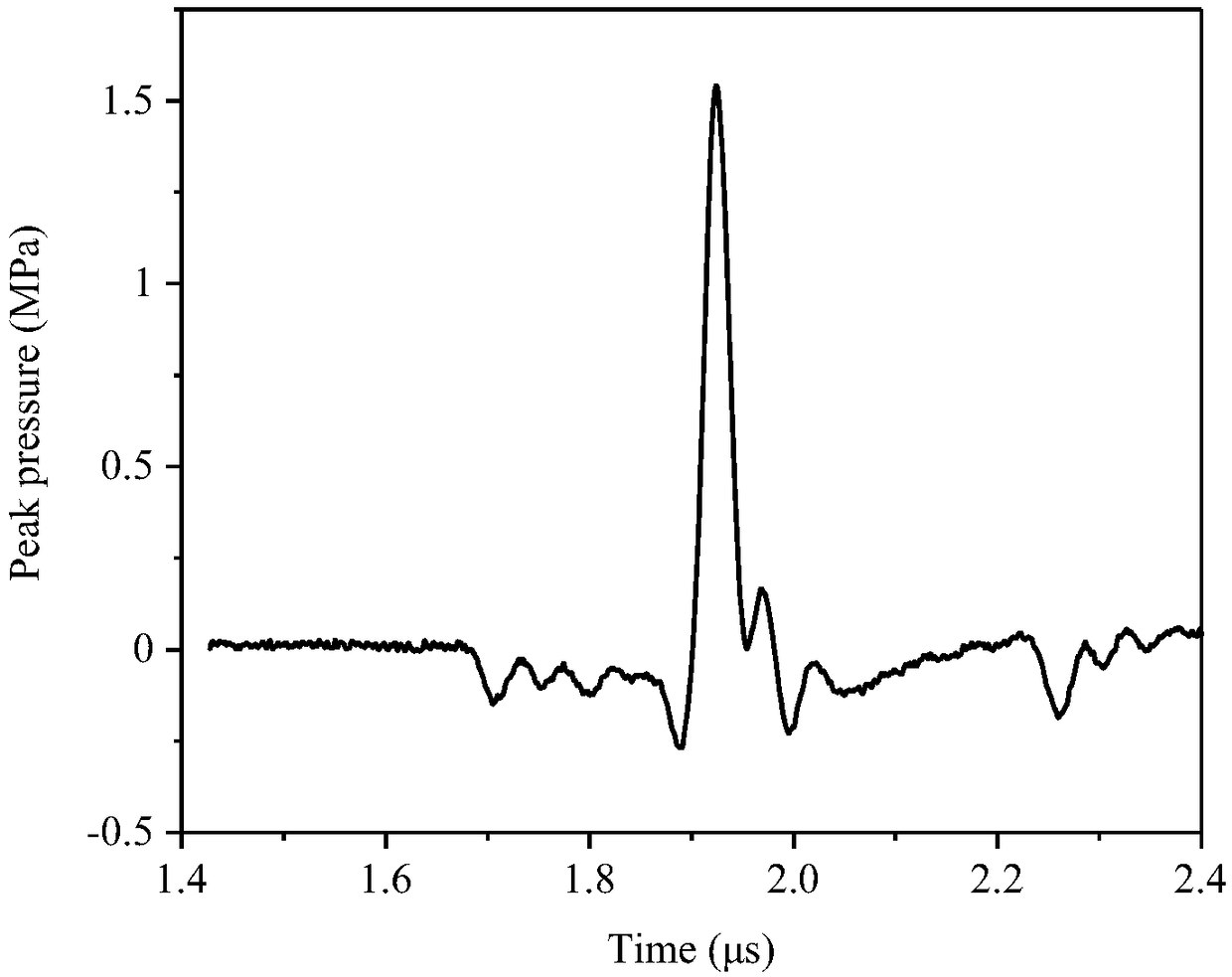
Flexible photoinduced ultrasonic thin film transducer and preparation method thereof
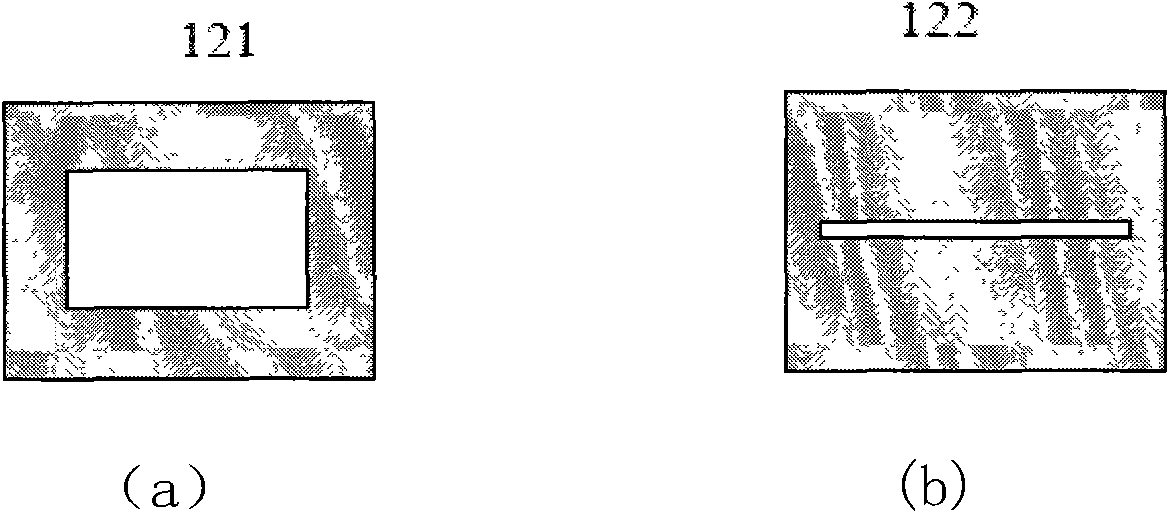
ActiveCN109433571AHigh photoacoustic conversion efficiencyHigh-resolutionMechanical vibrations separationPolymer substrateCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a flexible photoinduced ultrasonic thin film transducer and a preparation method thereof. The ultrasonic thin film transducer comprises a flexible transparent substrate (120),a light absorbing layer (130) and a thermos-elastic layer (140) from top to bottom in sequence. The flexible transparent substrate (120) is transparent polydimethylsiloxanepolymers; the light absorbing layer (130) is carbon nanotubes; and the thermo-elastic layer (140) is polydimethylsiloxane polymers. The preparation method of the flexible photoinduced ultrasonic thin film transducer comprises the steps that a glass substrate is spin-coated with a polydimethylsiloxane agent, and the flexible transparent substrate is prepared; an aluminum oxide inorganic screening film deposited with a carbonnanotube filter cake is pressed onto the transparent polymer thin film prepared in the second step, the aluminum oxide inorganic screening film is peeled off, and a carbon nanotube thin film transferred with the light absorbing layer is obtained on a transparent polymer substrate; and a carbon nanotube thin film layer is spin-coated with the polydimethylsiloxane polymers, and the thermos-elastic layer is formed after solidification. After the thermo-elastic layer is solidified, the glass substrate is peeled off.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Passive static triangle common path interference imaging spectral full-polarization detecting device
InactiveCN101799327AHyperspectral resolutionIncrease luminous fluxInterferometric spectrometryOptical elementsMoving partsAll optical
The invention relates to a passive static triangle common path interference imaging spectral full-polarization detecting device, which comprises a fronting optical telescopic system. The rear part of the fronting optical telescopic system is provided with a static all-optical modulating module; the rear part of the static all-optical modulating module is provided with a Sagnac static interference imaging spectrometer; the rear part of the Sagnac static interference imaging spectrometer is provided with an imaging mirror group; the rear part of the imaging mirror group is provided with a detector which is connected with a signal acquiring and processing system; after light which is emitted by a target source is collimated and then subjected to phase modulation, the modulated transmission light is changed into two beams of parallel polarized light; the two beams of light are converged on the detector after passing through the imaging mirror to form the image and generate interference; and then a signal received by the detector is sent to the signal acquiring and processing system to be processed. The device has the characteristics of simple and compact structure, no moving parts, large light quantity and capability of acquiring target two-dimensional space images, one-dimensional spectral information and complete polarization information once.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Advanced Magnification Device and Method for Low-Power Sensor Systems
ActiveUS20120019671A1Advanced optical magnification functionHigh resolution imagingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsData valuePower sensor
A system and method is provided for enabling an advanced optical magnification (zooming) function for low-power sensors, such as a remote wireless camera, using electronic methods and enabling that magnification be performed in any part of the imager. An image sensor has a set of imager pixels that have a defined field of view. A display device is also provided, which has a far lower resolution than the imager. A magnification level is selected, which results in macroblocks being defined for the sensor. A display data value is generated for each macroblock, and the set of display data values is used to drive a data display. The area of magnification is flexibly selected on the imager. As the magnification level is increased, the number of imager pixels in each macroblock decrease, enabling the display to present increasingly higher resolution images. Accordingly, an aesthetically pleasing magnification function is provided for a low-power, battery operated mobile environment.
Owner:AVAAK
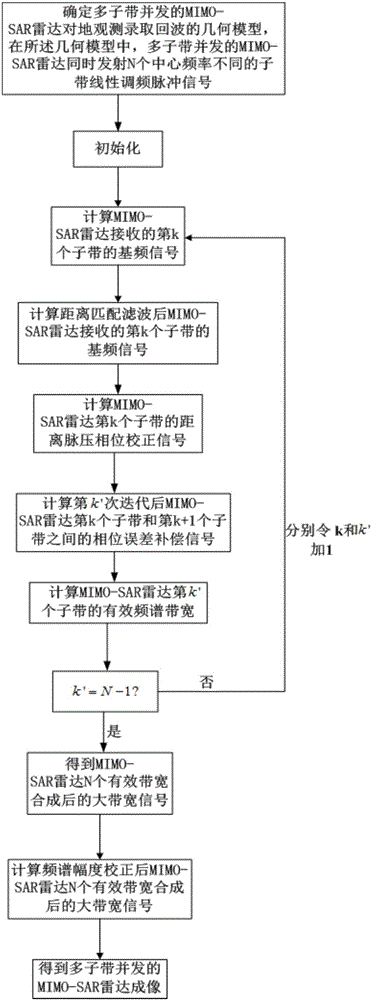
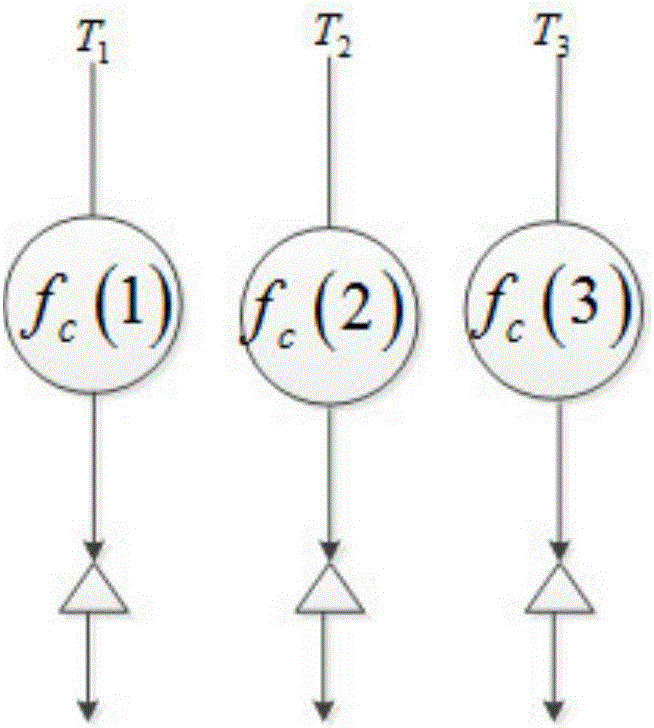
Multi-sub band concurrent MIMO-SAR radar imaging method
ActiveCN106338731AHigh resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEarth observationFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a multi-sub band concurrent MIMO-SAR radar imaging method mainly comprising the following steps: determining a geometrical model of earth observation recording echo of multi-sub band concurrent MIMO-SAR radar; calculating the baseband signal of a kth sub band received by MIMO-SAR radar and the baseband signal of the kth sub band received by the MIMO-SAR radar after range matching filtering; calculating the effective spectrum bandwidth of a k'th sub band of the MIMO-SAR radar; calculating a large-bandwidth signal S generated through synthesis of N effective spectrum bandwidths of the MIMO-SAR radar; correcting the spectrum amplitude of S to get a large-bandwidth signal S' generated through synthesis of N effective spectrum bandwidths of the MIMO-SAR radar after spectrum amplitude correction; and performing range IFFT on S' and performing imaging based on a range migration algorithm in turn to get a multi-sub band concurrent MIMO-SAR radar image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High Spatial Resolution X-ray and Gamma Ray Imaging System Using Crystal Diffraction Lenses
InactiveUS20050175148A1High resolution imagingHigh purityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
A method for high spatial resolution imaging of a plurality of sources of x-ray and gamma-ray radiation is provided. High quality diffracting crystals of 1 mm width are used for focussing the radiation and directing the radiation to an array of detectors which is used for analyzing their addition to collect data as to the location of the source of radiation. A computer is used for converting the data to an image. The invention also provides for the use of a multi-component high resolution detector array and for narrow source and detector apertures.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
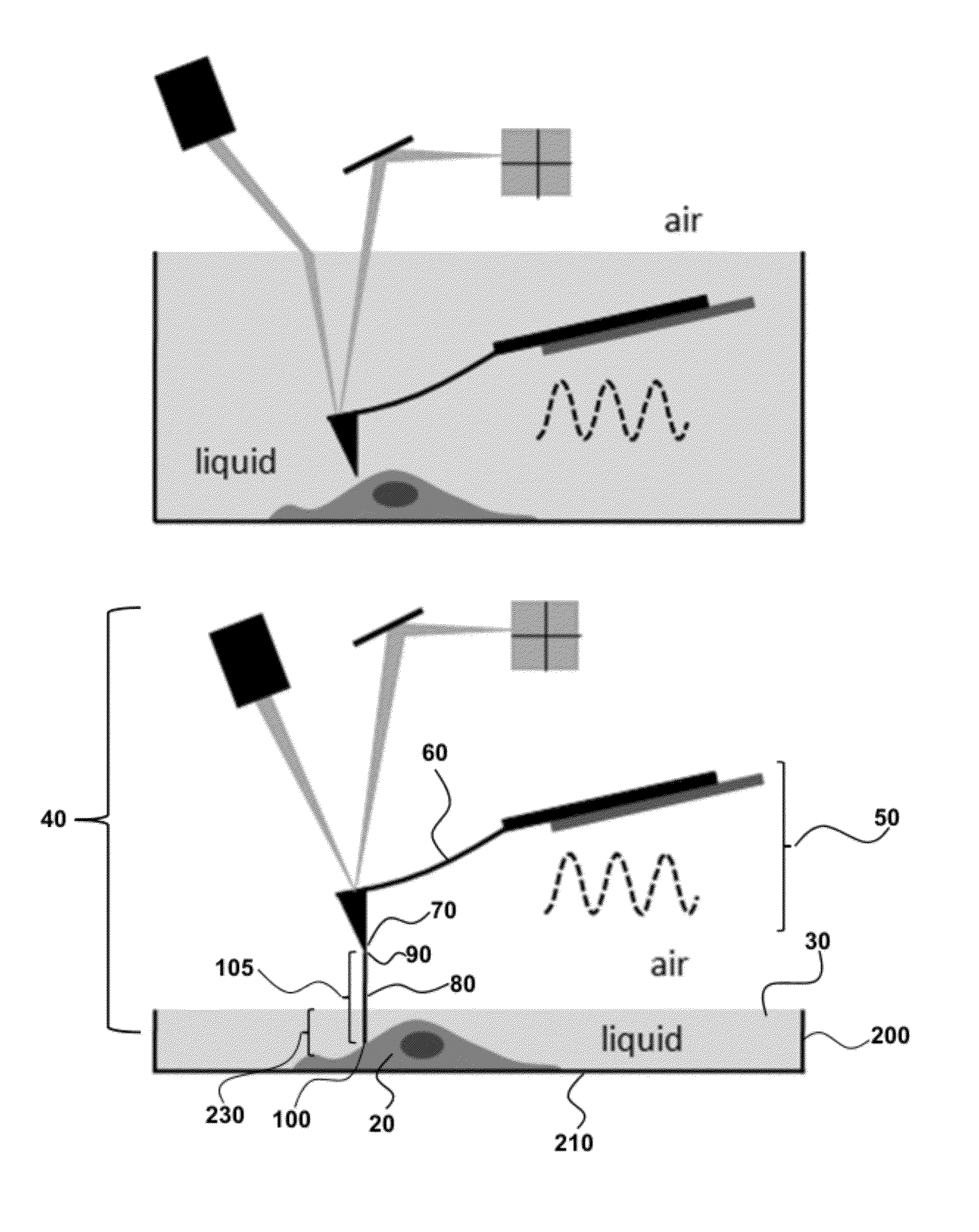
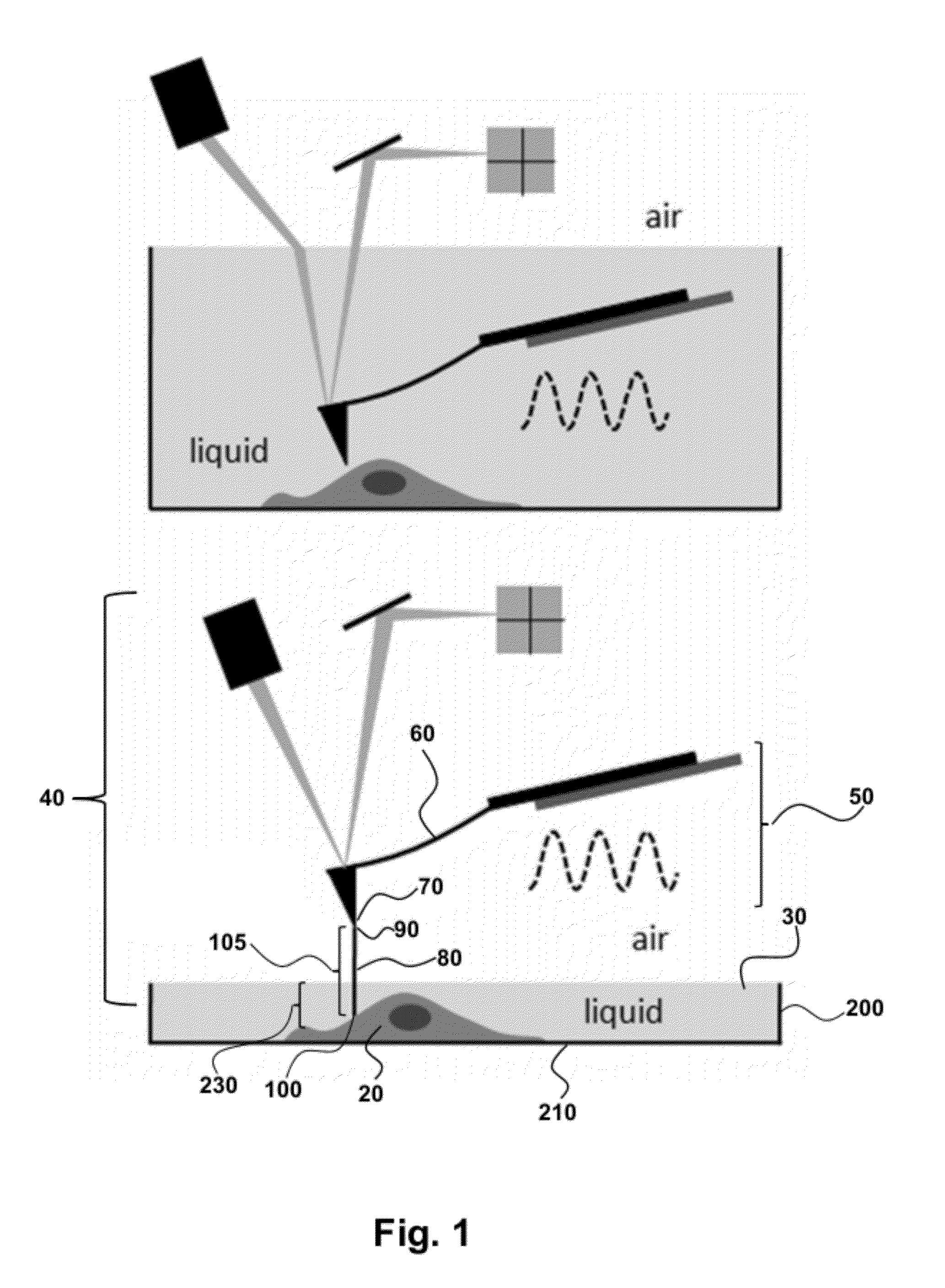
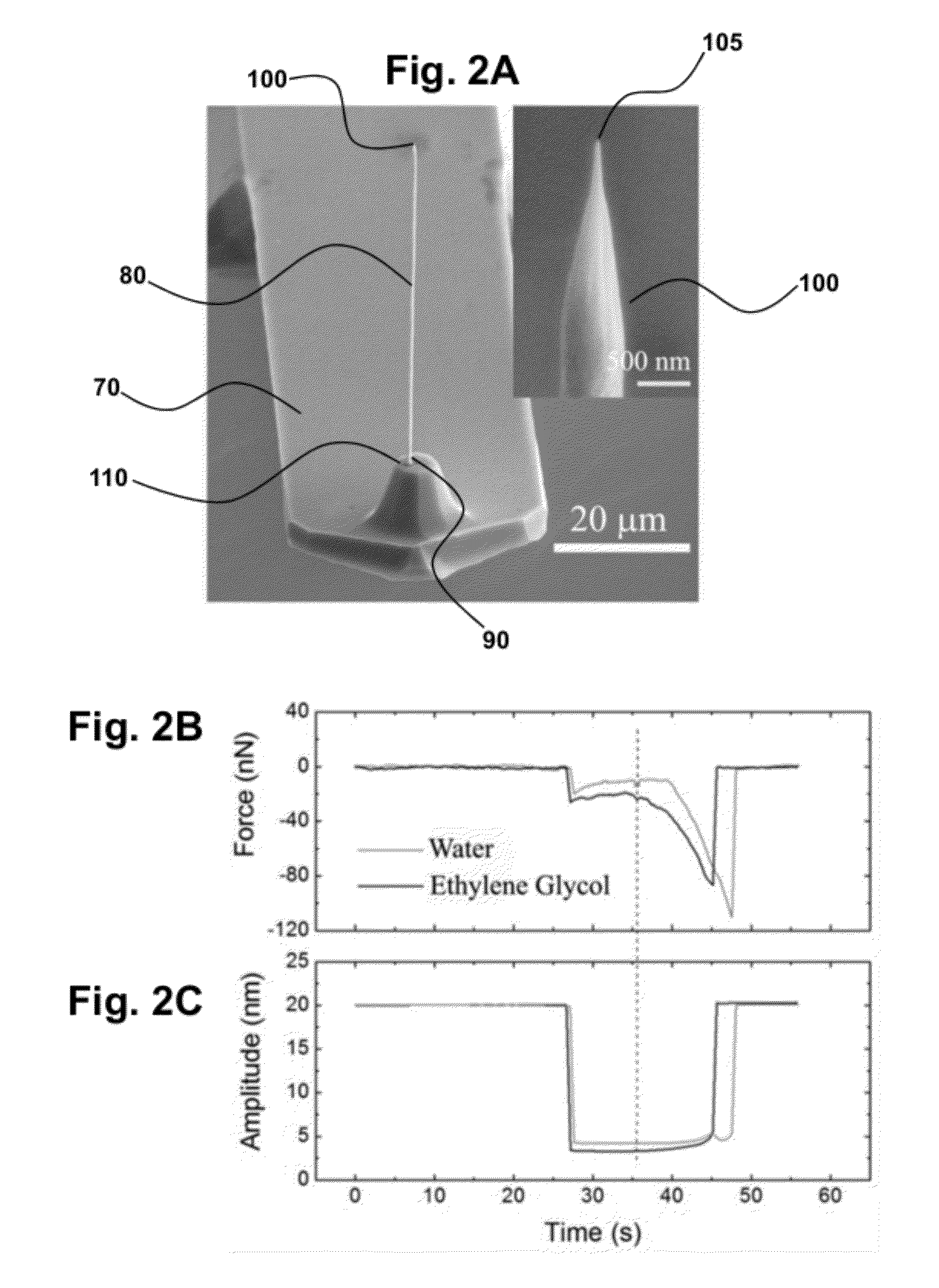
Ultra-Low Damping Imaging Mode Related to Scanning Probe Microscopy in Liquid
InactiveUS20120278958A1Ultra-low dampingHigh resolution imagingNanosensorsScanning probe microscopyAtomic force microscopyHigh resolution imaging
Provided are methods and systems for high resolution imaging of a material immersed in liquid by scanning probe microscopy. The methods further relate to imaging a material submersed in liquid by tapping mode atomic force microscopy (AFM), wherein the AFM has a microfabricated AFM probe comprising a nanoneedle probe connected to a cantilever beam. The nanoneedle probe is immersed in the liquid, and the rest of the AFM probe, including the cantilever beam to which the nanoneedle probe is attached, remains outside the liquid. The cantilever is oscillated and the nanoneedle probe tip taps the material to image the material immersed in liquid. In an aspect, the material is supported on a shaped substrate to provide a spatially-varying immersion depth with specially defined regions for imaging by any of the methods and systems of the present invention.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Miniature high-resolution multi-spectral objective lens
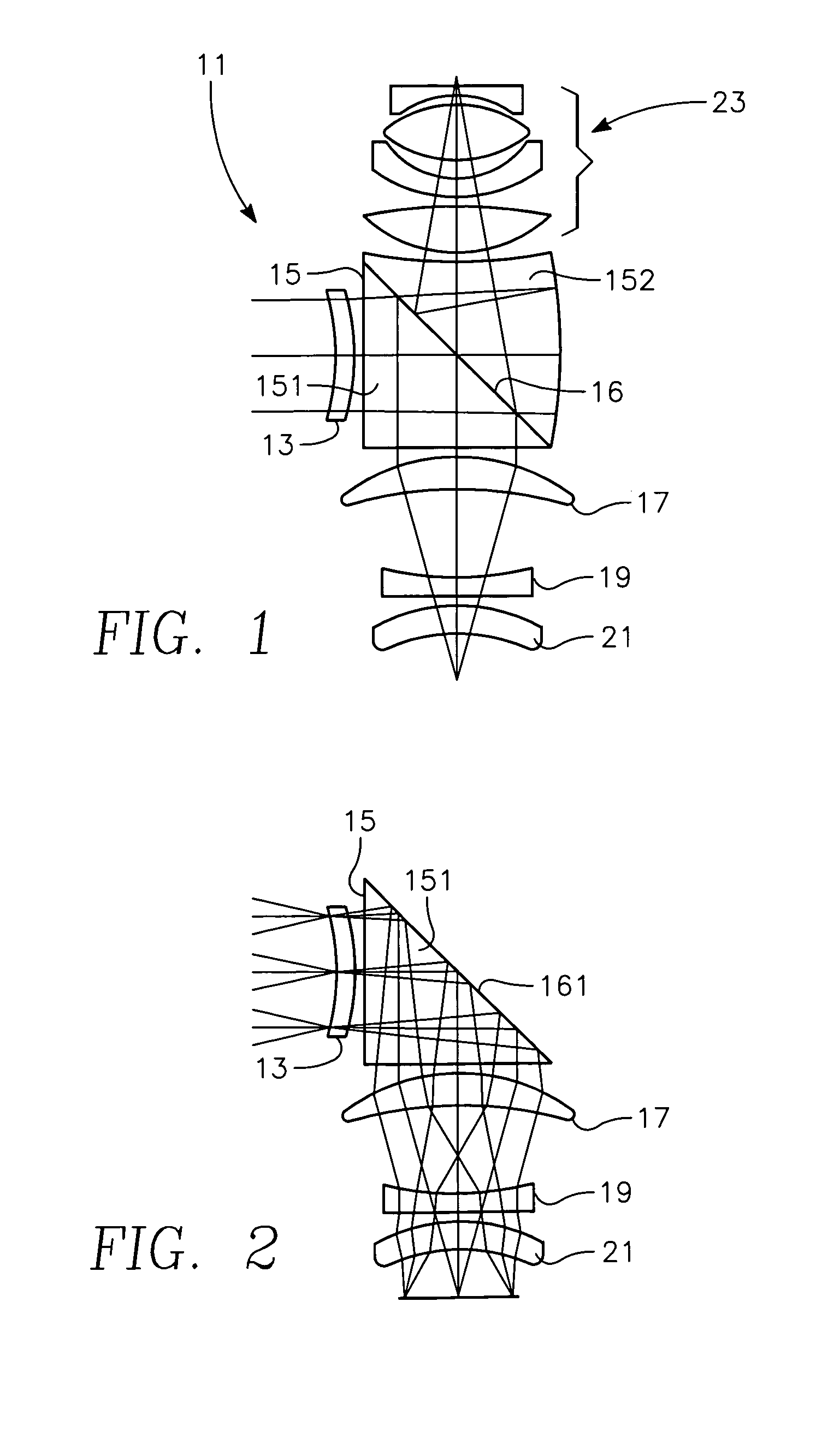
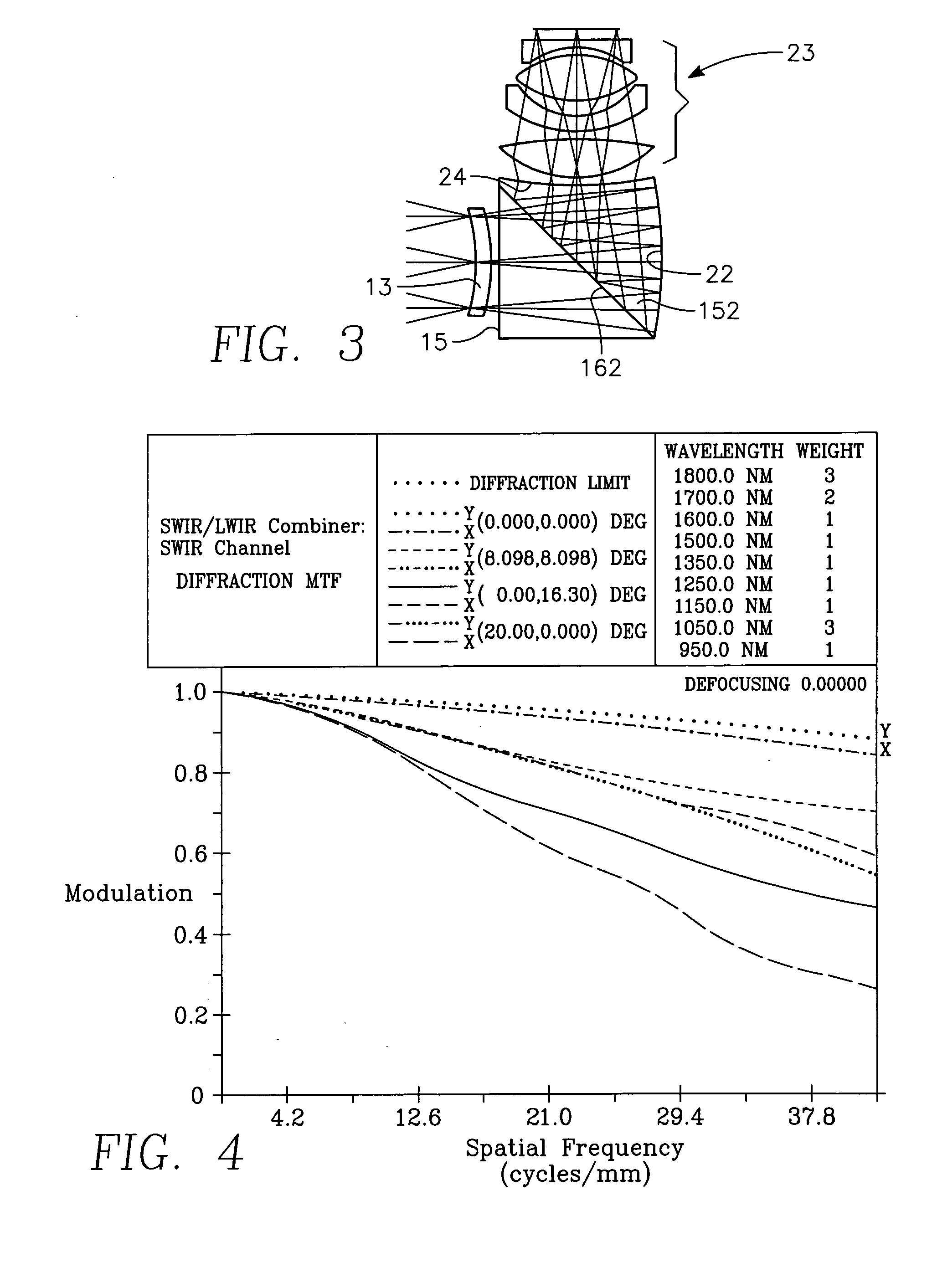
InactiveUS20050200946A1Small sizeSmall functional elementMirrorsOptical filtersElement spaceSpectral bands
A multi-spectral objective lens comprising a primary lens for receiving light reflected from an object, the light including wavelengths in the SWIR and LWIR spectral bands, and optical elements spaced from the receiving means for simultaneously imaging the SWIR light in one focal plane and the LWIR light in another focal plane, thereby allowing real-time image and sensor fusion.
Owner:ARMY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE
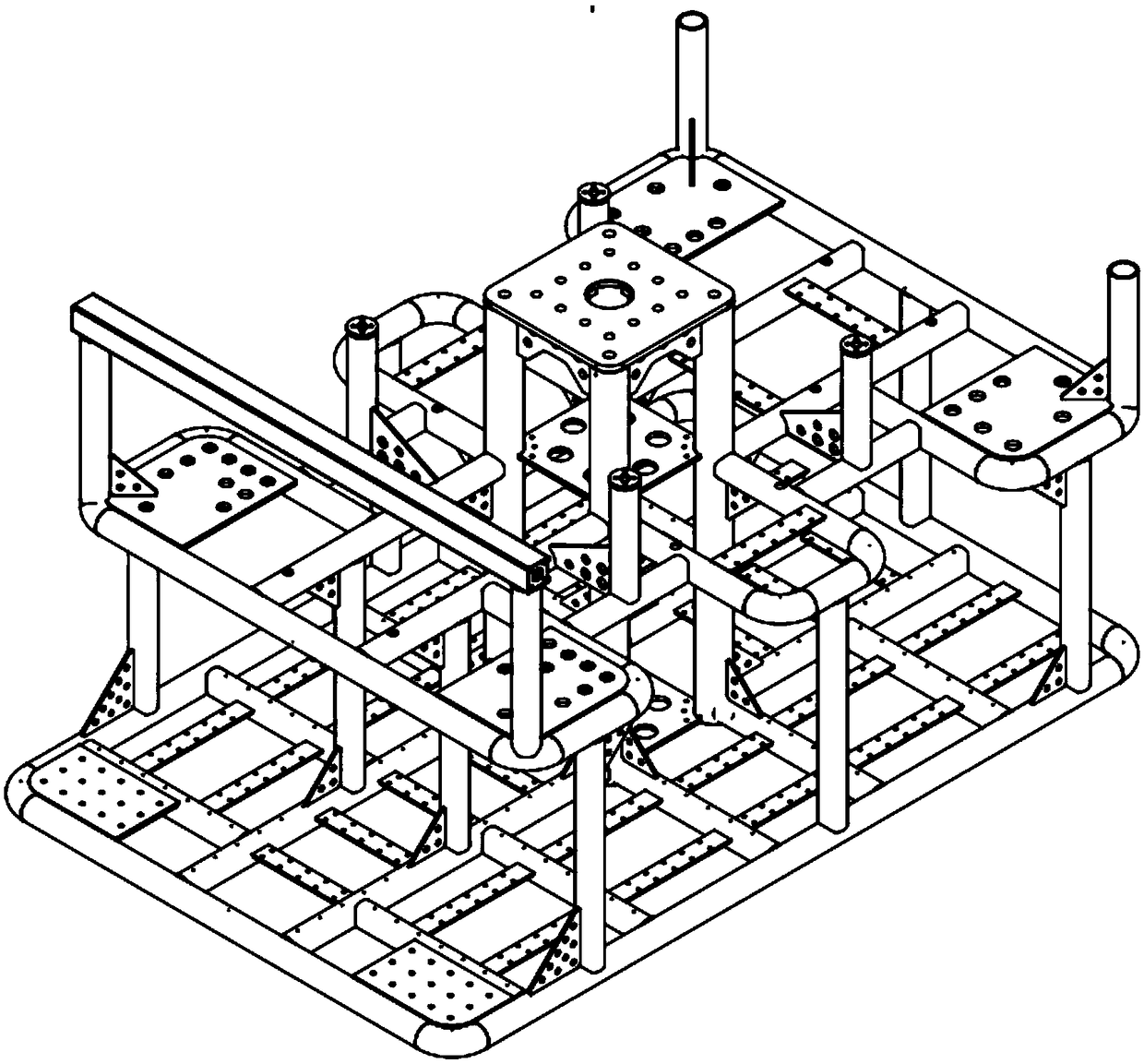
A large-depth all-electric drive operation type ROV platform
PendingCN109018268AReduce weight and sizeReduce power lossPropulsion power plantsPropulsive elementsEngineeringLED lamp
The invention discloses a large-depth all-electric driving operation type ROV platform, comprising a main frame structure, a power propulsion device fixed on the main frame structure, a pan head camera, a high-definition camera, a dimming LED, a functional robot arm I, a laser imaging device, an LED lamp, a functional robot arm II, a hydraulic power unit cabin, a drive unit pressure-resistant cabin, a main pressure-resistant cabin, a buoyancy mechanism, a conventional camera and a focusing camera; The main frame structure comprises a main frame load-bearing longitudinal pipe, a main frame hanging device, an equipment mounting plate, a base guard strip, a stiffening rib plate, a main frame square groove, a main frame center bracket and a main frame load-bearing horizontal pipe. The invention can be used for horizontal motion and rotational motion of an underwater vehicle, and the motion control of the underwater vehicle is realized.
Owner:CSSC SYST ENG RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com