Patents
Literature
61 results about "Boundary cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Boundary cells (also known as border cells or boundary vector cells) are neurons found in the hippocampal formation that respond to the presence of an environmental boundary at a particular distance and direction from an animal. The existence of cells with these firing characteristics were first predicted on the basis of properties of place cells. Boundary cells were subsequently discovered in several regions of the hippocampal formation: the subiculum, presubiculum and entorhinal cortex.
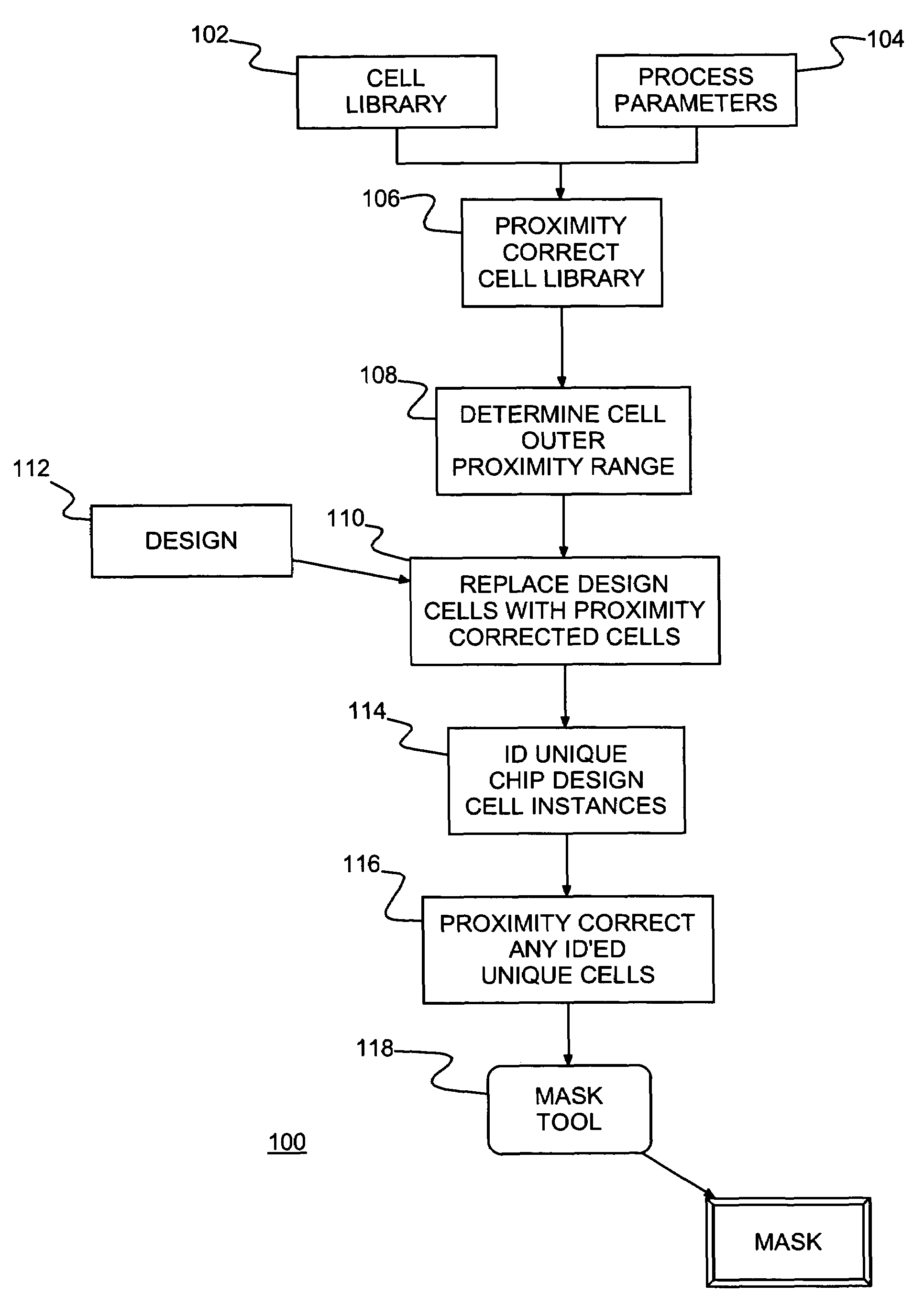
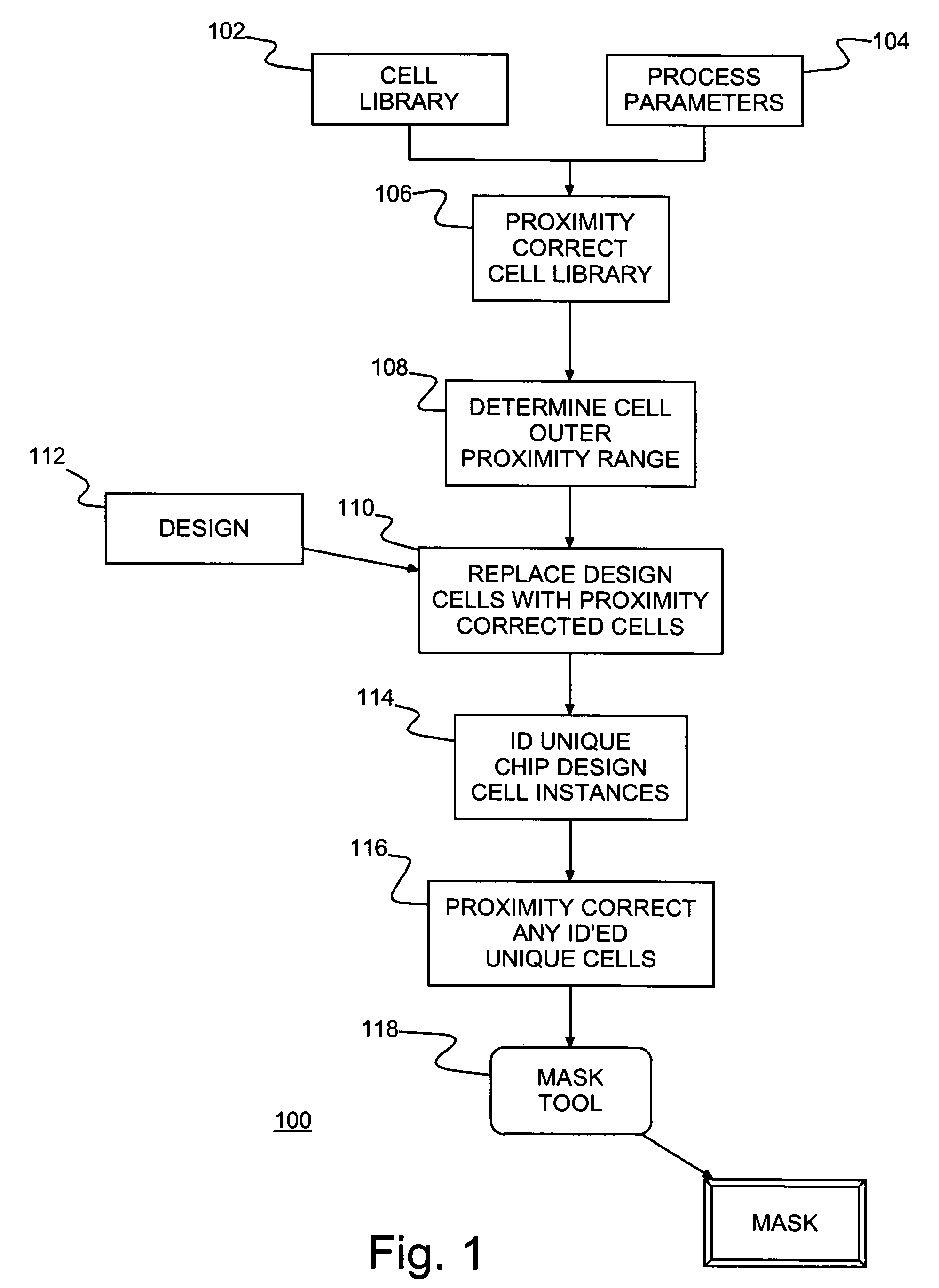
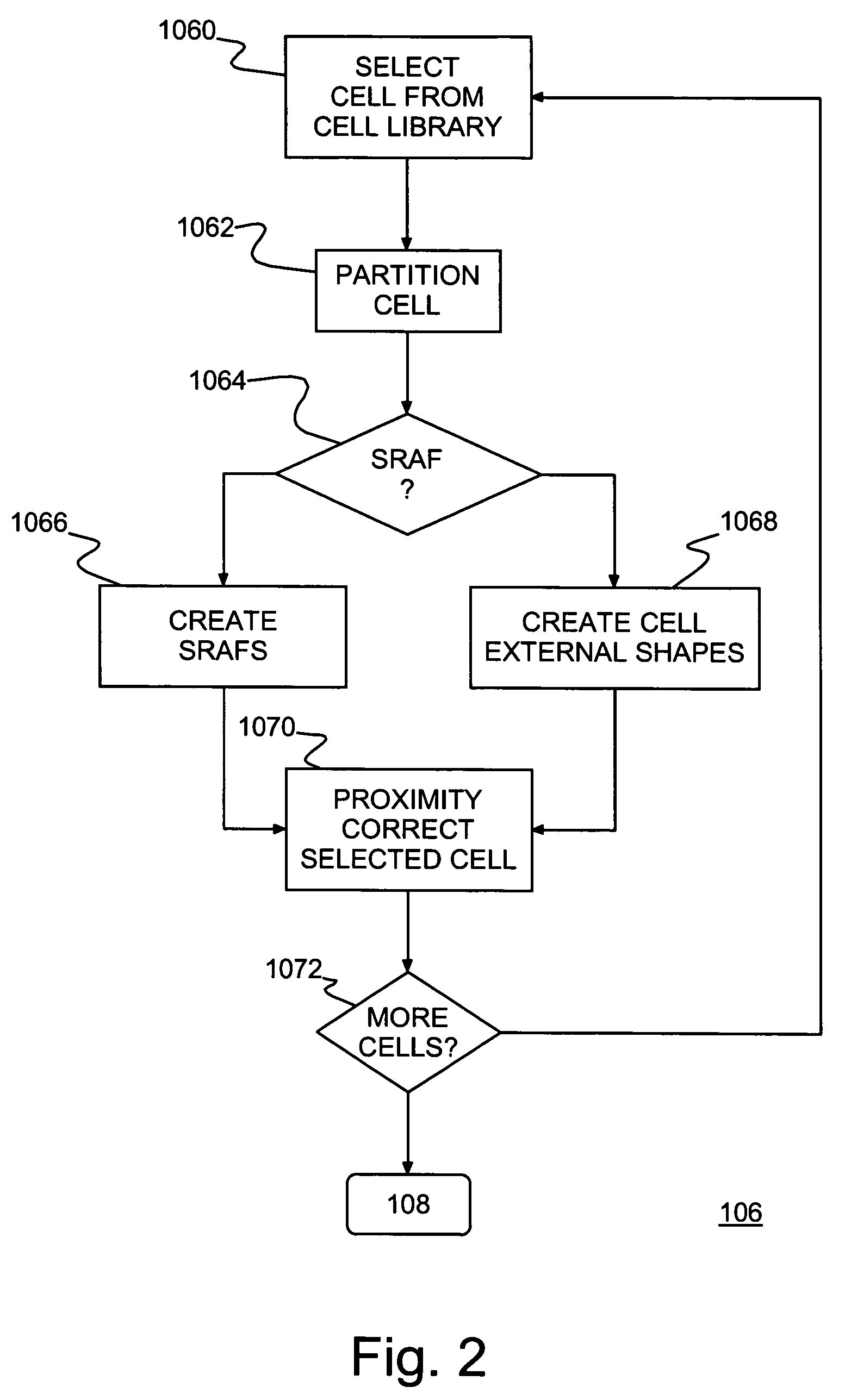
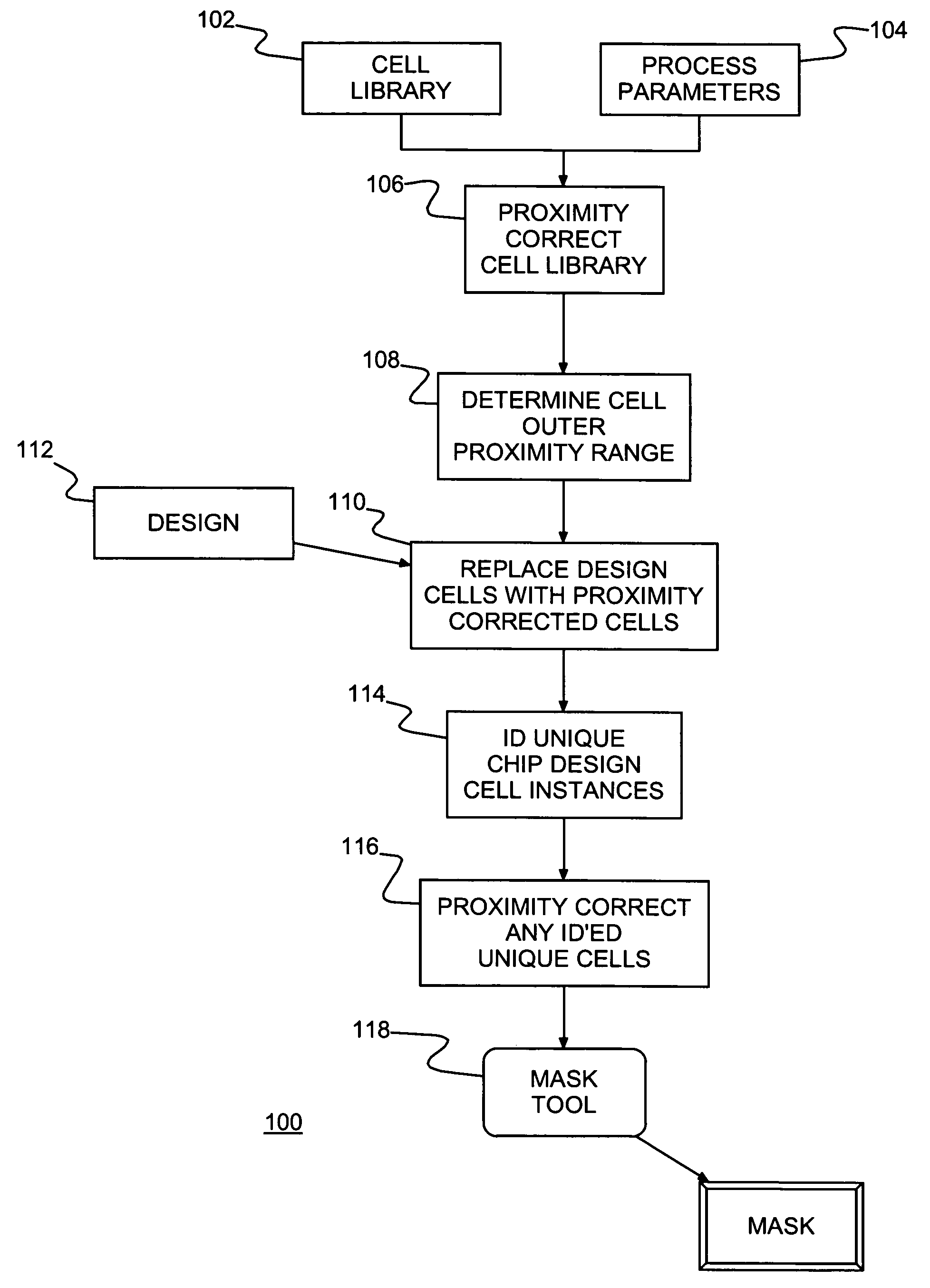
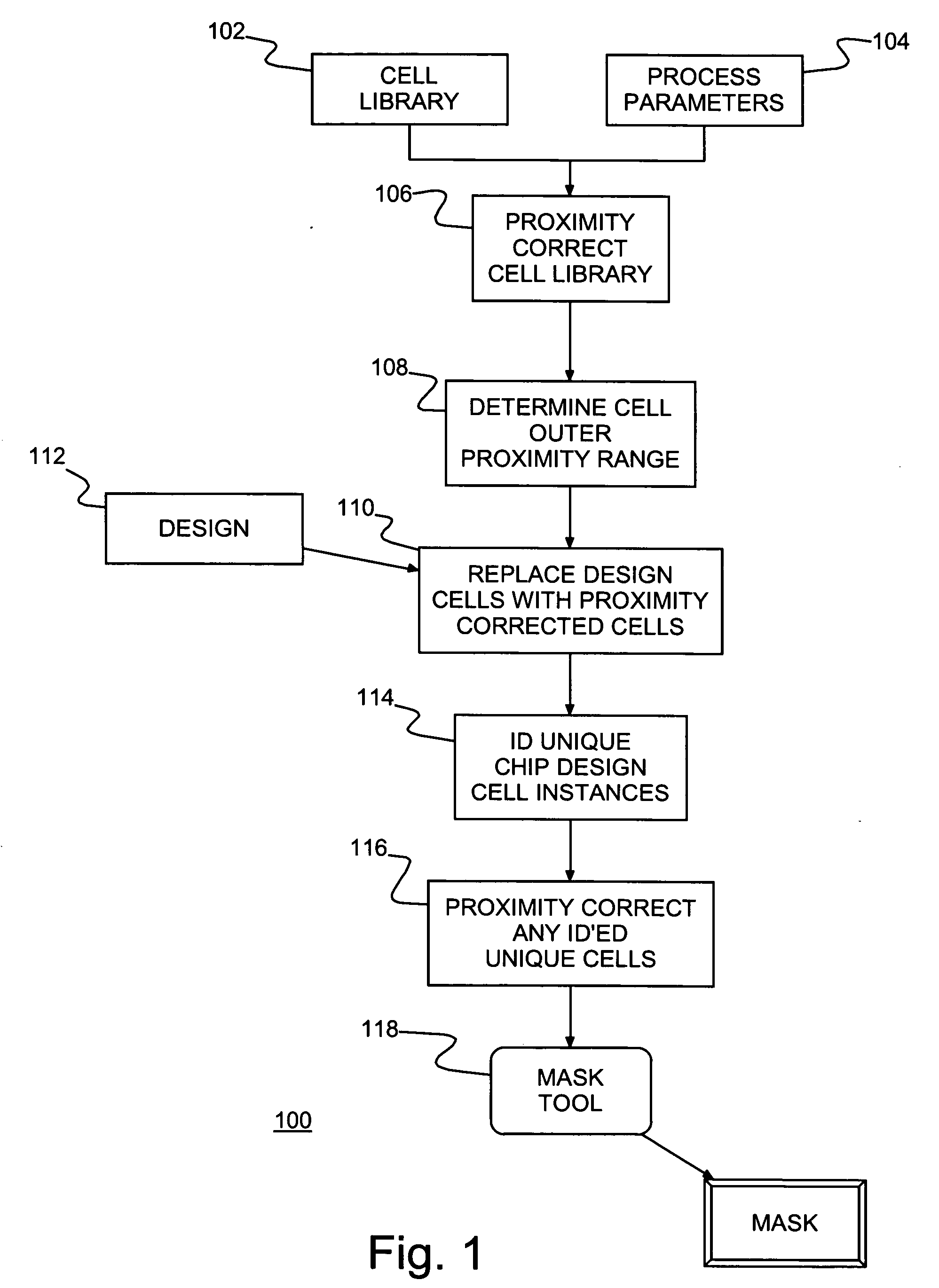
Method of IC fabrication, IC mask fabrication and program product therefor
InactiveUS7353492B2Reduce designReduce resource consumptionPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringBoundary cell
A method of forming integrated circuit (IC) chip shapes and a method and computer program product for converting an IC design to a mask, e.g., for standard cell design. Individual book / macro physical designs (layouts) are proximity corrected before unnesting and an outer proximity range is determined for each proximity corrected physical design. Shapes with a unique design (e.g., in boundary cells and unique instances of books) are tagged and the design is unnested. Only the unique shapes are proximity corrected in the unnested design, which may be used to make a mask for fabricating IC chips / wafers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Building datum extraction from laser scanning data
A method, apparatus, system, and computer program product provide the ability to extract level information and reference grid information from point cloud data. Point cloud data is obtained and organized into a three-dimensional structure of voxels. Potential boundary points are filtered from the boundary cells. Level information is extracted from a Z-axis histogram of the voxels positioned along the Z-axis of the three-dimensional voxel structure and further refined. Reference grid information is extracted from an X-axis histogram of the voxels positioned along the X-axis of the three-dimensional voxel structure and a Y-axis histogram of the voxels positioned along the Y-axis of the three-dimensional voxel structure and further refined.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Outline approximation for point cloud of building
A method, apparatus, system, and computer program product provide the ability to model a polyline boundary from point cloud data. Point cloud data is obtained and boundary cells are extracted. Potential boundary points are filtered from the boundary cells. Line segments are extracted from the potential boundary points and refined. A regularized polygon is obtained by intersecting the refined line segments.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
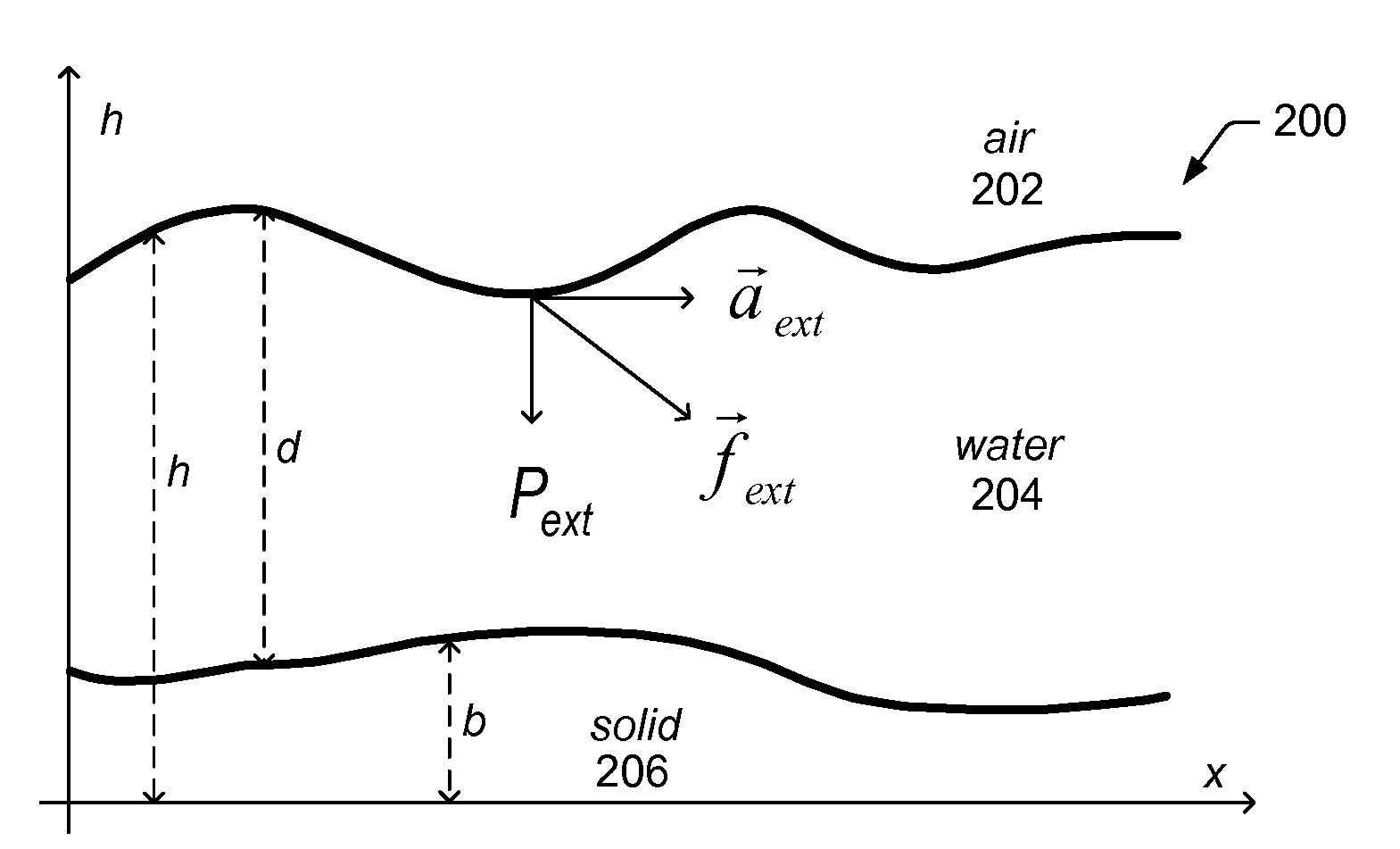
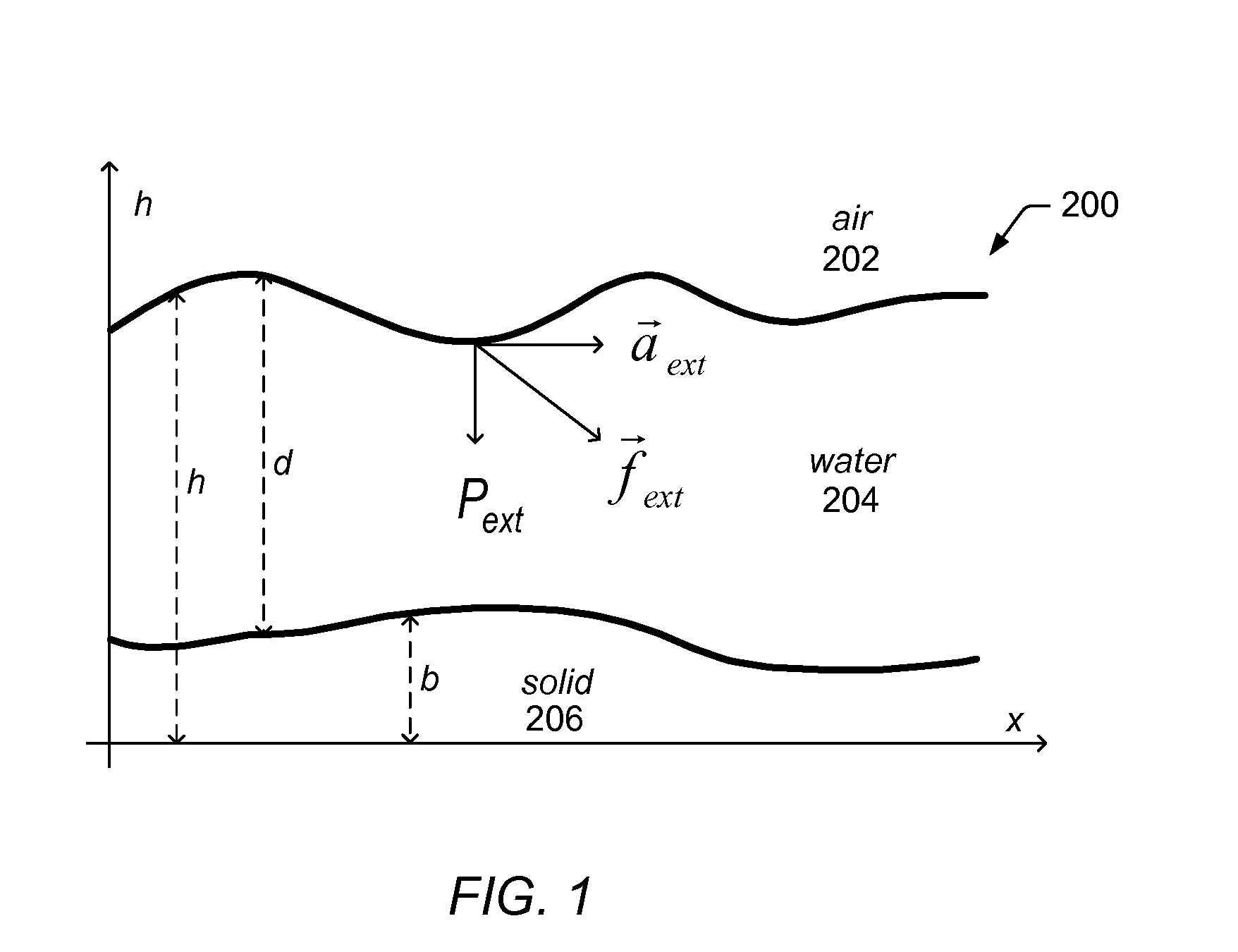
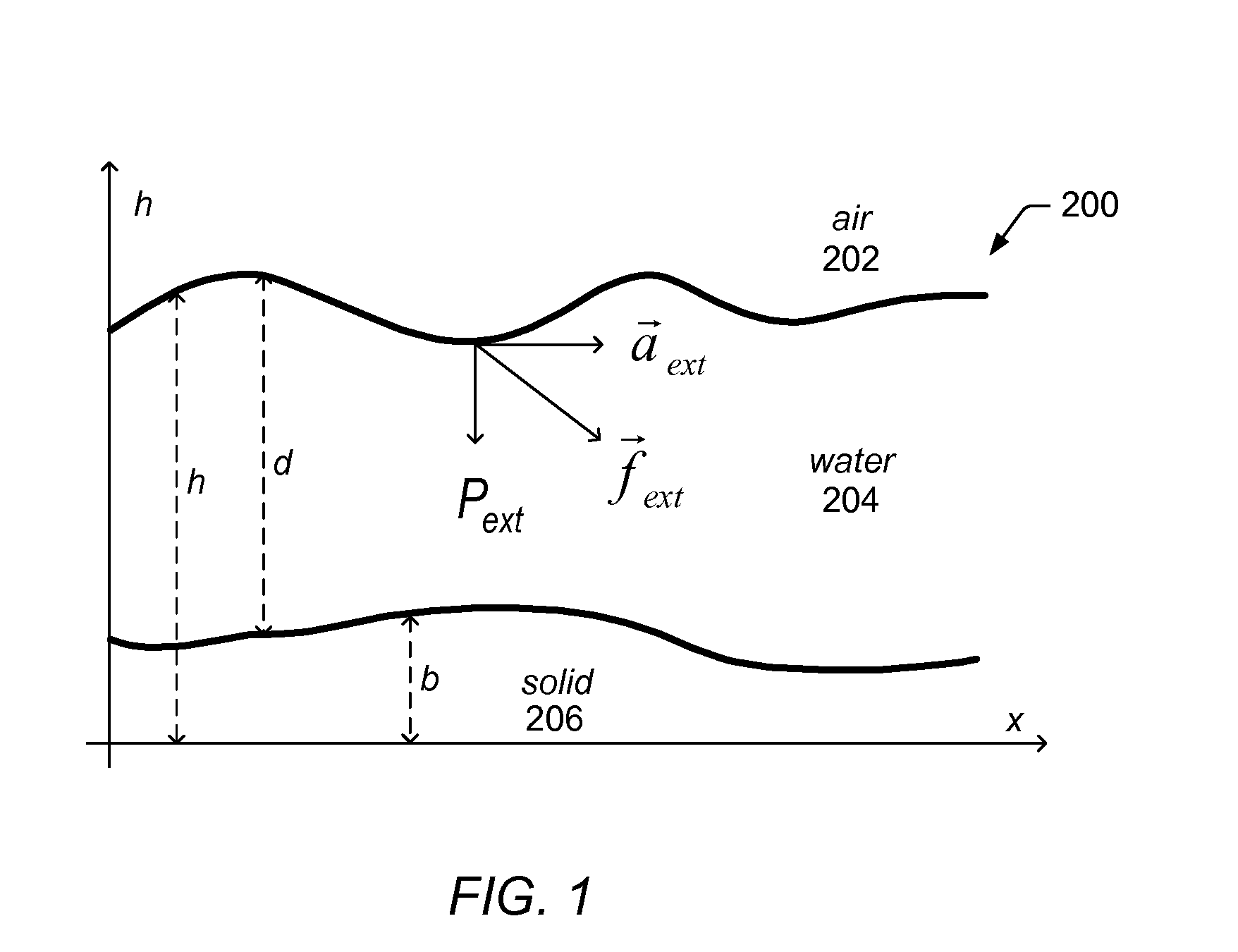
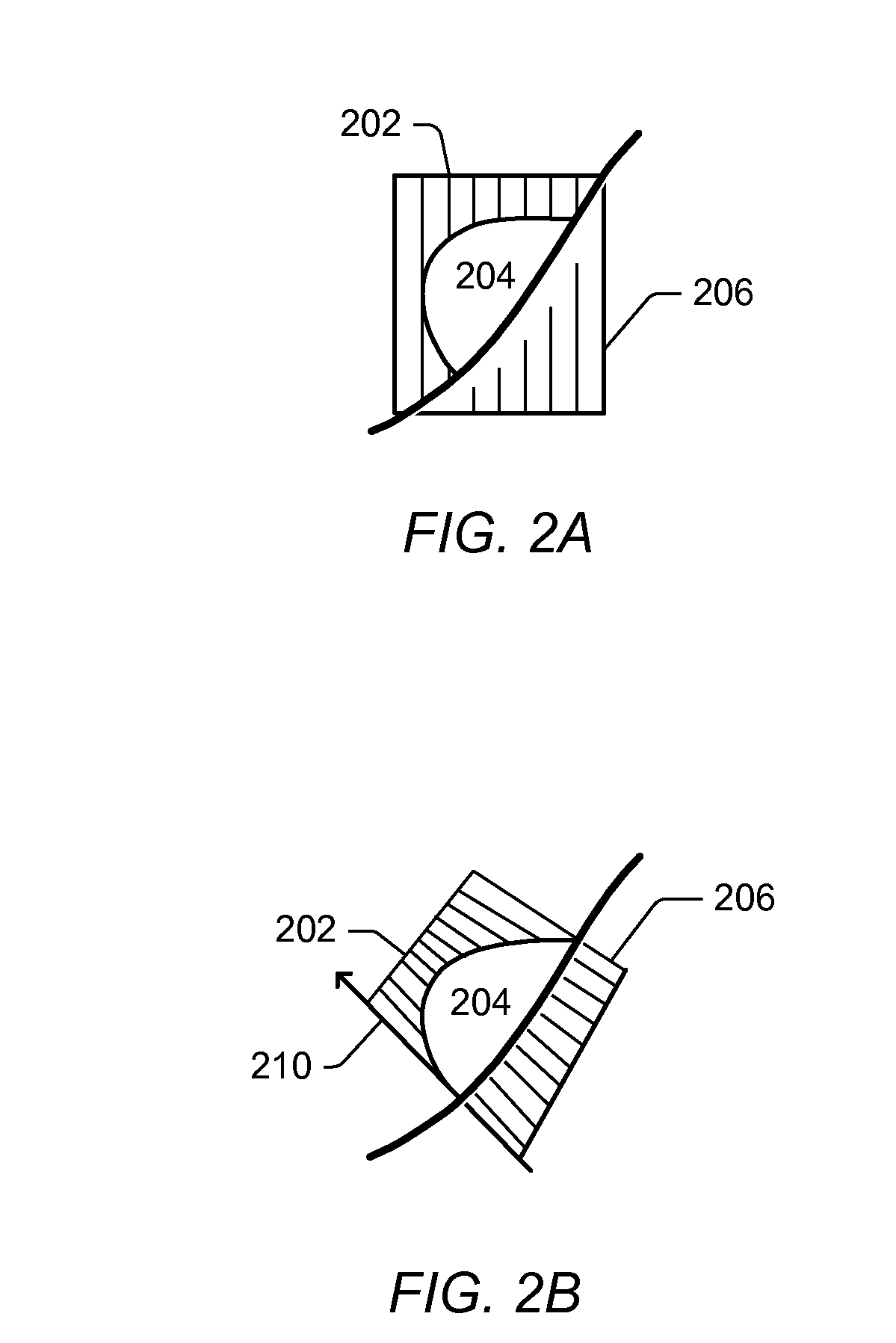
System and Method for Simulating Shallow Water Effects on Arbitrary Surfaces
ActiveUS20080177519A1Effective simulationFacilitate real-time fluid controlAnimationImage generationFluid controlWave equation
A system and method for shallow water simulation may provide a framework for solving General Shallow Wave Equations (GSWE) to efficiently simulate 3D fluid effects on arbitrary surfaces using a height field representation. The height field representation may include height columns constructed along surface normals, which may be dependent on a condition of boundary cells adjacent to fluid cells and / or artificial viscosity effects. The framework may provide implicit schemes for solving for the effects of external forces applied to the fluid, including gravity and surface tension, and explicit schemes for solving for advection effects. The system and method may be implemented on general-purpose CPU(s) and / or GPU(s) and may be capable of simulating a variety of fluid effects including: waves, rivulets and streams, drops, and capillary events. In some embodiments, the system and method may achieve real-time fluid control and fluid shape design through user-interaction (e.g., in a graphical painting application).
Owner:ADOBE INC
Method and device for numberical analysis of flow field of non-compressive viscous fluid, directly using v-cad data
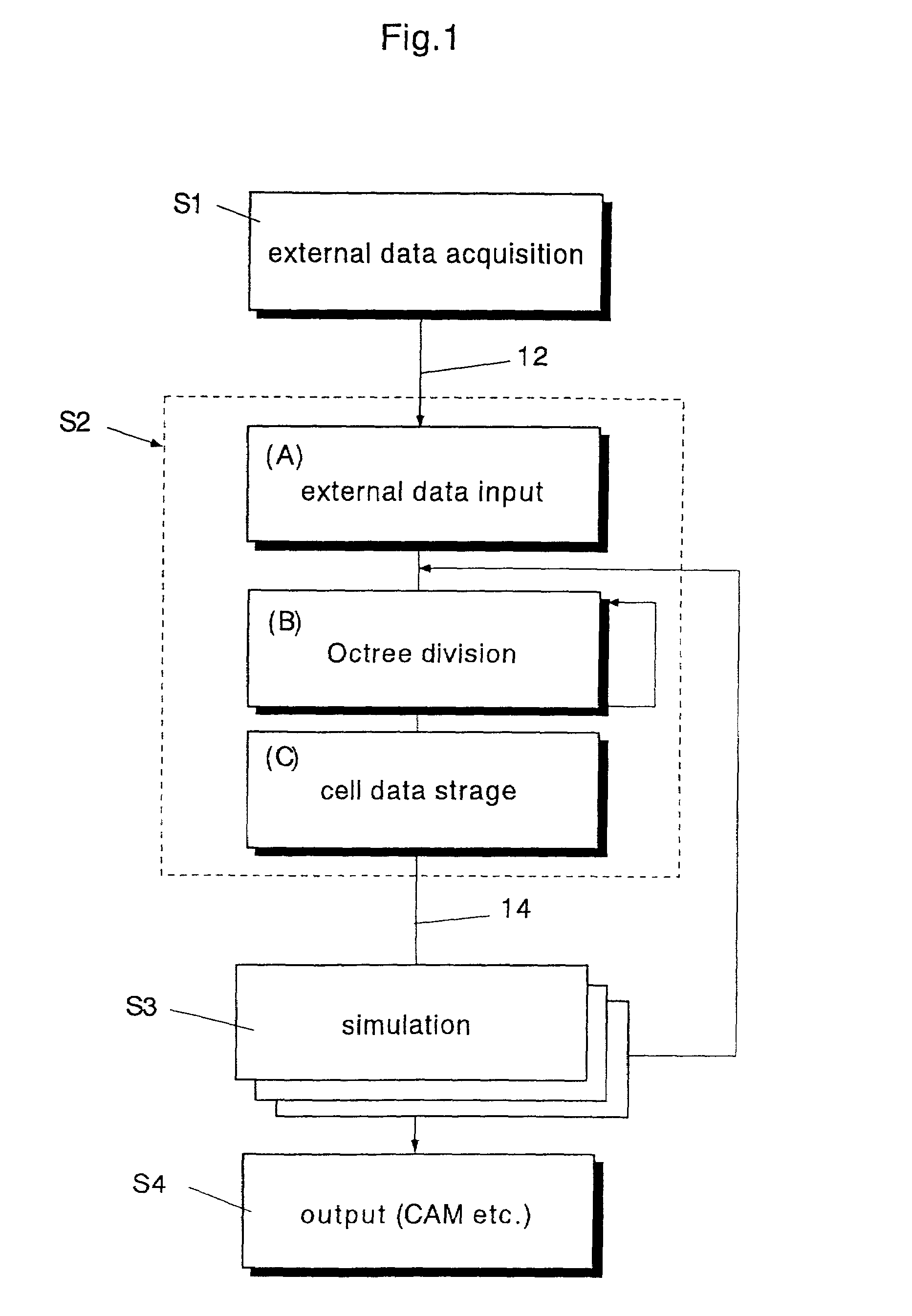
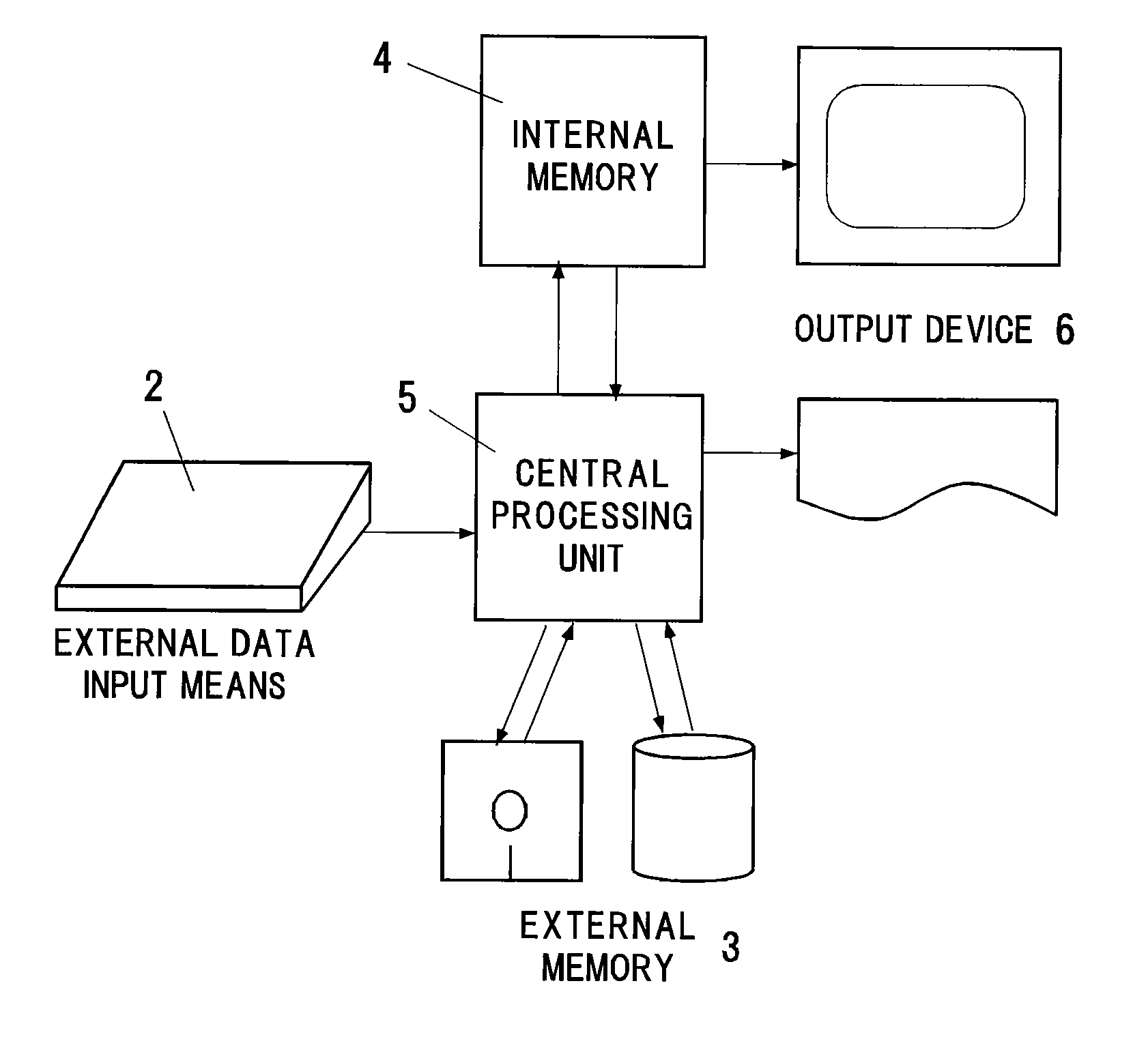
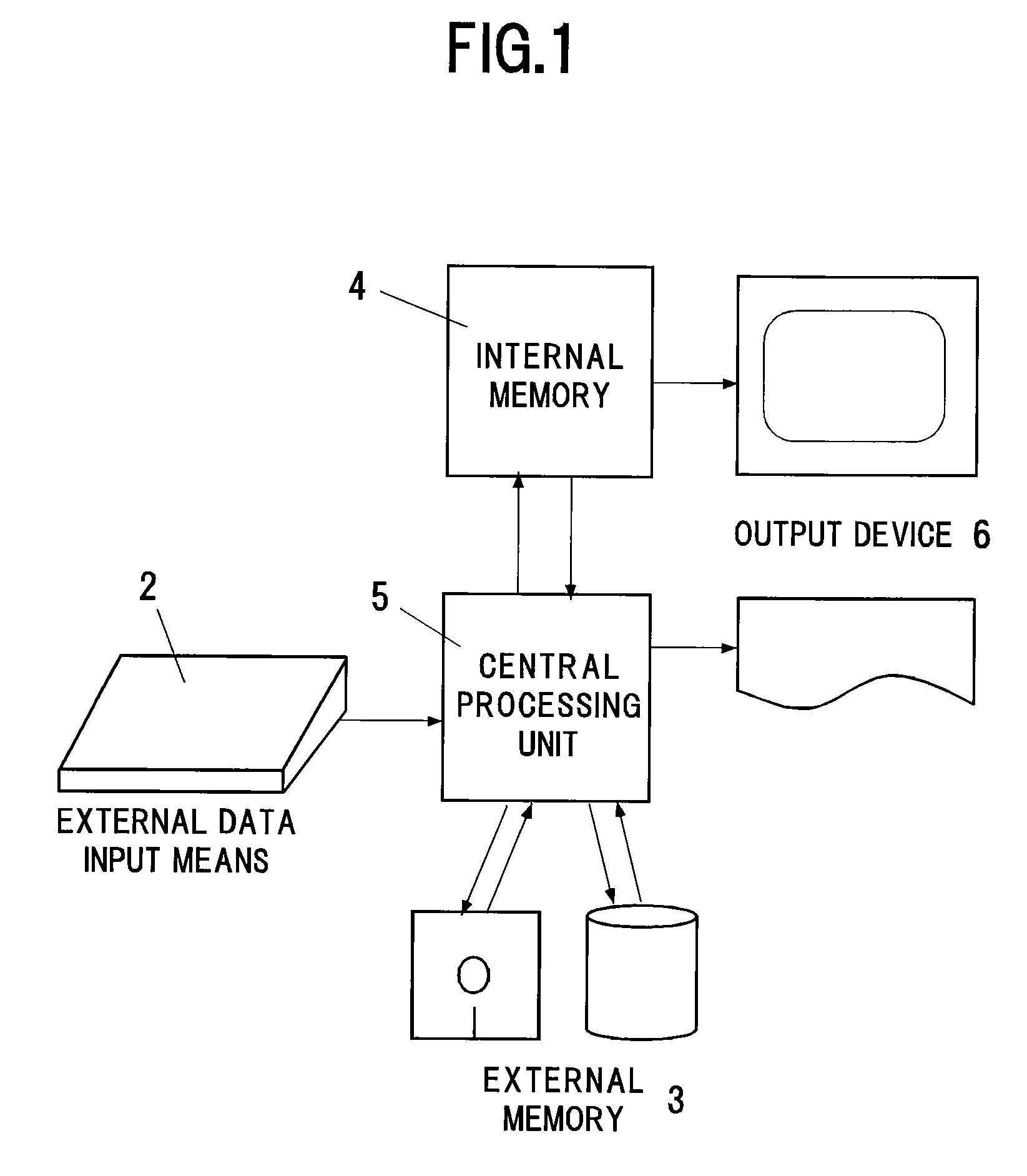
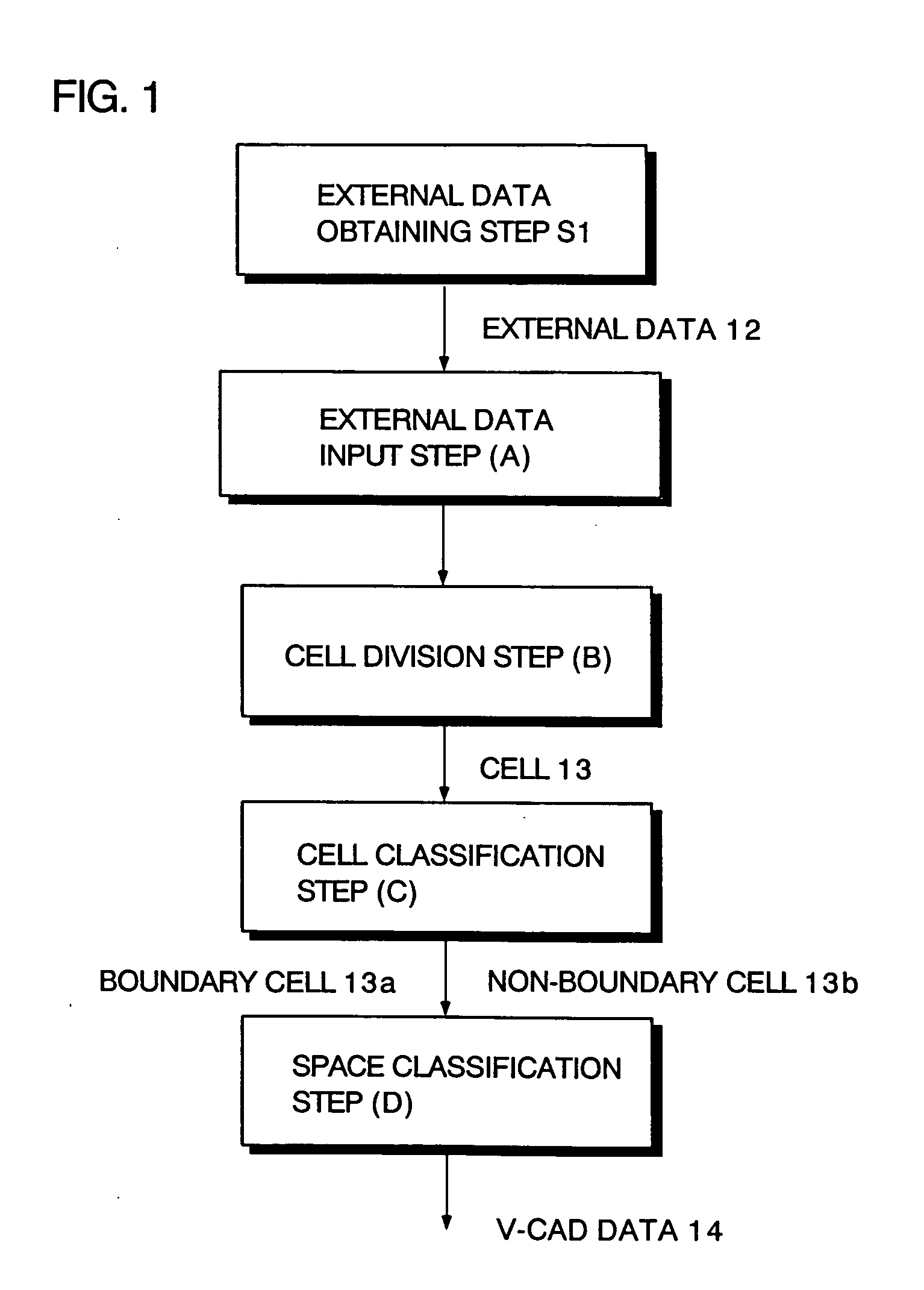
InactiveUS20060089803A1High expressionEnsure correct executionTesting/calibration apparatusVolume/mass flow measurementExternal dataDividing cell
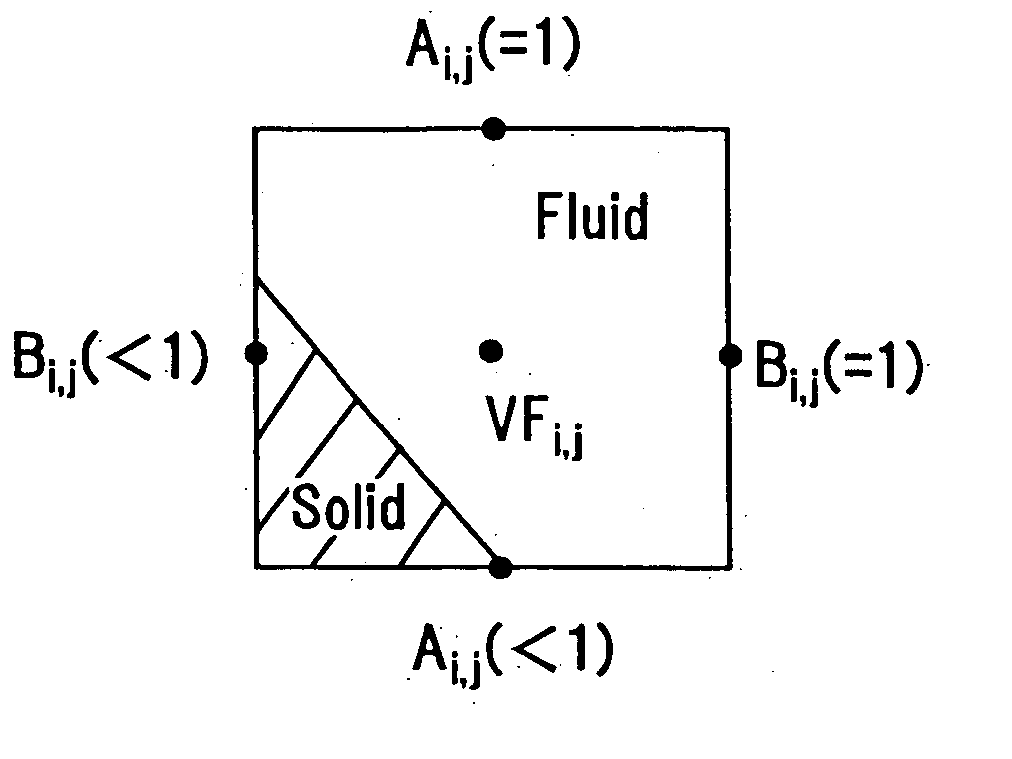
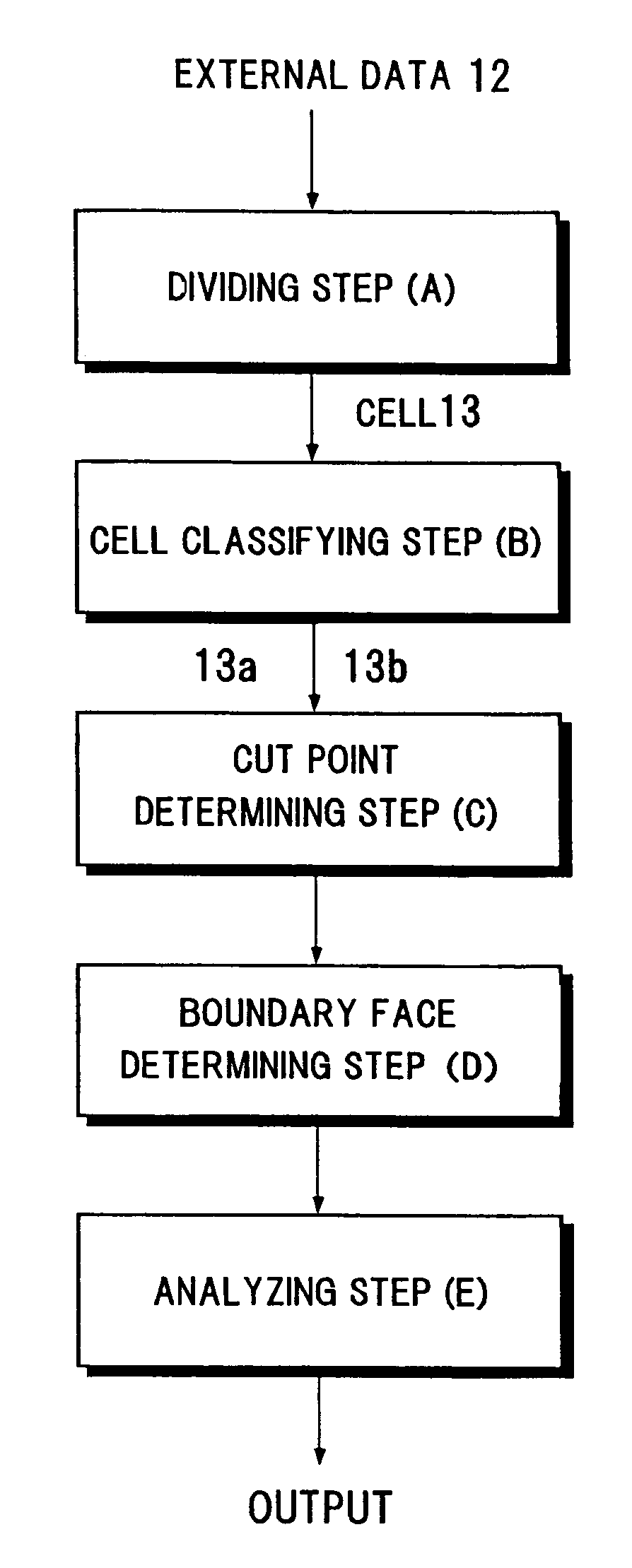
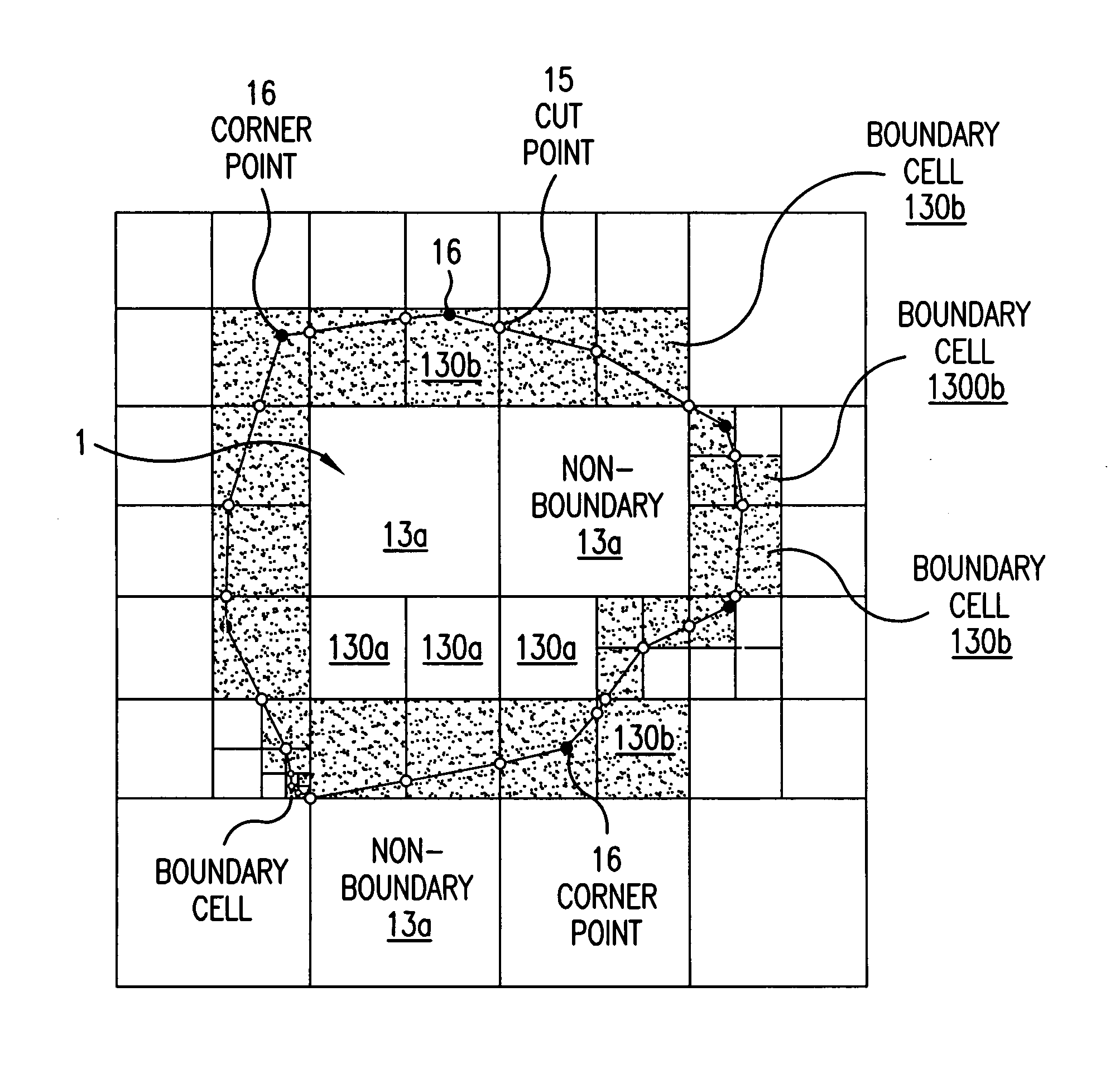
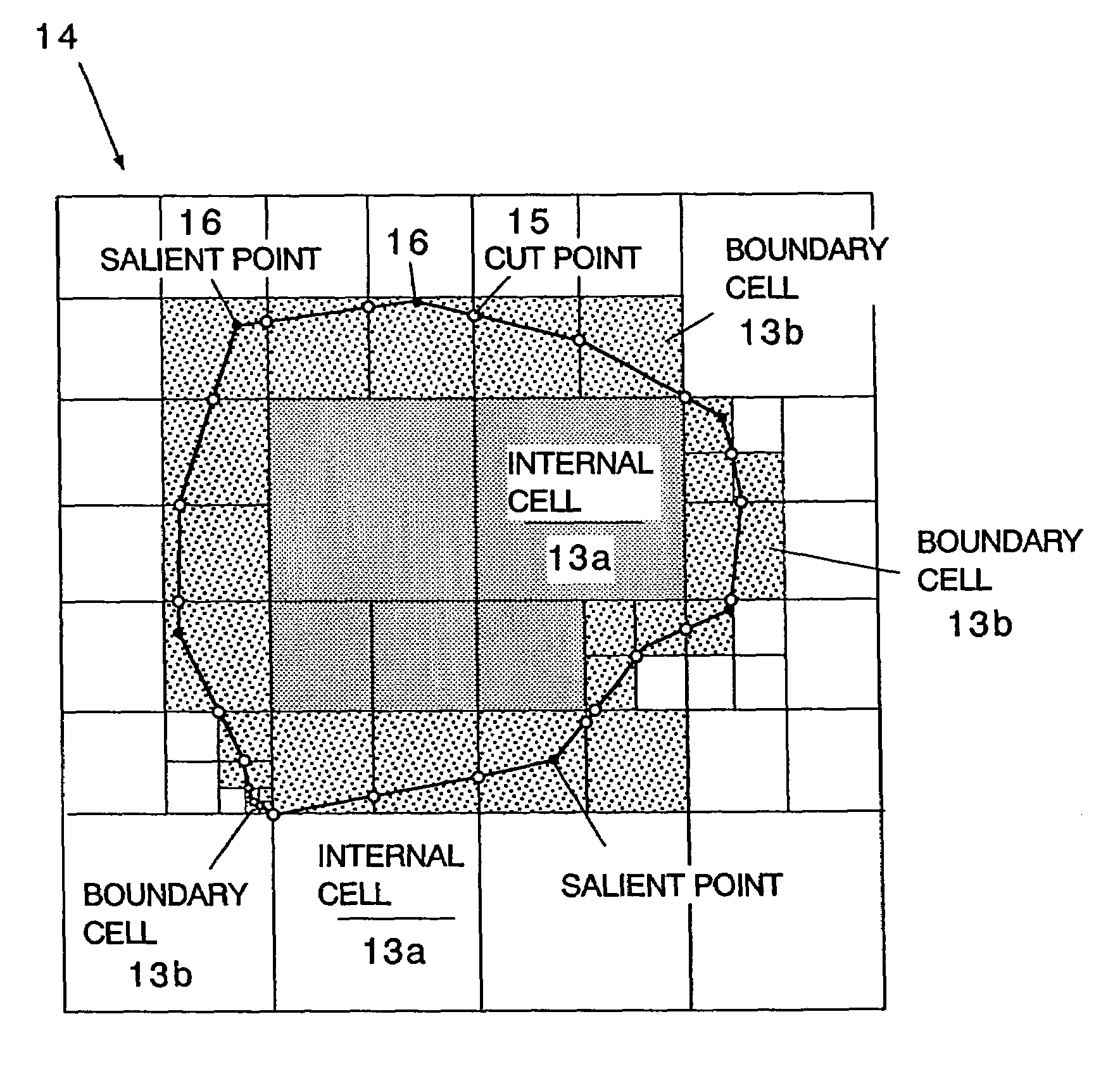
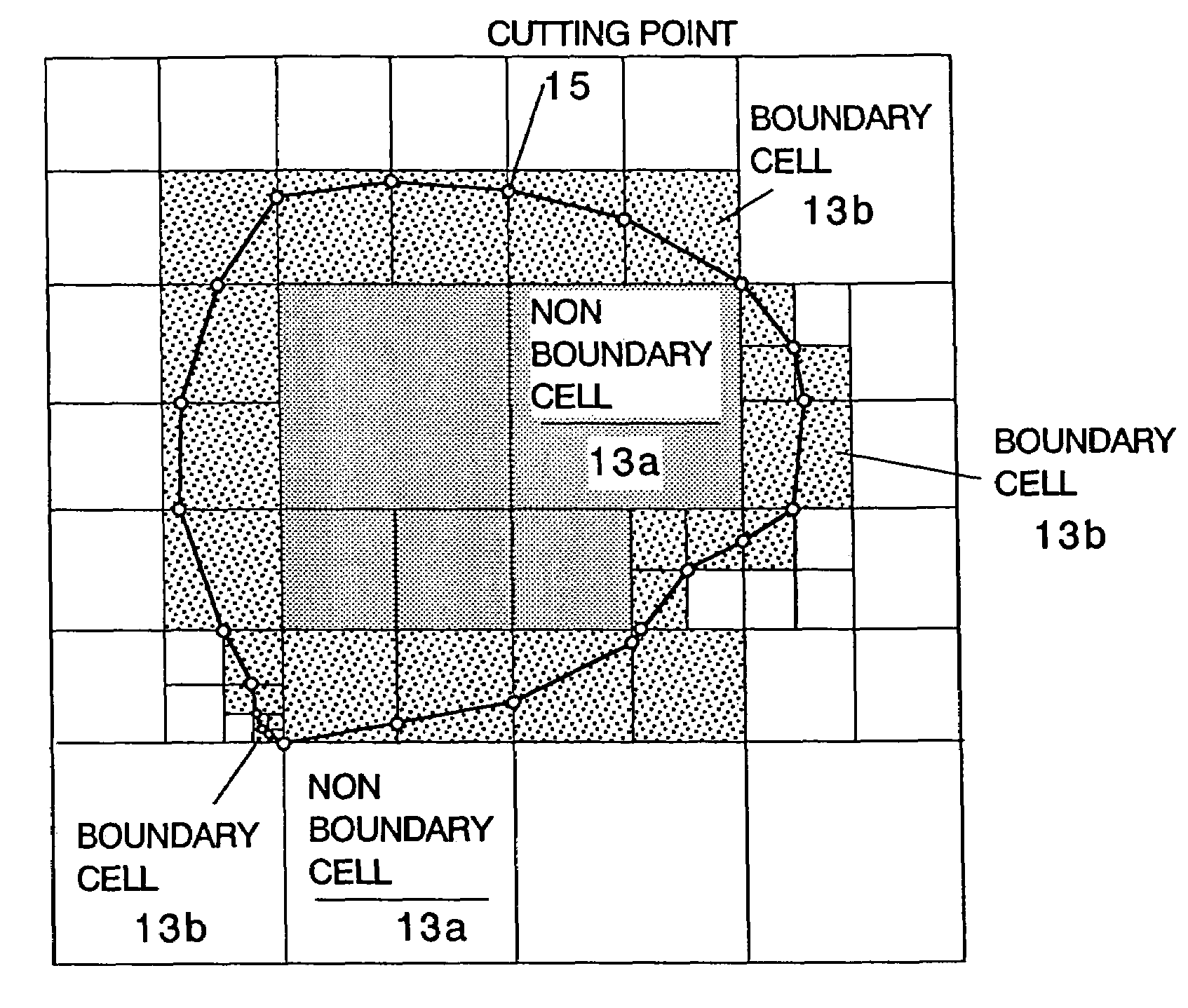
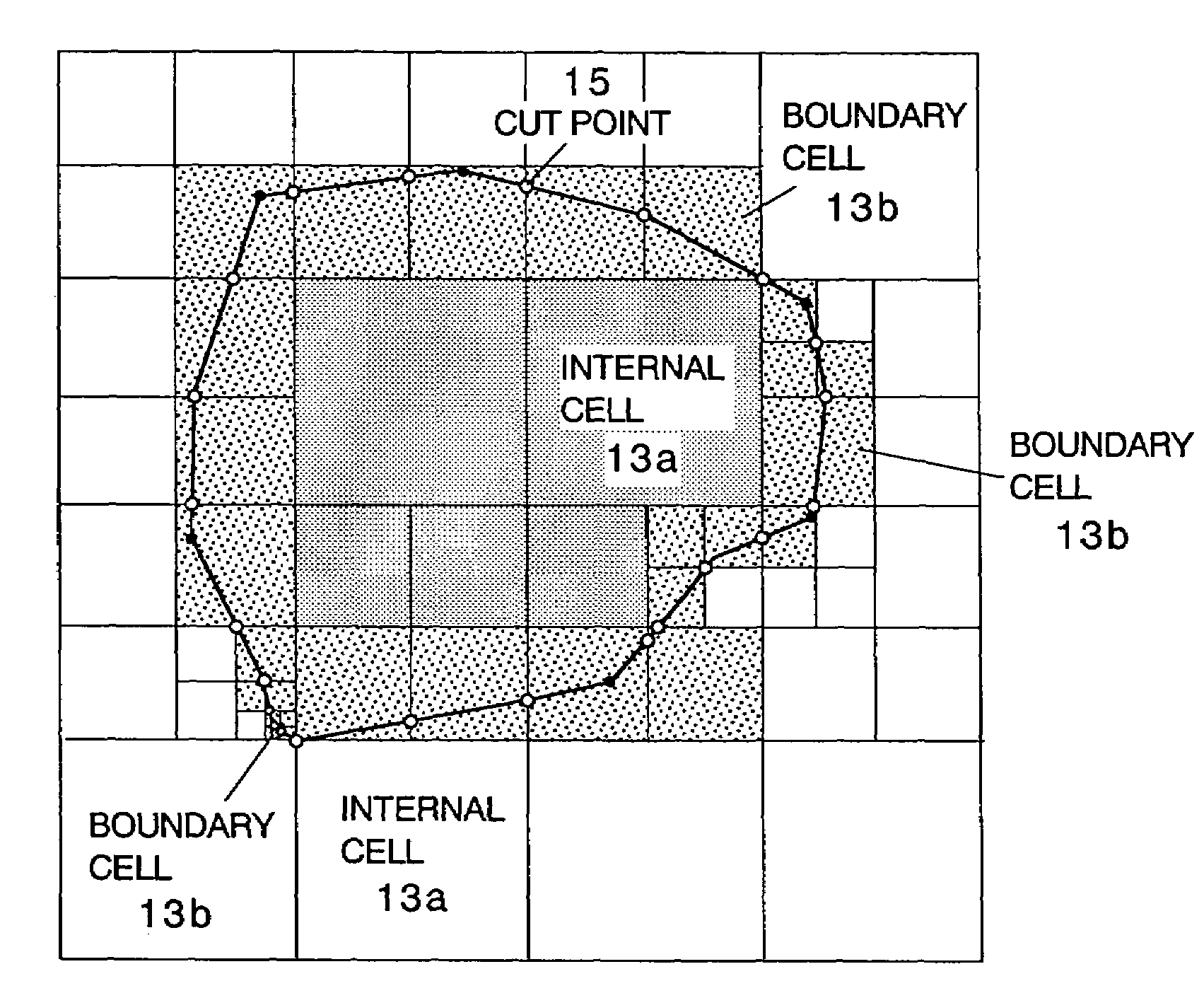
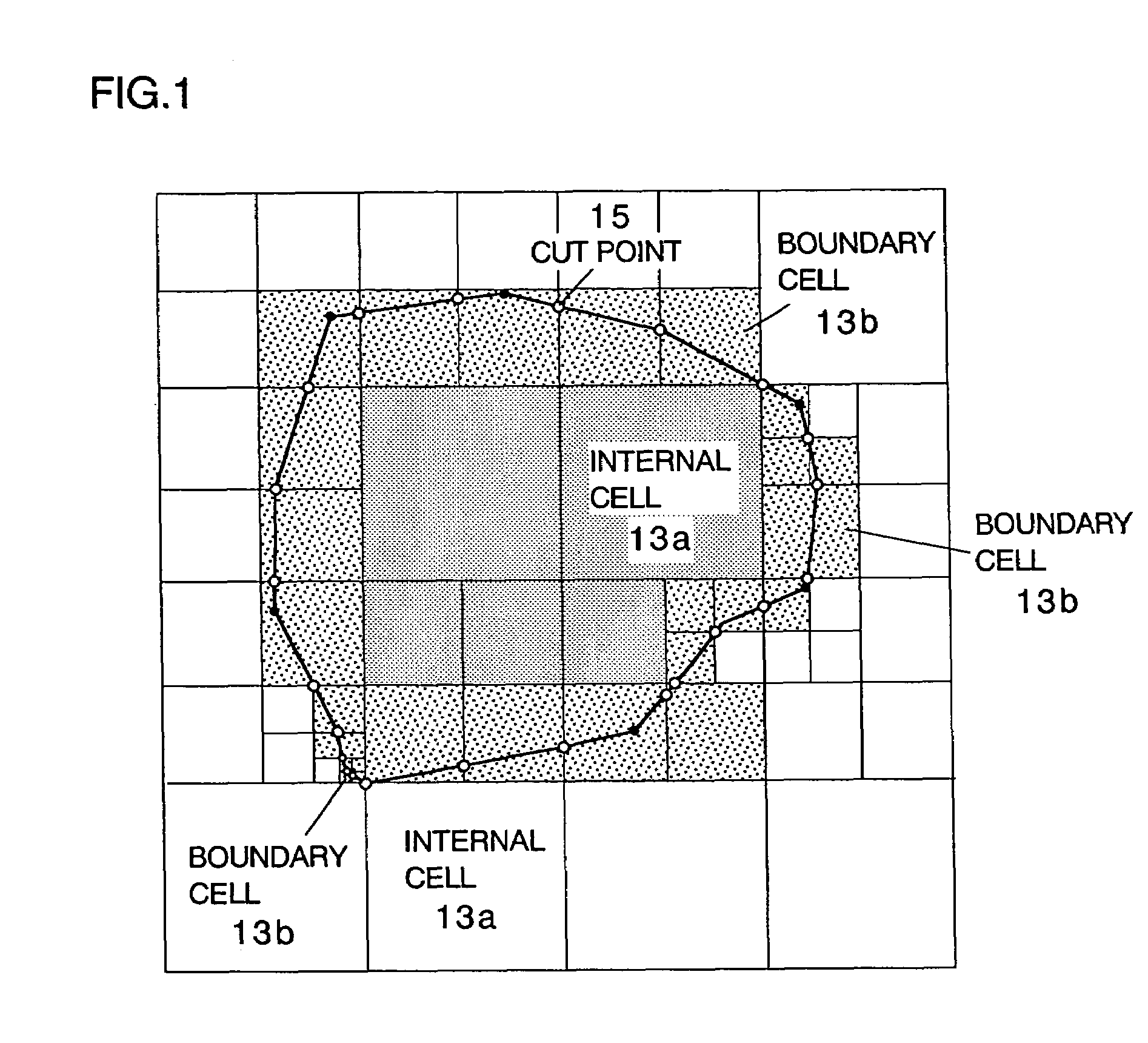
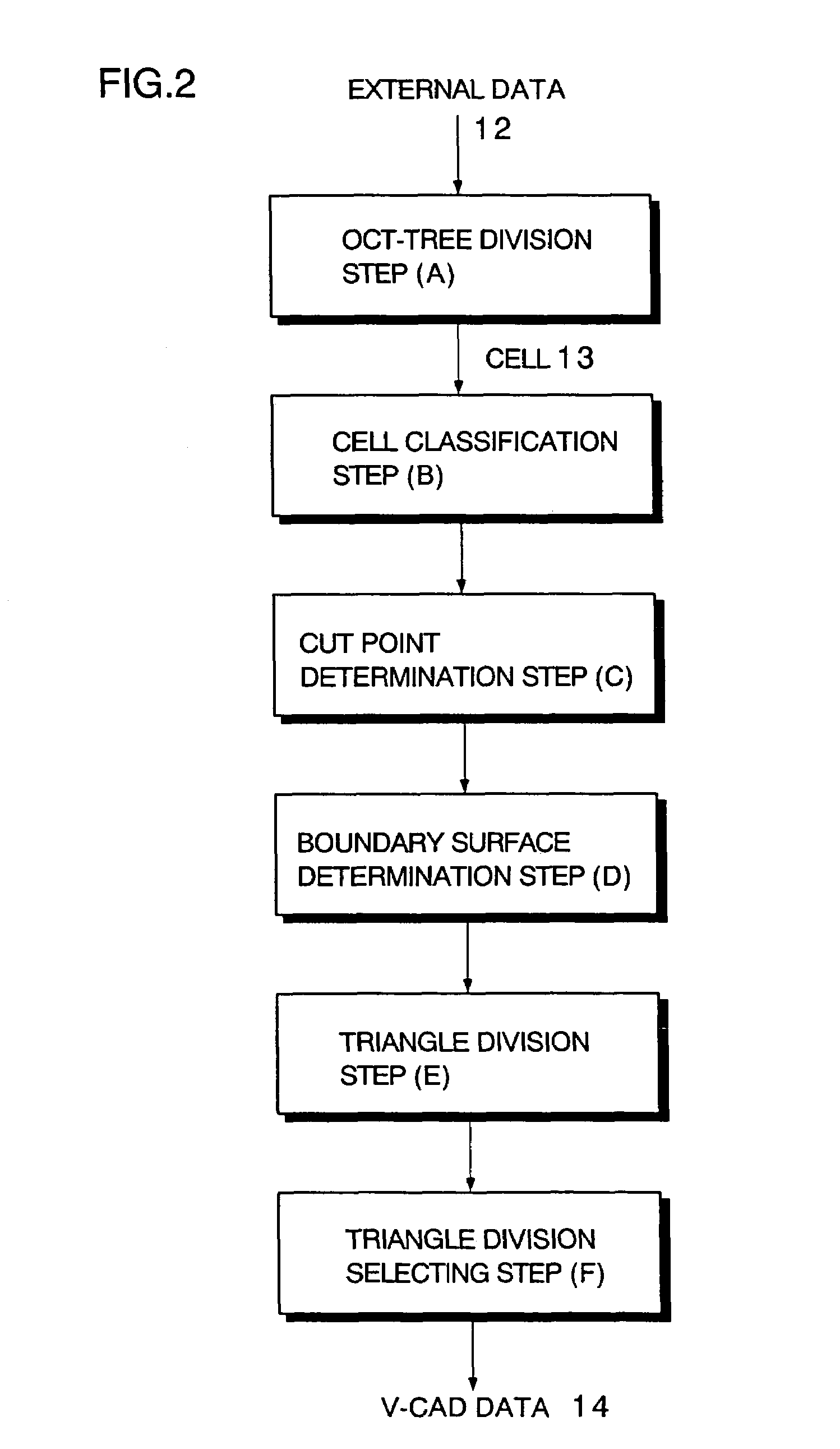
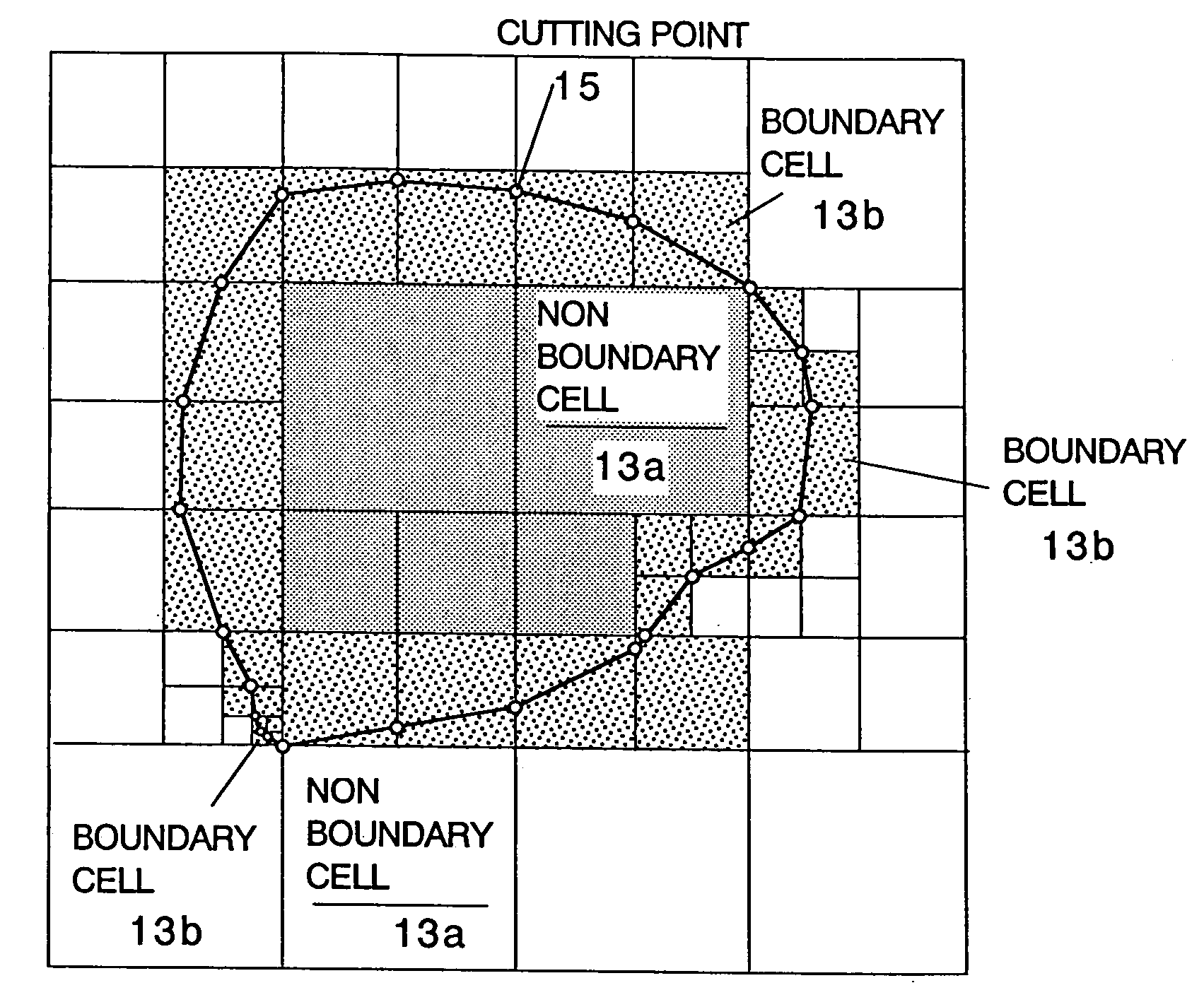
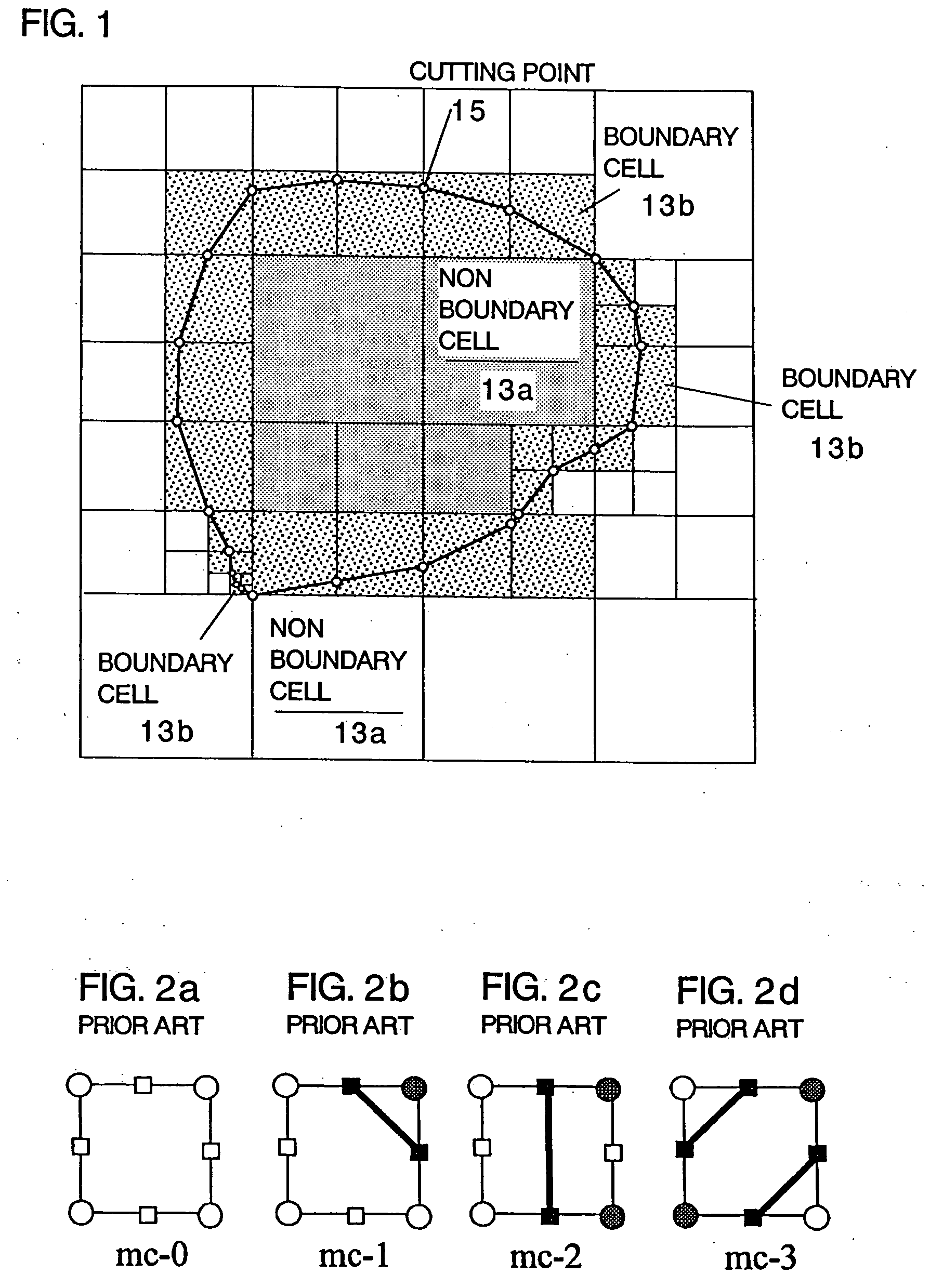
A method including: a dividing step (A) of dividing external data into a plurality of cells (13) having boundaries orthogonal to each other, the external data including boundary data of an object which contacts incompressible viscous fluid; a cell classifying step (B) of classifying the divided cells into an internal cell (13a) positioned inside or outside the object and a boundary cell (13b) including the boundary data; a cut point determining step (C) of determining cut points in ridges of the boundary cell on the basis of the boundary data; a boundary face determining step (D) of determining a polygon connecting the cut points to be cell internal data for the boundary face; and a analyzing step (E) of applying a cut cell finite volume method combined with a VOF method to a boundary of a flow field to analyze the flow field.
Owner:RIKEN
Method and device for numerical analysis of flow field of incompressible viscous fluid, directly using V-CAD data
InactiveUS7430500B2High expressionEnsure correct executionTesting/calibration apparatusVolume/mass flow measurementExternal dataDividing cell
A method including: a dividing step (A) of dividing external data into a plurality of cells (13) having boundaries orthogonal to each other, the external data including boundary data of an object which contacts incompressible viscous fluid; a cell classifying step (B) of classifying the divided cells into an internal cell (13a) positioned inside or outside the object and a boundary cell (13b) including the boundary data; a cut point determining step (C) of determining cut points in ridges of the boundary cell on the basis of the boundary data; a boundary face determining step (D) of determining a polygon connecting the cut points to be cell internal data for the boundary face; and a analyzing step (E) of applying a cut cell finite volume method combined with a VOF method to a boundary of a flow field to analyze the flow field.
Owner:RIKEN
Method for extending hard-handoff boundaries within a mobile telephone communications network
InactiveUS6122513ANetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCarrier signalTelephone communication
A method for extending hard-handoff boundaries within a mobile telephone communications network is disclosed. There are multiple cells within a CDMA cellular / PCS telephone communications network, in which some of the cells operate under two separate carrier frequencies. In order to extend the hard-handoff boundary of a boundary cell that operates under two carrier frequencies, a neighboring cell adjacent to the boundary cell but operating under only one of the two carrier frequencies of the boundary cell must first be located. Then, a repeater with a fixed or adjustable delay is placed between the boundary cell and the neighboring cell such that the hard-handoff boundary of the boundary cell is extended.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
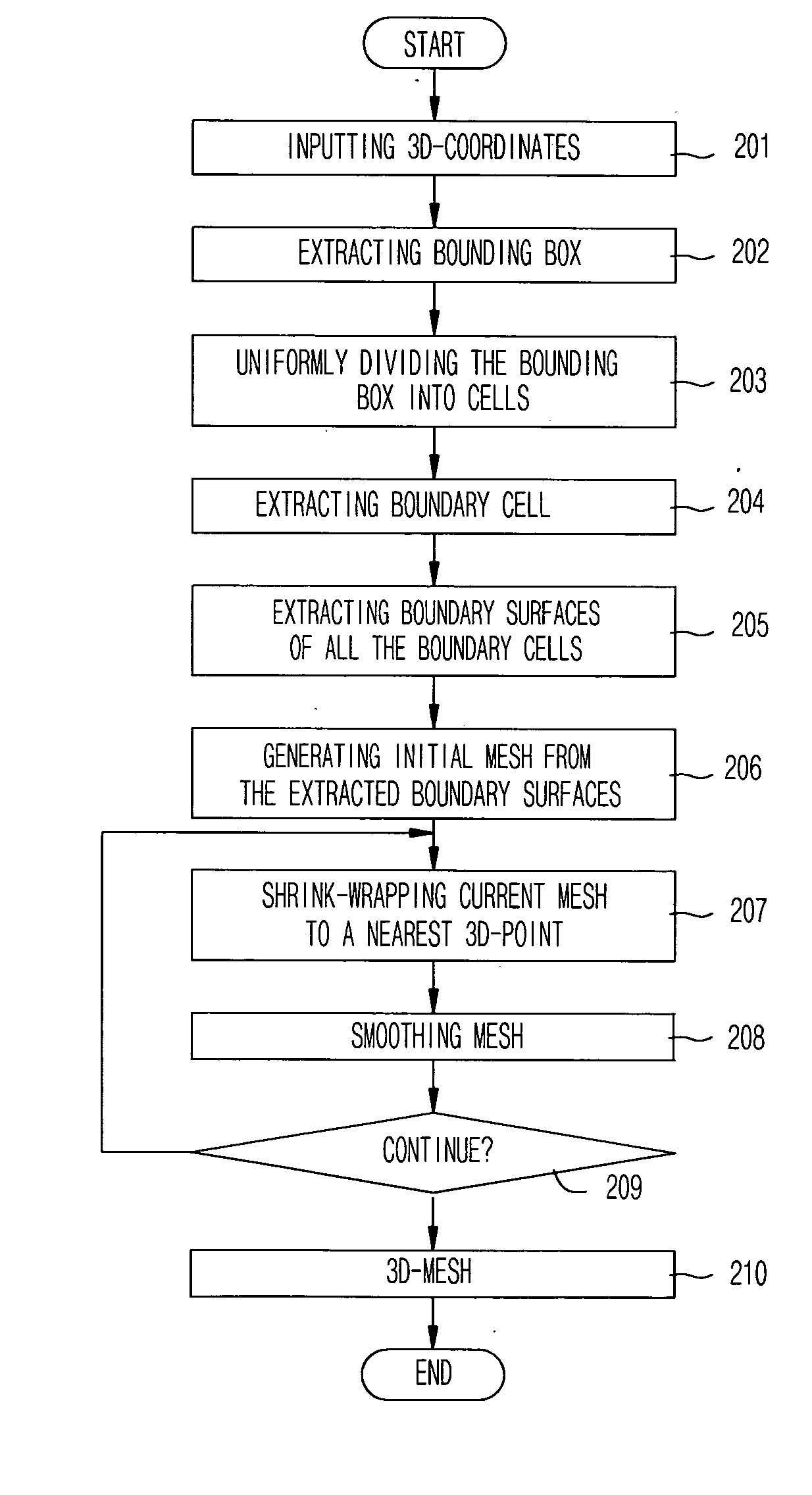
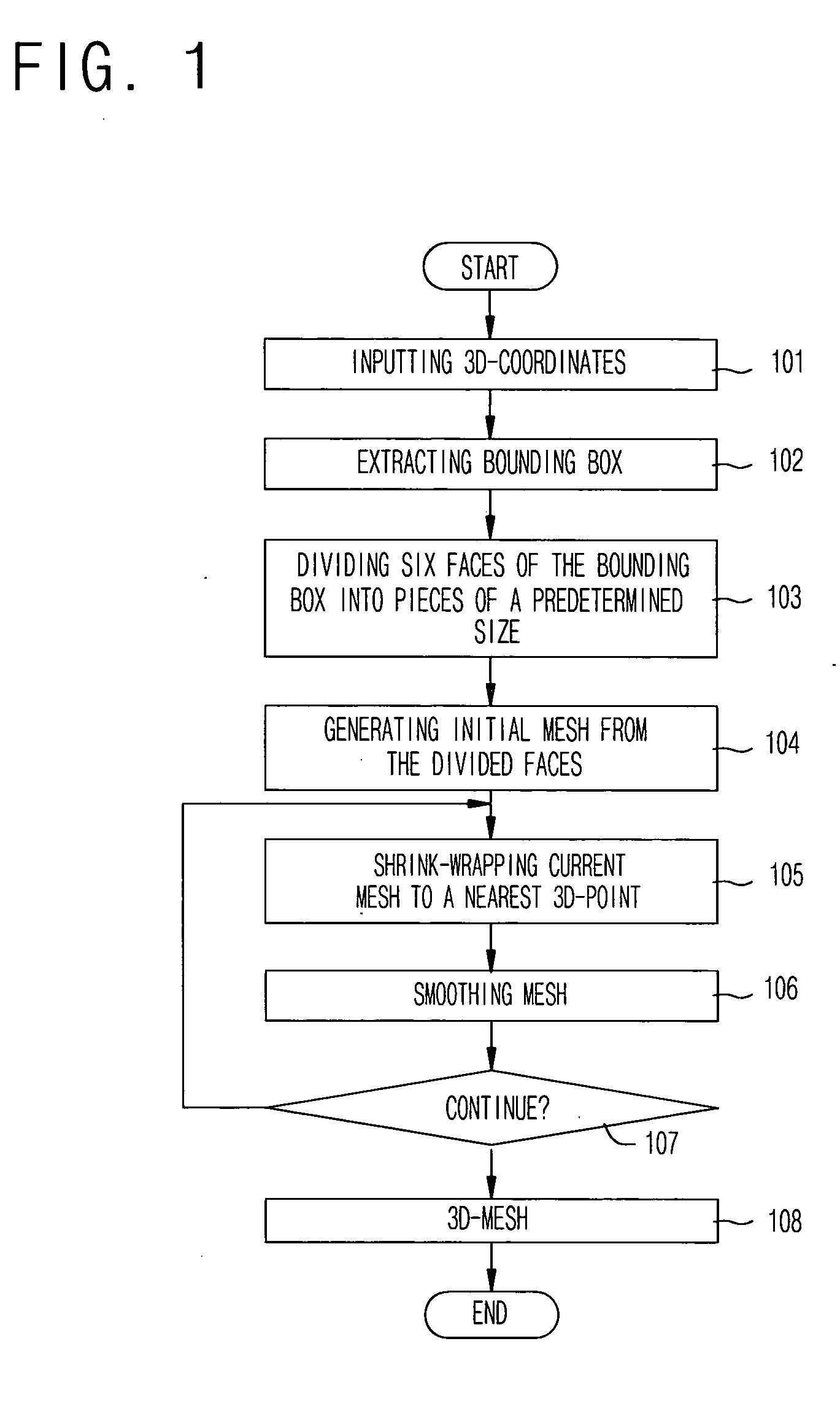
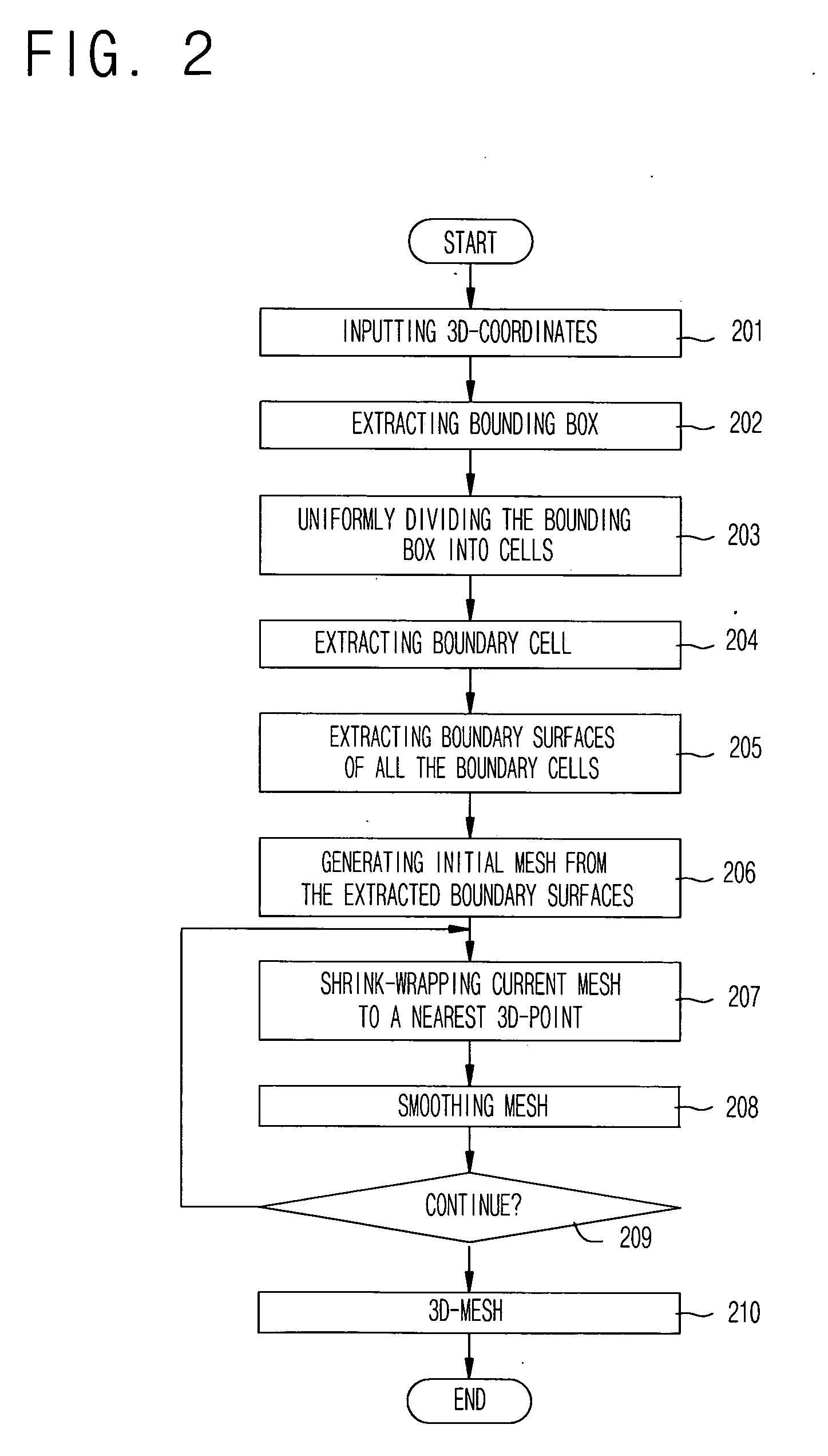
Method for generating 3D mesh from 3D points by using shrink-wrapping scheme of boundary cells
InactiveUS20050134586A1Decreasing elapsed timeShorten the timeImage generation3D-image renderingMinimum bounding boxComputer graphics (images)
The present invention relates to a method for generating a mesh model representing a 3D surface from unorganized 3D points extracted from a 3D scanner by using a shrink-wrapping scheme of boundary cells. A method for generating 3-dimensional mesh according to the present invention comprises the steps of: (a) receiving unorganized 3D point coordinates extracted by a 3D scanner or a digitizer; (b) extracting a minimum bounding box including all the point coordinates and uniformly dividing the extracted bounding box into cells of a predetermined size; (c) extracting a boundary cell including at least one point from the cells, extracting a boundary surface from all the boundary cells, and generating an initial mesh by summing extracted boundary surfaces; (d) calculating distances between each vertex constituting the mesh and the several points, finding a nearest point, and moving the vertex to the nearest point; and (e) averaging location of each shrink-wrapped vertex and location of the neighboring vertexes, and moving the shrink-wrapped vertex to center of neighboring vertexes.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Storage method of substantial data integrating shape and physical properties
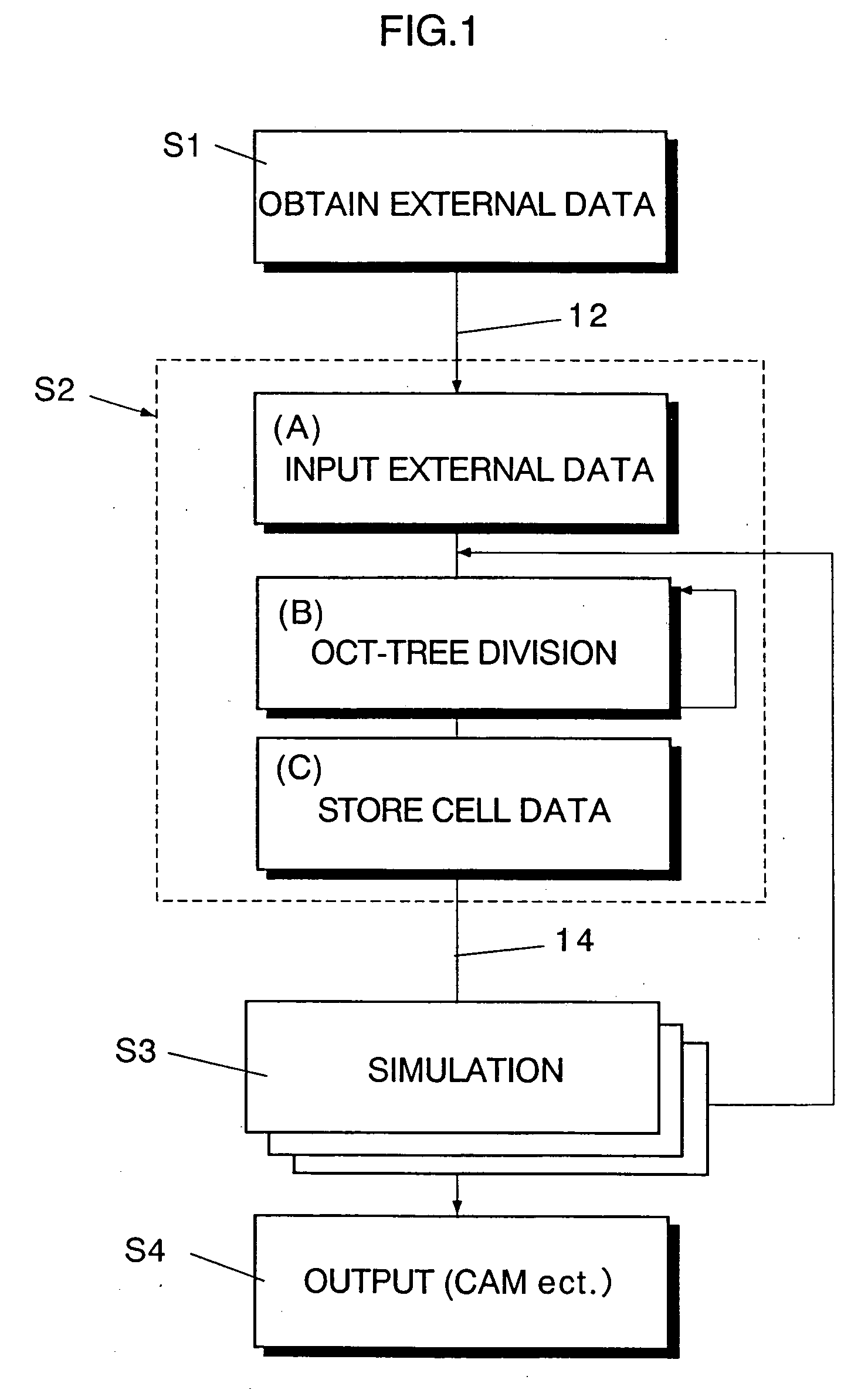
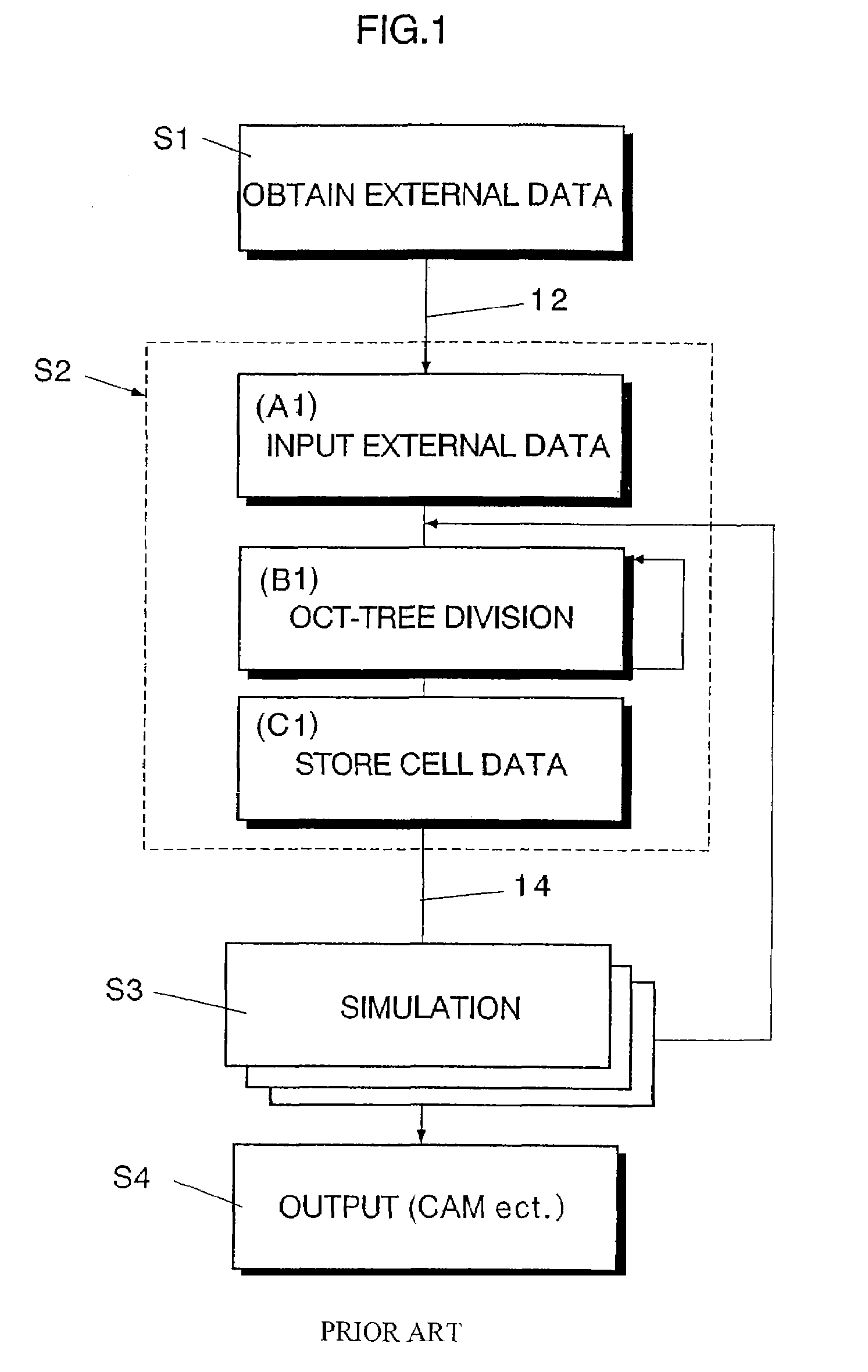
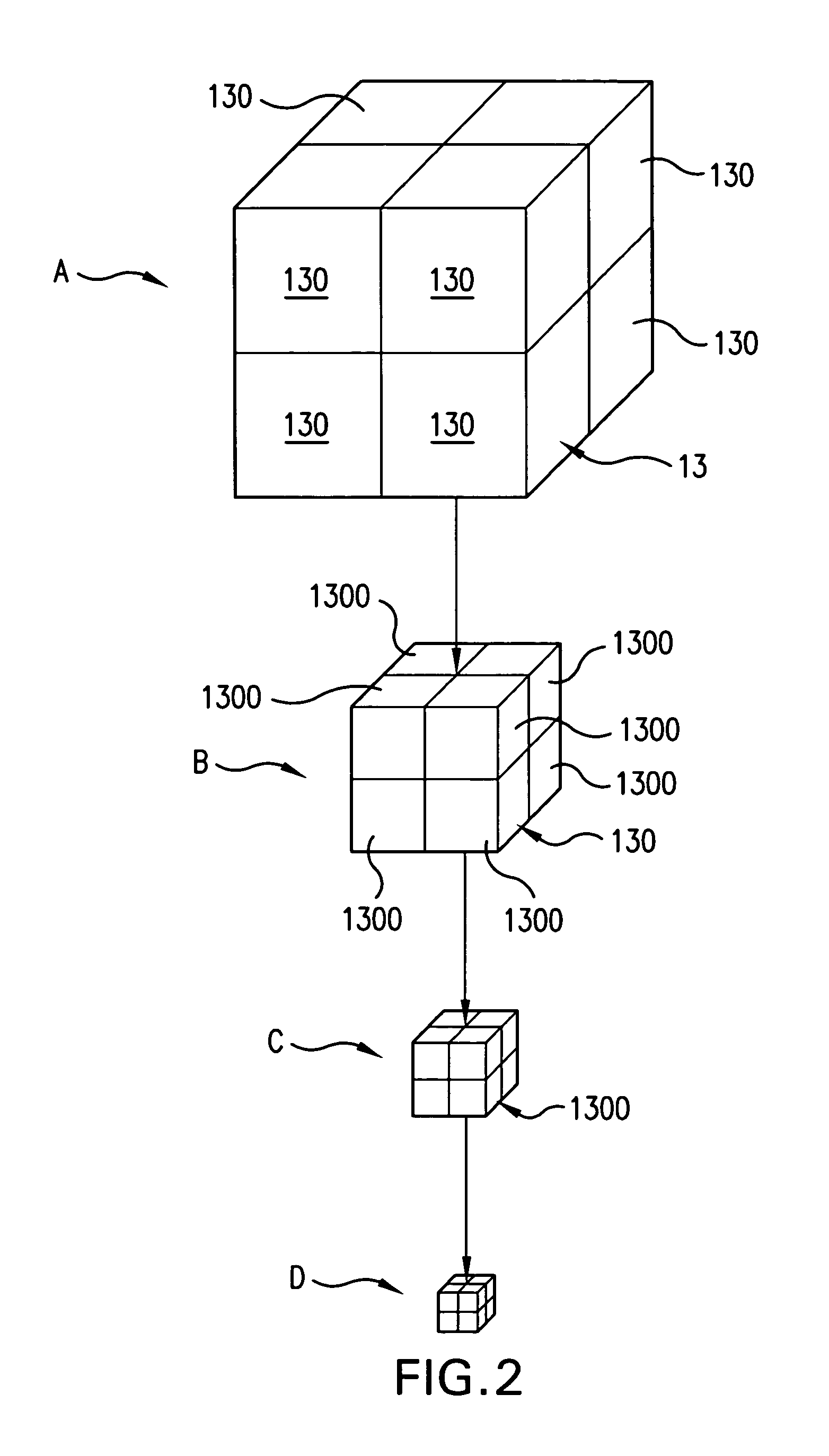
InactiveUS7088363B2Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)External data
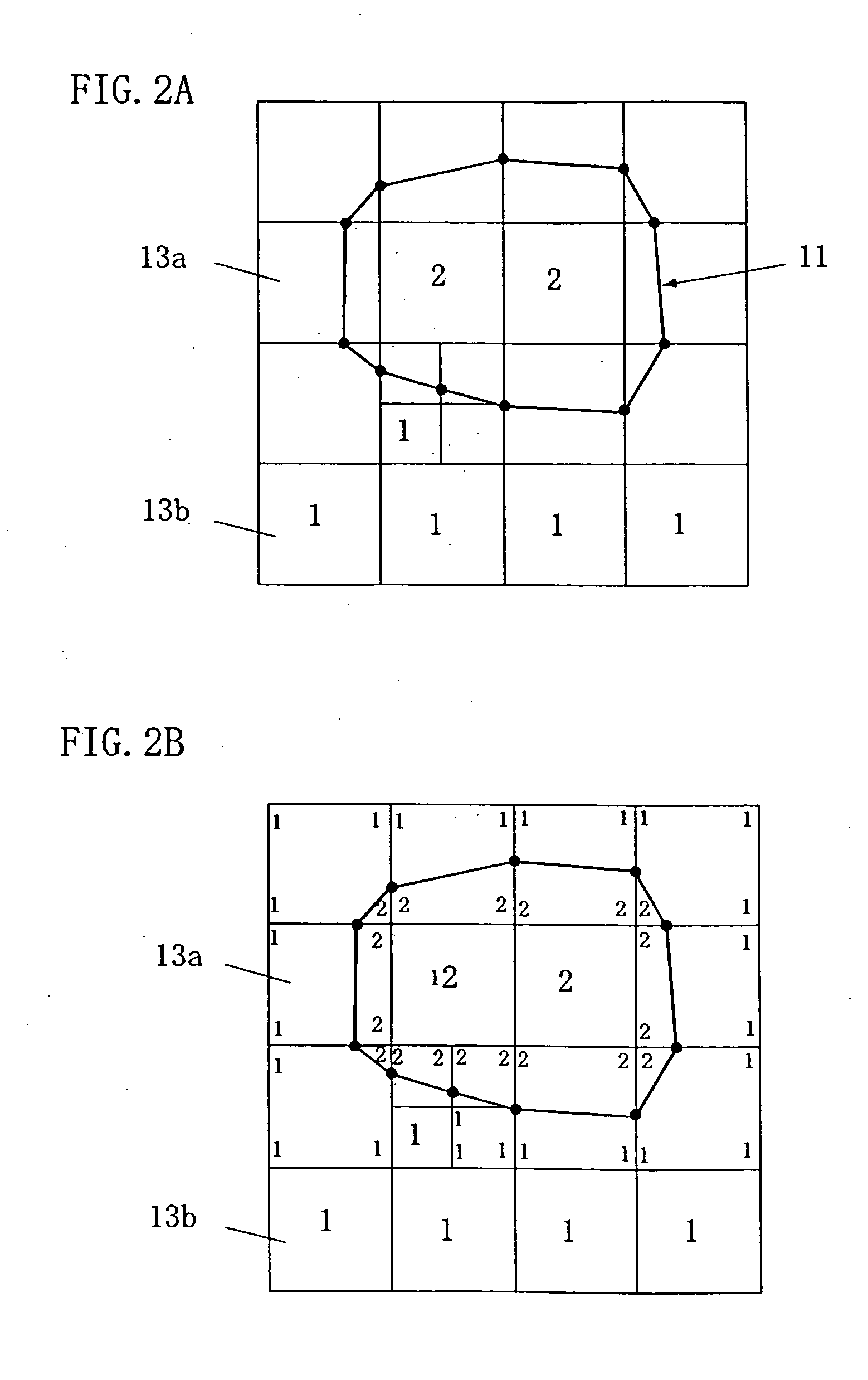
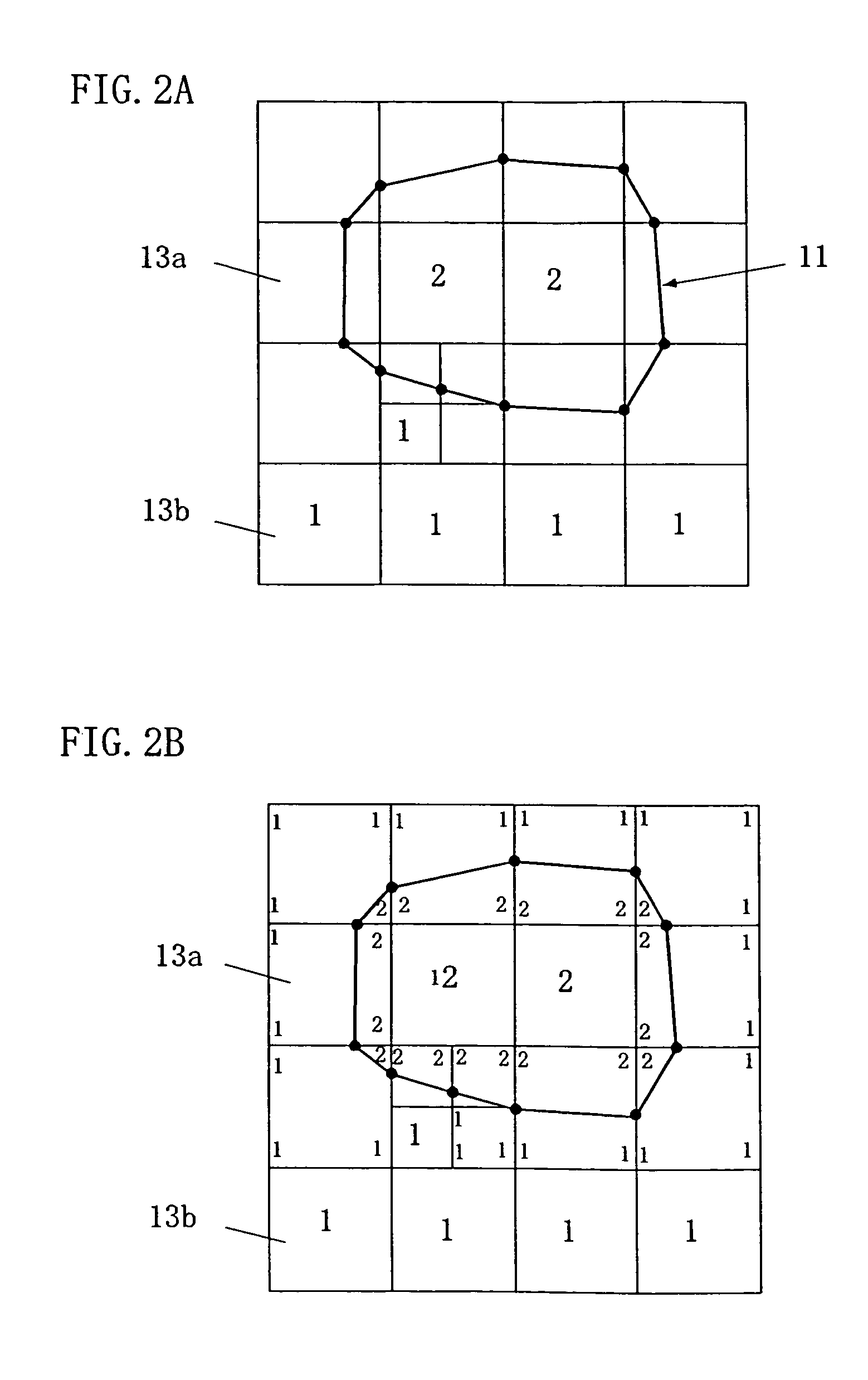
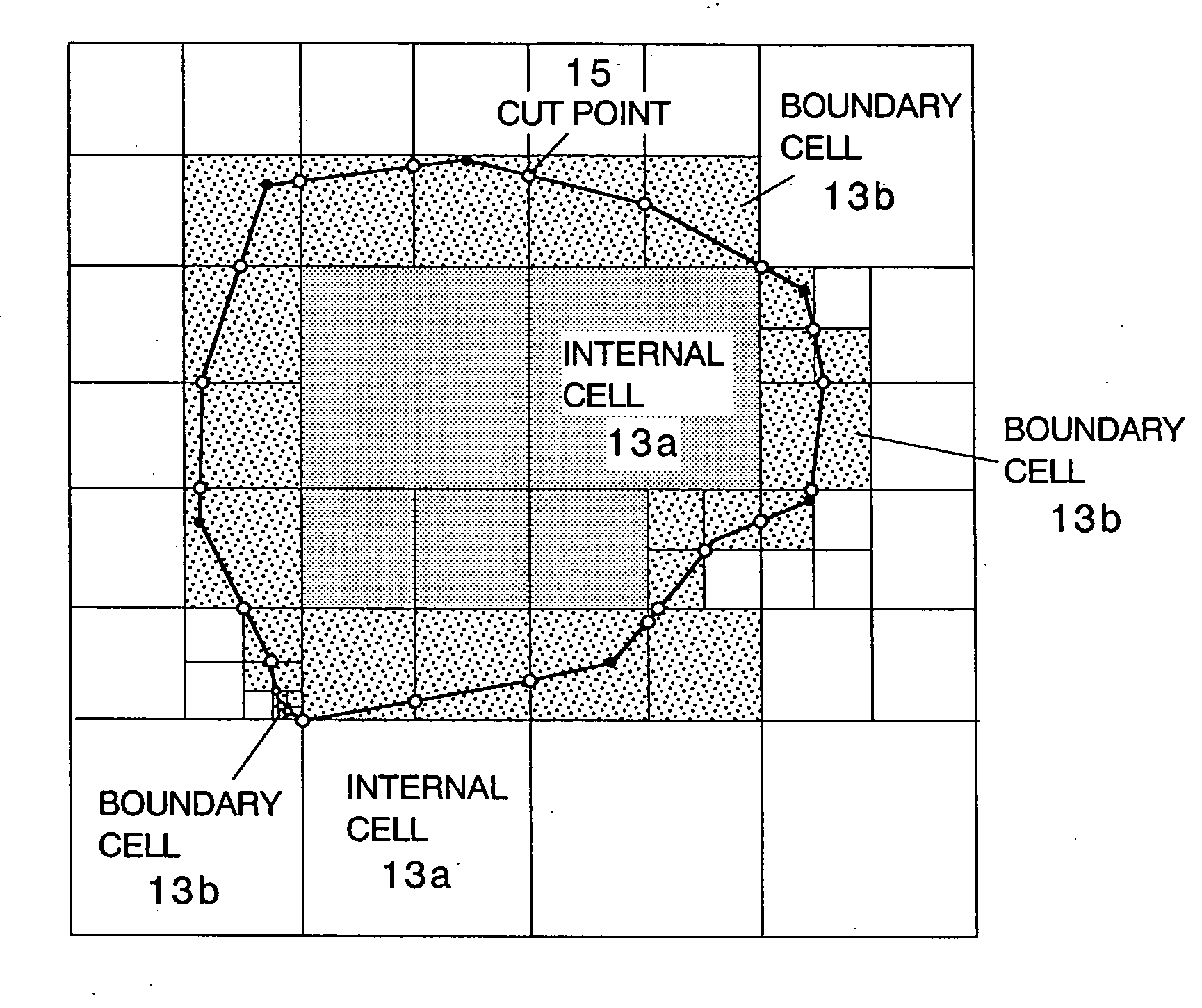
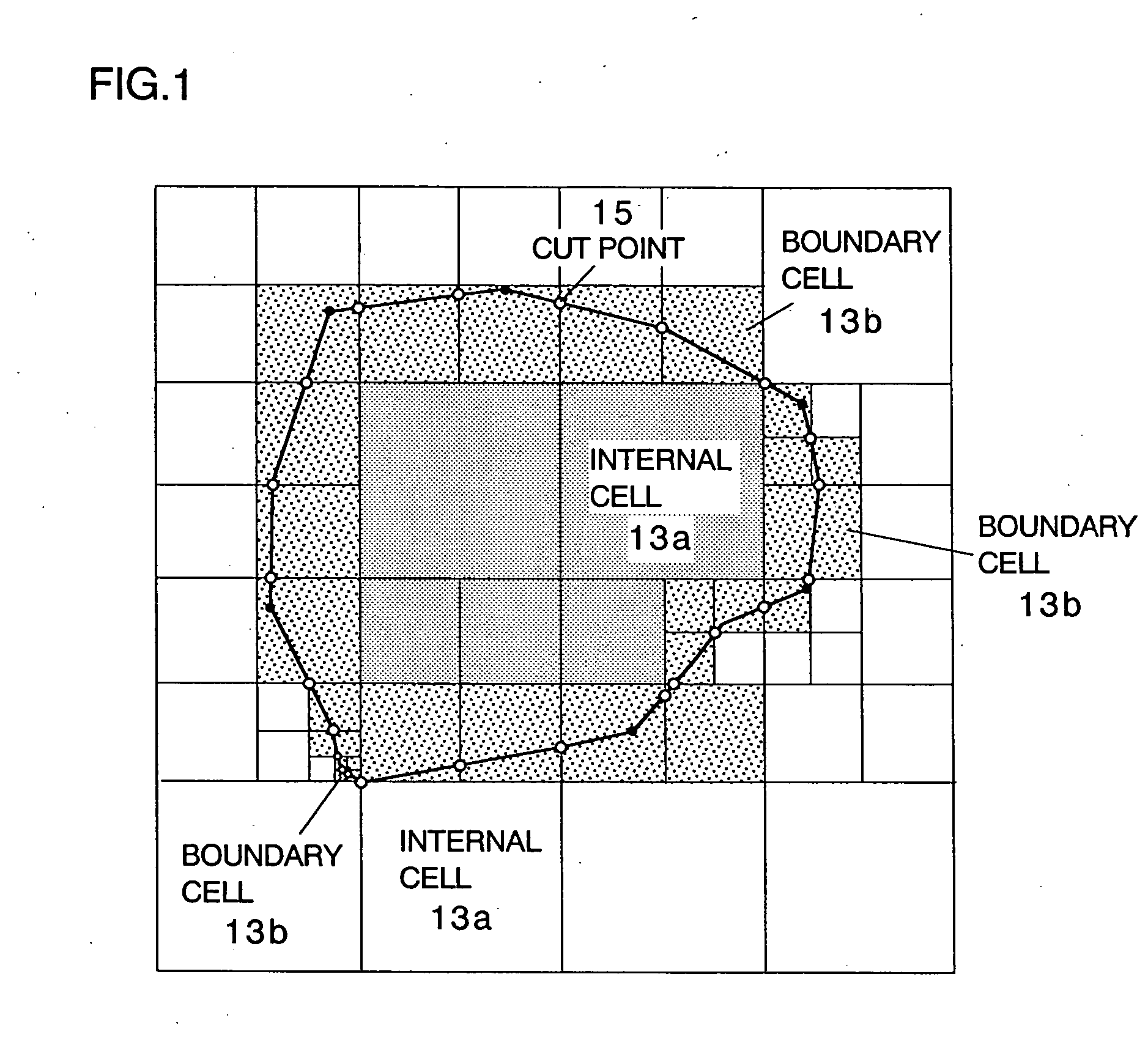
A method of storing substantial data integrating shape and physical properties comprising (A) inputting external data 12 consisting of boundary data of an object 1, (B) dividing, by modified Octree division, the external data into cubical cells 13 which boundary surfaces are orthogonal to each other, and (C) storing the values of various physical properties for each of the cells. Furthermore, in step (B), each of the divided cells 13 is classified to non-boundary cells 13a located in the interior of the object or in a region outside of the object, and boundary cells 13b including boundary surfaces. Thereby, substantial data integrating shape and physical properties can be stored in small storage capacity, thus enabling the integration of CAD and simulation.
Owner:RIKEN
Image processing-based erythrocyte and leukocyte classification counting method, system and device
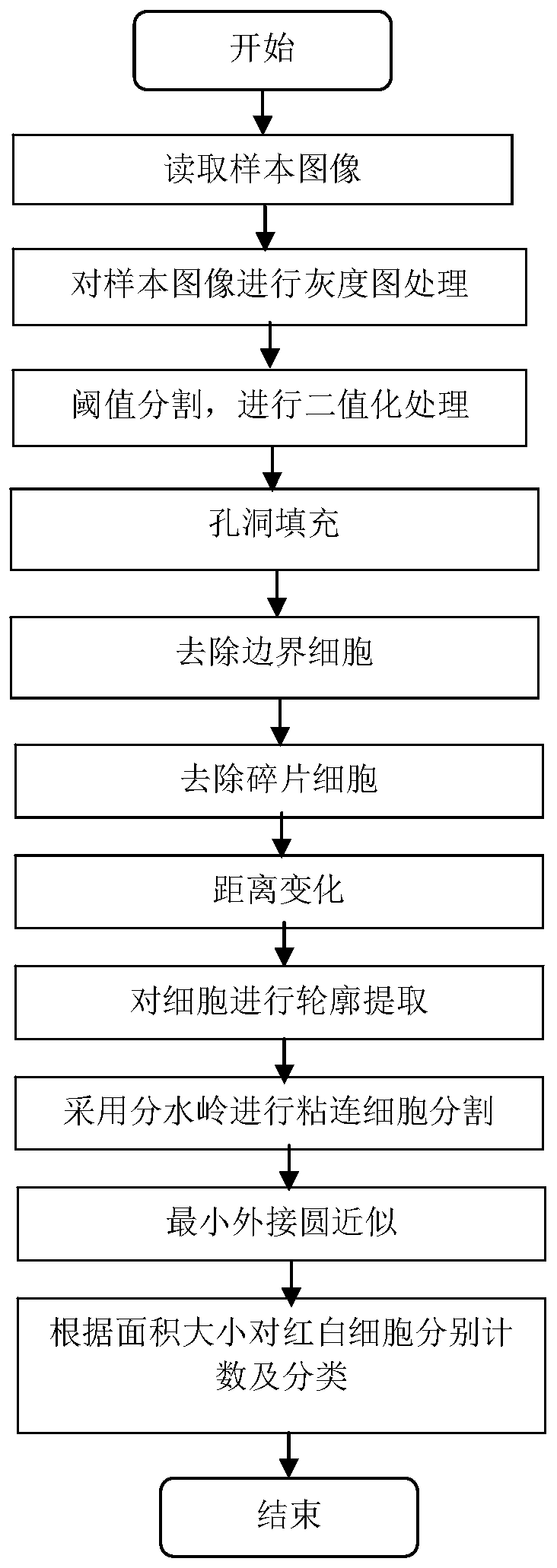
InactiveCN110110709AGuaranteed activityGuaranteed purityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingWhite blood cell
The invention discloses an image processing-based erythrocyte and leukocyte classification counting method, system and device, and the method comprises the steps of carrying out the graying processingon an acquired sample image, then carrying out the binarization processing, and obtaining a black-white binary image; preprocessing the black and white binary image to restore the cells with holes inside, and removing the fragment cells and boundary cells; adopting a segmentation algorithm to segment the cell populations adhering to clusters in the preprocessed image; extracting the cell contoursand counting the cell contours to obtain the number of integral cells; dividing the whole cell into the erythrocytes and the leukocytes according to the area of a region occupied by a single cell inthe image; and respectively counting to obtain the number of the erythrocytes and the number of the leukocytes, so that the problems of high detection equipment cost, personal errors and the like in the prior art are solved, the equipment cost is reduced, and the detection efficiency and the detection accuracy are improved.
Owner:湖南开启时代智能科技有限公司
System and method for simulating shallow water effects on arbitrary surfaces
ActiveUS7921003B2Effective simulationEasy to controlAnimationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationFluid controlWave equation
A system and method for shallow water simulation may provide a framework for solving General Shallow Wave Equations (GSWE) to efficiently simulate 3D fluid effects on arbitrary surfaces using a height field representation. The height field representation may include height columns constructed along surface normals, which may be dependent on a condition of boundary cells adjacent to fluid cells and / or artificial viscosity effects. The framework may provide implicit schemes for solving for the effects of external forces applied to the fluid, including gravity and surface tension, and explicit schemes for solving for advection effects. The system and method may be implemented on general-purpose CPU(s) and / or GPU(s) and may be capable of simulating a variety of fluid effects including: waves, rivulets and streams, drops, and capillary events. In some embodiments, the system and method may achieve real-time fluid control and fluid shape design through user-interaction (e.g., in a graphical painting application).
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Method of IC fabrication, IC mask fabrication and program product therefor
InactiveUS20050193363A1Reduce designReduce resource consumptionPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringBoundary cell
A method of forming integrated circuit (IC) chip shapes and a method and computer program product for converting an IC design to a mask, e.g., for standard cell design. Individual book / macro physical designs (layouts) are proximity corrected before unnesting and an outer proximity range is determined for each proximity corrected physical design. Shapes with a unique design (e.g., in boundary cells and unique instances of books) are tagged and the design is unnested. Only the unique shapes are proximity corrected in the unnested design, which may be used to make a mask for fabricating IC chips / wafers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Honeycomb structure body
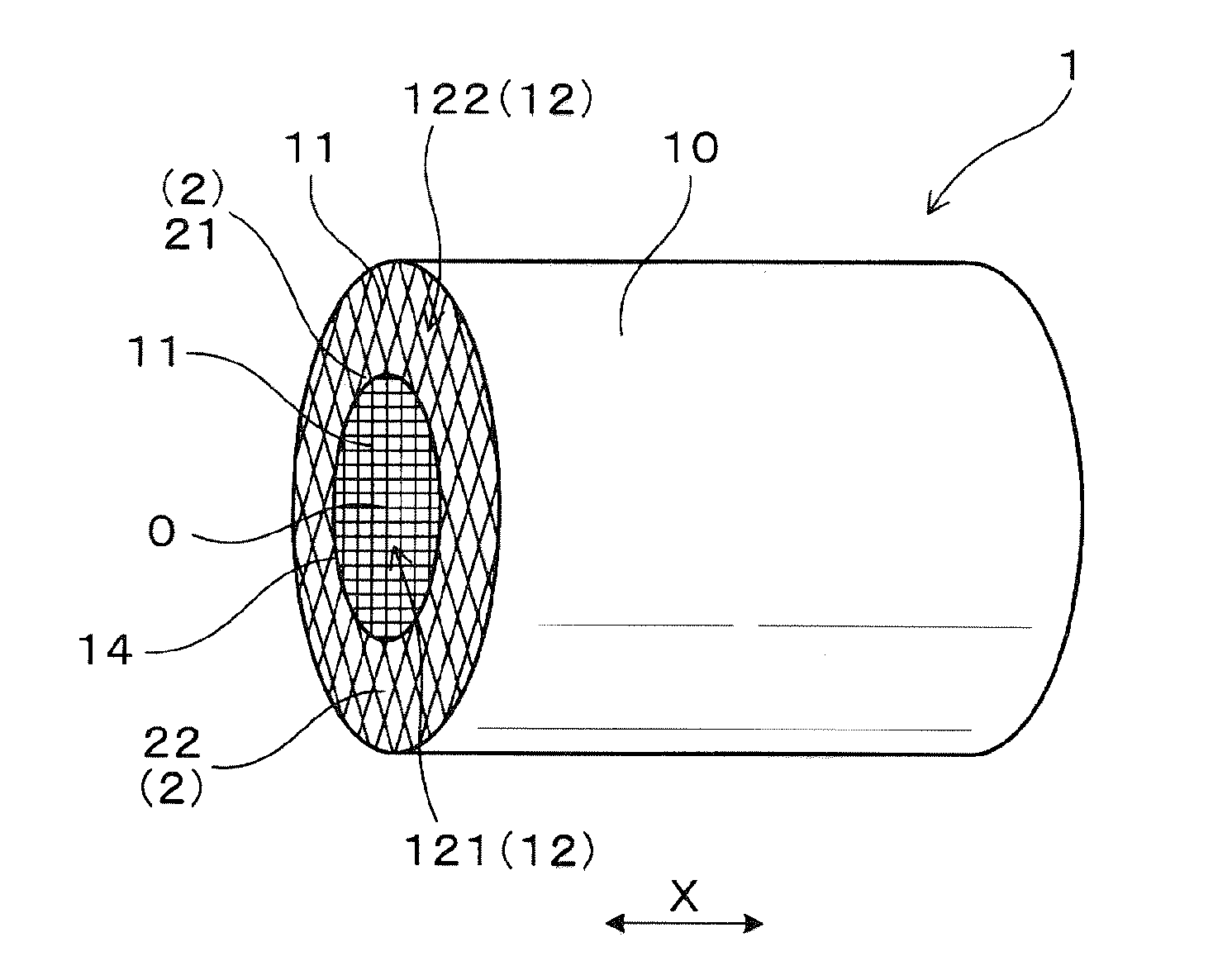
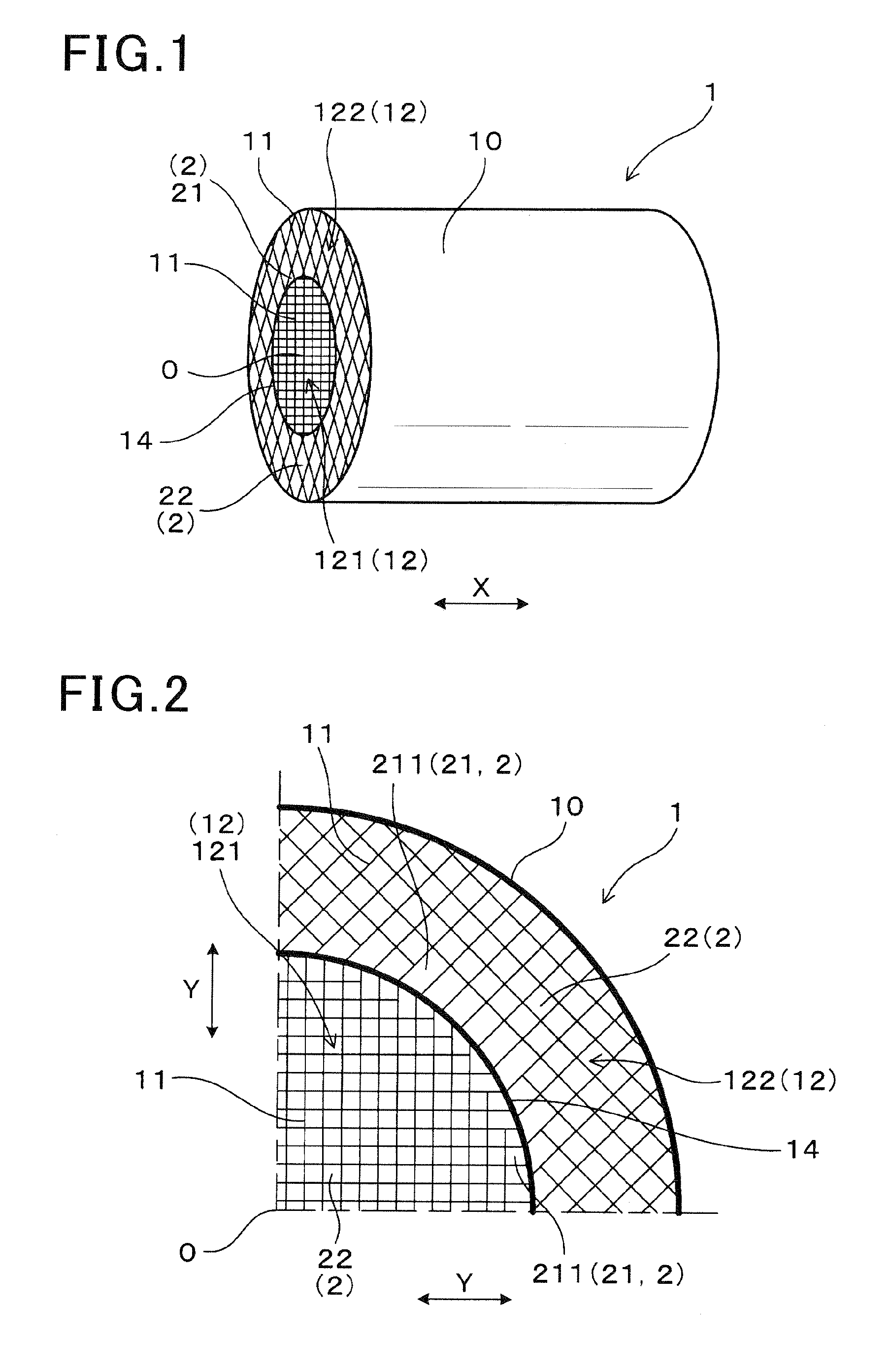
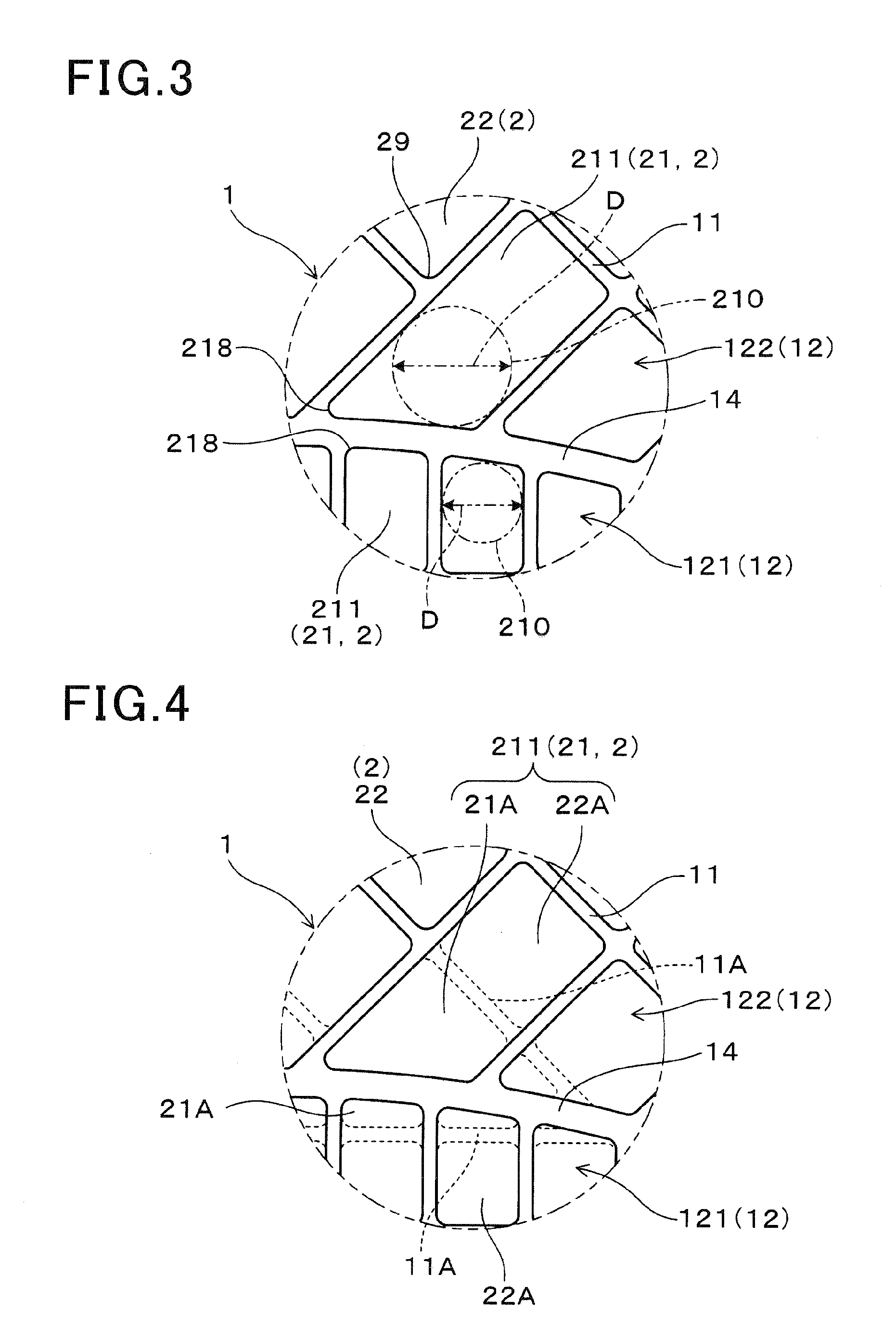
ActiveUS20150275726A1High mechanical strengthAvoid it happening againPhysical/chemical process catalystsDispersed particle filtrationEngineeringHoneycomb structure
A honeycomb structure body has a cylindrical outer peripheral wall, partition walls and cells. The cells are surrounded by the partition walls. In a radial cross section of the honeycomb structure body, the cells is divided into cell density sections having different cell densities formed from a central section to the outer peripheral wall. A boundary wall is formed between two cell density sections. Each cell density section has boundary cells and interior cells. The boundary cells are in contact with the boundary wall. The interior cells are not in contact with the boundary wall. In the radial cross section of the honeycomb structure body, an inscribed circle of each of the boundary cells has a diameter of not less than 0.5 mm. Further, an inscribed circle of an interior cell adjacent to the boundary cell also has a diameter of not less than 0.5 mm.
Owner:DENSO CORP
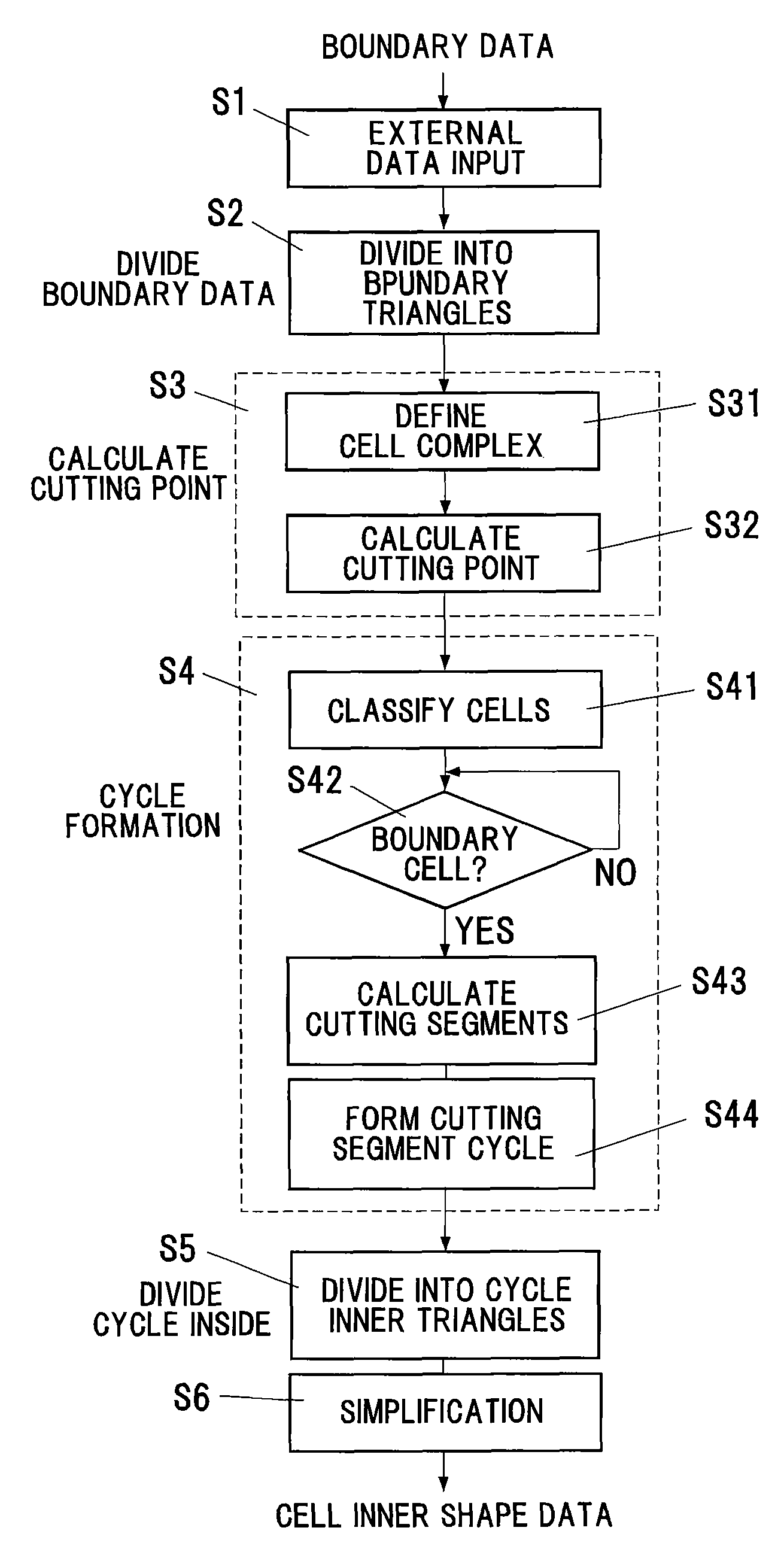
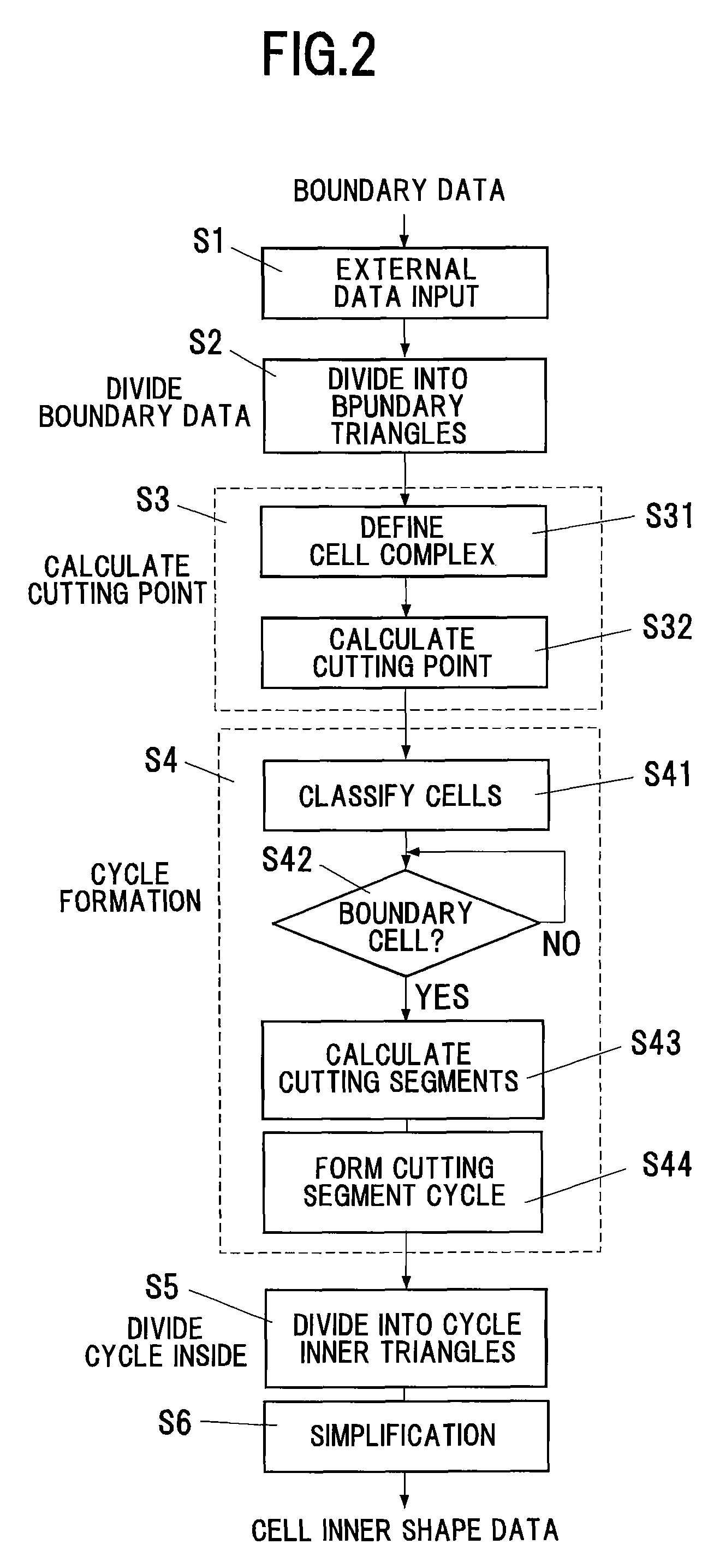
Method and program for converting boundary data into cell inner shape data
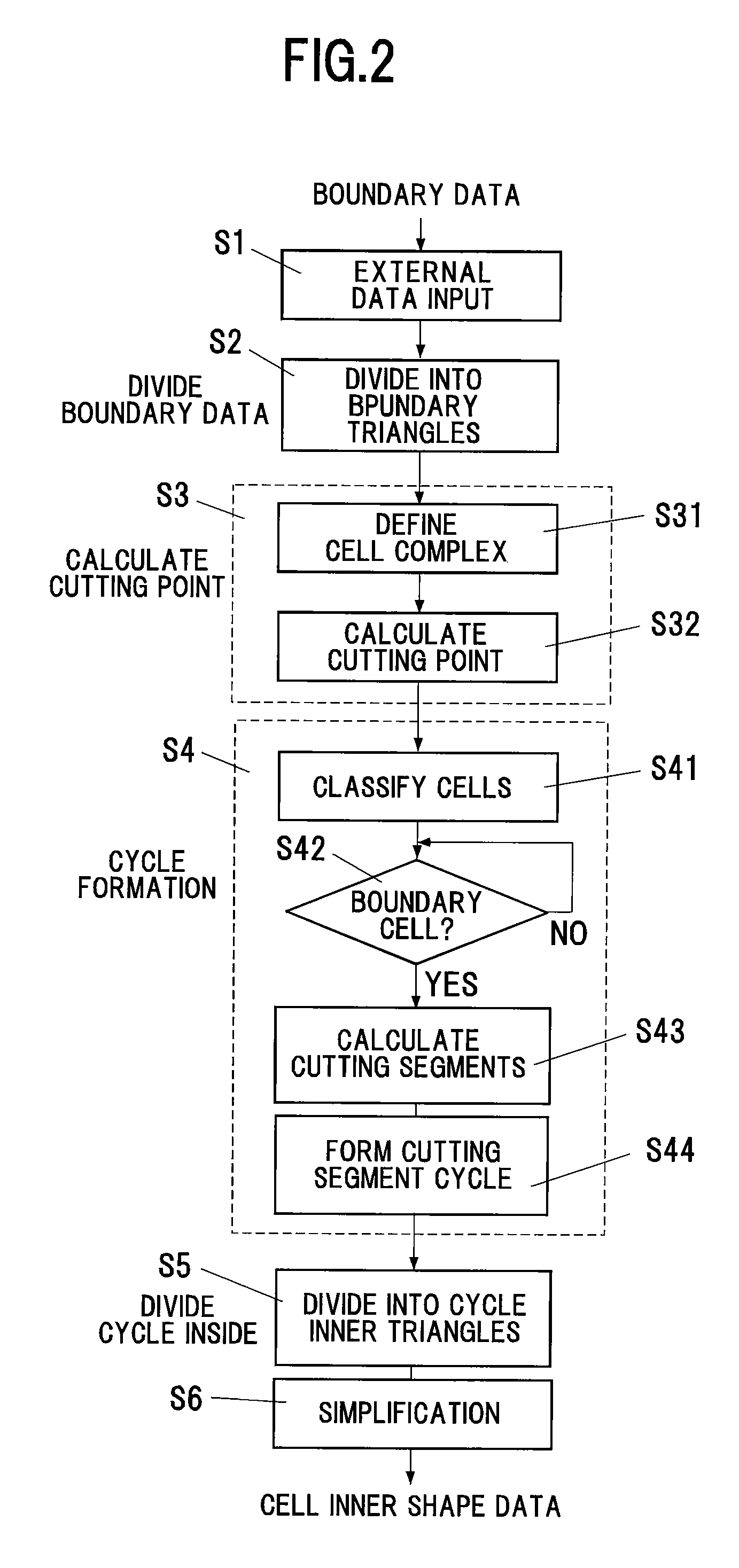
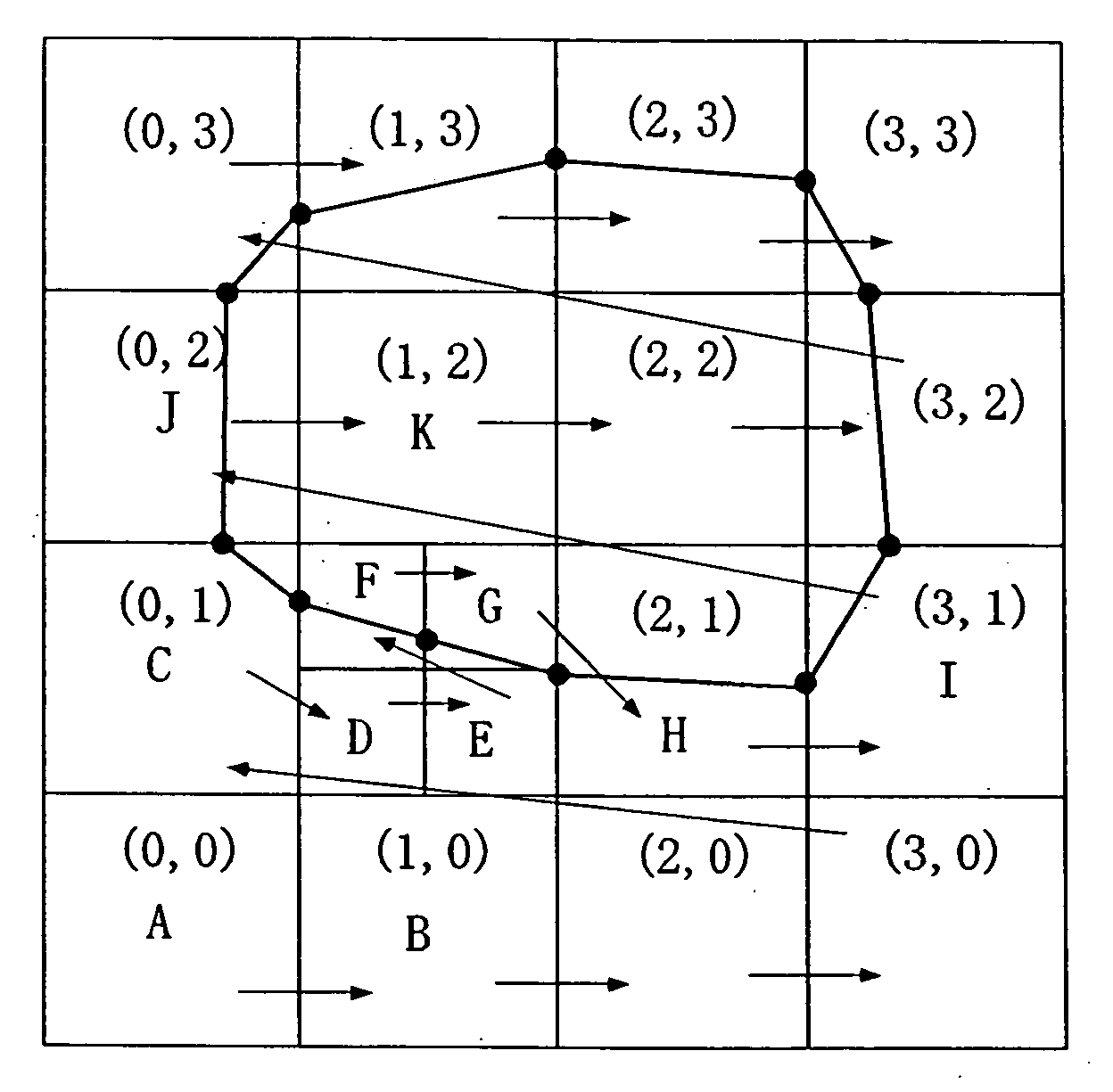
InactiveUS20070058455A1Reliable dataReduce calculationDigital storageDesign optimisation/simulationBoundary cellComputer science
A cutting point calculation step defines the cell complex that contains the boundary data, and calculating a cutting point where the boundary data cuts an edge or vertex of the rectangular parallelepiped cell of the cell complex. A cycle formation step classifies the rectangular parallelepiped cells into a boundary cell having the cutting point and a nonboundary cell having no cutting point, acquiring a cutting segment between a cell surface and boundary data for each boundary cell, and forming a cutting segment cycle closed by connecting the cutting points and the cutting segments alternately in sequence. A cycle internal division step divides the inside of the cutting segment cycle into cycle inner triangles sharing an adjacent side, for each boundary cell. A simplification step of unifying a plurality of cutting points on each edge, and registering the cycle inner triangles in the cell, for each boundary cell.
Owner:RIKEN
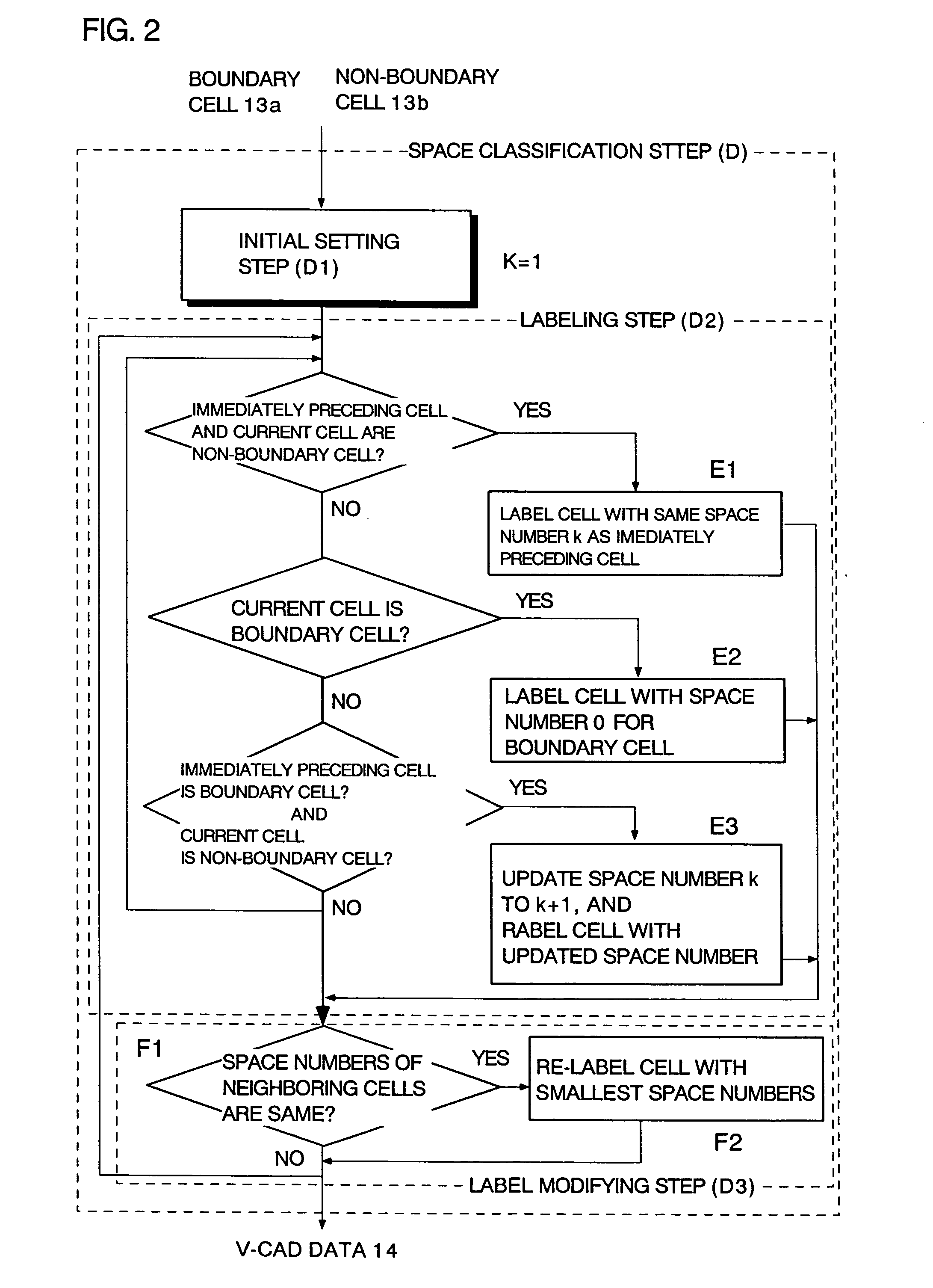
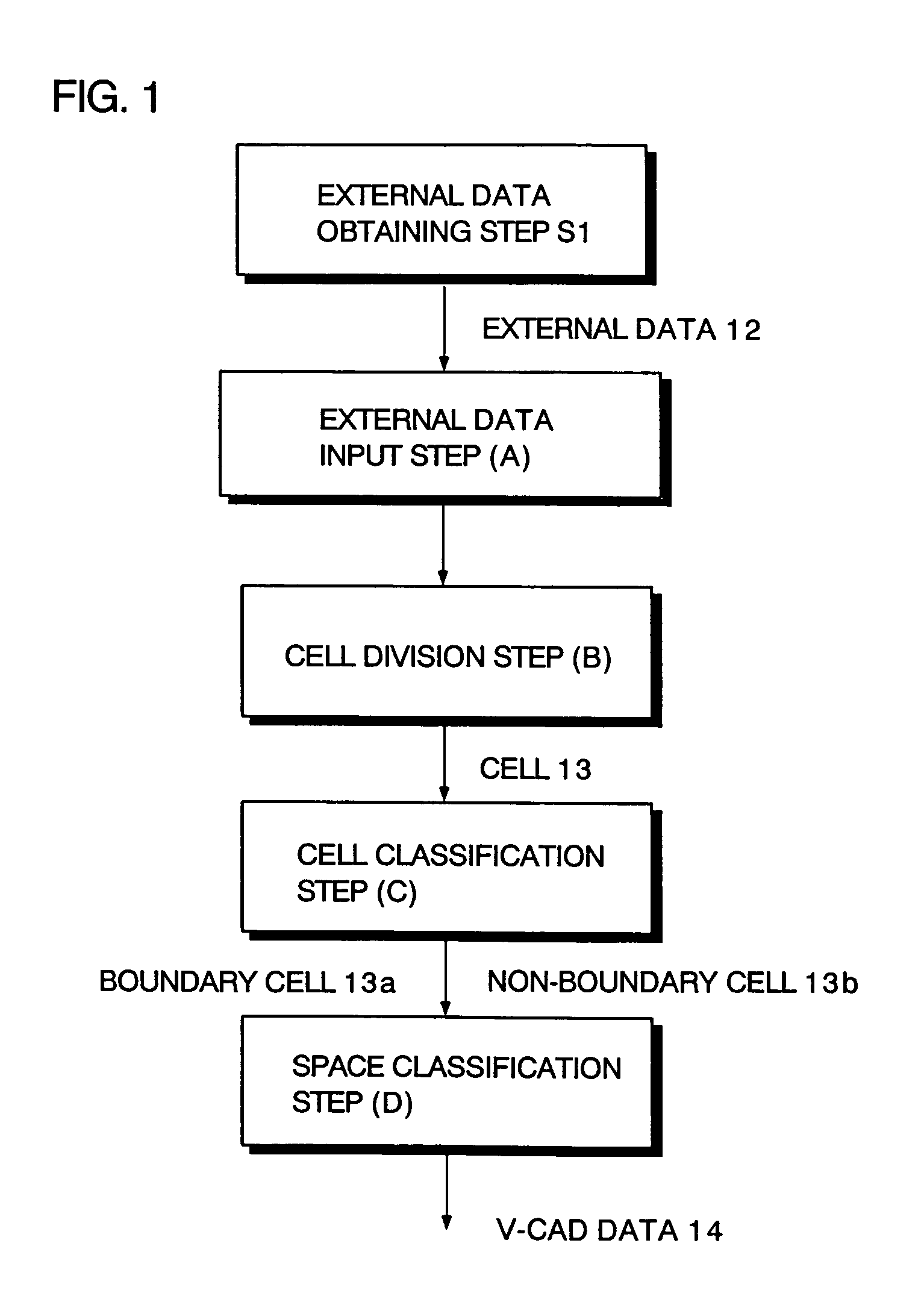
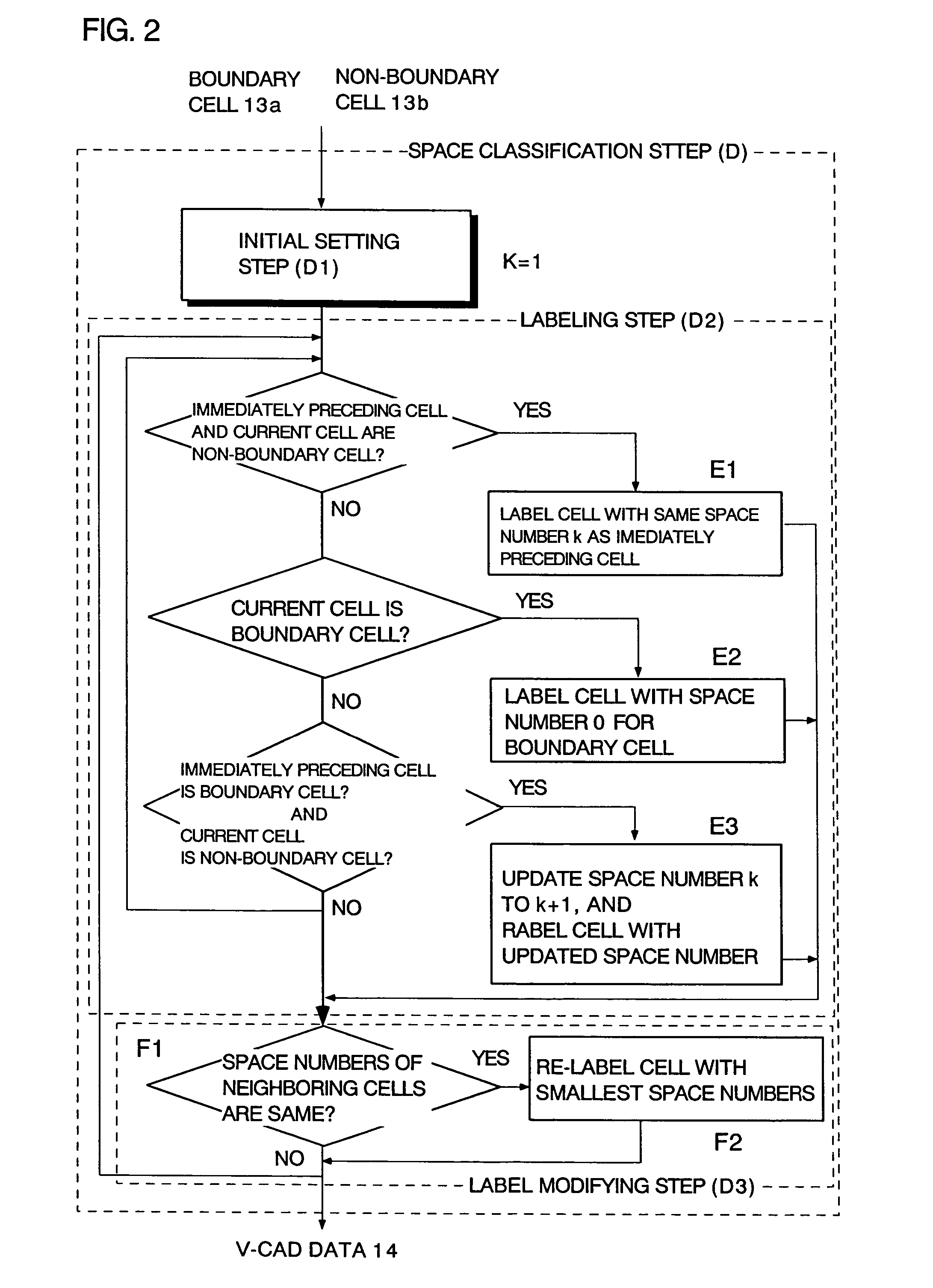
Boundary data inside/outside judgment method and program thereof
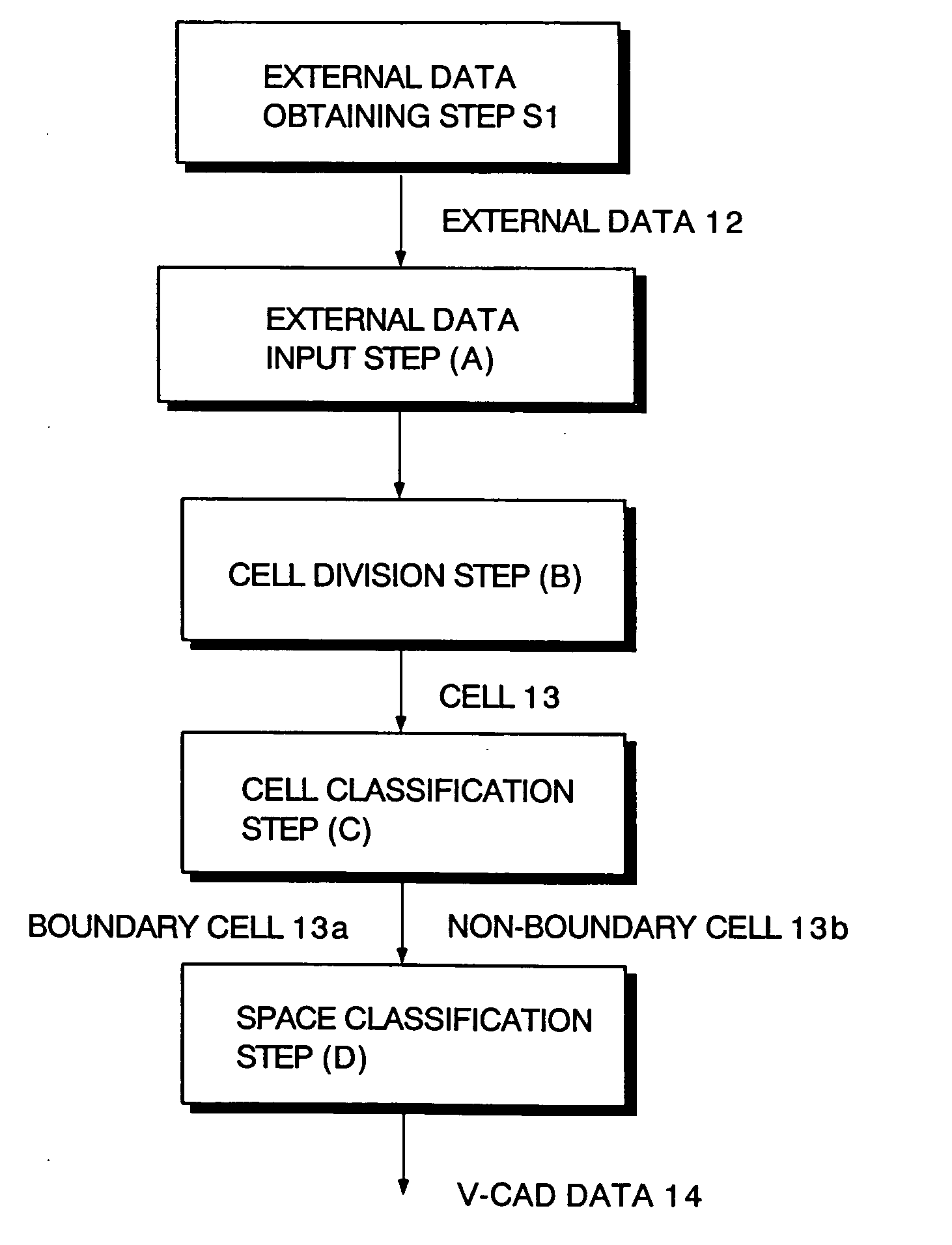
InactiveUS20050162418A1Fast processingEasy to implementImage enhancementImage analysisCell divisionExternal data
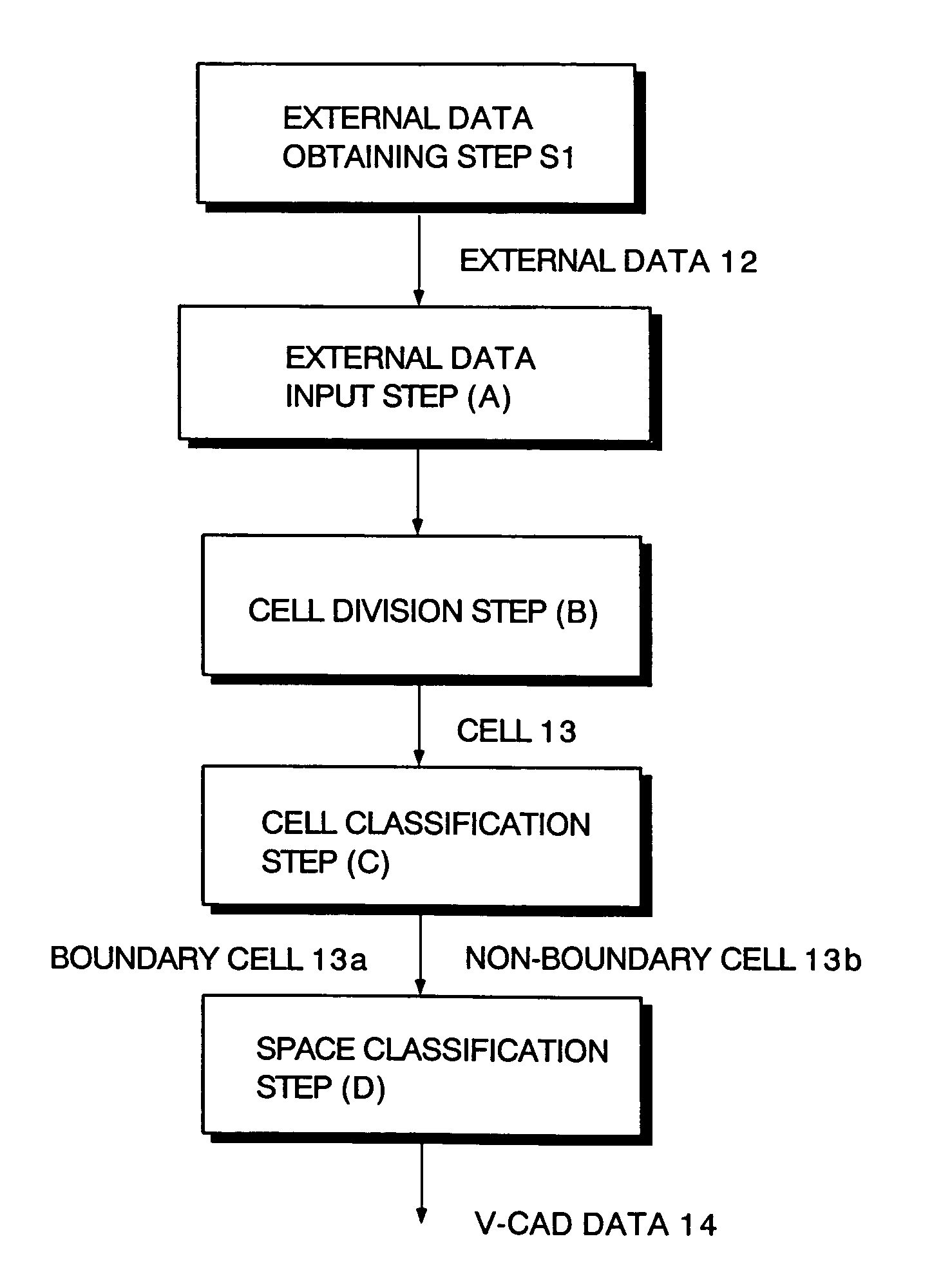
A method for determining insides and outsides of boundaries includes an external data input step of inputting external data constituted by boundary data of objects, a cell division step of dividing the external data into rectangular parallelepiped cells having boundary planes orthogonal to each other, a cell classification step of classifying the cells into a boundary cell that includes the boundary data and a non-boundary cell that does not include the boundary data, and a space classification step of classifying the non-boundary cells into a plurality of spaces that are partitioned by the boundary cells.
Owner:RIKEN
Method and program for labeling multi material data
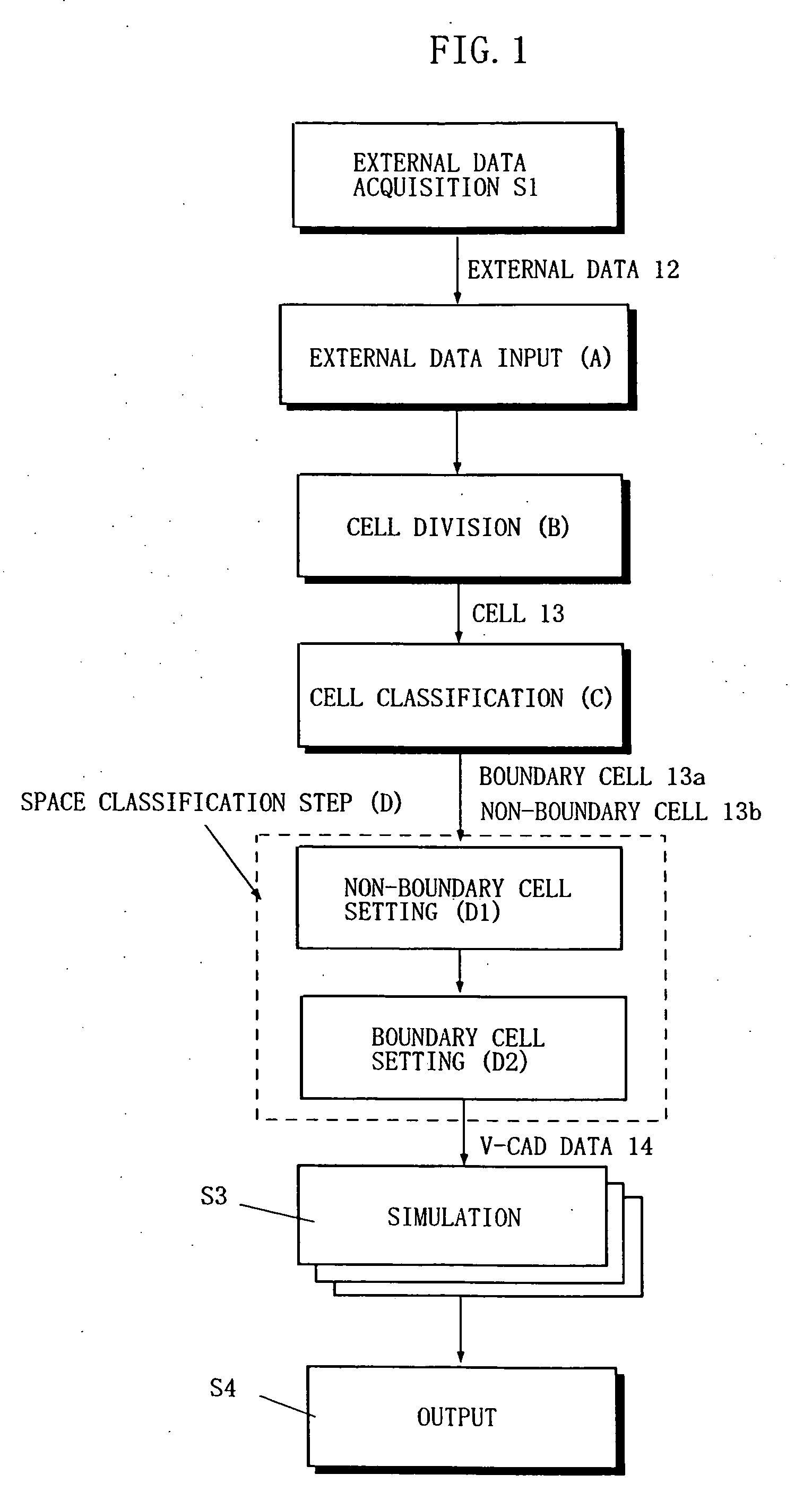
InactiveUS20060267974A1Short processing timeFast processingComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationCell divisionMulti material
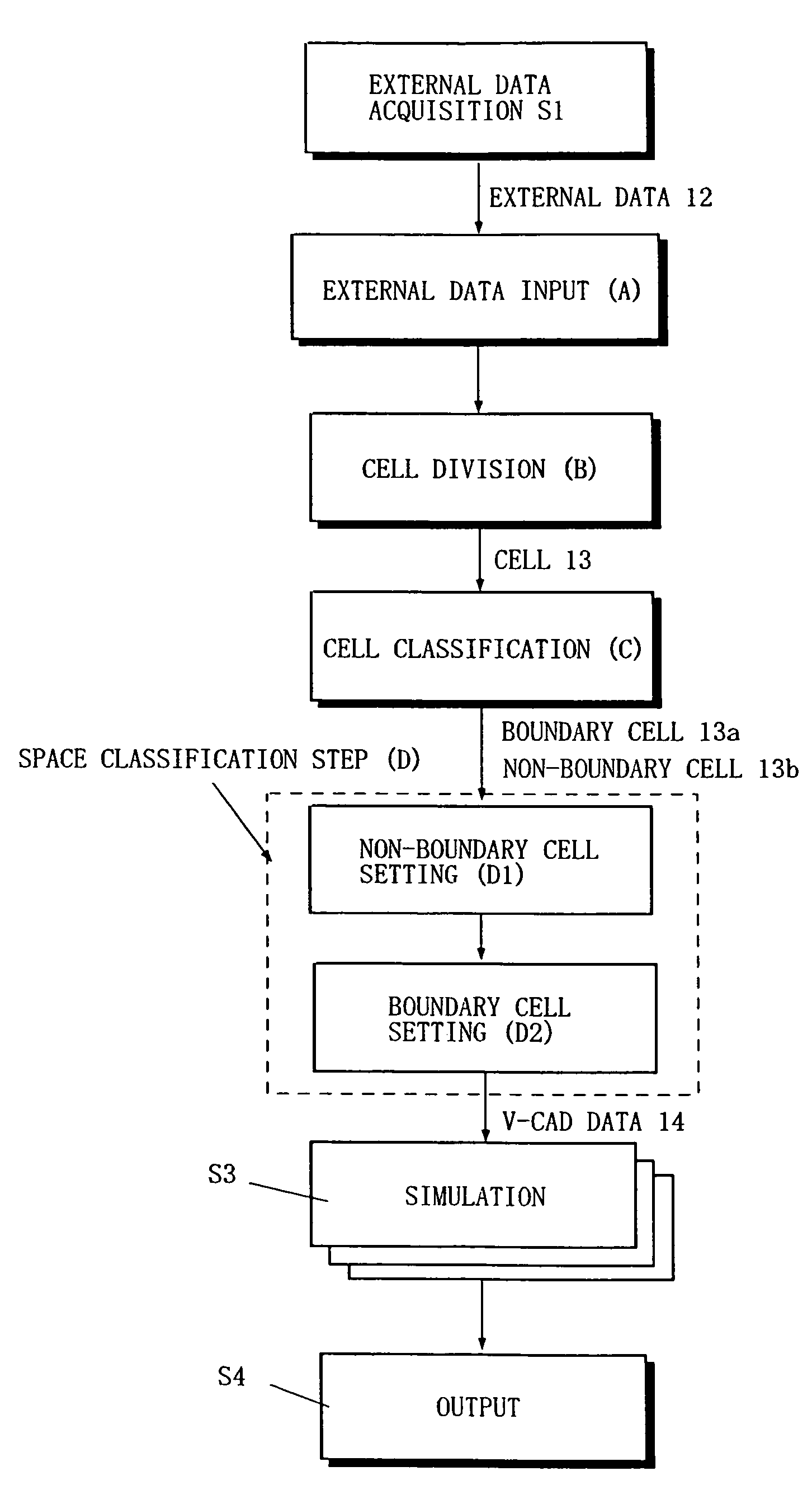
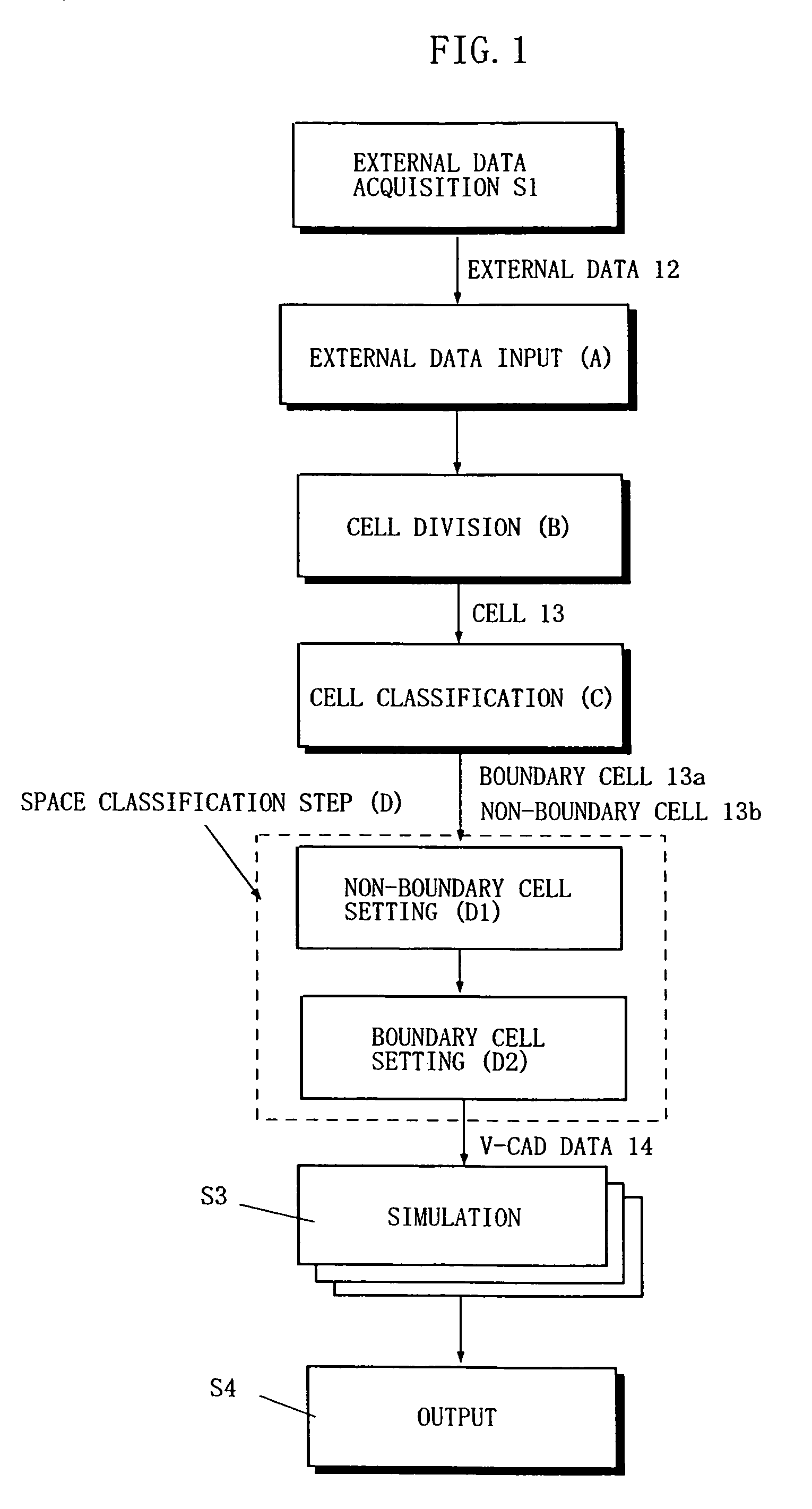
The present invention includes an external data acquisition step (S1), an external data input step (A), a cell division step (B), a cell classification step (C), a space classification step (D), a simulation step (S3), and an output step (S4). The cell classification step (C) includes a step of further classifying each of the boundary cells (13a) into a first type cell and a second type cell. The first type cell has a cutting point at which an edge line or vertex is cut by the boundary data. The second type cell has a cutting point that lies on a boundary with another cell of different hierarchy, and is larger than the another cell. The cell classification step (C) further includes a step of assigning a material number to each cell vertex.
Owner:RIKEN
Rapid prototyping method and apparatus using V-CAD data
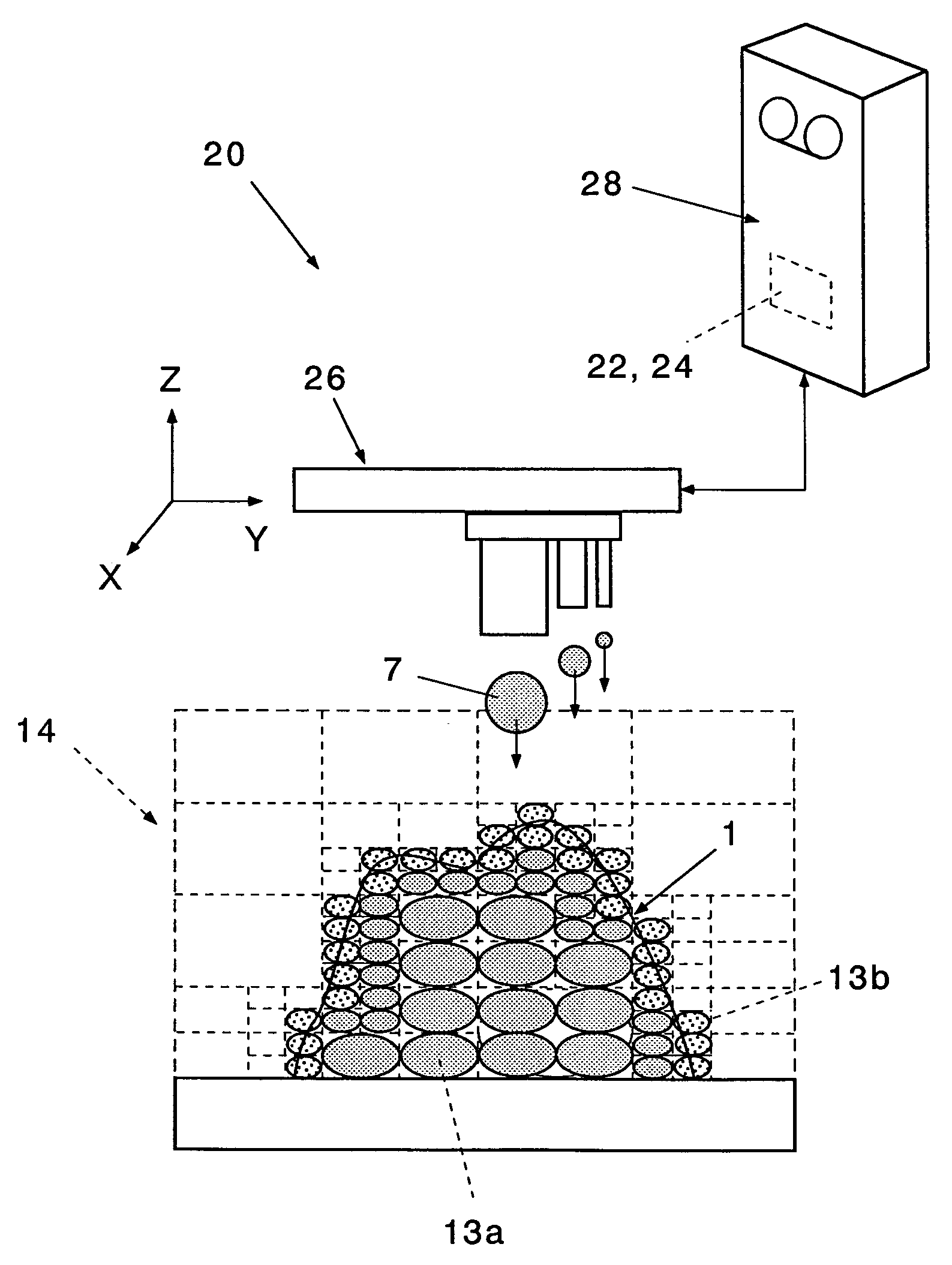
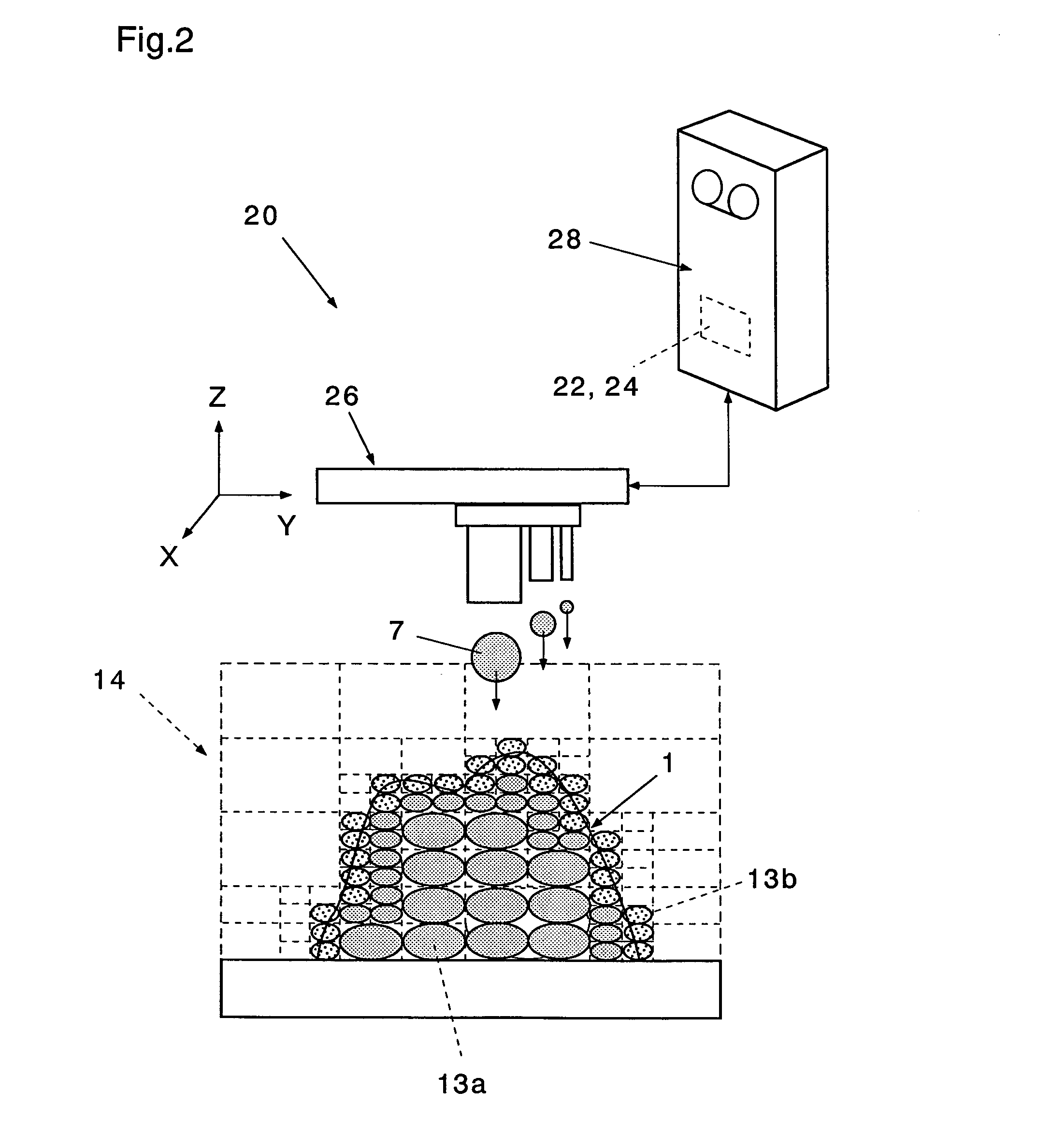
InactiveUS7406361B2Easy programmingFast formingAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with solidsDividing cellExternal data
V-CAD data is prepared by dividing external data 12 consisting of boundary data of an object into rectangular parallelepiped cells 13 having boundary planes orthogonal to each other in accordance with octree division and separating the respective divided cells into internal cells 13a positioned on the inner side of the object and boundary cells 13b including a boundary face, and a modeling unit quantity of a prototyping material 7 is changed in accordance with sizes of the internal cell 13a and the boundary cell 13b of a modeling portion. The prototyping material 7 is a resin, lumber powder, a low-fusing-point metal, metal powder, ceramics powder or a mixture of a binder and one of these materials, and its modeling unit quantity is set in such a manner that the modeling unit quantity is smaller than a capacity of a corresponding cell and does not protrude from the boundary plane of the cell. As a result, by using the V-CAD data, a program for rapid prototyping can be simplified, and a model production time can be greatly reduced.
Owner:RIKEN
Method and device for mining outlier
InactiveCN106649339ASmall amount of calculationHeavy calculationSpecial data processing applicationsData setOutlier
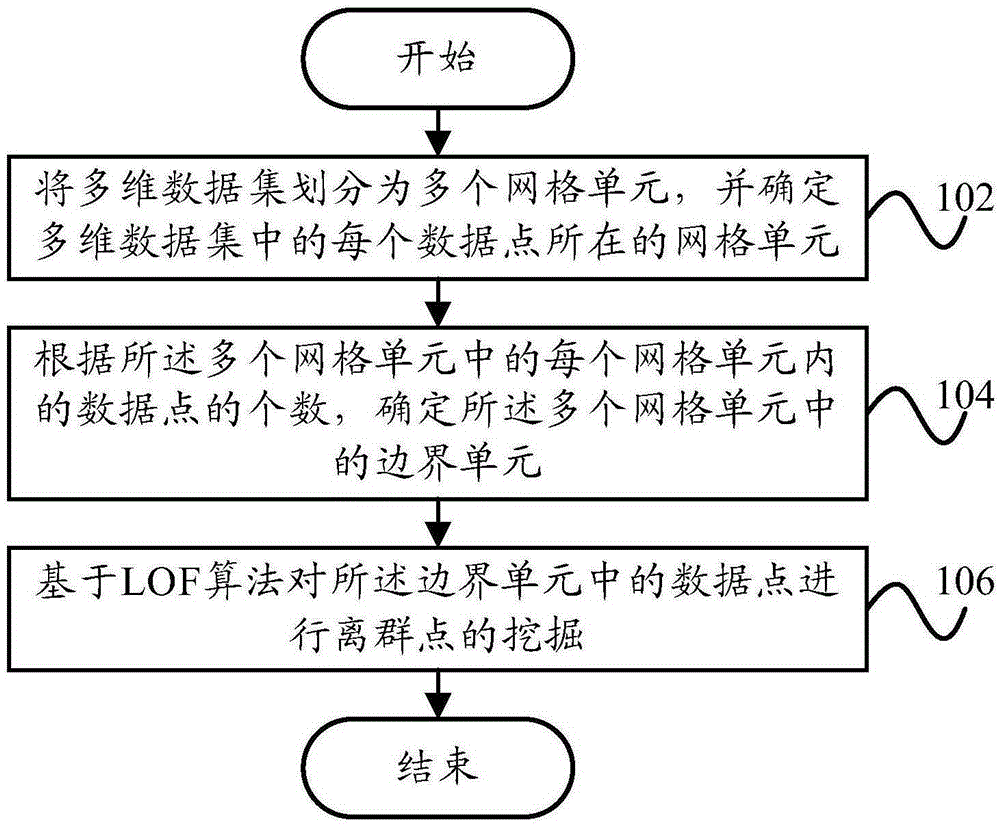
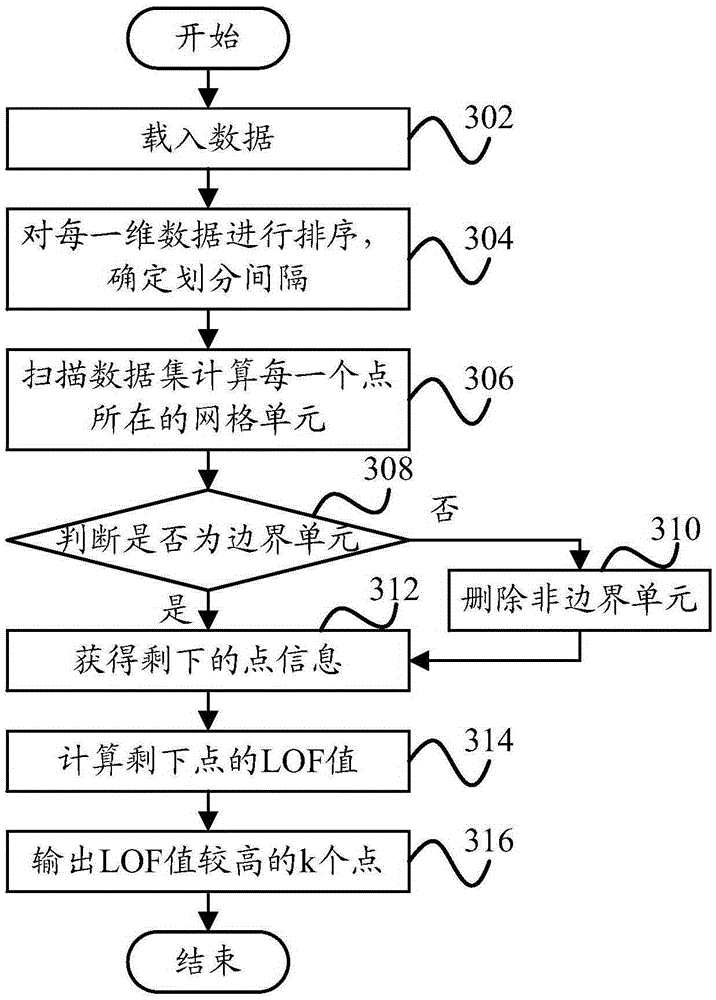
The invention provides a method and device for mining an outlier. The method for mining the outlier comprises the steps that a multi-dimensional data set is divided into a plurality of grid cells, and the grid cell where each data point is located in the multi-dimensional data set is determined; a boundary cell in the grid cells is determined according to the number of the data points in each of the grid cells; the data points in the boundary cell are subjected to outlier mining based on an LOF algorithm. According to the technical scheme, the data size needing to be detected during outlier mining can be effectively reduced, therefore, the calculation amount of a mining algorithm is reduced, and the operation time of the mining algorithm is shortened.
Owner:PEKING UNIV FOUNDER GRP CO LTD +1
Die machining method and device by V-CAD data
InactiveUS7110852B2Simple processReduce processing timeProgramme controlComputer controlExternal dataDividing cell
There is prepared V-CAD data obtained by dividing external data 12 consisting of boundary data of an object into rectangular parallelepiped cells 13 having boundary planes orthogonal to each other in accordance with octree division and separating the respective divided cells into internal cells 13a positioned on the inner side of the object and boundary cells 13b including a boundary face, and mold data and mold processing data used to manufacture the object are generated from data of a reference plane which at least partially comes into contact with the object 1 and the V-CAD data. Further, in the mold processing data, a plurality of the processing tools 2 are selected in descending order of a size in accordance with sizes of the internal cells 13a of a processing portion, and the processing tool 2 is moved in a plane of the mold and in the thickness direction, thereby processing the mold. As a result, by using the V-CAD data, the NC processing program for mold processing can be simplified, and the mold processing time can be greatly reduced.
Owner:RIKEN
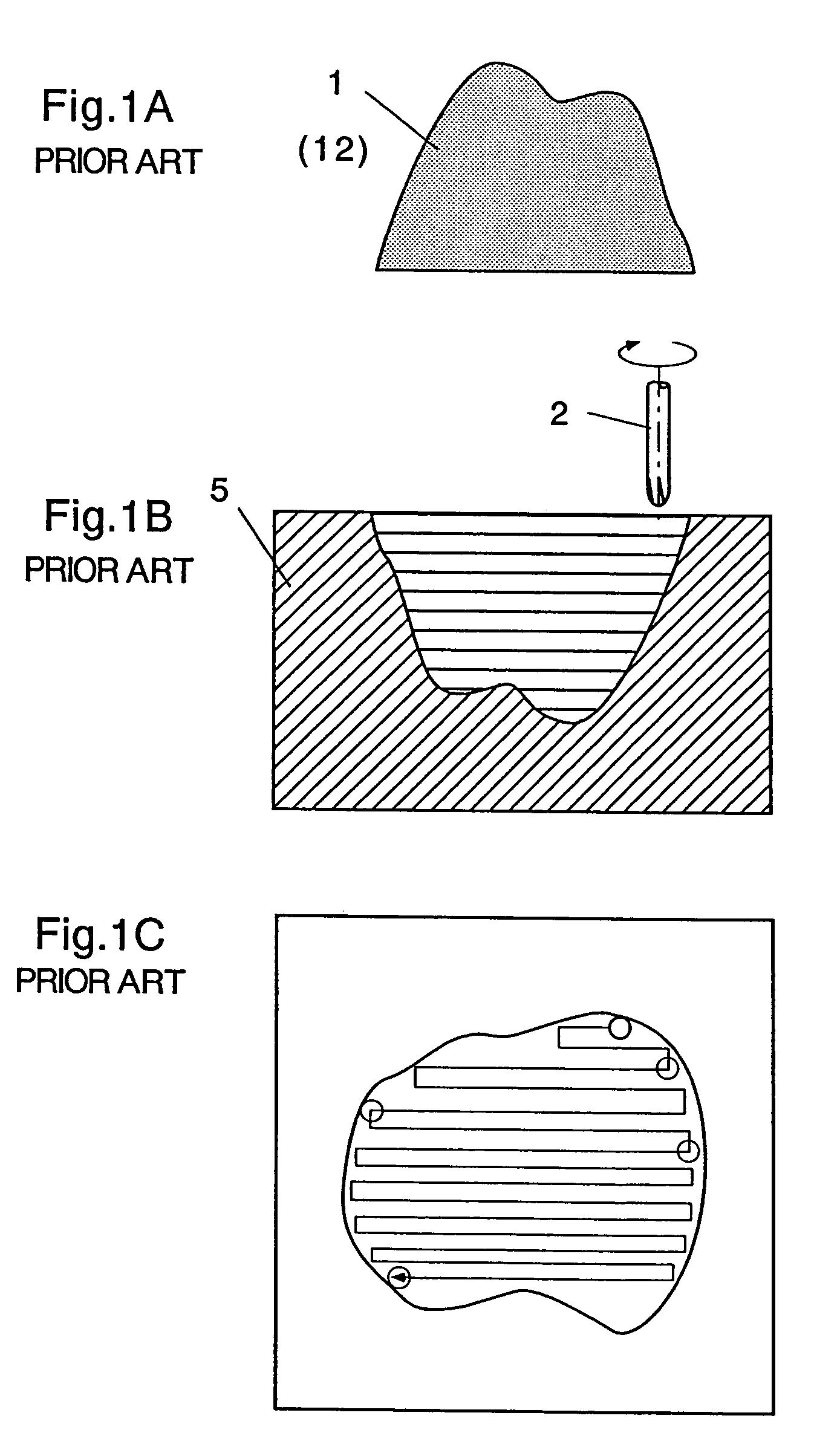
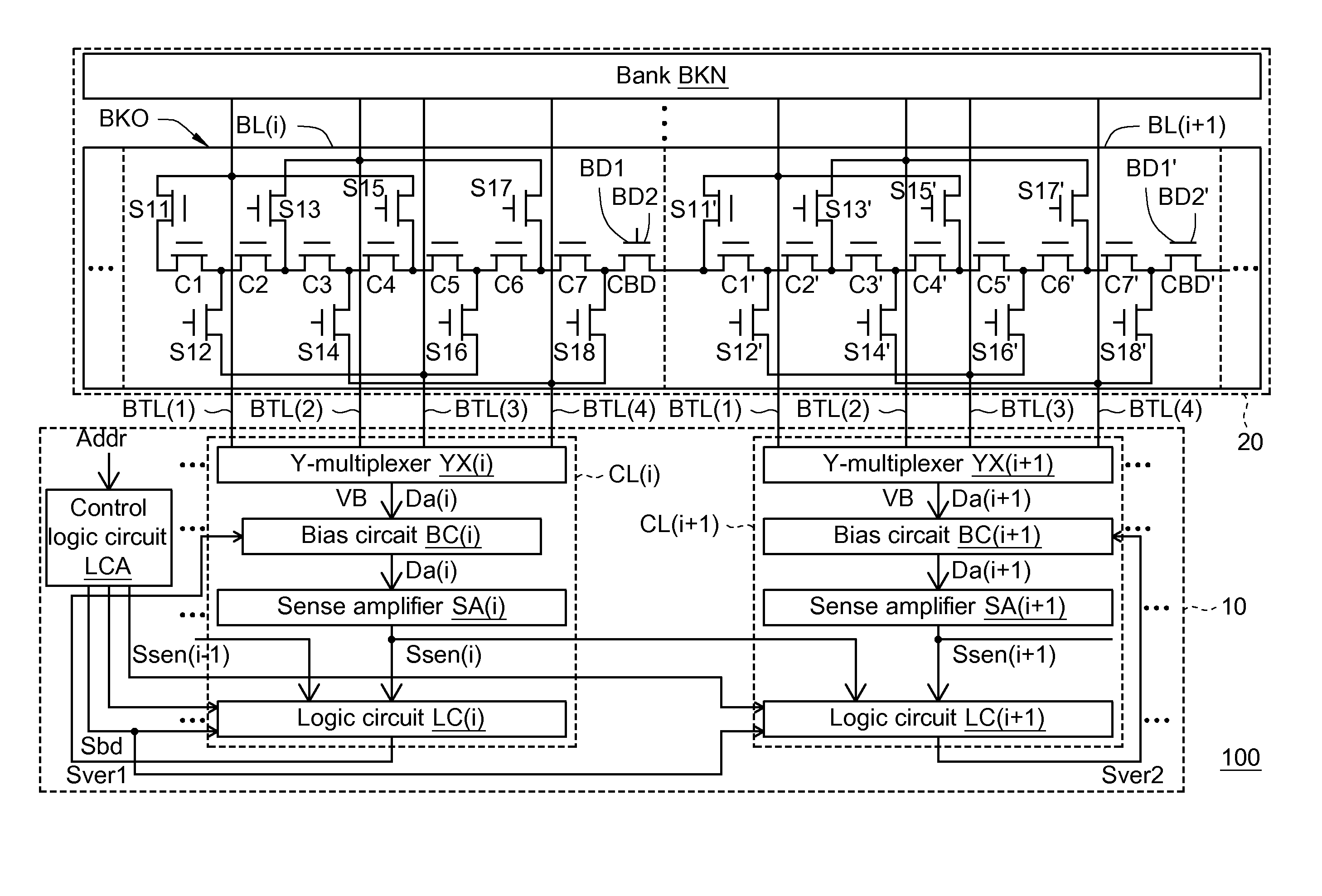
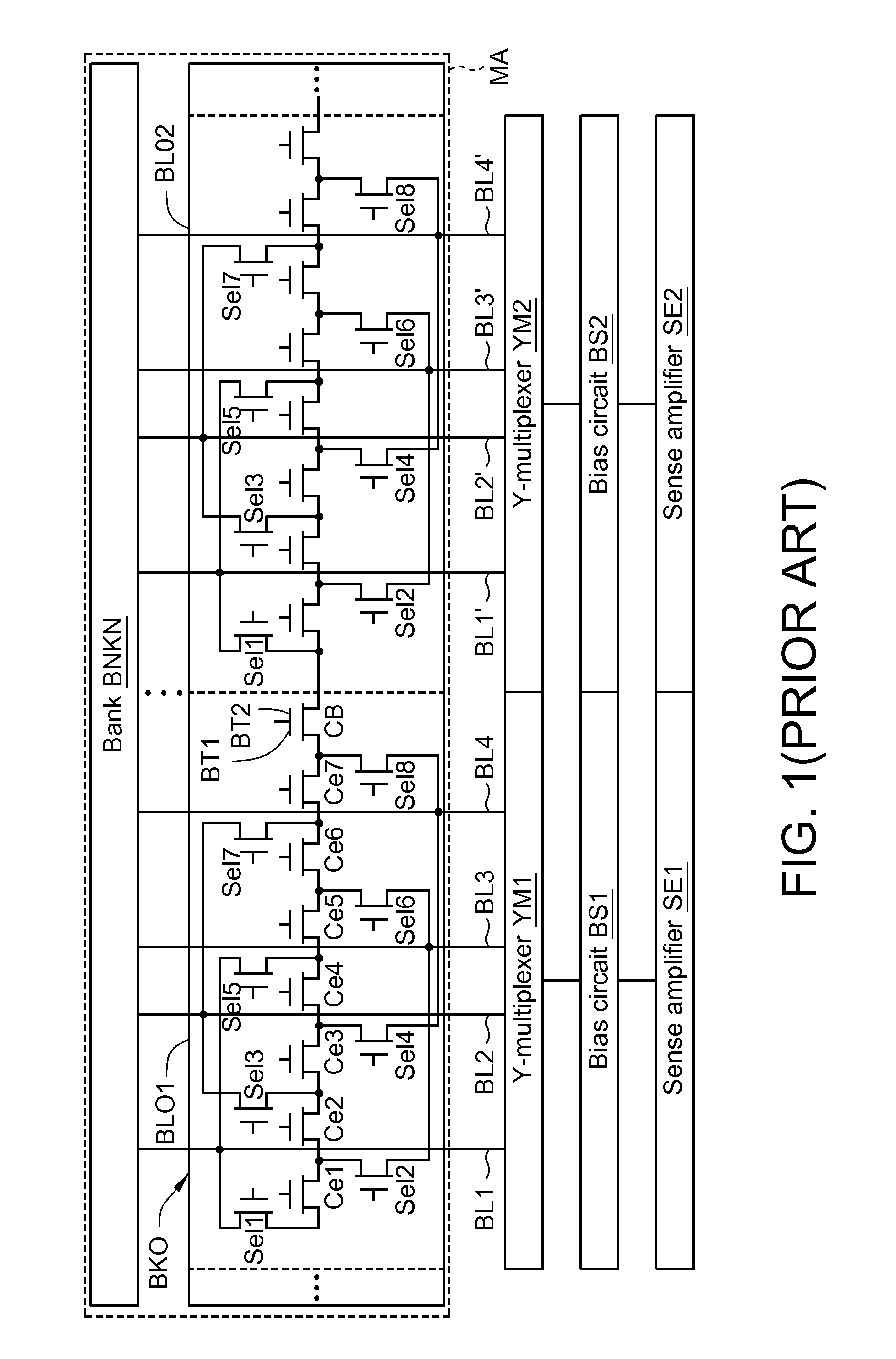
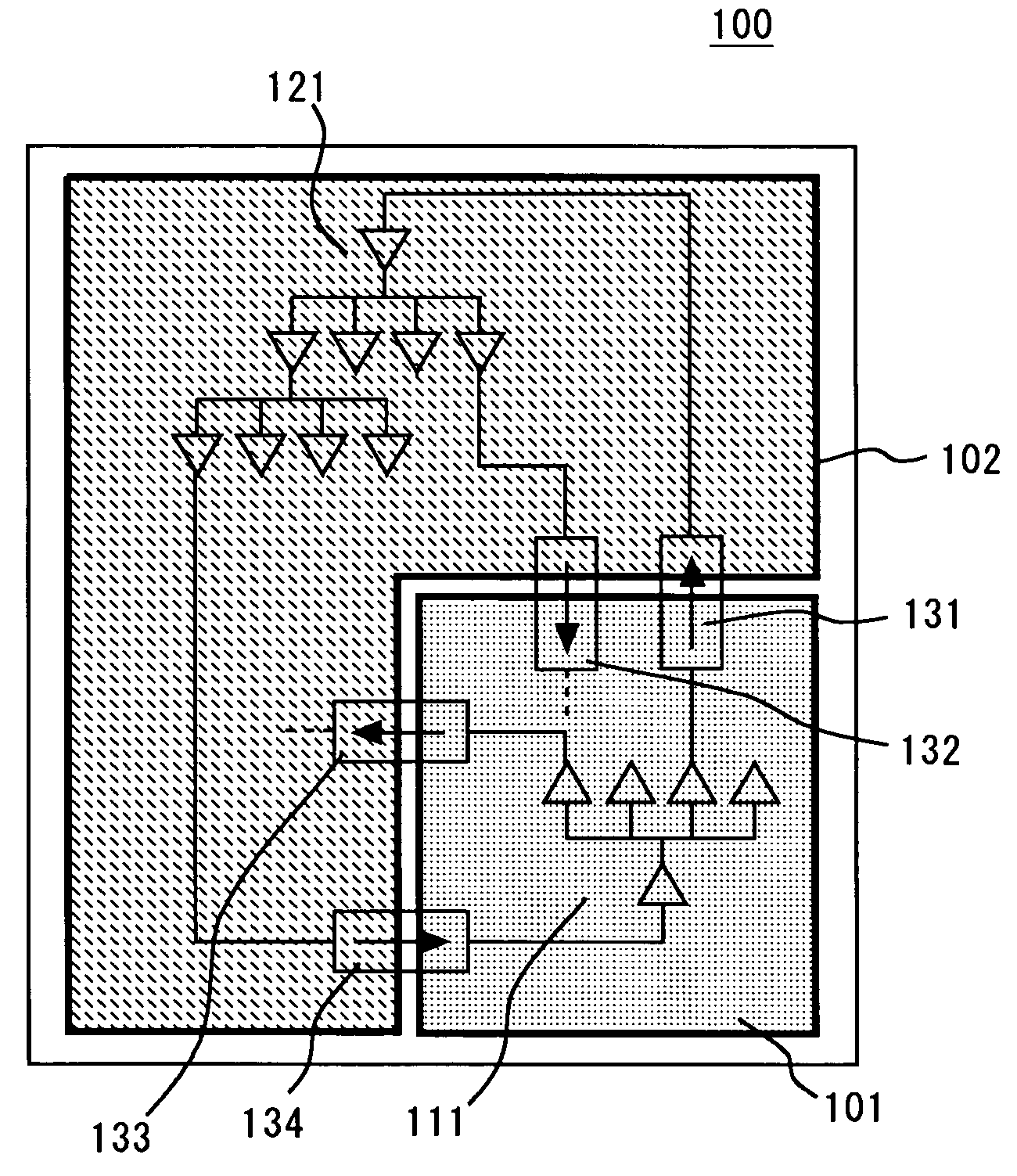
Memory control circuit and memory accessing method
A control circuit applied in a memory that comprises a first memory block and a second memory block, and each of the first and the second memory blocks includes a boundary cell. The control circuit comprises an address decoder, a first Y-multiplexer, and a second Y-multiplexer. The address decoder provides a plurality of column selection signals capable of being a boundary value. The first Y-multiplexer corresponds to the first memory block and provides a first boundary data channel for a boundary cell of the first memory block. The second Y-multiplexer corresponds to the second memory block and provides a second boundary data channel for a boundary cell of the second memory block. The first and the second boundary data channels are enabled simultaneously in response to the boundary value for outputting boundary data stored in the boundary cell of the first memory block and that of the second memory block.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
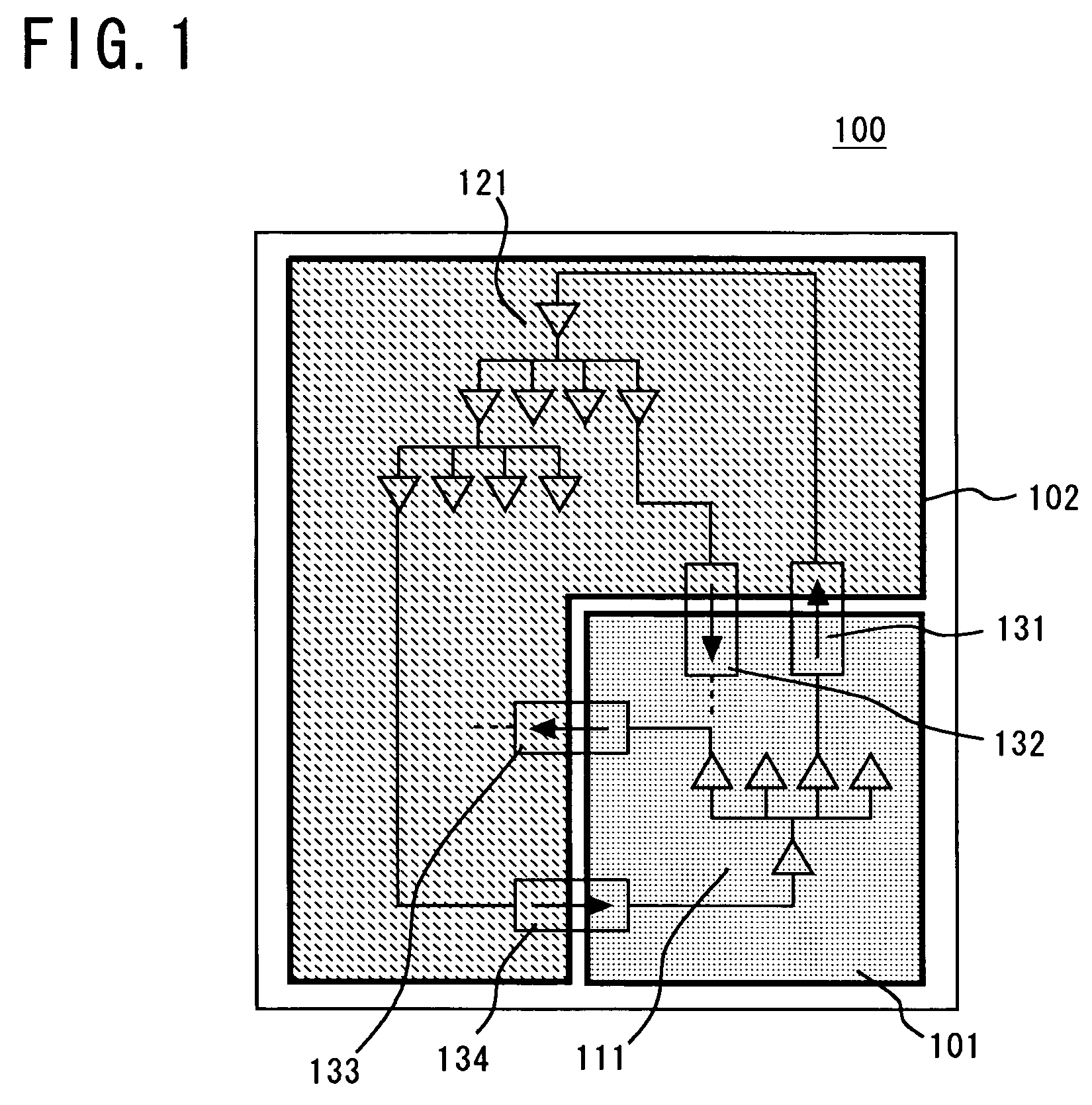
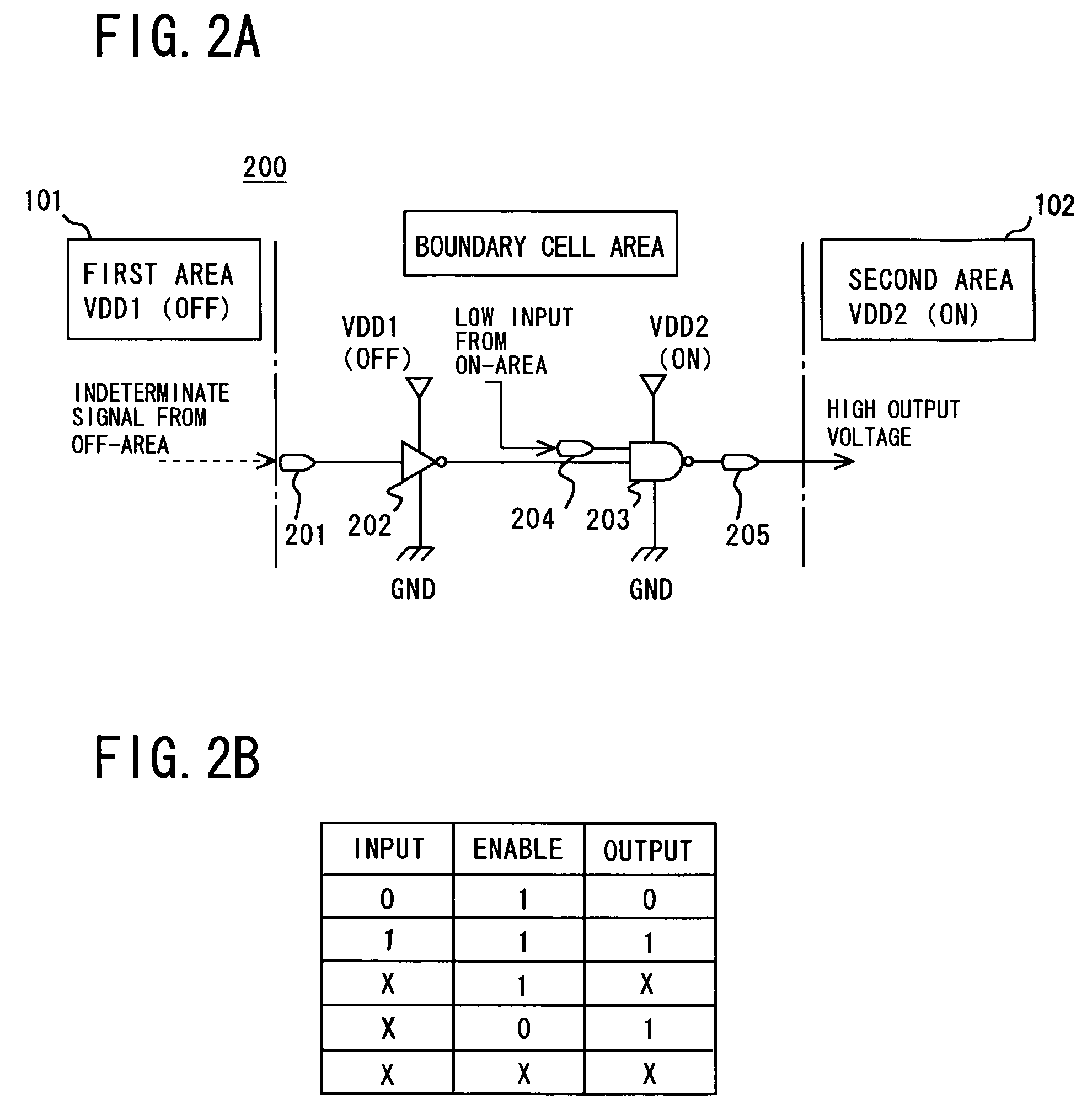
Method for designing semiconductor circuit device, utilizing boundary cells between first and second circuits driven by different power supply systems
InactiveUS7103866B2Simple designEfficient designSewerage structuresSolid-state devicesEngineeringDrain current
To design a chip having a plurality of circuit areas driven by different power supplies, a boundary cell to be inserted on the boundary between the circuit areas is prepared. After creating a logic circuit netlist with a design tool, the boundary cell is inserted on the boundary. The boundary cell is connected on a signal transmission path between the circuit areas. A circuit for suppressing shoot-through current or leakage current is used as the boundary circuit. By preparing the boundary cell in a cell library, chip design is facilitated.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and program for converting boundary data into cell inner shape data
InactiveUS7321366B2Maintain continuityAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationExternal dataDividing cell
A method and a program for converting boundary data into cell inner shape data, includes a division step (A) of dividing external data (12) constituted of the boundary data of an object into cells (13) in an orthogonal grid, a cutting point deciding step (B) of deciding an intersection point of the boundary data and a cell edge as a cell edge cutting point, a boundary deciding step (C) of deciding a boundary formed by connecting the cell edge cutting points as the cell inner shape data, a cell classification step (D) of classifying the divided cells into a nonboundary cell (13a) including no boundary surface and a boundary cell (13b) including a boundary surface, and a boundary cell data classification step (E) of classifying cell data constituting the boundary cell into internal cell data inside the cell inner shape data and external cell data outside the cell inner shape data.
Owner:RIKEN
Method and program of converting three-dimensional shape data into cell internal data
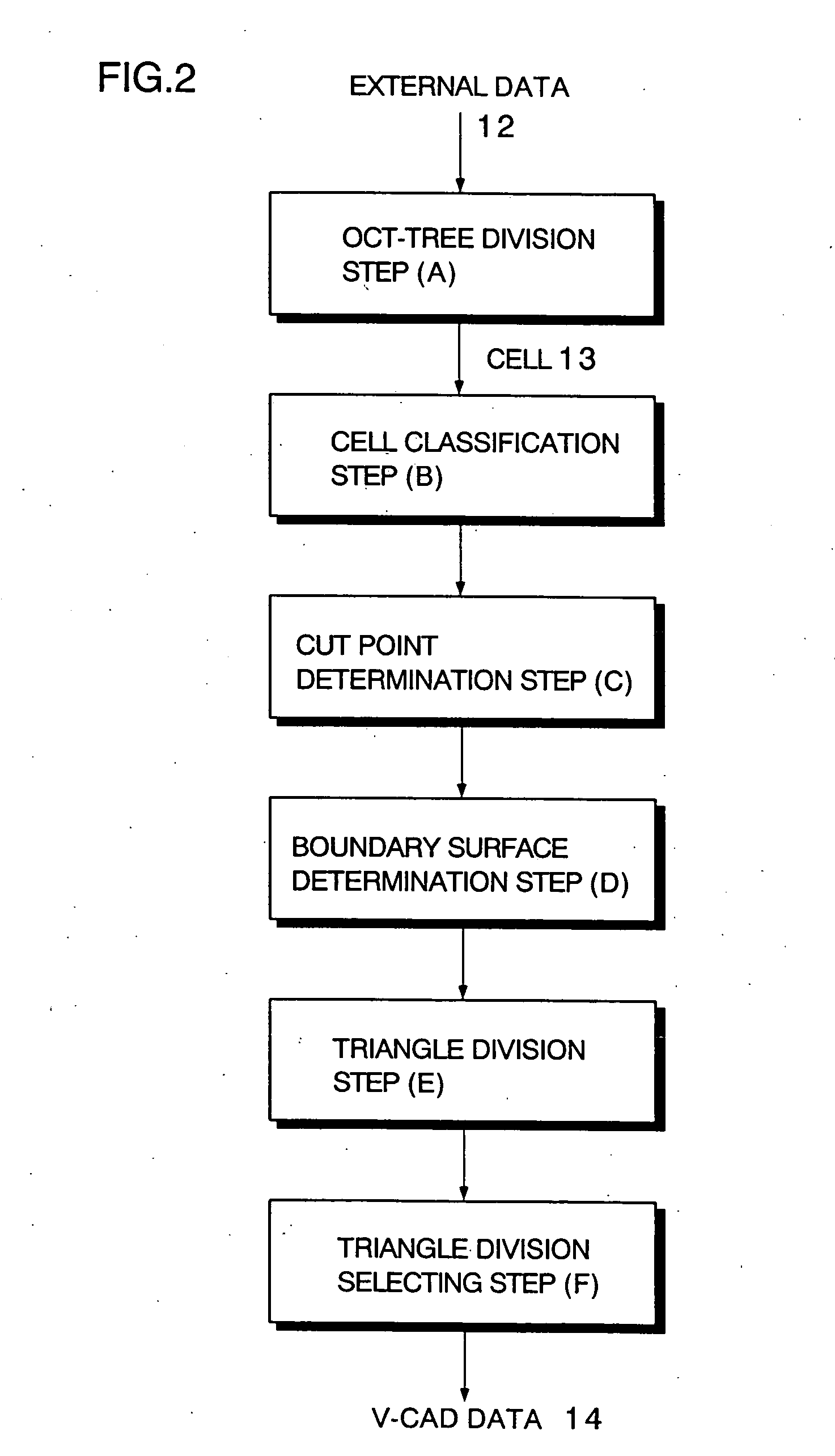
InactiveUS7333104B2Improve accuracyComputation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsExternal dataThree dimensional shape
A method of converting three-dimensional shape data into cell internal data. The method includes an oct-tree division step of dividing external data including boundary data of a target object into rectangular parallelepiped cells having boundary planes orthogonal to each other by oct-tree division. The method further includes a cell classification step of classifying each of the cells into an internal cell positioned inside or outside the target object or a boundary cell including the boundary data, and a cut point determination step of determining cut points of edges of the boundary cell based on the boundary data. The method further includes a boundary surface determination step of connecting cut points to form a polygon, and determining the polygon as the cell internal data when the number of the determined cut points is no fewer than 3 and no more than 12.
Owner:RIKEN
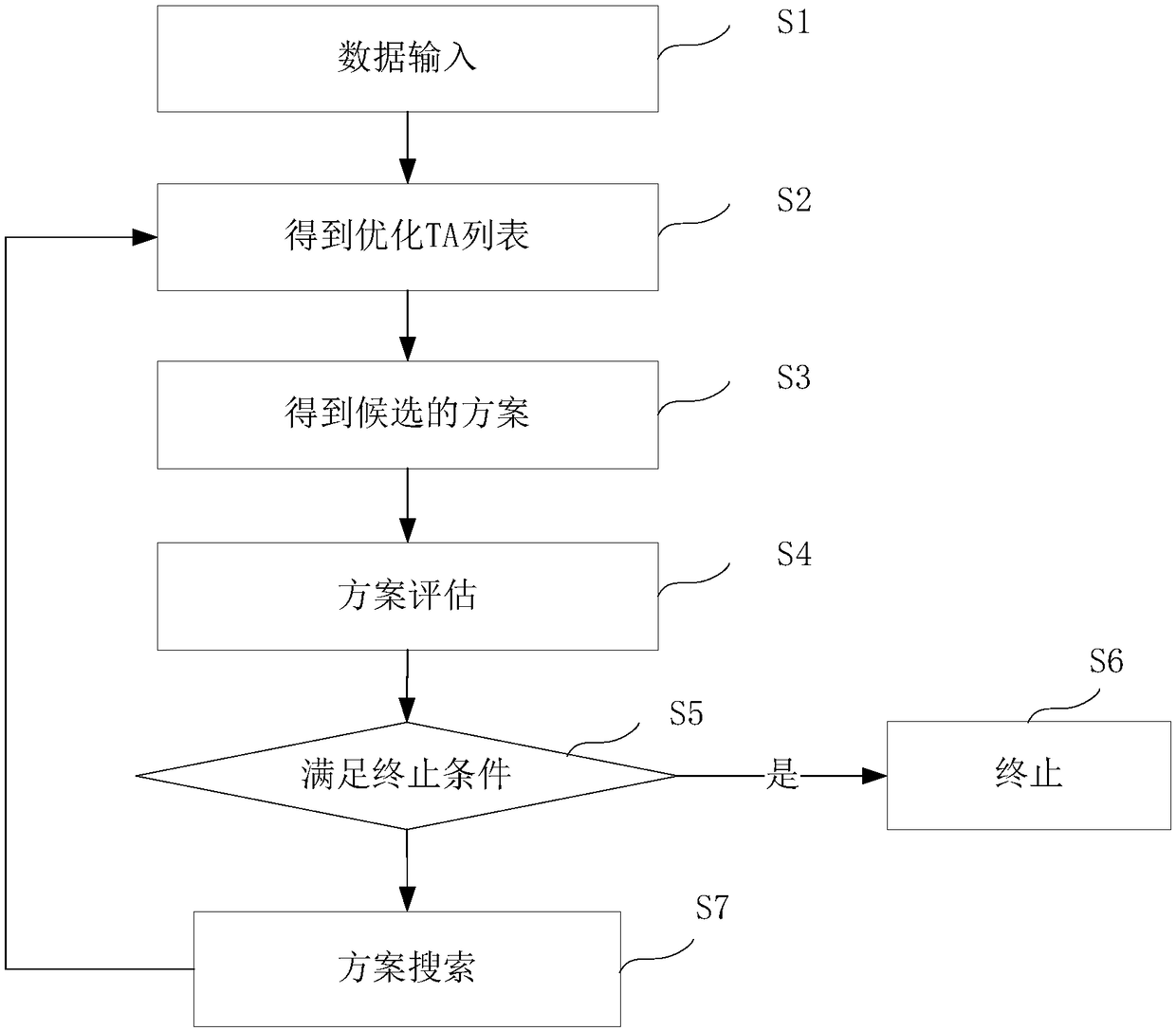
Method and apparatus for confirming boundary cell of tracking area
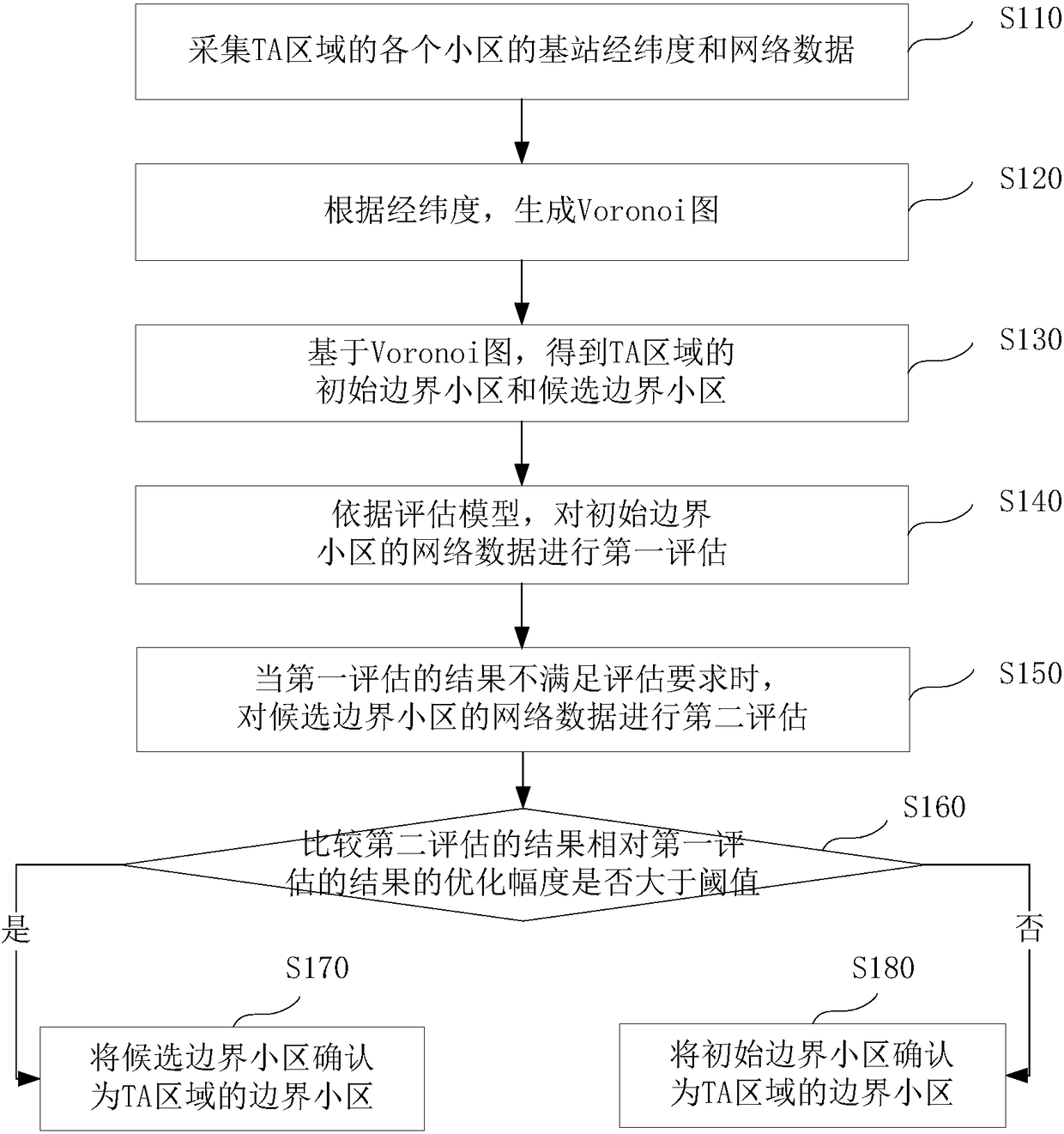
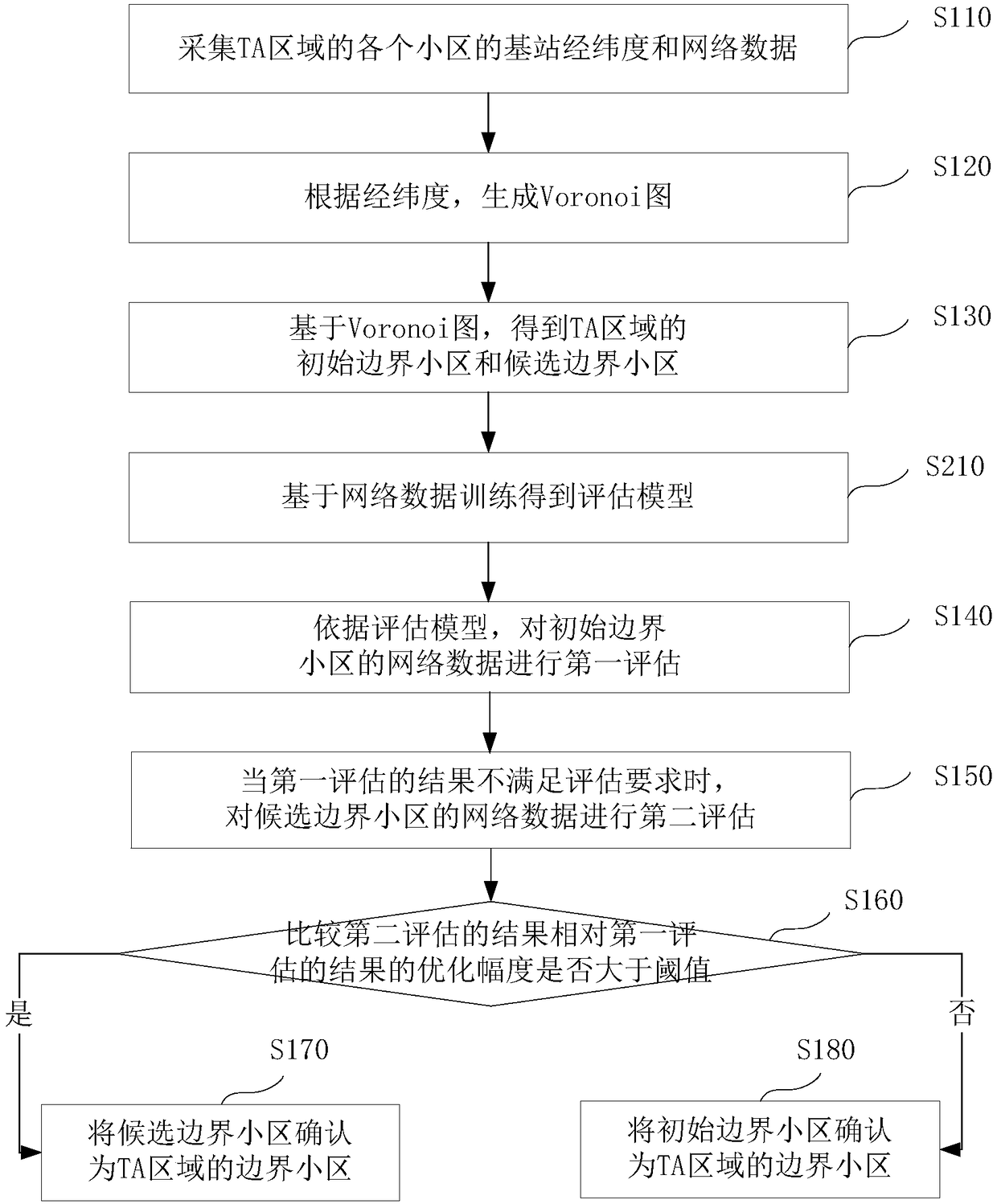
The invention discloses a method and apparatus for confirming a boundary cell of a tracking area. The method comprises the following steps: collecting base station longitude and latitude and network data of each cell in the tracking area TA; generating a Voronoi diagram according to the longitude and latitude; obtaining an initial boundary cell and a candidate boundary cell of the TA based on theVoronoi diagram; performing first evaluation on the network data of the initial boundary cell according to an evaluation model; when the result of the first evaluation does not satisfy the evaluationrequirements, performing second evaluation on the network data of the candidate boundary cell; comparing an optimization amplitude of the result of the second evaluation relative to the result of thefirst evaluation; when the optimization amplitude is greater than a threshold, confirming the candidate boundary cell as the boundary cell of the TA; and when the optimization amplitude is less than or equal to the threshold, confirming the initial boundary cell as the boundary cell of the TA. By adoption of the method and apparatus disclosed by the embodiment, the impact of the TA boundary changeon a network indicator can be accurately evaluated, thereby guiding the accurate designation of the TA boundary and reducing the signaling storm and the paging congestion rate.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP ANHUI +1
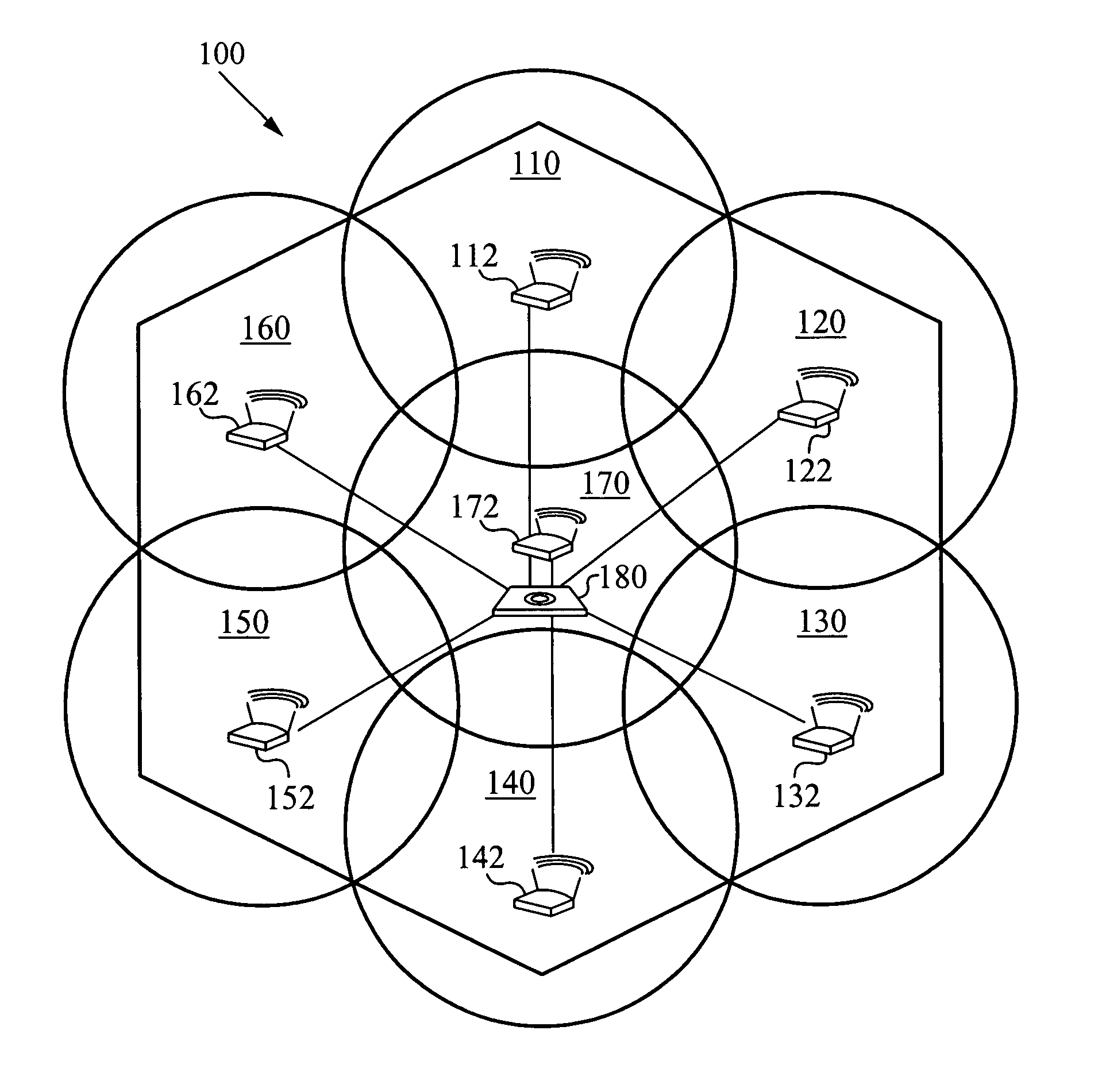
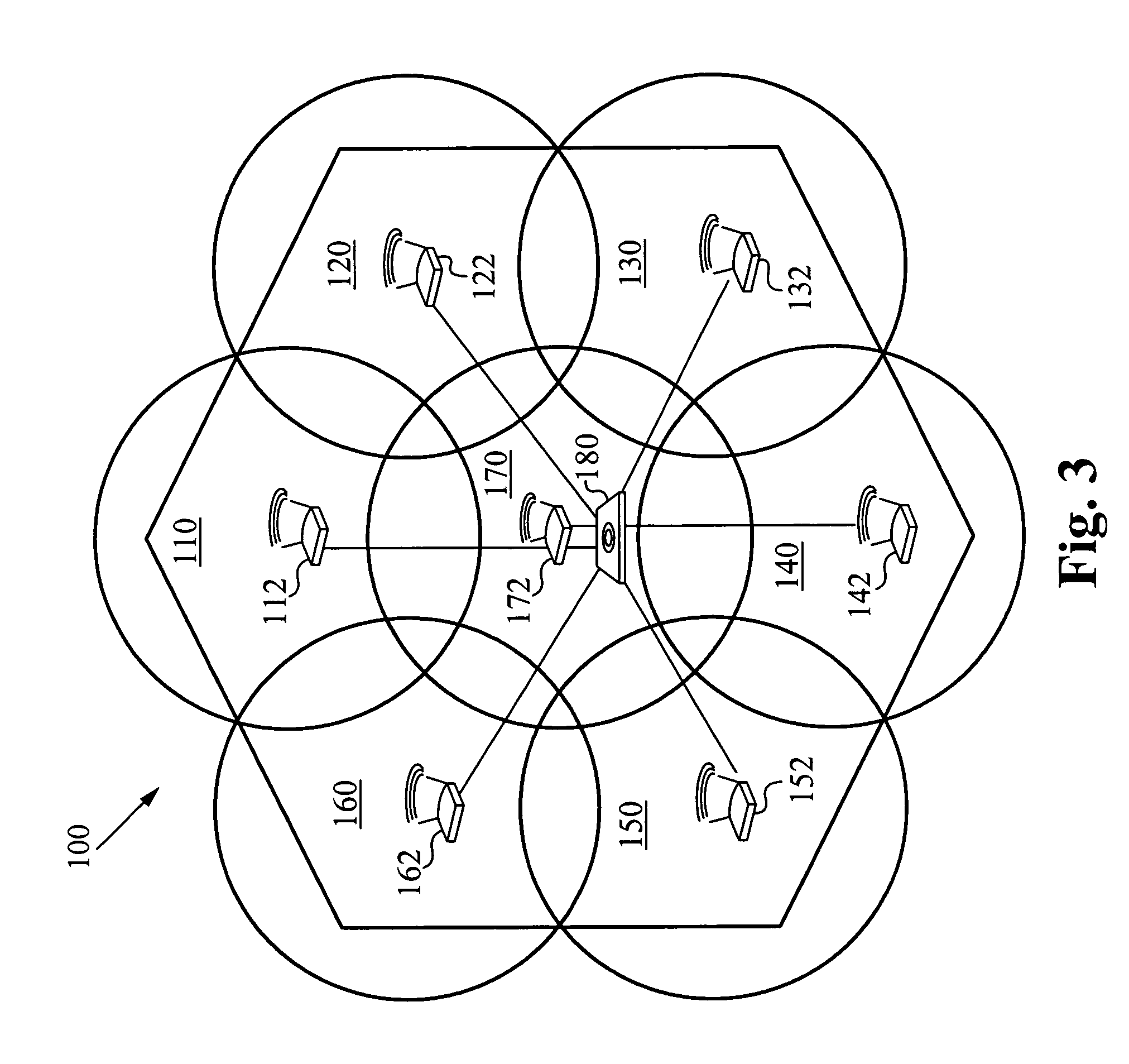
User movement prediction algorithm in wireless network environment
InactiveUS20050255849A1Improve overall utilizationNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationPrediction algorithmsTelecommunications
A wireless network including a plurality of cells is configured into groups, each group defining a supercell. Within each supercell, a plurality of boundary cells defines an outer boundary of the supercell. Each boundary cell is adjacent to at least two other supercells. The wireless network also include a plurality of control devices, one control device corresponding to each supercell. Each control device controls communications within the plurality of cells of the corresponding supercell. Each control device utilizes a predictive algorithm to identify the at least two supercells adjacent to a given boundary cell and transmits data packets to a wireless device located in the given boundary cell and to the at least two supercells adjacent to the given boundary cell.
Owner:AIR BROADBAND COMM
Method and program for labeling multi material data
InactiveUS7620528B2Short processing timeFast processingComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationCell divisionMulti material
The present invention includes an external data acquisition step (S1), an external data input step (A), a cell division step (B), a cell classification step (C), a space classification step (D), a simulation step (S3), and an output step (S4). The cell classification step (C) includes a step of further classifying each of the boundary cells (13a) into a first type cell and a second type cell. The first type cell has a cutting point at which an edge line or vertex is cut by the boundary data. The second type cell has a cutting point that lies on a boundary with another cell of different hierarchy, and is larger than the another cell. The cell classification step (C) further includes a step of assigning a material number to each cell vertex.
Owner:RIKEN
Method and program for determining insides and outsides of boundaries
InactiveUS7388584B2Fast processingEasy to implementImage enhancementImage analysisCell divisionExternal data
A method for determining insides and outsides of boundaries includes an external data input step of inputting external data constituted by boundary data of objects, a cell division step of dividing the external data into rectangular parallelepiped cells having boundary planes orthogonal to each other, a cell classification step of classifying the cells into a boundary cell that includes the boundary data and a non-boundary cell that does not include the boundary data, and a space classification step of classifying the non-boundary cells into a plurality of spaces that are partitioned by the boundary cells.
Owner:RIKEN
Method and program for converting boundary data into cell inner shape data
InactiveUS7898540B2Reliable dataReduce calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A cutting point calculation step defines the cell complex that contains the boundary data, and calculating a cutting point where the boundary data cuts an edge or vertex of the rectangular parallelepiped cell of the cell complex. A cycle formation step classifies the rectangular parallelepiped cells into a boundary cell having the cutting point and a nonboundary cell having no cutting point, acquiring a cutting segment between a cell surface and boundary data for each boundary cell, and forming a cutting segment cycle closed by connecting the cutting points and the cutting segments alternately in sequence. A cycle internal division step divides the inside of the cutting segment cycle into cycle inner triangles sharing an adjacent side, for each boundary cell. A simplification step of unifying a plurality of cutting points on each edge, and registering the cycle inner triangles in the cell, for each boundary cell.
Owner:RIKEN
Method and program of converting three-dimensional shape data into cell internal data
InactiveUS20050107992A1Improve accuracyComputation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsExternal dataThree dimensional shape
A method of converting three-dimensional shape data into cell internal data. The method includes an oct-tree division step of dividing external data including boundary data of a target object into rectangular parallelepiped cells having boundary planes orthogonal to each other by oct-tree division. The method further includes a cell classification step of classifying each of the cells into an internal cell positioned inside or outside the target object or a boundary cell including the boundary data, and a cut point determination step of determining cut points of edges of the boundary cell based on the boundary data. The method further includes a boundary surface determination step of connecting cut points to form a polygon, and determining the polygon as the cell internal data when the number of the determined cut points is no fewer than 3 and no more than 12.
Owner:RIKEN
Method and program for converting boundary data into cell inner shape data
InactiveUS20050216238A1Maintain continuityAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationExternal dataDividing cell
A method and a program for converting boundary data into cell inner shape data, includes a division step (A) of dividing external data (12) constituted of the boundary data of an object into cells (13) in an orthogonal grid, a cutting point deciding step (B) of deciding an intersection point of the boundary data and a cell edge as a cell edge cutting point, a boundary deciding step (C) of deciding a boundary formed by connecting the cell edge cutting points as the cell inner shape data, a cell classification step (D) of classifying the divided cells into a nonboundary cell (13a) including no boundary surface and a boundary cell (13b) including a boundary surface, and a boundary cell data classification step (E) of classifying cell data constituting the boundary cell into internal cell data inside the cell inner shape data and external cell data outside the cell inner shape data.
Owner:RIKEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com