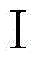Patents
Literature
663 results about "Cell division" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle. In eukaryotes, there are two distinct types of cell division: a vegetative division, whereby each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell (mitosis), and a reproductive cell division, whereby the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is reduced by half to produce haploid gametes (meiosis). Meiosis results in four haploid daughter cells by undergoing one round of DNA replication followed by two divisions. Homologous chromosomes are separated in the first division, and sister chromatids are separated in the second division. Both of these cell division cycles are used in the process of sexual reproduction at some point in their life cycle. Both are believed to be present in the last eukaryotic common ancestor.
Transformation method for plants
InactiveUS6140553AImprove conversion efficiencyIncreasing frequency of stable transformationBryophytesSugar derivativesCell divisionDNA Integration
A process for integrating a DNA fragment into the genome of a cell of a monocotyledonous plant, the process comprising the steps of: 1) incubating, prior to contacting with the DNA fragment, a culture of untransformed monocotyledonous plant cells on a medium comprising a plant phenolic compound, for a period of time sufficient to stimulate cell division and enhance competence for integration of foreign DNA; and 2) contacting the untransformed cells with the DNA fragment under conditions in which the DNA fragment is taken up by the untransformed cells and is stably integrated in the genome of the untransformed cells, to generate transformed cells.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE NV
Differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of notch gene
There is provided a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of a Notch gene. Specifically, the invention provides a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells in vitro, which method comprises introducing a Notch gene and / or a Notch signaling related gene into the cells, wherein the finally obtained differentiated cells are the result of cell division of the bone marrow stromal cells into which the Notch gene and / or Notch signaling related gene have been introduced. The invention also provides a method of inducing further differentiation of the differentiation-induced neural cells to dopaminergic neurons or acetylcholinergic neurons. The invention yet further provides a treatment method for neurodegenerative and skeletal muscle degenerative diseases which employs neural precursor cells, neural cells or skeletal muscle cells produced by the method of the invention.
Owner:SANBIO
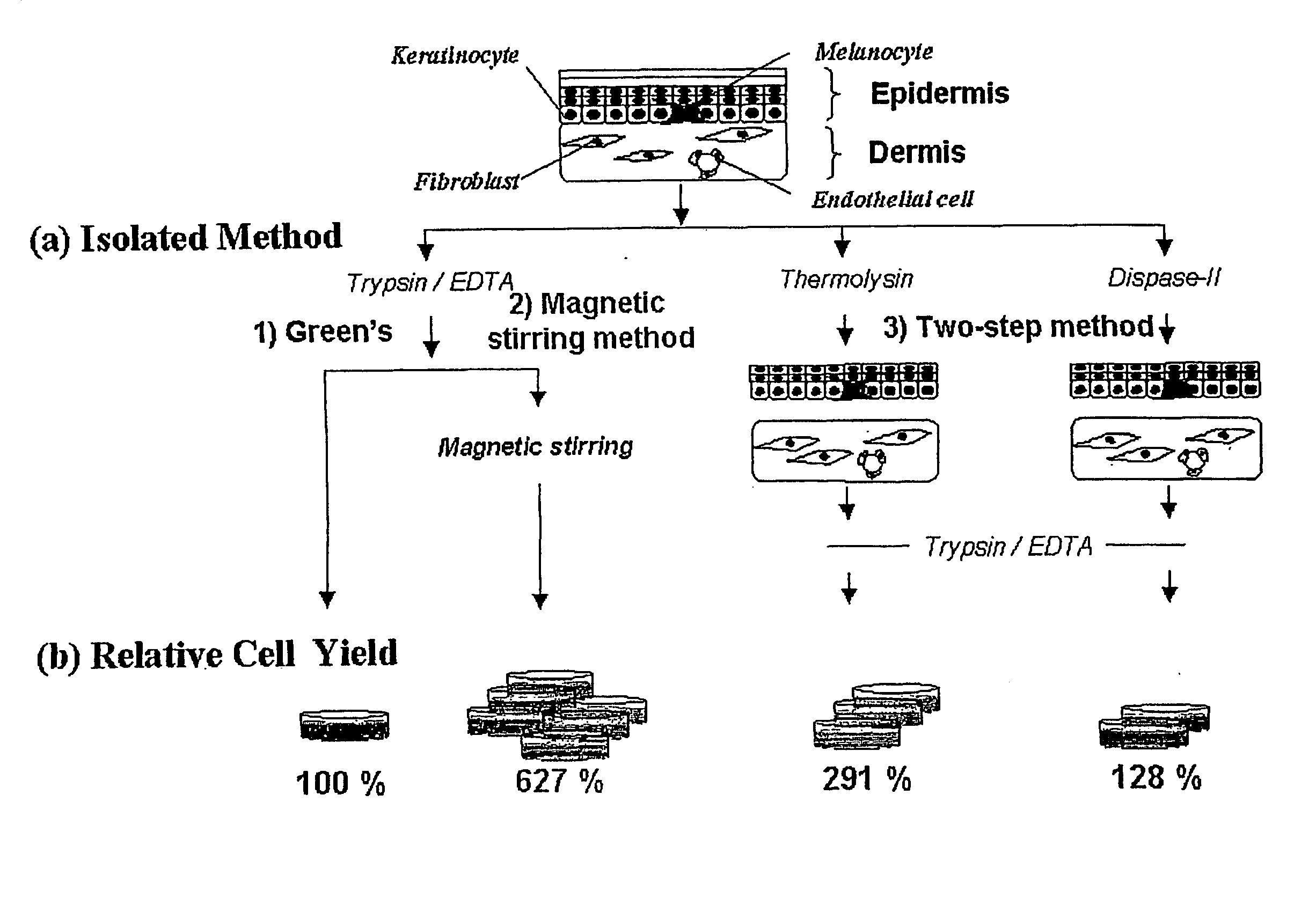
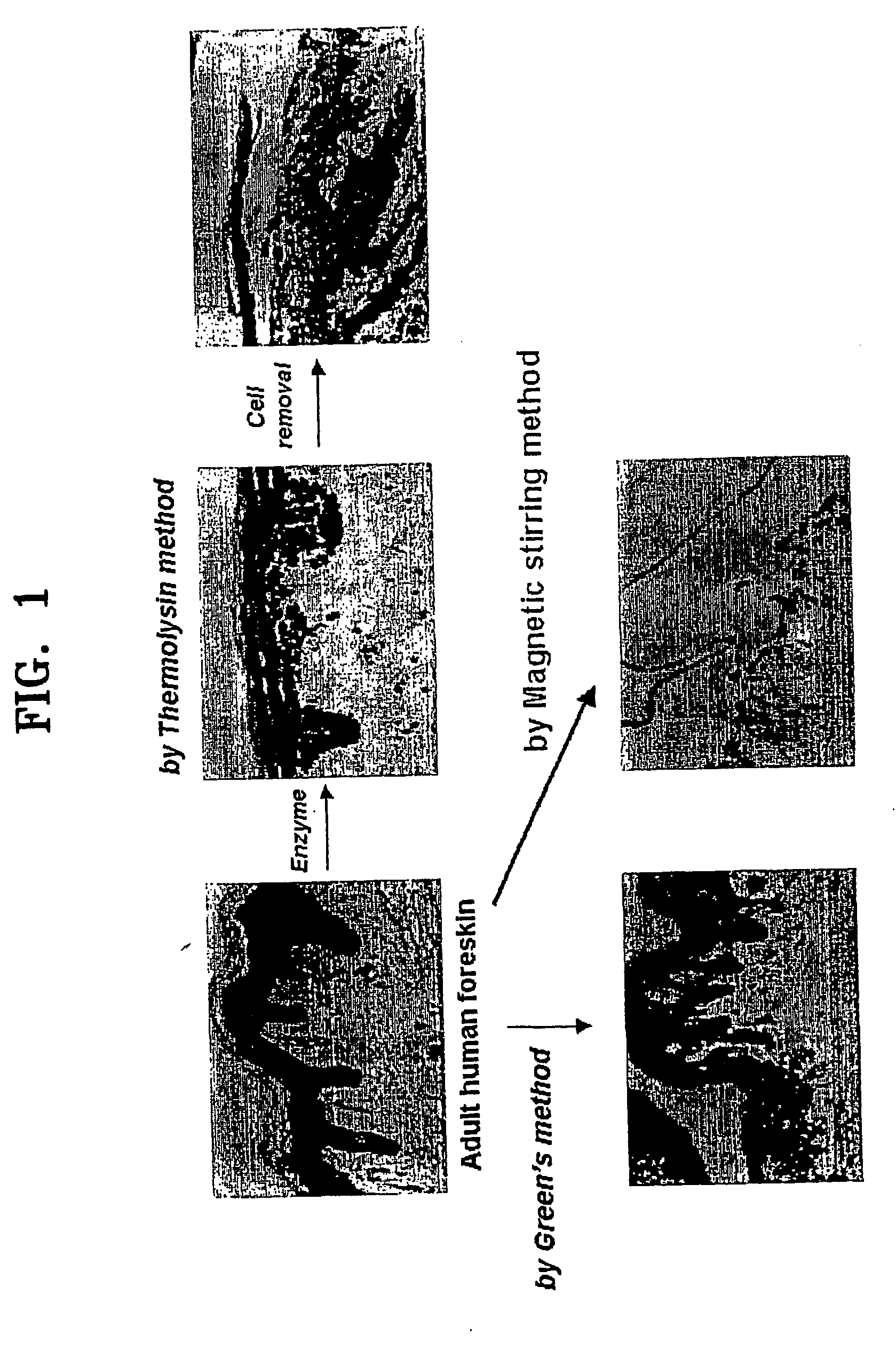
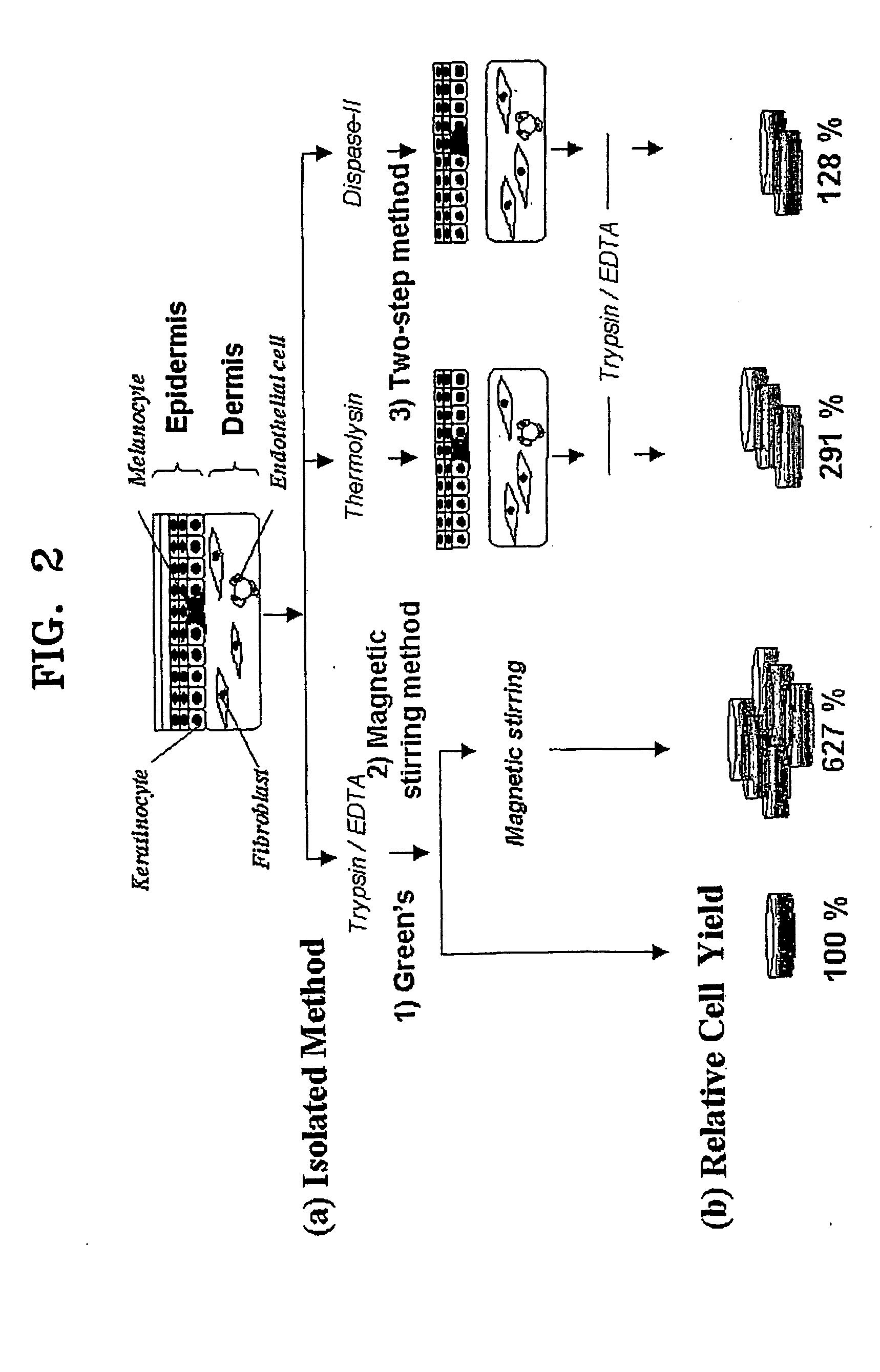
Method of isolating epithelial cells, method of preconditioning cells, and methods of preparing bioartificial skin and dermis with the epithelial cells or the preconditioned cells
InactiveUS20060105454A1Increased cell yieldEasy to implantCell dissociation methodsEpidermal cells/skin cellsDamages tissueTrypsin
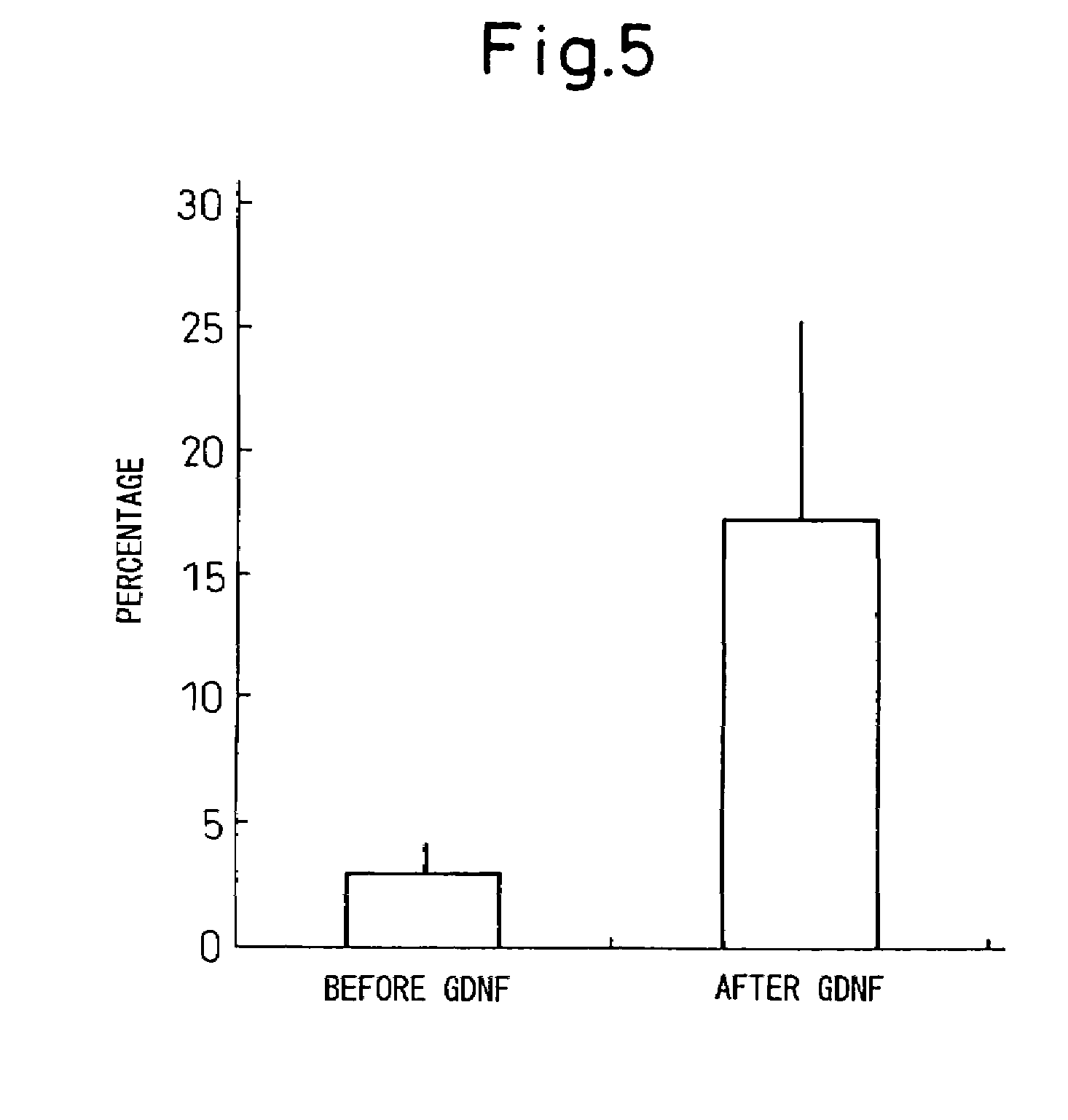
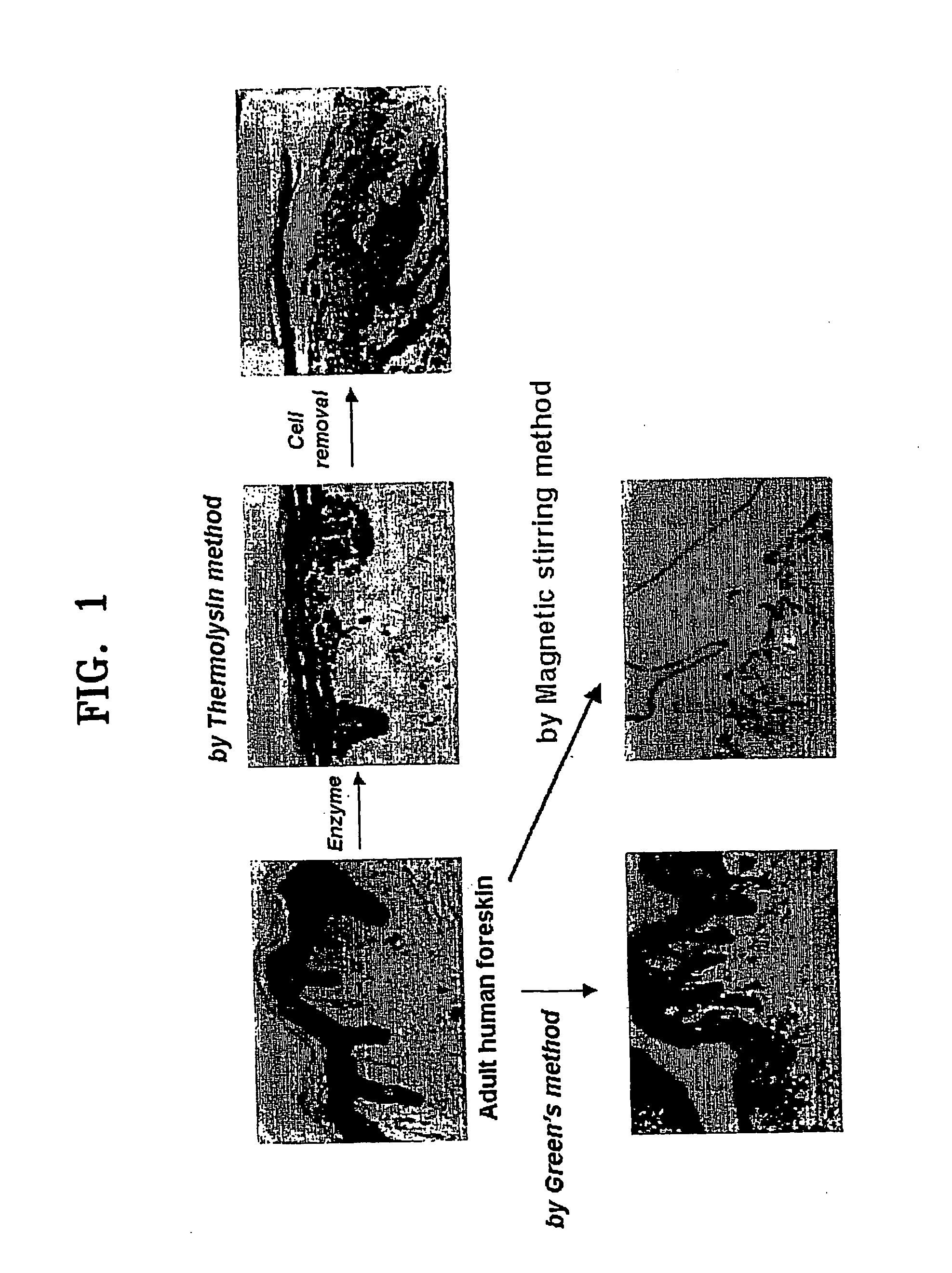
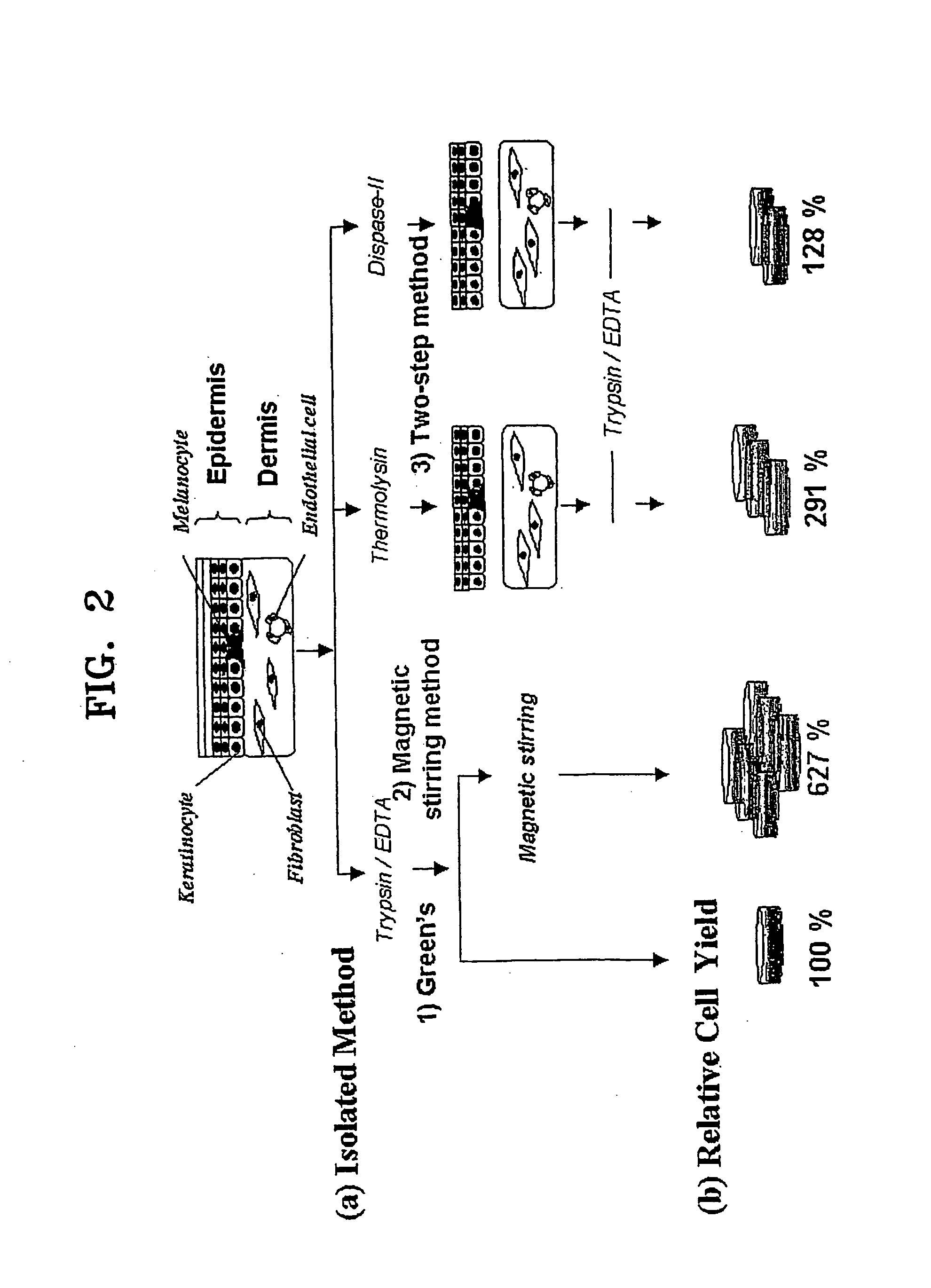
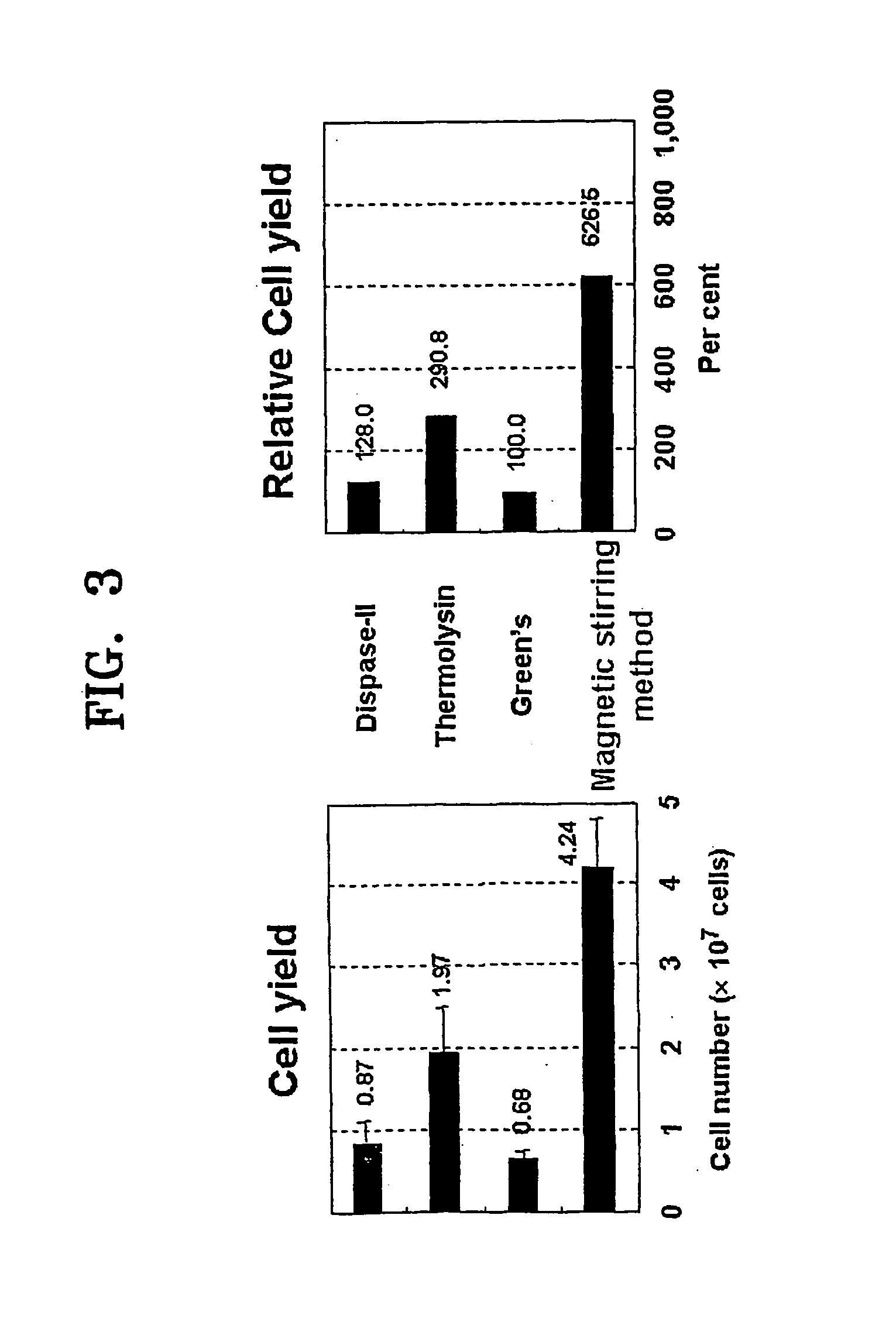
A method of isolating epithelial cells from a human skin tissue or internal organ tissue using trypsin and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) simultaneously with the application of magnetic stirring, a method of preconditioning isolated biological cells by the application of physical stimulus, i.e., strain, are provided. Epithelial cells can be isolated by the method with increased yield, colony forming efficiency (CFE), and colony size. Also, the increased percentage of stem cells in isolated cells is advantageous in therapeutic tissue implantation by autologous or allogeneic transplantation. In skin cells preconditioned by the application of strain, cell division is facilitated, and the secretion of extracellular matrix components and growth factors and the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are improved. When preconditioned cells are implanted by autologous or allogeneic transplantation to heal a damaged tissue, the improved cell adhesion, mobility, and viability provides a biological adjustment effect against a variety of stresses or physical stimuli which the cells would undergo after implantation, with improved capability of integration into host tissue, thereby markedly improving the probability of success in skin grafting.
Owner:KOREA INST OF RADIOLOGICAL & MEDICAL SCI
Method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of notch gene
There is provided a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of a Notch gene. Specifically, the invention provides a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells in vitro, which method comprises introducing a Notch gene and / or a Notch signaling related gene into the cells, wherein the finally obtained differentiated cells are the result of cell division of the bone marrow stromal cells into which the Notch gene and / or Notch signaling related gene have been introduced. The invention also provides a method of inducing further differentiation of the differentiation-induced neural cells to dopaminergic neurons or acetylcholinergic neurons. The invention yet further provides a treatment method for neurodegenerative and skeletal muscle degenerative diseases which employs neural precursor cells, neural cells or skeletal muscle cells produced by the method of the invention.
Owner:SANBIO
Day-dimension regional traffic index prediction method considering influences of multiple factors
ActiveCN107610469AAccurate portrayalEasy to operateDetection of traffic movementForecastingState predictionOriginal data
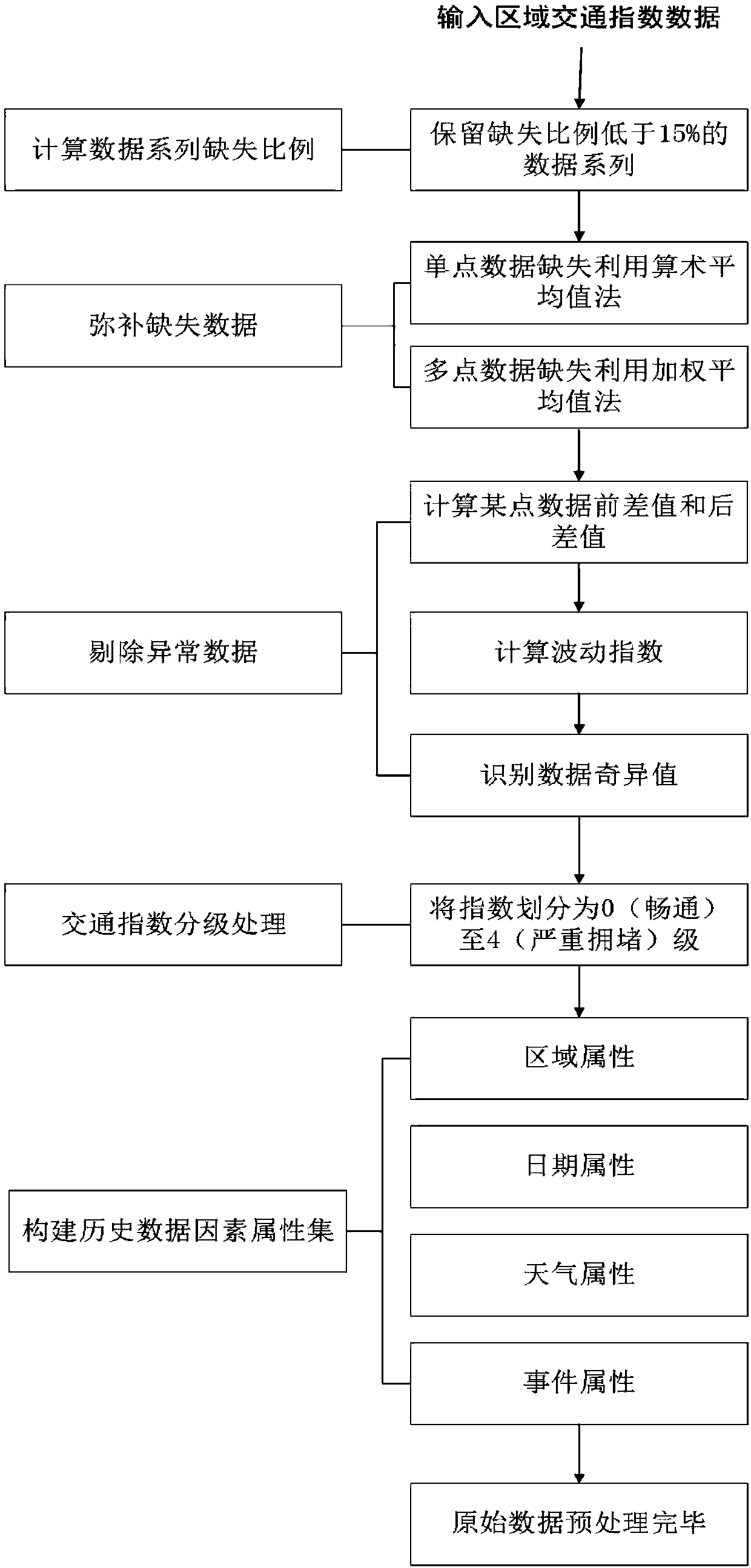
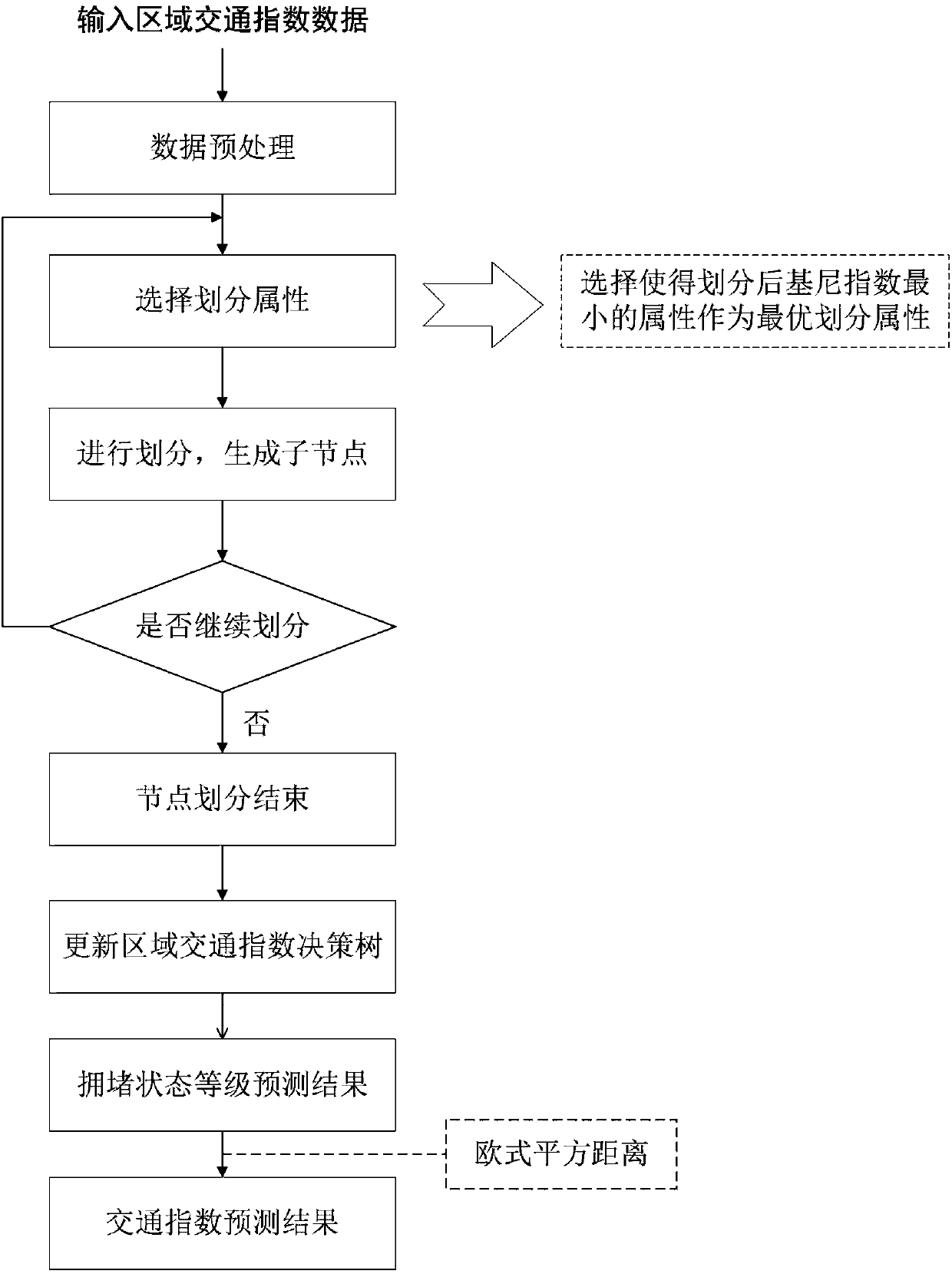
The invention discloses a day-dimension regional traffic index prediction method considering influences of multiple factors. The method comprises the steps that regions are divided and aggregated; regional traffic index original data preprocessing is carried out; the influences of multiple factors are considered, and regional traffic index prediction under the day dimension is carried out. According to the specific technical scheme of the method, on the basis of traffic cell division, traffic cells with the same aggregation property are aggregated, and regional traffic indexes are calculated;on the basis of road network operation early warning requirements, a prediction time period and a prediction cycle are determined; regional traffic data is extracted, made up for and removed, and preprocessing such as comprehensive building of a historical data factor attribute set from different angles is conducted on the data; on the basis of a decision tree theory, regional road network operation congestion state prediction is carried out; a final prediction result of the regional traffic indexes is determined by means of the square euclidean distance. By means of the method, on the one hand, monitoring and application of the urban road network operation state is deepened, and on the other hand, technical support is provided for early warning and forecasting work of the road network operation state.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Rapid detection of replicating cells
ActiveUS7582415B2Reduce riskFast resultsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNon destructiveMicroorganism
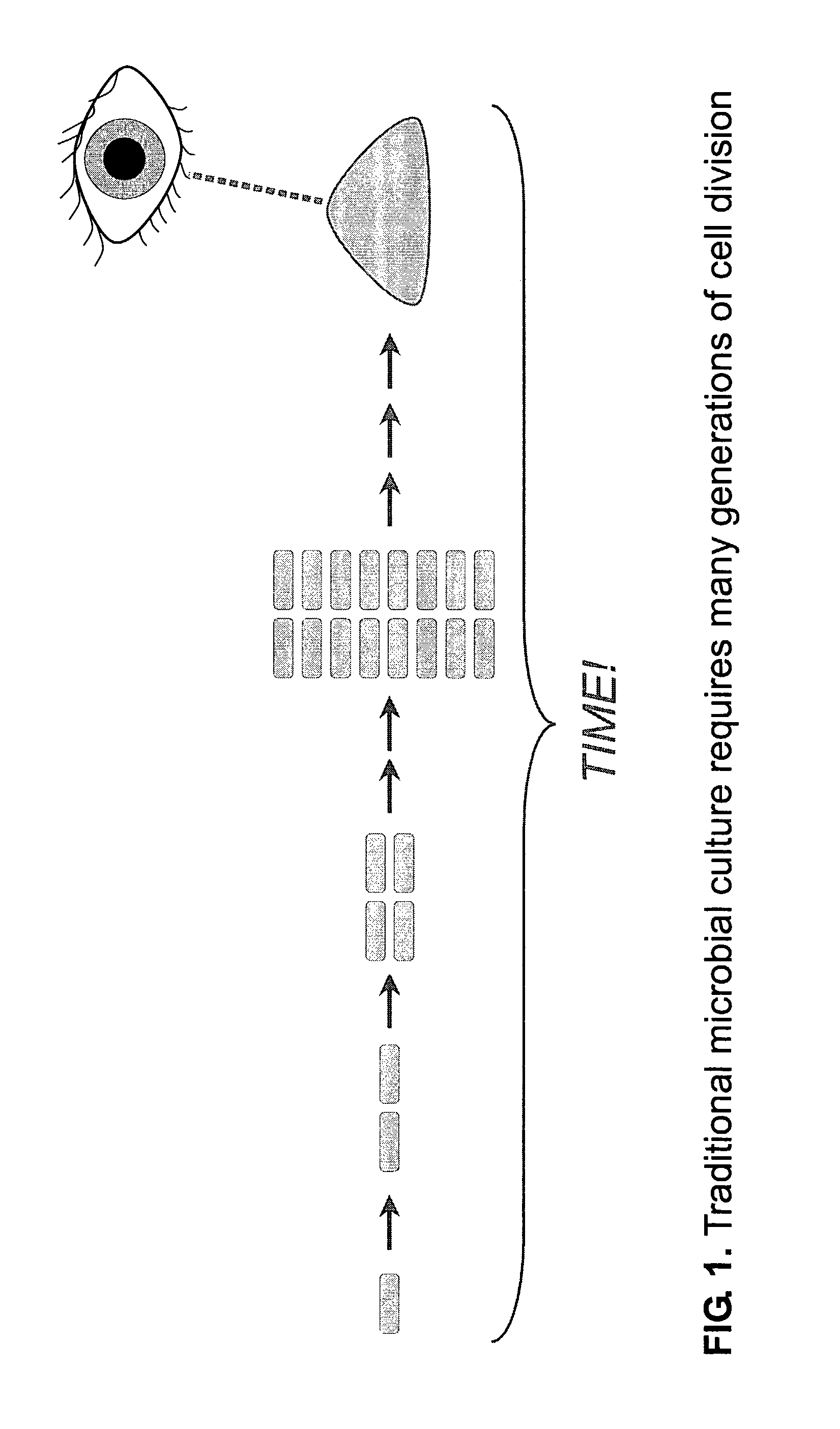
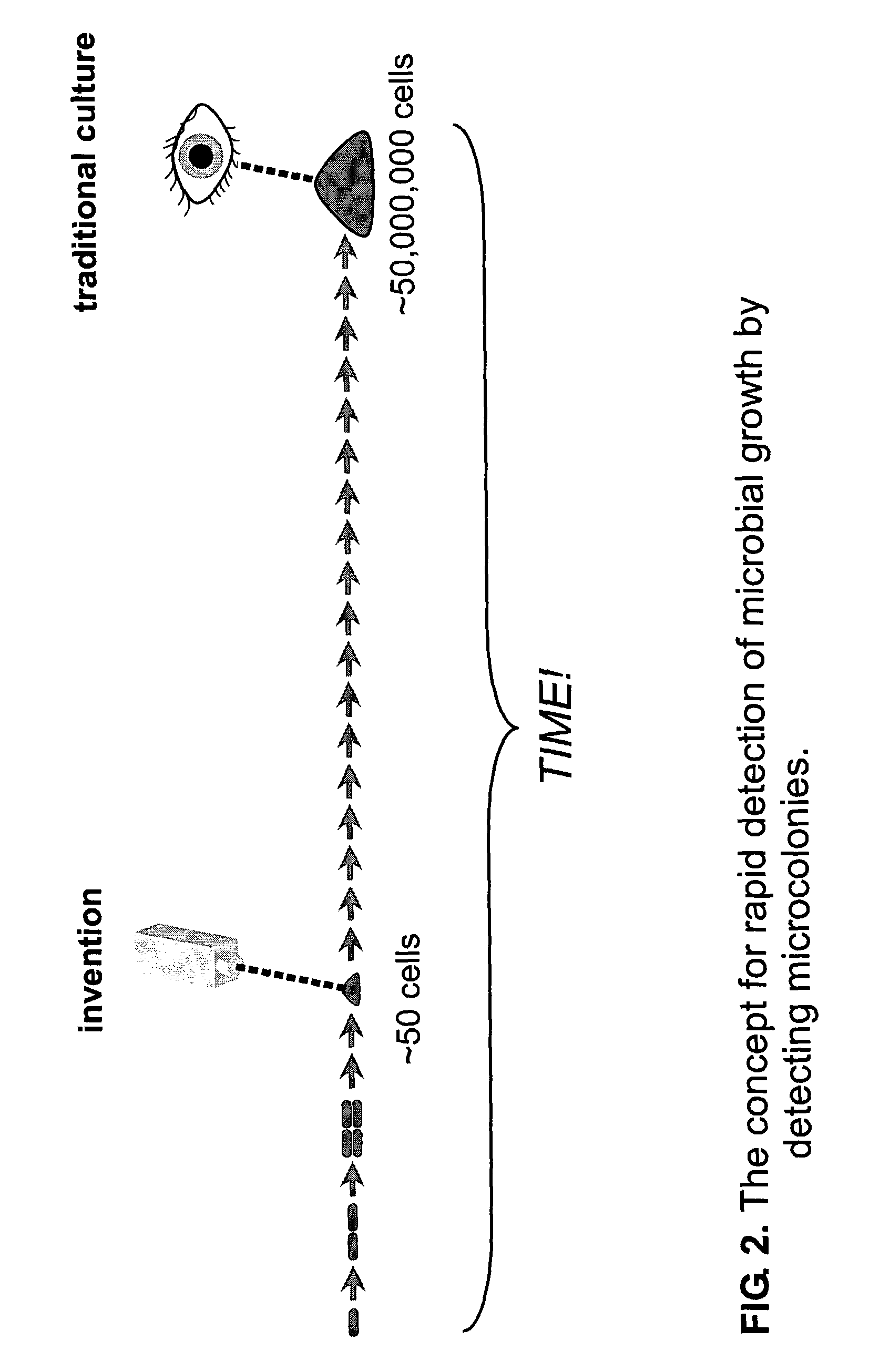
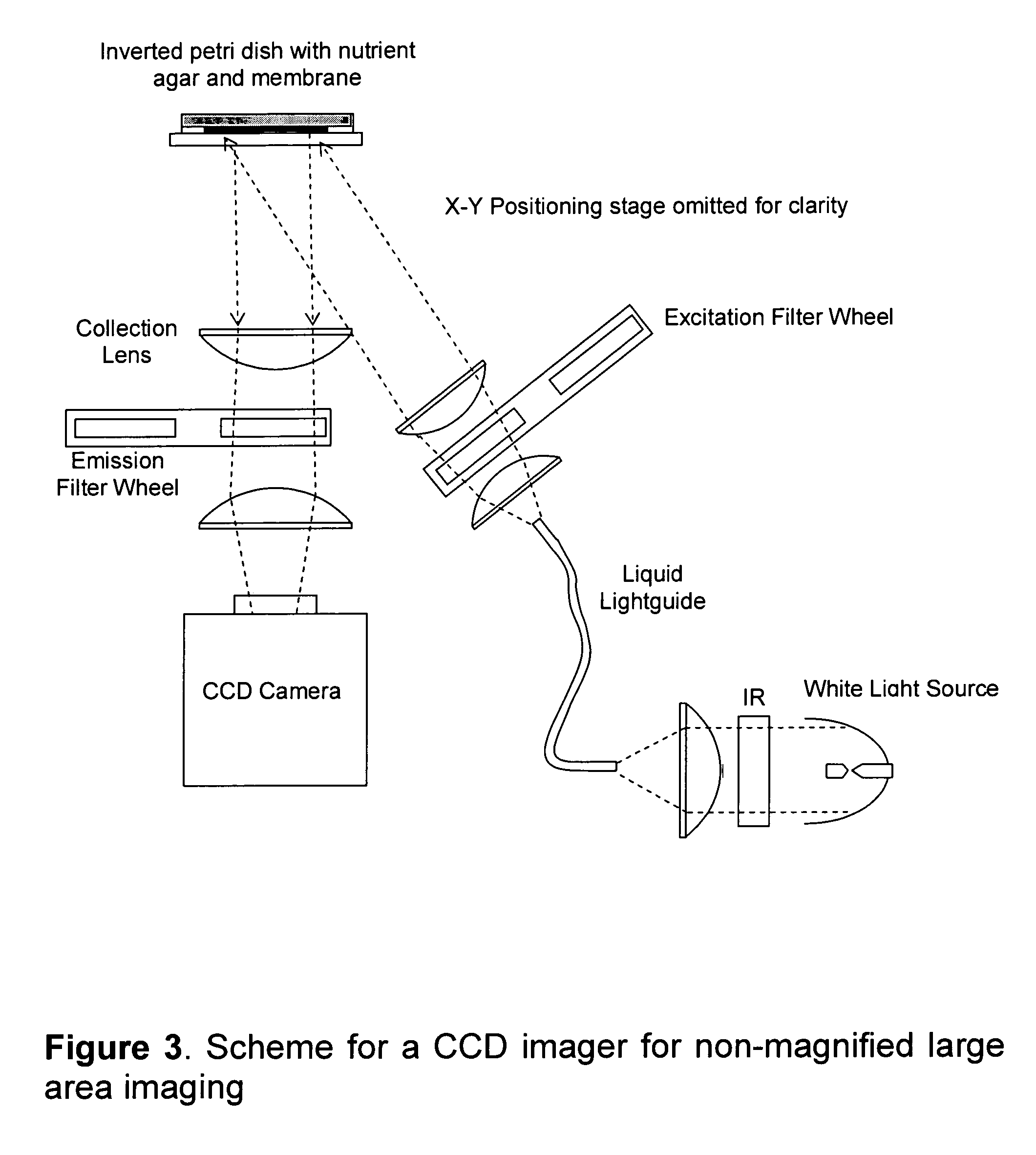
The invention enables efficient, rapid, and sensitive enumeration of living cells by detecting microscopic colonies derived from in situ cell division using large area imaging. Microbial enumeration tests based on the invention address an important problem in clinical and industrial microbiology—the long time needed for detection in traditional tests—while retaining key advantages of the traditional methods based on microbial culture. Embodiments of the invention include non-destructive aseptic methods for detecting cellular microcolonies without labeling reagents. These methods allow for the generation of pure cultures which can be used for microbial identification and determination of antimicrobial resistance.
Owner:RAPID MICRO BIOSYSTEMS INC
Cytokinin oxidase promoter from maize
InactiveUS20060037103A1Modulation rateEasy to controlSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyCell division
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating expression of nucleotide sequences in a plant. Compositions may comprise a novel nucleic acid sequence for a promoter with tissue specificity and / or cytokinin. inducibility. A method for expressing a heterologous nucleotide sequence in a plant using the promoter sequence is also provided. The method comprises transforming a plant cell to contain a heterologous nucleotide sequence operably linked to the promoter of the present invention and regenerating a stably transformed plant from the transformed plant cell. Other methods provide for downregulation of cytokinin oxidase in a plant.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Modulation of telomere length by oligonucleotides having a G-core sequence
InactiveUS7067497B2Effective of telomere lengthReduce telomere lengthSugar derivativesHydrolasesCell divisionCellular Aging
Modified oligonucleotides having a GGG motif sequence and a sufficient number of flanking nucleotides to modulate the telomere length of a chromosome are provided. Methods of modulating telomere length of a mammalian chromosome in vitro and in vivo are also provided, as are methods for inhibiting the division of a malignant mammalian cell and for modulating the effects of cellular aging.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Cell migration inhibiting compositions and methods and compositions for treating cancer
Methods for treating an individual having cancer are provided. The method may include administering a cell migration inhibitor and a chemotherapeutic agent to the individual to inhibit migration of cancer cell. Inhibiting cell migration may increase cell division. In this manner, the cell migration inhibitor and the chemotherapeutic agent in combination may have increased efficacy compared to the chemotherapeutic agent alone due to the increased cell division. The cell migration inhibitor may include any of the inhibitors described herein. For example, the cell migration inhibitor may be an organic molecule having a molecular weight of less than about 700, a monoclonal antibody, or a natural product.
Owner:AVOLIX PHARMA
Dominant negative mutant krp protein protection of active cyclin-cdk complex inhibition by wild-type krp
InactiveUS20070056058A1Speed upIncreasing cell proliferationBacteriaSugar derivativesMutated proteinPlant cell
Disclosed are mutant CDK inhibitor (CKI) polypeptides having dominant negative antagonist activity against wild-type CKI proteins, as well as related compositions, including nucleic acids and vectors encoding the mutant CKI polypeptides and transformed host cells and transgenic plants comprising such nucleic acids and vectors. Also disclosed are related methods for using the mutant proteins to modulate cell division in cells, particularly plant cells.
Owner:TARGETED GROWTH
Paraffin section method for fern gametophytes
InactiveCN102607907AAvoid poor resultsGood slice methodPreparing sample for investigationParaffin waxMicroscopic exam
The invention discloses a paraffin section method for fern gametophytes, which comprises the steps of material selection and fixation, washing, coloration and bluing, dehydration and hyalinizing, waxing and embedding, sectioning, patching, dewaxing and mounting, as well as microscopic examination and photographing, wherein improved FAA (formalin, acetic acid and alcohol) stationary liquid is adopted in the fixation, and the stationary liquid consists of formalin, acetic acid and 30% alcohol (formalin:acetic acid:30% alcohol = 1:1:18). The method is adopted, so that the disadvantage of much youngness of the fern gametophytes can be effectively overcome; the fixation can be well performed for cell divisions at all stages; from a paraffin section in a later stage, a plurality of mitotic sections can be observed, so that a whole development process can be reflected detailedly; therefore, the method has high development and application values.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for modulating plant growth and biomass
InactiveUS7371927B2Improve efficiencyPromote regenerationSugar derivativesHydrolasesGrowth plantCell division
This application discloses methods for modulating plant growth and biomass comprising stably incorporating into the genome of the plant a genetic construct comprising a gene promoter that is active in wood-forming tissues, a polynucleotide sequence encoding polypeptide regulators of cell division and a gene termination sequence.
Owner:ARBORGEN
In vivo assay for identification of antimicrobial agents
InactiveUS7011946B2Improve bioavailabilityMinor side effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMicroorganismCell division
The present invention provides novel in vivo assay systems and methods of using these assays systems to identify compounds that affect microbial cell division. The present invention further provides pharmaceutical compositions that have anti-microbial activity and methods of treating microbial infections.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Compounds useful for inhibiting Chk1
Aryl- and heteroaryl-substituted urea compounds useful in the treatment of diseases and conditions related to DNA damage or lesions in DNA replication are disclosed. Methods of making the compounds, and their use as therapeutic agents, for example, in treating cancer and other diseases characterized by defects in DNA replication, chromosome segregation, or cell division also are disclosed.
Owner:ICOS CORP
Modulation of telomere length by oligonucleotides having a G-core sequence
Modified oligonucleotides having a GGG motif sequence and a sufficient number of flanking nucleotides to modulate the telomere length of a chromosome are provided. Methods of modulating telomere length of a mammalian chromosome in vitro and in vivo are also provided, as are methods for inhibiting the division of a malignant mammalian cell and for modulating the effects of cellular aging.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Treating a tumor or the like with electric fields at different orientations
Cells that are in the late anaphase or telophase stages of cell division are vulnerable to damage by AC electric fields that have specific frequency and field strength characteristics. The selective destruction of rapidly dividing cells can therefore be accomplished by imposing an AC electric field in a target region for extended periods of time. Some of the cells that divide while the field is applied will be damaged, but the cells that do not divide will not be harmed. This selectively damages rapidly dividing cells like tumor cells, but does not harm normal cells that are not dividing. Since the vulnerability of the dividing cells is strongly related to the alignment between the long axis of the dividing cells and the lines of force of the electric field, improved results are obtained when the field is sequentially imposed in different directions. The field may also be rotated through 360° by applying AC waveforms with different phases to the electrodes.
Owner:ノボキュアゲーエムベーハー
Benzo [c] phenanthridines as antimicrobial agents
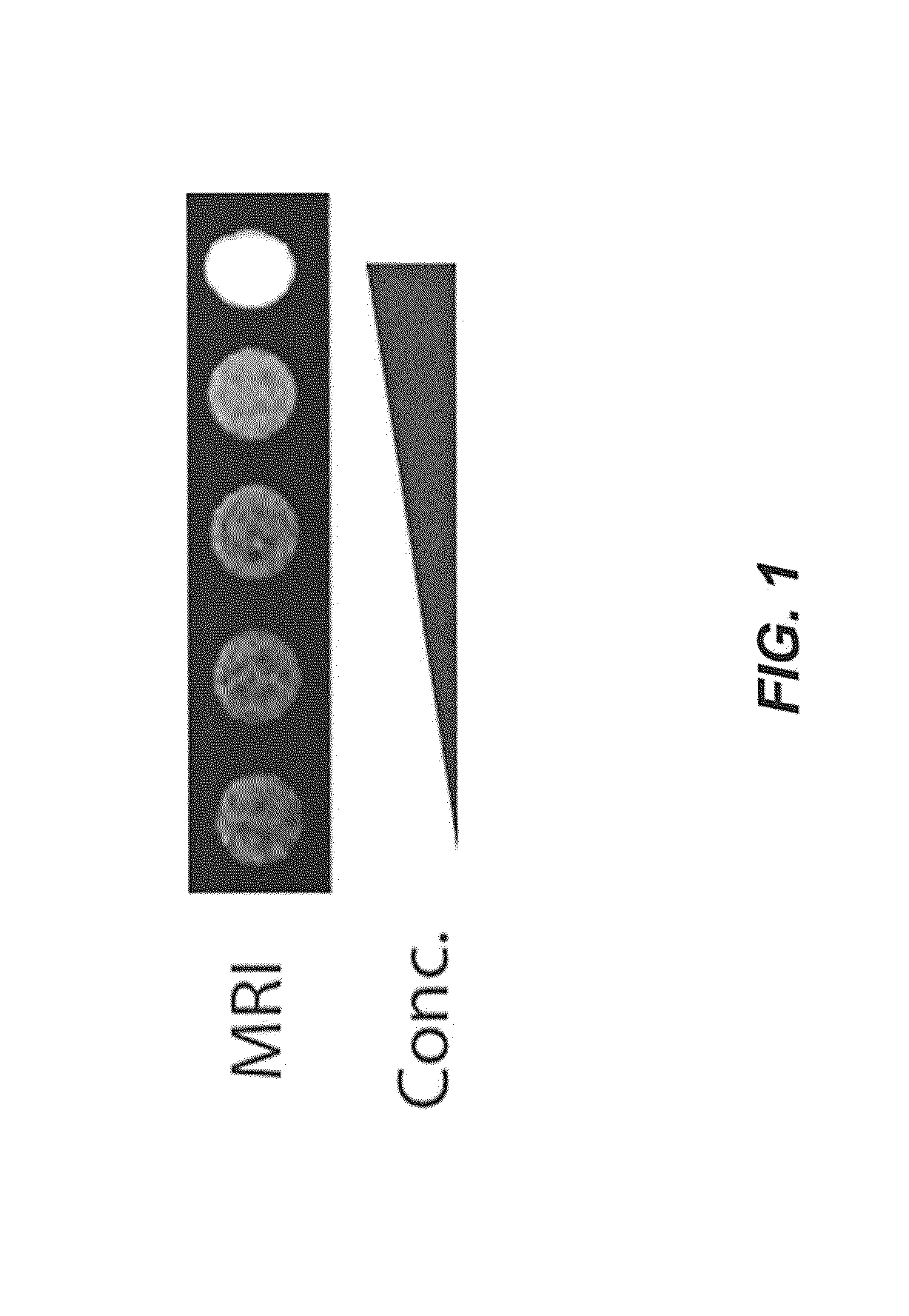
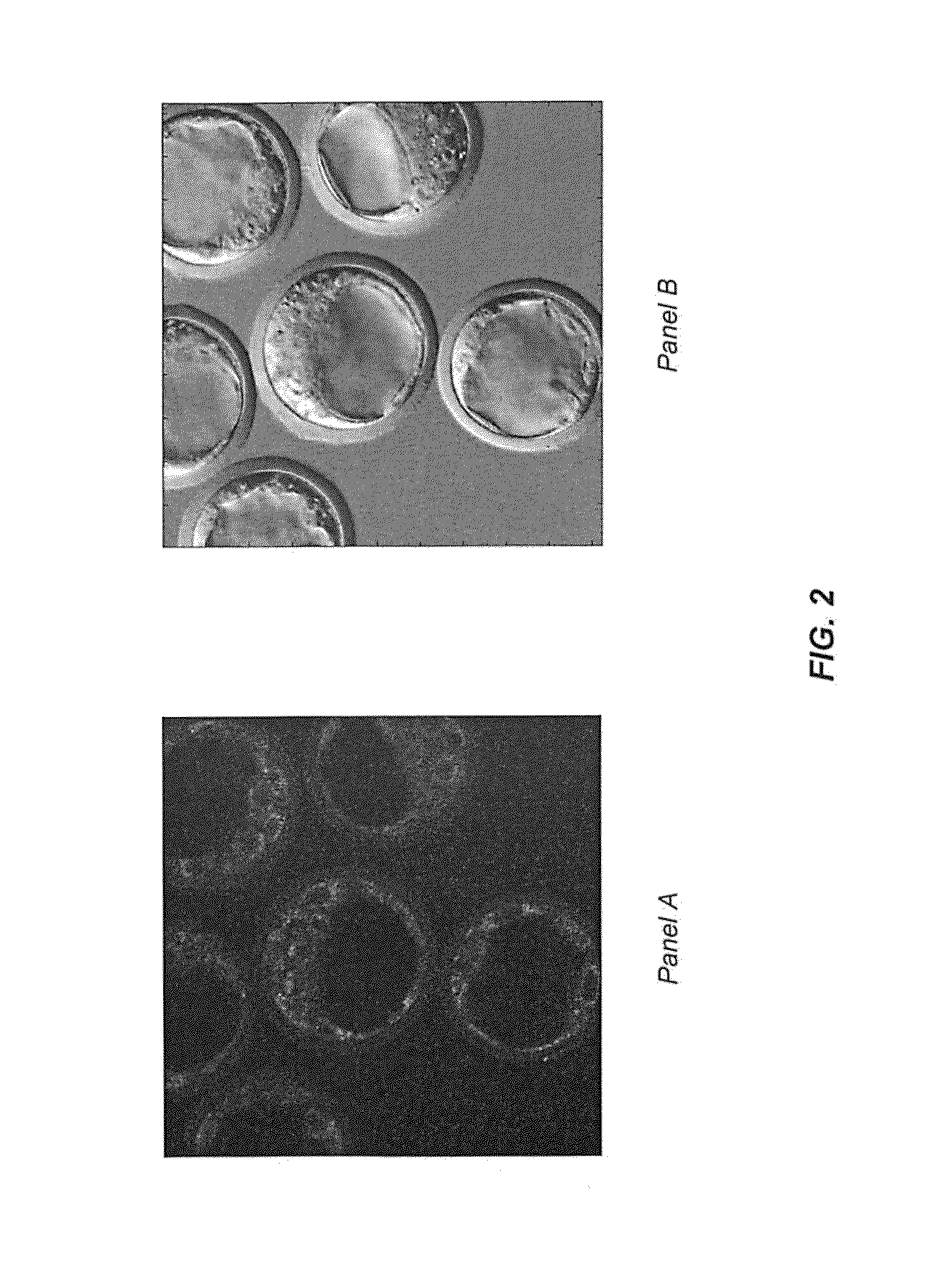
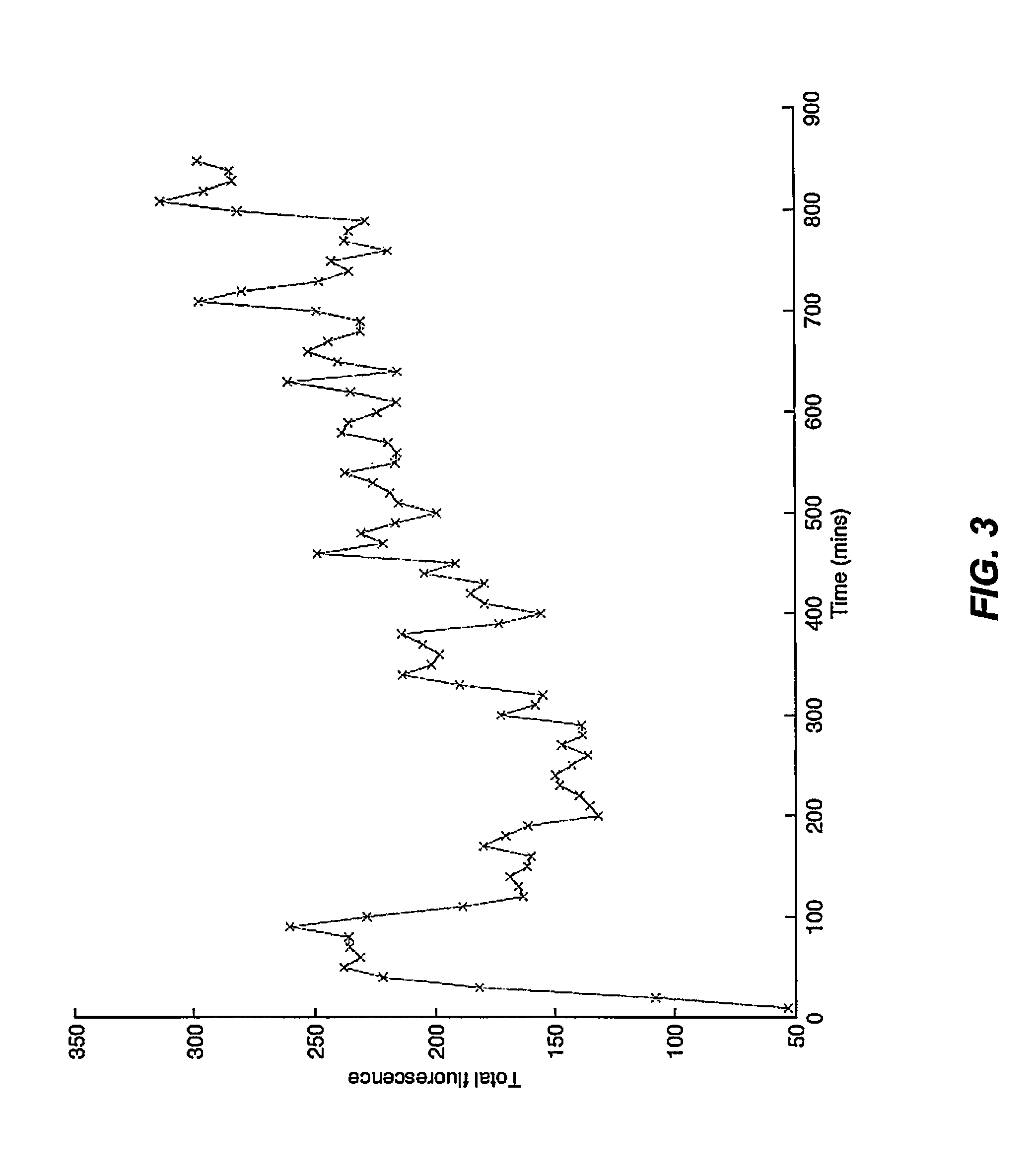
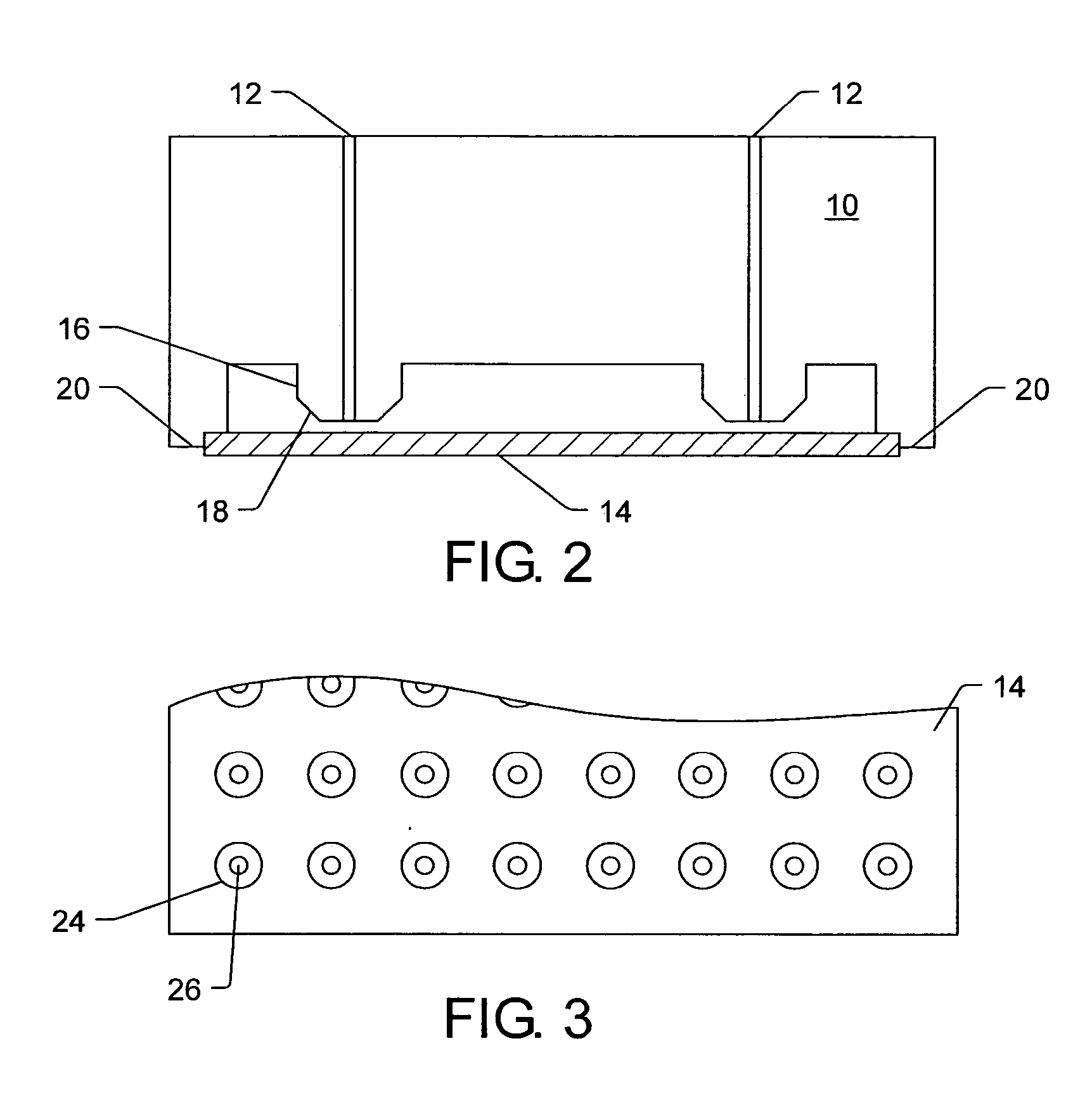
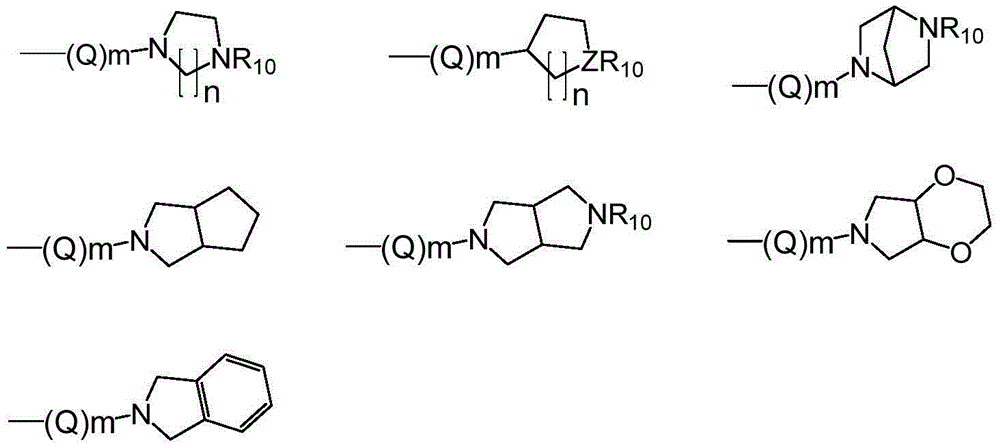
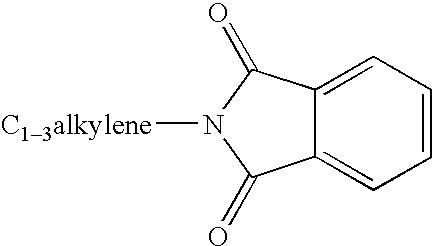
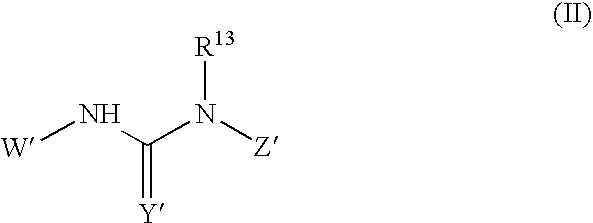
ActiveUS20120022061A1Reduce polymerizationAntibacterial agentsBiocideCell divisionBenzo(c)phenanthrene
The present invention provides compounds of formula I: formula (I) wherein X1-X4 and R1-R12 have any of the values defined in the specification, as well as salts and prodrugs thereof, which inhibit major molecular mechanisms associated with bacterial cell division and proliferation so as to be useful for the treatment and / or prevention of bacterial infections. The invention also provides compositions comprising these compounds as well as methods for using these compounds to inhibit bacterial cell division and proliferation and to treat bacterial infections.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
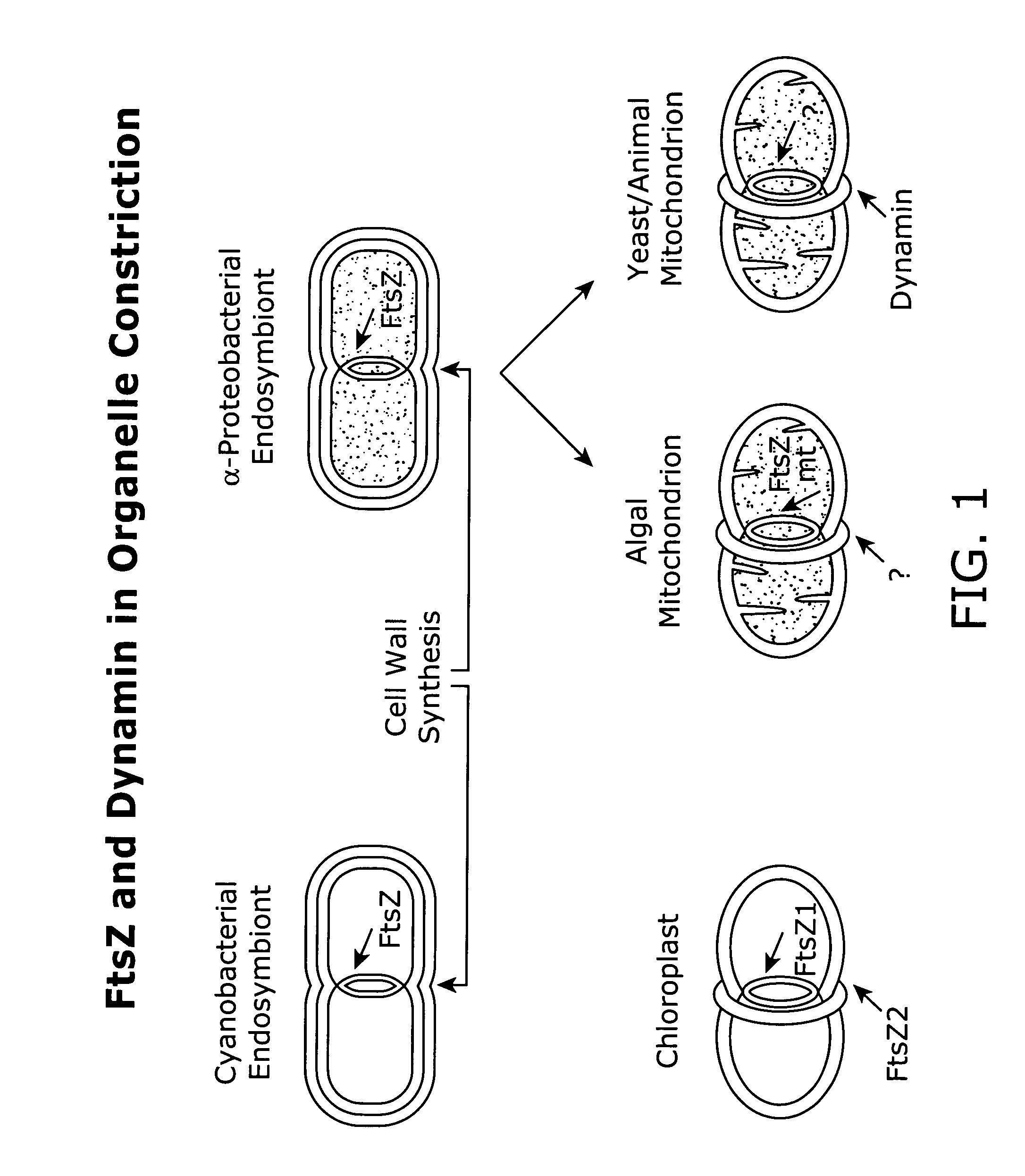
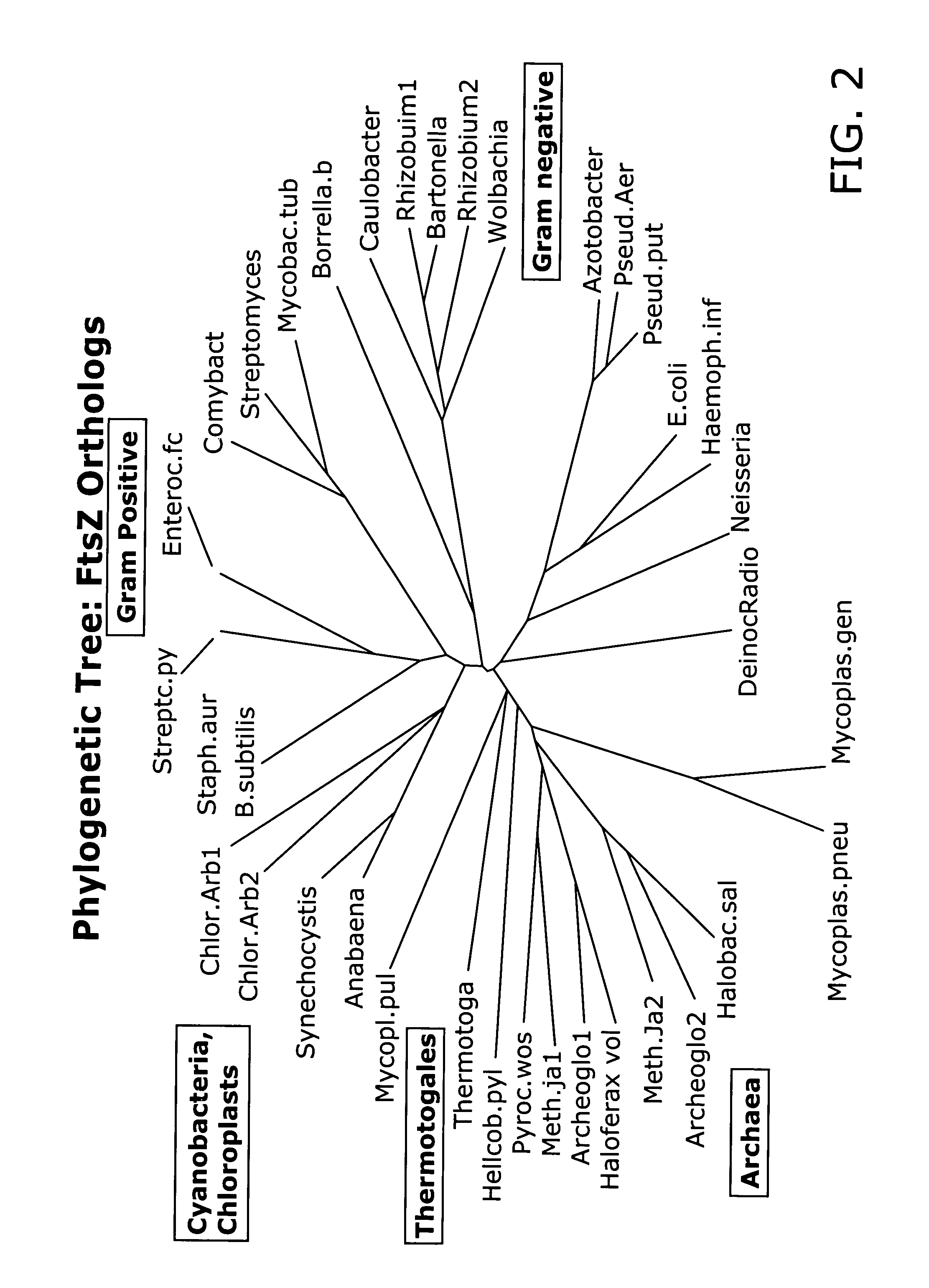
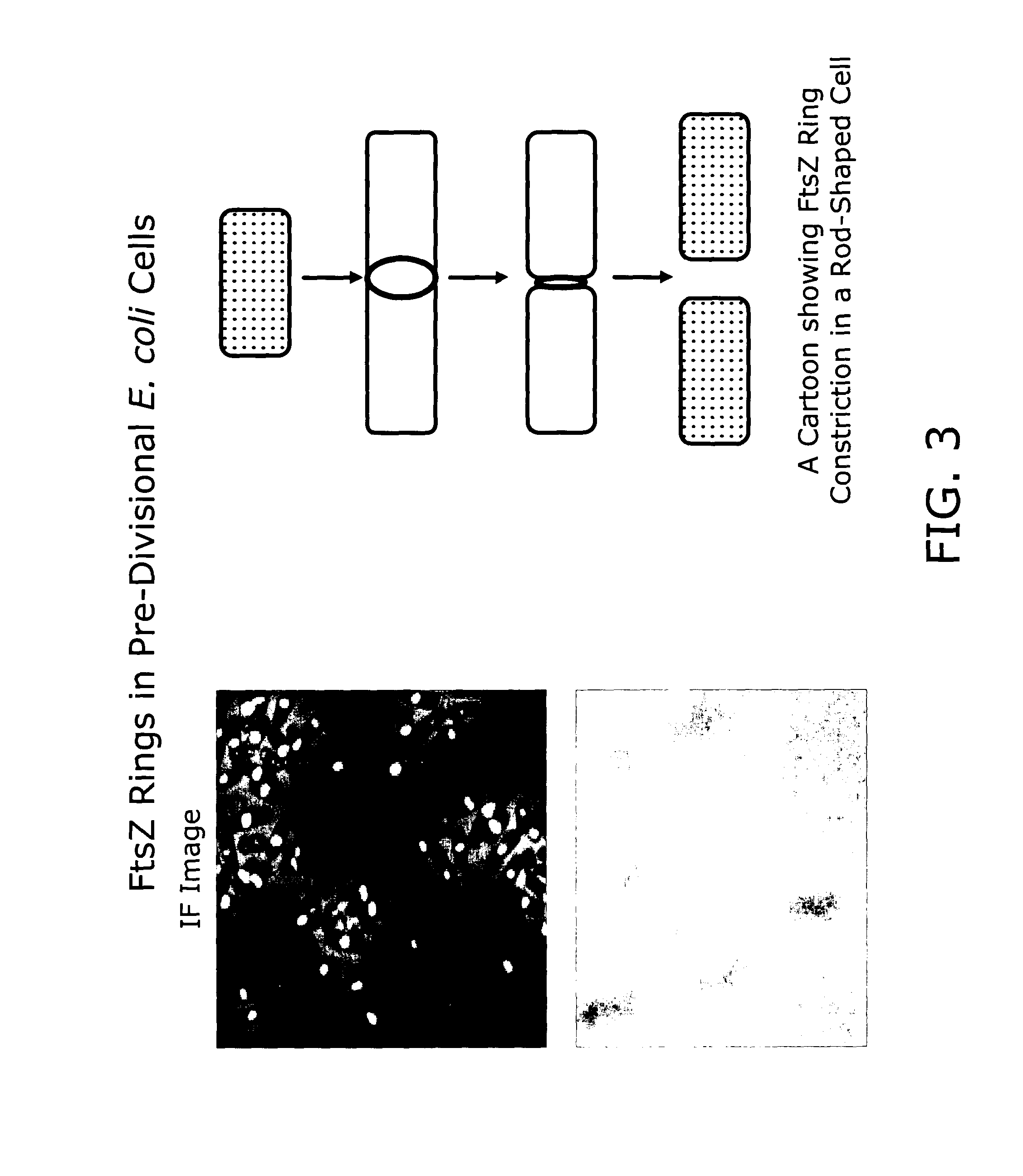
Host cells with artificial endosymbionts
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic cells comprising single-celled organisms that are introduced into the eukaryotic cell through human intervention and which transfer to daughter cells of the eukaryotic cell through at least five cell divisions, and methods of introducing such single-celled organisms into eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides methods of using such eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides single-celled organisms that introduce a phenotype to eukaryotic cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
System and method for tracking the movement of biological materials
This invention provides an automated system and method that allows a user to track the movement of an object, such as at least one cell amongst a plurality of cells as it moves from one point to another over time in order for the user to determine how the at least one cell functions. The user is able to track the movement of the at least one cell and determine if the at least one cell structure has changed, such as the at least one cell experiencing cell division or if two or more cells merge together. This user is able to optimally track the at least one cell to find an approximate location of at least one the cell as it moves in time and distance. Thus, this invention provides the user with a means to track cell movement to study the cell function.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Cell migration inhibiting compositions and methods and compositions for treating cancer
Methods for treating an individual having cancer are provided. The method may include administering a cell migration inhibitor and a chemotherapeutic agent to the individual to inhibit migration of cancer cell. Inhibiting cell migration may increase cell division. In this manner, the cell migration inhibitor and the chemotherapeutic agent in combination may have increased efficacy compared to the chemotherapeutic agent alone due to the increased cell division. The cell migration inhibitor may include any of the inhibitors described herein. For example, the cell migration inhibitor may be an organic molecule having a molecular weight of less than about 700, a monoclonal antibody, or a natural product.
Owner:AVOLIX PHARMA
Rice big grain gene and uses thereof
ActiveCN101161675ALarge grainIncrease productionImmunoglobulins against plantsPlant peptidesCell divisionAgricultural science
The present invention discloses a rice large-grain gene GW2 and the application thereof, the GW2 gene can be used to control the grain size of the crop, improve the yield or quality of the crop, regulate the cycle duration of cellular mitosis, and used as a molecular marker to identify the species of the crop to be a large-grain one or a small-grain one. The present invention also discloses a method to ameliorate the crop. The gene GW2 has a wide prospect on high-yield breeding of crops such as rice.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
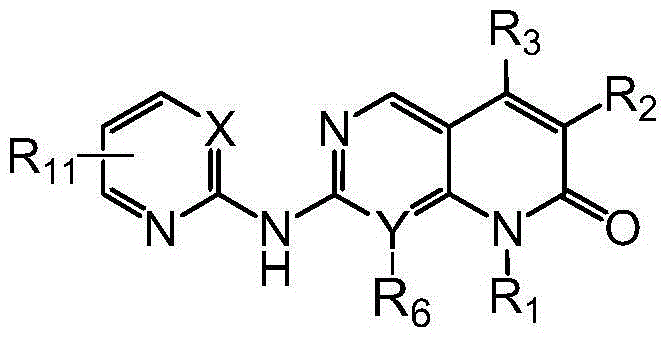
Pyrimido or pyridopyridone compound and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN105622638AApplicable treatmentHigh selectivityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDrugs preparationsPyridine
The invention discloses a pyrimido or pyridopyridone compound shown in the formula I and its preparation method and use and belongs to the technical field of drug preparation. The pyrimido or pyridopyridone compound can efficiently and selectively inhibit cyclin-depedent kinase (Cdks) CDK4 and CDK6 activity and prevent tumor cell division through inhibiting CDK4 / CDK6. The pyrimido or pyridopyridone compound can be used for treating various diseases caused through imbalance of cell cycle control based on CDK4 and CDK6 and is especially suitable for cancer treatment.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BEBETTER MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Plants with modified growth
InactiveUS6559358B1Improve the level ofModulating level of expression and activityClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesCell divisionPlant cell
A process is provided for modifying growth or architecture of plants by altering the level or the functional level of a cell division controlling protein, preferably a cell-division controlling protein that binds phosphorylates retinoblasoma-link proteins, more preferably a cyclin, particularly a D-type cyclin within cells of a plant. Also provided are chimeric genes comprising a transcribed DNA region encoding an RNA or a protein, which when expressed either increases or decreases the level or functional level of a cell-division controlling protein, and plant cells and plants expressing such chimeric genes.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE UNIV TECH SERVICES LTD
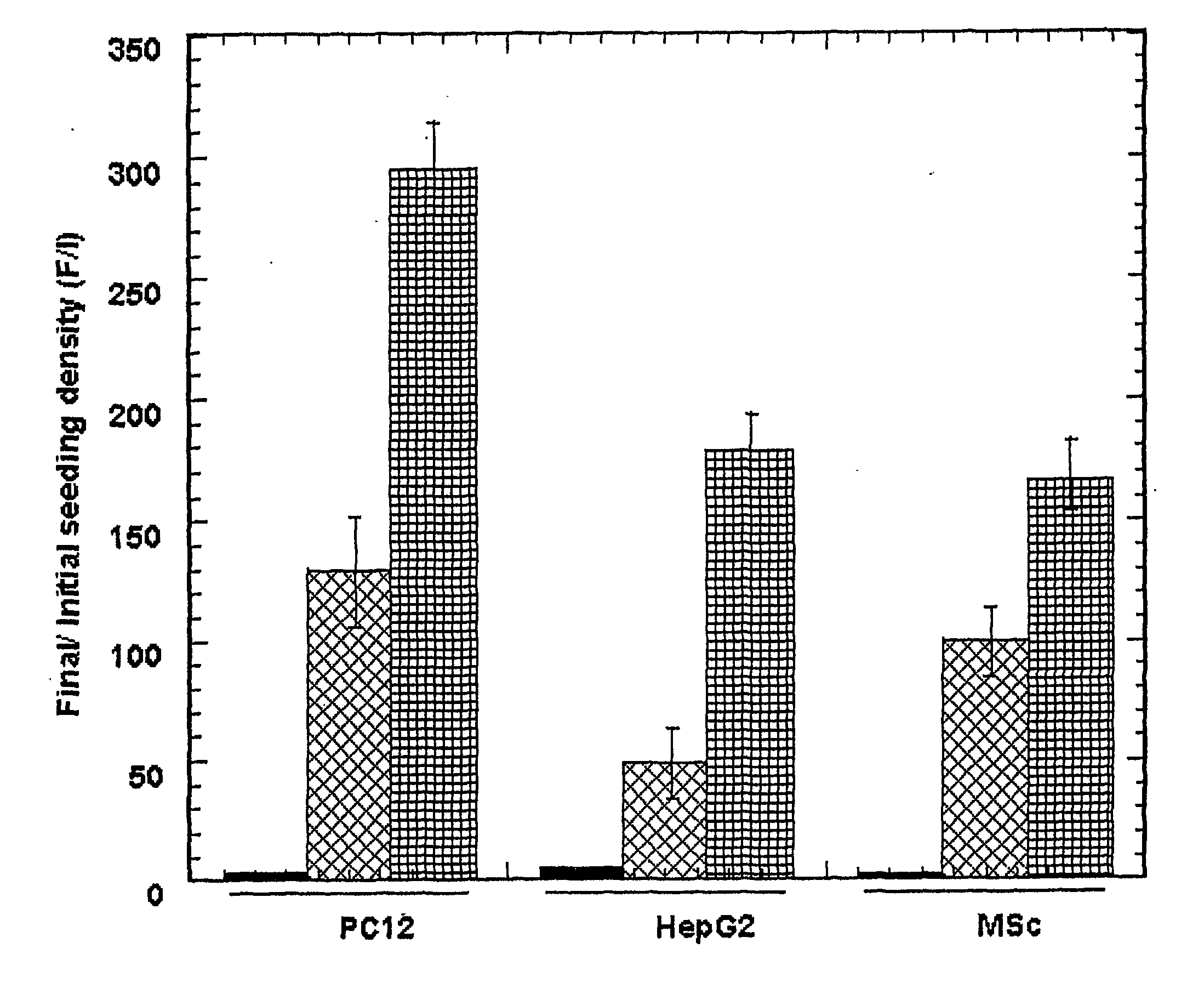
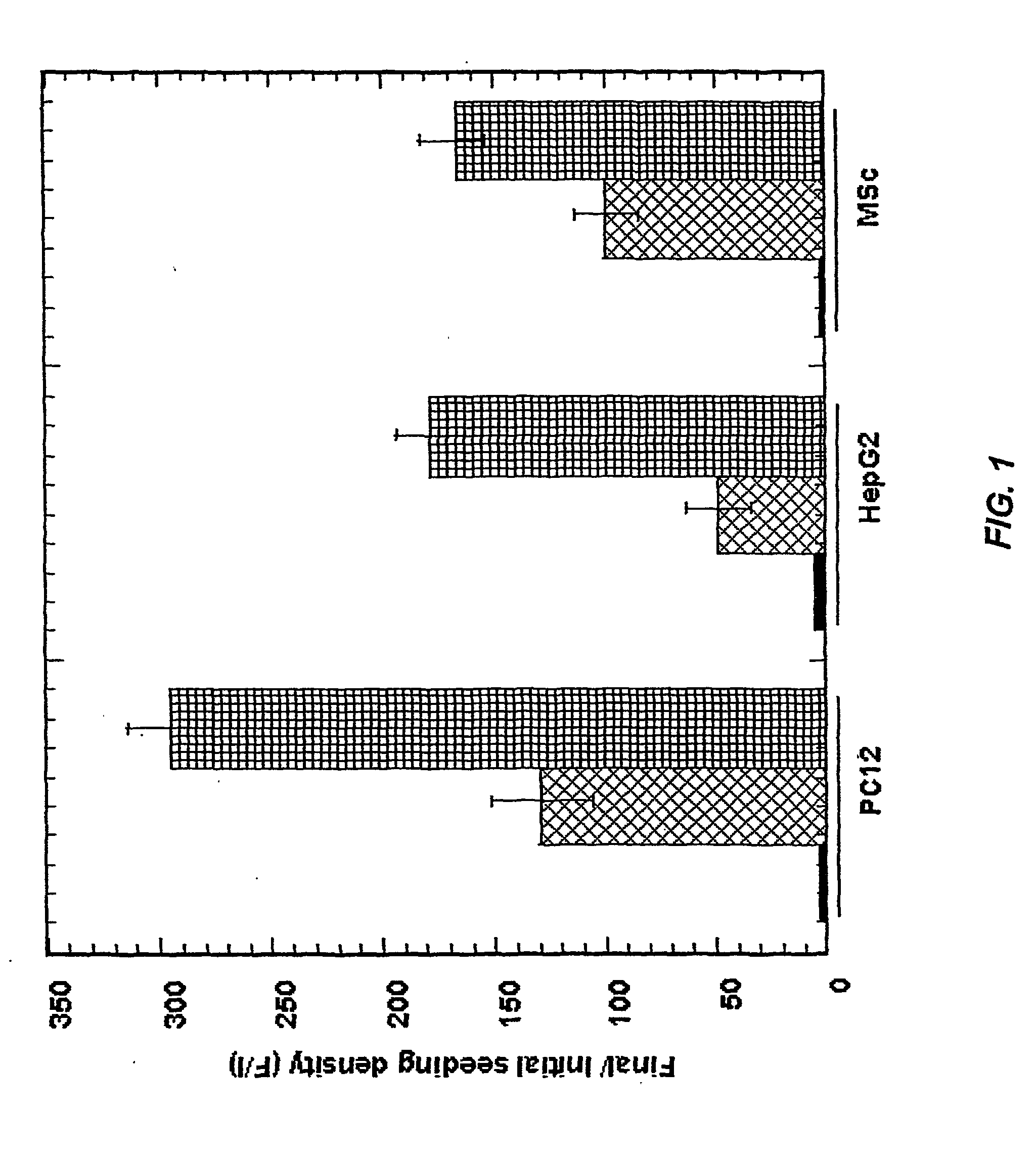
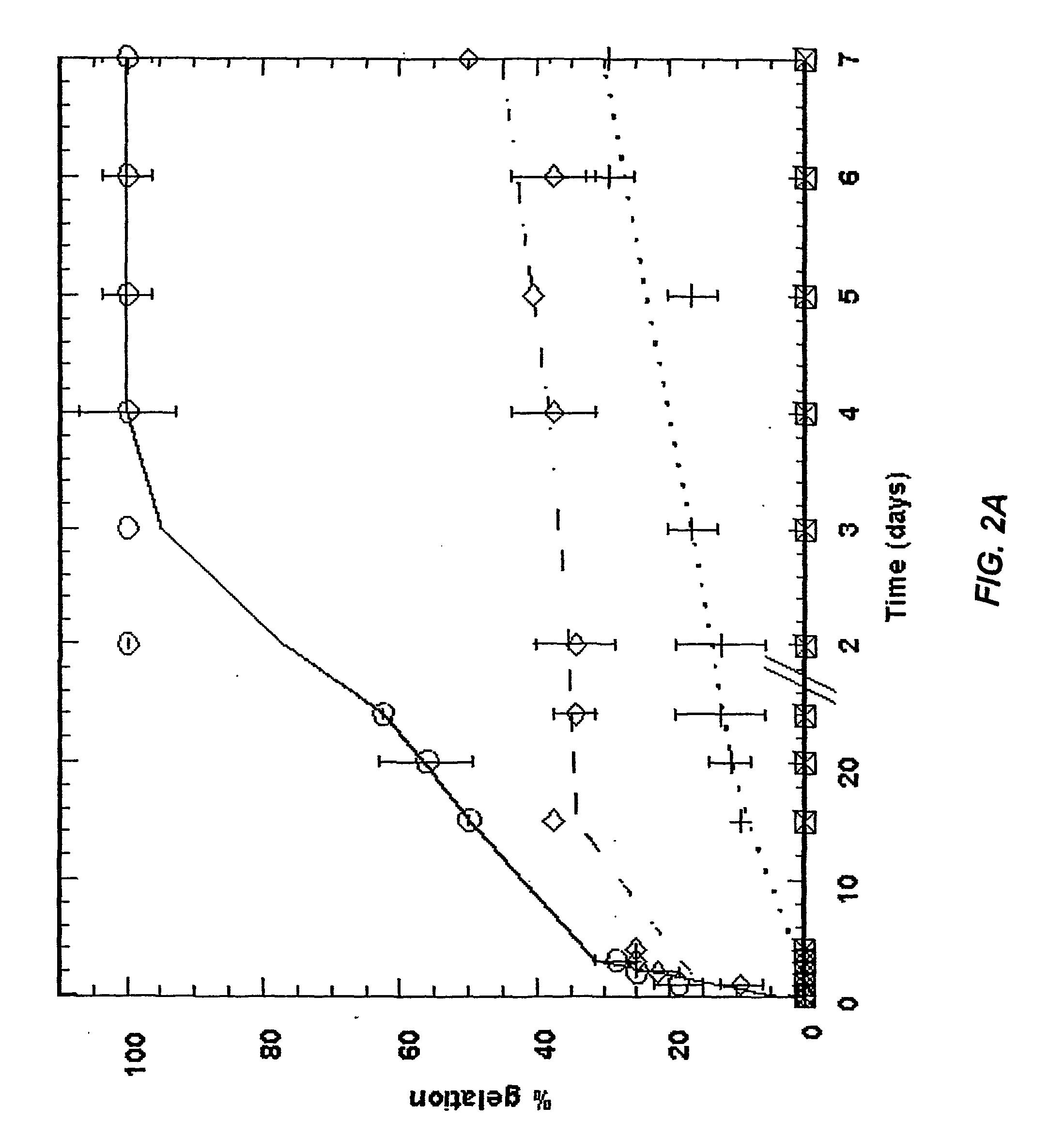
Non-disruptive three-dimensional culture and harvest system for anchorage-dependent cells
InactiveUS20040023370A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNon destructiveCell division
A non-disruptive three-dimensional culture system allows cell growth and proliferation in three dimensions, permitting cell splitting without subjecting cells to disruptive conditions that affect cell structure and functions. An extracellular matrix provides a good environment for culturing or co-culturing anchorage-dependent cells. The cells cultured this manner can be readily used in such applications as cell transplantation, tissue engineering seeding of cells on scaffolds, and other applications that require immediate availability of functioning cells.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
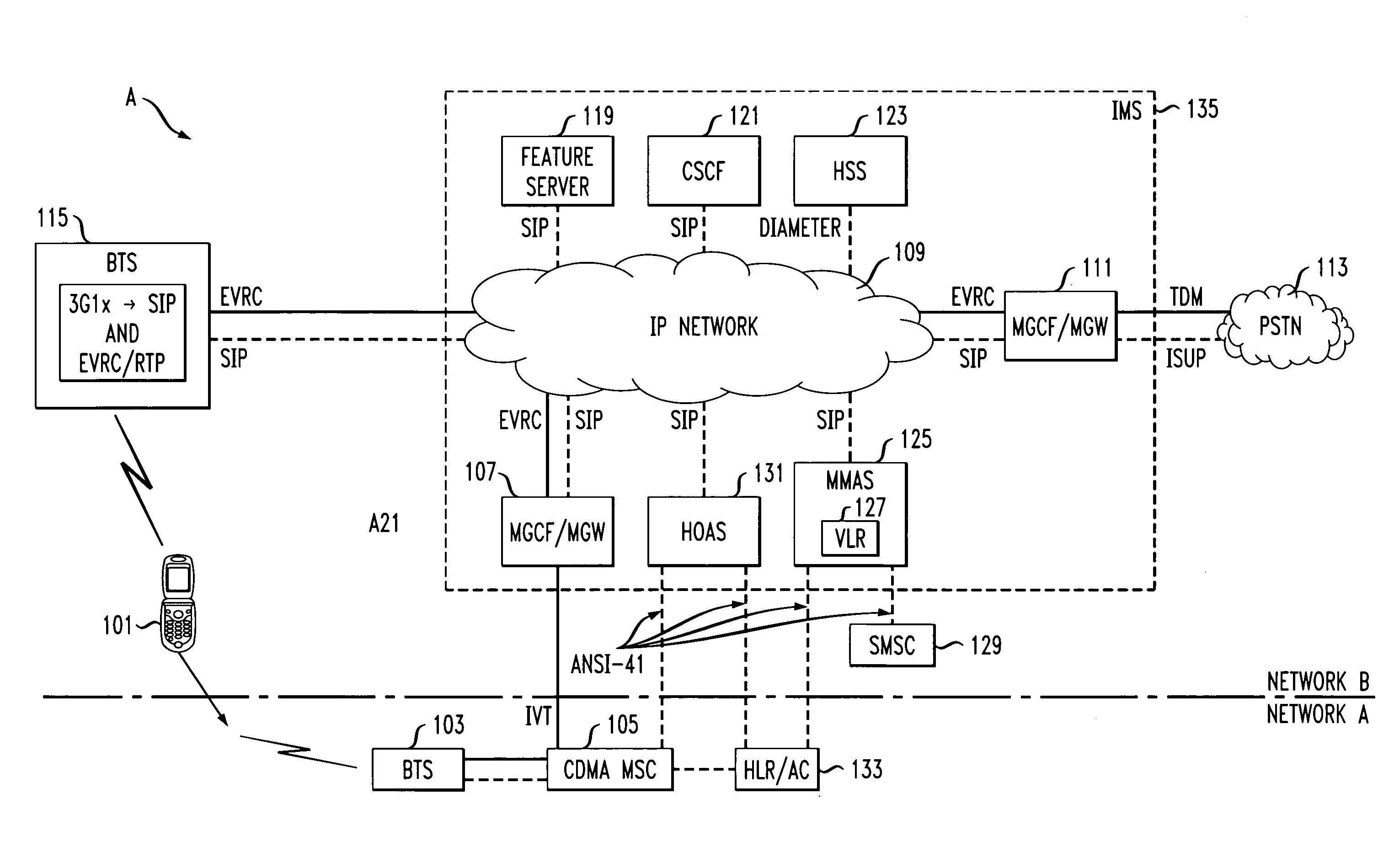
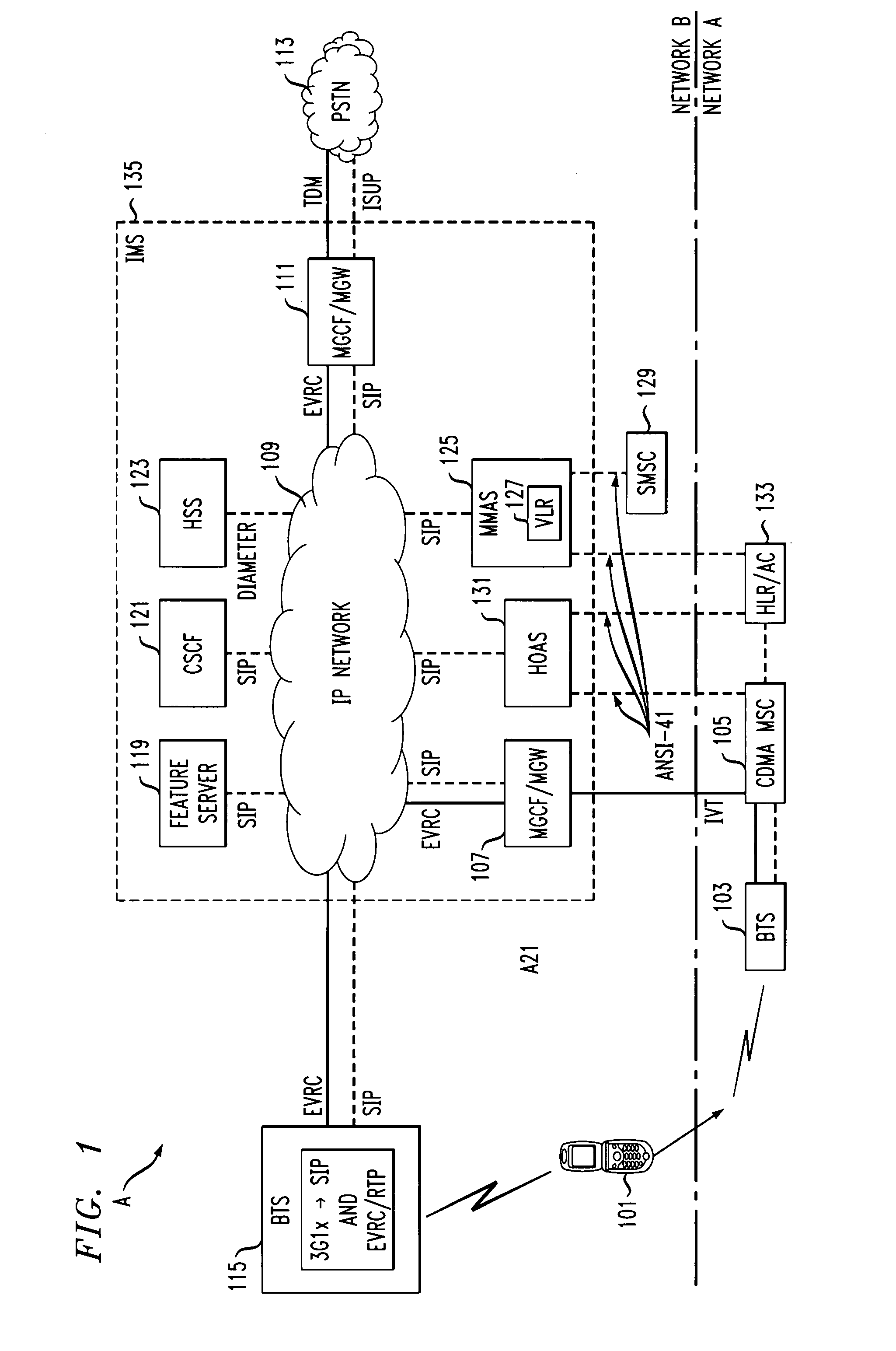
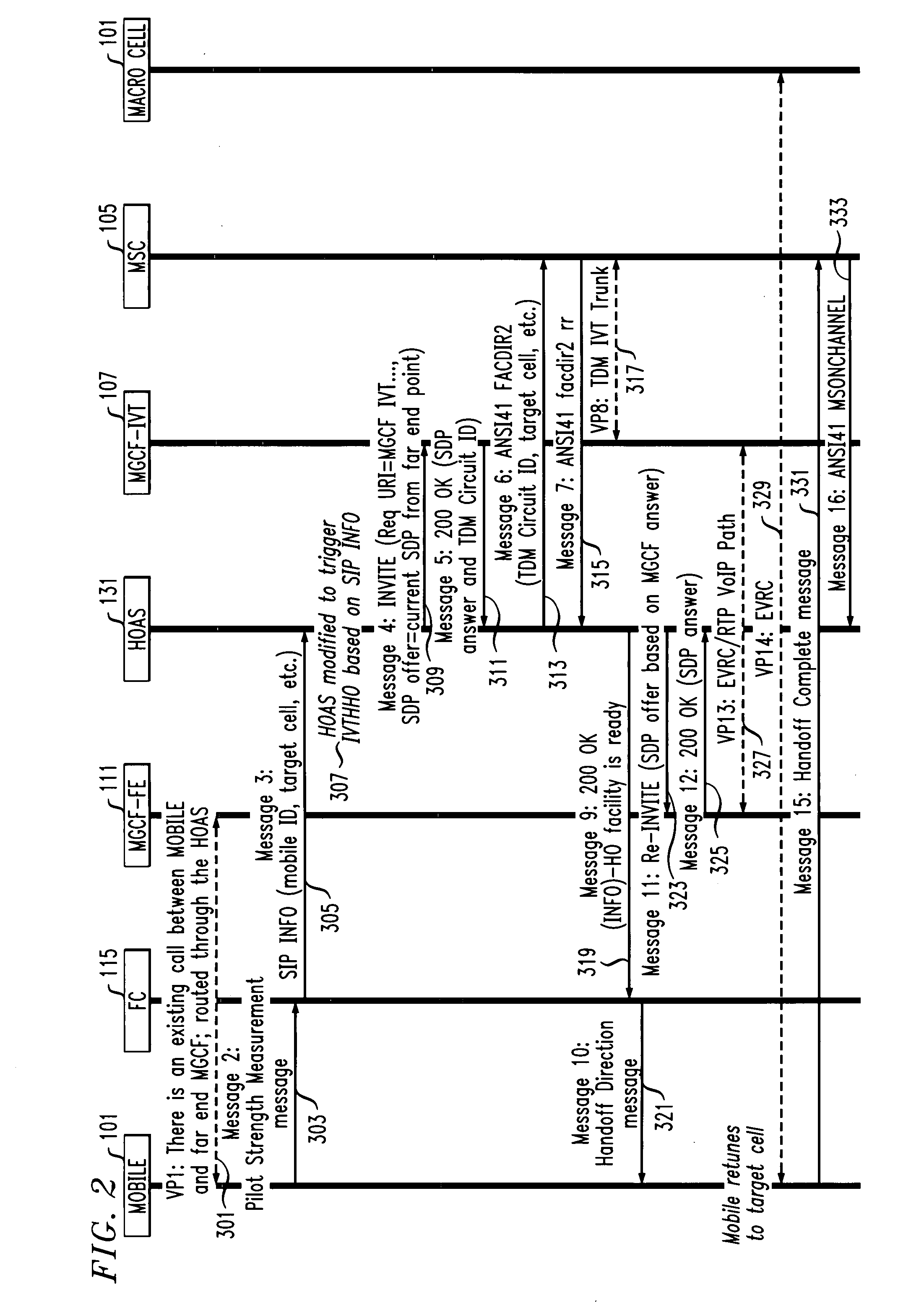
Method to allow hand-off of a CDMA mobile from IMS femtocell to circuit msc
A method for hand-off of a cell division multi-access mobile from an internet protocol base network to a circuit mobile switching center is disclosed. The system includes determining whether a hand-off is appropriate based at least in part on signal strength of a call for a mobile unit. The method continues with sending a message indicating that the mobile identification of the mobile unit and a target cell locating the circuit identification of a circuit that is available to support a hand-off. The method continues on with allocating the circuit and reconfiguring the mobile unit to a macrocell (CDMA access network) and legacy MSC via the circuit.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Use of human stem cells and/or factors they produce to promote adult mammalian cardiac repair through cardiomyocyte cell division
A method for treating a subject afflicted with a cardiac disorder, in vivo, comprising (i) producing a solution comprising media conditioned from the culture of cells, in vitro, and (ii) administering the solution of step (i) to the subject, thereby treating the cardiac disorder in the subject. Methods for determining whether an agent stimulates or inhibits myocyte proliferation.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Method for predicting congestion duration and spatial diffusion of urban road traffic
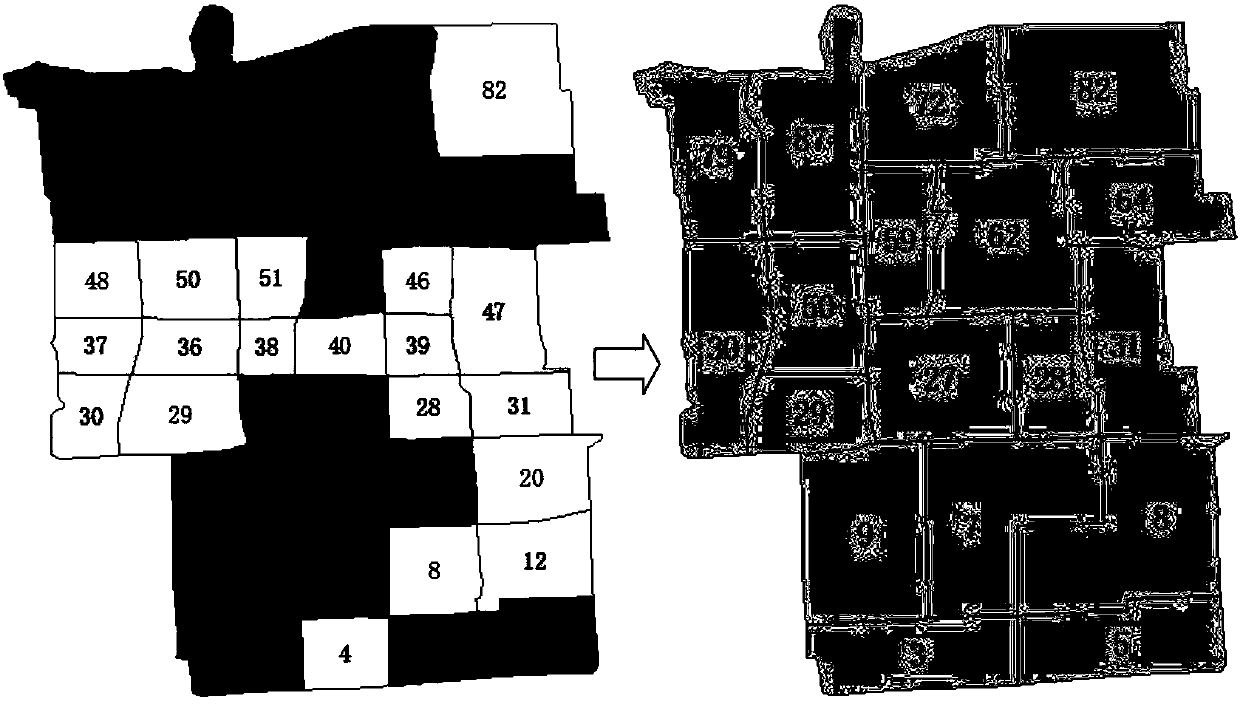
ActiveCN102568194AEfficient Predictive Diffusion EstimationPracticalRoad vehicles traffic controlCell divisionEngineering
The invention discloses a method for predicting congestion duration and spatial diffusion of urban road traffic. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out cell division on an area constituted by a target road section, an upstream road section and a downstream road section according to a road traffic flow characteristics after initial congestion occurs, wherein tail cells are defined as the cells located at a canalization region at downstream outlets of the road sections; (2) initializing each key parameter of each cell; (3) making a judgment according to a judgment rule (1) of the cell of the target road section after each time step is up, and with respect to the cells of the upstream road section and the downstream road section, making judgments according to a rule (2) and a rule (3) respectively in an observation period after each time step is judged to be up; and (4) if a termination condition of the judgment rule (1) is satisfied, terminating the judgment and calculating to predict the congestion duration, or else, turning to (3), and if the termination condition of the rule (2) or rule (3) is satisfied, terminating the judgment and calculating to predict congestion diffusion time, or else, turning to (3). The method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively predicting the congestion duration and carrying out spatial diffusion estimation and is good in practicability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
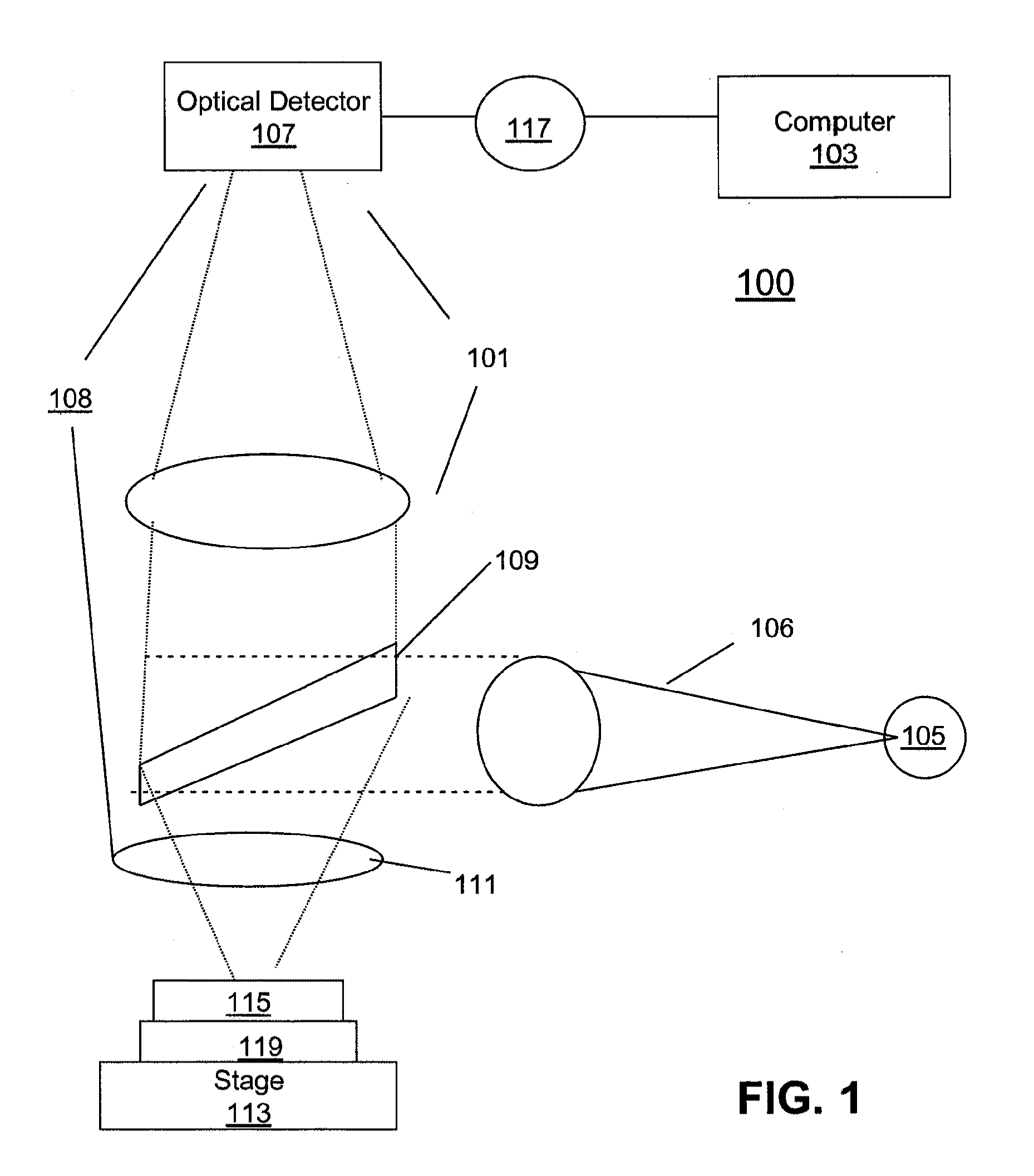
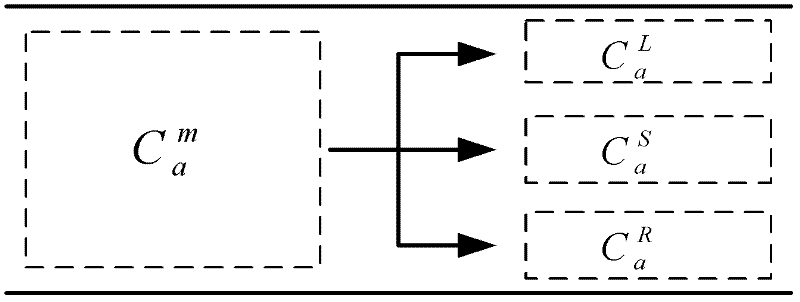
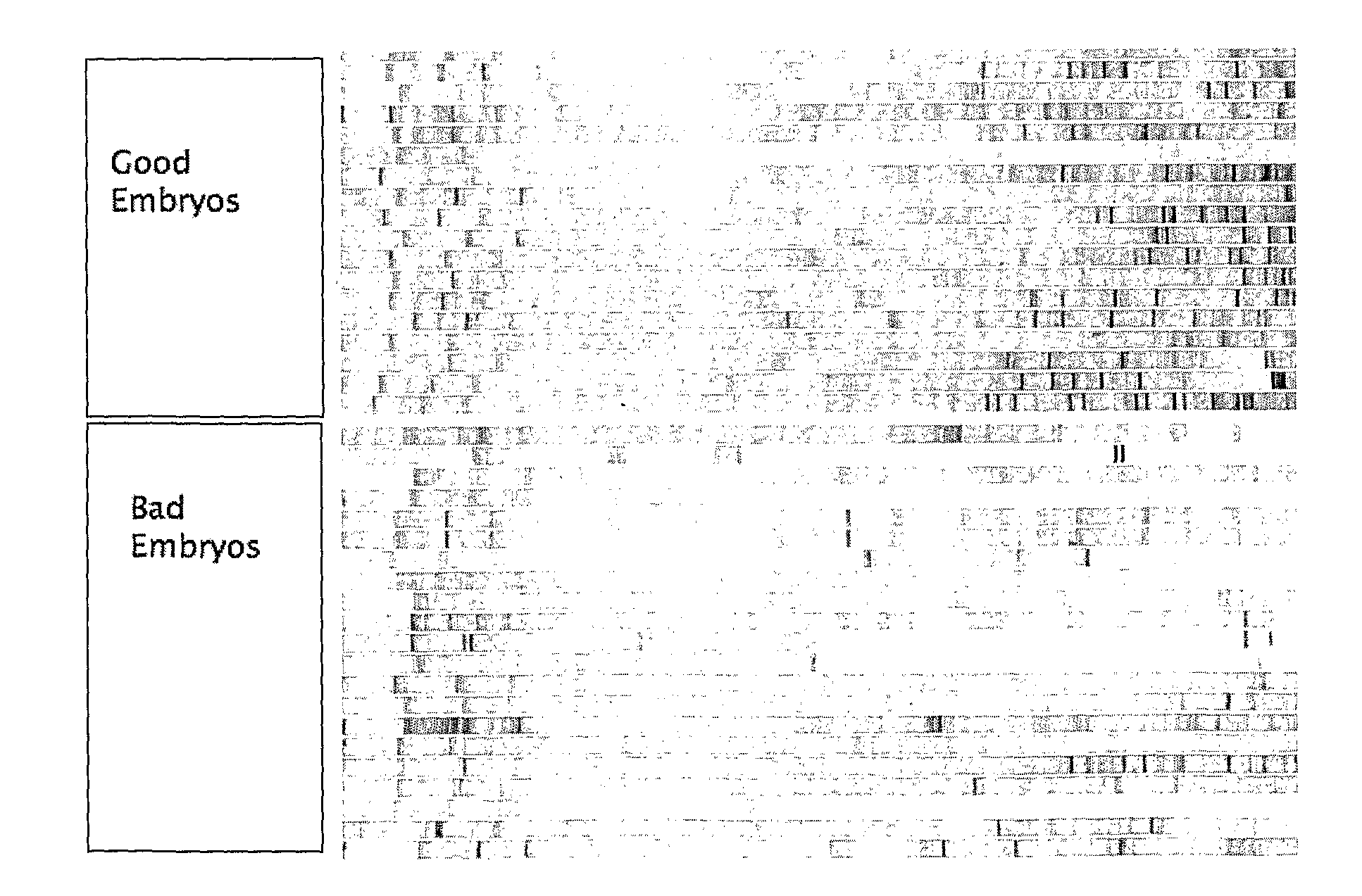
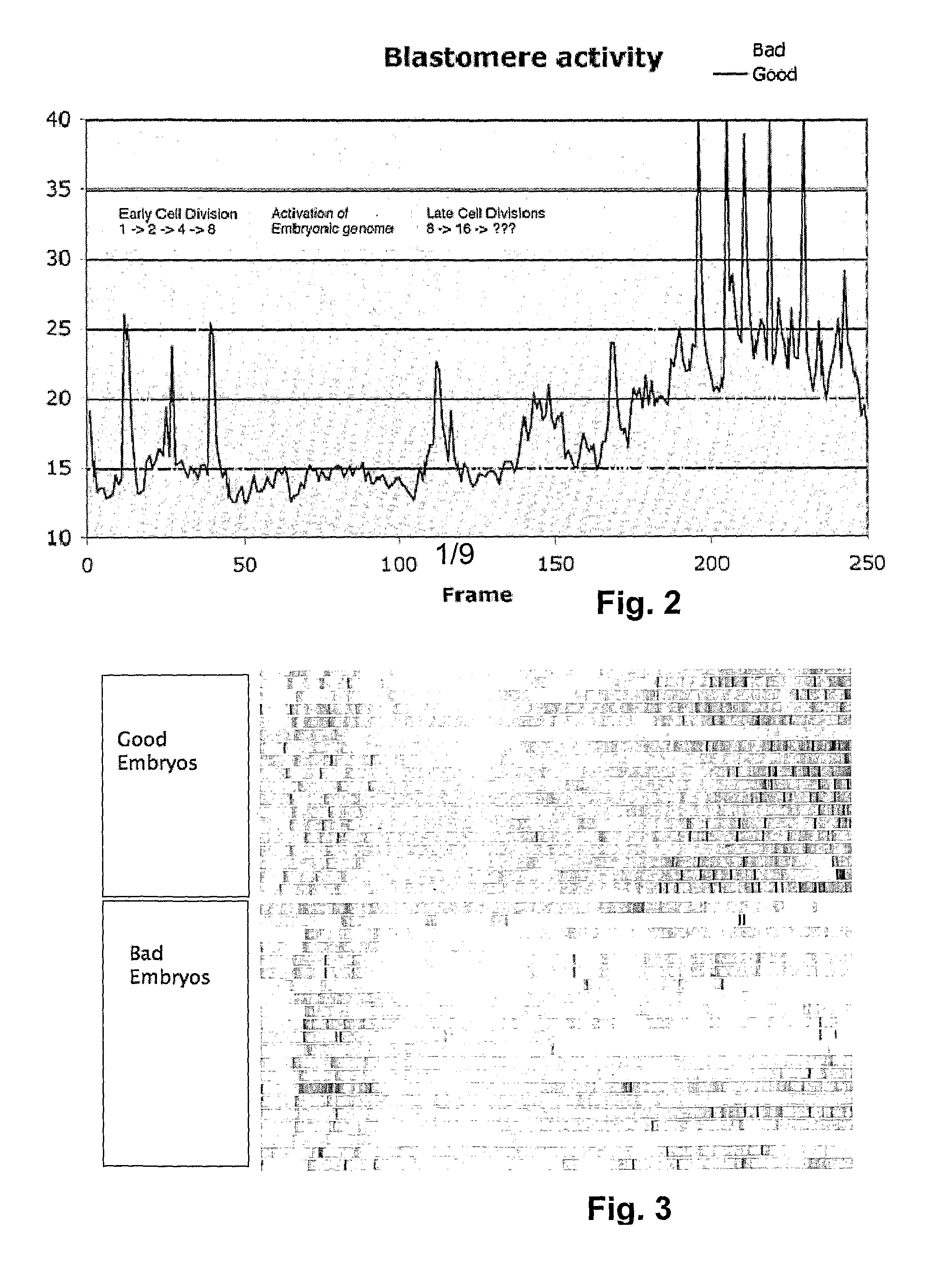
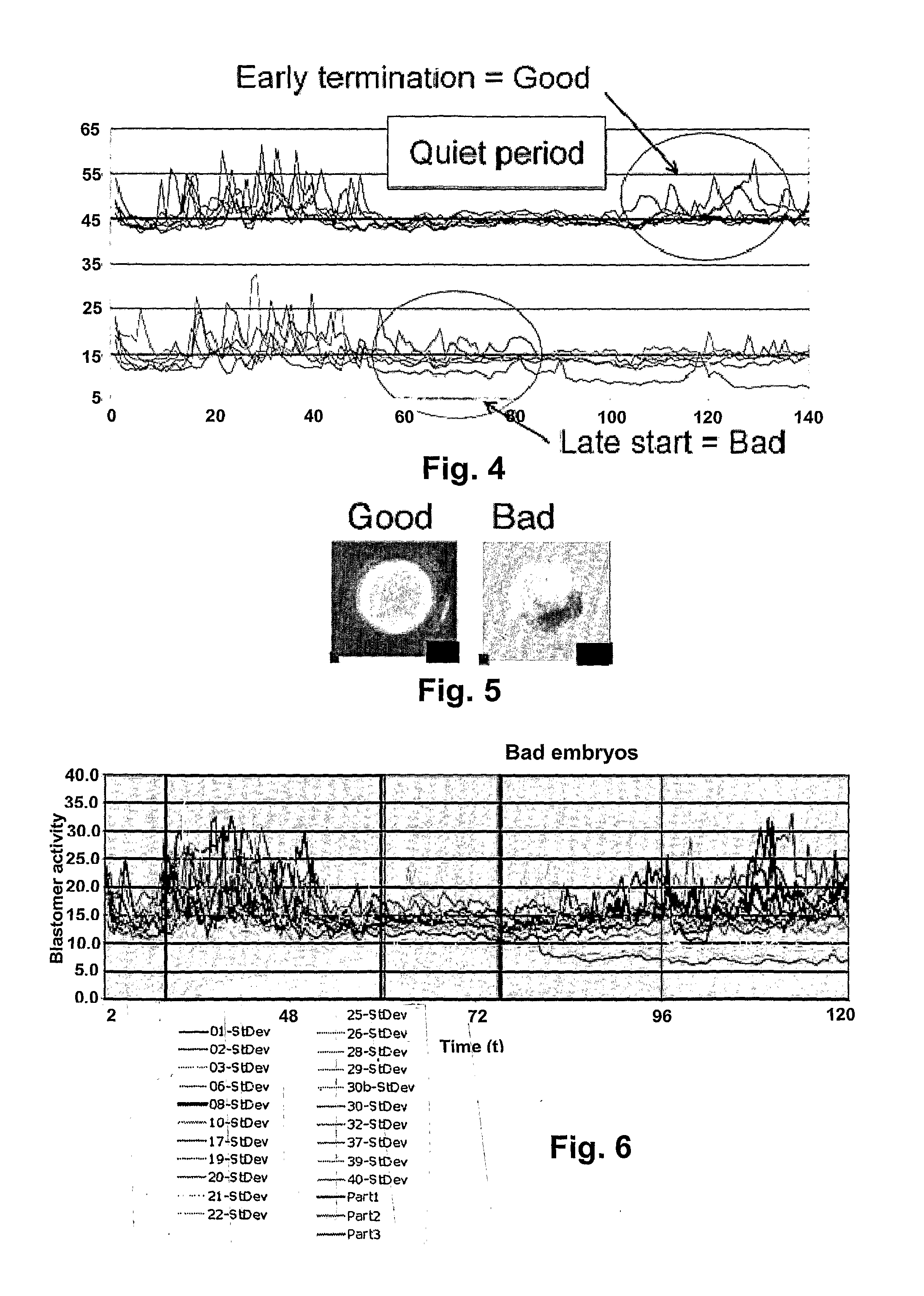
Embryo quality assessment based on blastomere division and movement
InactiveUS20100041090A1Quality improvementHigh baseline valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCell divisionEmbryo
The invention concerns a system and method for determining embryo quality comprising monitoring the embryo for a time period, said time period having a length sufficient to comprise at least one cell division period and at least a part of an inter-division period, and determining the length of the at least one cell division period; and / or ii) determining the extent and / or spatial distribution of cellular or organelle movement during the cell division period; and / or iii) determining duration of an inter-division period; and / or iv) determining the extent and / or spatial distribution of cellular or organelle movement during the inter-division period thereby obtaining an embryo quality measure. Thus, the selection of optimal embryos to be implanted after in vitro fertilization (IVF) is facilitated based on the timing, duration, spatial distribution, and extent of observed cell divisions and associated cellular and organelle movement.
Owner:UNISENSE FERTILITECH AS
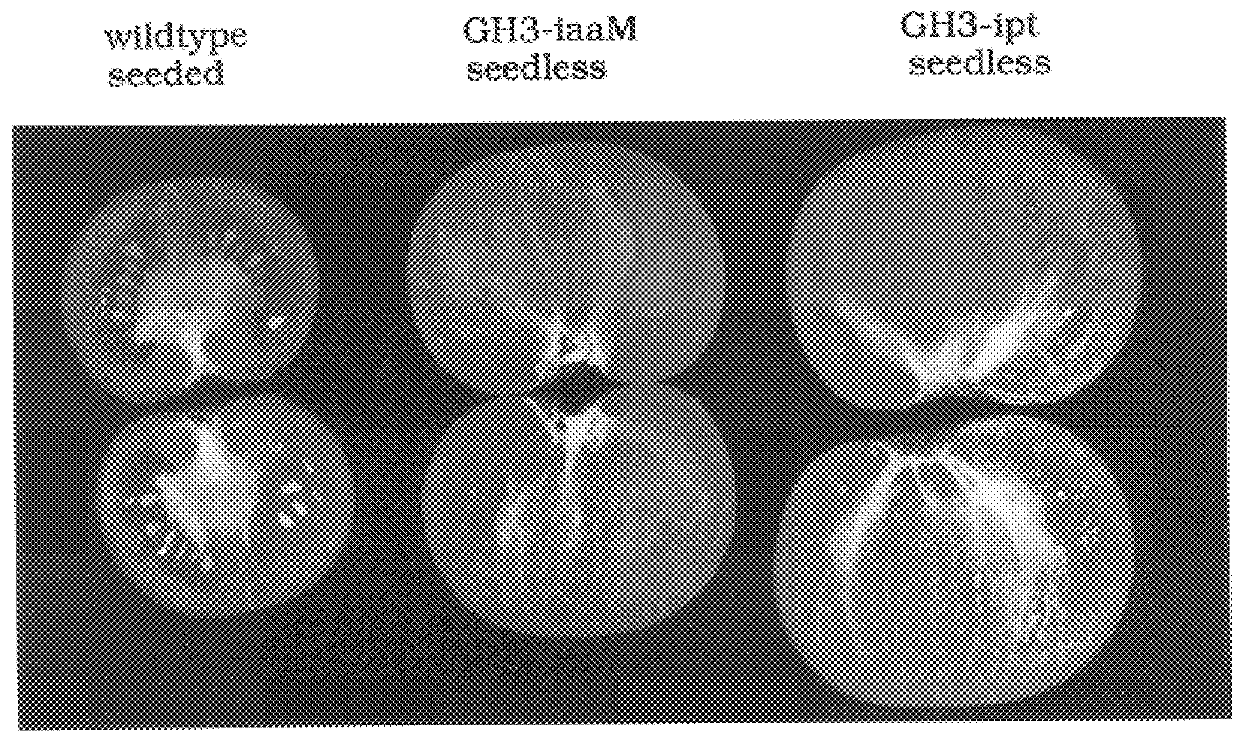
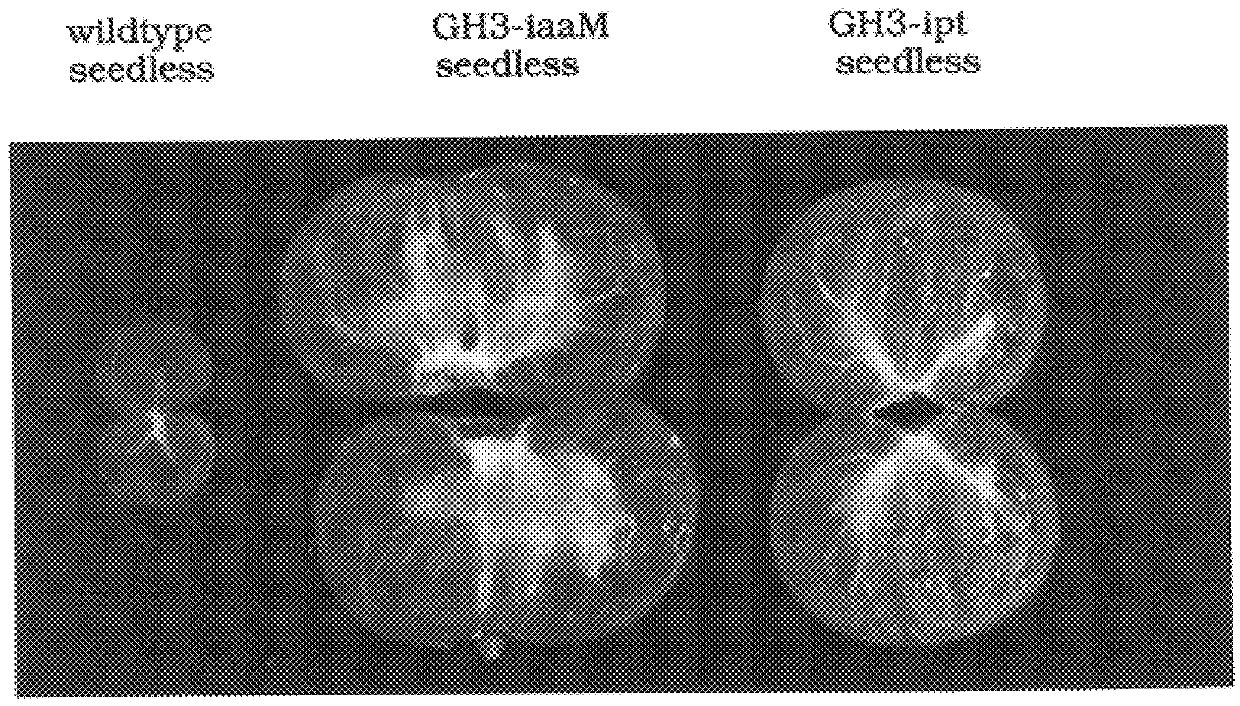
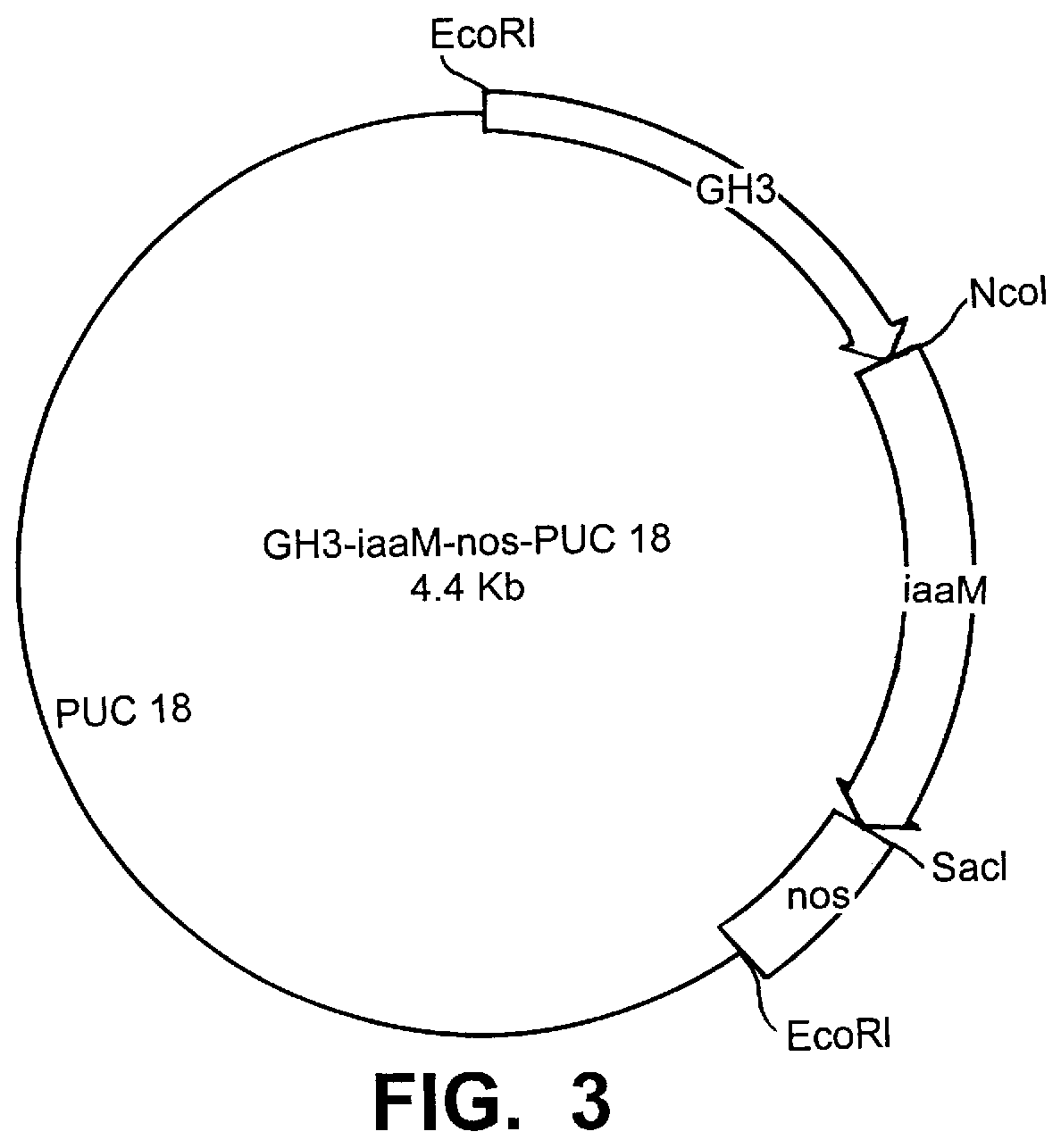
Transgenic seedless fruit comprising AGL or GH3 promoter operably linked to isopentenyl transferase or tryptophan monooxygenase coding DNA
InactiveUS6268552B1TransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesBiosynthetic genesDNA construct
The present invention provides methods and DNA constructs for the genetic engineering of plant cells to produce plants which produce substantially seedless fruit in the absence of exogenous growth factors (auxins or cytokinins) and in the absence of pollination. The substantially seedless fruits produced by the methods described herein are about the size of wildtype seeded fruit (or somewhat larger) and these fruits are equal to or superior to the wildtype seeded fruit with respect to solid content and flavor. The seedless fruits of the present invention are produced in transgenic plants which contain and express auxin or cytokinin biosynthetic genes, e.g., tryptophan oxygenase or isopentenyl transferase coding sequences expressed under the regulatory control of GH3 or AGL promoter sequences directing preferential or tissue specific expression of a downstream gene in the ovaries or developing fruit.
Owner:LI YI
Method of isolating epithelial cells, method of preconditioning cells, and methods of preparing bioartificial skin and dermis with the epithelial cells and preconditioned cells
InactiveUS20050164388A1Increased cell yieldEasy to implantCell dissociation methodsSkin implantsDamages tissueTrypsin
A method of isolating epithelial cells from a human skin tissue or internal organ tissue using trypsin and ethylene-diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) simultaneously with the application of magnetic stirring, a method of preconditioning isolated biological cells by the application of physical stimulus, i.e., strain, are provided. Epithelial cells can be isolated by the method with increased yield, colony forming efficiency (CFE), and colony size. Also, the increased percentage of stem cells in isolated cells is advantageous in therapeutic tissue implantation by autologous or allogeneic transplantation. In skin cells preconditioned by the application of strain, cell division is facilitated, and the secretion of extracellular matrix components and growth factors and the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are improved. When preconditioned cells are implanted by autologous or allogeneic transplantation to heal a damaged tissue, the improved cell adhesion, mobility, and viability provides a biological adjustment effect against a variety of stresses or physical stimuli which the cells would undergo after implantation, with improved capability of integration into host tissue, thereby markedly improving the probability of success in skin grafting.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



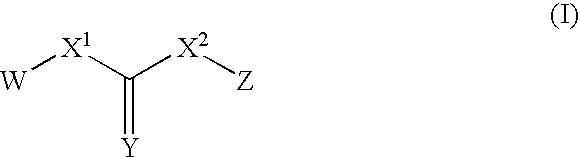
![Benzo [c] phenanthridines as antimicrobial agents Benzo [c] phenanthridines as antimicrobial agents](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/764a375c-7353-41c5-a263-27ec9326a293/US20120022061A1-20120126-D00000.png)
![Benzo [c] phenanthridines as antimicrobial agents Benzo [c] phenanthridines as antimicrobial agents](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/764a375c-7353-41c5-a263-27ec9326a293/US20120022061A1-20120126-D00001.png)
![Benzo [c] phenanthridines as antimicrobial agents Benzo [c] phenanthridines as antimicrobial agents](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/764a375c-7353-41c5-a263-27ec9326a293/US20120022061A1-20120126-D00002.png)