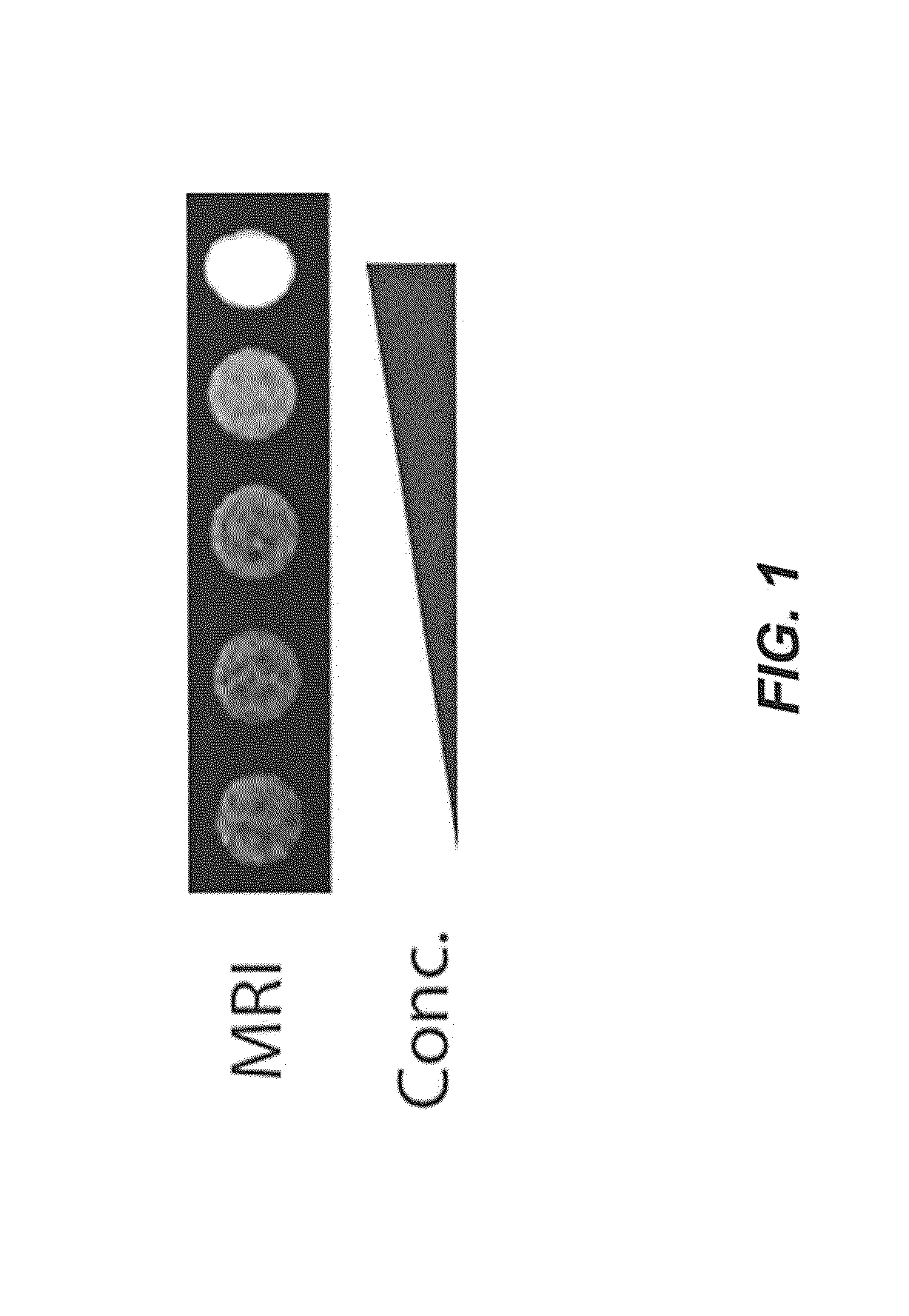
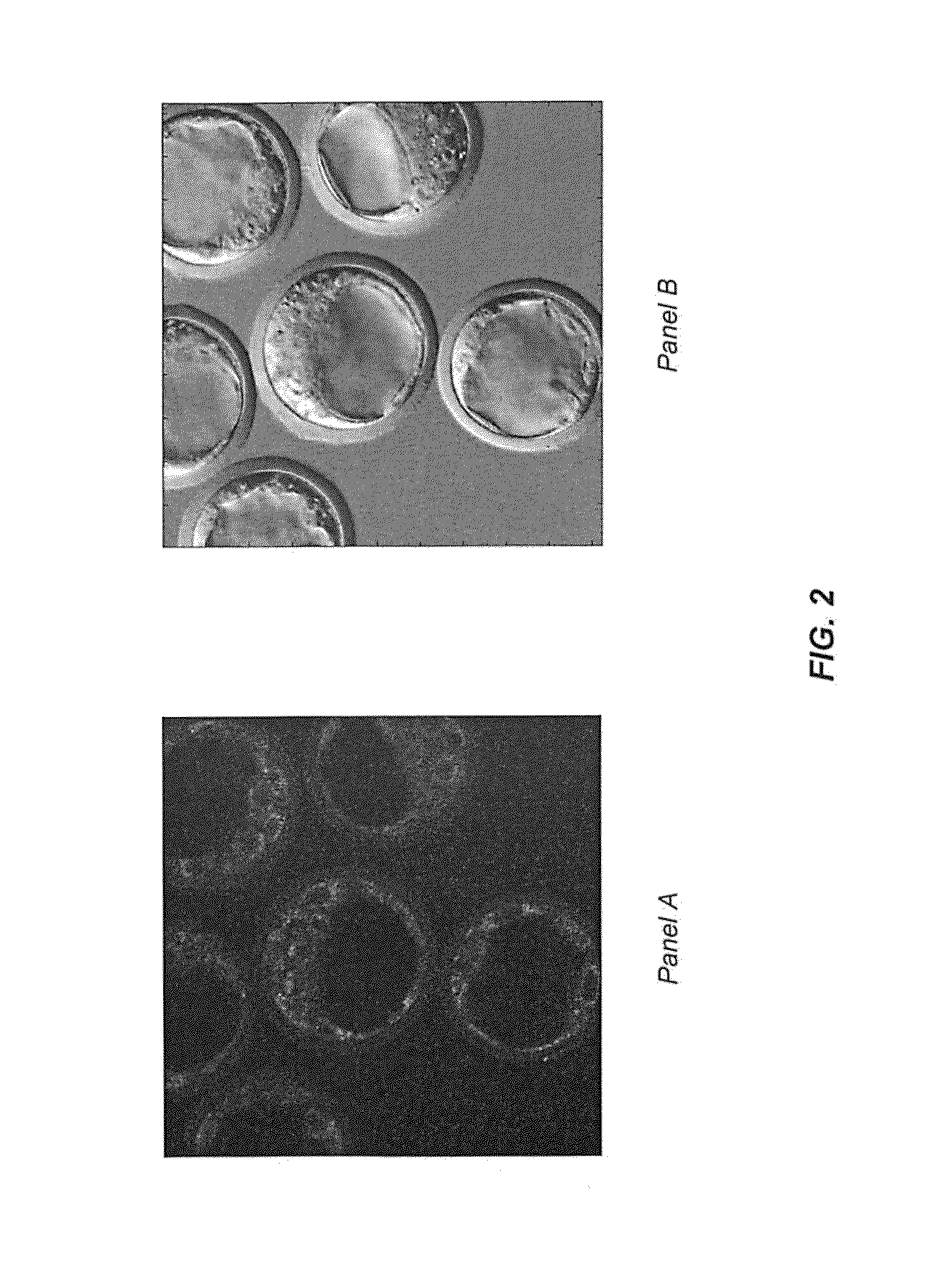
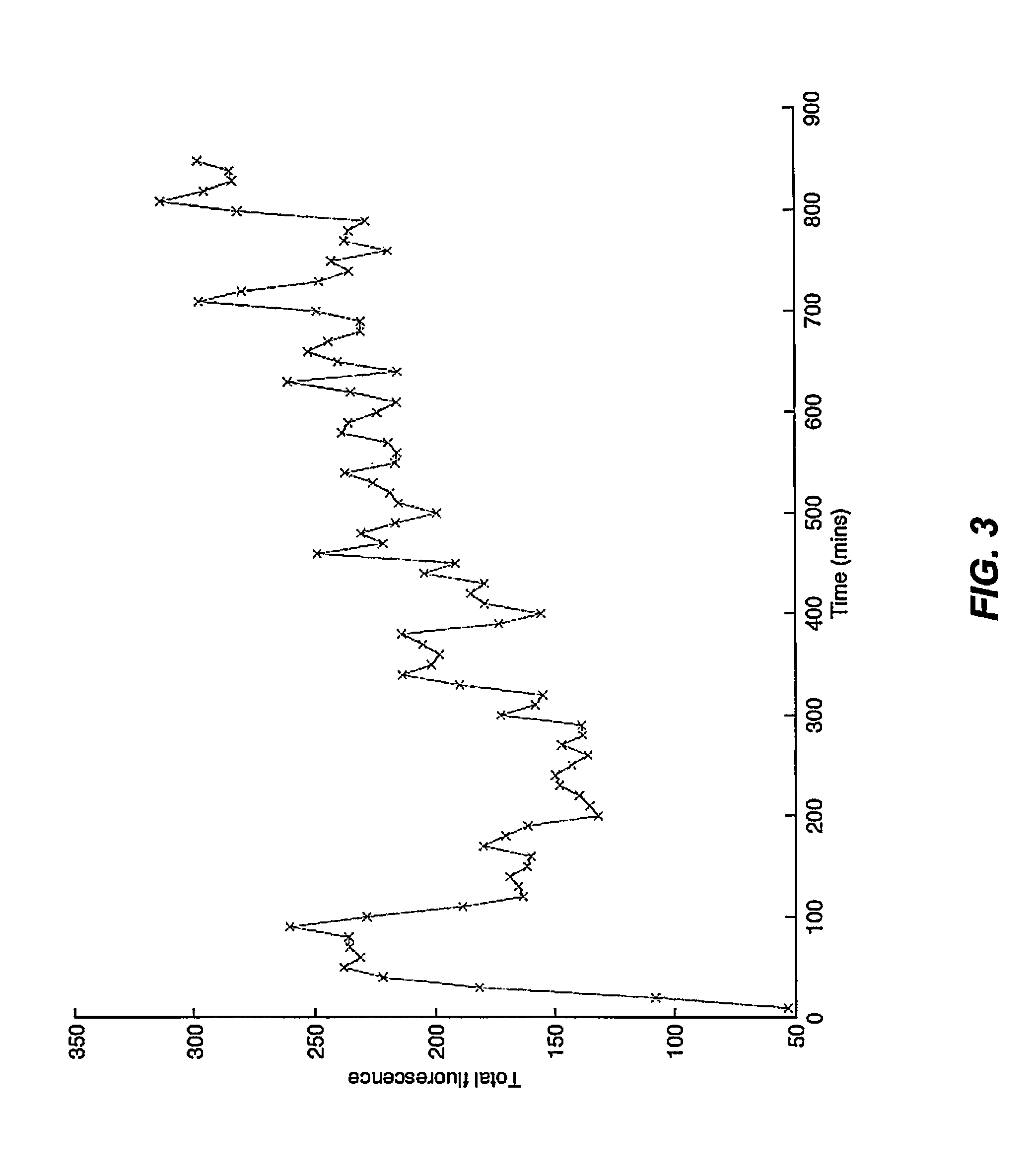
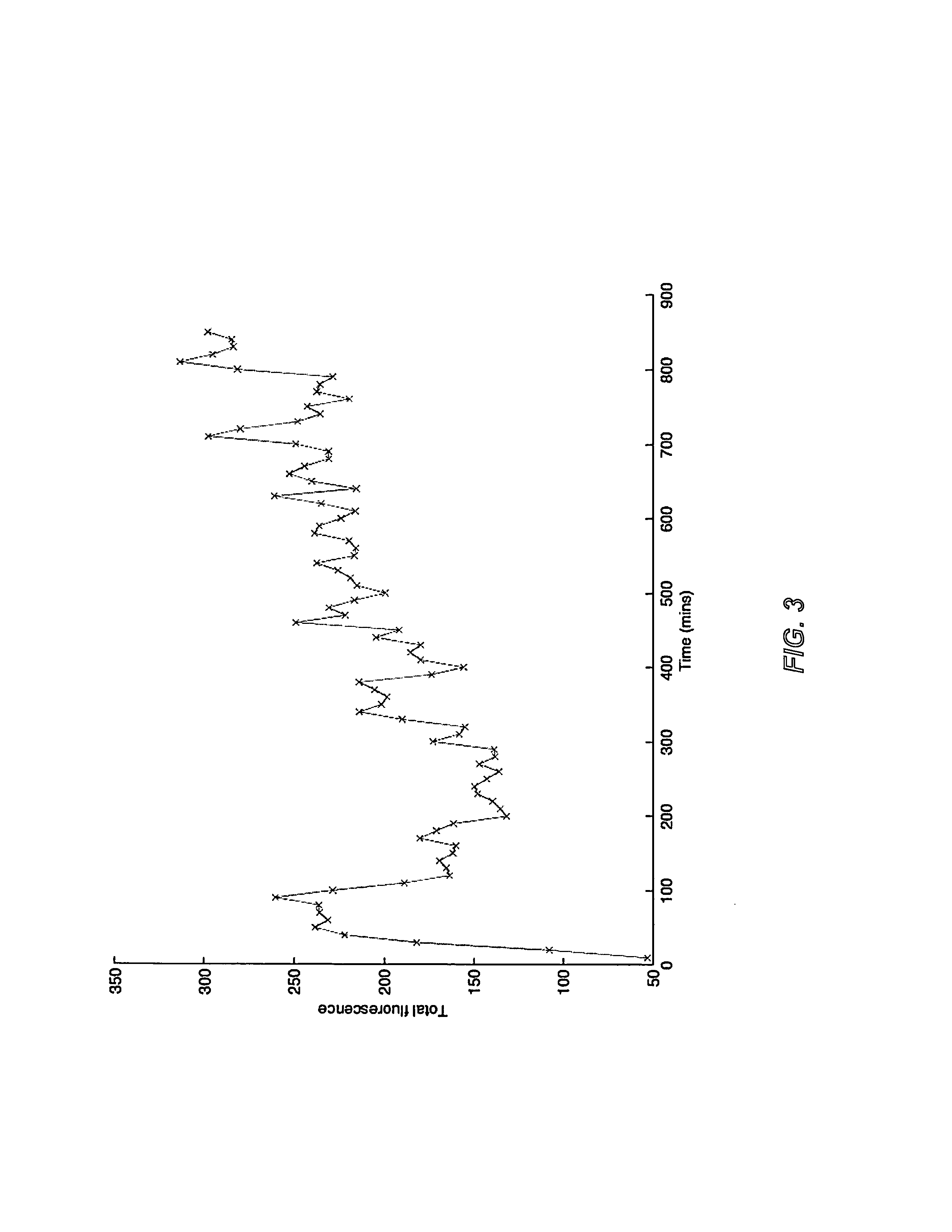
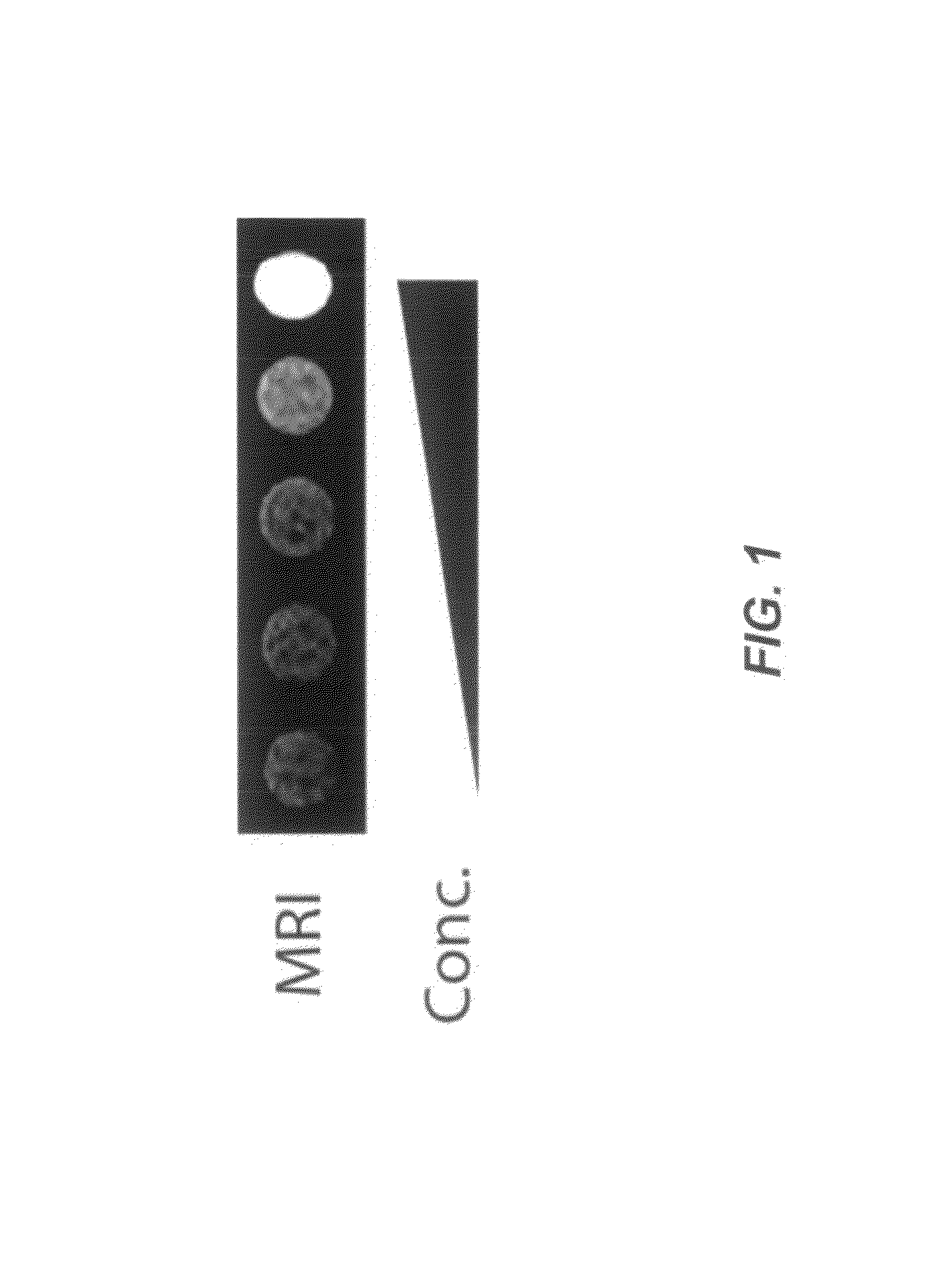
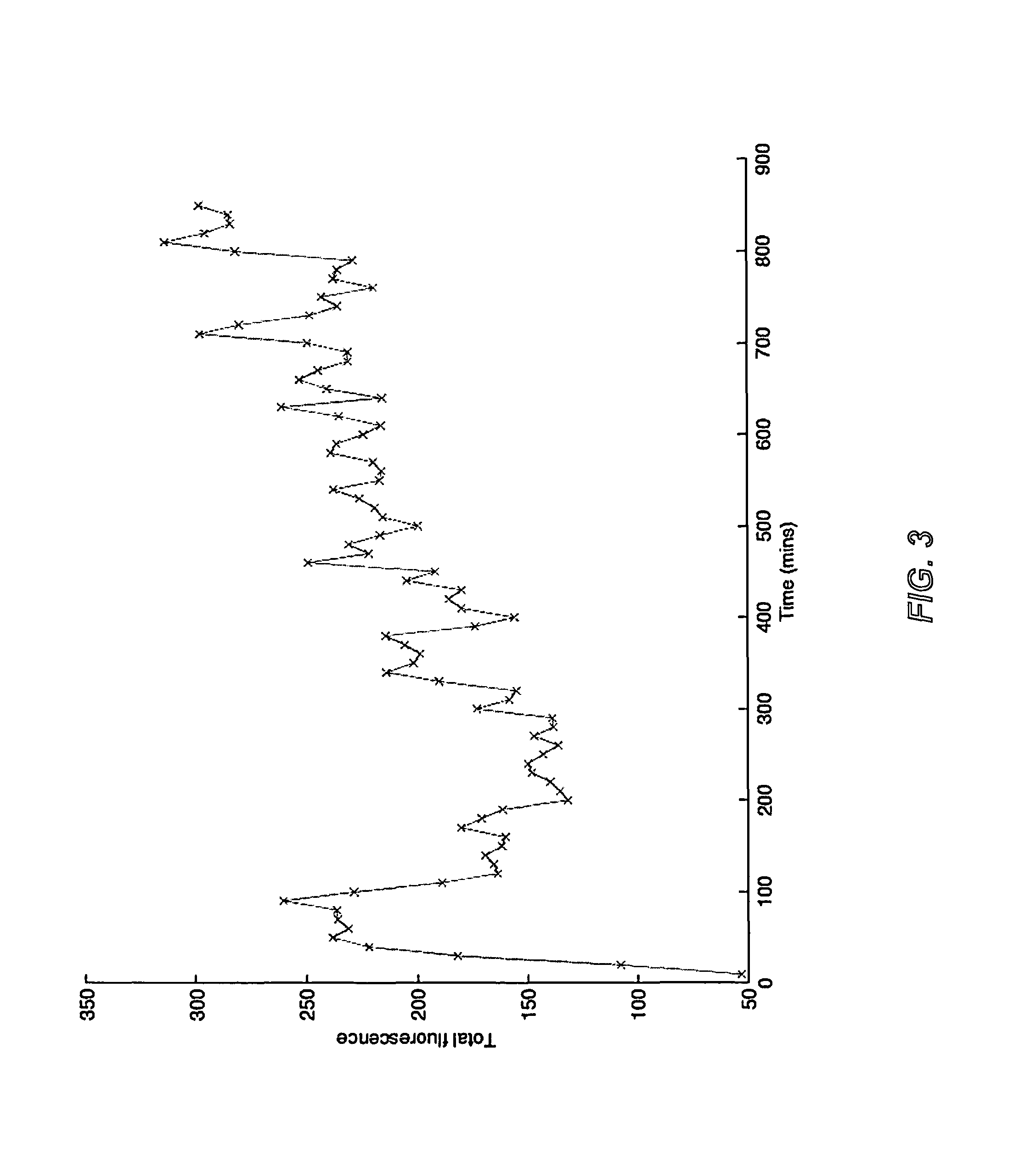
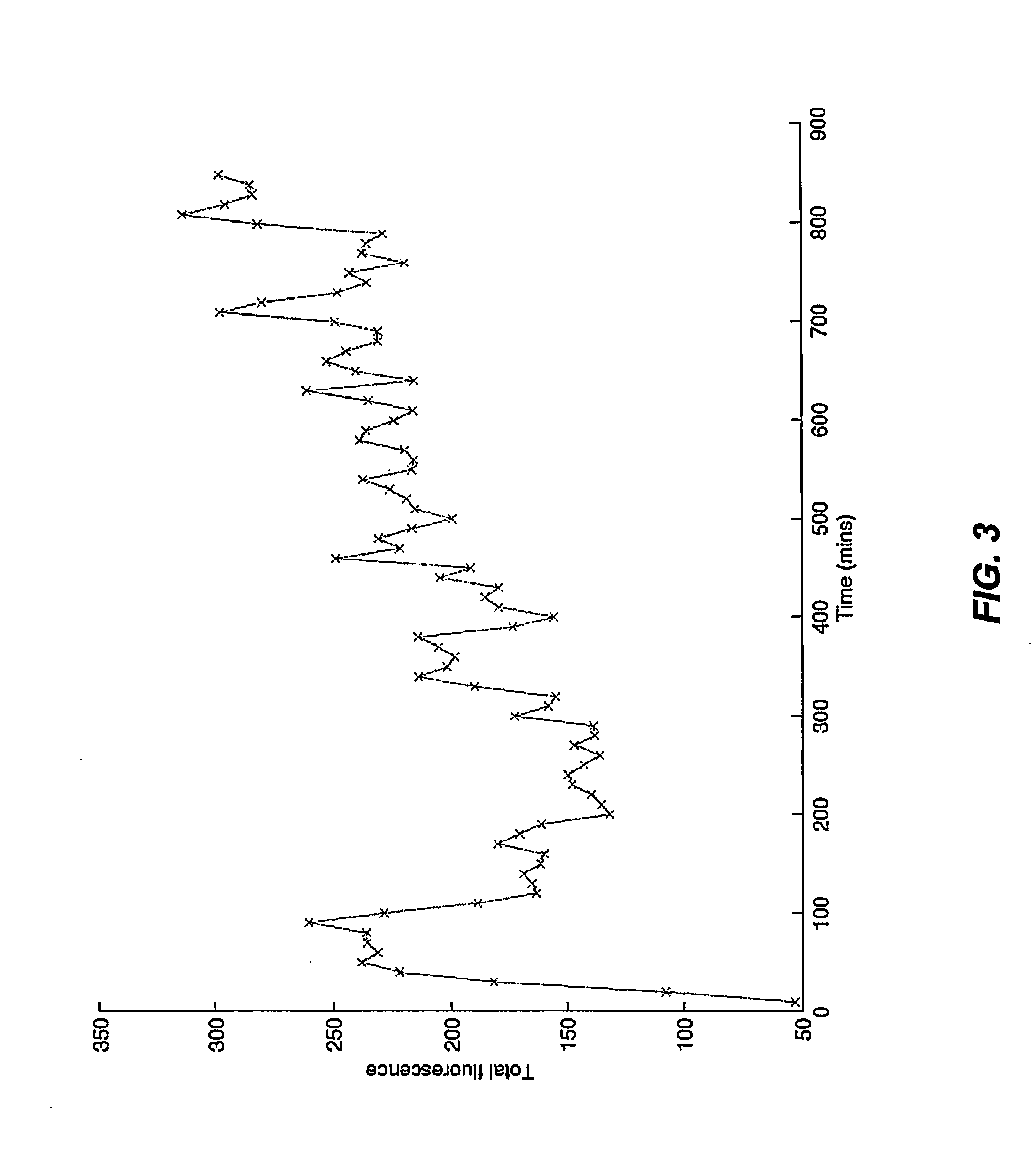
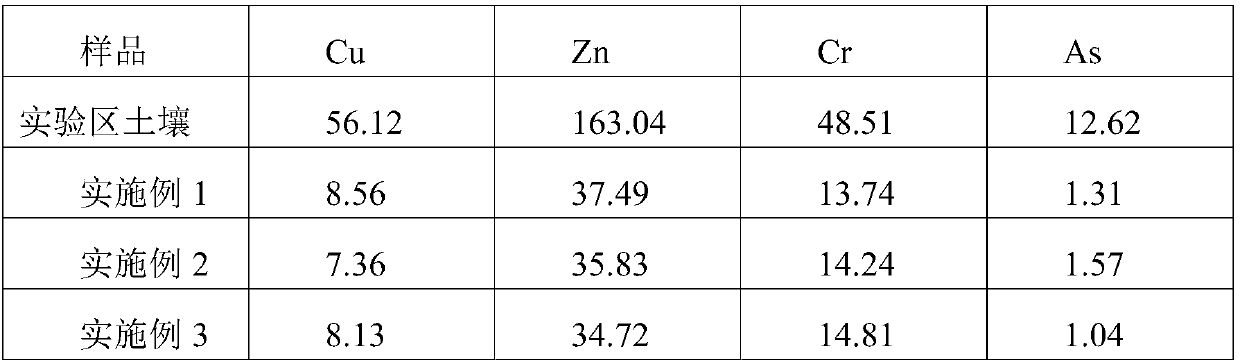
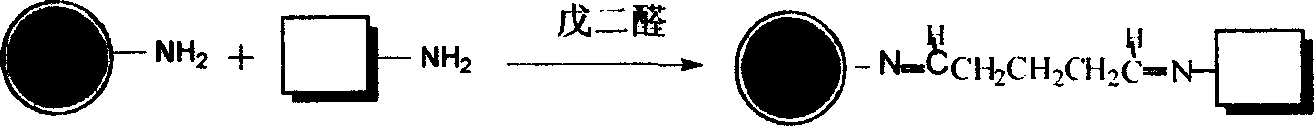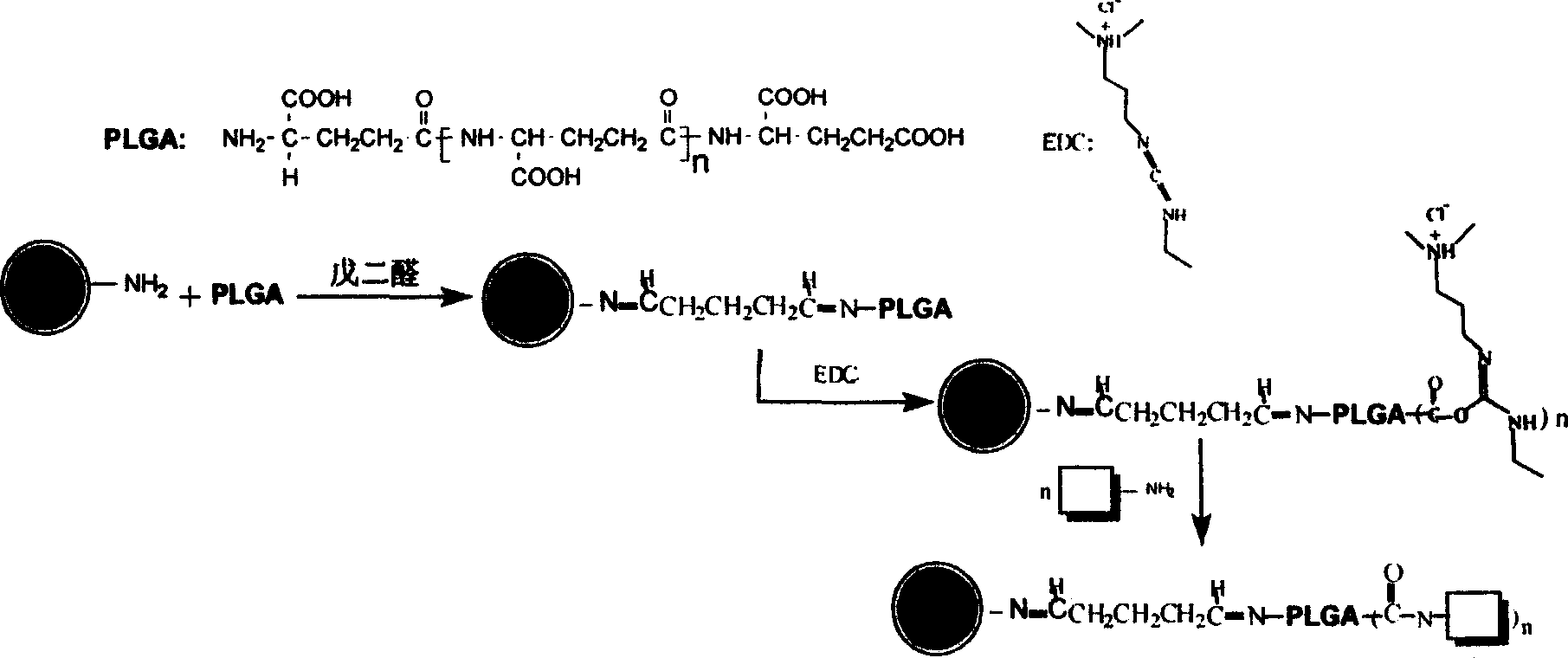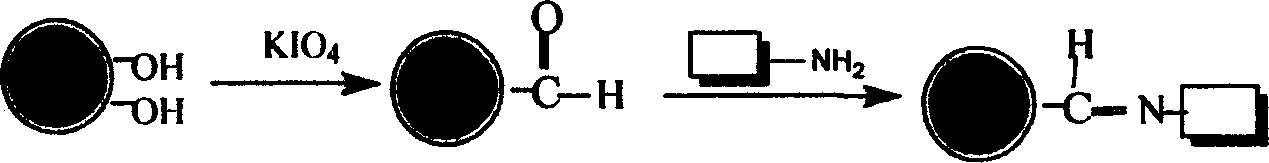Patents
Literature
87 results about "Magnetotactic bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
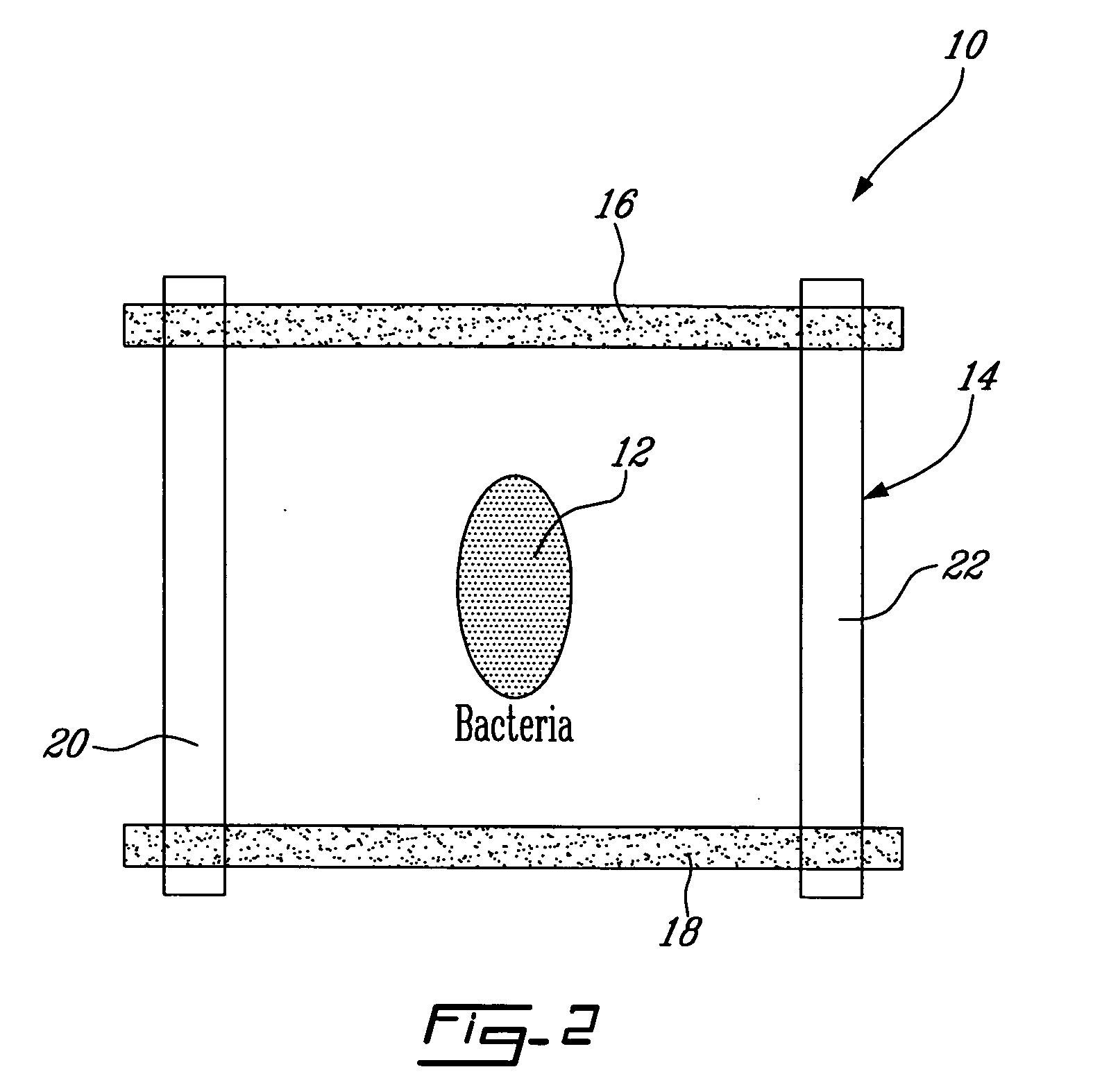
Magnetotactic bacteria (or MTB) are a polyphyletic group of bacteria that orient themselves along the magnetic field lines of Earth's magnetic field. Discovered in 1963 by Salvatore Bellini and rediscovered in 1975 by Richard Blakmore, this alignment is believed to aid these organisms in reaching regions of optimal oxygen concentration. To perform this task, these bacteria have organelles called magnetosomes that contain magnetic crystals. The biological phenomenon of microorganisms tending to move in response to the environment's magnetic characteristics is known as magnetotaxis. (However, this term is misleading in that every other application of the term taxis involves a stimulus-response mechanism.) In contrast to the magnetoreception of animals, the bacteria contain fixed magnets that force the bacteria into alignment—even dead cells are dragged into alignment, just like a compass needle.
Host cells with artificial endosymbionts
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic cells comprising single-celled organisms that are introduced into the eukaryotic cell through human intervention and which transfer to daughter cells of the eukaryotic cell through at least five cell divisions, and methods of introducing such single-celled organisms into eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides methods of using such eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides single-celled organisms that introduce a phenotype to eukaryotic cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
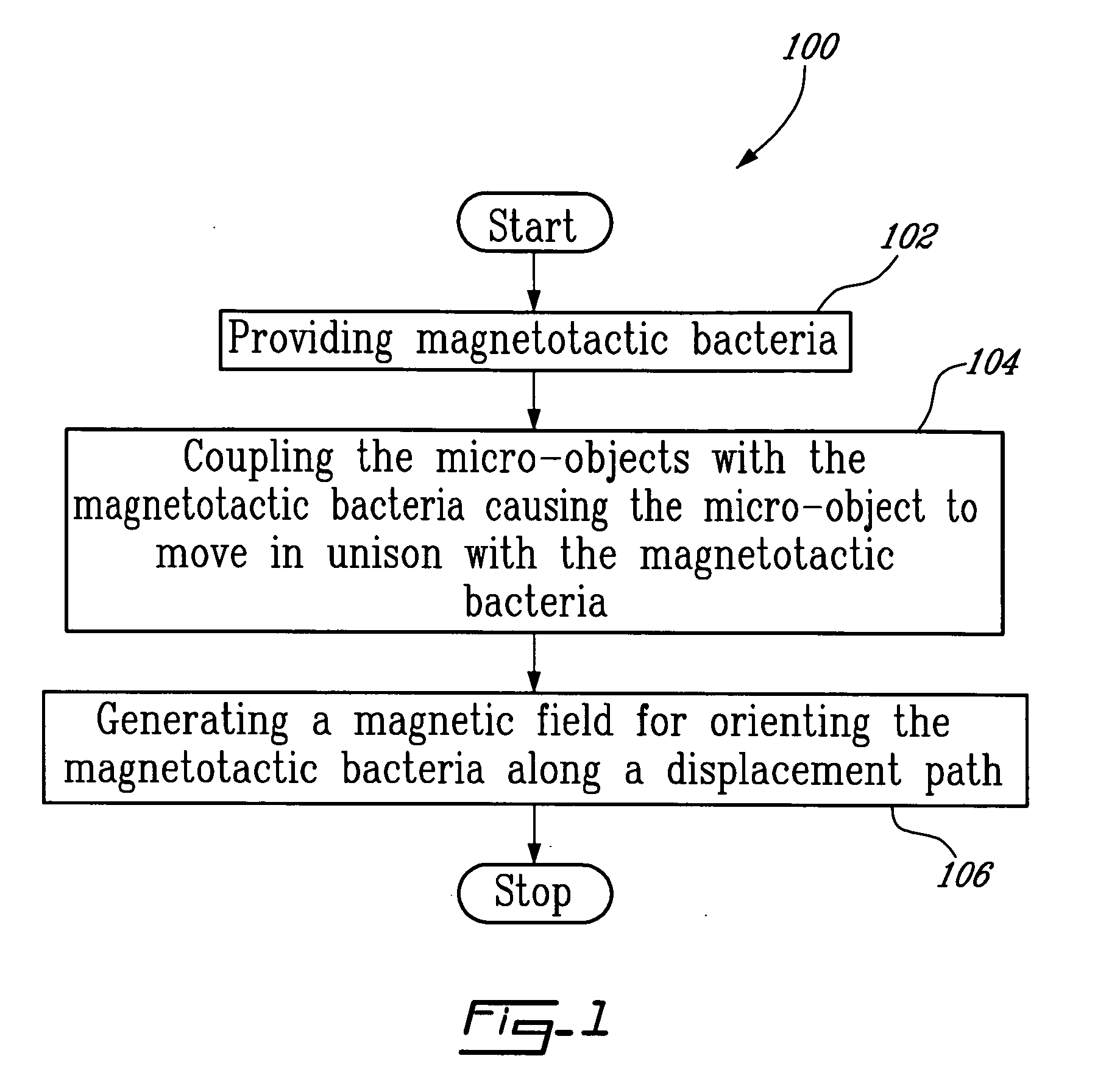
Method and system for controlling micro-objects or micro-particles
InactiveUS20060073540A1Minimize powerBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEngineeringMicroelectromechanical systems
Moving components with dimensions much smaller than what micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) technology can accomplish in terms of force generated and power efficiency, are integrated onto micro-systems. These moving components referred to herein as “bio-components” are special bacteria (magnetotactic bacteria) where the motion of these bio-components can be controlled by generating an “artificial pole” by a magnetic field generated by a constant electrical current that can be varied to change the location of the “artificial pole” from an electrical system such as an embedded electronic micro-circuit. According to the present invention, it is possible through a software program or codes, to control the direction of motion of these magnetotactic bacteria, for example, by downloading such program onto the embedded electronics (controller or the like), and to generate the required magnetic field to control such bacteria to accomplish a particular task. Moreover, though integrated sensory means and new algorithms, the magnetotactic bacteria-based system could adapt or change the direction of motion from new occurring conditions.
Owner:CORP DE LECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE DE MONTREAL
Host cells with artificial endosymbionts
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic host cells comprising artificial endosymbionts and methods of introducing artificial endosymbionts into eukaryotic host cells. The invention provides artificial endosymbionts that introduce a phenotype to host cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic host cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Host cells with artificial endosymbionts
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
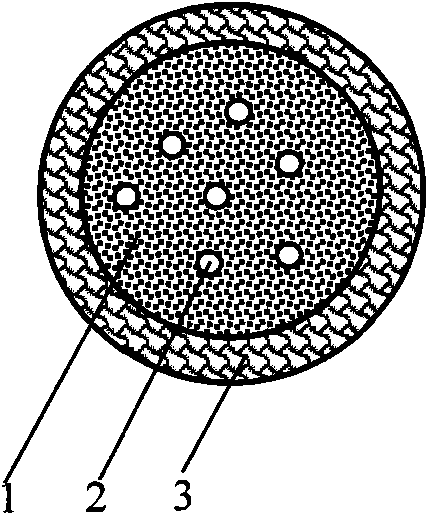
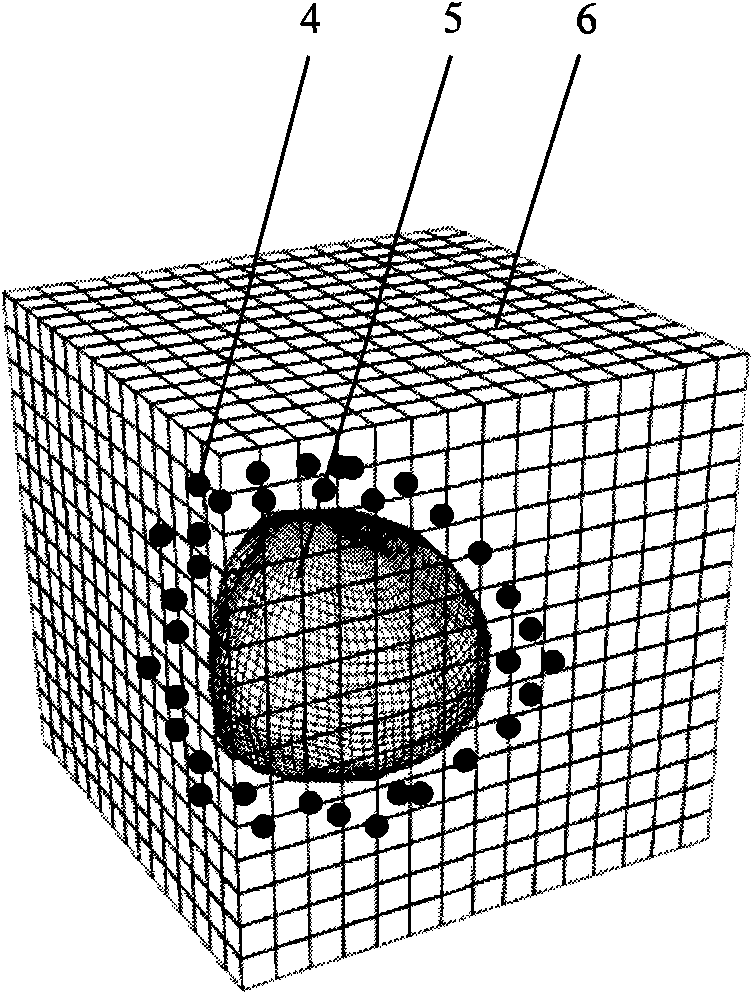
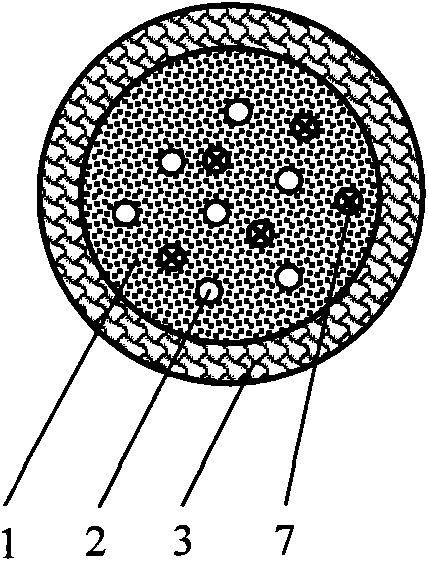
Magnetic phase-change microcapsule for performing thermal protection on normal structure in thermal physical therapy
InactiveCN101836915AGood biocompatibilityLow toxicityUltrasound therapySurgical instrument detailsMean diameterMagnetic phase
The invention discloses a magnetic phase-change microcapsule for performing thermal protection on a normal structure in thermal physical therapy. The magnetic phase-change microcapsule is a spherical microcapsule which is composed of a phase-change material (1), magnetic particles (2) and a liposome shell (3), and the mean diameter thereof is 1nm-1mm. In the invention, the phase-change material (1) is solid-liquid or / and liquid-solid phase-change material with high phase change heat and the phase change temperature at -10-0 DEG C or 38-100 DEG C according to different thermal physical therapeutic processes such as thermal therapy, cold therapy, cryosurgery or cold-heat alternating therapy and the like; the magnetic particles (2) are magnetic micro / nano-particles or magnetotactic bacteria; and a liposome is taken as a capsule carrier for lowering toxicity of the material and protecting an encapsulated material. The invention provides a safe and effective thermal protection material with novel concept. In the invention, the magnetic phase-change microcapsule can be gathered into a target organ with blood circulation under the action of an applied magnetic field; phase-change latent heat and low thermal conductivity of the phase-change material are adopted to carry out thermal protection on the normal structure; and the material is widely applied to thermal physical therapy, and the application method thereof is simple, feasible and reliable.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Host Cells with Artificial Endosymbionts
InactiveUS20130253303A1ElectrotherapyMaterial analysis by optical meansCell divisionMagnetotactic bacteria
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic cells comprising single-celled organisms that are introduced into the eukaryotic cell through human intervention and which transfer to daughter cells of the eukaryotic cell through at least five cell divisions, and methods of introducing such single-celled organisms into eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides methods of using such eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides single-celled organisms that introduce a phenotype to eukaryotic cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Biomagnetism nano target anti-cancer drug and its preparation
ActiveCN1927400AGood biocompatibilitySmall side effectsInorganic material magnetismRadioactive preparation carriersChemical reactionSide effect
The invention relates to a biological nanometer magnetic target anti-cancer drug, which is formed by coupled biological nanometer magnetic smalls and anti-cancer chemical drug. Wherein, the biological nanometer magnetic small is nanometer magnetic particle formed in magnetic bacterial cell, at 35-120nm diameter, while its main component is Fe3O4 or Fe3S4; single magnetic particle is packed by film; and the coupled anti-cancer chemical drug comprises chemotherapy drug, nucleic acid drug, radioactive nuclide or antibody drug. The invention also provides relative production that using physical adsorption couple or based on the active function group contained by smalls and anti-cancer drug, to select right coupler via chemical reaction to couple them. And the smalls has better bioavailability, less side effect, therefore, the anti-cancer drug can be accurately transmitted to ill part via external magnetic field, to reduce the contact between drug and normal organism., to realize target positioning treatment.
Owner:南京英睿杰生化科技有限公司
Host Cells with Artificial Endosymbionts
InactiveUS20140273203A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCell divisionMagnetotactic bacteria
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic cells comprising single-celled organisms that are introduced into the eukaryotic cell through human intervention and which transfer to daughter cells of the eukaryotic cell through at least five cell divisions, and methods of introducing such single-celled organisms into eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides methods of using such eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides single-celled organisms that introduce a phenotype to eukaryotic cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
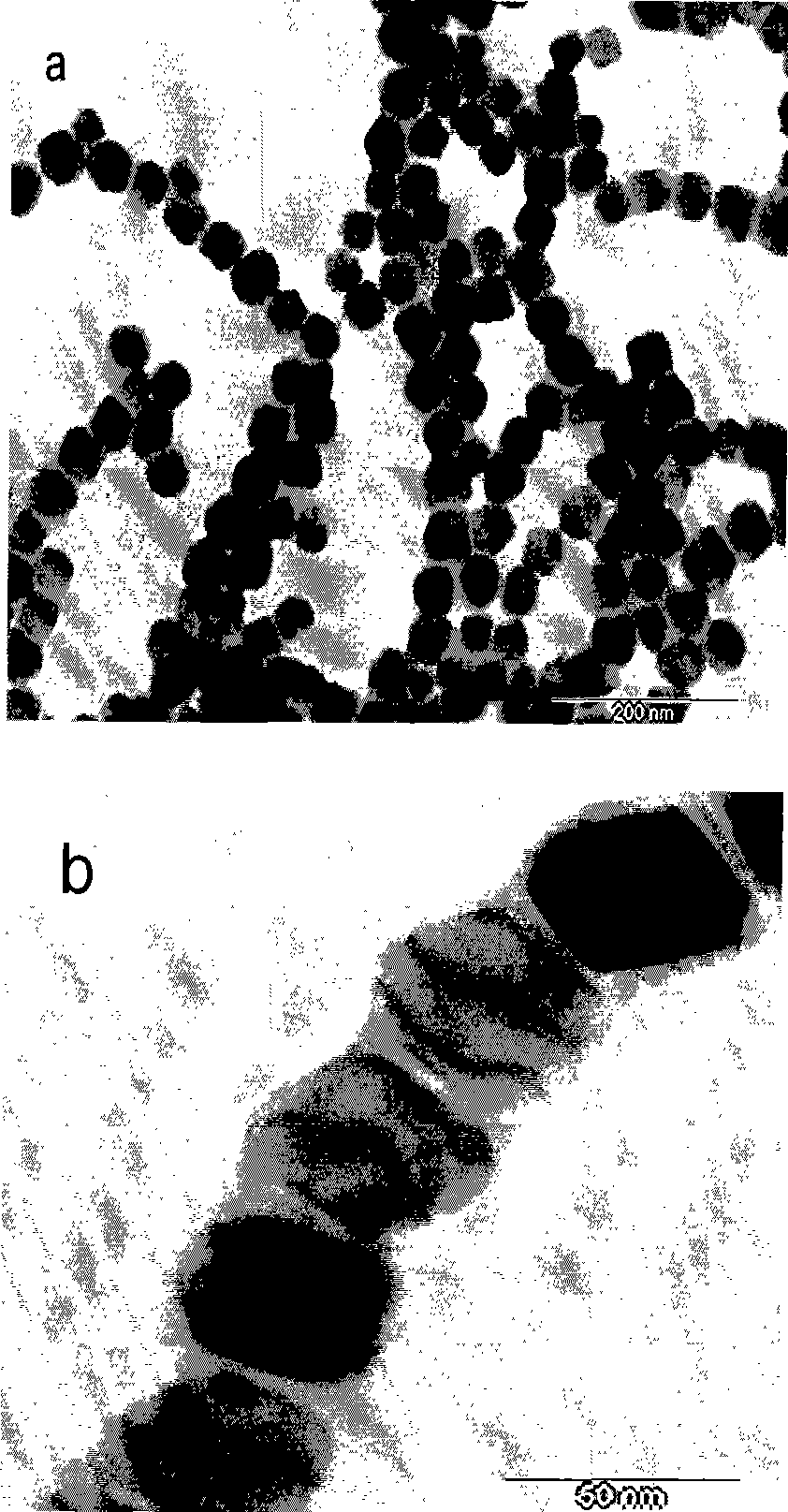
Method for producing magnetosome by cultivating magnetotactic bacteria
InactiveCN101434921AGuaranteed normal growthEasy to operateBacteriaMagnetotactic bacteriaMagnetosome
The invention provides a method for producing magnetosome by cultivating magnetic bacteria, which takes air as an oxygen supplying way and maintains the continuous growth of the magnetic bacteria with a material feeding way, and when dissolved oxygen reaches or gets lower than the dissolved oxygen suitable for magnetosome production, the dissolved oxygen is controlled at a proper dissolved oxygen range that is suitable for magnetosome production through agitating rotation speed, air flow speed and the dissolved oxygen in cascade. The magnetic bacteria cultivating method does not need air distribution and pure inert gases, but uses air aeration for oxygen supply, thus lowering initial dissolved oxygen from the saturation state of 100 percent to 0 percent, and the coordinated adjustment of agitating rotation speed and air flow speed can control the dissolved oxygen to be any value between the saturation states of 0 percent and 20 percent, thus lowering the production cost of magnetosome and providing technical guarantee for researching the physiological and biochemical characteristics of the magnetic bacteria under different dissolved oxygen levels.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Facultative anaerobic magnetotactic bacterium, and separation and culturing method therefor, and process for extracting and purifying magnetosome thereof
The invention is about a kind of magnetotactic bacterium which is separated from the mud sample in the iron-affluent watershed. The bacterium is preserved in the Chinese typical culture collection center. The preserving code is CCTCC NO:M205105 while the classified name is Magnetotactic bacterium MB-TZ. The bacterium is facultative anoxybiontic bacterium and the state of the thallus is circular staff. A thallus can produce 3-20 circular magnetic globules which are mainly comprised by iron, calcium, fosforus, oxygen and magnesium. The bacterium has many advantages such as short producing cycle, easy to cultivate and easy to be produced in factories. During the extracting and purifying of the magnetic globules, the invention adopts the treating method of repeating freeze thawing combining with supersonics, so it can dissolve the thallus more thoroughly and increase the yield of magnetic globules.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
Chemostatic high density culture method of magnetotactic bacteria high yield magnetosome
InactiveCN101376900AShorten the fermentation cycleEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDry weightVolumetric Mass Density
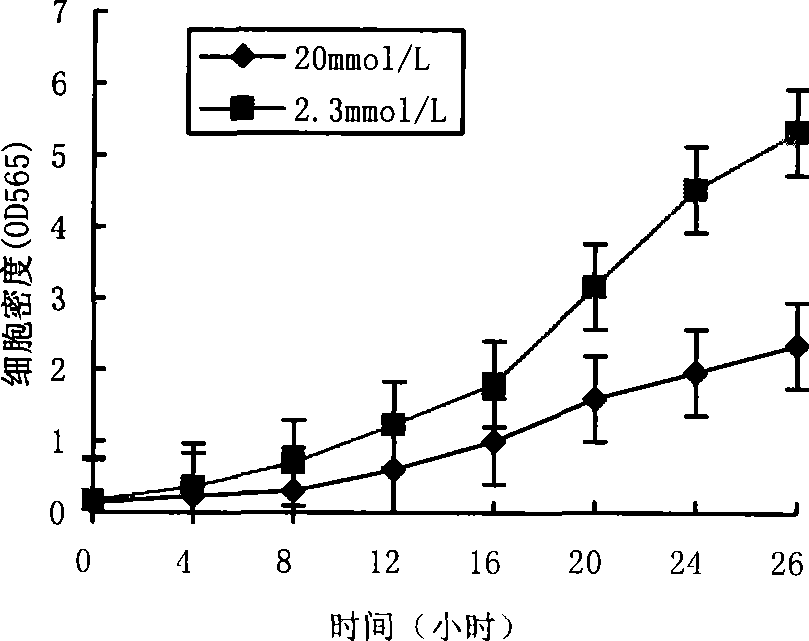
The invention provides a method for culturing magnetotactic bacterium high-yield magnetic particles chemostatically with high density; magnetotactic bacterium is cultured through a submerged fermentation culture method; the fermentation culture medium contains a carbon source, a nitrogen source and an iron source; dissolved oxygen is controlled in the fermentation process by stages, and materials are supplemented by regulating the pH value. The method realizes the chemostatical high-density culture of the magnetotactic bacterium and the mass production of the magnetic particles; the density of the cells cultured for 36h to 48h is 12OD565nm, the dry weight of the magnetic particles is 80mg / L to 100mg / L, and the fermentation cycle is shortened. The method lays solid foundation for the industrialized production of bacterium magnetic particles.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for the recombinant production of magnetic nanoparticles
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the size-adjusted recombinant production of magnetic nanoparticles. More particular, the invention relates to a method, comprising: providing one or more cells being capable of producing magnetic nanoparticles; modifying in the one or more cells the expression of one or more genes involved in the formation of the magnetic nanoparticles; cultivating the modified cells obtained in step (b); and isolating the magnetic nanoparticles from the cultivated cells, wherein the magnetic nanoparticles have a defined size. In preferred embodiments, the method comprises modifying the expression of one or more genes of the mamGFDC operon in magnetotactic bacterial cells. The invention is further directed to host cells bearing said modifications, the recombinant magnetic particles isolated from such cells as well as to the use of such particles for the detection and / or separation of biomolecules or as a contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:LUDWIG MAXIMILIANS UNIV MUNCHEN +1
Adsorption and magnetic separation coupling method for recycling precious metal ion in precious metal
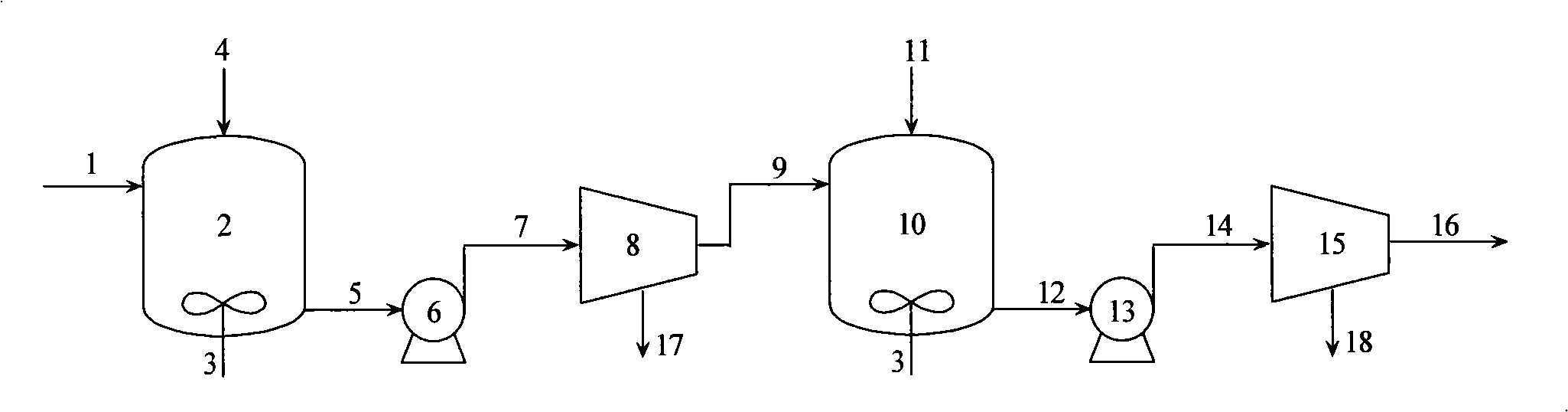
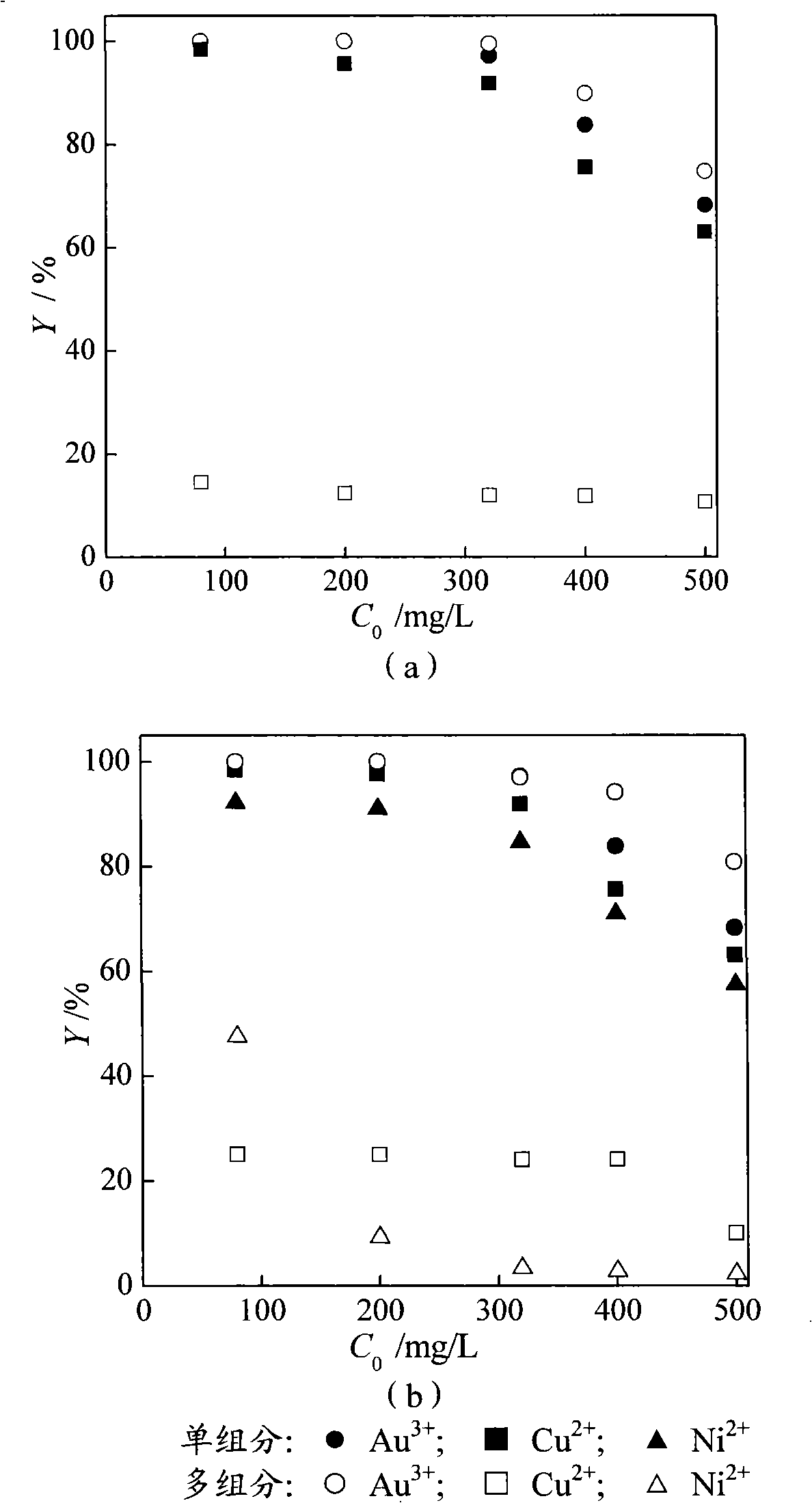
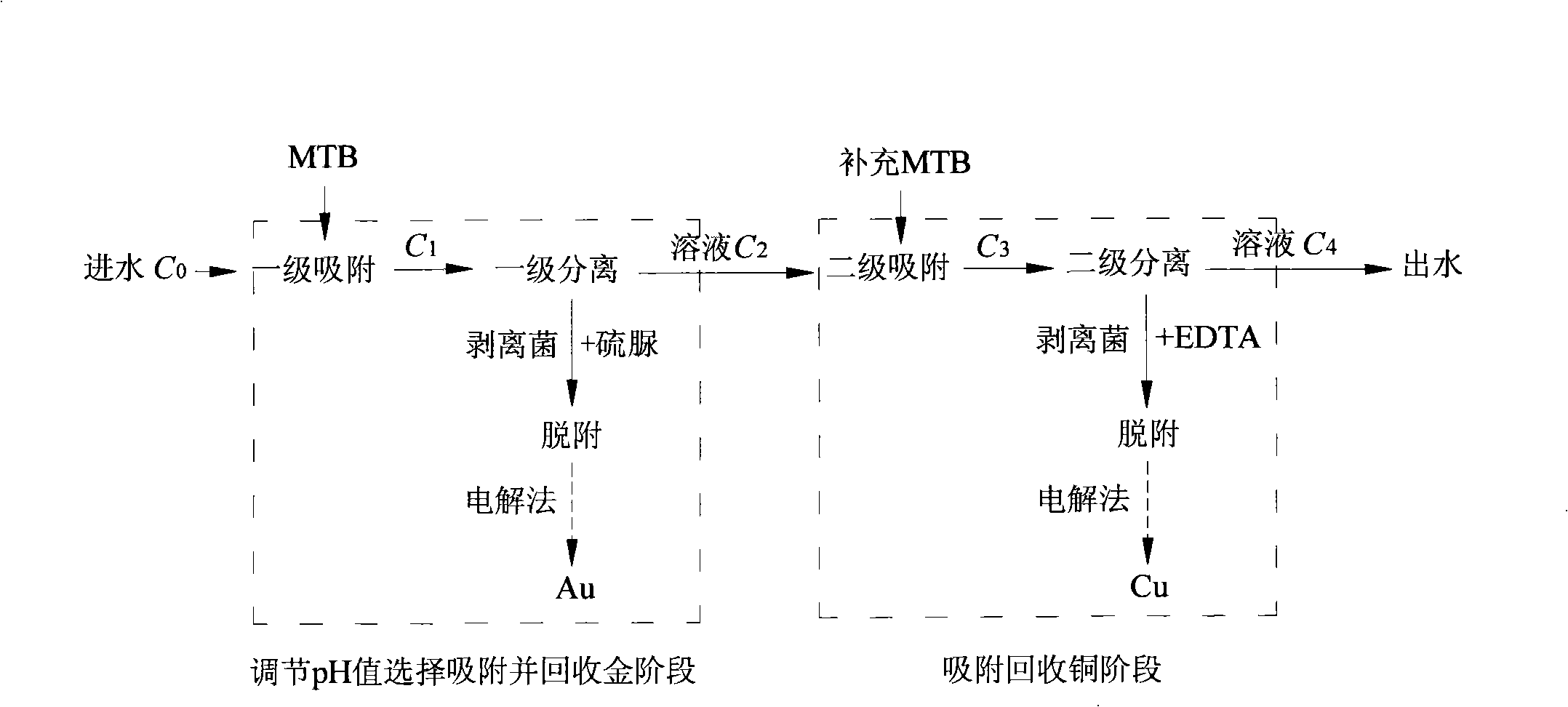
InactiveCN101343102AEfficient use ofEfficient recyclingWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsBiological water/sewage treatmentDesorptionCoupling
The invention discloses an adsorption and magnetic separation coupling method for recovering noble metal ions in wastewater, comprising the steps of: firstly, selecting and adsorbing noble metal ions in a solution by magnetotactic bacteria in an adsorber; secondly, separating out the magnetotactic bacteria after adsorbing the metal ions from the mixture obtained in the first step by utilizing a magnetic separator; and thirdly, implementing the metal ion desorption treatment to the magnetotactic bacteria separated off from the second step and adsorbed with noble metal ions, and if an electrolytic method is adopted to carry out the further purification and recovery, the noble metal in wastewater can be finally acquired. The method utilizes the selective adsorption characteristic of magnetotactic bacteria and combines the high gradient magnetic separation technique to recover noble metal ions efficiently from liquid and purify the wastewater. The noble metal ions in the wastewater solution can be utilized and recovered effectively on the premise of ensuring high efficiency and environmental protection through implementing the technical proposal of the method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
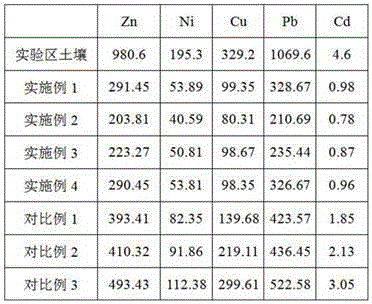
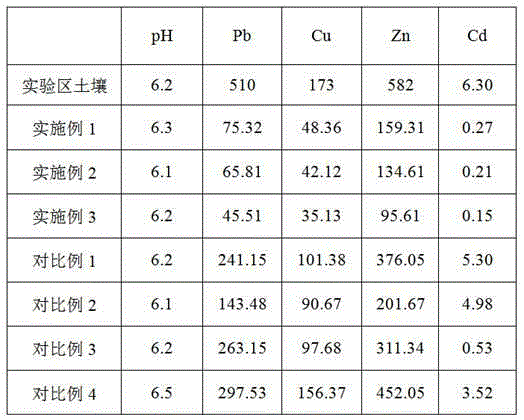
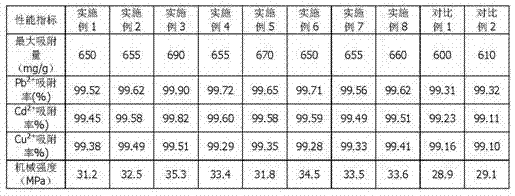
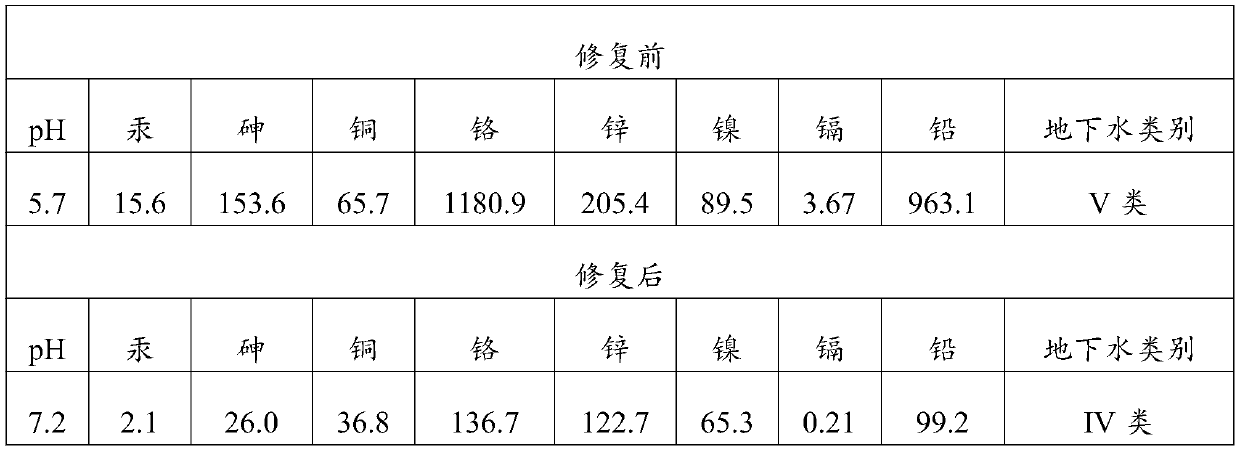
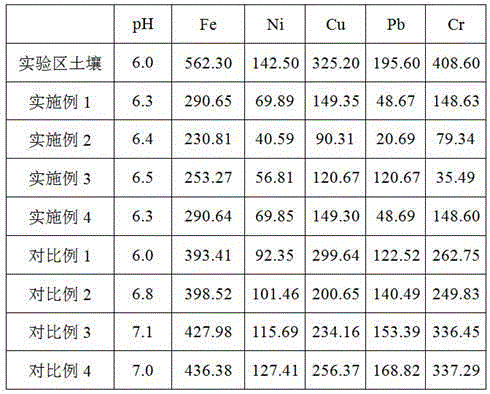
Microbe and solidifying agent combined in-situ remediation method of heavy metal contaminated soil
ActiveCN105149342AImprove adsorption capacityLow oxygenContaminated soil reclamationIn situ remediationPollution soil
The invention provides a microbe and solidifying agent combined in-situ remediation method of heavy metal contaminated soil. The microbe and solidifying agent combined in-situ remediation method comprises the following steps: mixing magnetotactic bacteria and heavy metal contaminated soil; irrigating heavy metal contaminated soil mixed with magnetotactic bacteria; arranging a magnetic field on heavy metal contaminated soil; collecting heavy metal contaminated soil containing magnetotactic bacteria; leaching the collected heavy metal contaminated soil and back-filling; adding a solidifying agent into heavy metal contaminated soil subjected to magnetotactic bacteria adsorption treatment, and curing for 30-45 days; and circularly repeating the steps till the content of heavy metals in soil reaches the safe standard, wherein the solidifying agent consists of SiO2, Fe2O3, Al2O3 and C3N3S3Na3. The microbe and solidifying agent combined in-situ remediation method belongs to in-situ remediation, is simple to operate, low in cost and good in remediation effect, avoids secondary contamination of soil, and is suitable for remediation of large-area contaminated soil.
Owner:江苏环保产业技术研究院股份公司
Method for microorganism-chemical method combined remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil
InactiveCN107617637AFast adsorptionReduce accumulationContaminated soil reclamationSolubilitySoil treatment
The invention provides a method for microorganism-chemical method combined remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. The method comprises the following steps: magnetotactic bacteria is inoculatedinto heavy metal contaminated surface soil for culture for 55-60 days; the soil, treated in the previous step, is covered by using a plastic film, and a magnetic field is kept for 35-40 days; shallow-layer soil, treated in the previous step, is collected and leached by using water, and an original place is filled with the soil after leaching; the steps are circularly repeated until the contents ofheavy metals besides As reach the national environmental requirement standards; and dissoluble iron salt is added in the soil remediated in the previous step, then, calcium salt is added, wherein thedissoluble iron salt comprises at least one of ferrous sulfate, iron chloride and ferrous chloride, and the adding quantity is 0.5-15 wt% of the weight of the soil. Compared with a traditional arsenic-contained heavy metal contaminated soil treatment method, the method is low in investment and technical requirement, prevents activation of other heavy metal in arsenic stabilization, and is excellent in soil remediation effect and high in practicability.
Owner:湖南新九方科技有限公司 +1
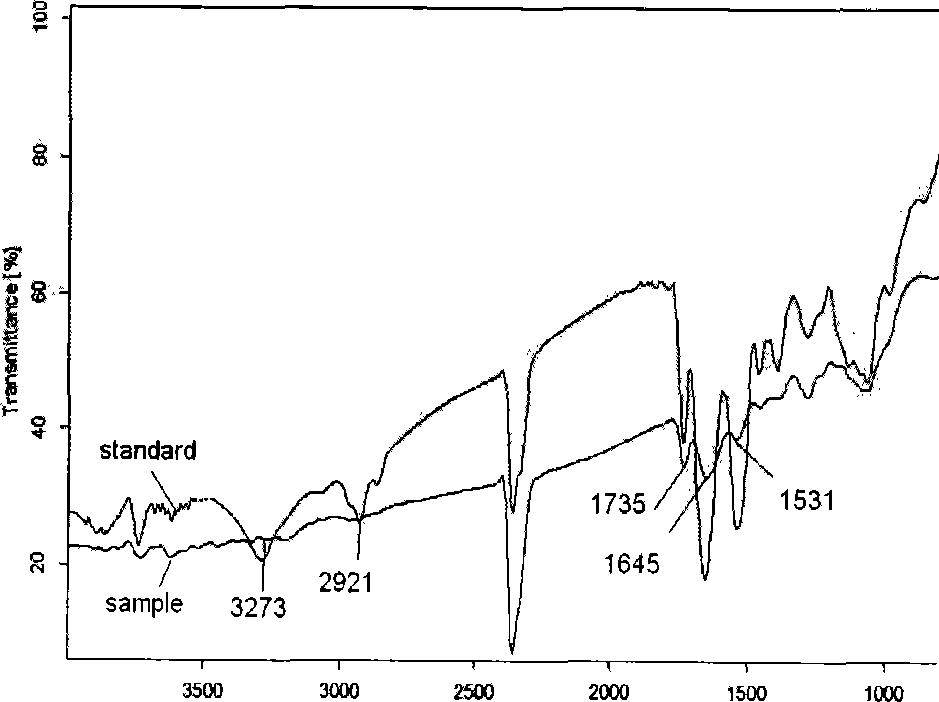
Medicine slow-release nanoparticle wrapping magnetosomes of magnetotactic bacteria and preparation method of medicine slow-release nanoparticle
InactiveCN105193733AOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMedicineMicrosphere
The invention relates to a medicine slow-release nanoparticle wrapping magnetosomes of magnetotactic bacteria and a preparation method of the medicine slow-release nanoparticle. The medicine slow-release nanoparticle comprises the magnetosomes of magnetotactic bacteria, chitosan, pharmaceutic adjuvant and medicine components. The preparation method includes the steps of collecting the magnetosomes of magnetotactic bacteria, mixing the materials, conducting spray drying to obtain the nanoparticle, wherein the grain size of the nanoparticle ranges from 100 nanometers to 50 micrometers. According to different treatment aims, the nanoparticle can serve as an oral slow-release formulation, can be used as a slow-release formulation for preparing targeted medicine as well, and can be widely applied to the field of biological medicine.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Remediation method for heavy metal polluted soil
InactiveCN109332376AReduce the risk of contaminated agricultural productsIncrease selenium contentContaminated soil reclamationHyperaccumulatorMagnetotactic bacteria
The invention discloses a remediation method for heavy metal polluted soil. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding a magnetotactic bacteria liquid culture medium to the heavy metal polluted soil; inoculating magnetotactic bacteria; and turning over; (2) adding the magnetotactic bacteria liquid culture medium to the heavy metal polluted soil; and arranging a magnetic field; (3) collecting the surface layer of the heavy metal polluted soil; (4) showering the collected heavy metal polluted soil; (5) spreading a soil conditioning agent on the surface of the heavy metal polluted soil;(6) planting heavy metal hyperaccumulators in the heavy metal polluted soil; (7) spraying a heavy metal blocking agent after the hyperaccumulator seeds are formed; and (8) cycling the steps (1) to (7) twice or three times. The method has the advantages of being low in planting difficulty, easy to manage, applicable to remediating of wide-range polluted soil, small in environmental disturbance, and good in soil treatment effect; and moreover, the environment is beautified while the polluted soil is treated; and the popularization is high.
Owner:云南惟绿环保科技有限公司
Microorganism restoration method for soil polluted by heavy metal
ActiveCN105127195AHas negative aerobic propertiesImprove adsorption capacityContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismRestoration method
The invention provides a microorganism restoration method for soil polluted by heavy metal. The microorganism restoration method comprises the following steps of 1, separation of magnetotactic bacteria; 2, cultivation of the magnetotactic bacteria; 3, restoration of the soil polluted by the heavy metal through the magnetotactic bacteria; 4, recovery of the magnetotactic bacteria; and 5, separation of the magnetotactic bacteria and the heavy metal. The microorganism restoration method for the soil polluted by the heavy metal can effectively reduce the content of the heavy metal in the soil, thereby reducing the accumulation amount of the heavy metal in plants. The microorganism restoration method for the soil polluted by the heavy metal belongs to in-situ restoration, and is easy to operate, low in cost and good in restoration effect; in addition, the microorganism restoration method does not damage soil fertility and secondary pollution to the soil is avoided.
Owner:山东省神农生态科技股份有限公司
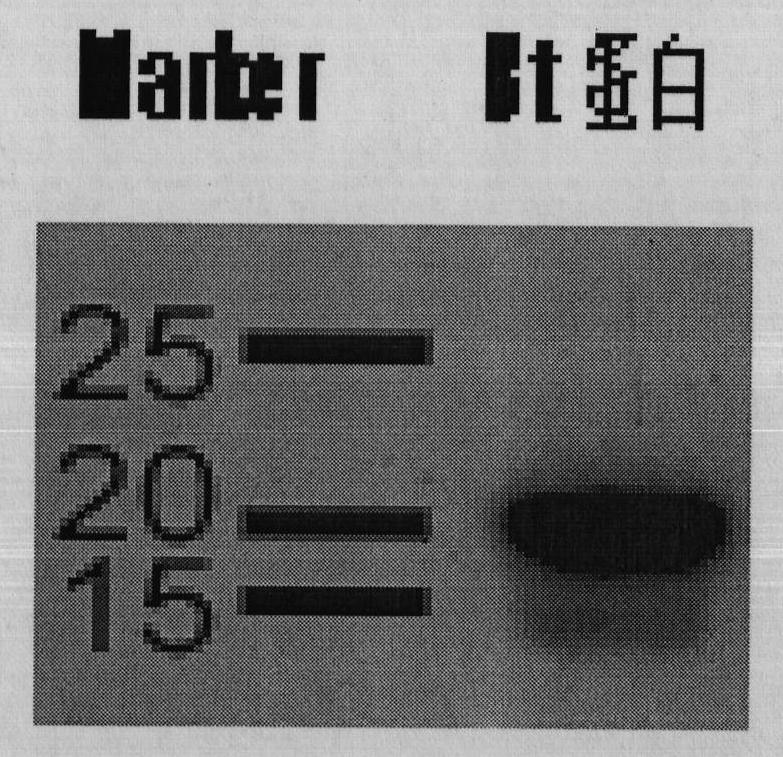
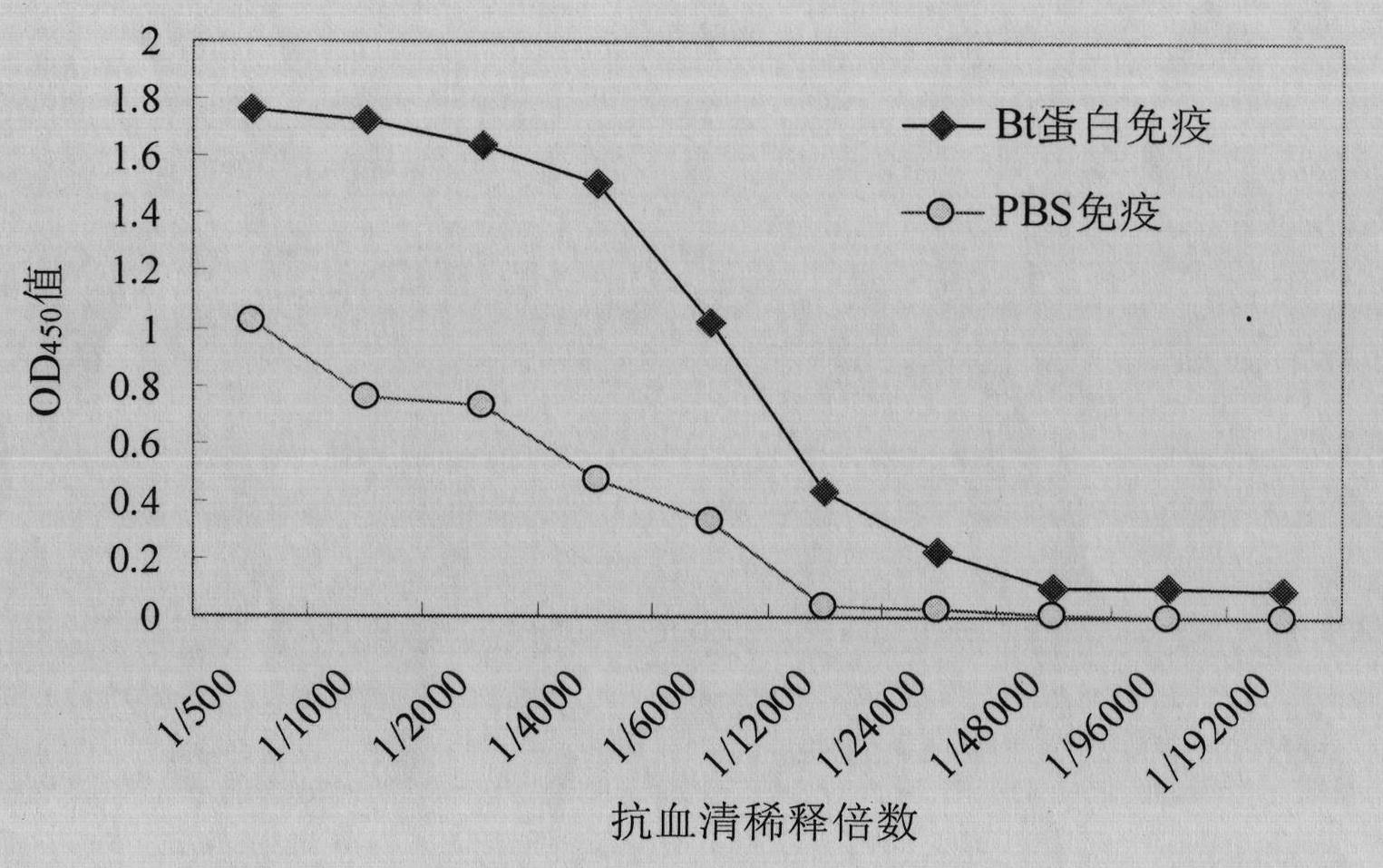
Immune magnetosome for detecting Bt insecticidal protein in mice tissue and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102419370ASmall and uniform particle sizeGood conditionBiological testingLuminous intensityAdjuvant
The invention relates to an immune magnetosome for detecting Bt insecticidal protein in mice tissue and a preparation method thereof. The immune magnetosome is coated by anti-Bt insecticidal protein polyclonal antibody with the particle size being 50nm. The preparation method of the immune magnetosome comprises the following steps of: performing ultrasonic disruption and magnetic adsorption to obtain purified magnetosome of magnetotactic bacteria, mixing adjuvant and Bt insecticidal protein, immunizing mice, performing separation and purification to obtain mouse anti Bt insecticidal protein polyclonal antibody and coupling the antibody and the magnetosome by a carboxy-amino chemical coupling method to obtain the immune magnetosome for detecting Bt insecticidal protein in mice tissue. By chemiluminescence EIA detection, the immune magnetosome provided by the invention has a luminous unit of 83kcounts / microgram magnetosome. The correlation of luminous intensity and Bt protein concentration shows that as the protein concentration goes up, the luminous intensity goes down with a range being 1-103ng / ml and with a minimum detectable concentration being 1ng / ml. The method for the practical detection of Bt insecticidal protein content in mice tissue has advantages of high sensitivity, stable result and simple operation, and shows a good application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Repairing method of heavy metal contaminated soil
InactiveCN109396166AImprove repair effectShort repair cycleContaminated soil reclamationPhosphoric acidSoil surface
The invention discloses a repairing method of heavy metal contaminated soil. The repairing method includes the steps of (1), breaking heavy metal contaminated soil to obtain fine soil; (2), spreadingmixed repairing additives to the fine soil, spraying phosphoric acid solution to the fine soil to keep soil moisture at 45%, covering the fine soil with thin film, and repairing for 25 days; (3), adding excrement to repaired soil, adding in earthworms, inoculating magnetotactic bacteria to the fine soil, and culturing for 30 days; (4), keeping the soil submerged, placing magnets on the surface ofsoil, removing earthworms crawling out the soil, and cleaning the surface soil after 12 days; (5), planting grass in the soil. The repairing method can effectively solve the problems that fixing efficiency is low, heavy metal is easy to release again, repairing cycle is long, and repairing cost is high of the conventional repairing method.
Owner:CHENGDU TECHCAL UNIV
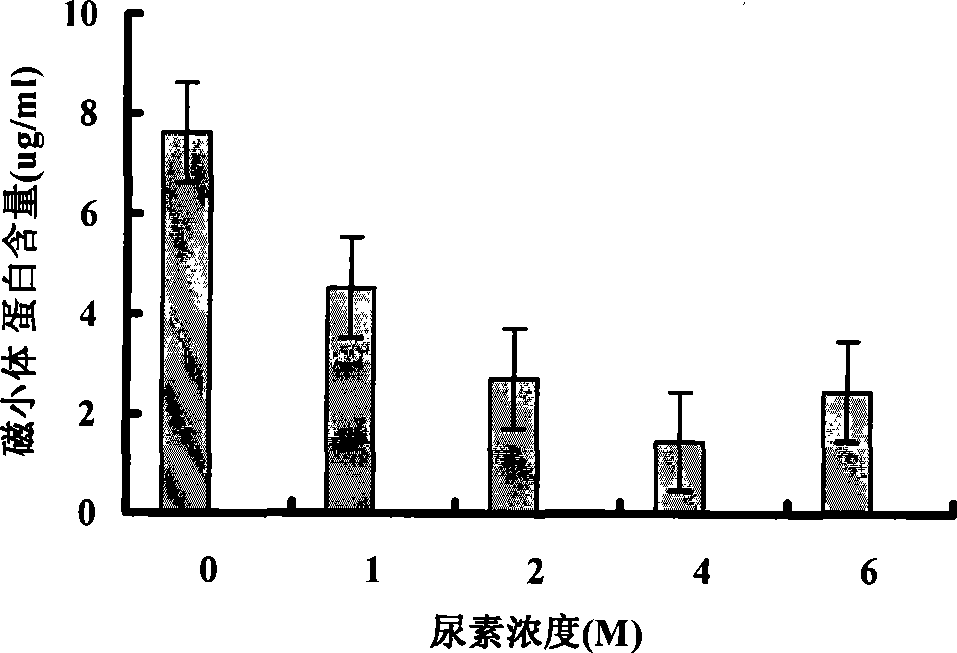
Method for continuous and batch purification of bacterial magnetic particles
InactiveCN101372364AResidue reductionContinuous operationFerroso-ferric oxidesIron sulfidesHigh pressureMagnetotactic bacteria
The invention provides a method for purifying a bacterial magnetosome at a large scale, which comprises the following steps: breaking magnetotactic bacterial cells by a high-pressure homogenizer, separating and cleaning the magnetosome by a magnetic chromatography system, digesting membrane protein with protease k, electroeluting, desalting by a magnetic stirring system, etc. The method has the advantages of continuous operations, and that the purification period is shortened from 2-3 months to less than one week, damage caused by ultrasonication to the plasma membrane of the magnetosome is effectively reduced, the membrane protein on the surface of the magnetosome is reduced and the immunogenicity of the purified magnetosome is lowered.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for restoring soil polluted by heavy metal through combination of magnetotactic bacteria and plants
ActiveCN105127196APromote growthToleratedContaminated soil reclamationSoil mixingMetal contaminated soils
The invention provides a method for restoring soil polluted by heavy metal through a combination of magnetotactic bacteria and plants. The magnetotactic bacteria and the soil polluted by the heavy metal are mixed and irrigated, and magnetic fields are arranged on the soil polluted by the heavy metal to collect heavy metal polluted soil containing the magnetotactic bacteria, drip washing of the soil polluted by the heave metal is conducted and backfill is conducted; bamboo willows and crimson leafbeet are planted on the soil polluted by the heavy metal at the same time, and the crimson leafbeet is removed after 50-60 days; then crimson leafbeet is planted again, and the crimson leafbeet is removed after 50-60 days; the steps of planting and removal of the crimson leafbeet are repeated; and the bamboo willows and the crimson leafbeet are removed at the same time 1.5-2.5 years later, and the steps are executed circularly and repeatedly until the content of the heavy metal in the soil is up to the safety standard. Compared with the prior art, the magnetotactic bacteria are easy to collect, the growth cycle of the bamboo willows is short and the absorption efficiency of the heavy metal is high. The crimson leafbeet is easy to grow and has a hyperaccumulation ability of cadmium. The method is capable of restoring the soil which is polluted by various heavy metals at the same time, and free of secondary pollution to the soil.
Owner:湖南省和清环境科技有限公司
Treatment process for heavy metal sewage
ActiveCN107324616ANo side effectsGood biocompatibilityWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentElectrolysisAdsorption equilibrium
The invention discloses a treatment process for heavy metal sewage. The process includes the steps of (1) conducting pretreatment including sediment and decolorization on the sewage to be treated; (2) adding a compound of magnetotactic bacteria and gel into the sewage after pretreatment and fully blending the mixture to achieve adsorption equilibrium of heavy metal; (3) using an external magnetic field to separate the compound of the magnetotactic bacteria and the gel to achieve the purposes of removing the heavy metal and purifying the sewage; (4) placing the separated compound of the magnetotactic bacteria and the gel in an electric field for electrolytic reduction to replace metal simple substances and achieve cyclic utilization of the heavy metal and the compound of the magnetotactic bacteria and the gel. The gel adopted in the process can achieve chelation and adsorption of metal ions, and is high in adsorption amount, excellent in adsorption capability and capable of being widely applied to comprehensive treatment of the sewage.
Owner:衡水睿韬环保技术有限公司
Remediation method for improving remediation effect of heavy metal contaminated soil
PendingCN111570501AImprove adsorption capacityFast adsorptionAgriculture tools and machinesContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a remediation method for improving the remediation effect of heavy metal contaminated soil. The method comprises the following steps: (1), stripping soil with the thickness of10-50cm from the surface layer of heavy metal contaminated soil, stacking the soil into a remediation pool, and inoculating magnetotactic bacteria; (2), after culturing for 15-25 days, enabling the soil in the remediation pool to be completely soaked in water, setting a magnetic field, and keeping the state for 20-25 days; (3), draining water in the remediation pool, and then leaching the soil inthe pool with clear water; (4), spraying liquid humic acid into the soil in the remediation pool; (5), adding molasses into the heavy metal contaminated soil with the surface soil stripped, spraying liquid humic acid after ploughing and standing, backfilling the soil in the (4), and planting plants capable of enriching heavy metal; and (6), regularly harvesting, removing and reseeding the plants capable of enriching the heavy metals in the (5), and regularly detecting the content of each heavy metal in the heavy metal contaminated soil until the content of the heavy metals in the heavy metal contaminated soil reaches the safety standard.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIV QIANJIANG COLLEGE
A production method of a compound bacterial preparation and an application thereof in sewage treatment
InactiveCN109234214AImproved salt toleranceStrong ammonia nitrogen removal effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNitrate nitrogenMicrobiology
The invention provides a production method of a compound bacterial preparation and an application thereof in sewage treatment. The compound bacterial preparation comprises 25 parts of transgenic marine facultative bacillus, 9 parts of magnetotactic bacteria, 2.5 parts of Halobacterium cordiformis, 3.8 parts of starch salt-solubilizing granular bacteria, 2.5 parts of mycobacterium halophilum, 5 parts of Mycobacterium sporangii, 6.5 parts of salt denitrifying mycobacterium and 2 parts of denitrifying kastraniella. The compound bacterial preparation provided by the invention has strong nitrate nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen removal effect in addition to salt tolerance, and is suitable for the treatment of high-salt wastewater.
Owner:宜兴市永洁环保设备有限公司
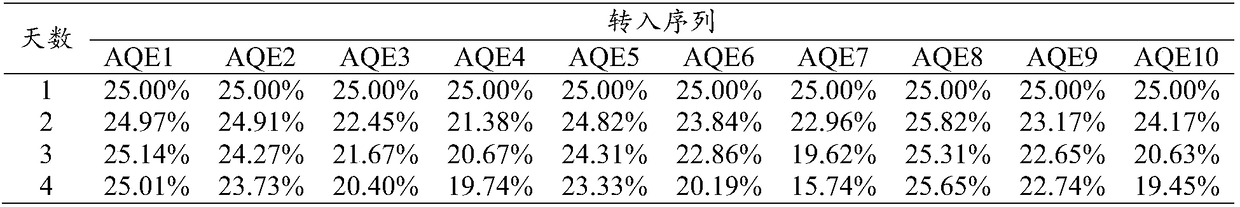
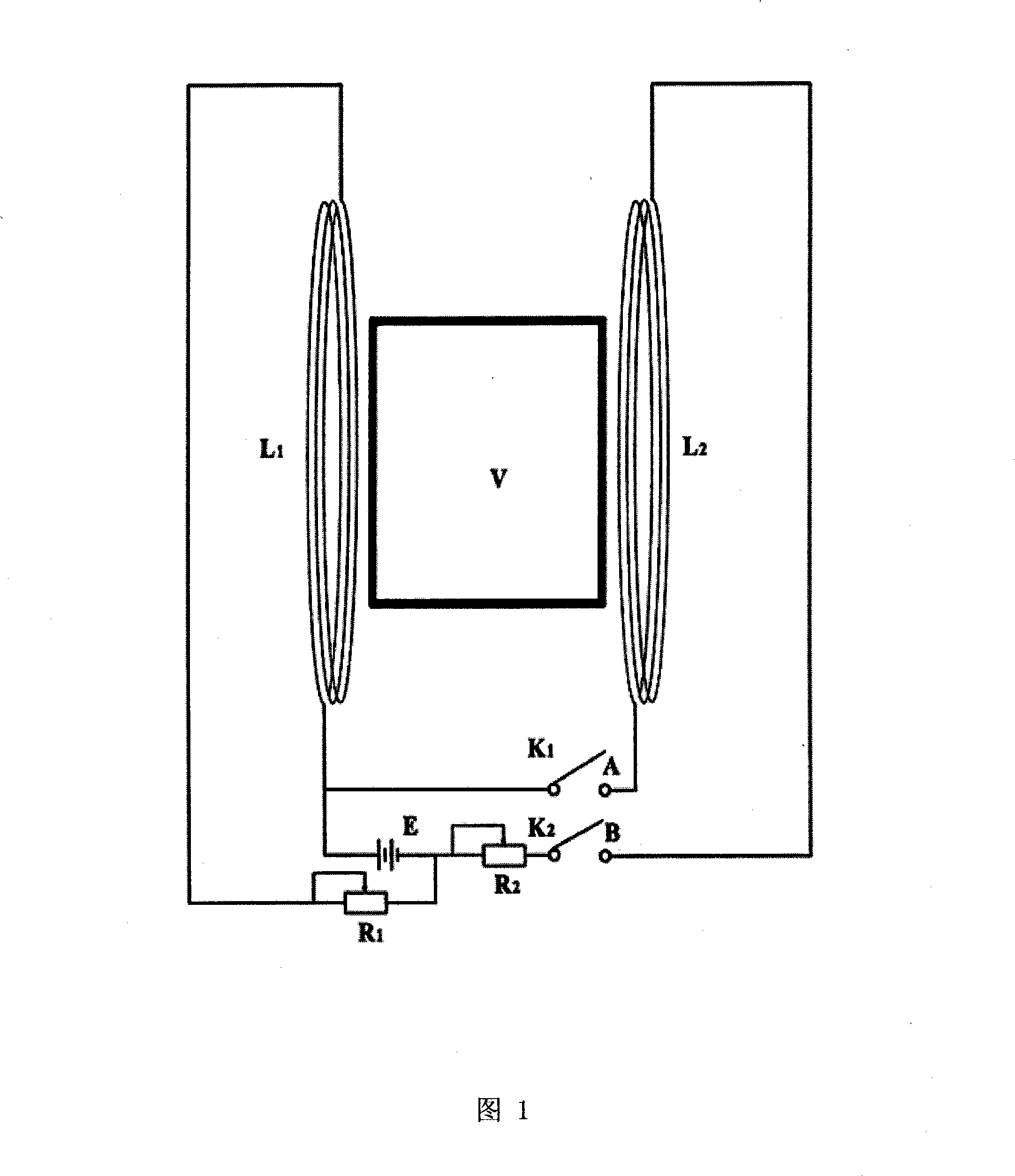
Device for observing magnetism tendency bacteria habit
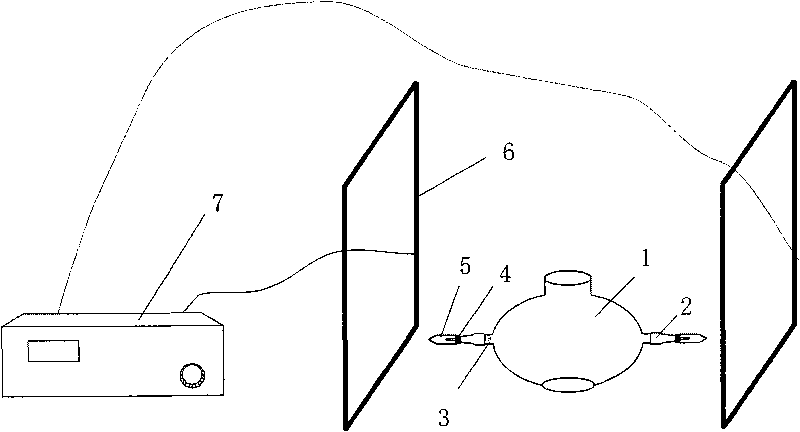
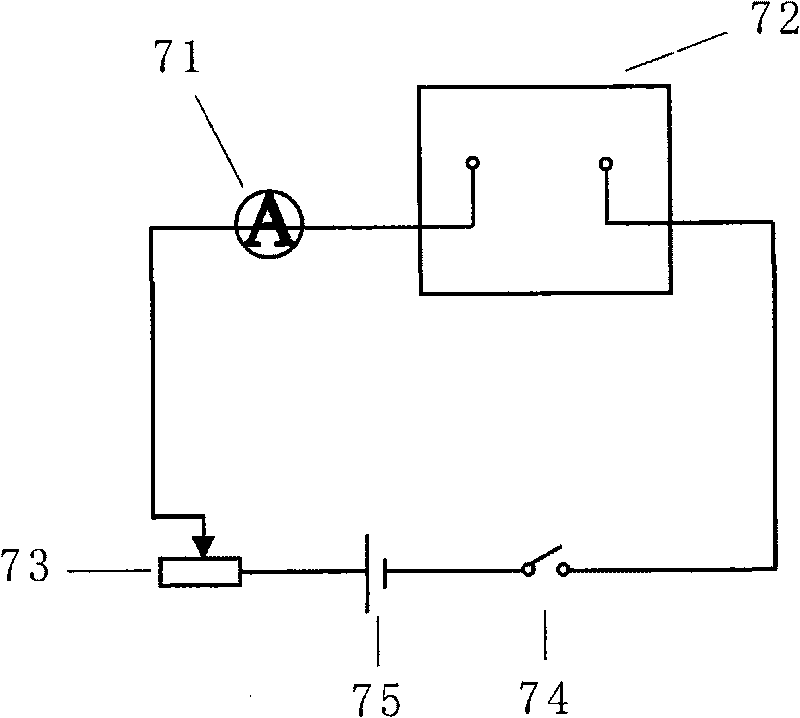
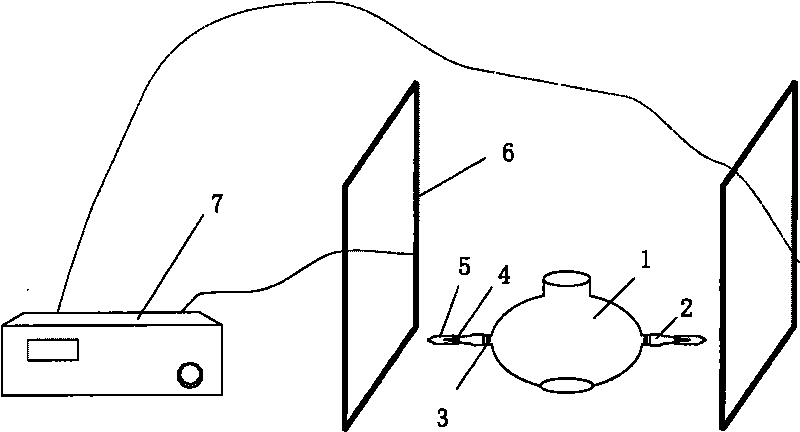
InactiveCN101235352AChange intensityChange directionStress based microorganism growth stimulationEngineeringHabit
The invention relates to a viewing device of magnetotactic bacteria habit, which belongs to the microbiology field. The invention is provided with a magnetotactic bacteria bacterial suspension container, which is characterized in that the container is a transparent cuboid structure, the left portion and the right portion of the container are respectively provided with a left magnet coil and a right magnet coil, one end of the left magnet coil is connected with the positive pole of a direct current power supply, and the other end of the left magnet coil is connected with the negative pole of the direct current power supply through a slide rheostat R1, one end of the right magnet coil is connected with the positive pole of the direct current power supply through a switch K1, and the other end of the right magnet coil is connected with the negative pole of the direct current power supply through a switch K2 and a slide rheostat R2. The strength and direction of electromagnetic field in the container is changed through adjusting resistance value of the slide rheostat and the current direction of the left and the right magnet coil, which are convenient for viewing growth habit of magnetotactic bacteria in different magnetic field conditions under oxygen dissolution condition.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV AT WEIHAI
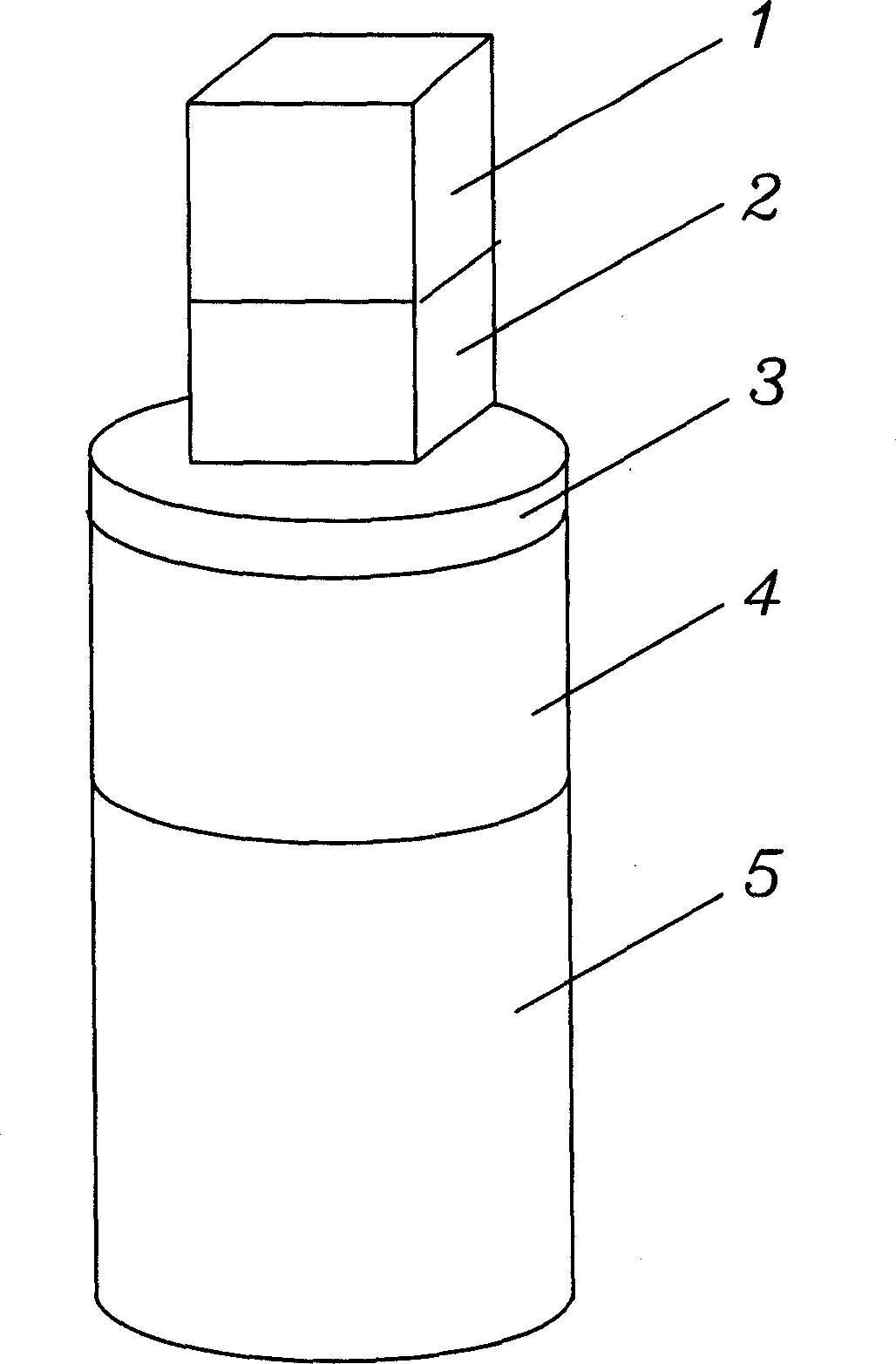
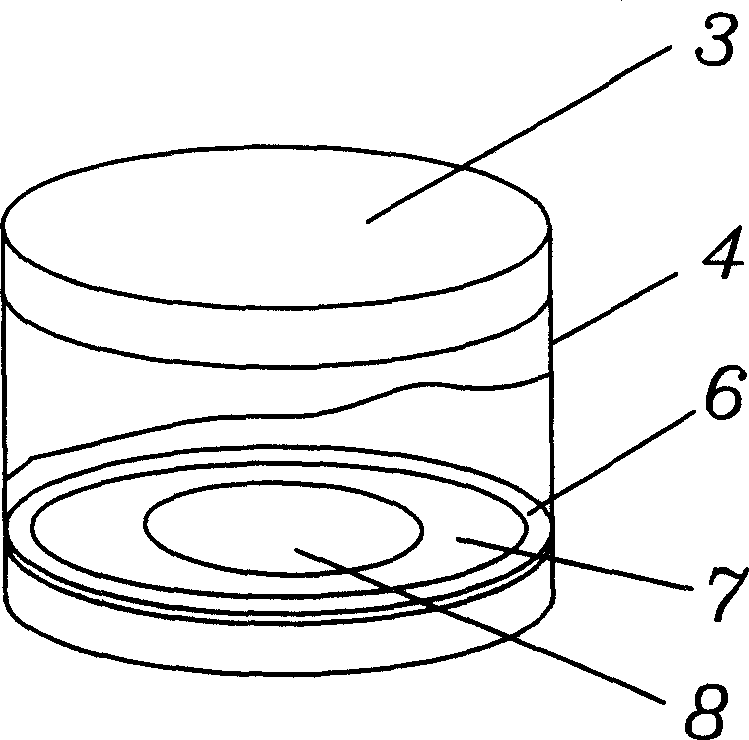
Magnetotactic bacteria or magnetotactic microbe separator
InactiveCN1884471AResolve separabilitySolve purificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRubber ringMicroorganism
The invention relates the segregator, comprising permanent magnet components, cover (3), separating cap (4) and sample cap (5). In the separating cap (4) there is inner edge (6) which is connected with inner wall of separating cap (4); under interior extent (6) there is rubber ring (7), and between them there is filter paper; permanent magnet components comprises N magnet and S magnet; separating cap (4) is connected with sample cap (5). The invention solves the problem that the magnetic bacteria is not easy to separate, and the invention has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, easy usage and strong practicality.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Bacterial magnetic particles with recombinant protein G expression capability and application thereof
The invention provides bacterial magnetic particles with recombinant protein G expression capability. The bacterial magnetic particle with recombinant protein G expression capability are obtained by performing enlarged culture and separation and purification on magnetotactic bacteria MSR-1 recombinant strains. The invention further provides application of the bacterial magnetic particles with recombinant protein G expression capability in detection of blood type irregular antibody IgG. By use of the magnetic property of the bacterial magnetic particles and the effect of an applied magnetic field, the bacterial magnetic particles with recombinant protein G expression capability, provided by the invention, are capable of assisting agglutination of sensitized erythrocytes, so that on the one hand, the usage amount of the bacterial magnetic particles is reduced to the greatest extent, and on the other hand, the detection sensitivity of low-potency IgG antibodies is improved to the greatest extent.
Owner:BEIJING GUO KE RONG ZHI BIOTECH CO LTD
Two-way device for collecting magnetotactic bacteria
InactiveCN101735937AEfficient collectionSimple structureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityForce lines
The invention provides a two-way device for collecting magnetotactic bacteria, and relates to the technology of bacteria collection. A collector of the device is a container of which the upper end is provided with an opening; side walls of the container are oppositely provided with an opening respectively; a tubular separation tube is arranged in two openings respectively; a sample tube is sleeved on the outer ends of two separation tubes respectively; two sample tubes are communicated with an inner cavity of the collector through the separation tubes respectively; the collector is arranged between two Helmholtz coils; the two Helmholtz coils are opposite, in parallel and vertically arranged; the two separation tubes on the collector face one coil respectively; and the axes of the separation tubes are consistent with the direction of a magnetic force line; and the two coils are electrically connected with a controller respectively. The device applies uniform weak field to a sample containing the magnetotactic bacteria, makes a magnetic field between 0.1 and 1 mT, can simultaneously collect the magnetotactic bacteria moving along or against the magnetic force line and can effectively and rapidly collect the maximum magnetotactic bacteria without preference from an environment. The device has the advantages of simple structure, low cost and convenient use, and provides high-quality equipment for researches of the diversity and magnetic properties of the magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for combining microorganisms with curing agent to remediate heavy metal contaminated soil
ActiveCN105149344AImprove adsorption capacityReduce accumulationContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismIn situ remediation
The invention provides a method for combining microorganisms with a curing agent to remediate heavy metal contaminated soil. The method comprises the following steps: mixing magnetotactic bacteria with heavy metal contaminated soil, irrigating the heavy metal contaminated soil which is mixed with the magnetotactic bacteria, setting magnetic fields on the heavy metal contaminated soil, collecting the heavy metal contaminated soil containing the magnetotactic bacteria, leaching the heavy metal contaminated soil, and re-filling the heavy metal contaminated soil; embedding a porous hard plastic capsule containing the curing agent into the heavy metal contaminated soil subjected to adsorption treatment by the magnetotactic bacteria, culturing the porous hard plastic capsule for 20-25 days, then, taking back the embedded porous hard plastic capsule; and repeating the steps in a circulating mode until content of the heavy metals in the soil reaches the safety standards. The method for combining microorganisms with a curing agent to remediate heavy metal contaminated soil disclosed by the invention belongs to in-situ remediation, is simple to operate, low in cost, good in remediation effect, capable of directly removing heavy metal ions without causing secondary pollution on the soil, and suitable for large-area contaminated soil governance.
Owner:张智平
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com