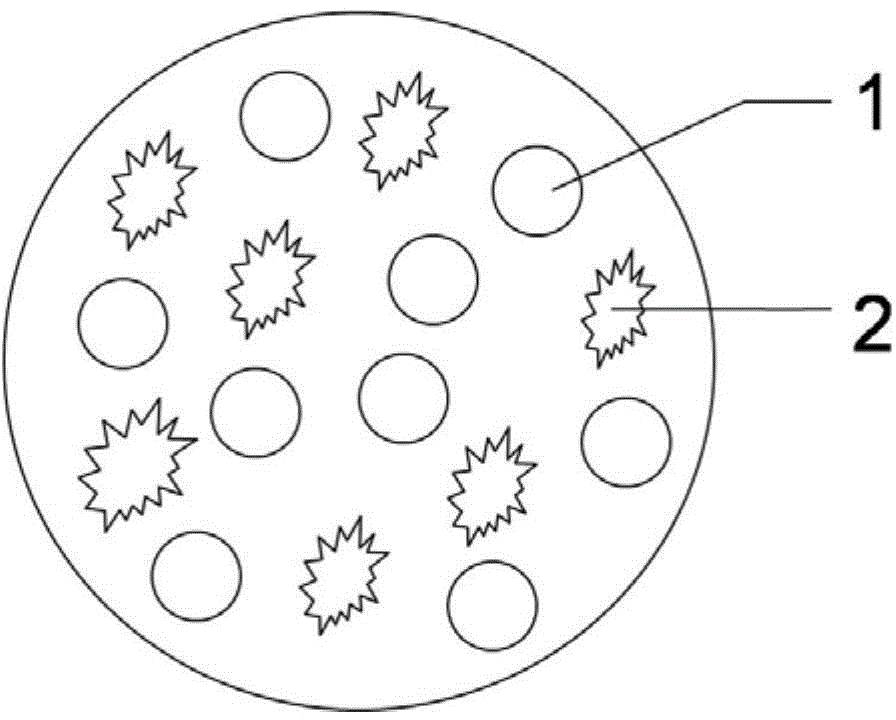
Medicine slow-release nanoparticle wrapping magnetosomes of magnetotactic bacteria and preparation method of medicine slow-release nanoparticle
A technology of magnetotactic bacteria and nano-microspheres, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as poor water solubility, poor tolerance, and affecting clinical application of drugs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1 A drug sustained-release nanosphere embedded with magnetotactic bacterial magnetosomes
[0029] The composition of the sustained-release nanometer microsphere is: 1 part of magnetosome of magnetotactic bacteria, 1 part of chitosan, 1 part of methyl cellulose and 10 parts of camptothecin.
[0030] The preparation of slow-release nanospheres embedded with magnetotactic bacterial magnetosomes is achieved by the following methods:
[0031] (1) Collect magnetotactic bacteria after culturing Magnetospiri-llumsp.AMB-1, break the wall with 500W ultrasound for 1 hour, release magnetosomes, and apply an external magnetic field to absorb and recover magnetosomes.
[0032] (2) Rinse the magnetosomes with physiological saline for 3 times, mix chitosan, methylcellulose, and camptothecin with a molecular weight of 10KDa and a deacetylation degree of 50% according to the above ratio, and prepare nano Microspheres; spray drying conditions are: inlet air temperature 80°C, outl...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 A drug slow-release nanosphere embedded with magnetotactic bacterial magnetosomes
[0035] The composition of the sustained-release nano microspheres is: 9 parts of magnetosomes of magnetotactic bacteria, 20 parts of chitosan, 4 parts of hydroxypropyl cellulose, and 10 parts of adriamycin.
[0036] The preparation of slow-release nanospheres embedded with magnetotactic bacterial magnetosomes is achieved by the following methods:
[0037] (1) Collect the magnetotactic bacteria after culturing M. gryphiswaldenseMSR-1, break the wall with 600W ultrasound for 0.5h, release the magnetosomes, and apply an external magnetic field to absorb and recover the magnetosomes.
[0038] (2) Rinse the magnetosomes with physiological saline for 5 times, mix chitosan, hydroxypropyl cellulose, and doxorubicin with a molecular weight of 100KDa and a degree of deacetylation of 80% according to the above ratio, and prepare by spray drying Nano microspheres; spray drying conditions ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 A drug slow-release nanosphere embedded with magnetotactic bacterial magnetosomes
[0041] The composition of the sustained-release nano microspheres is: 10 parts of magnetosomes of magnetotactic bacteria, 5 parts of chitosan, 5 parts of pectin and 10 parts of vincristine.
[0042] The preparation of slow-release nanospheres embedded with magnetotactic bacterial magnetosomes is achieved by the following methods:
[0043] (1) Collect the magnetotactic bacteria after culturing M. magnetotacticumMS-1, break the wall with 300W ultrasound for 2 hours, release the magnetosomes, and apply an external magnetic field to absorb and recover the magnetosomes.
[0044] (2) Rinse the magnetosomes with normal saline for 3 times, mix chitosan, pectin, and vincristine with a molecular weight of 2000KDa and a degree of deacetylation of 90% according to the above ratio, and prepare nanospheres by spray drying ; Spray drying conditions are: inlet air temperature 180°C, outlet te...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com