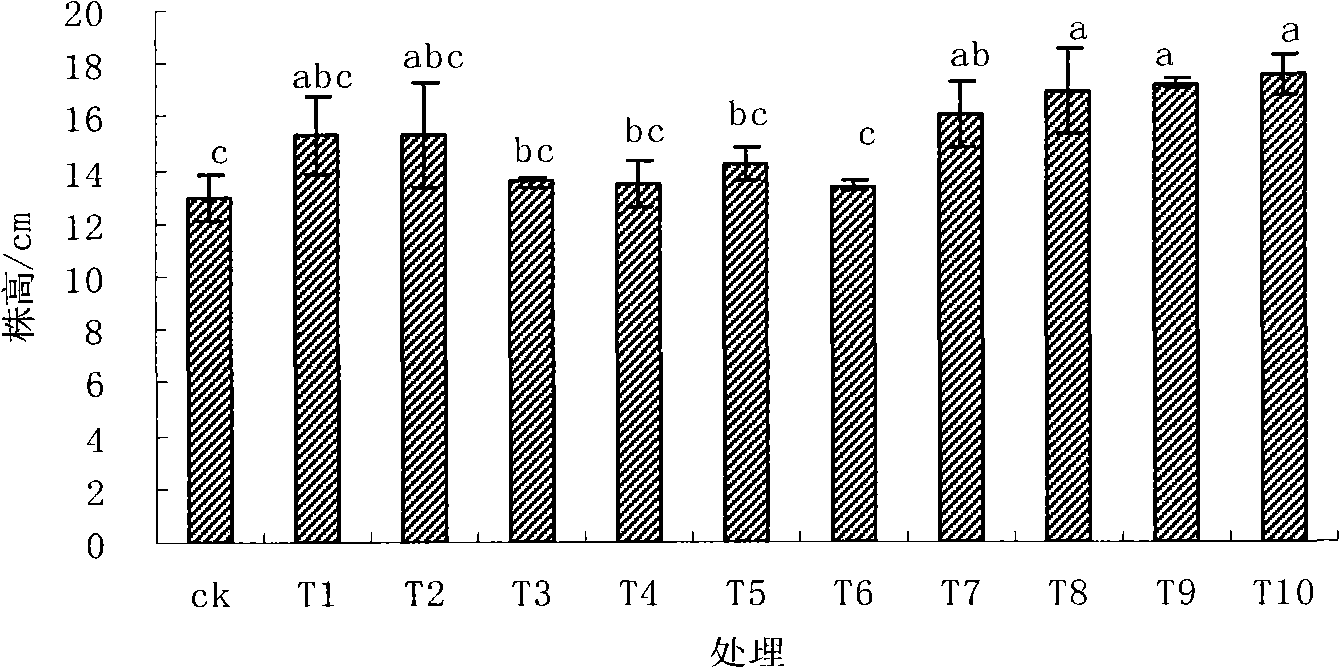
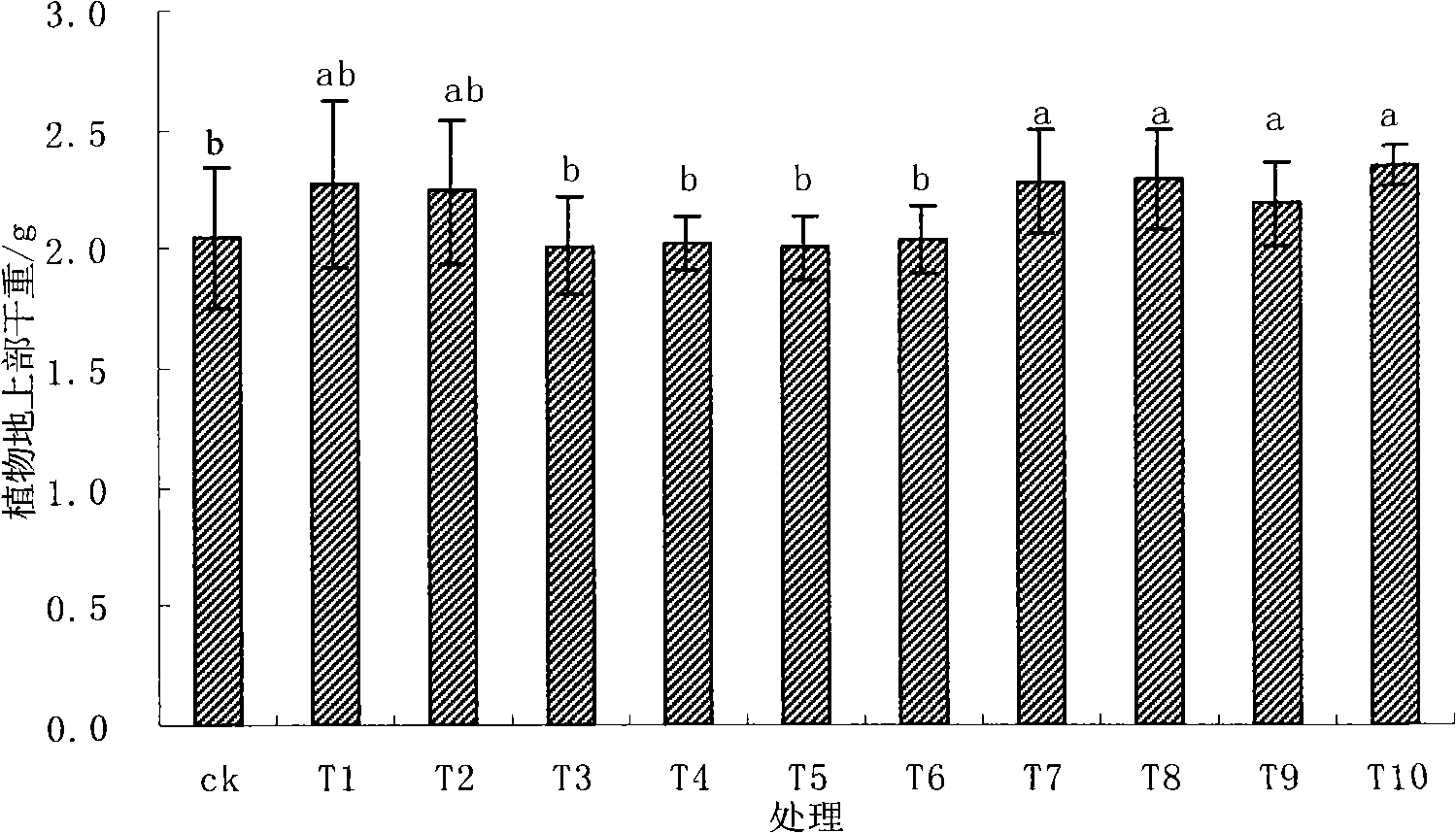
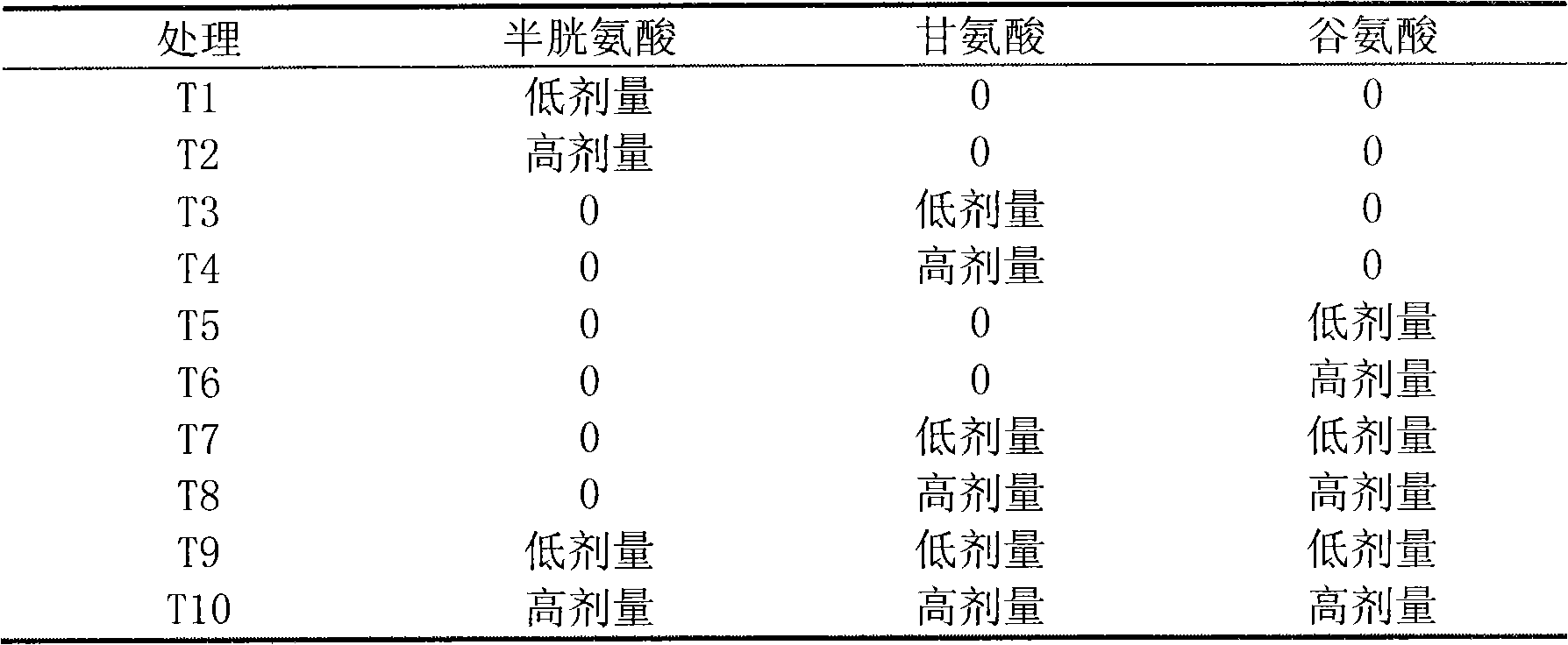
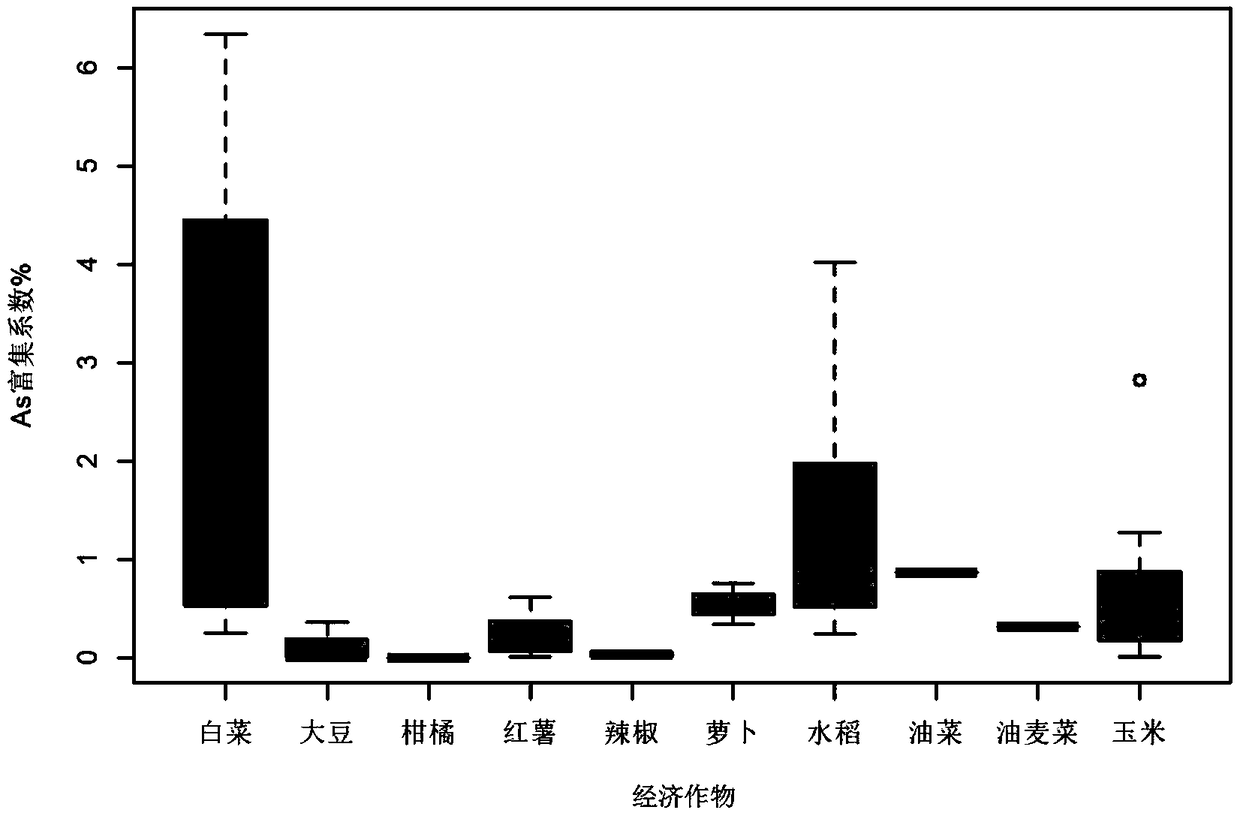
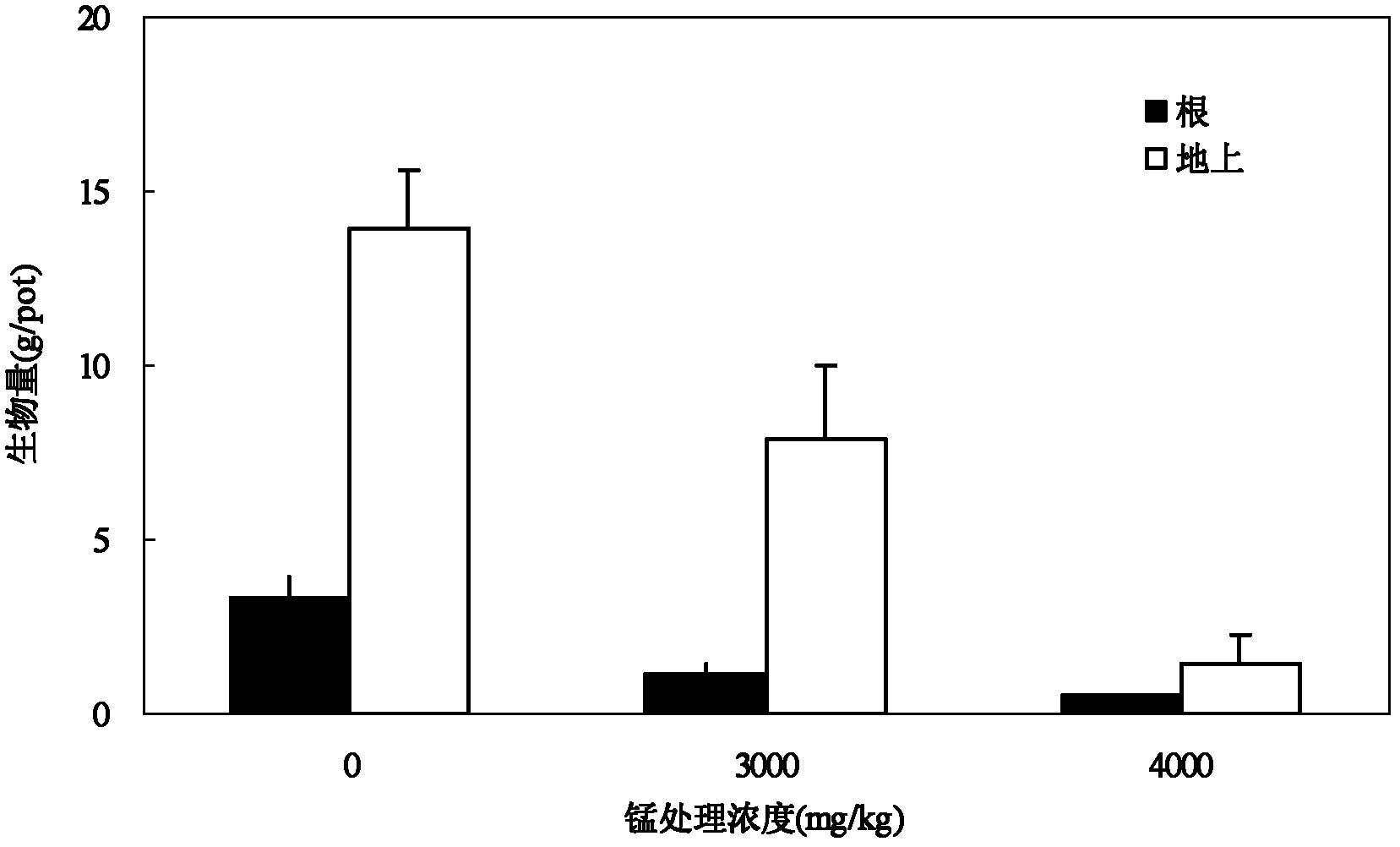
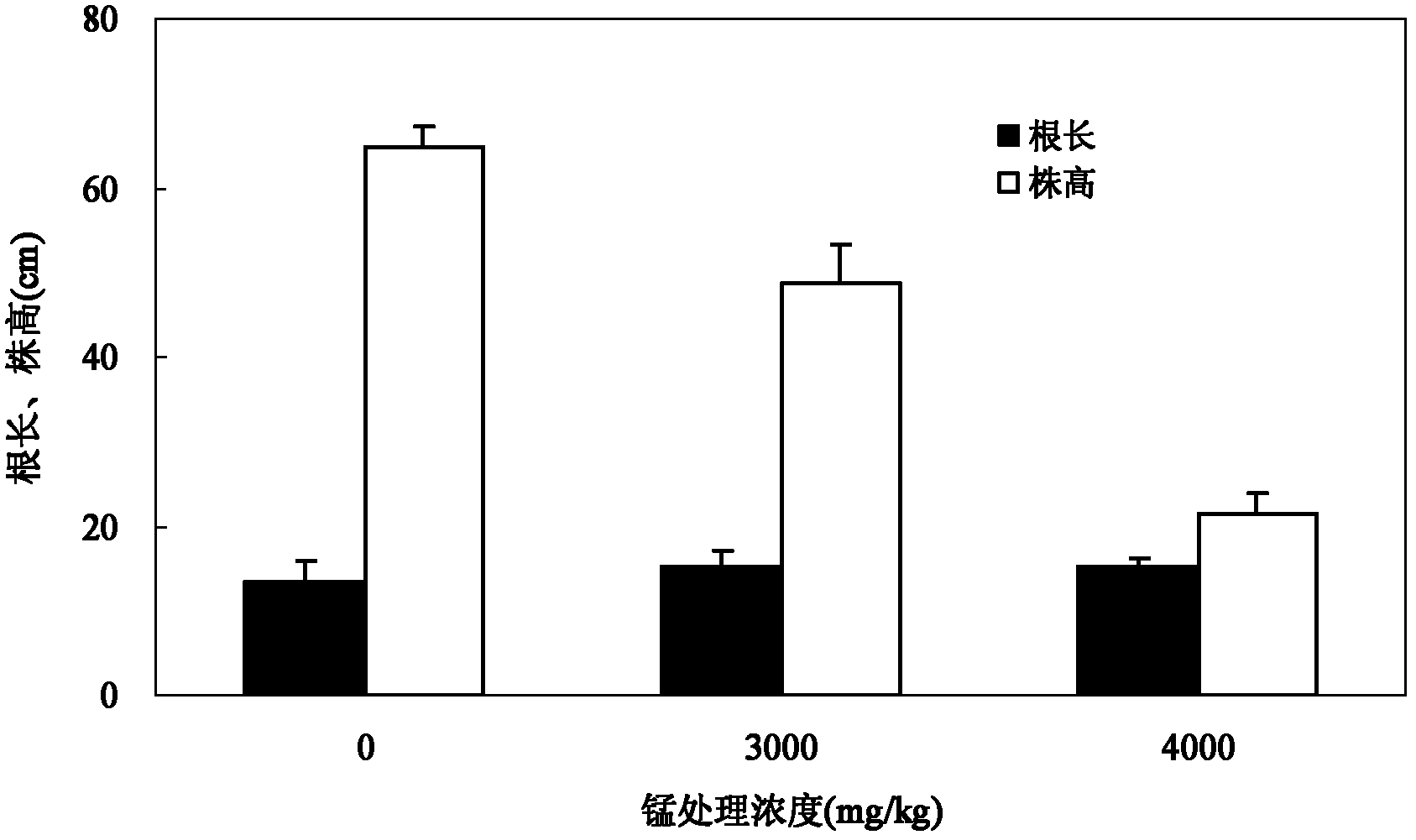
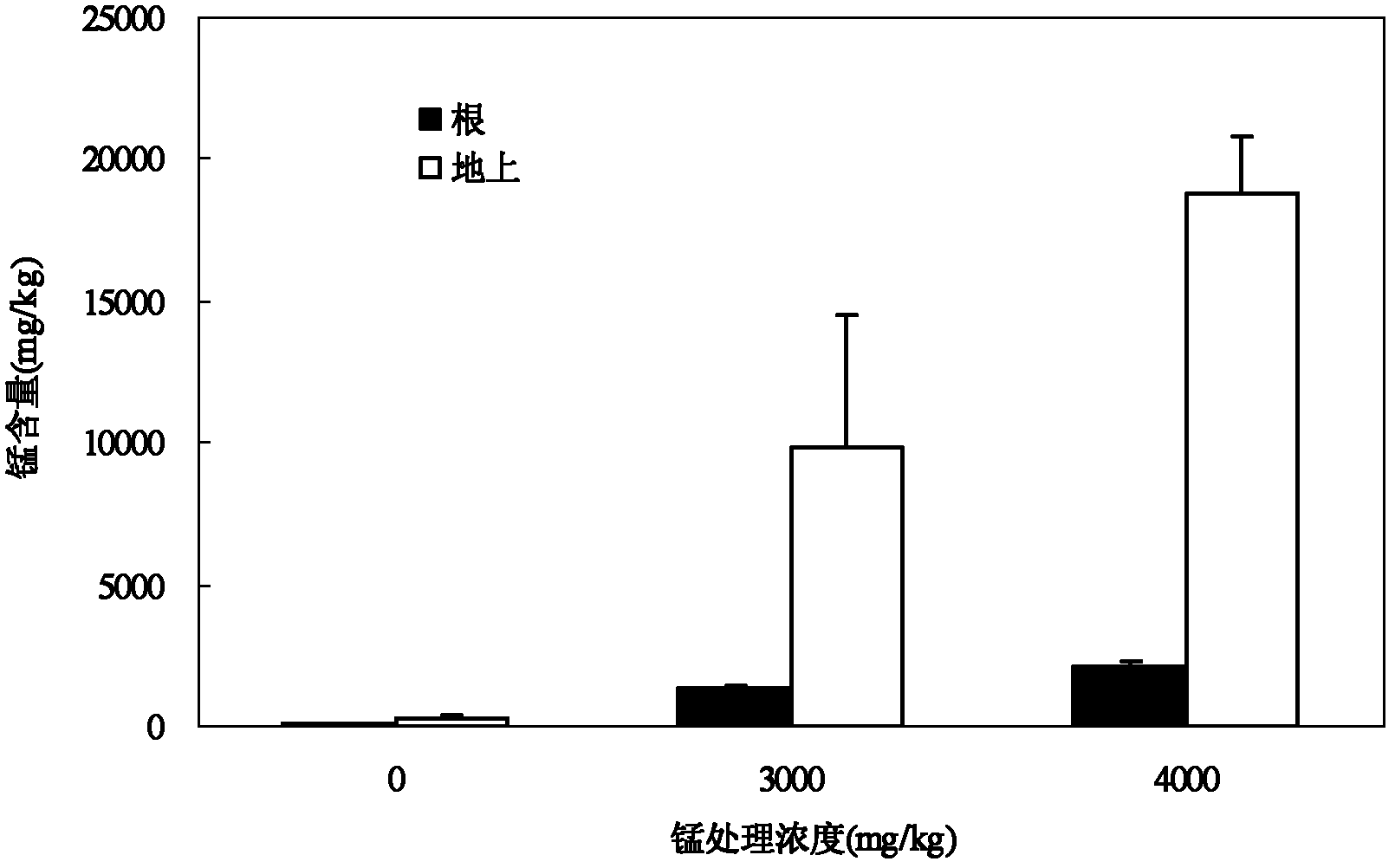
Patents
Literature
138 results about "Hyperaccumulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A hyperaccumulator is a plant capable of growing in water with very high concentrations of metals, absorbing these metals through their roots, and concentrating extremely high levels of metals in their tissues. The metals are concentrated at levels that are toxic to closely related species not adapted to growing on the metalliferous soils. Compared to non-hyperaccumulating species, hyperaccumulator roots extract the metal from the soil at a higher rate, transfer it more quickly to their shoots, and store large amounts in leaves and roots. The ability to hyperaccumulate toxic metals compared to related species has been shown to be due to differential gene expression and regulation of the same genes in both plants.
Plant repair method for treating soil having combined pollution of arsenic, lead and cadmium
InactiveCN101372016ADoes not destroy physical and chemical propertiesAvoid churnContaminated soil reclamationHyperaccumulatorPollution soil
The invention relates to a plant repair method for treating soil polluted by arsenic, lead and cadmium. In the soil combinedly polluted by arsenic, lead and cadmium, the method of single planting, interplanting of another crop, interval seeding or hybride are adopted to directly transplant or sow aster subulatus and ghostplant sagebrush. The treatment and restoration on the soil combined polluted by arsenic, lead and cadmium is completed by the following steps: the hyperaccumulator property of two plants on arsenic, lead and cadmium is used for vastly absorbing arsenic, lead and cadmium enriched in soil; the elements are upward transported and shifted to the over ground part; and the harmful elements such as arsenic, lead and cadmium in the soil are removed by reaping the over ground part.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for restoring hexavalent chromium-polluted soil by utilizing microbial fermentation
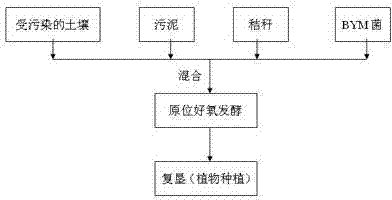
The invention belongs to the technical field of heavy-metal pollution restoration of soil and particularly relates to a method for restoring soil chromium-polluted soil. According to the main principle of the method, sludge, straws, the chromium-polluted soil and composite strains BYM (Bacterial Enzyme) are mixed and fermented and biological enzyme, organic sugar, and other substances which are generated in a microbial fermentation process are used for reducing hexavalent chrome contained in soil into trivalent chromium; and then chromium pollutants contained in the soil are thoroughly removed by planting a chromium hyperaccumulator. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention belongs to an in-situ restoration technology, has the advantages of small investment, low operation cost and minimal environmental disturbance, can improve the hardening degree of the soil, enhance the loose degree of the soil and increase the content of organic matters contained in the soil and is favorable to the plant growth of the restored soil.
Owner:HENAN JINGU IND DEV
Method of producing while recovering for cadmium-polluted vegetable field
InactiveCN103109651AImprove qualityProduction does not declineHorticultureHyperaccumulatorFood sanitation
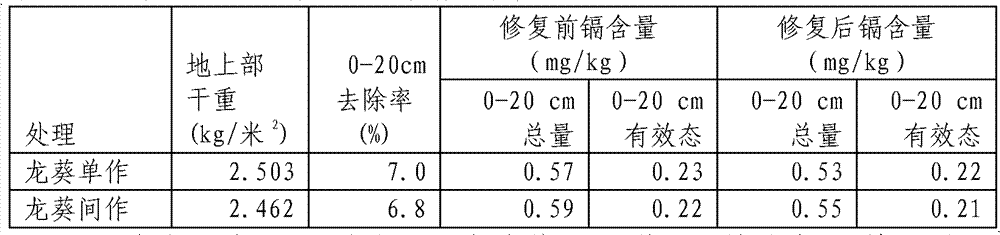
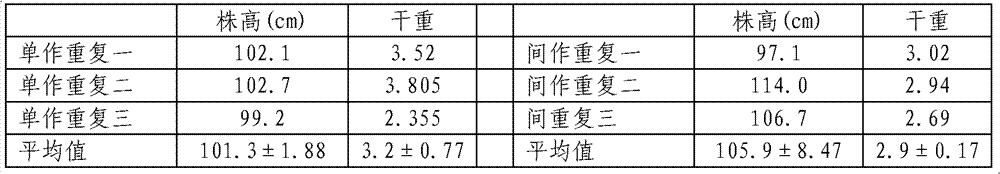
The invention relates to a method of plant recovering and agriculture safe utilization for cadmium-polluted vegetable field soil, in particular to a method of producing while repairing for a cadmium-polluted vegetable field. The method comprises planting green Chinese onions with low cadmium accumulation and cadmium-hyperaccumulator plants of nightshade in an intercropping mode on the cadmium-polluted soil, and after the green Chinese onions with low cadmium accumulation and the cadmium-hyperaccumulator plants of nightshade are fully grown, respectively removing the entire plants from the cadmium-polluted soil so as to achieve the aim of removing a pollutant of cadmium in the soil and simultaneously harvesting the green Chinese onions with low cadmium accumulation to serve as pollution-free vegetables. The harvested green Chinese onions meet the requirements of our country for food sanitation so as to be safely consumed. By means of the steps, a recovering and utilizing period is completed. According to the method of producing while recovering for the cadmium-polluted vegetable field, large amount of cadmium is taken away from the cadmium-polluted soil by utilizing the cadmium-hyperaccumulator plants, the polluted soil is recovered while the green Chinese onions meeting the sanitation standards of our country are produced, and the polluted soil can be safely utilized.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
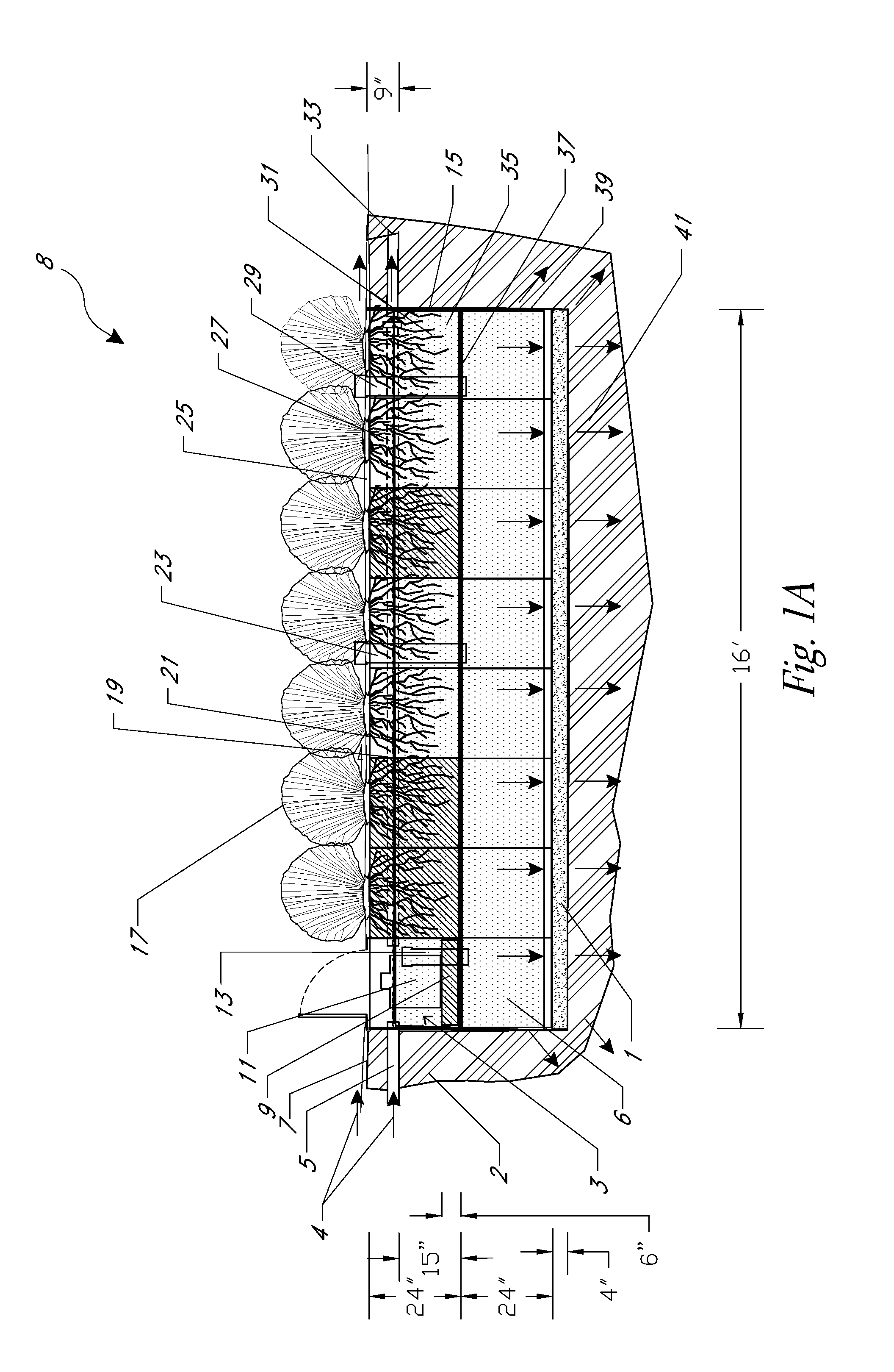
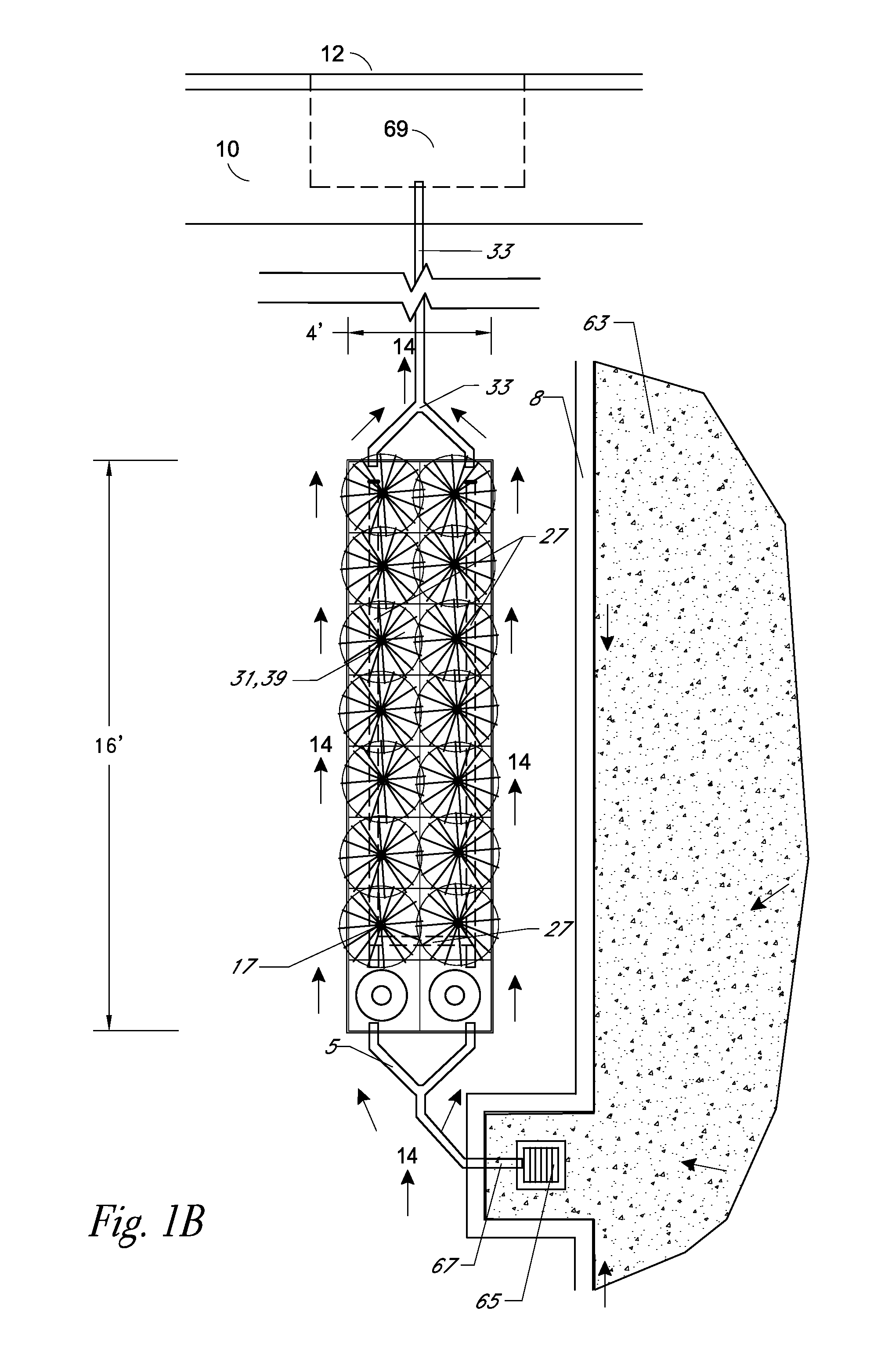
Underground water heavy metal pollution remediation device
ActiveCN104692531AImprove repair effectGood removal effectWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentHyperaccumulatorChemical adsorption
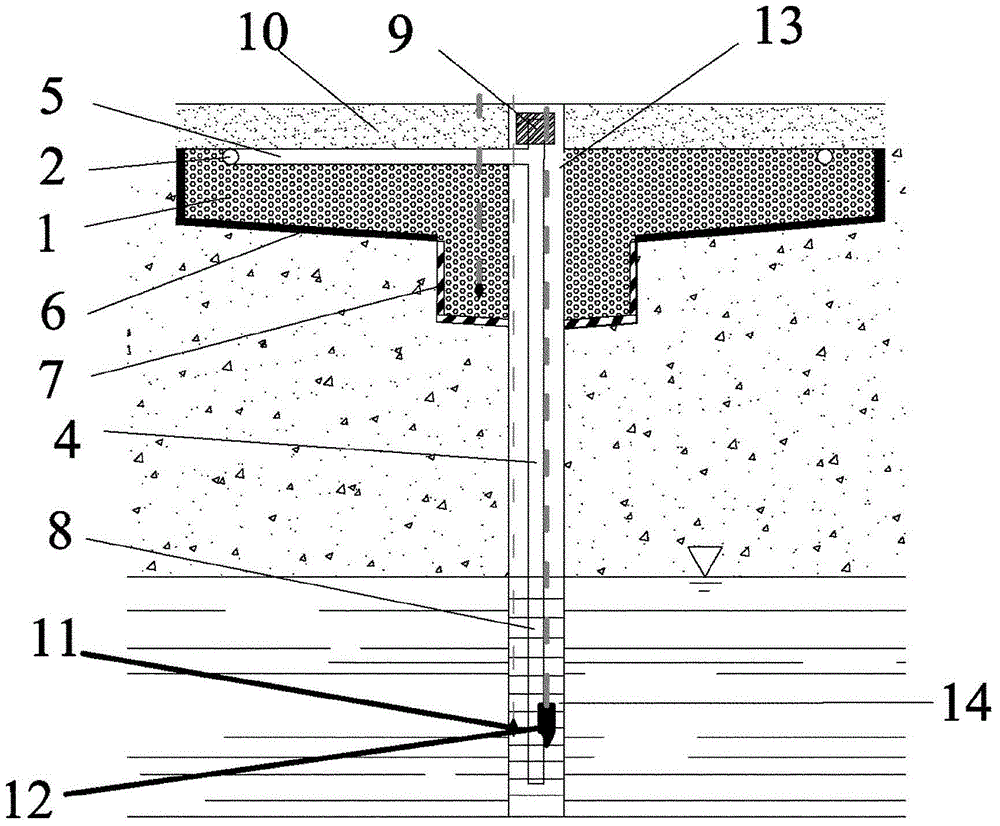
An underground water heavy metal pollution remediation device mainly includes a pumping system, a water distribution system, an adsorption reaction zone, a phytoremediation zone, a rapid seepage zone and a monitoring system. The adsorption reaction zone is filled with a medium for the adsorption of heavy metals in order to remove the heavy metals in the underground water. The phytoremediation zone is planted with hyperaccumulator with absorption and enrichment effects on heavy metals, so as to enhance the removal effect of heavy metals. The technique organically combines physical adsorption, chemical adsorption and phytoremediation, and can remediate heavy metals pollution of As, Zn, Cd, Mn, Cu, Cr and Pb and reach good removal effect; replacement of the adsorption reaction medium filler is simple; and the device has low operation cost, and is applicable to groundwater pollution sites in different water depths.
Owner:北京德瑞科森环保科技有限公司
Method of sustaining plant growth in toxic substrates polluted with heavy metal elements as well as fertilization and beneficiation of normal horticultural and agricultural soils
InactiveUS20070219096A1Growth has been successfulEasy disposalBiocideSeed and root treatmentPlant growthBiology
A method of sustaining plant growth in toxic substrates polluted with heavy metal elements comprising amendment and remediation of the toxic substrates with an organo-zeolitic mixture. Vegetation, such as hyperaccumulator plants or native plants and grasses for in situ remediation, will now grow. The method can also be used as a fertilizer and for benefication of normal, uncontaminated soils.
Owner:LEGGO PETER J +1
Heavy metal-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon combined pollution reinforcing repairing agent and application thereof
InactiveCN101992207AGood processing effectCd content increasedContaminated soil reclamationGlycinePolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bacillus cereus TH-35 capable of activating heavy metal cadmium in soil and application thereof
Belonging to the technical field of soil pollution biological treatment, the invention in particular discloses a Bacillus cereus TH-35 strain capable of activating heavy metal cadmium in soil. The strain is preserved in Guangdong microbiology culture center (GDMCC) on June 13, 2016, and the preservation number is GDMCC No.60044. According to the invention, an indigenous microorganism with efficient cadmium activation function is screened out from farmland soil, and is utilized to activate soil mineral nutrients at the rhizosphere and promote plant growth, at the same time, the indigenous microorganism also can effectively dissolve soil carbonate bounded forms, phosphate bounded forms and other major bounded forms of cadmium, thus effectively improving the efficiency of remediation of soil heavy metal cadmium by hyperaccumulator plants. In the process of activating soil heavy metal cadmium with the strain, no emission pollutant unfriendly to the environment is generated, therefore the Bacillus cereus TH-35 strain has great application prospects in preparation of environment friendly soil conditioners.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
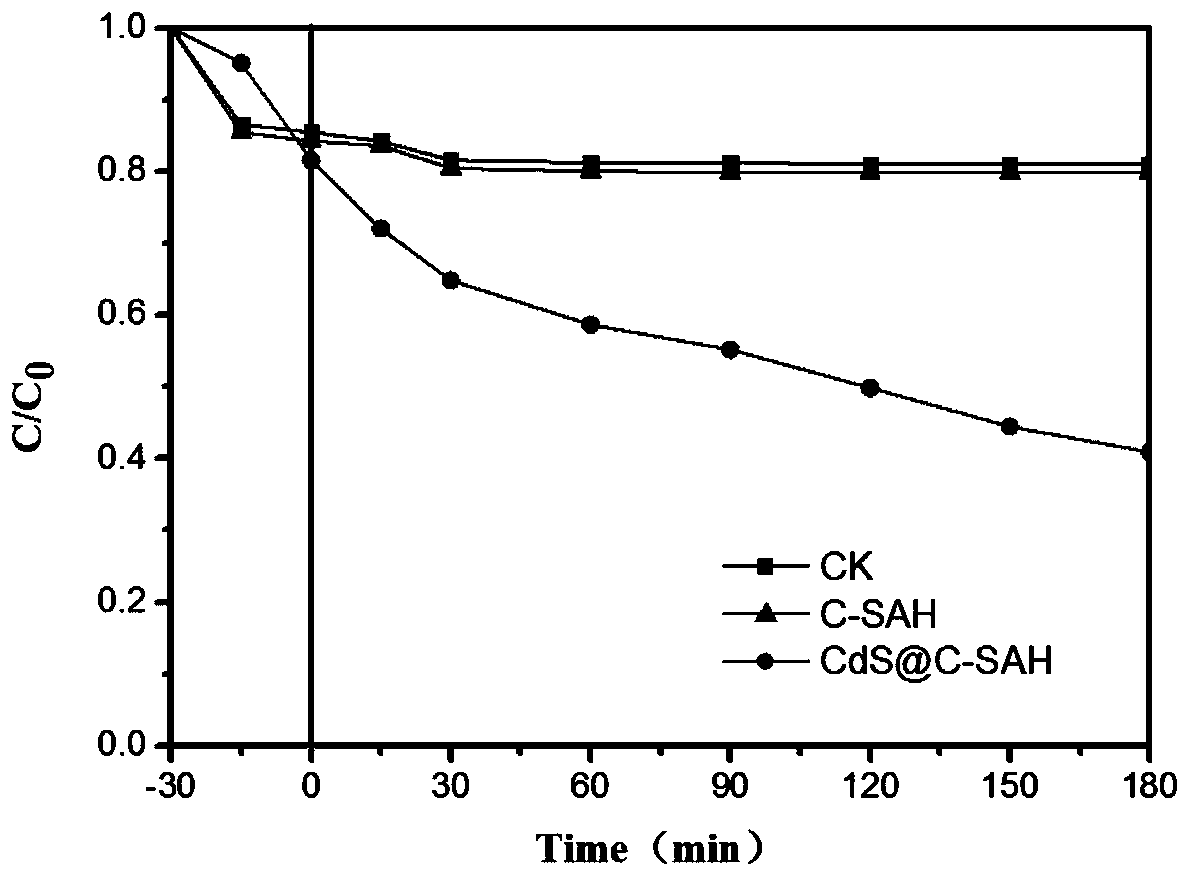
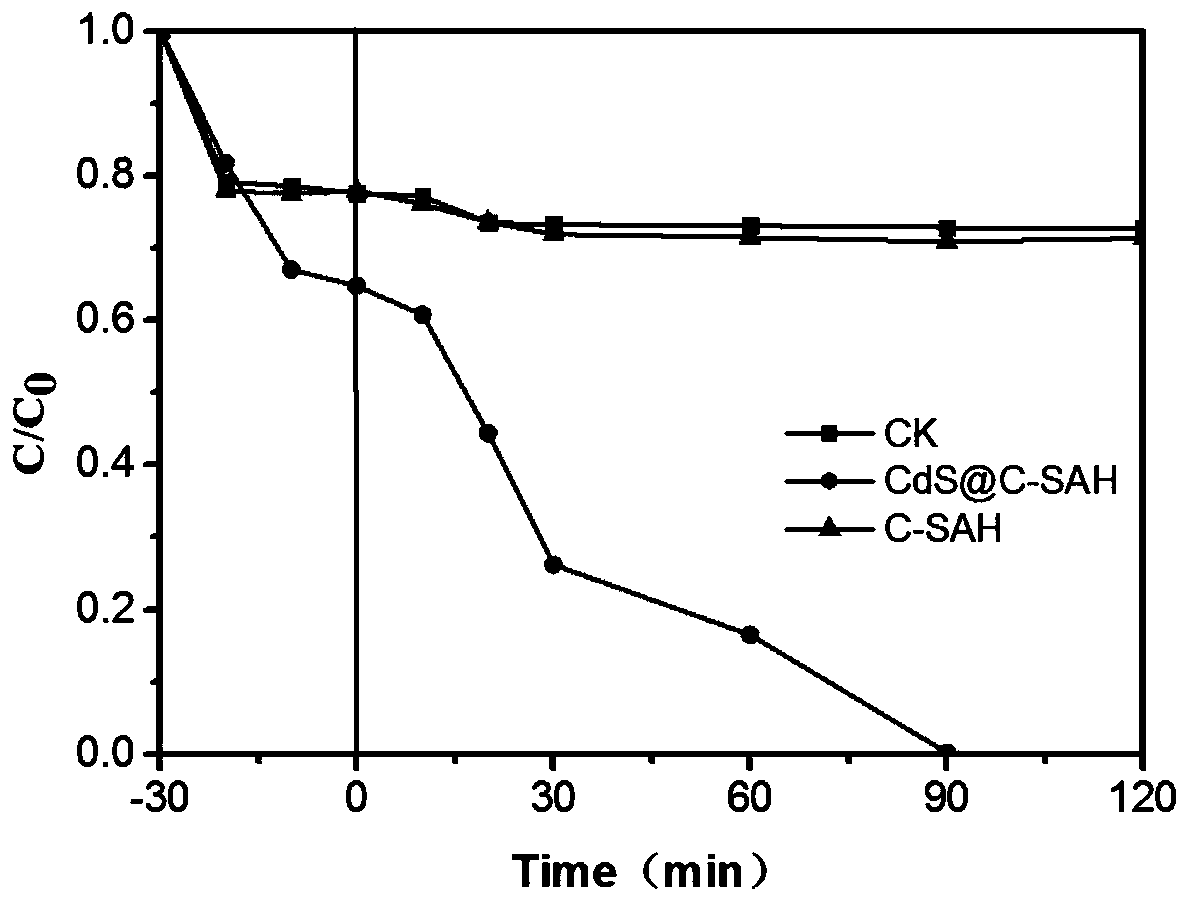
Method for preparing photocatalytic material from cadmium hyperaccumulator and application
ActiveCN109794262ARealize full resource utilizationRealize high-value recyclingPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationCadmium sulfateHyperaccumulator
The invention discloses a method for preparing a photocatalytic material from a cadmium hyperaccumulator and application. A cadmium-enriched hyperaccumulator harvested product is converted into a carbon loaded cadmium sulfate photocatalytic material with the small forbidden band width and efficient photocatalytic activity, full-dose recycling and high-value recycling of the cadmium hyperaccumulator can be achieved, the problems of high cost and secondary environment contamination for cadmium contaminated site plant repairing are solved, and application and popularization of the cadmium hyperaccumulator in soil contamination repairing are promoted.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for restoring and using vegetable field soil combinedly polluted by cadmium and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
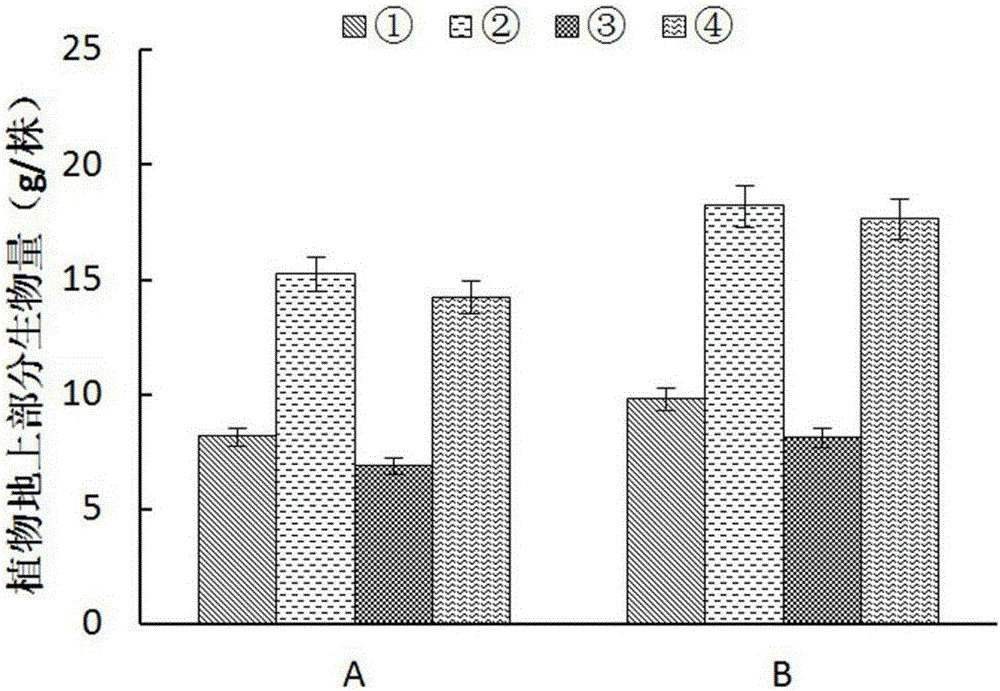
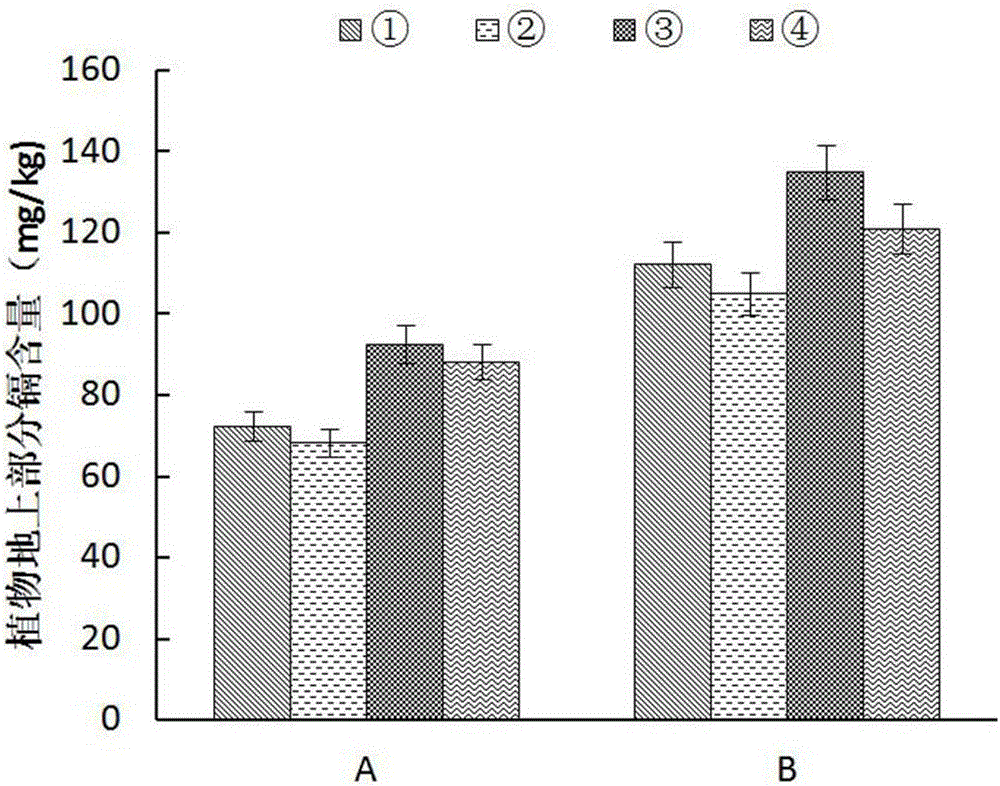
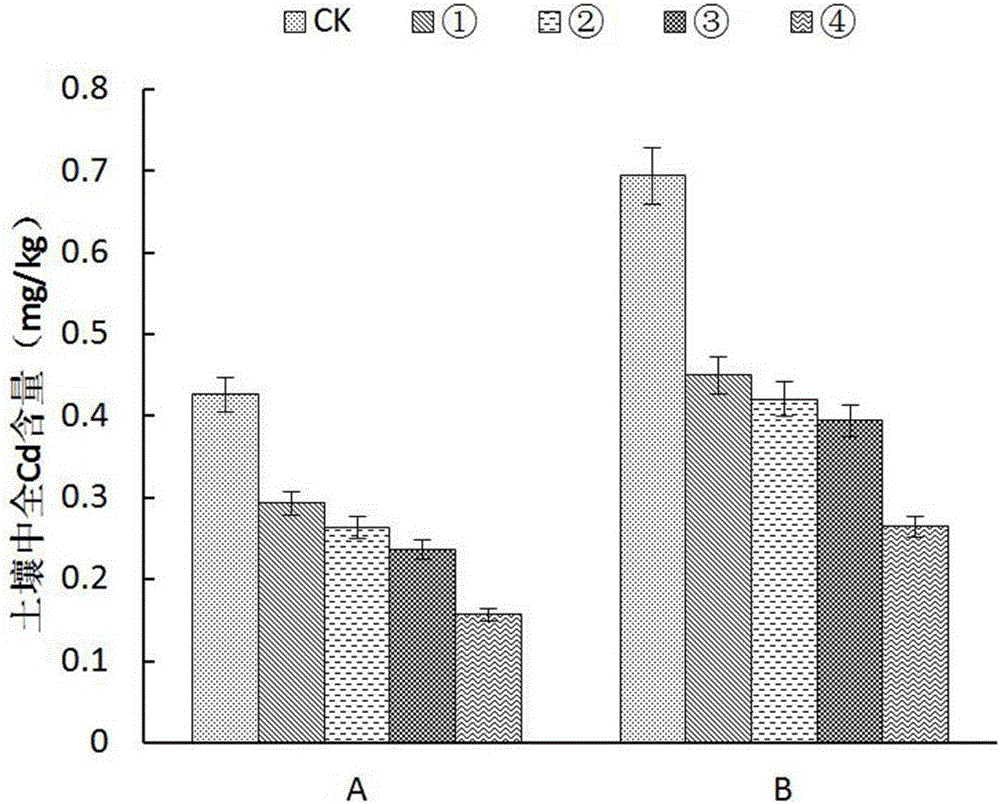
The invention relates to technology for synchronous restoration and production of vegetable field soil combinedly polluted by cadmium and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. The technology comprises the following steps of: 1) planting cadmium hyperaccumulator solanum nigrum L in the vegetable field which is combinedly polluted by the cadmium and the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in spring in a mode of furrow drilling and row planting, harvesting the solanum nigrum L when the solanum nigrum L grows for 63 to 67 days and bears fruits, and applying glycine, glutamic acid and cysteine about one month before the solanum nigrum L is harvested; 2) pulling the solanum nigrum L with roots out after the solanum nigrum L is harvested, and then planting cadmium low accumulation cabbage navy camps 91-12, wherein the row space and the plant space are 50cm respectively; harvesting the cabbage after the cabbage grows for about 80 days; and completing the steps in a restoring and using cycle. By the technology, a great amount of cadmium is taken away from the soil combinedly polluted by the cadmium and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon by using the hyperaccumulator, the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in the soil is obviously reduced, the cabbages meeting Chinese health standards can be produced, and the polluted soil can be safely used when the polluted soil is restored.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Hyperaccumulator-based biochar, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110564433ASolve security handling issuesWide variety of sourcesBiofuelsSpecial form destructive distillationHyperaccumulatorBiochar
The invention discloses hyperaccumulator-based biochar, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method of the hyperaccumulator-based biochar comprises the following steps:natural air drying, crushing and anaerobic pyrolysis. The hyperaccumulator-based biochar is prepared by the preparation method. The application is the application of the hyperaccumulator-based biochar in adsorption and solidification of heavy metal ions. A Hyperaccumulator is subjected to anaerobic pyrolysis to prepare the biochar, so that heavy metals in the hyperaccumulator are harmless, and the hyperaccumulator is reutilized; and the hyperaccumulator-based biochar can be used for solidifying and adsorbing heavy metal ions, has the advantages of greenness, energy saving and environmental friendliness, and has a very wide market application prospect.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
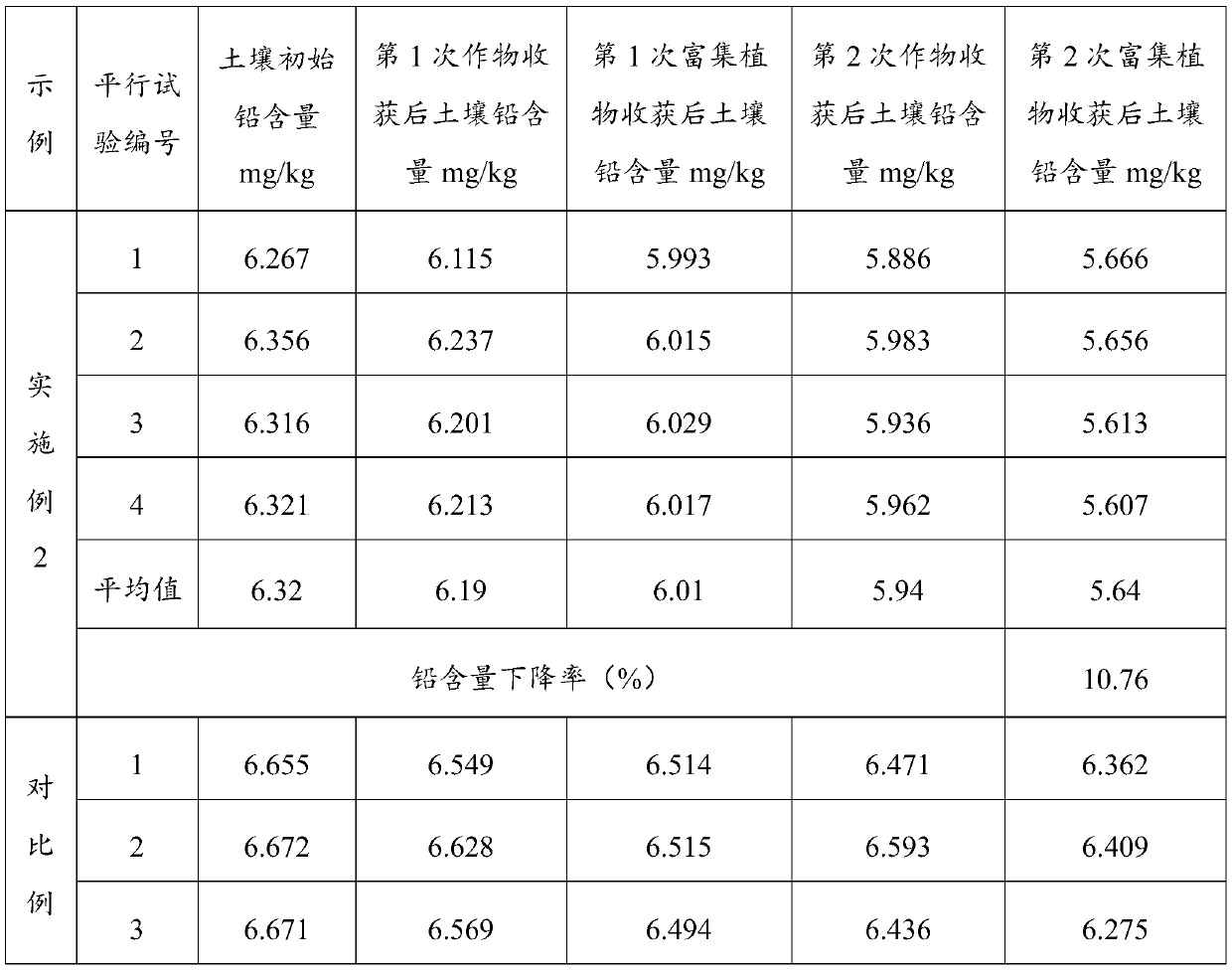
Remediation method for heavy metal pollution of farmland soil
ActiveCN110014032AImprove efficiencyReduce risk of leachingContaminated soil reclamationHyperaccumulatorMaterials science
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil protection, in particular to a remediation method for heavy metal pollution of farmland soil. A heavy metal passivator is uniformly mixed with soil, after conservation, the first crop is planted, and then hyperaccumulators are planted, at that same time, a heavy metal activator is applied and the passivator is applied, after the second crop is planted, the heavy metal passivator is applied at first, so as to reduce the risk of heavy metal leaching, at that same time, heavy metals are avoided to be enriched in crops, and then the heavy metalactivator is applied to plant hyperaccumulators to absorb heavy metals and reduce the content of heavy metals in the soil, and the heavy metals in the soil not covered by the plant roots are kept at alow leaching risk due to the existence of heavy metal passivators. The invention adopts a plant enrichment technology and a method of applying a heavy metal passivator, which can not only fundamentally remove the problem of heavy metals, but also passivate the heavy metals when planting crops, thereby improving the use efficiency of the soil.
Owner:BCEG ENVIRONMENTAL REMEDIATION CO LTD
Recovering metals from soil
InactiveUS20080134364A1Increasing nickel uptakeContaminated soil reclamationProcess efficiency improvementAbove groundHyperaccumulator
The invention relates to recovering metals, such as nickel and cobalt, by phytomining or phytoextracting soils rich in metals wherein the desired metal is selectively accumulated in hyperaccumulator plants by adjusting the soil pH. The metals are ultimately recovered from above-ground plant tissues at economically acceptable levels without further contaminating the metal-containing sites. The invention also relates to metal-hyperaccumulating plants.
Owner:CHANEY RUFUS L +3
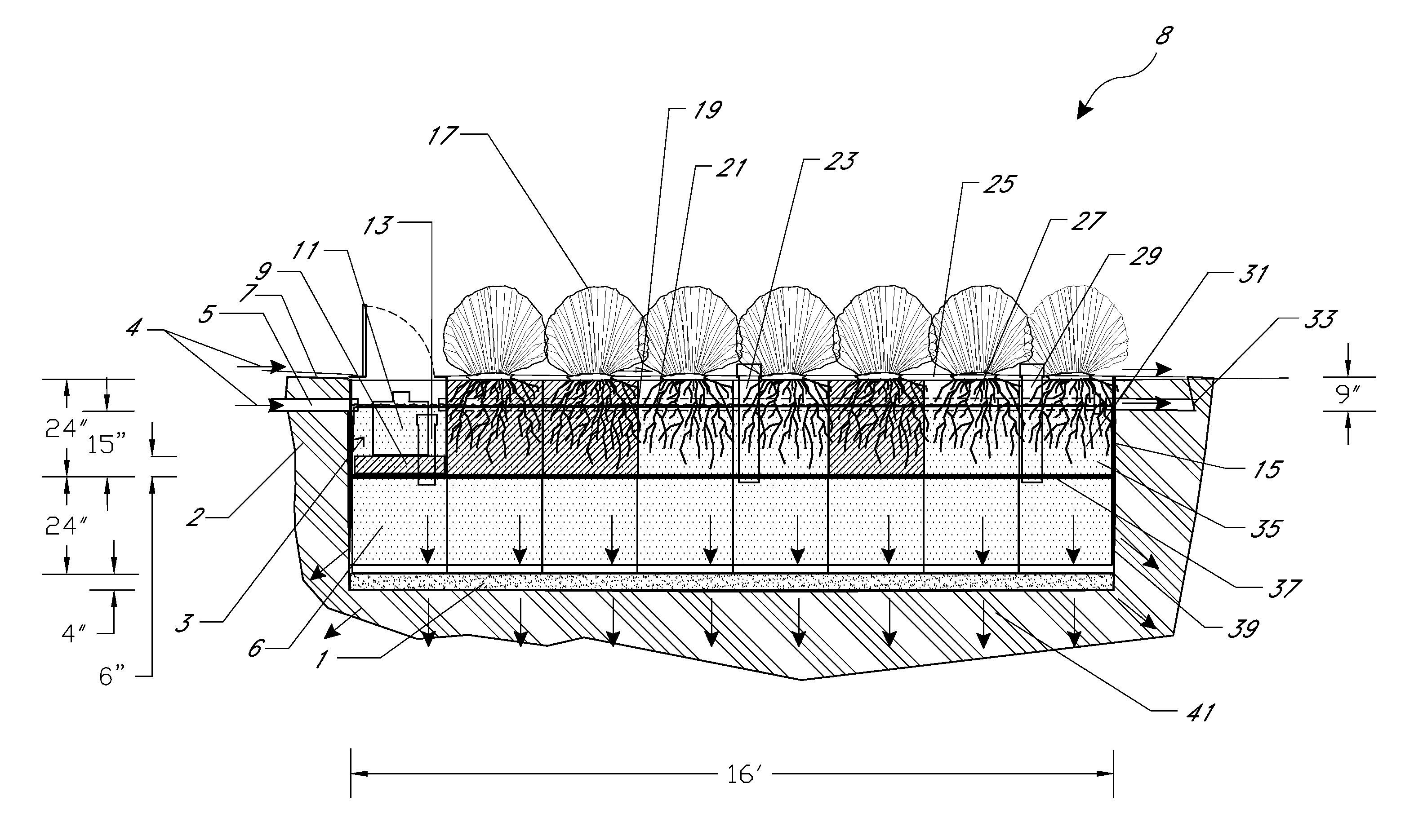
Modular high performance bioswale and water treatment system and method
InactiveUS20140138307A1Avoid erosionPrevent water erosionWater cleaningBiological treatment apparatusTerrainVegetation
A scalable, modular water filtration and re-capture system is disclosed, such as for use as a high performance bioswale, or other purposes. The system includes a filter container with a removable cartridge that contains a filter media soil and planted vegetation, which may be for example one or more hyperaccumulators. The filter container is stacked together with a cistern container and in fluid communication therebetween to form a stacked container pair as a water filter and capture module. This allows for efficient servicing and removability of the filter cartridge, such as in bioswale, below ground, or above ground configurations. Water inflows and outflows may be circulated for varieties of reclamation uses, or treated water may simply be stored or conveyed into the ground. Multiple such modules may be secured together in custom scalable configurations to meet various needs and intended uses for water volumes, available space or terrain, or specific water treatment needs. In some embodiments, a single individual can replace the cartridges as needed.
Owner:COFFMAN JEFF HOWARD +1
Mixed reinforcer for reinforcing repair of nightshade on composite contaminated soils and application thereof
InactiveCN102059245AGood processing effectImprove repair efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonHyperaccumulator
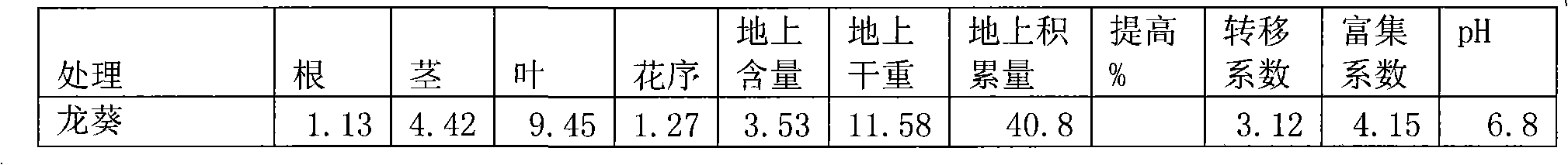
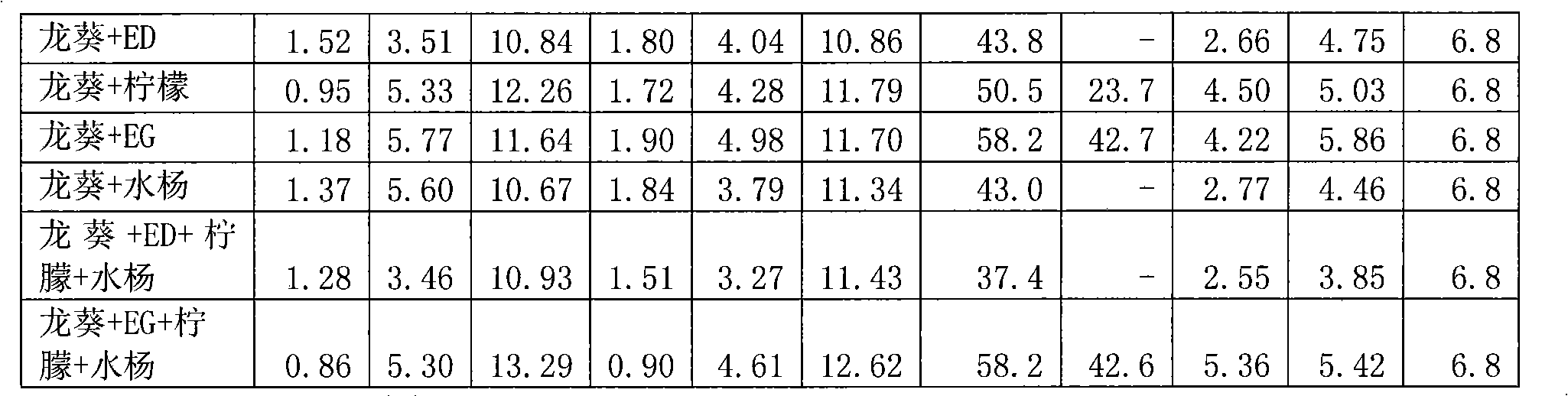
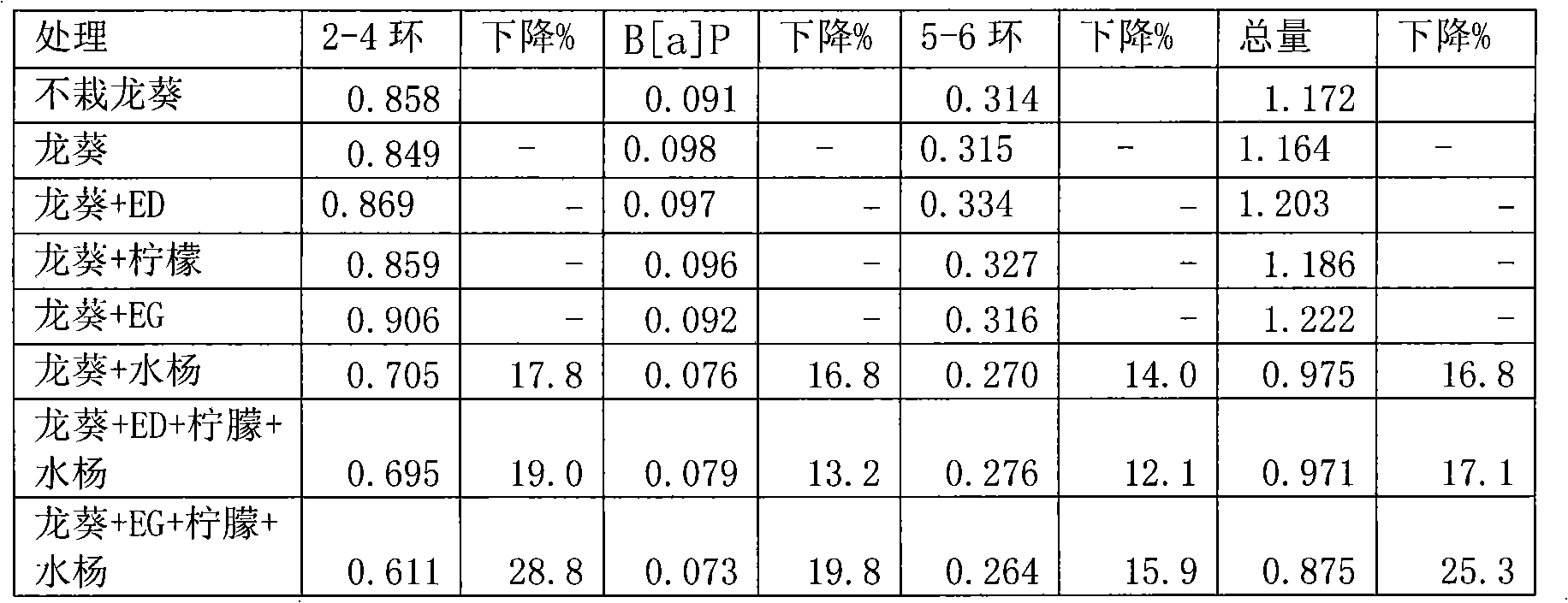
The invention relates to a phytoremediation technology of cadmium-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon composite contaminated soils, and in particular relates to a mixed reinforcer for reinforcing repair of nightshade on composite contaminated soils and an application thereof. The reinforcer is composed of the following components of EGTA (ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid), citric acid and salicylic acid with the molar ratio of (0.1-1.0): (0.5-5.0): (0.1-1.0). The reinforcer is added into heavy metal-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon composite contaminated soils planted with hyperaccumulators and / or accumulators. The citric acid and the salicylic acid are mixed to be dissolved into water to serve as the reinforcer; then, the reinforcer is applied in the heavy metal-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon composite contaminated soils planted with hyperaccumulators and / or accumulators, especially contaminated soils planted with nightshade; when the nightshade is mature, plants and soil samples are collected and are compared with those in which the reinforcer is not applied; the result shows that the processing effect is better if the reinforcer is applied, and the upper Cd extraction ratio of the nightshade is improved by 42.6%; and meanwhile, the removal rate of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon of the soils can reach 25.3%, and the repair efficiency is obviously improved.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Agrobacterium T29 capable of realizing high efficiency activating of mineral elements and heavy metal cadmium
ActiveCN108485998AEffective dissolutionPromote growthBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPotassiumSoil heavy metals
The invention discloses an agrobacterium sp. T29 capable of realizing high efficiency activating of mineral elements and heavy metal cadmium. The agrobacterium sp. T29 is preserved at Guangdong culture collection center (GDMCC) on 29th, Jan., 2018, and the preservation number is GDMCC No:60321. The agrobacterium sp. T29 is capable of realizing high efficiency activating of mineral elements potassium and phosphor and heavy metal cadmium. The agrobacterium sp. T29 is used for root activating of soil mineral nutrients and promoting plant growth, and is capable of dissolving soil cadmium effectively, and increasing hyperaccumulator plant soil heavy metal cadmium repairing efficiency. In soil heavy metal cadmium activating process using the agrobacterium sp. T29, no pollutant harmful for the environment is discharged, and the application prospect in the field of soil improvement is promising.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Endophyte for promoting growth of plants and remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil and application
InactiveCN102161976AAvoid competitionHigh pollution efficiencyPlant growth regulatorsBiocideFungal endophytePlant growth
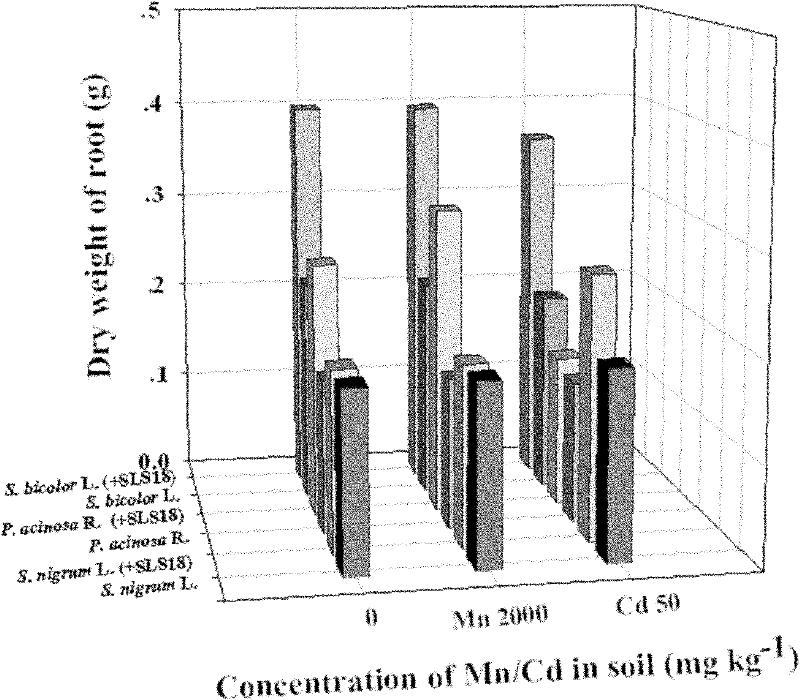
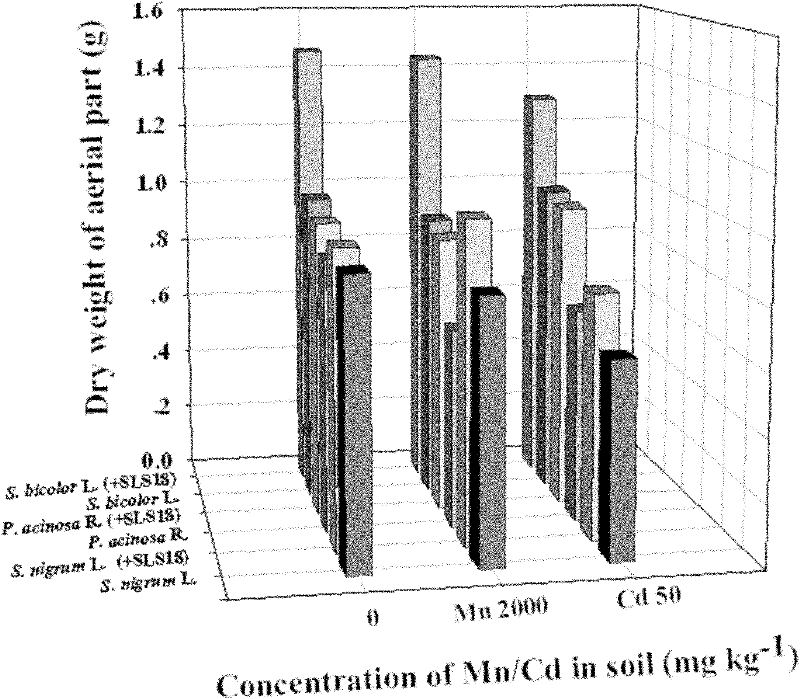
The invention provides an endophyte for promoting the growth of plants and the remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil and application thereof. Bacterial liquid of endophyte SLS18 is utilized to dip-dye Sorghum bicolor L. in a mode of seed bacteria dipping to colonize the endophyte SLS18 into the Sorghum bicolor L. to accompany each stage of the growth of the Sorghum bicolor L., so that the growth of the Sorghum bicolor L. on heavy metal-contaminated marginal land and the remediation of soil are promoted. The endophyte SLS18 is separated from the stem of a hyperaccumulator, namely pokeberry root, is obtained through screening, and is an endophyte which can be successfully colonized in the Sorghum bicolor L., has a remarkable effect of promoting the growth of the Sorghum bicolor L. and has the heavy metal resistance. A method is easy to operate, and is safe and economic, no new pollution is introduced into soil environment, heavy metal-contaminated marginal land resources can be effectively utilized so as to avoid the rival of energy crops and food crops against finite cultivated land, and heavy metal-contaminated land can also be effectively remediated.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for enhancing cadmium-polluted soil phytoremediation through phosphate solubilizing bacteria
InactiveCN106540958AIncrease plant biomassFast growthContaminated soil reclamationHyperaccumulatorPollution soil
The invention discloses a method for enhancing cadmium-polluted soil phytoremediation through phosphate solubilizing bacteria. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the phosphate solubilizing bacteria with the proportion being 10-50 kg for per mu of the soil are uniformly applied to cadmium-polluted soil, the soil is ploughed, base fertilizer is applied to the soil, and the soil is ploughed again; and (2) hyperaccumulators are planted in the cadmium-polluted soil, and a chelating agent with the proportion being 100-300 kg for per mu of the soil is applied to the soil 10-15 days before the hyperaccumulators are harvested. The phosphate solubilizing bacteria and the chelating agent are adopted for enhancing the phytoremediation technology, and the synergistic effect of the phosphate solubilizing bacteria and the chelating agent is sufficiently achieved; and compared with other physical and chemical remediation technologies, the method for enhancing cadmium-polluted soil phytoremediation through the phosphate solubilizing bacteria has the advantages of being low in cost, free of secondary pollution, easy to operate, good in remediation effect and the like.
Owner:HUNAN YONKER ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION RES INST
Planting method of low-aluminum zinc-containing rich-selenium health care tea in hilly red soil region
InactiveCN102668859AEffectively control enrichmentControl enrichmentHorticultureFertilizer mixturesRed soilTea leaf
The invention relates to a planting method of low-aluminum zinc-containing rich-selenium health care tea in a hilly red soil region. The method comprises the following steps that: mixing agents of zinc vitriol, sodium selenite, ammonium nitrate and monosodium phosphate are added into soil external sources according to the major trace element content of red soil and the growth characteristics of tea trees, and then, zinc and selenium annual hyperaccumulators are utilized for relay intercropping after the spring tea picking completion. The planting method has the technical effects that the relay intercropping is carried out, the enriching of the zinc and the selenium in a tea garden is effectively controlled, and the continuous utilization of the soil and the ecological safety of the tea garden are ensured. The zinc content and the selenium content in the tea respectively reach a value higher than 1mg / g and a value higher than 0.3mg / kg, the contents of the organic zinc and the organic selenium are respectively higher than 80 percent, and other qualities of the tea are not obviously changed.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Soil remediation process
InactiveCN110496857ARepair large areaEasy to operateContaminated soil reclamationHyperaccumulatorSoil remediation
The invention discloses a soil remediation process, which is characterized by including the steps of: 1) turning-over of soil, i.e. circularly turning over the soil at the bottom layer to the surfacesoil; 2) planting of hyperaccumulators, i.e. planting hyperaccumulators in the soil subjected to circulating soil turning; 3) application of fertilizer, i.e. applying a phytoremediation agent to the soil where the hyperaccumulators are planted; and 4) irrigation watering, i.e. carrying out water-saving irrigation on the soil where the hyperaccumulators are planted and the hyperaccumulators. The soil remediation process provided by the invention turns over the bottom soil to the upper soil, and plants the hyperaccumulators in the soil and applies fertilizer, not only can remediate the heavy metal polluted soil in a large range, but also is environment-friendly and convenient for operation, and lowers the remediation cost.
Owner:苏州碧青环境科技有限公司
Method for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil or water body by utilizing hyperaccumulator polymerization
InactiveCN105689376AWide range of growthImprove enrichment capacityWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationOperabilityMetal contamination
The invention relates to the technical field of phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated environment, in particular to a method for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil or water body by utilizing hyperaccumulator polymerization. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being capable of removing multiple pollutants, being low in cost, good in effect and strong in operability, and being capable of avoiding damage to the basic structure and functions of the water body or soil, avoiding secondary pollution, preserving water and soil and beautifying environment at the same time, and can be popularized and applied in a large scale. According to the technical scheme adopted by the invention, symphytum officinale is planted in the soil or water body polluted by cadmium, copper, lead and zinc, and when the symphytum officinale grows to a mature period, the overground part or the whole plant is harvested and is removed from the polluted soil or water body, and then the processes of planting and harvesting and removing the symphytum officinale can be repeated in the soil or water body polluted by cadmium, copper, lead and zinc, until the contents of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc in the soil or water body reach environmental quality standards.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Phytoextraction repairing method for heavy metal cadmium contaminated calcicolous farmland soil
InactiveCN106903157AReduce disturbanceWon't breakContaminated soil reclamationRepair processesChromium
The invention discloses a phytoextraction repairing method for heavy metal cadmium contaminated calcicolous farmland soil, and belongs to the technical field of phytoremediation for contaminated soil. The phytoextraction repairing method for the heavy metal cadmium contaminated calcicolous farmland soil particularly comprises the following steps that S1, hyperaccumulators of which the enrichment coefficient and transfer coefficient meet the standards are planted in the heavy metal cadmium contaminated calcicolous farmland soil; S2, a chelating agent is added to improve biological effectiveness of heavy metals; S3, growth conditions of plants are periodically observed; and S4, sampling is conducted on the plants, and the content of metal chromium at different positions of the plants is analyzed. The phytoextraction repairing method for the heavy metal cadmium contaminated calcicolous farmland soil belongs to an in-situ remediation technology, disturbance to the environment is small, landscape ecology cannot be destroyed, the environment can be greened, operation is easy, and the phytoextraction repairing method has a wide application prospect in environmental protection. According to the phytoextraction repairing method, soil fertility and ecological structure cannot be destroyed in the soil repairing process, and other crops can be planted without secondary treatment.
Owner:PINGDINGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Organic fertilizer for modifying plow layer of low-yield land and repairing heavy metal plants
The invention relates to an organic fertilizer for modifying the plow layer of a low-yield land and repairing heavy metal plants. For the modification of the plow layer (0-35 cm deep) of the low-yield land, the soil should comprise 30% of organic matters, 6% of inorganic nutrients, 5% of calcium (including chelated calcium, complexed calcium and and ionized calcium), 10% of silicon, and 0.5% of magnesium, zinc, manganese, molybdenum, selenium and on the like by weight percent. For the repair of the heavy metal plants in the plow layer of the soil, the following types of plants are involved: cadmium absorption accumulator plants: Pteris VittataL., Pteris CreticaL., Sedum Olfre diiL., and Phyto Cacca atinosa ROXL.; cadmium hyperaccumulator plants: Vio la booshanensis and Solanym nigrumL.; chromium absorption accumulator plants: Digitaria Sanguinnalis; arsenic hyperaccumulator plants: ciliate desert-grass lead accumulator plant: E.Canadensis; nickel accumulator plant: taraxacum officimale.
Owner:林炳营 +1
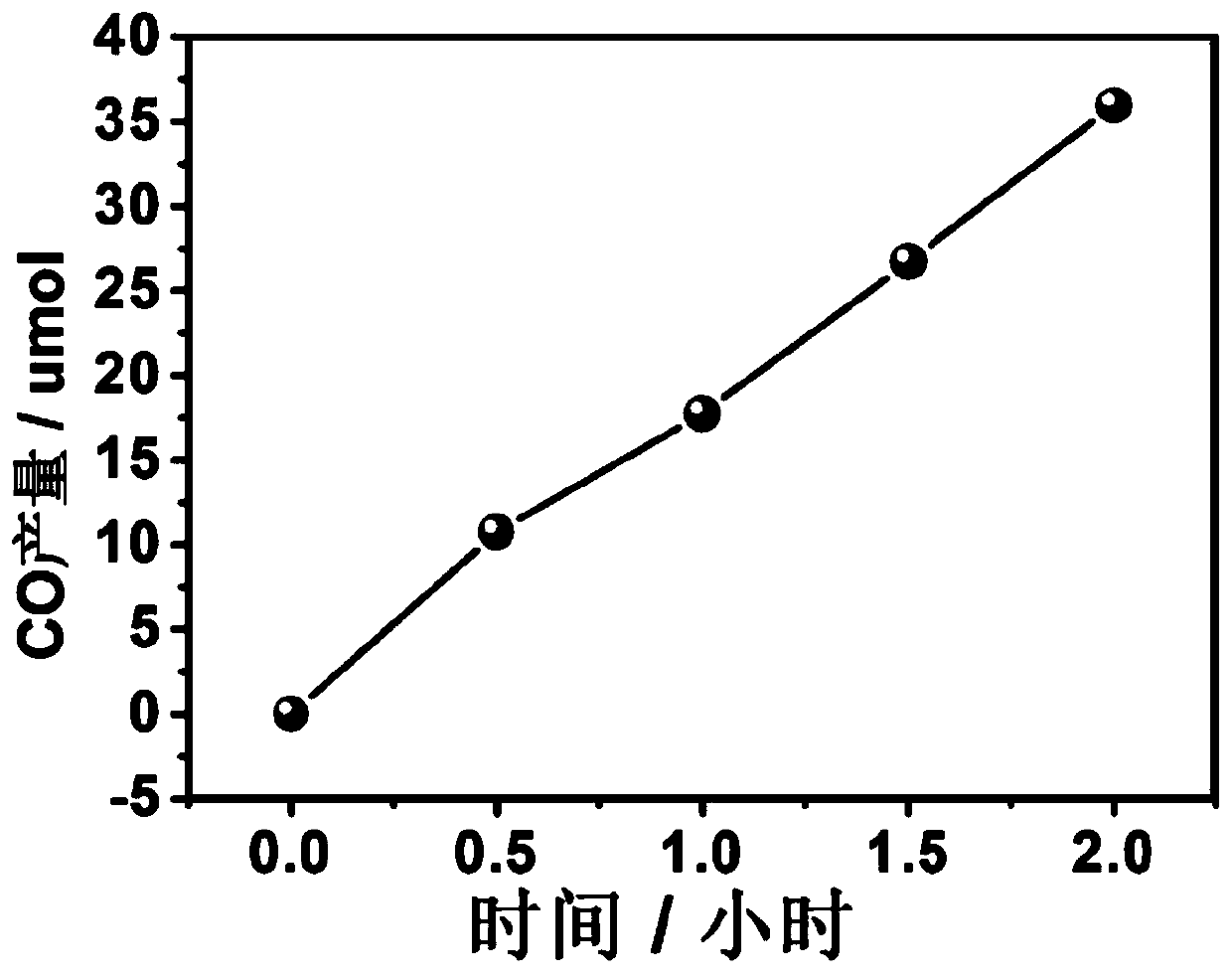
Method for preparing carbon dioxide reduction photocatalyst by utilizing hyperaccumulators
ActiveCN111111660AWide variety of sourcesSimple preparation processCarbon monoxideMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPhoto catalyticHyperaccumulator
The invention provides a method for preparing a carbon dioxide reduction photocatalyst by utilizing hyperaccumulators. The method comprises the steps: firstly, carrying out crushing and sand removal treatment on the hyperaccumulators; adding distilled water into the hyperaccumulators, uniformly mixing, and carrying out hydrothermal reaction at the temperature of 120-250 DEG C for 2-50 h to obtaina reaction product; and finally, centrifuging, washing and drying the obtained reaction product to obtain the carbon dioxide reduction photocatalyst. The preparation method is simple; the prepared carbon dioxide reduction photocatalyst can realize the reduction of carbon dioxide, and high added value products such as carbon monoxide are obtained; in addition, the invention provides a new method for resource utilization of the hyperaccumulators, and the method has wide application prospects in the fields of treatment of the hyperaccumulators containing heavy metals, reduction of carbon dioxideand other energy and chemical engineering.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Remediation method for heavy metal polluted soil
InactiveCN109332376AReduce the risk of contaminated agricultural productsIncrease selenium contentContaminated soil reclamationHyperaccumulatorMagnetotactic bacteria
The invention discloses a remediation method for heavy metal polluted soil. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding a magnetotactic bacteria liquid culture medium to the heavy metal polluted soil; inoculating magnetotactic bacteria; and turning over; (2) adding the magnetotactic bacteria liquid culture medium to the heavy metal polluted soil; and arranging a magnetic field; (3) collecting the surface layer of the heavy metal polluted soil; (4) showering the collected heavy metal polluted soil; (5) spreading a soil conditioning agent on the surface of the heavy metal polluted soil;(6) planting heavy metal hyperaccumulators in the heavy metal polluted soil; (7) spraying a heavy metal blocking agent after the hyperaccumulator seeds are formed; and (8) cycling the steps (1) to (7) twice or three times. The method has the advantages of being low in planting difficulty, easy to manage, applicable to remediating of wide-range polluted soil, small in environmental disturbance, and good in soil treatment effect; and moreover, the environment is beautified while the polluted soil is treated; and the popularization is high.
Owner:云南惟绿环保科技有限公司
Recovering metals from soil
InactiveUS7268273B2Increasing nickel uptakeContaminated soil reclamationBlast furnace detailsNickelHyperaccumulator
The invention relates to recovering metals, such as nickel and cobalt, by phytomining or phytoextracting soils rich in metals wherein the desired metal is selectively accumulated in hyperaccumulator plants by adjusting the soil pH. The metals are ultimately recovered from above-ground plant tissues at economically acceptable levels without further contaminating the metal-containing sites. The invention also relates to metal-hyperaccumulating plants.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE +2
Method for remediating soil with single or combined contamination of Cd and Pb by hyperaccumulator Emilia sonchifolia L.
InactiveUS20150101247A1Low costWide applicationContaminated soil reclamationCultivating equipmentsHyperaccumulatorPlanting seed
A method for remediating soil which is contaminated by an individual or a mixture of Cd and Pb with a hyperaccumulator Emilia sonchifolia L. includes steps of: planting seeds or seedlings of Emilia sonchifolia L. in soil which is contaminated by an individual or a mixture of Cd and Pb; watering regularly to maintain the soil moist; after Emilia sonchifolia L. flowers or completely matures, removing all of or an aboveground part of the plant from a contaminated spot of the soil and disposing the removed plant properly; repeating the above steps until a Cd and Pb content of the soil fall within an environmental security standard. Besides being adaptable and widely available, the Emilia sonchifolia L. is both a Cd hyperaccumulator and a Pb hyperaccumulator by respectively satisfying four indexes of the Cd hyperaccumulator and the Pb hyperaccumulator.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
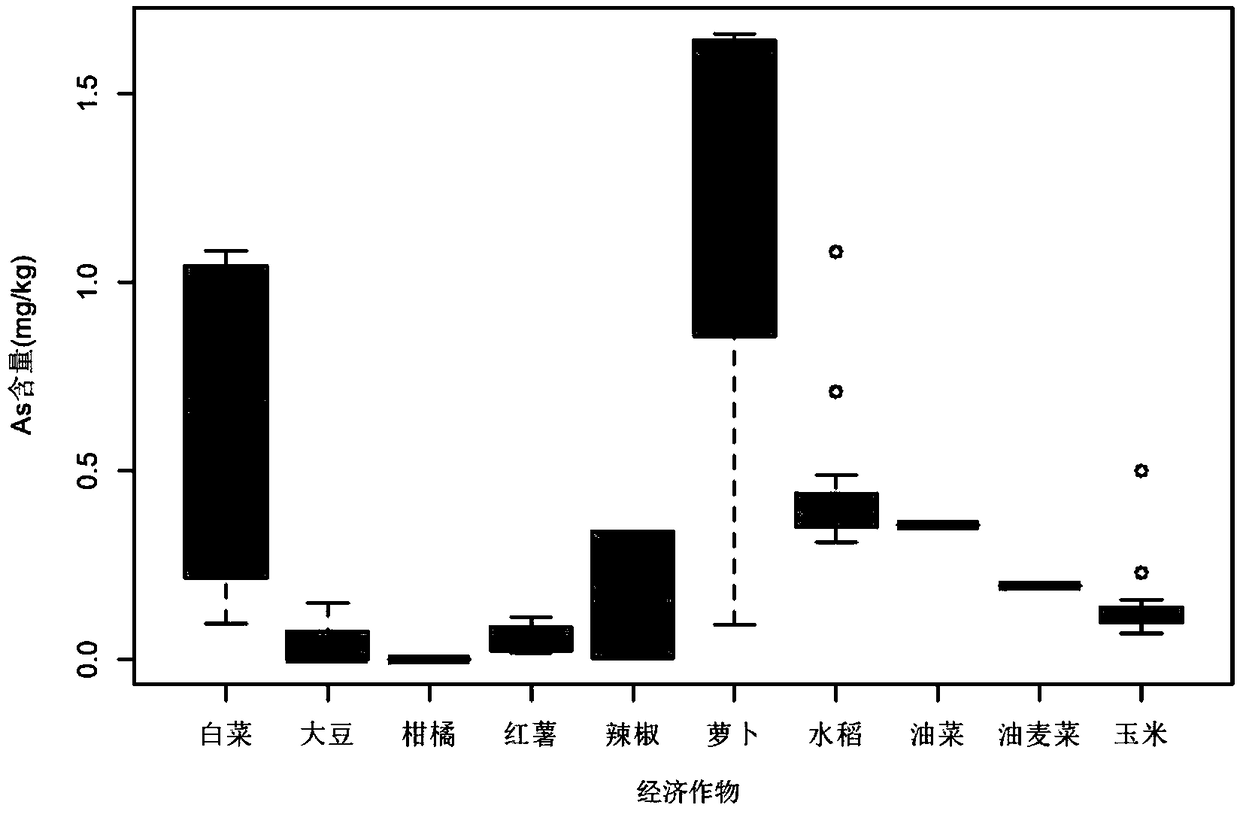
Method for remediating arsenic polluted soil by interplanting hyperaccumulators and commercial crops
InactiveCN108655172ASolve the problem of fear of direct sunlightAvoid light competitionContaminated soil reclamationSocial benefitsAbsorption capacity
The invention provides a method for remediating arsenic polluted soil by interplanting hyperaccumulators and commercial crops. In the arsenic polluted soil, the hyperaccumulators and the commercial crops are interplanted; the safe commercial crops are harvested by utilizing the low absorption capacity of the screened commercial crops on soil arsenic; meanwhile, by utilizing the enrichment capacityof the hyperaccumulators on the soil arsenic, the arsenic is enriched onto a plant shoot, and the mature plant (such as ciliate desert-grass) shoot is harvested and fed to an exclusive site so as tobe centrally and harmlessly treated, so that the aims of remediating and producing at the same time are achieved. The method for remediating the arsenic polluted soil by interplanting the hyperaccumulators and the commercial crops provided by the invention is reasonable in design, low in cost and high in operability, can be applied to the arsenic polluted soil, achieves the aims of remediating andproducing at the same time, has favorable economic benefit and social benefit, and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Method for repairing heavy metal polluted soil by using radix achyranthis bidentatae as manganese hyperaccumulator
InactiveCN102632074ALarge biomassStrong patienceContaminated soil reclamationHyperaccumulatorManganese
The invention relates to a technology for repairing heavy metal polluted soil, and in particular relates to a method for repairing heavy metal polluted soil by using radix achyranthis bidentatae as a manganese hyperaccumulator. The radix achyranthis bidentatae belongs to a renascent herb, and found by field investigation, the radix achyranthis bidentatae has strong tolerance and enrichment capacity on manganese. Indoor culture experiments prove that the radix achyranthis bidentatae is planted in manganese polluted soil, absorbs manganese from the soil by roots, and transports the manganese to an overground part for accumulation; and when growing to maturity, the radix achyranthis bidentatae is harvested and duly handled, thus the purpose of removing excessive manganese from the soil is achieved. Through a mode of continuously planting the radix achyranthis bidentatae on the manganese polluted soil and continually harvesting the radix achyranthis bidentatae, the manganese in the polluted soil is continuously extracted until the content of the manganese in the soil reaches the standard of environmental safety. The method is used for repairing the manganese polluted soil, and is a green and safe polluted soil treatment method.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Adsorbent based on photosynthetic spore bacterium treatment of soil heavy metals, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107597060APromote growthFacilitate Expansion DepthBacteriaOther chemical processesSorbentPlant cell
The invention discloses an adsorbent based on photosynthetic spore bacterium treatment of soil heavy metals, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the adsorbent comprises the following steps: preparing a composite powder, preparing a bacterium culture solution, preparing a photosynthetic bacterium culture solution, preparing a spore bacterium culture solution, and culturing photosynthetic bacteria. The photosynthetic bacteria and the spore bacteria promote the growth of hyperaccumulators, enrich microbial florae, promote the root expansion depth, improve the selectivity to heavy metals, inhibit the transshipment trend of the heavy metals from the root to the aboveground part, shorten the repairing time and accelerate the repairing efficiency. The heavy metal ion enrichment ability of the photosynthetic bacteria and the spore bacteria and the heavy metal ion adsorption and removal ability of zeolite, vermiculite and agriculture and forestry waste active carbon arecombined to make the heavy metal ions adsorbed into the adsorbent, solidify the soil heavy metal ions and transform the heavy metal ions into a low-toxicity form, so the soil heavy metal ions are effectively adsorbed, and the influence of plant cell metabolism disorder caused by the heavy metals on normal growth of the plants is reduced.
Owner:XINJIANG GUANGHEYUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Plant adsorbing material capable of reducing lead content of tree moss extract and application thereof
ActiveCN104353430AWide range of growthLarge biomassOther chemical processesSeparation with moving sorbentsHyperaccumulatorPlant Sources
The invention relates to a plant adsorbing material capable of reducing the lead content of a tree moss extract. The plant adsorbing material is characterized by being obtained through treatment, namely crushing, dilute acid soaking, filtration, ionized water washing, drying and the like by taking the leaves of ciliate desert-grass as raw materials. The lead content of the tree moss extract can be reduced by adding the plant adsorbing material to the tree moss extract for adsorption and then filtering to remove the plant adsorbing material. The plant adsorbing material disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the ciliate desert-grass is a heavy metal hyperaccumulator plant, has high adsorption effect on arsenic and lead and can release the adsorption site of a heavy metal contained in a material by being modified through dilute acid, the treated plant adsorbing material is capable of adsorbing lead ions contained in the tree moss extract by being added to the tree moss extract and the possibility of adding a non-plant source component to the tree moss extract is prevented. The plant adsorbing material disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low price of the used materials, easiness for operation of treatment means and obviousness in lead removal effect.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com