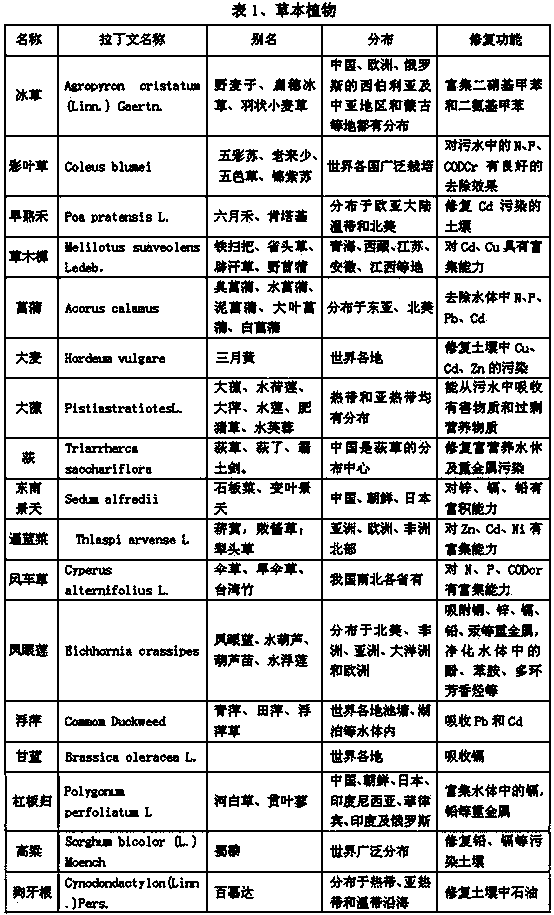
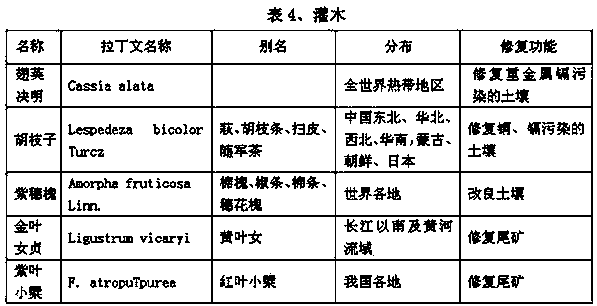
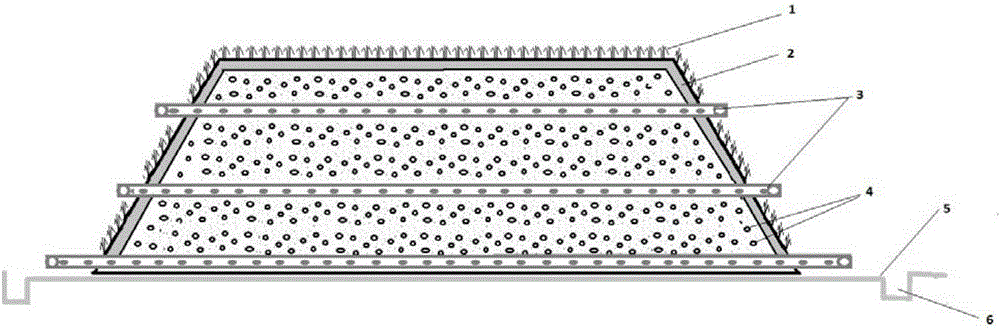
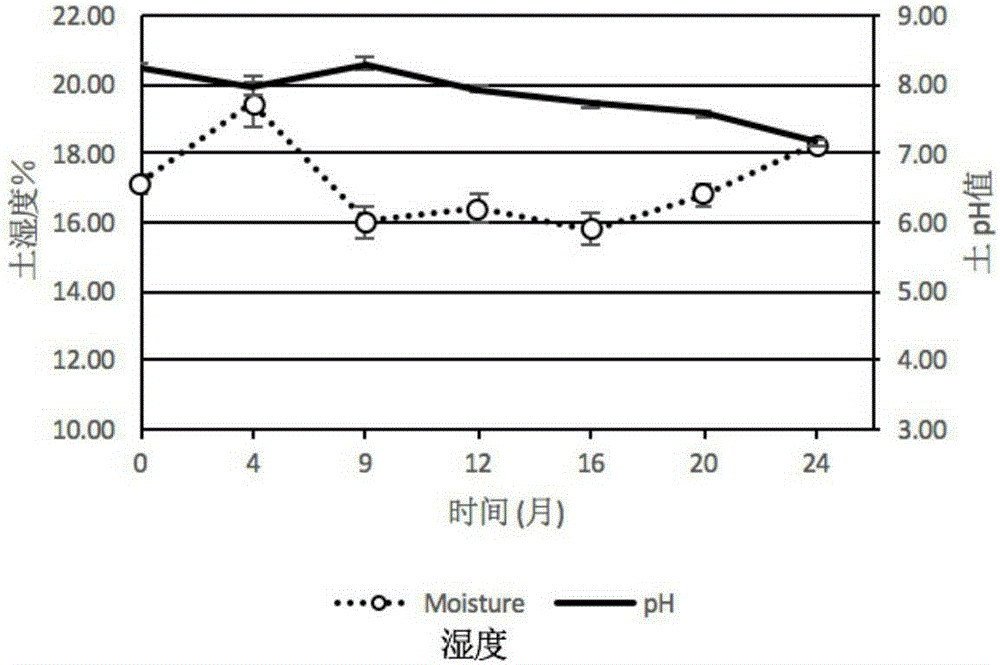
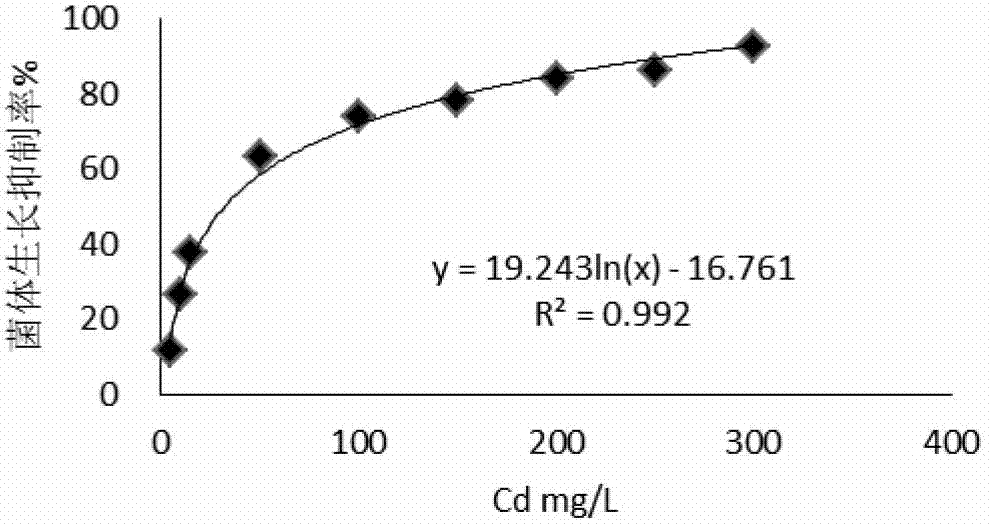
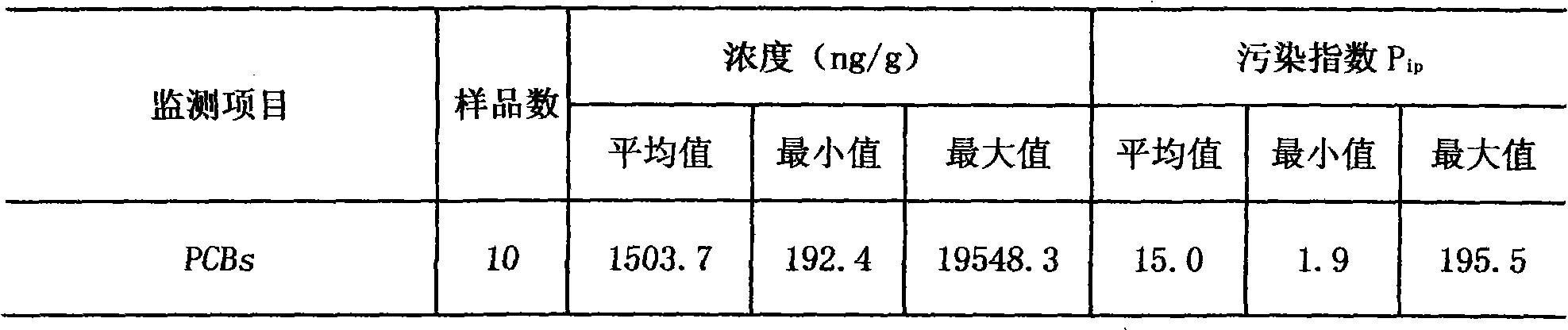
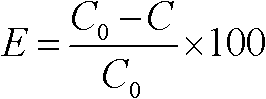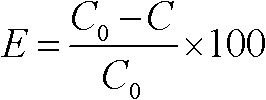Patents
Literature
840 results about "Phytoremediation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phytoremediation /ˌfaɪtəʊrɪˌmiːdɪˈeɪʃən/ (from Ancient Greek φυτό (phyto), meaning 'plant', and Latin remedium, meaning 'restoring balance') refers to the technologies that use living plants to clean up soil, air, and water contaminated with hazardous contaminants. It is defined as "the use of green plants and the associated microorganisms, along with proper soil amendments and agronomic techniques to either contain, remove or render toxic environmental contaminants harmless".
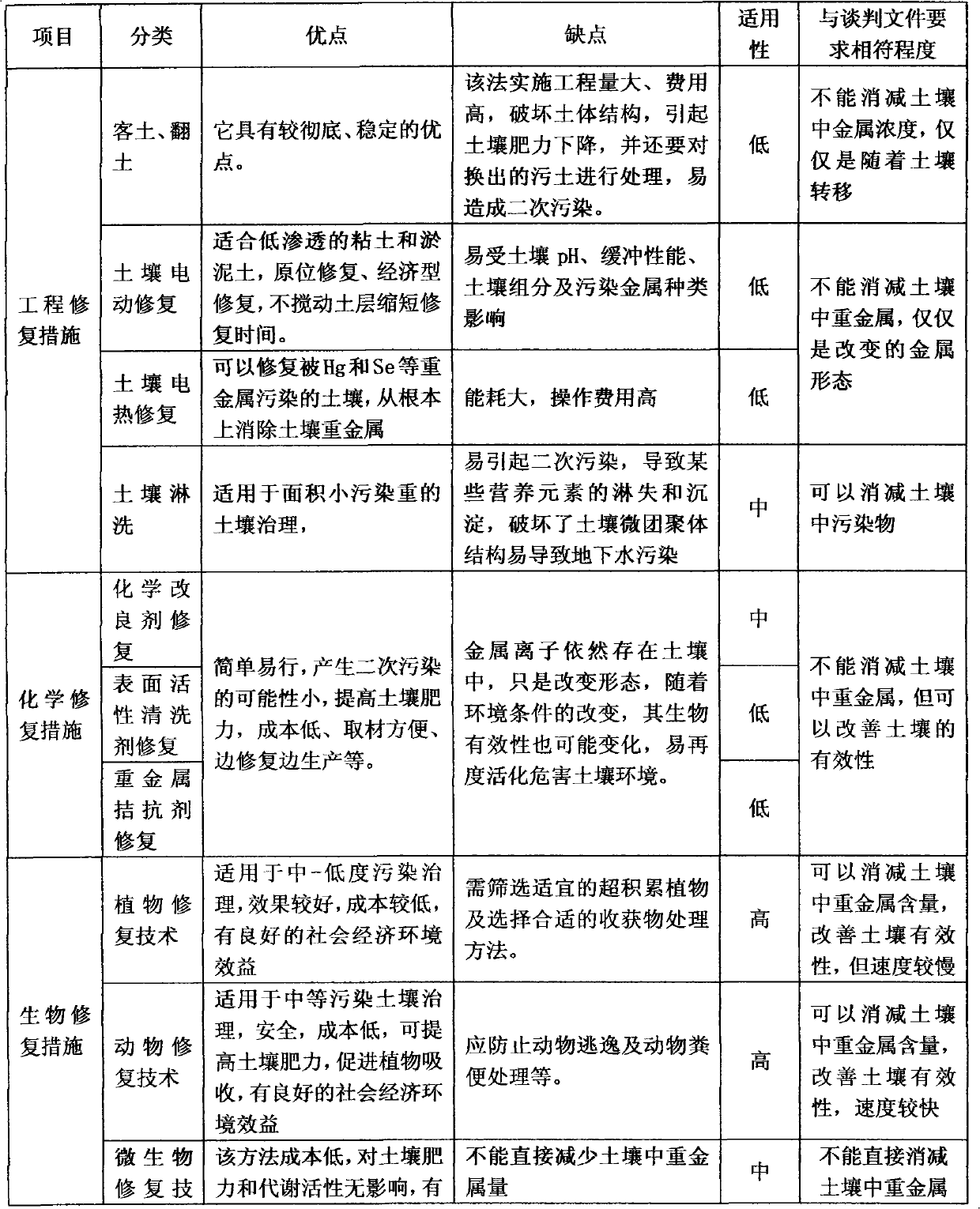
Soil remediation method for treating heavy metal pollutants
ActiveCN101947539AReduce the amount requiredNo secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceSoil remediation
Owner:浙江博世华环保科技有限公司
Solid-chemical compositions, geochemical binder system, and improved high-shear granulation process for both conventional and slow-release fertilizer and bioremediation nutrient compositions
InactiveUS20020178772A1Less-expensive to produceWiden meansSolid/semi-solid fertilisersMatrix fertilisersSolubilityAdditive ingredient
This invention discloses advanced means for the formulation and preparation of solid-chemical compositions which provide sources of water-soluble nutrients, electron acceptors and other agents for agriculture and waste-treatment, in particular, the bioremediation of contaminated environmental media. The disclosed formulations and means of production of the slow-release solid-chemical compositions of the present invention utilize a novel and economical "biphasic" chemical-system technology which involves a combination of a first "nutrient" component (1) which comprises water-soluble nutrients and other biologically utilizable substances with a second component (2) which comprises an inorganic geochemical-binder system. The simplest embodiment of the geochemical-binder system comprises one or more salts of phosphoric acid. In the preferred embodiments of the present invention intended for the slow-release of the ingredients contained in the "nutrient" component (1), the geochemical-binder system of component (2) comprises a combination of one or more salts of phosphoric acid with a inorganic binder matrix preferably containing a mixture of low-solubility carbonates, carbonate minerals, phosphates and phosphate minerals. The different embodiments of the geochemical-binder system of this invention allows a wide variation of formulations of the nutrient component (1) to be prepared in both conventional and slow-release forms using an improved high-shear granulation process whereby the dangerous chemicals typically used in the granulation process are largely or completely replaced with water. The present invention discloses means by which such compositions can be economically prepared in large quantities so as to meet the specific needs of different sectors of the agricultural / agribusiness and phytoremediation / bioremediation markets. The disclosed solid-chemical compositions of the present invention provide improved, cost-effective means for slowing and controlling the release-rate profiles of water-soluble nutrients, such as nitrogen- and phosphorus-rich compounds, and improved means for enhanced and / or time-targeted nutrient uptake by plants and microorganisms. The present invention also provides improved means for the reduction of nutrient run-off from agricultural areas into surface waters and means of preventing or minimizing nutrient-contamination of ground-water aquifers.
Owner:HINCE ERIC CHRISTIAN MR
Method for biologically remediating water body and soil comprehensively utilizing resources
ActiveCN103736721ALow costSimple technologyContaminated soil reclamationSustainable biological treatmentAlgal growthBioremediation
The invention discloses a method for biologically remediating a water body and soil comprehensively utilizing resources. The method comprises the steps: (1), determining main pollutants in a selected land area or water body area; (2), selecting to plant and / or cultivate fast-growing herbaceous plants, fast-growing alga, trees, bushes, fungi or microorganisms with high remediation efficiency in the selected land area or water body area; (3), harvesting or collecting the fast-growing herbaceous plants and the fast-growing alga after growing to reach a suitable height or size; (4), concentratedly processing the harvested or collected fast-growing herbaceous plants and the fast-growing alga, and comprehensively utilizing to prevent the pollutants from dispersing; (5), remediating an eutrophic water body by adopting an artificial floating island; (6), remediating a heavy metal polluted water body by confining floating plants; (7), repairing cadmium and zinc polluted soil by mixed-cropping festuca arundinacea and bluegrass; (8), remediating polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) polluted soil by mixed-cropping alfalfa and italian ryegrass; and (9), extracting and recovering silver from silver-containing wastewater remediation plants.
Owner:湖南绿心科技有限公司
A method for the remediation of harmful organics and/or heavy metal contaminated matrix
ActiveCN105344709APlay a role in loosening and ventilatingRestoration concepts for green sustainabilityContaminated soil reclamationBiostimulationMicrobial agent
The present invention provides a method for the remediation of harmful organics and / or heavy metal contaminated matrix in order to remediate harmful organics and / or heavy metal contaminated soil, sediment and / or sludge. The method involves the processes of biostimulation, bioaugmentation, rhizoremediation, phytoremediation and a passive biopile. The method comprises steps of: a) designing a microbial agent comprising pollutant degrading bacteria, plant promoting bacteria and / or biosurfactant producing bacteria; b) preprocessing the matrix; c) constructing a passive biopile; and d) capping the biopile with plants for phytoremediation. The method achieves internationally-dominant green and persistent remediation while achieving bioremediation / phytoremediation degrading the organics and removing heavy metal.
Owner:山东迈科珍生物科技有限公司
Slow-release fertilizer with effect of soil remediation and remediation method of soil polluted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
ActiveCN101928188AImprove repair efficiencyImprove biological activityContaminated soil reclamationFertilizer mixturesSolubilityPhytoremediation
The invention discloses slow-release fertilizer with the effect of soil remediation, which is prepared by polyhydroxyalkanoates which can be completely biodegraded, organic and inorganic nutrients and other substances, by slow-releasing the organic and inorganic nutrients, microorganism propagation and sustained and rapid growth of plants can be promoted, the bioactivity and water solubility of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are quickened, and simultaneously, the defects of fertilizer loss and repeated fertilization can be avoided, thereby saving the cost and enhancing the soil remediation efficiency. The invention also discloses a soil pollution remediation method by utilizing the slow-release fertilizer, plants with the remediation effect are planted in the soil with the slow-release fertilizer, and efficient, environment-friendly and sustained remediation of the soil polluted by the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) can be realized by utilizing the microorganism-plant remediation technology.
Owner:SHENZHEN ECOMANN BIOTECH
Energy crops for improved biofuel feedstocks
InactiveUS20070250961A1Low costIncrease productionBryophytesSugar derivativesDownstream processingBiofuel feedstock
The present invention is directed to improved systems and methods for reducing costs and increasing yields of cellulosic ethanol. In particular, the present invention provides plants genetically transformed for increased biomass, expression of lignocellulolytic enzymes, and simplification of harvesting and downstream processing. Also provided are methods for using these transgenic plants in the production of clean, marketable feedstocks for production of renewable fuels and chemicals and in other applications including phytoremediation.
Owner:EDENSPACE SYST CORP
Mutiple gene expression for engineering novel pathways and hyperexpression of foreign proteins in plants
InactiveUS20030041353A1High expressionHigh copy numberClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesPosition effectOperon
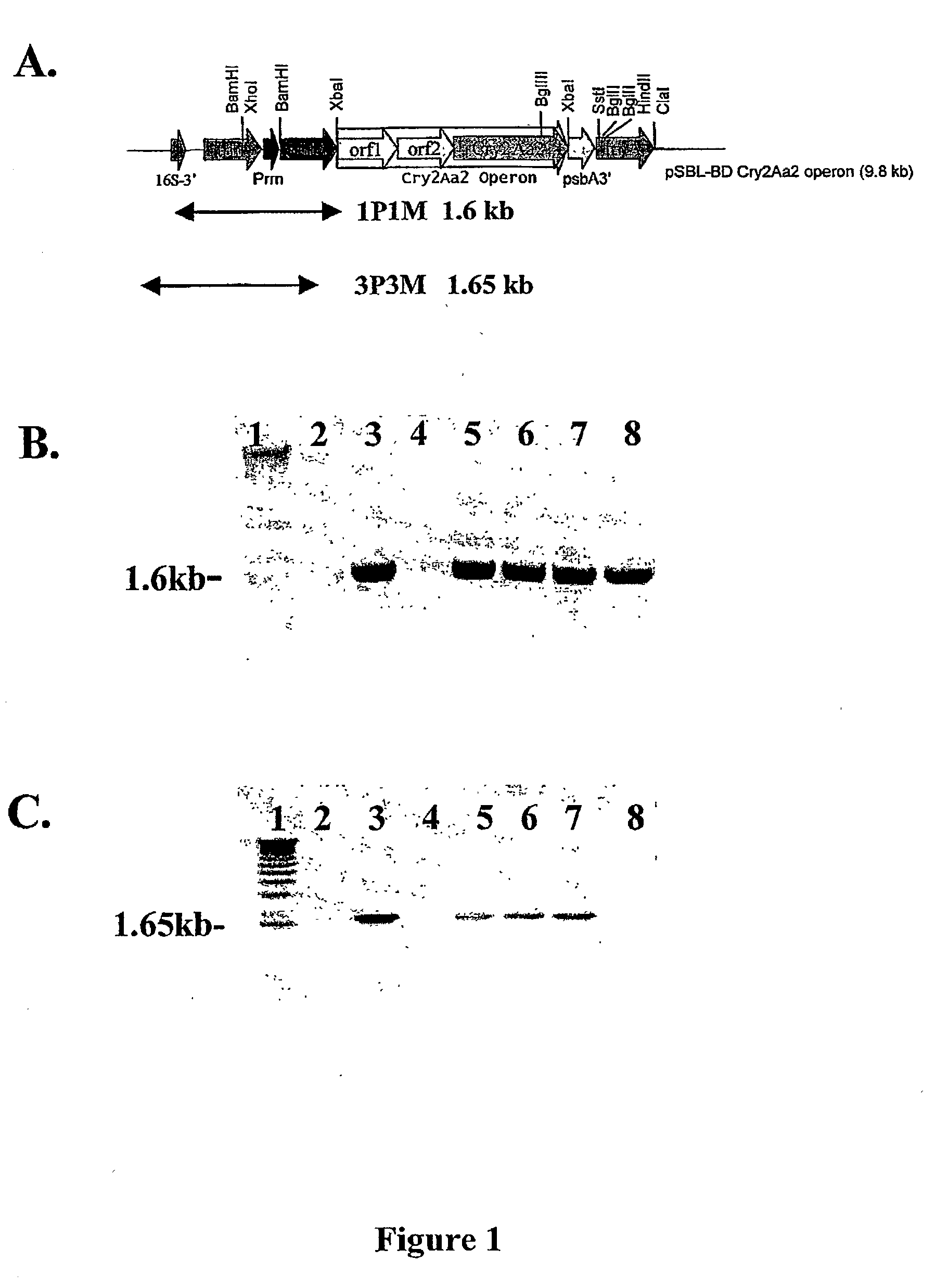
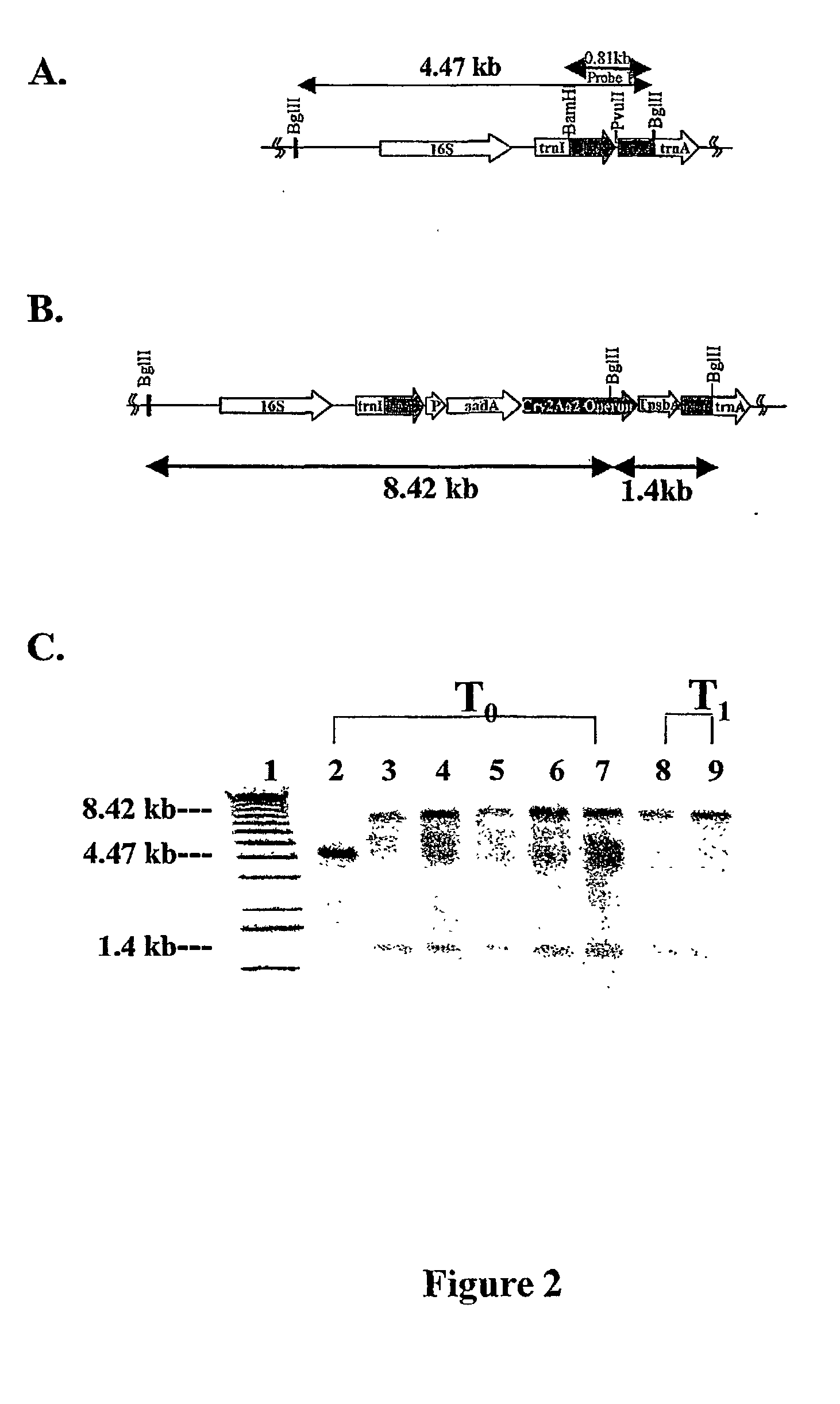
Introducing blocks of foreign genes in a single operon would avoid complications such as position effect and gene silencing inherent in putting one gene at a time into random locations in the nuclear genome. Cloning several genes into a single T-DNA does not avoid the compounded variable expression problem encountered in nuclear transgenic plants. This disclosure shows that a bacterial operon can be expressed in a single integration event as opposed to multiple events requiring several years to accomplish. Expression of multiple genes via a single transformation event opens the possibility of expressing foreign pathways or pharmaceutical proteins involving multiple genes. Expressing the Cry2aA2 operon, including a putative chaperonin to aid in protein folding, in the chloroplast via a single transformation event leads to production of crystalized insecticidal proteins. Expressing the Mer operon via a single transformation event leads to a phytoremediation system.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Heavy metal contaminated soil conditioner and plant and chemistry combined remediation method
ActiveCN101724404AImprove stabilityImprove bindingContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSoil propertiesSoil remediation
The invention discloses a heavy metal contaminated soil conditioner and a plant and chemistry combined remediation method. The heavy metal contaminated soil conditioner is a mixture of red mud and slaked lime. In the invention, the plant and chemistry combined remediation method is used, the pH of the soil is regulated by a chemical method, and heavy metals in the soil are absorbed by planting energy crops, hyperaccumulative plants and the like, thereby improving the soil properties, gradually reducing the content of heavy metals in the soil, finally achieving the purpose of soil remediation, improving the plant remediation efficiency, and being favorable to large-scale commercial application.
Owner:广东华农大城市规划设计院有限公司
Plant restoration method for heavy metal pollution of soil
InactiveCN1593797AImprove extraction efficiencyNo secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationRestoration methodSoil heavy metals
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for repairing urban house refuse compost heavy-metal composite pollution by synergistic lawn plant
InactiveCN1709834AImprove enrichment capacityPlay a repairing roleClimate change adaptationOrganic fertilisersHeavy metal compoundLitter
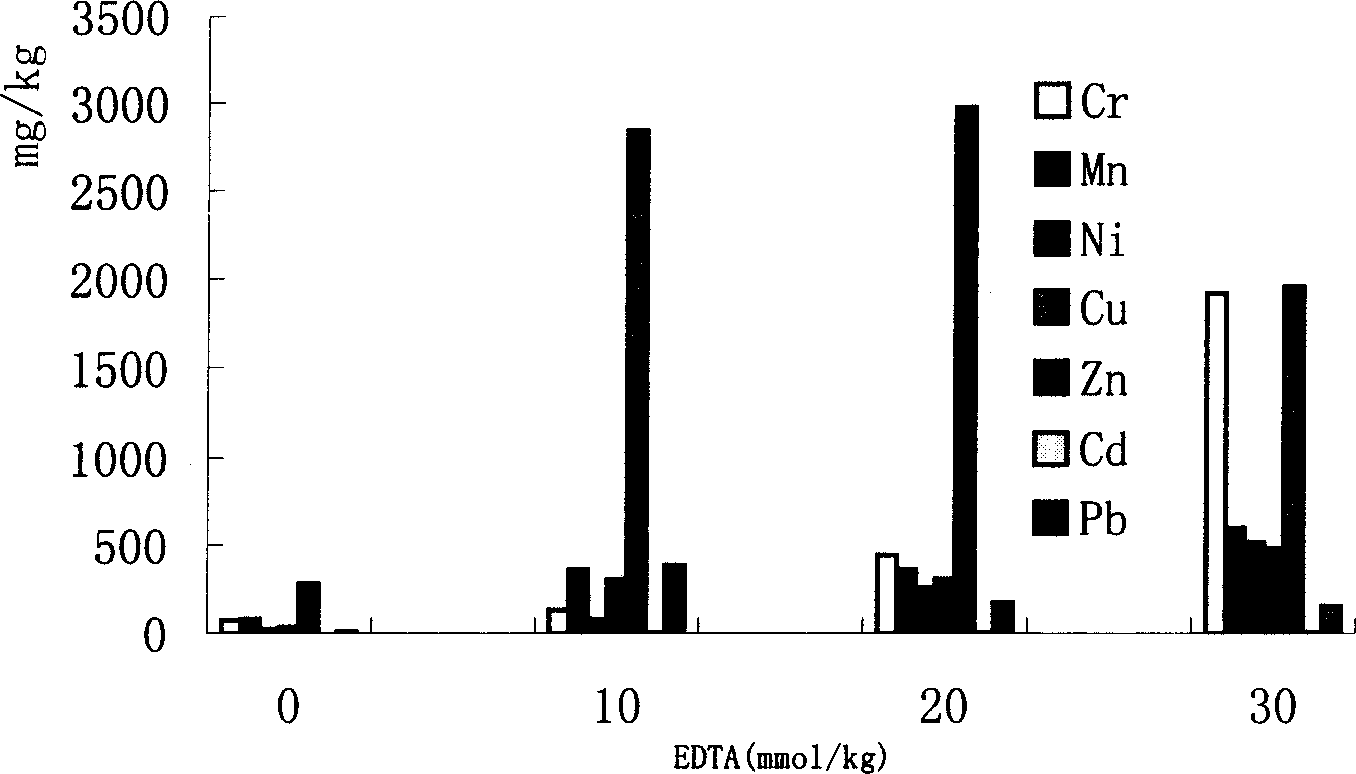
The invention relates to the method of a kind of using synergizing lawn plant to restore the heavy metal compound pollution in city life waste compost. In the period from seeding to mowing of grasses on lawn, fertilize EDTA into the waste compost base substance as per 5 - 30 mmol / kg; through fertilize EDTA, increase the extracting effect of lawn grasses to heavy metal in city life waste compost base substance, to make the effect of lawn glasses corresponding to the effect of heavy metal super-enriching plant. The application of the invention can not only rebuild waste compost industry, and realize the effective resource use of waste compost, but also provide scientific basis for complexing restoration of lawn grasses to heavy metal pollution area.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
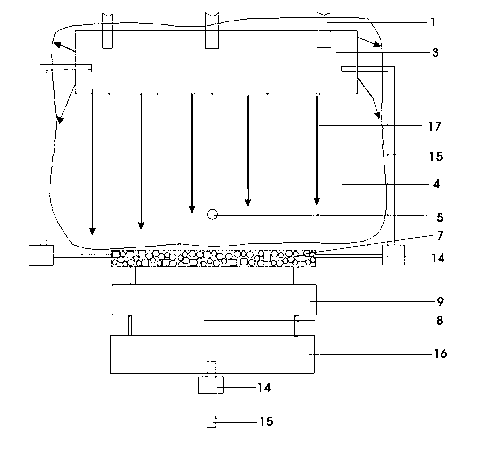
In-situ rainwater leaching repair system for contaminated soil
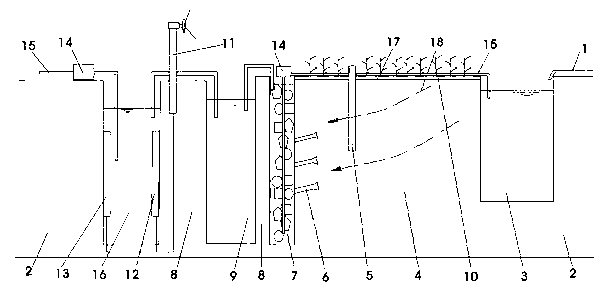
The invention relates to an in-situ rain leaching repair system for contaminated soil. The in-situ rain leaching repair system at least comprises three parts, namely a rain collection part, a leaching repair part and a waste water treatment part, wherein the rain collection part is provided with water guiding pipes, a water collecting tank and canals, the leaching repair part is provided with an observation well, water collecting pipes and plants planted for the soil phytoremediation, the observation well is built in a middle-upper layer of contaminated soil, and the water collecting pipes are in the middle-lower layer; and the waste water treatment part is provided with a filter tank, a microorganism putting tank, an electric separation tank, a wind power generating set and the like, leaching waste water is firstly filtered by the filter tank, and is then repaired by the microorganism putting tank, and finally, the leaching waste water passes through the electric separation tank to process heavy metal so as to obtain the purified liquid. The in-situ rain leaching repair system establishes a complete contaminated soil simulated repairing system for the soil in an aeration zone, and combines repair technologies of leaching, plants, microorganisms, electric separation and the like. The in-situ rain leaching repair system has the characteristics of energy conservation, emission reduction and no secondary pollution, and is suitable for repairing the soil in a large-area aeration zone with little pollution.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Lead and cadmium tolerant bacteria and method for plants renovation of soil pollution by heavy metal
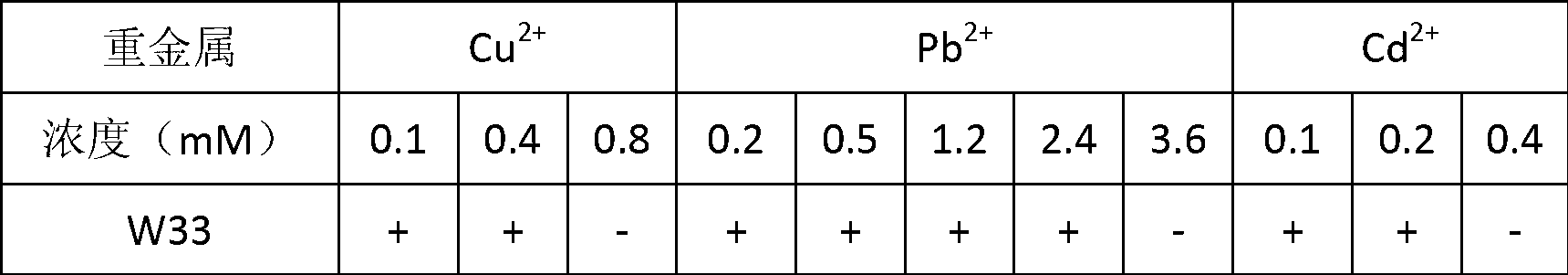
InactiveCN101153272AHas nitrogen fixationWith characteristicsBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPhosphateAntibiotic resistance
The invention relates to a heavy metal lead and cadmium antibiotic-resistant bacterium and a method for strengthening lead and cadmium heavy metals in the vegetable extraction soil, and belongs to the agricultural and environmental pollution treatment technical field. The J62 culture stain is appraised as the Burkholderia sp, has antibiotic resistance to a plurality of heavy metals, in particular to lead and cadmium, respectively reaching Pb<2+>1000mg / L and Cd<2+>2000mg / L. The invention has the characteristics of nitrogen fixation and phosphate solubilizing, and can promote the growth of the plant and improve the stress resistance of the plant. The effective living microbial numbers of the liquid preparation are above a billion per millimeter, and the effective living microbial numbers of the solid preparation are 200 millions per gram. When the seeds of the plant are seminated in humid soil containing heavy metals, 10 to 20mL of the bacteria liquid of 10<8> bacteria J62 / mLs is inoculated in each grams of soil once or in two times. The invention promotes the growth of the plant, strengthens the enrichment of heavy metal lead and cadmium of the plant, and improves the extraction and recovery efficiency of the plant.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Screening method for heavy metal enriched / accumulated plant
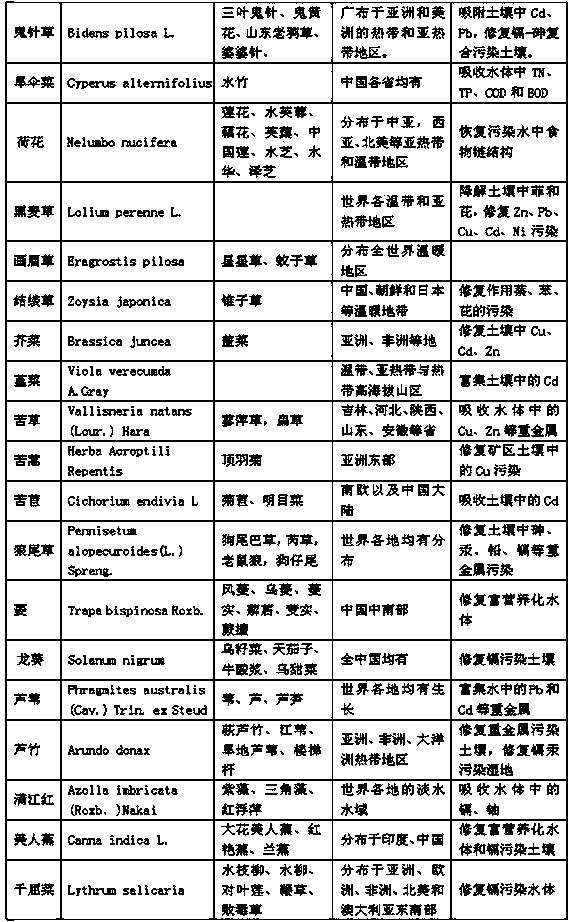
InactiveCN1568668AStrong targetingIncrease or decrease quantityPlant phenotype modificationEcological safetyScreening method
The invention relates to environmental pollution plant restoration, specifically to a screening method for heavy metal enriching / accumulating plant. 1)choosing experimental field 2) determining the screening object 3) determining the polluted object 4) potted plant screening experiment for heavy metal The invention chooses weeds as screening object, potted plant experiment , wild sampling and analysis, plot experiment as main means, screen plant for plant restoration. The invention is economic, highly effective, high ecological safety, wide adaptability,
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
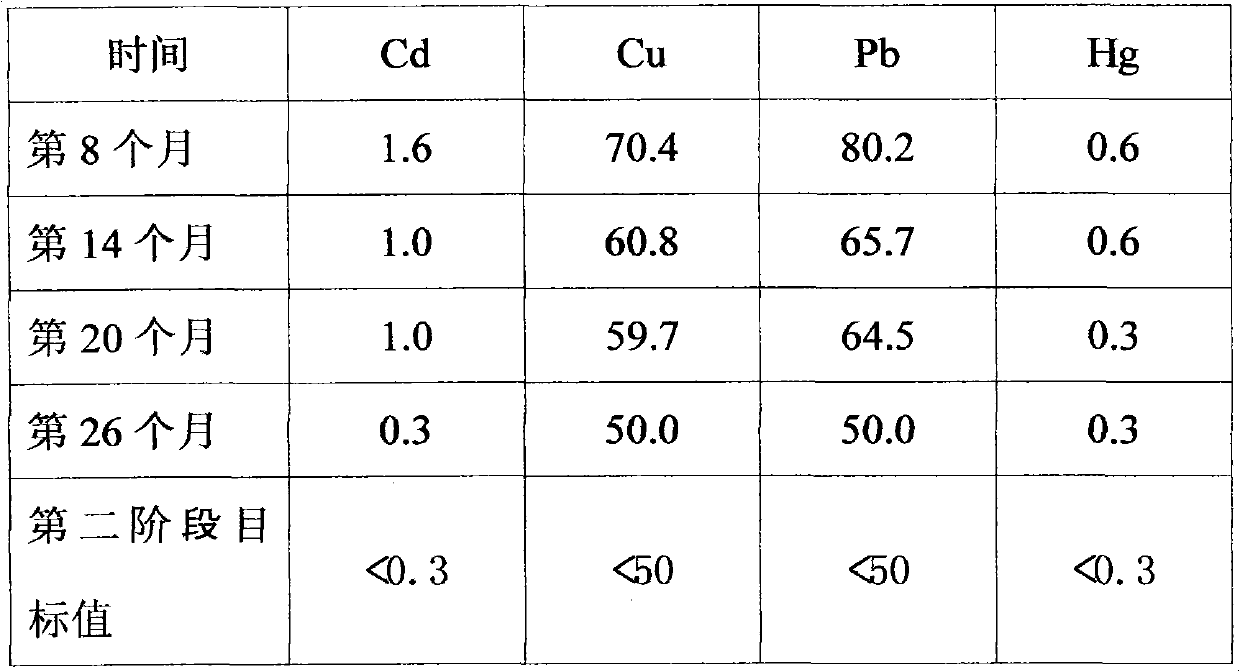
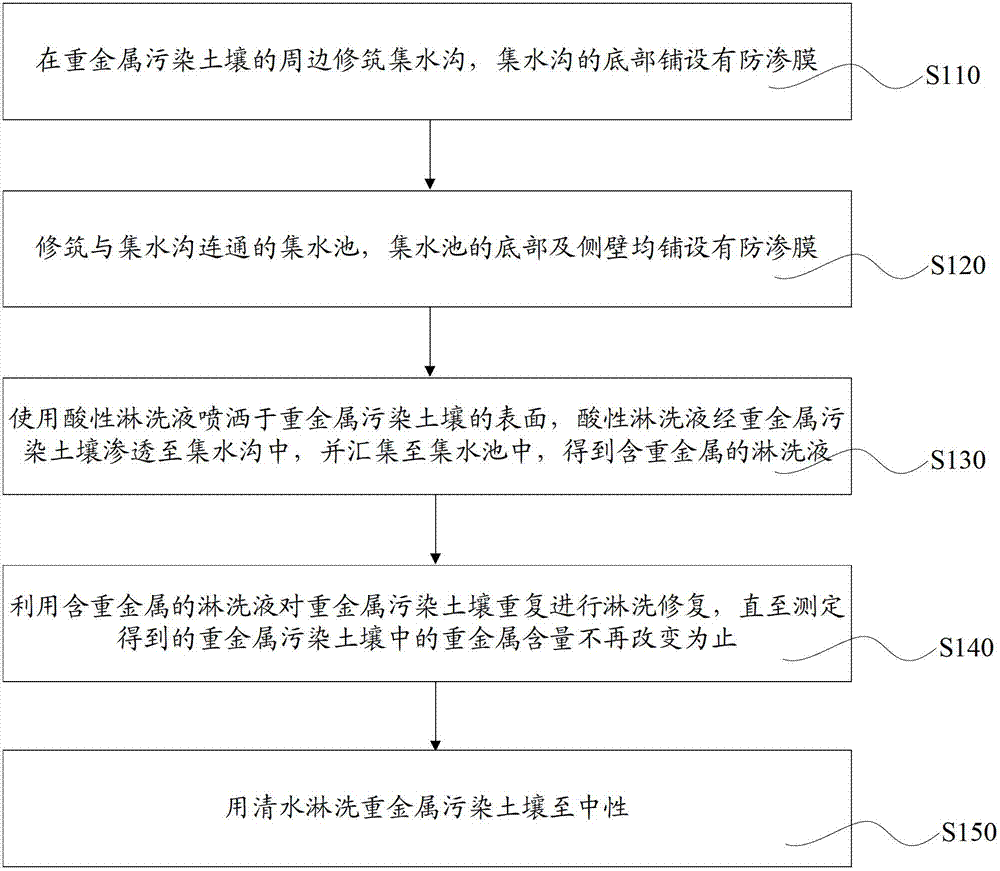
Remediation method of heavy metal contaminated soil
ActiveCN103111463AIncrease profitGood effectContaminated soil reclamationSoil remediationPhytoremediation
The invention relates to a remediation method of heavy metal contaminated soil, and the method comprises the following steps of: building a water collecting ditch around the heavy metal contaminated soil, and paving an impermeable membrane on the bottom of the water collecting ditch; building a water collecting tank communicated with the water collecting ditch, and paving impermeable membranes on the bottom and side walls of the water collecting tank; spraying acid leachate to the surface of the heavy metal contaminated soil, wherein the acid leachate permeates into the water collecting ditch through the heavy metal contaminated soil and gathers in the water collecting tank to obtain heavy metal-containing leachate; performing leaching remediation on the heavy metal contaminated soil by use of the heavy metal-containing leachate until the measured content of heavy metal in the heavy metal contaminated soil does not change; and leaching the heavy metal contaminated soil with clean water until the soil is neutral. The method provided by the invention is widely applicable and has the advantage of large processing capacity. After the soil remediation is finished, the method also can be used for performing microbial remediation and phytoremediation on the soil not reaching the state-specified standard in terms of heavy metal content.
Owner:深圳市先科环保有限公司
Heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium and method of promoting tailings area plant restoration by using same
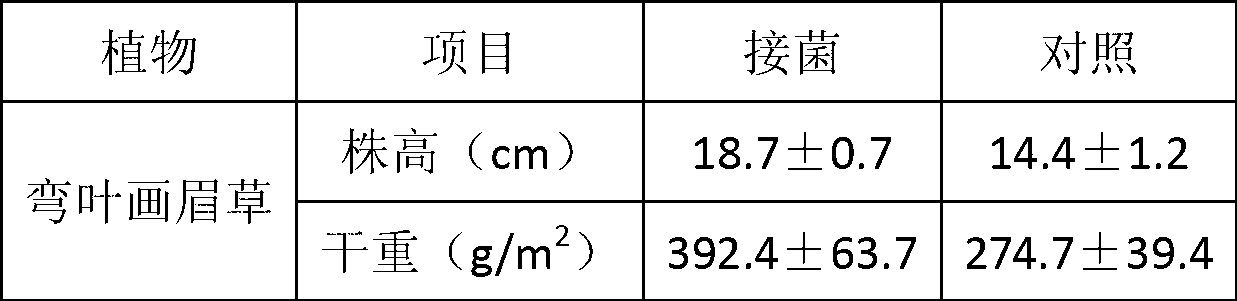
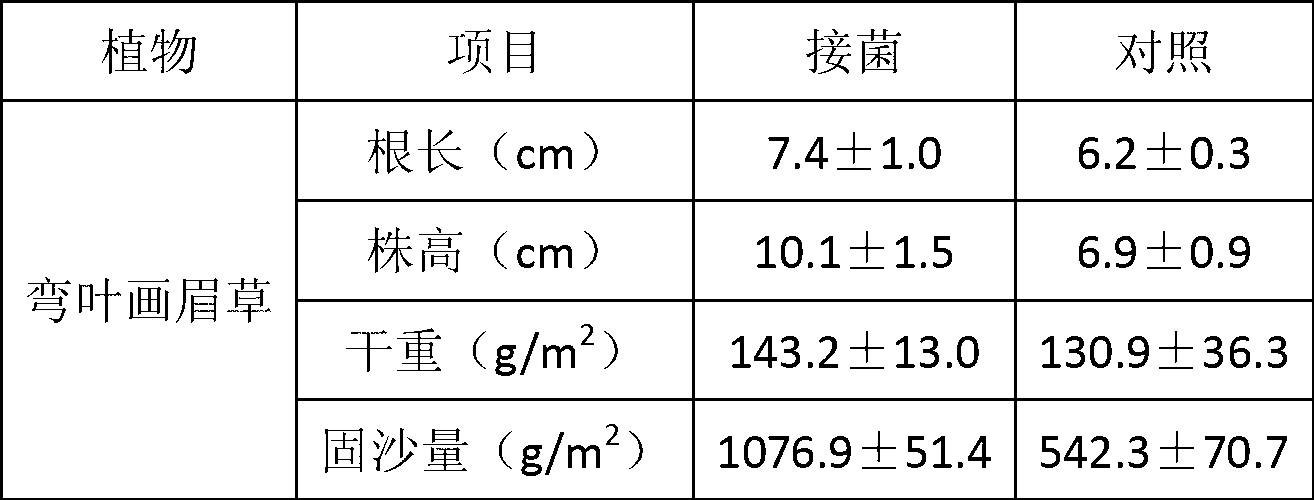
ActiveCN102936574APromote growthImprove stress resistanceBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPlant hormoneBacterial strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of agriculture and environmental pollution improvement and relates to a heavy metal resistant plant endogenous nodule bacterium and application thereof. The heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium is preserved at the China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) with the preservation date to be 2012 / 9 / 18 and culture preservation number to be CCTCC NO:M2012357. The bacterial strain liquid preparation contains more than a billion of effective living bacteria per milliliter, and the bacterial strain solid preparation contains 0.2 billion of effective living bacteria per gram. The heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium strain can secrete plant hormones indole acetic acid (IAA) and siderophores, and resists heavy metal copper and cadmium. When plants are planted in moist soil or tailings containing heavy metal and bioremediation preparation is inoculated, the heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium can promote plant growth and absorbs heavy metal copper, can improve plant restoration efficiency, can fix sandy soil and reduces water and soil loss.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for repairing soil of cadmium polluted by solanaceae plant
InactiveCN1724184APrevent water erosionReduce water erosionContaminated soil reclamationPollution soilInflorescence
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
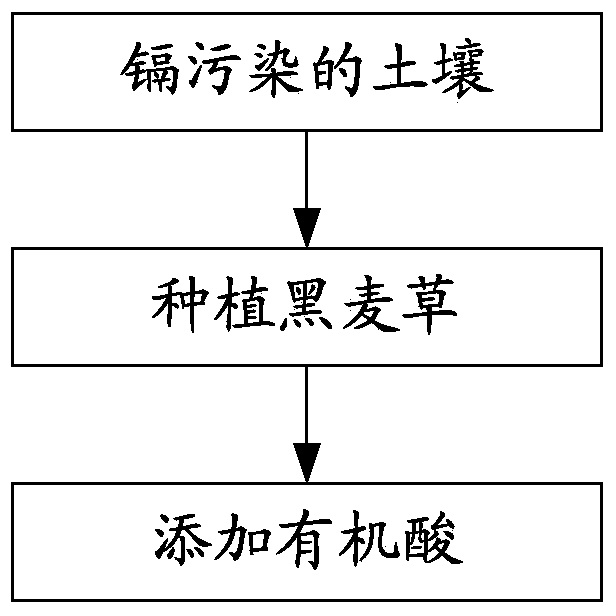
Phytoremediation method for soil with cadmium pollution
ActiveCN103521508APromote absorption and enrichmentImprove repair rateContaminated soil reclamationBiological activationPhytoremediation
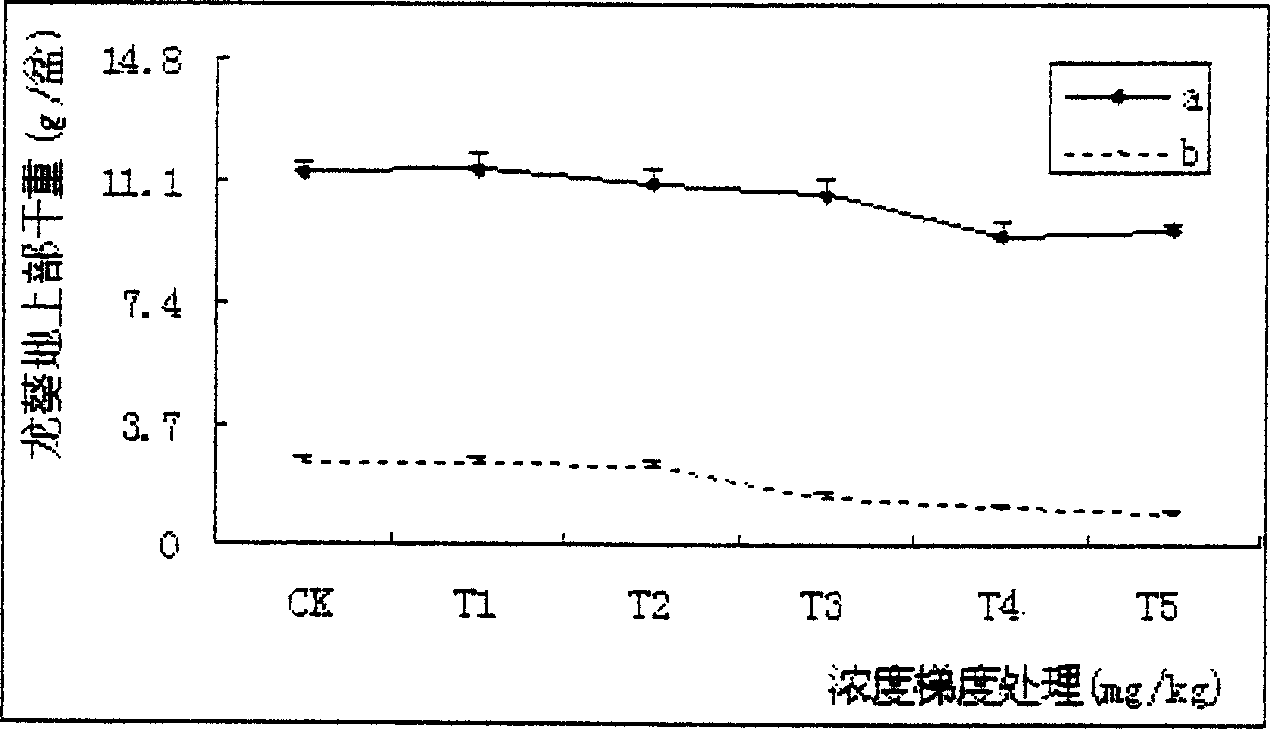
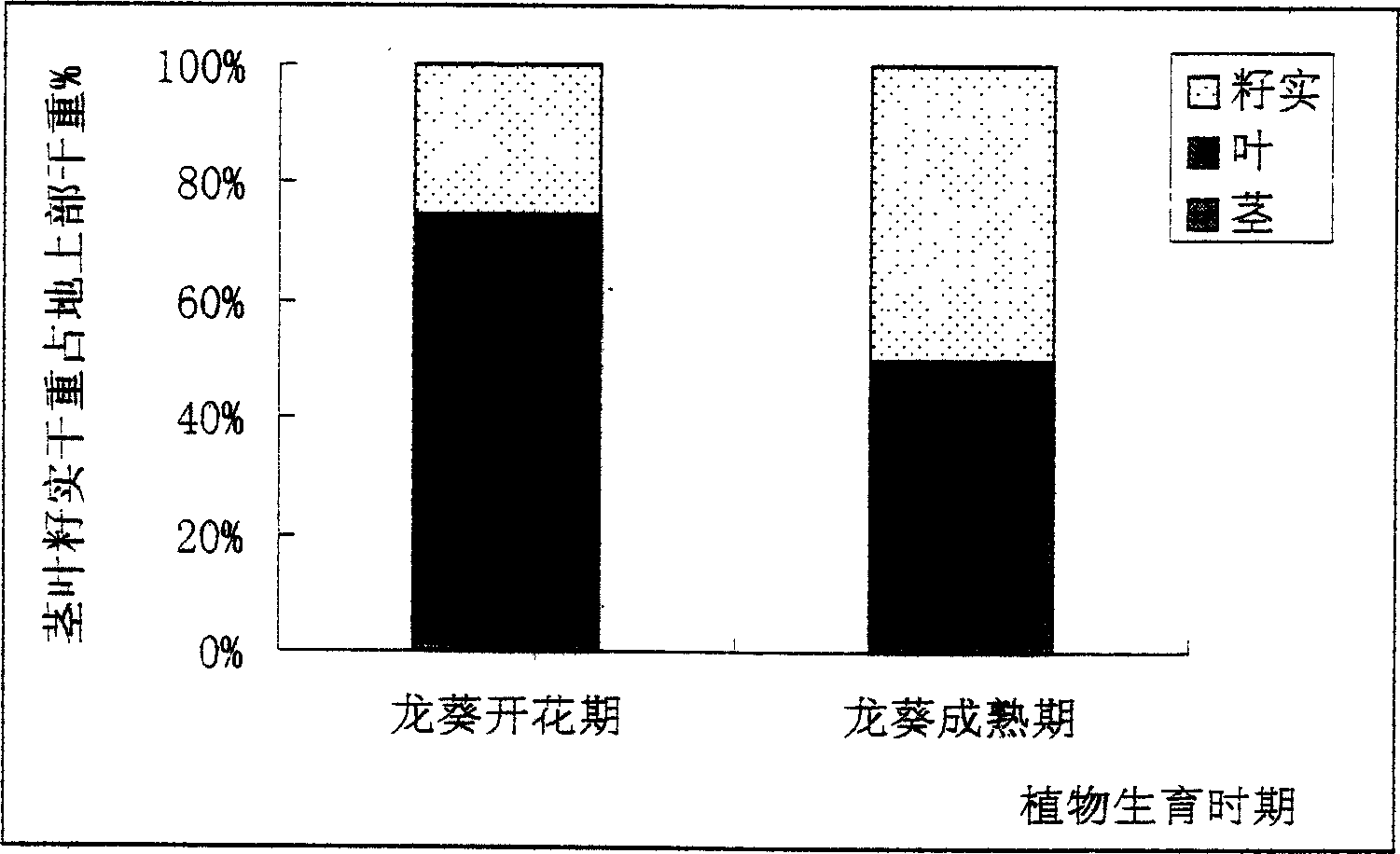
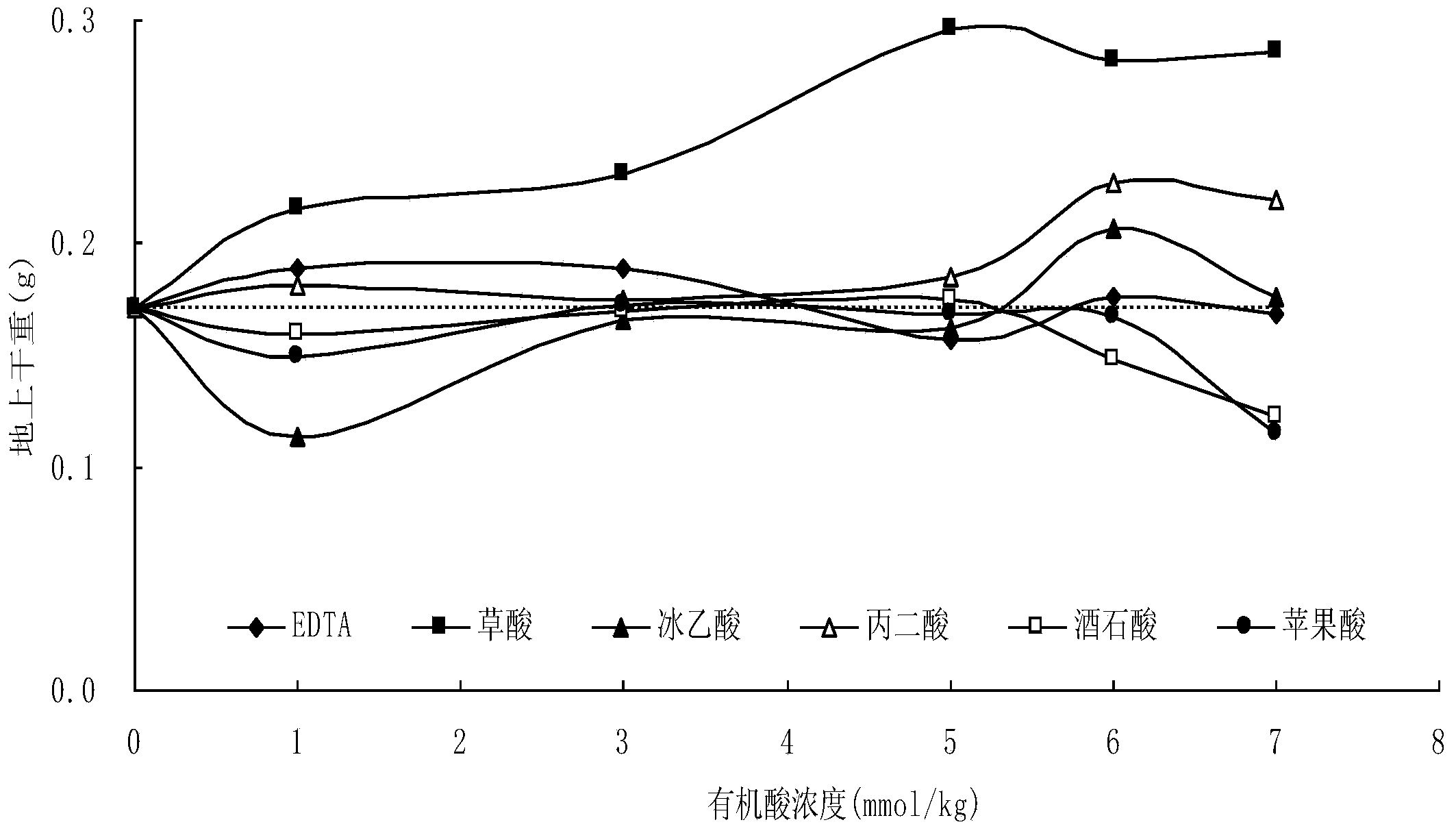
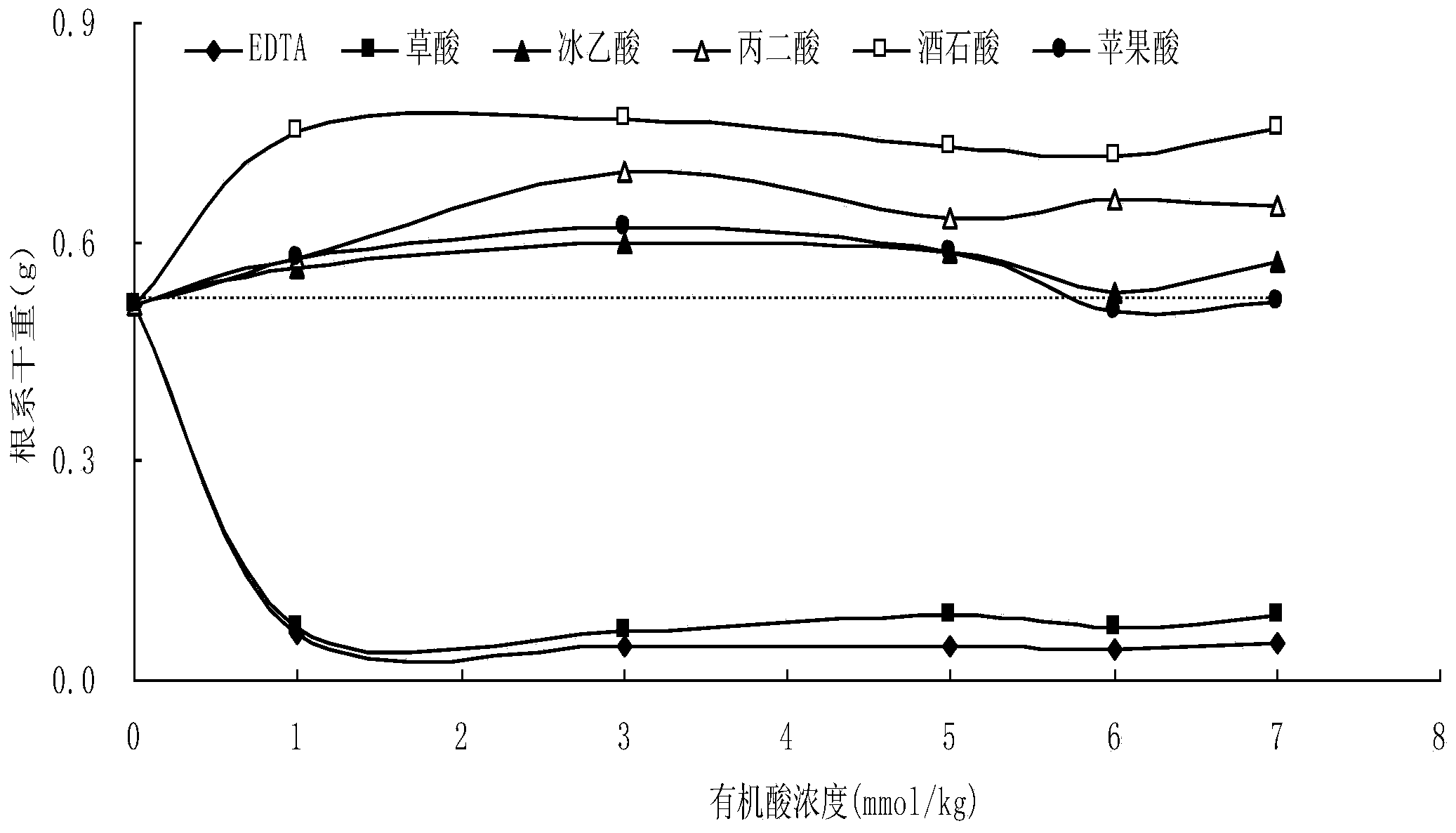
The invention discloses a phytoremediation method for soil with cadmium pollution. The method comprises the following steps: ryegrass is planted in soil with cadmium pollution; organic acid is added before harvest, and the organic acid is one selected from ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, oxalic acid, glacial acetic acid, propane diacid, tartaric acid or malic acid. In the method, based on ryegrass as a biomass raw material, when the ryegrass is used to restore the soil with cadmium pollution, through activation and induction actions of the organic acid, the bio-availability of heavy metal cadmium is raised, absorption and enrichment of cadmium of plants are promoted, and therefore the phytoremediation speed of soil with heavy metal pollution is raised. In addition, the organic acid can promote increase of amount of dry matter of overground parts and root systems of ryegrass to some extent, and finally, long-term goals of harmony of soil productivity restoration and local landscapes, ecological balance and sustainable development are achieved.
Owner:FARMLAND IRRIGATION RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Agent for phytoremediation of soil polluted by heavy metals using the waste active Sludge as the original material and the method of the phytoremediation of soil polluted by heavy metals
InactiveCN101036917AThe enrichment effect is obviousRealize ecological restorationContaminated soil reclamationActivated sludgePhosphoric acid
Provided is a heavy metal pollution soil repairing agent using excess activated sludge as the rawmaterial, a method of extraction and a method for repairing the heavy metal pollution soil, which relates to a heavy metal pollution soil repairing agent and a method thereof and a method for repairing the heavy metal pollution soil, and solves the problems of high cost, easily secondary pollution and complex operation existing in the repair of the heavy metal pollution soil. The heavy metal pollution soil repairing agent is composed of amylose, protein, nucleic acid, phosphoric acid, amino acid, humic acid compound, uronic acid and the organic substance required for cell lifecycle. The method for distilling the heavy metal pollution soil repairing agent is as follows: the wastewater treatment excess activated sludge reacts under the condition of 80-120 KPa and 60-100 DEG for 8-20 minutes; then centrifuges for 8-20 min at the rotating speed of 5000-7000r / min. The invention adopts the home position repairing or the heterotopia repairing to repair the heavy metal pollution. The invention has low cost and no secondary pollution, simple operation, short repairing period, strong activity and wide range of application.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Plant repairing method of agricultural land polluted by heavy metal
InactiveCN1559711ARepair pollutionDoes not affect the use of agricultural landContaminated soil reclamationAgricultural landSoil heavy metals
A plant method for restoring the agicultural field polluted by heavy metals includes such steps as screening the agricultural crops which features that their roots can absorb heavy metals but their seeds contains less heavy metals, and planting them in said polluted field.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Use of Debregeasia orientalis C. J. Chen in remediation of cadmium heavy metal contaminated soil
InactiveCN102172607ASignificantly enriched featuresIncrease vitalityContaminated soil reclamationUrticaceaeSoil heavy metals
The invention relates to a plant remediation technique for heavy metal contaminated soil and discloses the use of urticaceae plants in remediation of cadmium contaminated soil, in particular the use of Debregeasia orientalis C. J. Chen in remediation of cadmium heavy metal contaminated soil, which is to plant Debregeasia orientalis C. J. Chen in the heavy metal contaminated soil. Based on the cadmium enriching characteristic of Debregeasia orientalis C. J. Chen, the Debregeasia orientalis C. J. Chen is planted in the cadmium contaminated soil to absorb accumulated cadmium heavy metal and transfer most cadmium heavy metal to the parts above group, the parts above the group are harvested and ashed to extract heavy metal, and thus, the cadmium contaminated soil is remediated. In the growing process of the Debregeasia orientalis C. J. Chen, plant management is not required and stools can be left for growing braches, so the cost is low and the operability is high; meanwhile, new plant resource varieties are development for plant remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil, and new improvement and development space is provided for the deep development of the plant remediation technique.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV +8
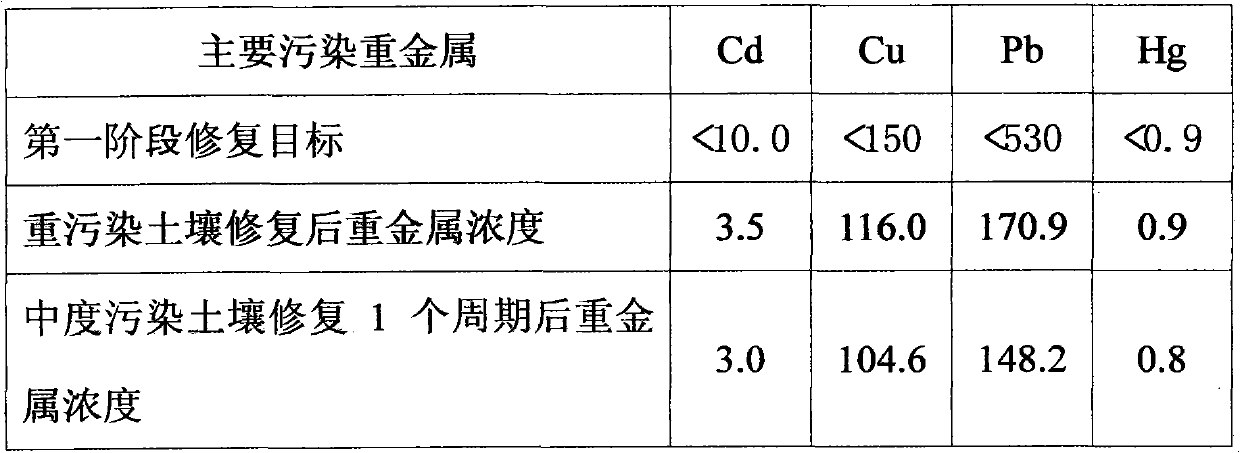
Phytoremediation method for managing composite cadmium-lead-arsenic contaminated soil
ActiveCN103894401ADoes not destroy physical and chemical propertiesAvoid churnContaminated soil reclamationAlkalinityGrowth height
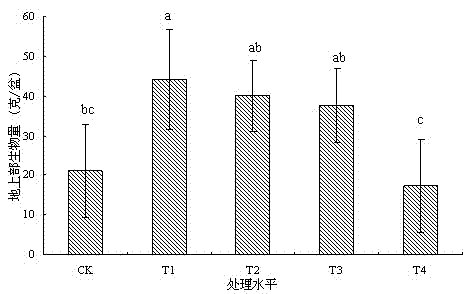
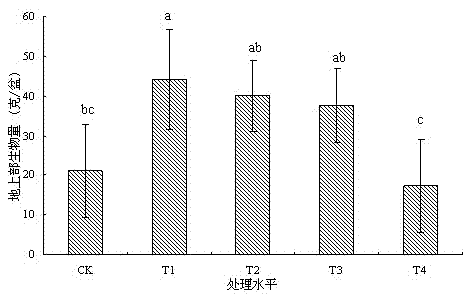
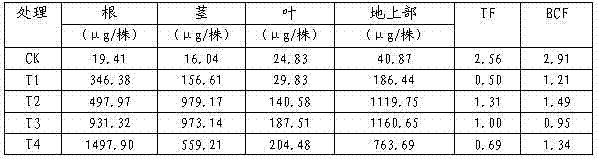
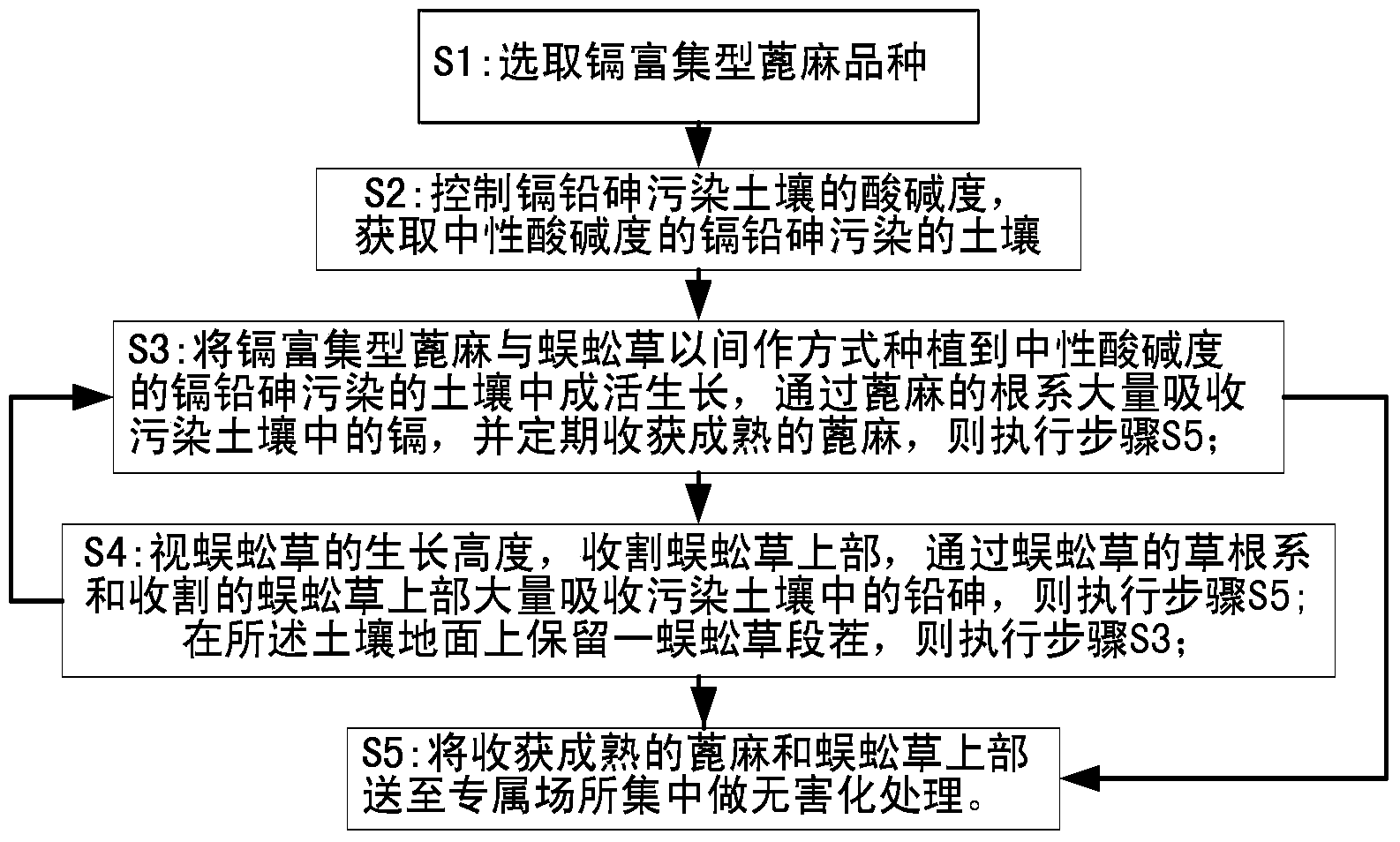
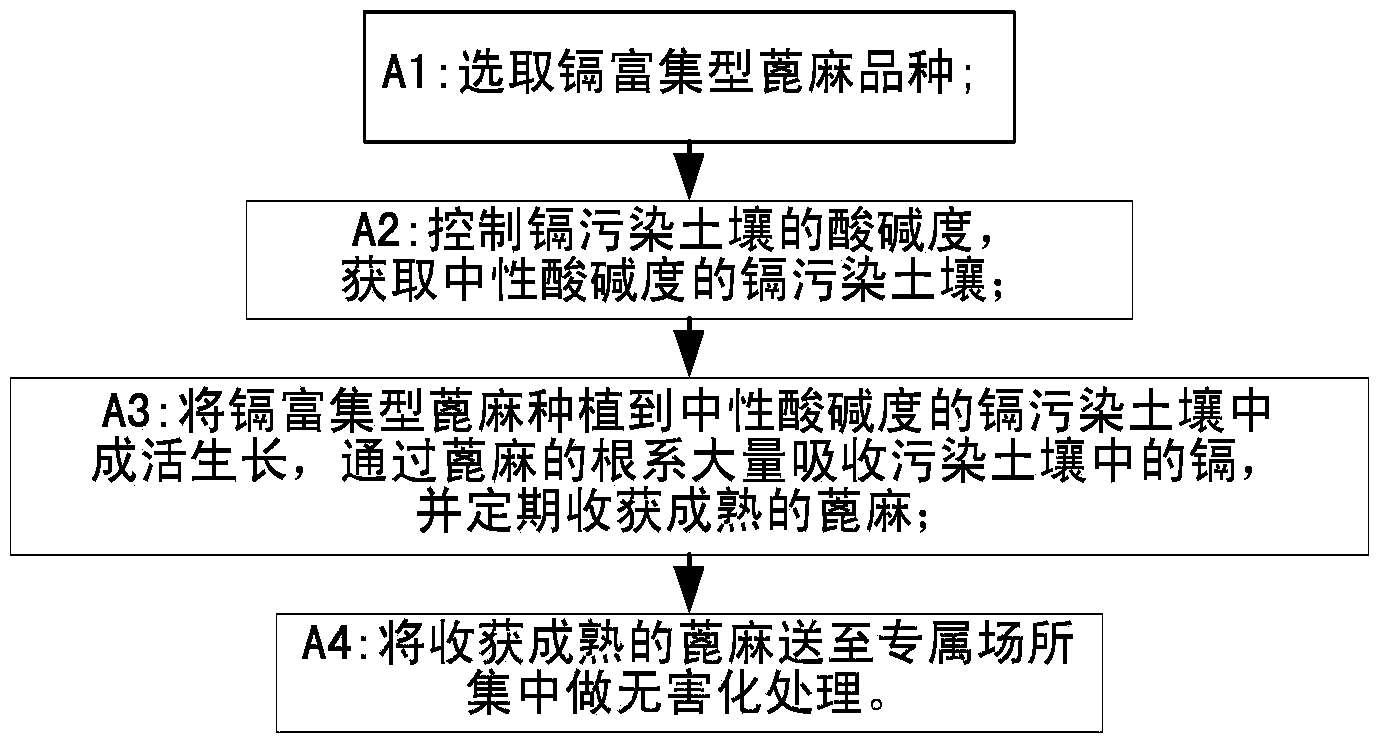
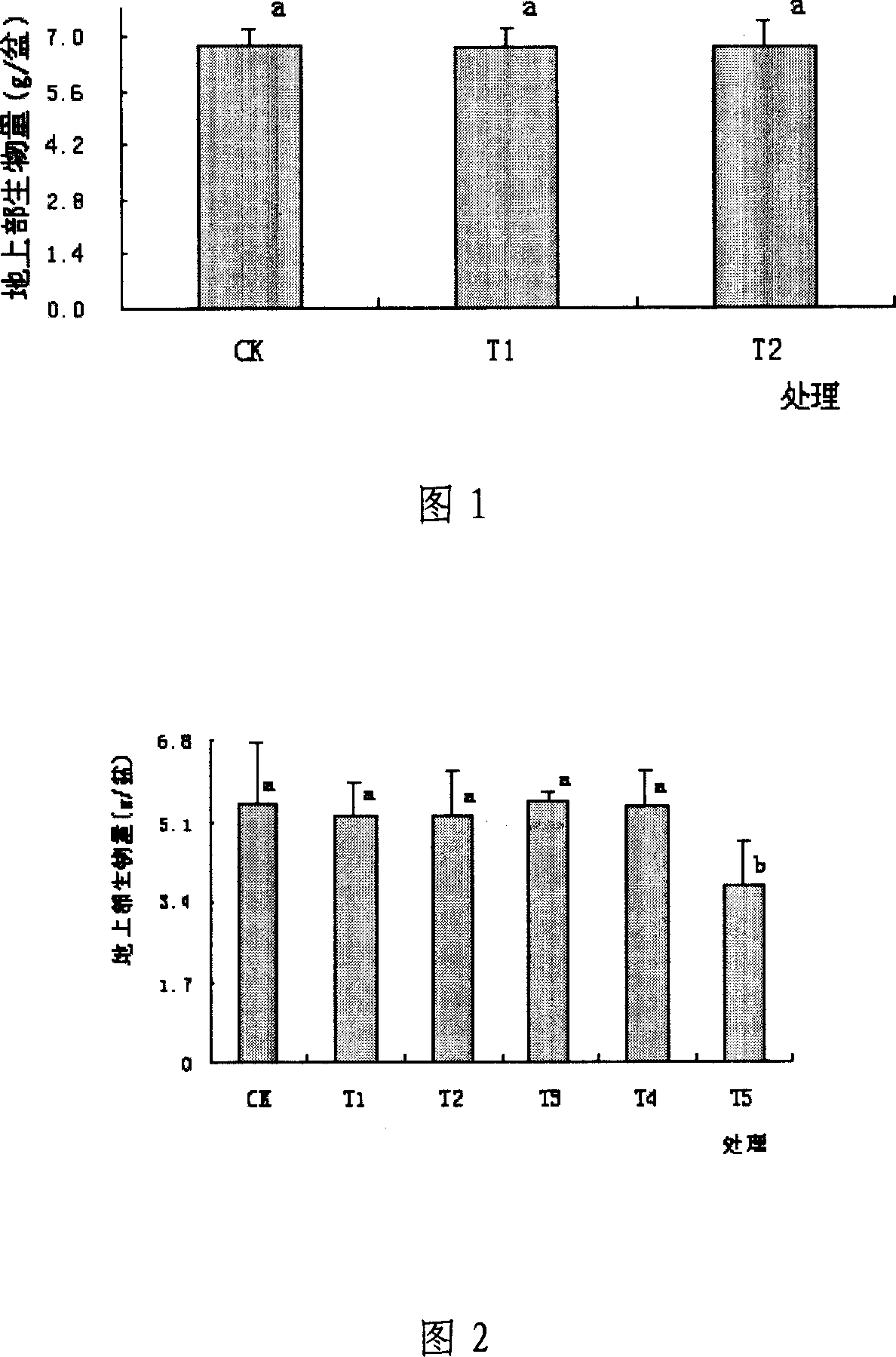
The invention provides a phytoremediation method for managing composite cadmium-lead-arsenic contaminated soil. The method comprises the following steps: step S1: selecting a cadmium-enriched castor-oil plant variety; step S2: obtaining cadmium-lead-arsenic composite contaminated soil with neutral acidity and alkalinity; step S3: planting cadmium-enriched castor-oil plants and ciliate desert-grass in an intercropping manner in the cadmium-lead-arsenic composite contaminated soil with neutral acidity and alkalinity for surviving and growth, and harvesting matured castor-oil plants at regular intervals, and carrying out step S5; step S4: harvesting the upper part of the ciliate desert-grass according to the growth height of the ciliate desert-grass, and carrying out the step S5; retaining stubble of the ciliate desert-grass on the soil surface, and carrying out the step S3; step S5: feeding the harvested and matured castor-oil plants and ciliate desert-grass to an exclusive place for concentration and carrying out innocent treatment. The invention further provides a phytoremediation method for managing cadmium contaminated soil. The phytoremediation method is suitable for managing and repairing cadmium-lead-arsenic moderately and slightly contaminated soil, and has good practical application prospect.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Method for restoring uranium milltailings by utilizing plants
ActiveCN101642768ASolve the hazard puzzleReduce entrySolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationUranium mineHydrometallurgy
The invention provides a method for restoring uranium milltailings by utilizing plants, which is a technique for restoring the uranium milltailings by utilizing uranium-enriched plants (macleaya cordata) as the material. The method directly plants macleaya cordata into the uranium milltailings without other supplementary means and comprises the following steps: (1) sterilizing seeds; (2) plantingseedlings in pots; (3) transplanting the plants into the uranium milltailings; (4) and carrying out the centralized processing on the reaped overground part. The method solves the problem that the prior uranium milltailings release uranium and heavy metals under natural conditions to damage the environment. The method has the advantages of simple operation and management, high restoration rate aswell as low cost and environmental risk and beautifies the environment. The method is suitable for treating solid uranium waste storage yards in uranium mines, hydrometallurgy plants, various ettle and milltailing warehouses, and the like.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV +1
Plants repairing method based on uranium tail SLAG pollution
InactiveCN101249501ASolving difficult problems that harm the environmentDrag reduction diffusionContaminated soil reclamationSlagHydrometallurgy
A phytoremediation method based on soil contaminated by uranium tailings comprises the steps for culturing pokeberry seedlings on a substrate containing uranium tailings, surviving, growing, harvesting and centrally processing. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing soil contaminated by uranium tailings, surface oil of forest and pig manure according to a ratio to obtain a culture substrate; (2) adding sodium silicate in the culture substrate; (3) sterilizing seeds; and (4) potting. By adopting the comprehensive processing scheme combined with the pokeberry, the uranium tailings, the surface oil of forest, the pig manure and the sodium silicate, the method can solve the difficult problem that the environment can be endangered by heavy metal, uranium, which is released by uranium tailings under natural condition. The method has the advantages of convenient operation and management, high remedying efficiency, low cost, low environment risk, environment beautification, etc., and is suitable for processing solid-state uranium waste storage fields such as uranium mines, hydrometallurgy plants and waste ore and tailings reservoirs.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process of botany for repairing soil composite polluted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
InactiveCN1792483AImprove degradation rateLow costSeed and root treatmentContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMyriophyllum
A phytologic method for repairing the soil polluted by polycycloarylhydrocarbon features that the leguminous plant such as alfalfa, trifolium, etc is planted in said polluted soil and it is harvested after it is growing for 85-95 days.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for repairing cadmium pollution soil using with asteraeae plant
InactiveCN101147914ADoes not destroy physical and chemical propertiesNo secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationPollution soilCadmium Cation
The present invention relates to a method for repairing soil contaminated by cadmium. It is characterized by that said invention utilizes plantation of bidens tripartite in the soil contaminated by cadmium so as to attain the goal of repairing said soil. Said invention also provides the plantation method of bidens tripartite and its field management method.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for removing heavy metal in soil
InactiveCN102319725AEasy to handleGood effectContaminated soil reclamationPollution soilCombined use
The invention discloses a method for removing heavy metal in soil, and belongs to the field of polluted soil treatment. The method comprises the following steps: adjusting the water content of the soil to be treated to 8%-12%; uniformly adding a magnetic adsorption material into the soil with adjusted water content, wherein the adding amount of the magnetic adsorption material is 10-50 g per 1 kg of soil; regularly adjusting the water content of the soil after magnetic adsorption material addition, maintaining the water content of the soil to 8%-12%, regularly and uniformly stirring the soil; collecting the magnetic adsorption material in the soil treated by above procedures for a certain period in a manner of magnetic separation so as to complete the removal of heavy metal in the soil. The method has simple operations, can realize high-efficient low-cost treatment of heavy metal-polluted soil, and has the advantages of low energy consumption and environment protection; the method can be combined with common technology of phytoremediation of heavy metal-polluted soil, and has good popularization and application value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Dredged sediment based plant adaptability matrix and ecological restoration method of bare slope
InactiveCN102229485AImprove stabilityNot easy to corrodeExcavationsHorticultureVegetationRestoration method
According to the invention, by using dredged sediment from water body such as eutrophicated rivers and lakes as the aggregate, plant straws, plant ash, ordinary portland cement, an organic fertilizer, a release fertilizer, a water-retaining agent and the like are added into the dredged sediment with uniformly stirring to form the bare slope plant adaptability matrix with certain adhesive performance. By employing the wet-type guniting technology for two-layer matrix guniting, the plant adaptability matrix is used for the plant restoration of bare mountain slope and can form a new plant cover layer in a short period. The dredged sediment is used as the matrix to control the loss of water and soil, thus minimizing the dependence on the clay resource and the restoration cost in slope restoration and solving the issue of dredged sediment treatment by the resource mode; and furthermore, the restoration method provided by the invention has high environmental, ecological and economic benefits.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Remediation technology and process for heavy metal and organic matter composite contaminated soil
InactiveCN106694535AEfficient degradationShort repair cycleContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonPollution soil
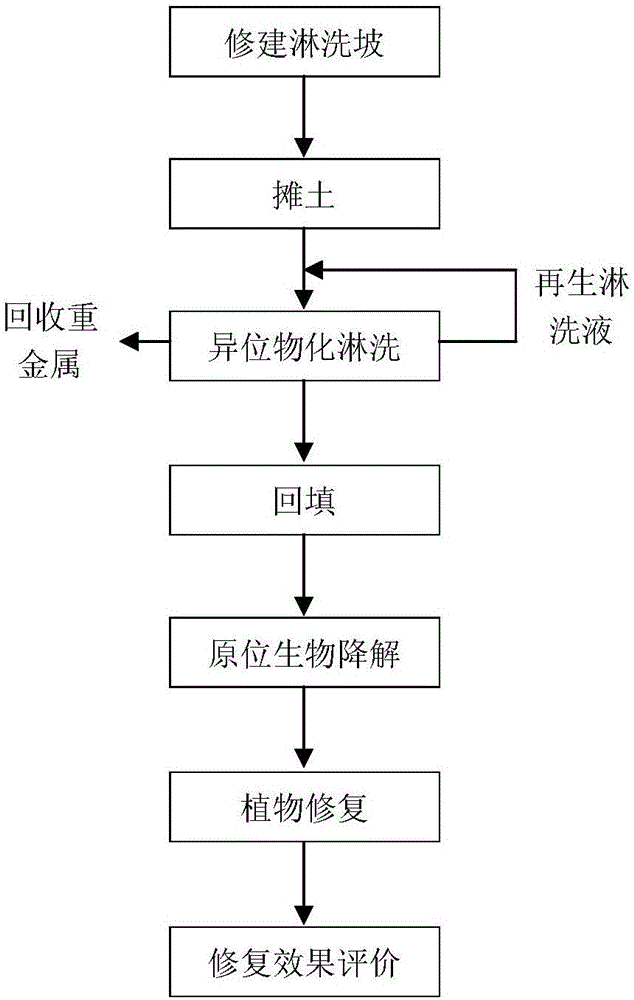
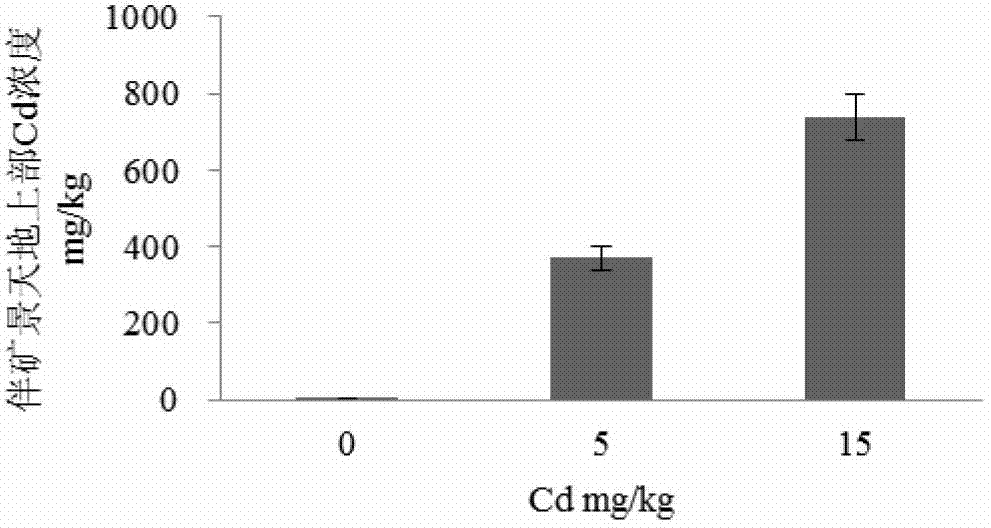
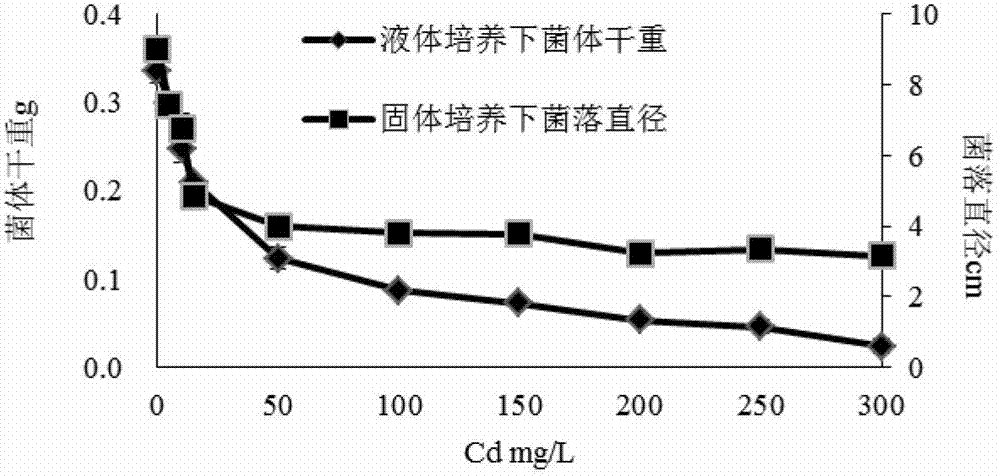
The invention provides a method for remediating heavy metal-organic matter composite contaminated soil. The method sequentially comprises the steps of building a leaching slope, paving the soil, carrying out heterogeneous physical and chemical leaching, backfilling, carrying out in-situ biodegradation and carrying out phytoremediation. According to the method, contaminants in the soil can be rapidly and effectively degraded, the remediation period of the contaminated soil is shortened, the remediation cost is low, no secondary contamination is caused, the method is simple and feasible, the fertility of the soil in contaminated sites can be improved, and the method is suitable for remediating the contaminated sites with various scale. The method can be used for remediating the soil contaminated by heavy metal such as Mn, Pb, As and Cu and the soil compositely contaminated by the organic matter such as petroleum and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon.
Owner:BEIJING FENGZELVYUAN ENVIRONMENT TECH
Application of trichoderma reesei and sedum plumbizincicola in remediation of cadmium-polluted farmland soil
ActiveCN103191914AImprove micro-ecological environmentImprove repair efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentTrichoderma reesei
The invention provides the application of trichoderma reesei and sedum plumbizincicola in the remediation of cadmium-polluted farmland soil. The application comprises the following steps of: cutting sedum plumbizincicola seedlings with about 10cm of plant height into soil to be remedied, applying trichoderma reesei FS10-C fermentation liquor or microbial preparation to the rhizosphere of the plant, keeping the soil water content to be 70%wt of the maximum field capacity in the process of remediation, and scissoring the plant along the surface of soil after the plant grows for 60-150 days to complete one remediation process. According to the application, the plant remediation efficiency of the cadmium-polluted farmland soil can be improved; and the sedum plumbizincicola plant remediation efficiency can be improved according to the trichoderma preparation, the biomass of the soil microorganism can be enhanced, the micro-ecological environment of the soil can be improved, and the application is good in ecological efficiency, and suitable for the remediation of the cadmium-polluted farmland soil.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Soil repair method for treating polychlorinated biphenyl pollutants
ActiveCN101966529AFree from destructionNo pollution in the processContaminated soil reclamationAnaerobic aerobicPolychlorinated biphenyl
The invention relates to a soil repair method for treating polychlorinated biphenyl pollutants, which comprises steps of greenhouse construction, anaerobic-aerobic alternated piling and plant repair, wherein the plant repair step comprises that: alfalfa for decomposing polychlorinated biphenyl and cocozelle for enriching the polychlorinated biphenyl are planted after the piled body is flattened, one-time plant repair time is controlled to be between 2 and 6 months, and the planted alfalfa and the planted cocozelle are directly returned to a field. The method repairs the soil by using anaerobic-aerobic alternated piling and plant repair modes, so different from a chemical method which produces new pollutants, the method has no pollution or damage to the repaired place; and the method is also different from obligate bacteria treatment technology for treating the soil. The soil repair method is an optimized soil repair method with low cost, no pollution and no damage to a soil ecologicalsystem.
Owner:浙江博世华环保科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com