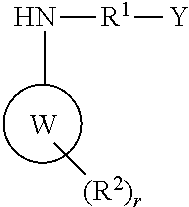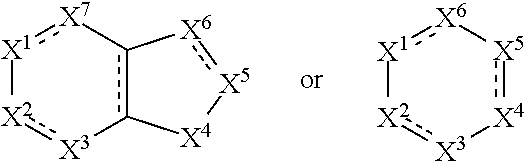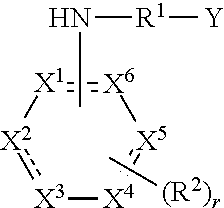Patents
Literature
305 results about "Monocotyledon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Monocotyledons (/ˌmɒnəˌkɒtəlˈiːdən/), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae sensu Chase & Reveal) are flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of the major groups into which the flowering plants have traditionally been divided, the rest of the flowering plants having two cotyledons and therefore classified as dicotyledons, or dicots. However, molecular phylogenetic research has shown that while the monocots form a monophyletic group or clade (comprising all the descendants of a common ancestor), the dicotyledons do not. Monocotyledons have almost always been recognized as a group, but with various taxonomic ranks and under several different names. The APG III system of 2009 recognises a clade called "monocots" but does not assign it to a taxonomic rank.
Transformation method for plants
InactiveUS6140553AImprove conversion efficiencyIncreasing frequency of stable transformationBryophytesSugar derivativesCell divisionDNA Integration
A process for integrating a DNA fragment into the genome of a cell of a monocotyledonous plant, the process comprising the steps of: 1) incubating, prior to contacting with the DNA fragment, a culture of untransformed monocotyledonous plant cells on a medium comprising a plant phenolic compound, for a period of time sufficient to stimulate cell division and enhance competence for integration of foreign DNA; and 2) contacting the untransformed cells with the DNA fragment under conditions in which the DNA fragment is taken up by the untransformed cells and is stably integrated in the genome of the untransformed cells, to generate transformed cells.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE NV
Promoter BgIosP587, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a promoter, in particular to a promoter for monocotyledons such as rice, and a preparation method and application thereof. The promoter of the invention has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, or has a variant which has the functions of the promoter and is selected from the following sequences: 1) a nucleotide sequence hybridized with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 under the condition of advanced tightness; 2) a nucleotide sequence carrying out substitution, loss, modification and addition of one or more basic groups on the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; and 3) a nucleotide sequence having at least 90 percent of sequence identity with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. In addition, the invention also relates to a method for preparing the promoter and the application of the promoter in adjusting and controlling the target gene expression in the monocotyledons.
Owner:深圳华大基因农业控股有限公司
Method and apparatus for substantially isolating plant tissues
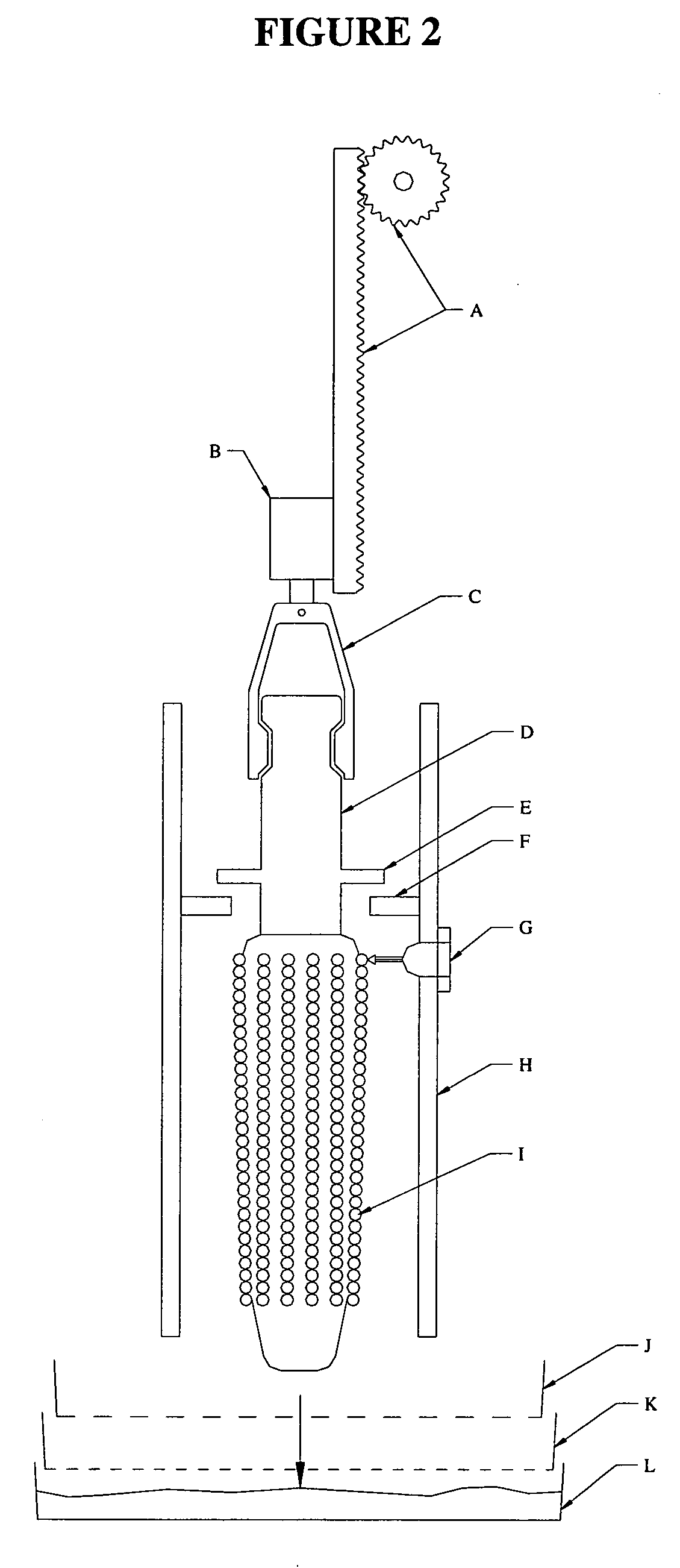
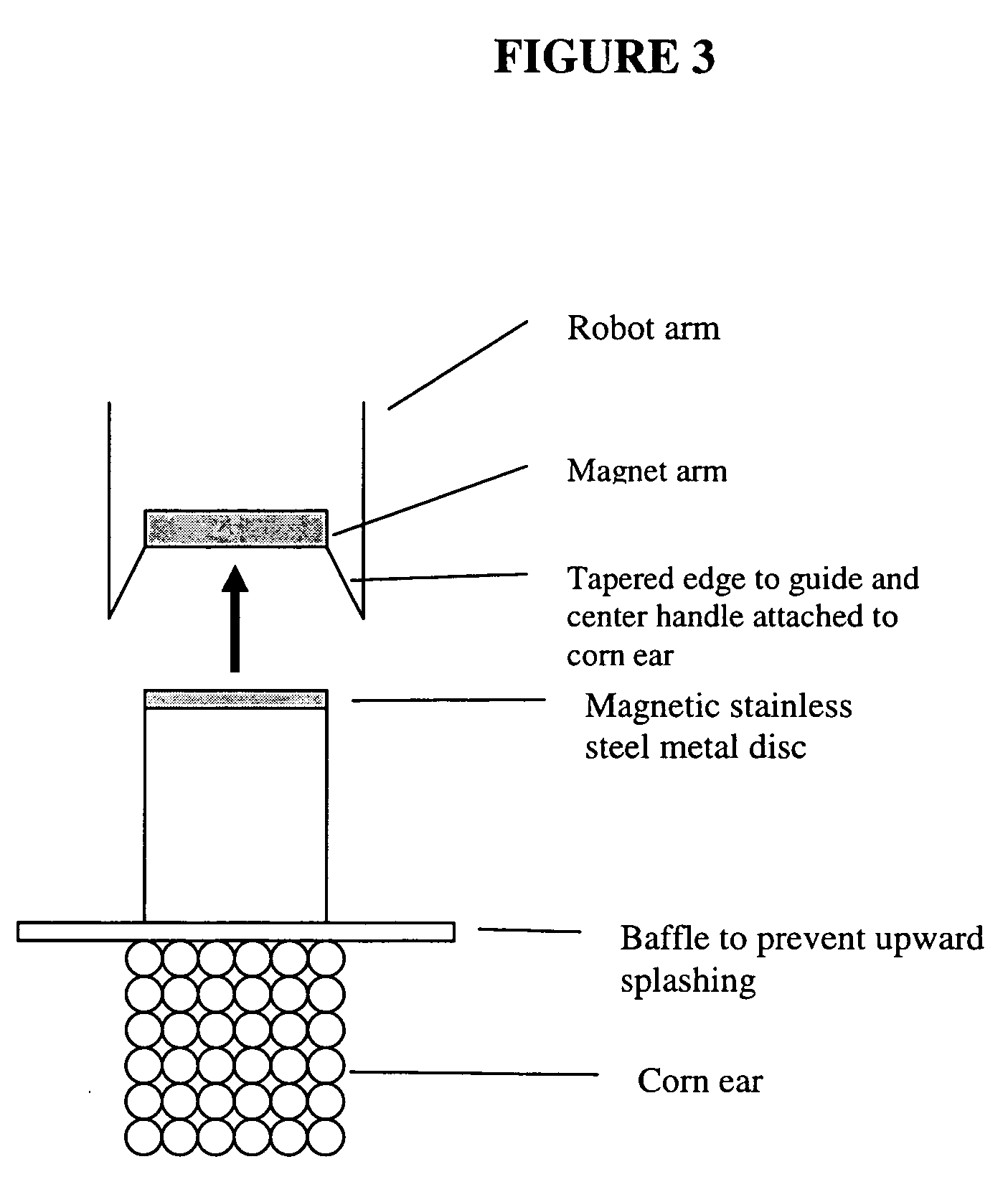
ActiveUS20050246786A1Improve reliabilityReduce harmOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant tissueGMO Plants
The present invention discloses and claims methods and devices for the rapid mechanical isolation of monocot plant tissues suitable for transformation or tissue culture. The invention includes mechanical devices for substantially isolating target plant tissues for use as transformable explants, and propagation of transgenic plants and plant tissues.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
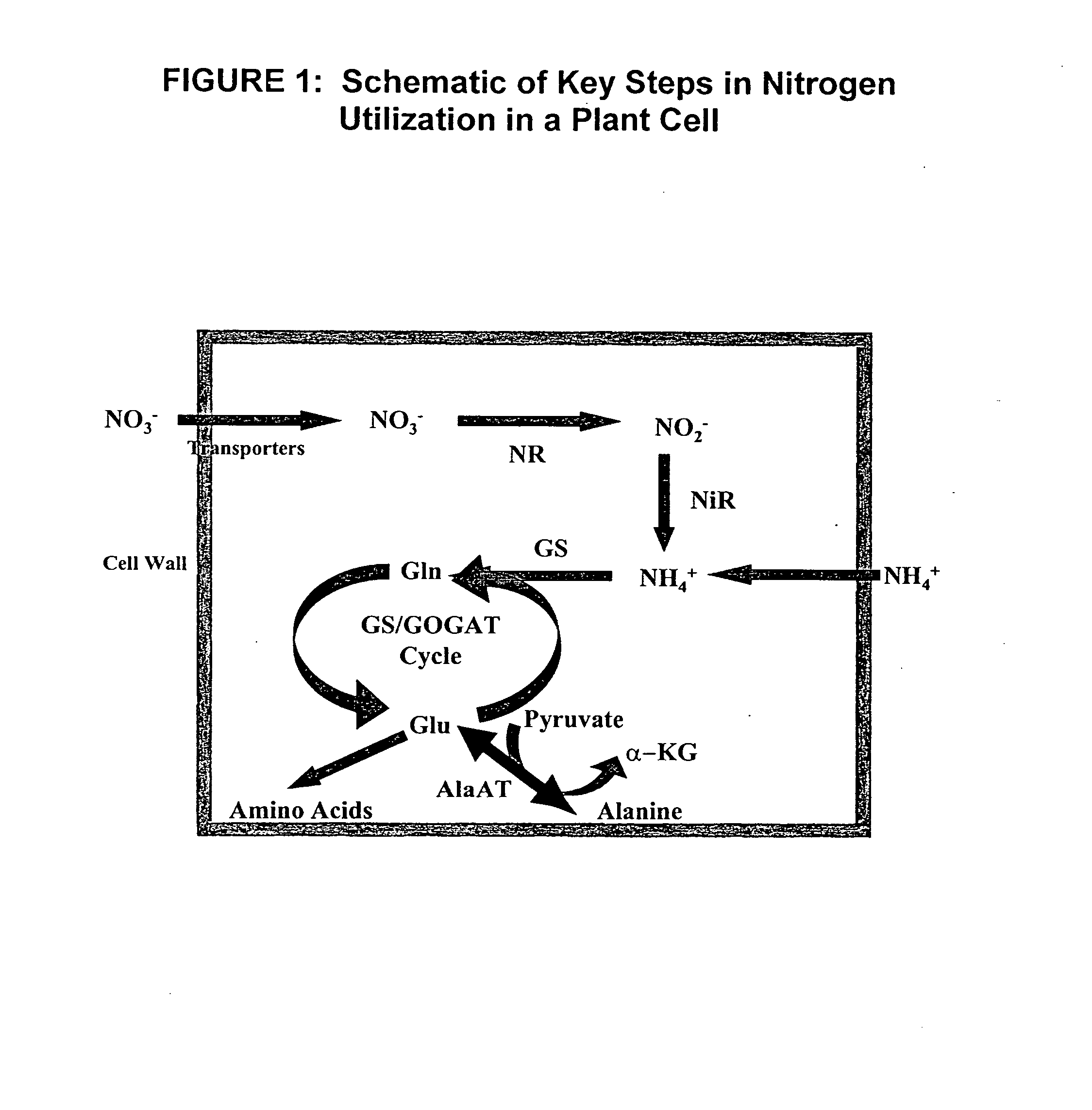
Nitrogen-efficient monocot plants
Methods of increasing nitrogen utilization efficiency in monocot plants through genetic modification to increase the levels of alanine aminotransferase expression and plants produced there from are described. In particular, methods for increasing the biomass and yield of transgenic monocot plants grown under nitrogen limiting conditions compared to non-transgenic plants are described. In this way, monocot plants may be produced that maintain a desired yield while reducing the need for high levels of nitrogen application.
Owner:BLUE HORSE LABS INC
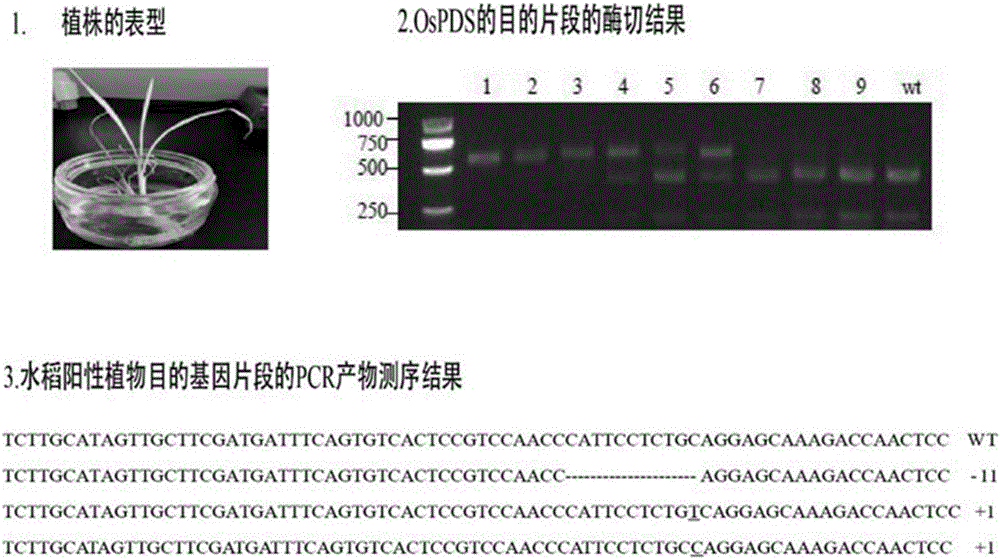
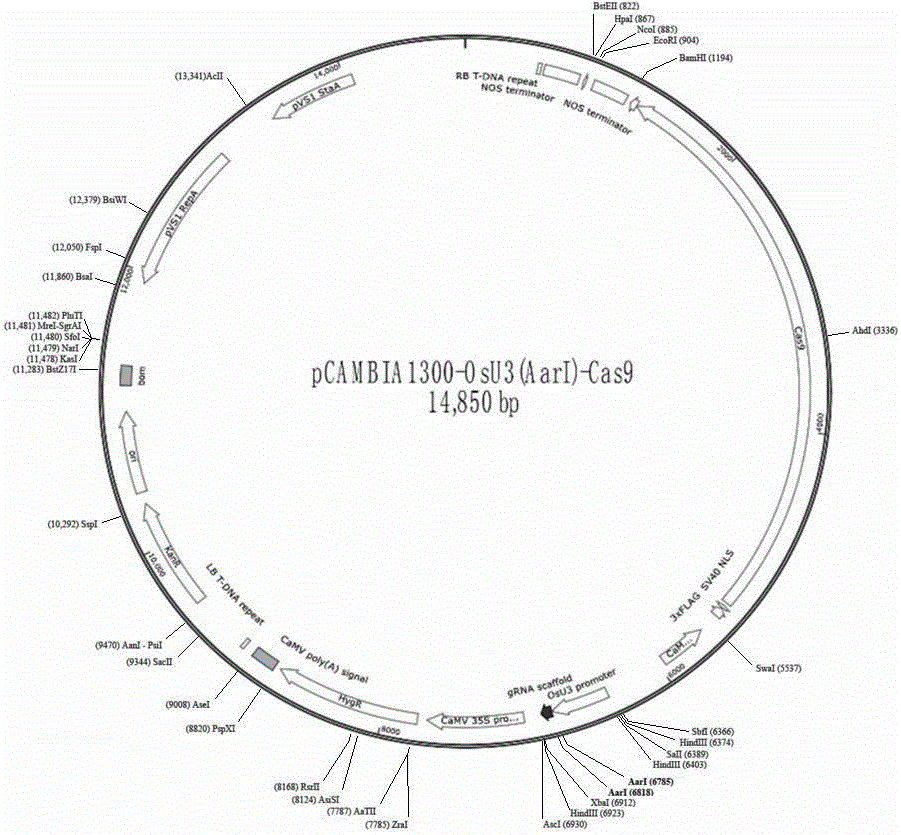
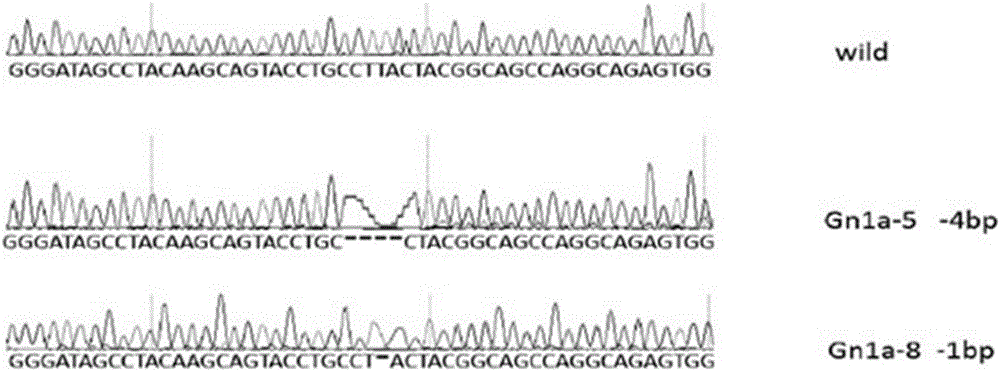
Monocotyledon plant gene knockout vector based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology, and applications thereof
InactiveCN106167810AEfficient constructionKnockout EfficientNucleic acid vectorPlant peptidesDigestionInsertion site
The invention discloses a plant gene knockout vector based on a CRISPR / Cas9 technology. The monocotyledon plant gene knockout vector is characterized in that the plant gene knockout vector is a monocotyledon plant CRISPR / Cas9 knockout vector pCambin1300-OsU3-Cas9, and contains the AarI insertion site. According to the present invention, with the CRISPR / Cas9 plant knockout double-component vector pCambin1300-OsU3-2x35s-Cas9 formed from a sgRNA-OsU3 structure sequence comprising the AarI insertion site and a 2x35s-Cas9-ter sequence, the purpose of the efficient and rapid construction of the monocotyledon plant gene knockout vector can be achieved through the one-step digestion linkage method; and the provided CRISPR / Cas9 knockout vector pCambin1300-OsU3-2x35s-Cas9 has characteristics of high targeting efficiency and extremely low undershoot efficiency, and can be used for plant target gene knockout or can be used for plant gene editing in a kit form.
Owner:内蒙古中科正标生物科技有限责任公司
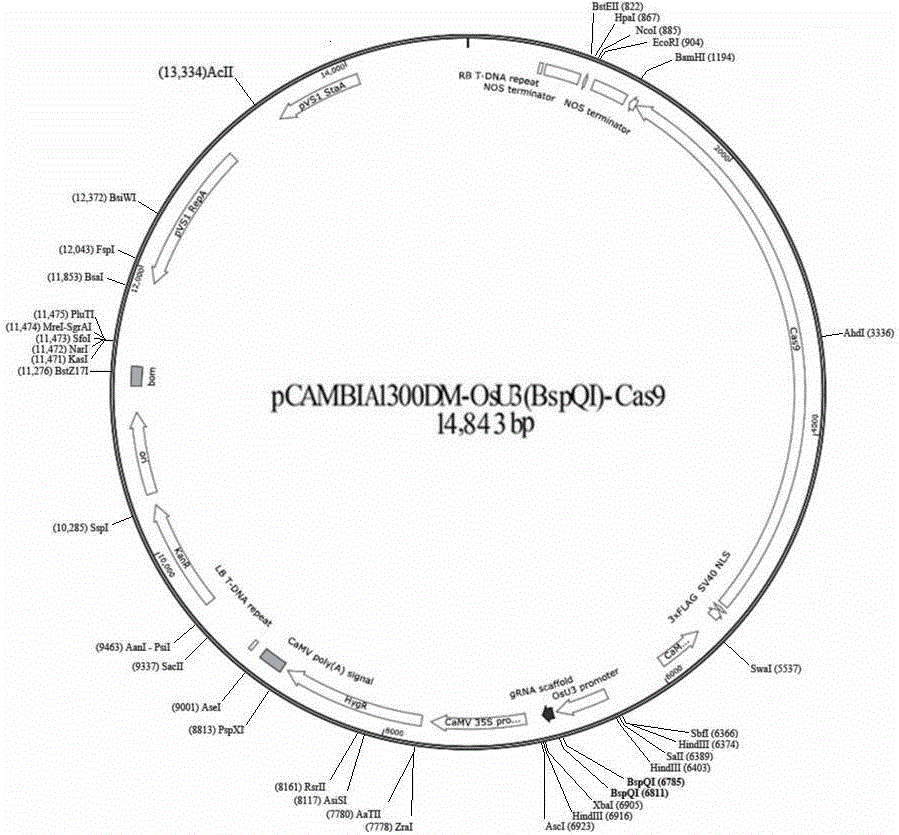
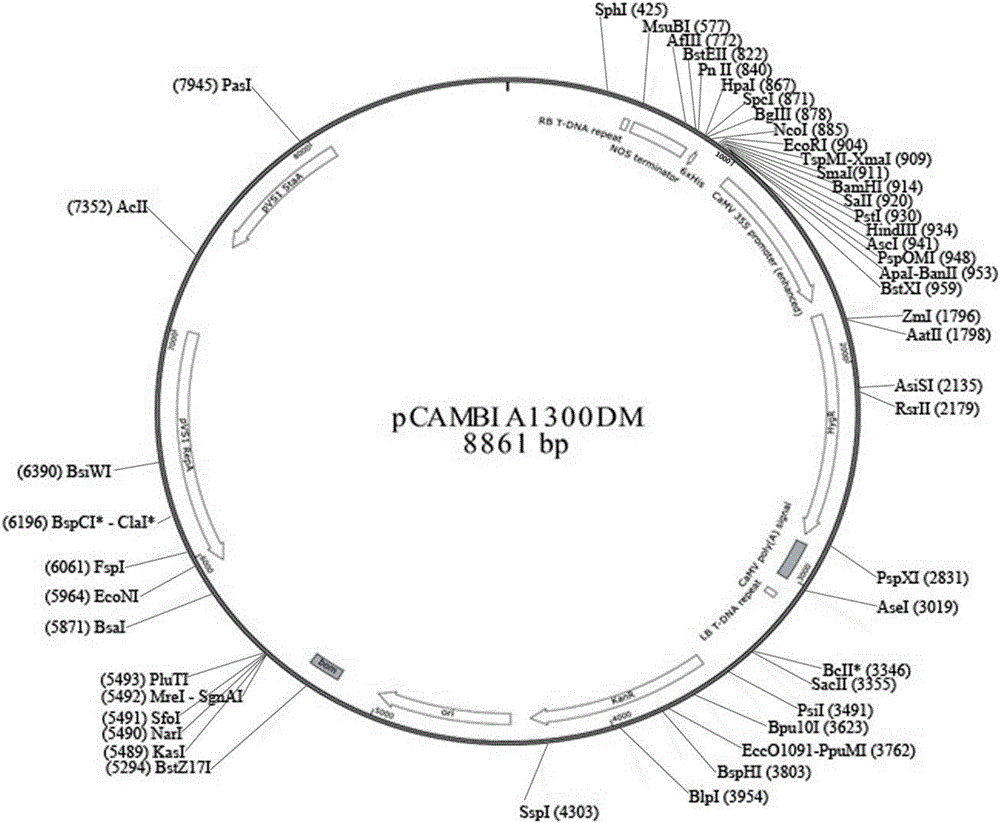
CRISPR/Cas9 technology-based monocotyledon gene knockout vector and application thereof
InactiveCN106434737AKnockout EfficientKnockout fastNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionInsertion siteOff targets
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cas9 technology-based plant gene knockout vector and an application thereof. The plant gene knockout vector is monocotyledon CRISPR / Cas9 knockout vector pCAMBIA1300DM-OsU3(BspQ I)-Cas9, and contains a BspQ I insertion site. The CRISPR / Cas9 plant knockout binary vector pCAMBIA1300DM-OsU3(BspQ I)-Cas9 commonly constructed by an sgRNA-OsU3 sequence composed of the BspQ I insertion site and a 2x35s-hSpCas9-ter sequence can realize high-efficiency rapid construction of the monocotyledon gene knockout vector through a one-step restriction and ligation method; and the CRISPR / Cas9 knockout vector pCAMBIA1300DM-OsU3(BspQ I)-Cas9 has the characteristics of high targeting efficiency and low off-target efficiency, and can be applied to plant target gene knockout or applied to plant gene editing in a kit form.
Owner:内蒙古中科正标生物科技有限责任公司
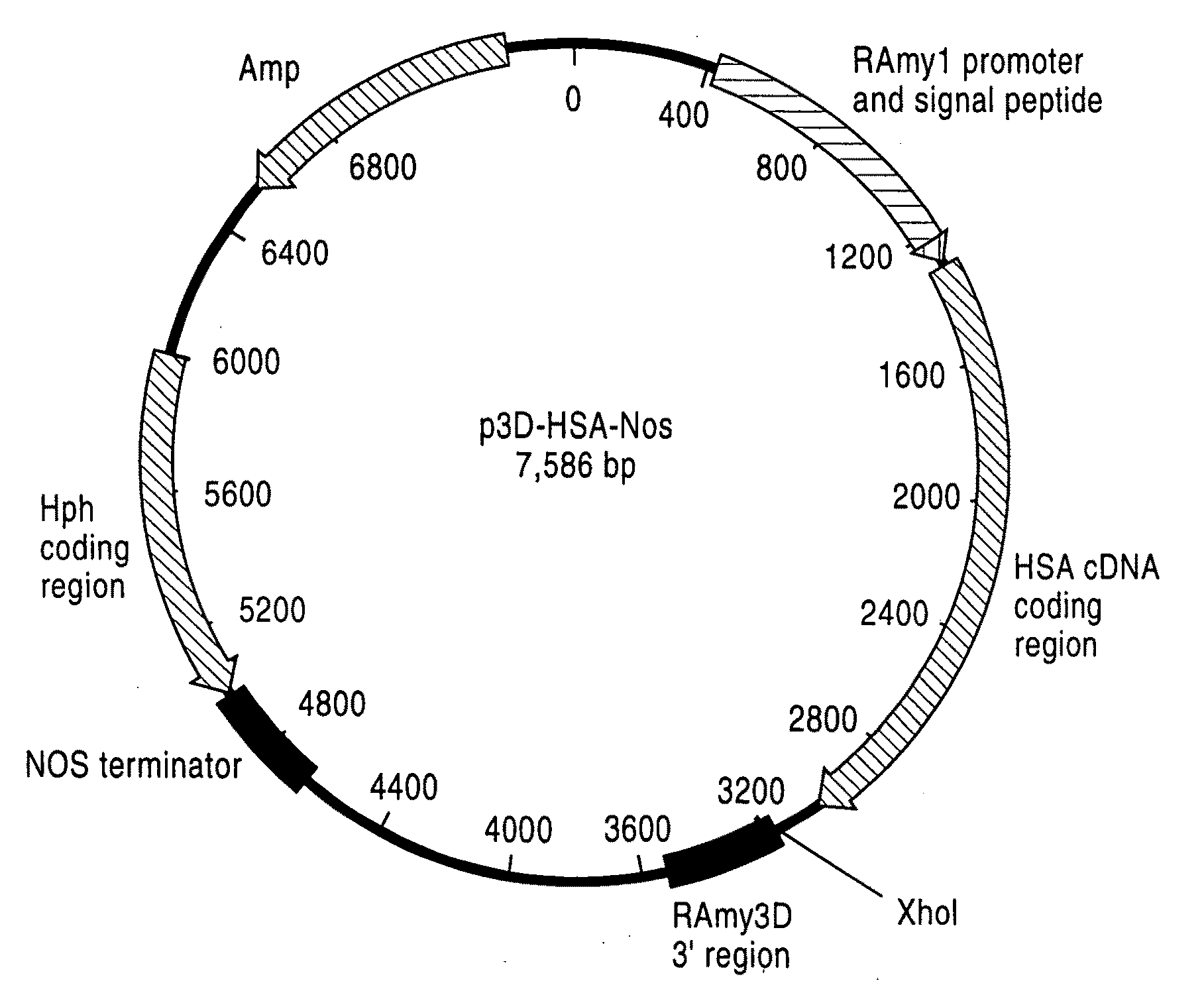
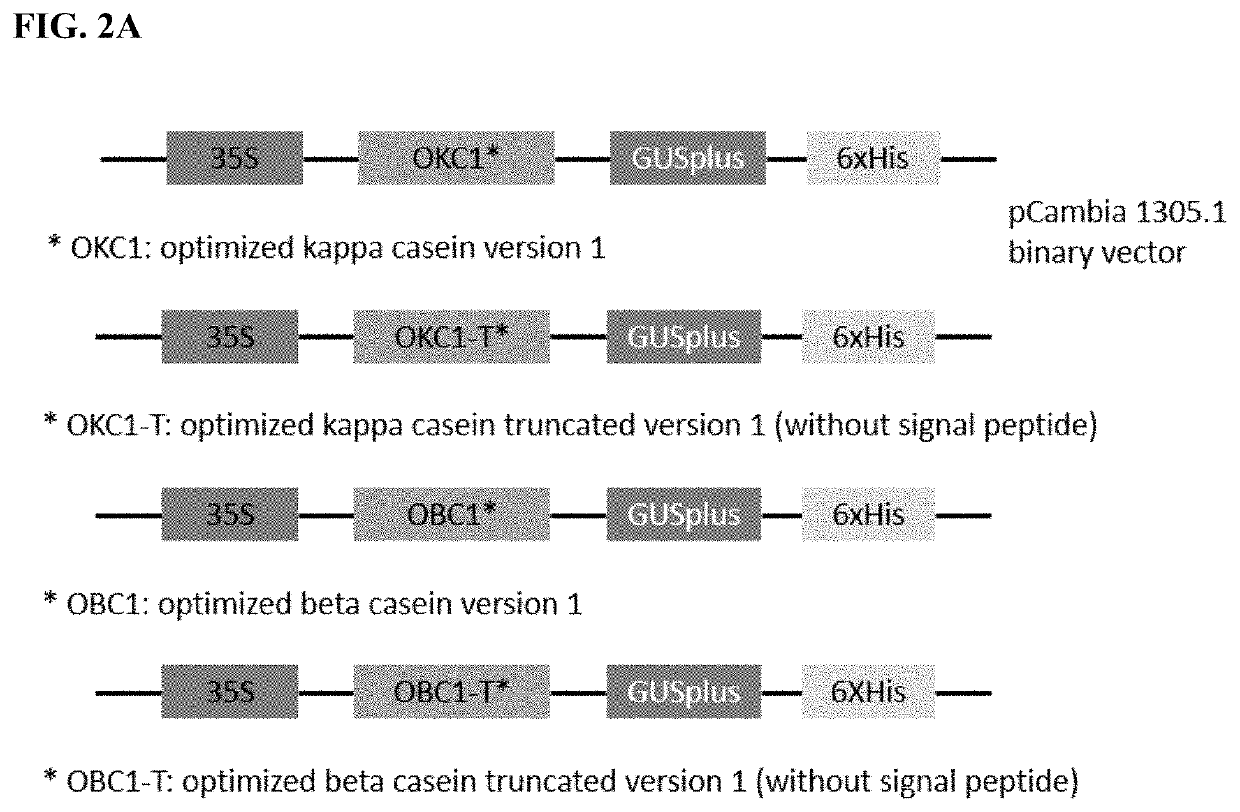
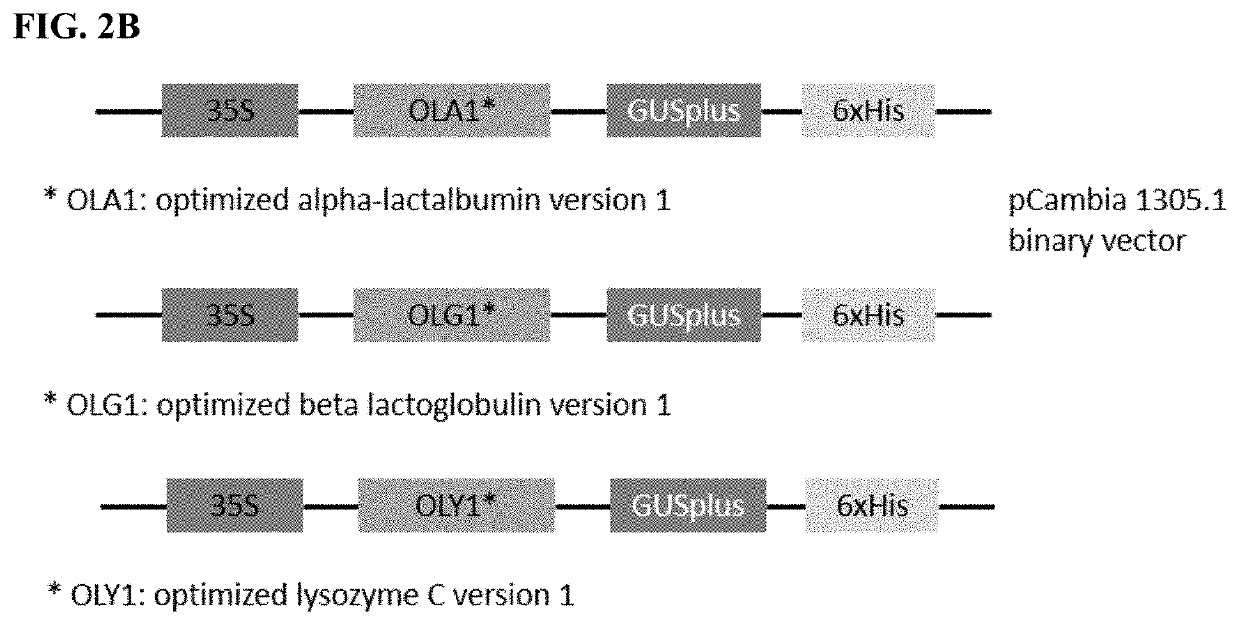
Human Blood Proteins Expressed in Monocot Seeds
The invention is directed to blood proteins produced in monocot seeds and isolated therefrom for use in therapeutic compositions, and to methods of making these isolated blood proteins and to therapeutic compositions comprising them.
Owner:INVITRIA INC
Expression of human milk proteins in transgenic plants
InactiveUS20080318277A1Material nanotechnologyVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTransgenesis
Owner:INVITRIA INC
Methods and compositions for enhanced plant cell transformation
InactiveUS7279336B2Improve conversion efficiencyImprove the level ofOther foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesPlant cellTransformation efficiency
Methods and compositions to increase Agrobacterium transformation efficiency (frequencies) in both dicot and monocot host plants include adding histones to the host plant at most transiently, and using histones and L-cysteine at certain stages in monocot transformation.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
Plant endosperm specificity promoter and its application
ActiveCN101063136AHigh expressionIncrease accumulation levelFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDicotyledonNucleotide
The invention discloses a special expressing promoter of plant endosperm and appliance, which is characterized by the following: 1) possessing DNA sequence of sequence 1 in sequence table; 2) possessing 70% or above 70% homologous property with limited DNA sequence of sequence 1 in sequence table; possessing DNA sequence with same function; 3) possessing crossing nucleic acid sequence with limited NDA sequence of sequence 1 in sequence table under high strict condition. This promoter can start special expression of external source gene in plant endosperm, which is fit for any plant with endosperm such as monocotyledon or dicotyledon.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gene deletion system for security control of transgene monocotyledon
InactiveCN101624594AImprove deletion efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsMultiple cloning siteTissue specific
The invention relates to a gene deletion system for the security control of transgene monocotyledon, comprising two homodromous loxP and FRT fused specificity recognition sites loxP-FRT, wherein a section of multiple clone site sequence for inserting a target gene to be led in plant is contained between the two specificity recognition sites. The gene deletion system can completely delete foreign genes in a specific plant organ by a plant expression vector which is formed by leading a monocotyledon tissue-specific promoter sequence, and can achieve the deletion efficiency of 99.8 percent, thereby being used for preparing the safe transgene monocotyledon.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method of enhancing the seed yield and promoting the growth of plants
InactiveCN103097401AIncrease productionHarvest size improvementClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesNucleotideWild type
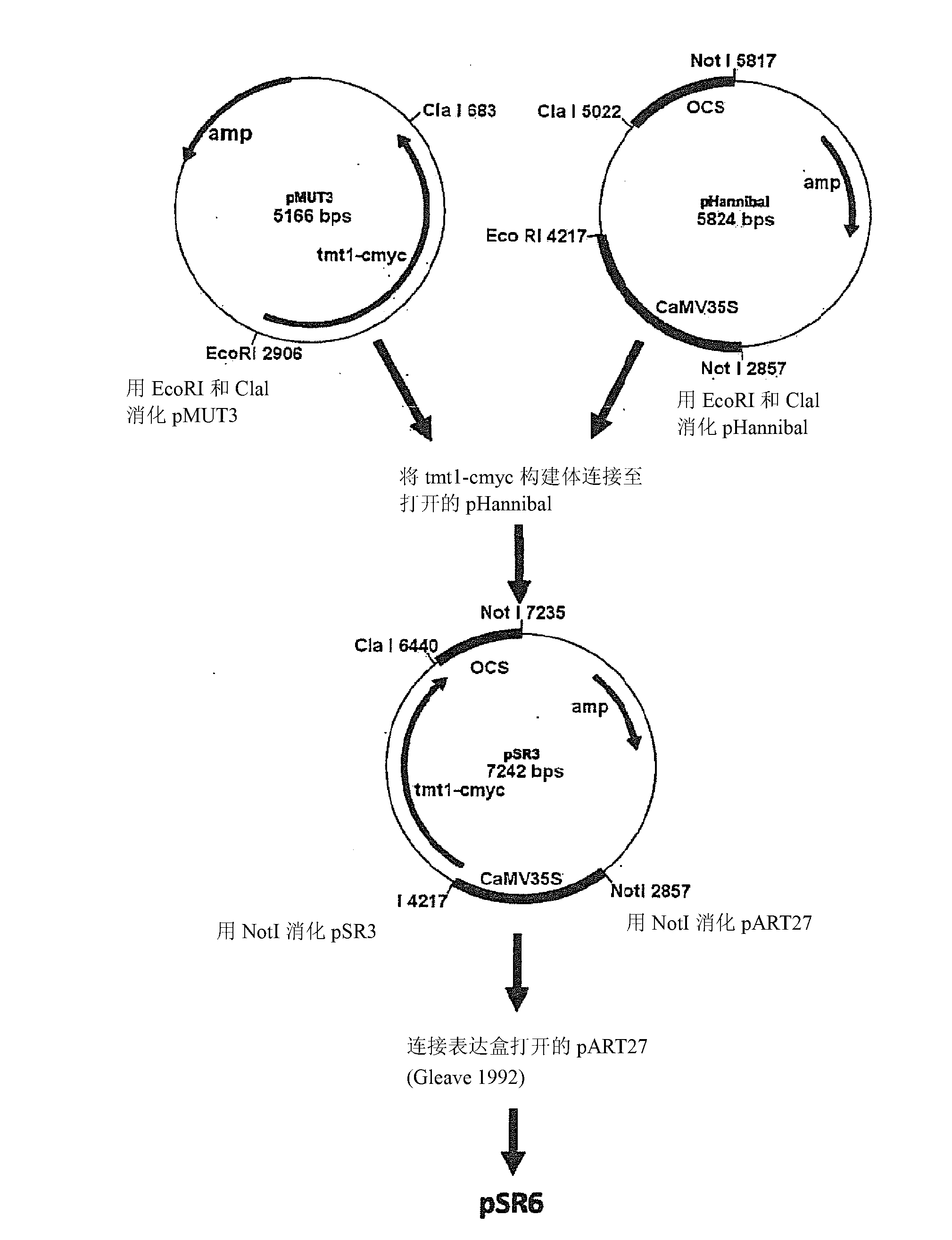
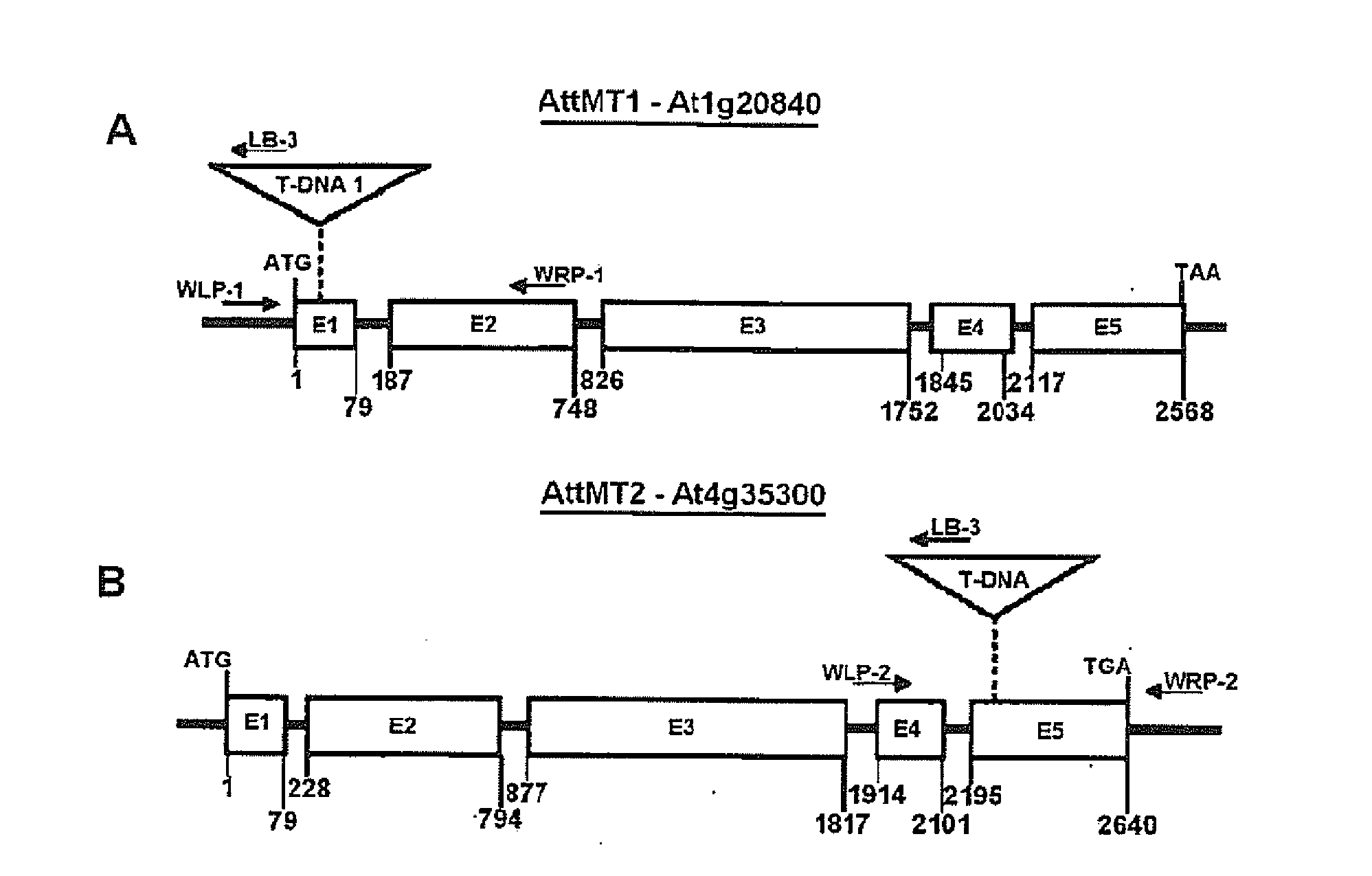
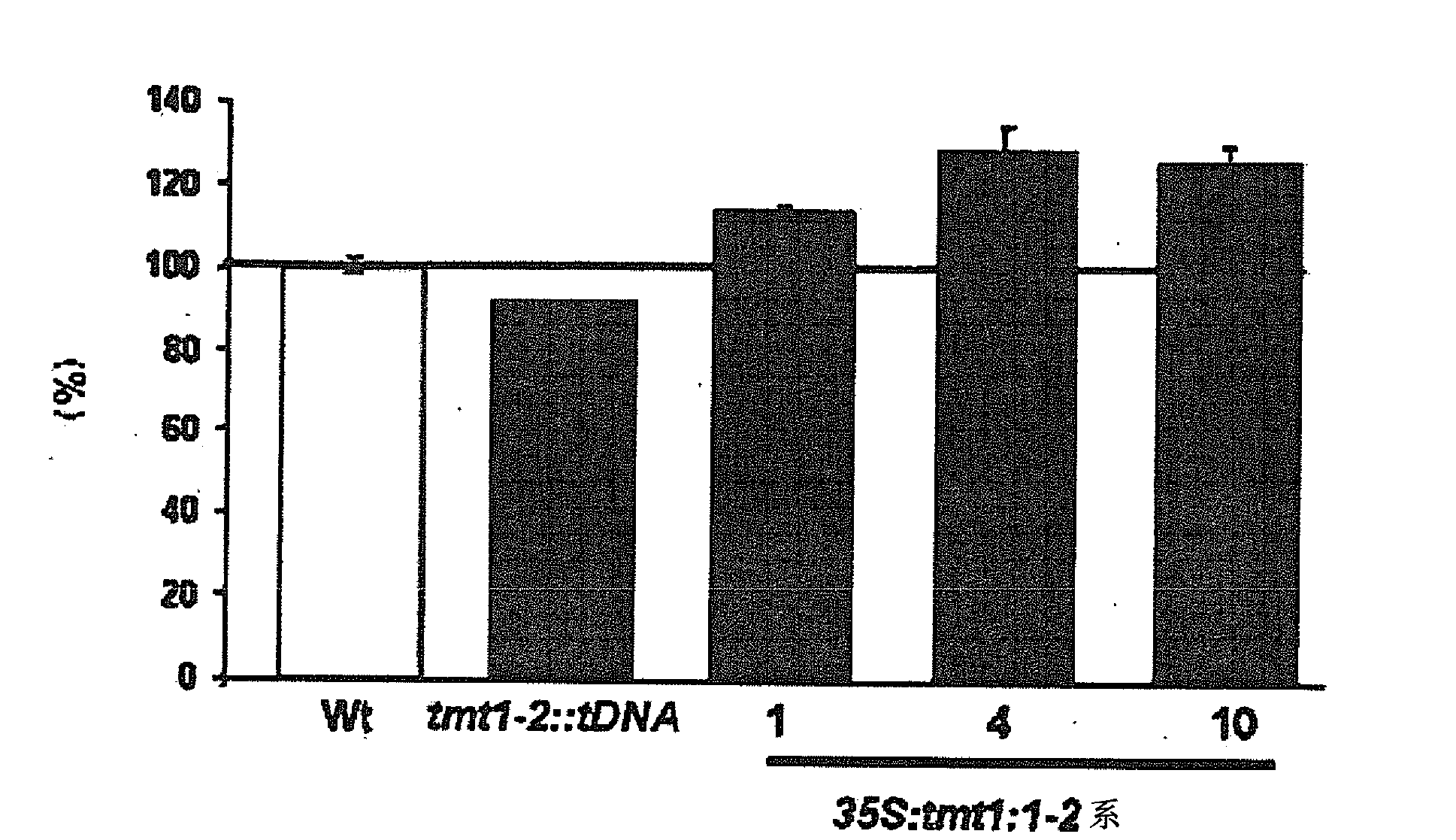
The invention relates to a method of enhancing the seed yield and promoting the growth of monocotyledonous or dicotyledonous plants by overexpression of TMT (tonoplast monosaccharide transporter) protein in osogenic or transgenic plant cells. The invention further concerns a transgenic plant having the property of an enhanced seed yield and increased growth as compared with the wild type, comprising a nucleotide sequence which codes for a TMT (tonoplast monosaccharide transporter) protein, as well as a regulatory nucleotide sequence, operably linked therewith, for the control of an increased gene expression of the TMT protein in the plant cells of the transgenic plant. It further relates to the use of the transgenic plant for the cultivation or production of cultivated plants or useful plants, or biomass, oils or proteins produced therefrom.
Owner:TECH UNIV KAISERSLAUTERN
Expression of human milk proteins in transgenic plants
InactiveUS7718851B2Material nanotechnologyVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTransgenesis
The invention is directed to seed and seed extract compositions containing levels of a human milk protein between 3-40% or higher of the total protein weight of the soluble protein extractable from the seed. Also disclosed is a method of producing the seed with high levels of extractable human milk protein. The method includes transforming a monocotyledonous plant with a chimeric gene having a protein-coding sequence encoding a protein normally present in human milk under the control of a seed maturation-specific promoter. The method may further includes a leader DNA sequence encoding a monocot seed-specific transit sequence capable to target a linked milk protein to a storage body.
Owner:INVITRIA INC
Plant endosperm specificity expression promoter and its application
InactiveCN101063135AHigh expressionImprove qualityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDicotyledonNucleotide
The invention discloses a special expressing promoter of plant endosperm and appliance, which is characterized by the following: 1) possessing DNA sequence of sequence 1 in sequence table; 2) possessing 70% or above 70% homologous property with limited DNA sequence of sequence 1 in sequence table; possessing DNA sequence with same function; 3) possessing crossing nucleic acid sequence with limited NDA sequence of sequence 1 in sequence table under high strict condition. This promoter can start special expression of external source gene in plant endosperm, which is fit for any plant with endosperm such as monocotyledon or dicotyledon.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and compositions for analysis of plant gene function
The invention provides novel methods and compositions for modulating gene function in plants. In particular, the invention provides methods and compositions that allow, for the first time, virus-induced gene silencing in rice. The invention is significant in that prior techniques were not available for rice and because of the major importance of rice to agriculture. The invention therefore provides techniques for the analysis of gene function in rice, as well as in other monocotyledonous species and dicotyledonous plant species.
Owner:SAMUEL ROBERTS NOBLE FOUND
Human blood proteins expressed in monocot seeds
InactiveUS20090258004A1Material nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsBlood proteins
The invention is directed to blood proteins produced in monocot seeds and isolated therefrom for use in therapeutic compositions, and to methods of making these isolated blood proteins and to therapeutic compositions comprising them.
Owner:INVITRIA INC
Pesticidal protein encoding gene Cry1Ab-Ma and expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN102094030AHigh expressionEfficient and stable expressionClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesBacillus thuringiensisResistant genes
The invention provides an insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-Material. The synthesis of the gene is as follows: according to the amino acid sequence of the N-terminal of the original Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) protein (Cry1Ab), the preferred codons of monocotyledon (corn) is used to perform human reformation and synthetize a new Cry1Ab DNA sequence; and the prokaryotic expression vector and plant expression vector are constructed, and transformation is performed in the host cells. Vitro tests prove that the transformed and synthetized Bt gene toxic protein has obvious insecticidal effect on Ostrinia nubilalis. The expression of the insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-Ma in monocotyledon is stable and efficient, thus the gene can be used to produce insect-resistant transgenic plant.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
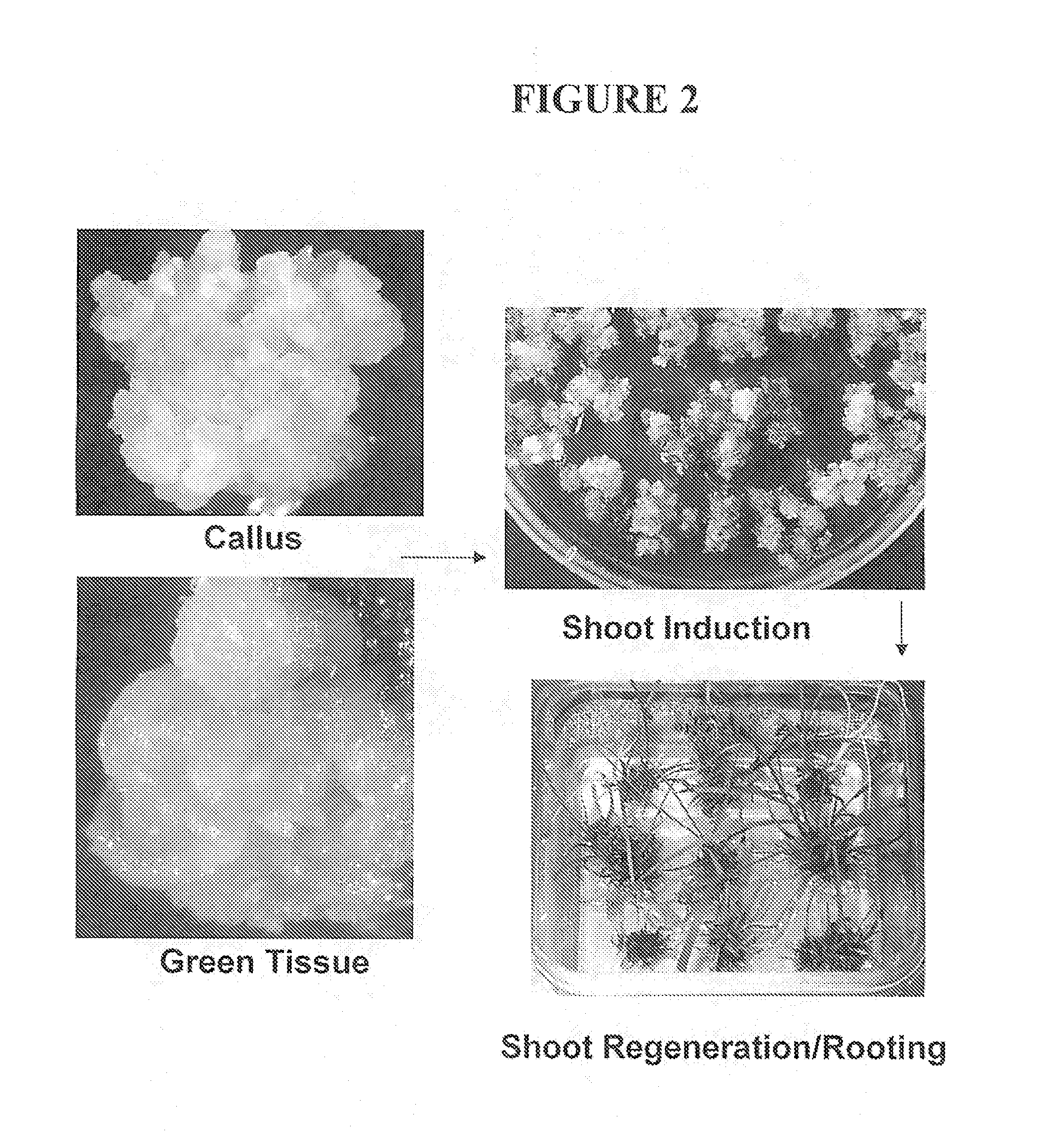
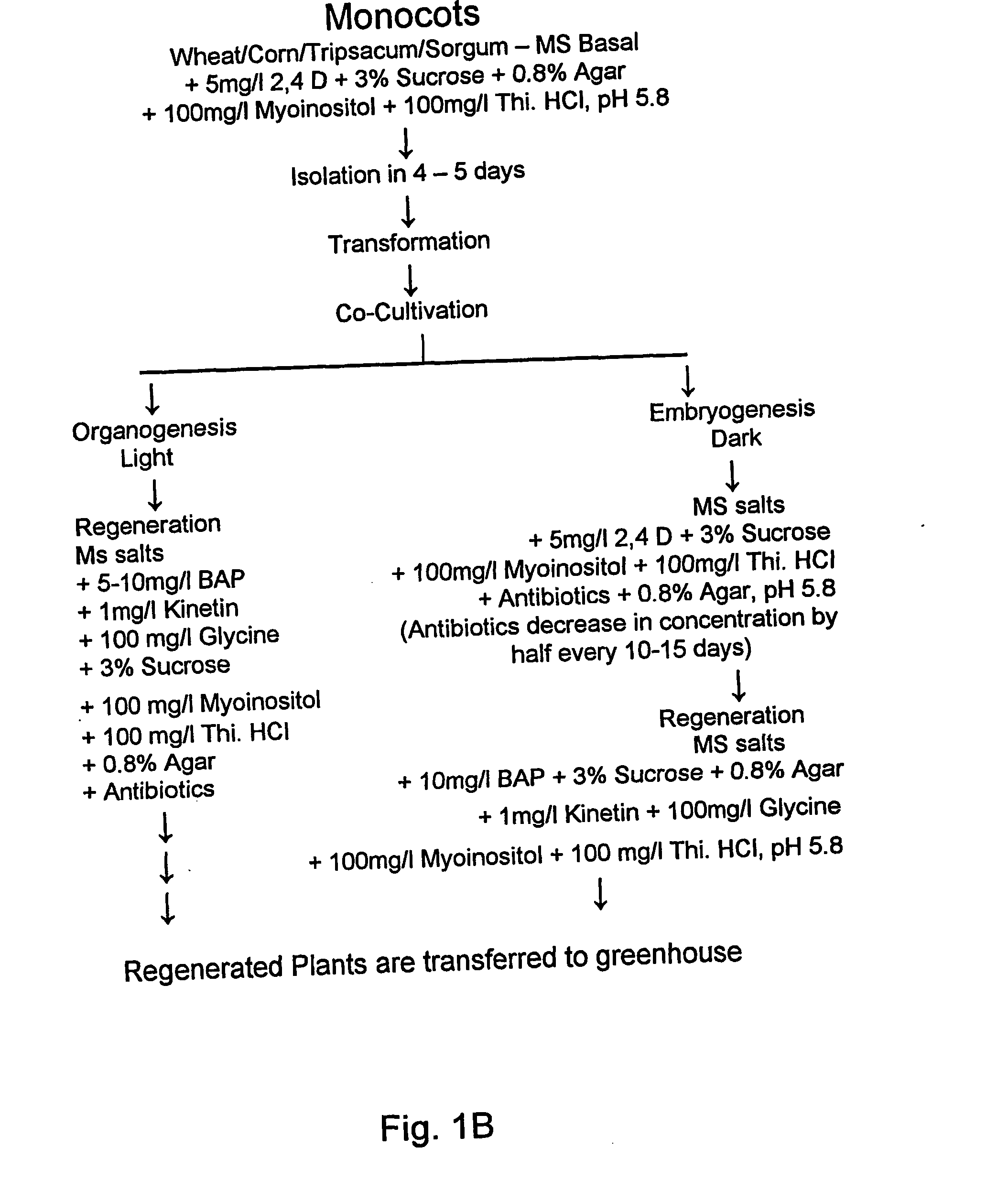
Methods for tissue culture and transformation of sugarcane
InactiveUS20130055472A1Efficient regenerationLong-term regenerabilityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationTransformation efficiencyGMO Plants
Compositions and methods for the efficient transformation and regeneration of monocot plants are provided. The methods of transformation involve infection with Agrobacterium. In this manner, any gene of interest can be introduced into the monocot plant with high transformation efficiency and in low copy number. Transformed and regenerated monocot cells, tissues, plants, and seed are also provided. The invention encompasses regenerating transformed plants, transgenic seeds produced therefrom, and transgenic plants and transgenic seeds from subsequent generations.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
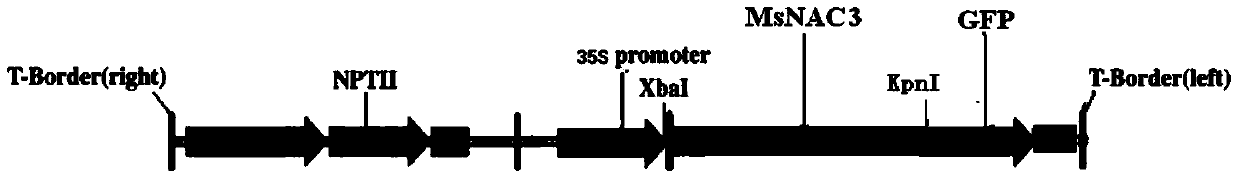
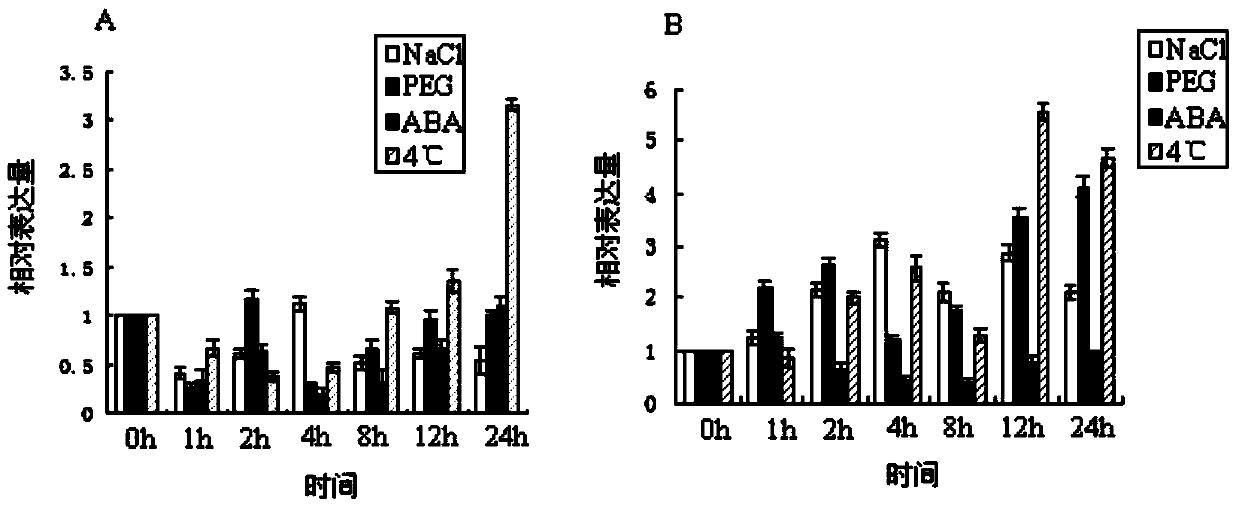
Alfalfa stress response gene MsNAC3 and application thereof
InactiveCN103740731AImprove cold resistanceImprove drought resistanceFermentationPlant genotype modificationNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
The invention relates to an alfalfa stress response gene MsNAC3 and an application thereof. A novel NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine) family related gene is cloned and authenticated from an alfalfa genome by using an RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology and is named as MsNAC3 with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.11, and a fusion expression vector containing an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene is constructed. The expression pattern of the gene MsNAC3 in alfalfa and the relation between the gene and adversity stress (cold damage, salt damage and drought) are analyzed by using a fluorescent quantitative PCR technology, in such a way, people find that the cold resistance, drought resistance and salt resistance of a transgenic tobacco plant can be improved through the overexpression of the gene in tobacco; the gene can be used for genetically transforming other monocotyledons and dicotyledons and improving the stress resistance of the monocotyledons and the dicotyledons.
Owner:申玉华 +5
Soybean drought-resistant zinc finger protein gene STF-2
InactiveCN102703467AImprove drought resistanceImprove stress tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyDicotyledon
The invention discloses a soybean zinc finger protein gene STF-2 which is a C2H2 type zinc finger protein gene related to drought and newly discovered in soybeans. Experiments show that: the STF-2 encoded protein can be located in the nucleus; after over-expression, the gene can obviously improve the drought resistance of the transgenic plants, and has a function of improving the comprehensive stress resistance of the plants; the gene disclosed by the invention comes from soybeans and has an optimized codon suitable for the dicotyledons such as soybeans and the like, and the genetic engineering receptor thereof is mainly suitable for the dicotyledons such as soybeans, tobaccos, cotton and the like; and moreover, the gene is also suitable for the monocotyledons such as rice, wheat, corn and the like.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
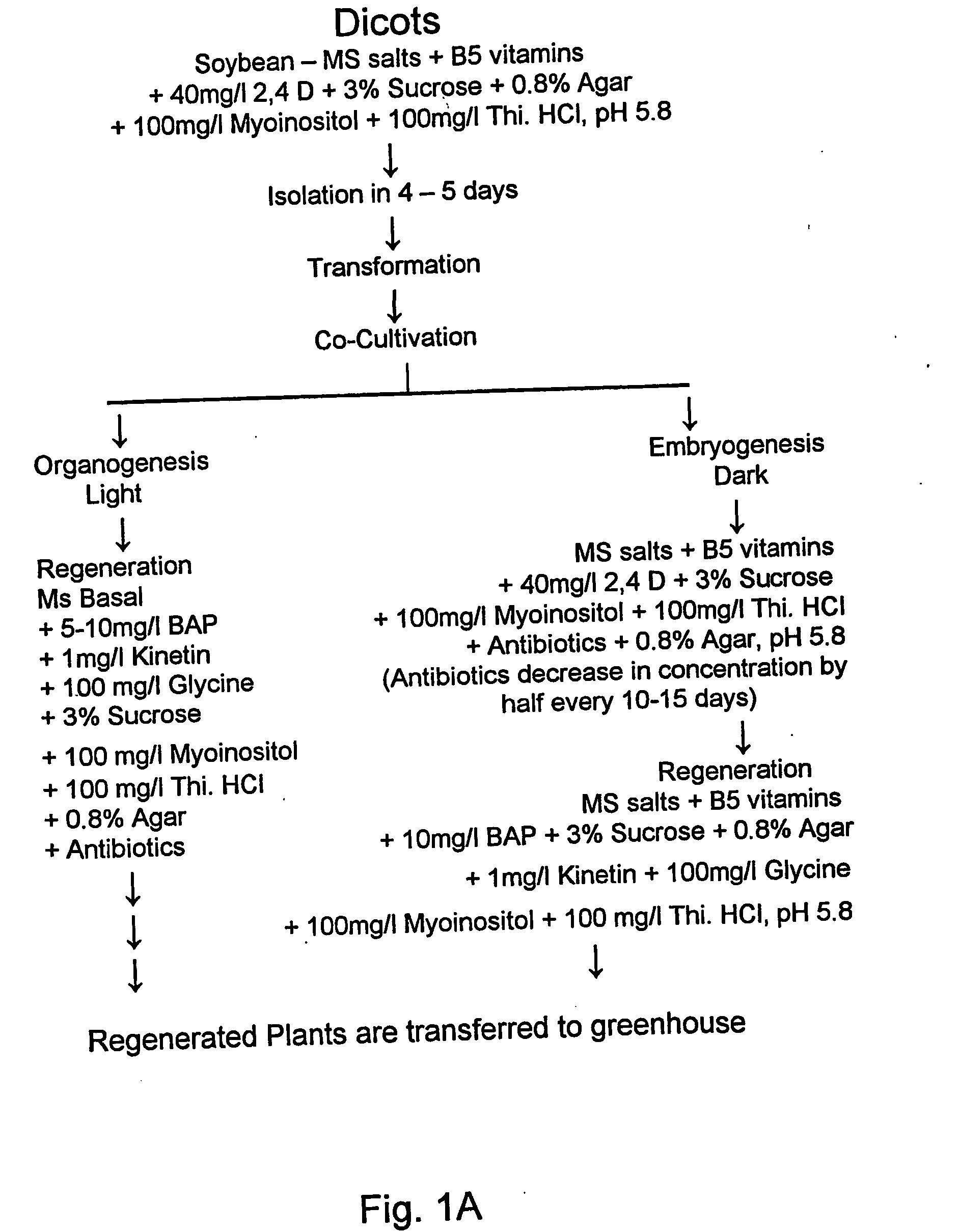
Plant regeneration
A method of plant micopropagation is provided whereby a thin section of non-callus tissue obtained from a monocotyledonous plant, such as sugarcane, wheat or sorghum, is cultured in the presence of a cytokinin and / or an auxin. Optimal regeneration occurs when a basal surface of the thin section is oriented so as to be substantially not in contact with the culture medium. This micropropagation method produces mature monocotyledonous plants by either organogenic or embryogenic regeneration without substantial callus formation. By avoiding use of callus as a starting tissue, this method reduces the likelihood of propagated plants displaying somaclonal variation.
Owner:SUGAR RES & DEV CORP +2
Monocotyledon transgenic method for invading growing points of seed buds minimally and fully
InactiveCN102876712AEasy to operateImprove conversion efficiencyGenetic engineeringFermentationTriticeaeGenotype
The invention relates to a monocotyledon transgenic method for invading growing points of seed buds minimally and fully. According to the technical key point, the monocotyledon transgenic method comprises the following steps of: germinating seeds for 1 to 2 days, and when buds extend to be 0.2 to 2 centimeters long, removing coleoptile to expose the growing points; pricking and brushing the growing points by using a minimally-invasive brush of which the diameter of a single brush hair is 4 to 20 micrometers, the exposed length is 0.5 to 3 millimeters and the number of the brush hairs is 100 to 5,000 and which is dipped with agrobacterium mediated conversion liquid to perform full minimally-invasive conversion; after performing co-culture, developing further to form seedlings, promoting the development of spikes and grains, and harvesting in a plant division mode; and performing identification on T1 generation. The monocotyledon transgenic method has the advantages that tissue culture, the limit of genotypes and resistance screening are avoided, the method is easy and convenient to operate and easy to realize in large scale and is suitable for all monocotyledons which bear seeds. By the monocotyledon transgenic method, the transformation effects that the genetic transformation rate of wheat is 49 percent, the genetic transformation rate of paddy is 66.3 percent and the genetic transformation rate of corn is 100 percent are achieved.
Owner:HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI INST OF GENETICS & PHYSIOLOGY
Milk protein production in transgenic plants
Owner:ALPINE ROADS INC
Media, kits, systems and methods for the micropropagation of monocotyledonous plants
InactiveUS20120159847A1Improving soil tilth/healthCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureMicropropagationBotany
Disclosed herein are media, systems and methods for achieving micropropagation of monocotyledonous plants.
Owner:BOOSHOOT
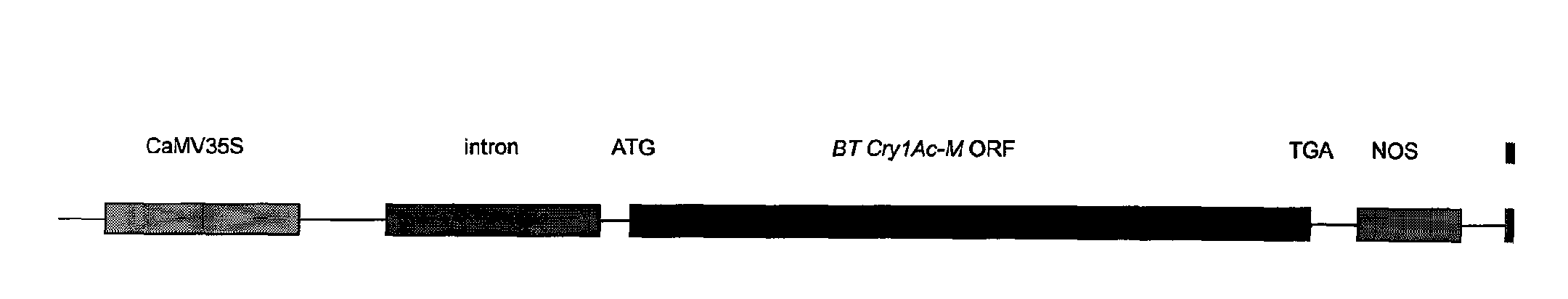
Artificial synthesized Bt insecticidal gene for transgenic anti-insect plants
The invention discloses an artificial synthesized Bt insecticidal gene for transgenic anti-insect plants, further, the invention relates to the optimization and transformation systematically to a coding frame and a codon of a CrylAc anti-insect gene, according to an activity analysis to Bt protein in different regions and in accordance with the coding characteristics of the monocotyledons, obtaining anti-insect gene CrylAc-M which can be expressed in a monocotyledons efficiently, with the optimized codon and coding frame. The CrylAc-M gene after being transformed is connected on an expression carrier with CaMV35S-Adhl as promoter, and then the Bt gene CrylAc-Adhl is transferred into a maize inbred line with highly efficient conversion rate by a gene gun co-transformation method. A transgenic progeny is positive through Bt protein testing and a field anti-insect test of the field is tested to be highly resistant.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
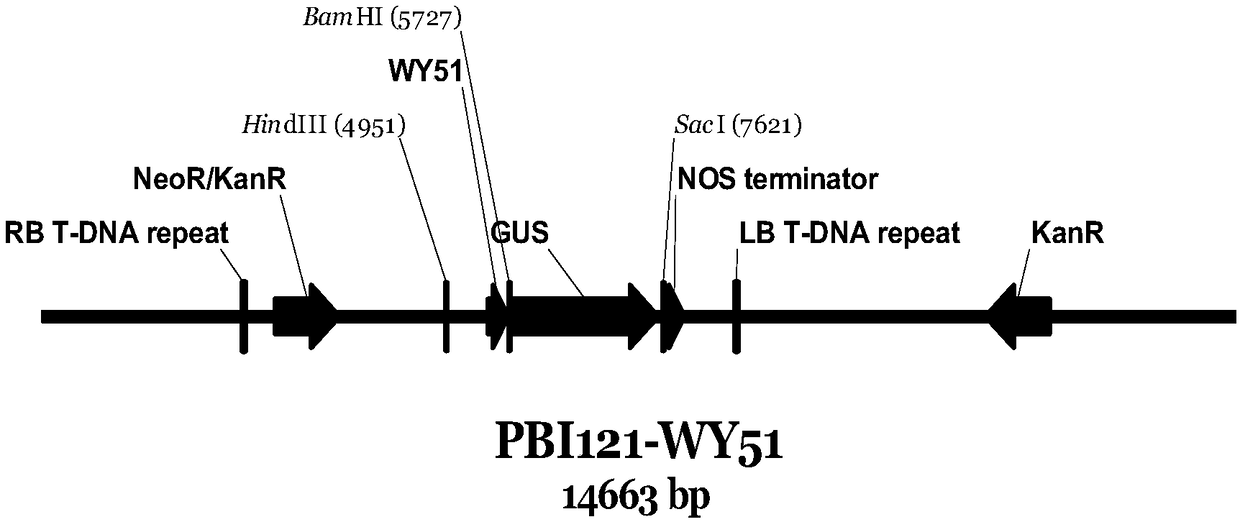
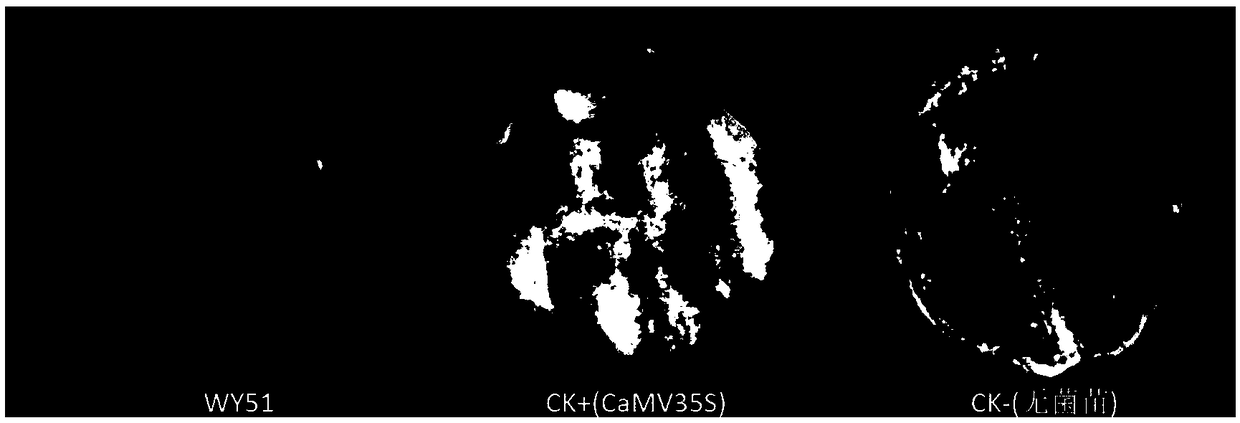
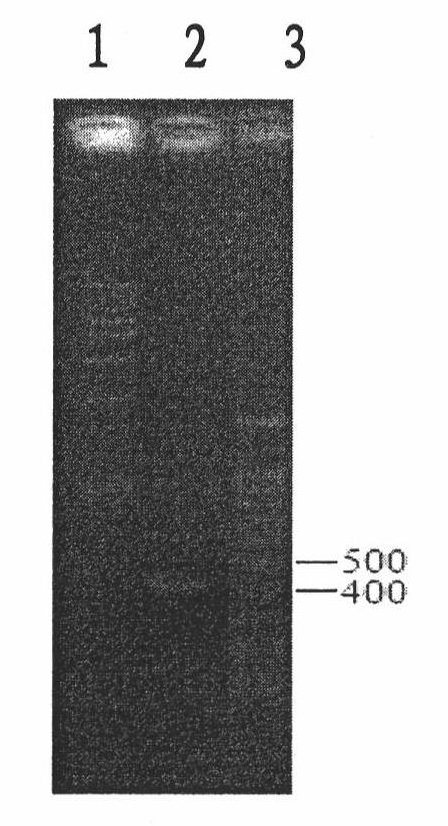
Oidium heveae Steinmann in-vivo promoter WY51 and application thereof
The invention discloses an oidium heveae Steinmann in-vivo promoter WY51 and application thereof. The promoter WY51 has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, or is provided with a variant with functions of the promoter. The invention further relates to a nucleic acid builder, a carrier, reconstitution cells, a transgenic plant, an explant and a callus which comprises the promoter. The promoter can be used for regulating and controlling expression of exogenous genes in dicotyledon and monocotyledon, and a brand-new tool and selection are provided for expression of genes of the transgenic plant.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Promoter BgIosP513 and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a promoter, in particular to a promoter of a monocotyledon such as paddy rice, and a preparation method and application of the promoter. The promoter has a nucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1, or has a variant which has a function of the promoter and is selected from the following sequences: 1) a nucleotide sequence in hybridization with the nucleotide sequence shown by the SEQ ID NO:1 under a high-grade stringent condition; 2) a nucleotide sequence for performing substitution, deletion and adding modification on one or more basic groups of the nucleotide sequence shown by the SEQ ID NO:1; and 3) a nucleotide sequence having at least 90 percent of sequence identity with the nucleotide sequence shown by the SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also relates to the preparation method of the promoter and the application of the promoter in adjusting the expression of a target gene in the monocotyledon and adjusting rice breeding.
Owner:HUADA GENE RES & DEV CENT HANGZHOU
Soybean zinc finger protein SCTF-1 and applications thereof
InactiveCN102181454AImprove cold resistanceImprove stress tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a soybean zinc finger protein gene SCTF-1 which is a C2H2-type zinc finger protein gene which is discovered in soybean and is relevant with low temperature. The experiment shows that the protein coded by SCTF-1 can be located to a cell nucleus; after being excessively expressed, the gene can obviously improve cold resistance of transgenic plants, and has a function of improving plant comprehensive stress tolerance. The gene provided by the invention is derived from soybean, and comprises an excellent codon of dicotyledon, such as soybean and the like; and the gene engineering receptor of the gene is mainly suitable for dicotyledon, such as soybean, tobacco and cotton and the like, and also suitable for monocotyledon, such as rice, wheat and corn and the like.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for transformation of mono-and di-cotyledonous plants using meristematic tissue and nodal callus from dicotyledonous plants
InactiveUS20040237133A1Efficient productionIncrease productionOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyNODAL
This invention relates to a method for the introduction of genes encoding desirable traits into both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants and to plants and parts thereof produced by growing plants using this method. The time required for the production of transgenic plants is significantly decreased, while the number of transgenic plants is significantly increased. These increases are not dependent upon the use of super-virulent Agrobacterium strains. The invention also relates to an improved technique for in vitro regeneration of mono- and di-cotyledonous plants in a suitable medium containing a novel growth regulator regime that promotes cell elongation in the production of numerous somatic embryos that are regenerable into fertile plants.
Owner:TOLEDO UNIV OF
N-pyridine aryloxyphenoxy carboxylic acid derivatives, preparation method and applications thereof
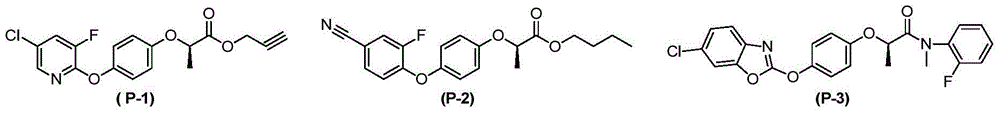
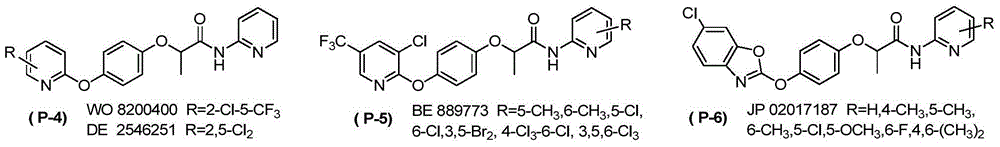
The invention discloses N-pyridine aryloxyphenoxy carboxylic acid derivatives represented by the formula (I), a preparation method and applications thereof. In the formula (I), the definitions of Ar1, Ar2, R, R', R1, R2, R3, R4, m, n, p, q, and X are represented in the description. The compounds (I) has activities on killing weeds, bacteria, and insects, and has extremely high activity on killing monocotyledon weeds such as Chinese sprangletop.
Owner:HUNAN CHEM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com