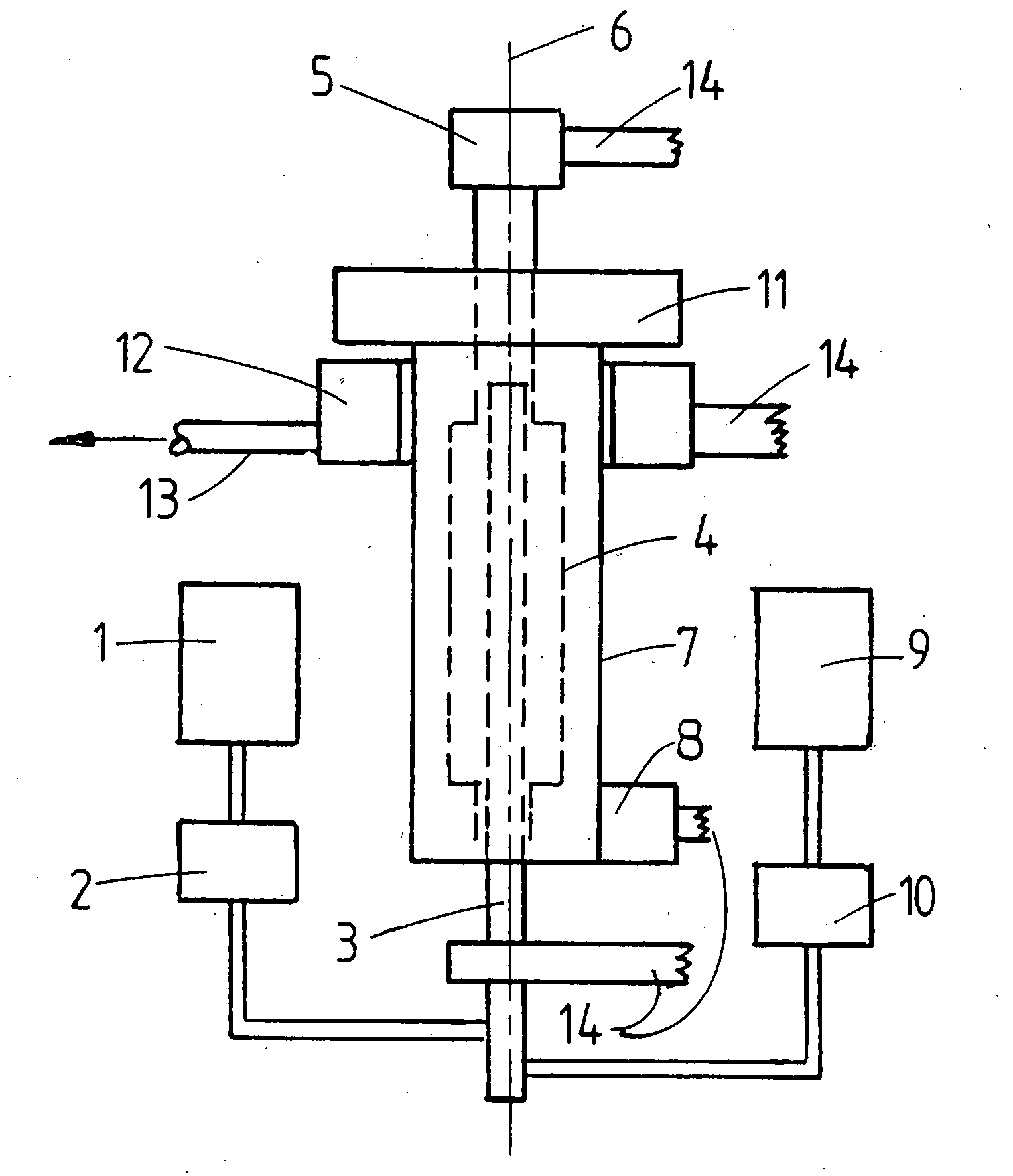
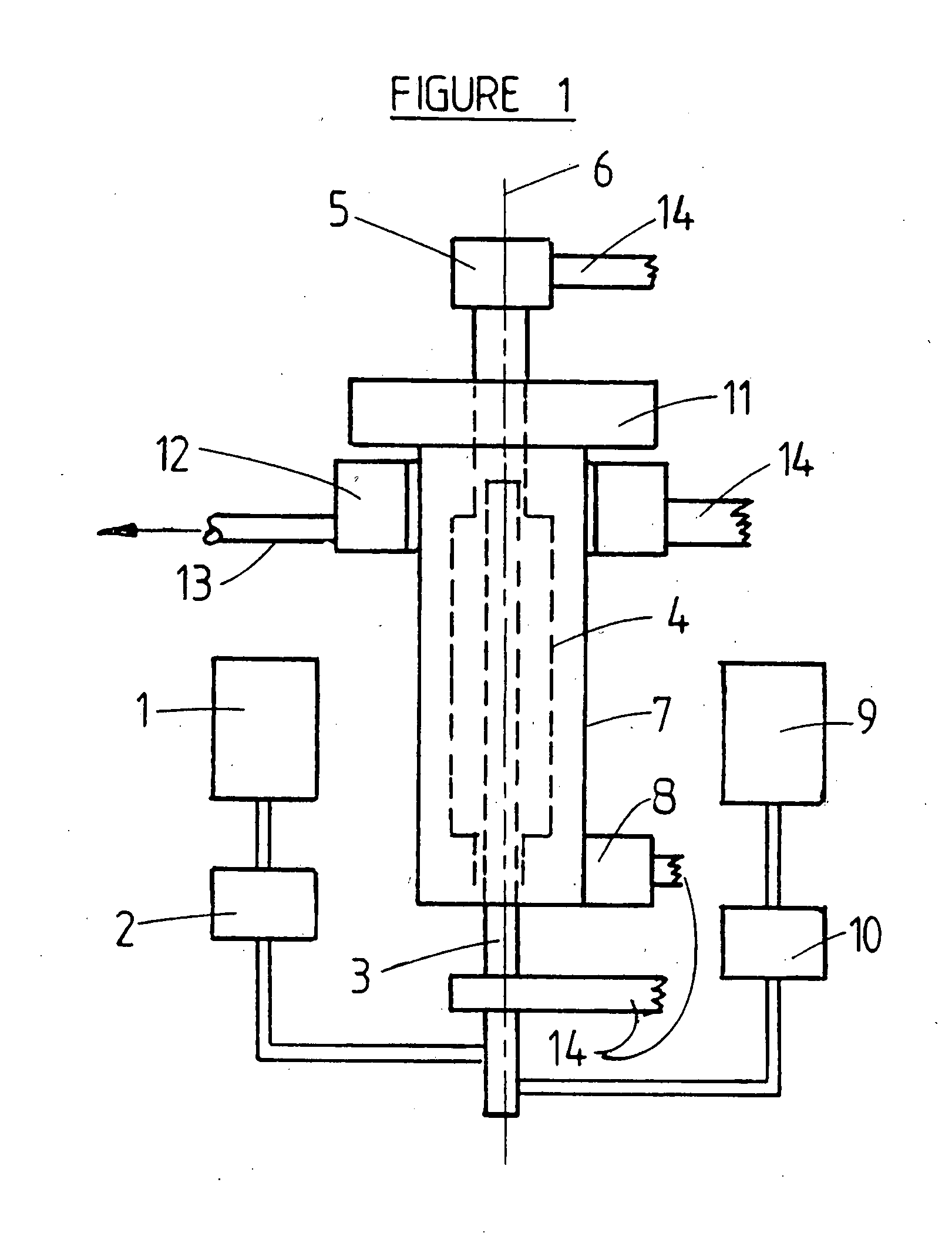
Patents
Literature
179 results about "Fluid particle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
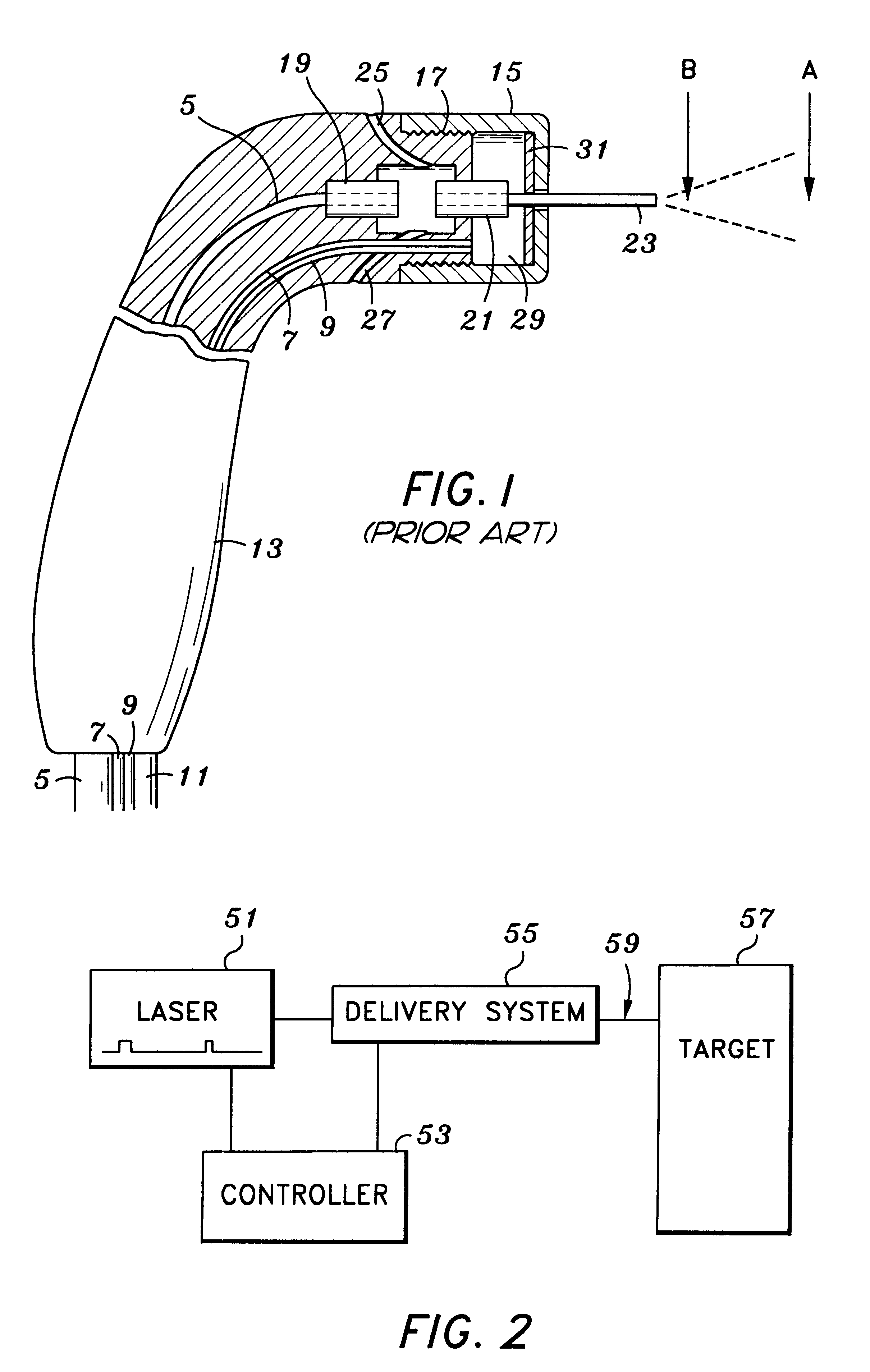
Tissue remover and method
InactiveUS6669685B1Fine and smooth incisionEasy to controlMedical devicesFluid jet surgical cuttersMedicineCutting force
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. The cannula is provided with a cannula distal end. The proximal end of the cannula is provided with fluid flow connection to an aspiration source. Separated soft tissue and fluid are aspirated through the cannula distal end and the cannula by an aspiration source at the proximal end of the cannula.
Owner:BIOLASE TECH INC
Tissue remover and method
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A non-thermal tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced mechanical cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. The cannula is provided with an aspiration inlet port adjacent the cannula distal end. The proximal end of the cannula is provided with fluid flow connection to an aspiration source. Separated soft tissue and fluid are aspirated through the aspiration inlet port and the cannula by an aspiration source at the proximal end of the cannula.
Owner:BIOLASE INC
Tissue remover and method
InactiveUS20040068256A1Fine and smooth incisionEasy to controlFluid jet surgical cuttersSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesCutting forceBiomedical engineering
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. The cannula is provided with a cannula distal end. The proximal end of the cannula is provided with fluid flow connection to an aspiration source. Separated soft tissue and fluid are aspirated through the cannula distal end and the cannula by an aspiration source at the proximal end of the cannula.
Owner:BIOLASE INC
Electrostatic fluid accelerator
InactiveUS6888314B2Not produce substantialMaximum speedSamples introduction/extractionElectric arc lampsHigh pressureBreakdown voltage
An electrostatic fluid accelerator having a multiplicity of closely spaced corona electrodes. The close spacing of such corona electrodes is obtainable because such corona electrodes are isolated from one another with exciting electrodes. Either the exciting electrode must be placed asymmetrically between adjacent corona electrodes or an accelerating electrode must be employed. The accelerating electrode can be either an attracting or a repelling electrode. Preferably, the voltage between the corona electrodes and the exciting electrodes is maintained between the corona onset voltage and the breakdown voltage with a flexible top high-voltage power supply. Optionally, however, the voltage between the corona electrodes and the exciting electrodes can be varied, even outside the range between the corona onset voltage and the breakdown voltage, in to vary the flow of fluid. And, to achieve the greatest flow of fluid, multiple stages of the individual Electrostatic Fluid Accelerator are utilized with a collecting electrode between successive stages in order to preclude substantially all ions and other electrically charged particles from passing to the next stage, where they would tend to be repelled and thereby impair the movement of the fluid. Finally, constructing the exciting electrode in the form of a plate that extends downstream with respect to the desired direction of fluid flow also assures that more ions and, consequently, more fluid particles flow downstream.
Owner:TESSERA INC
System and method for suppressing dust and odors
InactiveUS20070186778A1Lower water usageLow costUsing liquid separation agentDust removalEngineeringHigh velocity
A system and method for suppressing dust and / or odors. The system includes a fan-propelled mister that propels air through one or more discharge tubes to create a high velocity airflow. A misting ring having a plurality of nozzles adjacent the end of the discharge tube acts to create a mist of small fluid particles. In one embodiment, the misting ring includes a first set of nozzles for generating a mist having fluid particles of a first size for controlling or suppressing dust and a second set of nozzles for generating a mist having fluid particles of a second set for suppressing odor. The system may also include one or more high pressure hoses to saturate a particular area or zone. The mister may also be adjusted to direct the output and / or oscillate to cover a greater area.
Owner:DUST CONTROL TECH
Gas turbine combustor, and gas turbine with the combustor
InactiveCN1705815AReduce combustion vibrationContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsInterior spaceCombustor
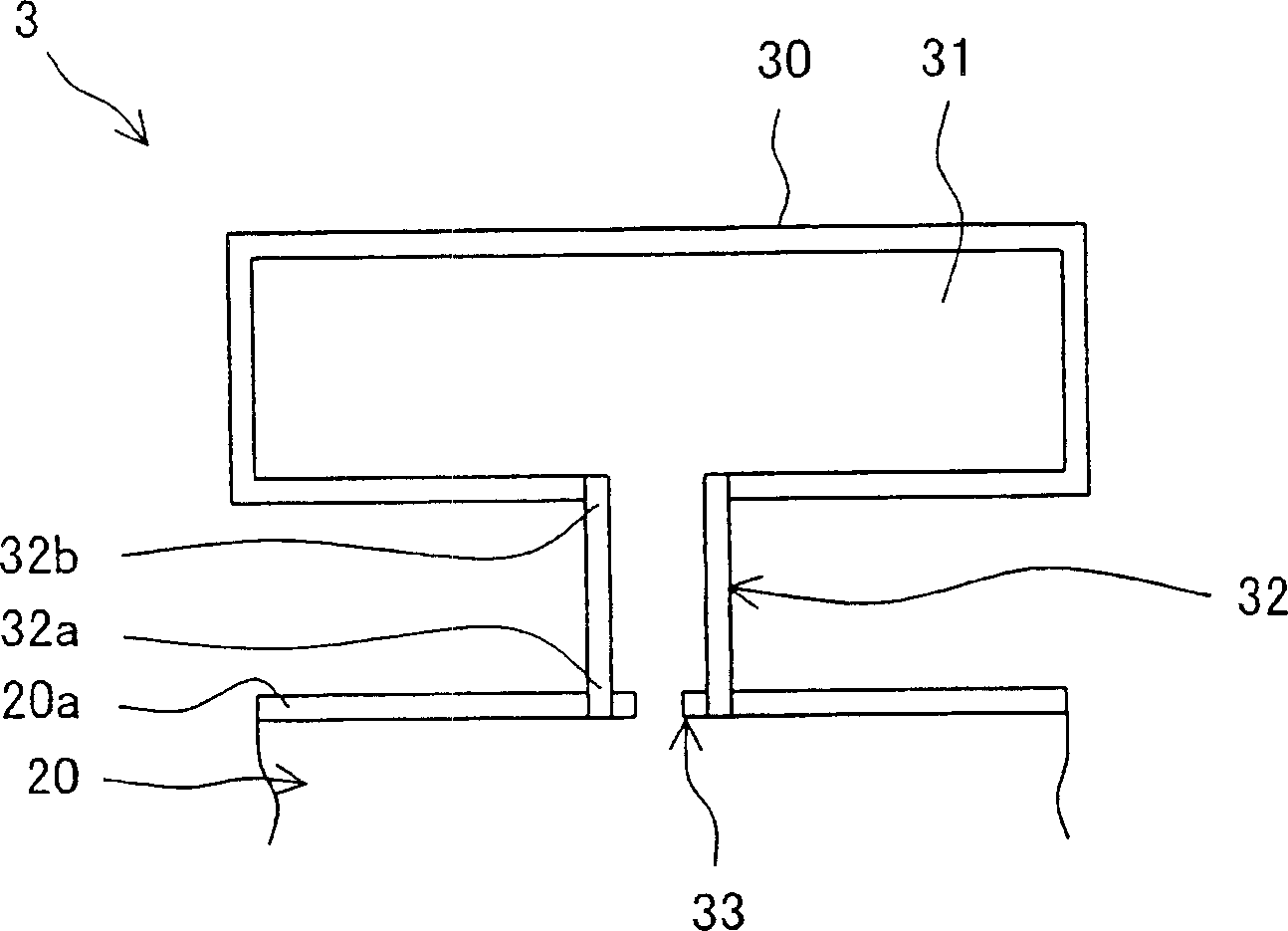
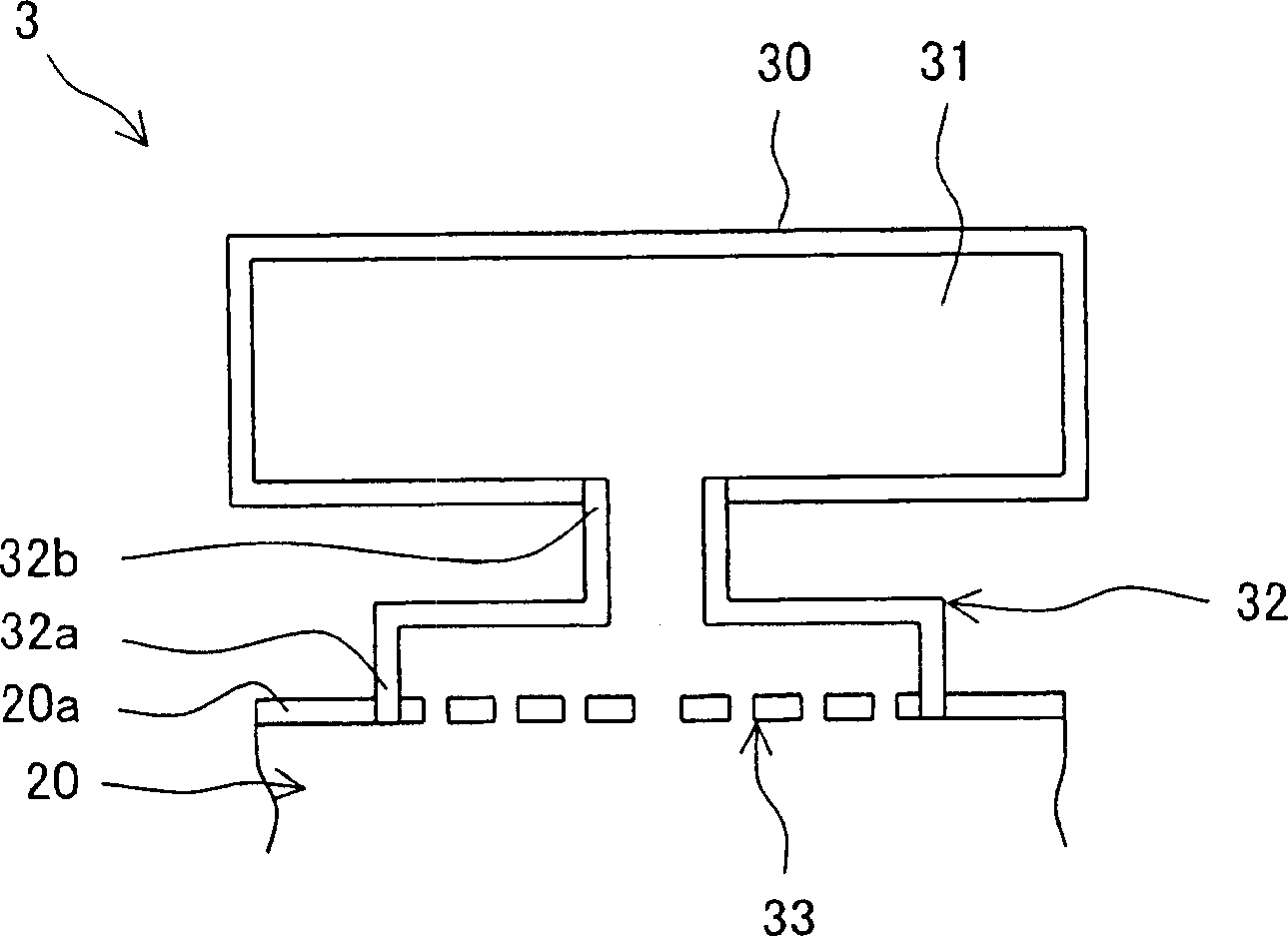
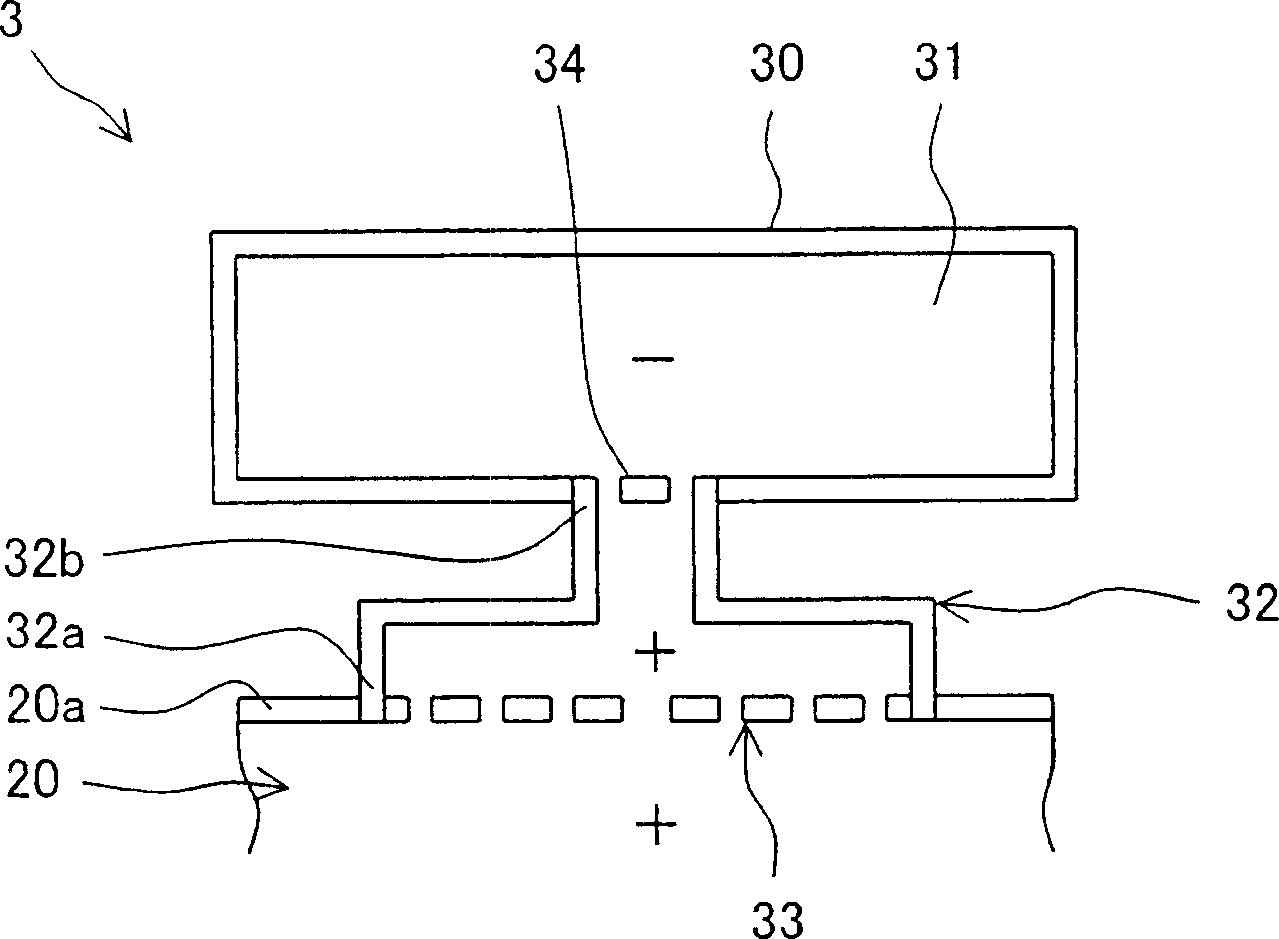
A gas turbine combustor (3) capable of reducing combustion vibration to stably reduce NOx, comprising a first box body (30) disposed on the outside of an objective body (20) having an inner tube (6), a tail tube (7), and a bypass duct (11) and forming a first internal space (31) of a specified volume and a first throat (32) of a specified length having one end (32a) opening to the side wall (20a) of the objective body (20) and the other end (32b) opening into the first internal space (31), wherein a first resistance body (33) having a large number of through-holes is fittedly inserted into one end (32a), fluid particles as vibration elements for the combustion vibration produced in a combustion area are effectively captured by the first resistance body (33) and resonated with air in the first internal space (31) connected thereto through the first throat (32) to vibrate near the first resistance body (33) so as to attenuate the amplitude of the vibration thereof.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
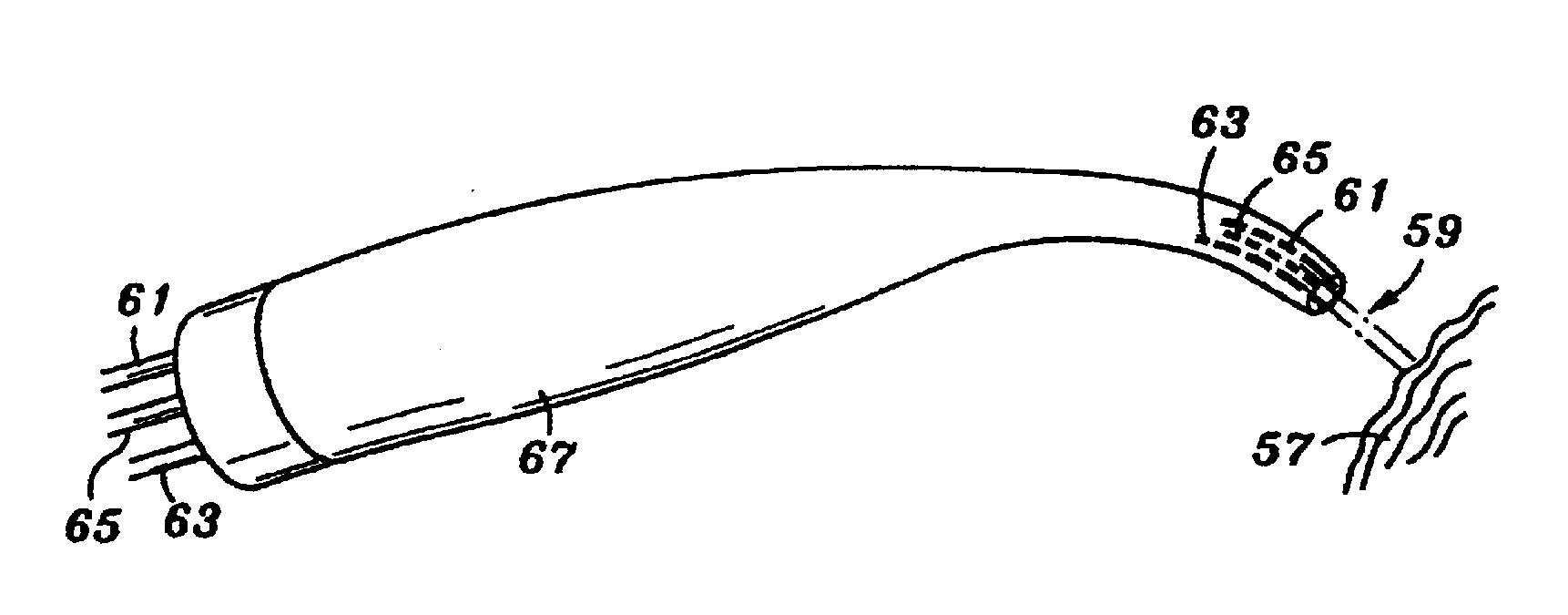
Tunnelling probe
InactiveUS20090298004A1Accurate cutting operationPromote absorptionTeeth fillingSurgical instrument detailsFiberActive agent
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. An endodontic probe is used to perform disinfection procedures on target tissues within root canal passages and tubules. The endodontic probe can include an electromagnetic radiation emitting fiber optic tip having a distal end and a radiation emitting region disposed proximally of the distal end. According to one aspect, the endodontic probe can include a porous structure that encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip excluding the radiation emitting region and that is loaded with biologically-active particles, cleaning particles, biologically-active agents, or cleaning agents for delivery from the porous structure onto the target tissues. Another aspect can include provision of the endodontic probe with an adjustable channel-depth indicator, which encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip besides the radiation emitting region and which is movable in proximal and distal directions along a surface of the fiber optic tip to facilitate the provision of depth-of-insertion information to users of the endodontic probe.
Owner:BIOLASE TECH INC
Fluid-solid coupling method based on smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) and nonlinear finite elements
InactiveCN103699715ASolve problems that are difficult to directly coupleEasy to implement in parallelSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsElement model
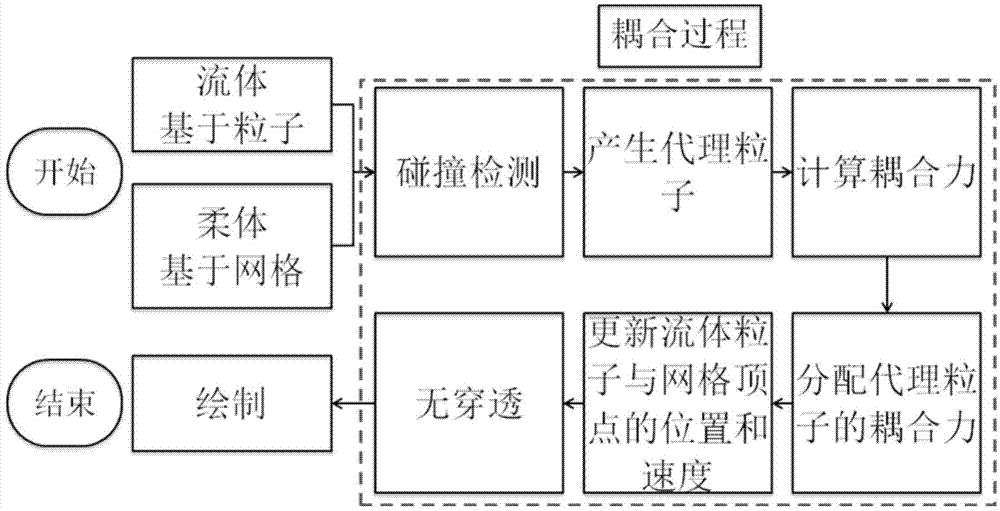
The invention provides a fluid-solid coupling method based on smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) and nonlinear finite elements. The method comprises the following six steps: at a collision detection stage, detecting collision information of fluid particles with a finite element network; at an agent particle generation stage, generating collision agent particles presenting a finite element model according to the collision information for processing the collision between a fluid and a solid; at a coupling force calculation stage, calculating force generated by collision between agent particles and fluid particles according to the position and speed relations of the agent particles and the fluid particles; at a coupling force allocation stage, controlling the position relation of the agent particles and the finite element model and allocating the coupling force to a finite element stress model; at a position and speed updating stage, driving the position and speed update of the finite element model and a fluid particle model according to the calculated coupling force; at a non-penetration modification stage, modifying penetration fluid particles according to an updated position.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Electrostatic fluid accelerator
InactiveUS20050200289A1Not produce substantialMaximum speedSamples introduction/extractionElectric arc lampsHigh pressureBreakdown voltage
Owner:TESSERA INC
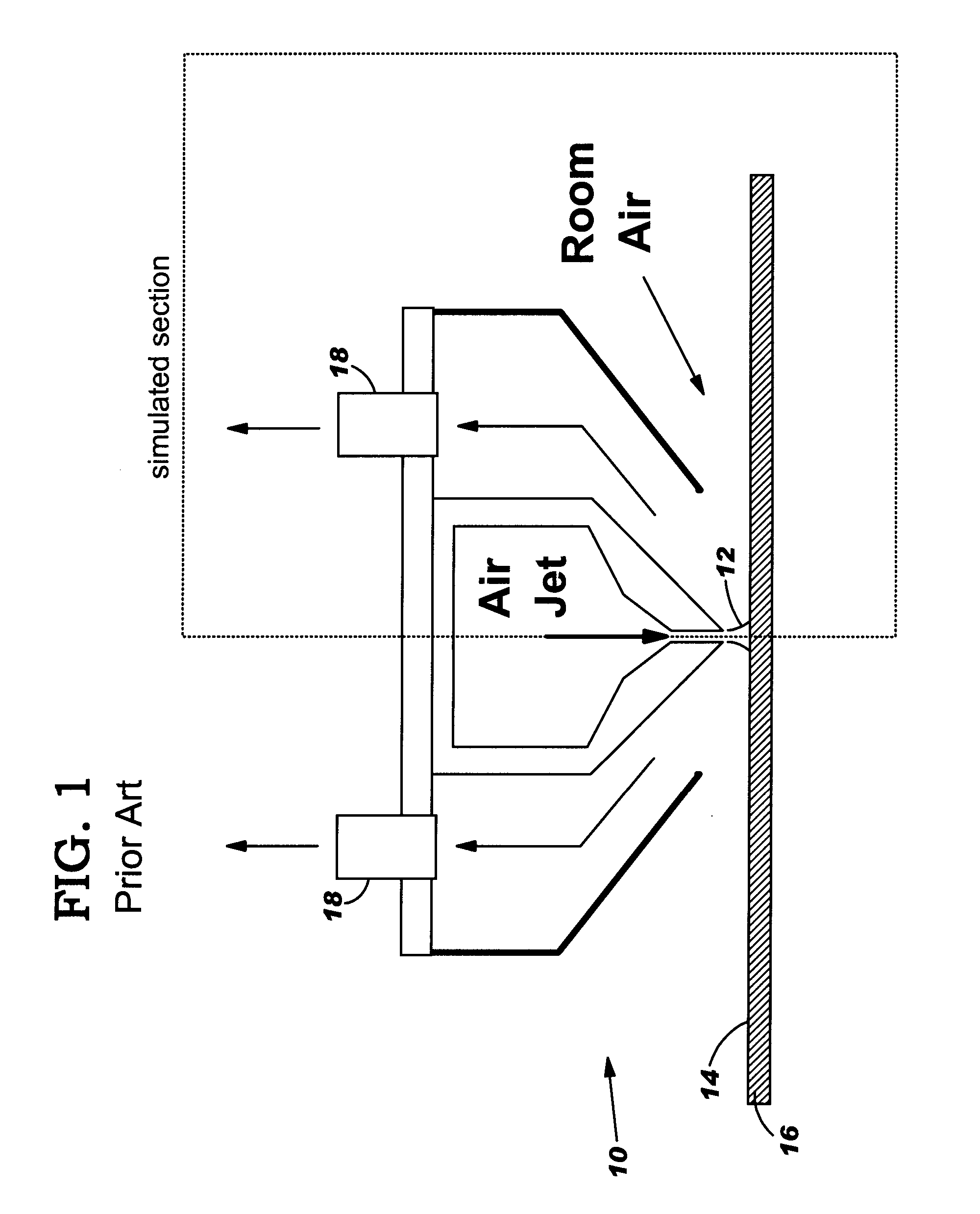
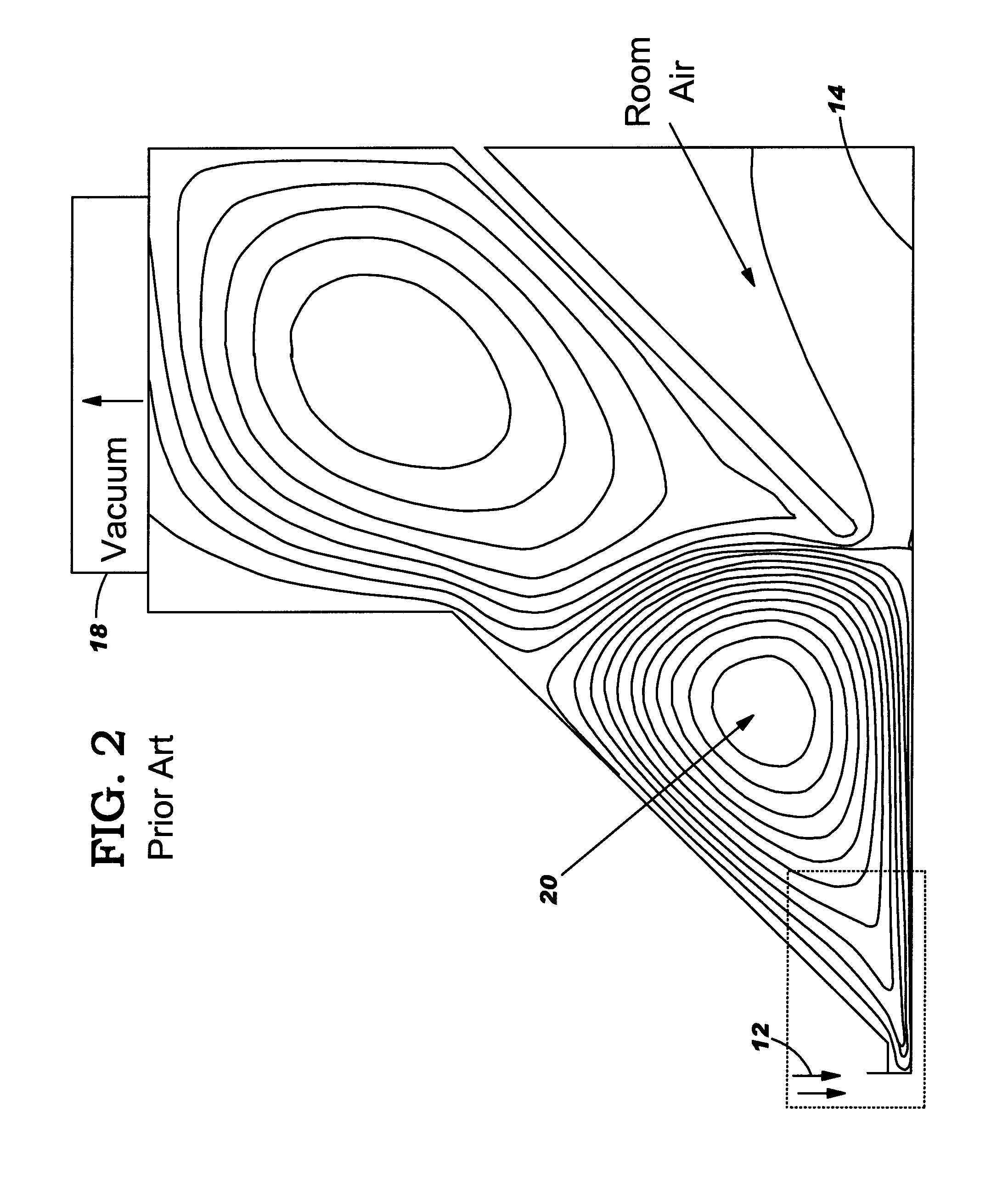
Non-contact fluid particle cleaner and method
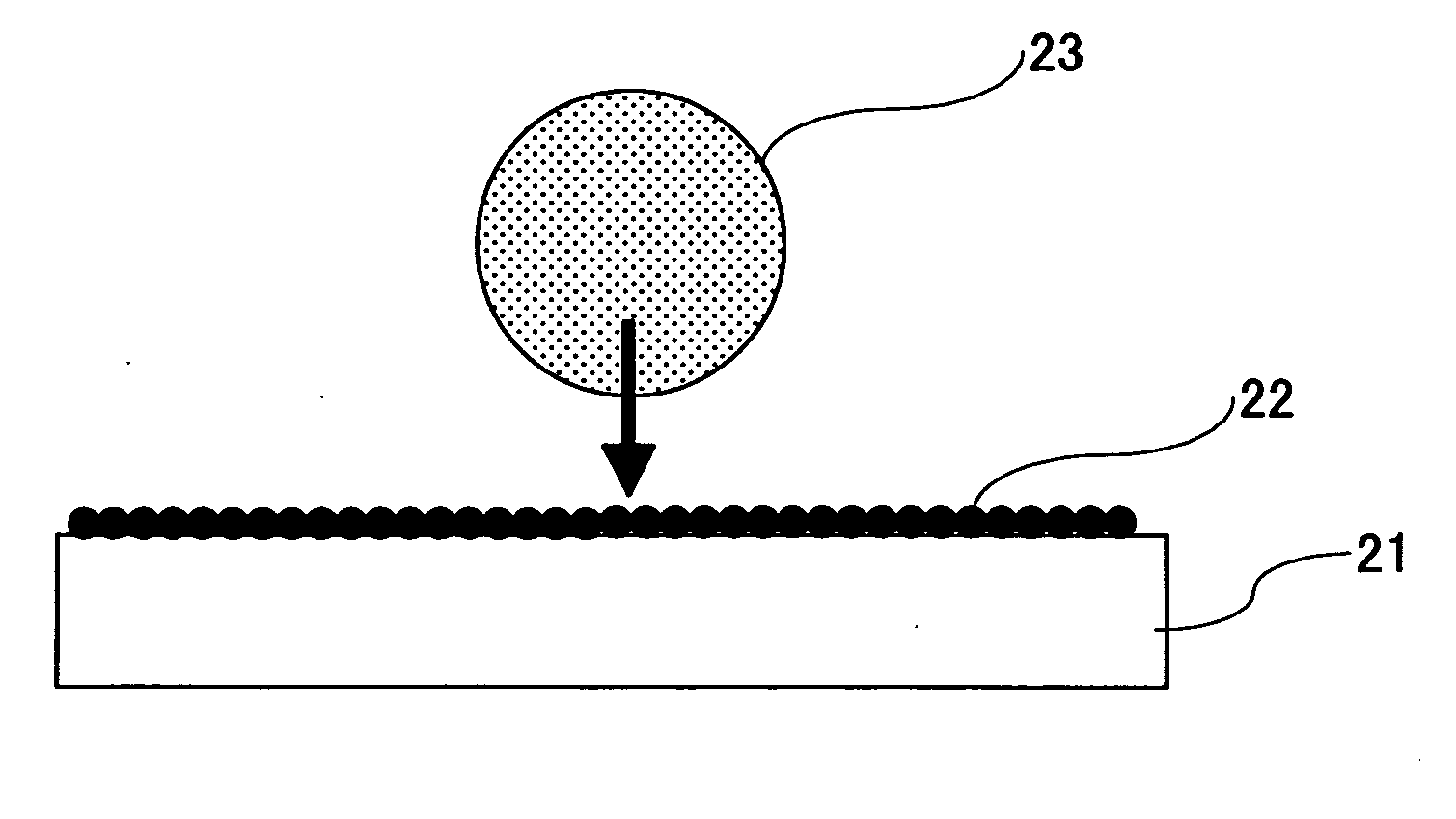
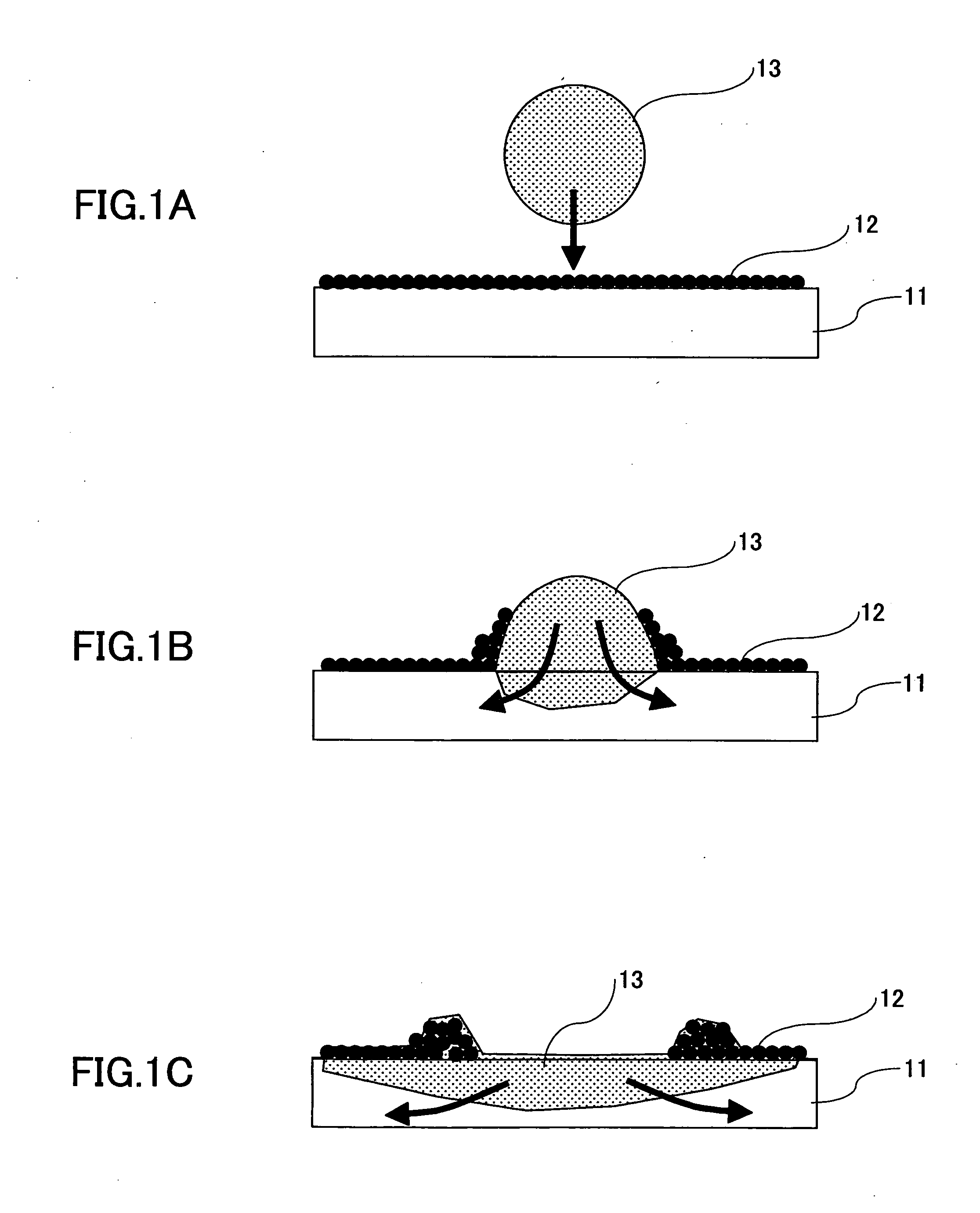
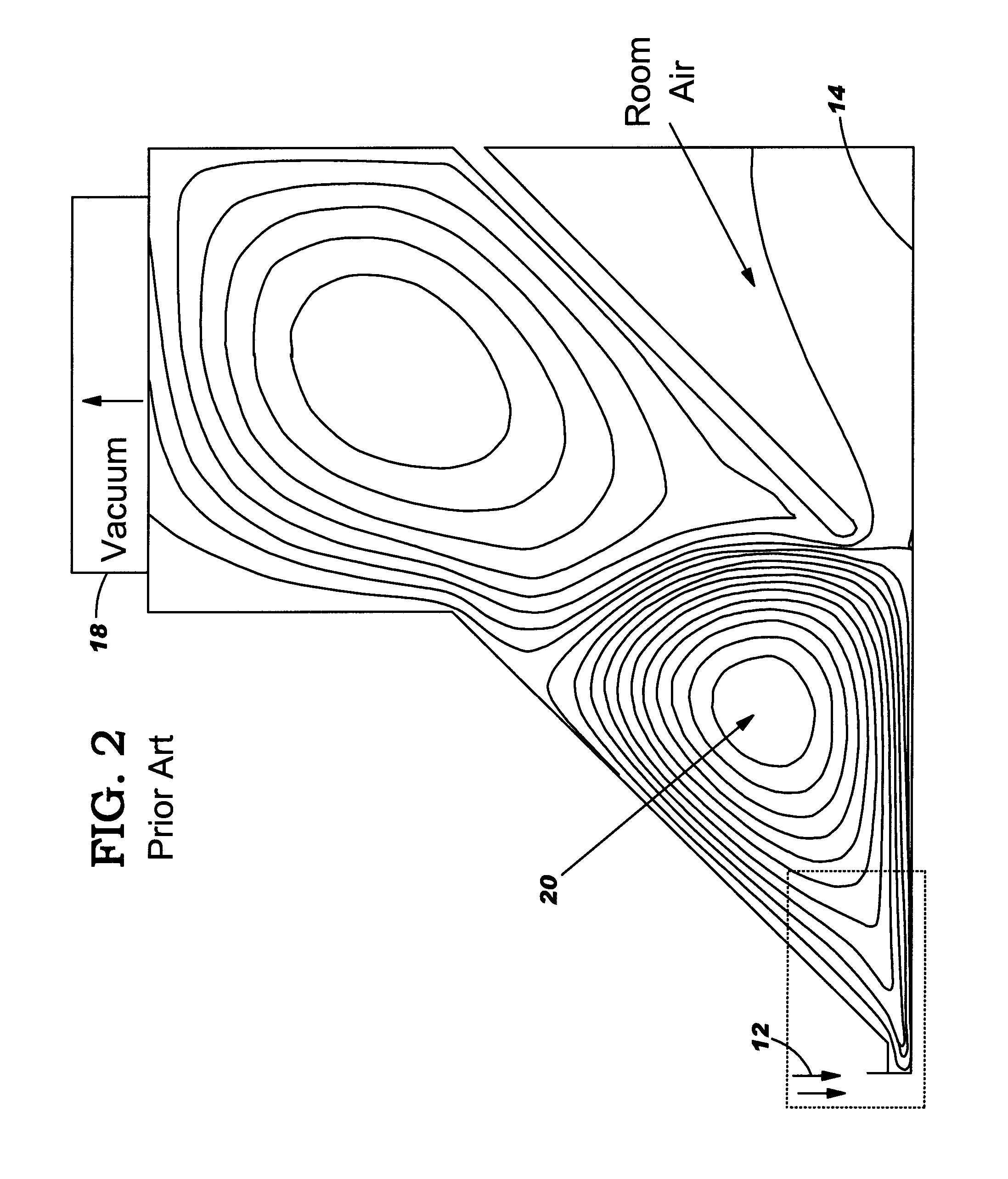
A fluid particle cleaner and method are disclosed. The invention provides a partition to a side of a fluid nozzle to form: a central cavity configured to define the fluid departing the surface into a central cavity vortex; and a side cavity adjacent the central cavity to define fluid escaping from the central cavity into a side vortex. The vortices interact in a counter-rotating and stationary fashion. The strong and smaller central vortex creates an upward air velocity field that forces any airborne particle to move away from the surface. The side vortex is designed to: connect the central vortex velocity field to the vacuum flow and allow airborne particles to remain suspended until they reach the vacuum flow; and create a decelerating field for high speed particles traveling parallel (horizontally) to the surface to increase the residence time in the central vortex with positive vertical velocity.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Microwave measuring device for detecting the charge of a two-phase flow
InactiveCN1618012ALow costAccurate measurementVolume/mass flow measurementMaterial analysis using microwave meansTransport systemCarrier signal
The invention relates to a microwave measuring device for detecting the charge of a two-phase flow with a gaseous carrier medium containing small and minuscule solid and / or fluid particles and for detecting gas contained in a fluid flow, preferably by means of waveguide carrier waves. A preferred application of the invention is the detection of solid particles contained in the flow of gas of voluminous pneumatic solid matter transport systems used, for example, for pulverized coal furnaces of coal power stations. The inventive microwave measuring device is provided with field rods, which protrude into the inside of the feed pipe, are arranged before and after a measuring section formed by a transmission antenna and a reception antenna, said rods interacting with the feed pipe made of conductive material as a resonator for microwaves injected into the feed pipe via the transmission antenna, whereby microwaves that differ from the injected microwaves in their plane of polarization and / or phase as a result of diffraction, superposition, and / or reflection outside the measuring section are essentially short-circuited in order to prevent the results of the measurement from being distorted. The inventive device has the particular advantage of being simple to build and easy to install even in voluminous and branched feed pipe systems.
Owner:PROMECON PROZESS & MESSTECHN CONRADS
Fixing liquid, toner fixing method, toner fixing device, image forming method, and image forming apparatus
A fixing liquid is provided which fixes a toner comprising a resin on a recording medium, in which a fluid particle comprising a component which dissolves or swells at least a portion of the resin comprised in the toner is dispersed in a dispersive medium, as a micro-emulsion.
Owner:RICOH KK
Simplified smoothed particle hydrodynamics
InactiveCN102768698ADesign optimisation/simulationEducational modelsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsParticle physics
The invention relates to simplified smoothed particle hydrodynamics. For efficient smooth particle hydrodynamics using more particle information, virtual particles are created. Each virtual particle represents an averaging of properties for the fluid particles in a cell. For density, force, or other calculations for a given fluid particle, the interaction between the particles within a cell are calculated. For calculating the influence of particles outside the cell on the particle in the cell, the virtual particles from the neighboring cells are used. The interaction with these aggregate particles reduces the number of calculations while still including the influence from particles of other cells.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Distorted Dammann grating and system for simultaneously imaging multiple object planes
ActiveCN102628970ASimultaneous imaging achievedSolve the problem of uneven energy distributionDiffraction gratingsGratingLight spot
The invention discloses a distorted Dammann grating and a system for simultaneously imaging multiple object planes. The system for simultaneously imaging multiple object planes which consists of a distorted Dammann grating and a focusing lens can be used for forming a multi-focus array of multiple equal-strength focusing light spots which are deviated simultaneously along axial and transverse directions in a back field of the focusing lens. The focus quantity and focus interval of the multi-focus system can be adjusted by changing the parameters of the distorted Dammann grating. An equal-strength multi-focus system can be used for imaging a plurality of axial planes of an object space in the same image plane. According to the system, a real-time three-dimensional imaging technology which does not require axial scanning can be realized. The real-time three-dimensional imaging technology has an important practical value in three-dimensional real-time monitoring of biological living body cell microscopy and fluid particles.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
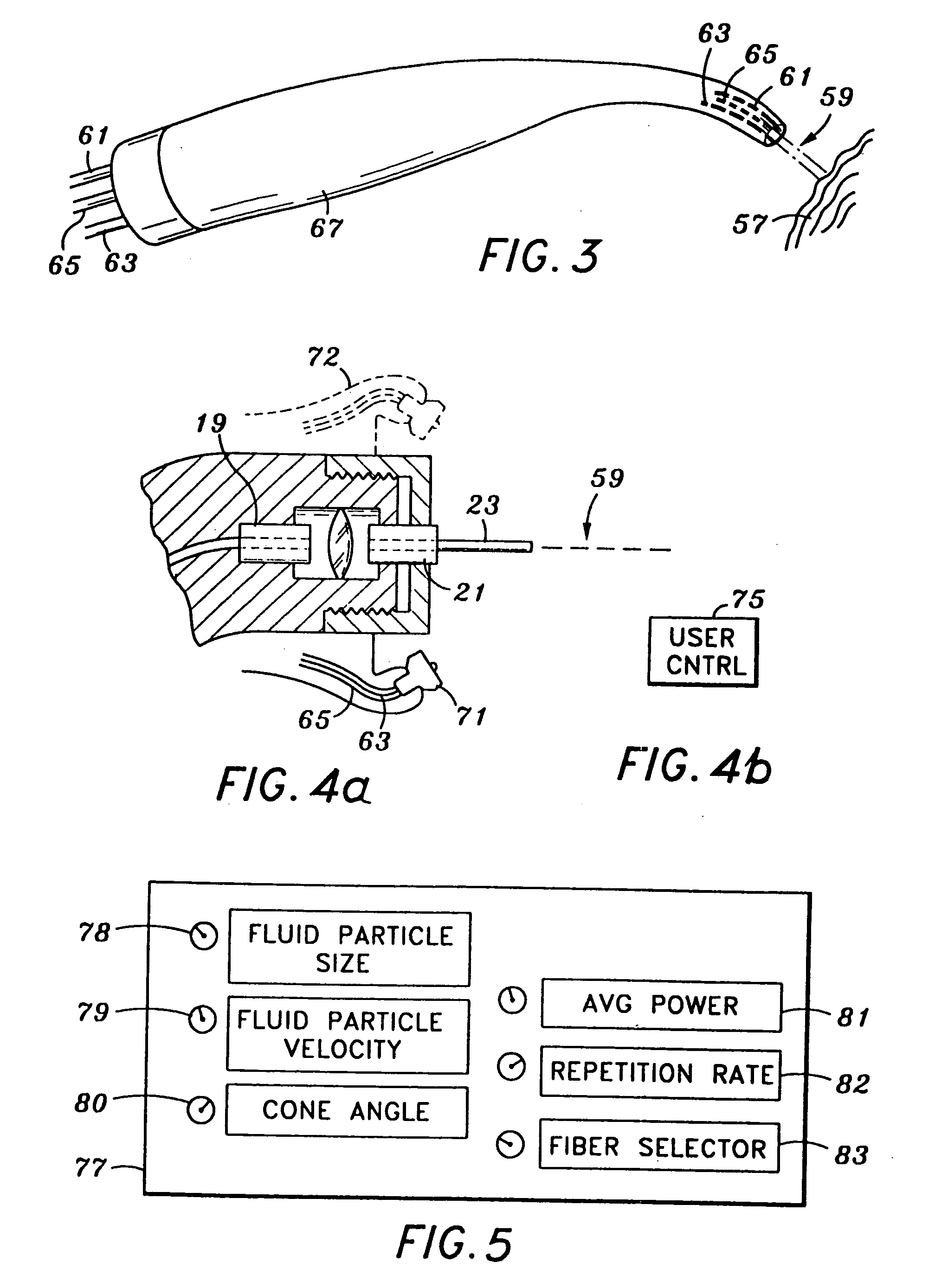
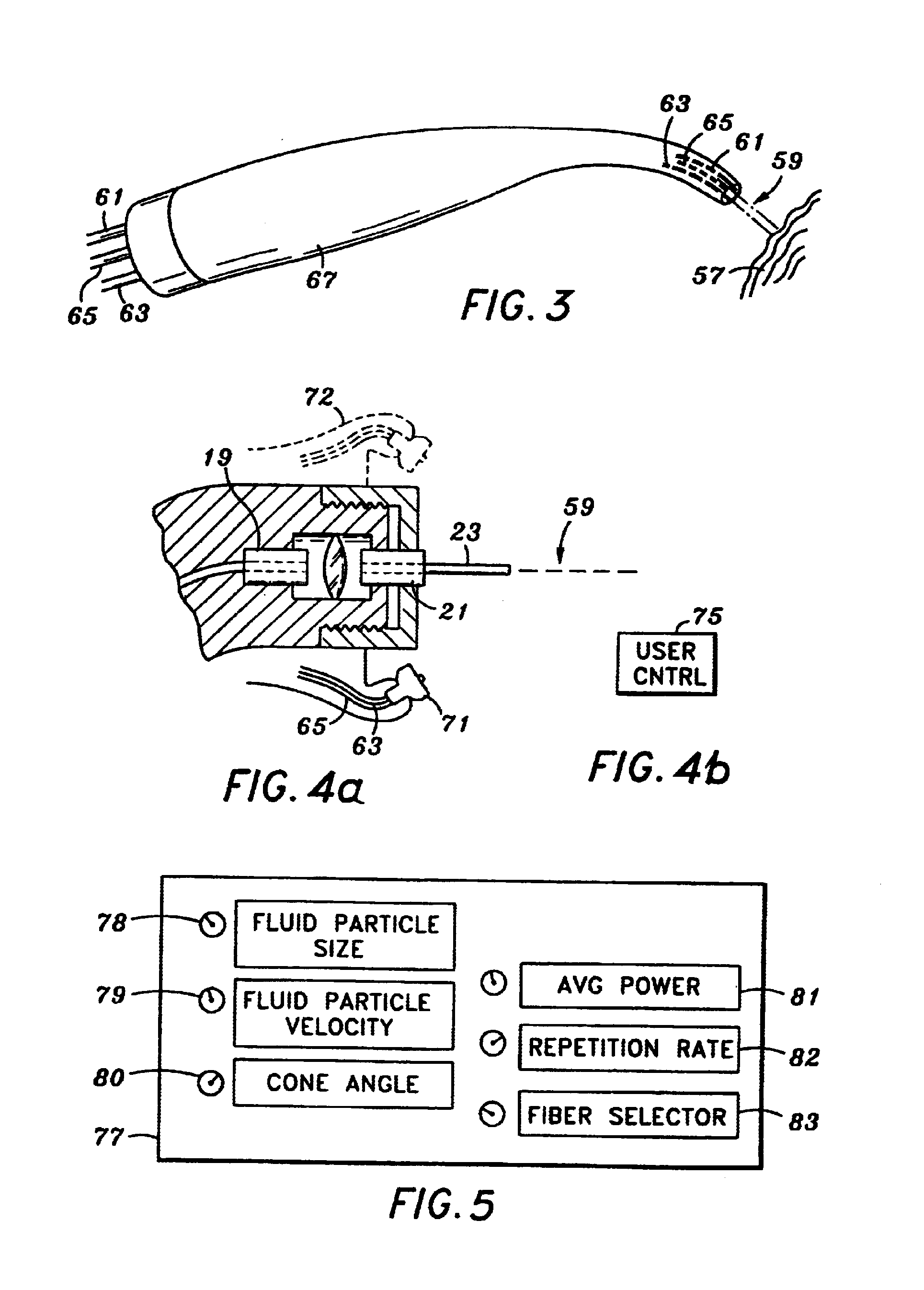
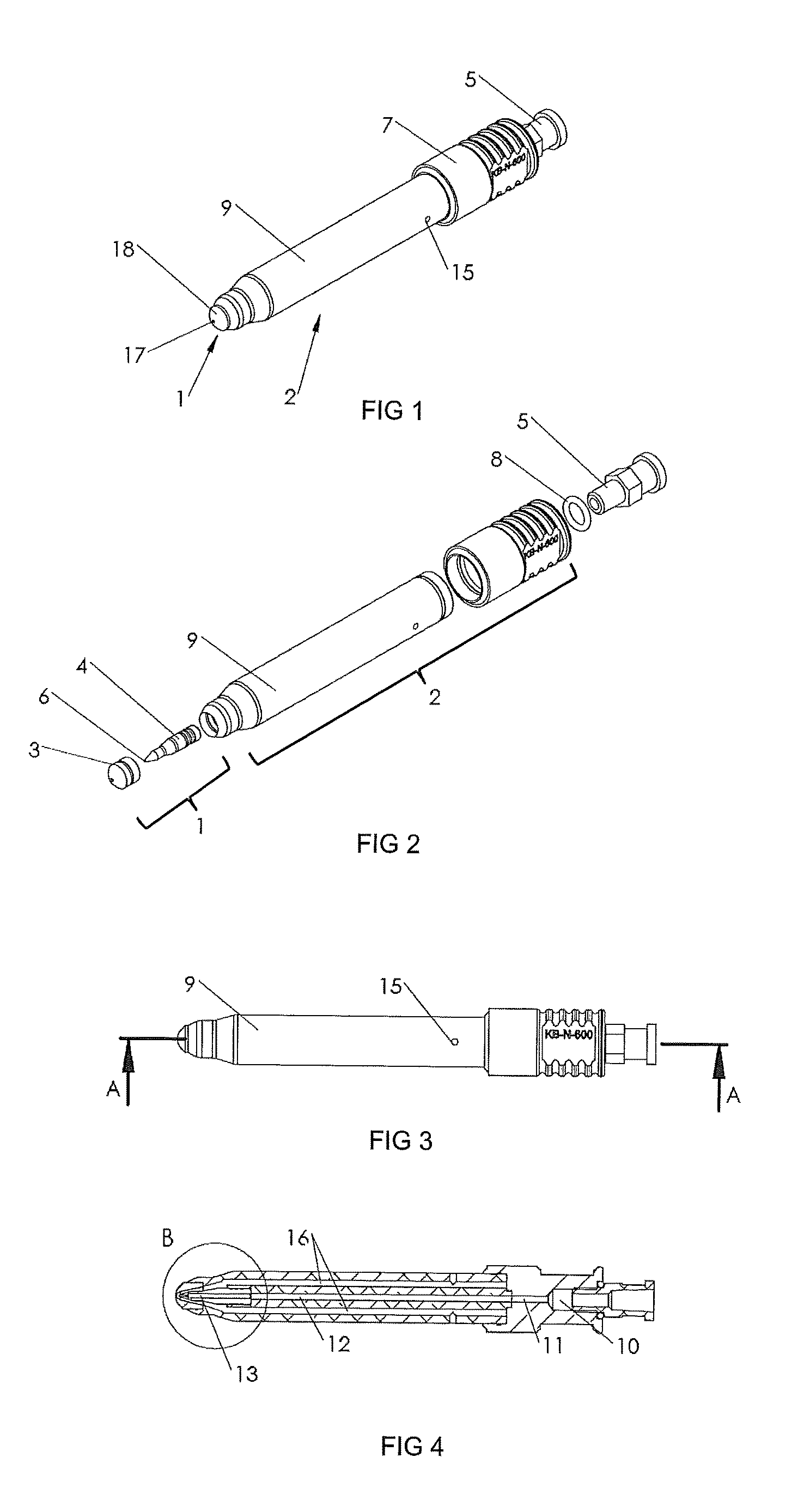
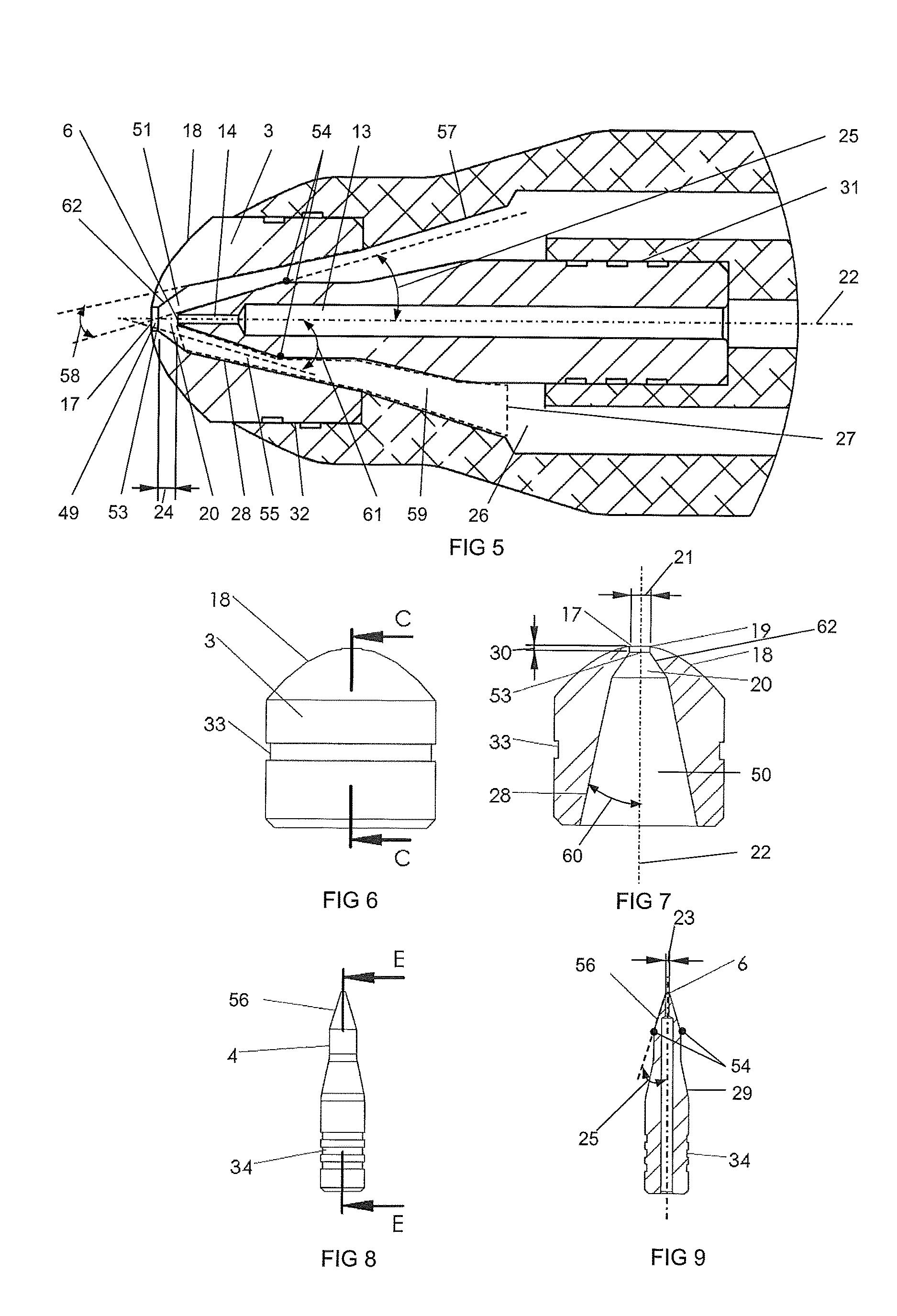
Drill and flavored fluid particles combination
A medical apparatus is constructed to have a proximal end and a distal end, with the distal end including a source of mechanical tissue disruption that is configured to treat or ablate a target surface. The source of mechanical tissue disruption includes a tissue-disrupting distal end, and the medical apparatus further includes a flavored particle output for directing flavored particles in a direction toward the tissue-disrupting distal end. Another feature of the present invention includes a medical apparatus having a proximal end and a distal end. The distal end of the medical apparatus includes a source of tissue displacement that is configured to move or displace a portion of the target surface, and that is formed to have a tissue-displacing distal end. The medical apparatus can be configured to have a flavored particle output for directing flavored particles in a direction toward the tissue-displacing distal end.
Owner:BIOLASE TECH INC
Aerosolizing nozzle and method of operating such aerosolizing nozzle
ActiveUS9573147B1High viscosityReduce surface tensionSpray nozzlesMedical devicesAcute angleEngineering
A nozzle and a method of generating an aerosol from a fluid and a gas by operating the nozzle. The nozzle has an aerosol exit orifice of a larger diameter and a fluid exit orifice of a smaller diameter aligned on a common central axis. A pressurized gas from a pressurized gas exit in close proximity to the fluid exit orifice intersects a fluid jet exiting from the fluid exit orifice at that acute angle and in a distance from the aerosol exit orifice. The method includes aerosolizing a fluid with a viscosity exceeding 4 cSt delivering an inhalable medication at a rate of more than 1 ml / minute, thereby delivering a medication at a mass flow rate of at least 30 mg / minute in form of the fluid particles having a mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) of 6 μm or less.
Owner:KAER BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
Spray nozzle and the application
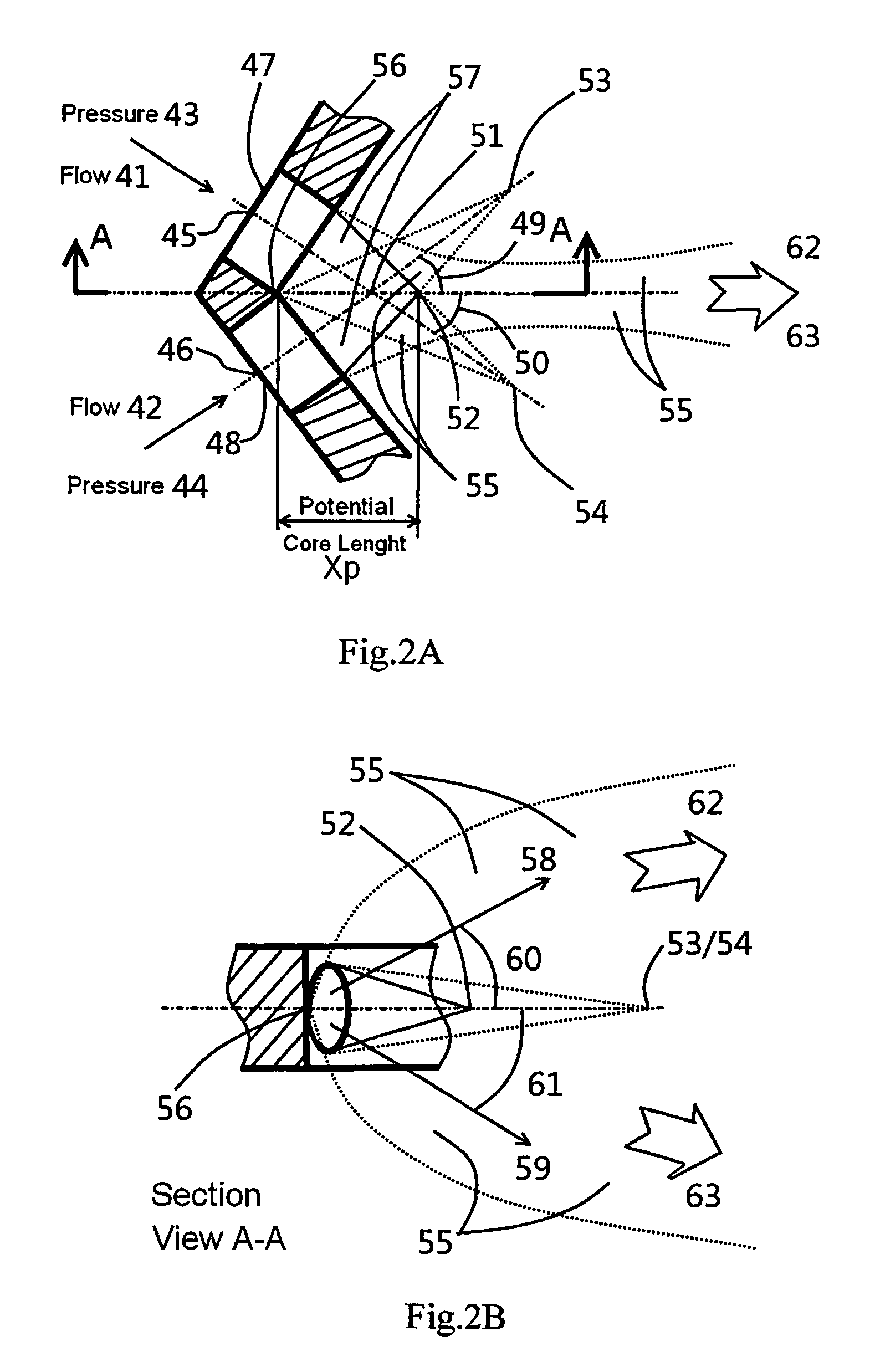
A spray nozzle for providing a high efficient atomization and a uniform fluid flow pattern, includes an internal fluid channel, sealing and a spray nozzle, on which two of spray orifices are designed close to each other. The fluid flow is guided in the internal fluid channel smoothly and separated to two fluid flows inside of spray nozzle. These two fluid flows are pressed out from the spray orifices and interfered with each other right after flow out from the spray orifices. The fluid is being atomized efficiently because the spray nozzle is designed to fully utilize both flow velocity energy and flow pressure potential energy, which is well known as “Potential Core” or “Potential Zone” and will disappear in a very short distance right after fluids flow out from the spray orifices. During the fluid flows collide with each other by using the flow velocity right after flow out from the orifices, the fluid flows explode within the potential core by using the flow pressure potential energy. And then, the fluid flow and the fluid particles are continuously atomized by using the velocity difference between the fluid flow and the air around the fluid flow to have very fine particles.
Owner:TAKAHARA HIROSHI
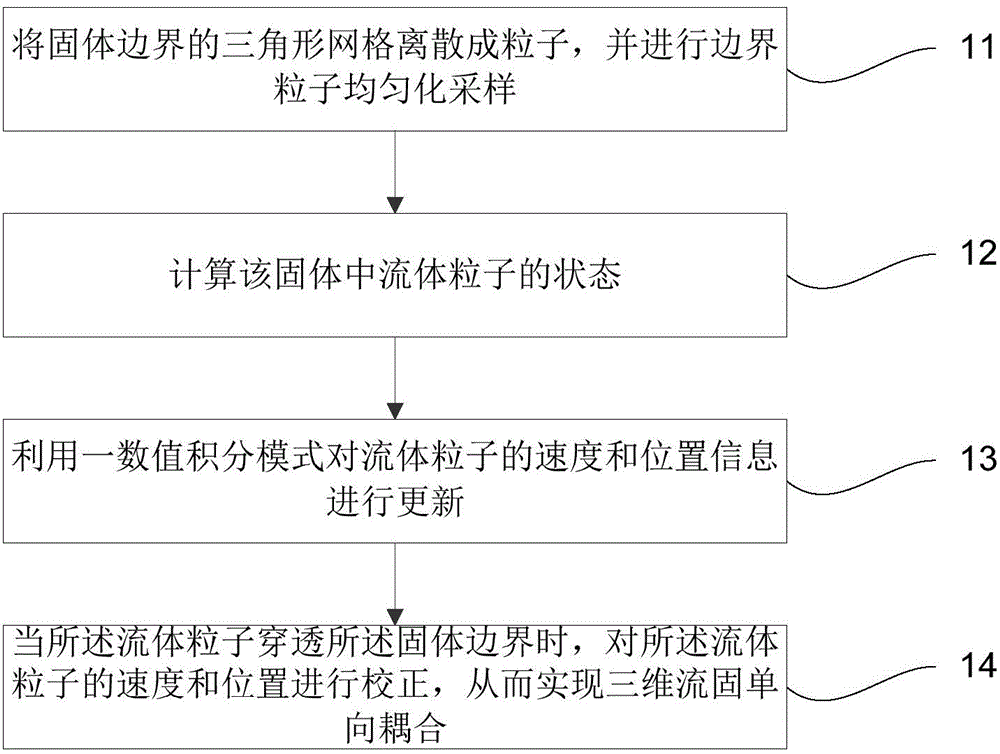
Implement method and system for three-dimensional fluid-solid one-way coupling
The invention discloses an implement method and an implement system for three-dimensional fluid-solid one-way coupling. The implement method includes: dispersing triangular meshes at the boundary of a solid into particles, and performing homogenized sampling on boundary particles; calculating state of fluid particles in the solid, wherein the state includes density of the fluid and the fluid particles at the boundary of the solid, pressure and viscous force of the fluid particles, and surface tension of the fluid particles; updating speed and position information of the fluid particles by a numerical integration mode; correcting the speed and the position of the fluid particles when the fluid particles penetrate through the boundary of the solid, and thereby achieving three-dimensional fluid-solid one-way coupling. According to the method and the system provided by the invention, stability during boundary treatment is increased, when pressure and viscous force is successfully simulated and penetrating effect is prevented, computation complexity is greatly reduced, and macroscopic effect of the surface tension is effectively simulated, furthermore, the mesh distorting phenomenon in the case of directly simulating aggregation force does not appear.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Drill and flavored fluid particles combination
A medical apparatus is constructed to have a proximal end and a distal end, with the distal end including a source of mechanical tissue disruption that is configured to treat or ablate a target surface. The source of mechanical tissue disruption includes a tissue-disrupting distal end, and the medical apparatus further includes a flavored particle output for directing flavored particles in a direction toward the tissue-disrupting distal end. Another feature of the present invention includes a medical apparatus having a proximal end and a distal end. The distal end of the medical apparatus includes a source of tissue displacement that is configured to move or displace a portion of the target surface, and that is formed to have a tissue-displacing distal end. The medical apparatus can be configured to have a flavored particle output for directing flavored particles in a direction toward the tissue-displacing distal end.
Owner:BIOLASE INC
Drill and flavored fluid particles combination
A medical apparatus is constructed to have a proximal end and a distal end, with the distal end including a source of mechanical tissue disruption that is configured to treat or ablate a target surface. The source of mechanical tissue disruption includes a tissue-disrupting distal end, and the medical apparatus further includes a flavored particle output for directing flavored particles in a direction toward the tissue-disrupting distal end. Another feature of the present invention includes a medical apparatus having a proximal end and a distal end. The distal end of the medical apparatus includes a source of tissue displacement that is configured to move or displace a portion of the target surface, and that is formed to have a tissue-displacing distal end. The medical apparatus can be configured to have a flavored particle output for directing flavored particles in a direction toward the tissue-displacing distal end.
Owner:BIOLASE TECH INC
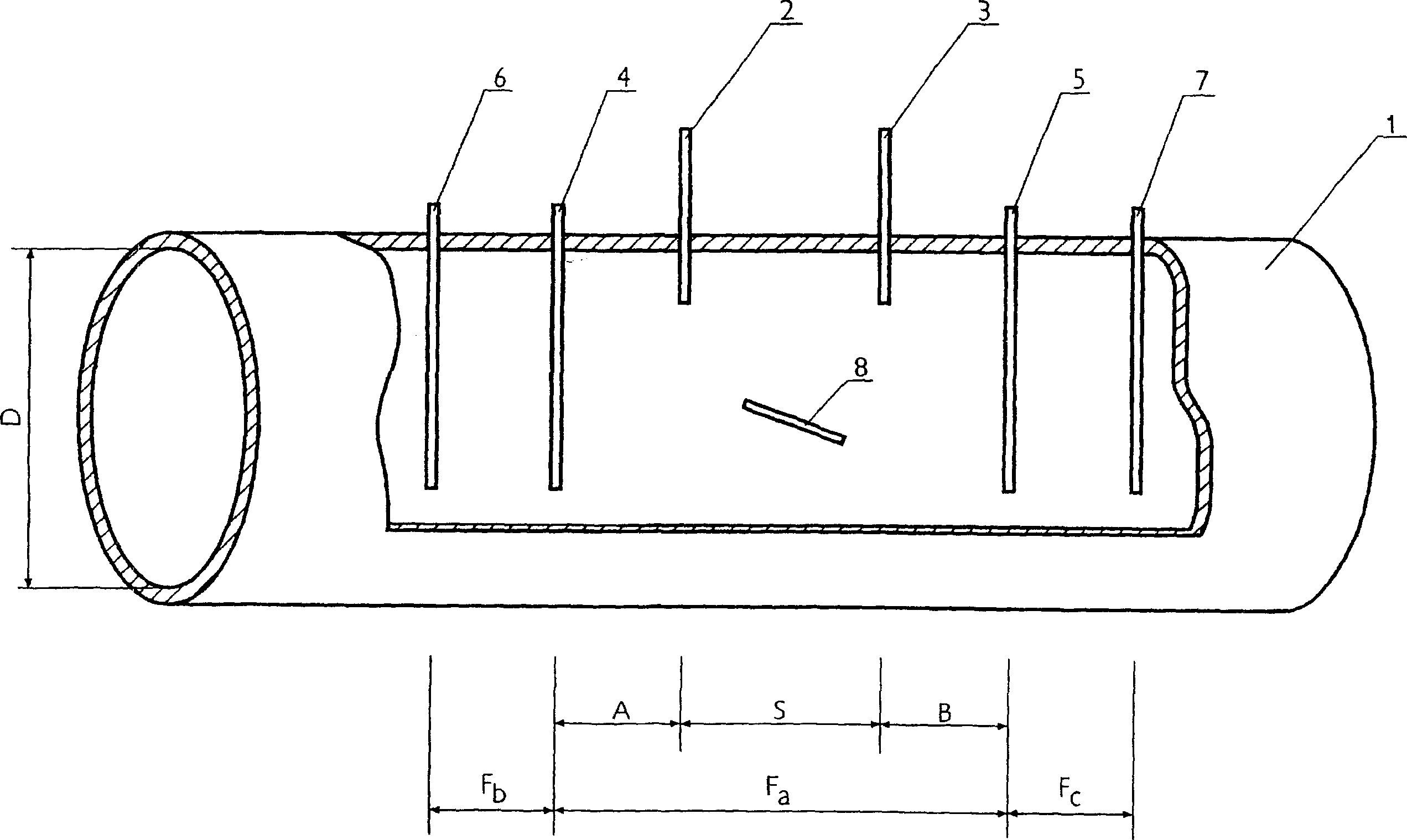
Motor with cooling duct
ActiveCN107623390ASimple designIncrease disturbanceMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsForced-airEngineering
The invention provides a motor with a cooling duct. The motor is a totally enclosed forced air-cooled traction motor. The motor comprises a motor inlet, a motor outlet and a stator. A number of statorcooling ducts are arranged in a circumferential direction in the stator. The stator cooling ducts are respectively communicated with the motor inlet and the motor outlet. A number of turbulence blocks are arranged on the inner wall of the stator cooling ducts. The invention is further applicable to a variety of other motors. The turbulence blocks are arranged in the cooling ducts, which enhancesthe disturbance to a cooling medium, exacerbates the irregular change of a fluid, and enhances the pulsation of fluid particles in all directions in the cooling ducts. The fluid turbulence is enhanced. The convection heat transfer coefficient of the side of the cooling ducts is increased, and the heat transfer rate is increased. The weight of the motor can be effectively controlled, which is conducive to lightweight design.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
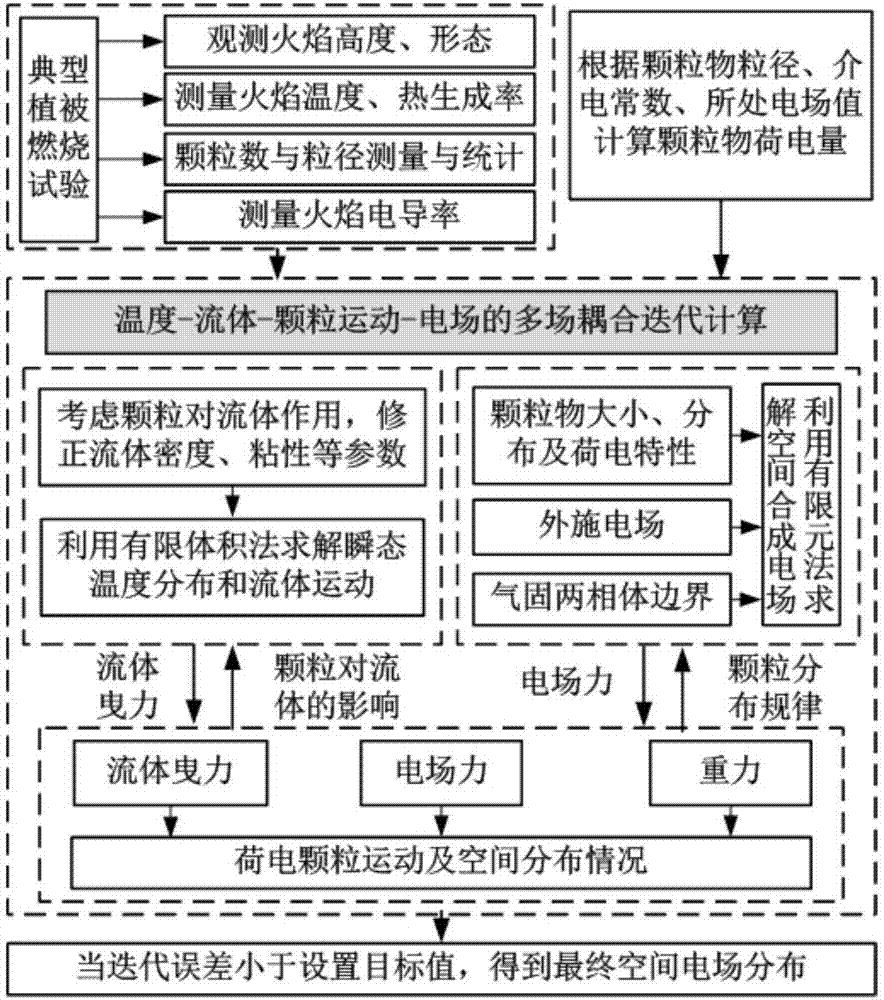
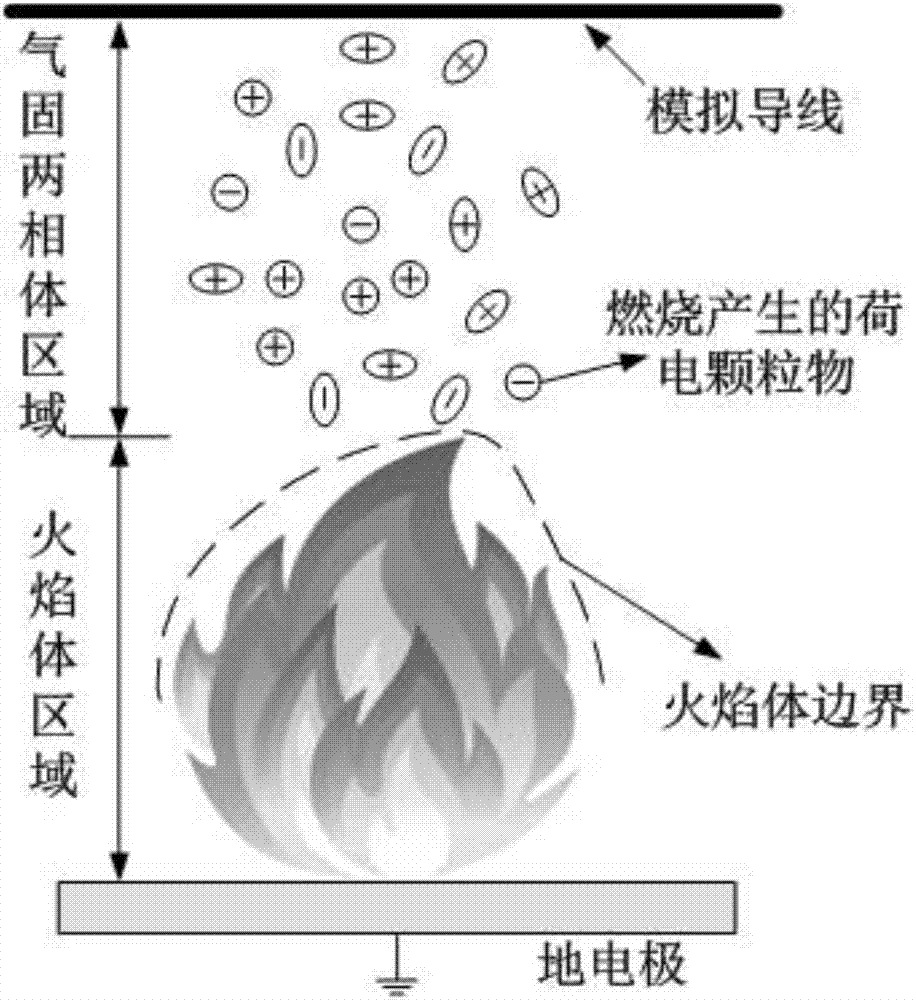
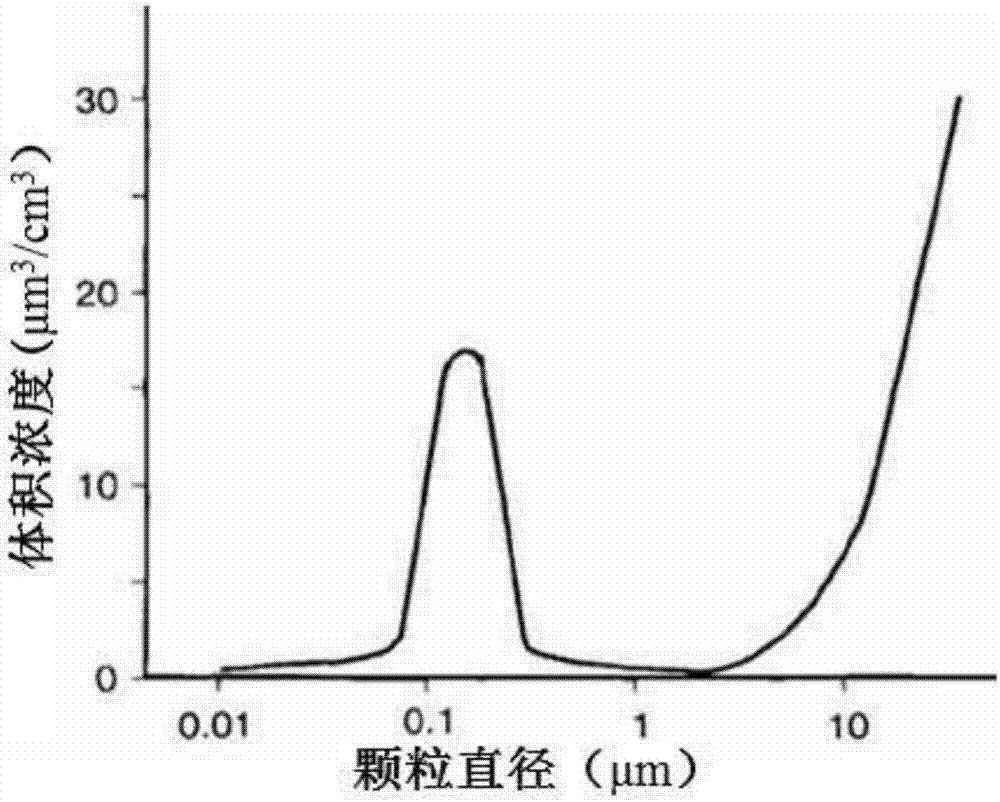
Calculation method for transmission line clearance spatial synthetic electric field under mountain fire condition
ActiveCN106980712AConvenient researchRealize quantitative analysisDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMulti fieldBody area
The invention discloses a calculation method for a transmission line clearance spatial synthetic electric field under a mountain fire condition. According to the method, the height, temperature and form of a flame are obtained according to a typical vegetation burning test, a stable burning area is selected, and clearance below a transmission line is divided into a flame body equivalent area and a gas-solid two-phase body area; a difference moving particle sizing instrument is adopted to measure small particles, a vernier caliper is adopted to measure big particles, and the statistical law of particle volume concentration and particle size is obtained; the electric quantity qk of the particles in the flame is calculated; a simulation model is established, and a finite volume method is utilized to solve transient temperature distribution and fluid motion; simulation calculation is performed on particle movement in the flame clearance to obtain particle distribution in the flame clearance; particle positions and carrying capacity are set, and a finite element method is utilized to solve a spatial synthetic electric field to obtain electric fields E at different positions; and initial particle distribution and an initial electric field value are set, temperature-fluid-particle movement-electric field multi-field coupling calculation is performed, and a final spatial synthetic electric field is obtained. The method can provide a basis for research on the discharge mechanism and breakdown characteristics of clearance.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Meshless particle method for analyzing trapped air mass-containing transient pipe flow
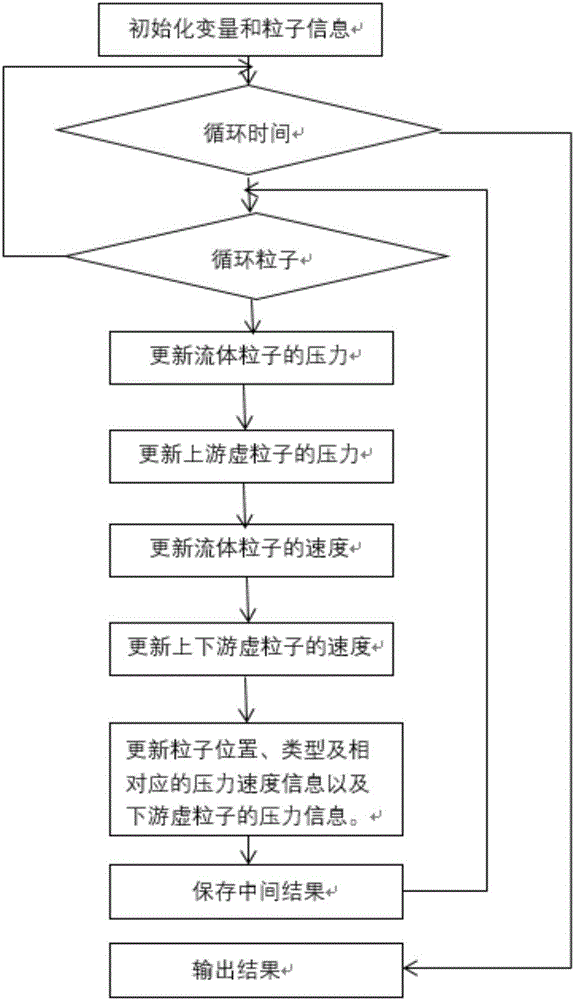
InactiveCN106570308AHigh simulationReduce mistakesSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsCompressibility
The invention discloses a meshless particle method for analyzing trapped air mass-containing transient pipe flow. The meshless particle method comprises the following steps of (1) initializing relevant variable and particle information; (2) carrying out iterative computation, namely circulating a time variable, circulating particles, calculating pressure information of fluid particles of the initialized particles and updating the pressure information of the fluid particles, the pressure information of upstream virtual particles, speed information of the fluid particles, speeds of upstream and downstream virtual particles, particle positions and corresponding pressure and speed information and the pressure information of downstream virtual particles; and (3) outputting the result. A water hammer equation under a lagrange system is solved by adopting a smoothed particle hydrodynamics method; the influences caused by movement of a gas-liquid interface and weak compressibility of water are fully considered; various errors caused by interpolation and gas-liquid interface tracking technologies are reduced; and the trapped air mass-containing transient pipe flow can be more conveniently simulated on the premise of meeting the numerical precision.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Coupling type inertial cyclone fluid particle heterogeneous separation device and method
InactiveCN104971830AImprove separation efficiencyIncrease concentrationReversed direction vortexCycloneParticle penetration
The invention relates to a coupling type inertial cyclone fluid particle heterogeneous separation device and method. The device comprises an inertial curve and a cyclone separator coupled with the inertial curve and provided with an integrated volute tangential inlet. The inertial curve and the cyclone separator are integrally coupled, the fluid phase and the particle phase firstly enter an inertial curve body through an external pipeline, the differential particle concentration gradient is generated, the fluid phase and the particle phase enter the cyclone separator integrally coupled with the inertial curve to be separated, and therefore the defects existing in the separation process under the particle concentration uniformity or concentration-gradient-free condition in the traditional separation process are overcome. The inertial curve is organically integrated into fluid-particle radial concentration space, the concentration gradient with the outer portion higher than the inner portion is generated under the effect of a centrifugal field, the particle penetration amount caused by short-circuit current entrainment after particles enter the cyclone separator can be reduced, the distance or time of the particles moving towards the capture wall is shortened, and the heterogeneous separation efficiency is effectively improved under the condition that the pressure drop of the separator is not obviously increased.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Electrostatic fluid accelerator
InactiveUS7652431B2Not produce substantialMaximum speedSamples introduction/extractionElectric arc lampsHigh pressureBreakdown voltage
An electrostatic fluid accelerator having a multiplicity of closely spaced corona electrodes. The close spacing of such corona electrodes is obtainable because such corona electrodes are isolated from one another with exciting electrodes. Either the exciting electrode must be placed asymmetrically between adjacent corona electrodes or an accelerating electrode must be employed. The accelerating electrode can be either an attracting or a repelling electrode. Preferably, the voltage between the corona electrodes and the exciting electrodes is maintained between the corona onset voltage and the breakdown voltage with a flexible top high-voltage power supply. Optionally, however, the voltage between the corona electrodes and the exciting electrodes can be varied, even outside the range between the corona onset voltage and the breakdown voltage, in to vary the flow of fluid. And, to achieve the greatest flow of fluid, multiple stages of the individual Electrostatic Fluid Accelerator are utilized with a collecting electrode between successive stages in order to preclude substantially all ions and other electrically charged particles from passing to the next stage, where they would tend to be repelled and thereby impair the movement of the fluid. Finally, constructing the exciting electrode in the form of a plate that extends downstream with respect to the desired direction of fluid flow also assures that more ions and, consequently, more fluid particles flow downstream.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Non-contact fluid particle cleaner and method
A fluid particle cleaner and method are disclosed. The invention provides a partition to a side of a fluid nozzle to form: a central cavity configured to define the fluid departing the surface into a central cavity vortex; and a side cavity adjacent the central cavity to define fluid escaping from the central cavity into a side vortex. The vortices interact in a counter-rotating and stationary fashion. The strong and smaller central vortex creates an upward air velocity field that forces any airborne particle to move away from the surface. The side vortex is designed to: connect the central vortex velocity field to the vacuum flow and allow airborne particles to remain suspended until they reach the vacuum flow; and create a decelerating field for high speed particles traveling parallel (horizontally) to the surface to increase the residence time in the central vortex with positive vertical velocity.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fixing liquid, toner fixing method, toner fixing device, image forming method, and image forming apparatus
A fixing liquid is provided which fixes a toner comprising a resin on a recording medium, in which a fluid particle comprising a component which dissolves or swells at least a portion of the resin comprised in the toner is dispersed in a dispersive medium, as a micro-emulsion.
Owner:RICOH KK
Rotary residual fuel slurrifier
A rotary slurrifier of this invention comprises a pair of spinning discs, which throw a first fluid into a larger mass of second fluid in paired and flow connected impact cavities, within a counter-rotating cavity shell. The first fluid is to be largely insoluble in the second fluid. Impact of the first fluid with the larger mass of second fluid, in the impact cavities, causes atomization of the first fluid into a slurry of many small first fluid particles suspended in a continuous phase of second fluid. The final slurry flows out of the rotating cavity shell via a slowdown reaction turbine.High viscosity residual petroleum fuels and tars as first fluids can be thusly preatomized in a fuel in water slurry, and can then be cleanly and efficiently burned in small bore, high speed, diesel engines, which now require use of expensive low viscosity distillate fuels, which are in short supply.
Owner:FIREY JOSEPH CARL
Beauty fluid atomization spraying device
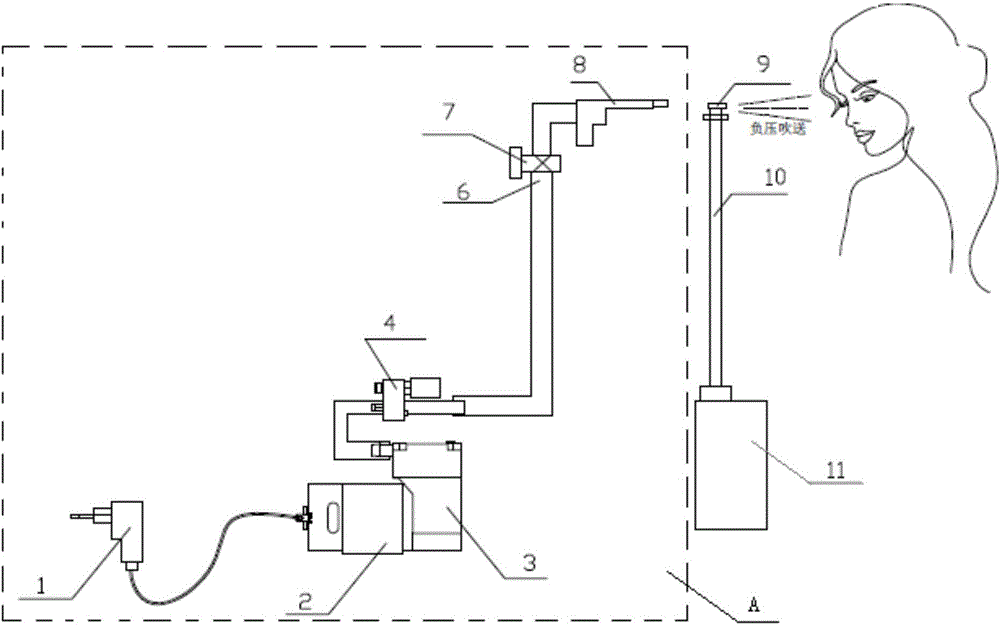
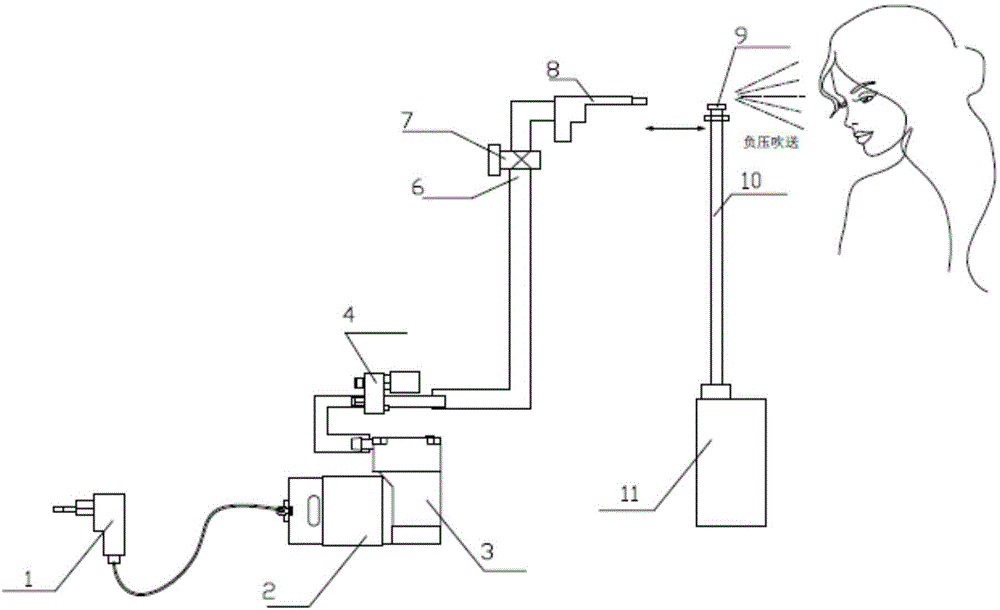
The invention provides a beauty fluid atomization spraying device which comprises a pressurizing device. The pressurizing device comprises an air tap for spraying high-pressure air and a fluid container for containing beauty fluid. The beauty fluid is guided to flow to a spray nozzle by the fluid container through a mist outlet pipeline. The spray nozzle is located nearby the air tap. The high-pressure air sprayed out of the air tap enables negative pressure to be generated nearby the spray nozzle. The beauty fluid flows to a negative-pressure area, and the beauty fluid in the negative-pressure area is sprayed out by a certain dispersion angle in a mist mode through the high-pressure air. The spray pressure of the air tap can be adjusted. The beauty fluid can be sprayed to the surface of human skin in a mist mode, the beauty fluid can be absorbed by the skin and a corium layer conveniently, and the high-pressure air of the device has no harm to a human body. The size of mist-shaped fluid particles and the dispersion angle of spraying can be adjusted. The overall structure is simple, and use is convenient.
Owner:SHENZHEN GUIZHIZUSHENG TECH CO LTD
Flow device and associated method and system
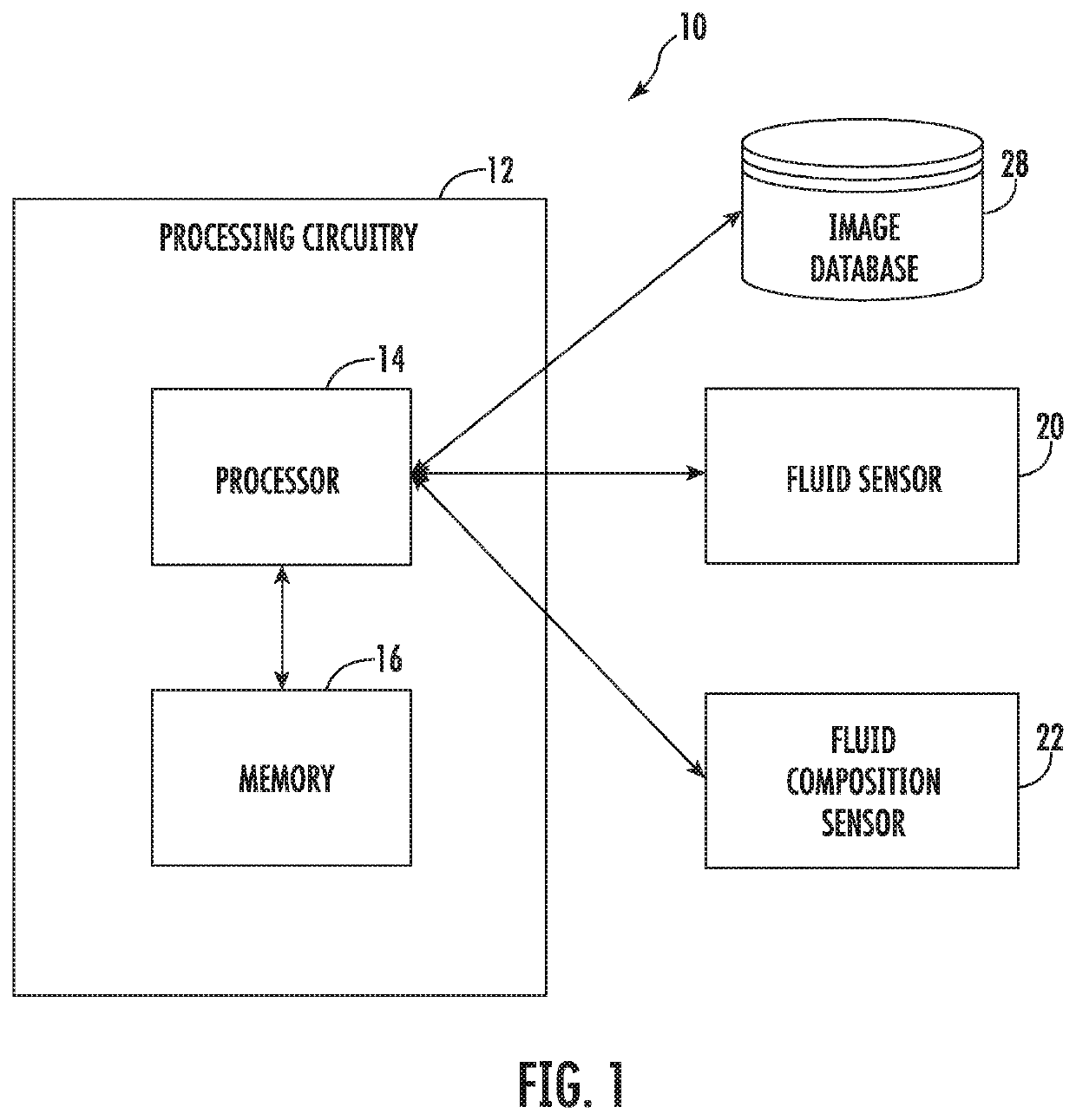
A flow device, method, and system are provided for determining the fluid particle composition. An example flow device includes a fluid sensor configured to monitor at least one particle characteristic of fluid flowing through the fluid sensor. The example flow device also includes at least one processor configured to, upon determining the at least one particle characteristic satisfies a particle criteria, generate a control signal for an external device. The example flow device also includes a fluid composition sensor configured to be powered based on the control signal and further configured to capture data relating to the fluid particle composition. The example flow device is also configured to generate one or more particle profiles of at least one component of the fluid based on the data captured by the fluid composition sensor.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com