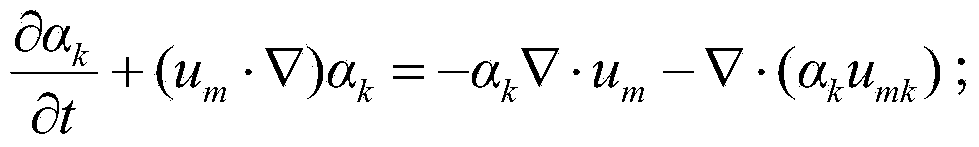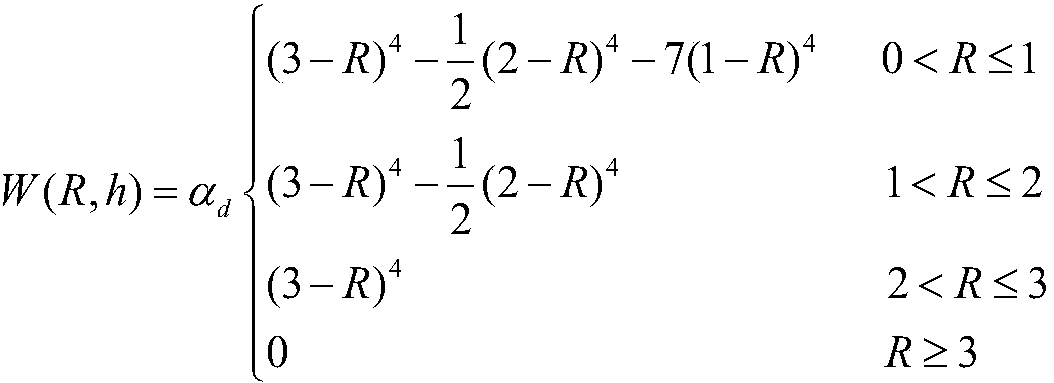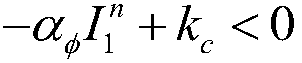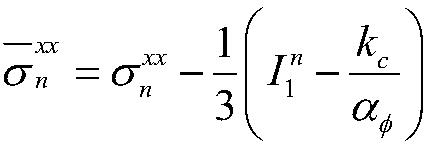Patents
Literature
73 results about "Smoothed-particle hydrodynamics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
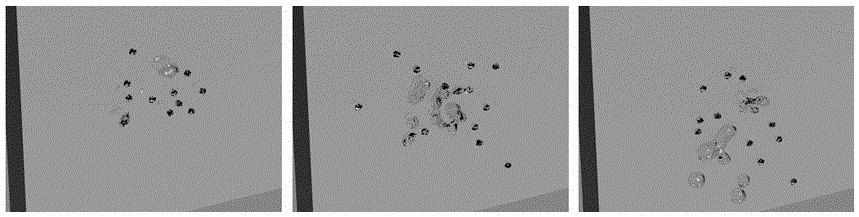
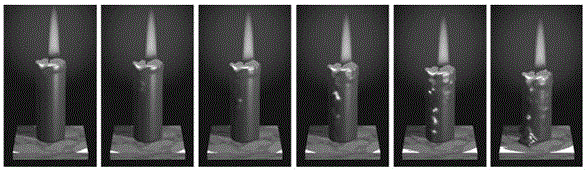
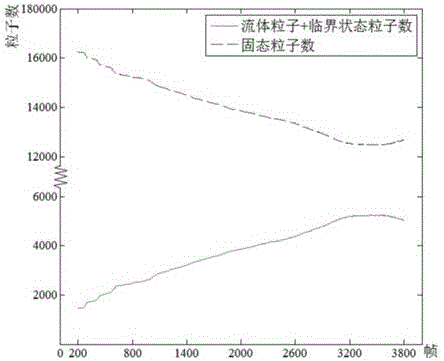
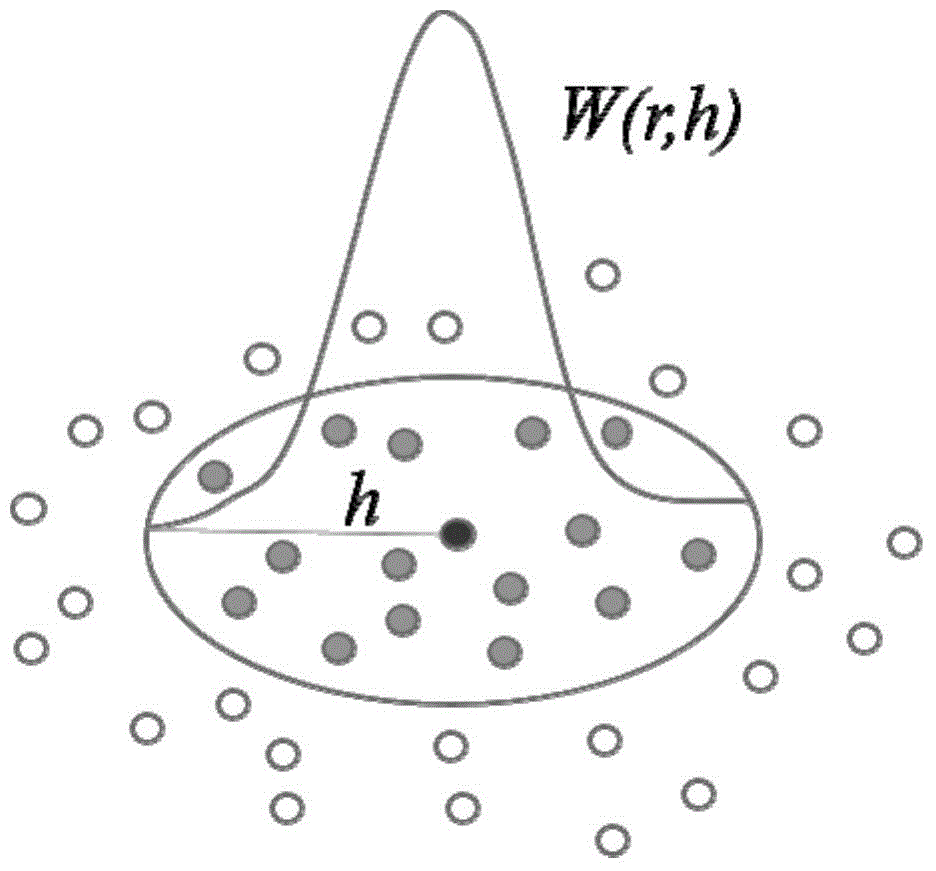
Smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) is a computational method used for simulating the mechanics of continuum media, such as solid mechanics and fluid flows. It was developed by Gingold and Monaghan and Lucy in 1977, initially for astrophysical problems. It has been used in many fields of research, including astrophysics, ballistics, volcanology, and oceanography. It is a meshfree Lagrangian method (where the co-ordinates move with the fluid), and the resolution of the method can easily be adjusted with respect to variables such as density.
Application programming interface for fluid simulations
ActiveUS7580821B2Design optimisation/simulationAnimationSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsApplication programming interface
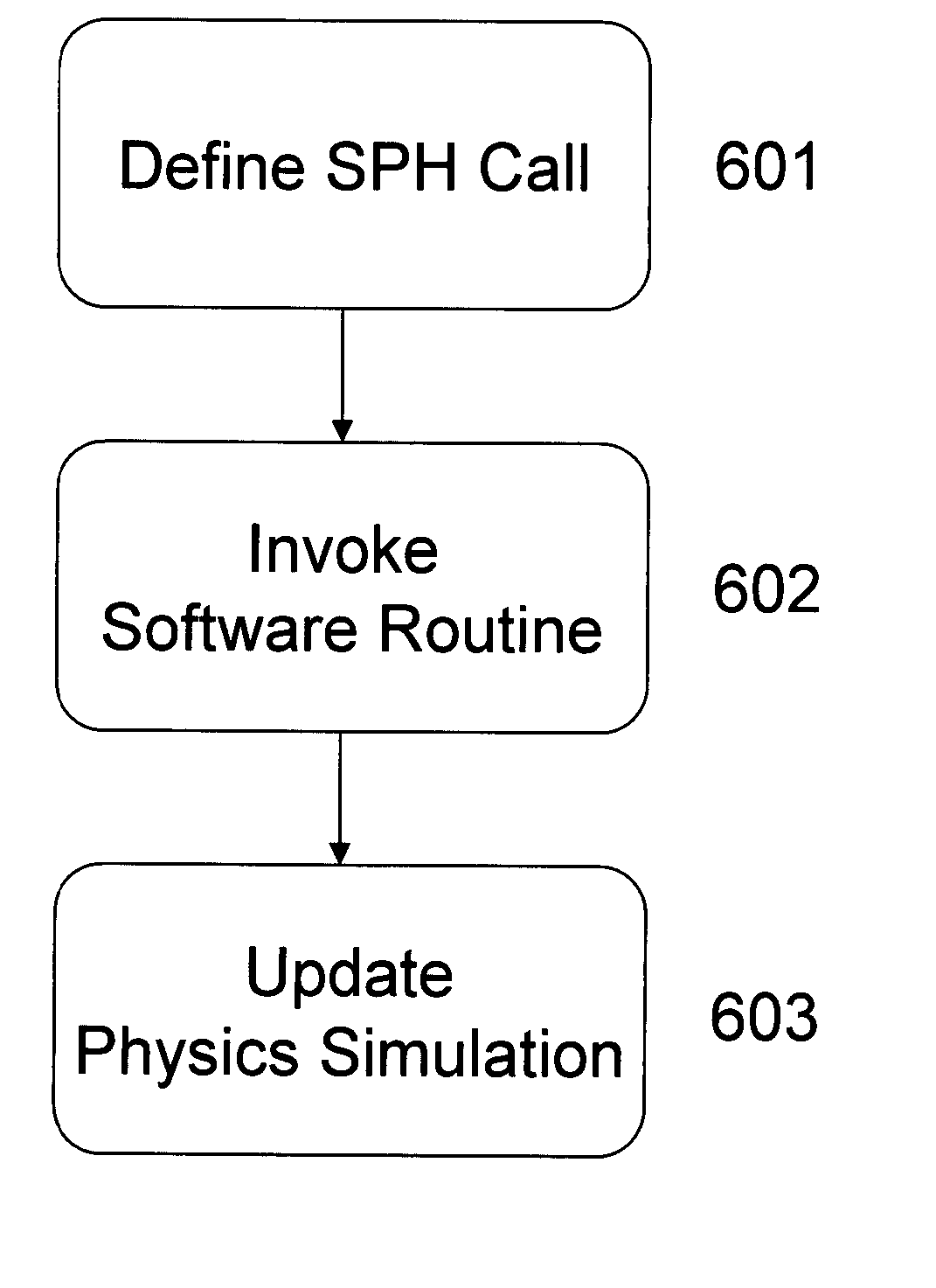
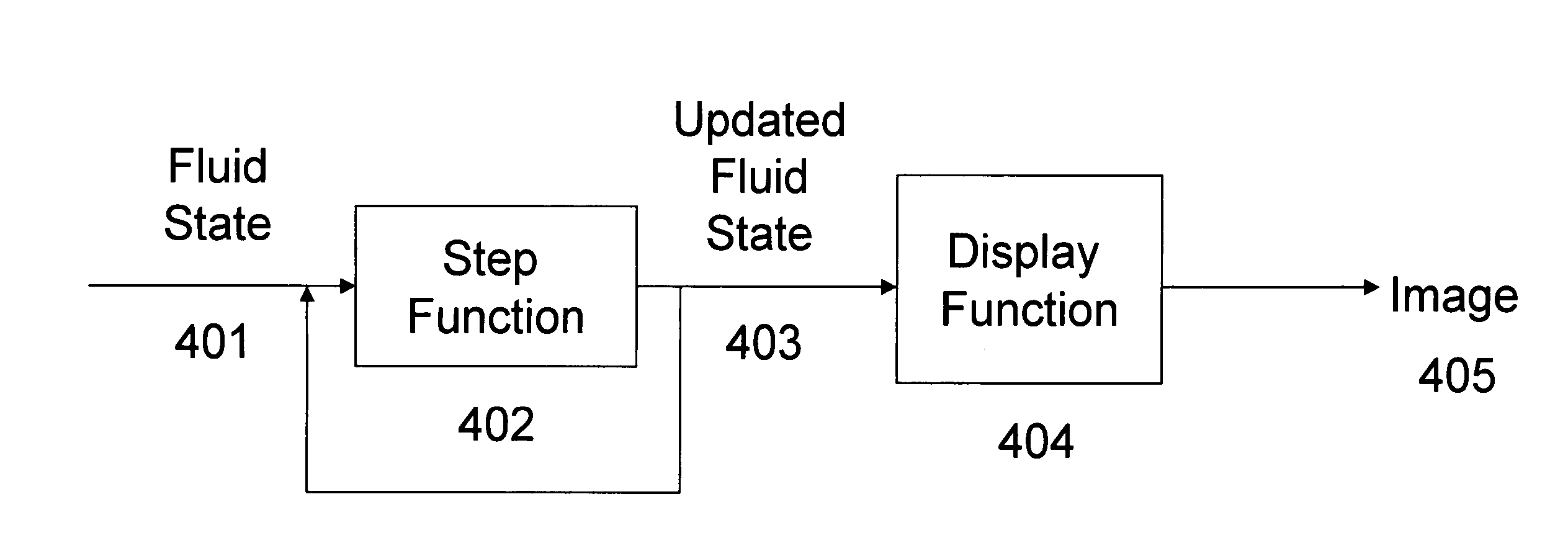
A method is disclosed for executing a physics simulation in a system comprising a computational platform, a main application stored in the computational platform, a secondary application stored in the computational platform, and a smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) application programming interface (API) implemented in the computational platform. The method defines a SPH call in the SPH API, and by operation of the main application, invokes a software routine using the SPH call. Additionally, by operation of the secondary application, a state of the physics simulation is updated in response to the software routine.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Soft tissue deformation simulation method
InactiveCN102044086AAvoid subsection calculationsSimplified representationSpecial data processing applications3D modellingSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsBiomechanics
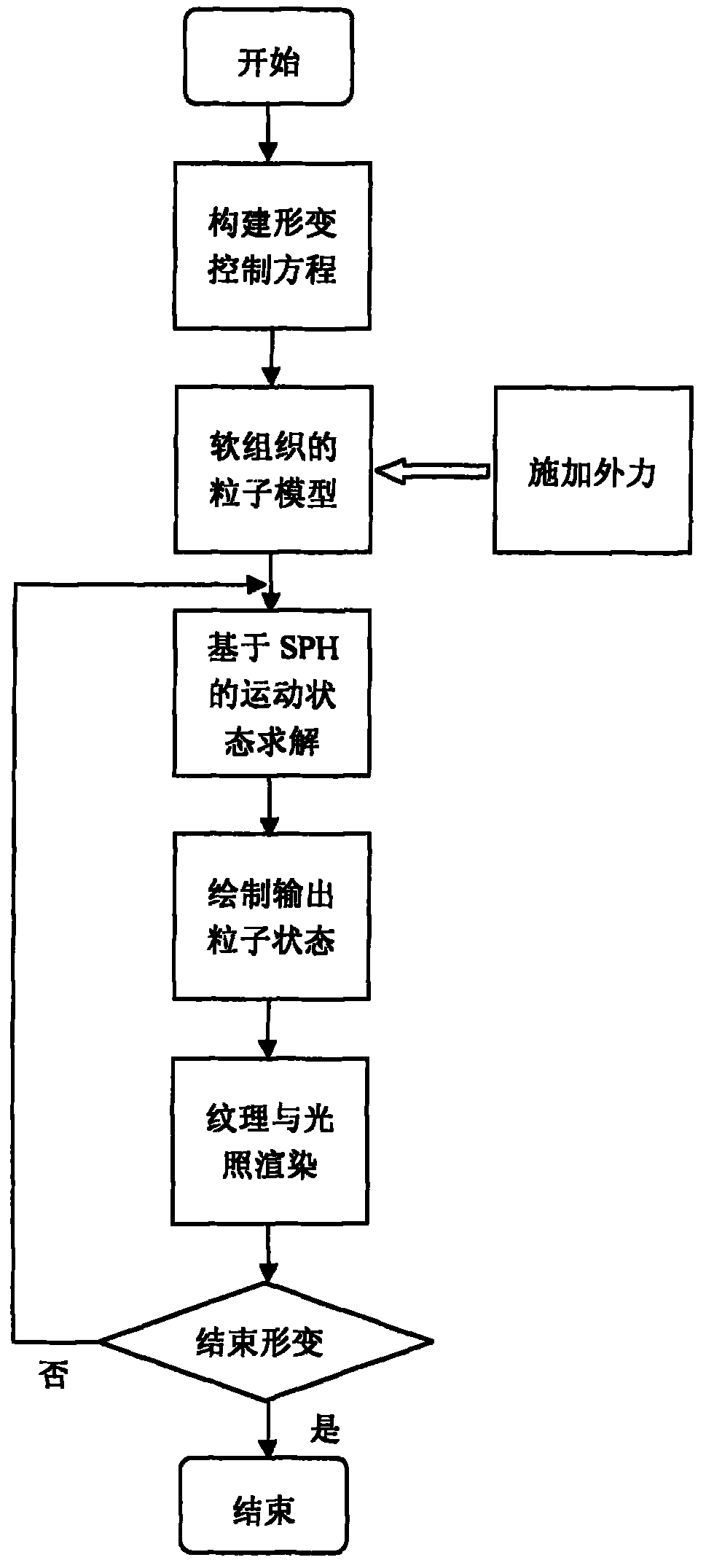
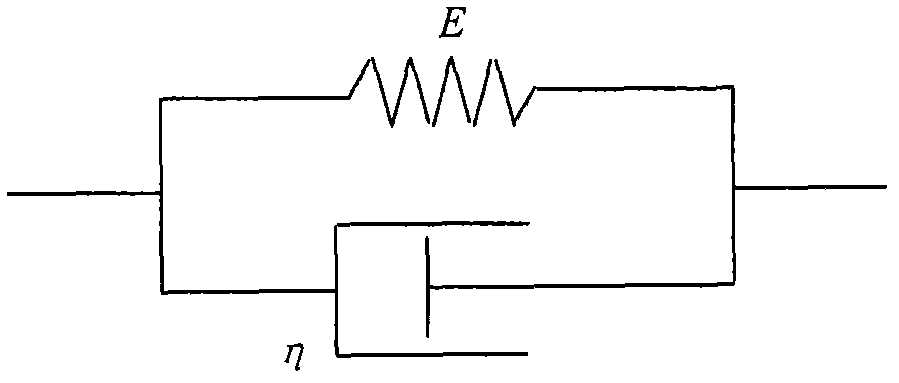
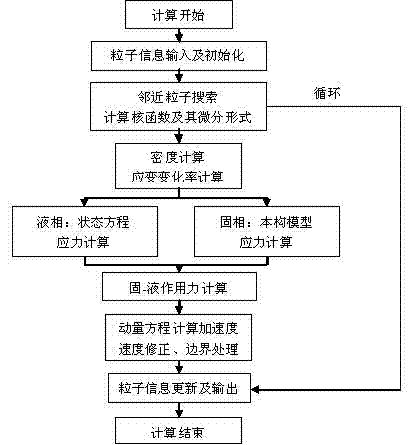
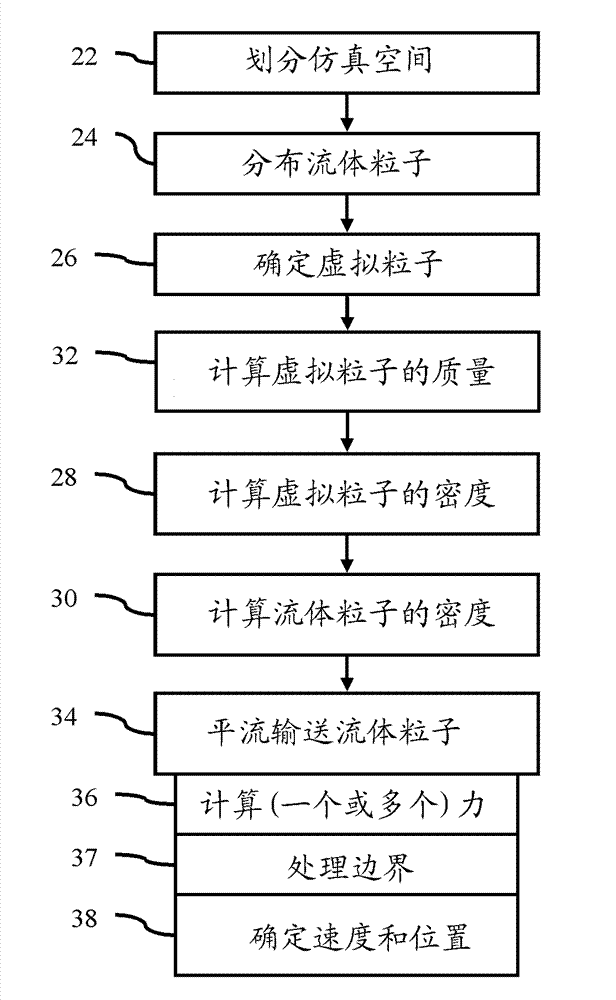
The invention relates to a soft tissue deformation simulation method based on smooth particle hydrodynamics, belonging to the technical field of graphic processing. In the method, a smooth particle hydrodynamics method is selected, and a viscoelastic mechanics model is used for reflecting the biomechanical characteristics of soft tissue. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a series of equations related to soft tissue deformation simulation according to the viscoelastic model; selecting a proper support domain search strategy and a smooth kernel function, approximately calculating each related item of the equation by adopting the particle approximation method, and calculating the variation values of the density, the position, the velocity and the like of each particle along with time through the display integration method; and dynamically outputting the status of each time step size of the particle model to a screen, rendering texture irradiation, and displaying the real-time deformation process of soft tissues and organs under stressing conditions. The method does not need troublesome grid computing, thereby increasing the accuracy and the real-time performance of soft tissue deformation simulation.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics) algorithm-based simulation method and simulation system of process of breaking dam by flood
ActiveCN102708227AHigh precisionRealistic effectClimate change adaptationSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsSpacetime
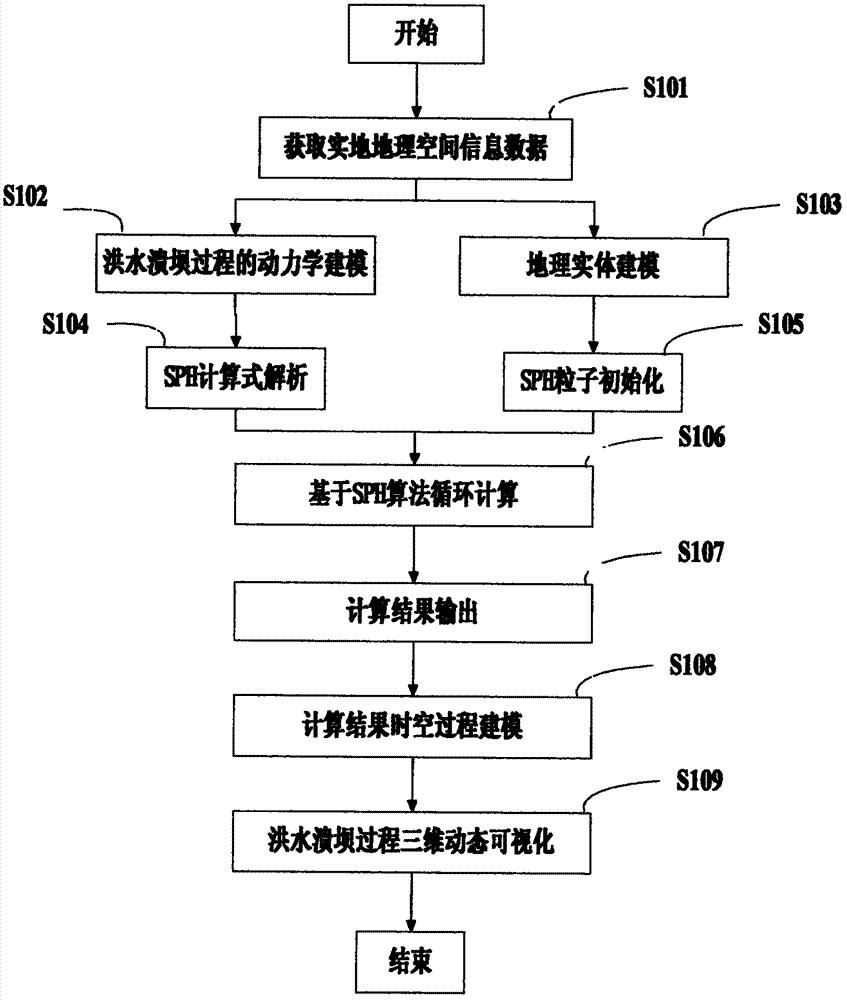
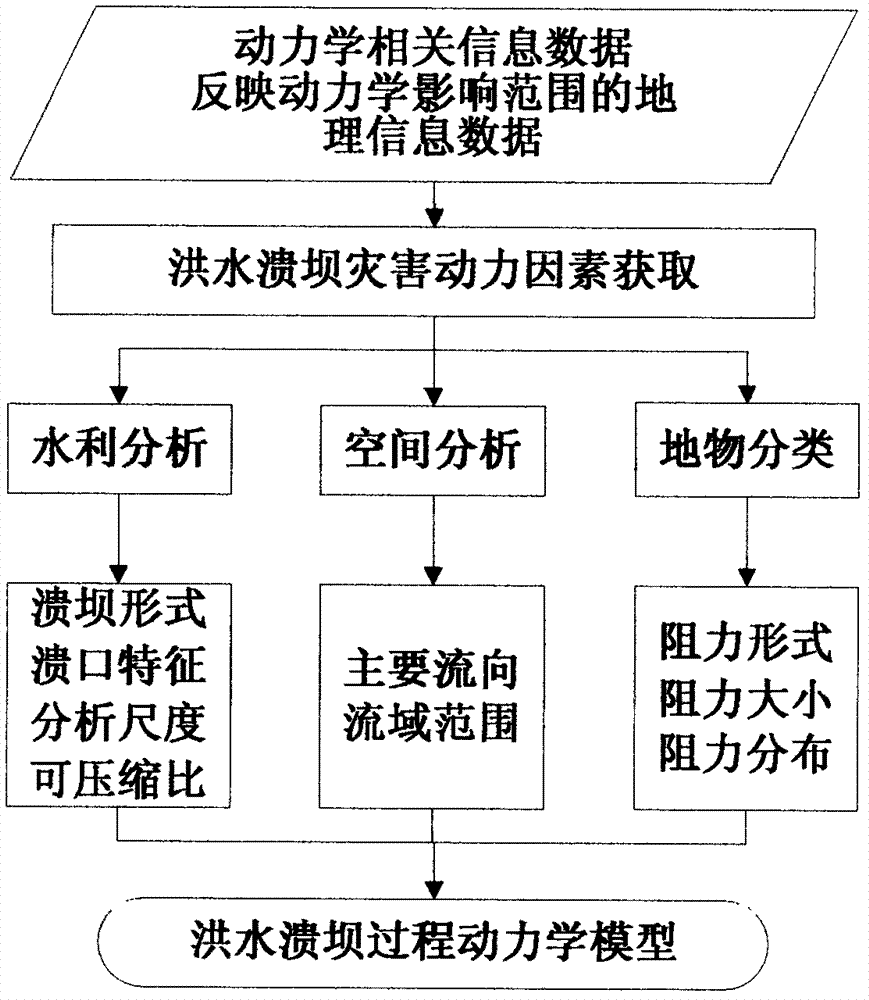
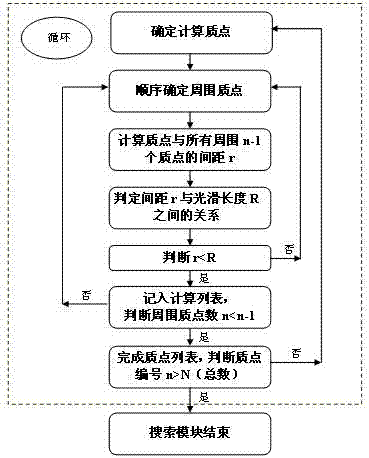
The invention provides an SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics) algorithm-based simulation method and an SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics) algorithm-based simulation system of the process of breaking dam by flood. The simulation method comprises the following steps: A. acquiring on-site geographic spatial information data; B. establishing a dynamical model of the process of breaking dam by flood based on the geographic spatial information data obtained in the step A; C. establishing a geographic entity model according to the geographic spatial information data obtained in the step A; D. analyzing the dynamical model obtained in the step B into an SPH calculation method; E. initializing the geographic entity model obtained in the step C to be hydrodynamics particles and boundary particles for the SPH calculation; F. circularly calculating based on the SPH algorithm; G. carrying out the spatial-temporal process modeling on the calculated value result obtained in the step F to obtain a 3D spatial-temporal model and a database of the process of breaking the dam by flood; and H. dynamically visualizing the 3D spatial-temporal model and the database of the process of breaking dam by flood obtained in the step G. By using the SPH method in the geographic process simulation, the authenticity of the simulation result is effectively improved.
Owner:自然资源部国土卫星遥感应用中心
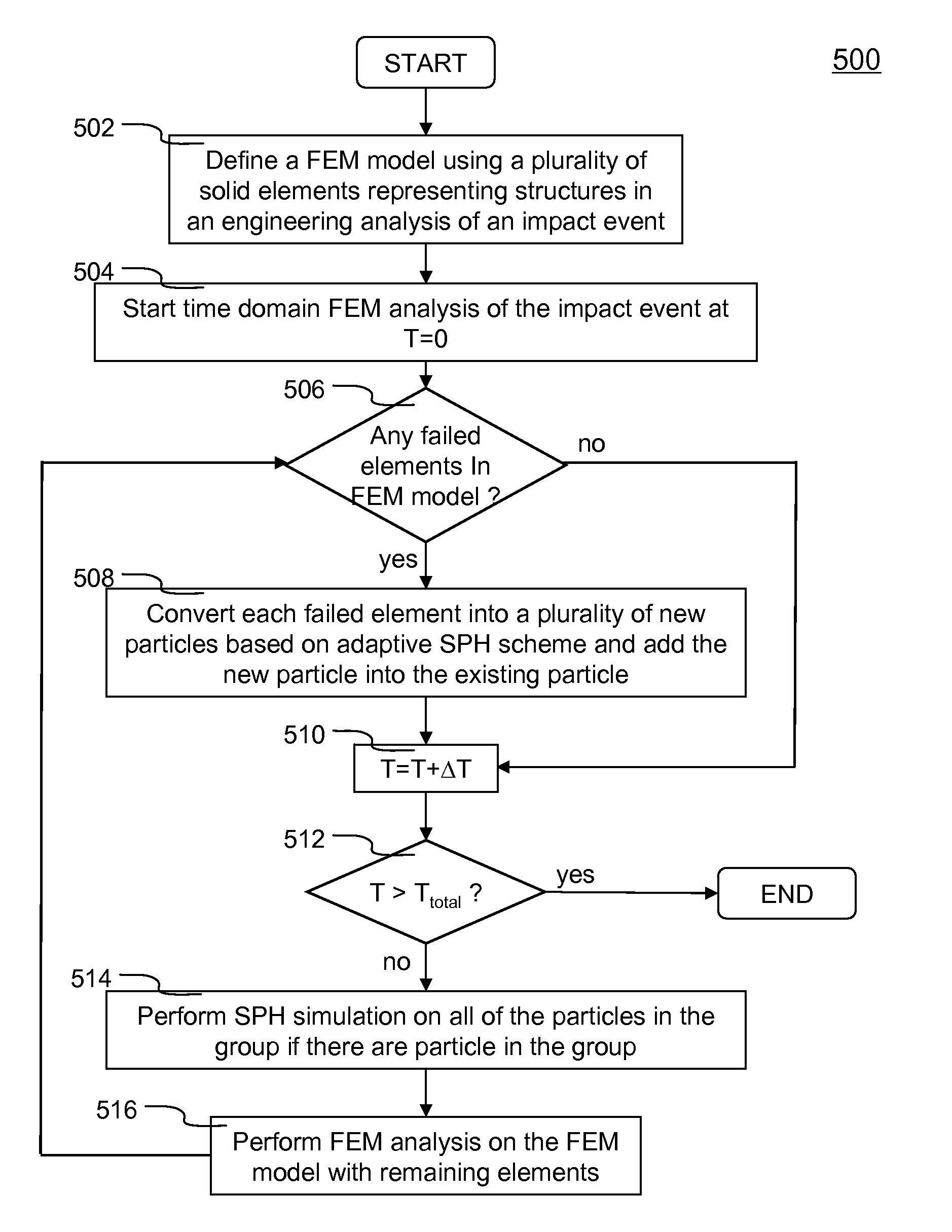
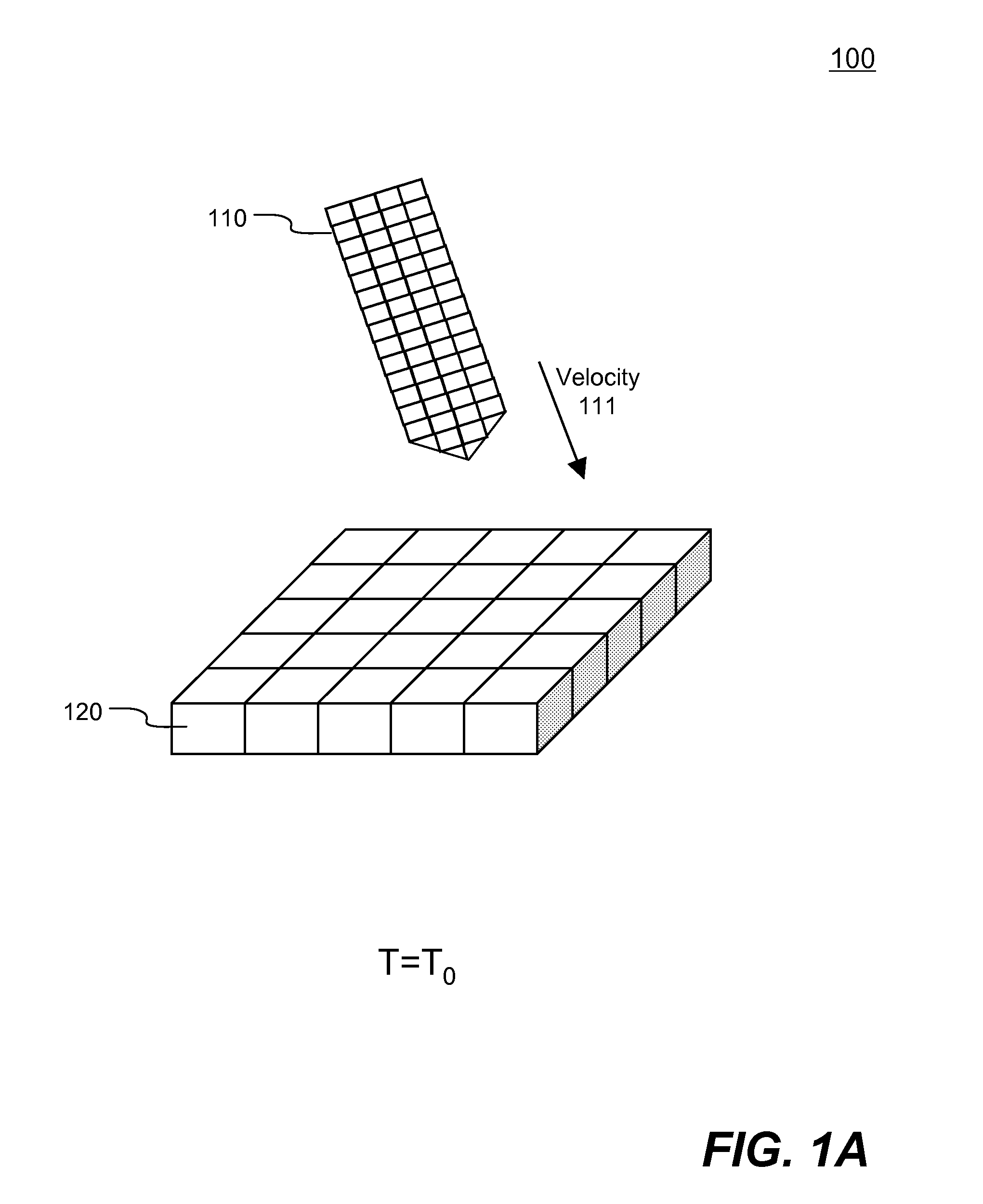
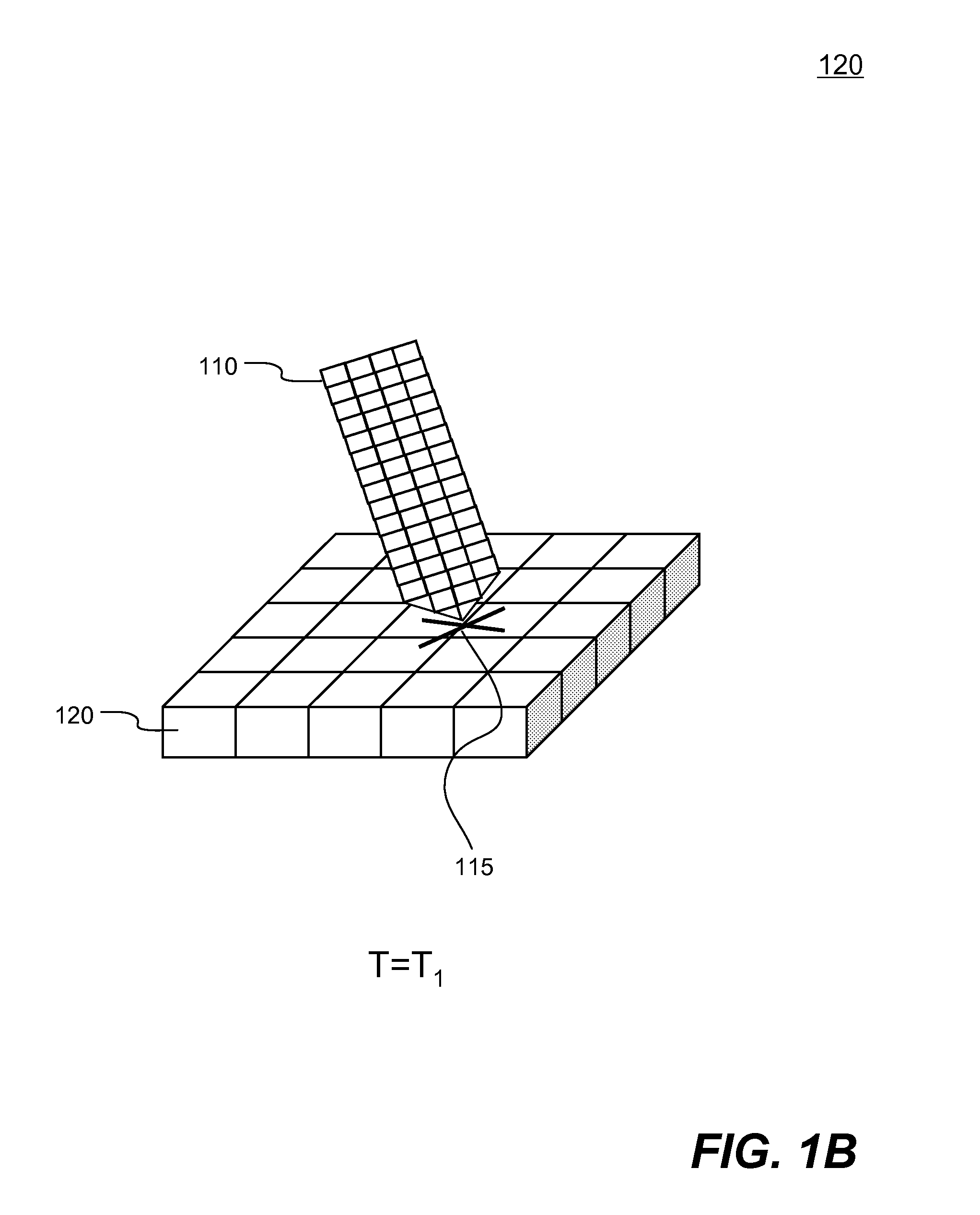
Methods and systems of engineering analysis using a hybrid approach with FEM and adaptive SPH
ActiveUS20090228246A1Real timeComputation using non-denominational number representationInvestigating material hardnessSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsMomentum
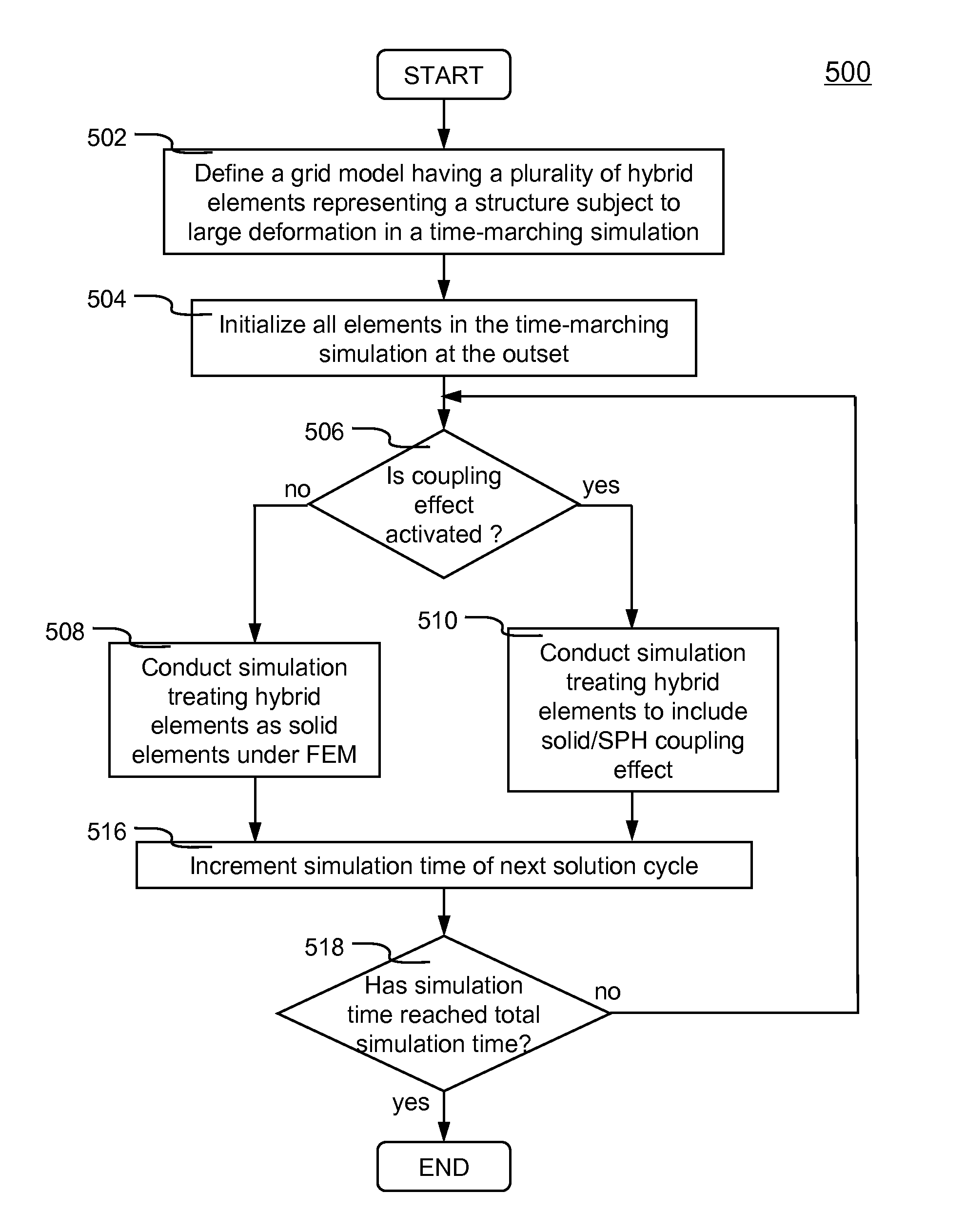
Systems and methods of computer aided engineering analysis using hybrid approach of finite element method (FEM) and adaptive smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) are described. According to one aspect, a computer-aided engineering analysis is performed to simulate an impact event between structures. A FEM grid model is created to represent the structures using a plurality of solid elements which represents geometry and material properties. Once a contact between two structures resulted into a material or structural failure according to predefined material constitutive equation, solid elements representing the failed portion of the structure are removed. Each failed solid element is then replaced by a plurality of particles to be analyzed using the SPH analysis. The particles replacing the failed element inherit all of the states and properties of the failed element, such as location, mass, velocity, acceleration, etc. The replacement is conducted according to the principles of mass, momentum and energy conservation.
Owner:ANSYS
Computational simulation method of flow slide catastrophe of rock and soil material
ActiveCN102819650AAccurate calculation of impact loadsReasonable prediction of flow-slip distanceSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsSoil mechanics
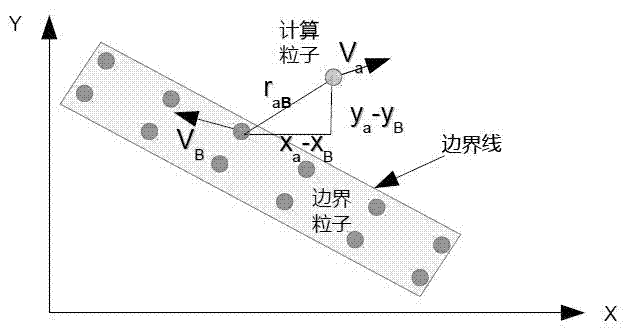
The invention relates to a computational simulation method of a flow slide catastrophe of a rock and soil material, belonging to the technical fields of computational rock and soil mechanics, geologic hazard prevention and control and geologic environment protection. Aiming at the limitation that the conventional grid-based computing method is only suitable for small-deformation analysis, the invention discloses a computational simulation method of an entire flow slide catastrophe process of the rock and soil material based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). According to the method, a Navier-strokes equation is used as a control equation, solid phase and liquid phase of the rock and soil material are described by using a sub-load face Cambridge model and an incompressible fluid constitutive model respectively, porous medium theory and darcy law are introduced to calculate solid-liquid coupling acting force, and a computation model, which considers the full coupling of water and soil, of the flow slide catastrophe of the rock and soil material, is established. According to the computational simulation method, the entire process of large-deformation flow damage of the rock and soil material can be effectively represented, and the fluidization characteristic of the rock and soil material is captured, so that powerful scientific basis is provided for engineering design, engineering construction, disaster prevention and reduction and the like of high-risk areas of the flow slide disaster, and meanwhile, application of the computational rock and soil mechanics in the technical fields of actual engineering construction, geologic hazard prevention and control and the like is forcefully promoted.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
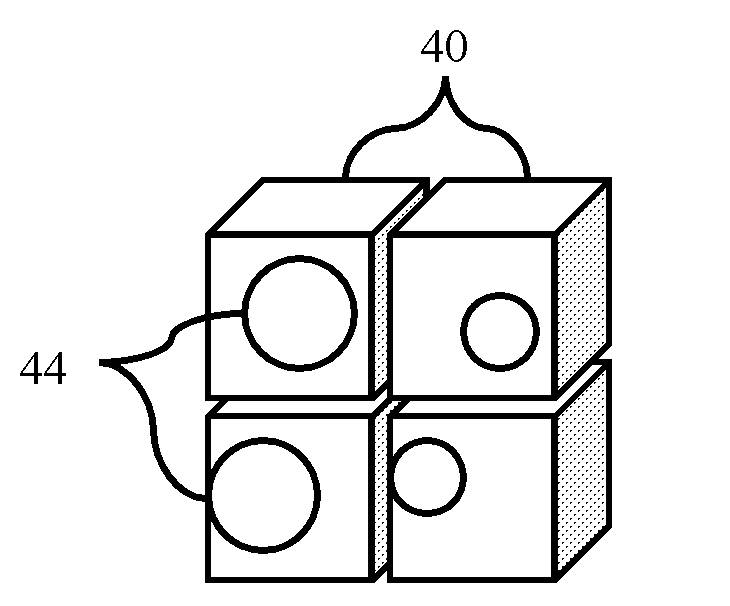
Hybrid Element Enabling Solid/SPH Coupling Effect
ActiveUS20110077912A1Geometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsEngineering
Hybrid elements that enable coupling effects between SPH particles and FEM solid are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, hybrid elements are configured to facilitate coupling effect of solid element based on finite element method (FEM) and one or more corresponding particles based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). Hybrid elements are defined in a computer aided engineering (CAE) grid model as a buffer or interface between the SPH particles and FEM solids. For example, a portion of the grid model comprises SPH particles because the likelihood of enduring large deformation, while the rest of the model comprises FEM solid elements. Hybrid elements are placed between the solids and the particles. Each hybrid element comprises two layers: solid layer and particle layer.
Owner:ANSYS
Fluid simulating method and device
ActiveCN104200015ASimulate extensively and preciselyImprove numerical stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsRelevant information
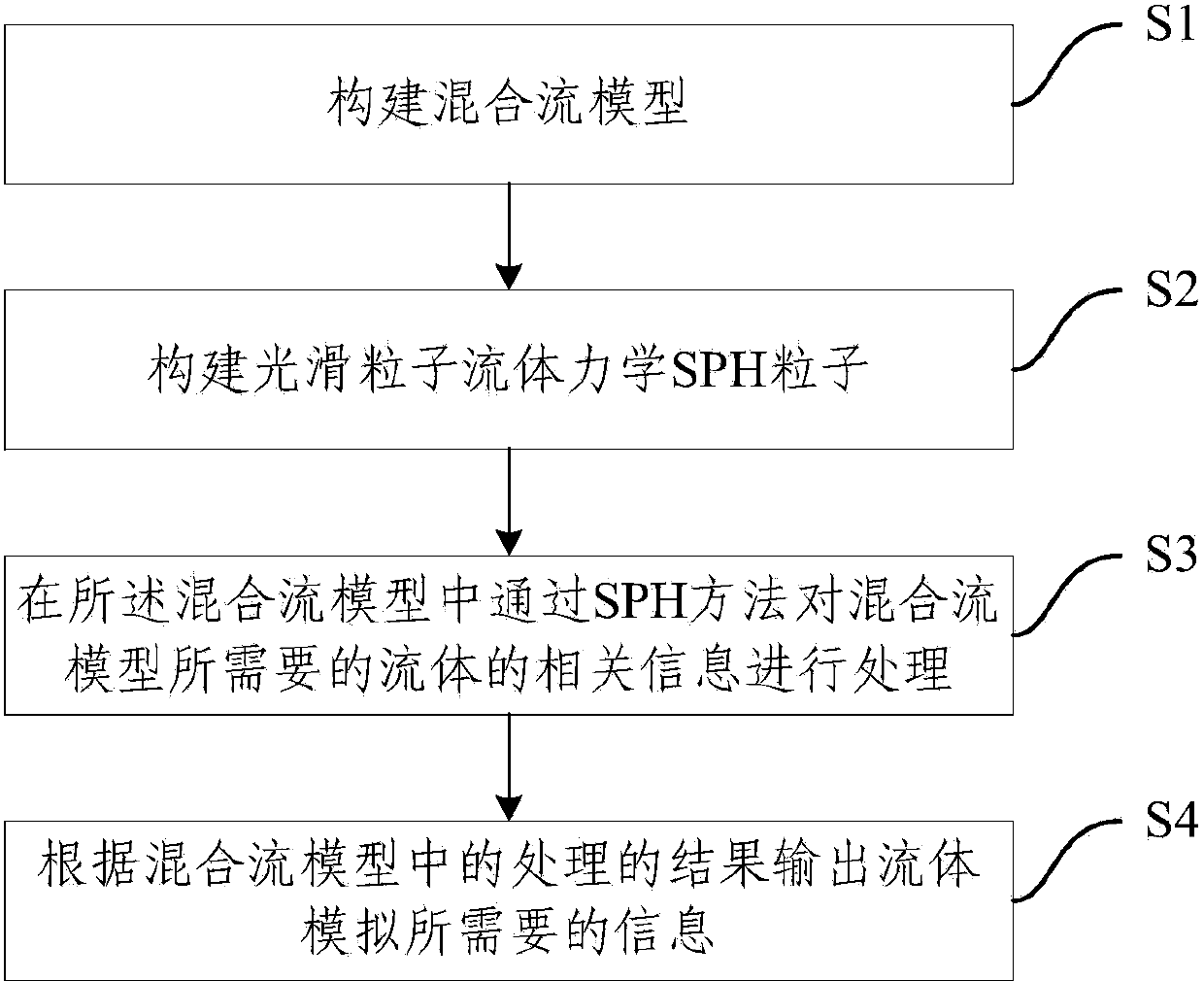
The invention provides a fluid simulating method and device. The method includes the steps that firstly, a mixed flow model is constructed; secondly, smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) particles are constructed; thirdly, relevant information of fluid needed by the mixed flow model is processed in the mixed flow model through an SPH method; fourthly, information needed in fluid simulating is output according to a processing result in the mixed flow model. According to the fluid simulating method and device, the moving process of multi-component fluid can be widely and accurately simulated.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
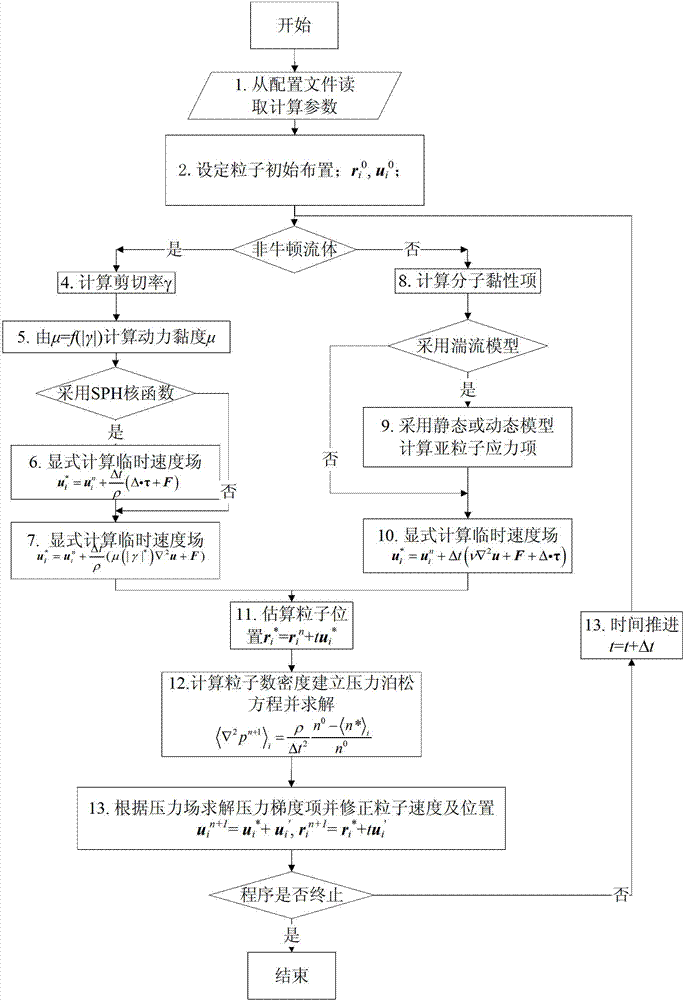
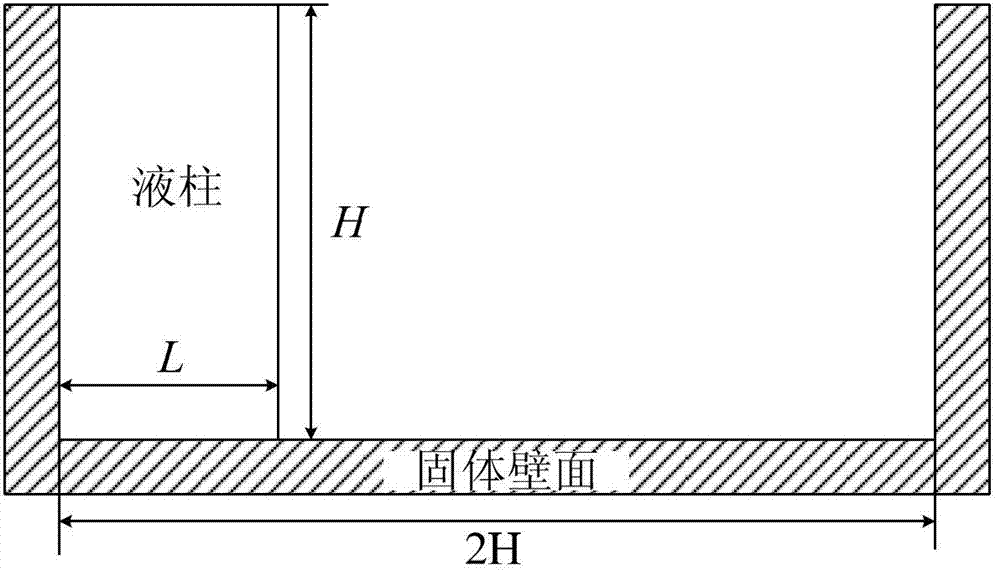
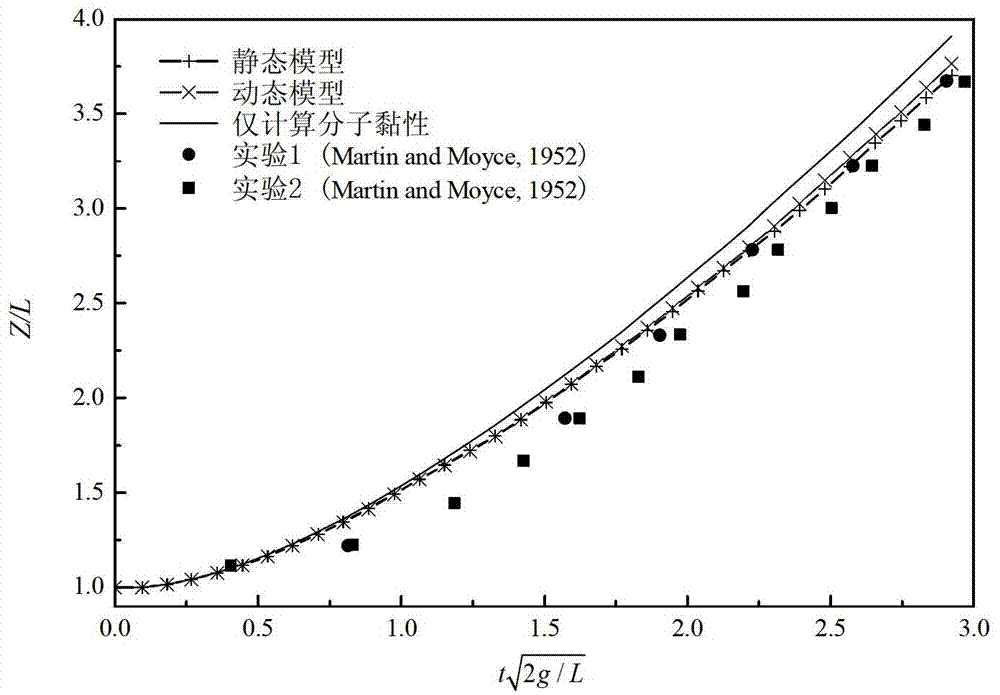
Establishment method for free surface flow model in moving particle semi-implicit algorithm
The invention provides an establishment method for a free surface flow model in a moving particle semi-implicit algorithm, comprising the following steps of: introducing a turbulence model which comprises a static Smagorinsky model and a dynamic Smagorinsky model in the form of Lagrange; treating a non-Newtonian fluid having a constitutive equation like mu = f(the absolute value ofgamma) by adopting a variable-viscosity Newtonian fluid model; and introducing a cubic spline kernel function, discretizing the shear stress of the non-Newtonian fluid by adopting the divergence discretization scheme of a smooth particle fluid dynamic method, and treating the free surface flow of the non-Newtonian fluid. According to the method provided by the invention, the sub-particle stress model of turbulence can be considered, and the method provided by the invention can be used for calculation for the non-Newtonian fluid.
Owner:江苏金洋造船有限公司
Fluid-solid coupling method based on smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) and nonlinear finite elements
InactiveCN103699715ASolve problems that are difficult to directly coupleEasy to implement in parallelSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsElement model
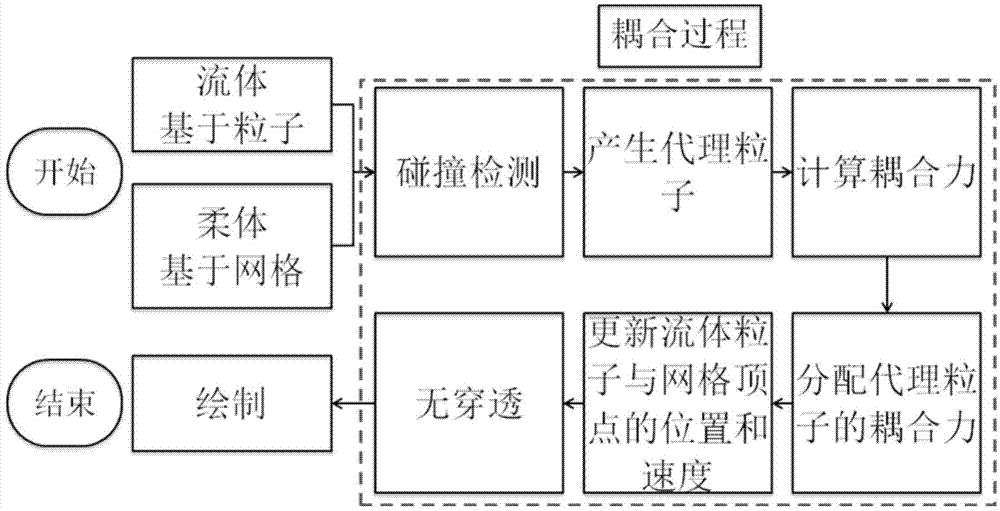
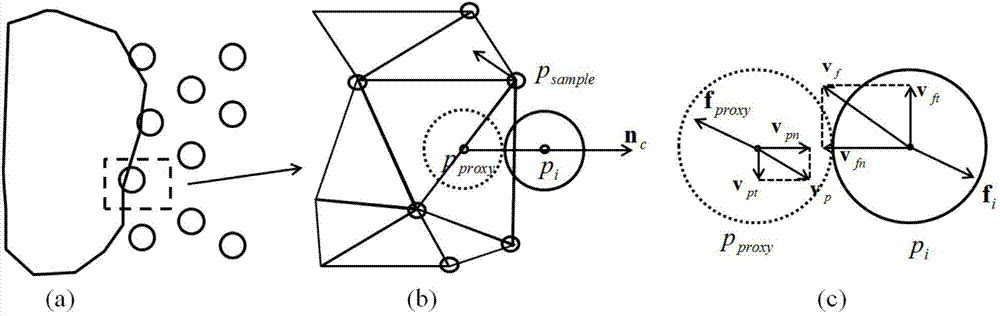
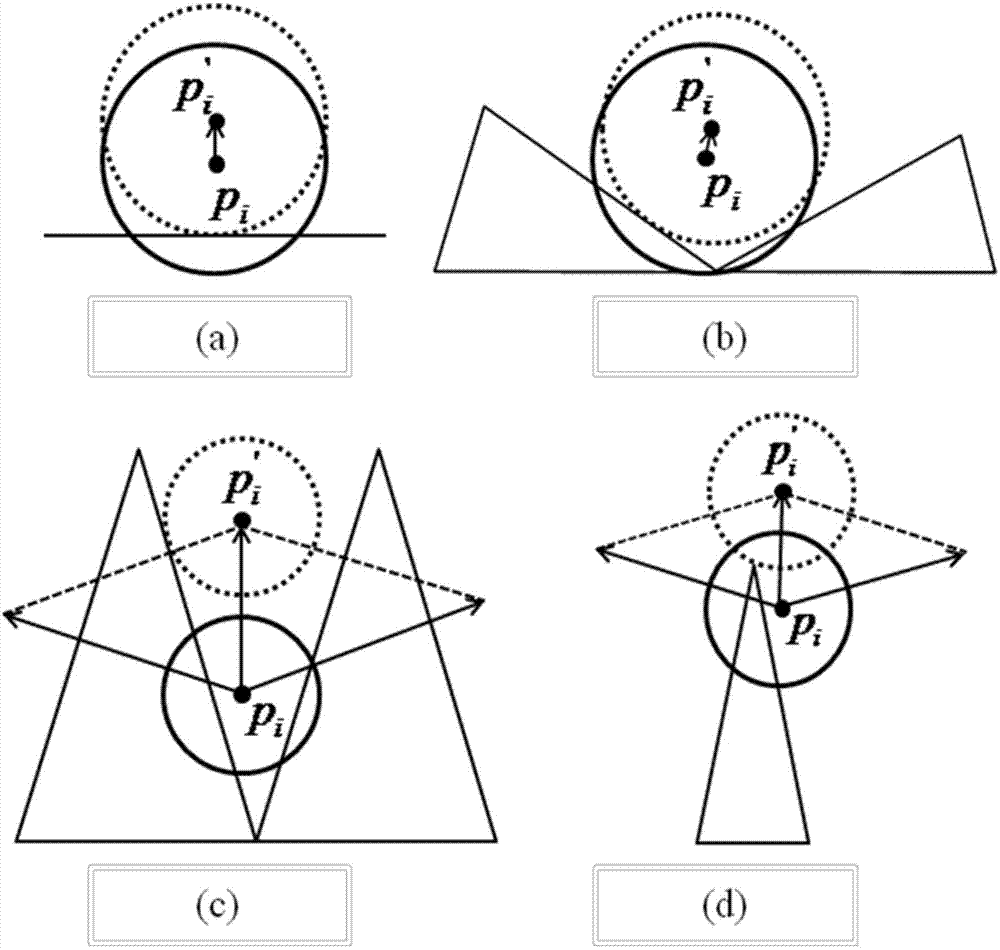
The invention provides a fluid-solid coupling method based on smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) and nonlinear finite elements. The method comprises the following six steps: at a collision detection stage, detecting collision information of fluid particles with a finite element network; at an agent particle generation stage, generating collision agent particles presenting a finite element model according to the collision information for processing the collision between a fluid and a solid; at a coupling force calculation stage, calculating force generated by collision between agent particles and fluid particles according to the position and speed relations of the agent particles and the fluid particles; at a coupling force allocation stage, controlling the position relation of the agent particles and the finite element model and allocating the coupling force to a finite element stress model; at a position and speed updating stage, driving the position and speed update of the finite element model and a fluid particle model according to the calculated coupling force; at a non-penetration modification stage, modifying penetration fluid particles according to an updated position.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Hybrid unit capable of solid/sph coupling
ActiveCN102262689ADesign optimisation/simulationAerodynamics improvementSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsEngineering
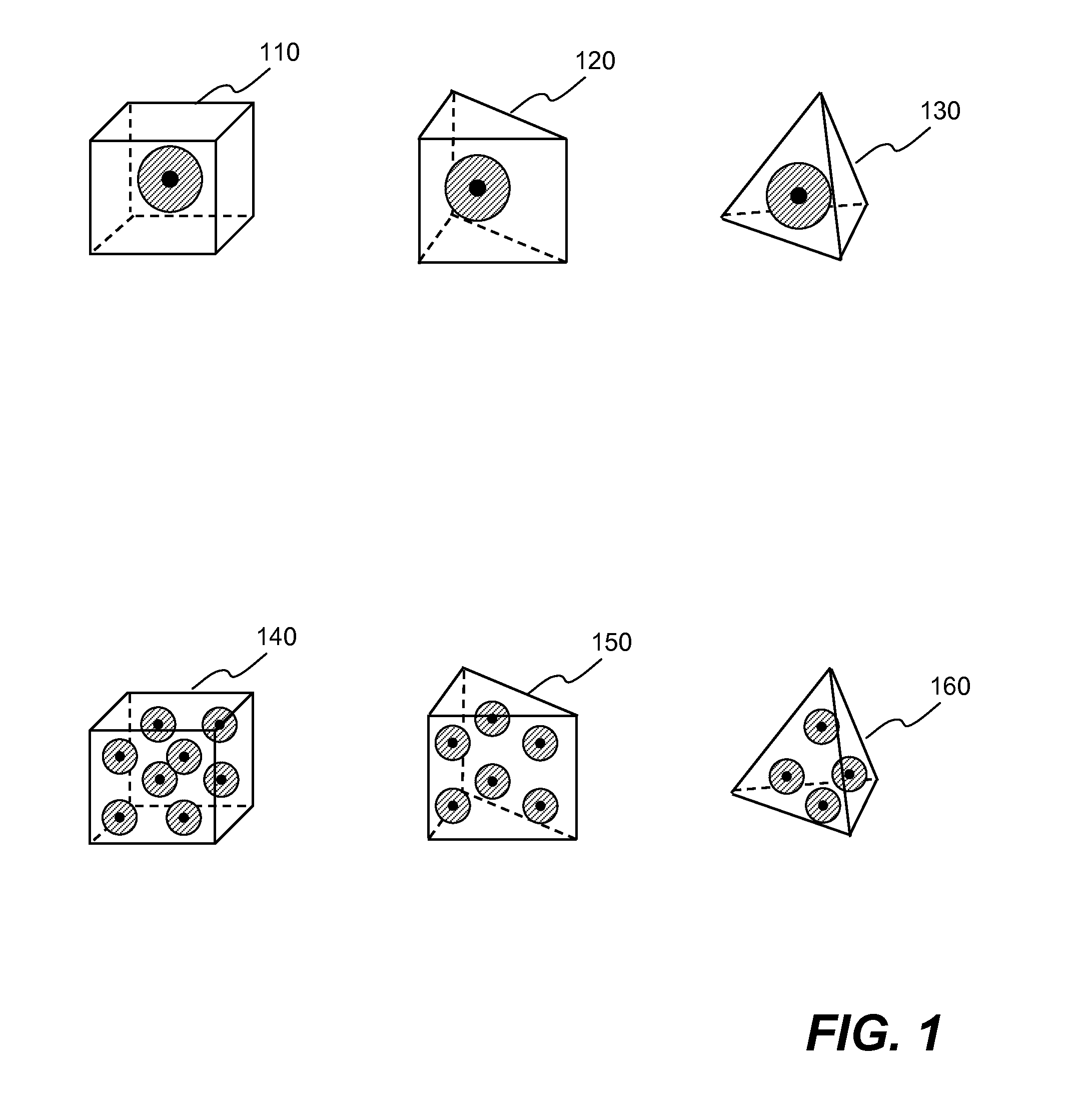
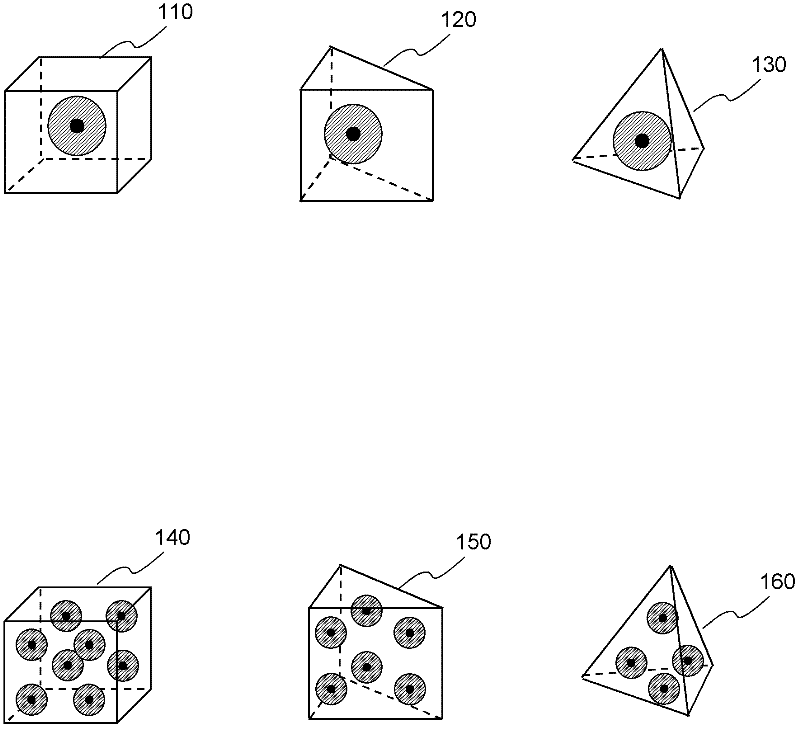
Hybrid elements (110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160) that enable coupling effects (510) between SPH particles and FEM solid elements are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, hybrid elements (110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160) are configured to facilitate coupling effect (510) of solid element based on finite element method, FEM, and one or more corresponding particles based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics, SPH. Hybrid elements (110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160) are defined in a computer aided engineering grid model (220) as a buffer or interface between the SPH particles and FEM solid elements. For example, a portion of the grid model (220) comprises SPH particles because the likelihood of enduring large deformation, while the rest of the model comprises FEM solid elements. Hybrid elements are placed between the solid elements and the particles. Each hybrid element further comprises two layers: a solid layer and a particle layer.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
Coagulation phenomenon simulation method based on particle model
ActiveCN106650064APrevent penetrationMake up for missing problemsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsParticle model
The invention discloses a coagulation phenomenon simulation method based on a particle model. The method includes the steps that 1, discrete modeling is conducted on the phenomenon that gas coagulates on the solid surface, wherein the influence of the dew point temperature and the relative humidity property in a humidity diffusion model on the details of the coagulation phenomenon is considered; 2, a soil-liquid coupled boundary density correction algorithm is proposed, the problem of particle loss of a smoothed-particle hydrodynamics model at the boundary is solved, and meanwhile particle penetration is prevented under the condition that the time step is not decreased; 3, a particle system is used for conducting discrete modeling on air, the simulation process can be expressed more visually, and adjustment and design can be conducted easily. By applying the method, the flow property, heat conduction property and the like of air can be conveniently adjusted, and the problems that existing air heat exchange phenomenon simulation is not visual in effect and lacks enough details are solved; the method has certain practical value.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application programming interface for fluid simulations
ActiveUS20070038424A1Design optimisation/simulationAnimationSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsApplication programming interface
A method is disclosed for executing a physics simulation in a system comprising a computational platform, a main application stored in the computational platform, a secondary application stored in the computational platform, and a smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) application programming interface (API) implemented in the computational platform. The method defines a SPH call in the SPH API, and by operation of the main application, invokes a software routine using the SPH call. Additionally, by operation of the secondary application, a state of the physics simulation is updated in response to the software routine.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
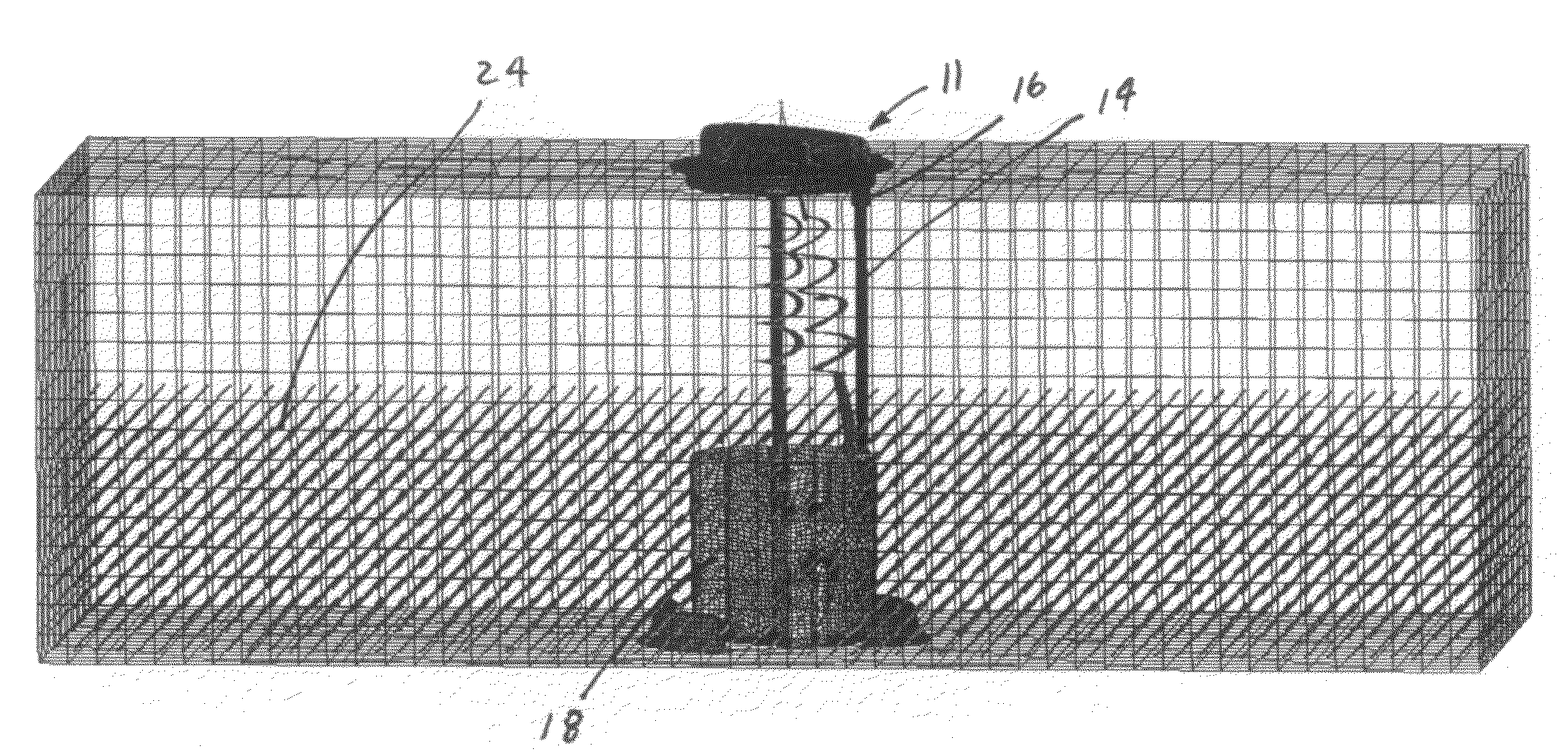
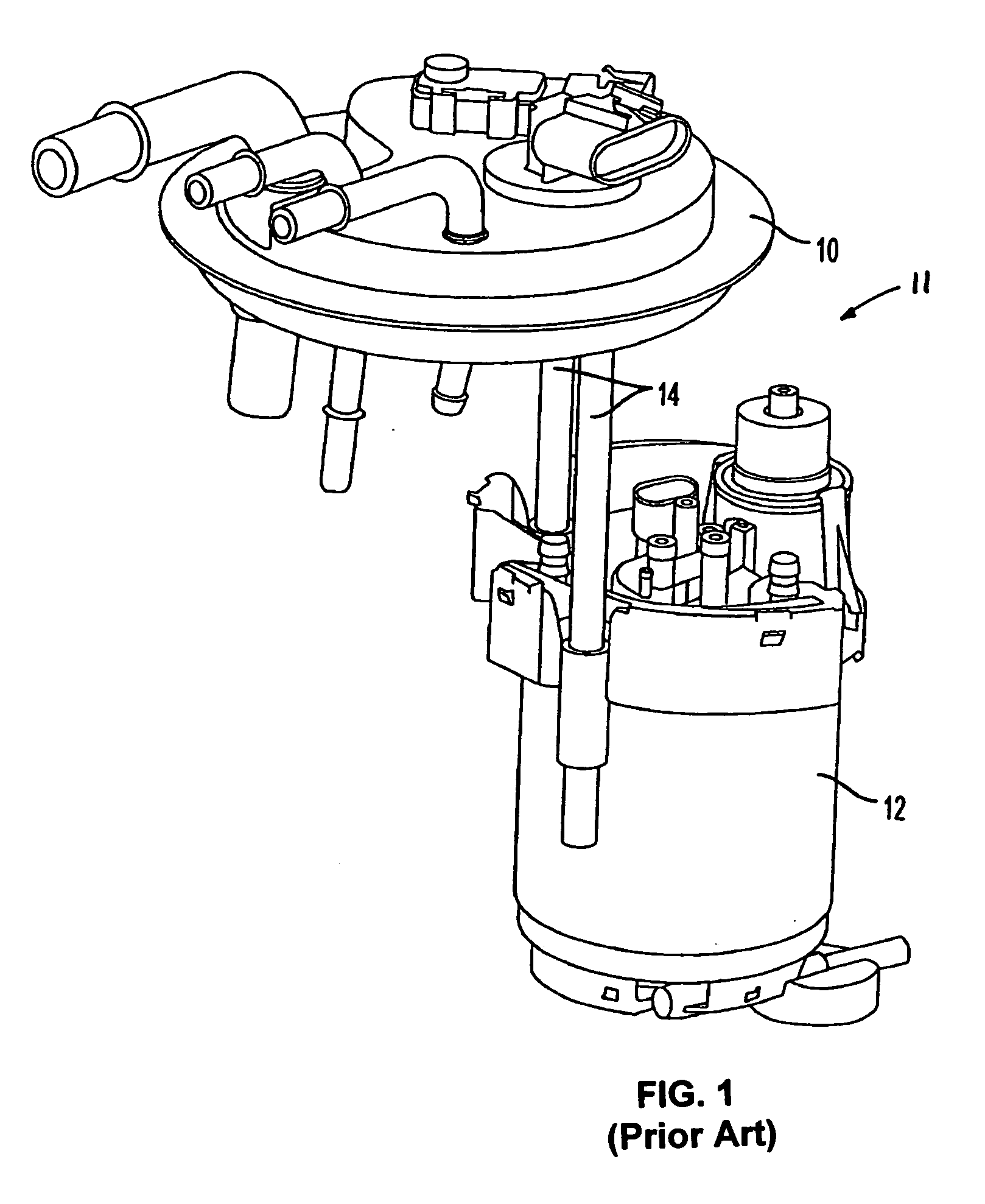
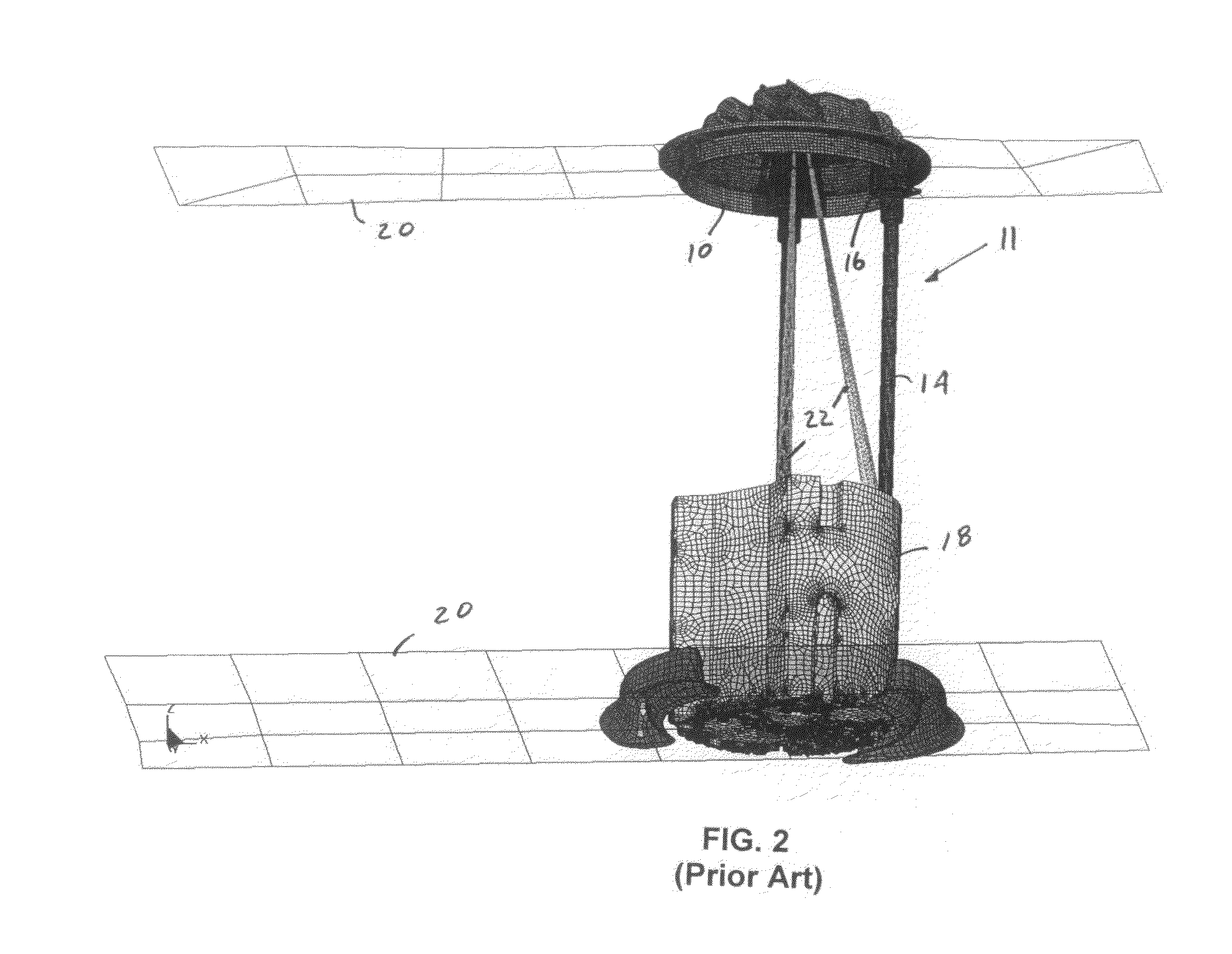
Fluid solid interaction included in impact simulation of fuel delivery module
A method is provided for simulating a vehicle crash on a fuel delivery module of a vehicle. The fuel delivery module (11) has a flange (10) constructed and arranged to be coupled to a fuel tank, a fuel pump (12) for delivering fuel from the tank and through the flange, a reservoir (18) housing the fuel pump, and strut rods (14). Each strut rod has an end coupled to the reservoir or fuel pump and another end coupled to the flange at an interface. The method models a fuel tank associated with the fuel delivery module as a rigid or elastic shell. A solid model of the fuel delivery module is created. The solid model is meshed to create a finite element model. Fluid in the fuel tank is modeled with Lagrangian or arbitrary Lagrangian Eulerian finite elements, or smoothed particle hydrodynamics particles. Solid fluid interactions are added to the meshed solid model. A vehicle crash simulation is run on the solid model together with the fluid interactions to determine the effect of the fluid interactions on the interface of each strut rod with the flange and to determine any effect on the flange.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
Third-dimensional fluid simulation method referring to heat conduction and dynamic viscosity
ActiveCN106096215ARealistic visual effectsGuaranteed realismComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsEngineering
The invention discloses a third-dimensional fluid simulation method referring to heat conduction and dynamic viscosity. The method comprises the steps that 1, discrete modeling is carried out on the heat conduction process in fluid and the heat conduction process between the fluid and the outside based on a smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) model, and the phase change process is simulated according to the influence of enthalpy of phase change on the phase change temperature; 2, calculation of the dynamic viscosity is introduced to show details in the fluid motion process; 3, a PCISPH algorithm is called to complete the remaining fluid motion simulating process; 4, a GPU accelerating algorithm is utilized for processing the processes of heat conduction, phase change, fluid viscosity changes and the like in parallel on a compute unified device architecture (CUDA), and fast simulation of third-dimensional phase change fluid is achieved. By means of the method, the heat conduction process between different kinds of fluid and the outside and the viscosity change process of the fluid can be simulated really and efficiently, simulation details in an existing method are enhanced, and the sense of reality of fluid simulation is improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
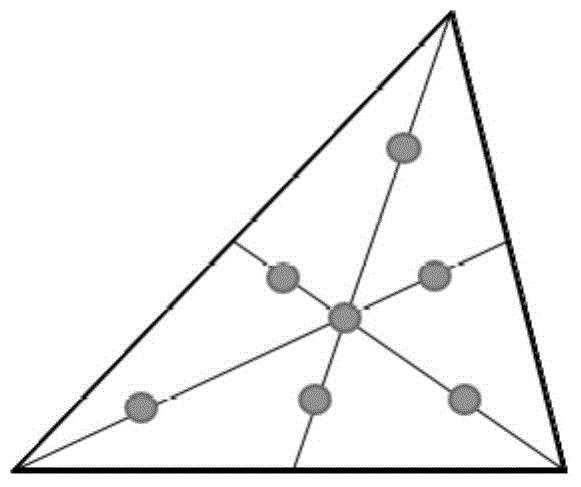
Simplified smoothed particle hydrodynamics
InactiveCN102768698ADesign optimisation/simulationEducational modelsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsParticle physics
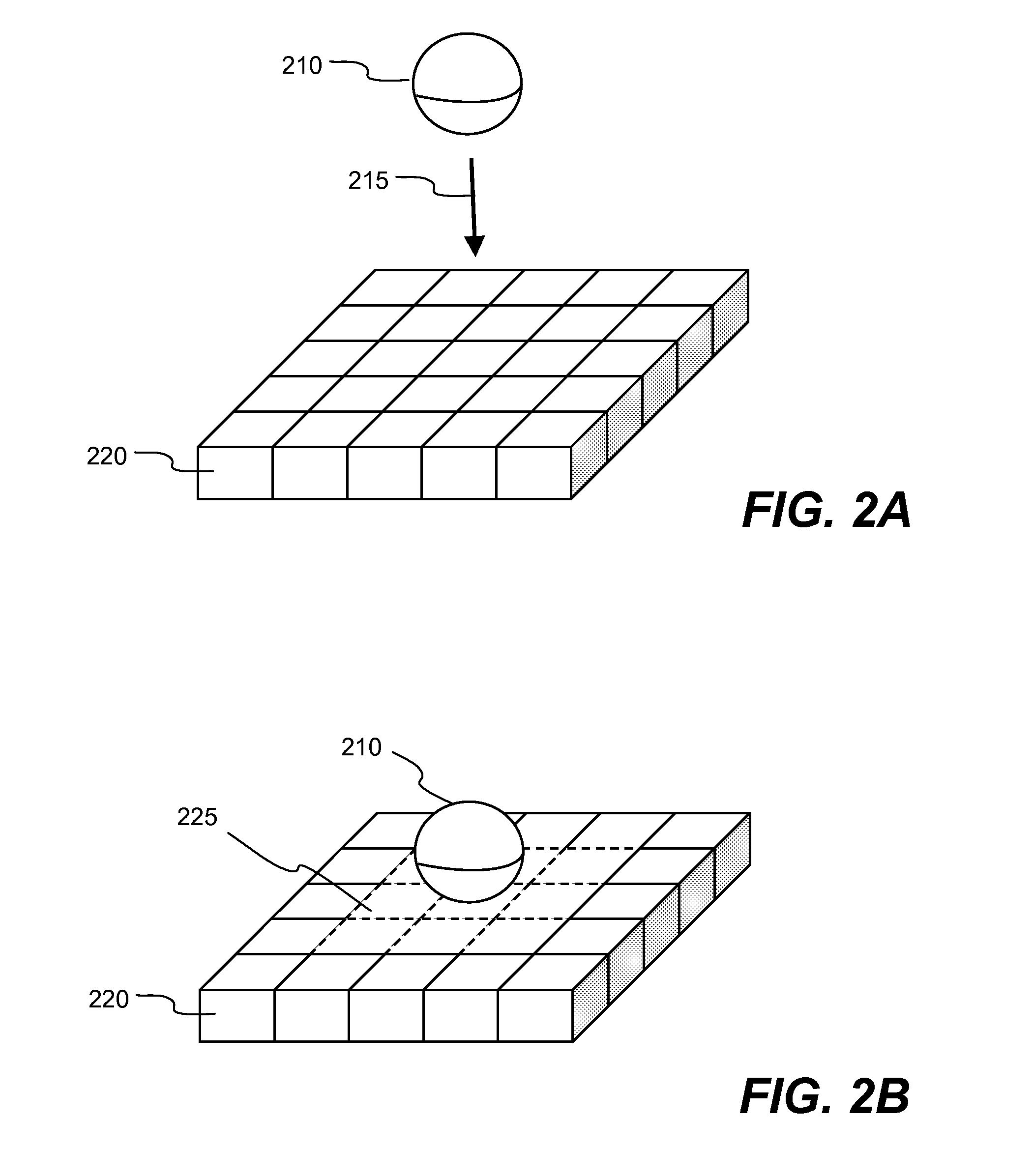
The invention relates to simplified smoothed particle hydrodynamics. For efficient smooth particle hydrodynamics using more particle information, virtual particles are created. Each virtual particle represents an averaging of properties for the fluid particles in a cell. For density, force, or other calculations for a given fluid particle, the interaction between the particles within a cell are calculated. For calculating the influence of particles outside the cell on the particle in the cell, the virtual particles from the neighboring cells are used. The interaction with these aggregate particles reduces the number of calculations while still including the influence from particles of other cells.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
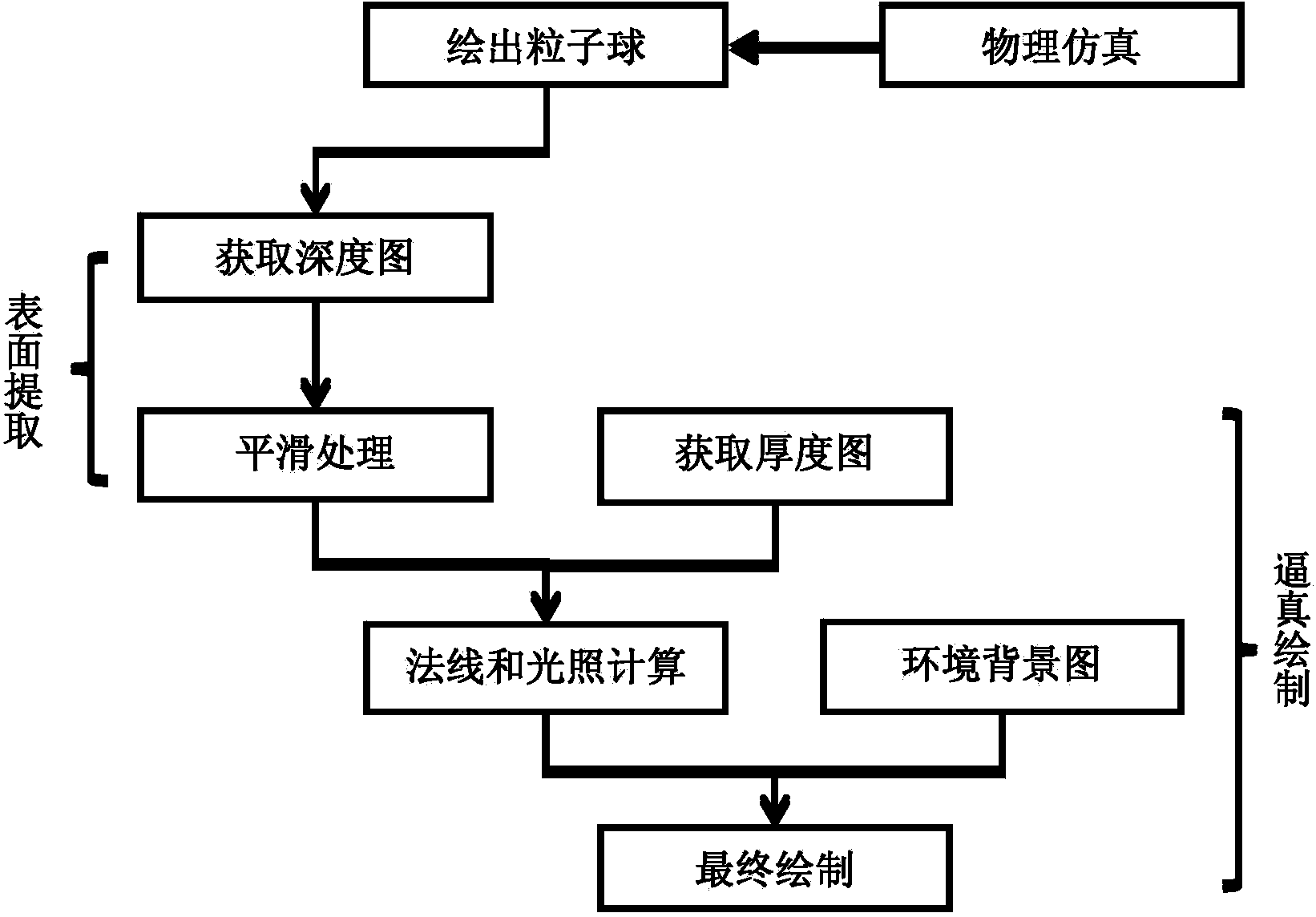
Method for drawing surface of SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics) fluid in real time on basis of screen spaces
InactiveCN103679802ARealistically show the impactImprove real-time performance3D-image rendering3D modellingSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsViewpoints
The invention provides a method for drawing the surface of SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics) fluid in real time on the basis of screen spaces. The method aims to track the surface of the fluid in real time and vividly draw the surface of the fluid on the basis of dynamic behavior of the fluid simulated by an SPH process, and research is carried out around an acceleration computation process on the basis of the screen spaces. The method includes generating depth graphs of the fluid in three-dimensional spaces from viewpoint positions; smoothing and filtering the depth graphs to dynamically extract the surface of the fluid relative to viewpoints; combining optical effects of environment mapping, fluid reflection, refraction and the like; simulating interaction among the fluid and other three-dimensional solid bodies in virtual scenes; vividly drawing flexible body and fluid interaction scenes on the basis of a GPU (graphics processing unit). The method has the advantages that various computation and rendering are carried out completely on the basis of the GPU, all operation can be carried out in a parallel mode, and the method is good in real-time performance and physical realism.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
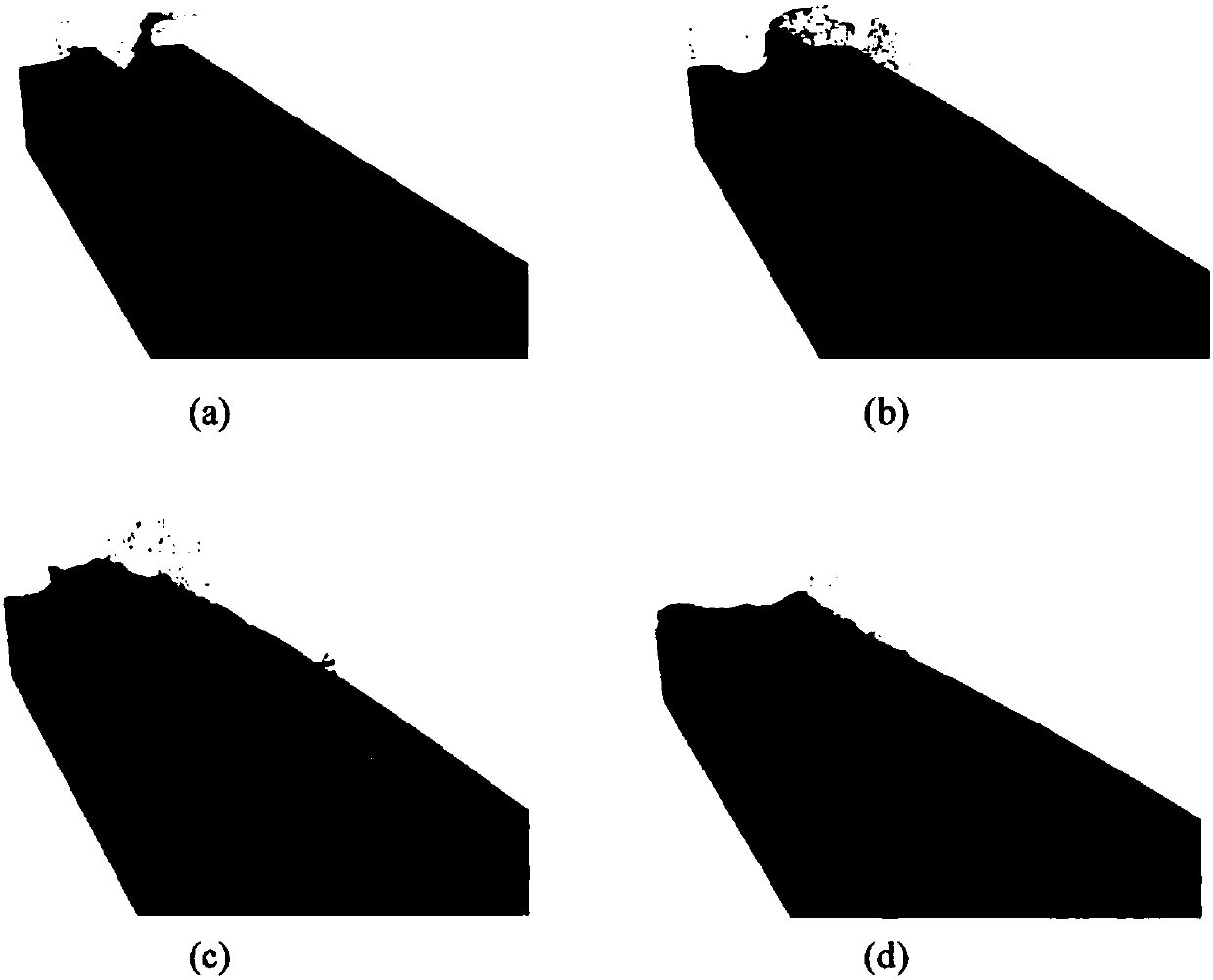
Method for analyzing stability of soil slopes and landslide movement procedures on basis of SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics) processes
ActiveCN108334719AGet range of influenceGet depthDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsInstability
The invention discloses a method for analyzing the stability of soil slopes and landslide movement procedures on the basis of SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics) processes. The method has the advantages that safety coefficients of the slopes and latent slide planes can be computed by the aid of the method, the landslide procedures after slope instability further can be analyzed by the aid of themethod, and indexes of influence ranges, submerged depths, impact force and the like after slope instability landslide further can be acquired; the stability of the slopes prior to instability can beanalyzed by the aid of the method, two instability criteria are proposed, accordingly, the safety coefficients of the slopes and the latent slide planes can be effectively acquired, and instability slide regions can be automatically computed by the aid of the method on the premise that slide planes (or slide ranges) are not specified in advance.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
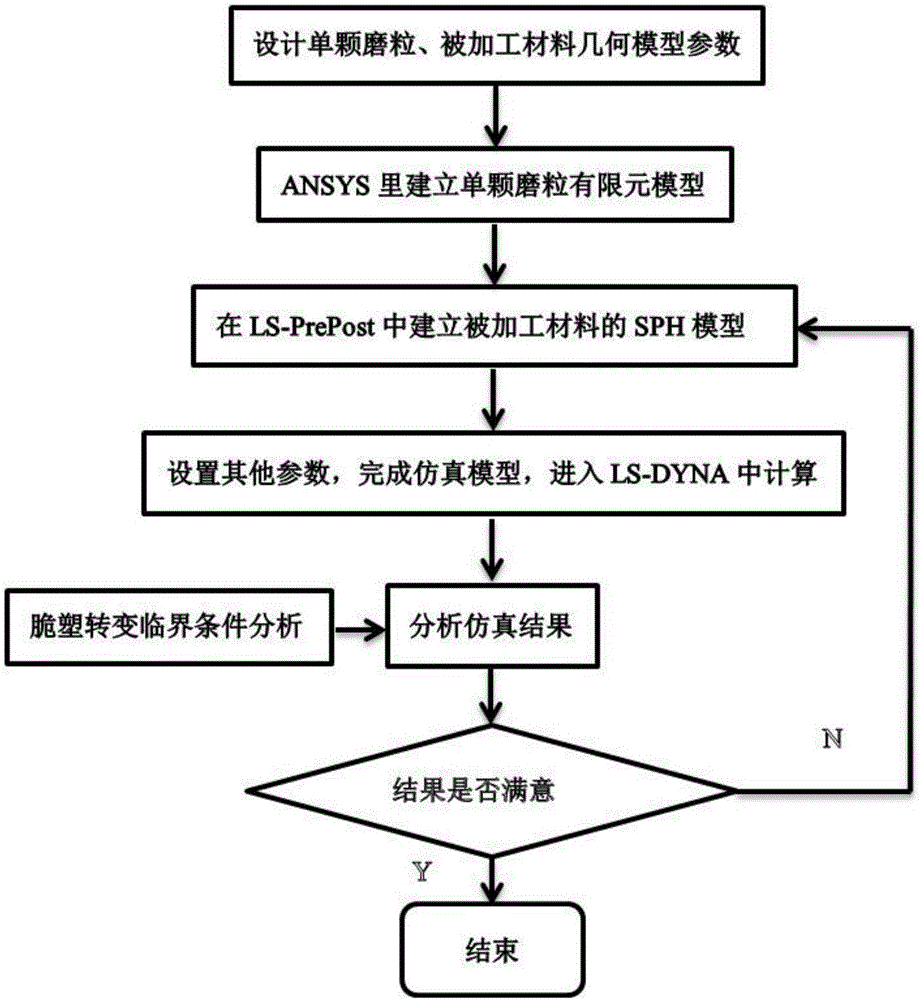
Brittle material grinding process modeling simulation method
InactiveCN106650021AAvoid the difficult problem of online observationImprove surface qualityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMicro nanoSmoothed-particle hydrodynamics
The invention discloses a brittle material grinding process simulation method, belongs to the field of micro-nano ultraprecision machining numeric simulation, and relates to a three-dimensional micro-nano single grain grinding simulation method based on a smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. The method comprises the steps of firstly setting the sizes of a grinding grain and a machined material; secondly, building a three-dimensional single grinding grain finite element model in ANSYS, building an SPH model of a workpiece material in LS-PrePost, setting related model parameters, and performing calculation in LS-DYNA; and finally, analyzing a simulation result. According to the simulation method, data such as a stress, a strain, density and the like in the grinding process can be obtained more clearly and accurately; a brittle material is removed in a plastic region by controlling a processing depth, and a damage mechanism of the brittle material is analyzed, so that relatively ideal surface quality is obtained; and a large amount of labor costs, experimental costs and economic costs are reduced and the difficult problem of difficult online observation of an experimental method is avoided.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
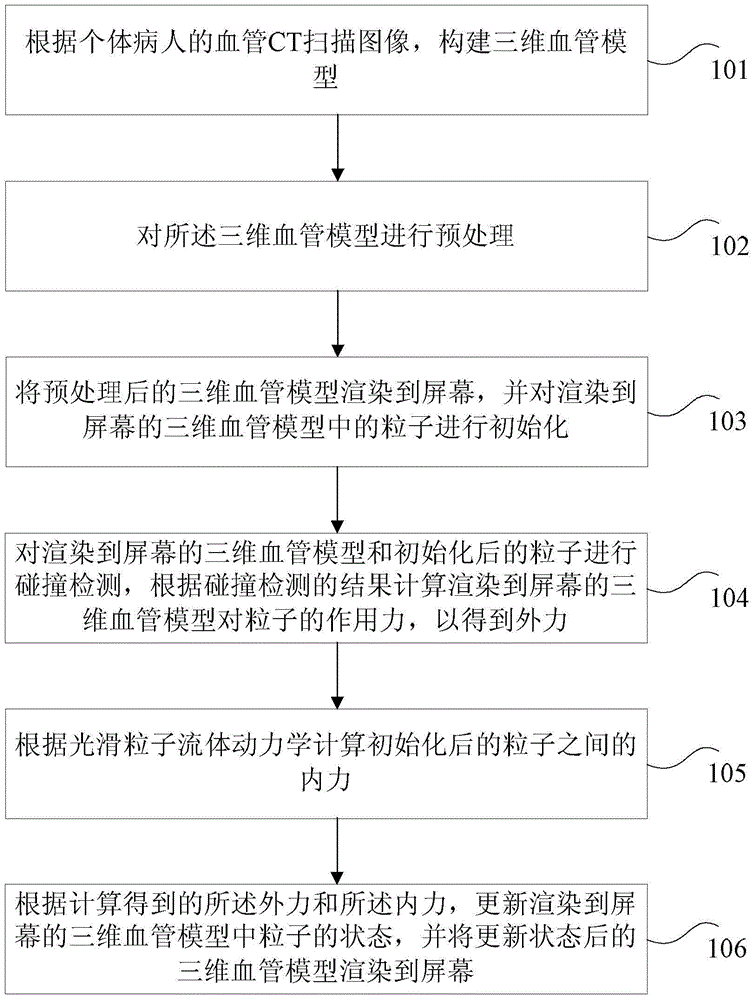
Method and device for simulating diffusion process of contrast agent
ActiveCN104574503AImprove accuracySave computing space3D-image rendering3D modellingSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsMedicine
The invention provides a method and device for simulating a diffusion process of a contrast agent. The method comprises steps as follows: a three-dimensional blood vessel model is built according to a blood vessel CT scanning image; the three-dimensional blood vessel model is pre-processed; the pre-processed model is rendered to a screen, and particles are initialized; the three-dimensional blood vessel model rendered to the screen and the initialized particles are subjected to collision detection, the action force of the three-dimensional blood vessel model on the particles is calculated according to a collision detection result to obtain external force; internal force among the initialized particles is calculated according to smoothed particle hydrodynamics; the state of the particles in the three-dimensional blood vessel model rendered to the screen is updated and rendered to the screen. The method and device solve the technical problems of large calculation amount, difficulty in acquisition of parameters and low authenticity of a simulation effect with a conventional method for simulating the diffusion process of the contrast agent in the prior art, and realize the technical effects of good instantaneity, high simulation effect accuracy and simple simulation process.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantitative analysis method of slope instability consequence
ActiveCN109359361AEffective Disaster Prevention Cost BudgetDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsInstability
A quantitative analysis method of slope instability consequence is disclosed. At first, that critical slip surface is calculated by the limit equilibrium method, Secondly, the displacement field of the landslide is calculated by using the smooth particle hydrodynamics method, and then the effective displacement threshold is determined by comparative analysis, Then a series of slope instability conditions are used to fit the relationship between the final sliding surface area of slope instability and its safety factor, Finally, the sliding area under the condition of safety factor less than 1is calculated by using the fitting relationship, and the sliding surface area histogram is used to quantify the consequences of slope instability, which overcomes the shortcomings of the traditional method, such as poor quantification effect of slope instability consequences, and can reasonably and effectively quantify the consequences of slope instability, which is of great significance for the prevention and control of landslide risk.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Physical and non-physical mixture-based complex scene fluid-solid coupling efficient simulation method
InactiveCN108491619AEnsure incompressibilityRich detail effectDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsFracture mechanics
The invention discloses a physical and non-physical mixture-based complex scene fluid-solid coupling efficient simulation method. The method comprises the steps of 1) performing incompressible fluid simulation, combining an Euler method and a Lagrange method, and proposing an implicit particle method-based zero-divergence smooth particle fluid dynamics method; 2) performing dynamics problem solving in fluid-solid coupling, subdividing a motion problem of a simulation object into three sub-problems according to object attributes, and solving the three sub-problems by using different methods respectively to realize a multi-dimensional classification combination computing framework; and 3) combining a strain energy density concept in fracture mechanics with Voronoi spatial segmentation to realize a physical perception-based crushing method. The simulation efficiency problem difficult to solve in complex fluid-solid coupling scene simulation is solved. Compared with a conventional fluid-solid coupling method, the method can simulate a fluid scene with richer details under the same system resources, and can meet the demand of simulating solid crushing under fluid impact.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
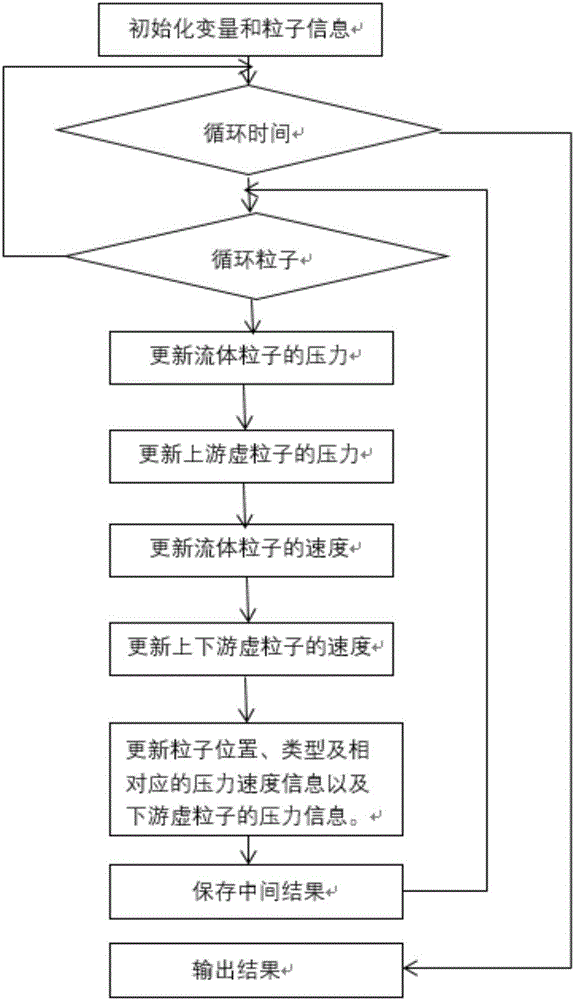
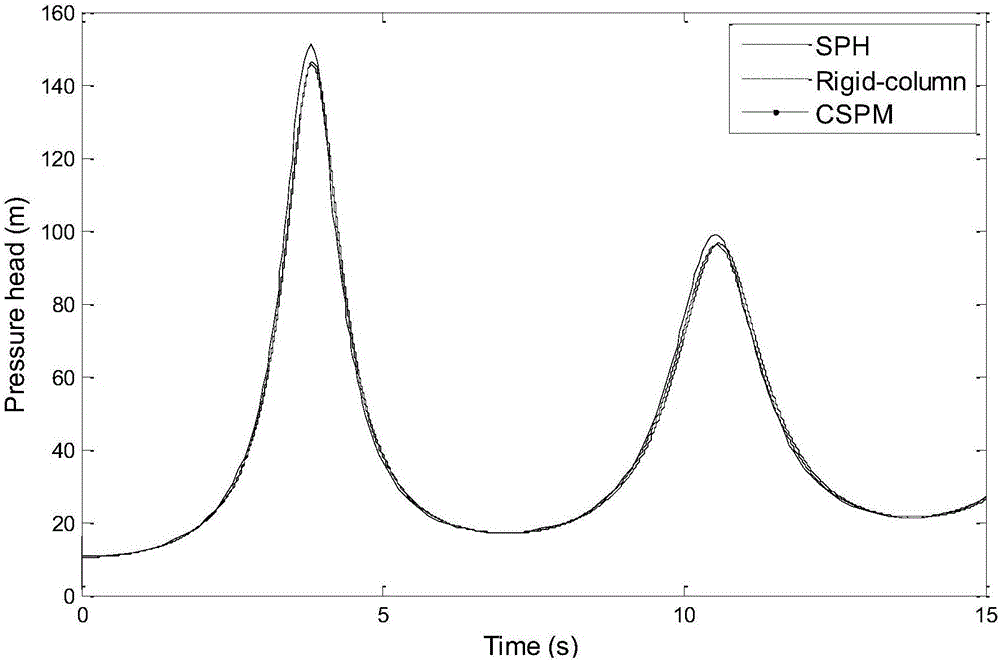
Meshless particle method for analyzing trapped air mass-containing transient pipe flow
InactiveCN106570308AHigh simulationReduce mistakesSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsCompressibility
The invention discloses a meshless particle method for analyzing trapped air mass-containing transient pipe flow. The meshless particle method comprises the following steps of (1) initializing relevant variable and particle information; (2) carrying out iterative computation, namely circulating a time variable, circulating particles, calculating pressure information of fluid particles of the initialized particles and updating the pressure information of the fluid particles, the pressure information of upstream virtual particles, speed information of the fluid particles, speeds of upstream and downstream virtual particles, particle positions and corresponding pressure and speed information and the pressure information of downstream virtual particles; and (3) outputting the result. A water hammer equation under a lagrange system is solved by adopting a smoothed particle hydrodynamics method; the influences caused by movement of a gas-liquid interface and weak compressibility of water are fully considered; various errors caused by interpolation and gas-liquid interface tracking technologies are reduced; and the trapped air mass-containing transient pipe flow can be more conveniently simulated on the premise of meeting the numerical precision.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
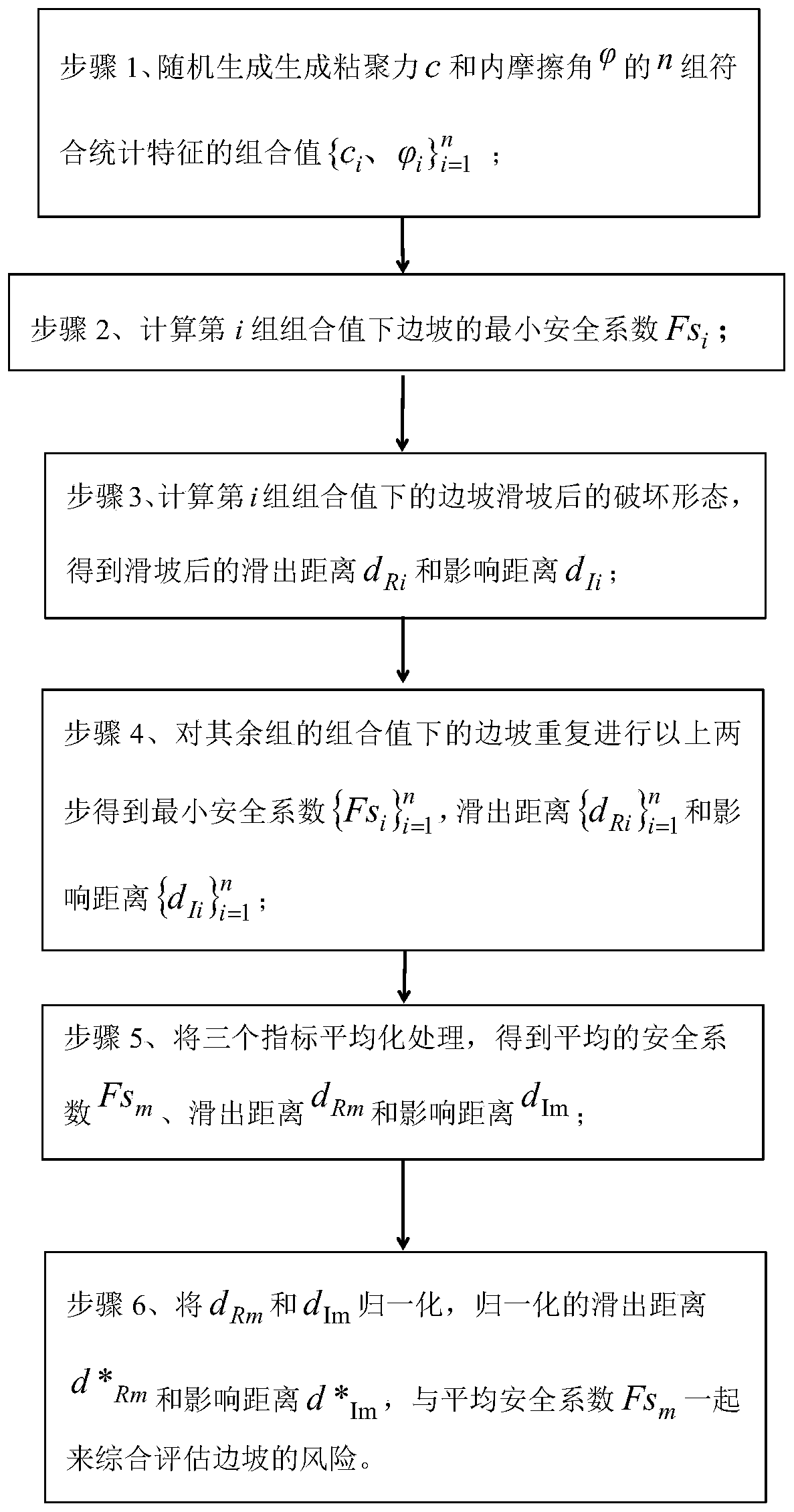
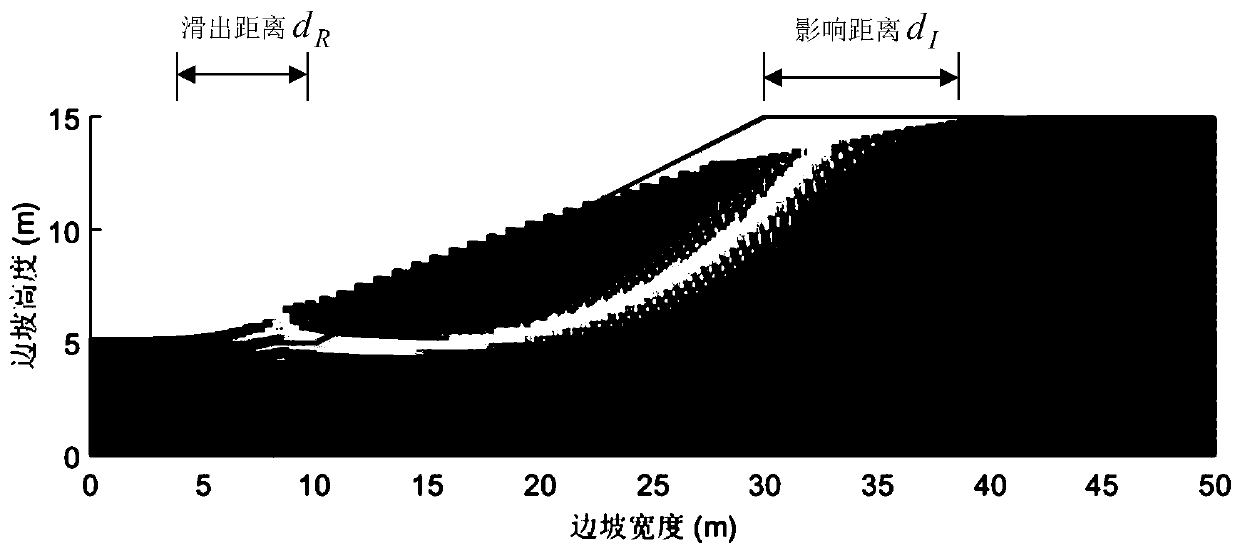
Slope risk comprehensive evaluation method based on landslide failure form
InactiveCN110765614AIntuitive Risk AssessmentReasonable risk assessmentDesign optimisation/simulationResourcesSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsClassical mechanics
The invention belongs to the field of slope stability and risk evaluation, and particularly relates to a slope risk comprehensive evaluation method based on a landslide failure form, which comprises the following steps: randomly generating n groups of combined values conforming to statistical characteristics according to the statistical characteristics of cohesive force c and an internal frictionangle, and recording the n groups of combined values as the ith group of combined values to obtain the minimum safety factor Fsi of a slope; analyzing the slip-off distance dRi and the influence distance dIi of the slope under the ith group of combined values by using a smoothed particle hydrodynamics method; making i= i + 1, repeating the previous two steps, and obtaining the minimum safety coefficient, the sliding-out distance and the influence distance of the slope under all the combined values; averaging to obtain an average safety coefficient, slip-off and influence distance; and calculating a normalized slide-out distance and an influence distance according to the positions of the slope crest and slope bottom structures, and comprehensively evaluating the landslide risk together withthe average safety coefficient. The smooth particle hydrodynamic method is introduced, and the slope stability and risk are evaluated more visually and reasonably by using the slip-off distance and the influence distance and combining the classical limit equilibrium method.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
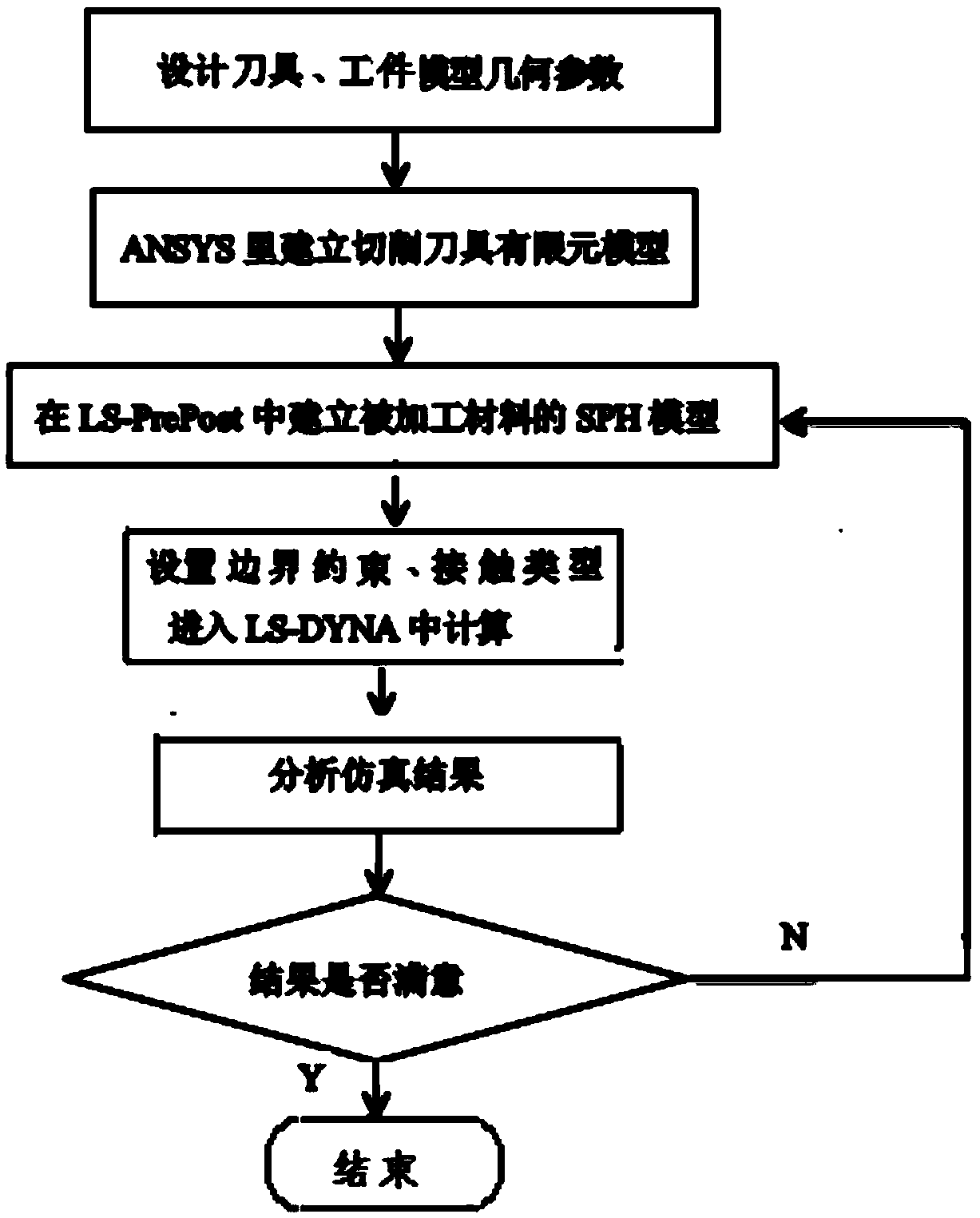
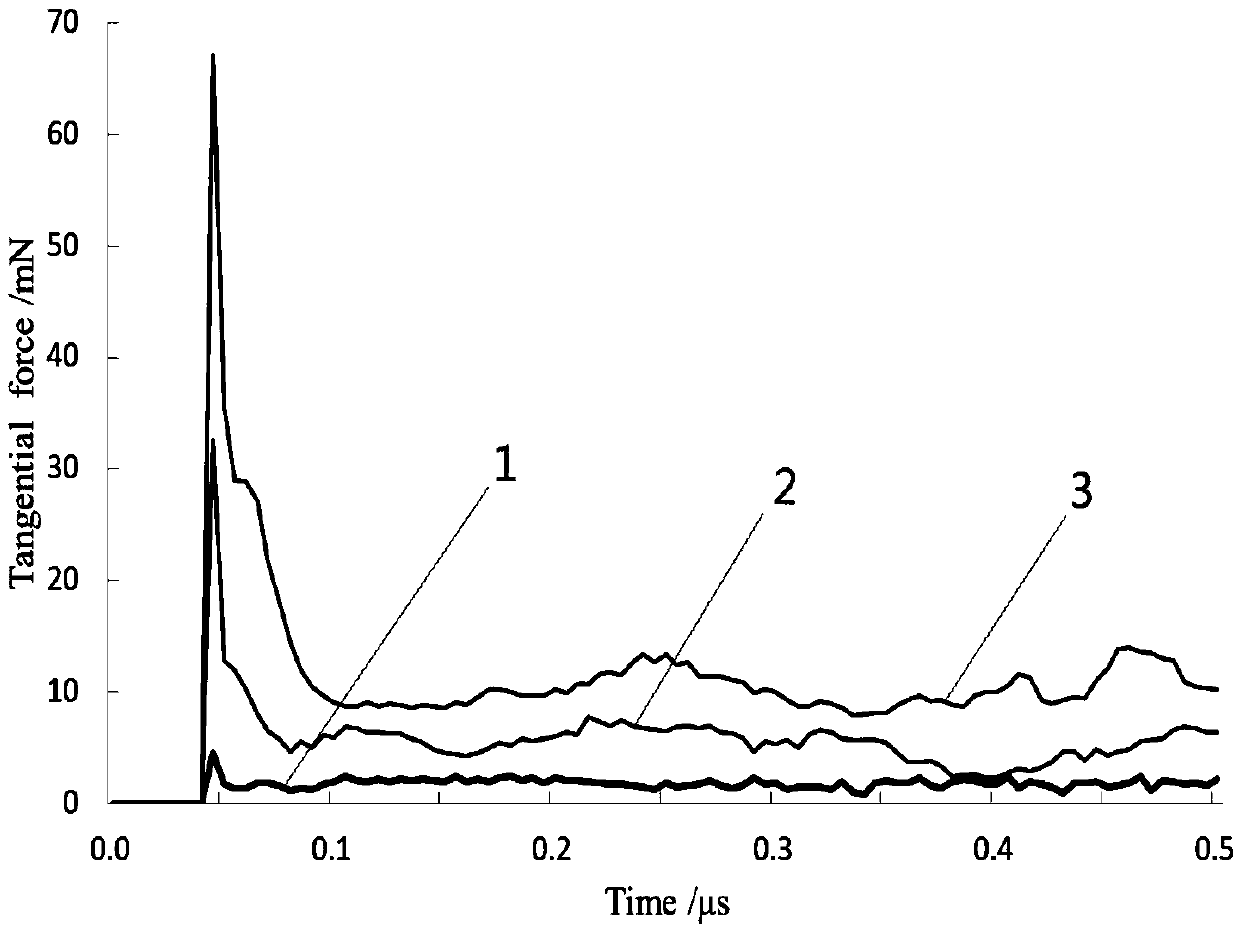
Cutting process simulation process for brittle materials
InactiveCN105512400AAvoid the difficult problem of online observationImprove surface qualitySpecial data processing applicationsMicro nanoSmoothed-particle hydrodynamics
The invention provides a cutting process simulation process for brittle materials, belongs to the field of micro-nano ultraprecision machining numerical simulation and relates to a three-dimensional micro-nano cutting machining simulation method based on an SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics) method. According to the simulation method, dimensions of a cutter and a workpiece material are set firstly; then a three-dimensional cutter finite element model is established in ANSYS, an SPH model of the workpiece material is established in LS-PrePost, parameters of contact, boundary, the material and the like are set, and calculation is performed in LS-DYNA; finally, a simulation result is analyzed, and whether the result meets the actual machining condition is judged. The simulation method has the advantages that data including stress, strain, density and the like in a cutting machining process can be obtained more clearly and more accurately, the brittle materials are removed from a ductile region through control of cutting depth, and acquisition of more ideal surface quality is more facilitated. A large quantity of labor cost, experimental cost and economic cost is saved, and the problem of on-line observation difficulty of an experimental method is solved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Melting phenomenon reality simulation method based on physics
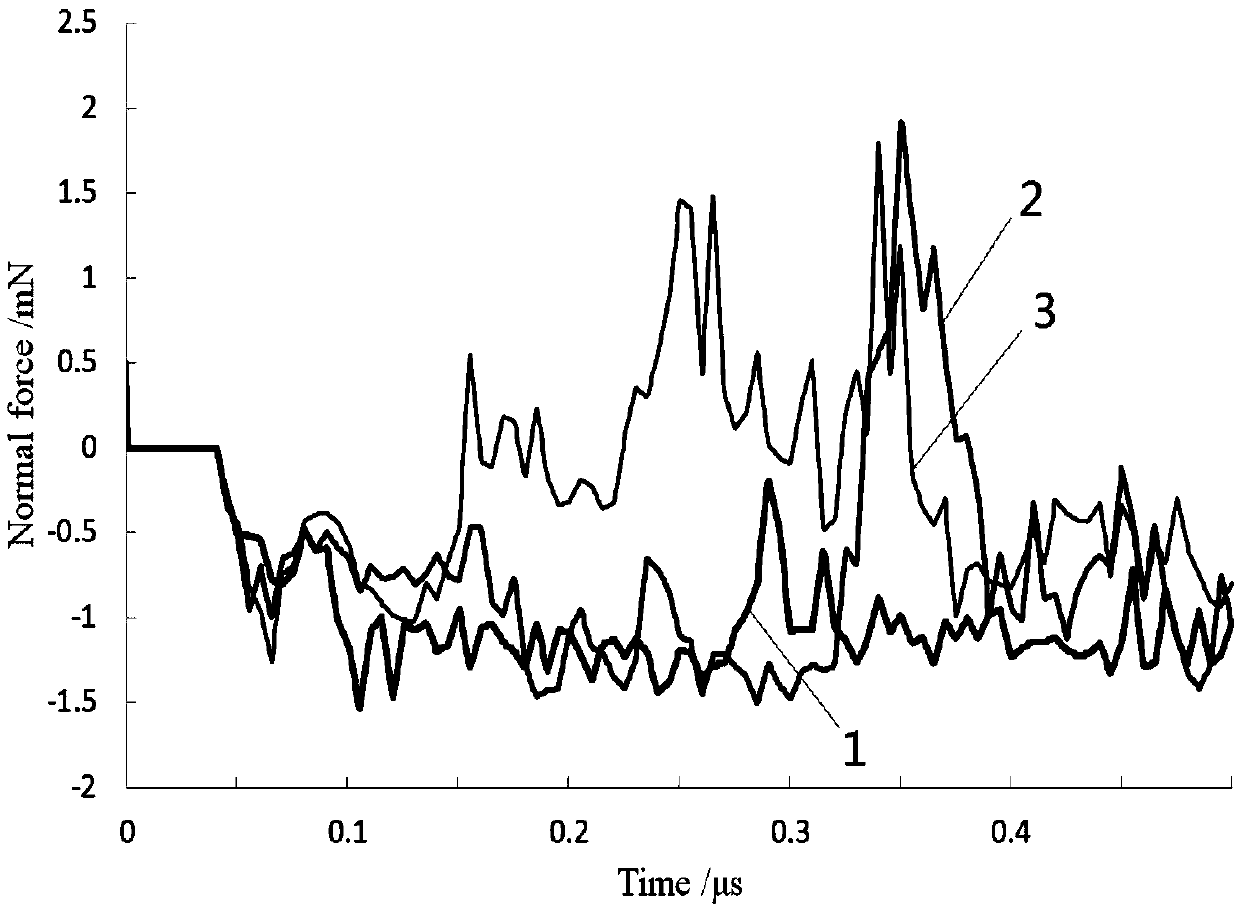
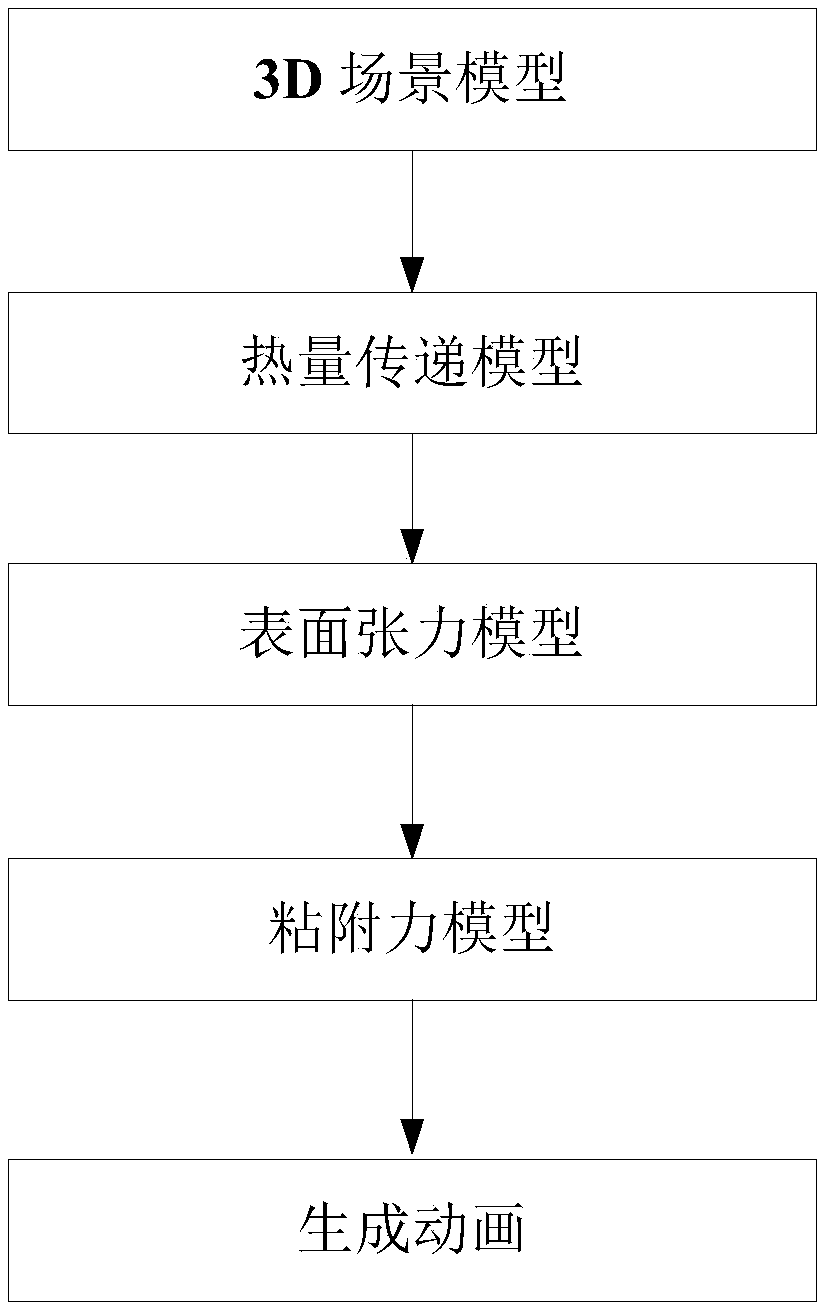
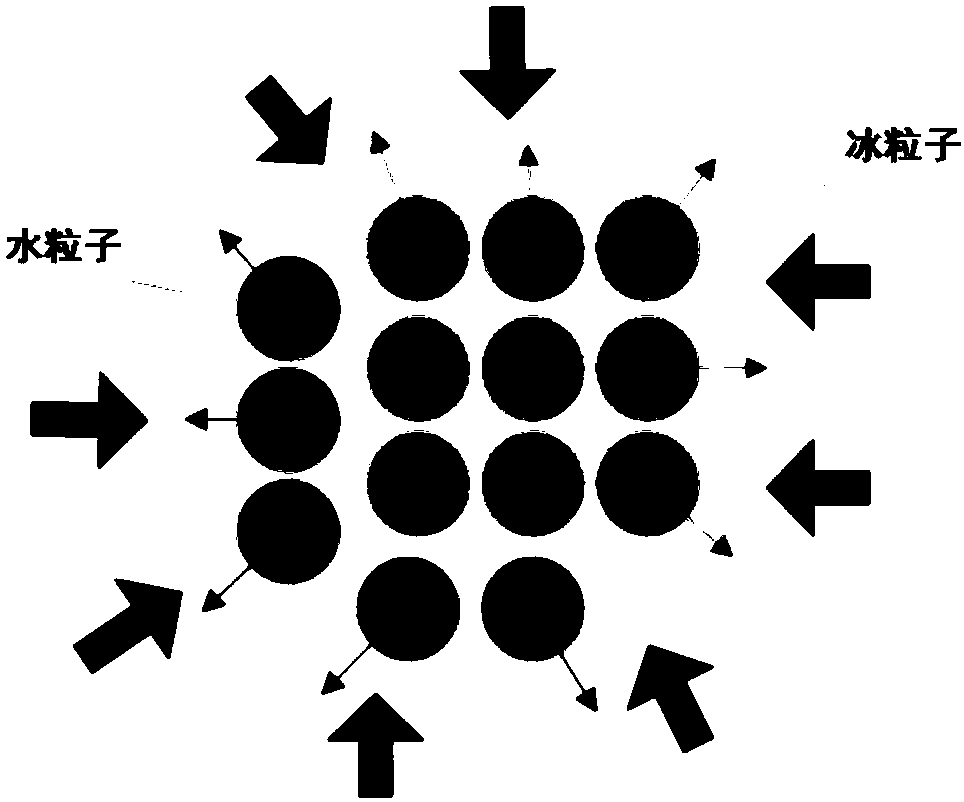
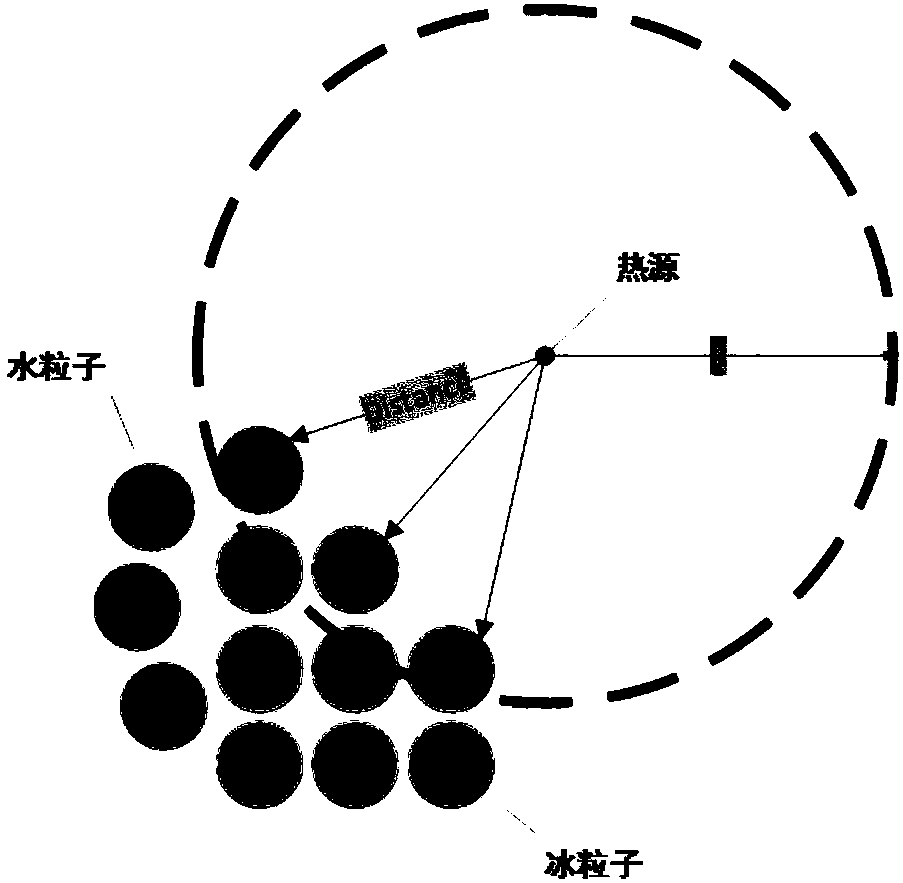
ActiveCN107798198AReduce complexityReduce consumptionDesign optimisation/simulationAnimationSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsLiquid state
The invention relates to a melting phenomenon reality simulation method based on physics. The melting phenomenon reality simulation method is suitable for modeling of a melting phenomenon in the natural world and comprises the steps that 1, the solid-to-liquid particle relation, heat transfer model, heat source radiation temperature model calculation mode of an object are established according toa particle model; 2, a liquid drop surface tension model is calculated by using a smooth particle fluid dynamical model and an interface theory of mechanics; 3, after liquid drops are generated, an adhering strength model when flow exists between the liquid drops and a solid also needs to be established so as to complete real flow of the liquid drops, and then a real effect is drawn. By adopting the melting phenomenon reality simulation method, a melting phenomenon protecting details can be quickly obtained, and the heat transfer model, a surface tension model constraining liquid drop behaviors and the adhering strength model embodying melting flow, which are needed for object melting, are designed. The melting phenomenon reality simulation method can achieve reality simulation of common object melting scenes, is simple and good in stability and has a certain practical value.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
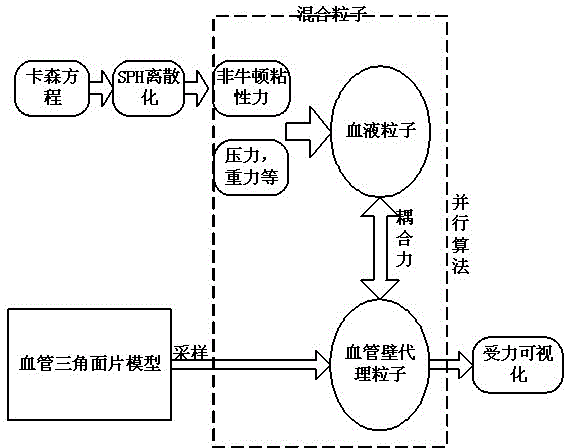
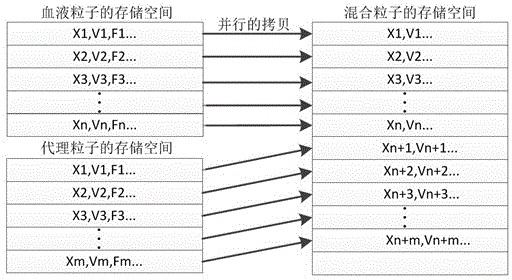
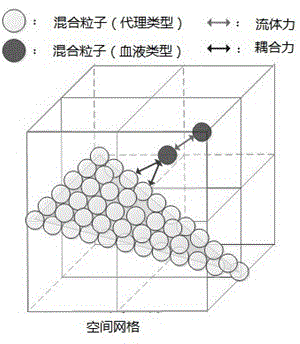
GPU (graphics processing unit) acceleration based real-time hybrid particle blood flow-blood vessel coupling method
InactiveCN104462830AGuaranteed coupling effectReal coupling effectSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsGraphics
The invention discloses a GPU (graphics processing unit) acceleration based real-time hybrid particle blood flow-blood vessel coupling method. According to the method, a Casson equation is solved in a discretized mode by an SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics) method, and further non-Newtonian viscosity force of blood is solved; a layer of surrogate particles are sampled on the blood vessel wall by referring to a classical surrogate particle based boundary processing method in graphics, and coupling force applicable to the surrogate particles and blood particles is defined; the surrogate particles and the blood particles are merged into hybrid particles, and acting force between each pair of mutually neighboring hybrid particles is calculated uniformly in a GPU so as to realize blood flow-blood vessel coupling; force data of the surrogate particles are mapped to colors of the surrogate particles for display to realize blood vessel force visualization. By the viscosity force solving method, authenticity in blood modeling is enhanced, the coupling method is quick and effective, authenticity and real-time performance in coupling are guaranteed, the force visualization method is simple and direct, and rich information about blood vessel wall force distribution is provided.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
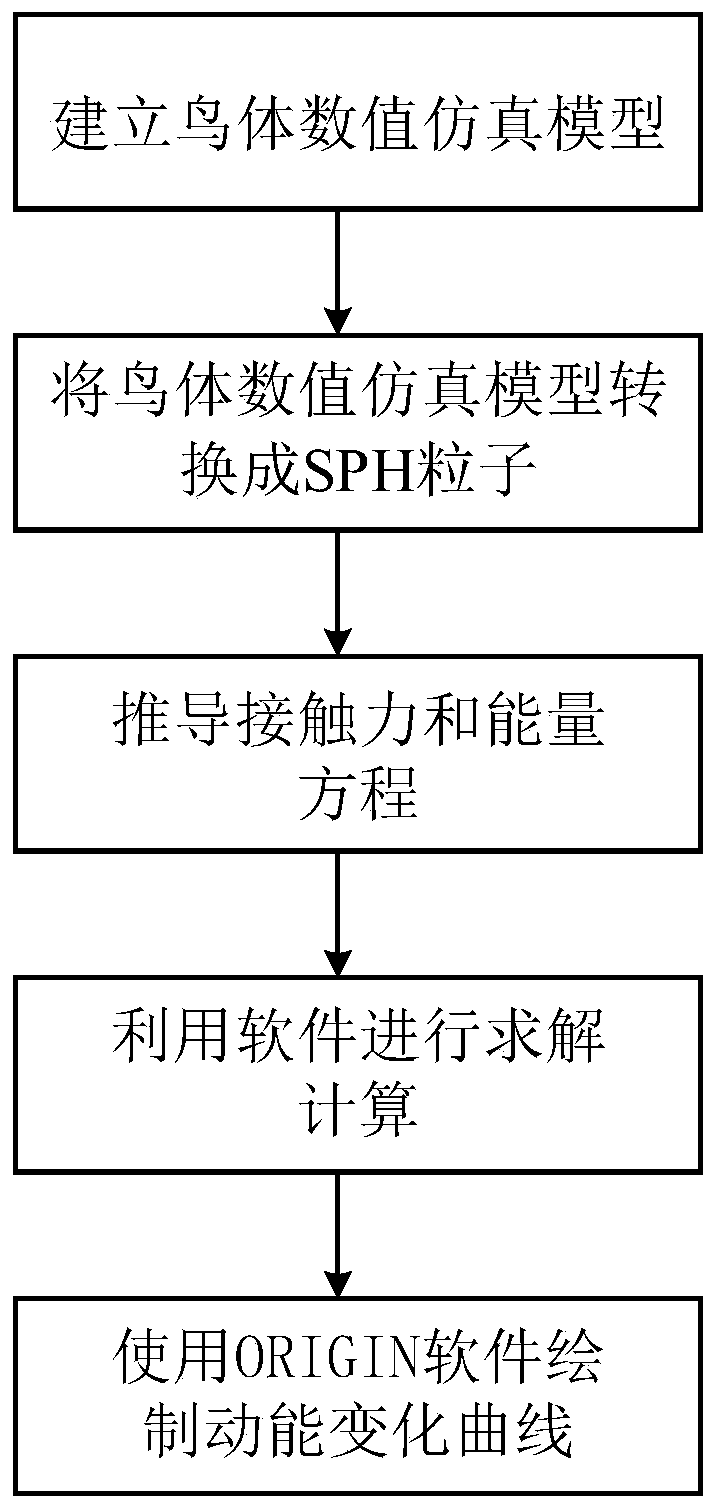
A method of calculating bird strike high speed rotation engine blade
The invention relates to a numerical simulation method for calculating response of bird strike on an engine blade. Based on a smooth particle method (Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics SPH) and a finiteelement method (Finite Element Method FEM), a numerical simulation model considering the impact environment factor influence of the bird body attitude angle is established, and dynamic response simulation is carried out under the model. In addition, technicians in the field can more simply modify different parameters for research in the bird impact dynamics response research process, and a reference basis is provided for research on the design and optimization of the aero-engine structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
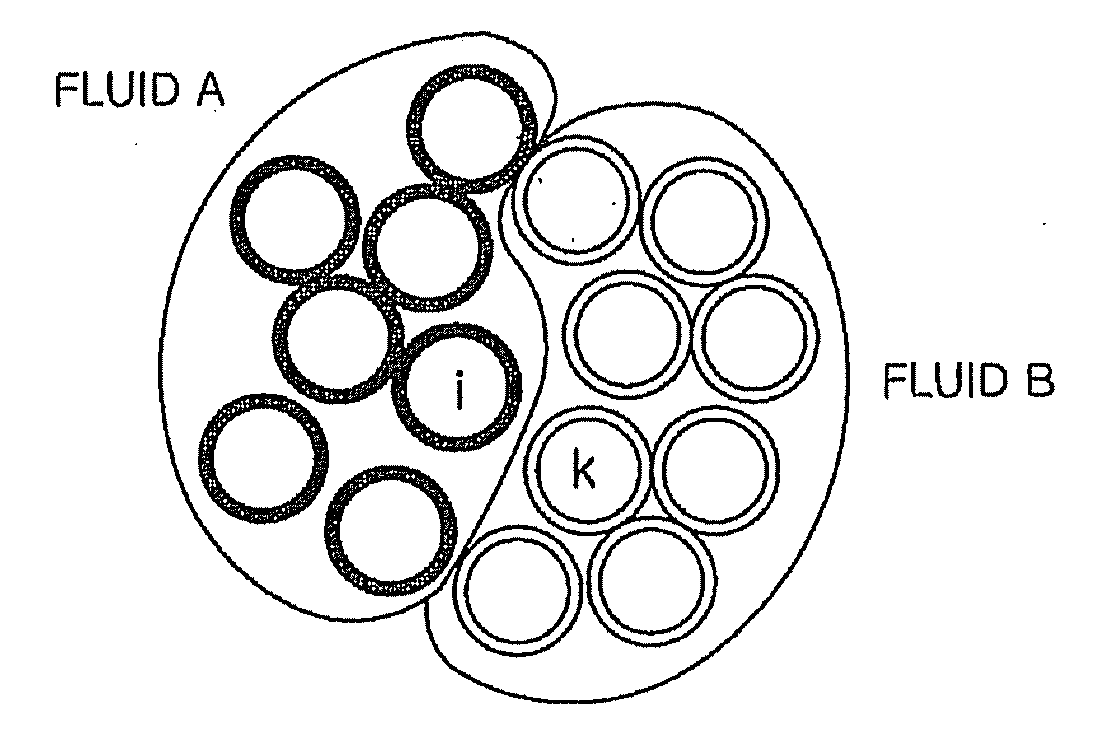
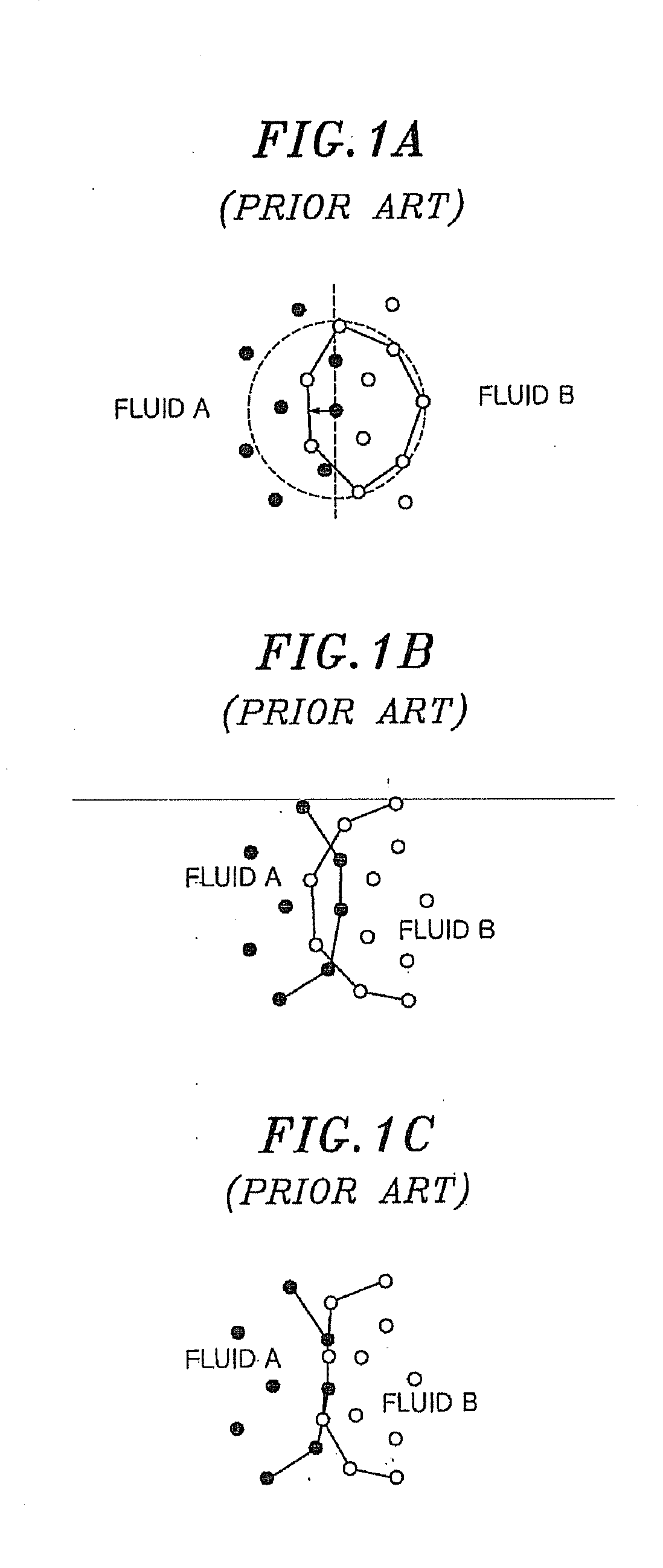
Method for calculating force acting on interface between immiscible fluids in fluid simulation
InactiveUS20100161298A1Realistic and excellent visualization resultReduced simulation timeComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsEngineering
A method for calculating a force acting on an interface between immiscible fluids in an SPH (Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics) based fluid simulation includes: calculating a force caused by viscosities of the fluids; calculating a force caused by pressures of the fluids; calculating an external force applied to the fluids from outside; and calculating an interactive force caused by interaction between the fluids. The force acting on the interface between the immiscible fluids are obtained by using sum of the force caused by the viscosities, the force caused by the pressures, the external force and the interactive force. The interactive force is a surface tensional force calculated based on a pressure acting on the interface between the fluids.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
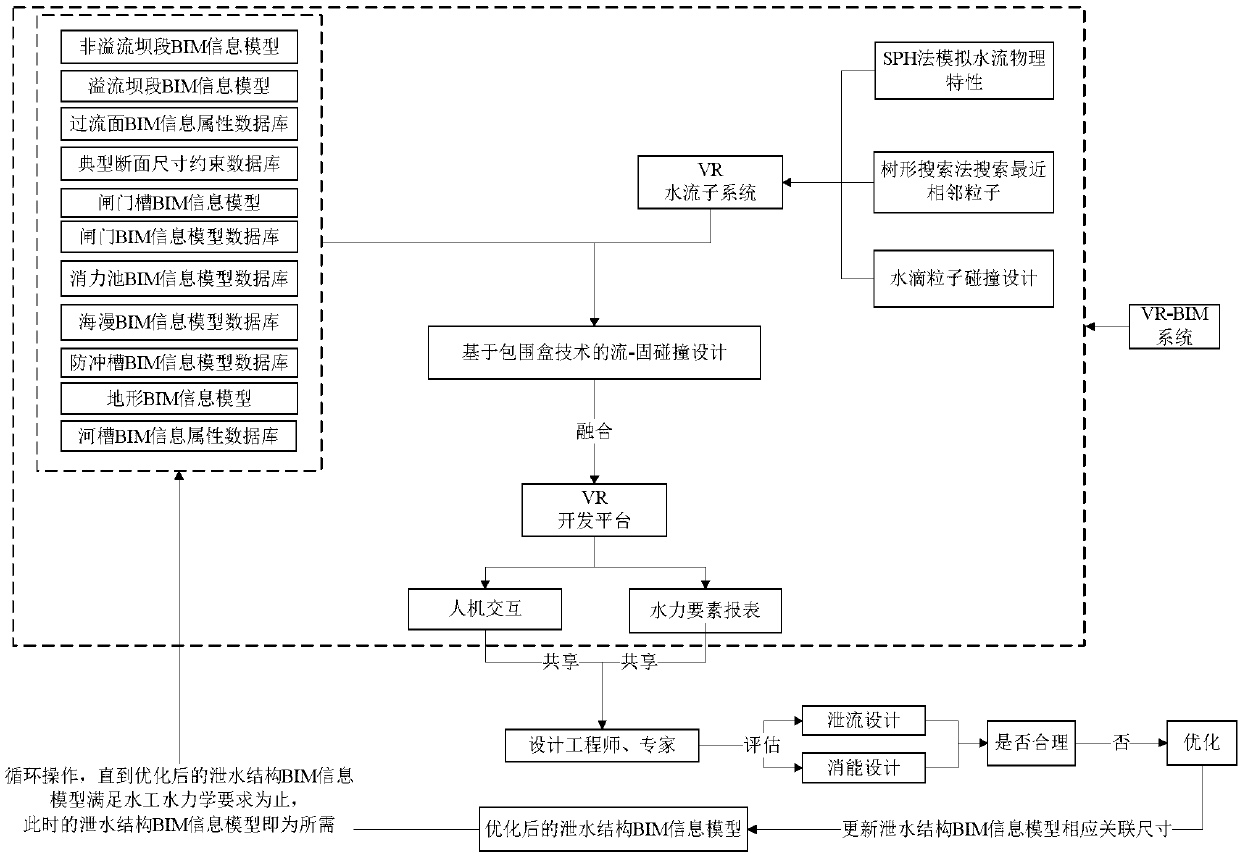
Optimization design method of drainage structure based on VR-BIM technology
InactiveCN108287979AOvercome the shortcomings of time-consuming and laborious testing, high cost, non-recyclable, etc.Improve design efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsTree shaped
The invention discloses an optimization design method of a drainage structure based on a VR-BIM technology. The innovative application of the VR-BIM technology in the field of drainage and energy dissipation structure design is achieved, according to the core of the method, water flow physical characteristics and water flow and structure collision characteristics are simulated in a VR platform, and a VR water flow subsystem is formed. According to the system, a smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method is used for simulating the water flow physical characteristics, a tree-shaped search method is used for searching for closest adjacent particles, and a condition is provided for simulation of interaction of water drop particles. Finally, in the VR platform, by using a fluid-solid collision design method based on a bounding box technology, a drainage structure BIM information model and a VR water flow subsystem which are generated at the primary design stage are fused into a VR-BIM system, and according to the water flow state in the system and hydraulics element distribution rules, whether or not the drainage and energy dissipation design is reasonable is judged. If not, corresponding optimization is conducted, and meanwhile the BIM information model is updated until the hydraulic engineering and hydraulics requirement is met.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
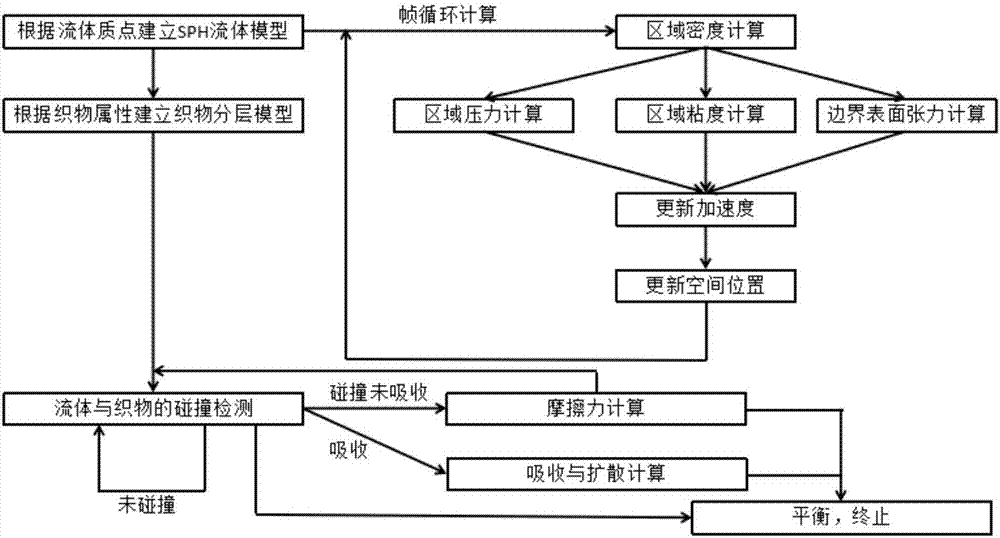
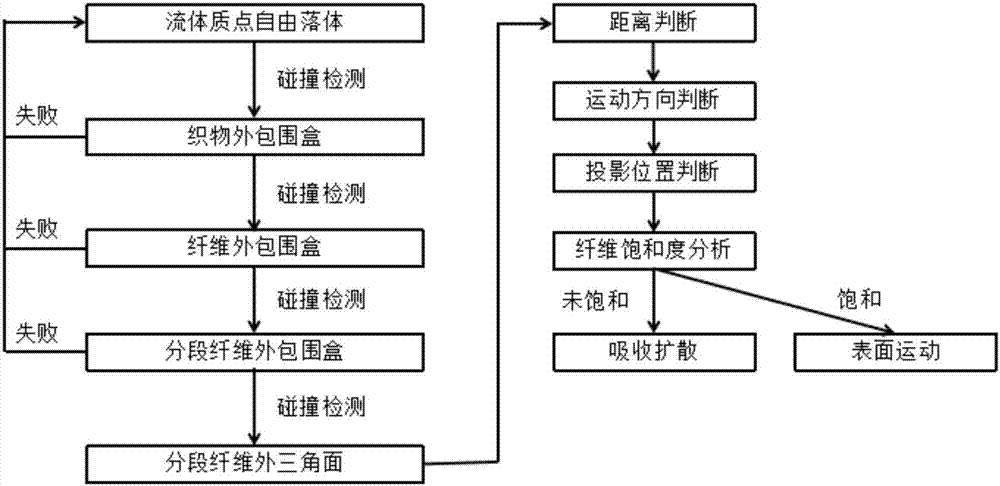
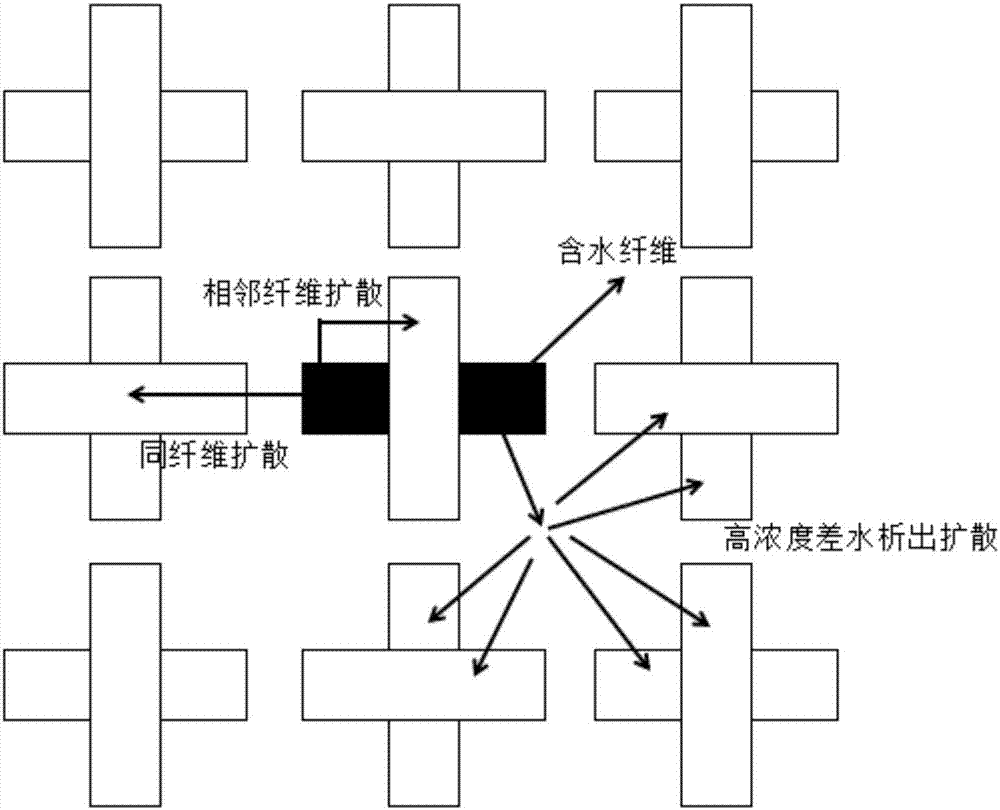
Fabric surface microcosmic water diffusion process visualization method based on SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics)
ActiveCN107025332ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDiffusionSmoothed-particle hydrodynamics
The invention discloses a fabric surface microcosmic water diffusion process visualization method based on SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics). The method comprises following steps: creating an SPH microcosmic water fluid; looking up space grids of the SPH microcosmic water fluid; acquiring surface tension and a contact angle based on the SPH microcosmic water fluid; designing a fabric structure; designing diffusion channels based on the fabric structure; designing collision and absorption of the microcosmic water fluid and fabric. From the point of the small-scale water fluid, the method is mainly specific to reactions between different small-scale fluids in a three-dimensional space and fabric made of different materials during contact as well as simulation of the diffusion process of fluid molecules in the fabric, and visualized display of results is performed.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com