Patents
Literature
535 results about "Strain energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
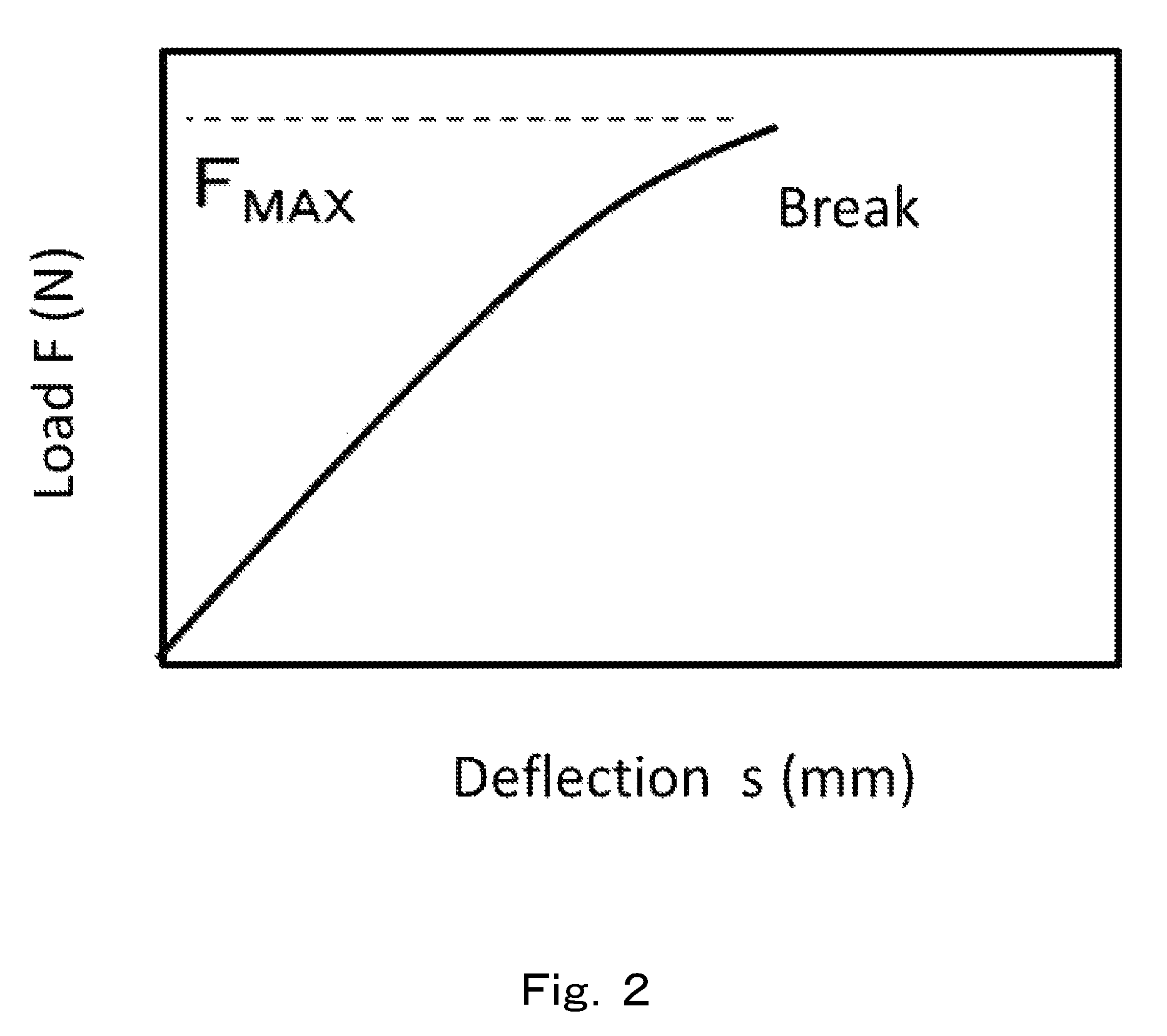
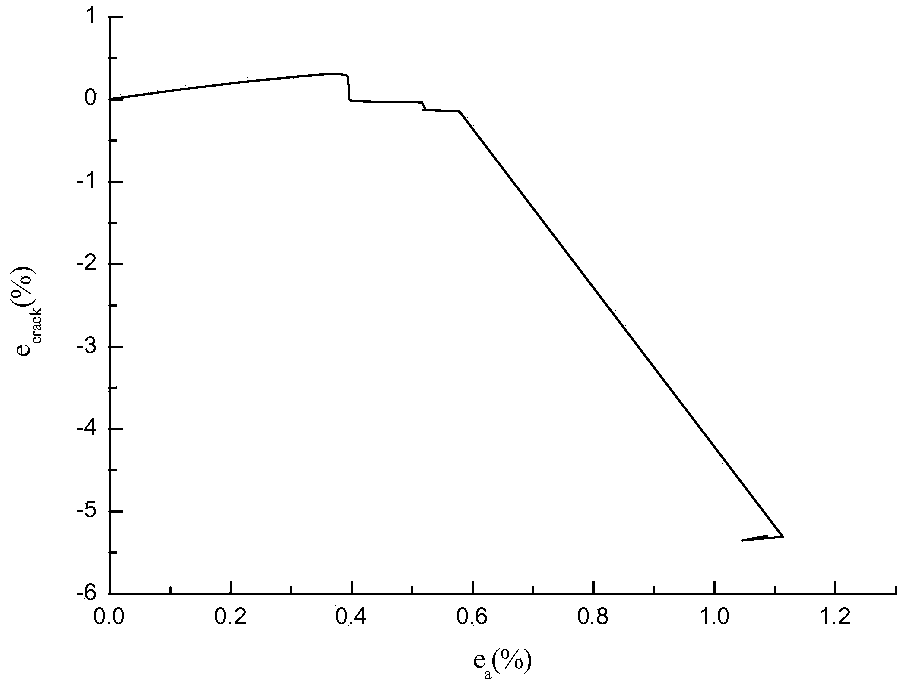
In physics, strain energy is the energy stored by a system undergoing deformation. For linearly elastic materials, strain energy is: U=1/2Vσε=1/2VEε²=1/2V/Eσ² where σ is stress, ε is strain, V is volume, and E is Young's modulus: E=σ/ε
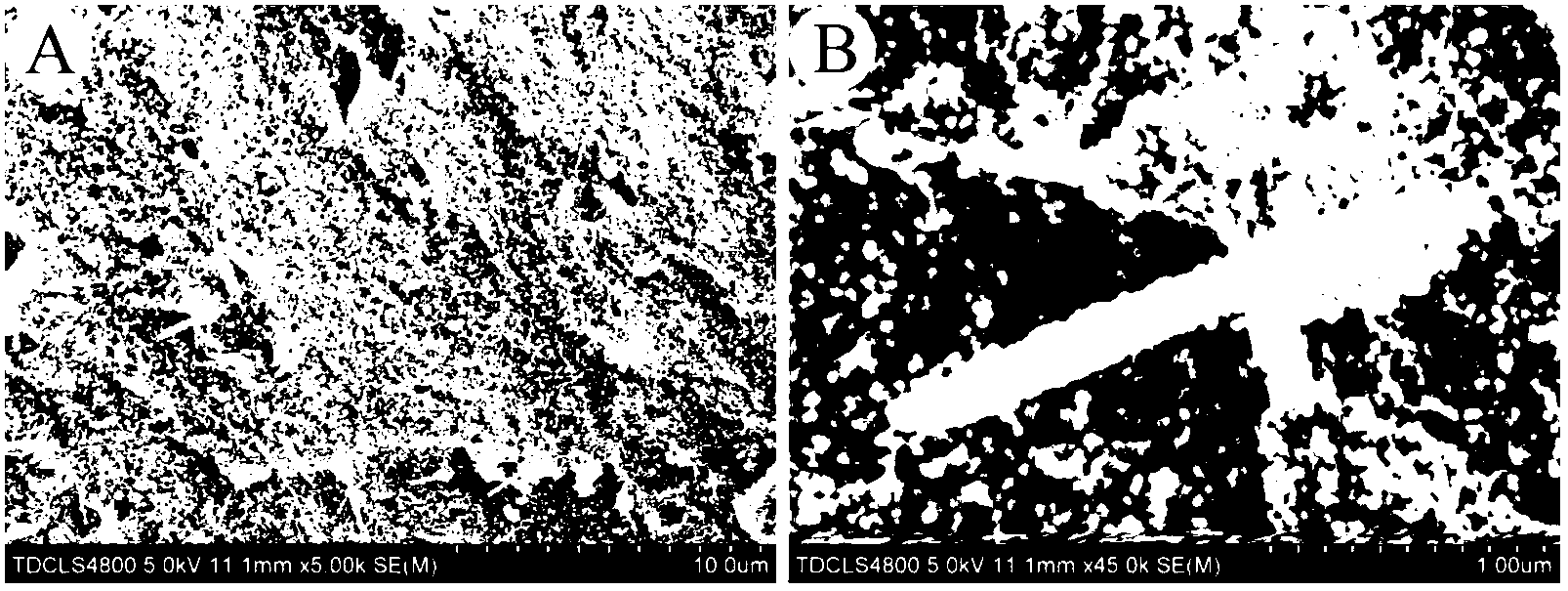
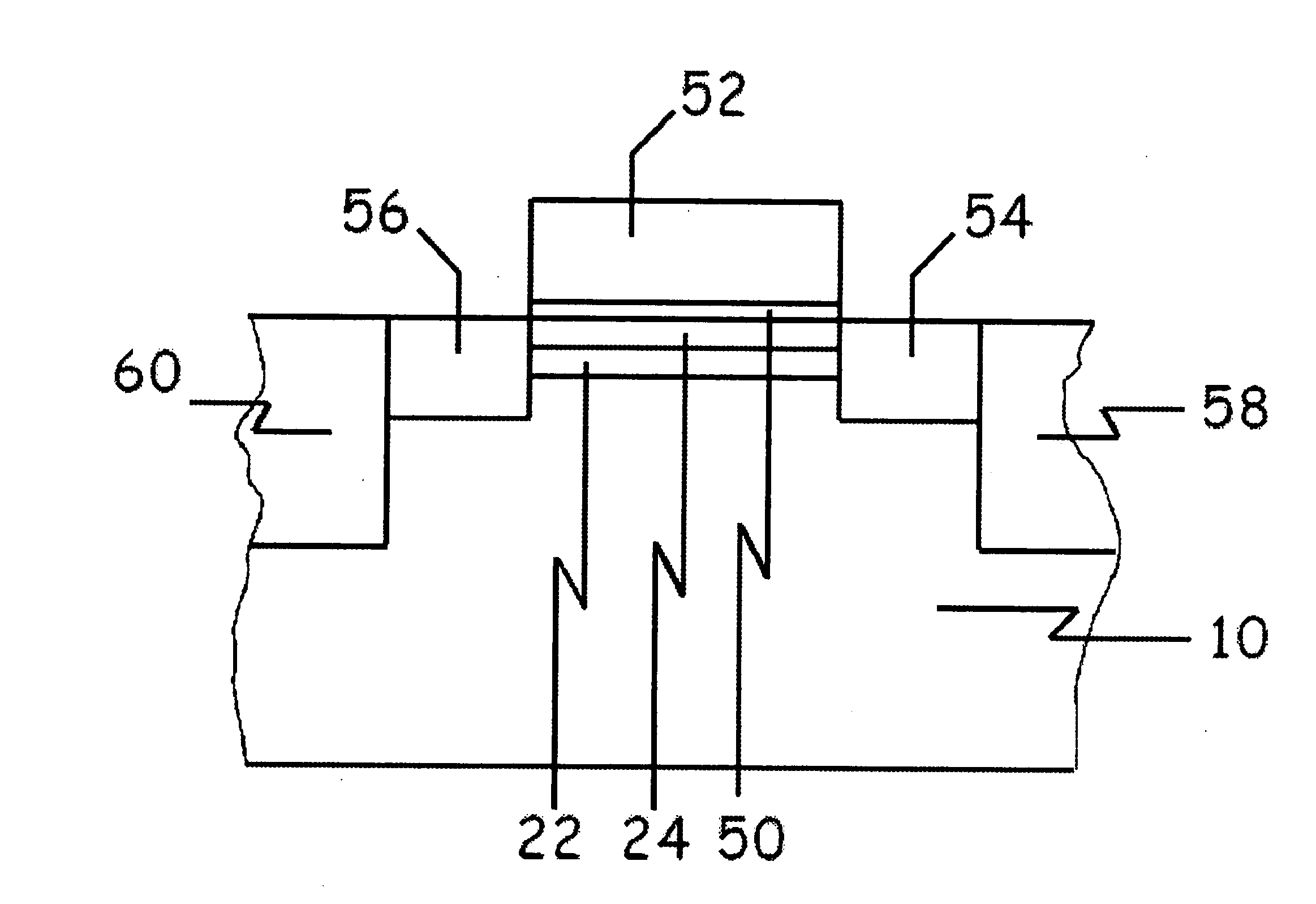
Method for cutting tempered glass plate
InactiveUS20150183679A1Precise cuttingGlass reforming apparatusGlass severing apparatusStrain energyToughened glass
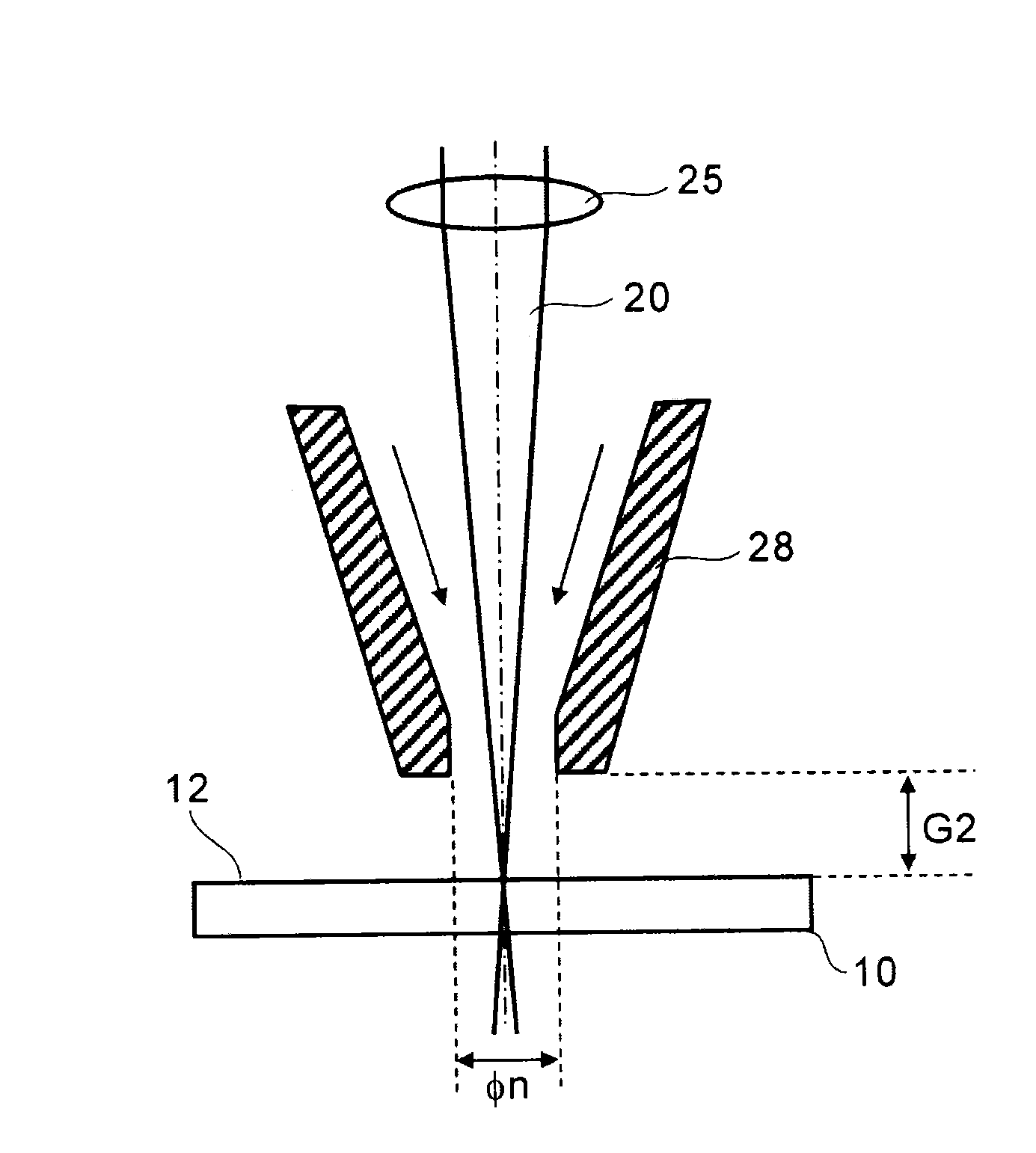
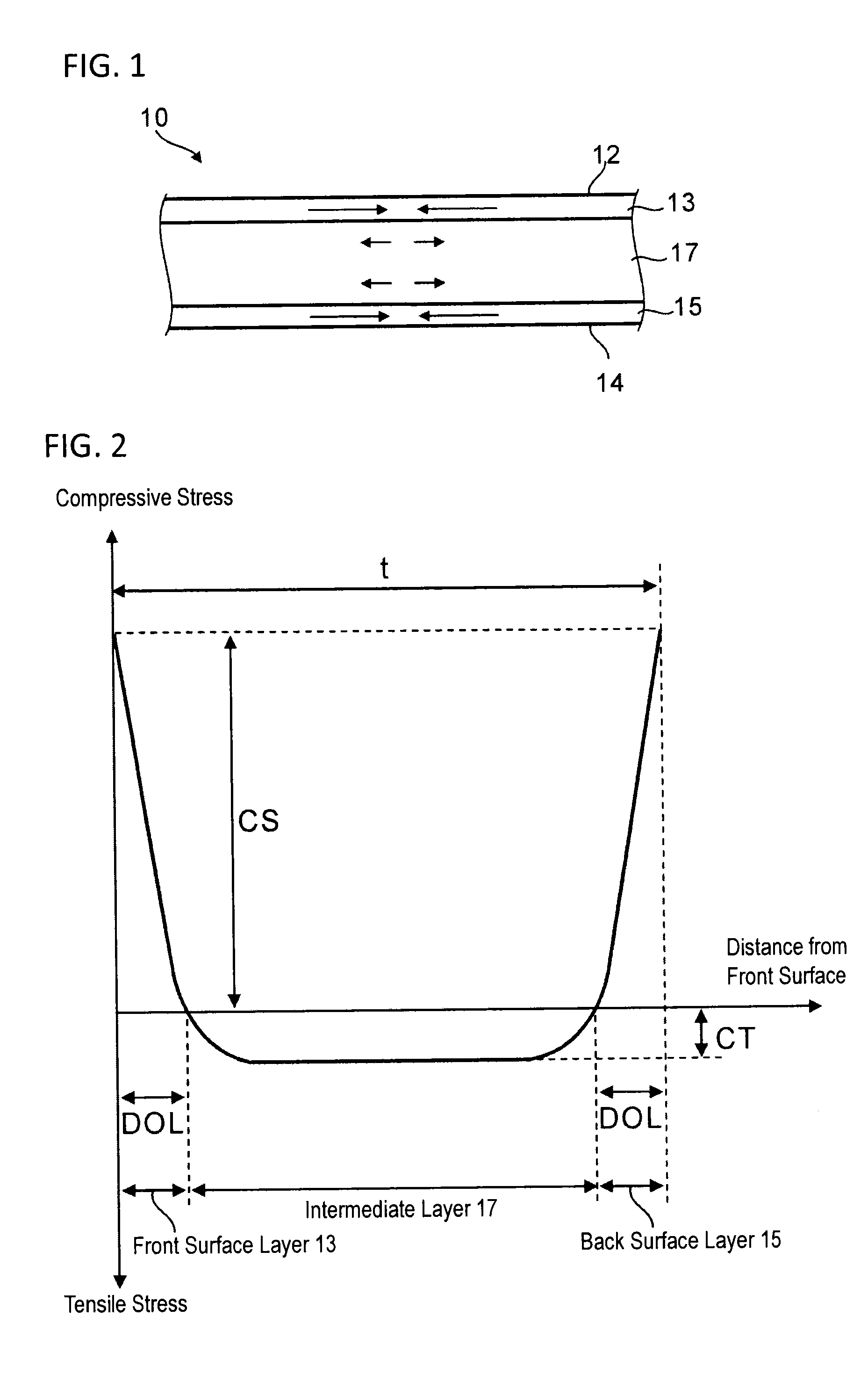
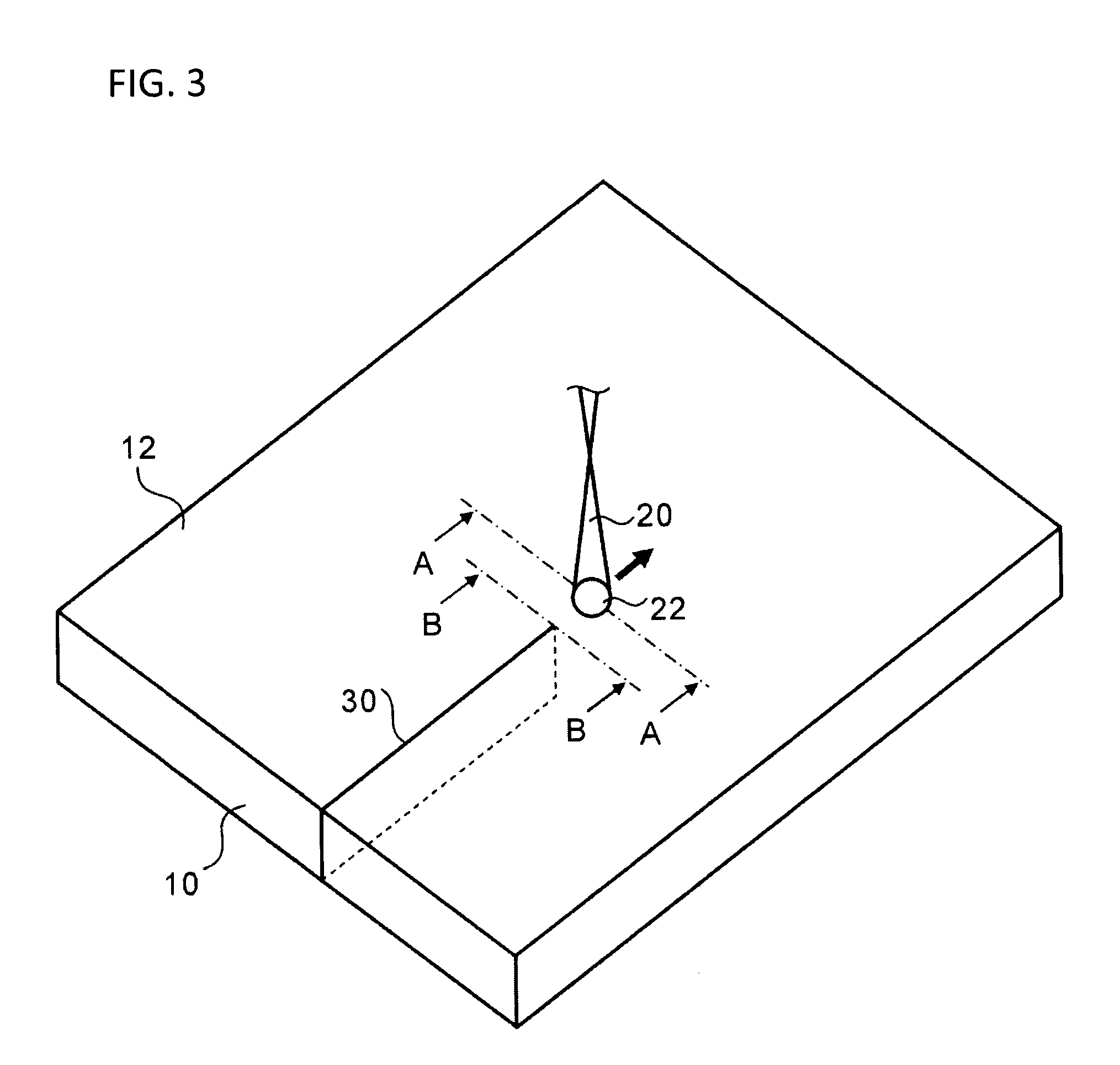
A method for cutting a strengthened glass sheet through laser irradiation. The sheet includes a front surface layer and back surface layer each having a residual compressive stress and an intermediate layer which is formed therebetween and has an internal residual tensile stress CT (MPa). A strain energy UCT (J / m2) expressed by UCT={CT2×(t1−2×DOL)} / (2×Y) is 2.5 J / m2 or more. A cutting index K (N / mm) expressed by K=Pe / v×exp(−α×t2)×(Y×αL) / (t2×ρ×c) is 150 N / mm or less.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
A lightweight forward design method and system for automobile structure based on multiple performance constraints
ActiveCN109063389AImprove the level of positive developmentSolve high time-consuming problemsGeometric CADInternal combustion piston enginesElement analysisStrain energy
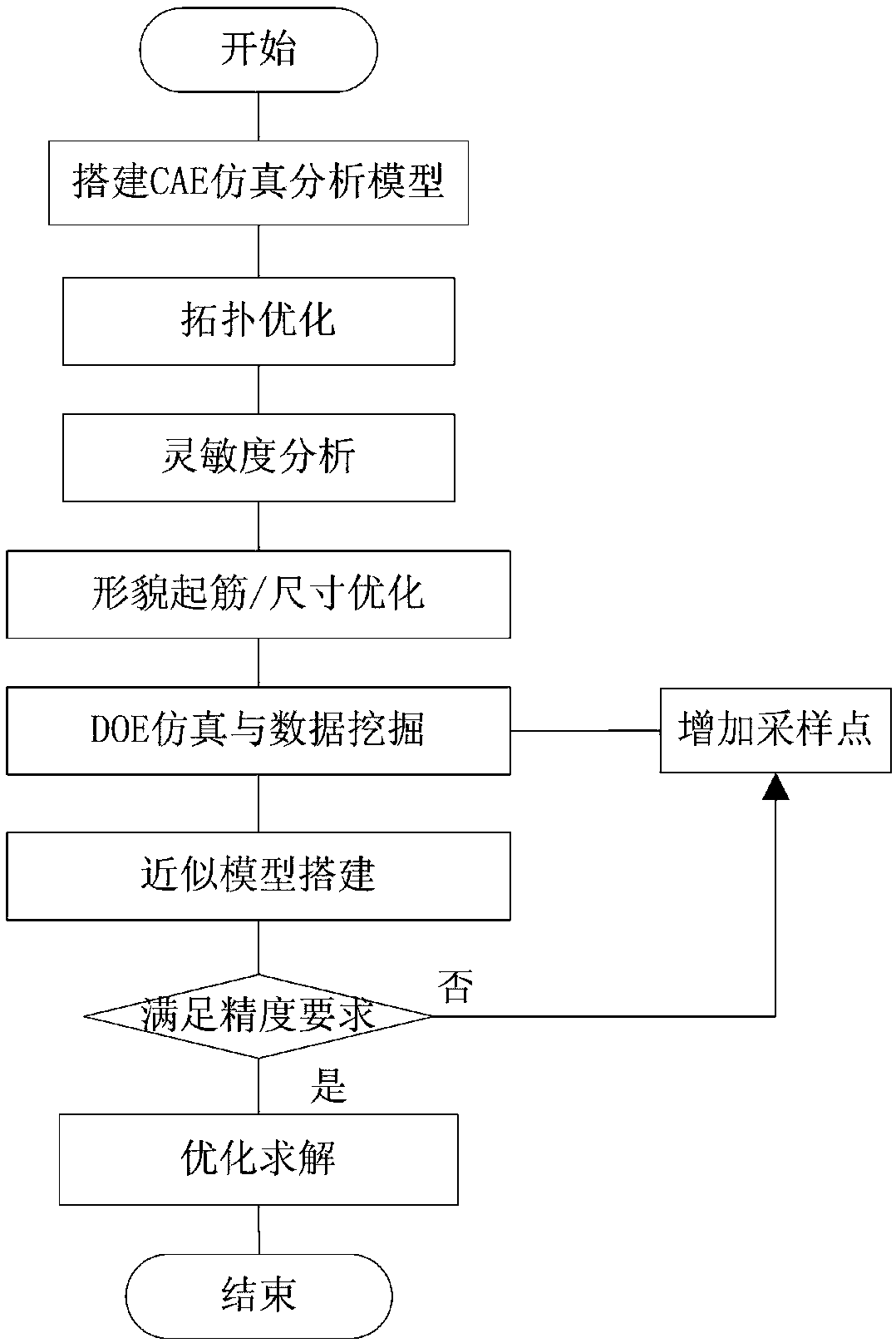
A lightweight forward design method and system of automobile structure based on multi-performance constraints is disclosed. The finite element analysis model of automobile body structure is established by using finite element modeling technology. The typical force transfer path of automobile structure is identified by using topology optimization technology and the bending / torsional rigidity performance of automobile body is taken as constrained working condition, and lightweight design in conceptual stage is carried out. Then the strain energy analysis and the material thickness sensitivity analysis are carried out by using the sensitivity analysis technology, and the weak links and the critical design area of the vehicle body are found. Topography optimization is used to improve vehicle performance; Finally, based on business integration optimization software, The multi-performance target of automobile body is analyzed by integrated simulation, and the correlation between design parameters and performance, performance and performance is studied by using DOE sampling and data mining technology, and then the lightweight design of automobile body structure considering multi-disciplinary performance is carried out, which reduces the quality of automobile body structure, improves product performance, shortens R D and manufacturing cycle, and saves cost.
Owner:CHONGQING CHANGAN AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
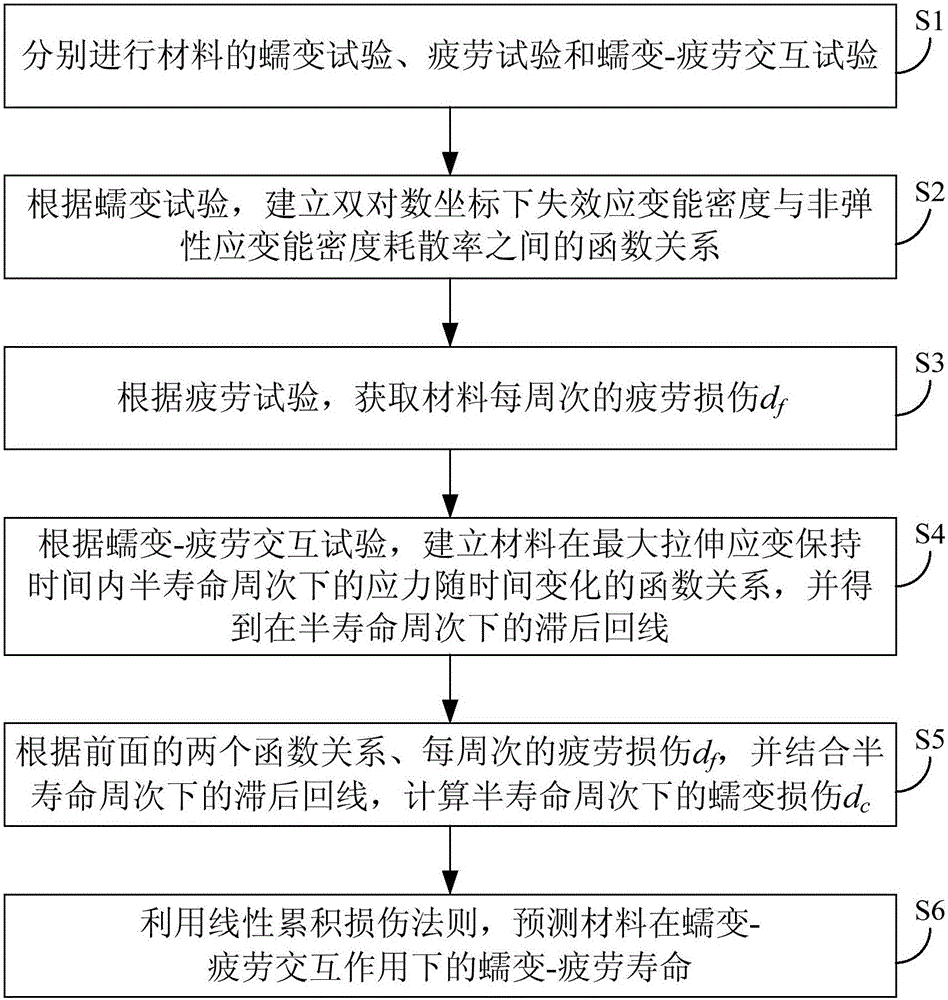
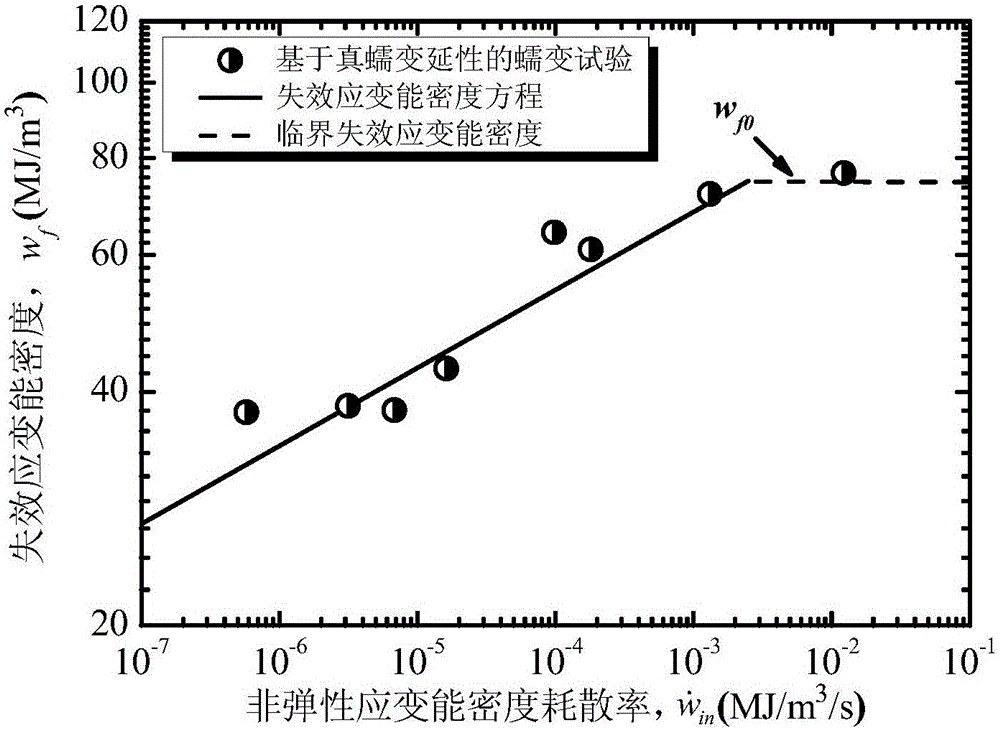
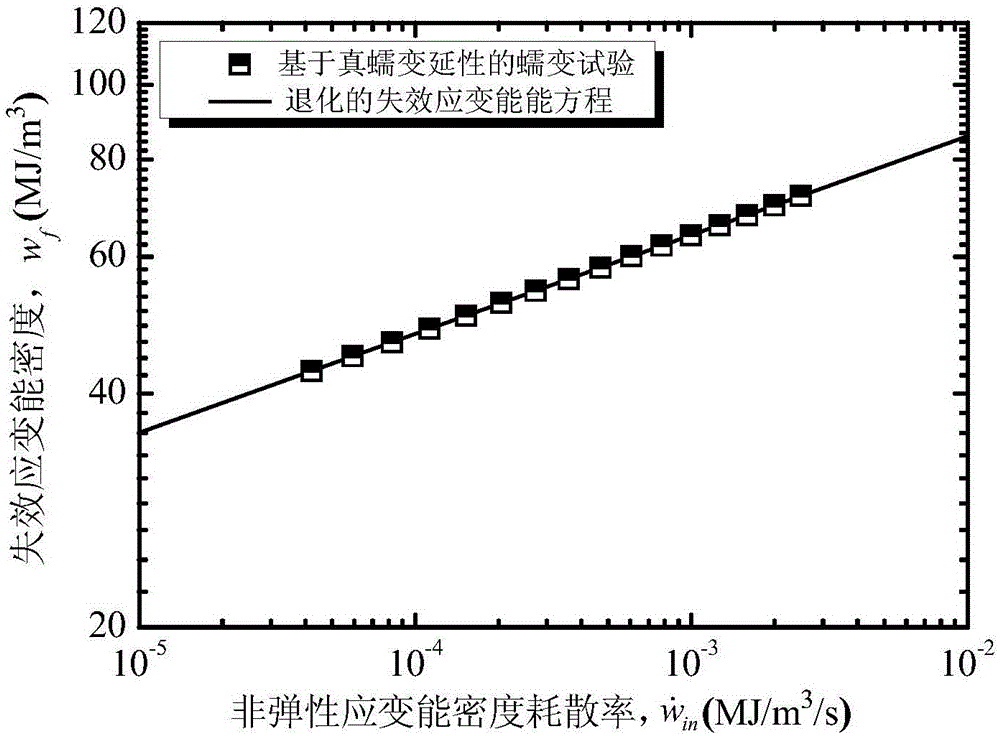
Forecasting method for creep-fatigue life of material
ActiveCN105158084ALife expectancyReal-time Damage DetectionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFatigue damageHysteresis
The invention provides a forecasting method for creep-fatigue life of a material. The method comprises the following steps: respectively performing a creep test, a fatigue test and a creep-fatigue interaction test for the material at a same test temperature; establishing a relation between the failure strain energy density wf and a non-elastic strain energy density dissipation rate of the material under a log-log coordinate according to the creep test; acquiring the fatigue damage df of the material per period according to the fatigue test; acquiring a hysteresis loop under a half-life period according to the creep-fatigue interaction test and establishing a function relation of the change of the stress Sigma (t) of the material under the half-life period within the maximum tensile strain maintaining time along with the change of time t; calculating the creep damage dc under the half-life period by combining with the hysteresis loop and based on the relation between wf and the function as shown in the specification and the relation of change of the fatigue damage df and the stress Sigma (t) along with the change of time t; and utilizing a linear accumulating damage rule to forecast the creep-fatigue life of the material under a creep-fatigue interaction. According to the method provided by the invention, the life of the material under the creep-fatigue interaction can be accurately forecasted.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Negative electrode for lithium secondary cell and lithium secondary cell
InactiveUS20050244711A1Improve charge and discharge cycle characteristicsImprove featuresElectrode carriers/collectorsActive material electrodesLithiumSilicon alloy
A negative electrode for a lithium secondary cell having a collector composed of an electroconductive metal foil and, provided on the surface thereof, an active material layer containing active material particles containing silicon and / or a silicon alloy and a binder, characterized in that the binder has mechanical characteristics of a tensile strength of 50 N / mm2 or more, an elongation at break of 10% or more, a strain energy density of 2.5×10−3 J / mm3 or more and a coefficient of elasticity of 10000 N / mm2 or less, and preferably characterized in that the collector has mechanical characteristics of a tensile strength of 80 N / mm2 or more, a proportional limit 30 N / mm2 or more, an elongation at break of 1.0% or more and an elastic elongation limit of 0.03% or more.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
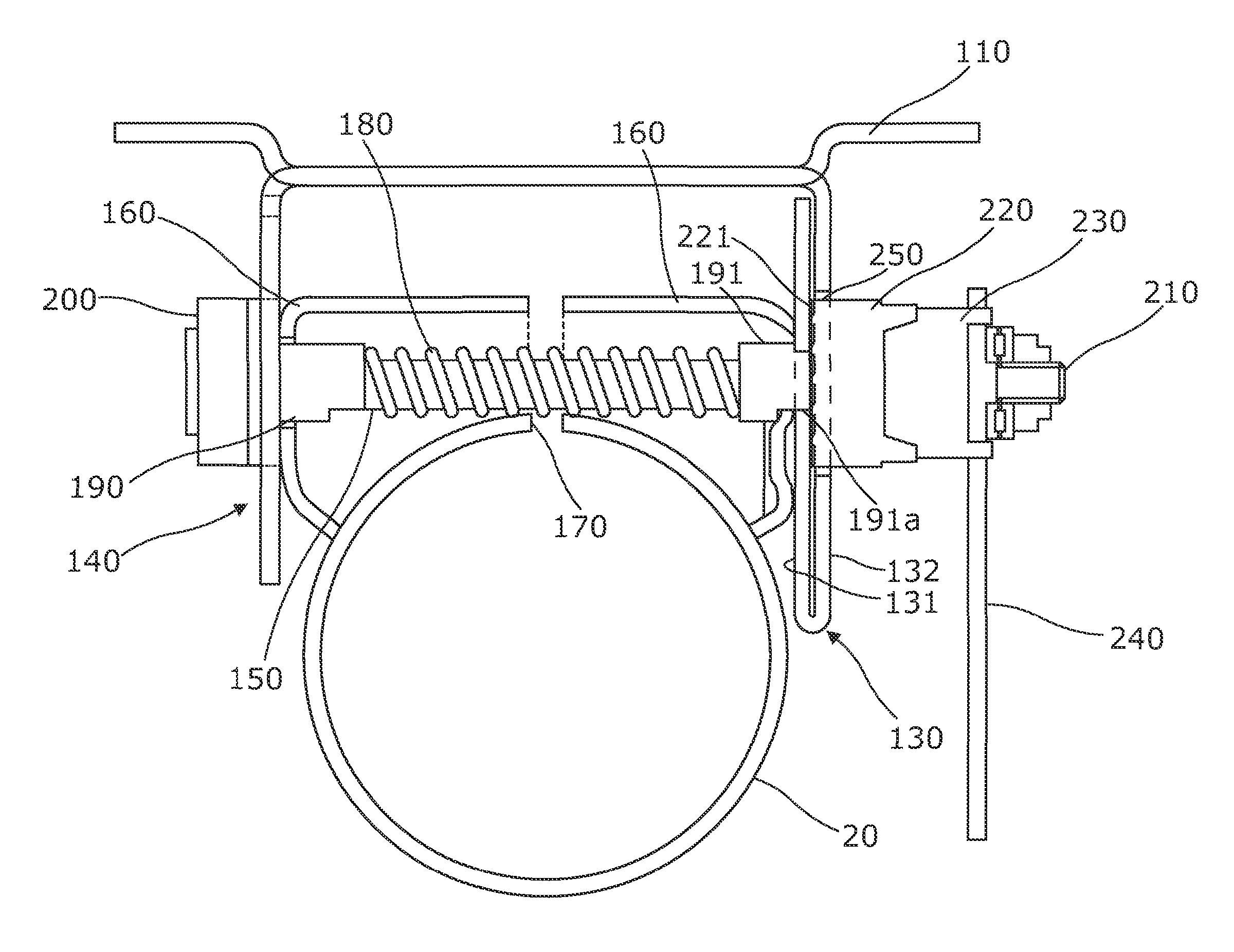
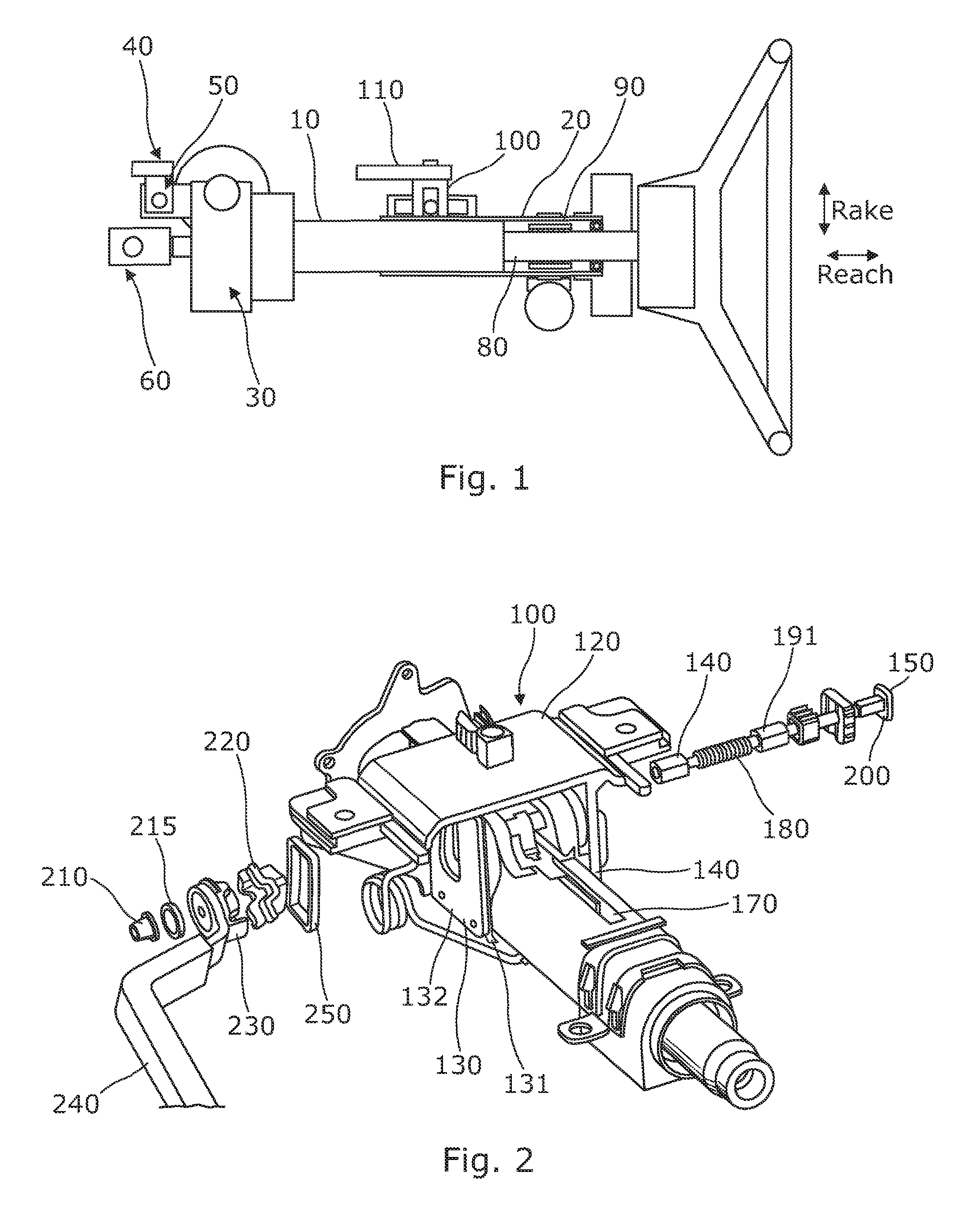
Steering column assembly
A steering column assembly comprises a steering column shroud comprising an inner and an outer tubular member, a support bracket which is fixed to part of the vehicle, and a clamp assembly which includes a cab mechanism having a fixed portion and a moving portion and a clamp pin which passes through arms of the support bracket, the clamp pin being provided with a first reaction member located towards one end of the pin outside of one arm of the support bracket and a second reaction member located towards the other end of the clamp pin outside of the other arm of the support bracket such that the arms of the bracket are located on the clamp pin between the reaction members and with the cam assembly located between the outside of one arm and one of the reaction members. The fixed cam portion is mechanically connected to the support bracket such that at least during an initial release phase of the clamp assembly the force required to produce a rotational movement of the fixed cam portion relative to the support bracket exceeds any rotational force exerted on the fixed part due to strain energy stored in the assembly.
Owner:TRW STEERING SYST POLAND Z O O +1
Silicon-dioxide aerogel heat insulation composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103011745AImprove mechanical propertiesChange the chemical state of the surfaceFiberSupercritical drying
The invention provides a fiber-reinforced silicon-dioxide aerogel heat insulation composite material and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method, mineral fibers with high mechanical strength, low heat conductivity and good heat stability serve as a reinforcing phase, silicon alcoholate serves as a precursor, fiber-composite silicon-dioxide wet gel is prepared by adopting an acid-base two-step catalysis method, and the block-shaped fiber-reinforced silicon-dioxide aerogel heat insulation composite material is then obtained through aging, modification, solvent displacement and supercritical drying. The prepared aerogel heat insulation composite material has the advantages of excellent mechanical property, good heat-insulating property and higher heat resistance. The aerogel composite material has a three-dimensional porous network-like structure, the compatibility between fibers and an aerogel matrix is good, the interfacial bonding is firm, and no obvious interfaces exist; and according to the block-shaped aerogel composite material, the density is 0.15-0.25 g / cm<3>, the compressive strength is 10%, the strain energy reaches 0.4-2.0MPa, and the coefficient of heat conductivity is 0.016-0.027 W / mK.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Device and method for connecting two parts of a craft
InactiveUS6454214B1Cosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic component separationStrain energyRotational energy
A device for releasably connecting a first part and a second part of a spacecraft. A clamp is operable to releasably connect the first part and the second part of the spacecraft and to store a prestress strain energy releaseable upon separation of the first part and second part of the spacecraft. The clamp includes a first end and a second end. At least one energy storing system is operable to convert at least a portion of the prestress on the clamp to rotational energy upon opening of the clamp and separation of the first part and the second part of the spacecraft. The energy storing system includes a first fitting part that includes a threaded section, a second fitting part that includes a threaded section, and a connecting device that includes a threaded section complementary to and operable to engage the threaded section of the first fitting part and the second fitting part. The connecting device is operable to link the first end and the second end of the clamp. During separation the fitting parts and the connecting device are operable to rotate in relation to one another to release the first fitting part and second fitting part from the connecting device.
Owner:SAAB ERICSON SPACE
A constant-resistance energy-absorbing bolt for strengthening large-deformation rock mass
InactiveCN102286975AIncrease ultimate elongationHigh and constant resistanceBulkheads/pilesEnergy absorptionStrain energy
The invention discloses a constant-resistance energy-absorbing anchor rod for strengthening a large-deformation rock body. The constant-resistance energy-absorbing anchor rod for strengthening the large-deformation rock body comprises a rod body, a constant-resistance energy-absorbing device, a nut and a tray, wherein the rod body is a smooth rod body with a round section; two ends of the rod body are provided with threads; the middle section of the rod body is wrapped by a plastic sleeve; the constant-resistance energy-absorbing device is arranged on the head part of the anchor rod and consists of a diameter-expanding cylinder, a conical cylinder, an anchorage device and a protective cover; the head of the rod body passes through the anchorage device to be connected with the diameter-expanding cylinder and the conical cylinder; and the protective cover is wrapped out of the diameter-expanding cylinder, the conical cylinder and the anchorage device. The constant-resistance energy-absorbing anchor rod can improve the capacity of the anchor rod in absorbing rock strain energy by utilizing the constant-resistance energy-absorbing device, is applicable to strengthening large-deformation surrounding rock of underground engineering or large-deformation rock creeping on the side slope under the high stress condition, has large ultimate elongation quantity, high and constant initial resistance and a simple structure, is convenient to manufacture and construct.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Carbon fiber reinforced base material, preform and composite material comprising the same
A carbon fiber reinforced substrate comprising a fabric composed of carbon fiber bundles and a first resin adhering to the fabric. Each of the carbon fiber bundles comprises numerous continuous carbon filaments, has the tensile modulus of 210 GPa or more, and has the fracture strain energy of 40 MJ / m3 or more. The amount of the first resin adhering to the fabric is in a range from 1 to 20 parts by weight per 100 parts by weight of said fabric. A preform comprising a laminate composed of plural layers of the carbon fiber reinforced substrate, wherein the layers are integrated by means of the first resin. A composite comprising the preform impregnated with a matrix resin.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
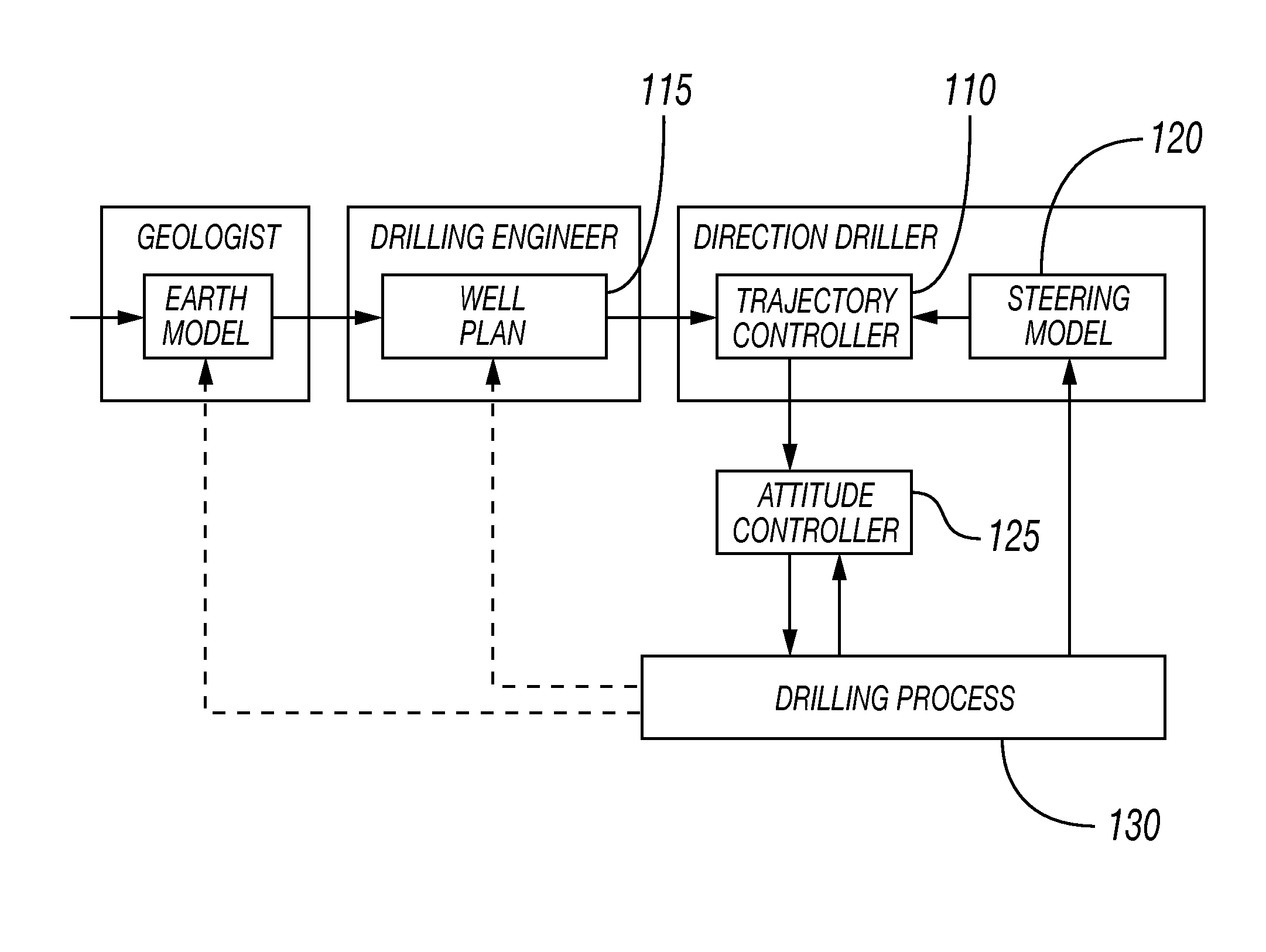
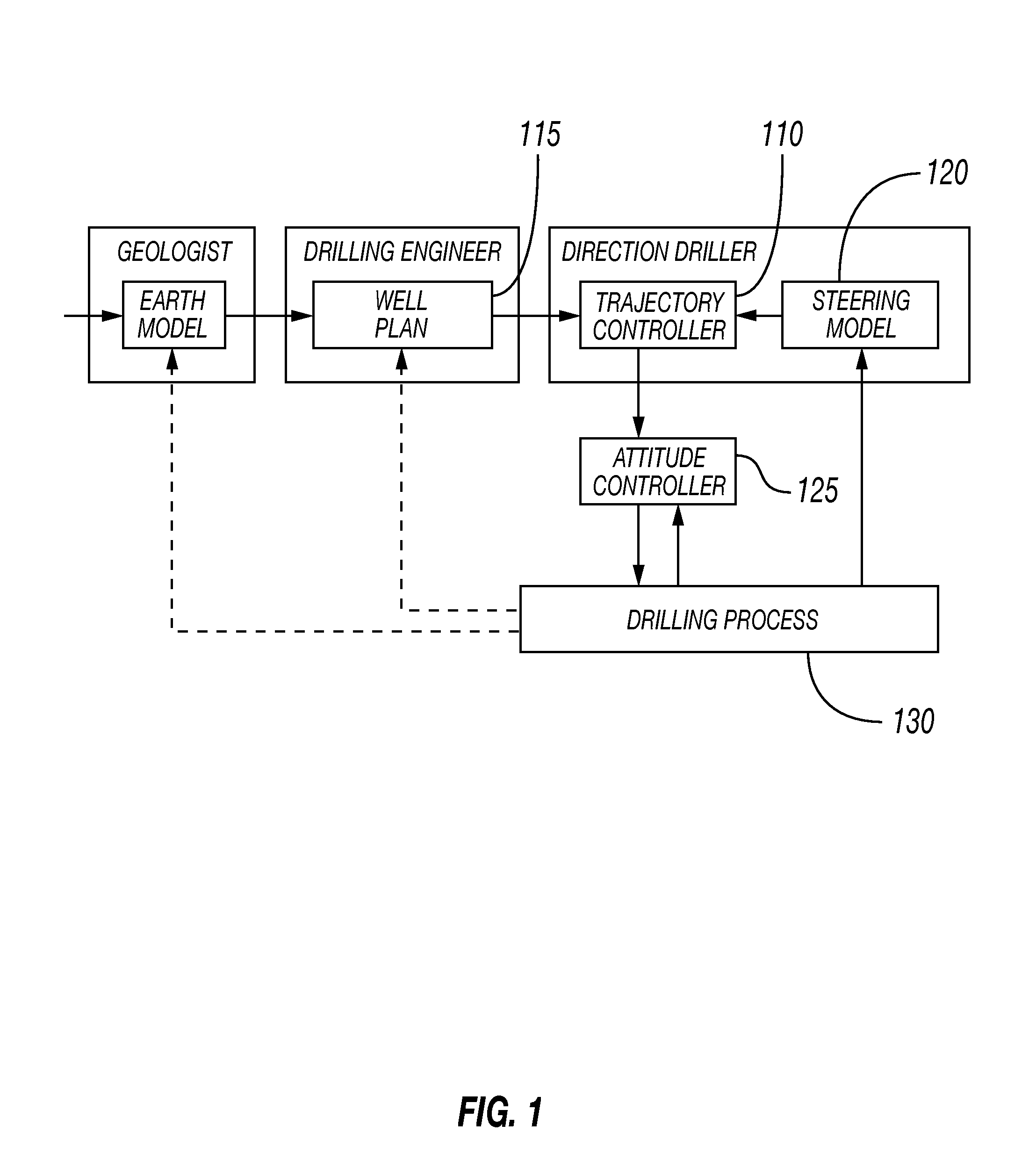
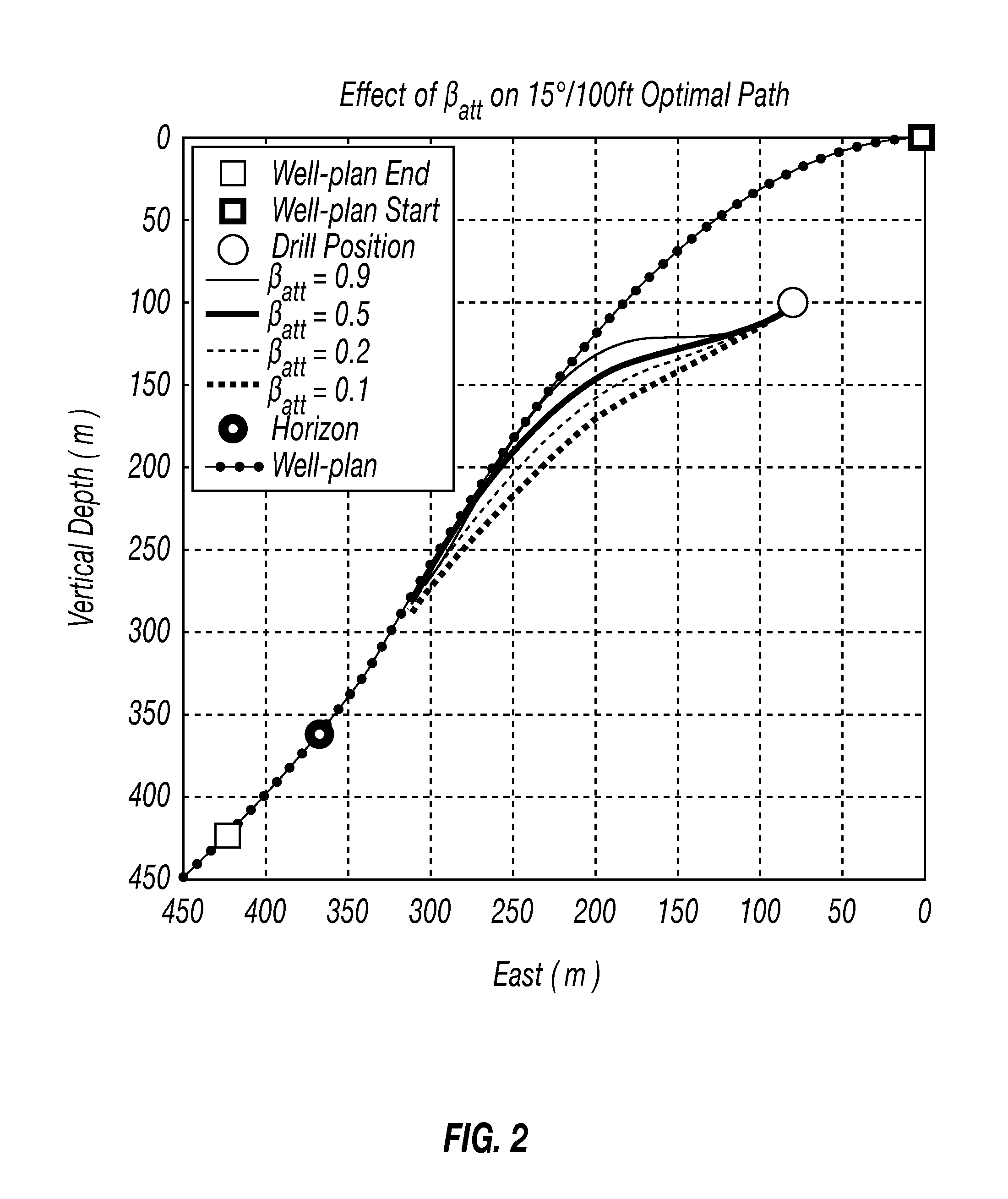
Optimal trajectory control for directional drilling
InactiveUS20150330209A1Strain energy is minimizedMinimize biasSampled-variable control systemsSurveyStrain energyOptimal trajectory
A feedback control system for steering a tool along a well-plan. Optimum steering instructions may be generated by a recursive optimization of multiple objectives. These objectives can include accuracy and quality. The quality objective can include the objective of drilling a smooth borehole by minimizing strain energy and torsion. The accuracy objective can include the objective of minimizing the deviation of the borehole trajectory during the real-time drilling process from a predefined well-plan. The trajectory control problem, therefore, can be a multi-objective problem where, in some embodiments, the weightings of the individual objectives can be adjusted along the process.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Strain energy shuttle apparatus and method for vibration energy harvesting
ActiveUS7521841B2Overcoming inherent structural stiffnessHighly susceptiblePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesStrain energyEngineering
An apparatus for use in low frequency vibration energy harvesting (VEH) and with actuators requiring a low deflection force. The apparatus includes a piezo flexure that is loaded with a compressive pre-load force to place the piezo flexure under compression. The piezo flexure may be supported at an intermediate point or at one end thereof. The compressive pre-load force produces flexes the piezo flexure into one or the other of two stable positions, these positions being offset on opposite sides of a longitudinal centerline representing the position of the piezo flexure that would be produced without the compressive pre-load force applied thereto. The compressive pre-load effectively provides a negative spring constant which “softens” the piezo flexure and enhances a responsiveness of the piezo flexure to low frequency vibration energy. The piezo flexure also operates over a much wider frequency bandwidth than conventional systems incorporating a tip mass.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
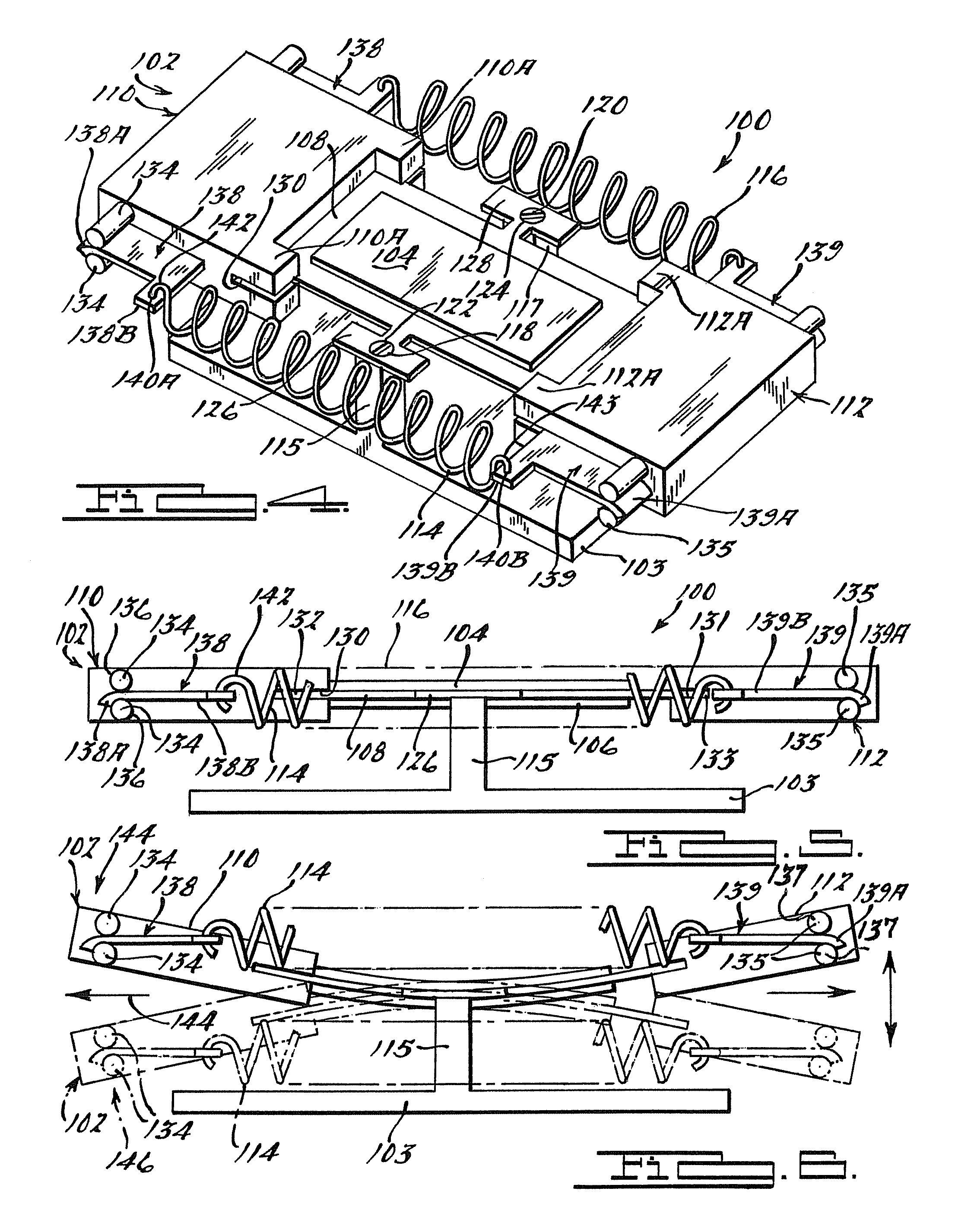
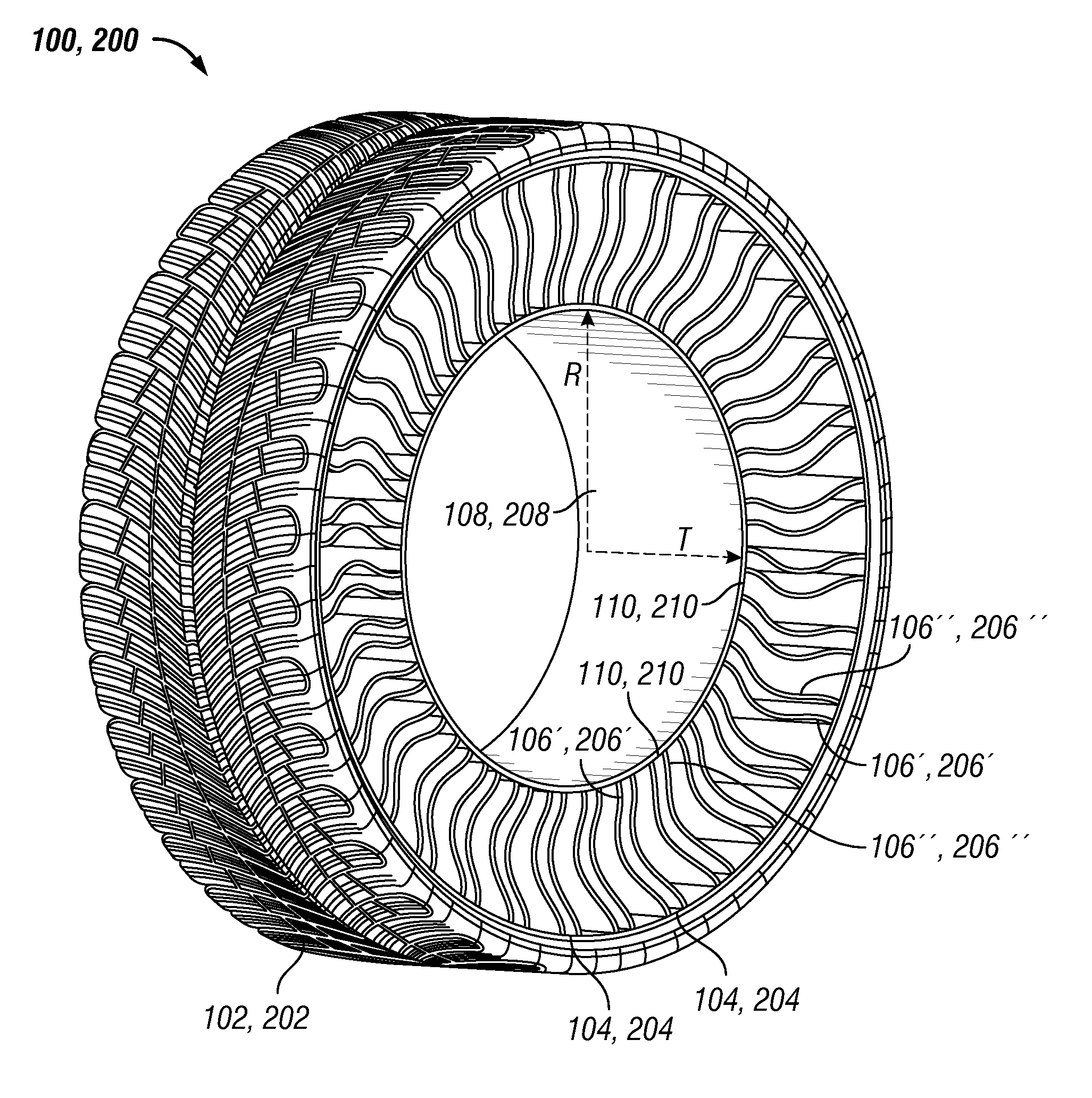
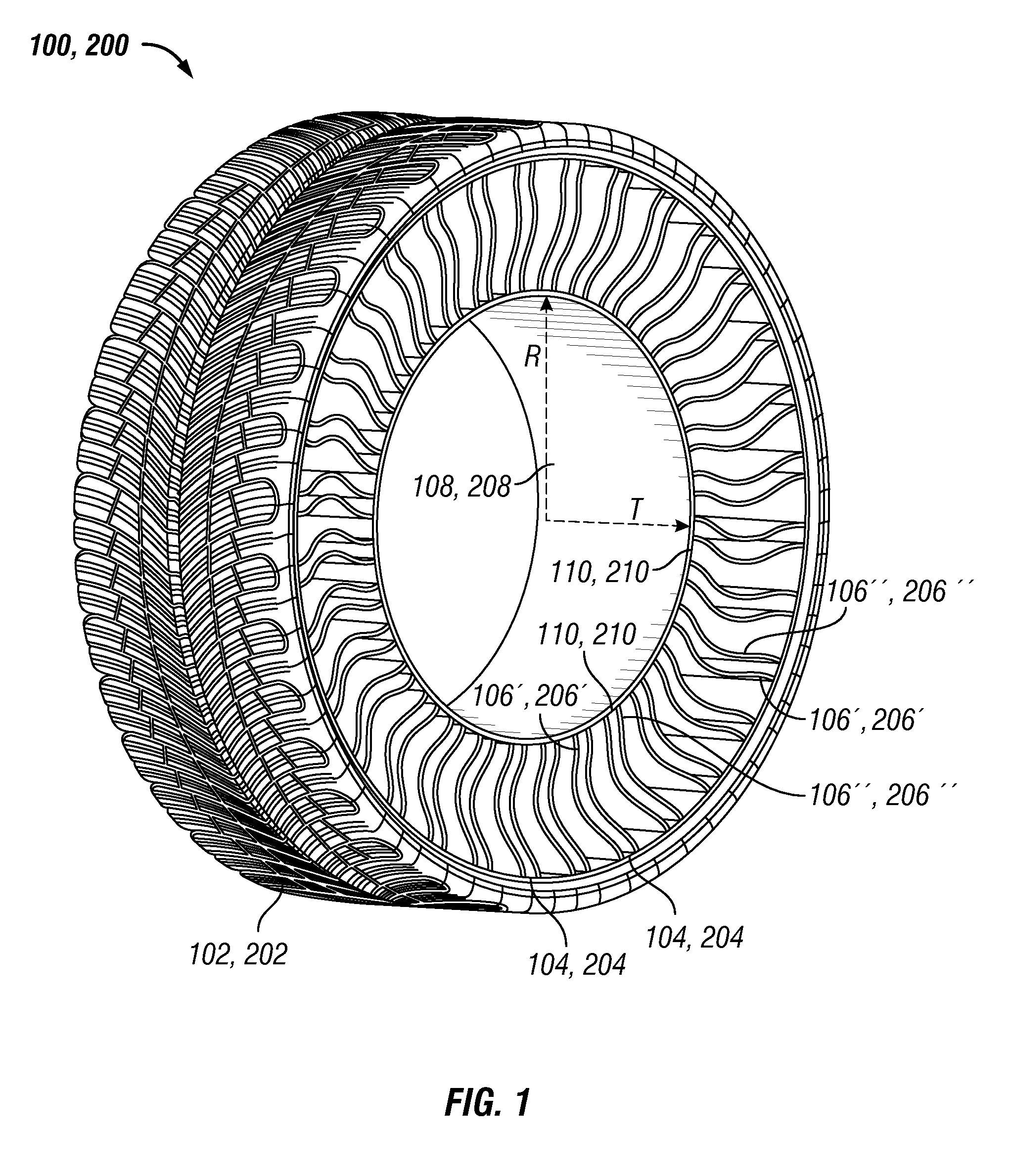
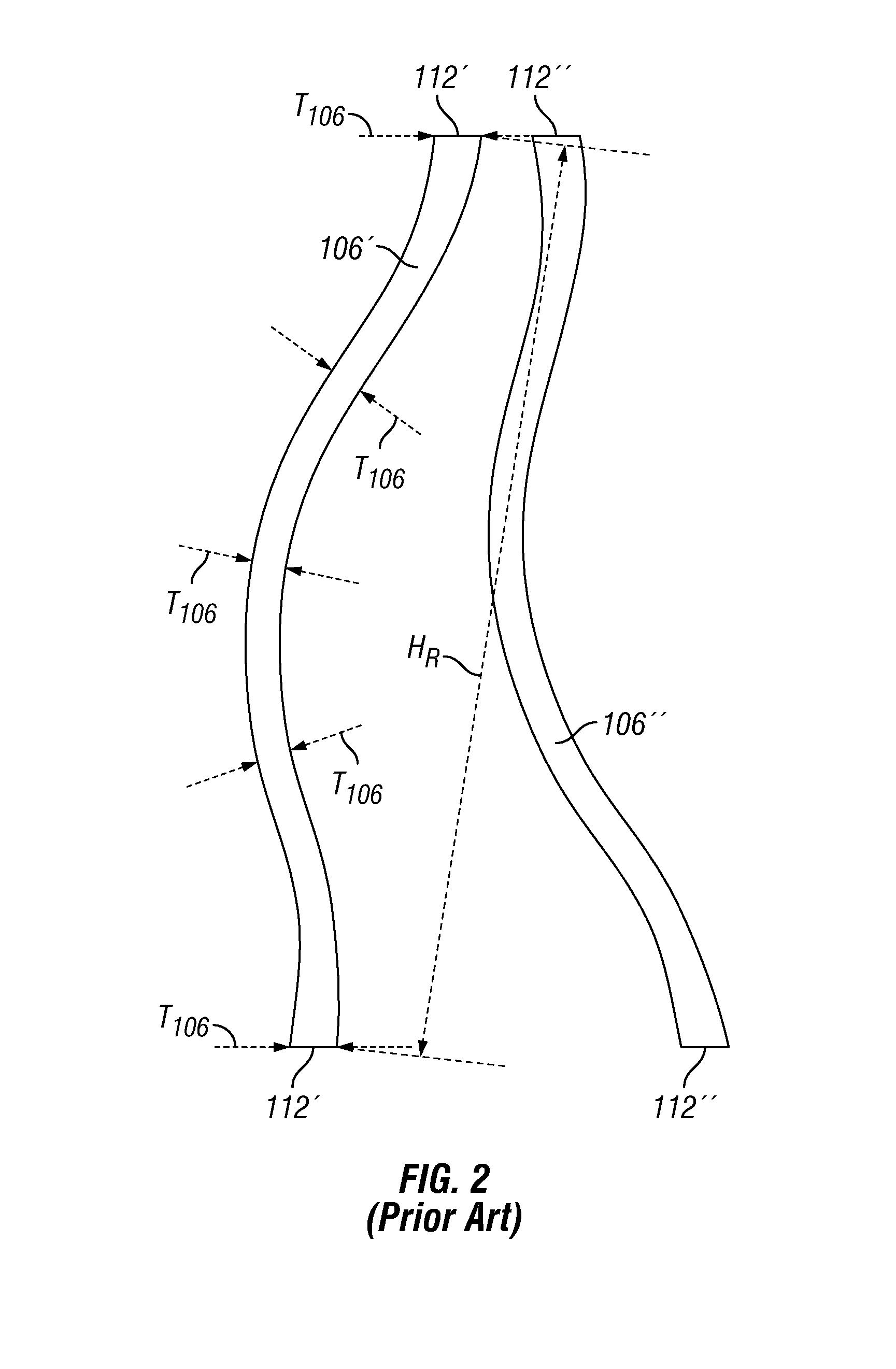
Spoke for a tire with optimized thickness for improved durability
ActiveUS20150174953A1Non-inflatable tyresNon-metallic wheel bodyStrain energyVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention provides spoke geometry for a non-pneumatic tire that is less prone to fatigue when used. In particular, the spoke geometry is provided with an optimized thickness profile over the length of the spoke. This optimization results in a reduction in the peak strain energy density levels in the spoke, thereby reducing the likelihood of crack initiation and propagation which in turn enhances the durability of the spoke and tire.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN +1
Strained silicon with elastic edge relaxation
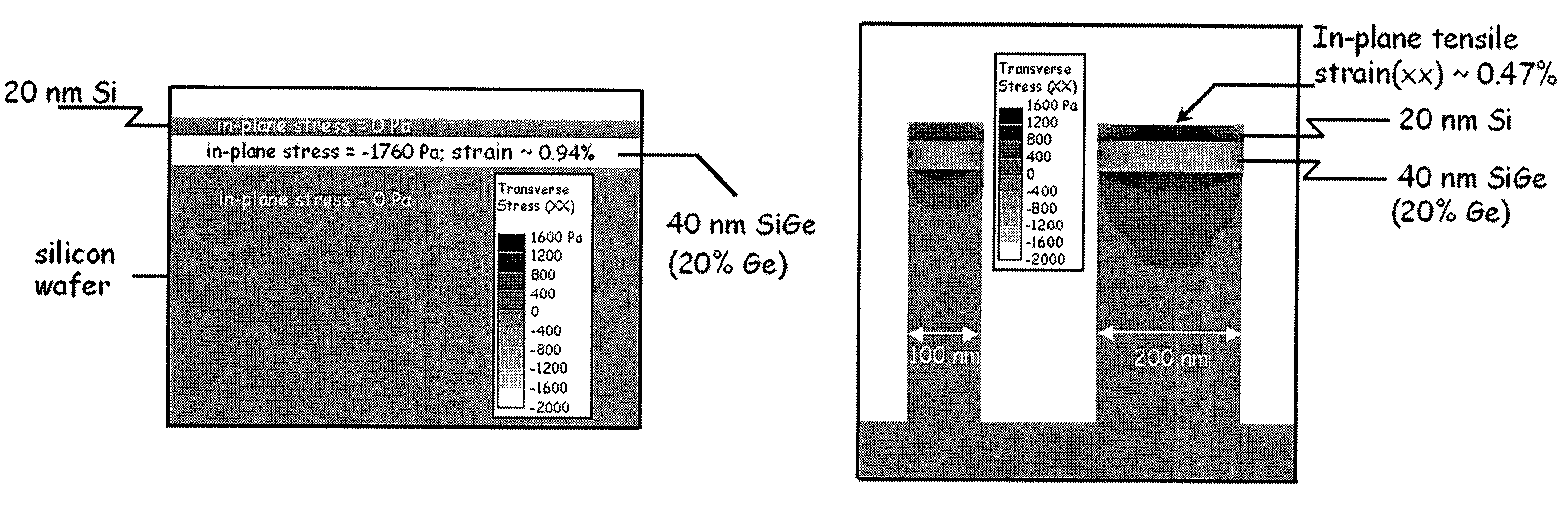
ActiveUS7338834B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTensile strainStrain energy
A thin blanket epitaxial layer of SiGe is grown on a silicon substrate to have a biaxial compressive stress in the growth plane. A thin epitaxial layer of silicon is deposited on the SiGe layer, with the SiGe layer having a thickness less than its critical thicknesses. Shallow trenches are subsequently fabricated through the epitaxial layers, so that the strain energy is redistributed such that the compressive strain in the SiGe layer is partially relaxed elastically and a degree of tensile strain is induced to the neighboring layers of silicon. Because this process for inducing tensile strain in a silicon over-layer is elastic in nature, the desired strain may be achieved without formation of misfit dislocations.
Owner:ACORN TECH INC
Toner
A toner has toner particles containing a binder resin that comprises a block polymer as a main component, obtained by chemically bonding a crystalline polyester resin with an amorphous polyurethane resin, wherein the binder resin has a specific content of a crystalline polyester resin component, and has a concentration of ester bonds derived from the crystalline polyester resin component of not more than 5.2 mmol / g, and The maximum value EMAX of the flexural elasticity modulus E in a three-point bending test on the toner and the strain energy u for the toner satisfy specific values.
Owner:CANON KK
Deployable antenna with foldable resilient members
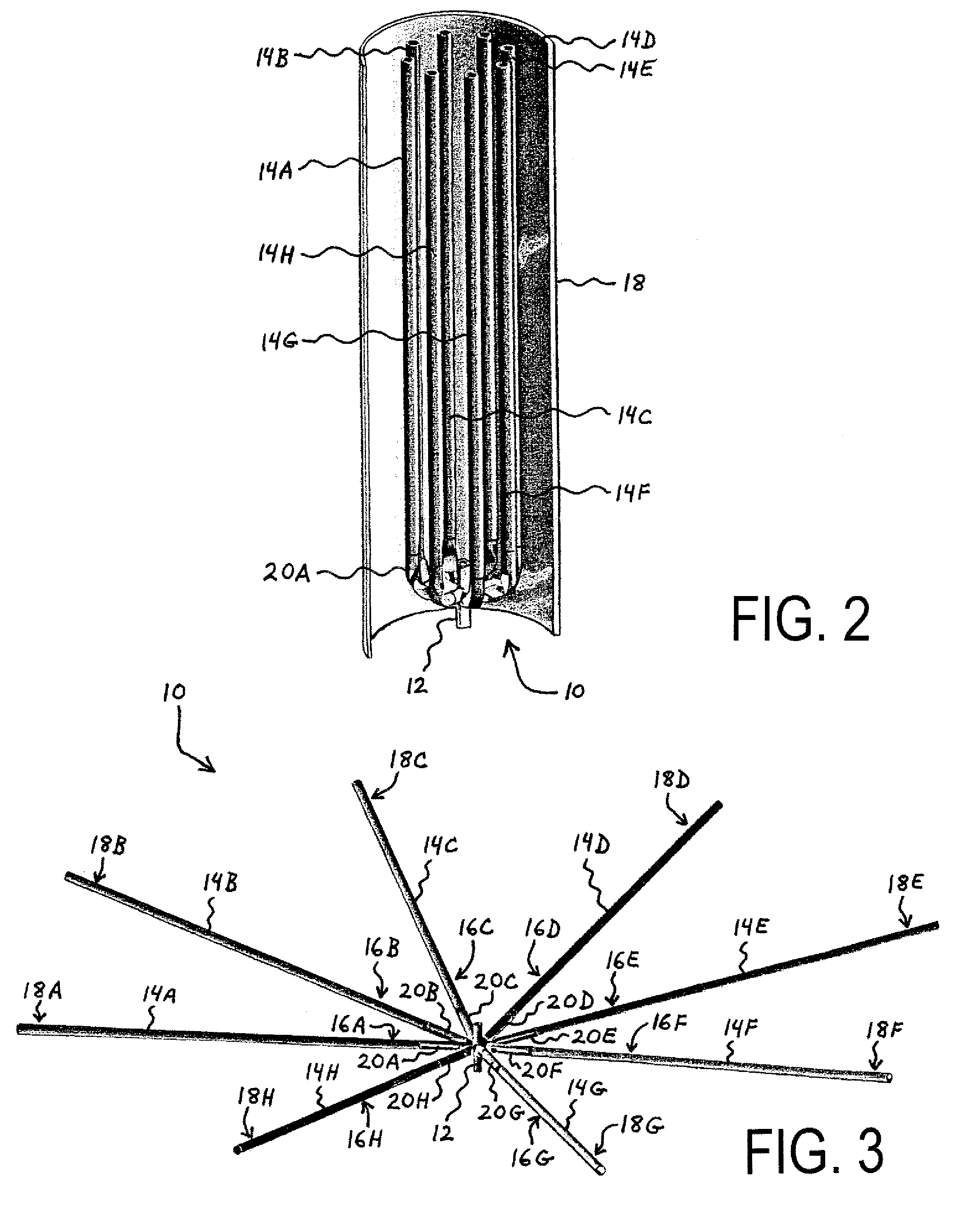
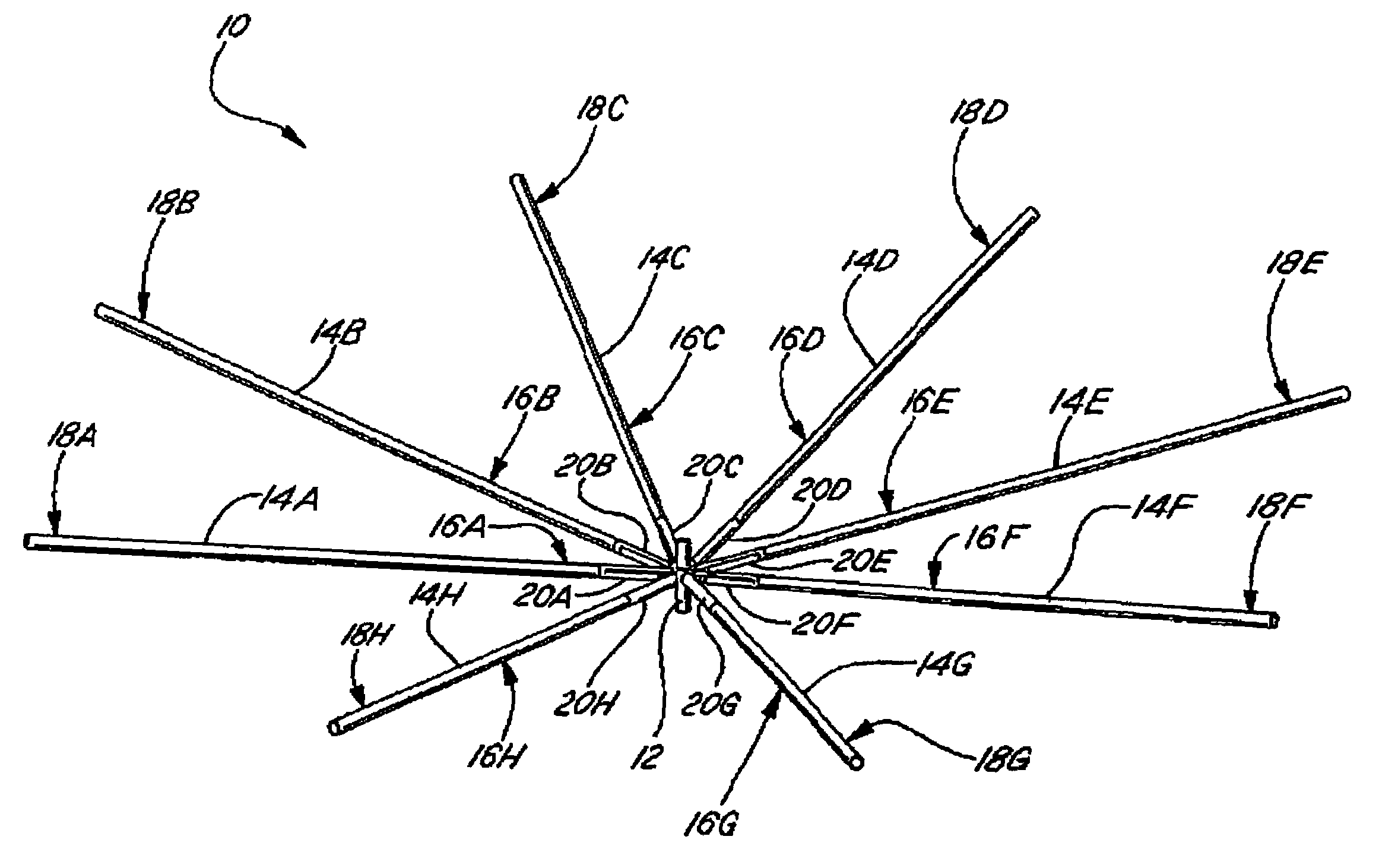
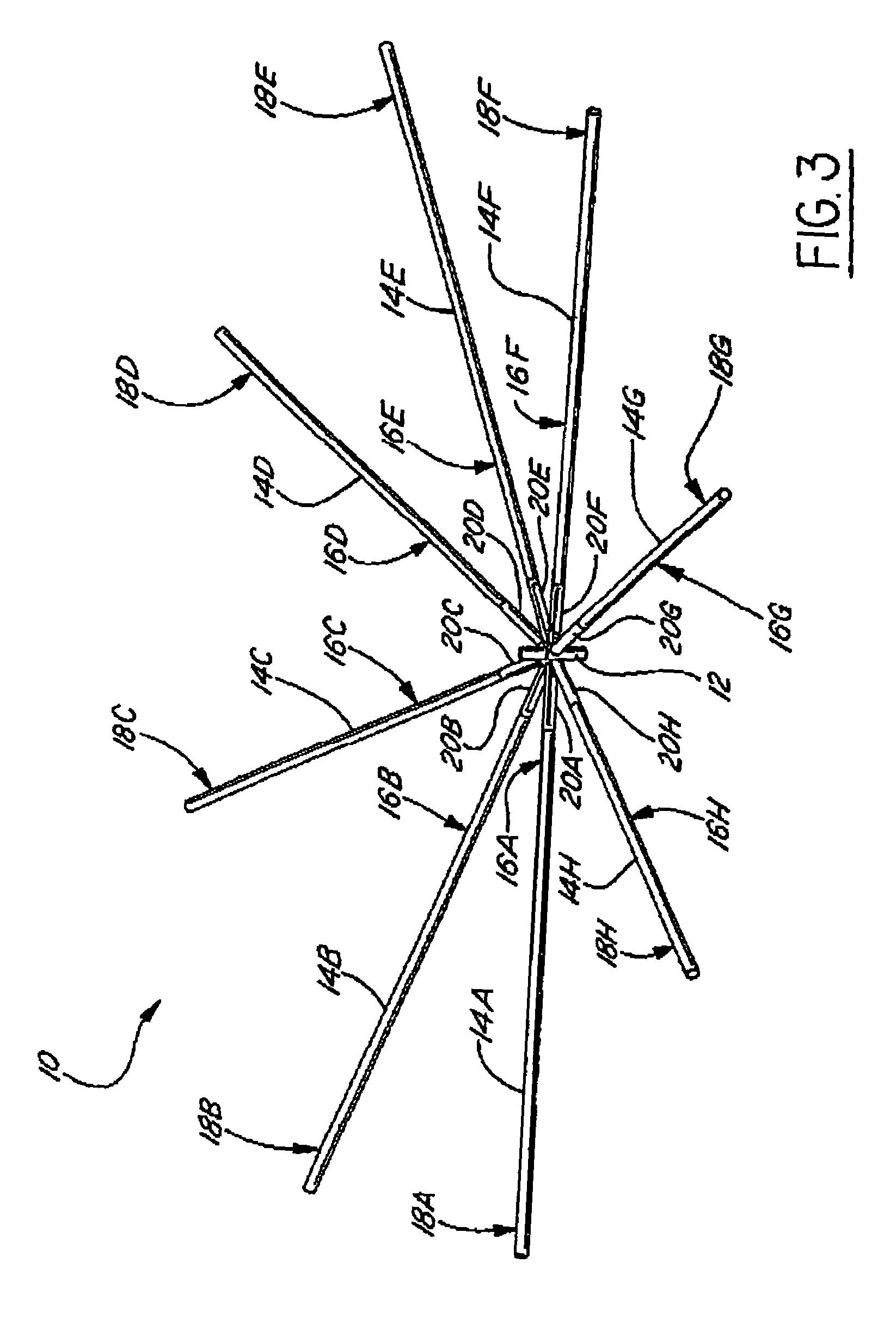
A framework for a deployable antenna is disclosed herein. The framework basically includes a plurality of elongate ribs, a matching plurality of foldable resilient members, and a hub. Each of the elongate ribs has both a proximal end and a distal end. The foldable resilient members serve to interconnect the proximal ends of the elongate ribs to the hub. Within such a configuration, each of the foldable resilient members is capable of storing strain energy whenever forcibly folded and also releasing the strain energy whenever subsequently permitted to elastically unfold. Thus, whenever the elongate ribs are released from a stowed position in which the foldable resilient members are forcibly folded, the strain energy causes automatic deployment of the antenna as the foldable resilient members are permitted to elastically unfold. In sum, therefore, the framework obviates many conventional uses of electro-mechanical motors or actuators in deploying various antennas.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Deployable antenna with foldable resilient members
A framework for a deployable antenna is disclosed herein. The framework basically includes a plurality of elongate ribs, a matching plurality of foldable resilient members, and a hub. Each of the elongate ribs has both a proximal end and a distal end. The foldable resilient members serve to interconnect the proximal ends of the elongate ribs to the hub. Within such a configuration, each of the foldable resilient members is capable of storing strain energy whenever forcibly folded and also releasing the strain energy whenever subsequently permitted to elastically unfold. Thus, whenever the elongate ribs are released from a stowed position in which the foldable resilient members are forcibly folded, the strain energy causes automatic deployment of the antenna as the foldable resilient members are permitted to elastically unfold. In sum, therefore, the framework obviates many conventional uses of electro-mechanical motors or actuators in deploying various antennas.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Strained silicon with elastic edge relaxation
ActiveUS20070215859A1Less thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTensile strainStrain energy
A thin blanket epitaxial layer of SiGe is grown on a silicon substrate to have a biaxial compressive stress in the growth plane. A thin epitaxial layer of silicon is deposited on the SiGe layer, with the SiGe layer having a thickness less than its critical thicknesses. Shallow trenches are subsequently fabricated through the epitaxial layers, so that the strain energy is redistributed such that the compressive strain in the SiGe layer is partially relaxed elastically and a degree of tensile strain is induced to the neighboring layers of silicon. Because this process for inducing tensile strain in a silicon over-layer is elastic in nature, the desired strain may be achieved without formation of misfit dislocations.
Owner:ACORN TECH INC
Rockburst active control method based on blasting excavation disturbance control
The invention discloses a rockburst active control method based on blasting excavation disturbance control. The rockburst active control method aims at overcoming the shortcoming that only blast load induction disturbance is considered in traditional blasting disturbance control, the rock mass strain energy release amount caused by single-section blasting is reduced by changing blasthole arrangement and an explosion initiation network, so that the goal of weakening overall release rate of rock mass strain energy is achieved on the basis of controlling blast load induction disturbance to achieve control of deep rock mass excavation disturbance, and active control of rockburst is achieved finally. The rockburst active control method is suitable for blasting excavation construction of deeply buried underground engineering in the fields of hydraulic and hydro-power engineering, traffic and mines and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Topological optimization design method for high-speed vertical machining centre long-span beam
InactiveCN101950319AImprove optimization efficiencyGuaranteed availabilitySpecial data processing applicationsSolid structureStrain energy
The invention belongs to the technical field of mechanical design and relates to a topological optimization design method for a high-speed vertical machining centre long-span beam. The method is mainly for the topological optimization of the three-dimensional solid structure of the long-span beam. The method consists two parts of early basis analysis and topological optimization design; the early basis analysis is to grasp the static and dynamic properties of the original beam, find out the parts of relatively weak static and dynamic properties and perform structural topological optimization on the beam correspondingly; and in the later topological optimization design, based on the result of the basic analysis, the later structural topological optimization including two-dimensional topological optimization and three-dimensional topological optimization of the beam is performed according to the characteristics of the beam. In the topological optimization method, a density method is adopted, the volume fraction response is used as a constraint function, and the static strain energy response is used as a target function; and finally an innovative model is established again according to the results of the two-dimensional and three-dimensional topological optimization analysis. The structural topological optimization method has the advantages of improving the optimization efficiency, along with accurate and reliable optimized results.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Rope net unfolding device based on thin-wall type stretching arm
InactiveCN102756811ANo need to consume energyRelease stabilityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsStrain energyEngineering
The invention discloses a rope net unfolding device based on a thin-wall type stretching arm, which is used for ontrack cleaning of space debris. The device does not need to be driven by external power, and a net body structure is driven to unfold by strain energy stored by the thin-wall type stretching arm, so as to capture the space debris. Through adoption of a thin-wall structure, the stretching arm has high flexibility and light weight, the stretching arm stretches out and contracts back to store strain energy and to enable the mechanism to achieve a high magnification ratio. Due to the design that the stretching arm drives the net body structure to unfold, the unfolding process of the net body structure has good controllability; and due to the design of a press plate and a limiting pin, the unfolding synchronism is ensured.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Weldability of alloys with directionally-solidified grain structure
ActiveUS20060157165A1Improve solderabilityFurnace typesElectron beam welding apparatusSand blastingStrain energy
A method of welding alloys having directionally-solidified grain structure. The methods improve the weldability of these alloys by creating a localized region of fine grain structure, wherein the welding occurs in these localized regions. The localized regions are formed by applying strain energy using a variety of different methods, such as by hammer peening, laser peening or sand blasting. Then, a heat treatment step may be used to create recrystallized grains having the fine grain structure. The region of fine grain structure provides better weldability.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
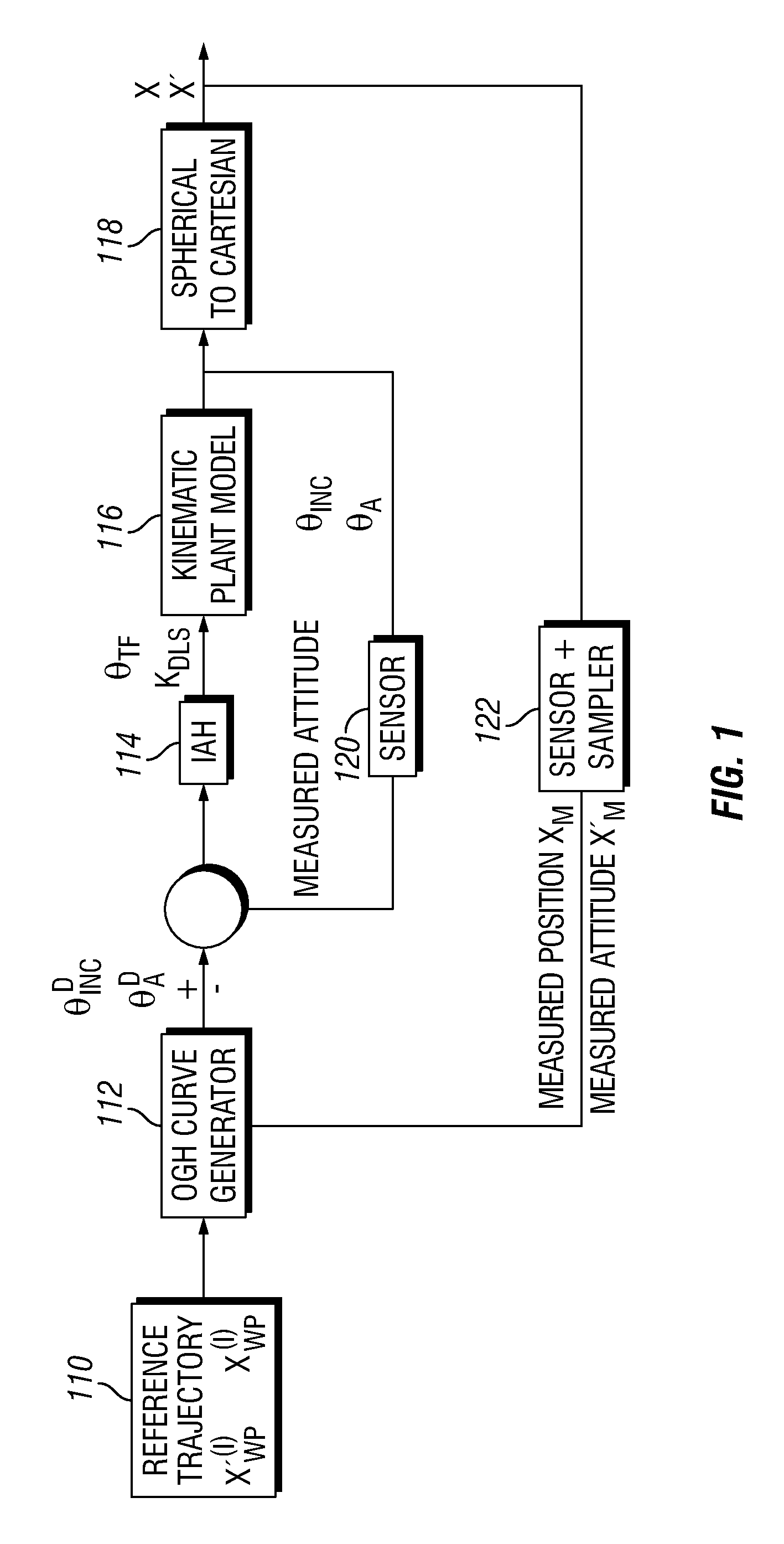
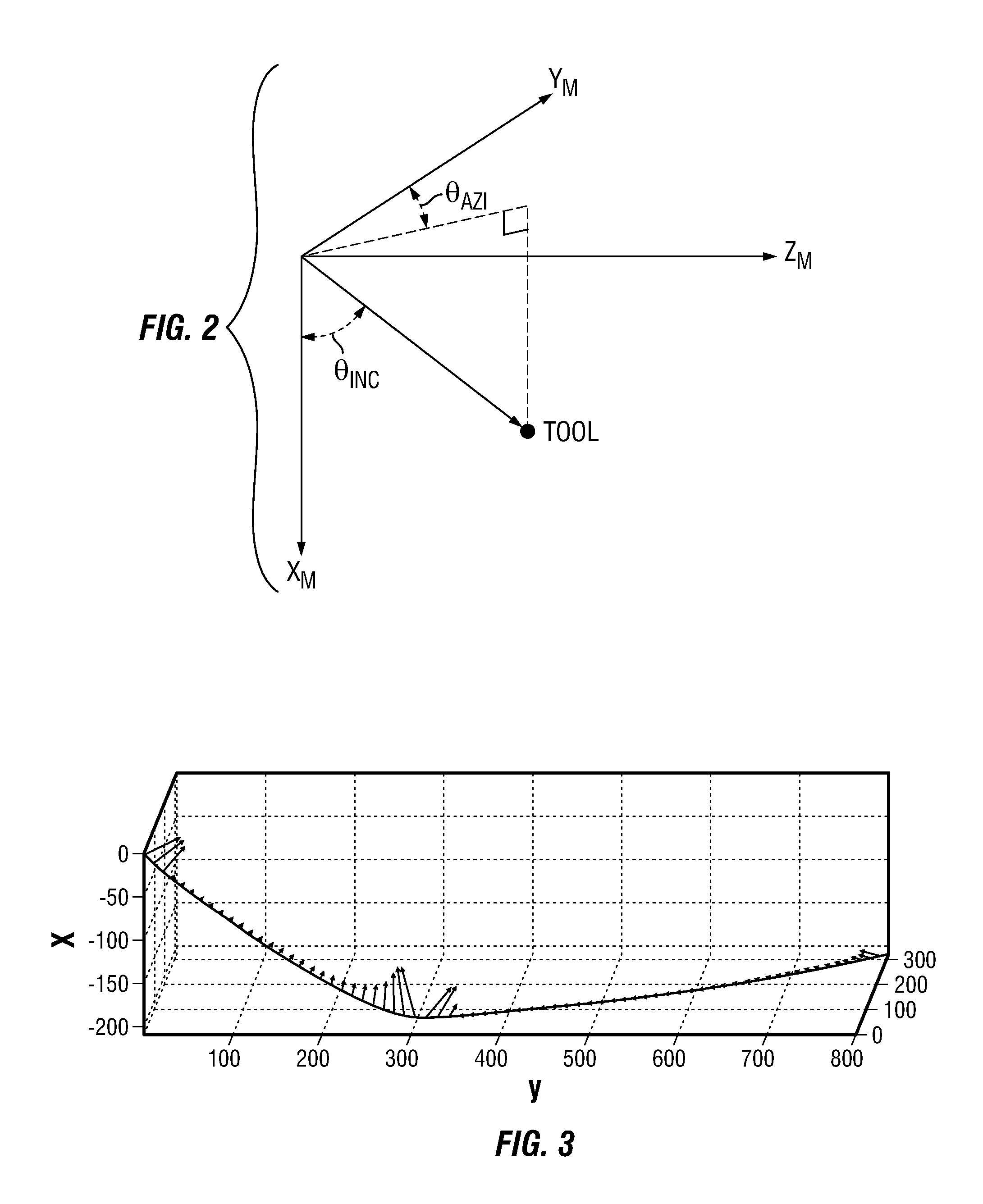
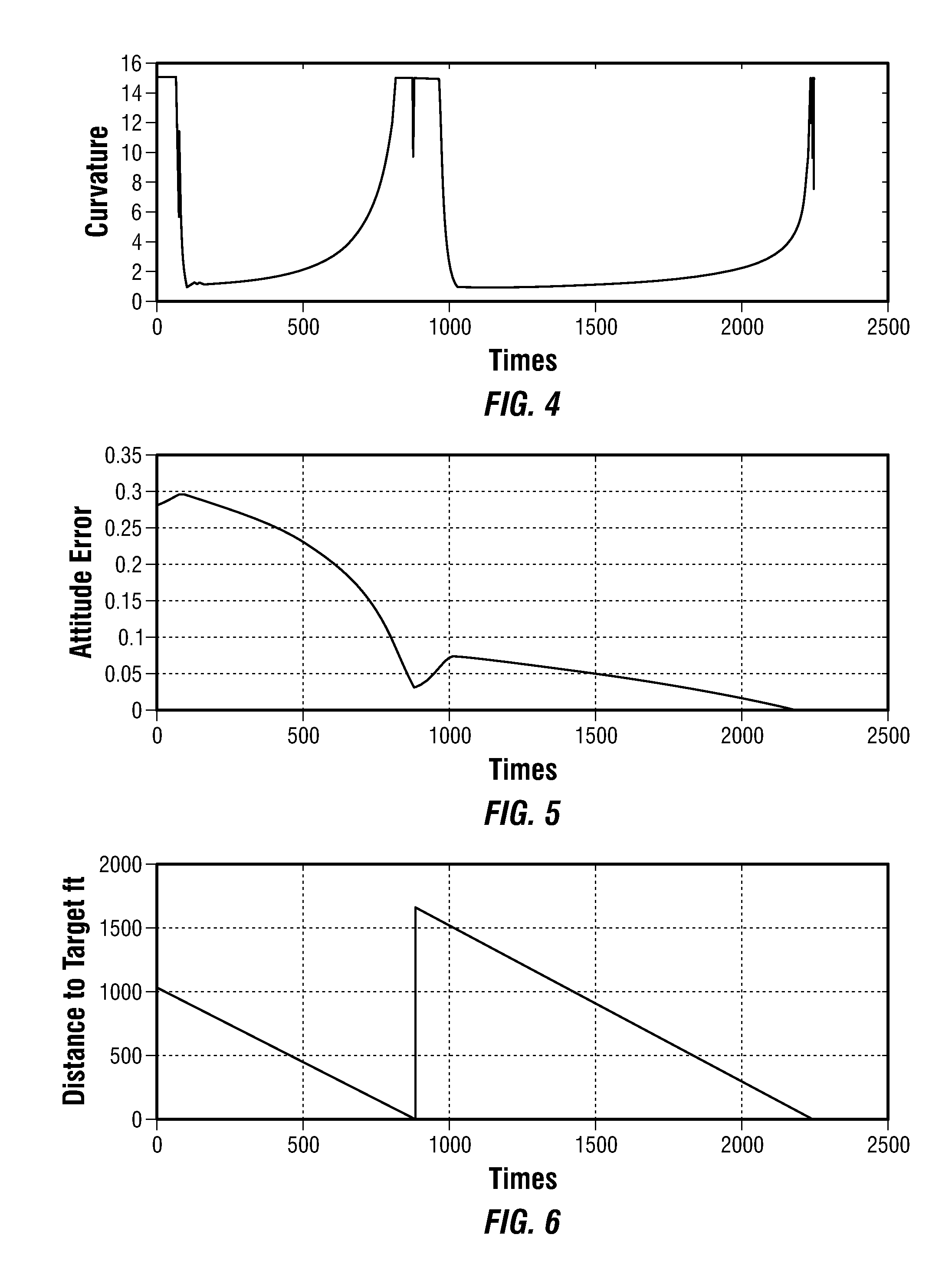
Minimum strain energy waypoint-following controller for directional drilling using optimized geometric hermite curves
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Paint and adhesive test system
InactiveUS6026680AWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesAdhesiveStrain energy
A testing system provides a quantitative way of measuring the adhesive strength of adhesives, paints, coatings, adhesive tapes, and other test substances to underlying adherends and substrates, such as metals. The test system of the invention consistently produces uniform results. First and second adherends are bonded together over a relatively small area near the centers and are then pulled apart by a force applied at one end of one of the adherends. The force is increased until the second adherend member is debonded from the first throughout the test bonding zone, thus determining the total energy expended in debonding the first and second adherend members plus strain energy expended in displacing the second member from the first. The force is then decreased until there is no longer any displacement of the second member from the first while concurrently measuring the decreasing force and displacement of the second adherend member from the first adherend member as a function of the decreasing force. This determines the strain energy apart from the total energy. The strain energy is then subtracted from the total energy and the resulting difference is divided by the area of the test bonding zone to determine the specific work of debonding. The strength of the adhesive properties of the test substances, and also the cohesive bonding strength of such substances may be determined utilizing the system of the invention.
Owner:MANN FAMILY TRUST OF 1994 THE
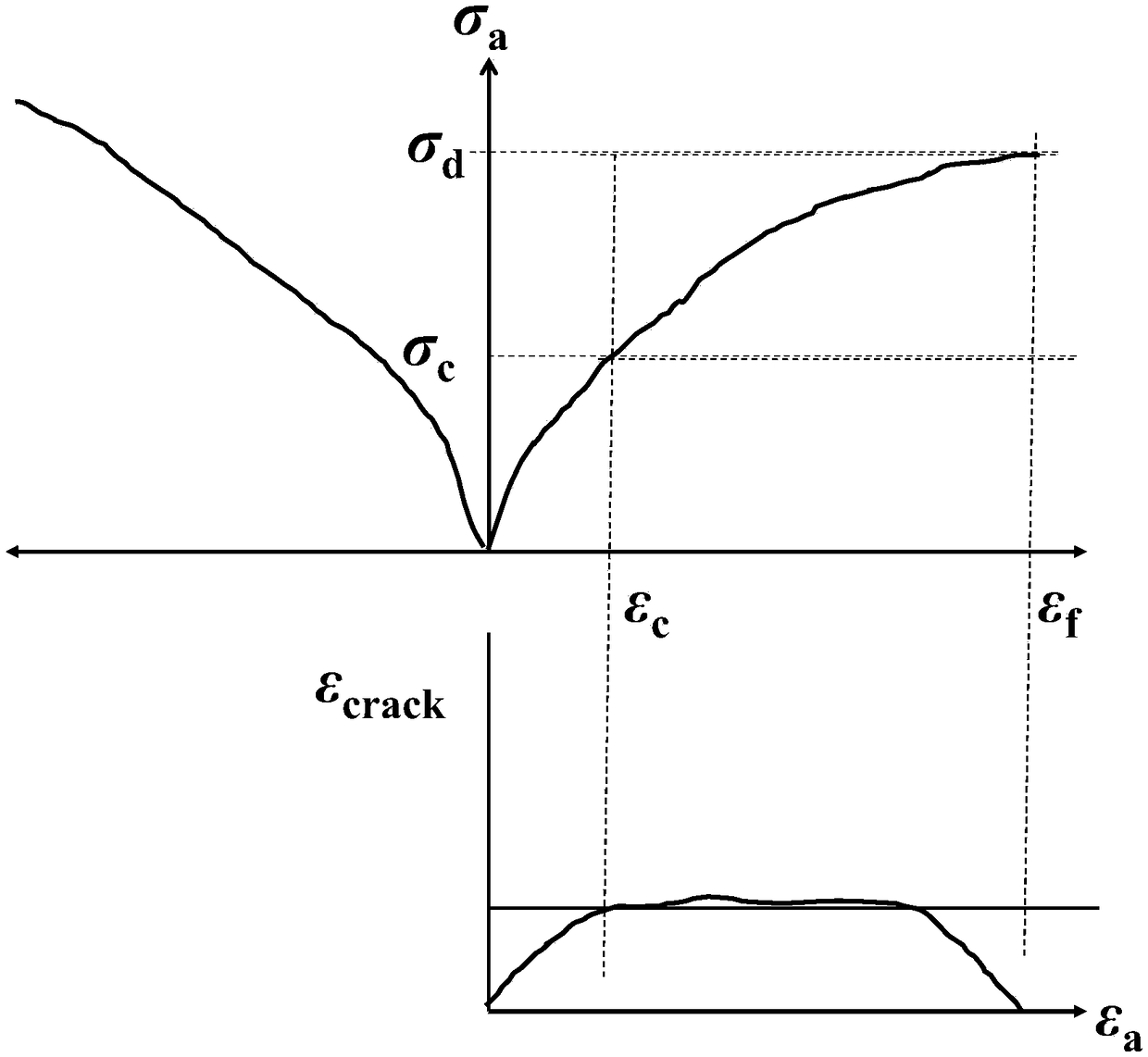
Method for evaluating compressibility of tight reservoir based on stress-strain curve
ActiveCN108593436AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMathematical modelStress–strain curve
The invention discloses a method for evaluating compressibility of a tight reservoir based on a stress-strain curve. The method comprises the following steps: testing the stress-strain curve of a rocksample under a certain confining pressure to obtain elasticity modulus and Poisson's ratio of an elastic deformation stage so as to obtain the volumetric strain of the elastic deformation stage and obtain crack volume strain; determining an expansion point of the rock sample according to an axial strain-crack volume strain relationship curve and obtaining the strain energy size through the stress-strain curve envelope area formed from the expansion point to the break point in an enclosing way; and establishing a compressibility index mathematical model of the surrounding rock by performing nondimensionalization on the change numerical value of the parameter, and calculating and comparing the size. The experimental evaluation method provided by the invention is suitable for the unconventional resources such as shale gas, coal bed gas, compact oil gas and a hot dry rock, and can be applied to the conventional oil and gas reservoir with low permeability and ultralow permeability. The confining pressure effect is considered and the artificial fracture density formed after the rock is expanded is considered, so the method can be used for evaluating the artificial joint network formingcapability of the formation condition and guiding the volumetric fracturing construction to select wells and select formations.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Segmented deployable boom structure for space applications
A long, elastically deployable tubular boom structure consisting of two or more thin-walled booms with a continuous longitudinal slit-opening along its entire length on the backside and a composite reinforced or metallic construction. The slit-opening, thin-walled tubular section accompanied by the boom elastic properties and unique fastening method between the boom segments allows the segmented boom to be flattened and then rolled up into an extremely compact cylindrical stowage volume. The boom elastically and immediately deploys from a rolled stowed configuration under its own strain energy without use of a motor or other complicated actuators / mechanisms. The segmented construction of multiple tube elements allows for unlimited boom lengths and enables unlimited structure scaling. In addition, the segmented slit-boom construction minimizes the overall boom cost and allows for tailoring of the boom stiffness along its length and facilitates repair of the boom if a material flaw is identified or localized damage occurs.
Owner:DEPLOYABLE SPACE SYST
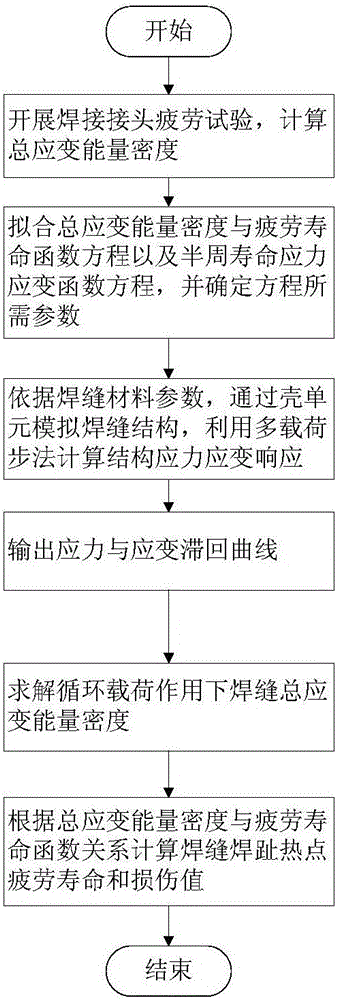
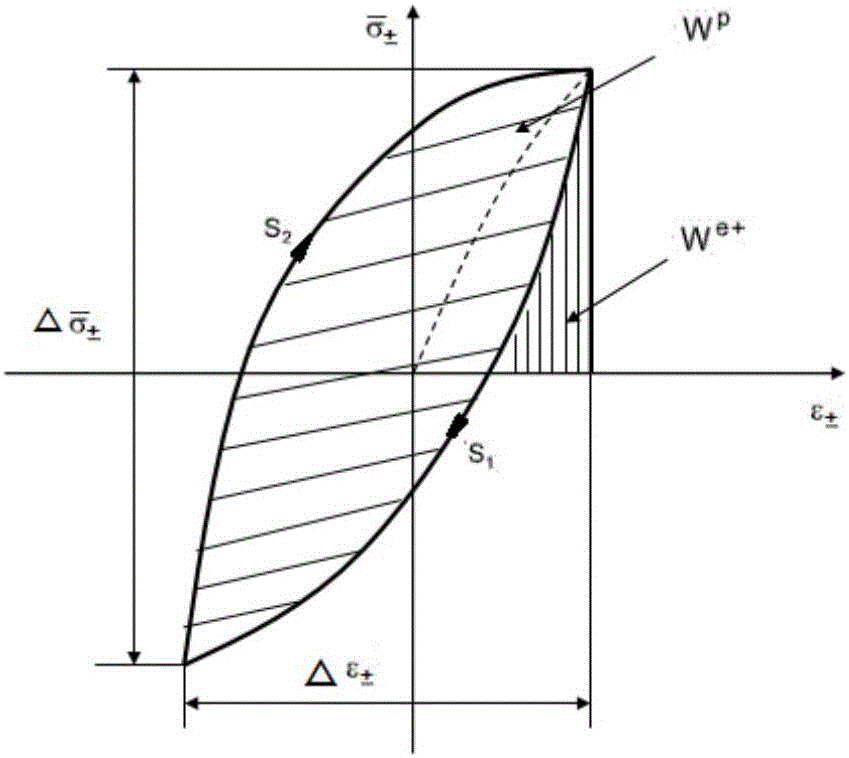
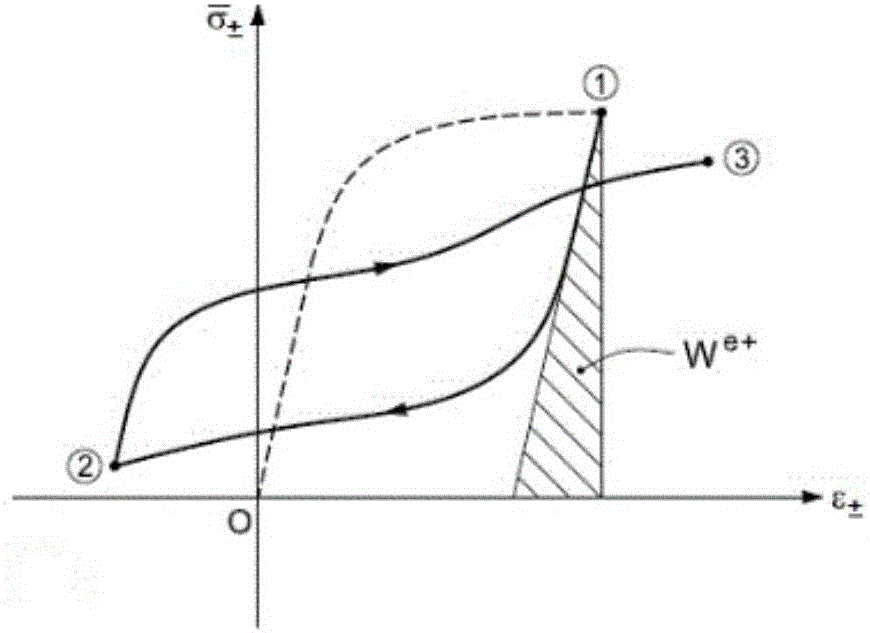
Weld seam fatigue life calculation method based on total strain energy density
ActiveCN106354898AImprove the accuracy of fatigue life calculationAvoid sureDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue IntensityFatigue damage
The invention discloses a weld seam fatigue life calculation method based on total strain energy density. The method mainly comprises the steps that 1, the weld-seam total strain energy density, a life function equation and a fatigue strength coefficient, a fatigue strength index, a cyclic strengthening coefficient and a cyclic strain hardening index which are needed by half-cycle life stress and a strain function equation are acquired through a welded joint fatigue test; 2, the weld seam structure is simulated through a shell unit module, the stress-strain response of the weld seam structure under the cyclic load action is calculated through a multi-load step method, and a stress-strain hysteretic curve is output; 3, the total strain energy density is calculated according to the stress-strain response, and the hot point fatigue life and a damage value of a weld toe of the weld seam are calculated by combining the energy density with the life function equation. According to the method, contribution of elastic-plastic stress and strain to the fatigue damage is comprehensively taken into account, scalar quantities are taken as damage parameters, the position and direction problems related to vectors are effectively avoided, the calculation precision is improved, and the time is saved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Rapid Thinning of GaN and SiC Substrates and Dry Epitaxial Lift-off
InactiveUS20150258769A1Minimize post lift-off polishingAvoid wasting substrate materialPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsEtchingCopper plating
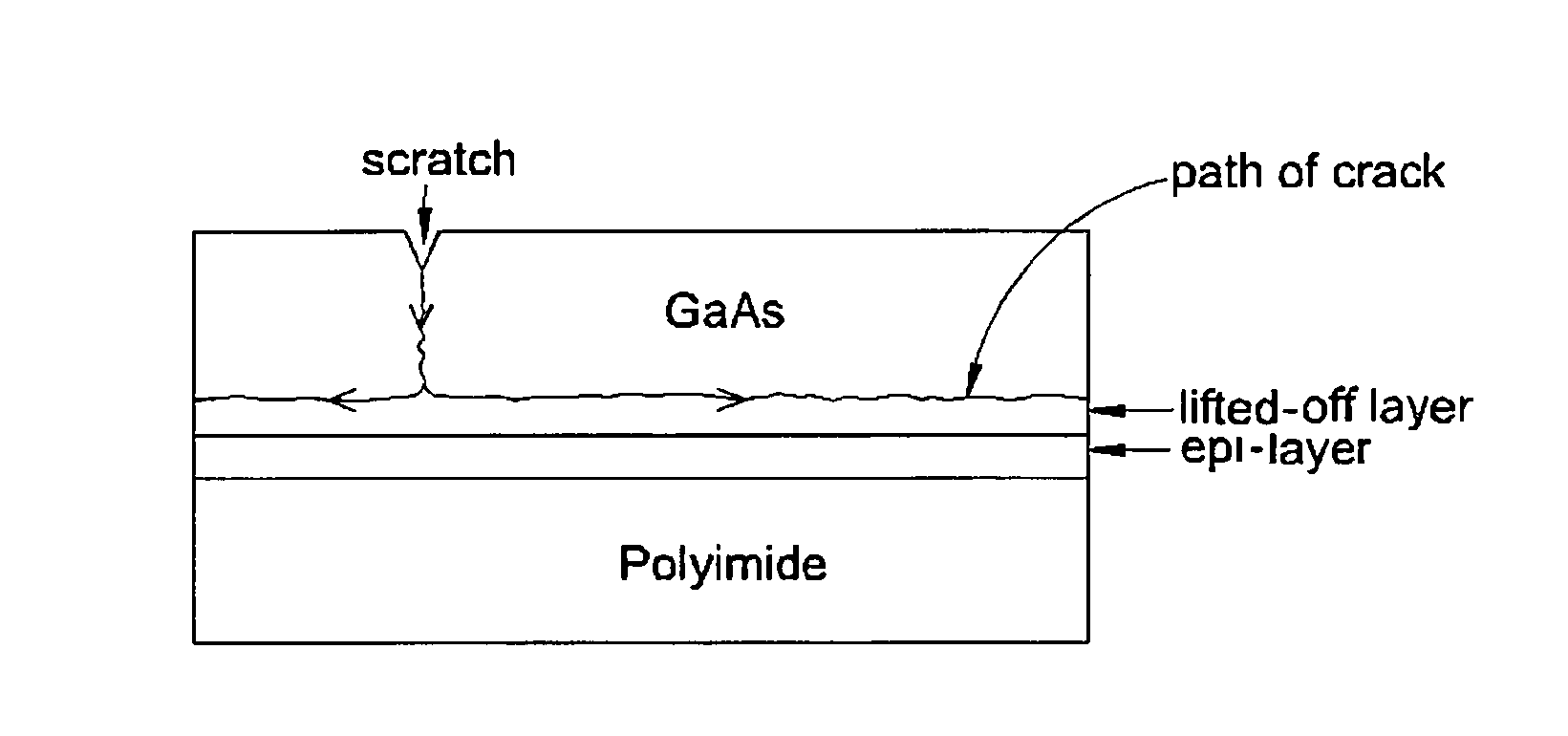
An epitaxially grown layer III-V solar cell is separated from the growth substrate by propagating a crack close to the epi / wafer interface. The crack is driven by the elastic strain energy built up due to thermal stresses between GaAs and polyimide by cooling below room temperature. A GaAs wafer is bonded to a polyimide substrate on the epi-side and scribed on the opposite side. The crack is initiated from the scratch and guided along the interface using an epitaxially grown sacrificial layer with lower fracture toughness under the solar cell. No expensive ion implantation or lateral chemical etching of a sacrificial layer is needed. The active layer is transferred wafer-scale to inexpensive, flexible, organic substrate. The process allows re-using of the wafer to grow new cells, resulting in savings in raw materials and grinding and etching costs amounting to up to 30% of the cost of the cell. Several cells are integrated on a common blanket polyimide sheet and interconnected by copper plating. The blanket is covered with a transparent spray-on polyimide that replaces the cover glass. The solar cell is stress-balanced to remain flat on orbit.Wide bandgap materials, such as Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) are very promising for light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and power electronics. These materials are extremely hard and difficult to machine and very expensive. The lack of good quality bulk GaN substrates with a smooth surface at a reasonable price is hampering the development of vertical devices.A rapid thinning technique is presented by lifting-off a 20-70 μm thick layer from the surface within a fraction of a second, which leaves the surface shiny and smooth. The savings in lapping and polishing add up to 60%, when this technique is incorporated in the crystal manufacturing process. This technology also has application for backside thinning where the savings are even larger.
Owner:FARAH JOHN
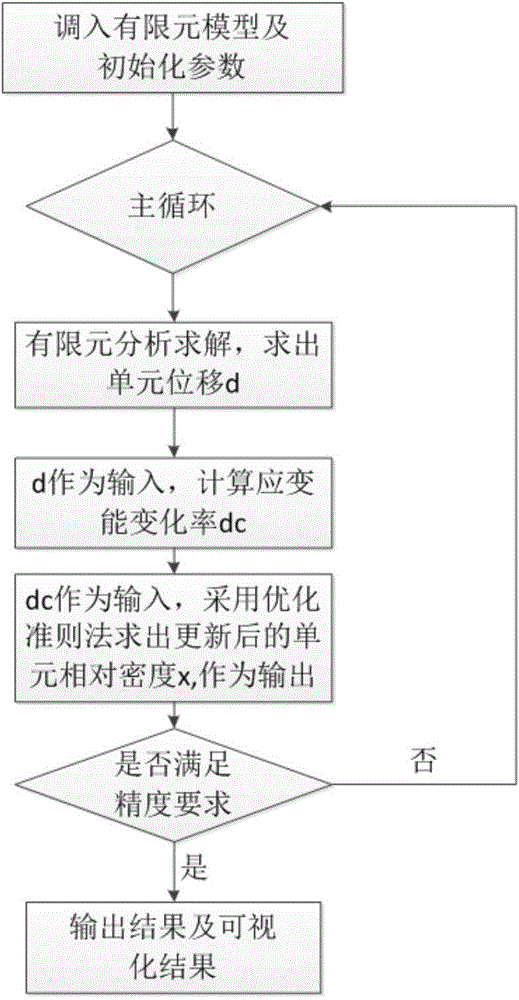
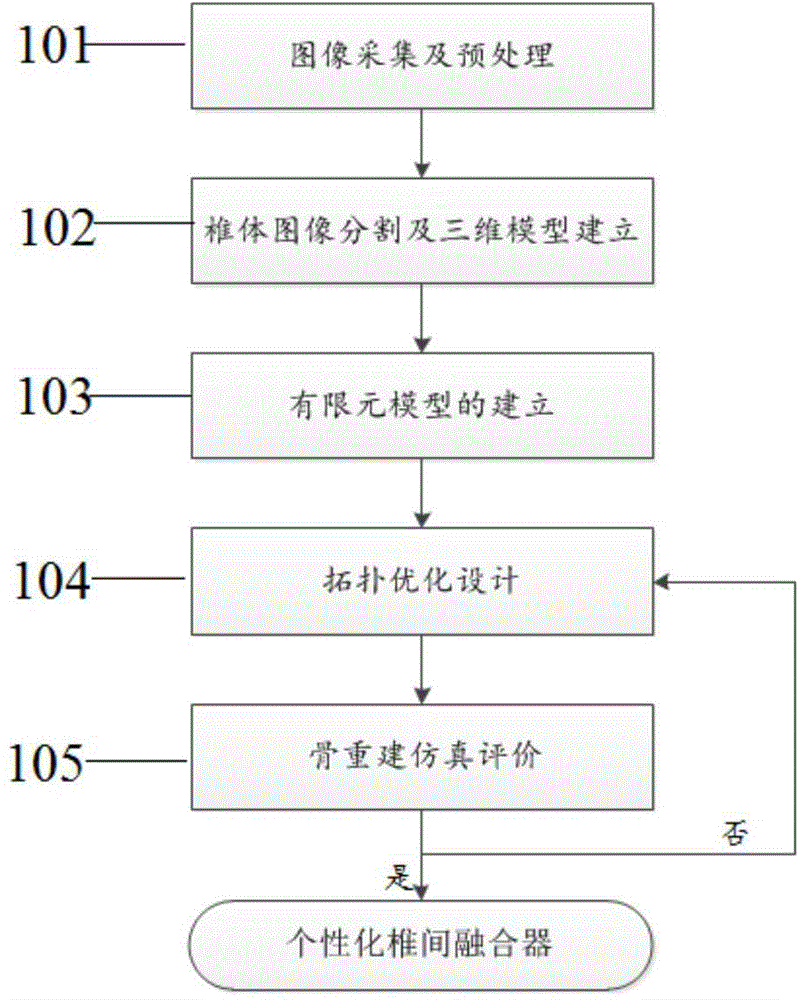
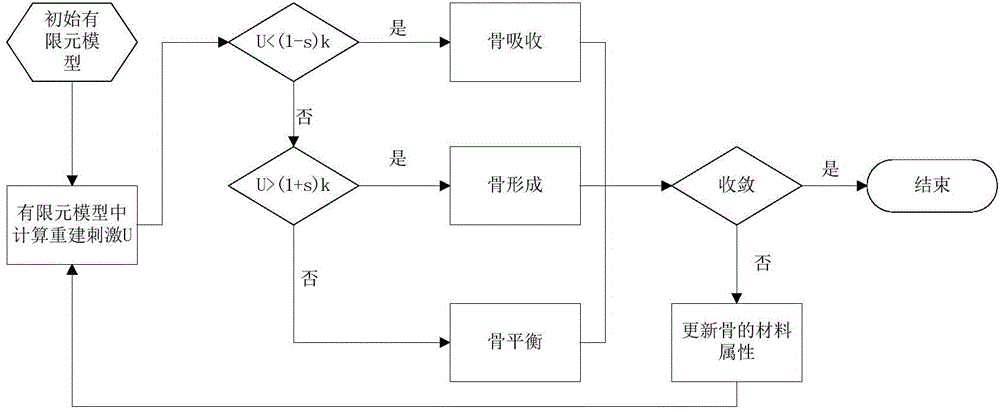
Personalized interbody fusion cage design method based on topological optimization and bony reconstitution simulation
InactiveCN104462723AGood for long termEase of evaluationSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationSpinal cage
The invention relates to a personalized interbody fusion cage design method based on topological optimization and bony reconstitution simulation. The method includes the steps of conducting CT / MRI scanning on a vertebral body, segmenting a CT / MRI continuous cross-sectional image of the vertebral body, establishing a three-dimensional model, establishing a finite element model through the substeps of grid dividing and smoothing, material assignment, boundary condition setting, mechanical loading and the like, conducting the topological optimization design on an interbody fusion cage through a density-variable method, and evaluating whether the design is reasonable or not by conducting bony reconstitution numerical analogue simulation on the vertebral body and the cage bone filling area according to the adaptation bony reconstitution theory on the basis of the strain energy density.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Shale hydraulic fracture propagation prediction method
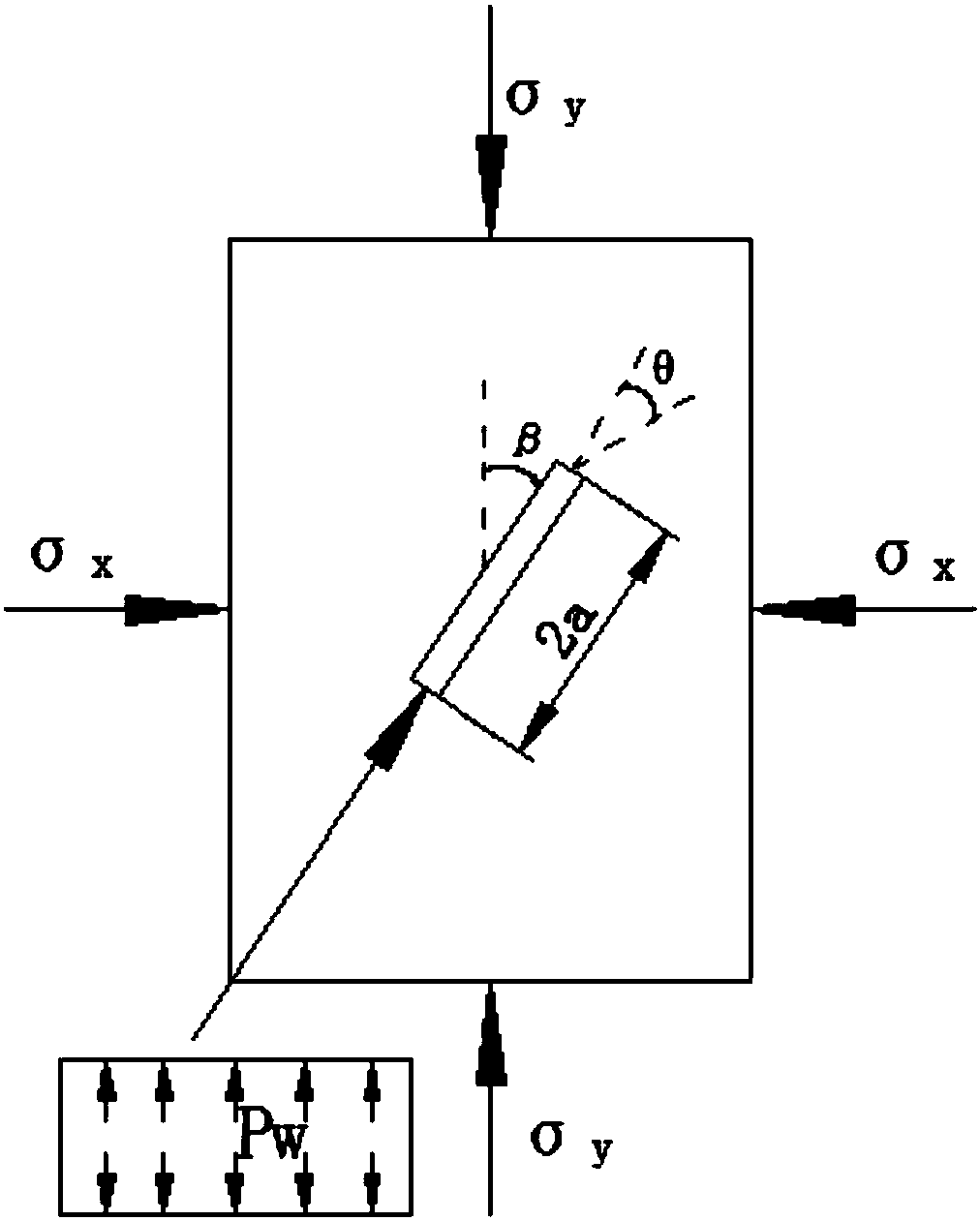
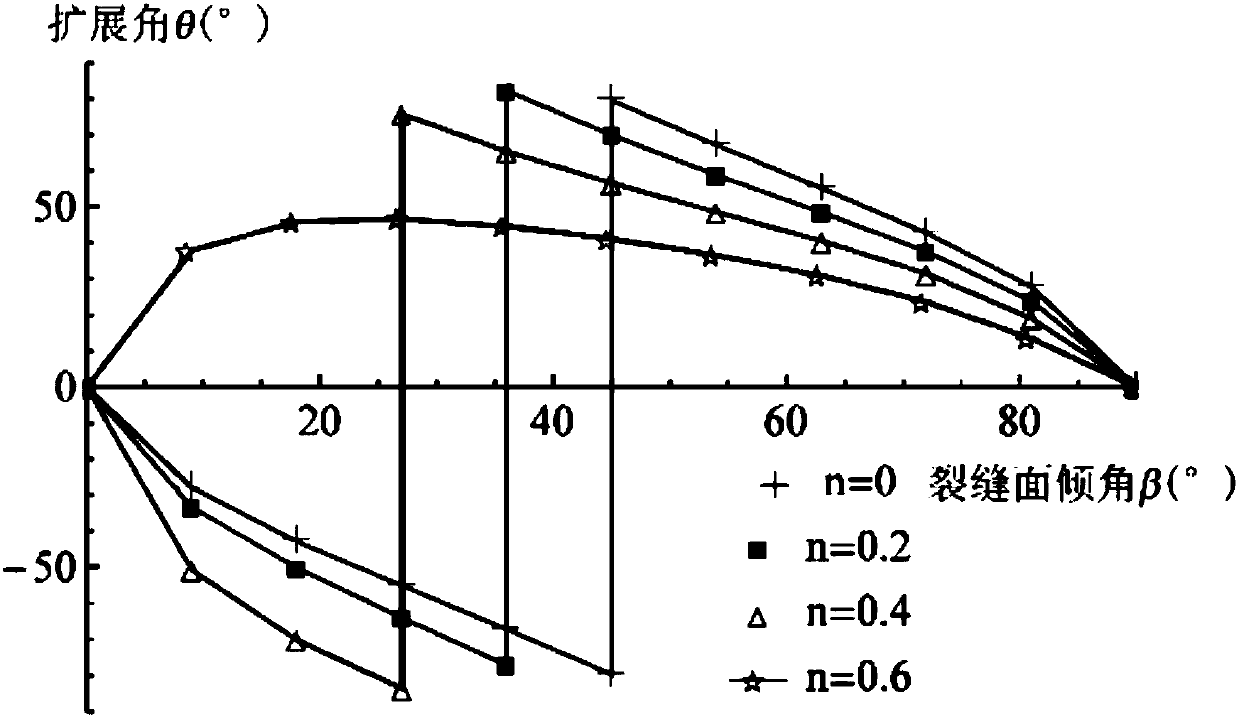
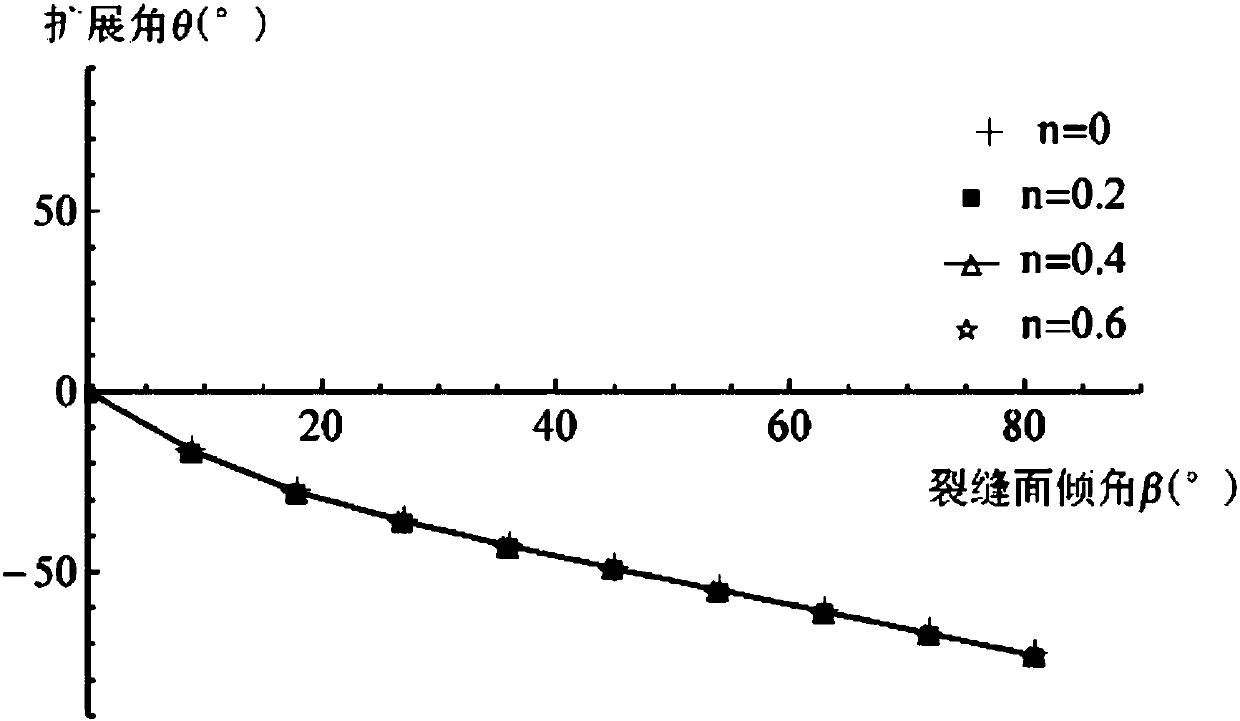
ActiveCN108468538AGuaranteed accuracyHigh precisionFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationFracture mechanicsStrain energy
The invention relates to the field of rock fracture prediction, in particular to a shale hydraulic fracture propagation prediction method. The method comprises the steps that 1, the normal direction,tangential stress and effect stress of an inclined fracture under the action of the external stress and water pressure are calculated; 2, a strain energy density function is obtained according to thetype of the fracture; 3, a strain energy density factor is obtained according to the strain energy density function; 4, the propagation direction and propagation angle of the fracture are judged according to a strain energy density criterion; 5, influences of stratification, natural fractures and the like on the propagation direction of hydraulic fractures are obtained through numerical simulation, so that fracture propagation under the effect of shale hydraulic pressure is predicted. The prediction method is based on fracture mechanics, a hydraulic condition factor is introduced, and the influences of different stratification directions on the propagation direction of the shale hydraulic fractures are obtained by researching the relation between the fracture propagation direction and themagnitude of the hydraulic pressure and utilizing an extended finite element method, so that accurate prediction of hydraulic fracture propagation is achieved, and higher prediction accuracy is obtained.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
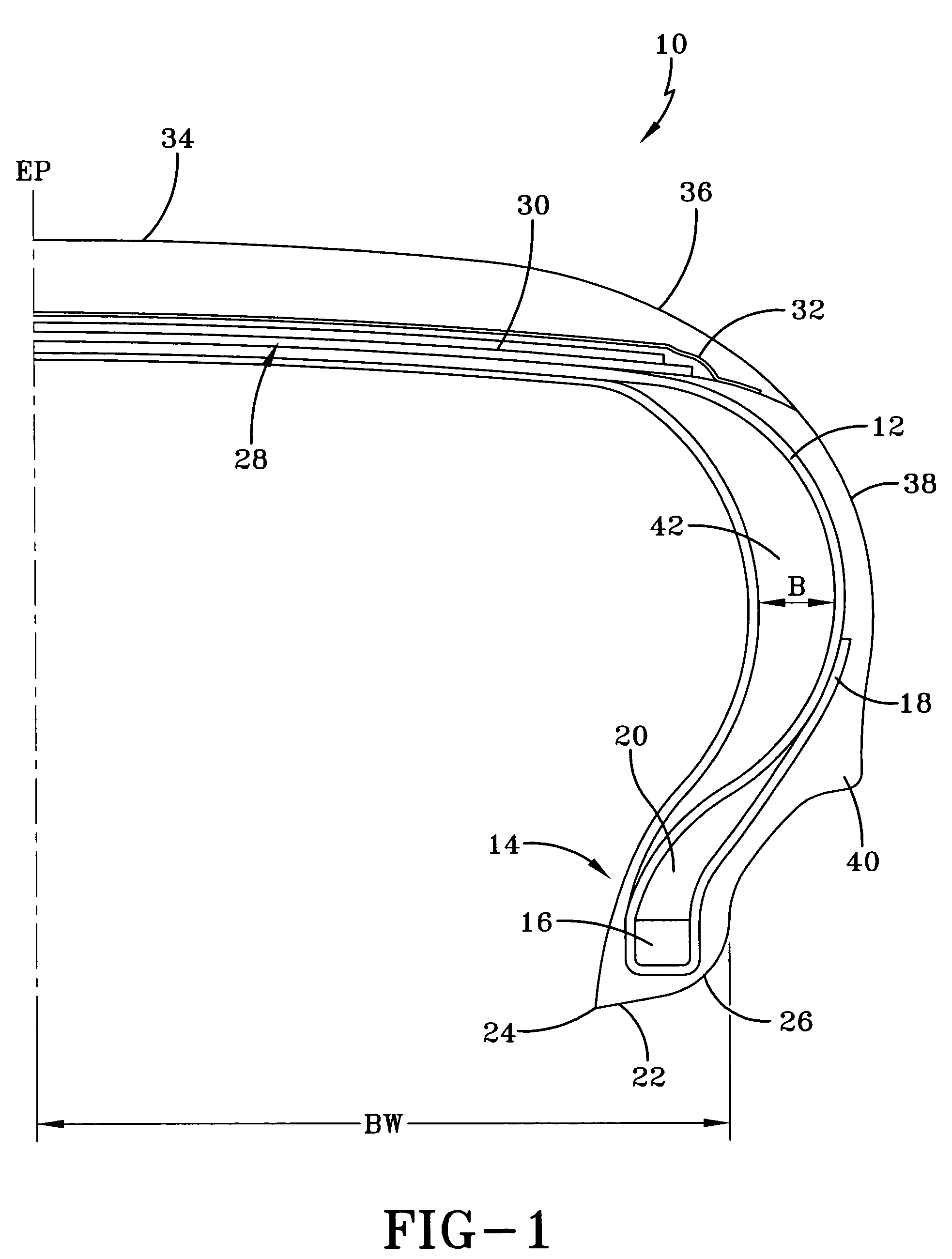
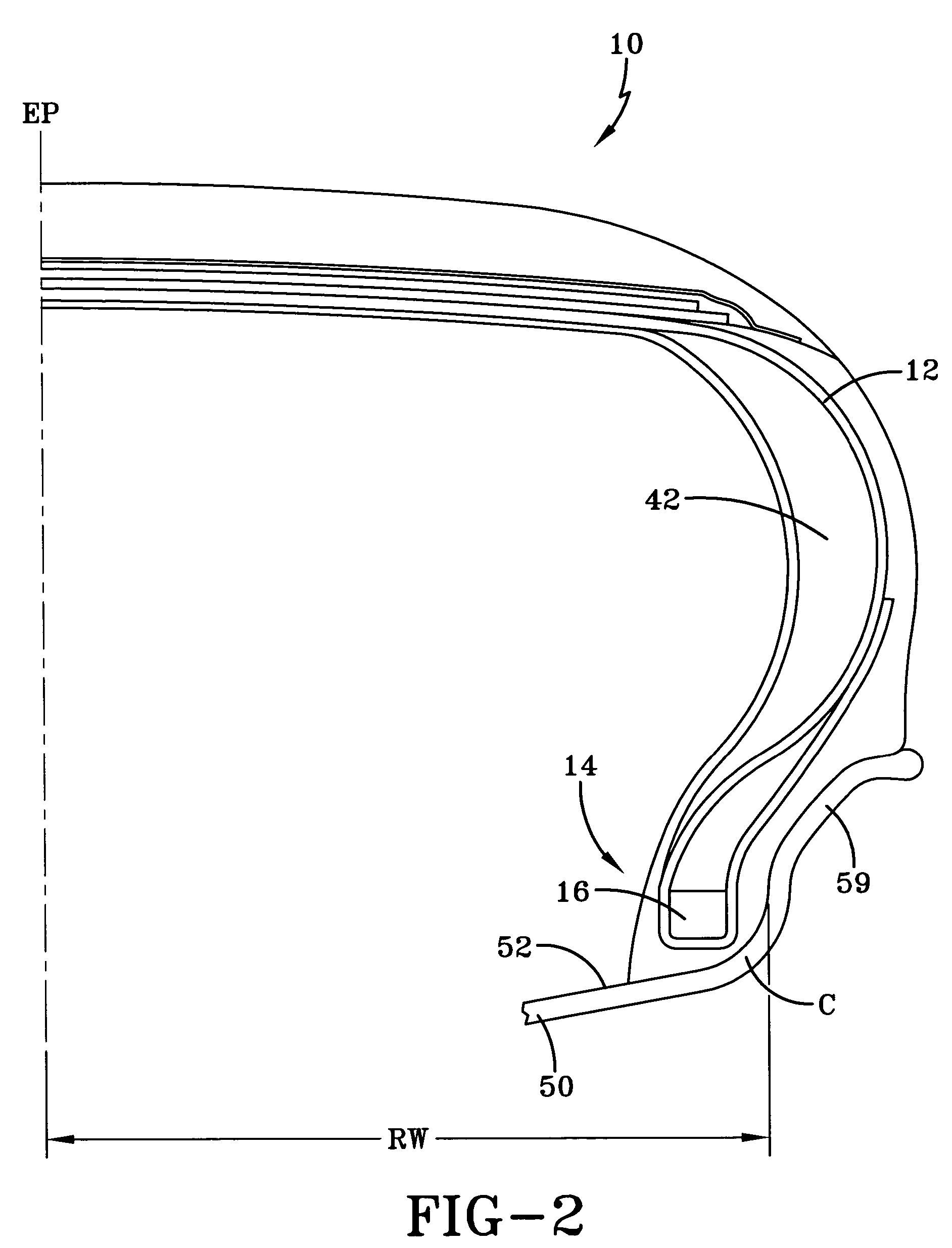
Self-supporting pneumatic tire
InactiveUS7093633B2Ride comfort is improvedIncreased durabilityWithout separate inflatable insertsRimsStrain energyEngineering
A self-supporting pneumatic tire is molded in such a manner that ride comfort is improved, durability is increased, and a greater run-flat capability can be achieved. The self-supporting run-flat tire is molded such that the molded bead base width is equal or less than the rim width of the intended rim upon which the tire is to be mounted. By molding the tire with a bead width less than or equal to the rim width, the sidewall inserts are not subjected to additional stress during and after inflation of the tire and the strain energy is more evenly distributed through the sidewall pillar construction.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com