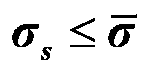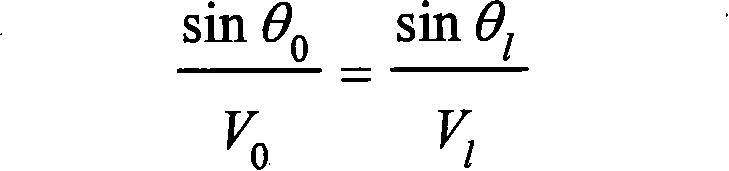Patents
Literature
113 results about "Tangential stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of tangential stress. : a force acting in a generally horizontal direction; especially : a force that produces mountain folding and overthrusting.
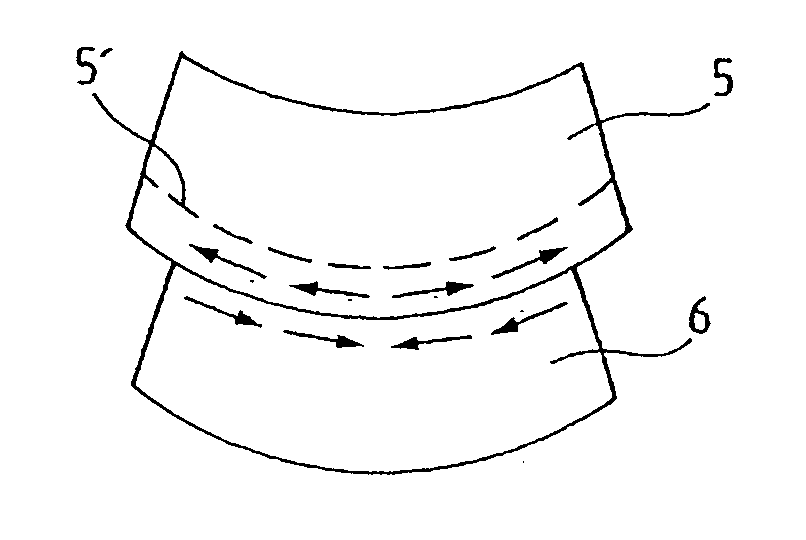
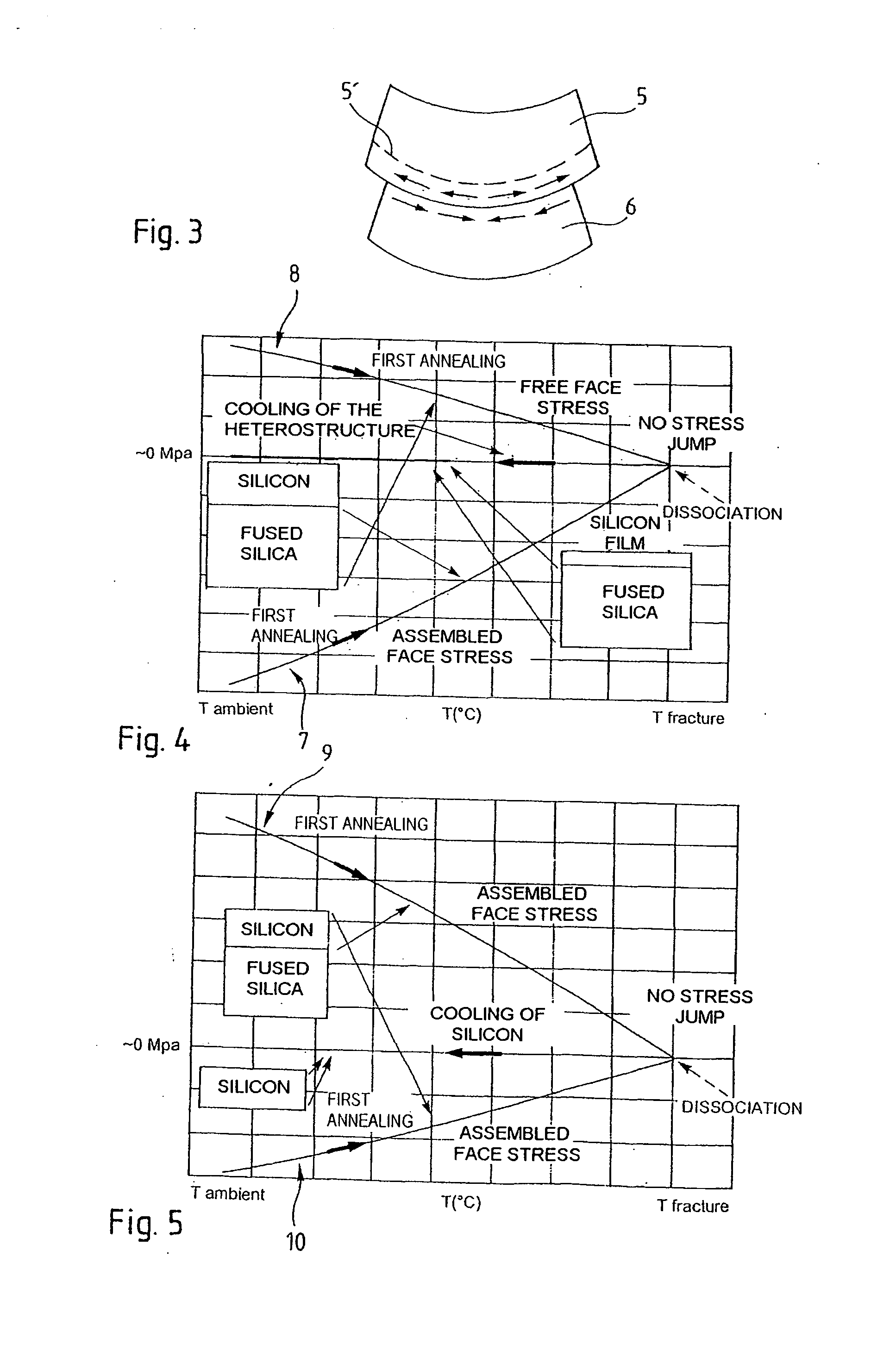
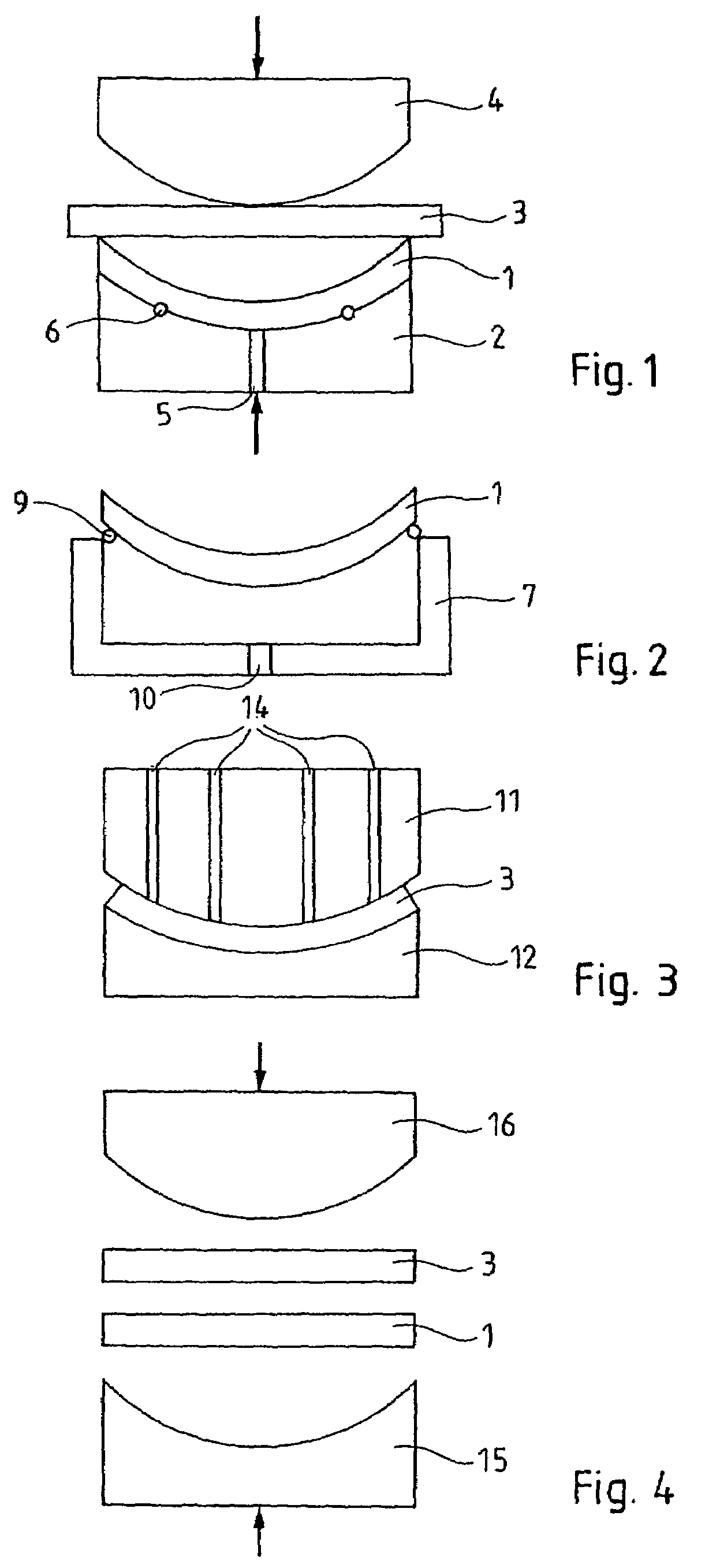
Method of producing a complex structure by assembling stressed structures
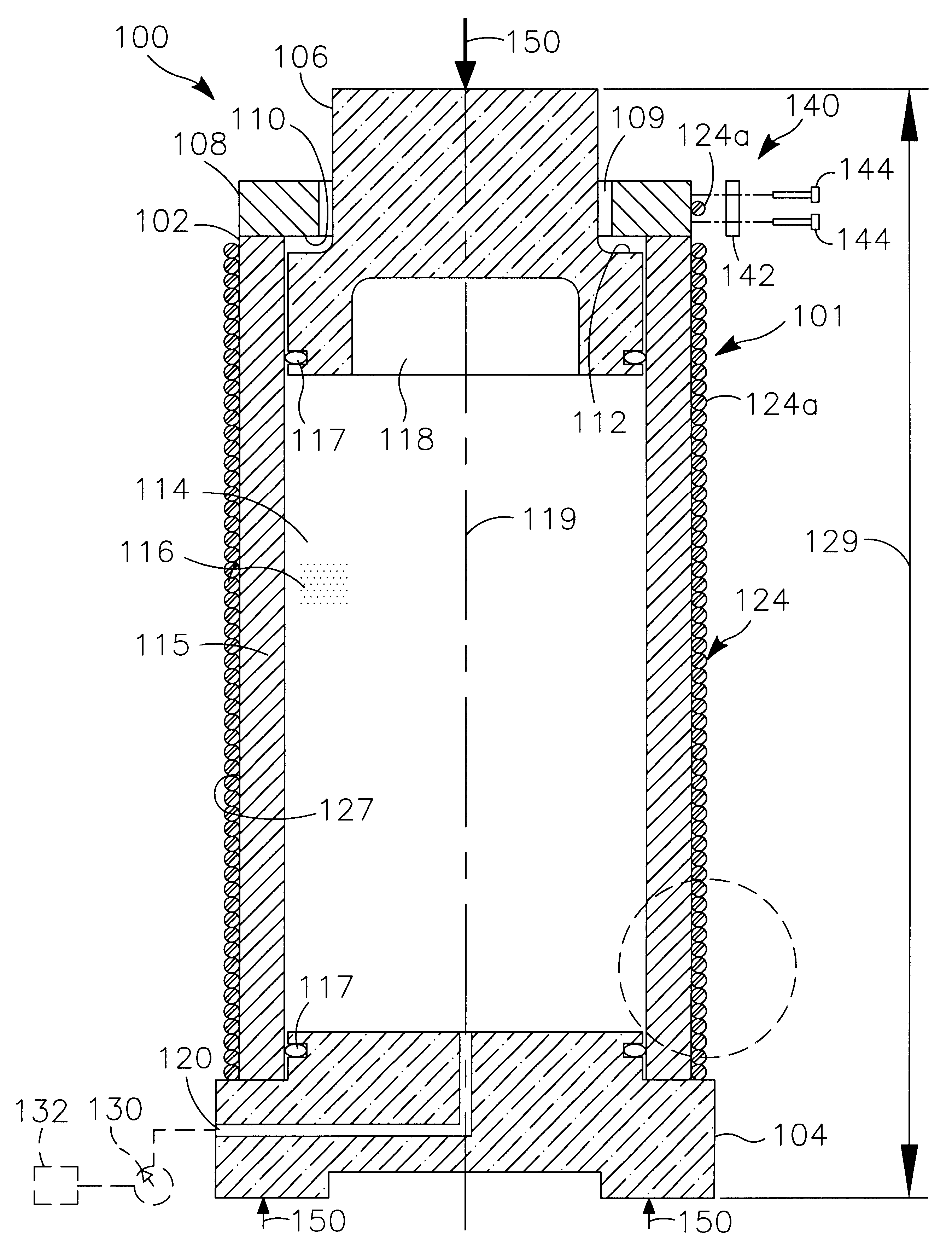
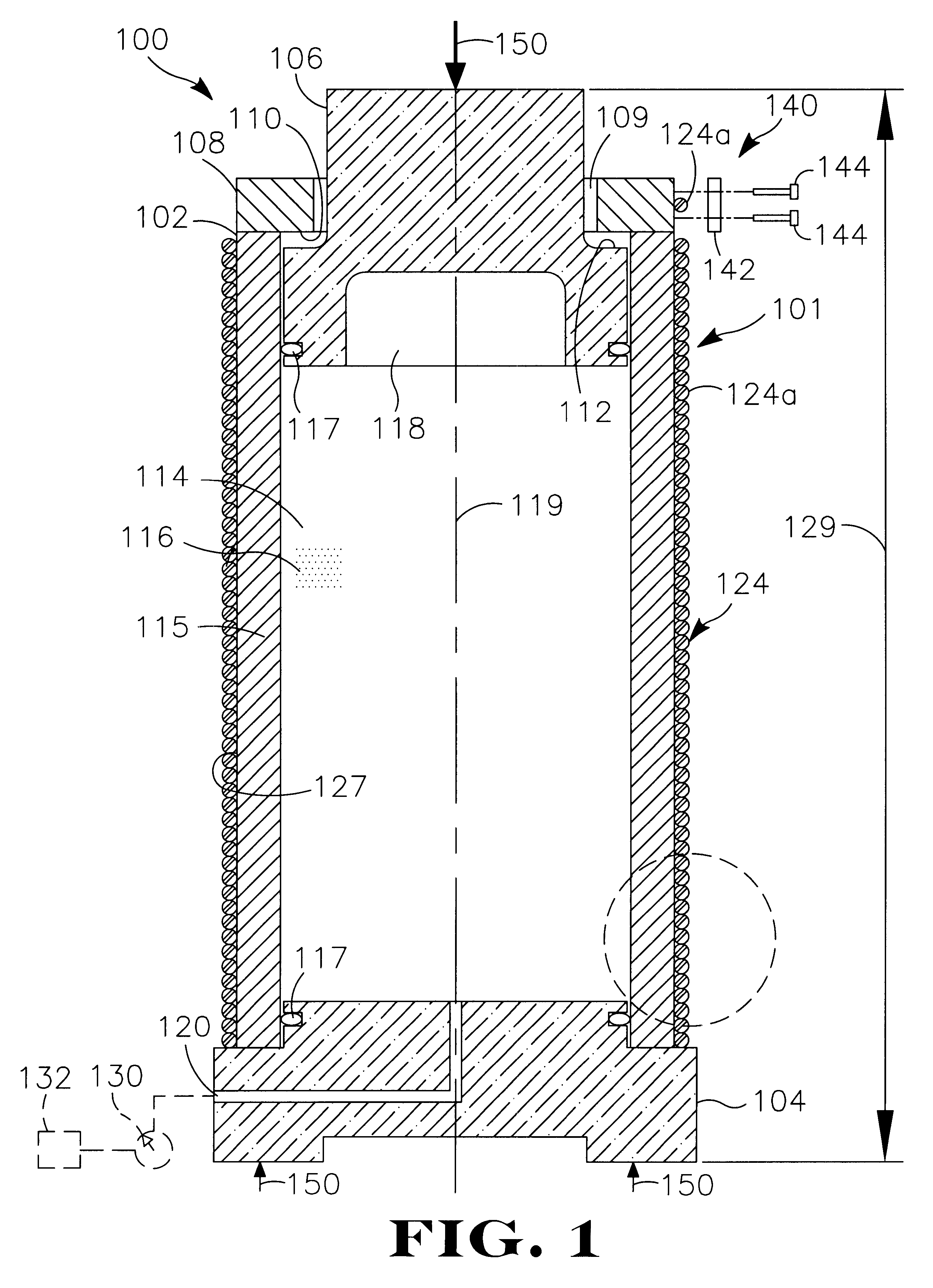
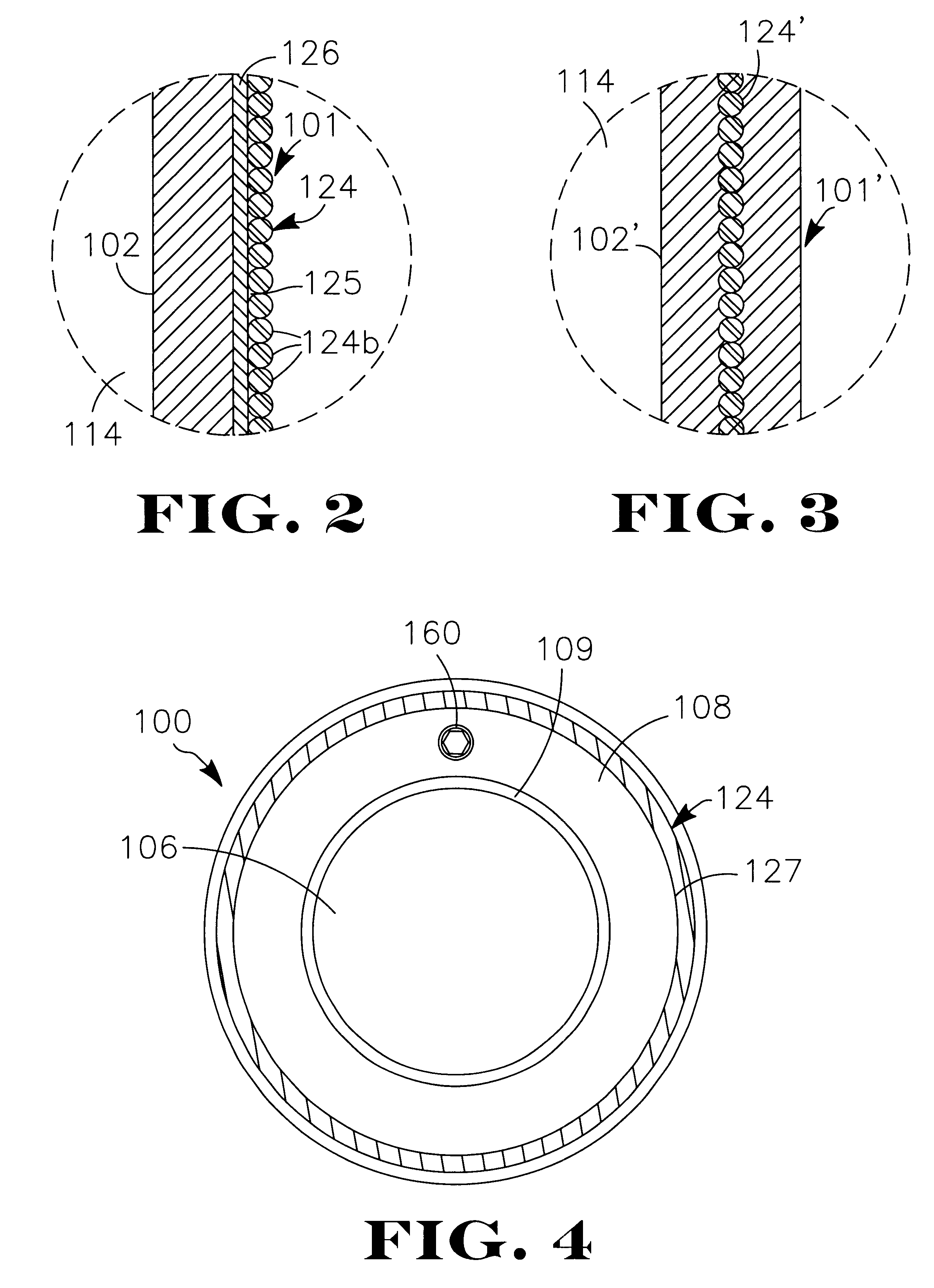
ActiveUS20060141742A1Easy to controlQuality improvementLamination ancillary operationsSolid-state devicesElectronic structureTangential stress
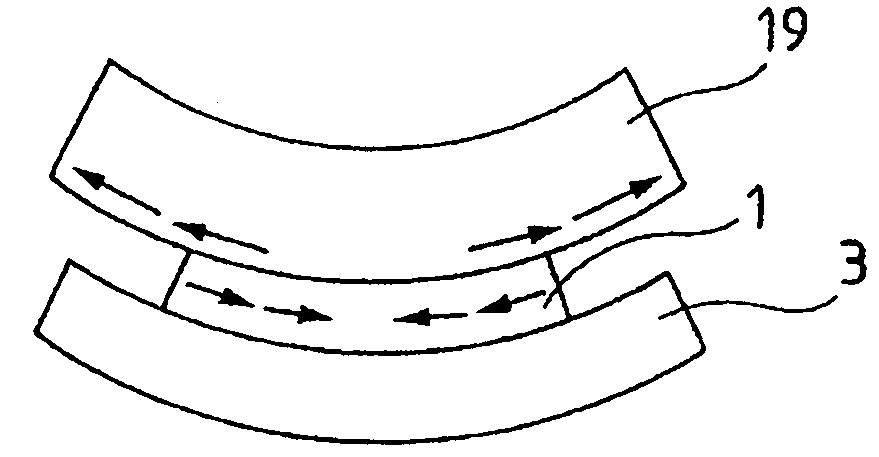
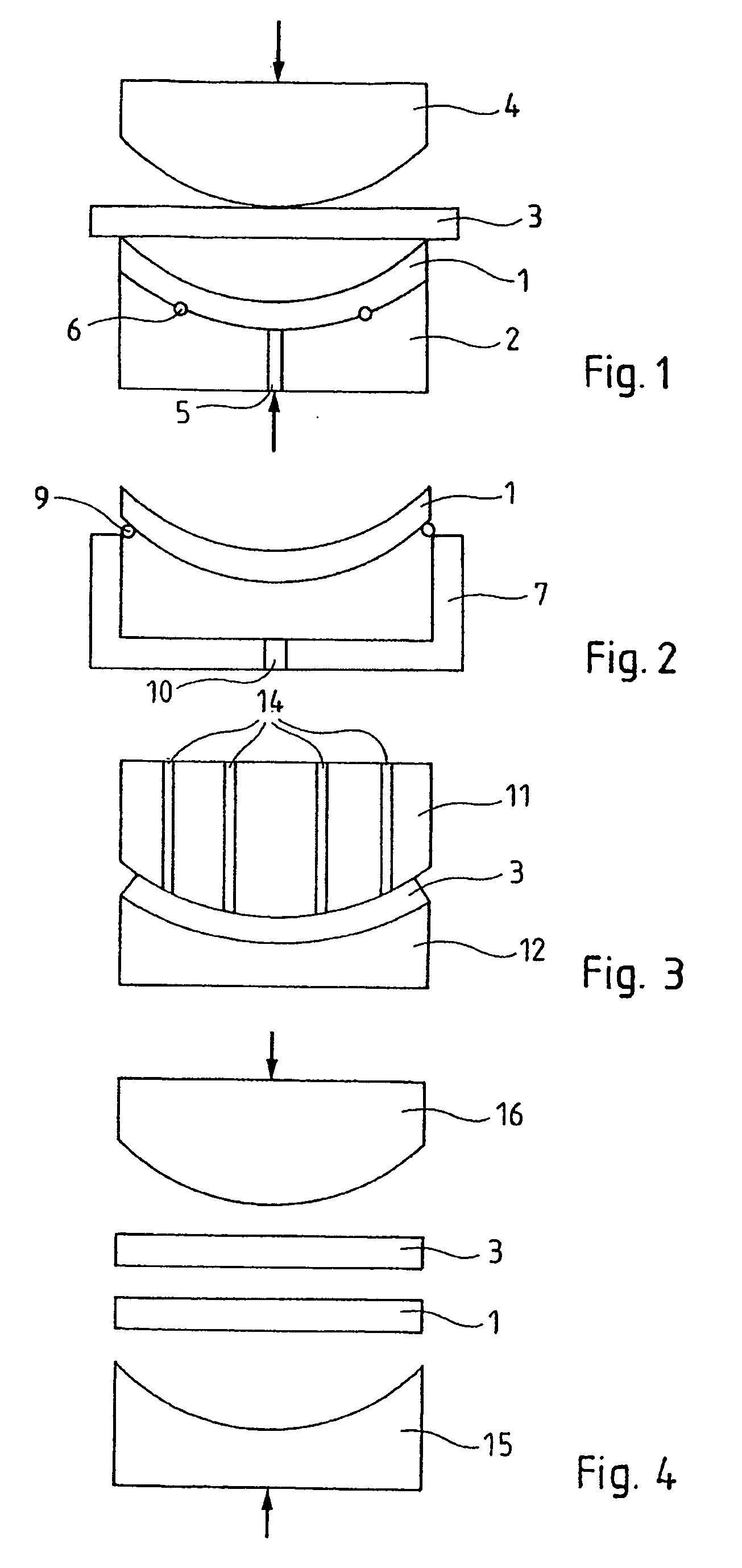
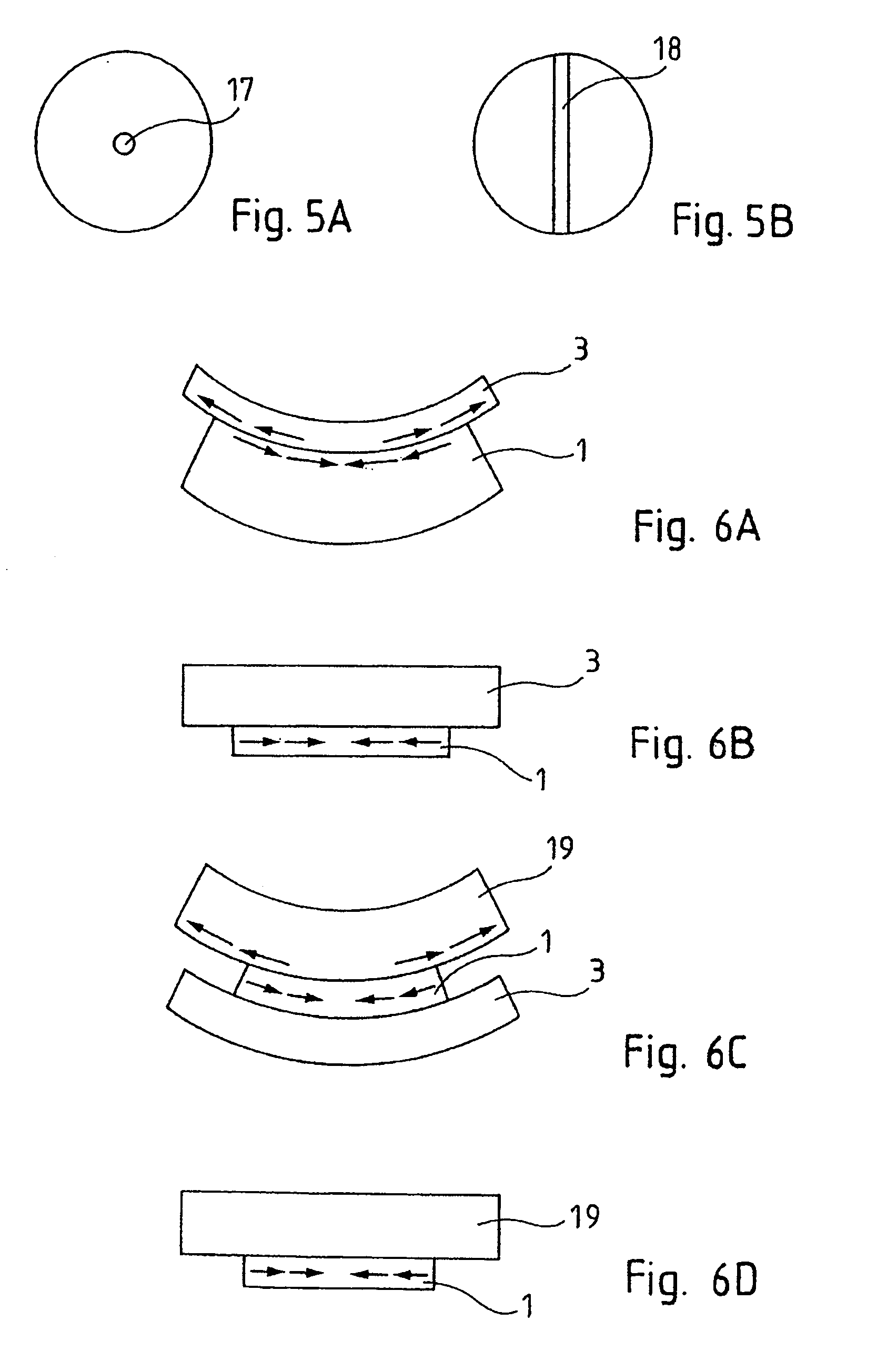
The invention relates to a method of producing a complex microelectronic structure, in which two basic microelectronic structures (1, 3) are assembled at the two respective connecting faces (3) thereof. The invention is characterised in that, before assembly, a difference is created in the tangential stress state between the two faces to be assembled, said difference being selected such as to produce a pre-determined stress state within the assembled structure under given conditions in relation to the assembly conditions.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
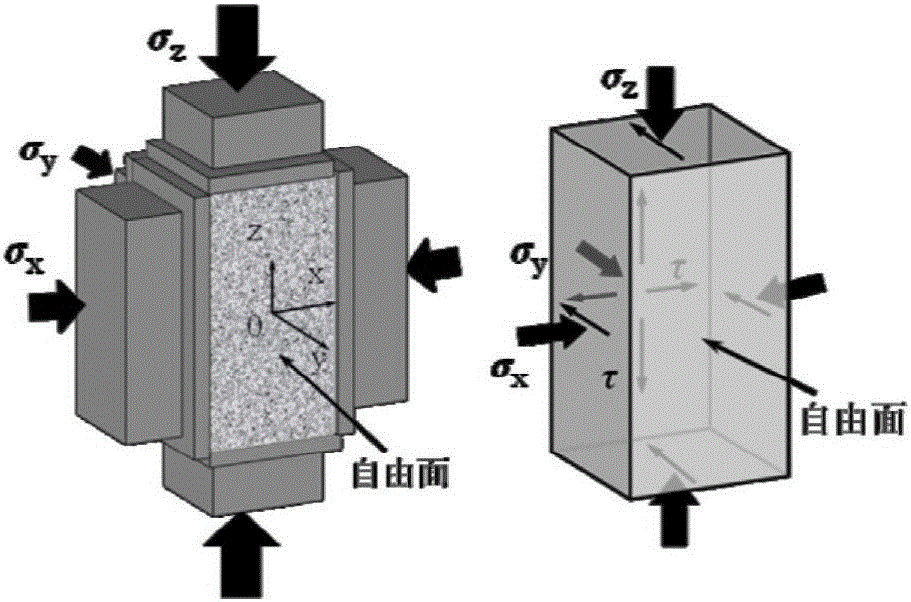
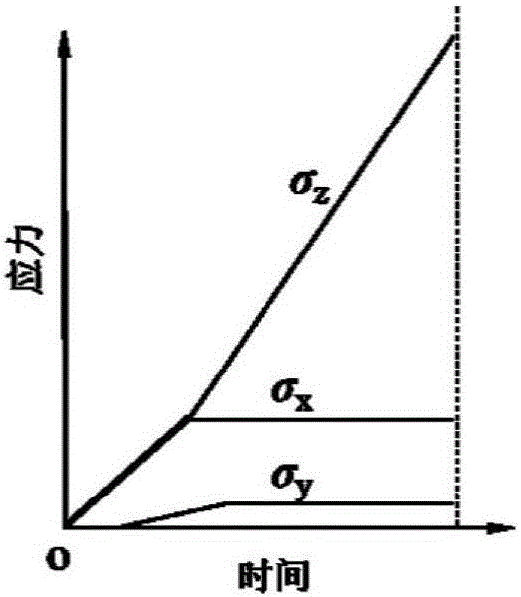
True triaxial test method for simulating shearing type rock burst
InactiveCN106442174APowerful testGet Deformation PropertiesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesTriaxial shear testStress conditions
The invention discloses a true triaxial test method for simulating shearing type rock burst. In the method, a true triaxial loading path and boundary condition characterized in that a single surface is free and five surfaces are stressed is adopted, a test piece with a large size is adopted, a certain three-dimensional load is applied, a loading rate of one direction is controlled, and a cuboid rock sample of which the single side is free under a three-dimensional compression stress state is used for simulating a special mechanical behavior of a field surrounding rock representativeness rock unit in a tangential stress centralization process. When the method is adopted, an inoculation and generation overall process of the shearing type rock burst can reappear in a laboratory, the problem that a traditional indoor test method cannot reasonably simulate the shearing type rock burst under a complex stress condition is solved, and the true triaxial test method has important practical significance and academic value for the mechanism and prediction studies of the type of rock burst.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
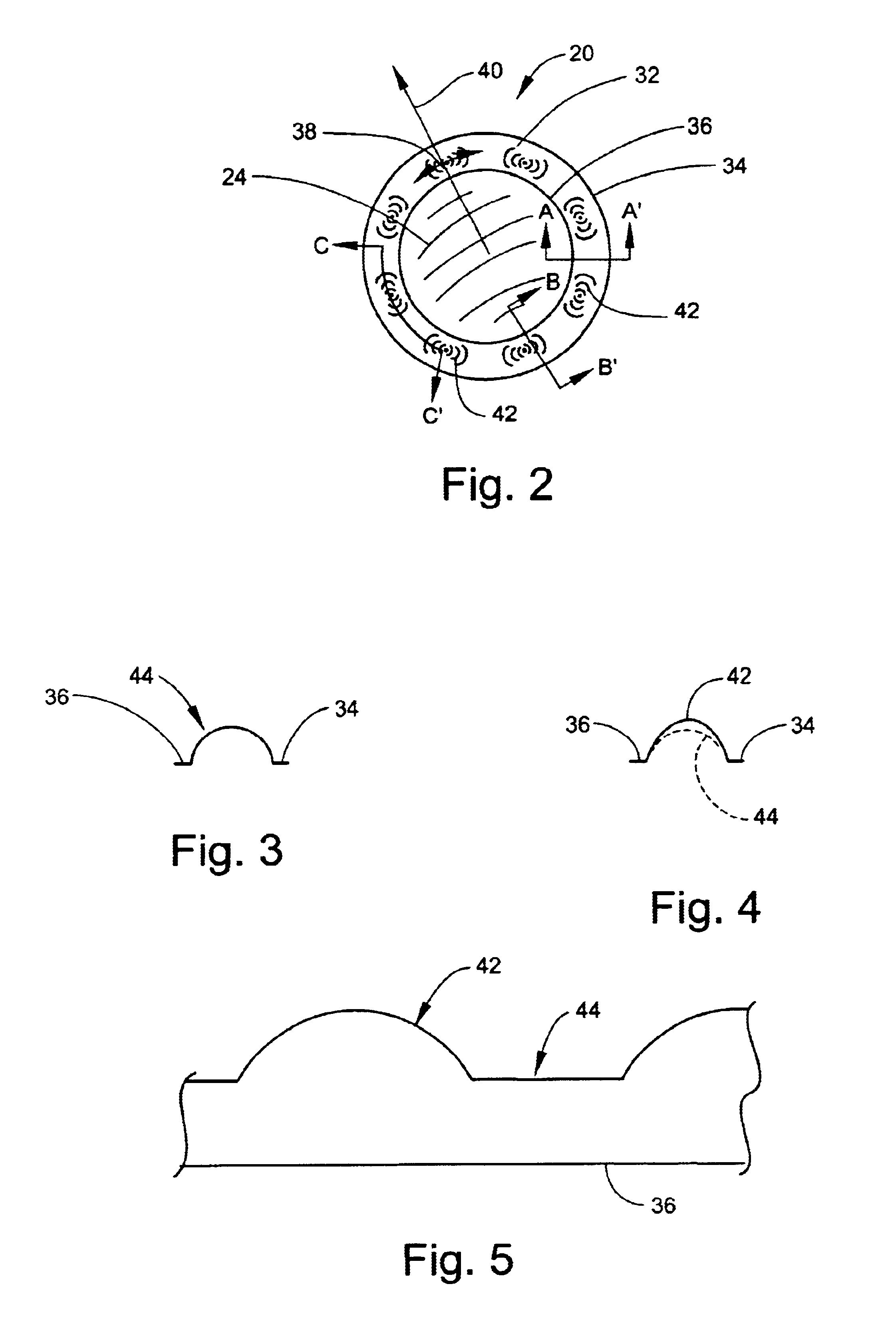
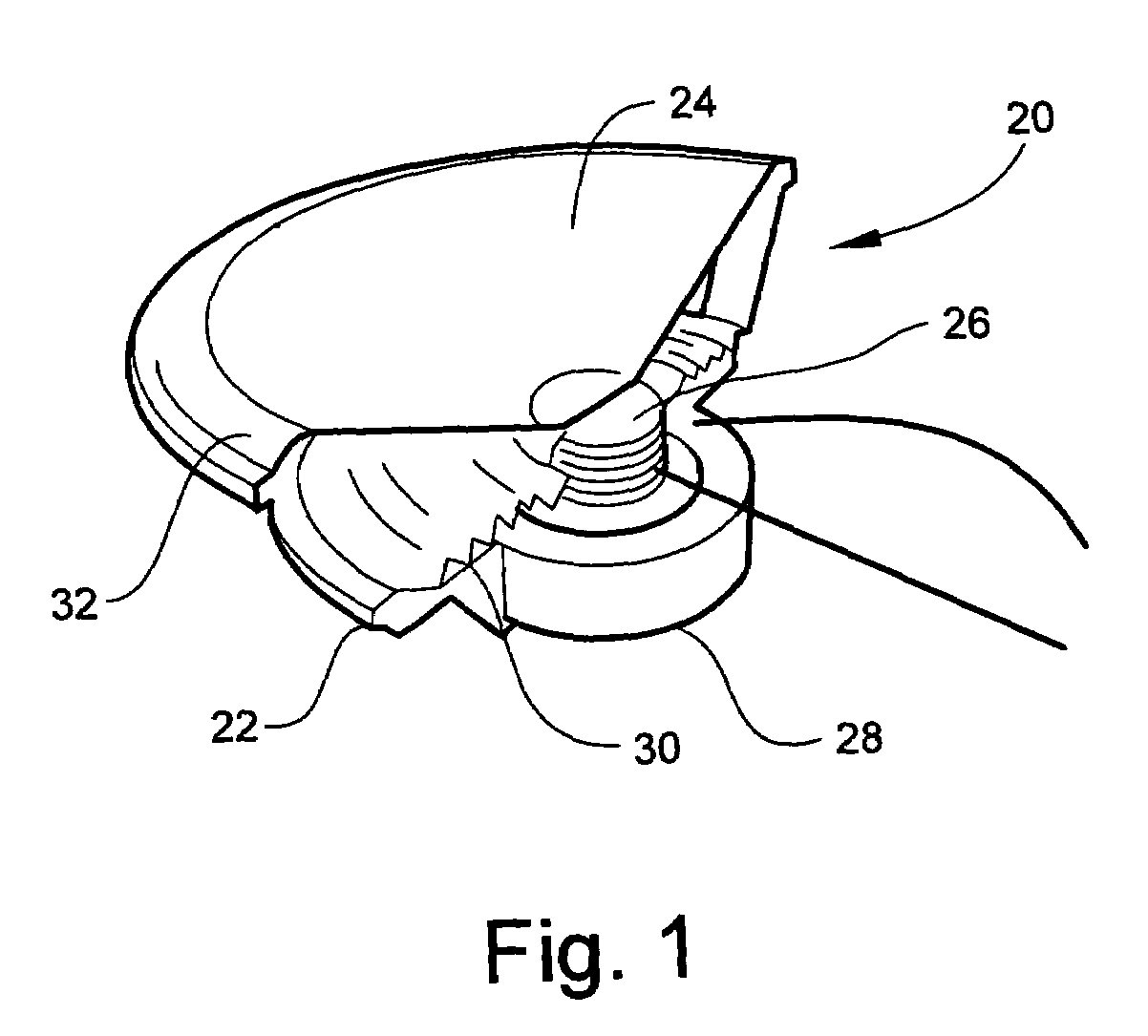
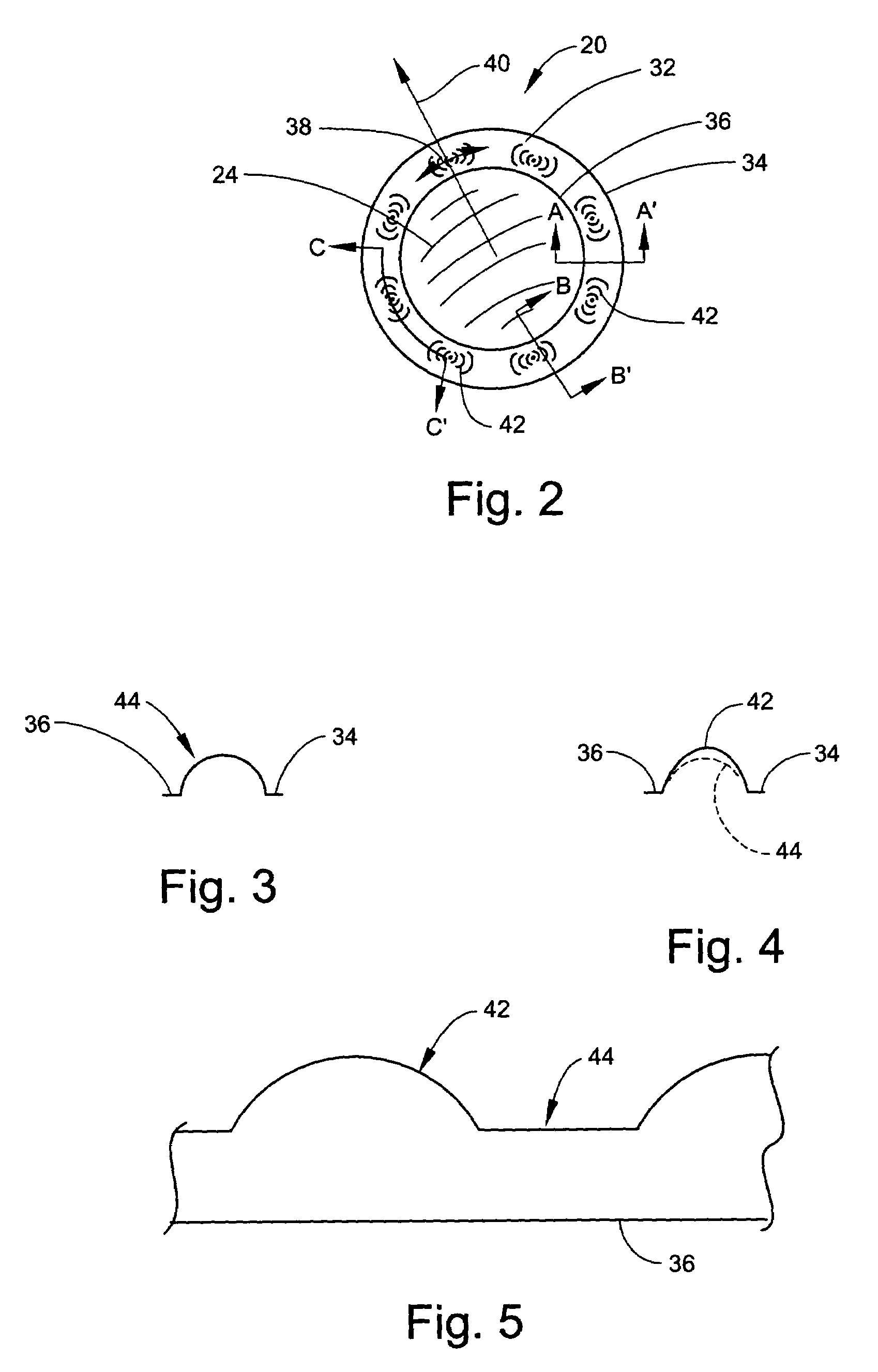
Tangential stress reduction system in a loudspeaker suspension
InactiveUS6851513B2Improve linearityImproved speaker performanceTransducer detailsLoudspeaker diaphragm shapeTangential stressEngineering
The invention is a suspension element having an outer edge and an inner edge. The suspension element, such as a spider or surround, varies in shape along at least a portion of the suspension element to help relieve both the radial and tangential stress placed on the suspension element when it is stretched. The shape employed in the suspension element allows the suspension element to stretch more easily, creating a higher performance speaker of the same size by increasing the diaphragm excursion and voice coil movement.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
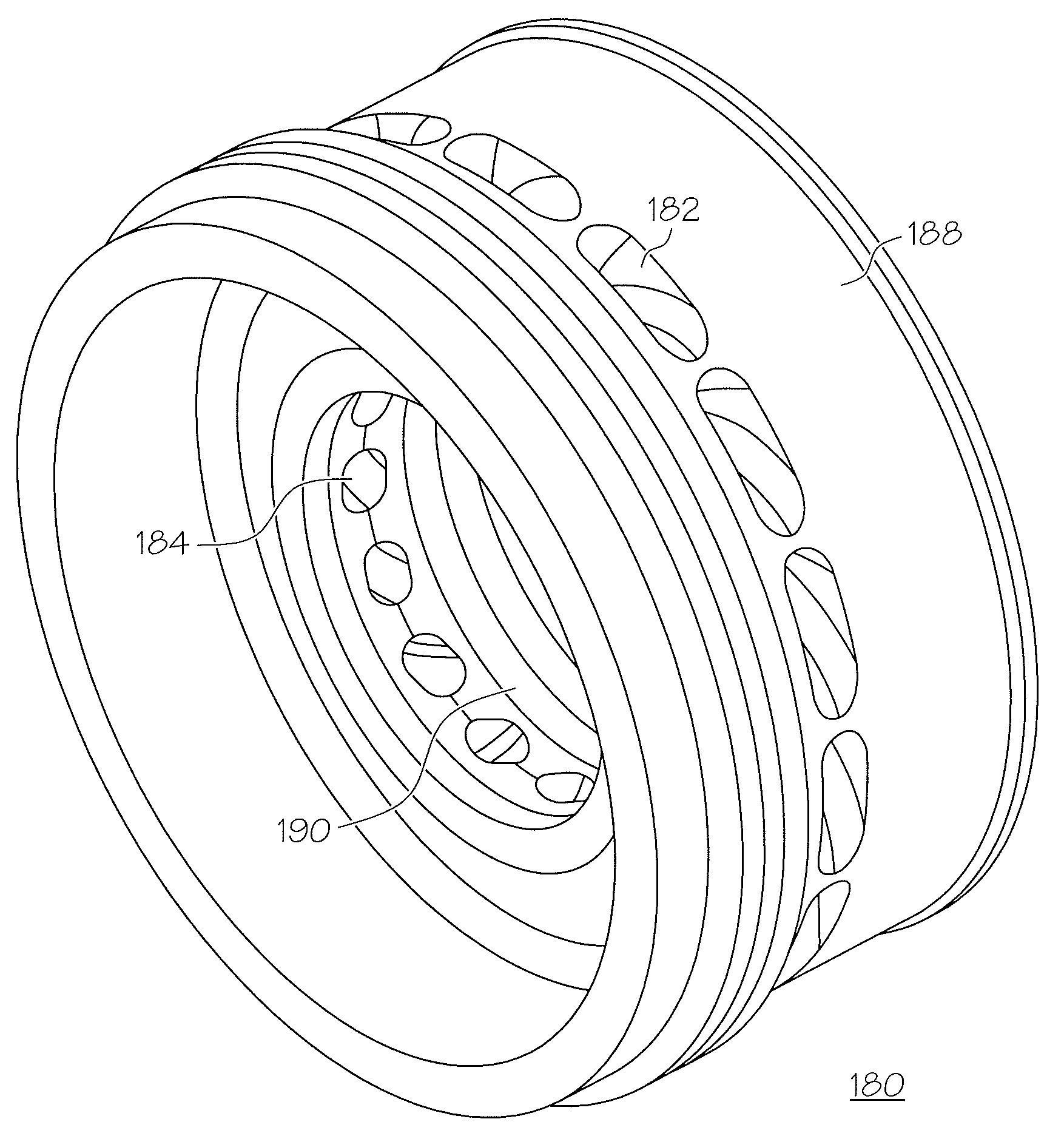
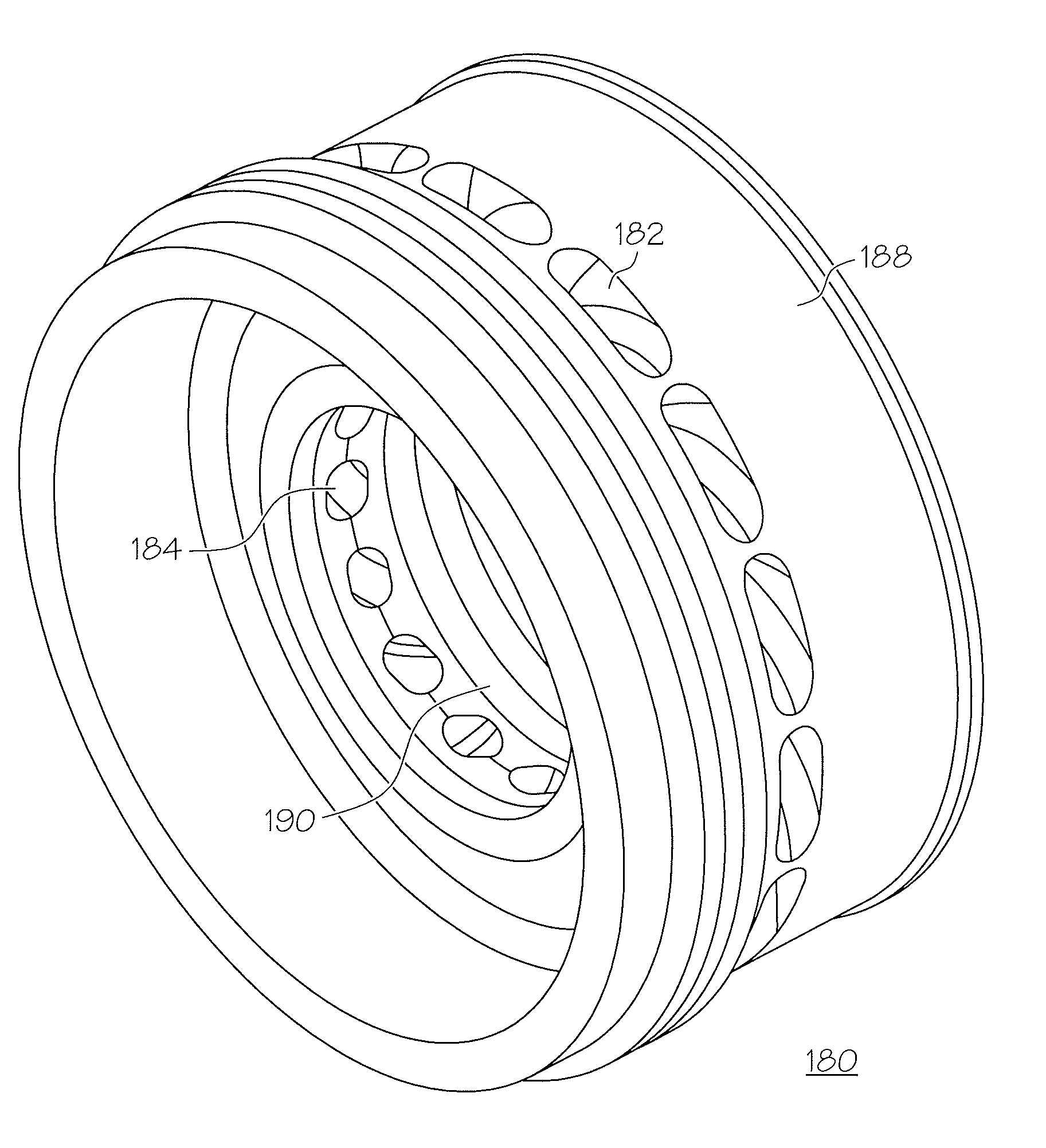
Vortex spoiler for delivery of cooling airflow in a turbine engine
InactiveUS7708519B2Minimal tangential stressStatic pressure lossPump componentsWind motor controlTangential stressEngineering
A vortex spoiler (180) for delivery of a cooling airflow (192) in a turbine (108) engine (100) including a plurality of inlet ports (182) formed circumferentially about a radial exterior sidewall (188), and a plurality of outlet ports (184) formed circumferentially about a radial interior sidewall (190). The plurality of inlet ports (182) are coupled to the plurality of outlet ports (184) via a plurality of ducts (186). Each of the ducts is formed having an interior diameter at the inlet port and the outlet port formed at a preselected angle normal to the surface of the each of the radial sidewalls to form a radially curved profile such that a cooling airflow (192) may pass radially inwardly through each of the plurality of ducts (186) with minimal tangential stress and minimal static pressure loss.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
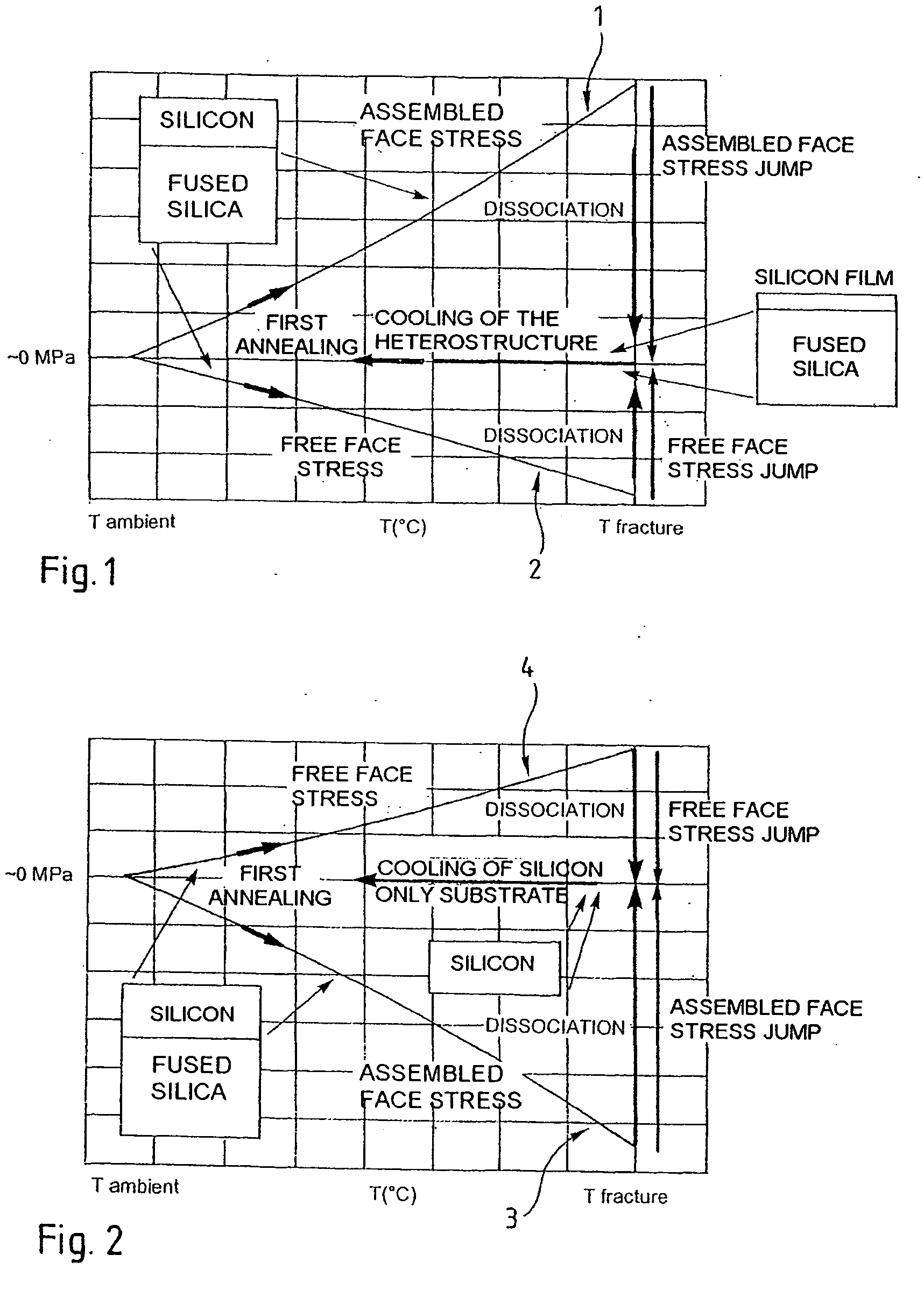
Method for making a stressed structure designed to be dissociated
InactiveUS20060205179A1Minimize stressImprove mechanical stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic structureTangential stress
The invention concerns a method of making a complex microelectronic structure by assembling two substrates through two respective linking surfaces, the structure being designed to be dissociated at a separation zone. The invention is characterized in that is consists, prior to assembly, in producing a state difference in the tangential stresses between the two surfaces to be assembled, said difference being selected so as to obtain in the assembled structure a predetermined stress state at the time of dissociation.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
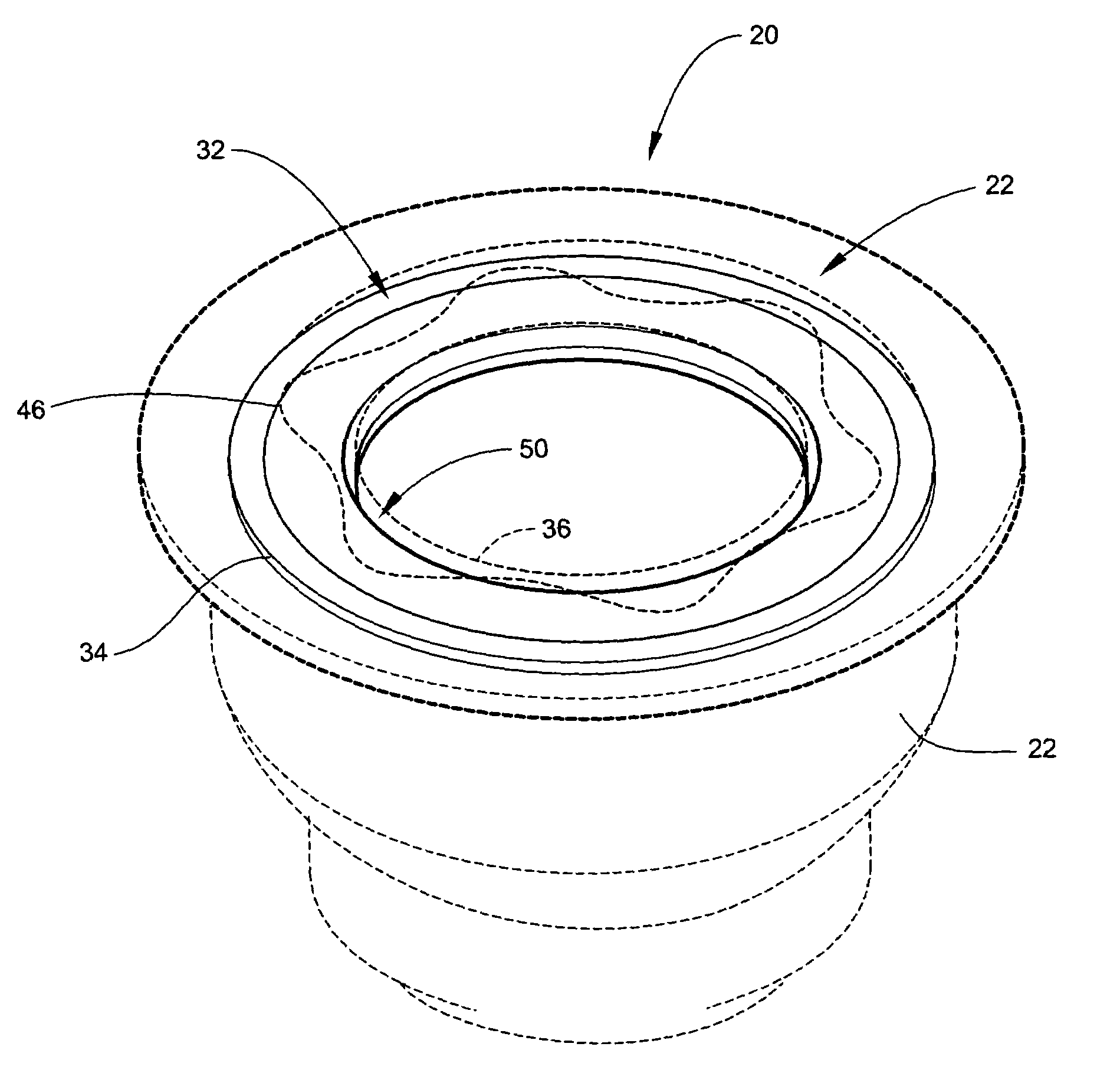
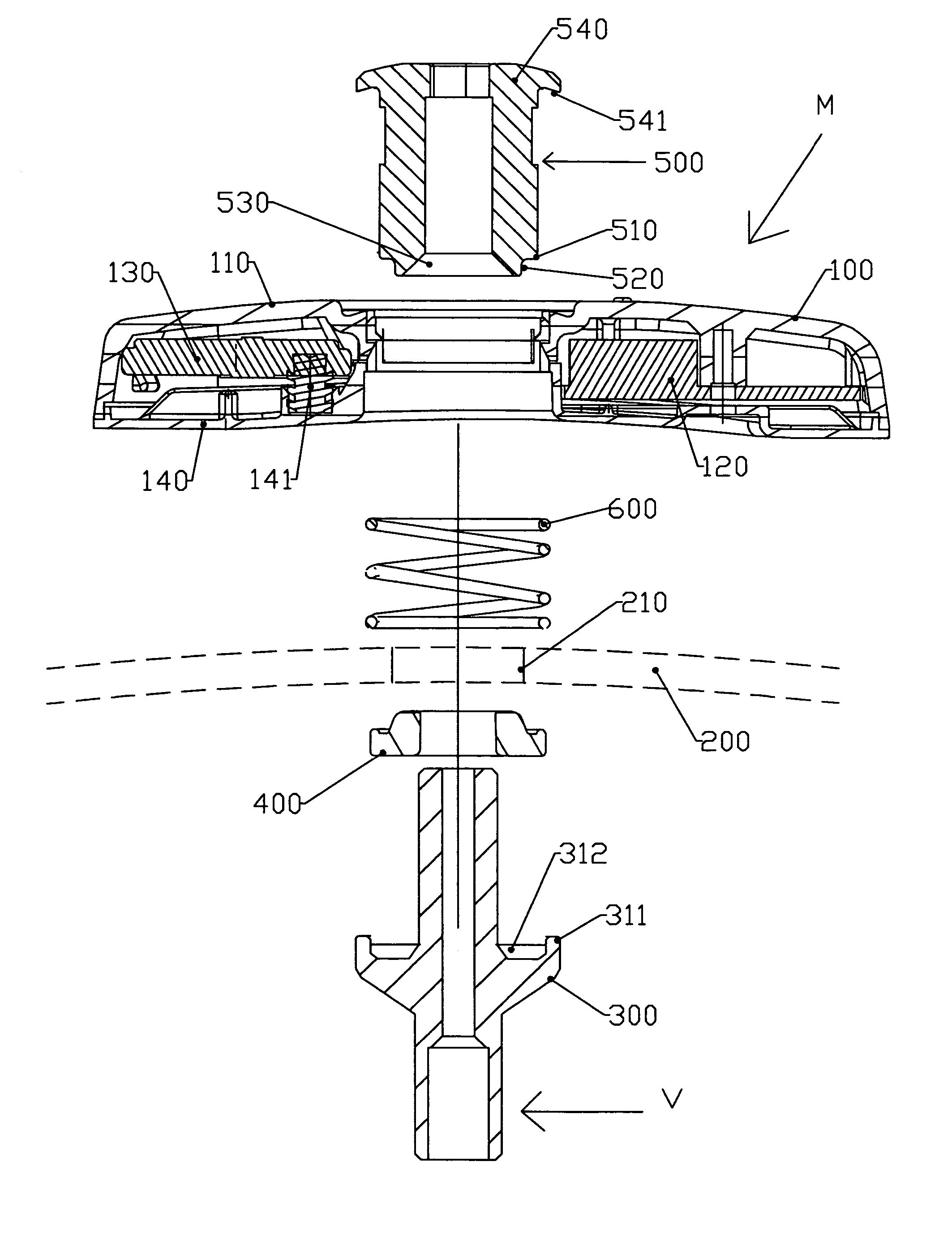
Assembly for attaching a detection unit, in particular for detecting tyre pressure, to a rim
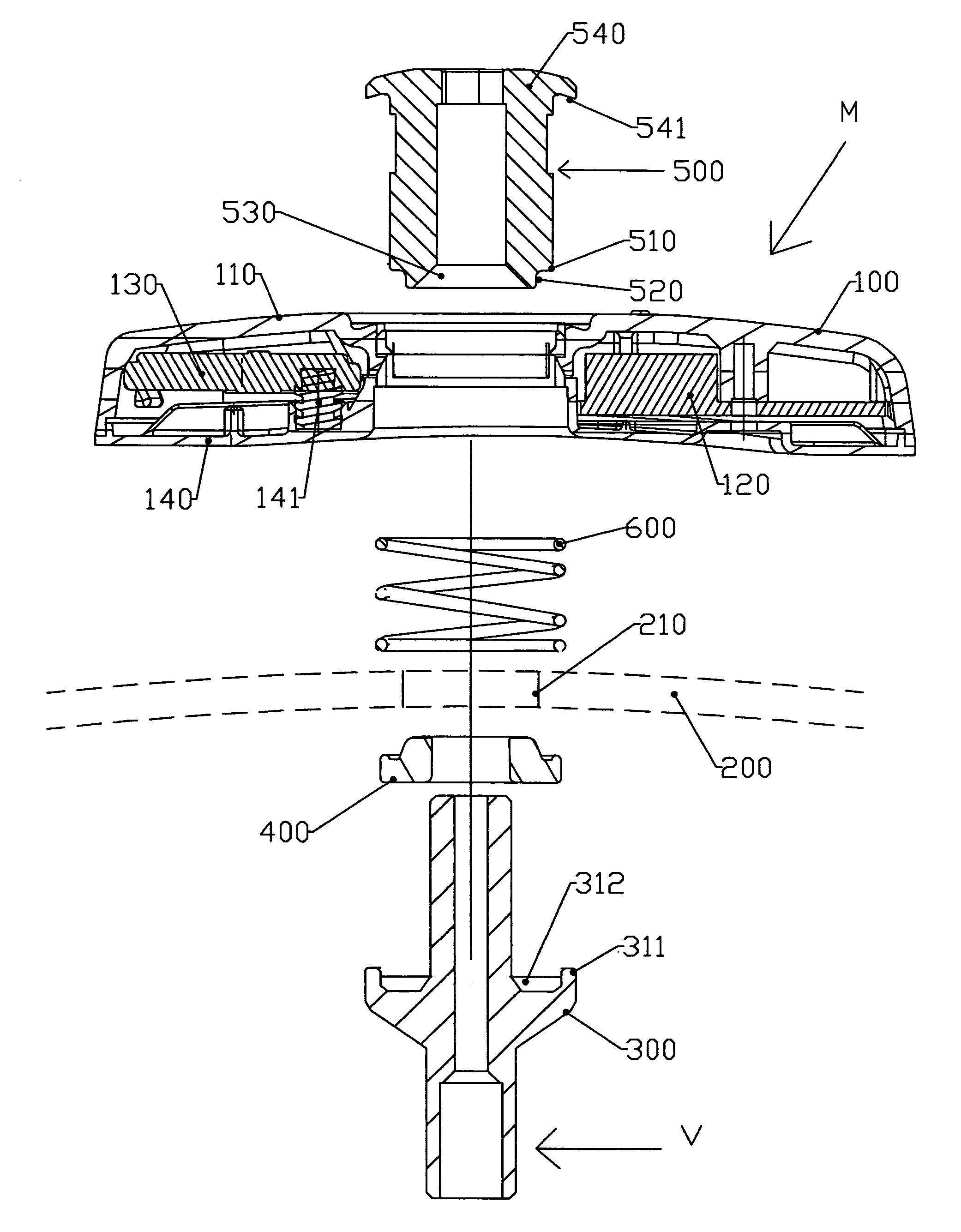
ActiveUS20060075812A1Hinders force applicationRelieve pressureTyre measurementsTangential stressEngineering
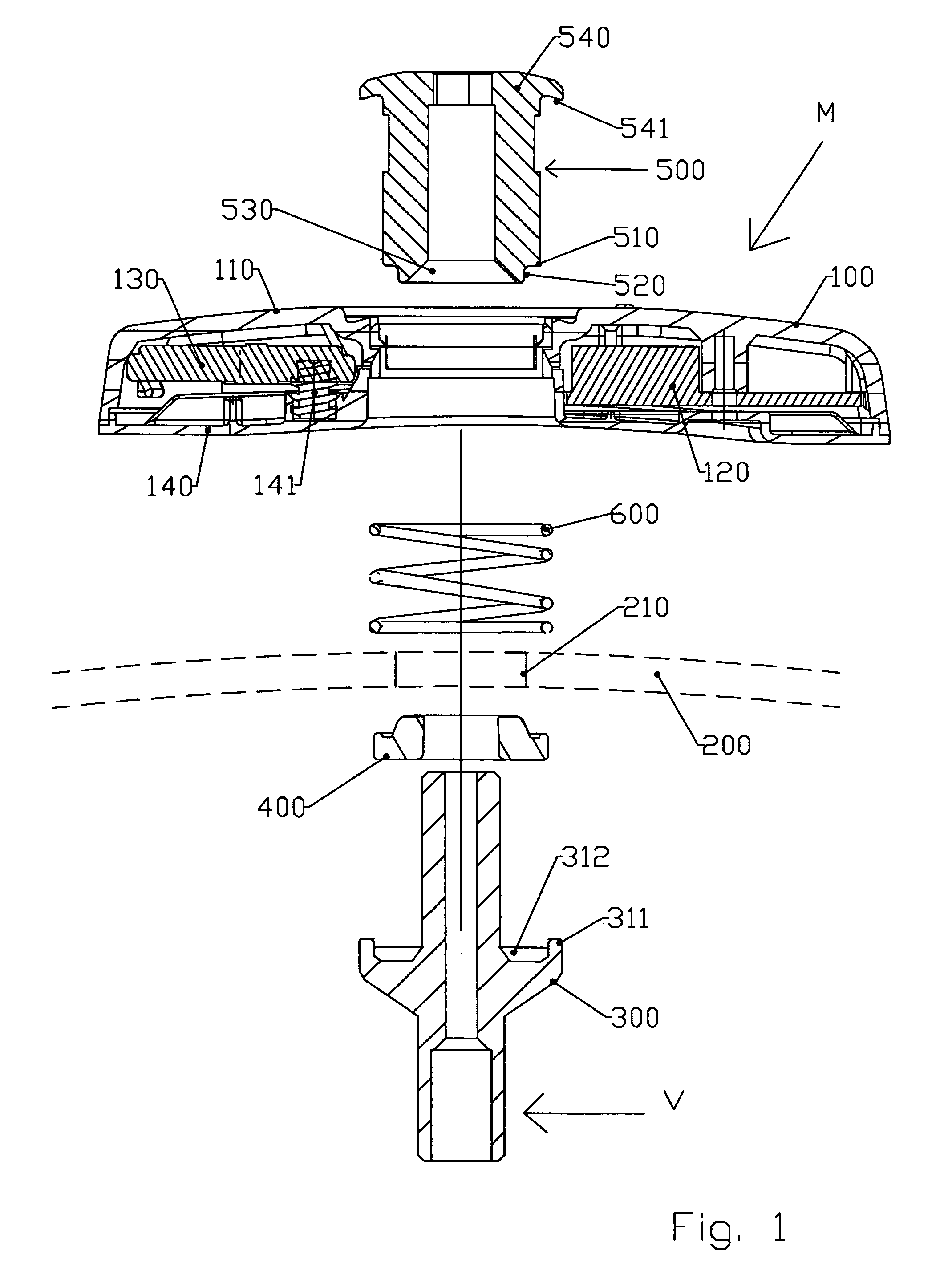
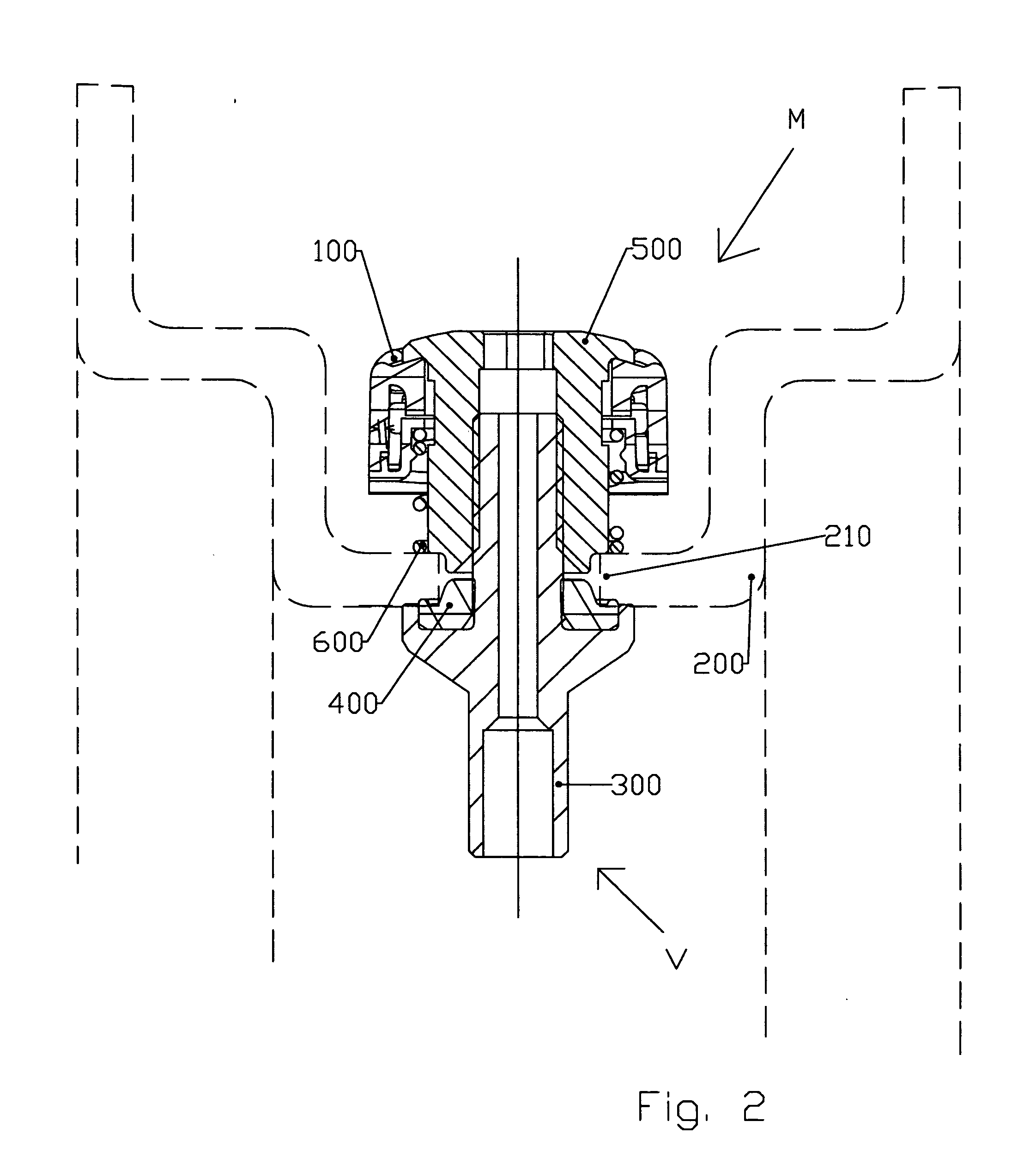
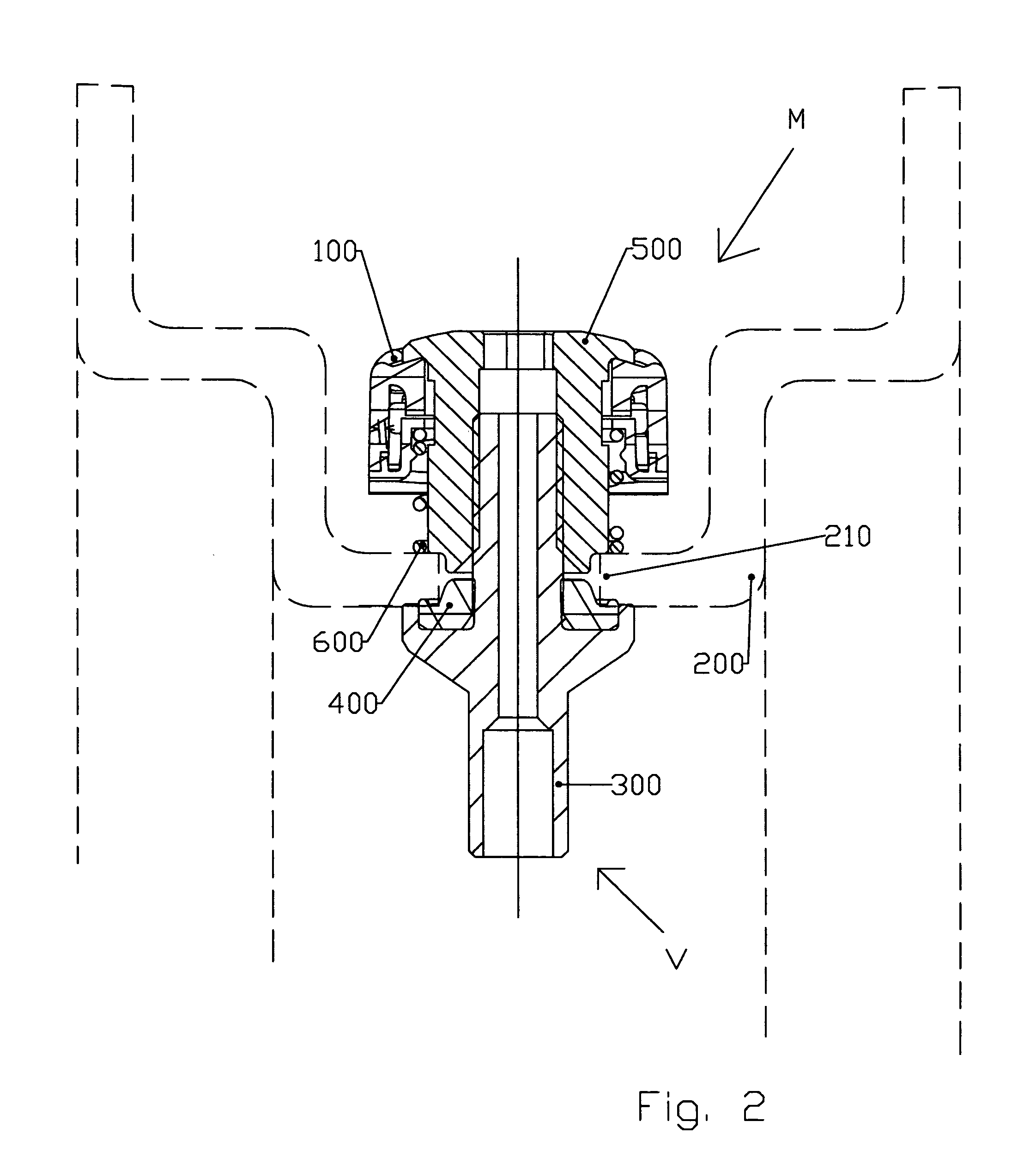
The invention relates to an assembly (M) of a detection unit (100) inside a tyre which is attached to the body (300) of a valve (V) and including the following elements: a detection unit (100) receiving detection components, a valve body (300), sealing means (400) for providing a seal between the valve body (300) and the rim (200), means (500) for holding the valve body (300) in position on the rim (200) which is preformed with a connection aperture (210) provided for this purpose, a module for connecting the detection unit (100) to the valve body (300). This assembly is remarkable in that at least one of the elements (500) of said assembly, aside from the sealing means (400), is preformed so that a portion of this element (500) penetrates the connection aperture (210) so as to engage it when the assembly is subjected to tangential stresses.
Owner:LDL TECH
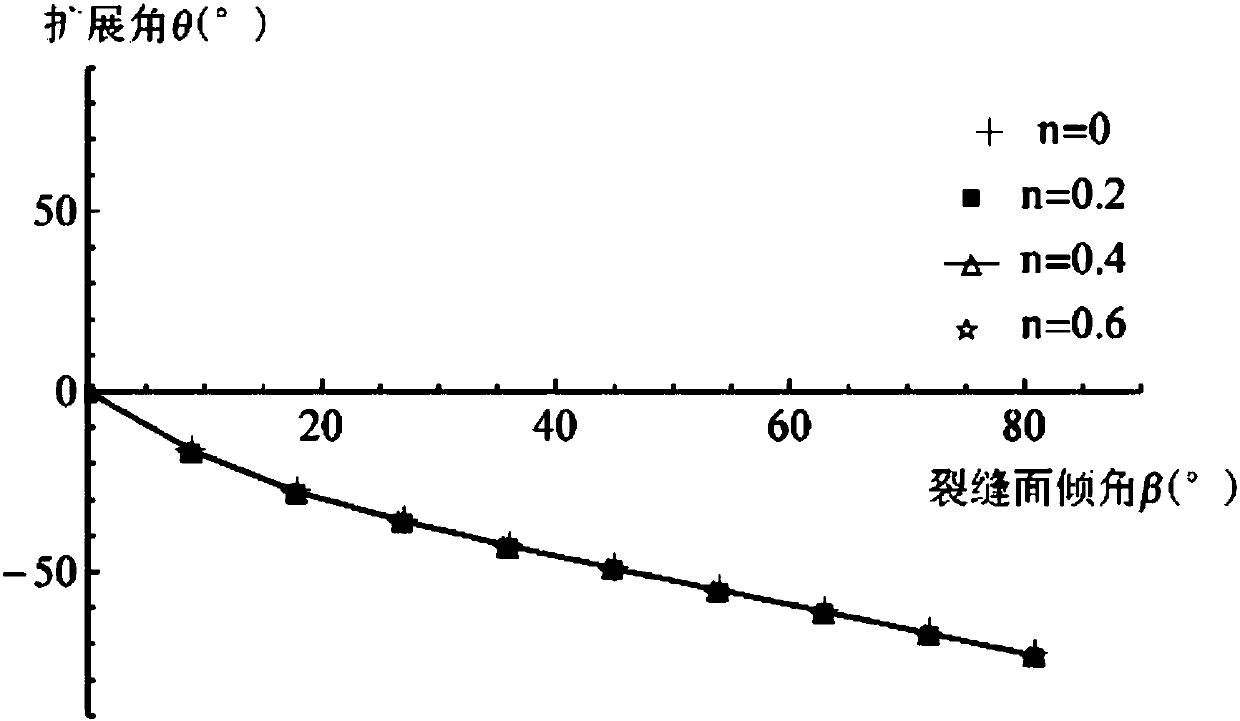
Shale hydraulic fracture propagation prediction method
ActiveCN108468538AGuaranteed accuracyHigh precisionFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationFracture mechanicsStrain energy
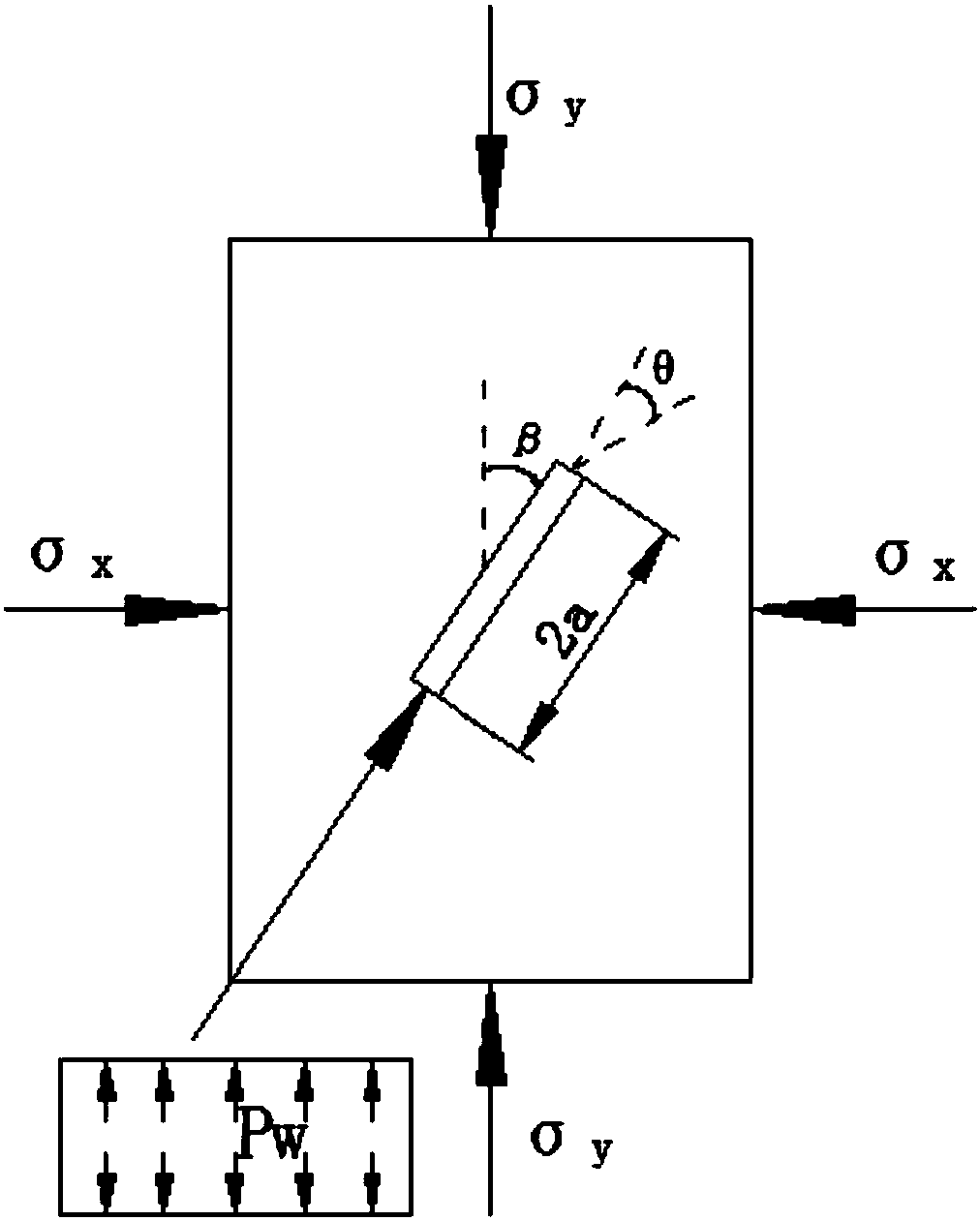
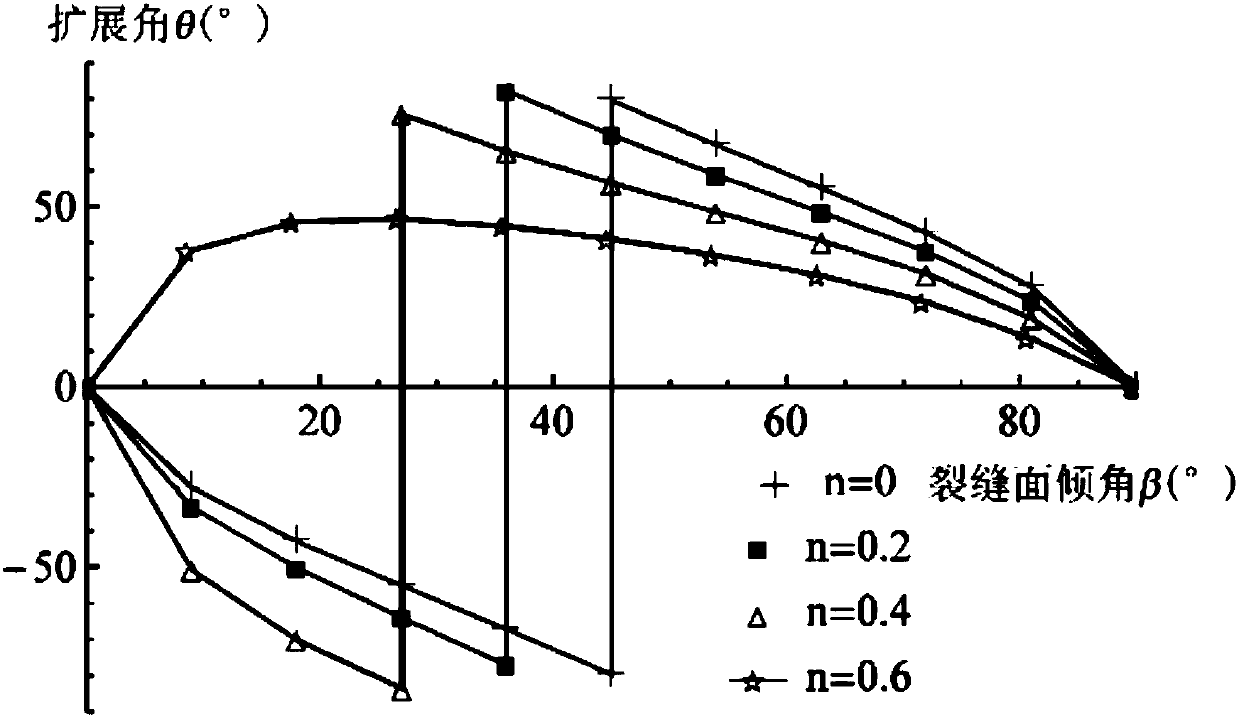
The invention relates to the field of rock fracture prediction, in particular to a shale hydraulic fracture propagation prediction method. The method comprises the steps that 1, the normal direction,tangential stress and effect stress of an inclined fracture under the action of the external stress and water pressure are calculated; 2, a strain energy density function is obtained according to thetype of the fracture; 3, a strain energy density factor is obtained according to the strain energy density function; 4, the propagation direction and propagation angle of the fracture are judged according to a strain energy density criterion; 5, influences of stratification, natural fractures and the like on the propagation direction of hydraulic fractures are obtained through numerical simulation, so that fracture propagation under the effect of shale hydraulic pressure is predicted. The prediction method is based on fracture mechanics, a hydraulic condition factor is introduced, and the influences of different stratification directions on the propagation direction of the shale hydraulic fractures are obtained by researching the relation between the fracture propagation direction and themagnitude of the hydraulic pressure and utilizing an extended finite element method, so that accurate prediction of hydraulic fracture propagation is achieved, and higher prediction accuracy is obtained.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Vortex spoiler for delivery of cooling airflow in a turbine engine
InactiveUS20090067986A1Minimal tangential stressStatic pressure lossWind motor controlPump componentsTangential stressEngineering
A vortex spoiler (180) for delivery of a cooling airflow (192) in a turbine (108) engine (100) including a plurality of inlet ports (182) formed circumferentially about a radial exterior sidewall (188), and a plurality of outlet ports (184) formed circumferentially about a radial interior sidewall (190). The plurality of inlet ports (182) are coupled to the plurality of outlet ports (184) via a plurality of ducts (186). Each of the ducts is formed having an interior diameter at the inlet port and the outlet port formed at a preselected angle normal to the surface of the each of the radial sidewalls to form a radially curved profile such that a cooling airflow (192) may pass radially inwardly through each of the plurality of ducts (186) with minimal tangential stress and minimal static pressure loss.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Experiment method for simulating different types of rock explosion
InactiveCN108519282AOvercome the disadvantage of sudden drop in loading pressurePowerful testMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSupporting systemTest sample
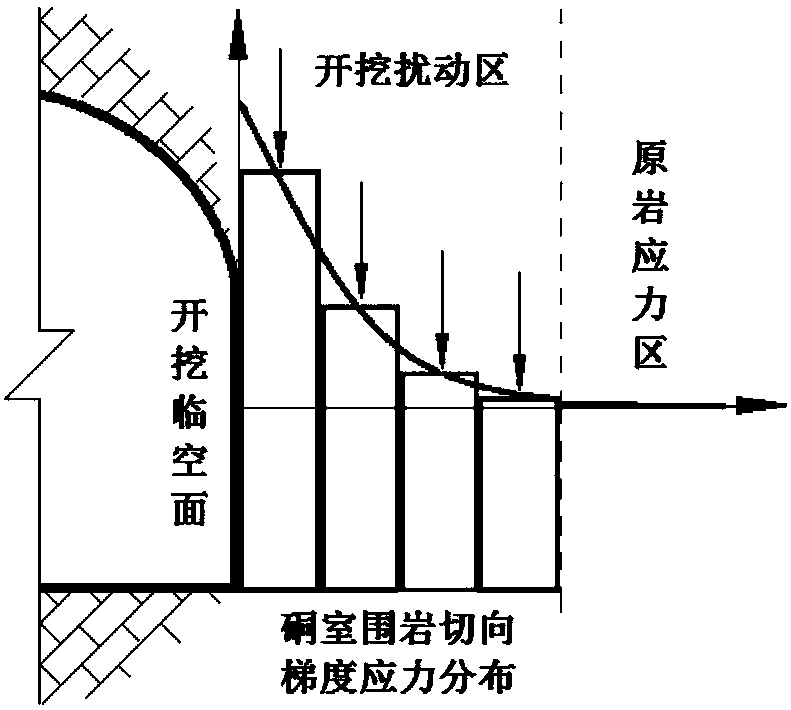
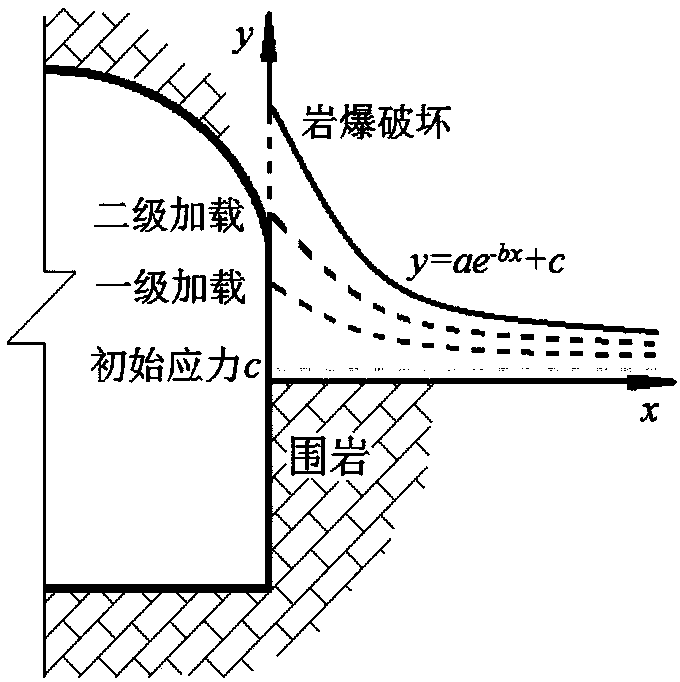
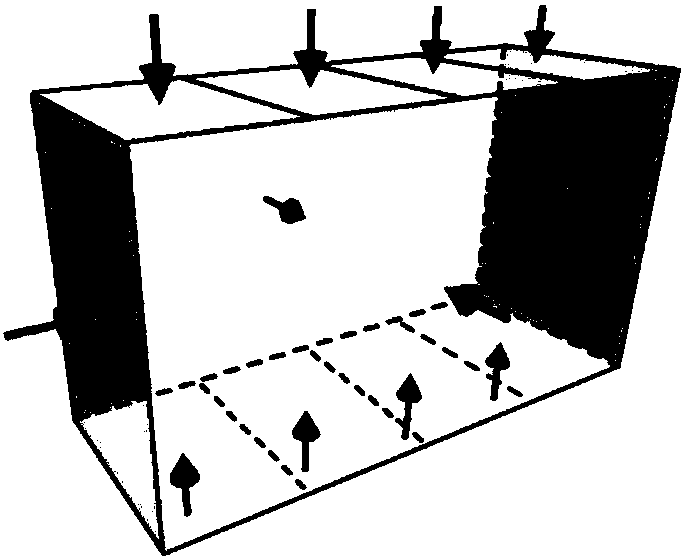
The invention discloses an experiment method for simulating different types of rock explosion. The experiment method is characterized by comprising the following steps: step 1, preparing a rock explosion test sample; step 2, performing a three-direction six-side loading, single-side unloading and top gradient loading experiment method on the rock explosion test sample; step 3, choosing appropriateinitial confining pressure, loading to initial confining pressure level and then simulating a chamber excavation process through horizontal single-side unloading under the situation that load of other sides are unchanged; step 4, achieving different gradient loading purposes by controlling four groups of independent loaders at the top of the rock explosion test sample, simulating chamber tangential stress concentration and gradient loading until the rock explosion test sample is damaged; step 5, in a rock explosion test sample loading damage process, monitoring and recording an experiment process; step 6, cleansing and analyzing experiment data. The method can recognize brittle failure modes partially happened in engineering and has important theoretical and engineering significance in choosing a reasonable surrounding rock construction method and a reasonable supporting system.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for testing stress of cavern wall
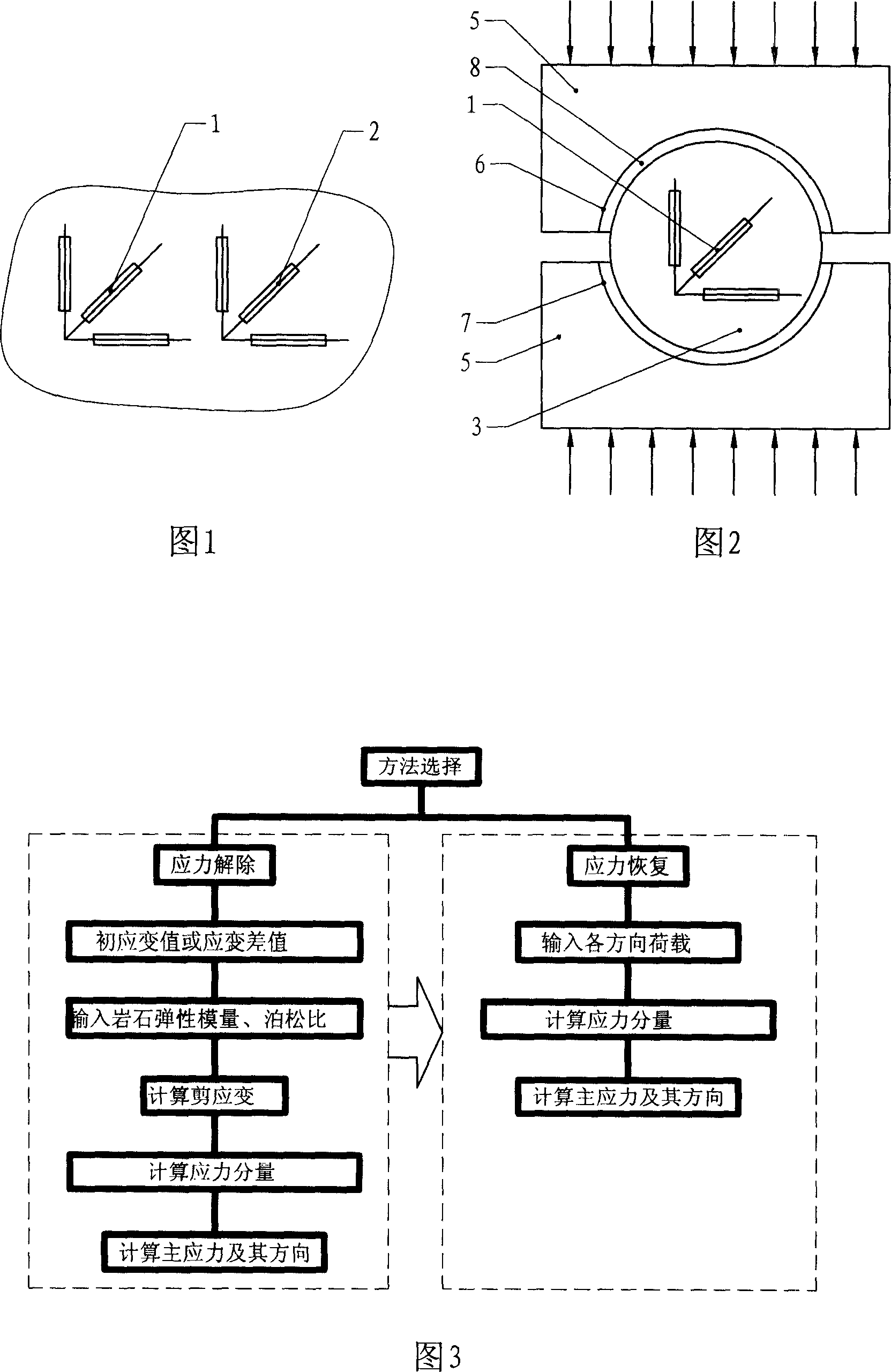
InactiveCN1963423AReduce measurement errorSuitable for on-site operationMining devicesForce measurementRock coreTangential stress
This invention discloses one spot measurement carve stress test method and device for channel stress test, which uses one same rock core and stress for stress elimination measurement and stress restore device, wherein, the rock wall stress test device comprises upper and down saddle pressure blocks to form round hole size and its load rock chip diameter matched; the saddle arc size is smaller than semi-round; the upper and down saddle pressure blocks arc tank and rock chip are set with at least one layer of film underlay pad.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Design method for row space between pressure relief boreholes
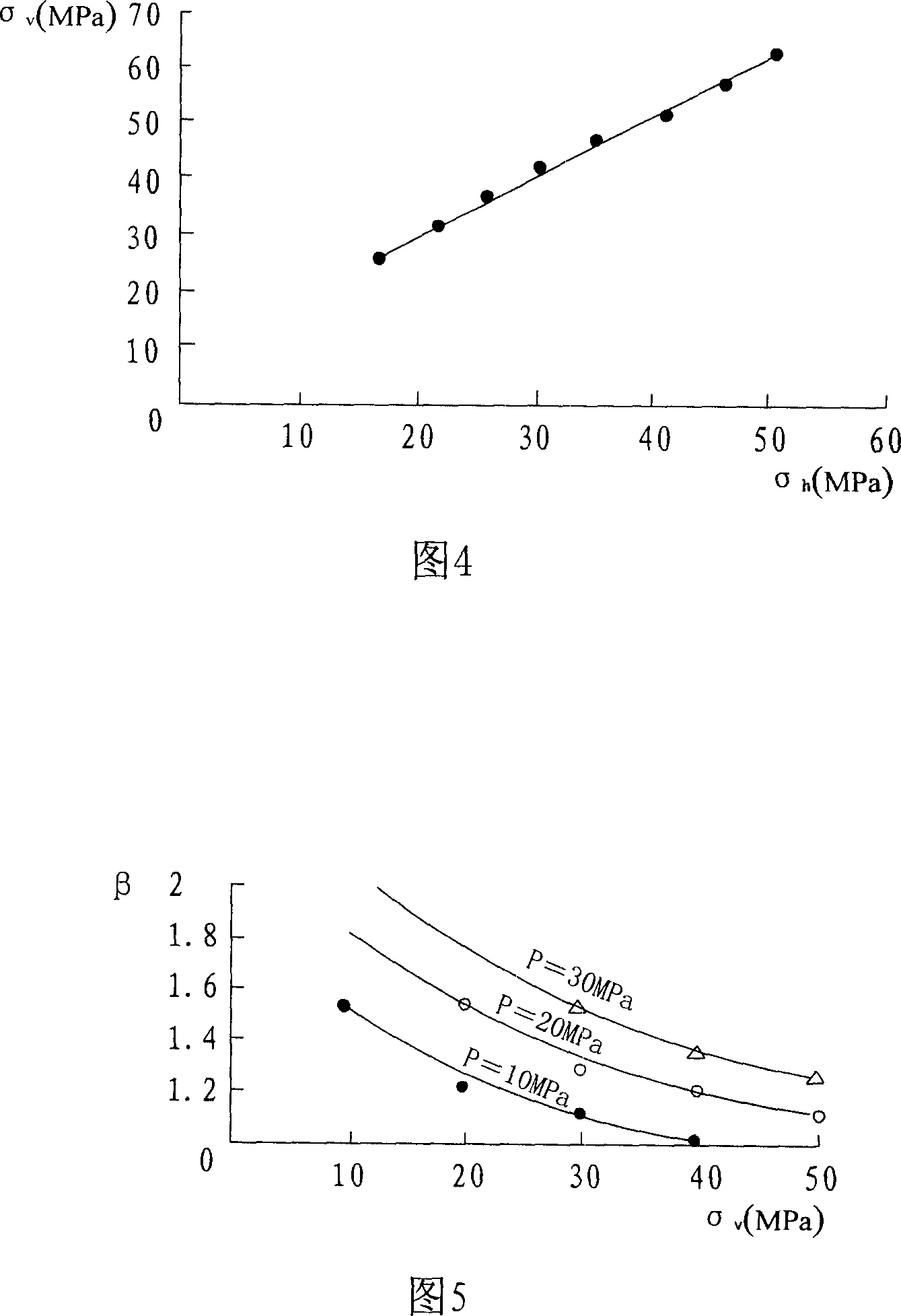
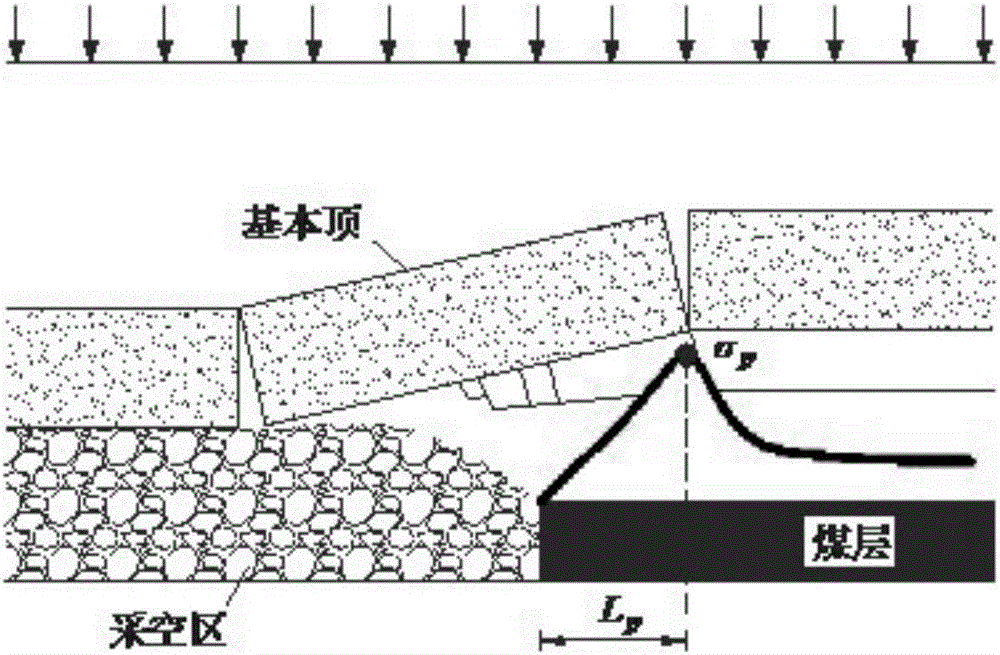
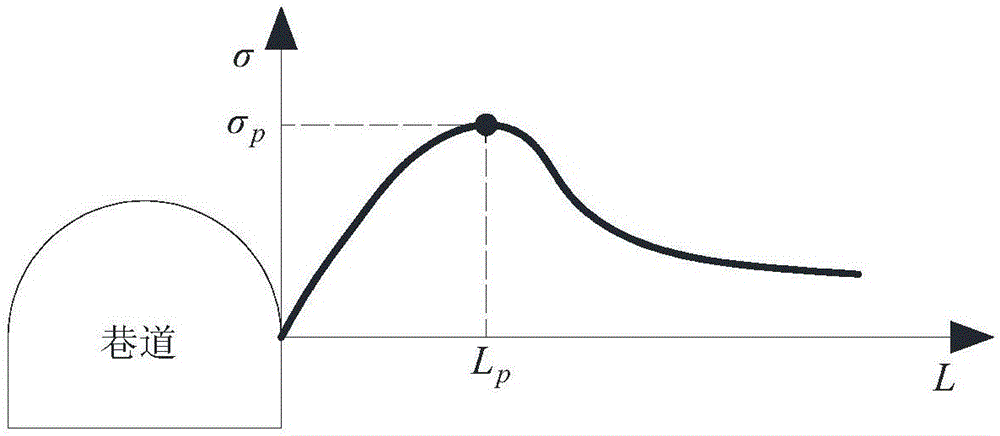
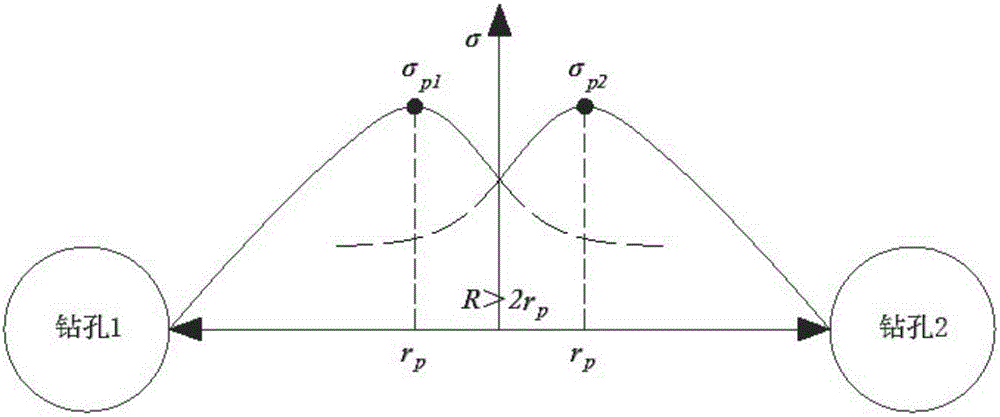
ActiveCN106528963ALess design parametersEvaluation indicators are few and simpleGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsTangential stressPeak value
The invention relates to a design method for row space between pressure relief boreholes. The method comprises the following three steps of: before the row space between the pressure relief boreholes is designed, firstly, requiring to evaluate the stress environment of a pressure relief site, and calculating a working face (roadway) surrounding rock supporting pressure peak value [Sigma]p and a peak value position Lp; selecting a surrounding rock on the Lp as an analysis object, adopting a corrected surrounding rock elastoplasticity analytical solution to calculate a borehole plastic zone radius rp, taking the rp as an index for evaluating the single-hole action range of the borehole, and determining the maximum row space between the boreholes as R which is less than or equal to 2rp; and meanwhile, adopting the elastoplasticity analytical solution to calculate the evolution curve of the circumferential stress [Sigma][Theta] of the borehole, taking the stress of a crosspoint of the circumferential stress curves of the adjacent boreholes as [Sigma]m, taking the stress [Sigma]0 of primary rock of an experiment site as an evaluation index, and determining the condition of the minimum row space R between the boreholes as [Sigma]m which is greater than or equal to [Sigma]0. The method is simple in operation and high in practicality and can be applied to fields including high-stress roadway pressure relief, rock burst prevention and treatment, high gassy seam permeability increasing and the like, the design accuracy of the row space between the boreholes can be effectively improved, and a borehole engineering quantity is lowered.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
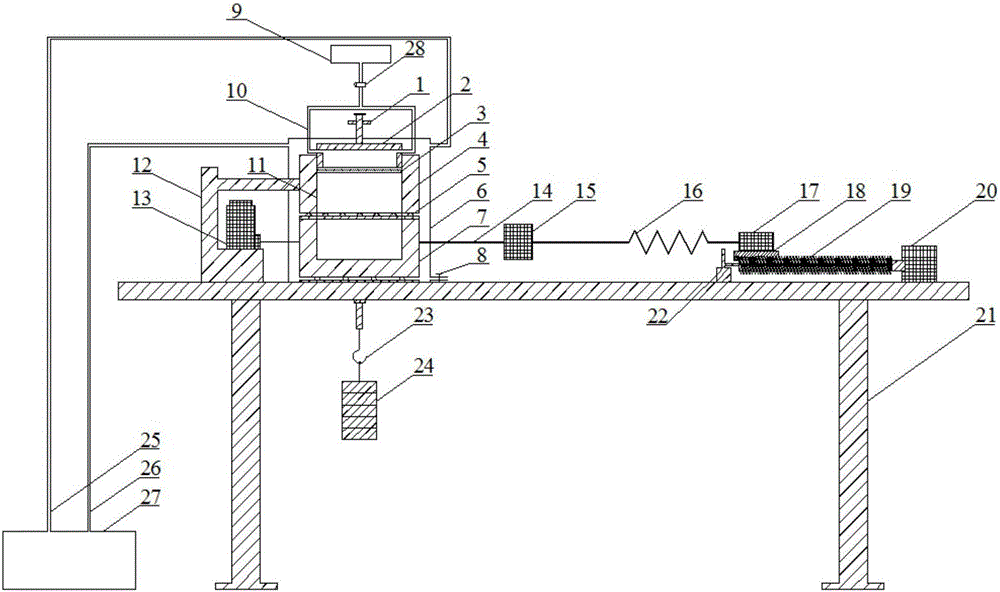
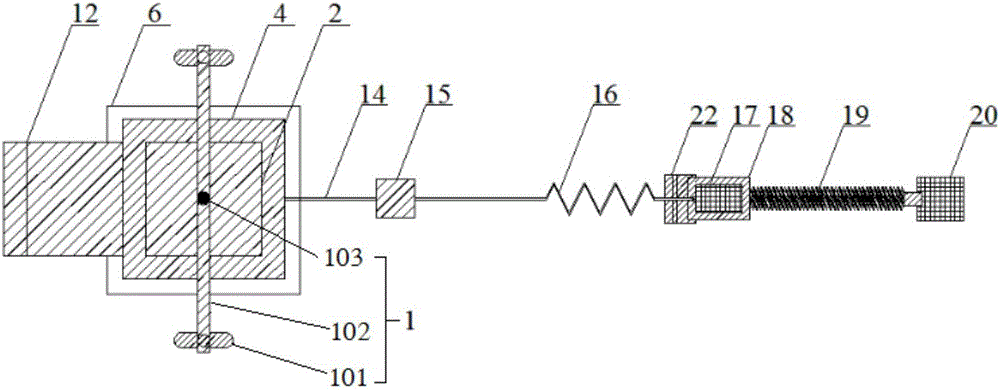
Rock-soil body shearing rheometer considering seepage-stress-chemical coupling
InactiveCN106769539AFully infiltratedNormal stress stabilityMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesData acquisitionTangential stress
The invention provides a rock-soil body shearing rheometer considering seepage-stress-chemical coupling. The rock-soil body shearing rheometer considering seepage-stress-chemical coupling comprises a test bench, a shearing box assembly, a loading assembly and a displacement-stress monitoring assembly; a large-size test sample can be placed in a shearing box unit, chemical liquid with a certain osmotic pressure is provided through a water pump, the test sample is dried through a hot air circulating unit, and seepage of the chemical liquid with different osmotic pressure and dry-wet circulation of the test sample are realized; normal pressure is loaded by weights, tangential pressure is loaded by a rigid spring, a vibration exciter acts on a spring so as to generate disturbance on tangential stress, and the deformation amount of the rigid spring is maintained by controlling a linear displacement mechanism to guarantee stability of the tangential stress; the displacement-stress monitoring assembly cooperates with a corresponding data acquisition system to monitor the displacement of a lower shearing box and the tensile force of the test sample. The rock-soil body shearing rheometer considering seepage-stress-chemical coupling can research the problems about rock-soil body disturbed by power, underwater, chemical corrosion, dry-wet circulation and long-term stability of single or combined action of stress.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Tangential stress reduction system in a loudspeaker suspension
InactiveUS7174990B2Increases amount of excursion and linearityImprove performanceEngine sealsTransducer detailsTangential stressEngineering
The invention is a suspension element having an outer edge and an inner edge. The suspension element, such as a spider or surround, varies in shape along at least a portion of the suspension element to help relieve both the radial and tangential stress placed on the suspension element when it is stretched. The shape employed in the suspension element allows the suspension element to stretch more easily, creating a higher performance speaker of the same size by increasing the diaphragm excursion and voice coil movement.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
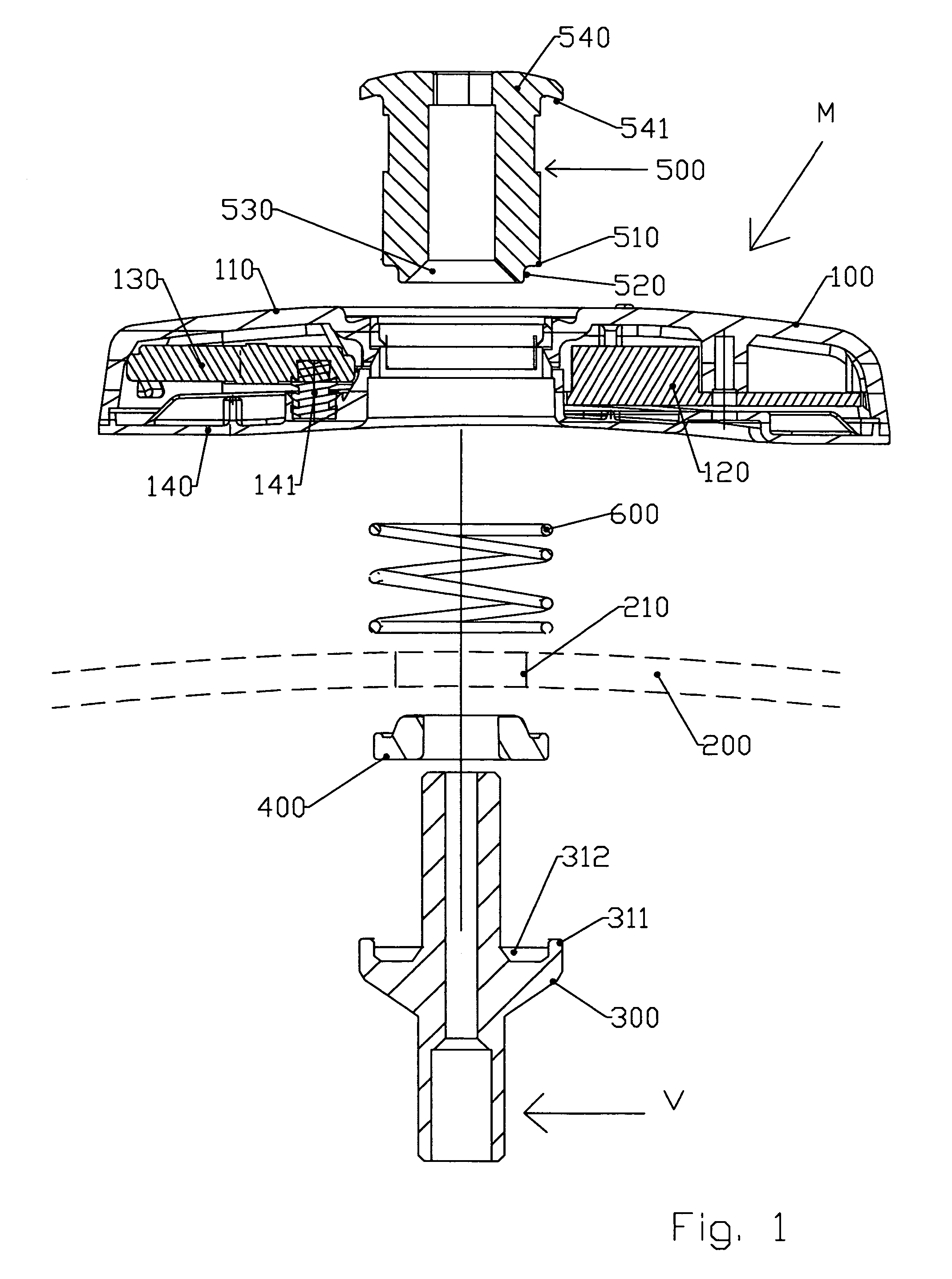
Assembly for attaching a detection unit, in particular for detecting tyre pressure, to a rim
ActiveUS7257998B2Relieve pressureReduce the total massTyre measurementsTangential stressBiomedical engineering
An assembly (M) of a detection unit (100) for placement inside a tire with a rim having a connection aperture (210) is provided. The assembly (M) can include a detection unit (100) for receiving detection components, a valve body (300), a seal (400) for providing a seal between the valve body (300) and the rim (200), and fastener (500) for holding the valve body (300) in position on the rim (200). One or more of the detection unit (100), the valve body (300), the fastener (500) for holding the valve body (300), or a combination thereof, is preformed to penetrate the connection aperture (210) so as to engage the connection aperture (210) when the assembly (M) is subjected to tangential stresses.
Owner:LDL TECH
Method for making a stressed structure designed to be dissociated
InactiveUS20100167499A1Minimize stressImprove mechanical stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic structureTangential stress
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Column structures and methods for supporting compressive loads
Owner:DRAKE WILLIAM E
Pile-soil interface three-axis model testing device under condition of seepage
ActiveCN104165797AGood repeatabilityIn line with engineering practiceStrength propertiesModel testingControl system
The invention discloses a pile-soil interface three-axis model testing device under a condition of seepage. The pile-soil interface three-axis model testing device comprises a three-axis confining pressure chamber, a vertical loading and unloading platform, a confining pressure control system, a seepage control system and a data acquisition system, wherein a pile-soil sample is arranged in the three-axis confining pressure chamber and has an interface between a pile body and a soil body; the vertical loading and unloading platform is used for loading tangential stress to the interface; the confining pressure control system is used for loading normal stress to the interface; the seepage control system is used for controlling seepage parameters in the pile-soil sample; and the data acquisition system is used for acquiring deformation data of the pile-soil sample in the three-axis apparatus confining pressure chamber. The pile-soil interface three-axis model testing device under the condition of seepage is capable of more conveniently studying stress characteristics of the pile-soil interface of the soil body under the action of coupling the seepage and the complex stresses.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Intelligent wind wheel used for vertical axis wind generating device
InactiveCN101581270ALow costEasy maintenanceWind motor controlWind motor supports/mountsTangential stressVertical axis wind turbine
The invention relates to an intelligent wind wheel, in particular to an intelligent wind wheel used for a vertical axis wind generating device. The intelligent wind wheel used for the vertical axis wind generating device comprises an upper wheel rim and a lower wheel rim; a support bar and a vane shaft are arranged between the wheel rims; the vane shaft is provided with a wind sail; the wheel rims, the support bar and the vane shaft form a regular prism; the middle part of the regular prism is provided with a wheel shaft; and a wheel hub is arranged between the wheel shaft and the wheel rim. The intelligent wind wheel used for the vertical axis wind generating device has the advantages and effects that the wind wheel does not need a windward adjusting system and can receive wind from any direction in an orientation of 360 degrees, and a main shaft permanently rotates towards the design direction. The wind sail rotates along a self shaft, and continually changes direction so that the tangential stress of the wind sail is maximized down the wind and the wind sail against the wind is parallel to the wind direction. The rotating angle of the wind sail is judged by a main controller according to the indication of a wind indicator and the current rotating relative position of the wind sail, and information is transmitted to a wind sail controller. The intelligent wind wheel used for the vertical axis wind generating device can reduce the cost, is convenient to maintain, and has low pneumatic noise.
Owner:肖玄同
Wing-spar structural topology optimization method based on stress constraint
ActiveCN103440378AReduce tangential stressGuaranteed structural rigidity performanceSpecial data processing applicationsStress concentrationLoad model
The invention discloses a wing-spar structure topology optimization method based on stress constraint. The method is used for solving the technical problem that nail load design through an existing method is large in tangential stress. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the steps that a nail load model is built through a three-dimensional entity unit. Stress serves as the constraint in the optimization process, the tangential stress in the position of a constrained nail load unit is the minimum, nail load sensitivity is obtained through an adjoint method, and nail load flexibility and material utilization amount jointly serve as stiffness optimization constraint to conduct structural topology optimization and obtain the design result. The method can guarantee structural stiffness performance and avoid concentrated stress because structural force transferring paths are reasonably distributed. According to the embodiment of the method, when the constraint structure material body subtraction proportions are 0.3 respectively, the smooth degree function of the constraint structure free of applied stress is 0.0207J, and under the condition that the smooth degree function of the constraint structure with applied stress is not changed, the maximum tangential stress of a bolt is reduced to 11.3MPa from 17.9MPa, and is reduced by 36.8%, and the tangential stress of a bolt unit is reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Piezoelectric stack-based vibration reduction ring device
The invention discloses a piezoelectric stack-based vibration reduction ring device, and belongs to the field of design for vibration reduction devices. The vibration reduction ring device comprises an inner ring, an outer ring, an inner ring end cover, an outer ring end cover, piezoelectric stacks and butterfly-shaped connection elements, wherein one piezoelectric stack is connected to the longitudinal symmetry axis of each butterfly-shaped connection element; the butterfly-shaped connection elements are uniformly distributed in aligned grooves between the inner ring and the outer ring; and the inner ring end cover and the outer ring end cover are further arranged at the upper ends of the inner ring and the outer ring separately. According to the novel vibration reduction ring design disclosed by the invention, the vibration reduction ring is capable of effectively reducing vibration transferred to supporting by a transmission system through a shaft and a bearing by virtue of a piezoelectric shunt damping technology, and capable of effectively preventing the piezoelectric stacks from bearing tangential stress and torque, thereby prolonging the service lives of the piezoelectric stacks.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
True triaxial test method of simulating extensional rock burst
InactiveCN106501081APowerful testGet Deformation PropertiesPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress conditionsTriaxial shear test
The invention discloses a true triaxial test method of simulating an extensional rock burst. The method employs a true triaxial loading route and a boundary condition of single side freeness and five side stressing, and utilize a cuboid rock sample in a single side freeness and three directional compressive stress state to simulate a special mechanical behavior of a representative rock unit of field wall rock in a tangential stress concentration process by applying a certain three directional load and controlling a loading speed of one direction. The method can be used for representing a whole inoculation and occurrence process of the extensional rock burst in a laboratory. The method solves the problem that the traditional indoor test method cannot simulate the extensional rock burst under a complex stress condition reasonably and has important practical significance and academic value in promoting mechanism and prediction studies of the rock burst.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Critical refraction longitudinal wave detection component inside tangential stress assistant device
InactiveCN101126741ALarge amplitudeImprove versatilityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLongitudinal waveTransducer
The utility model discloses an auxiliary device of internal tangential stress for critical refraction longitudinal wave detecting components, which is characterized in that: the inclined surface of the lower part (1) upward presents a concave cylindrical surface (3) and the inclined surface of the upper part (2) downward presents an outer convex cylindrical surface (4). The outer convex cylindrical surface (4) of the upper part (2) is meshed with the concave cylindrical surface (3) of the lower part (1). The upper part (2) can slide on the concave cylindrical surface (3) of the lower part (1). An indexing round graduation (6) is carved on borderline end face of the outer convex cylindrical surface (4) and the concave cylindrical surface (3). The receiving transducer and the transmitting transducer of ultrasonic wave are fixed at the upper part (2). The utility model has the advantages of overcoming the failures that different wedge structure is needed for measuring different components under test and the best incident angle can be get for the same kind of components under test for prior art, providing a micro angle-adjusting with good versatility, meeting the best angle incidence, receiving the biggest LCR wave amplitude device and being widely applied in stress measuring field.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Bendable electronic device modules, articles and methods of making the same
A foldable electronic device module includes a glass cover element having a thickness from about 25 [mu]m to about 200 [mu]m, an elastic modulus from about 20 GPa to about 140 GPa and a puncture resistance of at least 1.5 kgf. The module further includes a stack with a thickness between about 100 [mu]m and about 600 [mu]m; and a first adhesive joining the stack to the cover element with a shear modulus between about 1 MPa and about 1 GPa. The stack further includes a panel, an electronic device, and a stack element affixed to the panel with a stack adhesive. Further, the device module is characterized by a tangential stress at a primary surface of the cover element of no greater than about 1000 MPa in tension upon bending the module to a radius from about 20 mm to about 2 mm.
Owner:CORNING INC
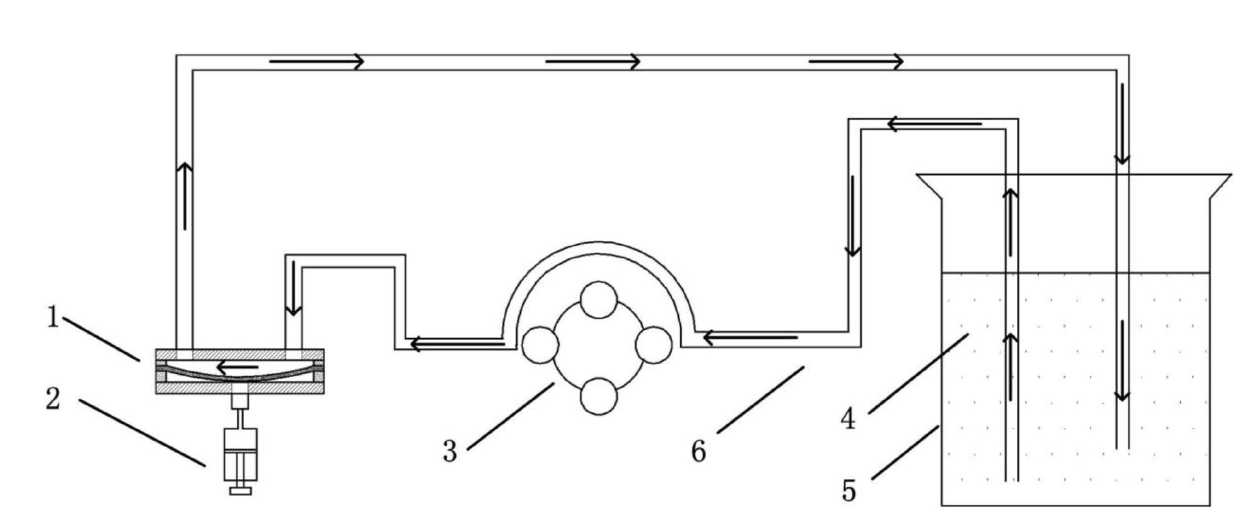
Method and device for loading cell fluid stress on deformable curved surface and experimental platform
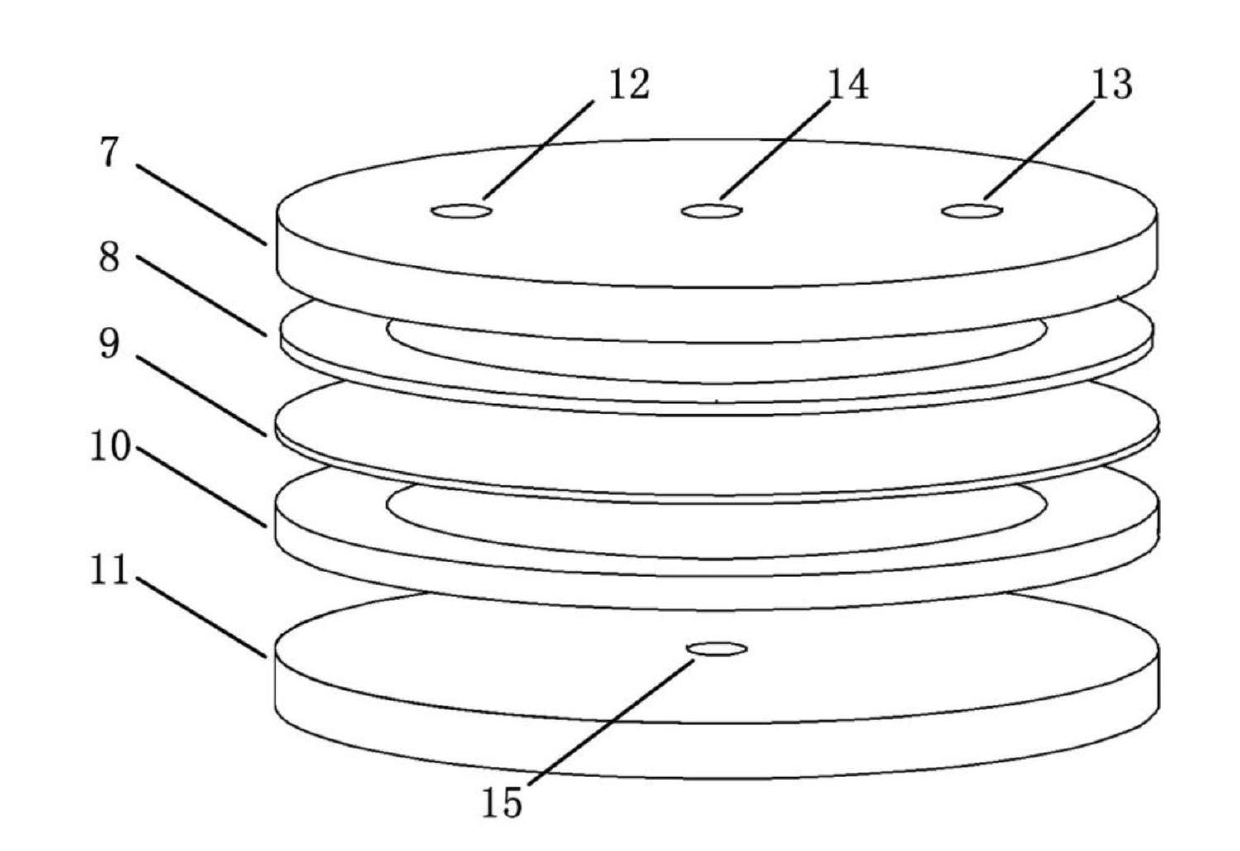
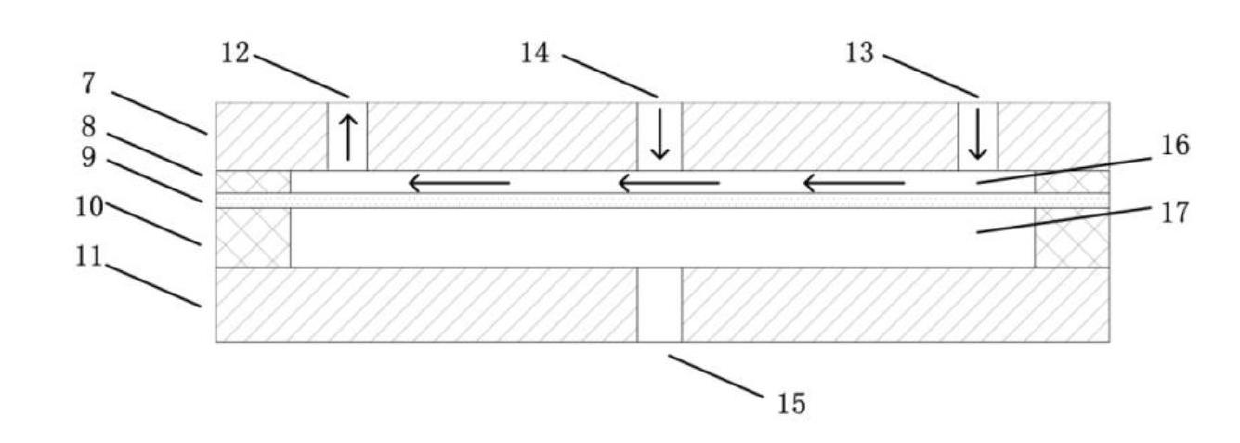
InactiveCN102676446AChange fluid shear stress stateChange stress stateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological cellPeristaltic pump
The invention discloses a method loading cell fluid stress on a deformable curved surface. A flowing cavity and a pressure cavity are isolated from each other through a transparent elastic membrane; biological cells are inoculated onto the surface of the transparent elastic membrane which faces the flowing cavity; the flowing cavity is full of a cell culture fluid; the transparent elastic membrane is deformed by applying a pressure through the pressure cavity; and the cell culture fluid is driven to circularly flow in the flowing cavity through a peristaltic pump, so that the biological cellsare subjected to the tangential stress and pressure of the fluid. The invention further provides a device for implementing the method. The device comprises a first cover plate, a first sealing gasket, a transparent elastic membrane, a second sealing gasket and a second cover plate from top to bottom, wherein a flowing cavity is formed among the first cover plate, the first sealing gasket and the transparent elastic membrane; and a pressure cavity is formed among the transparent elastic membrane, the second sealing gasket and the second cover plate. The shape of the bottom surface of the flowing cavity where the biological cells are positioned can be changed, and a fluid stress state in which the biological cells are kept is adjusted simultaneously, so that the shape and biological characteristic change rules of biological cells in different stress states are observed and detected.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
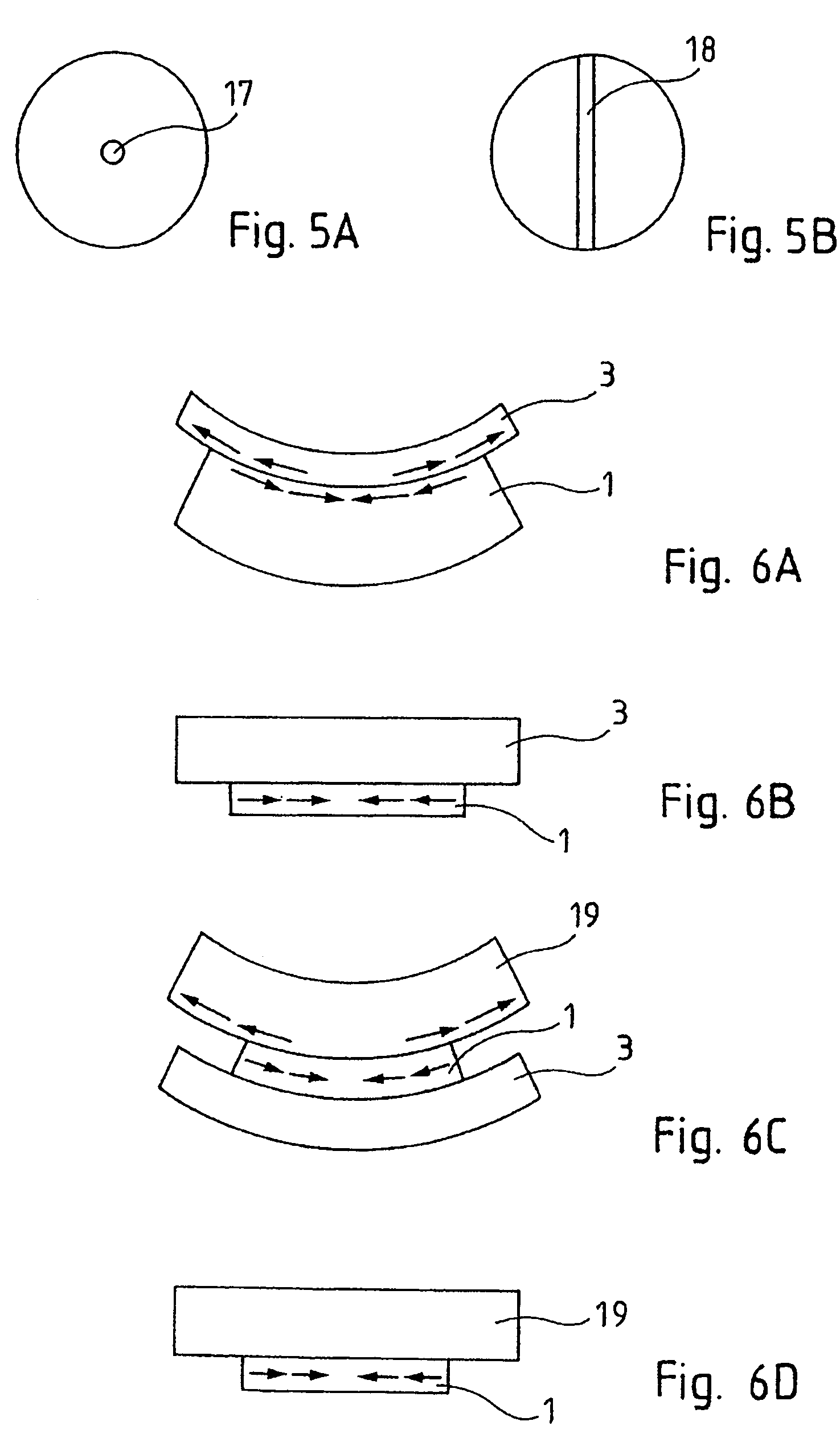
Method of producing a complex structure by assembling stressed structures
ActiveUS7550052B2Large temperature differenceLong durationLamination ancillary operationsSolid-state devicesElectronic structureTangential stress
The invention relates to a method of producing a complex microelectronic structure, in which two basic microelectronic structures are assembled at the two respective connecting faces thereof. The invention is characterized in that, before assembly, a difference is created in the tangential stress state between the two faces to be assembled, said difference being selected such as to produce a pre-determined stress state within the assembled structure under given conditions in relations to the assembly conditions.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Torque sensor
InactiveCN102865958ADirect torque measurementEliminate the effects ofWork measurementTorque measurementDrive shaftTangential stress
The invention provides a torque sensor which is composed of a supporting base, stress plates, a sleeve, a thin-wall plate and resistance strain gages. The supporting base, the stress plates and the sleeve are an integrated forming structure, the sleeve is coaxially and fixedly connected with the supporting base through the tangential stress plates on two sides, the stress plates on the two sides are symmetrical with the central axis of the sleeve as the center, the outer surfaces of the stress plates on the two sides serve as tangential planes of the edges of the sleeve, and the thickness of the stress plates is between 2mm to 5mm. The resistance strain gages are attached to the inner sides and the outer sides of the stress plates, the resistance strain gages on the stress plate on one side are distributed symmetrically with the center of the stress plate as the center, and the thin-wall plate along the normal direction of the sleeve is connected between the sleeve and the supporting base. The torque sensor can be used for measuring torque of a transmission shaft directly and does not need to dismantle a measuring device, the resistance strain gages symmetrically arranged on two sides of the stress plates can eliminate influence of temperature on measuring results, and torque of an object to be measured under the static condition can be measured.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A method for predicting fretting fatigue life of a nickel-base single crystal alloy turbine blade tenon
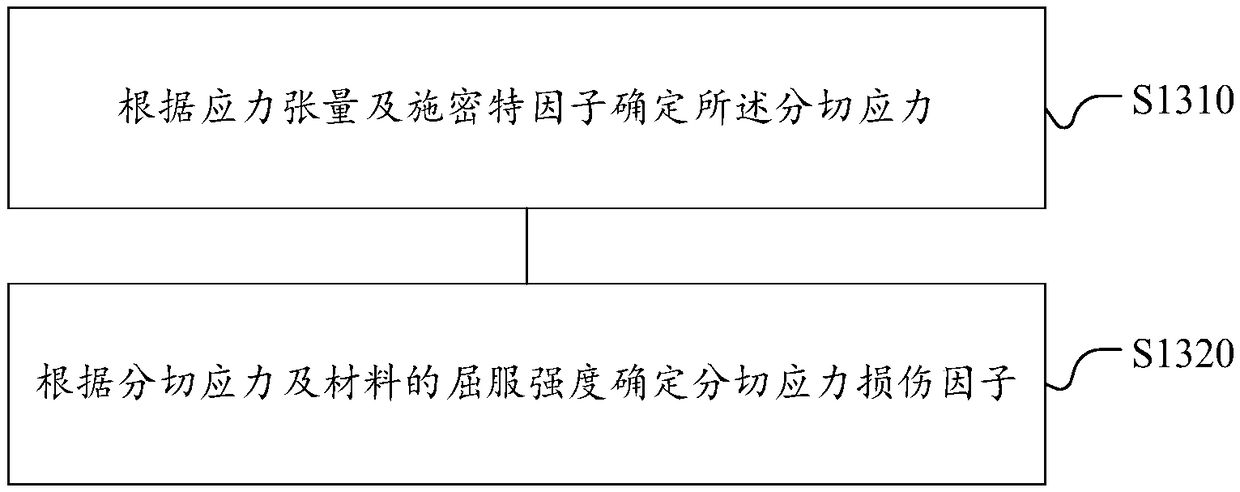
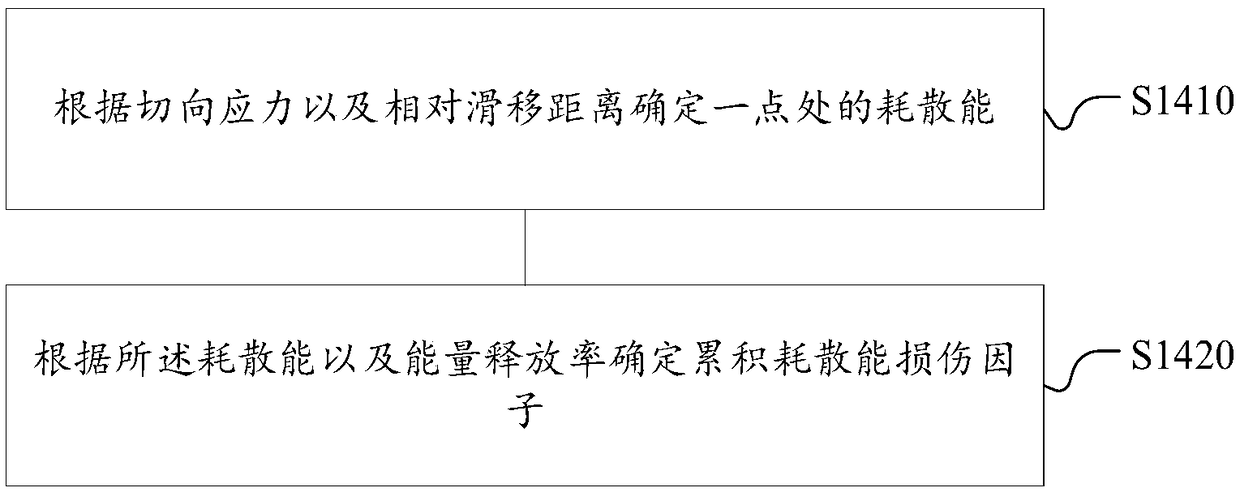
ActiveCN109408900AImprove accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsShear stressTurbine blade
A method for predicting fretting fatigue life of a nickel-base single crystal alloy turbine blade tenon includes establishing a fretting fatigue contact analysis model of that nickel-base single crystal alloy turbine blade tenon; calculating the model under the given working condition and obtain the analysis parameters, which include shear stress, tangential stress and relative slip distance at different positions of the contact surface; determining the shear stress damage factor at different positions of the contact surface of the model under a given working condition; the cumulative dissipative energy damage factors at different positions of the contact surface of the model are determined according to the given operating conditions and analysis parameters. According to the shear stress damage factor and cumulative energy dissipation damage factor, the fretting fatigue comprehensive damage factor is determined, and the fretting fatigue life of nickel-based single crystal alloy turbineblade tenon is obtained. The fretting fatigue life prediction method of the nickel-based single crystal alloy turbine blade tenon can accurately predict the fretting fatigue life of the nickel-basedsingle crystal alloy turbine blade tenon.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Measuring system and method for tangential piezoelectric strain constant of piezoelectric material by quasi-static method
InactiveCN101430352AEasy to measureAccurate and reliable measurement resultsElectrical measurementsElectricityDynamic method
The invention discloses a quasi-static measurement method for a tangential piezoelectric strain constant of a piezoelectric material d15, and a system thereof. In the method, a special tangential stressing component converts 'longitudinal force' of a piezoelectric test sample into a 'tangential force' on an existing quasi-static d33 measuring apparatus, and directly provides a measurement result of the d15 tangential piezoelectric strain constant of the piezoelectric test sample. The measurement system consists of the tangential stressing component, a force application device and a circuit component, wherein, the tangential stressing component consists of a strained compression fixing component which is composed of a strained compression fixing bracket, a fixing frame, a fixing shaft, an adjusting bolt, an insulating bush and a positioning shaft sleeve, and a strained compression component. The force application device and the circuit component are applicable to various types of quasi-static d33 measuring apparatuses, and the force application device and the circuit component of the quasi-static d33 measuring apparatus are connected by two multi-core cables according to requirements of the existing quasi-static d33 measuring apparatus. Compared with the existing dynamic method, the method and the system have the advantage of simple operation, strong practicability and easy popularization and implementation.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Testing device for rock three-axis external pressure and hole internal hydraulic pressure coupling loading and unloading
ActiveCN105784493AImprove sealingEven by forceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesAxial pressureTangential stress
The invention discloses a testing device for rock three-axis external pressure and hole internal hydraulic pressure coupling loading and unloading. The testing device is composed of a base, a confining pressure loading and unloading system, a hole internal hydraulic pressure loading and unloading system and an axial pressure loading and unloading system. The confining pressure loading and unloading system comprises a pressure chamber, a confining pressure bag, a protection tire, an oil inlet and outlet channel and a confining pressure electro-hydraulic servo system. The hole internal pressure loading and unloading system comprises an inner pressure bag, an upper sealing member, a lower sealing member, an upper L-shaped elbow, a lower L-shaped elbow, an upper cover plate, a lower cover plate and an internal pressure electro-hydraulic servo system. The axial pressure loading and unloading system comprises a loading block, a piston rod, an oil cylinder, an upper oil cavity channel, a lower oil cavity channel and an axial pressure electro-hydraulic servo system. The testing device is compact in structure, and all functions are independent and collaborative; different non-uniform radial stress fields and different non-uniform tangential stress fields, all of which are distributed in the circumferential direction can be constructed by adjusting the different confining pressure and internal pressure combinations, and linear and nonlinear radial unloading and tangential loading stress paths at points on the non-uniform stress fields in a rock sample can be achieved by adjusting the unloading rate of the internal pressure in a servo mode.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
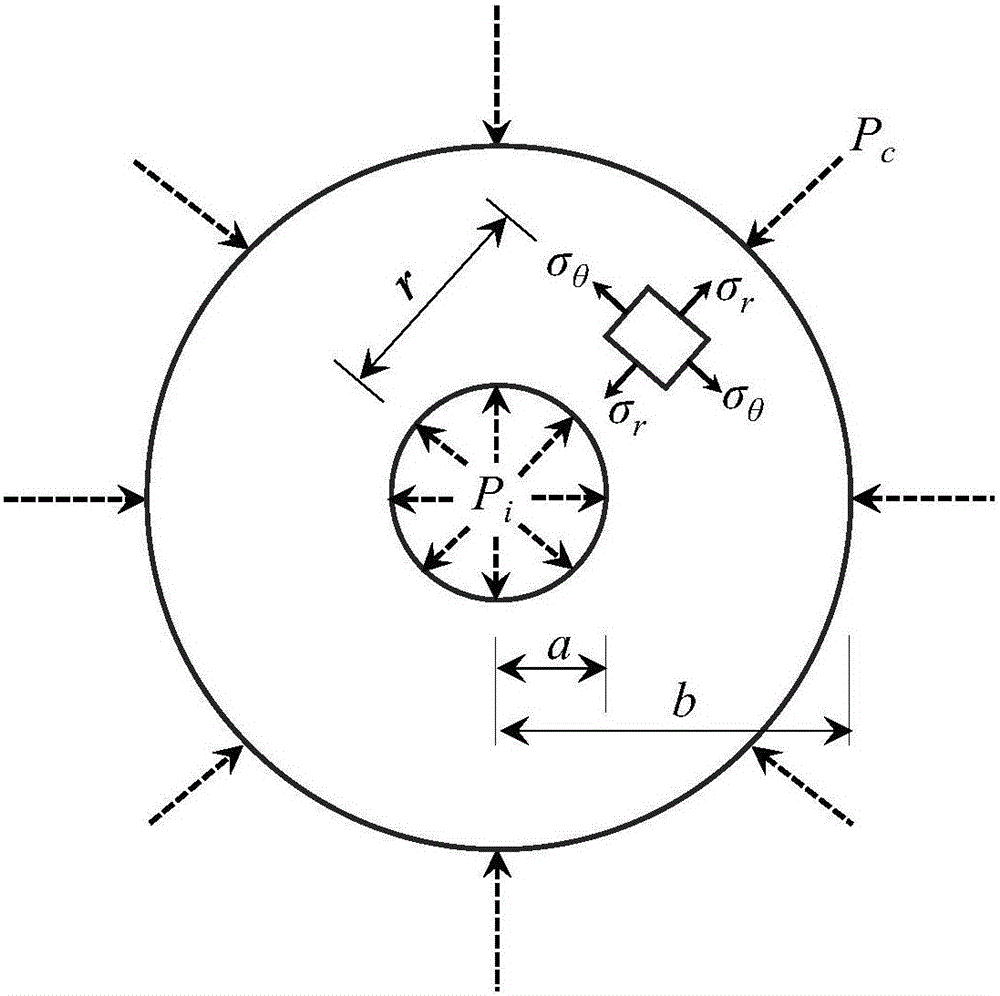
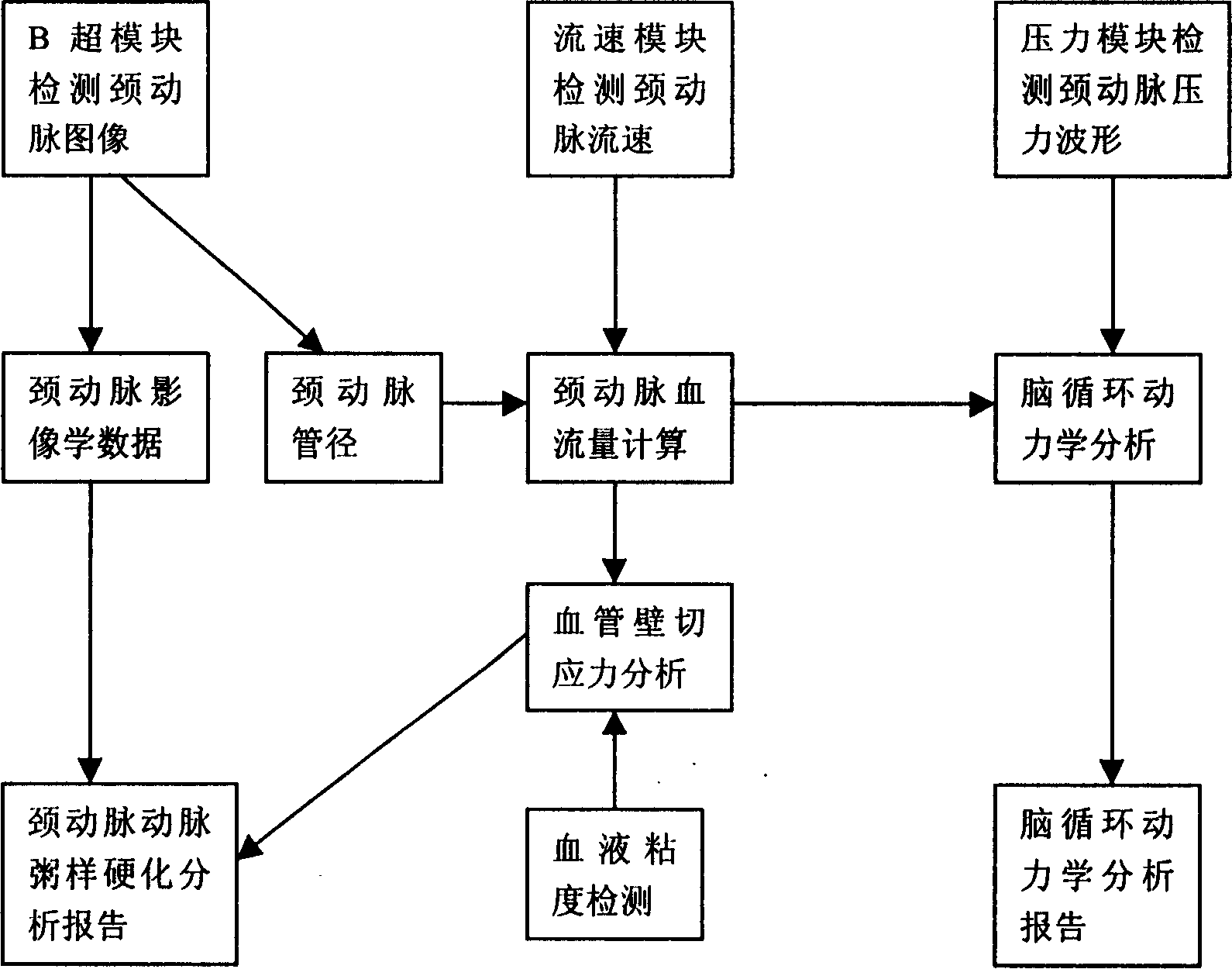
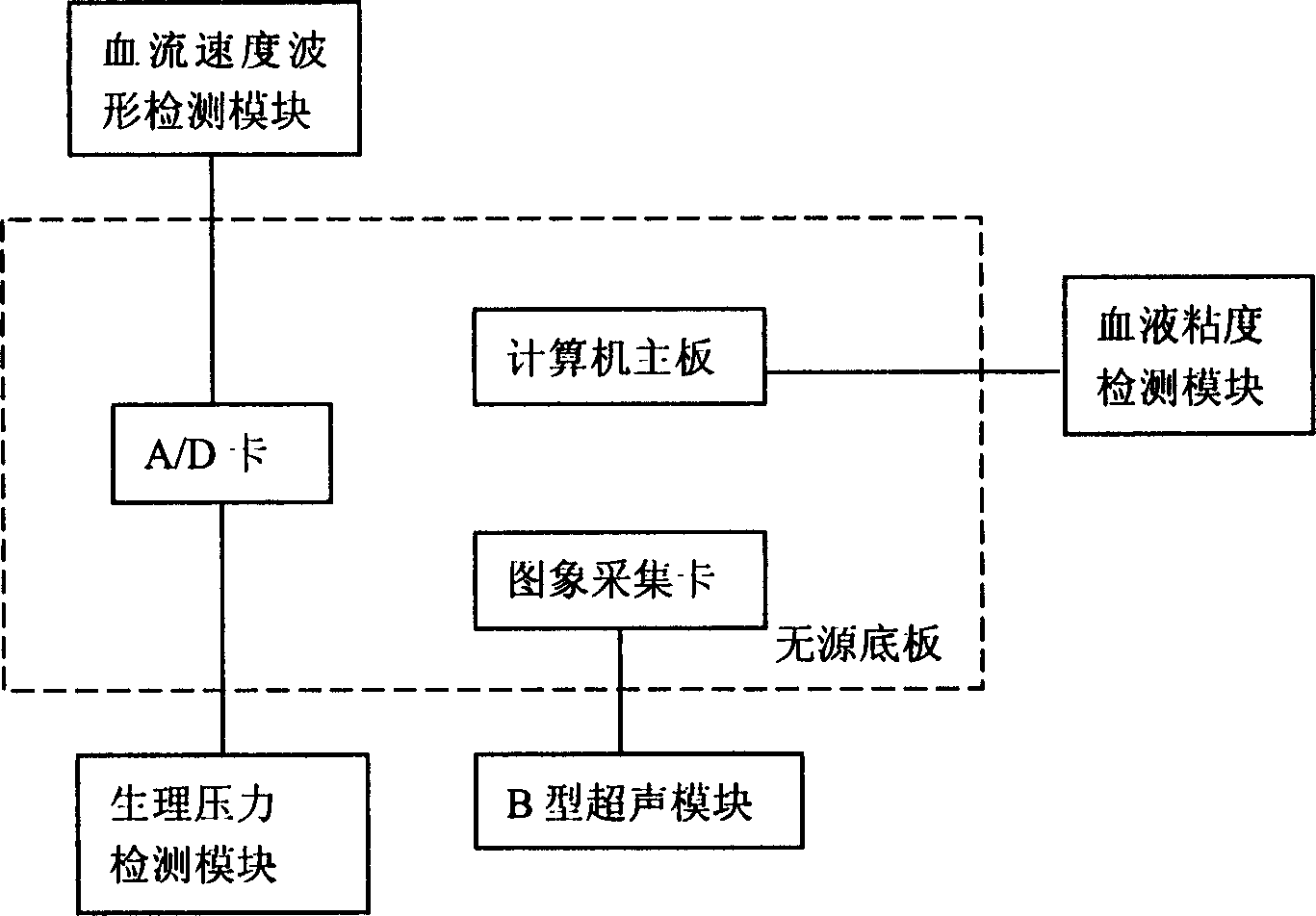
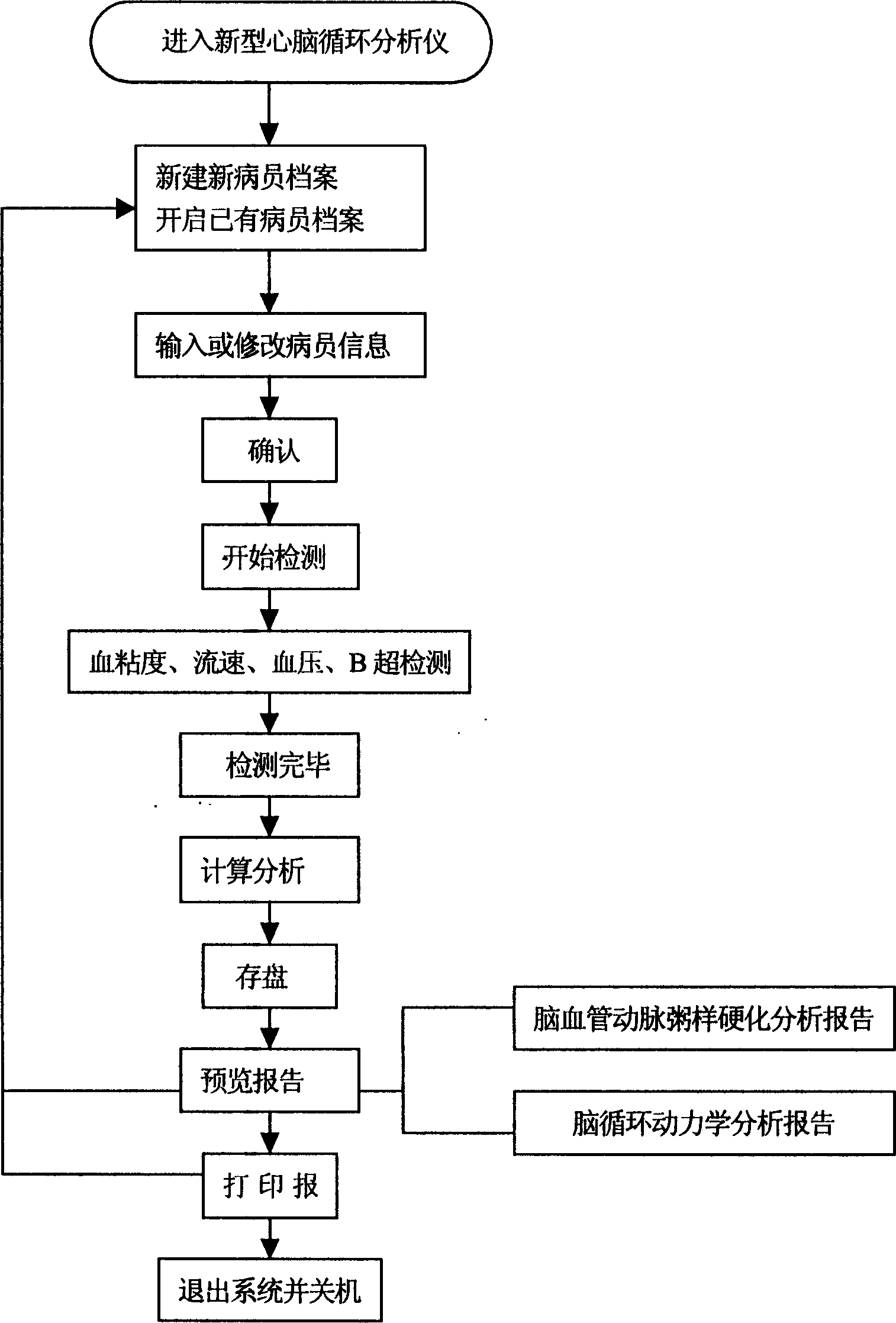
Cerebrovascular system function and brain recirculation dynamic analysis method and apparatus thereof
The invention discloses a cerebrovascular system function and brain recirculation dynamic analysis method, wherein iconographical index and tangential stress index for reflecting cerebrovascular atherosclerosis degree and arteria carotis blood vessel are added into the analytical method, these two indexes can perform early diagnosis and analysis to atherosclerosis and comprehensive analysis for the prevention and early stage diagnosis for cerebrovascular diseases. The invention also discloses the related analytic instrument based on the method for detecting blood vessel diameter by employing type B supersonic detection, which can improve detecting accuracy substantially.
Owner:上海德安生物医学工程有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com