Patents
Literature
222 results about "Dispersive medium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
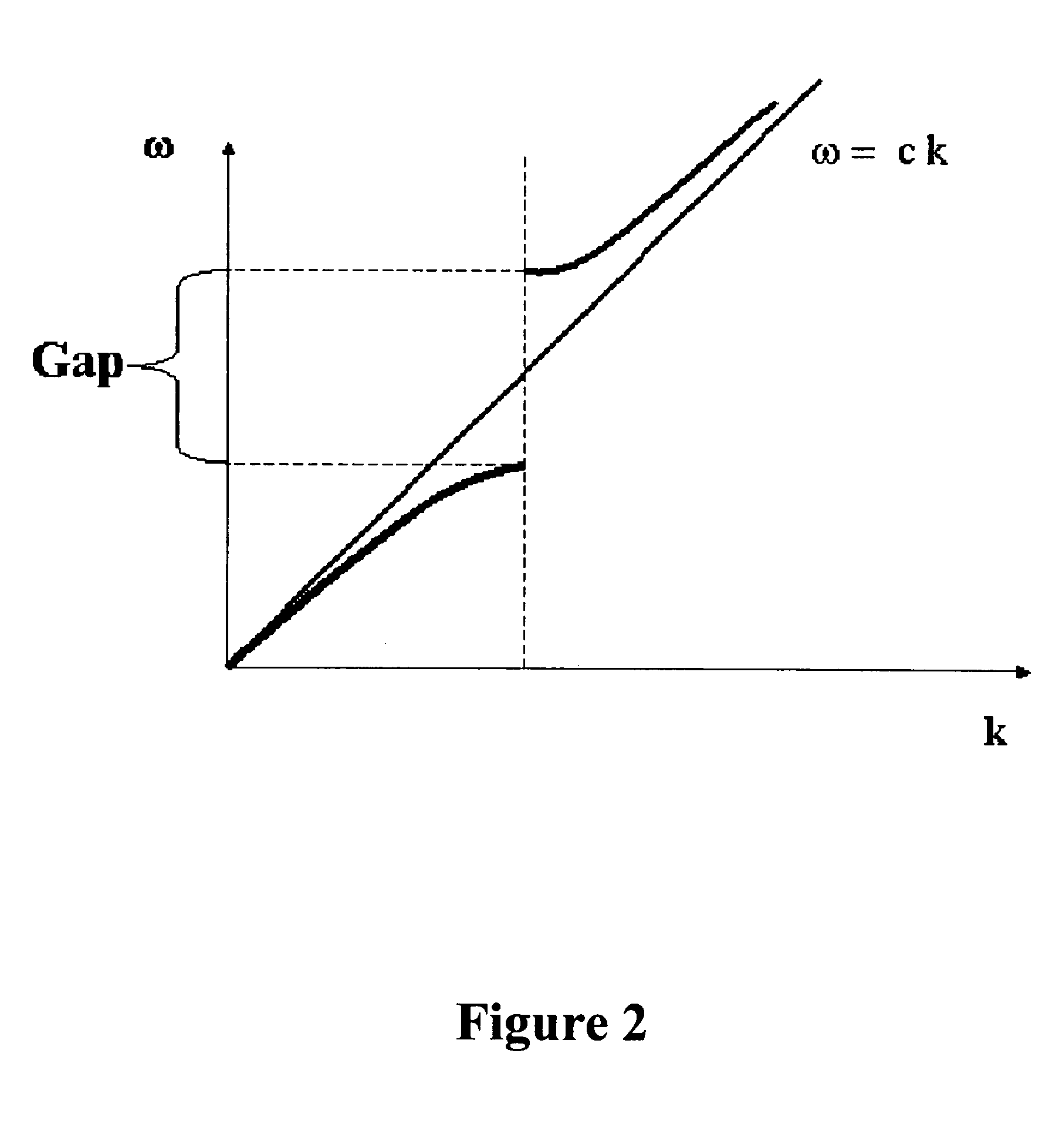
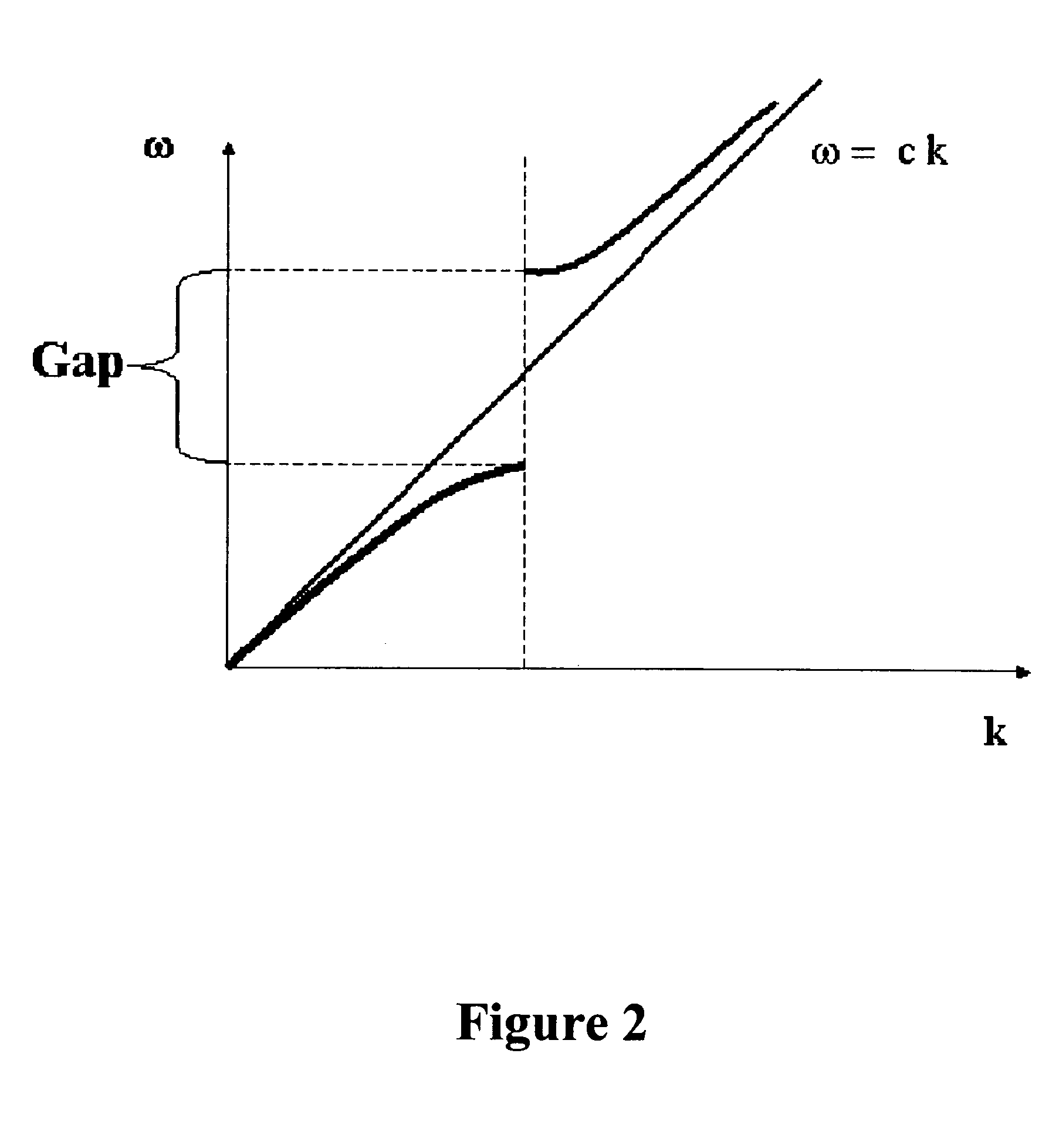
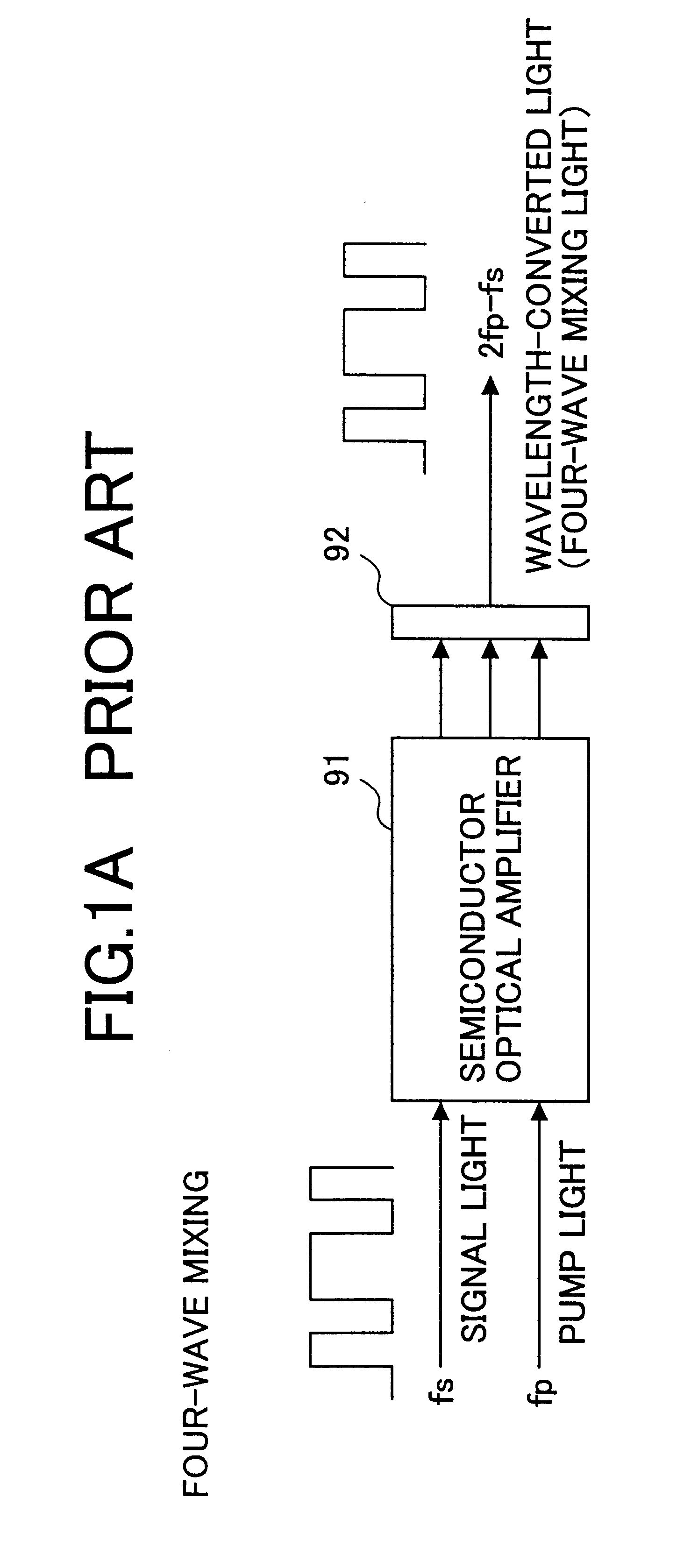
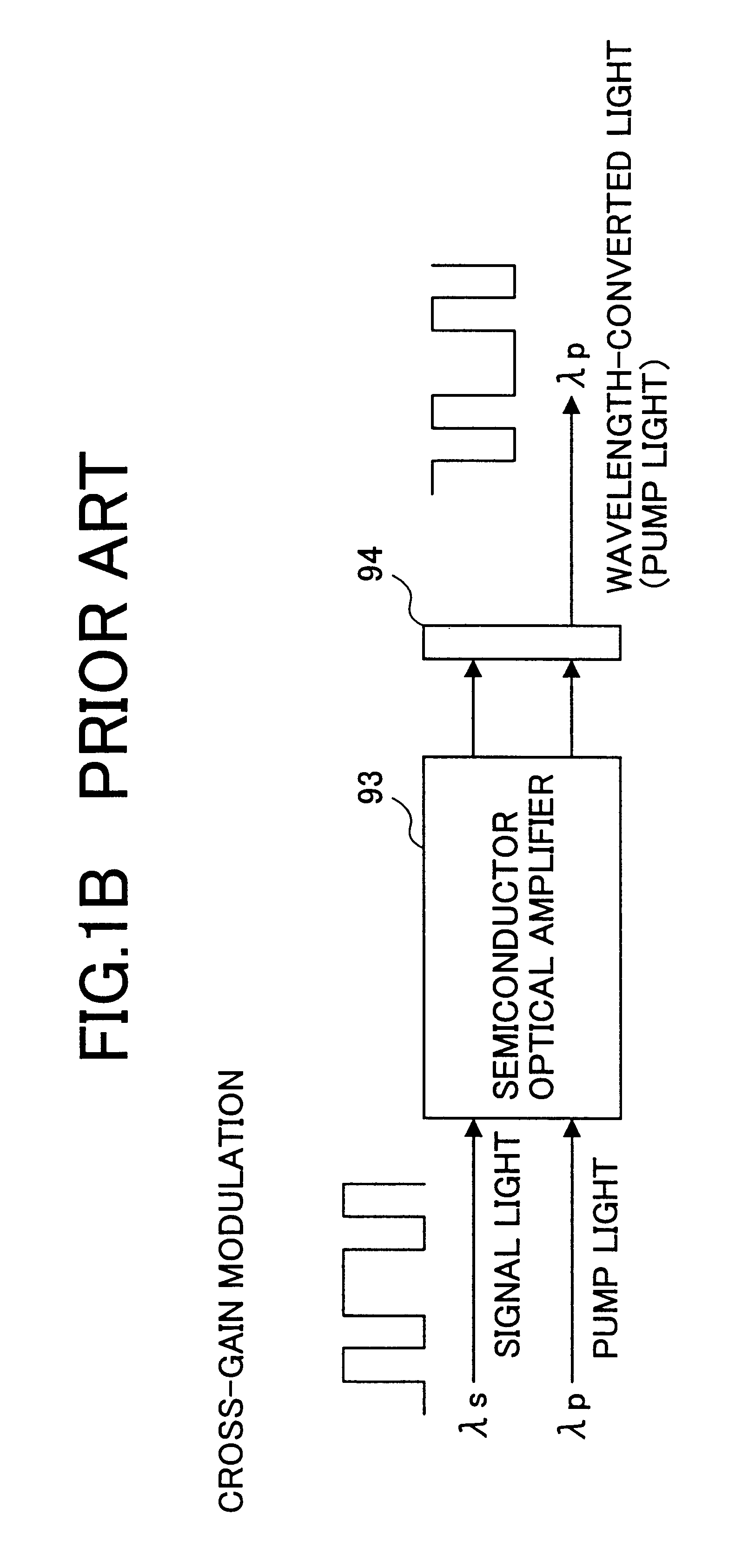
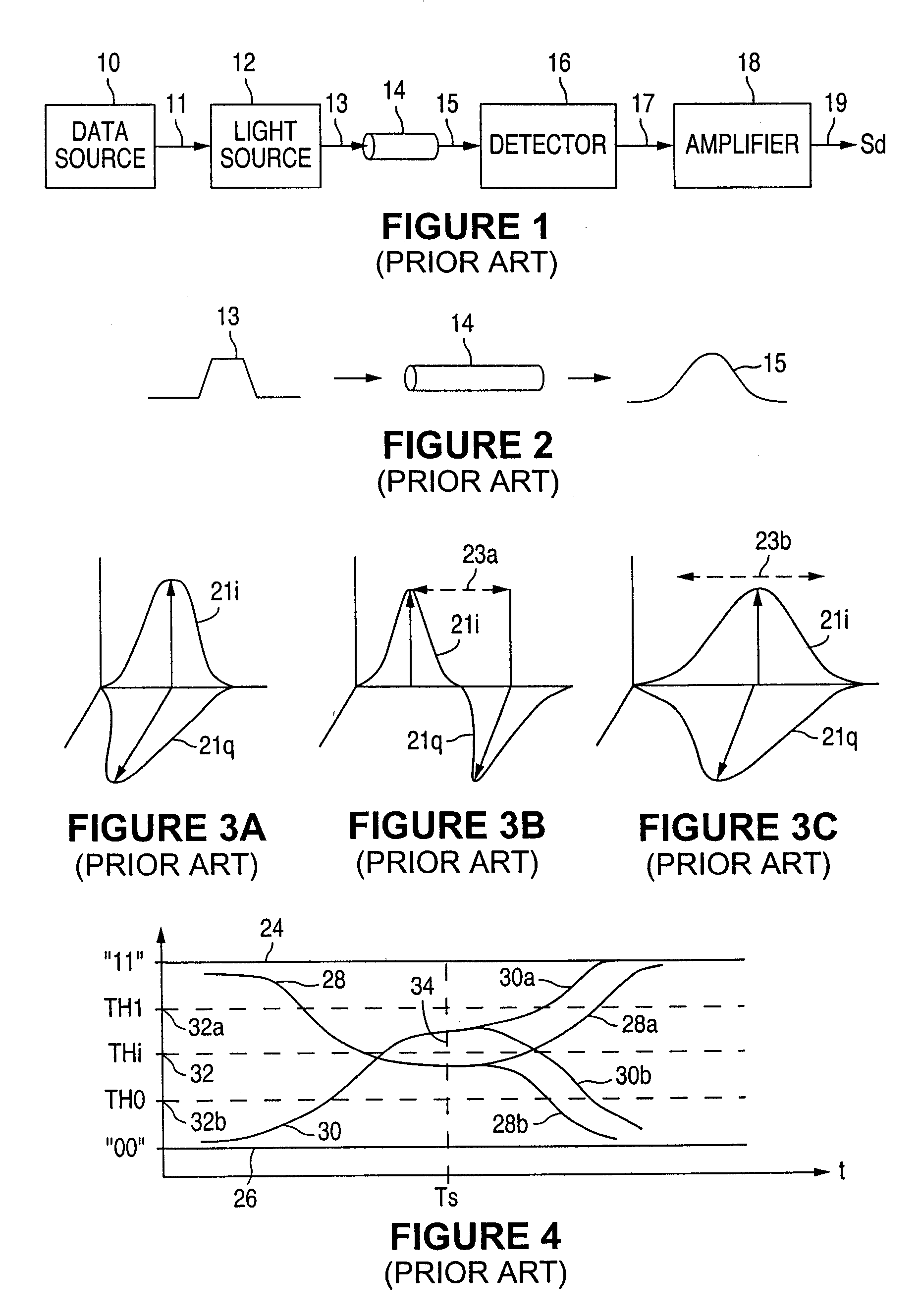
A dispersive medium is a medium in which waves of different frequencies travel at different velocities. With electromagnetic radiation (e.g. light, radio waves), dispersion corresponds to a frequency-dependent variation in the index of refraction of the medium.
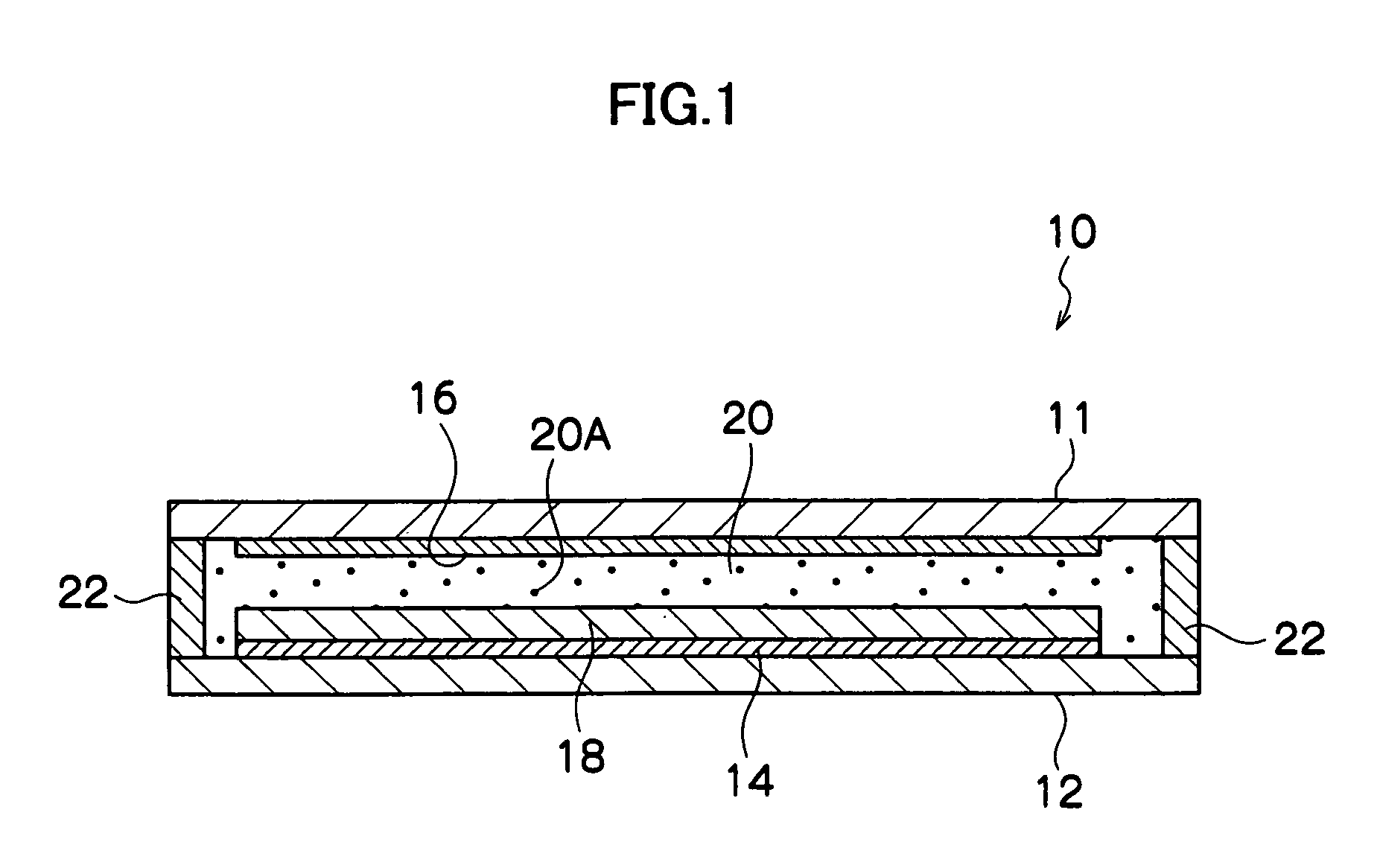
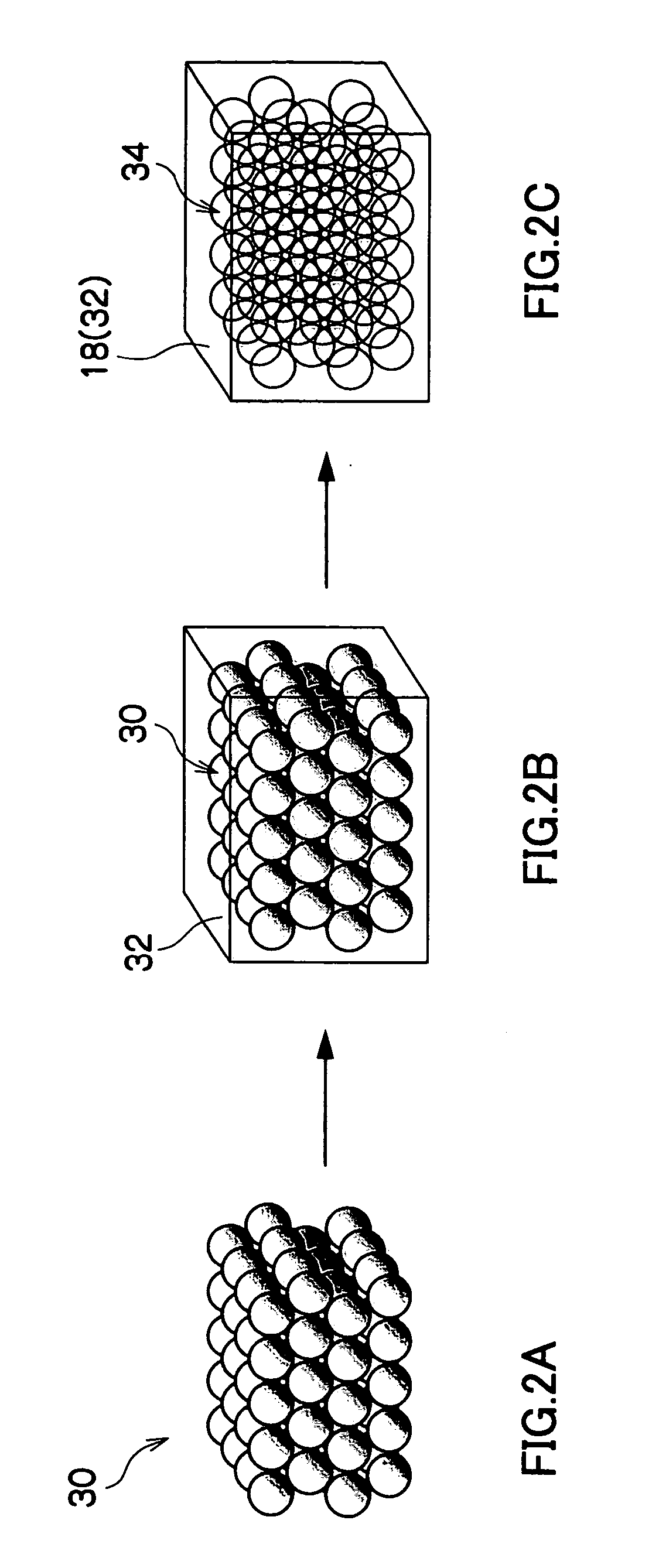
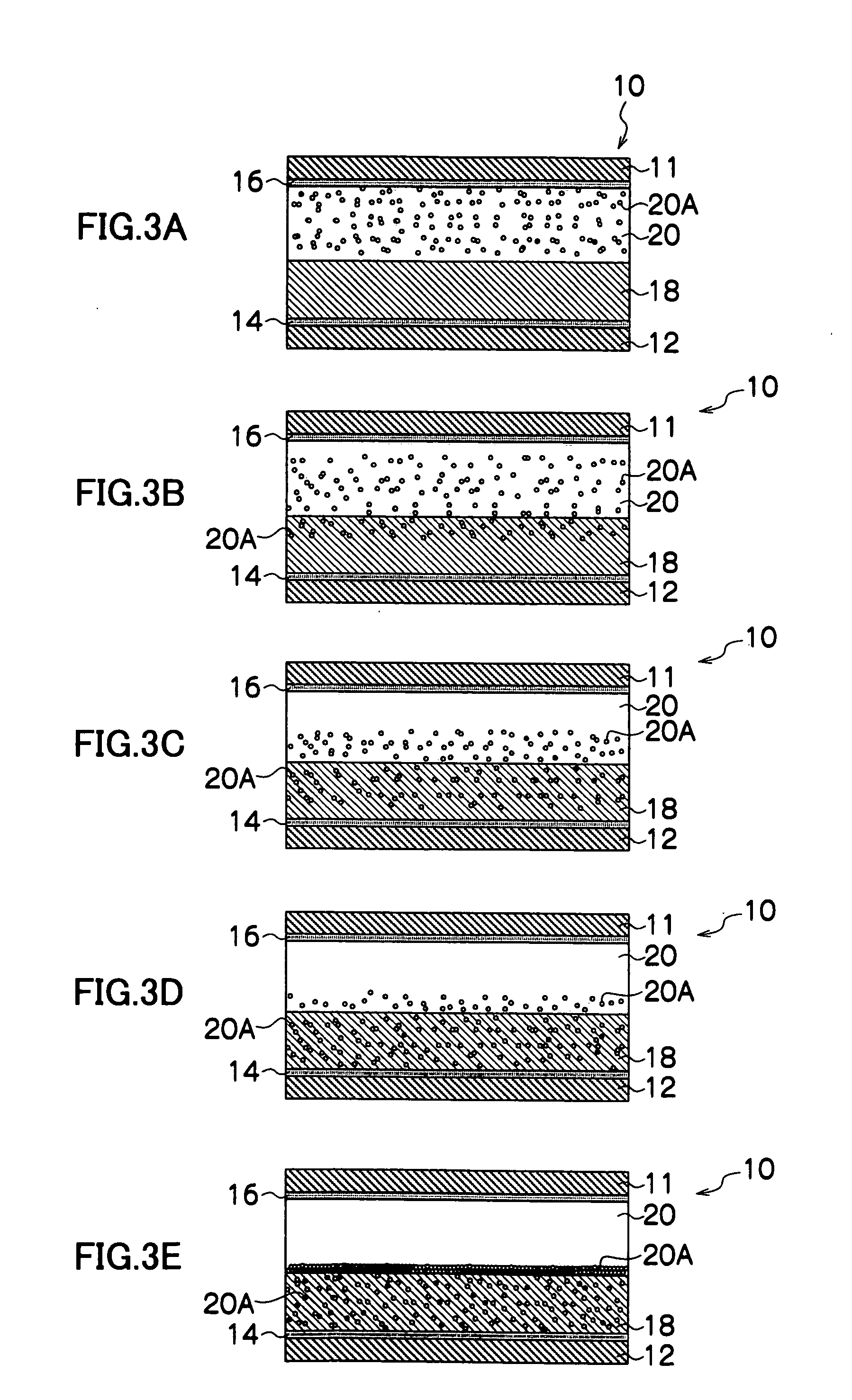
Quantum dot-wavelength converter, manufacturing method of the same and light emitting device including the same
InactiveUS20100051898A1Improve emission effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum dotLength wave
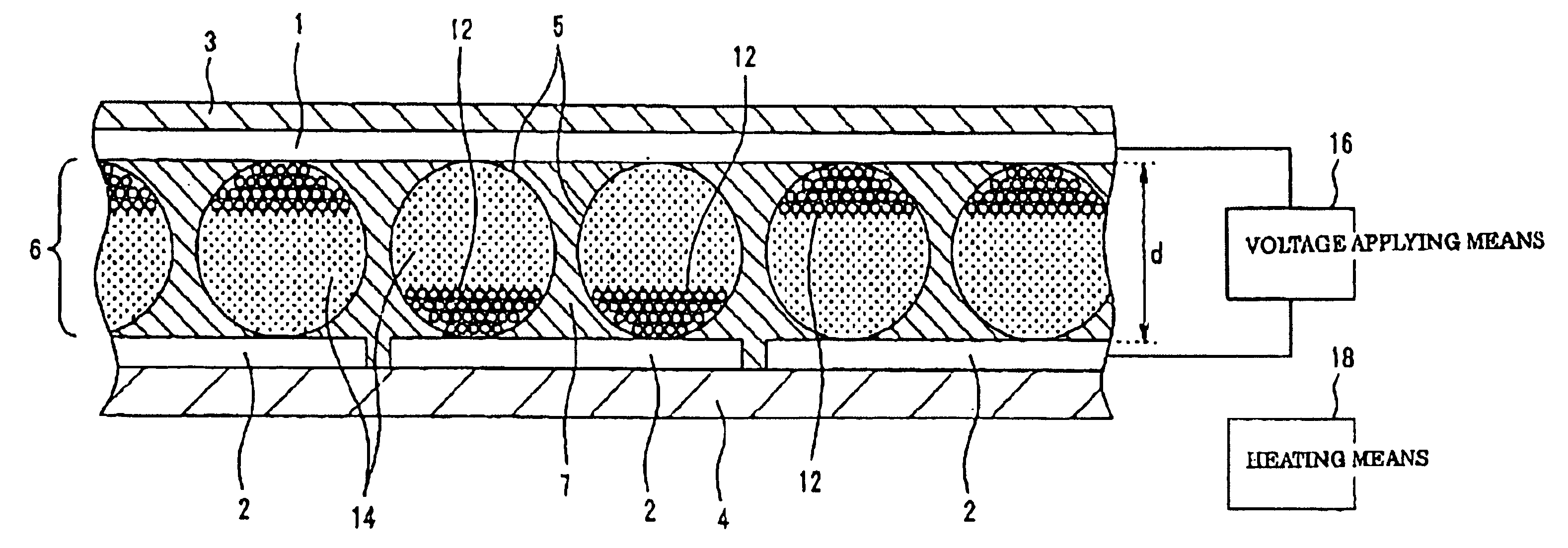
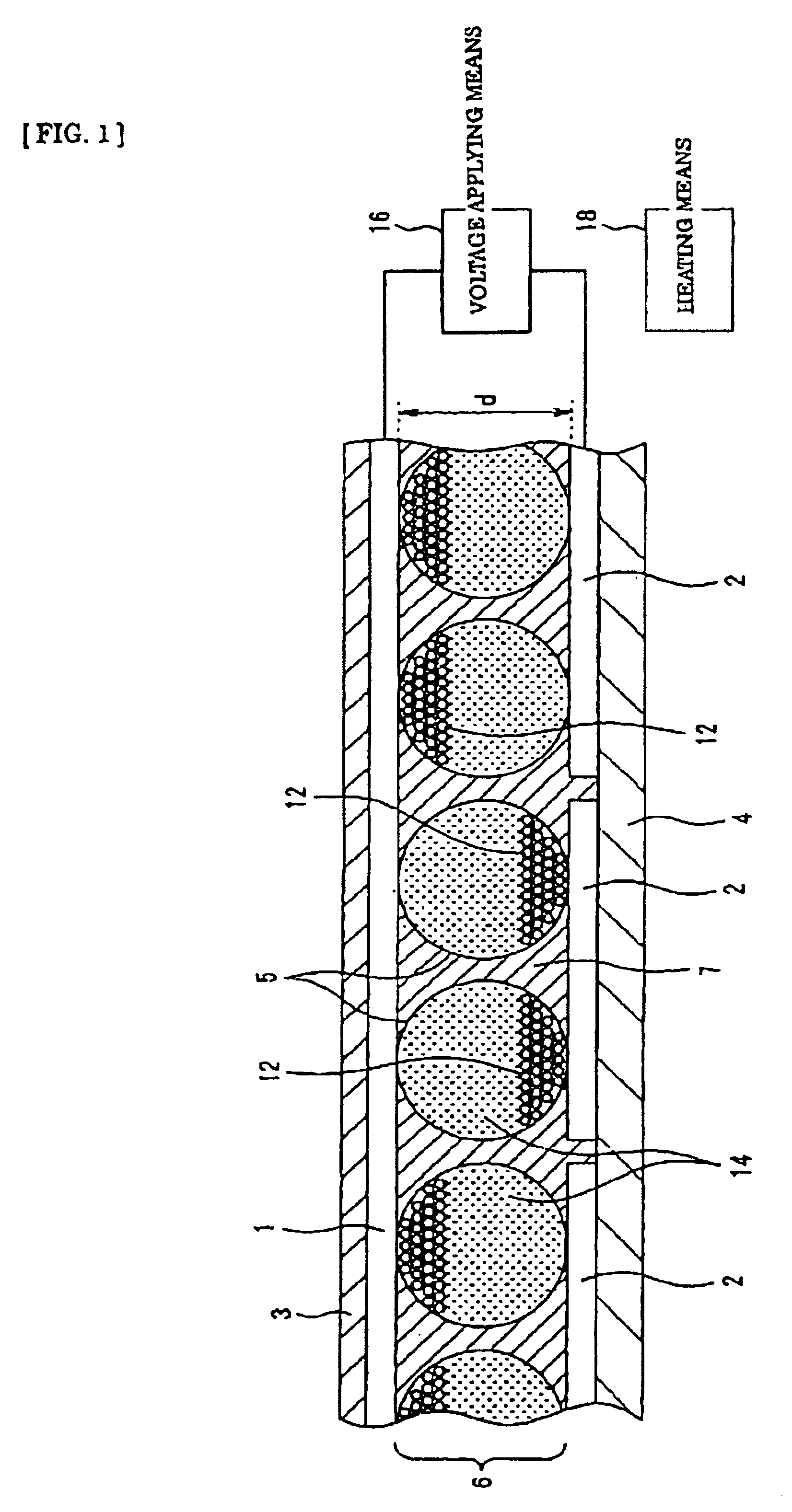
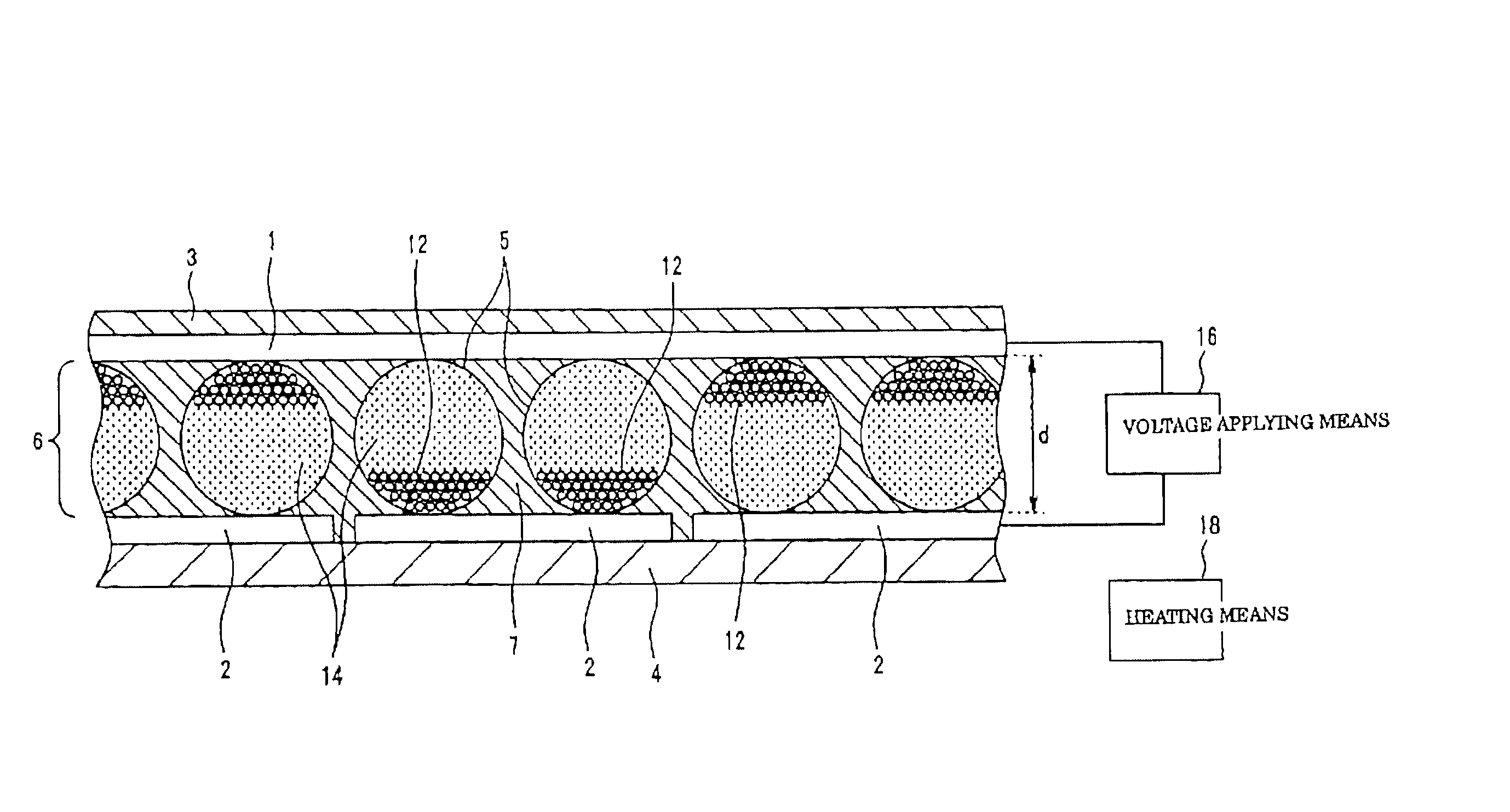
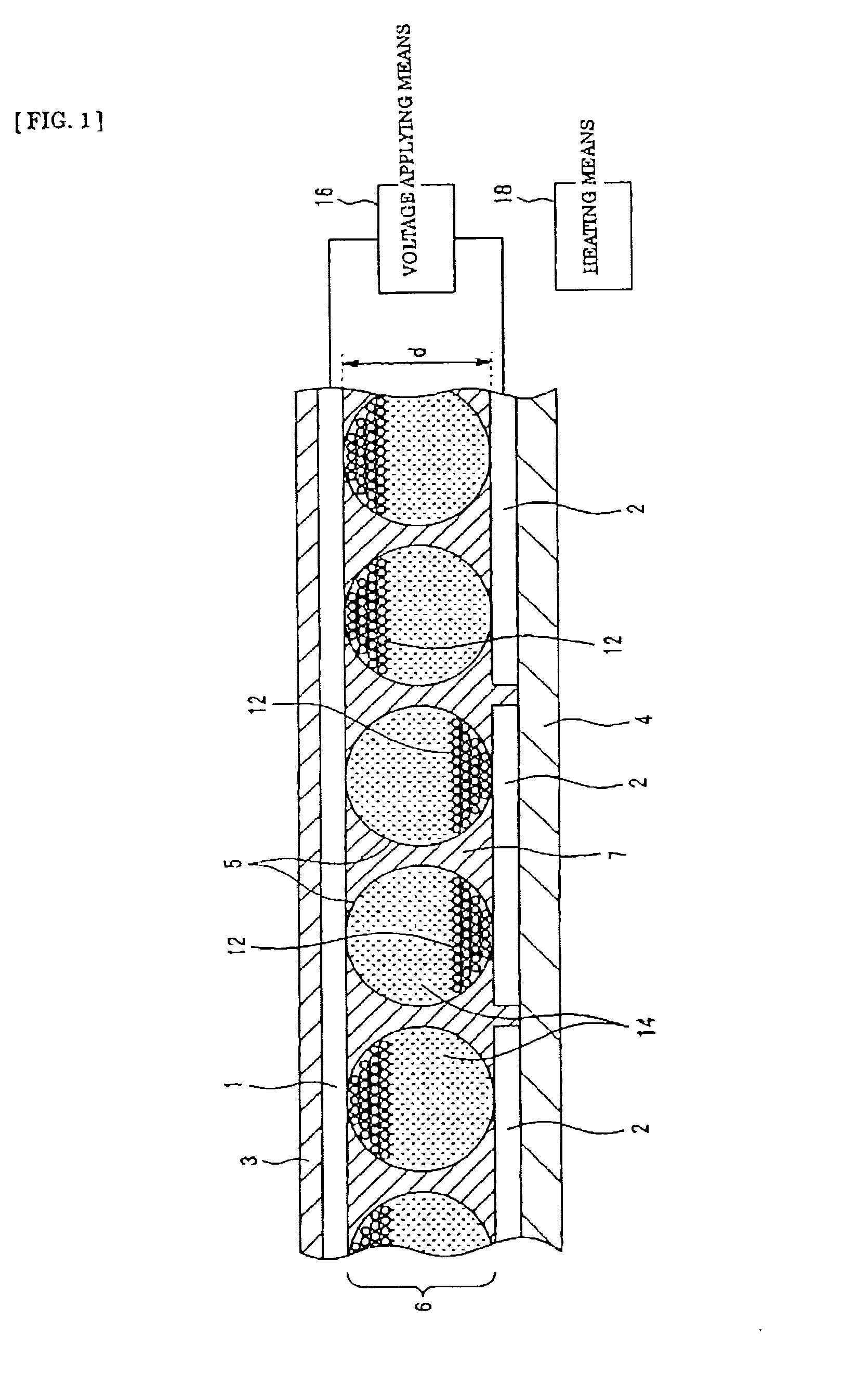
There is provided a quantum dot wavelength converter including a quantum dot, which is optically stable without any change in an emission wavelength and improved in emission capability. The quantum dot wavelength converter includes: a wavelength converting part including a quantum dot wavelength-converting excitation light and generating a wavelength-converted light and a dispersive medium dispersing the quantum dot; and a sealer sealing the wavelength converting part.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
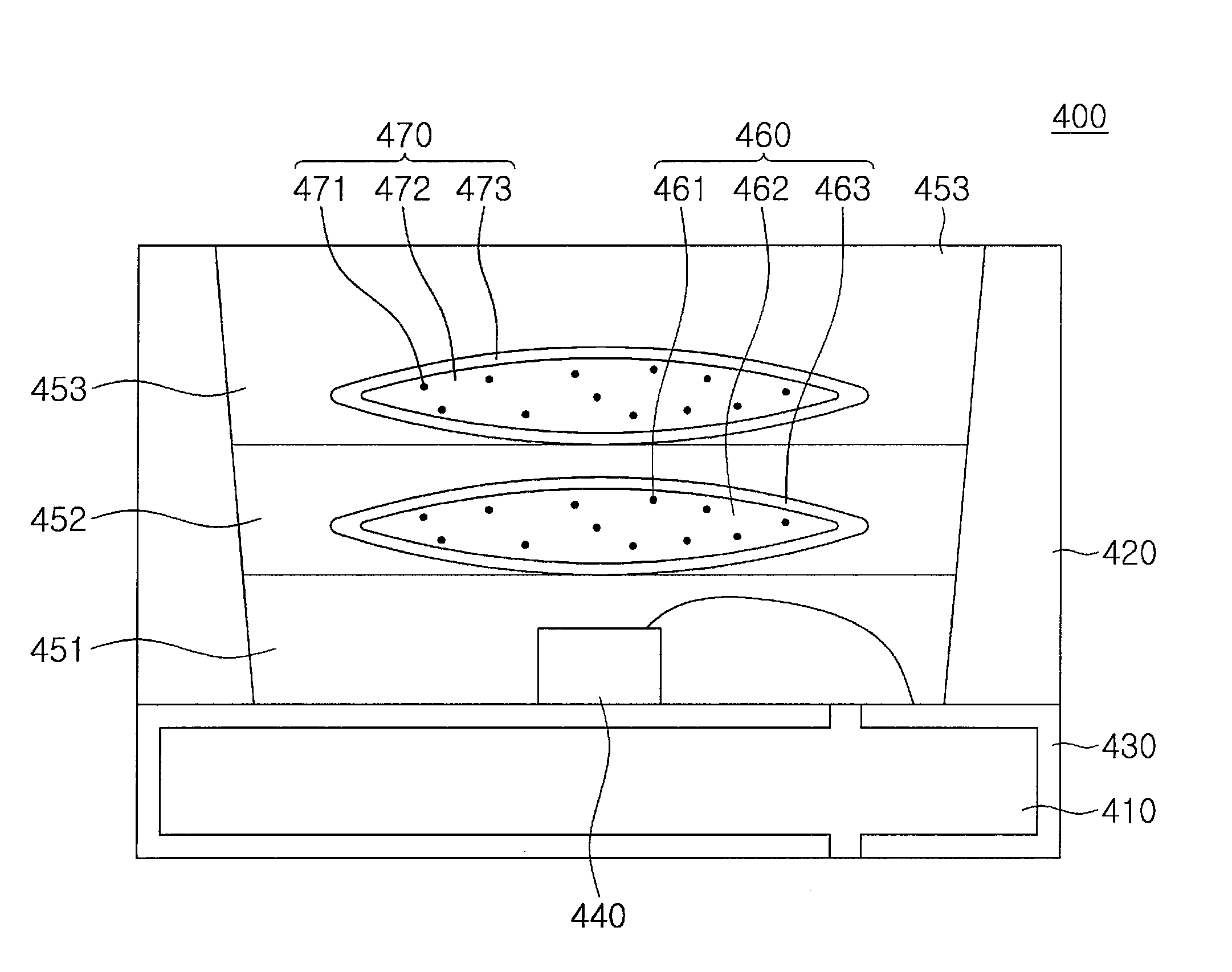
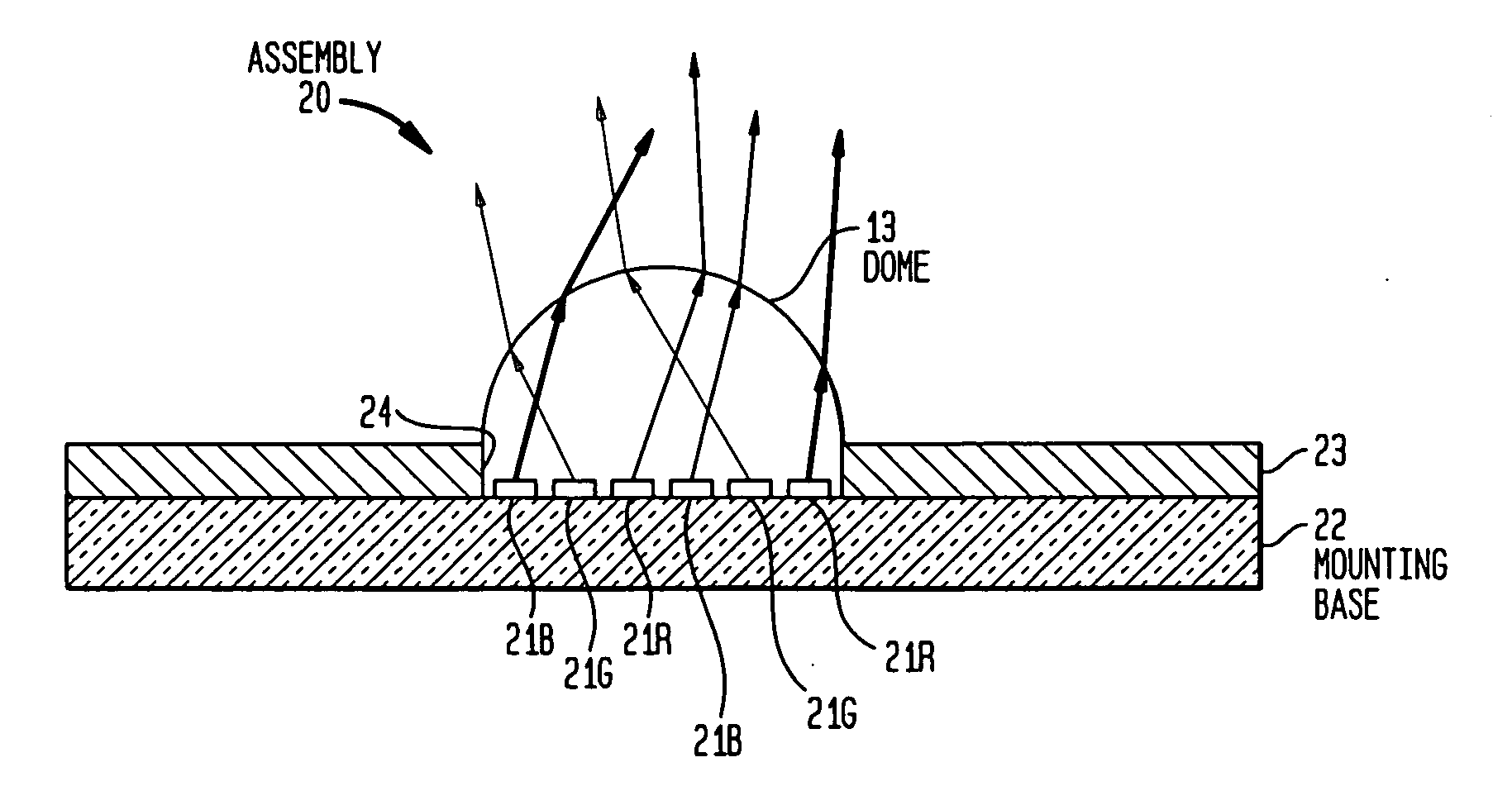
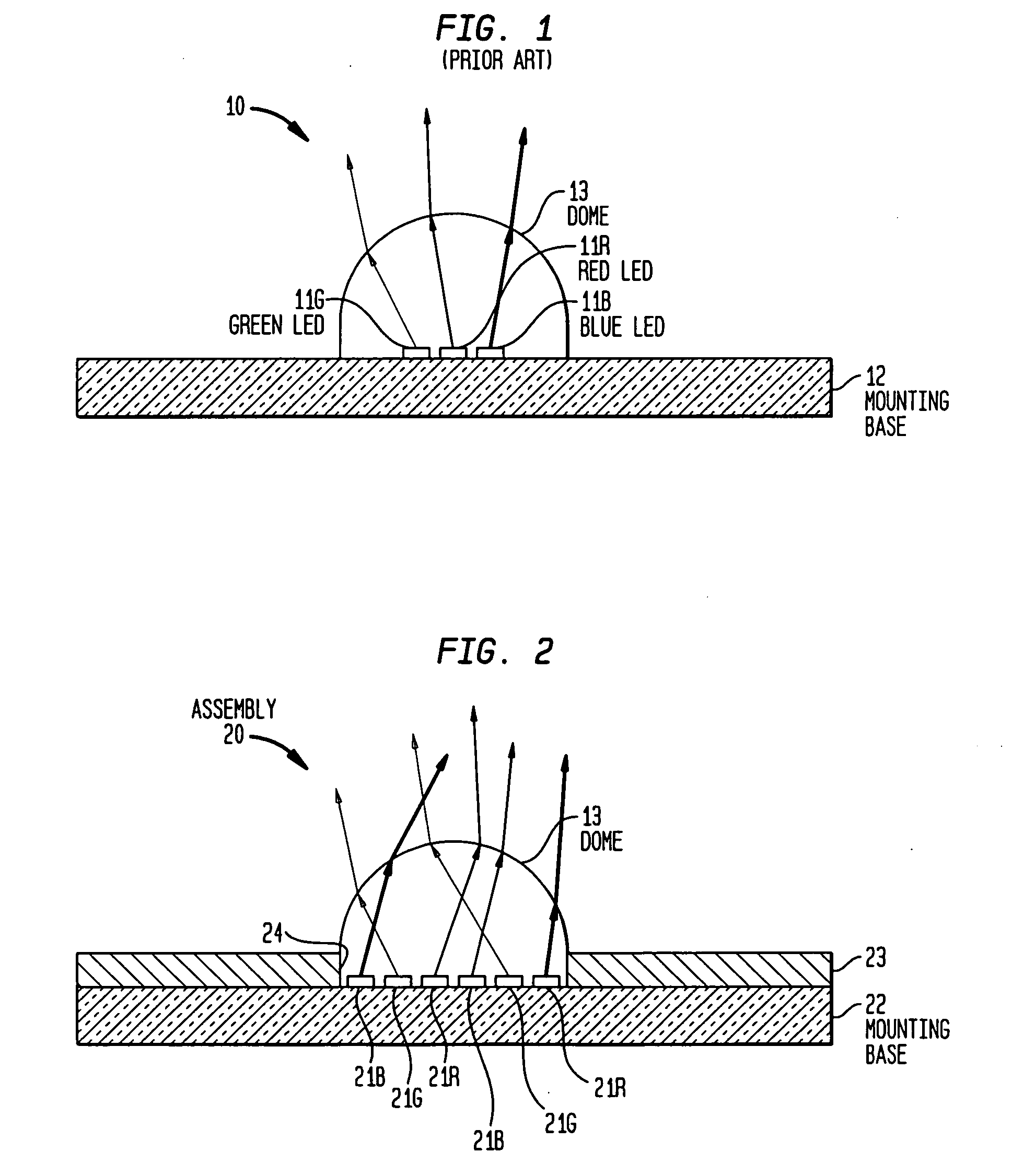
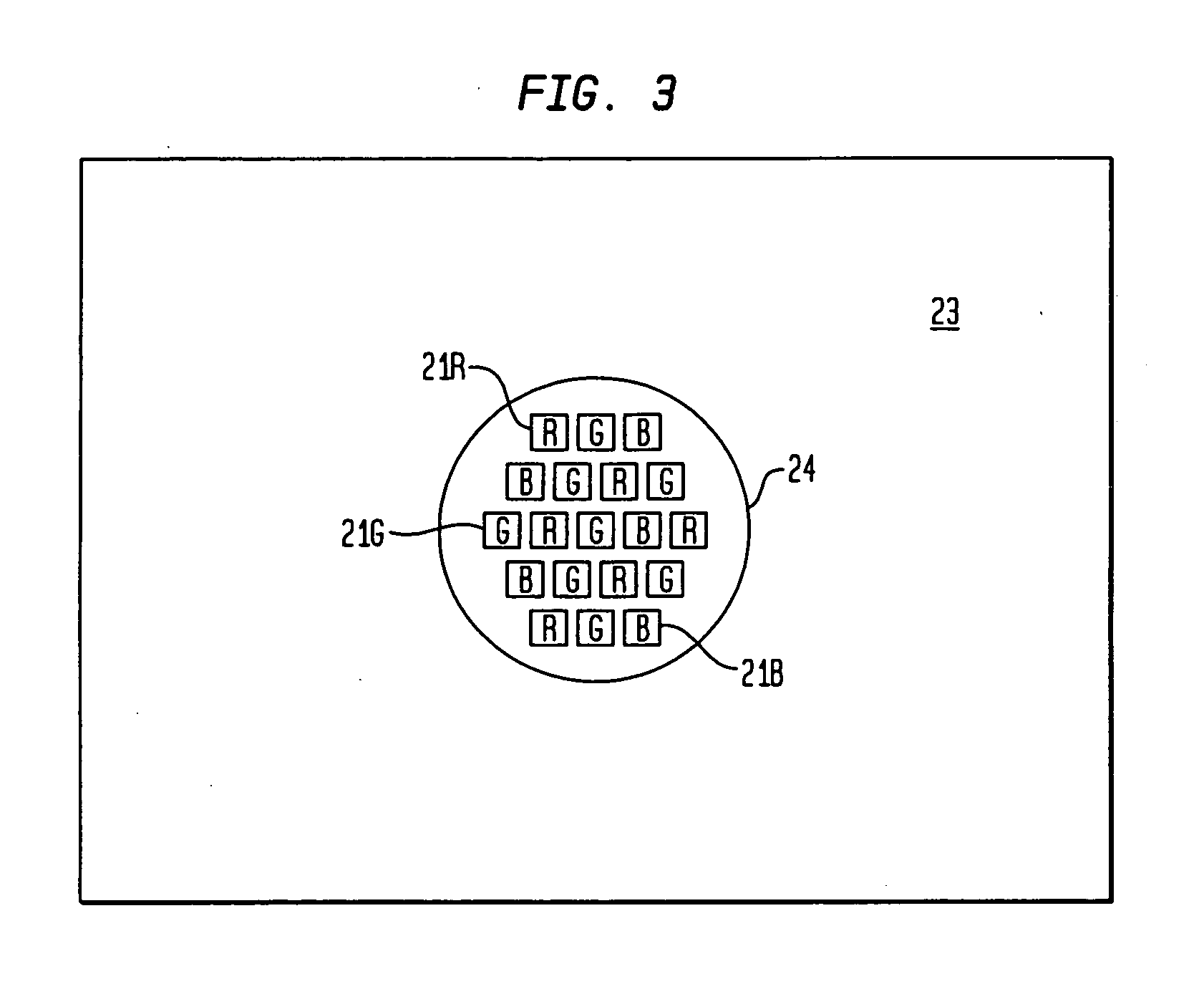
Multicolor LED assembly with improved color mixing
InactiveUS20070013057A1Improve color mixingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringColor mixing
In accordance with the invention, a multicolor LED assembly with improved color mixing comprises an assembly of closely-packed LED dice of different colors packaged for high temperature operation and arranged to minimize same-color adjacency to promote color mixing. The assembly of dice is encapsulated in a dispersive medium such as a transparent medium with entrained dispersive particles. The packaged assembly preferably includes a layer having light dispersing particles deposited directly on the LED.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
Nanophotonic devices based on quantum systems embedded in frequency bandgap media
InactiveUS20050185686A1Add nonlinearityImprove efficiencyQuantum computersLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonicsBinding state
The present invention describes nanophotonic materials and devices for both classical and quantum optical signal processing, transmission, amplification, and generation of light, which are based on a set of quantum systems having a discrete energy levels, such as atoms, molecules, or quantum dots, embedded in a frequency bandgap medium, such as artificial photonic crystals (photonic bandgap materials) or natural frequency dispersive media, such as ionic crystals, molecular crystals, or semiconductors, exhibiting a frequency (photonic) bandgap for propagating electromagnetic modes coupled to optical transitions in the quantum systems. If the frequency of one of optical transitions, called the working transition, lies inside the frequency bandgap of the medium, then spontaneous decay of the working transition into propagating photon modes is completely suppressed. Moreover, the excitation of the working transition and a photon form a photon-quantum system bound state lying inside the photonic bandgap of the medium, in which radiation is localized in the vicinity of the quantum system. In a quantum system “wire” or a quantum system “waveguide”, made of spatially disordered quantum systems, or in a chain quantum system waveguide made of a periodically ordered identical quantum systems, wave functions of the photon-quantum system bound states localized on different quantum systems overlap each other and develop a photonic passband lying inside bandgap of the photonic bandgap medium. Photons with frequencies lying inside the photonic passband propagate along the quantum system waveguide. Since the working transition cannot be excited twice, the passband photons interact with each other extremely strongly both in one waveguide and in different waveguides that are located sufficiently close to each other. These unique nonlinear properties of the quantum system waveguides are proposed to use for engineering key nanophotonic devices, such as all-optical and electro-optical switches, modulators, transistors, control-NOT logic gates, nonlinear directional couplers, electro-optical modulators and converters, generators of entangled photon states, passband optical amplifiers and lasers, as well as all-optical integrated circuits for both classical and quantum optical signal processing, including quantum computing.
Owner:ALTAIR CENT
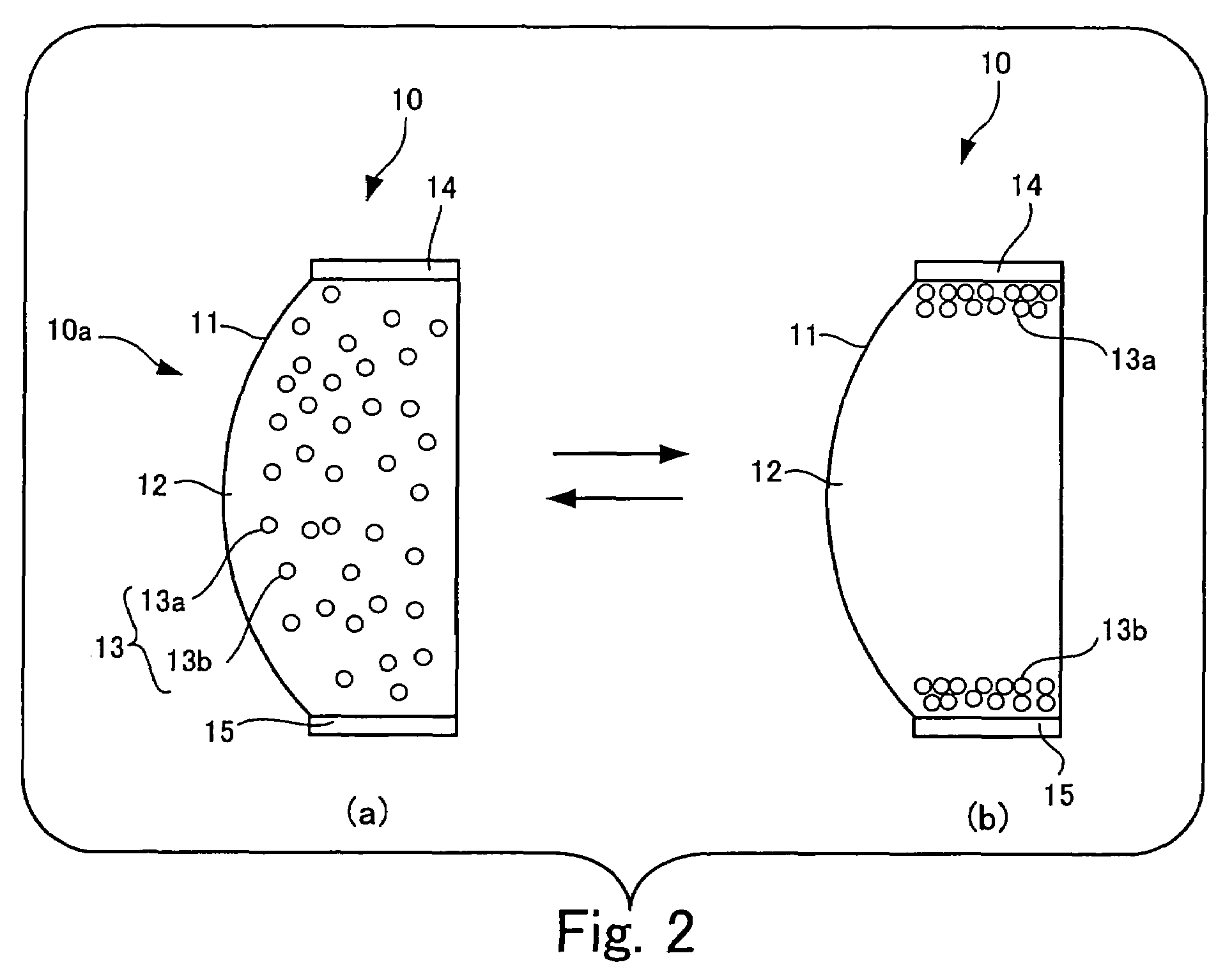
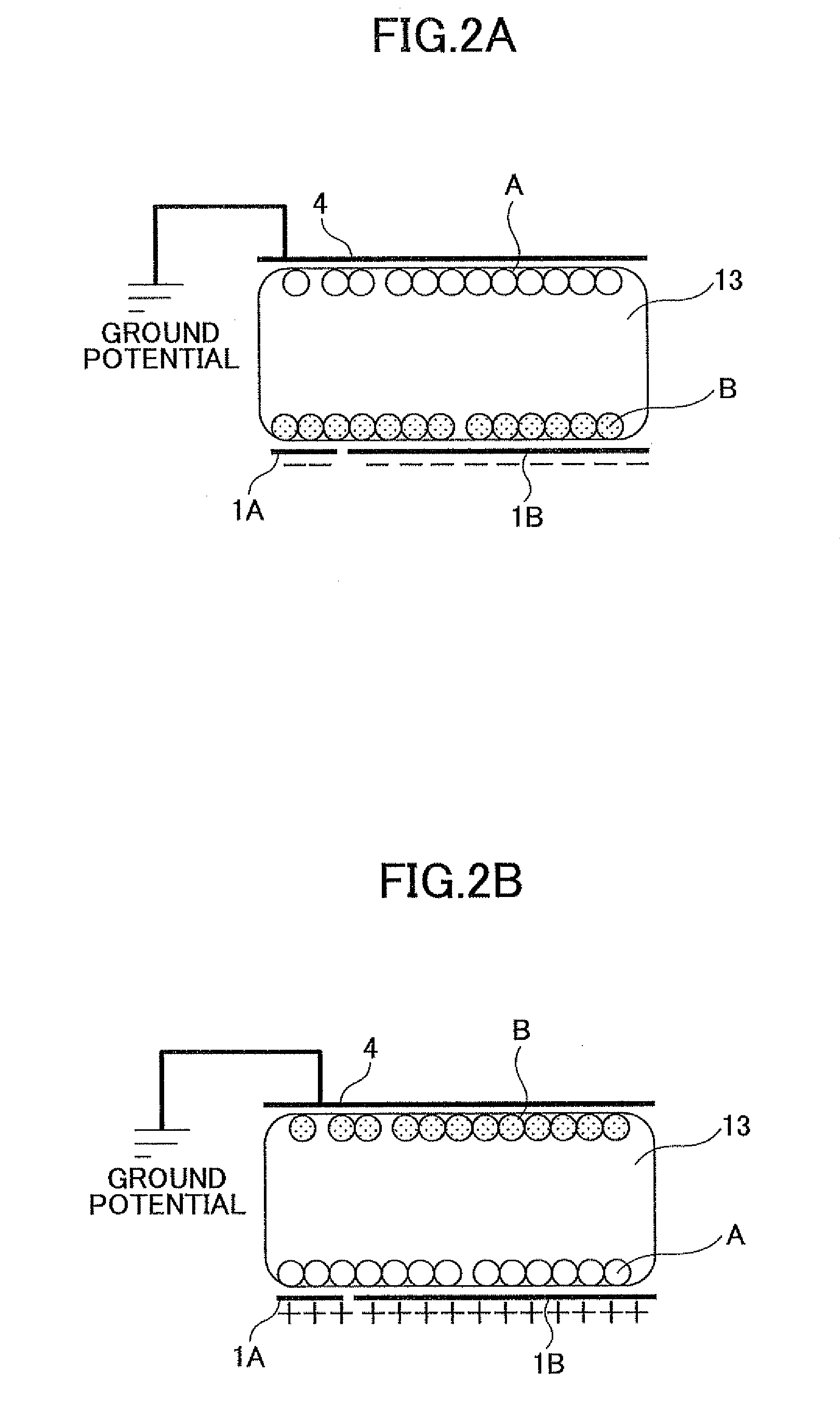
Electrophoretic device, driving method of electrophoretic device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS6788450B2Improving visibility and contrast characteristicMaintenance conditionStatic indicating devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresisEngineering
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Method and apparatus for arbitrary waveform generation using photonics
InactiveUS6724783B2Correction for dispersionLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionLow speedLow-pass filter
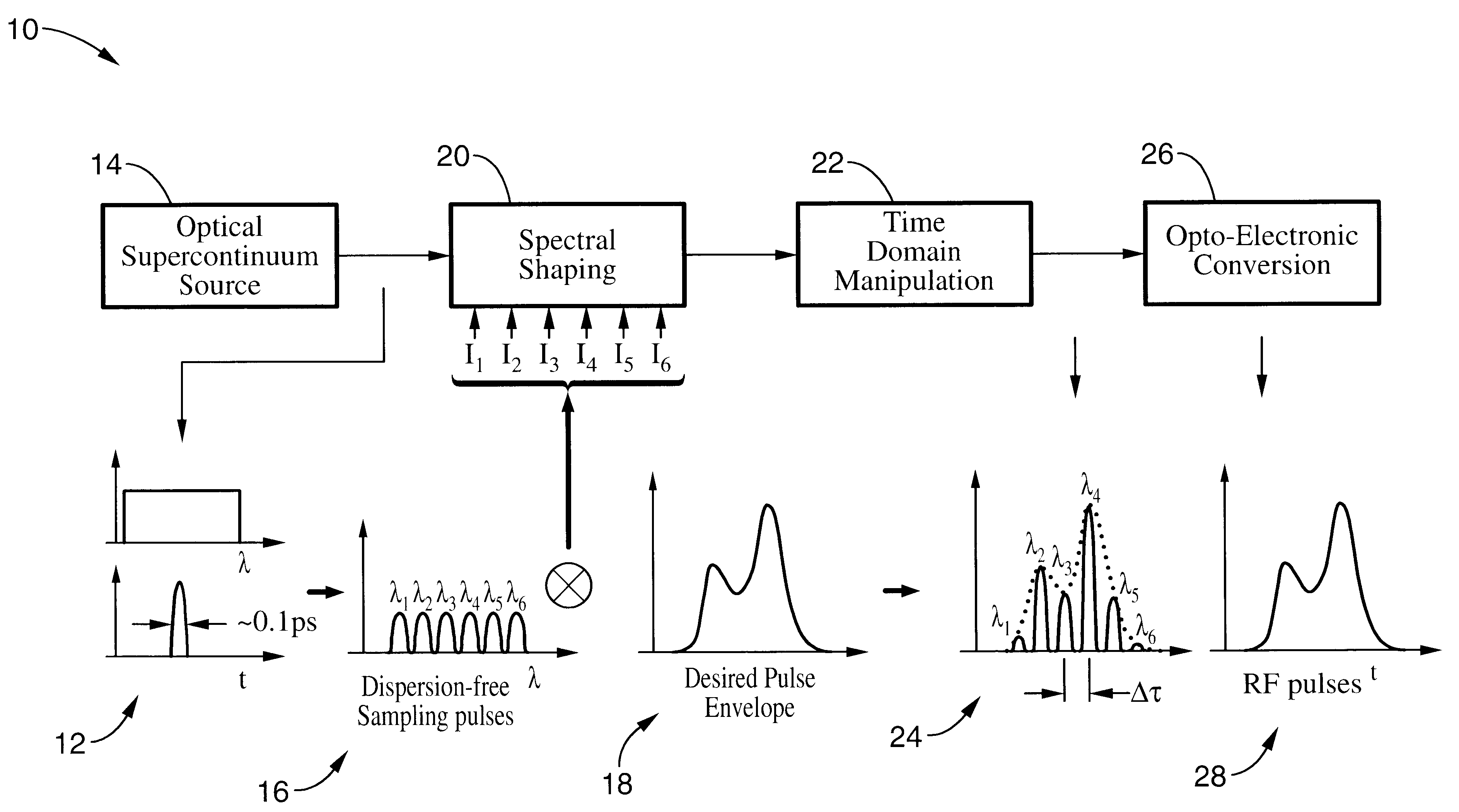
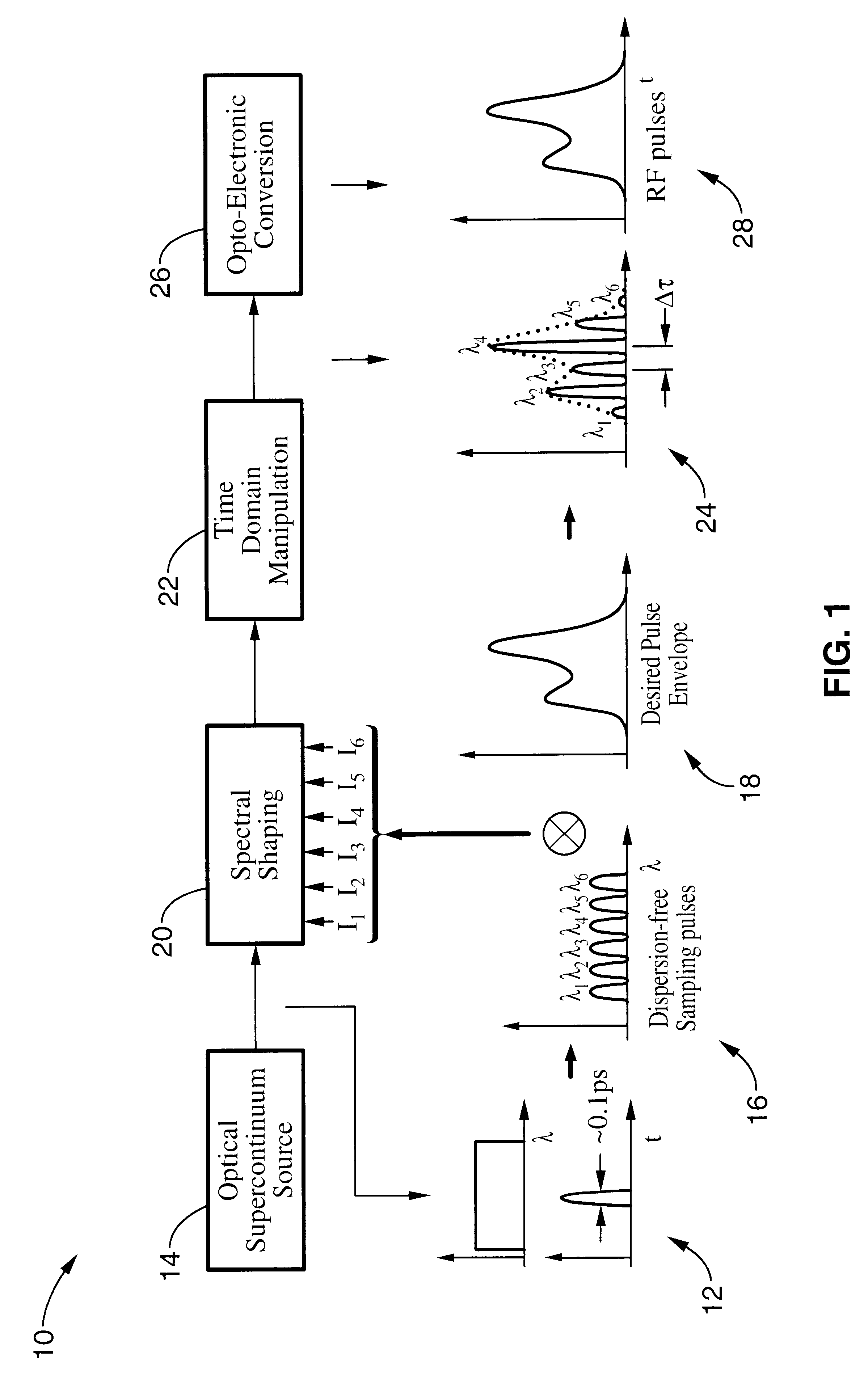
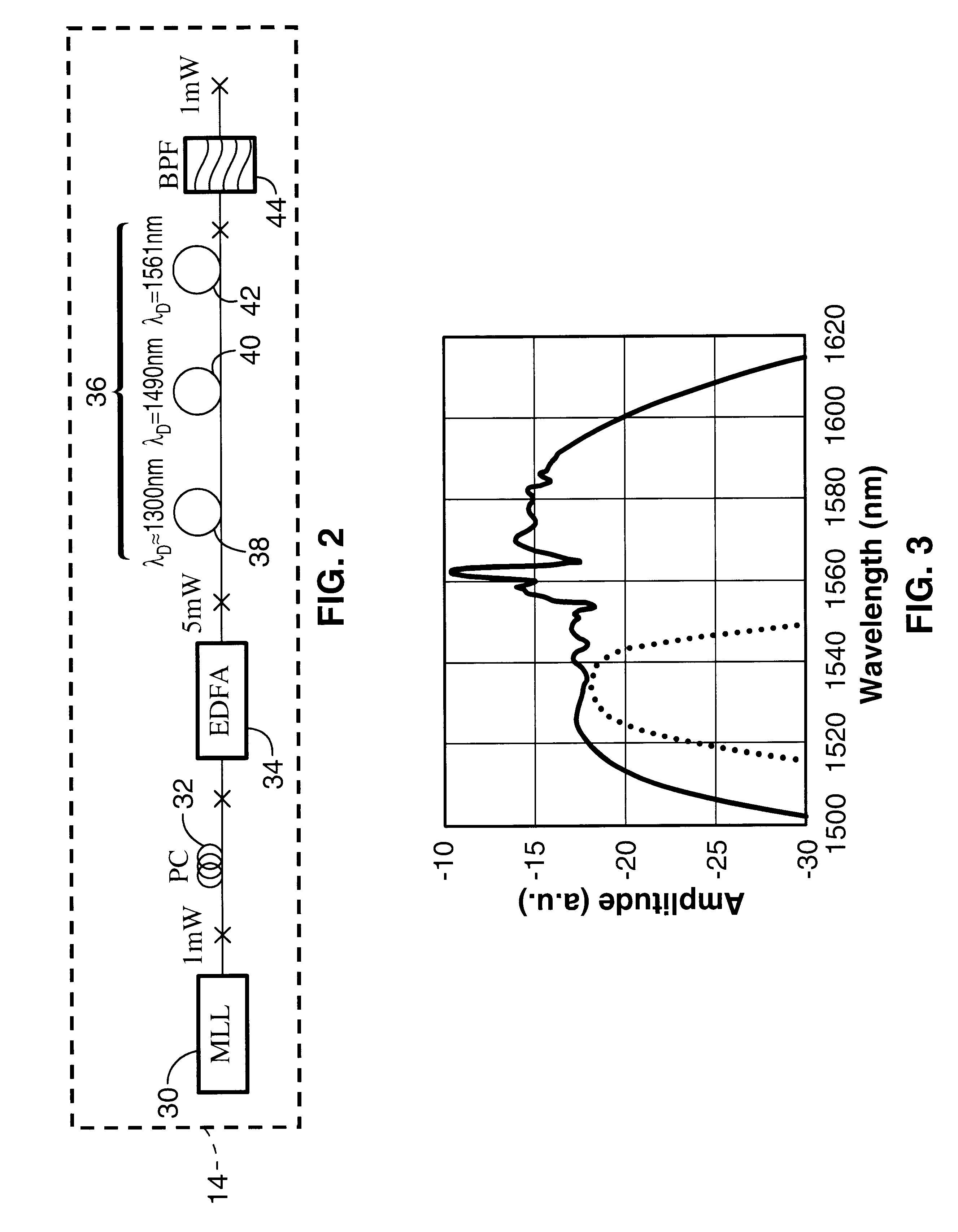
An apparatus and method for synthesizing waveforms with arbitrary amplitude, frequency, and phase modulation. Pulses from a broadband (supercontinuum) optical source are filtered into a plurality of wavelength channels, and the intensity of each wavelength channel is adjusted to an appropriate level depending on the desired shape of the envelope of the output pulse. The envelope of the sampling wavelength channels can be stretched, compressed, or inverted in the time domain later using a dispersive medium. After time domain manipulation, the optical pulse train is observed with a combination of high-speed photodetectors and a radio frequency low-pass filter, a low-speed photodetector.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Composition for manufacturing electrode of solar cell, method of manufacturing same electrode, and solar cell using electrode obtained by same method
InactiveUS20090250106A1Avoid alterationInhibit deteriorationConductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCarbon numberSolar cell
A composition for manufacturing an electrode of a solar cell, comprising metal nanoparticles dispersed in a dispersive medium, wherein the metal nanoparticles contain silver nanoparticles of 75 weight % or more, the metal nanoparticles are chemically modified by a protective agent having a main chain of organic molecule comprising a carbon backbone of carbon number of 1 to 3, and the metal nanoparticles contains 70% or more in number-average of metal nanoparticles having a primary grain size within a range of 10 to 50 nm.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Quantum dot-wavelength converter, manufacturing method of the same and light emitting device including the same
InactiveUS20110240960A1Improve emission effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor laser optical deviceQuantum dotLength wave
There is provided a quantum dot wavelength converter including a quantum dot, which is optically stable without any change in an emission wavelength and improved in emission capability. The quantum dot wavelength converter includes: a wavelength converting part including a quantum dot wavelength-converting excitation light and generating a wavelength-converted light and a dispersive medium dispersing the quantum dot; and a sealer sealing the wavelength converting part.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
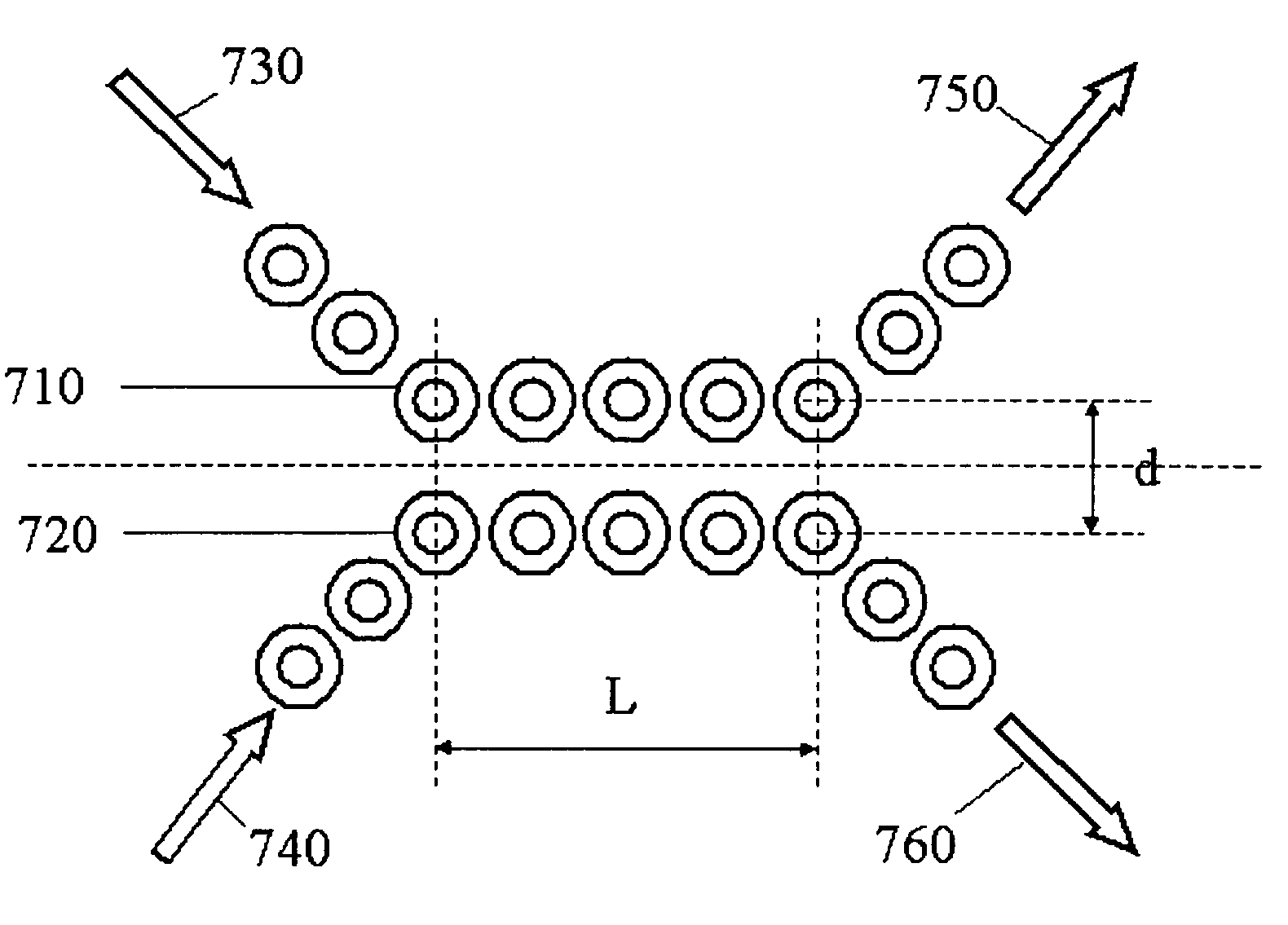
Method and system for interpreting and utilizing multimode dispersive acoustic guided waves
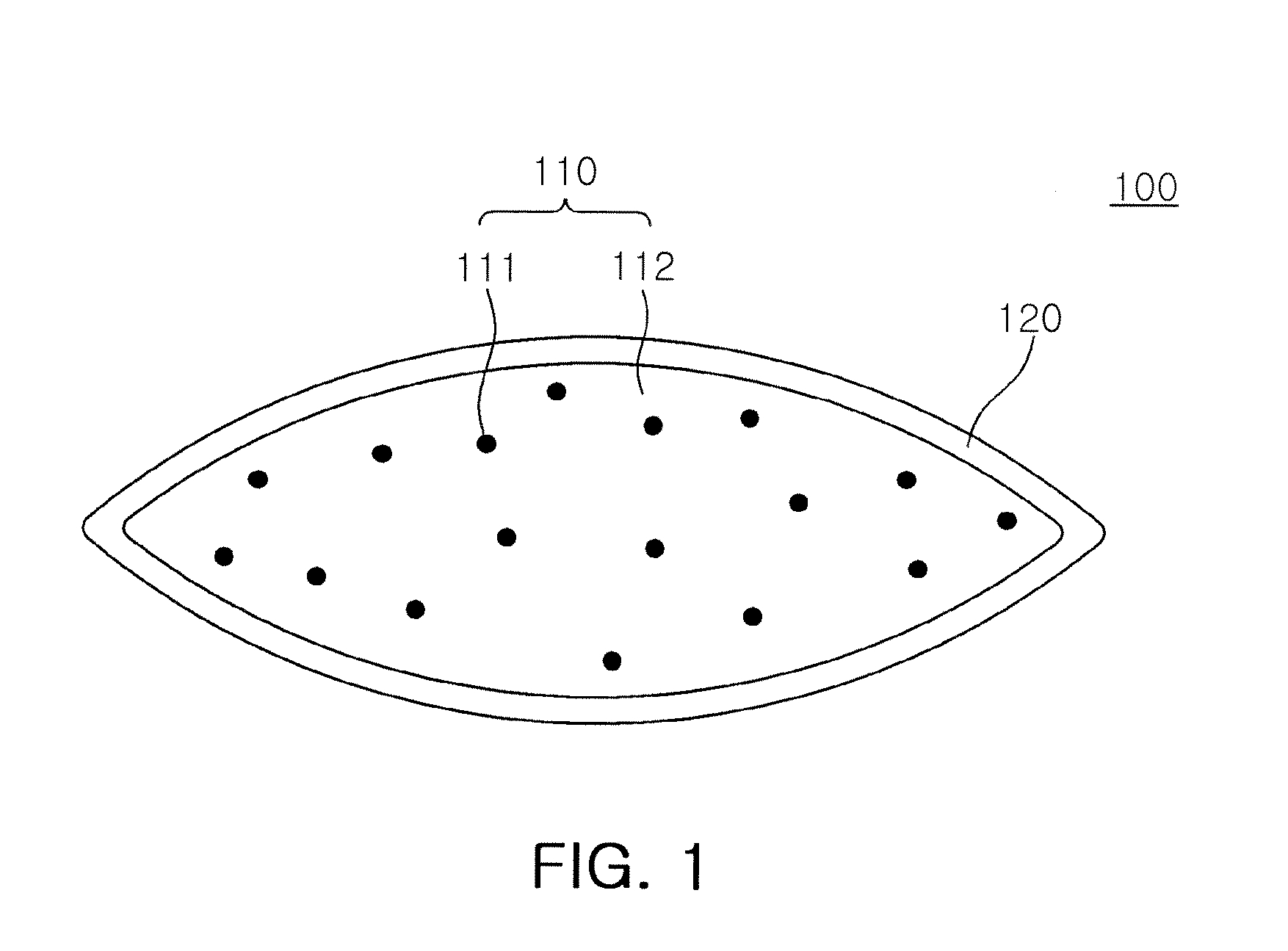
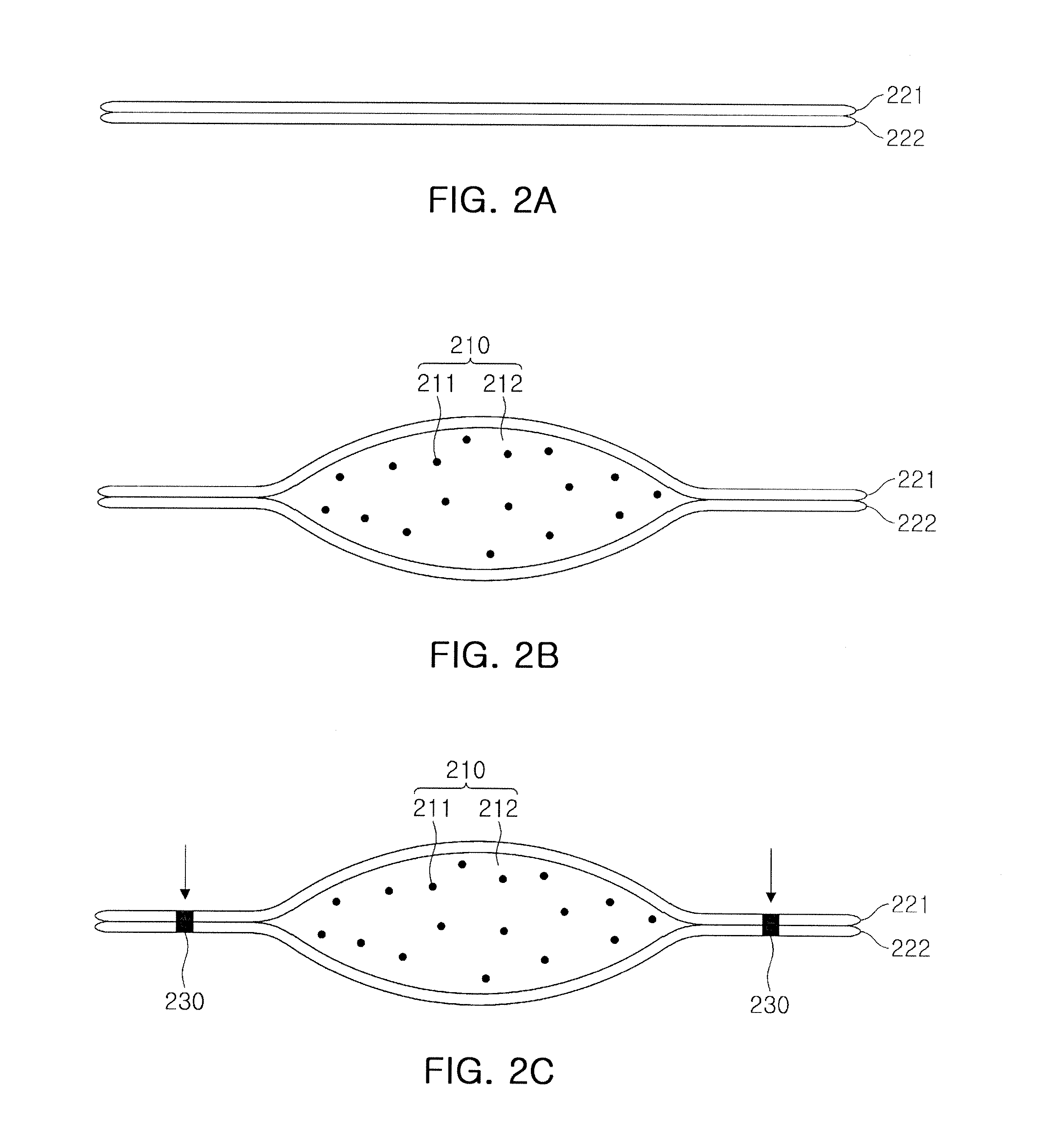
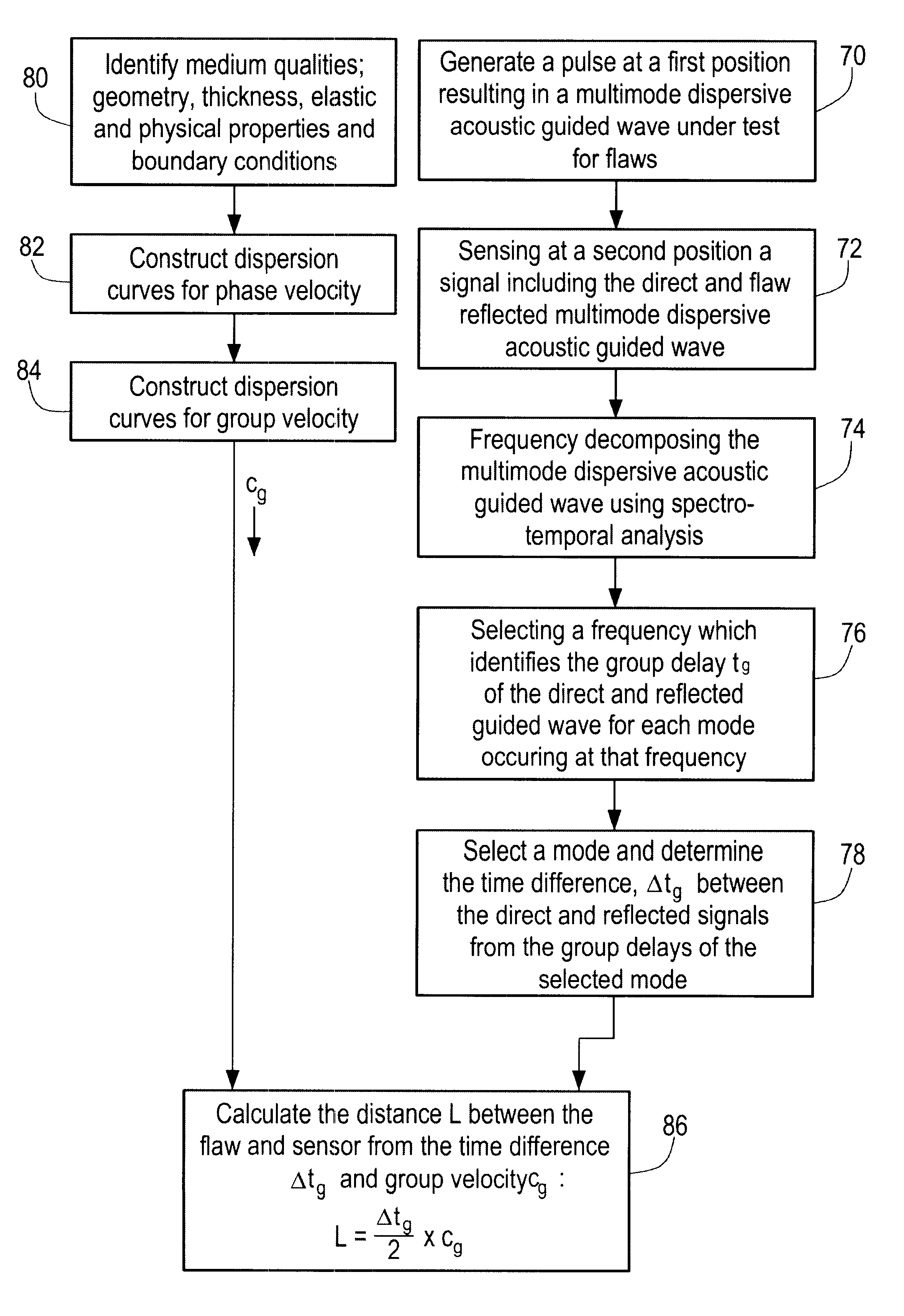
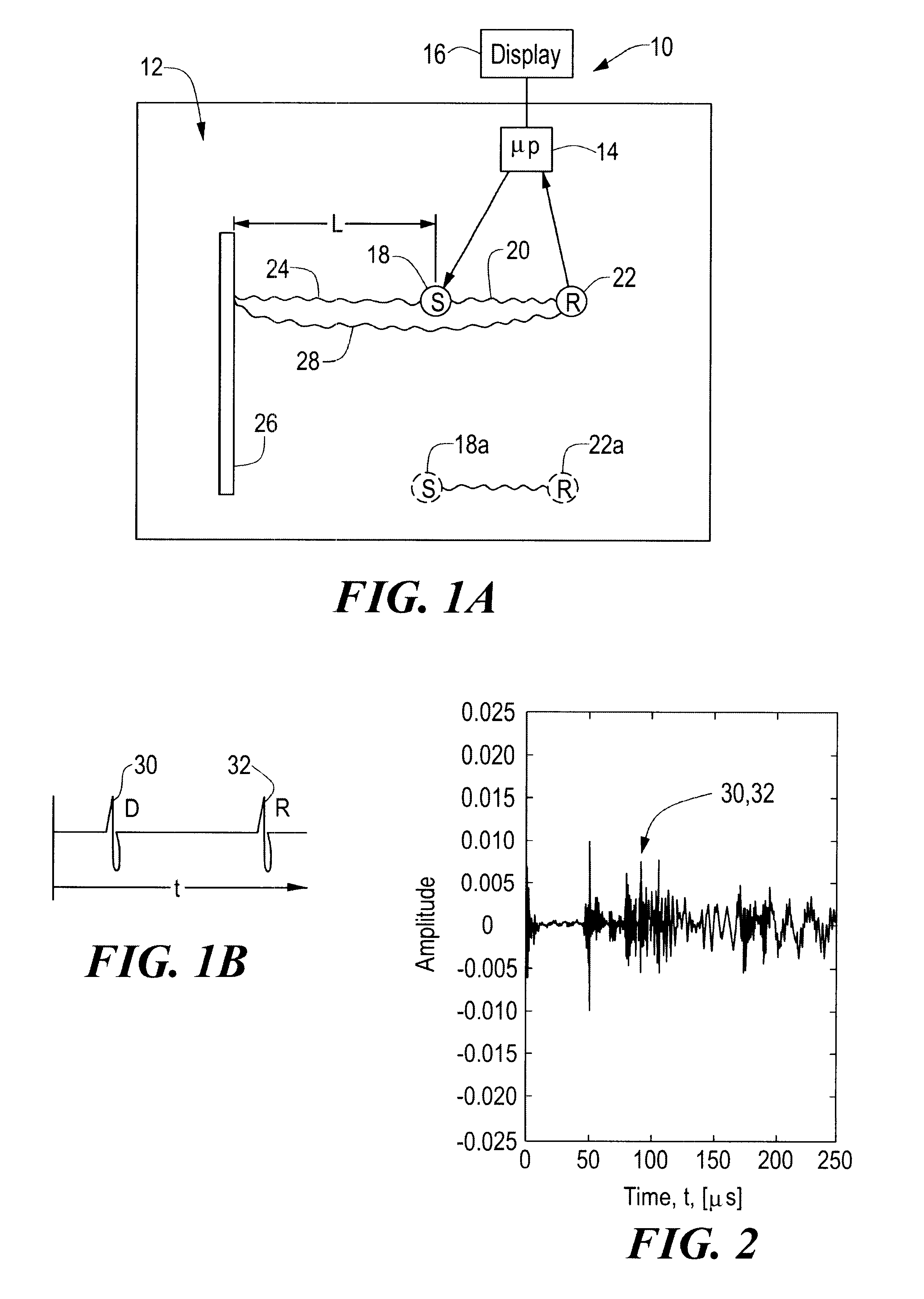
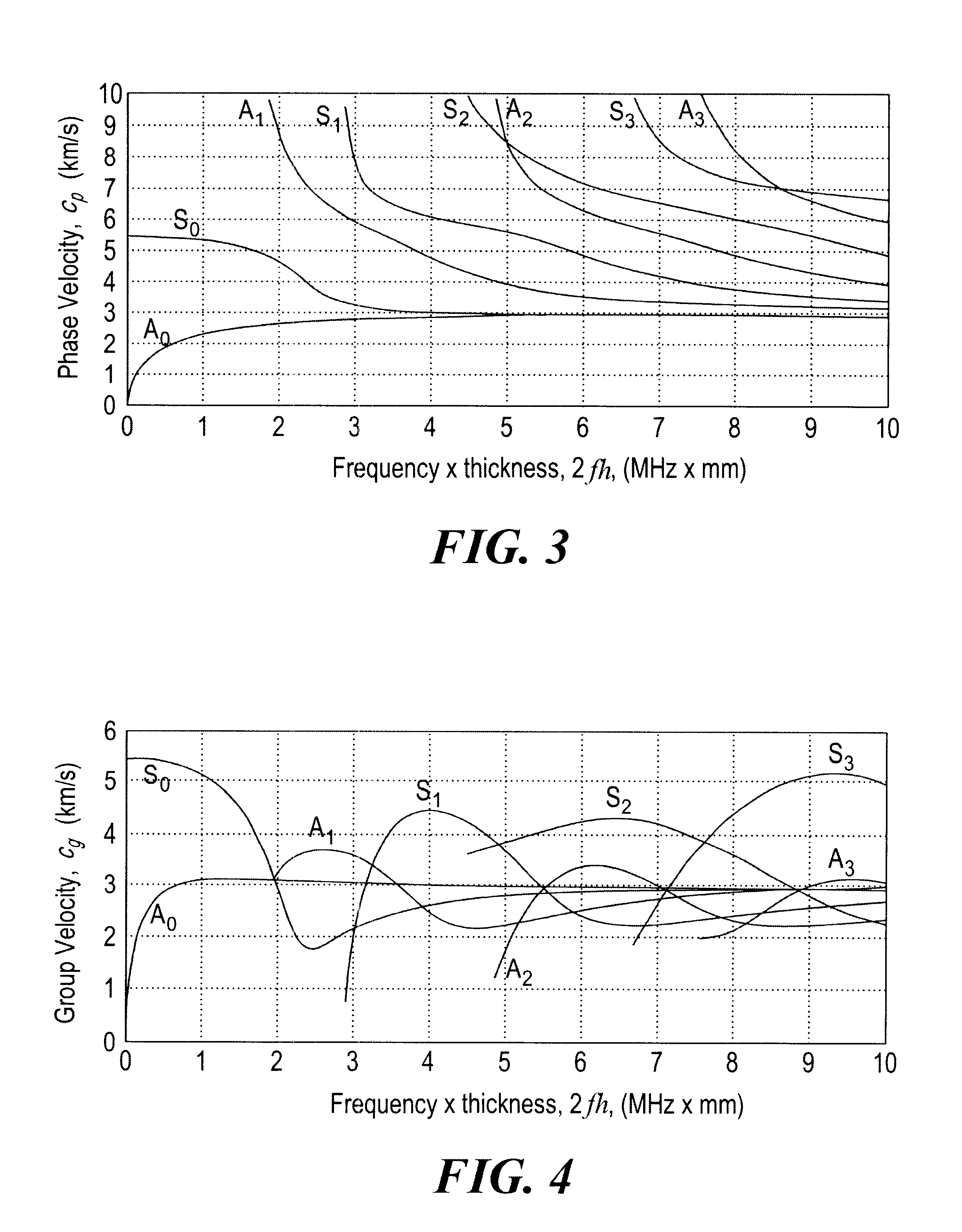
InactiveUS6360609B1Easy to measureAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionDispersion curveUnknown Source
A method and system of locating discontinuities, measuring distances, locating unknown sources, and measuring the thickness of multimode dispersive medium includes sensing a multimode dispersive acoustic guided wave and frequency decomposing that wave using spectral temporal analysis; selecting a frequency which identifies a group delay of the guided wave for each mode occurring at that frequency; selecting a mode from the group delays of the selected mode, determining the group velocity from the dispersion curves and computing the desired parameter.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
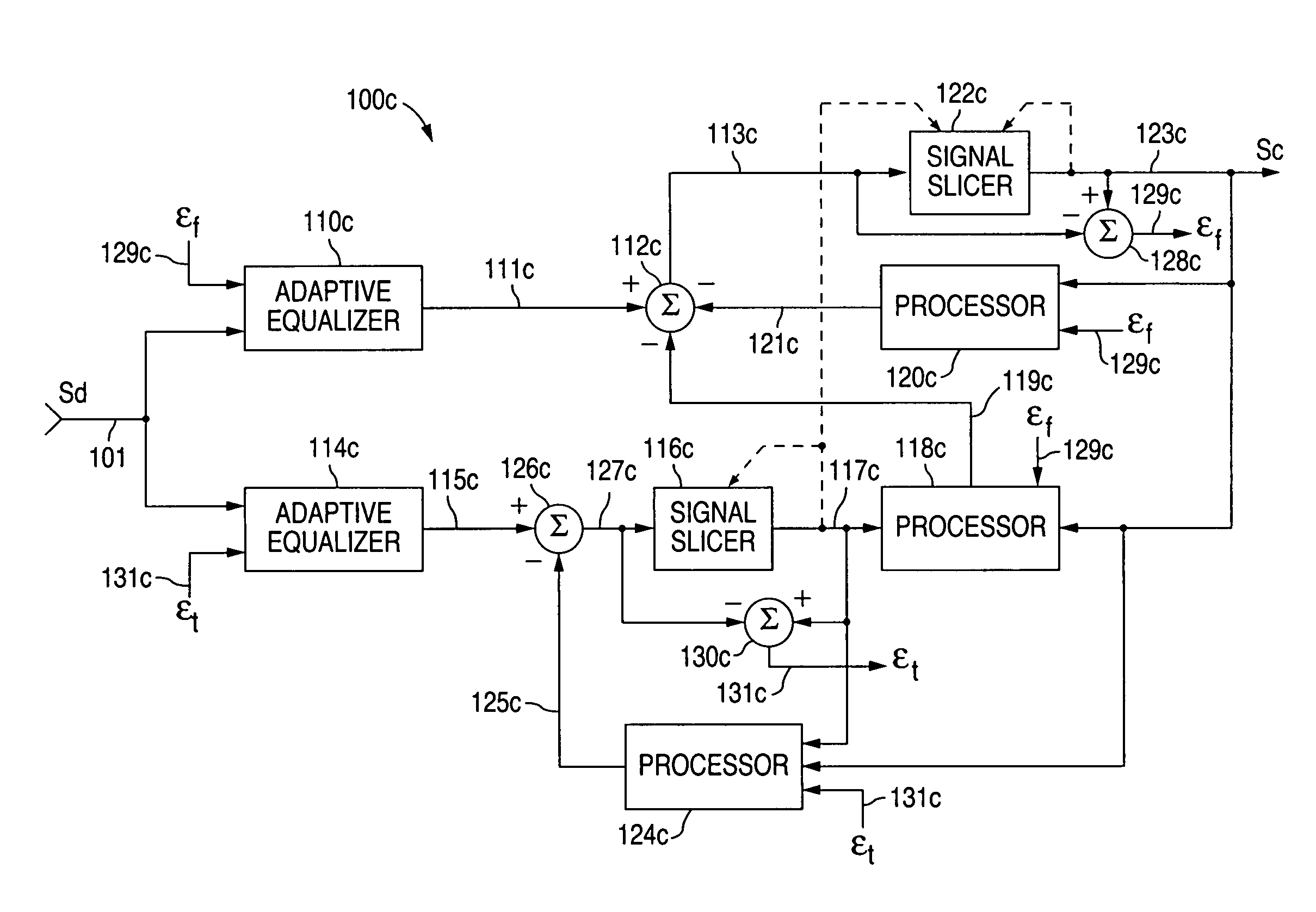
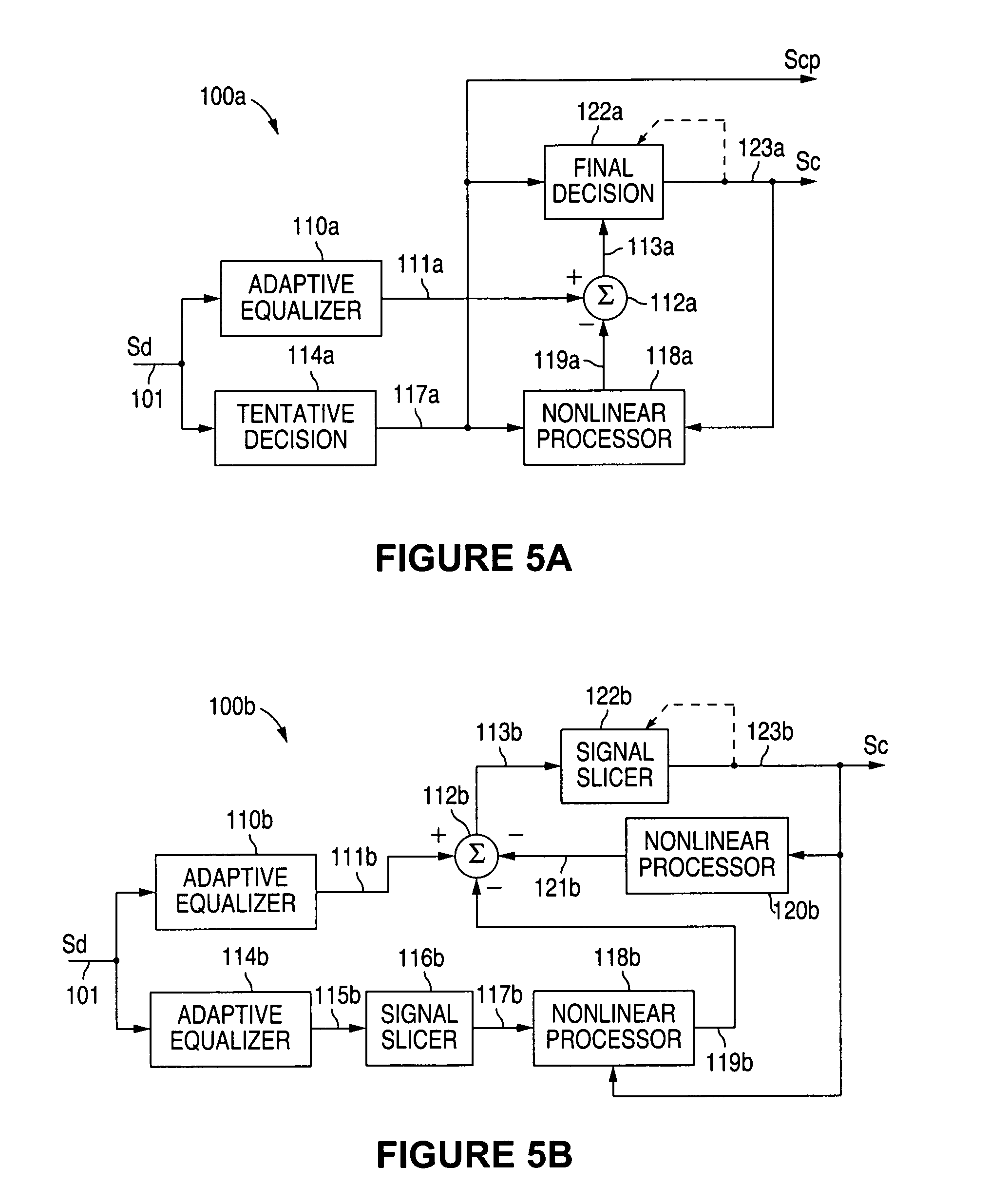
Compensation circuit and method for reducing intersymbol interference products caused by signal transmission via dispersive media
A compensation circuit and method for reducing ISI products within an electrical data signal corresponding to a detected data signal received via a signal transmission medium introduces distinct compensation effects for individual ISI products within the electrical data signal. Distinct data signal components within the detected data signal and corresponding to such ISI products can be selectively and individually compensated, thereby producing a compensated data signal in which each selected one of such individual data signal components is substantially removed. Individual data signal components or selected combinations of data signal components can be compensated as desired.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Electrophoretic device, driving method of electrophoretic device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20020150827A1Excellent characteristicsImprove visibilityLiquid crystal compositionsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresisEngineering
There is provided an electrophoretic device which comprises an electrophoretic layer containing dispersion medium and electrophoretic particles dispersed in the dispersion medium, controls the position of the electrophoretic particles according to the electric potential applied to electrodes, and can maintain the electrophoretic particles at a desired position for a long time by using the dispersion medium formed of mixture consisting of a plurality of substances having small mutual solubility.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Lens-eye model and method for predicting in-vivo lens performance
InactiveUS20020085172A1Predictive performanceAccurately predict in-vivo lens performanceSpectales/gogglesPhase-affecting property measurementsModel systemEngineering
An eye model system for remotely predicting the in-vivo performance of a vision altering optic includes a representative cornea, a dispersion medium, and a retinal surface. The corneal surfaces provide anatomical shape, optical power, and higher order aberration content. The dispersion medium mimics chromatic dispersion in an actual eye. The retinal surface is moveable to provide selected defocus. A humidity and temperature enclosure may be provided. Model eye elements can be tilted or decentered to simulate actual conditions. An associated method for remotely measuring the performance of a vision altering optic to predict its performance in-vivo includes making topography, wavefront, interferometry, PSF, MTF, or other optical and / or physical measurements of the model eye system with and without the optic in combination.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
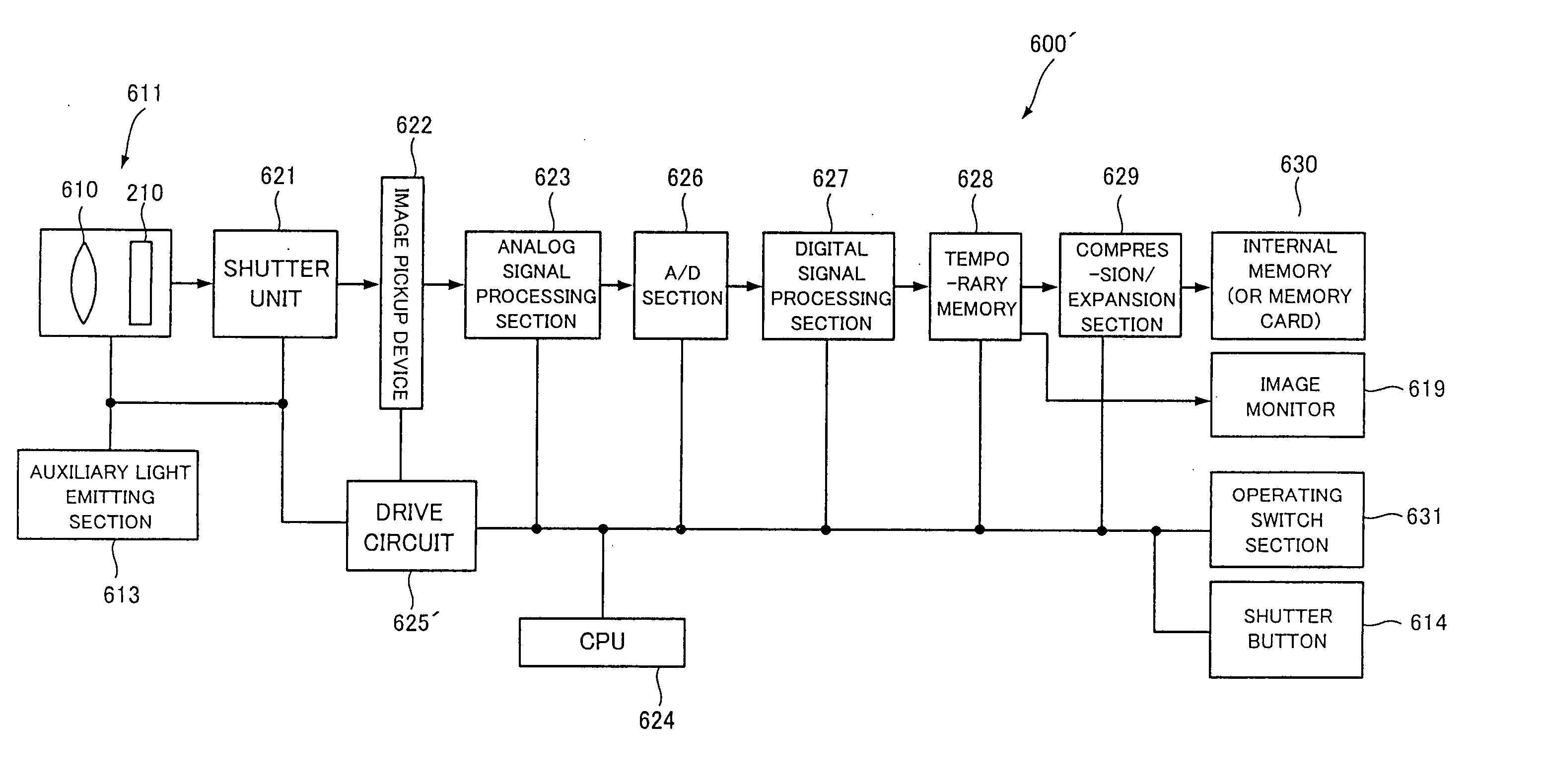
Optical unit, image taking apparatus and optical finder
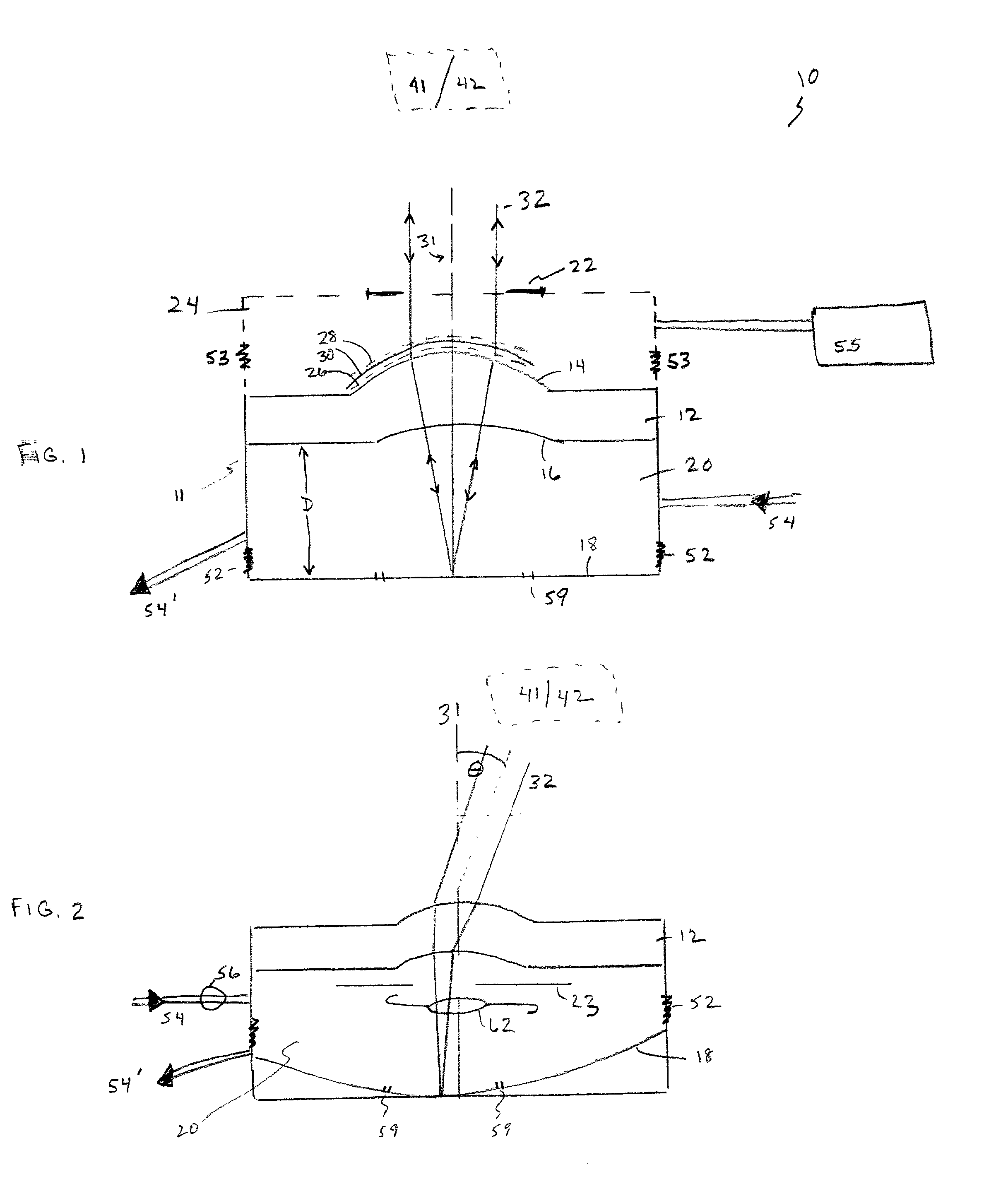
ActiveUS7265910B2Reduce performance degradationNon-linear opticsLensCamera lensAcquisition apparatus
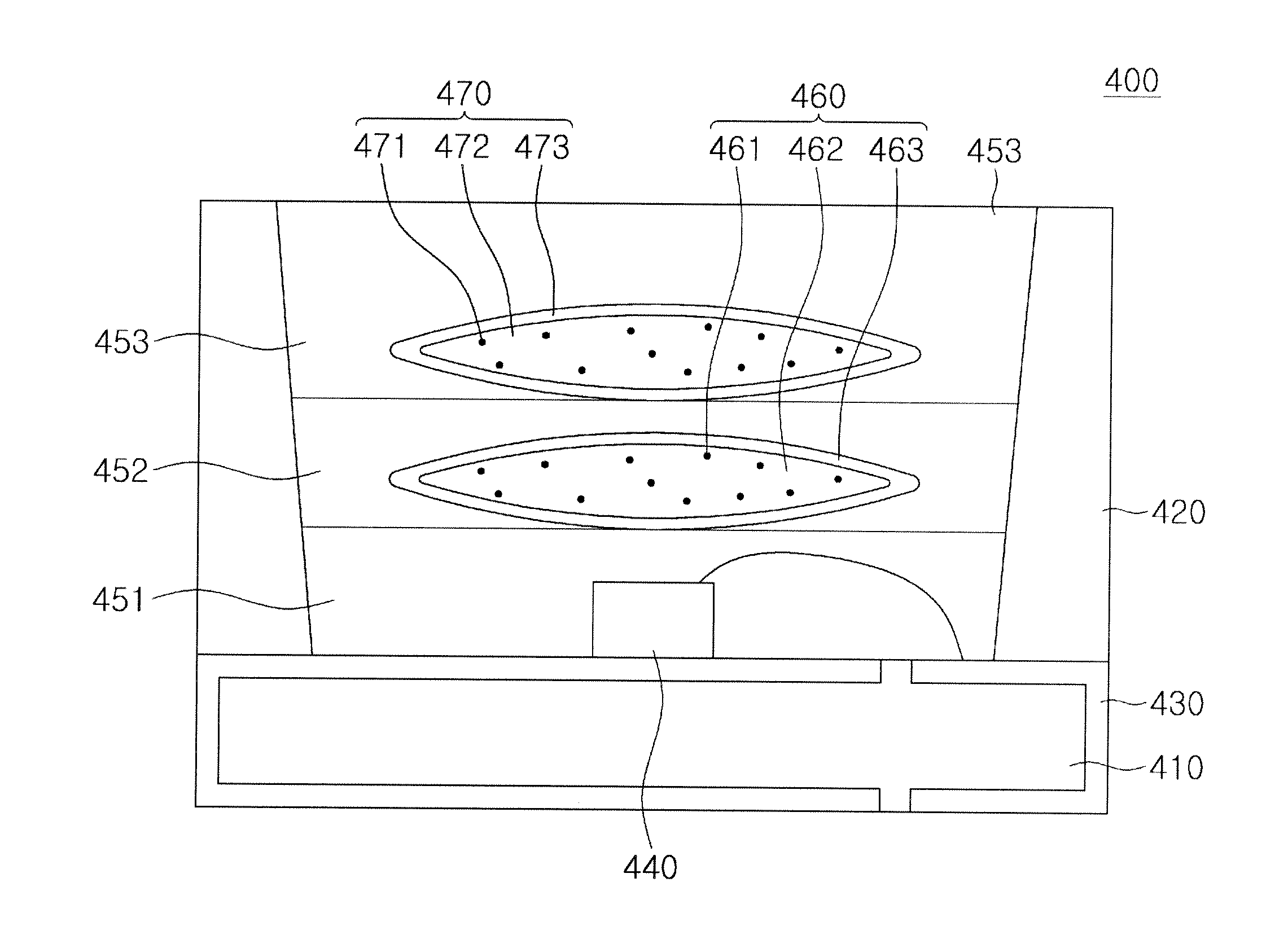
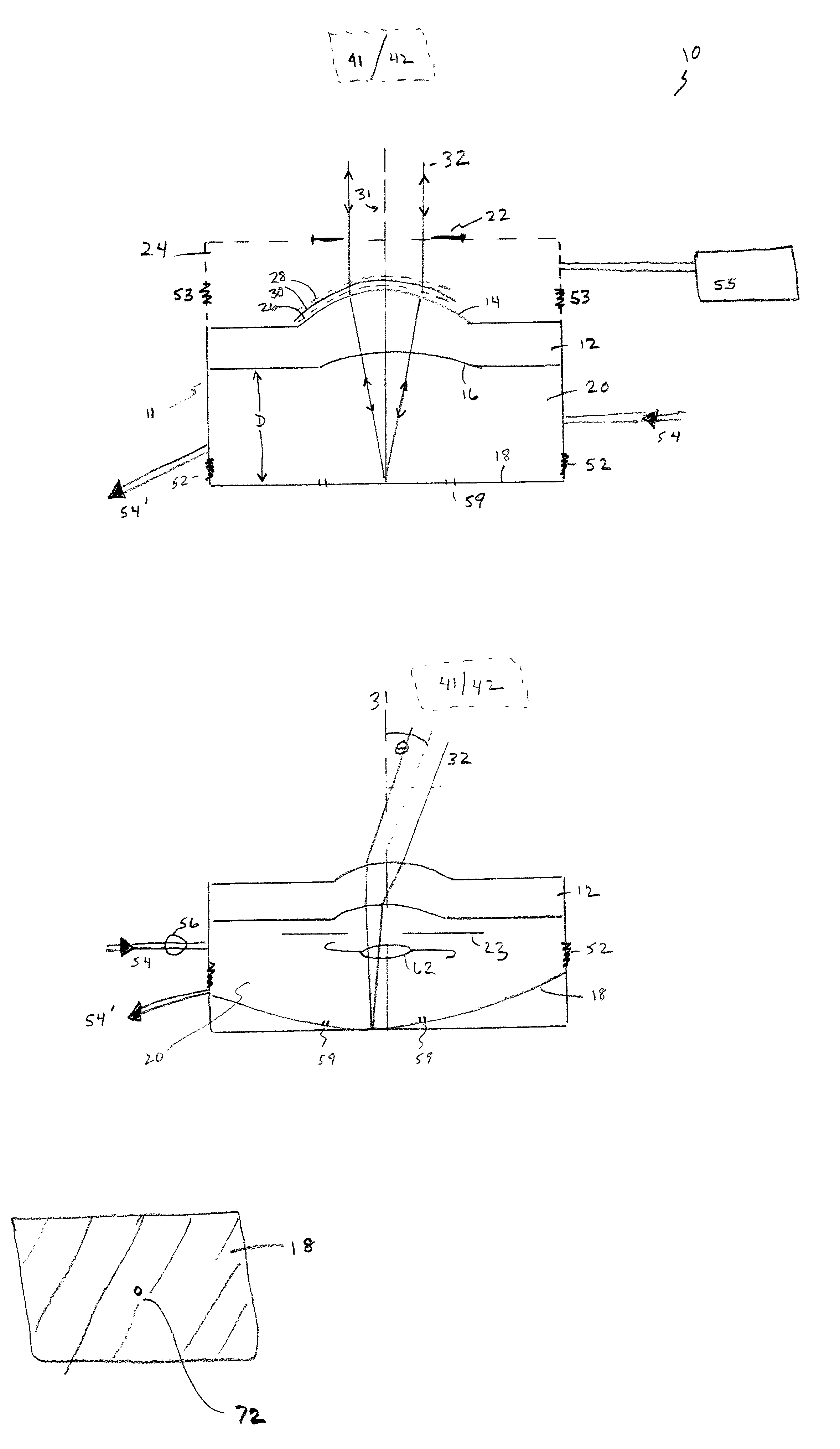
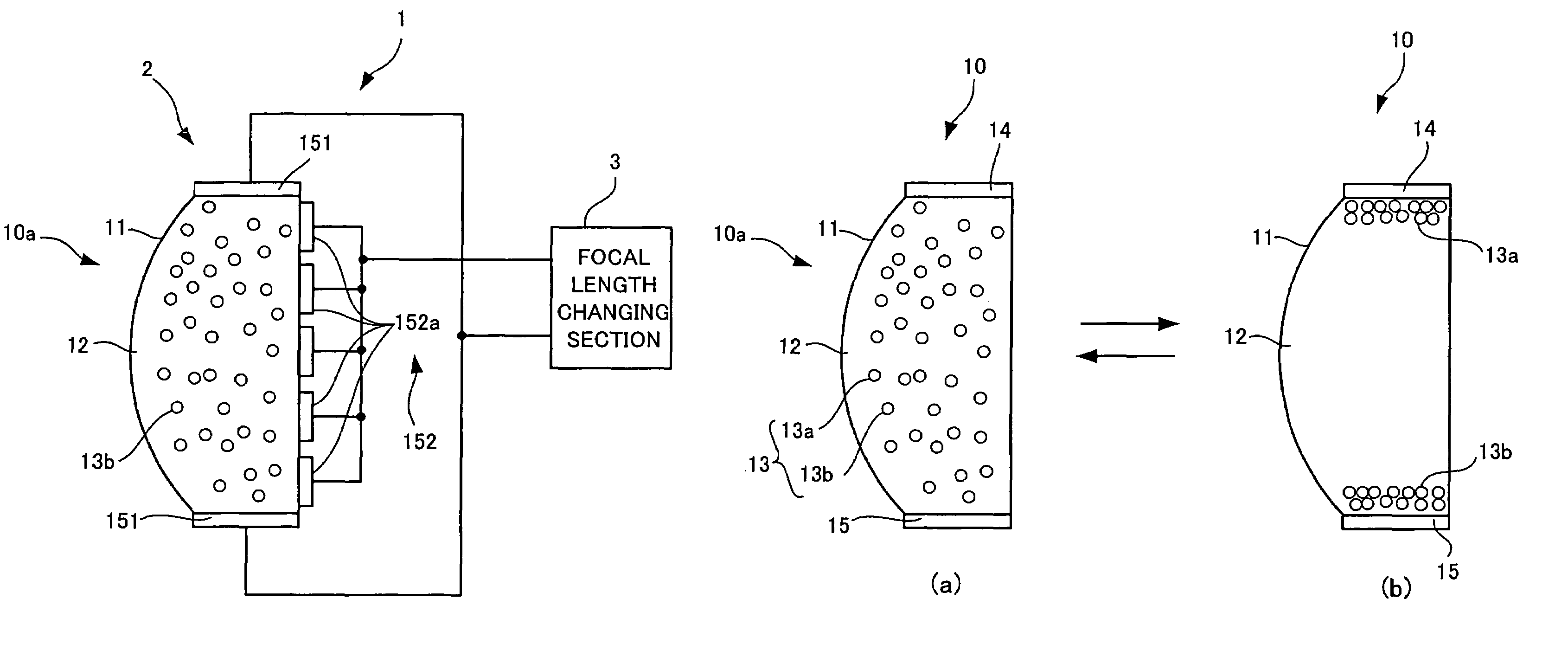
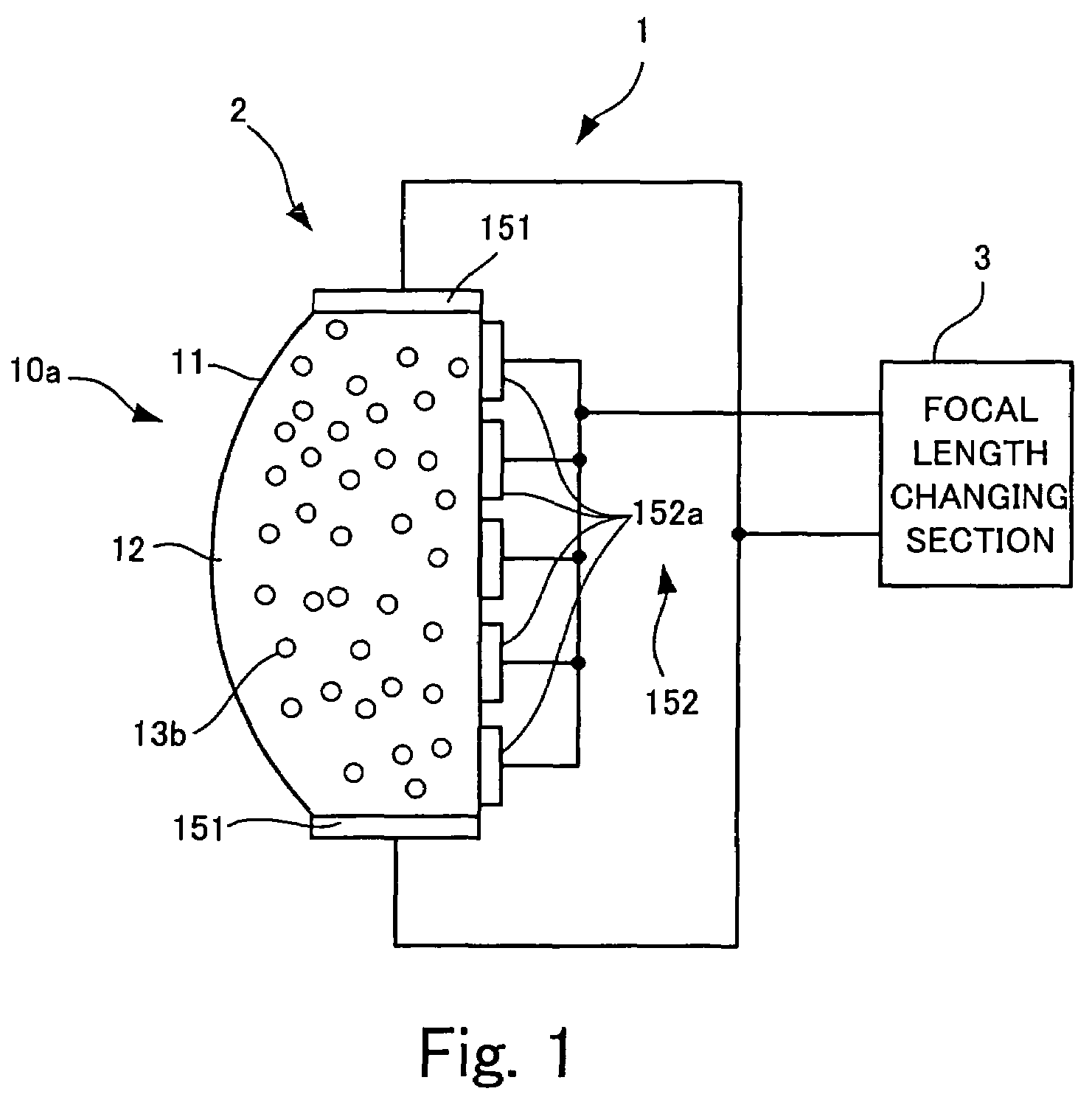
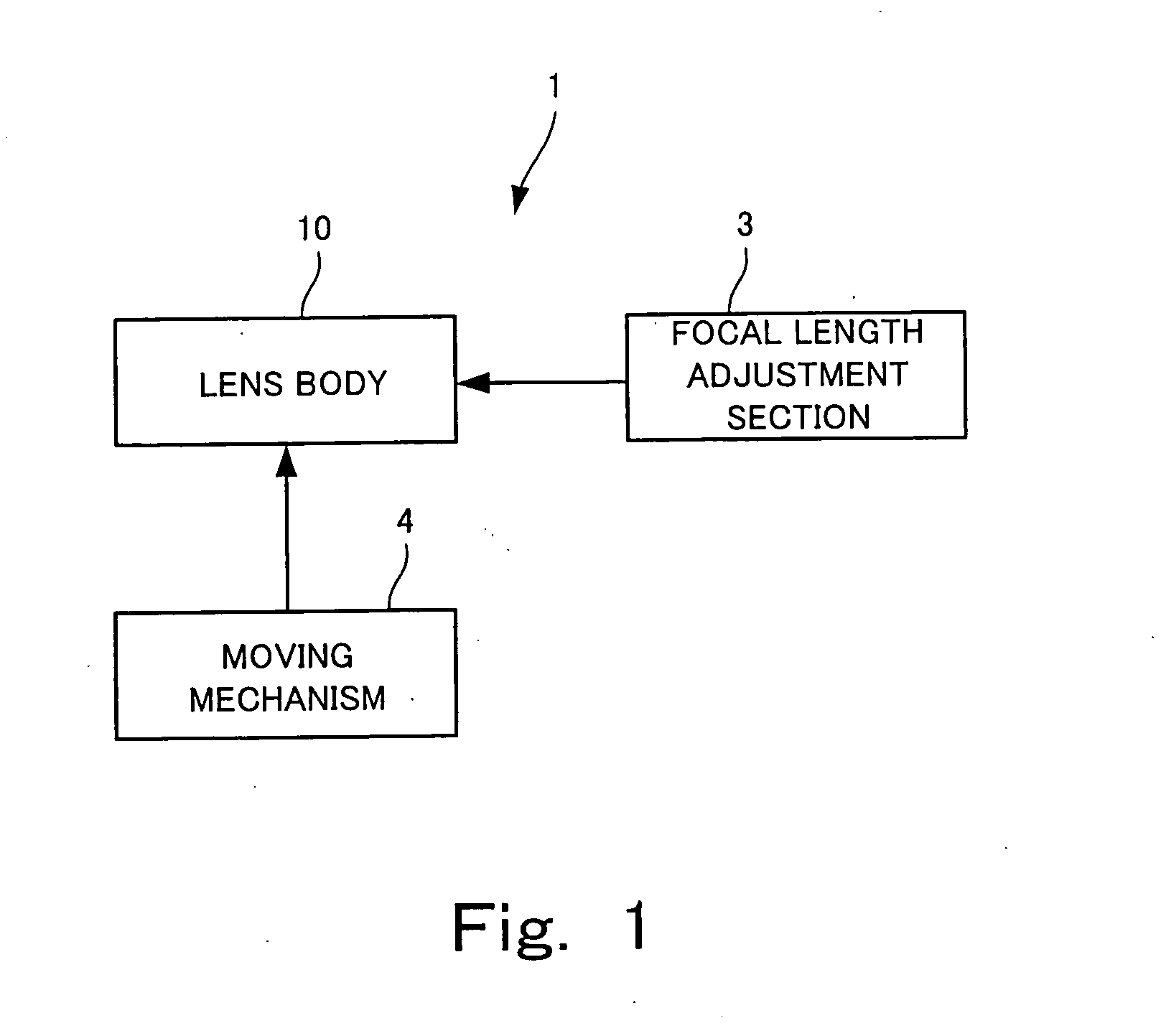
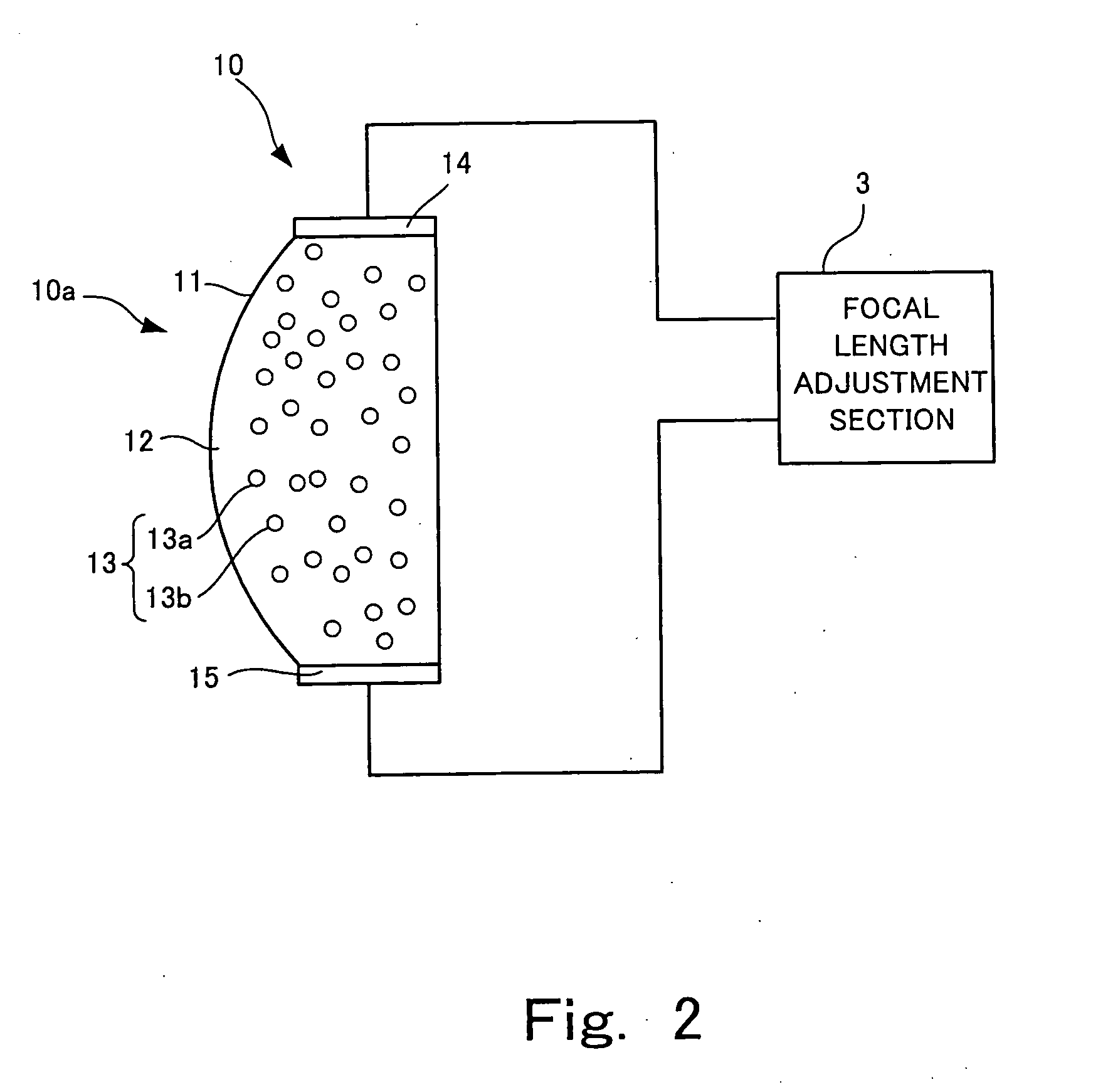
An optical unit capable of freely changing the refractive power and operating with a reduced deterioration in performance, an image taking apparatus having an image taking lens using the optical unit, and an optical finder using the optical unit. The optical unit includes a lens body having an electromagnetic field generator which changes the focal length of the lens body by moving, by an electromagnetic force, a dispersoid which is dispersed in a light-transmissive dispersion medium enclosed in a container, which is light-transmissive, and which has a refractive index different from the refractive index of the dispersion medium. The optical unit also includes a focal length changing section which changes the focal length of the lens body in three steps by controlling an electromagnetic field generated by the electromagnetic field generator.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +2
Method for preparing graphite series nano fluid
InactiveCN101186808AImprove thermal conductivityNo wearHeat-exchange elementsCarbon nanotubeMaterials science
The invention discloses a process for preparing nanophrase fluid of graphite, which comprises graphitic oxidation, surface modification and deoxidization of graphitic oxidation with surface modification. The surface modification means that surfaces of achieved 100 parts by mass of graphitic oxidation are modified to prepare graphitic oxidation with surface modification by 1-20 parts by mass of surface modifying agent. Deoxidization of graphitic oxidation with surface modification means that nanophrase graphite with surface modification is achieved by deoxidizing 100 parts by mass of products with 1-100 parts by mass of deoxidization agent. Finally the nanophrase graphite is prepared into nanophrase fluid of graphite, which is dispersed in dispersive medium by ultraphonic wave. The process of the invention can produce nanophrase fluid with high thermal conductivity, and replace nanophrase fluid of diamond, carbon nanotubes, carbon 60 and the like. Further the process of the invention has the advantages of simple technique, low cost, rich raw materials supply, and stable products, which cause no abrasion to heat exchangers.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Nanophotonic devices based on quantum systems embedded in frequency bandgap media
InactiveUS7076138B2Add nonlinearityImprove efficiencyQuantum computersLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonicsBinding state
The present invention describes nanophotonic materials and devices for both classical and quantum optical signal processing, transmission, amplification, and generation of light, which are based on a set of quantum systems having a discrete energy levels, such as atoms, molecules, or quantum dots, embedded in a frequency bandgap medium, such as artificial photonic crystals (photonic bandgap materials) or natural frequency dispersive media, such as ionic crystals, molecular crystals, or semiconductors, exhibiting a frequency (photonic) bandgap for propagating electromagnetic modes coupled to optical transitions in the quantum systems. If the frequency of one of optical transitions, called the working transition, lies inside the frequency bandgap of the medium, then spontaneous decay of the working transition into propagating photon modes is completely suppressed. Moreover, the excitation of the working transition and a photon form a photon-quantum system bound state lying inside the photonic bandgap of the medium, in which radiation is localized in the vicinity of the quantum system. In a quantum system “wire” or a quantum system “waveguide”, made of spatially disordered quantum systems, or in a chain quantum system waveguide made of a periodically ordered identical quantum systems, wave functions of the photon-quantum system bound states localized on different quantum systems overlap each other and develop a photonic passband lying inside bandgap of the photonic bandgap medium.
Owner:ALTAIR CENT
Electrophoretic liquid and display device using electrophoretic liquid
An electrophoretic liquid is disclosed that includes first particles that have the property of scattering light over an entire visible range and are positively or negatively charged; second particles that have the property of absorbing light of a specific wavelength range in the visible range and scattering light of ranges other than the specific wavelength range and are charged to a polarity opposite to that of the first particles; and a dispersion medium that has the property of allowing the light of the specific wavelength range absorbed by the second particles to pass through and absorbing the light of the ranges other than the specific wavelength range. In the electrophoretic liquid, the first particles and the second particles are dispersed in the dispersion medium.
Owner:TRANSCEND OPTRONICS (YANGZHOU) CO LTD
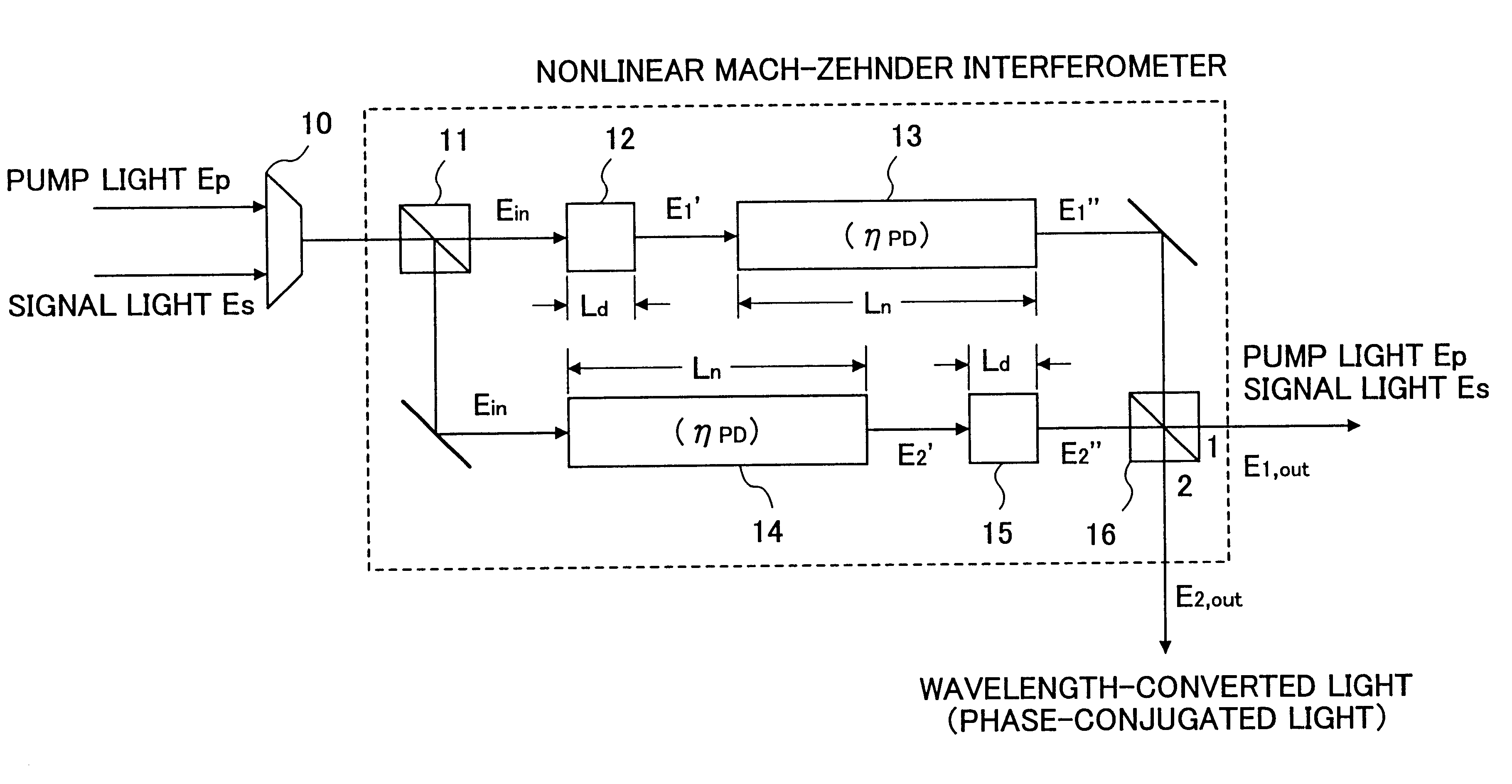
Optical parametric circuit
InactiveUS6867903B2Improve efficiencyCoupling light guidesLight demodulationReverse orderMach–Zehnder interferometer
An optical parametric circuit for separating an input signal light and a wavelength-converted light even when the wavelength difference is small is provided. The optical parametric circuit includes: a nonlinear Mach-Zehnder interferometer which includes a first optical path and a second optical path; optical dispersive mediums and second-order optical nonlinear mediums provided in the first and second optical paths; wherein optical dispersive medium and second-order optical nonlinear medium in the first optical path are placed in the reverse order of optical dispersive medium and second-order optical nonlinear medium in the second optical path.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Optical pulse compressor and optical function generator, optical pulse compressing method and optical function generating method
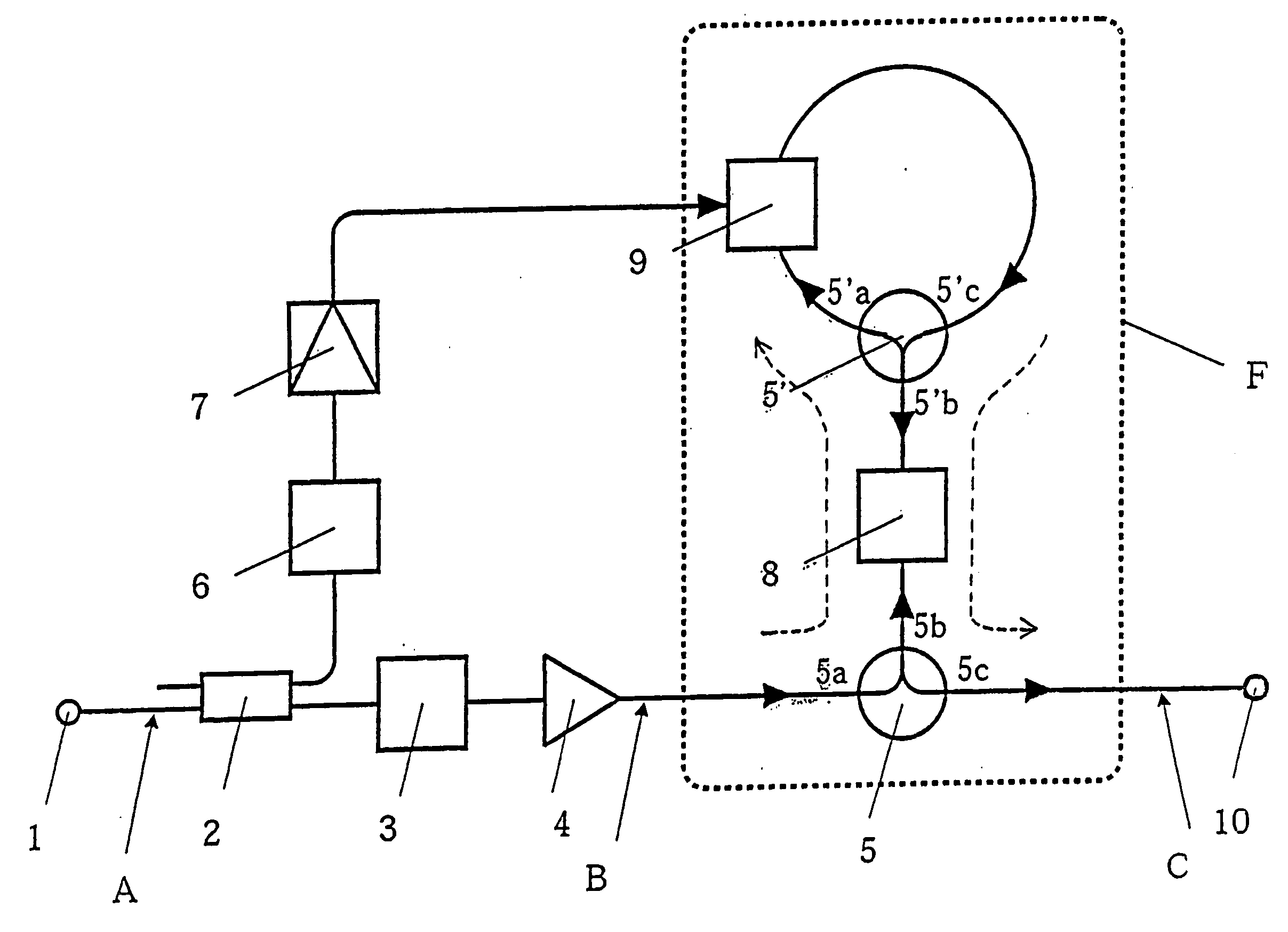
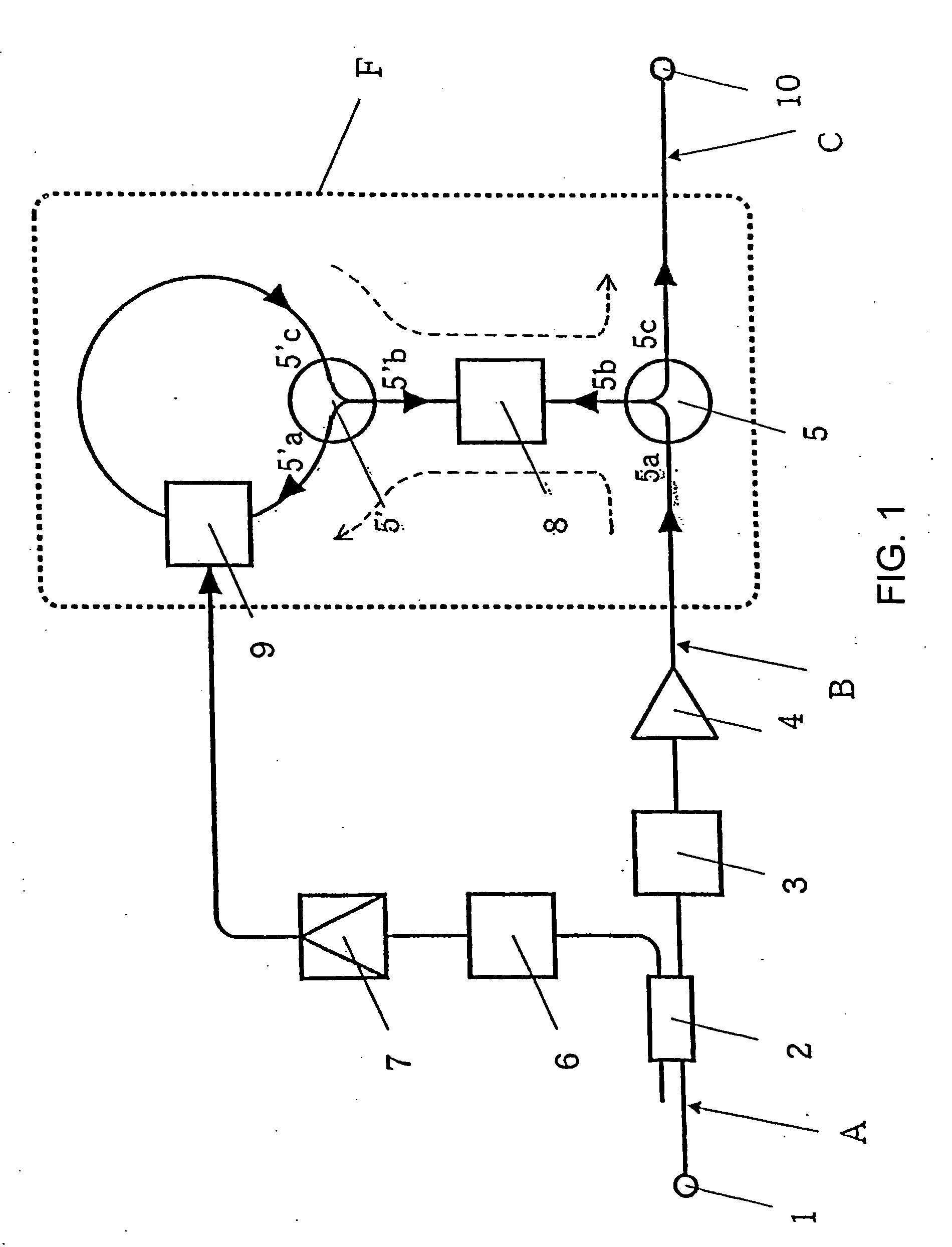
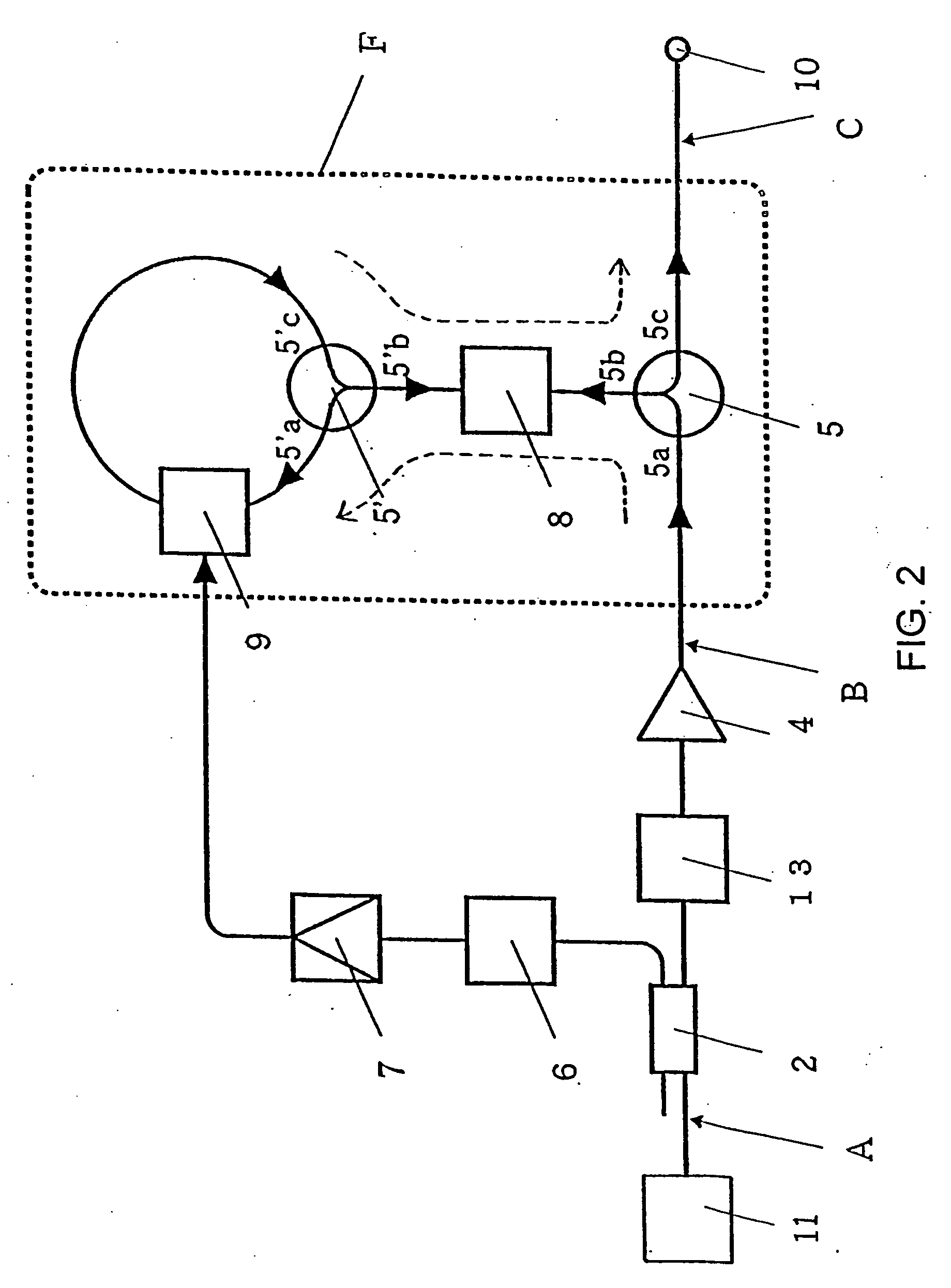
InactiveUS20070025728A1Promote generationEconomical high-qualityLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWaveform shapingOptical communication
A small-sized, high-functionality optical pulse compressor capable of generating a low-power, high-repetition-frequency ultrashort pulse train used for ultralast optical communication and photometry, and a simple-structure optical function generator for realizing an arbitrary time waveform. The optical pulse compressor comprises and optical Fourier transform device (F) having an optical phase modulator (9) driven by the repetition-frequency of an input optical pulse train and a dispersive medium (8), for converting the shape of an input optical pulse frequency spectrum into its time waveform, and an optical filter (3) inserted ahead of the optical Fourier transform device (F), for reducing the spectrum width of an input optical pulse, wherein the optical Fourier transform device (F) converts a small-spectrum-width optical pulse output from the optical function generator generates an optical pulse. The optical function generator generates an optical pulse having an arbitrary time waveform by reproducing, as it is, a spectrum waveform-shaped arbitrarily by an optical filter on a time-axis by tch optical Fourier transform device (F).
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Compensation circuit and method for reducing intersymbol interference products caused by signal transmission via dispersive media
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
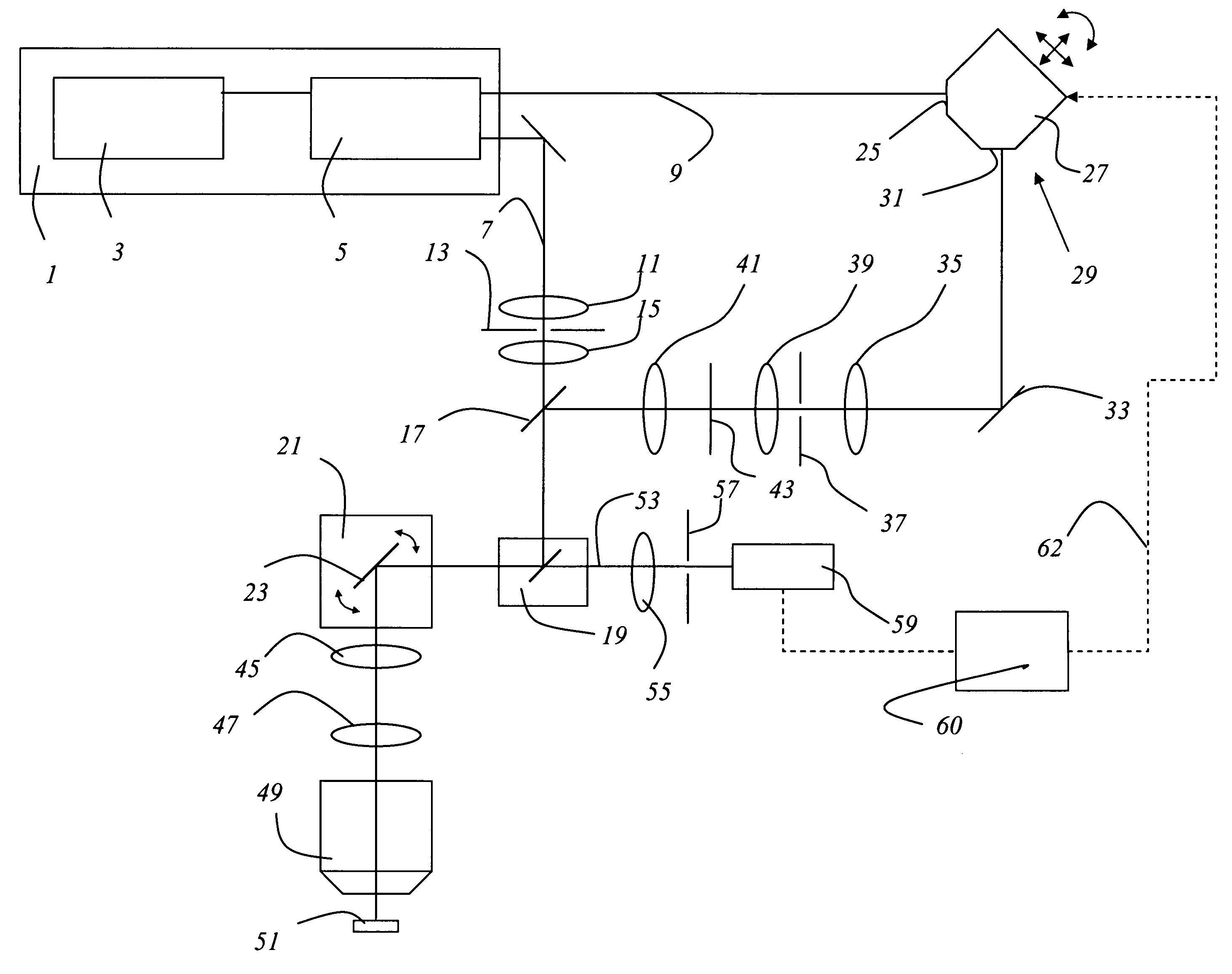
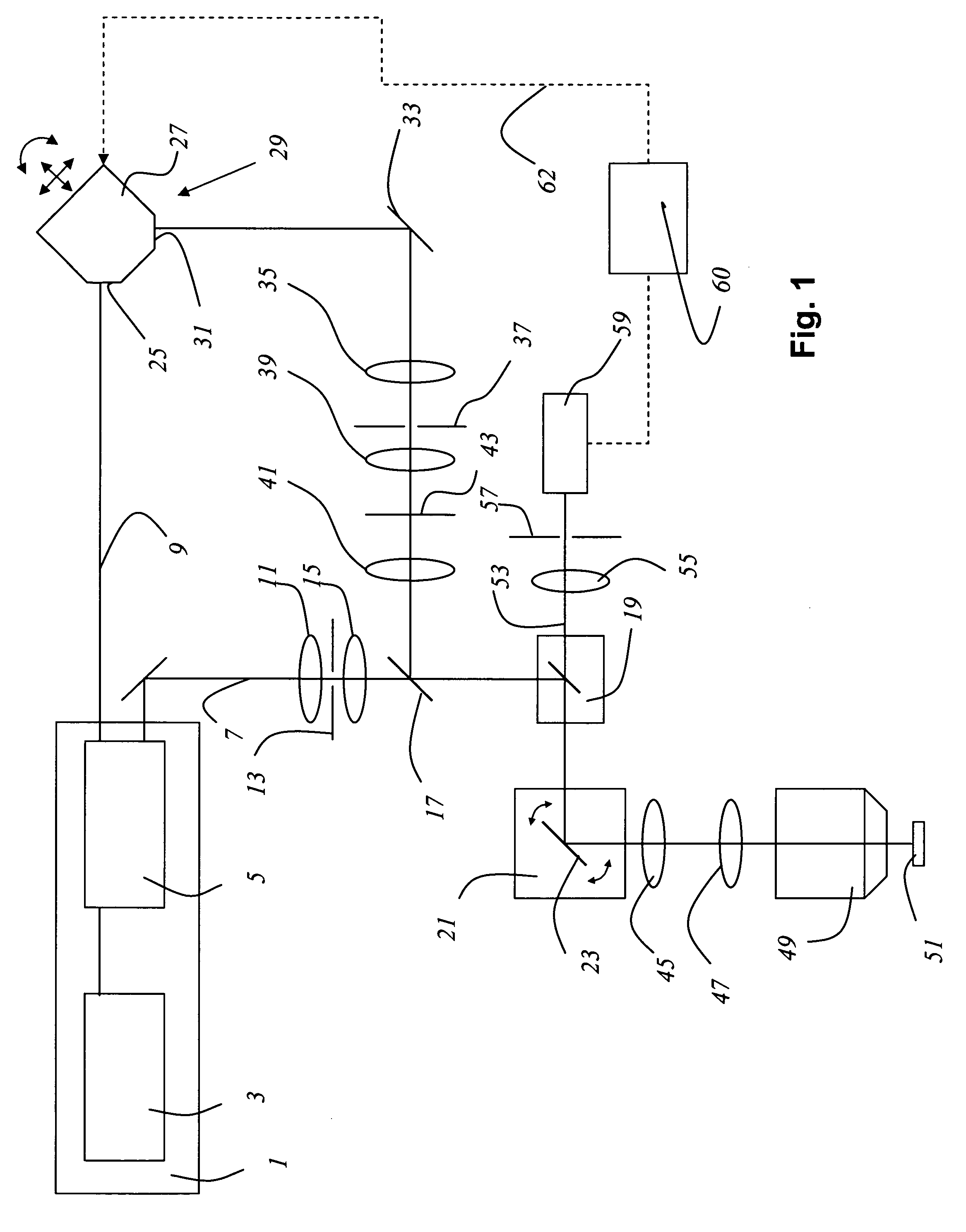
Scanning microscope
InactiveUS20050078363A1Simple and compact structureSignificant time delayPrismsMicroscopesLight beamMicroscope
In a scanning microscope that impinges upon a sample with a first light pulse and a second light pulse, a dispersive medium that modifies the time offset between the first and the second light pulse is provided in the beam path of at least one of the light pulses.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
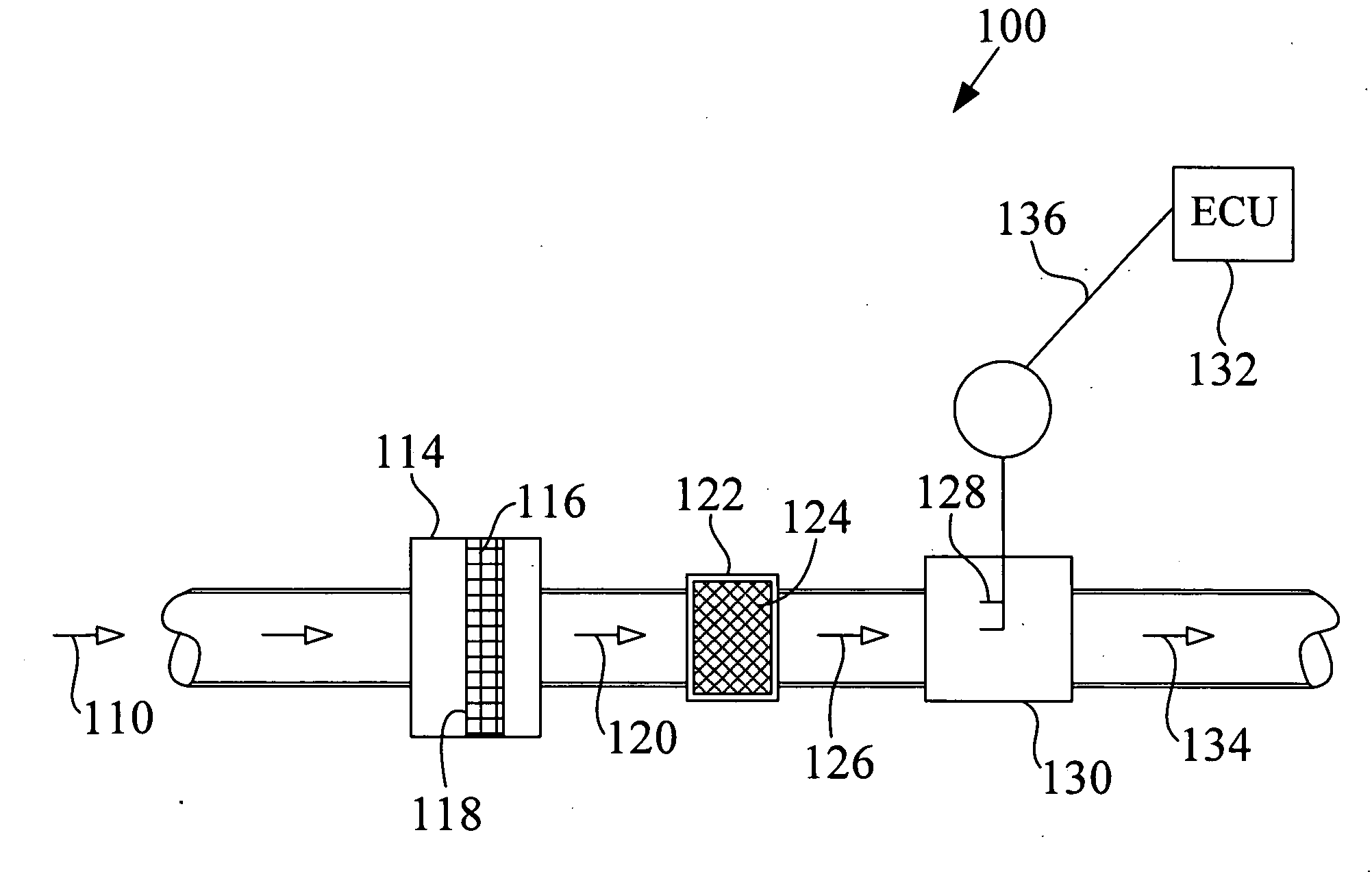
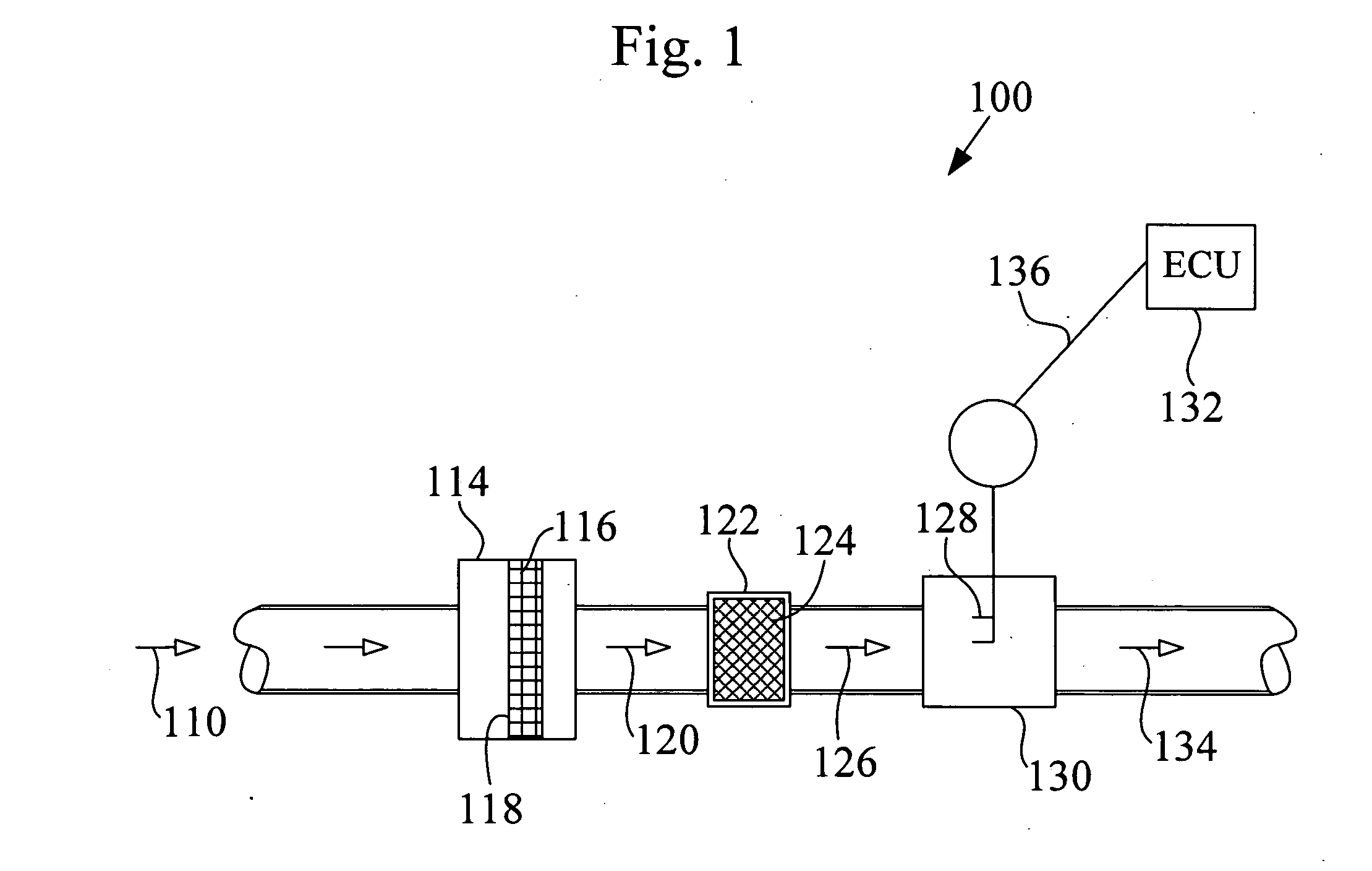
Flow vortex suppression apparatus for a mass air flow sensor
ActiveUS20100269583A1Reduce air turbulenceReduce turbulenceCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentFiberEngineering
In various aspects of the invention a flow vortex suppression apparatus for use in an air intake duct having a mass air flow sensor is disclosed. The flow vortex suppression apparatus includes an air flow permeable fibrous vortex dispersive media installed into the air duct in a position upstream of the mass flow sensor and configured to occlude the air duct such that air flow in the duct is constrained to pass through the vortex dispersive media. The vortex dispersive media is configured and adapted to diffuse vortices and reduce air turbulence of an air stream entering the mass flow sensor, thereby reducing variations and noise in a flow measurement signal from the mass air flow sensor.
Owner:MANN HUMMEL GMBH
Optical element and image taking apparatus
InactiveUS20060044448A1Reduce performance degradationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRefractive indexElectromagnetic field
An optical element including: a container which is light-transmissive at least in a light passage region; a light-transmissive dispersion medium enclosed in the container; a light-transmissive dispersoid dispersed in the dispersion medium and having a refractive index different from the refractive index of the dispersion medium; and an electromagnetic field generator which controls the refraction of light passing through the light passage region by moving the dispersoid dispersed in the dispersion medium by an electromagnetic force.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
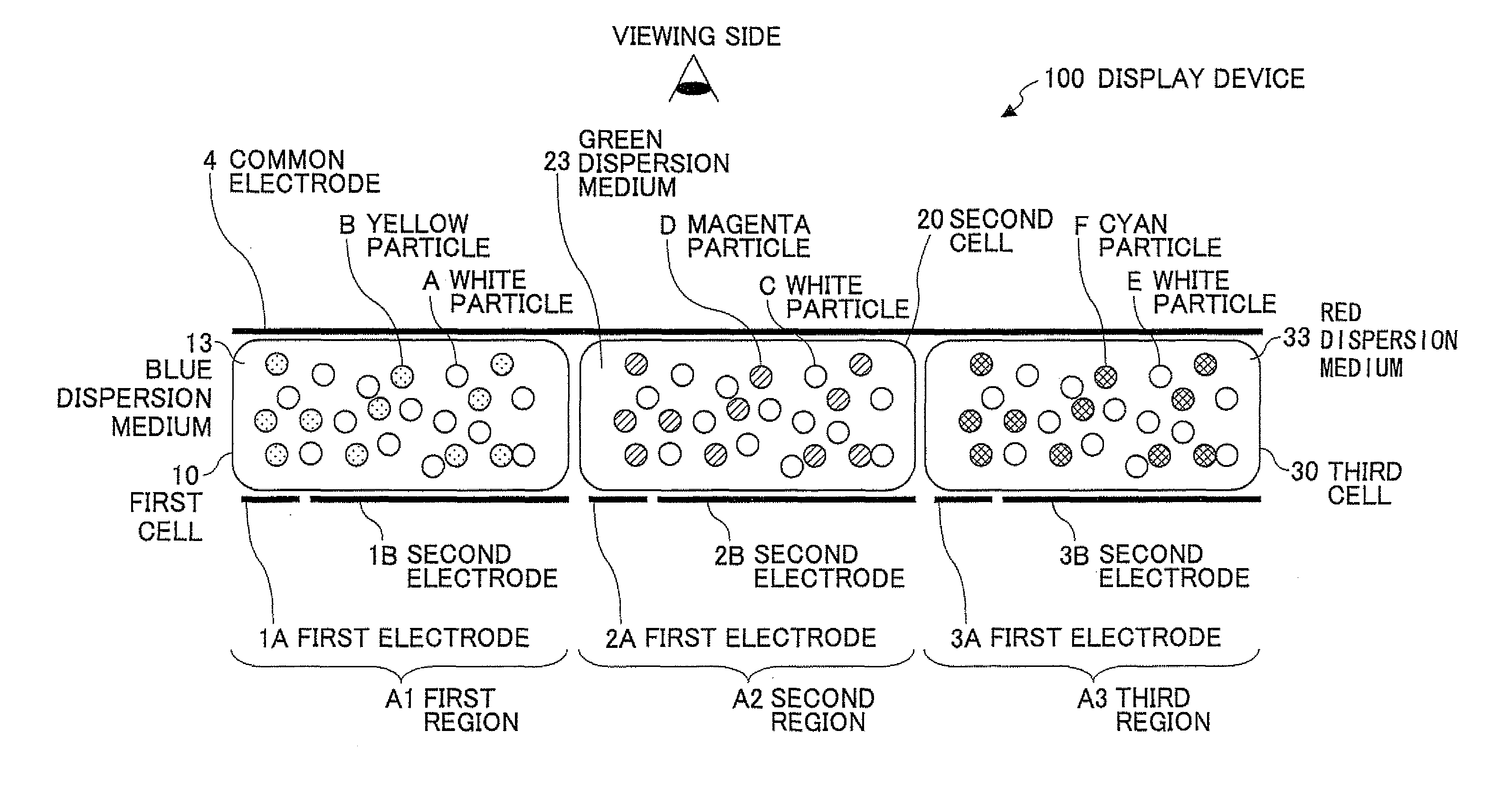
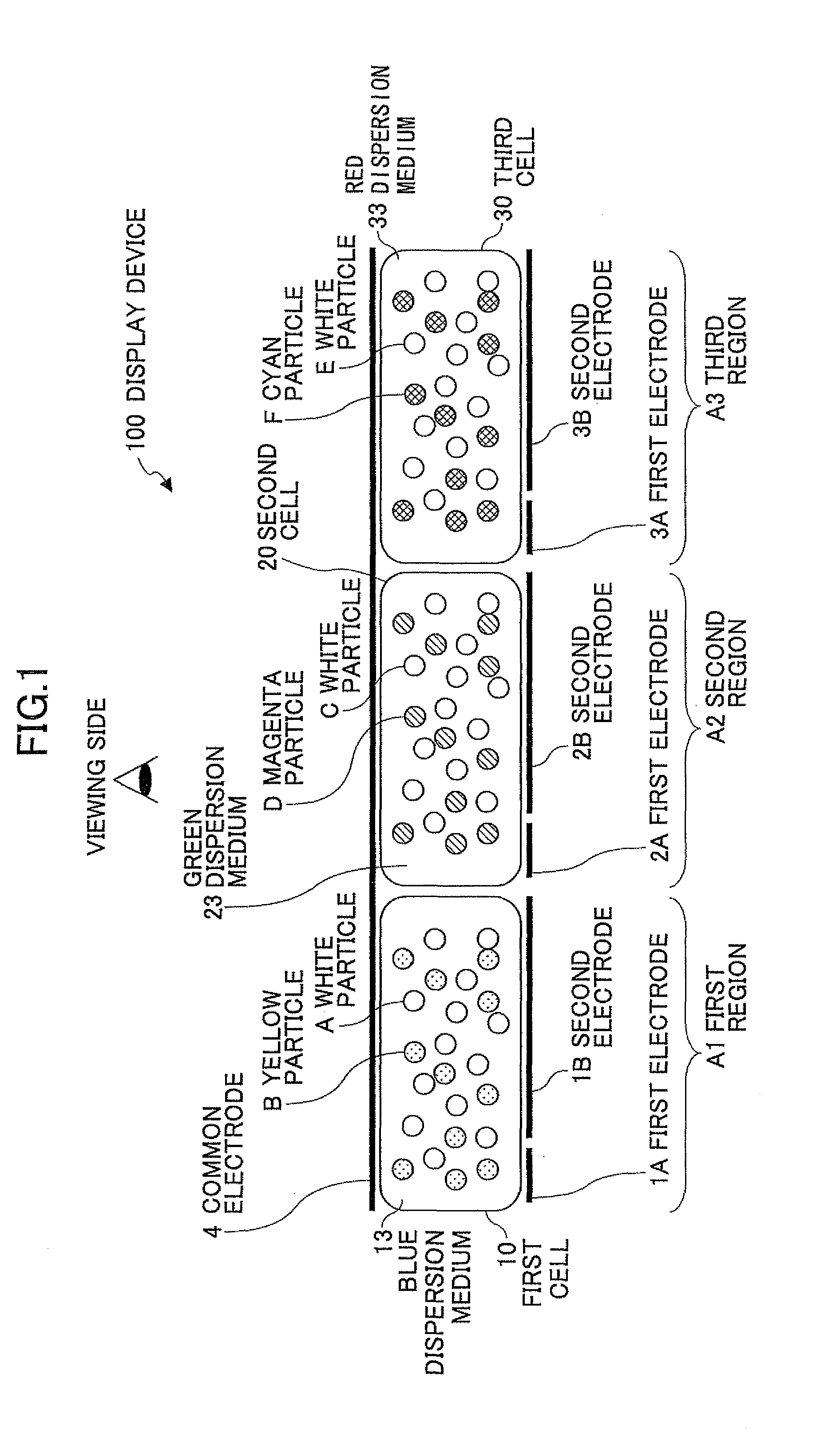
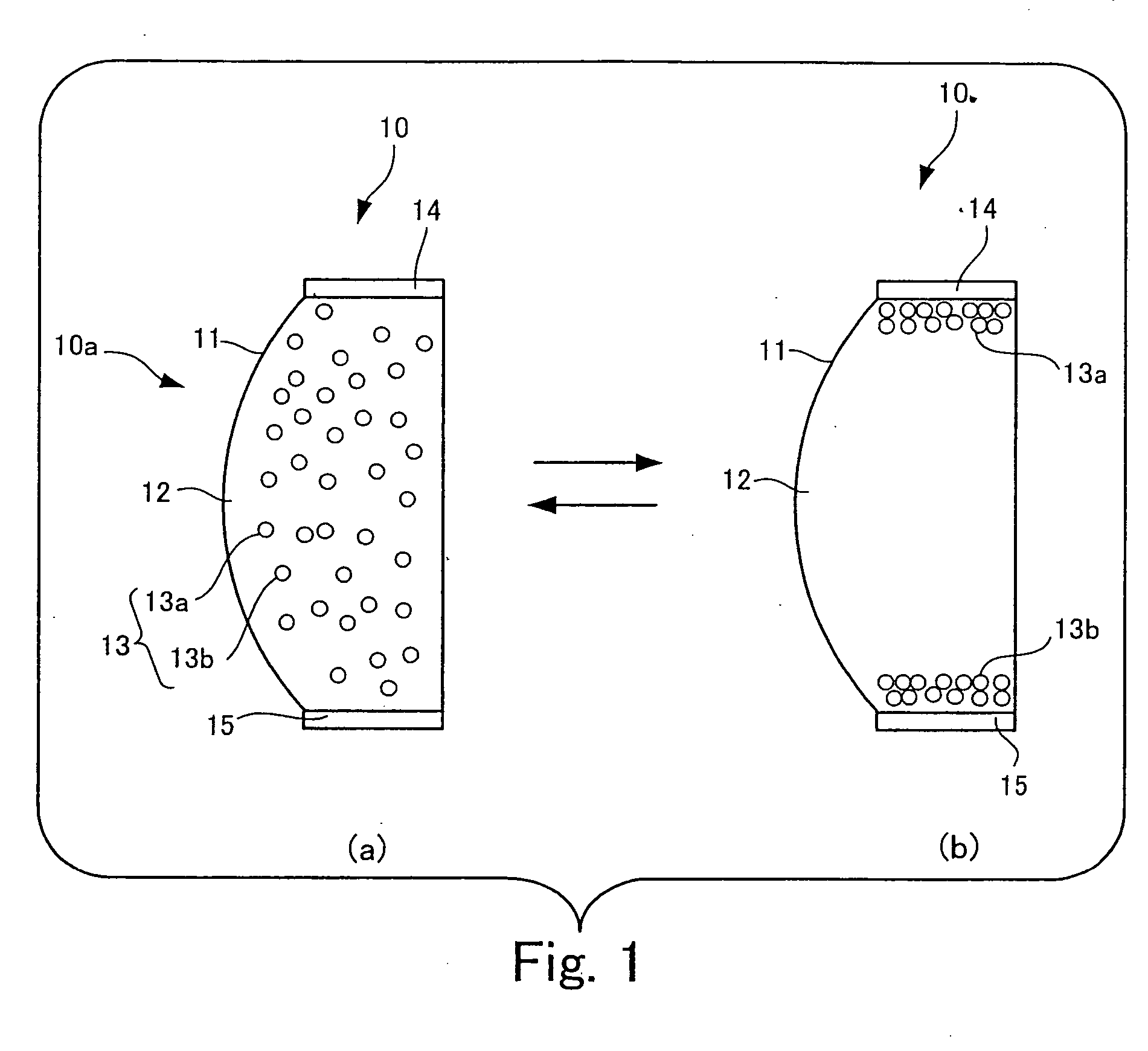
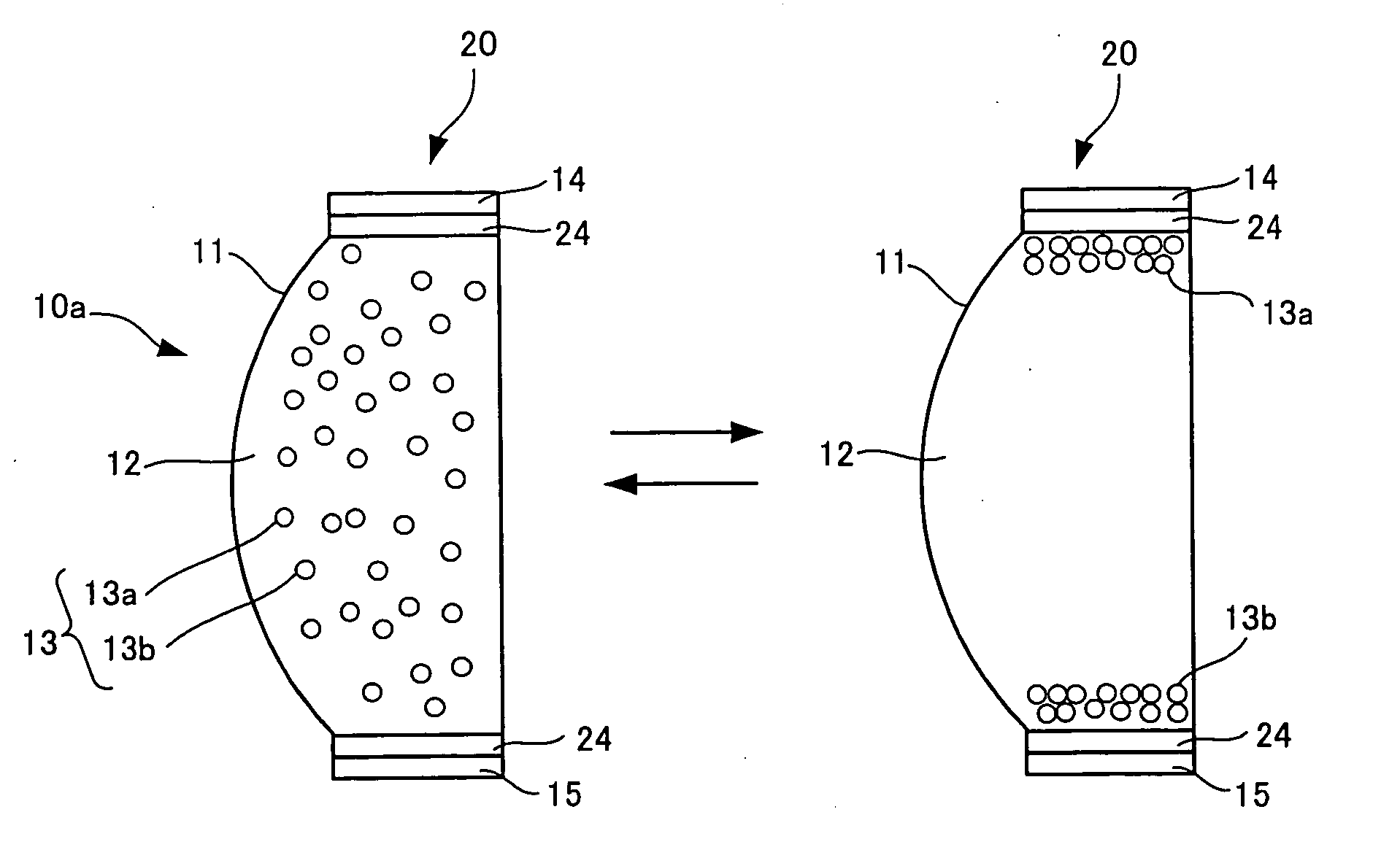
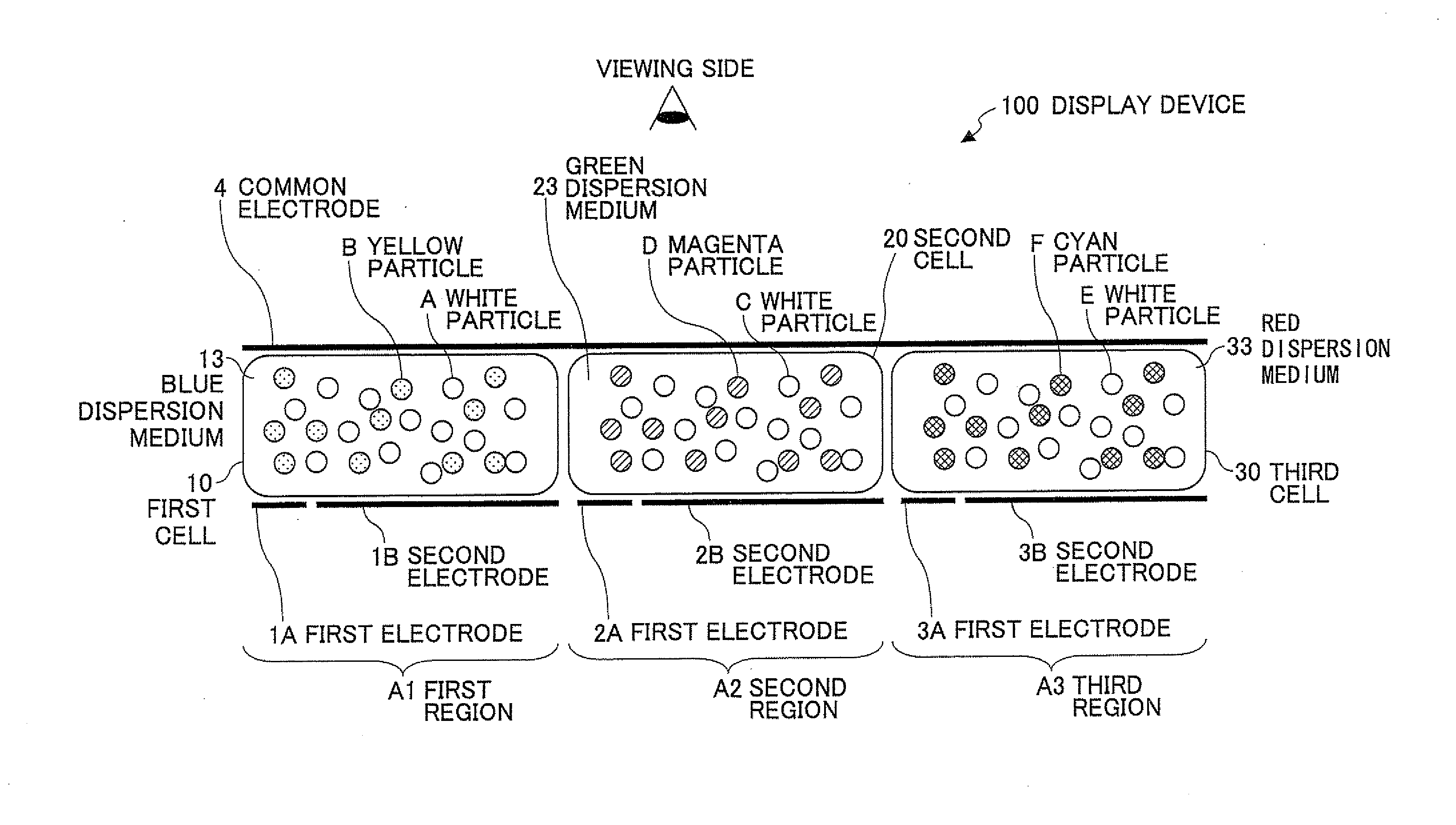
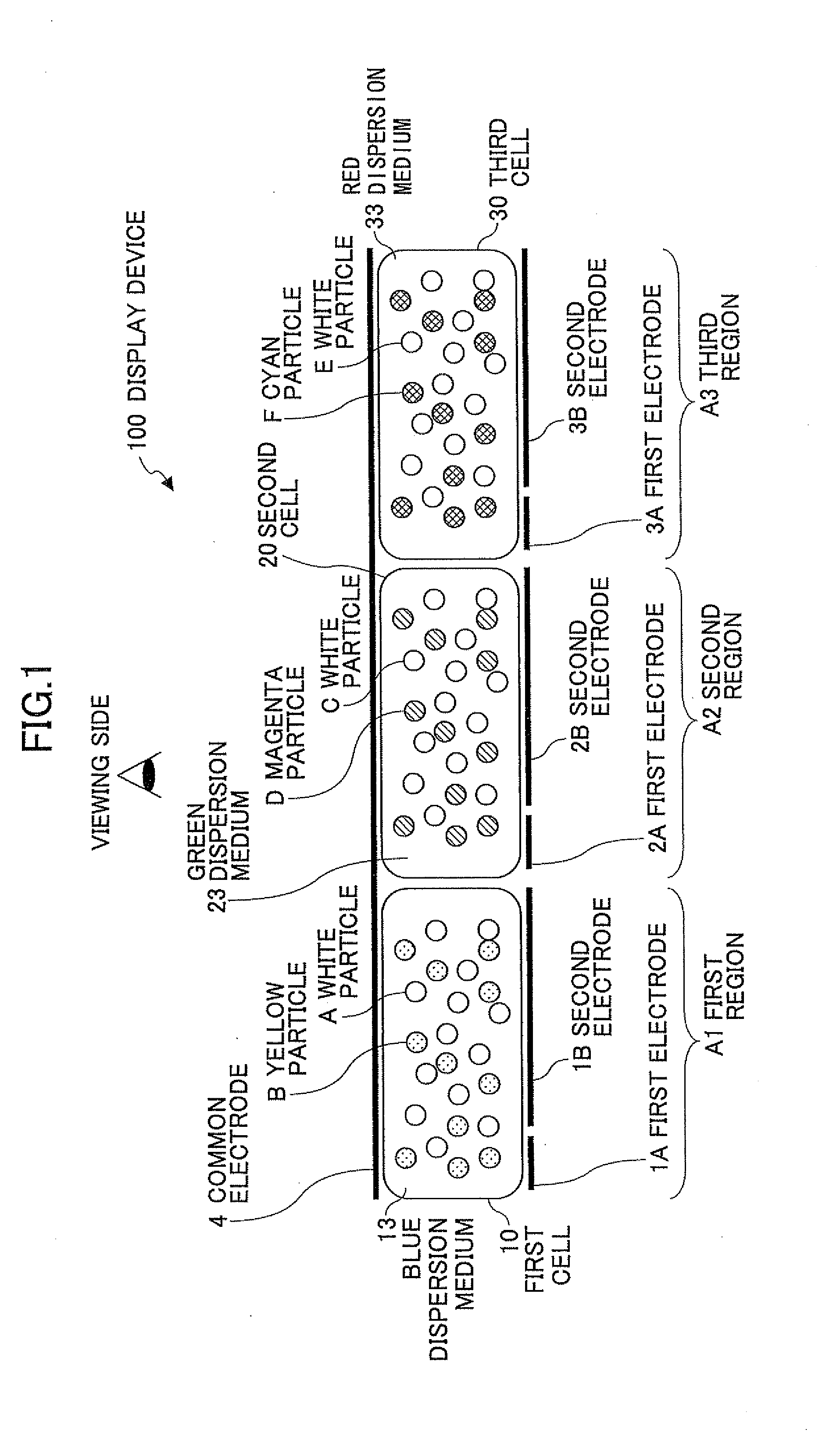
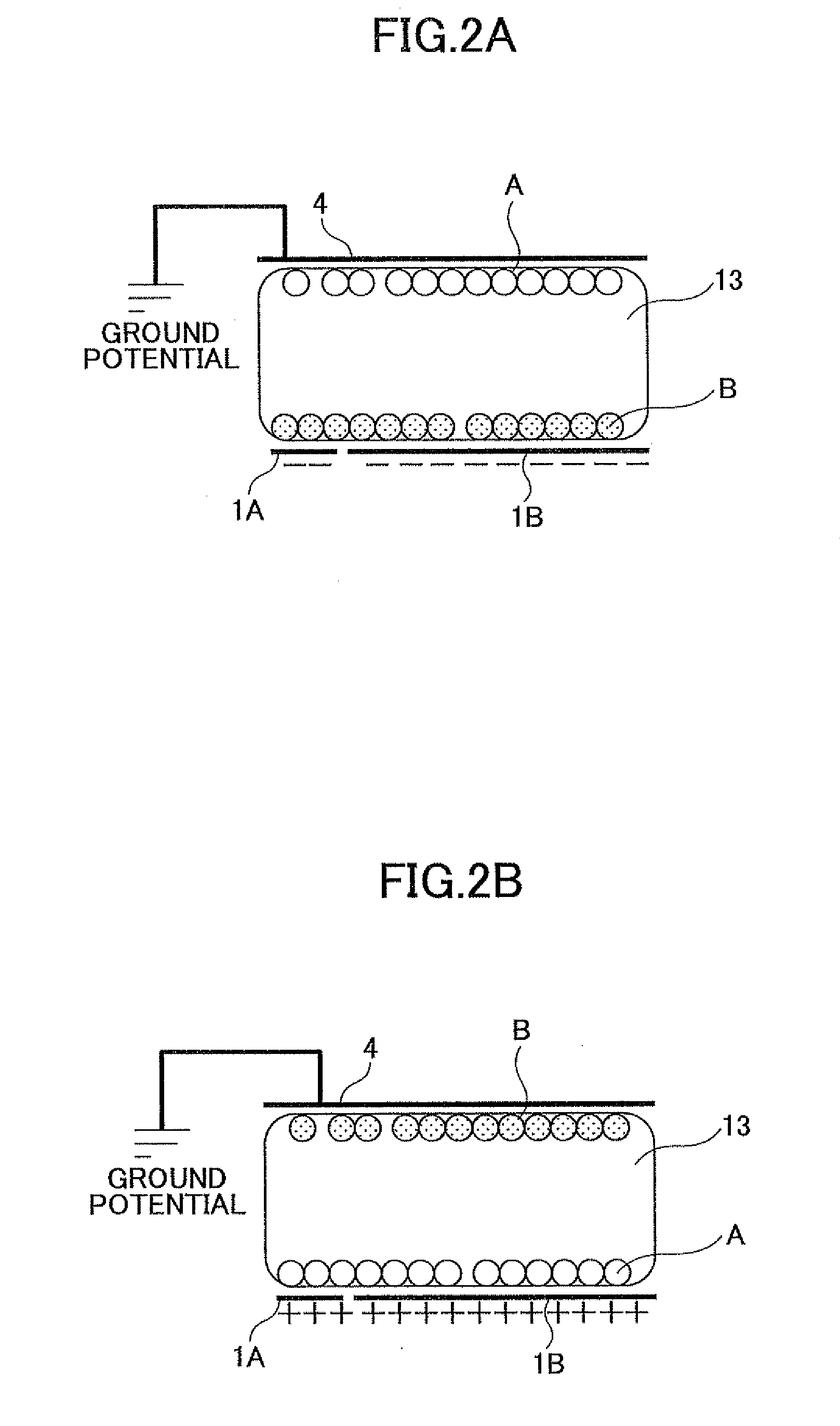
Image displaying medium, image display device, writing device and displaying method
The present invention provides an image display medium comprising a pair of substrates at least one of which having translucency, the substrates being disposed opposite to each other with a gap, a dispersion medium which has translucency and is enclosed in a space between the pair of substrates; and plural kinds of particle groups which are movably dispersed in the dispersion medium, move according to an electric field formed, and have different colors and forces for separation from the substrates.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Quantum entanglement generating system and method, and quantum entanglement generating and detecting system and method
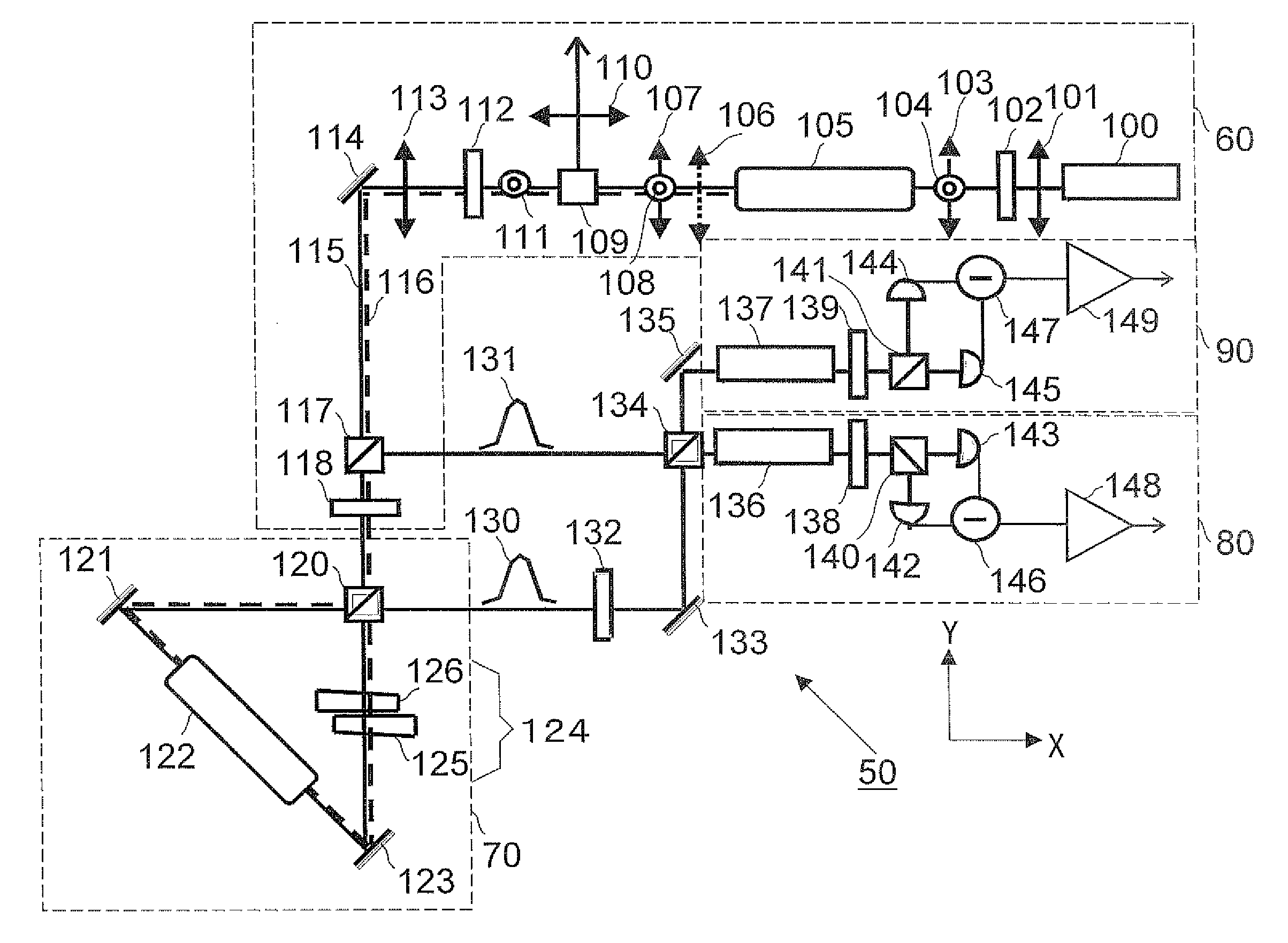
ActiveUS20110032532A1Improve stabilityGenerate an quantum entanglement stablyQuantum computersNanoinformaticsBeam splitterQuantum entanglement
A quantum entanglement generating system (30) comprises: a laser light source (1) for producing a light beam of light frequency 2f0; a ring interferometer (20) comprising a beam splitter (4) into which the light beam of light frequency 2f0 is incident and a plurality of mirrors (5, 7, 8), the beam splitter and the mirrors forming an optical path in the form of a ring; a parametric amplifier (6) inserted in the optical path of the ring interferometer for producing a beam of light of light frequency f0 upon receiving the light beam of light frequency 2f0 incident into the optical parametric amplifier; and a dispersive medium (9) inserted in the optical path of the ring interferometer for varying relative optical path length for the light beam of light frequency 2f0 and the light beam of light frequency f0, whereby two light beams of light frequency 2f0 split into at the beam splitter (4) so as to travel mutually contrariwise in direction of advance in the ring interferometer are incident into the optical parametric amplifier (6) to generate a first and a second squeezed light beam traveling mutually contrariwise in direction of advance in the ring interferometer (20), and the first and second squeezed light beams upon adjustment of their relative phase at a selected value through the dispersive medium (6) are combined in the beam splitter (4) to generate quantum entangled beams (10, 11).
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Variable-focus lens and image taking apparatus
The present invention provides a variable-focus lens capable of freely changing the refractive power and operating with a reduced deterioration in performance and an image taking apparatus having a focal-length-variable image taking lens including the variable-focus lens. The variable-focus lens includes: a lens body having an electromagnetic field generator which changes the focal length of the light passage region by moving, by an electromagnetic force, light-transmissive nanoparticles which are dispersed in a light-transmissive dispersion medium enclosed in a container having the shape of a lens, and which have a refractive index different from the refractive index of the dispersion medium; a moving mechanism which moves the lens body in an optical axis direction; and a focal length adjustment section which changes the focal length of the lens body by controlling an electromagnetic field generated by the electromagnetic field generator.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +2
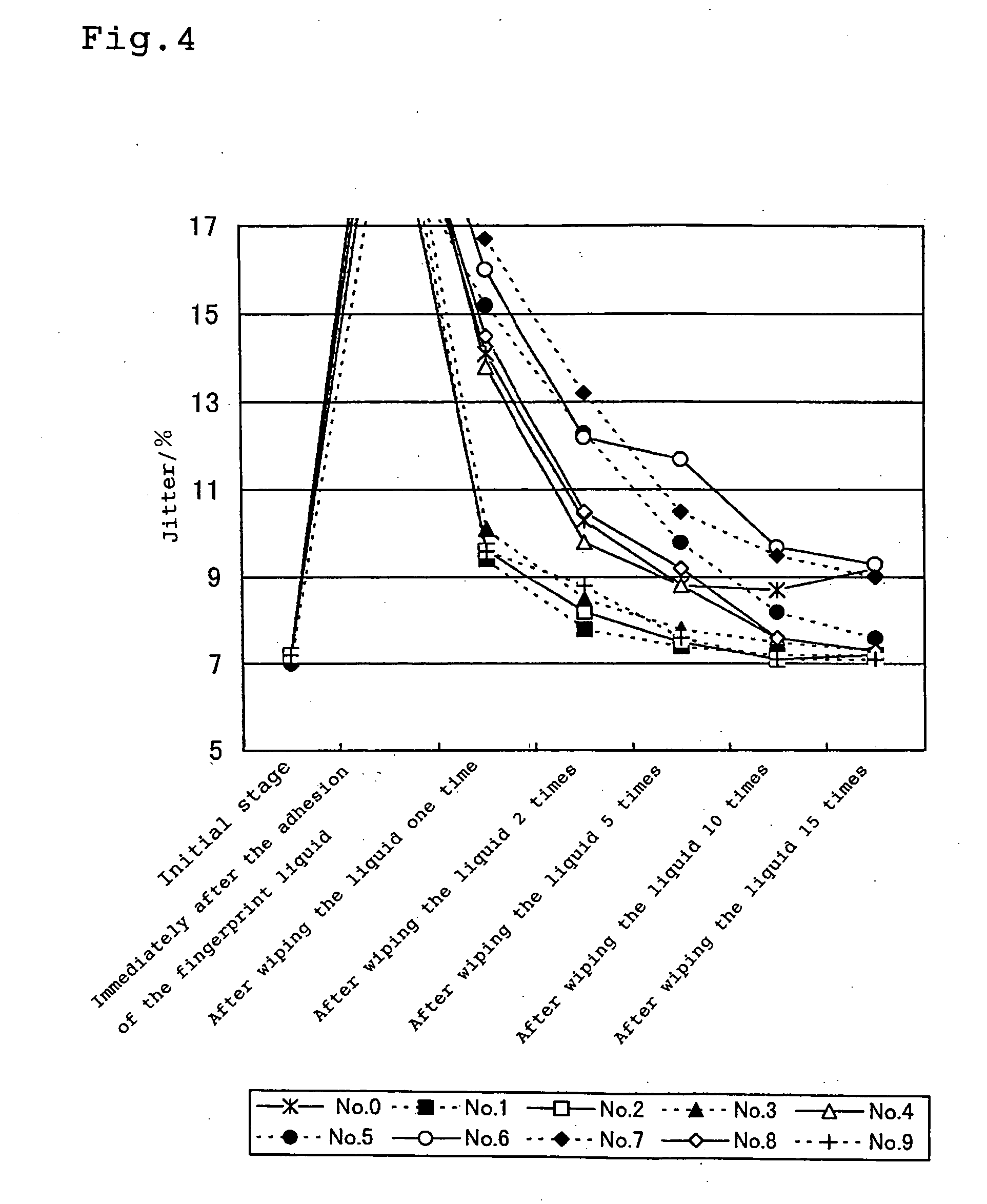
Artificial finger print liquid, testing method for optical information medium using it and optical information medium
The present invention provides a low-cost artificial fingerprint liquid for quantitatively and with a good reproducibility evaluating an anti-staining property, and a fingerprint adhering property or a fingerprint removing property on the surface of an optical disk such as a reproduction-only optical disk, optical recording disk, magneto-optical recording disk, various displays such as a CRT, and various substances such as glass. An artificial fingerprint liquid comprising a fine-particle-form substance and a dispersion medium capable of dispersing the fine-particle-form substance. The dispersion medium preferably has a surface tension ranging from 20 to 50 mN / m at 25° C., and preferably is selected from at least one of higher fatty acid, derivative of higher fatty acid, terpens, and derivatives of terpens. The fine-particle-form substance is at least one selected from inorganic fine particles and organic fine particles. The present invention provides a testing method for an optical information medium using the artificial fingerprint. The present invention provides an optical information medium which is good in the property of wiping off an organic stain, such as a fingerprint, adhering to a surface of the optical recording medium and which can maintain good recording / reproducing property over a long period.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Electrophoretic liquid and display device using electrophoretic liquid
An electrophoretic liquid is disclosed that includes first particles that have the property of scattering light over an entire visible range and are positively or negatively charged; second particles that have the property of absorbing light of a specific wavelength range in the visible range and scattering light of ranges other than the specific wavelength range and are charged to a polarity opposite to that of the first particles; and a dispersion medium that has the property of allowing the light of the specific wavelength range absorbed by the second particles to pass through and absorbing the light of the ranges other than the specific wavelength range. In the electrophoretic liquid, the first particles and the second particles are dispersed in the dispersion medium.
Owner:TRANSCEND OPTRONICS (YANGZHOU) CO LTD
Multicolor display optical composition, optical device, and display method of optical device
The present invention provides a multicolor display optical composition comprising a dispersion medium, a periodic structure having a porous structure inside communicated with the outside, and mobile particles contained in the dispersion medium so as to be movable and having a volume average primary particle diameter from 1 nm to 80 nm in a dispersion state in the dispersion medium, a volume average particle diameter of coagulated particles of 100 nm or larger in optical coagulation state by stimulation application, and having a refractive index different from that of the dispersion medium by 0.1 or more, wherein the mobile particles show no coloration in the dispersion state when the particles are dispersed in the dispersion medium and show white coloration with a predetermined whiteness value or higher in the coagulation state when the particles are coagulated, an optical device, and a display method of the optical device.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Stomach dissolved film coating pre-mix dose and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101199854AGood ratioGood performancePharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLow speedActive agent
The invention relates to a gastric-juice-soluble film-coating premix and the preparation method. The components include film-forming material (principal film-forming material and non-principal film-forming material), plasticizer, antisticking agent, surfactant and unorganic colorant. The preparation method of the gastric-juice-soluble film-coat premix is that: principle film-forming material is put into a super-mixer whose temperature is between 20 to 80 DEG C to mix at a low speed for 5minutes,and then after the plasticizer and the surfactant being added, to mix at a high speed for 20 minutes to get dispersive medium; then the dispersive medium, the lubricant and the unorganic colorant are added into the super-mixer to be dispersed at a high speed for 30 minutes; then the non-principal film-forming material and the plasticizer are added to mix at a low speed for 5 minutes; the finished product can be got after being screened. The gastric-juice-soluble film-coat premix which adopts complete hydrosolvent system is of moderate viscosity, so that good suspending state can be maintained; relatively low permeability can ensure the stability of the preparation; with improved production efficiency, improved moistureproof effect of the traditional Chinese medicine, more delicate coat and brighter color, the invention can better meet the requirements of the solid medicine for the film-coating.
Owner:AILEYI MEDICINE MATERIAL SCI & TECH TIANJIN CITY
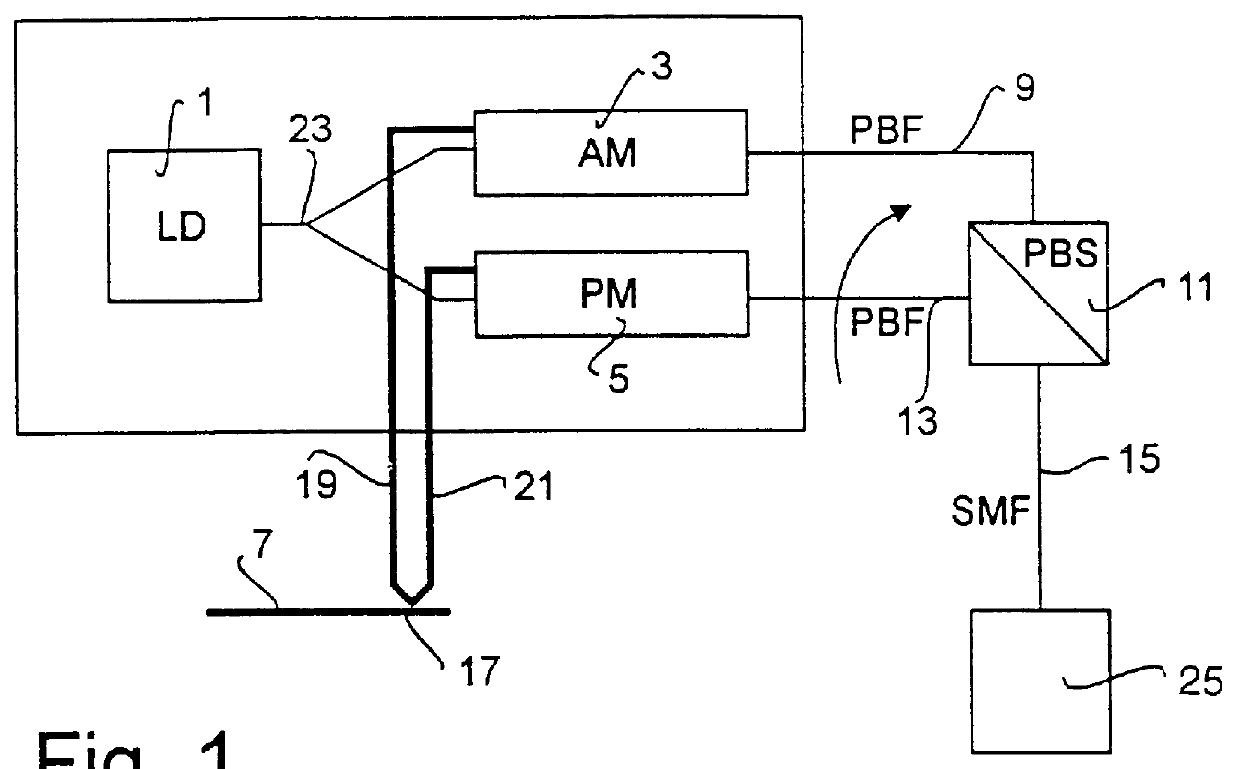
Compensation of dispersion
InactiveUS6122086AIncrease bitrateLaser detailsTransmission control/equlisationFiberPhase modulation
In transmission of optical signals in a dispersive medium, the signals are transmitted simultaneously in two modes in an optical fiber (15), which are orthogonal to each other, one of the signals being a non-chirped amplitude modulated signal modulated by an amplitude modulator (3), and the other signal is a phase modulated signal modulated by a phase modulator (5). The received signal is formed by the sum of the amplitude modulated contributions of the two signals. In an optical fiber system, two orthogonal modes of polarization in the same fiber can be chosen. In this manner it will be possible to transmit high bit rates and primarily over long distances.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
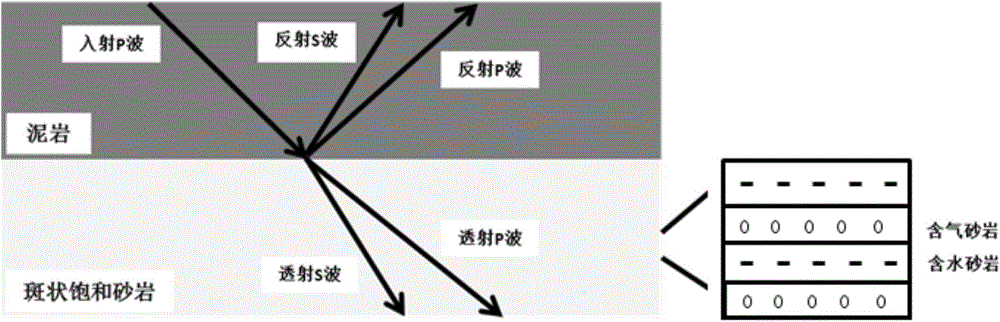
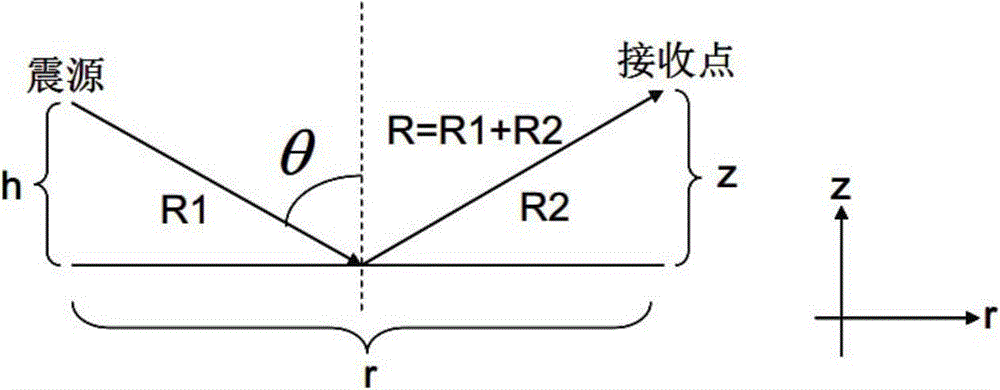
Method for modeling reflection coefficient of spherical PP wave in viscoelastic medium
The invention provides a method for modeling a reflection coefficient of a spherical PP wave in a viscoelastic medium and belongs to the field of geophysical prospecting for petroleum. The method comprises steps as follows: (1) a longitudinal wave phase velocity vp and a quality factor Q<-1> are calculated on the basis of a White model: the longitudinal wave phase velocity vp and the quality factor Q<-1> are calculated on the basis of the White model and reservoir parameters; (2) a reflection coefficient of a planar PP wave in a dispersive porous medium is calculated: the longitudinal wave phase velocity vp and the quality factor Q<-1> which are obtained in Step (1) are introduced in a Zoeppritz equation of the dispersive medium, and the reflection coefficient R<*>PP of the planar PP wave in the dispersive porous medium is calculated; (3) the reflection coefficient of the spherical wave is calculated: after the reflection coefficient R<*>PP of the planar PP wave is calculated in Step (2), the reflection coefficient of the spherical PP wave in the dispersive porous medium is modeled with a planar wave decomposition algorithm of the spherical wave, and the reflection coefficient R<spherical>PP of the spherical PP wave in the dispersive porous medium is calculated.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com