Patents
Literature
74 results about "Stereotaxy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stereotaxy (from stereo meaning "solidity", and tactile meaning "touch") refers to any technique that involves the recording and reproduction of three-dimensional haptic information or creating an illusion of depth to the sense of touch within an otherwise-flat surface. Unlike the current trend in haptic technology to provide haptic perception of simulated, virtual objects within an augmented-reality (that is, within a mostly-realistic) setting, stereohapty, which, when applied as a field of study, is known as stereohaptics or stereotactics, stereotaxy aims to provide an illusion of three-dimensional depth to the sense of touch by the human body. This resembles how stereoscopy, its visual counterpart, is meant to provide a visual illusion of depth to otherwise-flat images (such as 3-D films), a process known as stereopsis.
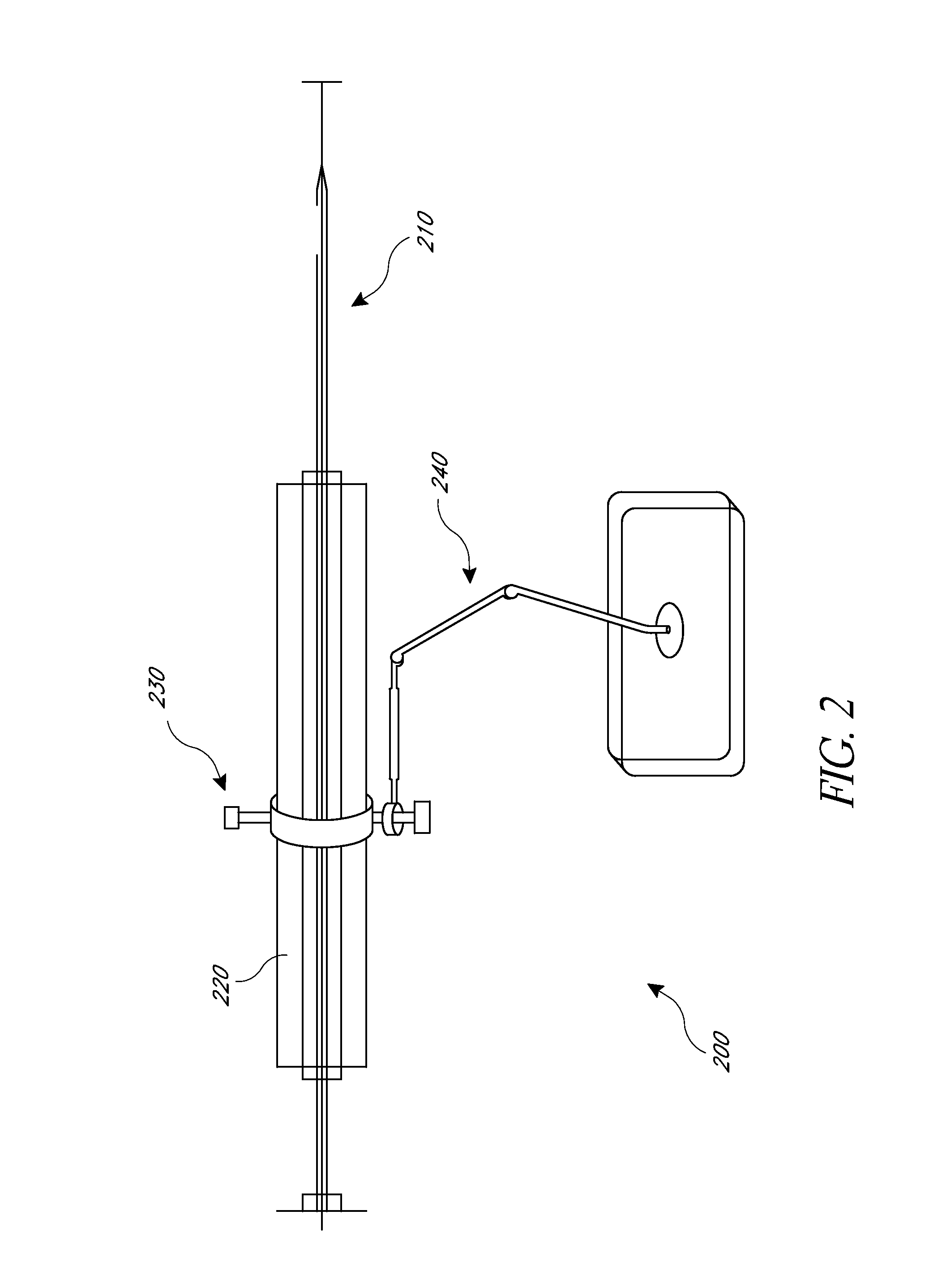
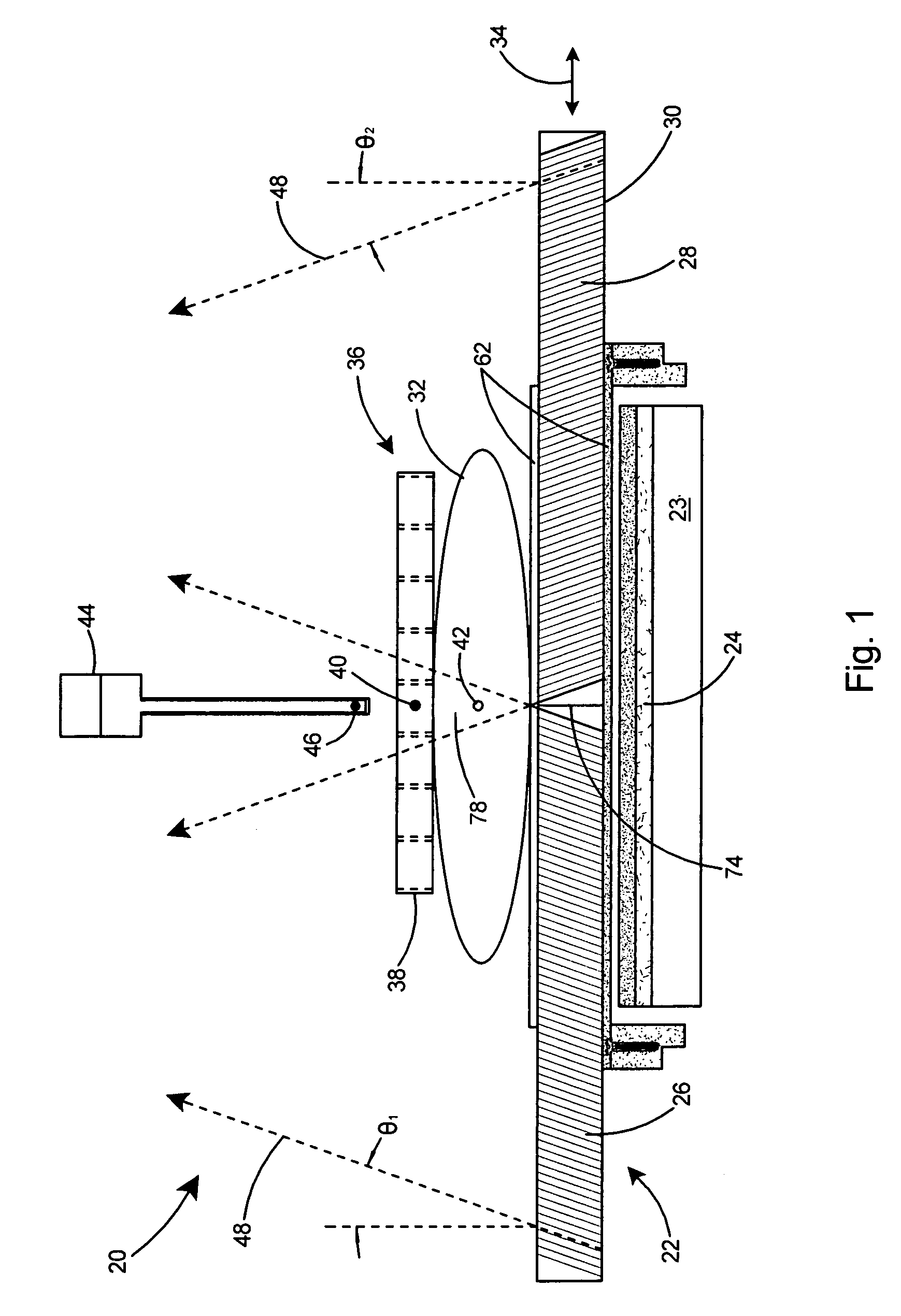
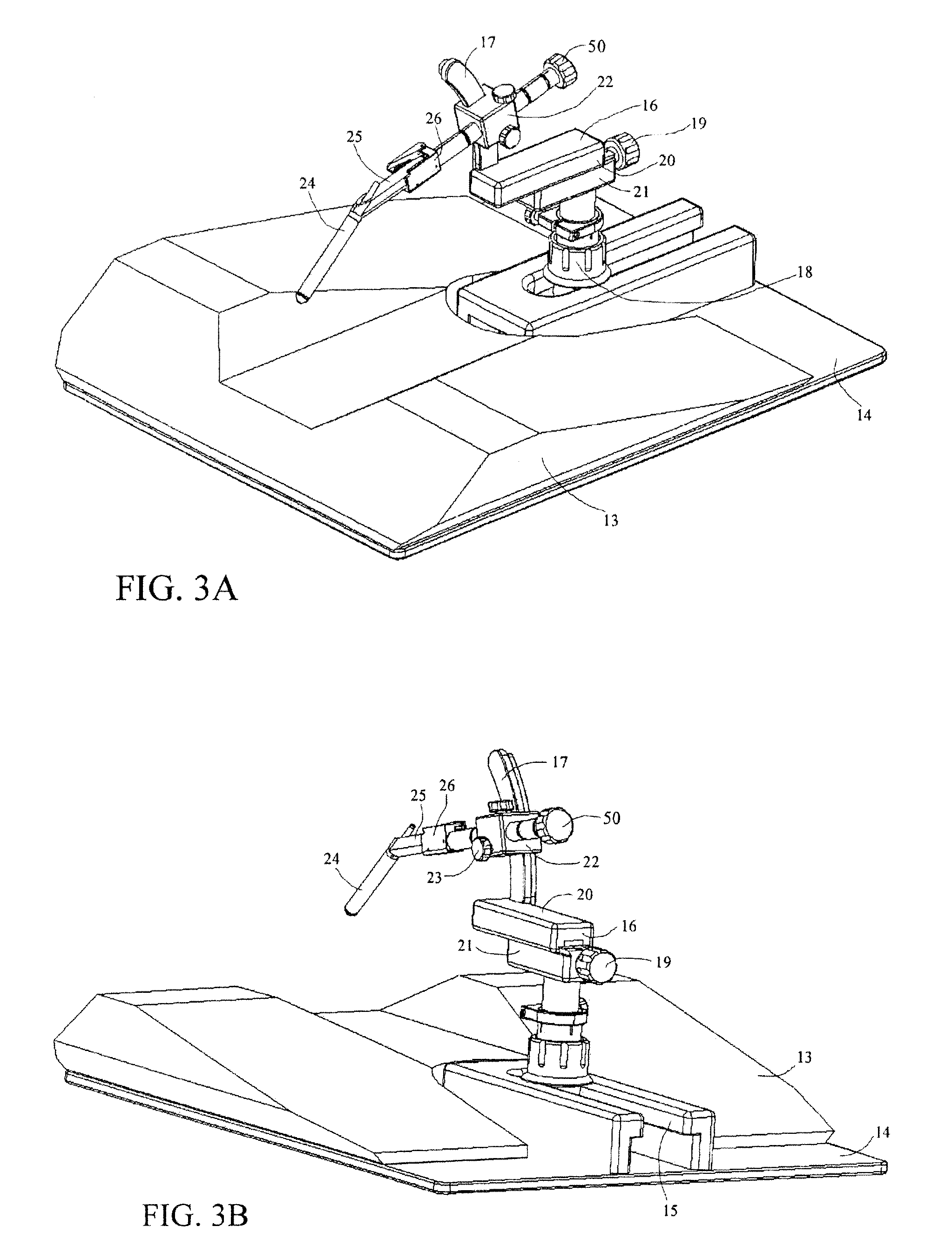
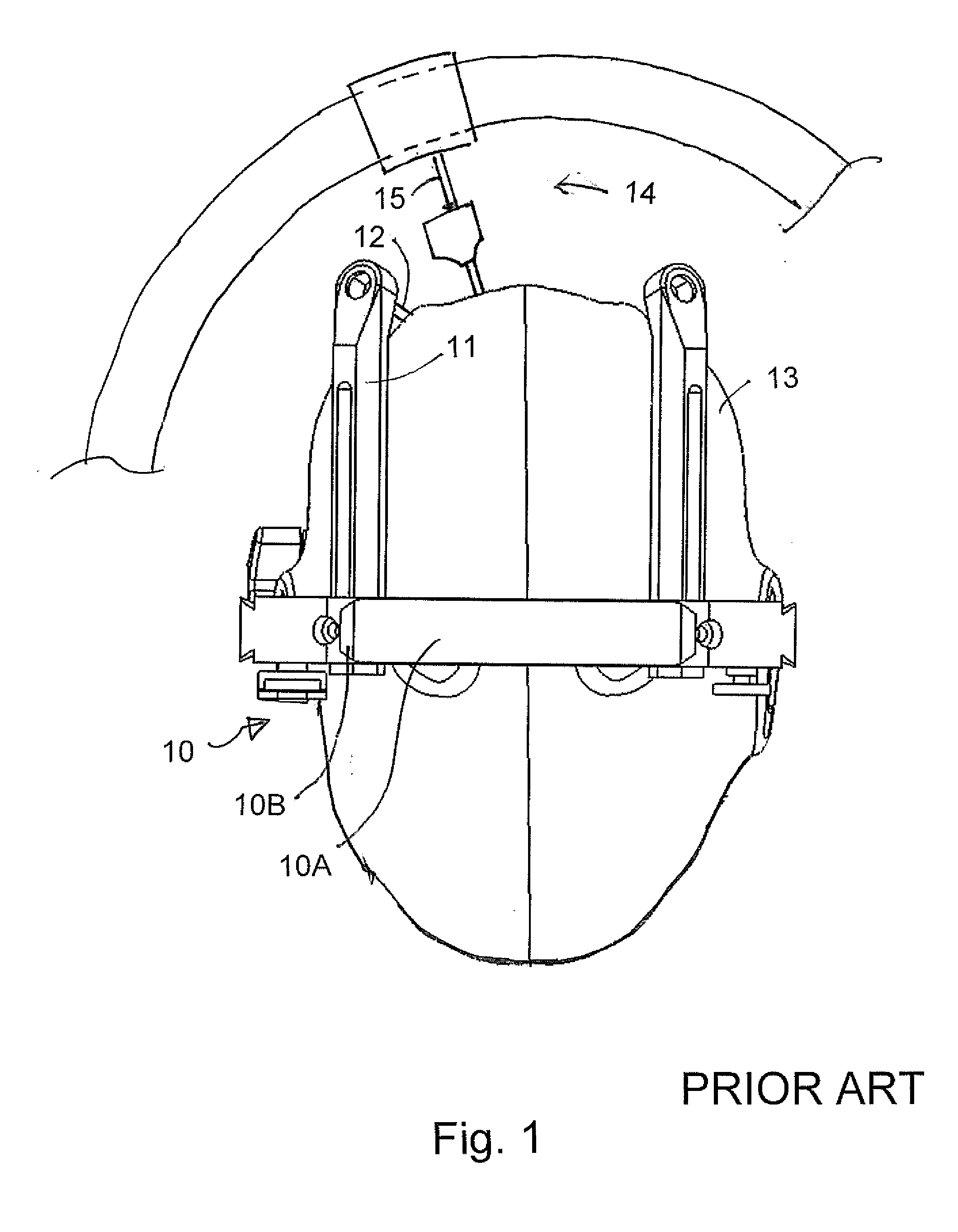
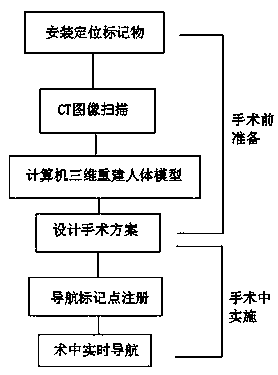
Method and apparatus for performing stereotactic surgery
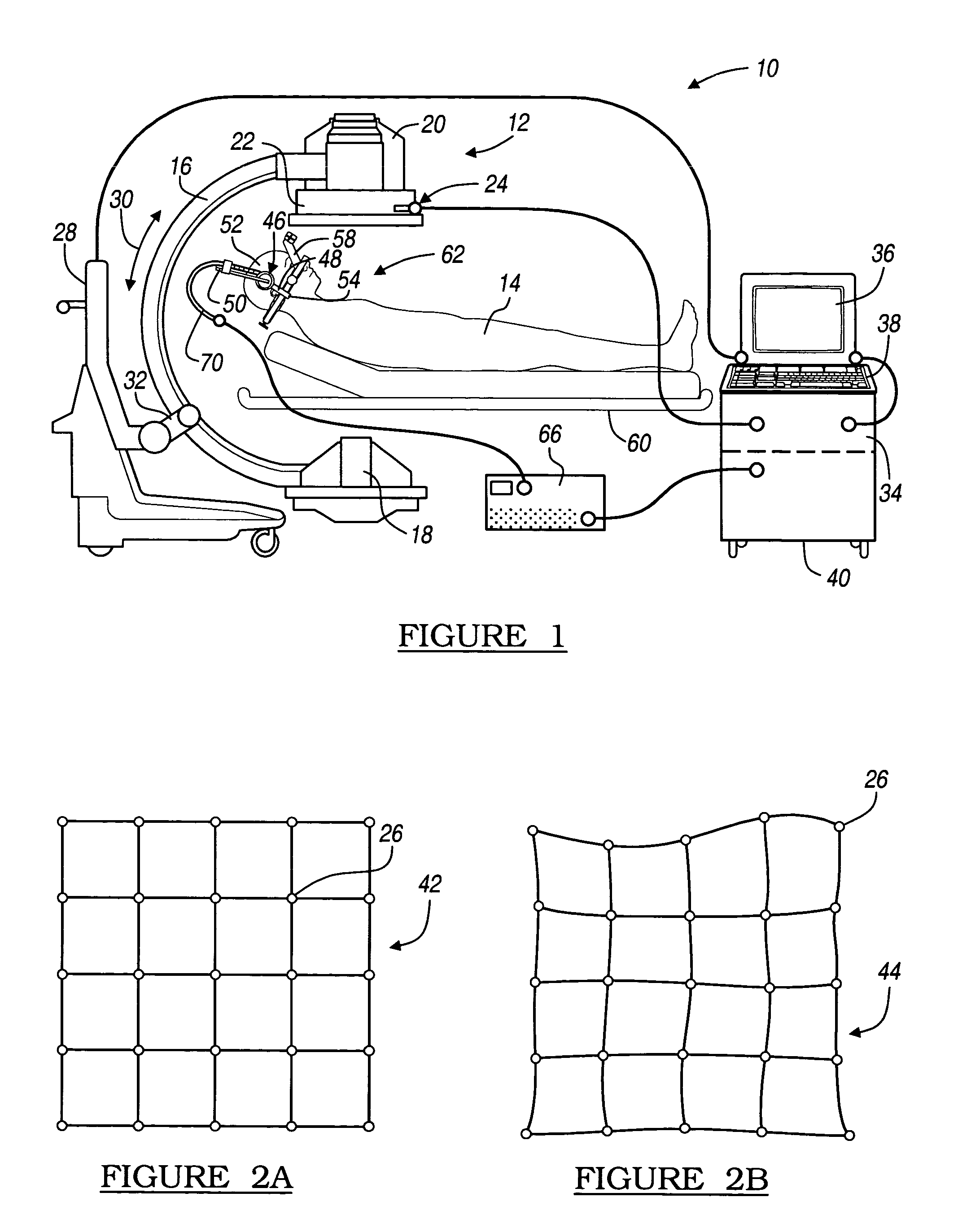
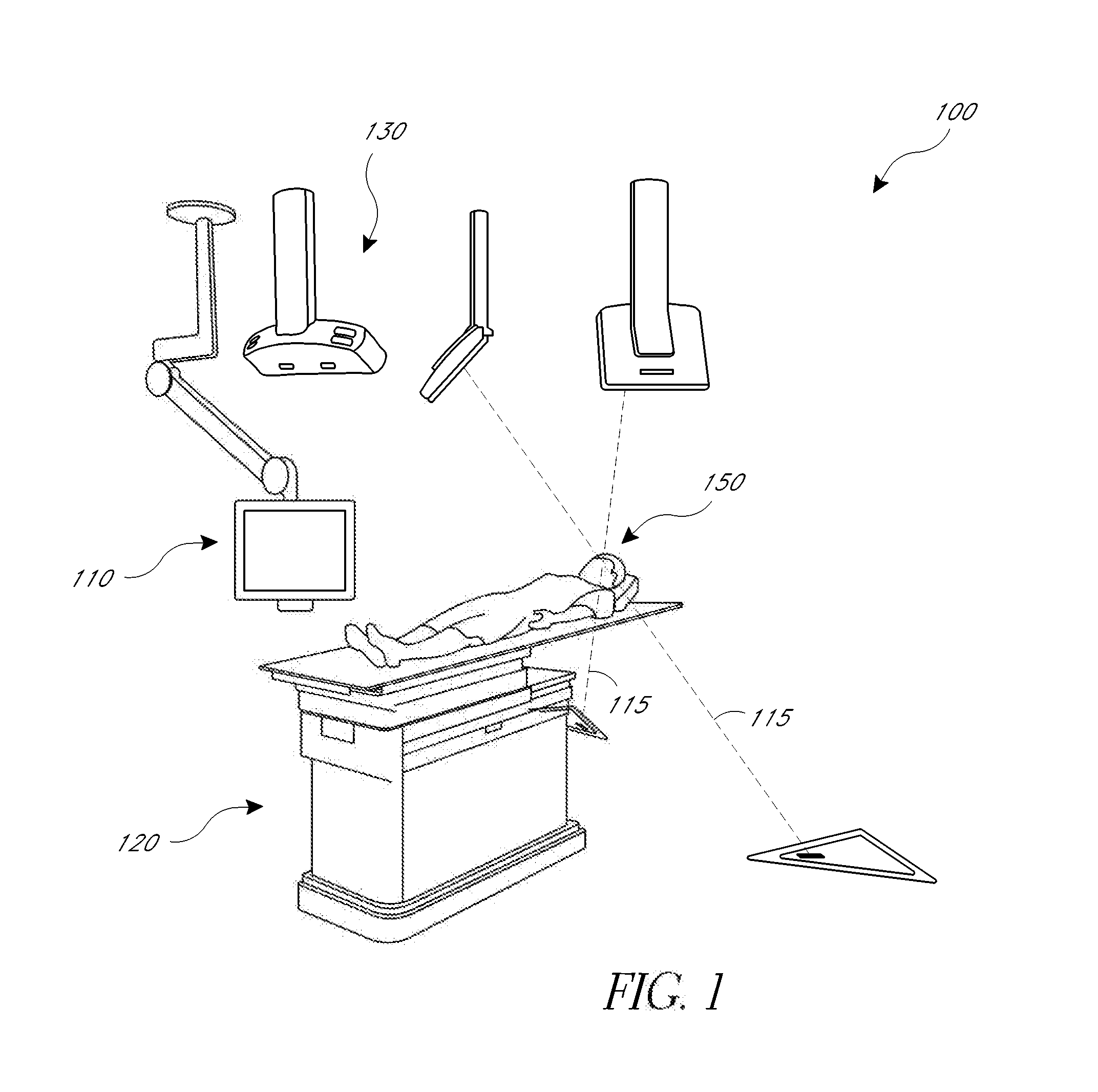
A stereotactic navigation system for navigating an instrument to a target within a patient may include a stereotactic head frame, an imaging device, a tracking device, a controller and a display. The stereotactic head frame is coupled to the patient and is used to assist in guiding the instrument to the target. The imaging device captures image data of the patient and of the stereotactic head frame. The tracking device is used to track the position of the instrument relative to the stereotactic head frame. The controller receives the image data from the imaging device and identifies the stereotactic head frame in the image data and automatically registers the image data with navigable patient space upon identifying the stereotactic head frame, while the display displays the image data.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH
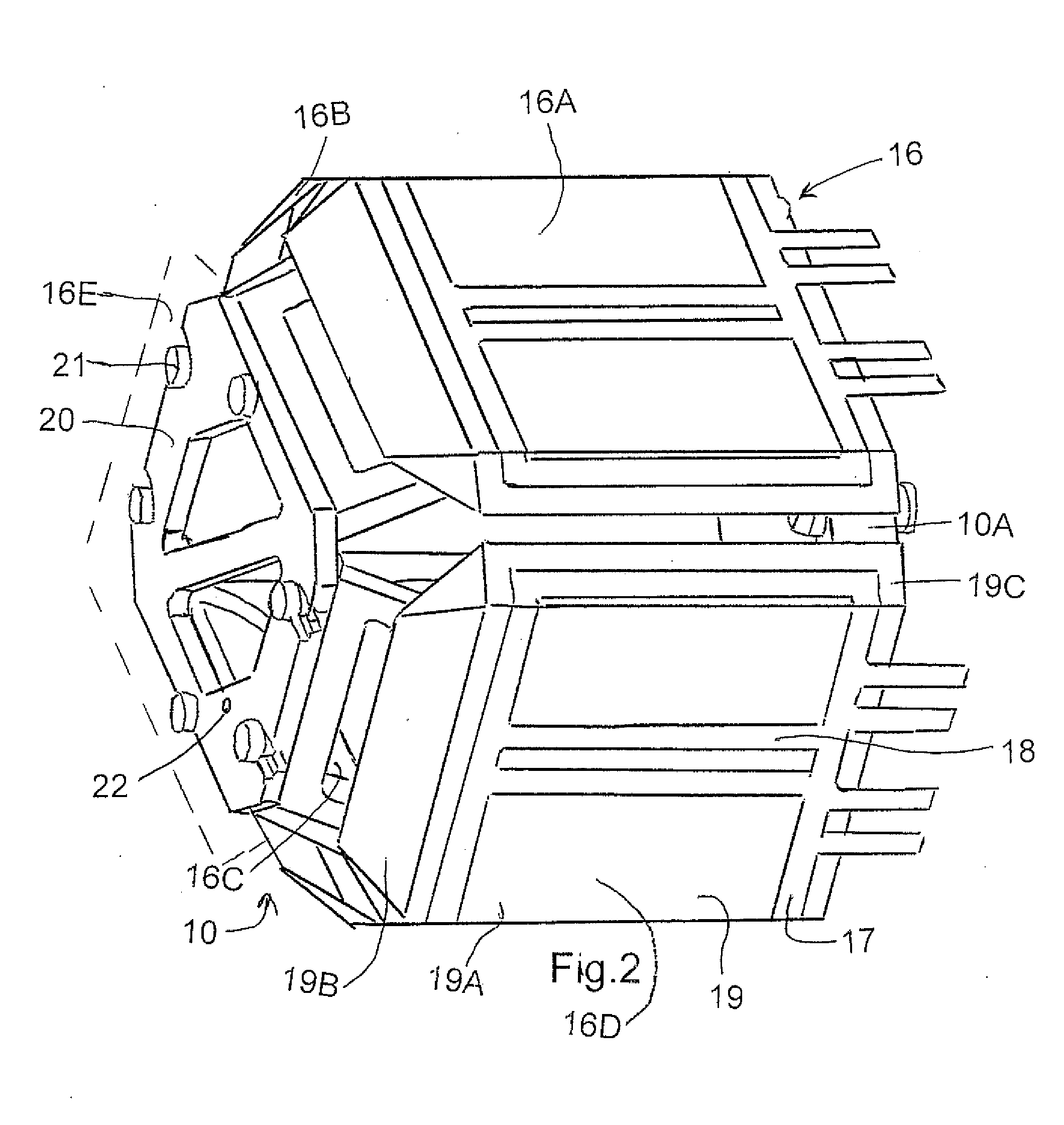
Method and stereotactic apparatus for locating intracranial targets guiding surgical instruments
A method and an instrument are presented for reliably, accurately and easily locating intracranial targets and guiding surgical instruments to intracranial targets in human patients. An adjustment apparatus and a portable guider 70 constitute main components of the invention. The method and instrument make use of images of natural reference points or fiducial markers found in CT / MRI images of patient's head. In accordance with the present method, after the adjustment apparatus is mechanically adjusted based on the information gathered from CT / MRI images, the adjustments are transferred by a special procedure to the portable guider. The portable guider is the only component employed during surgery, resulting in minimal general intrusion with the work of the surgeon.
Owner:OMURTAG AHMET +1
Excisional biopsy needle and method for use with image-directed technology
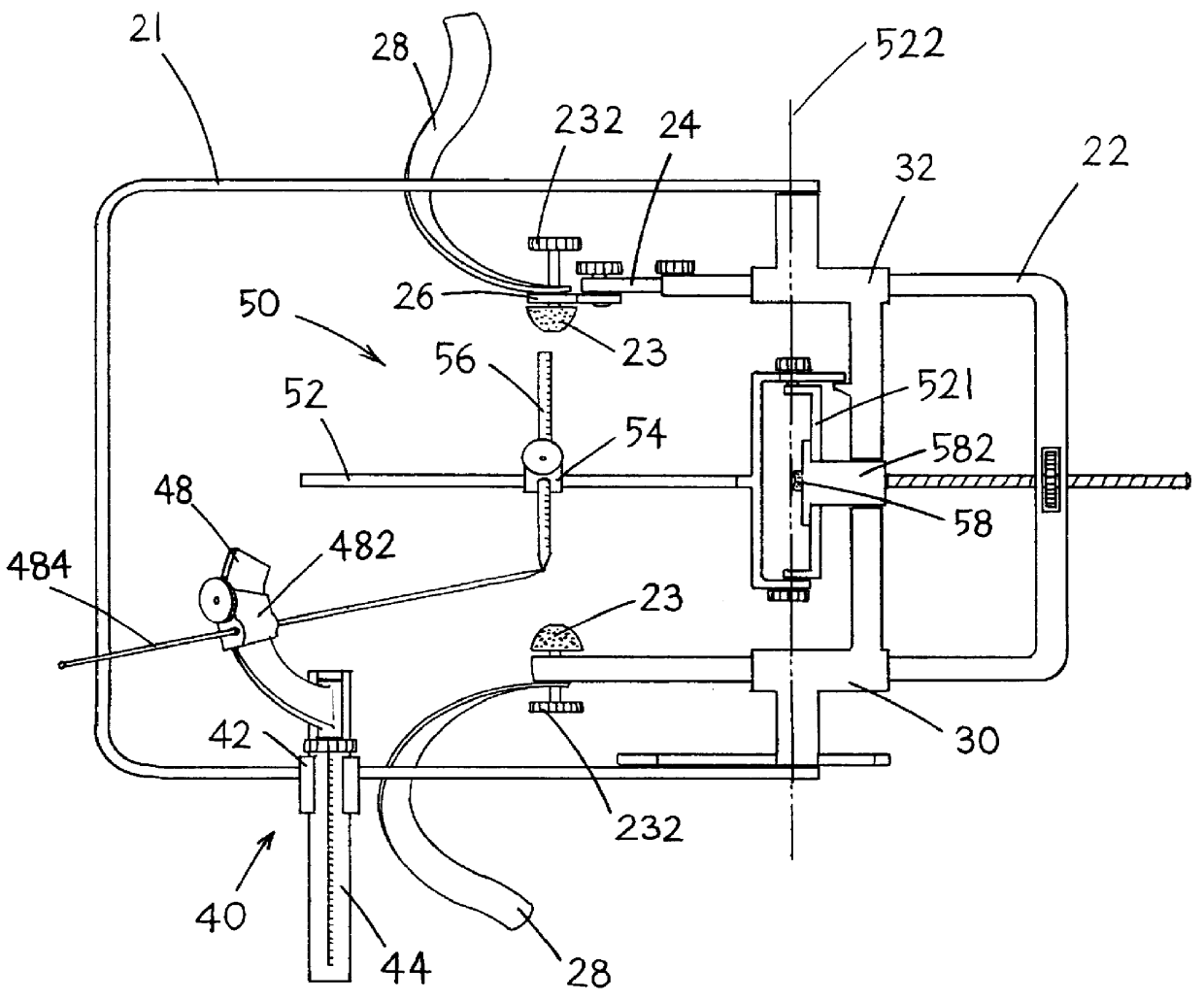
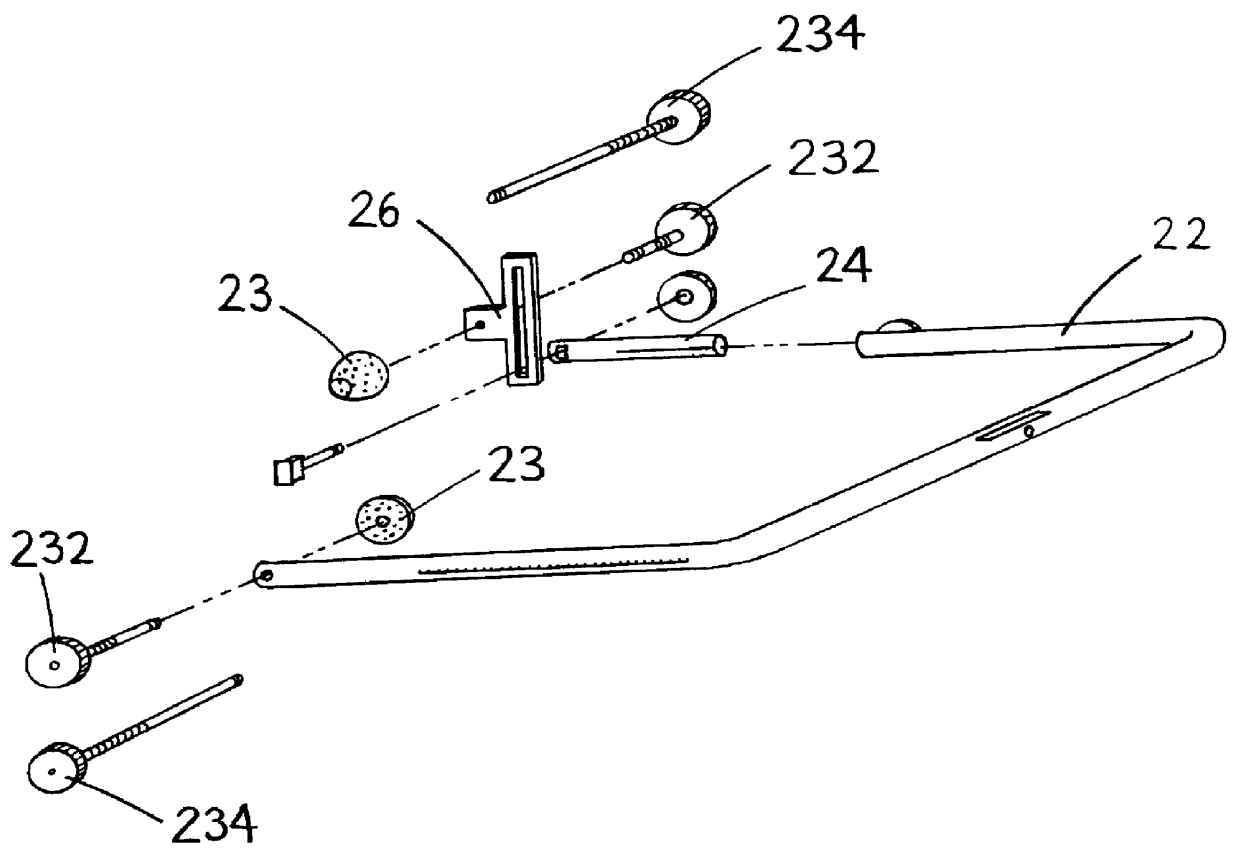
An excisional biopsy needle assembly for use in combination with a stereotactic platform for excising tissue from the interior of the body. The biopsy needle includes a rotatable flexible blade that is capable of transforming between a contracted configuration for piercing into the interior of the body and an expanded configuration in which the flexible blade is expanded relative to the shaft of the needle for excising tissue. The needle assembly may be mounted in a stereotactic needle for a breast biopsy procedure that digitally directs the needle tip into a lesion with the flexible blades in a contracted configuration, then expands the flexible blades to the expanded configuration and rotates the blades thus excising tissue in a region having a cross sectional dimension that is large in relation to the cross section of the needle shaft. The excised tissue is extracted from the needle tip through an aspiration channel.
Owner:KIETURAKIS MACIEJ J
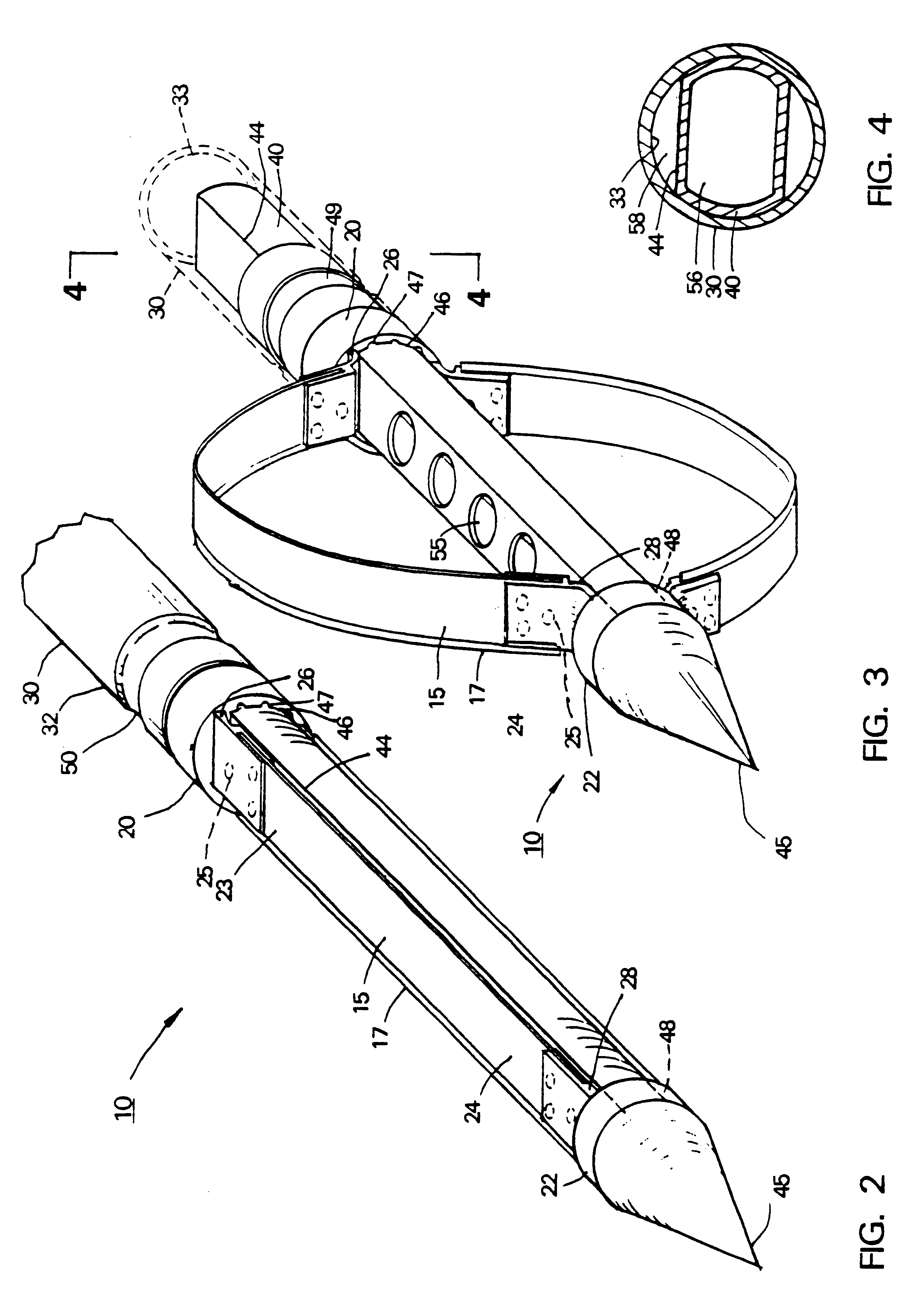
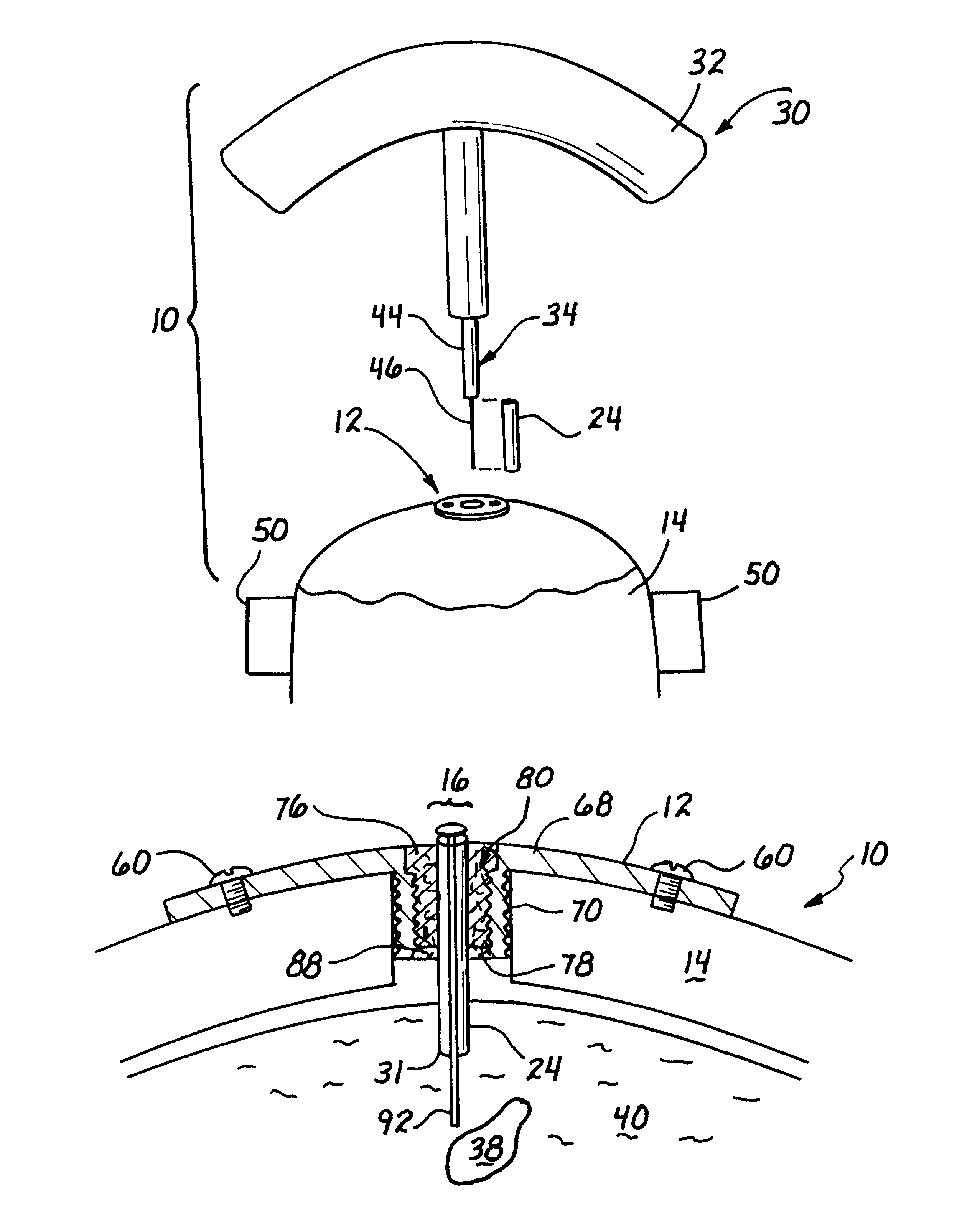
Stereotaxic detachable needle extension
InactiveUS6572624B2Easy to insertDiagnosticsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryStereotaxyBiomedical engineering
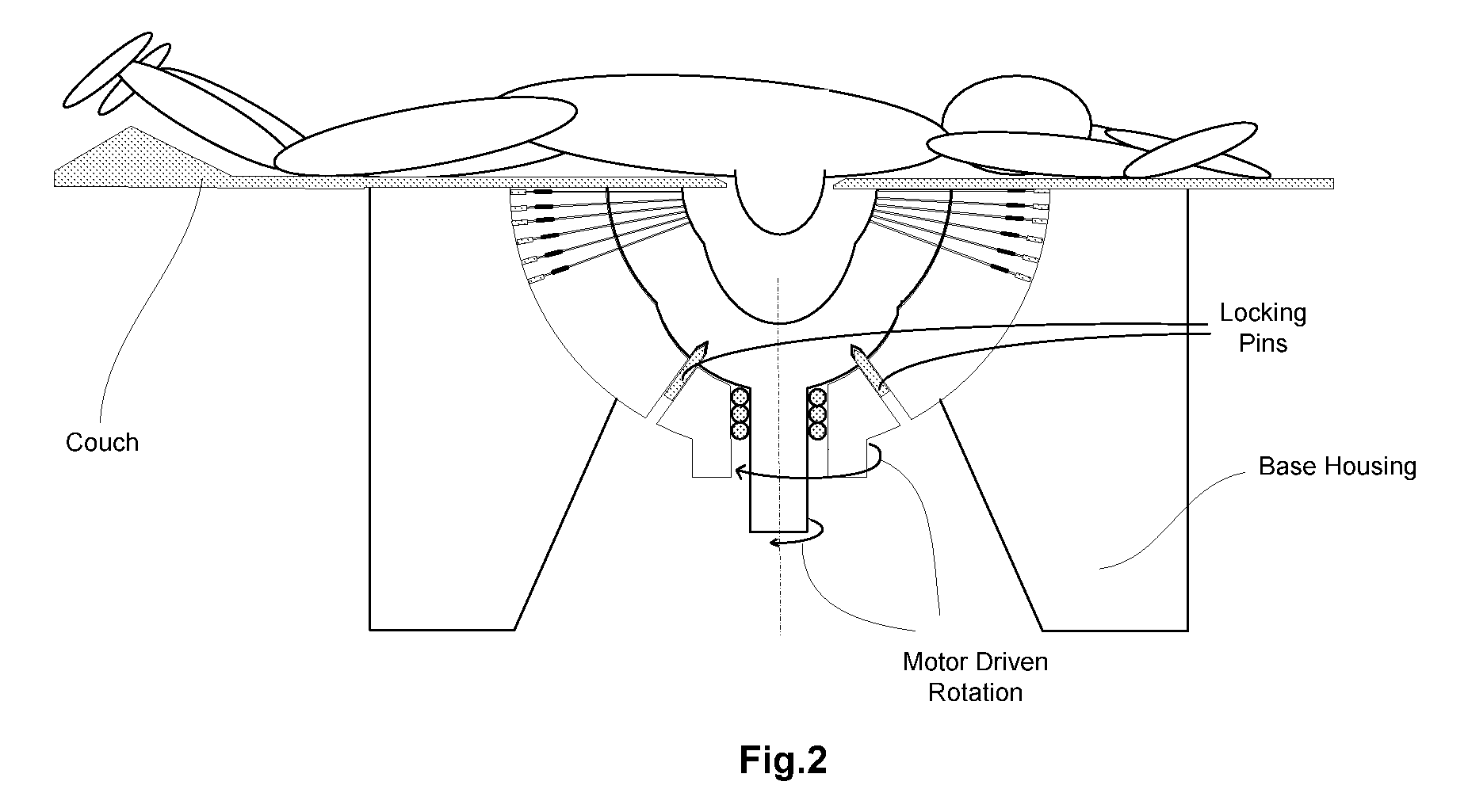
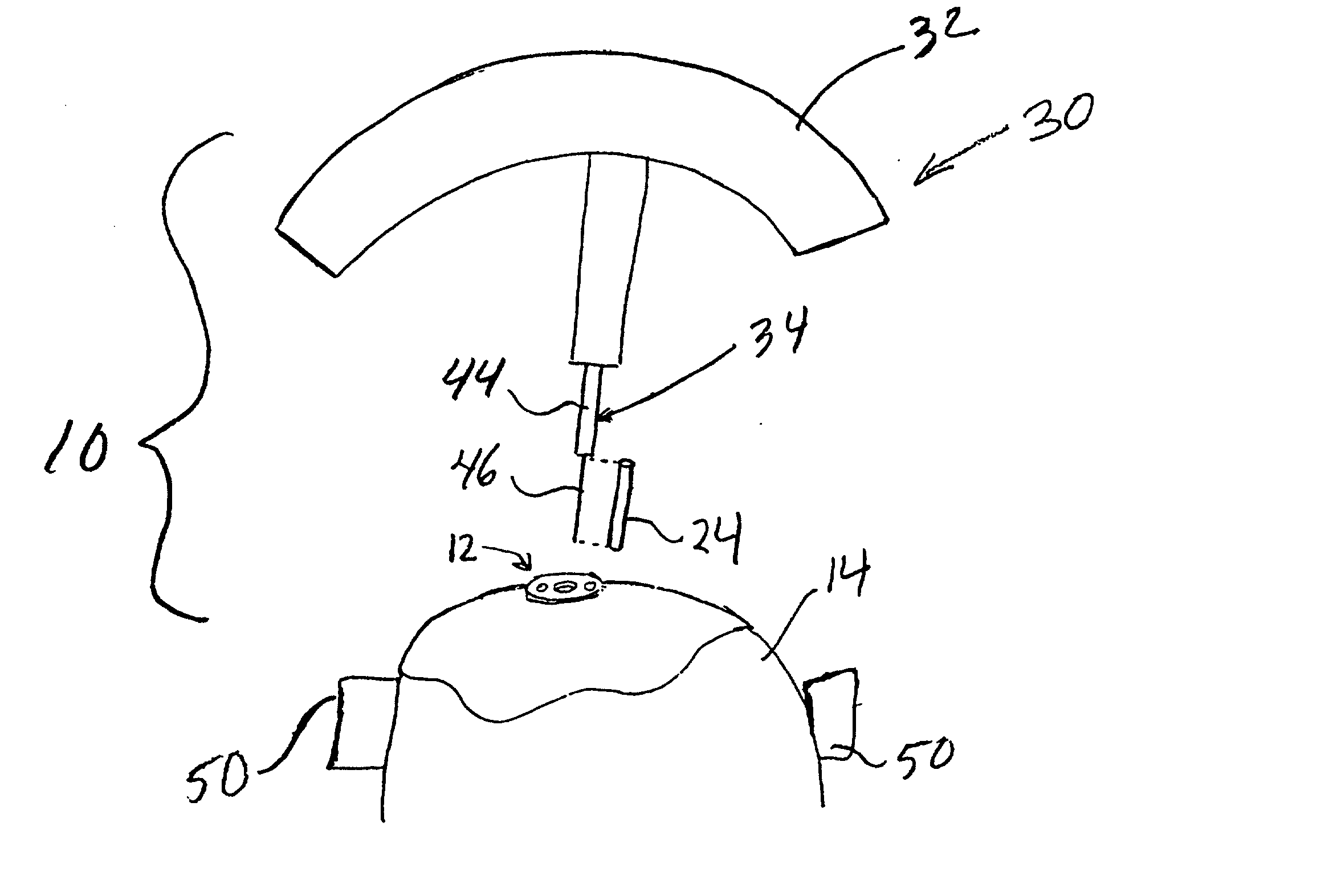
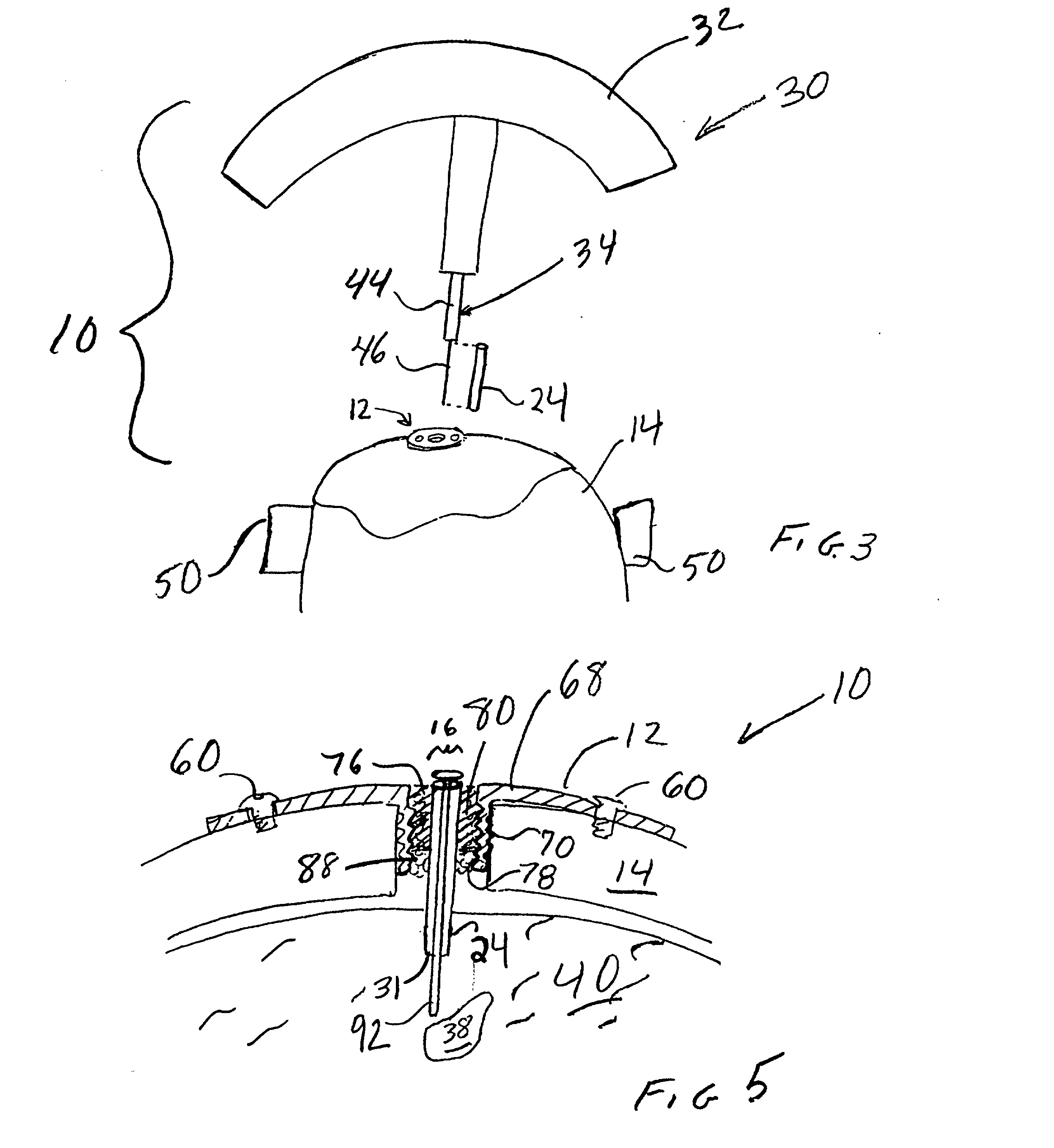
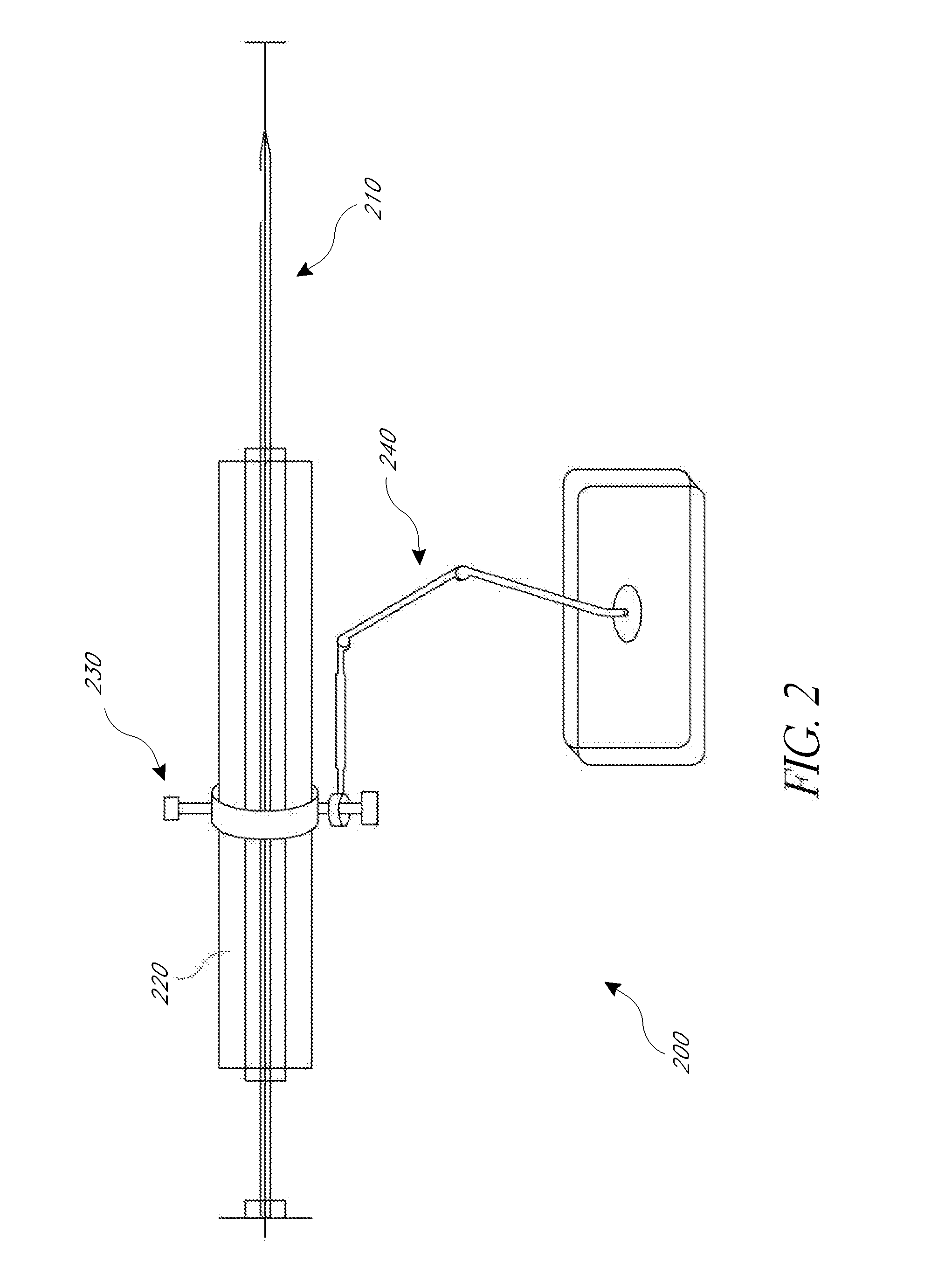
An apparatus for positioning instrumentation into a target region of a brain generally includes an attachment member, specifically a disc adapted to be secured to a cranium, and a marker assembly adapted to be connected to a locator device, for example a conventional stereotaxic assembly. The marker assembly includes a detachable cannula, and is further adapted to be secured to the attachment member in order to immobilize the cannula at a precise position in the brain, thus facilitating additional imaging of the patient in order to determine the position of the cannula with respect to the target region.
Owner:CYTORI THERAPEUTICS INC
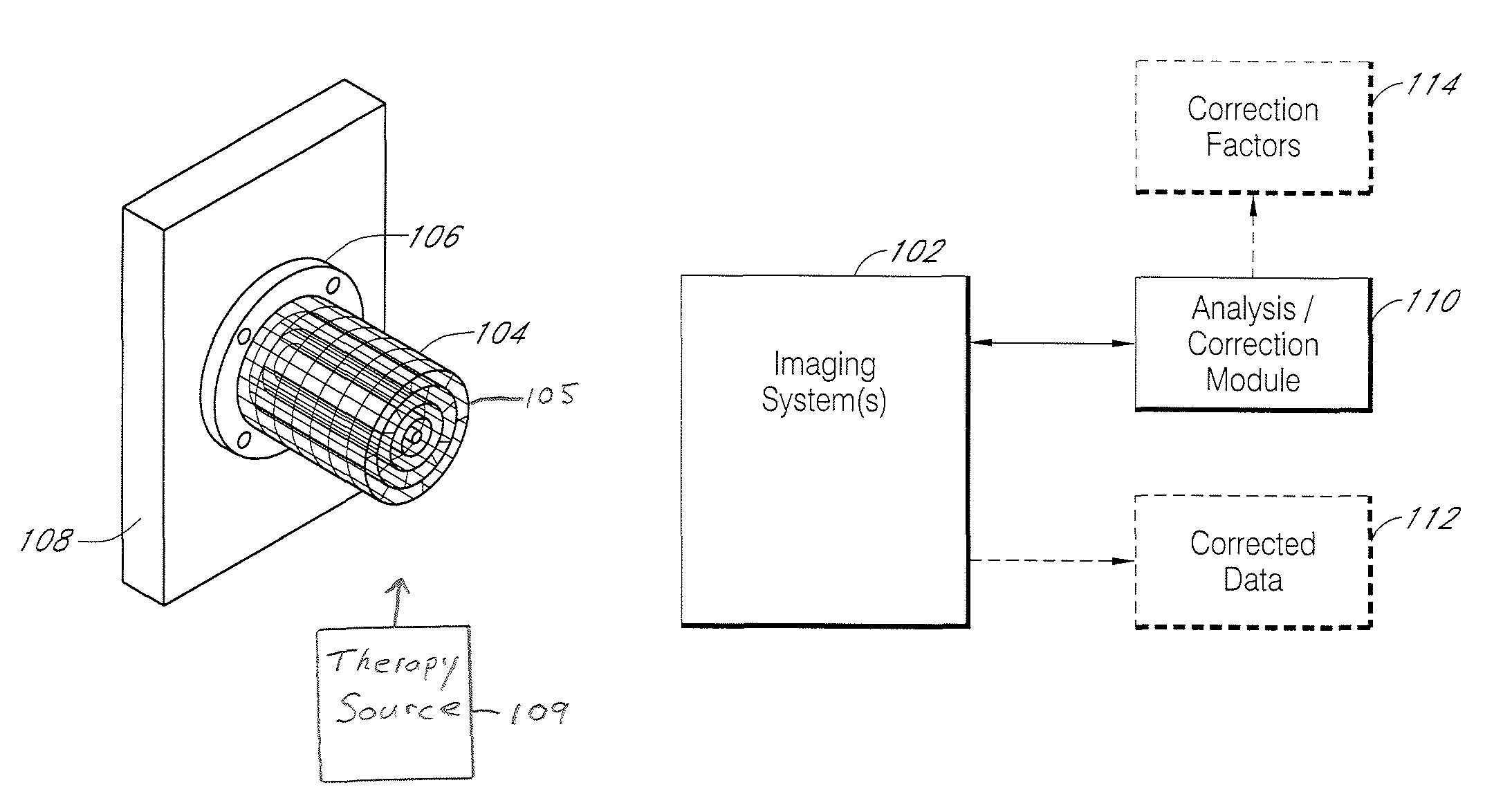
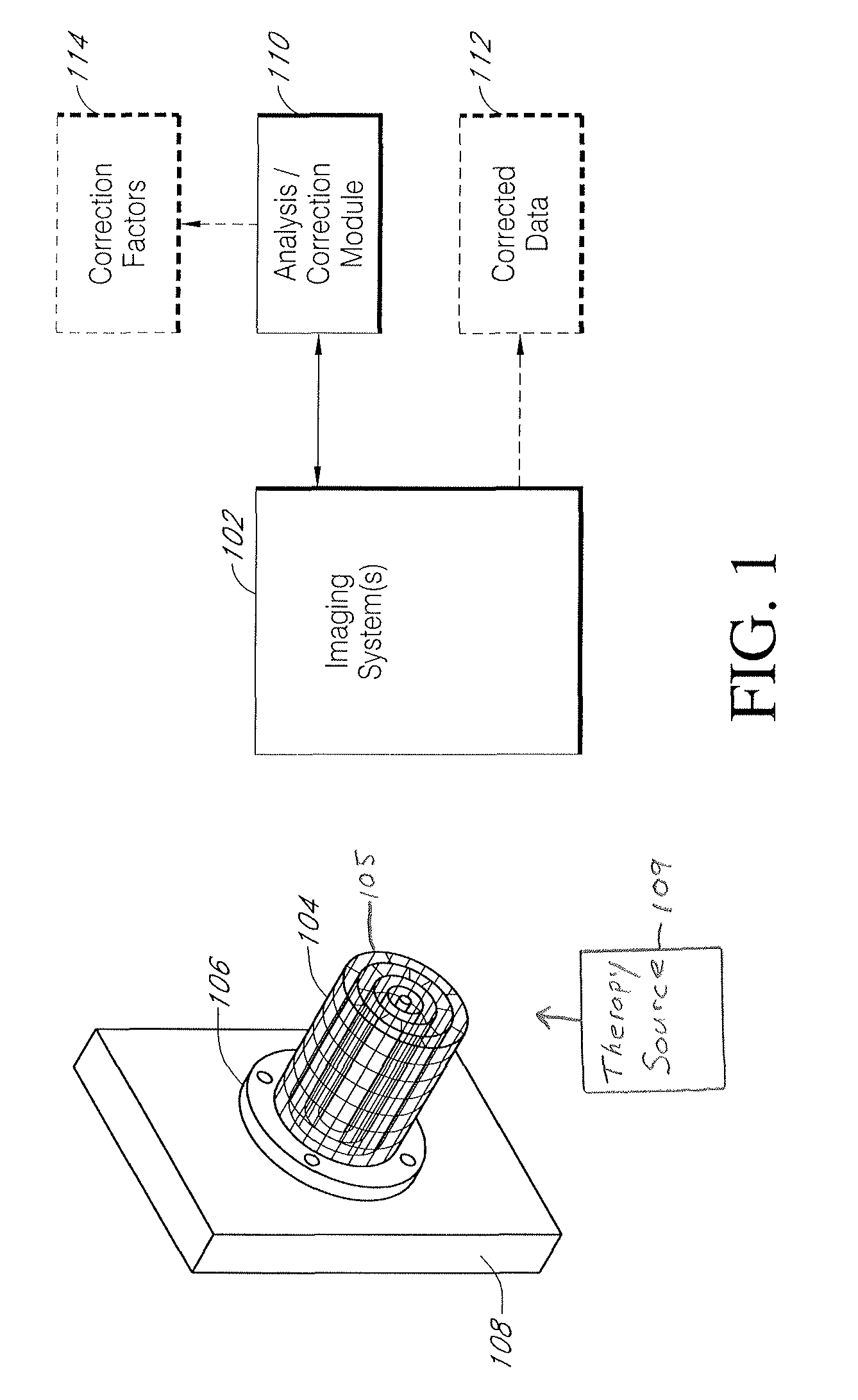
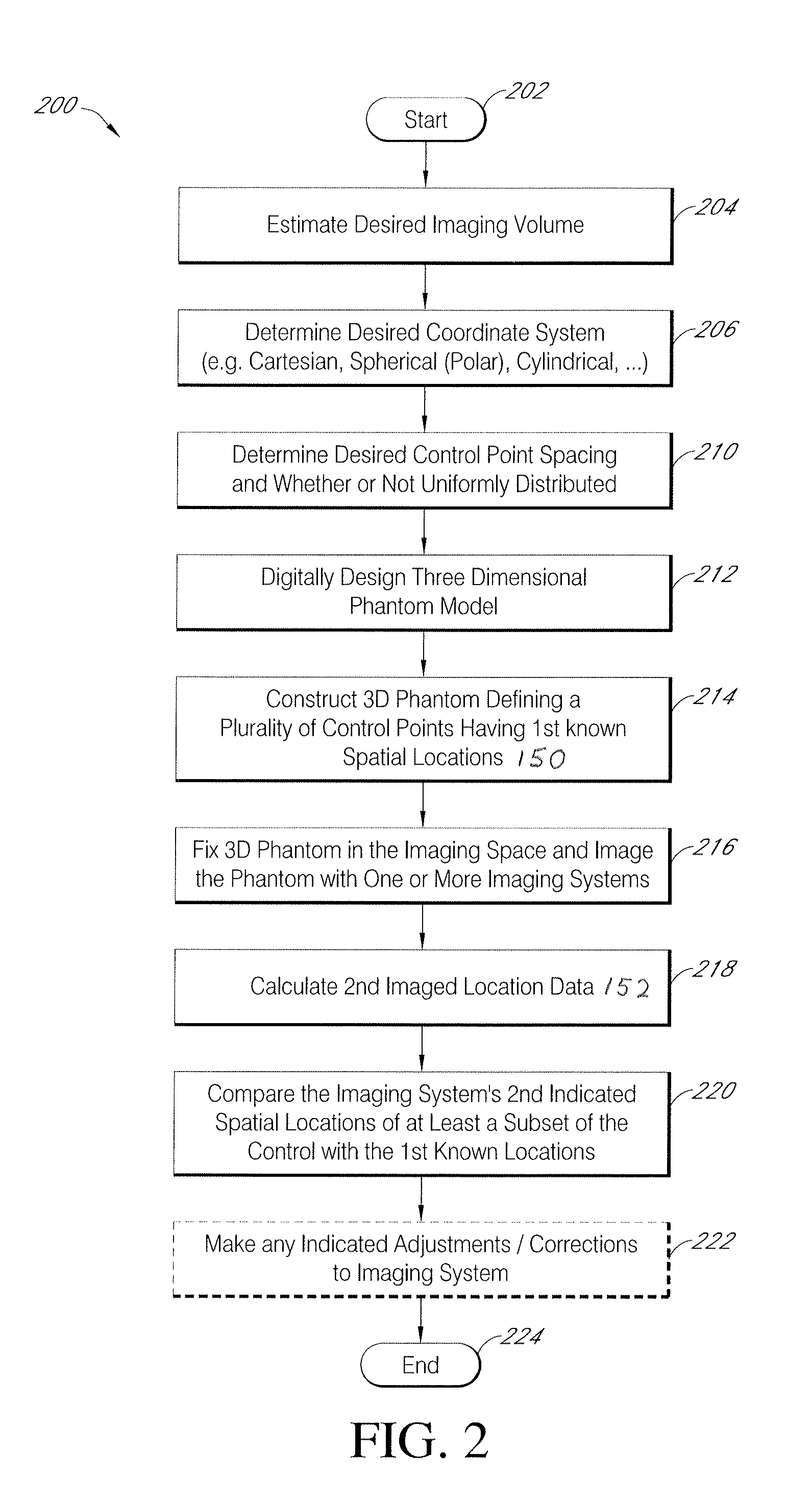
Systems and methods for characterizing spatial distortion in 3D imaging systems
Systems and methods for characterizing spatial distortions in location data determined by an imaging system, for example as employed in imaged guided therapy. A three dimensional phantom is custom formed for a desired imaging space of a given imaging system. The phantom includes a large plurality of control points fixed rigidly in space to a high degree of known accuracy. The phantom is fixed to a stereotactic frame defining a known calibrated reference or zero and imaged. An algorithm customized for the phantom determines the spatial locations of the control points. A comparison is made between the known and the determined spatial locations for at least a subset of the control points. The comparison results in indicia for any determined spatial distortions observed. The raw image data can be manipulated to compensate for any spatial distortion. The control points can have fixed locations known to an accuracy of 100μ or better. The algorithm can determine an initial estimate for the detected location of a control point accurate to ±0.5 pixel or better.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
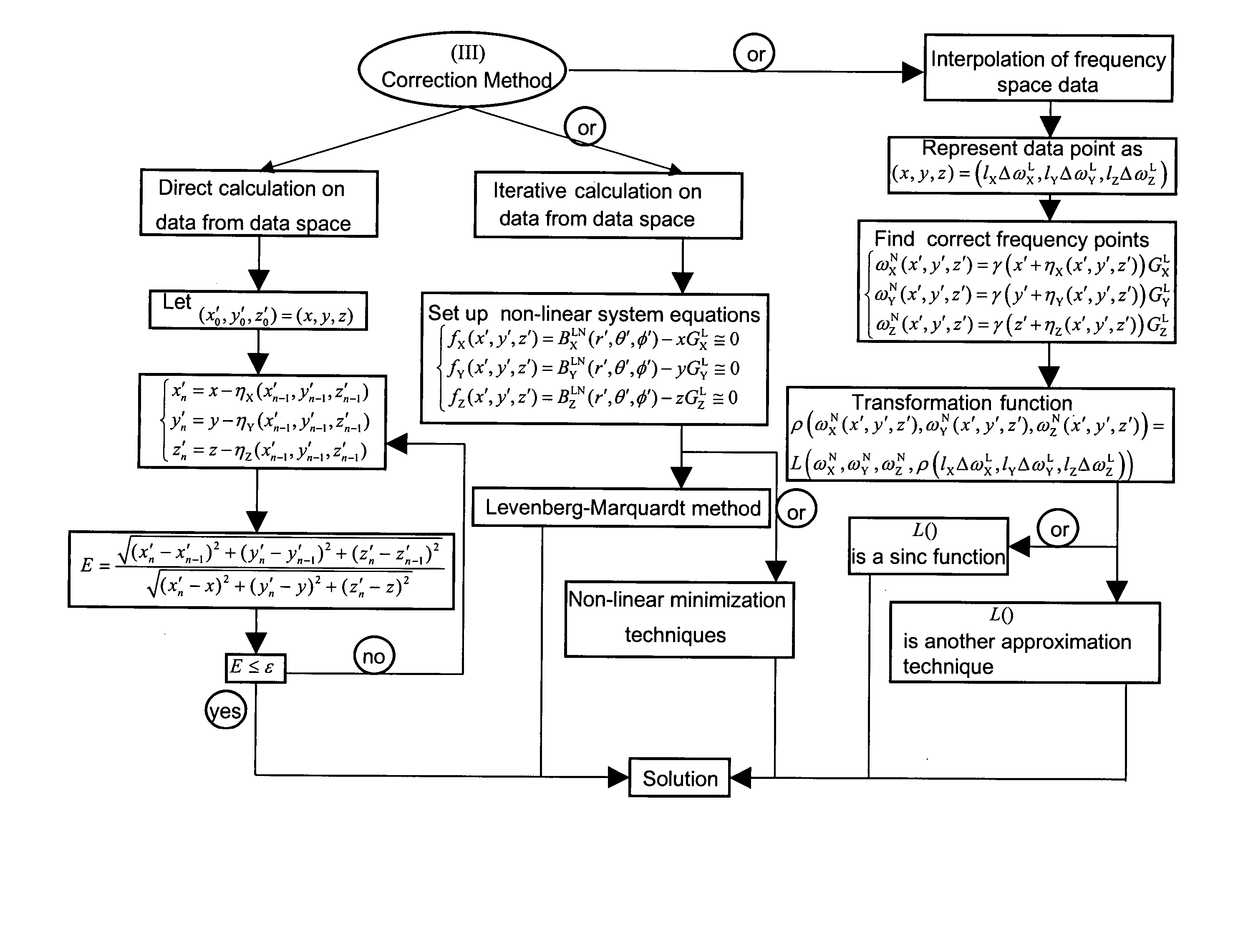
Correction of magnetic resonance images
InactiveUS20050024051A1Avoid artifactsAccurate imagingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientFourier transform on finite groups
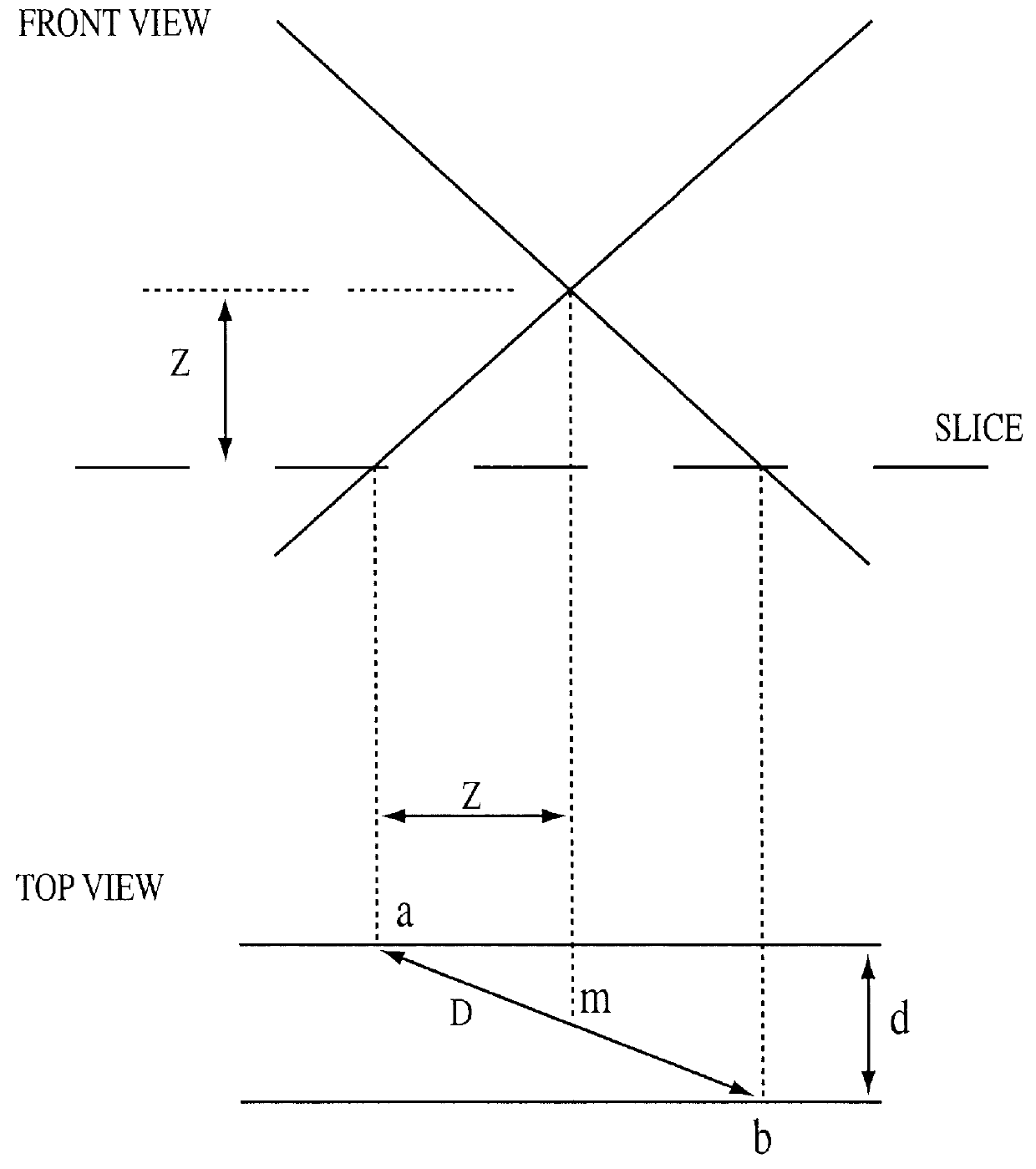
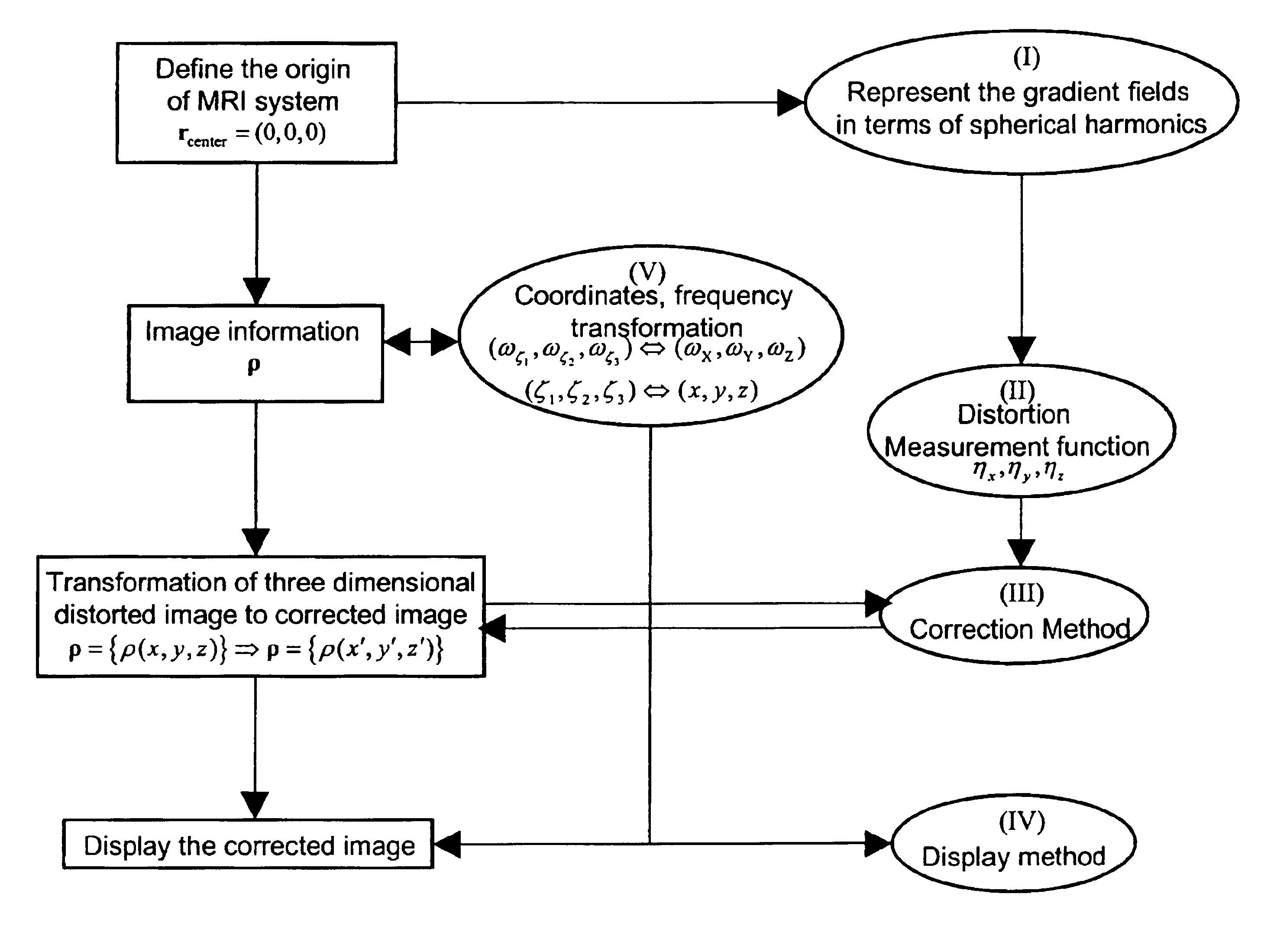
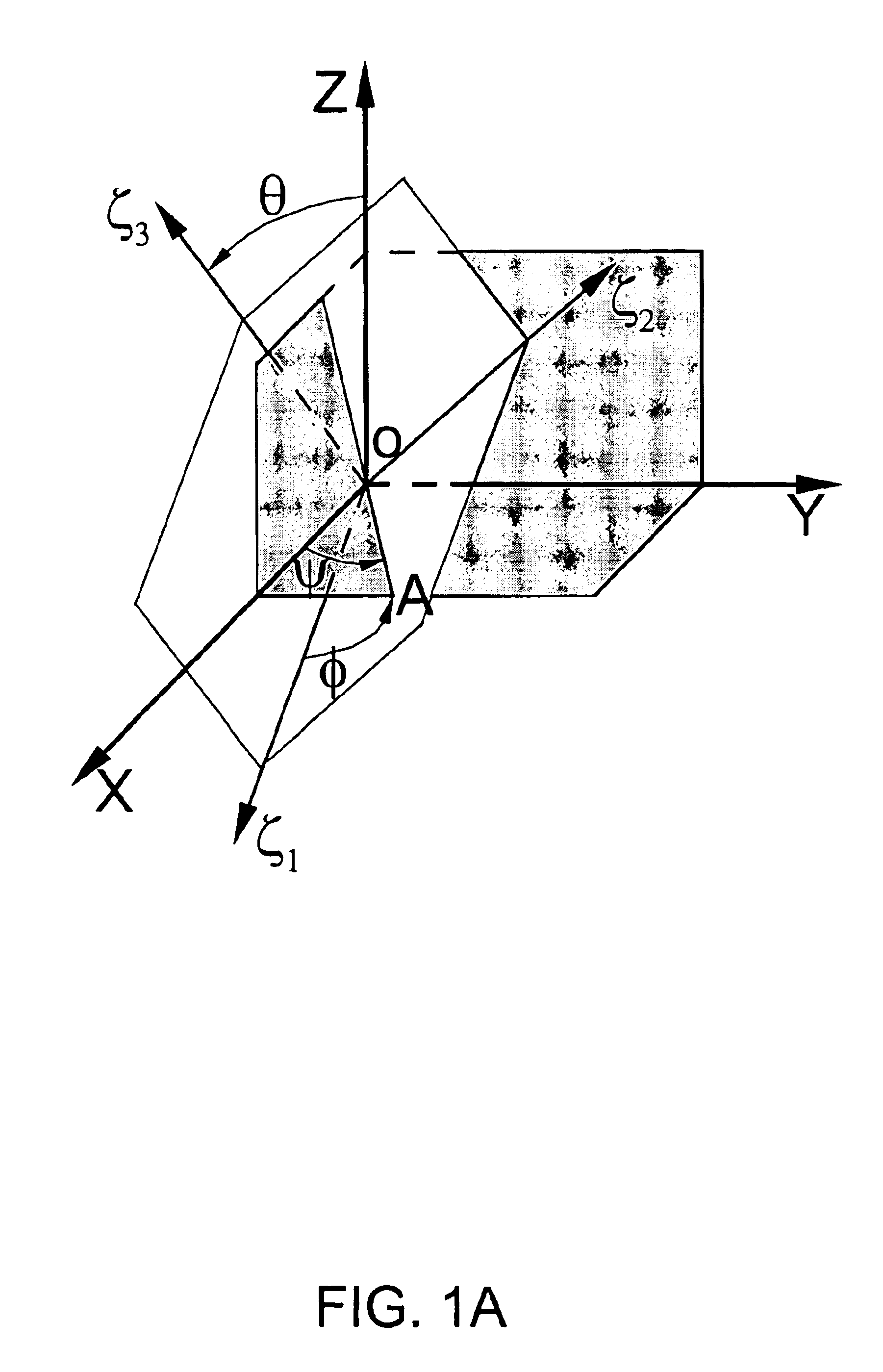
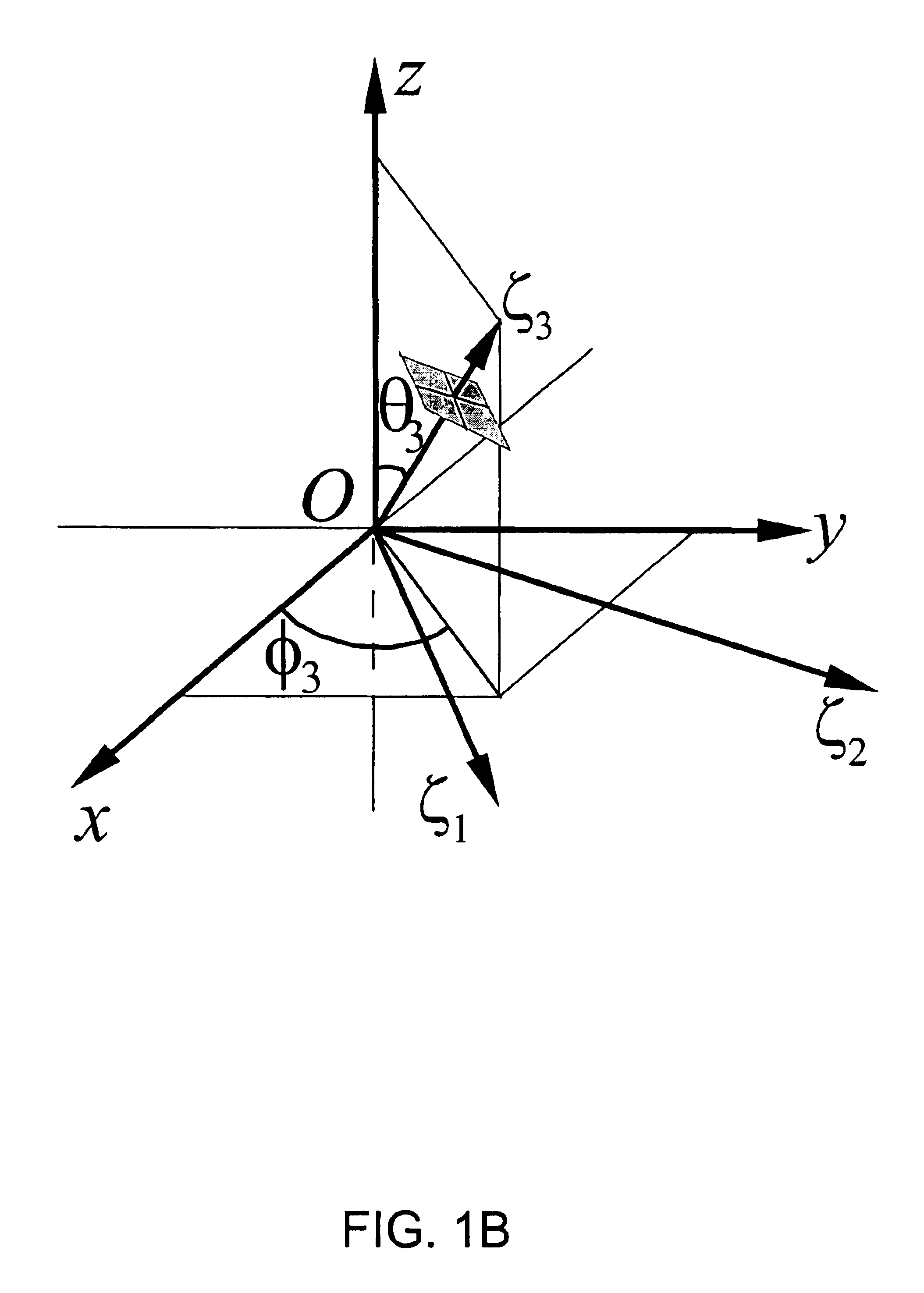
Spatial encoding in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques is achieved by sampling the signal as a function of time in the presence of magnetic field gradients, e.g., X, Y, and Z gradients. The gradient magnets have in the past been assumed to generate a linear gradient, and typical image reconstruction techniques have relied upon this assumption. However, to achieve high speed performance, gradient magnets often sacrifice linearity for speed. This non-linearity, in turn, results in distorted images, the distortion often being sufficiently large to compromise the usefulness of MRI images for stereotaxy or longitudinal studies, where precise volumetric information is required. The disclosure provides practical methods for correcting distorted images resulting from such non-linearity in the gradient fields, as well as distortions resulting from translational, rotational, and / or winding / design errors in the field generating devices. The methods employ spherical harmonic expansions of the gradient fields and fast Fourier transform techniques to provide well-corrected images without undue computational burdens.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
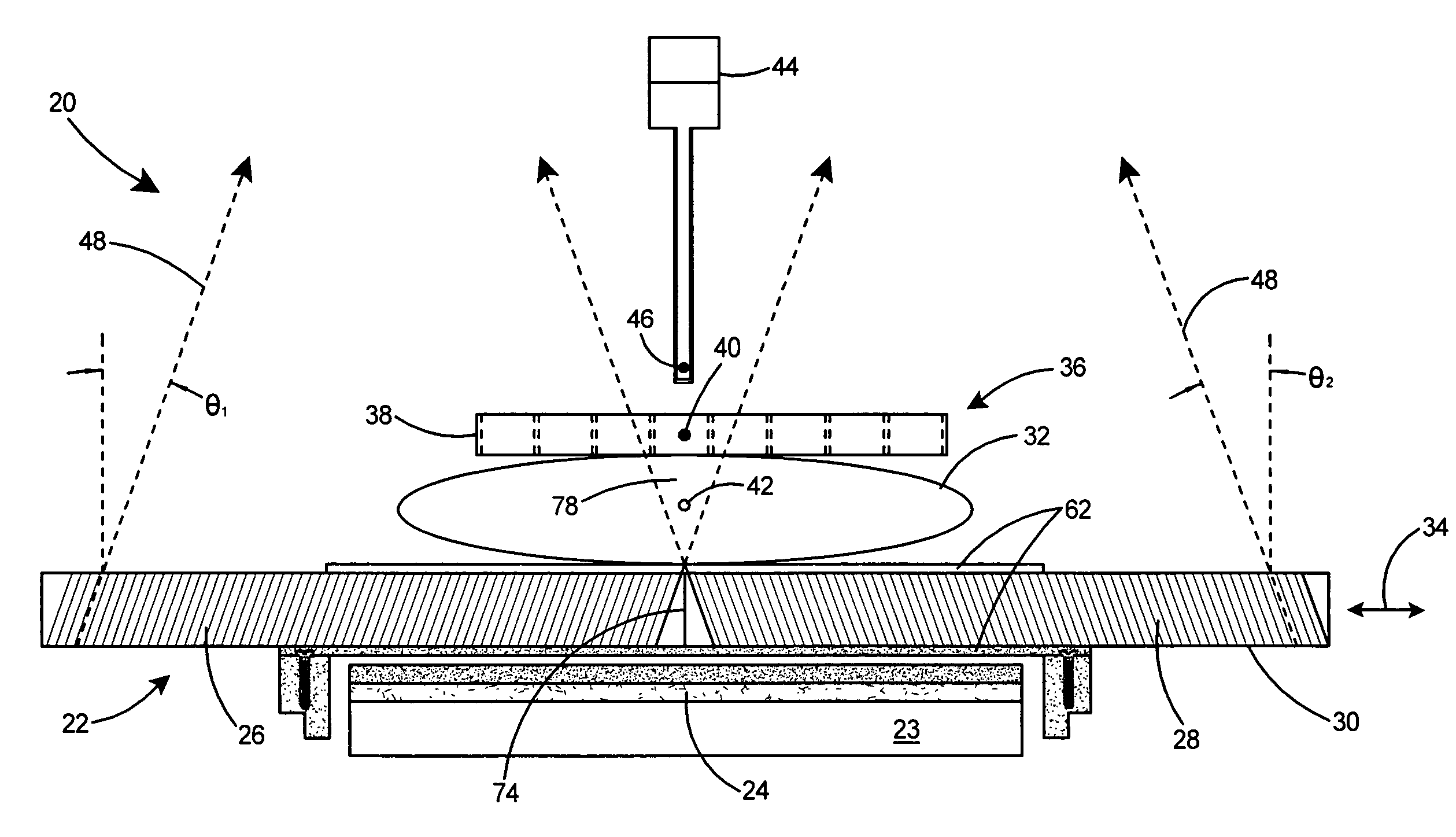
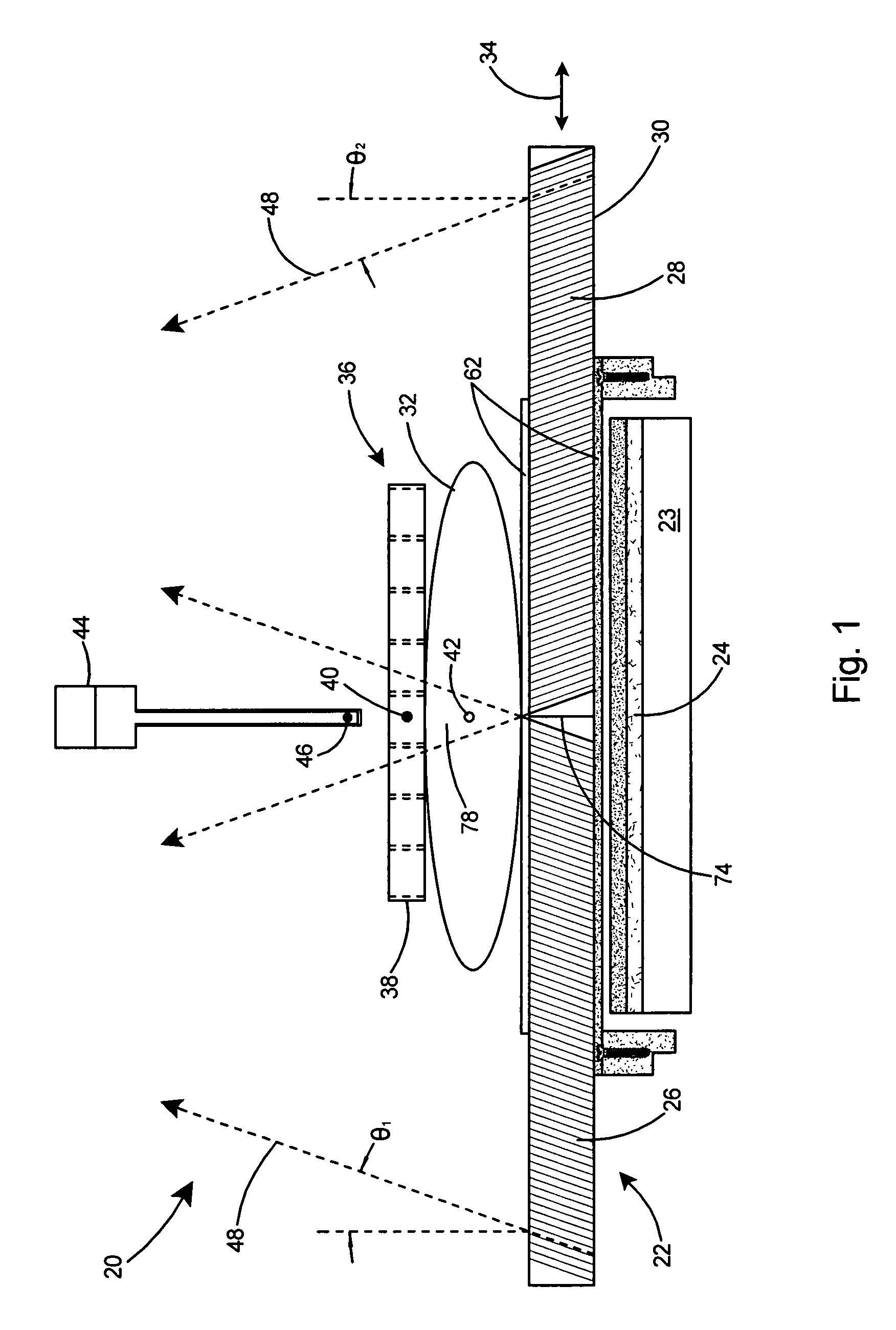
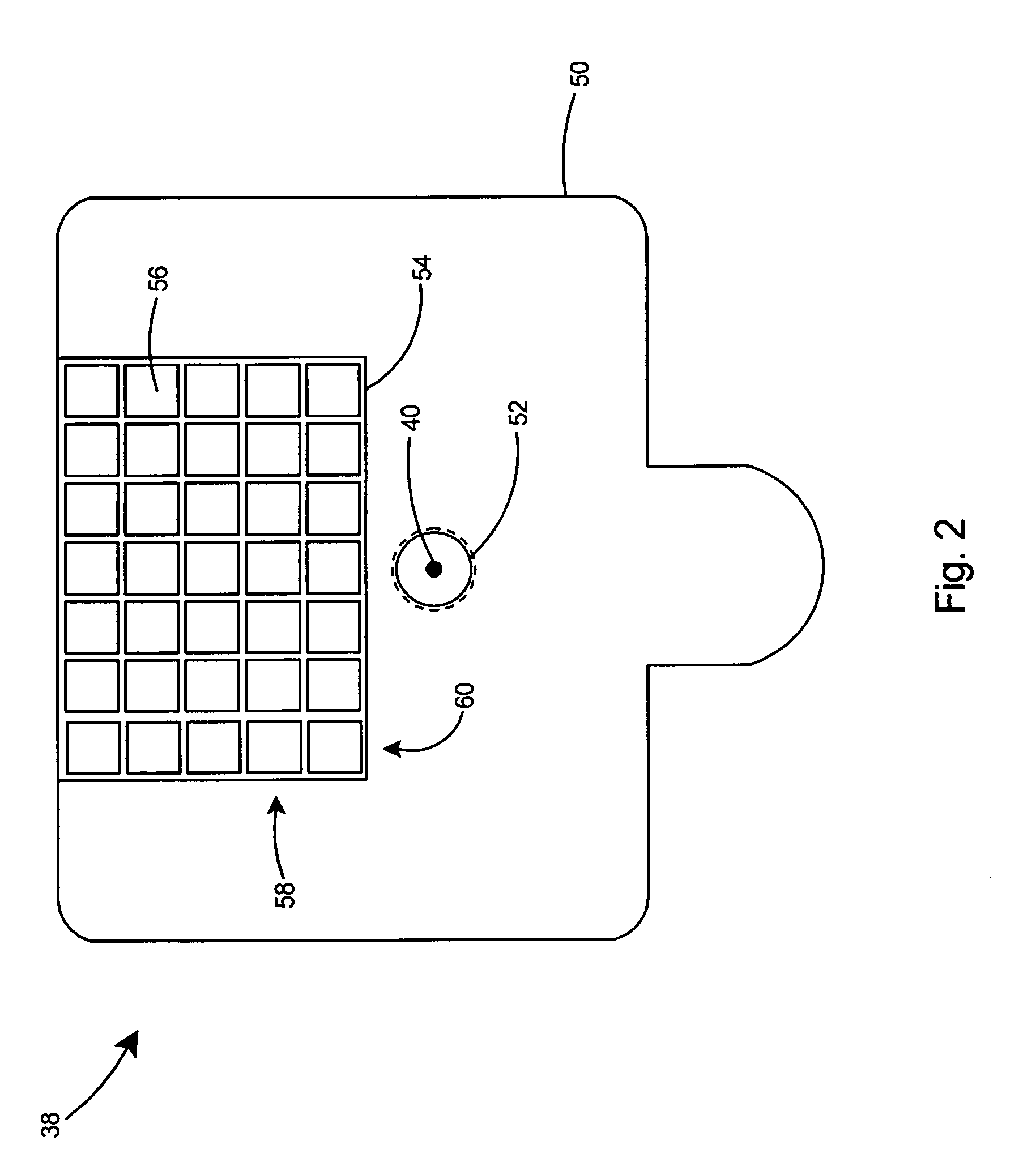
Systems and methods for frameless image-guided biopsy and therapeutic intervention
ActiveUS8758263B1Enhances patient comfortEliminate riskSurgical navigation systemsVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsComputed tomographyStereotaxy
A system and a method of performing a frameless image-guided biopsy uses imaging, a six-dimensional robotic couch system, a laser guidance system, an optical distance indicator, and a needle control apparatus. A planning CT scan is made of the patient with stereotactic fiduciary markers to localize and produce digitally reconstructed radiographs. Two stereoscopic images are generated using an imaging device to visualize and identify a target tumor. The images are fused with the digitally reconstructed radiographs of the planning CT scan to process tumor location. The tumor location data are communicated to the movable robotic couch to position the target tumor of the patient at a known isocenter location. A biopsy needle is guided with a laser alignment mechanism towards the isocenter at the determined depth using a needle positioning apparatus and an Optical Distance Indicator, and a biopsy sample of the target tumor is obtained.
Owner:VOXEL RAD
Small animal brain three-dimensional positioning system for magnetic resonance imaging scanning equipment
The invention relates to the technical field of medical experimental facilities, and discloses a small animal brain three-dimensional positioning system for magnetic resonance imaging scanning equipment. The system comprises a magnetic compatibility small animal brain three-dimensional positioning device used for conducting brain three-dimensional positioning on the head of a small animal and a magnetic resonance small animal radio frequency coil device which is used for receiving a magnetic resonance radio frequency signal in the X axis direction and transmitting the signal to a magnetic resonance imaging system. According to the system, in the piercing implementation process, magnetic resonance scanning can be carried out on an experimental animal, the magnetic resonance radio frequency signal is received through the small animal radio frequency coil, the signal is transmitted to the magnetic resonance imaging system, a magnetic resonance scanning image can be utilized for guiding and monitoring the piercing process, the magnetic resonance imaging scanning equipment can be utilized for guiding a small animal three-dimensional positioning operation or conducting positioning experiments such as piercing and stimulation exertion.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for locating an element of interest contained in a three-dimensional object, in particular during a stereotactic investigation in the X-ray examination of the breast
InactiveUS7035450B1Shorten the construction periodImprove matchImage enhancementImage analysisSelection criterionErrors and residuals
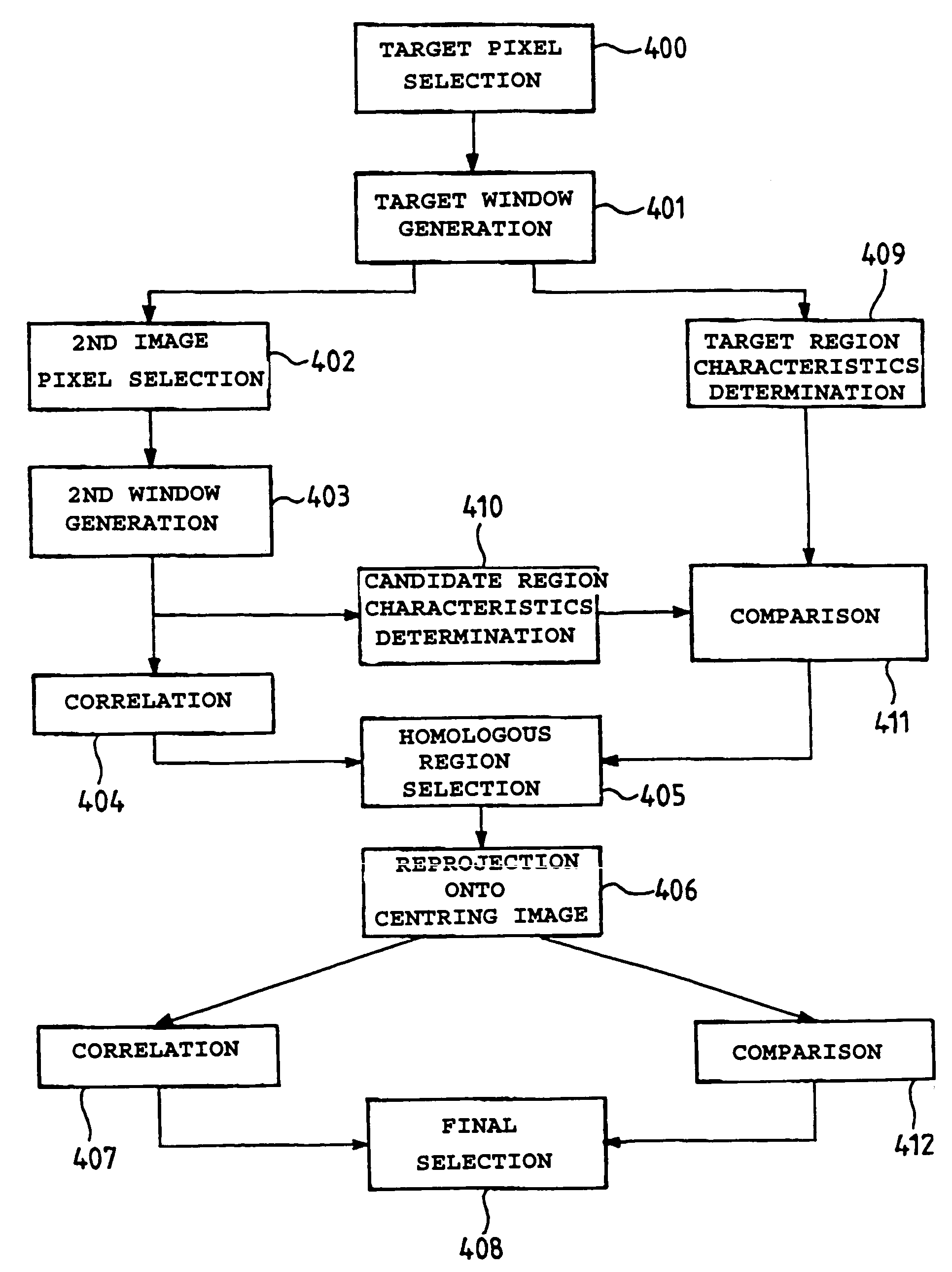
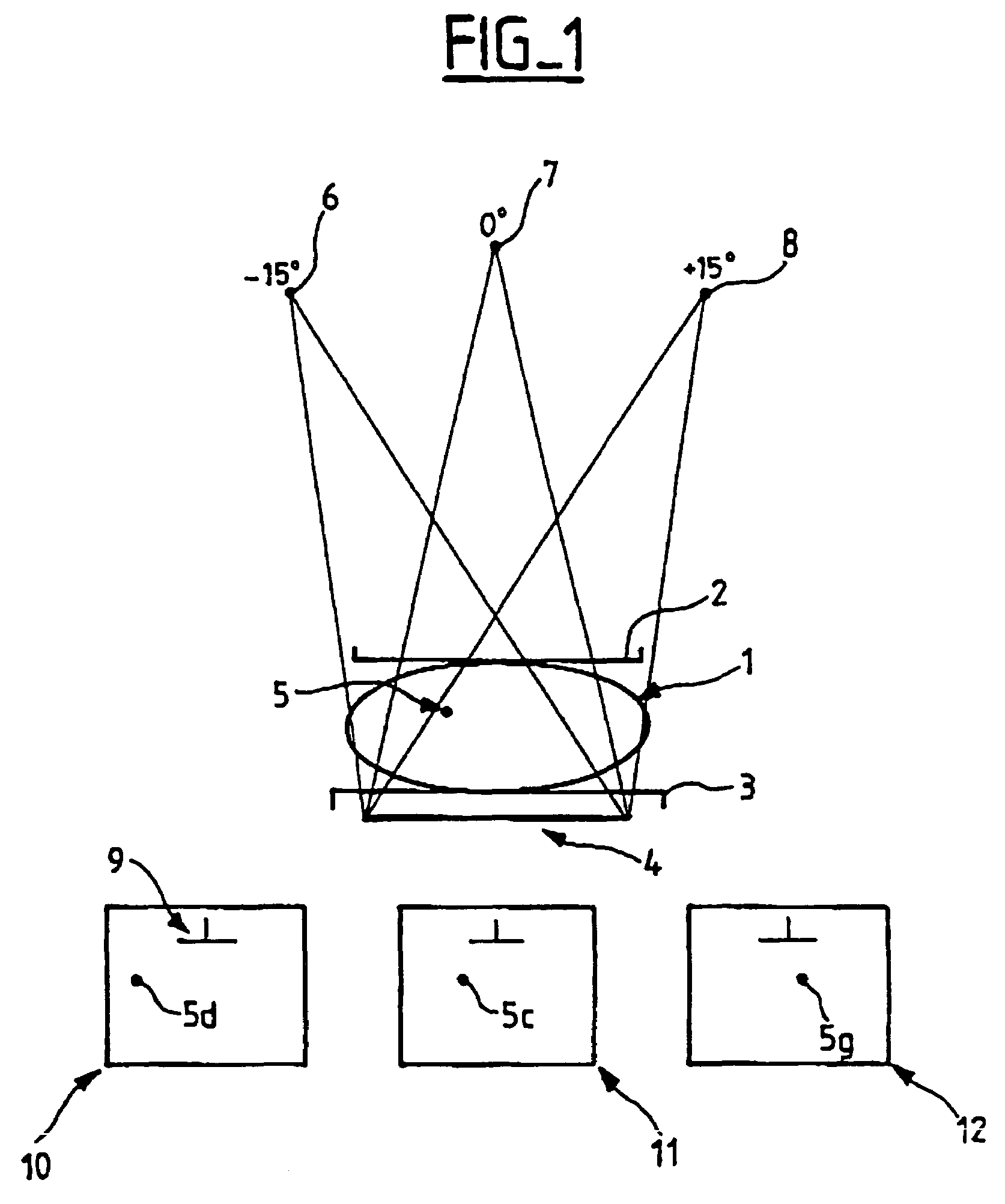
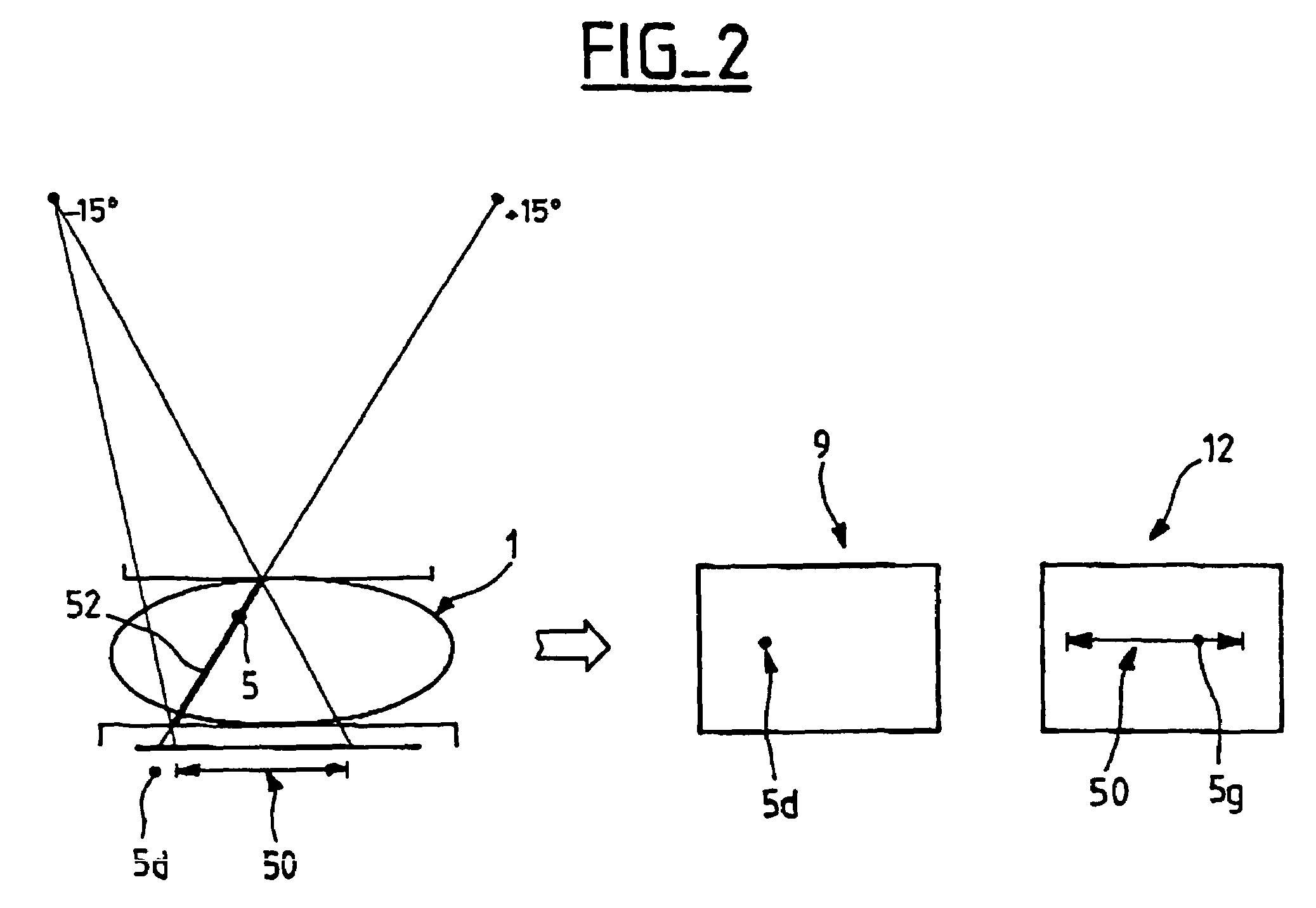
The stereotaxic images being digitized, a target pixel in a target region of interest is selected, a target window of chosen dimensional characteristics and containing the said target region of interest is generated around the selected target pixel, a set of pixels is determined in a second image, according to a predetermined selection criterion, a second window, of the same dimensional characteristics as the said target window, is generated around each selected pixel, a correlation processing between the grey-scale levels of the pixels of each second window and the grey-scale levels of the pixels of the target window is carried out so as to obtain a correlation value for each second window, and the region of interest homologous to the target region of interest is identified on the basis of the analysis of the set of correlation values thus obtained, so as to minimize the risks of matching error between the homologous regions of interest. The element of interest is then located on the basis of the positions of the two homologous regions.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYSTEMS INC
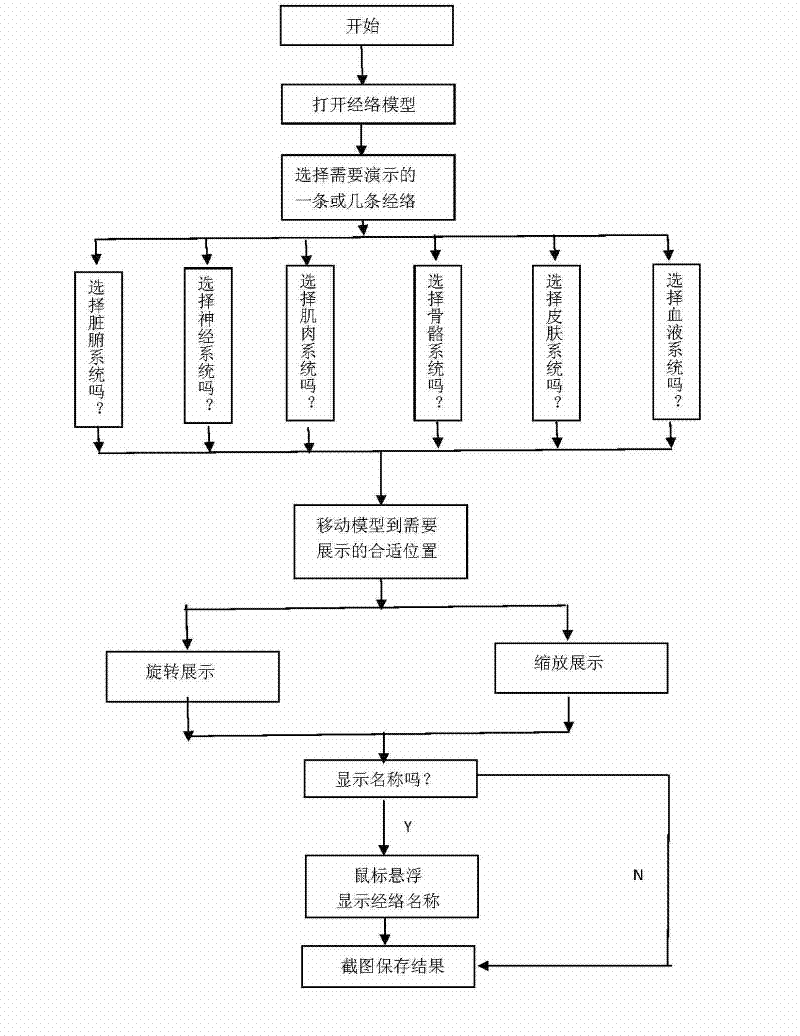
Three-dimensional meridian and acupoint positioning method under 3D MAX (three-dimensional Studio Max) environment
InactiveCN102393880AAcupoint selection is accurateClear pictureSpecial data processing applications3D-image renderingHuman body3d image
The invention belongs to the application field of traditional Chinese medicine meridian doctrine and acupuncture and moxibustion medical skill, in particular to a three-dimensional meridian and acupoint positioning method under a 3D MAX (Three-dimensional Studio Max) environment, which comprises the following steps of: (1) generating a real three-dimensional image of a human body by adopting a virtual reality technology; (2) constructing 3D meridian and acupoint models on a computer by utilizing a 3D model of the human body; (3) carrying out image combination processing to the real three-dimensional image of the human body and the 3D model of the human body so as to enable the images to be overlapped; and (4) comparing and correcting the meridian and acupoint data of the 3D model of the human body, finally forming the real meridian and acupoint data of the human body, and storing the data into a preset database. According to the invention, on the computer, meridians and acupoints are shown on skeletons, muscle, vessels, nerves, lymph, visceral organs and other related positions of the model in the 3D form by a three-dimensional way, so that the error that human body epidermis needle-inserting points are used as meridians and acupoints by mistakes can be corrected, and the defects of the traditional two-dimensional drawing or three-dimensional reality model in expression of meridians and acupoints of the human body can be overcome.
Owner:韩红
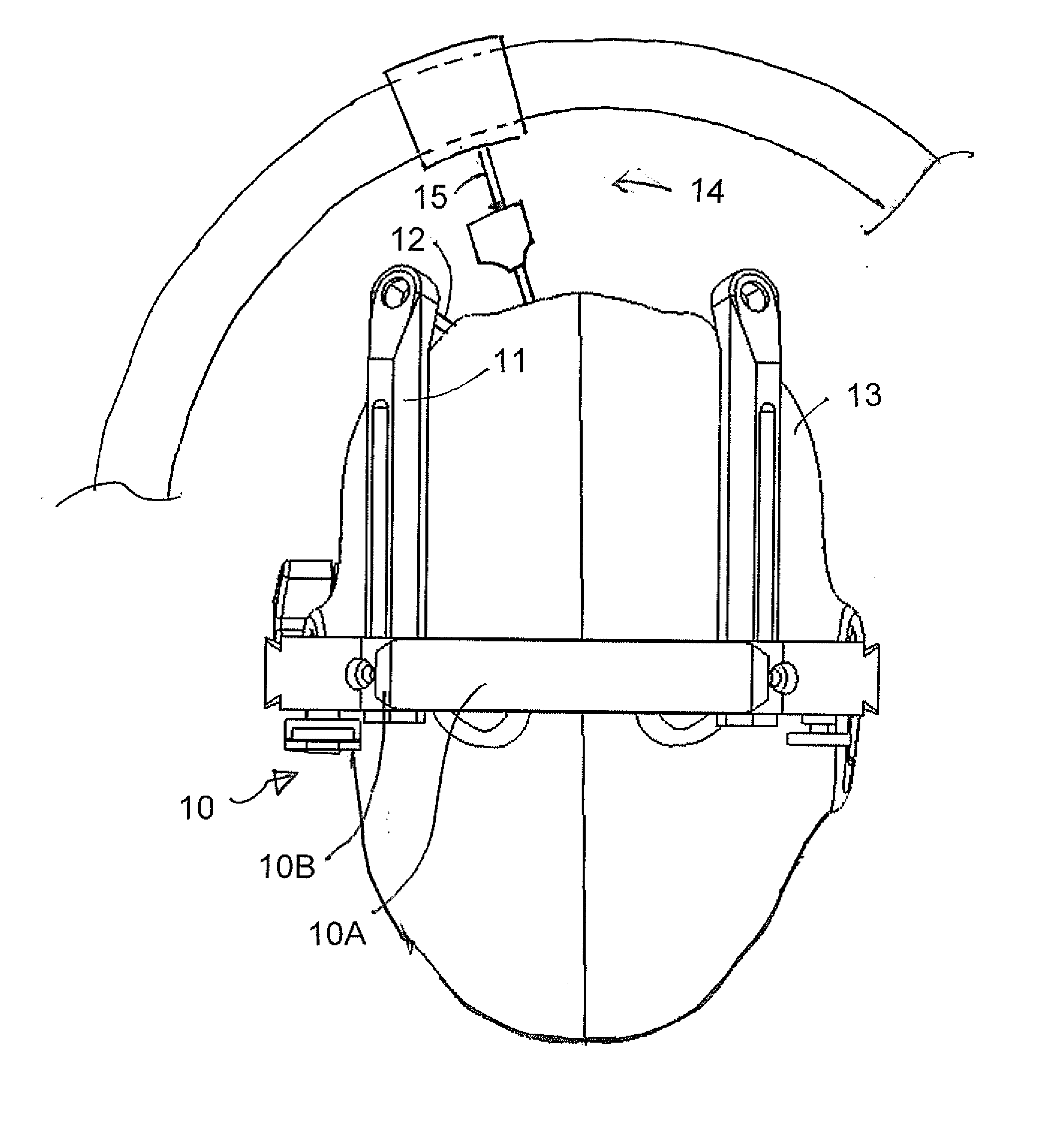
Versatile stereotactic device
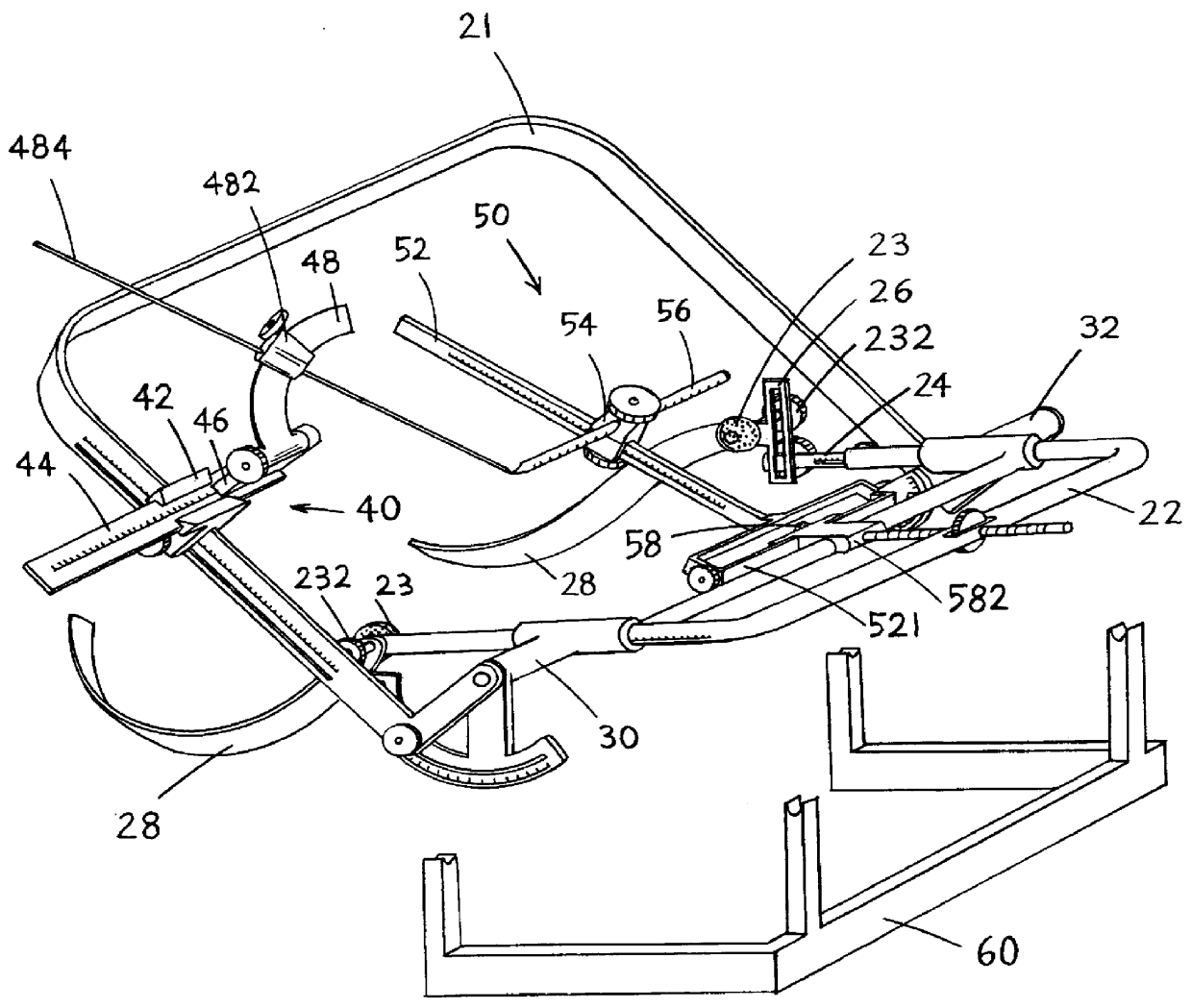
InactiveUS6080164AAccurate and reproducible resultEasy to useComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringFollow up examinationNon invasive
A stereotactic device for use with an imager is disclosed, which permits an imaging scan to be taken with reference to a personal coordinate system (or PCS) that is independent of a machine coordinate system (or MCS). Methods using the device to obtain imaging scans are described such that the imaging scans are superimposable even if taken at different time periods using the same or a different imager. The device comprises a frame that can be reproducibly positioned on a subject and which is equipped with non-invasive affixing means and localizing means that provide the PCS. The device and methods of the invention are particularly well suited for routine initial or follow-up examinations, pre-surgical planning and post-surgical evaluation.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Correction of magnetic resonance images
InactiveUS7088099B2Reduce computing timeExtension of timeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientSpatial encoding
Spatial encoding in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques is achieved by sampling the signal as a function of time in the presence of magnetic field gradients, e.g., X, Y, and Z gradients. The gradient magnets have in the past been assumed to generate a linear gradient, and typical image reconstruction techniques have relied upon this assumption. However, to achieve high speed performance, gradient magnets often sacrifice linearity for speed. This non-linearity, in turn, results in distorted images, the distortion often being sufficiently large to compromise the usefulness of MRI images for stereotaxy or longitudinal studies, where precise volumetric information is required. The disclosure provides practical methods for correcting distorted images resulting from such non-linearity in the gradient fields, as well as distortions resulting from translational, rotational, and / or winding / design errors in the field generating devices. The methods employ spherical harmonic expansions of the gradient fields and fast Fourier transform techniques to provide well-corrected images without undue computational burdens.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
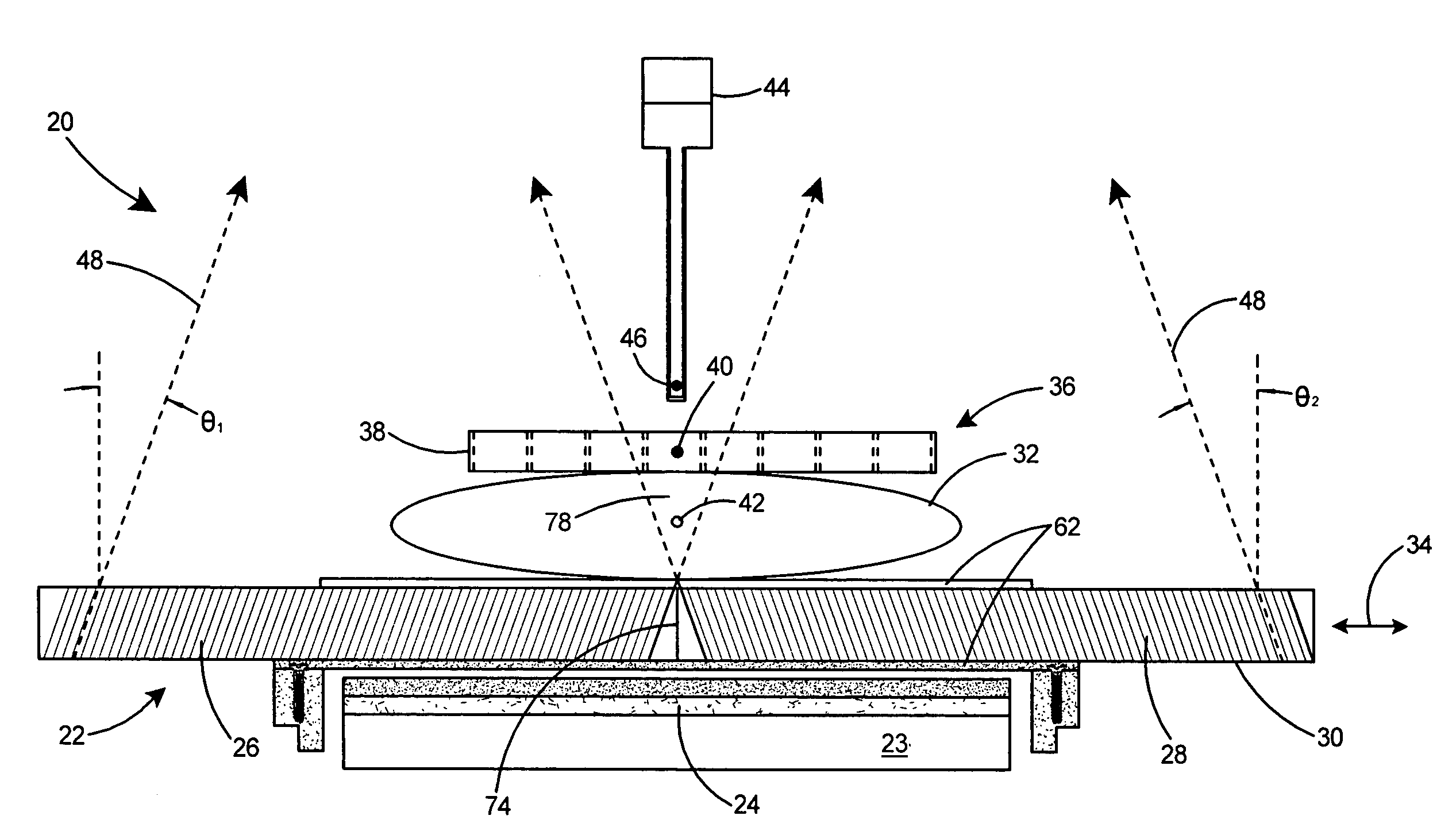
Needle breast biopsy system and method of use
ActiveCN102481146AEasy to catchCapture suitable forSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTomosynthesisBiopsy procedure
A tilted needle biopsy assembly is provided for mounting on an x-ray system. Because the biopsy needle is angied relative to at least one of the detector and the x-ray source, x-ray imaging may be performed during the biopsy procedure without interference by the biopsy device. The angled biopsy needle additionally allows improved access to the axilla and chest wall of the patient. The stereotactic biopsy device of the present invention may be coupled to any x-ray system, whether upright or prone, including but not limited to mammography systems, tomosynthesis systems, and combination mammography / tomosynthesis systems. The system flexibly supports the use of any mode of image capture (i.e., scout, two dimensional mammogram, three-dimensional reconstructed volume) for either or both target visualization and target localization. With such an arrangement, a needle biopsy assembly having improved patient coverage is provided for use with a variety of different x-ray imaging platforms.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
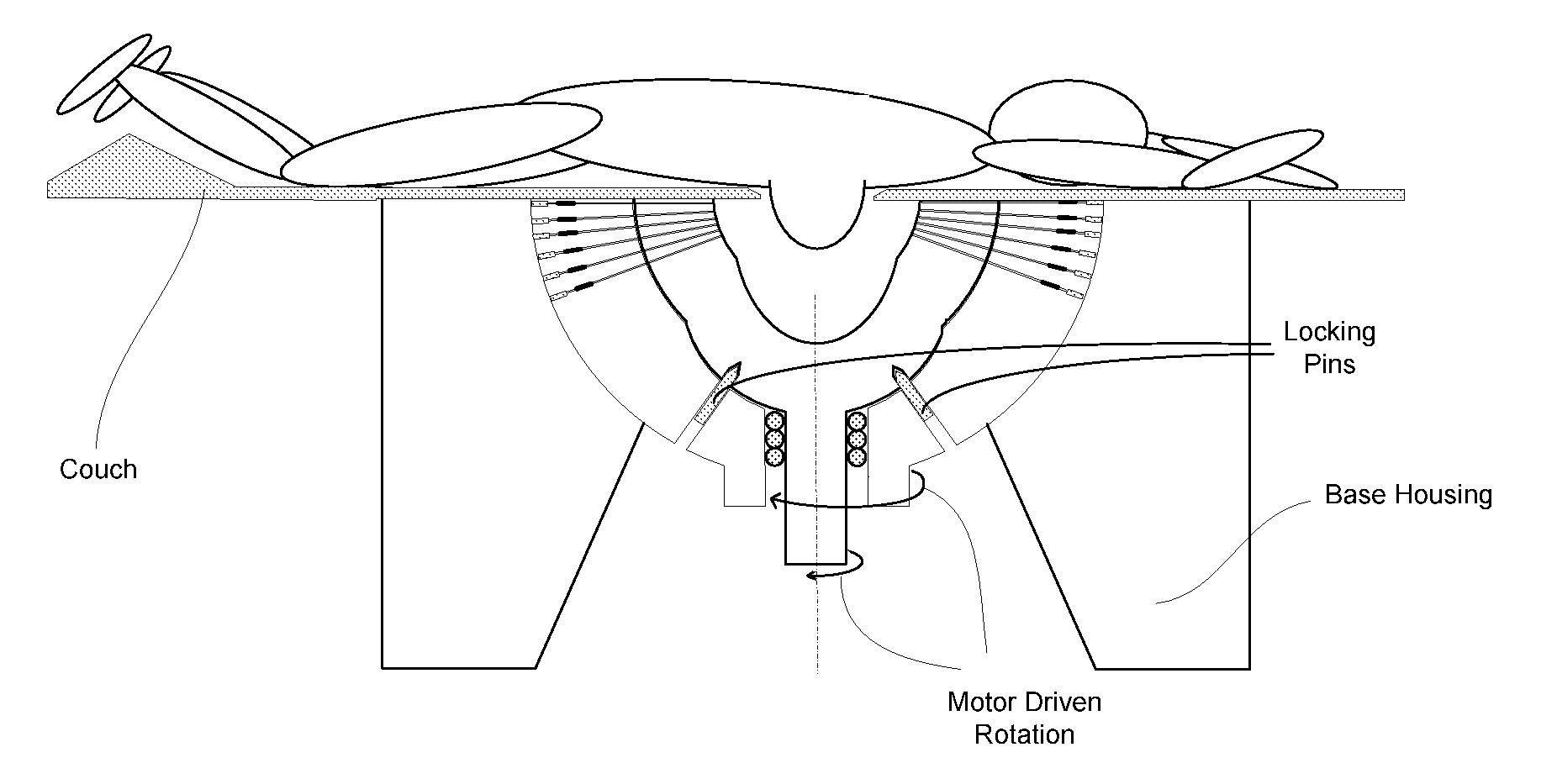
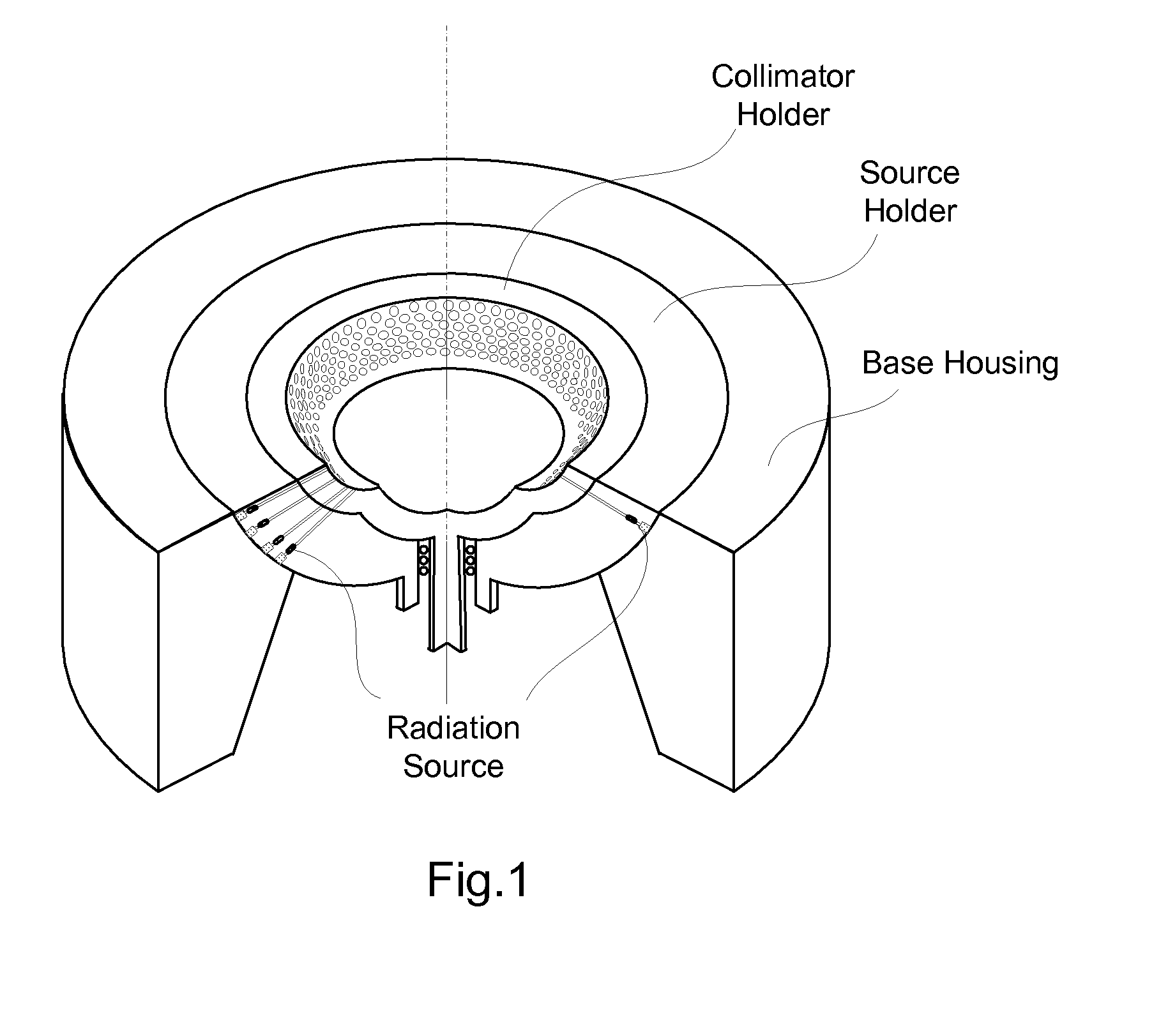
Gamma guided stereotactic localization system
InactiveUS20100016865A1Precise positioningPrecise supportSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringStereotactic localizationLocalization system
A stereotactic gamma-guided localization system for imaging a suspected cancer and guiding a physician in the removal of tissue samples for biopsy. The gamma-guided localization system includes a three step procedure including localization, correlation, and verification. The localization system includes a gamma camera with a set of slant-hole collimators for producing stereo images of a region of interest. A positioning system including a fiducial marker is placed adjacent to the object to be imaged and held rigidly in place to provide correlation of the location of the region of interest relative to the fiducial marker. A gamma emitting marker is then positioned at the calculated location of the region of interest and imaged to verify that that the calculated position corresponds to the actual location. The positioning system can then be used to accurately position and support any other hardware that needs to be positioned at the region of interest.
Owner:DILON TECH
Method and equipment for image-guided stereotactic radiosurgery of breast cancer
A method of treating a cancerous region in a breast of a patient comprising (i) imaging the breast in a three-dimensional coordinate system, (ii) stereotactically determining the location of the cancerous region in the breast, (iii) optionally determining the volume of the entire cancerous region to be treated, and (iv) while maintaining the breast in a three-dimensional coordinate system that is identical to or corresponds with the three-dimensional coordinate system used in (i), noninvasively exposing the cancerous region of the breast of the patient to a cancer-treatment effective dose of radiation; and equipment for use in such a method.
Owner:XCISION MEDICAL SYST +1
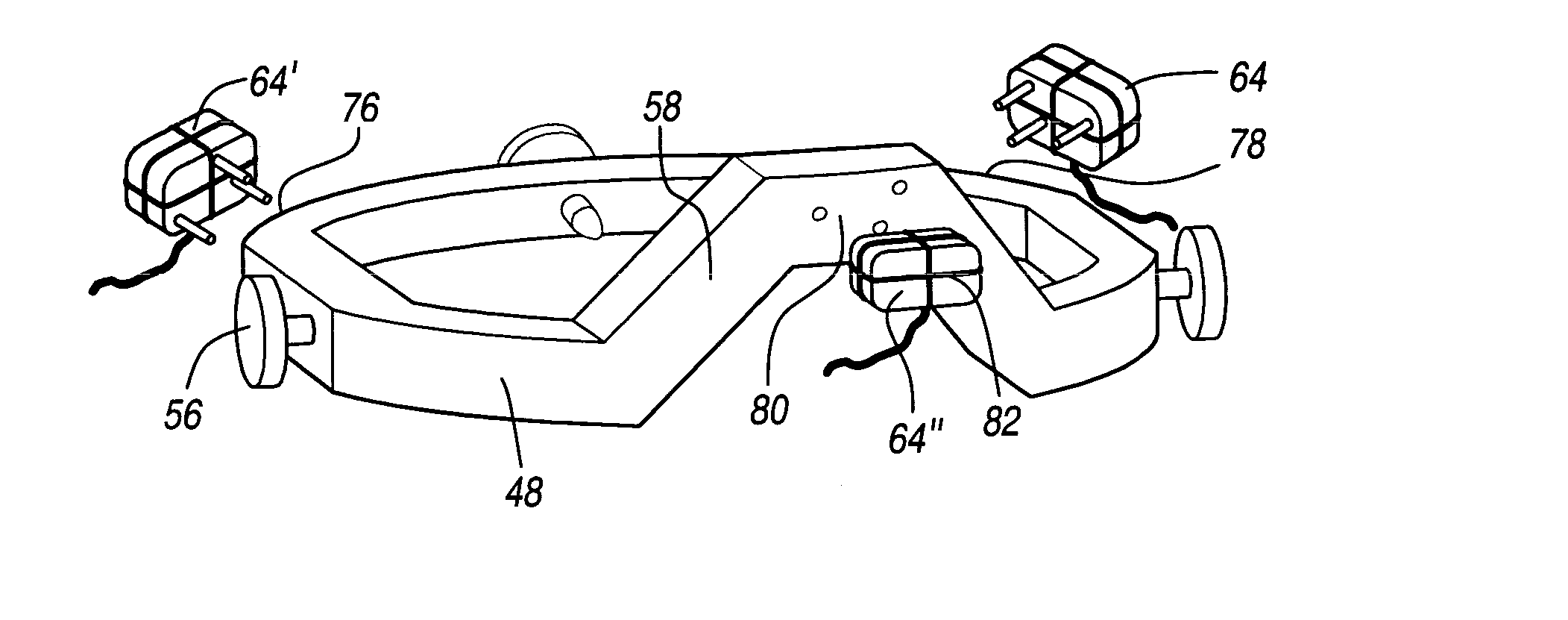
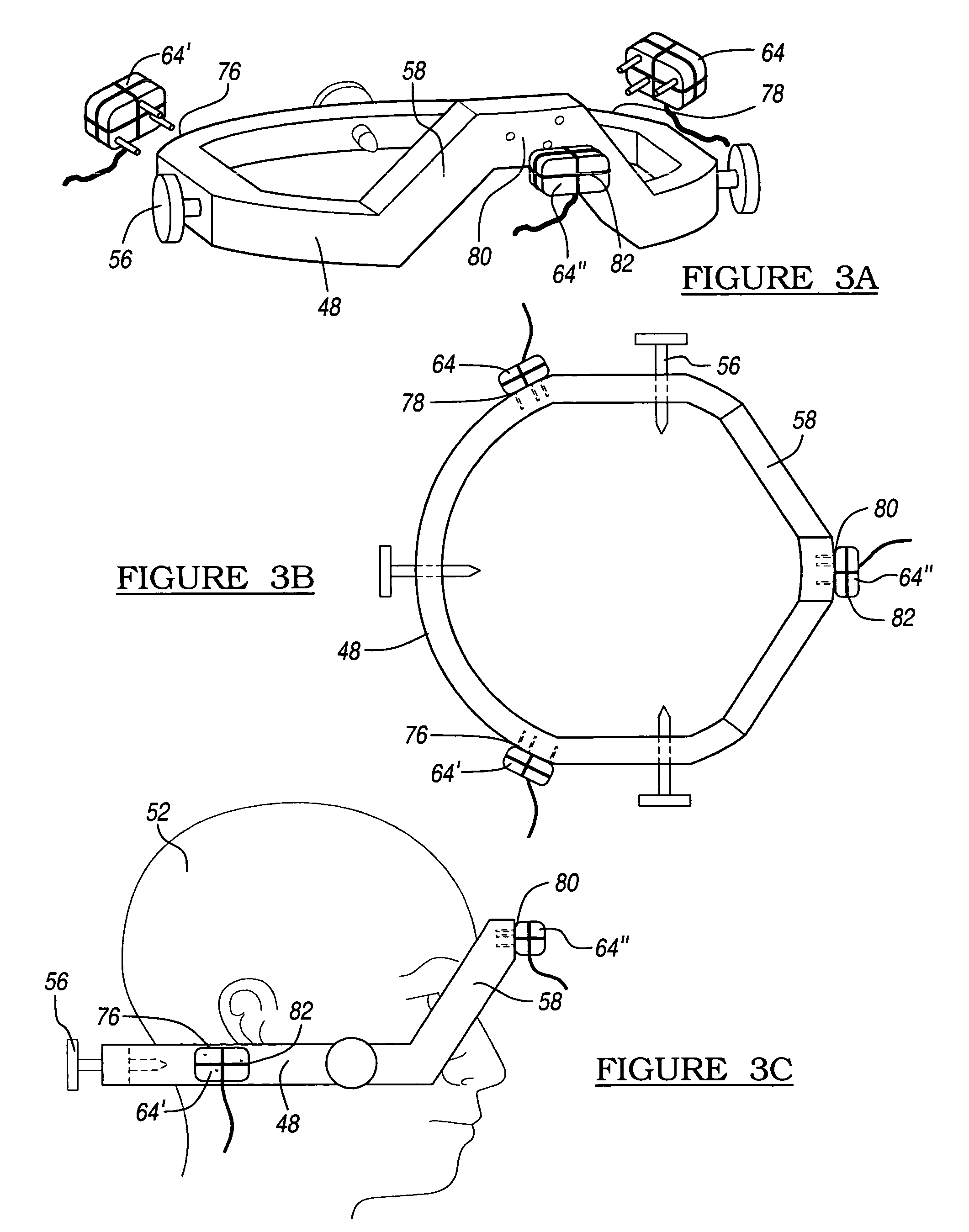
Stereotaxic detachable needle extension
InactiveUS20020007187A1Easy to insertDiagnosticsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryStereotaxyBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for positioning instrumentation into a target region of a brain generally includes an attachment member, specifically a disc adapted to be secured to a cranium, and a marker assembly adapted to be connected to a locator device, for example a conventional stereotaxic assembly. The marker assembly includes a detachable cannula, and is further adapted to be secured to the attachment member in order to immobilize the cannula at a precise position in the brain, thus facilitating additional imaging of the patient in order to determine the position of the cannula with respect to the target region.
Owner:CYTORI THERAPEUTICS INC
Method and equipment for image-guided stereotactic radiosurgery of breast cancer
ActiveCN101541236ASterographic imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringRadiosurgeryStereotactic neurosurgery
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE +1
Systems and methods for frameless image-guided biopsy and therapeutic intervention
ActiveUS20150018842A1High precisionAdverse effectSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsComputed tomographyLocation Equipment
A system and a method of performing a frameless image-guided biopsy uses imaging, a six-dimensional robotic couch system, a laser guidance system, an optical distance indicator, and a needle control apparatus. A planning CT scan is made of the patient with stereotactic fiduciary markers to localize and produce digitally reconstructed radiographs. Two stereoscopic images are generated using an imaging device to visualize and identify a target tumor. The images are fused with the digitally reconstructed radiographs of the planning CT scan to process tumor location. The tumor location data are communicated to the movable robotic couch to position the target tumor of the patient at a known isocenter location. A biopsy needle is guided with a laser alignment mechanism towards the isocenter at the determined depth using a needle positioning apparatus and an Optical Distance Indicator, and a biopsy sample of the target tumor is obtained.
Owner:VOXEL RAD
Method and apparatus for MR-guided biopsy
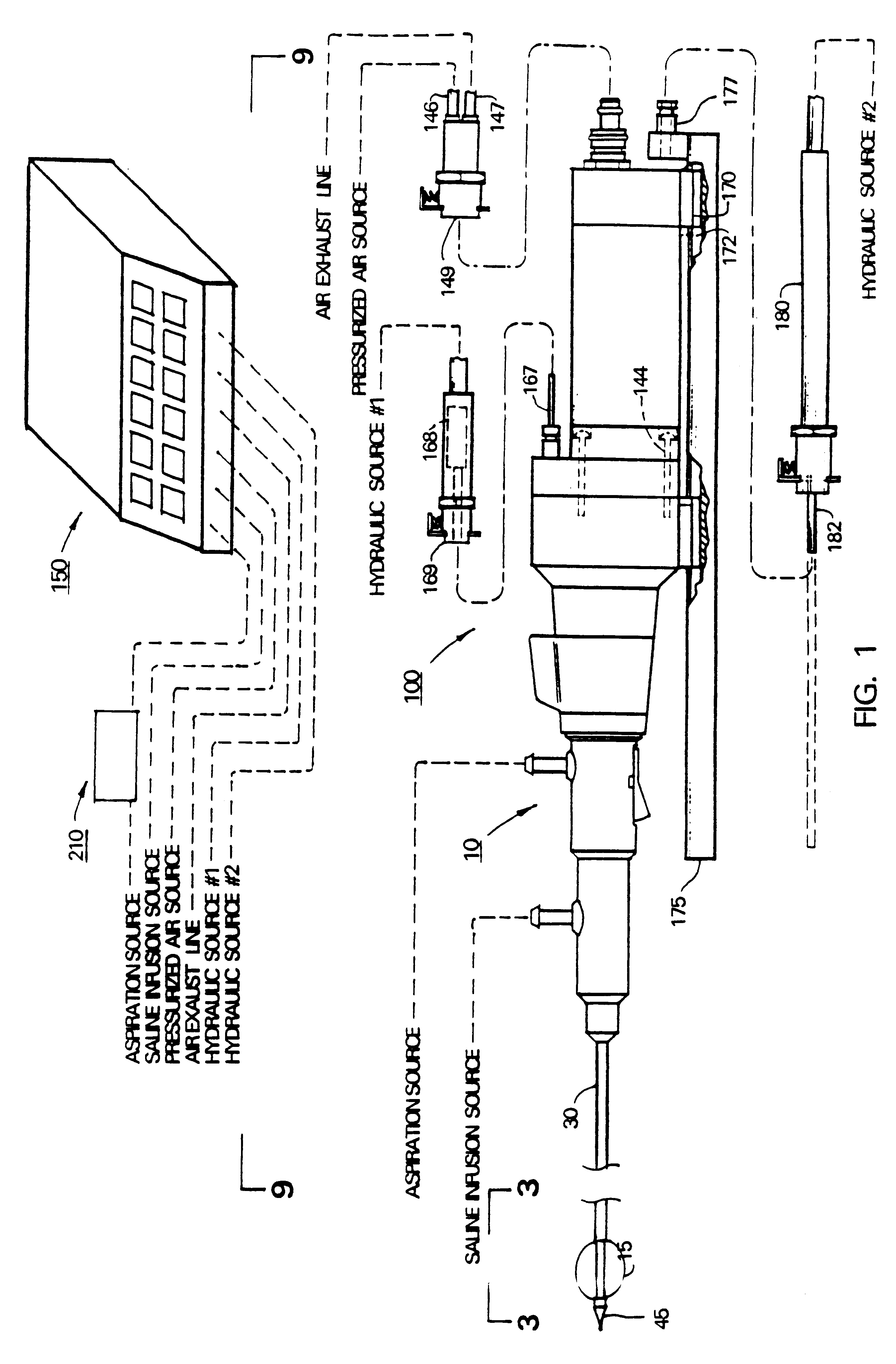
An MR-guided biopsy, for example, prostate biopsy, is performed by a mechanical tool for stabilizing the patient in prone position and for guiding the biopsy needle into defined targeted lesions in the prostate gland. The patient can lay prone in the MRI. The apparatus can guide an MR-visible, sterile needle sleeve, which can have a hollow tube filled with contrast media, through the anus onto the inner wall of the colon. Due to the visibility of the contrast media in the sleeve, the apparatus can be guided to the exact position. The sleeve can incorporate a tube within the contrast media filled sleeve to insert the biopsy needle and to push this needle forward into the prostate. The apparatus can utilize various mechanical mechanisms to stereotactically move the needle or needle sleeve in various directions.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Fiducial marker and method for gamma guided stereotactic localization
ActiveUS20100016713A1Accurate locationPrecise positioningSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic markersStereotactic localizationTissue sample
A fiducial marker for use in a gamma-guided stereotactic localization system for imaging a suspected cancer and guiding a physician in the removal of tissue samples for biopsy. The fiducial marker includes a fiducial source that can be accurately located in a positioning system and used to correlate the location of the positioning system with the detector and therefore the region-of-interest. The fiducial can be made radioactive such that it can be seen by the gamma camera. The fiducial marker enables the accurate positioning of other hardware in proximity to the object to be viewed.
Owner:SMART BREAST CORP
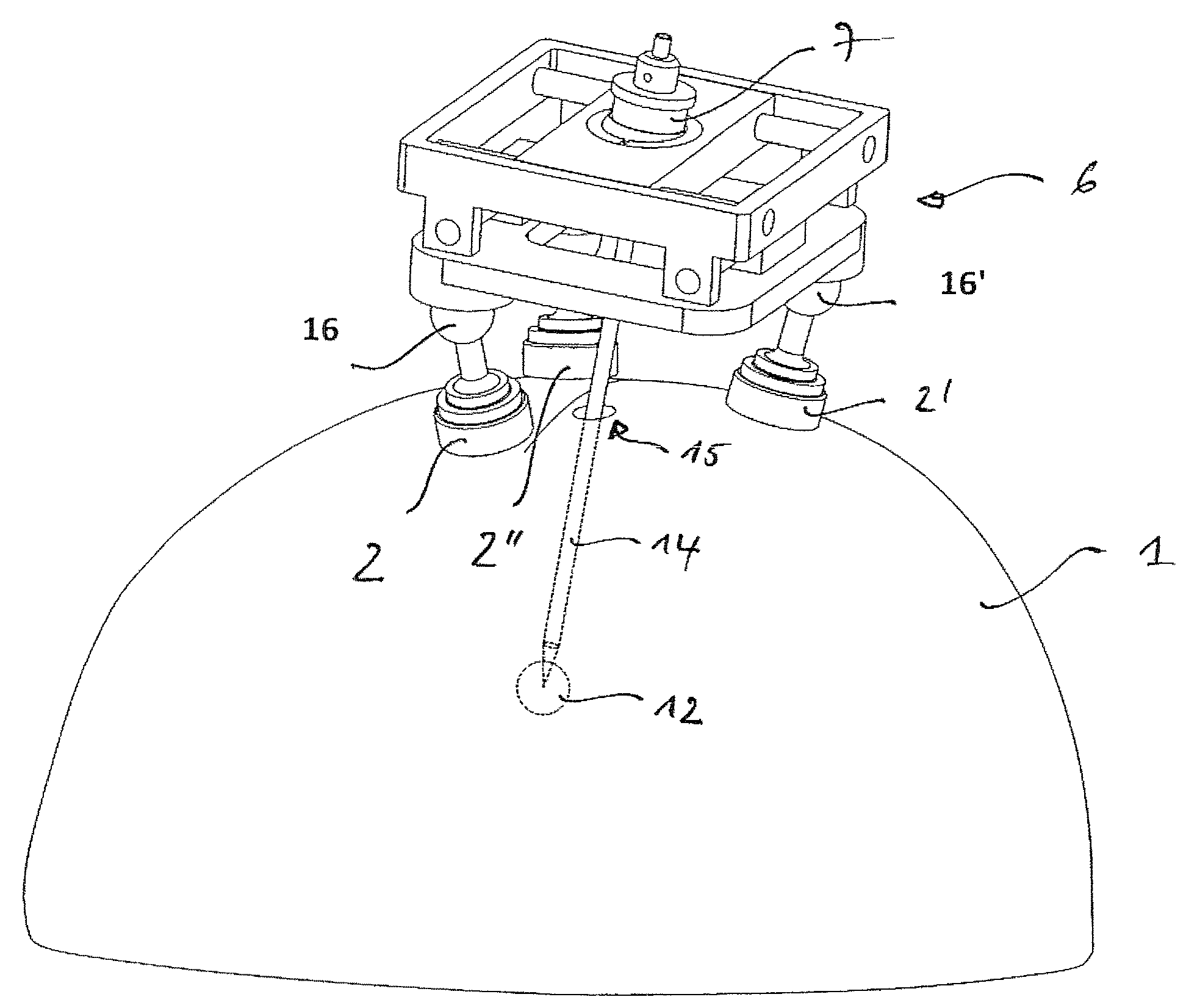
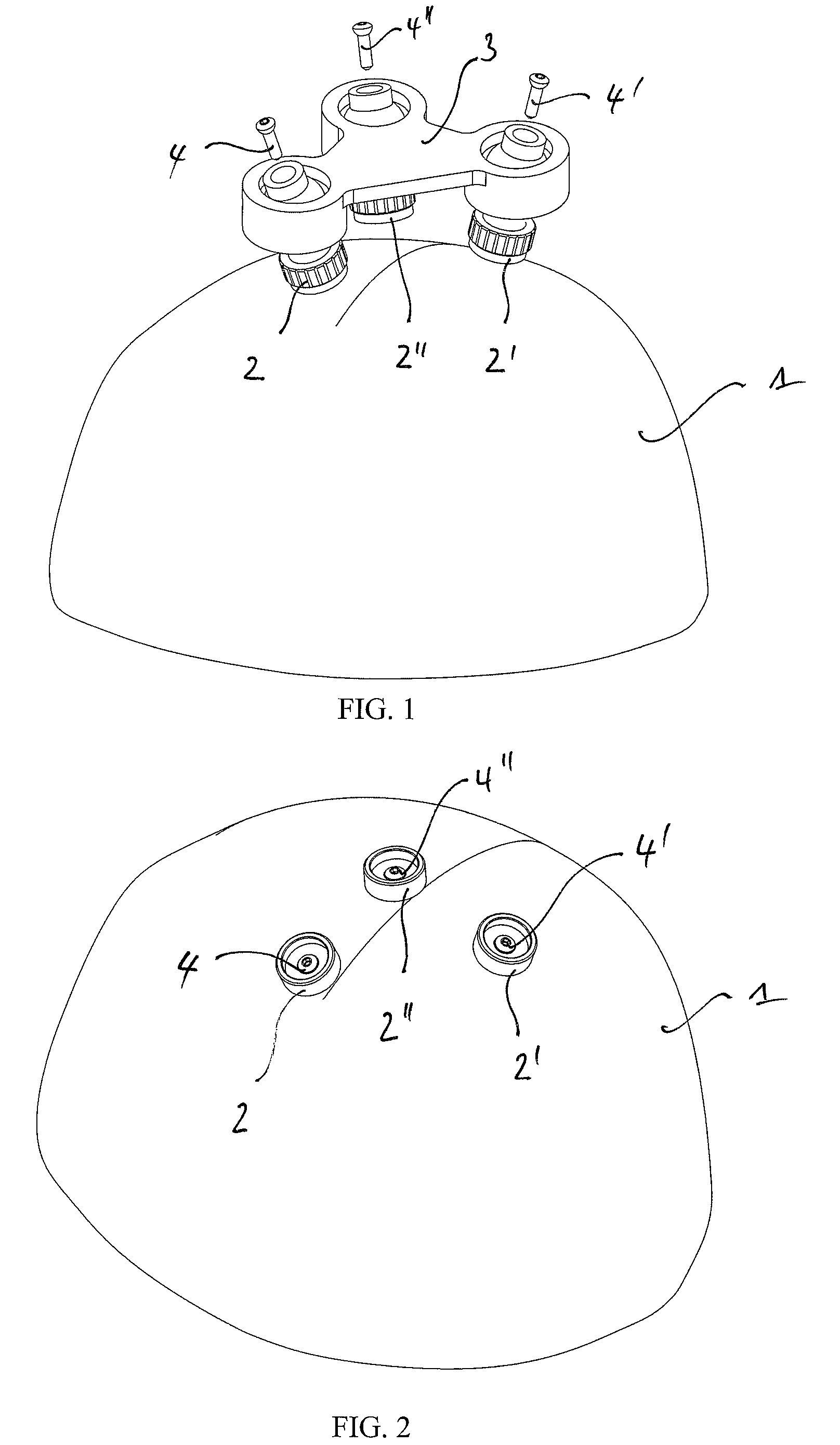
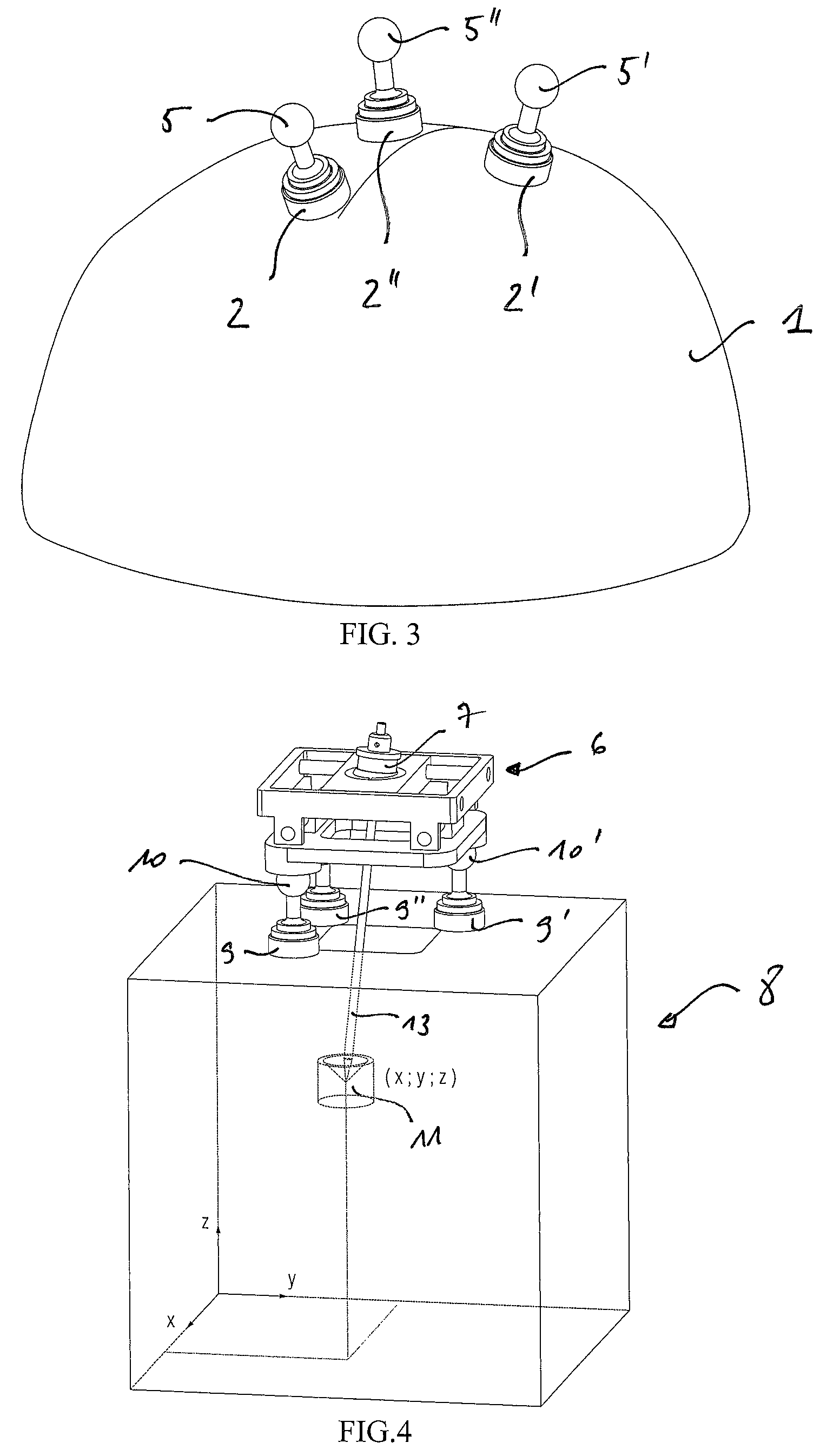
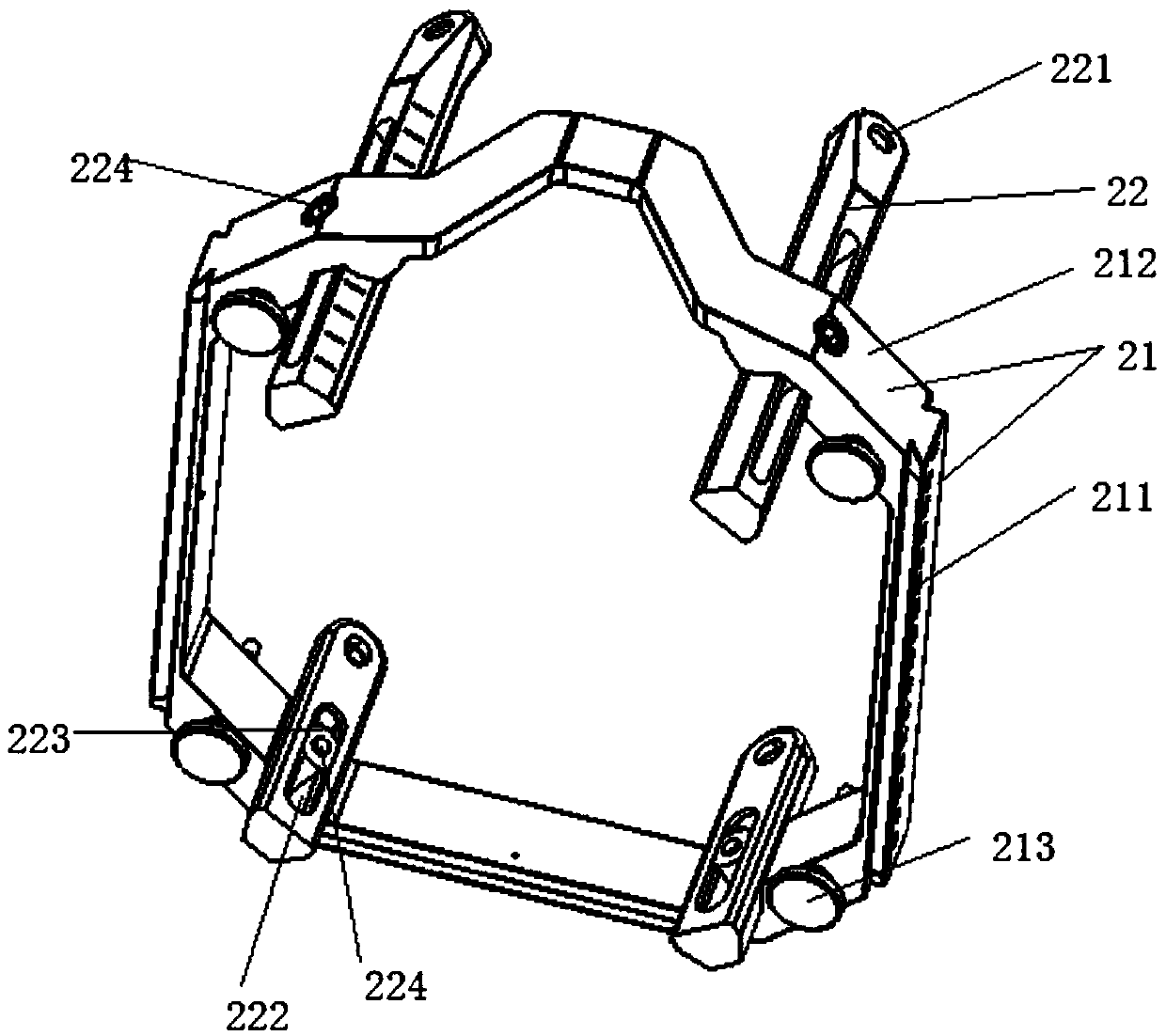
Adjustable stereotactic device and method for frameless neurosurgical stereotaxy
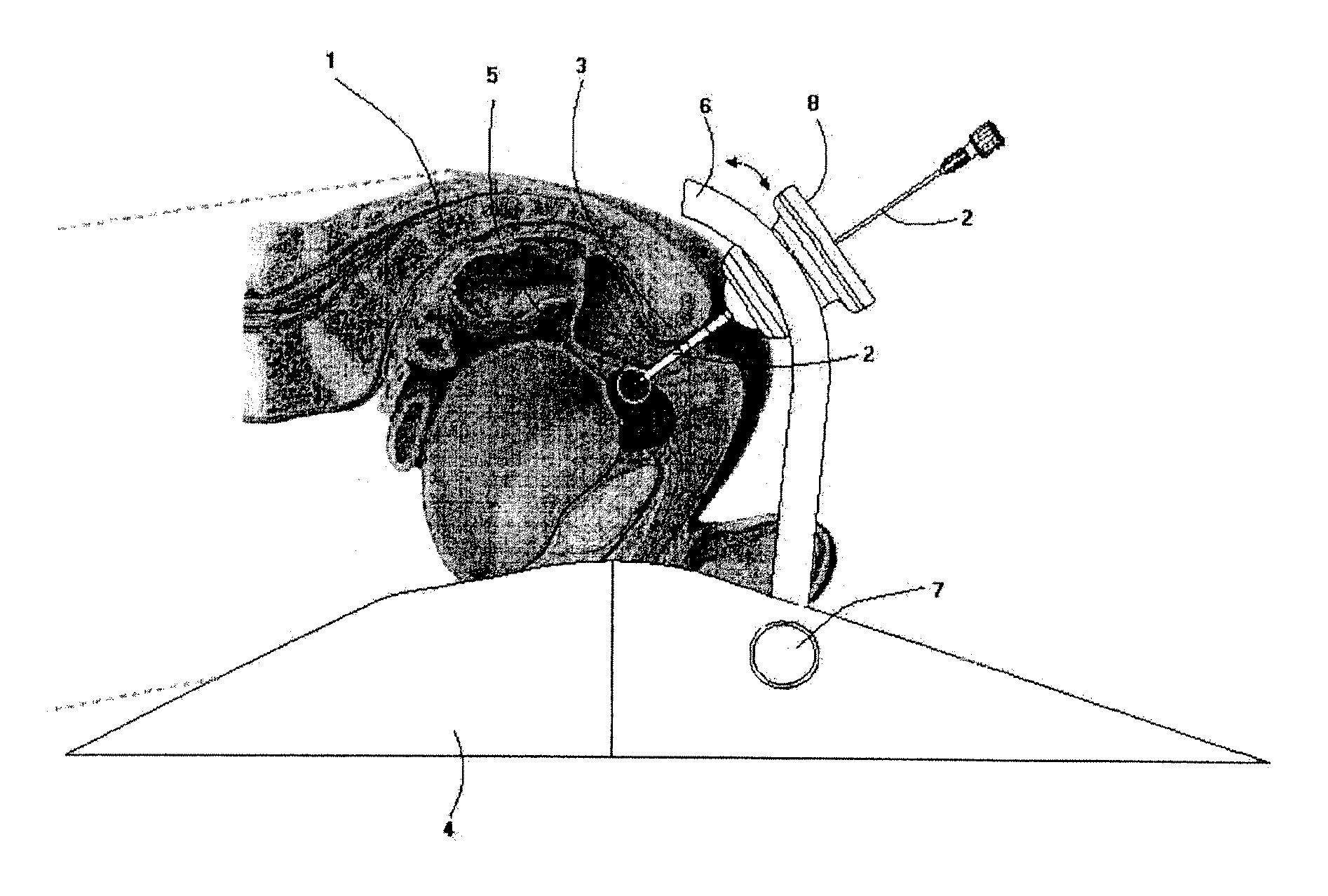
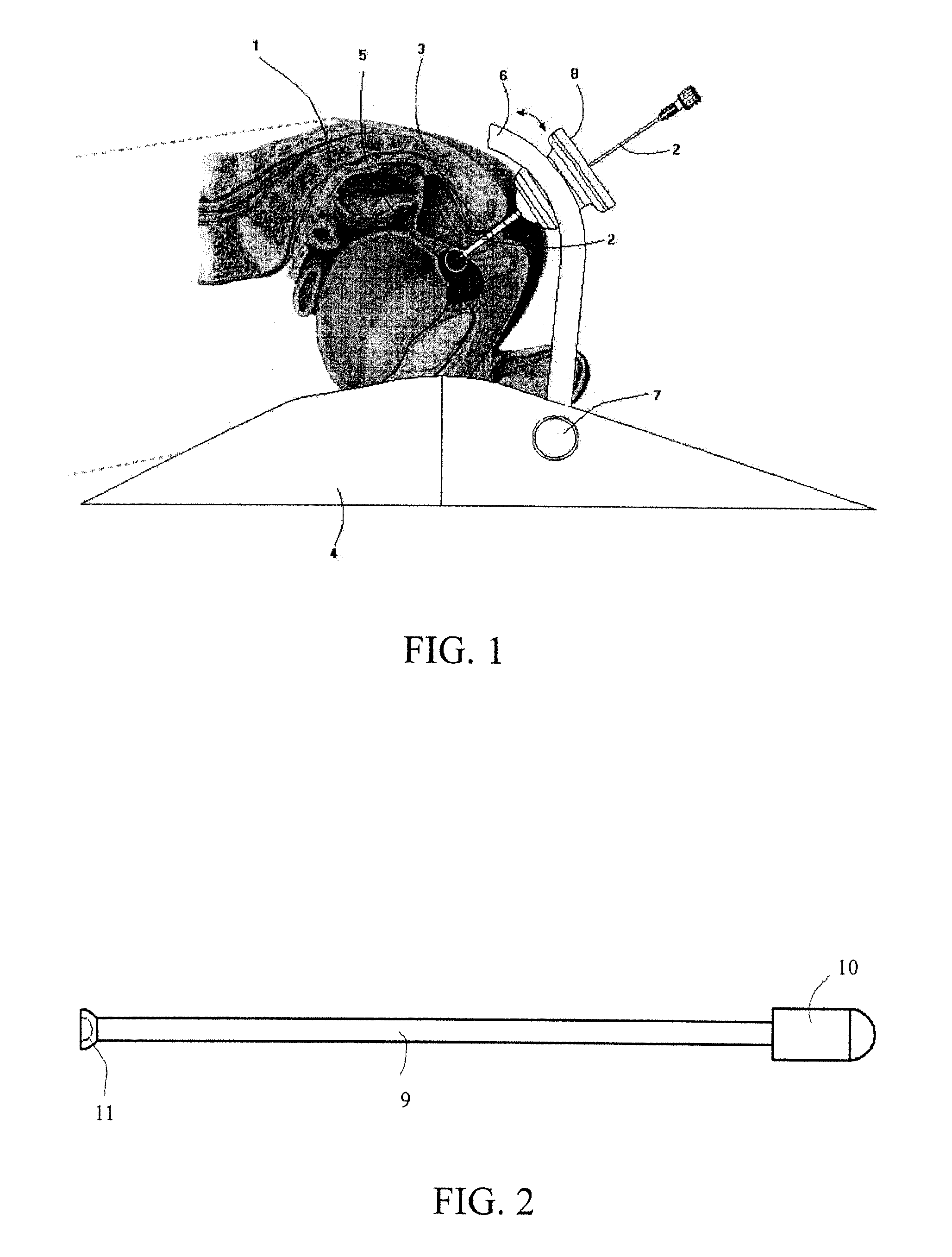
InactiveUS8617180B2Precise and controlled displacementSurgical needlesComputer-aided planning/modellingMedicineStereotaxy
The system comprises at least three anchors (2,2′,2″) intended to be attached to the patient and equipped with markers (5,5′,5″), an insertion guide device (6) with an insertion guide (7) intended to be attached to said anchors (2,2′,2″), an external calibration device (8) with at least three calibration markers (10,10′,10″) corresponding to said markers (5,5′,5″) and a planning and imaging software. The planning and imaging software is used to determine the position of a target point in the patient with respect to the markers (5,5′,5″), the calibration device is used to calibrate and orient the insertion guide (7) of the insertion guide device (6) mounted on said calibration markers (10,10′,10″) using the determination of the software before the insertion guide device is mounted on said markers (5,5′,5″) attached to the patient.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL) +1
Non-invasive transcranial ultrasound apparatus
ActiveUS8613714B2Reduce power consumptionEasy to assembleUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationTransducer
Disclosed is an autonomically functioning, battery-powered apparatus for non-invasive delivery of transcranial ultrasound. Insonation is directed by electronic circuitry and programmable instructions in memory and is modulated to achieve stereotemporal modulation of insonation so as to eliminate the need for assisted cooling. The apparatus is provided with registration members to facilitate stereotactic placement of transducer arrays and does not require diagnostic imaging guidance during setup and operation. Insonation is directed by electronic circuitry and programmable instructions in memory and is modulated to achieve stereotemporal modulation of insonation so as to eliminate the need for assisted cooling.
Owner:CEREVAST MEDICAL
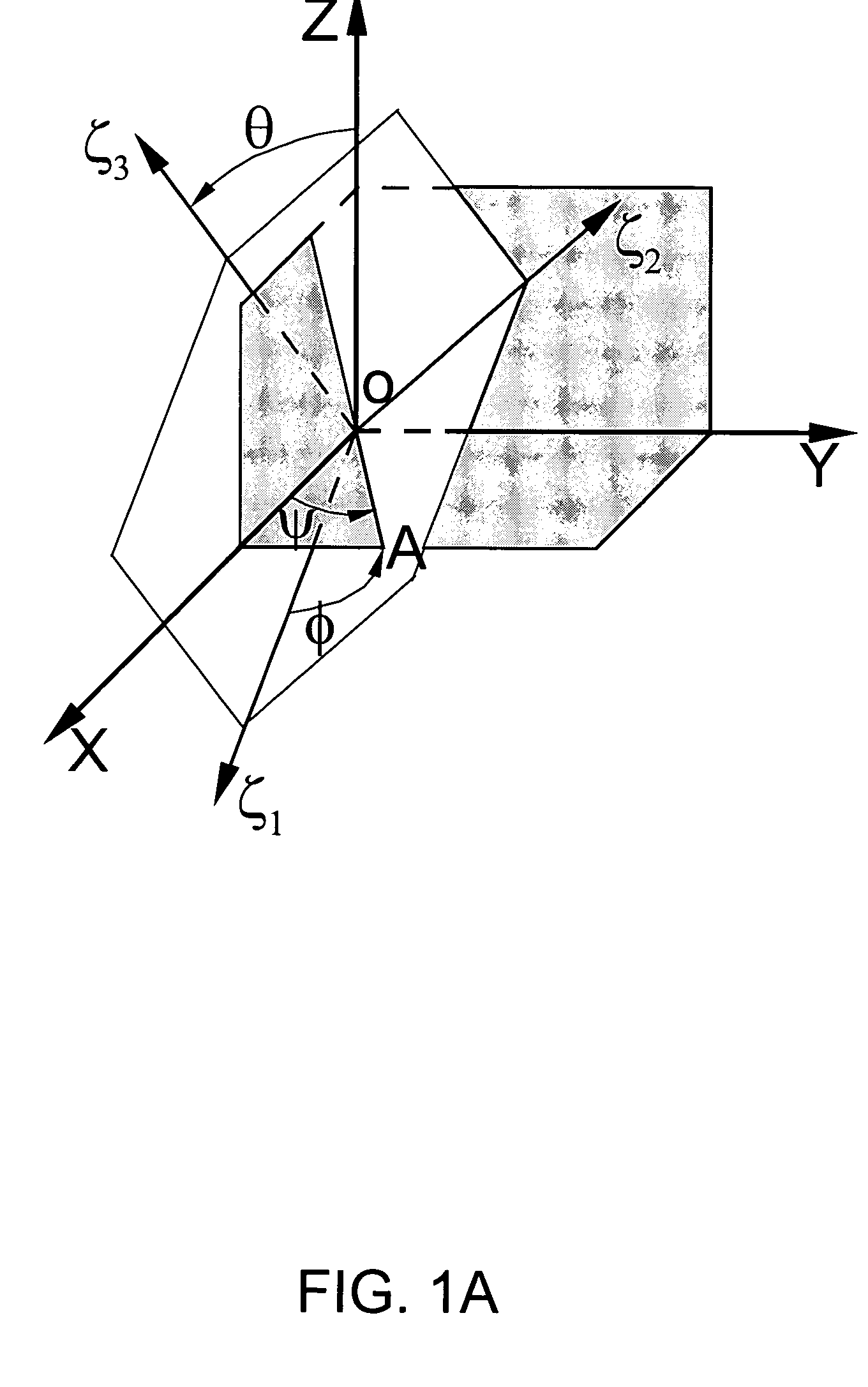
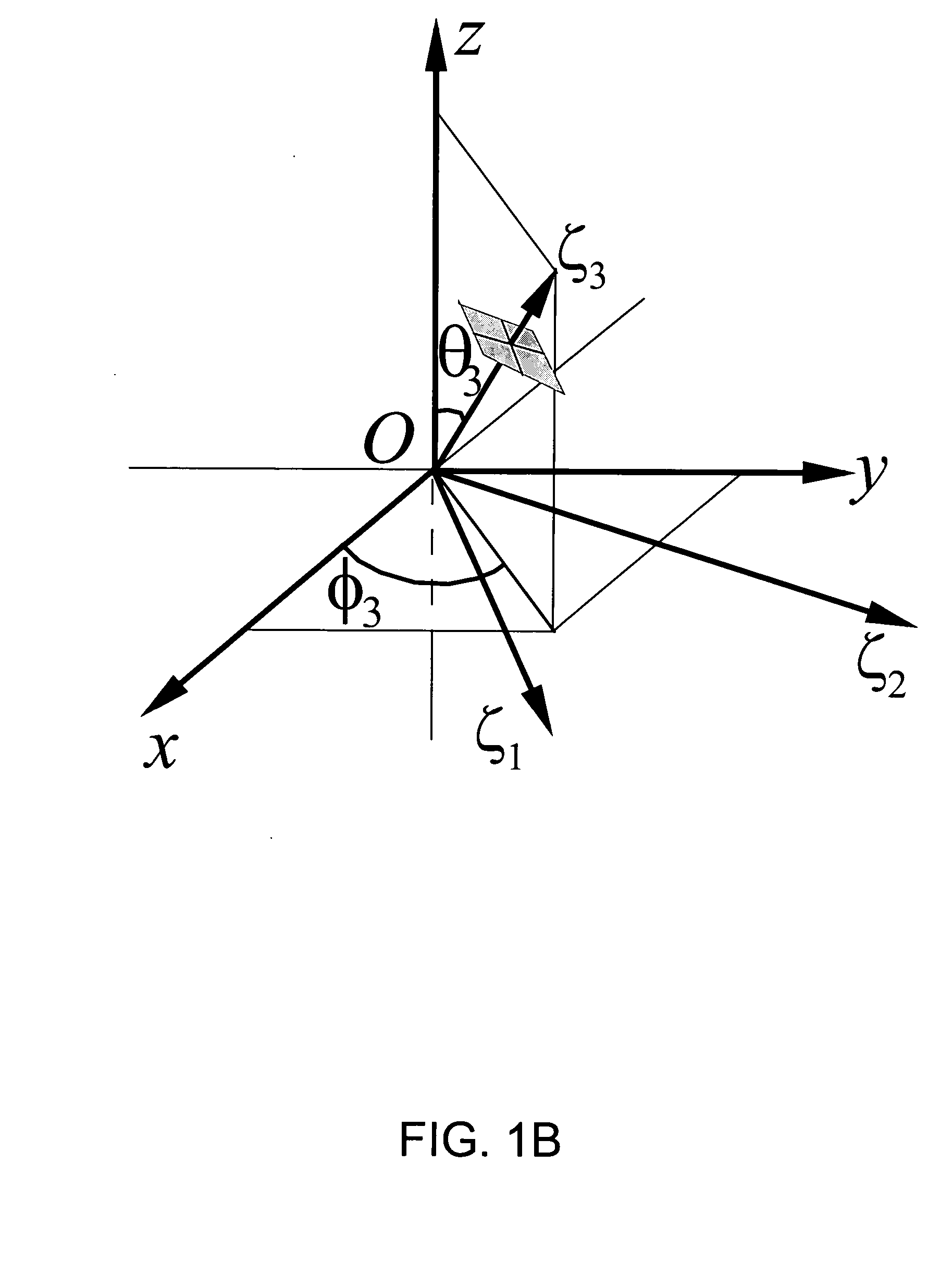
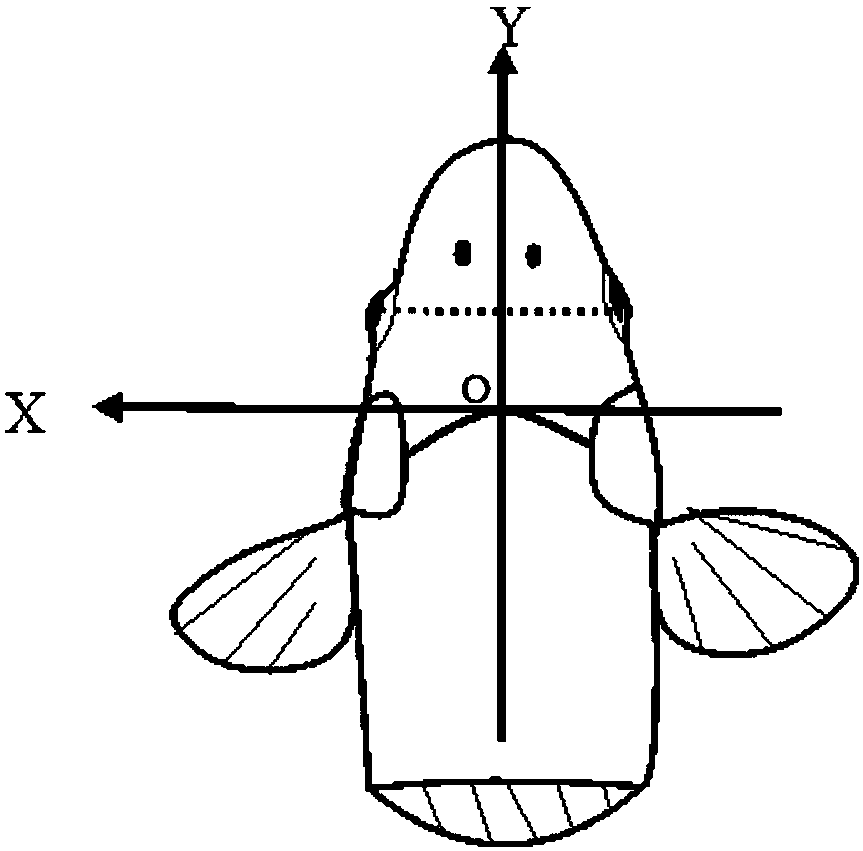
Method for converting carp magnetic resonance scanning coordinates into brain stereotaxic coordinates
ActiveCN107595287AImprove accuracyExact scale parameterInternal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceCarp
The invention discloses a method for converting carp magnetic resonance scanning coordinates into brain stereotaxic coordinates and belongs to the field of neuroscience. The method comprises the stepsthat a carp brain three-dimensional stereotaxic coordinate system and an auxiliary three-dimensional coordinate system on the surface of the skull are built; the two coordinate systems have a same coordinate origin O and a same X-axis, and both the included angles between the Y-axes and Z-axes of the two coordinate system are theta; the brain is subjected to magnetic resonance scanning imaging, and coordinate values of brain electrode implanting position points in the auxiliary coordinate system are determined; an algorithm is constructed by using the included angles theta, the magnetic resonance scanning coordinates are converted into the brain stereotaxic coordinates, and implanting of a brain electrode can be positioned and navigated. The method can position and navigate implanting ofthe brain electrode of a carp aquatic robot, and a new positioning and navigation method can also be provided for implanting of multiple biological brain electrodes.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
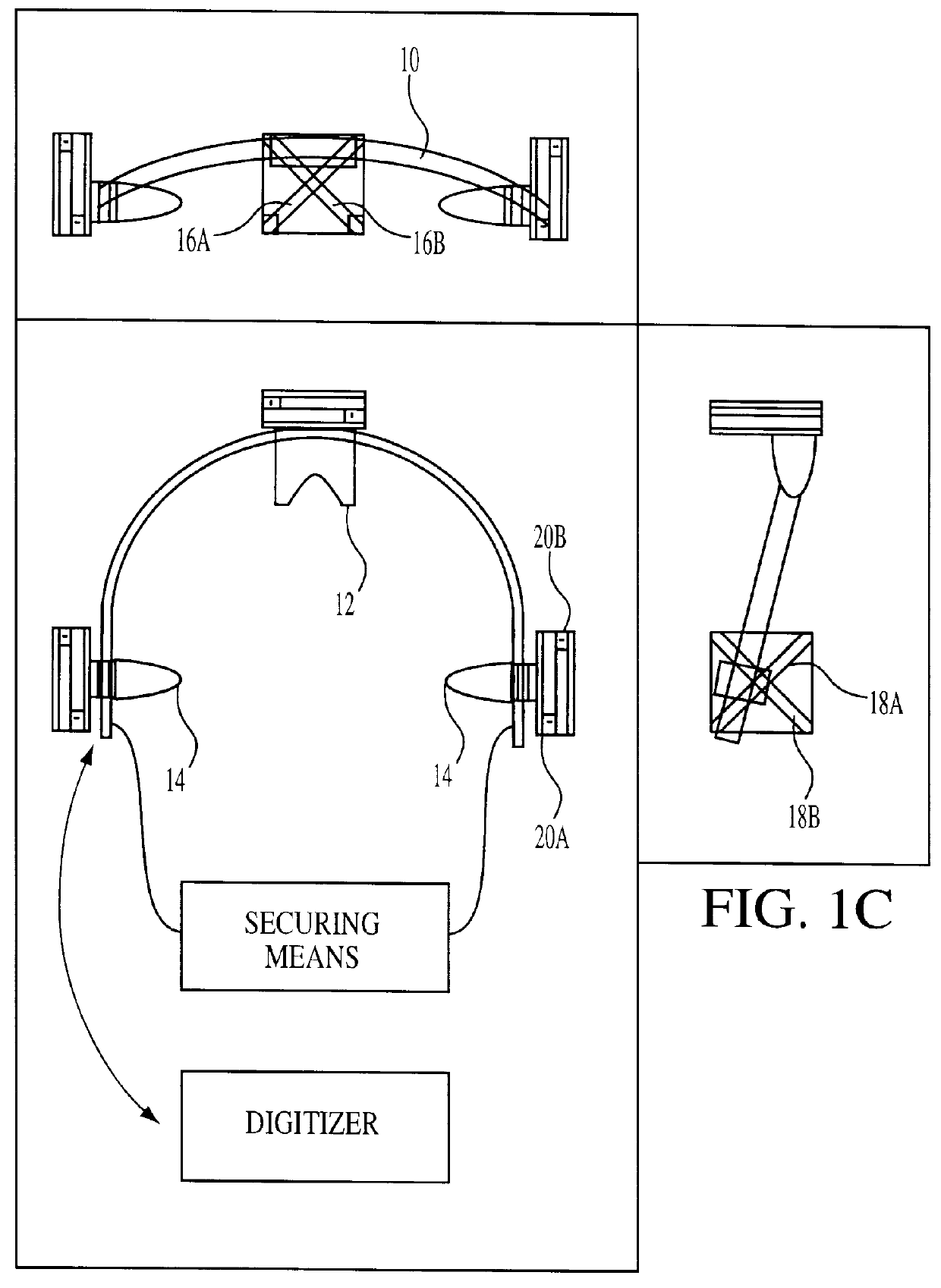
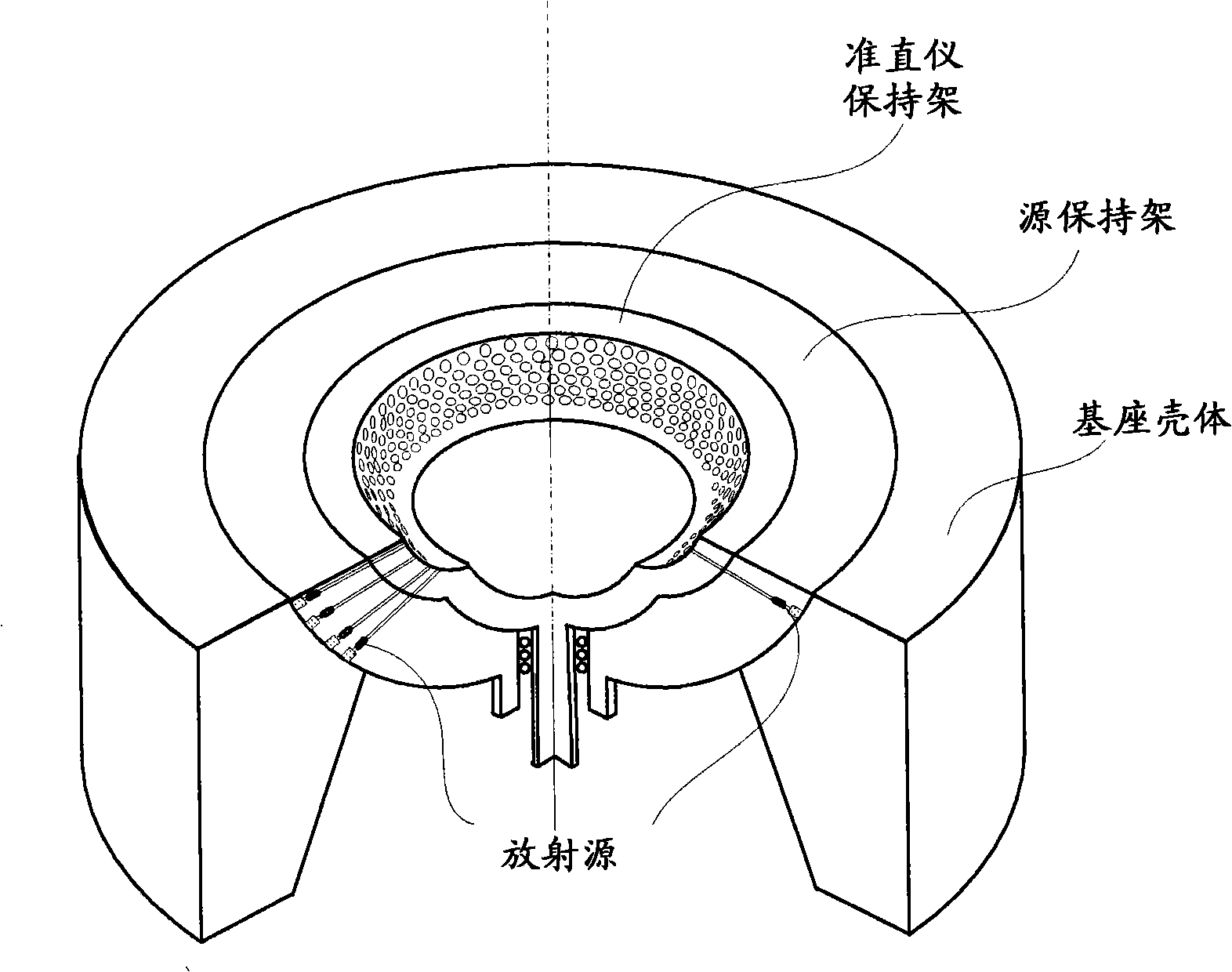
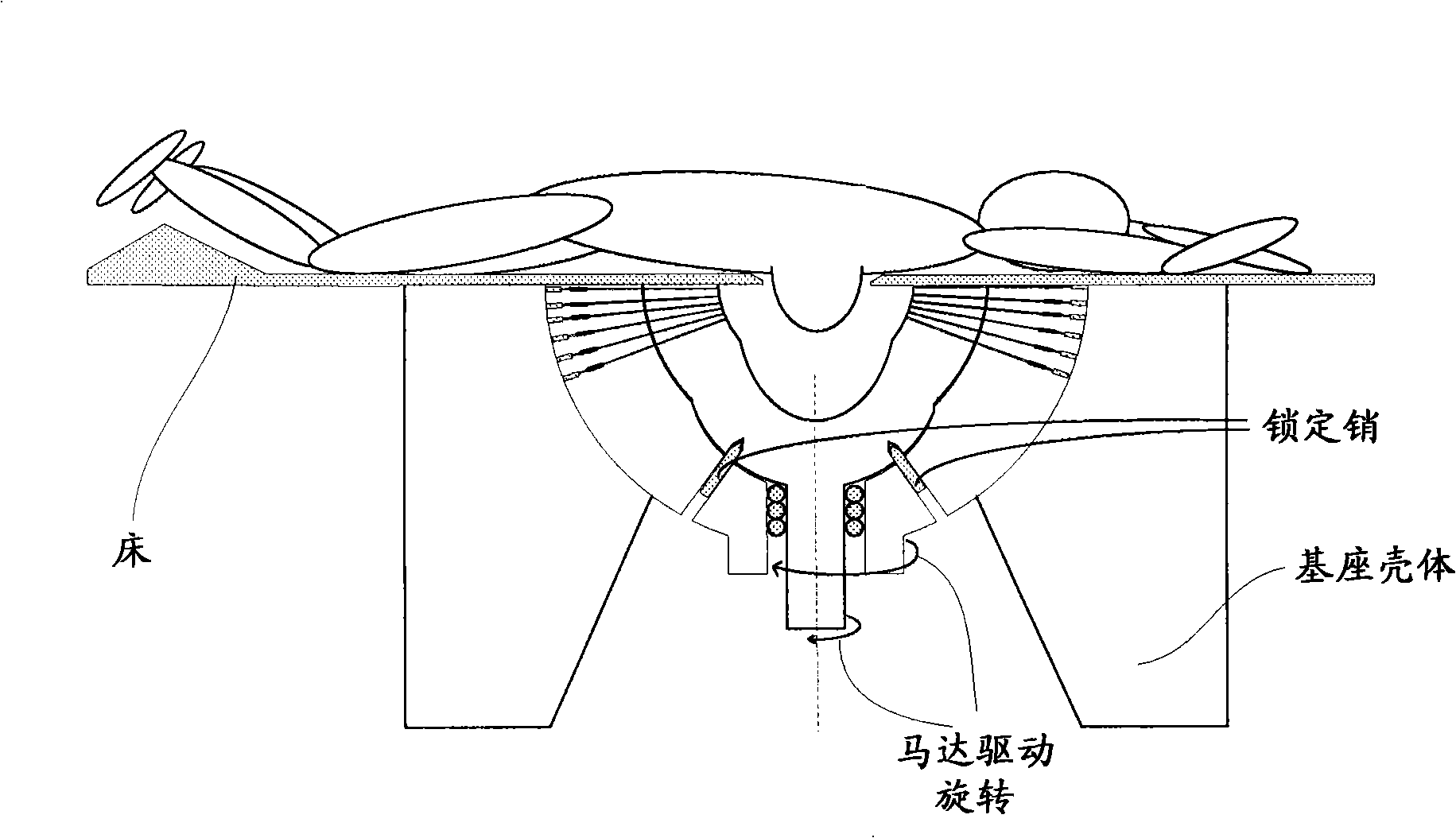
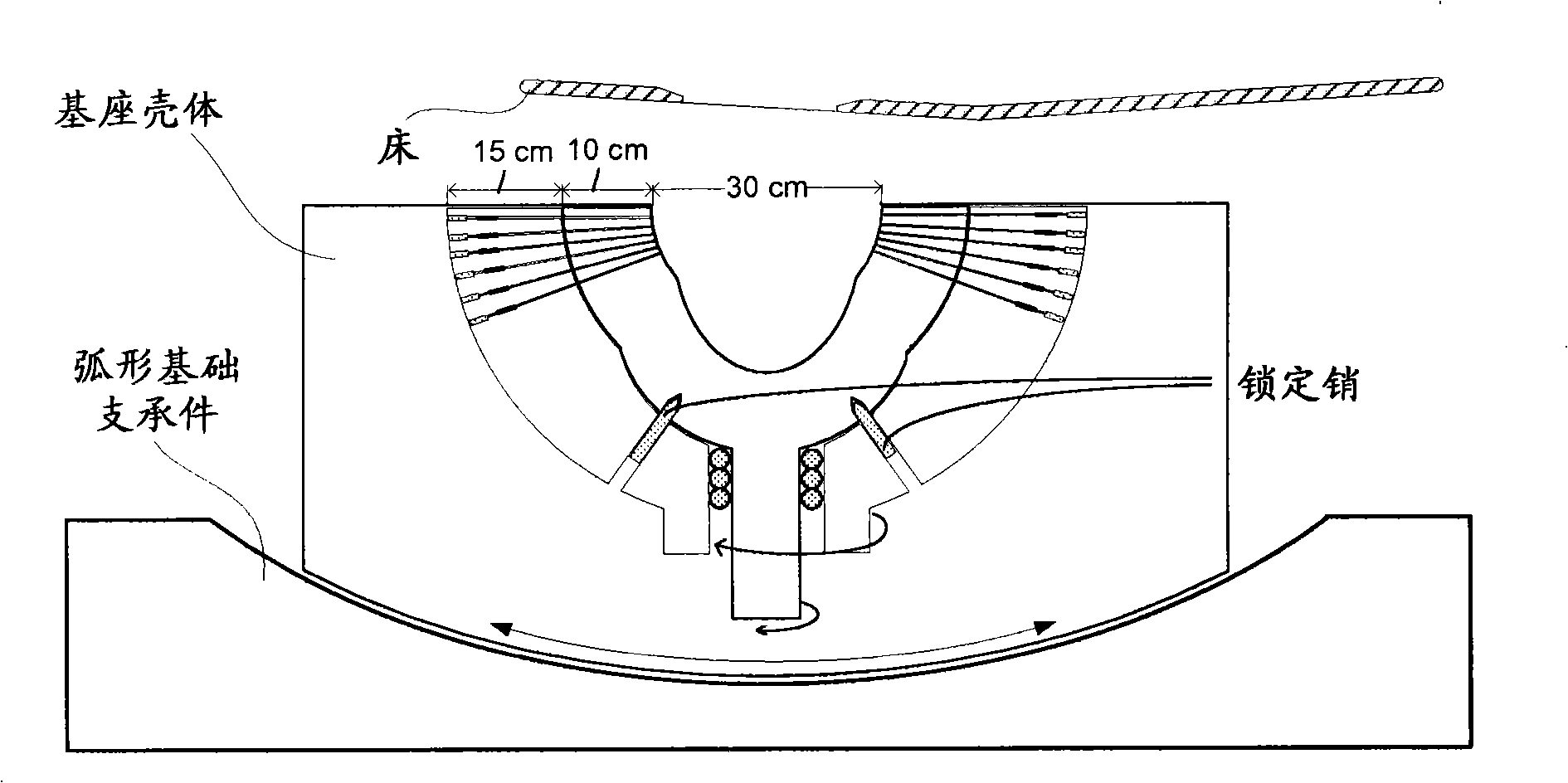
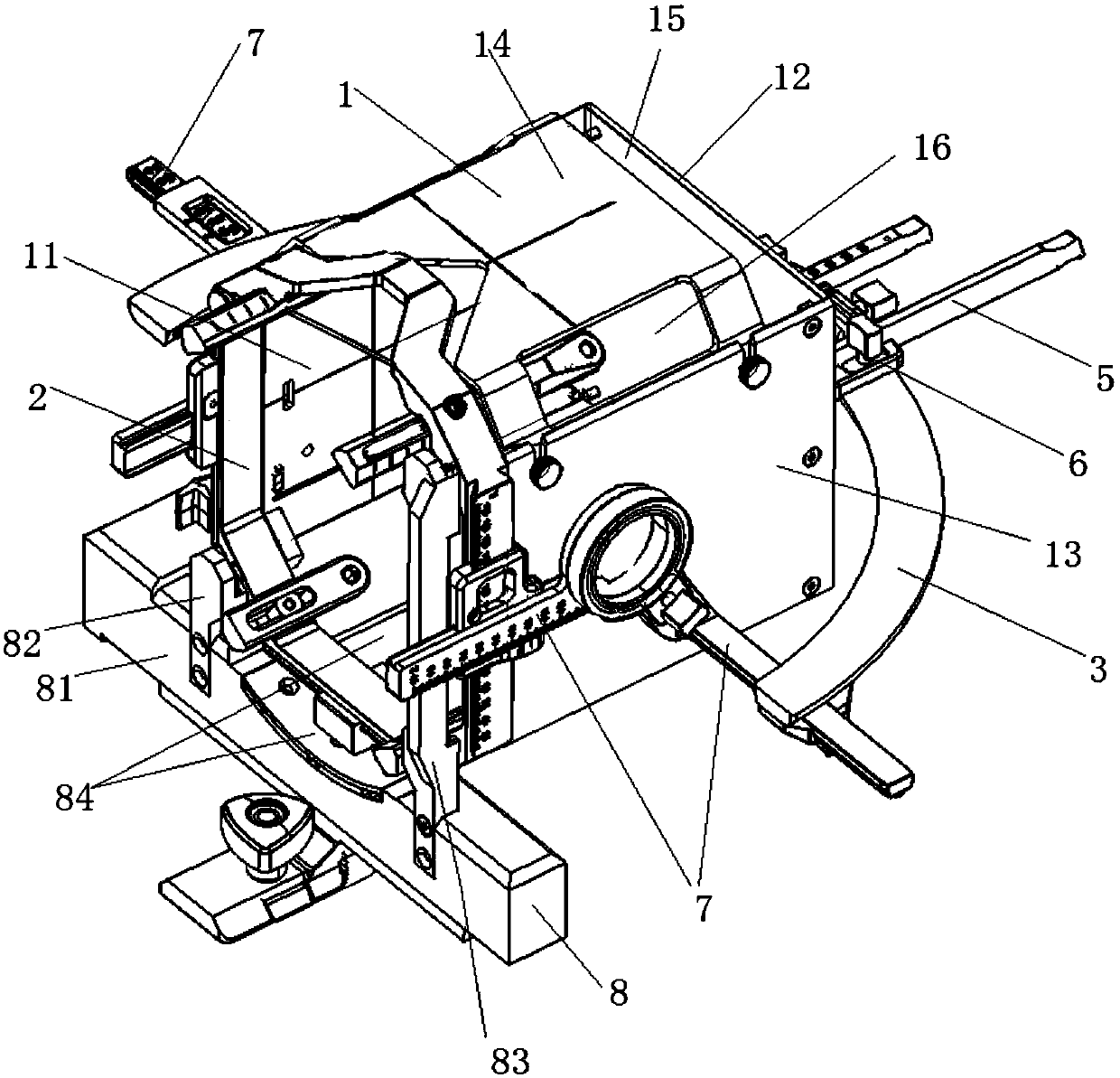
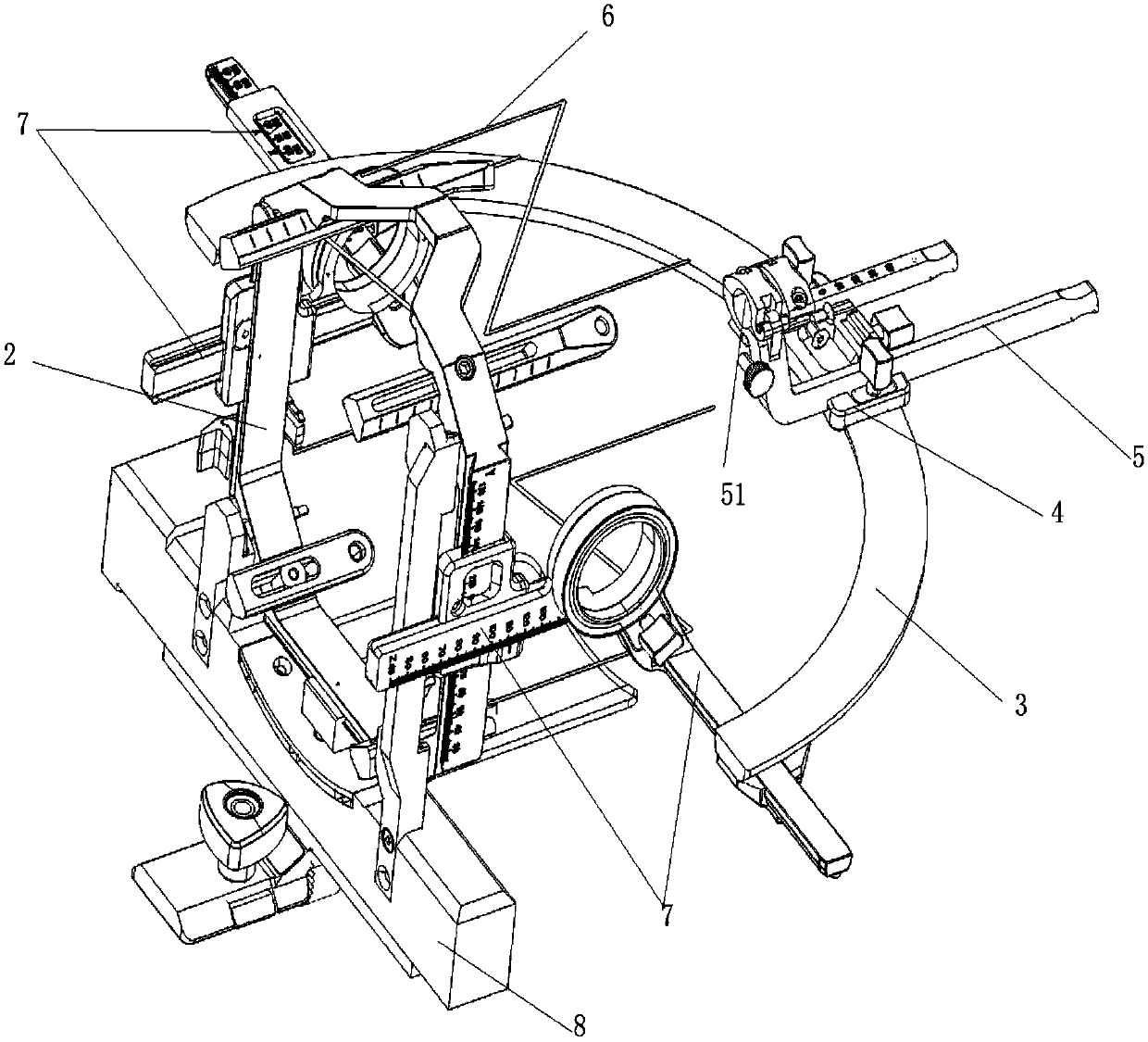
Brain stent stereotaxic instrument
InactiveCN110384543ATreatment safetyReduce the burden onSurgical needlesInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryCt technologyFixed frame
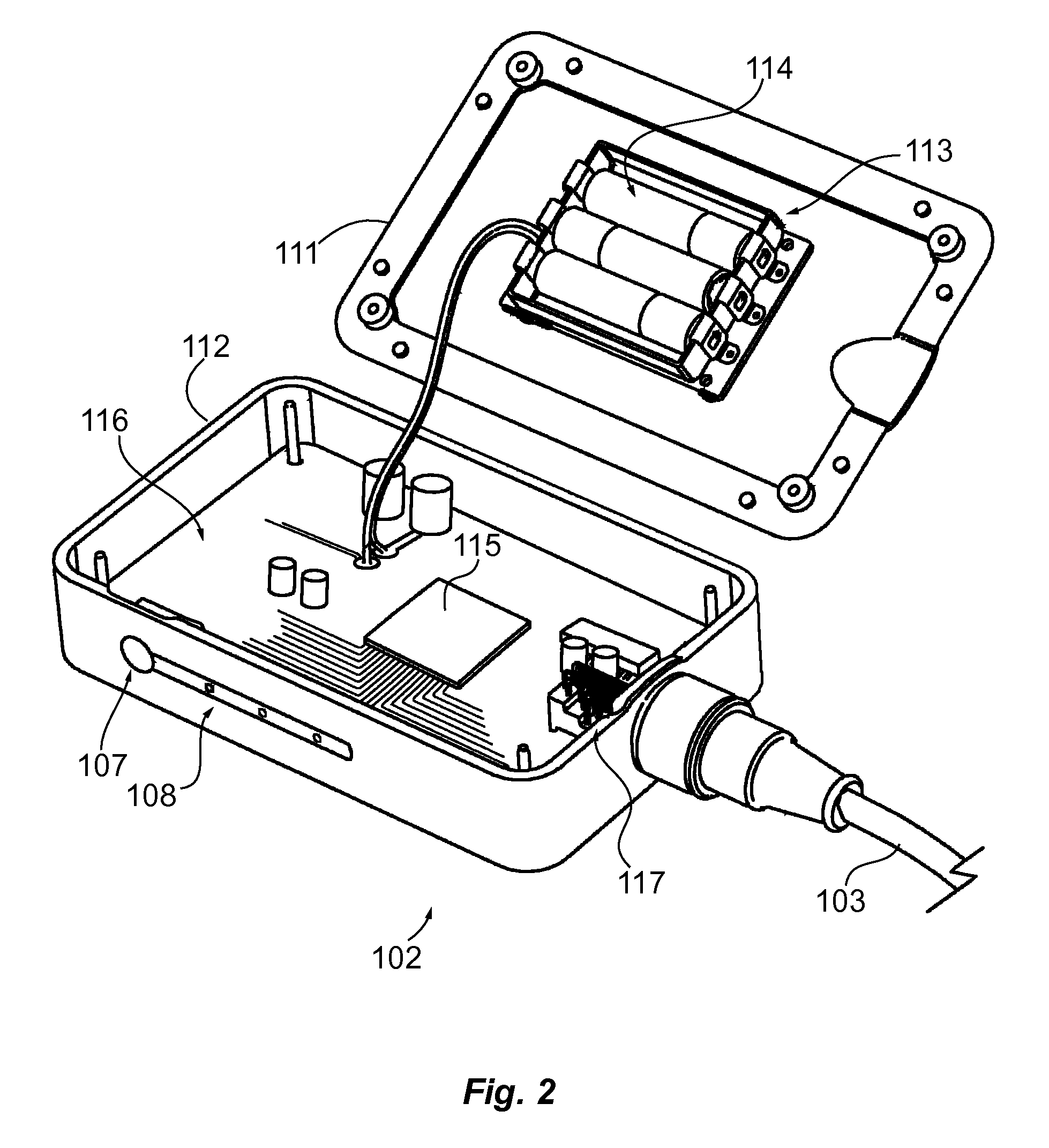
The invention discloses a brain stent stereotaxic instrument. The brain stent stereotaxic instrument comprises a shell, a head fixing frame, a semicircular arched positioning frame, a puncture needleslider and a puncture needle fixer. The novel brain stent stereotaxic instrument is a precise medical device capable of being matched with CT imaging equipment to be used and has high positioning precision; and the brain stent stereotaxic instrument is simple in structural design and practical, can assist a doctor in adjusting the puncture position and the needle entering angle, and can be combined with a CT technology, thus the accuracy, high efficiency and safety of minimally invasive stereotactic surgery are improved greatly, the surgery success rate of the minimally invasive stereotactic surgery is increased greatly, and the application field is enlarged accordingly.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROV MEDICAL INSTR INST +1
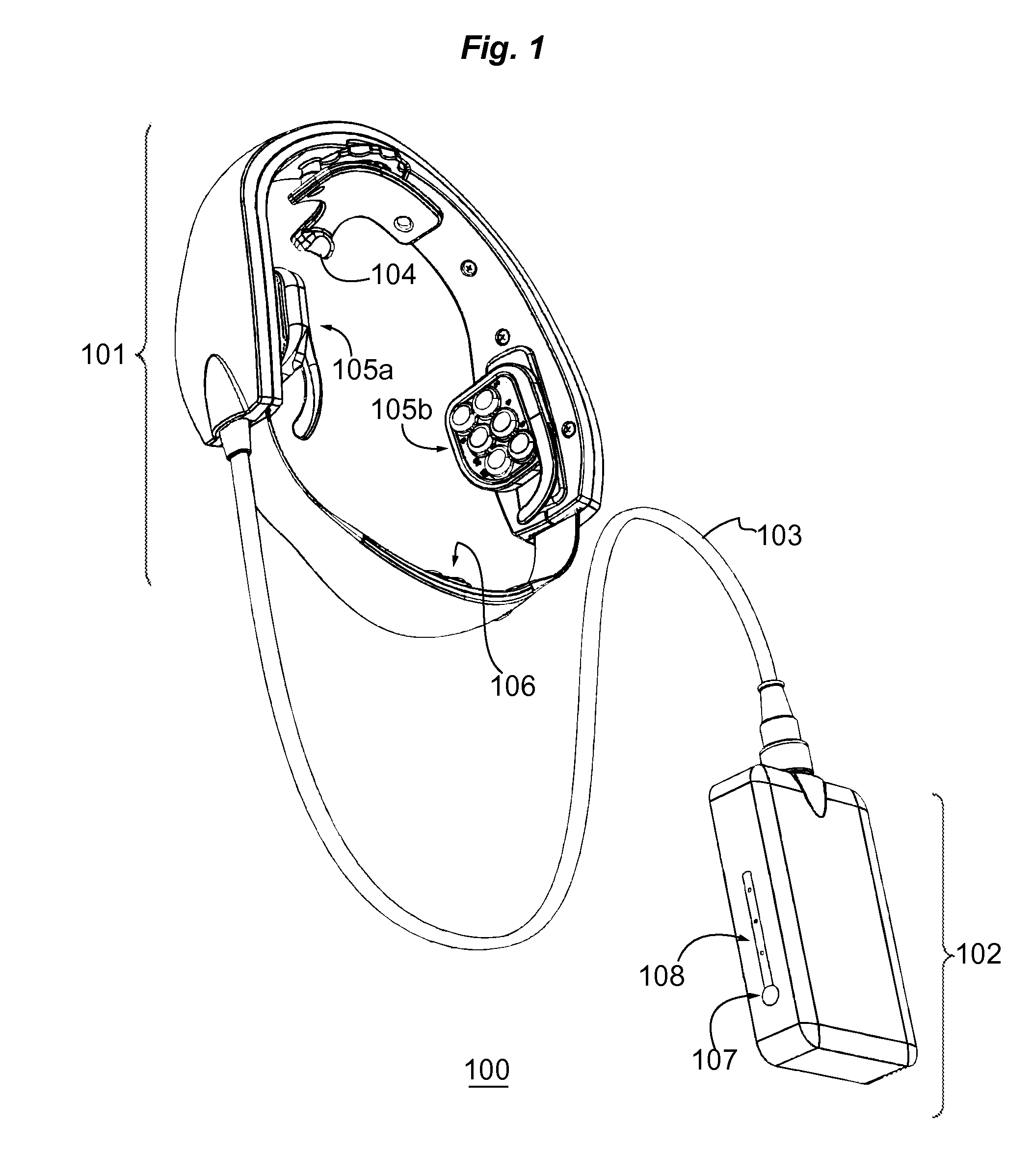
Multi Transmit/Receive Head Array Coil with Removable Panels
A modular multi-transmit head coil for use in Deep Brain Stimulation procedures includes a mounting frame arranged for attachment to the stereotactic head frame of the patient. An integrated MR stereotactic locating phantom is included as part of the coil structure which has attached MR / CT compatible fiducials on it to correlate pre-op, intra-op and post op images. The frame carries a series of modular removable coil elements in a transceive array that are connected to a set of RF power amplifiers that directly drive the coil elements. A control system including suitable software is arranged to control the signals to the coil elements so as to generate a required RF field with all the coil elements in place and with one or more the coil elements removed to allow access to the patent for the installation of the DBS leads.
Owner:DEERFIELD IMAGING INC
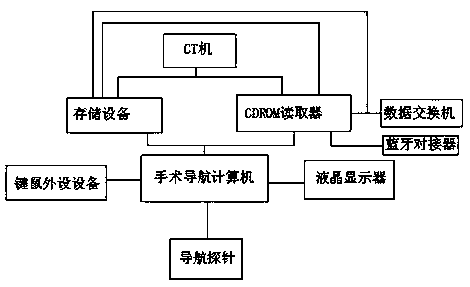
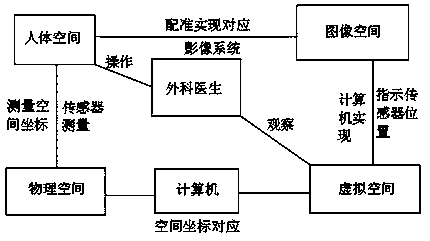
Hybrid positioning navigation system based on CT three-dimensional model mapping
PendingCN109864820AIntuitive Mixed Reality FusionHave the effect of seeing through the human bodyDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsHuman bodyMixed reality
The invention discloses a mixed positioning navigation system based on CT three-dimensional model mapping. The mixed positioning navigation system comprises a CT machine, a storage device, a CDROM reader, a data switch, a Bluetooth docking device, a surgical navigation computer, a keyboard and mouse peripheral device, a liquid crystal display and a navigation probe. The CT machine is a three-dimensional positioning device, plays a role in connecting medical images, surgical tools and surgical targets in a navigation system, plays a very important role in navigation positioning precision and surgical success rate, and has a main role in positioning human tissues and organs and surgical instruments; and the navigation probe is an operation tool. According to the CT three-dimensional model mapping-based hybrid positioning navigation system, hybrid reality fusion can be obtained very visually, the effect of human body perspective is achieved, direct comparison and fusion are achieved, an operation path is accurately measured, calculated and planned, risks are safely and effectively avoided, and a better use prospect is brought.
Owner:安徽紫薇帝星数字科技有限公司
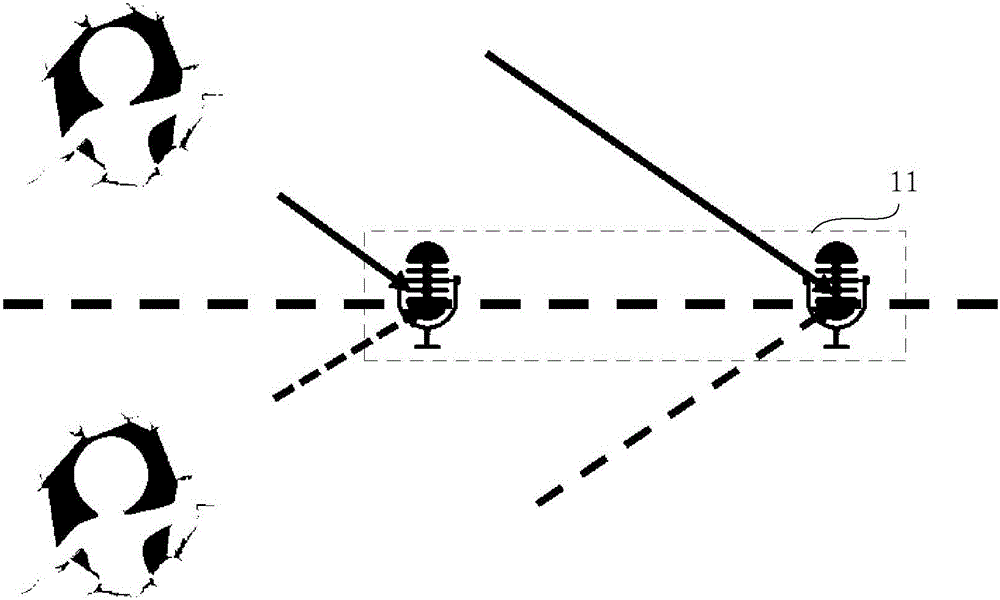
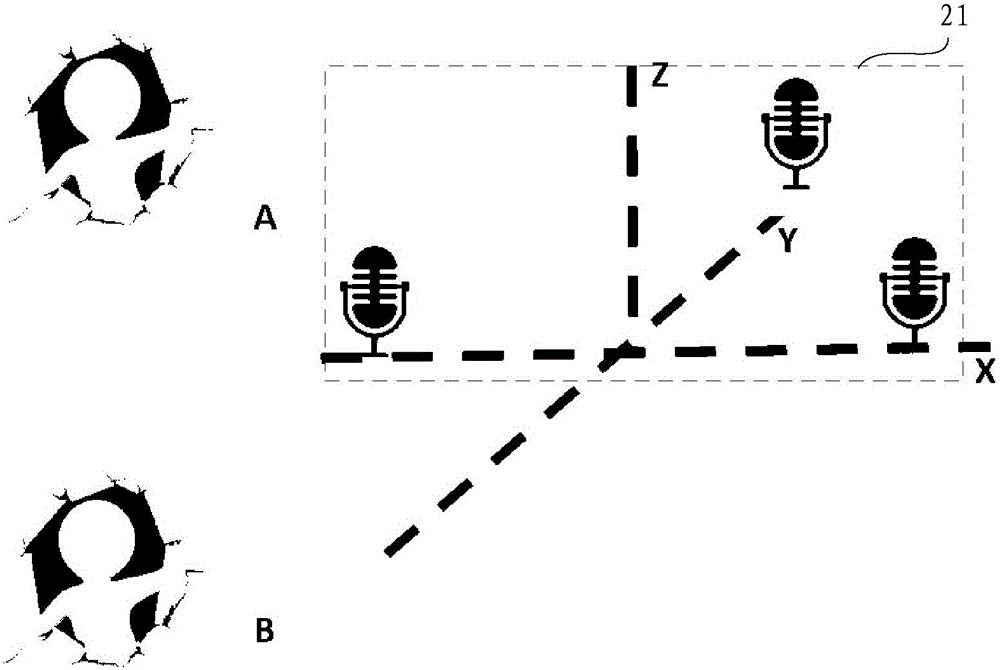
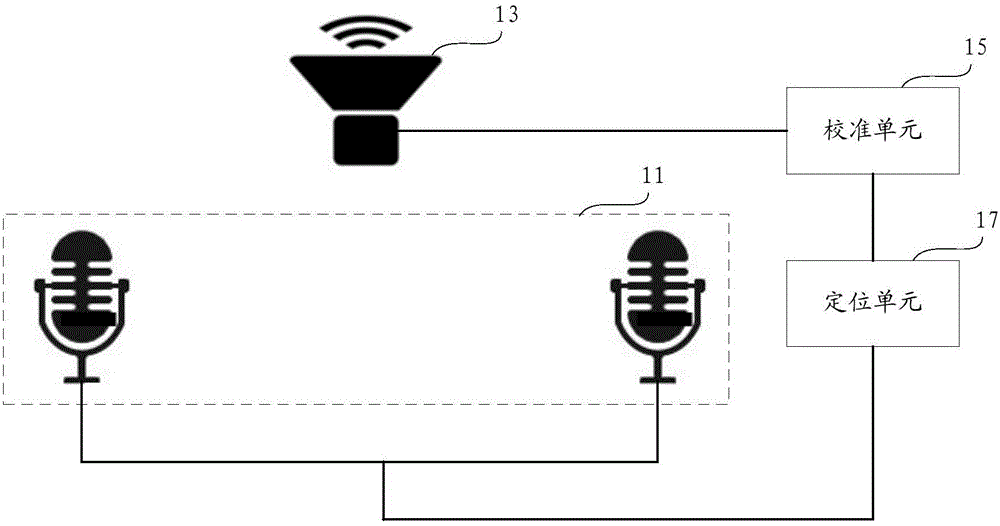
Sound source positioning system and method
The present invention provides a sound source positioning system and method. The system comprises a dual-microphone array used for acquiring the sound information; a loudspeaker used for acquiring the sound source feedback information, wherein the loudspeaker and the dual-microphone array are not located in a same straight line; a calibration unit used for calibrating the frequency response, phase and amplitude of the sound source feedback information according to a preset parameter; a positioning unit used for positioning two suspected positions of a sound source in a predetermined plane according to the sound information, and determining the position of the sound source in the two suspected positions according to the calibrated sound source feedback information. According to the present invention, the loudspeaker usually comprised in the conventional equipment is utilized to acquire the sound source feedback information, and the positioned suspected position of the microphone array is determined according to the sound source feedback information generated by the sound sources of different distances, thereby realizing the plane positioning without needing to increase a microphone by combining the dual-microphone array with the loudspeaker, or realizing the stereo positioning by combining a three-microphone array with the loudspeaker.
Owner:BEIJING HORIZON INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
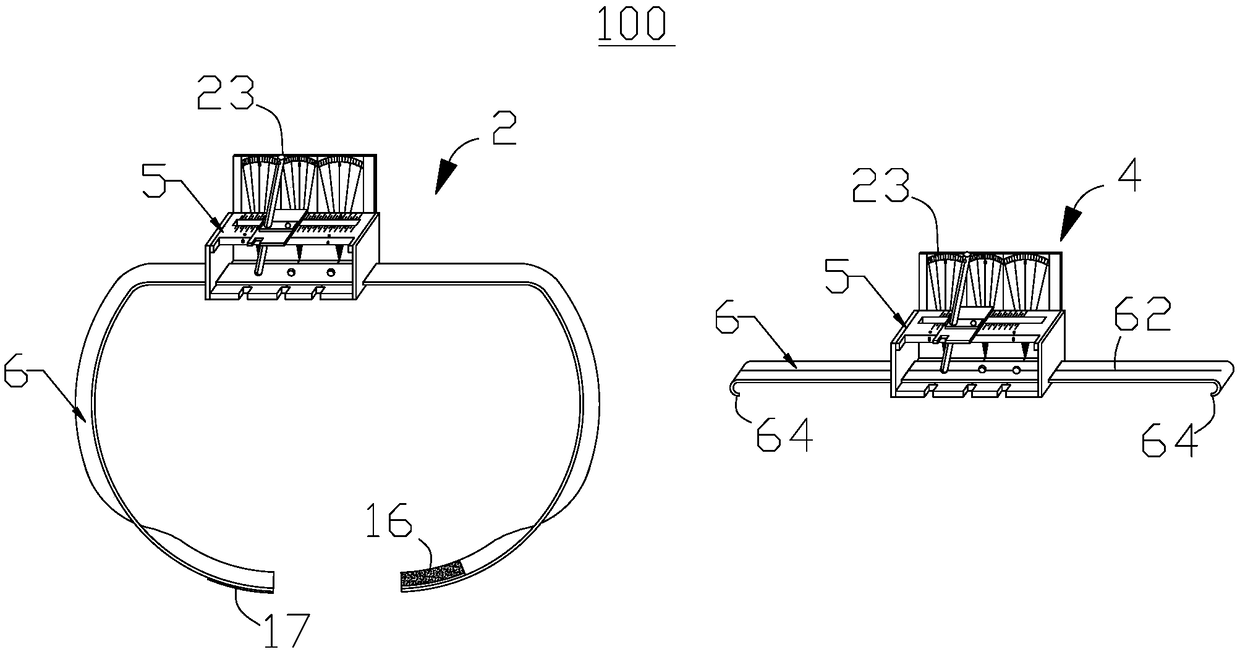
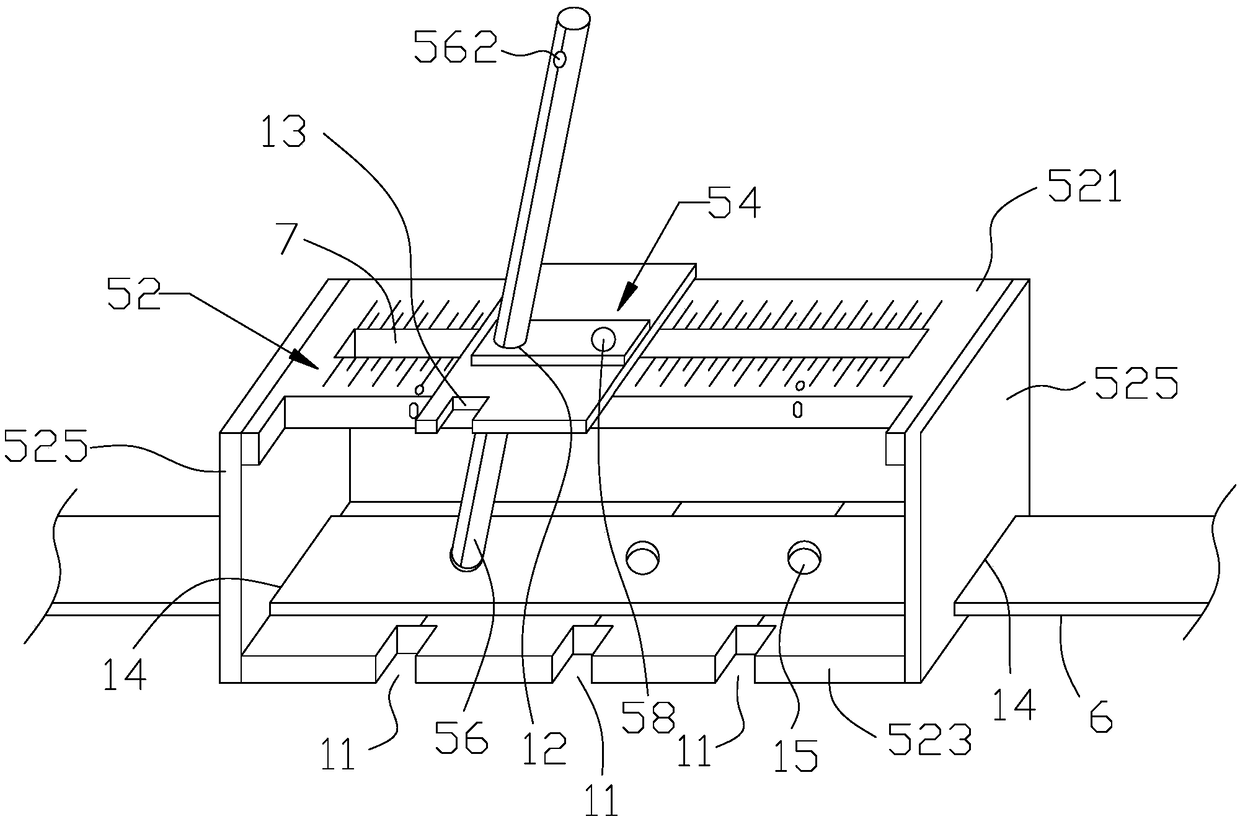
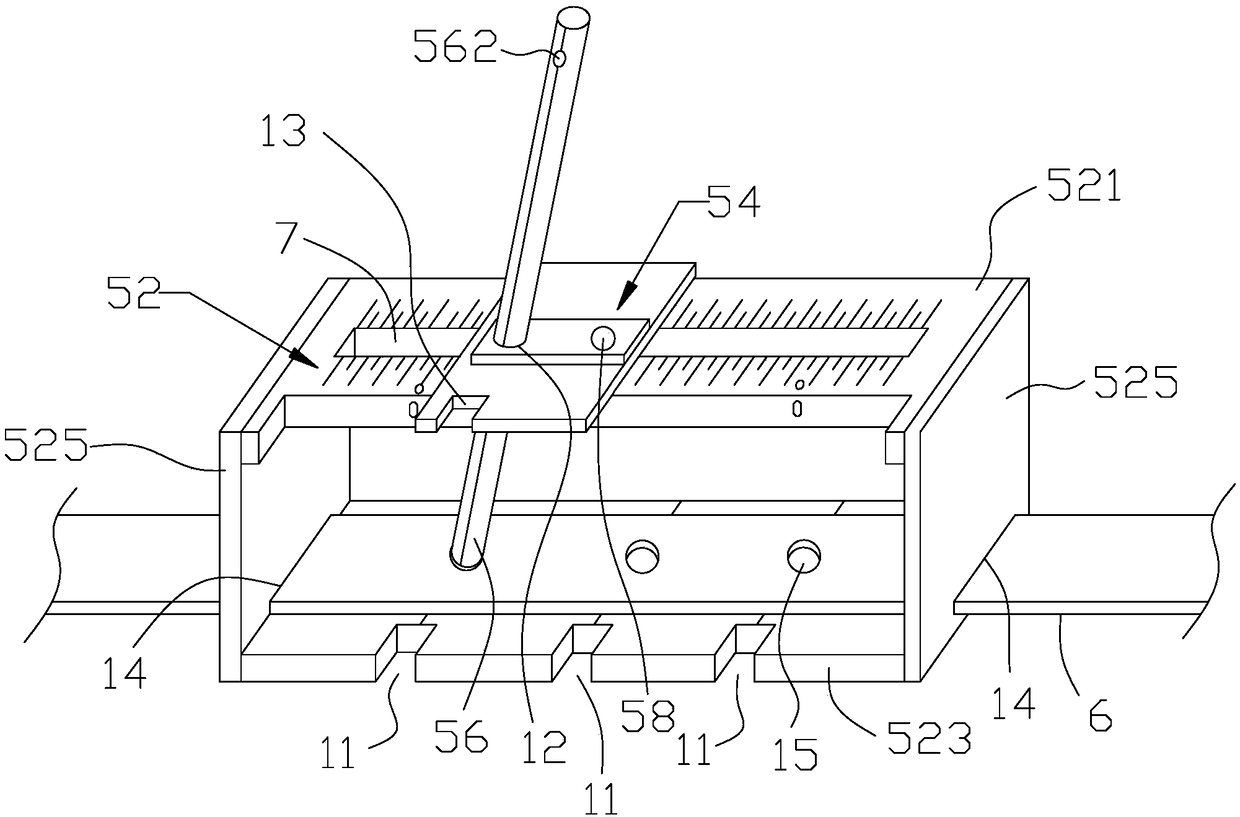
Puncture positioning system and precision stereoscopic positioner for minimally invasive paracentesis of intracranial hematoma
InactiveCN109091214AImprove puncture accuracyAvoid damageSurgical needlesTrocarParacentesisPulp and paper industry
The invention provides a precision stereoscopic positioner for minimally invasive paracentesis of intracranial hematoma. The precision stereoscopic positioner comprises a positioning device and a positioning belt. The positioning device comprises a support, a sliding part and a reference rod, the support comprises a top plate, a bottom plate and a connecting plate, the top plate opposite to the bottom plate is provided with a sliding hole and an angle positioning scale line, and the bottom plate is provided with three first reference rod positioning holes along the sliding hole and three firstdrainage tube positioning holes corresponding to the first reference rod positioning holes. The sliding part is mounted on the top plate through a bolt and is provided with a second reference rod positioning hole and a second drainage tube positioning hole at an interval, one end of the reference rod is inserted into the corresponding first reference rod positioning hole, the reference rod penetrates the sliding hole and the second reference rod positioning hole, and the positioning belt is mounted on the support. The precision stereoscopic positioner is capable of improving puncturing accuracy of the minimally invasive paracentesis of intracranial hematoma. The invention further provides a puncture positioning system for minimally invasive paracentesis of the intracranial hematoma.
Owner:刘国军
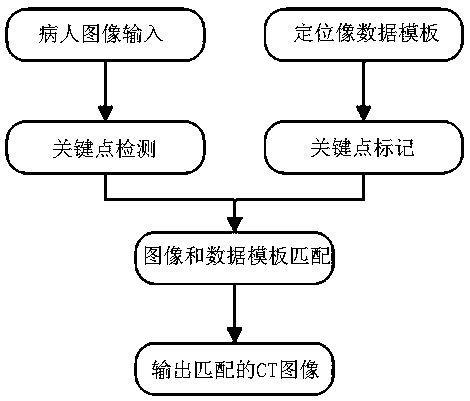
Rapid CT scanning method and system based on virtual stereotaxic image
ActiveCN110956633AReduce scan timeReduce workloadImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresRadiology
The invention discloses a rapid CT scanning method and system based on a virtual stereotaxic image. The rapid CT scanning method comprises the steps: inputting patient images which are photographed atdifferent angles and comprise a to-be-scanned region, and carrying out the key point detection of the patient images; inputting a positioning image data template and marking key points; performing matching calculation according to the key points in the patient image and the positioning image data template to obtain a three-dimensional virtual positioning image; and determining a CT scanning areaof the patient according to the three-dimensional virtual positioning image, and outputting a final CT image. The virtual positioning image generated by the optical image is used for replacing a traditional positioning image, and the time required for scanning the positioning image is shortened, and the radiation dose received by a patient is reduced, and the anatomical structure of the patient can be clearly displayed, and a doctor can more accurately position a scanning area, and the workload of the doctor is reduced.
Owner:NANJING ANKE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
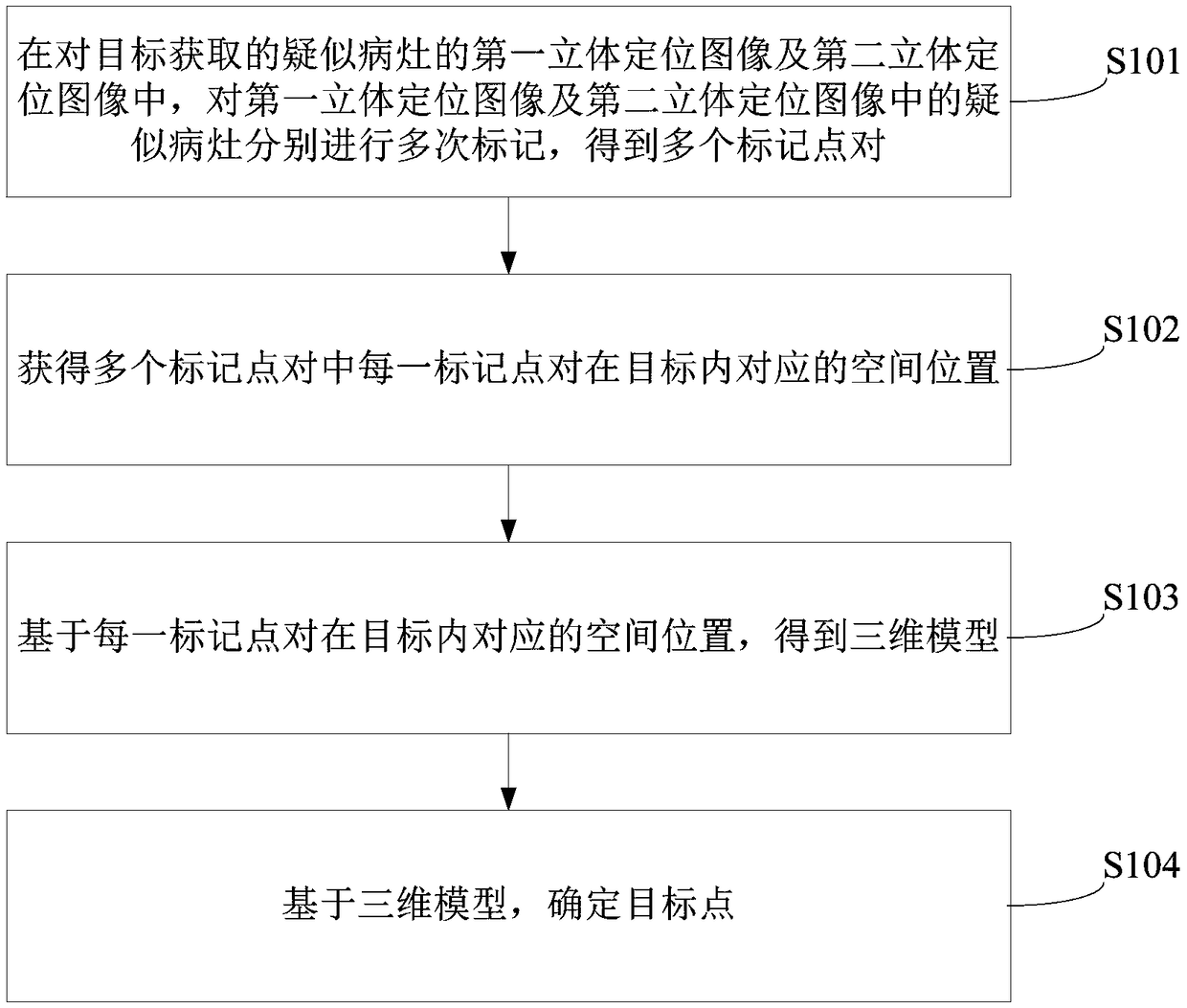
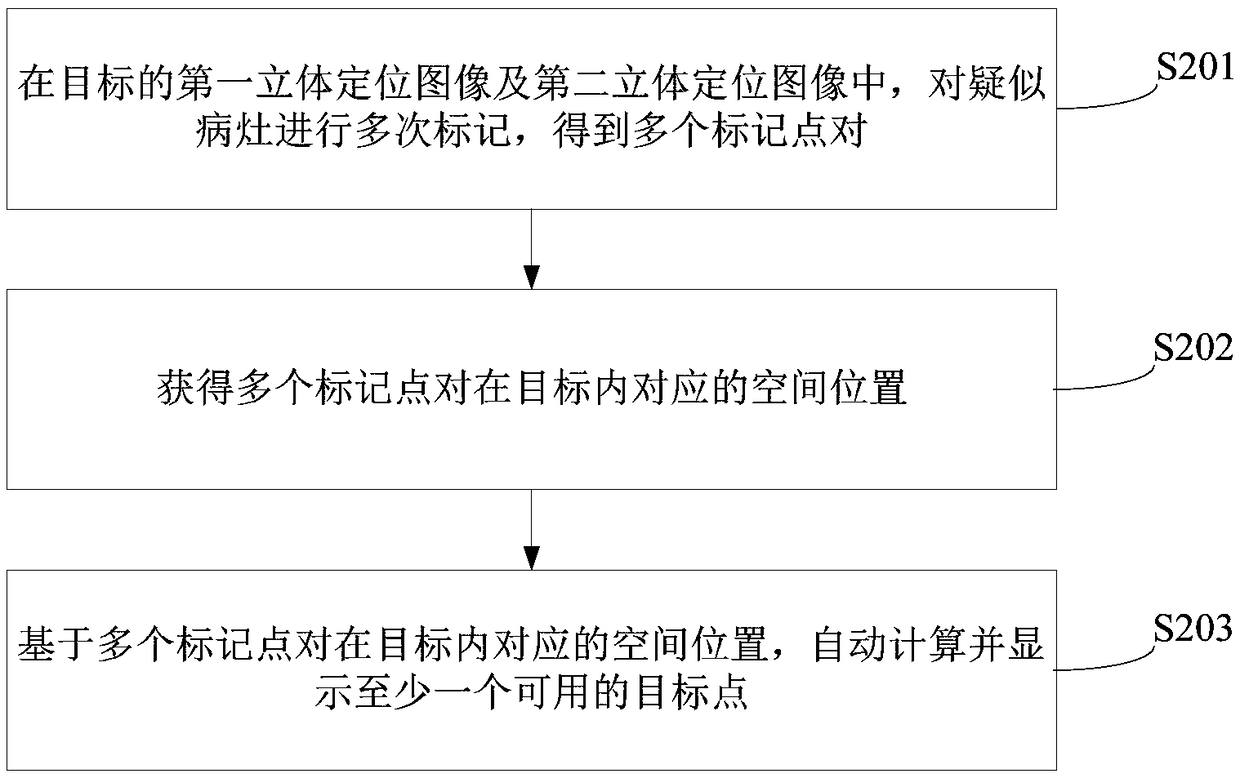
Method for determining target point and positioning system for mammary gland X ray photography system
The invention provides a method for determining a target point and a positioning system for a mammary gland X ray photography system. The method is applied to the mammary gland X ray photography system, and comprises steps of: repeatedly marking suspected lesions in a first stereo positioning image and a second stereo positioning image acquired by a target to obtain a plurality of mark point pairs; obtaining a spatial position corresponding to each of the plurality of mark point pairs in the target; based on the spatial position corresponding to each mark point pair in the target, obtaining athree-dimensional model, and determining a target point by the three-dimensional model. The method can help the user obtain the spatial position information of the suspected lesion, and comprehensively considers the spatial position information and the plane information of the mark points, thereby improving the accuracy of determining the target point.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com