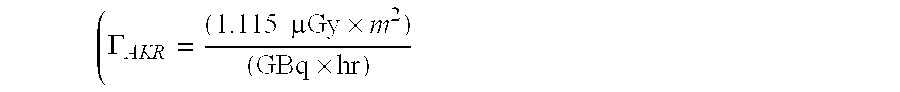Patents
Literature
59 results about "Stereotactic device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stereotactic surgery or stereotaxy is a minimally invasive form of surgical intervention which makes use of a three-dimensional coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, biopsy, lesion, injection, stimulation, implantation, radiosurgery (SRS), etc.
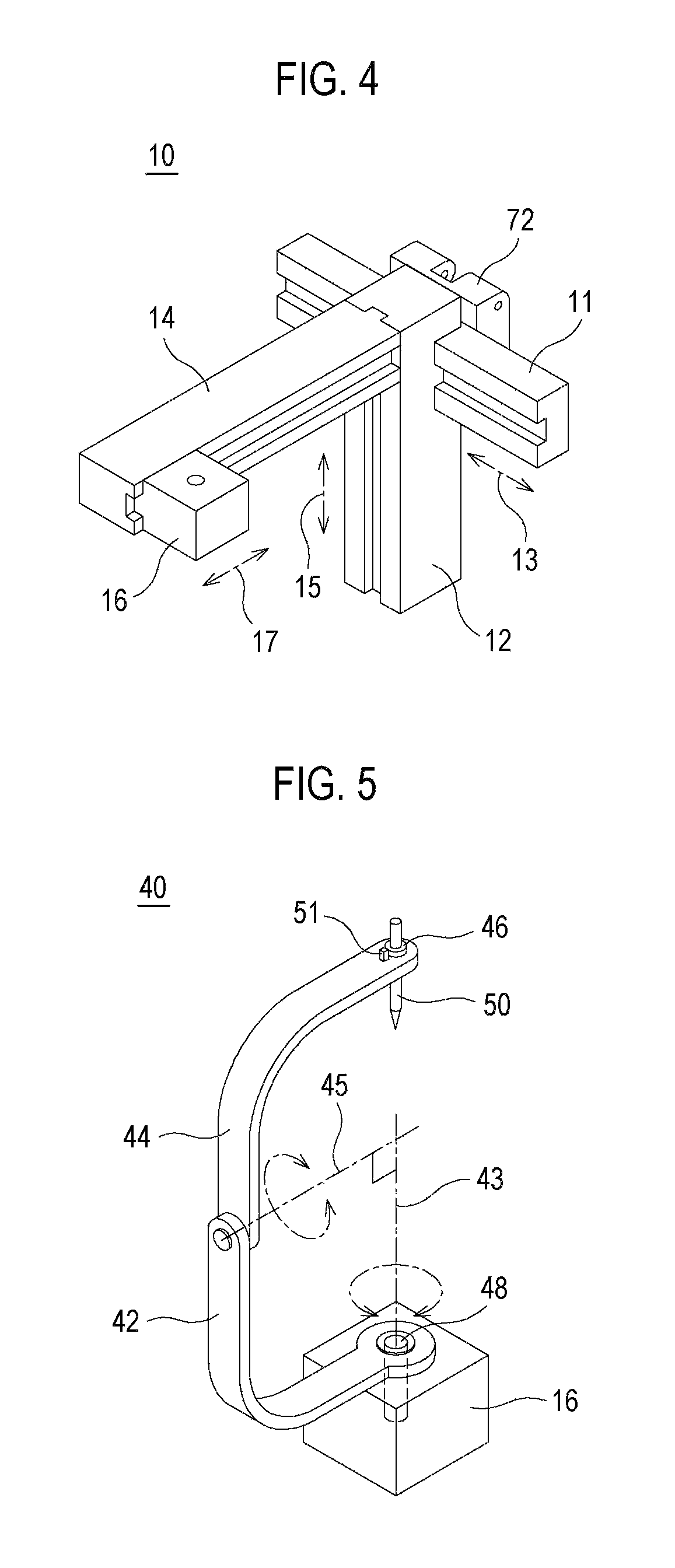
Method and apparatus for performing stereotactic surgery
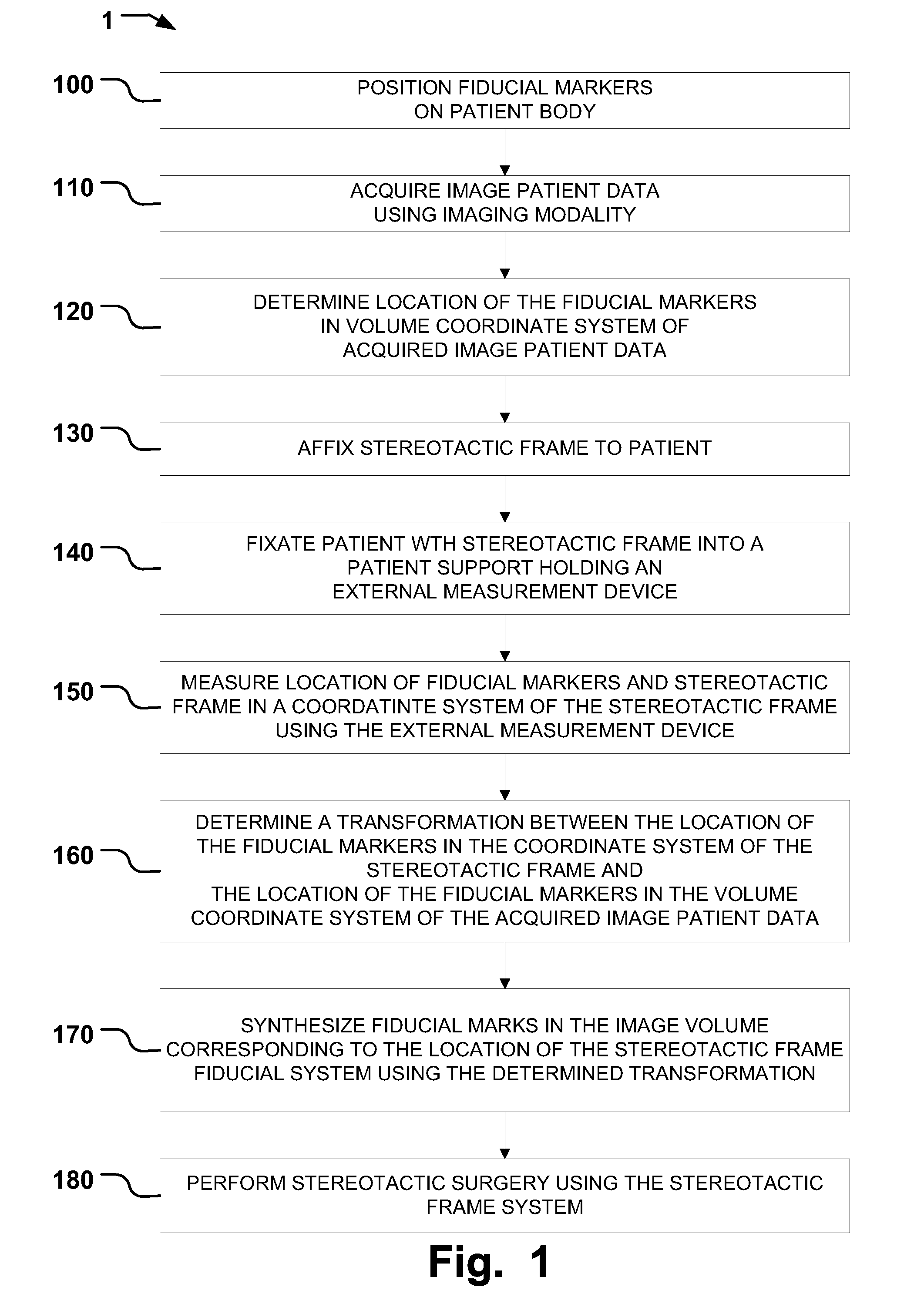
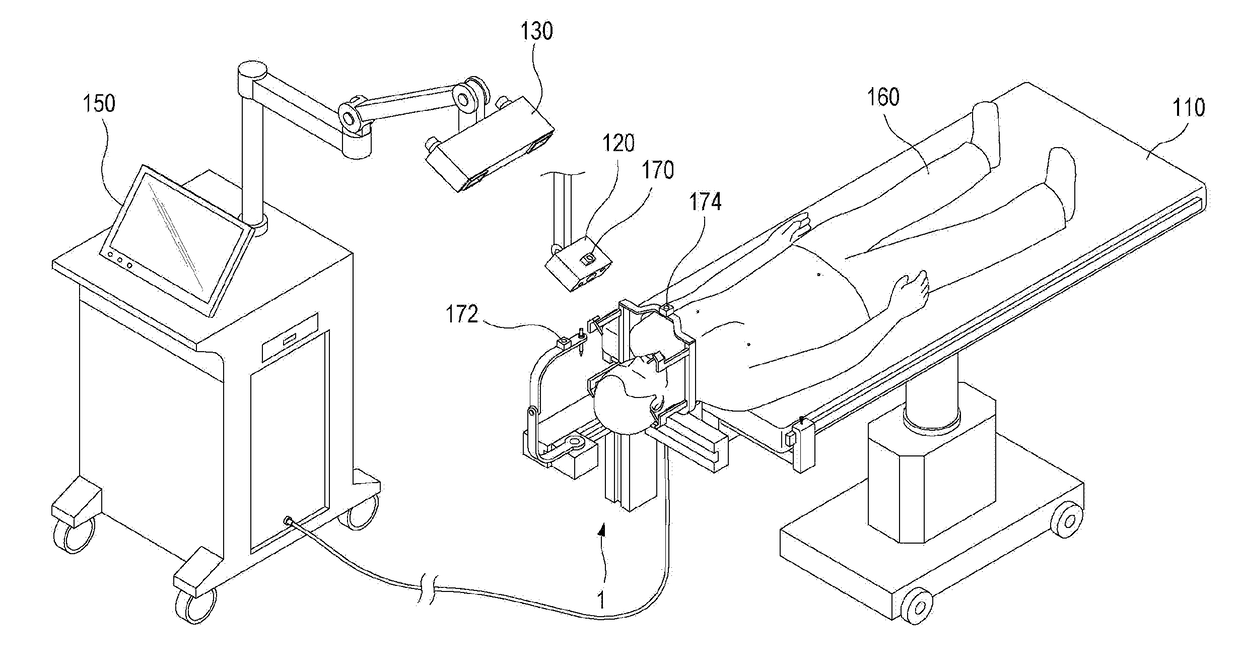
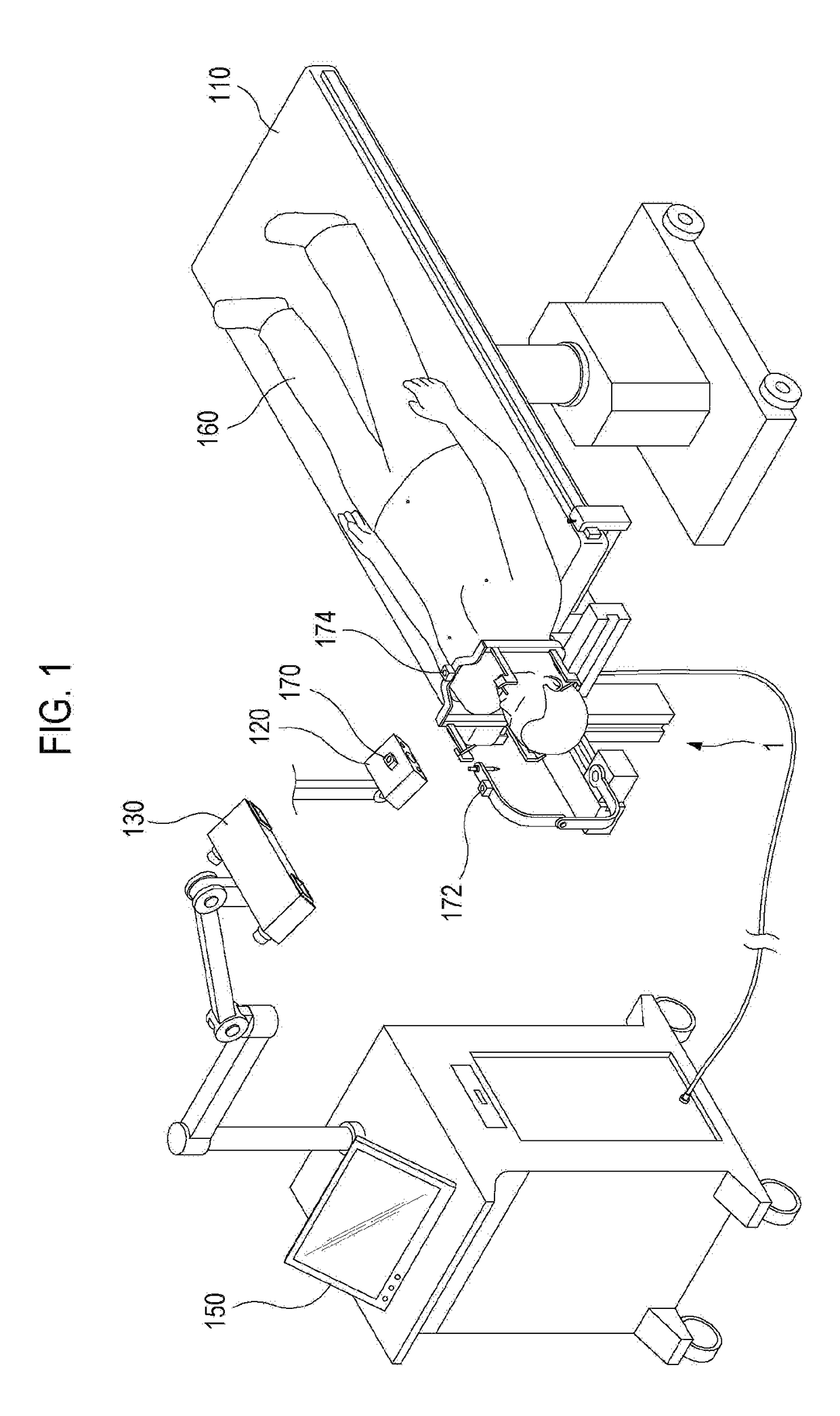
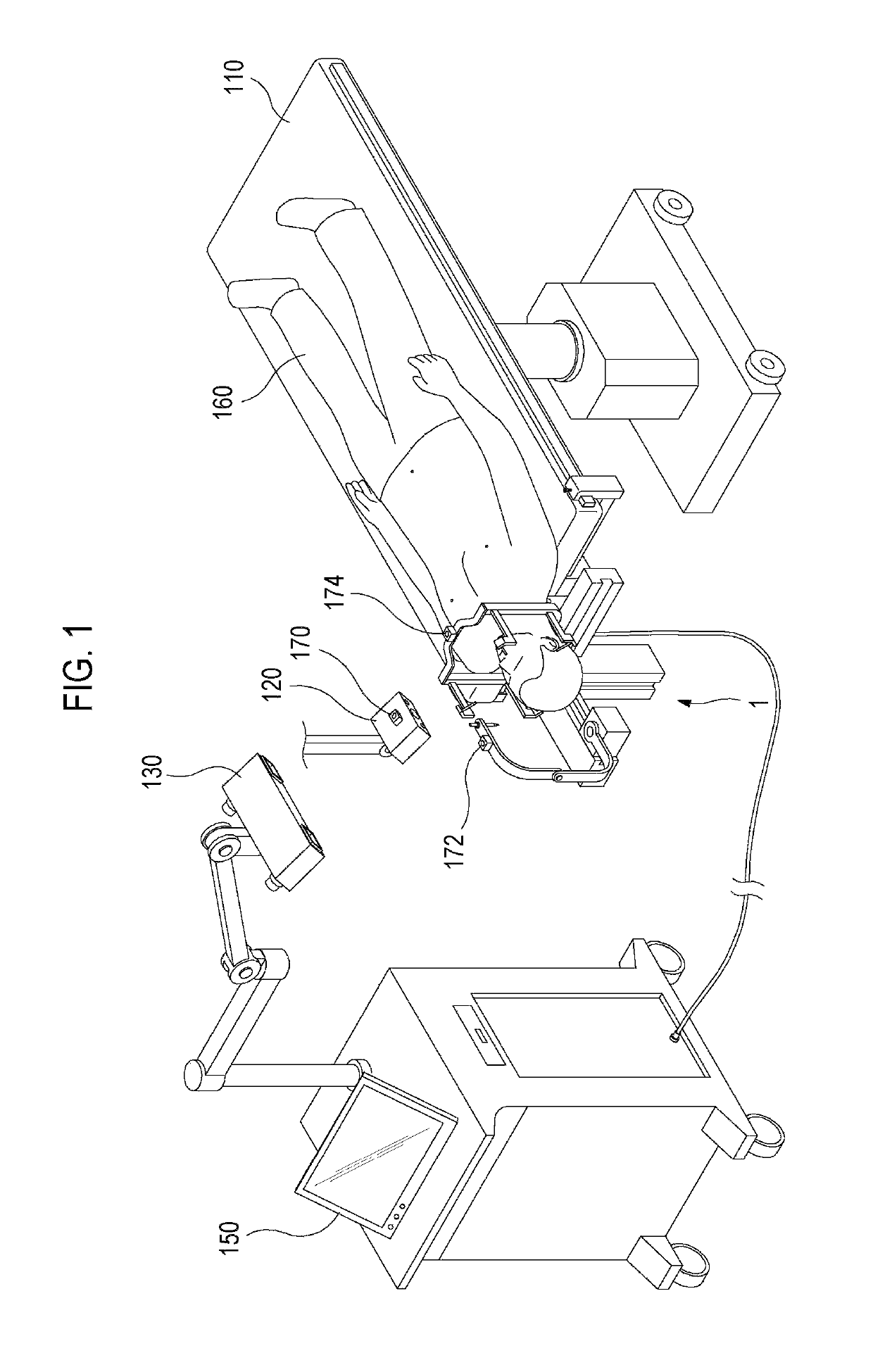
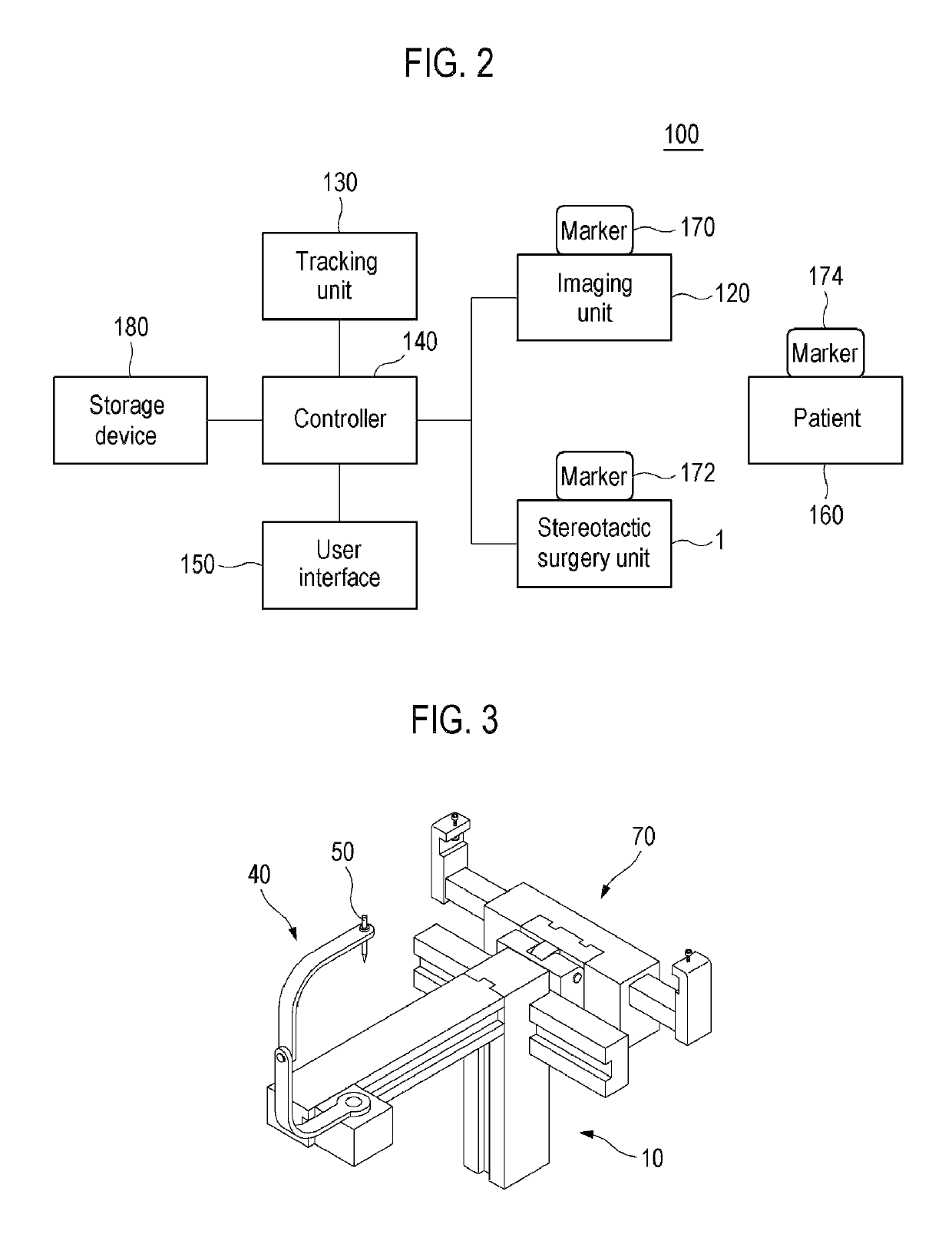
A stereotactic navigation system for navigating an instrument to a target within a patient may include a stereotactic head frame, an imaging device, a tracking device, a controller and a display. The stereotactic head frame is coupled to the patient and is used to assist in guiding the instrument to the target. The imaging device captures image data of the patient and of the stereotactic head frame. The tracking device is used to track the position of the instrument relative to the stereotactic head frame. The controller receives the image data from the imaging device and identifies the stereotactic head frame in the image data and automatically registers the image data with navigable patient space upon identifying the stereotactic head frame, while the display displays the image data.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH
Direct visualization robotic intra-operative radiation therapy applicator device
ActiveUS8092370B2Increase probabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryX-rayTherapeutic effect
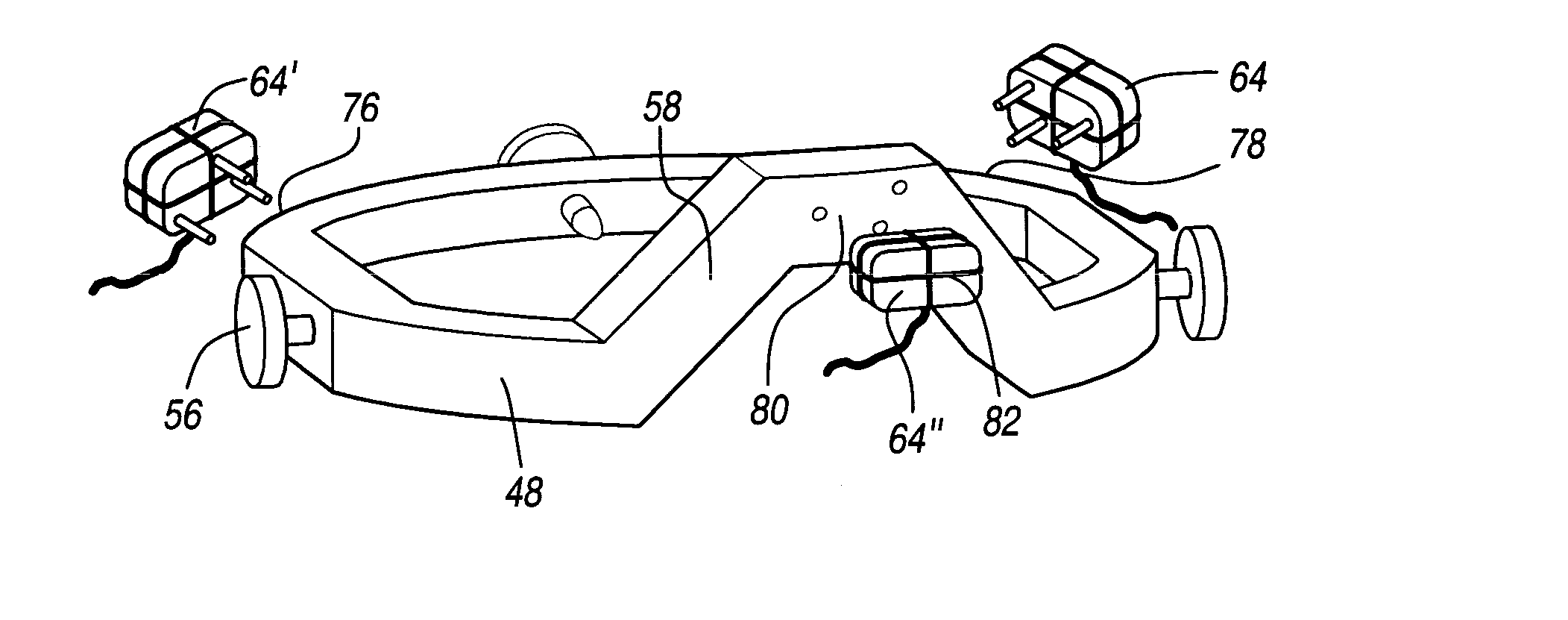
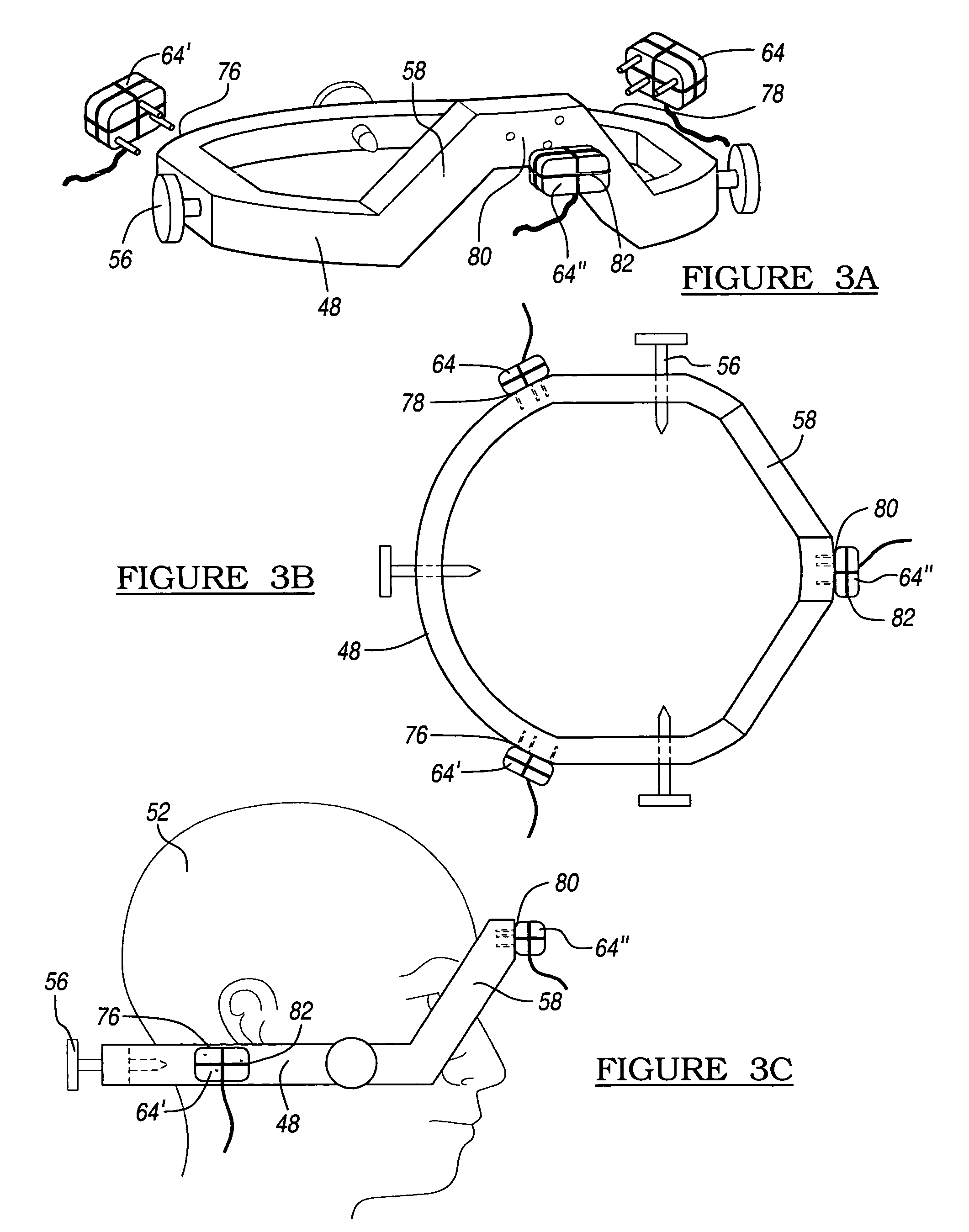
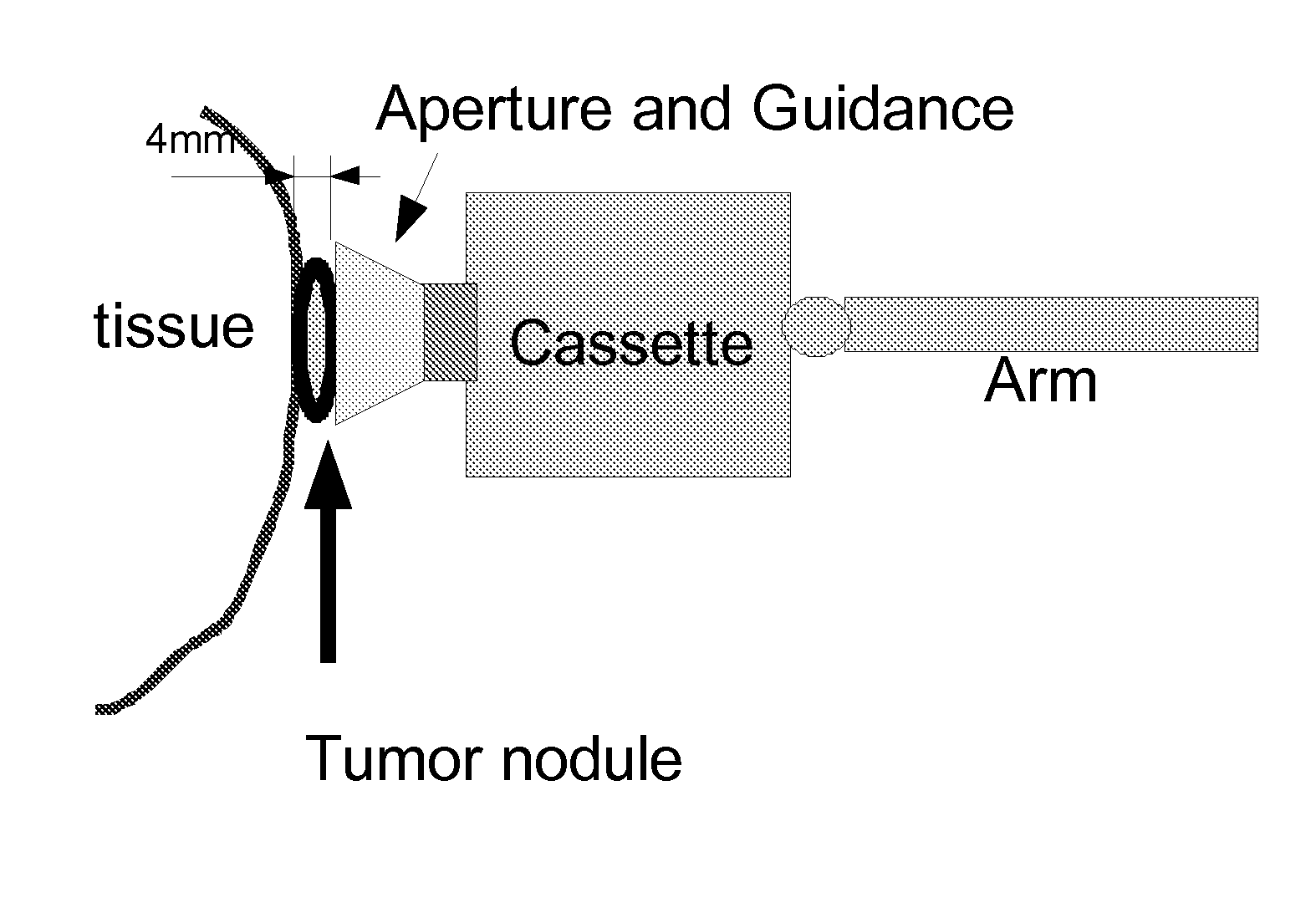
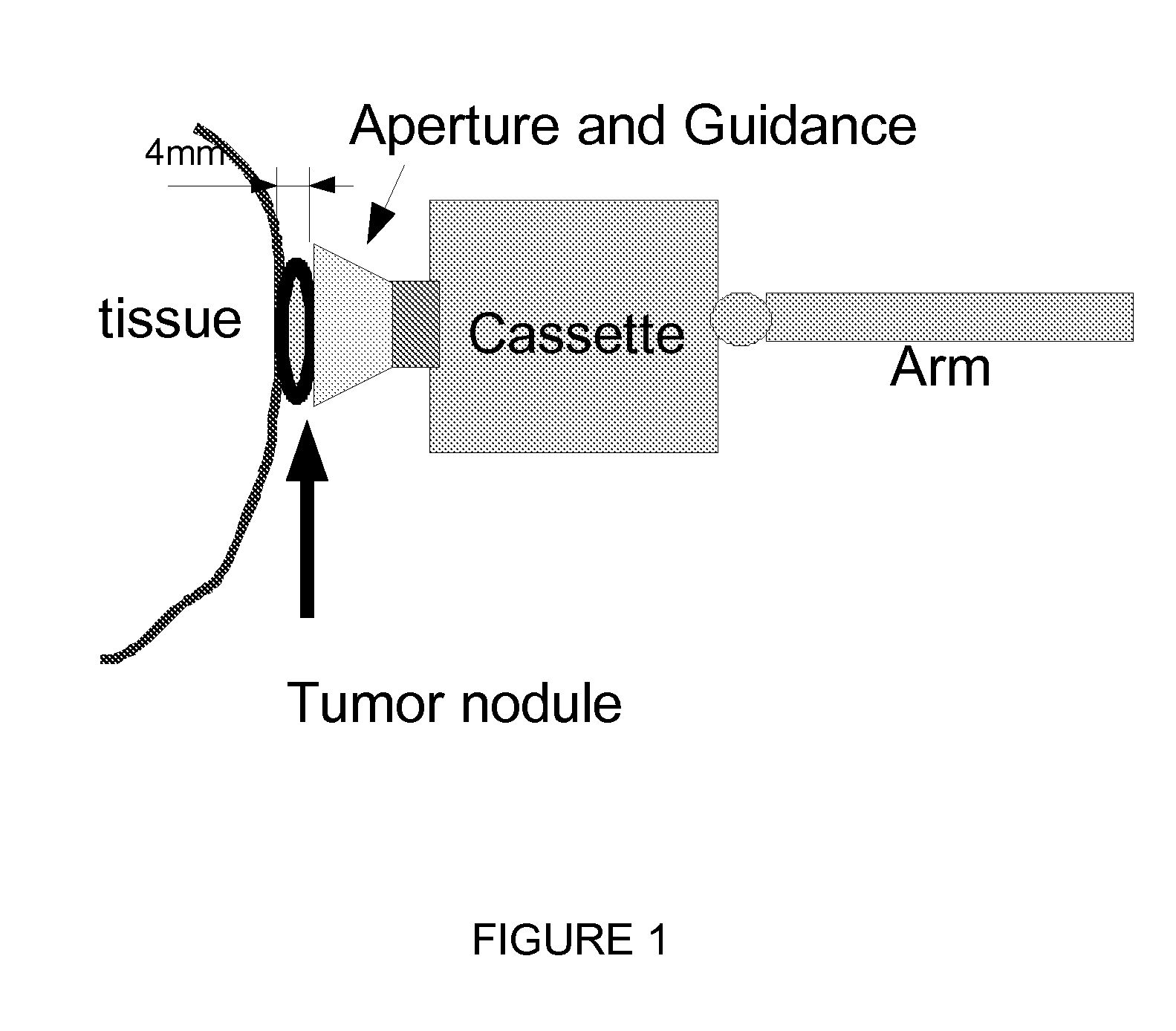
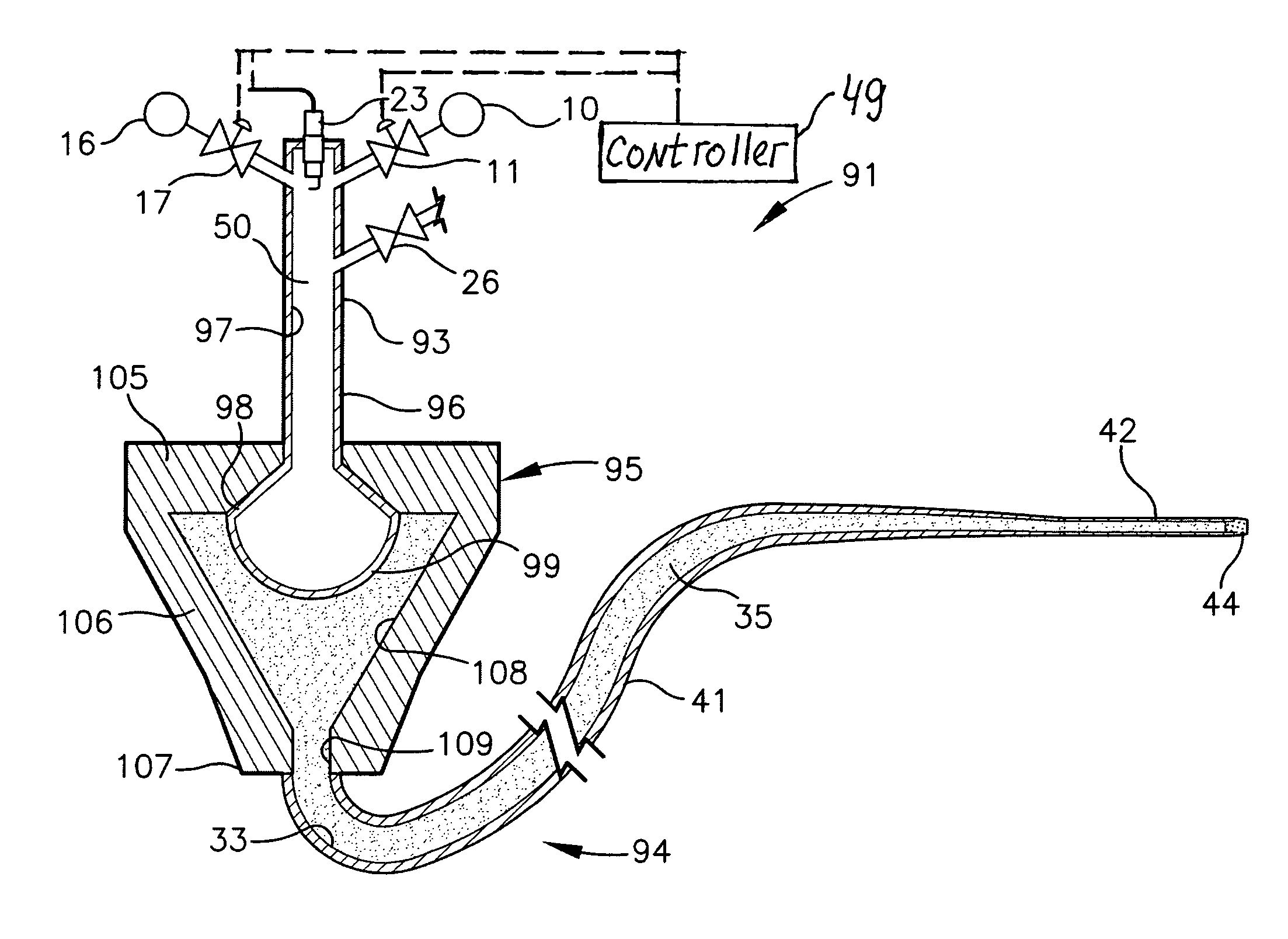
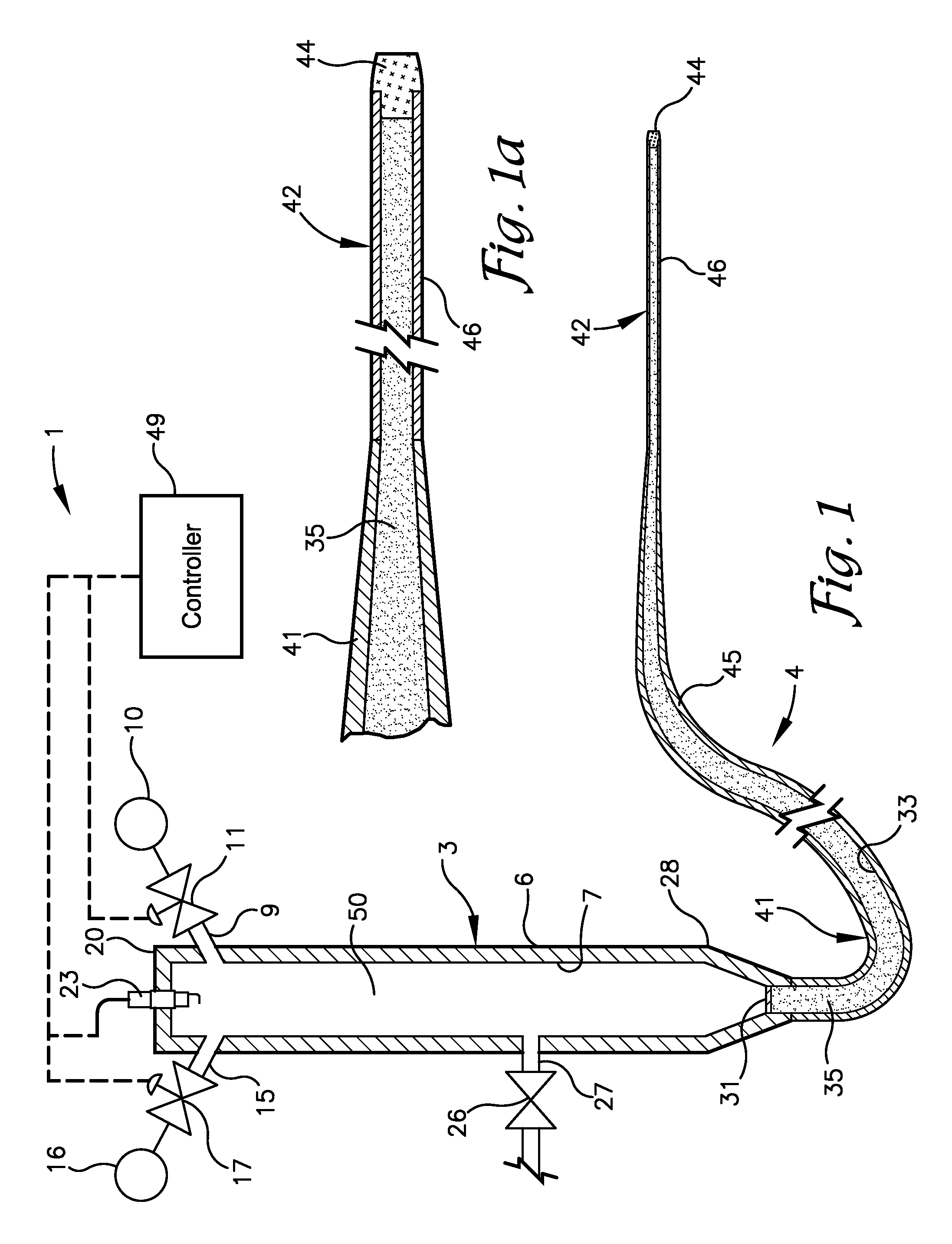
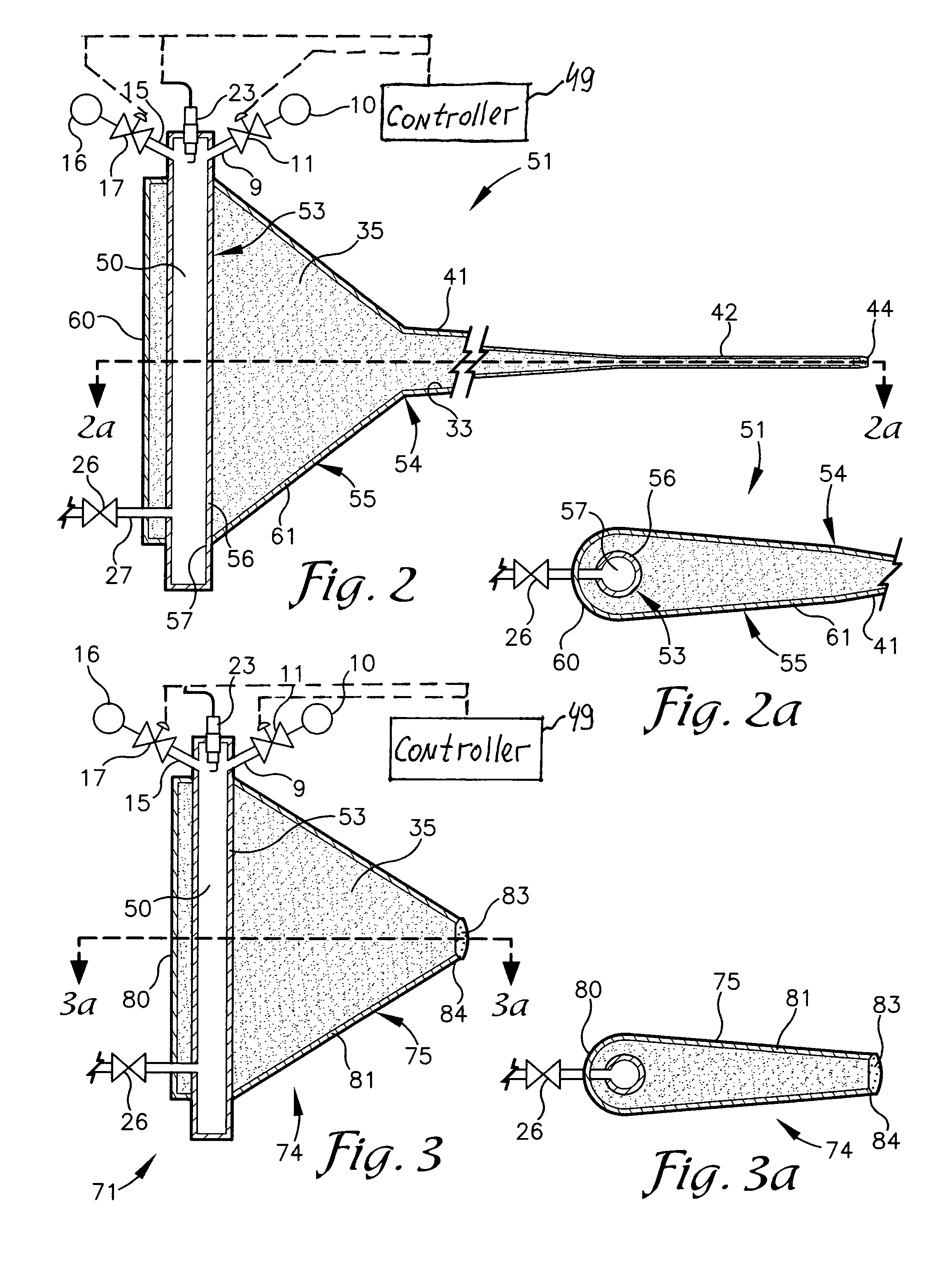
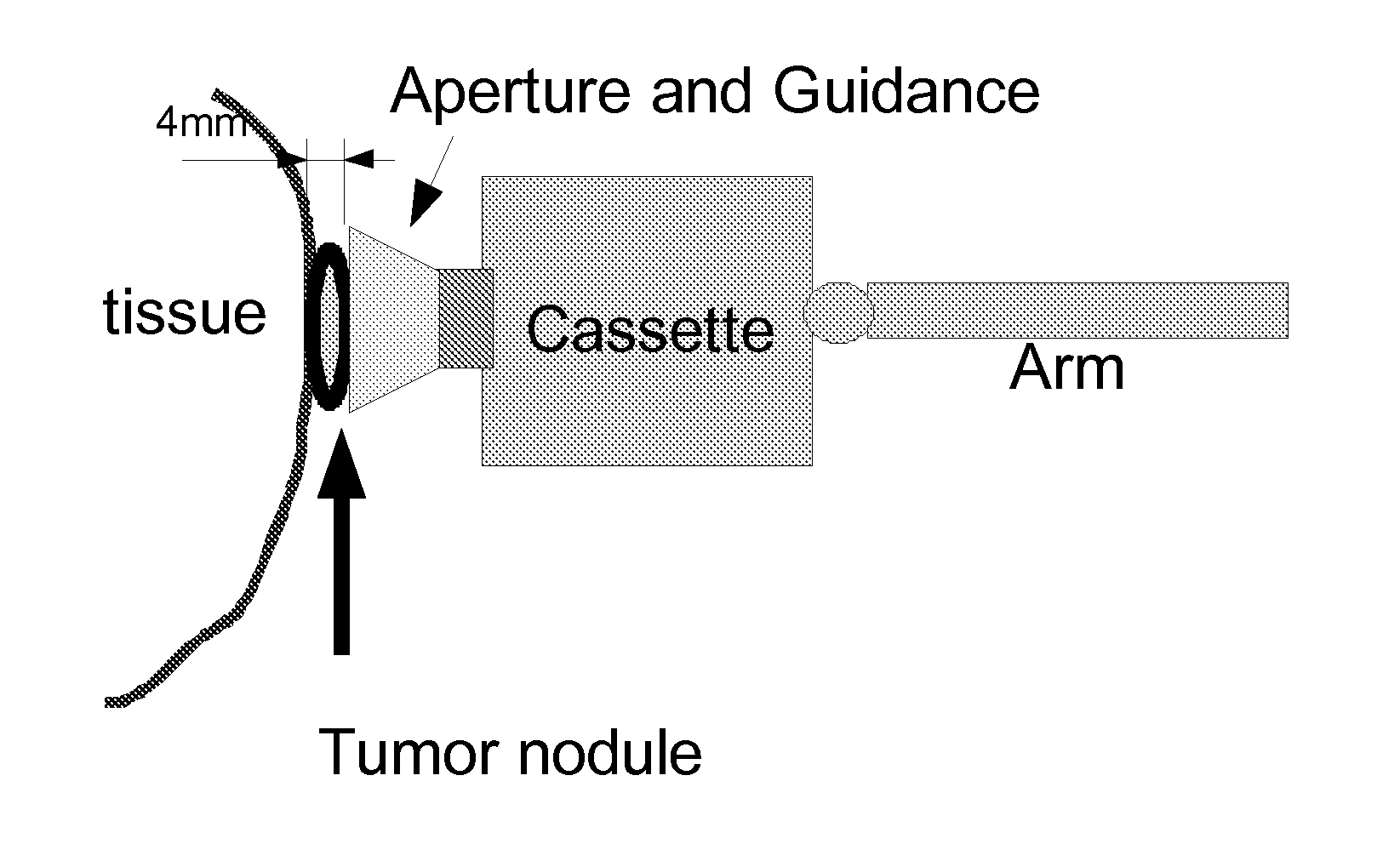
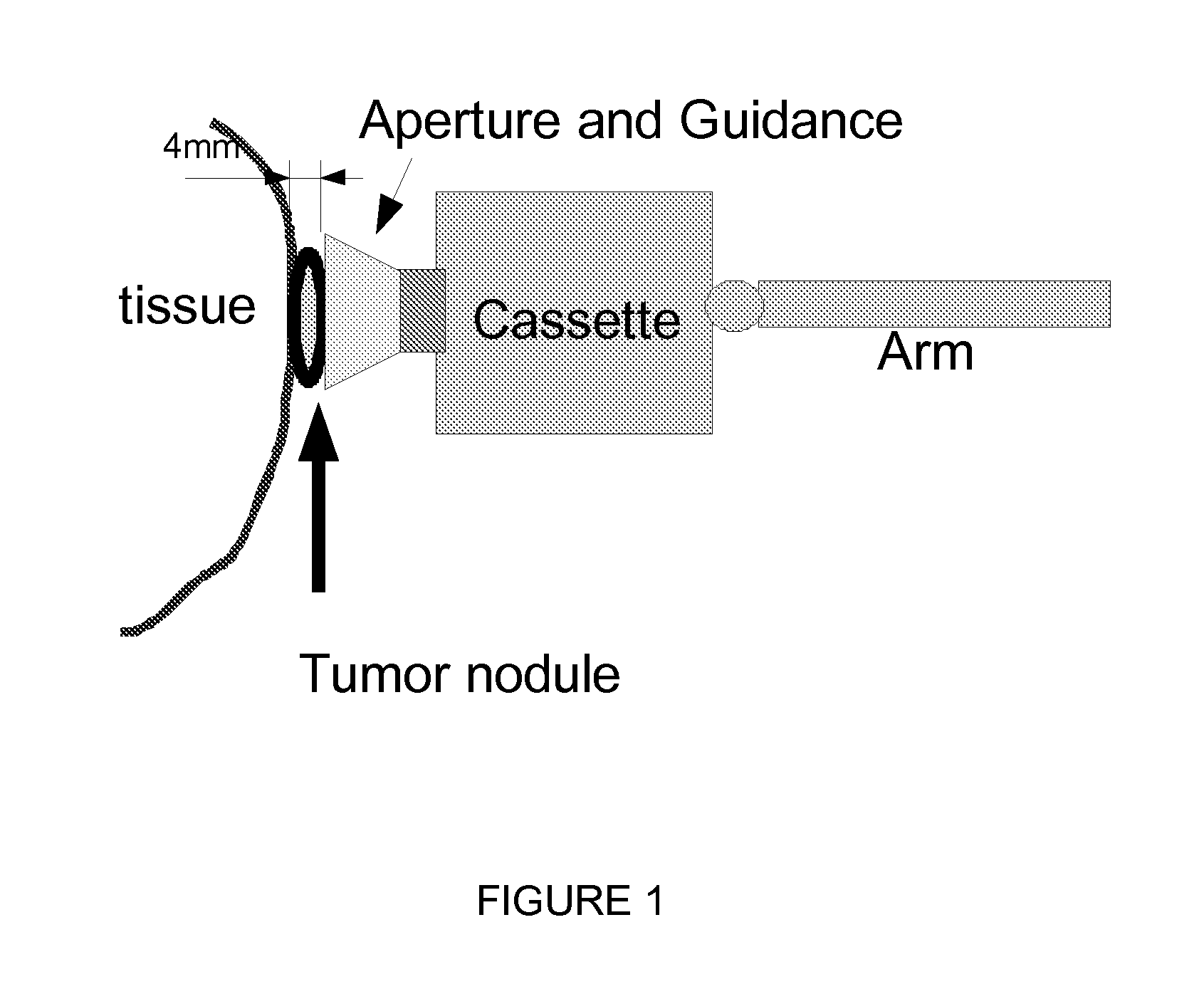
This invention proposes a robotic applicator device to be deployed internally to a patient having a capsule (also referred to as a cassette) and aperture with a means of alternately occluding and exposing a radioactive source through the aperture. The capsule and aperture will be integrated with a surgical robot to create a robotic IORT (intra-operative radiation therapy) applicator device as more fully described below. The capsule, radiation source, and IORT applicator arm would be integrated to enable a physician, physicist or technician to interactively internally view and select tissue for exposure to ionizing radiation in sufficient quantities to deliver therapeutic radiation doses to tissue. Via the robotic manipulation device, the physician and physicist would remotely apply radiation to not only the tissue to be exposed, but also control the length of time of the exposure. Control means would be added to identify and calculate margin and depth of tissue to be treated and the proper radiation source or radioactive isotope (which can be any particle emitter, including neutron, x-ray, alpha, beta or gamma emitter) to obtain the desired therapeutic effects. The invention enables stereotactical surgery and close confines radiation therapy adjacent to radiosensitive tissue.
Owner:SRIORT
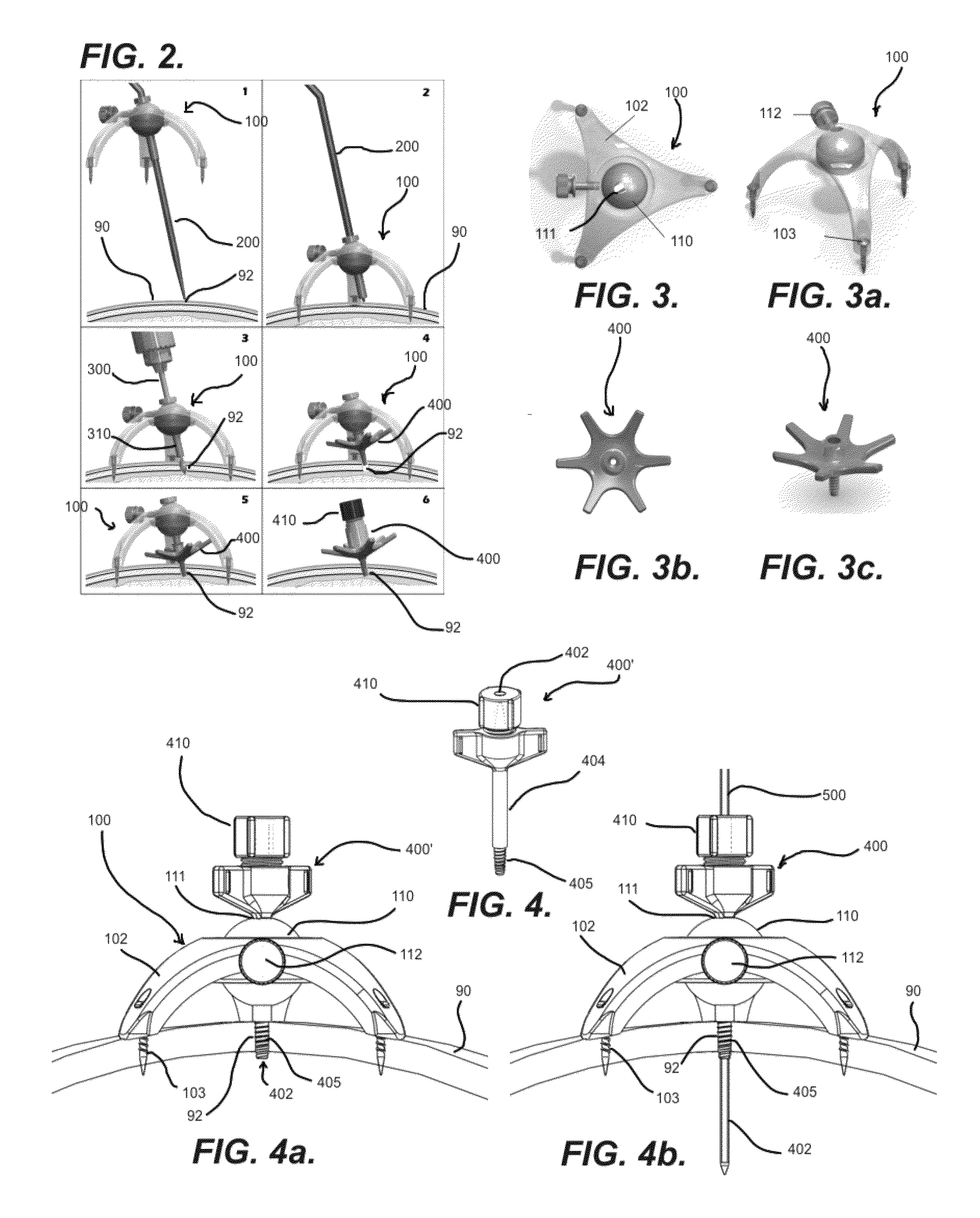
Versatile stereotactic device and methods of use
InactiveUS6684098B2Easy to checkEasily and repeatedly examinedDiagnostic markersComputer-aided planning/modellingFollow up examinationResonance
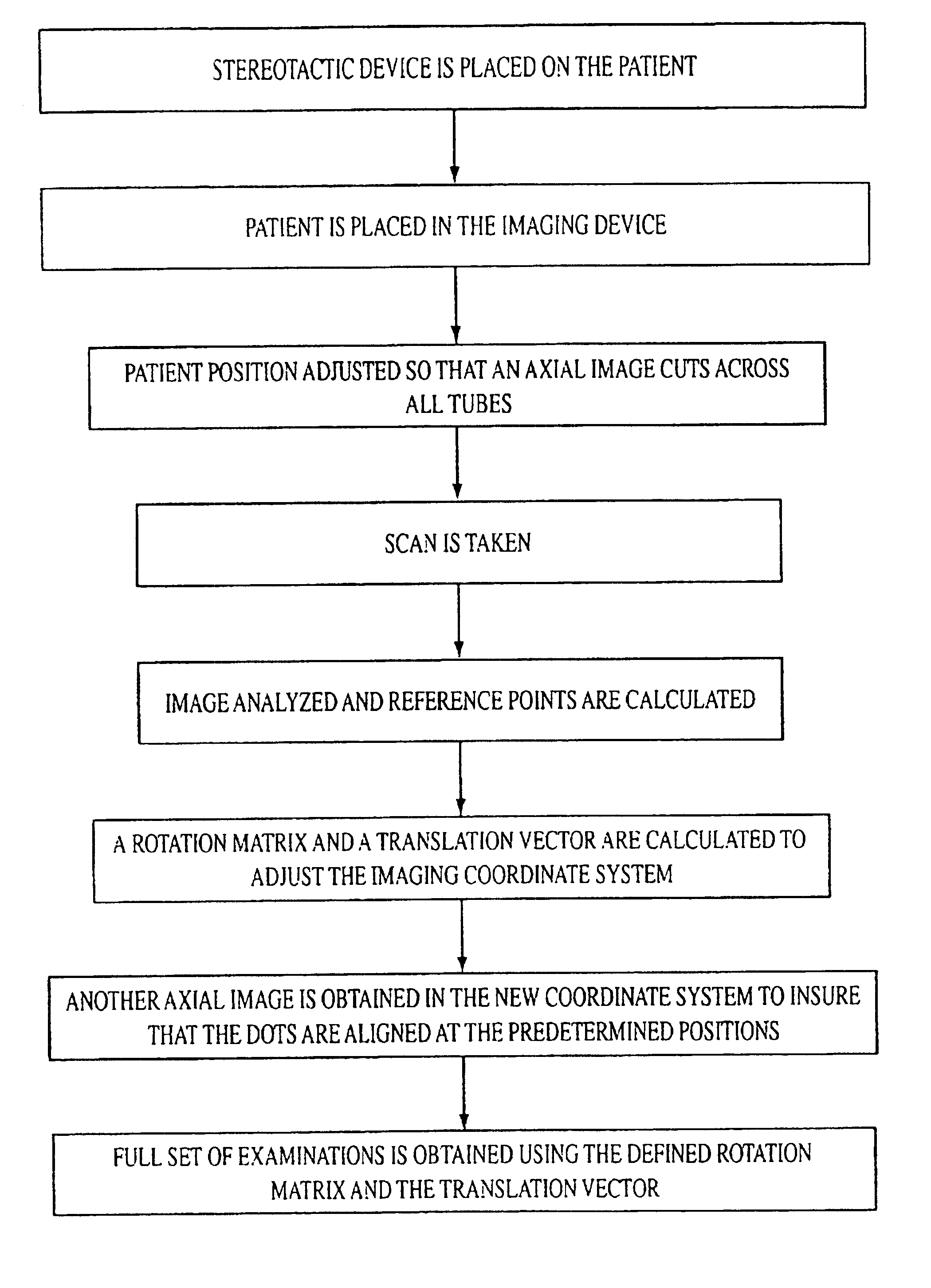
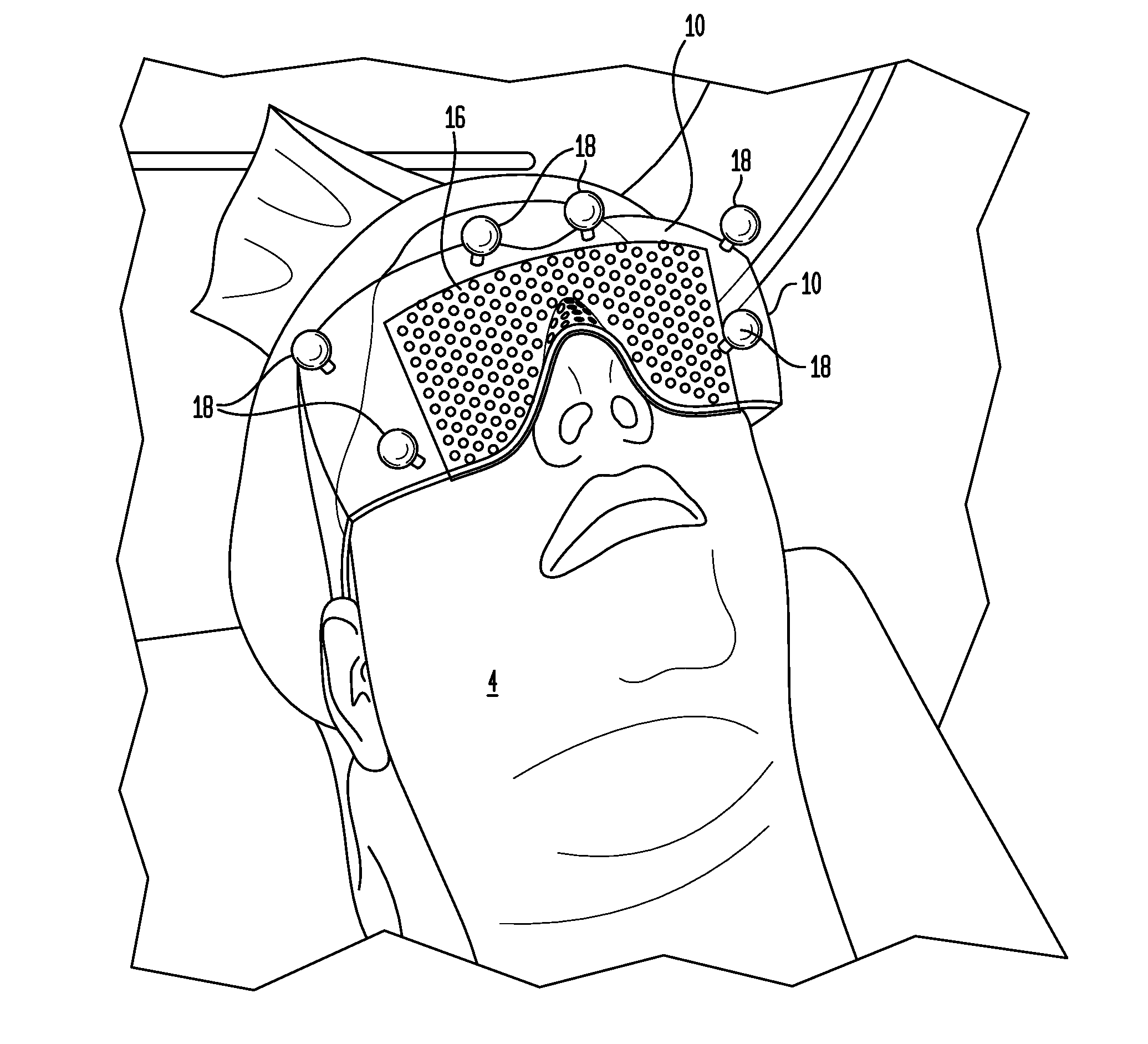
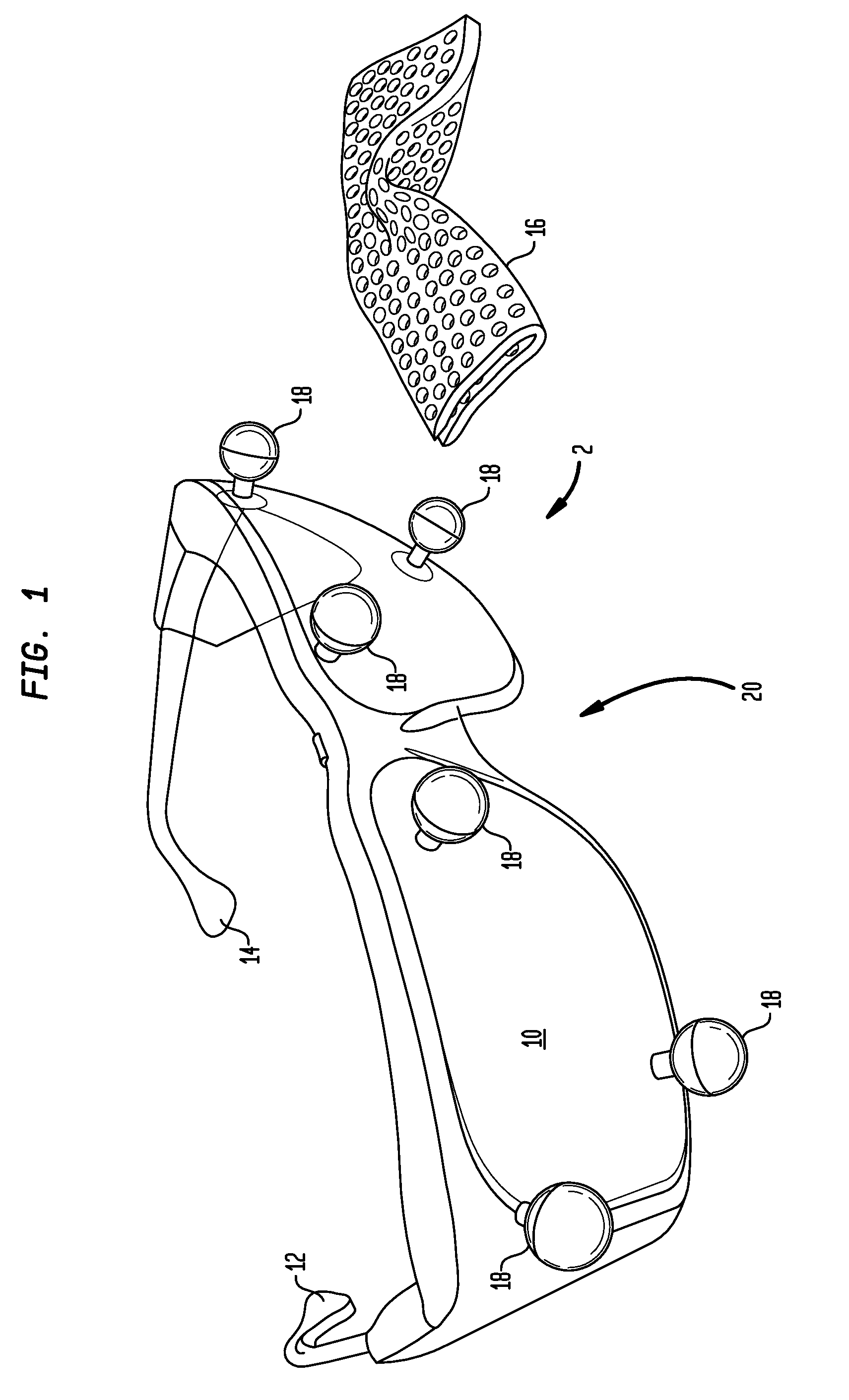
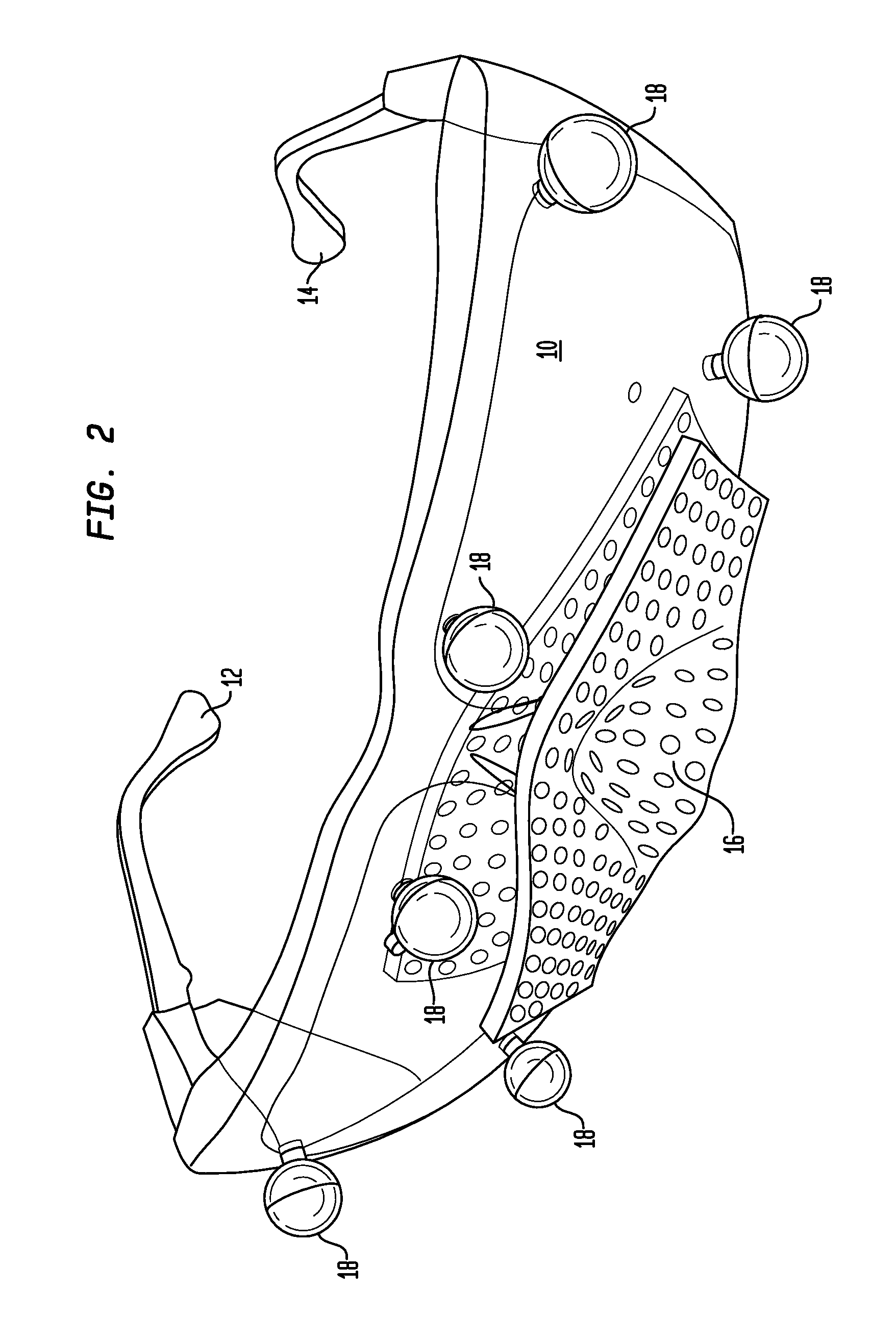
A stereotactic device for use with an imager such as a magnetic resonance imager is disclosed, which permits an imaging scan to be taken with reference to a personal coordinate system (or PCS) that is independent of a machine coordinate system (or MCS). Methods using the device to obtain imaging scans are described such that the imaging scans are superimposable even if taken at different time periods using the same or a different imager. The device comprises a frame that can be reproducibly positioned on a subject and which is equipped with non-invasive affixing means and localizing means that provide the PCS. The device and methods of the invention are particularly well suited for routine initial or follow-up examinations, pre-surgical planning and post-surgical evaluation. Markers on a stereotactic device can be tracked during an MRI scan to compensate for patient motion during the scan.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Stereotactic access devices and methods
ActiveUS20130053867A1Wide range of usesAccelerated trainingDiagnosticsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryStereotaxisMedical device
This invention is directed to devices and methods for stereotactic access, and particularly to a frameless stereotactic access device for accessing a body cavity and methods therefor. In general, a stereotactic device may include portions or features for fixing the device to a portion of a patient's body, such as, for example, a skull, such that the device may be generally spatially fixed in relation to the patient's body or part thereof. The stereotactic device may also generally include portions or features for guiding a medical device or other device at a particular trajectory in relation to the patient's body or part thereof.
Owner:VISUALASE
Versatile stereotactic device
InactiveUS6080164AAccurate and reproducible resultEasy to useComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringFollow up examinationNon invasive
A stereotactic device for use with an imager is disclosed, which permits an imaging scan to be taken with reference to a personal coordinate system (or PCS) that is independent of a machine coordinate system (or MCS). Methods using the device to obtain imaging scans are described such that the imaging scans are superimposable even if taken at different time periods using the same or a different imager. The device comprises a frame that can be reproducibly positioned on a subject and which is equipped with non-invasive affixing means and localizing means that provide the PCS. The device and methods of the invention are particularly well suited for routine initial or follow-up examinations, pre-surgical planning and post-surgical evaluation.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Stereotactic Therapy System
InactiveUS20110098722A1Less cumbersomeTime and cost-efficient therapyDiagnostic markersDiagnostic recording/measuringFrame basedStereotactic radiotherapy
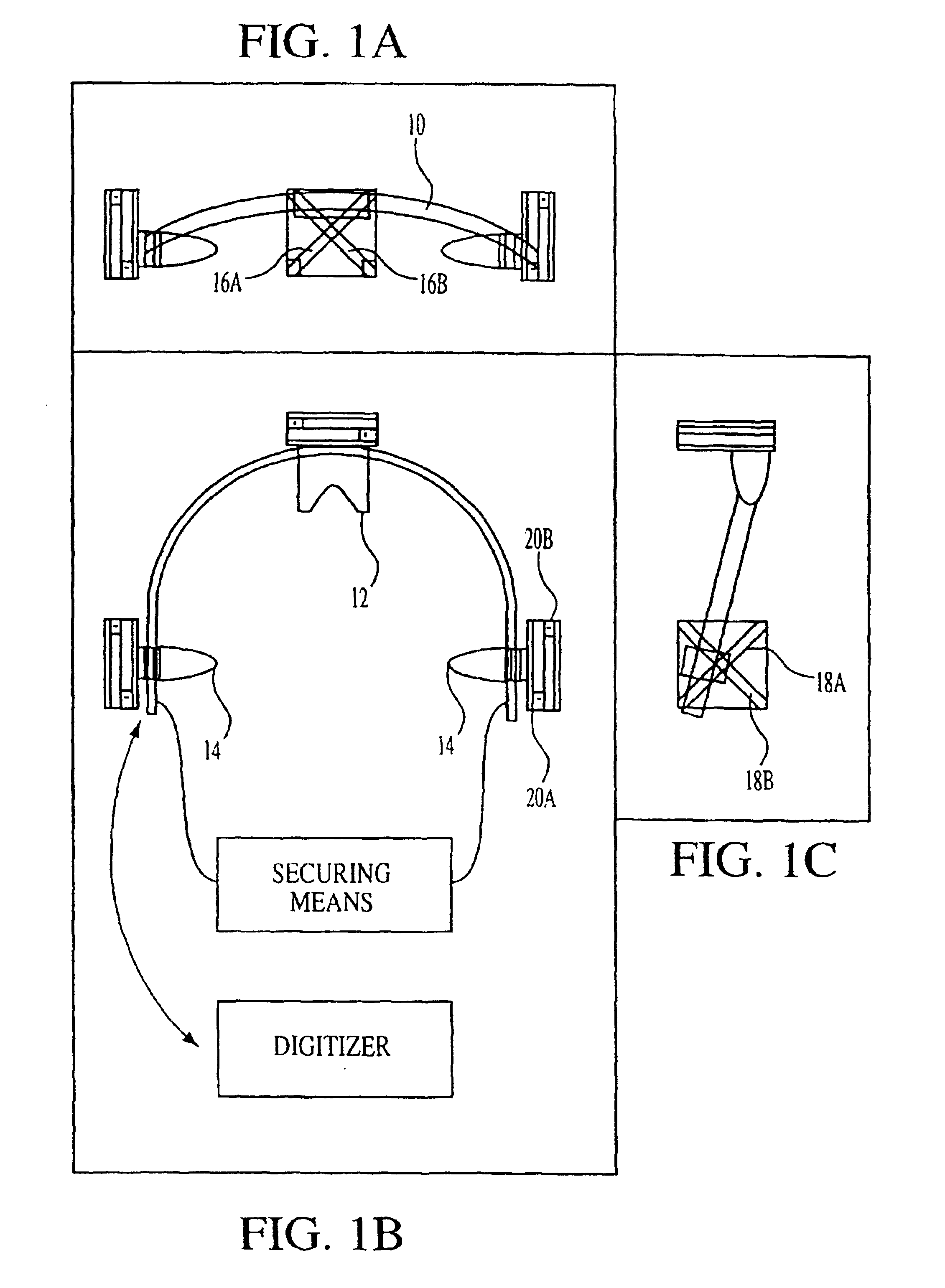
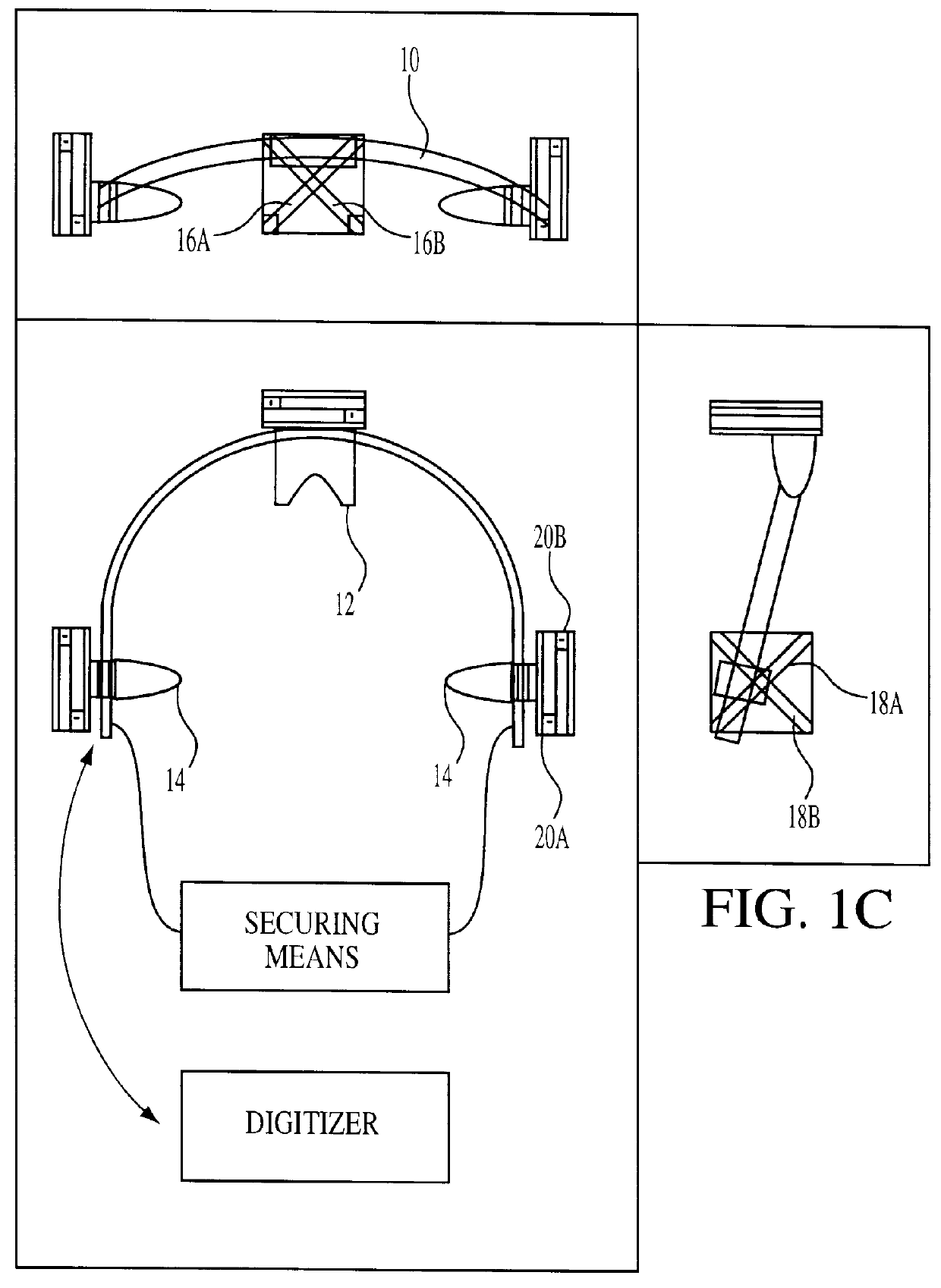
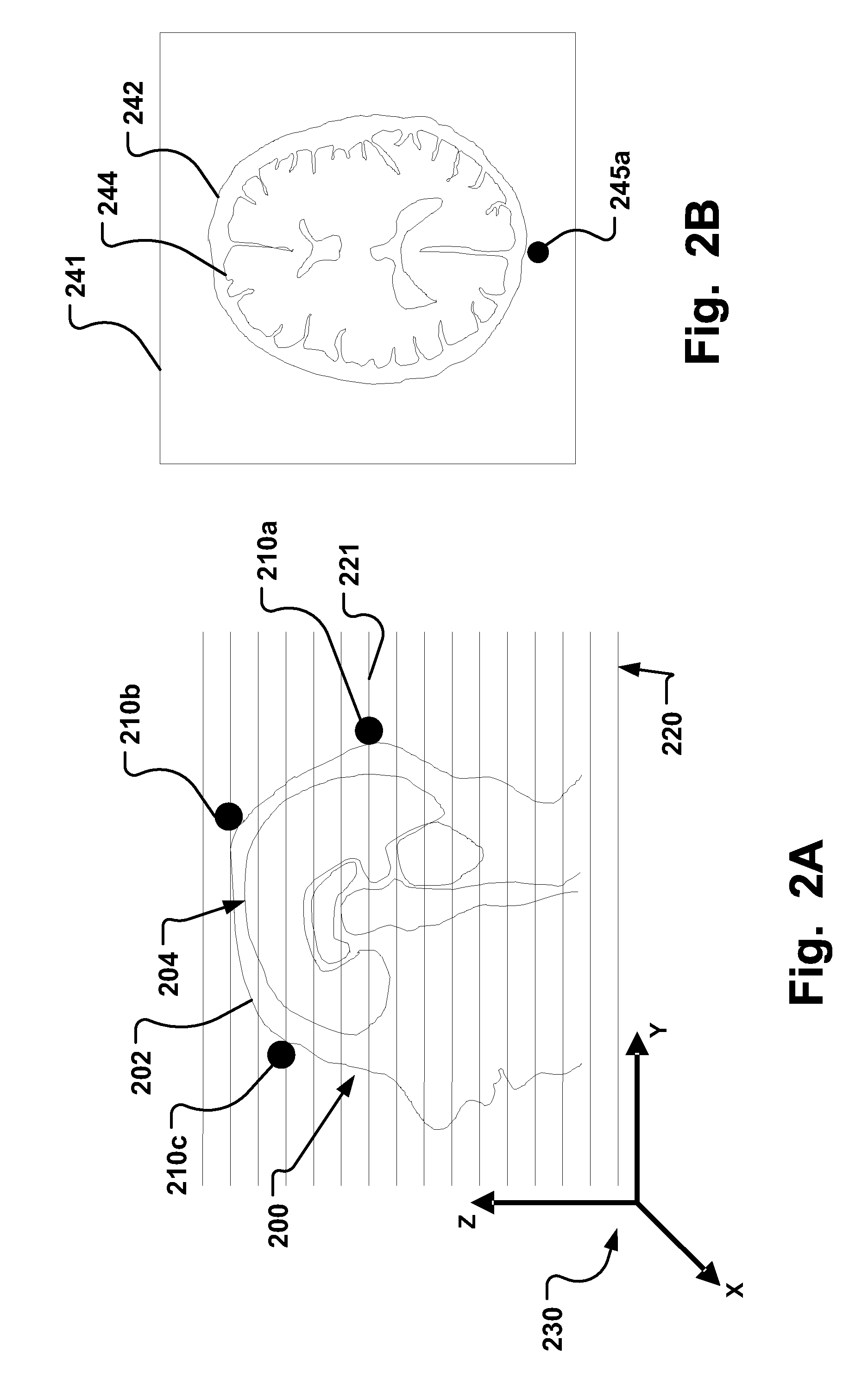
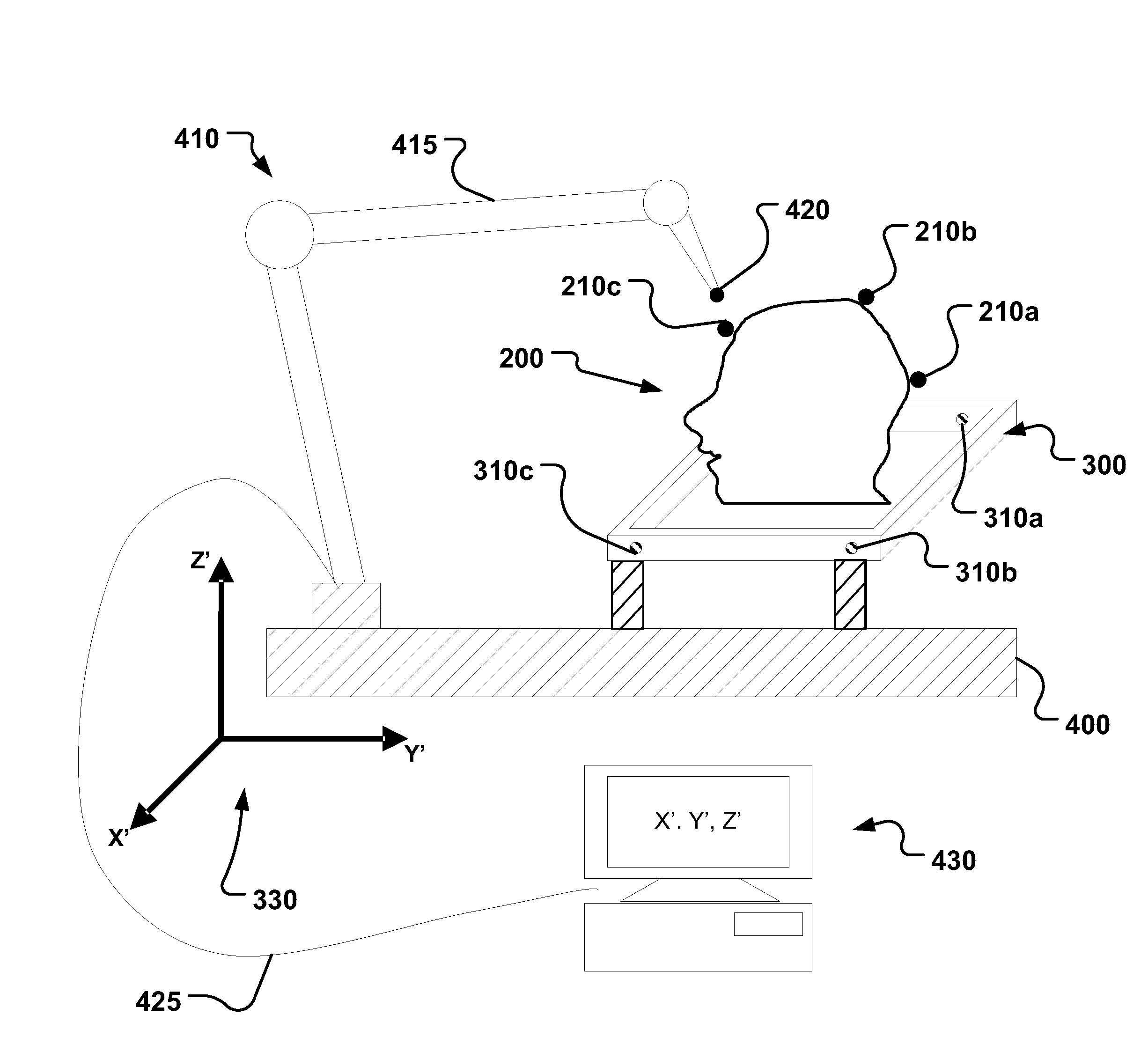
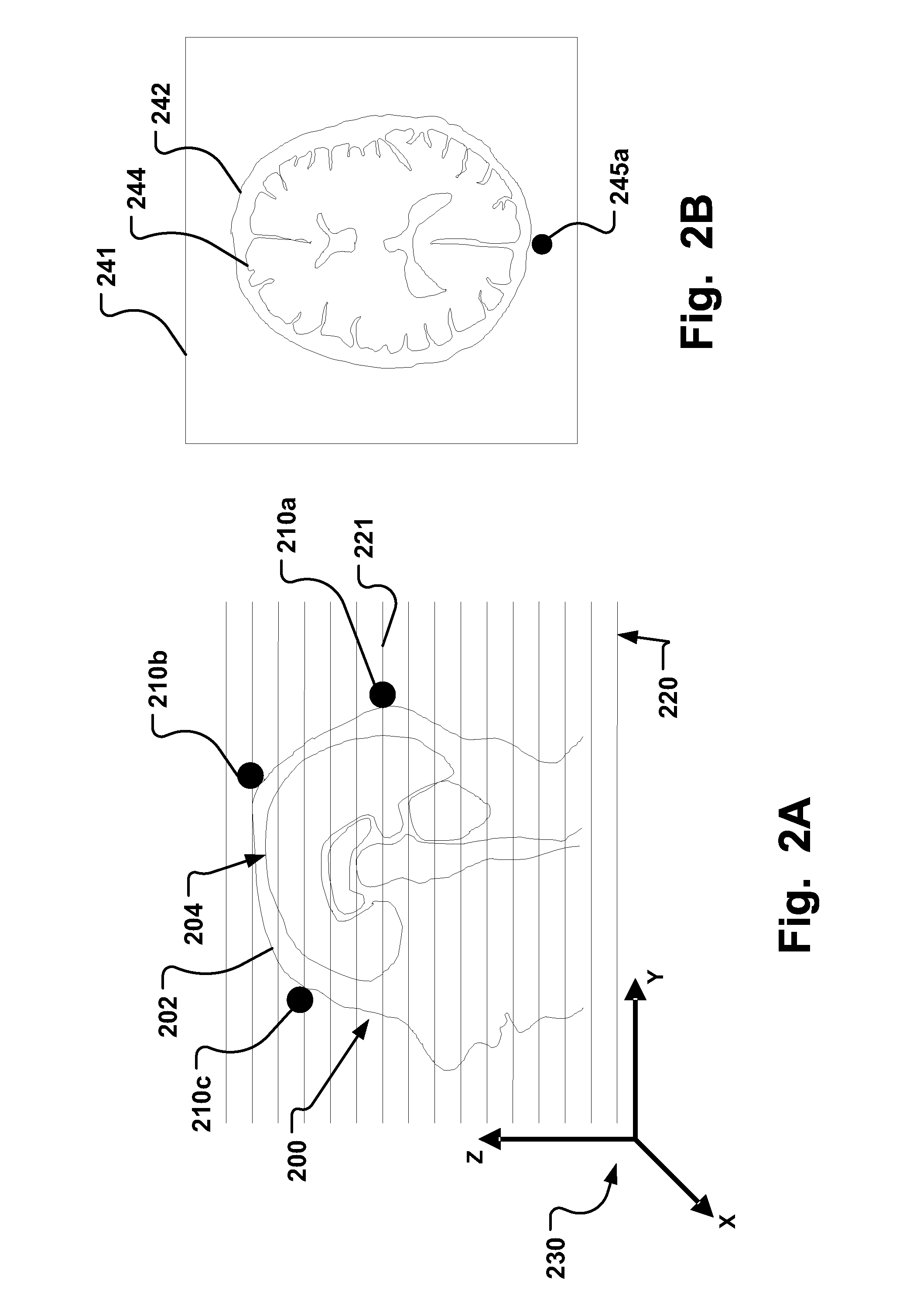
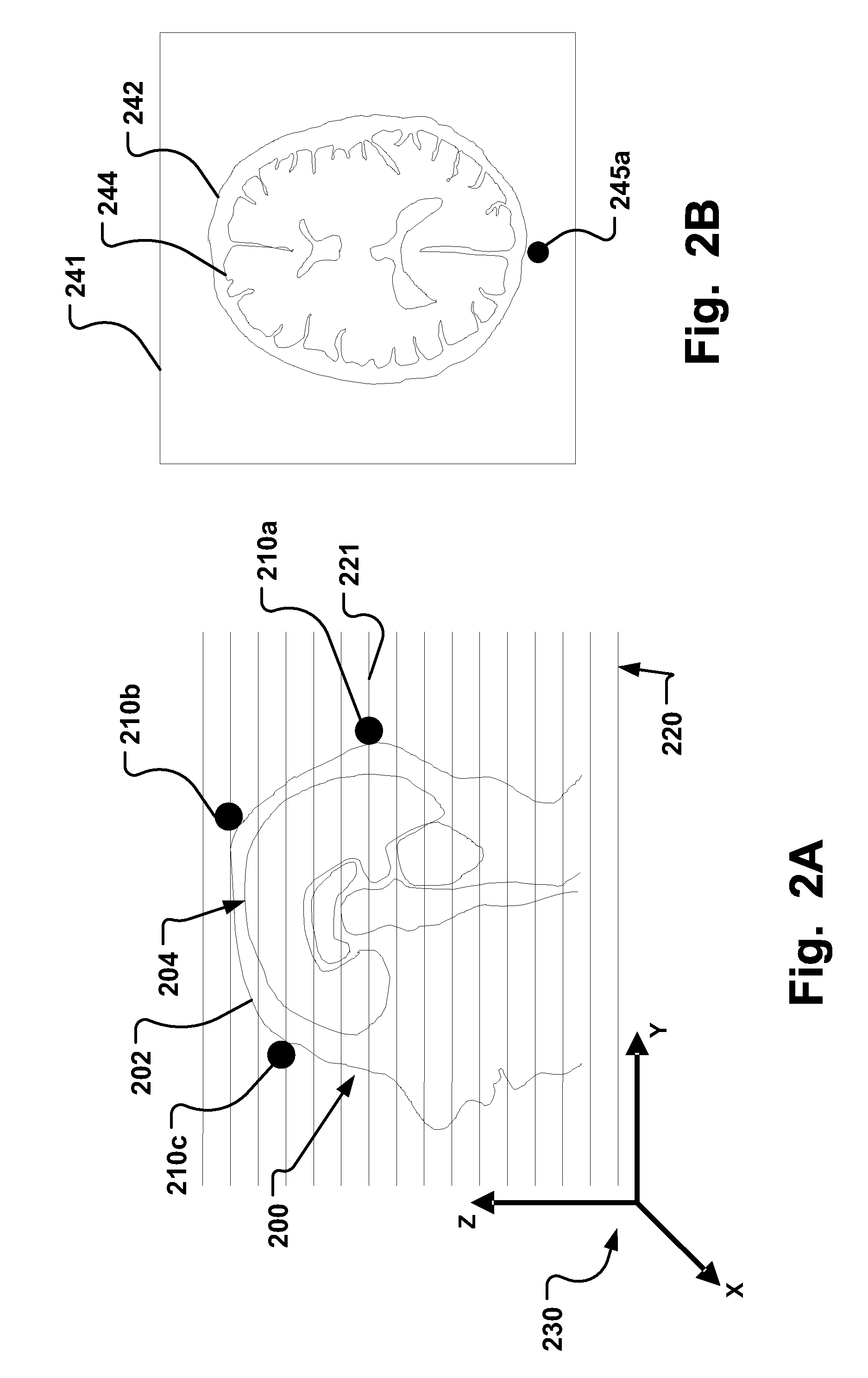
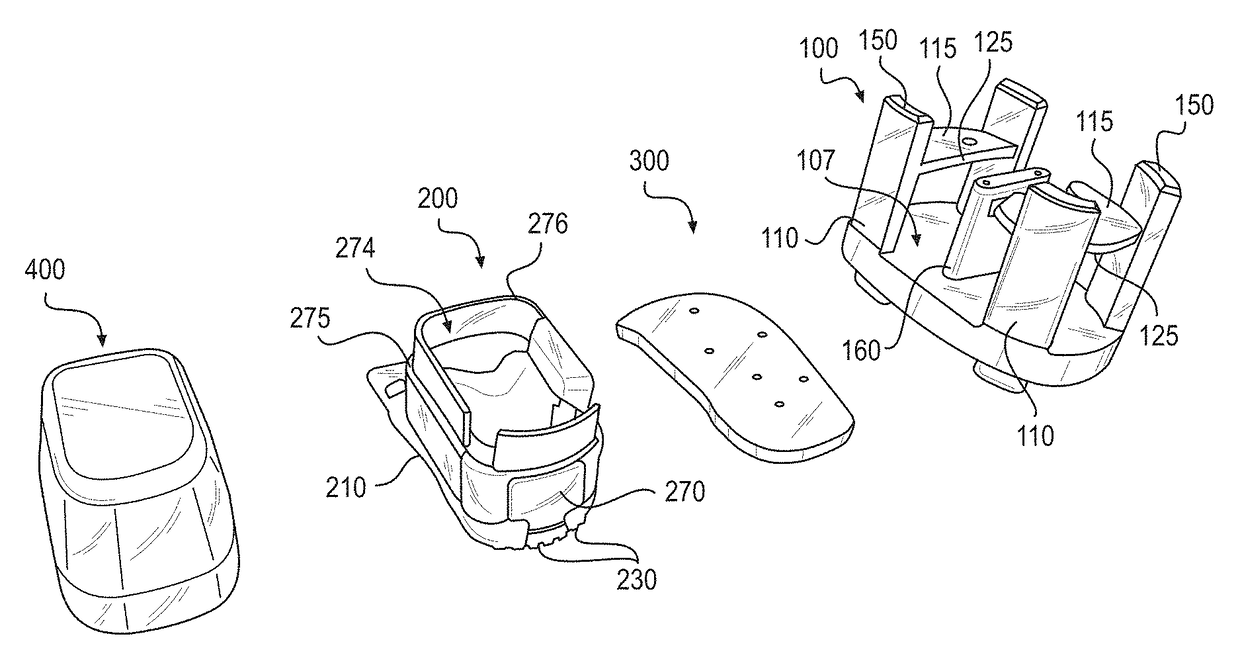
A fiducial marker system (210a-c) comprises a first unit and a second unit. The first unit is patient affixable and comprises a partly spherical inner surface having a first center point that is adapted to receive a touch probe measurement head for measuring the spatial position of the center point. The second unit is releasably attachable to an outer surface of the first unit, and has a second center point, wherein the first center point and the second center point are substantially identical when the second unit is attached to the first unit. For stereotactic therapy, a patient is imaged with the first and second unit assembled. Then the second unit is detached. A stereotactic frame (300) is attached to the first units via arms. Thus frameless imaging is provided in a frame based stereotactic surgery system with high precision. Repeated assembly of the frame (300) to the first units, remaining in the patient, provides advantageous fractionized stereotactic radiotherapy.
Owner:KAROLINSKA INNOVATIONS AB
Versatile stereotactic device and methods of use
InactiveUS20010020127A1Accurate and reproducible resultEasy to useDiagnostic markersSurgical instrument detailsFollow up examinationResonance
A stereotactic device for use with an imager such as a magnetic resonance imager is disclosed, which permits an imaging scan to be taken with reference to a personal coordinate system (or PCS) that is independent of a machine coordinate system (or MCS). Methods using the device to obtain imaging scans are described such that the imaging scans are superimposable even if taken at different time periods using the same or a different imager. The device comprises a frame that can be reproducibly positioned on a subject and which is equipped with non-invasive affixing means and localizing means that provide the PCS. The device and methods of the invention are particularly well suited for routine initial or follow-up examinations, pre-surgical planning and post-surgical evaluation. Markers on a stereotactic device can be tracked during an MRI scan to compensate for patient motion during the scan.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Head and facial marker semiautomatic calibration method for neurosurgical stereotactic surgery
InactiveCN103251457AEasy to operateImprove registration accuracyDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsSoftware systemStereotactic surgery
The invention relates to a head and facial marker semiautomatic calibration method for a neurosurgical stereotactic surgery. The method includes aiming to a feature that automatic calculation of a computer requires quantization rules, after selecting an initial marking point, selecting relative points as facial points on the head of a patient according to a certain rule; and allowing a computer software system to calculate corresponding facial marking points automatically according to a relative rule, and thus, applying the two groups of the marking points to realize registration between space and image space of the patient. The method can be used under the condition of unadaptable or insufficient time to stick facial markers, head and facial features of the patient can be selected by a computer in three-dimensional images semiautomatically, and the neurosurgical stereotactic surgery without sticking marking points outside and a frame can be performed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Stereotactic shockwave surgery and drug delivery apparatus
InactiveUS8684970B1Promote bone growthGood cell membrane permeabilityUltrasound therapyMedical devicesDetonationCatheter
A therapeutic apparatus for treating body tissue comprises a vessel enclosing a detonation chamber into which a detonatable mixture is introduced and then detonated using an igniter to form at least one shockwave and / or acoustic wave. A wave guide assembly having a converging geometry directs the wave to a tip of the wave guide assembly that is placed in contact with tissue to be treated by the wave. The wave guide assembly may include a wave focusing section surrounding the vessel, a flexible conduit connected to the wave focusing section and a needle connected to the conduit and sized for insertion into patient tissue to be treated. A cap connected to the end of the needle is formed from material permitting the wave or waves generated in the detonation chamber to pass therethrough to treat the patient tissue into which the needle is inserted.
Owner:MEDICAL SHOCKWAVES
Direct Visualization Robotic Intra-Operative Radiation Therapy Applicator Device
ActiveUS20100280374A1Increase probabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgerySurgical robotTherapeutic effect
This invention proposes a robotic applicator device to be deployed internally to a patient having a capsule (also referred to as a cassette) and aperture with a means of alternately occluding and exposing a radioactive source through the aperture. The capsule and aperture will be integrated with a surgical robot to create a robotic IORT (intra-operative radiation therapy) applicator device as more fully described below. The capsule, radiation source, and IORT applicator arm would be integrated to enable a physician, physicist or technician to interactively internally view and select tissue for exposure to ionizing radiation in sufficient quantities to deliver therapeutic radiation doses to tissue. Via the robotic manipulation device, the physician and physicist would remotely apply radiation to not only the tissue to be exposed, but also control the length of time of the exposure. Control means would be added to identify and calculate margin and depth of tissue to be treated and the proper radiation source or radioactive isotope (which can be any particle emitter, including neutron, x-ray, alpha, beta or gamma emitter) to obtain the desired therapeutic effects. The invention enables stereotactical surgery and close confines radiation therapy adjacent to radiosensitive tissue.
Owner:SRIORT
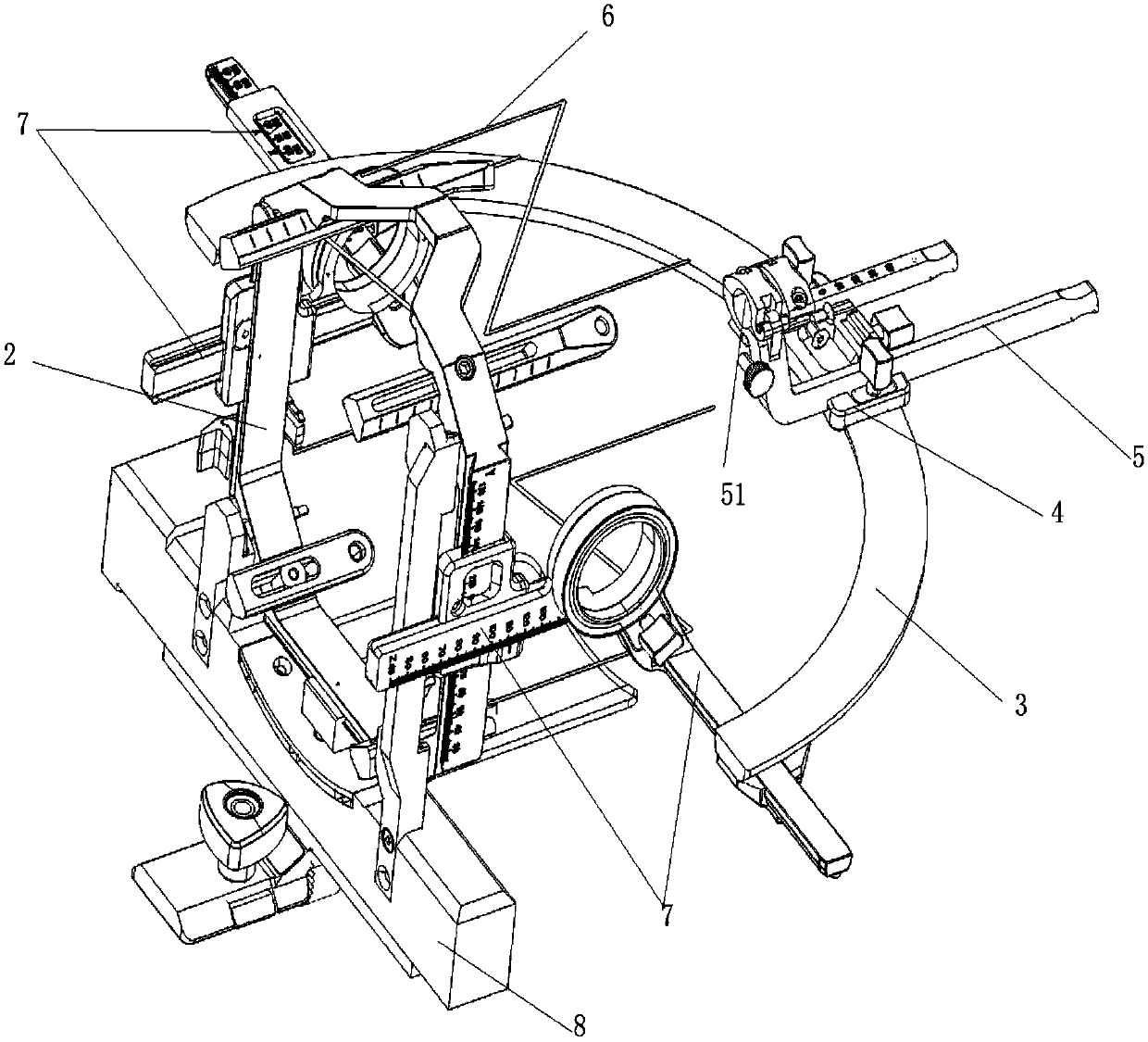
Surgical robot for stereotactic surgery and method for controlling stereotactic surgery robot
ActiveUS20180049825A1Improve surgical accuracySimple control methodDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsRotational axisSurgical robot
A stereotactic surgery robot according to the present disclosure may include: a rotating unit that is configured to have a surgical instrument that is able to be attached thereto, and is configured to rotate the surgical instrument on at least one of two rotational axes according to an entry posture of the surgical instrument; a moving unit that is configured to move the rotating unit in the direction of at least one of three linear axes according to the position of a surgical target; and a surgical portion support unit that is configured to be connected to the moving unit, and is configured to be detachable with respect to an operating table, wherein the moving unit may move the rotating unit such that an intersection point of the two rotational axes matches the surgical target.
Owner:KOHYOUNG TECH
Stereotactic Therapy System
InactiveUS20140005524A1Improve accuracyTime and cost-efficient therapyDiagnostic markersComputerised tomographsFrame basedStereotactic radiotherapy
A fiducial marker system (210a-c) comprises a first unit and a second unit. The first unit is patient affixable and comprises a partly spherical inner surface having a first center point that is adapted to receive a touch probe measurement head for measuring the spatial position of the center point. The second unit is releasably attachable to an outer surface of the first unit, and has a second center point, wherein the first center point and the second center point are substantially identical when the second unit is attached to the first unit. For stereotactic therapy, a patient is imaged with the first and second unit assembled. Then the second unit is detached. A stereotactic frame (300) is attached to the first units via arms. Thus frameless imaging is provided in a frame based stereotactic surgery system with high precision. Repeated assembly of the frame (300) to the first units, remaining in the patient, provides advantageous fractionized stereotactic radiotherapy.
Owner:KAROLINSKA INNOVATIONS AB
Stereotactic therapy system
InactiveUS8721660B2Improve accuracyTime and cost-efficient therapyDiagnostic markersDiagnostic recording/measuringFrame basedStereotactic radiotherapy
A fiducial marker system (210a-c) comprises a first unit and a second unit. The first unit is patient affixable and comprises a partly spherical inner surface having a first center point that is adapted to receive a touch probe measurement head for measuring the spatial position of the center point. The second unit is releasably attachable to an outer surface of the first unit, and has a second center point, wherein the first center point and the second center point are substantially identical when the second unit is attached to the first unit. For stereotactic therapy, a patient is imaged with the first and second unit assembled. Then the second unit is detached. A stereotactic frame (300) is attached to the first units via arms. Thus frameless imaging is provided in a frame based stereotactic surgery system with high precision. Repeated assembly of the frame (300) to the first units, remaining in the patient, provides advantageous fractionized stereotactic radiotherapy.
Owner:KAROLINSKA INNOVATIONS AB
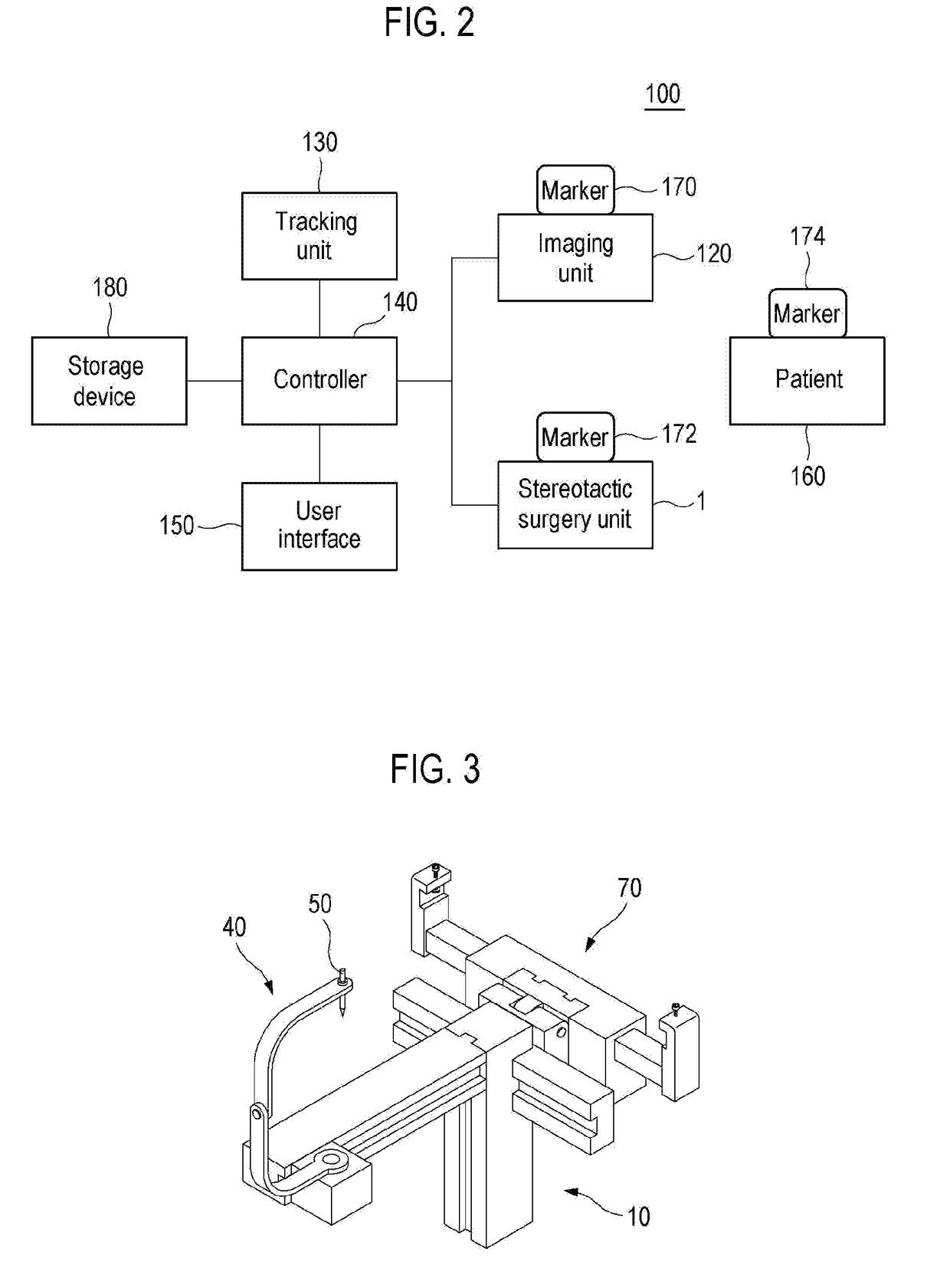
Surgical robot system for stereotactic surgery and method for controlling stereotactic surgery robot
ActiveUS20180049839A1Improve surgical accuracySimple control methodProgramme-controlled manipulatorGeometric image transformationStereotactic neurosurgerySurgical robot
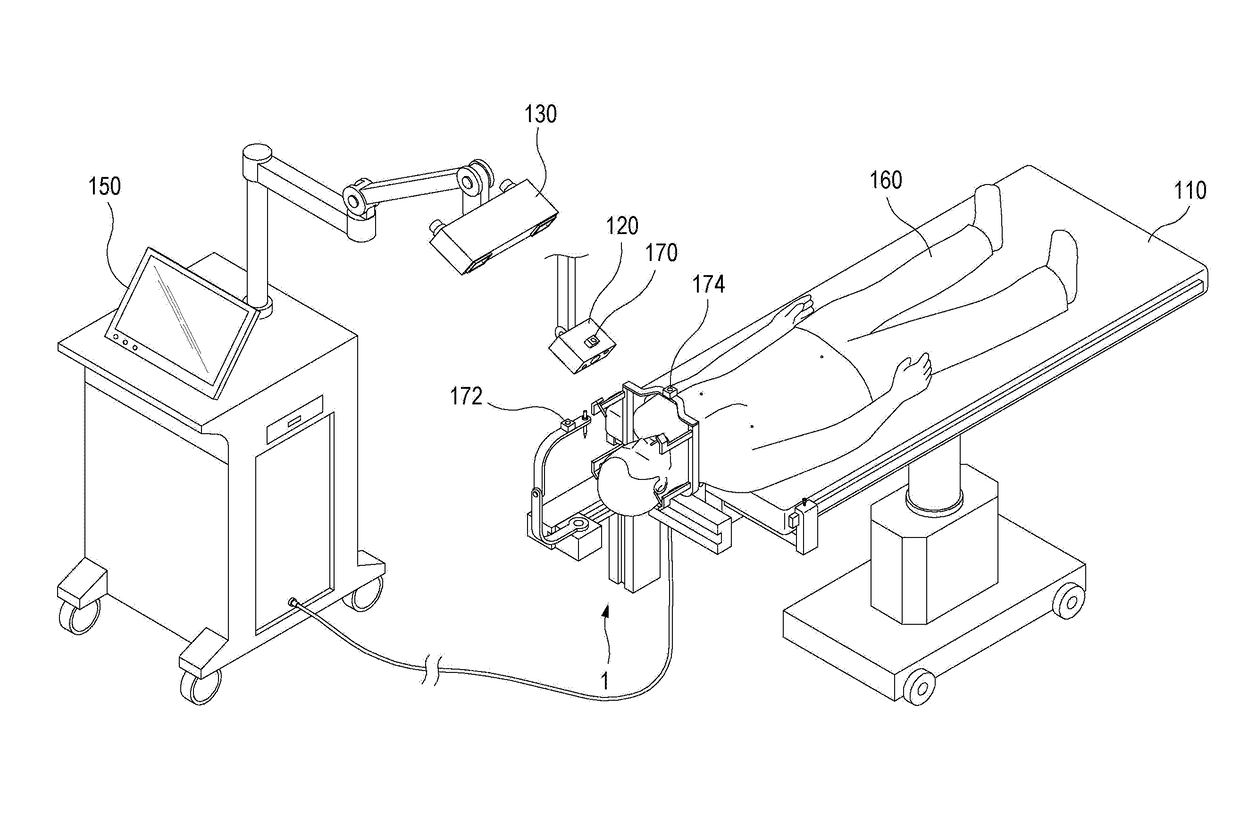
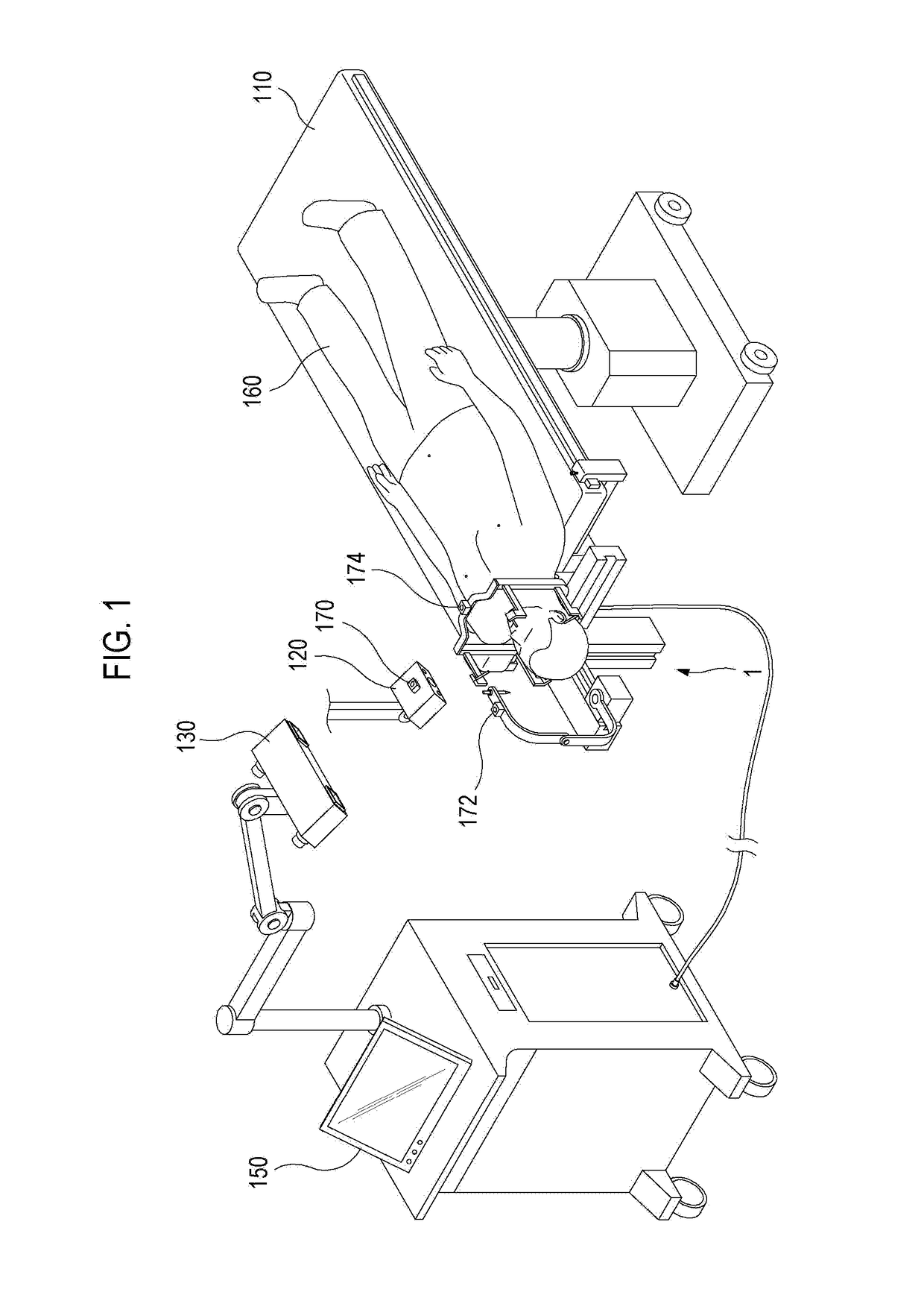
A surgical robot system for stereotactic surgery, according to the present disclosure, may include: a stereotactic surgery unit to move and rotate a surgical instrument; a controller to receive the first imaging data that represents a three-dimensional image of a surgical portion that includes a surgical target; one or more markers to be attached to, or disposed near, the surgical portion; an imaging unit to create the second imaging data that represents a three-dimensional external image of the surgical portion; and a tracking unit to track the positions and postures of the imaging unit and the markers. The controller may create the coordinate conversion relationships for converting a coordinate from the first coordinate system of the first imaging data into the fourth coordinate system of the stereotactic surgery unit and control the stereotactic surgery unit by using the coordinate conversion relationships above.
Owner:KOHYOUNG TECH
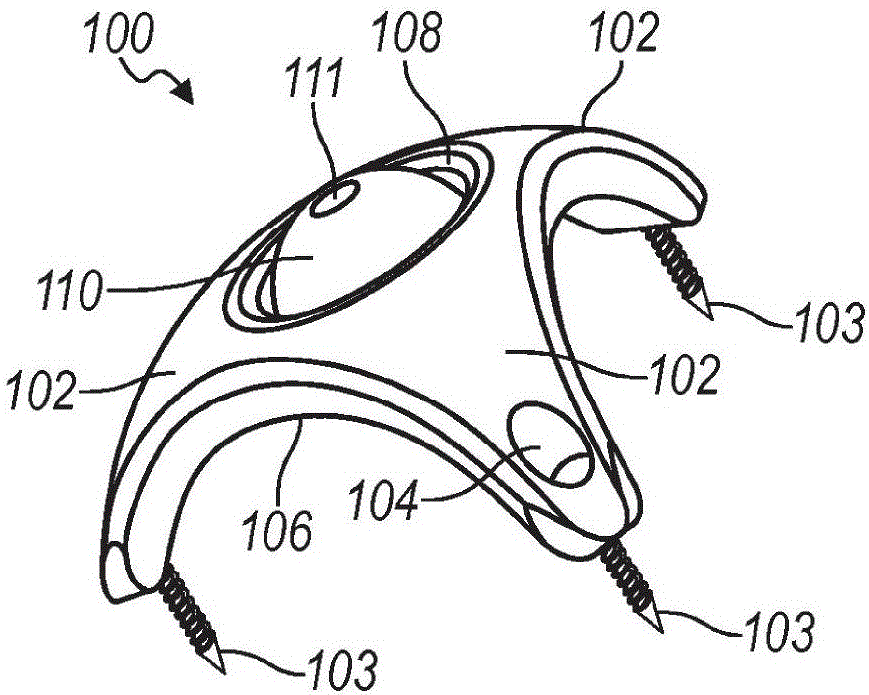
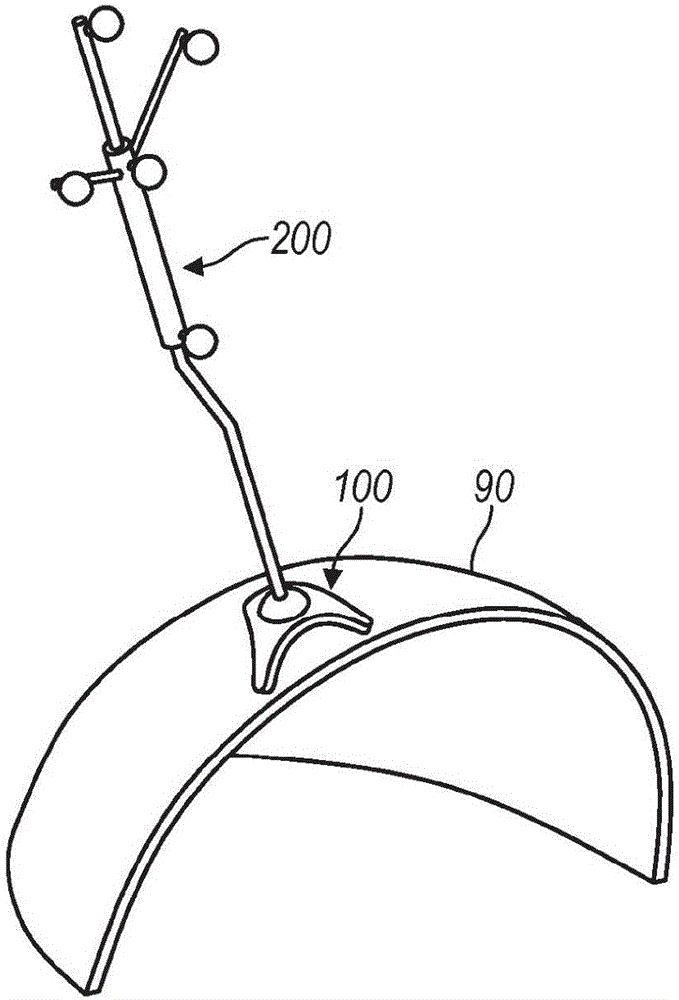
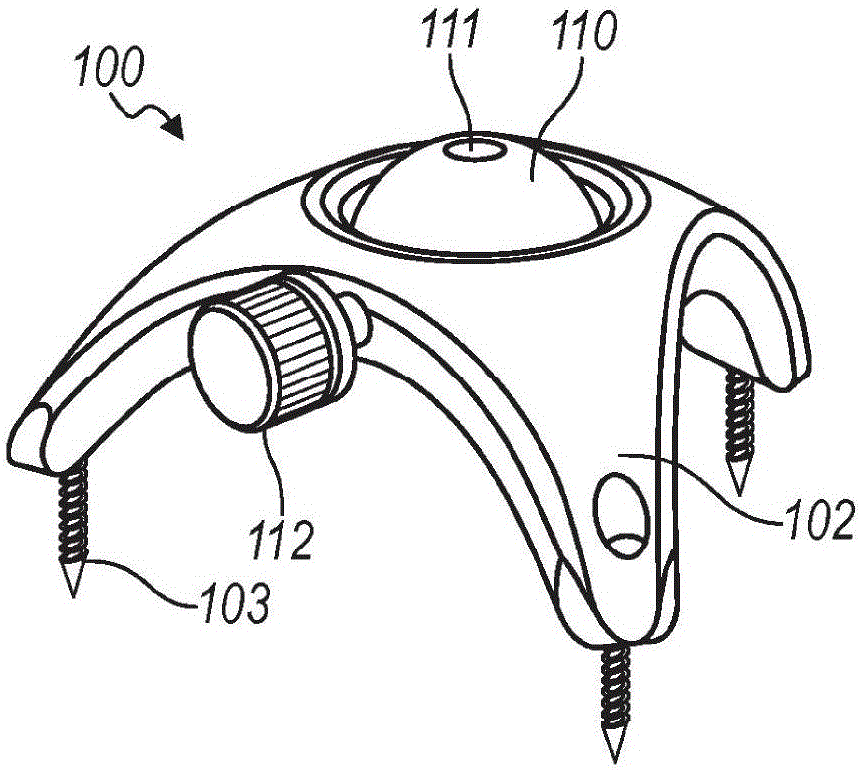
Surgical head clamp
InactiveUS20110092771A1Firmly attachedEndoscopesSurgical instrument supportStereotactic neurosurgeryComputer-assisted surgery
The invention relates generally to apparatus and devices for stereotactic surgery, computer aided surgery and other similar medical procedures. More particularly, a clamping device for firm attachment to a body part during surgery and for firmly and precisely positioning and orienting medical instruments attached to the clamping device is disclosed.
Owner:HYBEX HLDG
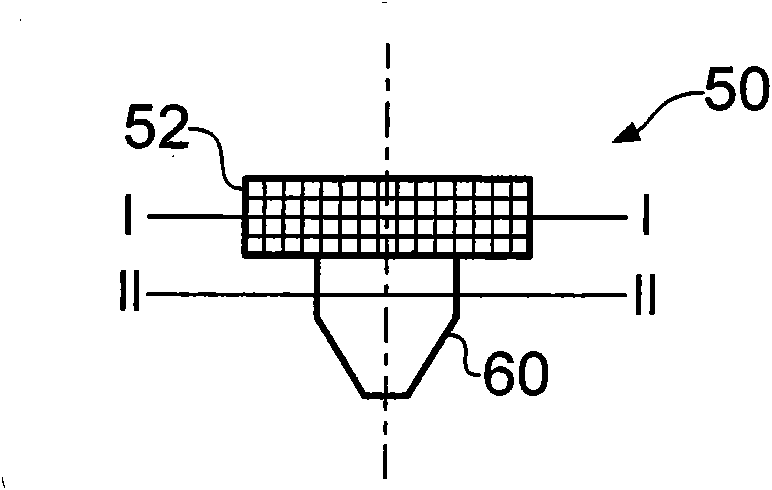
Apparatus for stereotactic neurosurgery
A skull mount (50;150;170;200;300) is described that is attachable to a hole (60) formed in the skull. The skull mount (50;150;170;200;300) comprises an alignment guide (62;152;172;216;306) defining an alignment axis (22;210;312) along which neurosurgical instruments can be passed. The skull mount, when attached to a hole in a skull, is arranged such that it does not substantially protrude from the outermost surface of the skull and does not extend into the brain parenchyma. Also described is a neurosurgical alignment instrument (30,206) for aligning such a skull mount (50;150;170;200;300) that comprises an elongate shaft (32) and an element (34,36) protruding from the distal end of the elongate shaft (32) for engaging and aligning the alignment guide (62;152;172;216;306) of an associatedskull mount (50;150;170;200;300). When the alignment instrument is engaged with a skull mount attached to a hole formed in the skull, the protruding element passes through the alignment guide of the skull mount and into the cortex of the subject's brain.
Owner:RENISHAW (IRELAND) LTD
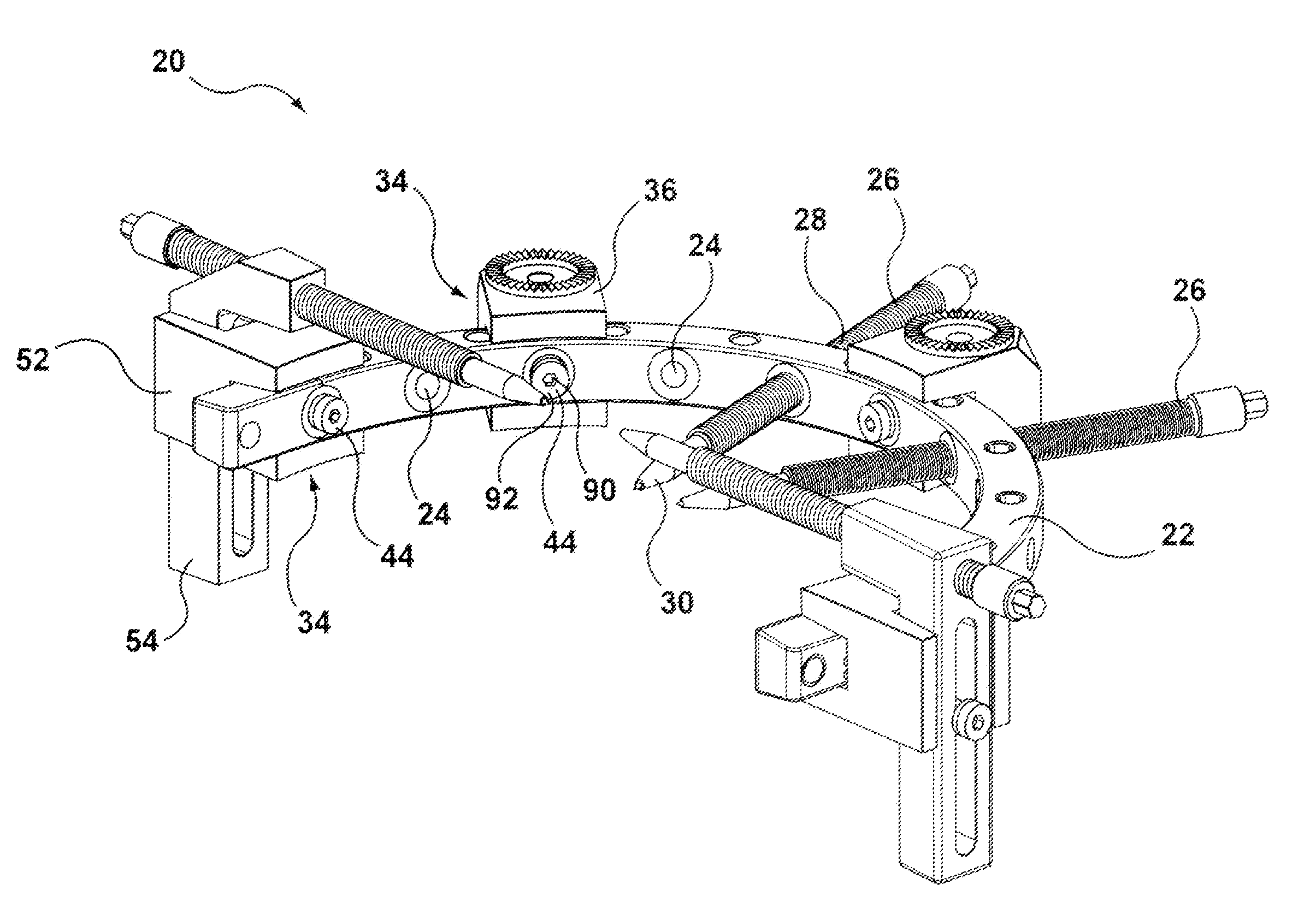
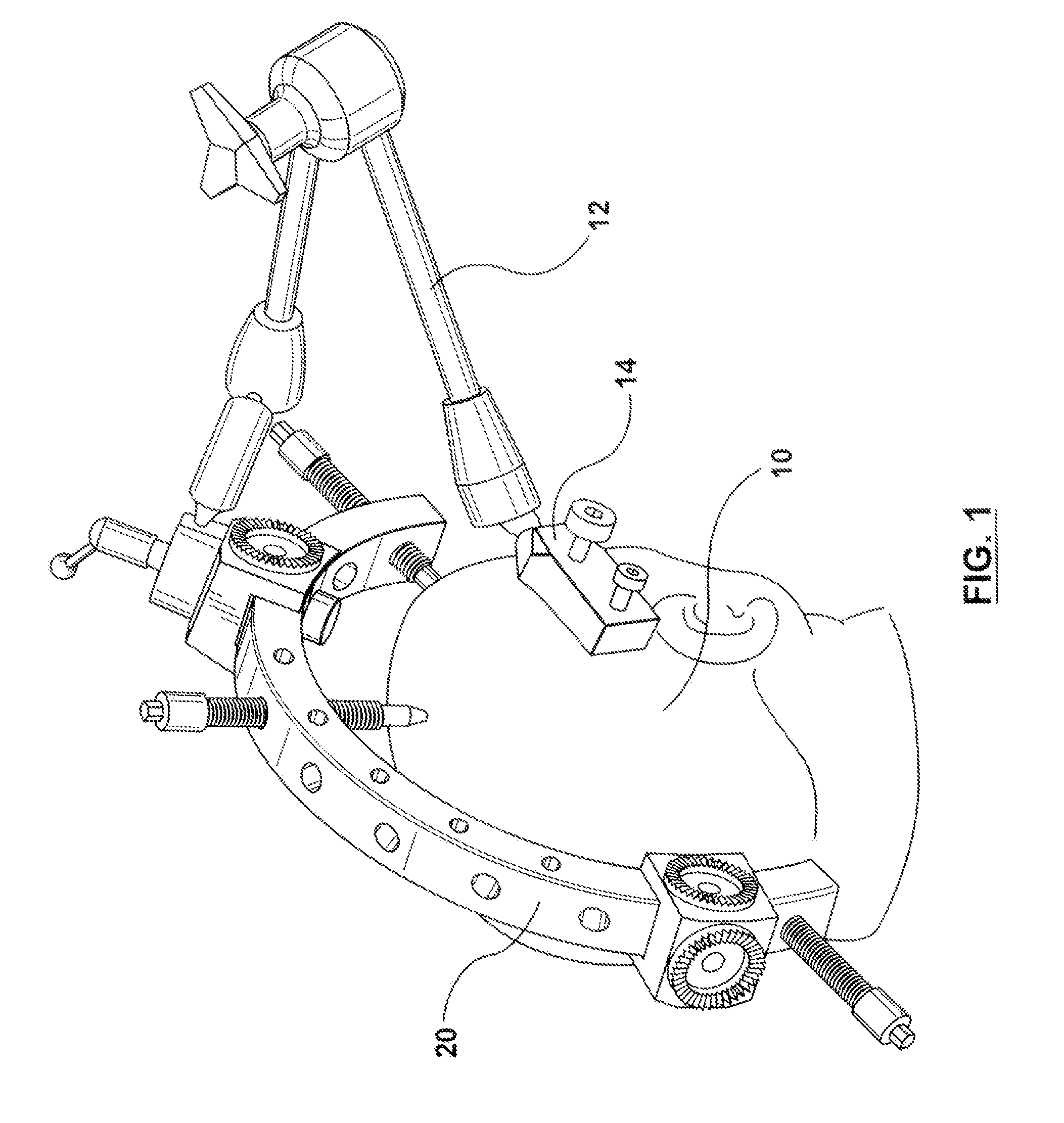
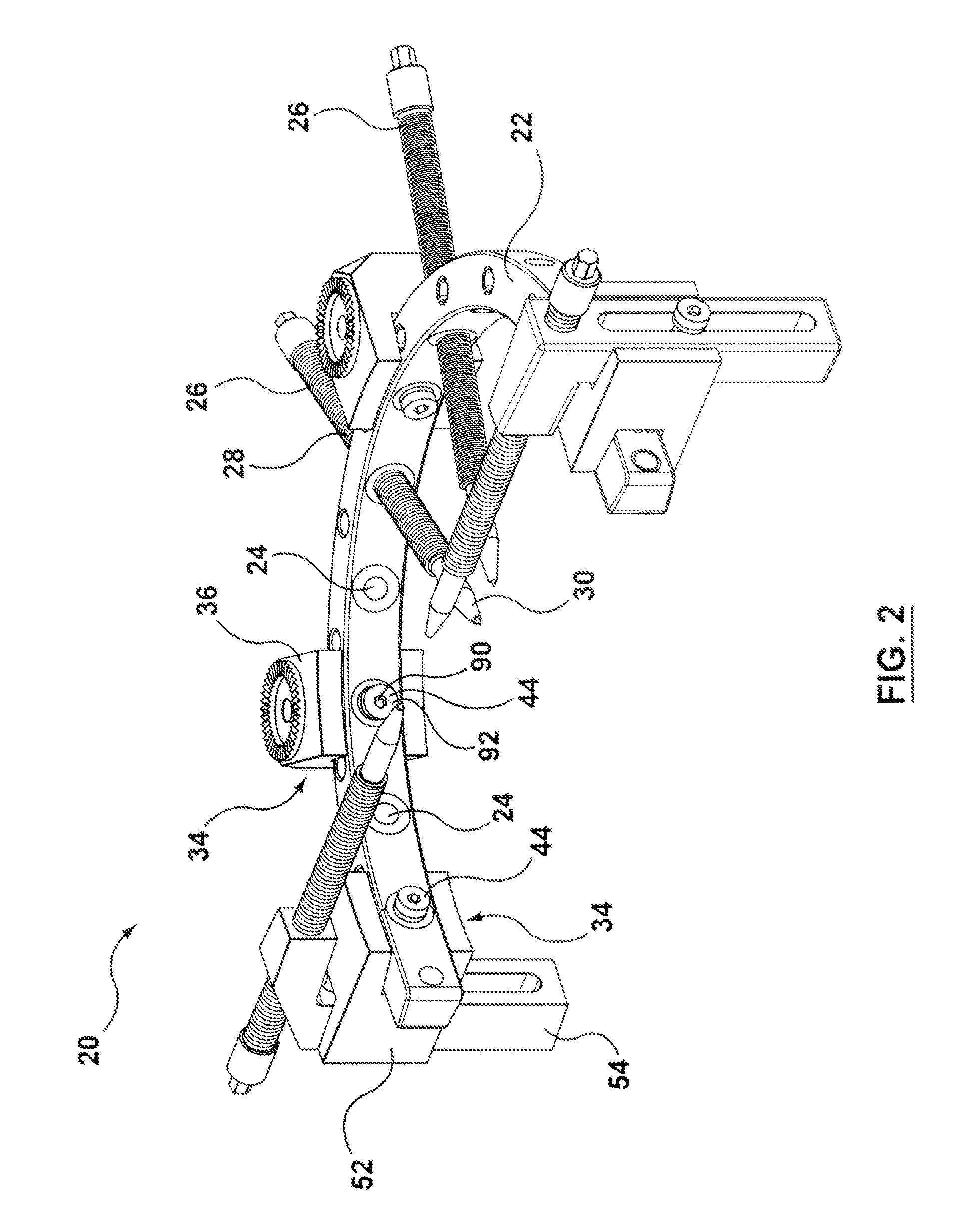
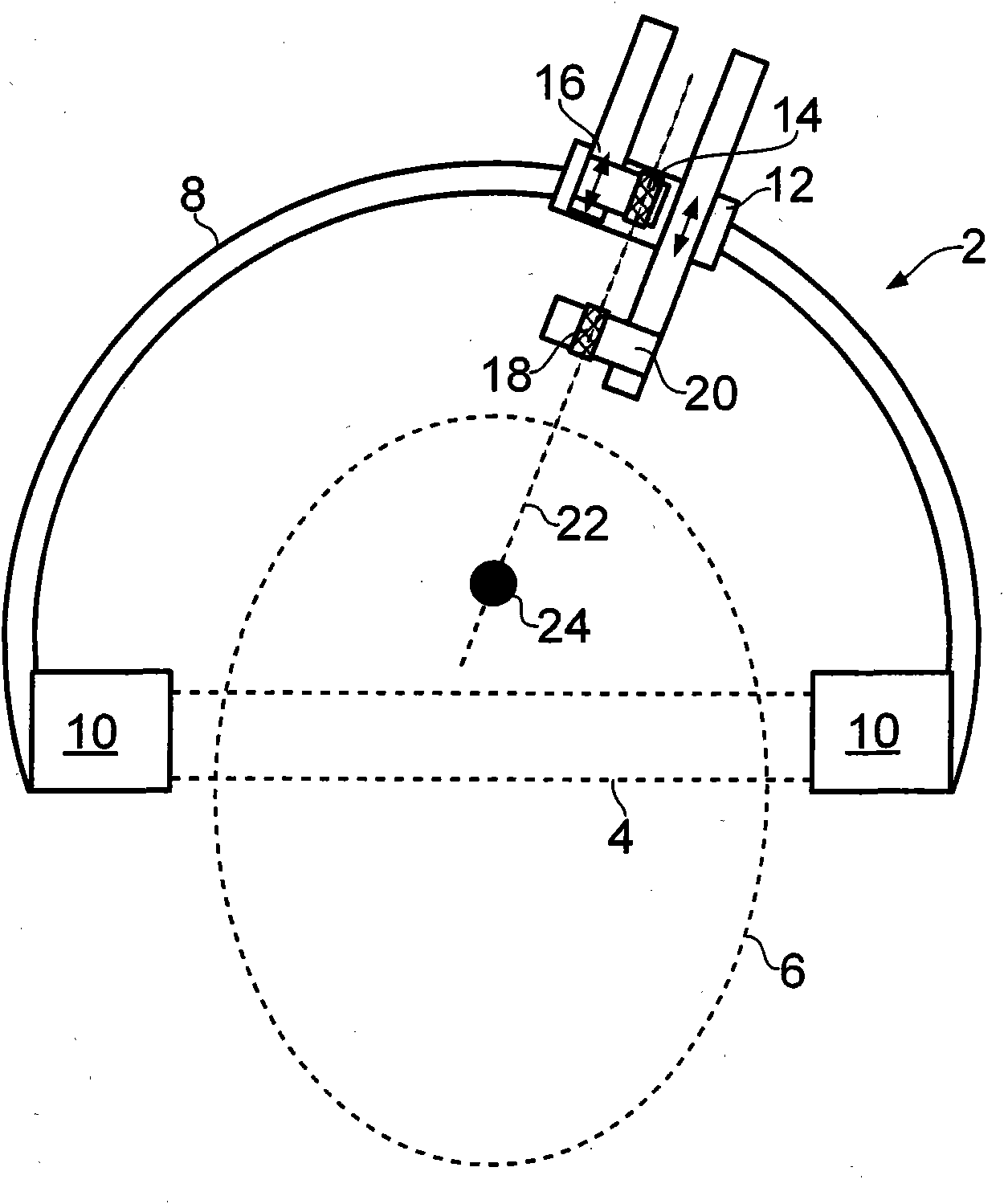
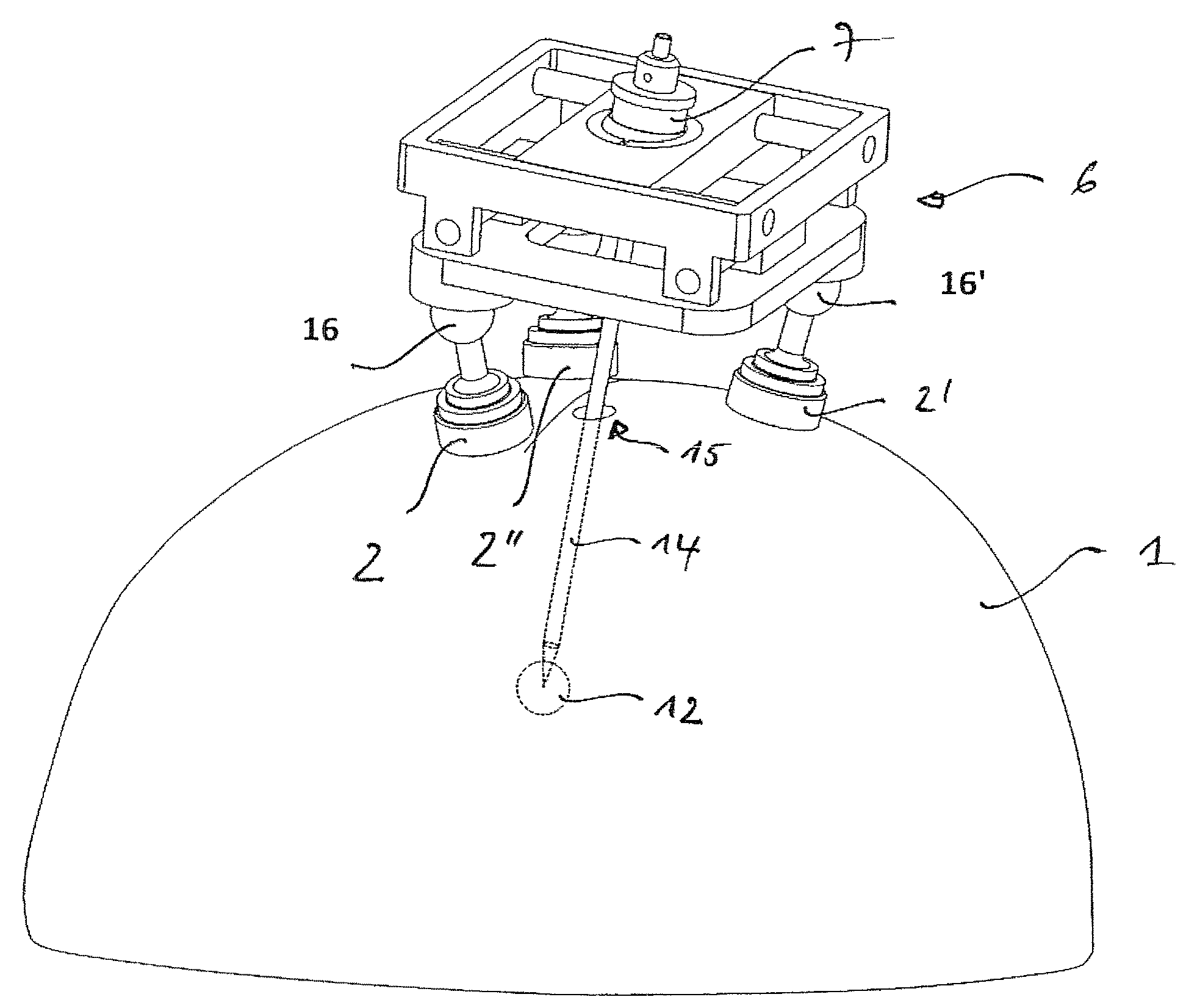
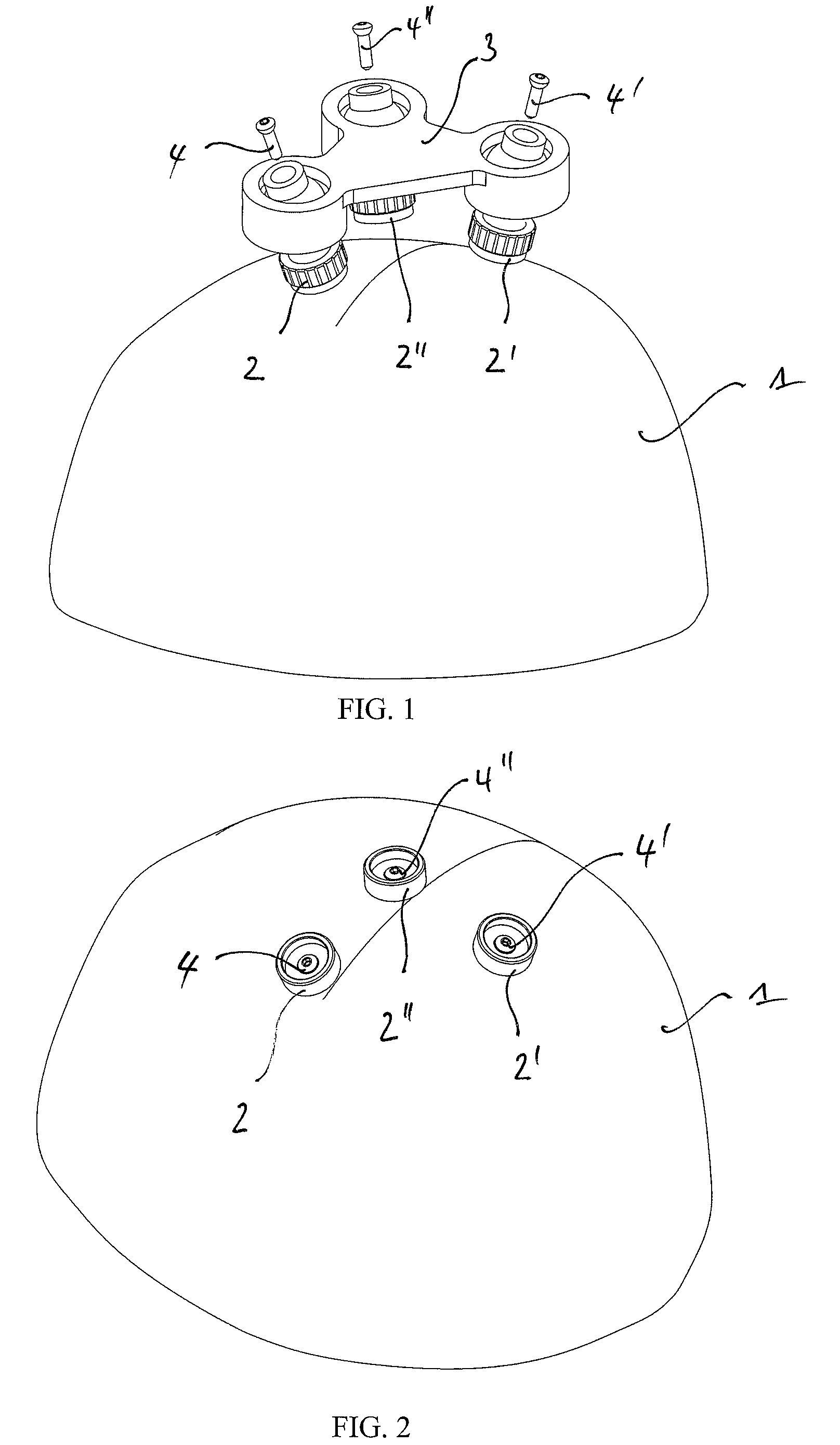
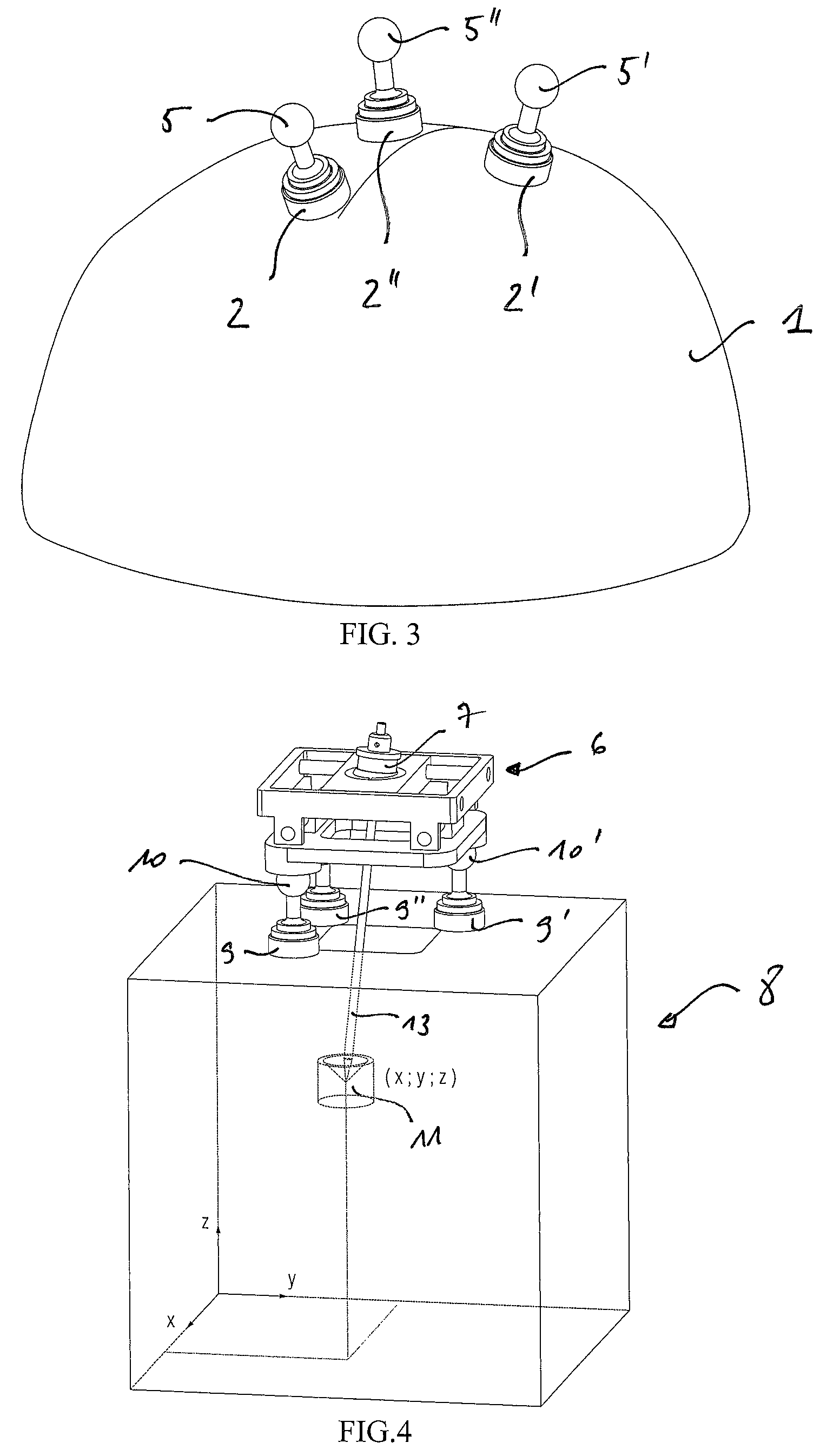
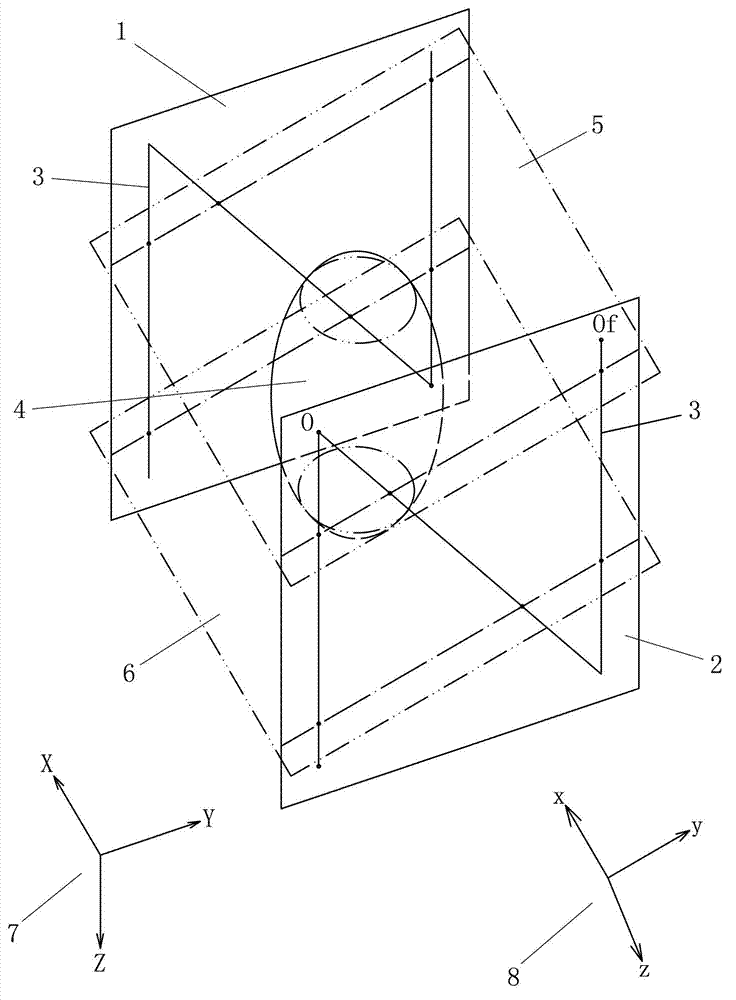
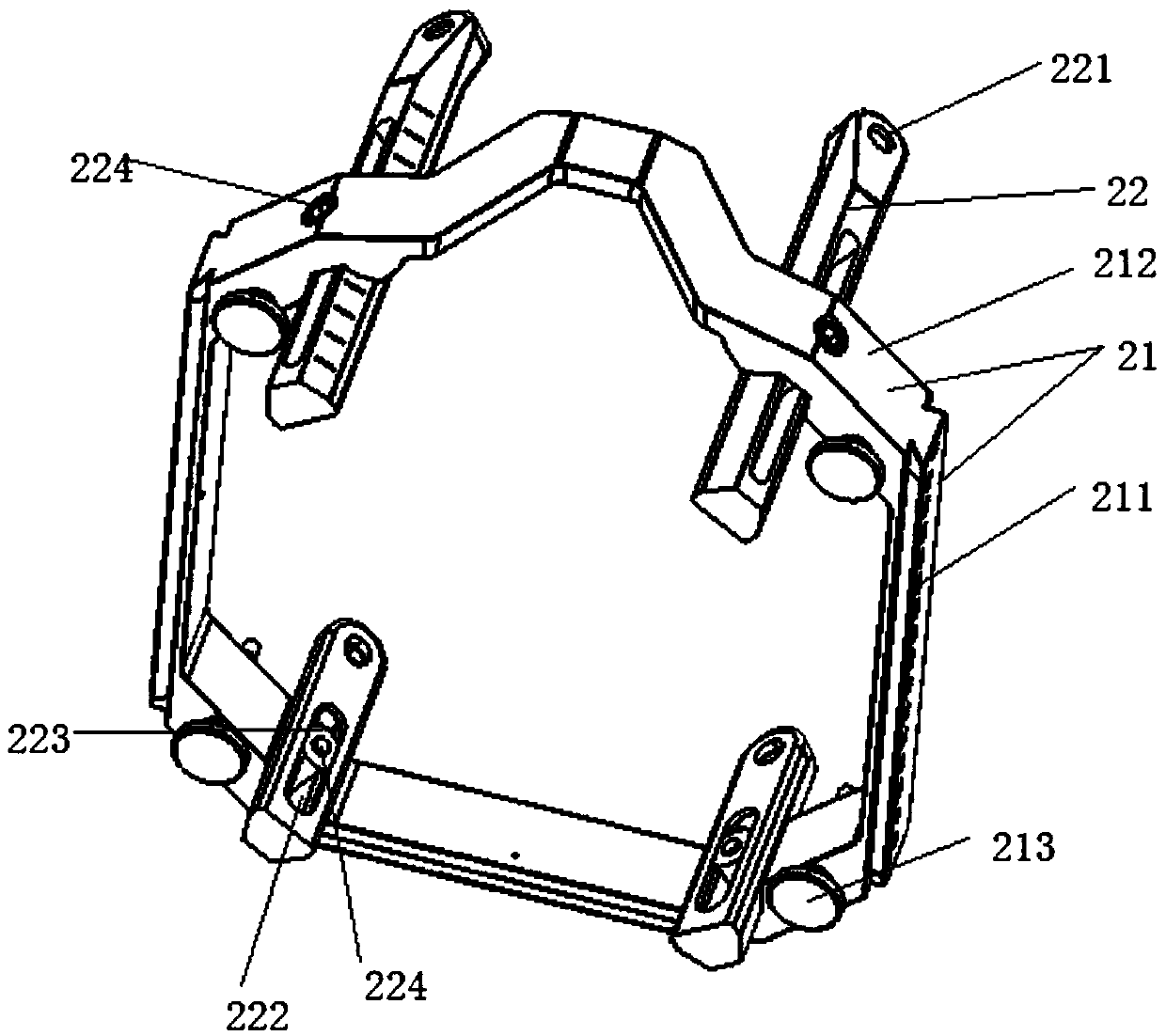
Adjustable stereotactic device and method for frameless neurosurgical stereotaxy
InactiveUS8617180B2Precise and controlled displacementSurgical needlesComputer-aided planning/modellingMedicineStereotaxy
The system comprises at least three anchors (2,2′,2″) intended to be attached to the patient and equipped with markers (5,5′,5″), an insertion guide device (6) with an insertion guide (7) intended to be attached to said anchors (2,2′,2″), an external calibration device (8) with at least three calibration markers (10,10′,10″) corresponding to said markers (5,5′,5″) and a planning and imaging software. The planning and imaging software is used to determine the position of a target point in the patient with respect to the markers (5,5′,5″), the calibration device is used to calibrate and orient the insertion guide (7) of the insertion guide device (6) mounted on said calibration markers (10,10′,10″) using the determination of the software before the insertion guide device is mounted on said markers (5,5′,5″) attached to the patient.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL) +1
Stereotactic access devices and methods
ActiveUS9237931B2Wide range of usesAccelerated trainingDiagnosticsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryStereotaxisStereotactic device
This invention is directed to devices and methods for stereotactic access, and particularly to a frameless stereotactic access device for accessing a body cavity and methods therefor. In general, a stereotactic device may include portions or features for fixing the device to a portion of a patient's body, such as, for example, a skull, such that the device may be generally spatially fixed in relation to the patient's body or part thereof. The stereotactic device may also generally include portions or features for guiding a medical device or other device at a particular trajectory in relation to the patient's body or part thereof.
Owner:VISUALASE
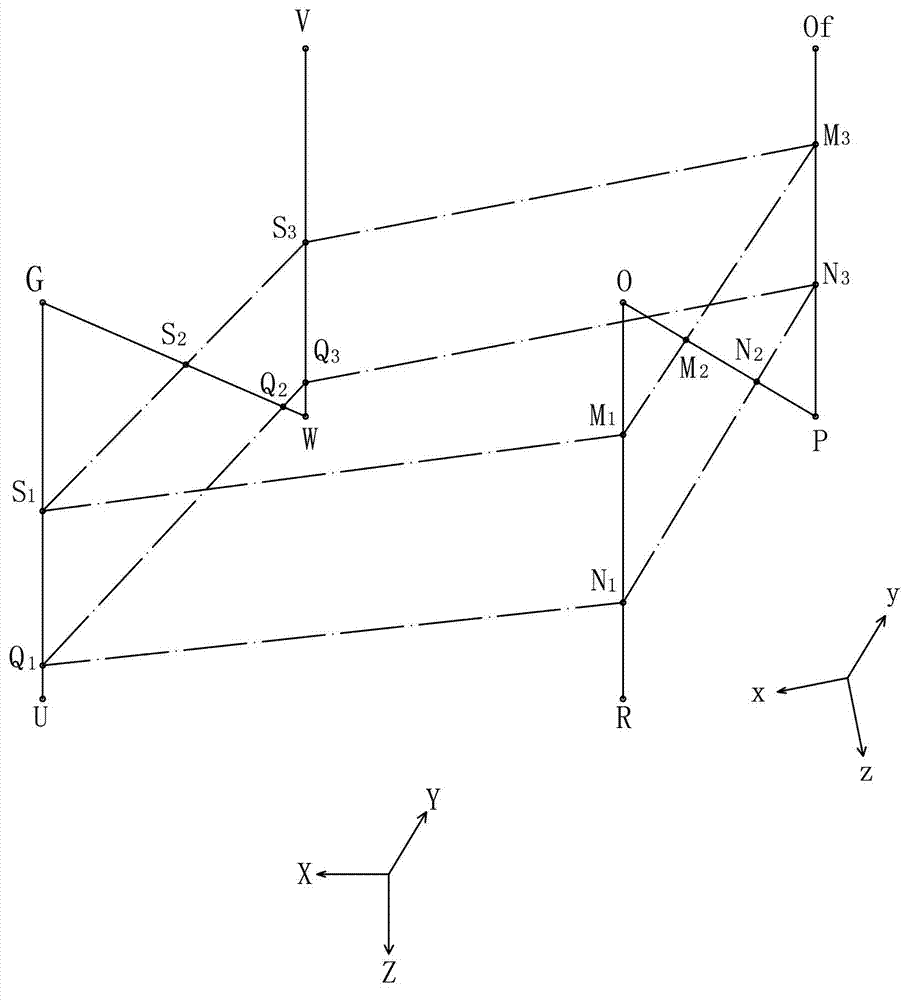
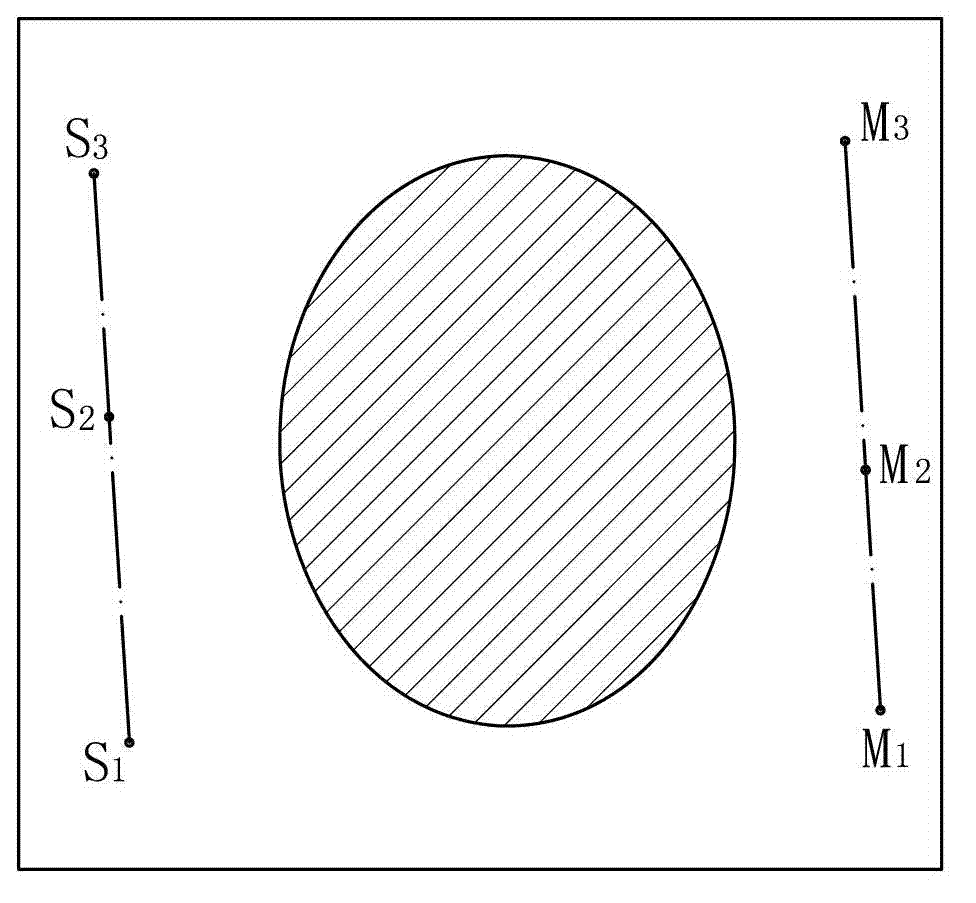
Method using cross-sectional image to obtain coordinate of target point in stereotaxic apparatus
InactiveCN103083090AReduce difficultyComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringStereotaxisComputer vision
The invention provides a method using a cross-sectional image to obtain a coordinate of a target point in a stereotaxic apparatus. The method comprises the steps: (1) selecting the cross-sectional image where six mark points of N-shaped metal lines of two positioning plates can be completely seen in the cross-sectional image, and measuring a coordinate parameter of the mark points; (2) establishing an equation in an image coordinate system of a Y-Z plane, an X-Z plane and an X-Y plane of a stereotaxic apparatus frame; (3) selecting the target point on the cross-sectional image, obtaining the three-dimension coordinate parameter in the image coordinate system, and calculating the distance from the target point to the Y-Z plane, the X-Z plane and the X-Y plane of the frame, and value of the distance is an X, Y and Z coordinate in the stereotaxic apparatus frame coordinate system of the target point. The method reduces installation difficulty of the stereotaxic apparatus frame, reduces difficulty of a stereotaxis operation, and especially is suitable for coordinate positioning of an intercranial 'invisible' target point.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
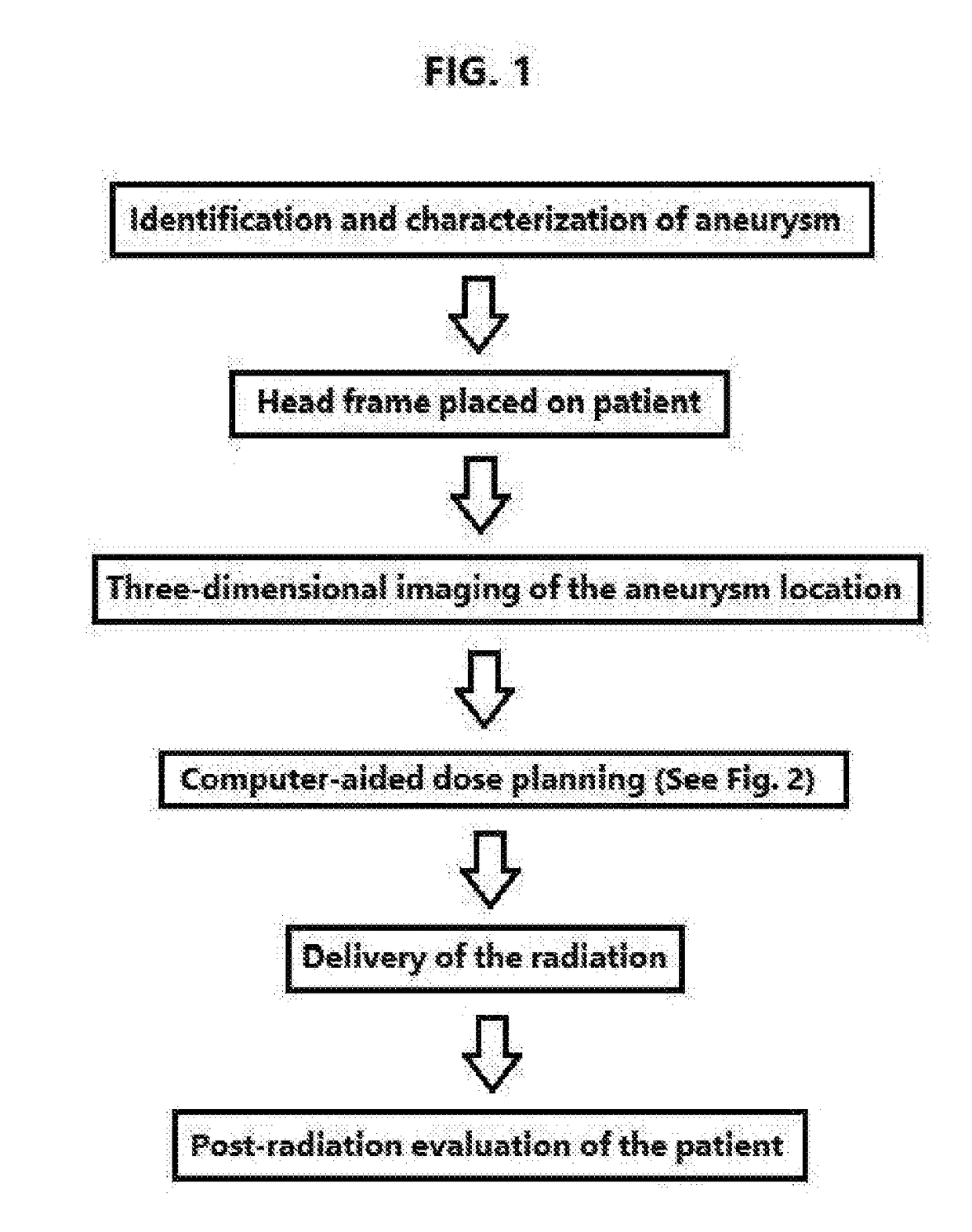
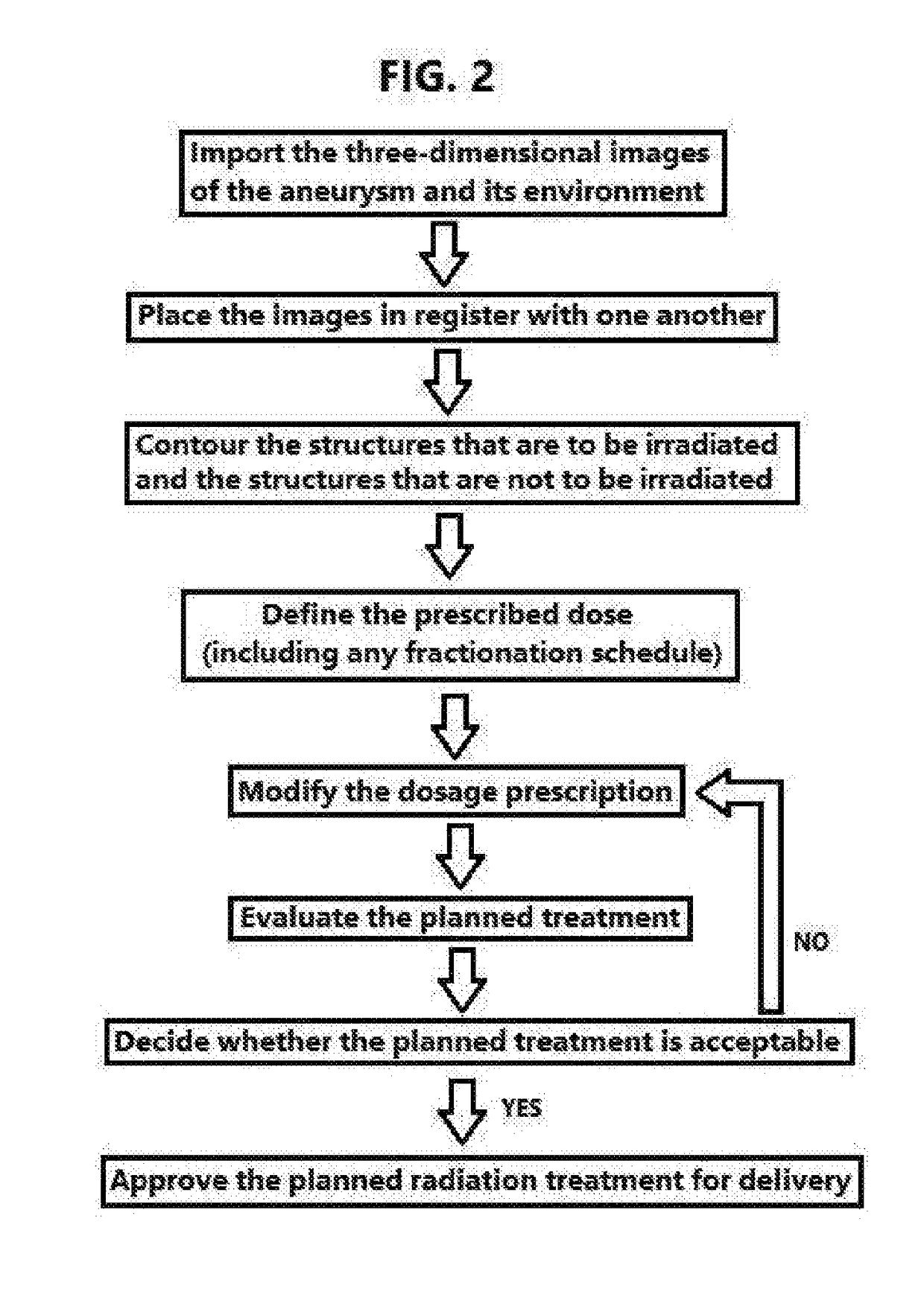
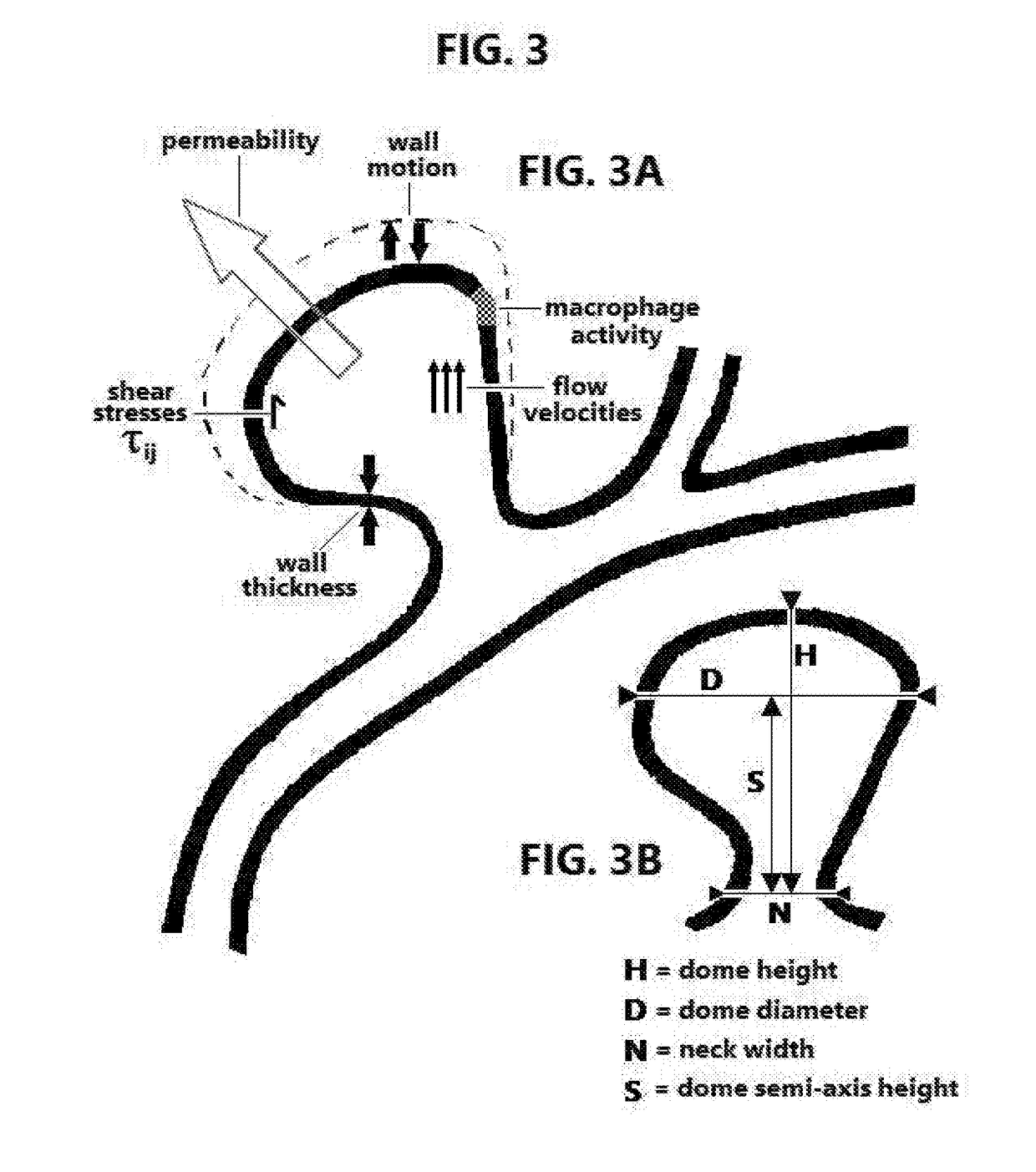
Treatment of unruptured saccular intracranial aneurysms using stereotactic radiosurgery
ActiveUS20190030368A1Facilitating formation of clotPrevent relapseDiagnosticsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryBrain sectionArteriovenous malformation
Methods and devices are disclosed for treating a patient with an unruptured saccular aneurysm that is not associated with an arteriovenous malformation, wherein ionizing radiation is delivered to the brain of a patient through stereotactic radiosurgery. The radiosurgery may be performed with a Gamma Knife, LINAC device such as CyberKnife, or particle-beam device. The treatment impedes a natural progression of the aneurysm towards rupture and may actually obliterate the aneurysm. The treatment plan may be based in part on measured geometric properties of the aneurysm or on physical aneurysm properties such as permeability, wall thickness, wall motion, the presence of macrophages, shear stress, and flow velocities. The methods may be used in conjunction with endovascular coil embolization.
Owner:LIPANI JOHN D
Brain stent stereotaxic instrument
InactiveCN110384543ATreatment safetyReduce the burden onSurgical needlesInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryCt technologyFixed frame
The invention discloses a brain stent stereotaxic instrument. The brain stent stereotaxic instrument comprises a shell, a head fixing frame, a semicircular arched positioning frame, a puncture needleslider and a puncture needle fixer. The novel brain stent stereotaxic instrument is a precise medical device capable of being matched with CT imaging equipment to be used and has high positioning precision; and the brain stent stereotaxic instrument is simple in structural design and practical, can assist a doctor in adjusting the puncture position and the needle entering angle, and can be combined with a CT technology, thus the accuracy, high efficiency and safety of minimally invasive stereotactic surgery are improved greatly, the surgery success rate of the minimally invasive stereotactic surgery is increased greatly, and the application field is enlarged accordingly.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROV MEDICAL INSTR INST +1
Surgical robot for stereotactic surgery and method for controlling stereotactic surgery robot
ActiveUS10363106B2Improve accuracySecure convenienceDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsRotational axisSurgical robot
A stereotactic surgery robot according to the present disclosure may include: a rotating unit that is configured to have a surgical instrument that is able to be attached thereto, and is configured to rotate the surgical instrument on at least one of two rotational axes according to an entry posture of the surgical instrument; a moving unit that is configured to move the rotating unit in the direction of at least one of three linear axes according to the position of a surgical target; and a surgical portion support unit that is configured to be connected to the moving unit, and is configured to be detachable with respect to an operating table, wherein the moving unit may move the rotating unit such that an intersection point of the two rotational axes matches the surgical target.
Owner:KOHYOUNG TECH
Stereotactic access devices and methods
This invention is directed to devices and methods for stereotactic access, and particularly to a frameless stereotactic access device for accessing a body cavity and methods therefor. In general, a stereotactic device may include portions or features for fixing the device to a portion of a patient's body, such as, for example, a skull, such that the device may be generally spatially fixed in relation to the patient's body or part thereof. The stereotactic device may also generally include portions or features for guiding a medical device or other device at a particular trajectory in relation to the patient's body or part thereof.
Owner:VISUALASE
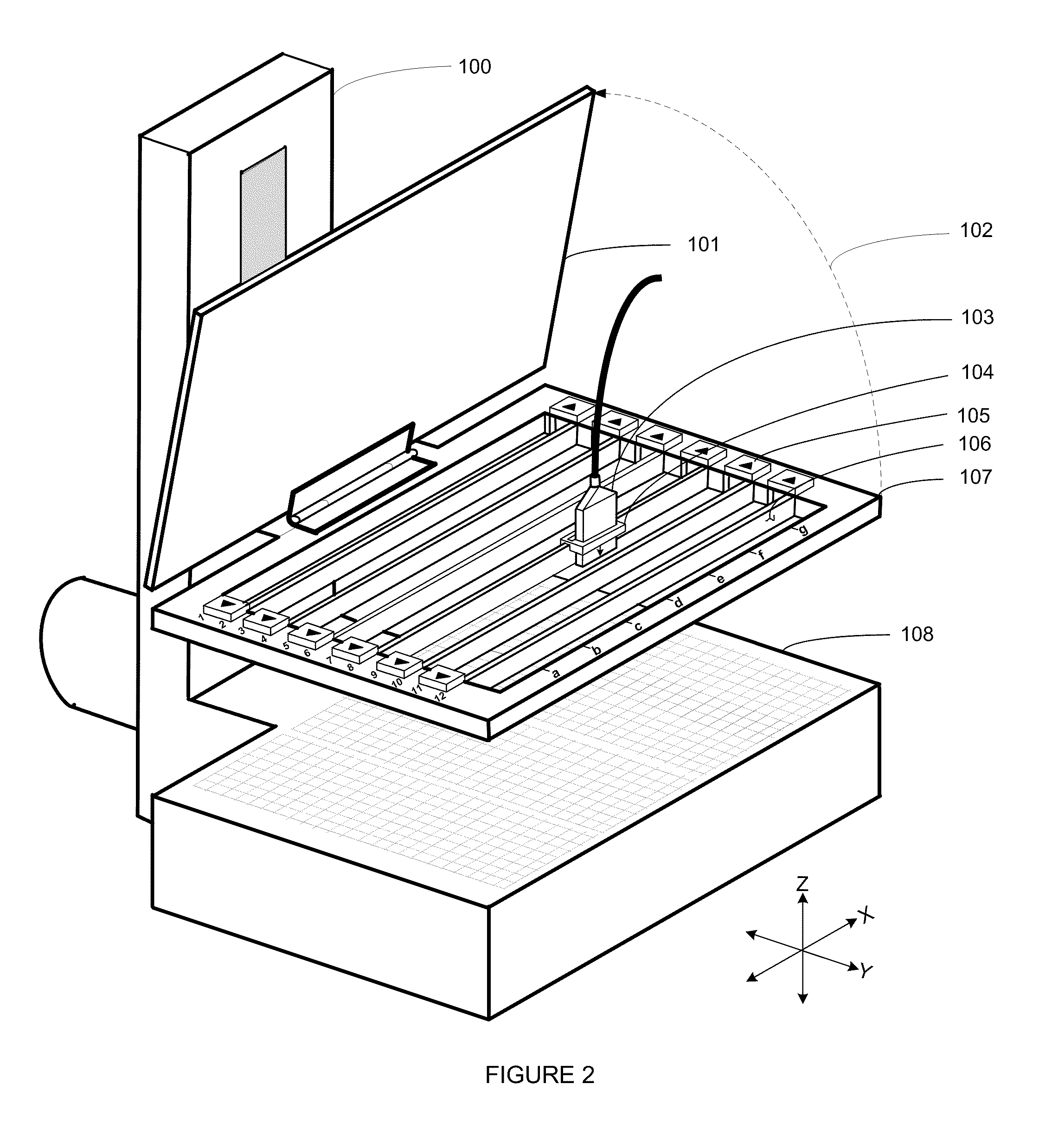
Interventions Using Correlated Nuclear and Ultrasound Imaging
InactiveUS20110295115A1Accurate and fast positioningSimple taskUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingStereotaxis
An apparatus and method for localizing a nuclear-emitting lesion during an intervention using correlated nuclear and ultrasound imaging. The apparatus provides interventional access and quasi-stereotactic positioning of interventional devices, with real-time ultrasound image visualization for tracking the approach of the device to the lesion. The apparatus is intended to overcome the shortcomings of fully-stereotactic nuclear-emission image localization.
Owner:YARNALL STEPHEN T
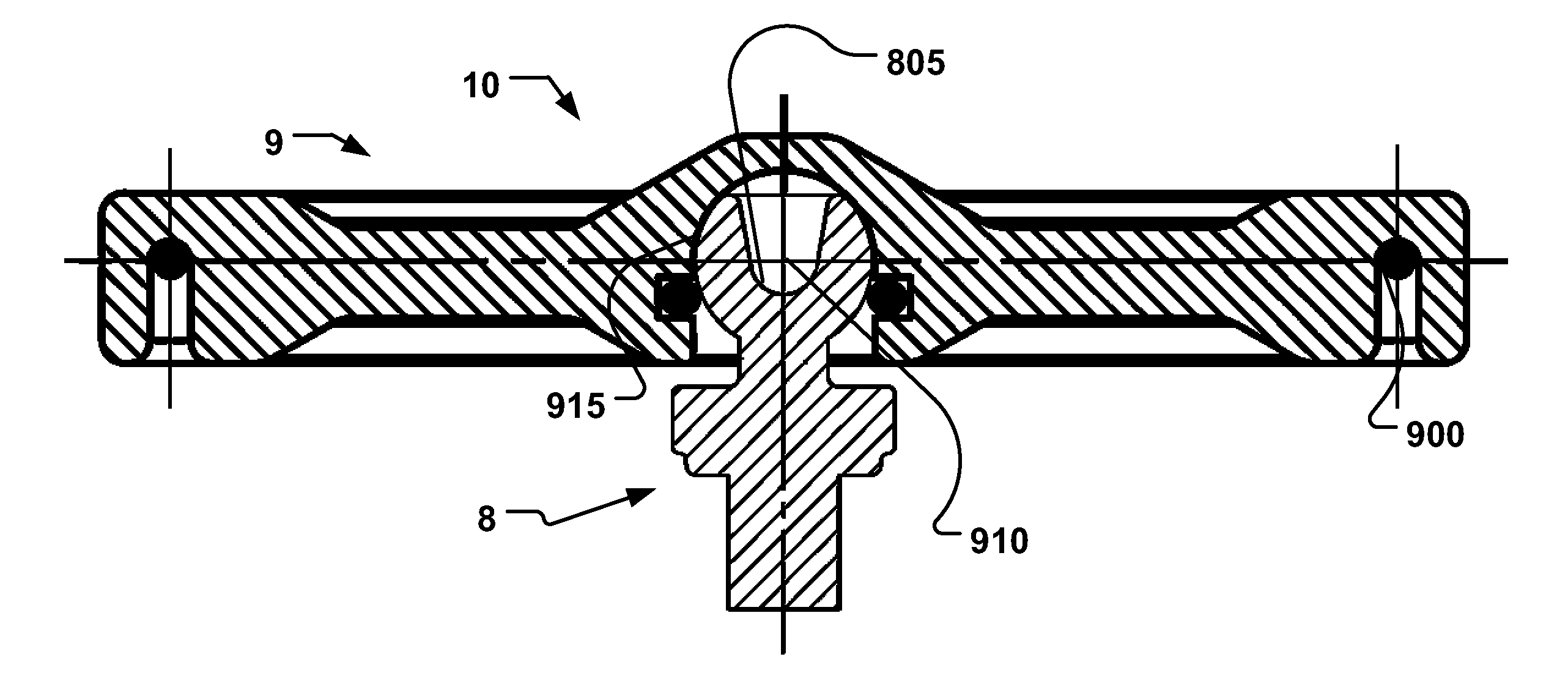
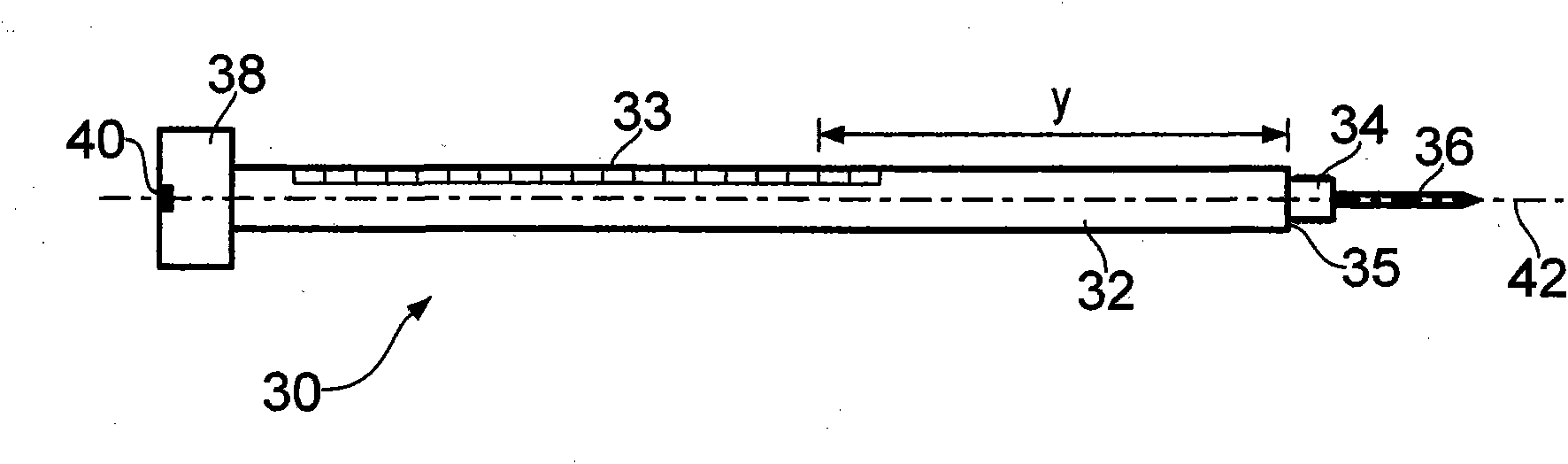
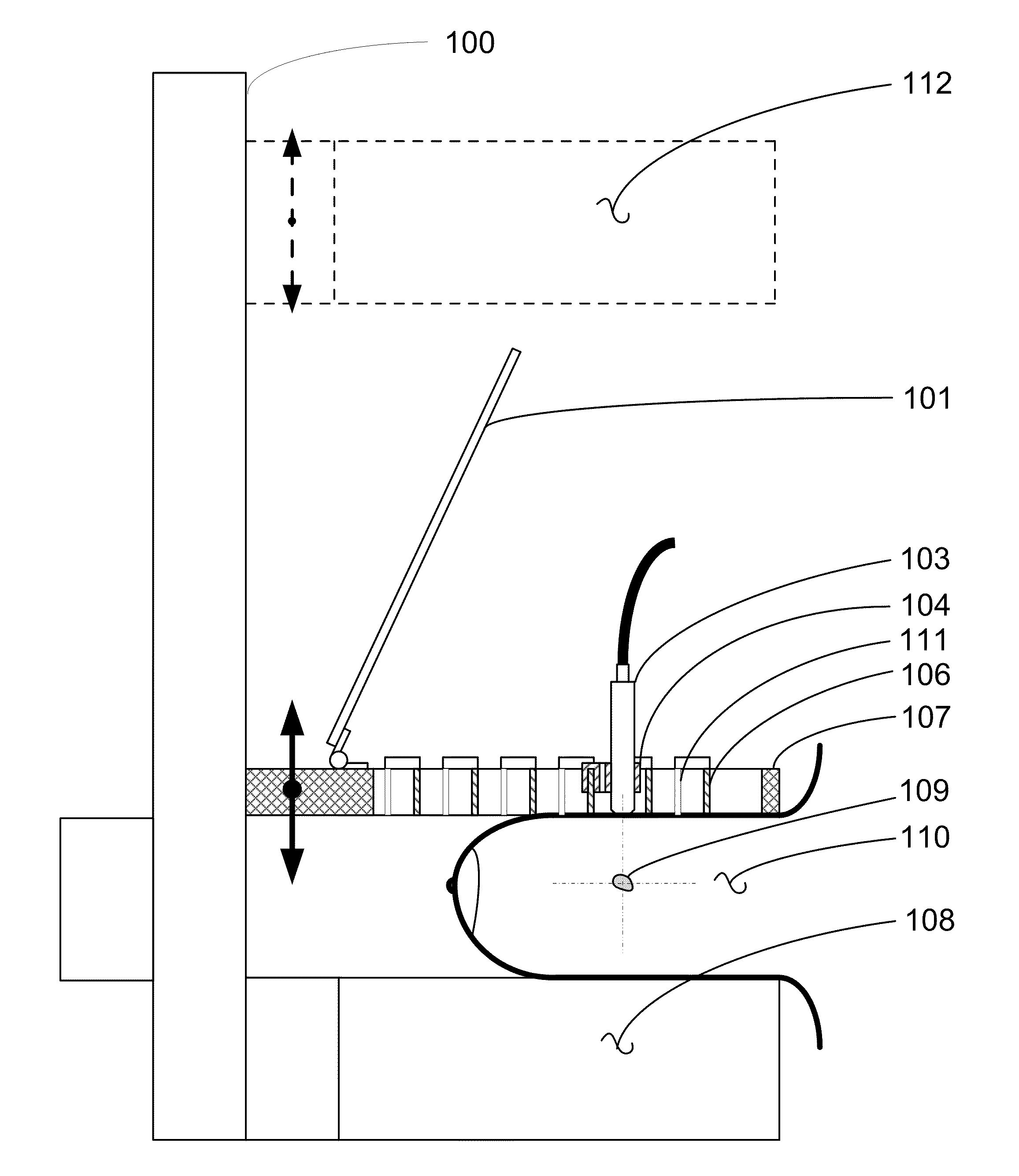
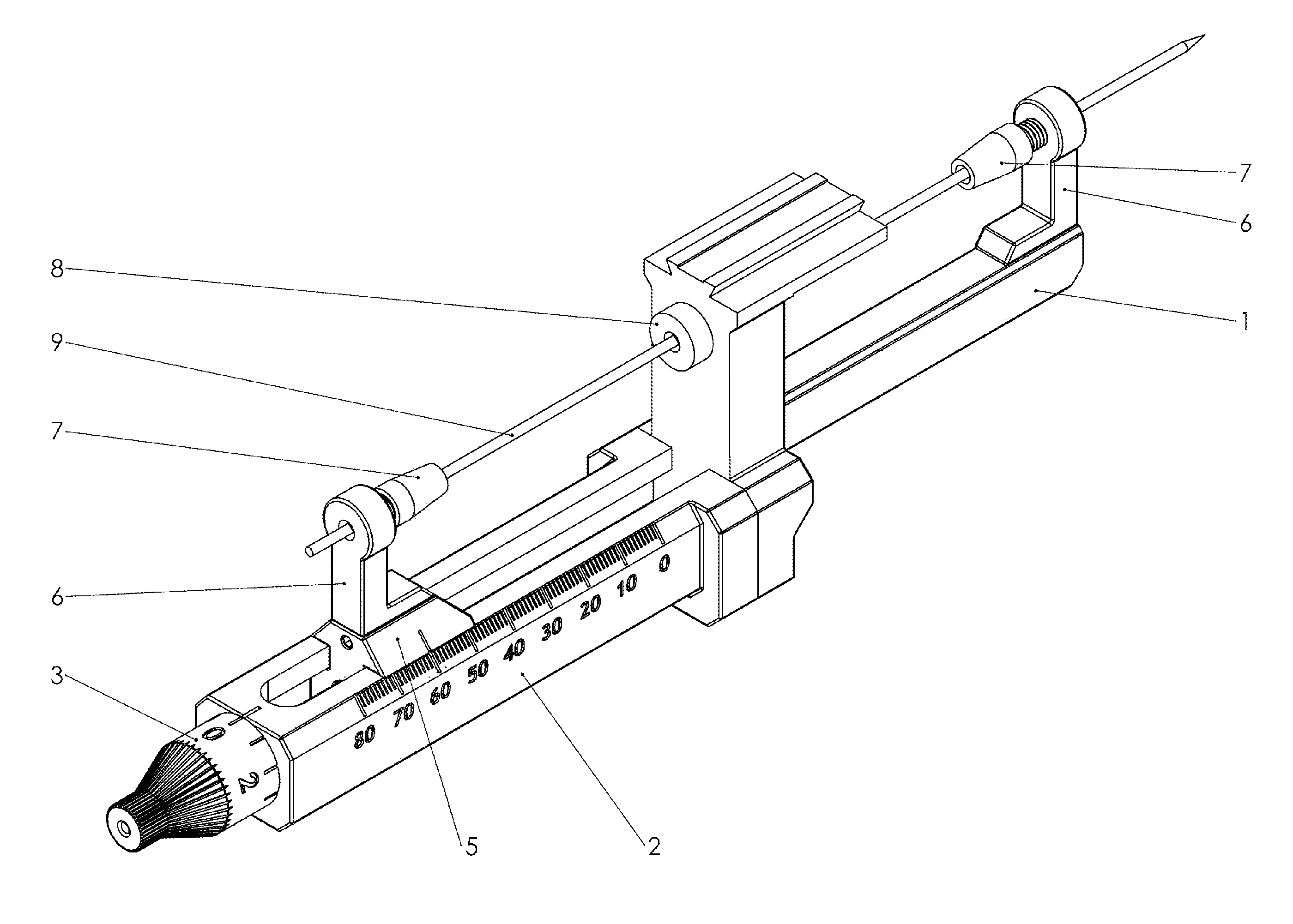
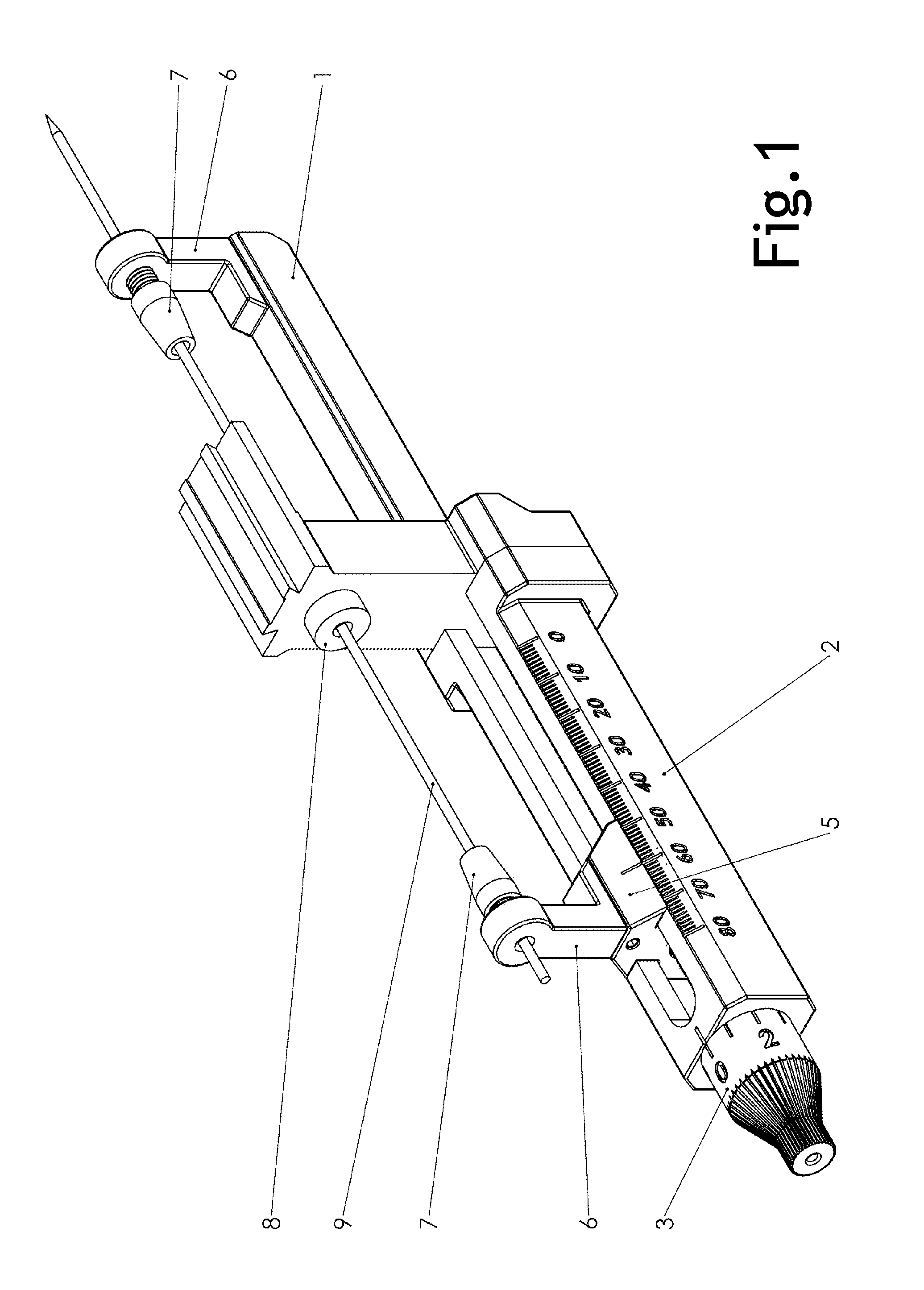
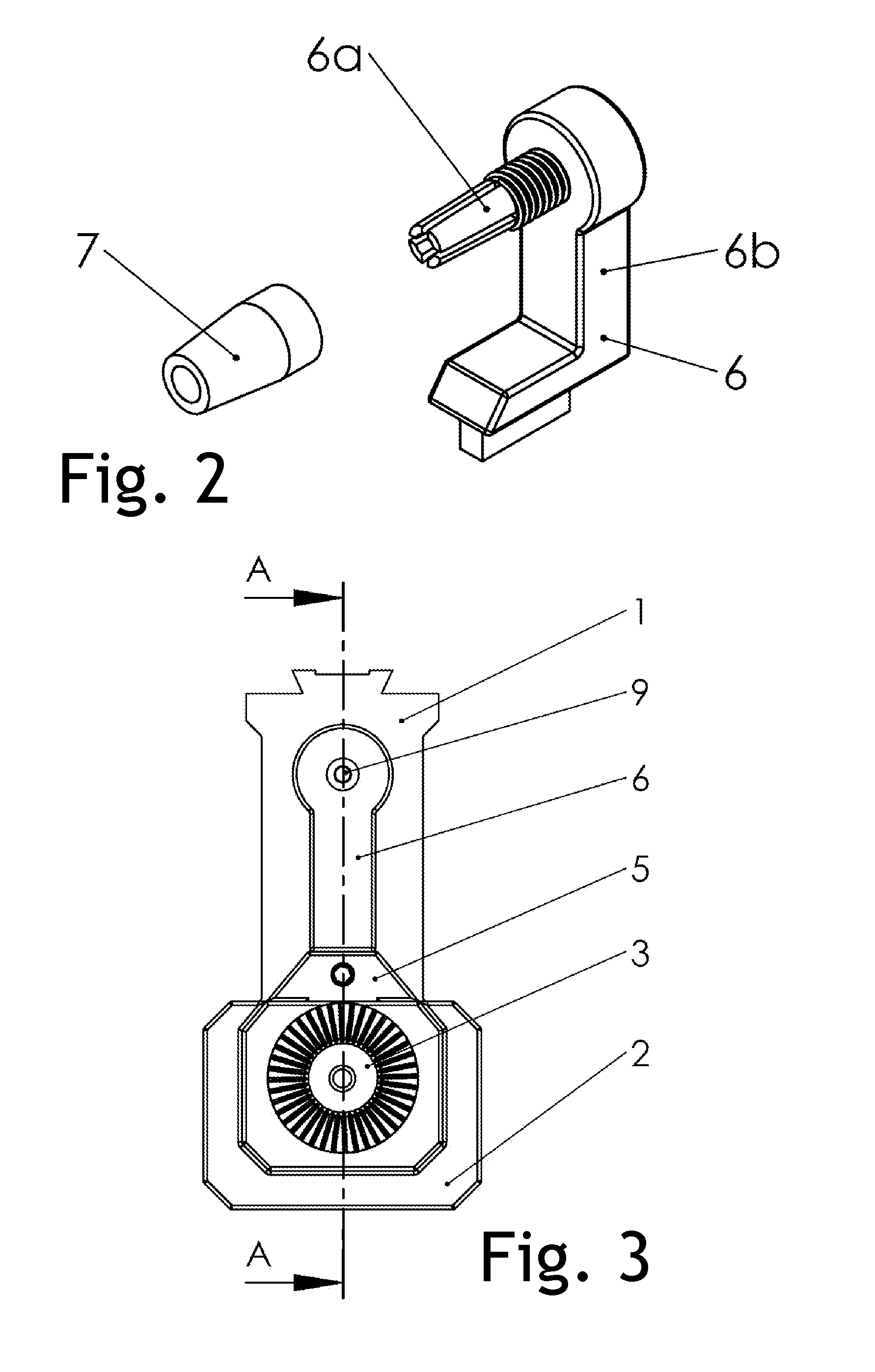
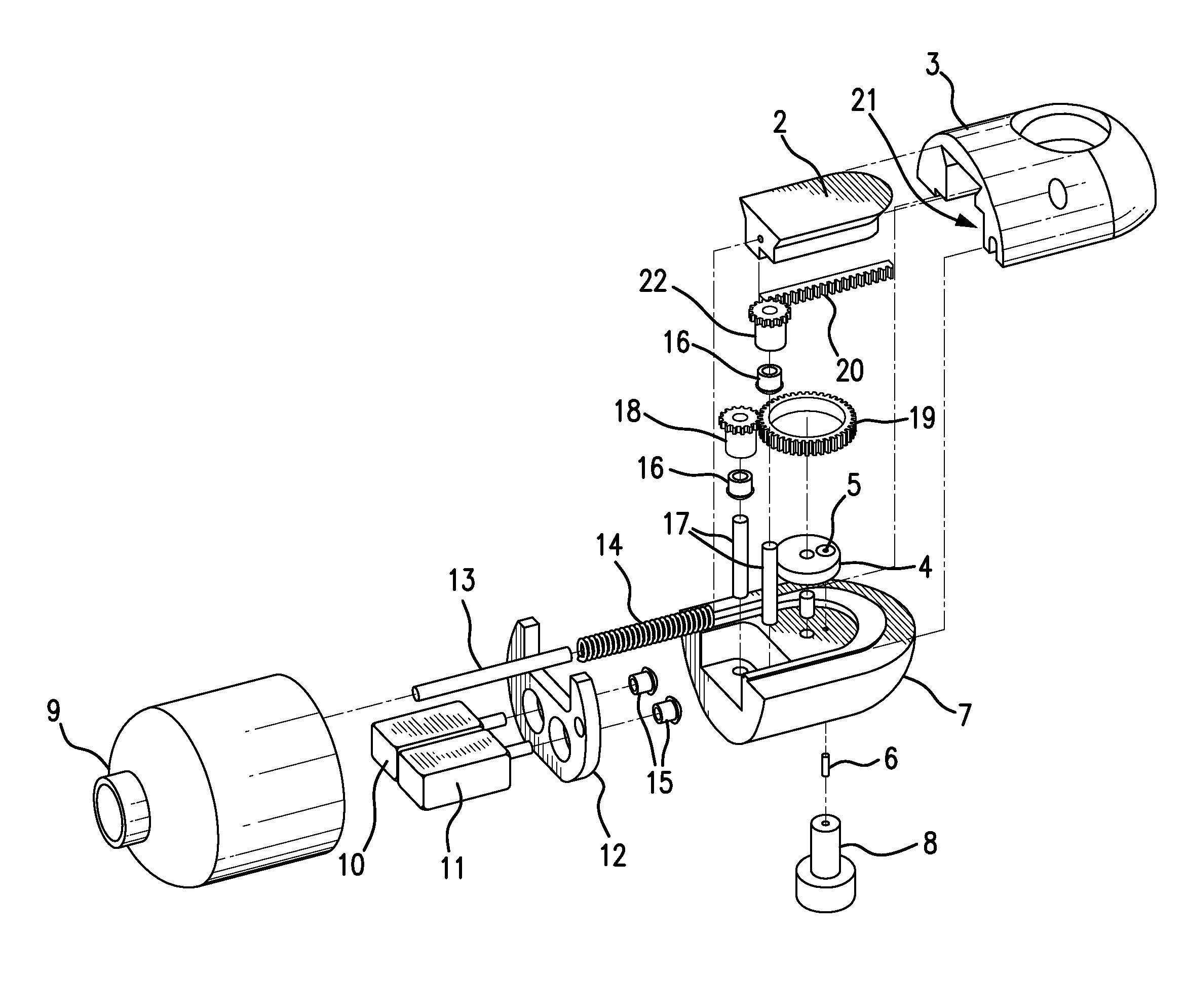
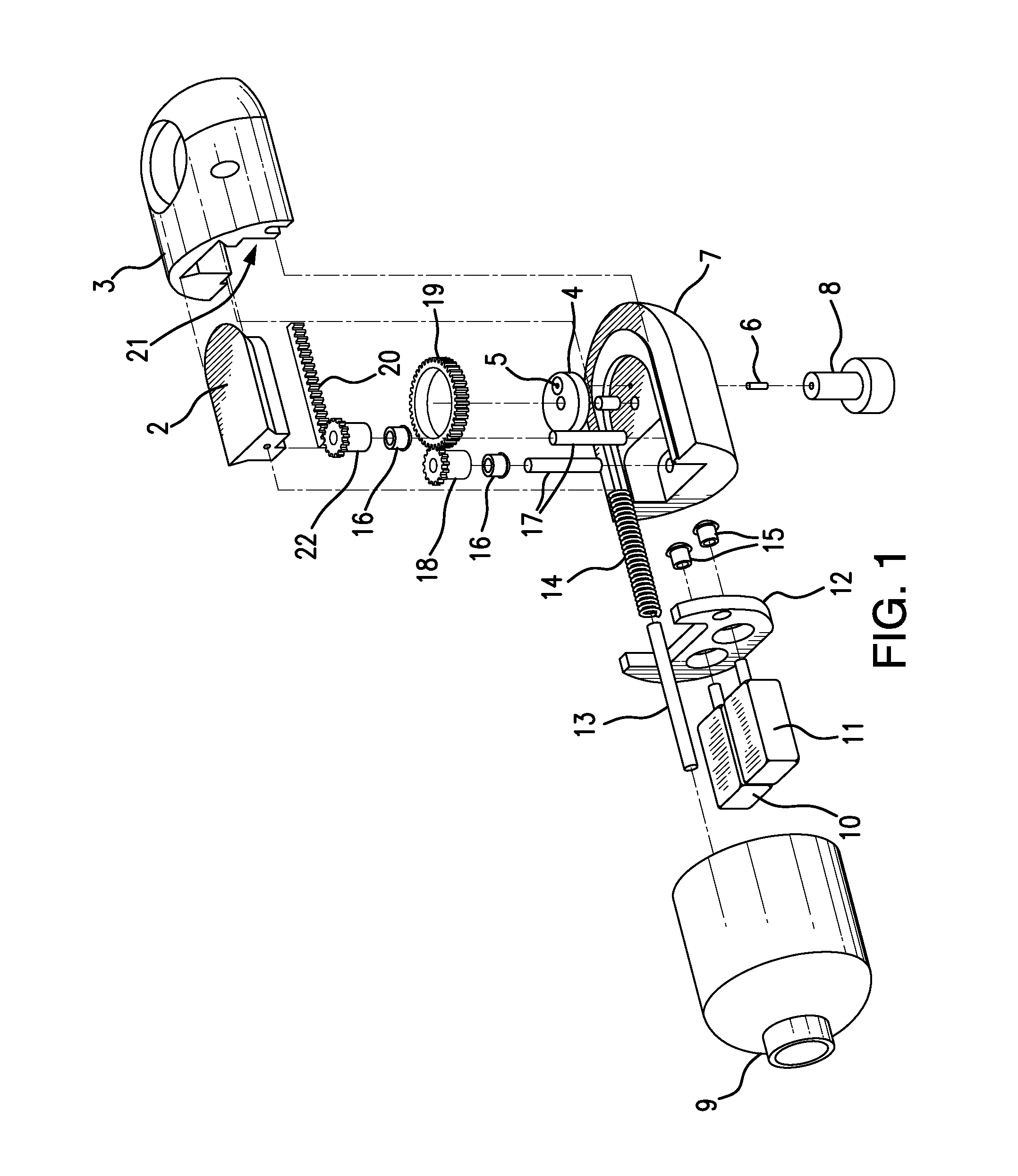
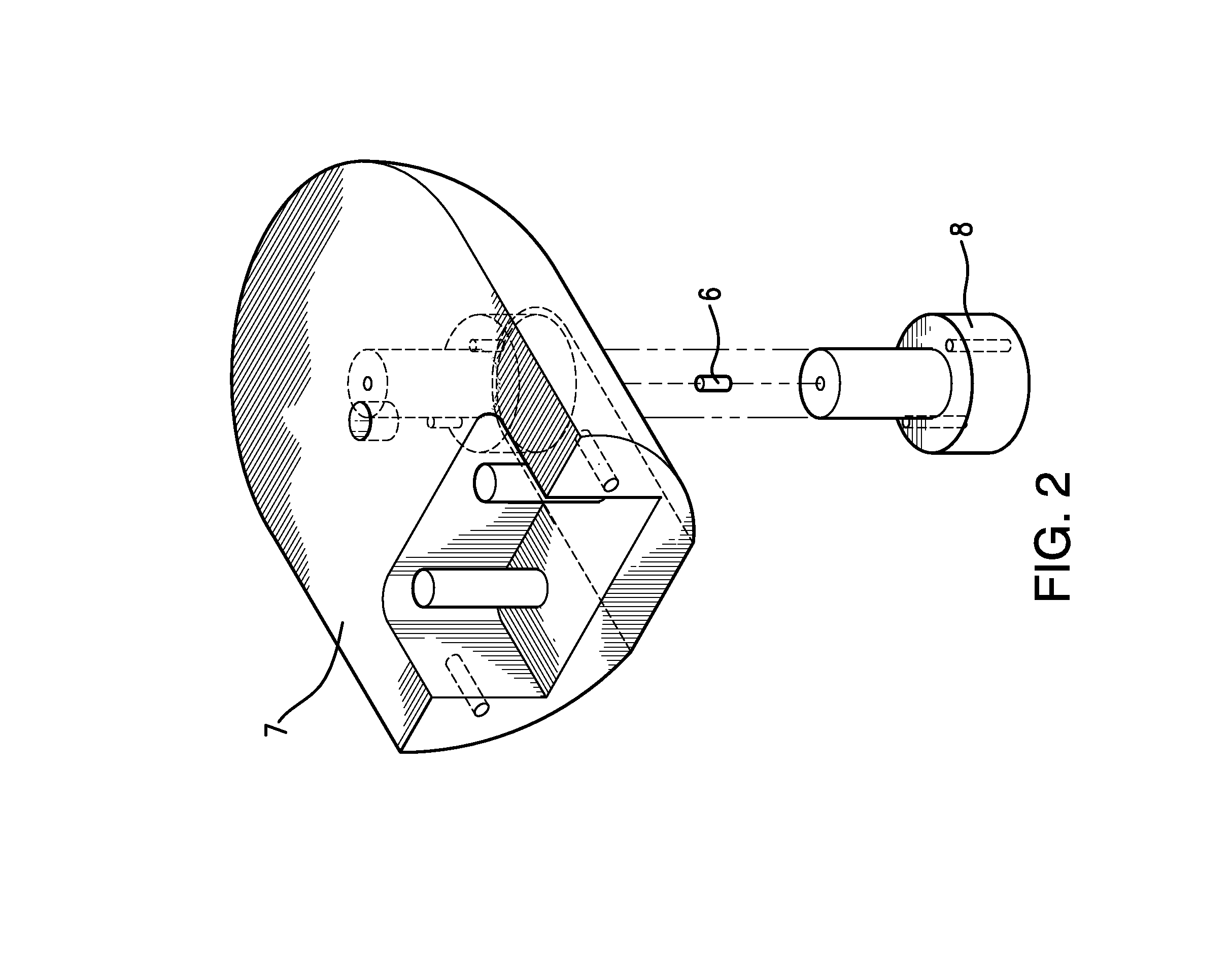
Microdrive for Use in Stereotactic Surgery
Instrument (9) micro positioning device on the stereotactic system consists of the linear drive with the collet-chuck and the bracket (1) with the instrument (9) guide. The collet-chuck fixes and positions the instrument (9) with the collet (6a, 6′a) and associated taper-nut (7, 7′). The collet (6a) with the associated nut (7) is intended for clamping and positioning a single instrument, whilst the collet (6′a) with the associated taper-nut (7) is intended for the simultaneous securing and positioning of five instruments (9) or microelectrodes at a time. Through holes of the collet (6′a) are coaxial with bores of the central spacer as instrument positioning guide (9), where the sections of the collet (6′a) form and define the four through holes, which are symmetrical and evenly-spaced around the central through-hole.
Owner:ORTOTIP D O O
Direct visualization robotic intra-operative radiation therapy device with radiation ablation capsule
InactiveUS8920300B2Increase probabilityNon-surgical orthopedic devicesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyX-rayIsotope
This invention proposes a robotic applicator device to be deployed internally to a patient having a capsule (also referred to as a cassette) and aperture with a means of alternately occluding and exposing a radioactive source through the aperture. The capsule and aperture will be integrated with a surgical robot to create a robotic IORT (intra-operative radiation therapy) applicator device as more fully described below. The capsule, radiation source, and IORT applicator arm would be integrated to enable a physician, physicist or technician to interactively internally view and select tissue for exposure to ionizing radiation in sufficient quantities to deliver therapeutic radiation doses to tissue. Via the robotic manipulation device, the physician and physicist would remotely apply radiation to not only the tissue to be exposed, but also control the length of time of the exposure. Control means would be added to identify and calculate margin and depth of tissue to be treated and the proper radiation source or radioactive isotope (which can be any particle emitter, including neutron, x-ray, alpha, beta or gamma emitter) to obtain the desired therapeutic effects. The invention enables stereotactical surgery and close confines radiation therapy adjacent to radiosensitive tissue.
Owner:SRIORT
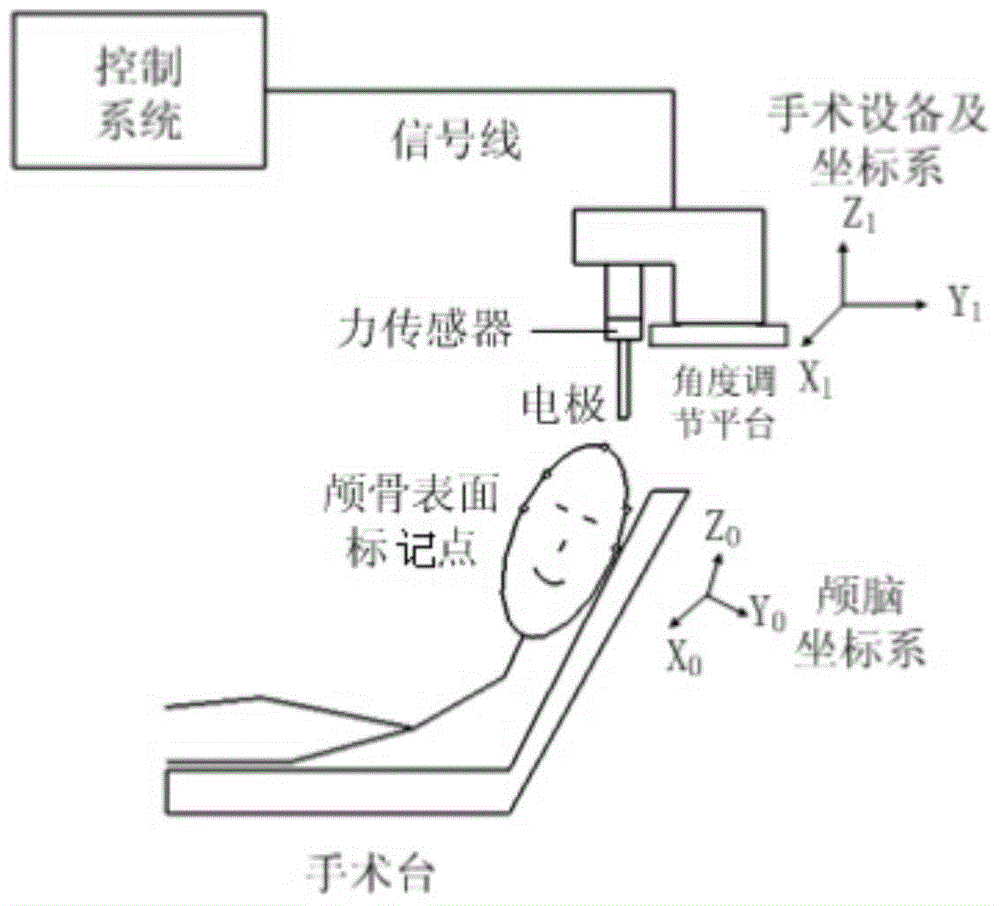
Force-sensor-based coupling method for extracranial and intracranial coordinate systems in brain stereotactic surgery of neurosurgery
The invention relates to a force-sensor-based coupling method for extracranial and intracranial coordinate systems in brain stereotactic surgery of neurosurgery. The method comprises the steps that a micro probe is mounted on the high-precision force sensor, and the force sensor is mounted on the Z-axis of the extracranial coordinate system where surgical equipment is located; a certain axial face of the extracranial coordinate system of the equipment is made to be parallel to a corresponding axial face of the intracranial coordinate system through mark points on the surface of the skull; the origin of the extracranial coordinate system is moved to coincide with an intracranial origin according to the mark point, namely the intersection point between a vertical line where the origin of the intracranial coordinate system is perpendicular to a median sagittal plane and the surface of the skull, so coupling between the extracranial coordinate system and the intracranial coordinate system is achieved. The method is ingenious in design concept and high in accuracy, and solves a series of problems existing in the prior art, operation is convenient, and the effect is remarkable.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
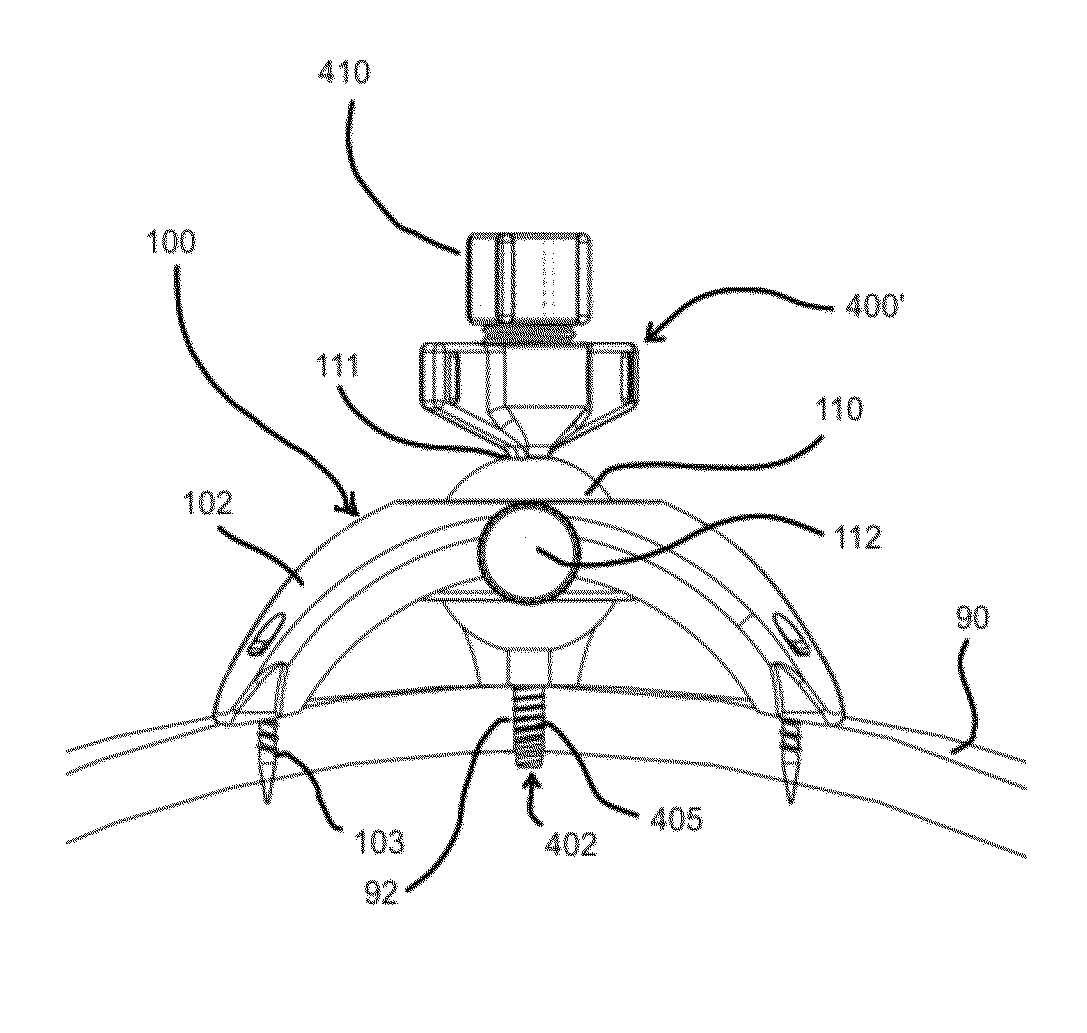
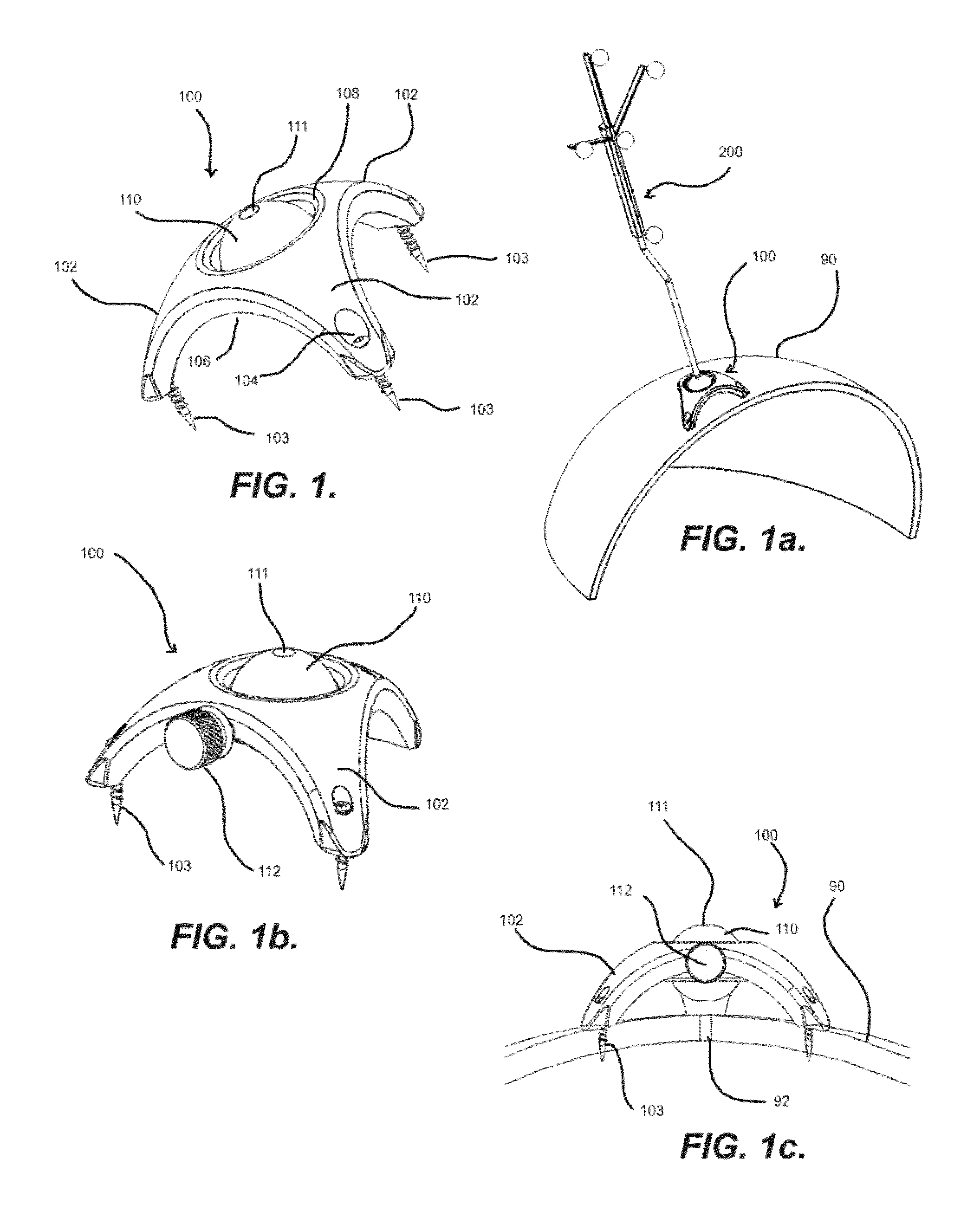
Cranial alignment device for use in intracranial stereotactic surgery
ActiveUS20150374443A1Simple processFit to patientOperating chairsDental chairsNoseStereotactic surgery
A cranial alignment device for use in intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy includes a nosepiece that is custom shaped to mate with the dorsum and alae of the patient's nose.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Stereotactic device for implantation of permanent implants into a rodent brain
ActiveUS9707049B1More accuracyImprove accuracyDiagnosticsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryPermanent implantMedicine
Stereotactic systems and implantation methods that can be designed for use with a specific species and further customized for use with an individual within the species are provided. The stereotactic system can include an implant jig that can model a tissue or organ in which a target tissue area is located. A neurocap can be coupled to the implant jig for pre-planning and pre-placement of implants. A stencil can be used to determine the location for placement of the neurocap on the individual, so that the implants can be precisely targeted at the desired location. Pre-surgical information and data can be obtained from an individual and used to customize components of a stereotactic system, which can improve accuracy of implant placement.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Stereotactic device for primate brains
ActiveUS20190175299A1Conveniently and accurately indicateConveniently insertedMedical devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringPrimateStereotaxis
A stereotactic device for primate brains indicates a brain coordinate reference point of a primate using a simulator for indicating a brain coordinate reference point, thereby providing an initial setting to a zero point corresponding to the brain coordinate reference point. The brain coordinate reference point is conveniently and accurately indicated without relatively expensive equipment, such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner, to determine brain coordinates of the primate, so that a targeting procedure can be conducted on the brain.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com