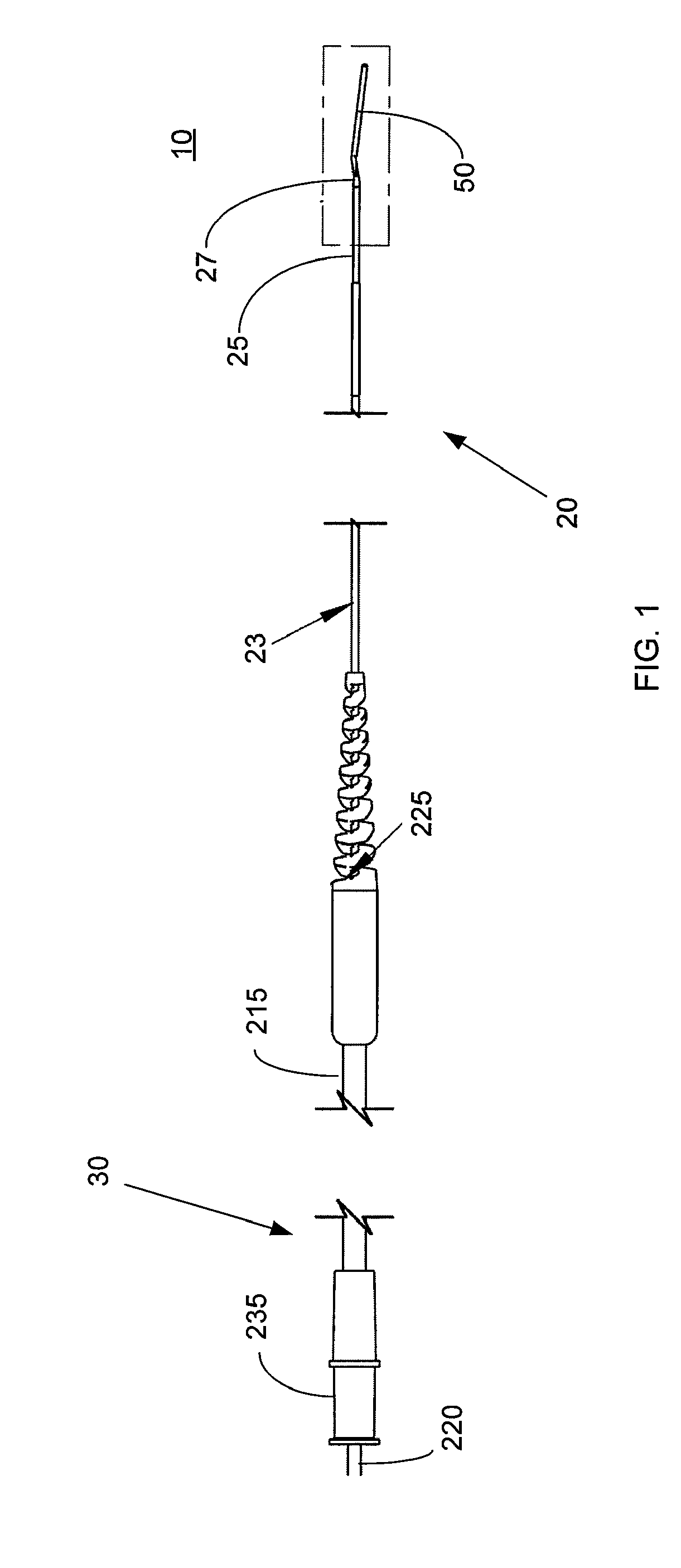
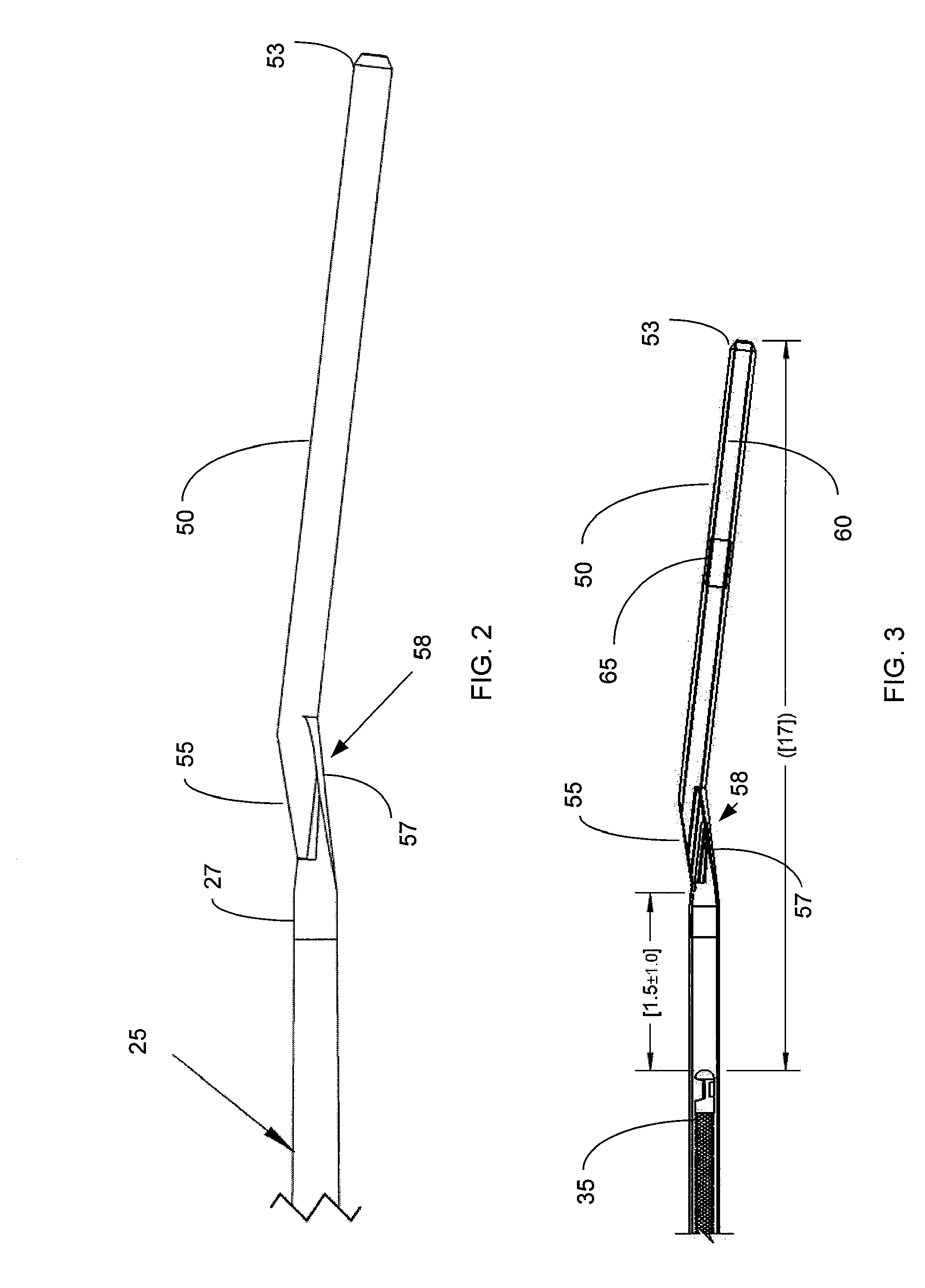
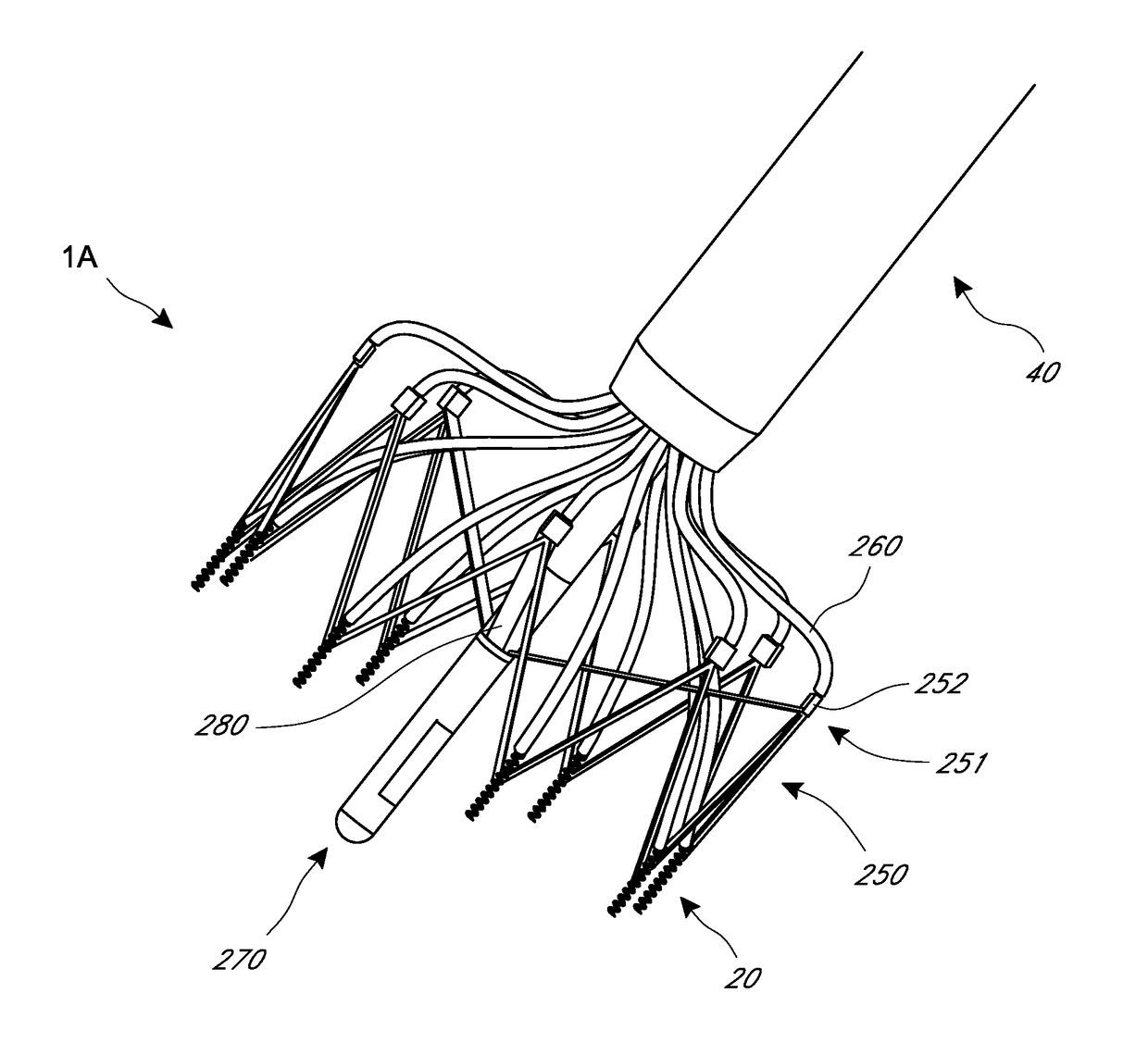
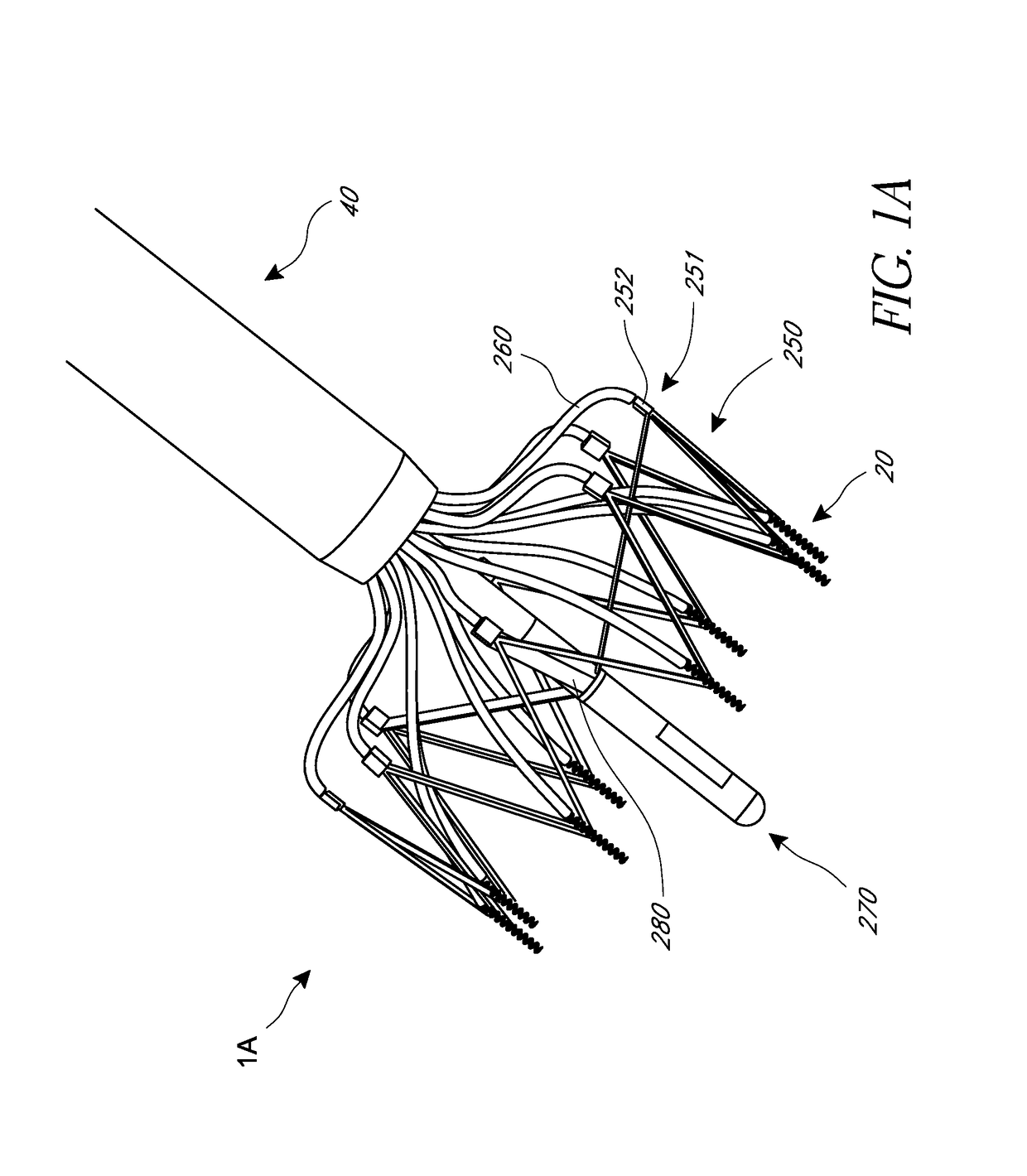
Patents
Literature
234 results about "Intravascular ultrasound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) is a medical imaging methodology using a specially designed catheter with a miniaturized ultrasound probe attached to the distal end of the catheter. The proximal end of the catheter is attached to computerized ultrasound equipment. It allows the application of ultrasound technology, such as piezoelectric transducer or CMUT, to see from inside blood vessels out through the surrounding blood column, visualizing the endothelium (inner wall) of blood vessels in living individuals.
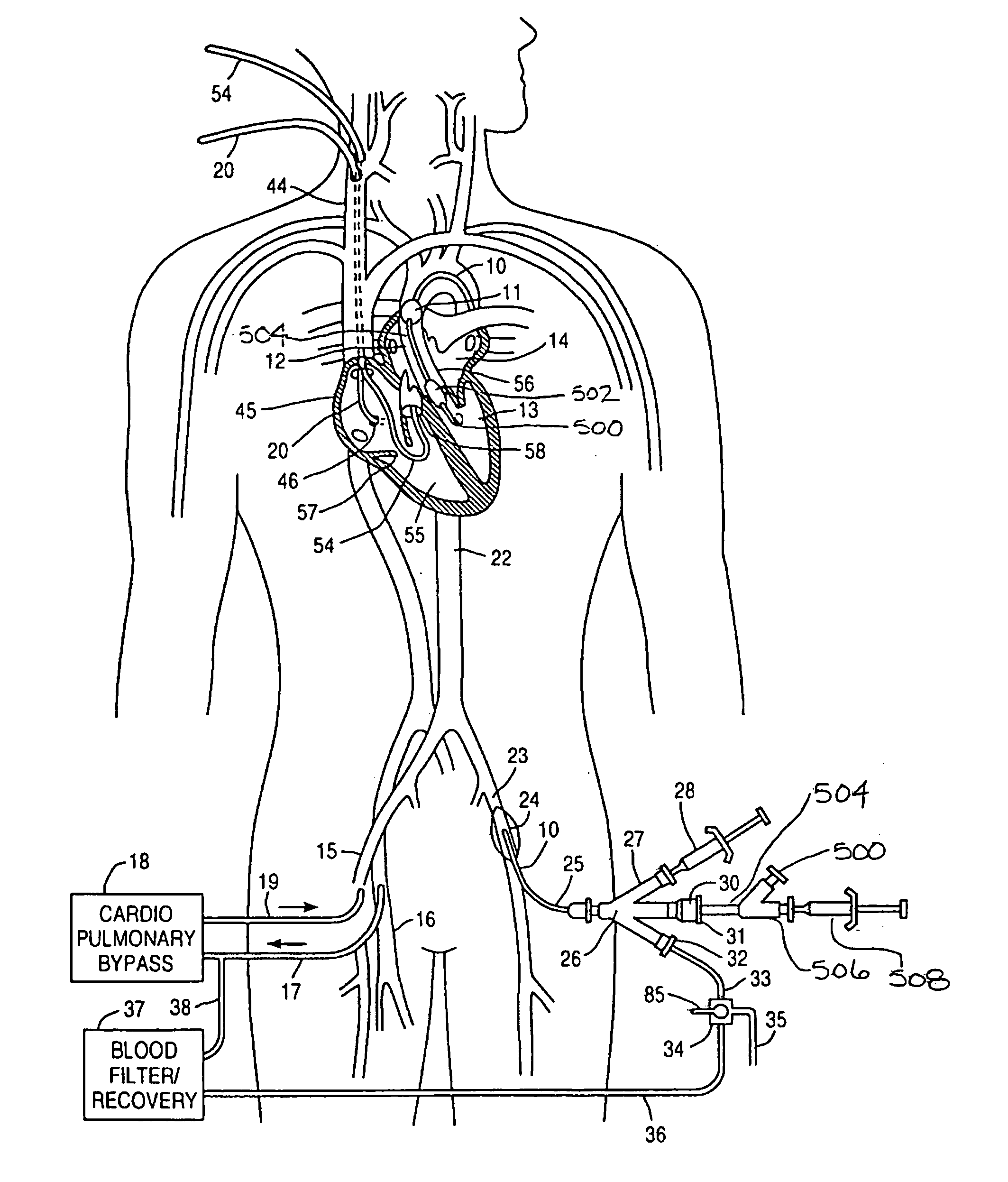
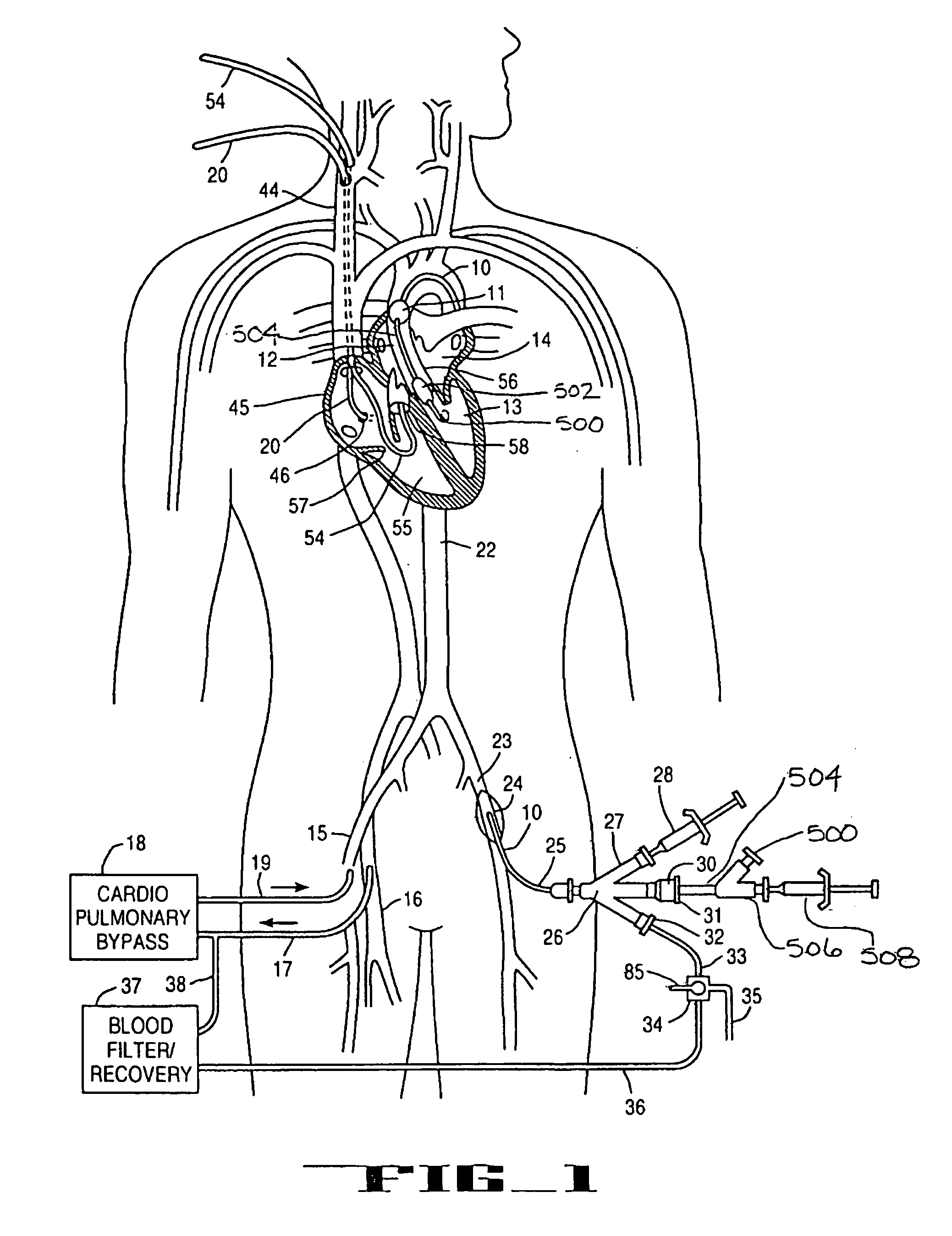
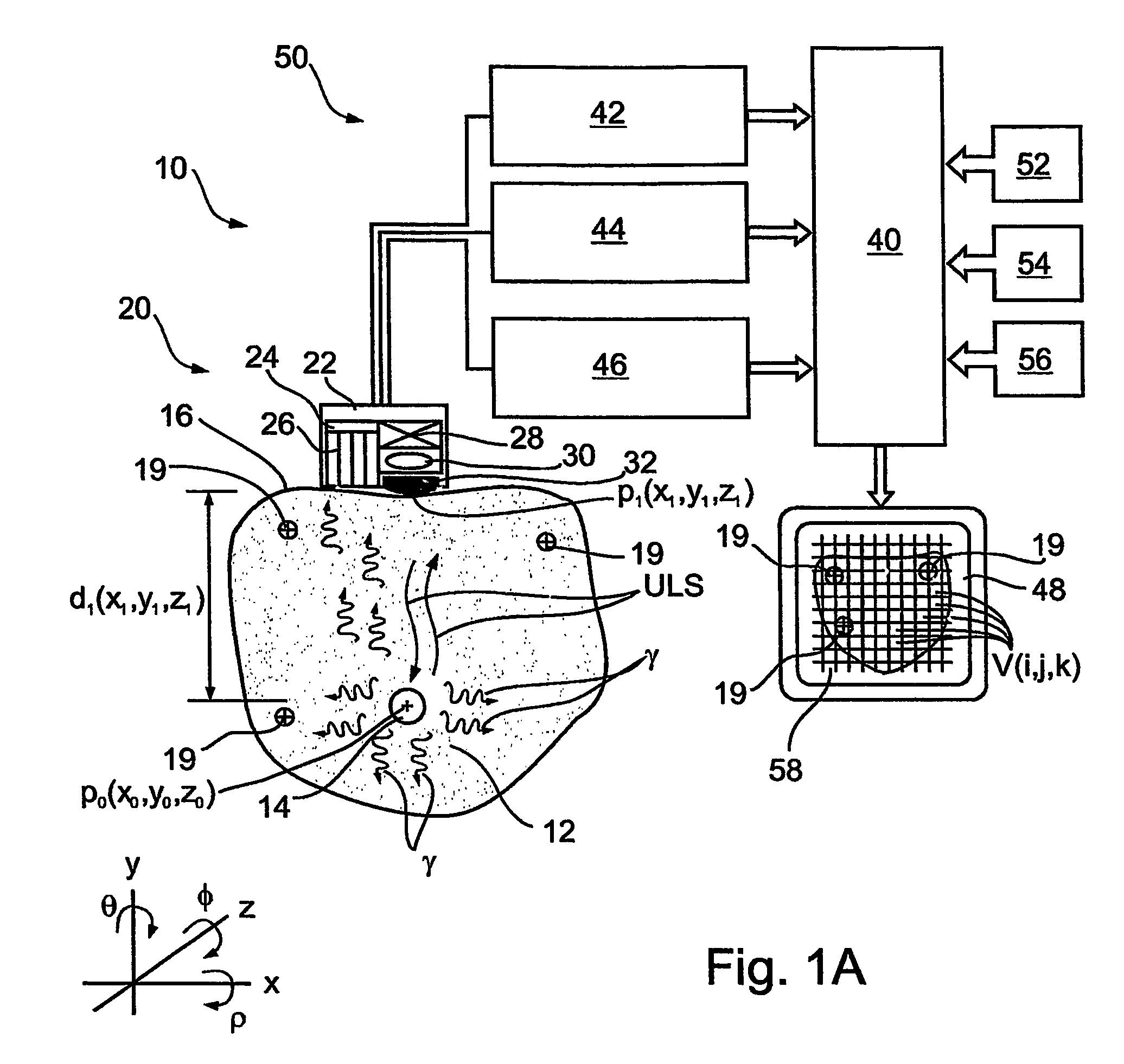
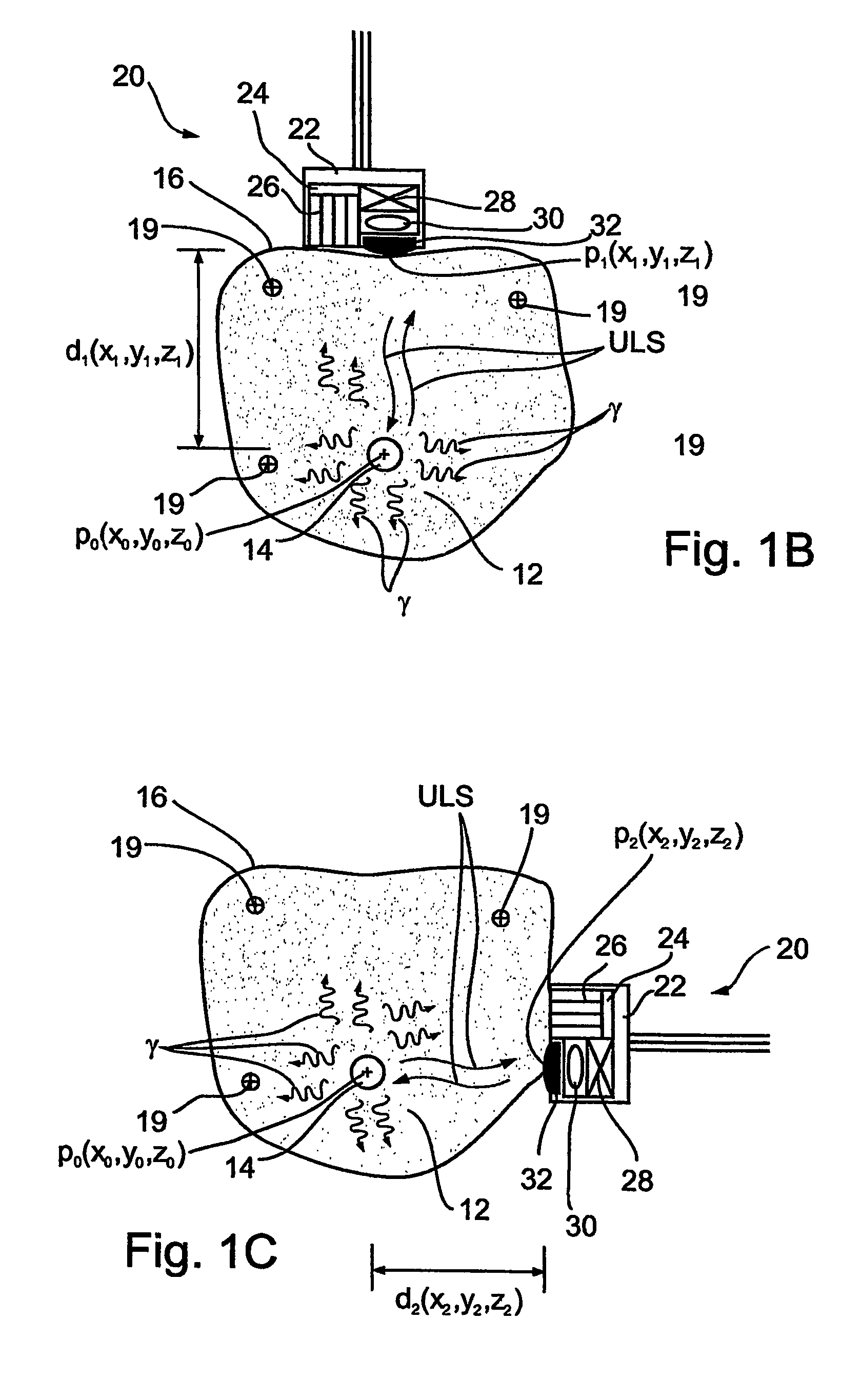
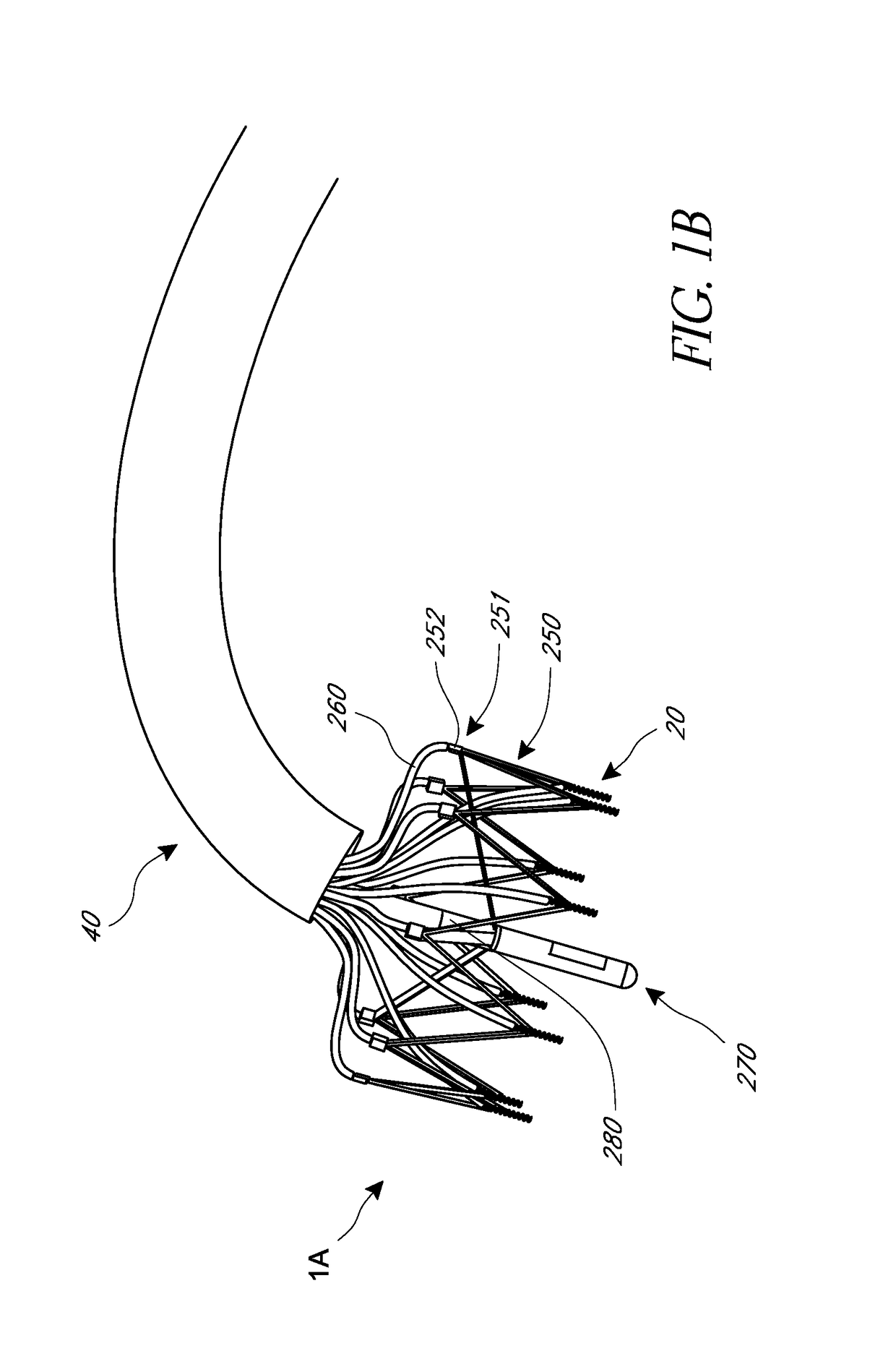
System and methods for performing endovascular procedures
InactiveUS20060058775A1Procedure is complicatedEasy to controlStentsGuide needlesExtracorporeal circulationAtherectomy
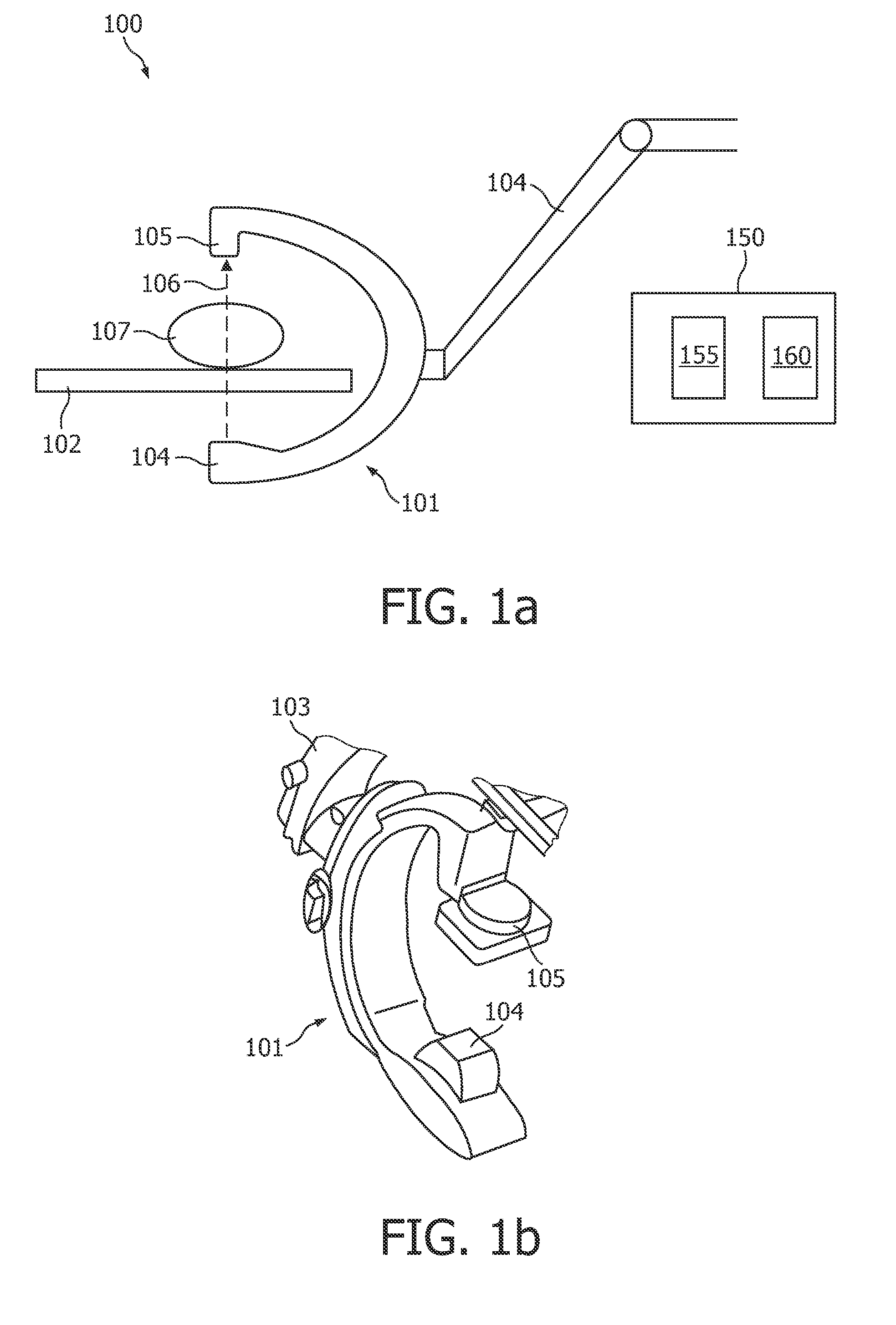
A system for inducing cardioplegic arrest and performing an endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of a patient. An endoaortic partitioning catheter has an inflatable balloon which occludes the ascending aorta when inflated. Cardioplegic fluid may be infused through a lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to stop the heart while the patient's circulatory system is supported on cardiopulmonary bypass. One or more endovascular devices are introduced through an internal lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to perform a diagnostic or therapeutic endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of the patient. Surgical procedures such as coronary artery bypass surgery or heart valve replacement may be performed in conjunction with the endovascular procedure while the heart is stopped. Embodiments of the system are described for performing: fiberoptic angioscopy of structures within the heart and its blood vessels, valvuloplasty for correction of valvular stenosis in the aortic or mitral valve of the heart, angioplasty for therapeutic dilatation of coronary artery stenoses, coronary stenting for dilatation and stenting of coronary artery stenoses, atherectomy or endarterectomy for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, intravascular ultrasonic imaging for observation of structures and diagnosis of disease conditions within the heart and its associated blood vessels, fiberoptic laser angioplasty for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, transmyocardial revascularization using a side-firing fiberoptic laser catheter from within the chambers of the heart, and electrophysiological mapping and ablation for diagnosing and treating electrophysiological conditions of the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Oct-ivus catheter for concurrent luminal imaging
The invention relates to an apparatus for in vivo imaging. More specifically, the present invention relates to a catheter that incorporates an Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) system and an Intravascular Ultrasound (“IVUS) system for concurrent imaging of luminal systems, such as imaging the vasculature system, including, without limitation, cardiac vasculature, peripheral vasculature and neural vasculature.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Apparatus and methods for imaging and attenuation correction
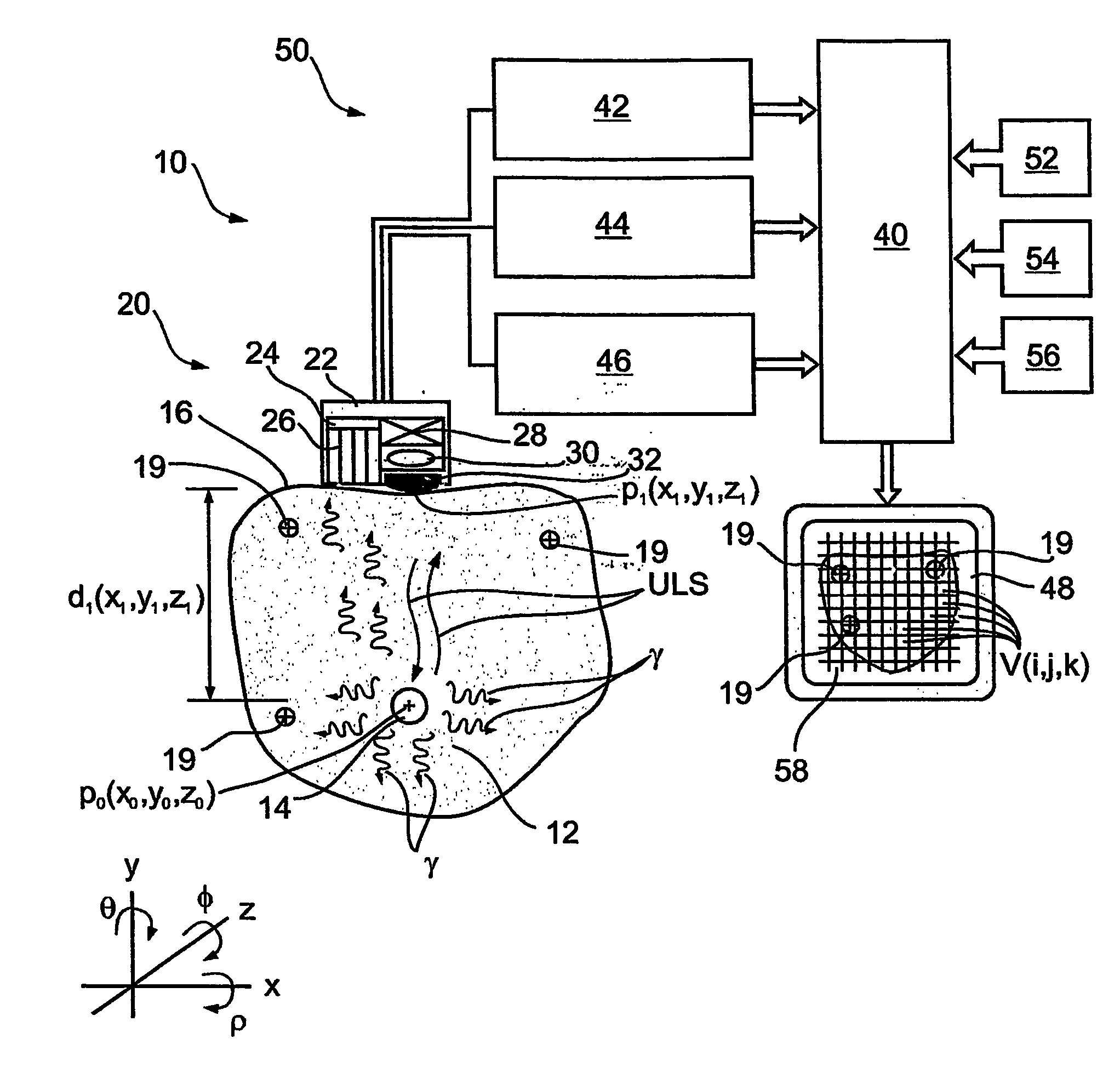
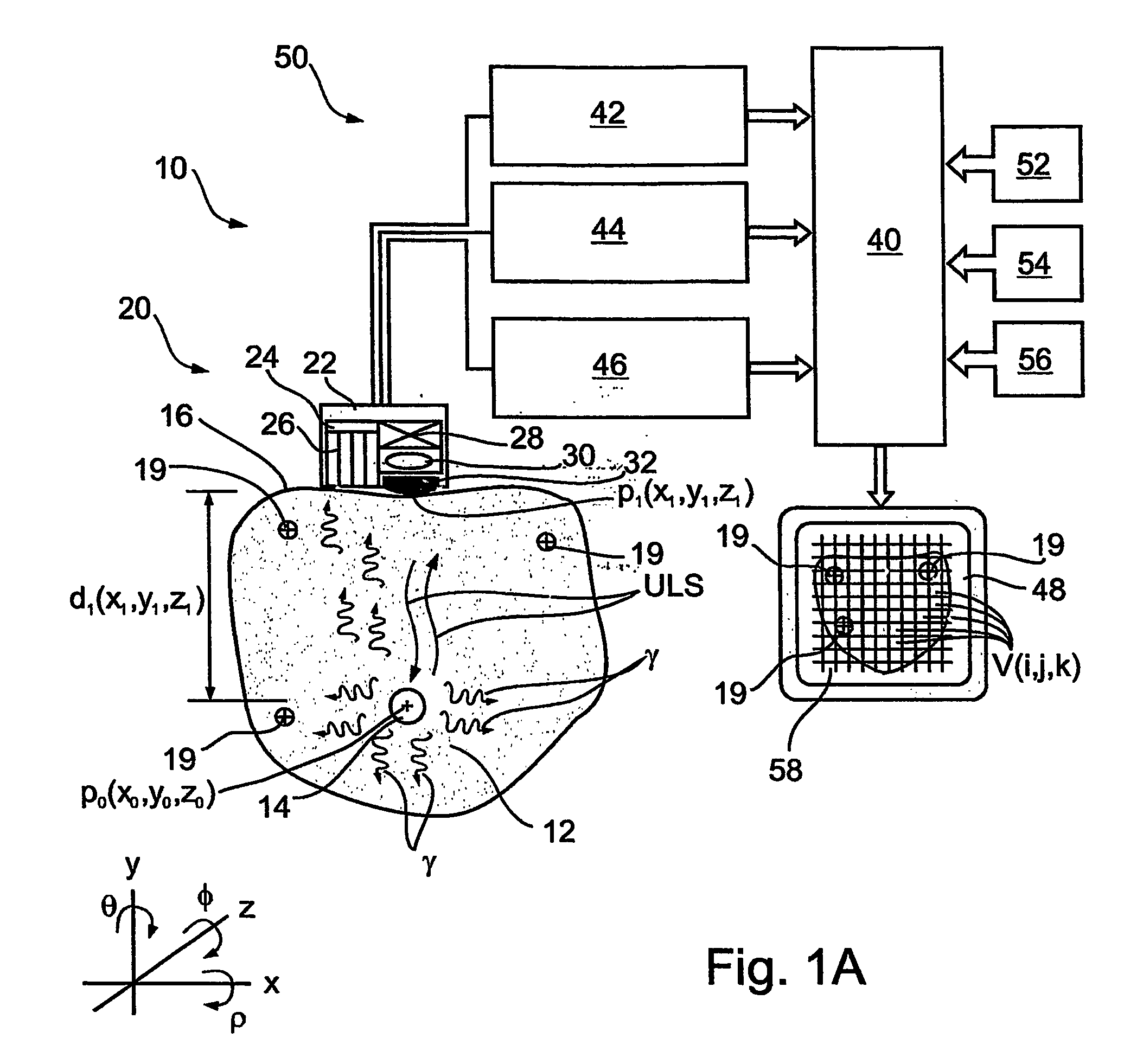
Imaging apparatus, is provided, comprising a first device, for obtaining a first image, by a first modality, selected from the group consisting of SPECT, PET, CT, an extracorporeal gamma scan, an extracorporeal beta scan, x-rays, an intracorporeal gamma scan, an intracorporeal beta scan, an intravascular gamma scan, an intravascular beta scan, and a combination thereof, and a second device, for obtaining a second, structural image, by a second modality, selected from the group consisting of a three-dimensional ultrasound, an MRI operative by an internal magnetic field, an extracorporeal ultrasound, an extracorporeal MRI operative by an external magnetic field, an intracorporeal ultrasound, an intracorporeal MRI operative by an external magnetic field, an intravascular ultrasound, and a combination thereof, and wherein the apparatus further includes a computerized system, configured to construct an attenuation map, for the first image, based on the second, structural image. Additionally, the computerized system is configured to display an attenuation-corrected first image as well as a superposition of the attenuation-corrected first image and the second, structural image. Furthermore, the apparatus is operative to guide an in-vivo instrument based on the superposition.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
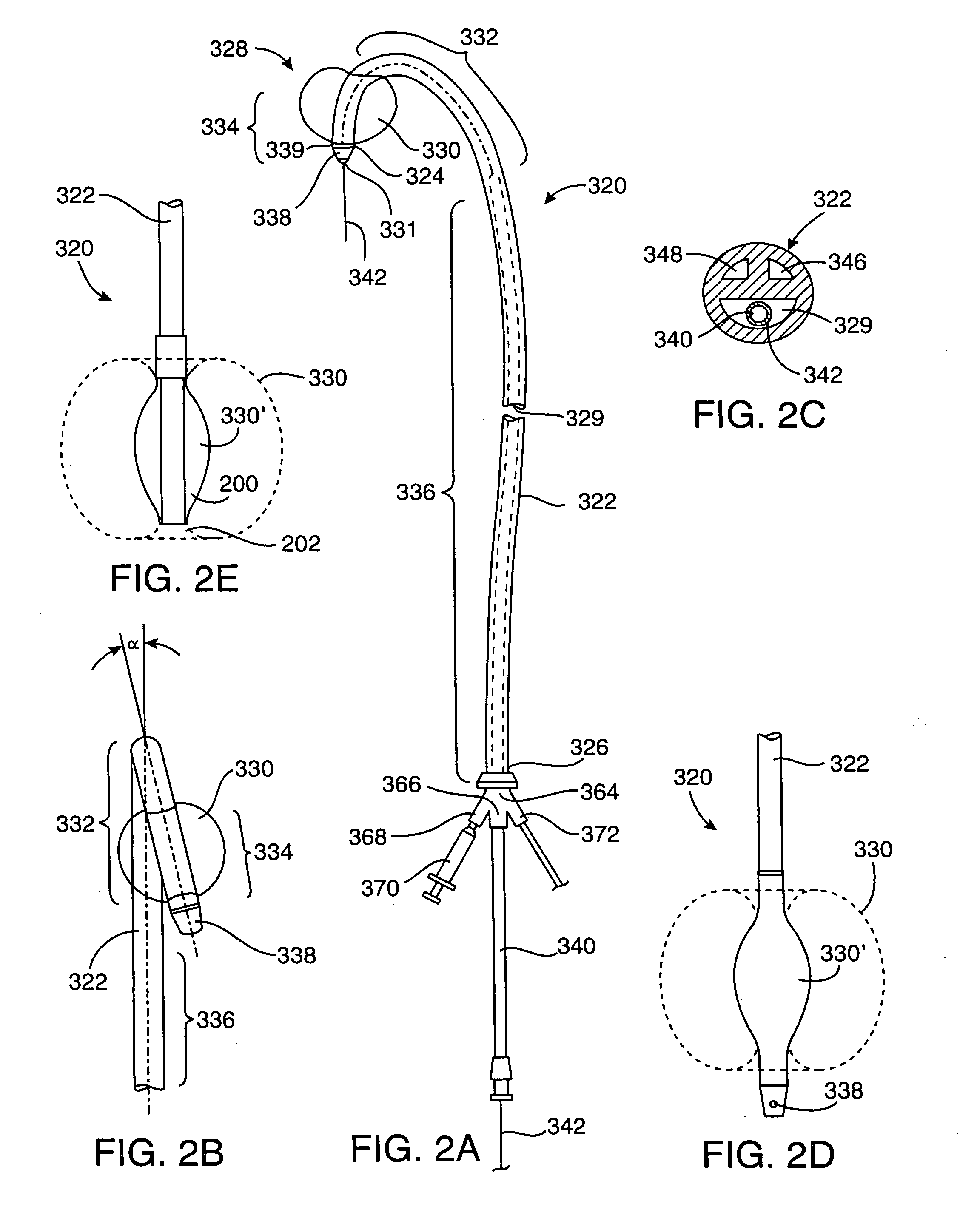
Medical system for inserting a catheter into a vessel
ActiveUS20060287595A1Improve assessmentMinimal stressUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsStentsUltrasound angiographyThree vessels
The invention relates to a medical system for introducing a catheter into a vessel, preferably a blood vessel of a patient, having at least a computer and control unit, a means for creating a transparent general view of the position of the vessel, a catheter with a reversible inflatable balloon located in the front area, to the outside of which a stent can be fitted for implanting into the vessel, a position locating system for the catheter with position and location sensors that can determine the position and location of the front area of the catheter in the space, the system being fitted in the front area with at least one OCT (optical coherence tomography) sensor at a catheter end for the close-up area, with at least one IVUS (intravascular ultrasound) imaging sensor at a catheter end for the remote area and the computer and control unit having image processing and image display functions for the image sensors.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Methods and apparatuses for medical imaging
InactiveUS20080051660A1Blood flow measurement devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionGratingUltrasound angiography
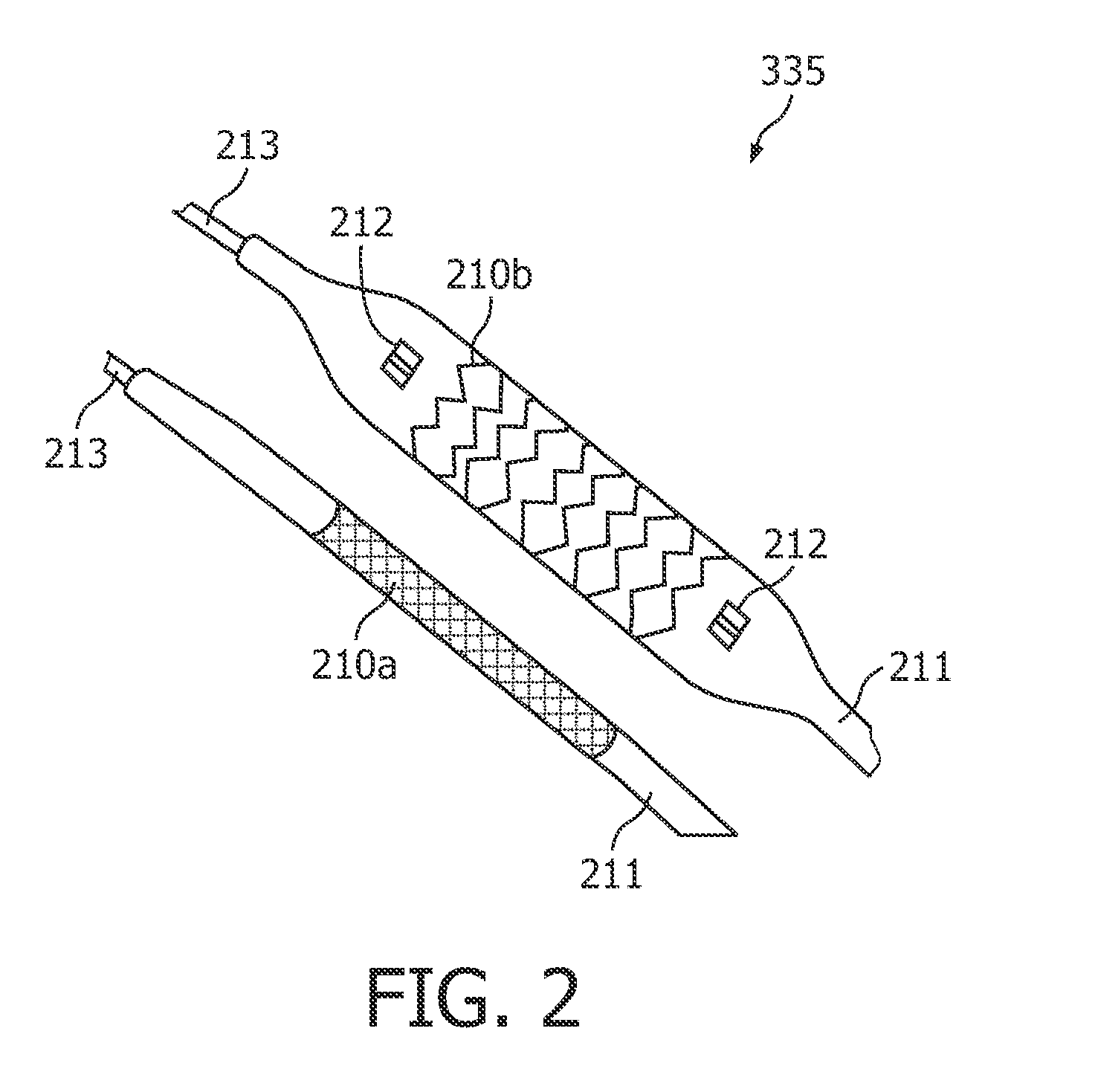
A set of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) related systems, apparatuses and methods are disclosed. New catheter designs including contrast agent introduction subsystems and / or Doppler subsystems are disclosed. Methods for acquiring and analyzing Doppler data from intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) catheters are disclosed. RF-based detection of blood and / or contrast agents such as micro-bubbles are disclosed. Methods for frame-grating image data analysis permitting frame registration before, during and after a contrasting effect is imposed on a system being imaged are disclosed. Methods for difference imaging for contrast detection are disclosed. Methods for quantification and visualization of IVUS data are disclosed. And methods for IVUS imaging are disclosed.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
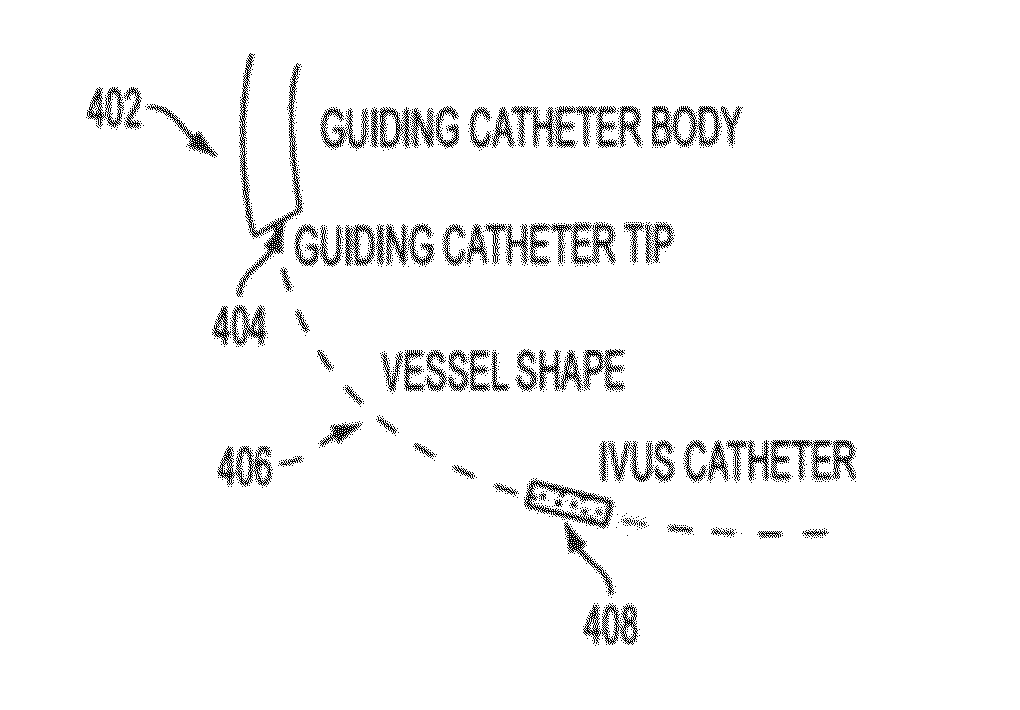
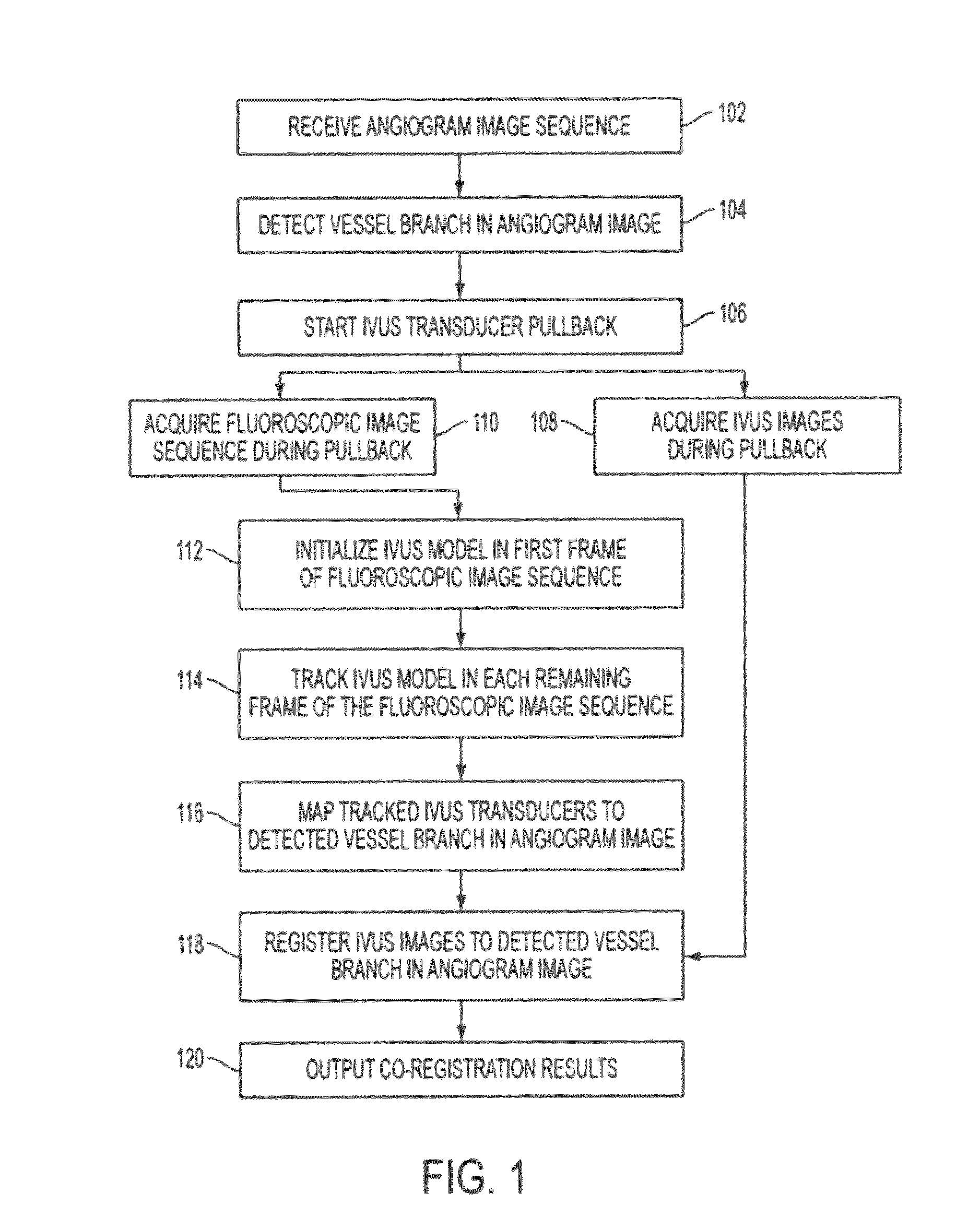
Method and System for Image Based Device Tracking for Co-registration of Angiography and Intravascular Ultrasound Images
ActiveUS20120059253A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular ultrasoundFluorescence
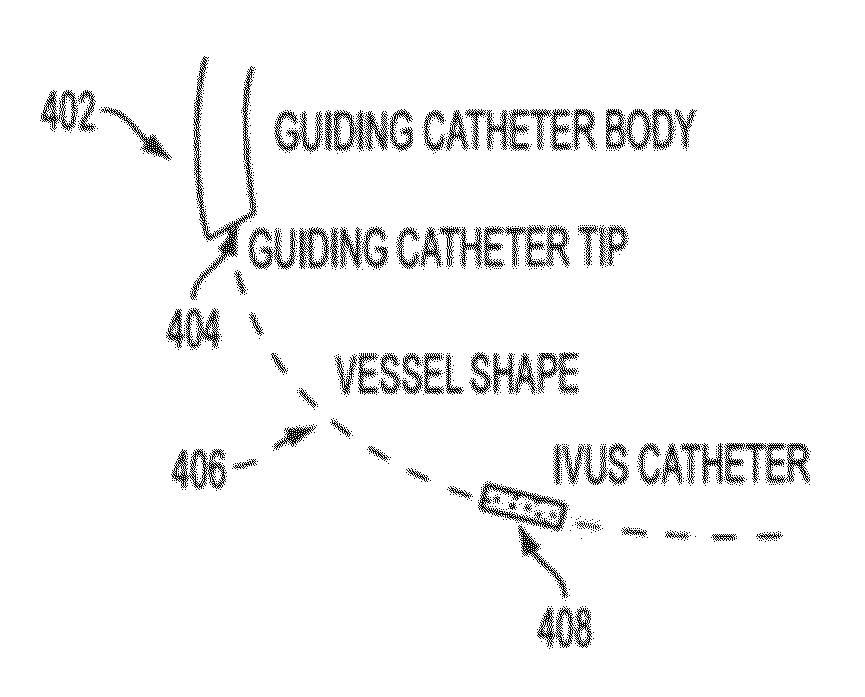
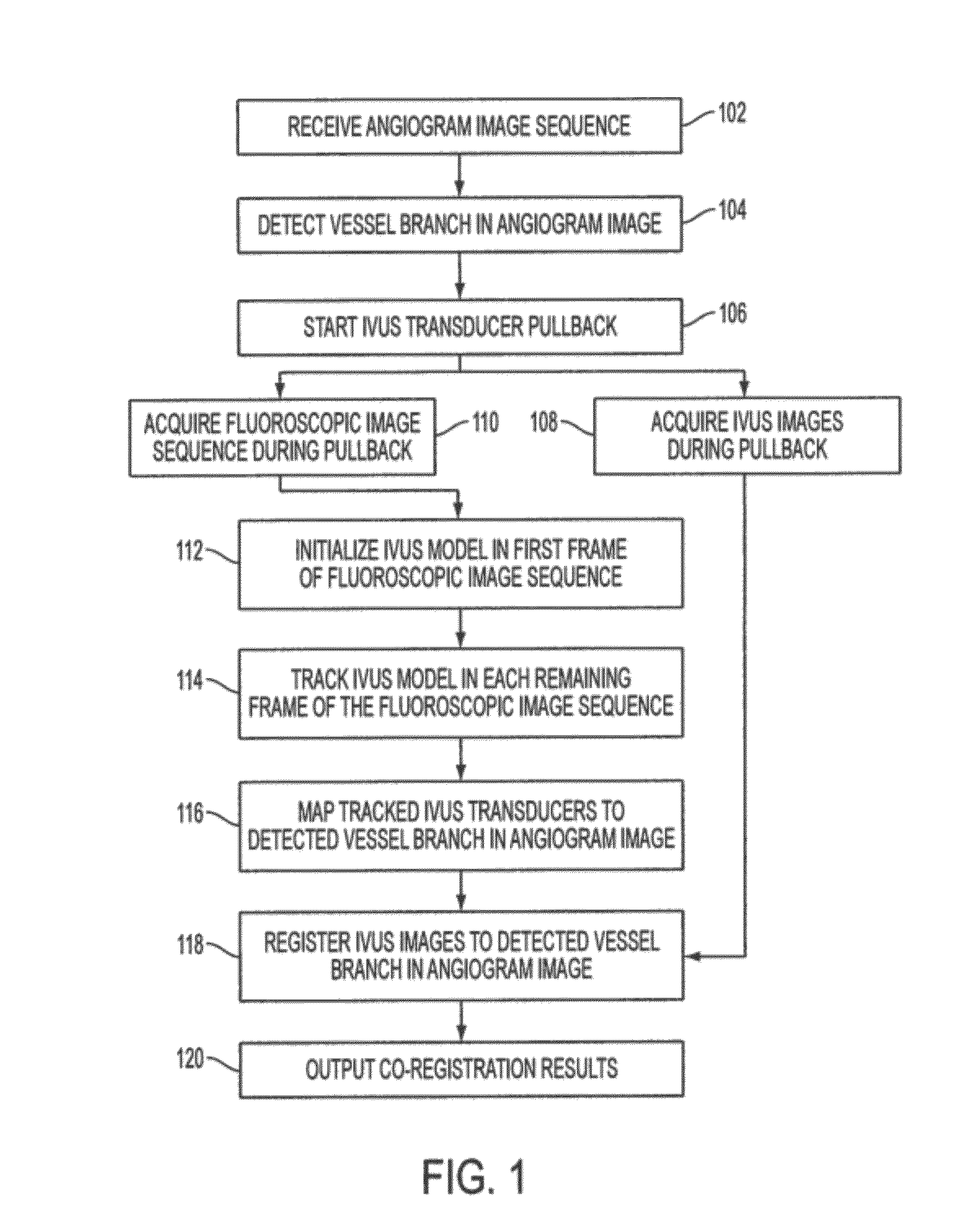
A method and system for co-registration of angiography data and intra vascular ultrasound (IVUS) data is disclosed. A vessel branch is detected in an angiogram image. A sequence of IVUS images is received from an IVUS transducer while the IVUS transducer is being pulled back through the vessel branch. A fluoroscopic image sequence is received while the IVUS transducer is being pulled back through the vessel branch. The IVUS transducer and a guiding catheter tip are detected in each frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence. The IVUS transducer detected in each frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence is mapped to a respective location in the detected vessel branch of the angiogram image. Each of the IVUS images is registered to a respective location in the detected vessel branch of the angiogram image based on the mapped location of the IVUS transducer detected in a corresponding frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
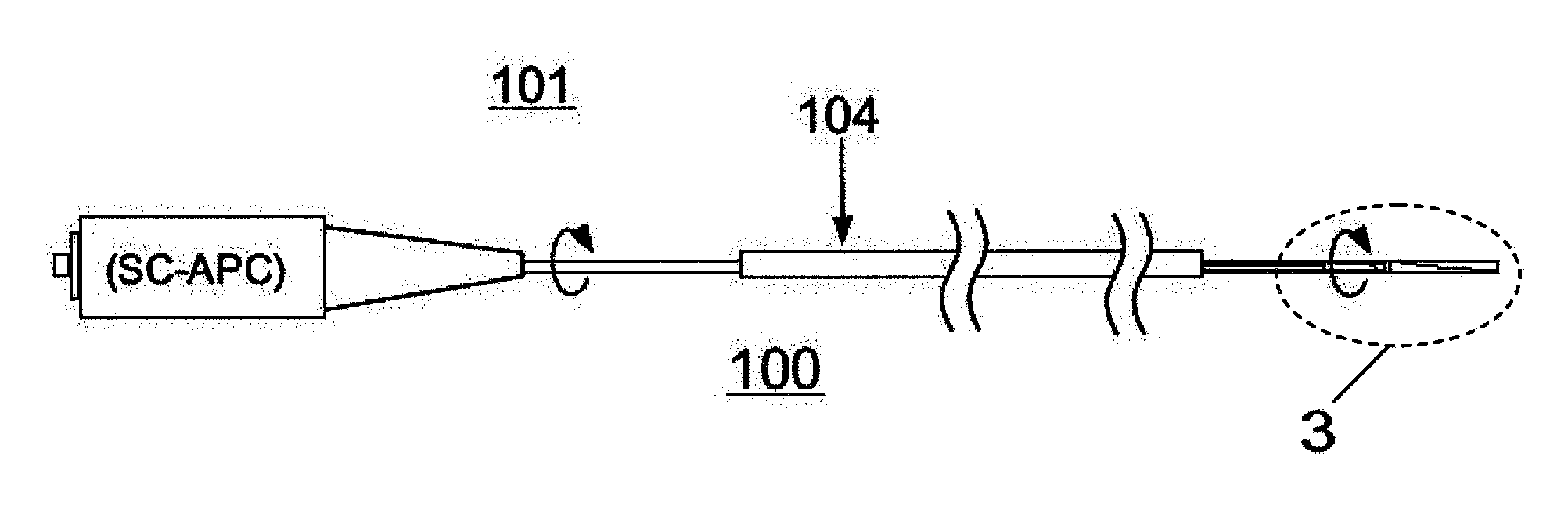
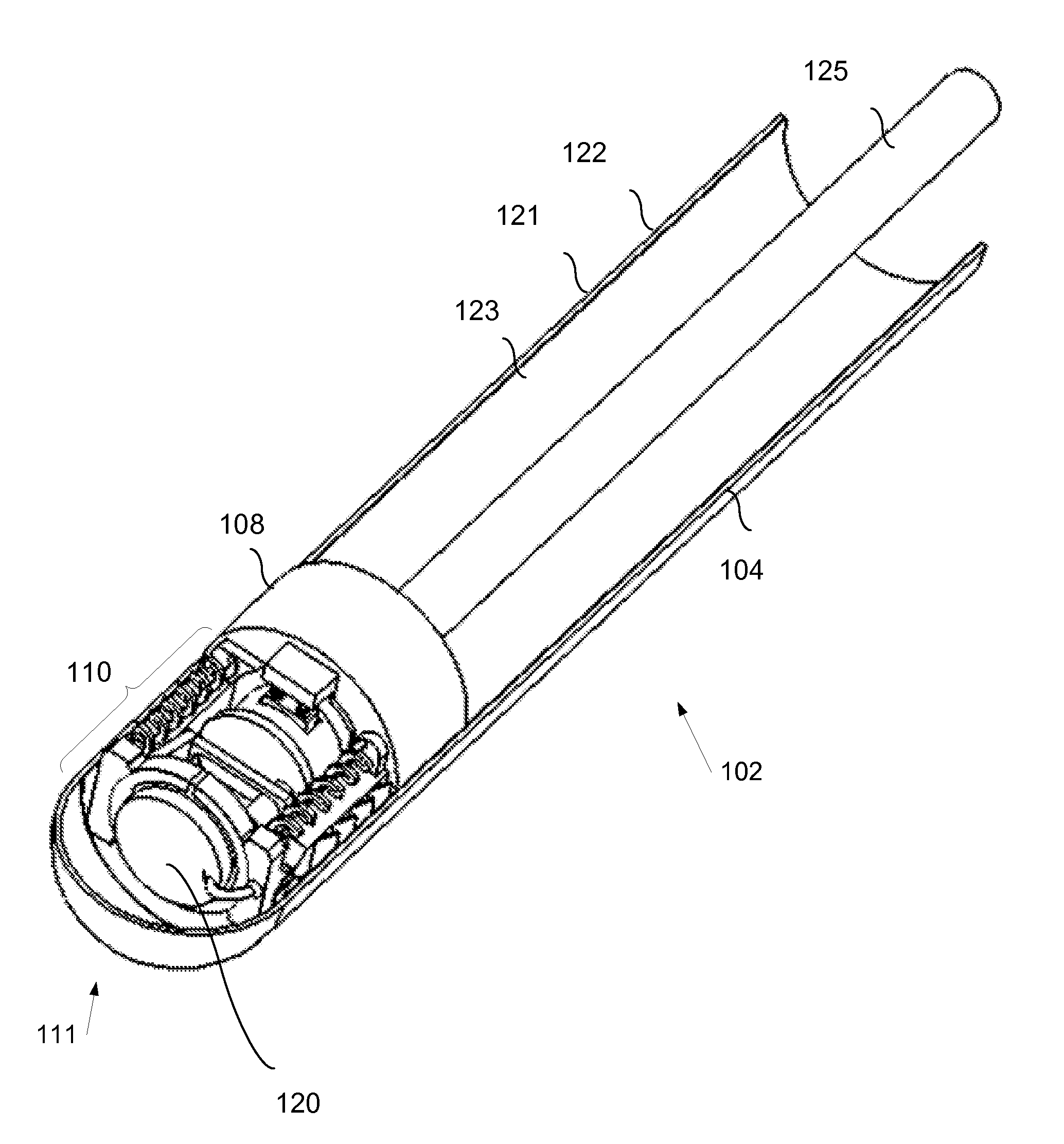
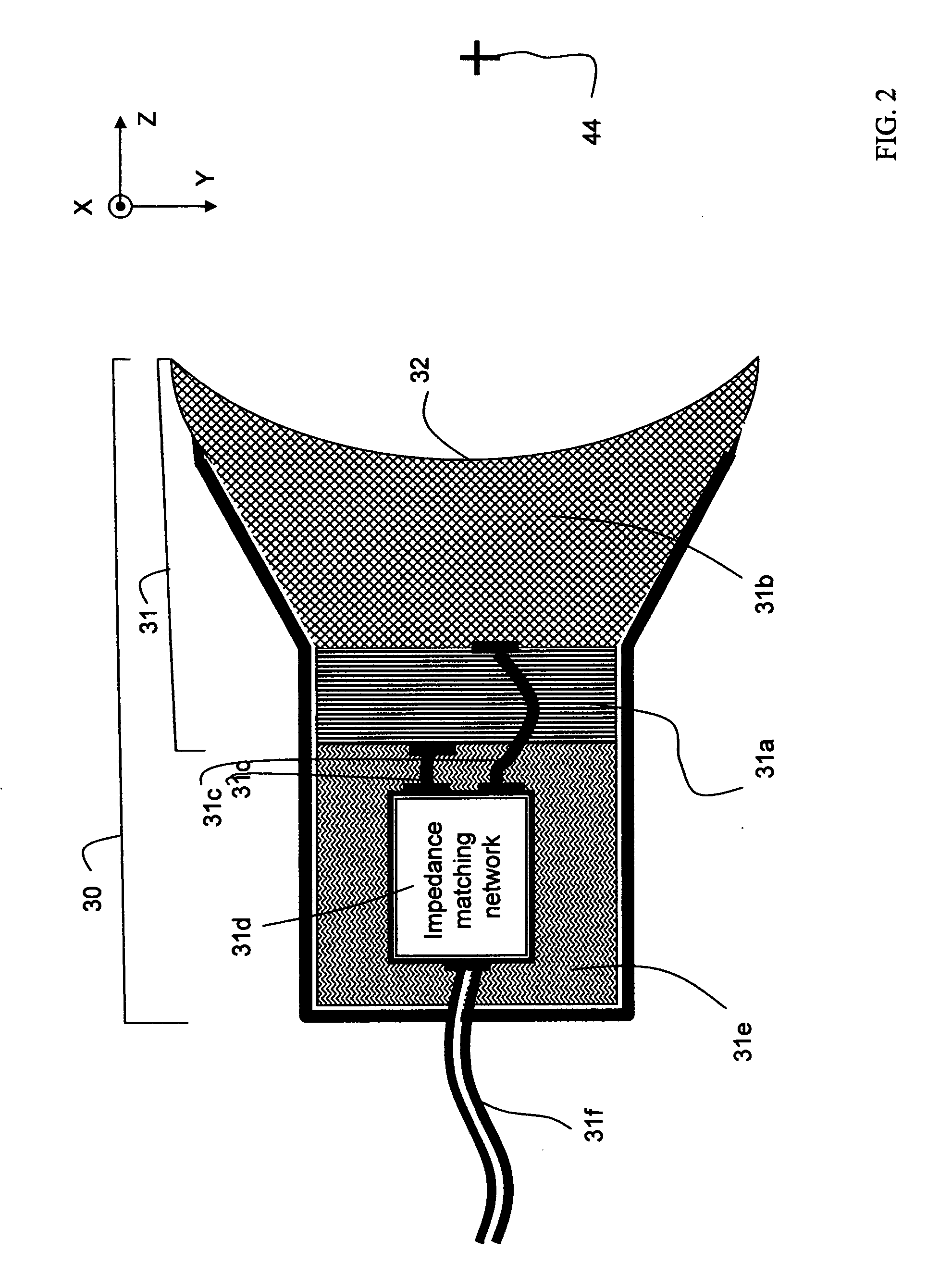
Rotational intravascular ultrasound probe with an active spinning element
ActiveUS20100234736A1Improve image qualityAccurate diagnosis of medicalCatheterInfrasonic diagnosticsManufacturing cost reductionSonification
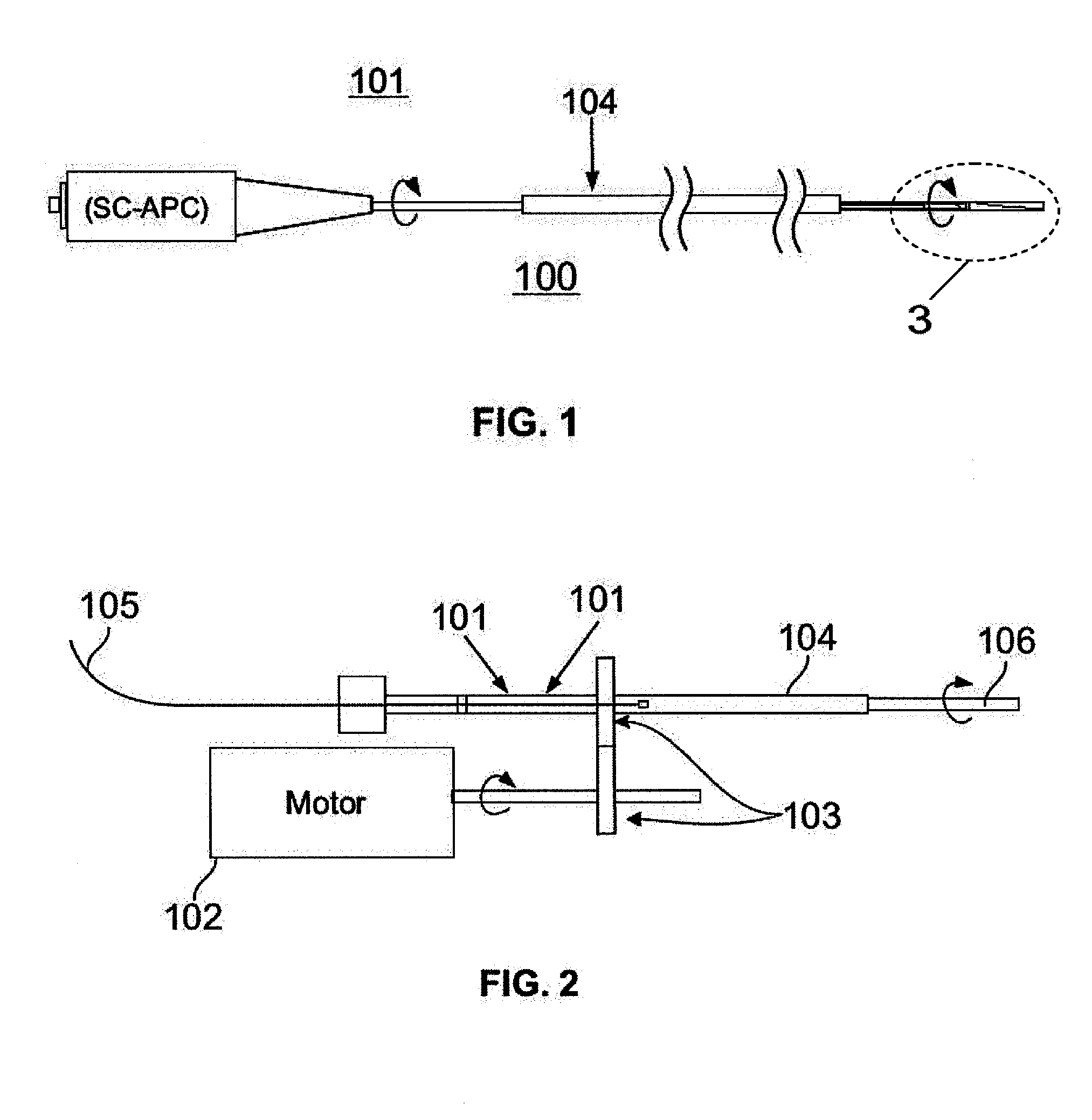
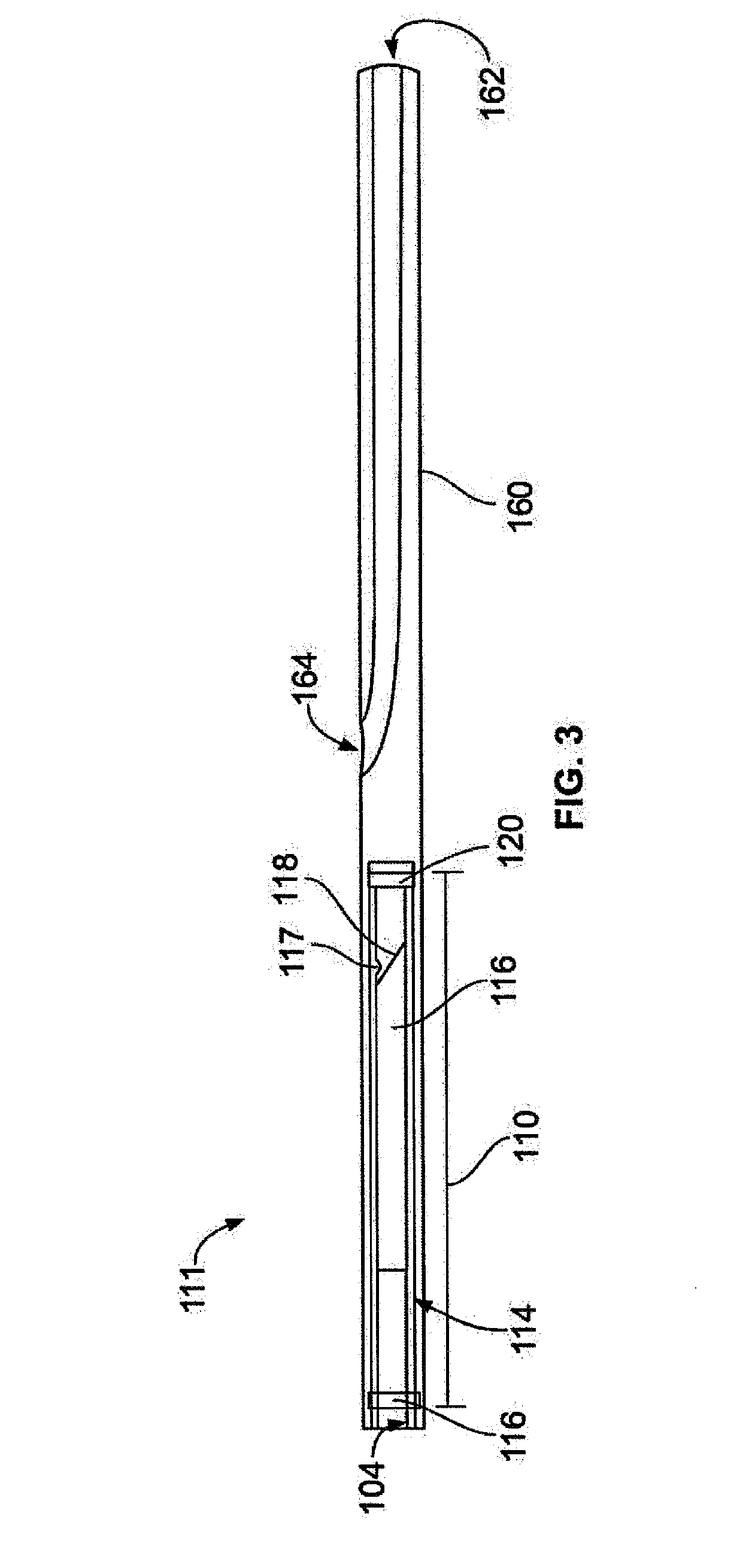
An intravascular ultrasound probe is disclosed, incorporating features for utilizing an advanced transducer technology on a rotating transducer shaft. In particular, the probe accommodates the transmission of the multitude of signals across the boundary between the rotary and stationary components of the probe required to support an advanced transducer technology. These advanced transducer technologies offer the potential for increased bandwidth, improved beam profiles, better signal to noise ratio, reduced manufacturing costs, advanced tissue characterization algorithms, and other desirable features. Furthermore, the inclusion of electronic components on the spinning side of the probe can be highly advantageous in terms of preserving maximum signal to noise ratio and signal fidelity, along with other performance benefits.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
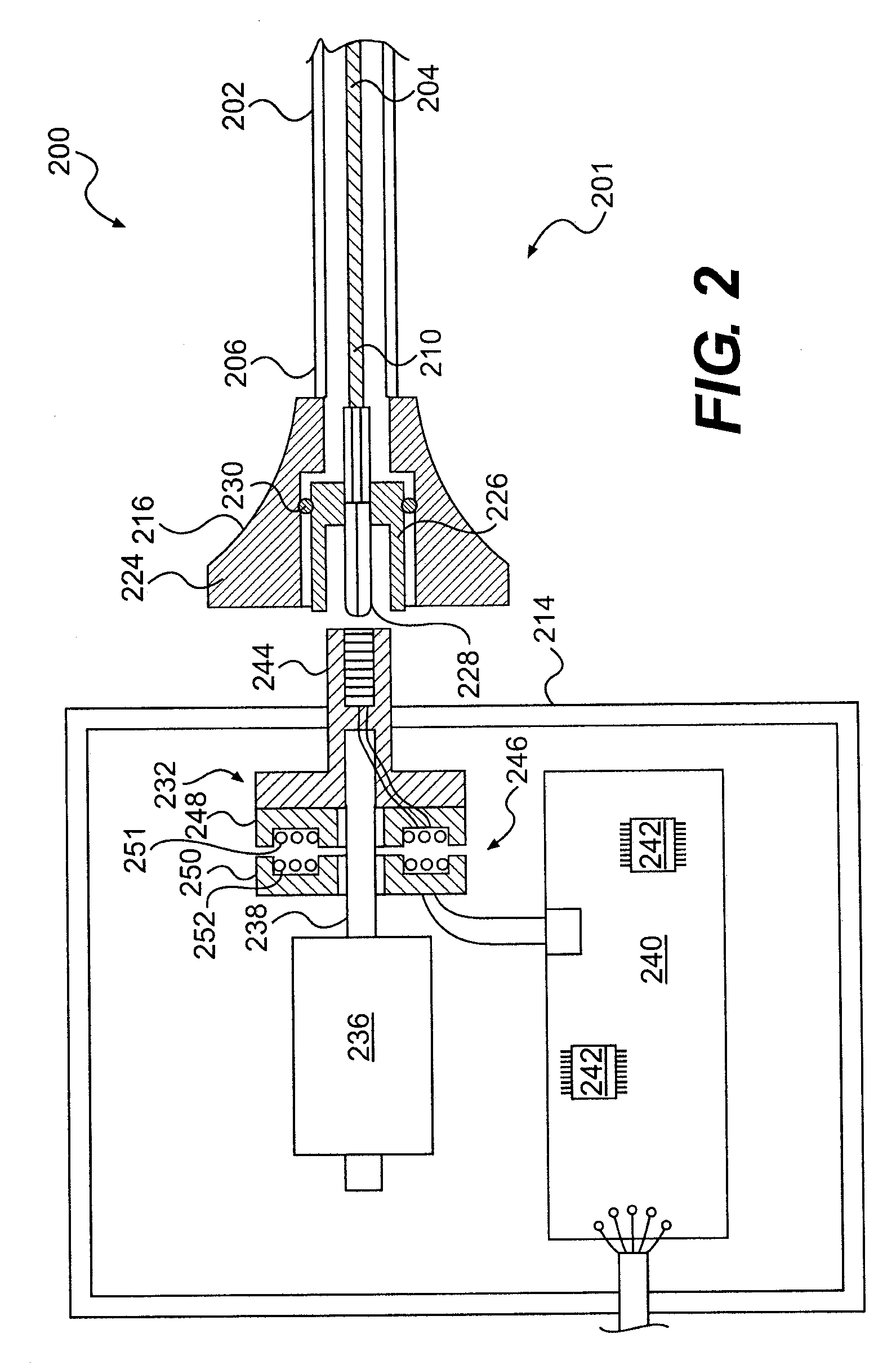
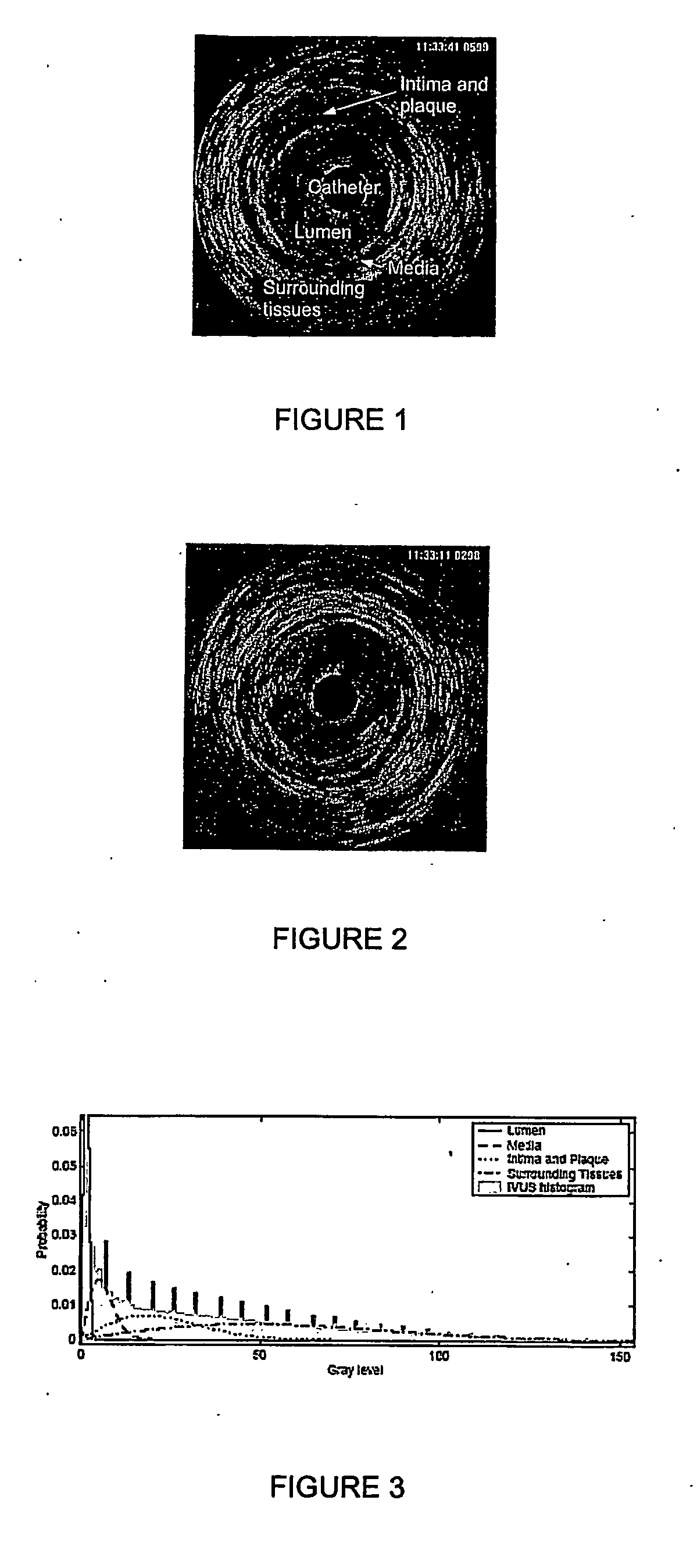
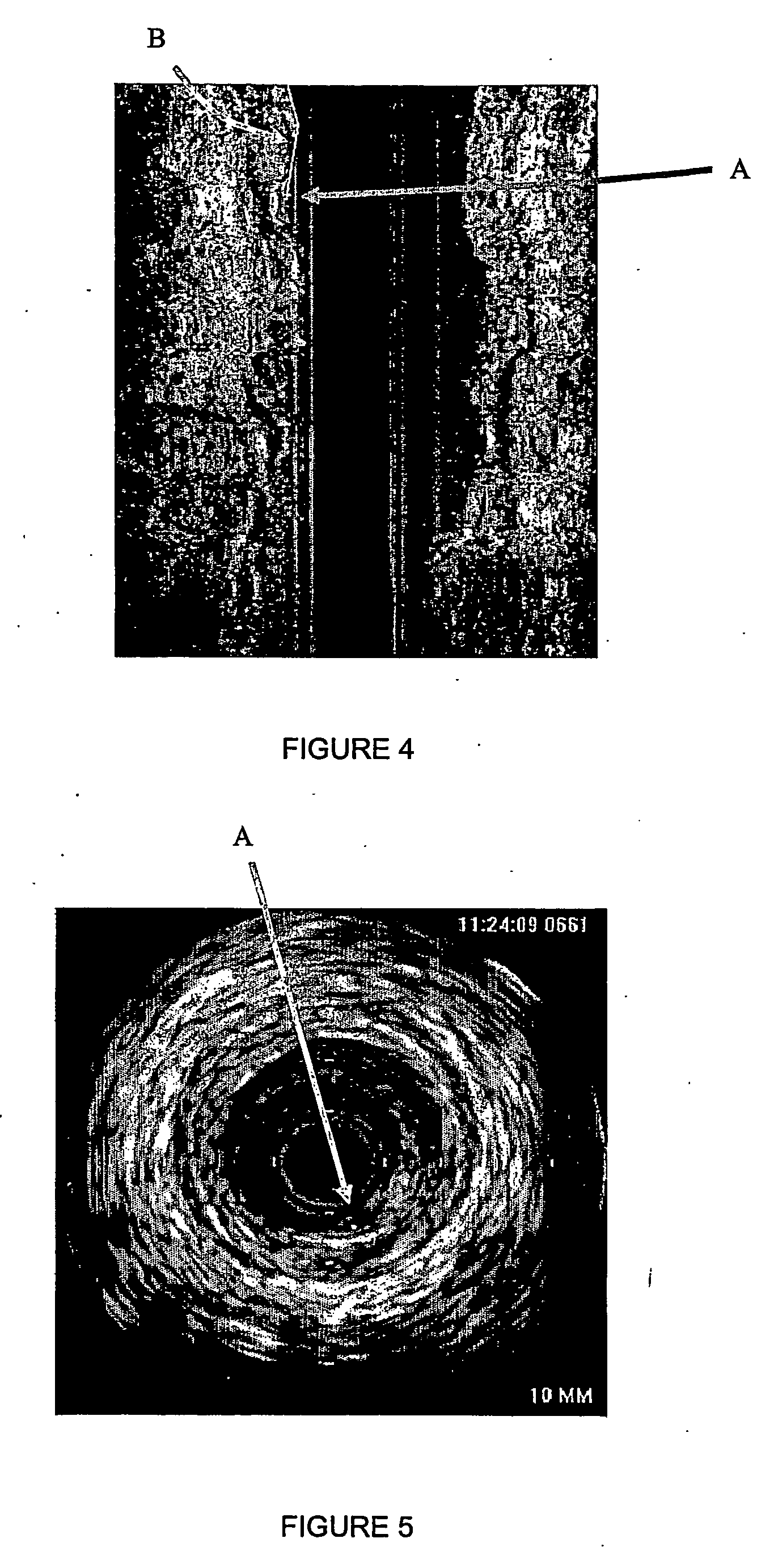
Automatic multi-dimensional intravascular ultrasound image segmentation method
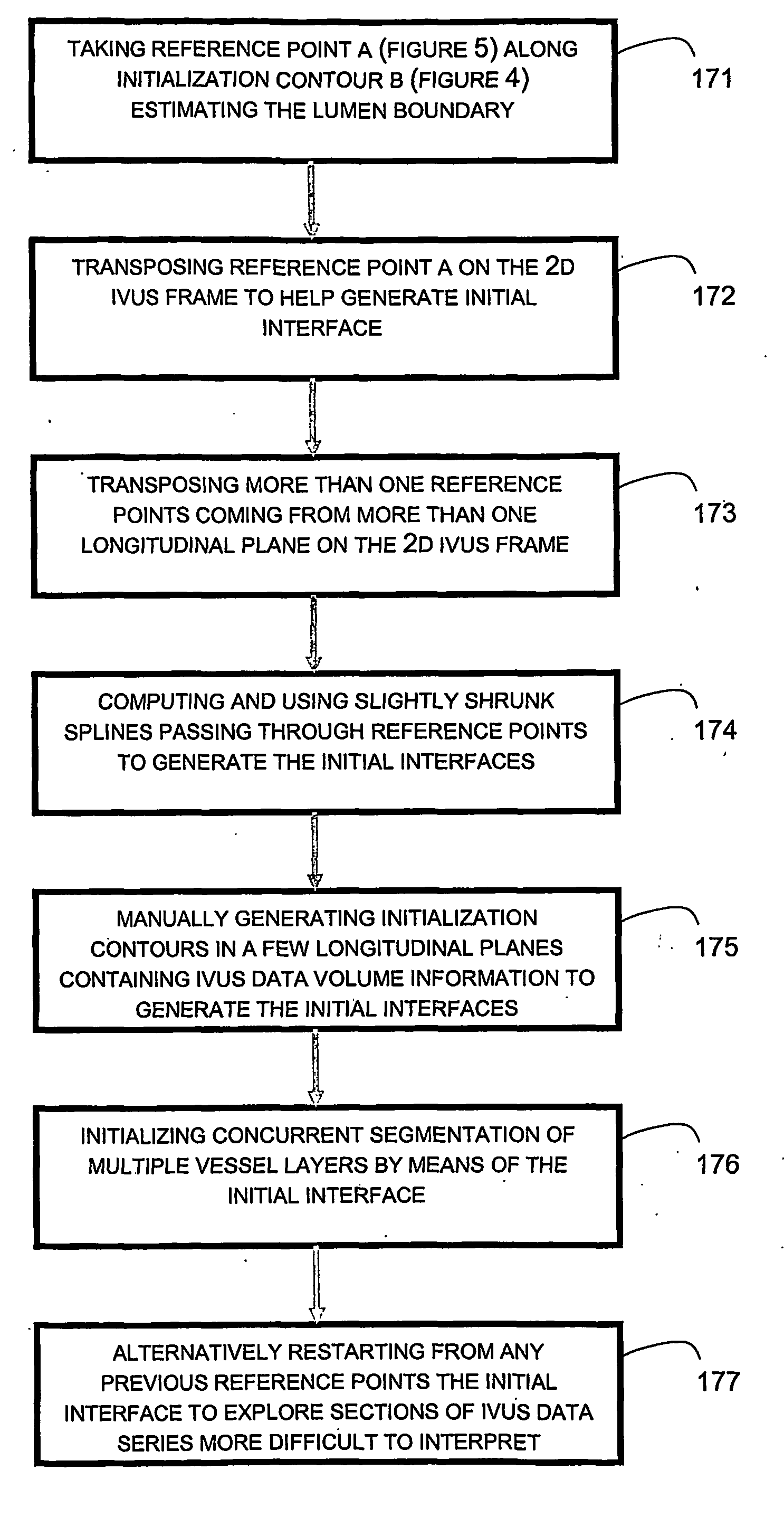
The present invention generally relates to intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) image segmentation methods, and is more specifically concerned with an intravascular ultrasound image segmentation method for characterizing blood vessel vascular layers. The proposed image segmentation method for estimating boundaries of layers in a multi-layered vessel provides image data which represent a plurality of image elements of the multi-layered vessel. The method also determines a plurality of initial interfaces corresponding to regions of the image data to segment and further concurrently propagates the initial interfaces corresponding to the regions to segment. The method thereby allows to estimate the boundaries of the layers of the multi-layered vessel by propagating the initial interfaces using a fast marching model based on a probability function which describes at least one characteristic of the image elements.
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP +1
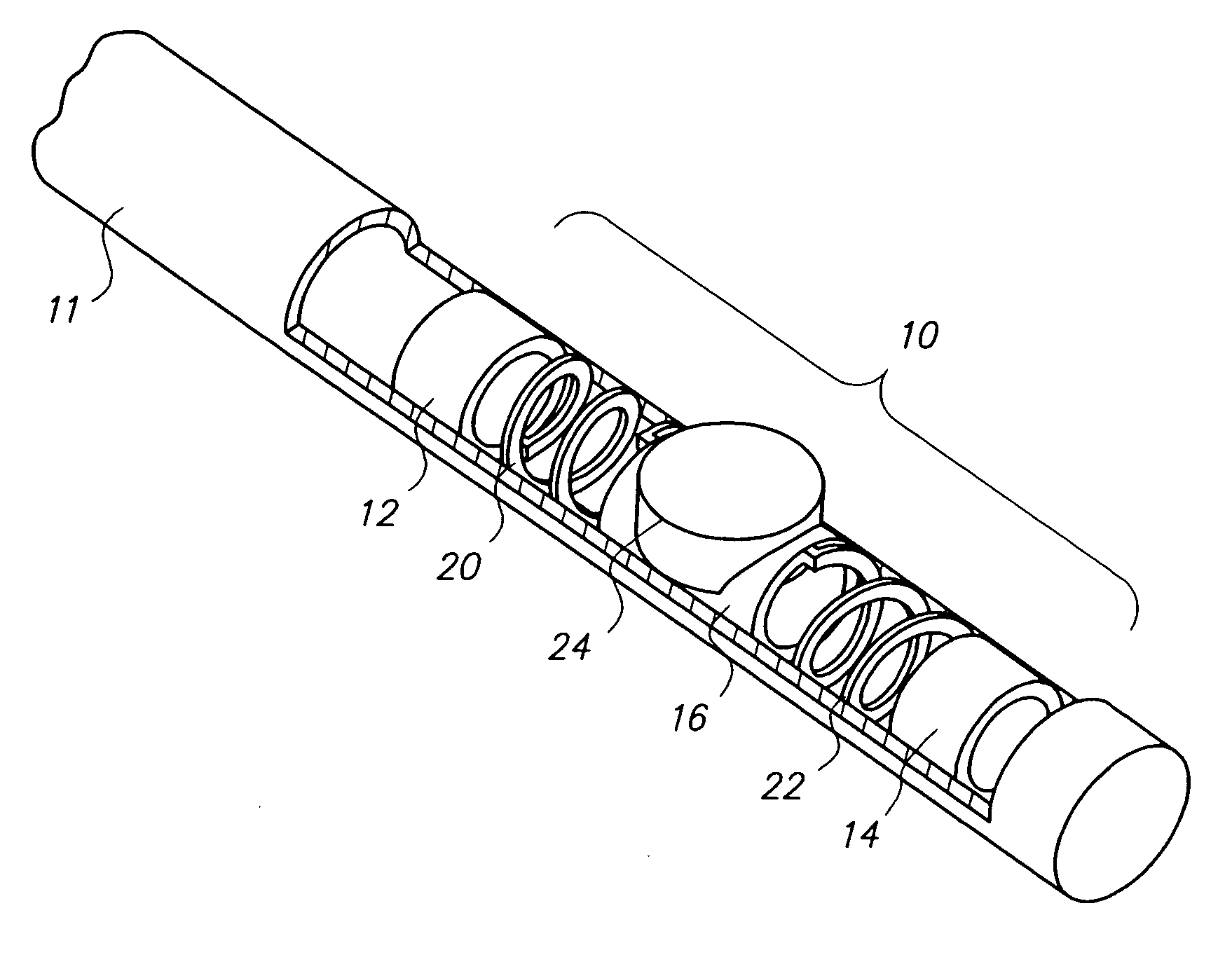
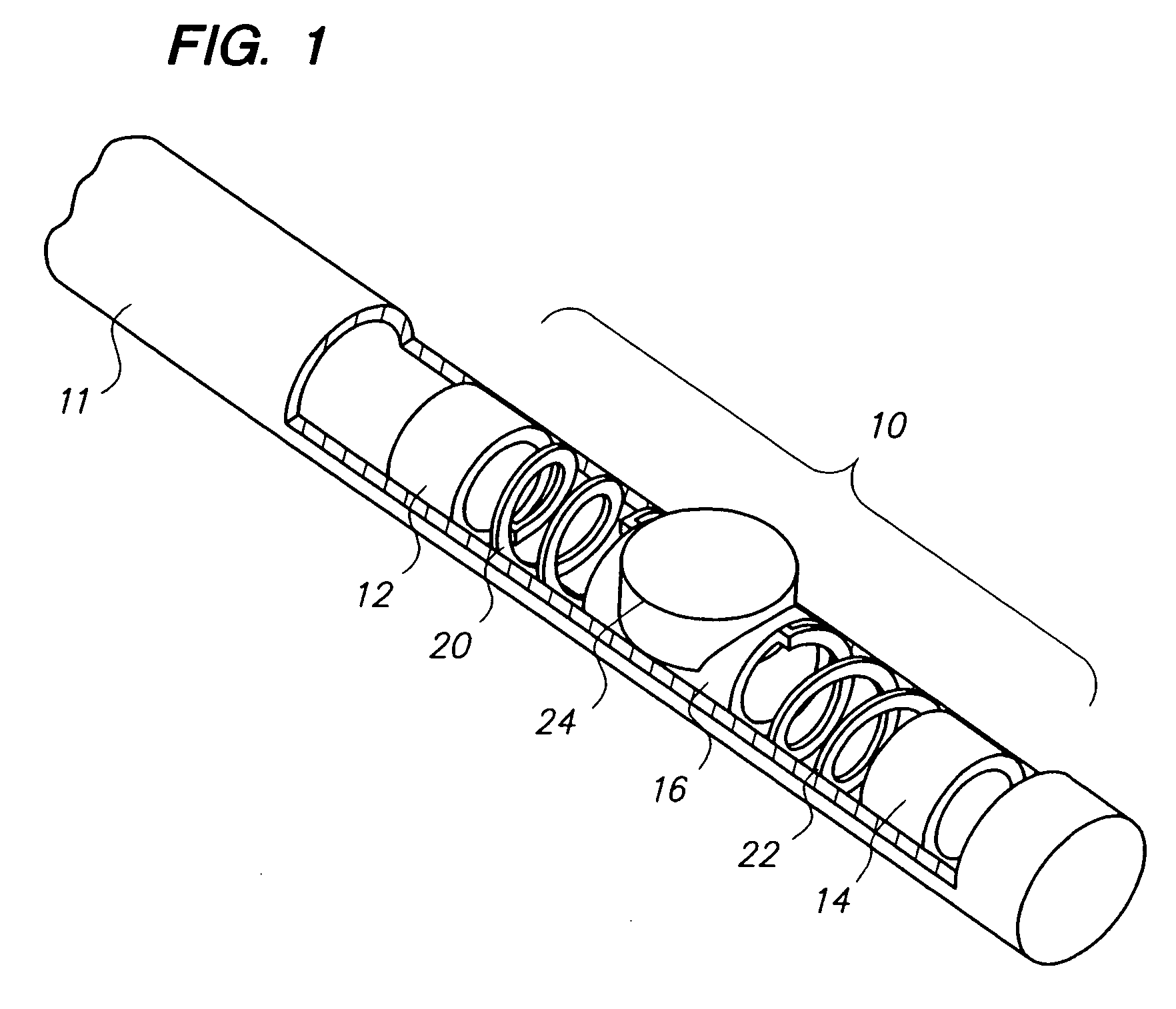
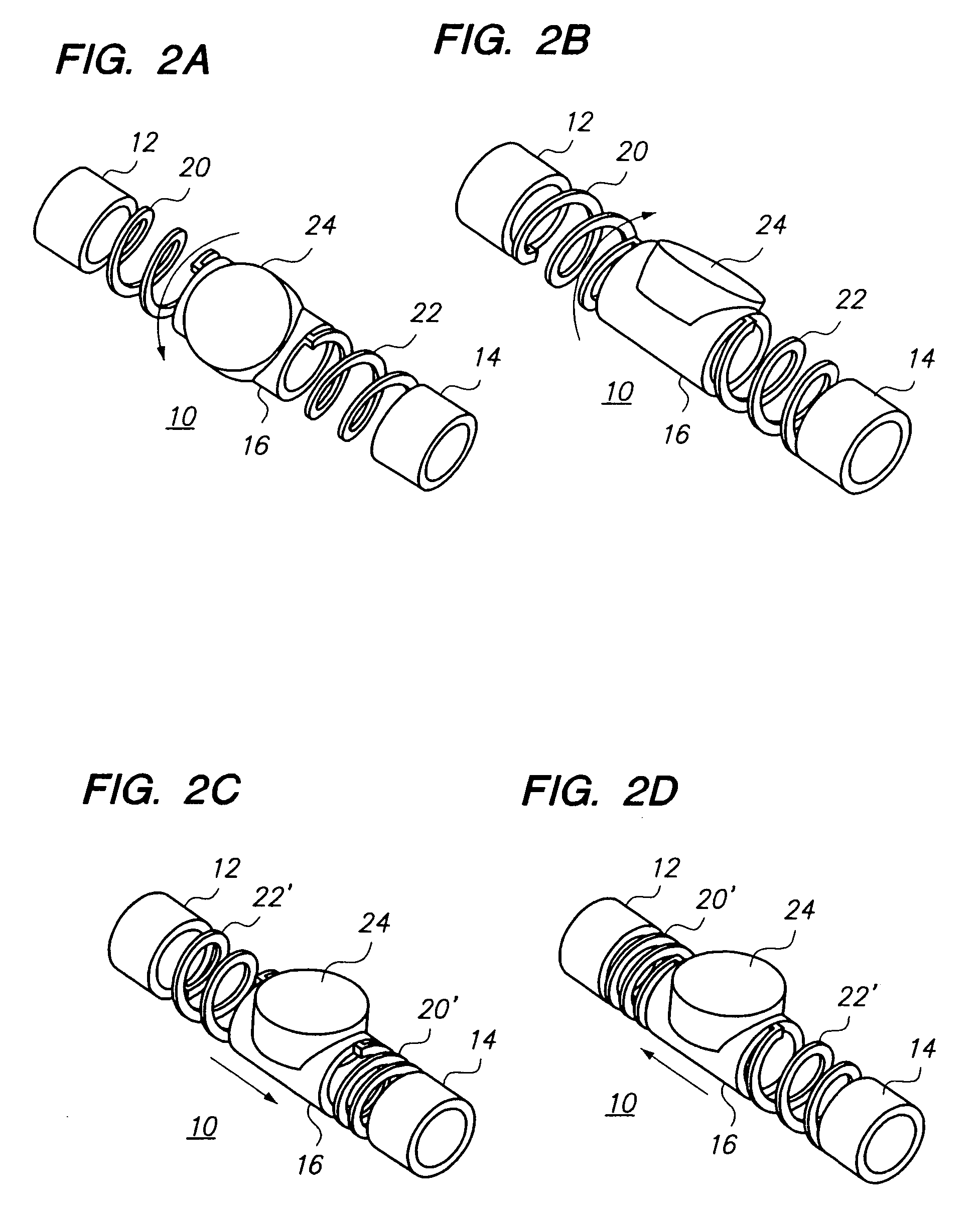
Multiple transducers for intravascular ultrasound imaging
The present invention relates to a new intravascular ultrasound imaging device with an increased field of view. By using more than one ultrasound transducer crystal that is capable of producing an ultrasonic signal for imaging, and preferably aligning the individual crystals on a shared backing with at least one edge of the crystals in contact, the field of view generated by a given actuator mechanism is increased without substantially increasing the overall dimensions of the device. Also disclosed are methods of using the same.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Apparatus and methods for imaging and attenuation correction
InactiveUS7652259B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySonification
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
Rotational intravascular ultrasound probe and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100160788A1Electrical transducersOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic sensorDrive shaft
A rotational intravascular ultrasound probe for insertion into a vasculature and a method of manufacturing the same. The rotational intravascular ultrasound probe comprises an elongate catheter having a flexible body and an elongate transducer shaft disposed within the flexible body. The transducer shaft comprises a proximal end portion, a distal end portion, a drive shaft extending from the proximal end portion to the distal end portion, an ultrasonic transducer disposed near the distal end portion for obtaining a circumferential image through rotation, and a transducer housing molded to the drive shaft and the ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Intravascular Ultrasound Imaging Device
InactiveUS20080114254A1Promote absorptionHigh indexUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterFiberUltrasound imaging
An optic fiber adapted for ultrasound imaging of the lumen of a vessel comprising: an inner core for transmitting light having an index of refraction that changes responsive to acoustic energy incident thereon; a ring core concentric with the inner core for transmitting light; a cladding material between the inner and ring cores that has an index of refraction smaller than the index of refraction of the material from which the inner core is formed; and at least one acoustic transducer comprising absorbing material formed on the surface of the ring core that absorbs optical energy transmitted along the ring core and generates ultrasound responsive thereto.
Owner:BIOSCAN
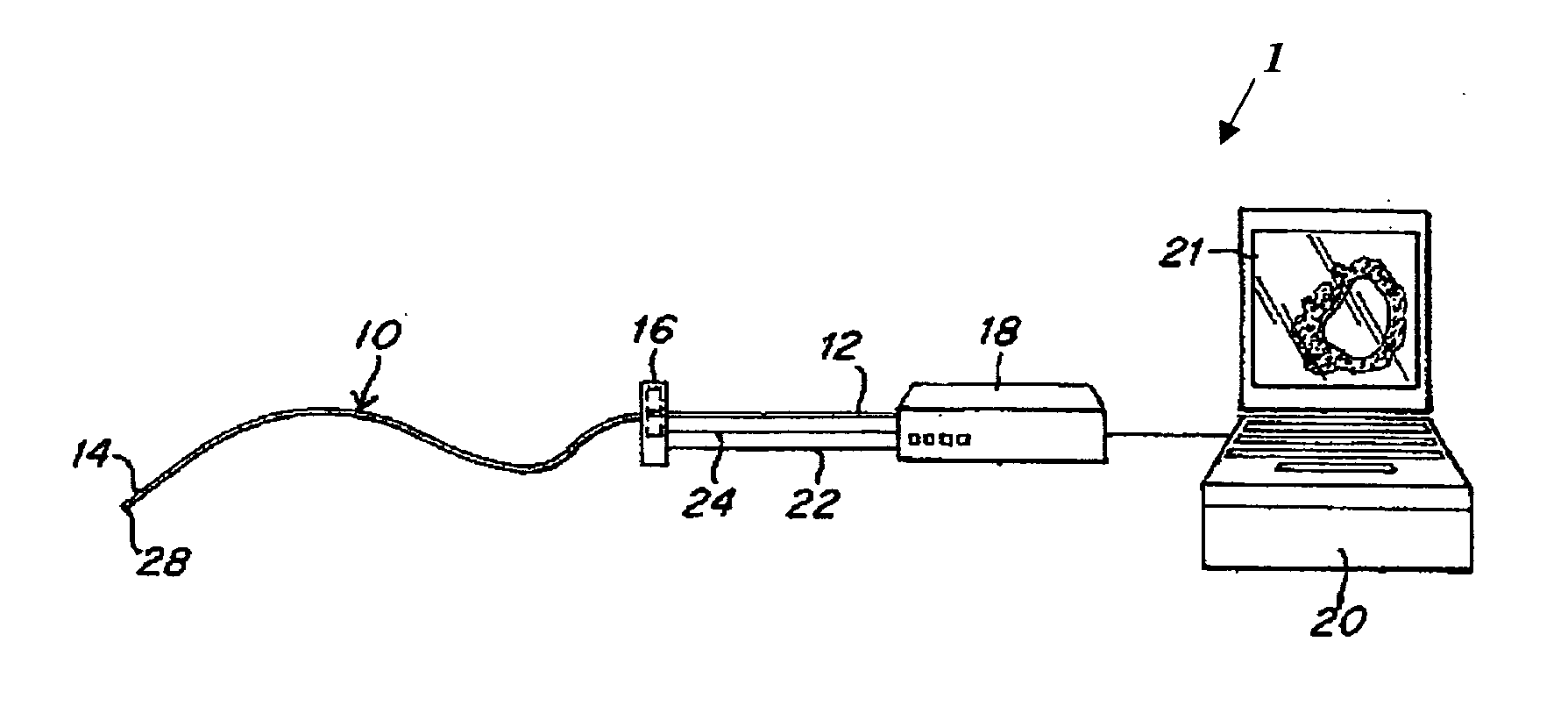
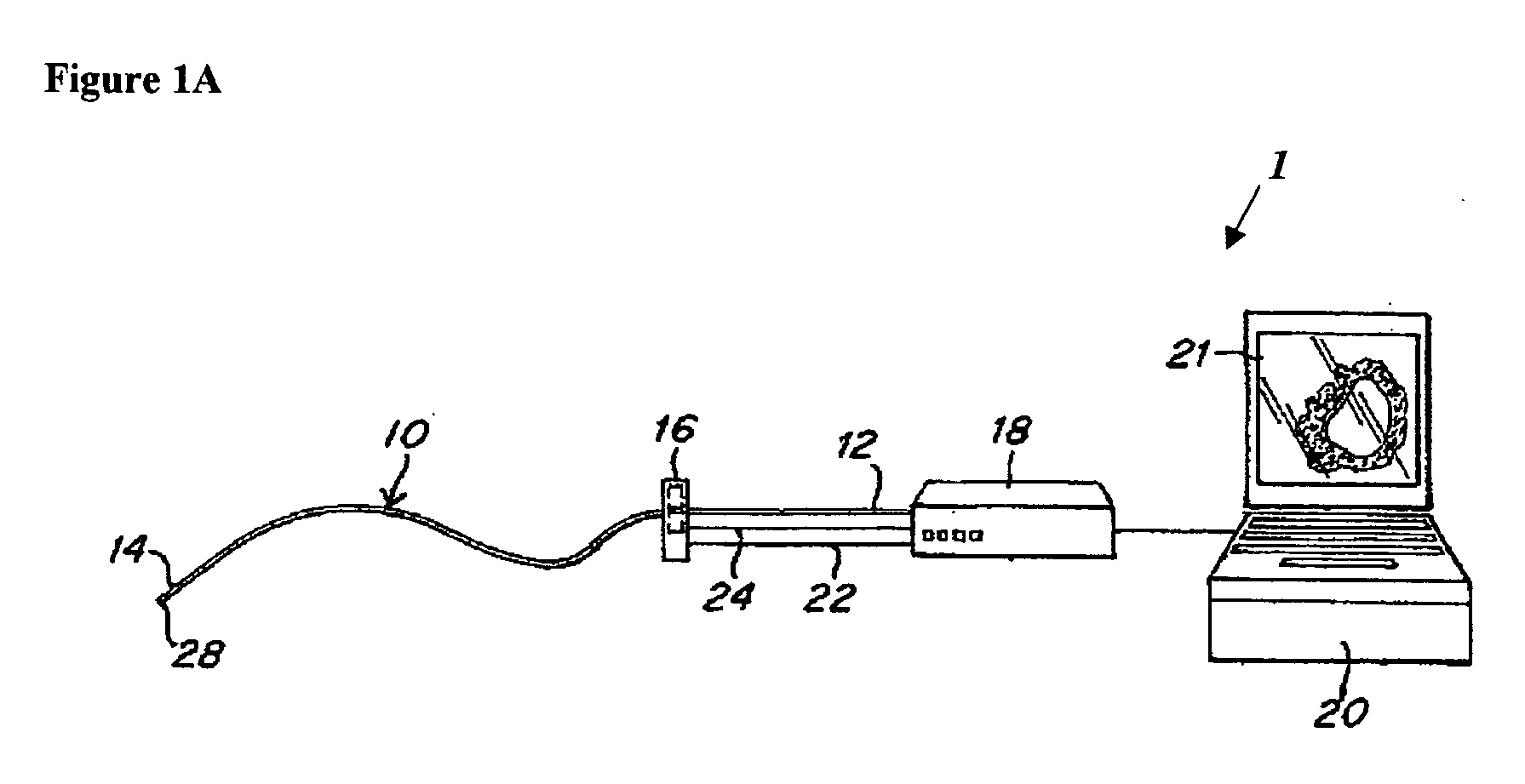
System and method for reducing angular geometric distortion in an imaging device
ActiveUS20070106155A1Reduce geometric distortionReduce and substantially eliminate angular geometric distortionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterTreatment choicesTreatment options
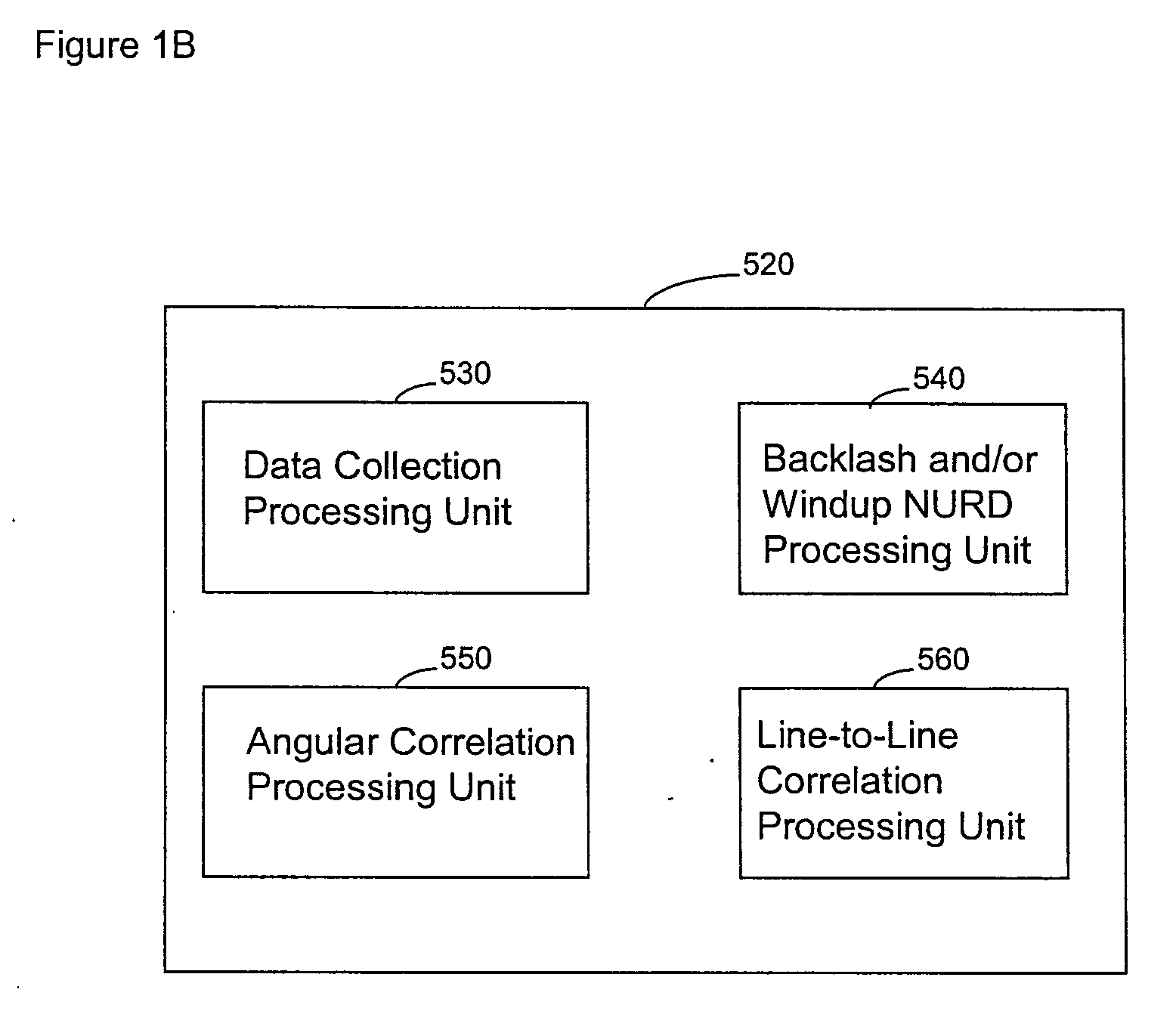
A system and method are provided for significantly reducing or substantially eliminating angular geometric distortions in devices designed for imaging and / or inspection of an interior portion or surface of a cavity. A series of processing steps or methods may be employed to eliminate Non-Uniform Rotational Distortion (NURD) in such devices, for example, unidirectional and bi-directional intravascular ultrasonic (IVUS) imaging systems. The system may include a processor and an electronic module which control operation of a transducer assembly provided at a distal end of a catheter assembly. The system invokes a first processing step or method to collect and store raw angle and line data, as well as one or more of second and third processing steps or methods which adjust for NURD experienced during backlash of a bi-directional imaging system and a fourth processing step or method which performs a line-to-line correlation function. The system and method provide more accurate and reliable angular orientations of anomalies identified during imaging and / or inspection of the interior portion or surface of the cavity, thus facilitating diagnosis and treatment options.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Flexible micro-electro-mechanical transducer
ActiveUS20070013269A1Convenient for fishingEasy to makeMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngineeringIntravascular ultrasound
A curved or bendable micro-electro-mechanical transducer (such as the cMUT) is disclosed. The transducer has a plurality of transducer elements built on a substrate. The substrate has a slot below every two neighboring device elements. Each slot is at least at least partially filled with a flexible material to allow bending of the substrate. A bending actuator may be included to facilitate the bending of the substrate. An exemplary bending actuator uses a nonuniformly shrinkable material to bend the substrate. A curved or bendable cMUT of the present invention can be configured to be an intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) device.
Owner:KOLO MEDICAL (SUZHOU) CO LTD
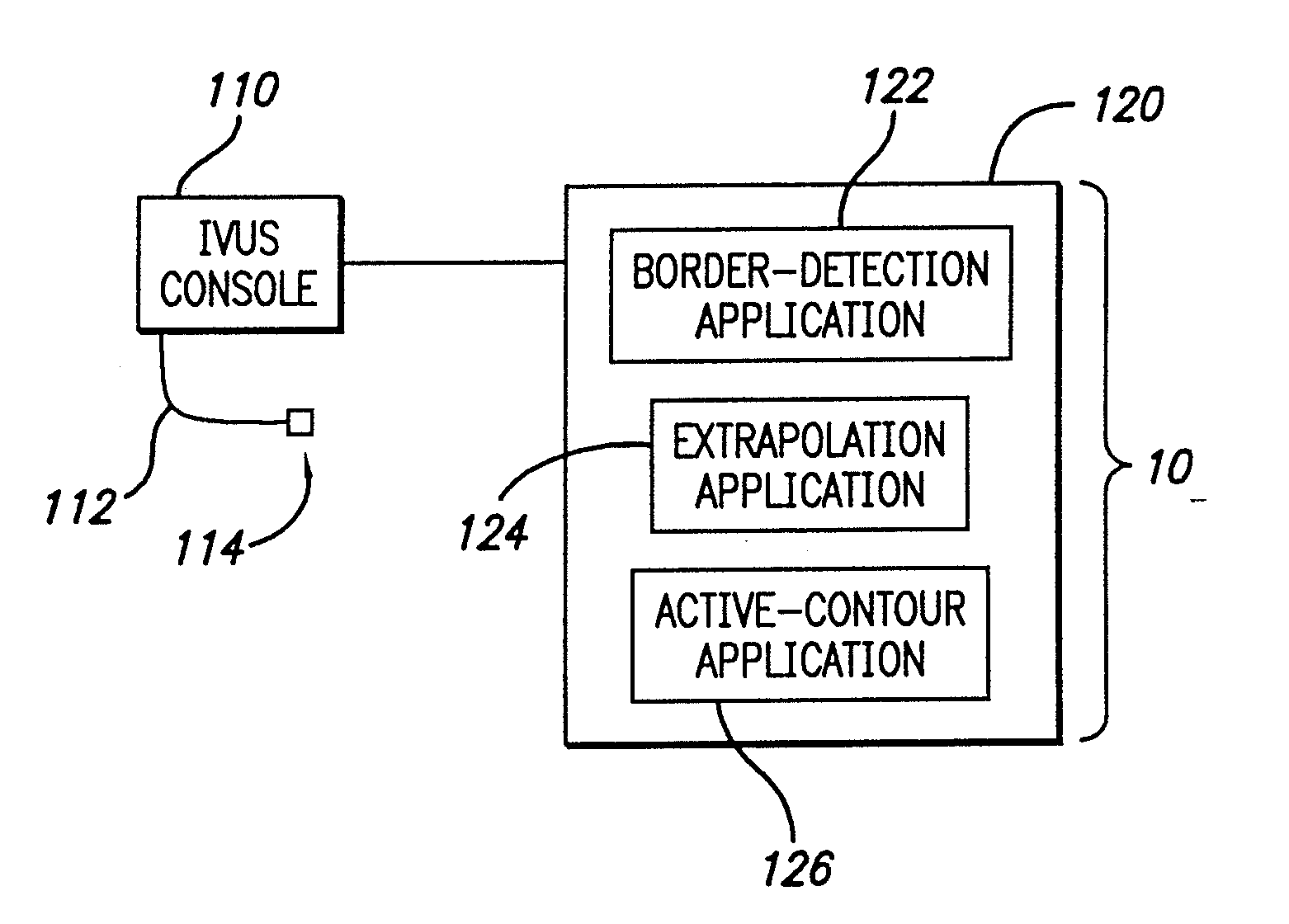
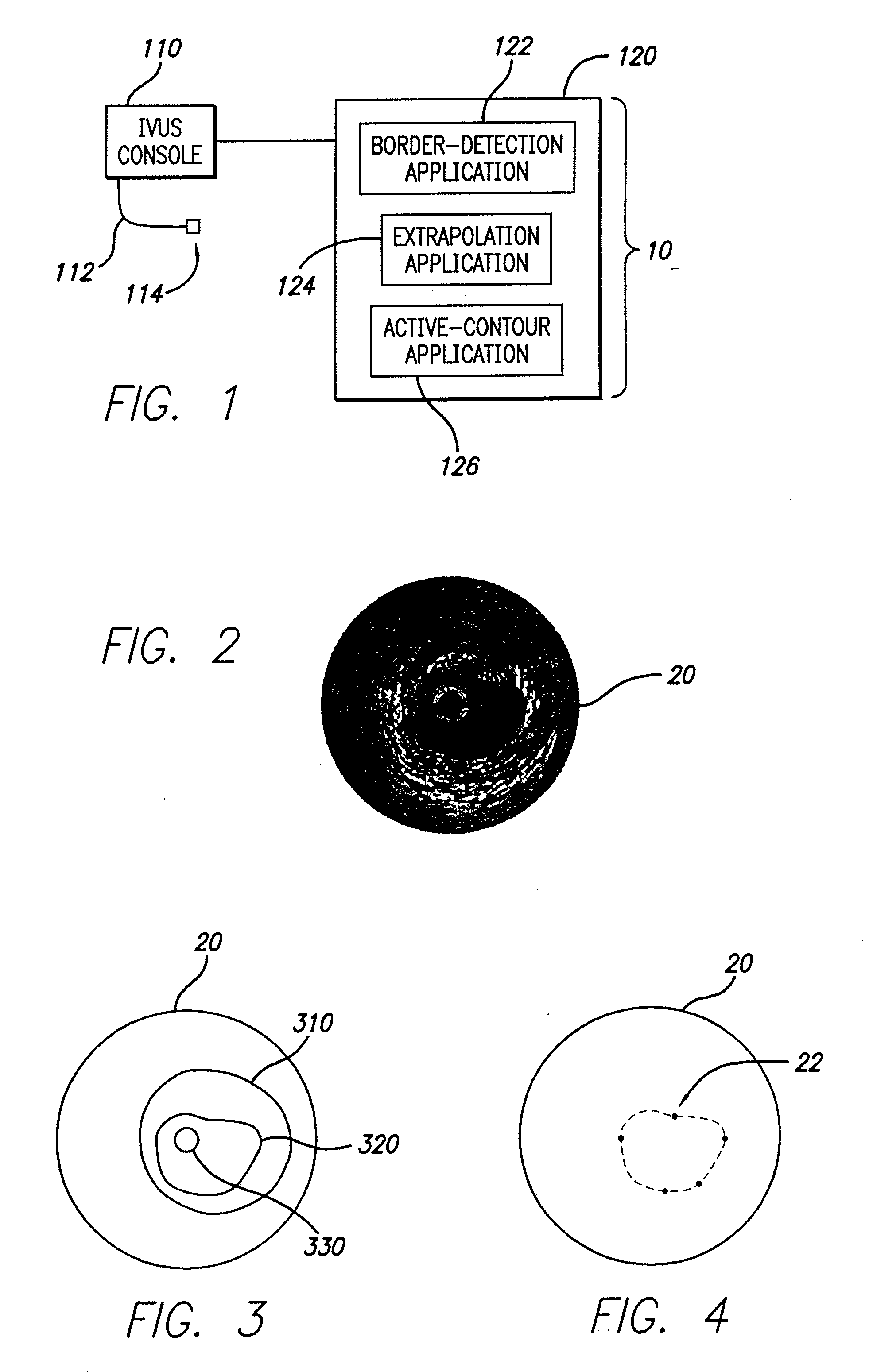
System And Method For Identifying A Vascular Border
InactiveUS20080287795A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular ultrasoundBoundary detection
A system and method is provided for using a first vascular image, or more particularly a plurality of control points located thereon, to identify a border on a second vascular image. Embodiments of the present invention operate in accordance with an intra-vascular ultrasound (IVUS) device and a computing device electrically connected thereto. Specifically, in one embodiment of the present invention, an-IVUS console is electrically connected to a computing device and adapted to acquire IVUS data. The IVUS data (or multiple sets thereof) is then provided to (or acquired by) the computing device. In one embodiment of the present invention, the computing device includes a plurality of applications operating thereon—i.e., a border-detection application, an extrapolation application, and an active-contour application. These applications are used to (i) identify a border and control points on a first IVUS image (i.e., any IVUS image), (ii) extrapolate the control points to a second IVUS image (i.e., another IVUS image), (iii) identify a border on the second IVUS image, and (iv) adjust the border on the second IVUS image in accordance with at least one factor. In one embodiment of the present invention, the at least one factor is selected from a group consisting of gradient factor, continuity factor, and curvature factor.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Automatic multi-dimensional intravascular ultrasound image segmentation method
The present invention generally relates to intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) image segmentation methods, and is more specifically concerned with an intravascular ultrasound image segmentation method for characterizing blood vessel vascular layers. The proposed image segmentation method for estimating boundaries of layers in a multi-layered vessel provides image data which represent a plurality of image elements of the multi-layered vessel. The method also determines a plurality of initial interfaces corresponding to regions of the image data to segment and further concurrently propagates the initial interfaces corresponding to the regions to segment. The method thereby allows to estimate the boundaries of the layers of the multi-layered vessel by propagating the initial interfaces using a fast marching model based on a probability function which describes at least one characteristic of the image elements.
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP +1
Forward-Looking Intravascular Ultrasound Devices and Methods for Making
InactiveUS20070287914A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasound angiographyForward looking
Embodiments of invention are directed to devices, and methods of forming them, that can be used for imaging interior volumes of the body. Particular embodiments are directed to improved intravascular ultrasound devices. In some embodiments the intravascular ultrasound devices are intended to be ‘forward-looking’; i.e., the image obtained by the device is of structures in front of, or distal to, the device.
Owner:MICROFAB
Spatial characterization of a structure located within an object by identifying 2d representations of the structure within section planes
InactiveUS20100099979A1Clear visualizationPrecise quantitative comparisonImage enhancementImage analysisSection planeSonification
It is described a virtual pullback as a visualization and quantification tool that allows an interventional cardiologist to easily assess stent expansion. The virtual pullback visualizes the stent and / or the vessel lumen similar to an Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) pullback. The virtual pullback is performed in volumetric data along a reference line. The volumetric data can be a reconstruction of rotational 2D X-ray attenuation data. Planes perpendicular to the reference line are visualized as the position along the reference line changes. This view is for interventional cardiologists a very familiar view as they resemble IVUS data and may show a section plane through a vessel lumen or a stent. In these perpendicular section planes automatic measurements, such as minimum and maximum diameter, and cross sectional area of the stent can be calculated and displayed. Combining these 2D measurements allows also volumetric measurements to be calculated and displayed.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and system for stabilizing a series of intravascular ultrasound images and extracting vessel lumen from the images
InactiveUS20110033098A1Accurate and effective diagnosticsAccurate and effective and therapeuticUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancement3d shapesSonification
A method and system for generating stabilized intravascular ultrasonic images are provided. The system may include a probe instrument, such as a catheter, connected to a processor and a post-processor. The method of using the system to stabilize images and the method for stabilizing images involve the process by which the processor and post-processor stabilize the image. A computer readable medium containing executable instructions for controlling a computer containing the processor and post-processor to perform the method of stabilizing images is also provided. The probe instrument, which has a transmitter for transmitting ultrasonic signals and a receiver for receiving reflected ultrasonic signals that contain information about a tubular environment, such as a body lumen, preferably is a catheter. The processor and post-processor are capable of converting inputted signals into one or more, preferably a series of, images and the post-processor, which determines the center of the environment at each reflection position, detects the edges of the tubular environment and aligns the image center with the environment center thereby limiting the drift of images, which may occur due to movement of the environment, and stabilizing the images. The processor may also be programmed to filter images or series of images to improve the image stabilization and remove motion interference and / or may be programmed to extract the 3D shape of the environment. The method and device are of particular use where motion causes image drift, for example, the imaging a body lumen, in particular a vascular lumen, where image drift may occur due to heart beat or blood flow.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
System and Method For Statistical Shape Model Based Segmentation of Intravascular Ultrasound and Optical Coherence Tomography Images
InactiveUS20080075375A1Improve segmentation qualitySufficient flexibilityImage enhancementImage analysisBoundary contourSonification
A method for segmenting intravascular images includes acquiring a series of digitized images acquired from inside a vessel, each said image comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a 2-dimensional grid of pixels, providing a precomputed set of shapes for modeling contours of vessel wall boundaries, wherein a contour can be expressed as a sum of a mean shape and a inner product of shape modes and shape weights, initializing a boundary contour for one of said set of images, initializing said shape weights by projecting a contour into said shape modes, updating said shape weights from differential equations of said shape weights, and computing a contour by summing said mean shape and said inner product of shape modes and updated shape weights.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
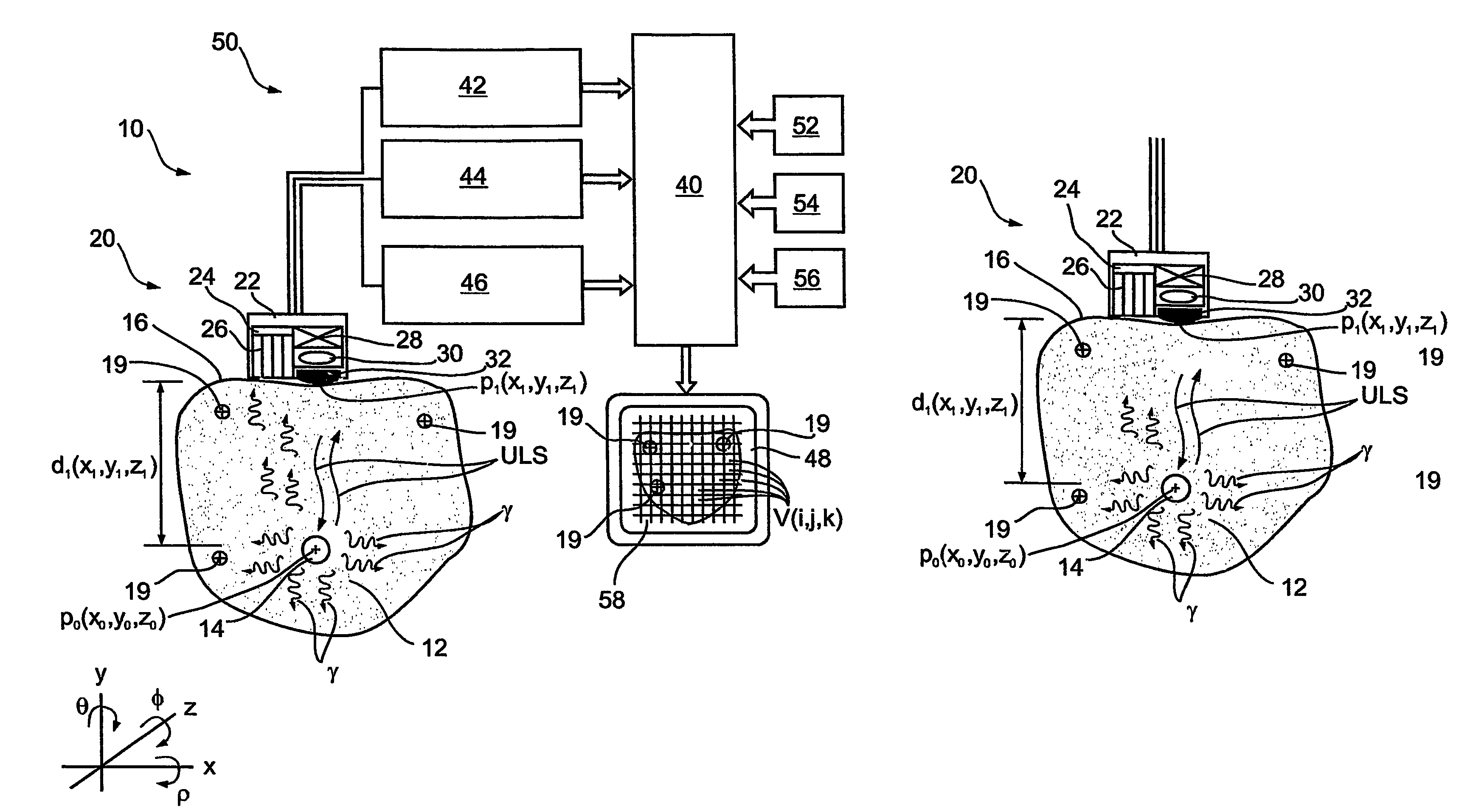
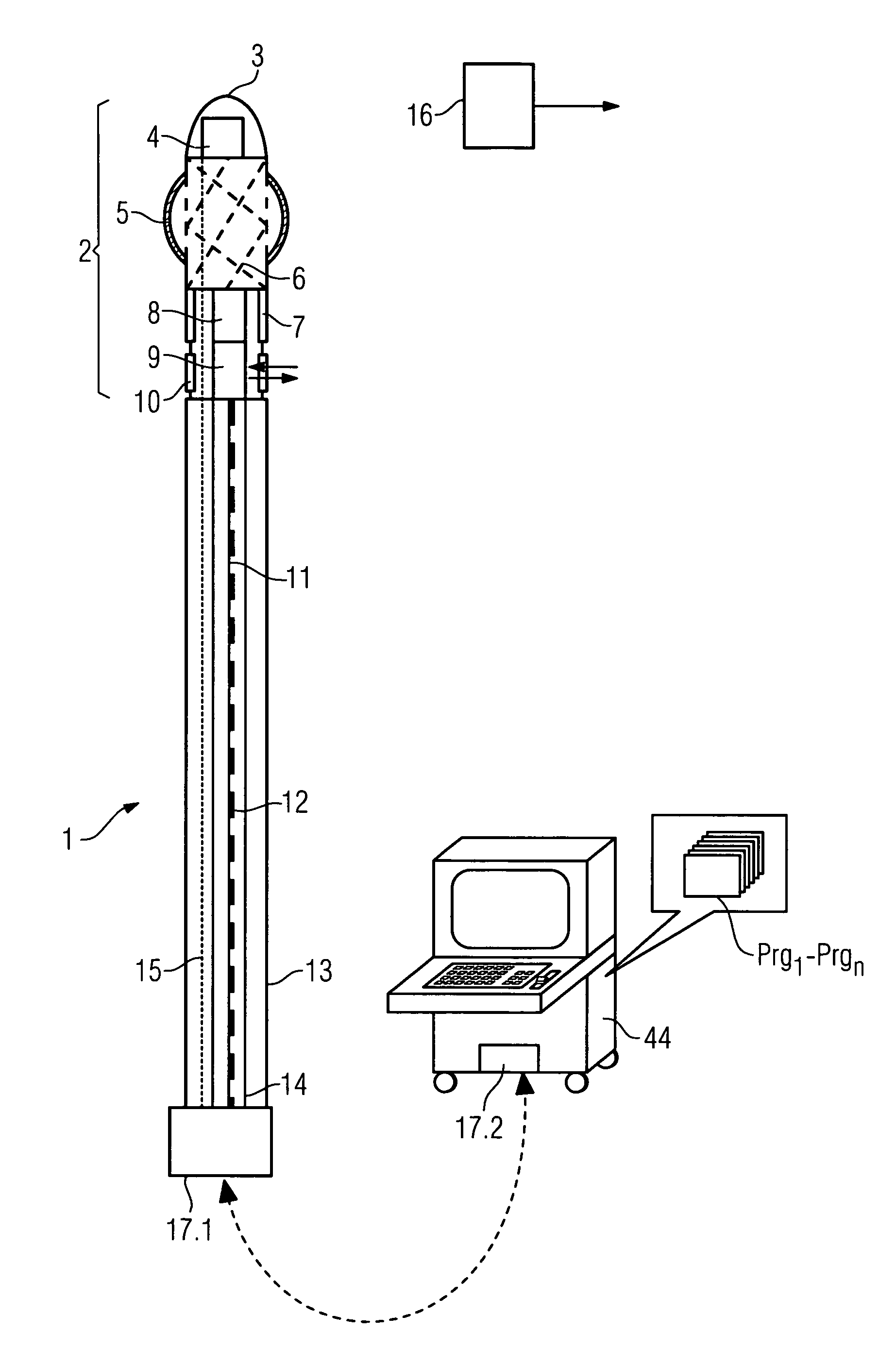
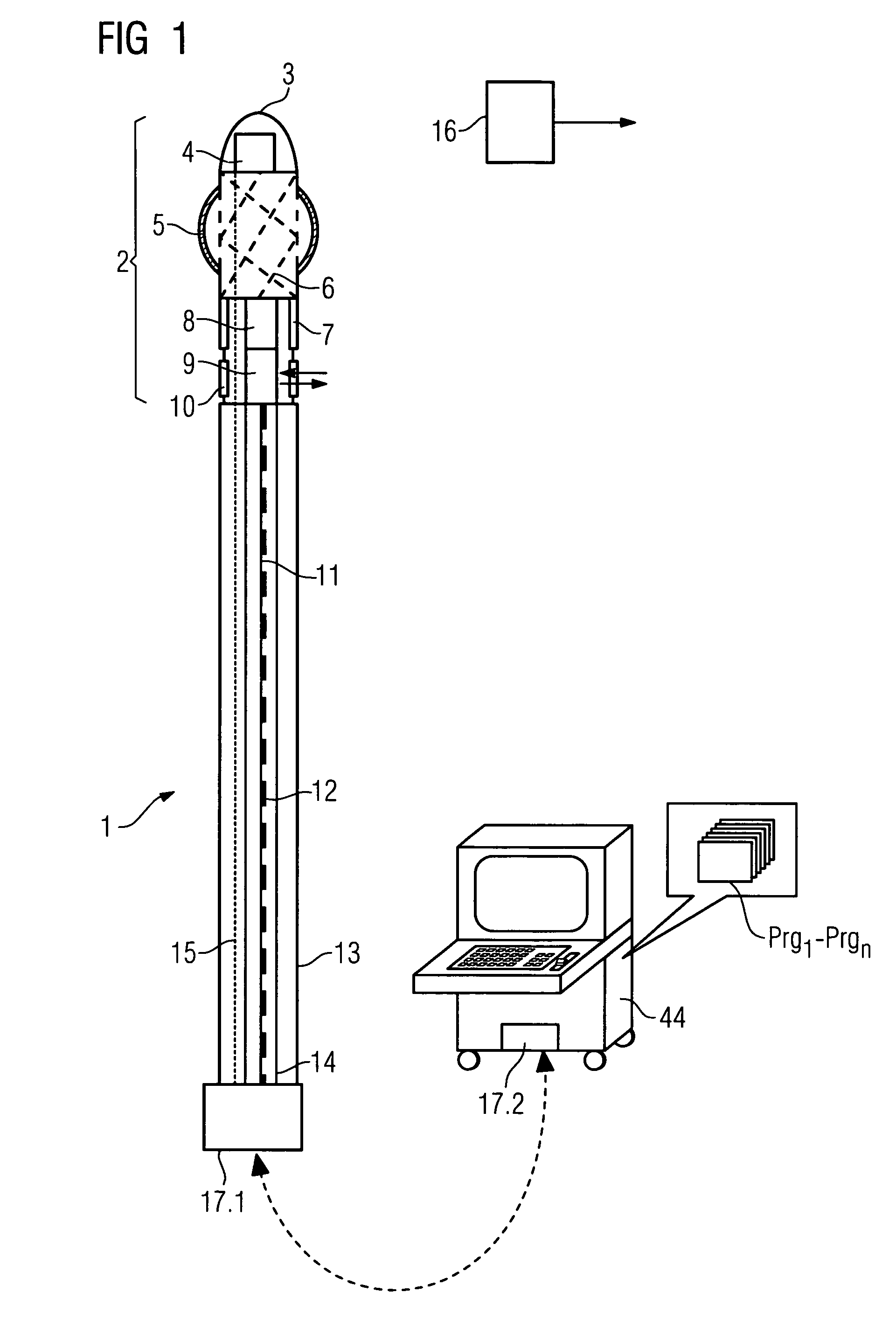
System for medical examination or treatment
ActiveUS7289842B2Improve image qualityEliminate disadvantagesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryFiberImaging processing
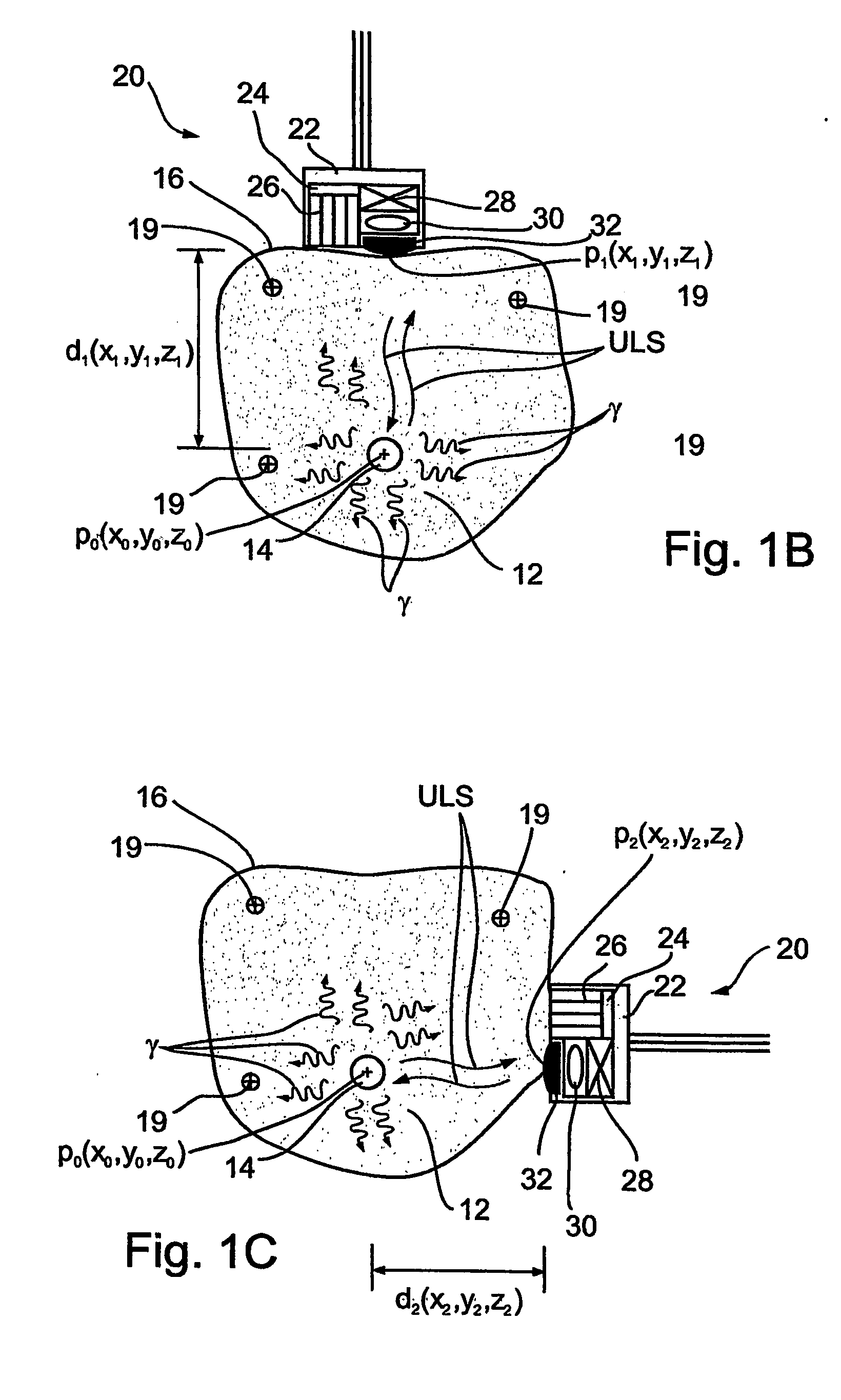
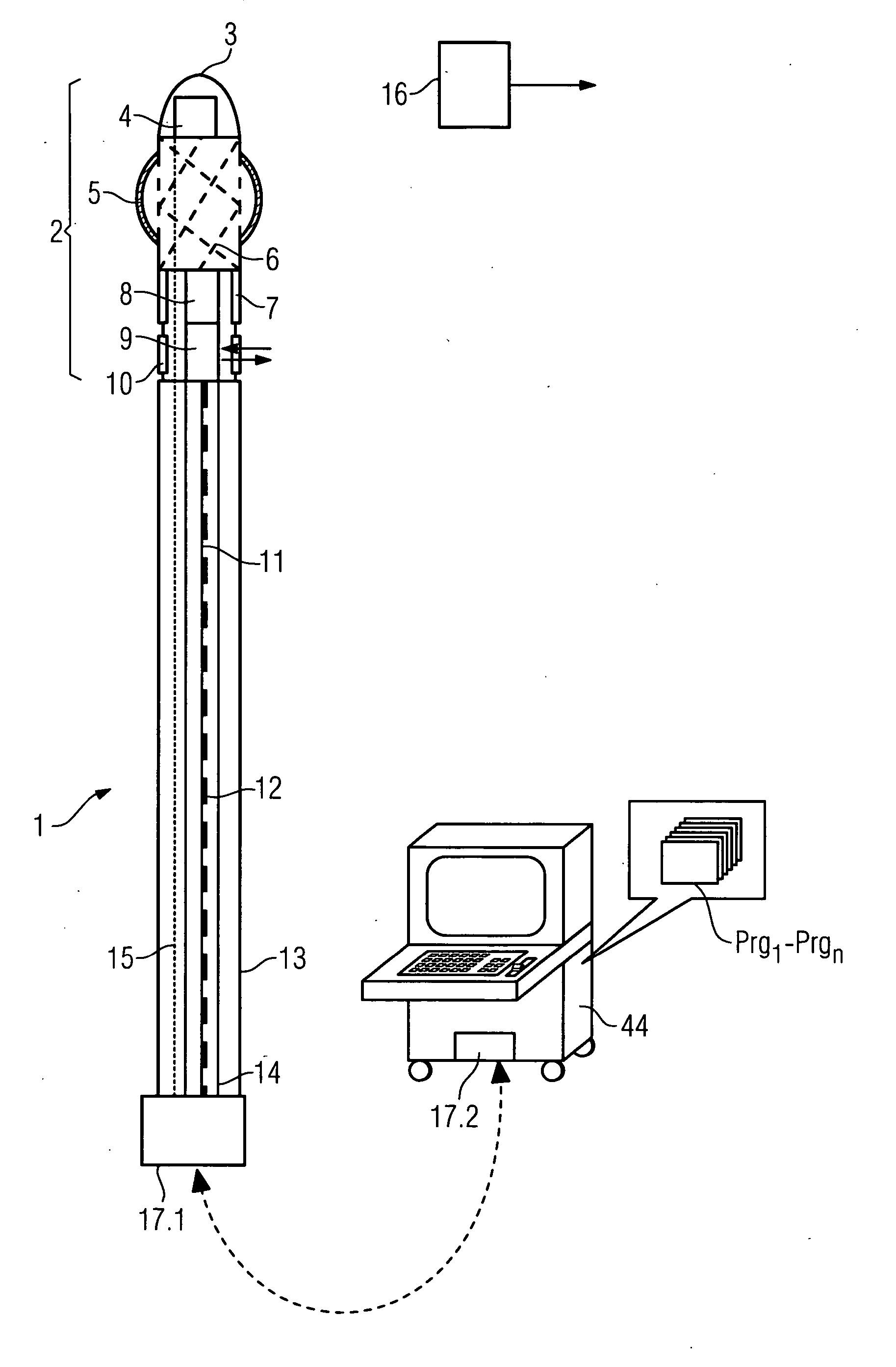
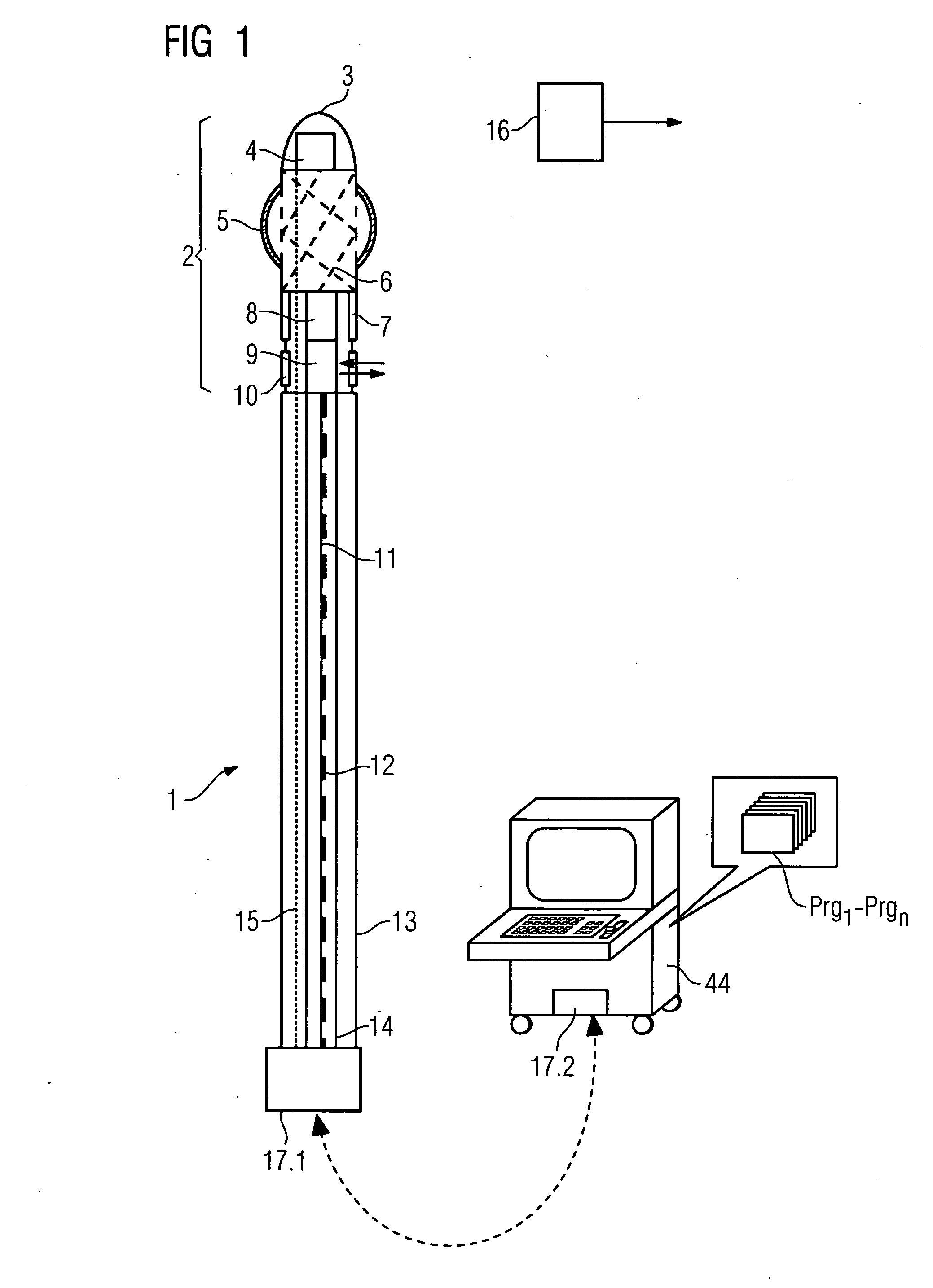
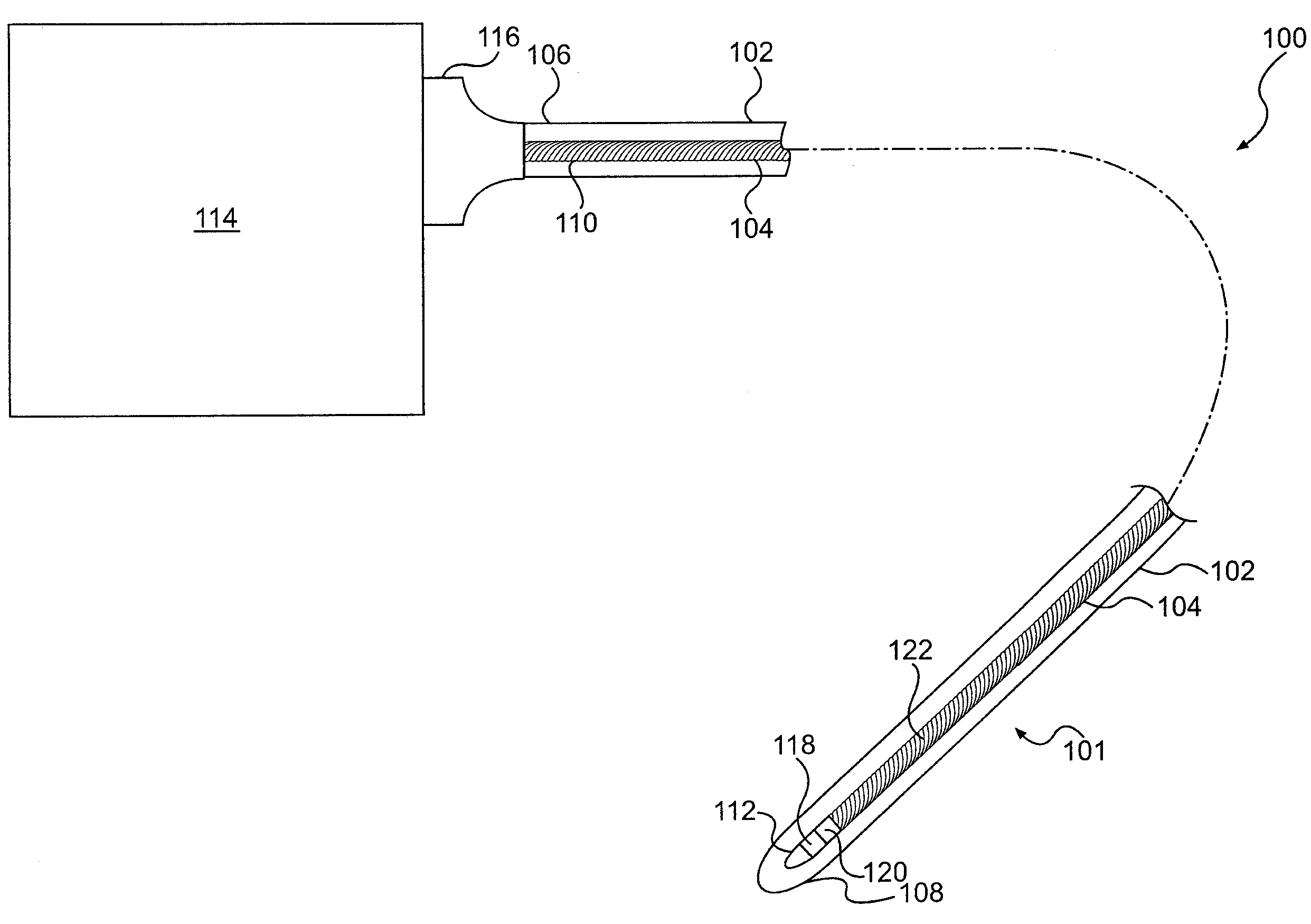
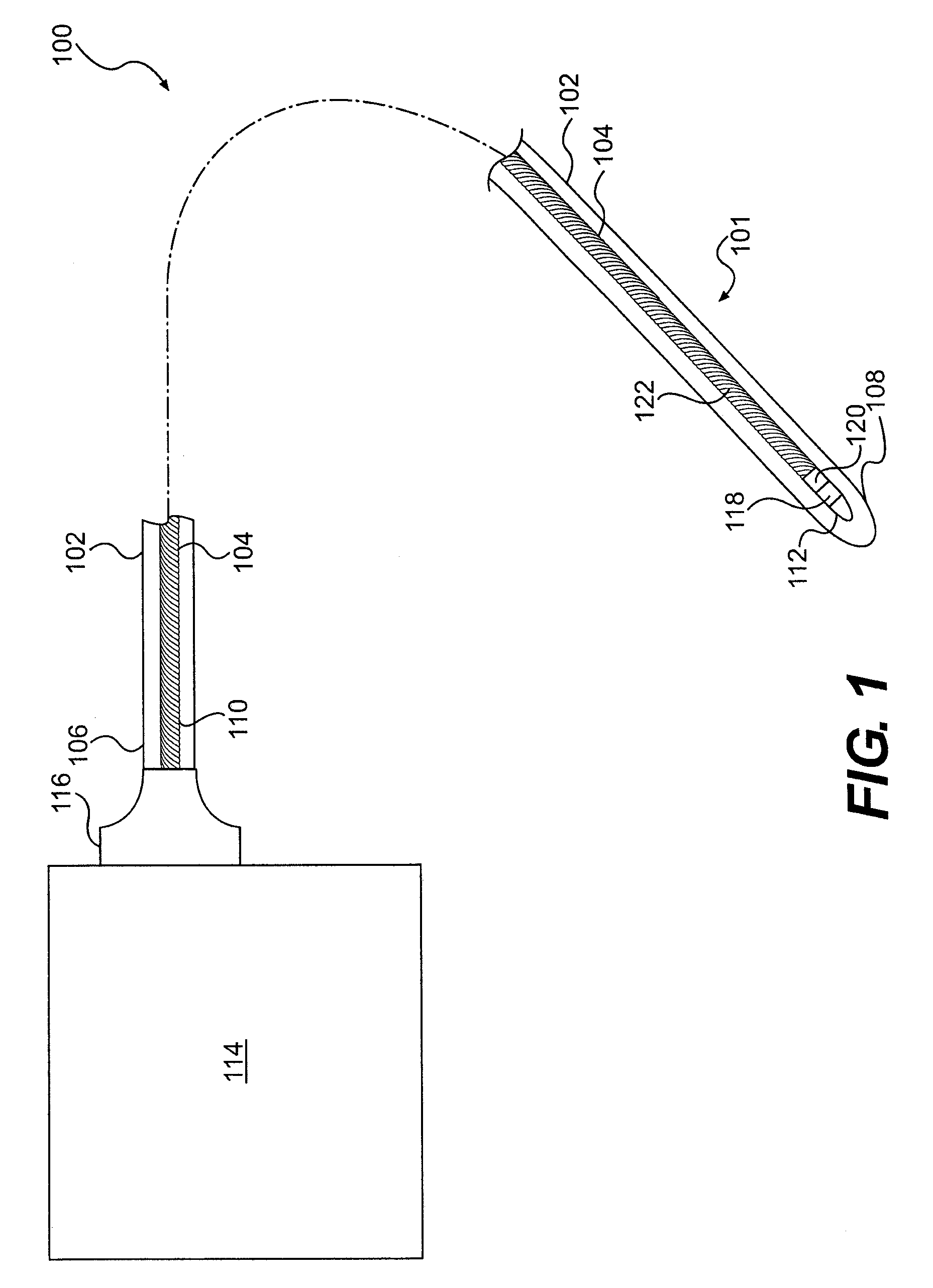
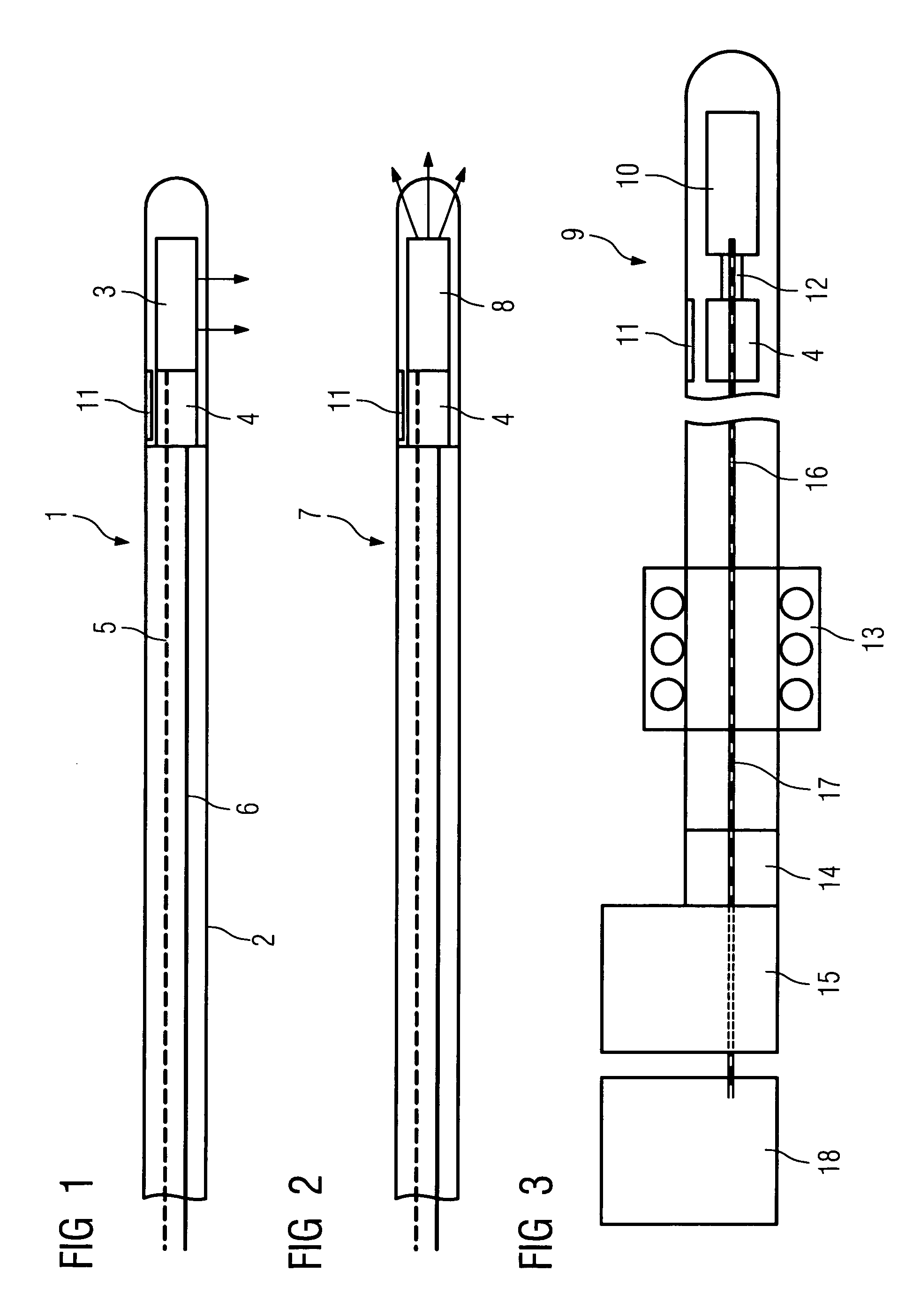
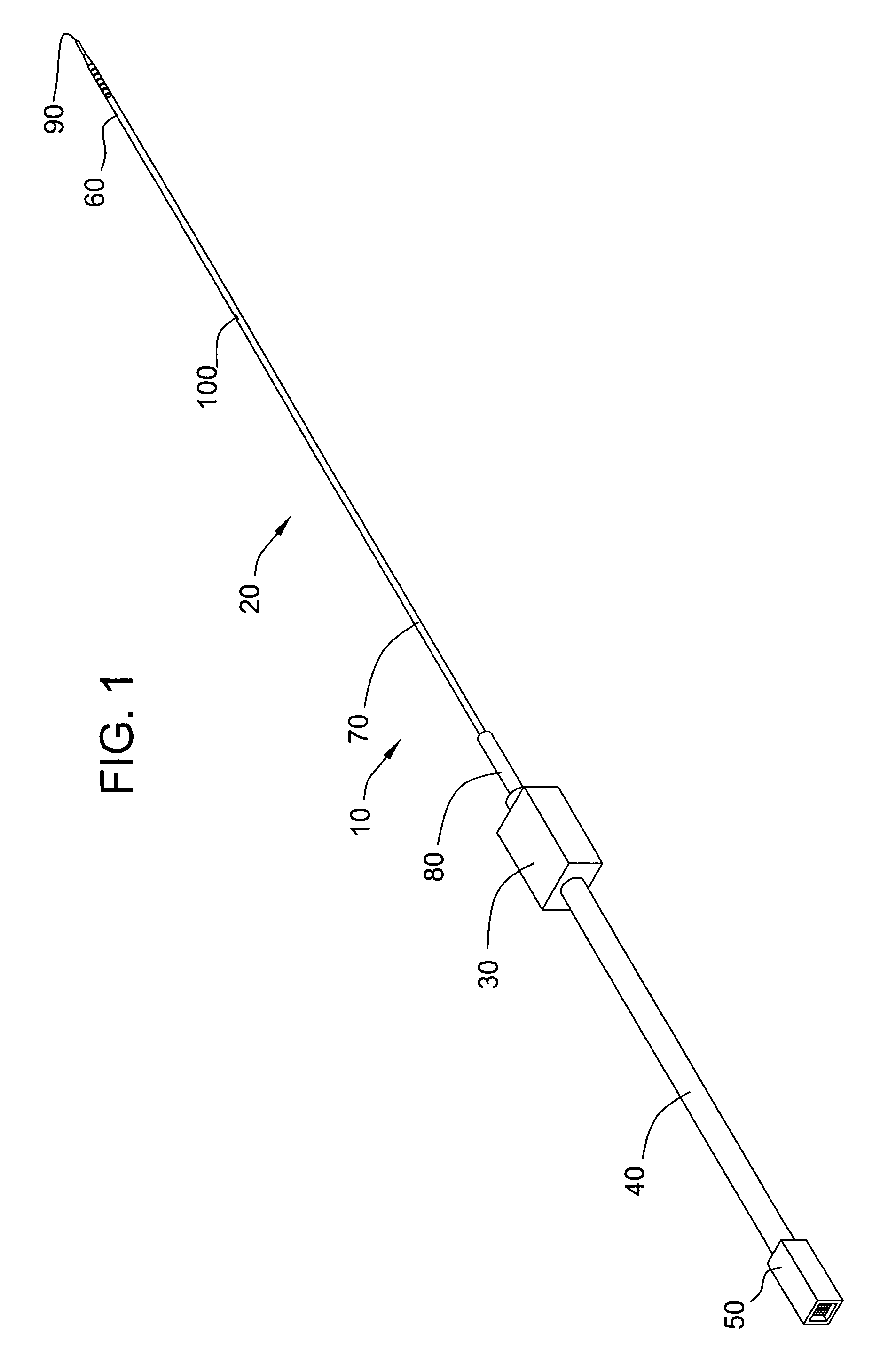
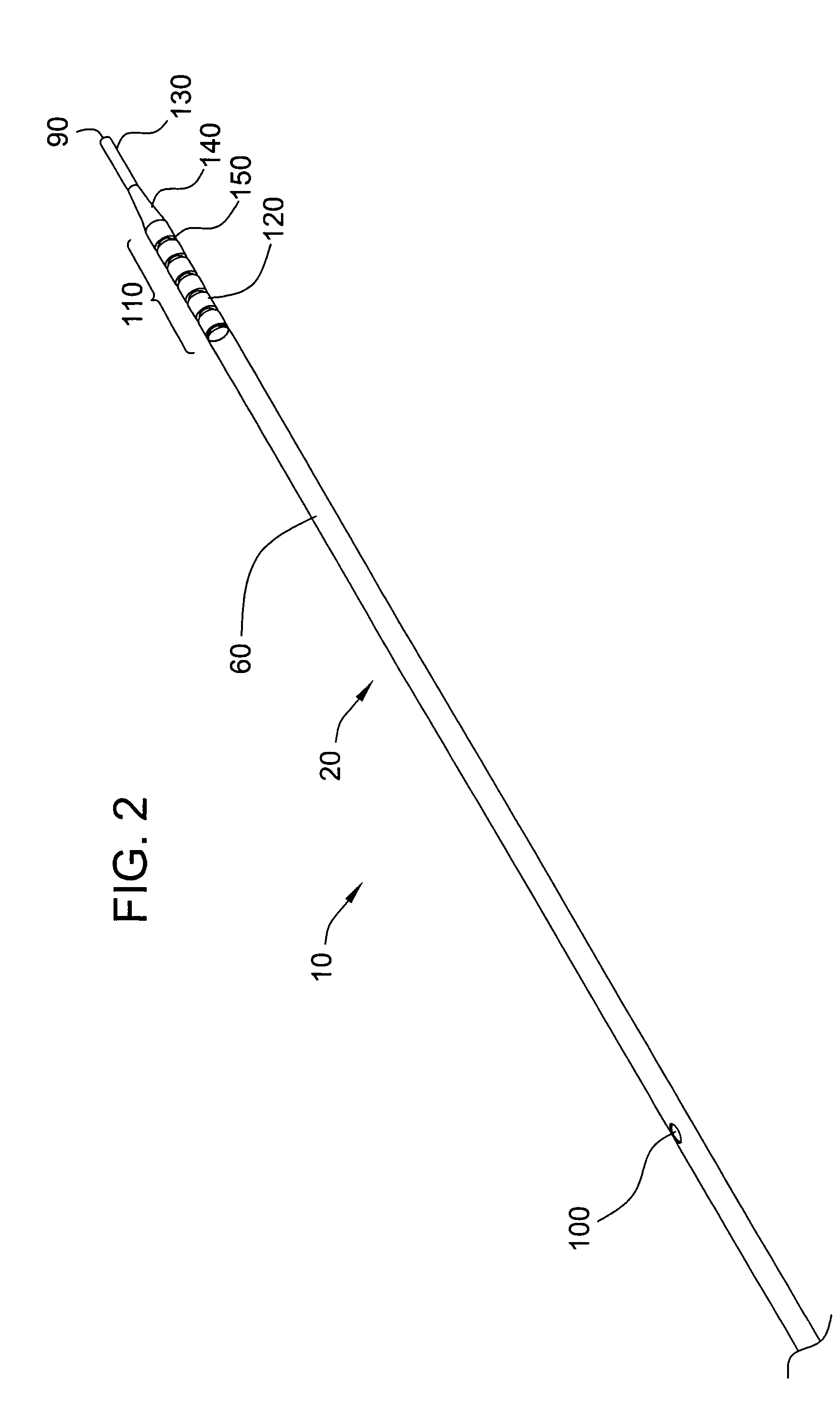
The invention relates to a medical investigation and / or treatment system comprising:a catheter system, comprising a catheter (1, 7, 9), witha first sensor (4, 11) of an imaging system for optical coherence tomography with an optical fiber via which the light is directed and is radiated in the area of a catheter tip introduced into an area to be investigated, via which fiber reflection light is directed from an illuminated investigation area to a first image processing unit (22),a second sensor (3, 8, 10) of an intravascular ultrasound imaging system to transmit and receive sound pulses which are fed as an electrical signal to a second image processing unit (23), undat least one display unit (24) for presenting the images of the first and second image processing unit (22, 23).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Intravascular ultrasound catheter device and method for ablating atheroma
InactiveUS20060241524A1Prolong time-integrated emulsificationEnhance reabsorptionChiropractic devicesMedical devicesCavitationUltrasound angiography
An intravascular catheter device having a catheter and an ultrasound ablation manifold is proposed for generating cavitations and acoustic jet streams in the blood to ablate atheroma. The ablation manifold has a power transducer and a coupled leaky acoustic cavity. The leaky acoustic cavity contains a first portion of ultrasonic power emission for intra-cavity ablation while allowing a second portion of ultrasonic power emission to leak outside for an extra-cavity ablation. The power transducer and the leaky acoustic cavity are configured to form a confocal resonant cavity. An intervening bird cage is coupled to the resonant cavity for stronger resonance while maintaining ultrasound leakage. A protective shield is mounted around the waist of bird cage to strengthen resonance and to prevent damaging the intima from an otherwise normal incidence of high intensity ultrasound. A microbubble releasing device and micro pump are also included to further increase the ablation efficacy.
Owner:YU QI
Method and system for image based device tracking for co-registration of angiography and intravascular ultrasound images
ActiveUS8565859B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationVascular ultrasound
A method and system for co-registration of angiography data and intra vascular ultrasound (IVUS) data is disclosed. A vessel branch is detected in an angiogram image. A sequence of IVUS images is received from an IVUS transducer while the IVUS transducer is being pulled back through the vessel branch. A fluoroscopic image sequence is received while the IVUS transducer is being pulled back through the vessel branch. The IVUS transducer and a guiding catheter tip are detected in each frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence. The IVUS transducer detected in each frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence is mapped to a respective location in the detected vessel branch of the angiogram image. Each of the IVUS images is registered to a respective location in the detected vessel branch of the angiogram image based on the mapped location of the IVUS transducer detected in a corresponding frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence.
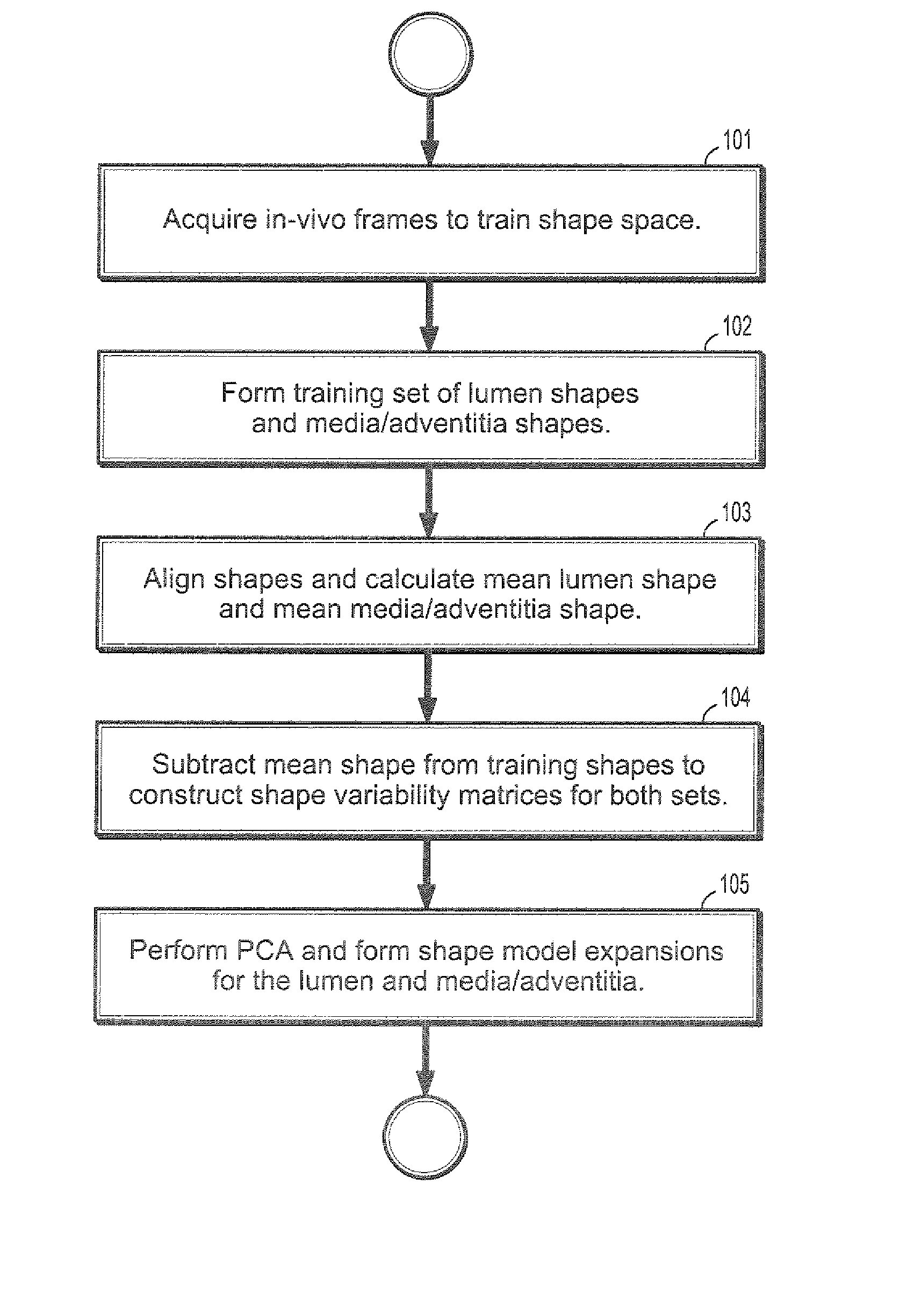
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for vascular border detection
ActiveUS20050196026A1Closely matchedOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryFrequency spectrumSonification
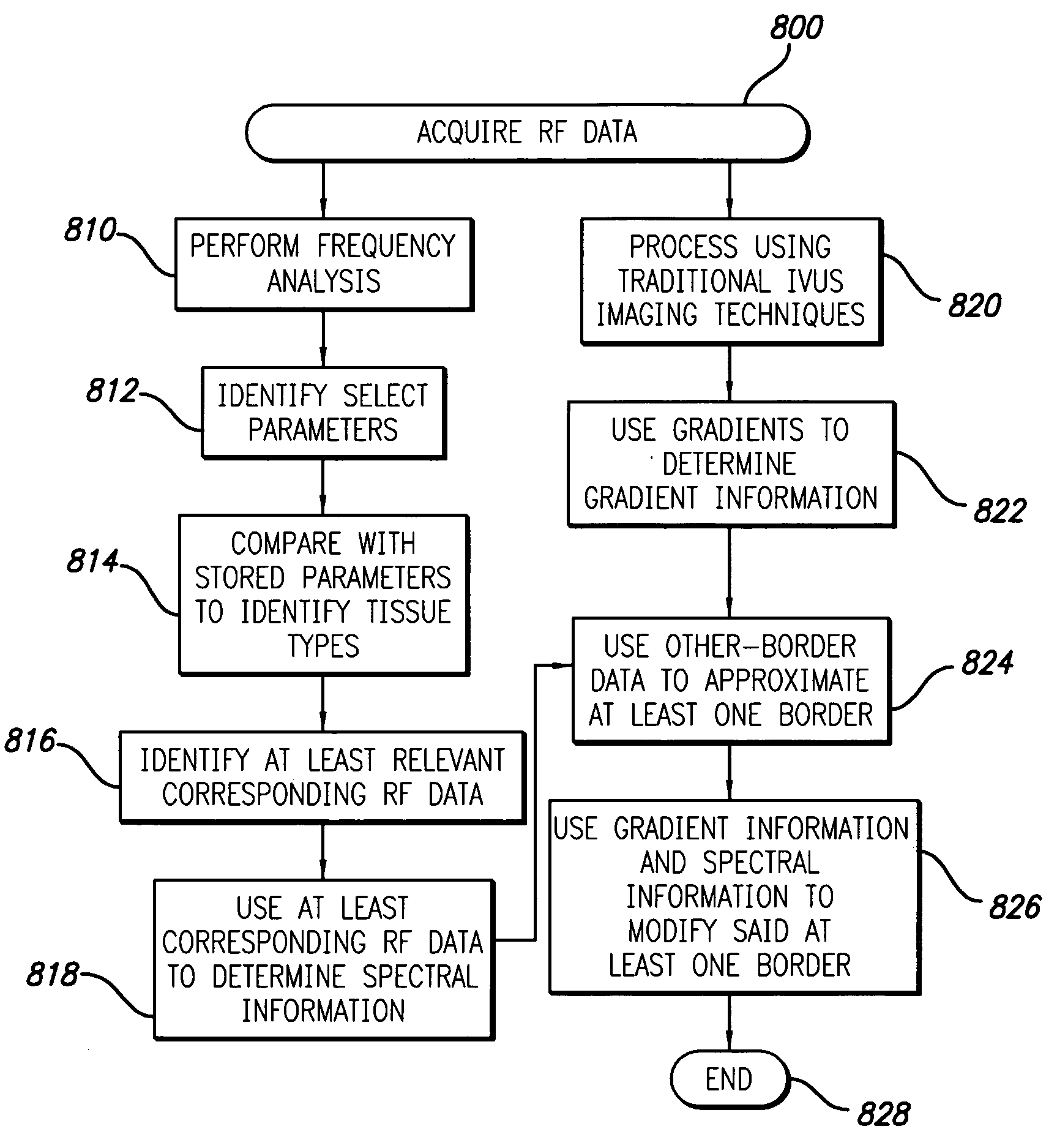
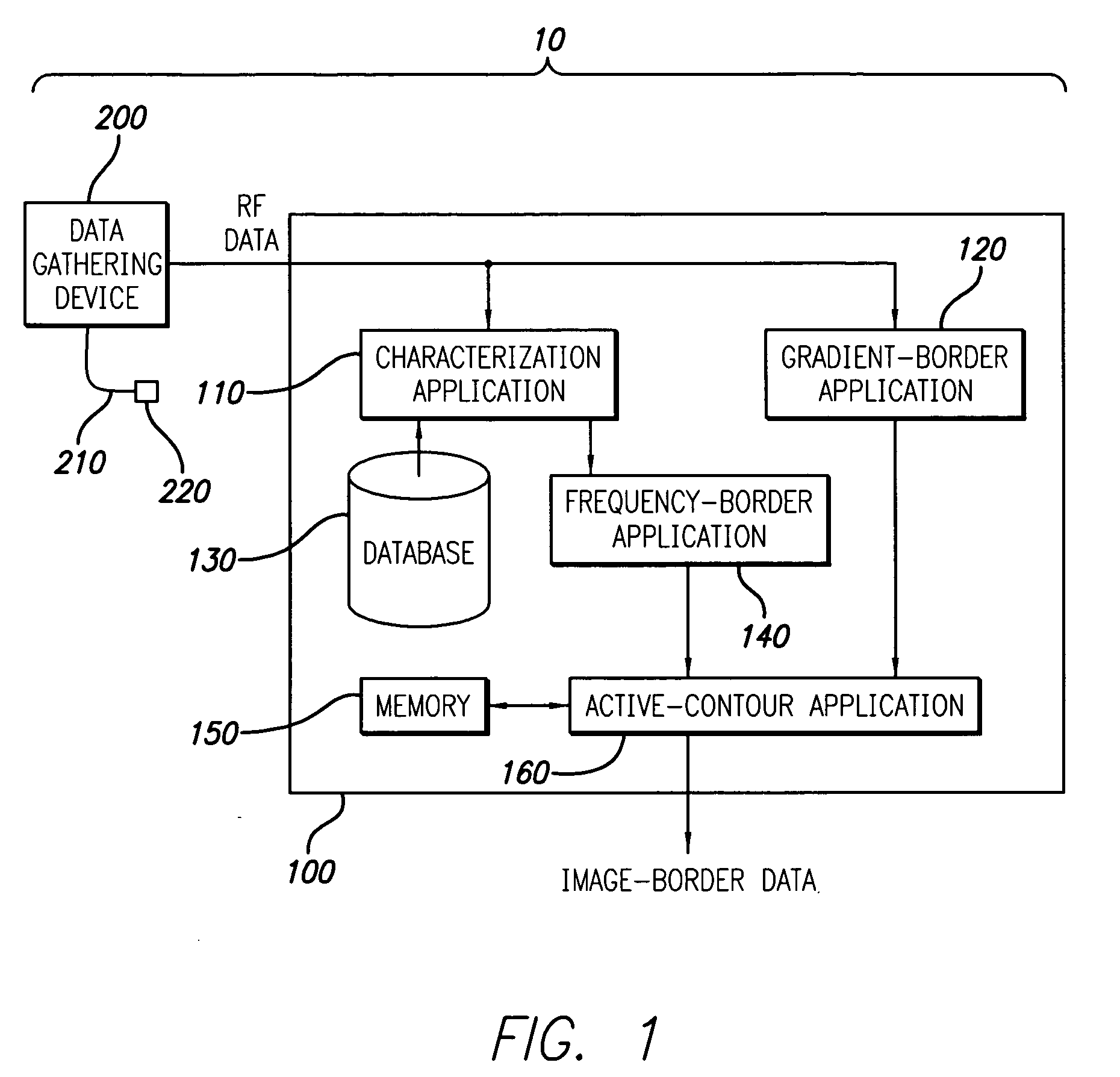
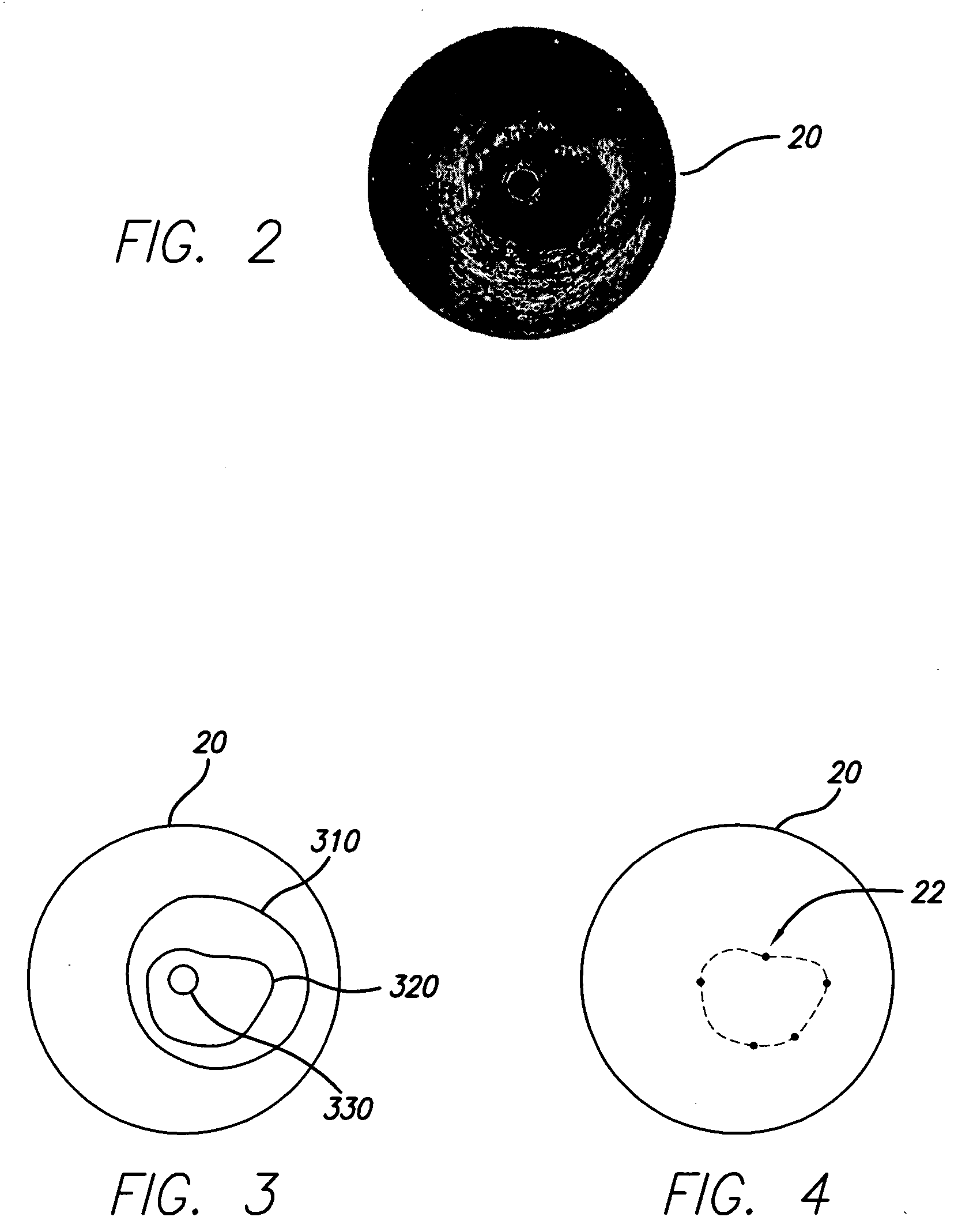
A system and method is provided for using the frequency spectrum of a radio frequency (RF) signal backscattered from vascular tissue to identify at least one border (e.g., tissue interface, etc.) on a vascular image. Embodiments of the present invention operate in accordance with a data gathering device (e.g., an intra-vascular ultrasound (IVUS) device, etc.) electrically connected to a computing device and a transducer via a catheter. The transducer is used to gather radio frequency (RF) data backscattered from vascular tissue. The RF data is then provided to (or acquired by) the computing device via the data-gathering device. In one embodiment of the present invention, the computing device includes (i) at least one data storage device (e.g., database, memory, etc.) for storing a plurality of tissue types and parameters related thereto and (ii) at least one application (e.g., a characterization application, a gradient-border application, a frequency-border application and / or an active-contour application). The characterization application is used to convert (or transform) the RF data into the frequency domain and to identify a plurality of parameters associated therewith. The identified parameters are then compared to the parameters stored in the data storage device to identify the corresponding tissue type. This information (e.g., tissue type, corresponding RF data, etc.) is then used, either alone or together with other border-related information (e.g., gradient information, other-border information, etc.), to determine at least one border on a vascular image.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
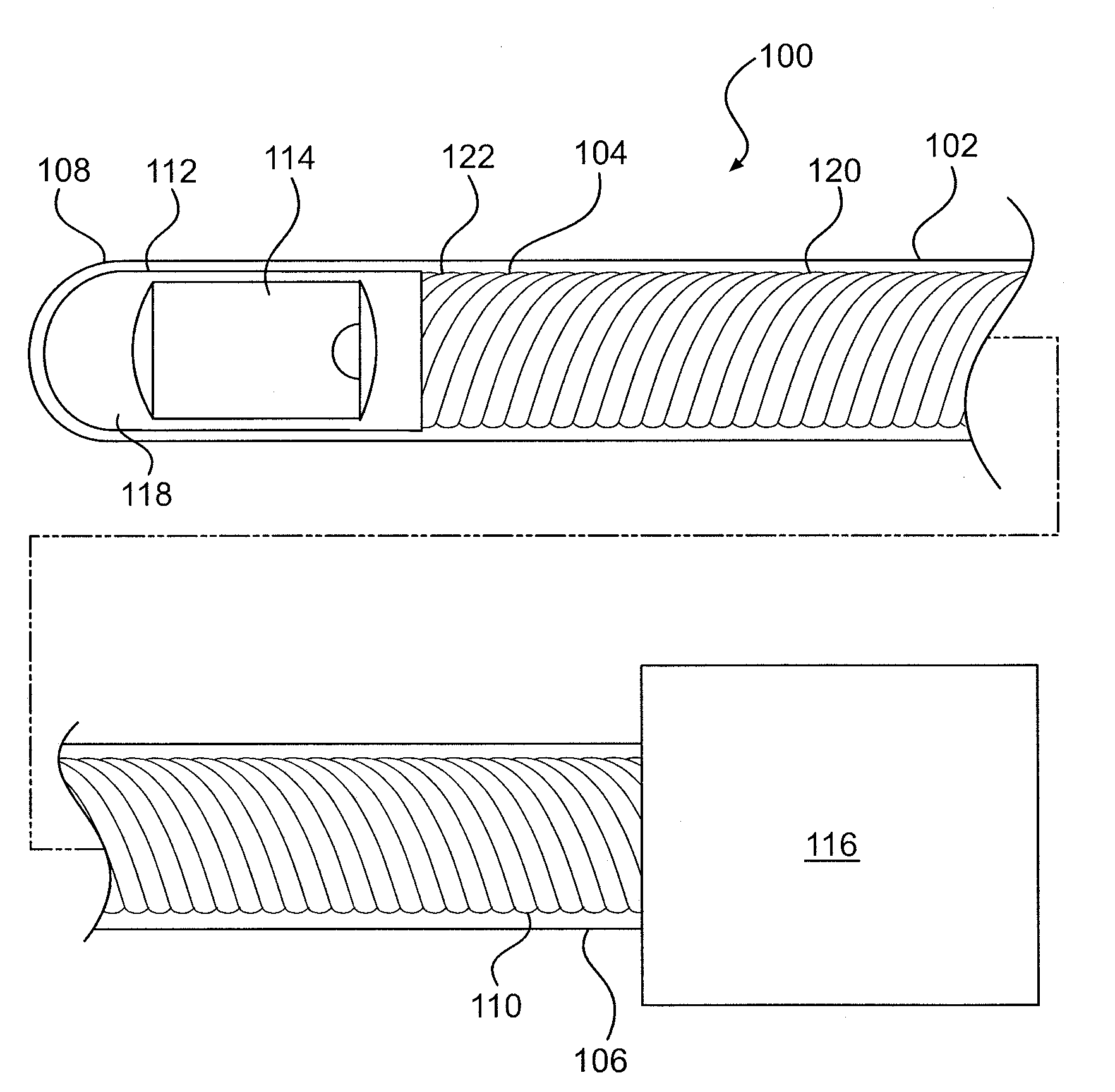
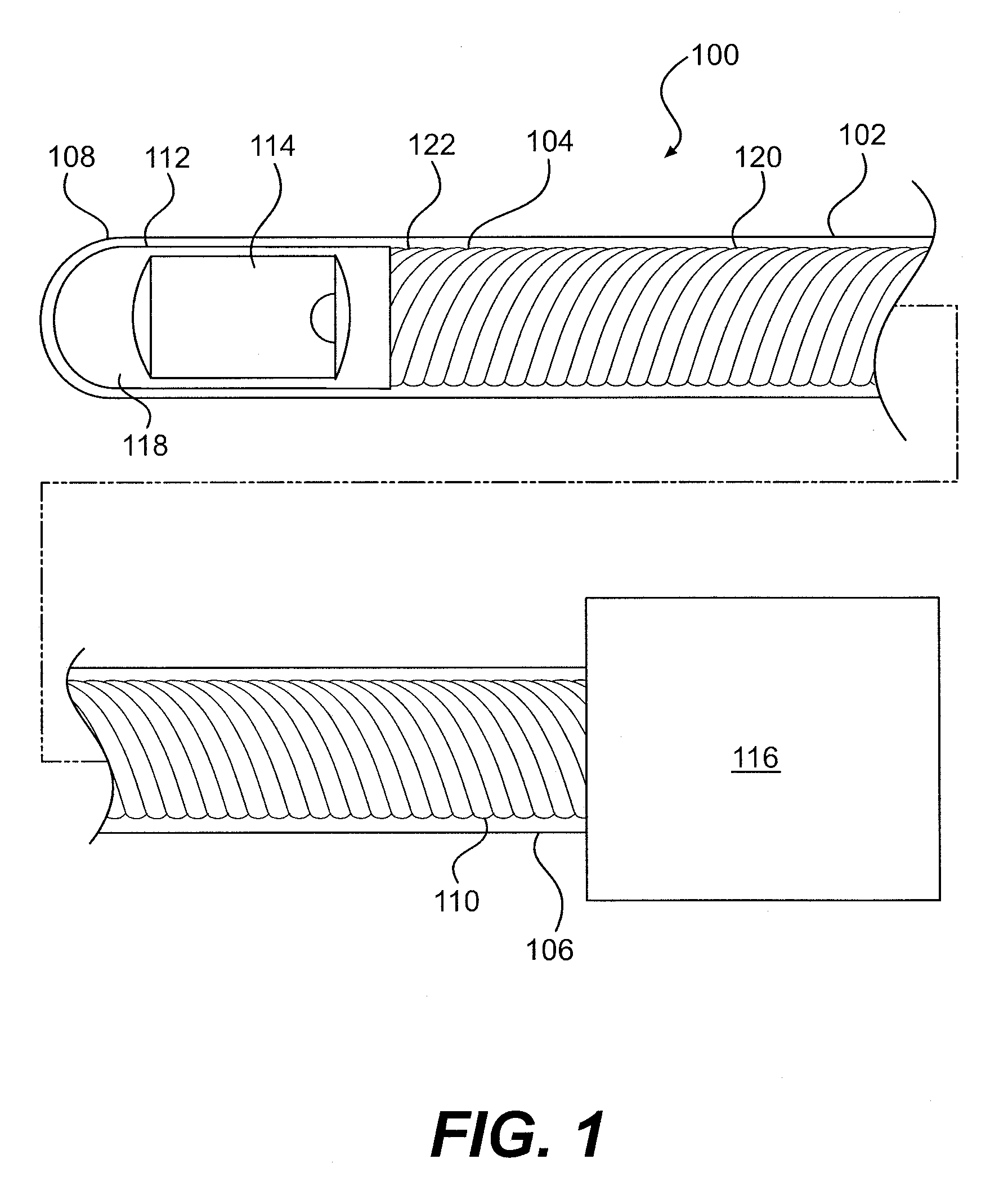
Low profile intravascular ultrasound catheter
ActiveUS20090163818A1Easy accessIncrease flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfusion syringesUltrasound imagingUltrasound angiography
The present invention provides low profile intravascular ultrasound catheters adapted to access sites within the patient's body through narrow blood vessels, e.g., the radial artery. In an embodiment, a low profile catheter comprises an catheter sheath, a short guidewire receiver attached to the distal end of the catheter sheath, and a telescope assembly at the proximal end. The catheter sheath comprises a main portion and a tapered portion for increased flexibility toward the distal end of the catheter. In one embodiment, a rotatable and translatable imaging core is received within the catheter sheath for ultrasound imaging. A short guidewire receiver is used to allow the imaging core to be advanced farther distally with respect to the distal end of the catheter. In an embodiment, the catheter sheath extends through a portion of the telescope assembly to provide enhanced support of the imaging core within the telescope assembly.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods for delivery of heart valve devices using intravascular ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS20170086974A1Shorten the construction periodReduce eliminateOrgan movement/changes detectionHeart valvesAnatomical landmarkBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
Methods related to delivery of various heart valve implants are described. The implant may be delivered using an ultrasound imaging delivery system. The ultrasound imaging delivery system may be used to deliver a variety of different devices, including mitral valve reshaping devices, mitral valve replacement valves, and others. A deployment catheter carrying an implant having a tissue anchor is advanced to a deployment site in a heart. An imaging element is positioned adjacent the implant and a relationship between the tissue anchor and an anatomical landmark in the heart is visualized. The implant is then attached by driving the tissue anchor into tissue in the heart.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Medical catheter and system for inserting a catheter into a vessel
ActiveUS8126534B2Better assessmentMinimal stressUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEndoscopesUltrasound angiographyBlood vessel
The invention relates to a medical system for introducing a catheter into a blood vessel of a patient, having a computer and control unit, a means for creating a transparent general view of the position of the vessel, a catheter with a reversible inflatable balloon located in the front area, to the outside of which a stent can be fitted for implanting into the vessel, a position locating system for the catheter with position and location sensors that can determine the position and location of the catheter, the system with at least one OCT (optical coherence tomography) sensor at a catheter end for the close-up area, with at least one IVUS (intravascular ultrasound) imaging sensor at a catheter end for the remote area and the computer and control unit having image processing and image display functions for the image sensors.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for stabilizing a series of intravascular ultrasound images and extracting vessel lumen from the images
InactiveUS8483488B2Accurate and clean imageEnhance the imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancement3d shapesSonification
A method and system for generating stabilized intravascular ultrasonic images are provided. The system includes a probe instrument, having an ultrasonic signal transmitter and a reflected ultrasonic signal receiver, the reflected signals containing information about a tubular environment, and a processor and post-processor, capable of converting inputted signals into one or more, preferably a series of, images. The method for stabilizing images involves the processor and post-processor input and output. The post-processor determines the environment center at each reflection position, detects the tubular environment edges, and aligns the image center with the environment center thereby limiting image drift and stabilizing the images. The processor may also filter images to improve image stabilization and remove motion interference and / or extract the environment's 3D shape. The method and device are of particular use in a vascular lumen, where image drift may occur due to heart beat or blood flow.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Capacitive microfabricated ultrasound transducer-based intravascular ultrasound probes
An ultrasound catheter is described herein for insertion into a cavity such as a blood vessel to facilitate imaging within a vasculature. The catheter comprises an elongate flexible shaft, a capacitive microfabricated ultrasonic transducer, and a sonic reflector. The elongate flexible shaft has a proximate end and a distal end. A capacitive microfabricated ultrasonic transducer (cMUT) is mounted to the shaft near the distal end. The reflector is positioned such that a reflective surface redirects ultrasonic waves to and from the transducer. In other embodiments, the catheter comprises a plurality of cMUT elements and operates without the use of reflectors. In further embodiments, integrated circuitry is incorporated into the design.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Intravascular ultrasound image and intravascular-OCT image fusing method
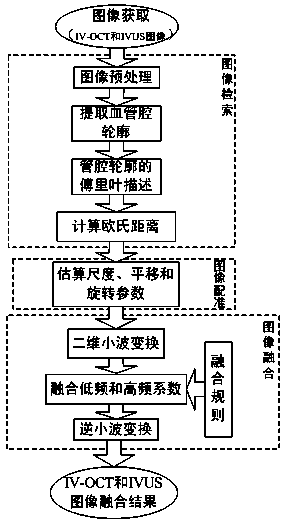
ActiveCN104376549AComprehensive descriptionStrong tissue penetrationImage enhancementReference imageUltrasound angiography
The invention relates to an intravascular ultrasound image and intravascular-OCT image fusing method. The method includes the following steps of (a) image retrieval, wherein for intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) images and intravascular (IV)-OCT images collected at the same position on a blood vessel section, a frame of IV-OCT image is taken as a reference image, and an image to be registered is selected from the n frames of IVUS images collected from the point; (b) IVUS image and IV-OCT image registration; (c) IVUS image and IV-OCT image fusion. IV-OCT image data and IVUS image data of the same blood vessel section are fused, the advantage of high tissue penetrating power of IVUS imaging and the advantage of high resolution of IV-OCT imaging are brought into full play, more comprehensive description of blood vessel walls and atherosclerotic plaques is obtained, and a reliable basis is provided for research on the coronary heart disease and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com