Method and apparatus for sequential authentication using one or more error rates characterizing each security challenge
a technology of security challenges and error rates, applied in the field of user authentication techniques, can solve the problems of inconsistent fingerprints, sequential challenges that are not beneficial, and the set of rules or algorithms for making a binary decision to accept or reject users may be more complicated than others, and achieve the effect of convenient adaptation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
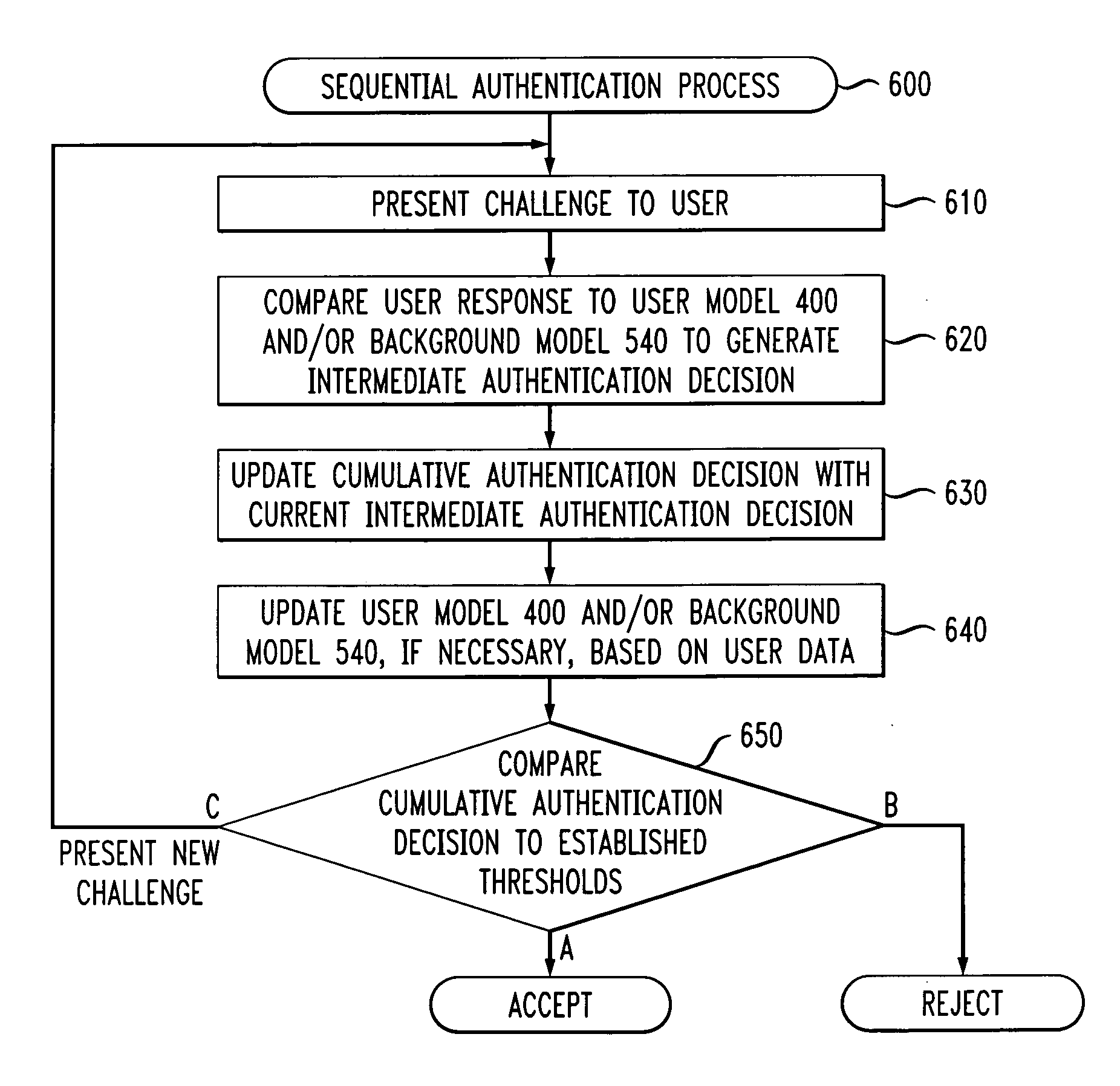
[0019] The present invention provides a sequential authentication system. The disclosed sequential authentication system is based on knowledge verification for the purpose of measuring a similarity score for every interaction turn. The disclosed sequential authentication system continuously estimates the probability that the user's identity claim is genuine and the probability that the user is not who he or she claims to be.
[0020] During a user authentication, a series of challenges is presented to the user, and each user response is compared to one or more models, resulting in an intermediate authentication decision (such as a log likelihood ratio (LLR)). At each interaction turn, the intermediate decisions from the individual turns are combined (such as a sum of LLRs) to create a cumulative authentication result to ultimately either accept or reject the user's identity claim. The models used for the sequential authentication process may also be adapted from the user data during a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com