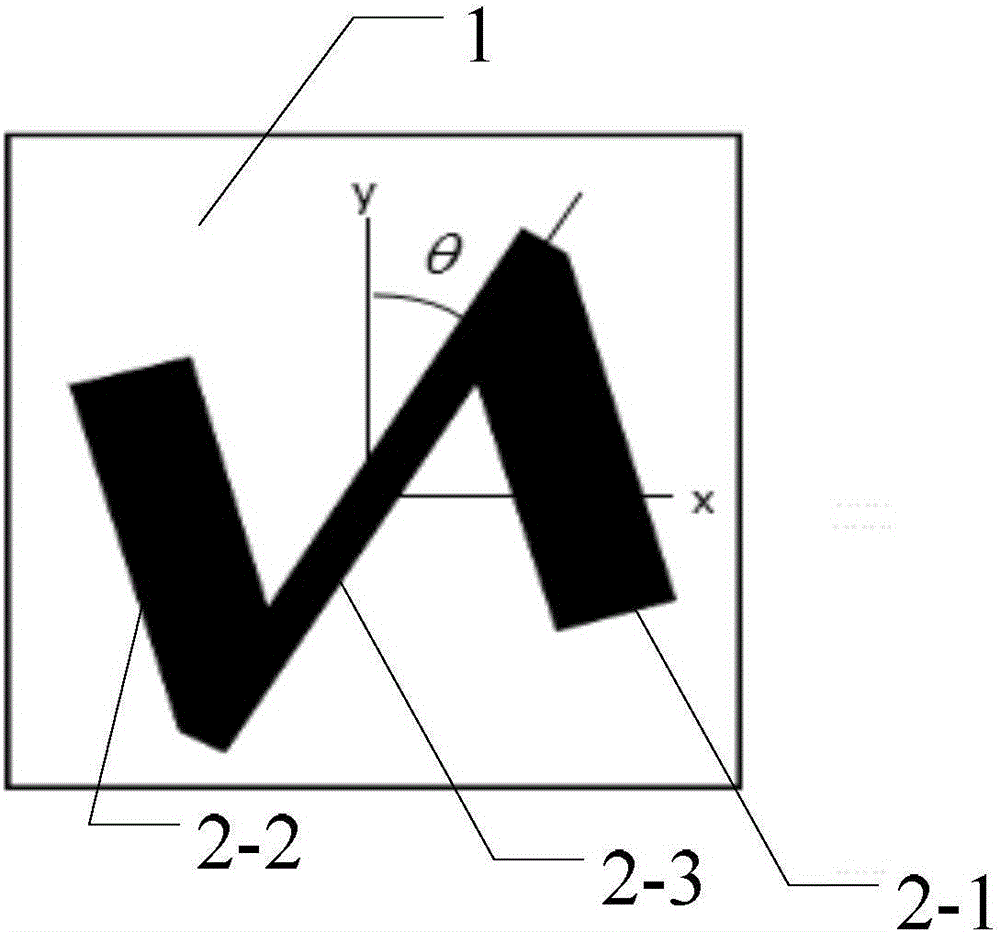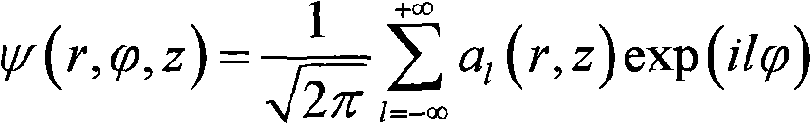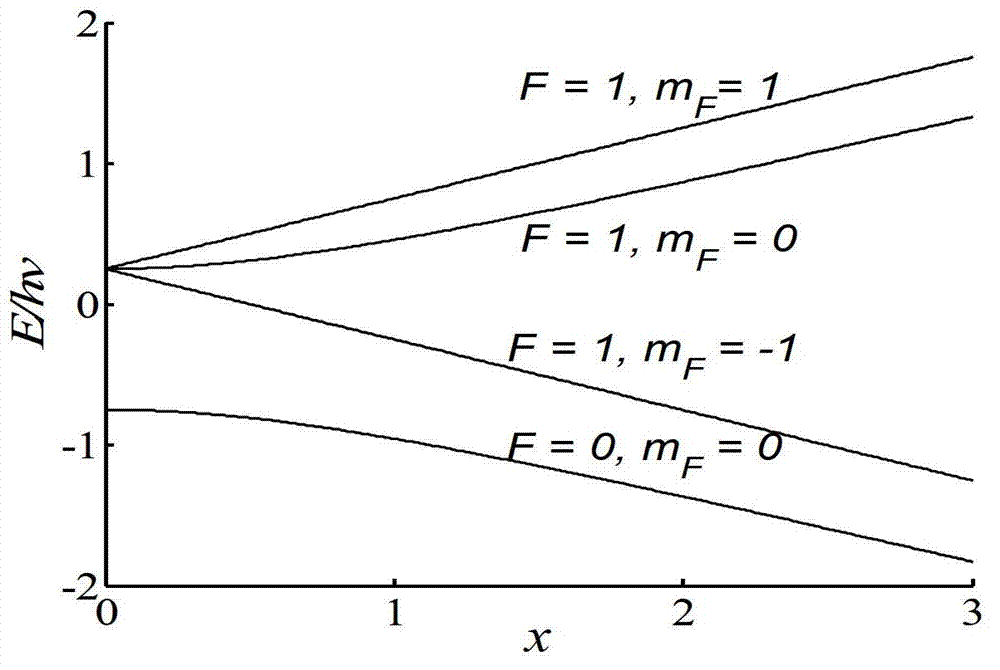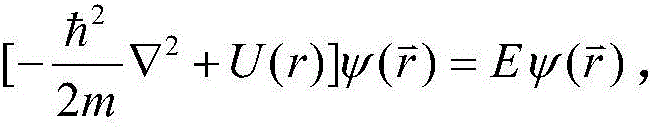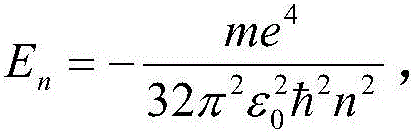Patents
Literature
36 results about "Quantum number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quantum numbers describe values of conserved quantities in the dynamics of a quantum system. In the case of electrons, the quantum numbers can be defined as "the sets of numerical values which give acceptable solutions to the Schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom". In more general cases, quantum numbers correspond to eigenvalues of operators that commute with the Hamiltonian—quantities that can be known with precision at the same time as the system's energy—and their corresponding eigenspaces. Together, a specification of all of the quantum numbers of a quantum system fully characterize a basis state of the system, and can in principle be measured together.
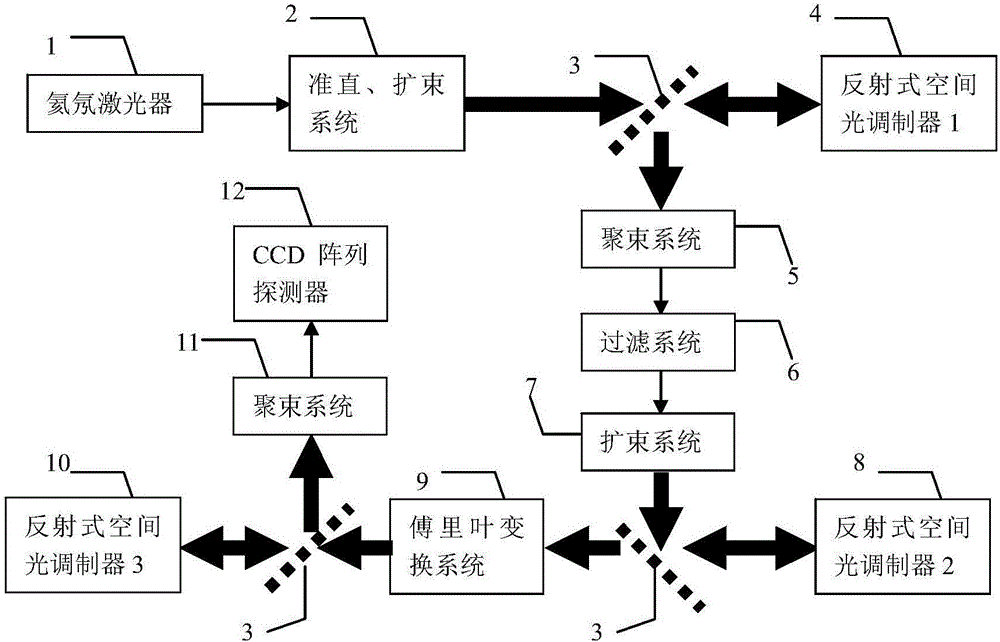
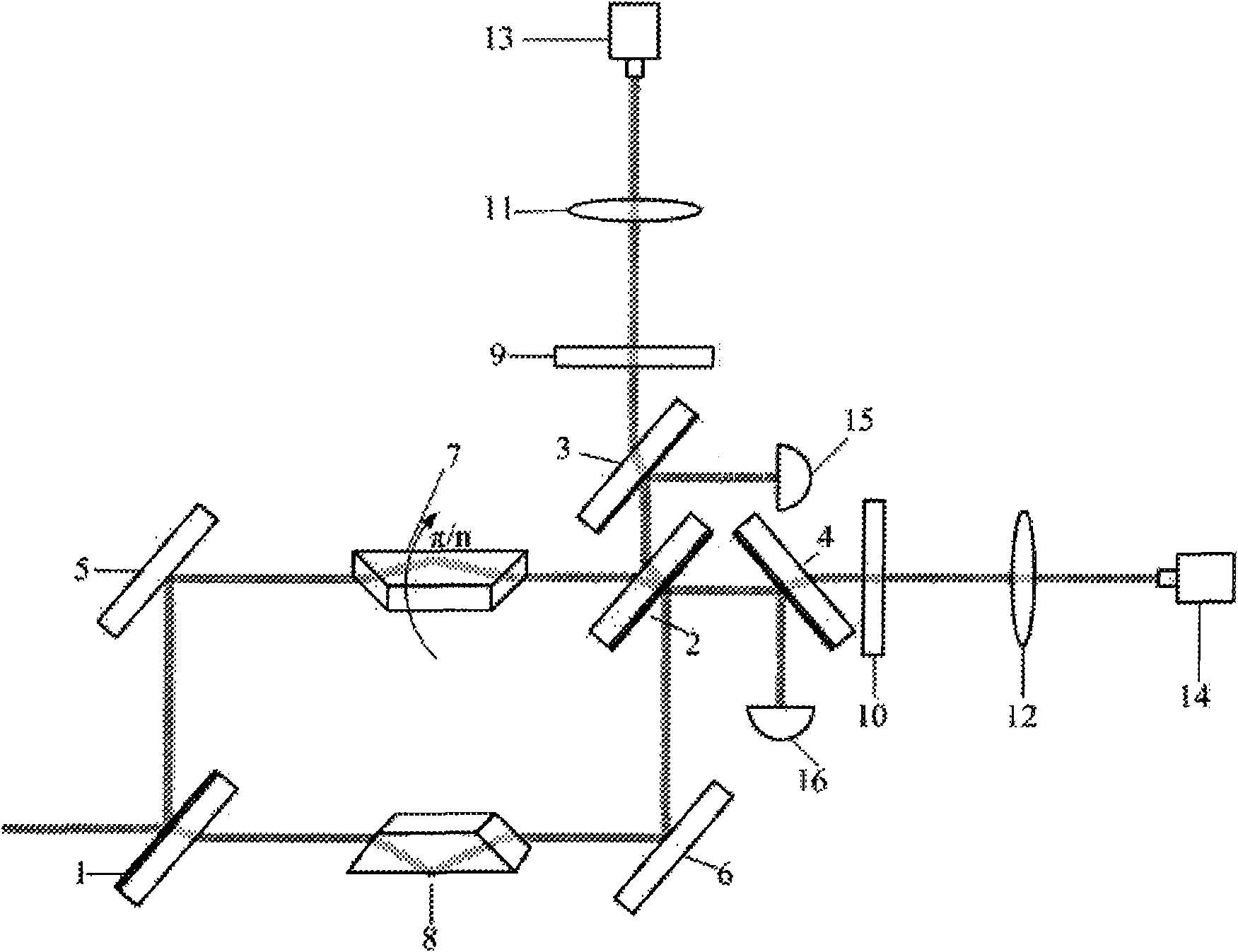
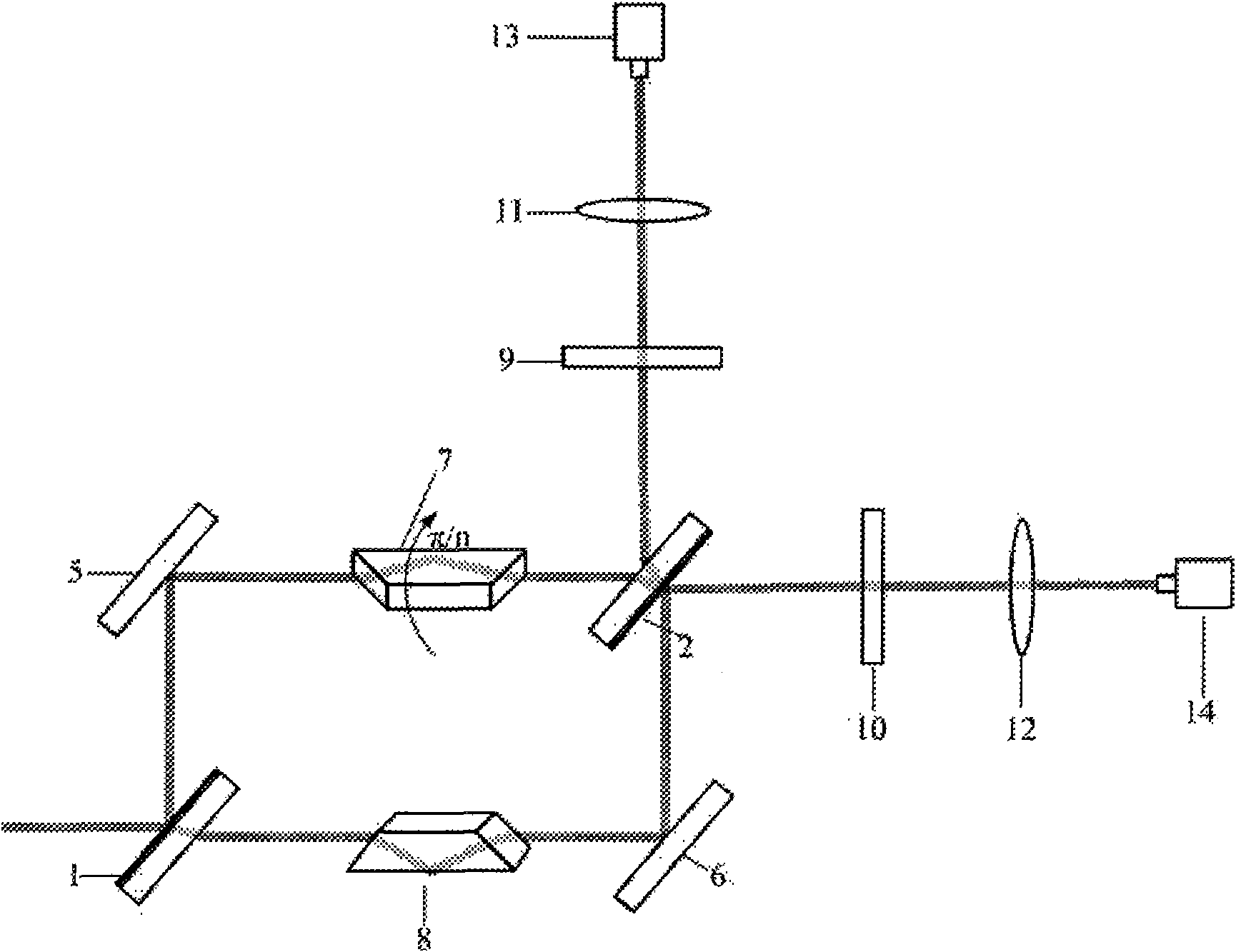
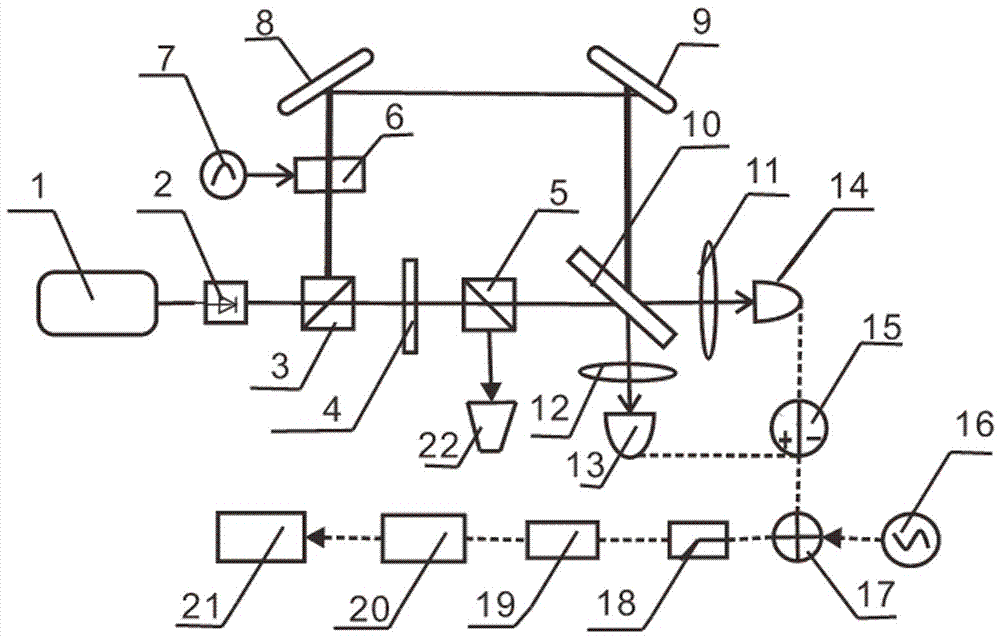
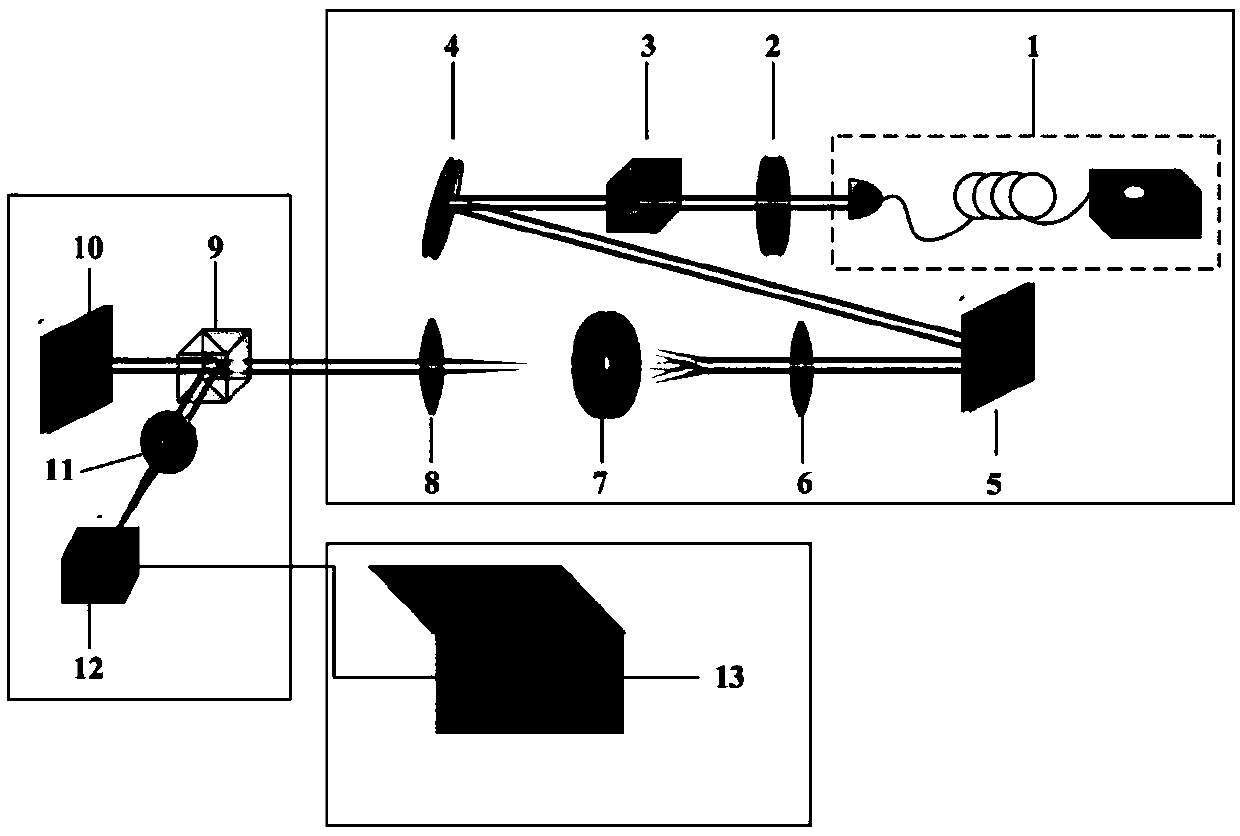
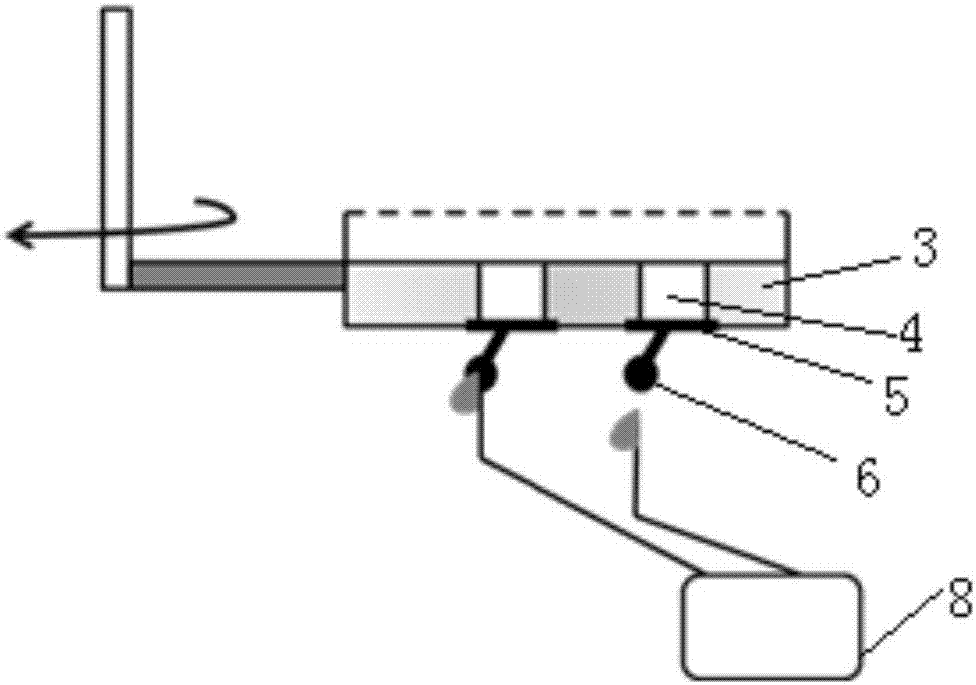
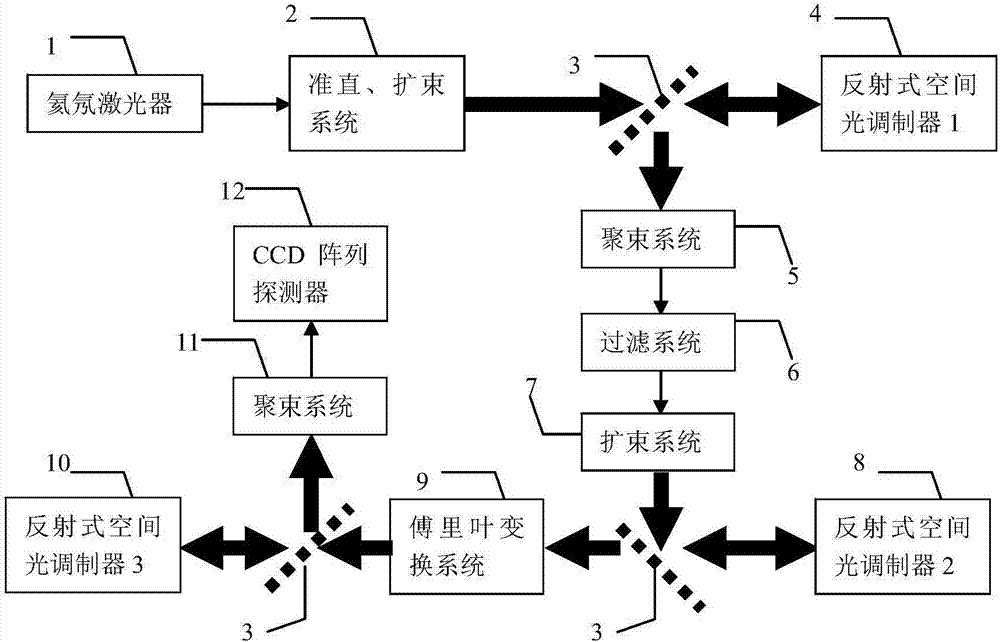
Photon orbit angular momentum measurement system and method based on wave-front conversion method
ActiveCN106289526AGood repeatabilityHigh operating freedomSpectrum investigationQuantum technologySpatial light modulator
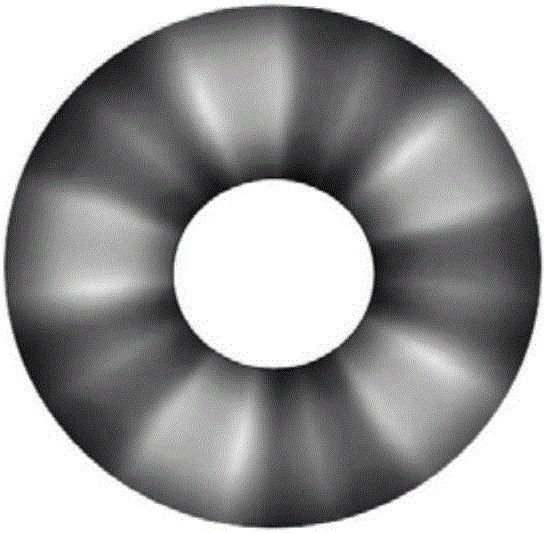
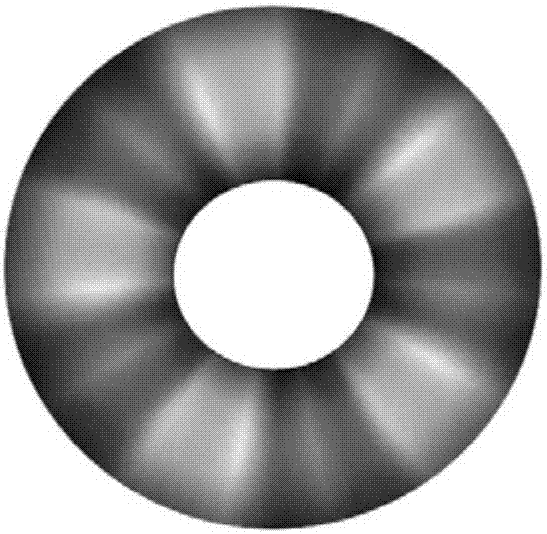
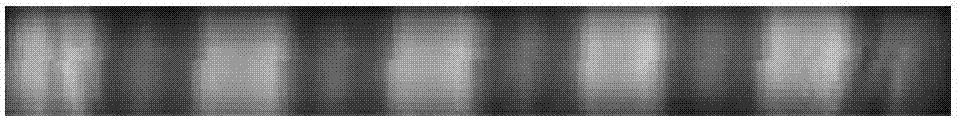
The invention discloses a photon orbit angular momentum measurement system and a method based on a wave-front conversion method, which belong to the technical field of single photon detection in a quantum technology, solve the problem that the existing photon-magnitude orbit angular momentum detection needs multiple interferometers to be cascaded, and can simply, conveniently and accurately measure the photon-magnitude orbit angular momentum. Transmitted laser signals are modulated through multiple times of a spatial light modulator and a Fourier transformation system; the modulated signal pulses with the orbit angular momentum are gathered to a CCD detection array; and the quantum number in the orbit angular momentum in the signals can be distinguished through a pattern position on the detector, different azimuth angles are corresponding to different lateral coordinates, and the quantum number 1 in the orbit angular momentum can be determined as coordinates are measured. The system and the method of the invention are applied to measurement on the quantum number in the single-photon magnitude orbit angular momentum.
Owner:黑龙江省工业技术研究院
Lens and method for generating vortex beam based on reflecting super-surface
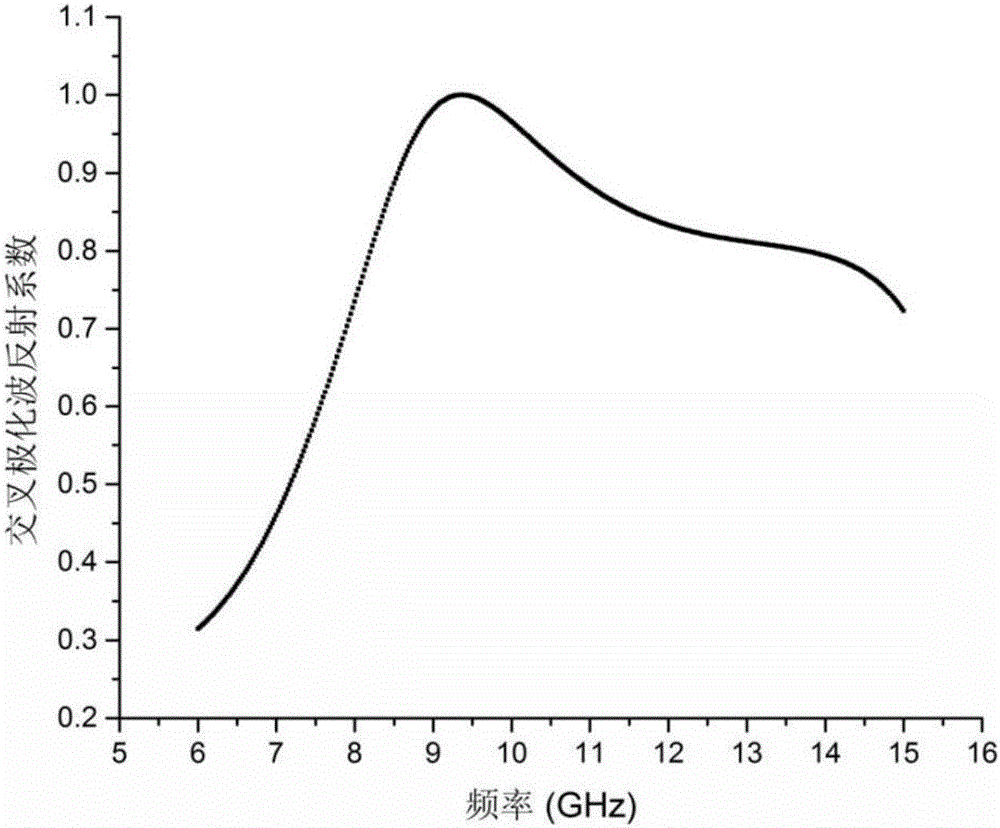
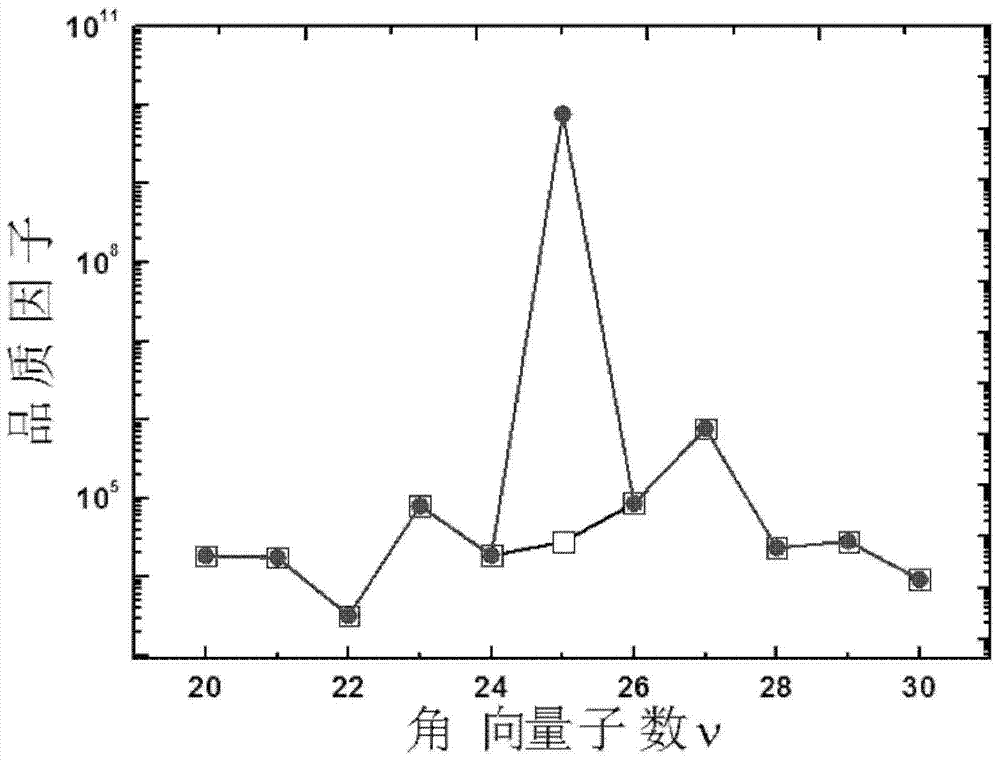
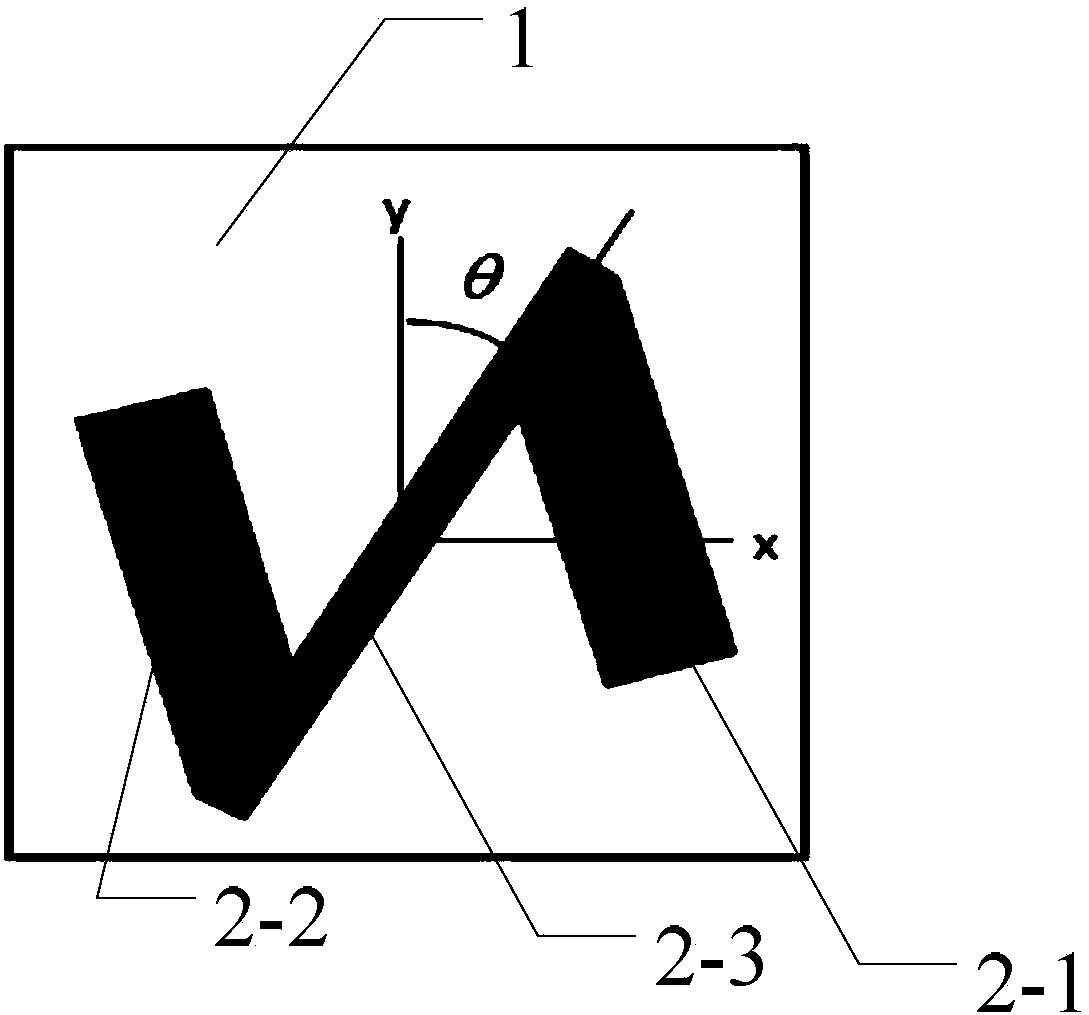
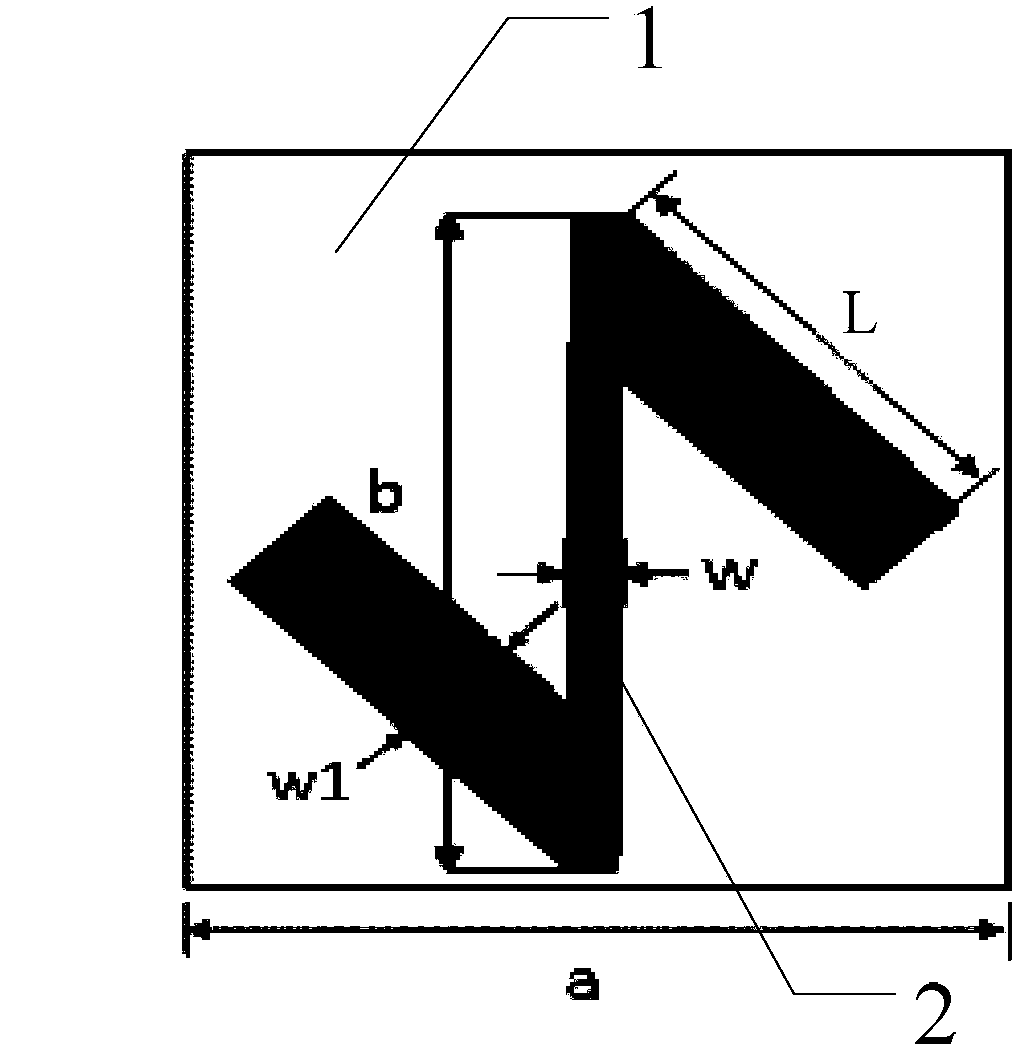
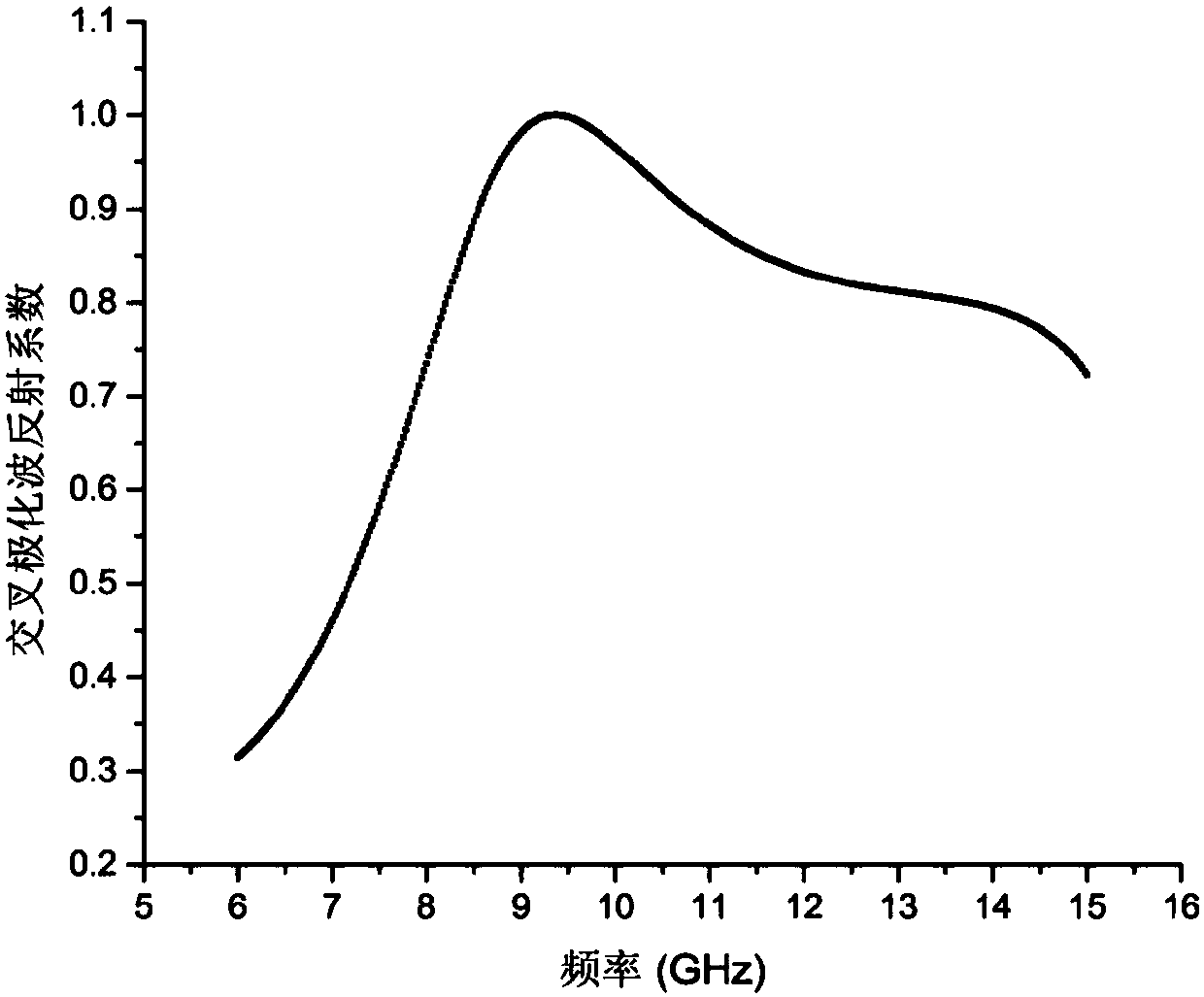
ActiveCN106025566AHigh cross-polarized wave reflectivityThe overall thickness is thinAntennasMetal stripsMomentum
The invention provides a lens and method for generating a vortex beam based on a reflecting super-surface, relates to a technology for generating the vortex beam based on a phase discontinuous super-surface, and aims at solving the problem that a traditional method for generating the vortex beam by a spiral phase wave plate is limited by the thickness when the wavelength is relatively large. The lens comprises m*n periodically arranged phase change units, wherein each phase change unit comprises a substrate and a reversed Z-shaped metal layer located on the surface of the substrate; each reversed Z-shaped metal layer comprises a metal strip I, a metal strip II and an inclined strip; employing one side of each substrate as an x axis and the side adjacent to the side as a y axis, the included angle between the central line of the corresponding inclined strip and the y axis is theta; the formula is as shown in the specification, wherein l is the orbital angular momentum quantum number; and the formula is as shown in the specification. Incident light, entering the lens, of a circularly polarized wave and abnormally reflected light generated when the circularly polarized wave vertically enters the lens are symmetrical about a normal line; a cross-polarized reflection wave is vertical to reflection of the lens; and the abnormal reflection angle is as shown in the specification. The lens and the method are suitable for generating the vortex beam.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
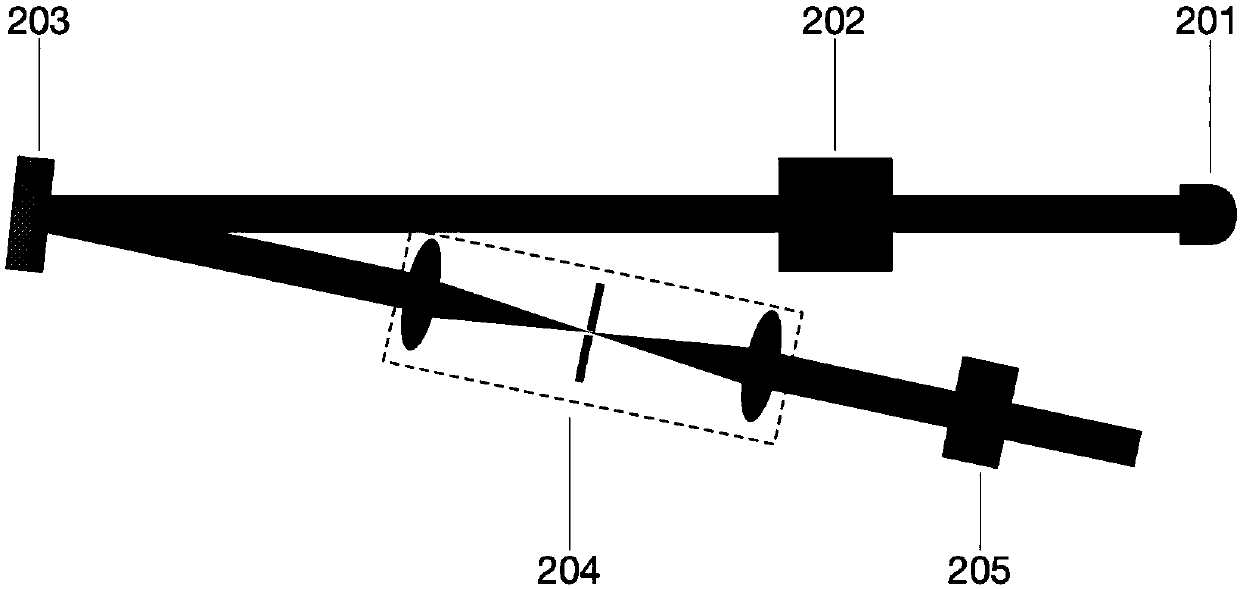
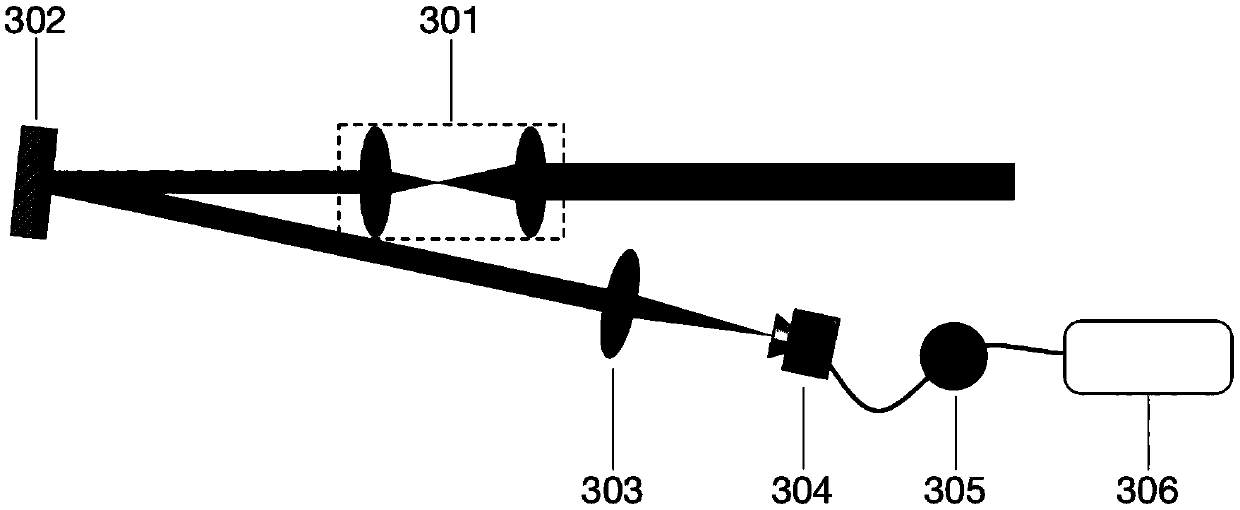
Method and device for realizing demodulation of mixing auger phase light beam orbit angular momentum state
InactiveCN101587281AOptical measurementsInterferometric spectrometryBeam splitterMach–Zehnder interferometer
The invention provides a method and device for realizing the demodulation of the orbit angular momentum state of the mixing auger phase light beam containing a plurality of orbit angular momentum states. the device comprises four 50 / 50 beam splitters, two 45 DEG total reflectors, two Dove prisms, two diffraction grids, two convex lenses, two CCD detectors and two energy meters. in the invention, the separation of the different angular-momentum quantum number helical light is realized, the measuring of each helical component energy in the light beam is realized, the measuring of the orbit angular momentum state containing the helical component in the light beam is realized. in the invention, the Mach-Zehnder interferometer having two arms with Dove prism is adopted for separating the helical component of different angular-momentum quantum number in the light beam, the beam splitter and the energy meter is used for measuring the energy distribution condition of each helical component in the light beam, and the diffraction grid is used for demarcating the separated orbit angular momentum state of the helical component. the invention can be widely used in the light orbit angular momentum information storing and transmitting field.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for producing random quantum number at high speed based on vacuum state quantum fluctuation
ActiveCN107220026AIncrease spawn rateIncreased entropy contentRandom number generatorsGeneration ratePhase space
The invention relates to a high-speed true random quantum number generating method, in particular to a method for producing random quantum number at high speed based on vacuum state quantum fluctuation. The problem that the production speed of an existing vacuum random quantum number generator is lower is solved. According to the specific scheme, the high-speed true random quantum number generating method mainly comprises the following steps that the translation effect of Gaussian distribution is firstly exerted to a vacuum state in a phase space, amplification of vacuum-state orthogonal amplitude component noise in the phase space is achieved, and the entropy content introduced by quantum noise in a system is increased; the true random bits which can be extracted in data postprocessing are increased; the background light of a homodyne detection system is strengthened, the sensitivity of the detection system to vacuum noise is improved, and a vacuum noise measurement value is amplified, so that the framing amount of vacuum noise statistics, namely sampling quantization bits are remarkably increased. By adopting the method, the vacuum random quantum number generating rate is effectively improved, and a new means is provided for manufacturing of high-speed random quantum number generators.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and device for detecting angular acceleration of rotator
ActiveCN108680768AThe method is simple and effectiveAcceleration measurementDevices using optical meansDual modeTime–frequency analysis
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting the angular acceleration of a rotator. In the method, a dual-mode multiplexed Laguerre-Gaussian beam having an opposite angular quantum numberis used as a detecting beam. The frequency of scattered light is modulated because of a rotational Doppler effect when the dual-mode multiplexed Laguerre-Gaussian beam irradiates the rotator along anaxis of rotation. By using a coherent detection method, the central light intensity of the interference spot is detected and recorded. The time-varying rule df / dt of the frequency of the central light intensity and the angular acceleration a(t)of the rotator satisfies a direct proportion relationship, namely a(t)=([pi] / l)(df / dt), wherein l is the orbital angular quantum number of the detecting beam. By using the short-time Fourier transform method, the change of the central light intensity of the interference spot is subjected to time-frequency analysis, the time-varying rule of the frequencyof an intensity signal can be obtained, and then the angular acceleration of the rotator is further deduced. The device is simple in system structure and easy to operate, can measure the angular velocity and the angular acceleration of the rotator in real time, and has great progress compared with the prior art.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
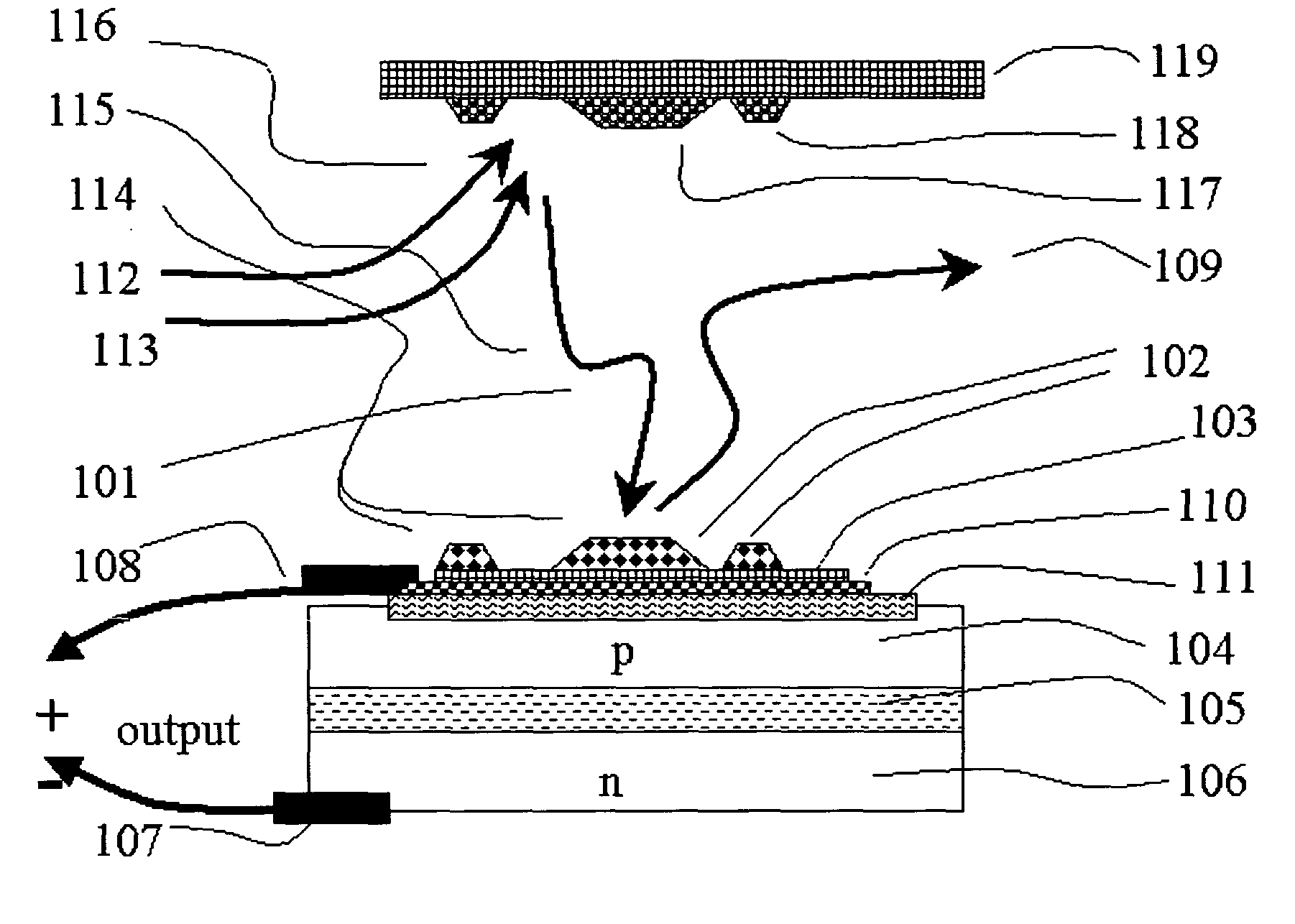
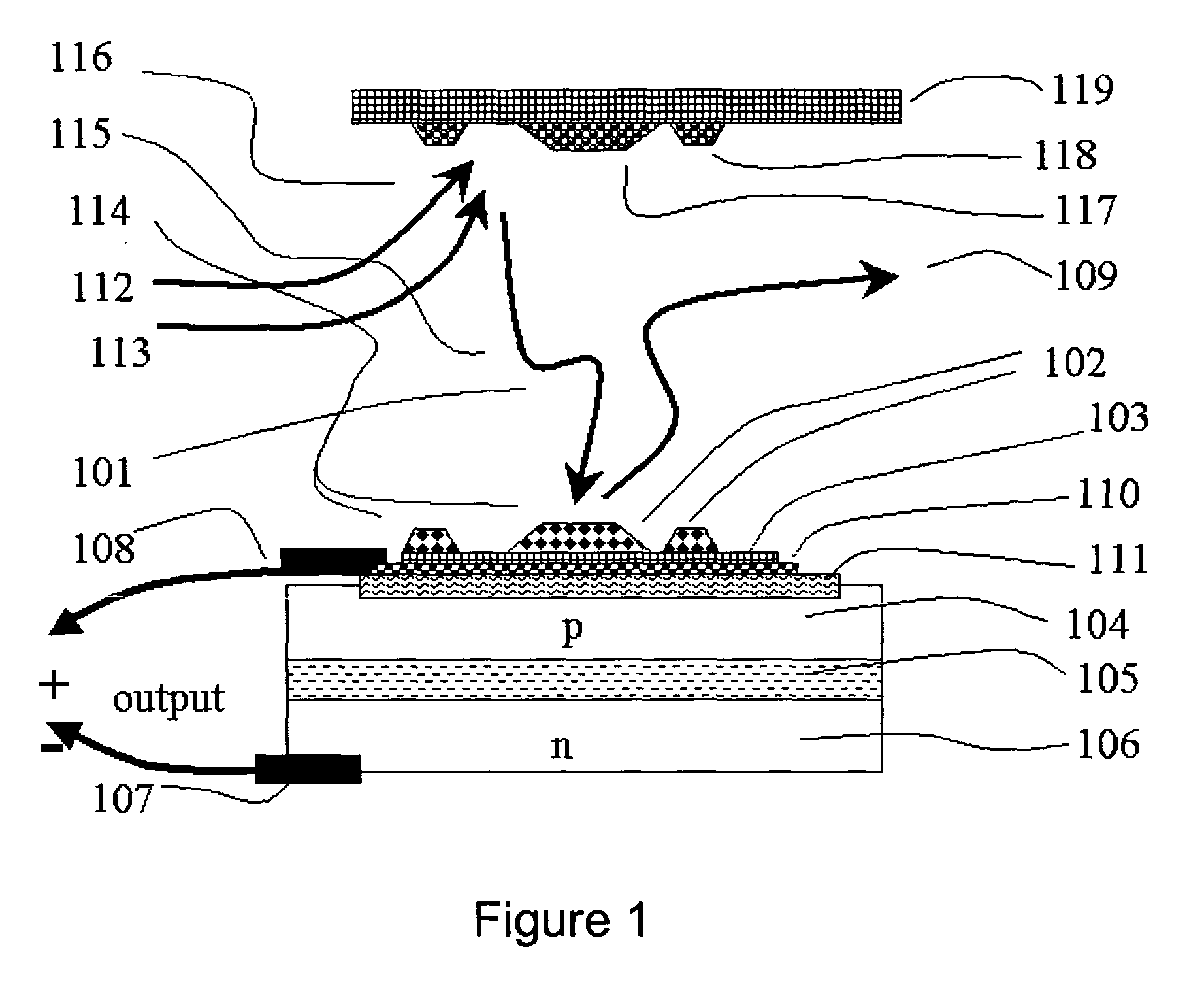
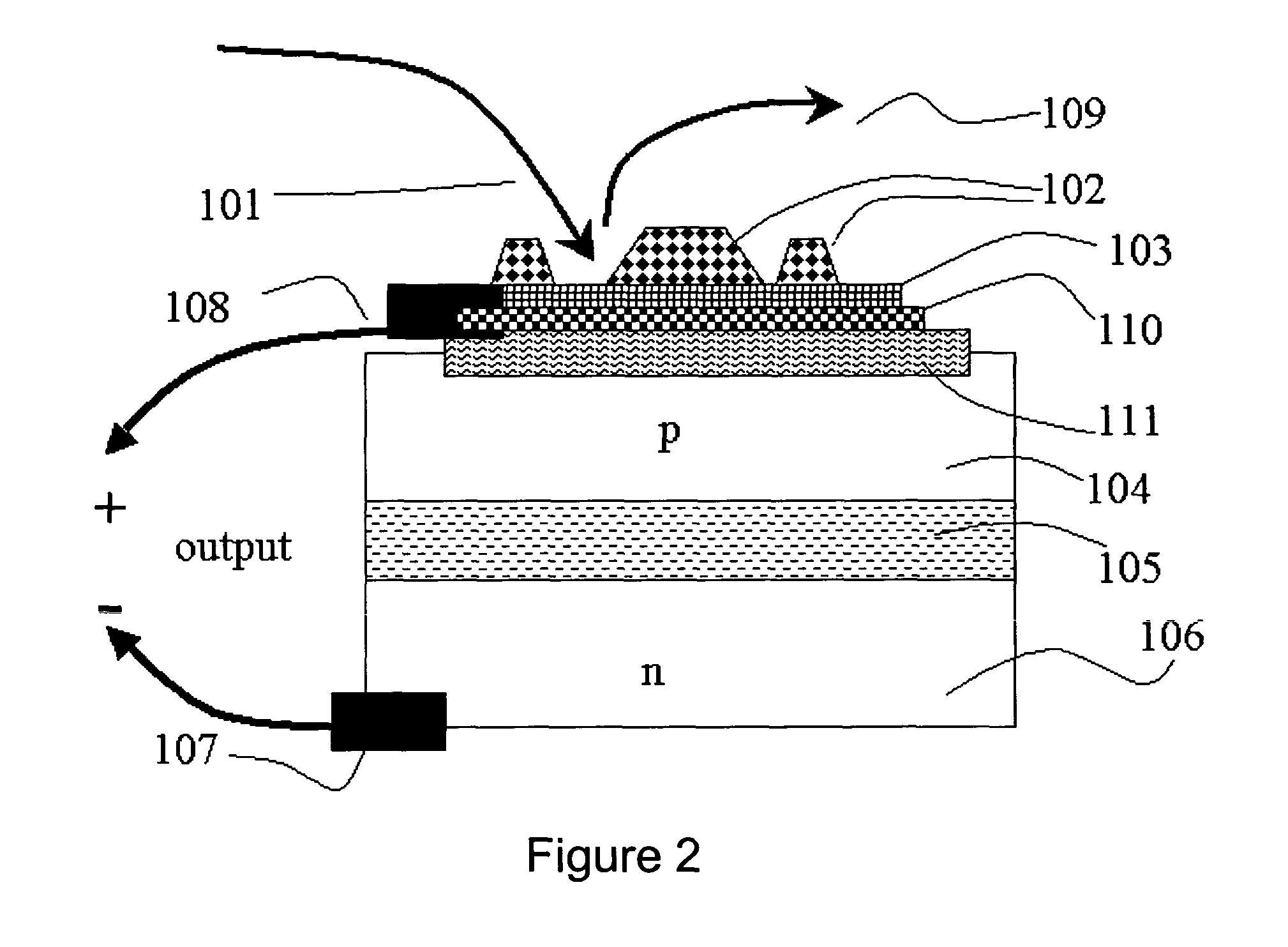
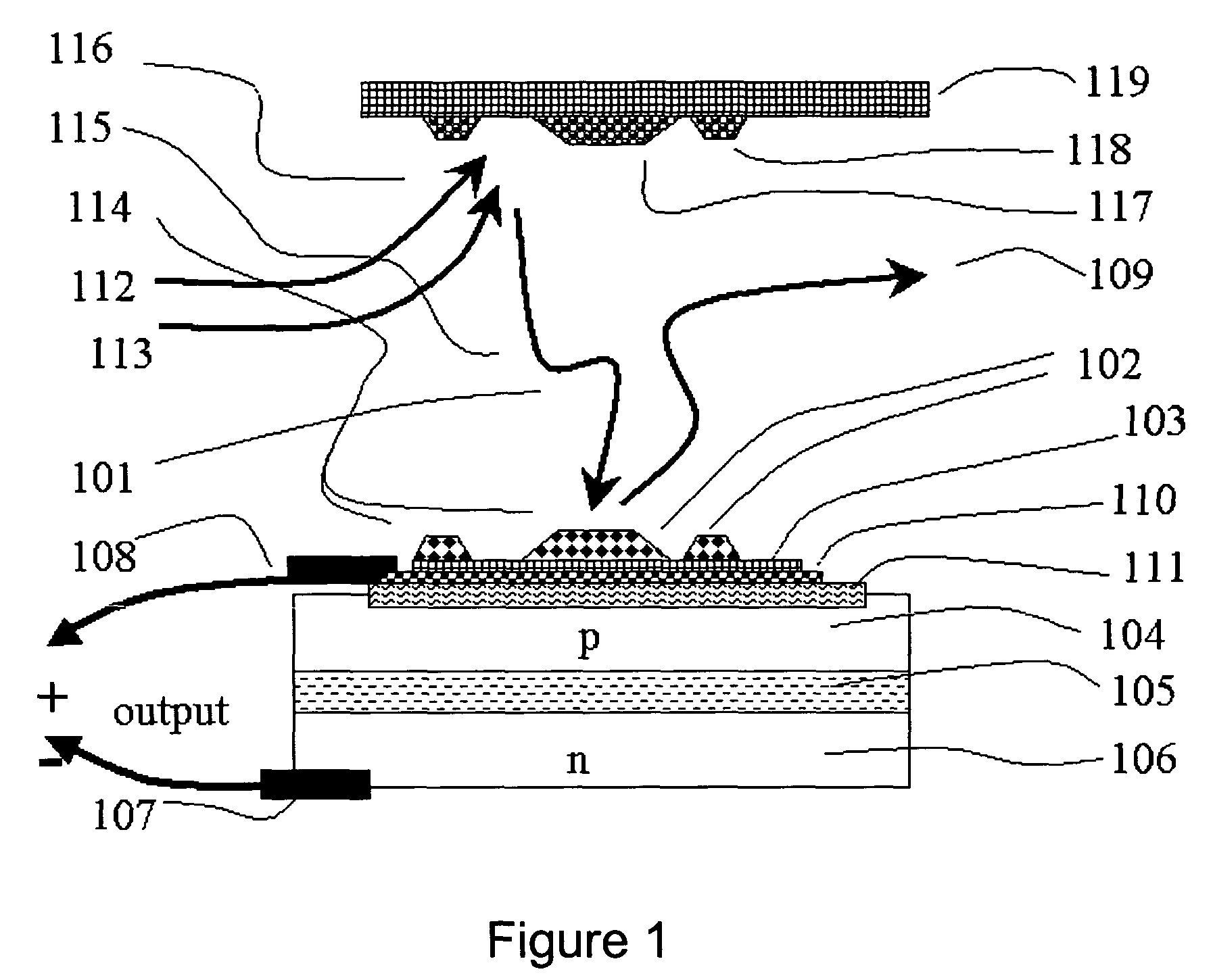
Gas specie electron-jump chemical energy converter
InactiveUS20050189011A1Thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesChemical reactionElectrical conductor
An apparatus and method for extracting energy is provided. In one aspect the method includes using chemical reactions to generate vibrationally excited molecules, such as high-quantum-number-vibrationally-excited gas molecules in a region. The vibration energy in the vibrationally excited molecules is converted into hot electrons when the excited molecules contact a conductor. A geometry is provided so that the excited molecules may travel, diffuse or wander into a conductor before loosing a useful fraction of the vibrational energy. Optionally, the generating and the converting process may be thermally separated, at least in part. The short lived hot electrons are converted into longer lived entities such as carriers and potentials in a semiconductor, where the energy is converted into a useful form.
Owner:NEOKISMET L L C
Double-wavelength single receiving channel-based rotation Raman temperature measurement laser radar
ActiveCN105182365AReduce the difficulty of adjustmentAvoid job performance varianceElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationAtmospheric temperatureRaman lidar
The invention discloses a double-wavelength single receiving channel-based rotation Raman temperature measurement laser radar. The laser radar is based on two working wavelengths and a single receiving channel. The two working wavelengths of the laser radar are respectively composed of odd number pulses and even number pulses. The low-quantum-number rotation Raman signals of one working wavelength and the high-quantum-number rotation Raman signals of the other working wavelength are extracted by the receiving channel of the laser radar. The laser radar is operated alternately at the two working wavelengths in the time division multiplexing manner. The atmospheric temperature is calculated based on the ratio of high-quantum-number rotation Raman signals to low-quantum-number rotation Raman signals. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the rotation Raman temperature measurement is realized only by means of a single filter, a single detector and a single acquisition card. Compared with a single-wavelength double receiving channel-based rotation Raman temperature measurement laser radar, the above laser radar is compact in structure, wherein the difficulty of optical path adjustment and the difficulty of system parameter calibration are lowered. Meanwhile, the double-wavelength single receiving channel-based rotation Raman temperature measurement laser radar is low in cost. The working performance difference between the filter and the detector caused by the inconsistence of working environments can be avoided. Moreover, the detection accuracy, the system stability and the environmental adaptability are improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Gas specie electron-jump chemical energy converter
InactiveUS7119272B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectElectrical conductorChemical reaction
An apparatus and method for extracting energy is provided. In one aspect the method includes using chemical reactions to generate vibrationally excited molecules, such as high-quantum-number-vibrationally-excited gas molecules in a region. The vibration energy in the vibrationally excited molecules is converted into hot electrons when the excited molecules contact a conductor. A geometry is provided so that the excited molecules may travel, diffuse or wander into a conductor before loosing a useful fraction of the vibrational energy. Optionally, the generating and the converting process may be thermally separated, at least in part. The short lived hot electrons are converted into longer lived entities such as carriers and potentials in a semiconductor, where the energy is converted into a useful form.
Owner:NEOKISMET L L C
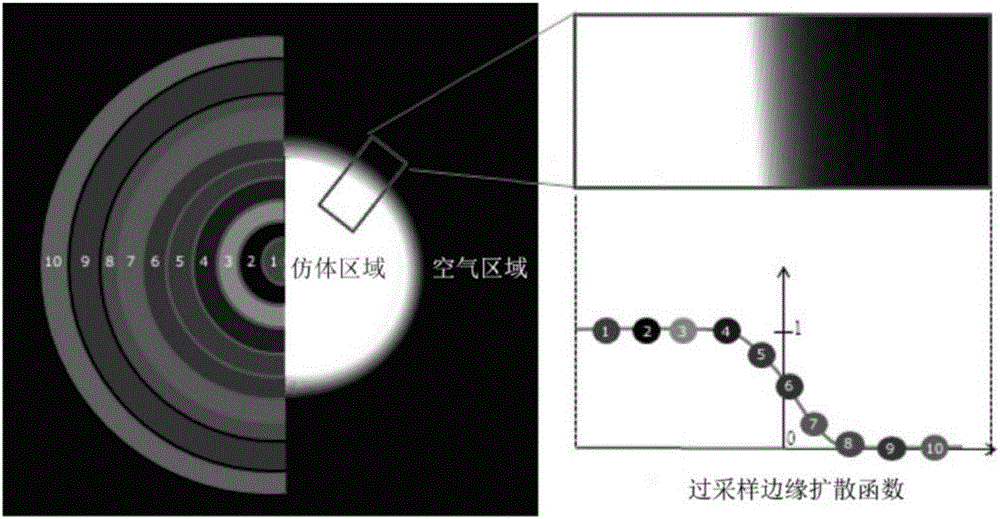
Cone-beam XCT (X-ray computed tomography) imaging quality estimation method under sparse projection
InactiveCN106725565AAccurate measurementAddressing Fundamental Issues in Imaging Quality AssessmentImage enhancementImage analysisNoise power spectrumDiffusion function
The invention discloses a cone-beam XCT (X-ray computed tomography) imaging quality estimation method under sparse projection; the method which estimates imaging system quality after a reconstructed three-dimensional image of a simulated body is obtained comprises: selecting a plurality of three-dimensional reconstruction result sections, overlapping and averaging the three-dimensional reconstruction result sections along z-axis direction to obtain an image in a polar coordinate system; performing threshold segmentation, recognizing a target area, and determining the center of the target area by centroid method; setting oversampling pixel size, subjecting pixels in various concentric circle ranges in the image in the polar coordinate system to pixel value averaging, ranking according to distances off the center of circle so as to obtain an oversampling edge spread function (ESF) curve; solving a modulation transfer function; calculating a two-dimensional noise power spectrum of a cone-beam XCT imaging system to obtain a one-dimensional noise power spectrum, and calculating a noise equivalent quantum number NEQ.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Single-mode emission orbital angular momentum (OAM) laser
ActiveCN108054633ALower threshold currentReduce volumeLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingMicro column
The invention relates to the technical field of a semiconductor laser, and proposes a single-mode emission orbital angular momentum (OAM) laser. A cavity body of a resonant cavity of the laser is of amicro column, micro ring or micro disc structure for supporting an echo wall mode, a grating or defect is etched on an outer side surface of the cavity body of the laser, the echo wall mode with special angular quantum number can be selected as a hot shot mode of the laser, the selected mode is vertically scattered and output by a top grating, the output is a travelling wave mode with a vortex phase, namely an OAM mode, the top grating is arranged at a position, near to an outer side edge of a micro column, of a grating layer and comprises a real part and a virtual part, the real part and thevirtual part comprise two groups of gratings and are used for respectively modulating effective reflectivity of the mode, so that scattering output of the travelling wave mode is formed. The laser issmall in cavity volume and low in loss, and thus, ultrahigh-speed modulation can be achieved. The semiconductor laser has the characteristics of small volume, single-mode working and low threshold current, and is convenient to detect, a two-dimensional array is easy to integrate, output light is easy to couple to optical fiber, and various advantages can be achieved on different material systems.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
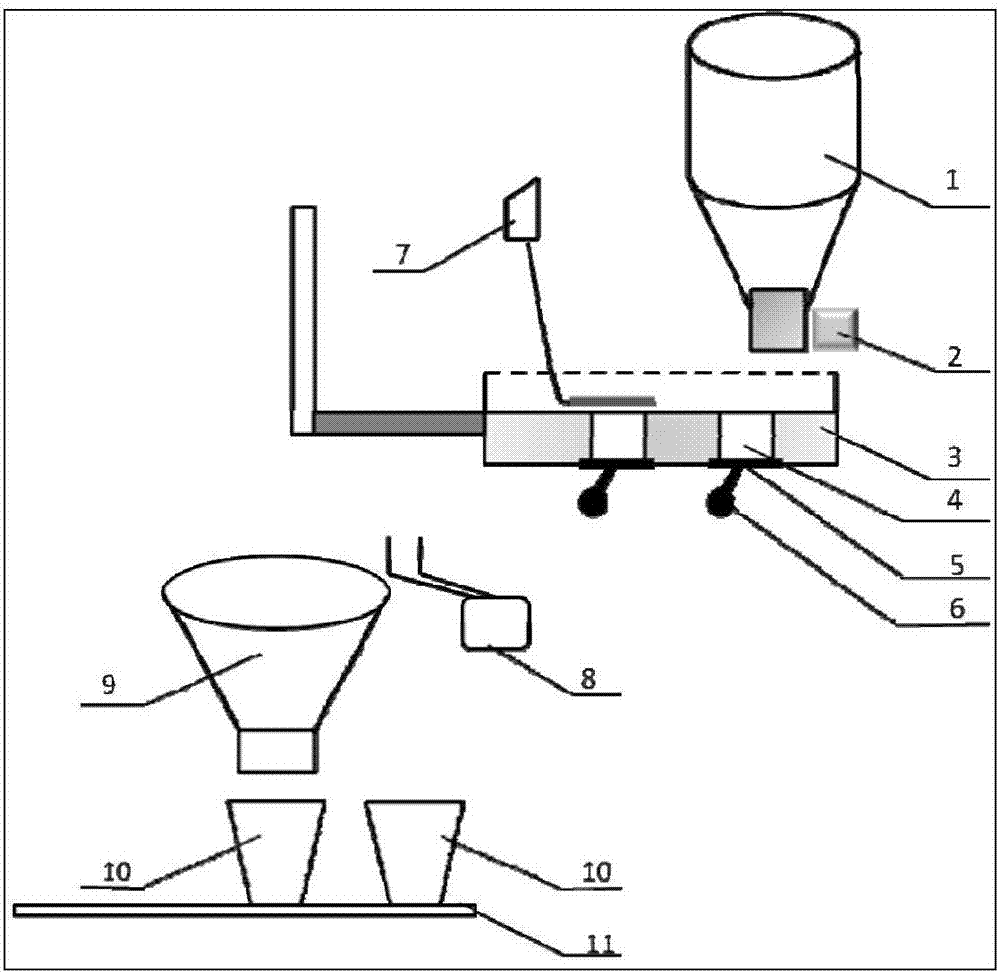
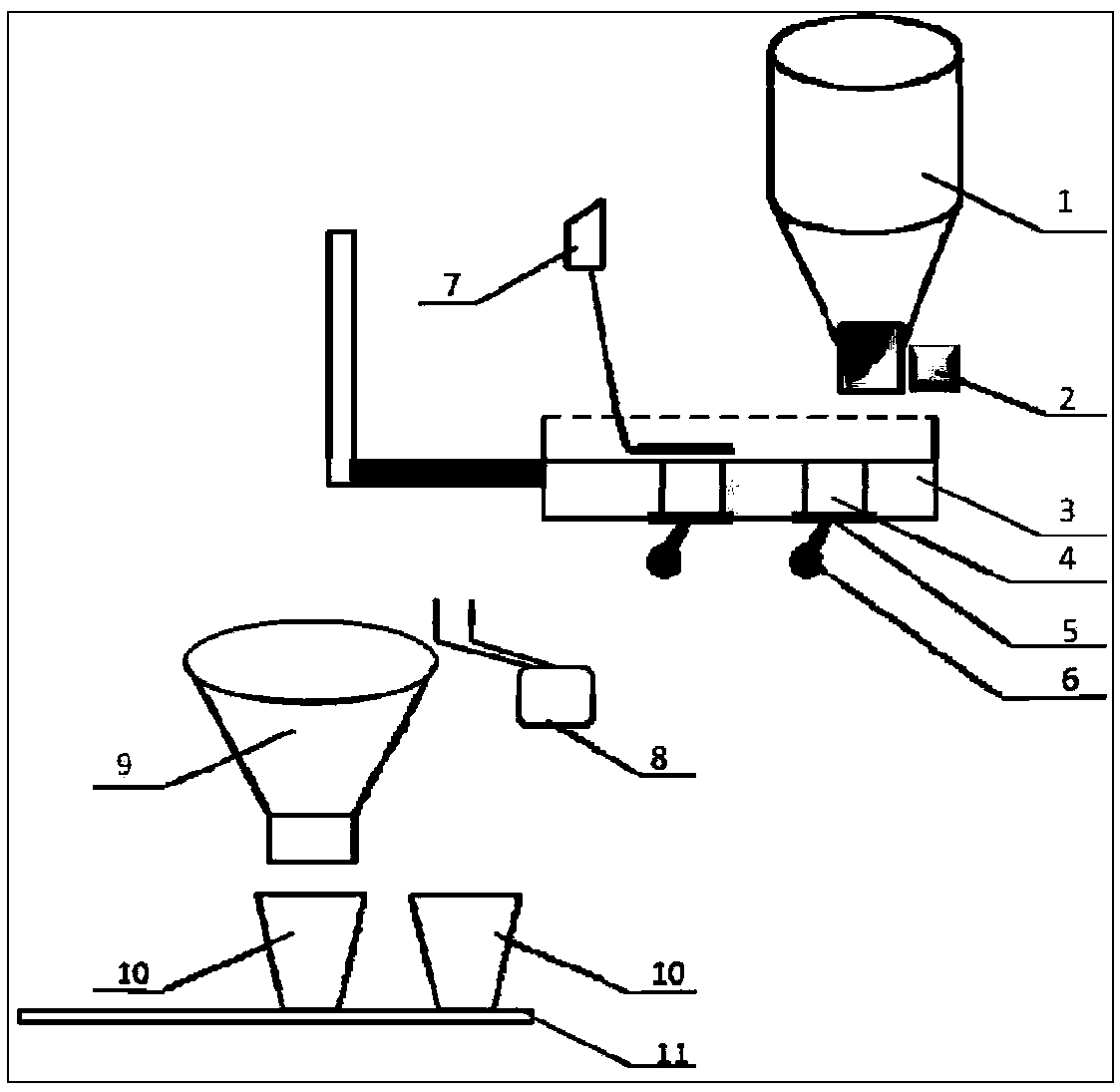
Chinese medicinal granule feeding device and application thereof
ActiveCN106976574ASimple structureEasy to operatePackaging automatic controlSolid materialControl systemEngineering
The invention provides a Chinese medicinal granule feeding device. The Chinese medicinal granule feeding device is composed of a material storage tank, a microfeeder, a metering panel, metering cylinders, bottom sealing plates, touch handles, a discharging brush, a tough key, a material collecting pipe, material receiving boxes and a flow guide rail. The entire device is connected with a control system for use. According to the Chinese medicinal granule feeding device, a metering method of materials achieves quantization, the metering range of all the dosages is divided according to the integral multiples of the minimum dosage, a special counter is designed for the quantum number N conversion dosage, the multielement metering cylinders in the metering panel are combined, broad-spectrum adjustable granule automation feeding is achieved, and the feeding device can be used for intelligent compatibility of Chinese medicinal granules. The Chinese medicinal granule feeding device is simple in structure, low in preparation cost, convenient to operate, stable in operation, capable of meeting the requirements in measuring accuracy, and suitable for industrial application and popularization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
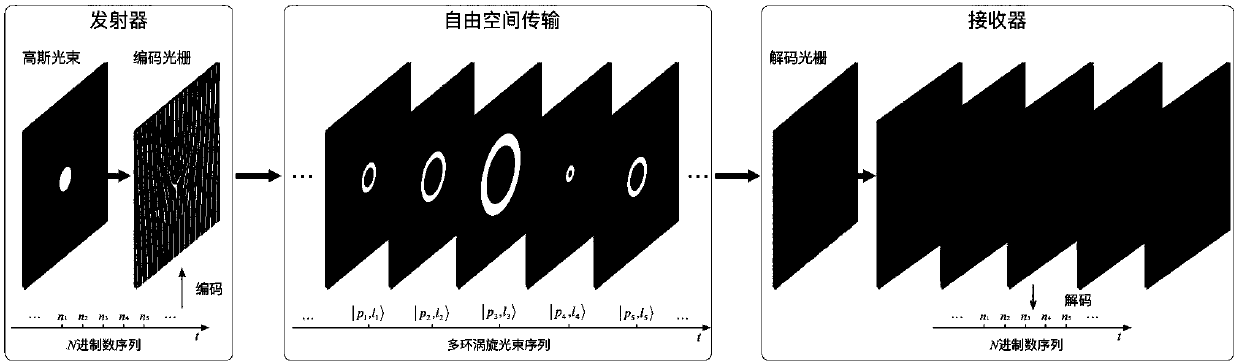
High-dimensional digital signal coding and decoding method and system based on multicyclic vortex beam
ActiveCN108667518AImprove coding efficiencySimple structureDiffraction gratingsElectromagnetic receiversDecoding methodsAngular momentum
The invention discloses a high-dimensional digital signal coding and decoding method and a high-dimensional digital signal coding and decoding system based on a multicyclic vortex beam. According to the method and system provided by the invention, two mutually independent dimensions, the orbital angular momentum and the radial quantum number of the multicyclic vortex beam simultaneously serve as coding features for performing high-dimensional coding of a digital signal, so that the coding efficiency is further enhanced under the condition of using the limited orbital angular momentum. In addition, according to the method and system provided by the invention, both the coding and decoding of the digital signal based on the multicyclic vortex beam can be achieved via a diffraction grating, the system is simple in structure and easy to control, and has relatively large progress compared with the prior art.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Wireless communication encryption method based on angular momentums
InactiveCN106899970AEnsure secure transmissionAchieve securityError preventionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesSpin angular momentum of lightComputer hardware
The invention relates to a wireless communication encryption method based on angular momentums. According to wireless spin angular momentum and orbital angular momentum channel parameter characteristics, cross-layer password negotiation is realized by utilizing the difference due to the randomness and the independence of the spin angular momentum in different polarization or polarization states, the orbital angular momentum in different characteristic quantum numbers, signal strength indication and the bit error rate, so that an expected user and an eavesdropper receive not exactly same password packets in a password negotiation stage; therefore, the eavesdropper cannot obtain a password among normal communication users; and thus, the purpose of ensuring security data transmission is achieved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
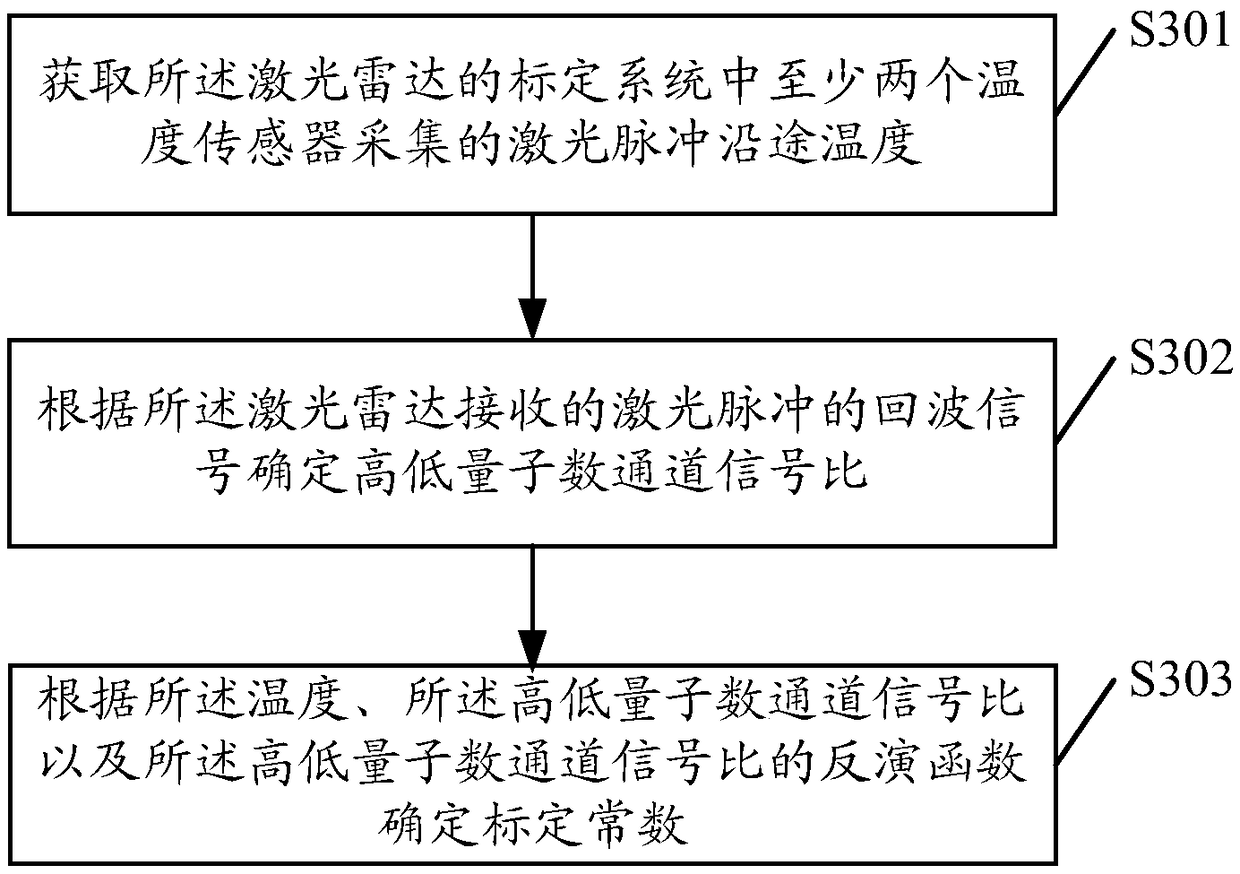
Laser radar calibration system and method
PendingCN108828565AImprove accuracyNo position shiftWave based measurement systemsTwo temperatureTemperature difference
The invention discloses a laser radar calibration system. The calibration system comprises a laser radar, a calibration cavity, a heating cavity and at least two temperature sensors; the heater is located inside the calibration cavity; the laser radar is located outside the calibration cavity and is used for emitting laser pulses to the calibration cavity; the laser pulses can pass through the calibration cavity so as to be transmitted outside; the temperature sensors are disposed inside and outside the calibration cavity and are used for collecting the temperature of the laser pulses along the transmission path of the laser pulses; and the laser radar is also used for receiving echo signals corresponding to the laser pulses, so that the ratio of the signals of a high-quantum number channel to the signals of a low-quantum number channel can be determined according to the echo signals, and therefore, the calibration of the laser radar is realized according to the temperature and the ratio of the signals of the high-quantum number channel to the signals of the low-quantum number channel. According to the laser radar calibration system of the invention, temperature difference can be generated artificially through the heater, and therefore, a large temperature gradient can be obtained; and calibration is performed along a horizontal direction, positional deviation will not be generated, and therefore, the accuracy of a calibration result can be further improved. The present invention also discloses a calibration method.
Owner:北京聚恒博联科技有限公司
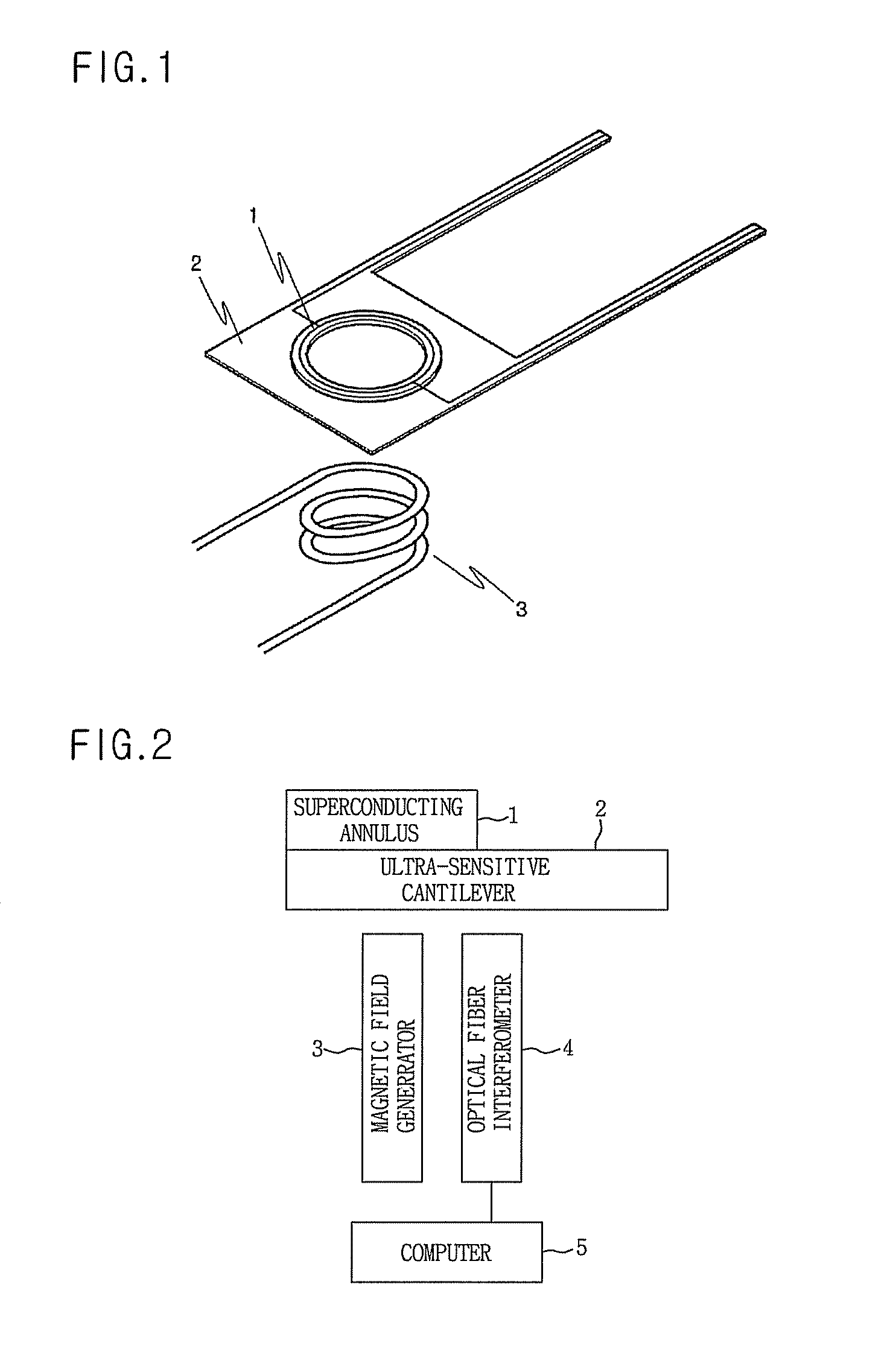
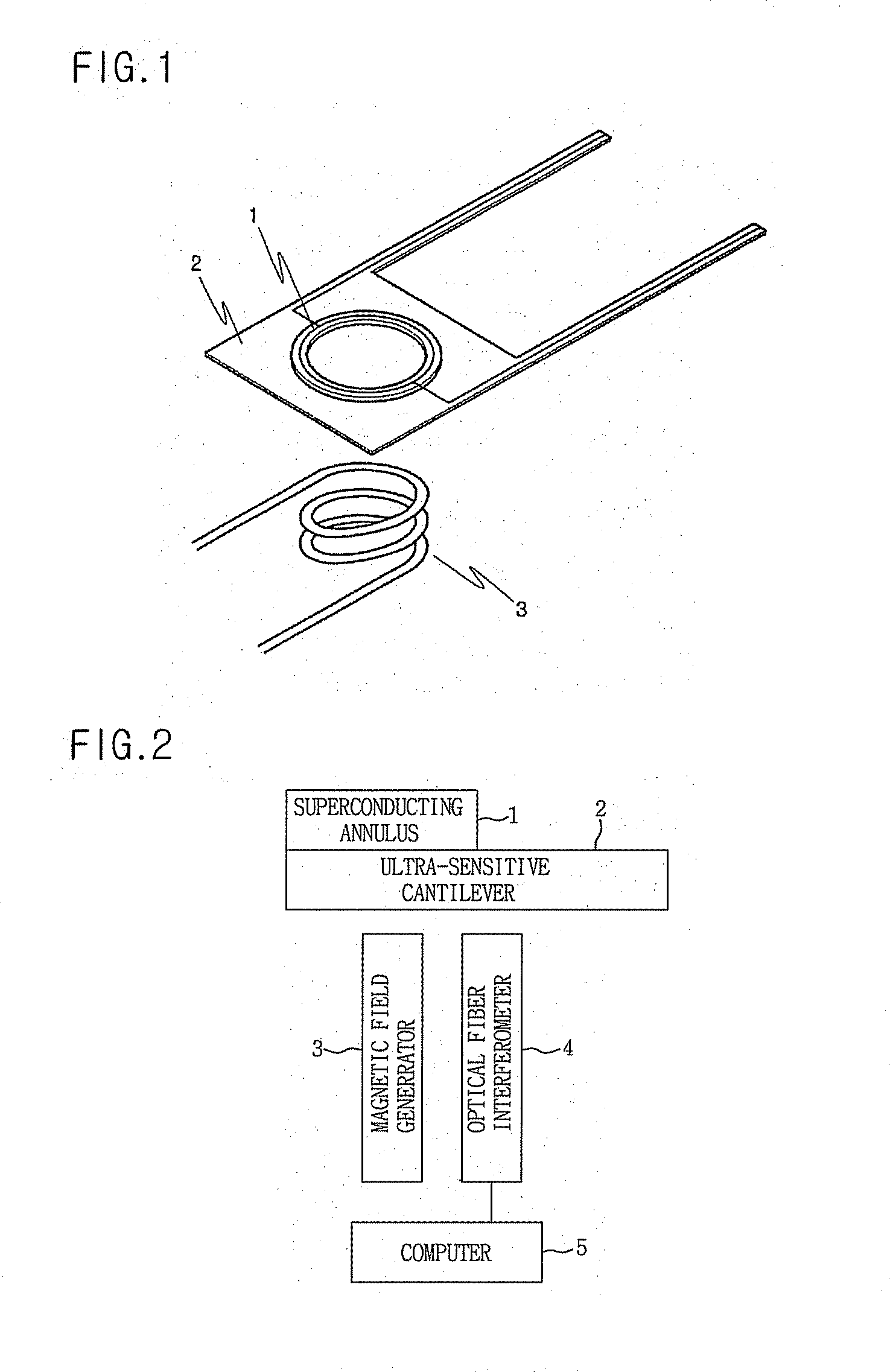
Quantum-based force realization apparatus and force measurer using the same
InactiveUS8033184B2Dissimilar materials junction devicesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementCantileverUltra sensitive
Disclosed herein are a force realization apparatus using a superconducting flux quantum, which is capable of generating force proportional to a flux quantum number by including a micron-sized superconducting annulus or superconducting quantum interference device in an ultra-sensitive cantilever, and a force measurer using the same.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Method and device for testing hyperfine structure energy level of hydrogen atom
InactiveCN102928080AReduce manufacturing costEasy to getRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationHigh energyData acquisition
The invention discloses a method for testing the hyperfine structure energy level of a hydrogen atom and a device for displaying the hyperfine structure energy level of the hydrogen atom. The device is suitable for the experiment research and teaching of a quantum physics specialty and used for testing and displaying the hyperfine structure energy level of the hydrogen atom. Pure hydrogen is ionized and then dissociated into the hydrogen atoms according to a quantum mechanics principle; each generated ground-state hydrogen atom is in four hyperfine structure energy states, namely |F=1, mF=+1)|F=1, mF=0)(high energy state) and |F=1, mF=-1)|F=0, mF=0)(low energy state), wherein F is the angular quantum number of the ground-state hydrogen atoms, and mF is a magnetic quantum number. The device is manufactured on the basis of a principle that the hydrogen atoms in the high energy states are focused towards a center and the hydrogen atoms in the lower energy states are deflected towards an edge after the ground-state hydrogen atoms pass through a magnetic field with a certain gradient and comprises a hydrogen source system, an ionization system, a tiny drainage hole collimator, a deflection magnet, an imaging target, a vacuum system, a distance adjusting device, a support frame, data acquisition and analysis software, and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Tera-hertz and infrared frequency band laser light source
InactiveCN102237635AEnhanced internal quantum conversion efficiencyGood monochromaticityLaser optical resonator constructionLaser active region structureLaser lightElectromagnetic field
The invention discloses a tera-hertz and infrared frequency band laser light source, which comprises a planar metal structure layer, a semiconductor active layer and a metal bottom plate layer, wherein the metal bottom plate layer is a support layer; the semiconductor active layer and the planar metal structure layer are overlapped on the metal bottom plate layer in sequence to form a coherent surface state; and the planar metal structure layer consists of one-dimensional or two-dimensional periodically-arranged metal units or metal gratings with concentric ring structures. The coherent surface state is coupled with external plane waves through a metal gap of the planar metal structure layer and is radiated to a free space, and the ratio of the metal gap of the planar metal structure layer to a unit cycle length is in an inverse relation with a coupling coefficient, so that the electromagnetic field intensity of the semiconductor active layer is amplified, and quantum number reversion is realized to generate lasing. The laser light source disclosed by the invention has a wide frequency band, high light power and a simple structure and is convenient to manufacture.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
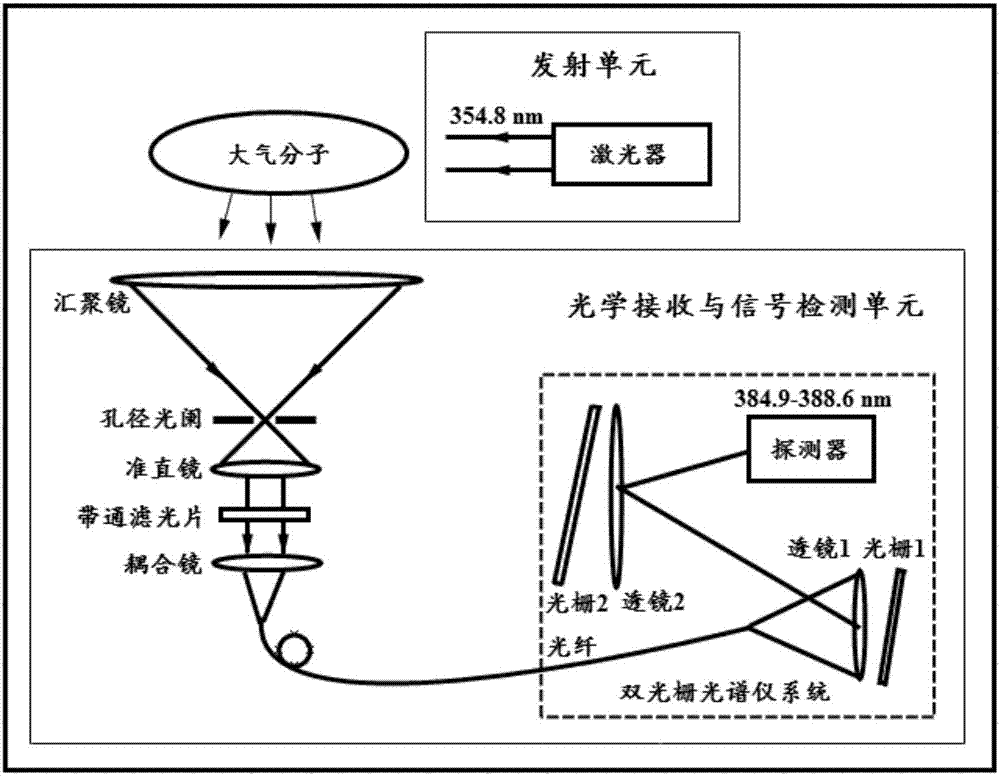
Measuring system of N2 molecule vibration-rotation Raman spectrum
ActiveCN105928922AAppropriate rangeAppropriate spectral resolving powerRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringGratingLinear dispersion
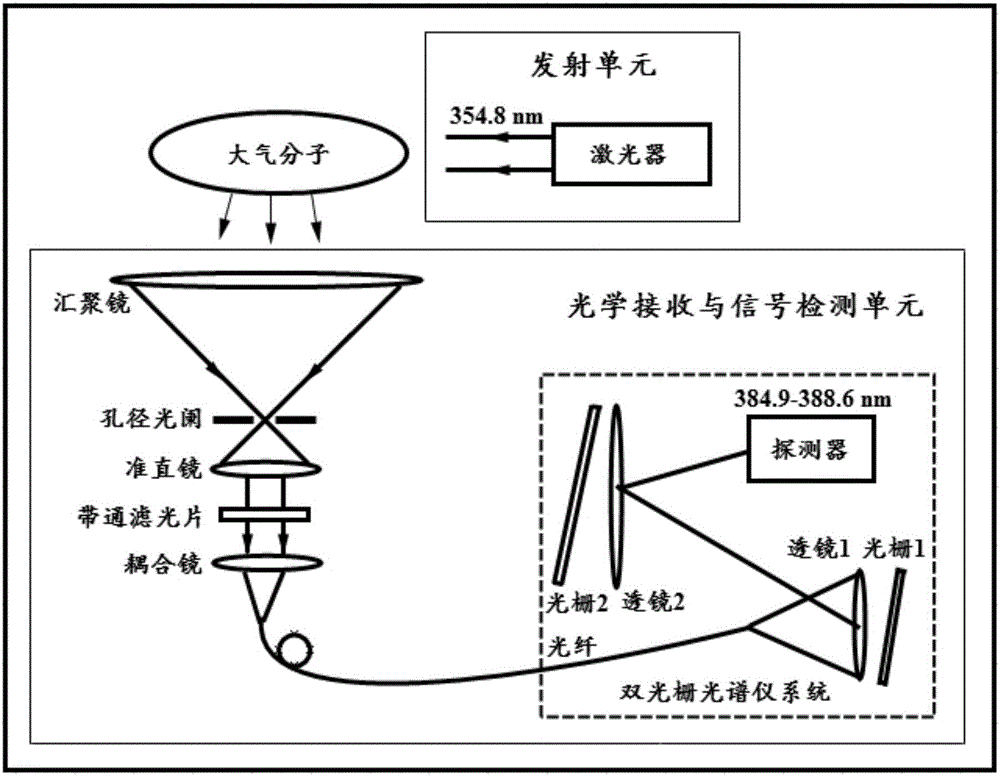
The invention discloses a measuring system of N2 molecule vibration-rotation Raman spectrum. The system comprises an emission unit and an optics reception and signal detection unit. The emission unit irradiates the atmospheric molecules by using the ultraviolet laser with extremely narrow linewidth of 354.8 nm outputted by a seed-injected solid-state laser. The optics reception and signal detection unit collects the signal of the vibration-rotation Raman spectrum produced by the N2 molecule, uses a double grating dispersion system to disperse the light in a range of 384.9-388.6 nm in space with a linear dispersion of 8.3 mm / nm, uses a linear array detector having 32 channels to distinguish and record discrete spectral line signals of O branch (rotation quantum number J=16-2) and S branch (rotation quantum number J=0-14) of N2 molecule vibration-rotation Raman spectrum, and produces inhibition better than 13 order of magnitude for the light near 354.8 nm. The system realizes the distinction and record of N2 molecule Stokes vibration-rotation Raman spectrum, and can obtain temperature information.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
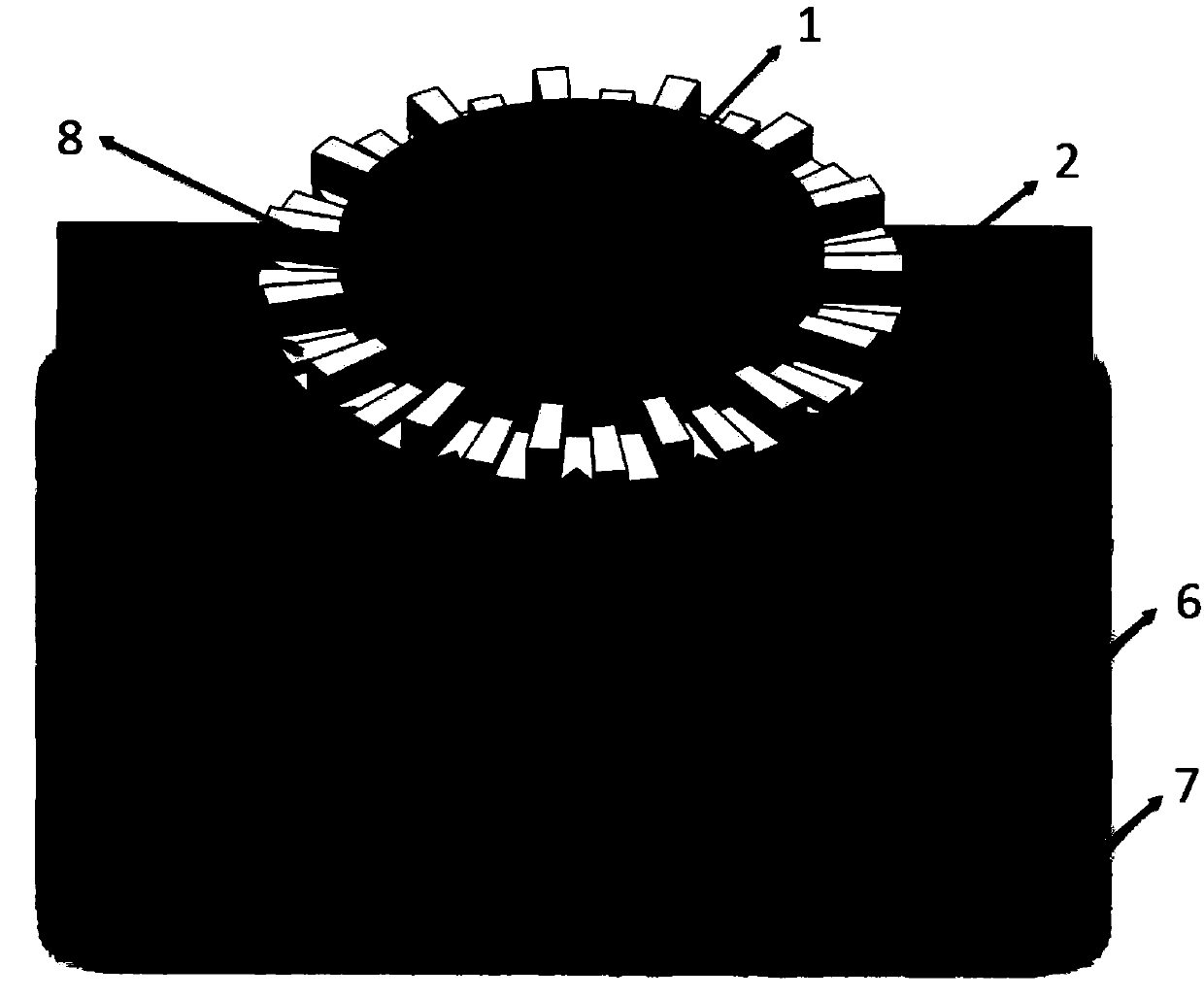
Device and method for generating controllable vortex electron beam
ActiveCN107919258AControllable quantum numberAdjust the magnetic field strengthElectric discharge tubesAngular momentumMagnetic monopole
The invention discloses a TEM based device for generating a controllable vortex electron beam. The device is characterized by comprising an electron gun for generating a planar electron beam, a magnetic field controller, and a magnetic needle wound by a conductive coil; the magnetic needle is arranged on a planar electron beam channel via a chip controlled by electrical equipment; the magnetic field controller generates an intensity controllable magnetic field; and the magnetic field is used to modulate the phase of the planar electron beam. The invention also discloses a method for generatingthe controllable vortex electron beam via the device. The device can form magnetic field distribution similar to magnetic monopole in an electronic microscope, so that the vortex electron beam with single track angular momentum and controllable quantum number is obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
All-optical fiber light splitting system based on sampled fiber Bragg grating
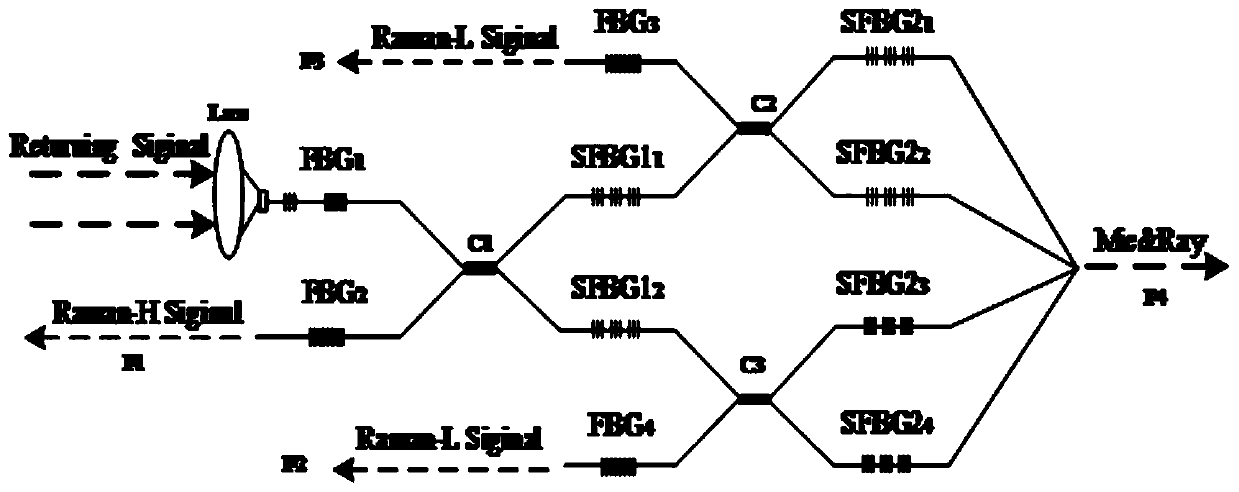
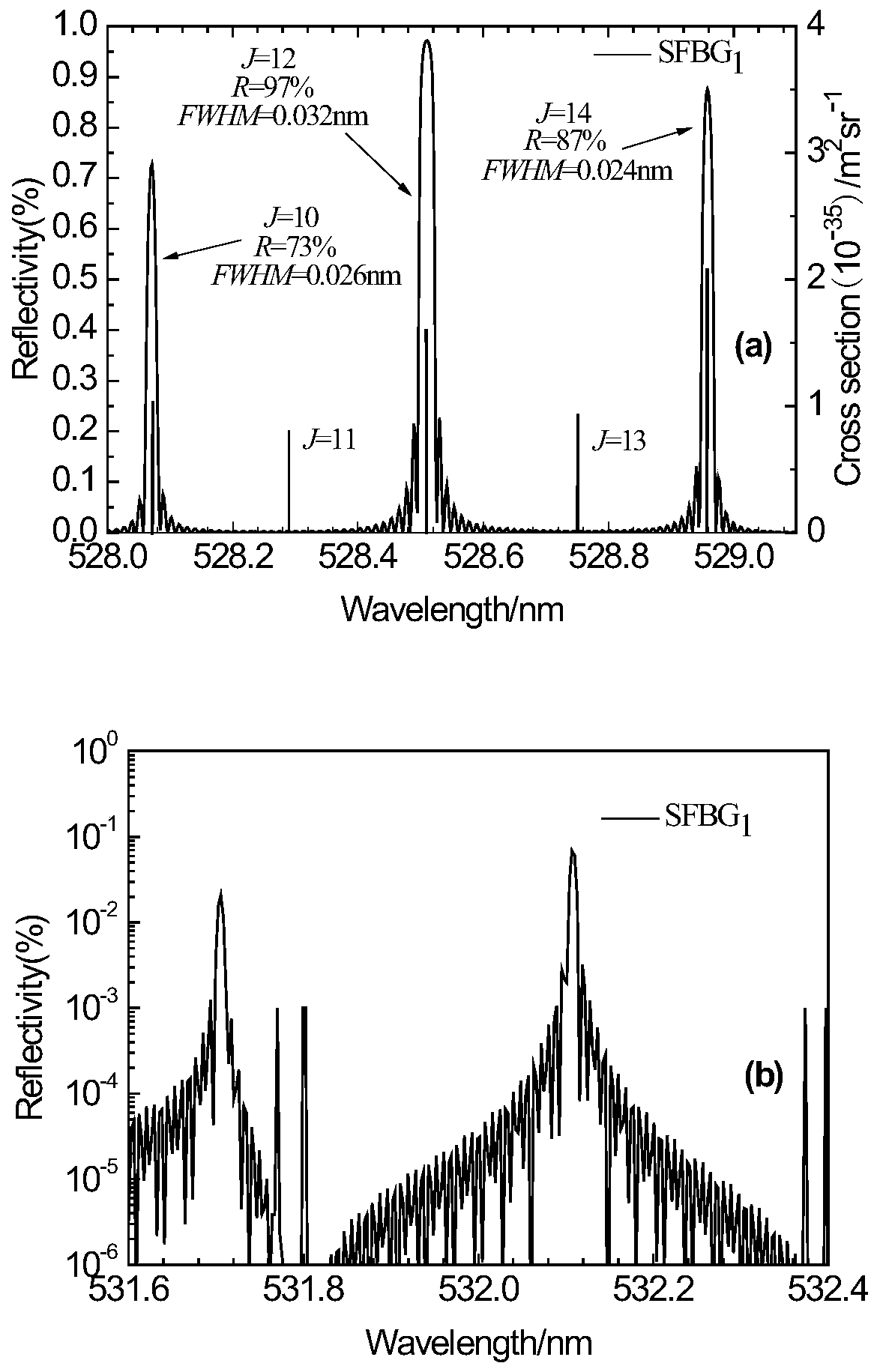
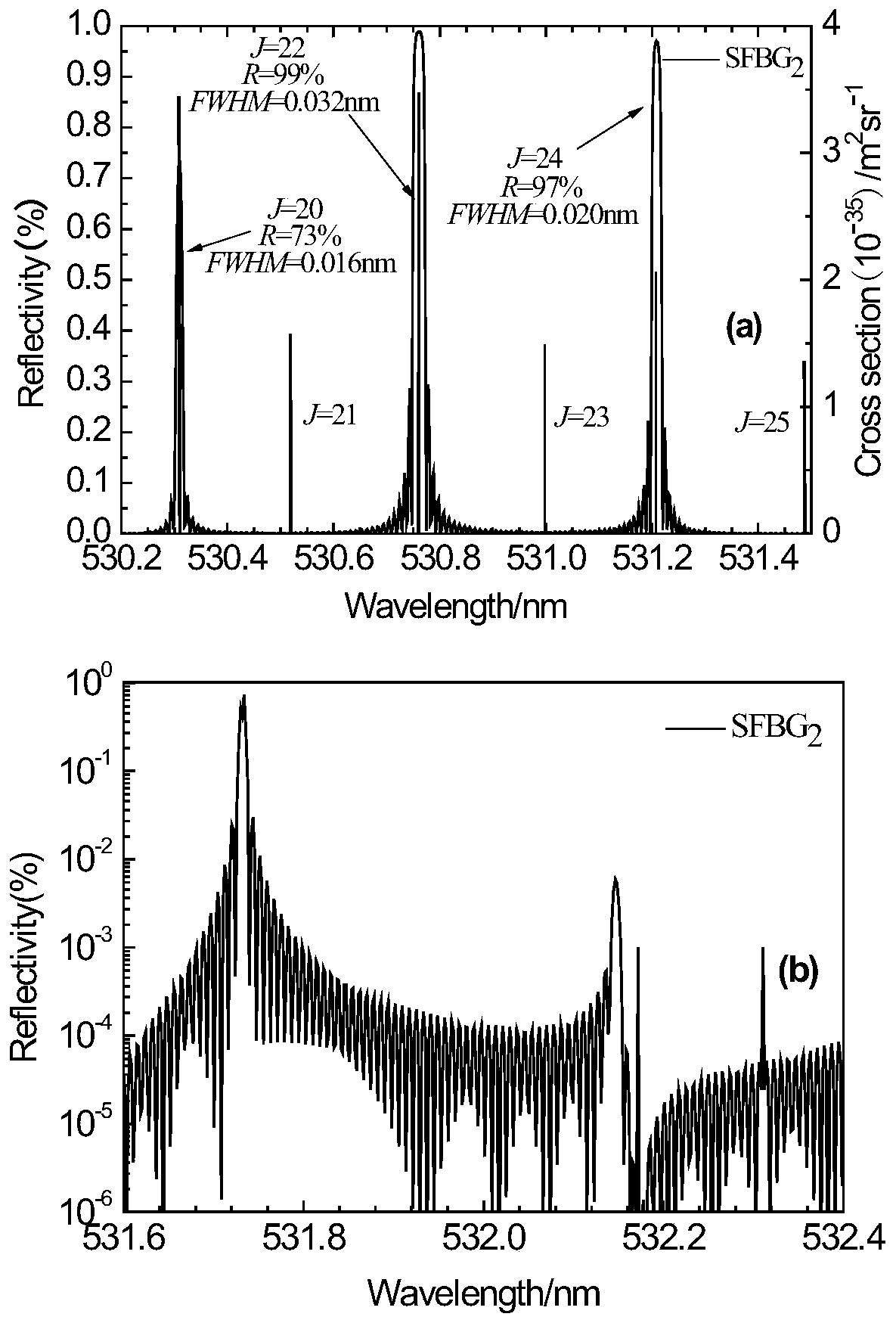
PendingCN110187326ASolve complexitySolution volumeThermometers using physical/chemical changesElectromagnetic wave reradiationFiberGrating
The invention provides an all-optical fiber light splitting system based on a sampled fiber Bragg grating. The all-optical fiber light splitting system comprises a lens, a first fiber Bragg grating, asecond fiber Bragg grating, a third fiber Bragg grating, a fourth fiber Bragg grating, a first superstructure fiber Bragg grating, a second superstructure fiber Bragg grating, a first coupler, a second coupler and a third coupler, wherein the first superstructure fiber Bragg grating, the second superstructure fiber Bragg grating, the first fiber Bragg grating, the second fiber Bragg grating, thethird fiber Bragg grating and the fourth fiber Bragg grating are in multi-stage cascade. According to the all-optical fiber light splitting system based on the sampled fiber Bragg grating provided bythe invention, when rotational Raman scattering high and low quantum numbers are obtained, the signal-to-noise ratio needs to be improved through twice reflection, the requirement for performance parameters of a visible light waveband fiber Bragg grating is greatly reduced, so that the processing of a feature signal by a subsequent system is facilitated, background noises can be well filtered out,and the problems of complex light splitting systems, large size and poor spectral light splitting stability are effectively solved.
Owner:BEIFANG UNIV OF NATITIES
Real-time quantum communication method
InactiveCN108306691AInstant Messaging SolutionPhotonic quantum communicationBeam splittingSignal generator
The invention discloses a real-time quantum communication method. The real-time quantum communication method comprises the following steps that a communication medium is prepared, a large quantity ofquanta such as photons, electrons and neutrons are divided into two parts through a beam splitting device, the two parts are injected into a storage device separately, one part is saved by a signal generator, and the other part is saved by a signal receiver; 2, the signal receiver moves to any place; 3, when a signal sender sends a signal, the signal sender converts a code of the signal into the characteristic changes such as the quantum number, the quantum energy and the quantum polarization direction of the part of the quantum state; and 4, the signal receiver monitors the changes of the overall quantum state in real time and converts the signal according to a pre-agreed protocol. The real-time quantum communication method has the advantage that a real-time communication scheme which truly does not need a channel is achieved. The real-time quantum communication method can achieve huge application by means of the three characteristics that communication cannot be tapped or intervenedand does not need time.
Owner:邓晓波
Manufacturing method of muon hydrogen atom type high-frequency laser
InactiveCN106207740AImproved energy level structureHigh energyWave amplification devicesWavelengthQuantum number
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a muon hydrogen atom type high-frequency laser. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of: colliding hydrogen atoms by using a muon beams to ensure that electronic around the hydrogen atoms are ionized by the muons and captured by the hydrogen atoms so as to generate muon hydrogen atoms; obtaining an energy level structure of the muon hydrogen atoms through a Schrodinger equation for solving the muon hydrogen atoms; taking a carbon monoxide laser with a wave length of 5.8 microns as a pump laser to realize the overturning of amount of the muons on a 2p excited state; and enabling the muons located at a 2p energy level to jump to a 1s energy level (muons at the 2p energy level jumps to the 1s energy level to carry out spontaneous radiation jump), so as to generate 1.9 Kev of high-frequency X waveband laser. According to the manufacturing method disclosed by the invention, a working substance which is likely to generate X waveband lasers is disclosed through theoretical analysis, and a feasible working principle is disclosed; under the condition that the main quantum number is smaller than 30, the energy level life of the muon hydrogen atoms is much shorter than the life of the muons; and a proper energy level structure is searched in the part with an energy level smaller than 30, so that X waveband light is generated.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Quantum-based force realization apparatus and force measurer using the same
InactiveUS20080047367A1Uniform levelDissimilar materials junction devicesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementMagnetic field gradientUltra sensitive
Disclosed herein are a force realization apparatus using a superconducting flux quantum, which is capable of generating force proportional to a flux quantum number by including a micron-sized superconducting annulus or superconducting quantum interference device in an ultra-sensitive cantilever, and a force measurer using the same. The quantum-based force realization apparatus includes: superconducting quantum trap means having a magnetic moment proportional to a flux quantum number; an ultra-sensitive cantilever which mounts therein the superconducting quantum trap means, has elasticity and is displaced by force generated by the superconducting quantum trap means located in a magnetic field gradient; and a magnetic field generator which applies a magnetic field to the superconducting quantum trap means.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
a n 2 Measurement System of Molecular Vibrational Raman Spectroscopy
ActiveCN105928922BGuaranteed normal transmissionEasy to detectRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringGratingLinear dispersion
The invention discloses a measuring system of N2 molecule vibration-rotation Raman spectrum. The system comprises an emission unit and an optics reception and signal detection unit. The emission unit irradiates the atmospheric molecules by using the ultraviolet laser with extremely narrow linewidth of 354.8 nm outputted by a seed-injected solid-state laser. The optics reception and signal detection unit collects the signal of the vibration-rotation Raman spectrum produced by the N2 molecule, uses a double grating dispersion system to disperse the light in a range of 384.9-388.6 nm in space with a linear dispersion of 8.3 mm / nm, uses a linear array detector having 32 channels to distinguish and record discrete spectral line signals of O branch (rotation quantum number J=16-2) and S branch (rotation quantum number J=0-14) of N2 molecule vibration-rotation Raman spectrum, and produces inhibition better than 13 order of magnitude for the light near 354.8 nm. The system realizes the distinction and record of N2 molecule Stokes vibration-rotation Raman spectrum, and can obtain temperature information.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A Chinese medicine formula granule feeding device and its application
ActiveCN106976574BSimple structureEasy to operatePackaging automatic controlSolid materialControl systemMedicine
The invention provides a Chinese medicinal granule feeding device. The Chinese medicinal granule feeding device is composed of a material storage tank, a microfeeder, a metering panel, metering cylinders, bottom sealing plates, touch handles, a discharging brush, a tough key, a material collecting pipe, material receiving boxes and a flow guide rail. The entire device is connected with a control system for use. According to the Chinese medicinal granule feeding device, a metering method of materials achieves quantization, the metering range of all the dosages is divided according to the integral multiples of the minimum dosage, a special counter is designed for the quantum number N conversion dosage, the multielement metering cylinders in the metering panel are combined, broad-spectrum adjustable granule automation feeding is achieved, and the feeding device can be used for intelligent compatibility of Chinese medicinal granules. The Chinese medicinal granule feeding device is simple in structure, low in preparation cost, convenient to operate, stable in operation, capable of meeting the requirements in measuring accuracy, and suitable for industrial application and popularization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Micro-alga experiment device
PendingCN108485936ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringBottle
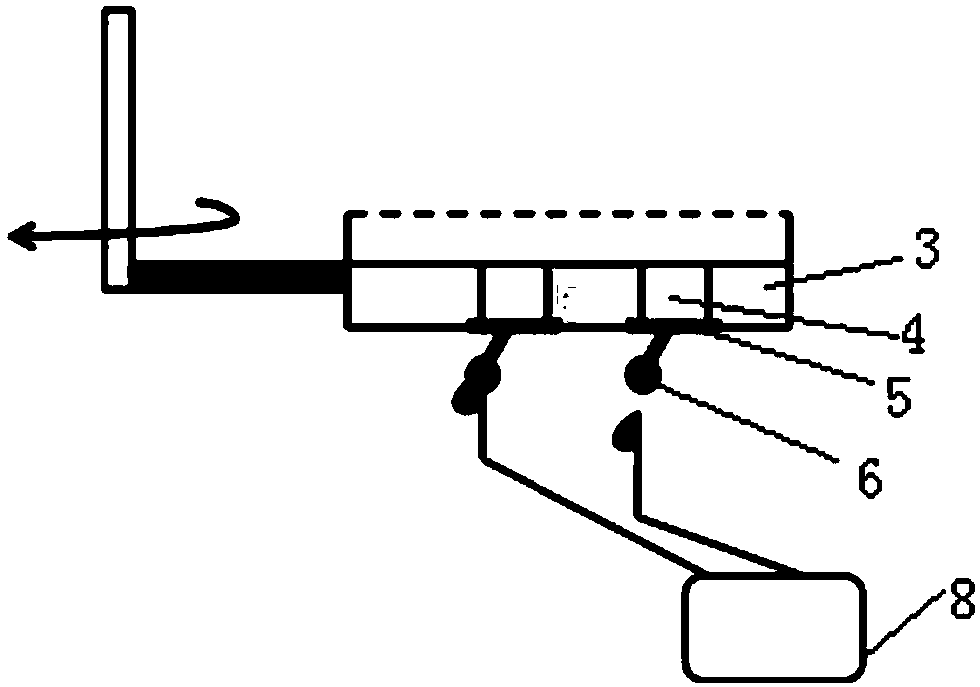
The invention discloses a micro-alga experiment device which comprises a cylinder, a conical bottle and an LED (Light Emitting Diode) lamp plate, wherein both sides of the cylinder are opened; the conical bottle is used for containing micro-algae; the conical bottle is positioned inside the cylindrical cylinder; the bottom of the conical bottle is tangent to the inner wall of the cylinder; the LEDlamp plate is arranged opposite to the opening of the conical bottle; the LED lamp plate is in sealed fixation with the openings of the cylindrical cylinder; the LED lamp plate is used for emitting light into the cylindrical cylinder; the light can be completely reflected inside the cylindrical cylinder. The micro-alga experiment device is a light quantum number controllable micro-alga experimentdevice.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Photon Orbital Angular Momentum Measurement System and Method Based on Wavefront Conversion Method
ActiveCN106289526BGood repeatabilityHigh operating freedomSpectrum investigationSpatial light modulatorQuantum technology
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
Gas specie electron-jump chemical energy converter
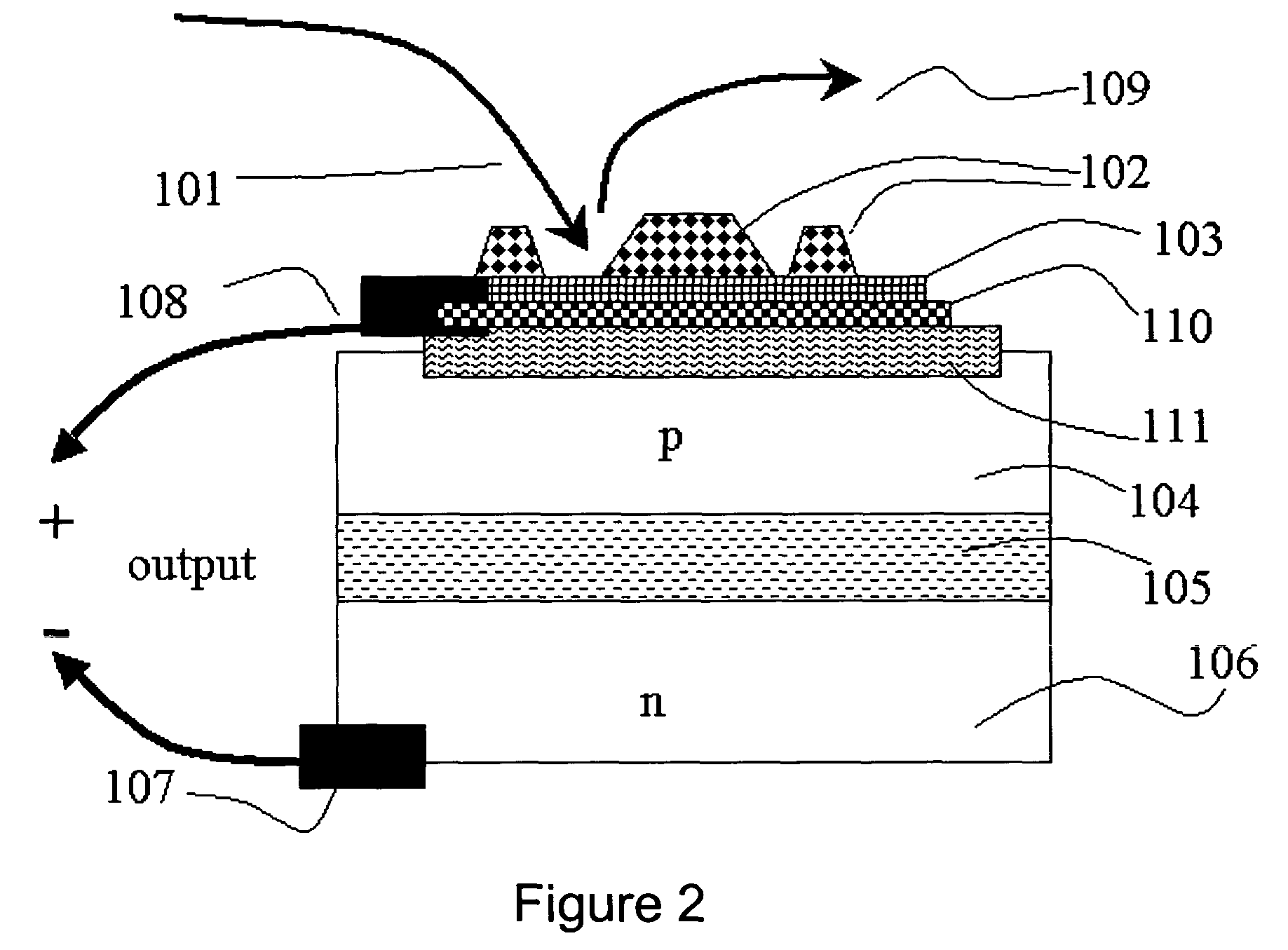
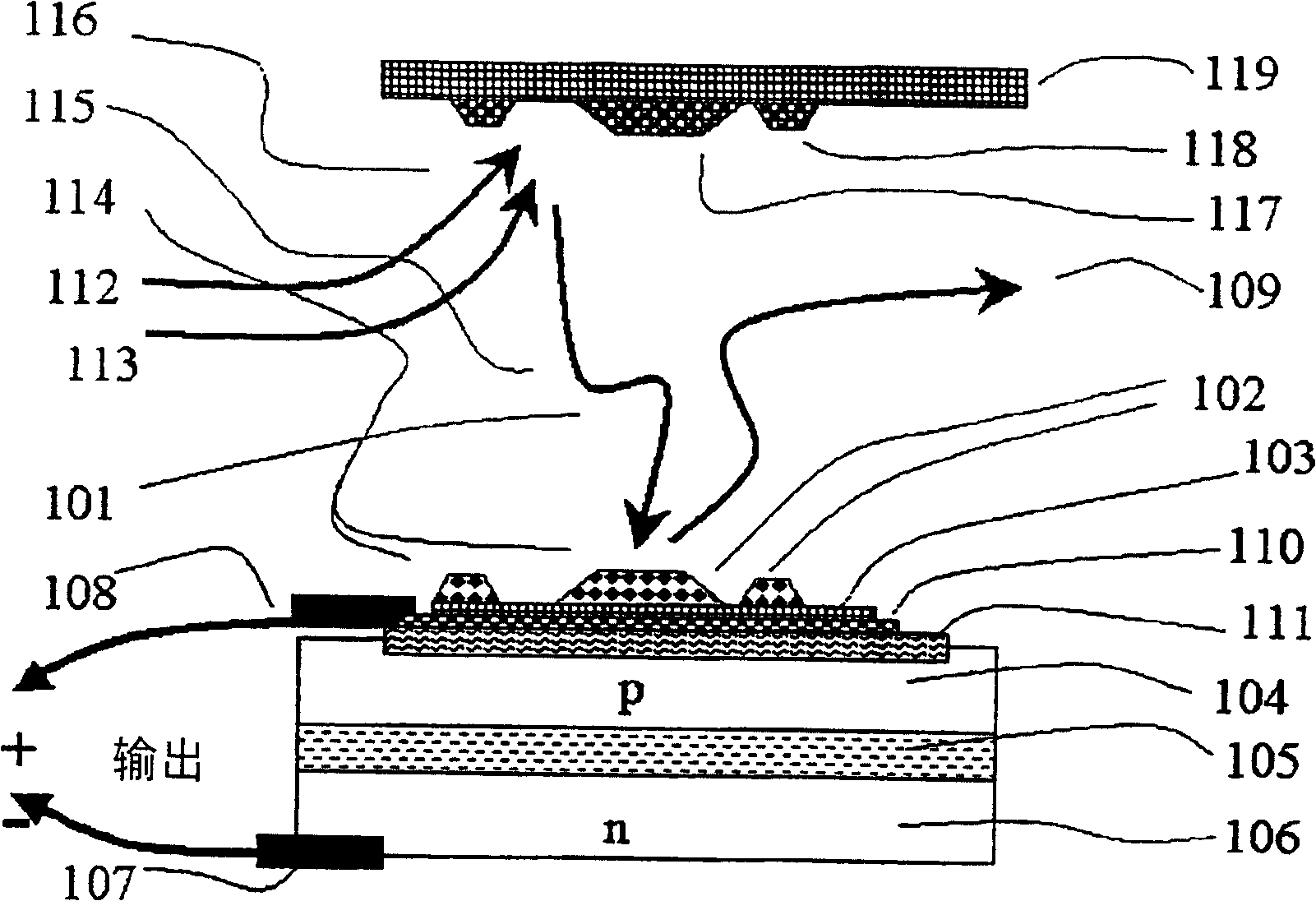
InactiveCN100416862CCombustion-air/fuel-air treatmentSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorChemical reaction
An apparatus and method for extracting energy is provided. In one aspect the method includes using chemical reactions to generate vibrationally excited molecules (101), such as high-quantum-number-vibrationally-excited gas molecules in a region. The vibration energy in the vibrationally excited molecules is converted into hot electrons when the excited molecules contact a conductor (103). A geometry is provided so that the excited molecules may travel, diffuse or wander into a conductor (103) before loosing a useful fraction of the vibrational energy. Optionally, the generating and the converting process may be thermally separated, at least in part. The short lived hot electrons are converted into longer lived entities such as carriers and potentials in a semiconductor, where the energy is converted into a useful form.
Owner:NEOKISMET L L C
A single-mode lasing ring microcavity laser
ActiveCN104993374BStable single mode lasingControl outward radiationLaser optical resonator constructionGratingQuantum
The invention discloses a single-mode lasing ring micro-cavity laser, which comprises: a ring-shaped micro-cavity resonator, and a grating structure is distributed on the inner wall of the ring-shaped micro-cavity resonator. The grating period number of the grating structure is equal to the angular vector quantum number of the single-mode lasing mode of the single-mode lasing ring microcavity laser. The annular microcavity resonator includes an upper confinement layer, an active region and a lower confinement layer. The grating structure is vertically distributed on the inner wall of the ring microcavity resonant cavity. The ring-shaped semiconductor microcavity laser provided by the present invention diffracts light through the grating structure distributed on the inner wall of the ring, can control the outward radiation of different modes of light fields, and suppress the quality factors of all other non-laser modes , so that the ring microcavity laser can achieve stable single-mode lasing.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
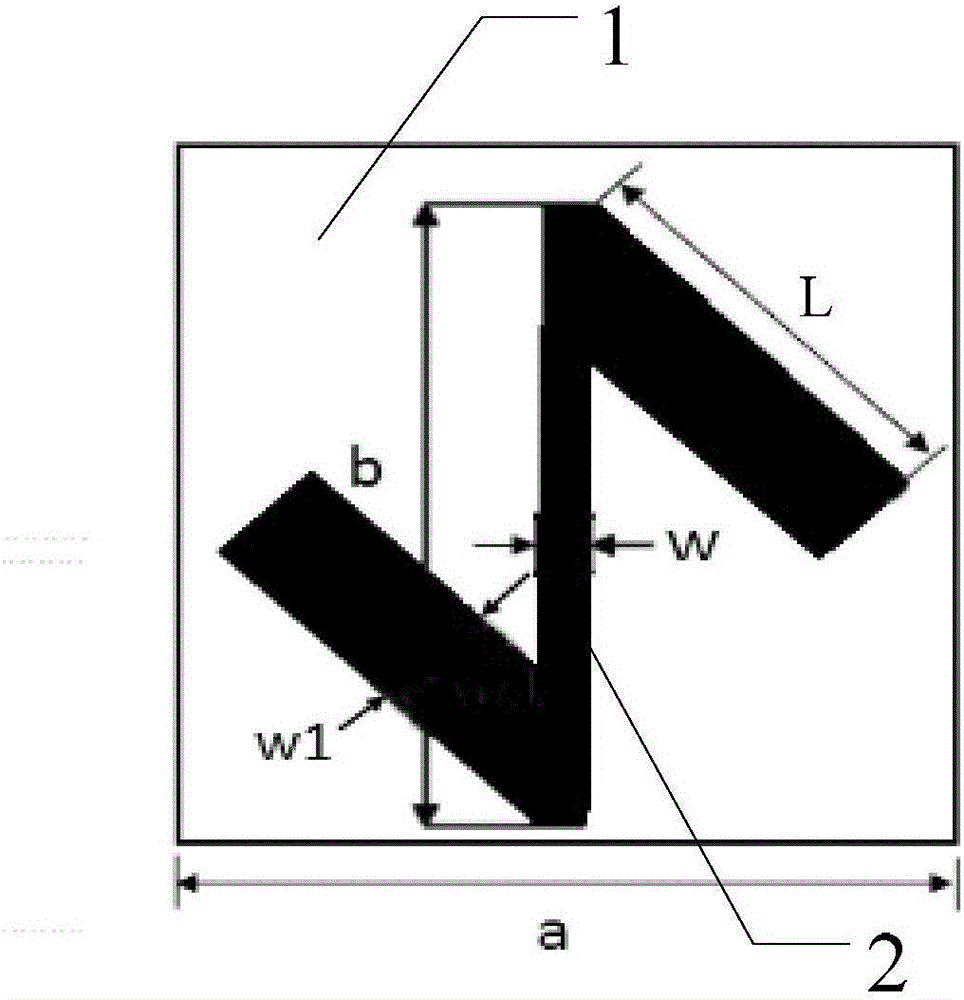
Lens and method for generating vortex beams based on reflective metasurface
ActiveCN106025566BHigh cross-polarized wave reflectivityThe overall thickness is thinAntennasMetal stripsAngular momentum
The invention provides a lens and method for generating a vortex beam based on a reflecting super-surface, relates to a technology for generating the vortex beam based on a phase discontinuous super-surface, and aims at solving the problem that a traditional method for generating the vortex beam by a spiral phase wave plate is limited by the thickness when the wavelength is relatively large. The lens comprises m*n periodically arranged phase change units, wherein each phase change unit comprises a substrate and a reversed Z-shaped metal layer located on the surface of the substrate; each reversed Z-shaped metal layer comprises a metal strip I, a metal strip II and an inclined strip; employing one side of each substrate as an x axis and the side adjacent to the side as a y axis, the included angle between the central line of the corresponding inclined strip and the y axis is theta; the formula is as shown in the specification, wherein l is the orbital angular momentum quantum number; and the formula is as shown in the specification. Incident light, entering the lens, of a circularly polarized wave and abnormally reflected light generated when the circularly polarized wave vertically enters the lens are symmetrical about a normal line; a cross-polarized reflection wave is vertical to reflection of the lens; and the abnormal reflection angle is as shown in the specification. The lens and the method are suitable for generating the vortex beam.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com