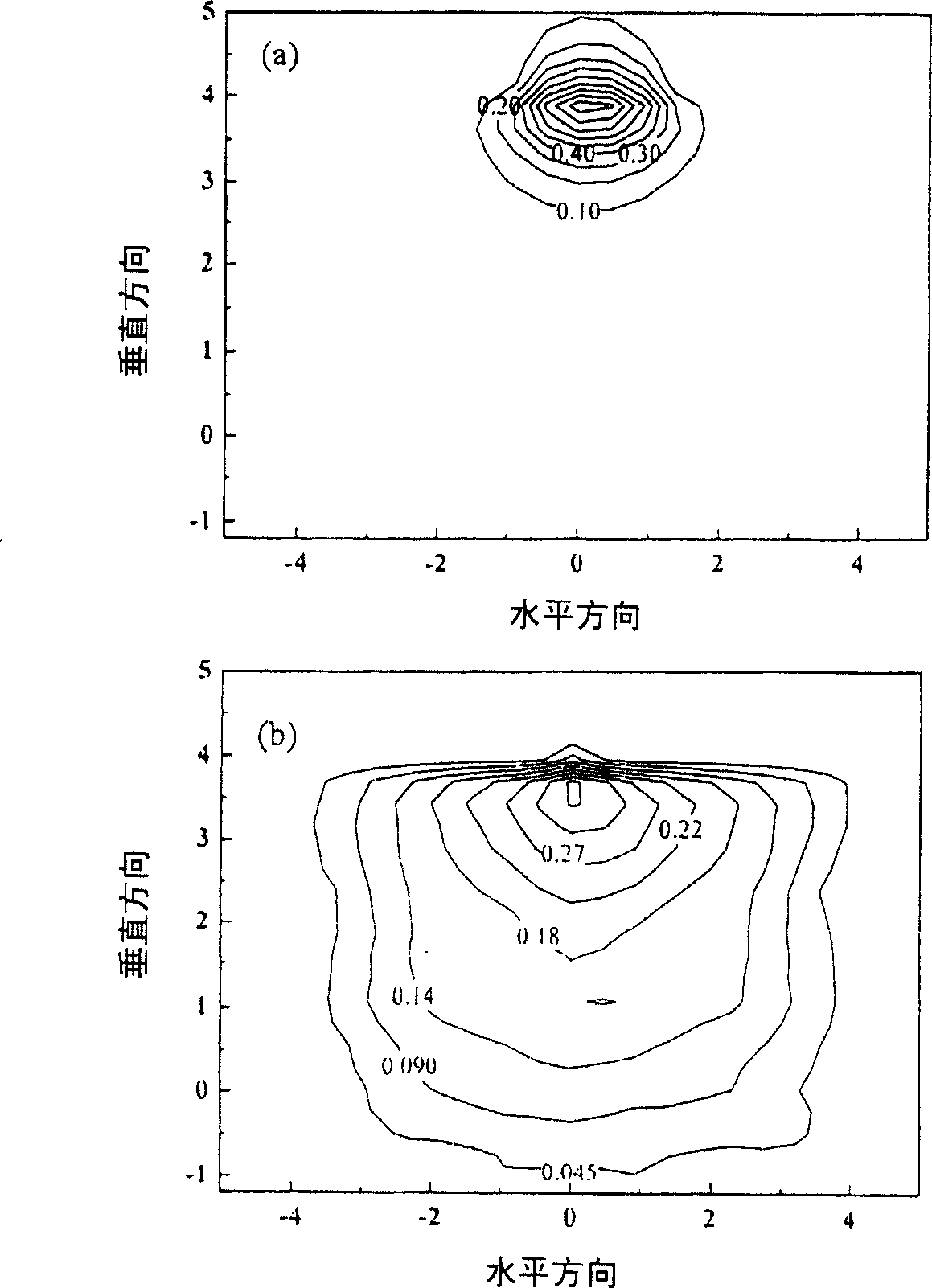
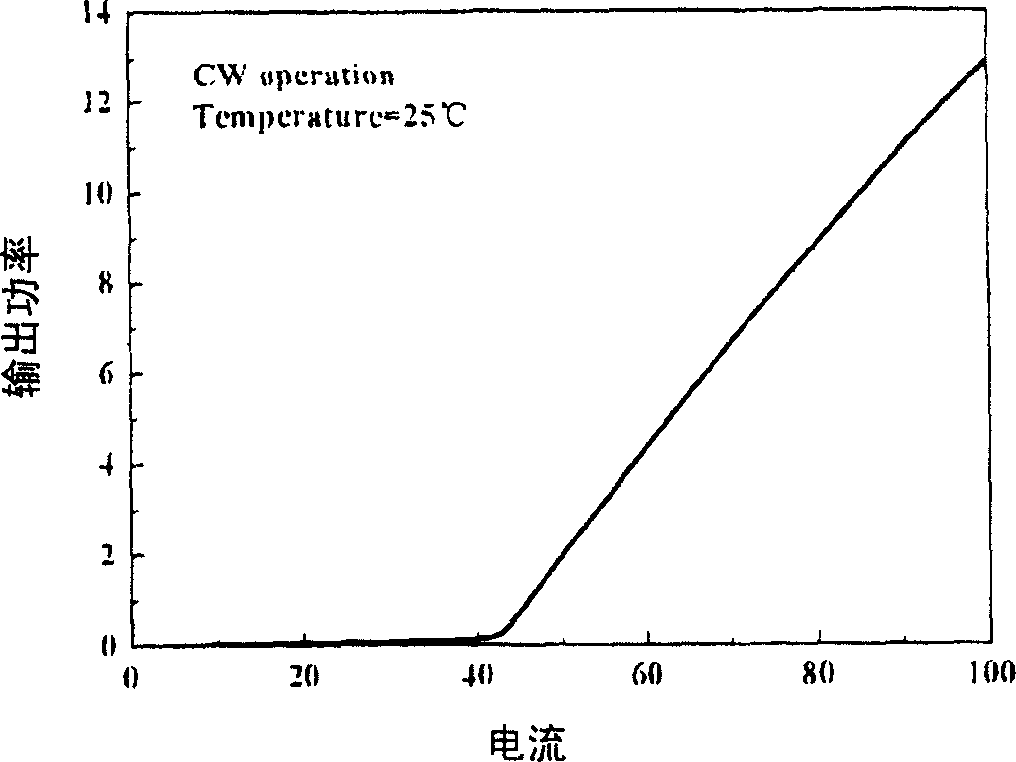
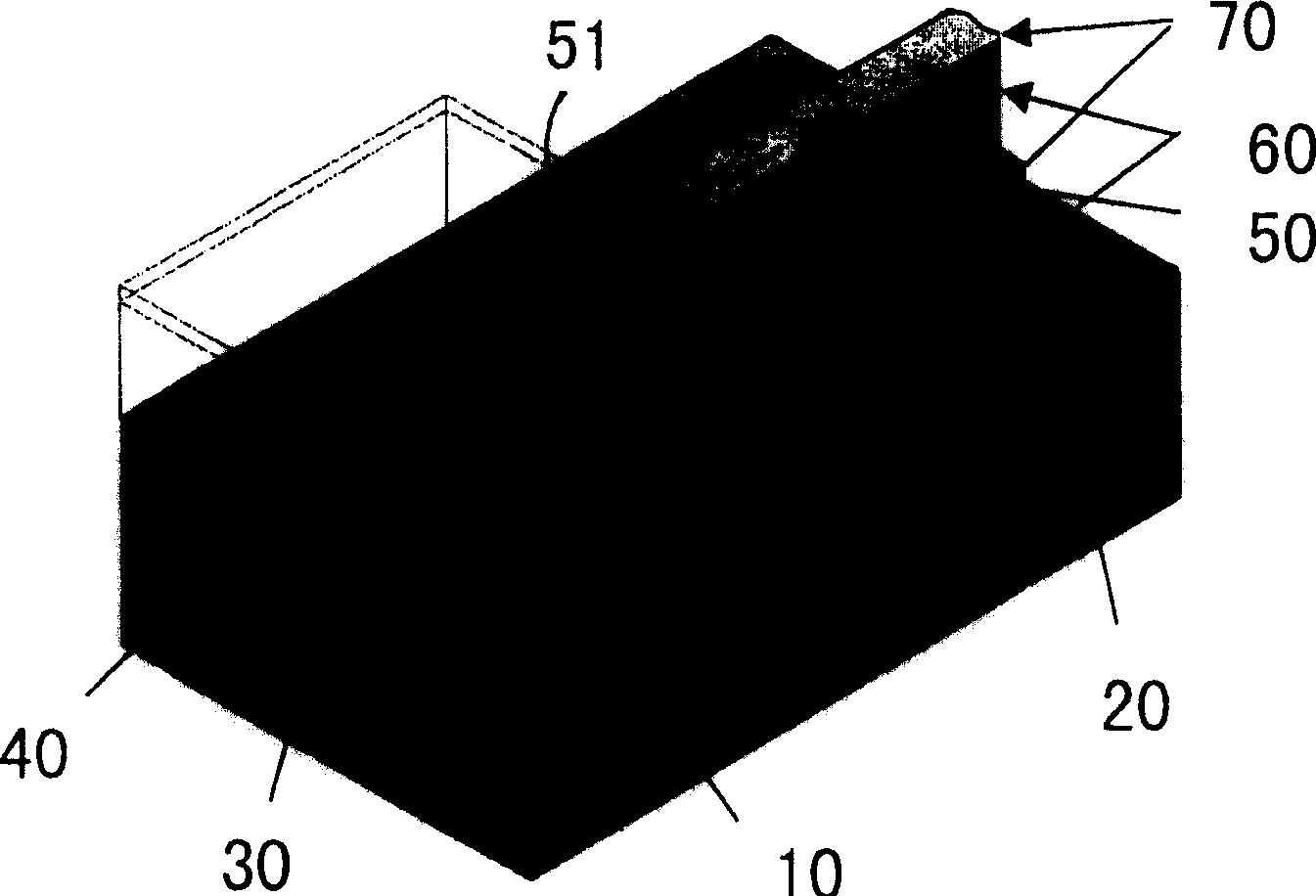
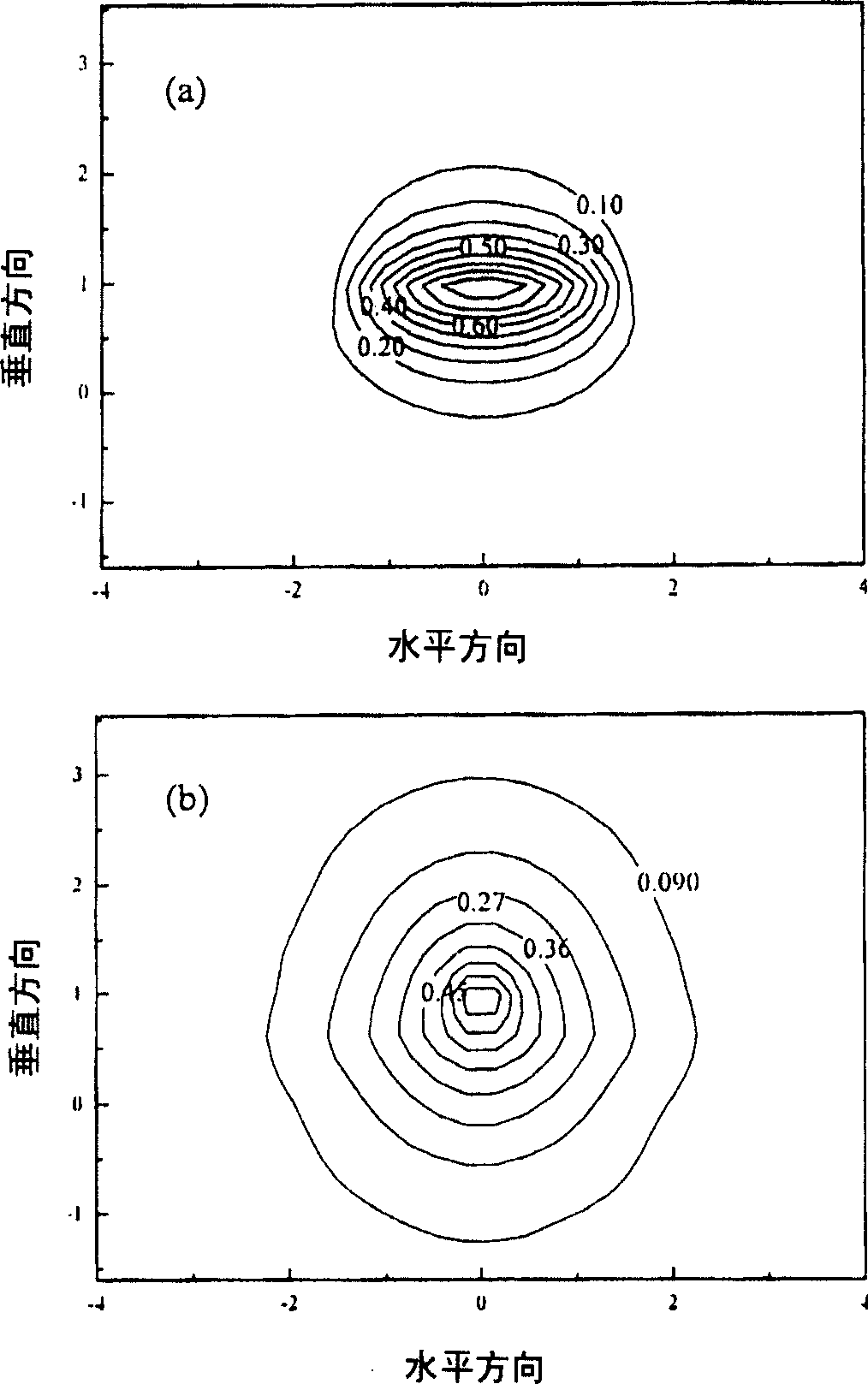
Patents
Literature
131results about How to "Lower threshold current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser and manufacturing method thereof
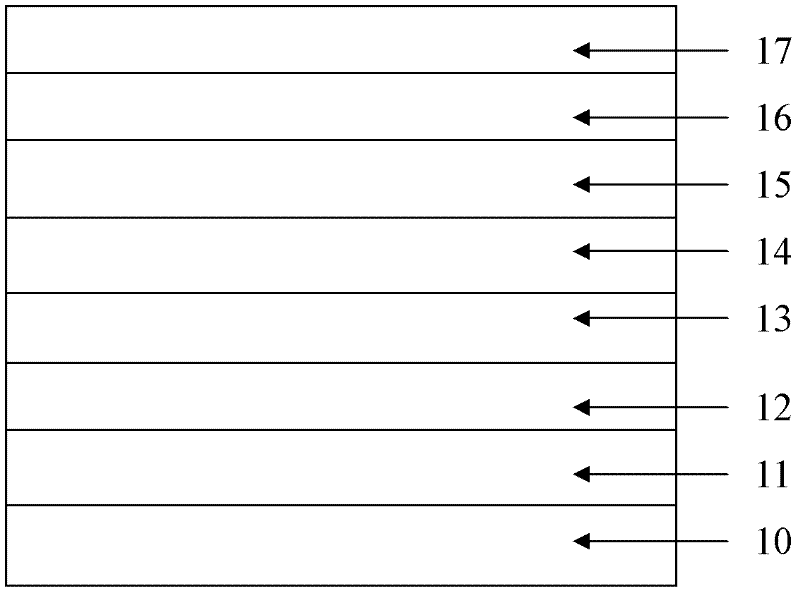
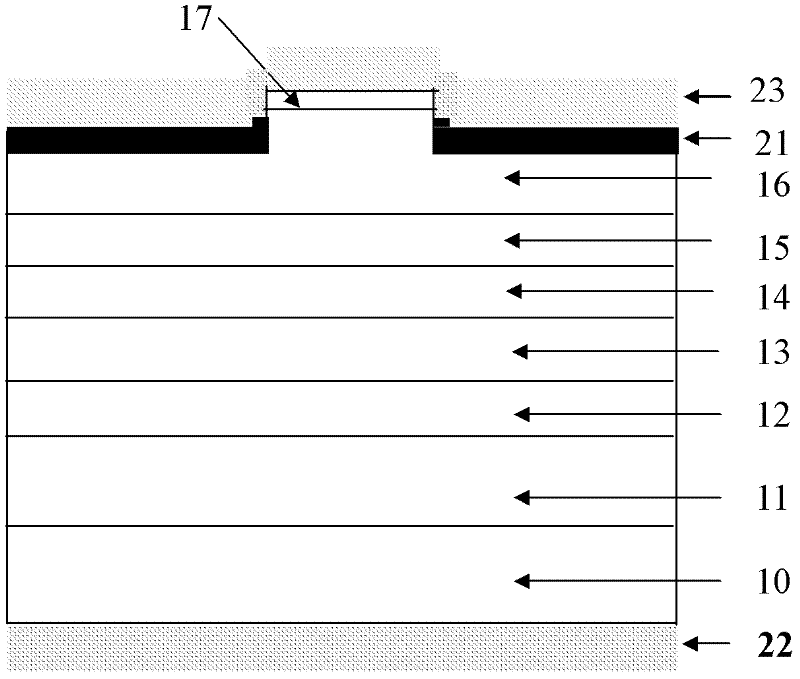
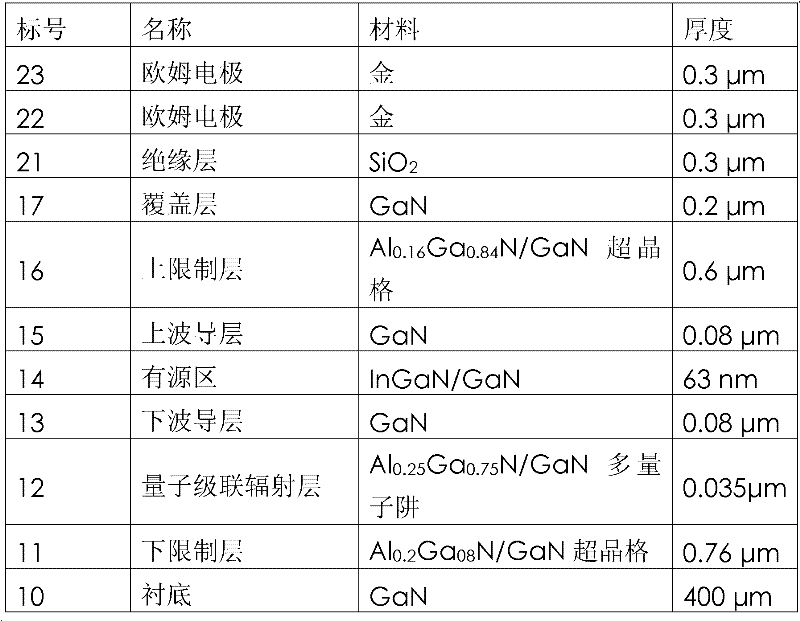
InactiveCN104577711AHigh gainEffective limitLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserPotential well
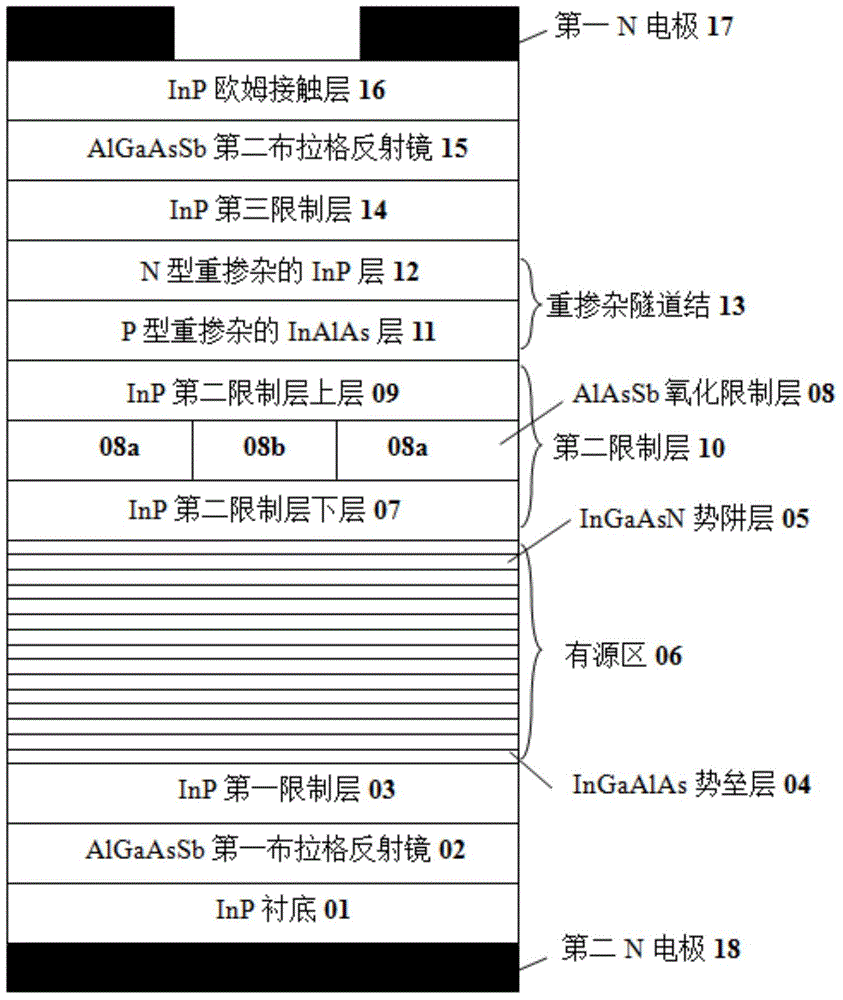
The invention discloses a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser which comprises a substrate, a first Bragg reflector, a first limiting layer, an active region, a second limiting layer, a second Bragg reflector and an Ohmic contact layer which are arranged in a laminated manner, wherein the active region adopts a quantum well structure, a potential barrier layer is made of InGaAlAs, and a potential well layer is made of InGaAsN; a heavily-doped tunnel junction and a third limiting layer are also arranged between the second limiting layer and the second Bragg reflector; an oxidized limiting layer is also arranged in the second limiting layer. The invention also provides a preparation method of the laser. The laser has the advantages that the laser uses an InGaAsN / InGaAlAs material system as the active region, has large conduction band order ratio and can effectively limit injected carriers, so that the threshold current is reduced, and the laser gain is improved; on an isometric wavelength band of 1550 nm, the content of N required by an active region material is lower, and devices with high material quality are easy to obtain.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Load circuit protection device
ActiveCN102265475ALower threshold currentPrevent false shutdownEmergency protective arrangement detailsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionLoad circuitCounter-electromotive force
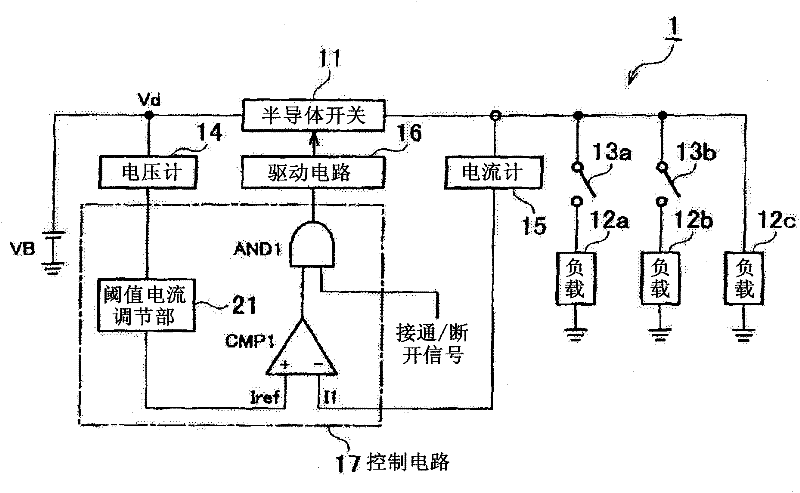
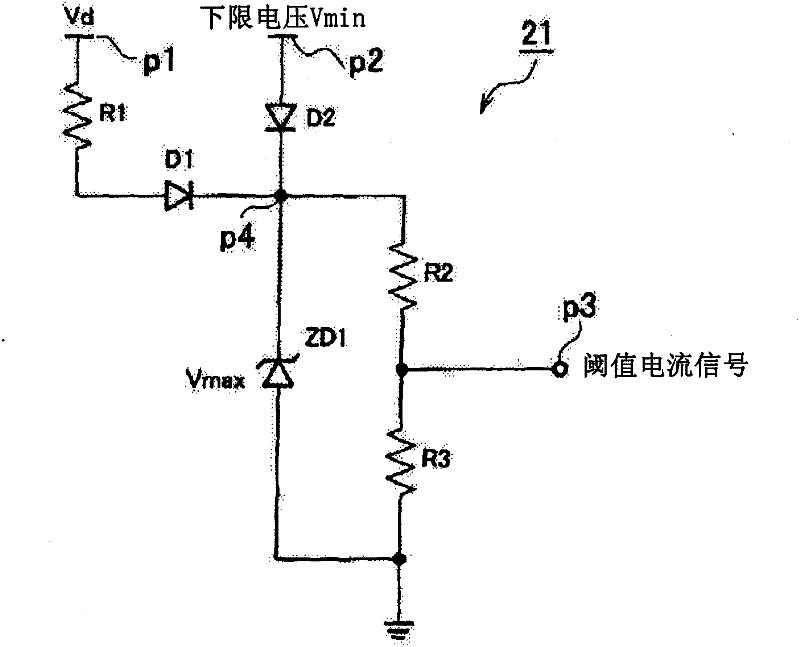
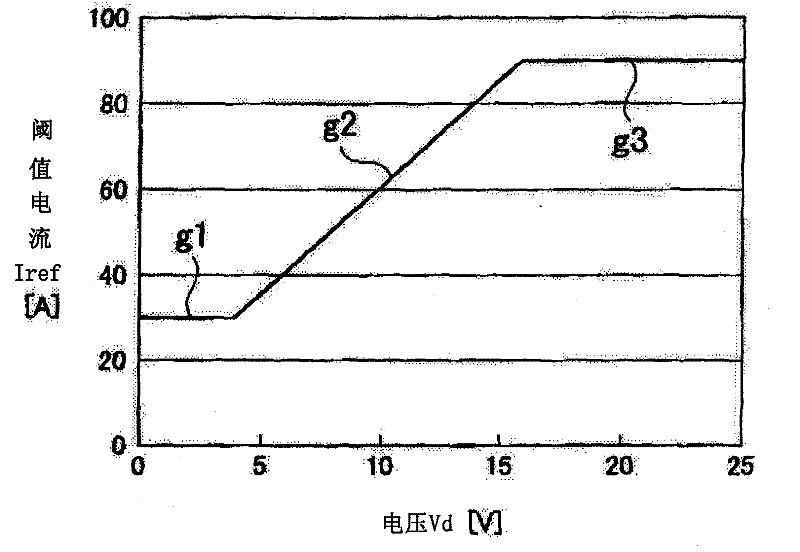
Provided is a load circuit protection device, which discriminates an inrush current, which is generated when a semiconductor switch or a switch provided in the downstream of the semiconductor switch is turned on, and an excess current generated in a load from each other, and protects a load circuit by turning off the semiconductor switch only when the excess current is generated. A detection current (I1) detected by an ammeter (15) and a preset threshold current (Iref) are compared with each other by means of a comparator (CMP1), and in the case where the detection current (I1) reaches the threshold current (Iref), the semiconductor switch (11) is turned off and the load circuit is protected. Furthermore, a voltage (Vd) in a cable connecting a battery (VB) and the semiconductor switch (11) is measured, and in the case where a counter-electromotive force is generated and the voltage (Vd) is reduced, the threshold current (Iref) is reduced. Therefore, when a dead short-circuit is generated, the detection current (I1) quickly reaches the threshold current (Iref) and turns off the semiconductor switch (11), and when the inrush current is generated, since the detection current (I1) does not reach the threshold current, erroneous interruption is prevented from being generated.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
GaN (gallium nitride)-based semiconductor laser and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102227046AReduce leakageIncrease the injection currentLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersIonizationMagnesium
The invention provides a GaN (gallium nitride)-based semiconductor laser and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the field of semiconductor lasers. The GaN-based semiconductor laser does not have an electronic barrier layer, thus reducing the working voltage of the laser and prolonging the service life of the laser. For the laser, a quantum cascade radiation layer is arranged between an n-type optical limited layer and an n-type waveguide layer of the laser and utilized to generate infrared radiation when the laser operates, thus realizing ionization of magnesium acceptor impurities in a p-type GaN waveguide layer and a AlGaN optical limited layer, improving carrier concentration in each p-type layer, increasing hole injection current, reducing leakage of electronics from an active area, avoiding introduction of a AlGaN electronic barrier layer and eliminating optical absorption loss caused by the magnesium-doped AlGaN electronic barrier layer, thereby reducing the threshold current of the laser, reducing the working voltage of the laser and prolonging the service life of the laser.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Active area of laser unit, semiconductor laser unit and manufacturing method of laser unit
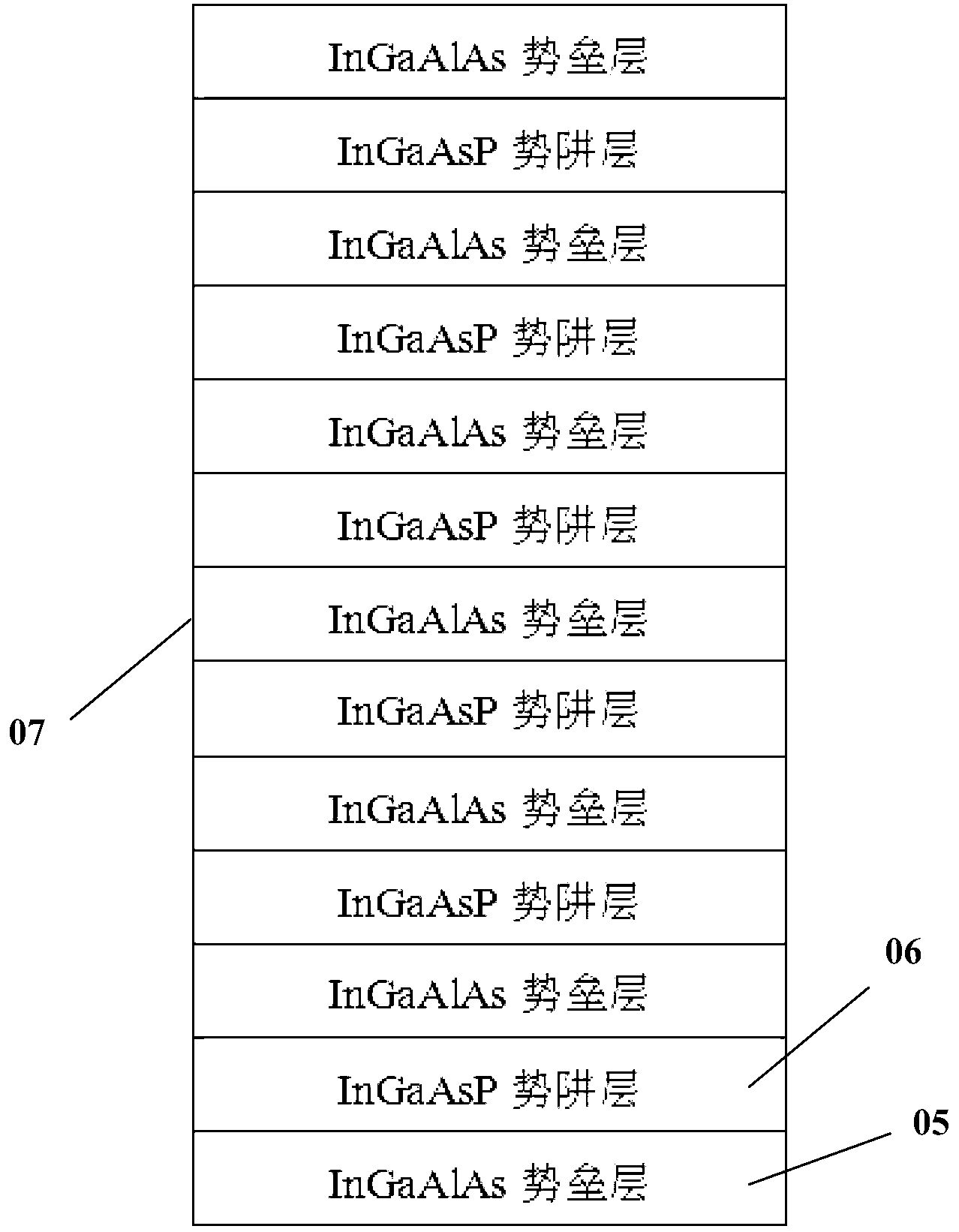
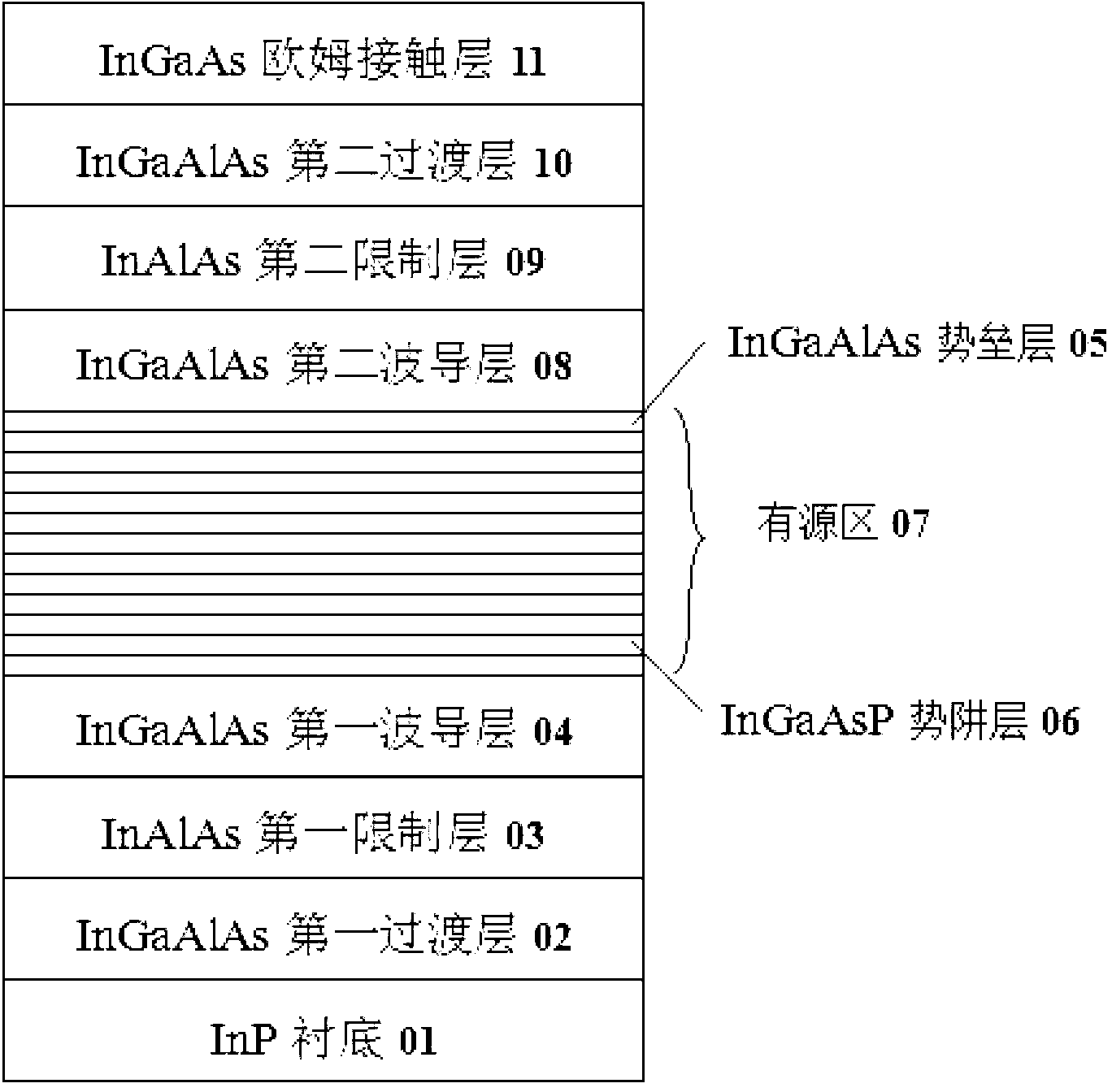
ActiveCN103326242ALower threshold currentRaise the characteristic temperatureLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPotential wellCharge carrier
The invention discloses an active area of a laser unit. The active area comprises a multiple-quantum well structure, wherein a potential well layer in the multiple-quantum well structure is made from InGaAsP, and a barrier layer in the multiple-quantum well structure is made from InGaAlAs; a cycle of the multiple-quantum well structure is K, and K ranges from 3 to 20. Furthermore, the invention discloses a semiconductor laser unit and a manufacturing method of the laser unit, wherein the semiconductor laser unit comprises the active area. The semiconductor laser unit provided by the invention has a lower threshold current and higher characteristic temperature, to realize no-refrigeration work; the laser unit has relatively high differential gain, and can provide a laser output in a Tencent Messenger (TM) mode; the laser unit has a relatively high conduction band order, so as to simultaneously restrict injected carriers effectively and distribute the carriers among wells uniformly and enhance the modulation characteristic of the laser unit.
Owner:苏州市吴中中科育成科技发展有限公司
Method for making laminated travelling wave electroabsorption modulation laser with epitaxial selection region
InactiveCN101471541ALower threshold currentGood far-field characteristicsOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsGratingQuantum well
The invention relates to the fabrication method of a travelling-wave electroabsorption modulated laser with a laminated structure formed by selective-area growth (SAG). The fabrication method comprises the following steps: fabricating a mask strip pattern on a semi-insulating InP substrate; sequentially epitaxially growing a heavily-doped n-InP buffer layer, a 1.2Q lower confinement layer, a multi-quantum well structure of a modulator, a multi-quantum well structure of a laser, a 1.2Q upper confinement layer and an n-InP inversion layer; etching off an upper laminated multi-quantum well structure in a SAG laminated multi-quantum well structure, and a lower laminated multi-quantum well structure and the 1.2Q lower confinement layer of an optical terminal region; fabricating a grating on a large-area growth area, and etching an inversion layer to the 1.2Q upper confinement layer by the grating; and sequentially epitaxially growing a p-InP protection layer, an etching stop layer, a p-InP cover layer and a p-InGaAs layer; and etching off the p-InGaAs layer in the electrical insolation area, and implanting ions in the p-InP cover layer in the area to produce a high-impedance area.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Edge-emitting diode semiconductor laser with raster structure
ActiveCN102545052AReduce carrier leakageLower threshold currentOptical wave guidancePhysicsHeat sink
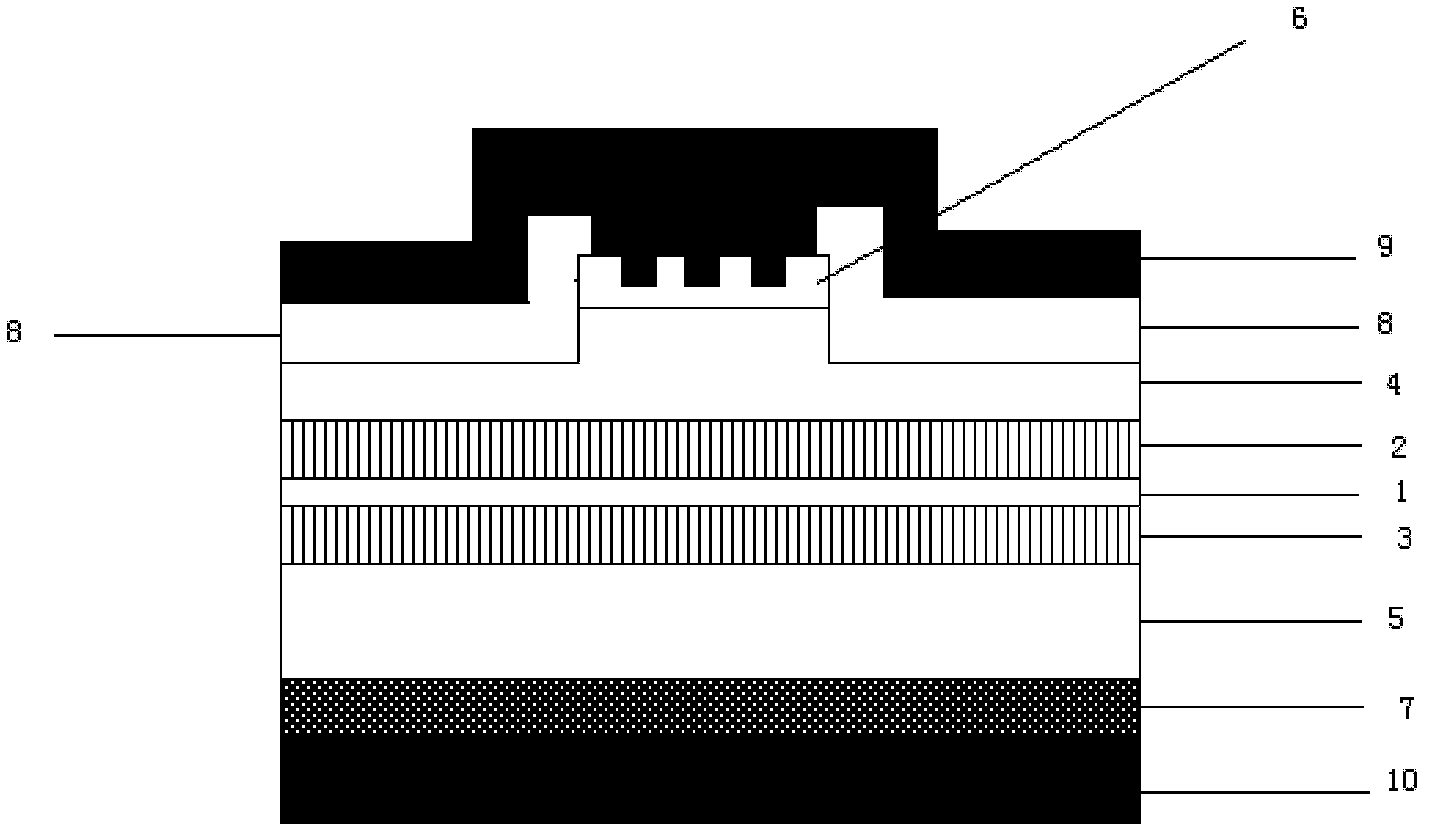
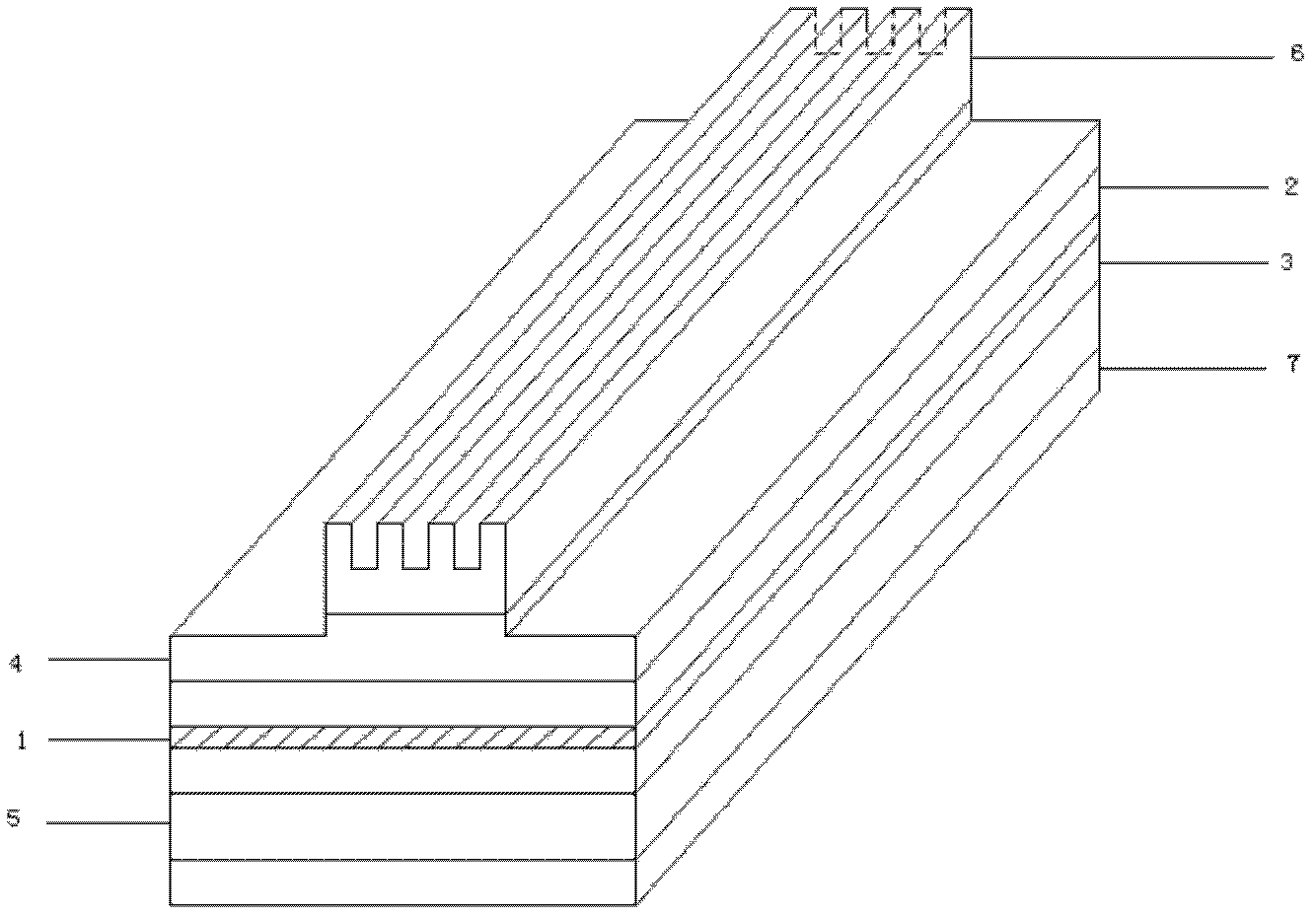
The invention discloses an edge-emitting diode semiconductor laser with a raster structure and belongs to the optoelectronic technical field of semiconductors. The edge-emitting diode semiconductor laser comprises a semiconductor laser epitaxial structure, a silicon dioxide insulating layer, an upper layer of P type electrode and a lower layer of P type electrode, wherein the semiconductor laser epitaxial structure consists of a substrate, an N type limit layer, an N type waveguide layer, a multi-quantum well active region, a P type waveguide layer, a P type limit layer and a P type ohmic contact layer; and the raster structure is grown on a crestiform table. The photolithographic process is adopted in a manufacturing process; and after scraping, a chip is sintered on a copper heat sink and is packaged and fixedly arranged on a radiating base. According to the structure, due to the introduction of the raster structure on the crestiform table, the lateral diffusion of current carriers injected into an active layer is inhibited, the uniformity of the current carriers in the active area is improved, and the threshold current of a semiconductor laser is reduced. The edge-emitting diode semiconductor laser is simple in manufacturing process, low in cost and good in repeatability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for forming semiconductor laser and spot-size converter by once epitaxy
InactiveCN1756008AReduce pollutionLow costLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersTime extensionSemiconductor package
Disclosed a method for one time extension forming the semiconductor laser and mode spot switch comprises following steps: (1), on the N type indium phosphide substrate, extending growing the N type indium phosphide breaker, a lower waveguide layer, a 2.4 ª–m indium phosphide space layer, a lower light-limited layer of active region, a compression strain quanta active region, a upper light-limited layer, a P type indium phosphide envelope, and a high doping P type indium gallium arsenide ohmic electrode contract layer; (2), utilizing the wet corrosion process to etch the upper carinate shape of laser and mode spot switch; (3) utilizing the auto-alignment process to etch the lower carinate shape; (4), growing the SiO2 insulating layer and opening a electrode window; (5) decreasing the substrate of extended plate to 100 ª–m, and manufacturing P / N electrodes to be scribed into the tube core of 250í‡600ª–m.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for making semiconductor laser and spot-size converter by double waveguide technology
InactiveCN1756009AReduce the number of growthLow costLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersSemiconductor packageIntrinsics
Disclosed a method for utilizing the dual-waveguide technology to manufacture the semiconductor laser and mode spot switch comprises following steps: on the N type indium phosphide substrate, sequentially extending growing the N type indium phosphide breaker, a lower waveguide layer, a space layer, a active region, and a thinner indium phosphide intrinsic layer, wherein, the indium phosphide intrinsic layer can prevent the oxidation of active region; removing the highest indium phosphide intrinsic layer, partly covering the laser with SiO2, and utilizing the wet corrosion process to etch the upper carinate shape of mode spot switch; utilizing the auto-alignment process to etch the lower carinate shape which comprises a lower waveguide layer, a space layer, a second growth P type indium phosphide coating layer, and a high doping P type indium gallium arsenide ohmic electrode contract layer; utilizing the SiO2 to partly cover the mode spot switch and etching the upper and lower carnate shapes again while the upper carinate shape comprises a active region, a P type indium phosphide coating layer and a high doping P type indium gallium arsenide ohmic electrode contract layer; and decreasing the substrate of extended plate to 100 ª–m, and manufacturing P / N electrodes to be scribed into the tube core of 250í‡500ª–m.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor light-emitting device and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN1602569ALower threshold currentControllable polarization plane of lightOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonic crystal structureCrystal structure
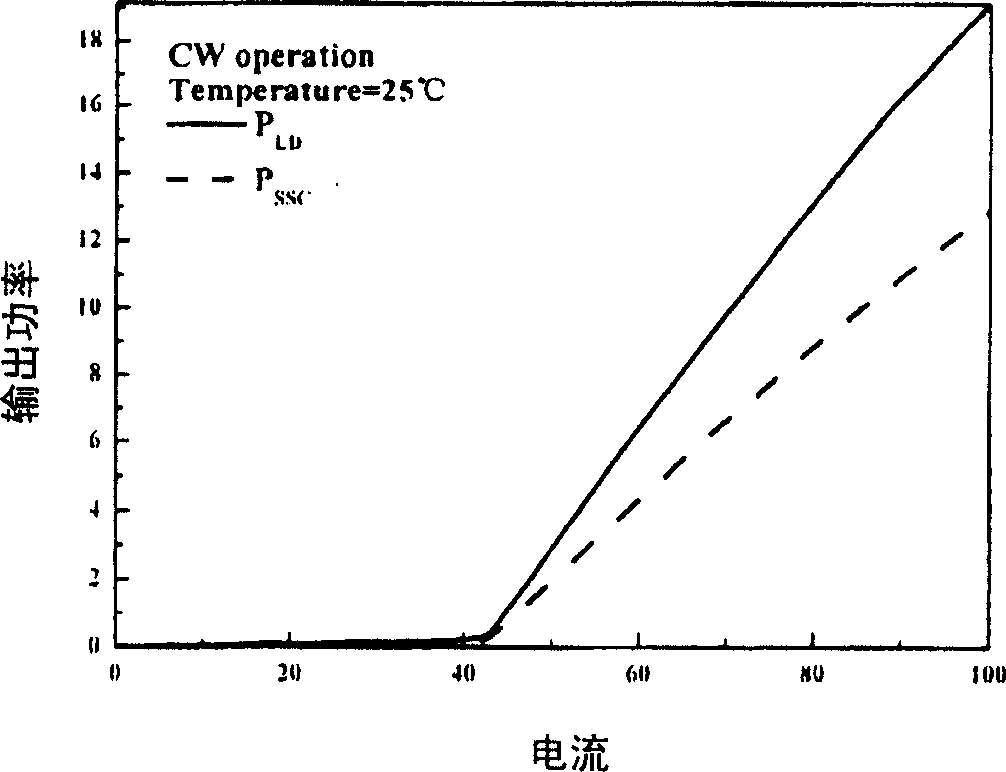
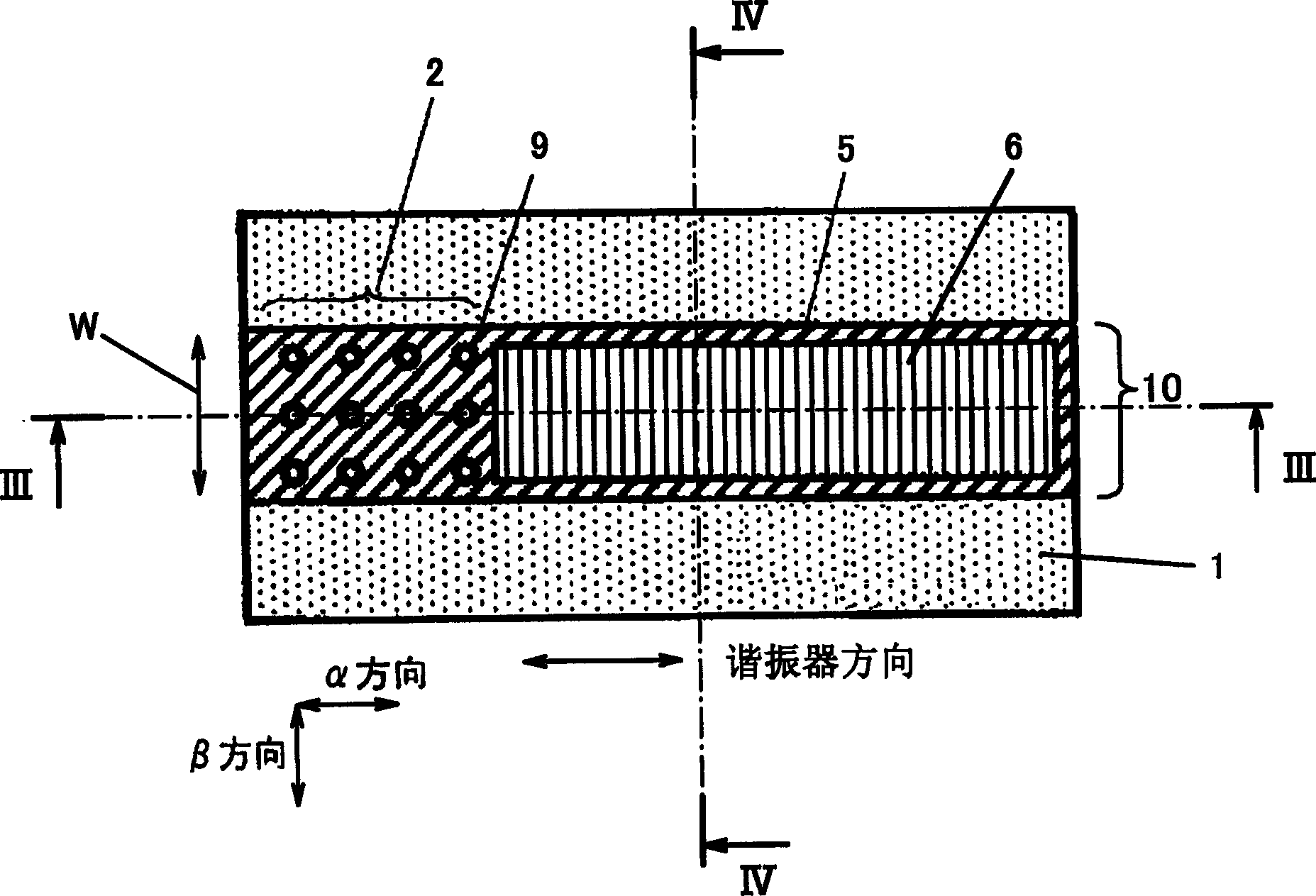
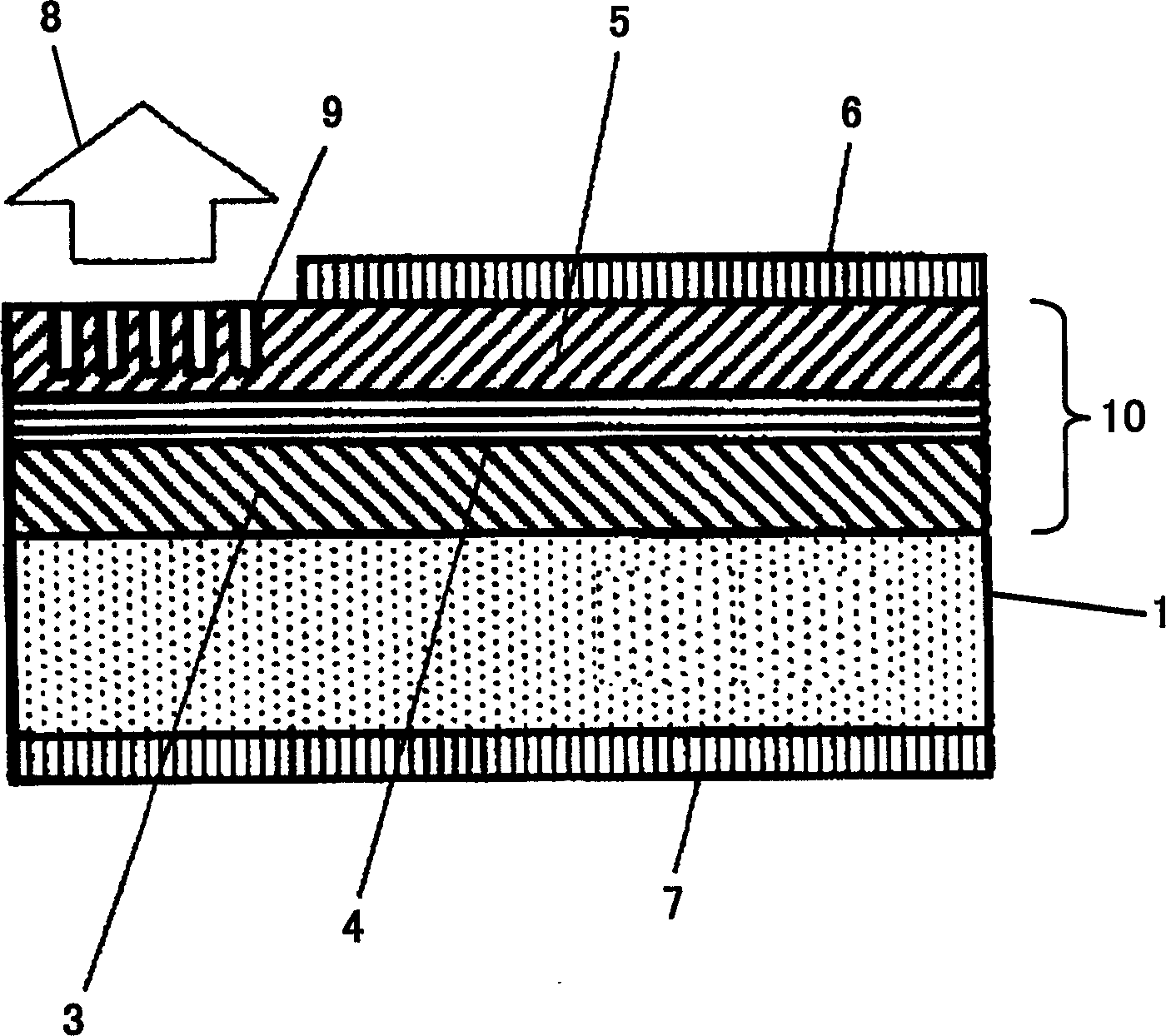
A semiconductor light emitting device of the present invention comprises a n-type InP substrate (1), and a stripe structure (10) formed in the stripe shape on the n-type InP substrate (1) and comprised of a n-type InP lower cladding layer (3), an active layer (4) having a resonator in a direction parallel to the n-type InP substrate (1), and a p-type InP upper cladding layer (5). The stripe structure (10) has a photonic crystal structure (2) with concave portions 9 arranged in rectangular lattice shape, and the direction in which the concave portions (9) of the photonic crystal structure (2) are arranged corresponds with a resonator direction. A stripe-shaped upper electrode (6) is formed on the stripe structure (10) to extend in the resonator direction. The semiconductor light emitting device of the present invention so structured is configured to radiate light in the direction perpendicular to the n-type InP substrate (1).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
VCSEL (Vertical cavity Surface Emitting Laser) epitaxial structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109728502AImprove power conversion efficiencyShallow depthLaser detailsLaser active region structureVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserHeat losses
The invention discloses a VCSEL epitaxial structure and a preparation method thereof. An N type DBR layer is composed of AlYGa1-YAs in which the Al content is different, barrier junctions between different AlYGa1-YAs layers are reduced, stress change between the adjacent AlYGa1-YAs layers is used to increase the barrier height, so that the total depth of the barrier junction of the N type DBR layer is reduced, the serial resistance of the N type DBR layer is reduced, the voltage between the two ends of the N type DBR layer is reduced, the threshold current of the DBR layer is reduced, and current consumed in the N type DBR layer is reduced, and further heat loss of the epitaxial structure is reduced, and the power conversion efficiency and gradient efficiency of the epitaxial structure areimproved. Steps are formed between the AlYGa1-YAs in different Al content, the barrier difference is reduced, electrons are easier to transit, the electron and cavity complex logarithm is increased,the number of counter rotating particles is increased, and the gain is improved.
Owner:YANGZHOU CHANGELIGHT
1300nm-1550nm semiconductor laser unit containing bismuthide and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103259193ARaise the characteristic temperatureSmall temperature coefficientLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserOhmic contact
The invention discloses a 1300nm-1550nm semiconductor laser unit containing bismuthide. The 1300nm-1500nm semiconductor laser unit containing bismuthide comprises a transitional layer, a lower limiting layer, a lower waveguide layer, an active area, an upper waveguide layer, an electron barrier layer, an upper limiting layer and an ohmic contacting layer all of which are connected sequentially. The active area adopts a strained quantum well made of a GaNAsBi / GaAs material system. The P-type AlGaAs electron barrier layer is placed between the P-type AlGaAs upper waveguide layer and the P-type AlGaAs or GaInP upper limiting layer, and the N-type AlGaAs transitional layer is placed between a GaAs substrate and the N-type AlGaAs or GaInP lower limiting layer. A semiconductor laser epitaxy structure grows on the GaAs substrate, the production cost of the semiconductor laser epitaxy structure is less than that of an InP substrate laser, has high feature temperature, can effectively keep a current carrier from overflowing the active area, and can be popularized to a vertical cavity surface emitting laser and other types of lasers.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
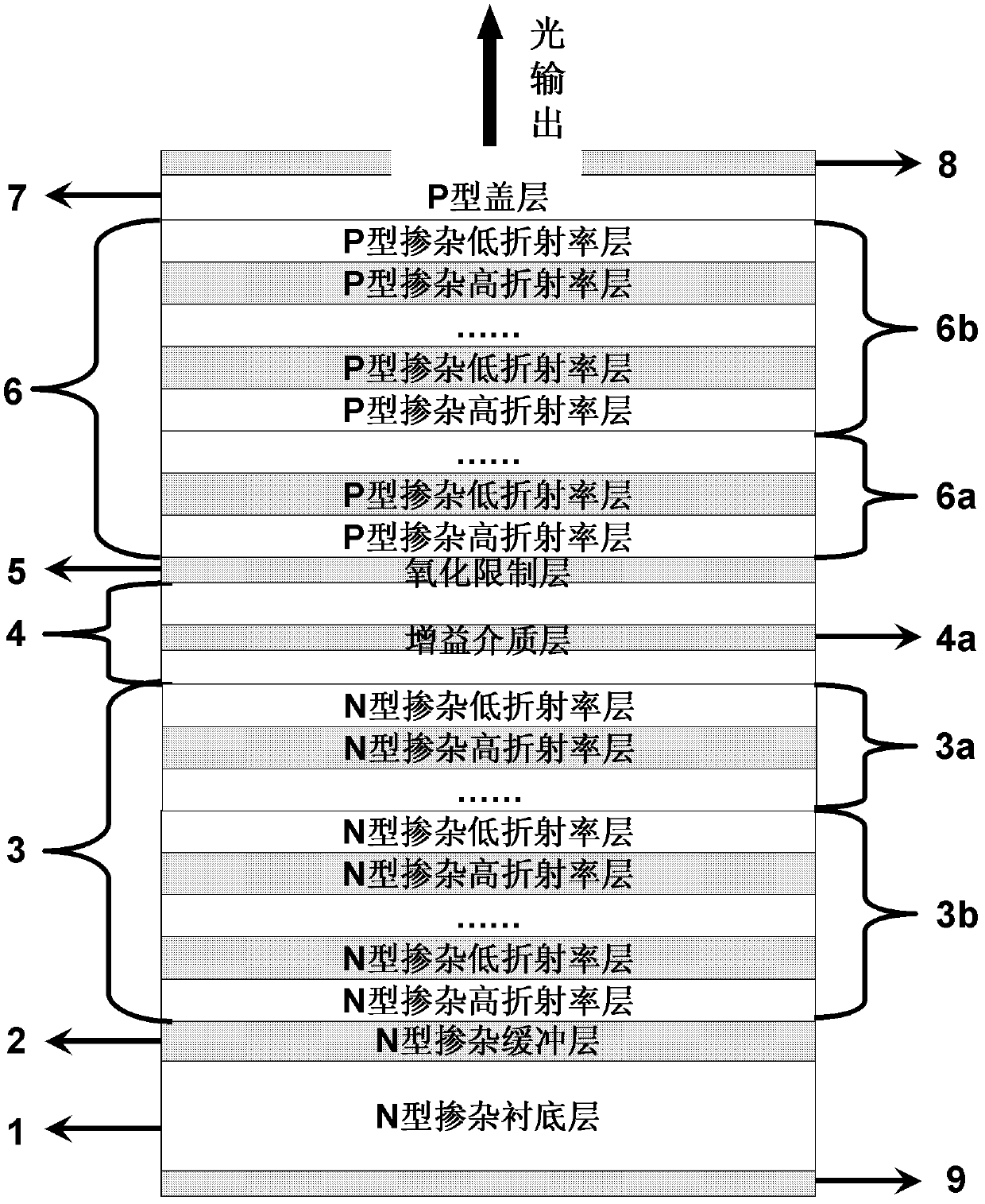
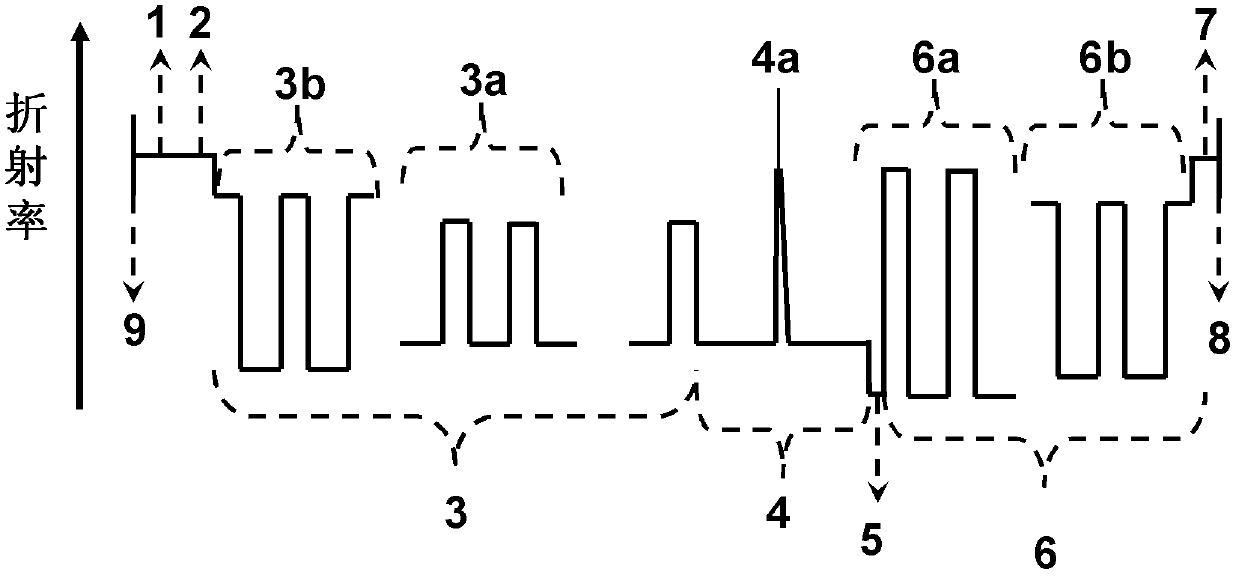
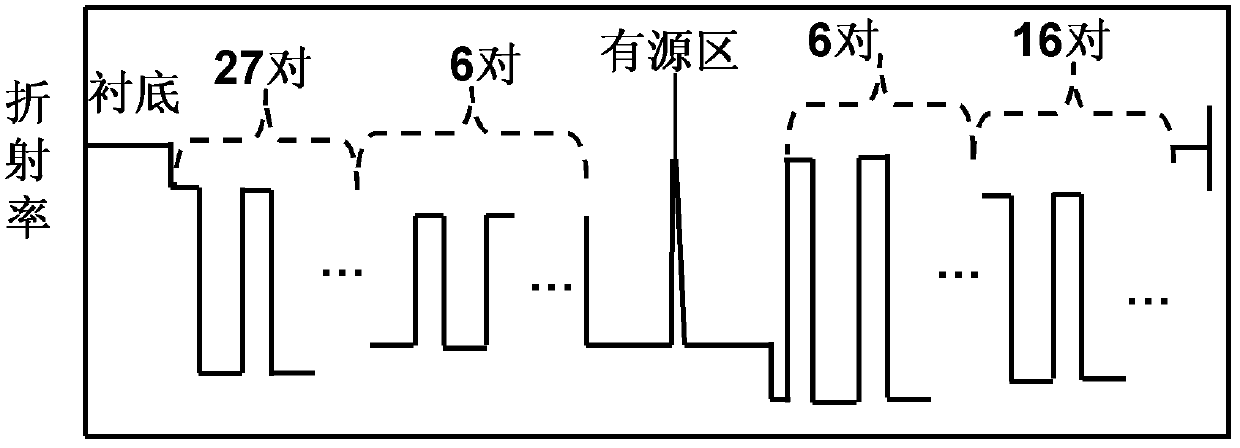
High-efficiency vertical cavity surface emitting semiconductor laser with asymmetric optical field distribution
ActiveCN102611000AImprove self-heating effectSimple preparation processLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersNon symmetricDistributed Bragg reflector
In order to solve the problems of high optical field loss on P-type DBR (distributed Bragg reflector) side and restricted conversion efficiency of the existing vertical cavity surface emitting semiconductor laser, the invention relates to a high-efficiency vertical cavity surface emitting semiconductor laser with asymmetric optical field distribution, which belongs to the technical field of semiconductor laser. The high-efficiency vertical cavity surface emitting semiconductor laser with asymmetric optical field distribution comprises, from bottom to top, an N-side electrode, an N-type substrate, an N-type buffer layer, an N-type segmented DBR, an active region, an oxidation confinement layer, a P-type segmented DBR, a P-type cover layer and a P-side electrode, wherein the refractive index difference of the former 6 to 8 pairs of high- and low-refractive index material of the N-type segmented DBR close to the active region is smaller than that of the latter low-refractive index material pairs; and the refractive index difference of the former 6 to 8 pairs of high- and low-refractive index material of the P-type segmented DBR close to the active region is larger than that of the latter low-refractive index material pairs. The high-efficiency vertical cavity surface emitting semiconductor laser provided by the invention has high photoelectrical conversion efficiency, and wide application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU EVERBRIGHT PHOTONICS CO LTD
N-type ZnO and p-type GaN combined ZnO-base vertical cavity surface emitting laser and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102195234ALower threshold currentIncrease output powerLaser detailsLaser output parameters controlVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserResonant cavity
The invention relates to an n-type ZnO and p-type GaN combined ZnO-base vertical cavity surface emitting laser and a manufacturing method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor light emitting devices and manufacturing methods thereof. The laser consists of a substrate 1, a p-type GaN epitaxial layer 2, a current lower limitation layer 3 and a lower electrode 5 which are prepared on the epitaxial layer 2 and independent of each other, an n-type ZnO-base material light emitting layer 4 prepared on the current lower limitation layer 3, an upper electrode 6 and the like, andis characterized in that: a multi-layer AlGaN / GaN thin film distributed bragg reflector (DBR) lower reflector 8 is grown and prepared between the substrate 1 and the p-type GaN epitaxial layer 2; an n-type broadband gap ZnO-base ternary system material current upper limitation layer 7 is prepared on the n-type ZnO-base material light emitting layer 4; and the upper electrode 6 and a multi-layer medium thin film DBR upper reflector 9 which are independent of each other are prepared on the current upper limitation layer 7. The n-type ZnO and p-type GaN combined ZnO-base vertical cavity surface emitting laser has the advantages that: due to a controllable resonant cavity, the output power of the device can be enhanced; the direction of laser becomes better; and the application range of the device is expanded.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Single-mode emission orbital angular momentum (OAM) laser
ActiveCN108054633ALower threshold currentReduce volumeLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingMicro column
The invention relates to the technical field of a semiconductor laser, and proposes a single-mode emission orbital angular momentum (OAM) laser. A cavity body of a resonant cavity of the laser is of amicro column, micro ring or micro disc structure for supporting an echo wall mode, a grating or defect is etched on an outer side surface of the cavity body of the laser, the echo wall mode with special angular quantum number can be selected as a hot shot mode of the laser, the selected mode is vertically scattered and output by a top grating, the output is a travelling wave mode with a vortex phase, namely an OAM mode, the top grating is arranged at a position, near to an outer side edge of a micro column, of a grating layer and comprises a real part and a virtual part, the real part and thevirtual part comprise two groups of gratings and are used for respectively modulating effective reflectivity of the mode, so that scattering output of the travelling wave mode is formed. The laser issmall in cavity volume and low in loss, and thus, ultrahigh-speed modulation can be achieved. The semiconductor laser has the characteristics of small volume, single-mode working and low threshold current, and is convenient to detect, a two-dimensional array is easy to integrate, output light is easy to couple to optical fiber, and various advantages can be achieved on different material systems.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
New method for realizing efficient electrofluorescence and low threshold laser
InactiveCN101707231AEnhanced electroluminescenceLower threshold currentLaser active region structureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
The invention belongs to the field of semiconductor optoelectronic materials and device technology, and relates to a new method for realizing efficient electrofluorescence and low threshold laser. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing a p-type material and an n-type material which have the same crystal structure and similar lattice constants, and taking the p-type material as a hole source of the n-type material; through the design of an energy band, regulating an energy band structure between the p-type material and the n-type material by adopting a dielectric layer to control the transport property of a current carrier, and accumulating electrons in an n-type material layer to form a hole and injecting electrons to the n-type material layer from the p-type material so as to realize the efficient electrofluorescence and low-threshold later emission in the n-type material. The new method for realizing the efficient electrofluorescence and the low threshold laser is suitable for heterojunction growth and device preparation of II-VI group semiconductor material, III-V group semiconductor material and other semiconductor materials with wide band gap, is a simple and practicable method for realizing semiconductor luminescence, expands the range for preparing high-efficiency luminescent devices greatly, and opens a new way for the research and the preparation of the luminescent devices.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
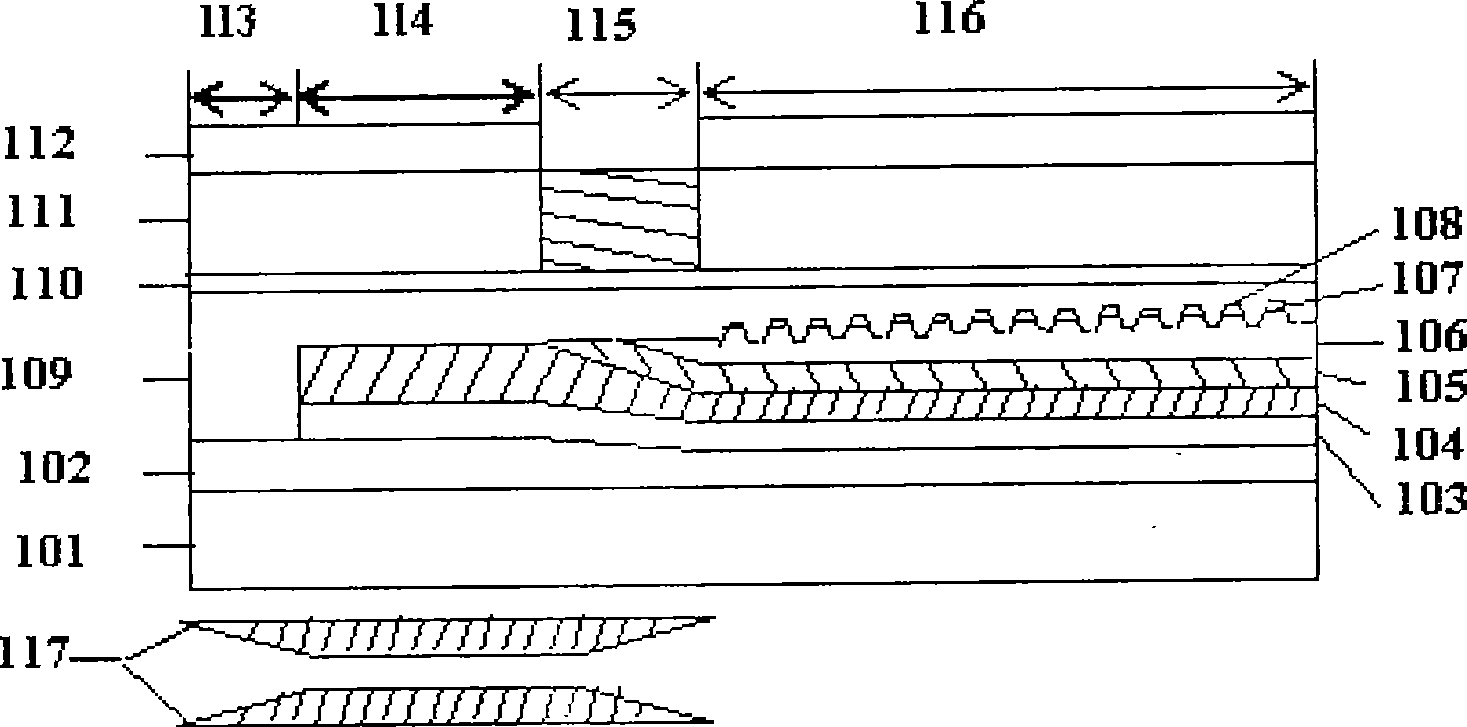
Integrated device of semiconductor laser and wedge shaped waveguide modular speckle converter
The integrated device one semiconductor laser and wedged waveguide mode spot converter includes substrate area, light guiding area, limiting arean and electrode area. The limiting arean on the substrate includes one n-type lower limiting layer of doped InP; one p-type upper limiting layer of doped InP, which includes two layers, one layer on the light guiding arean and the other layer below the electrode area; one p-type layer of un-oxidized InAlAs stripes and Al-containing oxide stripes arranged alternately between two p-type upper limiting layers; and one optical medium film on two ends of the device. The electrode arean is made on the limiting arean and below the substrate area. The Al-containing oxide layer limits the injected current and laser field in the semiconductor laser part and makes the lower light guiding area form wedged waveguide in the wedged waveguide mode spot converter part.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Epitaxy structure of InGaN quantum dot and growth method
The invention discloses an epitaxy structure of an InGaN quantum dot and a growth method. The epitaxy structure of the InGaN quantum dot comprises a substrate, a low temperature GaN buffering layer, a high temperature GaN layer, a plurality of InGaN quantum dots and a GaN coverage layer, wherein an atomic-scale step form is arranged on the surface of the substrate, and the chamfer angle of steps is 0.05-10 degrees; the low temperature GaN buffering layer is grown on the substrate, and the surface of the low temperature GaN buffering layer is provided with a step form the same as that the substrate; the high temperature GaN layer is grown on the low temperature GaN buffering layer, grooves are etched in the surface of the high temperature GaN layer, the surface of the high temperature GaN layer is of a staggered step form, and a latticed structure is formed on the surface of the high temperature GaN layer; the multiple InGaN quantum dots are distributed and grown on the latticed structure of the surface of the high temperature GaN layer; the GaN coverage layer is grown on the high temperature GaN layer and covers the multiple InGaN quantum dots; the multiple InGaN quantum dots and the GaN coverage layer are sequentially and repeatedly grown on the GaN coverage layer.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
GaN-based semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a GaN-based semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof. The GaN-based semiconductor device comprises a silicon substrate and an epitaxial layer formed on the silicon substrate, and is characterized in that the epitaxial layer comprises an AlN nucleating layer, an AlGaN buffer layer and a GaN buffer layer which are sequentially formed on the silicon substrate. According to the invention, a dielectric film is adopted to act as a mask layer, different effects are achieved through regulating and controlling the periodicity of a dielectric layer, and the dielectric layer can act as a limiting layer when the periodicity reaches the maximum, so that the optical loss can be effectively reduced, and threshold current of a laser and a super-radiation light-emitting diode is reduced; and the electric layer acts as an interface layer when the periodicity is small and forms another optical waveguide structure together with AlGaN at the bottom, a planar coupling optical waveguide laser and a super-radiation light-emitting diode are formed, and a nearly-circular light spot with a good shape can be acquired.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Semiconductor laser with elliptic annular window
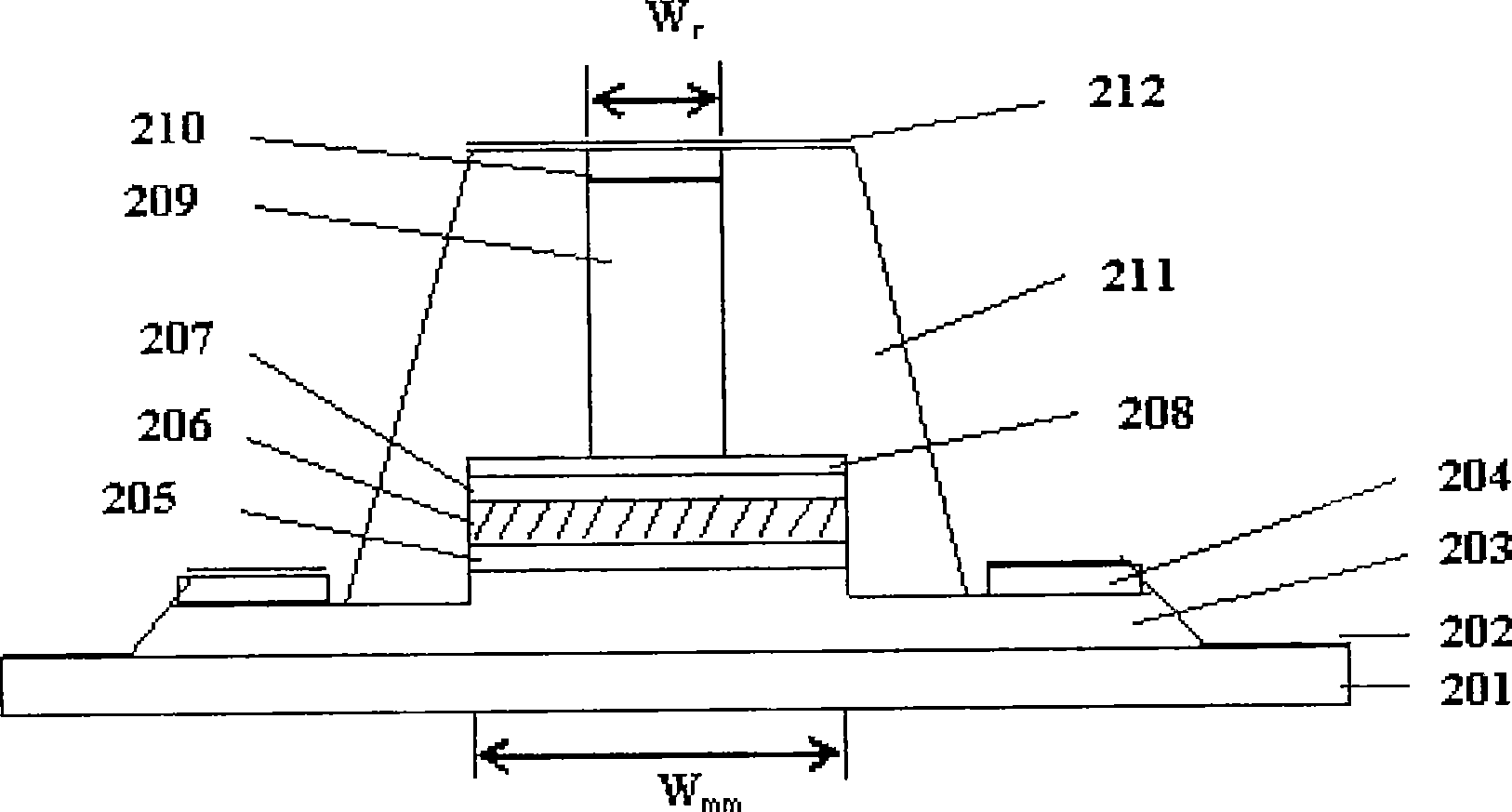
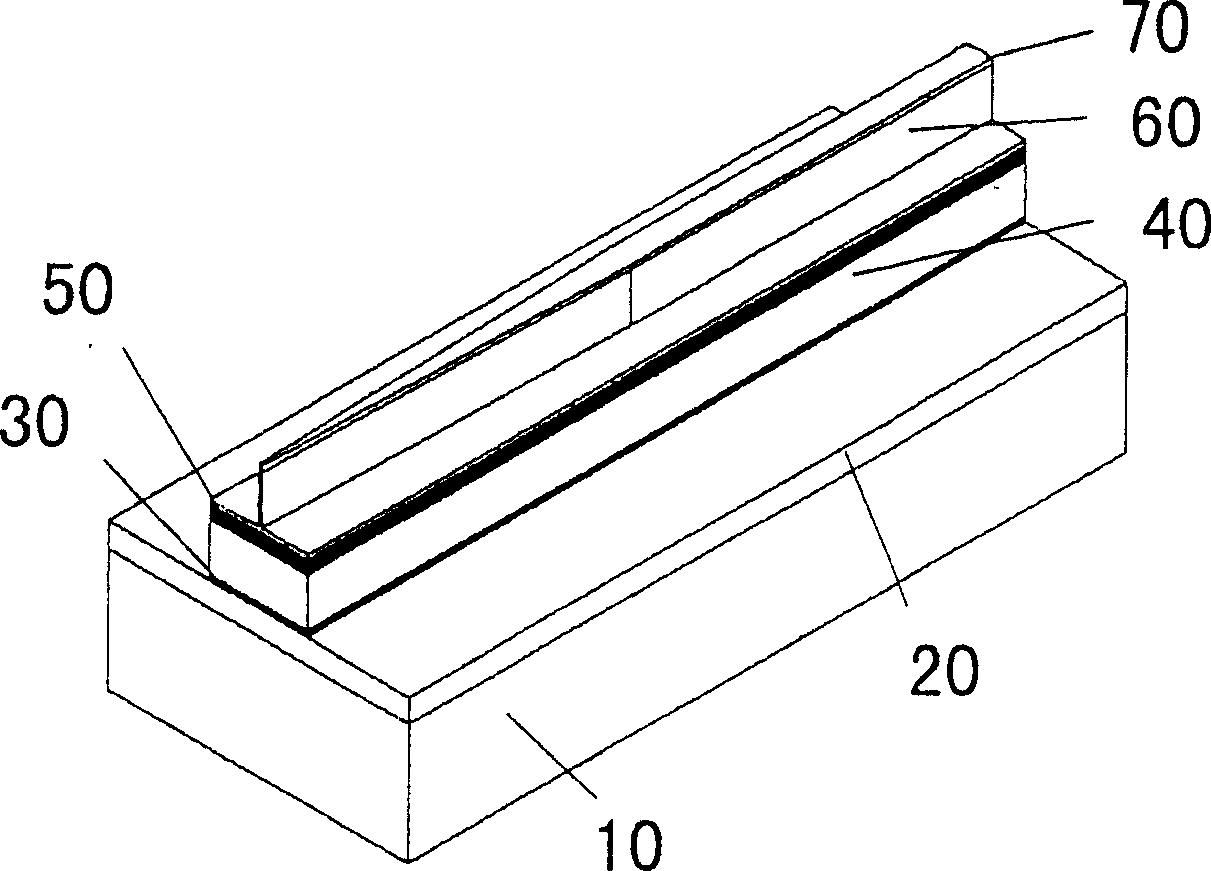
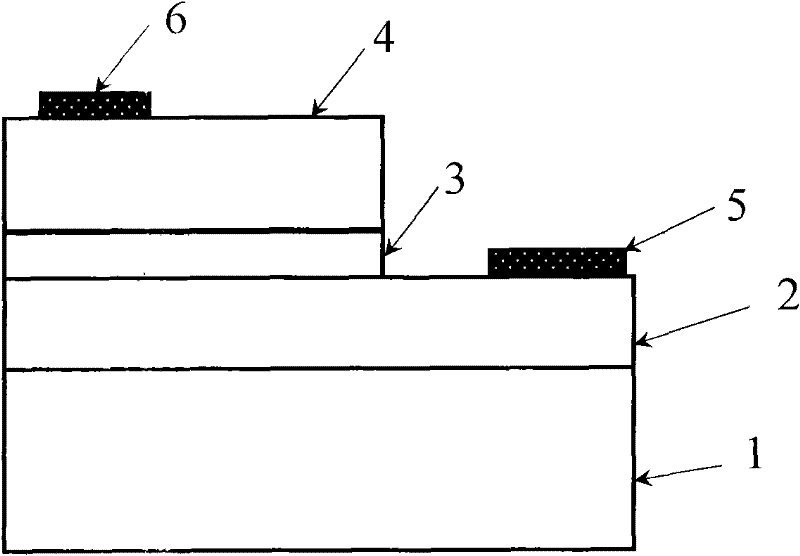
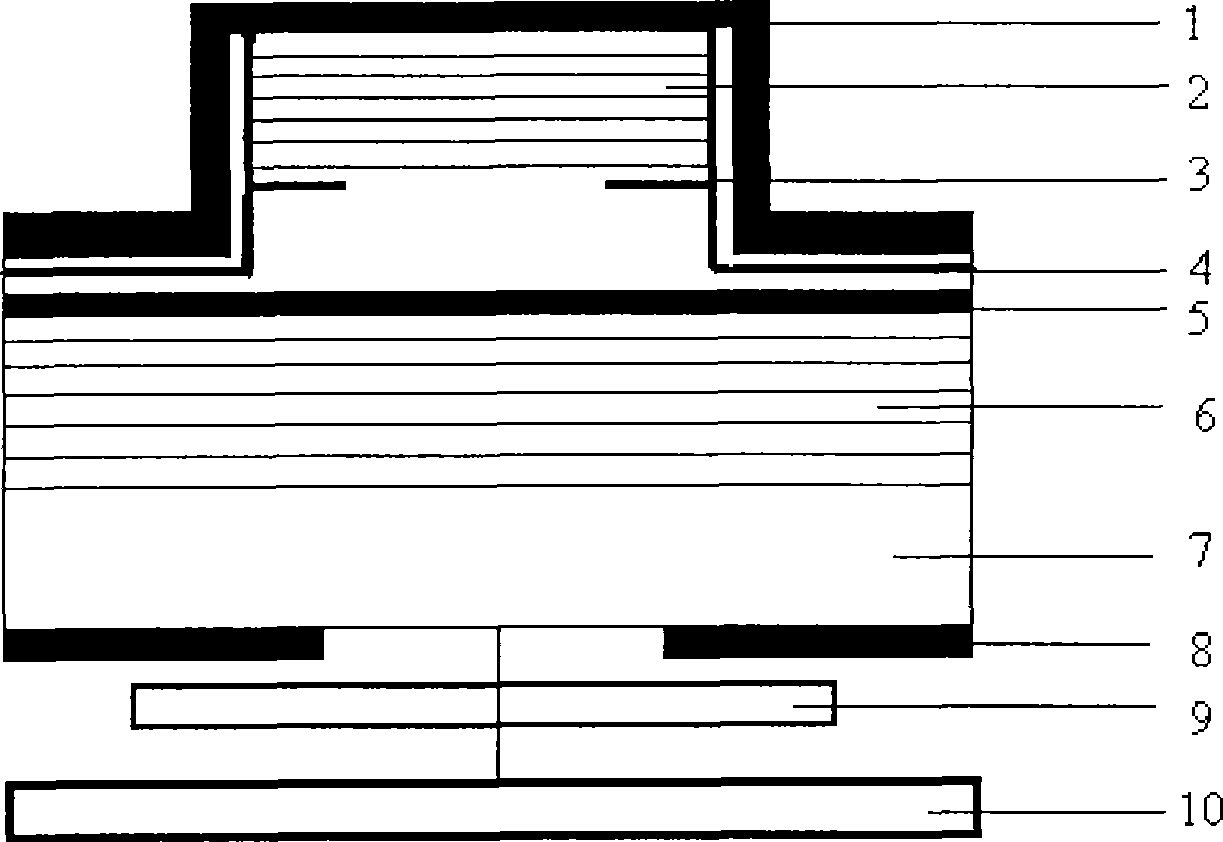
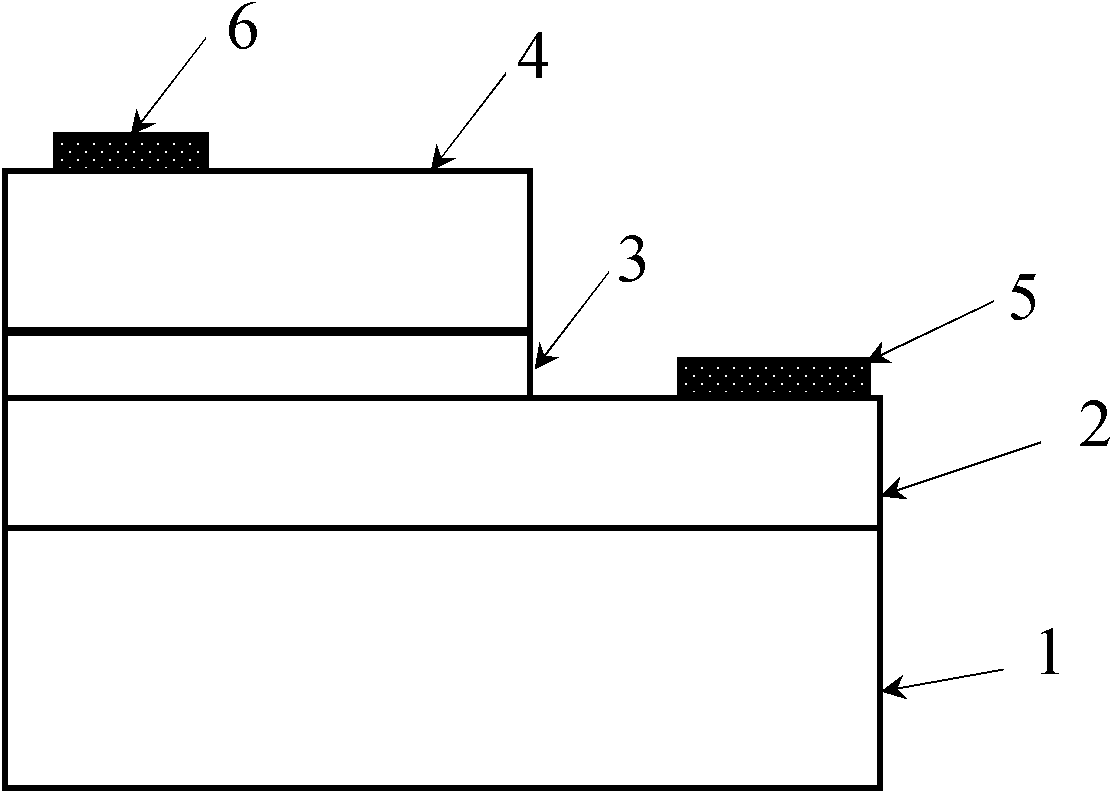
InactiveCN105790069APrevent proliferationReduce leakageLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor materialsOhmic contact
A traditional vertical cavity surface emission semiconductor laser is in a completely symmetric round shape, output light of the laser is round symmetric light beams, the light beams are not hollow and is in an instable polarization state. The invention provides a semiconductor laser with an elliptic annular window. The structure is shown as figures: the elliptic annular window 1, an upper electrode 2, an ohmic contact layer 3, an upper distributed Bragg reflection mirror 4, an oxide limitation layer 5, a semiconductor material active gain layer 6, a lower distributed Bragg reflection mirror 7, a substrate 8 and a lower electrode 9, the overall structure from the elliptic annular window to the active gain layer is an elliptic cylindrical structure, the ratio selection range between the length of a long shaft and the length of a short shaft of the elliptic structure is 3:2 to 5:4, a central region of the elliptic cylindrical structure is hollow, and an elliptic etching region 10 formed by etching is etched from the ohmic contact layer to the upper distributed Bragg reflection mirror. The semiconductor laser works in an electric pumping mode, elliptic hollow light beams can be emitted under the effect of the elliptic annular window, the emitted elliptic hollow light beams have favorable polarization characteristics, and the polarization is in a stable state.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High power 650nm semiconductor laser for digital multi-purpose optical disks and manufacturing method
InactiveCN1805027ALower threshold currentSmall working currentLaser active region structureOptical beam sourcesSemiconductorCarrier leakage
The invention relates to a digital multi-function disc used large power 650nm semiconductor laser, which comprises a substrate used to do laser material structure external growth, a buffer layer on the substrate, a N type cladding on the buffer layer to limit the leakage of the loading unit, an active region layer on the cladding, a first P type cladding on the active region layer to limit the leakage of the loading unit, a current barrier layer on the P type cladding to barriers the current spread to reduce the current leakage, a second P type cladding on the current barrier layer and the first P type cladding to limit the leakage of the loading unit, a basaltic layer on the second P type cladding, an electrode touching layer on the basaltic layer, a double groove structure on the electrode touching layer, the basaltic layer and the second P type cladding which adopts etching bath to etch the three grooves, and a silicon nitride oxide layer on the electrode touching layer which covers the double grooves.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Total-reflection optical waveguide semiconductor laser chip and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN108631153AAchieve light confinementLower threshold currentOptical wave guidanceThinningHigh reflectivity
A total-reflection optical waveguide semiconductor laser chip and a manufacturing method thereof are disclosed. The semiconductor laser chip comprises an epitaxial wafer. The epitaxial wafer comprisesa substrate, a lower cladding, an active area, an upper cladding and an Ohmic contact layer which are successively arranged from bottom to top. The center position of the epitaxial wafer is providedwith a ridge-type optical cavity. The two sides of the ridge-type optical cavity are provided with isolation grooves. The outer side of each isolation groove is provided with a shoulder area. The upper surface of the epitaxial wafer is provided with a high-reflectivity optical film layer and a P electrode layer. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of (1) forming the epitaxial wafer; (2) carrying out one-time photoetching; (3) evaporating a high-reflectivity optical film; (4) carrying out two times of photoetching; (5) carrying out three times of photoetching; (6) manufacturing the P electrode layer; (7) carrying out substrate thinning; (8) manufacturing an N electrode layer; (9) carrying out strip dissociation and coating; and (10) forming a single laser chip. In the invention, the optical limiting of an optical cavity is realized, the threshold current of the laser chip is reduced, photoelectric conversion efficiency is increased, an output light shape is obviouslyimproved, stray light is eliminated and chip reliability is increased.
Owner:Shandong Huaguang Optoelectronics Co. Ltd.
Three-dimensional sensing system based on vertical cavity surface transmission laser device array
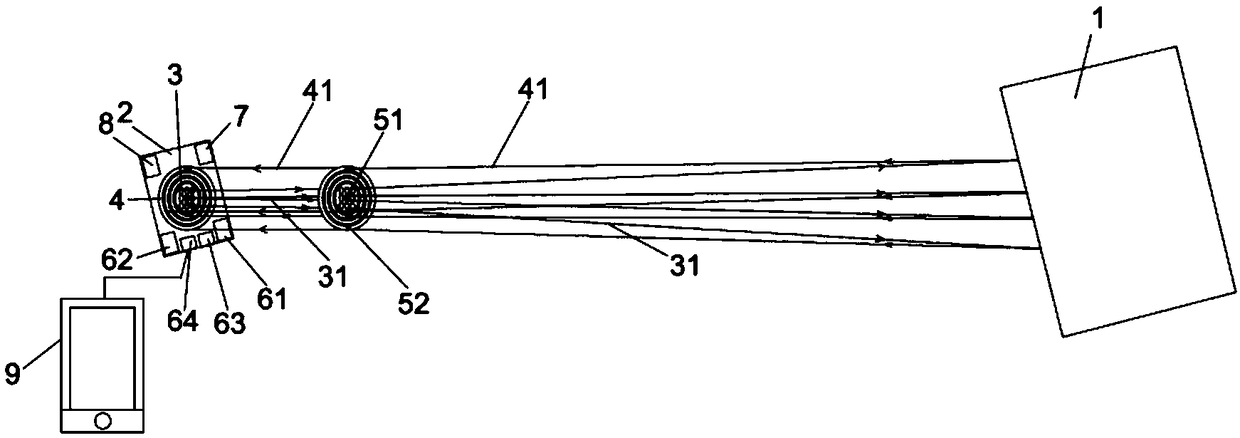
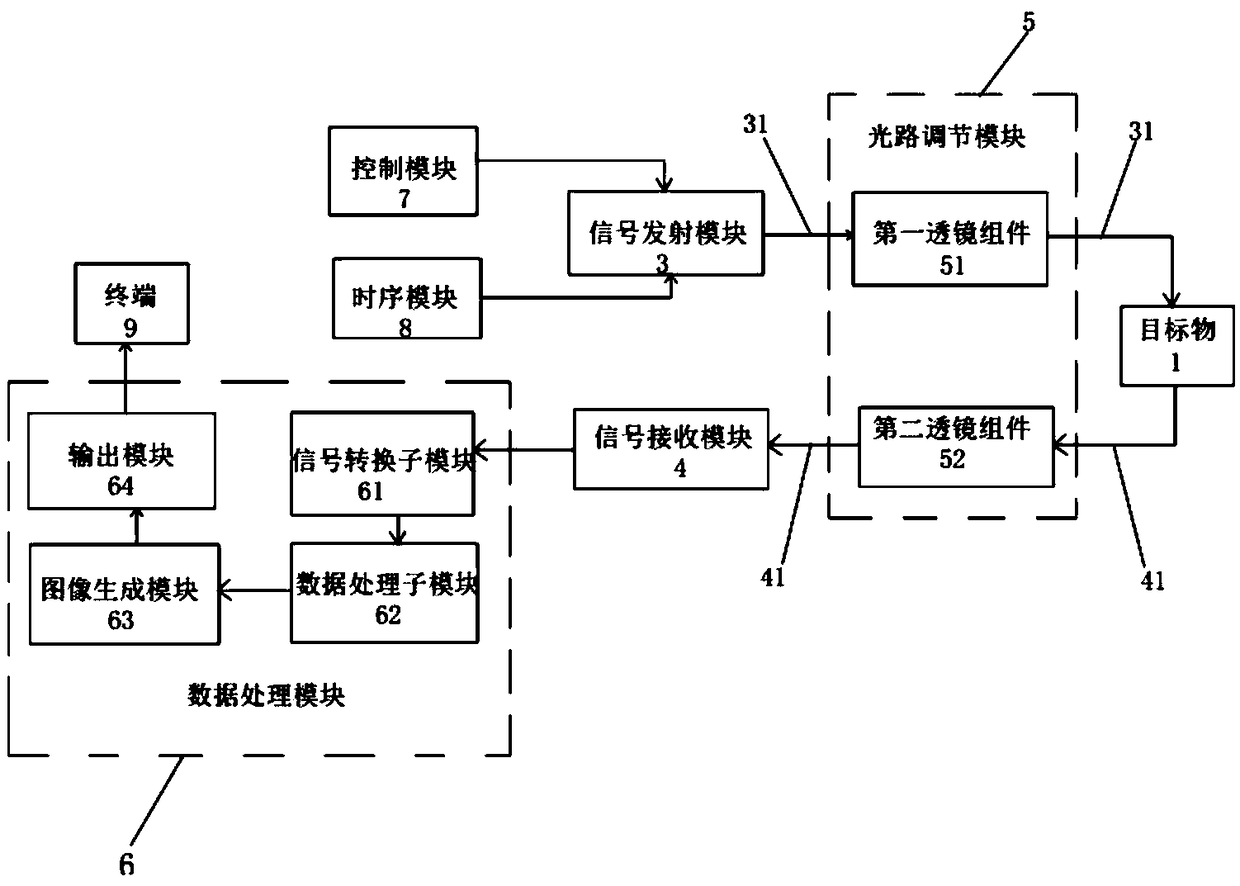
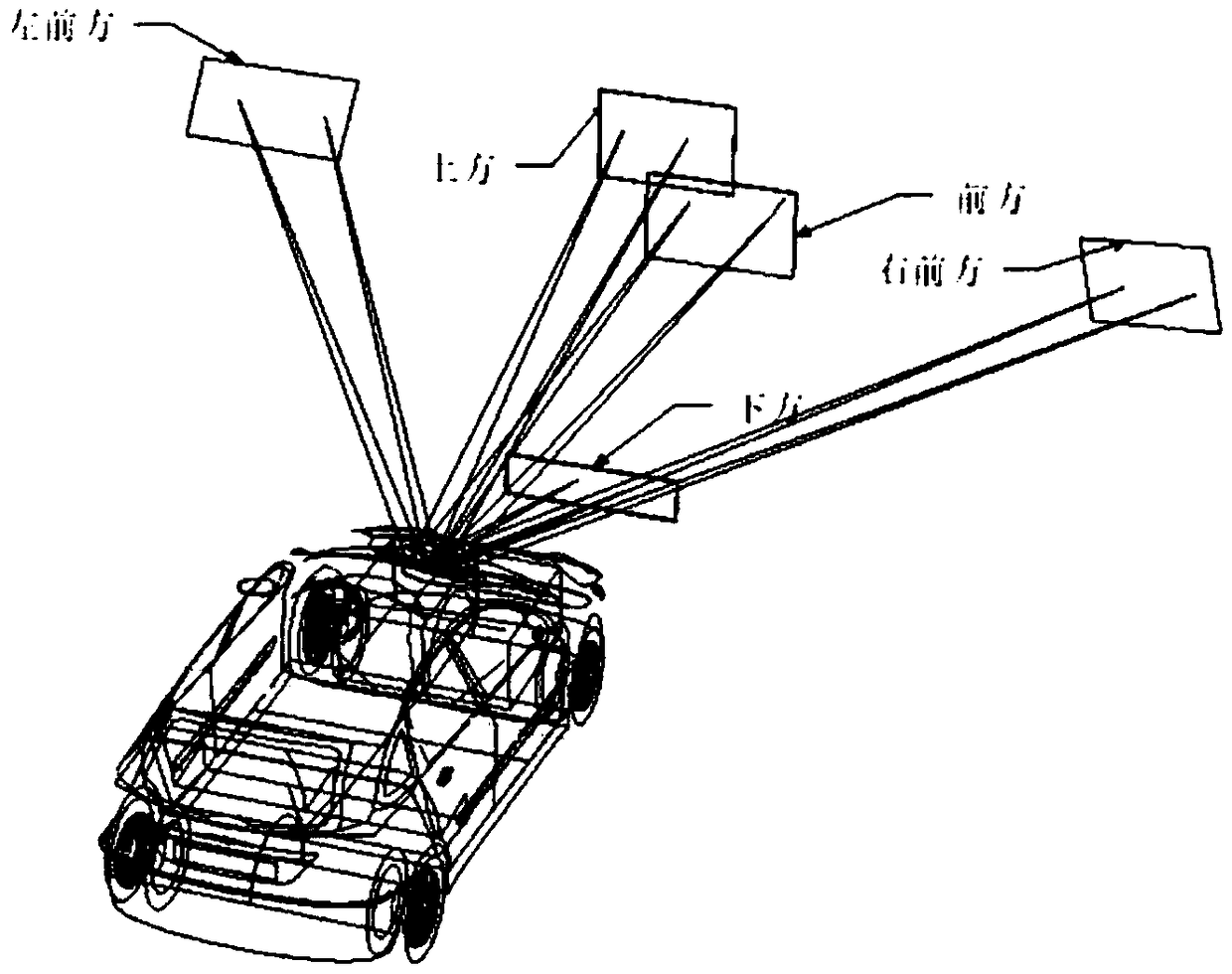
PendingCN108680929AReduce volumeIn line with the trend of miniaturizationLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersComputer moduleOptoelectronics
The invention relates to the sensing technology field and discloses a three-dimensional sensing system based on a vertical cavity surface transmission laser device array. The system comprises a signaltransmission sub-module, a signal receiving sub-module, an optical path adjustment module and a data processing module, wherein the signal transmission submodule is used for transmitting a laser signal to a target under the first condition, the signal receiving submodule is used for receiving the laser signal reflected by the target under the second condition, the optical path adjustment module is used for shaping the laser transmitted by the signal transmission sub-module into parallel light which is then transmitted to the target and used for shaping the laser reflected by the target into parallel light which is then transmitted to the signal receiving sub-module, and the data processing module is used for analyzing and processing the laser signal reflected by the target. The system isadvantaged in that both the signal transmission sub-module and the signal receiving sub-module are vertical cavity surface transmission laser device (VCSEL) arrays, the signal transmission sub-moduleand the signal receiving sub-module are integrated on the same motherboard, and the integration degree is relatively high.
Owner:度亘核芯光电技术(苏州)有限公司
Inner cavity type multiple-active region photon crystal vertical cavity surface transmission semiconductor laser device
InactiveCN101588018ALower threshold currentReduced series resistanceOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsLarge seriesPhotonic crystal structure
The invention relates to an inner cavity type multiple-active region photon crystal vertical cavity surface transmission semiconductor laser device, belonging to the semiconductor photoelectron field. The common oxidation limiting vertical cavity surface transmission semiconductor laser device has problems of multiple-transverse module laser shooting, low single module output power, large threshold current and large series resistance and so on. The invention adopts the multiple-active region structure on the active region of the device, meanwhile leads the defect type photon crystal structure into DBR on the vertical cavity surface transmission semiconductor laser device, the inner cavity type multiple-active region photon crystal vertical cavity surface transmission semiconductor laser device with dozens of micrometres of single module operation oxidation bore diameter, dozens of mws of single module power, dozens of Ohms of series resistances and more than 40 dbs of side module inhibition can be obtained by optimizing the photon crystal period, the air bore diameter, the etching depth, the device diameter and the oxidation bore diameter and so on reasonably.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation process of ridge waveguide DFB laser based on double-glue-layer structure
PendingCN112038218ALower threshold currentReduce the ratioOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsWaveguide lasersPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation process of a ridge-type waveguide DFB laser based on a double-glue-layer structure. Windowing of a ridge-type region current channelcomprises the steps: depositing a SiO2 insulating layer in a plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition mode; coating a first layer of photoresist on the surface of the SiO2 insulating layer, and baking the first layer of photoresist to prevent the first layer of photoresist from being corroded by a wet method; coating a second layer of photoresist on the first layer of photoresist; baking the second layer of photoresist, wherein the baking temperature and time are both lower than those of the first layer of photoresist; performing exposure and development on the second layer of photoresist by using the photomask; corrodingthe second layer of photoresist subjected to exposure and development by adopting a wet etching process; etching the first layer of photoresist by adopting an RIE dry etching process; and etching theSiO2 insulating layer by adopting an RIE dry etching process, and removing the SiO2 insulating layer on the ridge strips to form a current channel. According to the method, the ridge-shaped structurewith a complete vertical shape on the side surface can be prepared.
Owner:武汉敏芯半导体股份有限公司
Surface emitting laser and surface emitting laser array
ActiveCN109861078ALower threshold currentLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersSandwich likeInsulation layer
The invention discloses a surface emitting laser which comprises a substrate and a functional layer which is of a sandwich-like type structure. The functional layer comprises a first doped layer, an active layer, a limiting layer and a second doped layer, wherein the active layer and the limiting layer are positioned between the first doped layer and the second doped layer. The first doped layer and the second doped layer are used for conveying carriers to the active layer, and the carriers can firstly pass through the limiting layer and then be transmitted to the active layer to compositely emit light. The limiting layer comprises an insulation layer and a conductive column and the conductive column runs through the insulation layer according to a thickness direction, and thus, the carriers need to be transmitted to the active layer through the conductive column, an area of a carrier compounding region of the active region can be limited, and in a case of keeping the same carrier density, a required injection current is smaller, so that in the premise of not changing a volume and an area of photon crystals, a threshold current required for photon excitation is reduced. The invention further provides a surface emitting laser array which also has the beneficial effects above.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Long wavelength GaNAsBi/GaAs multiple-quantum well laser and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103280695ARaise the characteristic temperatureNo refrigeration workLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersLower limitOhmic contact
The invention discloses a long wavelength GaNAsBi / GaAs multiple-quantum well laser, comprising a lower limit layer, a lower wave guide layer, an active region, an upper wave guide layer, an upper limit layer and an ohmic contact layer, which are connected in sequence, wherein the active region adopts a GaNAsBi / GaAs multiple-quantum well structure. According to the invention, the threshold current of the laser can be lowered, the gain of the laser can be increased, the refrigeration-free work can be realized, the laser is suitable for multiple lasers such as a surface launching laser, the production cost of the laser is far lower than that of an INP (indium phosphide)-based laser, no Al exists in the active region of the multiple-quantum well laser, the growth technics difficulty can be reduced, and the yield of the laser can be increased and the service life of the laser can be prolonged.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Vertical cavity surface emitting laser capable of controlling outer cavity polarization
ActiveCN101521355AIncrease output powerEnhanced Polarization RatioLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserGrating
The invention relates to a vertical cavity surface emitting laser, in particular to a vertical cavity surface emitting laser capable of controlling outer cavity polarization. The laser mainly comprises a p type DBR layer, an active layer, an n type DBR layer, a GaAs substrate, a p electrode, an n electrode and an outer cavity high-reflection mirror, wherein the p electrode is coated on the p type DBR layer, the n electrode is laid at the bottom of the GaAs substrate, and the outer cavity high-reflection mirror is arranged on the optical axis of the emergent light. The invention is characterized in that an amorphous silicon grating is also arranged between the window of the emergent light and the outer cavity high-reflection mirror. With the outer cavity structure, the vertical cavity surface emitting laser capable of controlling outer cavity polarization can better stabilize and control the polarization characteristics of output light to obtain a higher polarization selection ratio; meanwhile, the output power of linear polarization light is improved.
Owner:吉光半导体科技有限公司
Laser radar device and laser radar system
PendingCN108828559ASimple structureReduce volumeWave based measurement systemsVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserRadar systems
The invention relates to the technical field of laser, and discloses a laser radar device. The laser radar device comprises a signal transmitting module, a signal receiving module, an optical path adjusting module and a data processing module, wherein the signal transmitting module is used for transmitting a laser signal to a target object; the signal receiving module is integrated with the signaltransmitting module on the same laser radar main board, and is used for receiving the laser signal reflected by the target object; the optical path adjusting module is arranged on an optical path inwhich the laser signal locates, and is used for adjusting the optical path of laser; and the data processing module is connected with the signal receiving module, and is used for analyzing and processing the laser signal reflected by the target object. The signal transmitting module is a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) array. The signal transmitting module and the signal receiving module are integrated on the same laser radar main board, thereby greatly simplifying the structure of the laser radar device, reducing the size of the existing laser radar device, improving the integration degree, and conforming to the trend of miniaturization of the current laser radar.
Owner:度亘核芯光电技术(苏州)有限公司
GaN-based laser unit and super-radiation light-emitting diode as well as manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN106711764ARaise the lateral limitLower threshold currentLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersOptical limitingElectron blocking layer
The invention discloses a GaN-based laser unit and a super-radiation light-emitting diode as well as a manufacturing method thereof. A ridged structure of the laser unit and the super-radiation light-emitting diode is directly formed through epitaxial growth, and comprises a substrate and an epitaxial layer, wherein strip-shaped step structures are distributed on the surface of the substrate, the epitaxial layer is arranged on the substrate, covers the strip-shaped step structures and is provided with the ridged structure, and the epitaxial layer comprises a lower contact layer, a lower limiting layer, a lower waveguide layer, an active layer, an upper waveguide layer, an electronic blocking layer, an upper limiting layer and an upper contact layer which are sequentially formed on the substrate. Through a method of forming a window area in the substrate or pre-etching to form the step structures, the ridge shape of laser unit and the super-radiation light-emitting diode is directly grown on the substrate, and optical limiting layers are grown at two sides of the ridge structure, so that transverse limit of an apparatus is effectively improved, threshold-value current of the apparatus is reduced, and etching operation can be further omitted, and therefore, etching loss is avoided, threshold-value current of the apparatus is further reduced, and reliability of the apparatus is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
ZnO and GaN-combined ZnO-based end surface transmitting laser and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101976800ALower threshold currentIncrease output powerLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlResonant cavityPower flow
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor light-emitting devices and preparation thereof and relates to a ZnO and GaN-combined ZnO-based end surface transmitting laser and a preparation method thereof. A chip of the ZnO and GaN-combined ZnO-based end surface transmitting laser comprises a substrate as well as a GAN epitaxial layer, a current lower limiting layer, a ZnO base material light-emitting layer and an upper electrode which are prepared on the substrate. The ZnO and GaN-combined ZnO-based end surface transmitting laser is characterized in that the substrate can be a conductive GaAs crystal slice, a conductive InP crystal slice, a conductive SiC crystal slice or a conductive GaN crystal slice, the conducting type of the substrate is the same as that of the GAN epitaxial layer, a lower electrode is prepared below the substrate, a front reflecting mirror and a back reflecting mirror are formed from a front end surface and a back end surface split by the chip, and the devices emit light through the front reflecting mirror and the back reflecting mirror. As a controllable resonant cavity of the ZnO base laser is prepared, the threshold current of the laser can be reduced, the output power of the devices is improved, the direction of laser is better, and therefore, the application range of the devices is further expanded.
Owner:EPITOP PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com