Method for forming semiconductor laser and spot-size converter by once epitaxy
A mode-spot converter and laser technology, applied in semiconductor lasers, lasers, laser parts, etc., can solve the problems of poor device fabrication repeatability, difficult interface processing, and deterioration of mode characteristics, and achieve high differential gain, low cost, and low cost. The effect of device cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
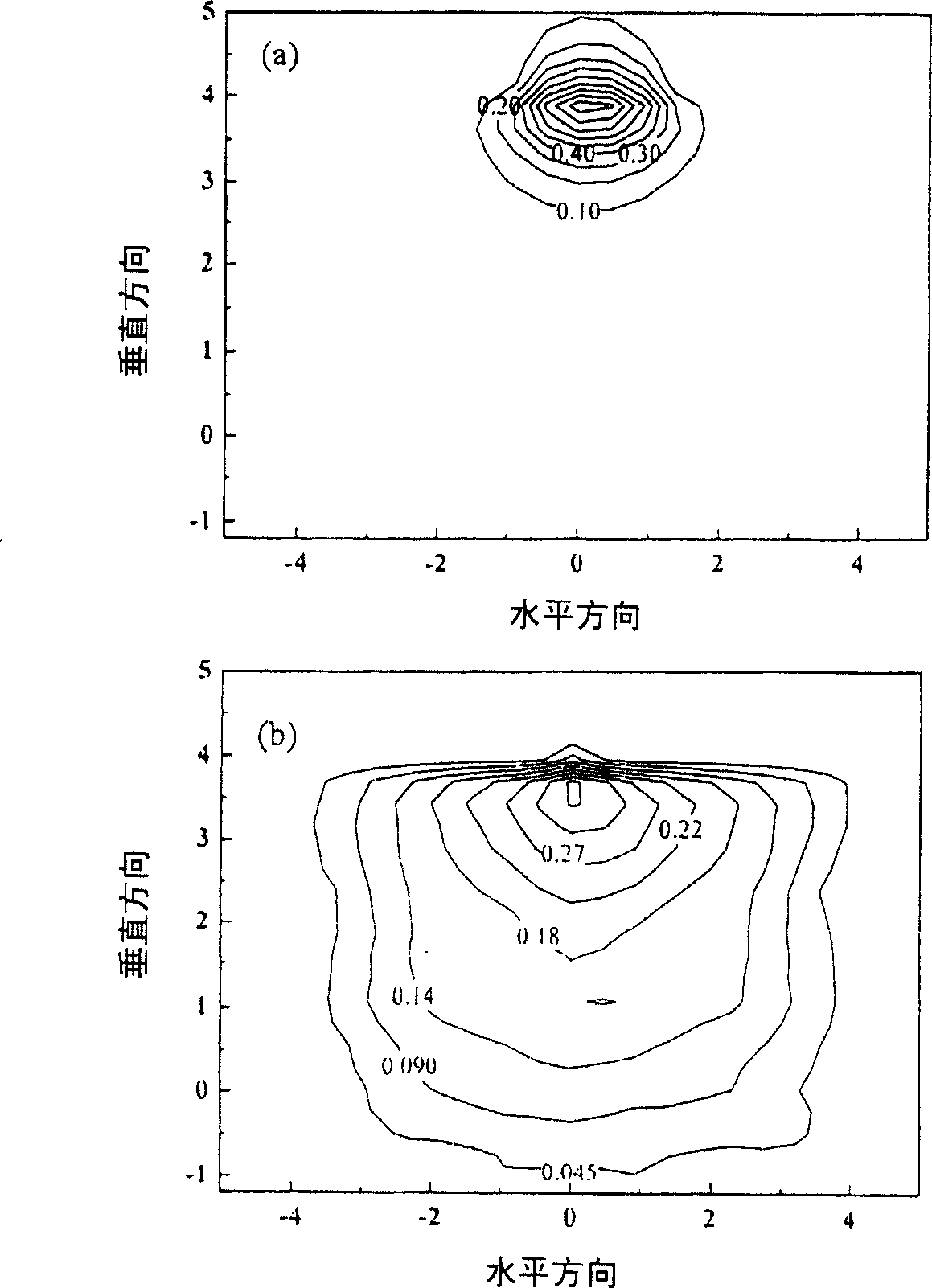
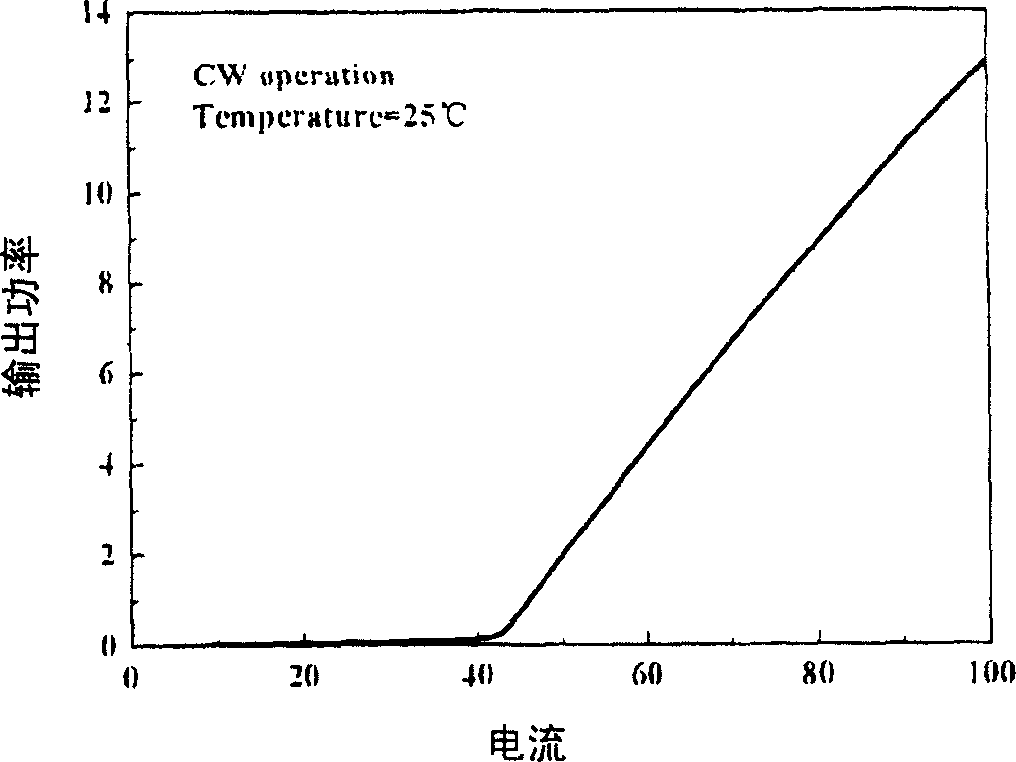
Image
Examples
Embodiment
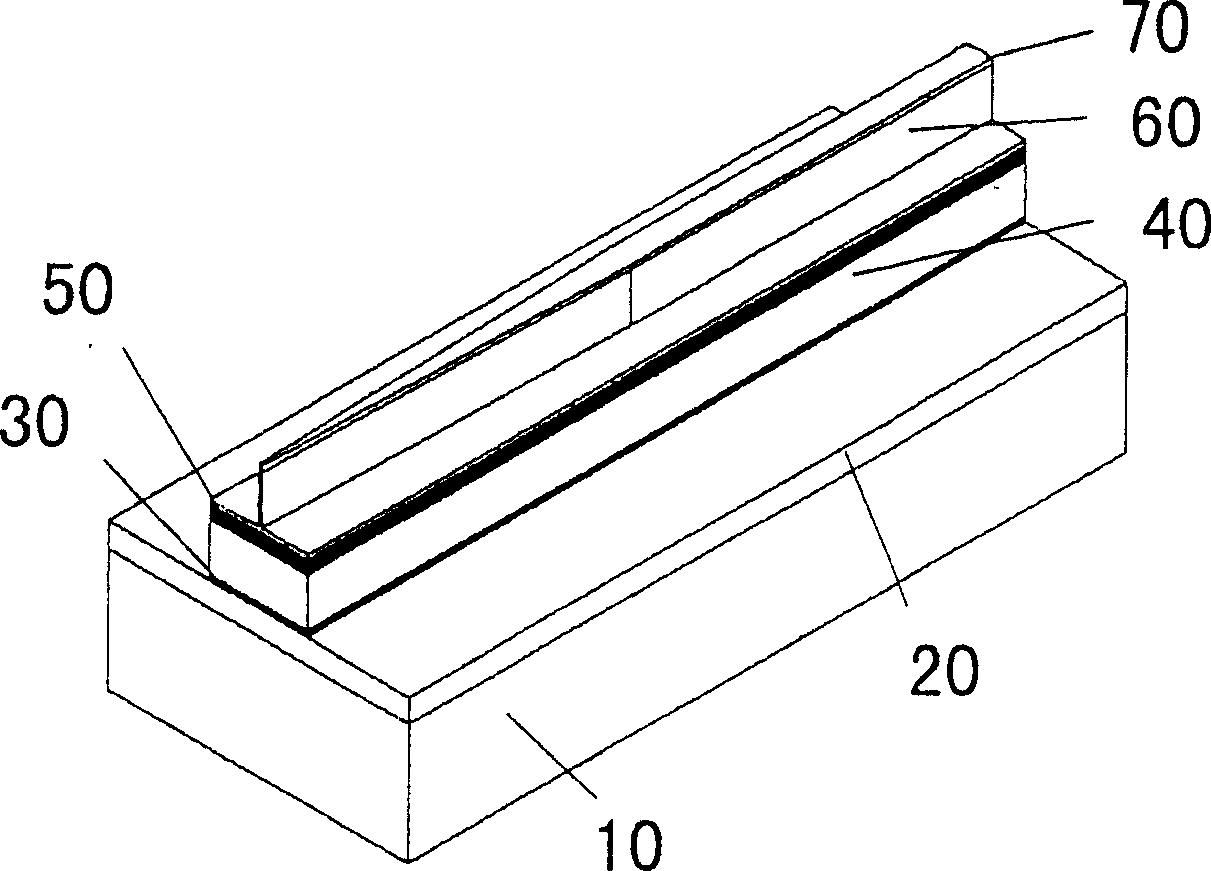
[0062] Please refer to figure 1 , the present invention relates to a kind of preparation method of novel LD-SSC, comprises following preparation steps:
[0063] (1) The 2-inch n-InP substrate undergoes strict decontamination (heating and boiling with ethanol, trichlorethylene, acetone, and ethanol in sequence) → pickling (soaking in concentrated sulfuric acid for 1 to 2 minutes) → water washing (rinsing with deionized water More than 50 times) → after drying treatment, put it into the growth chamber, the growth temperature is 655°C, the growth pressure is 22mbar, and the graphite boat speed is 75-80 rpm.
[0064] (2) On the n-type indium phosphide substrate (100) epitaxially grow n-type indium phosphide buffer layer (0.5 μm thick), lower waveguide layer (thickness 50nm, bandgap wavelength is 1.1 or 1.2 μm), 2.4 μm Indium phosphide space layer, lower optical confinement layer (thickness 80nm, bandgap wavelength 1.1 or 1.2μm), compressive strain quantum well active region, uppe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bandgap wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com