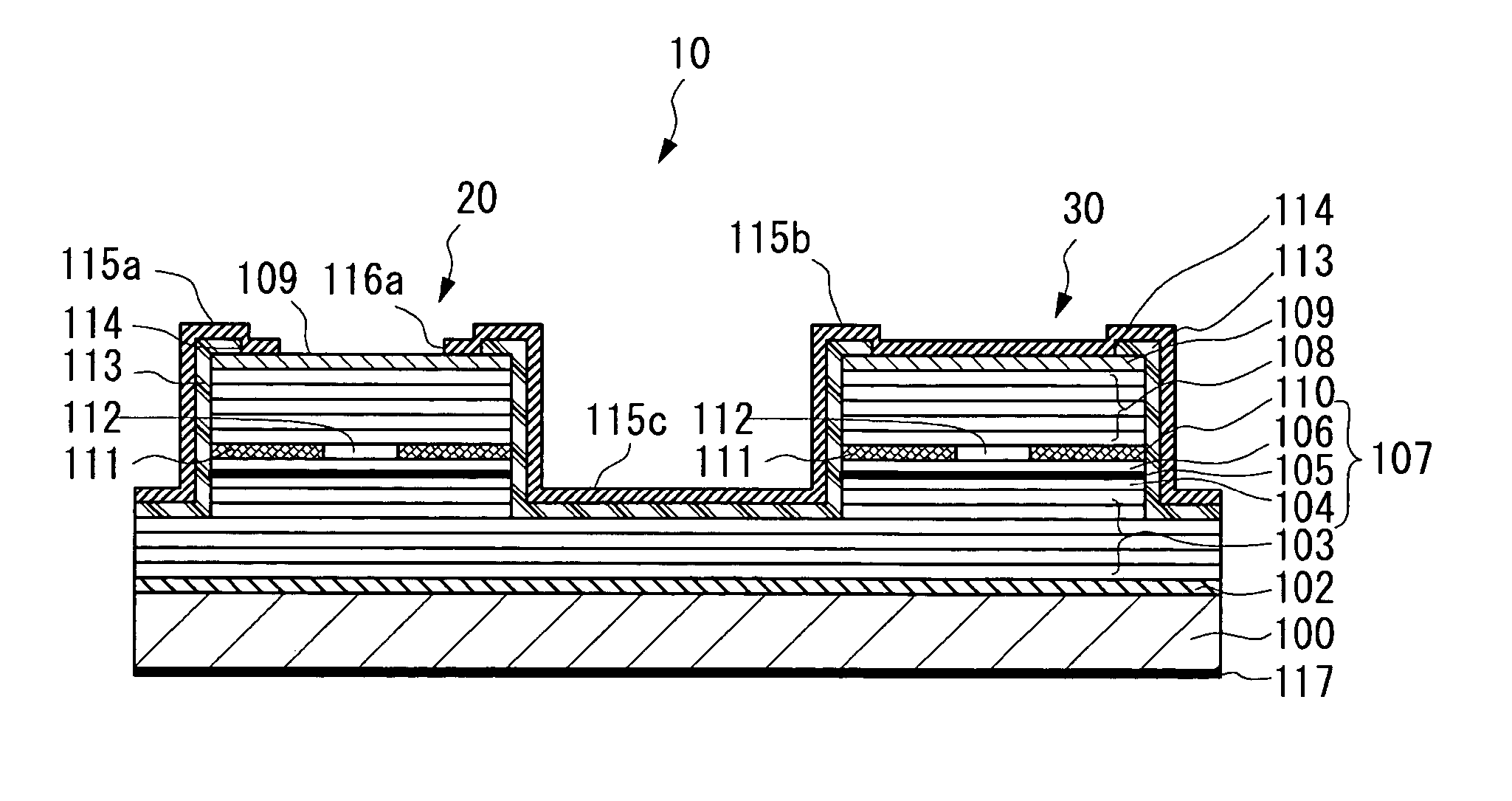
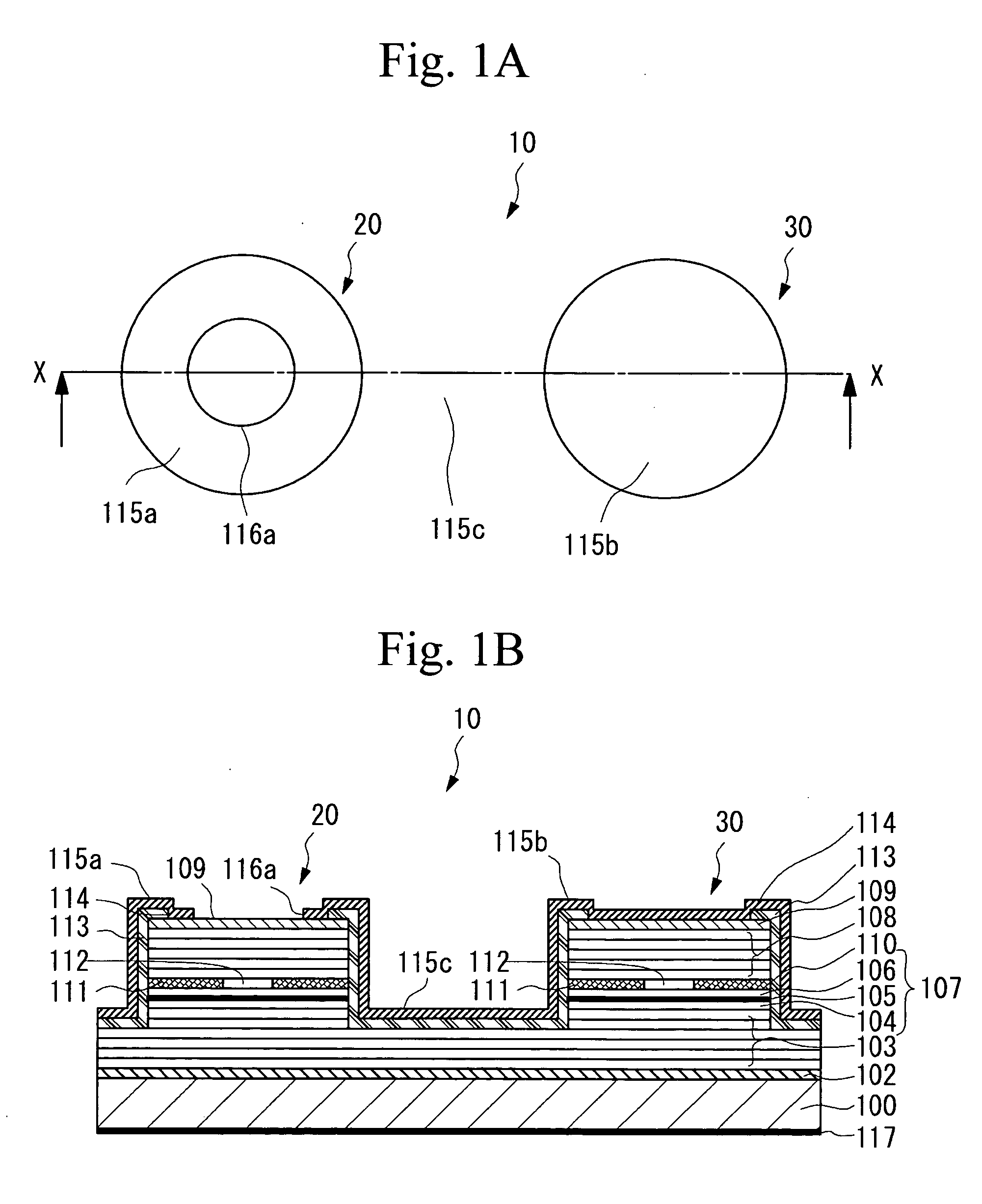
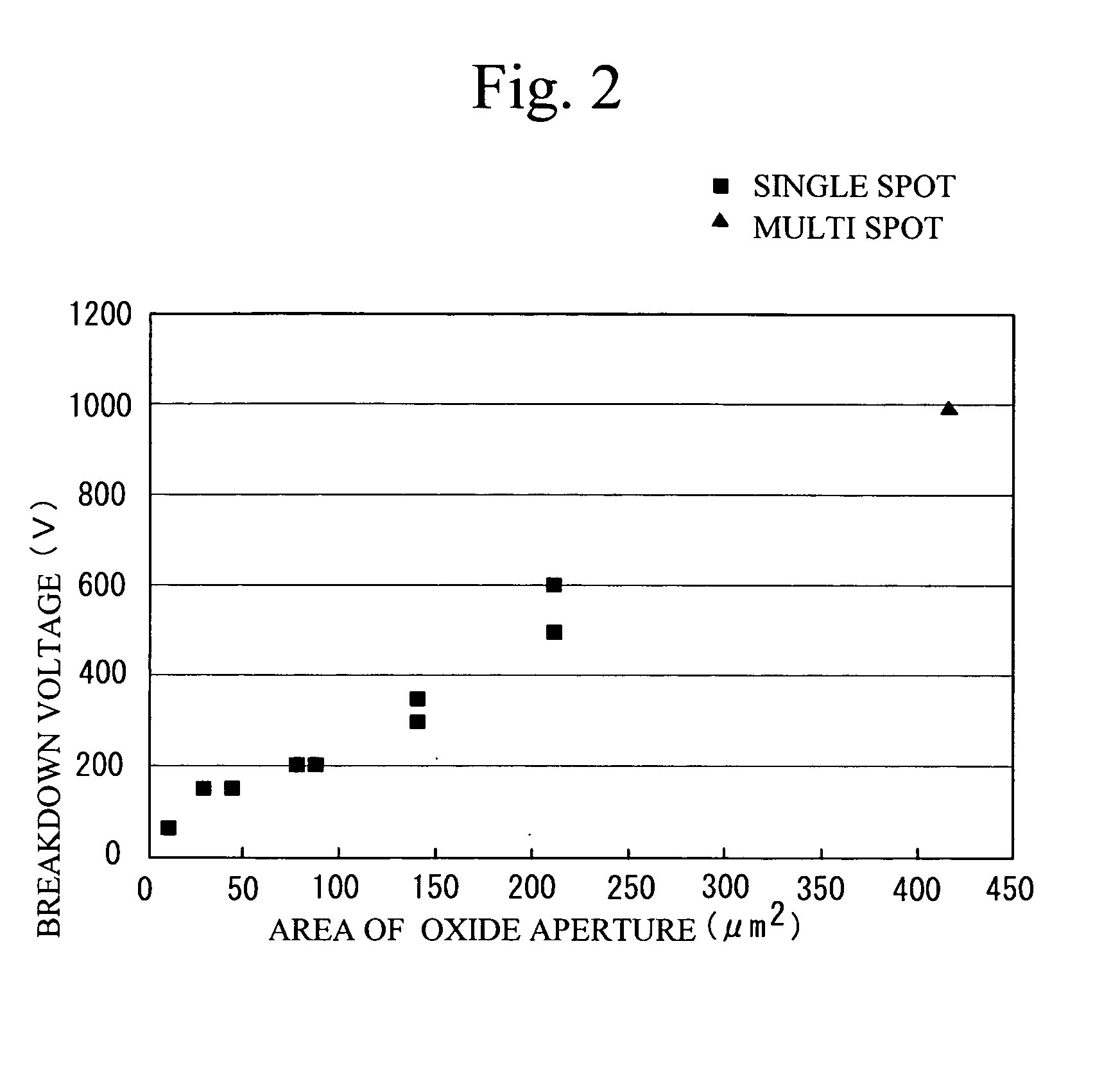
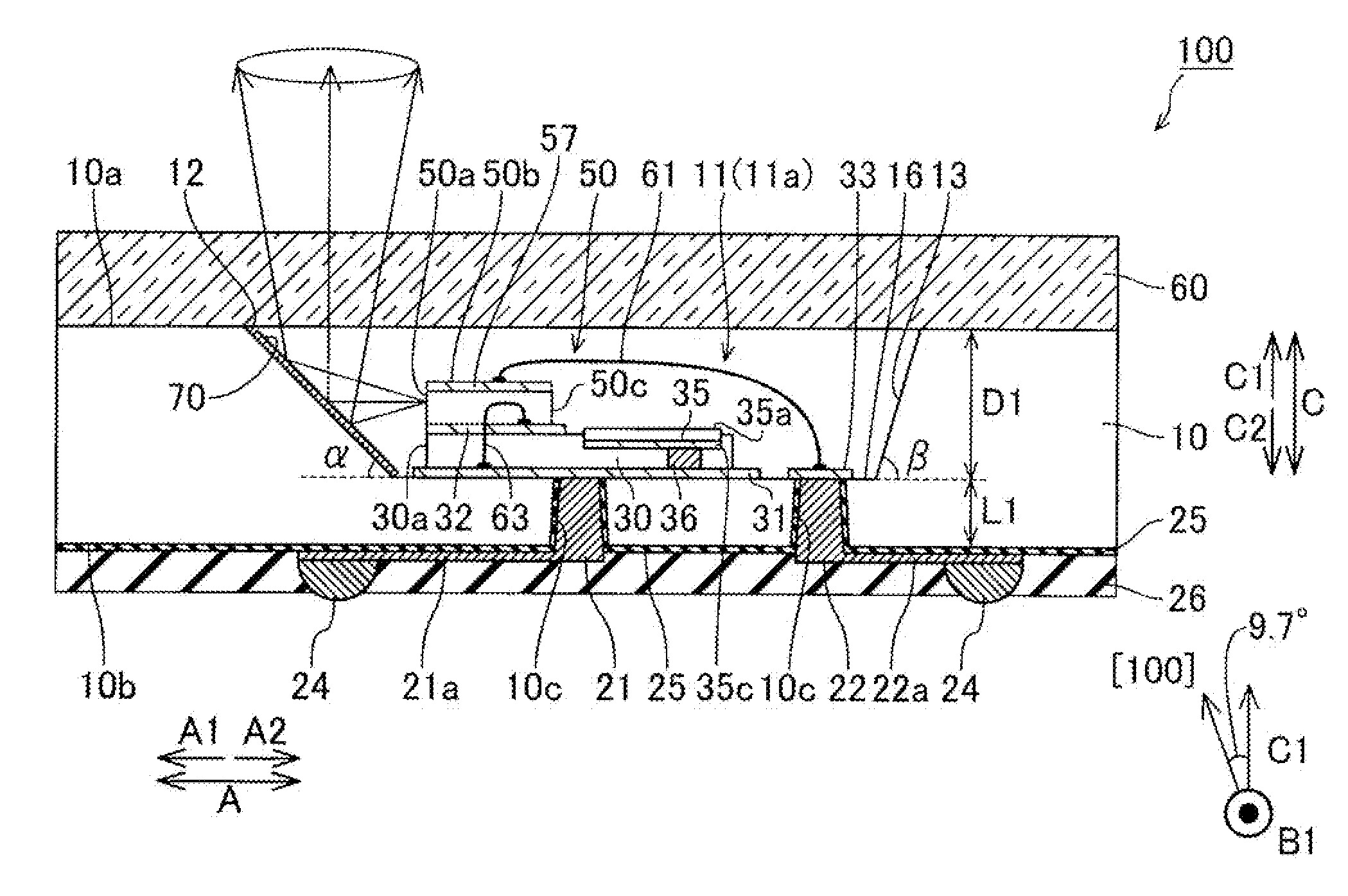
Patents
Literature
2340 results about "Semiconductor laser theory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
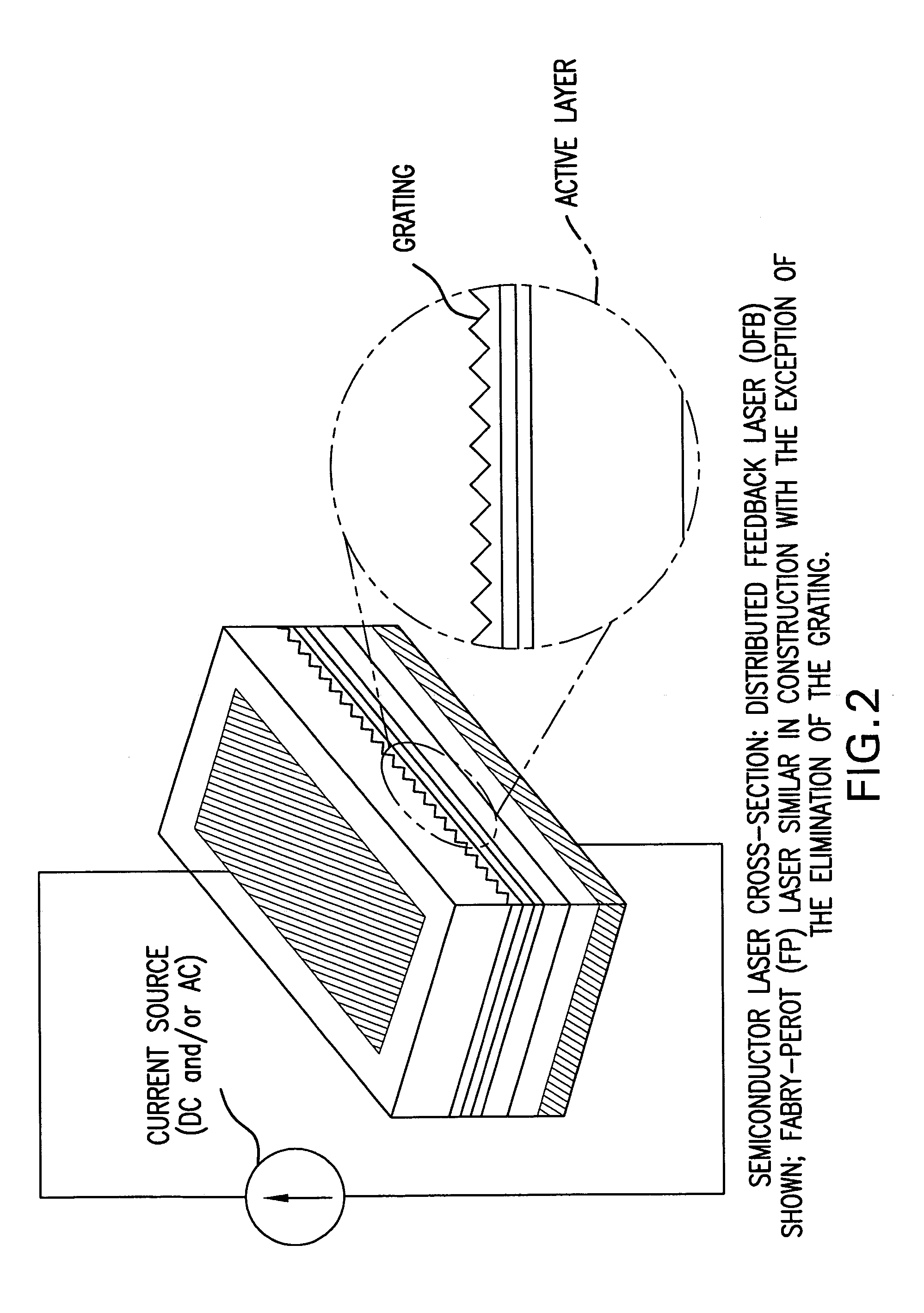
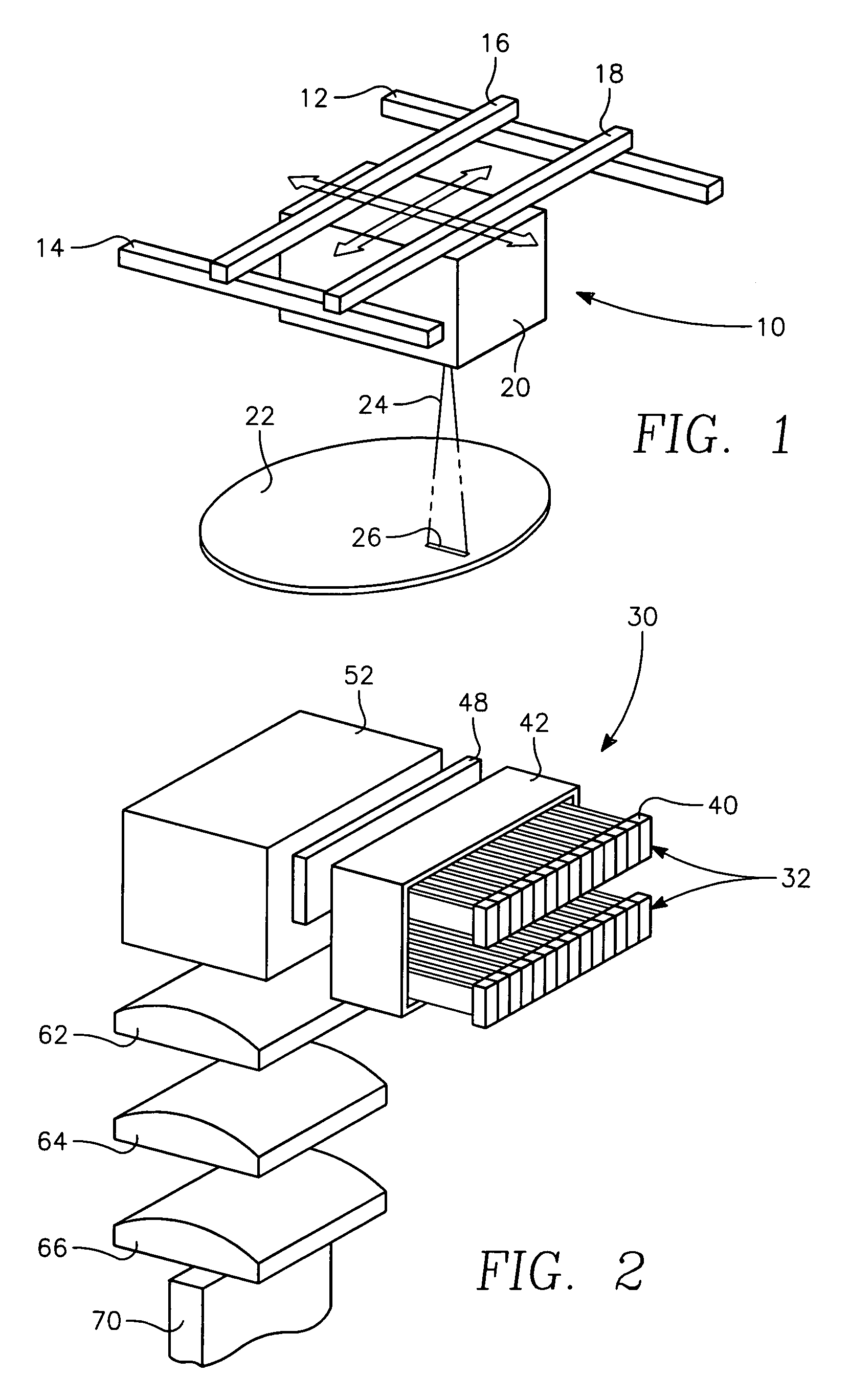
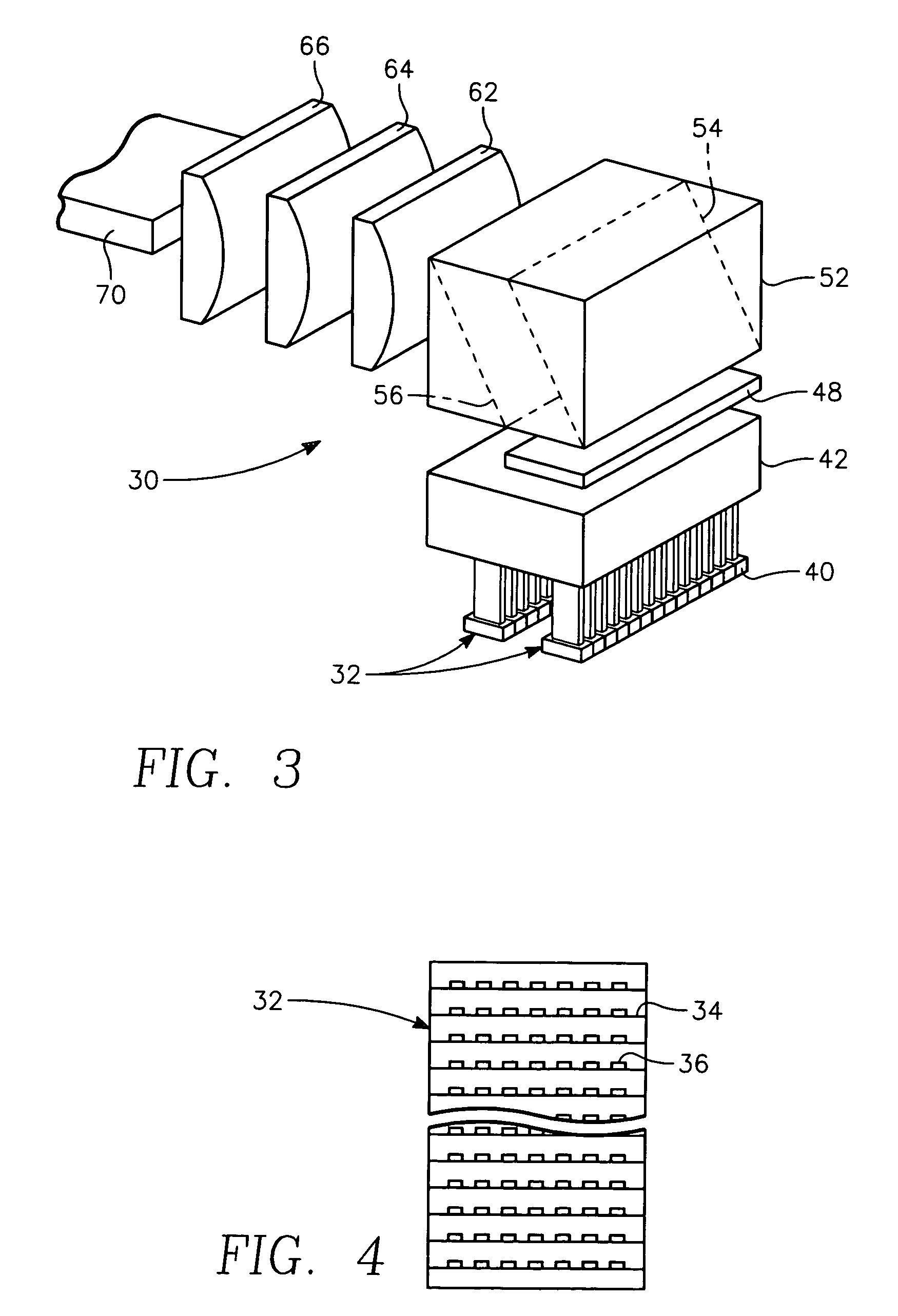
Semiconductor lasers or laser diodes play an important part in our everyday lives by providing cheap and compact-size lasers. They consist of complex multi-layer structures requiring nanometer scale accuracy and an elaborate design. Their theoretical description is important not only from a fundamental point of view, but also in order to generate new and improved designs. It is common to all systems that the laser is an inverted carrier density system.
Semiconductor laser diode
InactiveUS20080285609A1Improve luminous efficiencyAvoid polarizationLaser detailsLaser active region structureLight-emitting diodeCrystal growth
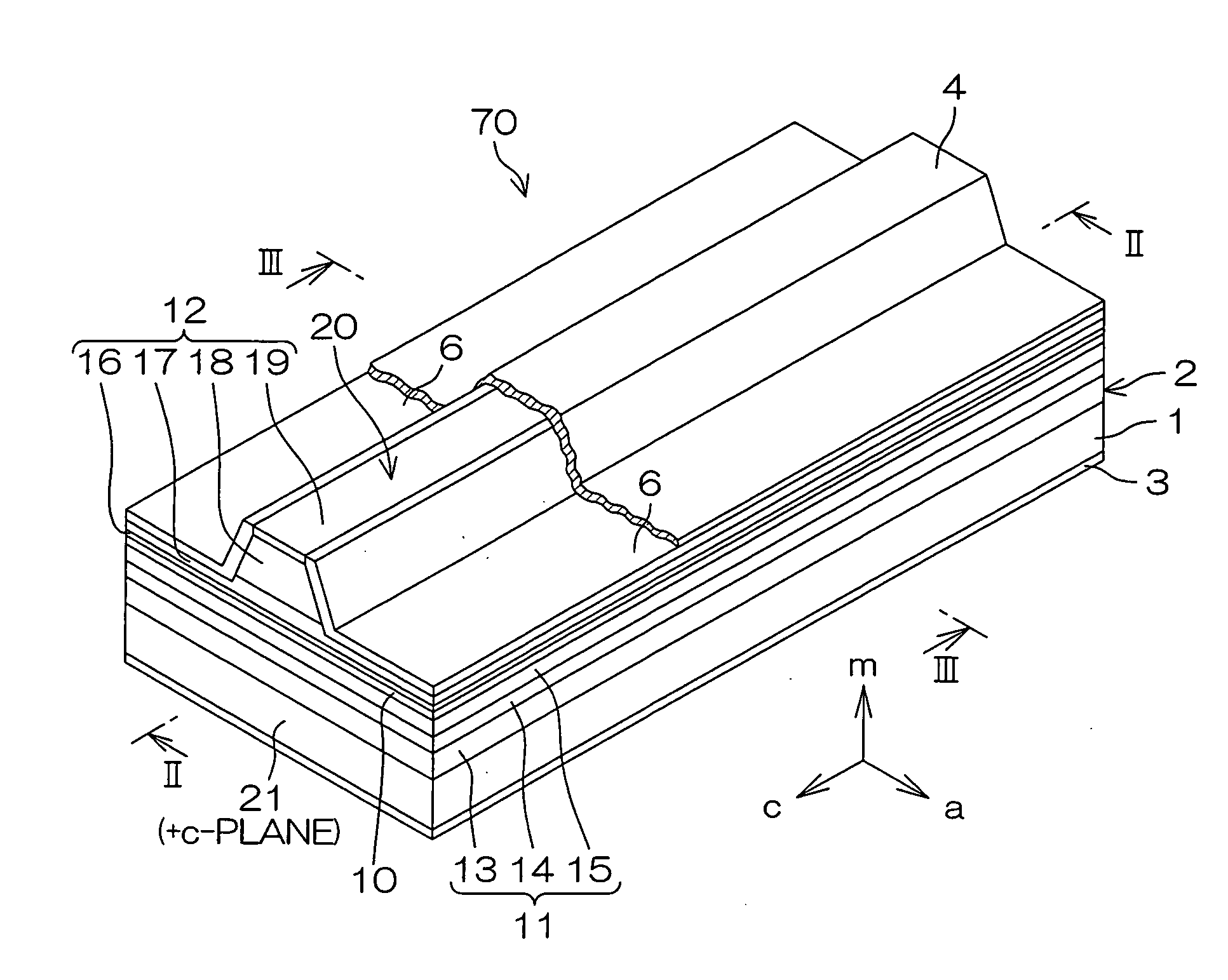
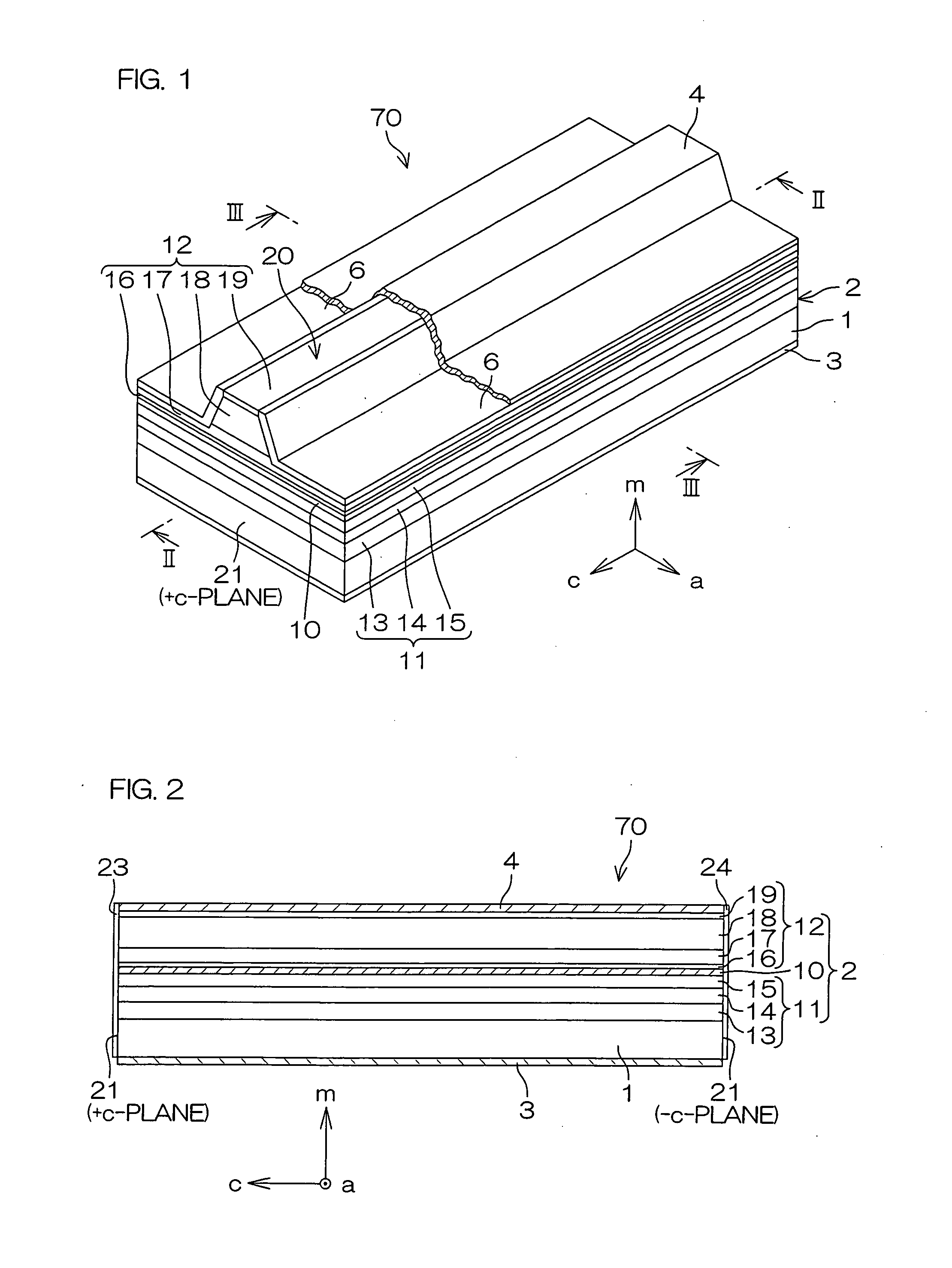
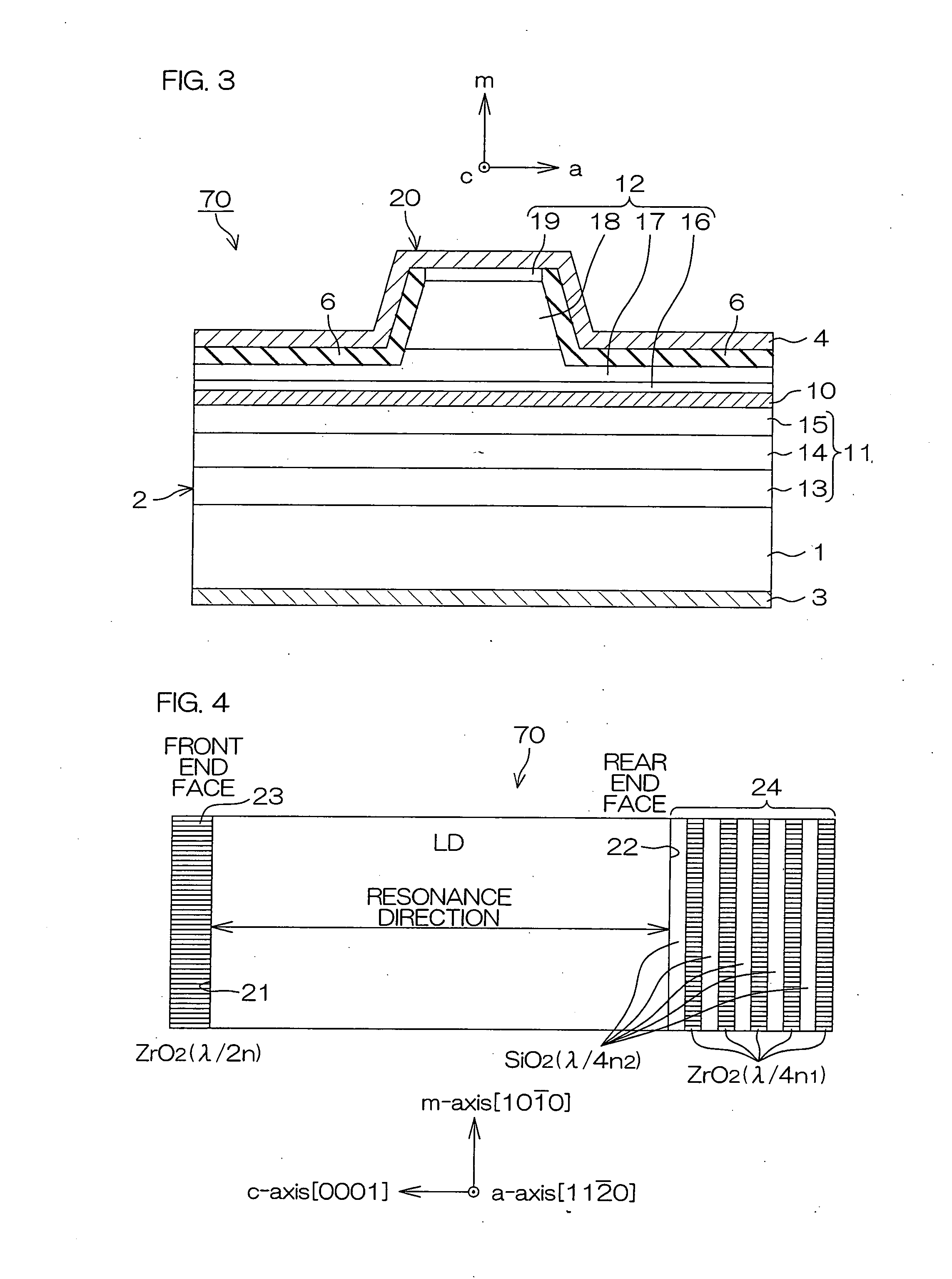
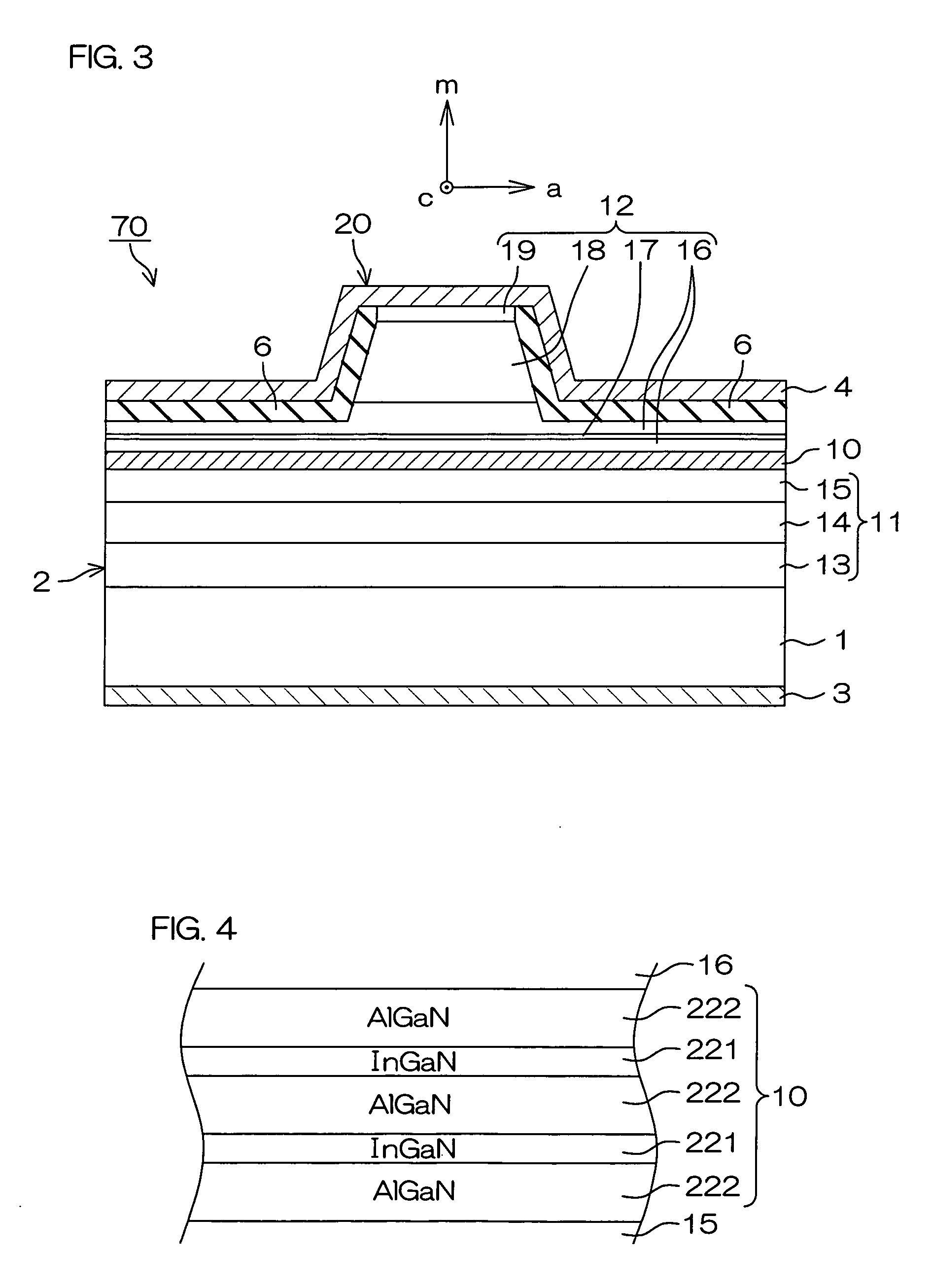
An inventive semiconductor laser diode includes a Group III nitride semiconductor layered structure having a major crystal growth plane defined by a non-polar or semi-polar-plane. The Group III nitride semiconductor layered structure includes: a p-type cladding layer and an n-type cladding layer; an In-containing p-type guide layer and an In-containing n-type guide layer held between the p-type cladding layer and the n-type cladding layer; and an In-containing light emitting layer held between the p-type guide layer and the n-type guide layer.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Semiconductor laser apparatus and optical apparatus
InactiveUS20120033695A1Improve sealingPromote absorptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor lasersPolyvinyl alcoholSemiconductor chip
This semiconductor laser apparatus includes a package constituted by a plurality of members, having sealed space inside and a semiconductor laser chip arranged in the sealed space, while surfaces of the members located in the sealed space are covered with a covering agent made of an ethylene-polyvinyl alcohol copolymer.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor laser device
InactiveUS20100195687A1Improve energy efficiencyTotal current dropLaser detailsLaser active region structureActive layerNitride semiconductors
A semiconductor laser device has a semiconductor laser diode structure made of group III nitride semiconductors having major growth surfaces defined by nonpolar planes or semipolar planes. The semiconductor laser diode structure includes a p-type cladding layer and an n-type cladding layer, a p-type guide layer and an n-type guide layer held between the p-type cladding layer and the n-type cladding layer, and an active layer containing In held between the p-type guide layer and the n-type guide layer. The In compositions in the p-type guide layer and the n-type guide layer are increased as approaching the active layer respectively. Each of the p-type guide layer and the n-type guide layer may have a plurality of InxGa1-xN layers (0≦x≦1). In this case, the plurality of InxGa1-xN layers may be stacked in such order that the In compositions therein are increased as approaching the active layer.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
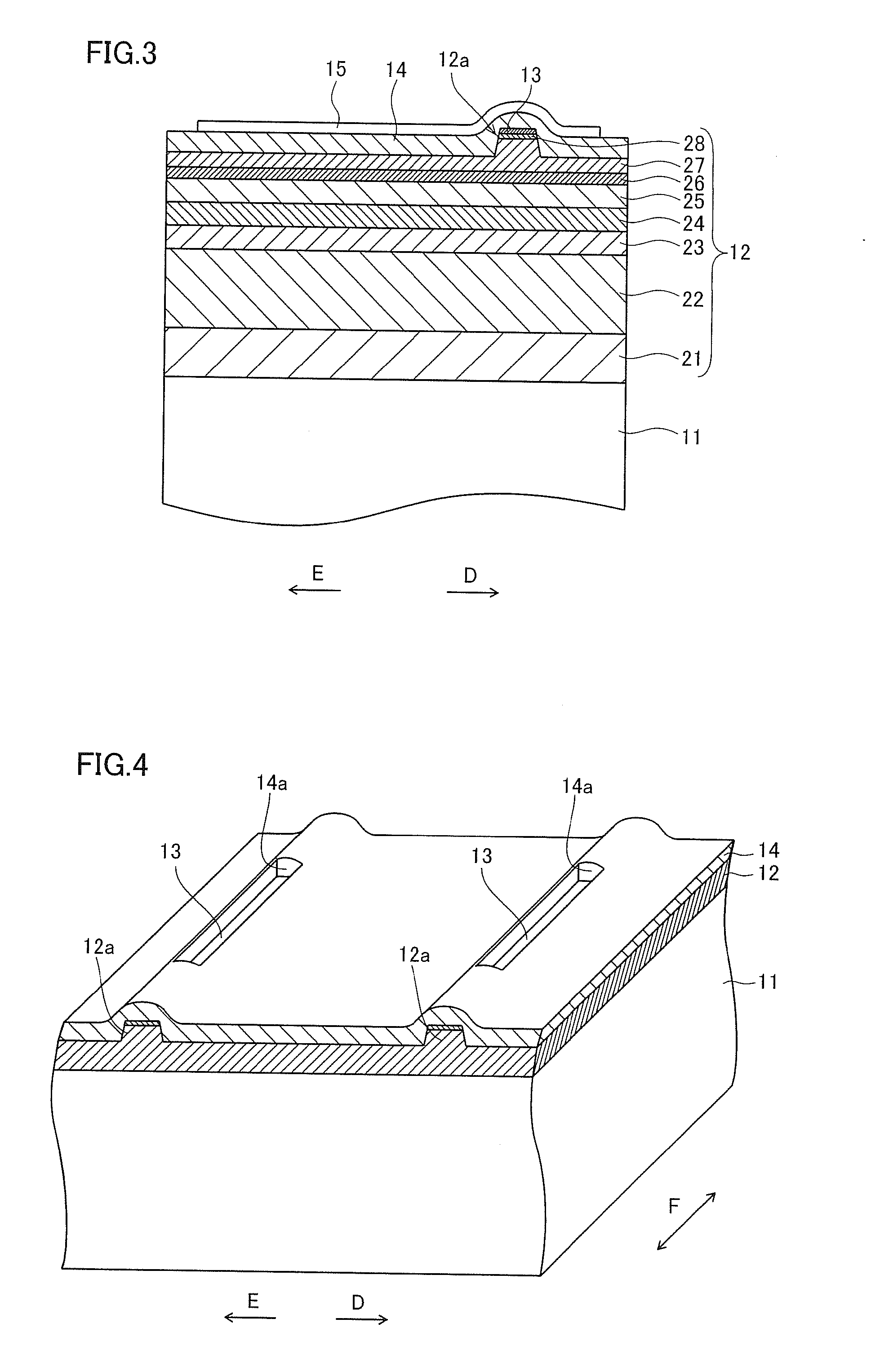
Semiconductor laser device
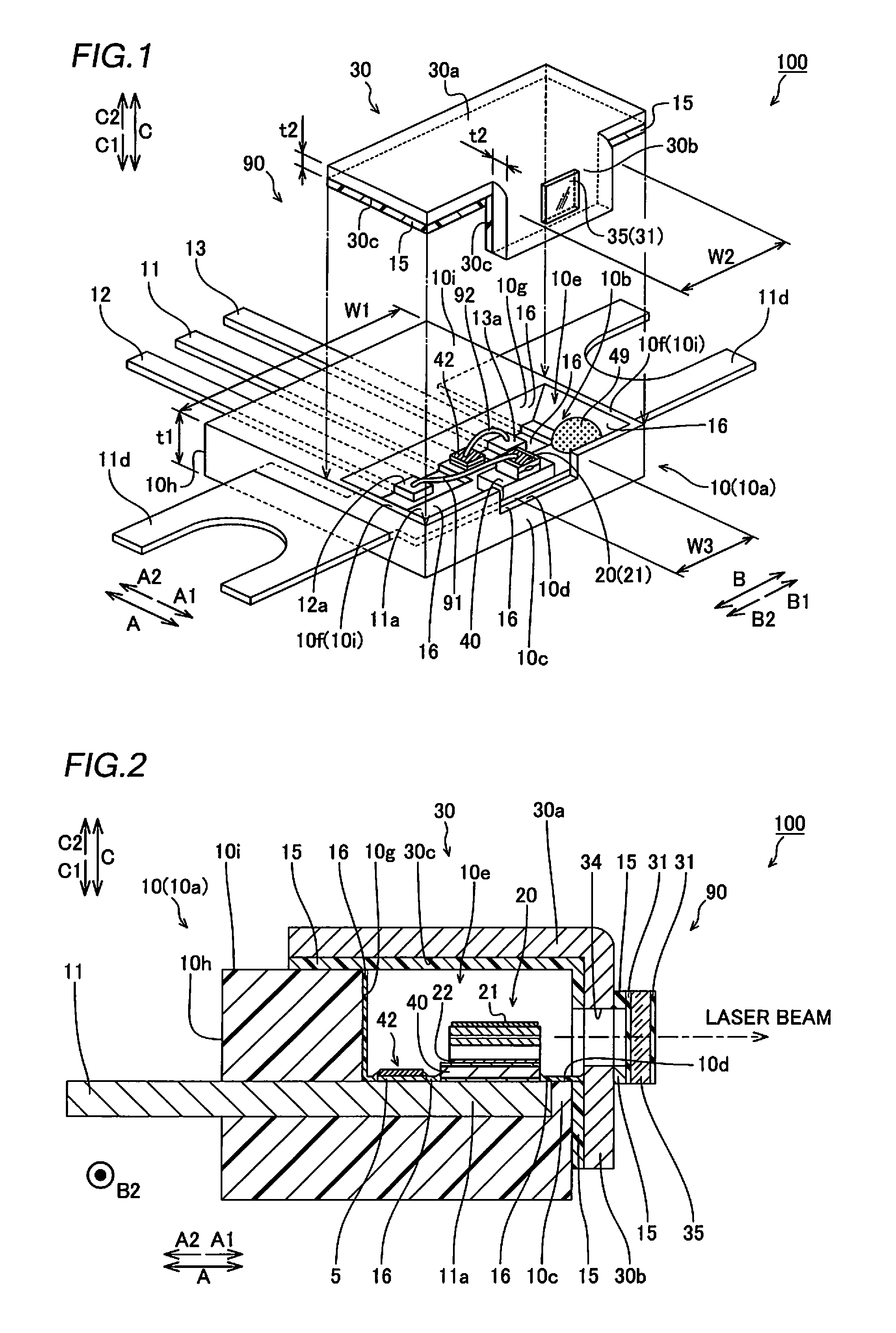
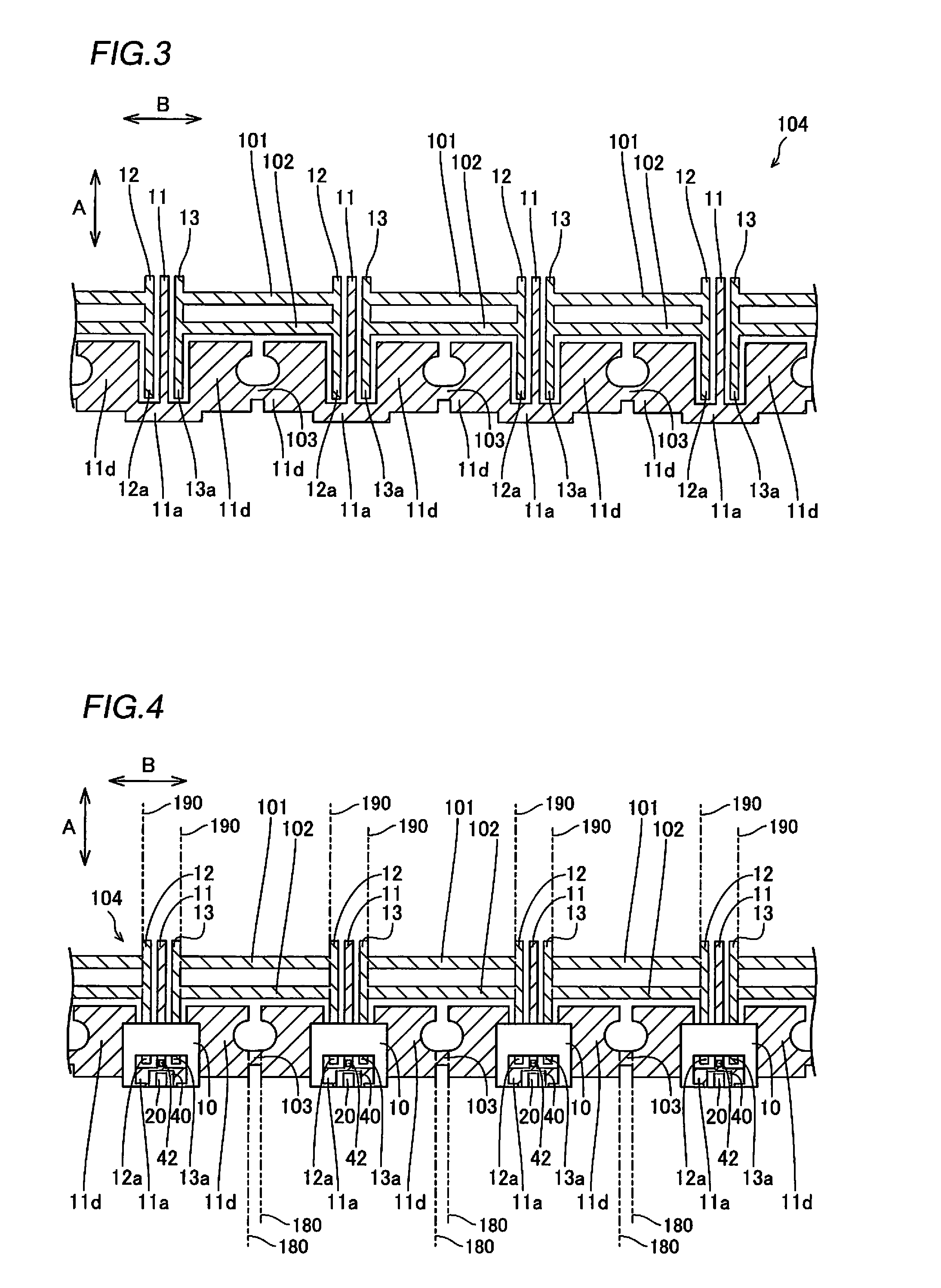
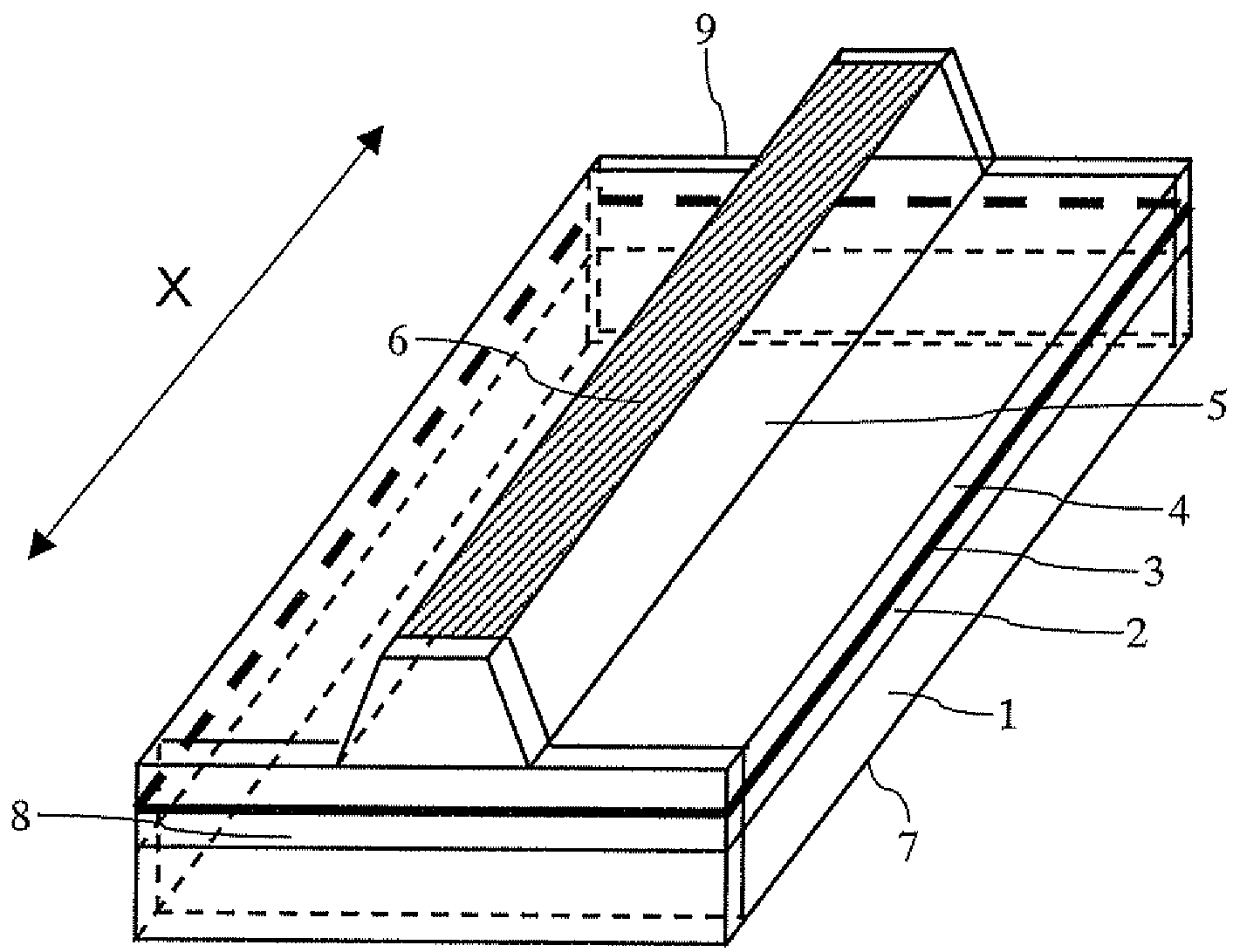
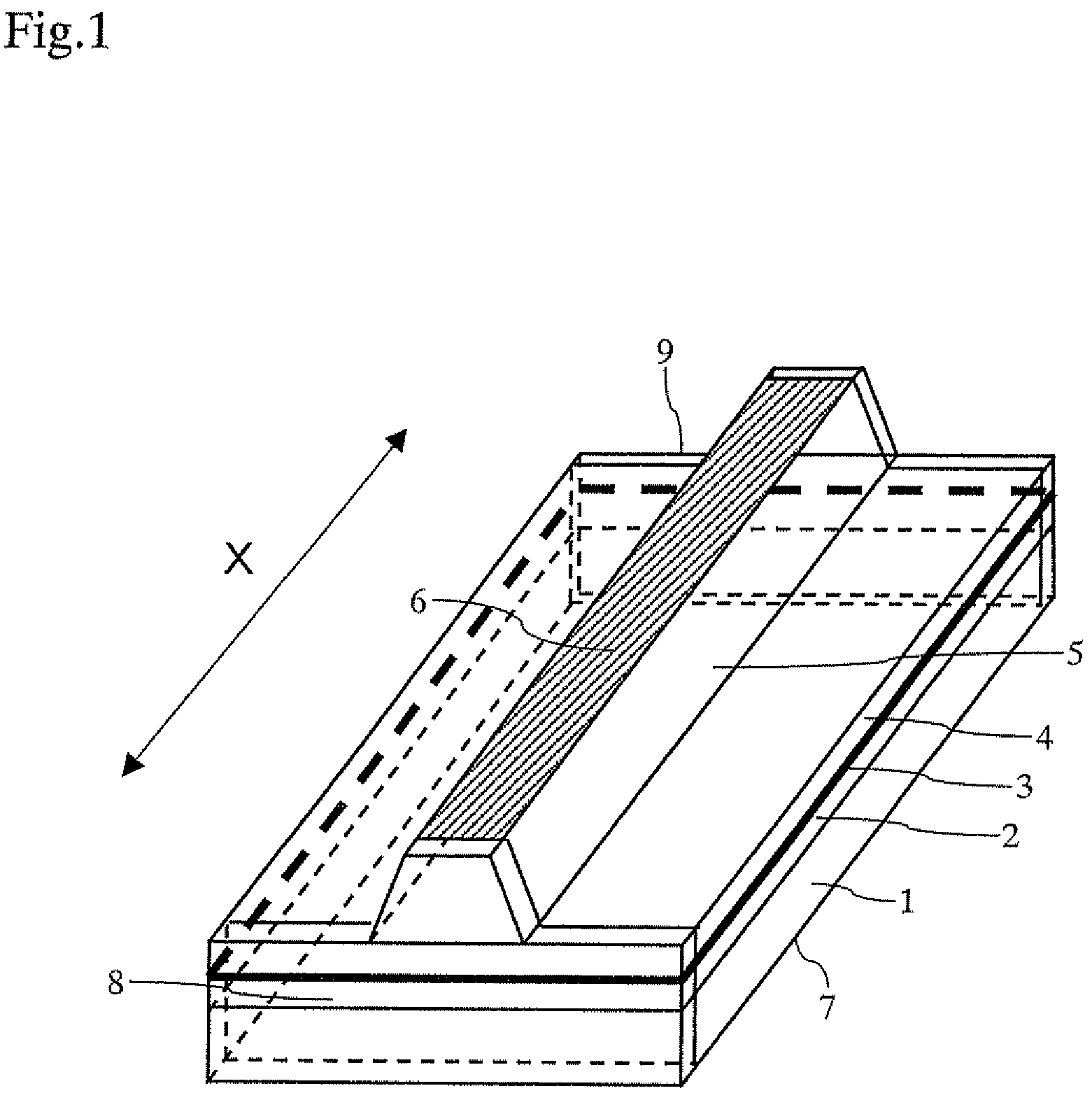
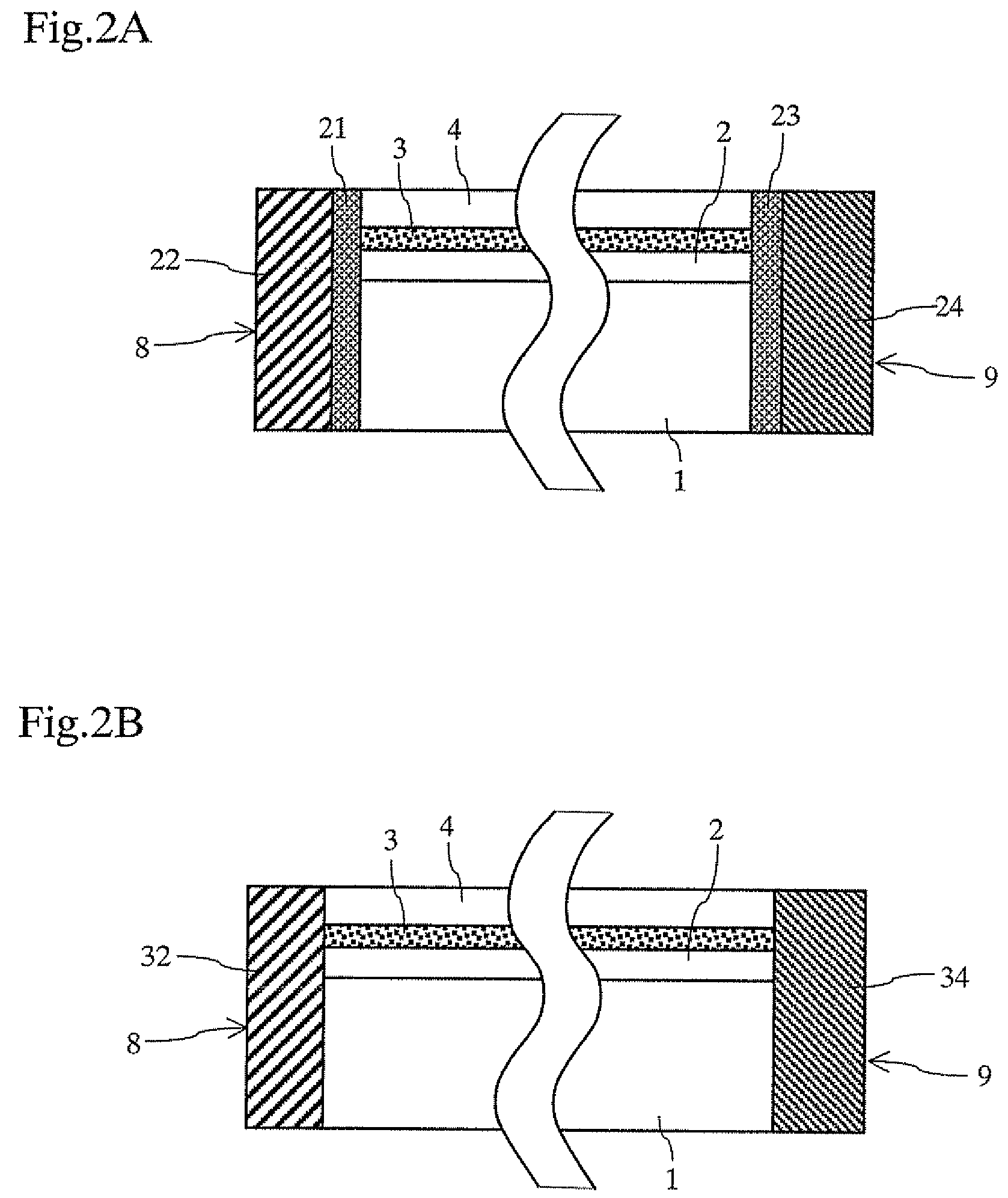
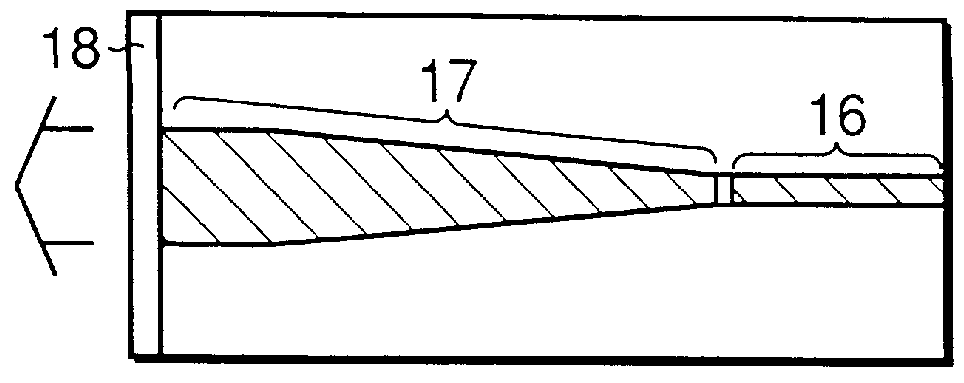
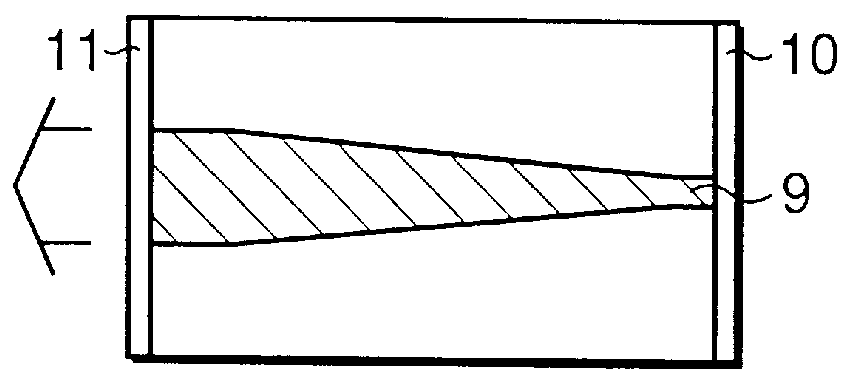
A semiconductor laser device includes a cavity extending in a propagation direction of a laser beam (X-direction). A front facet is on one end of the cavity through which the laser beam is emitted. A rear facet is on the other end of the cavity. Further, an adhesive layer and a coating film are on the front facet, and an adhesive layer and a coating film are on the rear facet. The adhesive layers preferably have a thickness of 10 nm or less and preferably include an anodic oxide film of one of Al, Ti, Nb, Zr, Ta, Si, and Hf.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
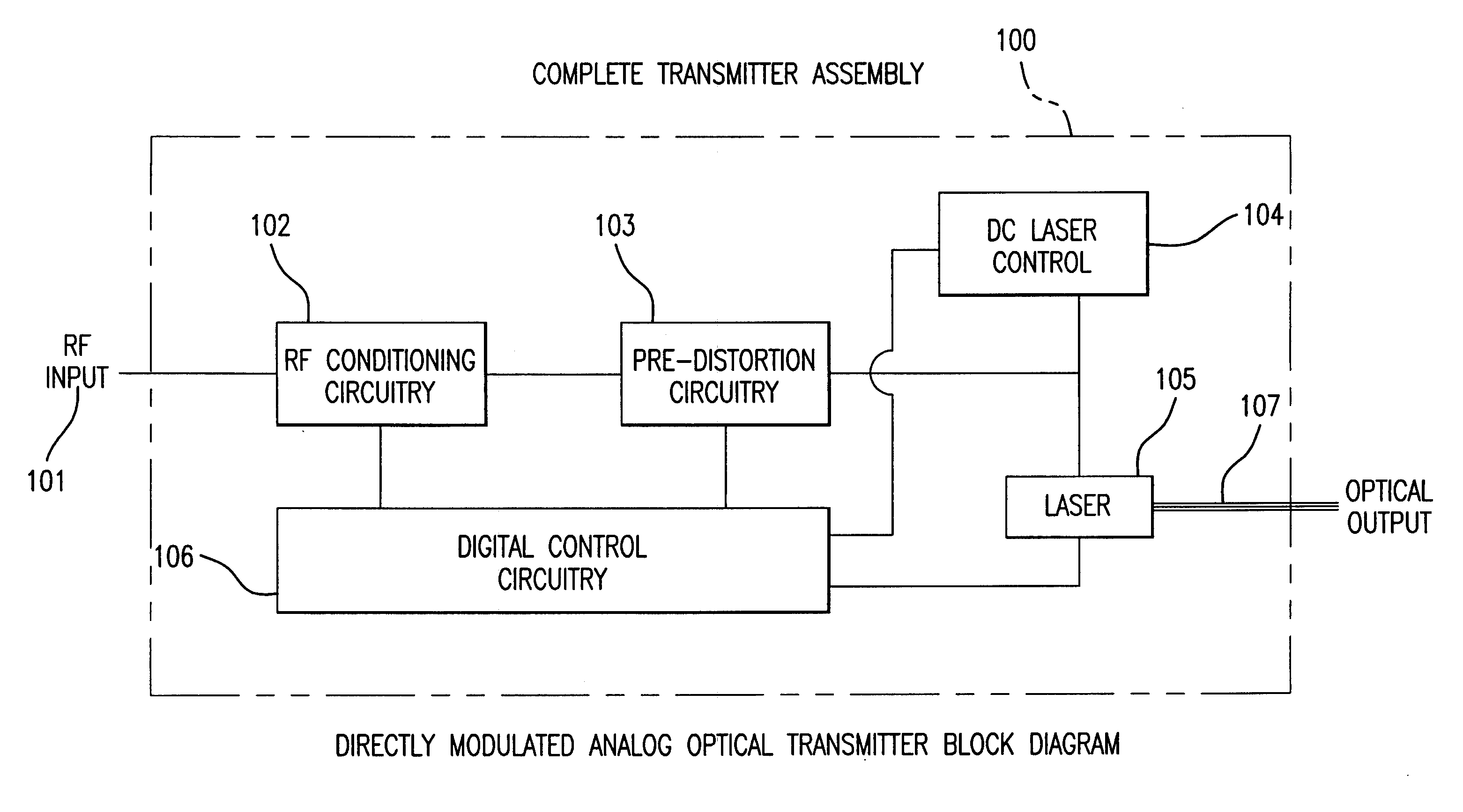
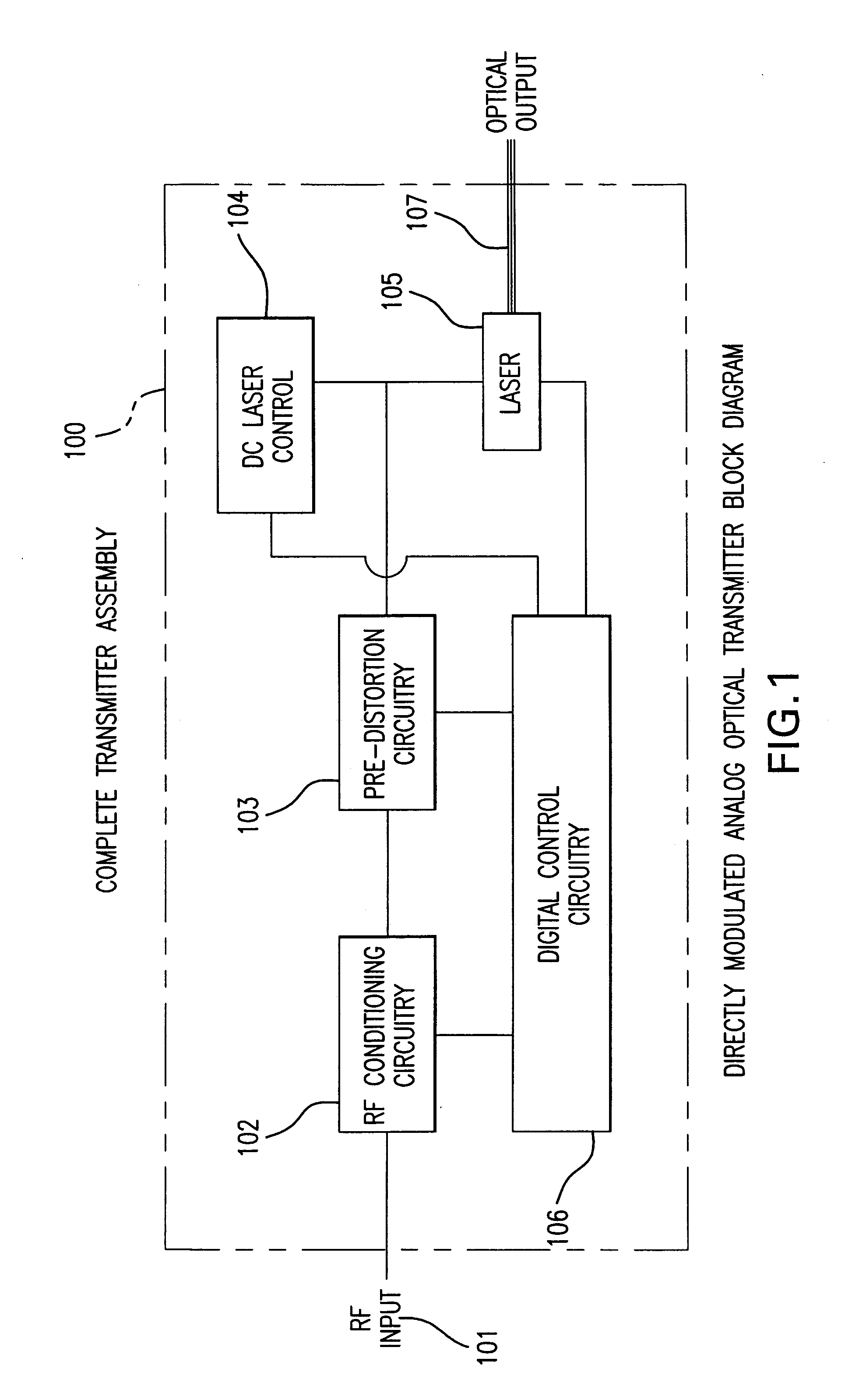
Directly modulated laser optical transmission system
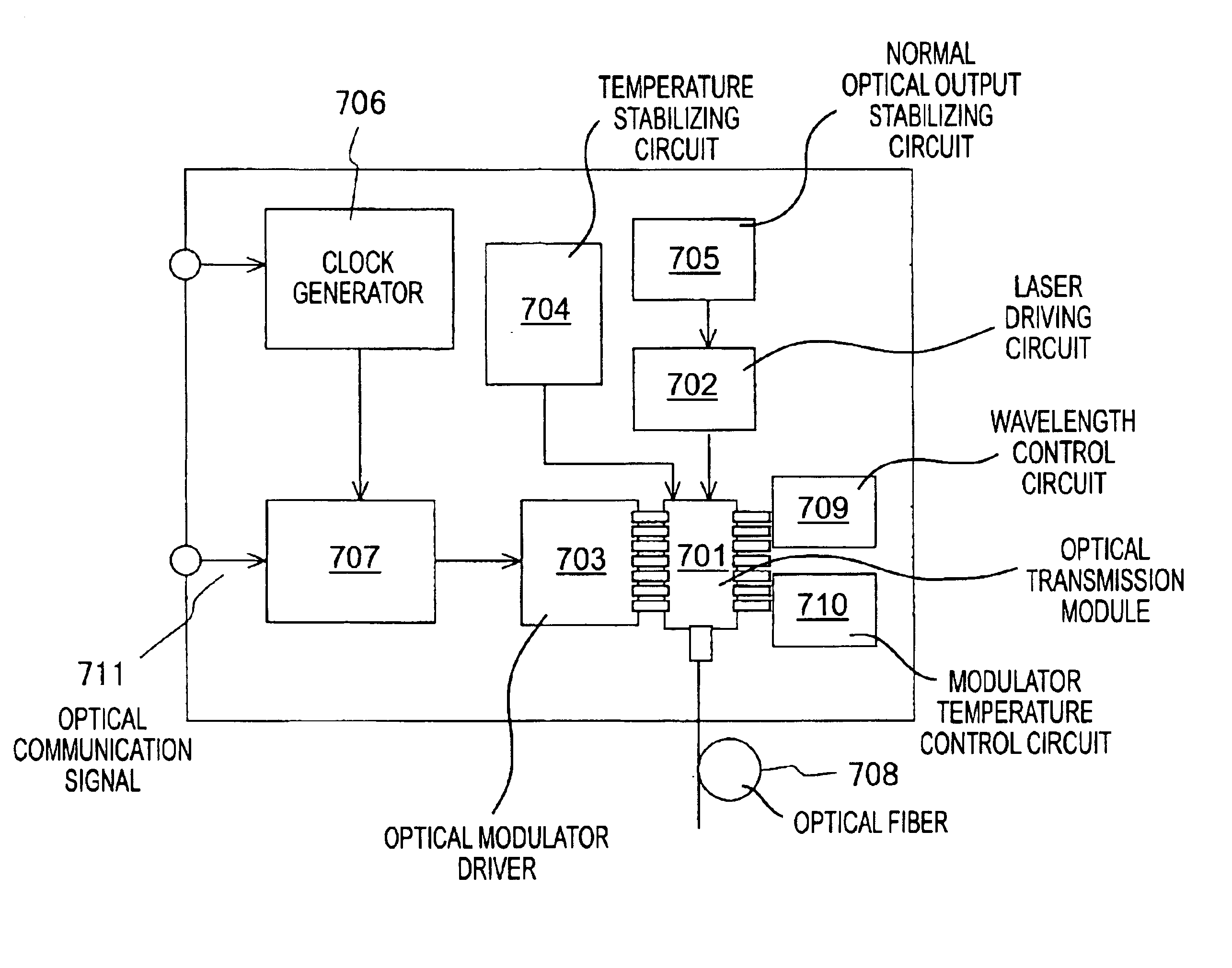
InactiveUS7466925B2Reduce signal distortionReducing frequency independent componentLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFiberEngineering
An optical transmitter for generating a modulated optical signal for transmission over dispersive fiber optic links in which a broadband analog radio frequency signal input is applied to a modulation circuit for directly modulating a semiconductor laser with the analog signal input. The transmitter may further include a temperature sensor in proximity to the laser and a negative feedback control circuit coupled to the temperature sensor for adjusting the temperature of the laser in response to an output characteristic of the laser, such as linearity.
Owner:EMCORE INC
Surface emitting semiconductor laser
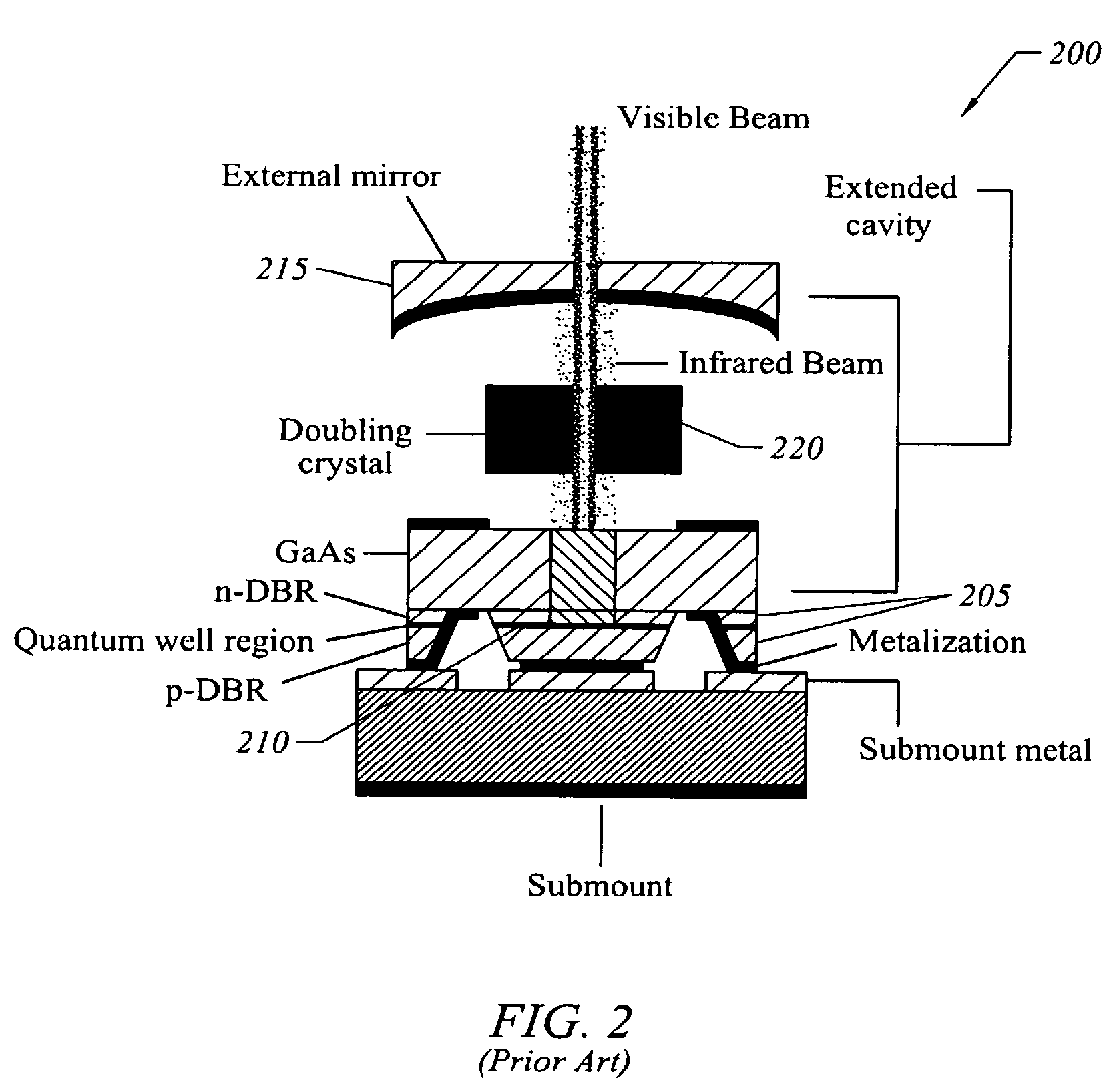
InactiveUS6052398AImprove reflectivityLower resistanceLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersOptical cavitySemiconductor package
Two semiconductor layers of the laser form a tunnel junction enabling an electrical current for pumping the laser to pass from an N doped semiconductor Bragg mirror to a P doped injection layer belonging to the light-amplifying structure. The Bragg mirror co-operates with another mirror of the same type having the same doping to include said structure in an optical cavity of the laser. In a variant, the tunnel junction may be buried and located so as to constitute confinement means for said pumping current. The laser can be used in an optical fiber communications network.
Owner:II VI LASER ENTERPRISE
Semiconductor laser, semiconductor device, and their manufacture methods
A substrate is made of SiC. A plurality of AlxGa1-xN patterns (0<=x<=1) is formed on a surface of the substrate and dispersively distributed in an in-plane of the substrate. An AlyGa1-yN buffer layer (0<=y<=1) covers the surface of the substrate and the AlxGa1-xN patterns. A laser structure is formed on the AlyGa1-yN buffer layer. Since the AlGaN buffer layer is grown by using the AlGaN patterns as seed crystals, a dislocation density of a predetermined region in the AlGaN buffer layer can be lowered. The characteristics of a laser structure can be improved by forming the laser structure above the region having a low dislocation density. Since the AlGaN pattern has electric conductivity, the device resistance can be suppressed from being increased.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
System and method for driving semiconductor laser sources for displays
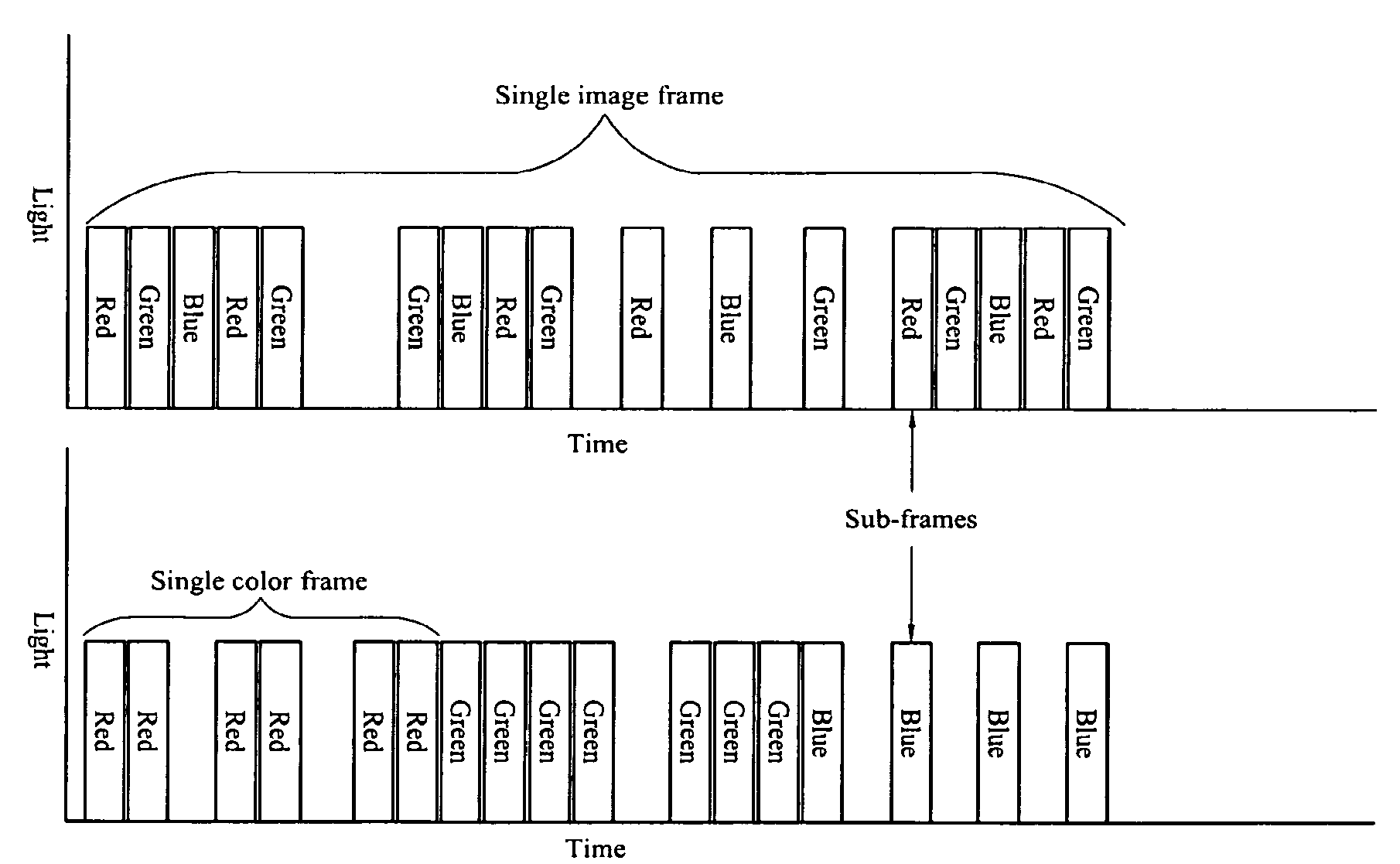
InactiveUS7357513B2Television system detailsLaser using scattering effectsDisplay deviceSemiconductor
A light engine includes a multi-color laser source having a set of semiconductor lasers. A controller synchronizes the operation of the laser source to operate in a color sequential order with a spatial modulator.
Owner:ARASOR ACQUISITION +1
Optical transmitter and optical signal transmitter
InactiveUS6757499B1Good reproducibilityPromote recoveryNanoopticsCoupling light guidesLength waveOptical transmitter
The optical transmitter includes a semiconductor laser device, and an optical modulator region optically connected to the semiconductor laser device and having the function of modulating the output light from the semiconductor laser device. The operating temperature of the optical modulator region is changed without changing the oscillation wavelength of the semiconductor laser device.
Owner:OCLARO JAPAN INC
Semiconductor laser devices and methods
InactiveUS7286583B2Increase speedImprove mobilityLaser detailsNanoopticsResonant cavitySemiconductor materials
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
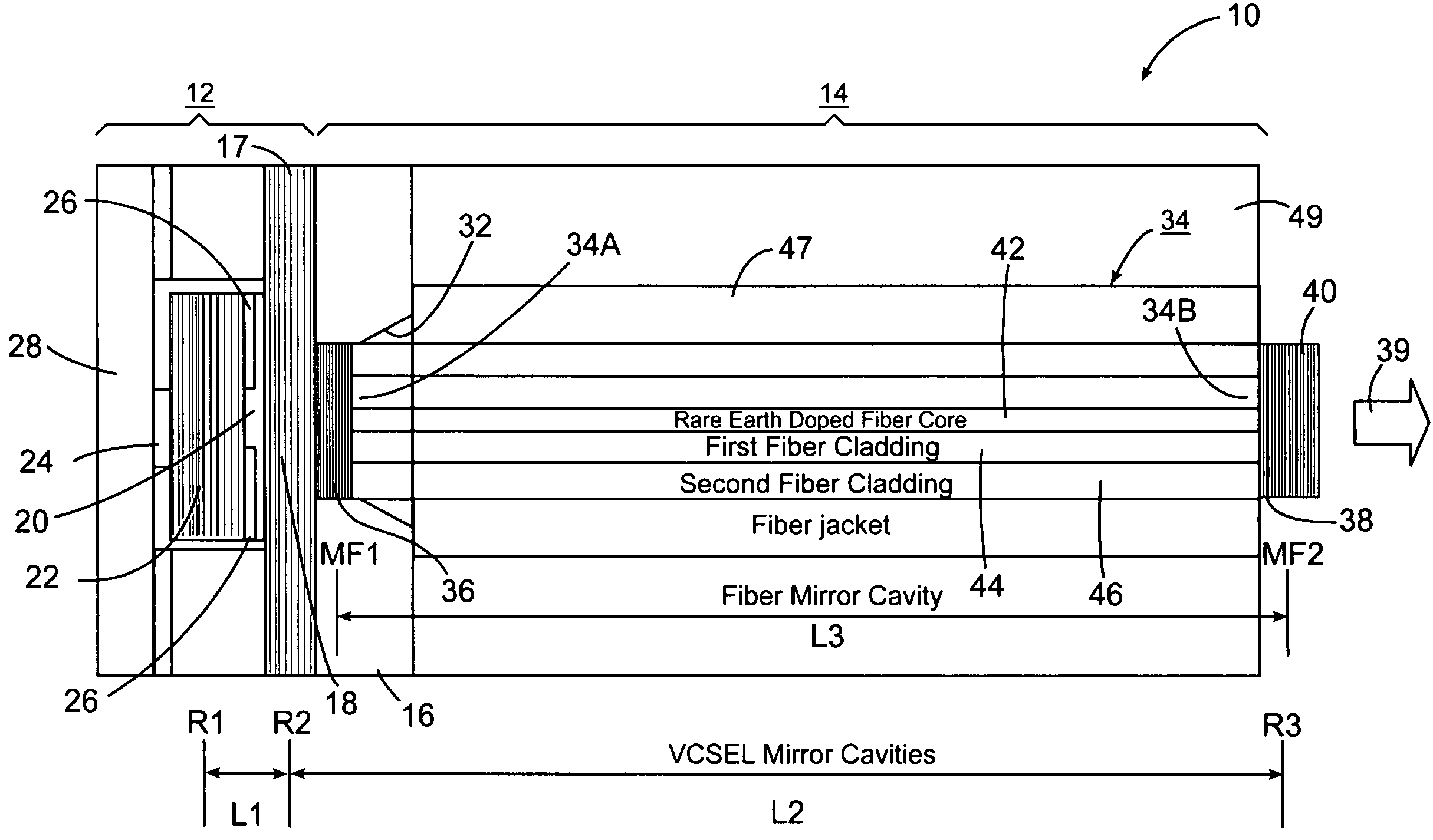
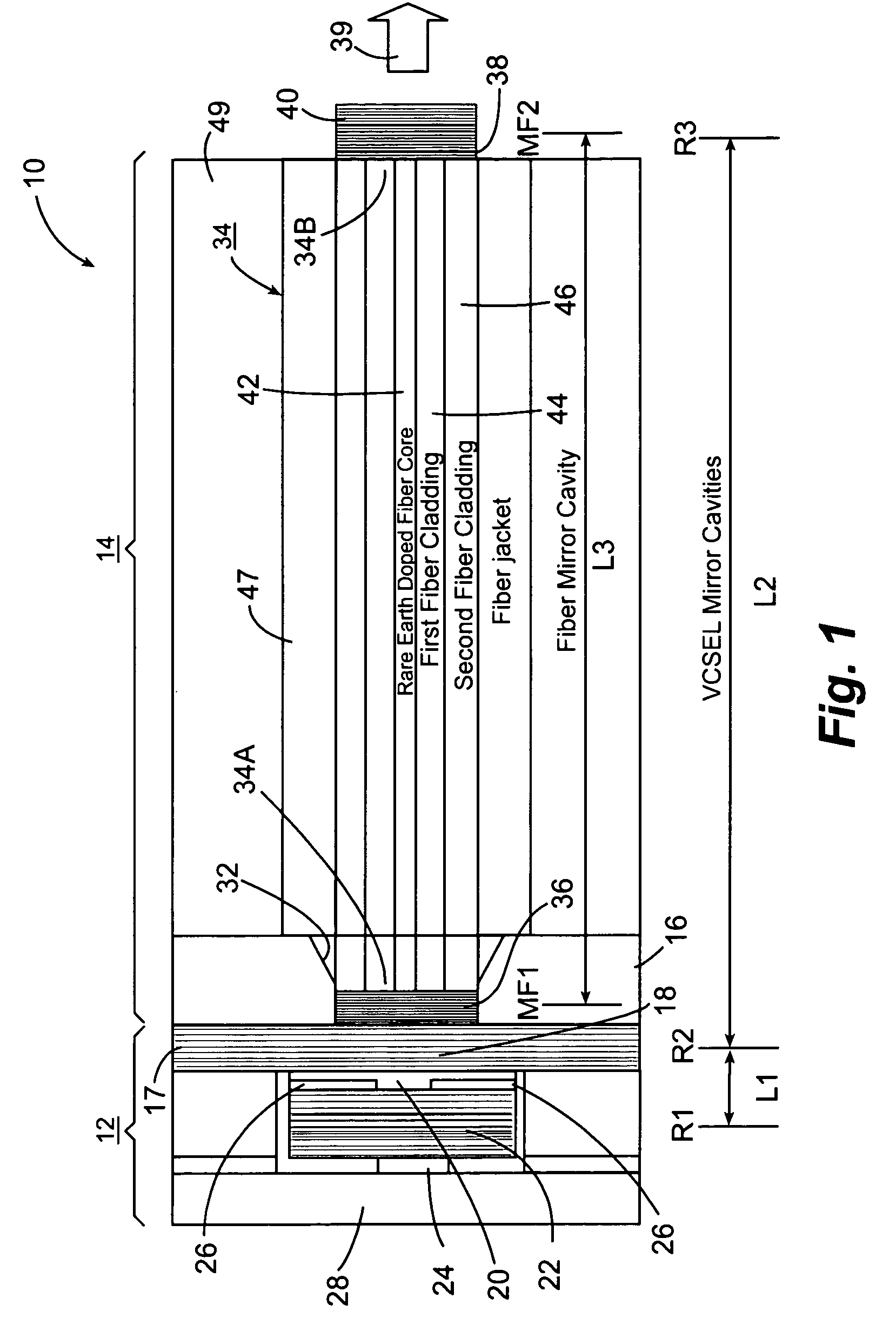
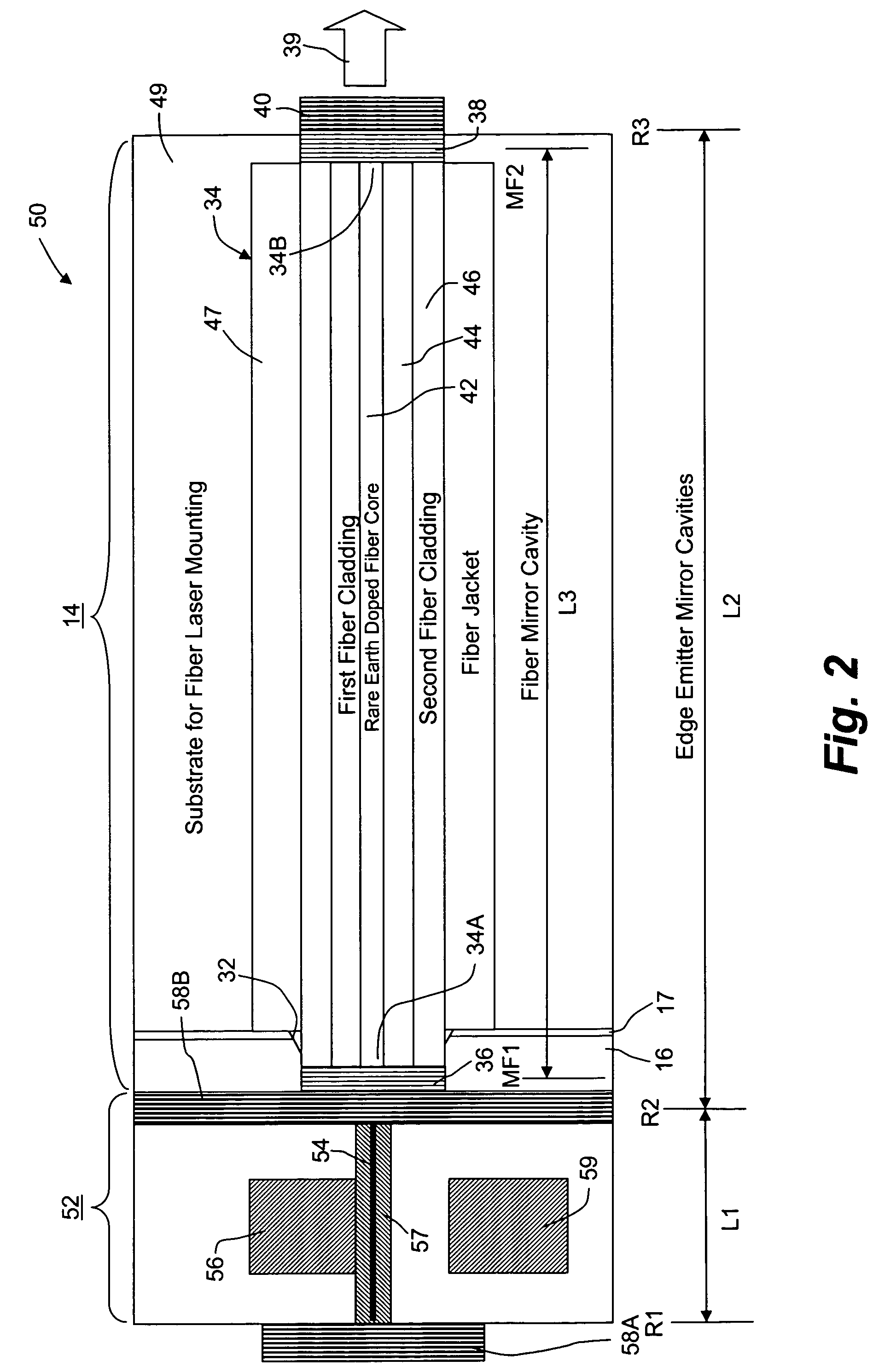
Optical spectroscopy apparatus and method for measurement of analyte concentrations or other such species in a specimen employing a semiconductor laser-pumped, small-cavity fiber laser
InactiveUS7283242B2Improve absorption efficiencyEffectively and efficiently utilizedMaterial analysis by optical meansLaser arrangementsRare earthSpectroscopy
An optical spectroscopy apparatus determines the concentration of analyte in a specimen that utilizes a single radiation source which is hybrid laser comprising a semiconductor pump laser and small-cavity rare earth fiber laser where laser cavities of both lasers are butt coupled or otherwise optically coupled to form a plurality of laser cavities that produce a plurality of emission wavelengths, one which may be the pump laser emission wavelength at the output of the fiber laser thereby forming a multi-wavelength combined output where the wavelengths substantially match distinguishing spectral characteristic features along at least a portion of a characteristic optical spectrum of the analyte under examination.
Owner:THORNTON ROBERT L
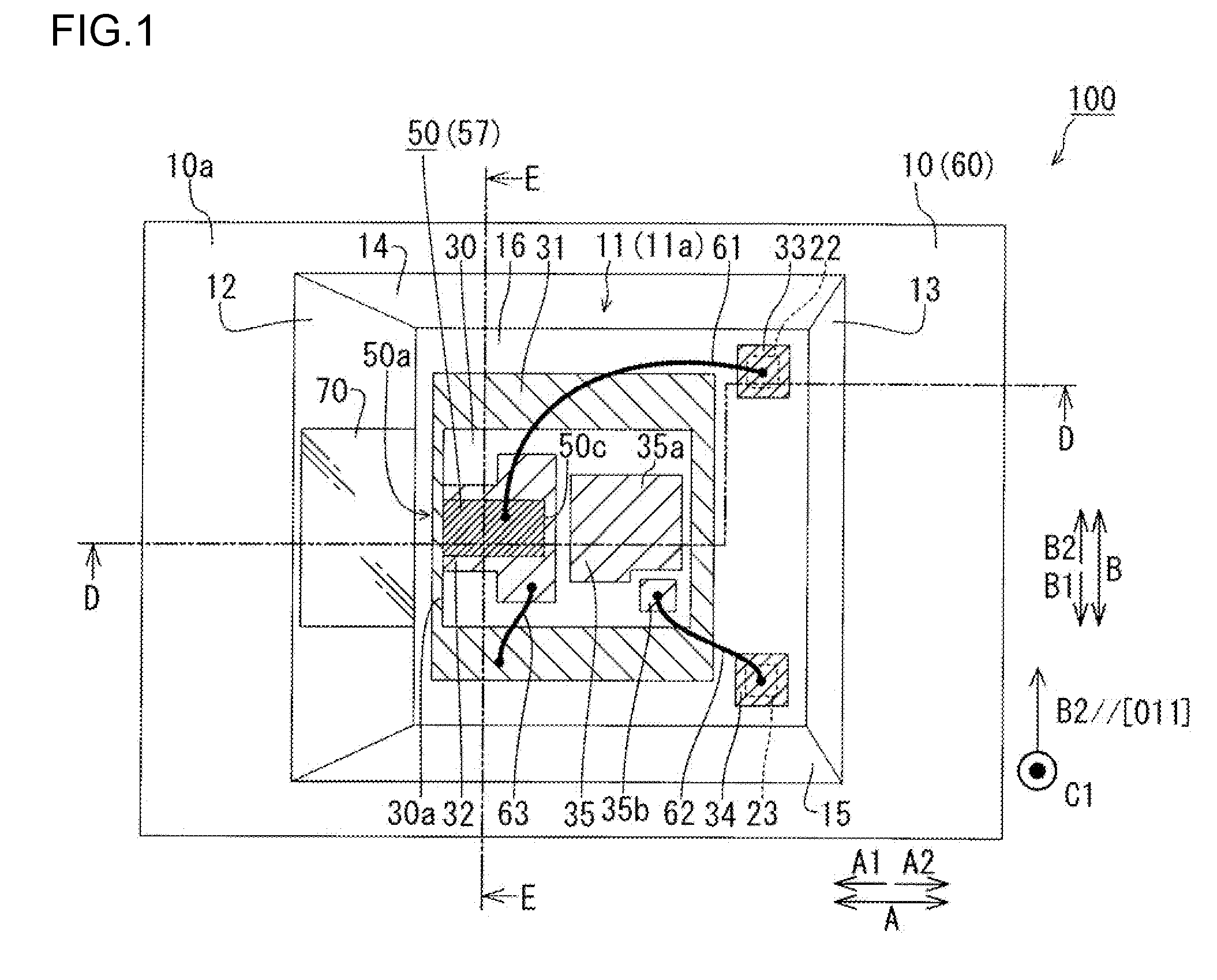
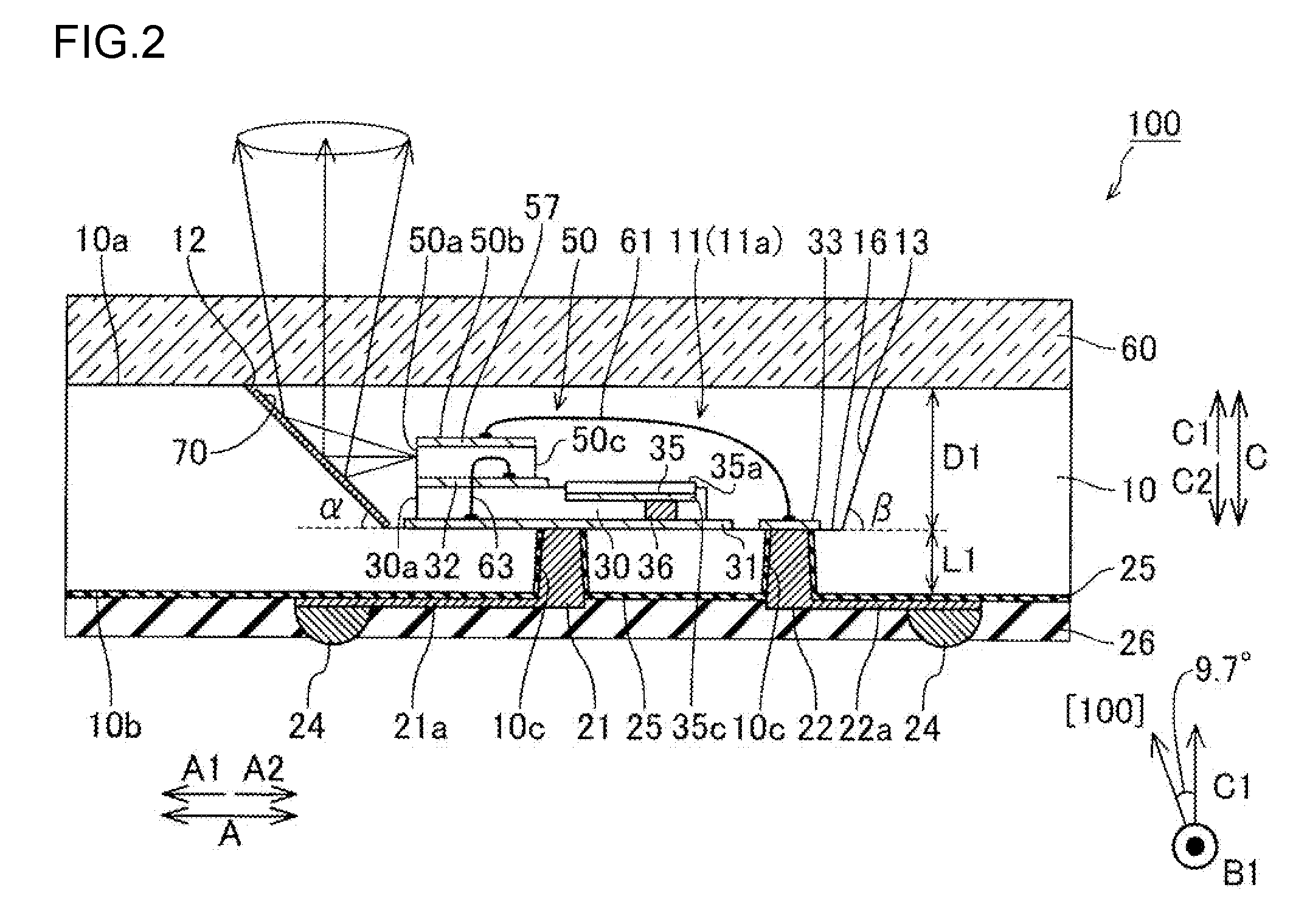
Semiconductor laser device
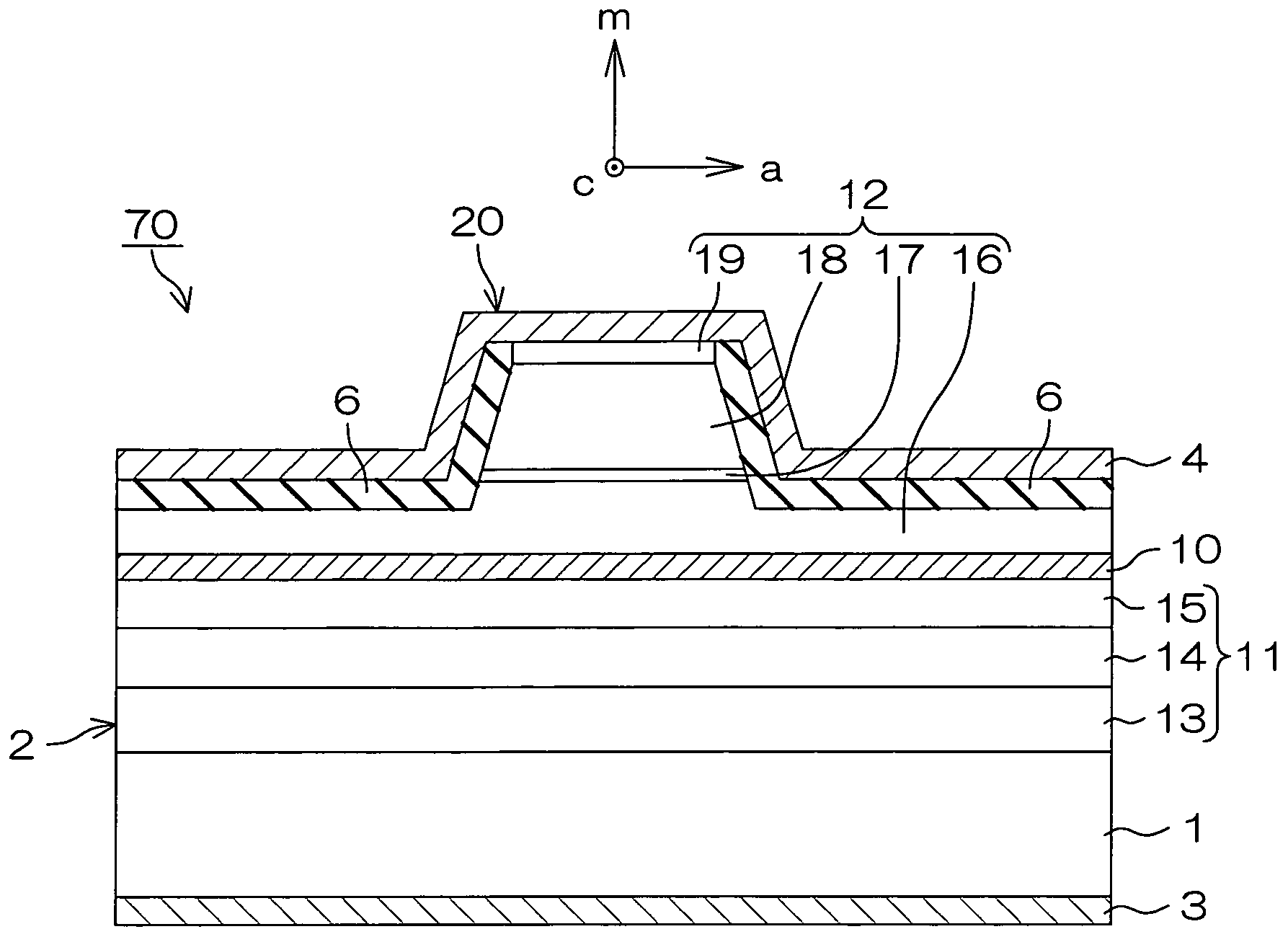
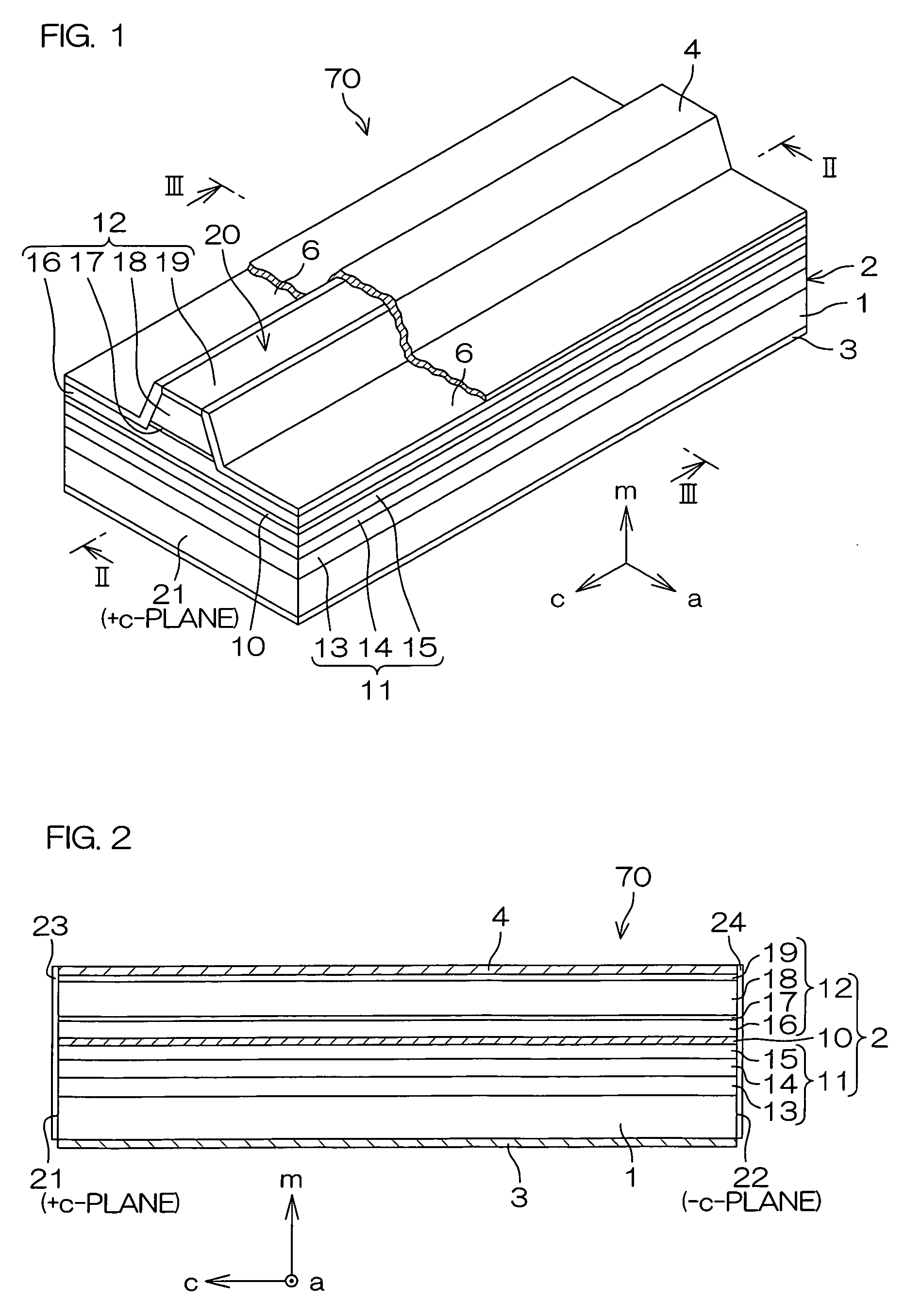
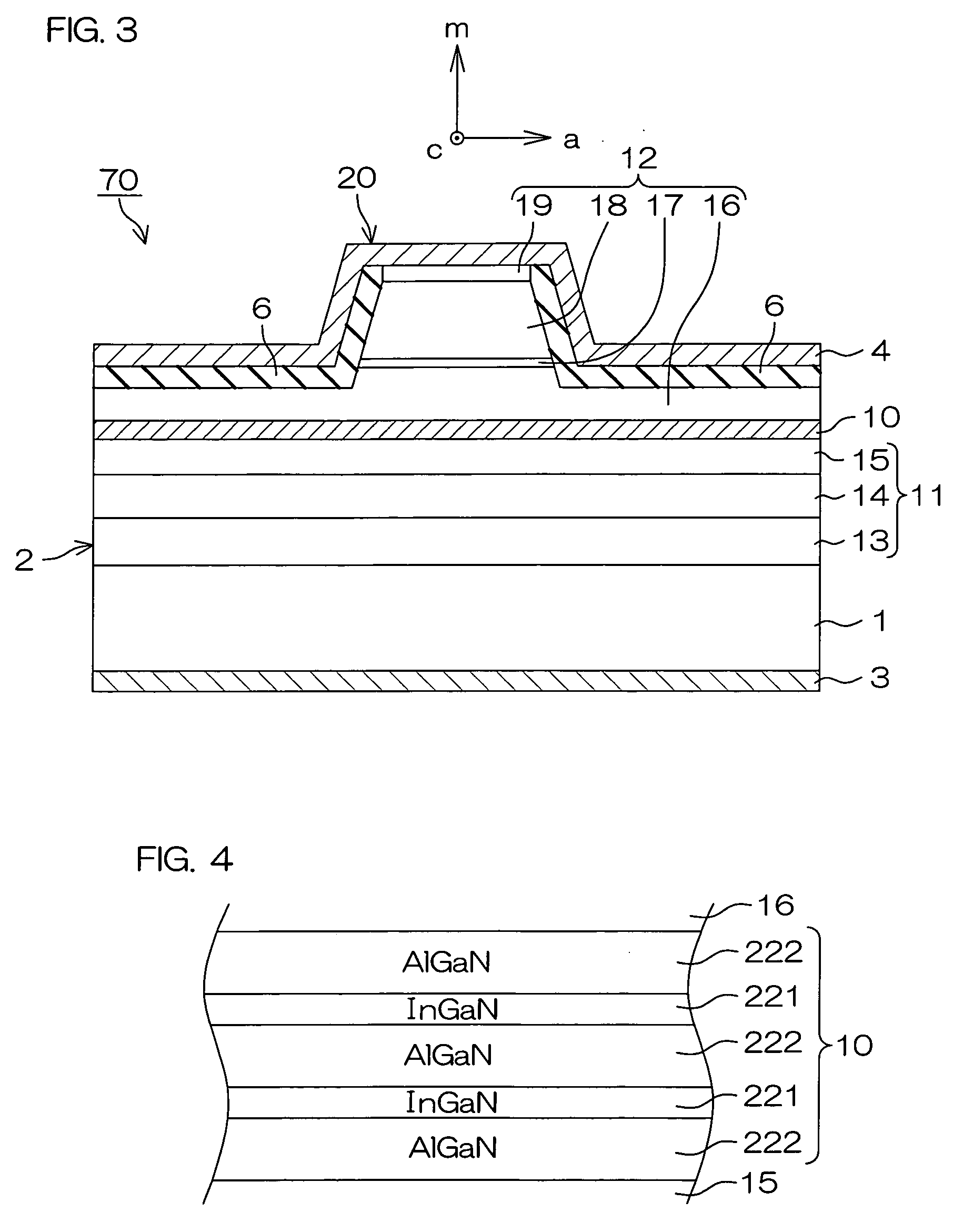
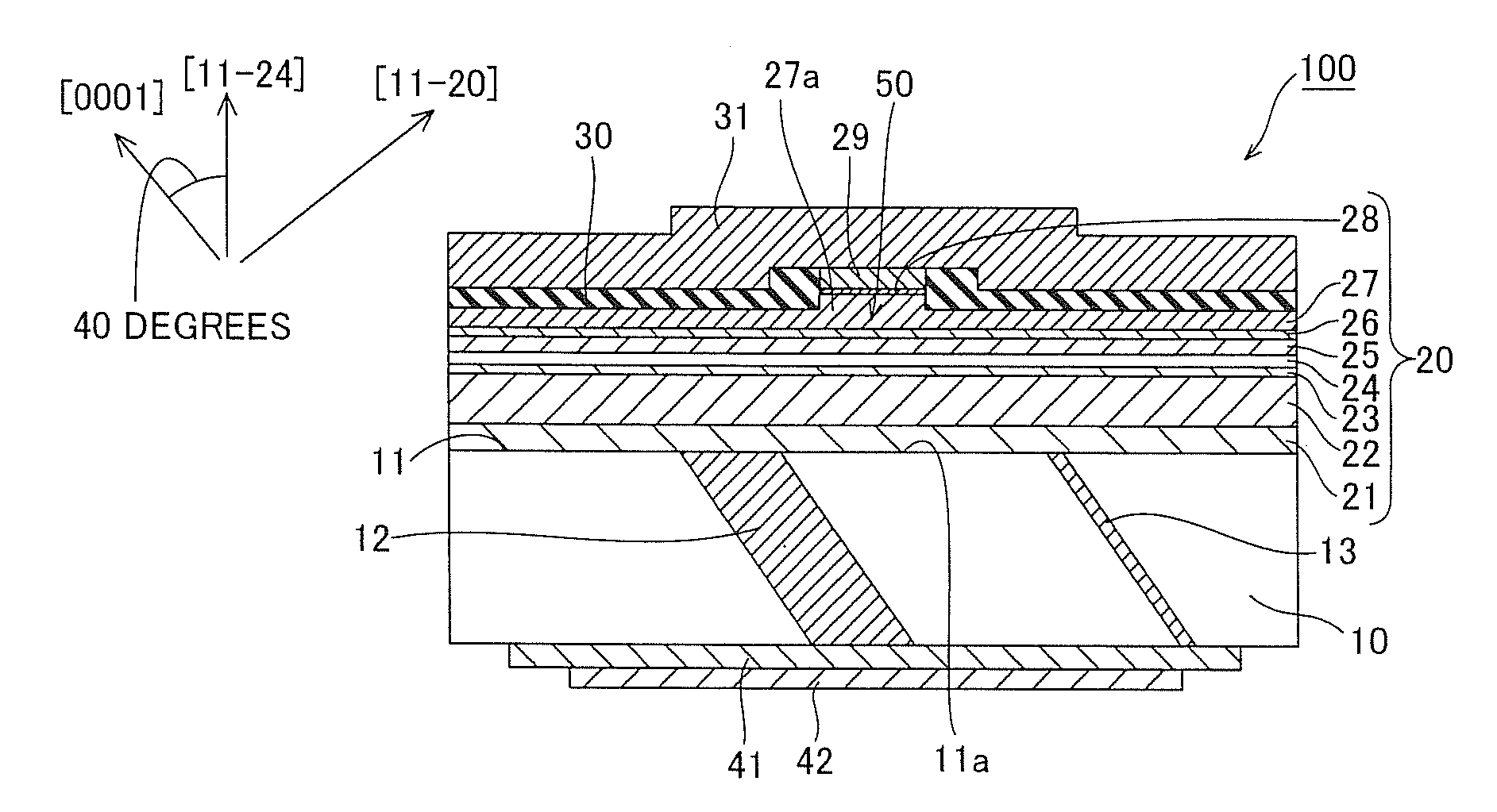
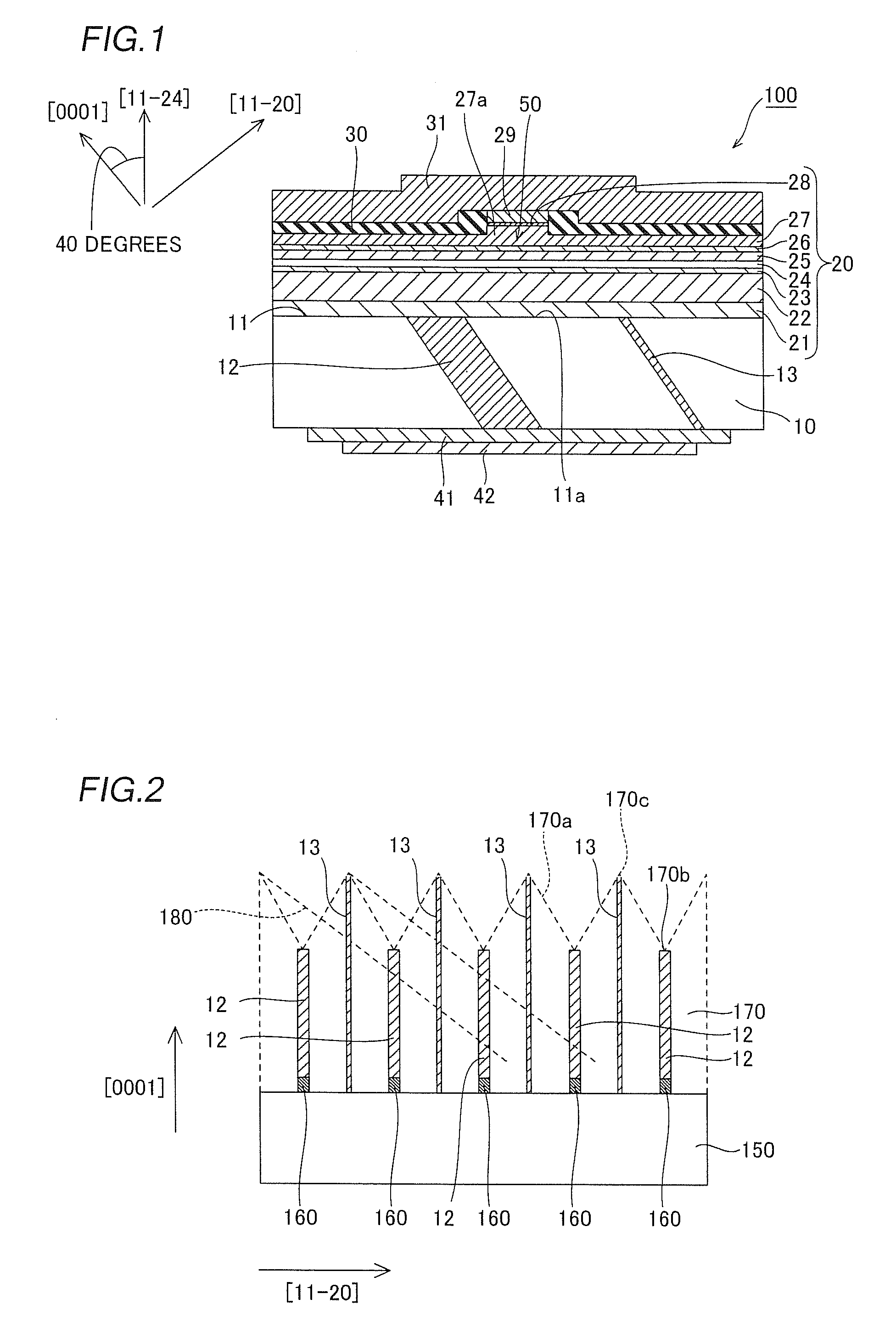
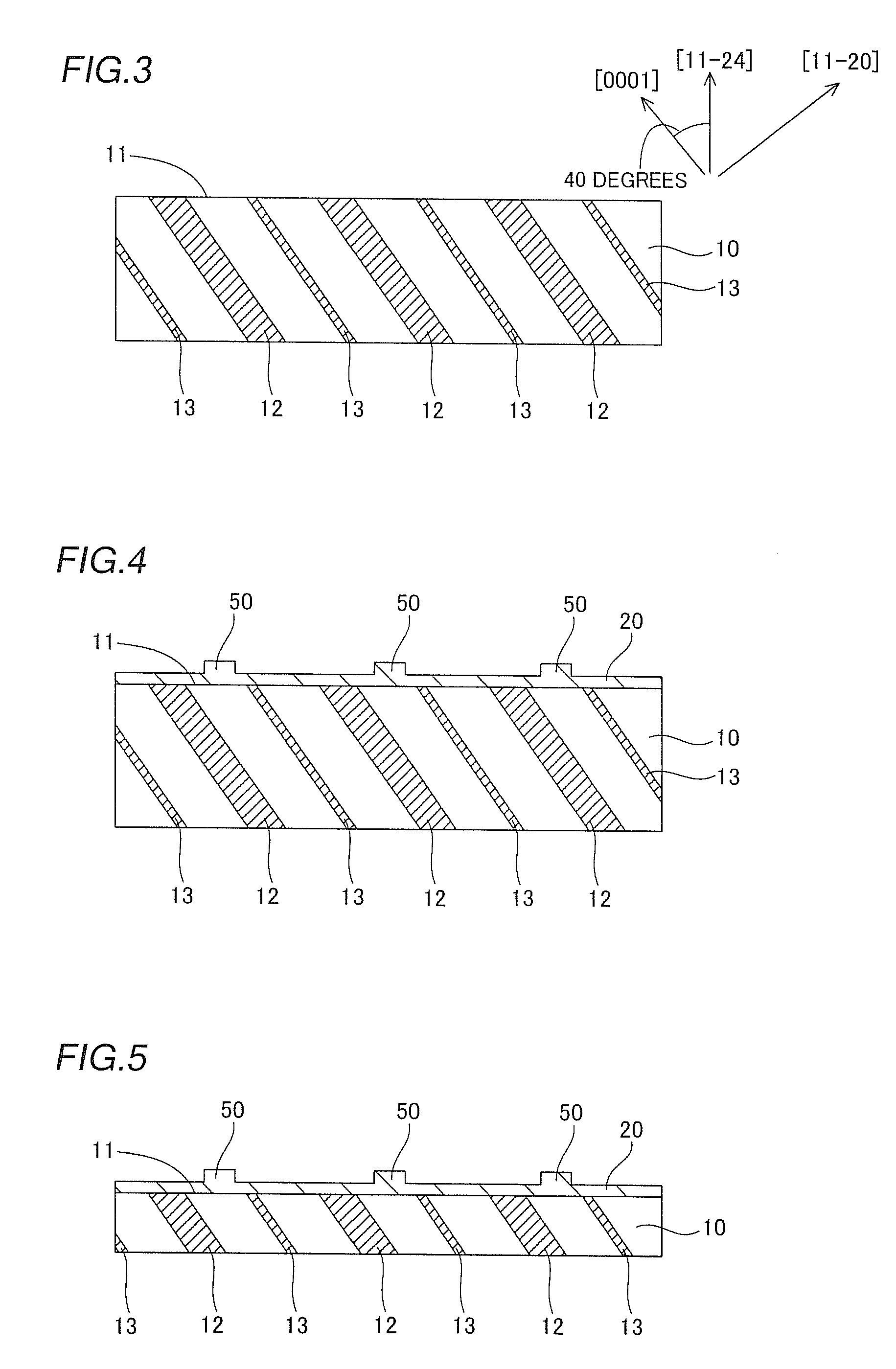
InactiveUS20090252191A1Polarization fieldOptical resonator shape and constructionNanoopticsDistributed Bragg reflectorLength wave
A semiconductor laser device is made of a group III nitride semiconductor having a major growth surface defined by a nonpolar plane or a semipolar plane. The semiconductor laser device includes a cavity having an active layer containing In and distributed Bragg reflectors coating both cavity end faces of the cavity respectively. In each of the distributed Bragg reflectors, a central wavelength λc of a reflectance spectrum satisfies the relation λSP−10 nm≦λc≦λSP+10 nm with respect to an emission peak wavelength λSP of spontaneous emission in the active layer.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
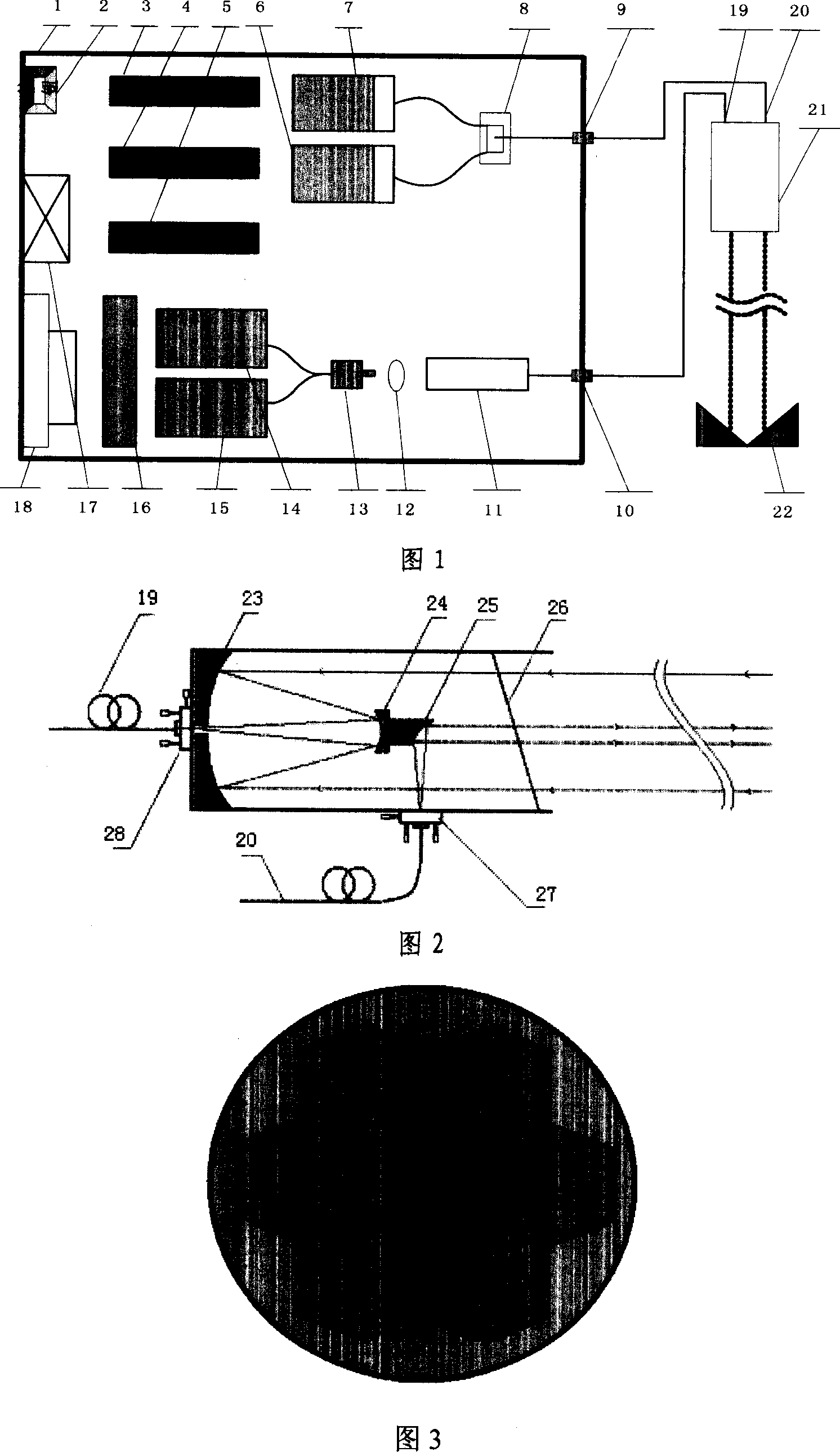
Opening gas multi-element monitoring instrument and monitoring method
InactiveCN101021474AReal-time online monitoringOvercome speedColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberFiber coupler
The invention discloses a multi-wavelength high-sensitivity online monitor of multi-component NH3 and H2O based on semiconductor laser absorption spectroscopy. It contains host chassis and open long-path system. Equip power receptacle, switch, fiber connector and data transmission interface. It is characterized in that: there are near-infrared semiconductor laser, semiconductor laser controller, phase-locked amplifier, signal generator, data collecting and controlling module and infrared detector in host chassis which is connected with field optical system by fiber. Open optical system contains send-receive optical telescope and multielement reflector array. Optical telescope has input and output fiber couplers. The device realizes simultaneous testing of gas multi-component by using multi-wavelength and frequency division multi-signal detecting technique.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
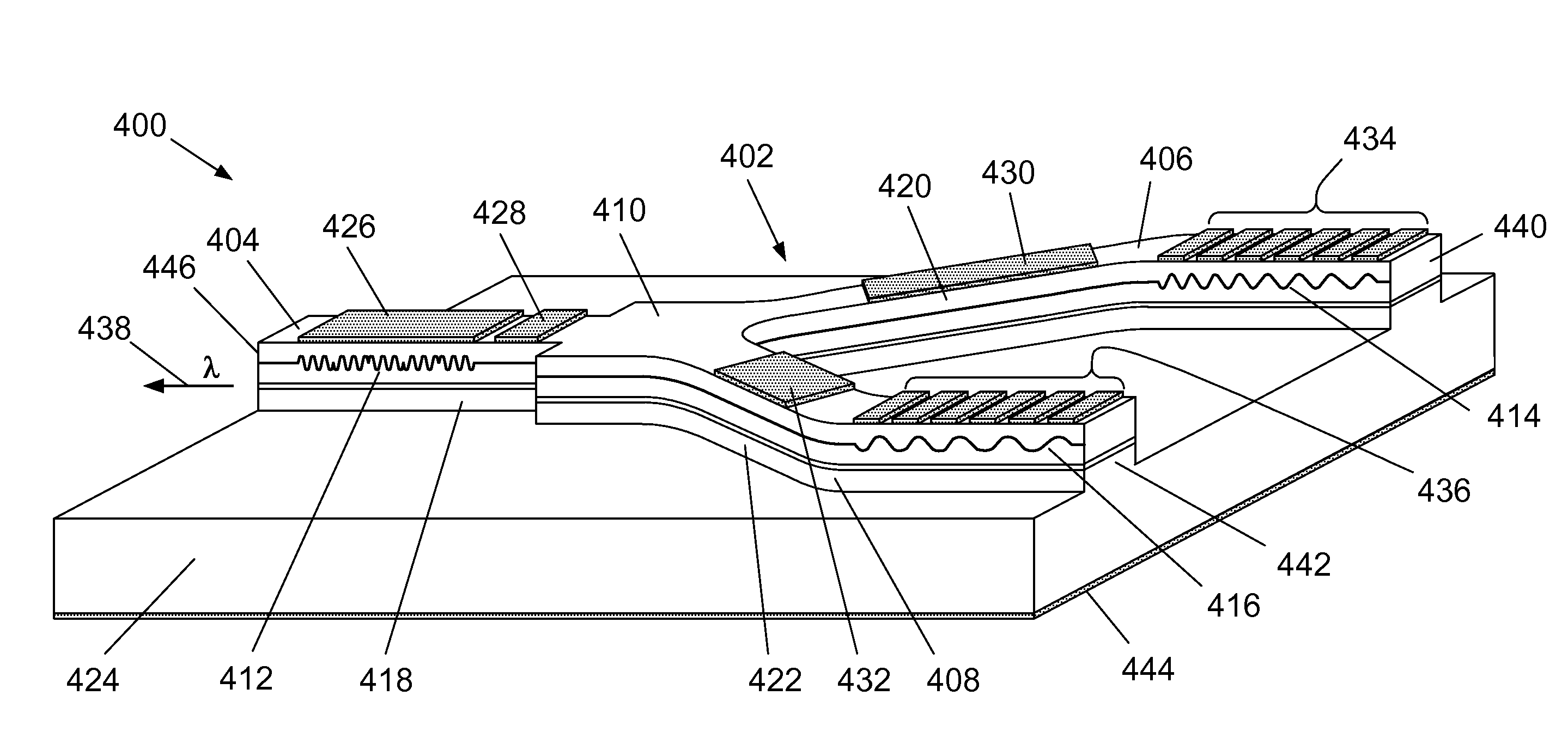
Branched waveguide multisection dbr semiconductor laser
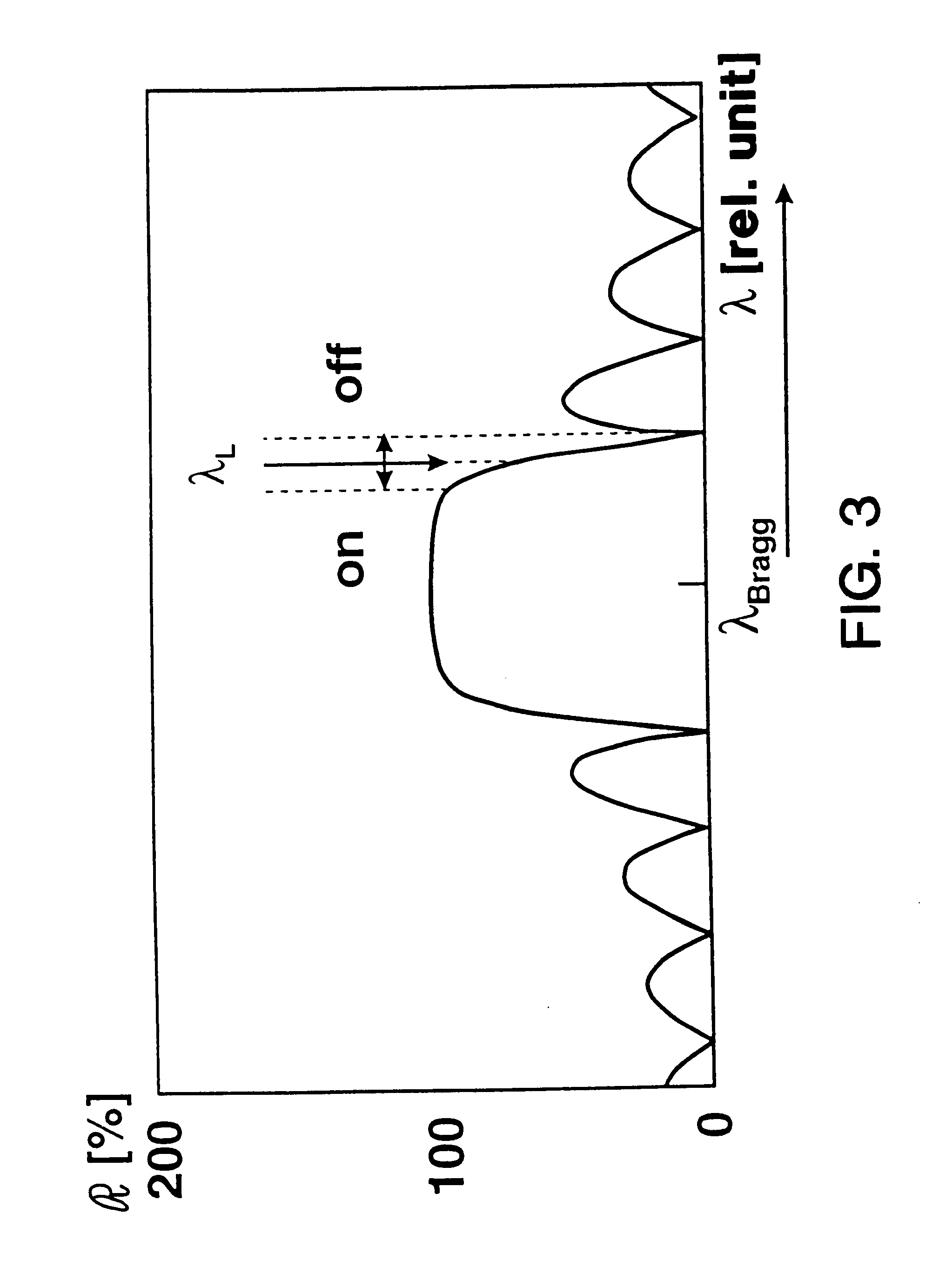
ActiveUS20100142567A1Cavity length lowImprove reflectivityLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingCoupling
The present invention concerns tunable distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) semiconductor lasers, in particular a DBR laser with a branched optical waveguide 5 within which a plurality of differently shaped lasing cavities may be formed, and a method of operation of such a laser. The laser may comprise a phase control section (418), gain section (420, 422), a sampled grating DBR (412) giving a comb-line spectrum and two tunable, chirped DBRs (414, 416) for broadband frequency training and a coupling section (410).
Owner:LUMENTUM TECH UK LTD
Surface emitting semiconductor laser
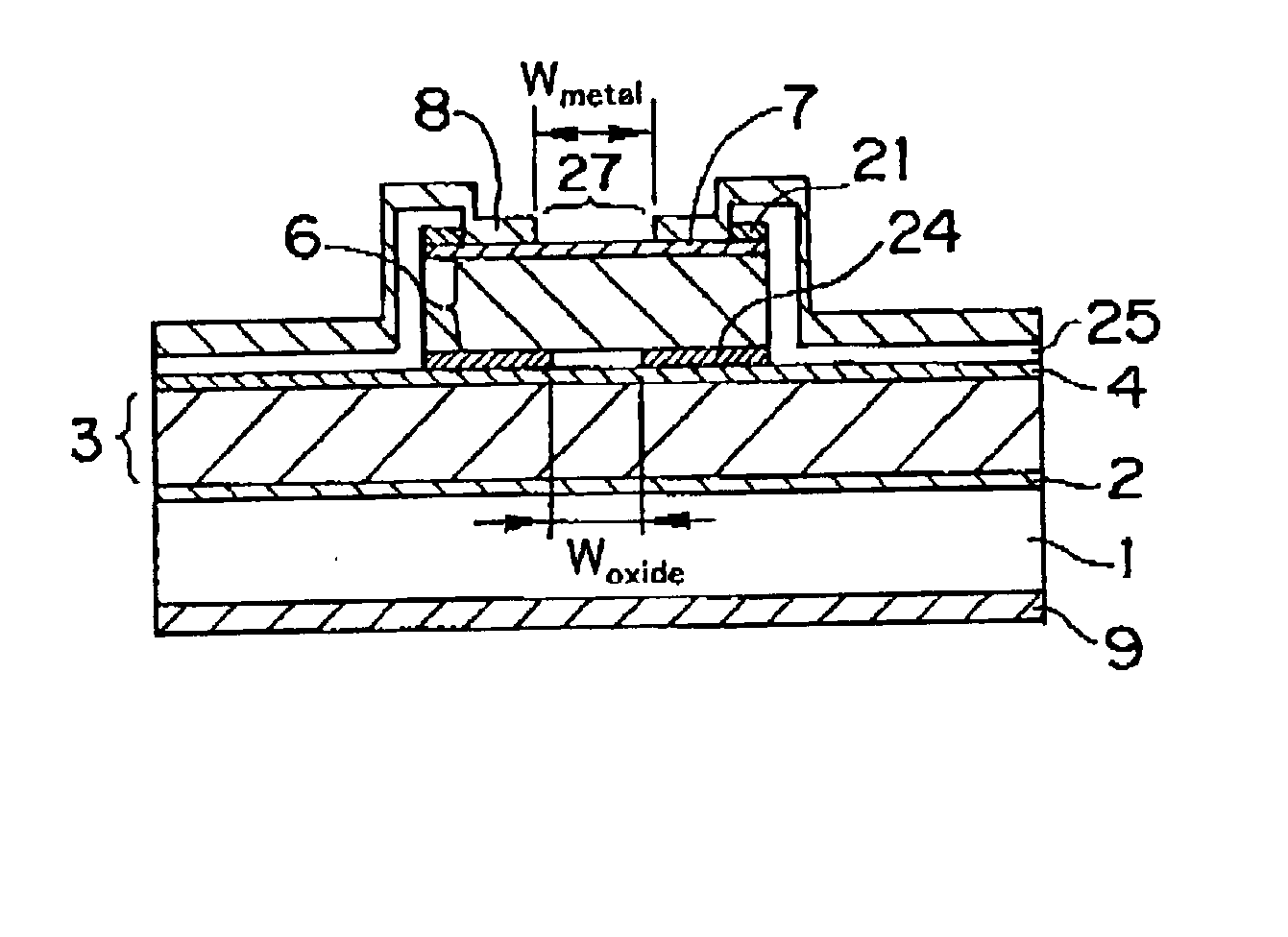
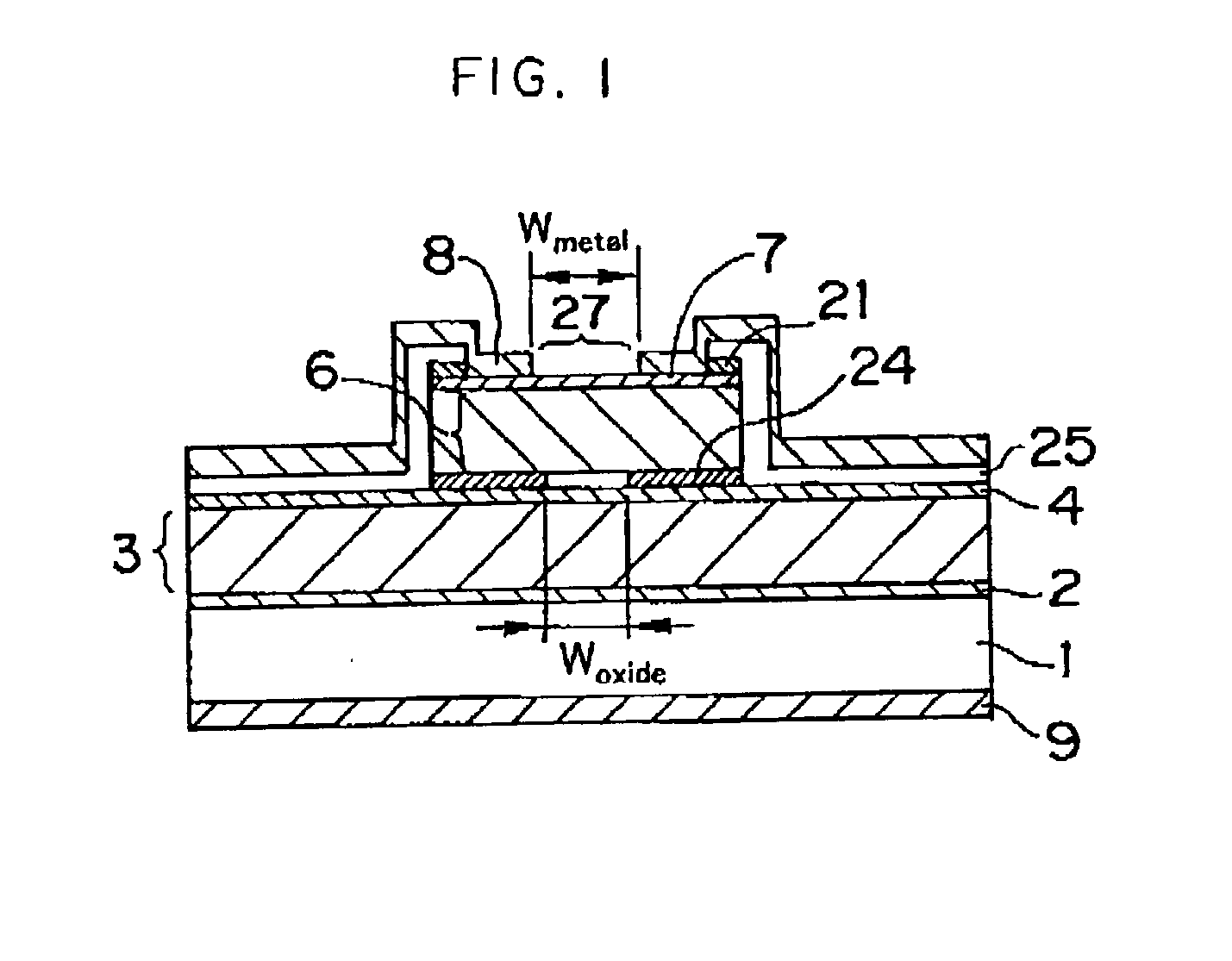
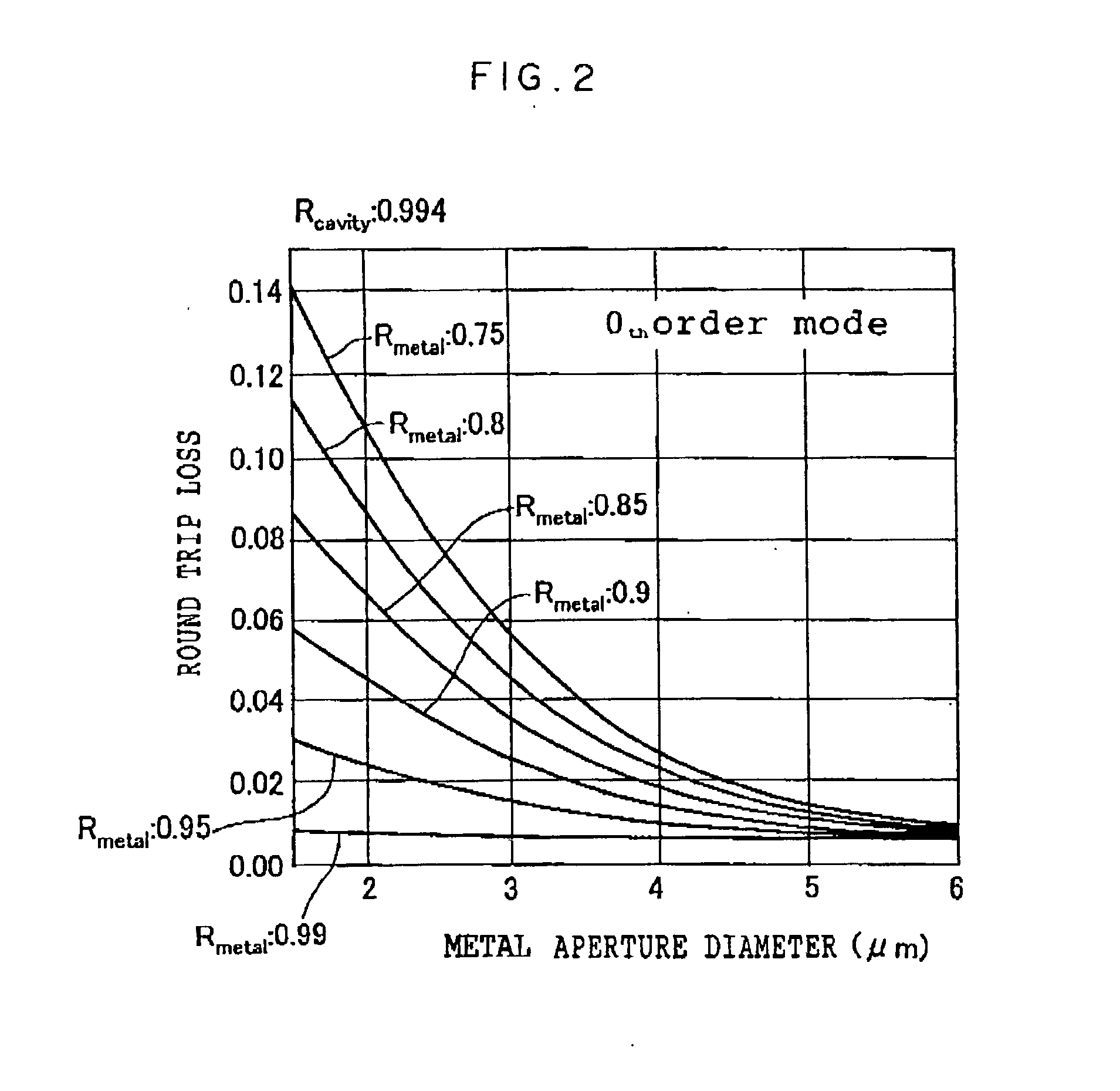
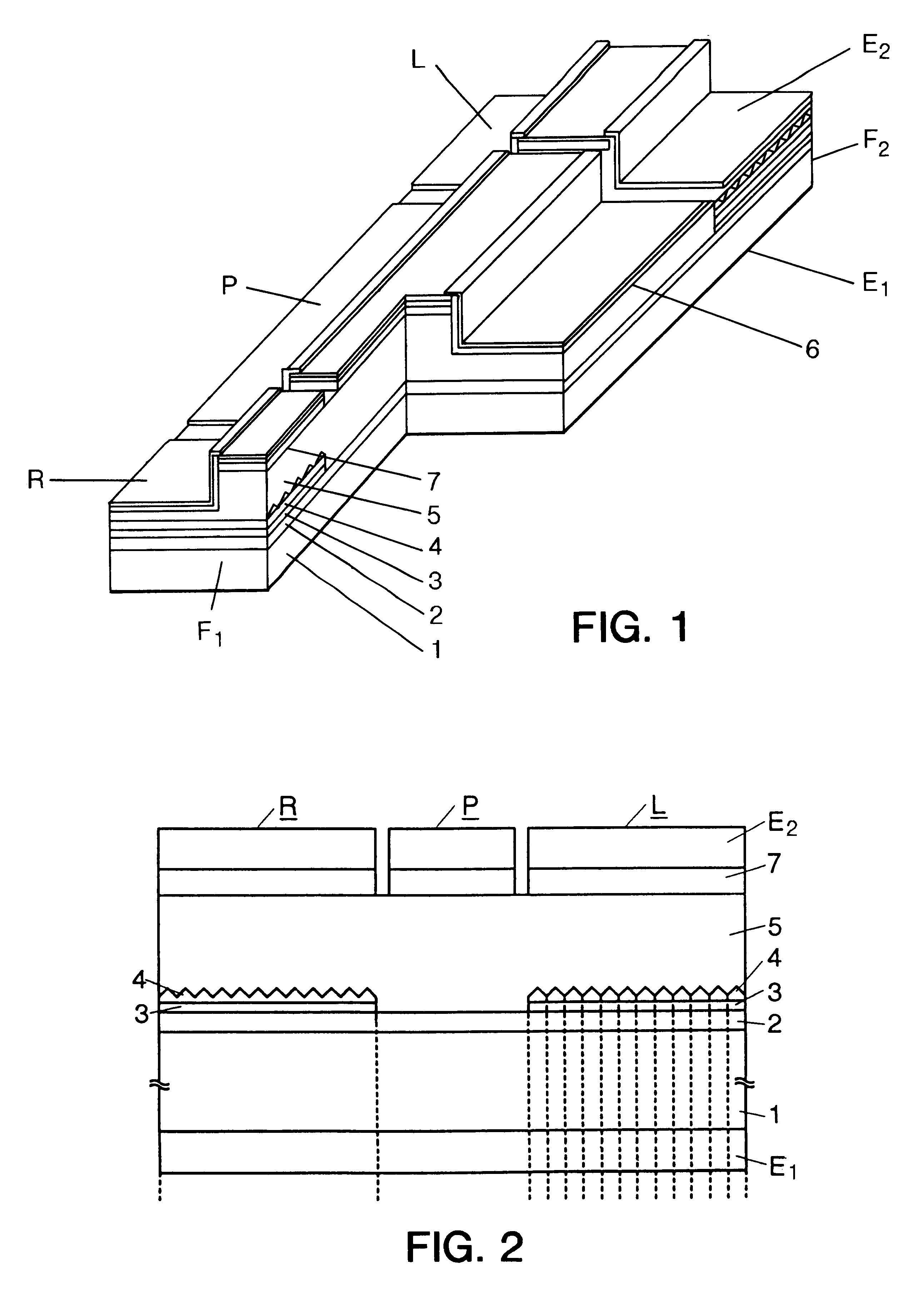
InactiveUS20030039294A1Optical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersCurrent limitingSemiconductor laser theory
The present invention provides a surface emitting semiconductor laser, comprising: a semiconductor substrate having sequentially layered thereon a lower multi-layer mirror, an active layer region, and an upper multi-layer mirror that, together with the lower multi-layer mirror, contributes to the formation of a cavity; an upper electrode disposed on an upper layer of the upper multi-layer mirror and provided with an aperture that forms an emission region of a laser beam generated at the active layer region; and a current confinement portion disposed between the upper electrode and the lower multi-layer mirror and provided with an aperture that forms a current path; wherein an aperture diameter of the upper electrode and an aperture diameter of the current confinement portion are determined such that a difference between an optical loss of the cavity in a higher-order lateral mode of the laser beam and an optical loss of the cavity in a fundamental lateral mode of the laser beam becomes a value in the vicinity of a maximum value, and the higher-order lateral mode is suppressed, and at least one of the aperture formed in the upper electrode and the aperture of the current confinement portion is formed into a two-fold symmetrical configuration having long and short axes with respect to arbitrary two axial directions orthogonal to each other in a plane.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Thermal flux laser annealing for ion implantation of semiconductor P-N junctions
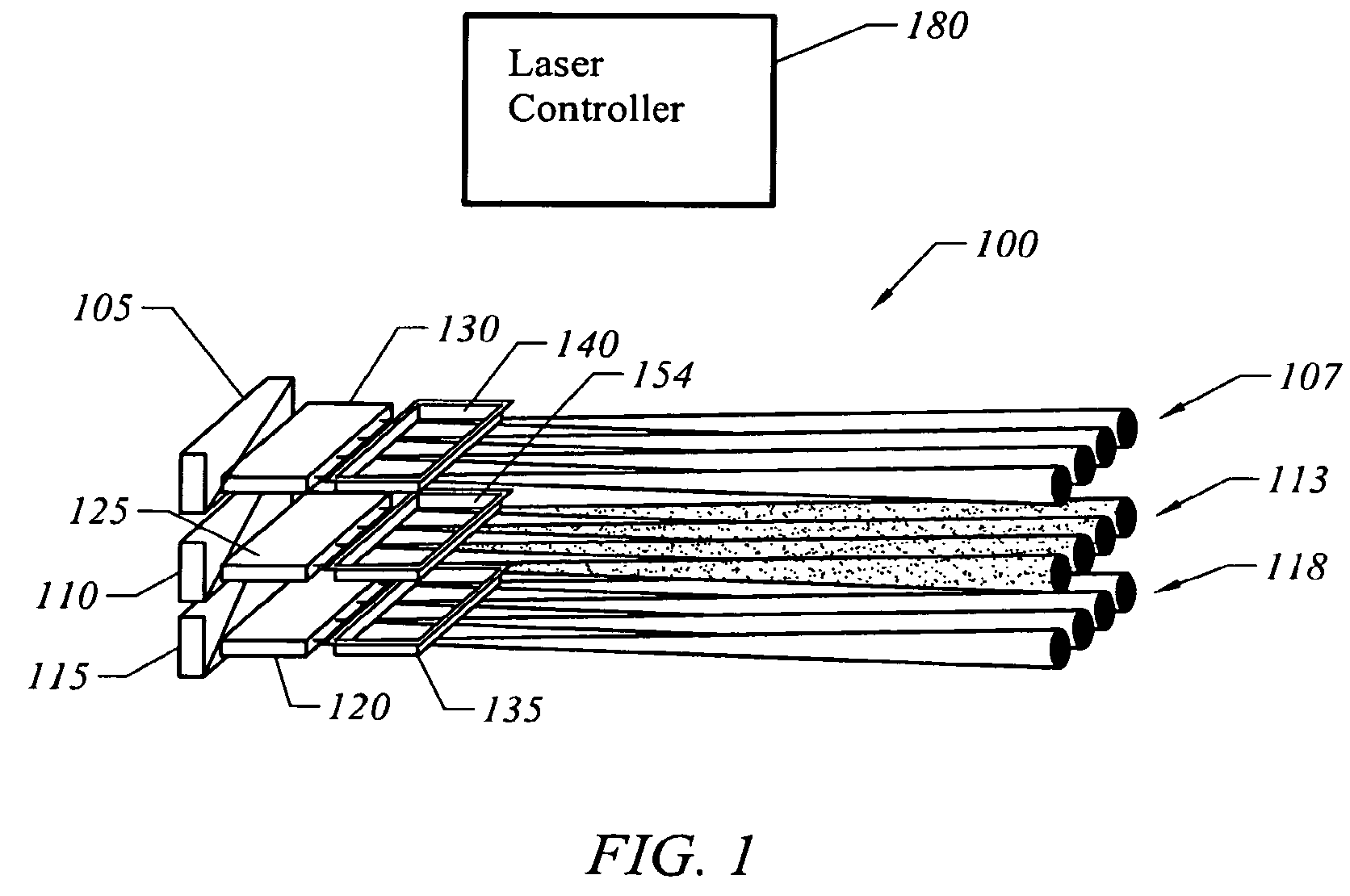
ActiveUS7135392B1Facilitate multiple reflectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersLaser transmitterHeat flux
A method for forming P-N junctions in a semiconductor wafer includes ion implanting dopant impurities into the wafer and annealing the wafer using a thermal flux laser annealing apparatus that includes an array of semiconductor laser emitters arranged in plural parallel rows extending along a slow axis, plural respective cylindrical lenses overlying respective ones of the rows of laser emitters for collimating light from the respective rows along a fast axis generally perpendicular to the slow axis, a homogenizing light pipe having an input face at a first end for receiving light from the plural cylindrical lenses and an output face at an opposite end, the light pipe comprising a pair of reflective walls extending between the input and output faces and separated from one another along the direction of the slow axis, and scanning apparatus for scanning light emitted from the homogenizing light pipe across the wafer in a scanning direction parallel to the fast axis.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Light emitting diode and semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20030132449A1Desirable crystallinityImprove luminous efficiencyLaser detailsSolid-state devicesUltraviolet lightsSingle crystal substrate
An ultraviolet-light-emitting semiconductor diode comprising an n-type ZnO layer with luminous characteristics formed on a transparent substrate, and a p-type semiconductor layer selected from the group consisting of SrCu2O2, CuAlO2 and CuGaO2, which is formed on the n-type ZnO layer to provide a p-n junction therebetween. The transparent substrate is preferably a single crystal substrate having atomically flat yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) (III) surface. The n-type ZnO layer is formed on the transparent substrate having a temperature of 200 to 1200° C., and the p-type semiconductor layer selected from the group of SrCu2O2, CuAlO2 and CuGaO2 is formed on the n-type ZnO layer. The n-type ZnO layer may be formed without heating the substrate, and then the surface of the ZnO layer may be irradiated with ultraviolet light to promote crystallization therein.
Owner:HOYA CORP
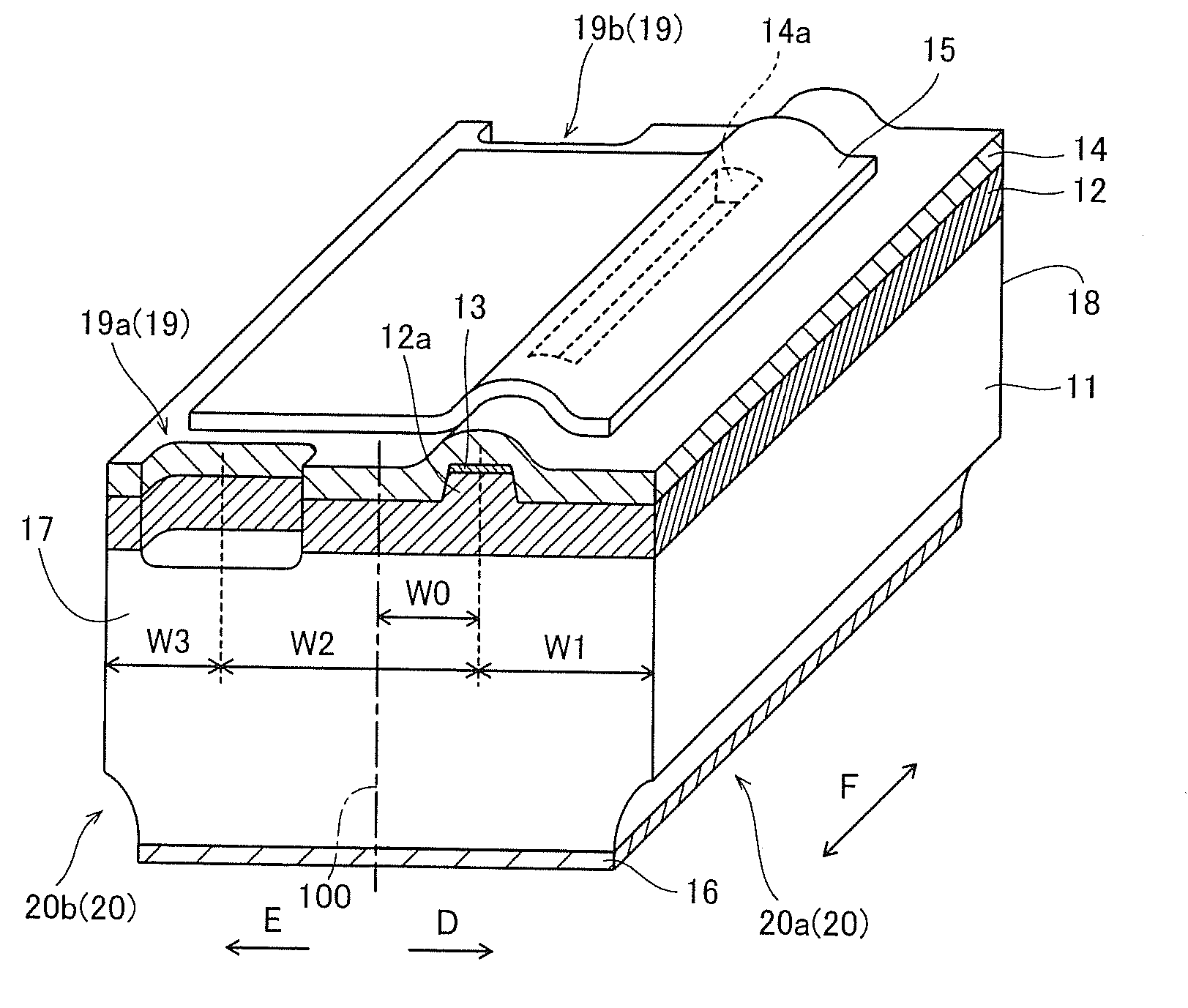
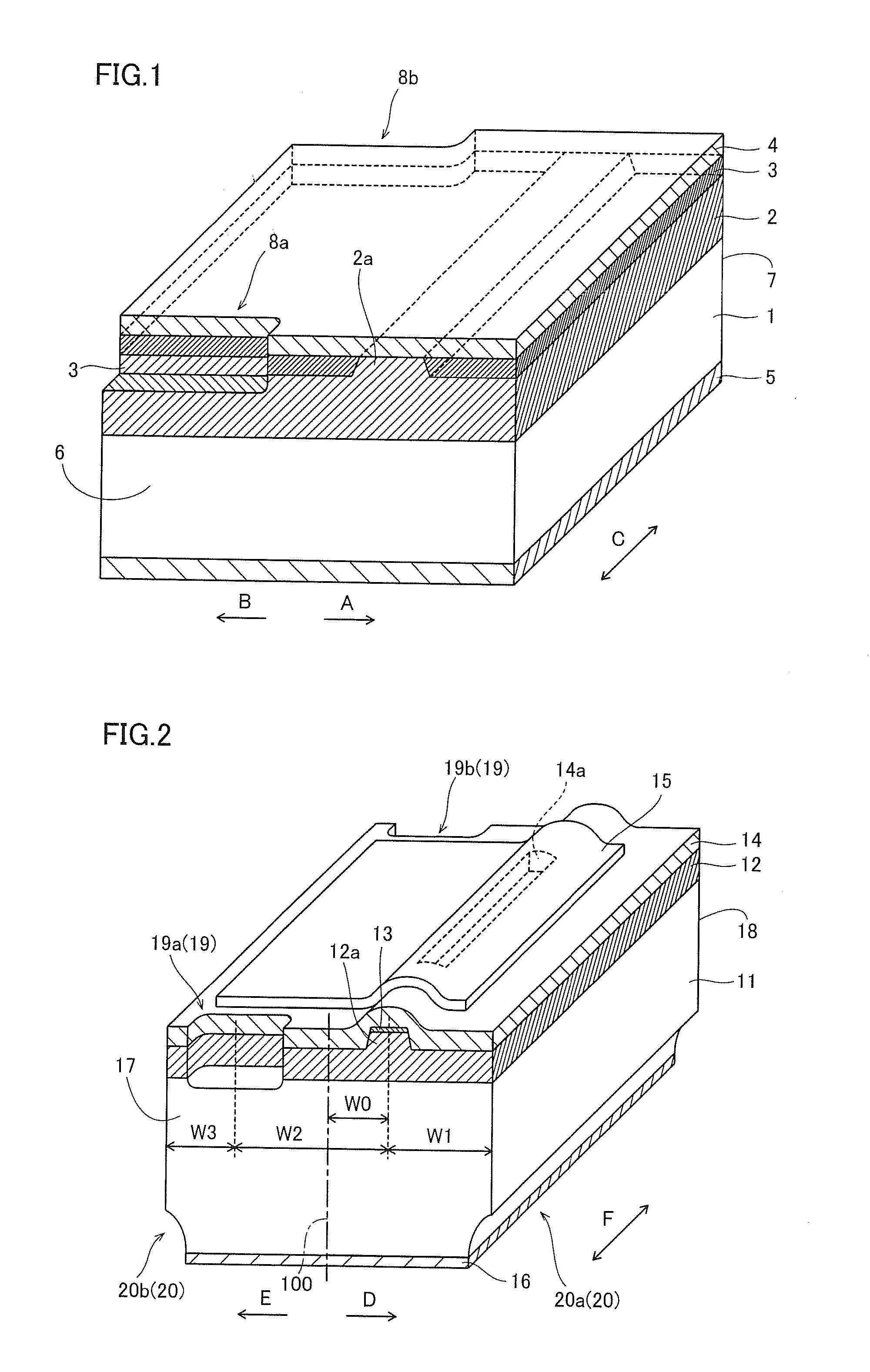
Semiconductor laser device and method of manufacturing the same
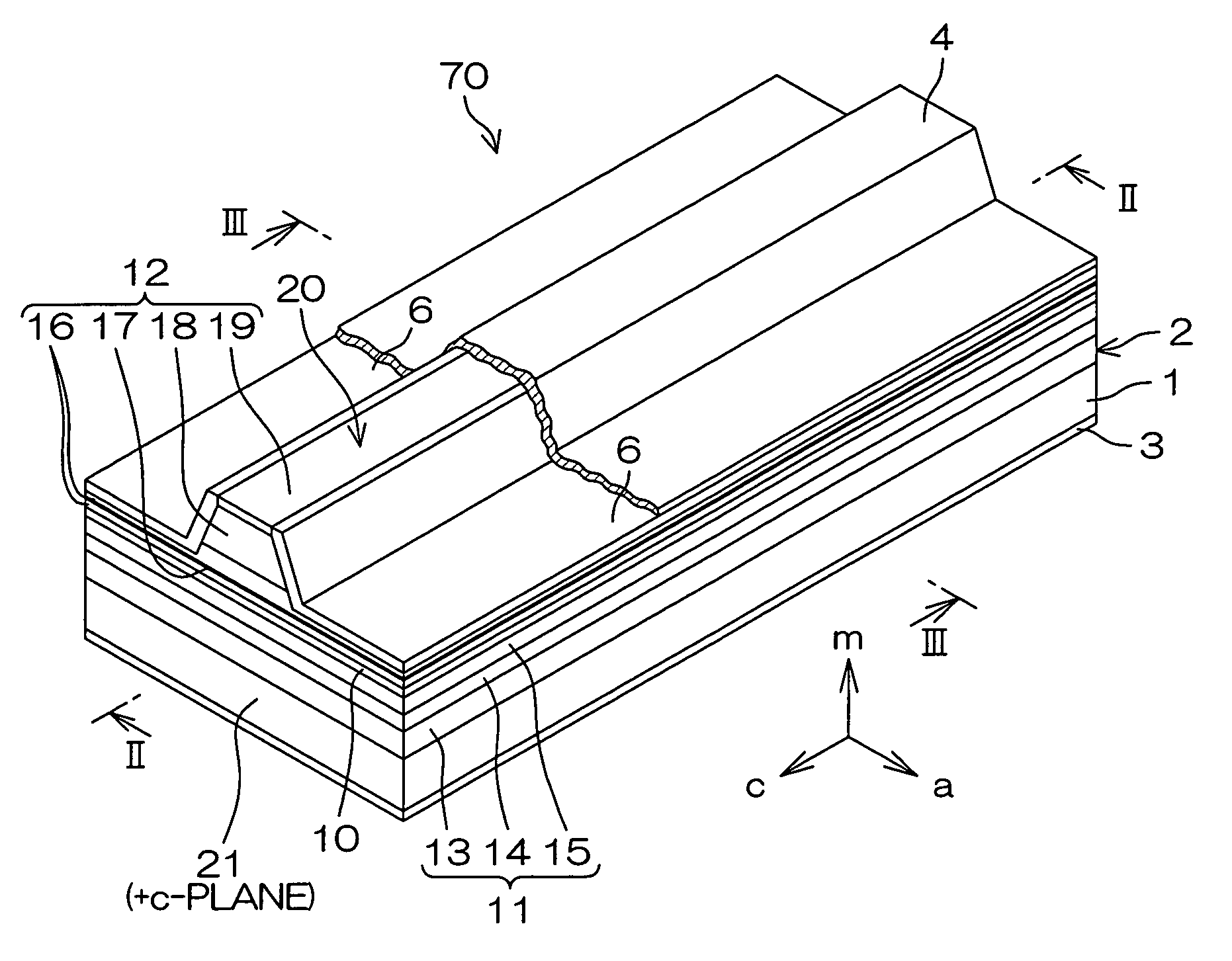
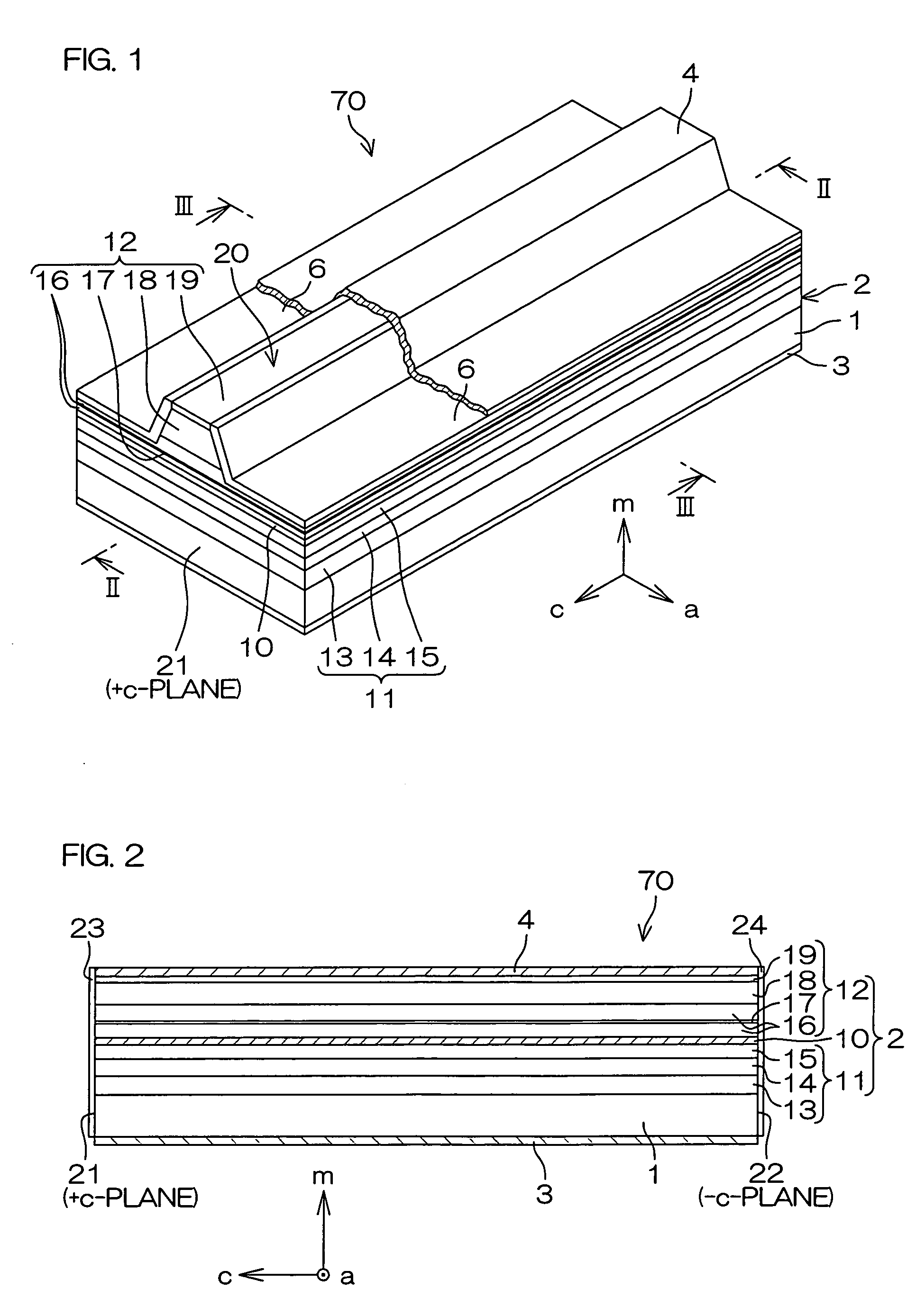
A semiconductor laser device capable of suppressing damage of a waveguide is obtained. This GaN-based semiconductor laser chip (semiconductor laser device) includes an n-type GaN substrate of a nitride-based semiconductor and a semiconductor layer of a nitride-based semiconductor formed on the n-type GaN substrate and provided with a ridge portion constituting a waveguide extending in a direction F. The ridge portion (waveguide) is formed on a region approaching a first side from the center of the semiconductor layer. On a region opposite to the first side of the ridge portion (waveguide), a cleavage introduction step is formed from the side of the semiconductor layer, to extend in a direction intersecting with the extensional direction F of the ridge portion (waveguide).
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
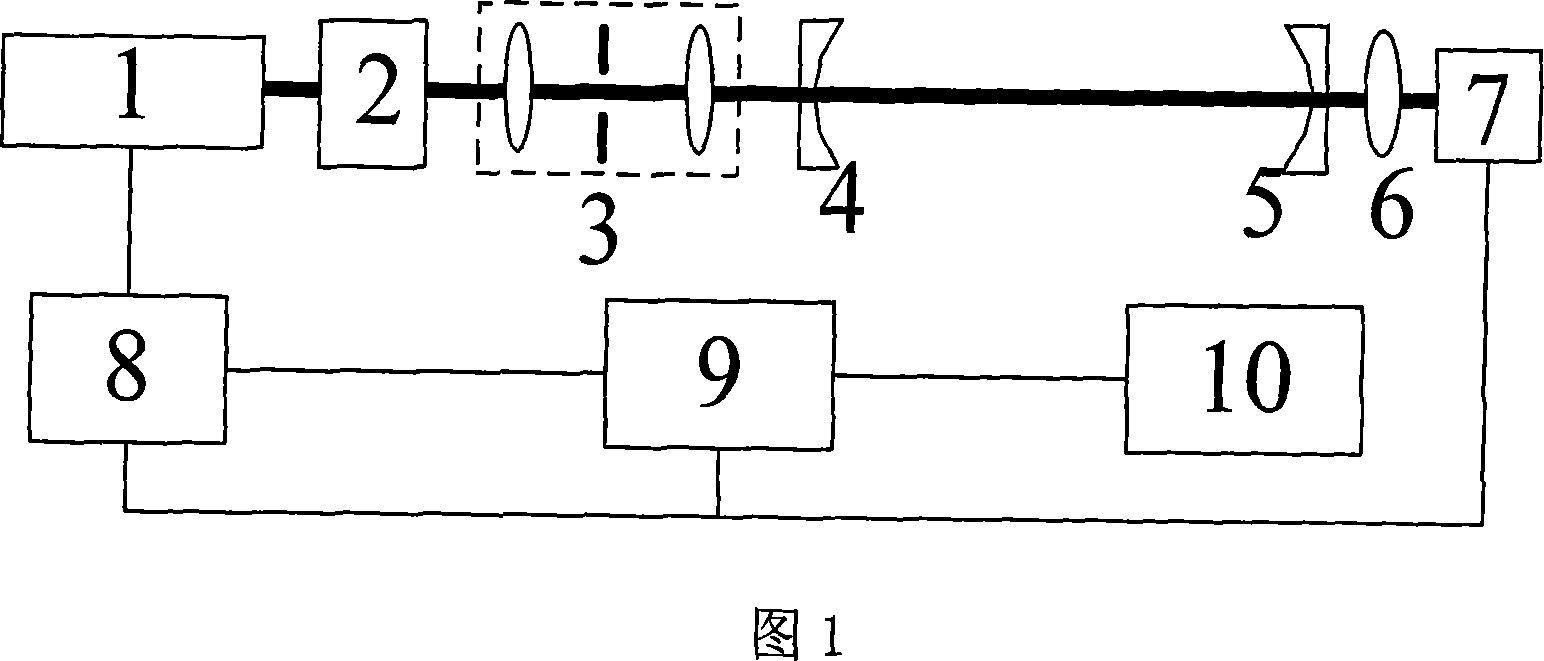
Semiconductor laser self-mixing effect based high reflectivity measurement method
InactiveCN101055224ALower requirementReduce the difficulty of adjustmentScattering properties measurementsTesting optical propertiesPolarizerHigh reflectivity
The invention discloses a method for measuring high reflectivity based on self-mixing effect of semiconductor laser which belongs to the technical field of measuring optical elements parameter. The present cavity ringdown technique for determining high reflectivity by measuring ringdown time, using the self-mixing effect of semiconductor laser, improves laser power to coupling efficiency of ringdown cavity by controlling back feedback optical intensity of continuous wave semiconductor laser, greatly improves the signal-noise ratio of cavity outputting signal, thereby improving measuring precision and measuring range of high reflectivity. The methods for controlling back feedback optical intensity which can make the cavity output signal reach the maximum include: inserting a linear polarizer, an attenuation plate, an optical isolator or a variable aperture between the semiconductor laser and the first cavity mirror, or adjusting the pitching of the first cavity mirror, or changing the distance of the laser and the first cavity mirror.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vertical-cavity surface-emitting semiconductor laser
A surface-emitting semiconductor laser includes comprising a substrate, a first mesa that is formed on the substrate and includes at least one mesa capable of emitting laser light, and a second mesa that is formed on the substrate and includes at least one mesa restraining emission of laser light.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Semiconductor laser device, optical pickup device and semiconductor device
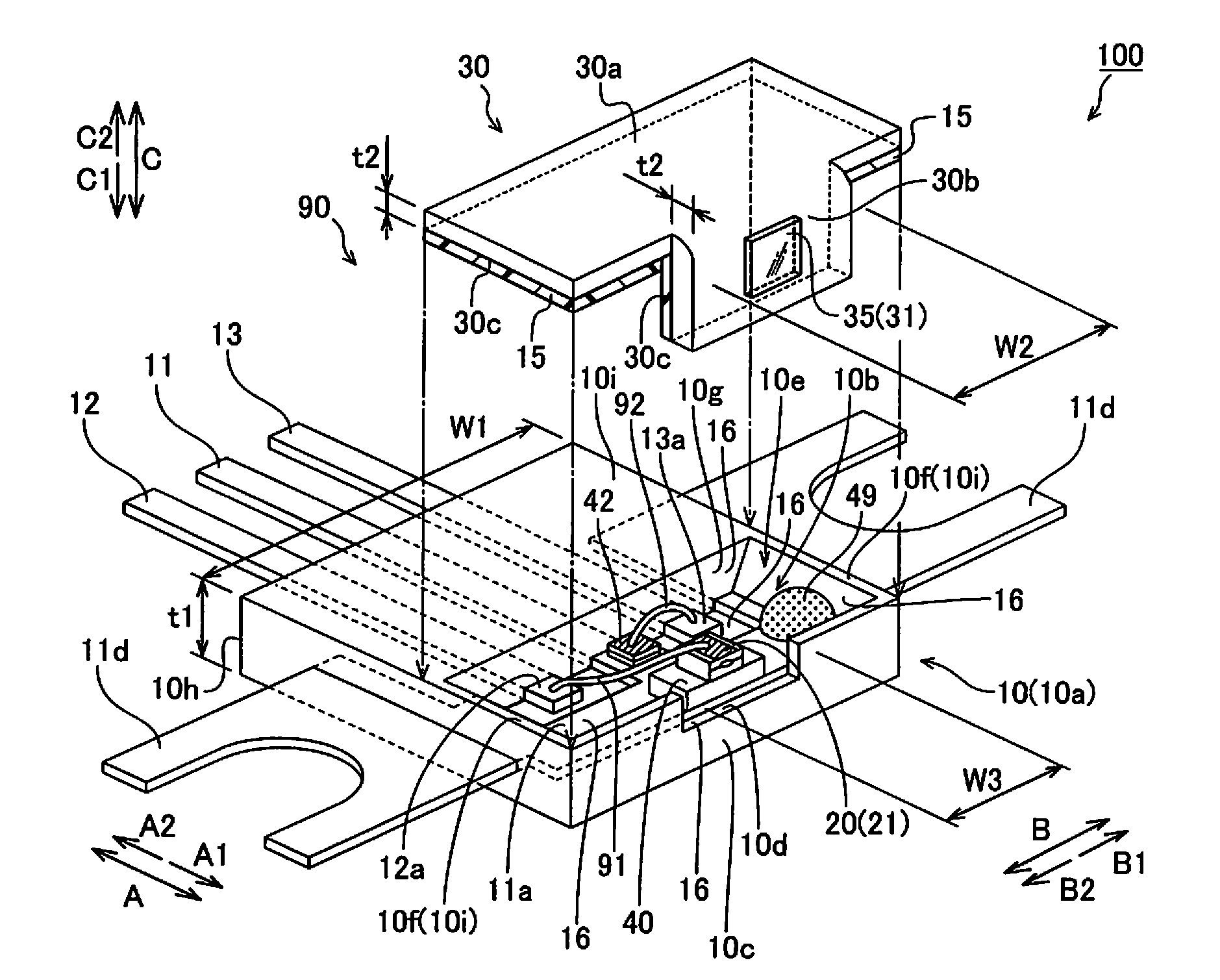
InactiveUS20110158273A1High resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsPower semiconductor deviceOptical pickup
A semiconductor laser device includes a Si(100) substrate in which a recess having an opening and a bottom face surrounded by inner wall surfaces is formed, a semiconductor laser element placed on the bottom face, and a translucent sealing glass, mounted on top of the Si(100) substrate, which seals the opening. The laser light emitted from the semiconductor laser element is reflected by a metallic reflective film formed on the inner wall surface and then transmits through the sealing glass so as to be emitted externally.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Laser Light Source and Optical Device
InactiveUS20090067453A1Highly-efficient monochrome light generationReduce coherenceCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsTransverse modeLaser light
A laser light source is provided with a pump light source (1) comprising a semiconductor laser, a solid laser medium (2) which is excited by the semiconductor laser, and multi-mode means for changing at least either a longitudinal mode or a transverse mode of laser oscillation of the solid laser. The oscillation light of the laser medium excited by the light outputted from the pump light source is changed by the multi-mode means into output light (5) having a plurality of oscillation spectra and is outputted, thereby a small, high power, and highly efficient low coherent light source can be realized, and a laser light source having reduced speckle noises can be provided.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
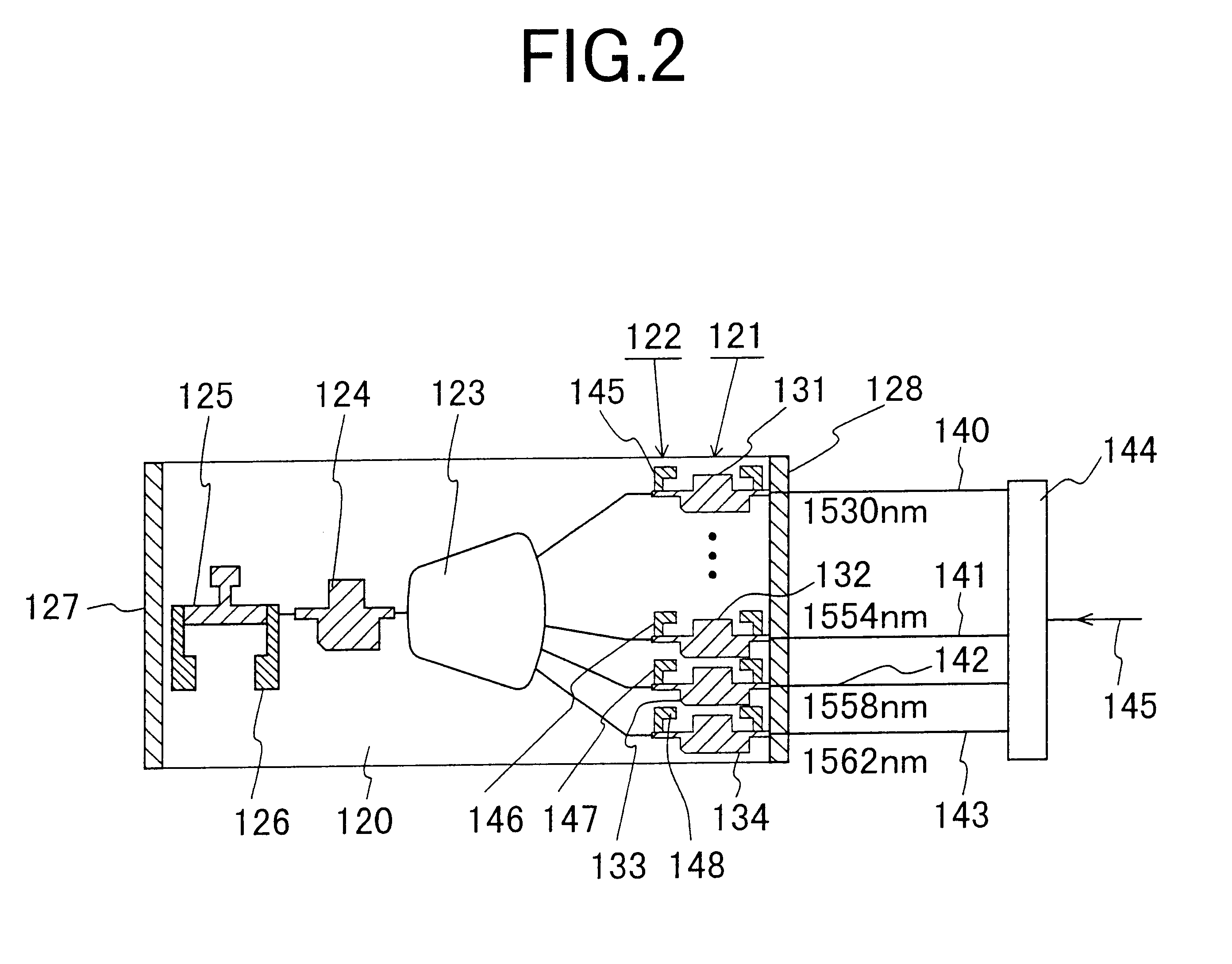
Wavelength monitor
InactiveUS20120147361A1Solve problemsRadiation pyrometryPhotoelectric discharge tubesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
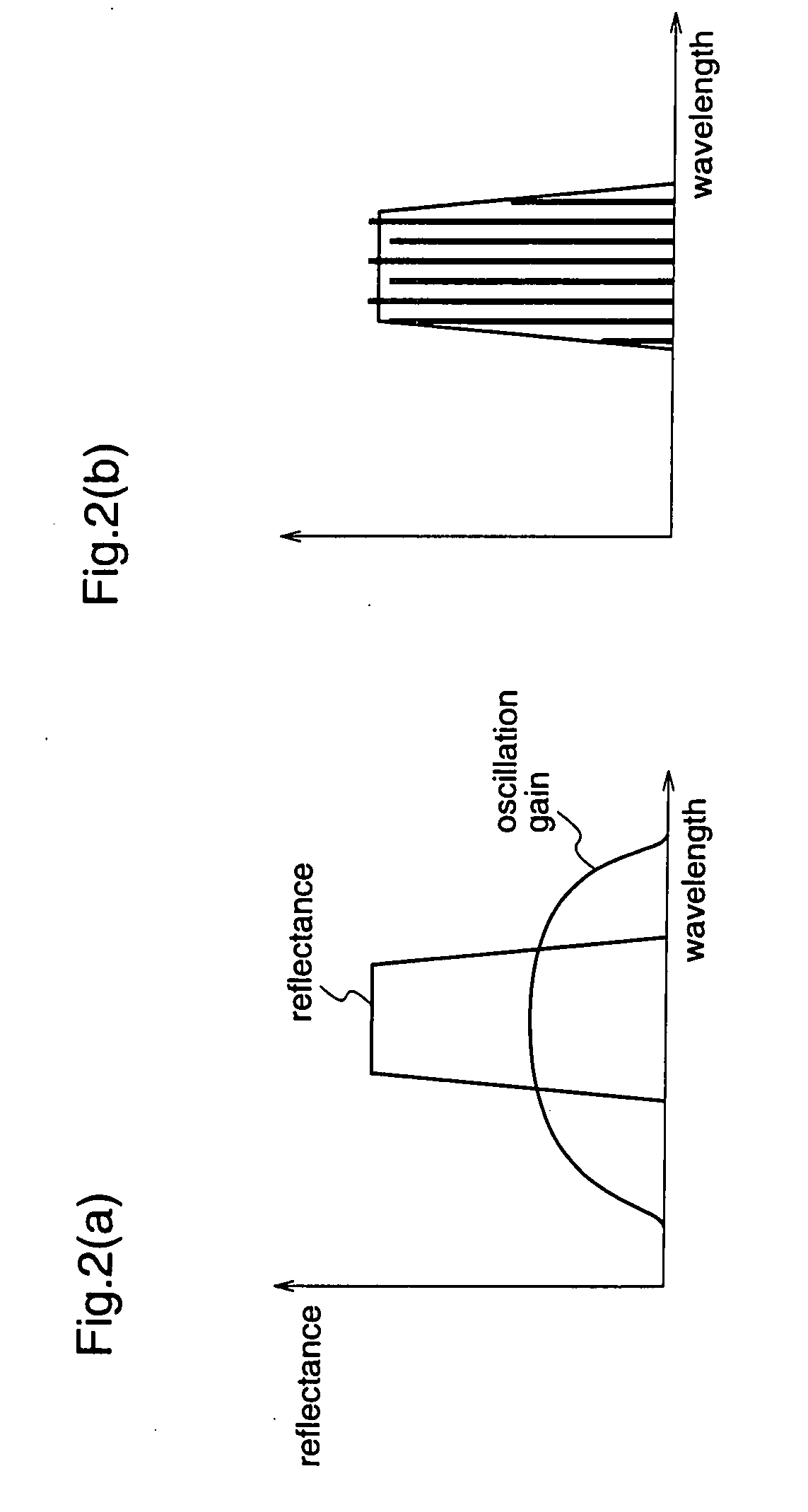
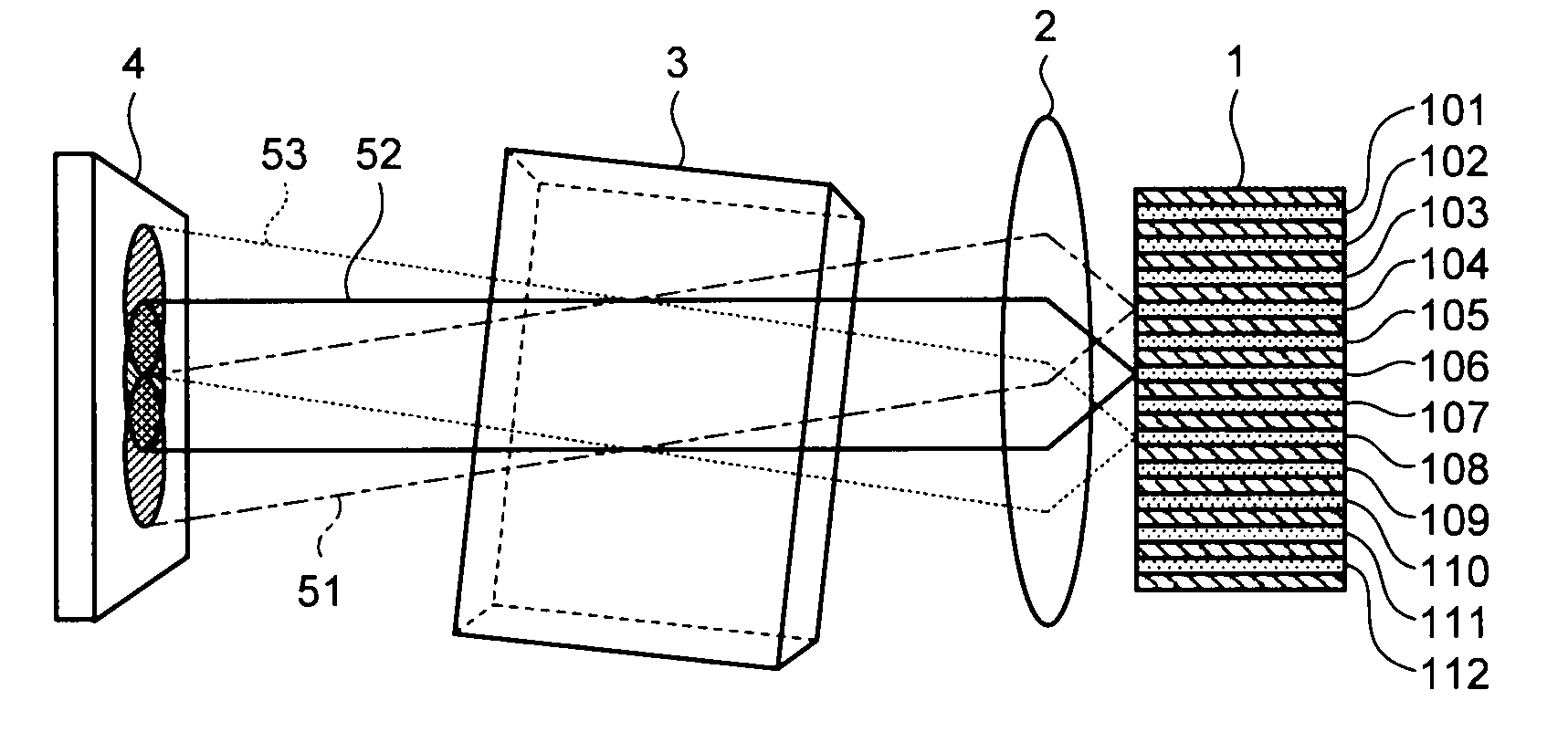
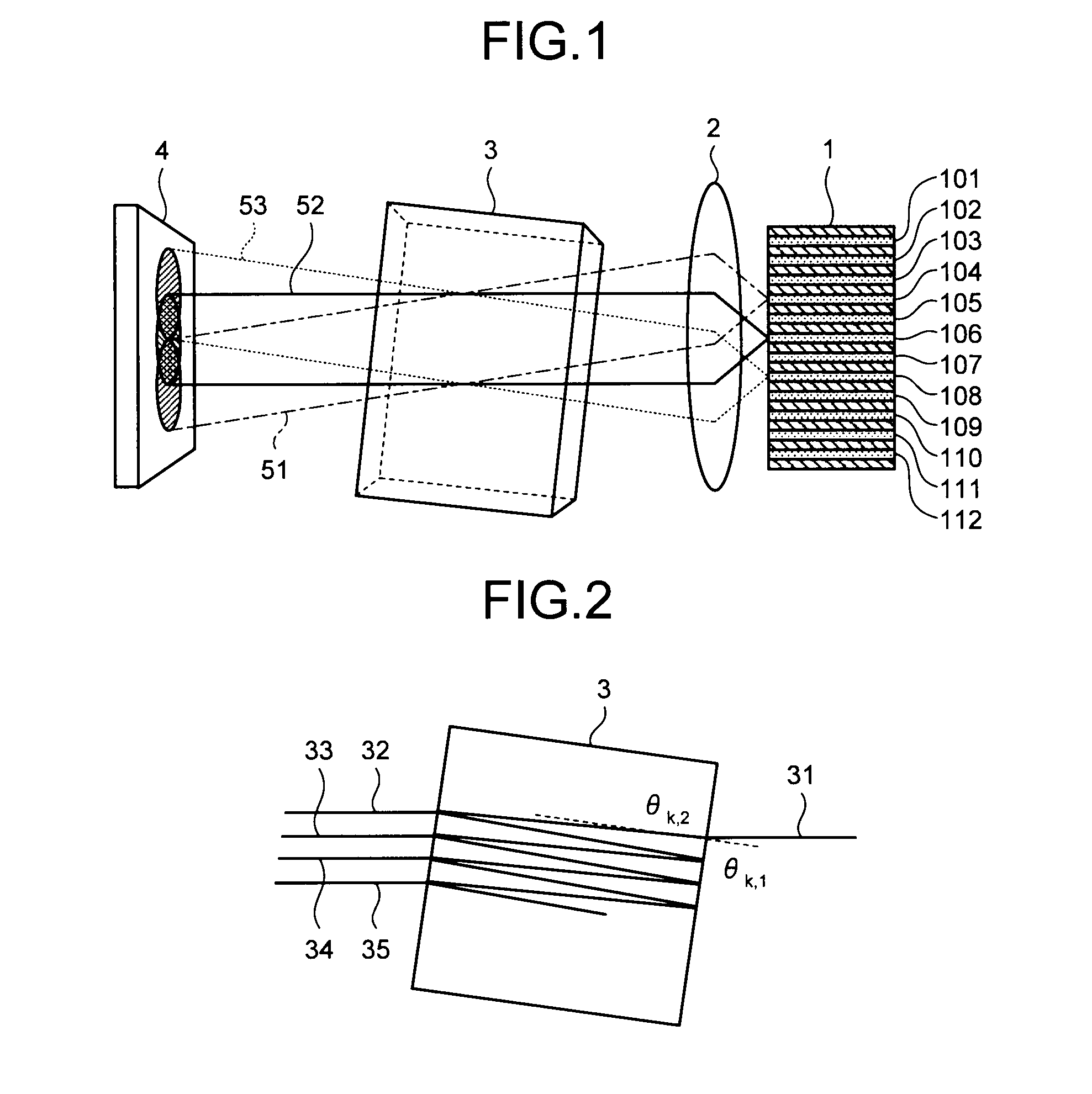
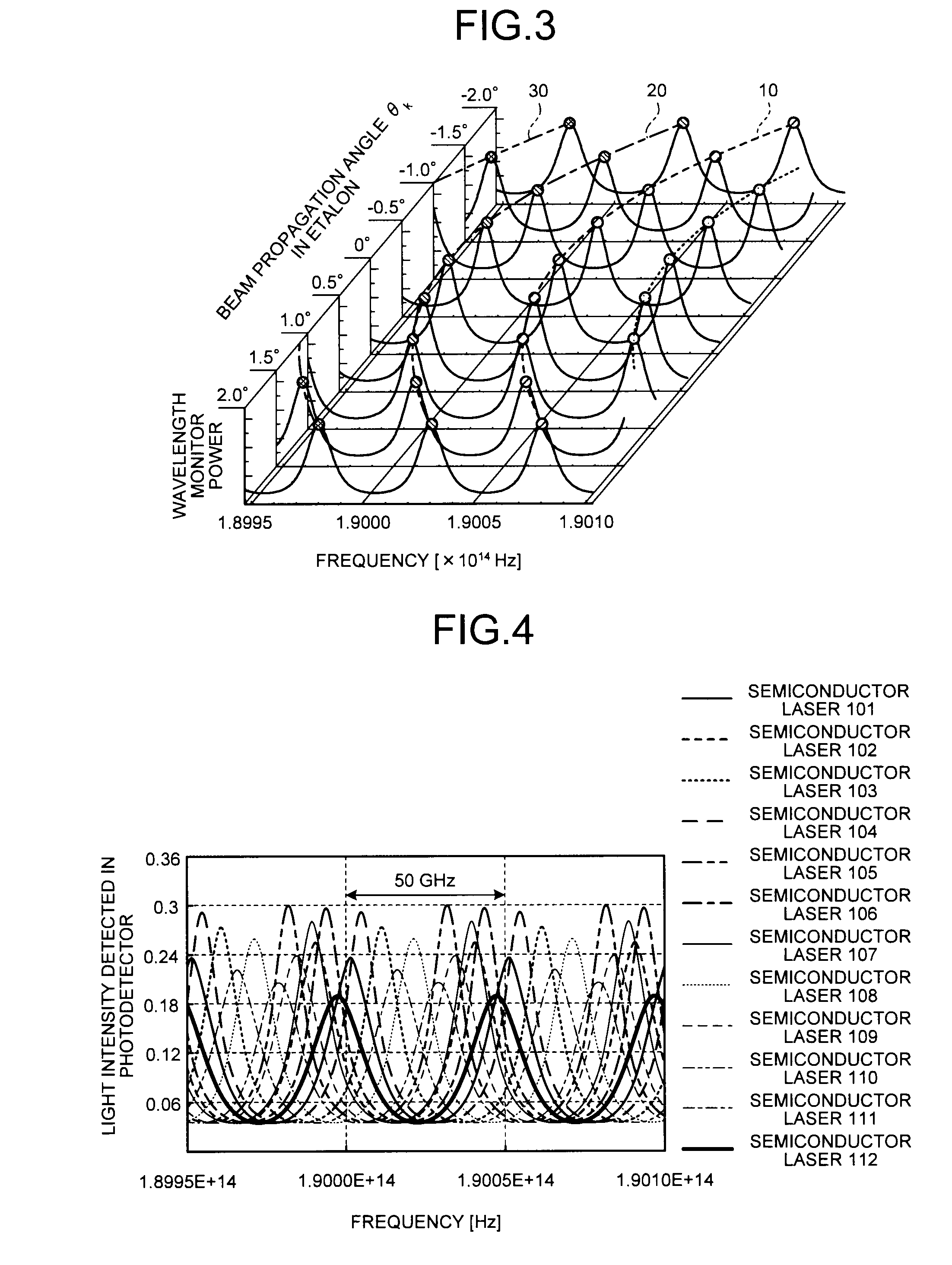
In a wavelength monitor that monitors a wavelength of laser light emitted from at least two semiconductor lasers formed in parallel on a semiconductor substrate, the wavelength monitor includes a collimating lens that collimates laser light from each of the semiconductor lasers, an etalon that is arranged so that laser light collimated by the collimating lens is capable of entering and has a periodicity, and a photodetector that receives laser light transmitted through the etalon and detects a light intensity, wherein a beam propagation angle in the etalon of laser light emitted from each of the semiconductor lasers becomes a predetermined angle obtained by formula 1.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
All-optical true random number generator
InactiveCN102681816AMeet the needs of high-speed secure communicationOvercome additional problemsRandom number generatorsOptical fiber couplerNumber generator
The invention discloses an all-optical true random number generator, which comprises an all-optical true random number entropy source, wherein the all-optical true random number entropy source injects output light of a continuous laser device I into a two-section semiconductor laser device through a 3dB optical fiber coupler I and a light attenuator, produces a high-speed chaos self-pulse signal and controls the repeated frequency of the chaos self-pulse signal by adjusting the light injection intensity and the frequency detuning amount. Sampling and subsequent processing are not required; the additional problem caused by signal distortion because of sampling in the prior art is solved; the complexity of a system is greatly reduced; a code rate can be tuned in a large range by changing the light injection intensity and the frequency detuning amount; and the code rate is up to Gbps and can be directly compatible with a light network.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Q-switched semiconductor laser
InactiveUS6215805B1High frequencyLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionRefractive indexElectron
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Production method and apparatus for single-slice integrated semiconductor laser array
ActiveCN101369718ALow costReduce manufacturing difficultyLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsGratingPhase shifted
Method for manufacturing a monolithic integrated semiconductor laser array, wherein each laser DFB grating structure in the array being sampling Bragg grating structure, the grating of each DFB semiconductor laser waveguide in the array is sampling Bragg grating, and the sampling Bragg grating containing equivalent grating corresponding to the common Bragg grating; the mase wavelength of the DFB semiconductor laser is determined by sampling period of the sampling structure of the sampling Bragg grating within the equivalent grating action bandwidth of the sampling Bragg grating, and it is able to change mase wavelength by changing sampling period. The sampling period is increased or decreased by mask plate with various sampling pattern, and various wavelength mases are implemented by closing in or outlying a center wavelength of the DFB laser mase wavelength, thus to implement multi-channel multi-wavelength laser array; the invention implements various complicated equivalent phase-shift with sub-micron stage accuracy, namely corresponding equivalent grating has Lambada / 4 phase-shift, Lambada / 8 phase-shift and a CPM structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Semiconductor laser device
A semiconductor laser device includes a substrate made of a nitride-based semiconductor and a waveguide formed on a principal surface of the substrate, wherein the substrate includes a dislocation concentrated region arranged so as to obliquely extend with respect to the principal surface of the substrate, and the waveguide is so formed as to be located above the dislocation concentrated region and also located on a region except a portion where the dislocation concentrated region is present in the principal surface of the substrate.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor laser device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20040184502A1Easy and high-volume fabricationImprove accuracyOptical wave guidanceSemiconductor laser arrangementsWaveguideNitride
A semiconductor laser device comprises: a first light-emitting element having a first laser part, an insulating layer, and an ohmic electrode layer; and a second light-emitting element having a second laser part, an insulating layer, and an ohmic electrode layer. The first laser part has a ridge waveguide, and is formed by stacking thin films of group-III nitride compound semiconductors (for example, GaN-based semiconductors). The second laser part has a ridge waveguide, and is formed by stacking thin films of group III-V compound semiconductors (such as GaAs). The first laser part and the second laser part are integrally bonded to each other by the interposition of an adhesive metal layer which is formed between the ohmic electrode layers. This provides the semiconductor laser device with a small distance between the light-emitting spots of the laser parts.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Semiconductor laser with wide side of tapered light gain region
InactiveUS6075801AOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor packageLight beam
The semiconductor laser disclosed includes a first conductivity type buffer layer, an active layer and a second conductivity type cladding layer which are sequentially positioned on a first conductivity type semiconductor substrate. The active layer has a laser gain region to which an electric current is injected. The laser gain region having a width varying linearly along a resonating direction is disposed between a high reflection film provided on a facet of a wide side of the laser gain region of the active layer and a low reflection film provided on a facet of a narrow side of the laser gain region of the active layer. The facet of the narrow side is for outputting oscillation beams of a high order mode. This provides a high electrical-to-optical conversion efficiency, and enables the outputting of a large output from a narrow light emission region.
Owner:NEC CORP
Semiconductor laser driving current control method and multi-mode working driving power supply
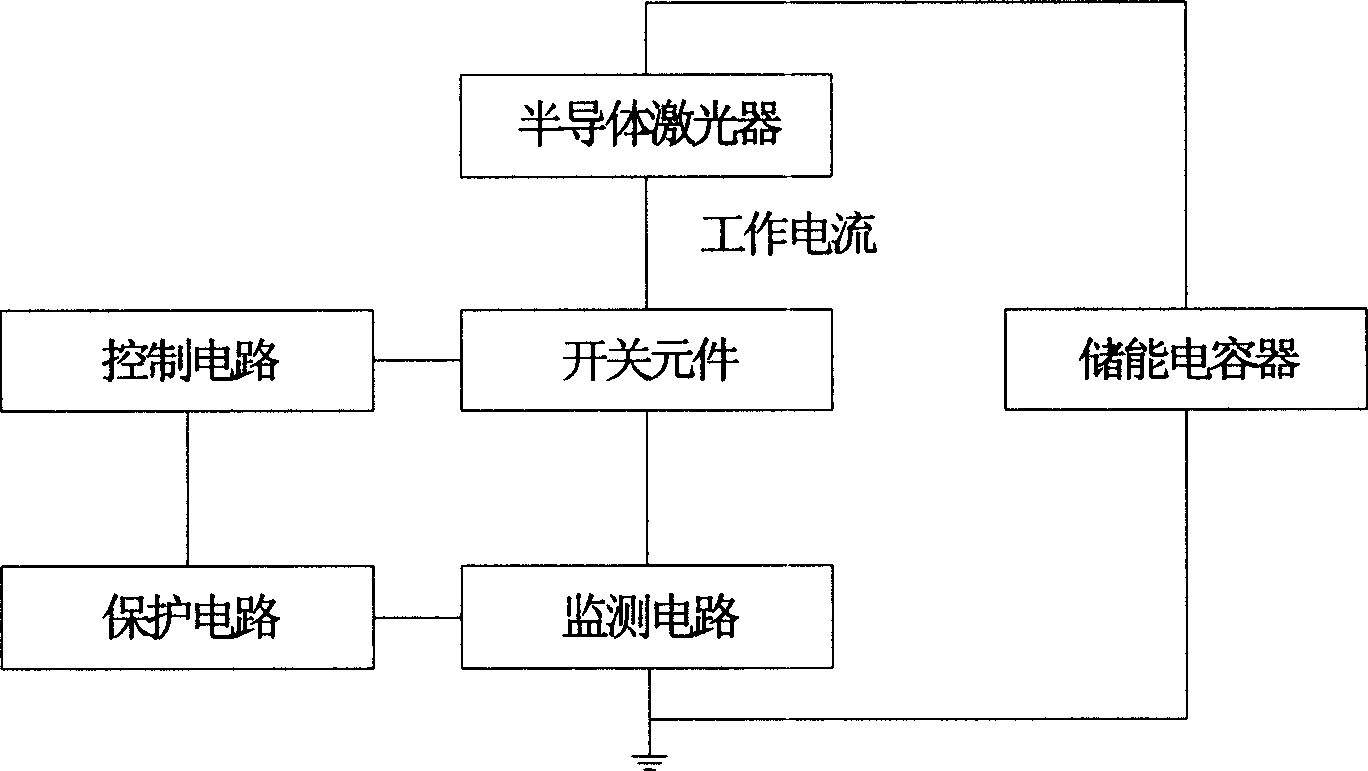
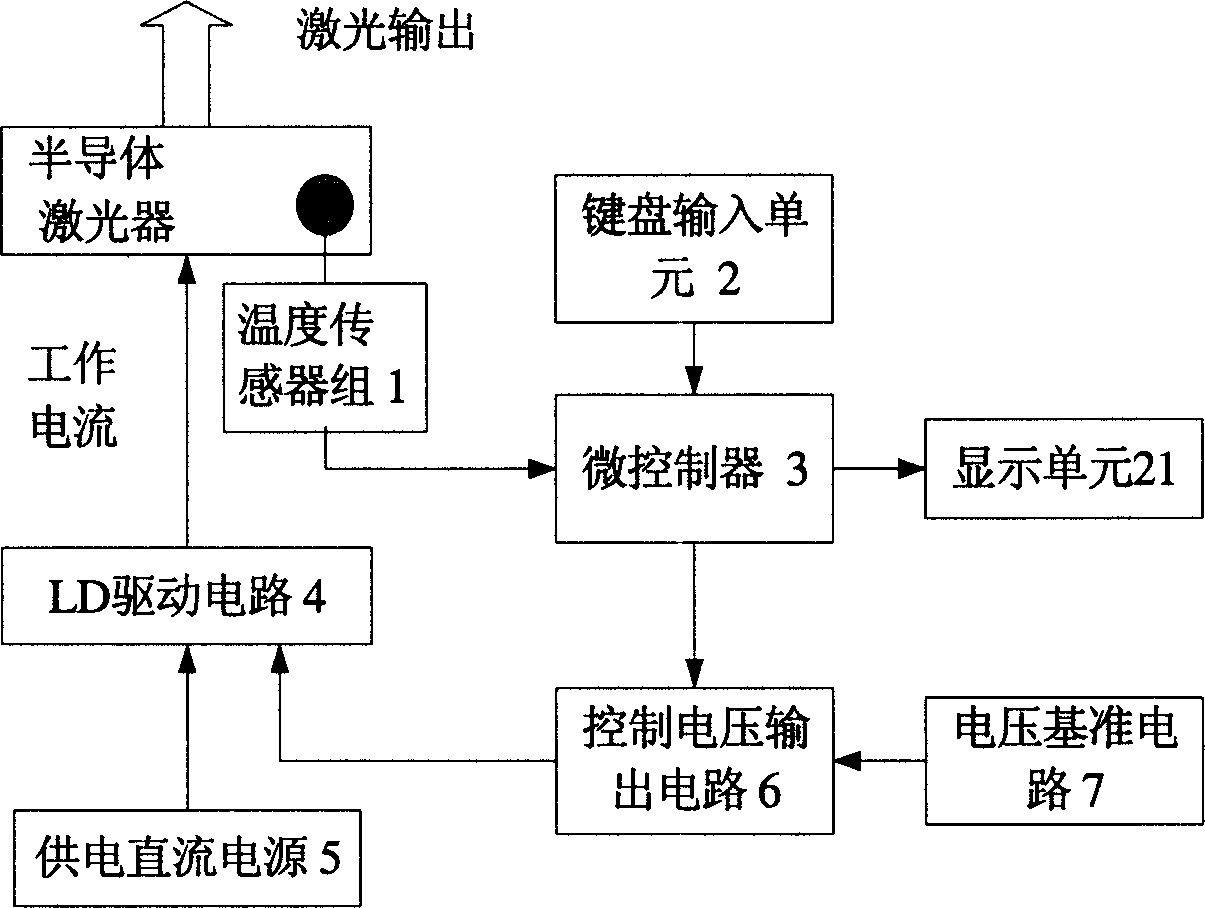
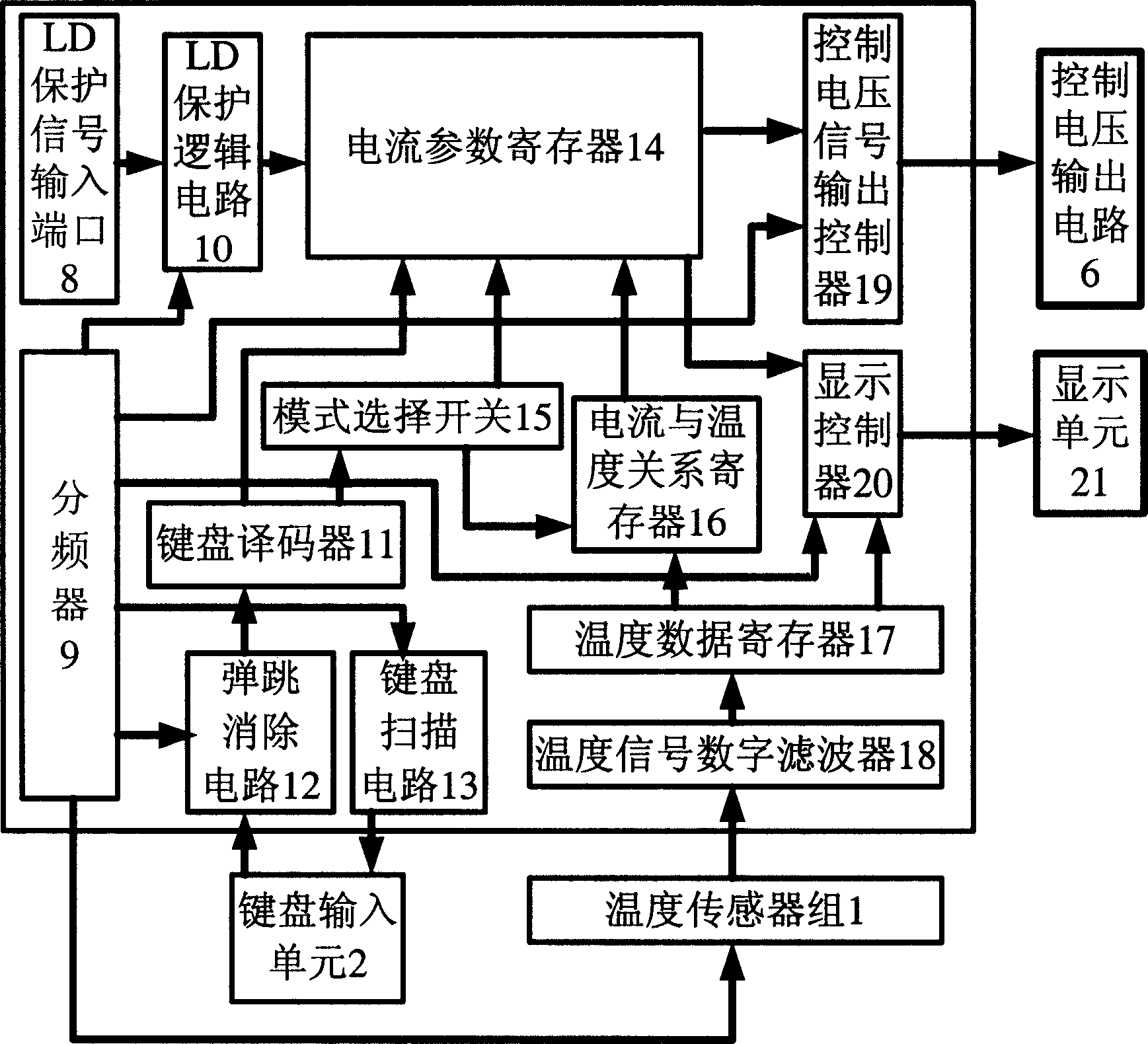
InactiveCN1652419AUndamagedStable working currentLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersDriving currentSemiconductor package
Driving current value needed is obtained through experiment testing calibration method for semiconductor laser to reach certain output power under different temperatures so as to get coincidence relation between temperature and driving current value. The said coincidence relation in list form is inputted into microprocessor by using keyboard input unit. Based on detected operating temperature of LD, changing driving current compensates variation of output power caused by changing temperature in order to realize stable LD output power. The invention also discloses driving power for semiconductor laser operated based on multiple modes in order to realize the disclosed method. The invention is applicable to diversified areas of semiconductor laser being as light source or pump source.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com