Patents
Literature
158 results about "Waveguide lasers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A waveguide laser is a laser which contains a waveguide as the gain medium. There are very different types of waveguide lasers: Solid-state waveguide lasers are usually based on some planar or channel waveguides in some crystal or glass pieces.
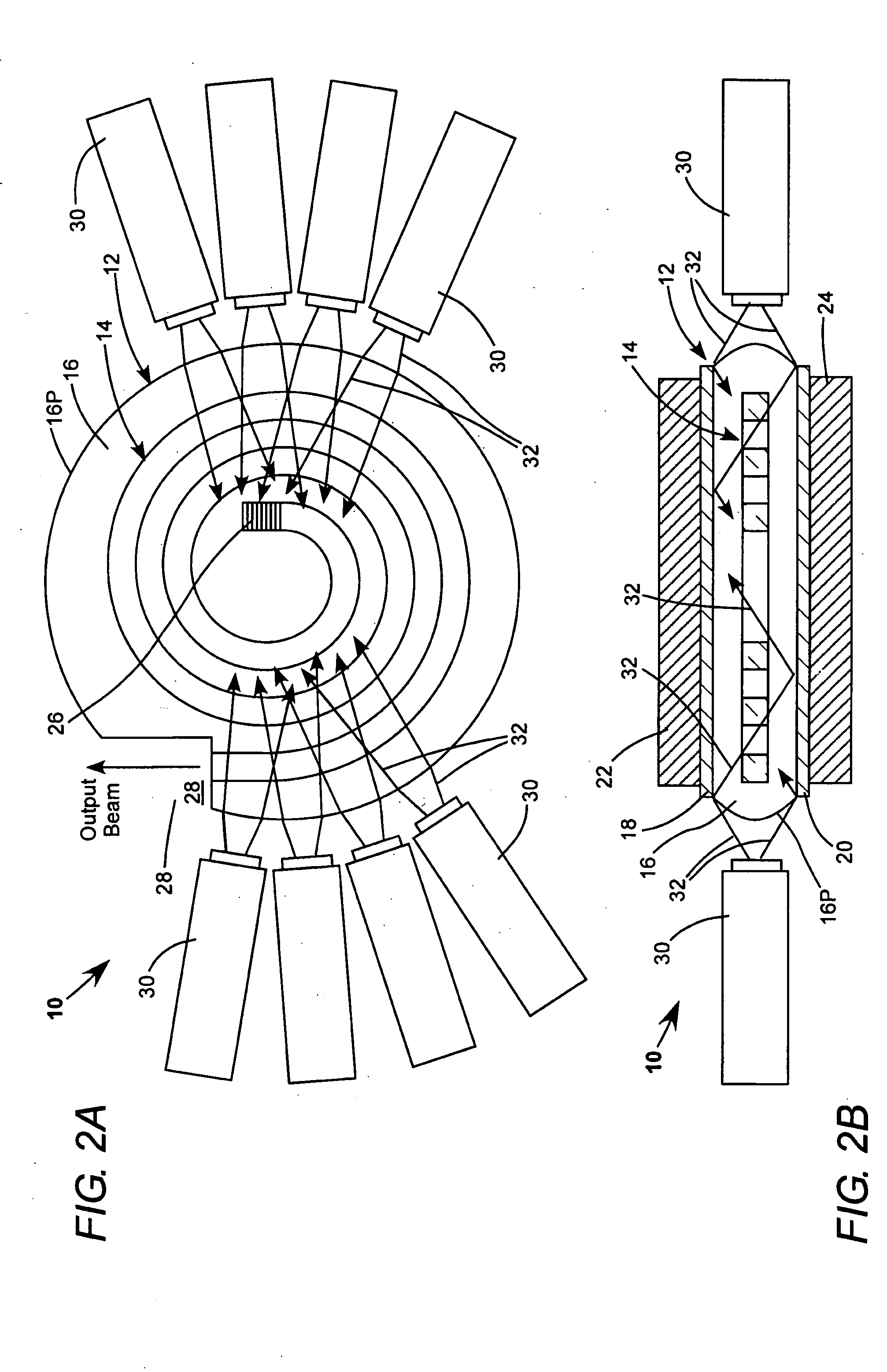
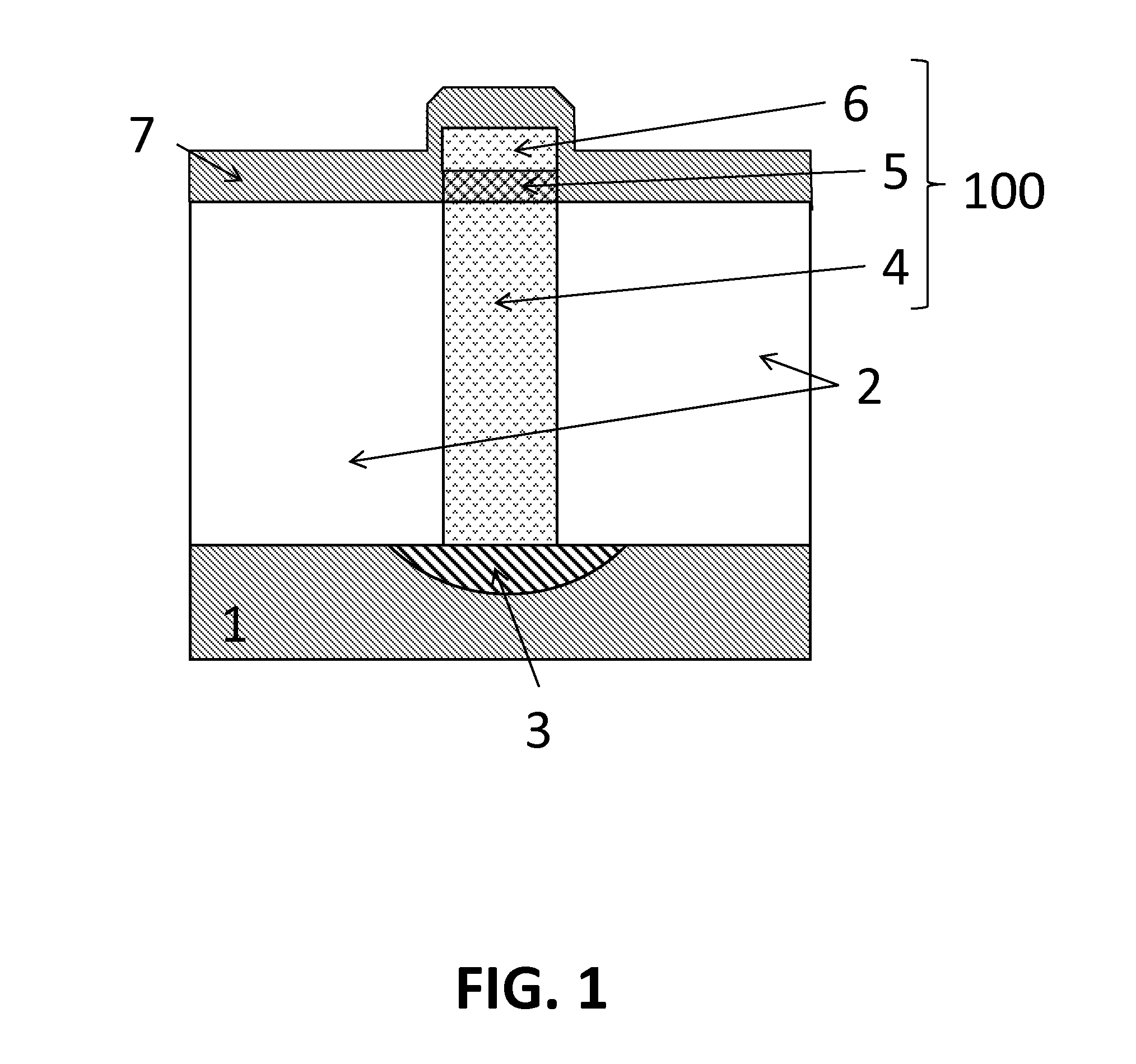
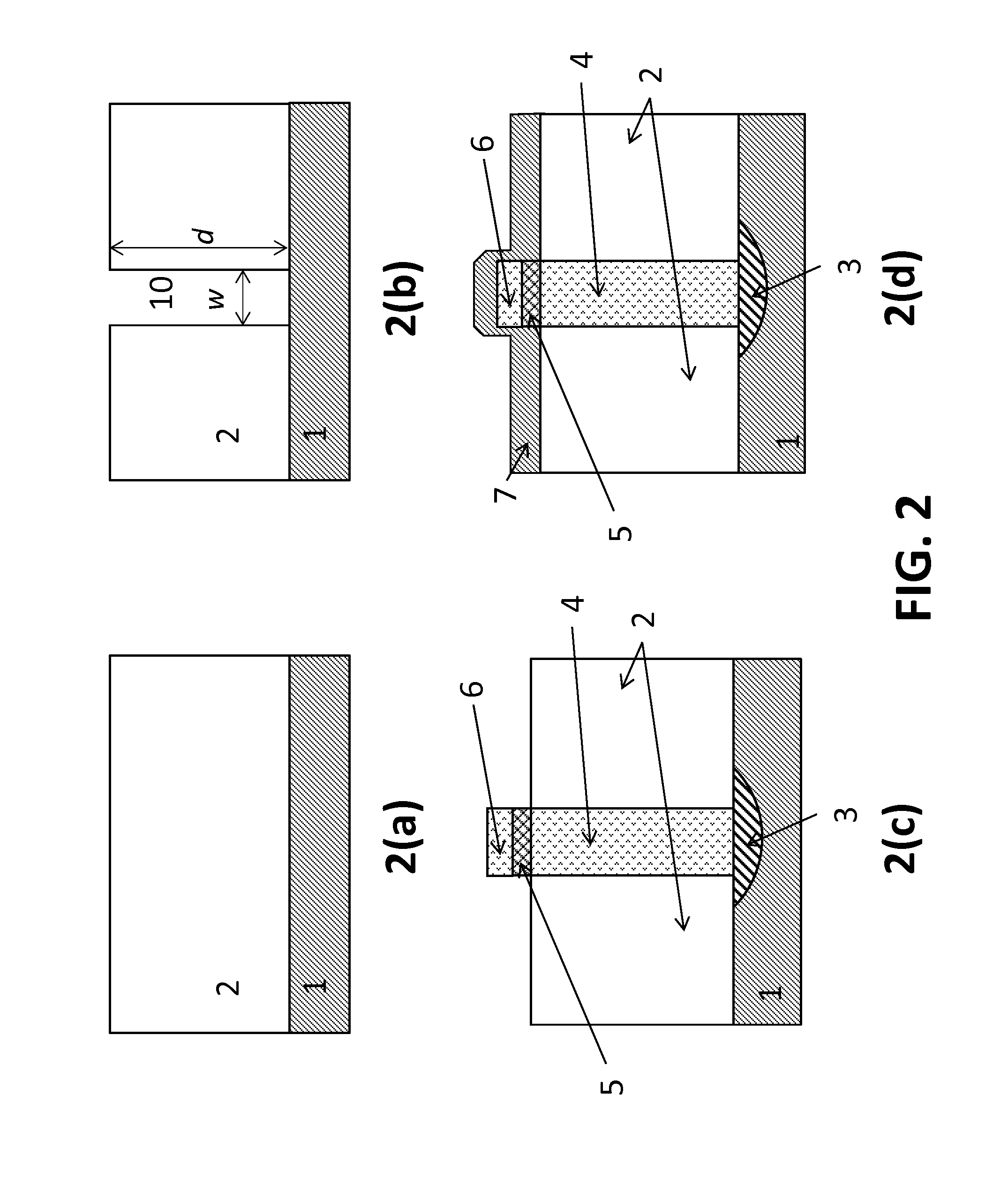
Polarisation asymmetric active optical waveguide, method of its production, and its uses
InactiveUS6151429AIncrease photosensitivityHigh refractive indexOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical resonator shape and constructionDopantWaveguide lasers
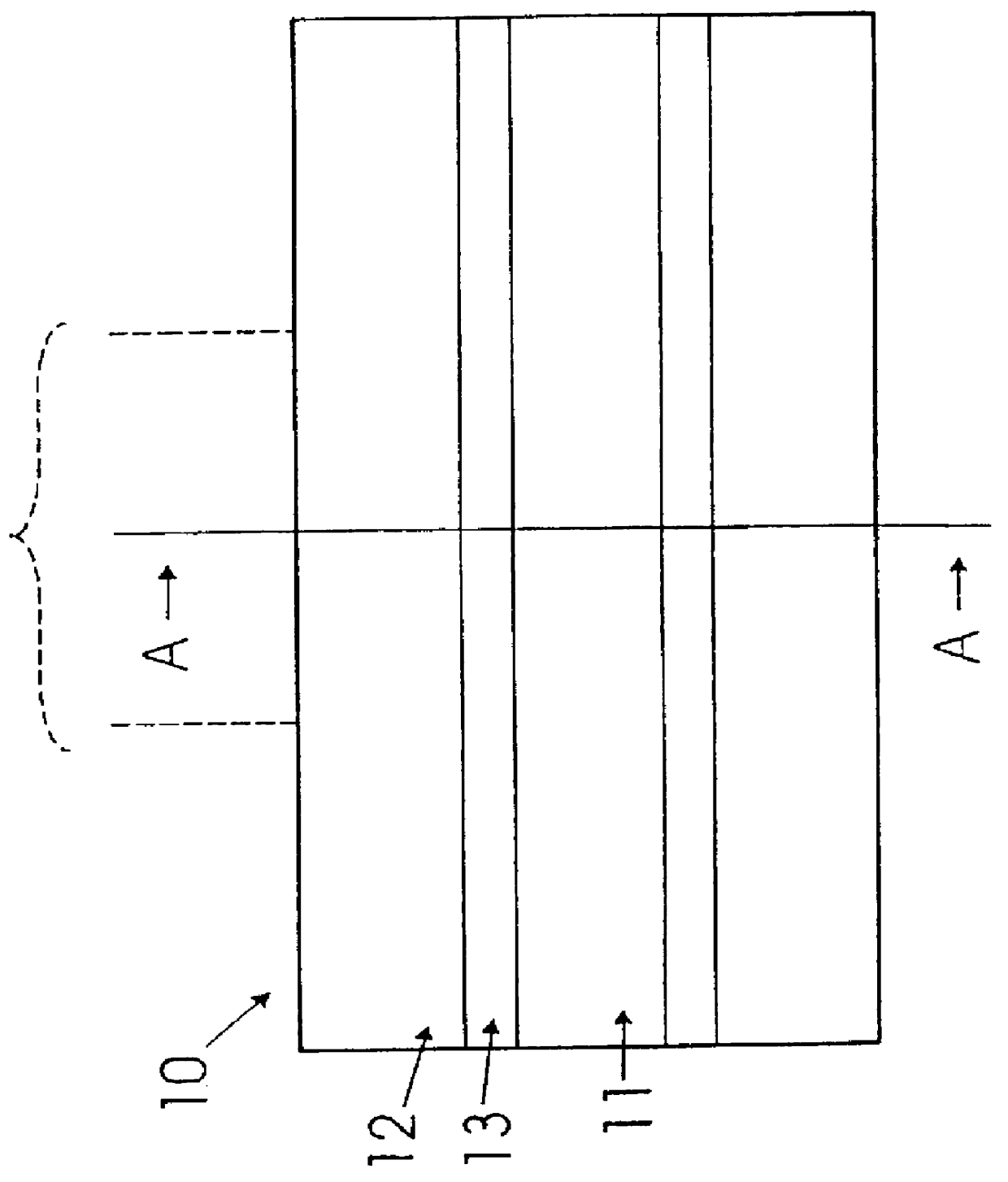
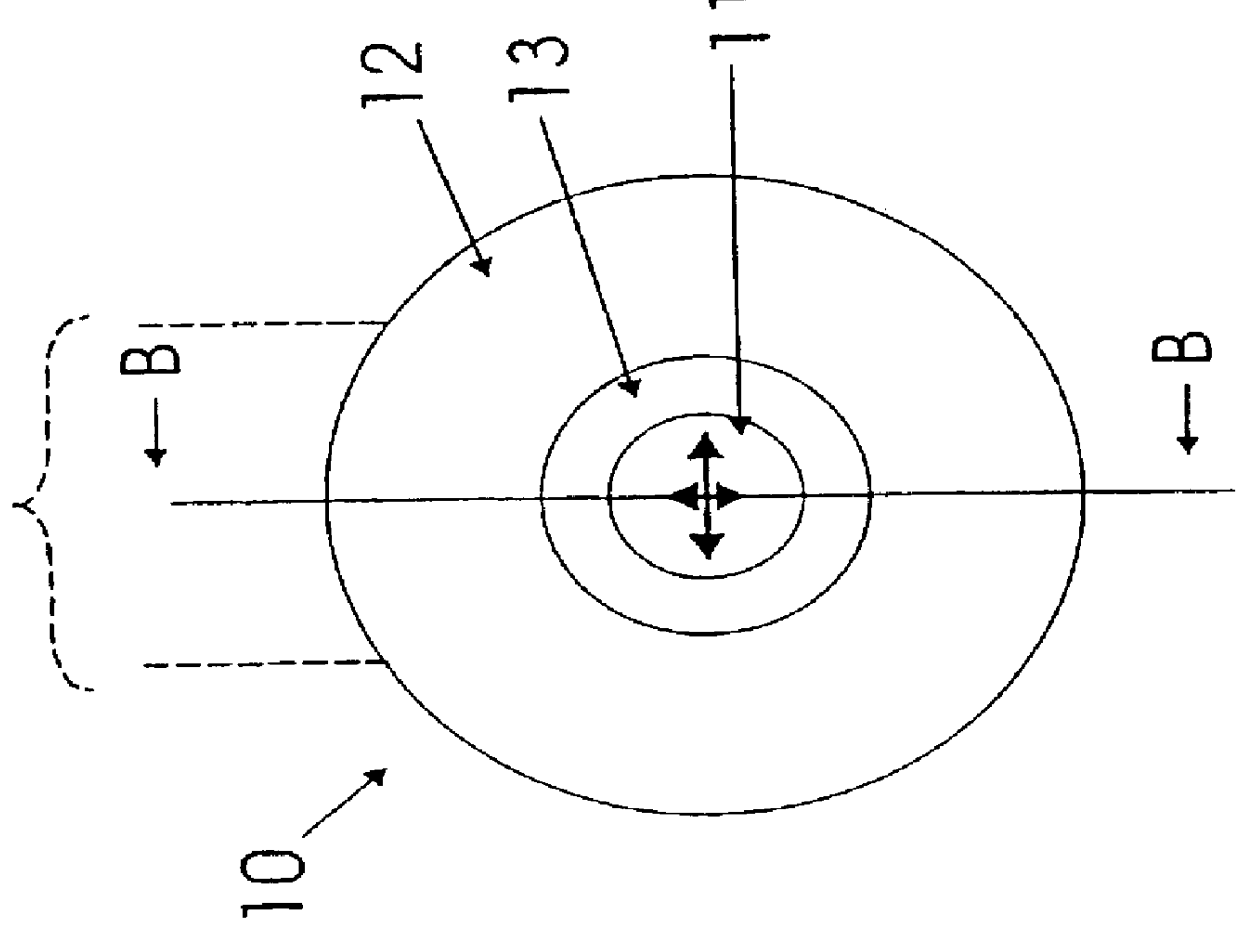
A method of producing an active optical waveguide having asymmetric polarization, said method comprising the steps of (a) providing an active optical waveguide (10) comprising: (i) a transverse refractive index profile (21) comprising a guiding region (11), an intermediate region (13), and a non-guiding region (12); (ii) a transverse photorefractive dopant profile (31) comprising a constant or graded photorefractive dopant concentration within at least one of the guiding, non-guiding and intermediate regions, except that the photorefractive dopant is not located solely in the guiding region; and (iii) exhibiting in said guiding region, intermediate region, or both, light guiding modes having different polarizations; and (b) exposing at least a part (10a, 10b) of the active optical waveguide to an effective transverse illumination of light (20) reacting with the photorefractive dopant and modifying said transverse refractive index profile; said part of the active optical waveguide being exposed to a fluence selectively suppressing the propagation of the light guiding modes having different polarizations so that the propagation of one mode is less suppressed than the propagation of the other mode(s). Such an active optical waveguide, single polarization mode optical waveguide lasers and multi-wavelength single polarization mode optical waveguide lasers comprising such an active optical waveguide, methods of their production, and their uses in telecommunications, in spectroscopy, in sensors and in absolute calibrated laser light sources.
Owner:KOHERAS +1
Optical fiber and integrated optic lasers with enhanced output power
InactiveUS6018533AEfficient pumpingIncrease powerCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsBasic modeLaser source
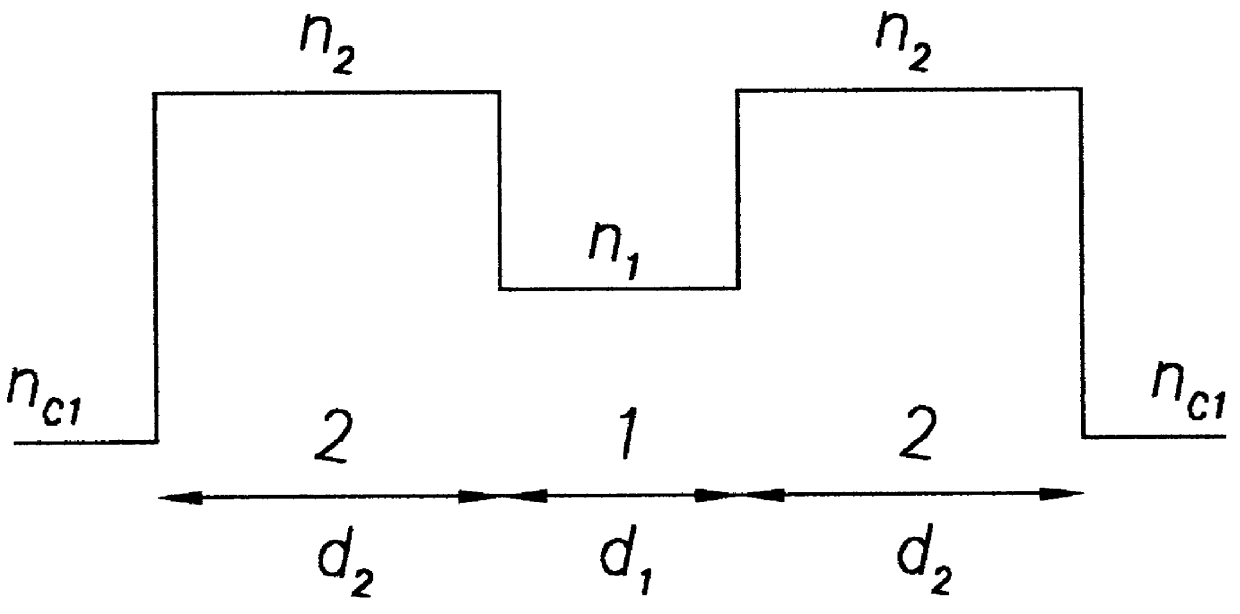
The invention describes a method of single-transverse-mode generation for waveguide lasers of various kinds having a large cross section of their active core and thus providing a possibility of efficient pump of the active core region. This results in a laser beam with enhanced power and high spatial quality for high efficiency coupling to standard single-mode optical fiber networks. It is found that a multimode waveguide having a central dip of special shape in the refractive index profile of its core is able to guide a higher order mode with sharp central peak of its field carrying the considerable part on the mode energy and whose width is well compatible with the width of the fundamental mode of standard single-mode fibers. The useful properties of this higher order mode can be employed to provide the single-transverse-mode regime of generation in optical fiber lasers, integrated optical micro-lasers and various semiconductor laser sources.
Owner:CERAMOPTEC IND INC
Frequency comb source with large comb spacing
InactiveUS20120133931A1Reduce lossLow-loss bandwidth controlRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsLow noisePhase noise
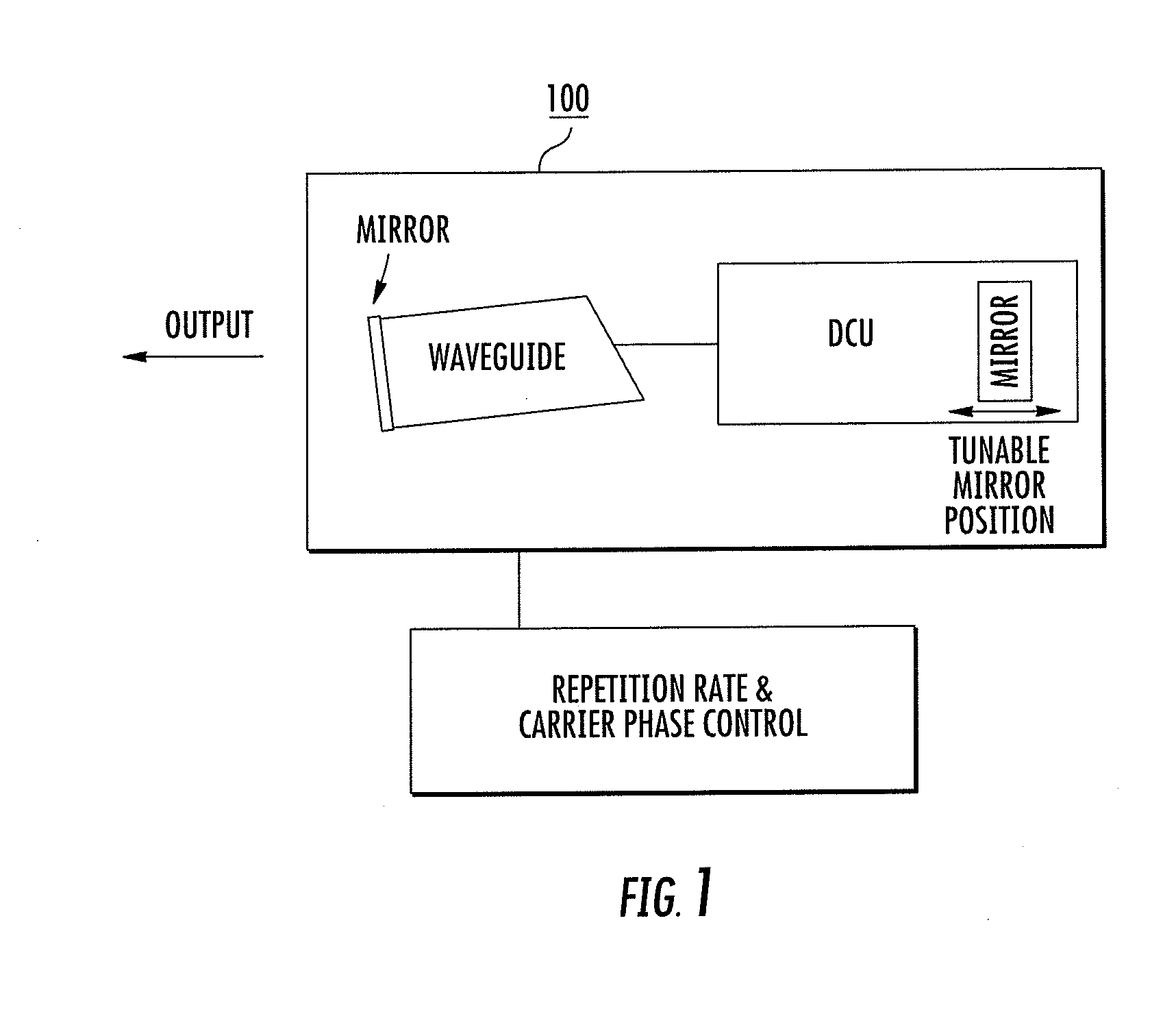
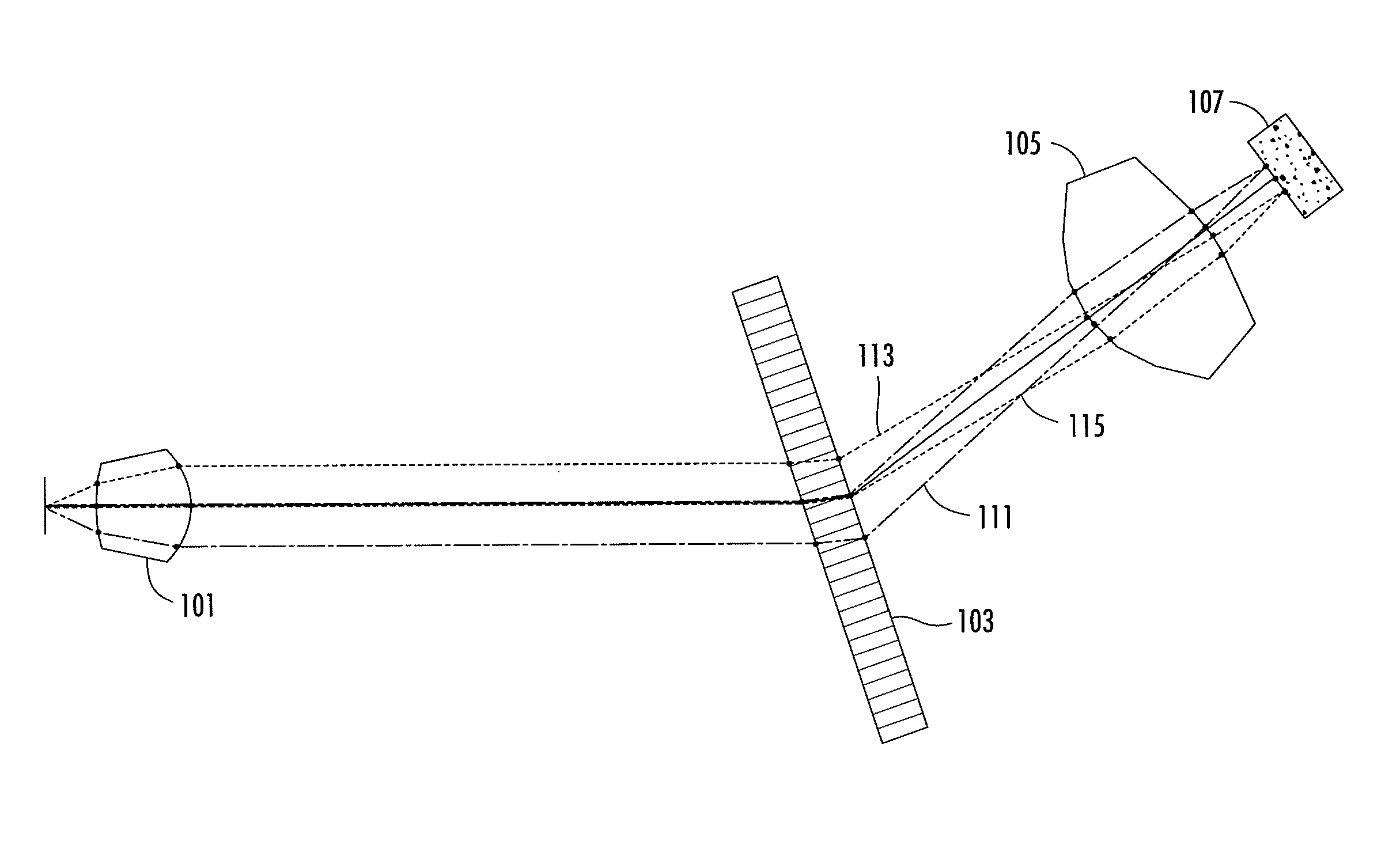
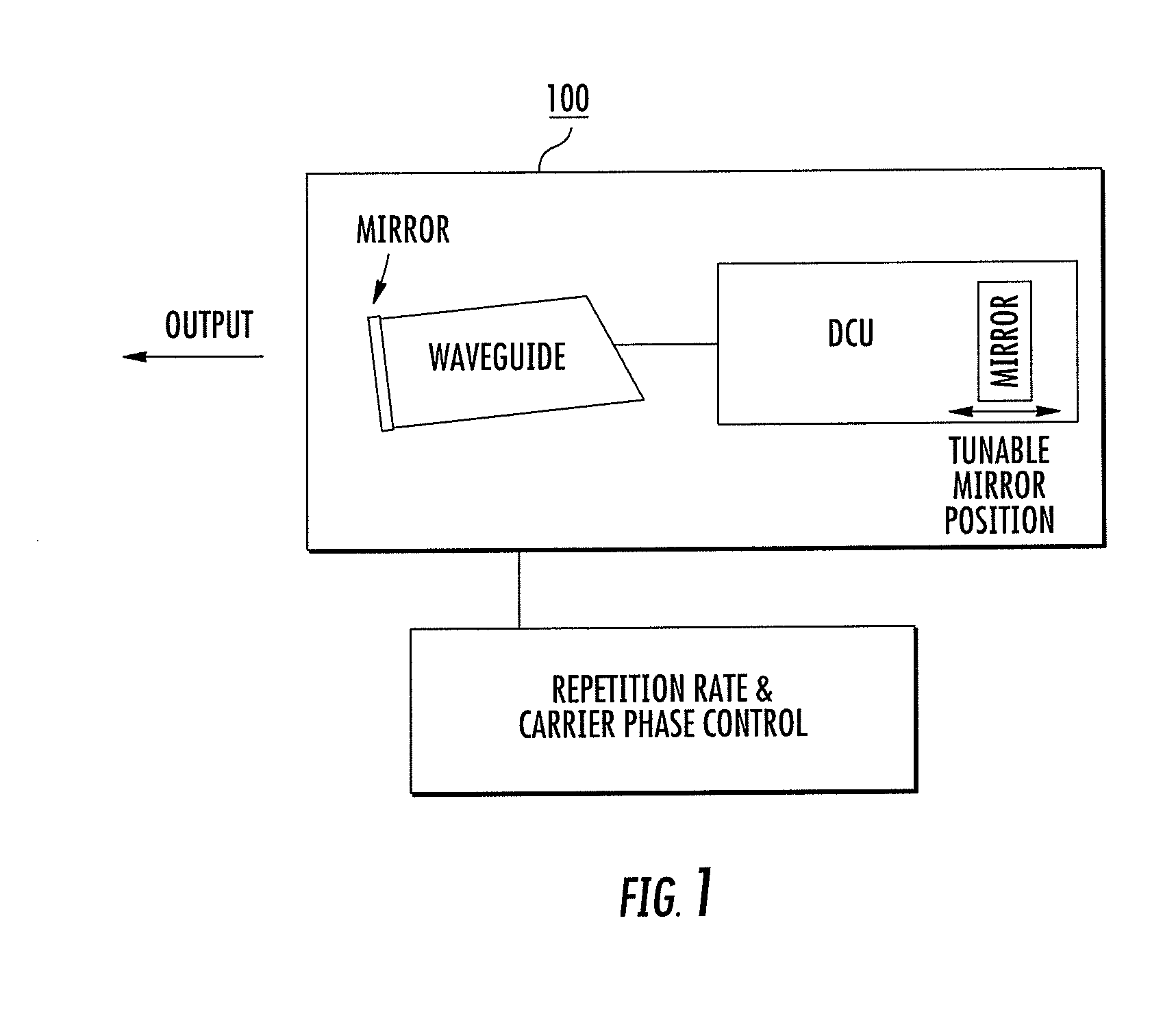
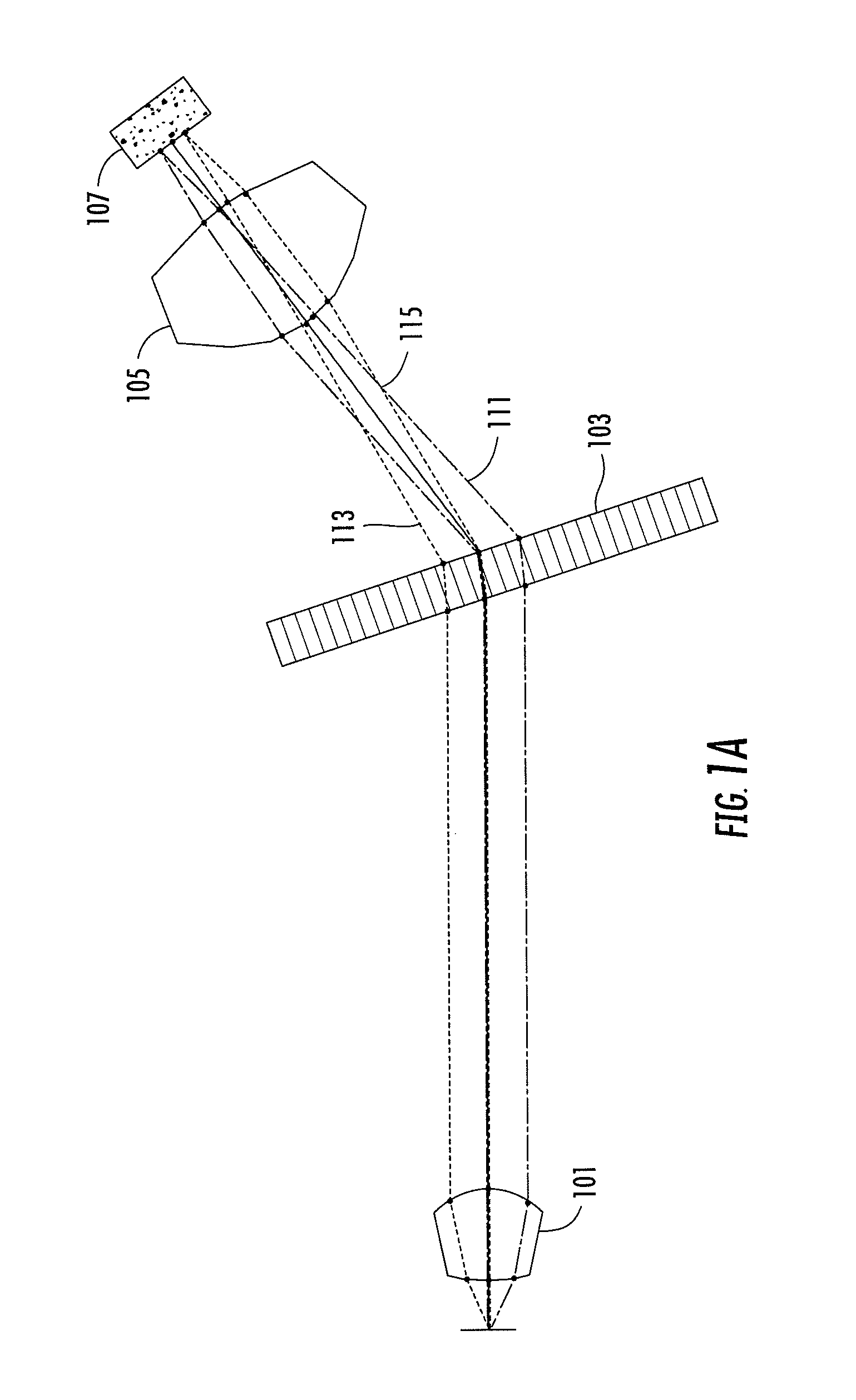
A frequency comb laser providing large comb spacing is disclosed. At least one embodiment includes a mode locked waveguide laser system. The mode locked waveguide laser includes a laser cavity having a waveguide, and a dispersion control unit (DCU) in the cavity. The DCU imparts an angular dispersion, group-velocity dispersion (GVD) and a spatial chirp to a beam propagating in the cavity. The DCU is capable of producing net GVD in a range from a positive value to a negative value. In some embodiments a tunable fiber frequency comb system configured as an optical frequency synthesizer is provided. In at least one embodiment a low phase noise micro-wave source may be implemented with a fiber comb laser having a comb spacing greater than about 1 GHz. The laser system is suitable for mass-producible fiber comb sources with large comb spacing and low noise. Applications include high-resolution spectroscopy.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Planar laser
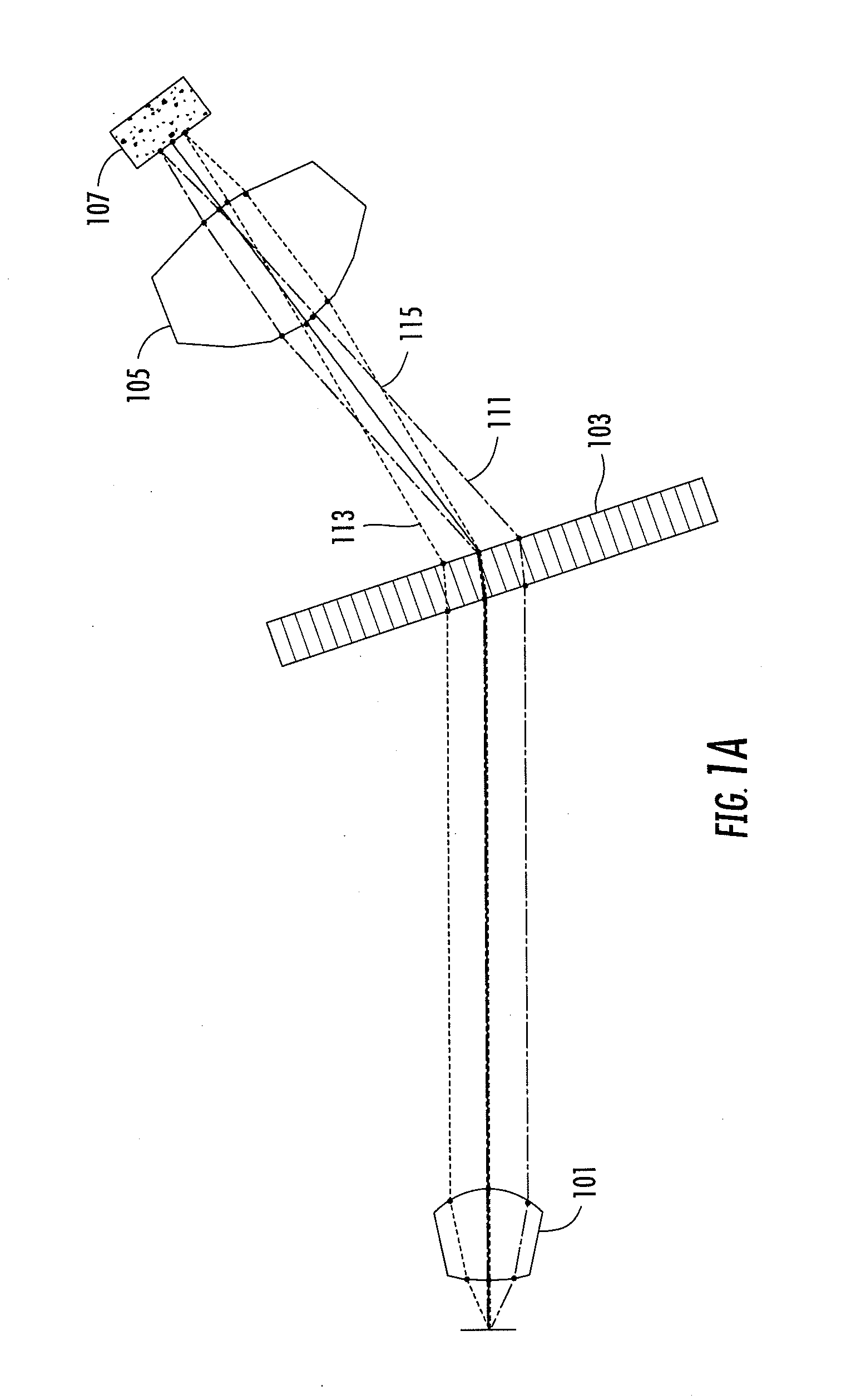
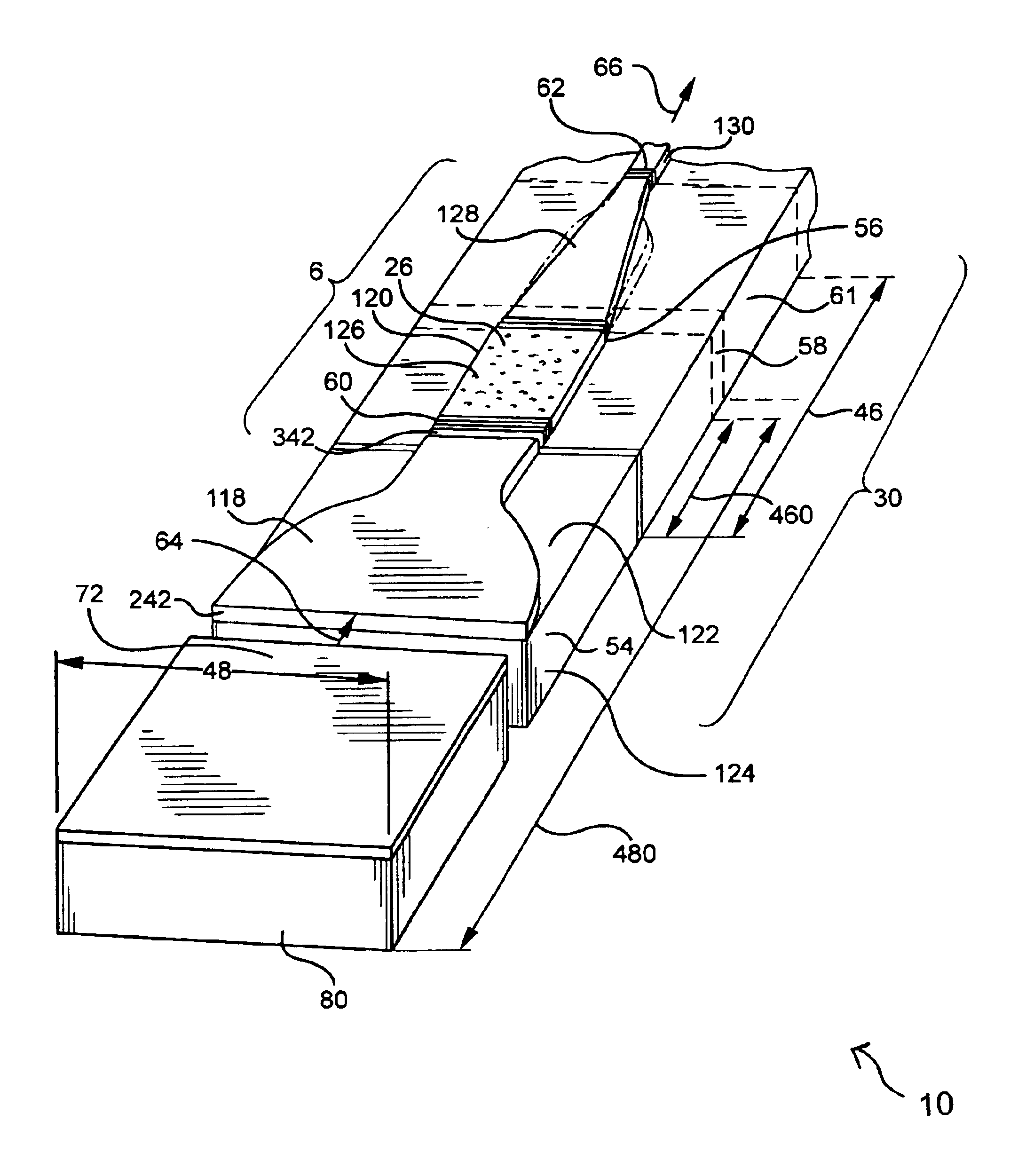
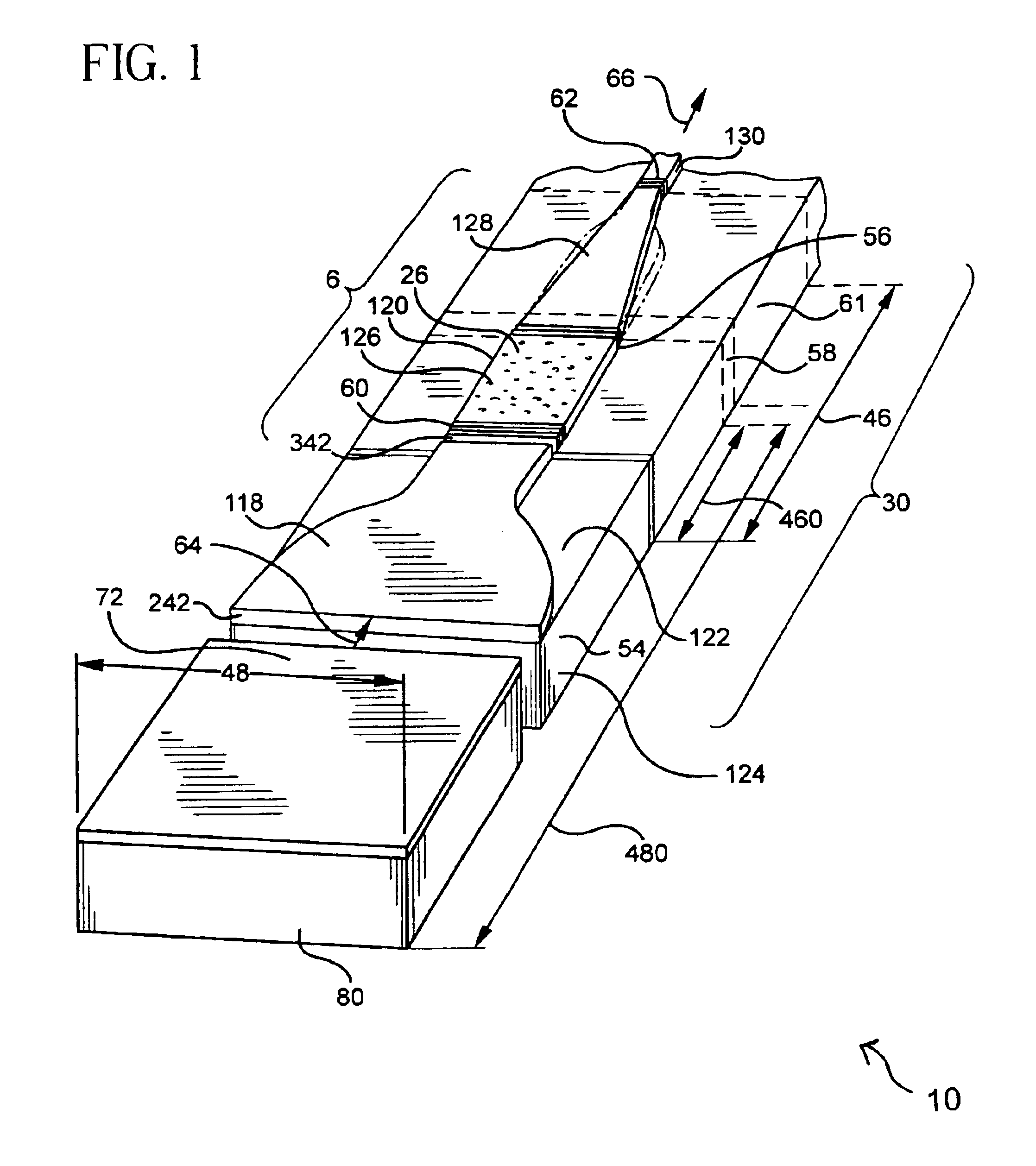
An optical device (10) includes a broad area laser (72) for lasing at a first wavelength (64), a multimode active-doped tapered waveguide laser (6); and a multimode passive planar mode transformer (118) coupling and tapering from the broad area laser (72) to the multimode active-doped tapered waveguide laser (6).
Owner:CORNING INC
Waveguide laser illuminator incorporating a despeckler
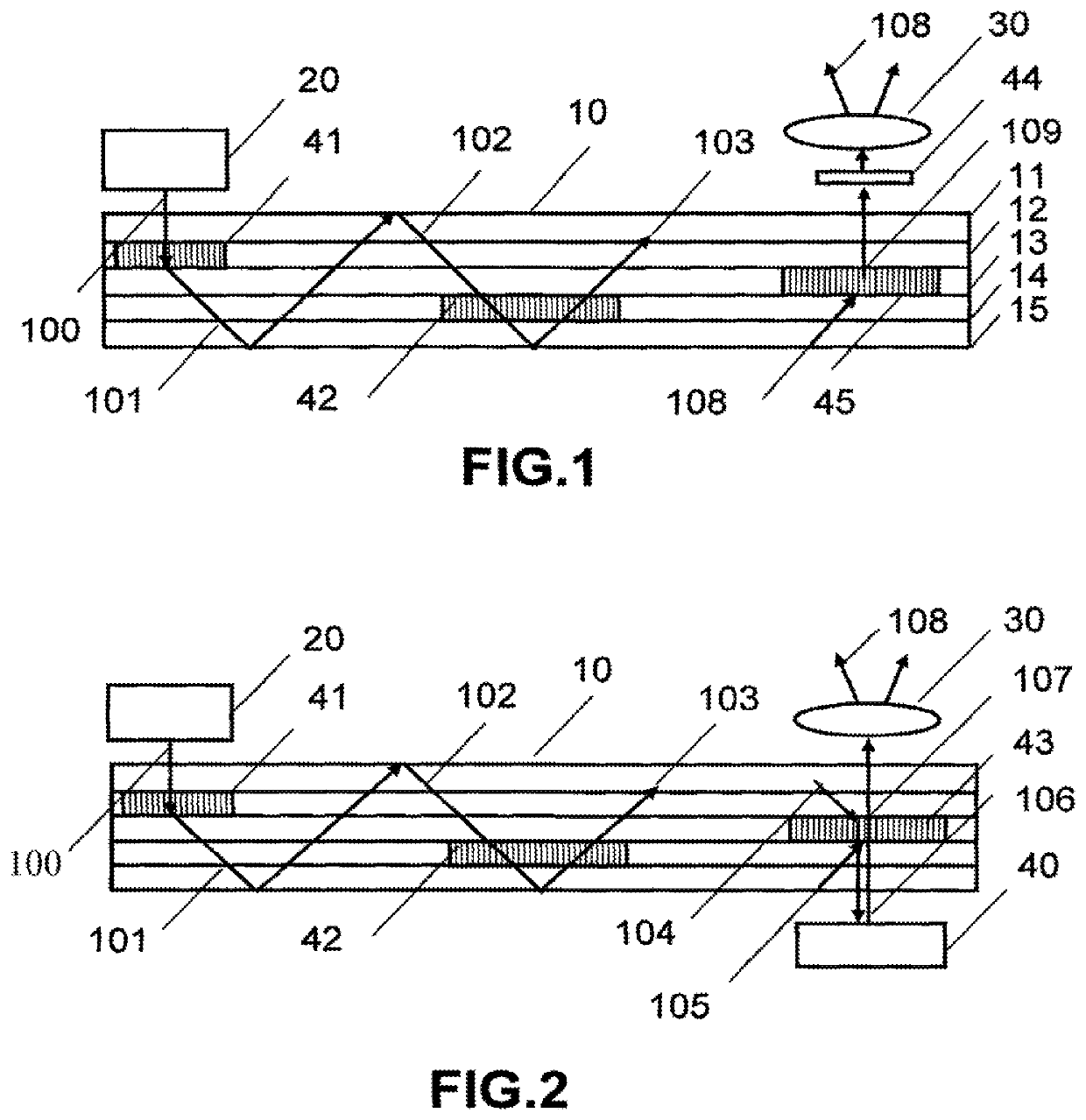
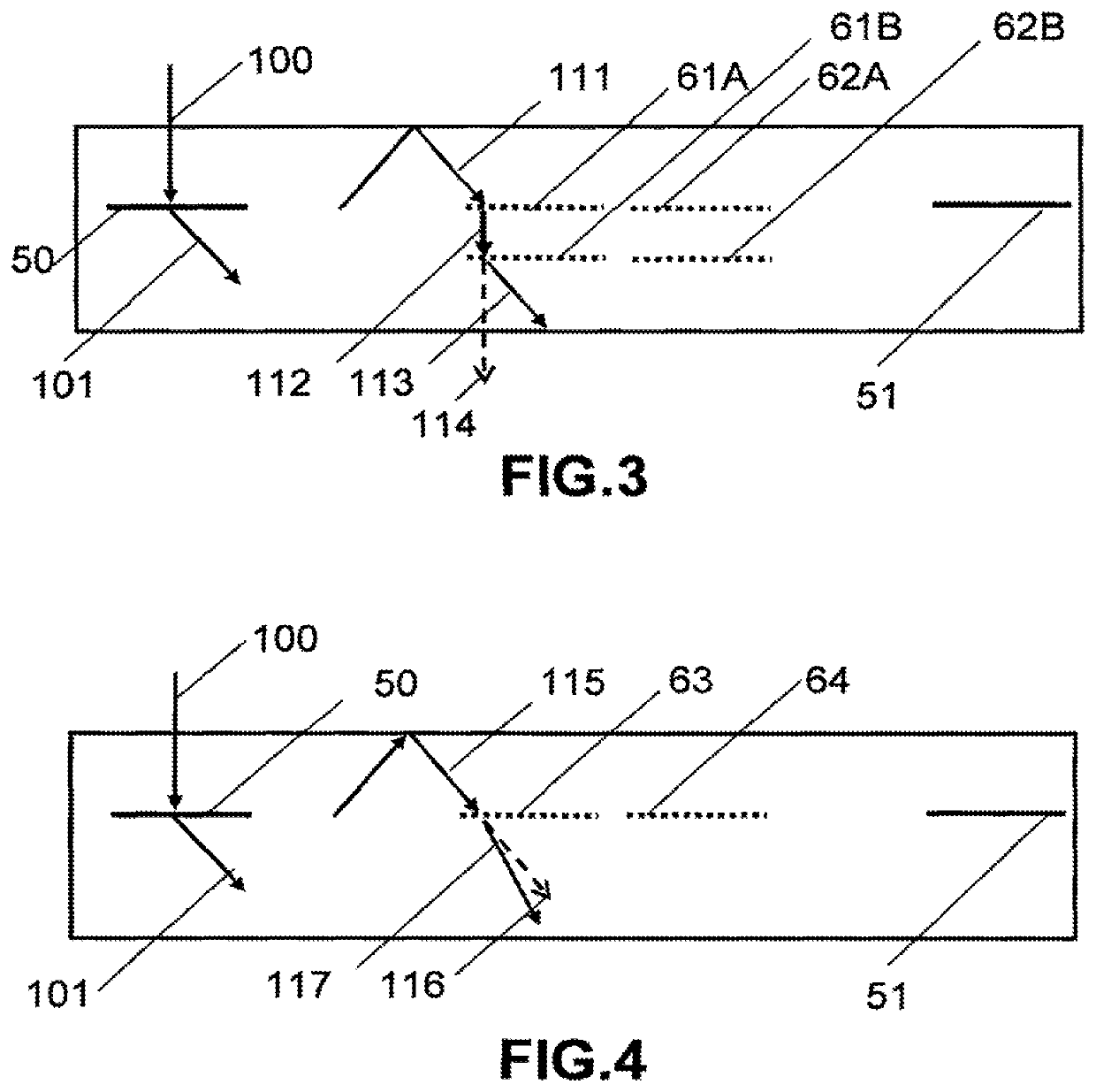
There is provided an illumination device having: a laser; a waveguide including at least first and second transparent lamina; a first grating device for coupling light from the laser into a TIR path in the waveguide; a second grating device for coupling light from the TIR path out of the waveguide; and a third grating device for applying a variation of at least one of beam deflection, phase retardation or polarization rotation across the wavefronts of the TIR light. The first second and third grating devices are each sandwiched by transparent lamina.
Owner:DIGILENS
CO2 waveguide laser with beryllium oxide waveguides
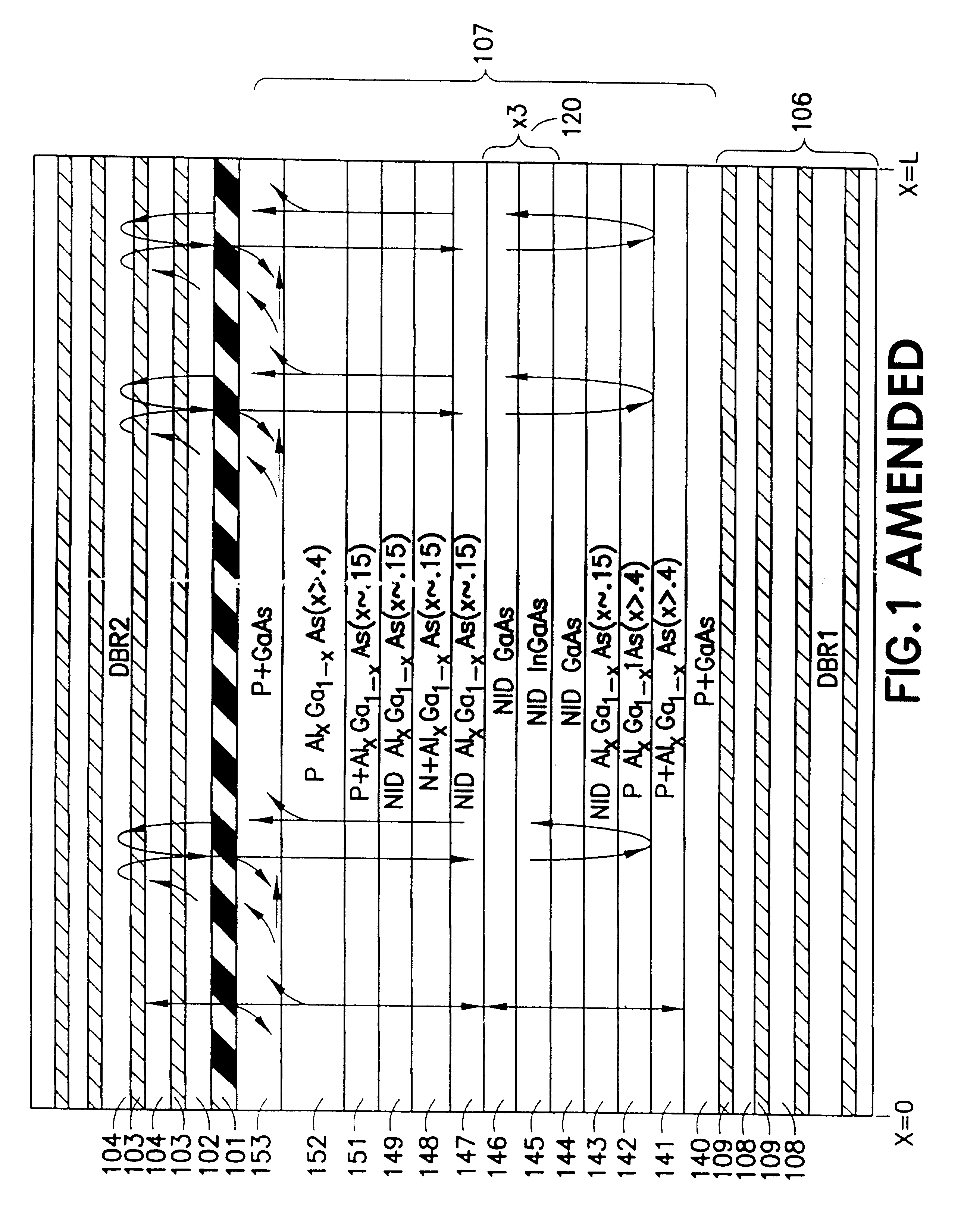
ActiveUS20050105581A1Active medium materialActive medium shape and constructionMicrometerWaveguide lasers
A pulsed, Q-switched, waveguide CO2 laser includes a plurality of waveguide channels formed in a block of a beryllium oxide ceramic material and is operated at a wavelength between about 9.2 and 9.7 micrometers. The laser has an output power up to 55% greater than that of a similarly configured laser, operated at the same wavelength and pulse conditions, but wherein the waveguide channels are formed in a block of an alumina ceramic material.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Monolithic ceramic laser structure and method of making same
A monolithic ceramic waveguide laser body is made by forming and grinding two or more plates of alumina ceramic to produce internal and external features otherwise impossible to fabricate in a single ceramic body. The plates are bonded together by use of glass frit or by self-friting (diffusion bonding) methods to achieve a vacuum tight enclosure. The ceramic surfaces to be bonded have an "as ground" finish. One internal structure created by this method includes a channel of dimensions from 8 to 1.5 mm square or round that confines an RF or DC electrical discharge and comprises a laser resonator cavity. The channel can be ground to form a "V", "U" or "Z" shape folded cavity. Another internal structure is a gas reservoir connected to the resonator cavity. Various other important features are described that can only be created by this method of building a laser. The plates are bonded together in a furnace at temperatures ranging between 450° C. and 1700° C., depending on the method used.
Owner:MORROW CLIFFORD E
System Comprising a Low Phase Noise Waveguide Laser, a Method of Its Manufacturing and Its Use
InactiveUS20070263676A1Reducing influence of vibrational pickReduce phase noiseLaser optical resonator constructionLaser using scattering effectsPhase noiseLine width
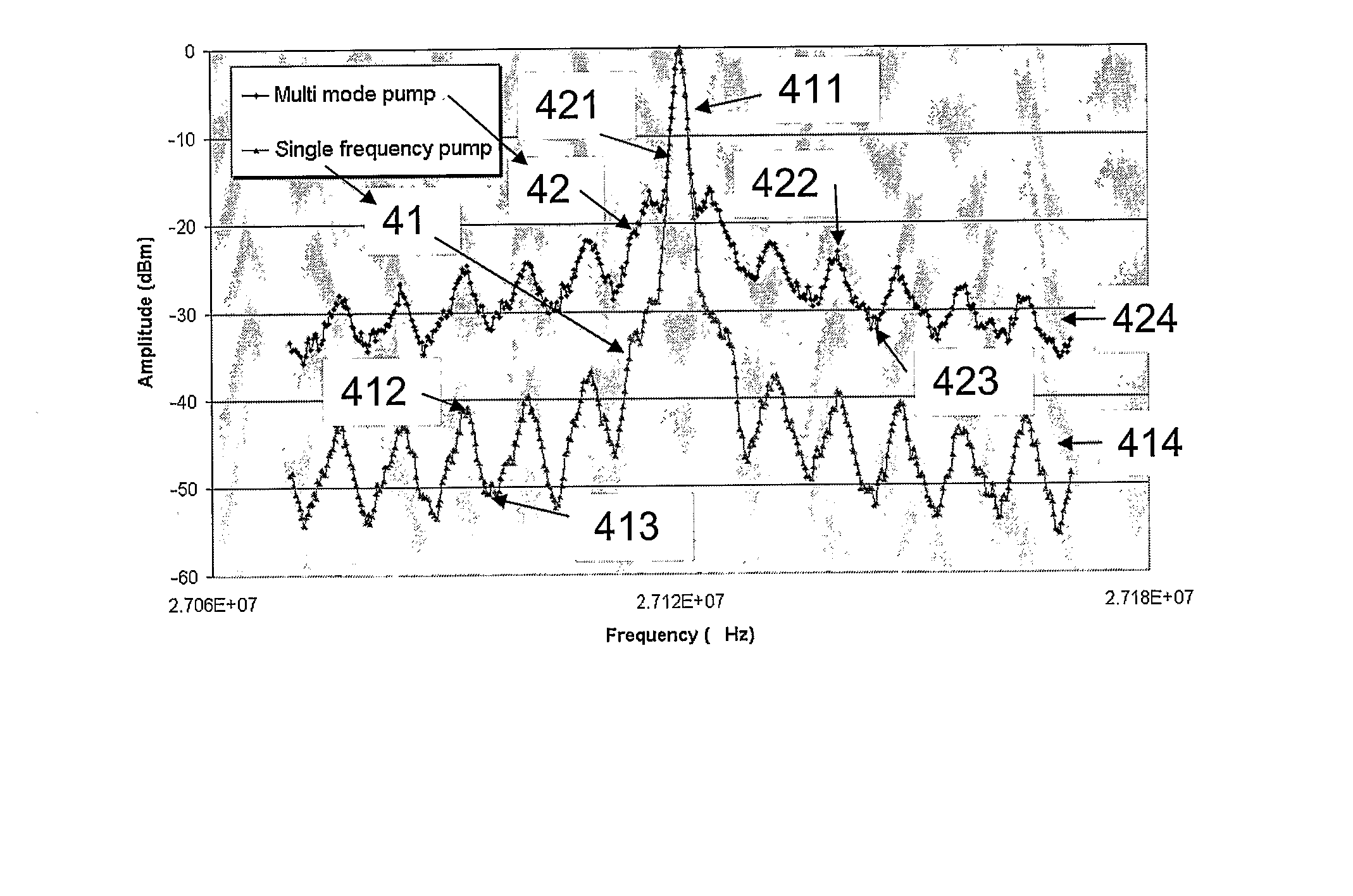
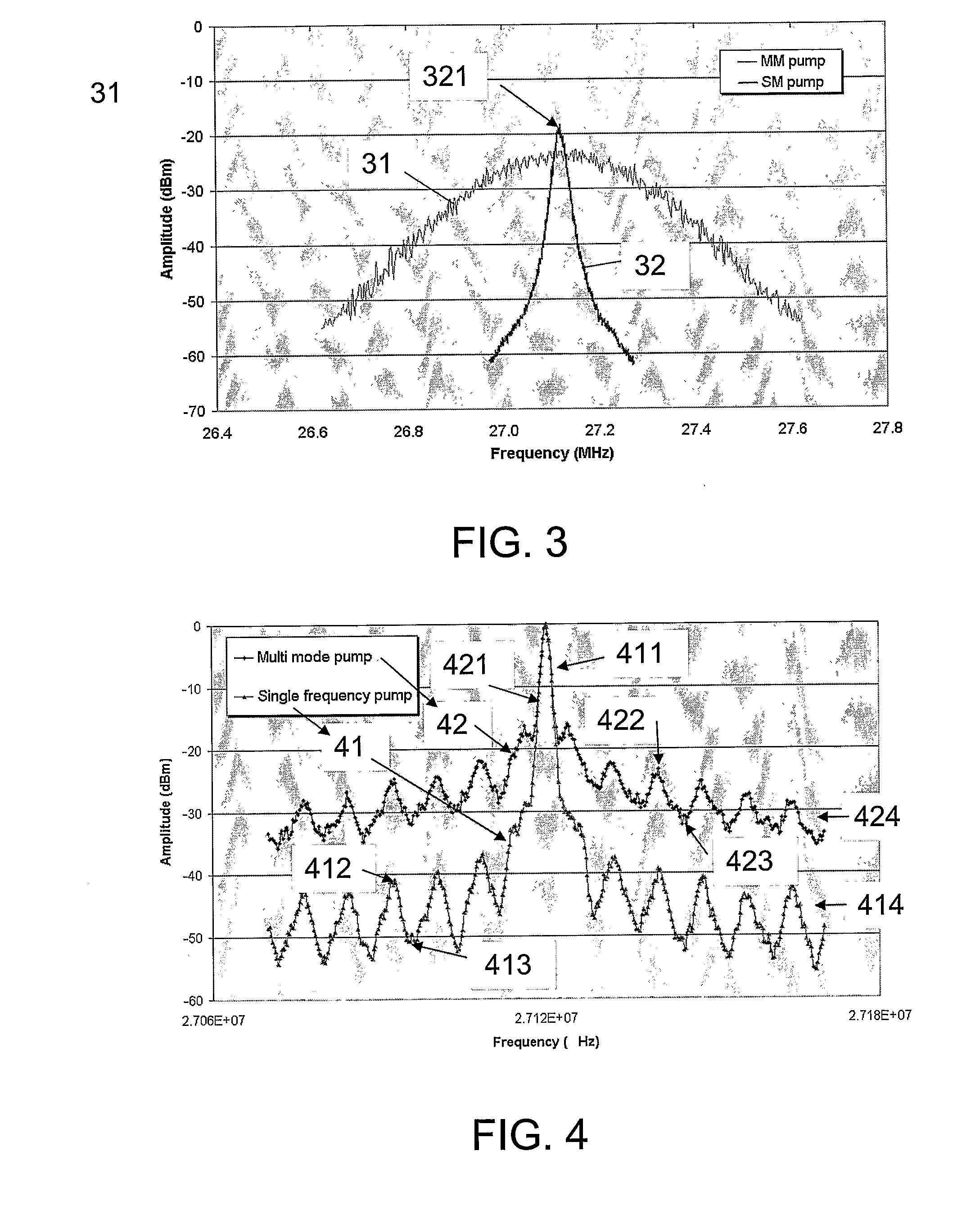
The invention relates to a system comprising a waveguide laser for exciting laser light at a lasing wavelength λs and a pump for pumping the waveguide laser at a pumping wavelength λp. The invention further relates to a method of providing such a system and its use. The object of the present invention is to provide a system comprising a waveguide laser with a reduced phase noise. The problem is solved in that the pump is a single frequency laser. The invention may e.g. be used in systems where an ultra-low phase noise and / or linewidth is required, e.g. in LIDAR or interferometric systems.
Owner:KOHERAS
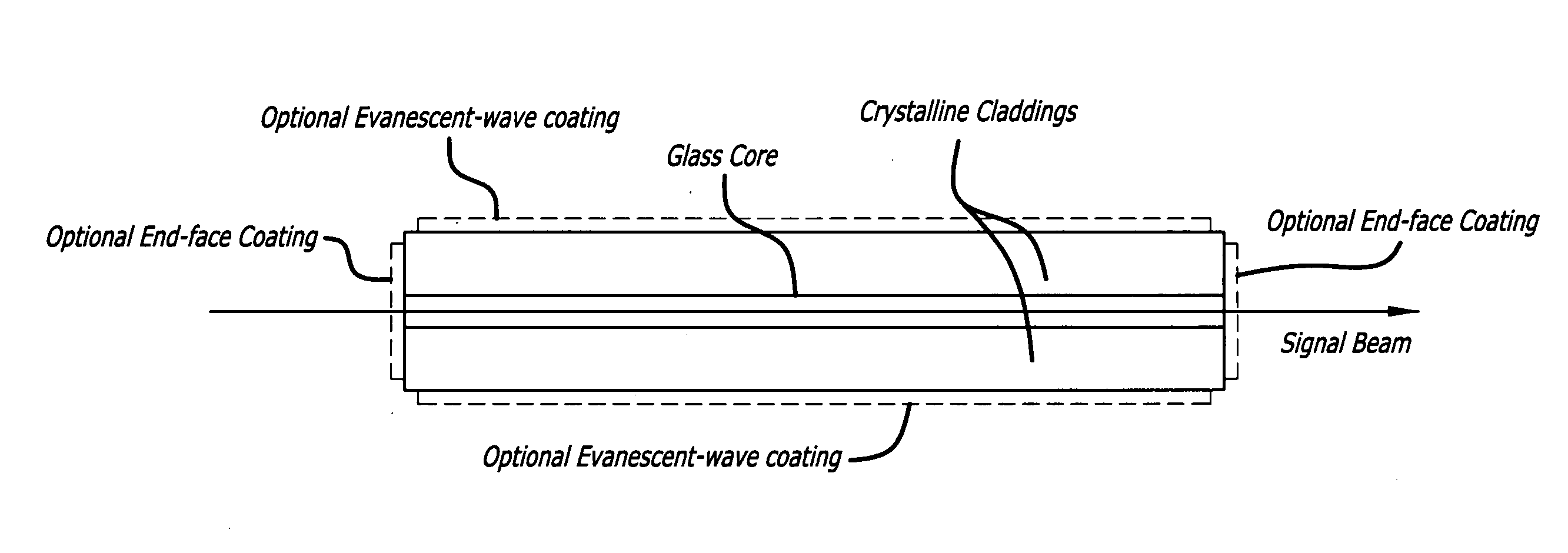
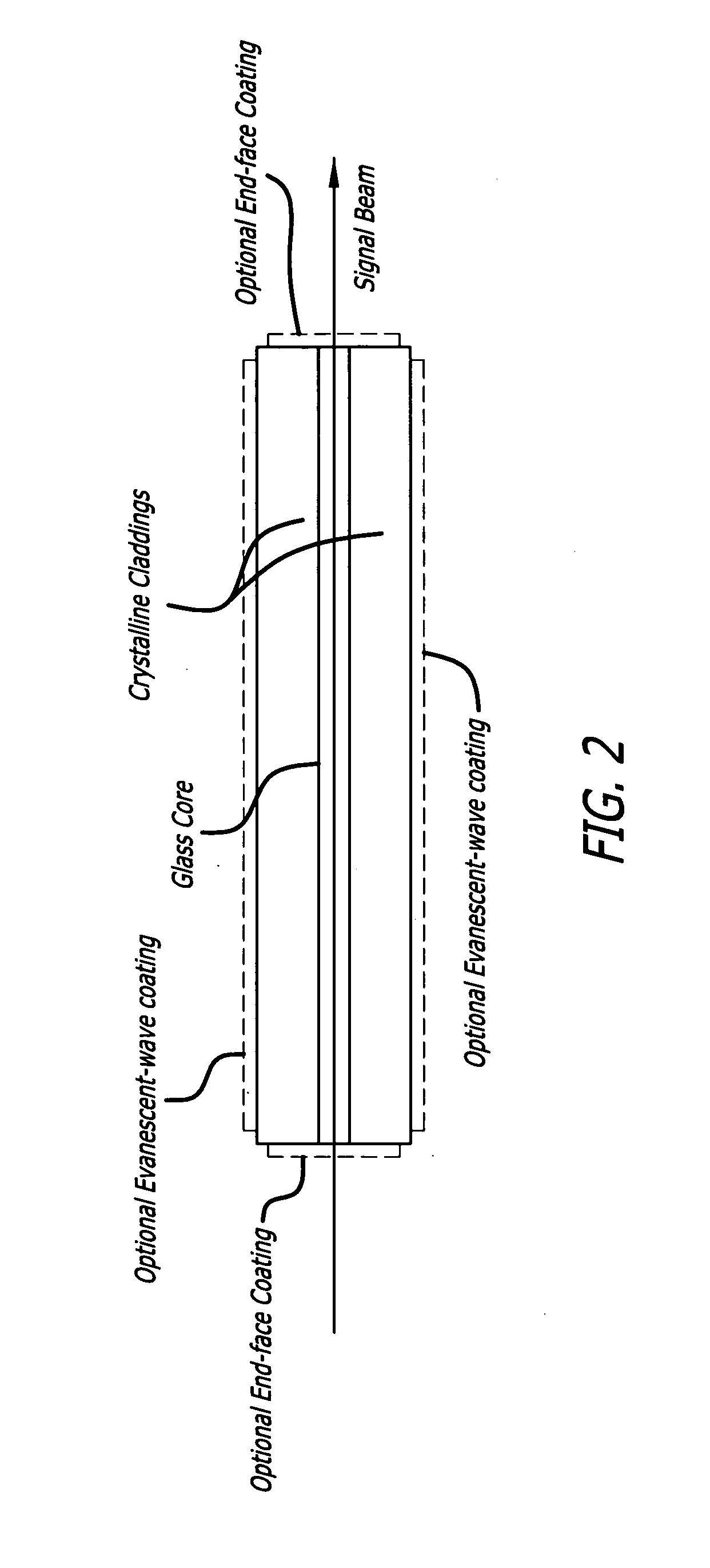
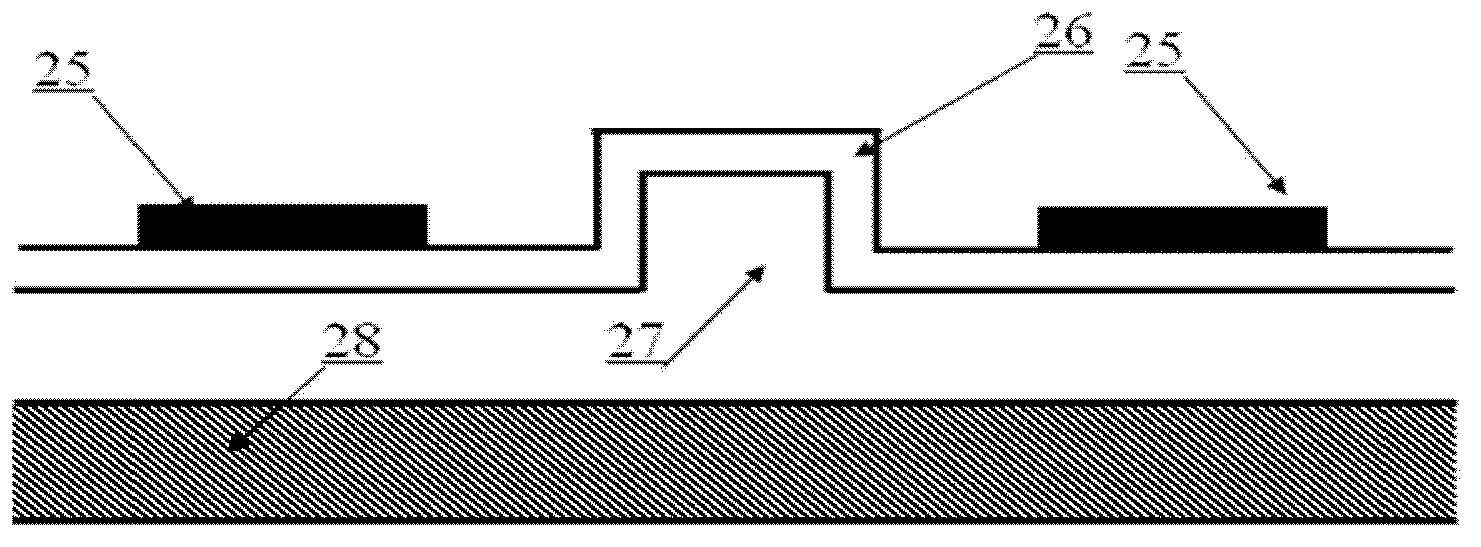
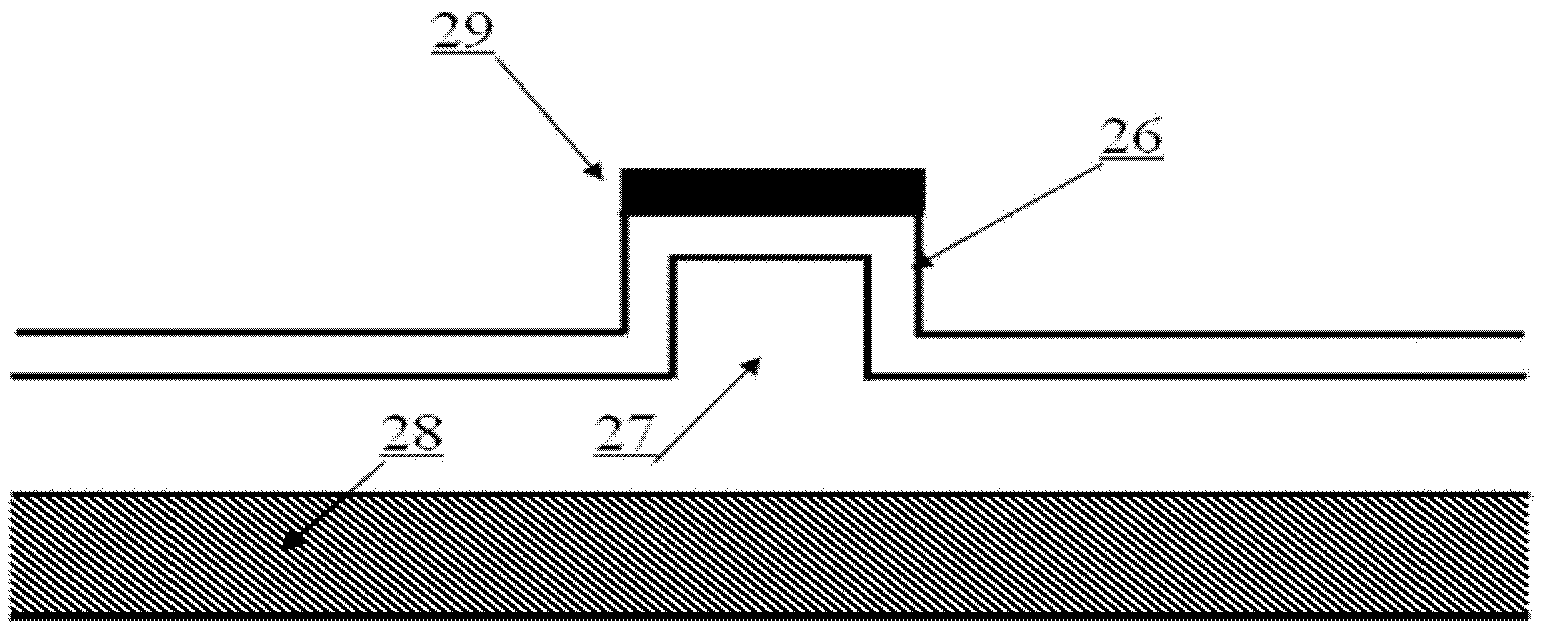
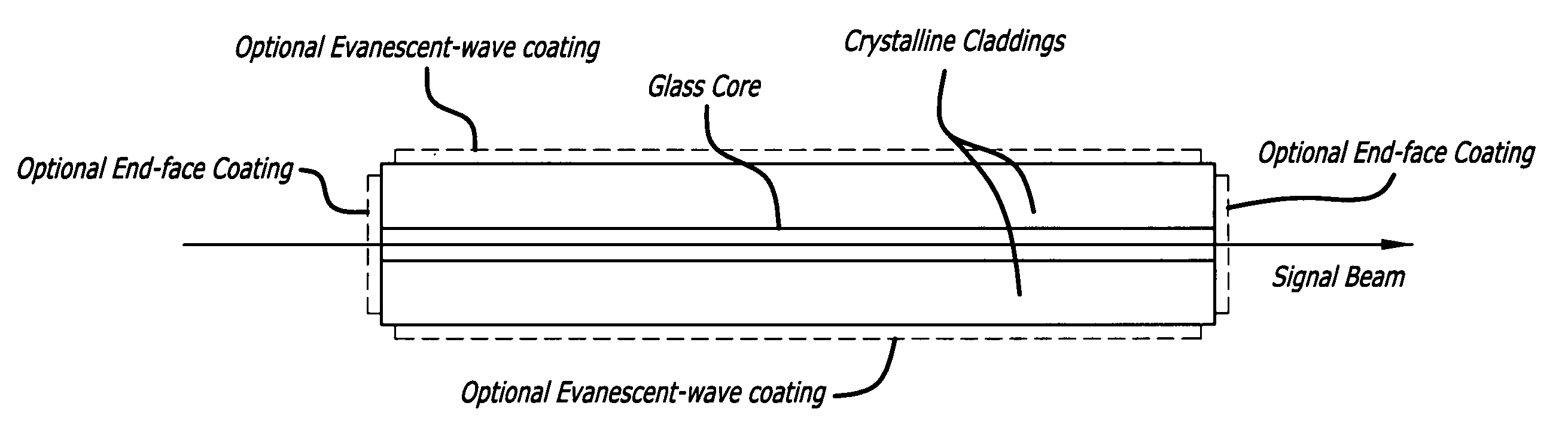
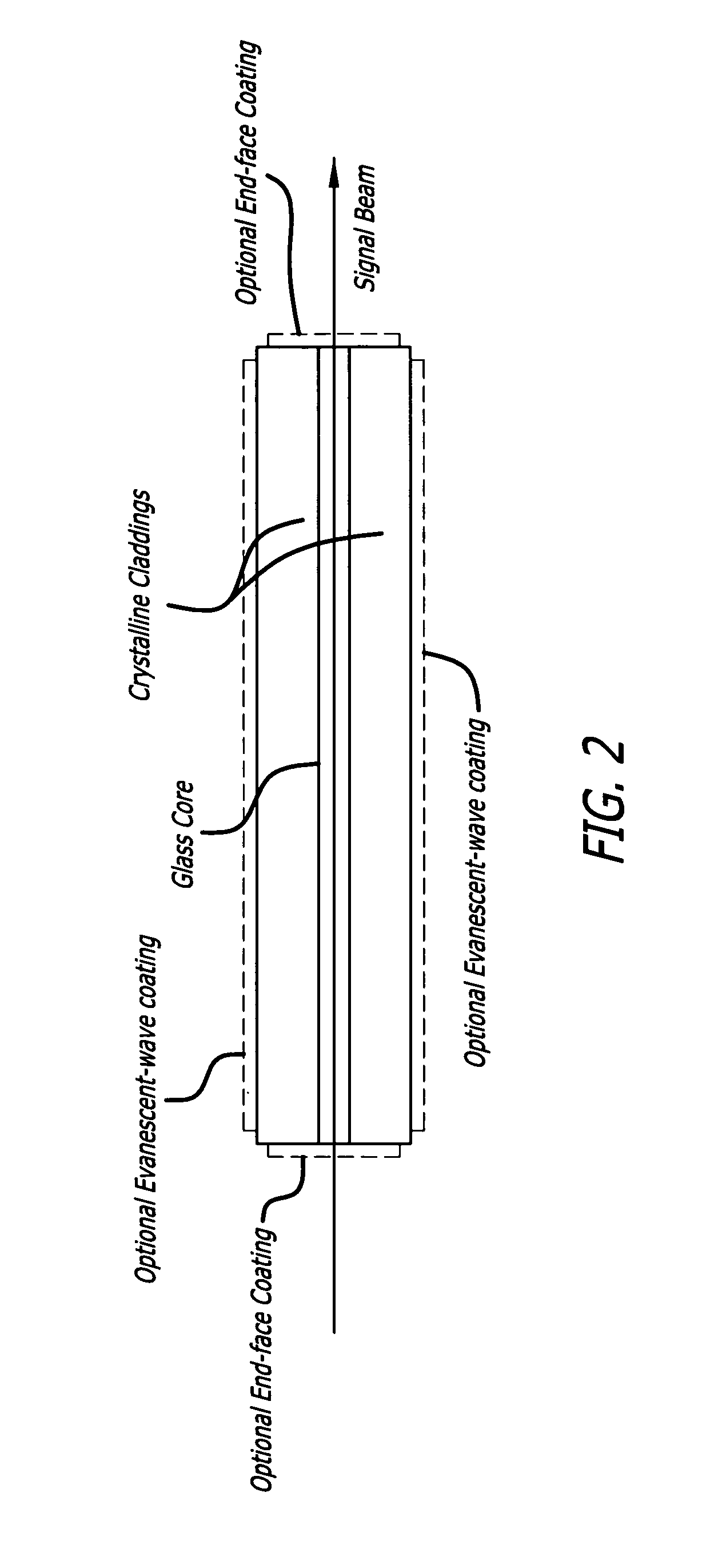
Glass core planar waveguide laser amplifier
ActiveUS20110200292A1High transparencyLow refractive indexLaminationLamination apparatusRefractive indexThermal expansion
A planar waveguide with a glass core and a crystalline cladding. In a specific embodiment, the core is doped preferably with Neodymium, Ytterbium, or Erbium. In the best mode, the core is athermal glass with a refractive index uniformity 10−6 or better and the crystalline cladding has a refractive index lower than that of the core by 10−4 to 10−3 with a refractive index uniformity of 10−4. The cladding has high transparency at pump and lasing wavelengths. The coefficient of thermal expansion of the cladding is close to that of the core. In illustrative embodiments, the cladding is Sapphire and the core is aluminate glass. In an alternative embodiment, the cladding is crystal quartz and the core—is phosphate glass. By utilizing different materials for the core and cladding, the properties of each are optimized. Use of glass for the core allows much more flexibility in tailoring the properties of the core and the PWG geometry readily accommodates the low thermal conductivity of a glass core because the overall thermal performance is dominated by the higher thermal conductivity of the crystalline cladding.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Hybrid integrated composite cavity wave length-tunable laser transmitter
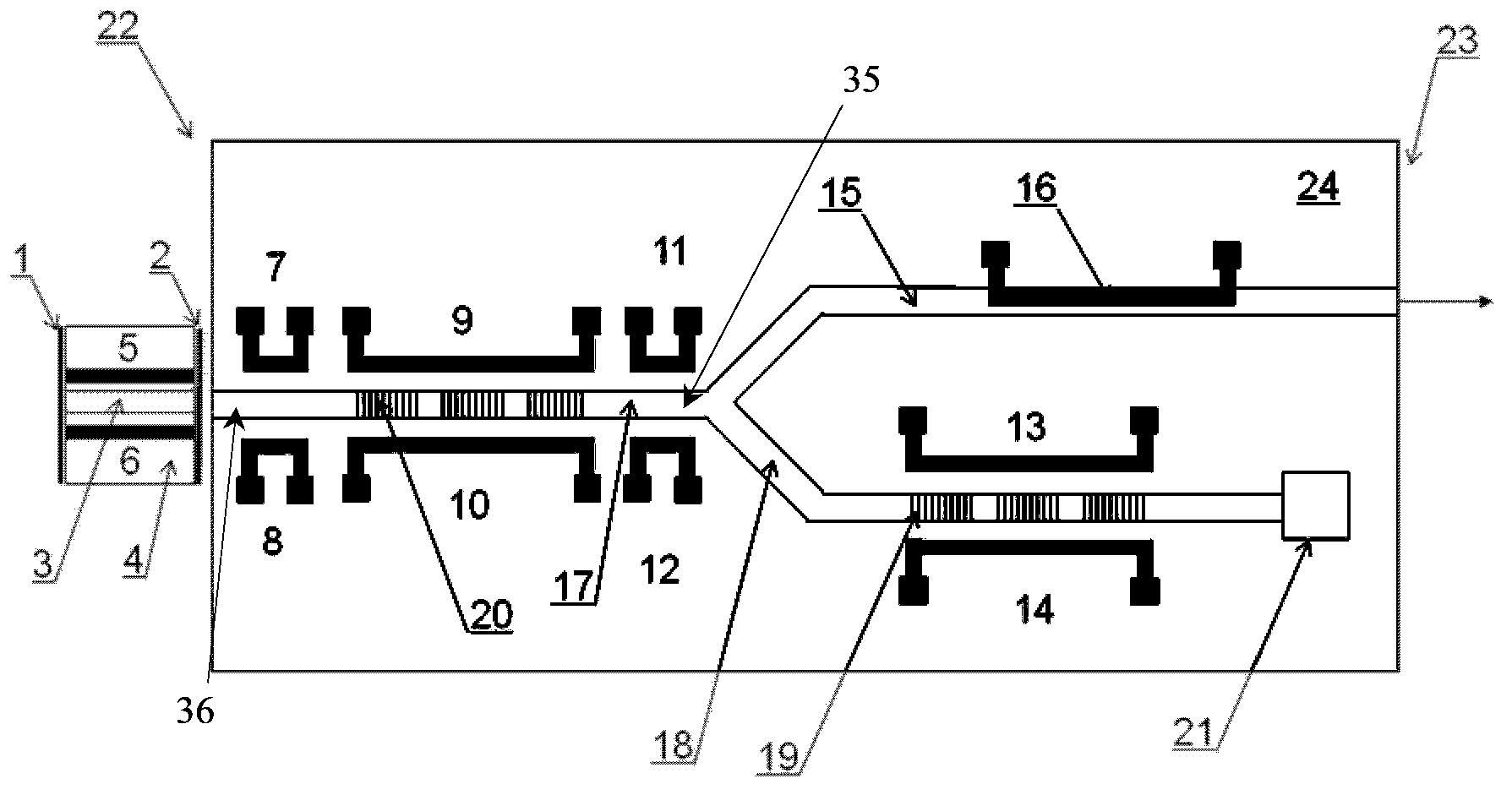
ActiveCN103457155ASmall sizeImprove continuityLaser detailsLaser output parameters controlLaser transmitterGrating
The invention discloses a hybrid integrated composite cavity wave length-tunable laser transmitter. Optical waveguides of a passive photonic chip sequentially comprise phase control regions, a first reflection grating, a phase coupling region and a second reflection grating, and a tunable laser outer cavity is formed by the phase control regions, the first reflection grating, the phase coupling region and the second reflection grating. Optical waveguides connecting the phase coupling regions are Y-branch waveguide couplers of two asymmetrical waveguide arms, wherein the second reflection grating is arranged on one waveguide arm, and a waveguide laser intensity modulator is arranged on the other waveguide arm; tunable lasers are output from the middle of a composite reflection mirror in a light split mode, and is then transmitted and output at the speed modulated according to the laser intensity of the lasers from a port of the waveguide arm provided with the waveguide laser intensity modulator. Because the second reflection grating and the waveguide laser intensity modulator are arranged on the two Y-branch waveguide couplers of the two asymmetrical waveguide arms respectively, the size of the hybrid integrated composite cavity wave length-tunable laser transmitter is reduced; the waveguide laser intensity modulator can achieve high-speed laser transmission.
Owner:马亚男
Glass core planar waveguide laser amplifier
ActiveUS8977097B2Active medium materialActive medium shape and constructionRefractive indexThermal expansion
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
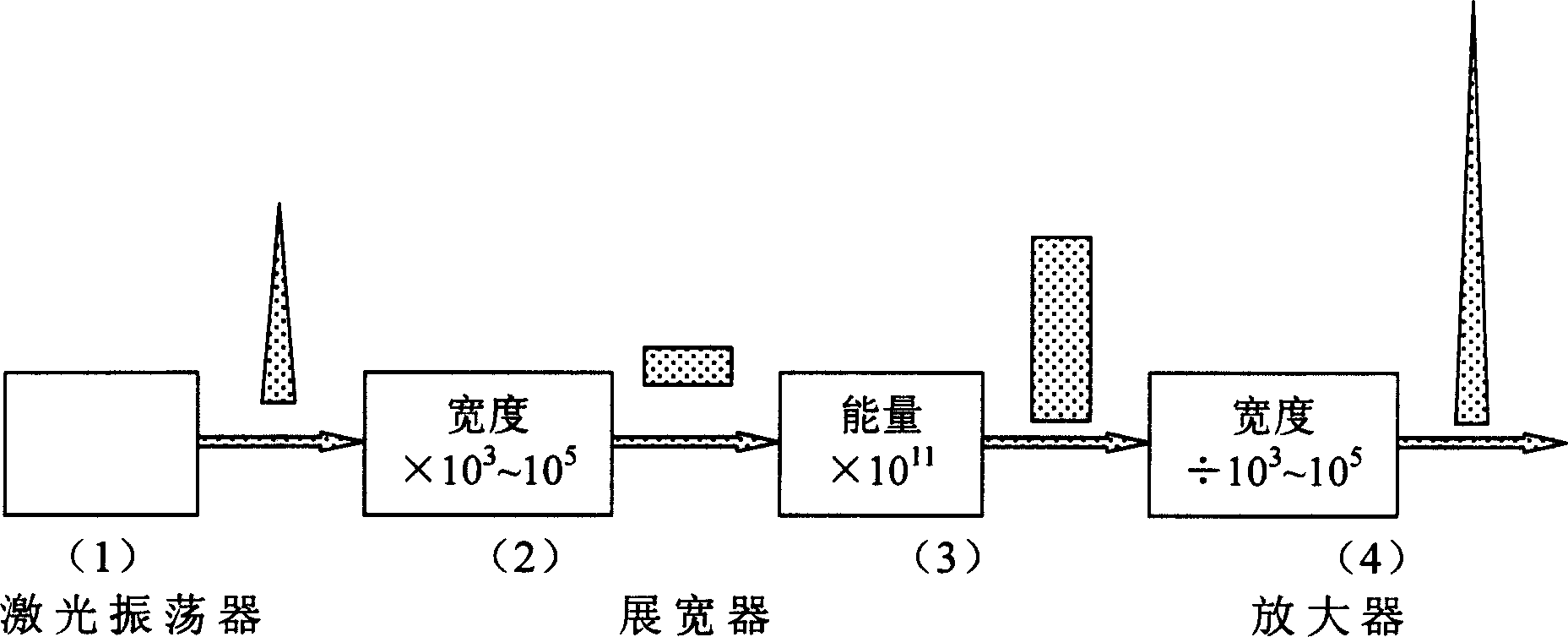
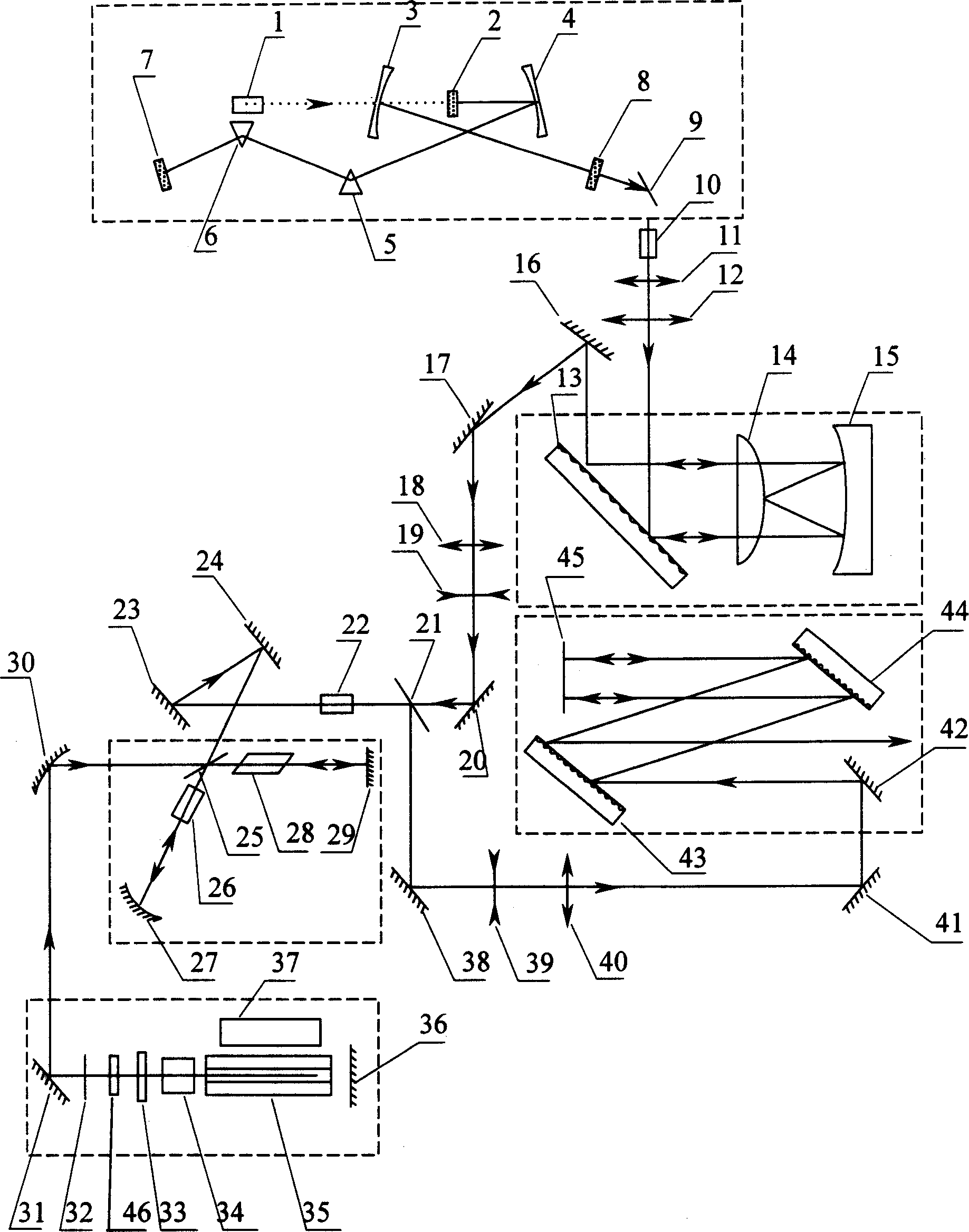
Table type fully solidified high repetition frequency femtosecond laser
The invention is a table-type all-solidified high-repeated frequency fly-second laser device, comprising fly-second pulse oscillator, pulse widening device, regenerative amplifier and pulse compressor, and its character: the pulse widening device is composed of grating, convex lens and concave reflector; the regenerative amplifier is composed of polarizing plate, Pockels cell, highly reflecting concave mirror, Ti-sapphire stick and reflector group; the pumping source of the regenerative amplifier is a Q-switch plane waveguide laser; the pulse width compressor is composed of reflector, two parallel-placed gratings and all reflector. Its output power can be up to 20W, higher 31 times than that of preceding technique, able to be applied to generate super ultraviolet or X rays, and has an extremely wide application prospect in photoetching, optical communication and micro-fabricating technique.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
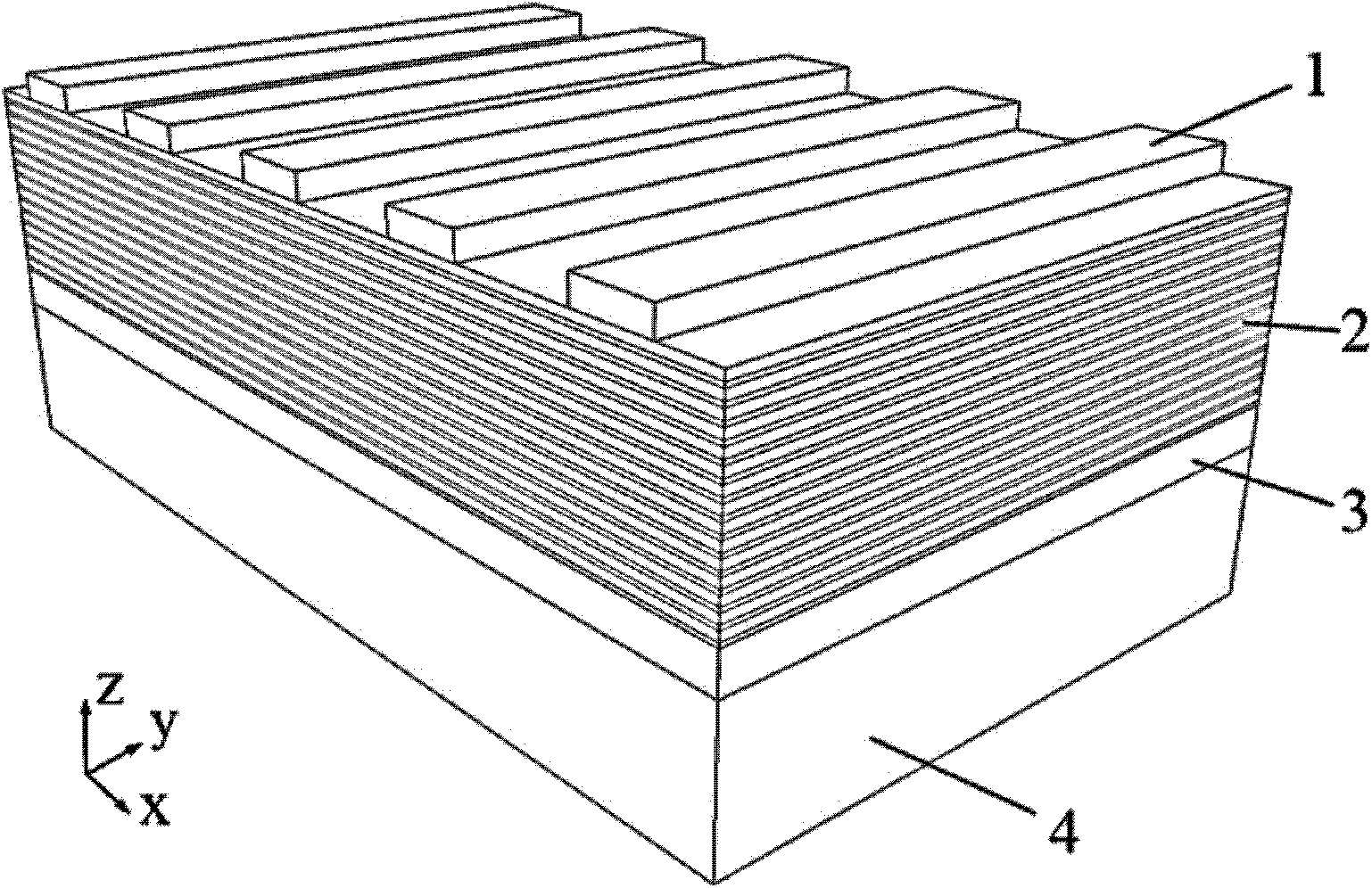
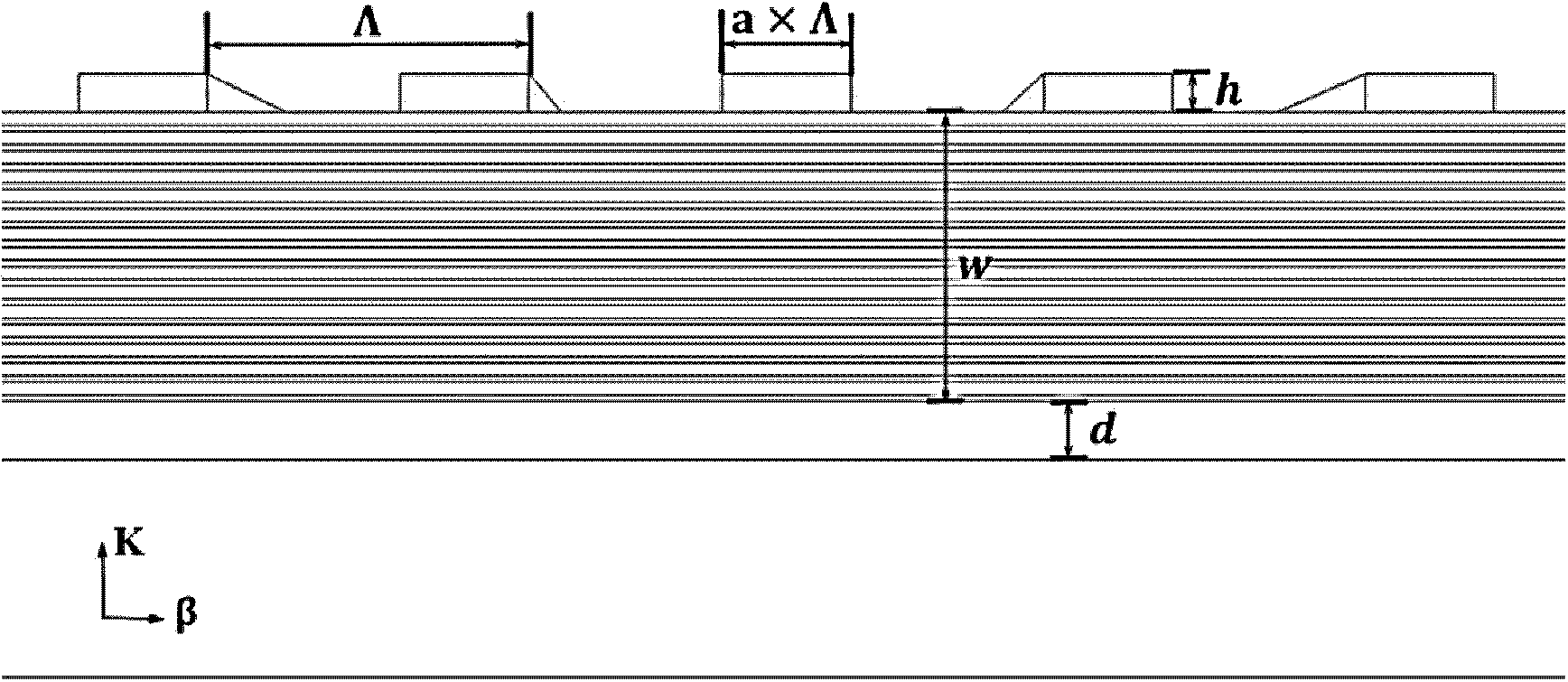
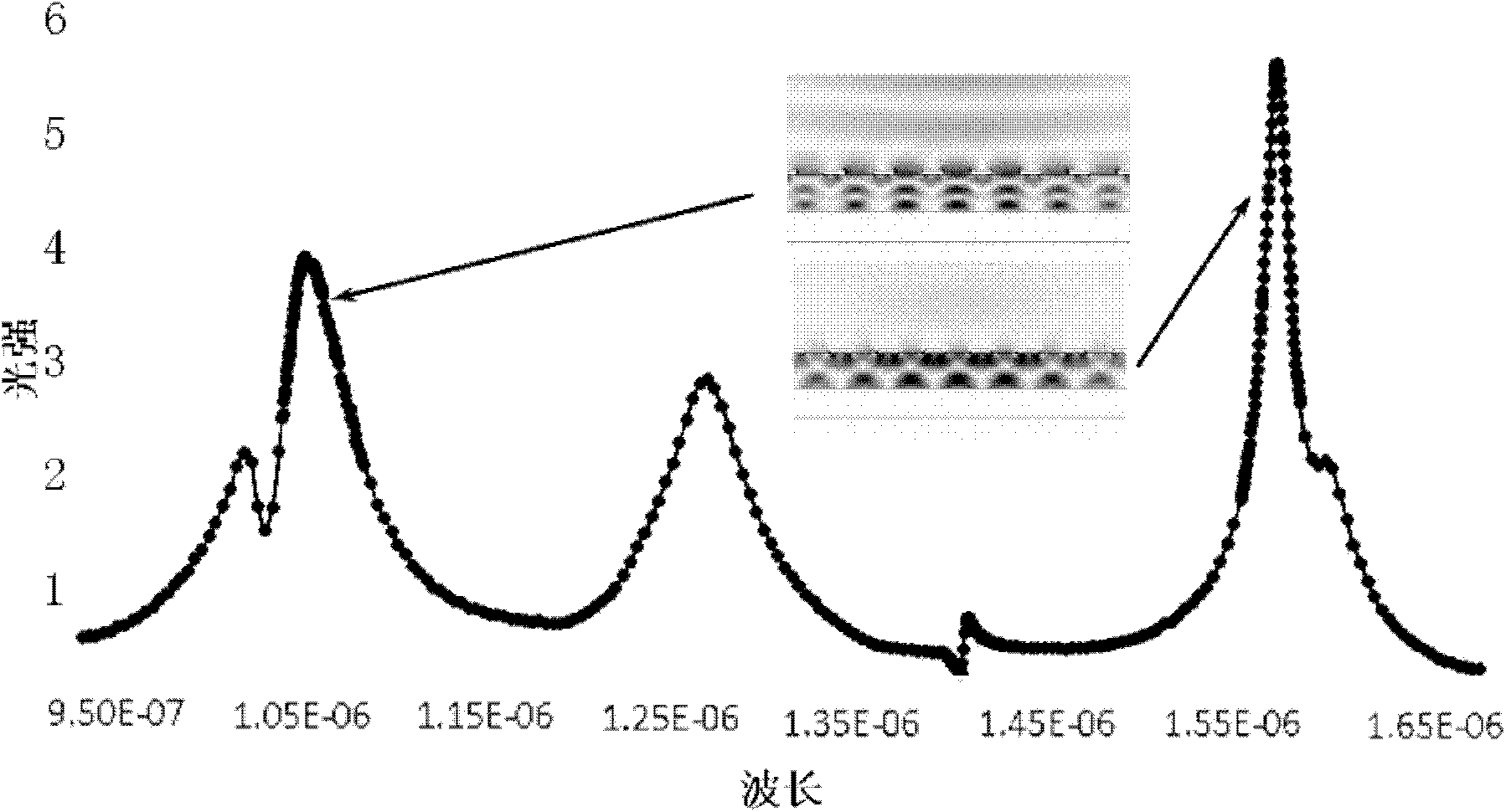
Asymmetric metal grating and coating semiconductor multi-quantum-well waveguide laser
The invention relates to the field of laser technologies and micro-nano optoelectronics and discloses an asymmetric metal grating and coating semiconductor multi-quantum-well waveguide laser. The waveguide laser comprises an upper metal grating layer (1), an active layer (2), a lower metal coating layer (3) and a substrate (4). The optical field is locally limited in the semiconductor active layer effectively through the upper metal grating layer and the lower metal coating layer. One-dimensional strip-shaped metal gratings are manufactured on the upper metal grating layer, FP-cavity-like resonance is formed in combination with local area surface plasma resonance, and thus wavelength mode can be effectively selected. The active layer is made of multi-quantum-well high-gain material, pump light is effectively absorbed and target light is sufficiently fed back through strong resonance between the pump light and the target light, and finally low-threshold laser emitting is achieved. The waveguide laser has the advantages of being capable of limiting one-dimensional sub-wavelength of light, good in unidirectionality and the like.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rare earth doped gallium germanium bismuth lead luminous glass material and its preparation method and uses
InactiveCN1807310AWith integrationWith miniaturizationGlass furnace apparatusWaveguide lasersRare earth
The disclosed Ga-Ge-Bi-Pb fluorescent glass material doped with rare earth is prepared by: mixing and fusing the Ga2O3, Bi2O3, GeO2, lead-contained compound and rare earth compound to obtain the fused glass liquor; clearing and pouring the liquor into the mold to obtain the glass; putting the glass rapidly into a muffle furnace with temperature as the glass transformation temperature for heat preservation; finally, cooling to room temperature. This product can be manufactured into different shape, and has wide application as the gain medium.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
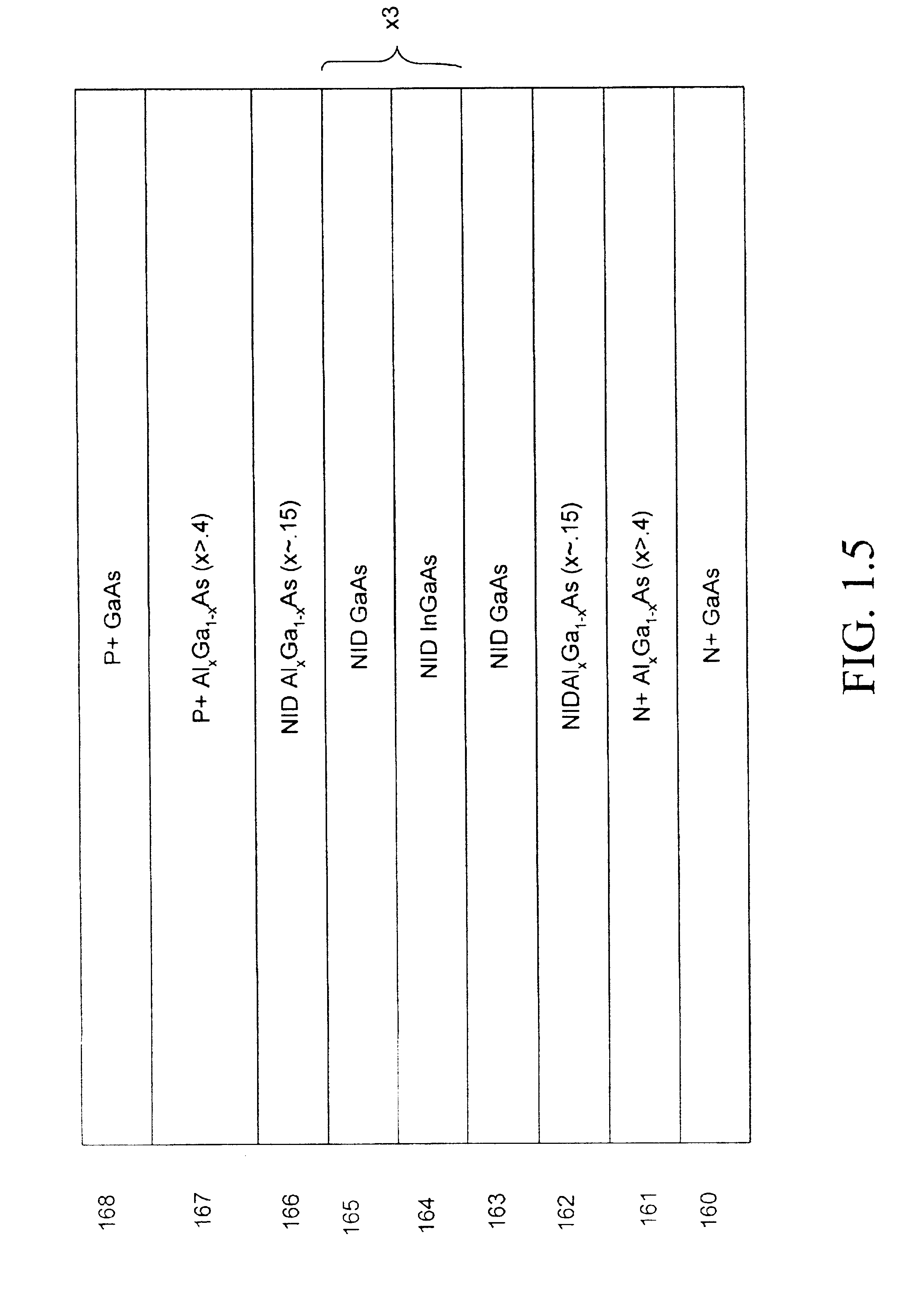
Monolithic wafer-scale waveguide-laser
InactiveUS20050169339A1Enhanced couplingActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionRare-earth elementCoupling
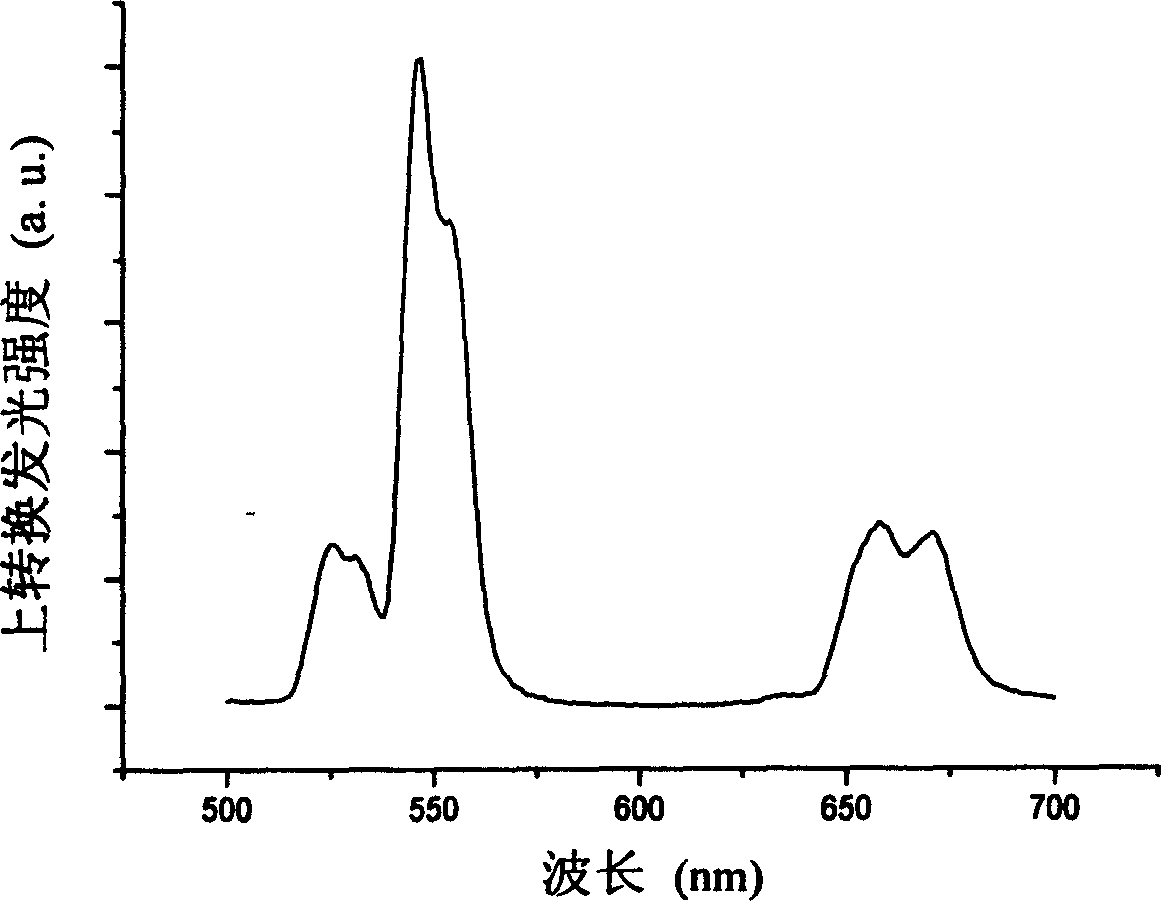
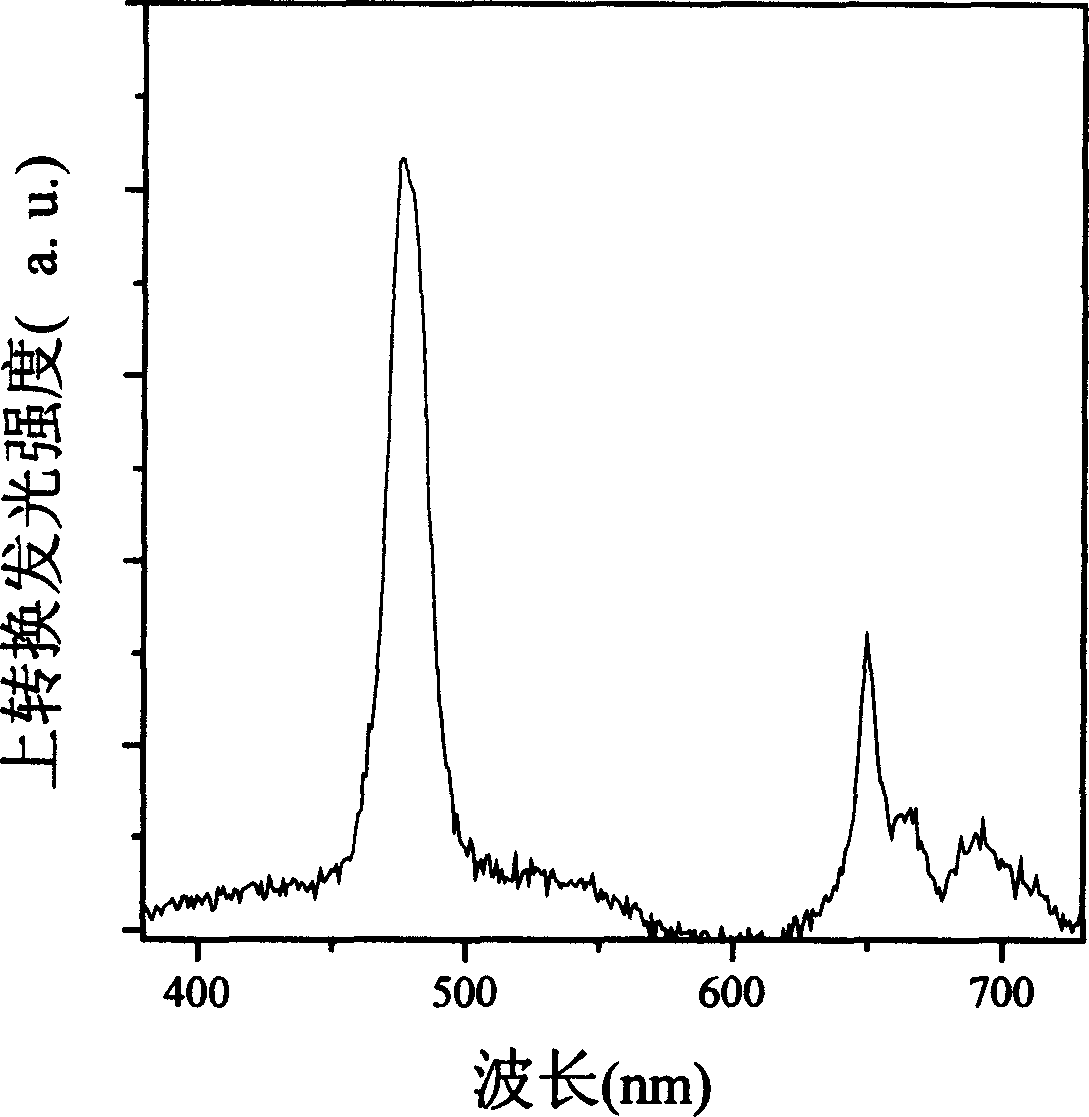
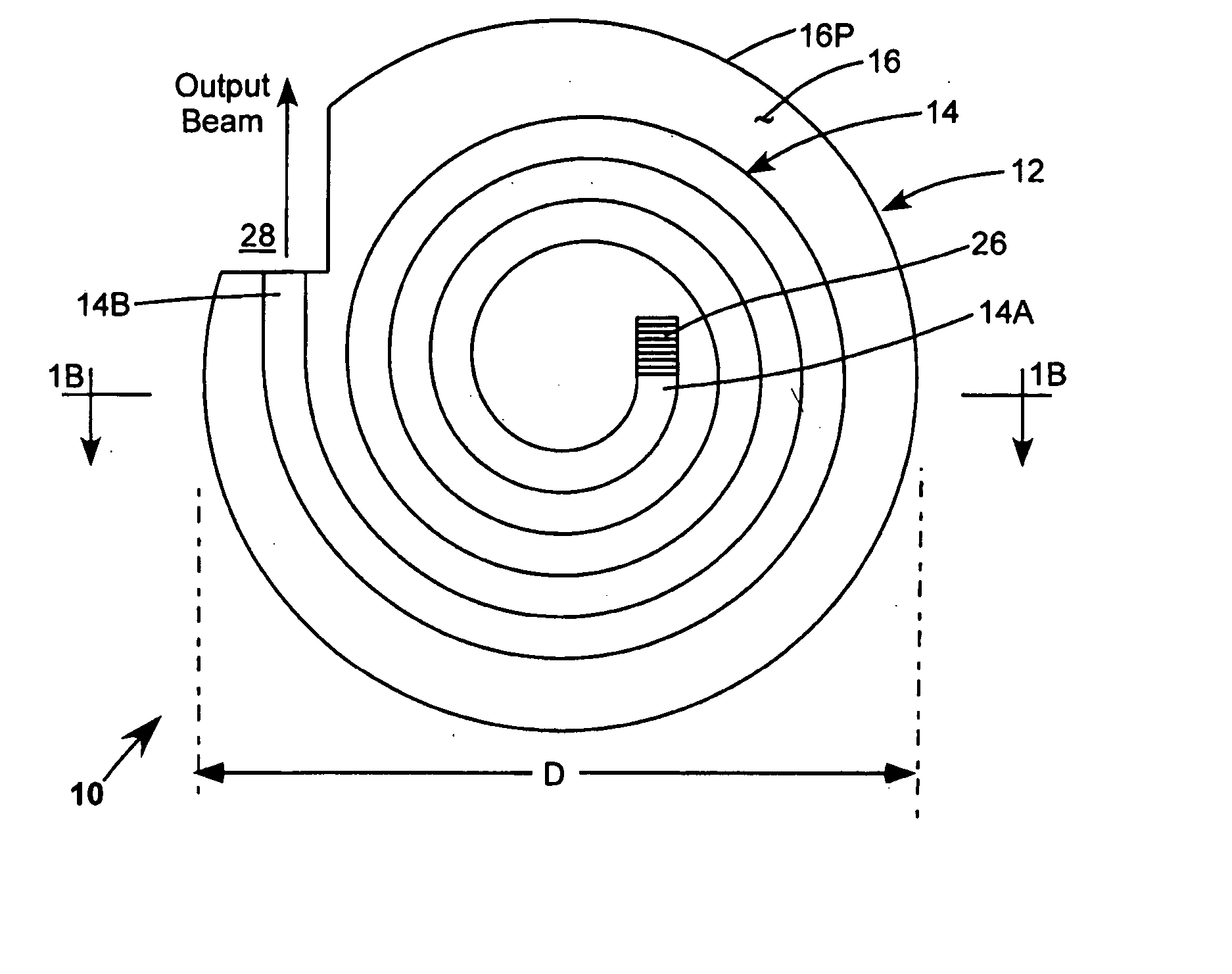
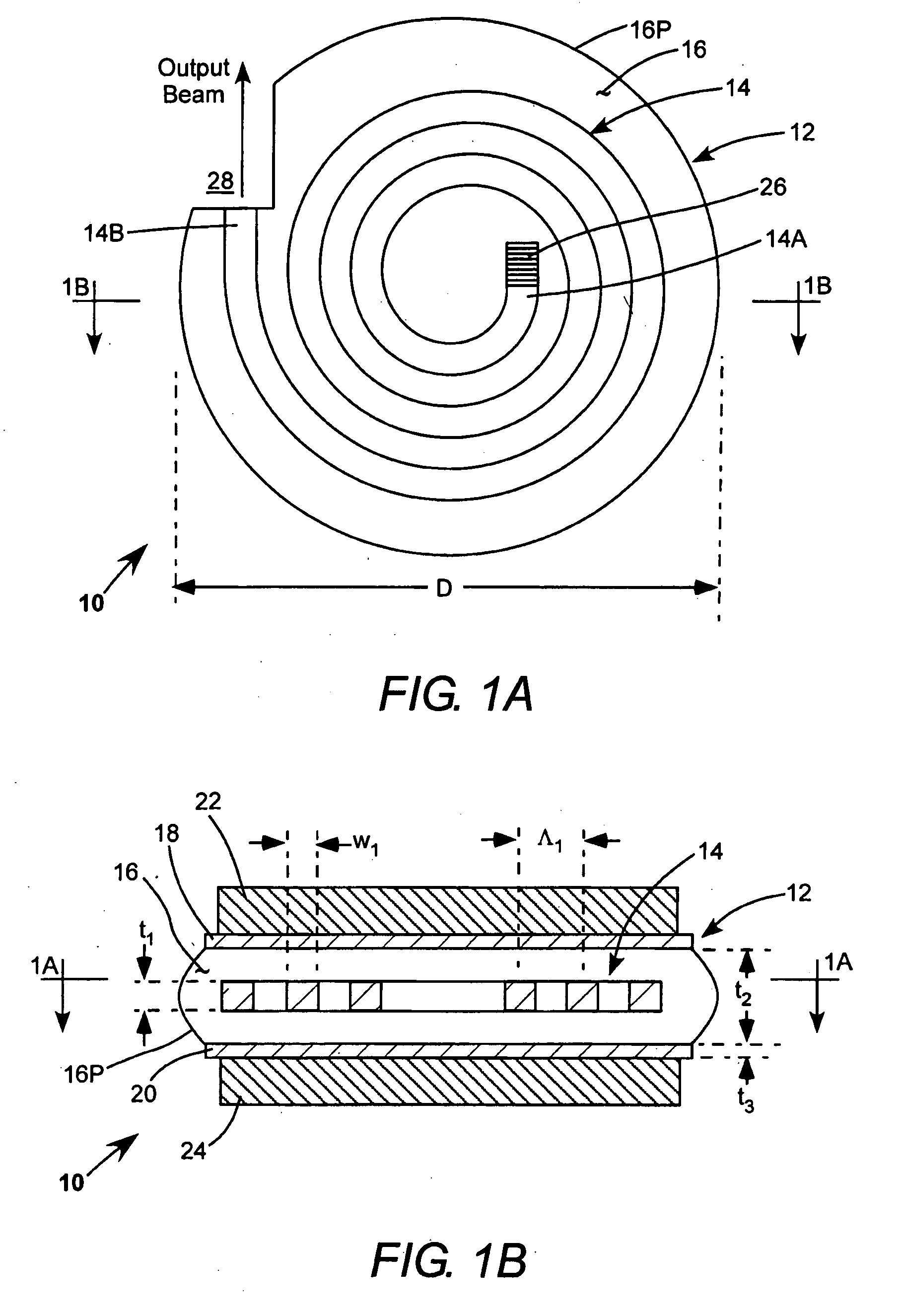
A waveguide laser is formed by starting with a glass disc doped with a rare earth element to define a lasant material. The disc is etched or machined to define an elongated waveguide channel having a spiral configuration. The open area between the walls of the waveguide channel is filled with a cladding material. An end reflector is formed on the radial inner end of the spiral waveguide. First cladding layers are formed on both sides of the spiral waveguide. A second cladding layer is deposited on at least one of the first cladding layers. A heat sink is connected to the second cladding layer. A plurality of optical pump sources are positioned about the side walls of the structure to excite the lasant material and generate a laser beam. In one preferred embodiment, the side walls of the structure are provided with a convex configuration to enhance pump coupling.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Optical waveguide laser, optical waveguide amplifier and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101436748AReduce gainLower the thresholdOptical resonator shape and constructionAudio power amplifierWaveguide lasers
The invention relates to the laser filed, in particular an optical waveguide laser, an optical waveguide amplifier and a manufacturing method thereof. A laser gain medium sheet or a laser gain medium sheet stuck with an underlayer together is manufactured through a plurality of times of optical processing, cutting and polishing; and the gain medium sheet is stuck with an underlayer material together through agglutination, optical cementing or deep agglutination method. The laser gain medium is processed to form a waveguide laser gain medium cavity of which four sides are wrapped with an adhesive layer or a deep optical cementing layer through a plurality of times of optical processing and agglutination; and the end face of the waveguide laser gain medium cavity is an optical surface and is plated with a laser cavity film layer, thereby forming the laser or the amplifier with a waveguide structure. The waveguide cavity structure provides a method which can reduce a threshold value and can obtain laser through low-power pumping for various laser gain materials with high threshold values. The method for manufacturing the waveguide cavity has a simple process and is suitable for large-scale popularization.
Owner:FUZHOU PHOTOP QPTICS CO LTD
Reflection cavity mirror structure for high-speed Q modulation and wavelength tunable type waveguide laser
InactiveCN103944064AIncreased range of tunable wavelengthsWith characteristicsLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlWaveguide lasersErbium lasers
The invention discloses a reflection cavity mirror structure for a high-speed Q modulation and wavelength tunable type waveguide laser. The reflection cavity mirror structure for the high-speed Q modulation and wavelength tunable type waveguide laser comprises a split beam coupling structure, a big tunable optical micro-ring, a small tunable optical micro-ring and a Mach-Zehnder modulation structure, wherein the split beam coupling structure serves as an input end and a reflection output end, the two optical micro-rings are connected with the split beam coupling structure by being coupled with a first waveguide evanescent wave and a second waveguide evanescent wave respectively so that wavelength tuning can be achieved, and the two ends of the Mach-Zehnder modulation structure are connected with corresponding optical micro-ring evanescent waves respectively in a coupled mode through straight waveguide, so that wavelength tuning of the laser is achieved. According to the reflection cavity mirror structure for the high-speed Q modulation and wavelength tunable type waveguide laser, the reflectivity can be adjusted rapidly, wavelength tuning can be achieved, and the reflection cavity mirror structure can be used for constructing the high-speed Q modulation and wavelength tunable type waveguide laser. Due to the adoption of the two optical micro-rings, the range of the adjustable wavelength of the environment can be widened according to the vernier and calipers effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Grating coupled vertical cavity optoelectronic devices
InactiveUSRE38682E1Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionStimulated emissionWaveguide
A edge emitting waveguide laser is obtained that derives its optical power from a vertical cavity laser structure. The vertical cavity laser with top and bottom Distributed Bragg Reflectors produces stimulated emission by resonance in the vertical direction but the optical power so generated is diffracted by a second order grating into an optical mode propagating in the optical waveguide formed by the upper and lower mirrors as cladding layers. The efficiency of the diffraction grating and the reflectivity of the mirrors are maximized so that essentially all of the light is coupled into the guide and the loss through the mirrors can be neglected. The same structure can be utilized as a detector, a modulator or an amplifier. The designated laser structure to achieve this form of operation is the inversion channel laser which is a laterally injected laser having both contacts on the top side of the device. Then the anode and cathode of the laser are essentially coplanar electrodes and the device is implemented in the form of a traveling wave laser, detector, modulator or amplifier which forms the basis for very high frequency performance.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
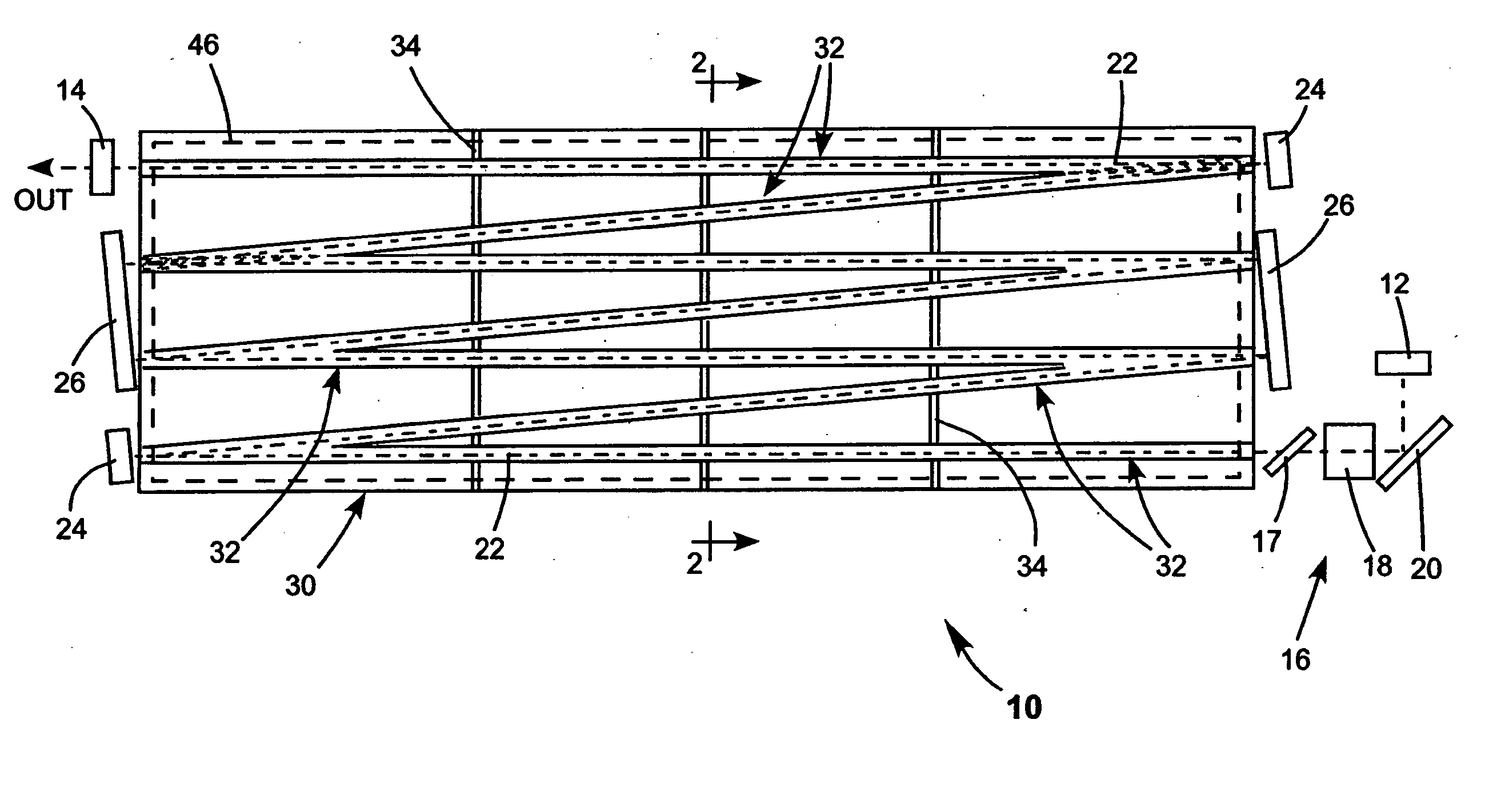
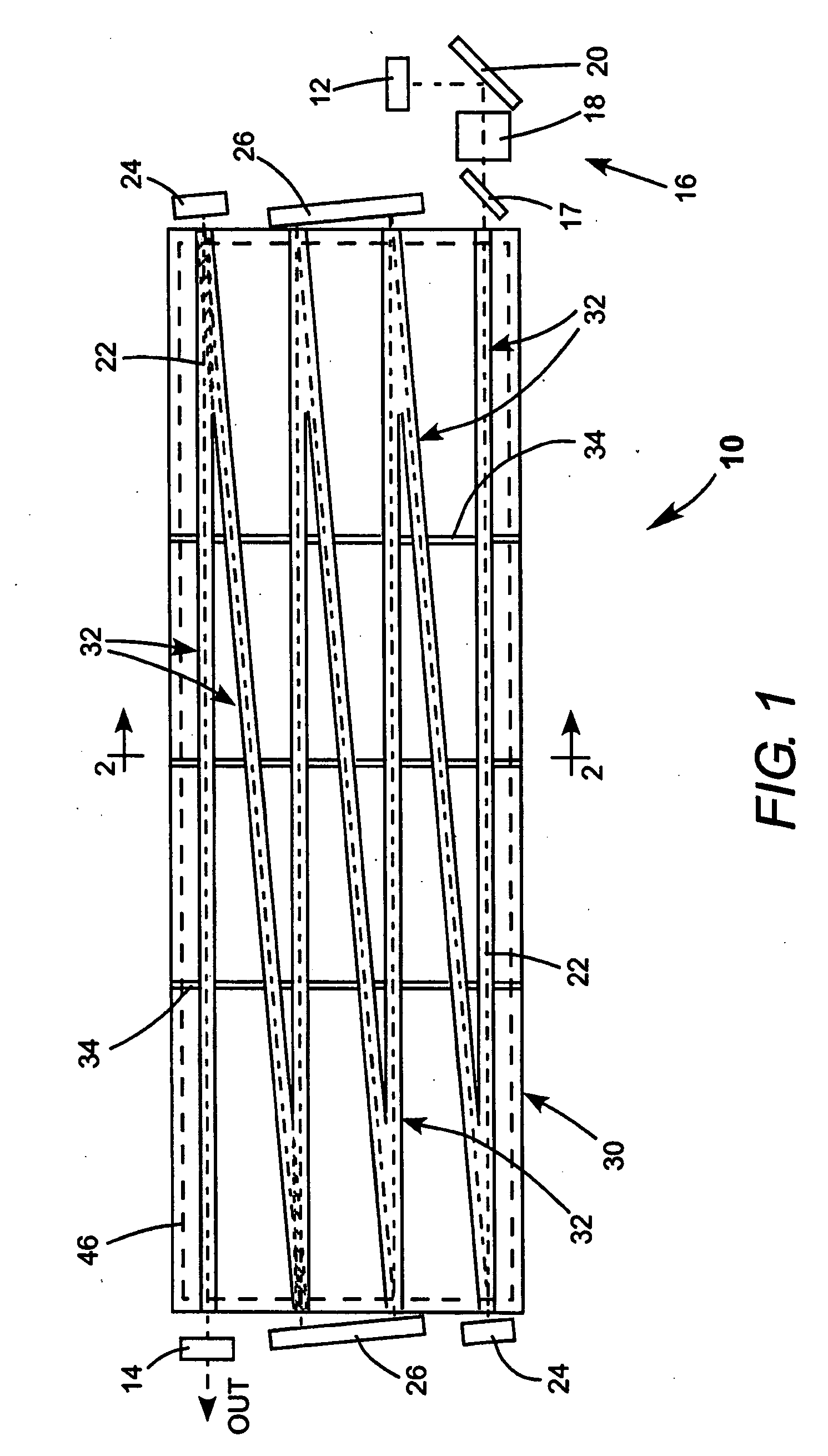
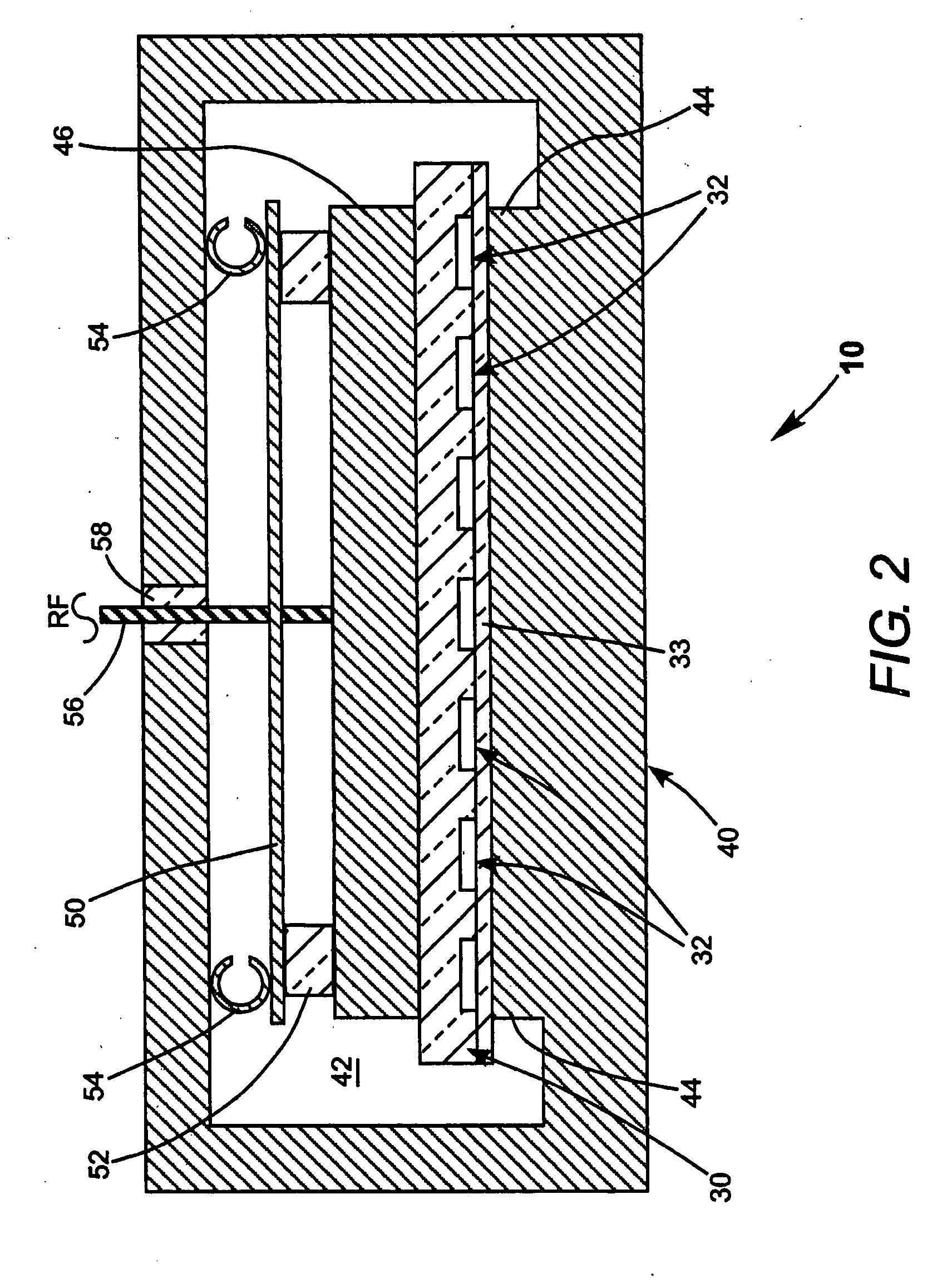
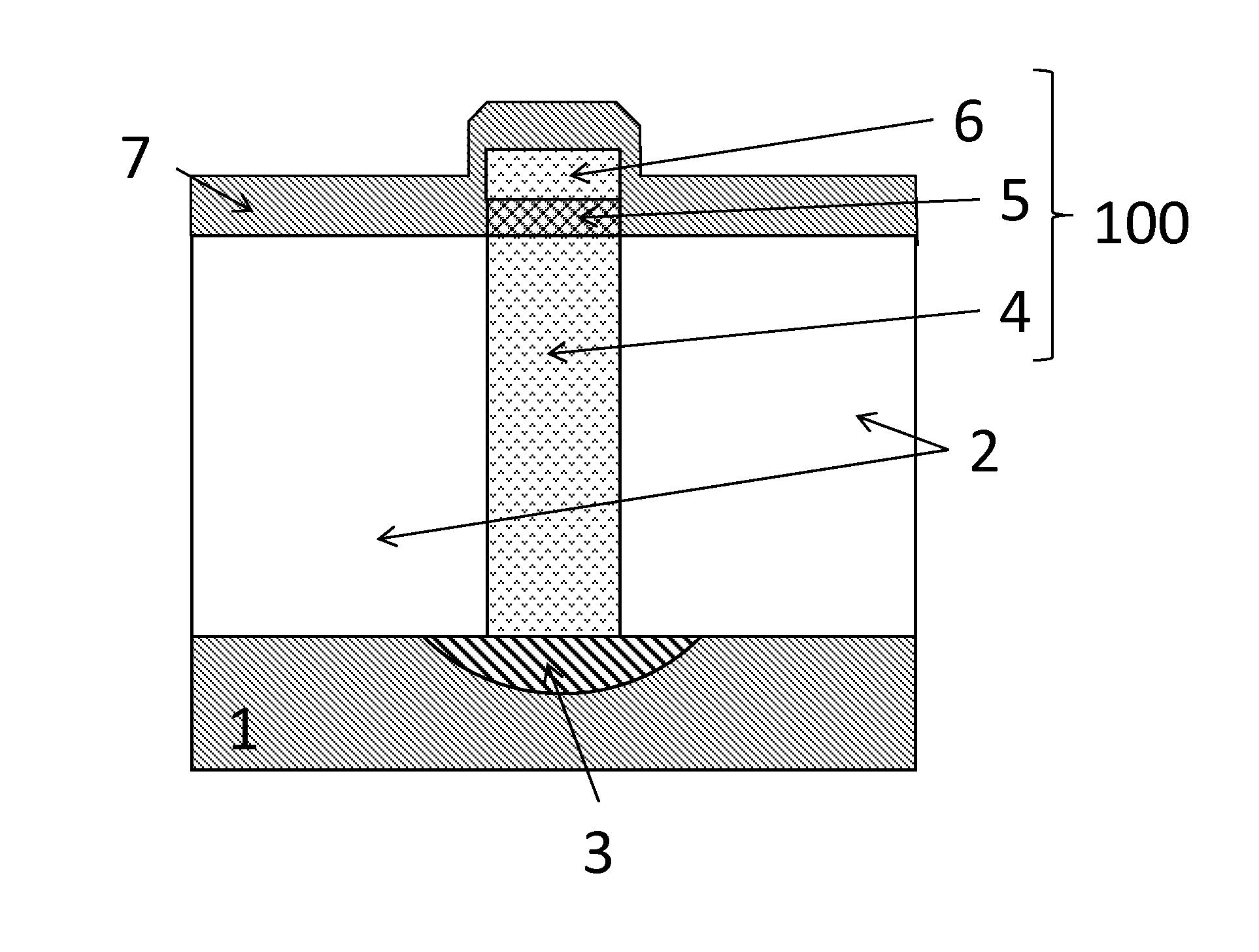
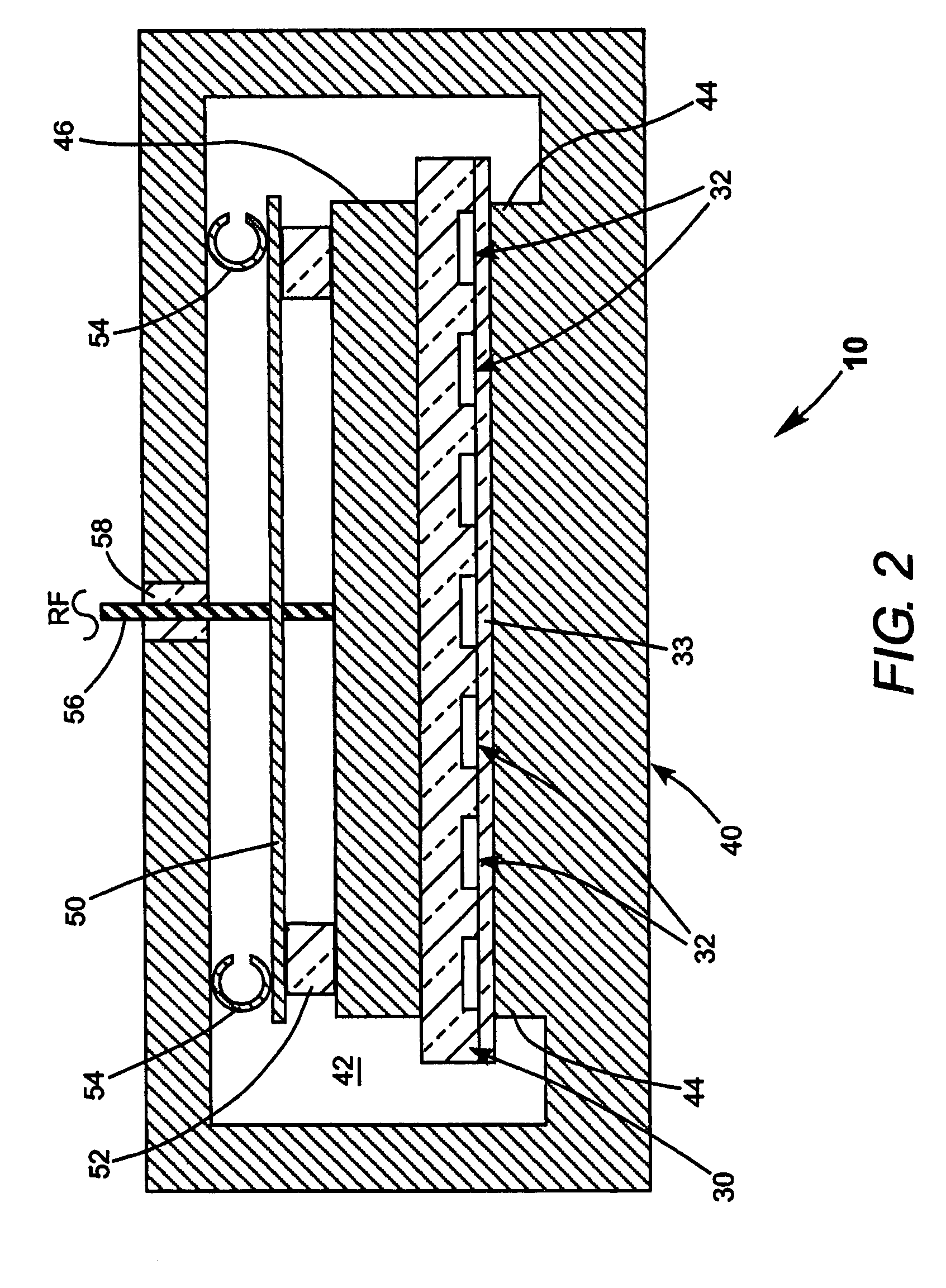
Waveguide laser having reduced cross-sectional size and/or reduced optical axis distortion
InactiveUS20070189353A1Reducing thermally induced distortionActive medium materialWaveguide lasersCoupling
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to waveguide lasers (e.g., RF-excited waveguide lasers). Certain example embodiments of this invention provide combined waveguide cover and non-coupled top electrodes, and / or heat load balancing vacuum vessels including multiple (e.g., two or more) chambers. In certain example embodiments, RF energy may couple through the combined waveguide cover and non-coupled top electrode without significantly traversing the insulating carrier material via one or more cutouts or gaps formed in the RF coupling region of the top (or even a bottom) electrode. In certain example embodiments, first and second chambers of the vacuum vessel may be arranged so that heat generated in the discharge region flows away from the first and second chambers, thereby reducing thermally induced distortion of the optical component during laser operation. These techniques may be used alone or in various combinations.
Owner:VIDEOJET TECH INC
Frequency comb source with large comb spacing
InactiveUS8571075B2Reduce lossEasy to adjustRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsLow noisePhase noise
A frequency comb laser providing large comb spacing is disclosed. At least one embodiment includes a mode locked waveguide laser system. The mode locked waveguide laser includes a laser cavity having a waveguide, and a dispersion control unit (DCU) in the cavity. The DCU imparts an angular dispersion, group-velocity dispersion (GVD) and a spatial chirp to a beam propagating in the cavity. The DCU is capable of producing net GVD in a range from a positive value to a negative value. In some embodiments a tunable fiber frequency comb system configured as an optical frequency synthesizer is provided. In at least one embodiment a low phase noise micro-wave source may be implemented with a fiber comb laser having a comb spacing greater than about 1 GHz. The laser system is suitable for mass-producible fiber comb sources with large comb spacing and low noise. Applications include high-resolution spectroscopy.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Single frequency thulium waveguide laser, an article comprising it, its use and a method of its manufacture
InactiveUS20070153839A1Simple and compact and economicLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionWaveguide lasersSpectroscopy
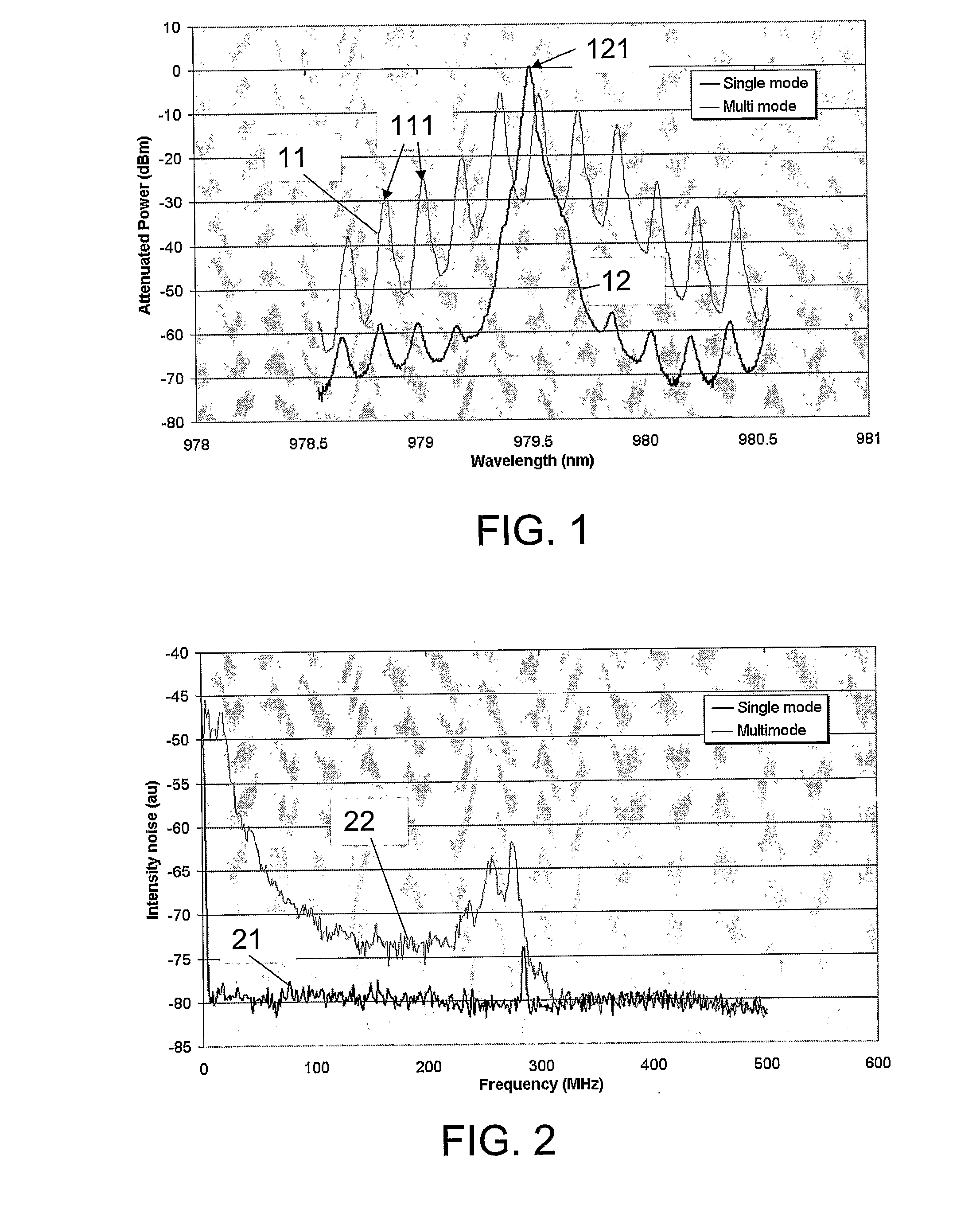
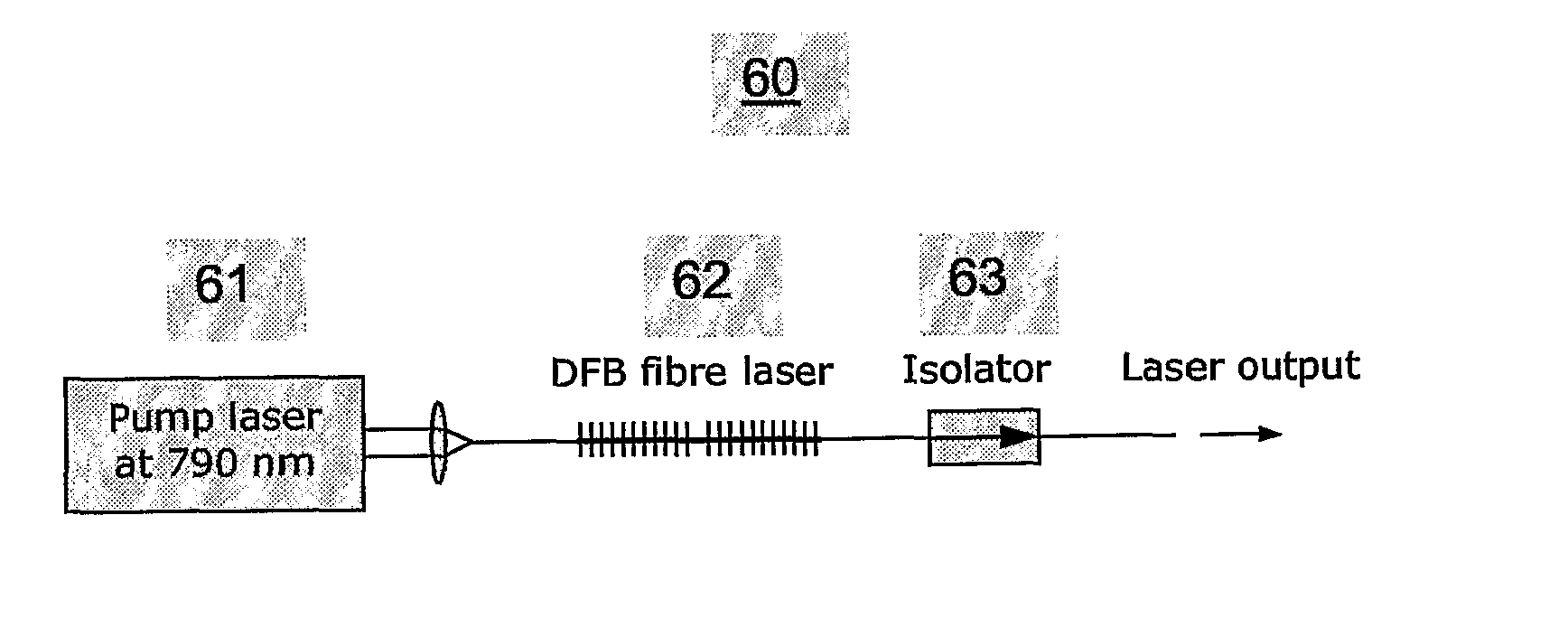
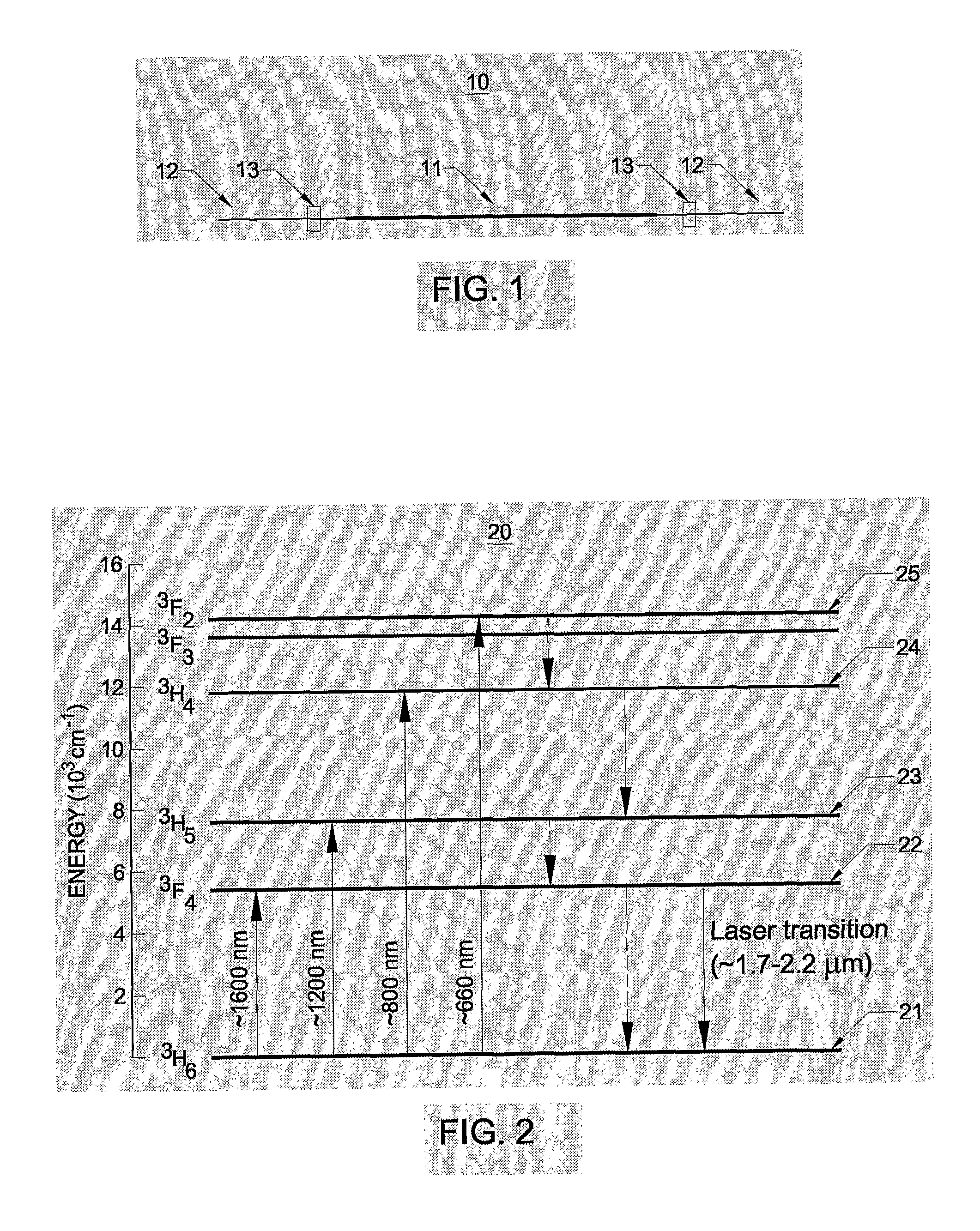
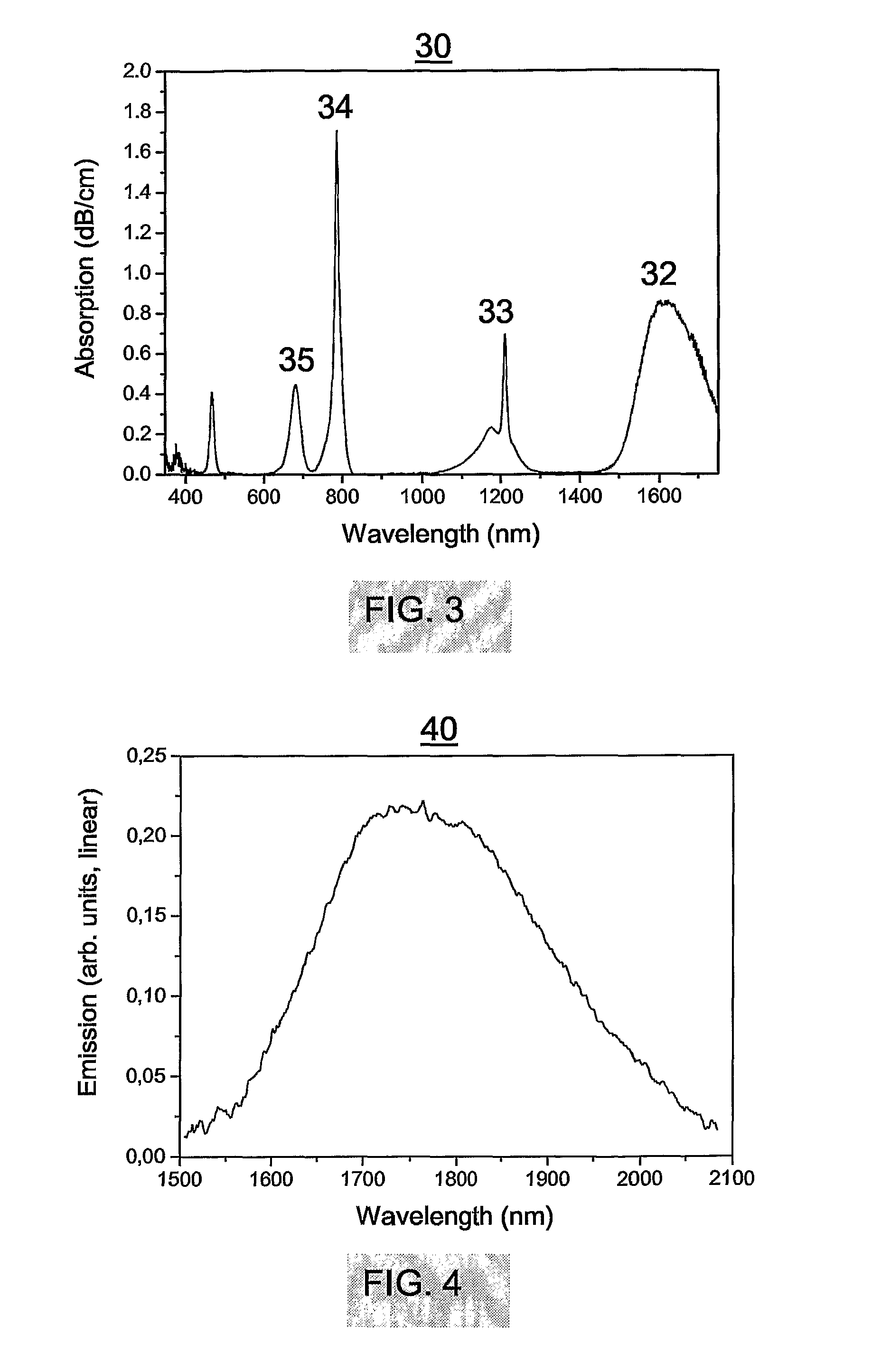
The invention relates to an optical waveguide laser comprising a) an active region formed over a length of the optical waveguide, comprising an excitable material emitting light in response to stimulation by pump light thereby defining an optical gain profile and the excitable material comprises Tm; b) a frequency discriminated feedback element adapted to select a single longitudinal lasing mode by coordination with the frequency response of the optical gain of the excitable material; and c) a polarisation asymmetry element adapted for selecting a single polarisation mode of a given longitudinal mode by selectively suppressing propagation of the other polarisation mode of said longitudinal mode. The object of the present invention is to provide relatively simple, compact and economic lasers for single-frequency operation in the wavelength range of 1.7 um to 2.2 um; in particular for a number of applications, including spectroscopy and for eye-safe optical sources in sensing and in LIDAR, etc.
Owner:KOHERAS
Hybrid Waveguide Lasers and Methods for Fabricating Hybrid Waveguide Lasers
ActiveUS20150333481A1Quality improvementControl leakageOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsWaveguide lasersPhotonics
The present disclosure relates to a method for integrating a sub-micron III-V waveguide laser on a semiconductor photonics platform as well as to a corresponding device / system. The method comprises providing on a semiconductor substrate an electrically insulating layer, etching a trench having a width in the range between 50 nm and 800 nm through the electrically insulating layer, thereby locally exposing the silicon substrate, providing a III-V layer stack in the trench by local epitaxial growth to form a channel waveguide, and providing a light confinement element for confining radiation in the local-epitaxial-grown channel waveguide.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
A mode selection waveguide laser
A mode selection laser comprises a recess which is formed in the surface of an electrode in a waveguide in the laser. The recess provides a region of free space propagation within the waveguide which preferentially selects the lowest order mode. A mode selective RF excited CO2slab laser may be constructed, having a stable resonator in the waveguide dimension and a negative branch unstable resonator in the non-waveguide dimension. The position and size of the recess is considered to provide low order mode selection.
Owner:ルクシナーリミテッド
Waveguide laser illuminator incorporating a despeckler
There is provided an illumination device comprising: a laser; a waveguide comprising at least first and second transparent lamina; a first grating device for coupling light from the laser into a TIR path in the waveguide; a second grating device for coupling light from the TIR path out of the waveguide; and a third grating device for applying a variation of at least one of beam deflection, phase retardation or polarization rotation across the wavefronts of the TIR light. The first second and third grating devices are each sandwiched by transparent lamina.
Owner:DIGILENS
Hybrid waveguide laser and method for manufacturing hybrid waveguide laser
ActiveCN104283093ALower the thresholdReduce power consumptionLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersElectricityWaveguide lasers
The invention relates to a hybrid waveguide laser and a method for manufacturing the hybrid waveguide laser. The hybrid waveguide laser is sub-micron III-V in level and comprises a channel waveguide, a lateral cladding layer adjacent to the waveguide in the transverse direction, and a light limiting element. The channel waveguide is 50 nm to 800 nm in width and 500 nm to 1200 nm in height. The light limiting element is used for limiting the light within the waveguide. The waveguide may comprise an III-V lamination comprising a lower cladding layer, an active region and an upper cladding layer. The laser may be optically coupled to an output waveguide which may be electrically pumped. The invention also provides a method for integrating the sub-micron III-V level waveguide laser onto a silicon photon platform. The method comprises the steps of providing an electricity insulating layer on a silicon substrate, etching a channel of 50 nm to 800 nm in width in the electricity insulating layer, forming a channel waveguide in the channel through providing an III-V lamination during the local epitaxial growth process, and providing a light limiting element to limit the light within the waveguide.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
Distributed feedback light waveguide laser
InactiveCN1585213AEasy to makeThe production process is stable and reliableOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialGratingWaveguide lasers
In this invention, in the minus or plus 15%area from the center of the sampling Prague grating which is etched on the light waveguide, on of the sampling period is jumping, while other sampling period is keeping unchanged. The jumped period is 1.4-1.6 or 0.4-0.6 times of the original. The sampling Prague grating makes the respective reflecting peak generate similar slit of the normal grating. The period of this grating possesses the property of linear chirp. When the period jumped to 1.5 or 0.5 times of the original, the -1 level chirp reflecting peak is about to zero.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
CO2 waveguide laser with beryllium oxide waveguides
ActiveUS7046709B2Active medium materialActive medium shape and constructionMicrometerWaveguide lasers
A pulsed, Q-switched, waveguide CO2 laser includes a plurality of waveguide channels formed in a block of a beryllium oxide ceramic material and is operated at a wavelength between about 9.2 and 9.7 micrometers. The laser has an output power up to 55% greater than that of a similarly configured laser, operated at the same wavelength and pulse conditions, but wherein the waveguide channels are formed in a block of an alumina ceramic material.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Planar waveguide laser device
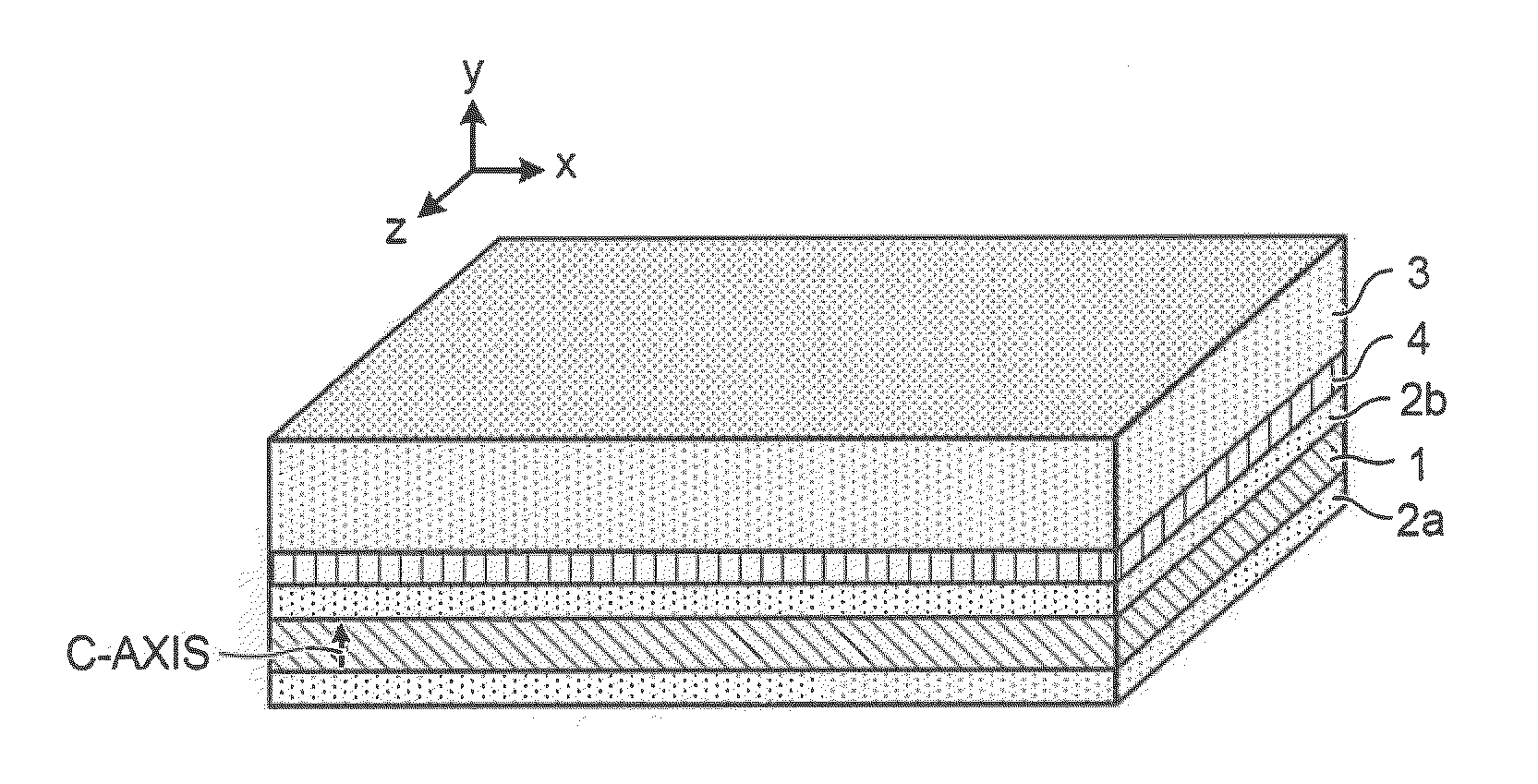
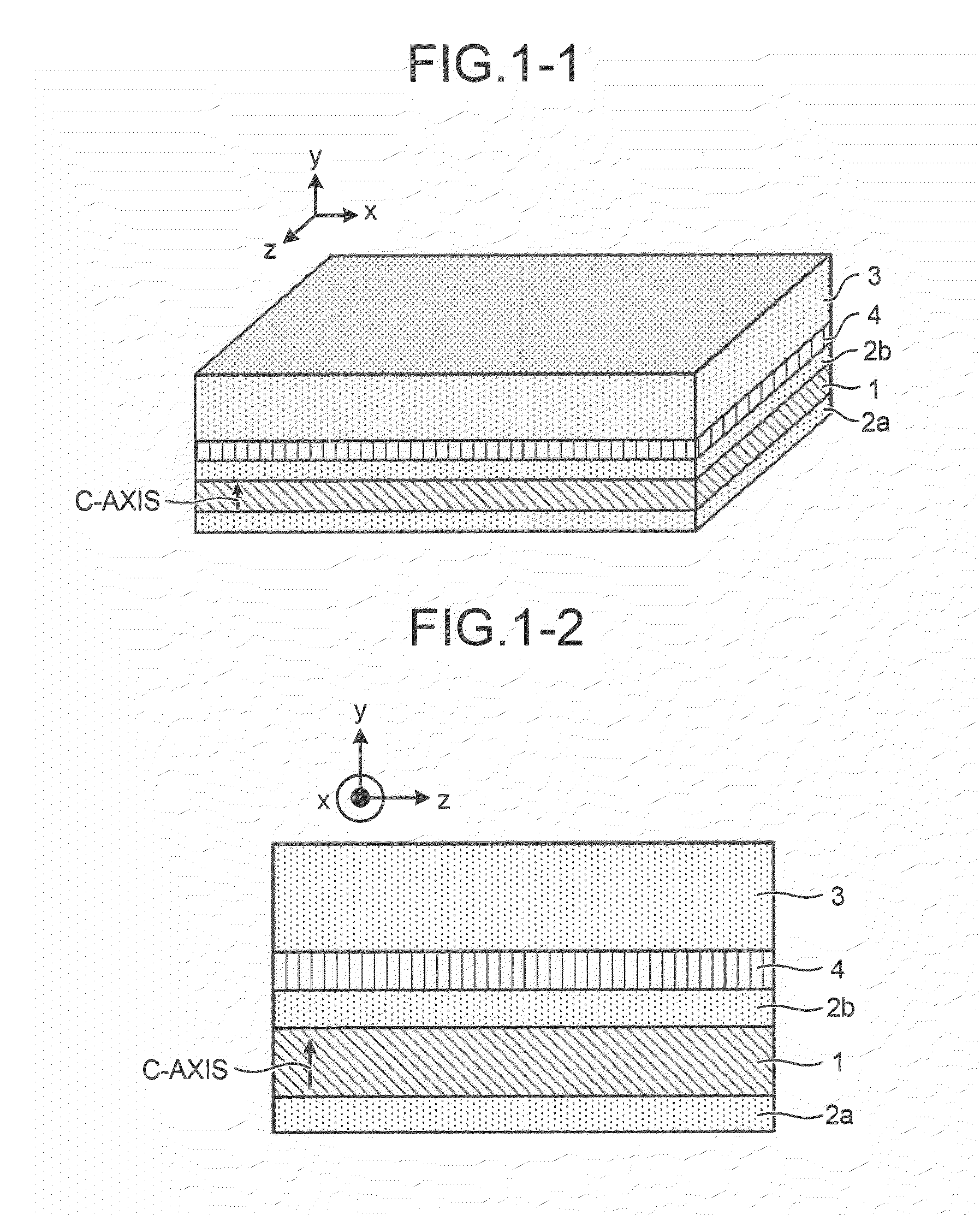
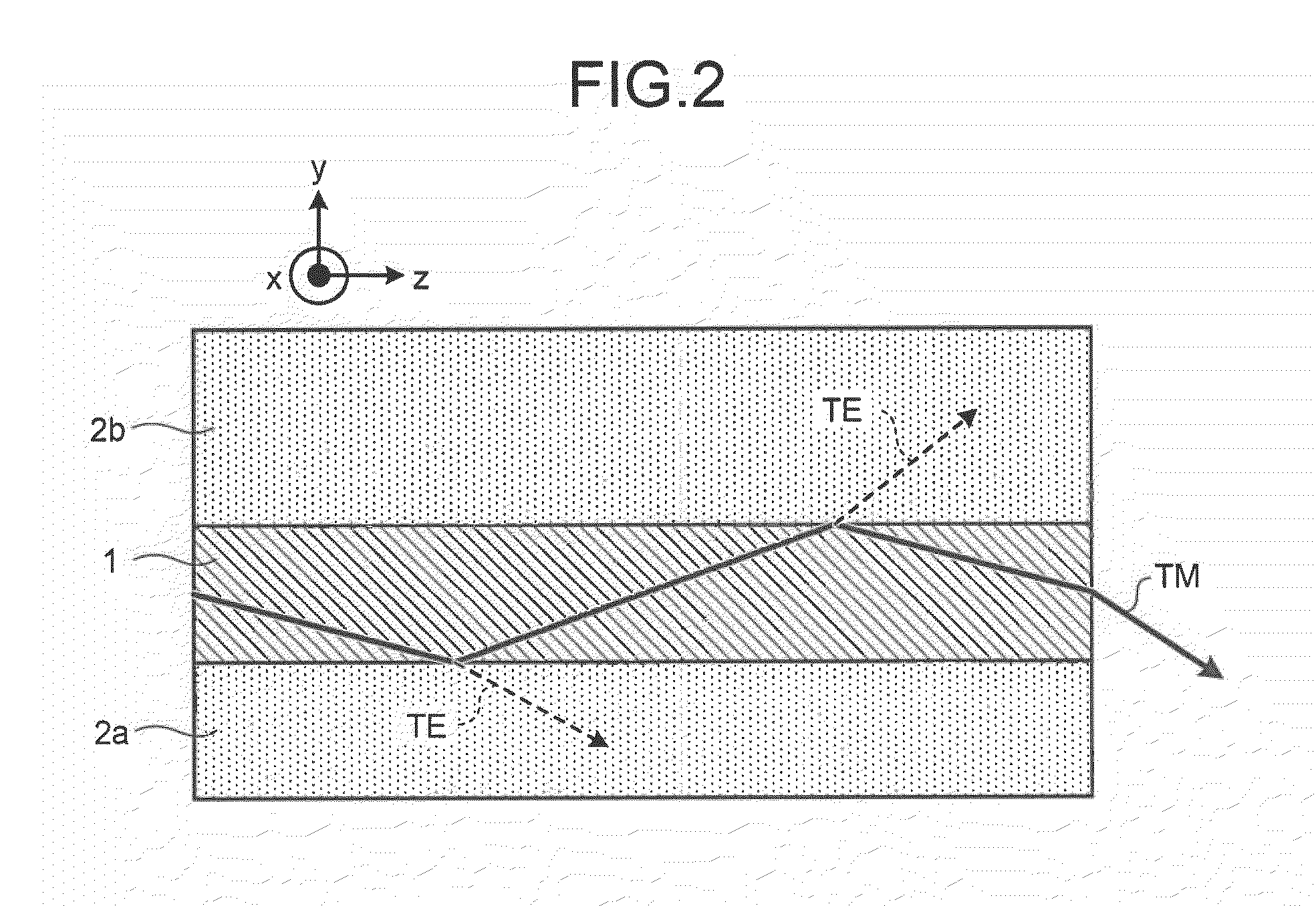
ActiveUS20100189151A1Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical axisWaveguide lasers
A planar waveguide laser device forms a waveguide by a plate-like laser medium having birefringence and clad attached to at least one of the surfaces of the laser medium perpendicular to its thickness direction, amplifies laser light by a gain produced by excitation light incident on the laser medium, and performs laser oscillation. The laser medium is formed of a material having an optic axis on a cross section perpendicular to the light axis, which is the laser travelling direction. The clad is formed of a material having a refractive index in a range between refractive indexes of two polarized lights that travel along the light axis in the laser medium and have oscillation surfaces that are orthogonal to each other. The planar waveguide laser device readily oscillates linearly polarized laser light.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
GaN-based semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
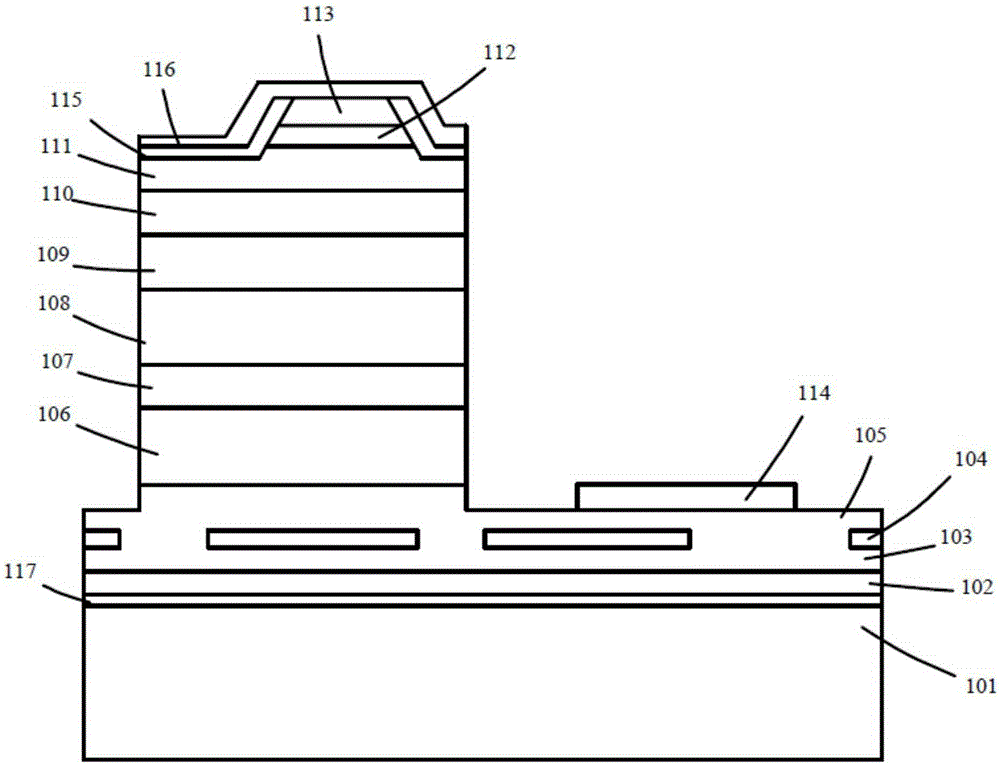
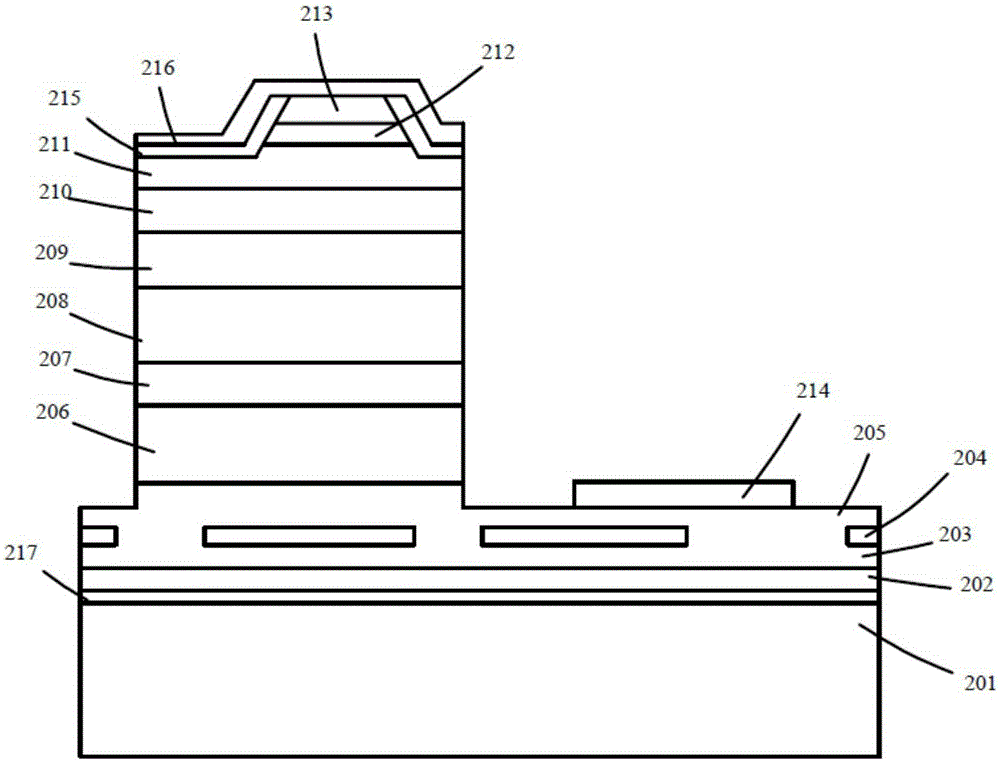
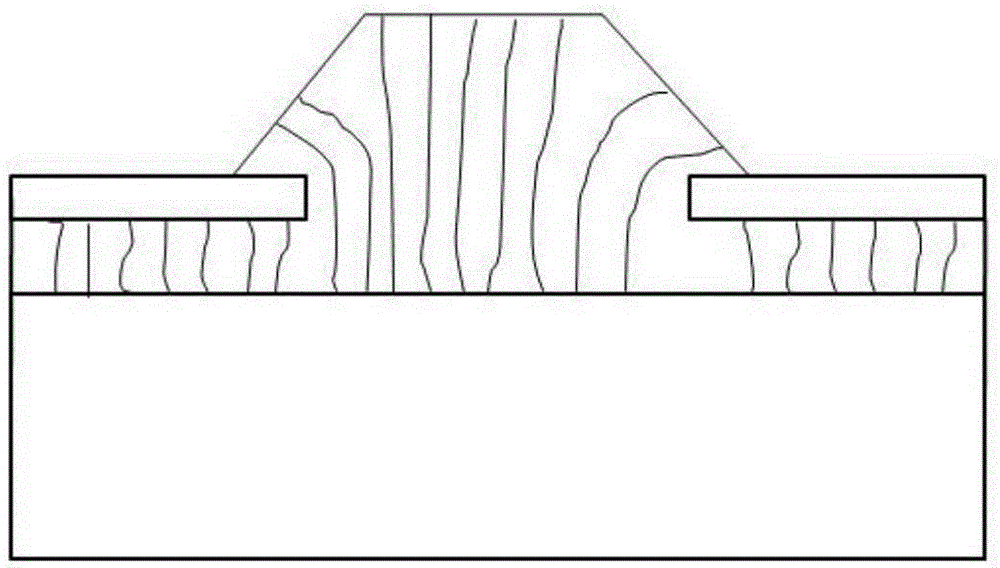
The invention discloses a GaN-based semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof. The GaN-based semiconductor device comprises a silicon substrate and an epitaxial layer formed on the silicon substrate, and is characterized in that the epitaxial layer comprises an AlN nucleating layer, an AlGaN buffer layer and a GaN buffer layer which are sequentially formed on the silicon substrate. According to the invention, a dielectric film is adopted to act as a mask layer, different effects are achieved through regulating and controlling the periodicity of a dielectric layer, and the dielectric layer can act as a limiting layer when the periodicity reaches the maximum, so that the optical loss can be effectively reduced, and threshold current of a laser and a super-radiation light-emitting diode is reduced; and the electric layer acts as an interface layer when the periodicity is small and forms another optical waveguide structure together with AlGaN at the bottom, a planar coupling optical waveguide laser and a super-radiation light-emitting diode are formed, and a nearly-circular light spot with a good shape can be acquired.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Rotary adjustable water waveguide laser processing device
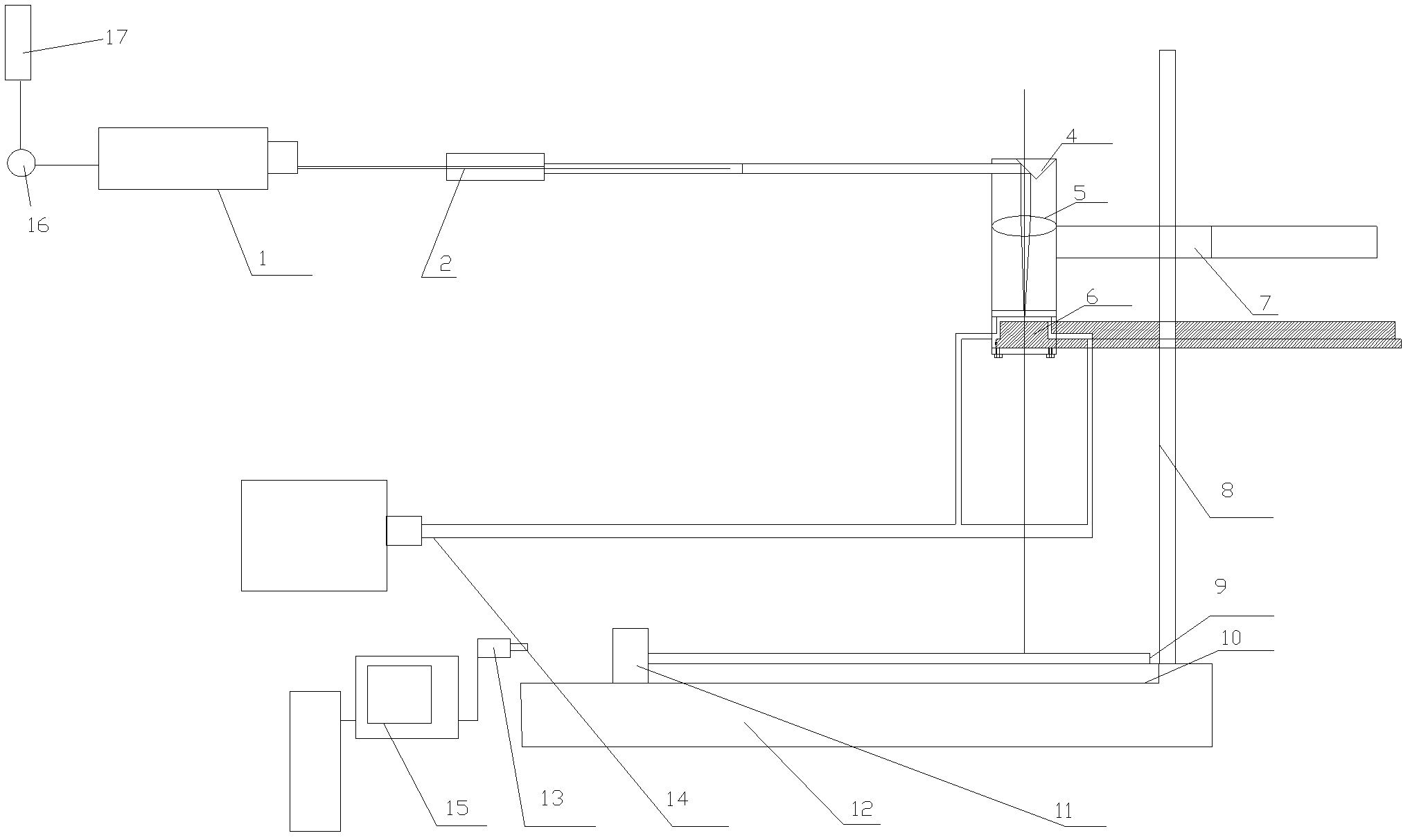
ActiveCN102248293AImprove processing efficiencyImprove efficiencyLaser beam welding apparatusNumerical controlData acquisition
The invention discloses a rotary adjustable water waveguide laser processing device relating to a laser processing device. The rotary adjustable water waveguide laser processing device is provided with a laser, an inverted telescope, a lens cone, a pipe joint, a pressing sheet, flat glass, a water cavity, a first reflecting mirror, a focusing lens, a nozzle body, a positioning mortise and tenon, a compression screw, a nozzle fixing frame, a bracket, a water collector, a clamp, a numerical control platform, a camera, a water circulating device, a data acquiring, processing and controlling computer, an observation laser and a second reflecting mirror. When different processing zones are selected, light path adjusting links can be reduced, thus the efficiency is increased; the technical problems of narrow processing range and low efficiency in the background art part can be solved; the poor processing flexibility and other defects can be overcome; and in a cavity with a certain pressure for the equipment, stable water waveguide jet flow processing can be formed and laser can be guided to a laser region through water waveguide, thereby the application field can be widened and the efficiency can be increased to the greater degree.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com