A mode selection waveguide laser
A technology of lasers and modes, which is applied in the direction of lasers, gas laser parts, laser parts, etc., can solve the problem of not describing the length and size information of the slit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
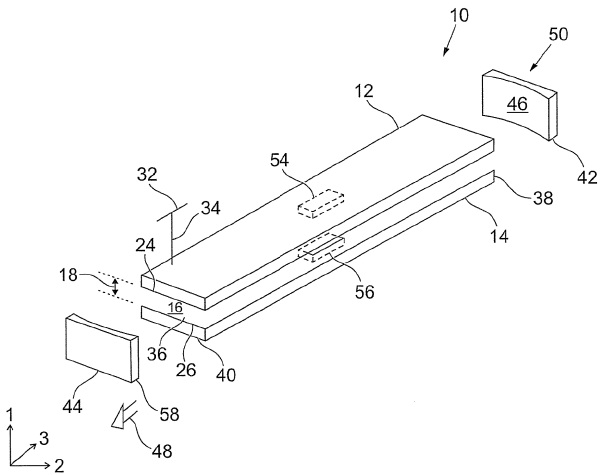
[0038] attached figure 1 A mode selective laser is shown, indicated with reference numeral 10 . Laser 10 includes a pair of elongated rectangular planar electrodes 12, 14 made of a conductive metal, such as aluminum. The planar dimensions of the electrodes 12 , 14 determine the size of the discharge region 16 formed between them, and thus determine the output power of the laser 10 . For 100w CO 2 For a laser, the electrodes may be approximately 480 mm long and 45 mm wide. The electrodes 12, 14 are typically adapted to include one or more coolant channels (not shown) through which water passes.
[0039] The electrodes 12, 14 are spaced apart by the height of a waveguide, or a gap 18 between the electrodes. Usually the height of the gap 18 is 1 mm to 4 mm, and in a preferred embodiment, the height is in the range of 1.3 mm to 2.8 mm. The electrodes 12 , 14 are spaced apart by a predetermined height 18 .
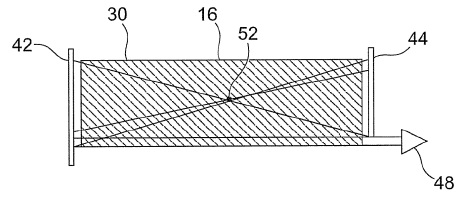
[0040] The discharge region 16 is then confined within the first and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com