Patents
Literature
1206results about How to "Reduced series resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
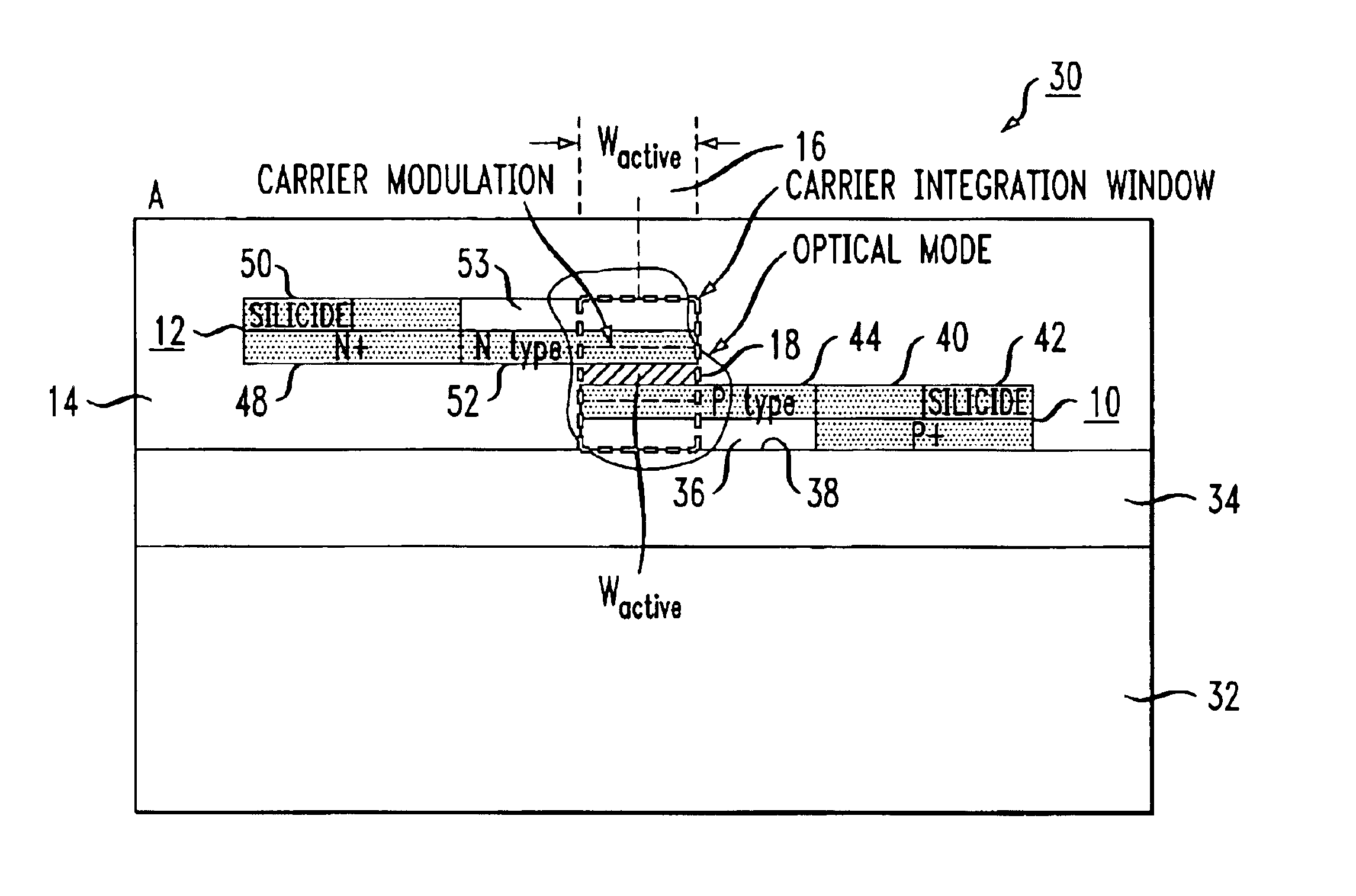
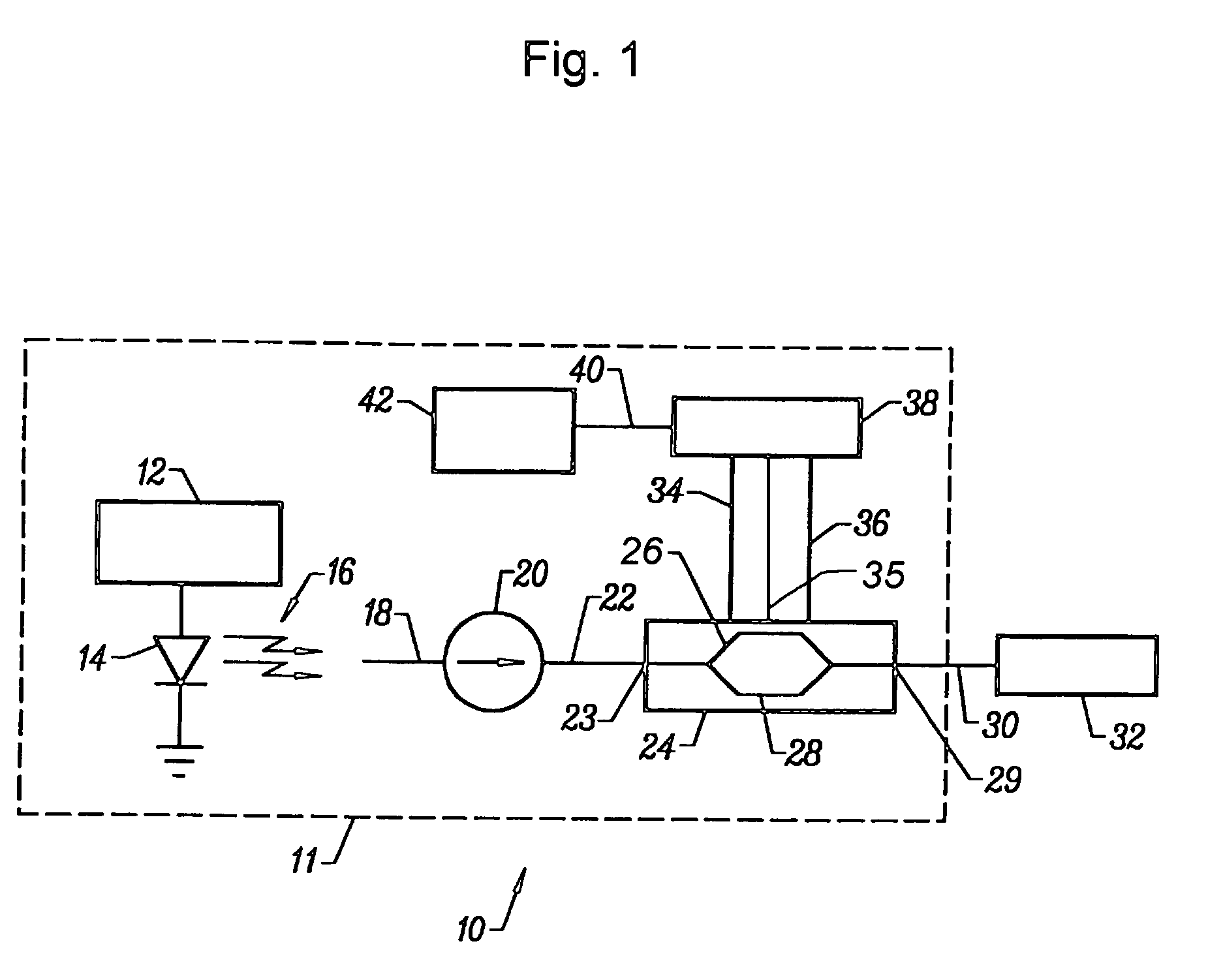
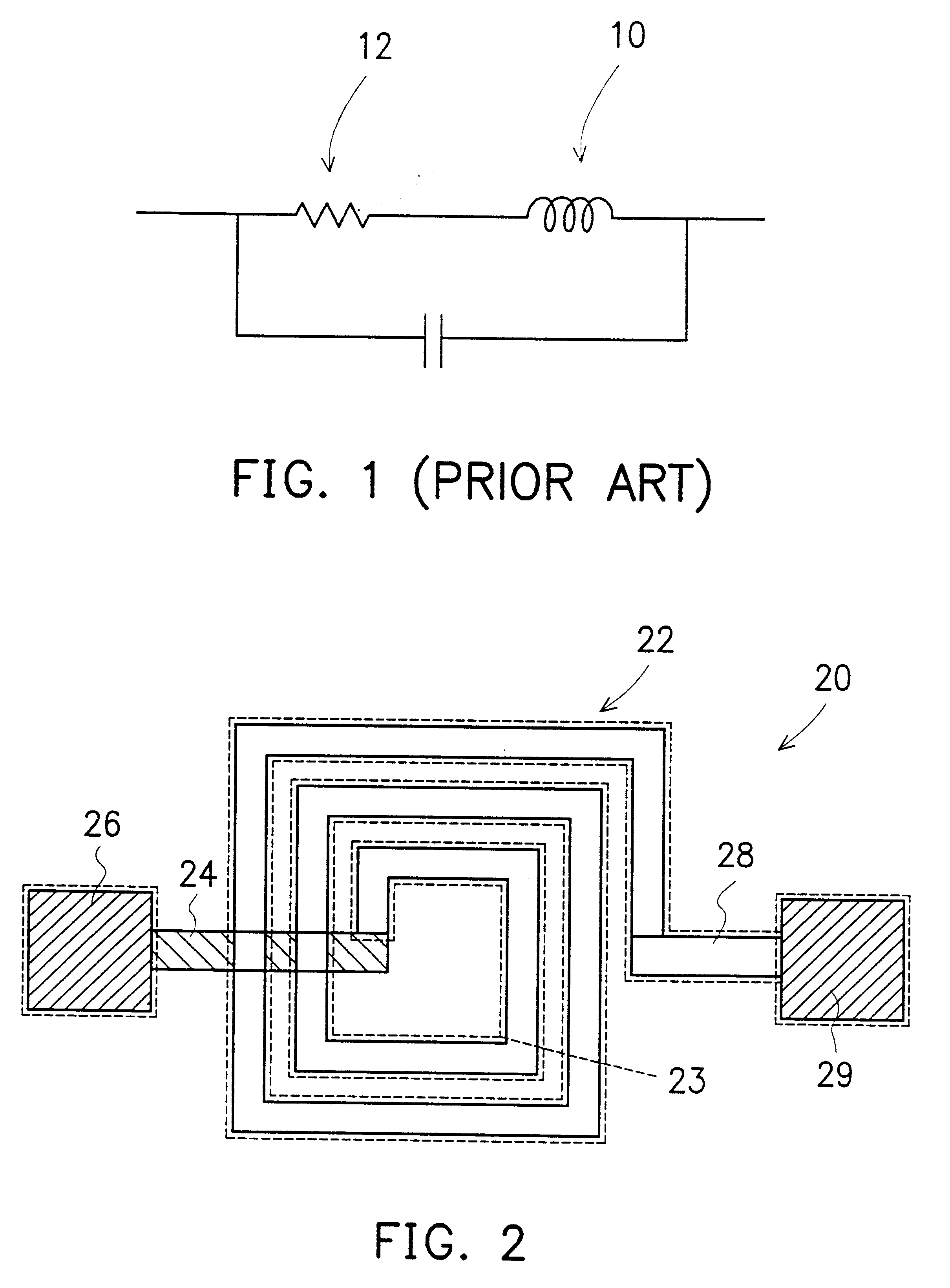
High-speed silicon-based electro-optic modulator
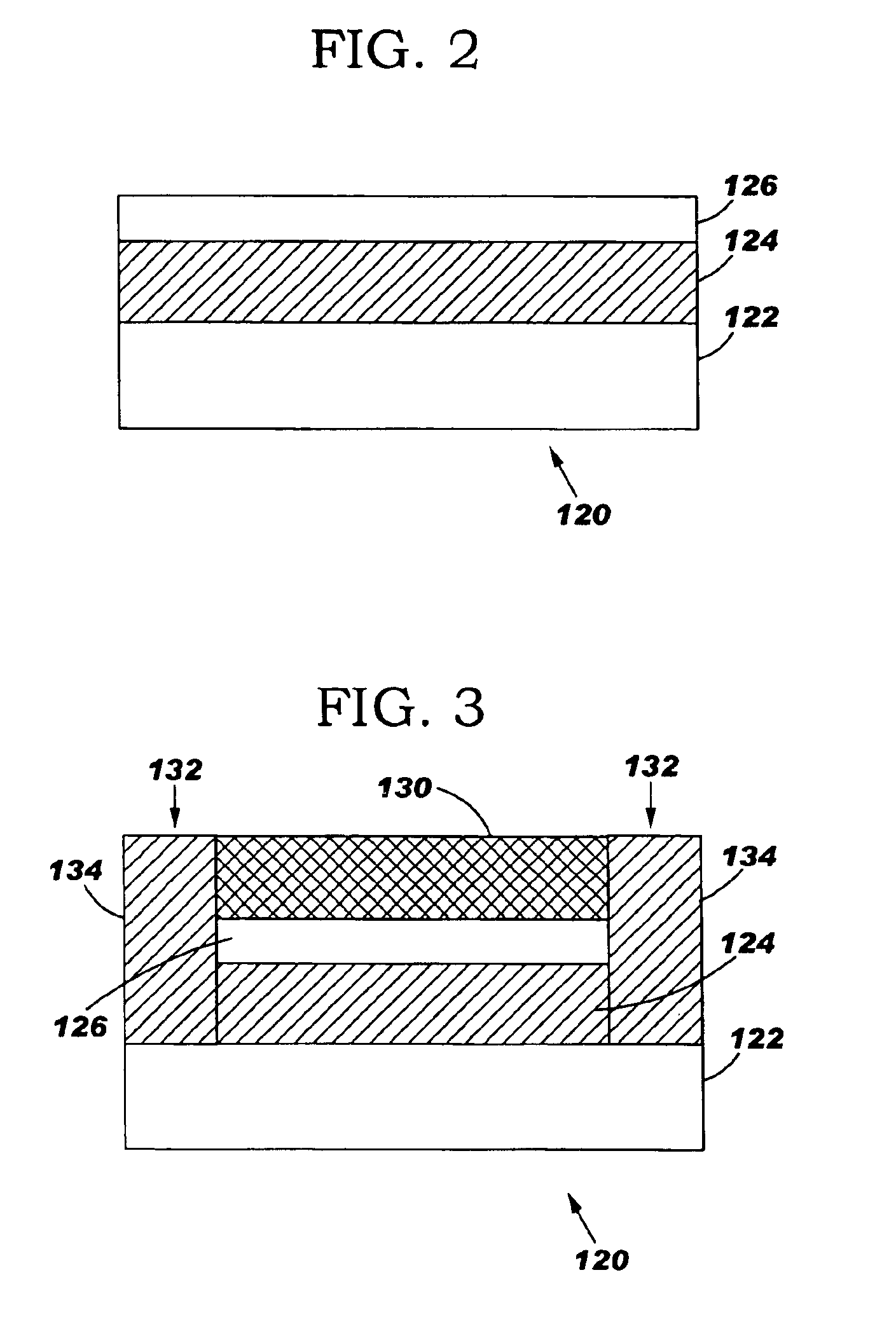
ActiveUS6845198B2Series resistance is minimizedLower optical lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideElectricitySurface layer
A silicon-based electro-optic modulator is based on forming a gate region of a first conductivity to partially overly a body region of a second conductivity type, with a relatively thin dielectric layer interposed between the contiguous portions of the gate and body regions. The modulator may be formed on an SOI platform, with the body region formed in the relatively thin silicon surface layer of the SOI structure and the gate region formed of a relatively thin silicon layer overlying the SOI structure. The doping in the gate and body regions is controlled to form lightly doped regions above and below the dielectric, thus defining the active region of the device. Advantageously, the optical electric field essentially coincides with the free carrier concentration area in this active device region. The application of a modulation signal thus causes the simultaneous accumulation, depletion or inversion of free carriers on both sides of the dielectric at the same time, resulting in high speed operation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
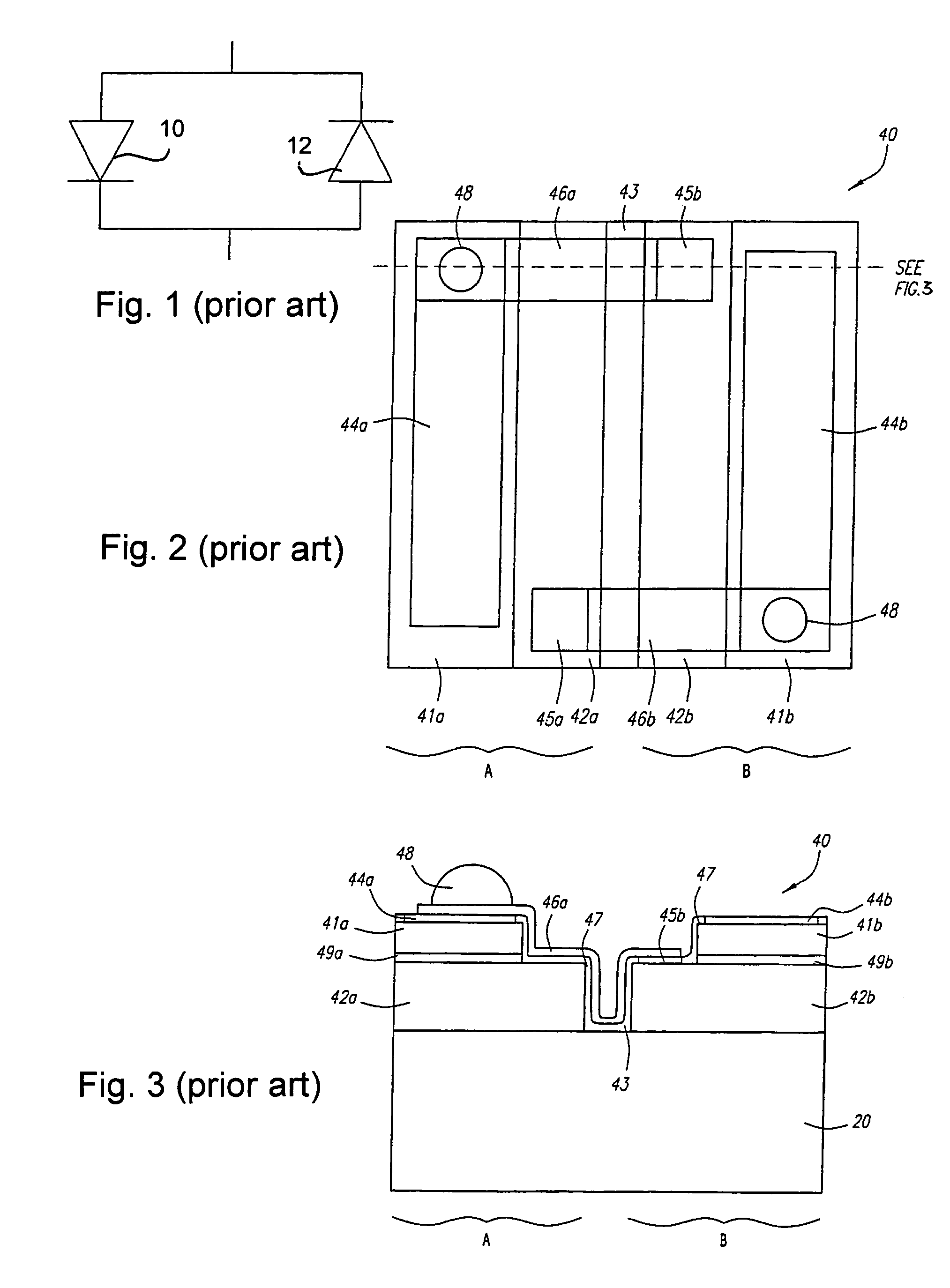
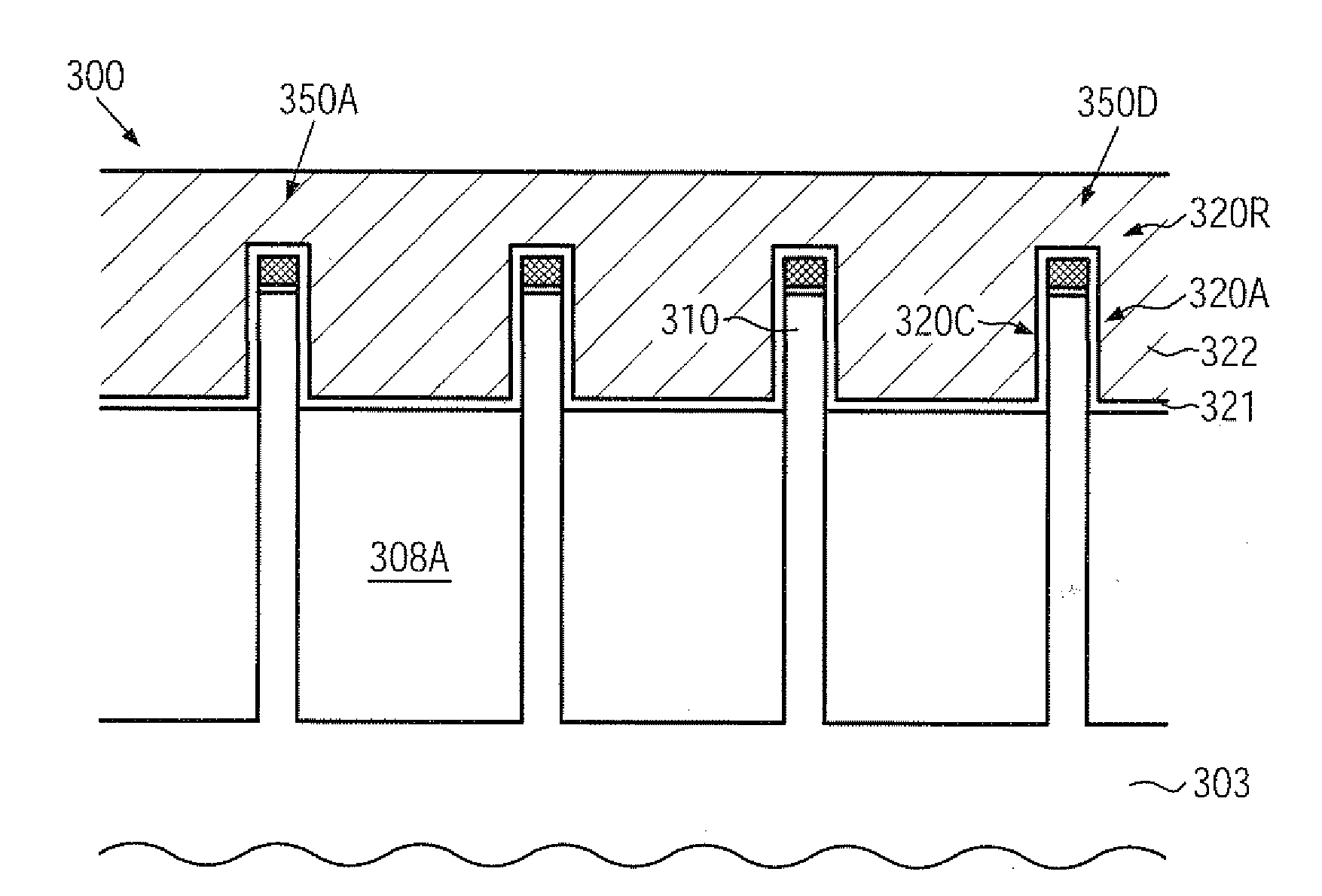
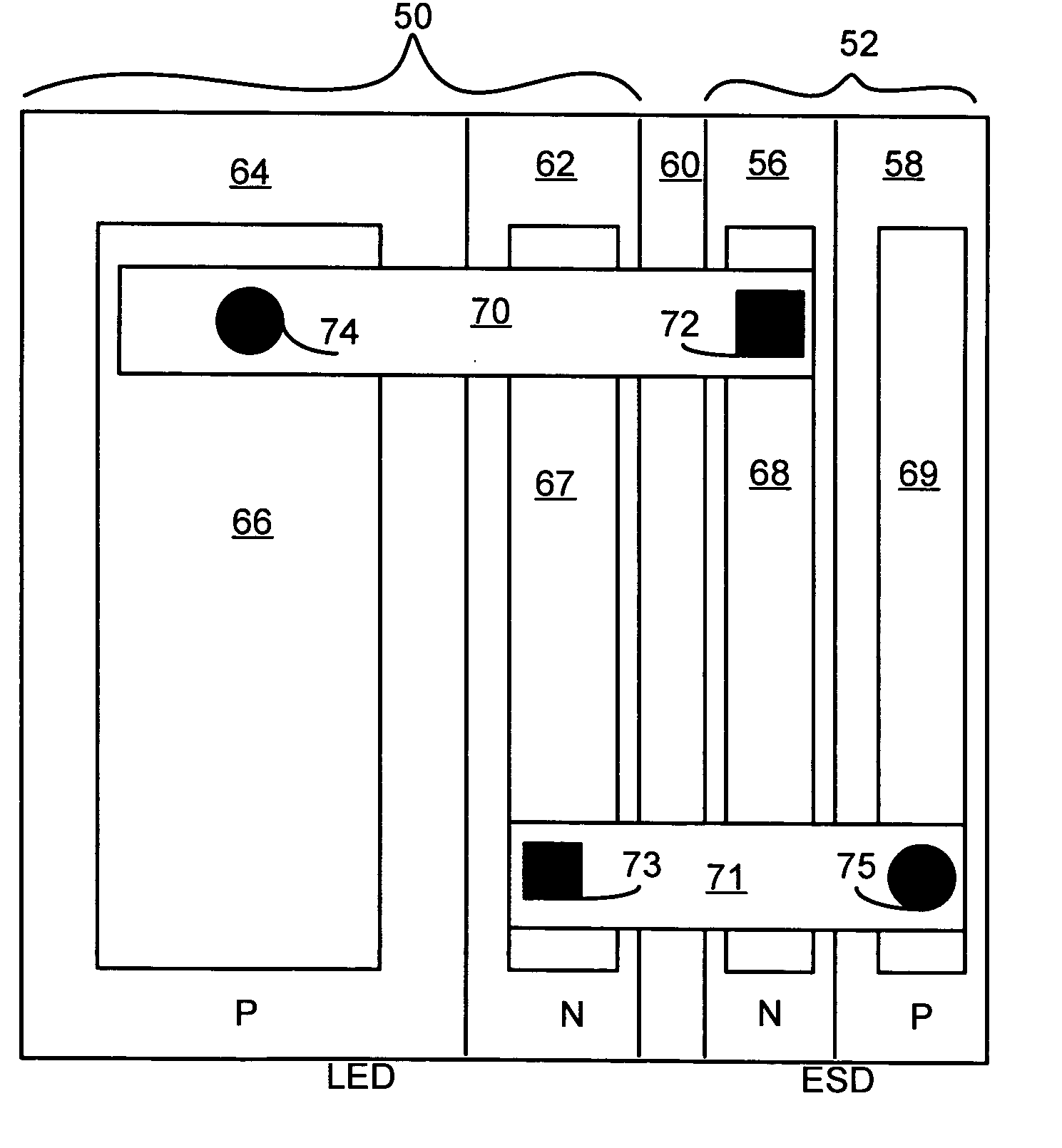
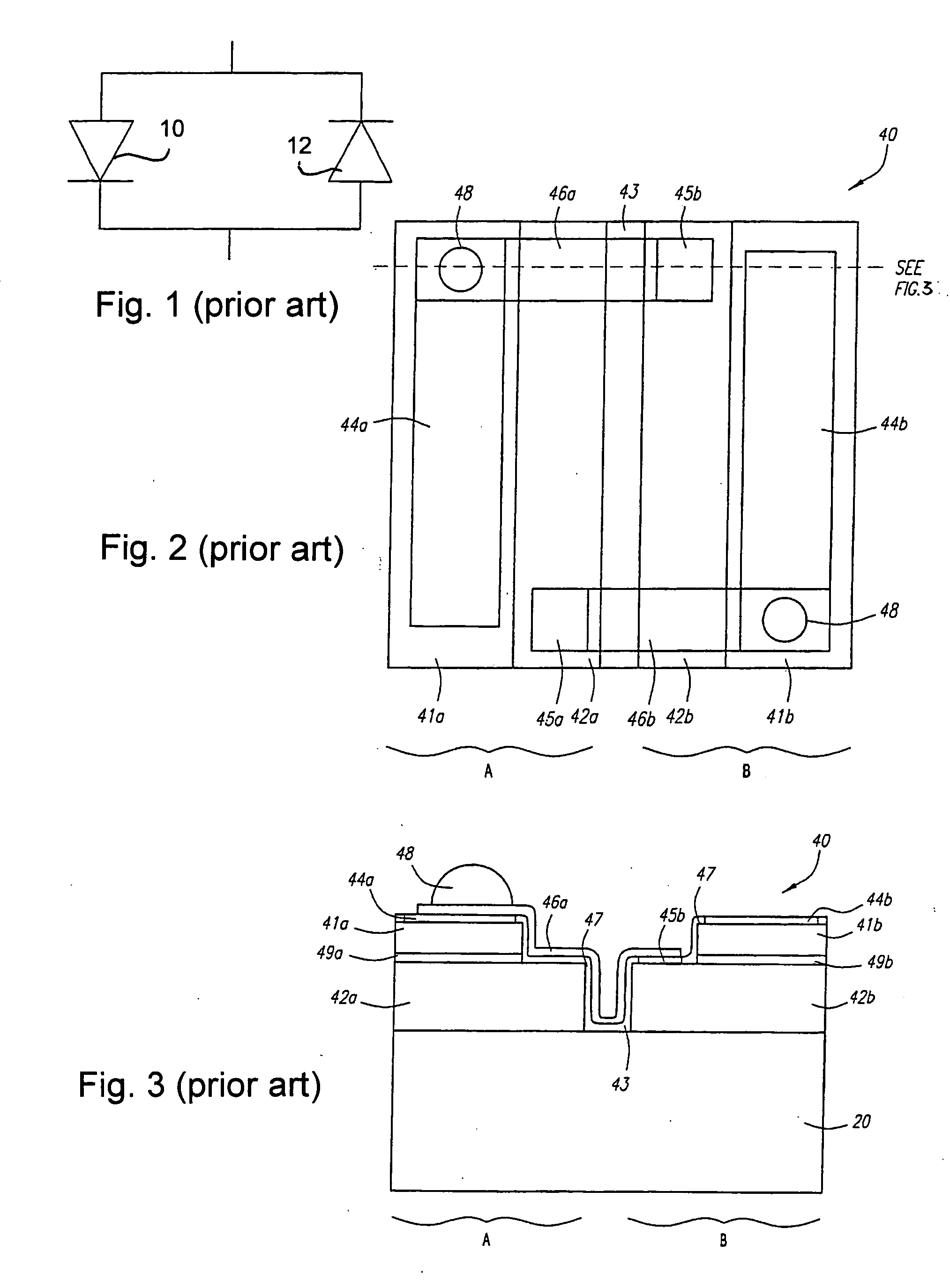
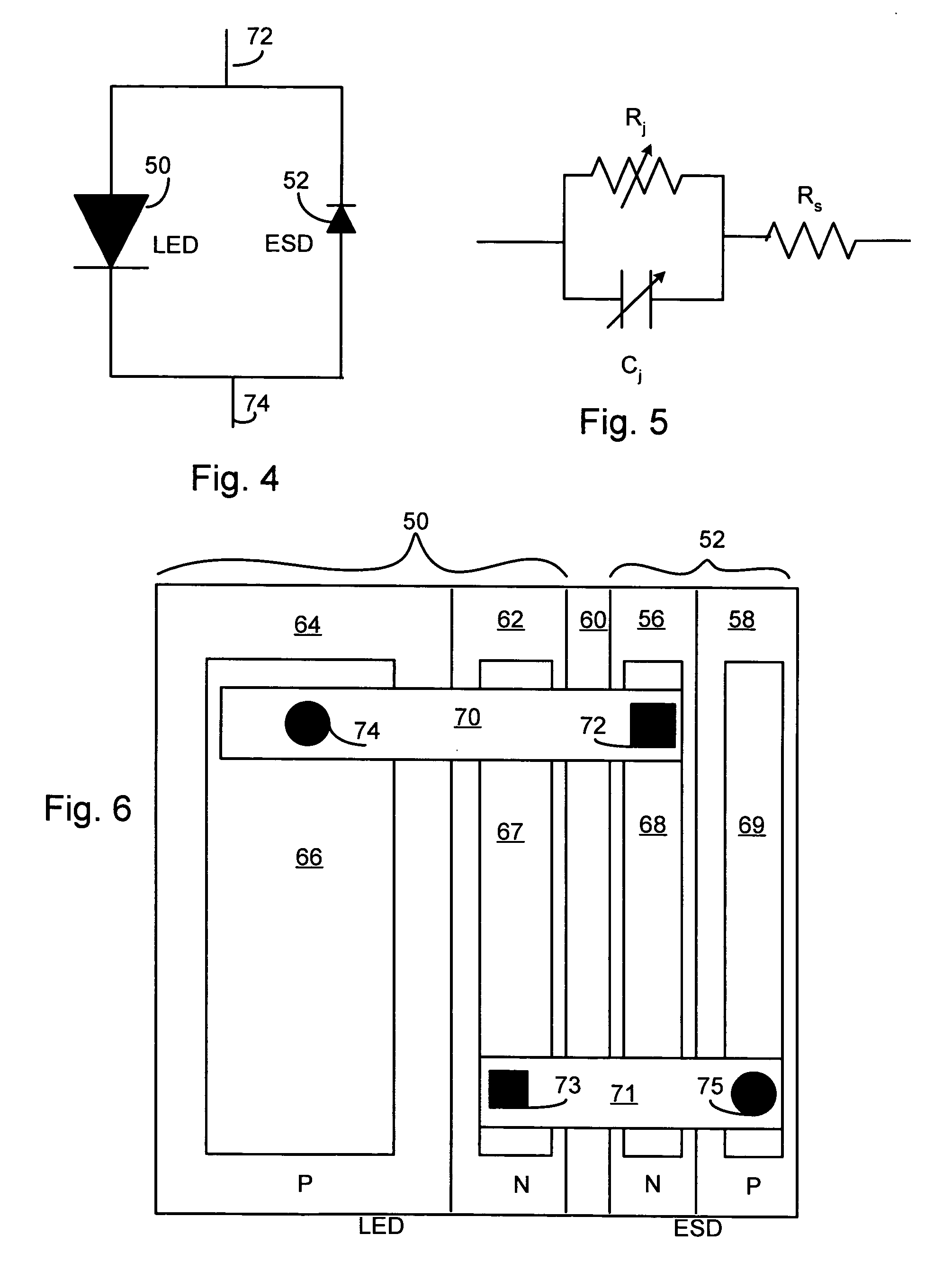
LED chip with integrated fast switching diode for ESD protection
ActiveUS7064353B2Reduced series resistanceIncrease widthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsP–n junction
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV +1
Electrode array for use in electrochemical cells
InactiveUS7368191B2Reduce leakageReduced series resistanceFinal product manufactureFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsEngineering
The invention features an electrode array (7) in which pairs of electrodes (1) are geometrically arranged so that the broadest faces of the exposed electrodes are not directly opposing to each other. Rather, the broadest facing surfaces of the electrodes in the array are parallel, adjacent, or offset at an angle. The electrode geometry of an electrode array of the invention permits electrodes to be in close proximity, thereby lowering series resistance, while minimizing the possibility for short circuits that can cause electrical leakage. An electrode array of the invention can be used in an electrochemical cell, such as a battery, e.g., a lithium battery, a capacitor, a flow-through capacitor, or a fuel cell.
Owner:BIOSOURCE INC
Electrode for photovoltaic cells, photovoltaic cell and photovoltaic module
ActiveUS7432438B2Low production costReduce contact resistancePV power plantsSolid-state devicesAlloyLow melting point
An electrode for contacting an electrically conductive surface of a photovoltaic element includes an electrically insulating optically transparent film, an adhesive layer provided on a planar surface of the film, and a plurality of substantially parallel, electrically conductive wires embedded into the adhesive layer. The plurality of wires lies over the planar surface of the film. A part of the surfaces of the wires protrude from the adhesive layer. At least the part of the surfaces protruding from the adhesive layer are covered by a coating consisting of an alloy having a low melting point to solder the wires to the electrically conductive surface and to a first terminal bar. The adhesive layer has a thickness less that a thickness of the wires embedded therein.
Owner:MEYER BURGER AG
Double gate and tri-gate transistor formed on a bulk substrate and method for forming the transistor
ActiveUS20090321836A1Increased silicon volumeReduced series resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDouble gateEngineering
Three-dimensional transistor structures such as FinFETS and tri-gate transistors may be formed on the basis of an enhanced masking regime, thereby enabling the formation of drain and source areas, the fins and isolation structures in a self-aligned manner within a bulk semiconductor material. After defining the basic fin structures, highly efficient manufacturing techniques of planar transistor configurations may be used, thereby even further enhancing overall performance of the three-dimensional transistor configurations.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
LED chip with integrated fast switching diode for ESD protection
ActiveUS20050274956A1Reduced series resistanceImprove breakdown voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsLight-emitting diode
A relatively small ESD protection diode is formed on the same chip as a light emitting diode. In one embodiment, the ESD diode is a mesa-type diode isolated from the light emitting diode by a trench. To reduce the series resistance of the ESD diode, the PN junction and metal contact to the semiconductor material is made long and expands virtually the width of the chip. Various configurations of the PN junction and the N and P metal contacts for the ESD diode are described for increasing the breakdown voltage and for improved testing.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV +1
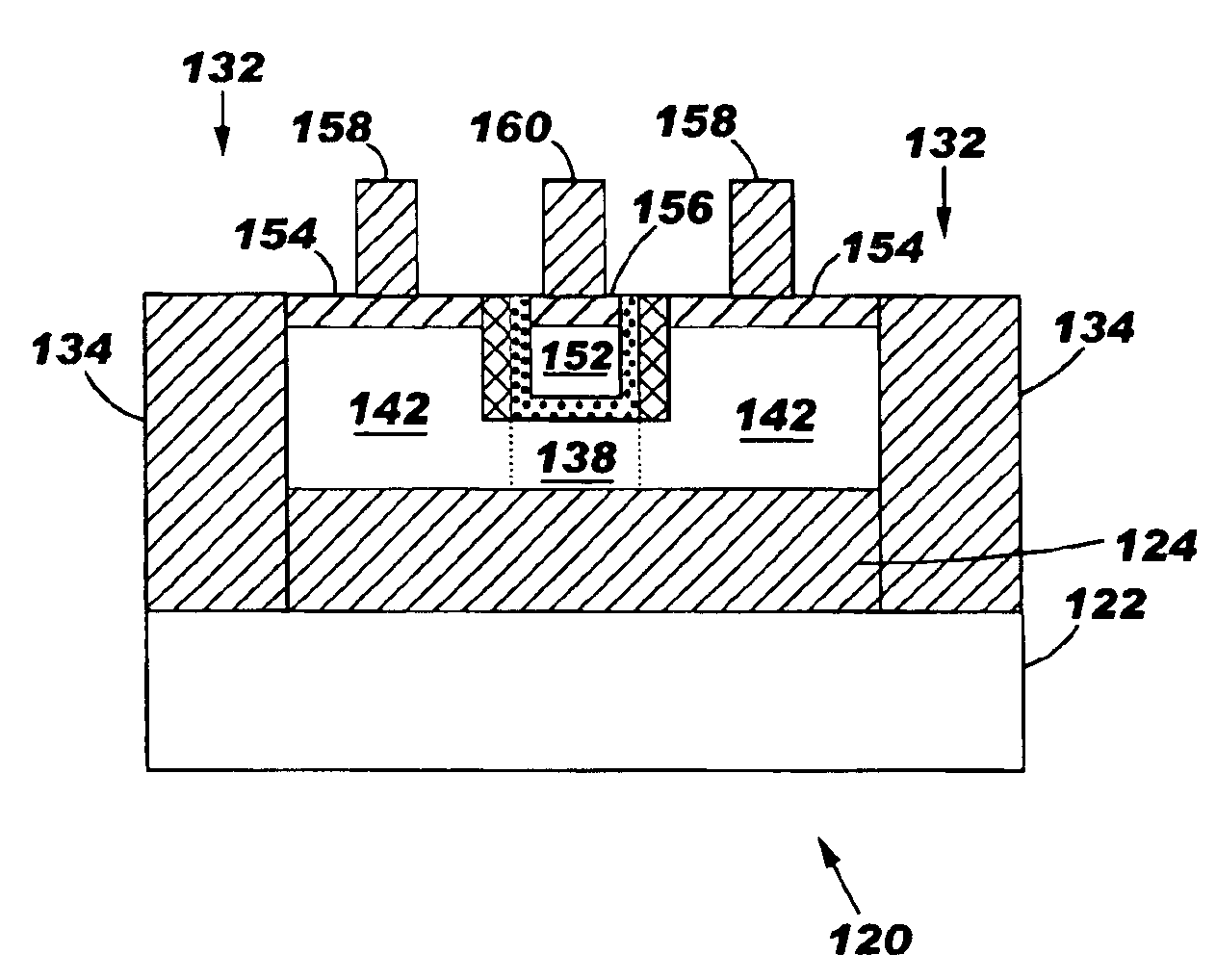
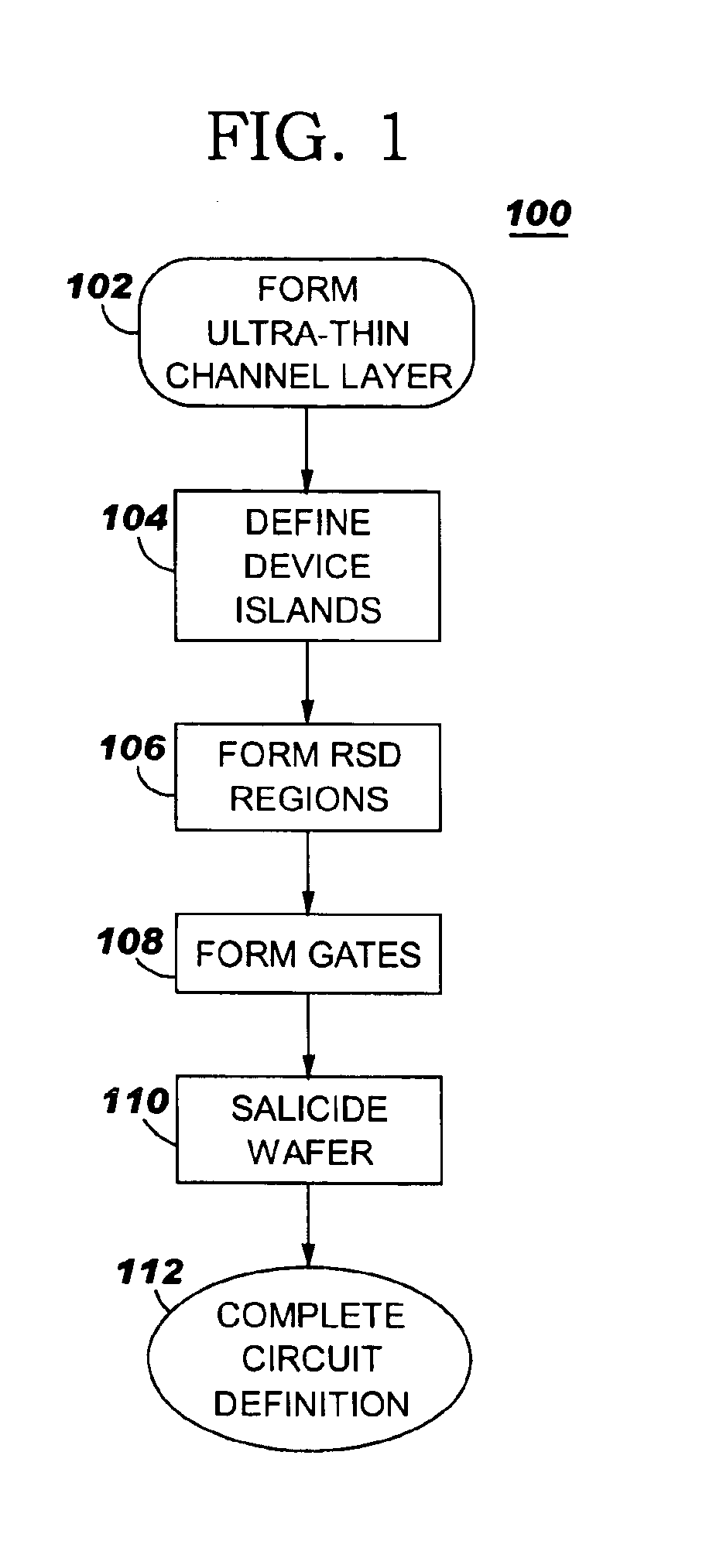
High performance FET with elevated source/drain region
InactiveUS6864540B1Improve field effect transistor (FET) performanceReduce ultra-thin channel FET series resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricSalicide
The invention includes a field effect transistor (FET) on an insulator layer, and integrated circuit (IC) on SOI chip including the FETs and a method of forming the IC. The FETs include a thin channel with raised source / drain (RSD) regions at each end on an insulator layer, e.g., on an ultra-thin silicon on insulator (SOI) chip. Isolation trenches at each end of the FETs, i.e., at the end of the RSD regions, isolate and define FET islands. Insulating sidewalls at each RSD region sandwich the FET gate between the RSD regions. The gate dielectric may be a high K dielectric. Salicide on the RSD regions and, optionally, on the gates reduce device resistances.
Owner:IBM CORP
Photoactive component with organic layers
ActiveUS20070090371A1Reduce recombination lossHigh yieldNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesQuantum yieldTransport layer
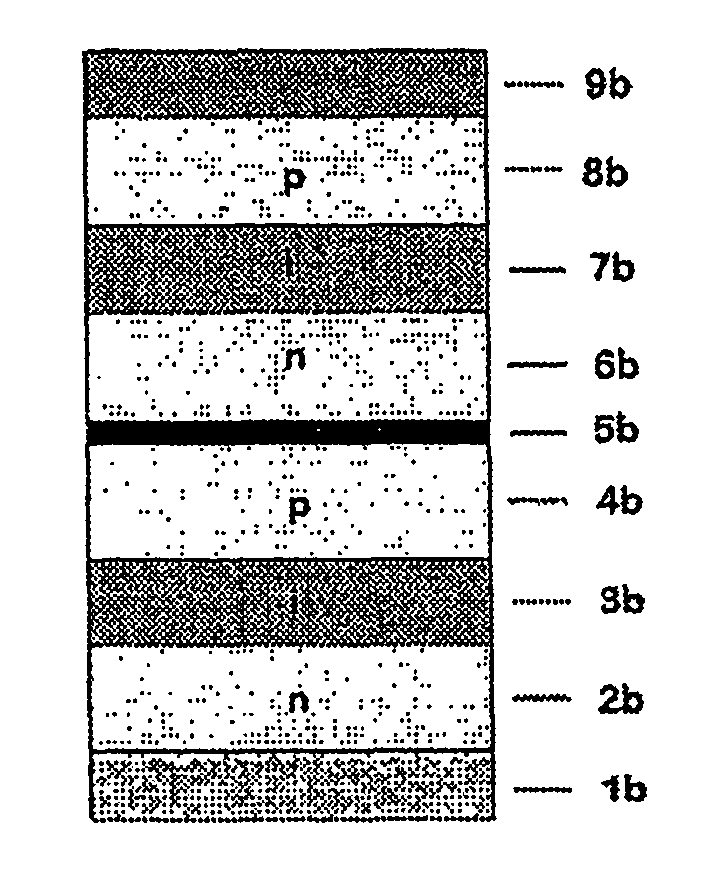
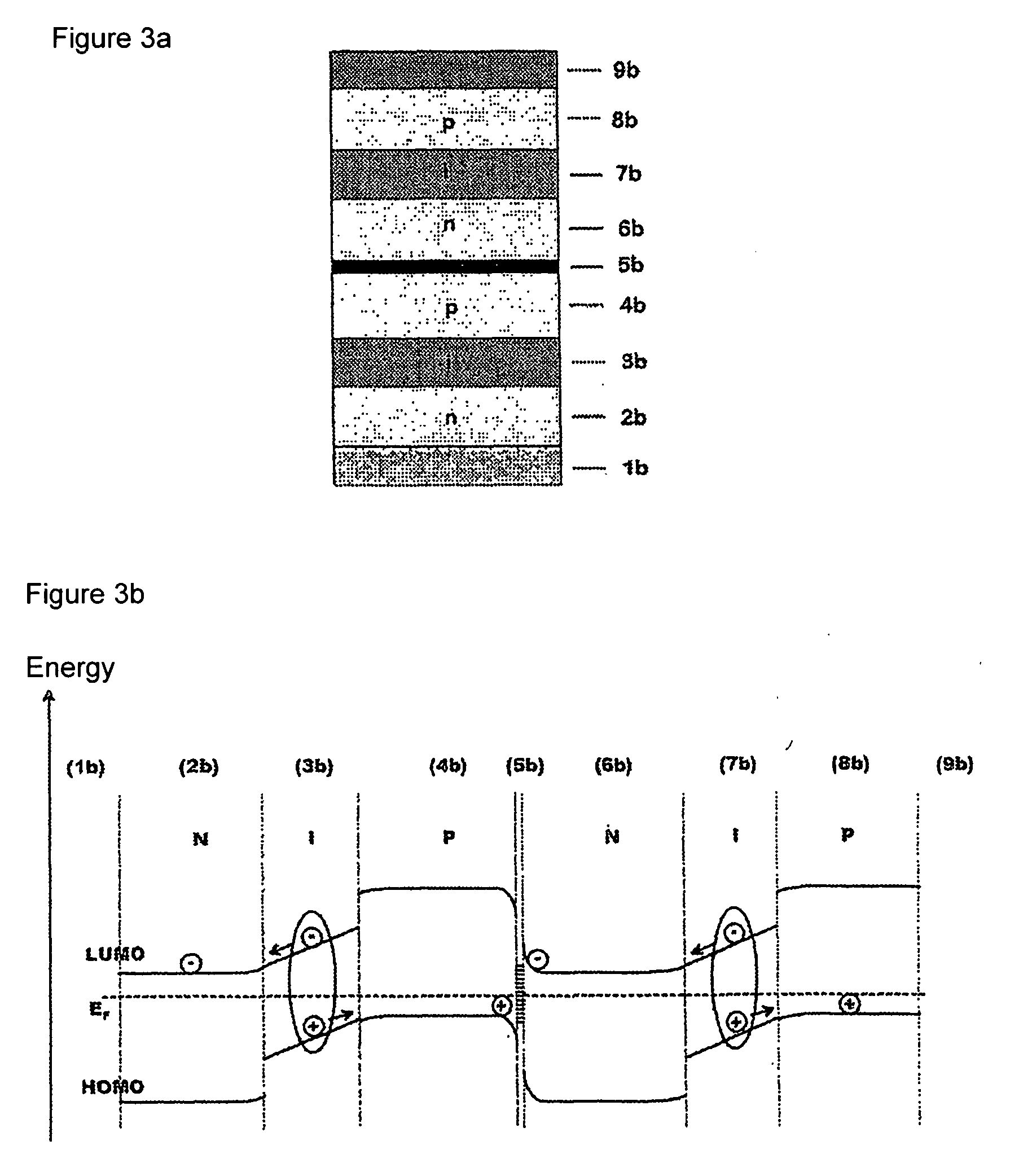
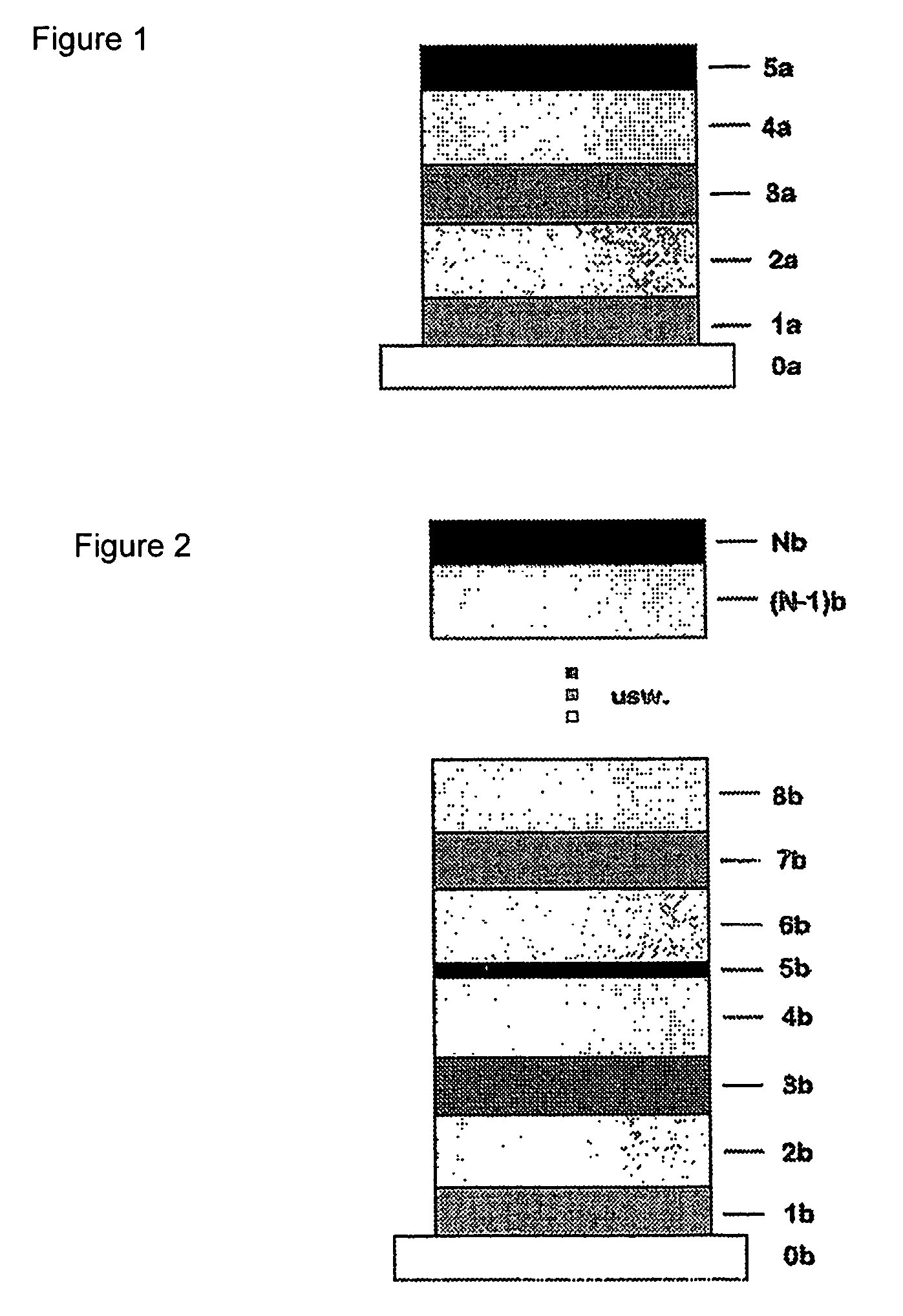
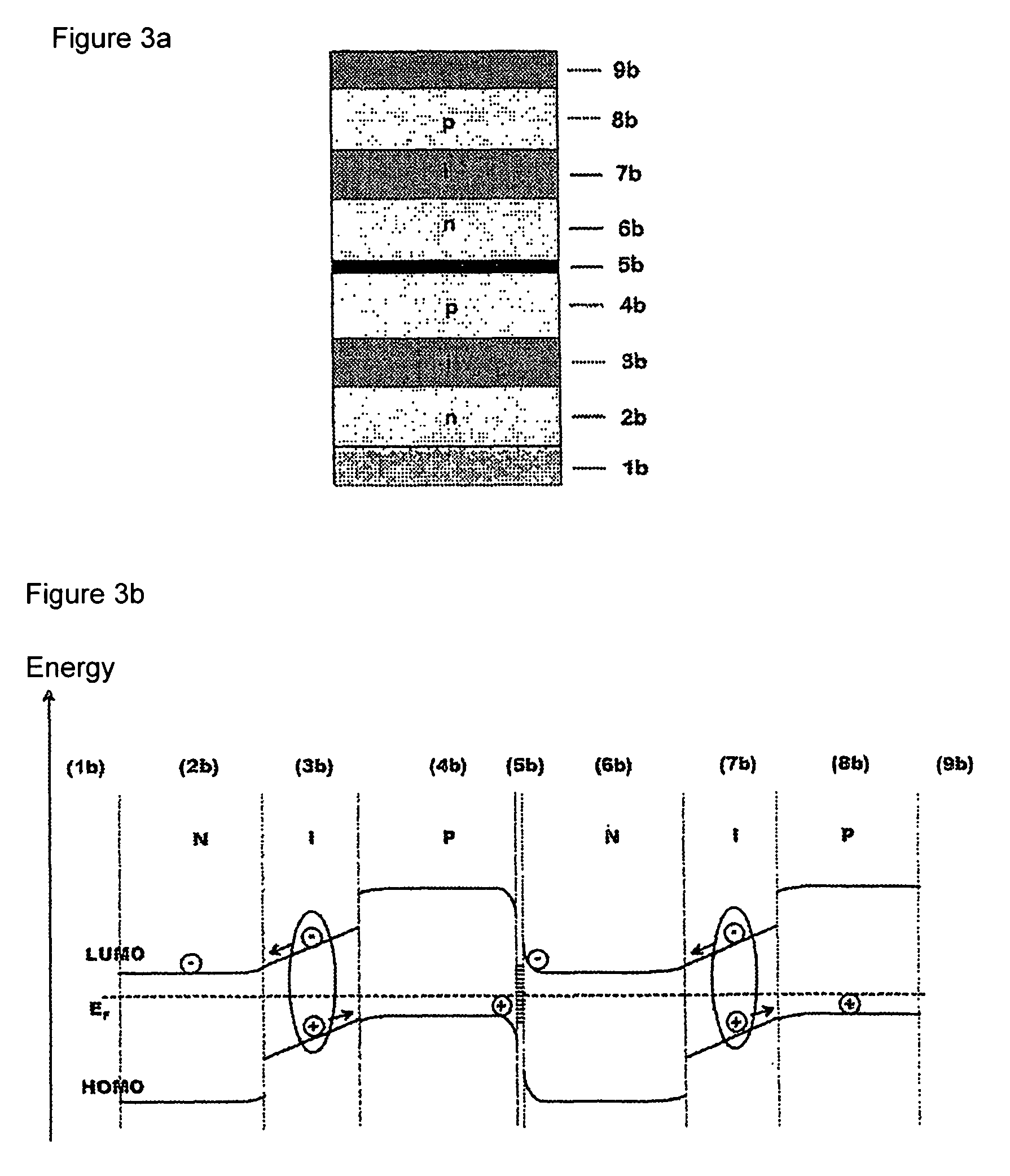
The invention relates to a photoactive component, especially a solar cell, comprising organic layers and formed by at least one stacked pi, ni, and / or pin diode. The diodes are characterised in that they comprise at least one p-doped or n-doped transport layer having a larger optical band gap than that of the photoactive layer. The individual diodes are characterised by a high internal quantum yield, but can be optically thin (peak absorption <80%). A high external quantum yield is obtained by either enlarging the optical path of the incident light in the diodes using light traps, or by stacking a plurality of the diodes. The transition between two diodes being facilitated by transition layers for the purposes of improved recombination and generation. Both forms of embodiment have a number of specific advantages using the doped transport layers with a large band gap.
Owner:HELIATEK GMBH
Flip-chip light emitting diode with resonant optical microcavity
InactiveUS6969874B1Improve efficiencyAccelerate emissionsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDielectric substrateGallium nitride
A flip-chip light emitting diode with enhanced efficiency. The device structure employs a microcavity structure in a flip-chip configuration. The microcavity enhances the light emission in vertical modes, which are readily extracted from the device. Most of the rest of the light is emitted into waveguided lateral modes. Flip-chip configuration is advantageous for light emitting diodes (LEDs) grown on dielectric substrates (e.g., gallium nitride LEDs grown on sapphire substrates) in general due to better thermal dissipation and lower series resistance. Flip-chip configuration is advantageous for microcavity LEDs in particular because (a) one of the reflectors is a high-reflectivity metal ohmic contact that is already part of the flip-chip configuration, and (b) current conduction is only required through a single distributed Bragg reflector. Some of the waveguided lateral modes can also be extracted with angled sidewalls used for the interdigitated contacts in the flip-chip configuration.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Microcavity oled device
ActiveUS20050037232A1Improve luminous efficiencyImproved chromaticity of redIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensDopantMetallic electrode
A microcavity OLED device including a substrate; a metallic bottom-electrode layer disposed over the substrate; a metallic top-electrode layer spaced from the metallic bottom-electrode layer; and an organic EL medium structure having a defined thickness, and including a light-emitting layer comprising a host material and at least one dopant disposed between the top-electrode layer and the bottom-electrode layer; wherein one of the metallic electrode layers is light transmissive and the other one is essentially opaque and reflective; wherein the material for reflective metallic electrode layer includes Ag, Au, Al, or alloys thereof, and the material for the light transmissive metallic electrode layer includes Ag, Au, or alloys thereof. The at least one dopant is selected to generate one of red, green, or blue light in the light-emitting layer. The defined thickness of the EL medium structure is selected so that the microcavity OLED device is tuned for emission of one of red, green, or blue light through the light transmissive electrode layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Drive current increase in transistors by asymmetric amorphization implantation
ActiveUS7855118B2Increased complexityImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDriving currentNon symmetric
By providing a substantially non-damaged semiconductor region between a pre-amorphization region and the gate electrode structure, an increase of series resistance at the drain side during the re-crystallization may be reduced, thereby contributing to overall transistor performance, in particular in the linear operating mode. Thus, symmetric and asymmetric transistor architectures may be achieved with enhanced performance without unduly adding to overall process complexity.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
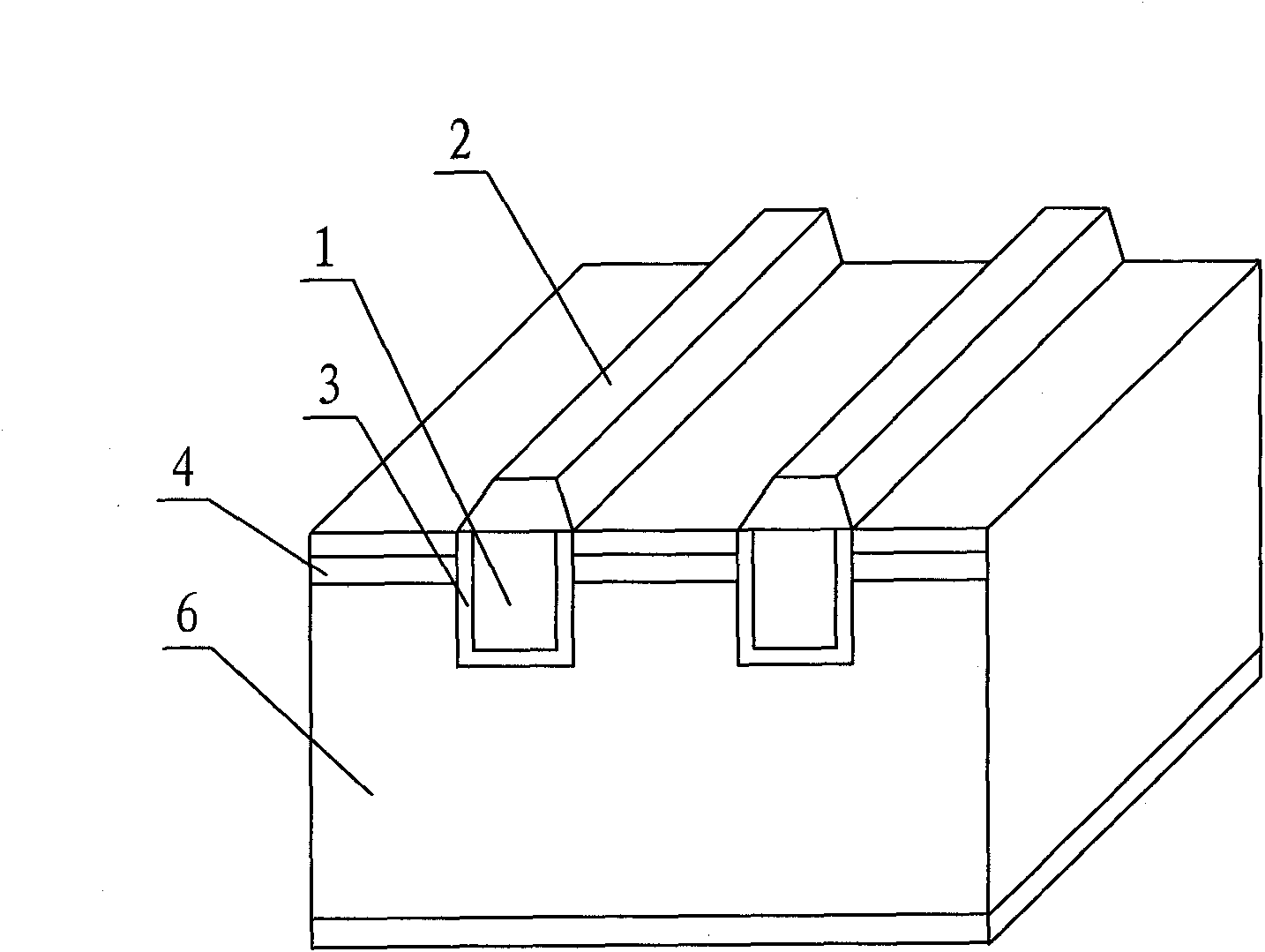
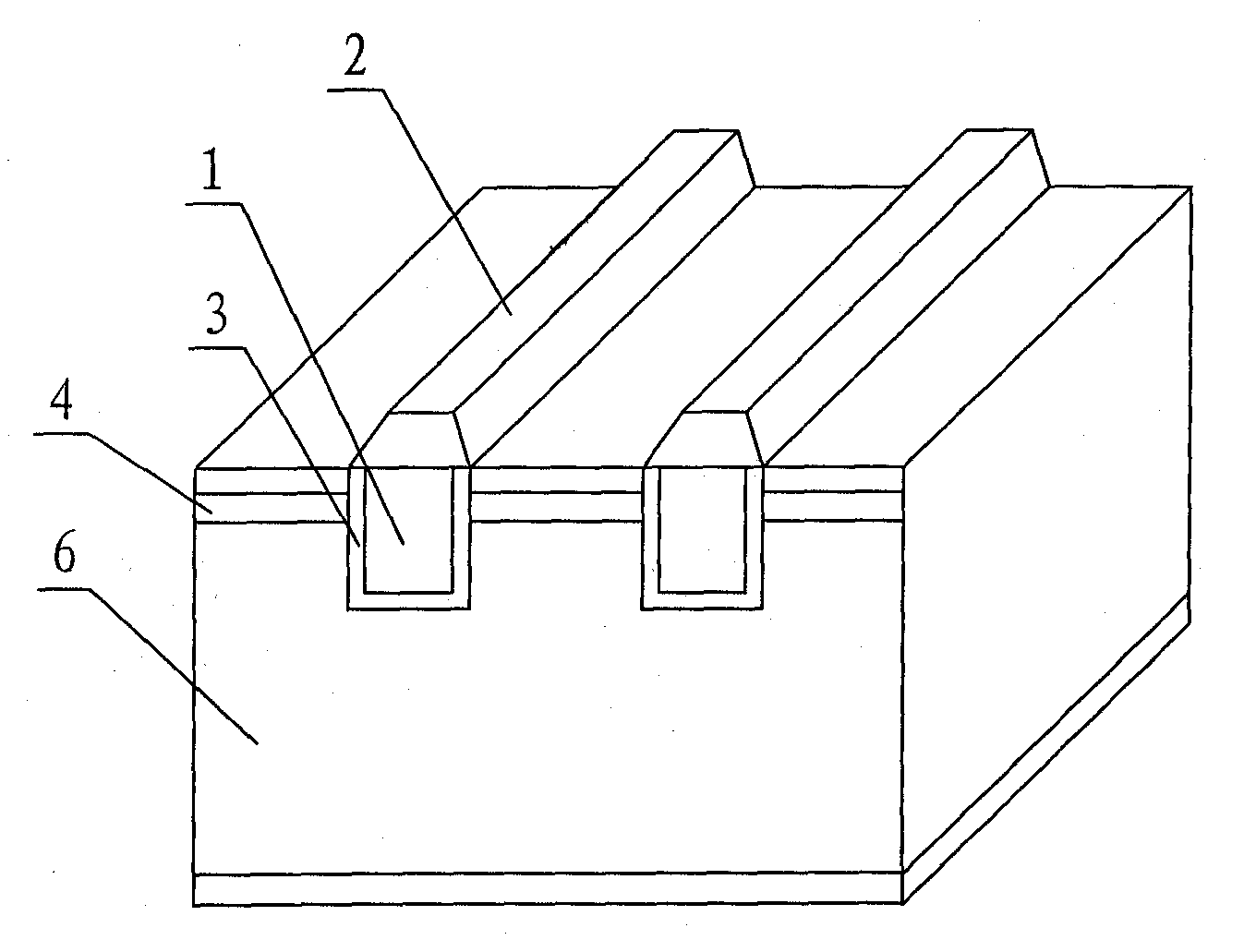
Contacts to semiconductor fin devices
InactiveUS7105894B2Reduce contact resistanceIncrease contact areaTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive materialsEngineering
A method for forming a contact to a semiconductor fin which can be carried out by first providing a semiconductor fin that has a top surface, two sidewall surfaces and at least one end surface; forming an etch stop layer overlying the fin; forming a passivation layer overlying the etch stop layer; forming a contact hole in the passivation layer exposing the etch stop layer; removing the etch stop layer in the contact hole; and filling the contact hole with an electrically conductive material.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Fabrication of back-contacted silicon solar cells using thermomigration to create conductive vias
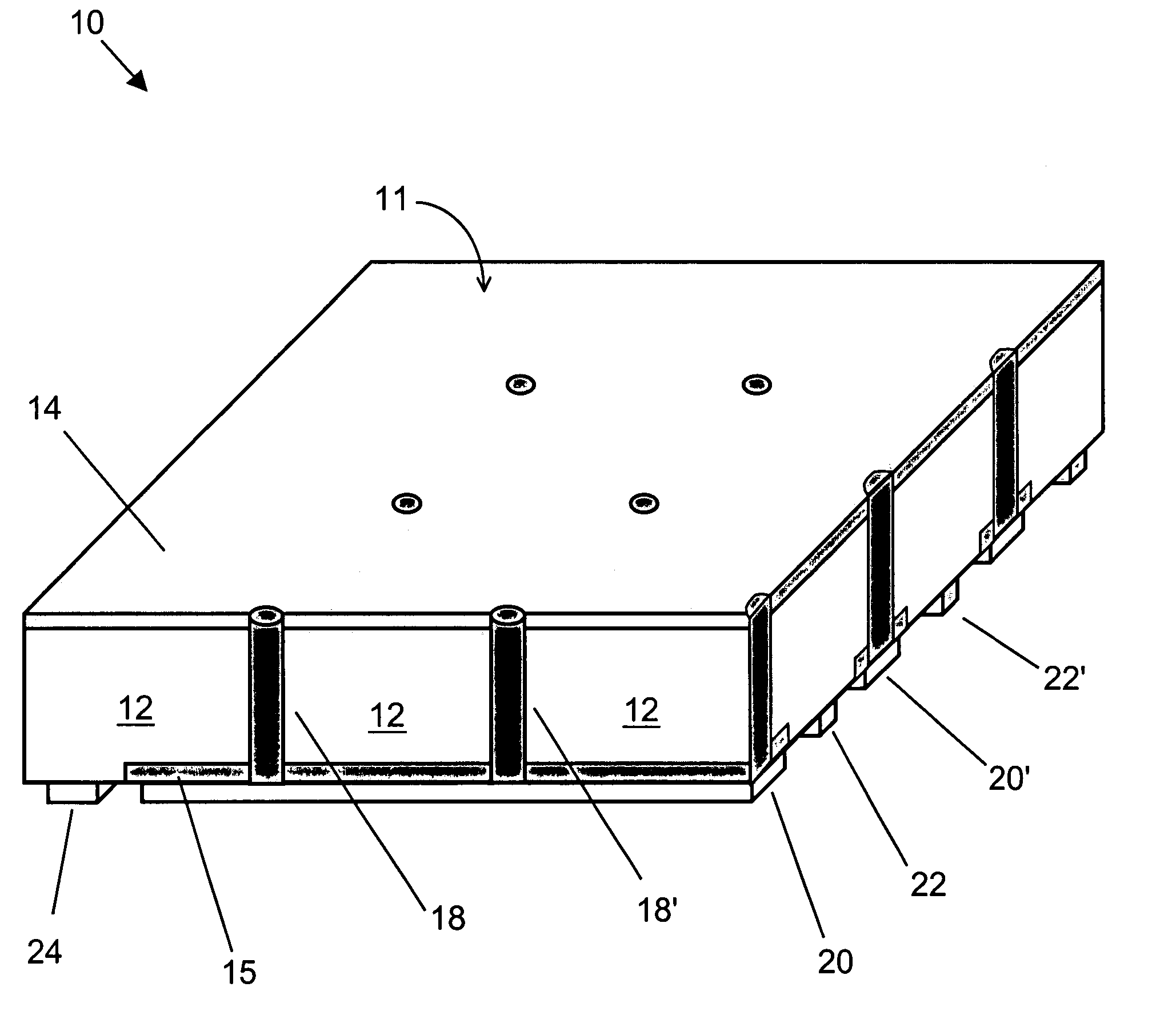
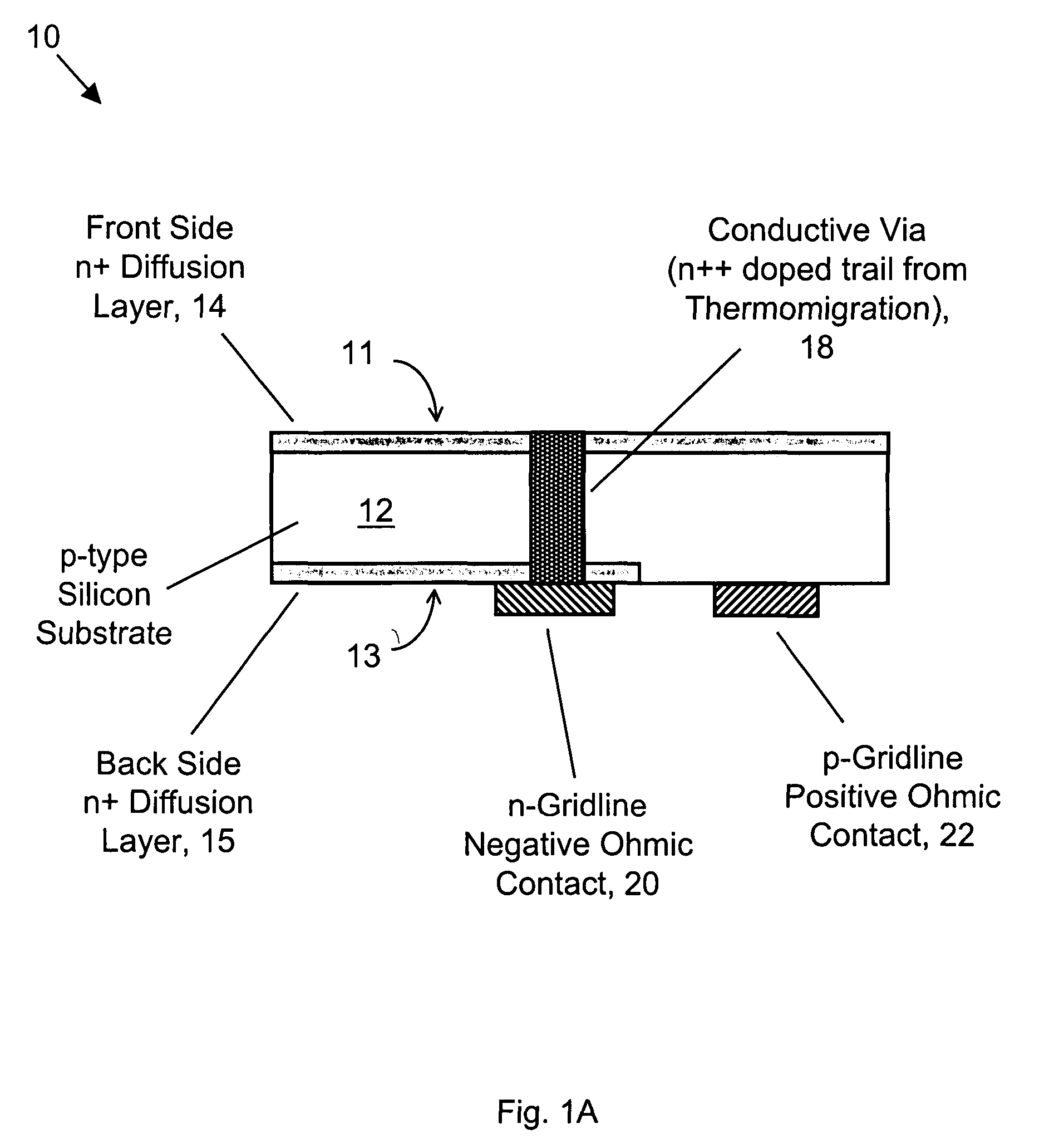
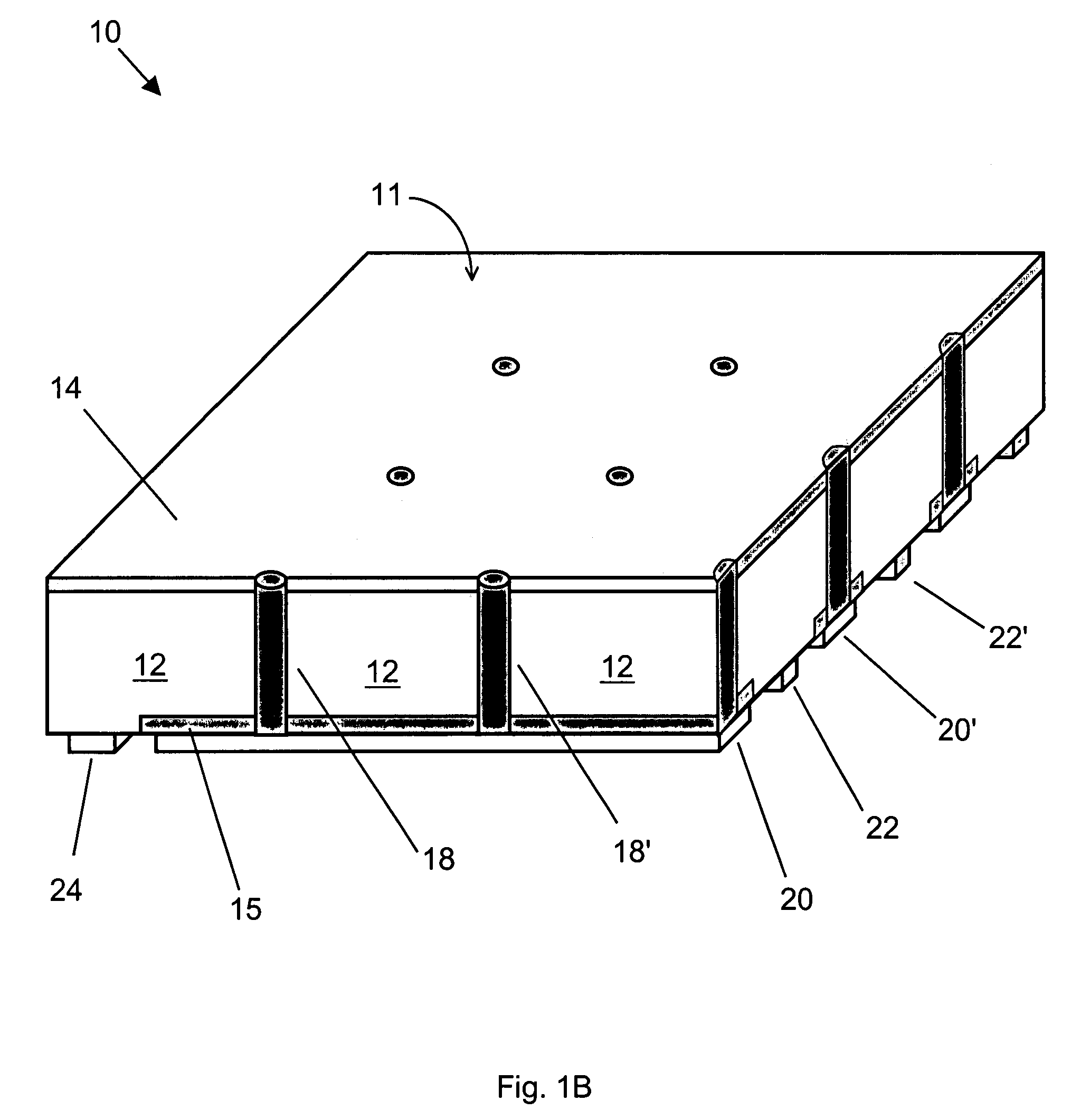
InactiveUS7170001B2Improve conversion efficiencyReduce contact resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationOhmic contactEngineering
Methods of manufacturing back-contacted silicon solar cells fabricated using a gradient-driven solute transport process, such as thermomigration or electromigration, to create n-type conductive vias connecting the n-type emitter layer on the front side to n-type ohmic contacts located on the back side.
Owner:ADVENT SOLAR INC +1
Through-hole vertical semiconductor devices or chips
InactiveUS20080029761A1Improve cooling efficiencyReduced series resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLead bondingEngineering
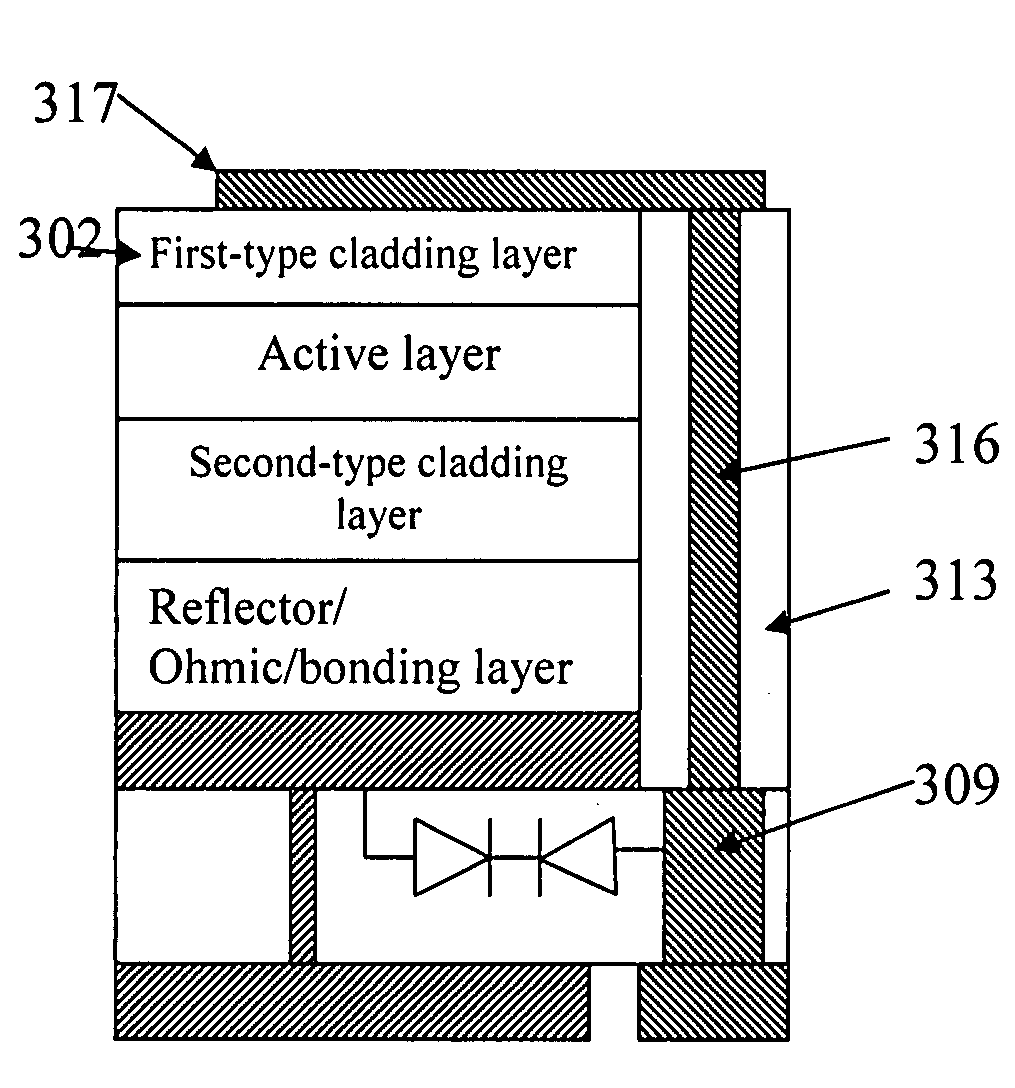
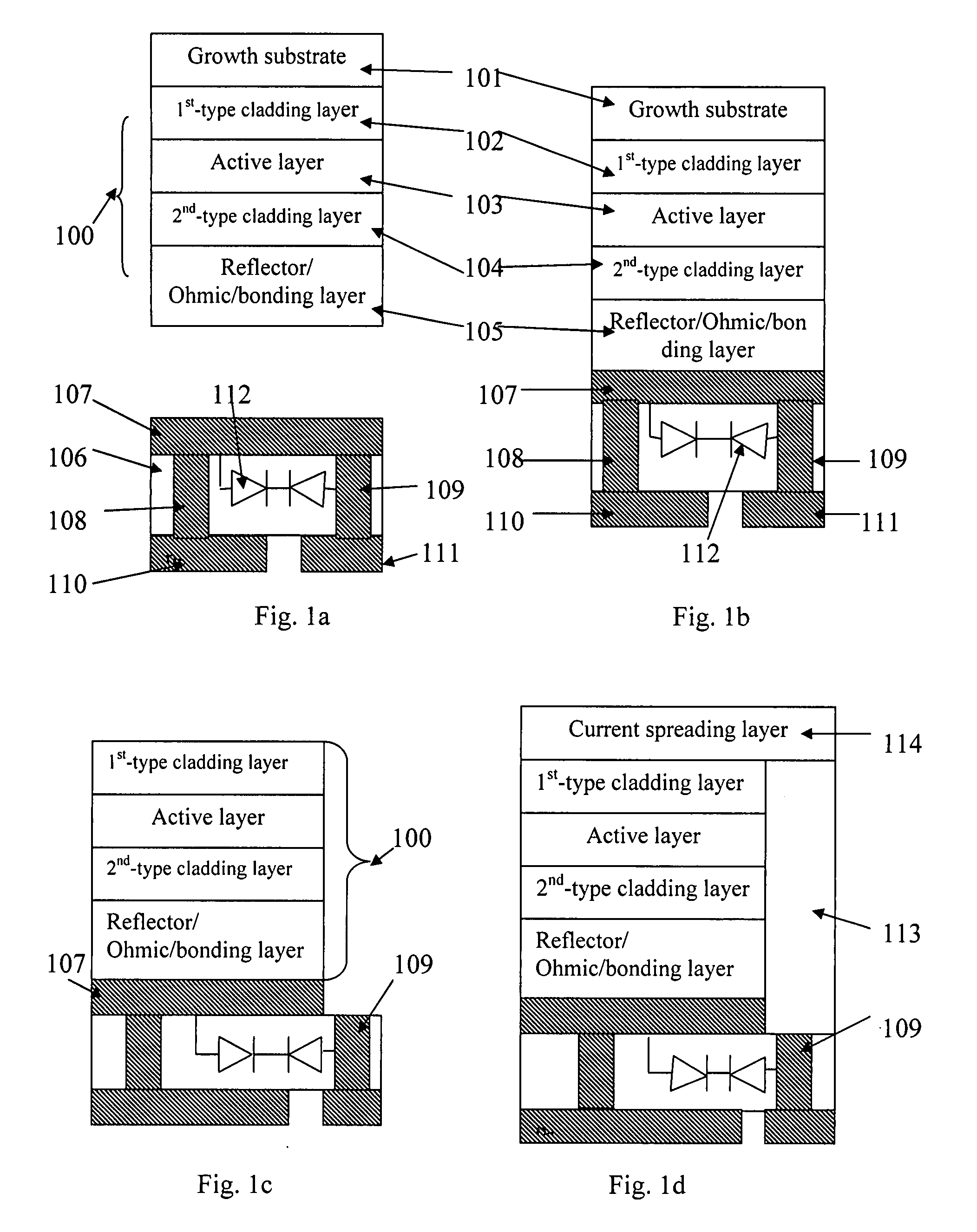
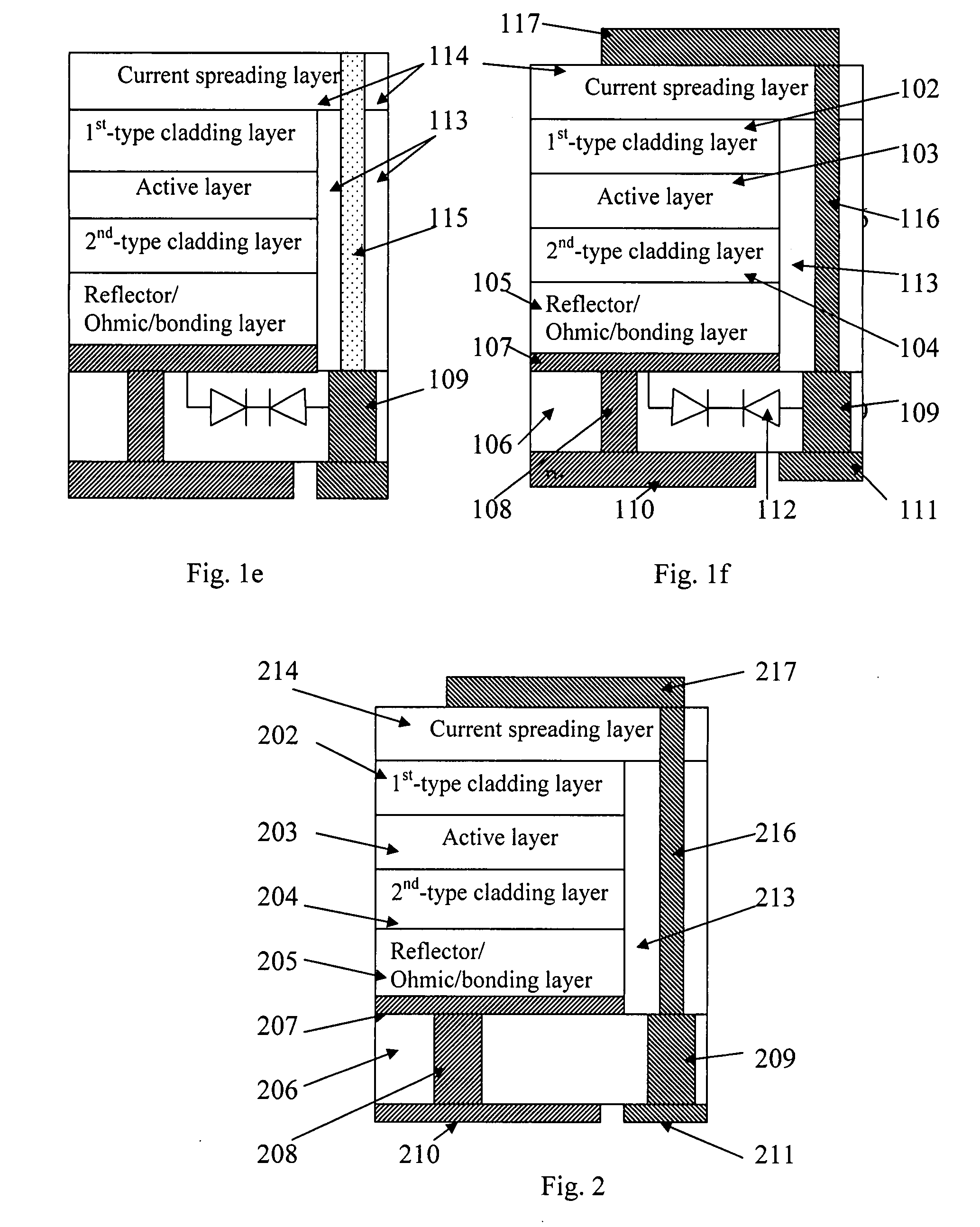
The present invention discloses through-hole vertical semiconductor devices and chips. The structure of an embodiment of through-hole vertical semiconductor devices and chips having static protection diodes is the following: a semiconductor epitaxial layer is bonded to the first surface of a supporting chip with static protection diode; the first-type cladding layer of the semiconductor epitaxial layer is electrically connected to a first electrode on the second surface of the supporting chip via a current spreading layer, a patterned electrode, a half-through-hole-metal-plug and a through-hole-metal-plug; the second-type cladding layer of the semiconductor epitaxial layer is electrically connected to a second electrode on the second surface of the supporting chip via a reflector / Ohmic / bonding layer and at least one through-hole-metal-plug. An external power source is electrically connected to the first and second electrodes without wire bonding.
Owner:JING PENG +2
III-nitride light-emitting device with increased light generating capability
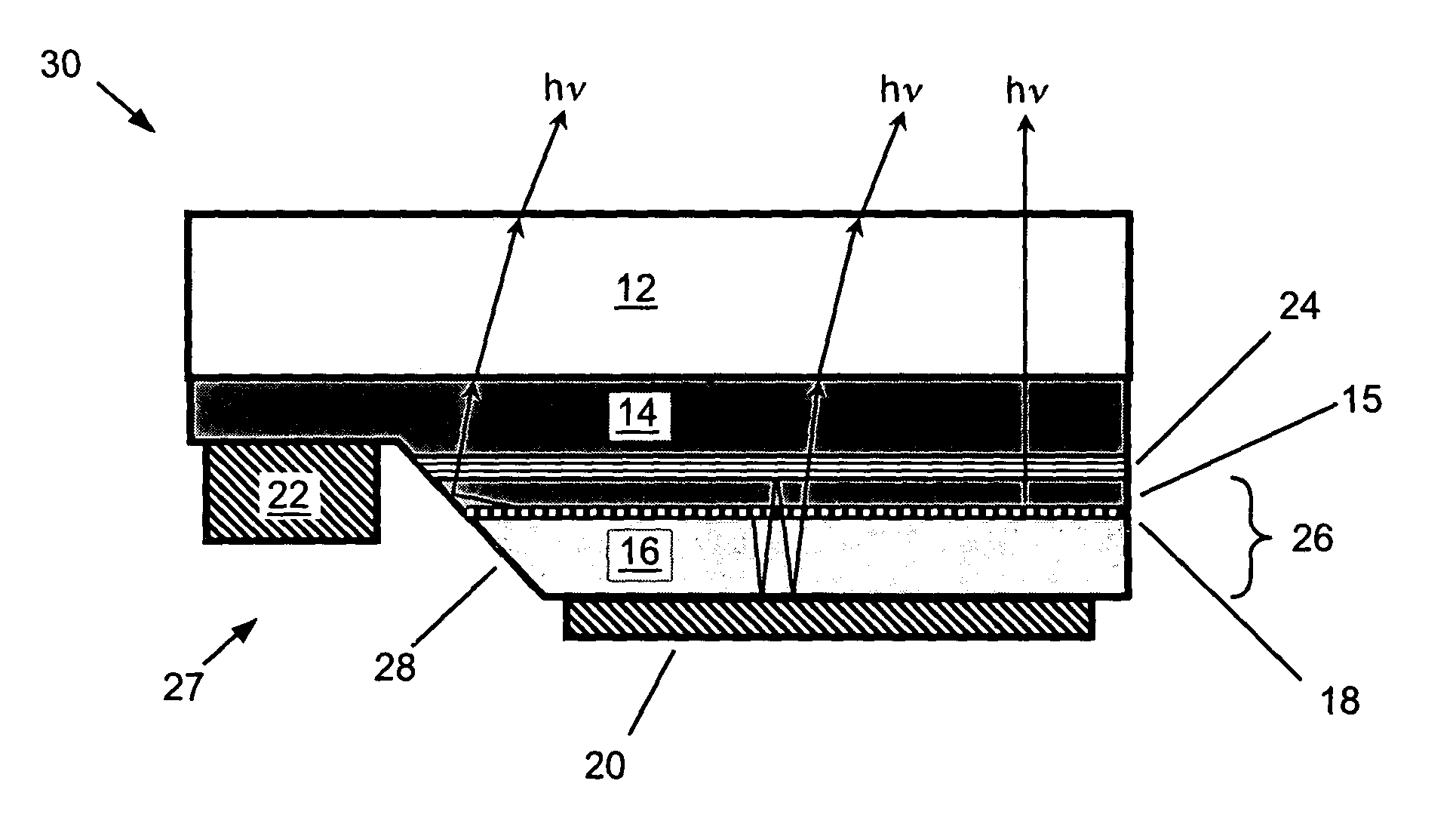
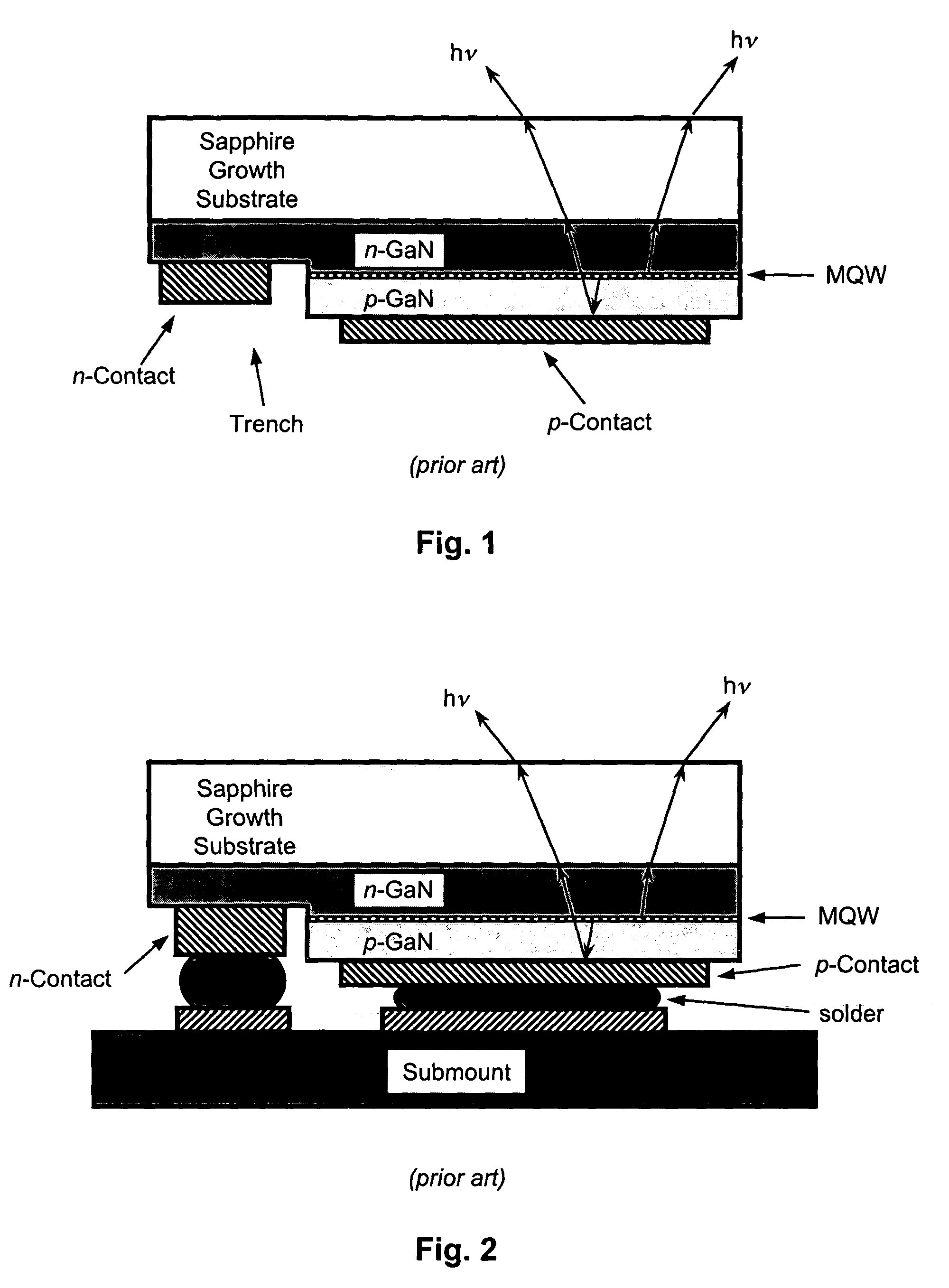
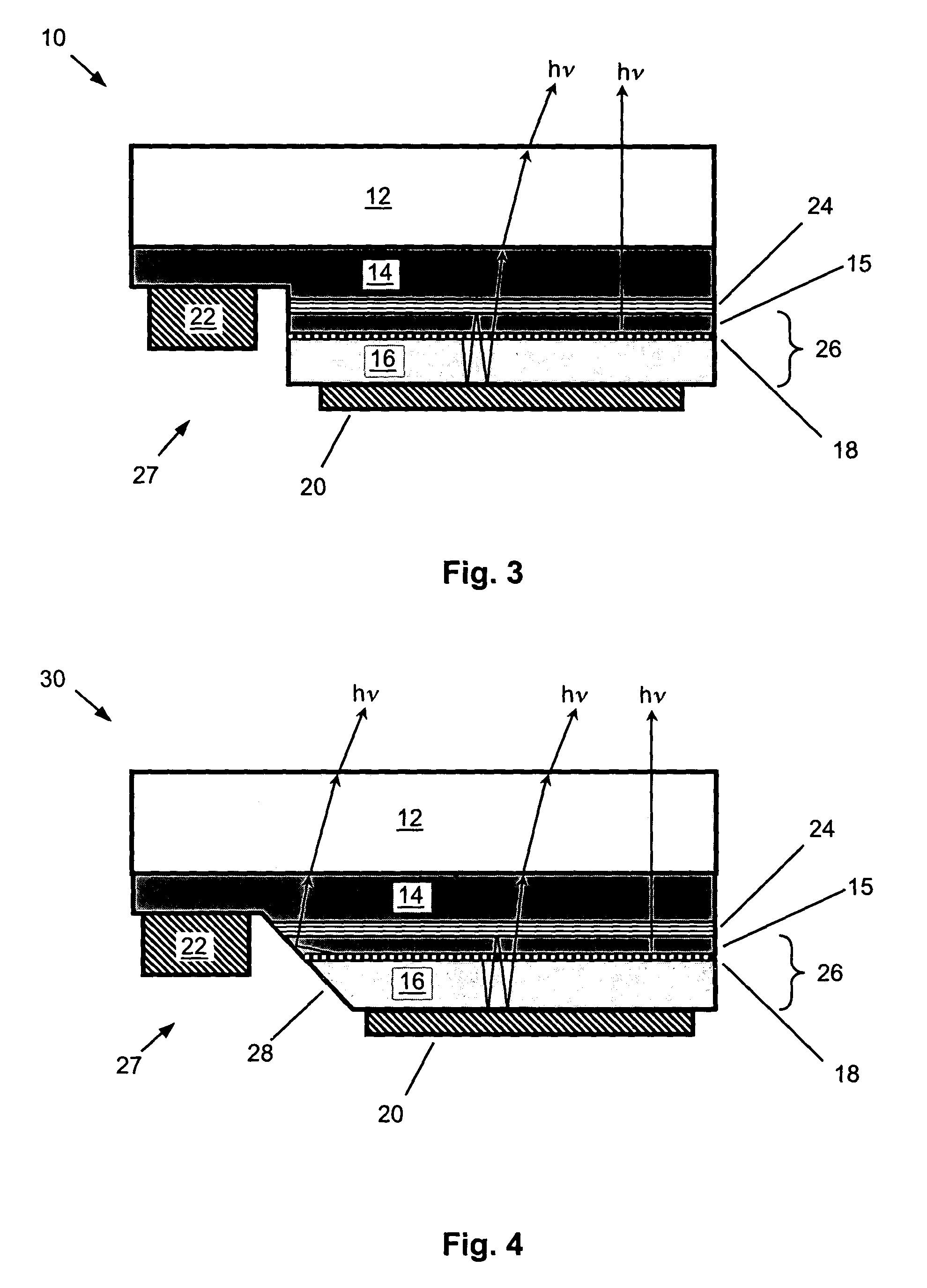
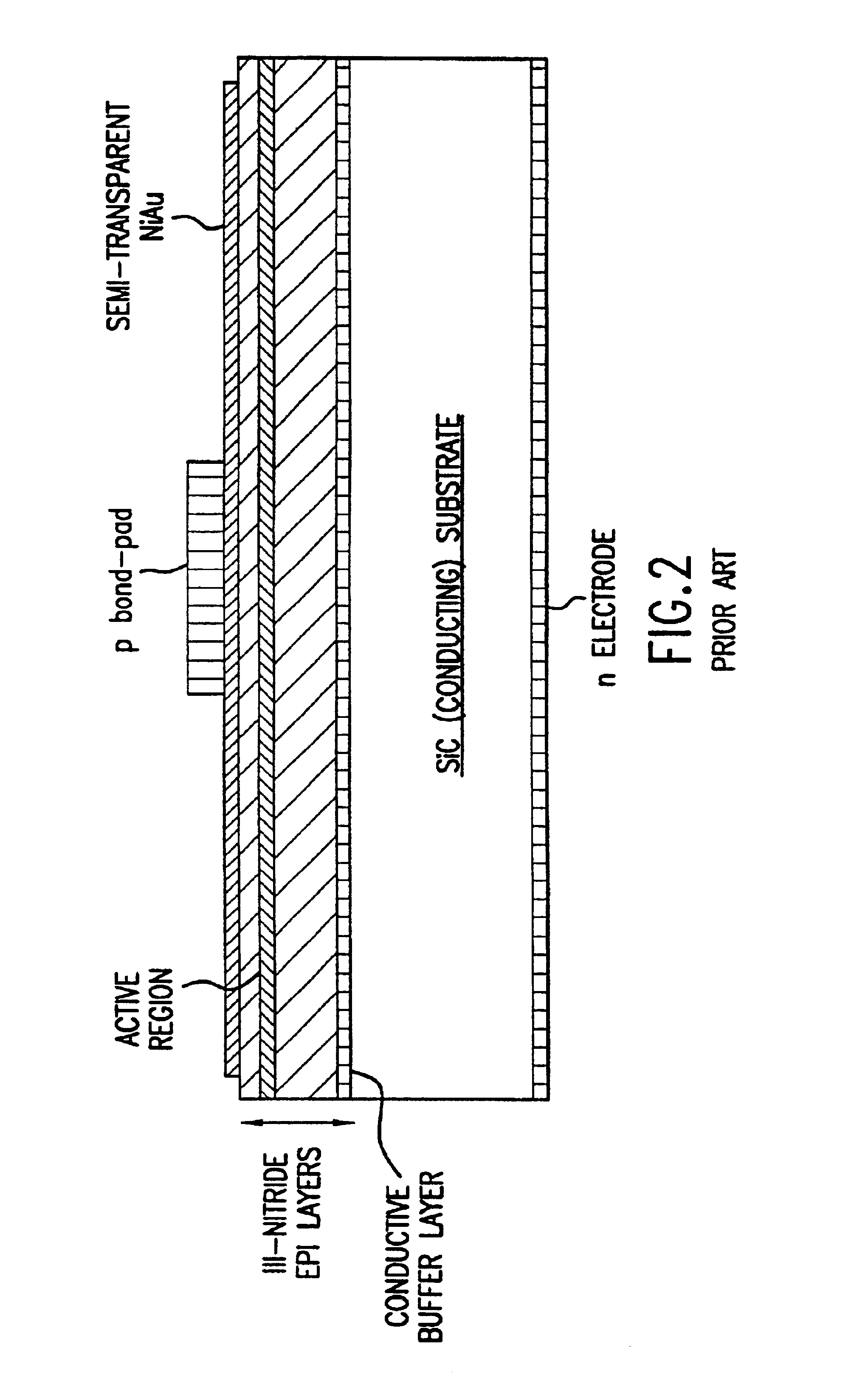
InactiveUS6844571B2Excellent current spreadingLow series resistanceStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesPeak valueElectricity
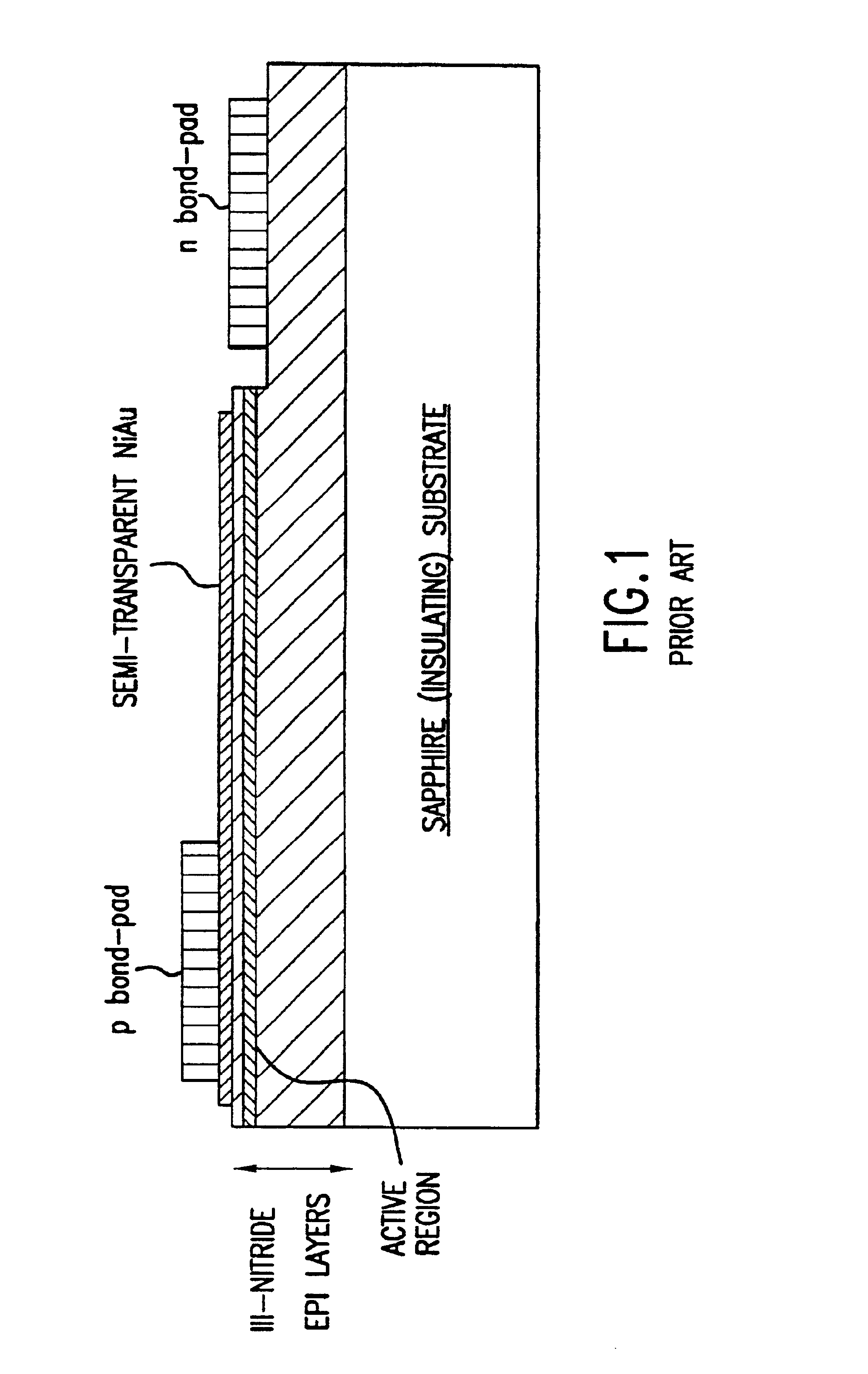
The present invention is an inverted III-nitride light-emitting device (LED) with enhanced total light generating capability. A large area device has an n-electrode that interposes the p-electrode metallization to provide low series resistance. The p-electrode metallization is opaque, highly reflective, and provides excellent current spreading. The p-electrode at the peak emission wavelength of the LED active region absorbs less than 25% of incident light per pass. A submount may be used to provide electrical and thermal connection between the LED die and the package. The submount material may be Si to provide electronic functionality such as voltage-compliance limiting operation. The entire device, including the LED-submount interface, is designed for low thermal resistance to allow for high current density operation. Finally, the device may include a high-refractive-index (n>1.8) superstrate.
Owner:LUMILEDS +1
Field effect transistor
ActiveUS20080258243A1Suppress generationReduced series resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringField effect
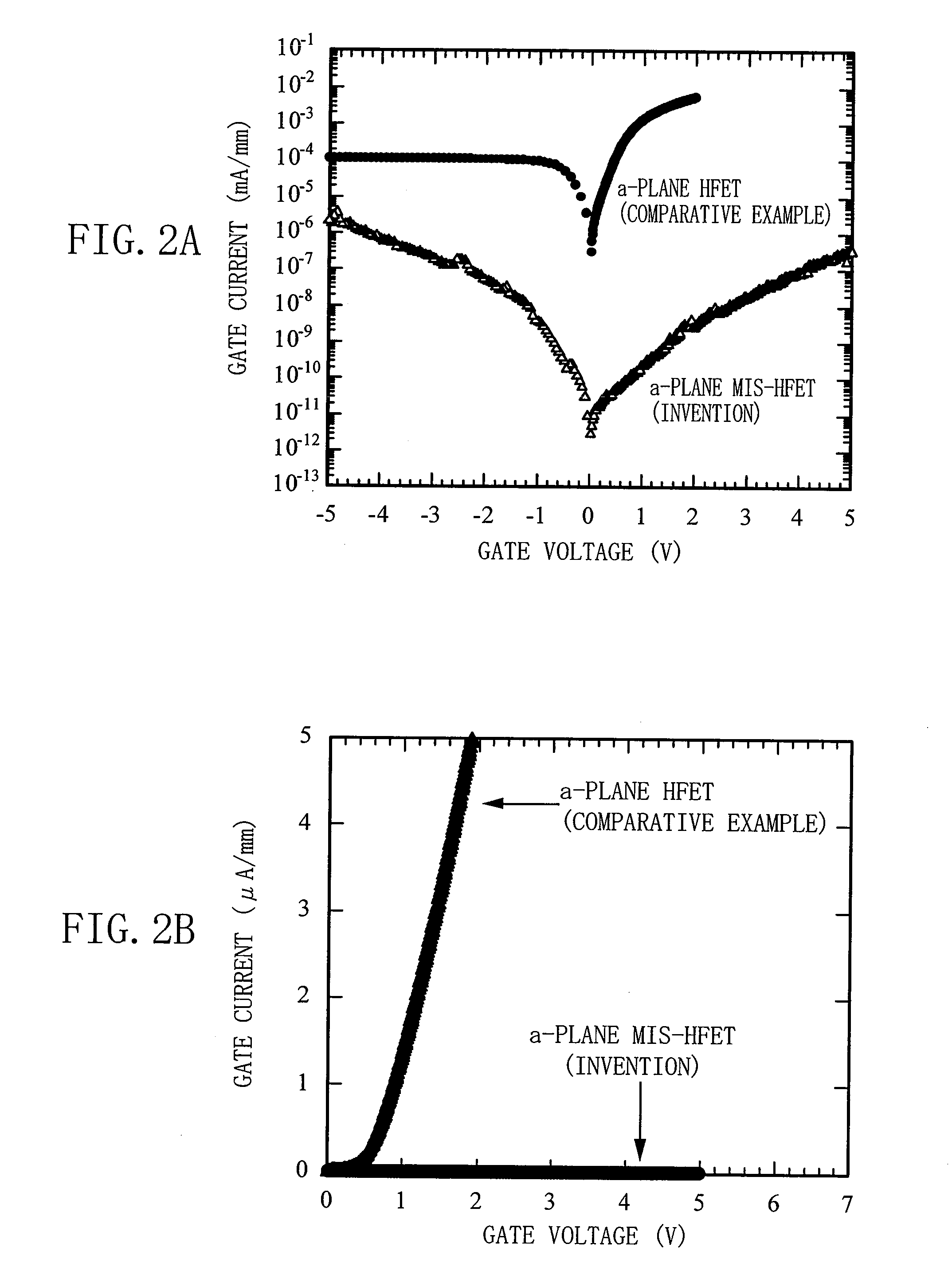
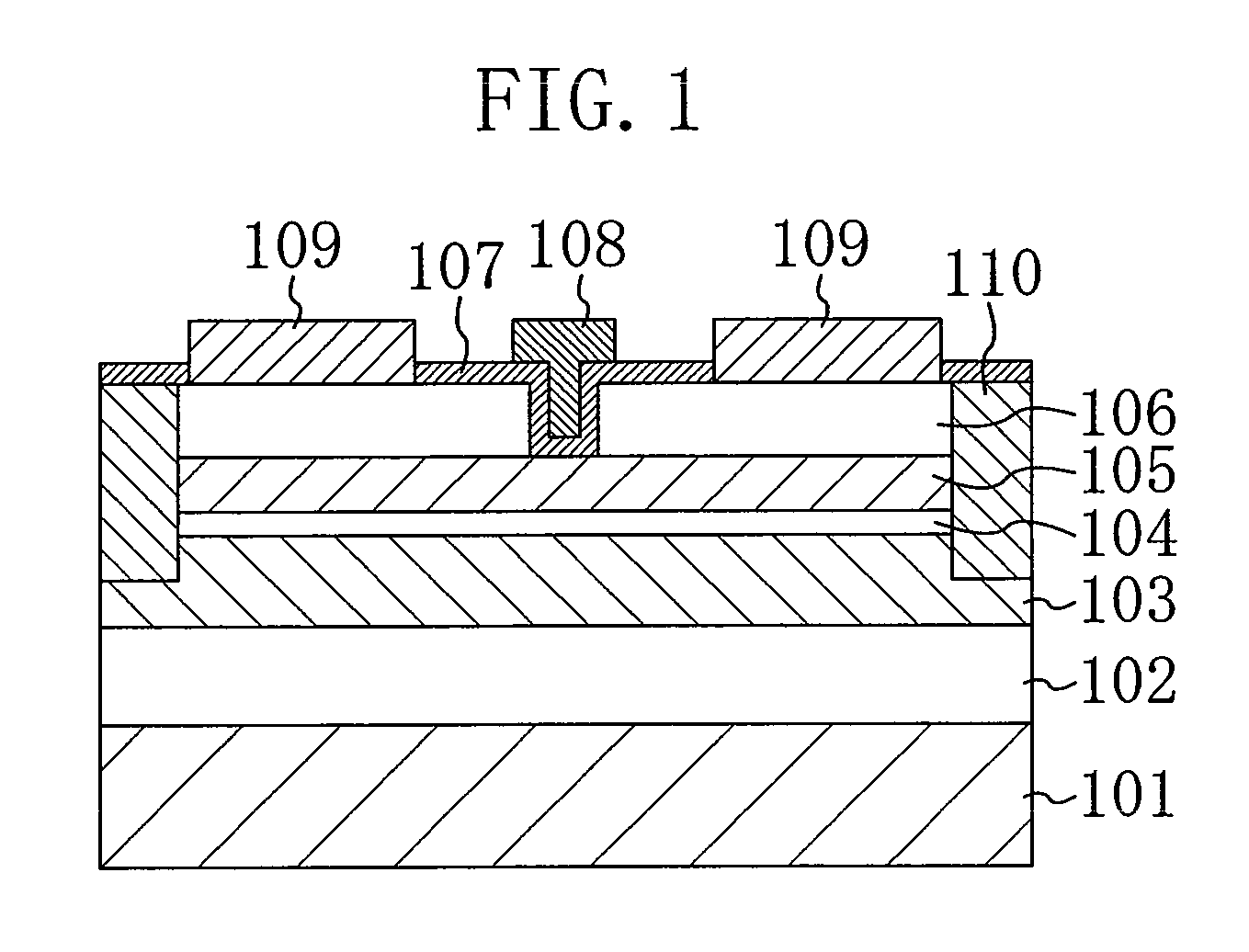
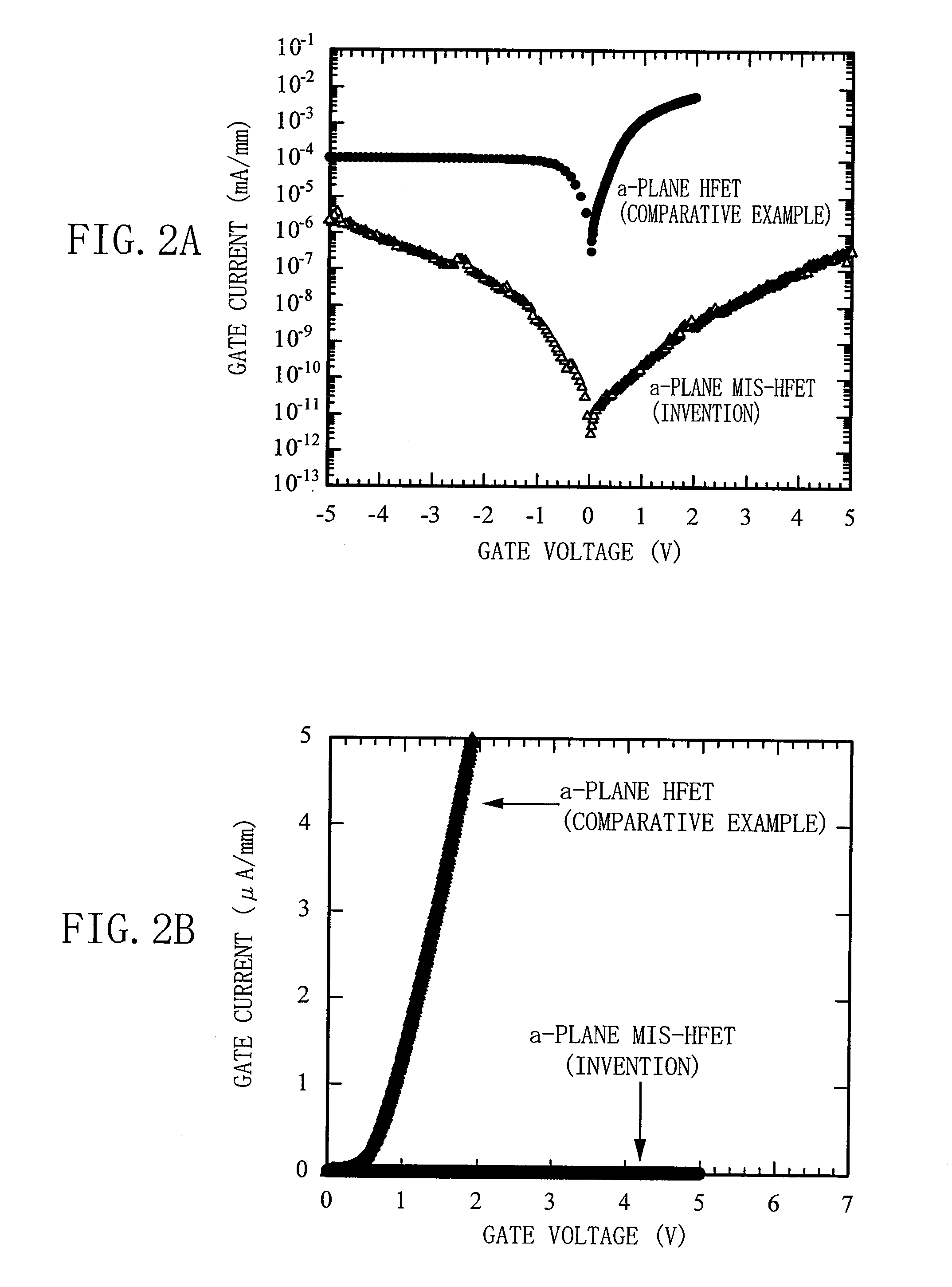
A field effect transistor includes: a first nitride semiconductor layer having a plane perpendicular to a (0001) plane or a plane tilted with respect to the (0001) plane as a main surface; a second nitride semiconductor layer formed on the first nitride semiconductor layer and having a wider bandgap than the first nitride semiconductor layer; a third nitride semiconductor layer formed on the second nitride semiconductor layer; and a source electrode and a drain electrode formed so as to contact at least a part of the second nitride semiconductor layer or the third nitride semiconductor layer. A recess that exposes a part of the second nitride semiconductor layer is formed between the source electrode and the drain electrode in the third nitride semiconductor layer. A gate electrode is formed in the recess and an insulating film is formed between the third nitride semiconductor layer and the gate electrode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Lead-free silver conductive paste used for positive electrode of solar battery and preparation technique thereof
InactiveCN101609850AStrong adhesionLower resistanceFinal product manufactureConductive materialConductive pasteSilver electrode
The invention provides a lead-free silver conductive paste used for positive electrode of solar battery and a preparation technique thereof. The paste comprises the following materials by weight percentage: 65 to 85 percent of silver powder, 2 to 8 percent of lead-free glass powder, 10 to 25 percent of organic carrier and 0.1 to 3 percent of additive. The paste adopts the lead-free glass powder of Si-B-Bi-Al-Ti-Zn-O series to replace the traditional lead-bearing glass powder; and the series glass powder has lower softening point, can lead the silver electrode to have good adhesive force after sintering, and ensures the silver electrode to be well contacted with a silicon substrate. In addition, zinc resinate is used as the additive in the invention, not only can well improve the printing performance of the paste, but also can improve the electrical property of the electrode.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Silver conductive paste used for positive electrode of solar battery and preparation technique thereof
InactiveCN101609849AReduce contact resistanceReduced series resistanceFinal product manufactureConductive materialMicrometerOhmic contact
The invention provides a silver conductive paste used for positive electrode of solar battery and a preparation technique thereof. The paste comprises silver powder, glass powder, an organic carrier and an additive, wherein the silver powder accounts for 65 to 85 percent of the total weight of the paste and consists of two types of silver powder with different particle sizes; the first type of silver powder has the particle size range of 3 to 15 micrometers and is spherical; the second type of silver powder has the particle size range of 0.1 to 3 micrometers and is spherical; the first type of silver powder accounts for 20 to 50 percent of the total silver powder; the glass powder is of Pb-B-Si-Zn-Ti-Al-O series and accounts for 1 to 10 percent of the total weight of the paste; the organic carrier accounts for 10 to 20 percent of the total weight of the paste; and the additive accounts for 0.1 to 3 percent of the total weight of the paste, and consists of BaO powder and CaO powder. The silver powder with different particle size ranges is mutually filled, thus greatly improving the electrical property of the electrode and improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the battery. In addition, the invention can ensure good ohmic contact between the paste and a substrate.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Composition and preparation method of silicon solar battery electrode slurry
InactiveCN101651155AEnhanced ohmic contactReduced series resistanceRenewable energy productsSemiconductor devicesBack surface fieldOhm
The invention relates to composition and a preparation method of silicon solar battery electrode slurry. The silicon solar battery electrode slurry comprises silicon solar battery sunny slope grid electrode silver slurry, back surface field silver-aluminium slurry and back surface field aluminium slurry which are used for preparing an ohm contact layer containing silicon alloy powder. In the invention, silver powder, aluminium powder, a simple substance element and the silicon alloy powder are used as raw materials, and an organic bond and an inorganic bond are used as accessories, and after the raw materials and the accessories are evenly mixed, a three-roller rolling mill is utilized to roll the mixture into the silicon solar battery electrode slurry of which the fineness is 20.0-25.0mum and the viscosity is 20000-40000mpa.s.
Owner:谭富彬
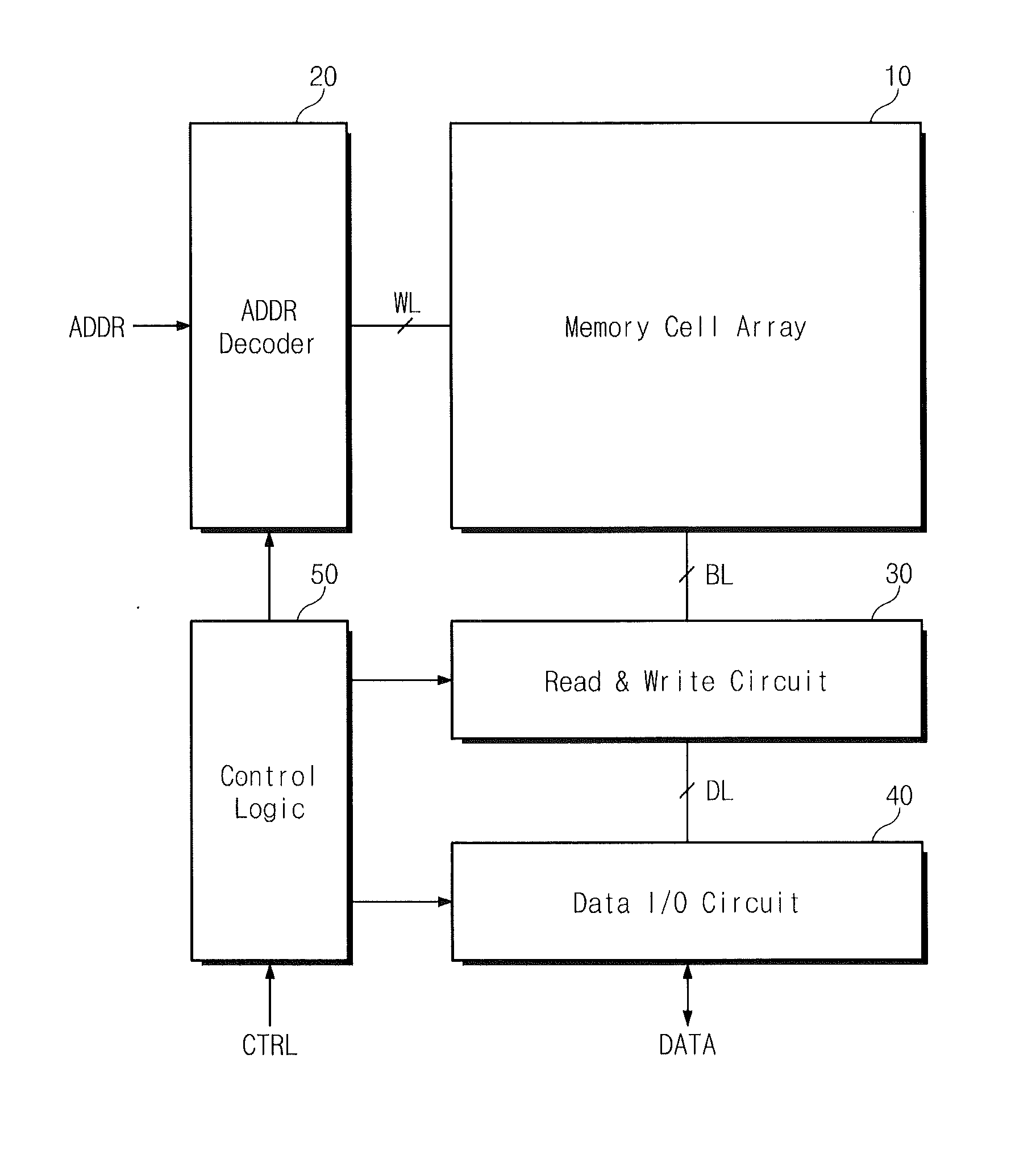
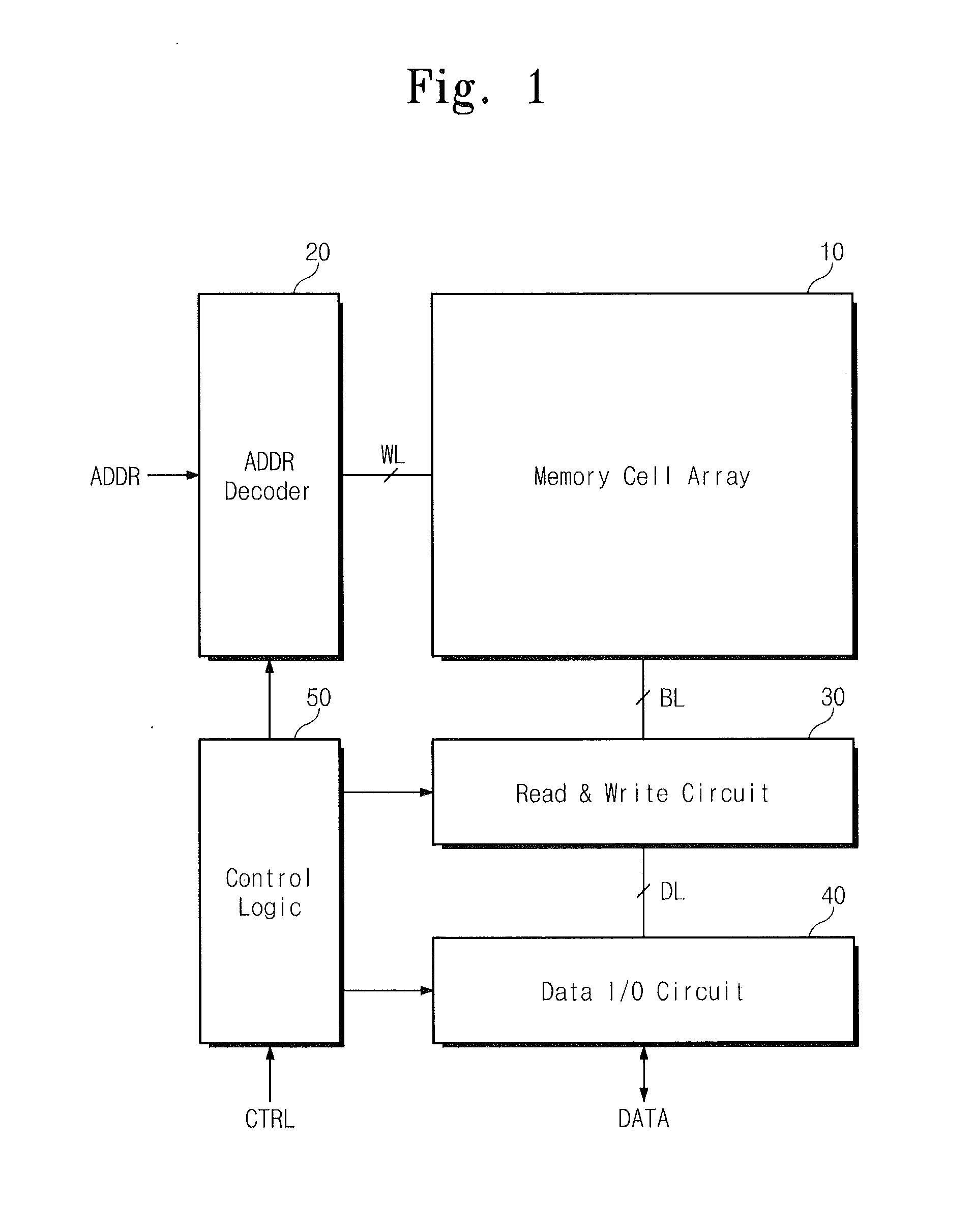
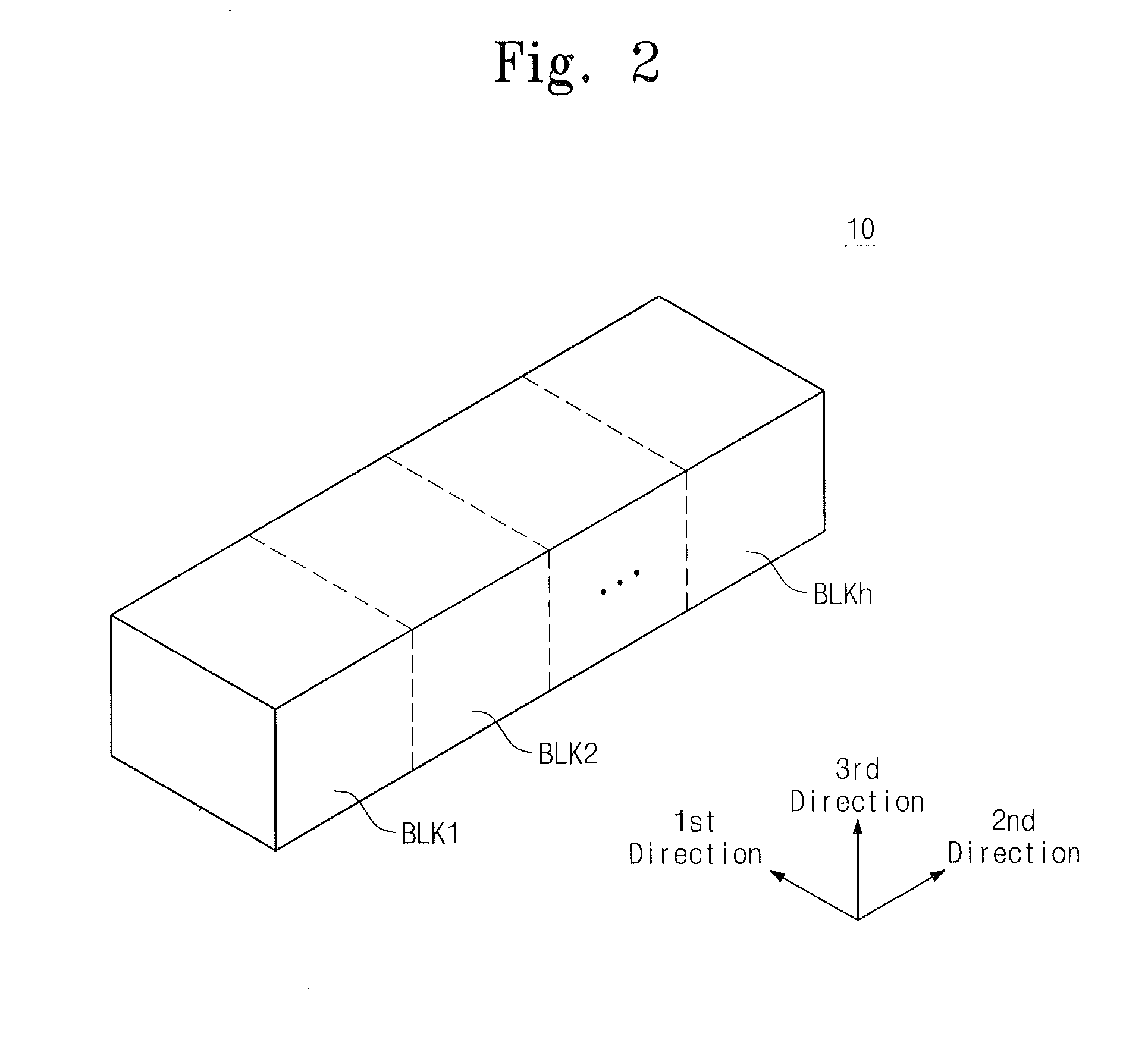
Vertically-integrated nonvolatile memory devices having laterally-integrated ground select transistors
ActiveUS20110310670A1Reduced series resistanceSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCouplingThreshold voltage
Nonvolatile memory devices utilize vertically-stacked strings of nonvolatile memory cells (e.g., NAND-type strings) that can be selectively coupled to common source lines within a substrate. This selective coupling may be provided by lateral ground select transistors having different threshold voltages that account for different lateral spacings between the vertically-stacked strings of nonvolatile memory cells and the common source lines.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Photoactive component with organic layers
ActiveUS7675057B2Reduce recombination lossHigh yieldNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesQuantum yieldTransport layer
Owner:HELIATEK GMBH
Contacts to semiconductor fin devices
InactiveUS20060244066A1Reduce contact resistanceIncrease contact areaTransistorSolid-state devicesConductive materialsSemiconductor
A method for forming a contact to a semiconductor fin which can be carried out by first providing a semiconductor fin that has a top surface, two sidewall surfaces and at least one end surface; forming an etch stop layer overlying the fin; forming a passivation layer overlying the etch stop layer; forming a contact hole in the passivation layer exposing the etch stop layer; removing the etch stop layer in the contact hole; and filling the contact hole with an electrically conductive material.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Deep-UV light-emitting diode and preparation method thereof
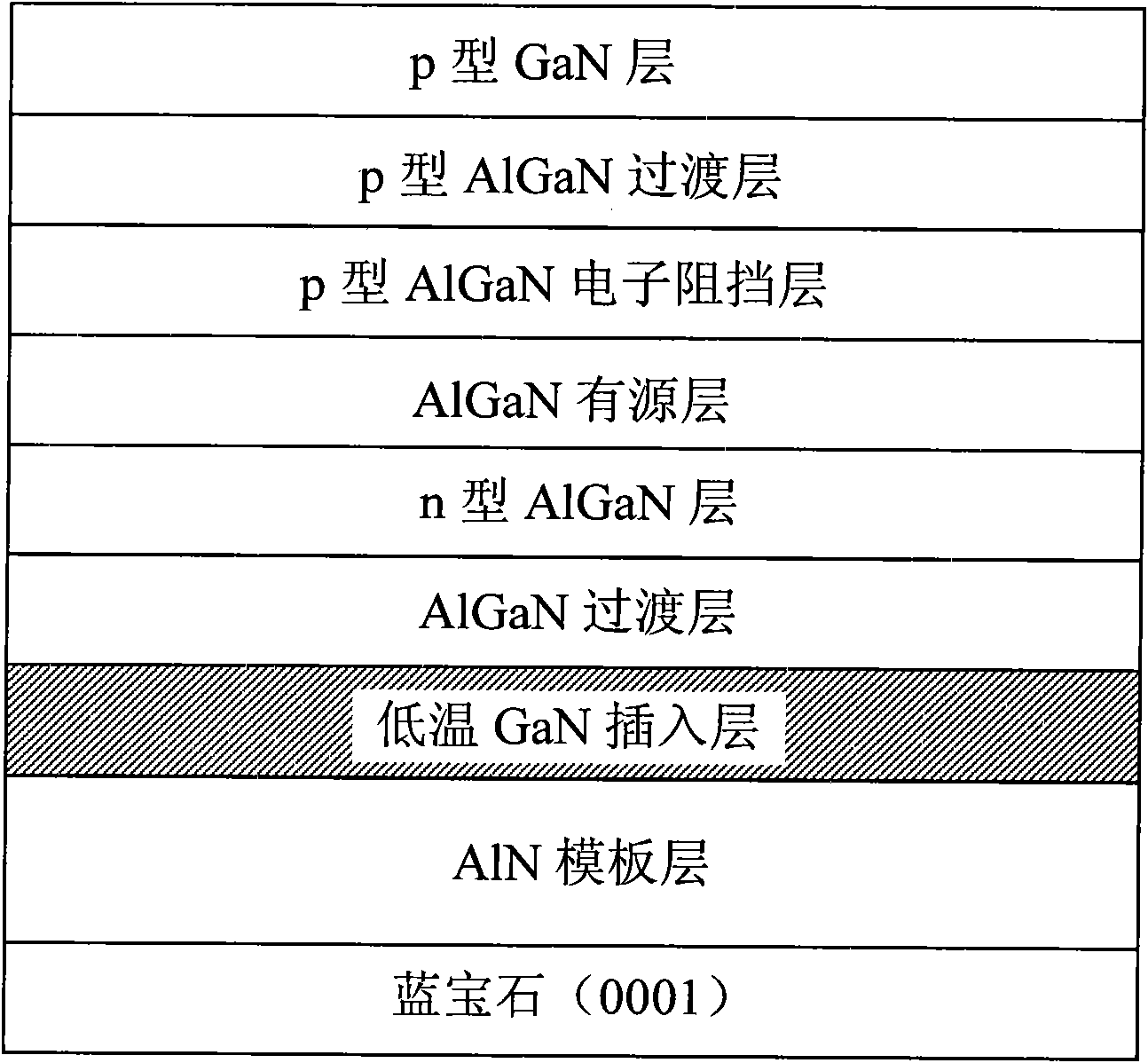
InactiveCN101604716AReduce dislocation densityImprove crystal qualitySemiconductor devicesDislocationSmooth surface
The invention provides a deep-UV light-emitting diode and a preparation method thereof. A low-temperature GaN insertion layer is used to replace an AlN / AlGaN superlattice or a high-temperature GaN insertion layer to grow the deep-UV light-emitting diode. The low-temperature GaN insertion layer is a GaN with thickness of 20-50nm under the conditions of temperature being 400-900 DEG C, pressure being 30-200torr, and V / III being 1500-2500. The method can effectively lower the dislocation density in an epitaxial AlGaN layer and a quantum well, and improves the surface planeness. The prepared LED component has smooth surface, better crystal quality, starting voltage reduction, and smaller serial resistances of the component; and the electroluminescene peak value is ranged from 300nm to 370nm.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for forming a raised source and drain without using selective epitaxial growth
InactiveUS6090691AEasily controllable depthGood coplanaritySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureEngineering
A method for forming a raised source and drain structure without using selective epitaxial silicon growth. A semiconductor substrate is provided having one or more gate areas covered by dielectric structures. Doped polysilicon structures are adjacent to the dielectric structures on each side and are co-planar with the dielectric structures from a CMP process. The first dielectric structures are removed to form gate openings and a liner oxide layer is formed on the bottom and sidewalls of the gate openings. Dielectric spacers are formed on the liner oxide layer over the sidewalls of the gate openings, and the liner oxide layer is removed from the bottom of the gate openings and from over the doped polysilicon structures. Source and drain regions are formed in the semiconductor substrate by diffusing impurity ions from the doped polysilicon layer. A gate oxide layer and a gate polysilicon layer are formed over the semiconductor structure and the gate polysilicon layer is planarized to form a gate electrode. In a key step, the dielectric spacers are removed to form spacer openings, and impurity ions are implanted through the spacer openings and annealed to form source and drain extensions. The dielectric spacers are reformed and a self-aligned silicide layer is formed on the doped polysilicon structure and the gate electrode. Alternatively, the self-aligned silicide layer can be formed prior to removing the dielectric spacers and implanting ions to form source and drain extensions.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Field effect transistor
ActiveUS7956383B2Suppress generationInhibition formationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringField effect
A field effect transistor includes: a first nitride semiconductor layer having a plane perpendicular to a (0001) plane or a plane tilted with respect to the (0001) plane as a main surface; a second nitride semiconductor layer formed on the first nitride semiconductor layer and having a wider bandgap than the first nitride semiconductor layer; a third nitride semiconductor layer formed on the second nitride semiconductor layer; and a source electrode and a drain electrode formed so as to contact at least a part of the second nitride semiconductor layer or the third nitride semiconductor layer. A recess that exposes a part of the second nitride semiconductor layer is formed between the source electrode and the drain electrode in the third nitride semiconductor layer. A gate electrode is formed in the recess and an insulating film is formed between the third nitride semiconductor layer and the gate electrode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Conductive paste for crystalline silicon solar cell and preparation method of conductive paste
ActiveCN104078090AHigh tear strengthImprove adhesion strengthNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCable/conductor manufactureSilver pasteConductive paste
The invention provides conductive paste for a crystalline silicon solar cell. The conductive paste comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of conductive metal powder, 1.0-10 parts of inorganic binder, 10-65 parts of organic carrier and 0.05-5.0 parts of conductive carbon. The conductive paste is excellent in conductivity; the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the cell is not influenced; and widely applied conductive paste for the crystalline silicon solar cell such as front-side silver paste, front-side seed layer silver paste, back-side silver paste and back electric field aluminum paste can be prepared.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
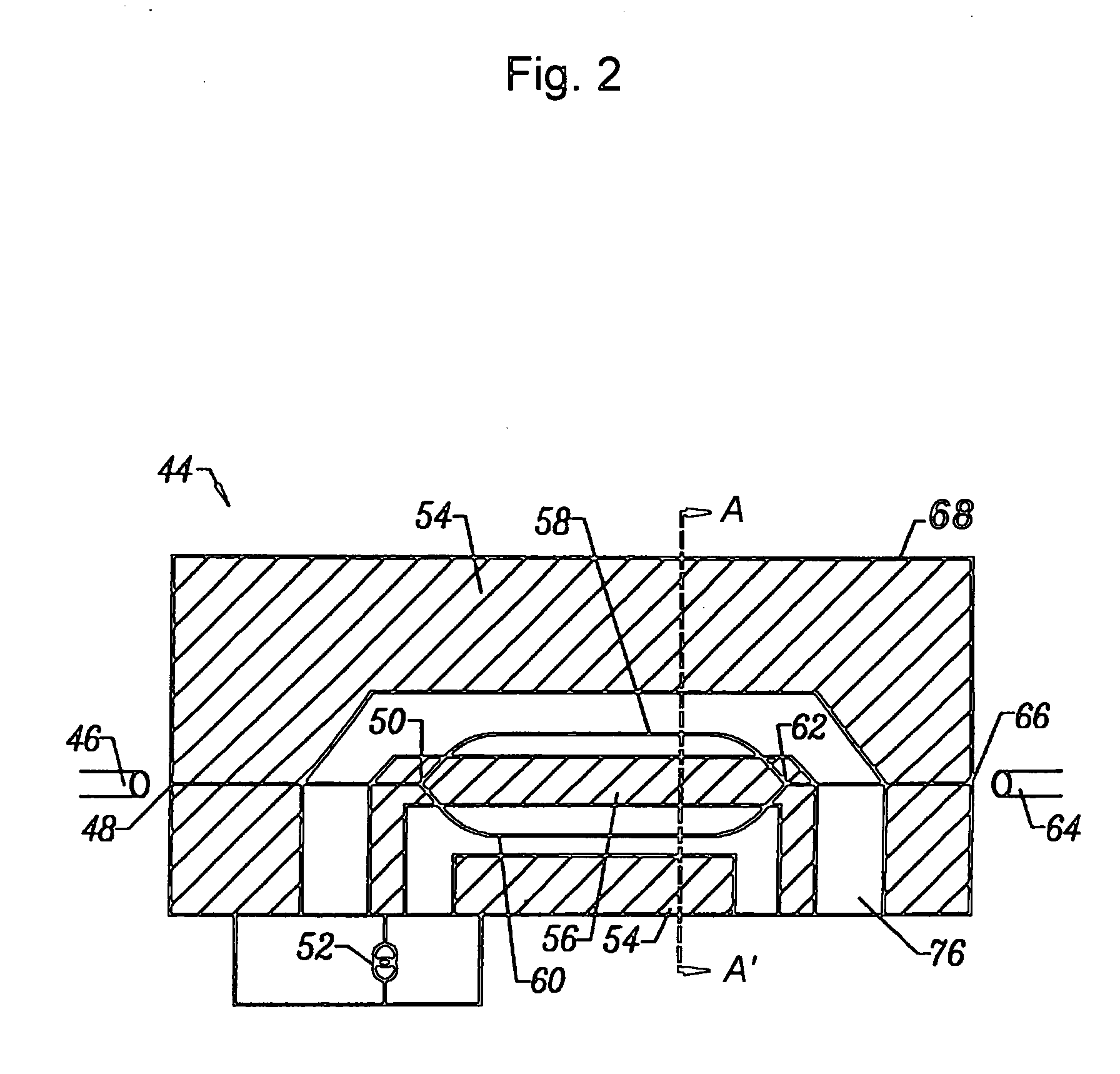
Low bias drift modulator with buffer layer
ActiveUS20060023288A1Reduced series resistanceHigh resistivityNon-linear opticsBias driftOperating point
The invention relates to an electro-optic modulator structure containing an additional set of bias electrodes buried within the device for applying bias to set the operating point. Thus the RF electrodes used to modulate incoming optical signals can be operated with zero DC bias, reducing electrode corrosion by galvanic and other effects that can be present in non-hermetic packages. The buried bias electrodes are also advantageous in controlling charge build-up with consequent improvement in drift characteristics. The bias electrode material is useful for routing bias signals inside the device, in particular to external terminals, as well as forming encapsulating layers to permit operation in non-hermetic environments, thereby lowering manufacturing costs. Embodiments using both X-cut and Z-cut lithium niobate (LiNbO3) are presented. For the latter, the bias electrodes can be split along their axis to avoid optical losses
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Process for manufacturing solar cell by twice screen printing and grooving
ActiveCN101969082AReduced series resistanceIncrease the conductive cross-sectional areaFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesScreen printingEngineering
The invention discloses a process for manufacturing a solar cell by twice screen printing and grooving, which is used for manufacturing the solar cell by twice electrode printing and comprises a grooving process and a twice printing process, wherein the grooving process comprises the step of performing grooving on an electrode grid line area on the surface of a silicon wafer so as to form an etched groove in the electrode grid line area; and the twice printing process comprises the following steps of: a, primary electrode printing, namely, filling printing electrode paste into the etched groove and performing drying to form a first layer of electrode in the etched groove; and b, secondary electrode printing, namely, printing the electrode on the outer surface of the first layer of electrode so as to form a second layer of electrode in the electrode grid line area on the surface of the silicon wafer. The solar cell manufactured by the method has relatively lower series resistance, a selective emitter and relatively higher conversion efficiency, and can reduce shading loss; and the electrode paste is difficult to spread in a sintering process.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD
Main-gate-free and high-efficiency back-contact solar cell module, main-gate-free and high-efficiency back-contact solar cell assembly, and preparation process thereof
ActiveUS20170222082A1Reduces electron collection distanceReduced series resistanceFinal product manufacturePV power plantsElectricityCrack resistance
The present invention relates to the field of solar cells, and in particular to a main-gate-free and high-efficiency back-contact solar cell module, a main-gate-free and high-efficiency back-contact solar cell assembly, and a preparation process thereof. The solar cell module, comprising cells and an electrical connection layer, a backlight side of the cells having P-electrodes connected to a P-type doping layer and N-electrodes connected to a N-type doping layer, is characterized in that the electrical connection layer comprises a number of parallel leads each electrically connected to the P-electrodes or the N-electrodes. The present invention has the beneficial effect that a main-gate-free and high-efficiency back-contact solar cell module, a main-gate-free and high-efficiency back-contact solar cell assembly, and a preparation process thereof are provided, which can effectively the short-circuiting of the P-electrodes and the N-electrodes and has the advantages of low cost, high hidden-cracking resistance, high efficiency and high stability.
Owner:JOLYWOOD SUZHOU SUNWATT
Method and structure of manufacturing a high-Q inductor with an air trench
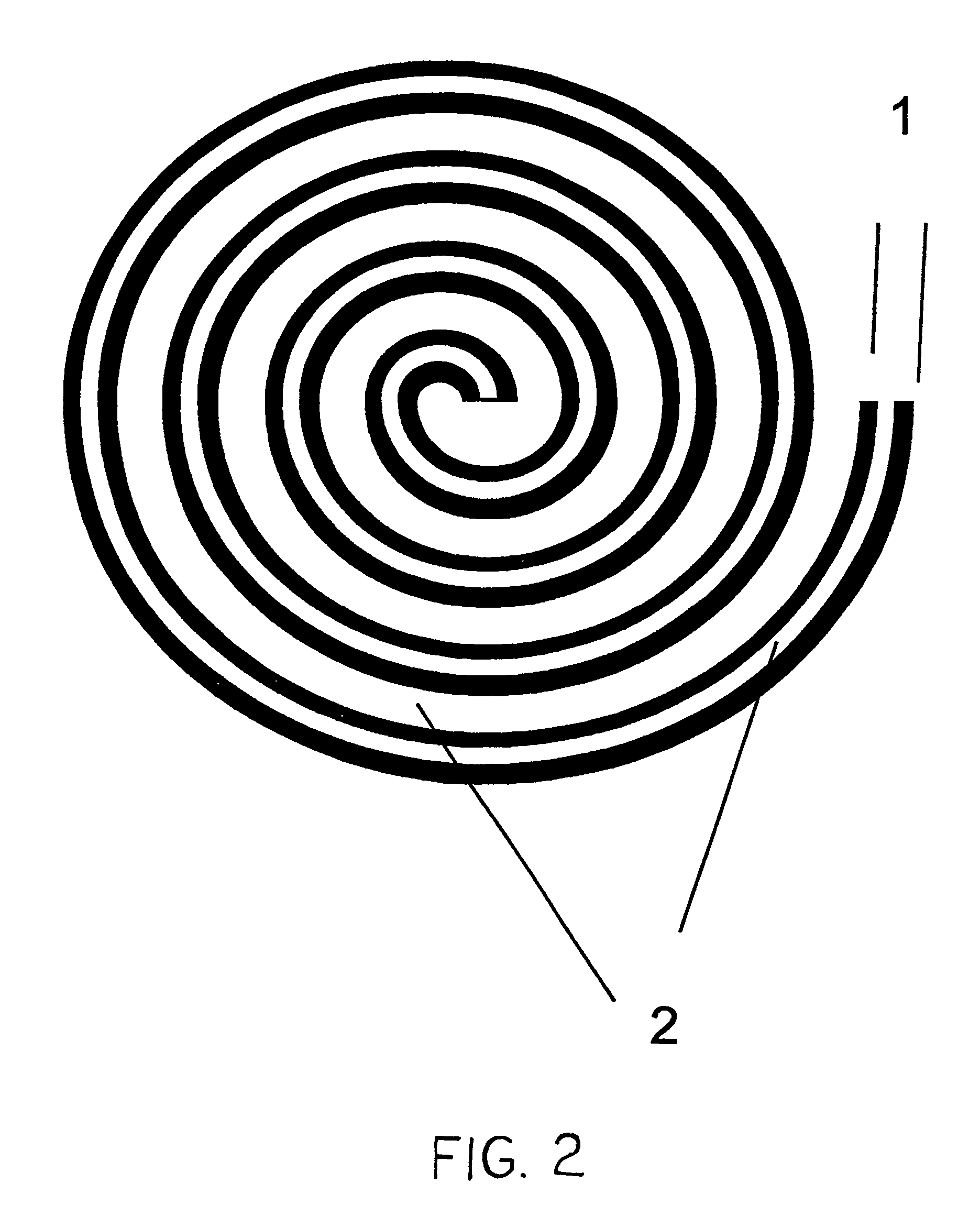
InactiveUS6355535B2Reduced series resistanceHigh quality factorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesParasitic capacitanceInductor
The structure of a high-Q inductor applied in a monolithic circuit according to the invention comprises a plurality of spiral metal lines and a plurality of dielectric layers, each dielectric layer formed between two adjacent spiral metal lines. Furthermore, via plugs are formed in each dielectric layer to electrically connect two adjacent spiral metal lines. A spiral air trench is formed along the spacing of the spiral metal lines in the dielectric layers. Therefore, the 3D-structure of the inductor of the invention can greatly reduce the series resistance thereof without widening the spiral metal lines. In addition, the spiral air trench, filled with air which has a lower dielectric constant, can efficiently reduce the parasitic capacitance between the spacing of the spiral metal lines. As a result, the inductor of the invention has a higher quality factor at a proper RF operating frequency region.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com