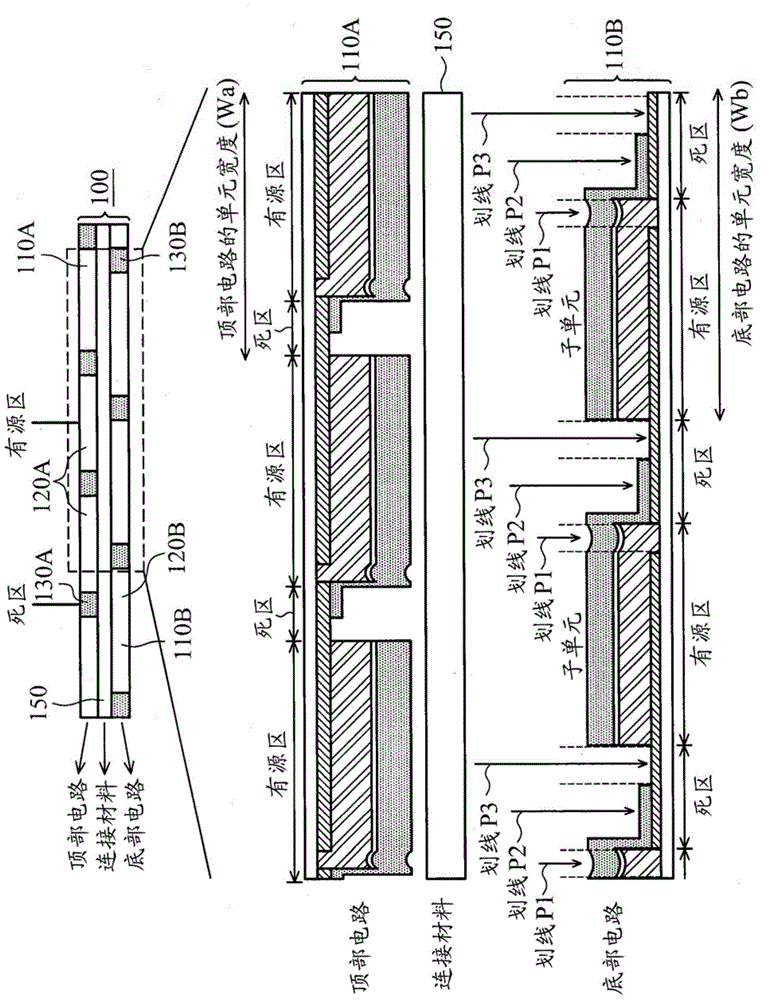
Patents
Literature
45results about How to "Reduce recombination loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
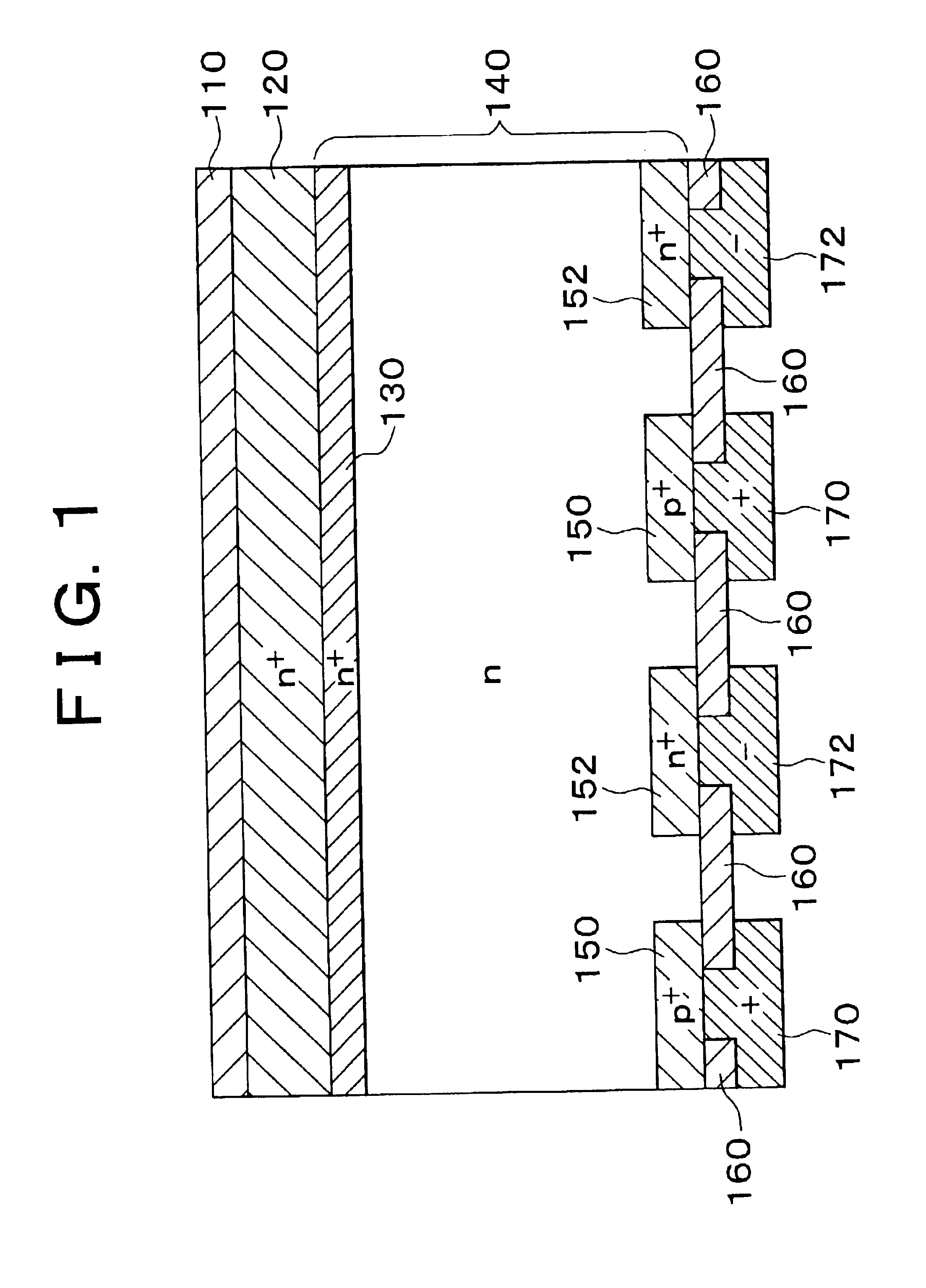
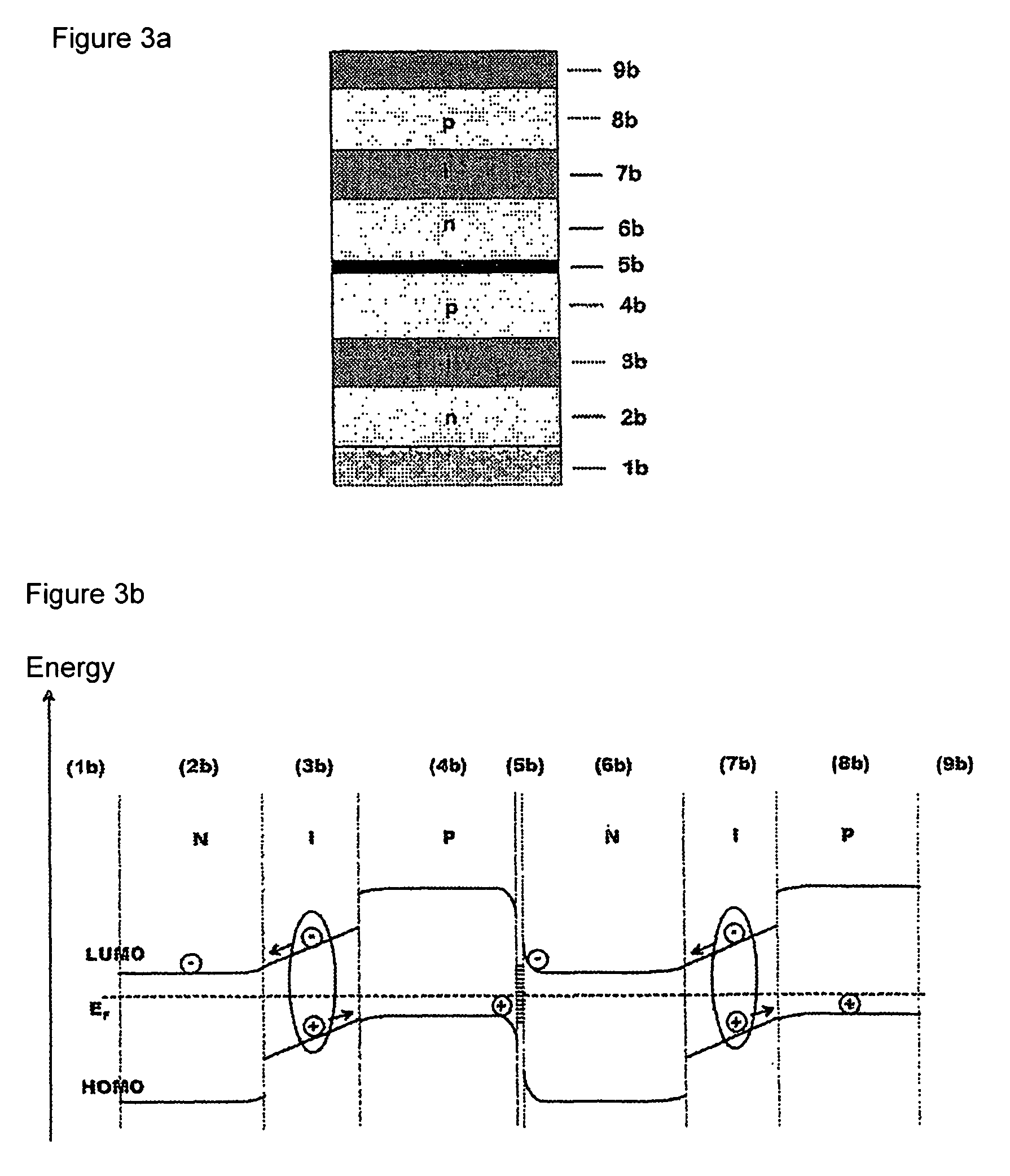
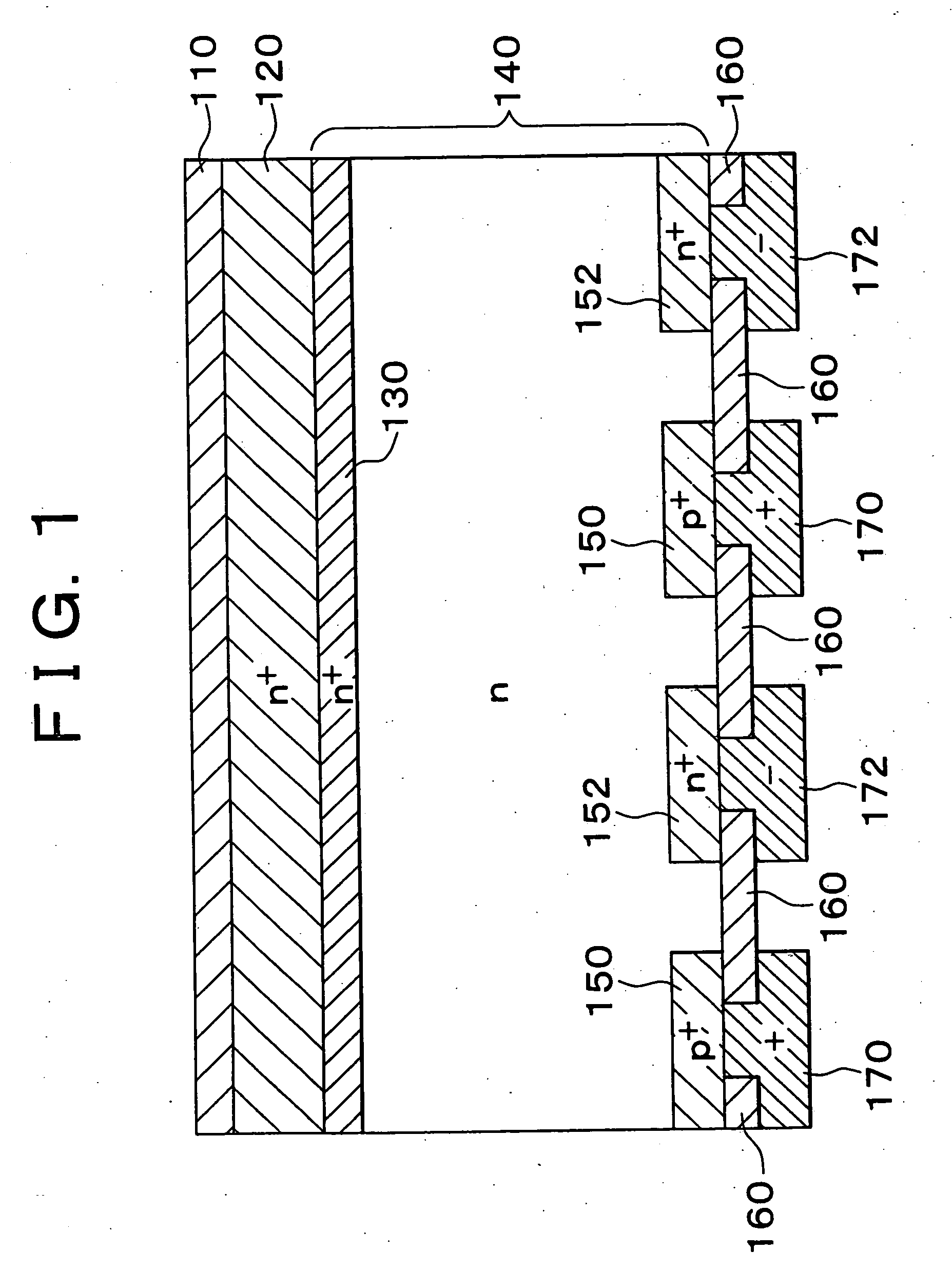
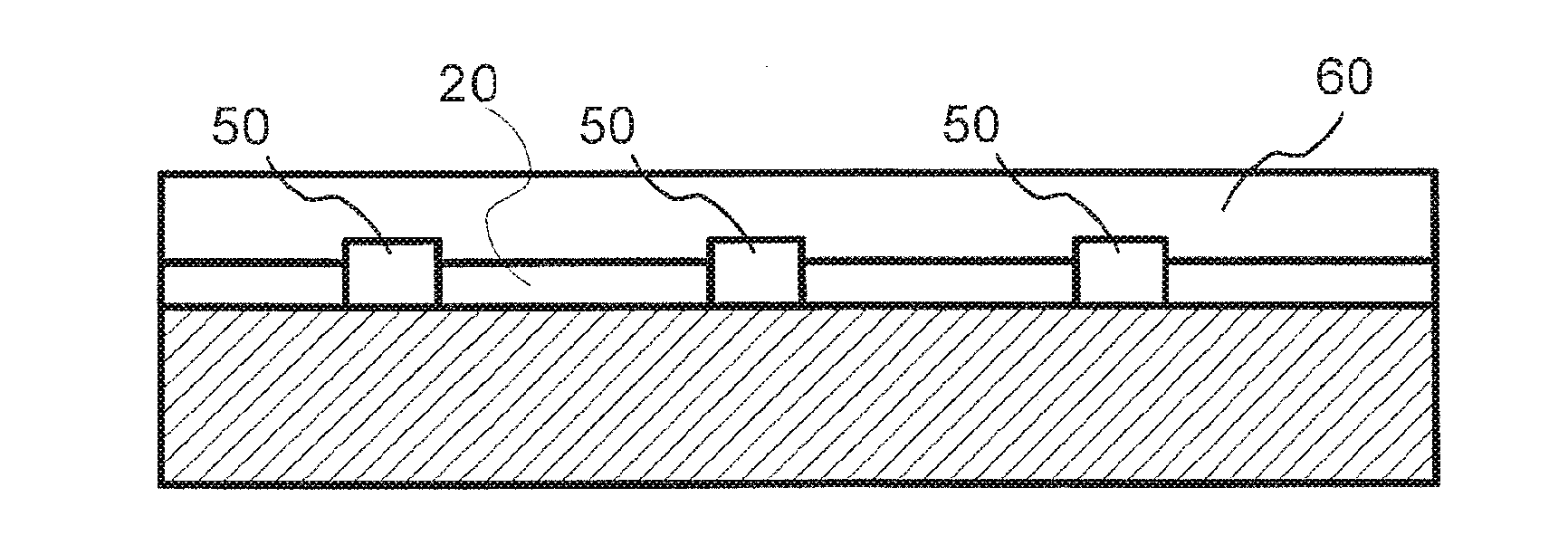
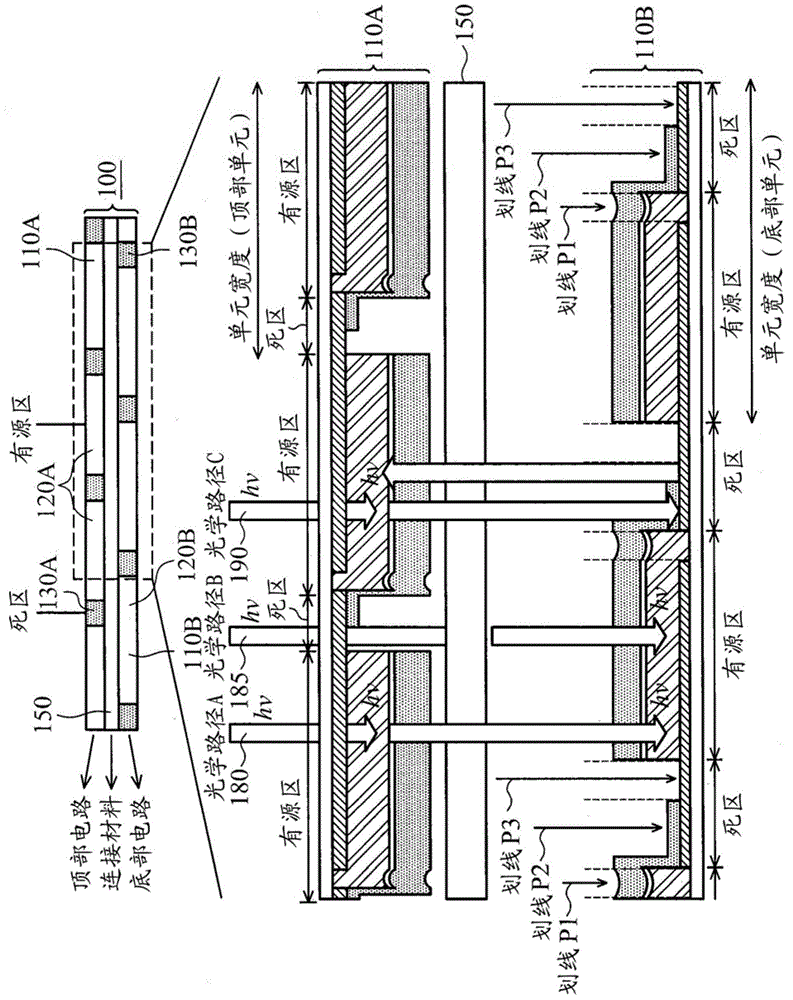
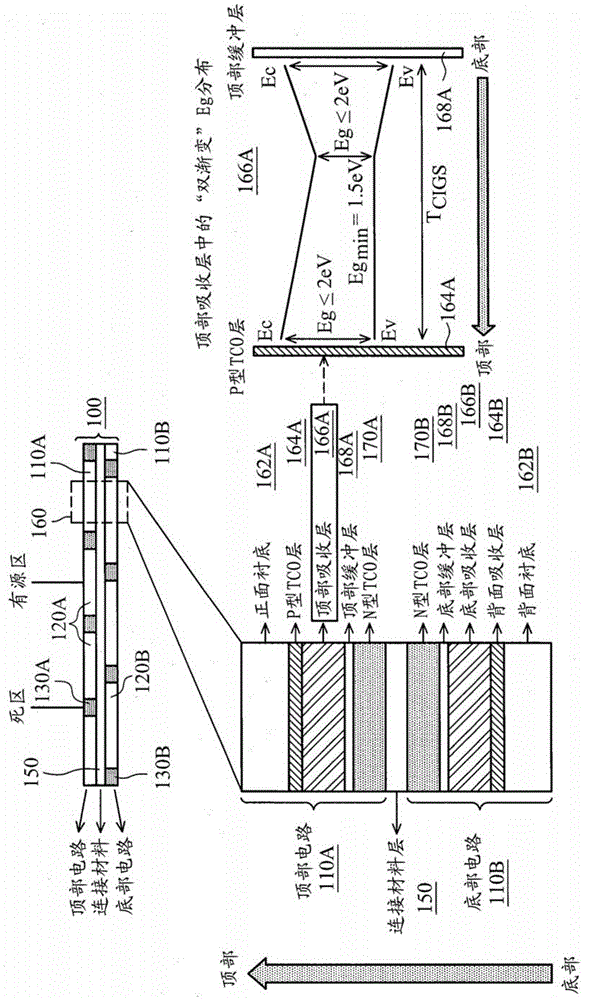
Photoactive component with organic layers
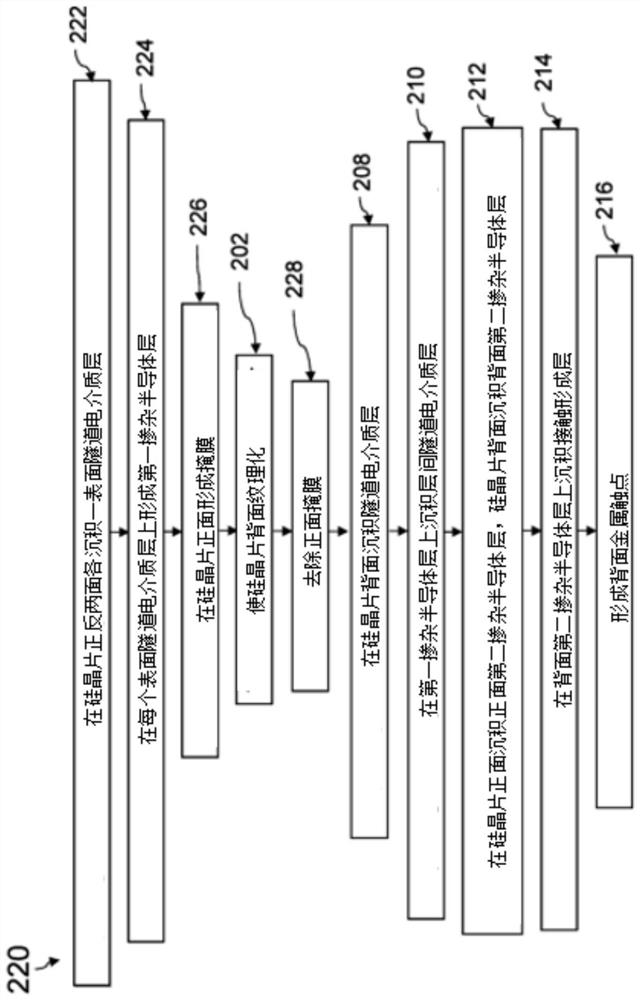
ActiveUS20070090371A1Reduce recombination lossHigh yieldNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesQuantum yieldTransport layer
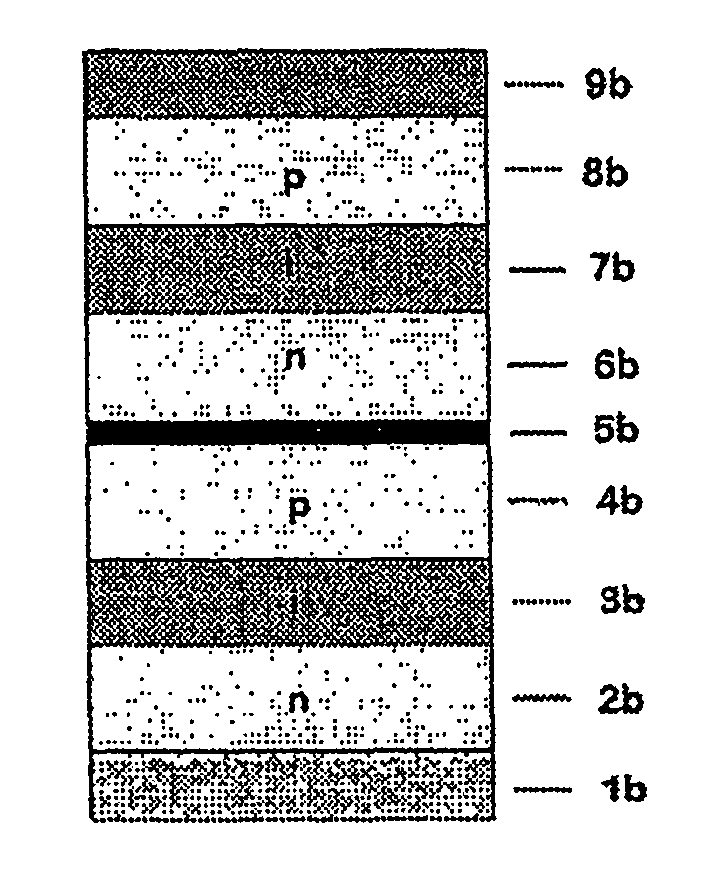
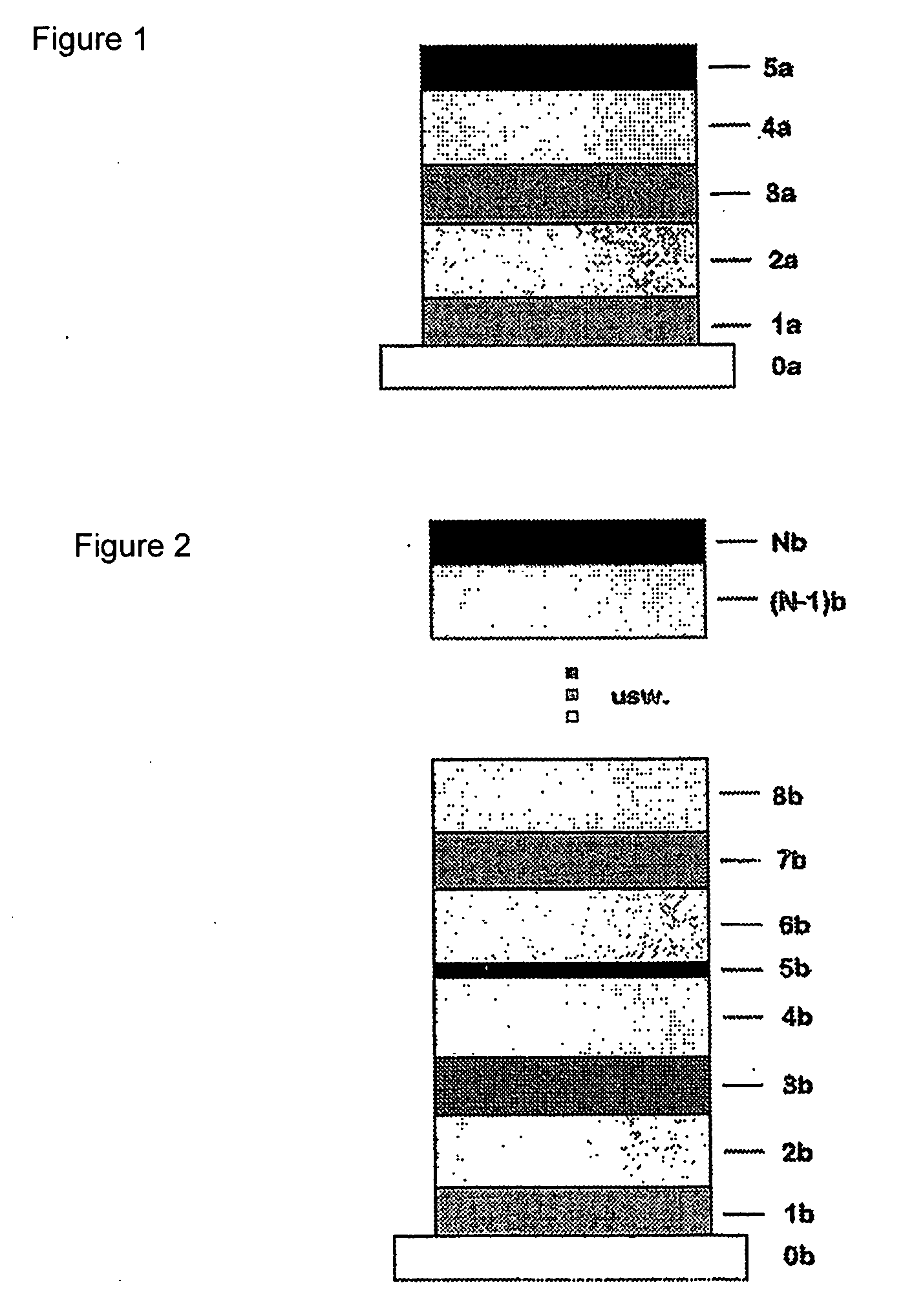
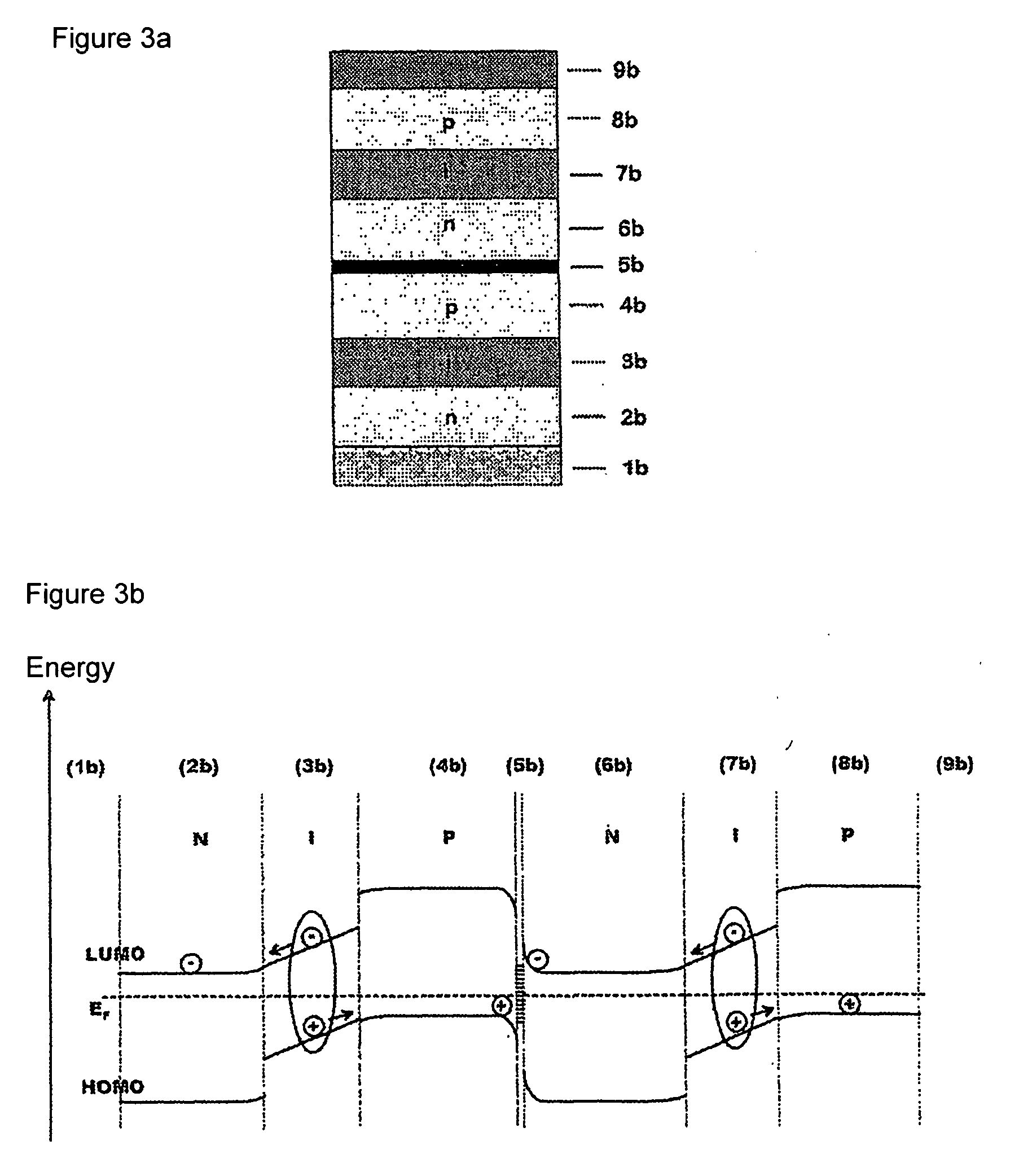
The invention relates to a photoactive component, especially a solar cell, comprising organic layers and formed by at least one stacked pi, ni, and / or pin diode. The diodes are characterised in that they comprise at least one p-doped or n-doped transport layer having a larger optical band gap than that of the photoactive layer. The individual diodes are characterised by a high internal quantum yield, but can be optically thin (peak absorption <80%). A high external quantum yield is obtained by either enlarging the optical path of the incident light in the diodes using light traps, or by stacking a plurality of the diodes. The transition between two diodes being facilitated by transition layers for the purposes of improved recombination and generation. Both forms of embodiment have a number of specific advantages using the doped transport layers with a large band gap.
Owner:HELIATEK GMBH
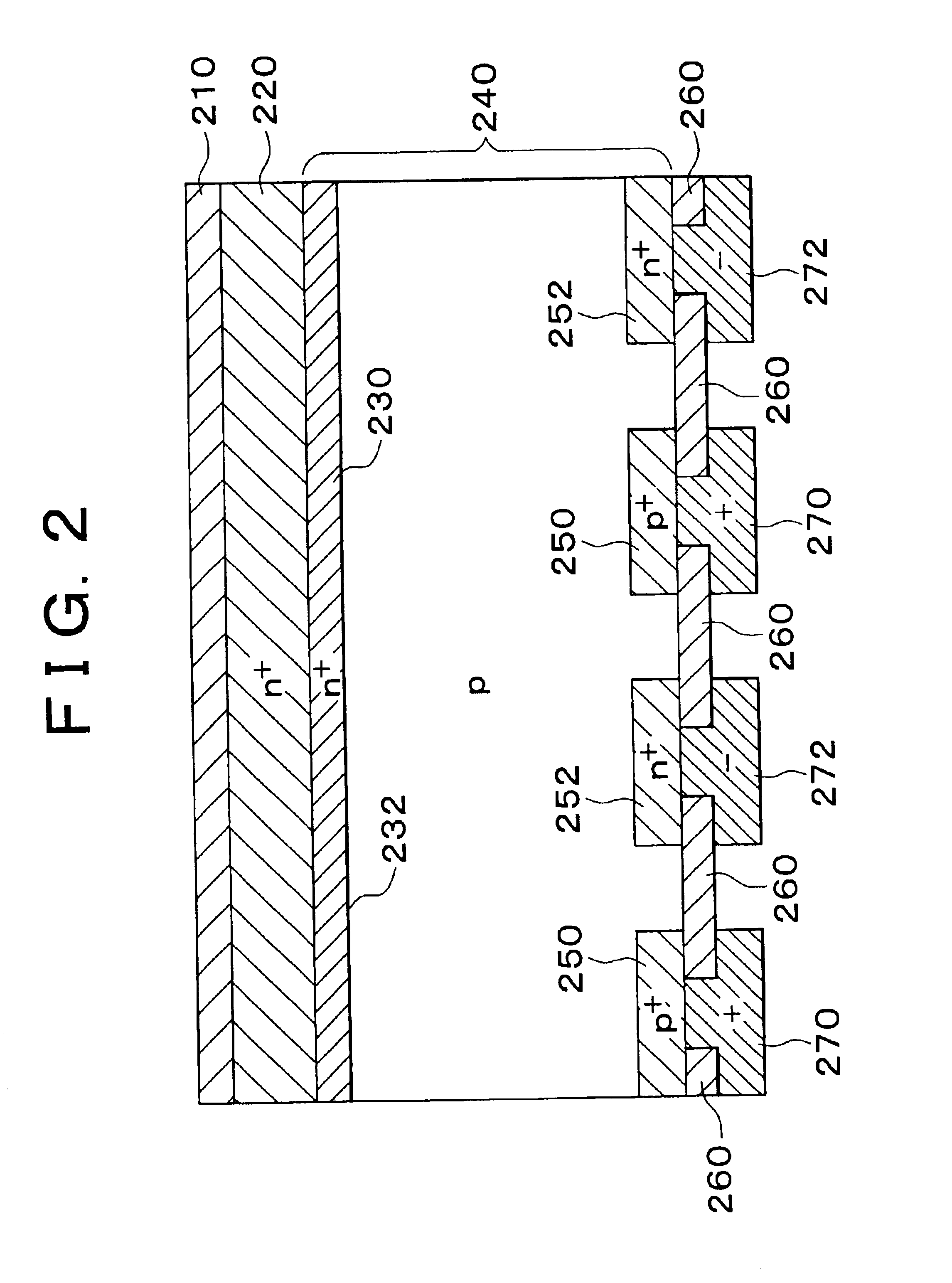
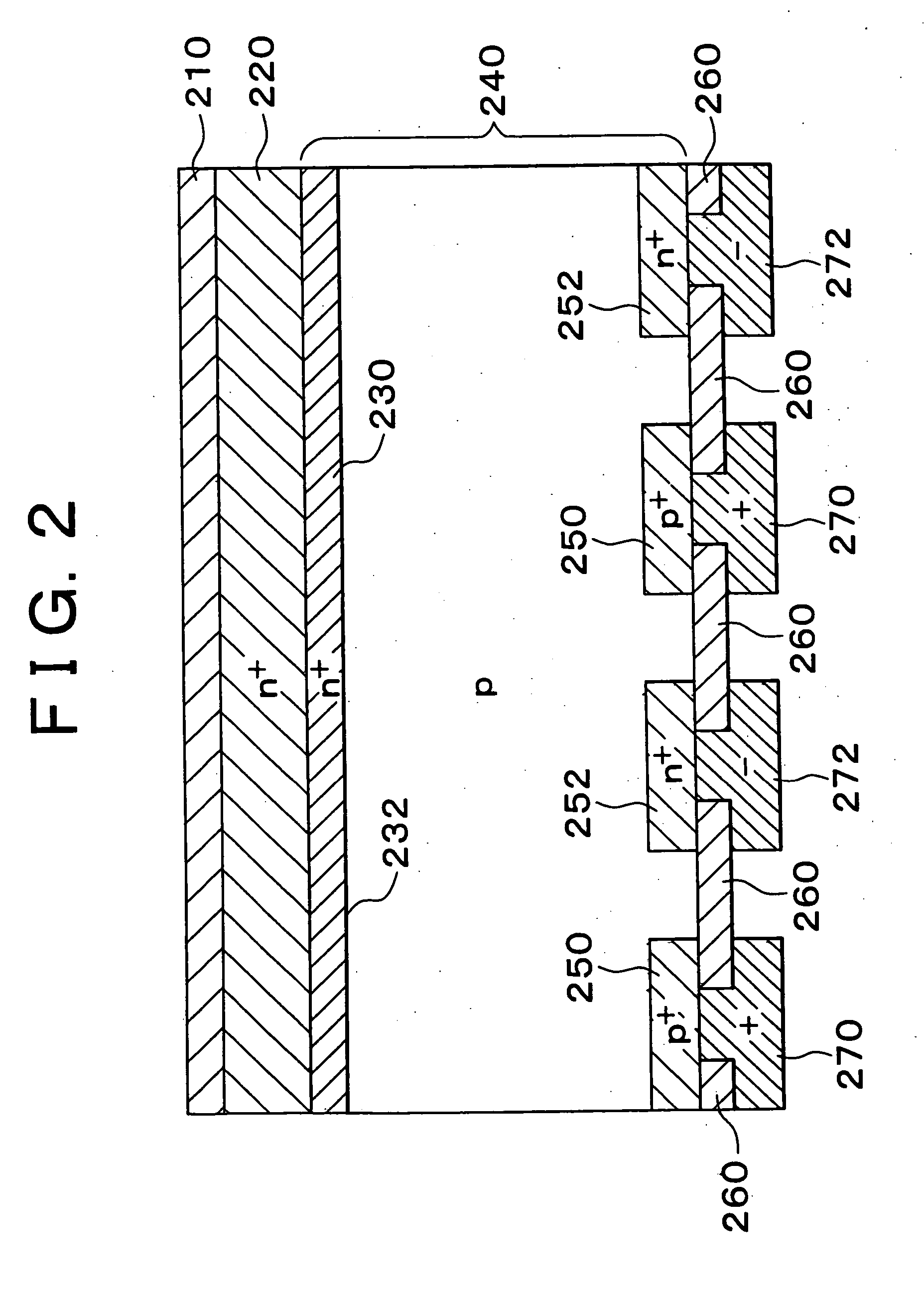
Photoelectric conversion element and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6927417B2Reduce carrier recombination lossImprove conversion efficiencyTransistorPV power plantsLight beamPhotoelectric conversion
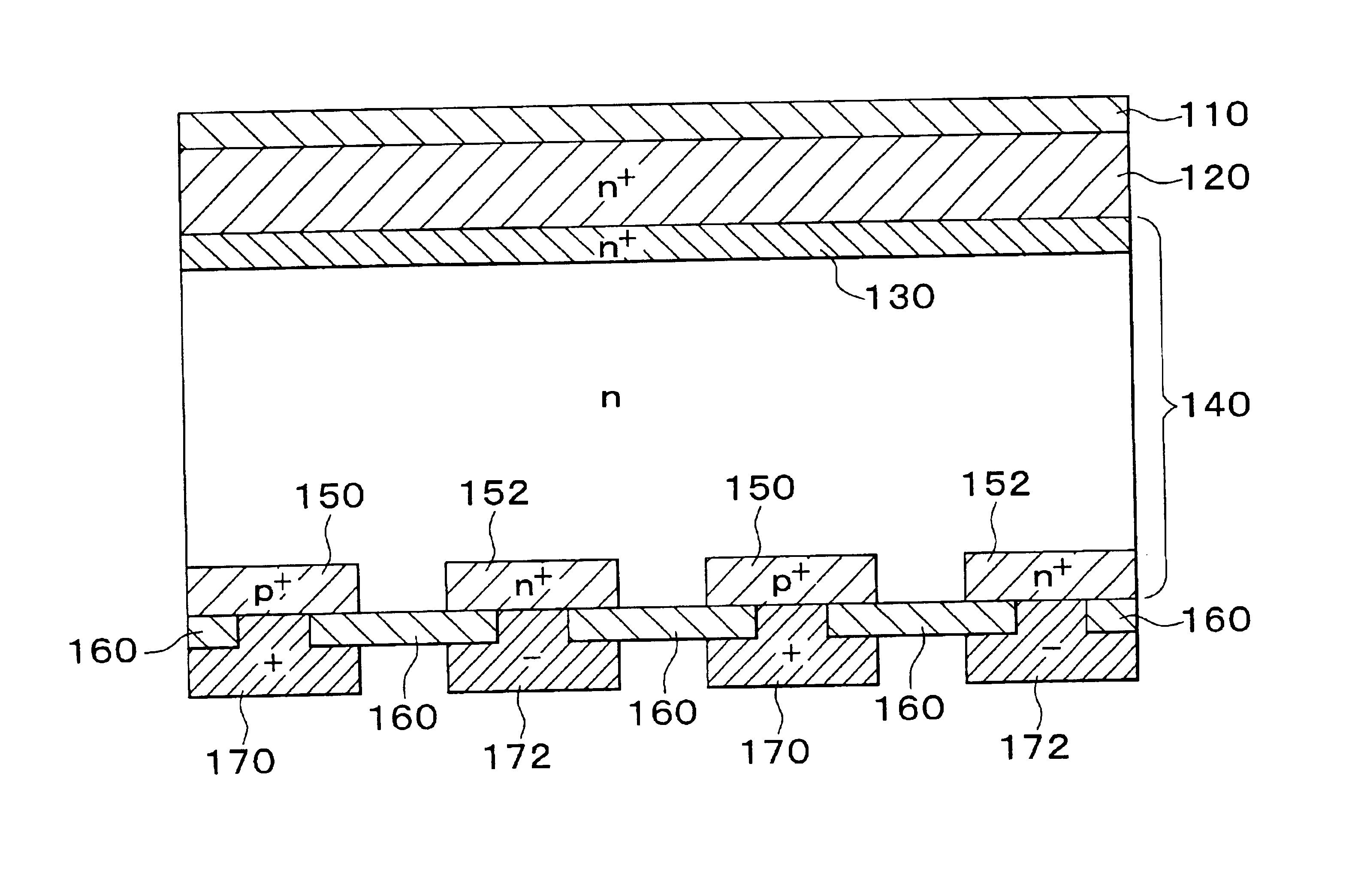
In a back-surface electrode type photoelectric conversion element having electrodes and semiconductor layers for collecting carriers disposed only on a back surface side of a semiconductor substrate, a semiconductor thin film that is larger in band gap than the semiconductor substrate and that contains an element causing a conductivity identical to or different from a conductivity of the semiconductor substrate is provided on a light-receiving surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and a diffusion layer is formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate. Alternatively, 95% or more of light beams having a wavelength of anywhere from 800 nm to 2000 nm are caused to penetrate the light-receiving surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and an insulative thin film containing an element causing a conductivity identical to or different from the conductivity of the semiconductor substrate is provided so as to form a diffusion layer on the surface of the semiconductor substrate through diffusion of the element.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Photoactive component with organic layers
ActiveUS7675057B2Reduce recombination lossHigh yieldNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesQuantum yieldTransport layer
Owner:HELIATEK GMBH
Heterojunction solar cell with absorber having an integrated doping profile
InactiveUS20110174374A1Moderate influenceIncrease fill factorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationCharge carrierBand gap
The invention relates to a heterojunction solar cell and a method for the production thereof. The heterojunction solar cell has an absorber layer made of silicon with a basic doping and at least one heterojunction layer of a doped semiconductor material whose band gap differs from that of the silicon of the absorber layer. The absorber layer has a doped layer at an interface directed toward the heterojunction layer, the doping concentration of said doped layer being greater than the basic doping concentration of the absorber layer. As a result of this doping profile, a field effect can be caused which prevents charge carrier pairs produced within the absorber layer from diffusing toward the interface between the absorber layer and the heterojunction layer and from recombining there.
Owner:INST FUR SOLARENERGIEFORSCHUNG
Solar cell
ActiveUS20120060917A1Increase open voltagePrevent be damagePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSolar cell
A solar cell is provided comprising a substrate, a first insulating layer on a first surface of the substrate, the first insulating layer having a plurality of first openings that expose portions of the substrate, and a plurality of first electrodes electrically connected to the substrate through the first openings, wherein one or more of the first electrodes are configured so that a width of an upper portion located on the first insulating layer is wider than a width of a lower portion located in a corresponding first opening.
Owner:SHANGRAO JINKO SOLAR TECH DEV CO LTD
Photoelectric conversion element and method of manufacturing the
InactiveUS20050205960A1Reduce carrier recombination lossImprove conversion efficiencyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLight beamPhotoelectric conversion
In a back-surface electrode type photoelectric conversion element having electrodes and semiconductor layers for collecting carriers disposed only on a back surface side of a semiconductor substrate, a semiconductor thin film that is larger in band gap than the semiconductor substrate and that contains an element causing a conductivity identical to or different from a conductivity of the semiconductor substrate is provided on a light-receiving surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and a diffusion layer is formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate. Alternatively, 95% or more of light beams having a wavelength of anywhere from 800 nm to 2000 nm are caused to penetrate the light-receiving surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and an insulative thin film containing an element causing a conductivity identical to or different from the conductivity of the semiconductor substrate is provided so as to form a diffusion layer on the surface of the semiconductor substrate through diffusion of the element.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
N-type crystalline silicon double-sided solar cell structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106409956AImprove conversion efficiencyEasy to prepareFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSilver pasteMetal electrodes
The invention discloses an N-type crystalline silicon double-sided solar cell structure and a preparation method thereof. The N-type crystalline silicon double-sided solar cell structure sequentially comprises a front metal wire, a front local contact metal electrode, a front antireflection film, a front passivation film, a P-type doped layer, an N-type crystalline silicon substrate, an N+ region, a back passivation film, a back local contact metal electrode and a back metal wire from top to bottom, wherein fine metal wires are combined with the local contact metal electrodes through a conductive bonded material to form a conductive assembly capable of replacing a fine grid line of a battery. A main grid line or an electrode lead exports current collected on the front surface and the back surface of the battery. Due to the structure of the battery, the contact area of metal and the silicon substrate is reduced, the composite loss is reduced, the light shading area of the grid lines is significantly reduced, so that the conversion efficiency of the battery is improved, and meanwhile, the production cost is reduced by reducing the dosage of silver paste.
Owner:LONGI SOLAR TECH (TAIZHOU) CO LTD
Photoelectric device
InactiveUS20140034119A1Reduce light lossReduce recombination lossPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
A photoelectric device that reduces optical loss, reduces recombination loss of carriers, and can be manufactured by using a simplified process is provided. The photoelectric device includes a semiconductor substrate, a first semiconductor stack on a first surface of the semiconductor substrate and having a first conductivity, and a second semiconductor stack on the first surface of the semiconductor substrate and having a second conductivity opposite to the first conductivity. Edge portions of the first and second semiconductor stacks face each other with an insulating portion therebetween.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL KEYSTONE TECH LLC
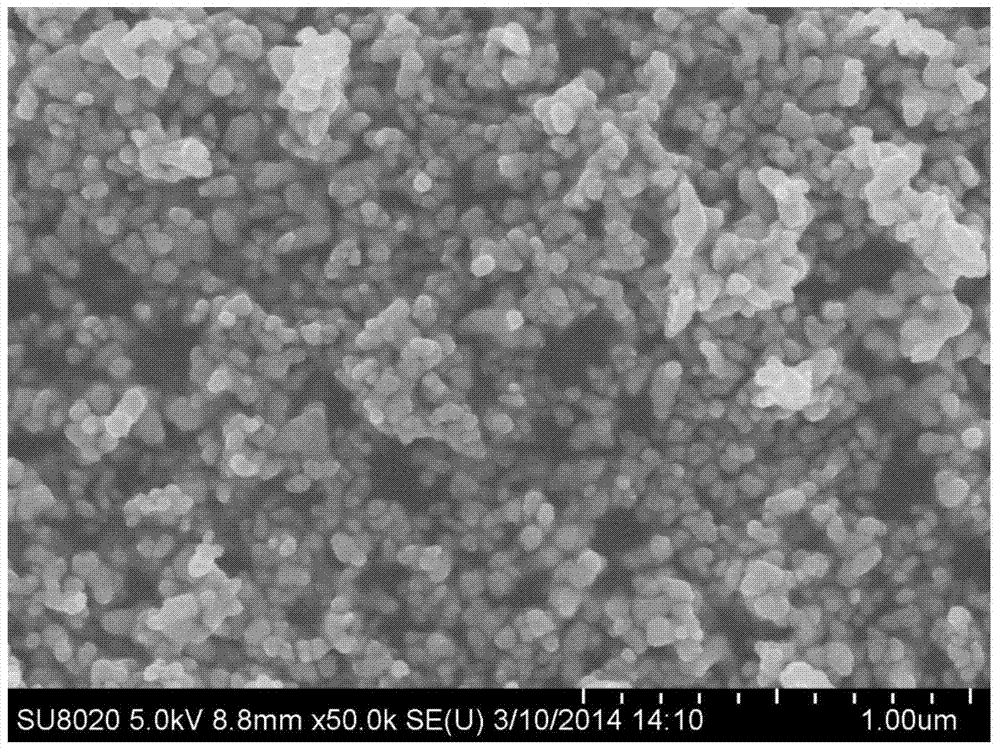
Preparation method of porous nanocrystalline Cu2S counter electrode of quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell
InactiveCN104332315ALarge specific surface areaIncrease contact surfaceLight-sensitive devicesCuprous sulfideSolar cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of solar cells and energies, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a porous nanocrystalline Cu2S counter electrode of a quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell. The preparation method comprises the steps of: regarding copper acetate and thioacetamide as precursors; obtaining 20-100 nm cuprous sulfide (Cu2S) nanometer particles through solvothermal reaction; preparing the cuprous sulfide (Cu2S) nanometer particles and ethanol into a thick liquid; forming 5-10 microns Cu2S nanocrystalline porous film on a conductive base body by utilizing a knife coating method, a silk screen print method or a spin-coating method; sintering at 300-500 DEG C in an inert atmosphere or vacuum for 10-60 min to obtain a battery electrode. The prepared Cu2S nanometer porous counter electrode extremely increases contact area of the counter electrode and electrolyte, further increases catalytic reaction site of the Cu2S and the electrolyte, and improves performance of the solar cell. In addition, the preparation method of the porous nanocrystalline Cu2S counter electrode of the quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell is simple in preparation technology, relatively low in cost and has wide application foreground and wide research values.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Heterojunction solar cell and interfacing processing method and preparing technology thereof
InactiveCN103762276AEnhanced built-in electric fieldReduce recombination lossPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionJunction formation
The invention discloses a heterojunction solar cell and an interfacing processing method and preparing technology thereof. According to the interface processing method of the heterojunction solar cell, in the preparing technology of the heterojunction solar cell, highly doping processing is conducted on the front surface of a crystalline silicon wafer with the ion implantation technology or the diffusion technology so that a heavy doped layer can be formed on the front surface of the crystalline silicon wafer, and then the Fermi level of the surface of the crystalline silicon water of the heterojunction solar cell is changed and an built-in electric field is enhanced. According to the method, the built-in electric field of the substrate interface of crystalline silicon can be enhanced, separation and conveyance of current carriers on the border of a depletion region can be promoted more effectively, film / crystalline silicon abrupt junction formation is facilitated, the width of a depletion layer on the base region of the crystalline silicone is reduced, light absorption efficiency is improved, recombination losses of the current carriers are reduced, and the voltage characteristic of a heterojunction efficient battery is improved.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD
Near-infrared flexible detector based on optical microcavity effect and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111490167AImprove detection performanceReduce recombination lossSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin membranePhotodetection
The invention relates to the technical field of photoelectric detection, in particular to a near-infrared flexible detector based on an optical microcavity effect and a preparation method of the near-infrared flexible detector. The invention discloses the near-infrared flexible detector based on an optical microcavity effect. The detector comprises a glass substrate, a flexible substrate is attached to the glass substrate, a transparent conductive electrode ITO is plated on the flexible substrate, the transparent conductive electrode ITO is sequentially coated with an electron transport layer,an organic functional layer and a hole transport layer from bottom to top in a spinning manner, a metal electrode layer is plated on the hole transport layer, and the flexible substrate comprises a plastic substrate, a stainless steel substrate, an ultrathin glass substrate, a paper substrate and a biological composite film substrate. According to the near-infrared flexible detector, the problemof large half-wave peak width of an organic photoelectric detector is solved, and the problems of poor detection performance and no dynamic detection capability in a near-infrared band are also solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Photo-electric equipment and batch spherical semiconductor grain producing equipment
InactiveCN1357927AEasy to manufactureEfficient aggregationPolycrystalline material growthFinal product manufactureElectrical conductorLight beam
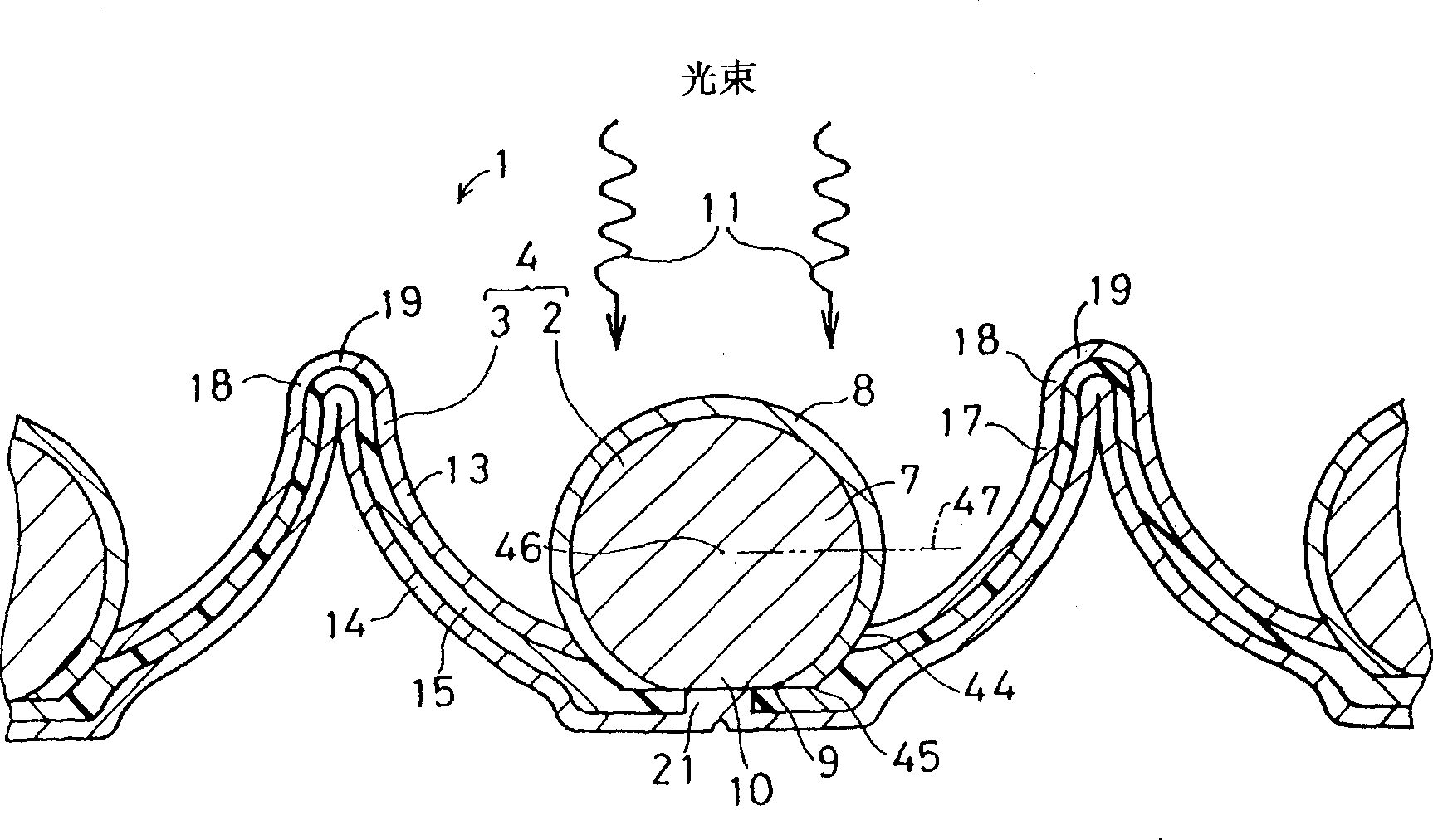
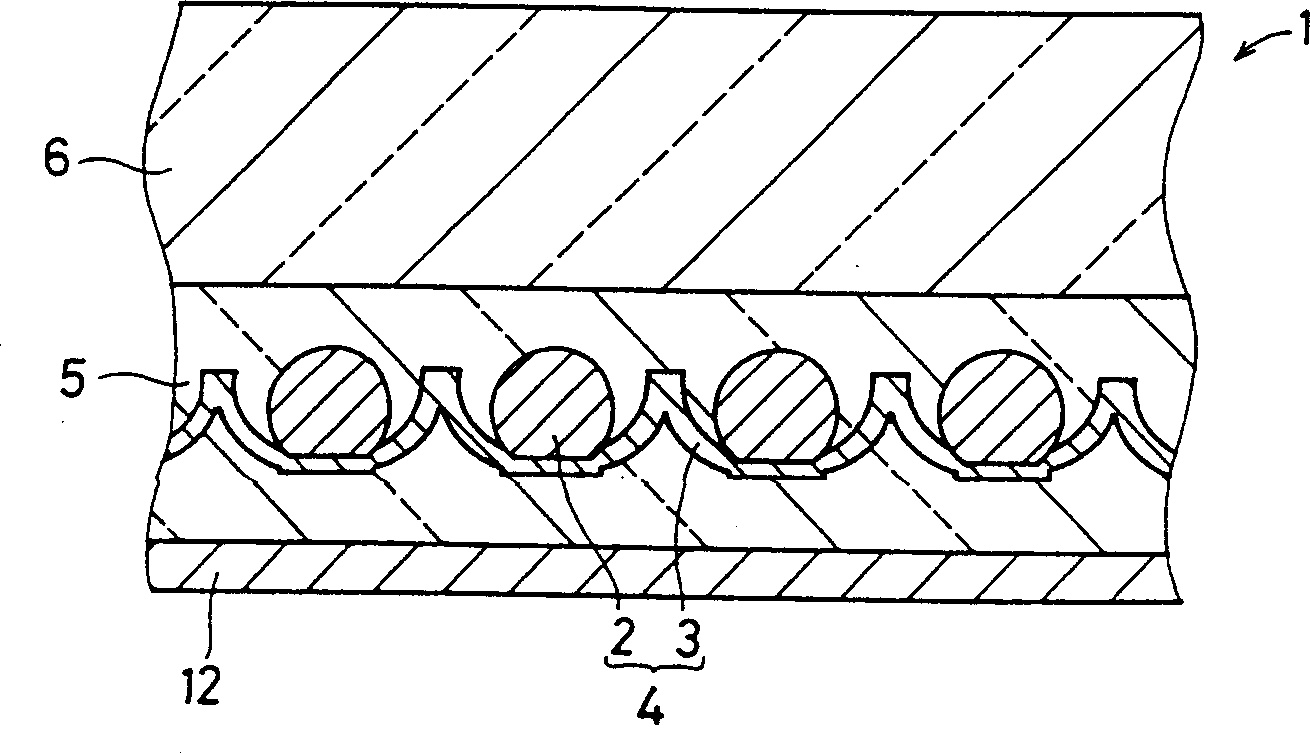
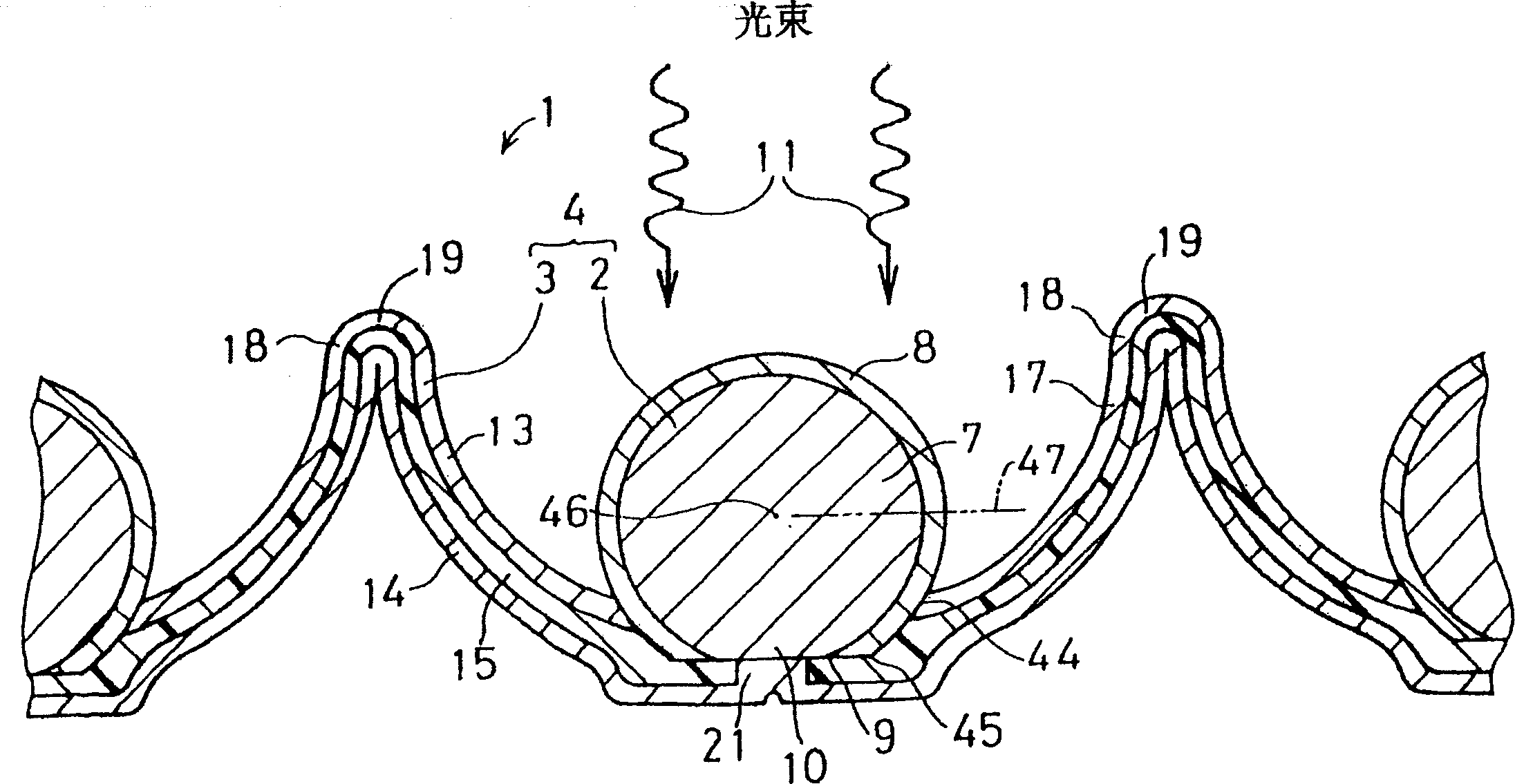
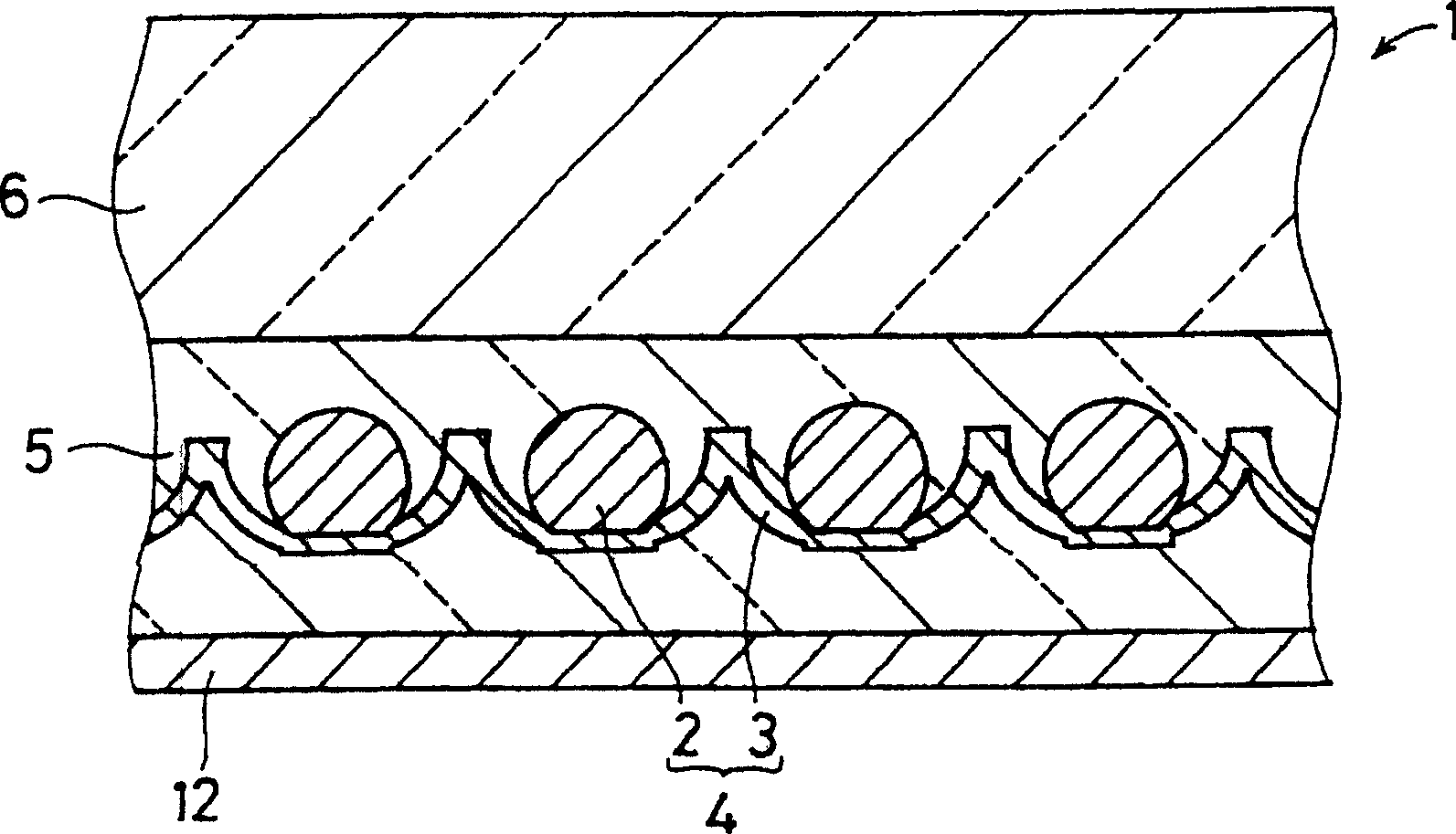
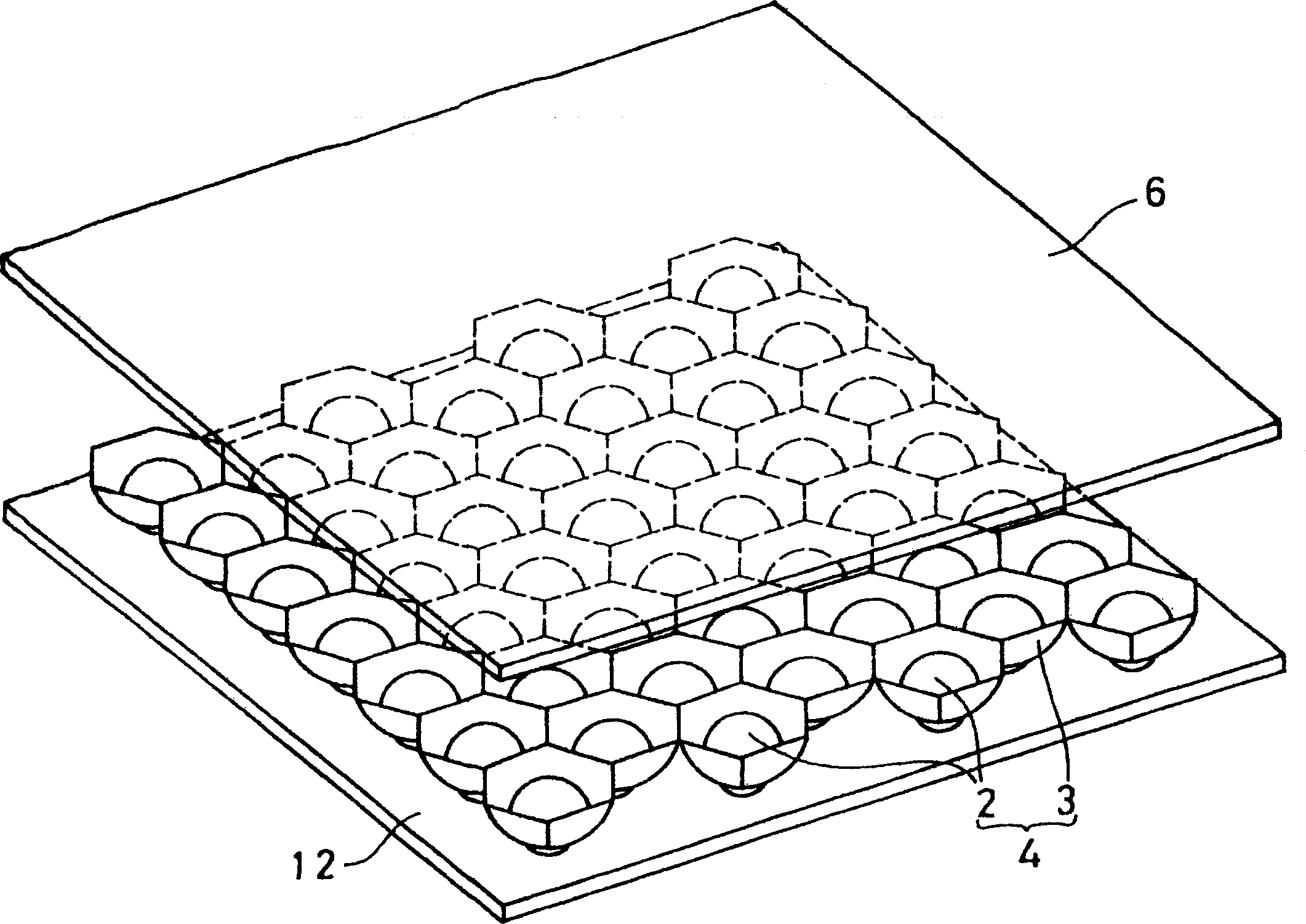
A photoelectric conversion element is disposed in each of a plurality of recesses of a support. Light reflected by the inside surface of the recess shines on the photoelectric conversion element. The photoelectric conversion element has an approximately spherical shape and has the following structure. The outer surface of a center-side n-type amorphous silicon (a-Si) layer is covered with a p-type amorphous SiC (a-SiC) layer having a wider optical band gap than a-Si does, whereby a pn junction is formed. A first conductor of the support is connected to the p-type a-SiC layer of the photoelectric conversion element at the bottom or its neighborhood of the recess. A second conductor, which is insulated from the first conductor by an insulator, of the support is connected to the n-type a-Si layer of the photoelectric conversion element.
Owner:CLEAN VENTURE 21
Batch spherical semiconductor grain producing equipment and method
InactiveCN1706993AFirmly connectedEasy to manufactureBy zone-melting liquidsPhotovoltaic energy generationGas phaseCrucible
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a photovoltaic device at low cost by reducing the consumption of high purity Si material. SOLUTION: Photoelectric conversion elements 2 are mounted in a plurality of recesses 17 formed on a support 3, respectively, and reflected light inside the recesses 17 is cast to the photoelectric conversion element 2. The photoelectric conversion element is almost spherical, and a p-type amorphous SiC (abbreviated a-SiC) layer 8 with an optical band gap wider than an n-type amorphous Si (abbreviated a-Si) is applied to the outer side of the n-type a-Si layer 7 on the center side. Then a p-n junction is formed. A first conductor 13 of the support is connected with the p-type a-SiC layer 8 of the photoelectric conversion element at the bottom of a recess or the nearby place thereof. A second conductor 14 through an electrical insulator 15 of the support is connected with the n-type a-Si layer 7 of the photoelectric conversion element.
Owner:CLEAN VENTURE 21
Collimated ionizer and method
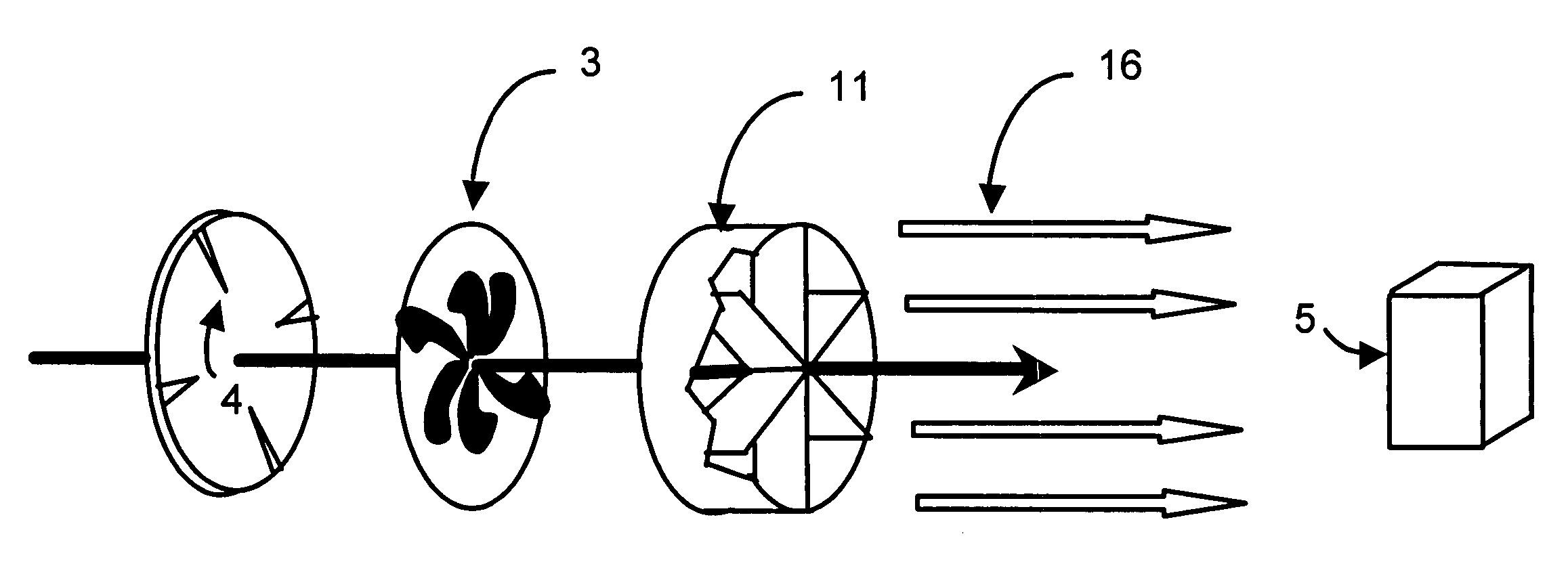
ActiveUS7295418B2Improve performanceDelivering generated ions more effectivelyParticle charging/ionising stationsVapor flow controlIon densityAir entrainment
An air ion collimator is added to ionizers with integrated fans that are used to remove static charge. Three mechanisms minimize air ion losses through recombination. Hence, the collimator increases the air ions that are available for charge removal. First, reducing turbulence slows air ion mixing. Second, air entrainment into fast moving air ion zones further slows the rate of air ion losses by dilution. The rate of recombination reaction slows with decreasing ion density. Third, vanes within the collimator delay mixing. In addition to conserving air ions, the collimator directs more ions to the target. Air ions lost to grounding are reduced. Again, more air ions are available to remove static charge from the target.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Two-sided differentiated textured structure for monocrystal silicon heterojunction solar cells and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109638103ASmall specific surface areaReduce dosageFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationPower flowSolar cell
The invention relates to a two-sided differentiated textured structure for monocrystal silicon heterojunction solar cells, which is characterized in that the light receiving side and the shady side ofa silicon wafer side structure are of different structures, the light receiving side is a pyramidal textured structure, and the shady side is a polished side or a pyramidal textured structure largerthan the light receiving side. A chain cleaning machine is used for texturing in the whole process, and the shady side is etched by wet chemical etching after groove texturing, so that the pyramidal textured structure is enlarged or polished. Then, RCA cleaning, HF natural oxidation layer removing, slow lifting and drying are carried out. The textured structures of the light receiving side and theshady side are designed separately based on the different light entry characteristics of the two sides, and the problem on how to produce and manufacture a differentiated textured structure is solved. A simplified process which can reduce the subsequent production cost and take into account the composite loss of the back surface and the short circuit current is provided.
Owner:JIANGSU WANJI DRIVE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Photovoltaic cell and method of manufacturing such a cell
InactiveUS20140137934A1Reduce lossReduce recombination lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationElectrical conductorSemiconductor
A fire through conductor paste is applied as a plurality of mutually separate islands on a dielectric layer on a semi-conductor body of a photo-voltaic cell. A connecting structure of a further conductor paste is applied connecting the islands, at least on the dielectric layer between locations of the islands, so that the islands are connected by the connecting structure. Different compositions are used for the fire through conductor paste and the further conductor paste, which behave differently during firing. The fire through conductor paste and the further conductor paste are fired under process conditions wherein the fire through conductor paste fires through the dielectric layer and the further conductor paste does not fire through the dielectric layer. In this way the fire through metal paste establishes electric contact through the dielectric layer between the semi-conductor body and a structure formed from the further conductor paste.
Owner:STICHTING ENERGIEONDERZOEK CENT NEDERLAND
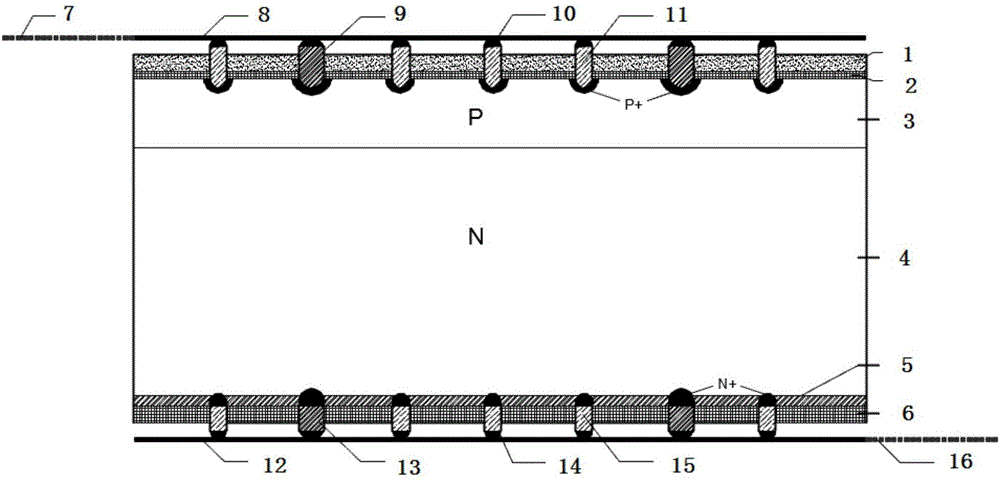
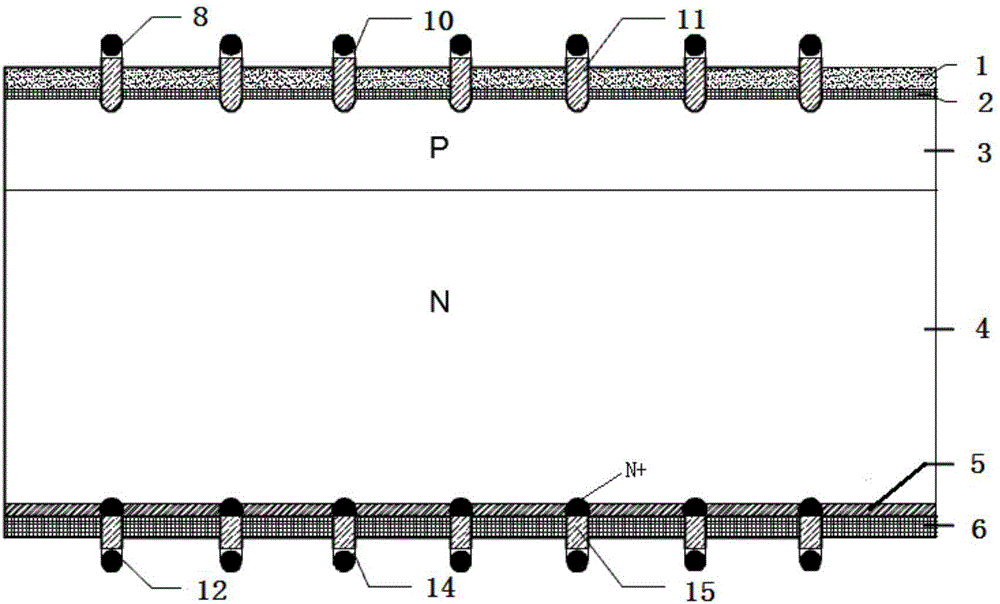
Deep hole staggered back contact solar battery structure and manufacturing method thereof
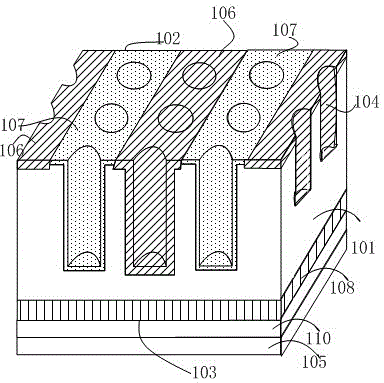
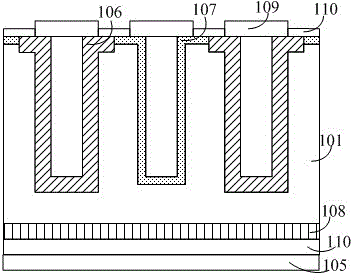
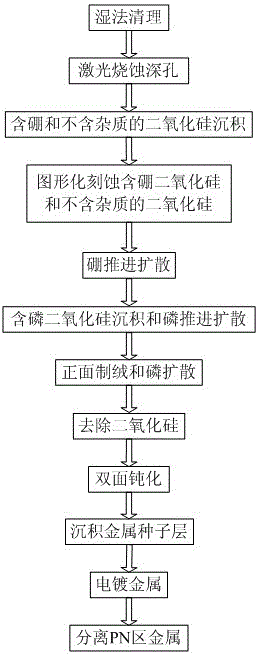
ActiveCN102779866AAddress effectivenessShorten the diffusion distanceFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar battery
The invention relates to a photovoltaic device for converting optical energy into electrical energy, and specifically relates to a deep hole staggered back contact solar battery structure and a manufacturing method of the photovoltaic device. By adopting a laser ablation method, deep holes with same depth are respectively formed on the upper surfaces of a P+ type diffusion zone and a N+ type diffusion zone which are formed on the back surface in a staggered manner, wherein the deep holes are not deep enough to reach a doping zone on the front surface of a silicon substrate. The deep holes respectively have same doping concentration and doping depth with the local diffusion zone. According to the invention, by the method of manufacturing the deep holes on a base electrode and an emitting electrode, the problems of failure in effective collection of some short life current carriers and high series resistance cased by long transmission distance of the current carriers in the conventional staggered back electrode scheme are solved. The deep hole structure greatly shortens the diffusion distance of the photon-generated carriers, thus, more photon-generated carriers are collected and the recombination loss of the photon-generated carriers is reduced, the series resistance of batteries is reduced, and the conversion efficiency of the solar battery is further improved.
Owner:张家口环欧国际新能源科技有限公司
Charge narrowing absorption effect-based perovskite photoelectric detector having vertical energy gap gradient and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN109904324AReduce recombination lossReduce half peak widthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron transmissionOptical detectors
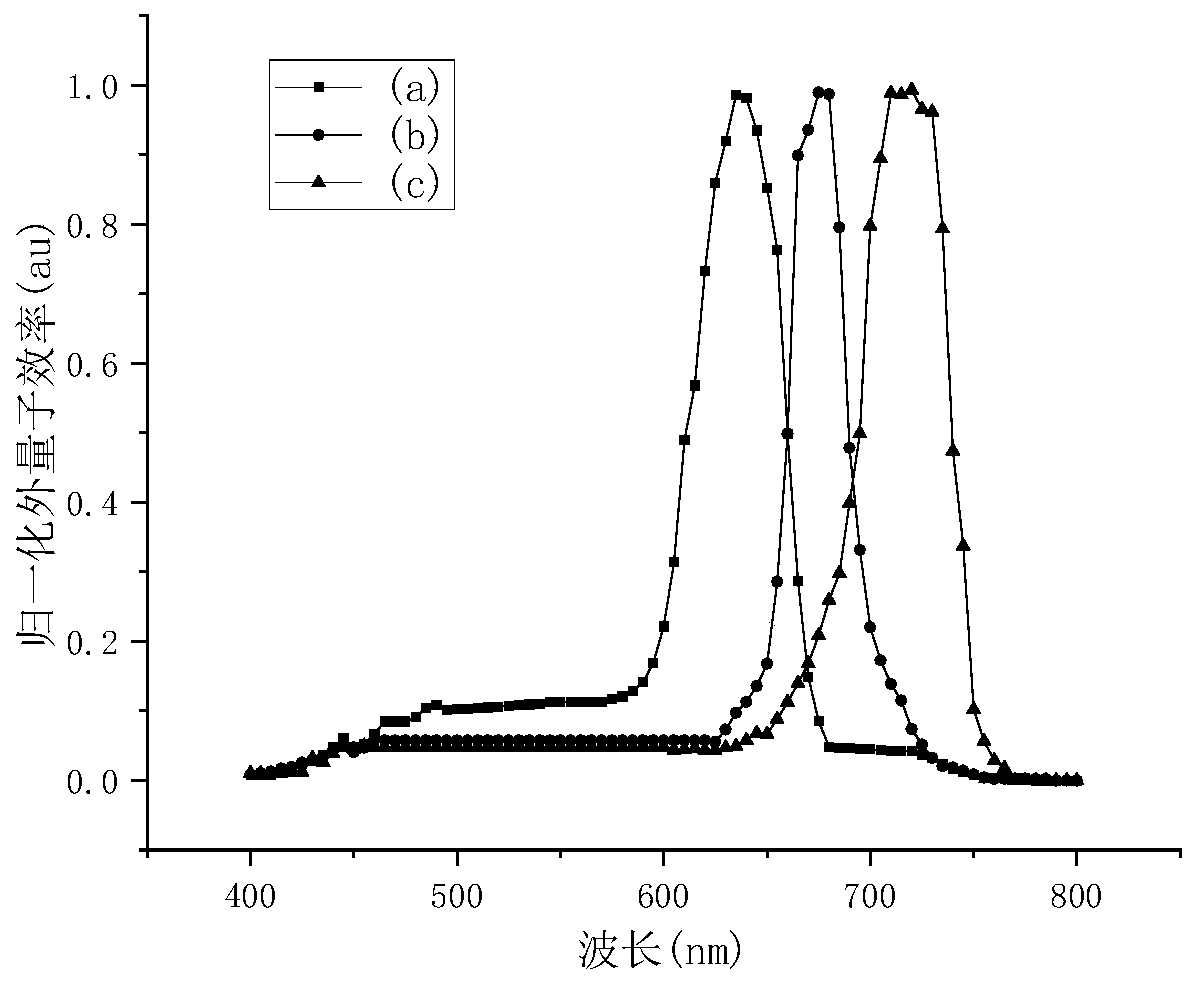
The invention discloses a charge narrowing absorption effect-based perovskite photoelectric detector having vertical energy gap gradient and a fabrication method thereof. The perovskite photoelectricdetector comprises a glass substrate, a first transparent conductive electrode layer, a first hole transmission layer, a perovskite sensitive layer a, a first electron transmission layer, a first holeblocking layer, a second transparent conductive electrode layer, a second hole transmission layer, a perovskite sensitive layer b, a second electron transmission layer, a second hole blocking layer,a third transparent conductive electrode layer, a third hole transmission layer, a perovskite sensitive layer c, a third electron transmission layer, a third hole blocking layer, a metal electrode layer. By the perovskite photoelectric detector, the half-wave peak width of the optical detector is effectively narrowed, the detection performance of the perovskite optical detector is improved, lightwaves of three different bands can be simultaneously detected, moreover, the fabrication method is simple and effective and is suitable for mass production.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Low-cost and efficient crystalline silicon solar cell module
InactiveCN109461776AShorten the transportation distanceReduce recombination lossFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationPolycrystalline siliconCrystalline silicon
The invention discloses a low-cost and efficient crystalline silicon solar cell module. The knotting is performed on a polished polycrystalline silicon wafer surface or monocrystalline silicon surfacewithout performing surface texturing processing, and then a passivation film and an anti-reflection film are orderly deposited, an electrode is prepared to form a cell, and then the cell and the EVAand the photovoltaic glass are packaged as the module. The carrier conveying distance is greatly shortened, and the passivation film and the anti-reflection film are separately optimized, so that thepassivation effect of the cell can reach the optimum, the composite loss is reduced, an open-circuit voltage and the filling factor of the cell are improved. Compared with the solar cell in the texturing technology, the influence of a system serial resistor caused by the solder strip in the module and the transmission loss in the conductor for system connection can be reduced; the dosage of the chemical reagent is greatly reduced, the fragment rate in the production and the sub-fissure in the module production can be reduced, the process is simple, the cost is low, and the efficiency is high;the absorption on the infrared radiation by the surface I s reduced, the cell temperature is reduced, and the module efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Solar cell module
InactiveCN104916718AReduce collection lossReduce thermal lossPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesConductive polymerCoupling
A tandem solar module includes first and second thin film solar cell circuits and a transparent coupling layer disposed between the first and second thin film circuits for securing the first and second thin film circuits together in a stack. Each solar cell circuit includes a multi-layer structure, the multi-layer structure including a substrate, a first conductive layer formed over the substrate, a buffer layer, an absorber layer formed between the first conductive layer and the buffer layer, and a second conductive layer formed over the buffer layer. The first thin film solar cell circuit and second thin film solar cell circuit are oriented with respect to one another such that the absorber layers are disposed between the substrates of the circuits. The first and second solar cell circuits have different bandgap profiles.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
PERC battery with novel front structure
InactiveCN111223945AIncrease IscRaise VocPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesOptical transparencyTransmission loss
The invention relates to a PERC battery with a novel front structure, which comprises a P-type silicon substrate and an N+ diffusion layer formed by diffusion on the upper surface of the P-type silicon substrate, and is characterized in that a SiNx passivation layer is arranged on the upper surface of the N+ diffusion layer, the SiNx passivation layer is provided with a plurality of open slots which penetrate through the SiNx passivation layer and are distributed in a grid line pattern, the SiNx passivation layer and the open slots are covered with a transparent conductive TCO film, and metalmain grids are printed on the surface of the TCO film and above the open slots corresponding to the main grids. According to the invention, a metal fine grid on the battery is cancelled; photogenerated current generated by a transmission silicon substrate is collected by utilizing the characteristics of optical transparency and conductivity of the TCO film; and compared with a traditional metal fine grid, the current collection effect is better, the transmission loss is less, and the composite loss can be reduced. In addition, the TCO film is transparent, so that the shielding of the metal fine grid on the light receiving surface of the battery is avoided, and the purpose of improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the battery is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG AIKO SOLAR ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Photovoltaic cell and method of manufaturing such a cell
InactiveCN103703568AReduce recombination lossPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorProcess conditions
A fire through conductor paste is applied as a plurality of mutually separate islands on a dielectric layer on a semi-conductor body of a photo- voltaic cell. A connecting structure of a further conductor paste is applied connecting the islands, at least on the dielectric layer between locations of the islands, so that the islands are connected by the connecting structure. Different compositions are used for the fire through conductor paste and the further conductor paste, which behave differently during firing. The fire through conductor paste and the further conductor paste are fired under process conditions wherein the fire through conductor paste fires through the dielectric layer and the further conductor paste does not fire through the dielectric layer. In this way the fire through metal paste establishes electric contact through the dielectric layer between the semi-conductor body and a structure formed from the further conductor paste.
Owner:STICHTING ENERGIEONDERZOEK CENT NEDERLAND
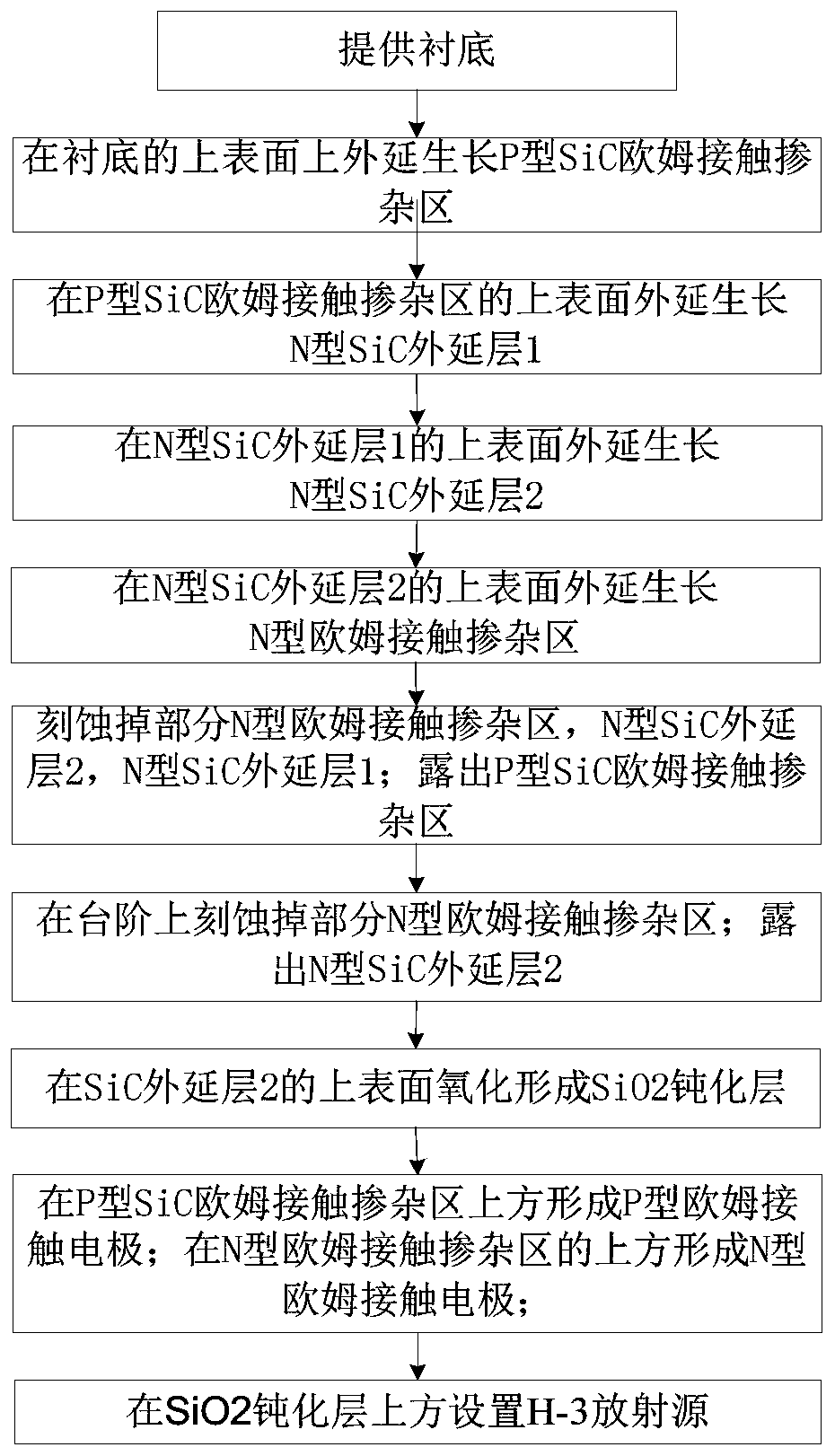
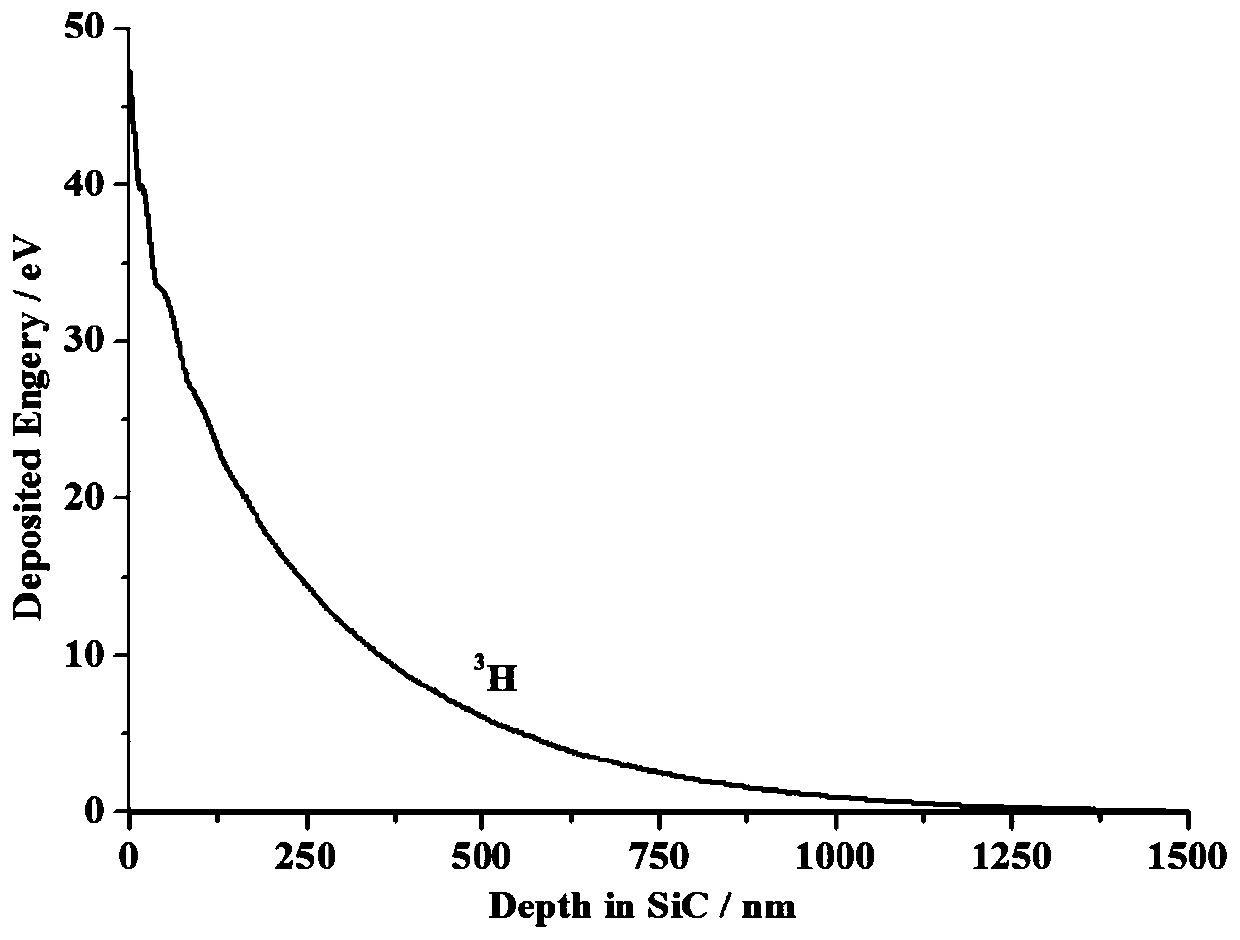
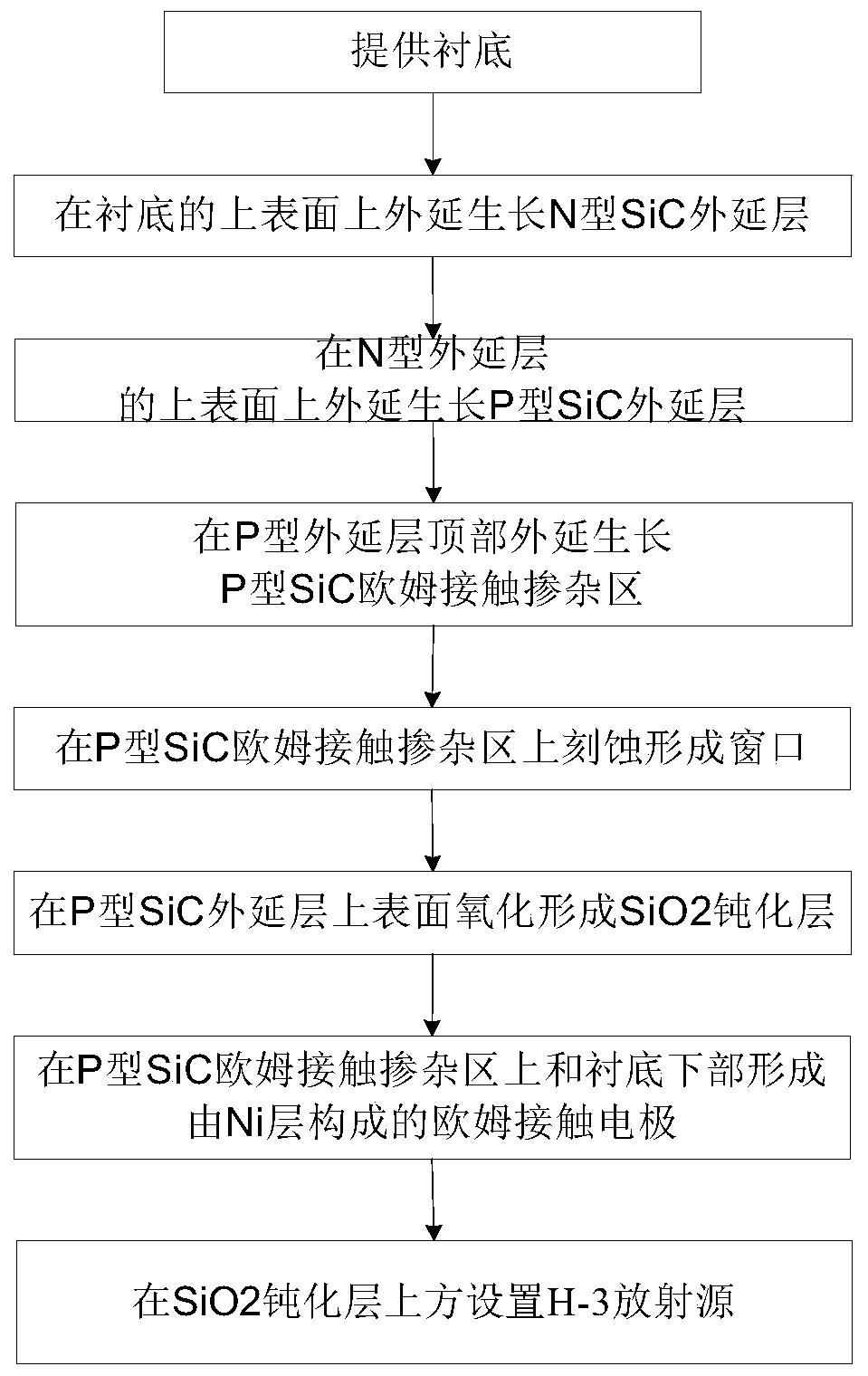
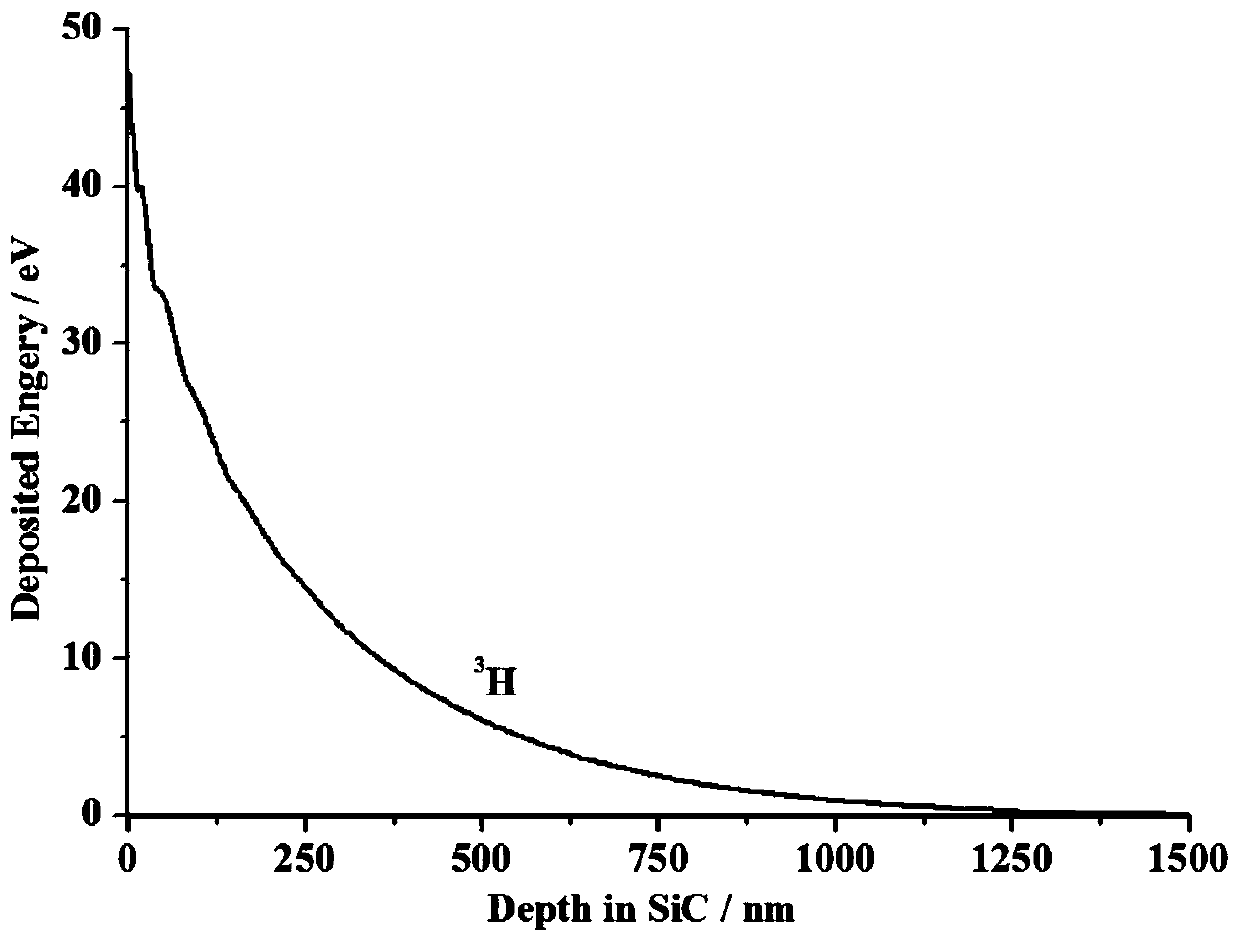
H-3 silicon carbide isotope battery and manufacturing method thereof
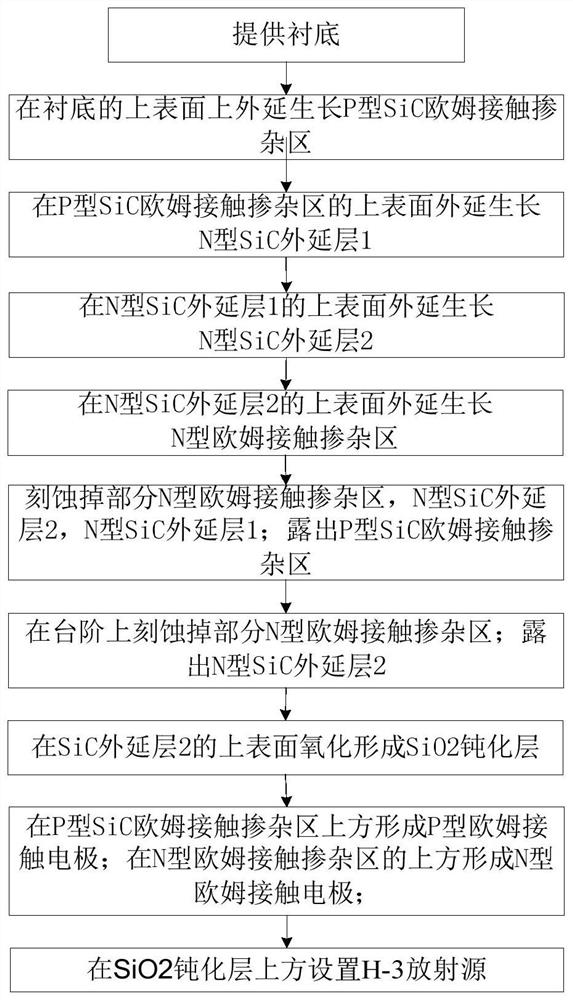
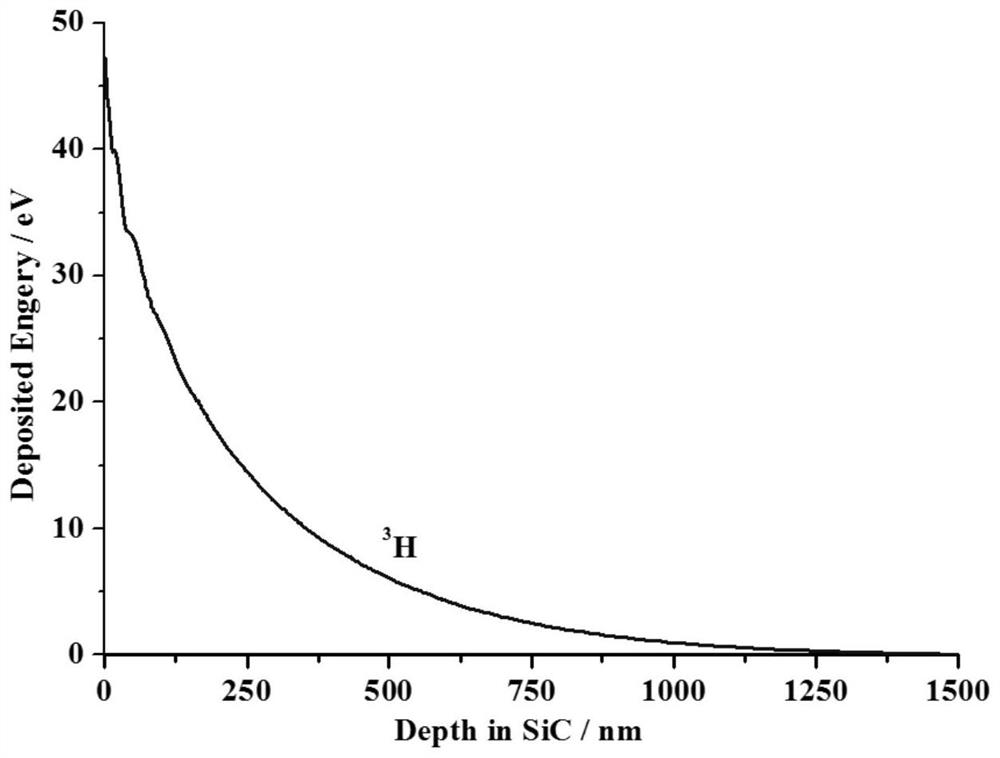
ActiveCN110491541AIncrease output powerReduce recombination lossFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationOhmic contactIsotope
The invention discloses an H-3 silicon carbide isotope battery and a manufacturing method thereof. The isotope battery comprises an N-type highly-doped SiC substrate and a P-type SiC ohmic contact doped region from bottom to top, wherein a first N-type SiC epitaxial layer is arranged in a partial region on the P-type SiC ohmic contact doped region; a second N-type SiC epitaxial layer is arranged on the first N-type SiC epitaxial layer; a P-type ohmic contact electrode is arranged in a region, except the first N-type SiC epitaxial layer, on the P-type SiC ohmic contact doped region; an N-type ohmic contact doped region is arranged partially in a region on the second N-type SiC epitaxial layer; an N-type ohmic contact electrode is arranged on the N-type ohmic contact doped region; a SiO2 passivation layer is arranged in a region, except the N-type ohmic contact doped region, on the second N-type SiC epitaxial layer; and an H-3 radioactive isotope source is arranged on the SiO2 passivation layer. The design is novel and reasonable, the problem of irradiation generated carrier recombination loss of H-3 on the surface can be effectively solved, and the output power and the energy conversion efficiency of the isotope battery are effectively improved.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Method of Manufacturing a Solar Cell and Equipment Therefore
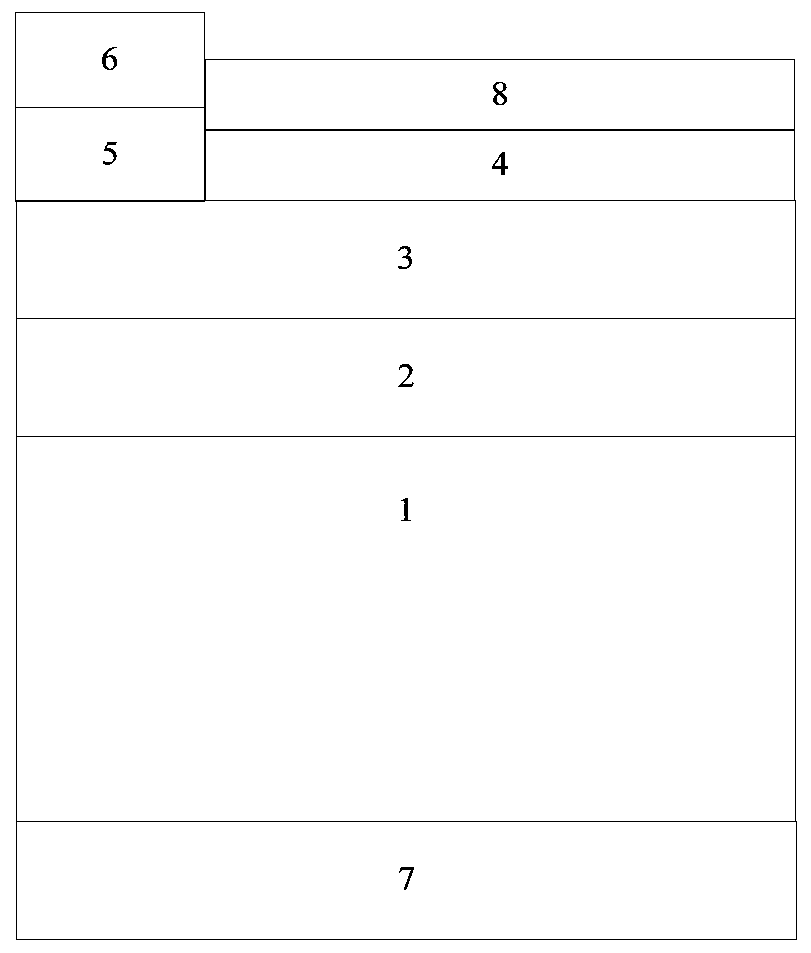
InactiveUS20150040974A1High resolutionReduce doping concentrationElectric discharge tubesFinal product manufactureCharge carrierEngineering
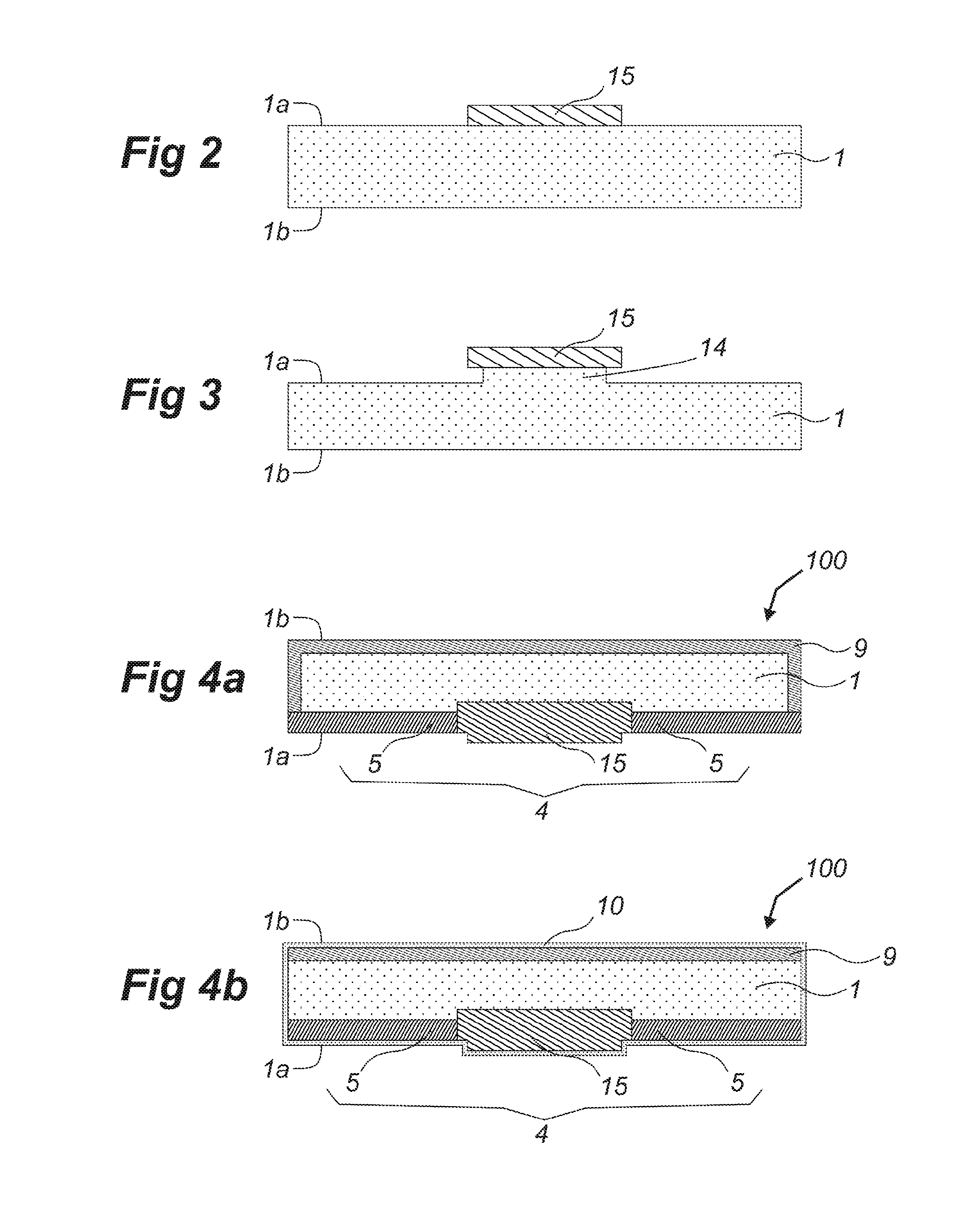
The method of manufacturing a solar cell, which comprises a semiconductor substrate (1) with a first side (1a) and an opposed second side (1b), at which first side an active region doped with charge carriers of a first conductivity type is defined selectively. The method comprises introducing said charge carriers into the substrate (1) on said first side (1a) by ion implantation in an implantation step at a dose level that induces surface amorphization, therewith forming an amorphized region. Thereafter, material in part of the amorphized region is selectively recrystallized to define a first, recrystallized subregion (5), a remaining part of the amorphized region defining a second subregion (15). Subsequently, the recrystallized material of the first subregion (5) is at least partially removed, therewith creating the selectively defined active region and inducing a surface topology between the at least partially removed first subregion (5) and the second subregion (15). An apparatus for carrying out said method and a resulting solar cell having surface topology are also provided.
Owner:TEMPRESS IP
Hybrid photovoltaic cells and related methods
InactiveUS20120028406A1Improve conversion efficiencyReduce recombination lossFinal product manufactureIndividual molecule manipulationElectron holeHeterojunction
Owner:NANOCO TECH LTD
Deep hole staggered back contact solar battery structure and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102779866BAddress effectivenessShorten the diffusion distanceFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar battery
The invention relates to a photovoltaic device for converting optical energy into electrical energy, and specifically relates to a deep hole staggered back contact solar battery structure and a manufacturing method of the photovoltaic device. By adopting a laser ablation method, deep holes with same depth are respectively formed on the upper surfaces of a P+ type diffusion zone and a N+ type diffusion zone which are formed on the back surface in a staggered manner, wherein the deep holes are not deep enough to reach a doping zone on the front surface of a silicon substrate. The deep holes respectively have same doping concentration and doping depth with the local diffusion zone. According to the invention, by the method of manufacturing the deep holes on a base electrode and an emitting electrode, the problems of failure in effective collection of some short life current carriers and high series resistance cased by long transmission distance of the current carriers in the conventional staggered back electrode scheme are solved. The deep hole structure greatly shortens the diffusion distance of the photon-generated carriers, thus, more photon-generated carriers are collected and the recombination loss of the photon-generated carriers is reduced, the series resistance of batteries is reduced, and the conversion efficiency of the solar battery is further improved.
Owner:张家口环欧国际新能源科技有限公司
A kind of h-3 silicon carbide pn type isotope battery and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN110459340BIncrease output powerReduce doping concentrationSemiconductor devicesRadiation electrical energyOhmic contactEngineering
Owner:南京绿能芯耀科技有限公司
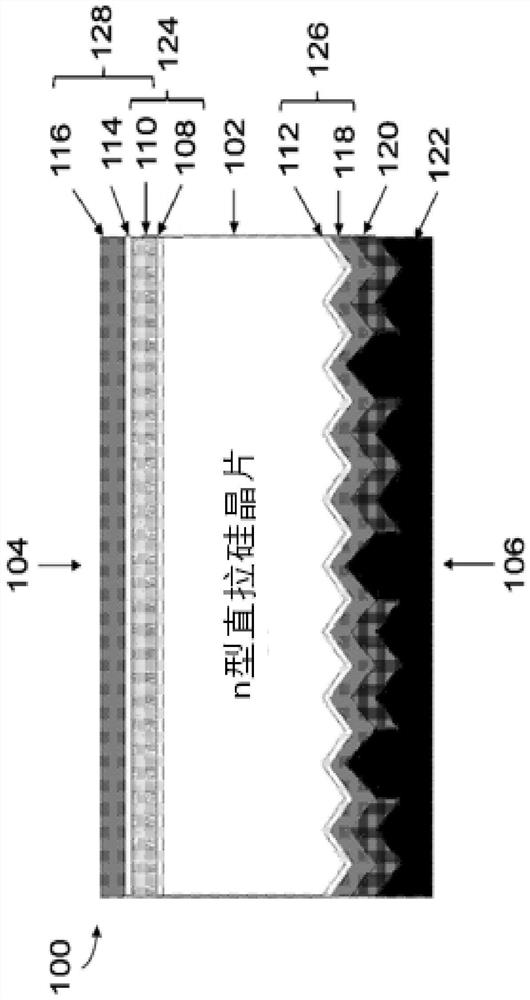
Solar cell and method for fabricating a solar cell
PendingCN113875025AIncrease the open circuit voltageImprove efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesPhysicsDoping
A solar cell is described. In an embodiment, the solar cell (100) comprises a silicon wafer having (102) a front side (104) arranged to receive incident light and a rear side (106), and a first doped semiconductor layer (110) formed on either the front side (104) or the rear side (106) of the silicon wafer (102). The solar cell (100) further comprises (i) a dielectric tunnel layer (112) deposited on one side of the silicon wafer (102) opposites to the side at which the first doped semiconductor layer (110) is formed, (ii) a front side second doped semiconductor layer (116) deposited on the front side (104) of the silicon wafer (102); and (iii) a rear side second doped semiconductor layer (118) deposited on the rear side (106) of the silicon wafer (102), the front side and the rear side second doped semiconductor layers (116), (118) each having a doping of an opposite polarity to the first doped semiconductor layer (110). The first doped semiconductor layer (110) cooperates with either the front side second doped semiconductor layer (116) or the rear side second doped semiconductor layer (118) to form a tunnel junction, and the dielectric tunnel layer (112) cooperates with either the rear side second doped semiconductor layer (118) or the front side second doped semiconductor layer (116) to form a passivated contact.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Sensitization method for PbS thin film, infrared photoelectric detector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112310242ANo high temperature requirementsSensitization temperature is lowFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsSpecific detection
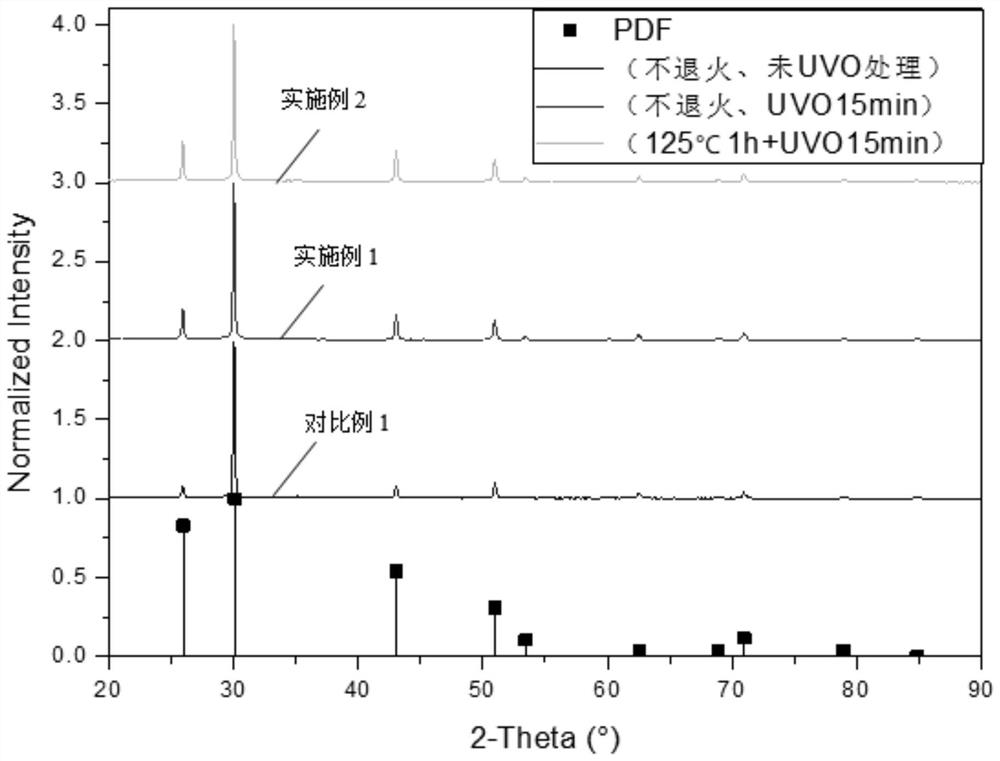
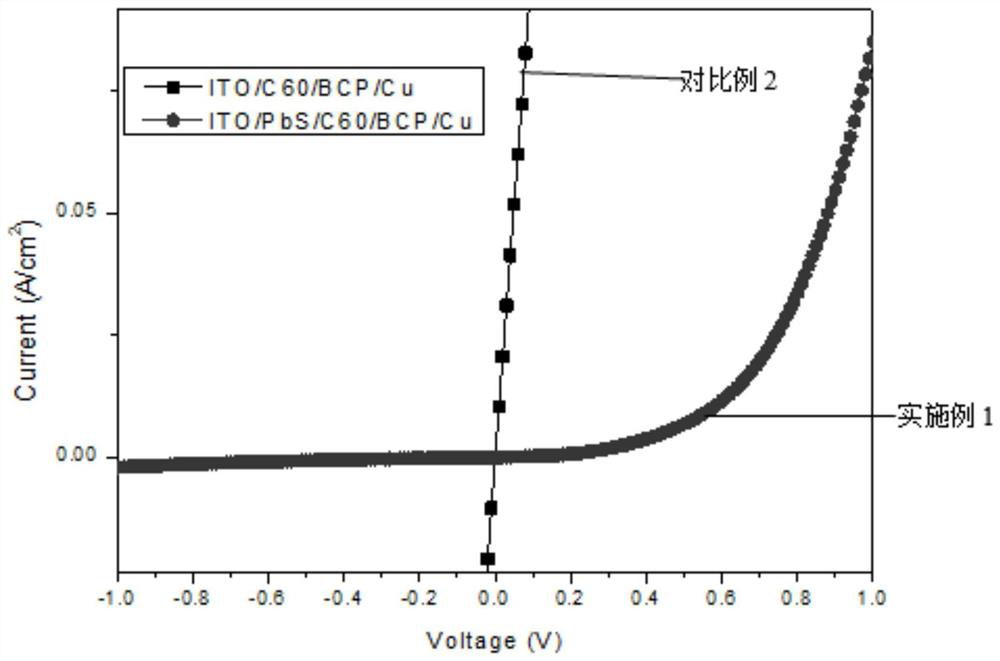
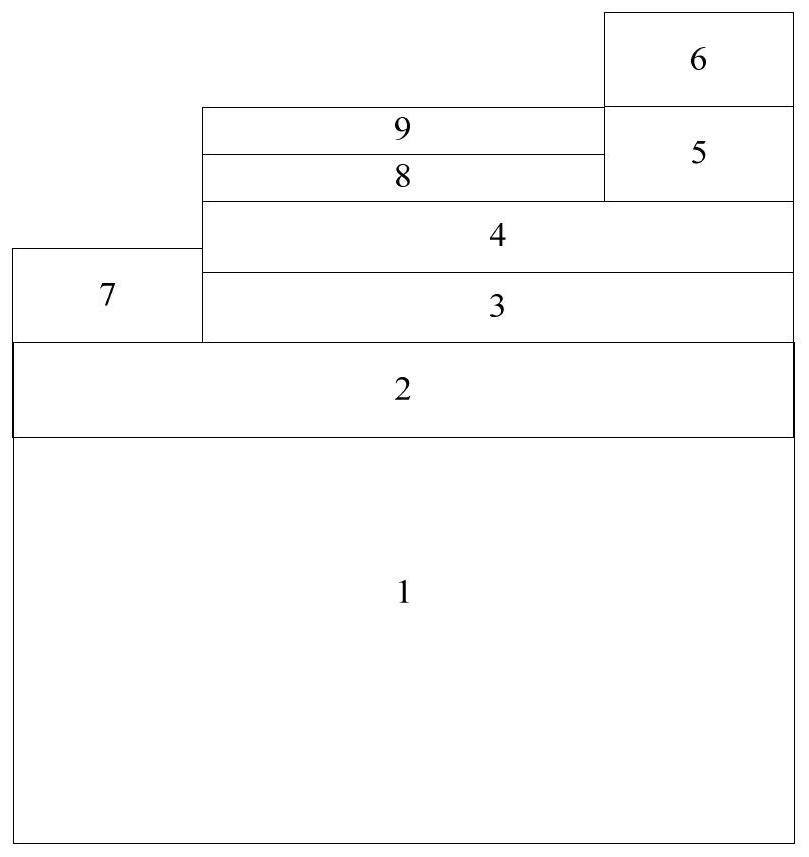
The invention relates to a novel sensitization method for a PbS thin film. According to the method, ultraviolet ozone treatment is carried out on the PbS thin film to sensitize the PbS thin film. Theinvention also relates to an infrared photoelectric detector based on the PbS film and a preparation method. The detector comprises a conductive glass or silicon wafer substrate layer, a p-type semiconductor layer, an n-type semiconductor layer, a buffer layer and an electrode layer. The p-type semiconductor layer is a PbS thin film subjected to ultraviolet ozone sensitization treatment; and the n-type semiconductor layer is fullerene C60 or a derivative thereof. According to the method, UVO sensitization treatment is adopted, the sensitization temperature is low, energy consumption is low, operation is easy, and the sensitization effect is remarkable. In addition, the infrared photoelectric detector is a high-sensitivity infrared photoelectric detector which is provided with a diode structure and can work at room temperature, and the specific detection rate is obviously superior to that of a traditional photoresistor type detector.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
A kind of h-3 silicon carbide isotope battery and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN110491541BIncrease output powerReduce recombination lossFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationCarbide siliconOhmic contact
The invention discloses a H-3 silicon carbide isotope battery and a manufacturing method thereof, comprising an N-type highly doped SiC substrate, a P-type SiC ohmic contact doping region, and a P-type SiC ohmic contact doping region from bottom to top. A first N-type SiC epitaxial layer is provided in a part of the upper part of the region, and a second N-type SiC epitaxial layer is arranged above the first N-type SiC epitaxial layer. In the upper part of the P-type SiC ohmic contact doped region, except for the first N-type SiC The region of the epitaxial layer is provided with a P-type ohmic contact electrode, and the upper part of the second N-type SiC epitaxial layer is provided with an N-type ohmic contact doped region, and an N-type ohmic contact electrode is provided above the N-type ohmic contact doped region. The area above the N-type SiC epitaxial layer except the N-type ohmic contact doped region is provided with SiO 2 passivation layer, on SiO 2 An H‑3 radioisotope source is provided above the passivation layer. The invention has a novel and reasonable design, can effectively solve the problem of recombination loss of H-3 irradiated carriers on the surface, and effectively improves the output power and energy conversion efficiency of the isotope battery.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com