Patents
Literature
48results about How to "Reduce carrier recombination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
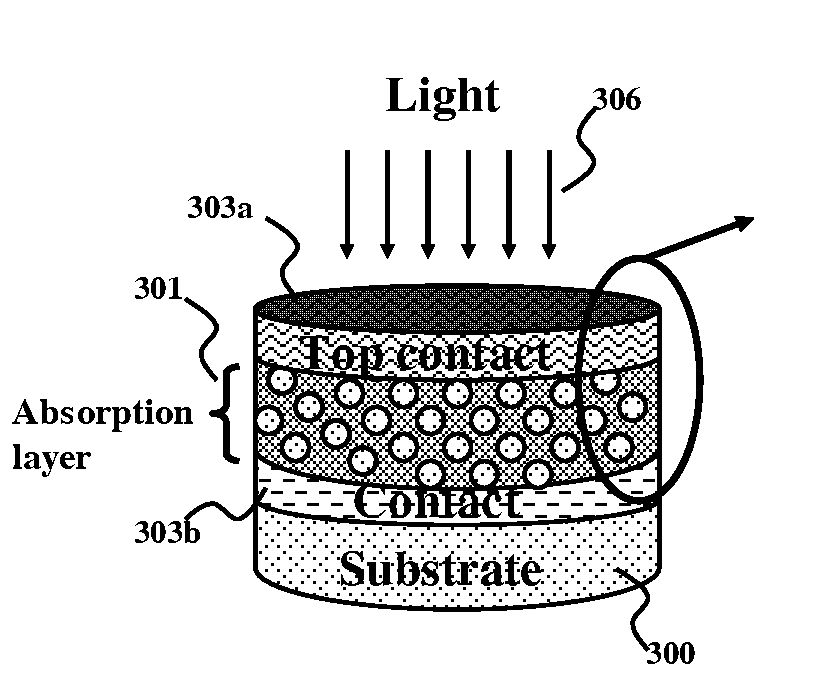
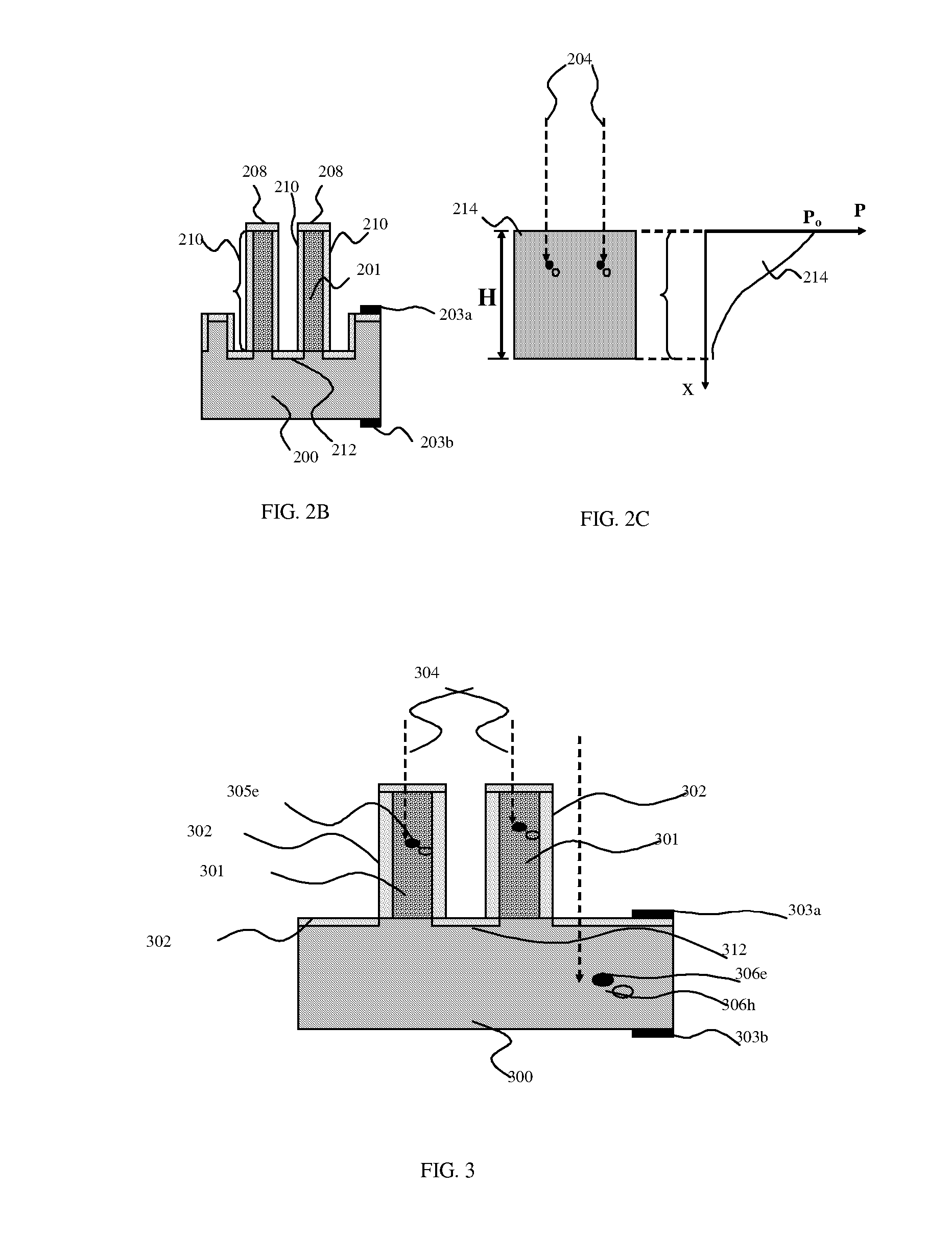
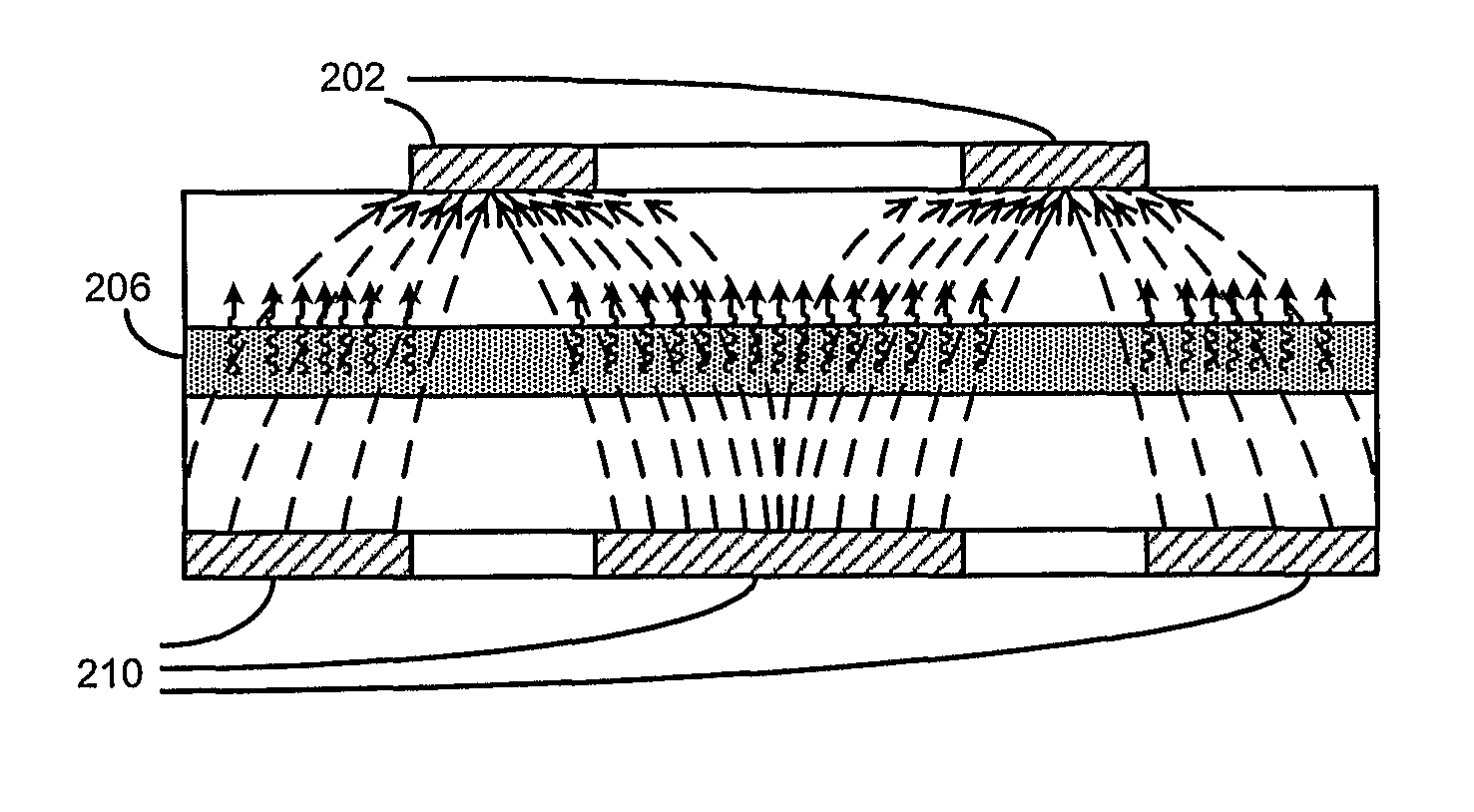
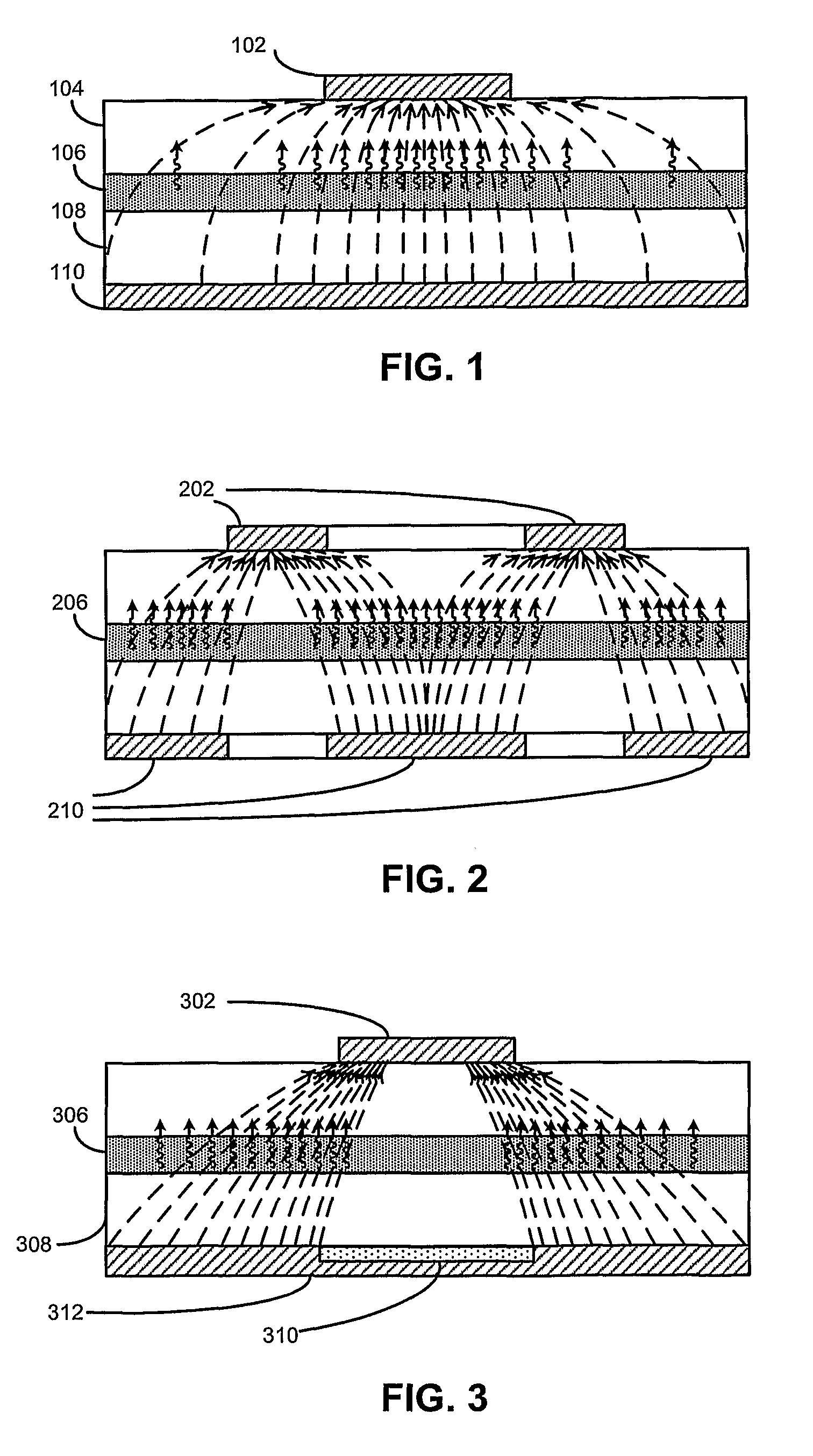
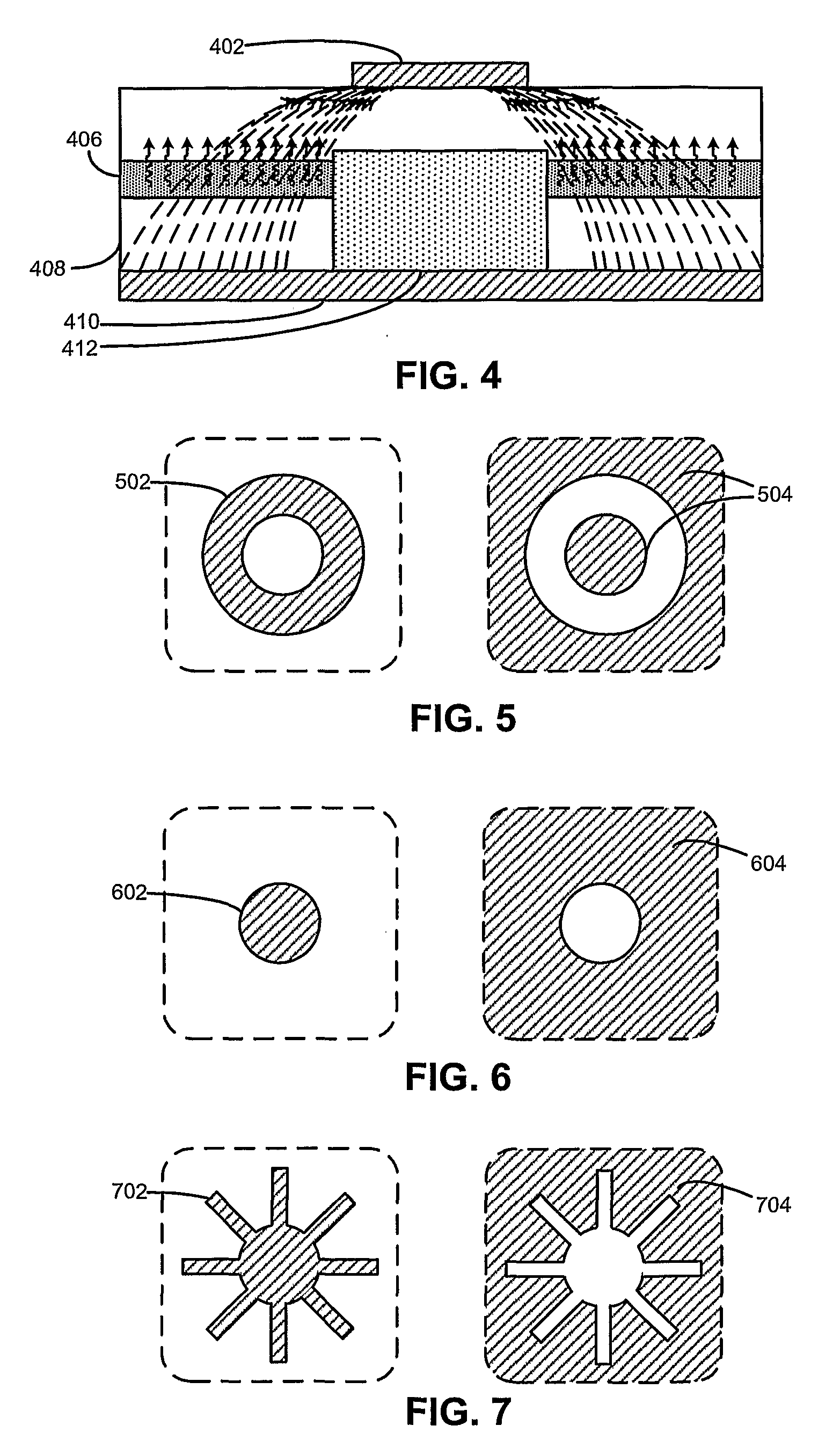
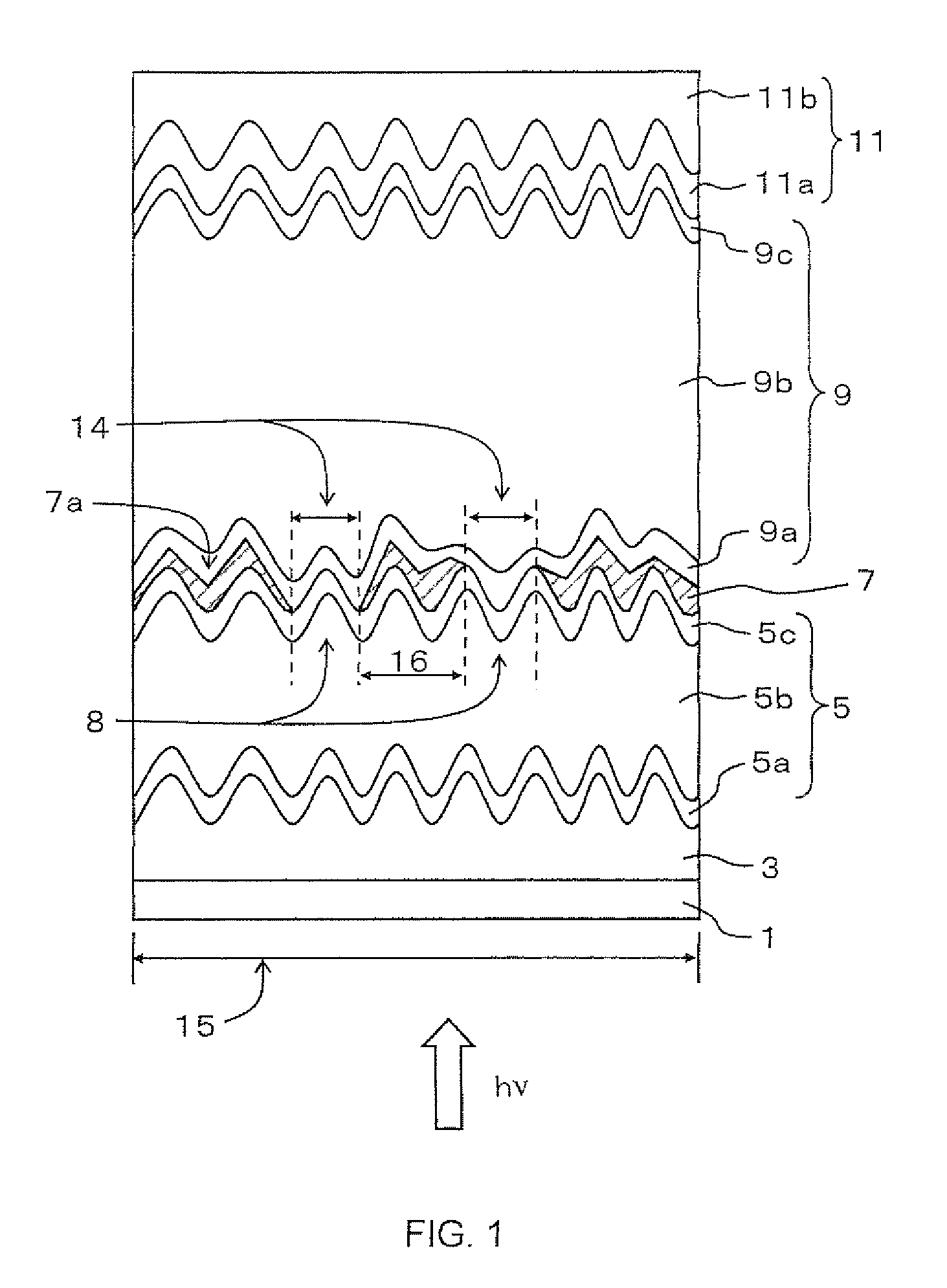
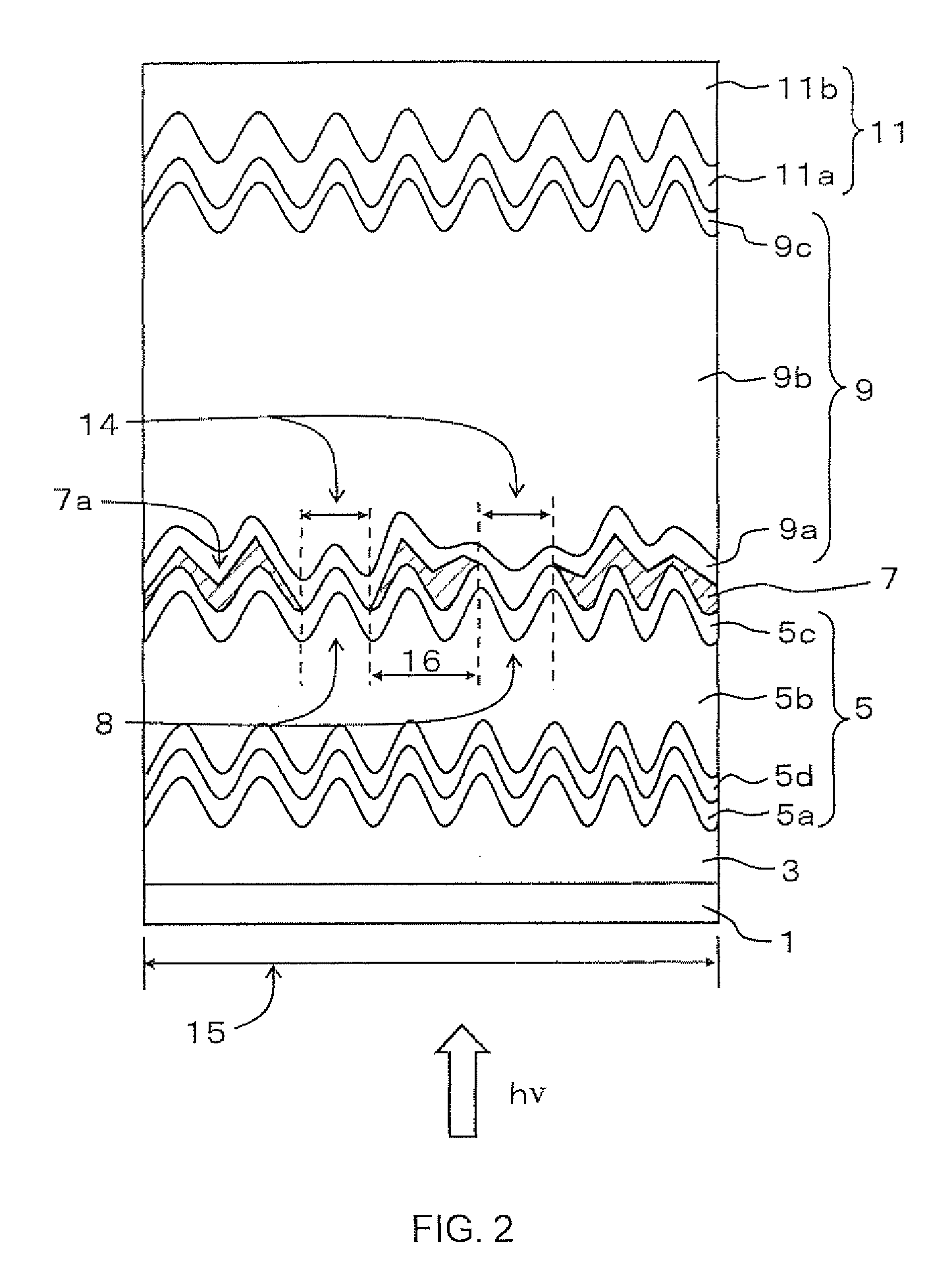
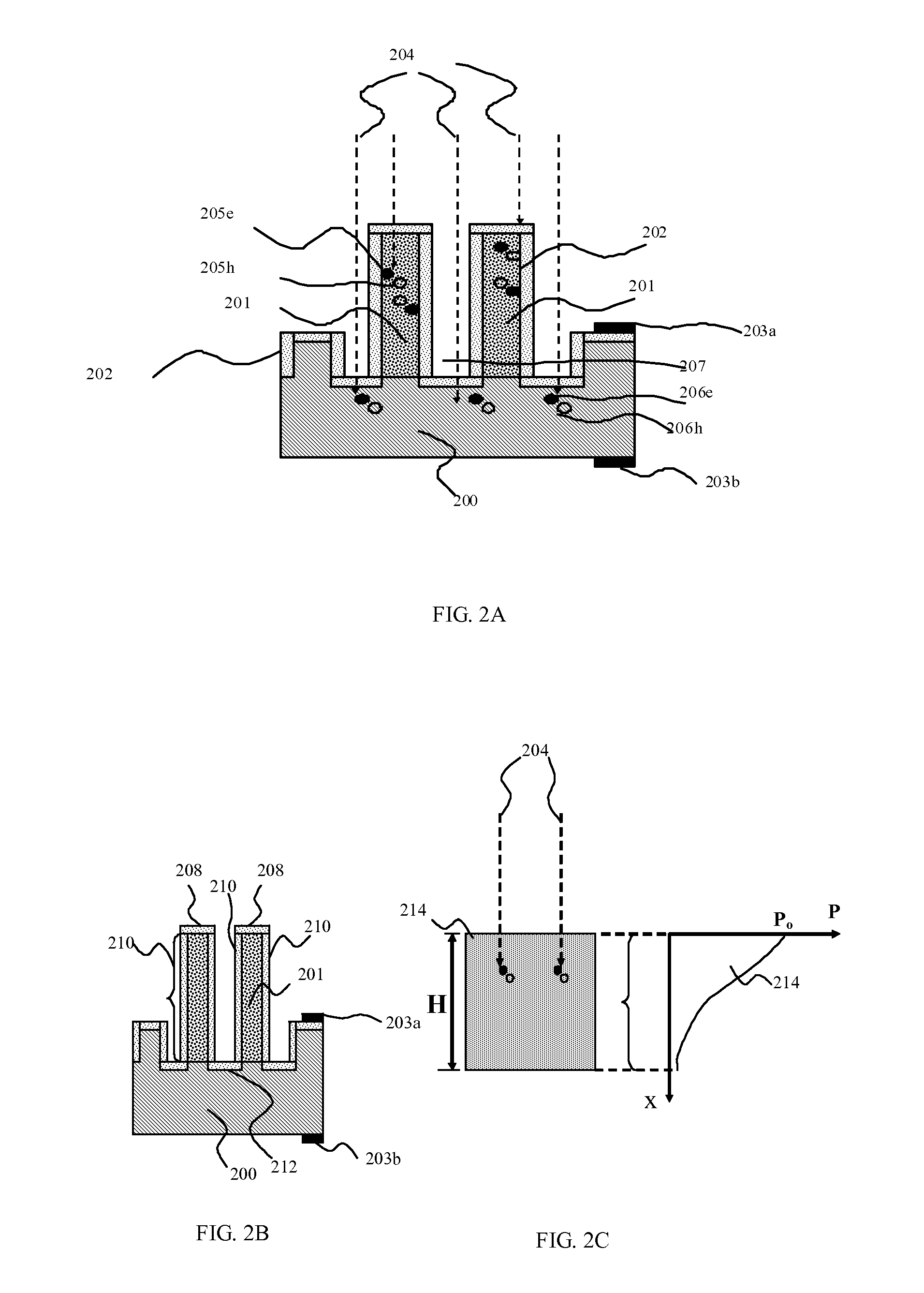
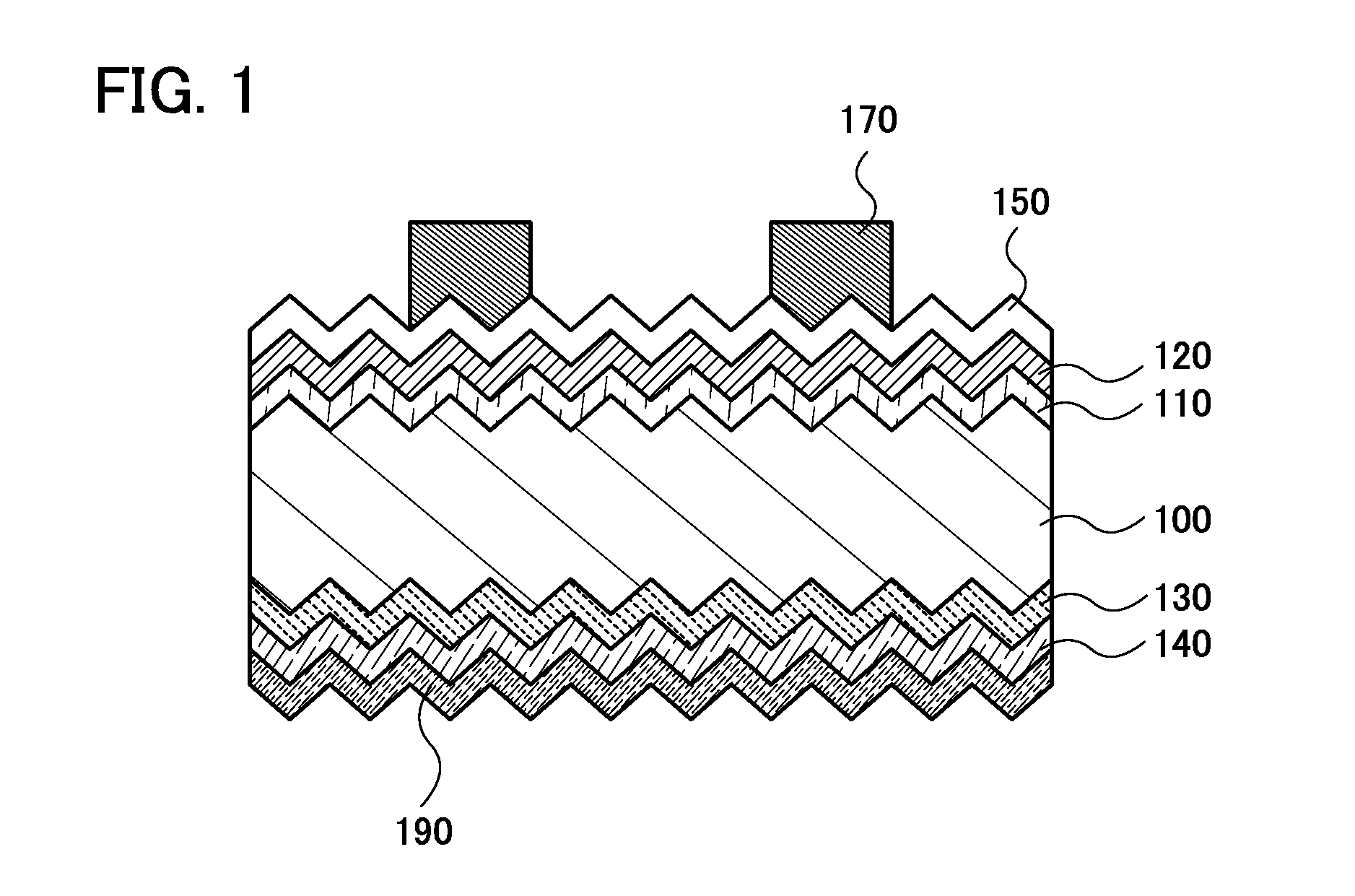
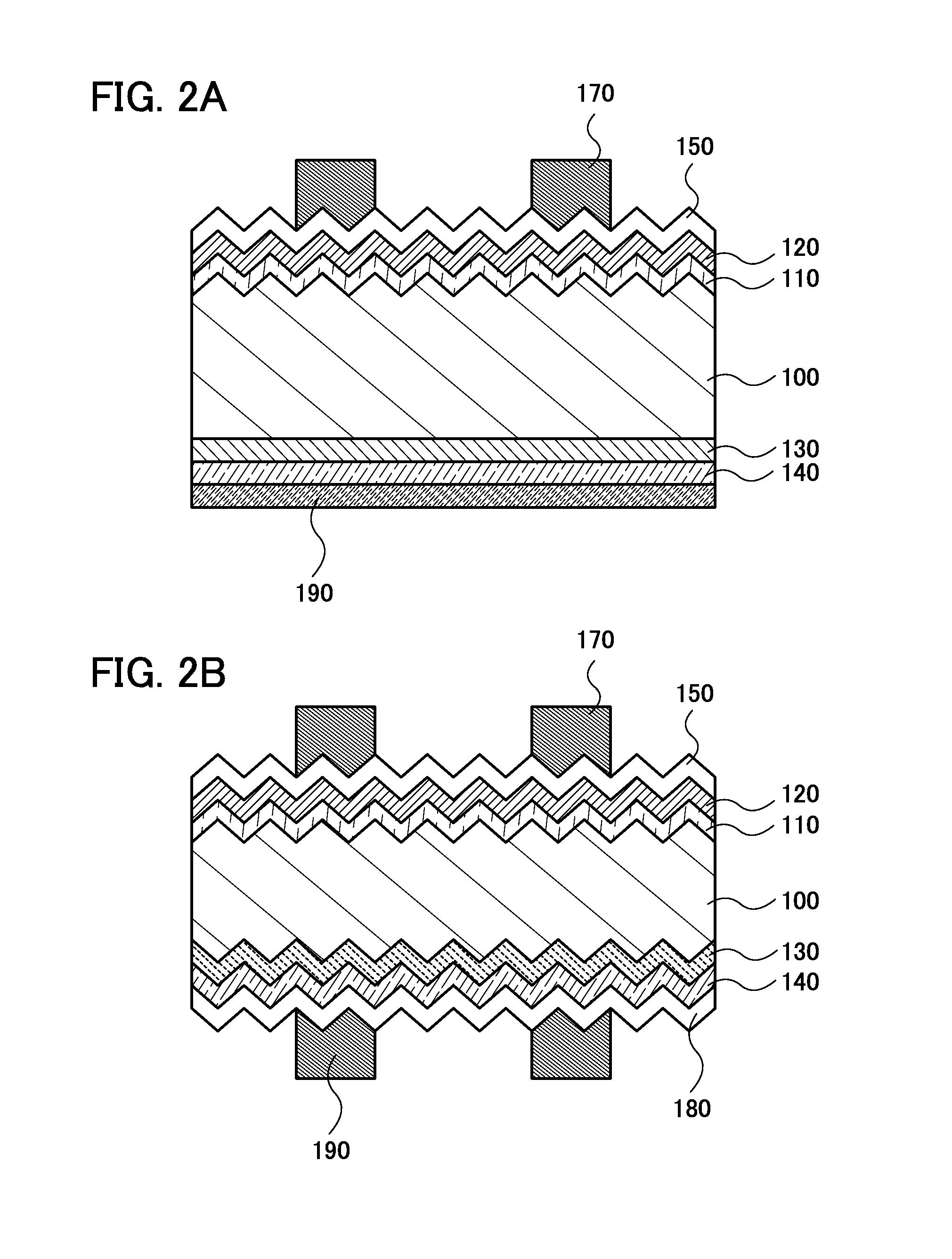
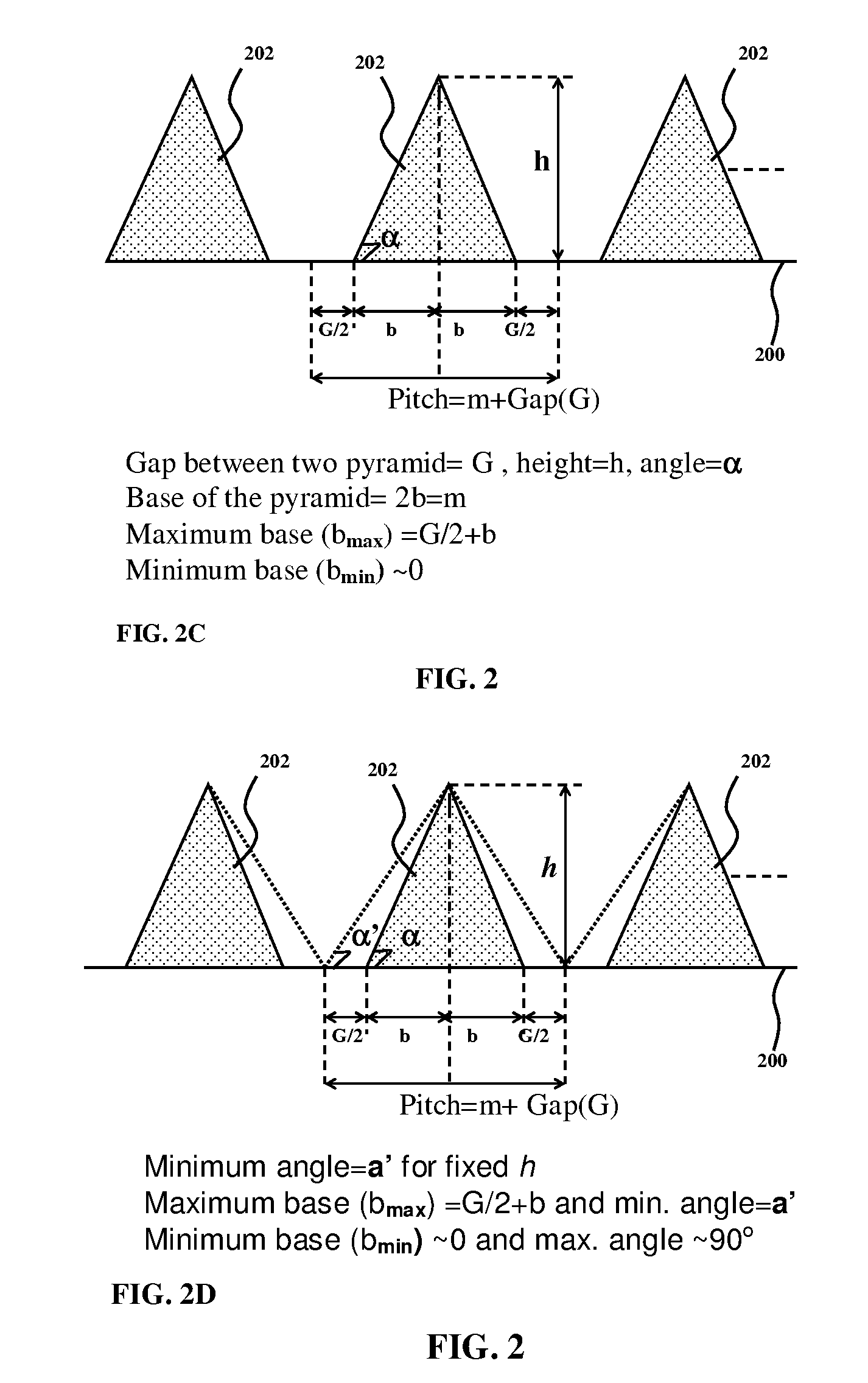
High efficiency photovoltaic cells with self concentrating effect
ActiveUS20080072958A1Low-cost manufacturing processEnhanced light absorptionPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesSolar cellNanostructure
Novel structures of photovoltaic cells (also called as solar cells) are provided. The Cells are based on the micro (or nano) structures which could not only increase the surface area but also have the capability of self concentrating the solar spectrum incident onto the cell. These photovoltaic cells have large power generation capability per unit physical area over the conventional cells. These cells will have enormous applications such as in space, in commercial, residential and industrial applications.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
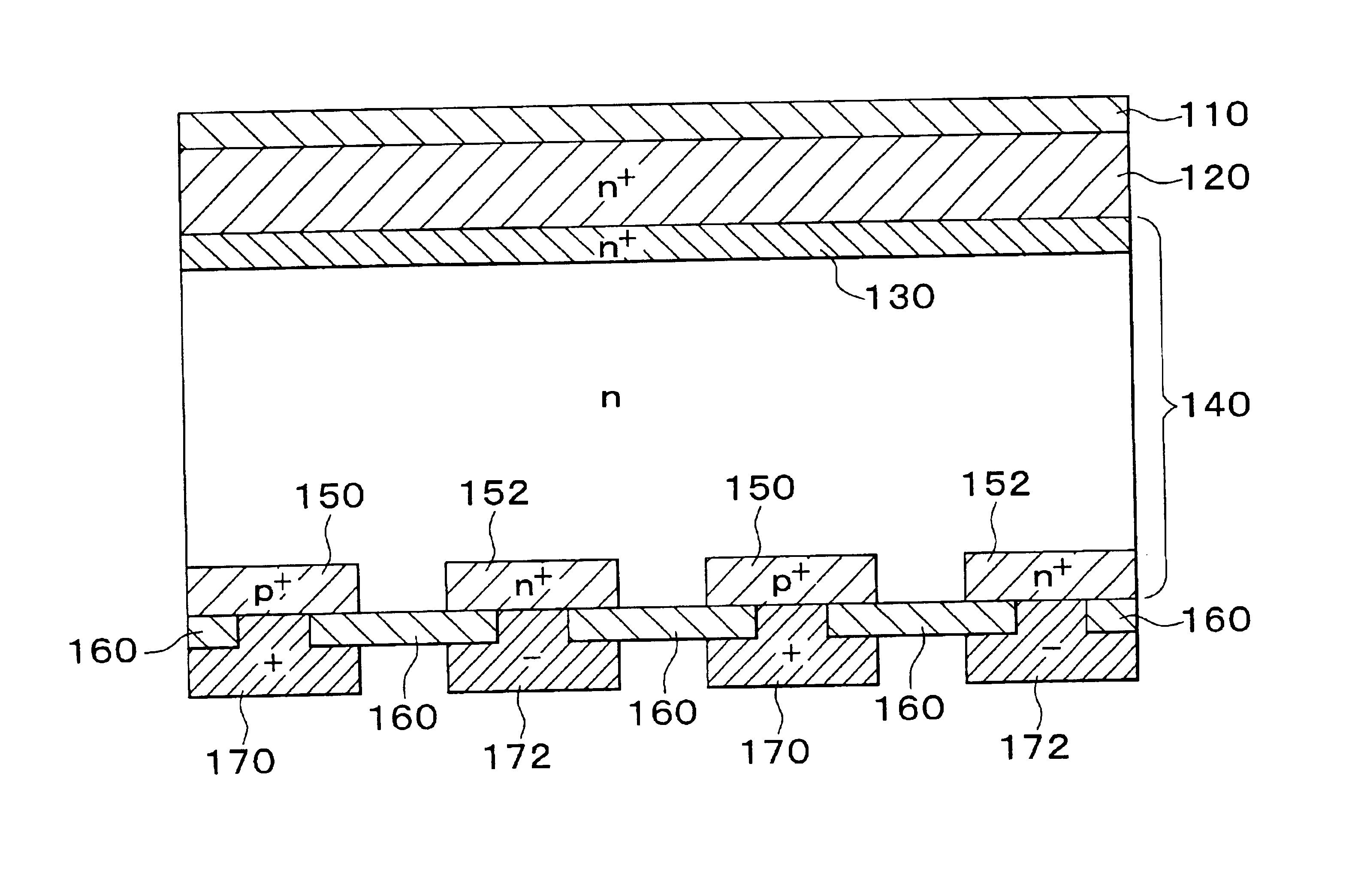
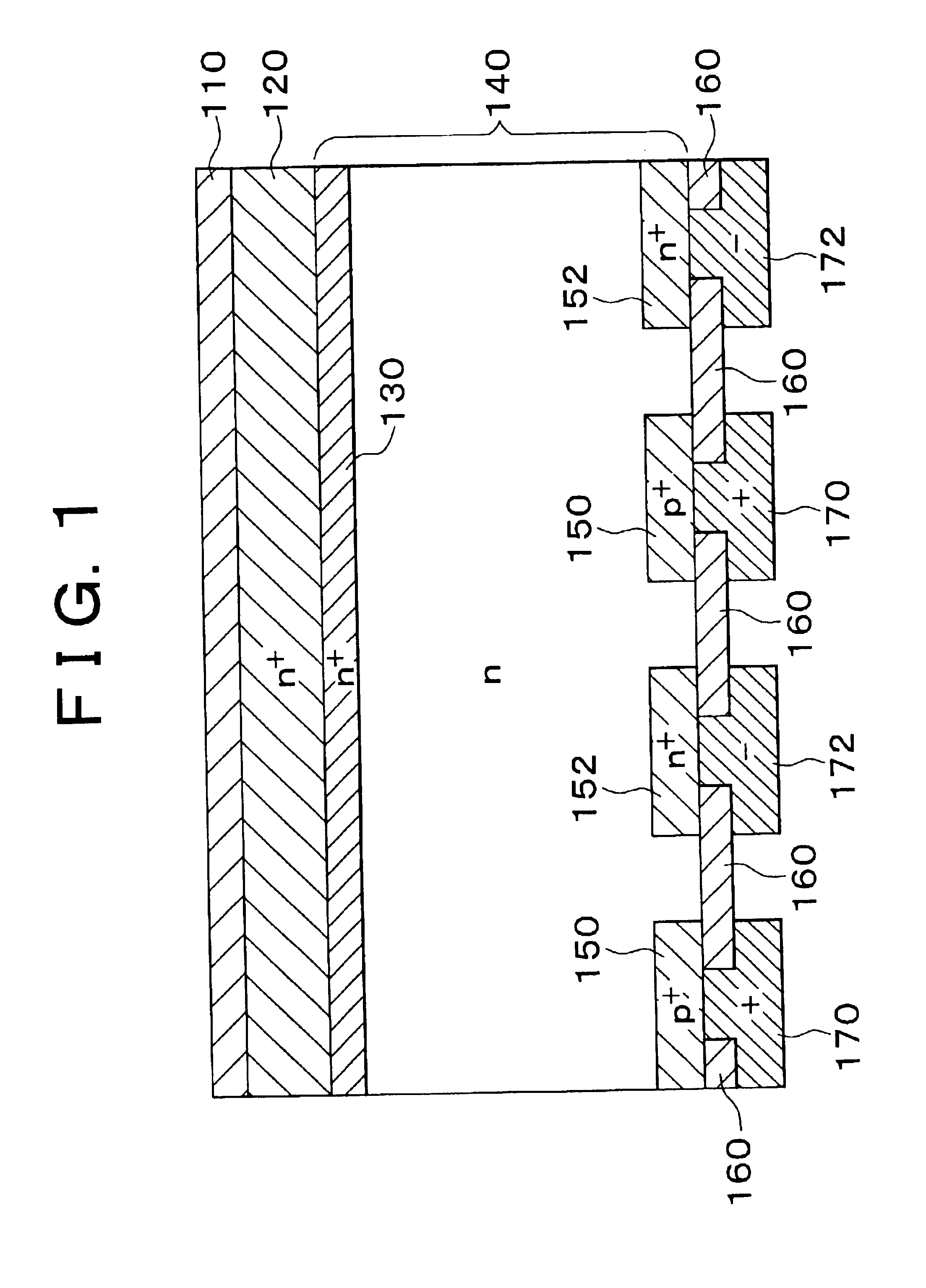
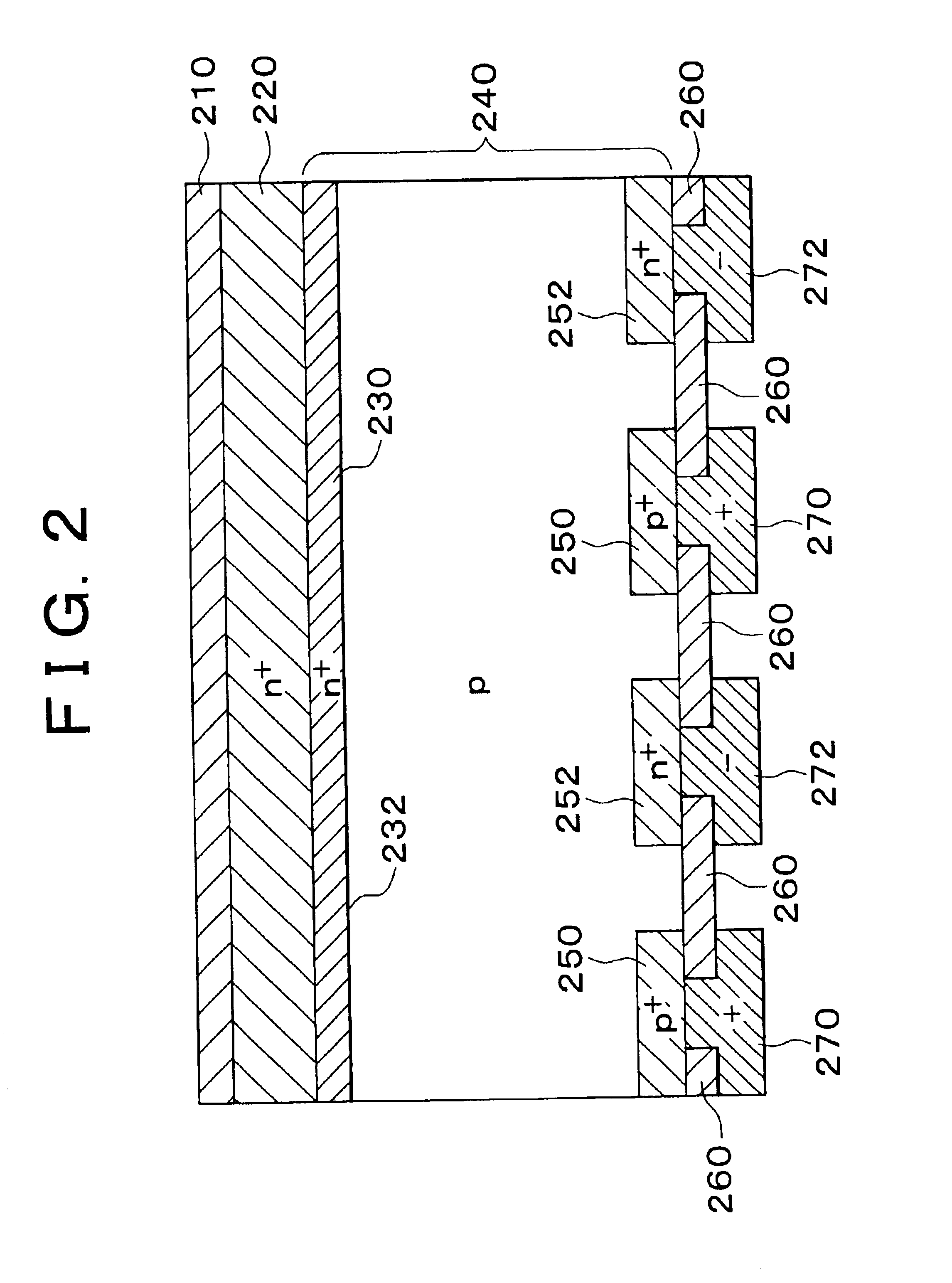
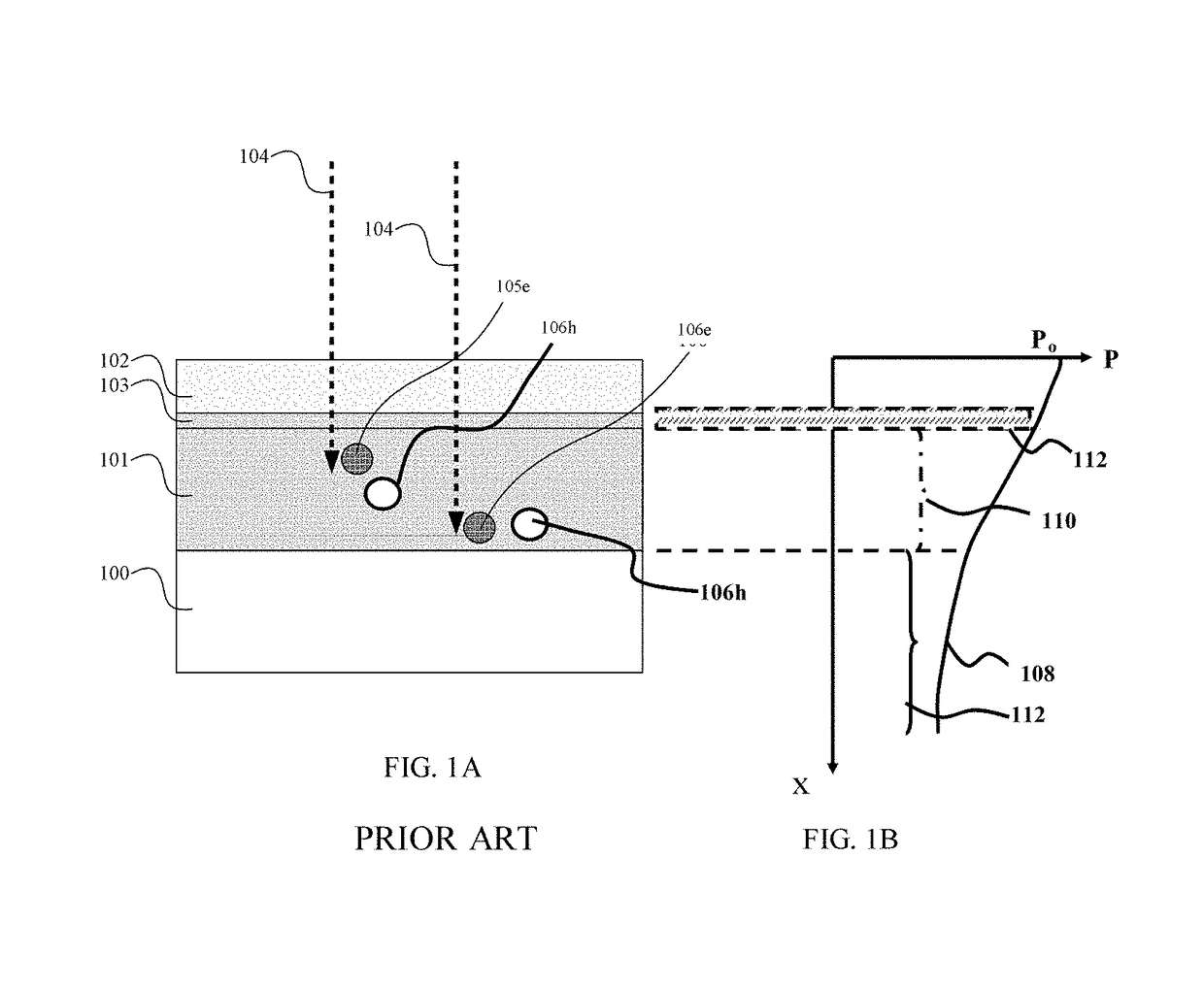
Semiconductor/electrode contact structure and semiconductor device using the same
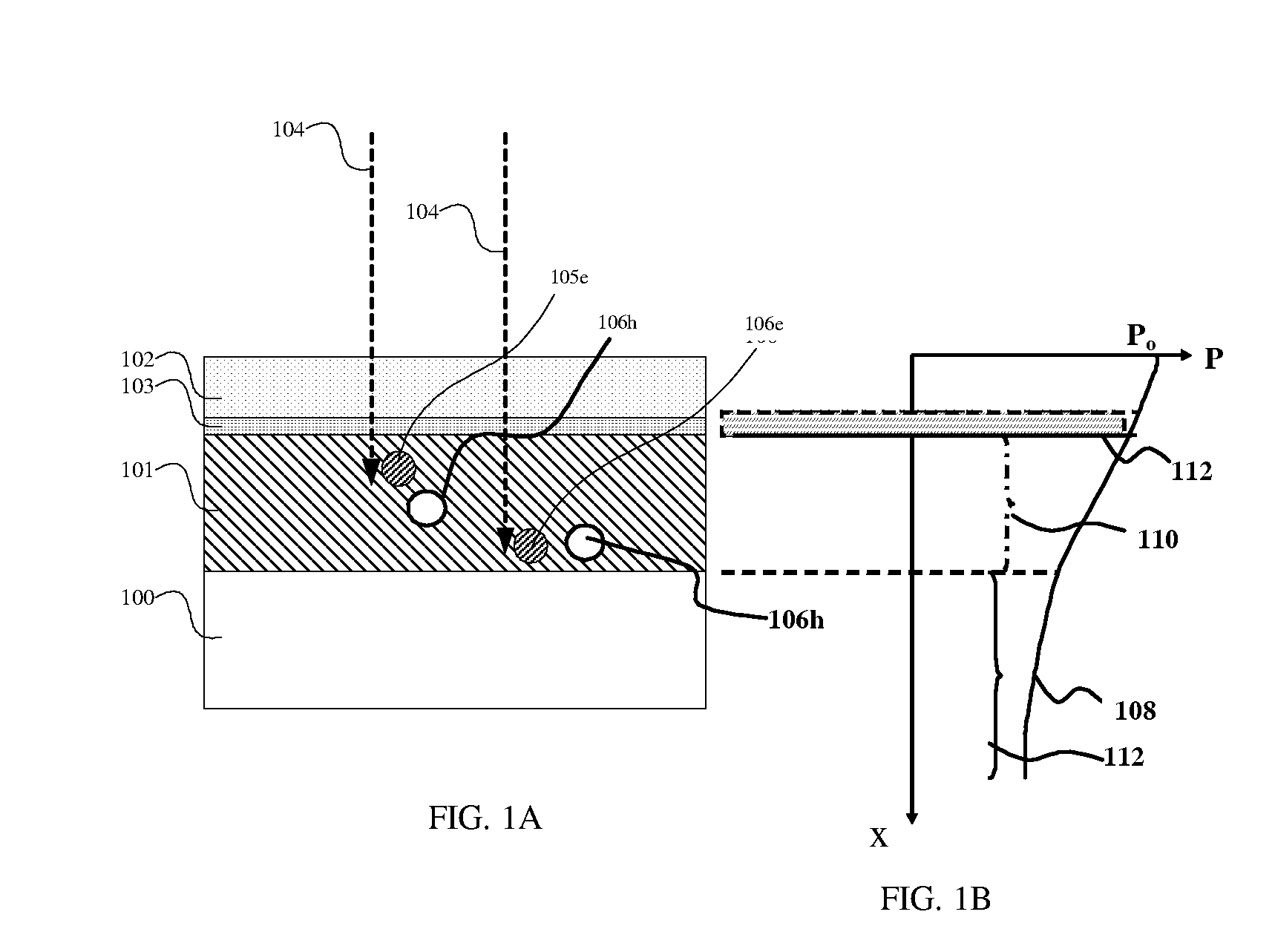
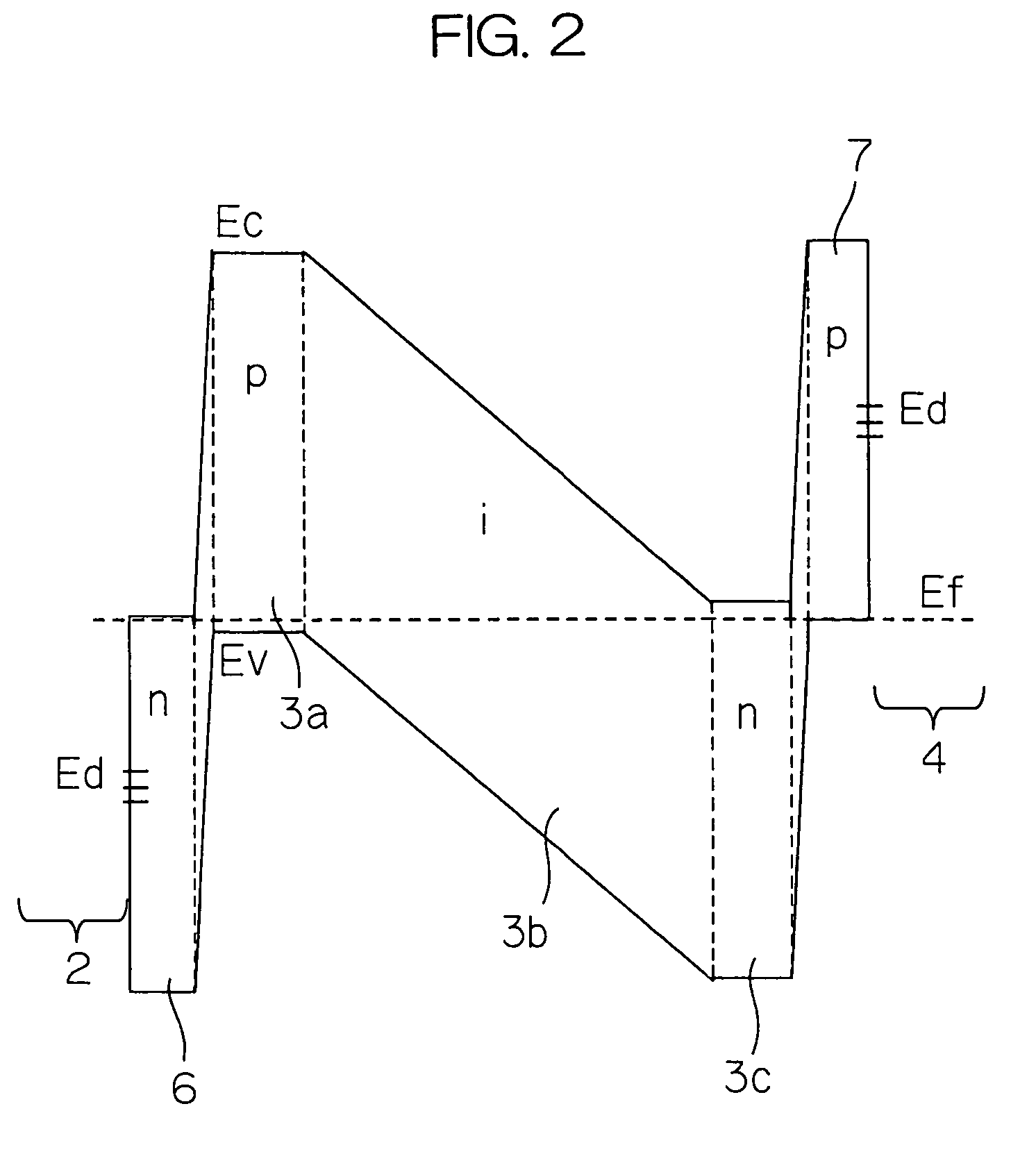
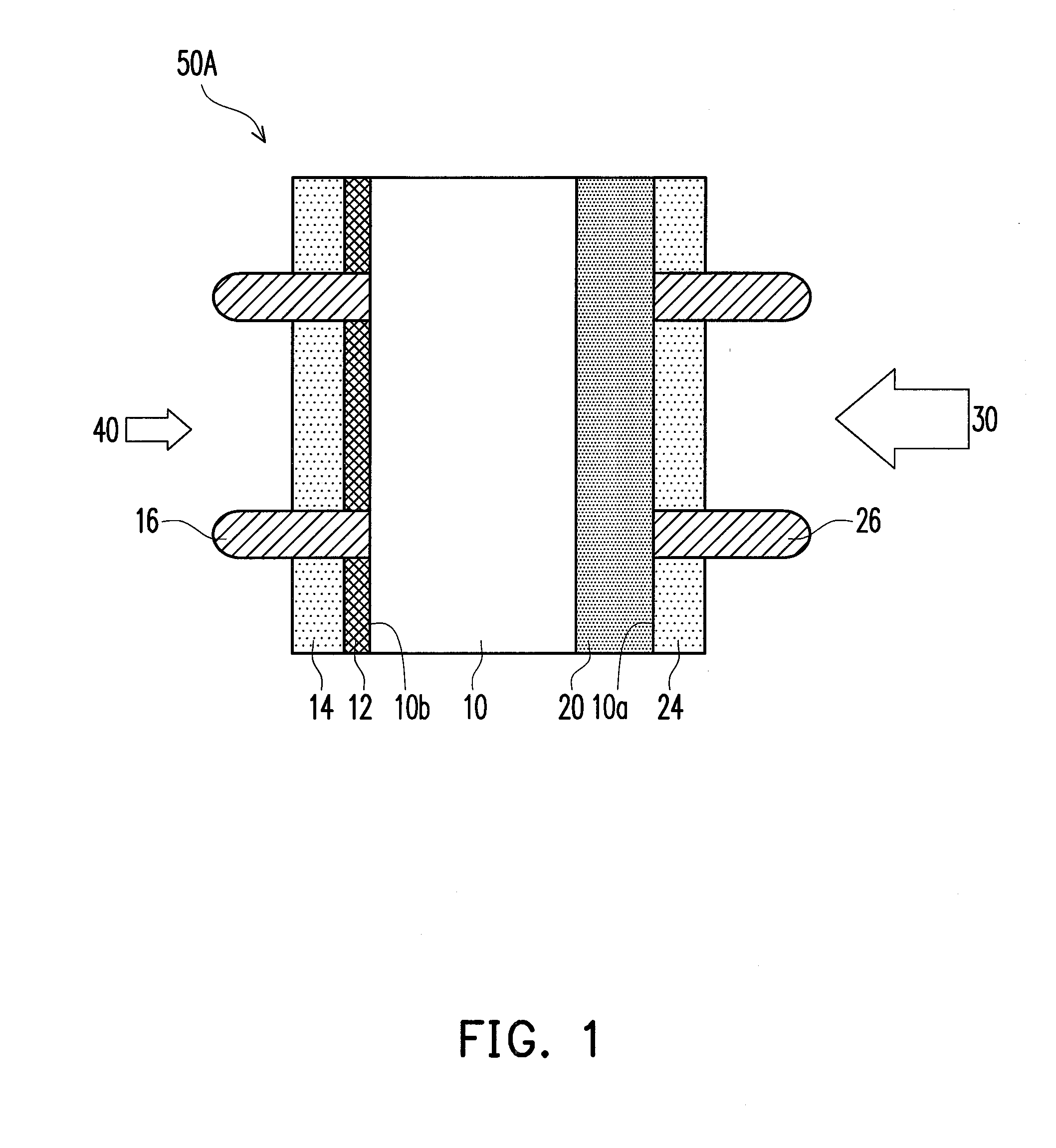
InactiveUS20050012095A1Reduce recombination rateLow densitySuperconductor devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor electrodeDevice material
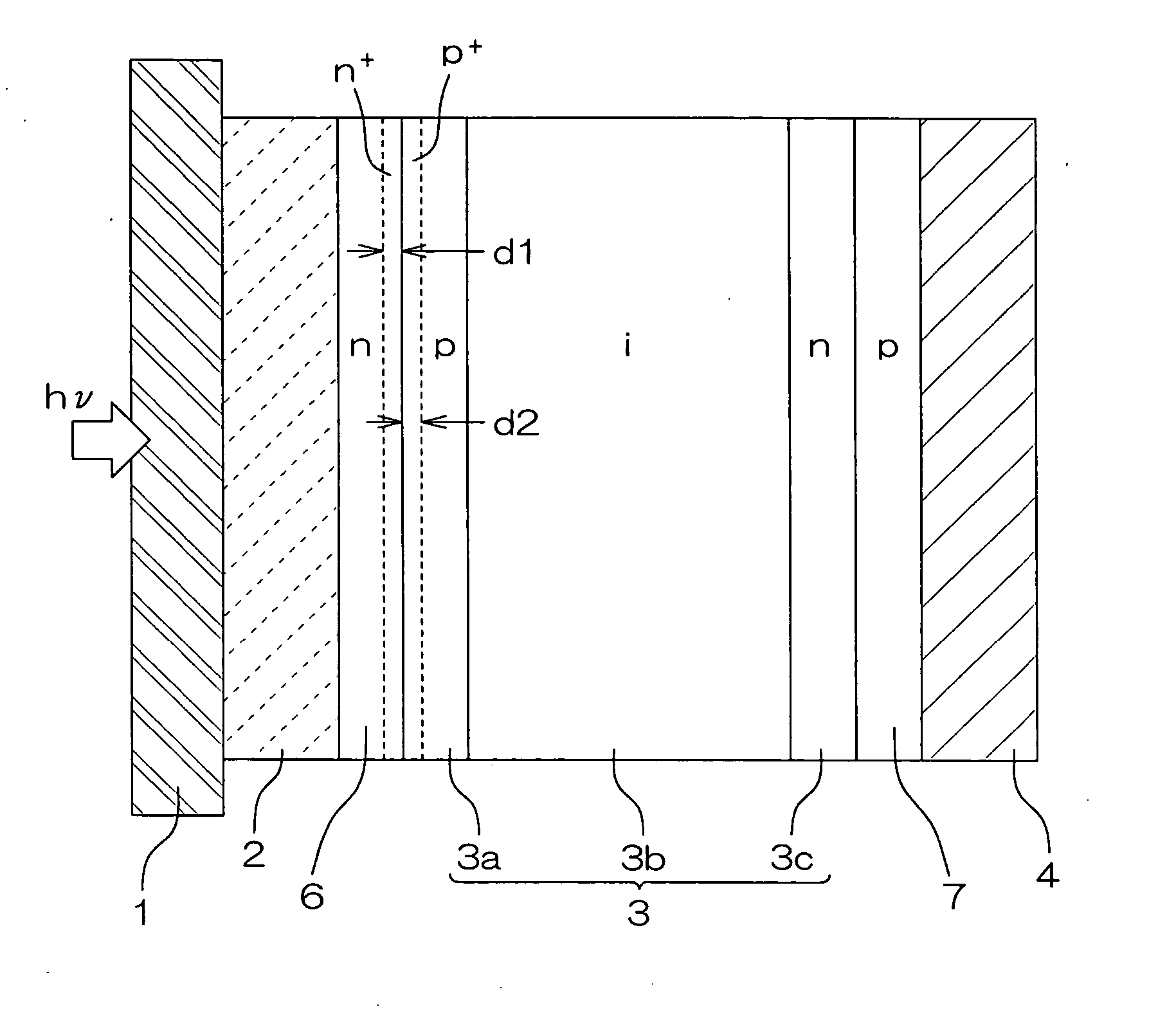
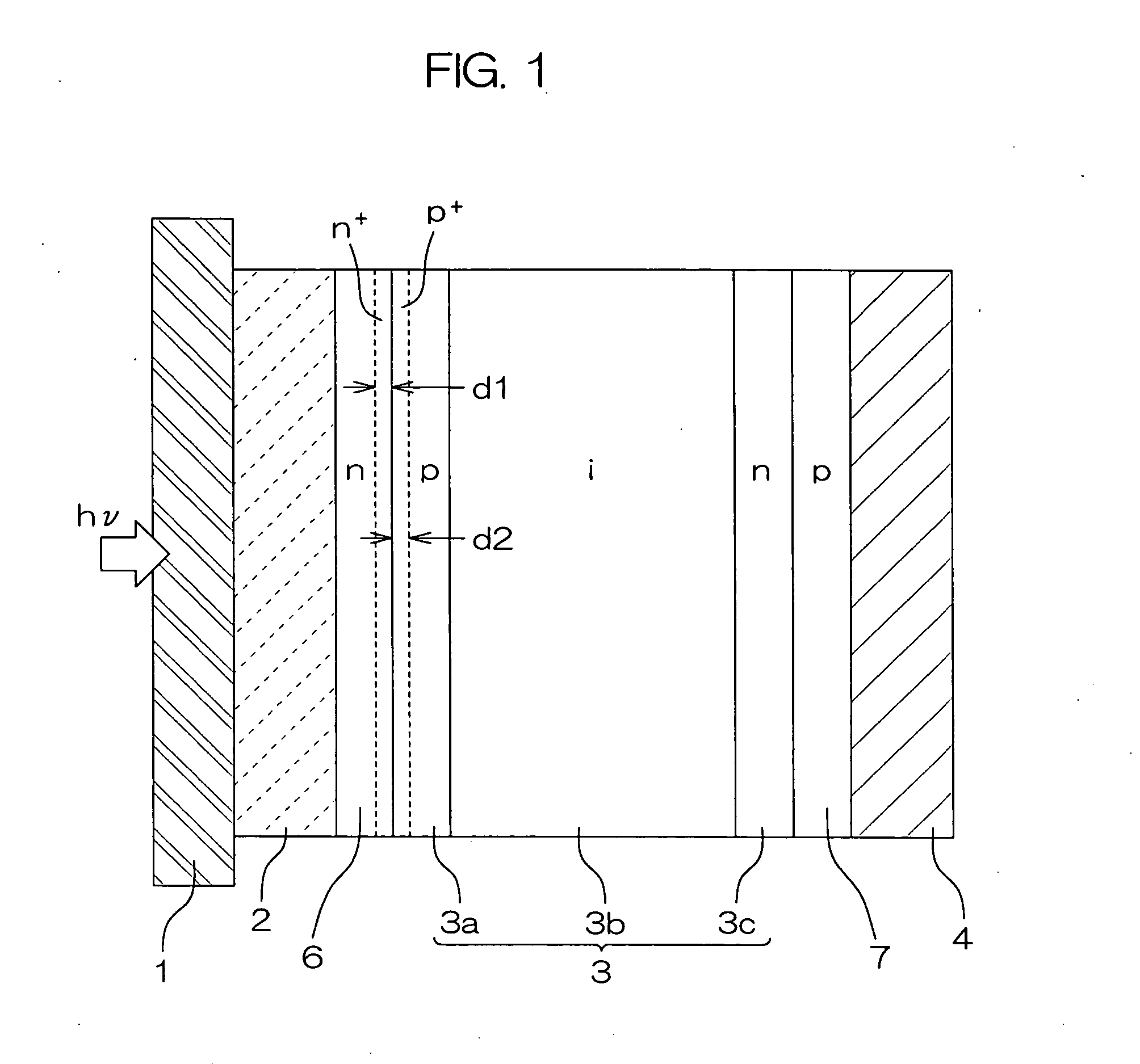
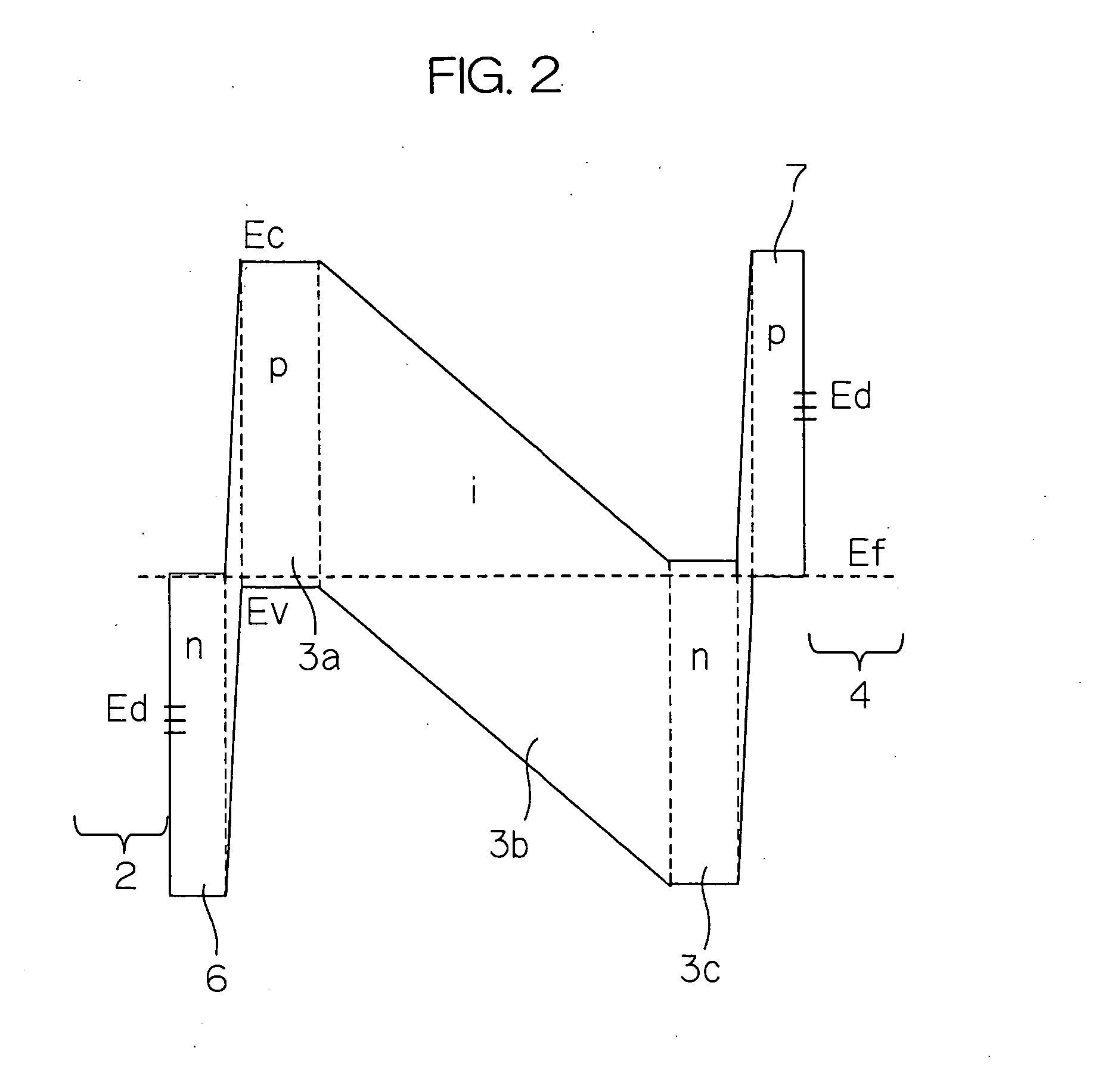
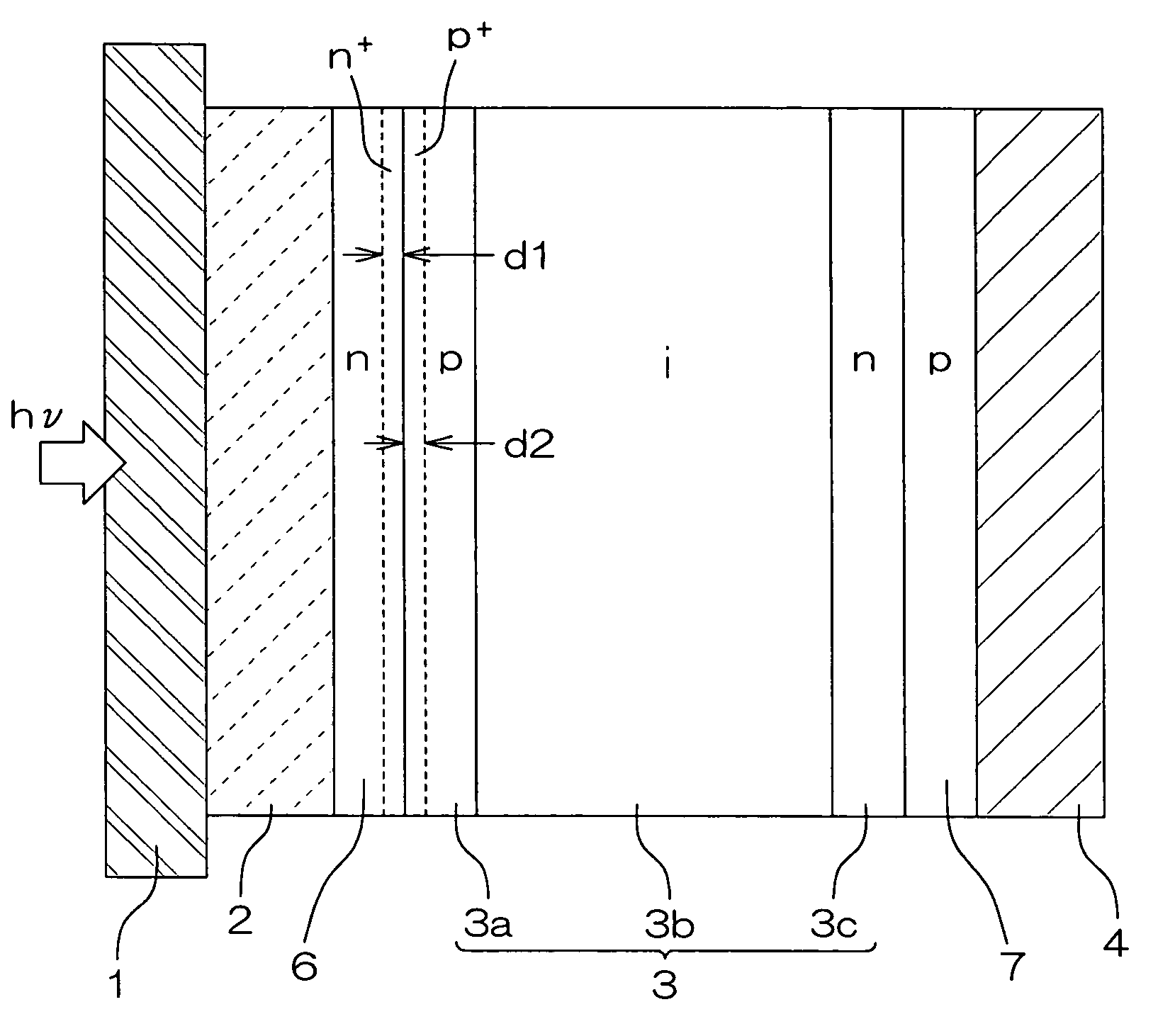
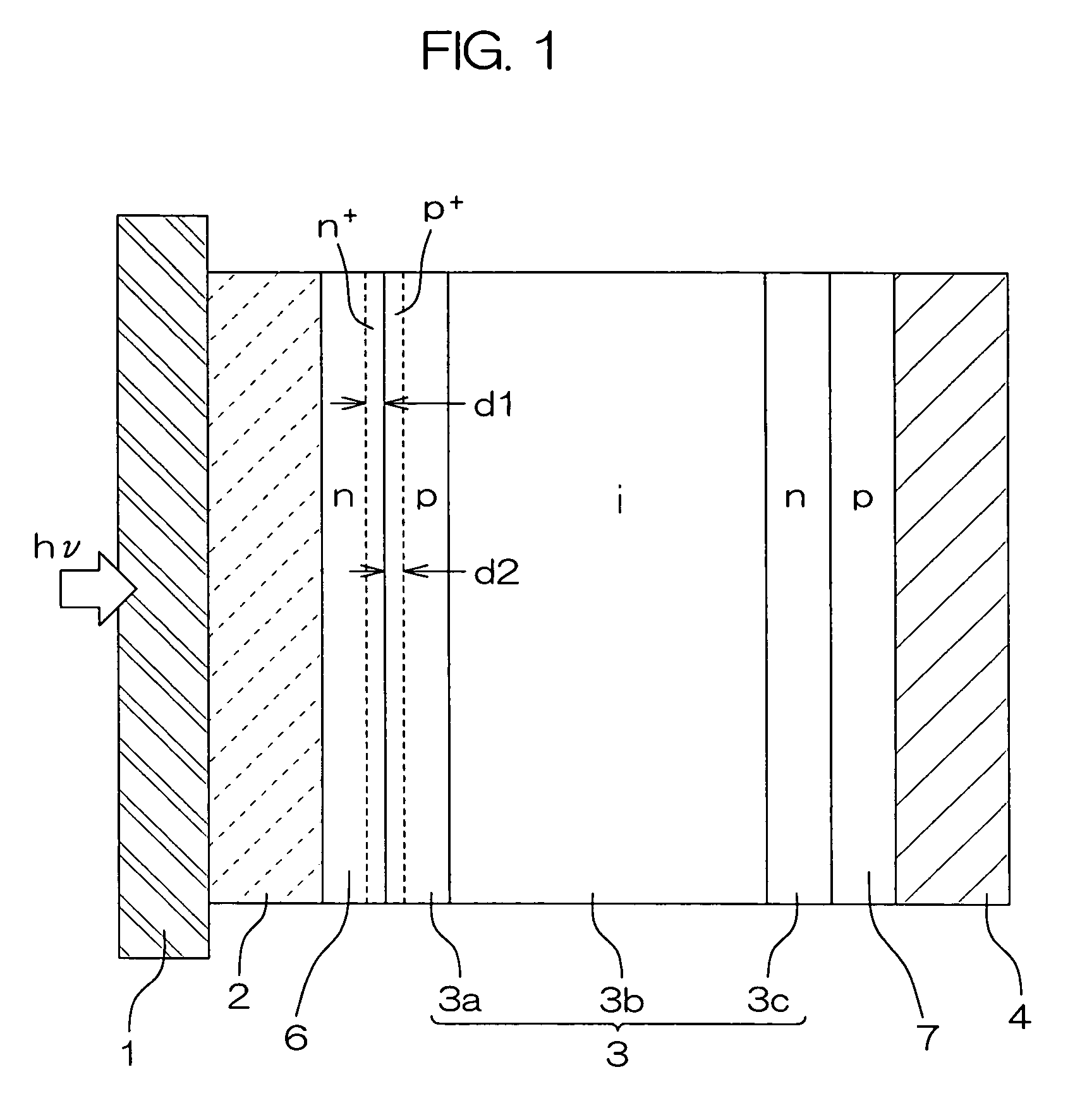
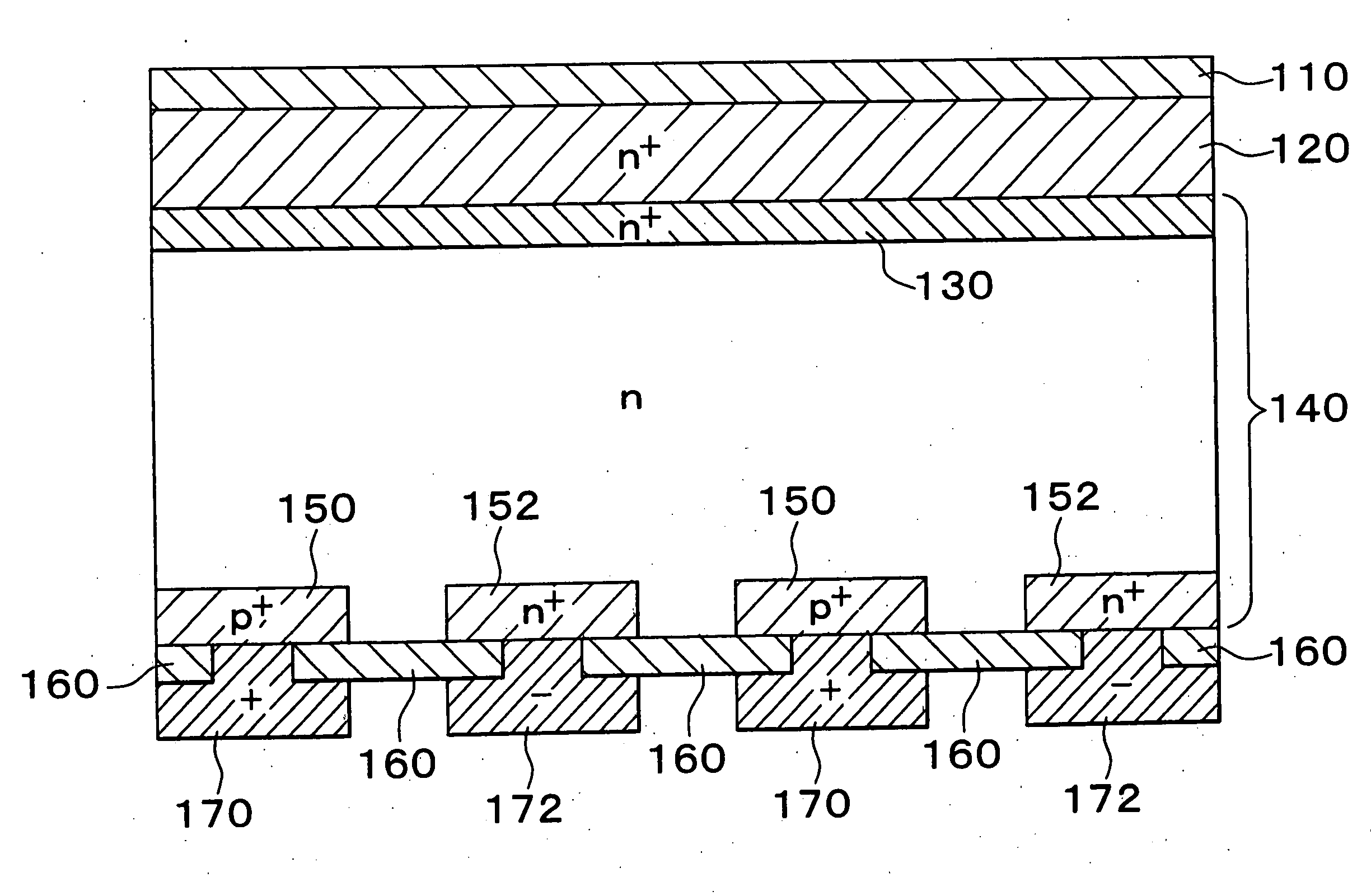
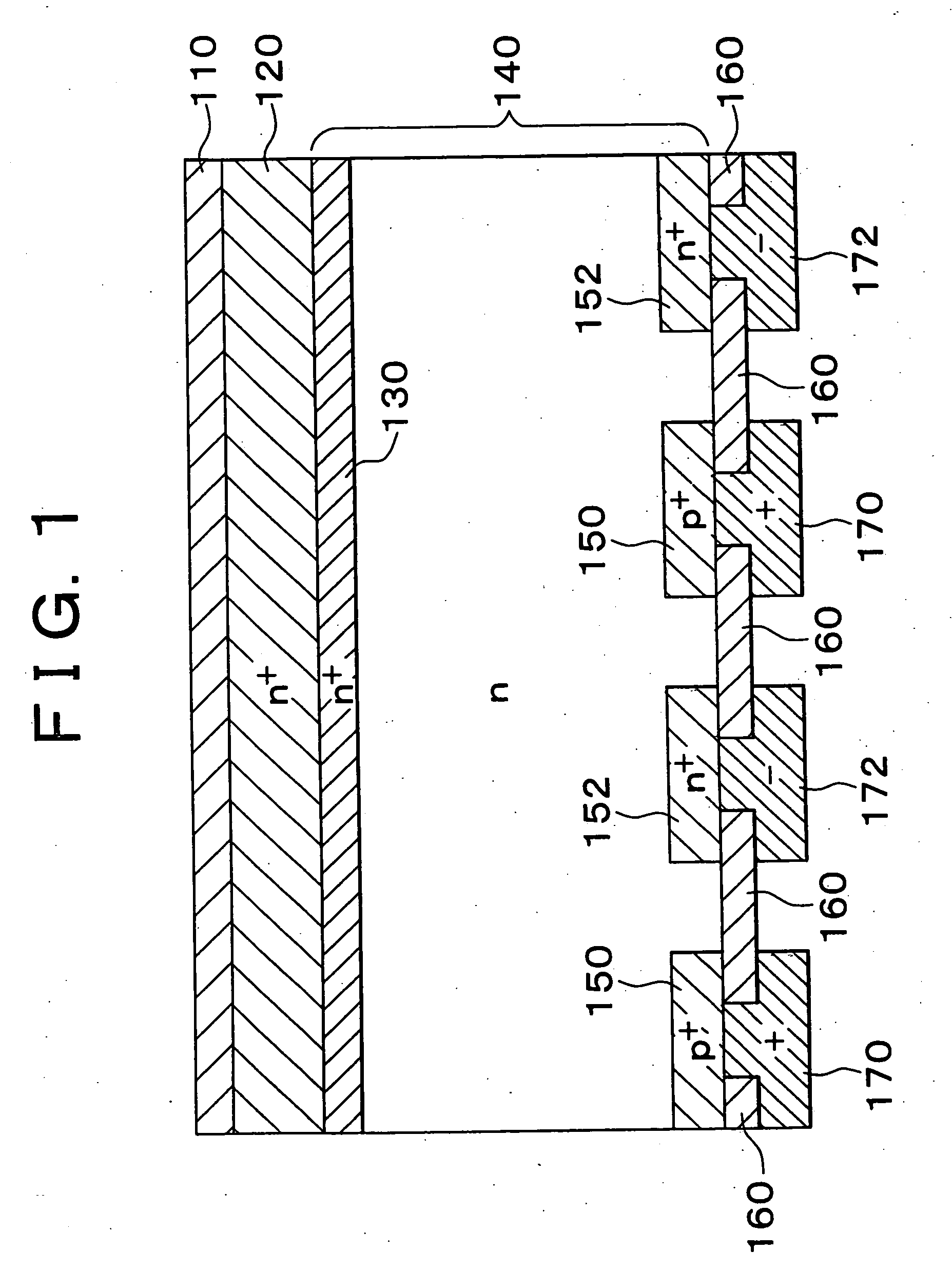
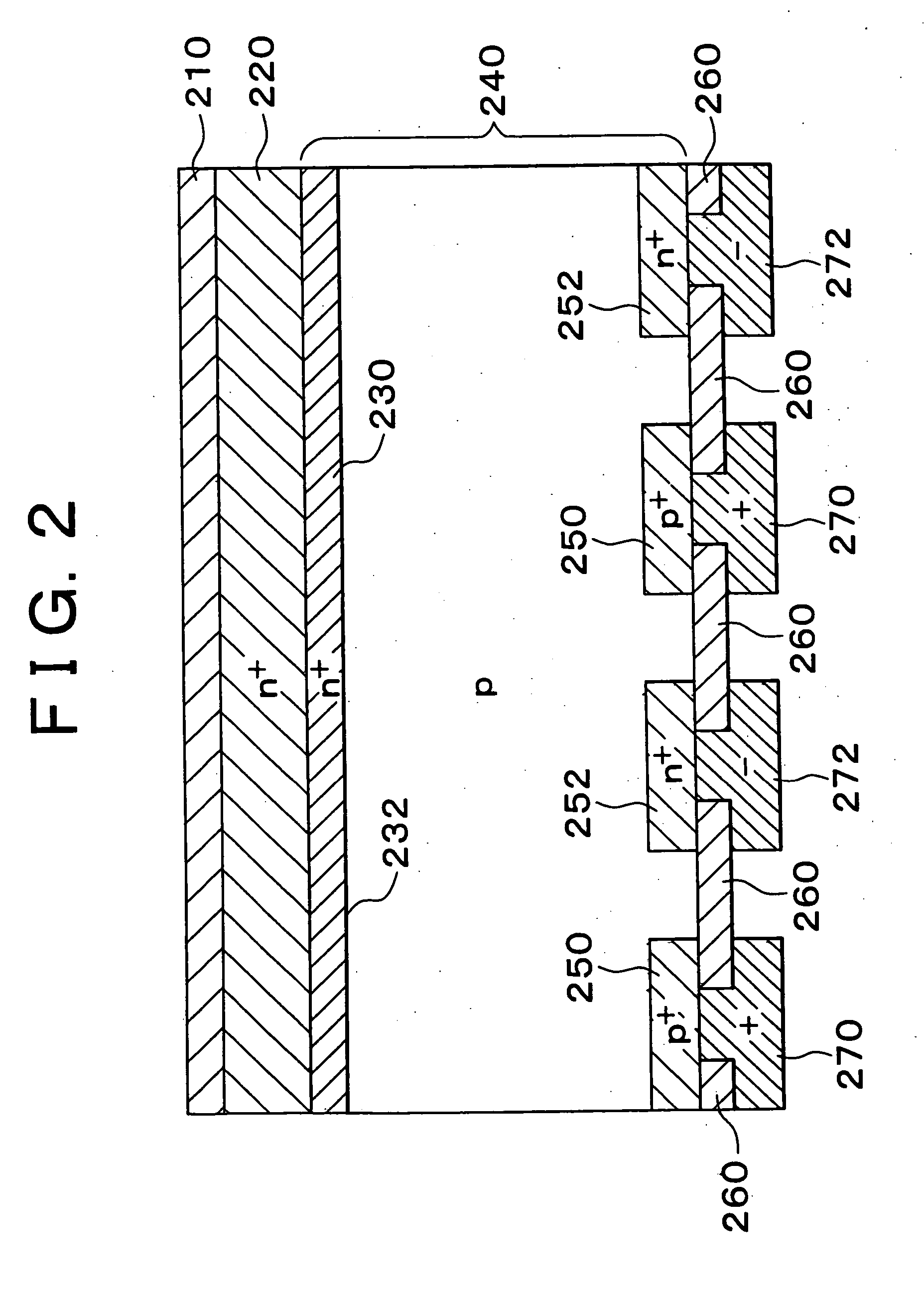
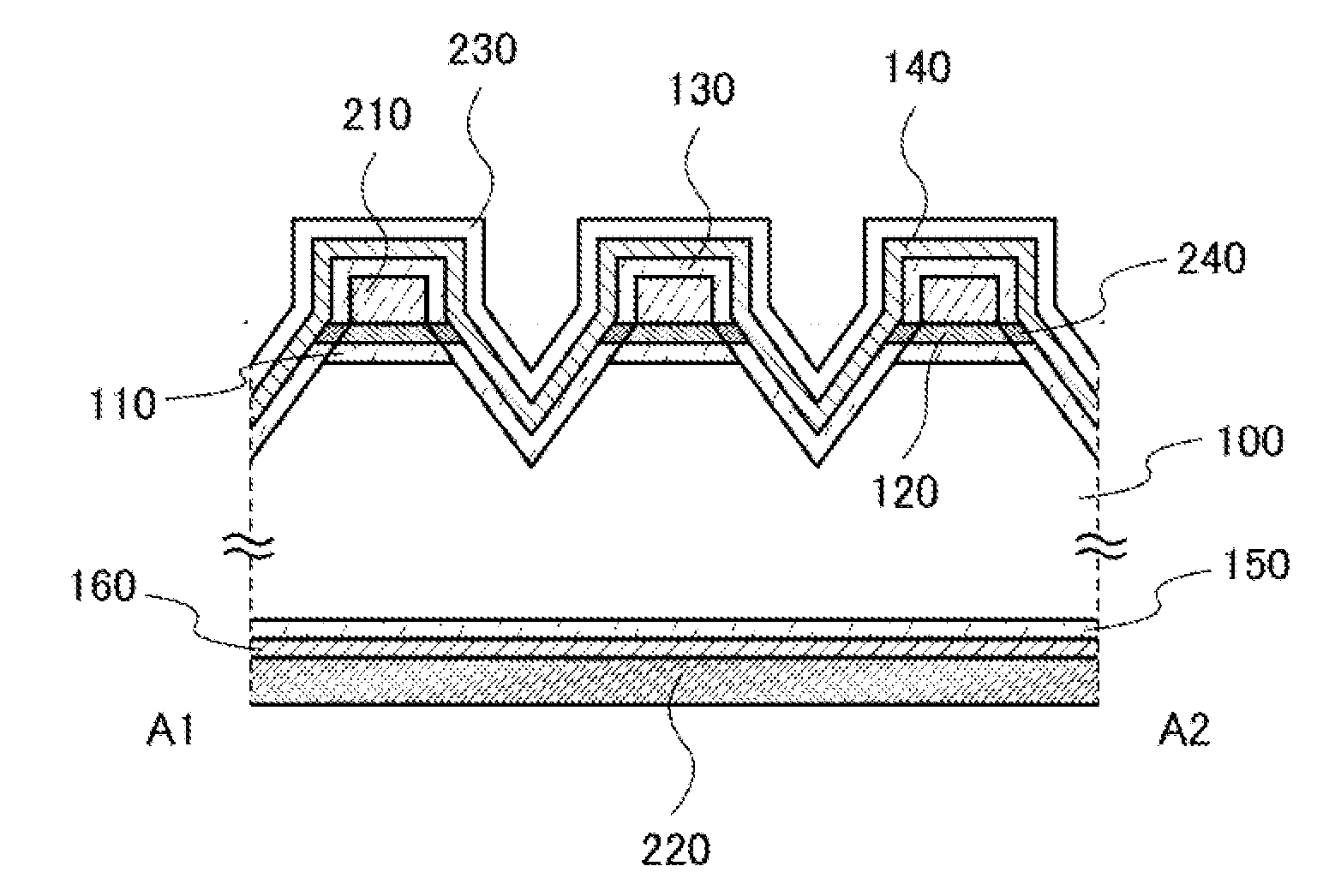
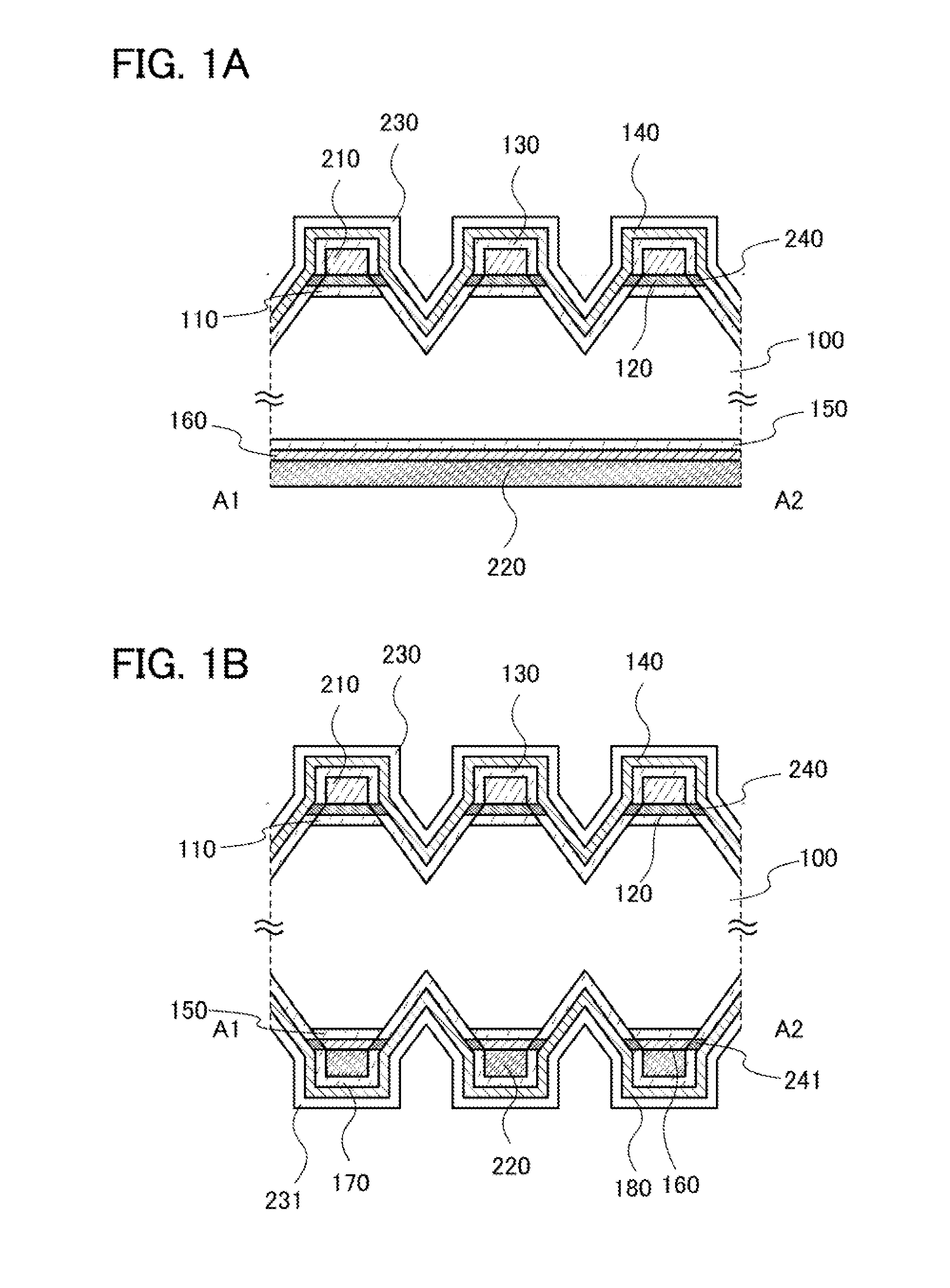
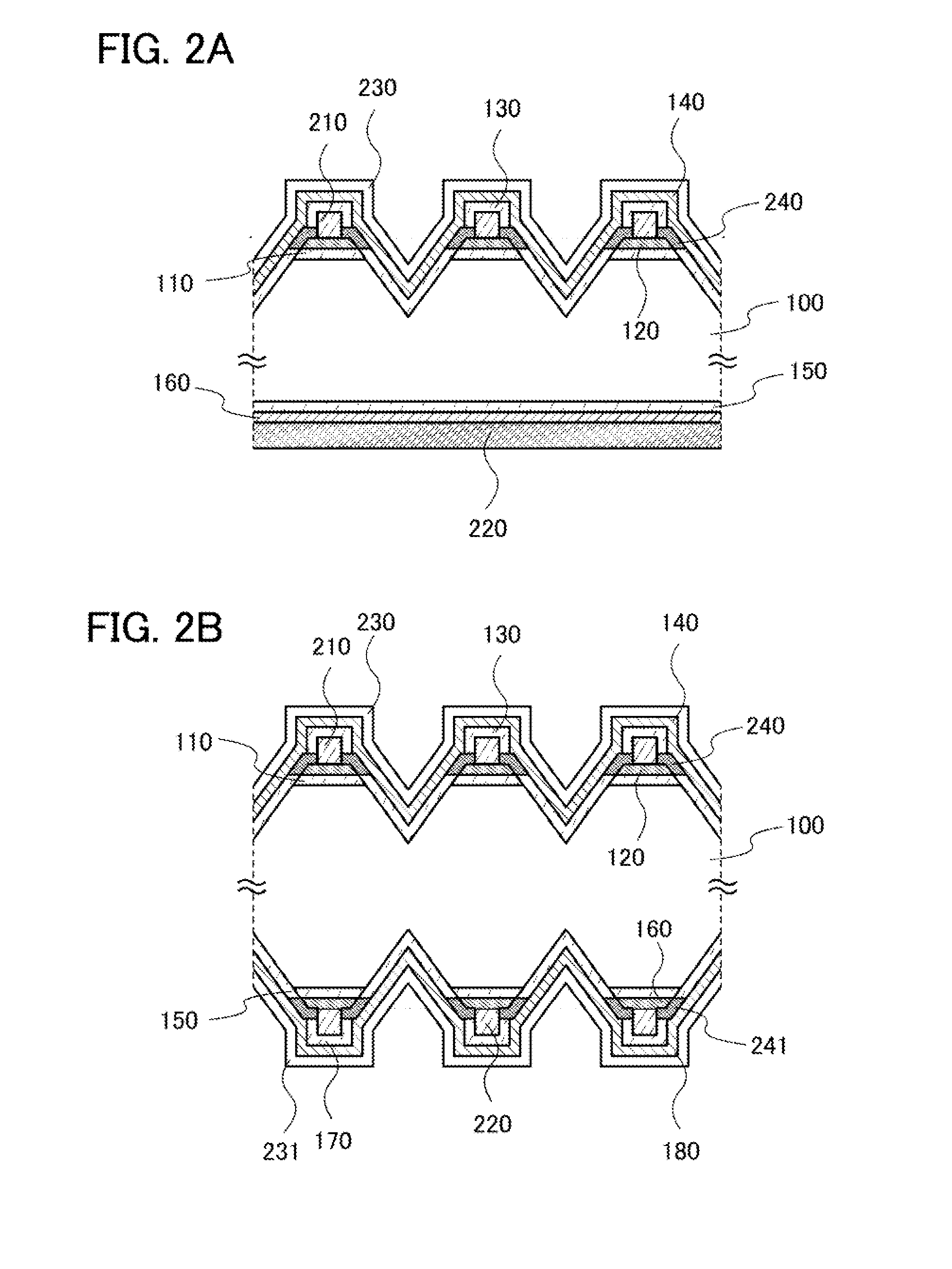
In a photoelectric conversion device, in a contact between a p-type semiconductor 3a and an electrode 2, an n-type semiconductor 6 of a conductivity type opposite to that of the p-type semiconductor is provided between the p-type semiconductor 3a and the electrode 2. The existence of the n-type semiconductor 6 allows a recombination rate of photo-generated carriers excited by incident light to be effectively reduced, and allows a dark current component to be effectively prevented from being produced. Therefore, it is possible to improve photoelectric conversion efficiency as well as to stabilize characteristics. Further, a tunnel junction is realized by increasing the concentration of a doping element in at least one or preferably both of the p-type semiconductor 3a and the n-type semiconductor 6 in a region where they are in contact with each other, thereby keeping ohmic characteristics between the semiconductor and the electrode good.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
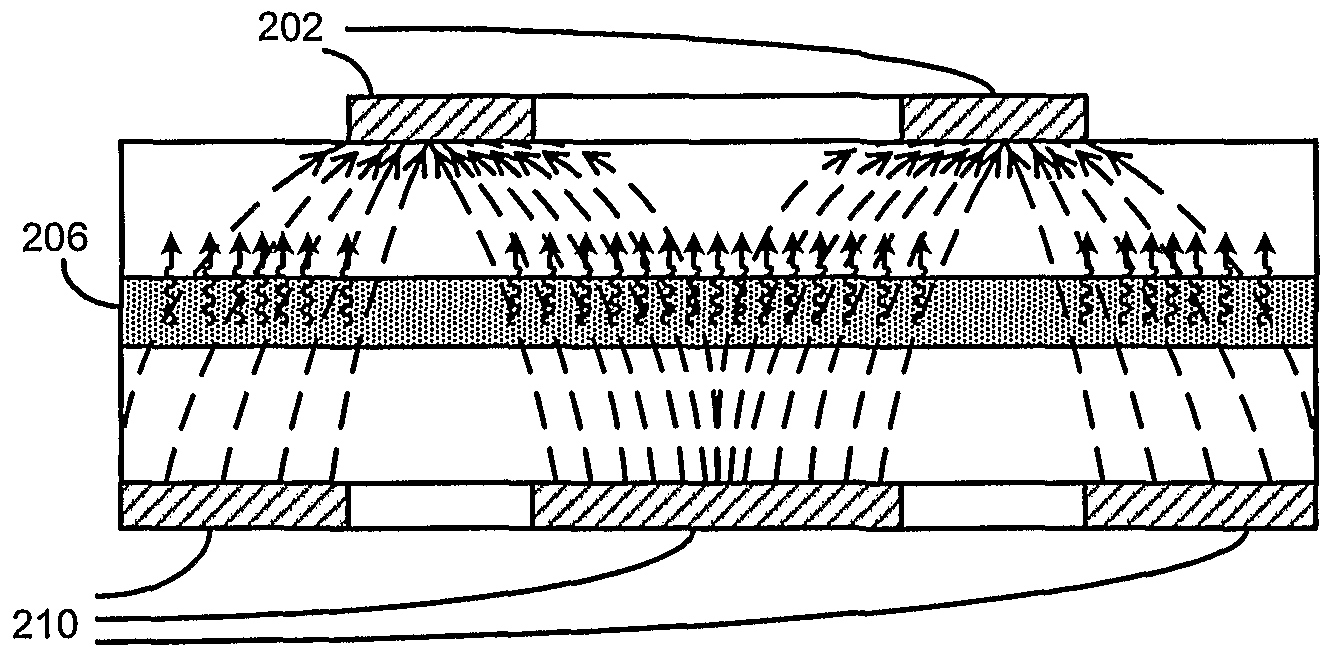
High efficiency photovoltaic cells and manufacturing thereof
ActiveUS20070204902A1Low costElectric power generatedElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureMicrometerEngineering
Novel structures of photovoltaic cells (also treated as solar cells) are provided. The cells are based on nanometer or micrometer-scaled wires, tubes, and / or rods, which are made of electronic materials covering semiconductors, insulators, and may be metallic in structure. These photovoltaic cells have large power generation capability per unit physical area over the conventional cells. These cells will have enormous applications such as in space, commercial, residential and industrial applications.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
Photoelectric conversion element and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6927417B2Reduce carrier recombination lossImprove conversion efficiencyTransistorPV power plantsLight beamPhotoelectric conversion
In a back-surface electrode type photoelectric conversion element having electrodes and semiconductor layers for collecting carriers disposed only on a back surface side of a semiconductor substrate, a semiconductor thin film that is larger in band gap than the semiconductor substrate and that contains an element causing a conductivity identical to or different from a conductivity of the semiconductor substrate is provided on a light-receiving surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and a diffusion layer is formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate. Alternatively, 95% or more of light beams having a wavelength of anywhere from 800 nm to 2000 nm are caused to penetrate the light-receiving surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and an insulative thin film containing an element causing a conductivity identical to or different from the conductivity of the semiconductor substrate is provided so as to form a diffusion layer on the surface of the semiconductor substrate through diffusion of the element.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
High efficiency photovoltaic cells
ActiveUS20070175507A1Low costReduce carrier recombinationPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesNanoparticleEngineering
Novel structures of photovoltaic cells (also called as solar cells) are provided. The cells are based on nanoparticles or nanometer-scaled wires, tubes, and / or rods, which are made of electronic materials covering semiconductors, insulators, and may be metallic in structure. These photovoltaic cells have large power generation capability per unit physical area over the conventional cells. These cells will have enormous applications such as in space, commercial, residential and industrial applications.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
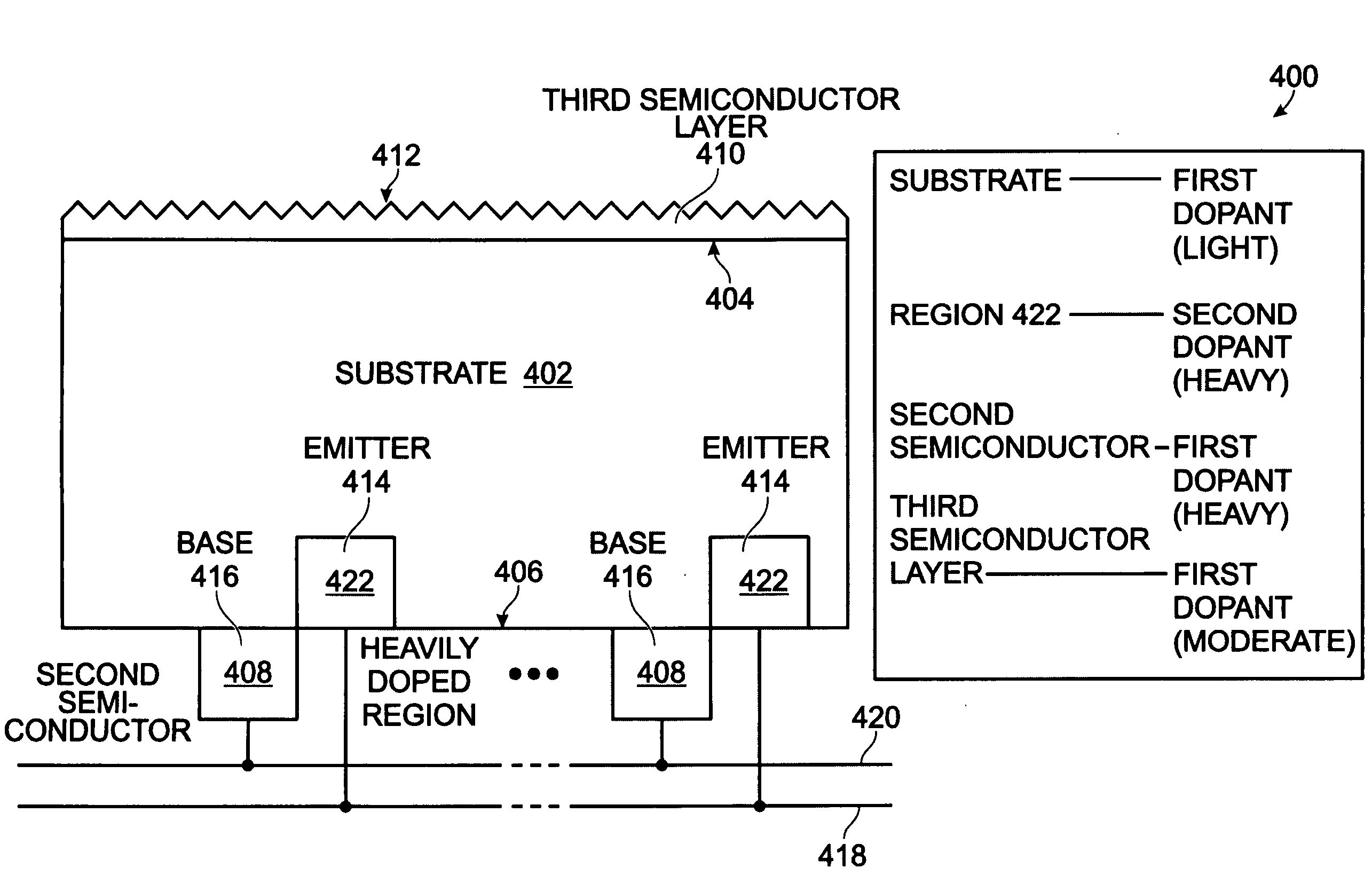
Single Heterojunction Back Contact Solar Cell
ActiveUS20100236613A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationDopantHeterojunction
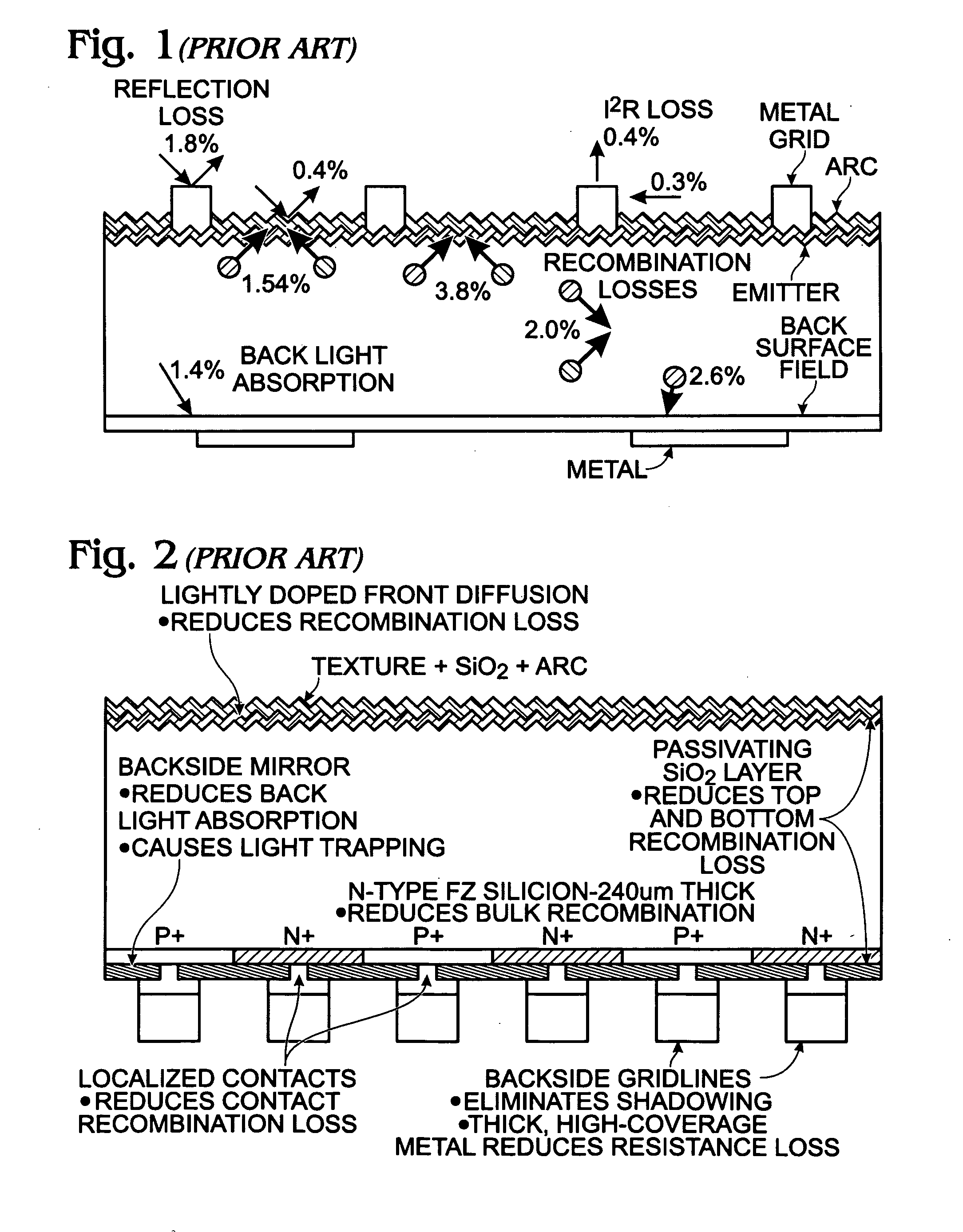
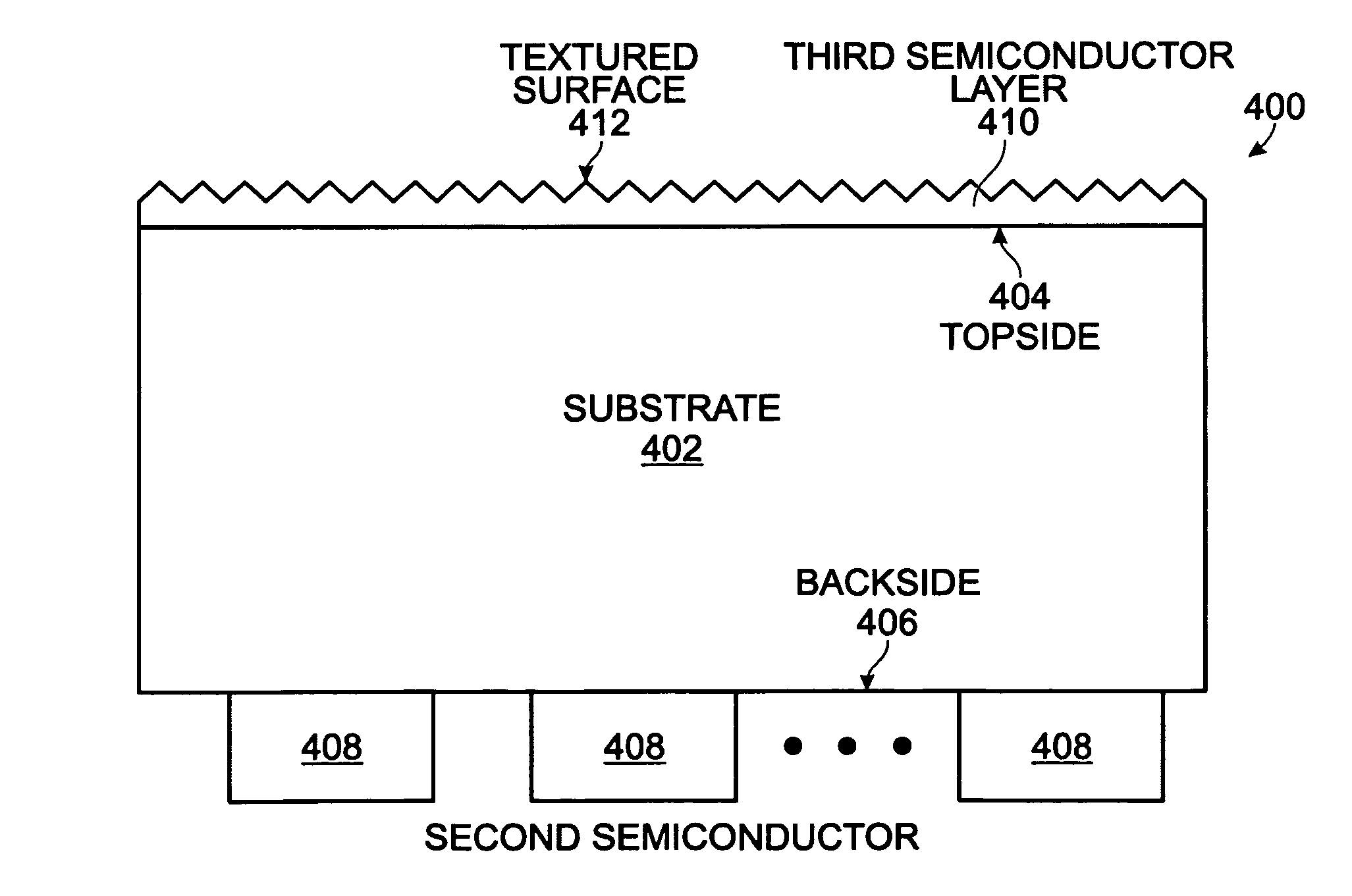
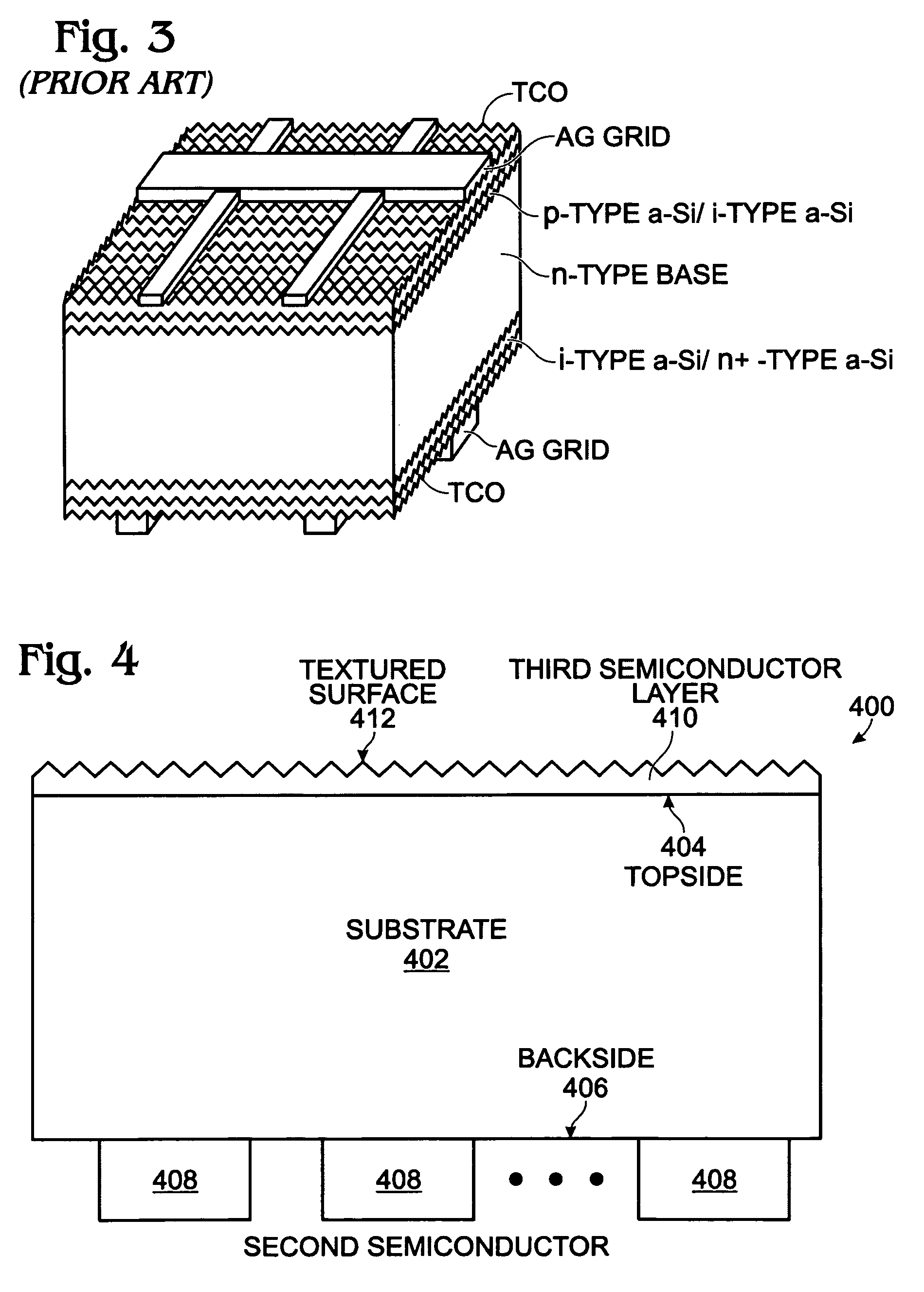
A back contact single heterojunction solar cell and associated fabrication process are provided. A first semiconductor substrate is provided, lightly doped with a first dopant type. The substrate has a first energy bandgap. A second semiconductor is formed over a region of the substrate backside. The second semiconductor has a second energy bandgap, larger than the first energy bandgap. A third semiconductor layer is formed over the first semiconductor substrate topside, moderately doped with the first dopant and textured. An emitter is formed in the substrate backside, heavily doped with a second dopant type, opposite of the first dopant type, and a base is formed in the substrate backside, heavily doped with the first dopant type. Electrical contacts are made to the base and emitter. Either the emitter or base is formed in the second semiconductor.
Owner:SHARP KK
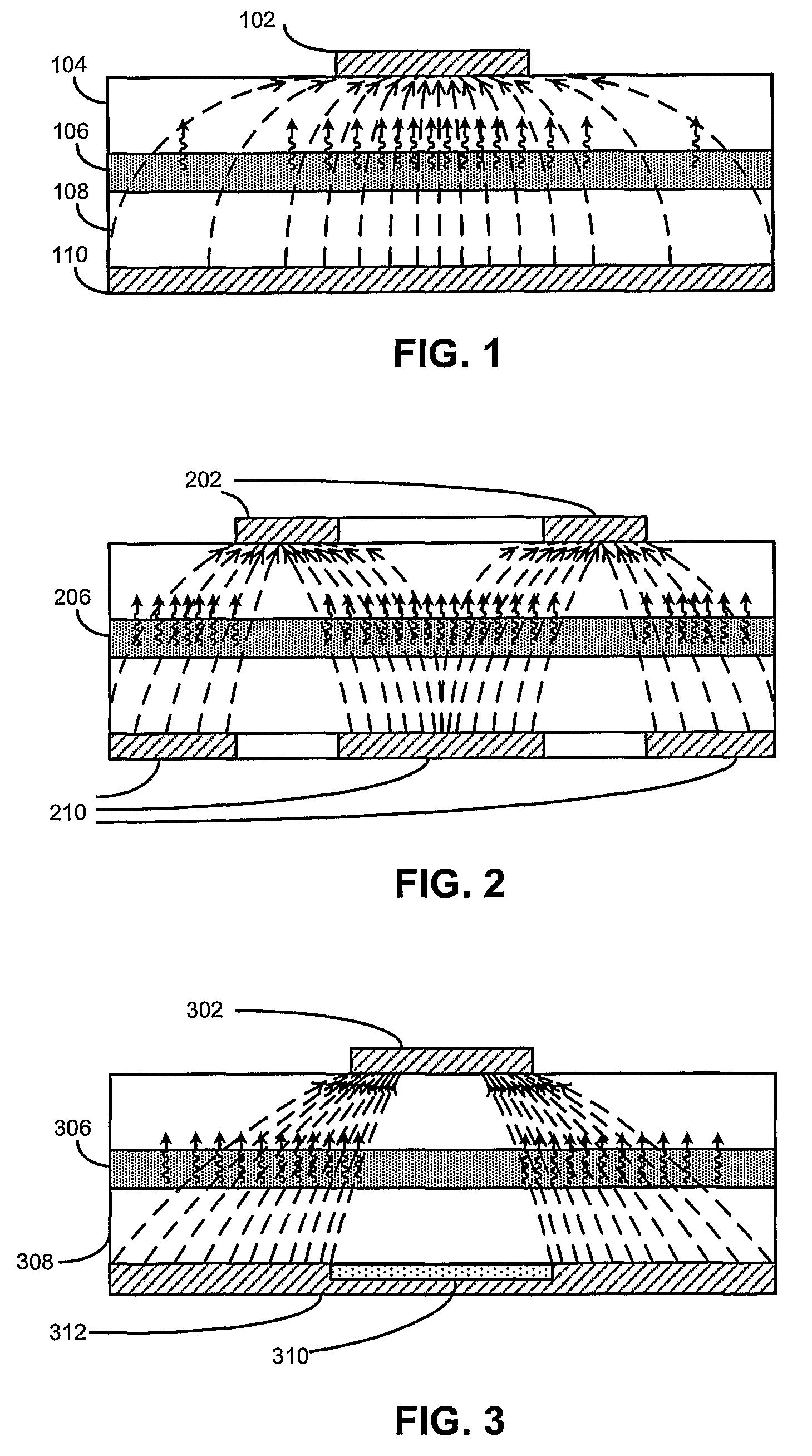
Photovoltaic cells based on NANO or micro-scale structures
ActiveUS20070204901A1Electric power generatedLarge power generation capabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScale structureEngineering
Novel structures of photovoltaic cells (also treated as solar cells) are provided. The cells are based on nanometer-scaled wires, tubes, and / or rods, which are made of electronic materials covering semiconductors, insulators or metallic in structure. These photovoltaic cells have large power generation capability per unit physical area over the conventional cells. These cells will have enormous applications in space, commercial, residential, and industrial applications.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
Semiconductor Light-Emitting Device with Electrode for N-Polar Ingaain Surface
ActiveUS20080230792A1Reduce carrier recombinationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactCharge carrier
One embodiment of the present invention provides a semiconductor light-emitting device, which comprises: an upper cladding layer; a lower cladding layer; an active layer between the upper and lower cladding layers; an upper ohmic-contact layer forming a conductive path to the upper cladding layer; and a lower ohmic-contact layer forming a conductive path the lower cladding layer. The lower ohmic-contact layer has a shape substantially different from the shape of the upper ohmic-contact layer, thereby diverting a carrier flow away from a portion of the active layer which is substantially below the upper ohmic-contact layer when a voltage is applied to the upper and lower ohmic-contact layers.
Owner:LATTICE POWER (JIANGXI) CORP
Backside illuminated image sensor with shallow backside trench for photodiode isolation
InactiveUS20100006908A1Improve performanceIncreasing image sensor die sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital imagingCharge carrier
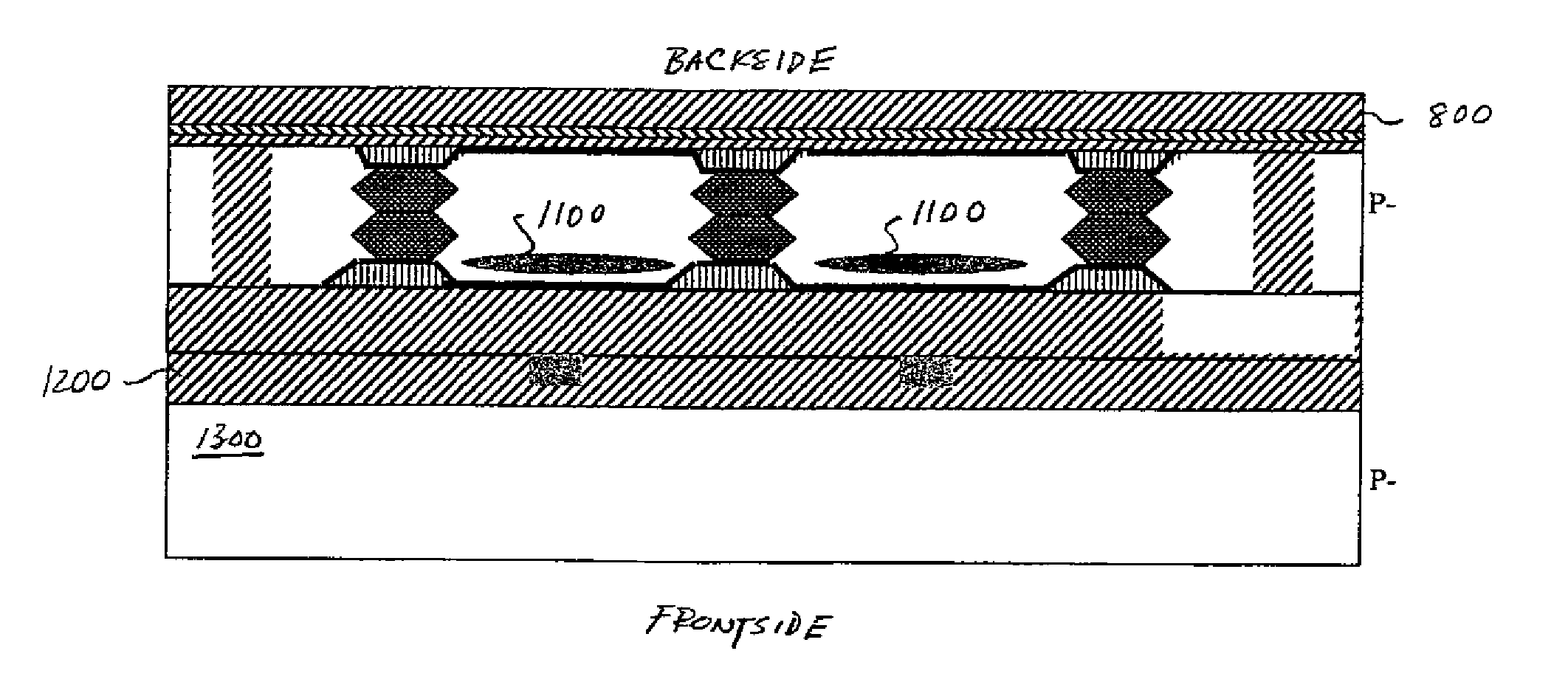
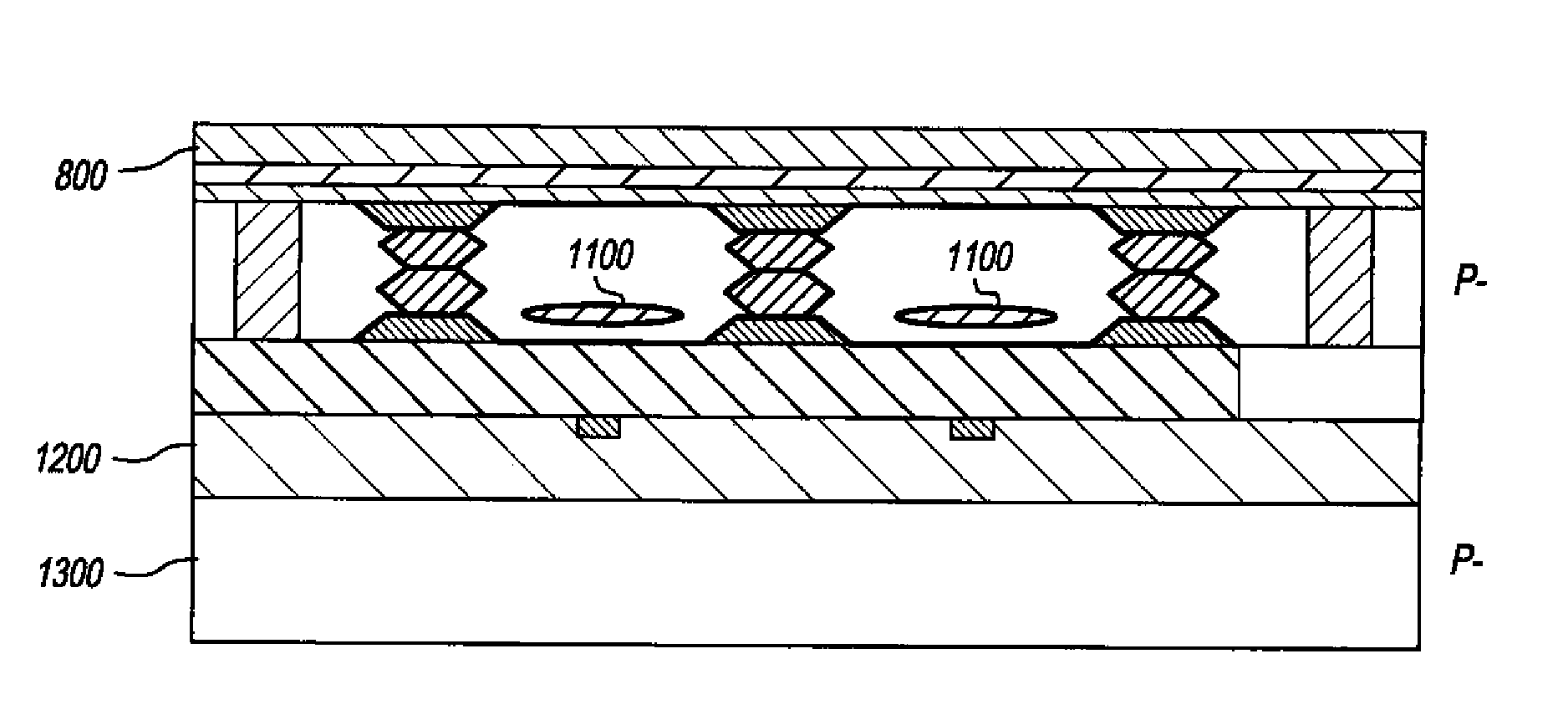
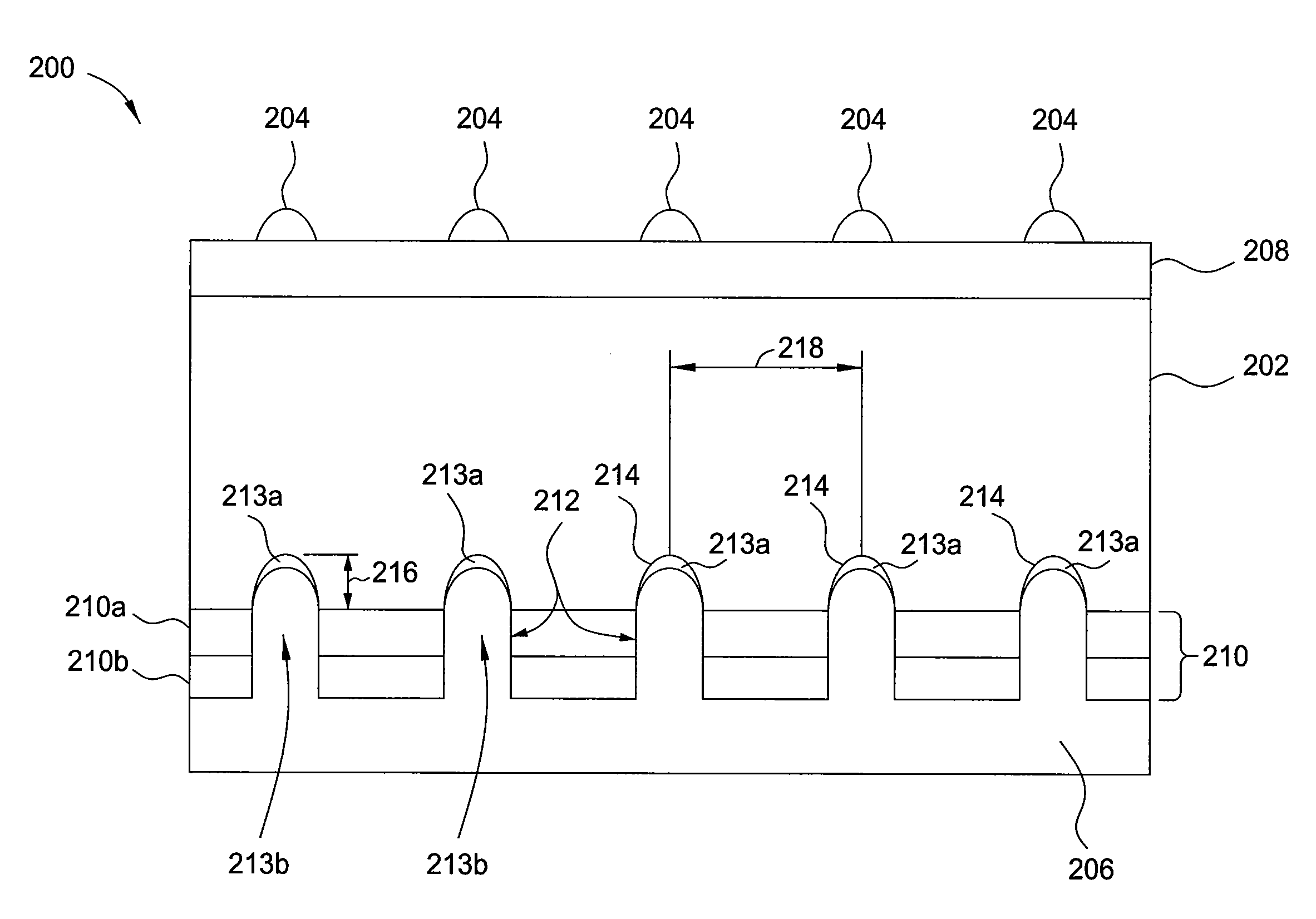
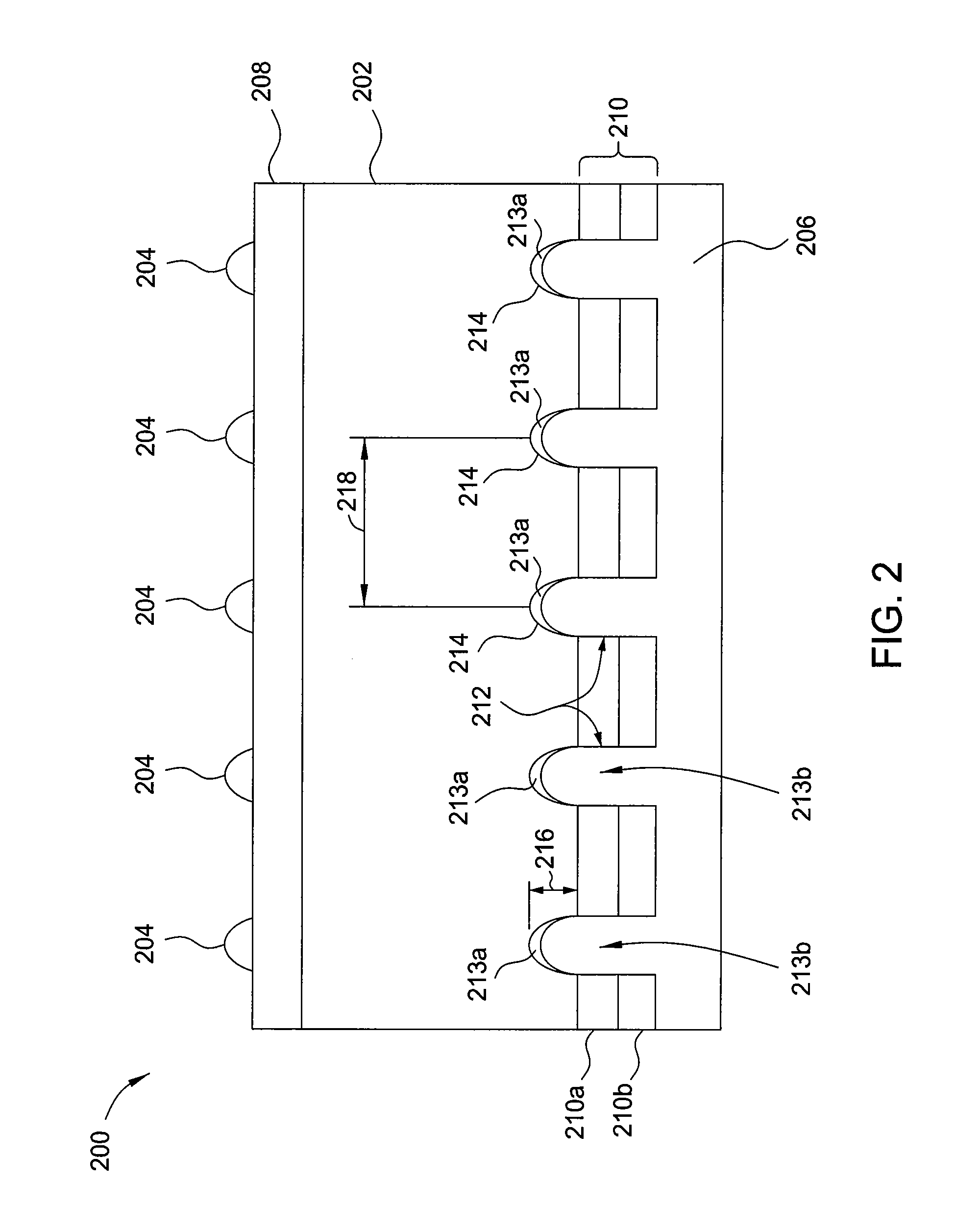
A backside illuminated image sensor comprises a sensor layer implementing a plurality of photosensitive elements of a pixel array, an oxide layer adjacent a backside surface of the sensor layer, and at least one dielectric layer adjacent a frontside surface of the sensor layer. The sensor layer further comprises a plurality of backside trenches formed in the backside surface of the sensor layer and arranged to provide isolation between respective pairs of the photosensitive elements. The backside trenches have corresponding backside field isolation implant regions formed in the sensor layer, and the resulting structure provides reductions in carrier recombination and crosstalk between adjacent photosensitive elements. The image sensor may be implemented in a digital camera or other type of digital imaging device.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Backside illuminated image sensor with shallow backside trench for photodiode isolation
ActiveUS20110059572A1Reduce carrier recombinationImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital imagingCharge carrier
A backside illuminated image sensor comprises a sensor layer implementing a plurality of photosensitive elements of a pixel array, an oxide layer adjacent a backside surface of the sensor layer, and at least one dielectric layer adjacent a frontside surface of the sensor layer. The sensor layer further comprises a plurality of backside trenches formed in the backside surface of the sensor layer and arranged to provide isolation between respective pairs of the photosensitive elements. The backside trenches have corresponding backside field isolation implant regions formed in the sensor layer, and the resulting structure provides reductions in carrier recombination and crosstalk between adjacent photosensitive elements. The image sensor may be implemented in a digital camera or other type of digital imaging device.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
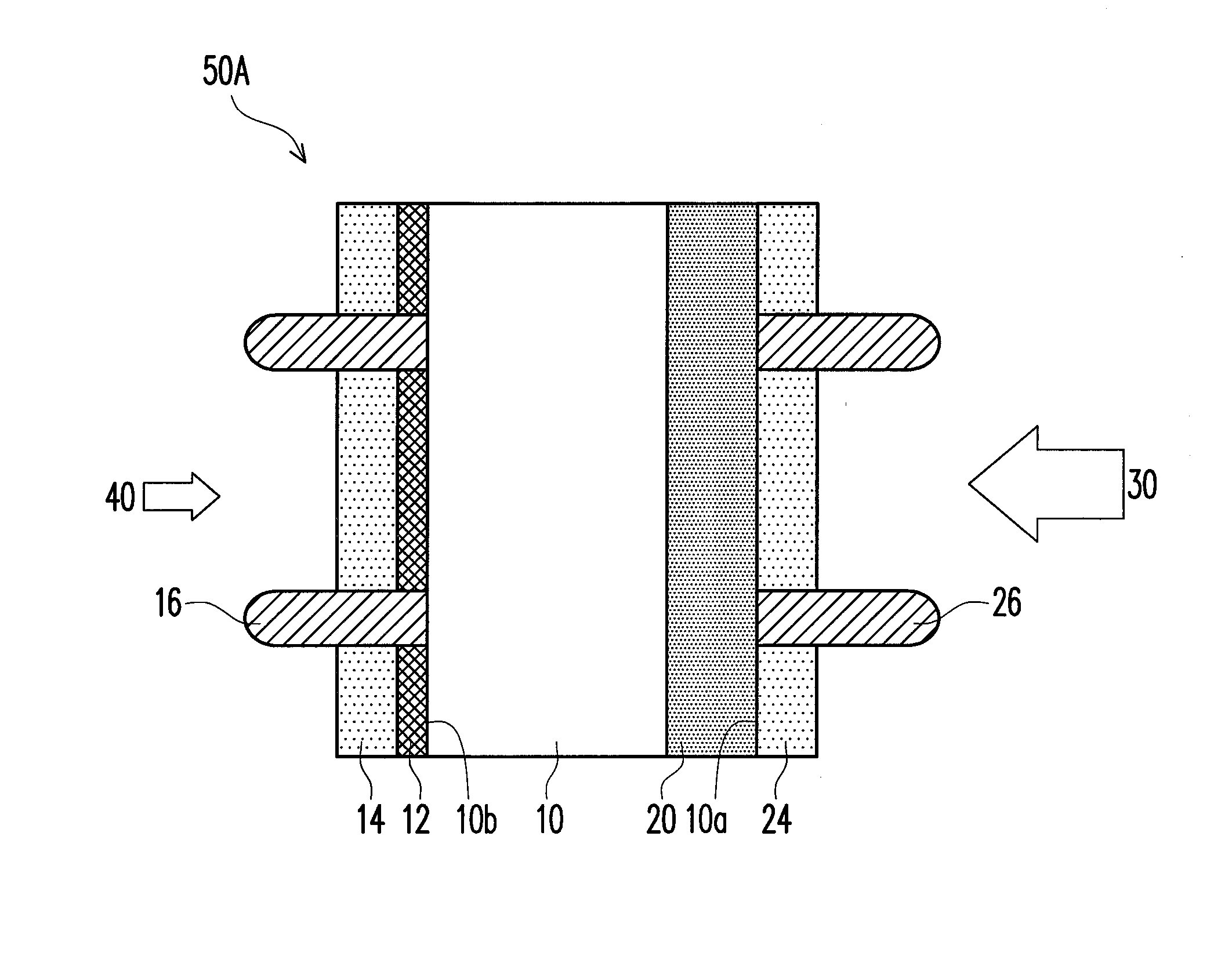
Solar cell device
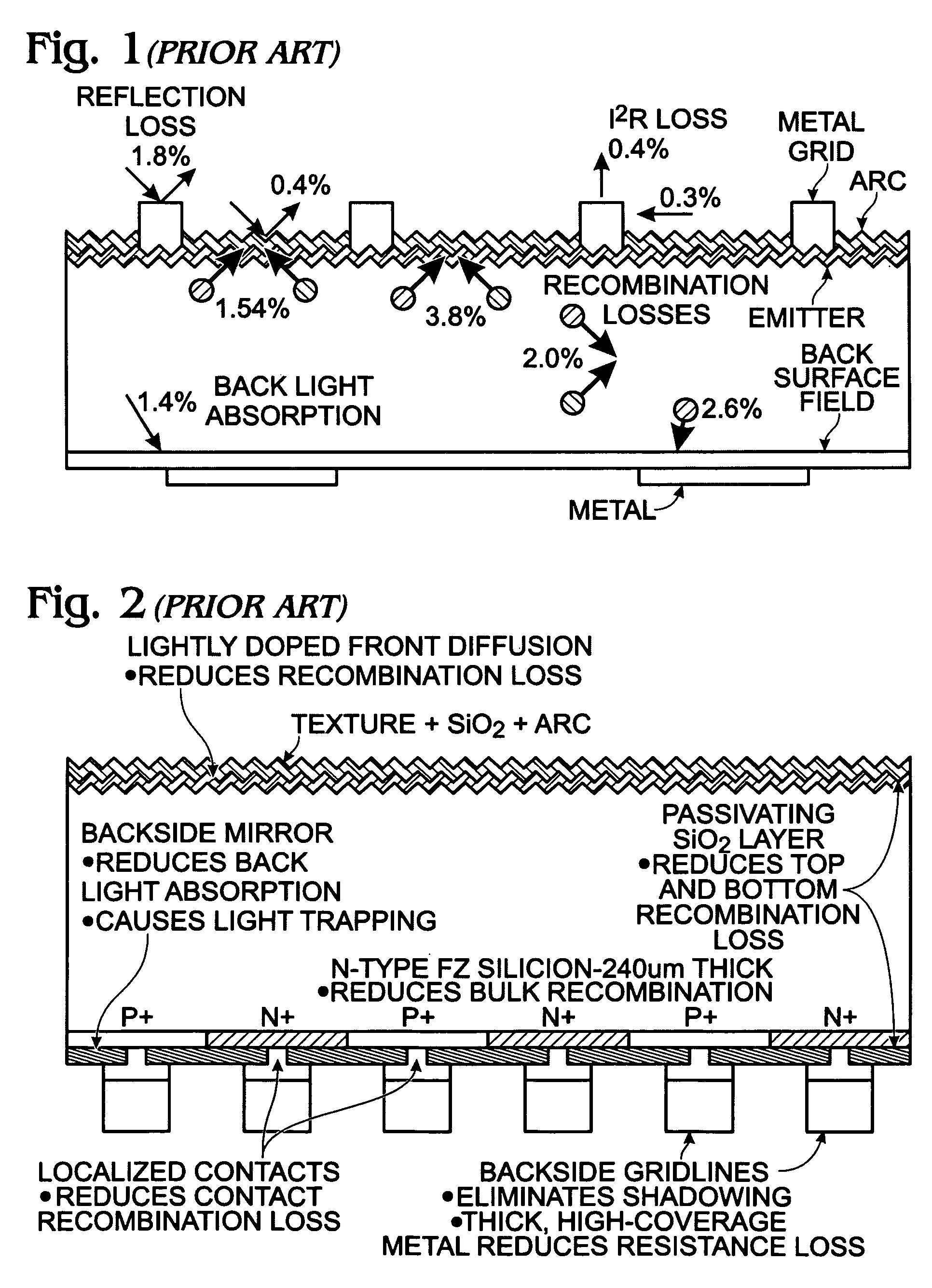
InactiveUS7560750B2Carrier recombination rate RReduce carrier recombinationThyristorSuperconductor devicesPhotoelectric conversionRecombination rate
In a photoelectric conversion device, in a contact between a p-type semiconductor 3a and an electrode 2, an n-type semiconductor 6 of a conductivity type opposite to that of the p-type semiconductor is provided between the p-type semiconductor 3a and the electrode 2. The existence of the n-type semiconductor 6 allows a recombination rate of photo-generated carriers excited by incident light to be effectively reduced, and allows a dark current component to be effectively prevented from being produced. Therefore, it is possible to improve photoelectric conversion efficiency as well as to stabilize characteristics. Further, a tunnel junction is realized by increasing the concentration of a doping element in at least one or preferably both of the p-type semiconductor 3a and the n-type semiconductor 6 in a region where they are in contact with each other, thereby keeping ohmic characteristics between the semiconductor and the electrode good.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Doped ai paste for local alloyed junction formation with low contact resistance
InactiveUS20130255765A1Reduce carrier recombinationReduces cost-per-wattSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationJunction formationCharge carrier
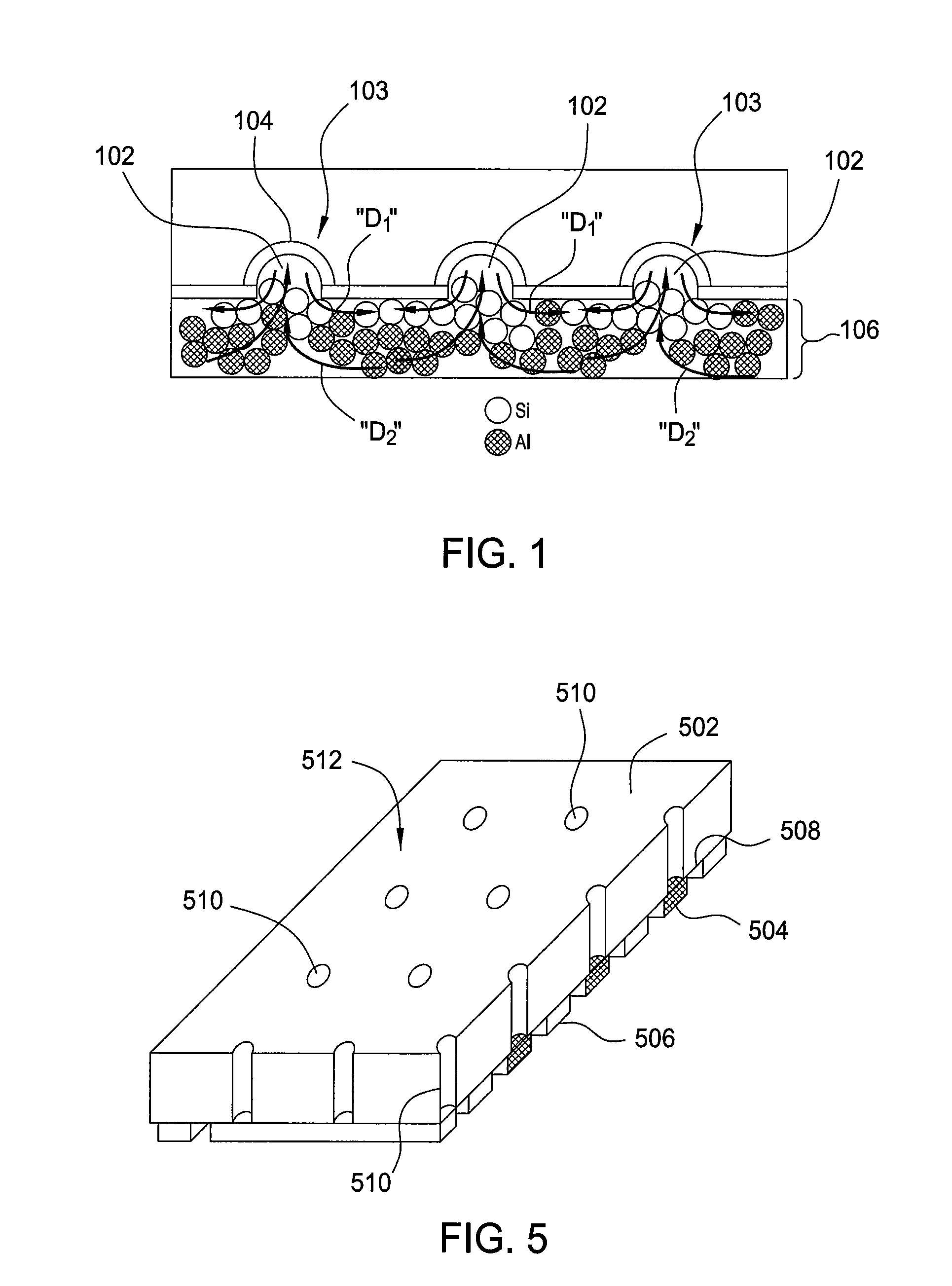
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to solar cells having reduced carrier recombination and methods of forming the same. The solar cells have eutectic local contacts and passivation layers which reduce recombination by facilitating formation of a back surface field (BSF). A patterned aluminum back contact doped with a Group III element is disposed on the passivation layer for removing current form the solar cell. The methods of forming the solar cells include depositing a passivation layer including aluminum oxide and silicon nitride on a back surface of a solar cell, and then forming openings through the passivation layer. An aluminum back contact doped with a Group III element is disposed on the passivation layer in a pattern covering the holes, and thermally processed to form a silicon-aluminum eutectic within the openings.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Bifacial solar cell
InactiveUS20110139250A1Reduce carrier recombinationIncrease efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesFixed chargeSolar cell
A bifacial solar cell including a semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type, a fixed charge layer, a first grid electrode, a semiconductor layer of a second conductivity type and a second grid electrode are provided. The fixed charge layer is located on a rear surface of the semiconductor substrate. The first grid electrode is located over the rear surface of the semiconductor substrate and electrically connected to the rear surface of the semiconductor substrate by penetrating through the fixed charge layer. The semiconductor layer is located on the front surface of the semiconductor layer. The second grid electrode is located over and electrically connected to the semiconductor layer.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
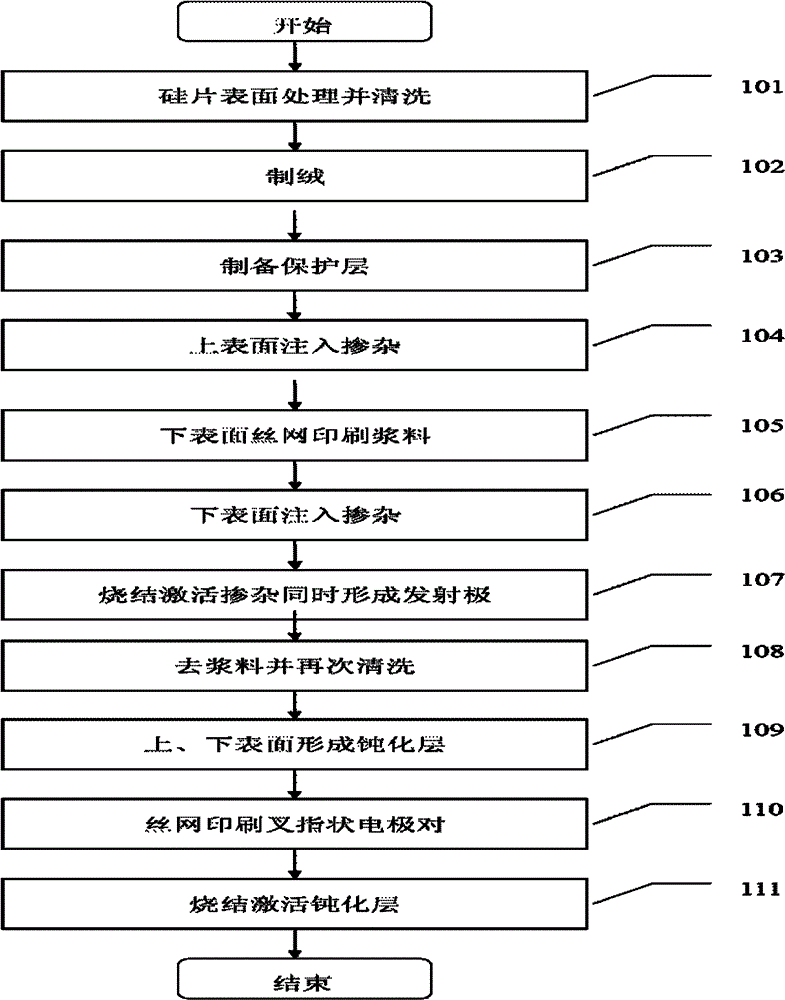
Interdigital back contact type solar battery and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102800738AReduce power generation costsReduce exposureOther printing apparatusPhotovoltaic energy generationElectrical batterySlurry
The invention relates to an interdigital back contact type solar battery and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: performing surface treatment and cleaning on a silicon chip; manufacturing velvet on the silicon chip; performing oxidation treatment on the silicon chip to form a protective layer for protection; performing doping treatment on the upper surface of the silicon chip with the protective layer; forming interdigital p and n areas on the lower surface of the silicon chip with the protective layer through slurry screen printing and ion injection; sintering the silicon chip; removing remnant aluminum, and cleaning again; forming a passivation layer on the silicon chip; printing an interdigital metal electrode couple; and sintering the silicon chip again. According to the method, the solar battery is prepared on the basis of ion injection doping and aluminum paste screen printing technologies, the technologies are simple, the process steps are obviously reduced, and the combination with the conventional P-type silicon solar battery process of enterprises is facilitated, so that the photoelectric conversion efficiency is improved, the battery power generation cost is reduced, and the interdigital back contact type solar battery and the method are convenient to popularize and use.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photoelectric conversion element and method of manufacturing the
InactiveUS20050205960A1Reduce carrier recombination lossImprove conversion efficiencyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLight beamPhotoelectric conversion
In a back-surface electrode type photoelectric conversion element having electrodes and semiconductor layers for collecting carriers disposed only on a back surface side of a semiconductor substrate, a semiconductor thin film that is larger in band gap than the semiconductor substrate and that contains an element causing a conductivity identical to or different from a conductivity of the semiconductor substrate is provided on a light-receiving surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and a diffusion layer is formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate. Alternatively, 95% or more of light beams having a wavelength of anywhere from 800 nm to 2000 nm are caused to penetrate the light-receiving surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and an insulative thin film containing an element causing a conductivity identical to or different from the conductivity of the semiconductor substrate is provided so as to form a diffusion layer on the surface of the semiconductor substrate through diffusion of the element.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
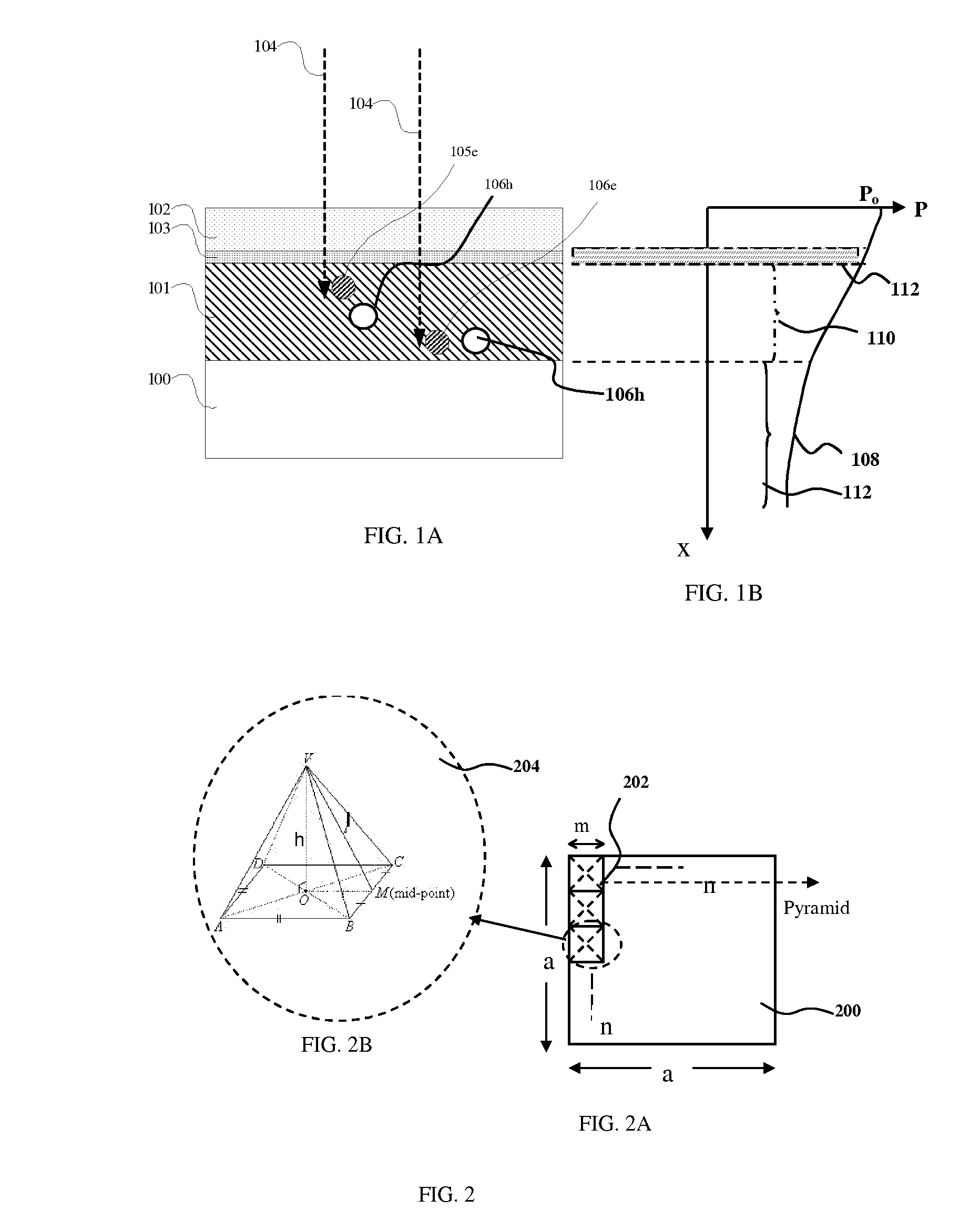
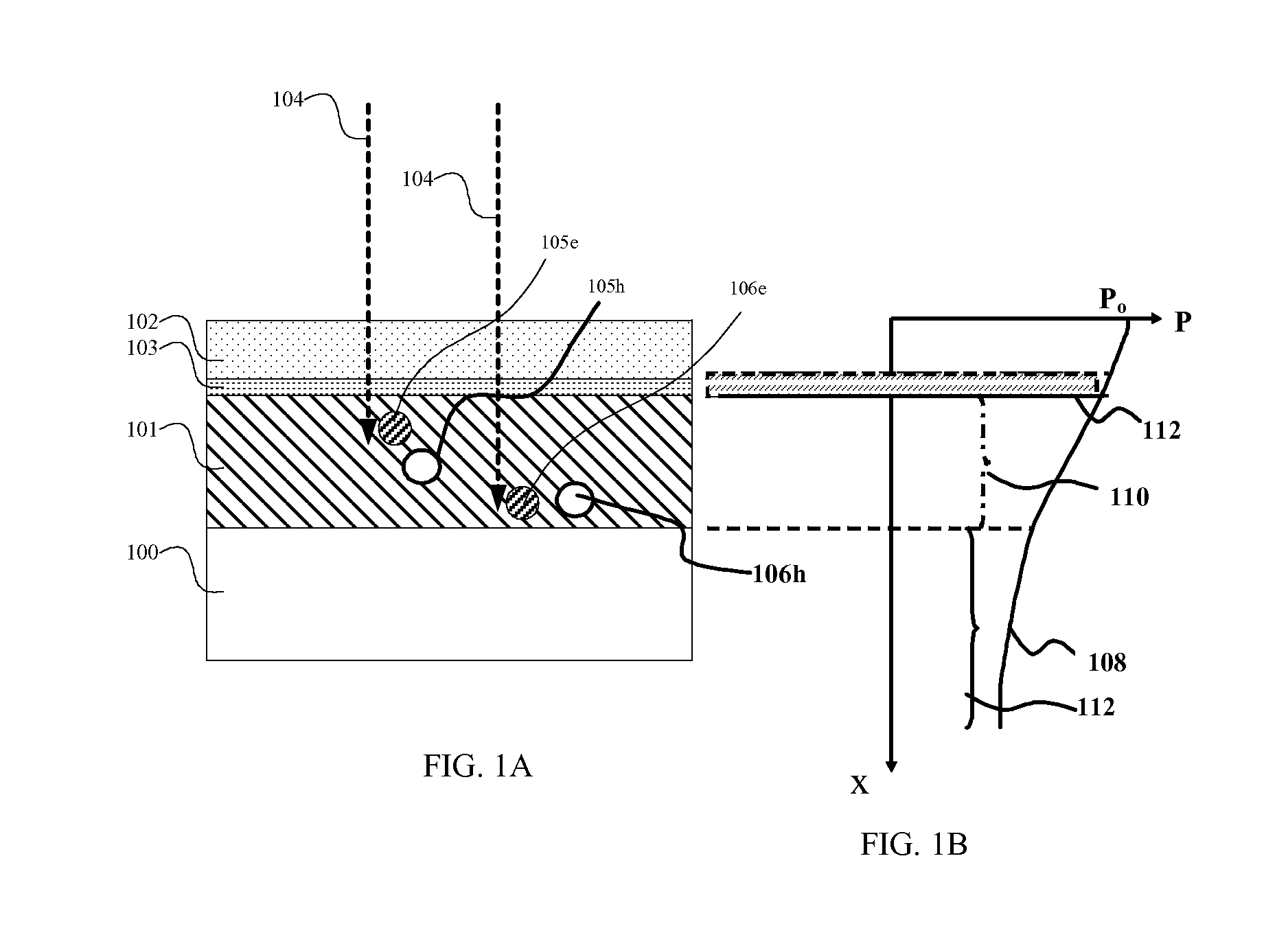
Light receiving element and light receiving device incorporating circuit and optical disc drive
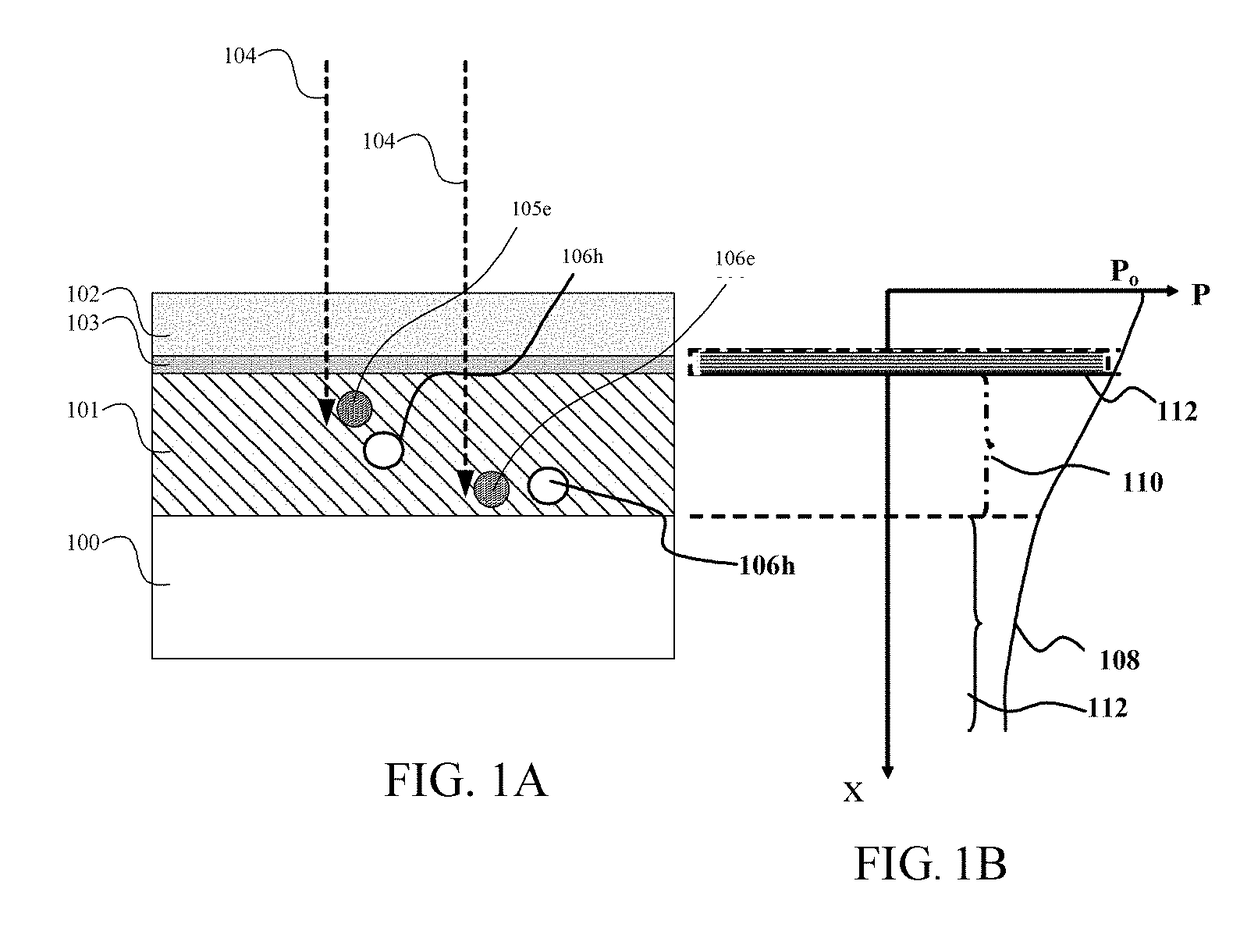
InactiveUS20050001231A1High sensitivityReduce carrier recombinationIntegrated optical head arrangementsSolid-state devicesCharge carrierPeak value
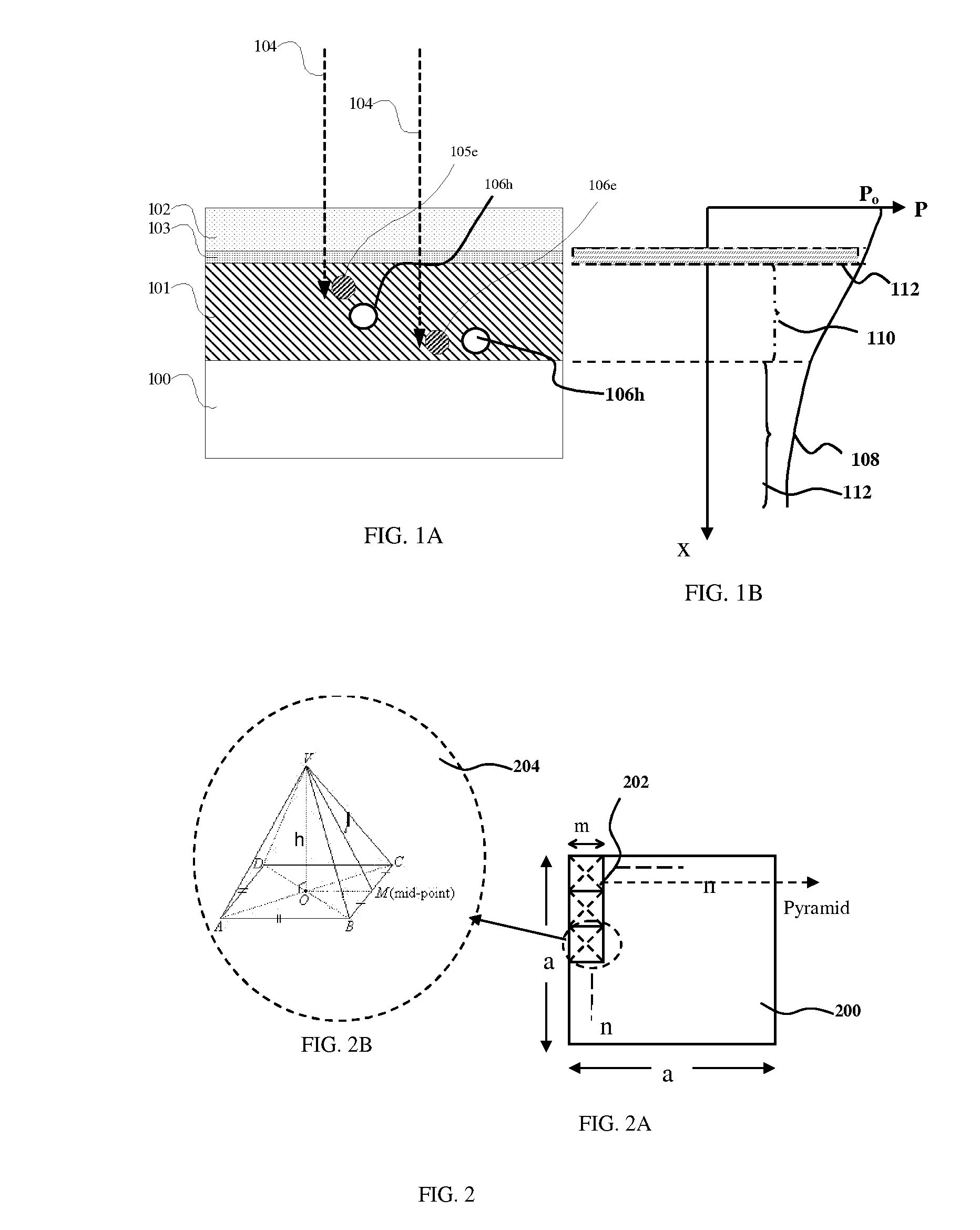
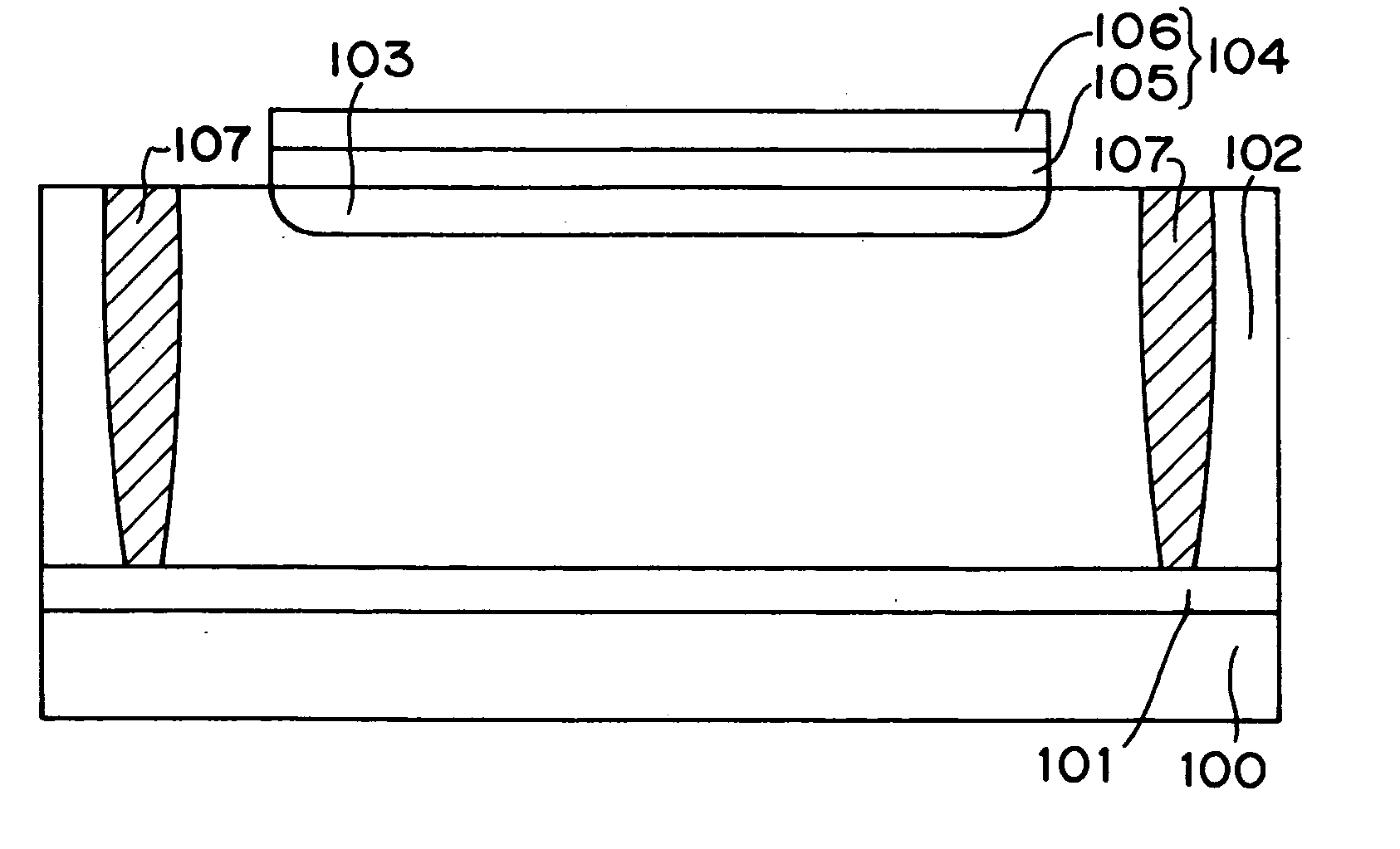
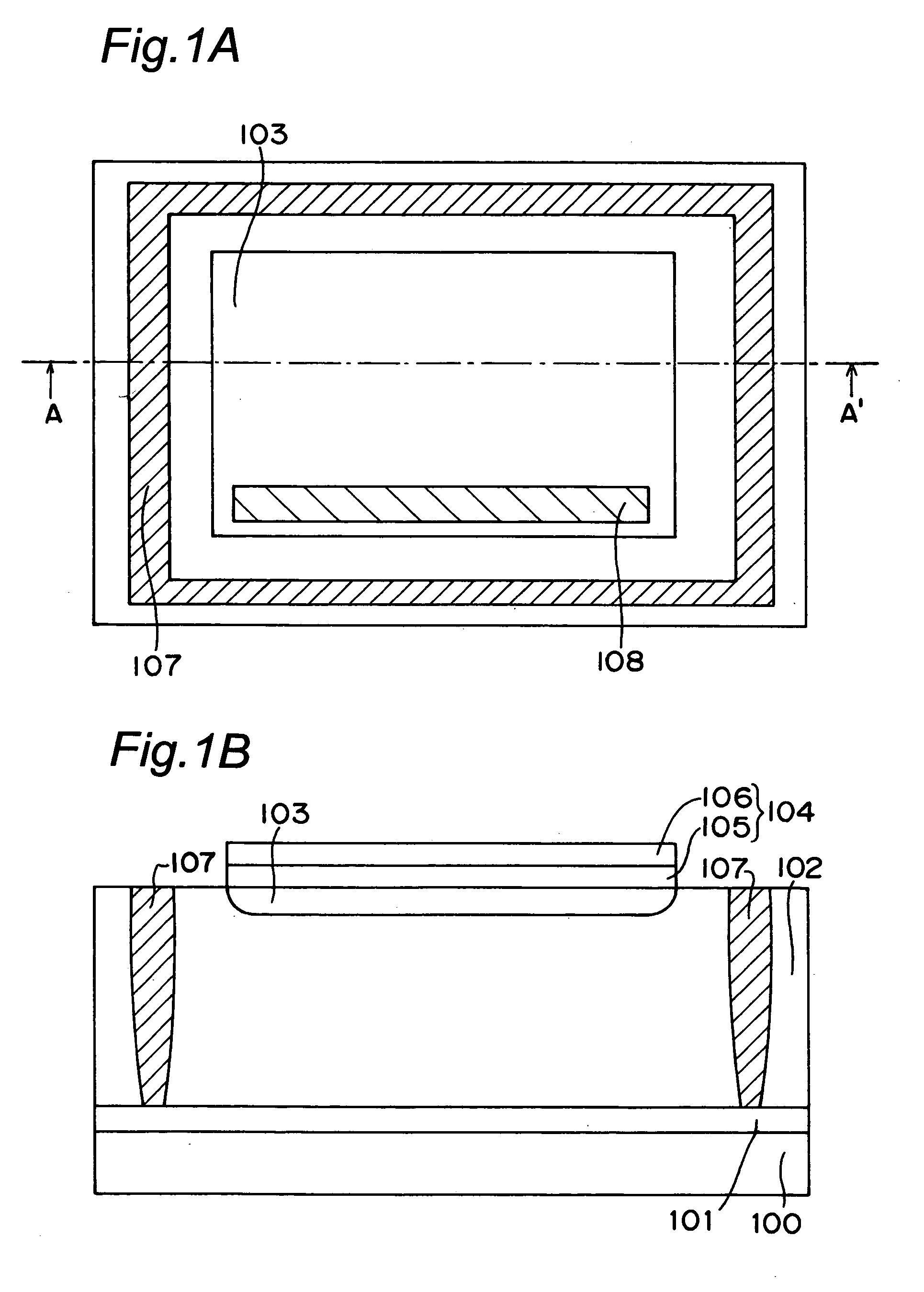
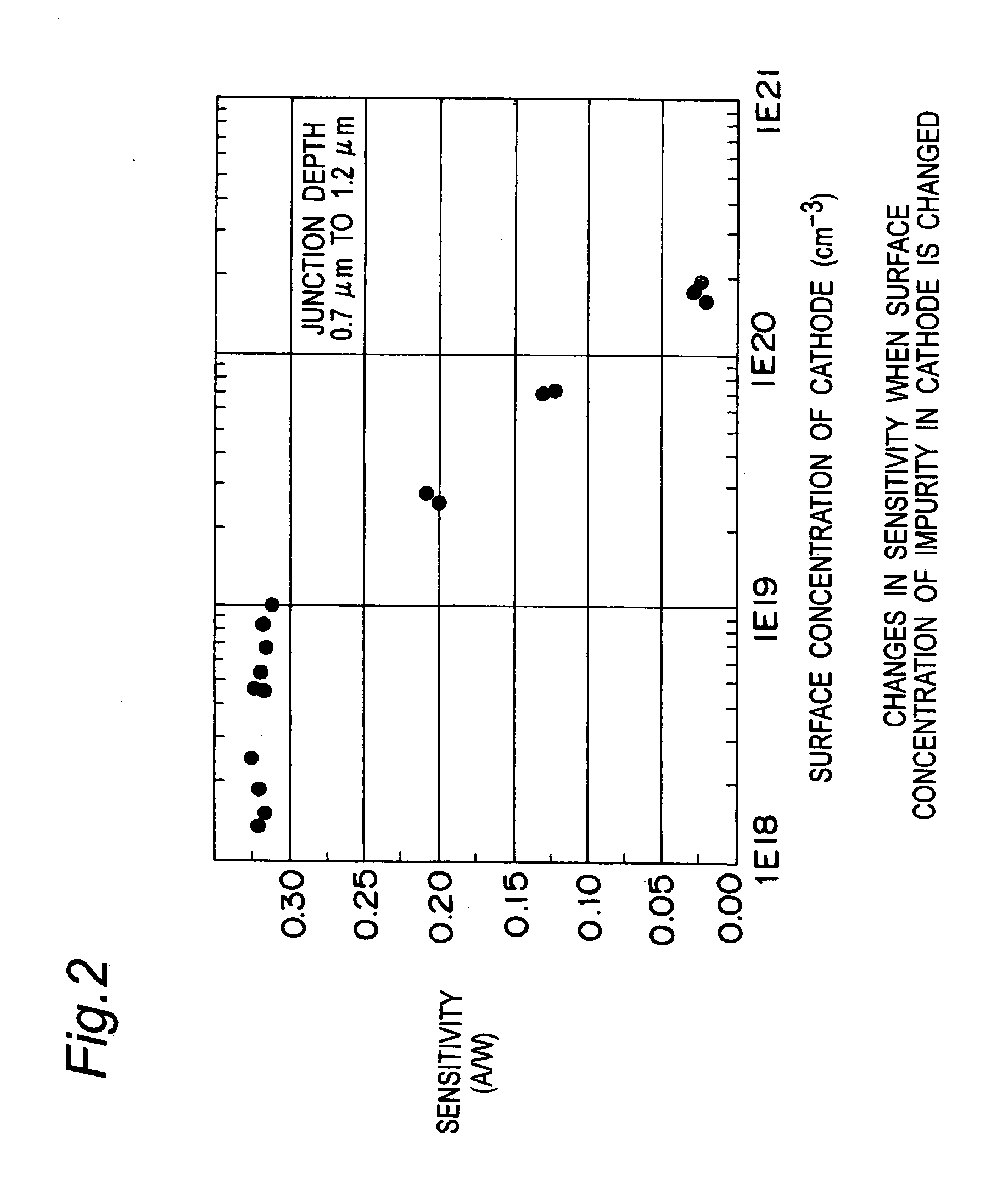
A light receiving device includes a P type diffusion layer (101), a P type semiconductor layer (102), an N type diffusion layer (103) serving as a light receiving part, and a light transmitting film (104), all formed on a p type silicon substrate (100). The N type diffusion layer (103) has a thickness of 0.8 μm to 1.0 μm which is larger than an absorption length of incident light having wavelength of 400 nm, and such a concentration profile that a impurity concentration is not higher than 1E19 cm−3 on a surface and has a peak in a vicinity of the surface. Since recombination of carriers generated by the incident light is prevented in the vicinity of the surface of the N type diffusion layer (103), sensitivity of the light receiving device is enhanced and response speed is increased by the low-resistance N type diffusion layer (103) having a larger junction depth.
Owner:SHARP KK
Single heterojunction back contact solar cell
ActiveUS8288645B2Reduce manufacturing costImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationDopantHeterojunction
A back contact single heterojunction solar cell and associated fabrication process are provided. A first semiconductor substrate is provided, lightly doped with a first dopant type. The substrate has a first energy bandgap. A second semiconductor is formed over a region of the substrate backside. The second semiconductor has a second energy bandgap, larger than the first energy bandgap. A third semiconductor layer is formed over the first semiconductor substrate topside, moderately doped with the first dopant and textured. An emitter is formed in the substrate backside, heavily doped with a second dopant type, opposite of the first dopant type, and a base is formed in the substrate backside, heavily doped with the first dopant type. Electrical contacts are made to the base and emitter. Either the emitter or base is formed in the second semiconductor.
Owner:SHARP KK
Stacked photoelectric conversion device and method for producing the same
InactiveUS8258596B2Reducing non-bonding handReduce carrier recombinationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationElectricityInter layer
To provide a stacked photoelectric conversion device and a method for producing the same, in which an interlayer is provided between photoelectric conversion layers to obtain an effect of controlling the amount of incidence light, and carrier recombination at an interface between the interlayer and a semiconductor layer is decreased to enhance photoelectric conversion efficiency.The stacked photoelectric conversion device of the present invention comprises a plurality of silicon-based photoelectric conversion layers having a p-i-n structure stacked, wherein at least a pair of adjacent photoelectric conversion layers have an interlayer of a silicon nitride therebetween, the pair of the photoelectric conversion layers are electrically connected with each other, and a p-type silicon-based semiconductor layer constituting a part of the photoelectric conversion layer and contacting the interlayer contains a nitrogen atom.
Owner:SHARP KK
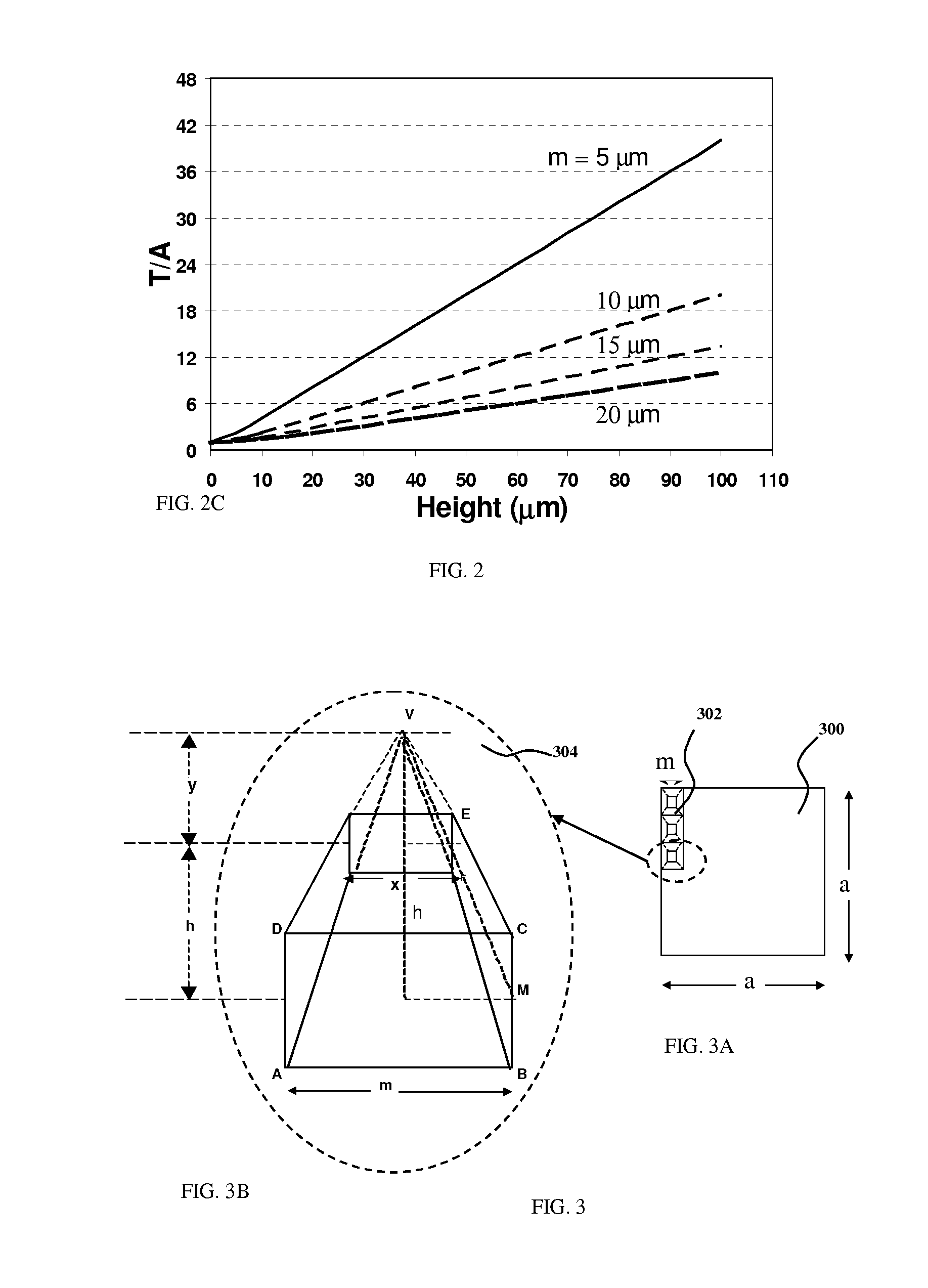
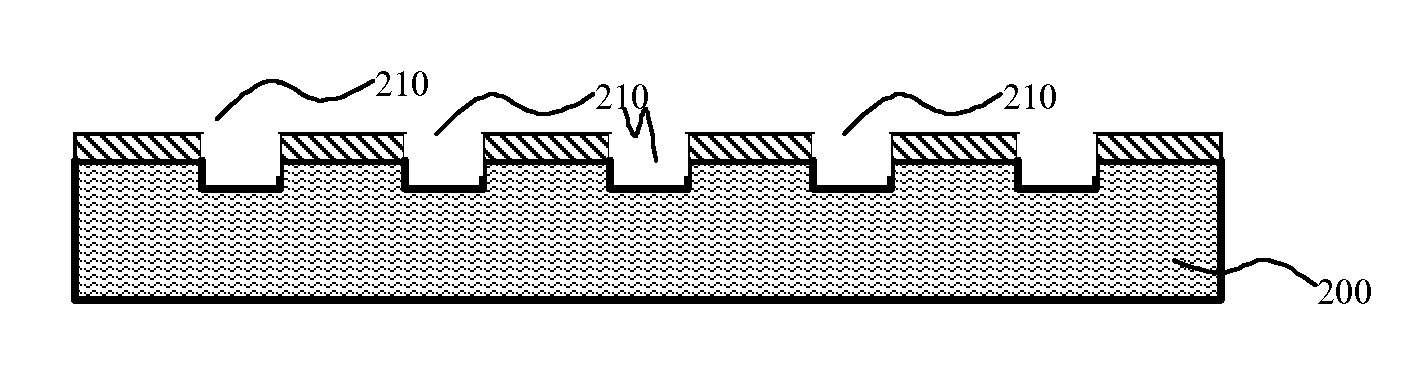
High efficiency photovoltaic cells with self concentrating effect
ActiveUS20170236953A1Enhanced light absorptionReduce carrier recombinationPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesReflection lossScale structure
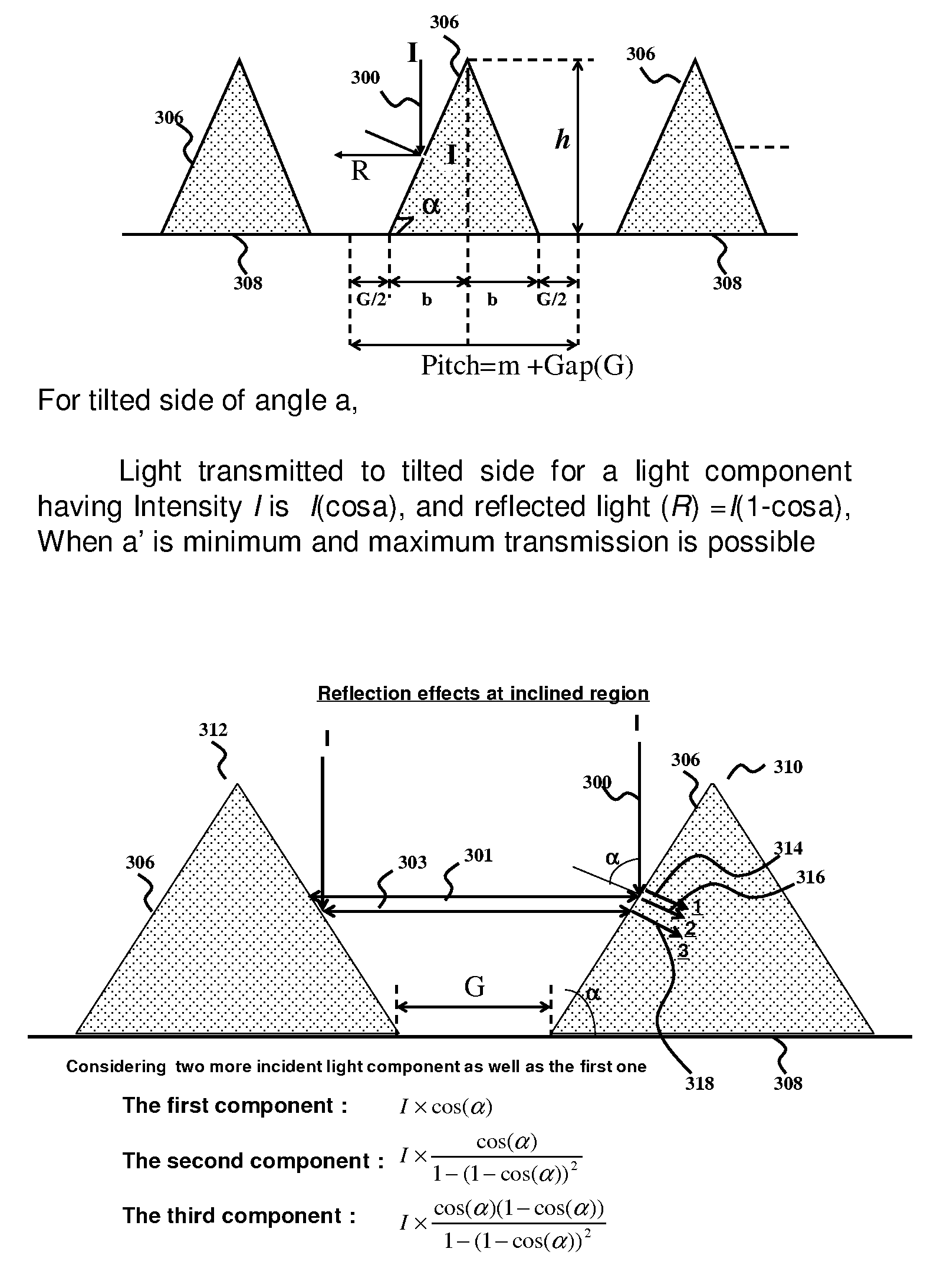
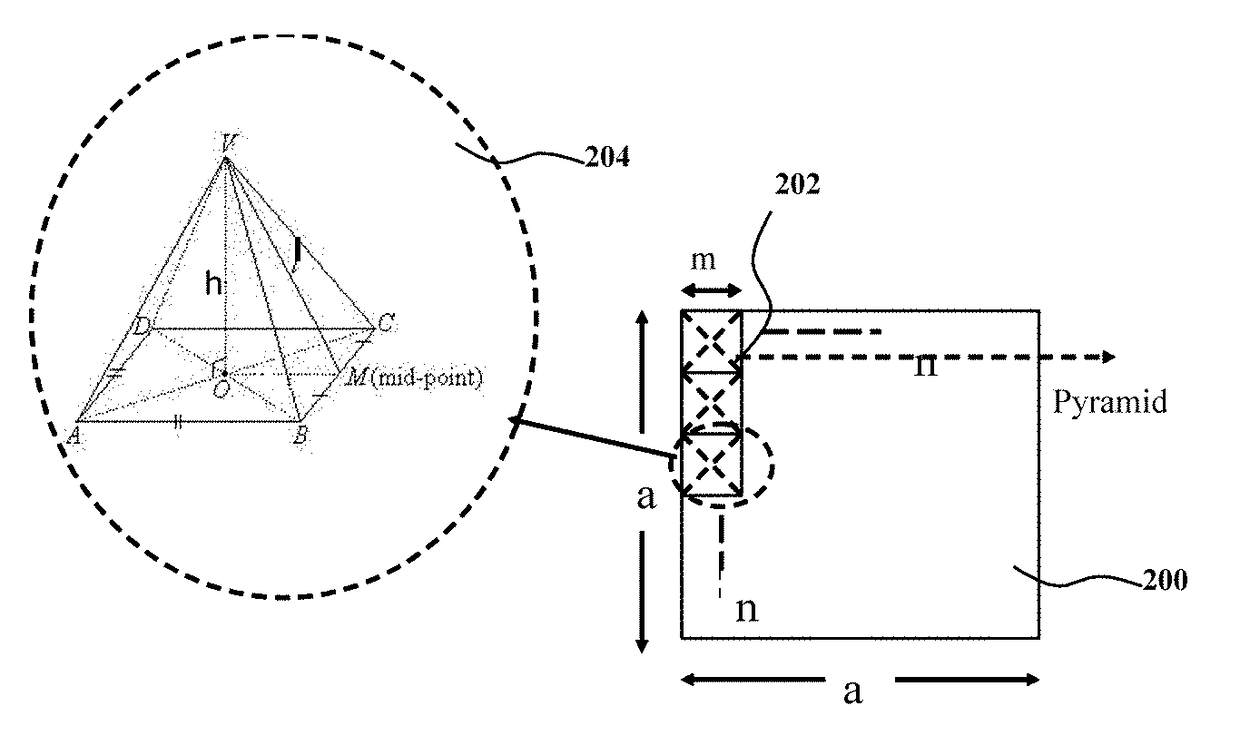
This invention relates to a novel structure of photovoltaic devices (e.g. photovoltaic cells also called as solar cells) are provided. The cells are based on the micro or nano scaled structures which could not only increase the surface area but also have the capability of self-concentrating the light incident onto the photonics devices. More specifically, the structures are based on 3D structure including quintic or quintic-like shaped micor-nanostructures. By using such structures reflection loss of the light from the cell is significantly reduced, increasing the absorption, which results in increasing the conversion efficiency of the solar cell, and reducing the usage of material while increasing the flexibility of the solar cell. The structures can be also used in other optical devices wherein the reflection loss and absorption are required to enhanced to significantly improve the device performances.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
Solar cell unit and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130276872A1Reduce carrier recombinationImprove light absorptionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolar cellImpurity
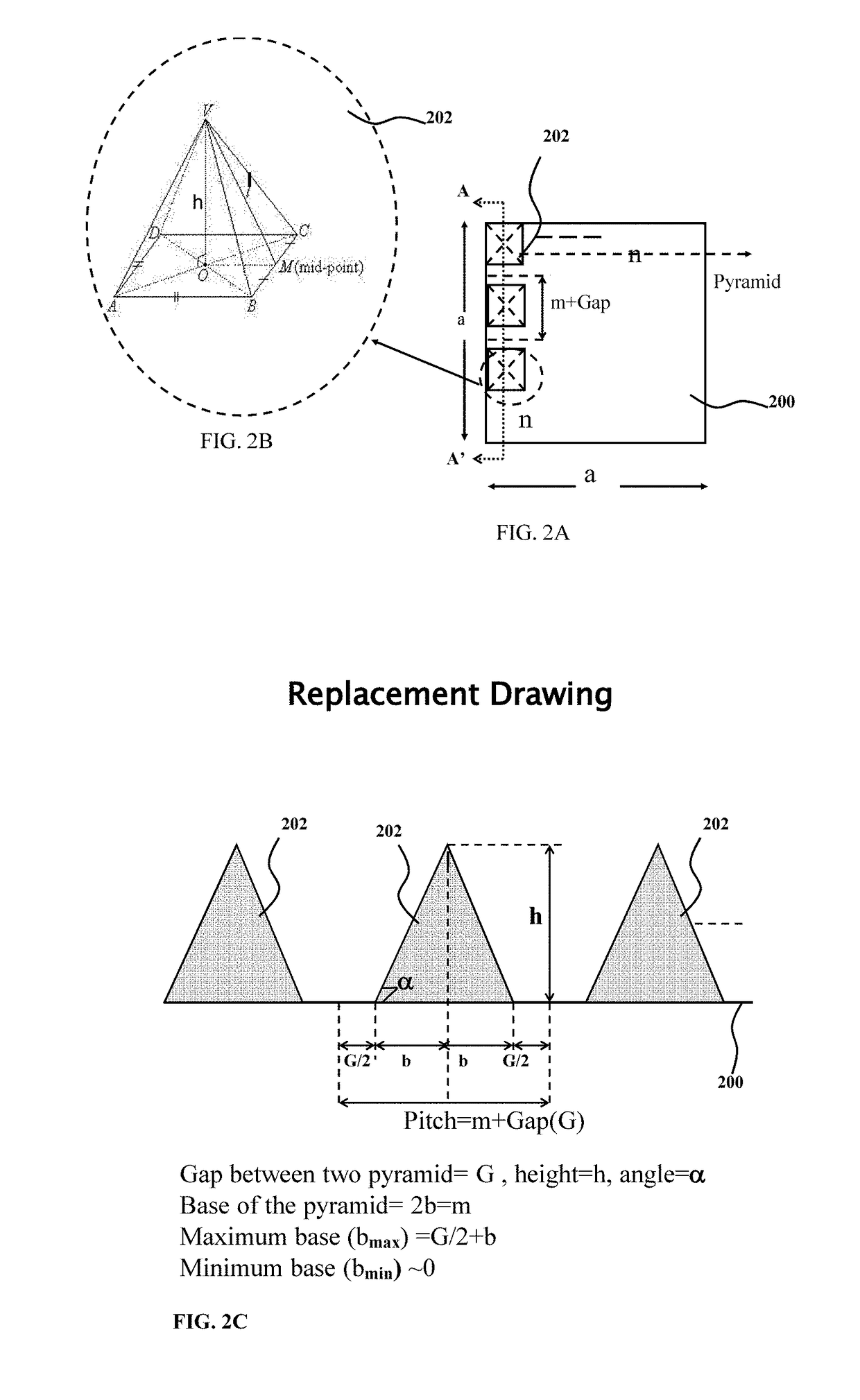
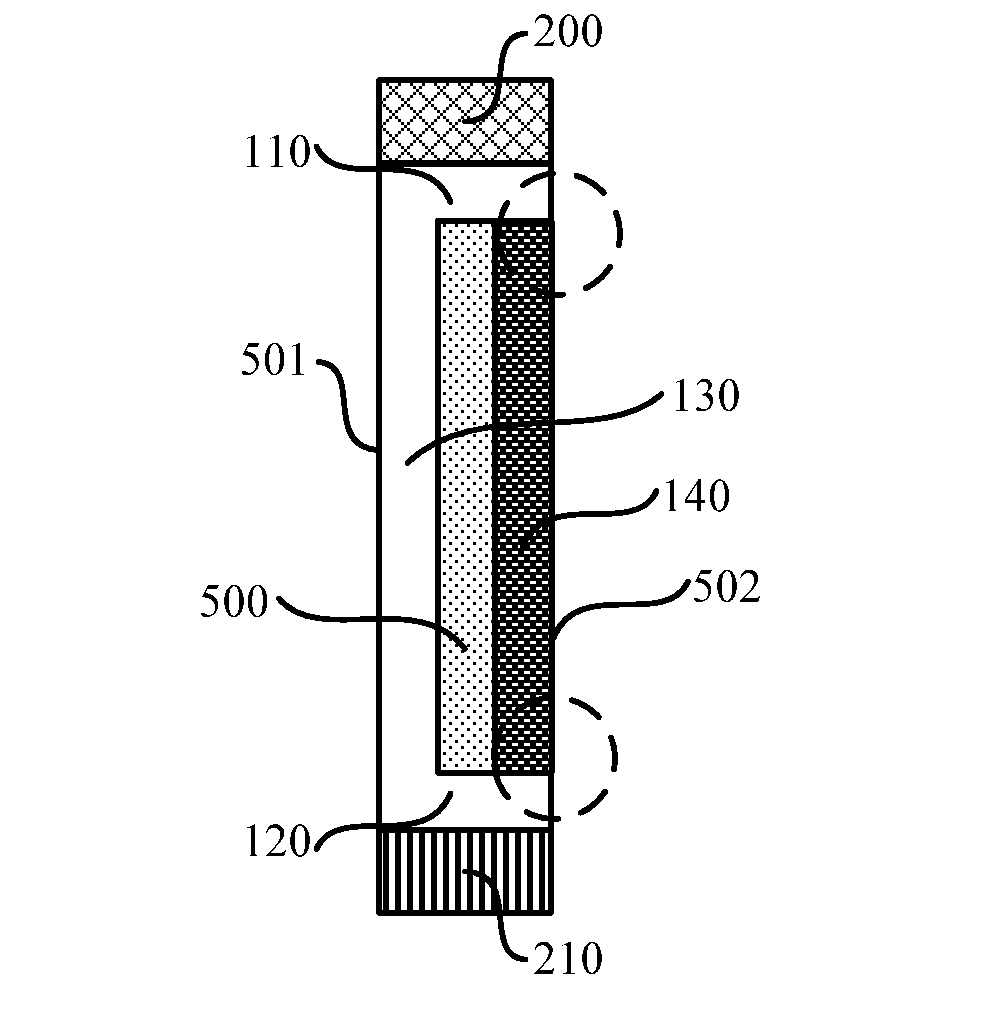
A solar cell unit comprising a strip plate which has a third surface and a fourth surface opposite to the third surface, wherein a third doping region and a fourth doping region are arranged on the third surface and the fourth surface respectively, and a first doping region and a second doping region are arranged on side surfaces adjacent to the third surface and the fourth surface respectively; the types of impurities in the third doping region and the fourth doping region are contrary to one another; the surfaces of the first doping region and the second doping region have uniform doping type. Accordingly, the present invention further provides a method for manufacturing a solar cell unit.
Owner:SUNOVEL SUZHOU TECH
Front grid line passivation contact-based PERC solar cell and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112186049AImprove efficiencyIncrease the open circuit voltageFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSilicon oxideMaterials science
The invention belongs to the technical field of crystalline silicon solar cells, and relates to a front grid line passivation contact-basedPERC solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The solar cell comprises a P type monocrystalline silicon substrate; a back aluminum oxide passivation layer and a back silicon nitride passivation layer are sequentially arranged on the back surface of the P type monocrystalline silicon substrate from inside to outside. A front silicon oxide passivation layer and a front silicon nitride passivation layer are sequentially arranged on the front face of the Ptype monocrystalline silicon substrate from inside to outside; a front metal silver grid line penetrating through the front silicon oxide passivation layer and the front silicon nitride passivation layer is arranged on the front face of the P type monocrystalline silicon substrate. An ultrathin tunneling silicon oxide layer and a phosphorus-doped polycrystalline silicon layer are sequentially arranged on the front face of the P type monocrystalline silicon substrate and located below the front face metal silver grid line from inside to outside. According to the solar cell and preparation method thereof of the invention, the open-circuit voltage of the cell can be improved, the carrier recombination of a metal contact region can be reduced, the parasitic absorption of the doped polycrystalline silicon layer to light can be reduced, the current loss can be reduced, and the efficiency of the PERC cell can be improved.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD +1
Graphene photoelectric detector based on interdigital electrode structure
InactiveCN110854234AIncrease contact resistanceIncrease photocurrentSemiconductor devicesPhysicsLight absorbance
The invention relates to a graphene photoelectric detector based on an interdigital electrode structure. The photoelectric detector comprises a substrate layer and an optical waveguide disposed on thesubstrate layer. The optical waveguide is provided with a dielectric isolation layer; the dielectric isolation layer is provided with two metal layers which are not in contact with each other; the two metal layers serve as electrodes; graphene layers are arranged on the two metal layers; and the graphene layers serve as light absorption layers. The provided graphene photoelectric detector based on the interdigital electrode is compatible with a CMOS process and has high performance.
Owner:苏州枫桥光电科技有限公司
Photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20120298191A1Reduce carrier recombinationSmall electrical conductivityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionHigh concentration
Provided is a photoelectric conversion device characterized by a lattice-shaped current-collection metal electrode and a depressed portion provided in opening regions of a lattice structured by the lattice-shaped. current collection electrode. This structure results in the reduction in the area of a heterojunction containing a highly-doped semiconductor layer, which decreases the influence of carrier recombination promoted by the high concentration of an impurity and leads to the improved electric Characteristic of the photoelectric conversion device. The lattice shape of the current collection electrode also makes it possible to exclude the use of a light-transmitting current collection electrode and allows a protective insulating layer having a high light-transmitting property to be formed over the current collection electrode, which contributes to the reduction of the light absorption loss.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
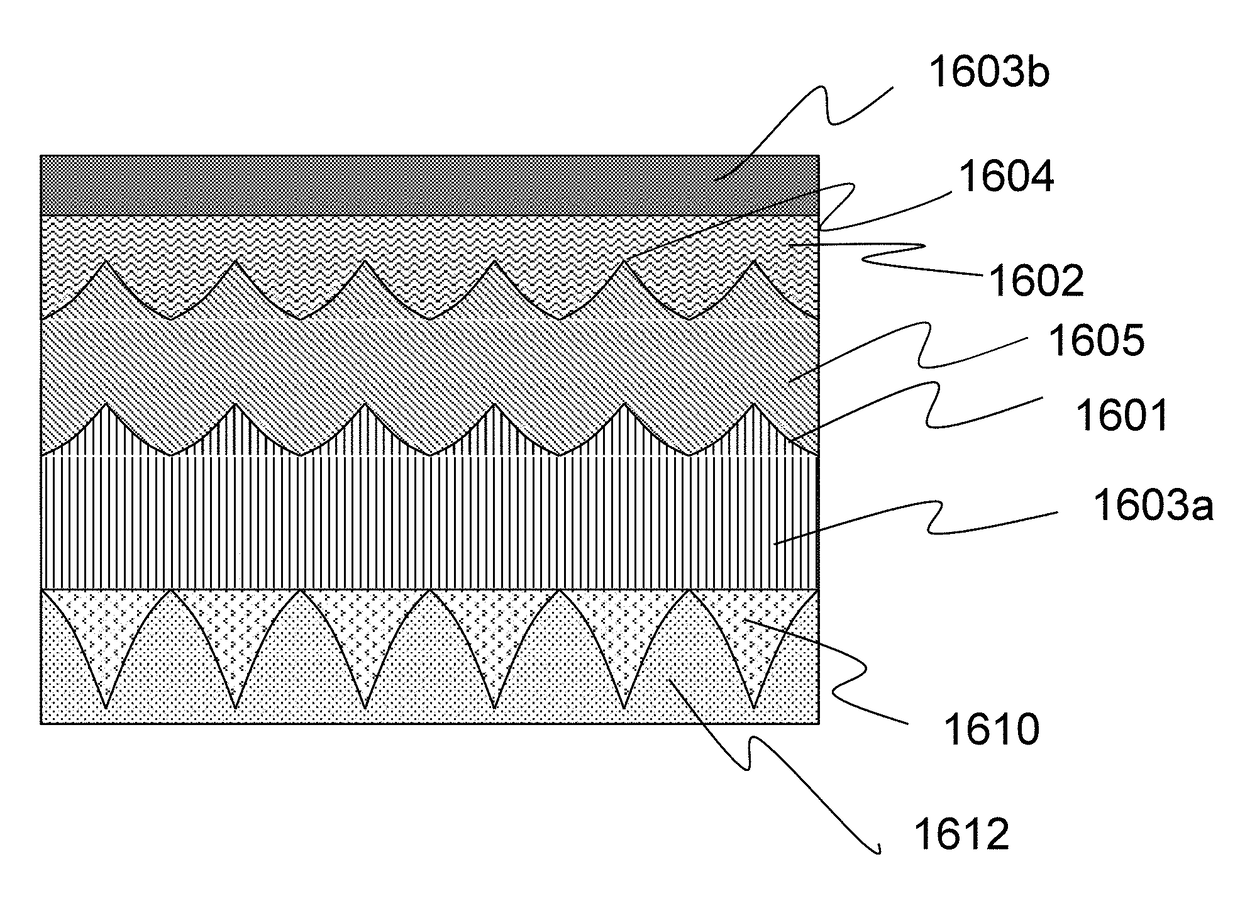
High efficiency photovoltaic cells and manufacturing thereof
ActiveUS20170301810A1Reduce reflectionHigh reflection coatingLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesElectricityReflection loss
This invention relates to a novel structure of photovoltaic devices (e.g. photovoltaic cells also called as solar cells) are provided. The cells are based on the micro or nano scaled structures which could not only increase the surface area but also have the capability of reducing the reflection and increasing the absorption of incident light. More specifically, the structures are based on 3D structure which are made of electric materials covering semiconductors, insulators, dielectric, polymer, and metallic type materials. By using such structures reflection loss of the light from the cell is significantly reduced, increasing the absorption, which results in increasing the conversion efficiency of the solar cell, and reducing the usage of material while increasing the flexibility of the solar cell. The structures can be also used in other optical devices wherein the reflection loss and absorption are required to enhance significantly improve the device performances.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
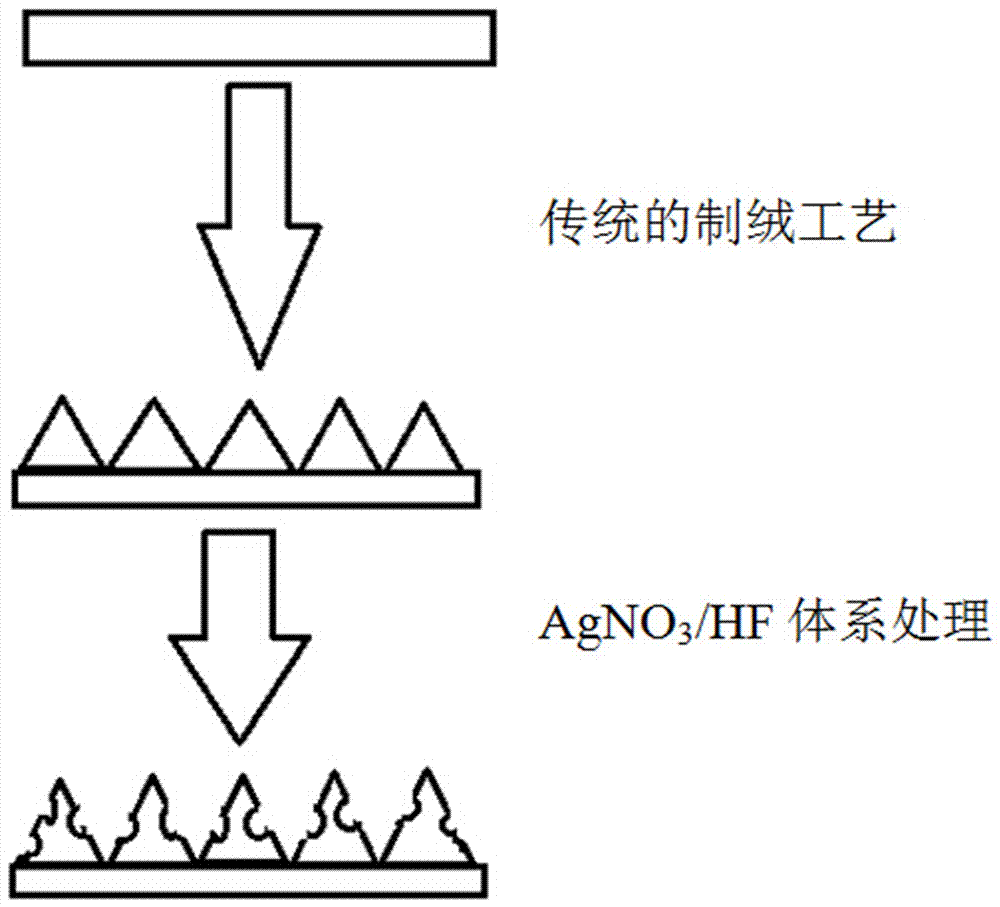
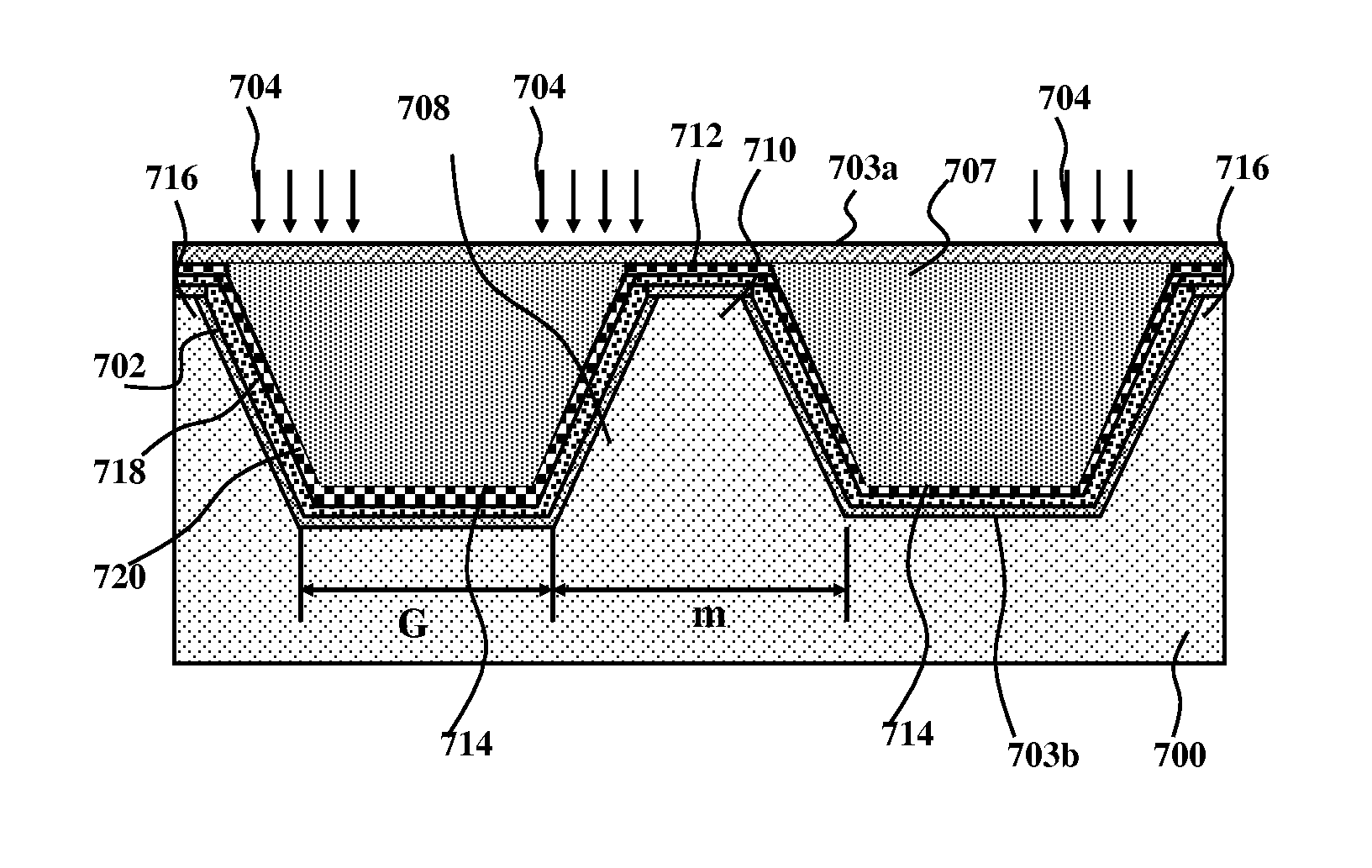
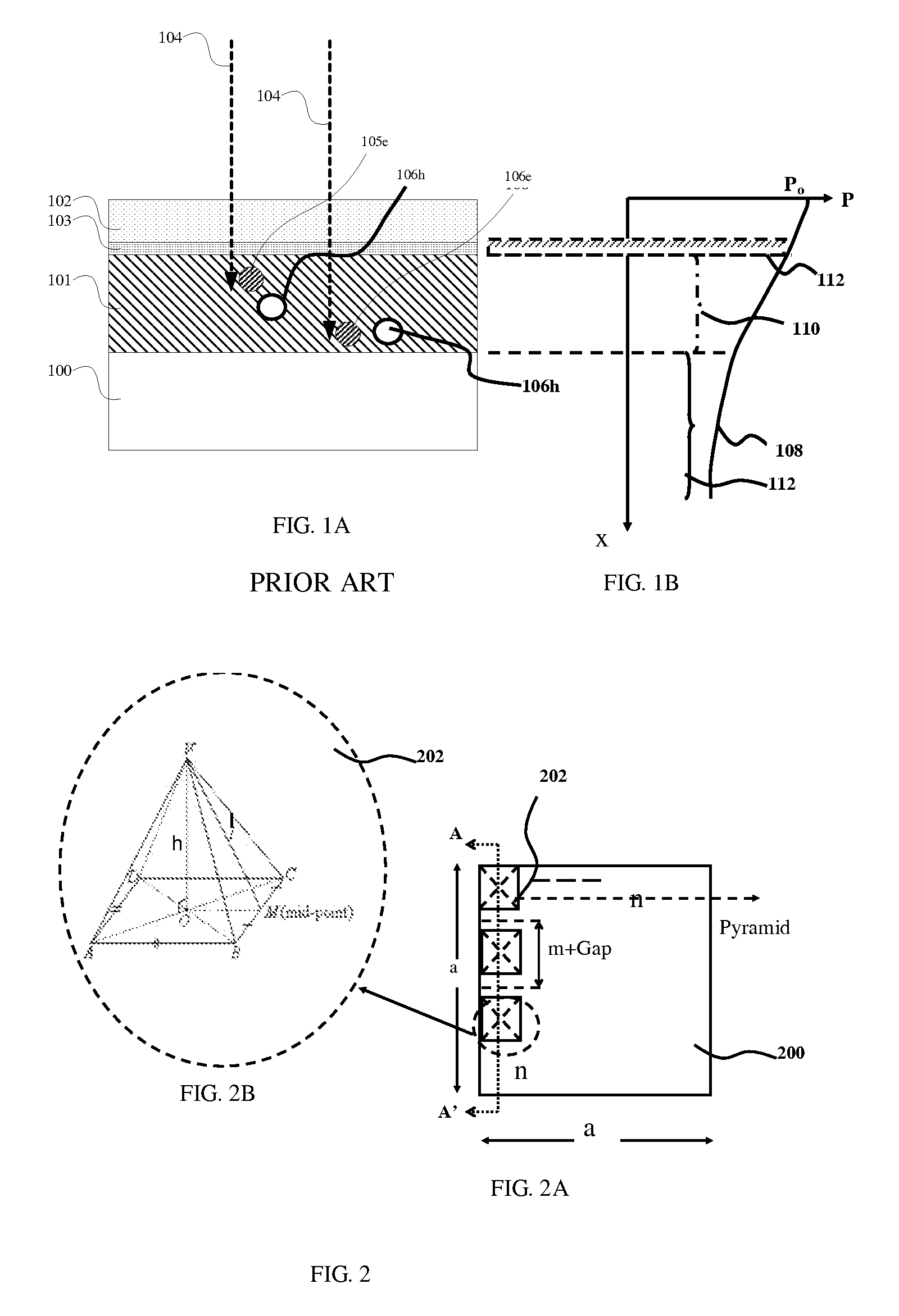
Method for preparing single-crystal silicon texture-surface structure with low reflectivity
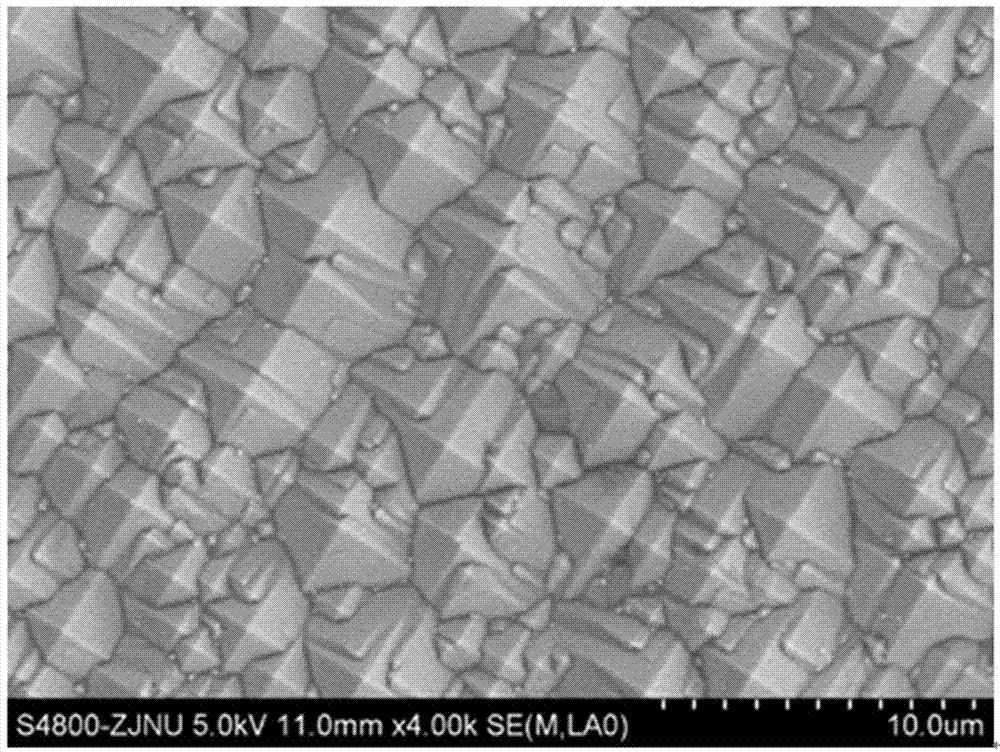
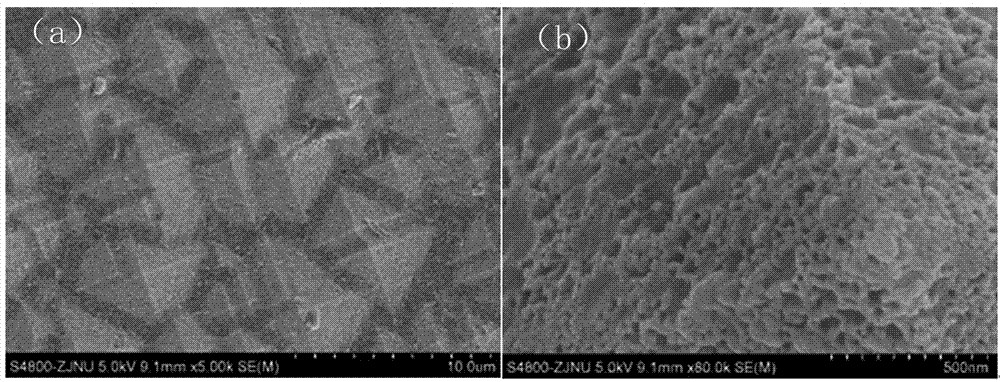
InactiveCN107316917ALow birthrate has no effectReduce reflectivityMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureAlcoholCharge carrier
The invention discloses a method for preparing a single-crystal silicon texture-surface structure with low reflectivity. A large amount of tetrahedral pyramids are formed on a surface of a silicon wafer by a traditional method, and many nanometer pores are formed in the surface of the silicon wafer by immersion processing of an alkali alcohol solution. The reflectivity of the surface of the silicon wafer with a nanometer structure in a pyramid shape can be further reduced; and meanwhile, the carrier recombination of the surface of the silicon wafer is only reduced slightly, almost no influence on the lifetime of a minority carrier of the silicon wafer is generated, so that the photoelectric conversion efficiency of a crystalline silicon solar cell can be effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
High efficiency photovoltaic cells and manufacturing thereof
ActiveUS8816191B2Reduce carrier recombinationEnhanced light absorptionLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureMicrometerEngineering
Novel structures of photovoltaic cells (also treated as solar cells) are provided. The cells are based on nanometer or micrometer-scaled wires, tubes, and / or rods, which are made of electronic materials covering semiconductors, insulators, and may be metallic in structure. These photovoltaic cells have large power generation capability per unit physical area over the conventional cells. These cells will have enormous applications such as in space, commercial, residential and industrial applications.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
Photovoltaic cells based on nano or micro-scale structures
ActiveUS8624108B1Electric power generatedLarge power generation capabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScale structureEngineering
Novel structures of photovoltaic cells (also treated as solar cells) are provided. The cells are based on nanometer-scaled wires, tubes, and / or rods, which are made of electronic materials covering semiconductors, insulators or metallic in structure. These photovoltaic cells have large power generation capability per unit physical area over the conventional cells. These cells will have enormous applications in space, commercial, residential, and industrial applications.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
Photoelectric conversion device
ActiveUS20130082344A1Reduce resistance lossImprove conversion efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationPhotoelectric conversionCrystalline silicon
A photoelectric conversion device with low resistance loss and high conversion efficiency is provided. The photoelectric conversion device includes a first silicon semiconductor layer and a second silicon semiconductor layer between a pair of electrodes. The first silicon semiconductor layer is provided over one surface of a crystalline silicon substrate having one conductivity type and has a conductivity type opposite to that of the crystalline silicon substrate, and the second silicon semiconductor layer is provided on the other surface of the crystalline silicon substrate and has a conductivity type which is the same as that of the crystalline silicon substrate. Further, the first silicon semiconductor layer and the second silicon semiconductor layer each have a carrier concentration varying in the film thickness direction.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
High efficiency photovoltaic cells with self concentrating effect
ActiveUS8716594B2Enhanced light absorptionReduce carrier recombinationPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSolar cell
Novel structures of photovoltaic cells (also called as solar cells) are provided. The Cells are based on the micro (or nano) structures which could not only increase the surface area but also have the capability of self concentrating the solar spectrum incident onto the cell. These photovoltaic cells have large power generation capability per unit physical area over the conventional cells. These cells will have enormous applications such as in space, in commercial, residential and industrial applications.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
Semiconductor light-emitting device and method for making same
ActiveUS7919784B2Reduce carrier recombinationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactCharge carrier
Owner:LATTICE POWER (JIANGXI) CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com