Patents
Literature
139results about How to "Reduce recombination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Photoelectrocatalytic fluid analyte sensors and methods of fabricating and using same
InactiveUS20080220535A1Reduce recombinationOptical radiation measurementImmobilised enzymesPhysicsOptical radiation
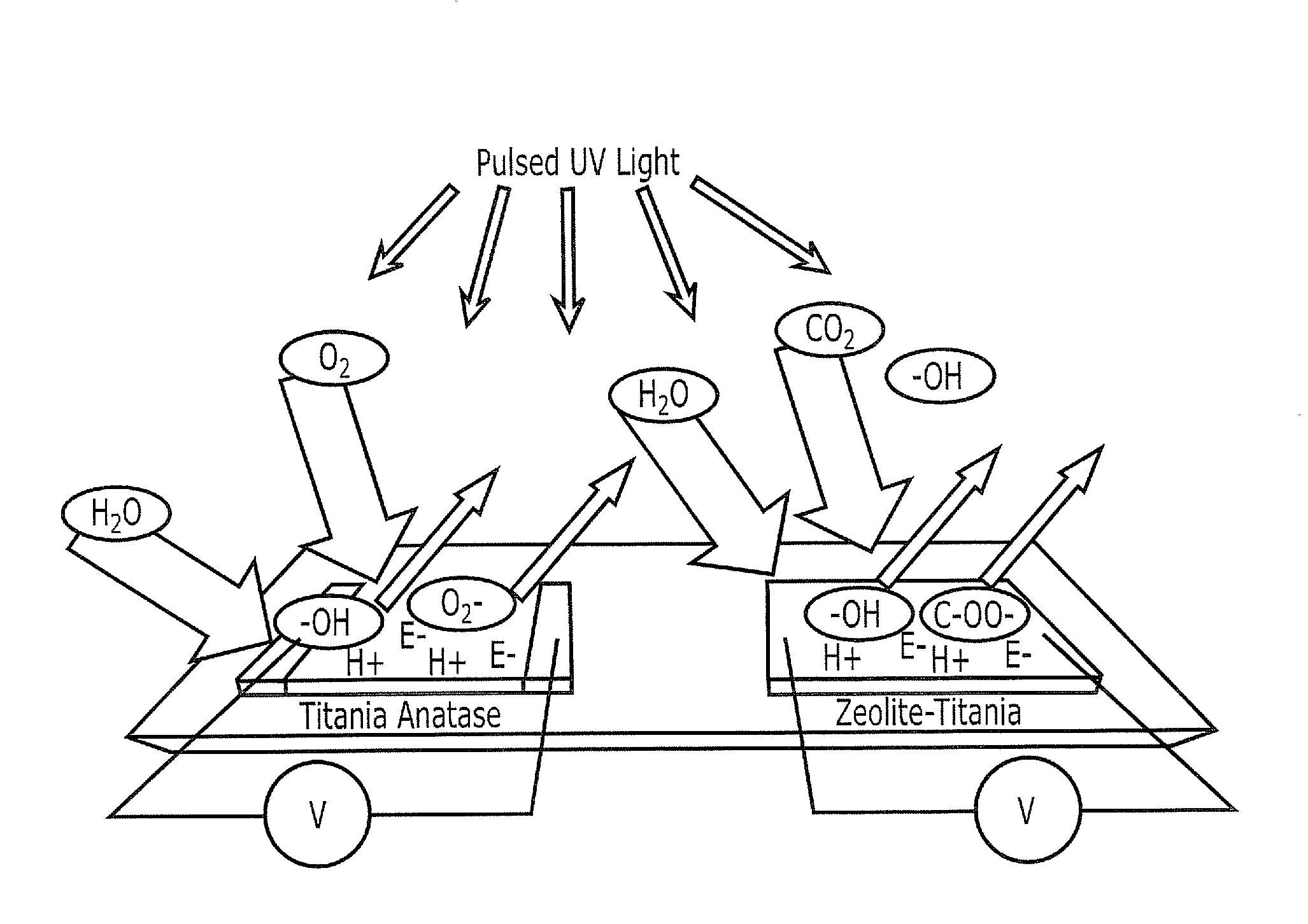
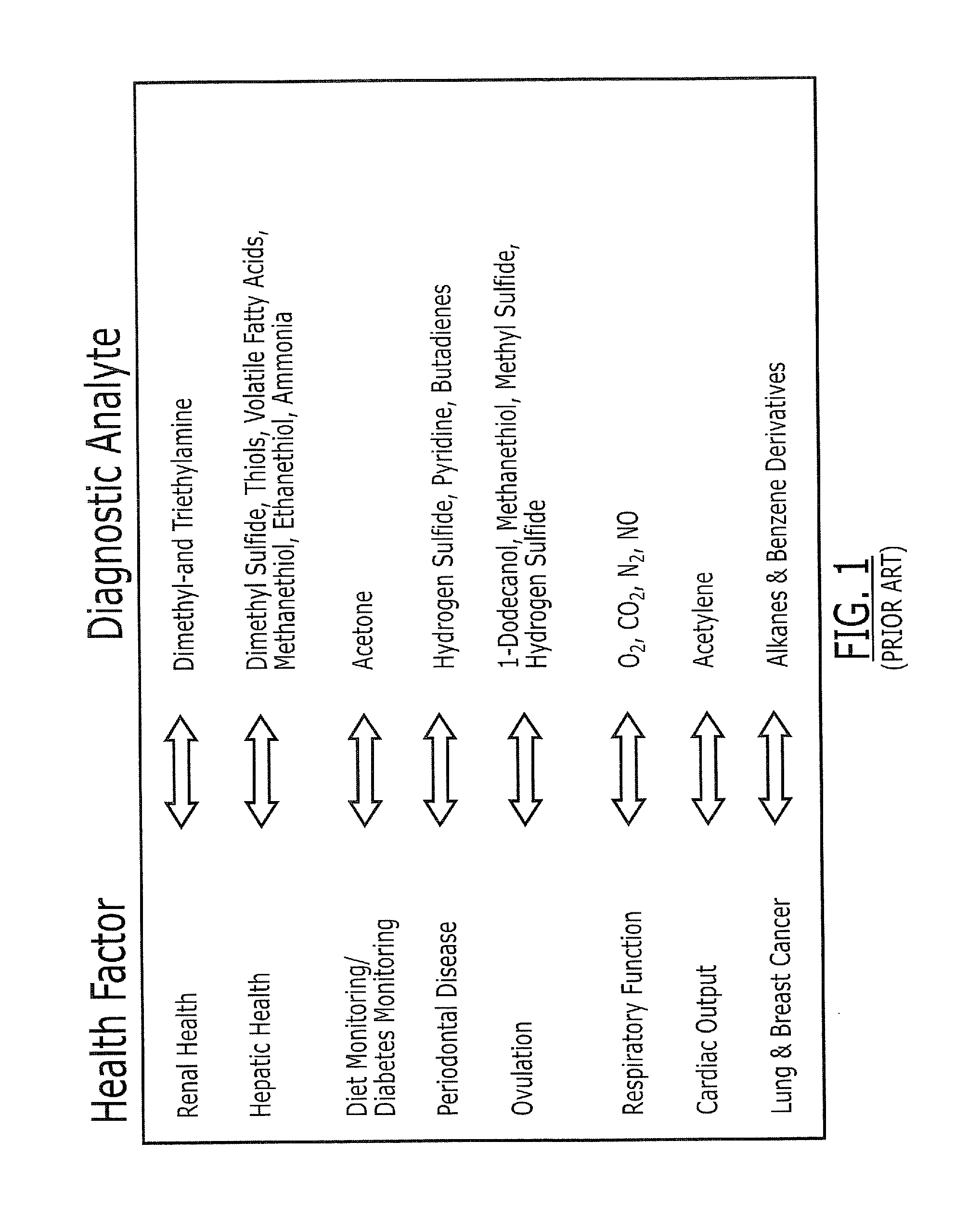
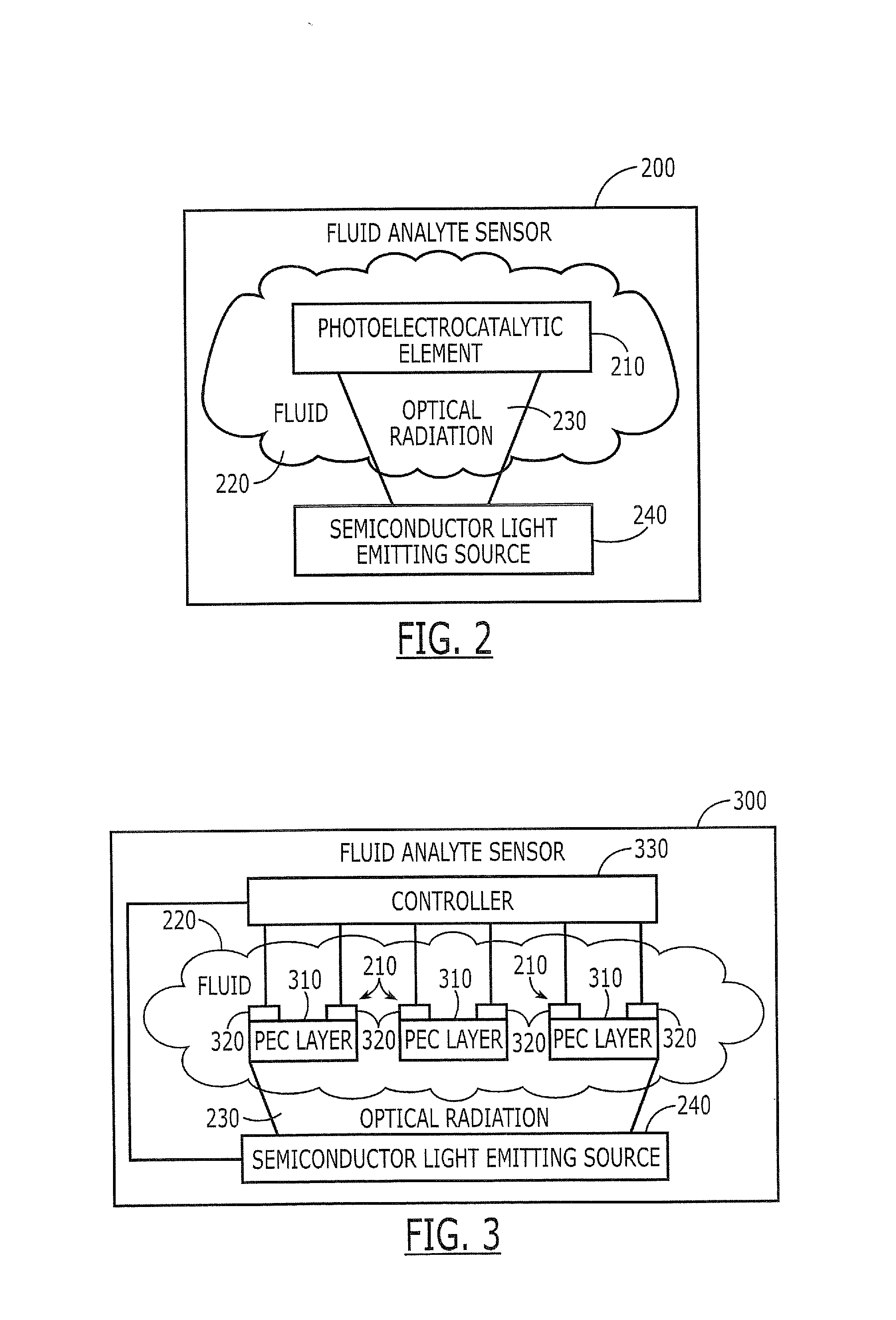
Fluid analyte sensors include a photoelectrocatalytic element that is configured to be exposed to the fluid, if present, and to respond to photoelectrocatalysis of at least one analyte in the fluid that occurs in response to impingement of optical radiation upon the photoelectrocatalytic element. A semiconductor light emitting source is also provided that is configured to impinge the optical radiation upon the photoelectrocatalytic element. Related solid state devices and sensing methods are also described.
Owner:VALENCELL INC
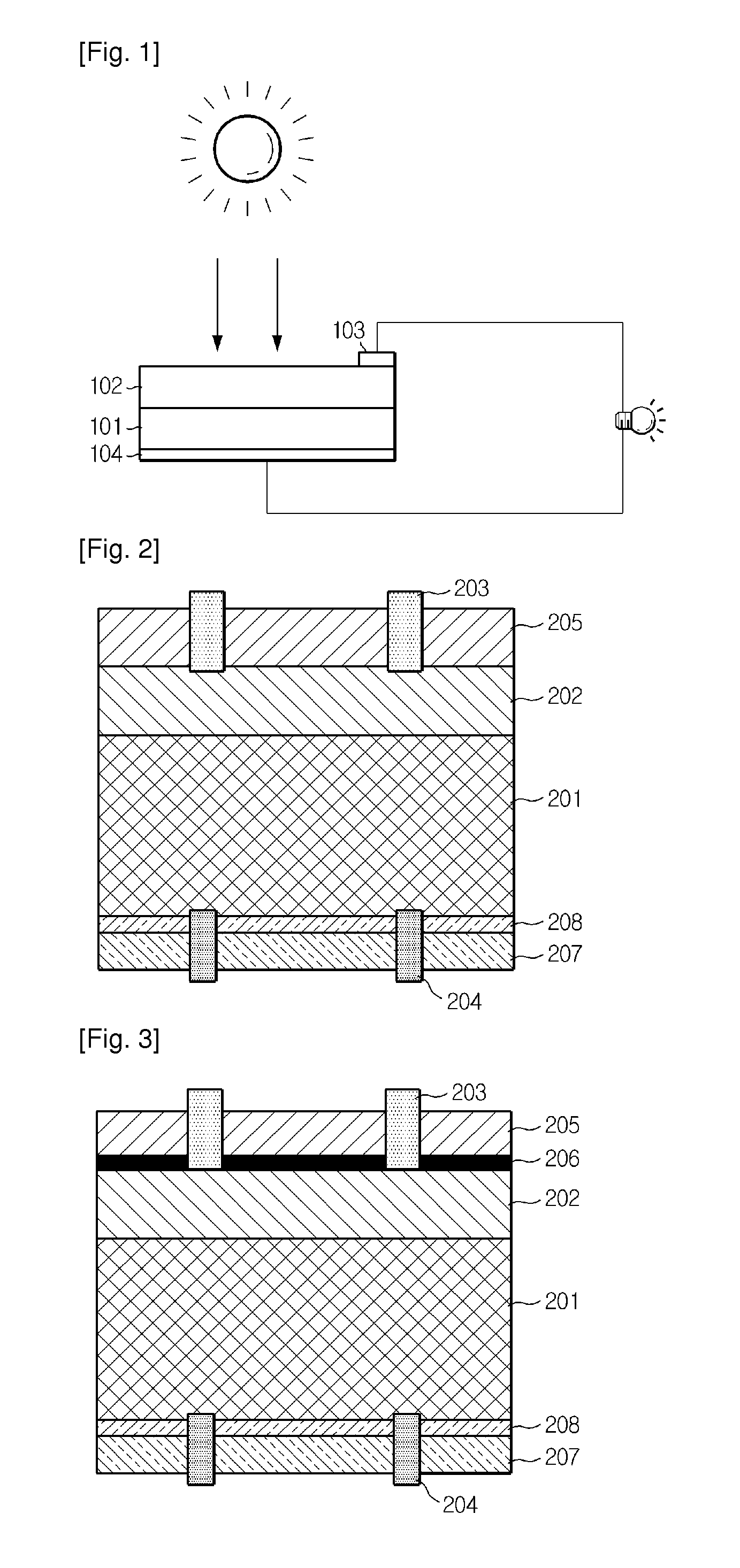
Solar cell and fabrication method thereof
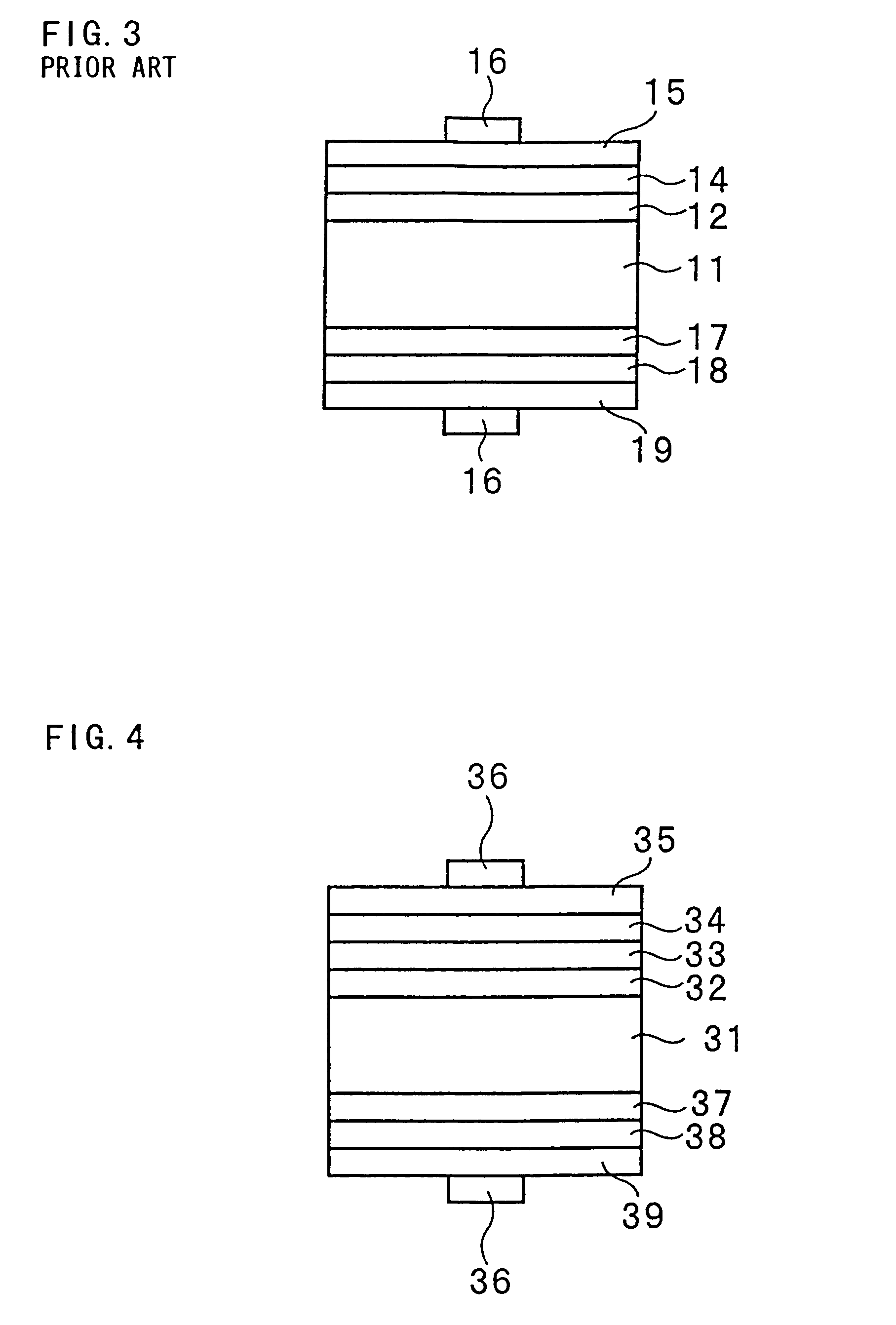
InactiveUS6130380AReduce layeringReduce recombinationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGermaniumSemiconductor
In a solar cell, a crystal defect layer by ion implantation or an amorphous layer by ion implantation is formed between p type diffusion layers provided in an island-like manner at a side opposite to a light receiving surface of a low concentration p type semiconductor single crystalline substrate. The element of the ion implantation may be at least one selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, silicon, germanium, fluorine, oxygen and carbon. The constituent substance of the semiconductor substrate, such as Si is preferably used for the ion implantation. In such a solar cell structure having the crystal defect or amorphous layer, relatively long wavelength light that could not effectively be utilized in the prior art solar cell may be utilized so that the photoelectric conversion efficiency may be improved.
Owner:SHARP KK
Photovoltaic device with intrinsic amorphous film at junction, having varied optical band gap through thickness thereof
InactiveUS7030413B2Reduce current consumptionQuality improvementFinal product manufacturePV power plantsCrystalline semiconductorCrystallization
In a photovoltaic device comprising a thin intrinsic amorphous semiconductor film inserted in a junction portion of a crystalline semiconductor substrate and an amorphous semiconductor film which have conductive types reverse to each other, an optical band gap of the intrinsic amorphous semiconductor film is expanded on a side in contact with the amorphous semiconductor film.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
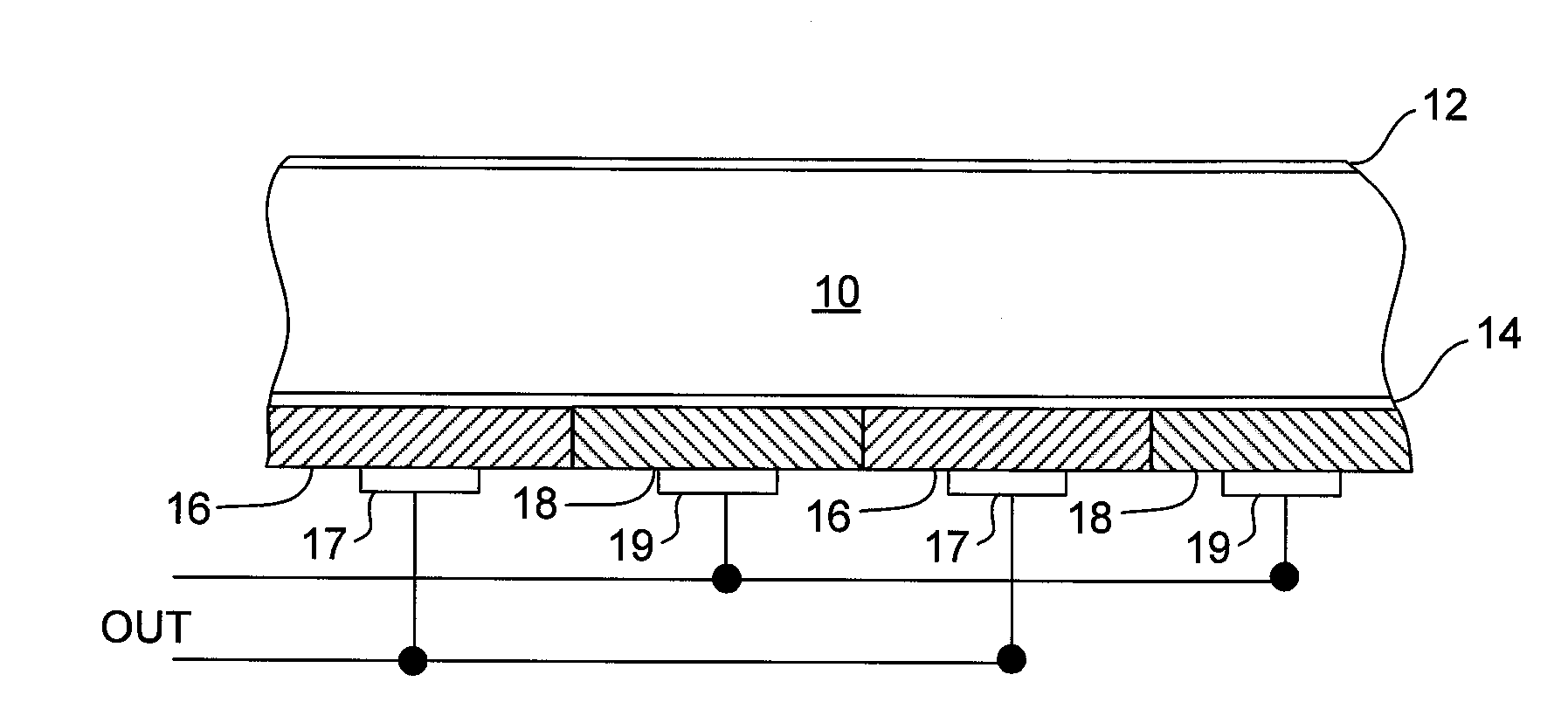
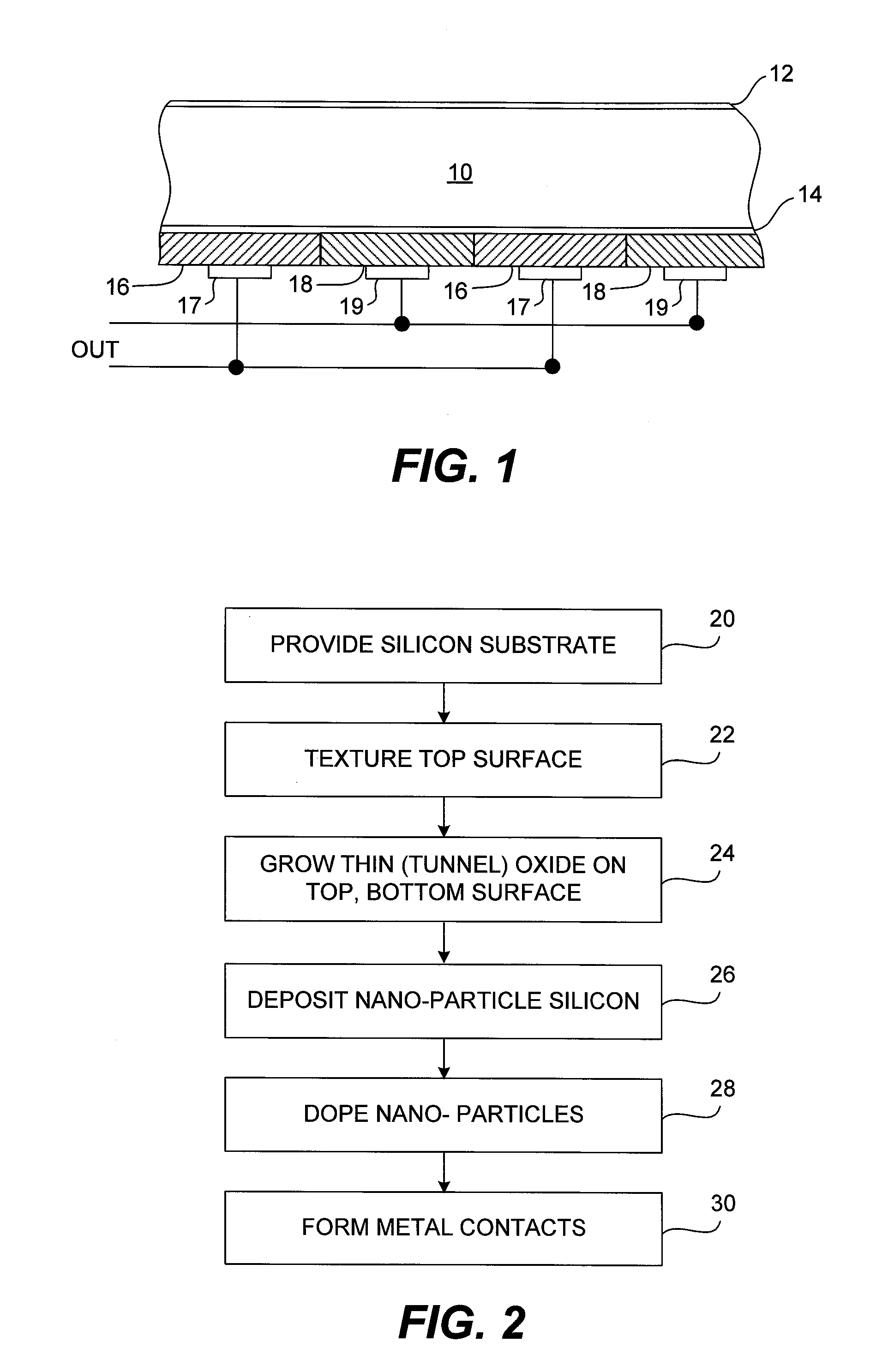
Solar cell having silicon nano-particle emitter
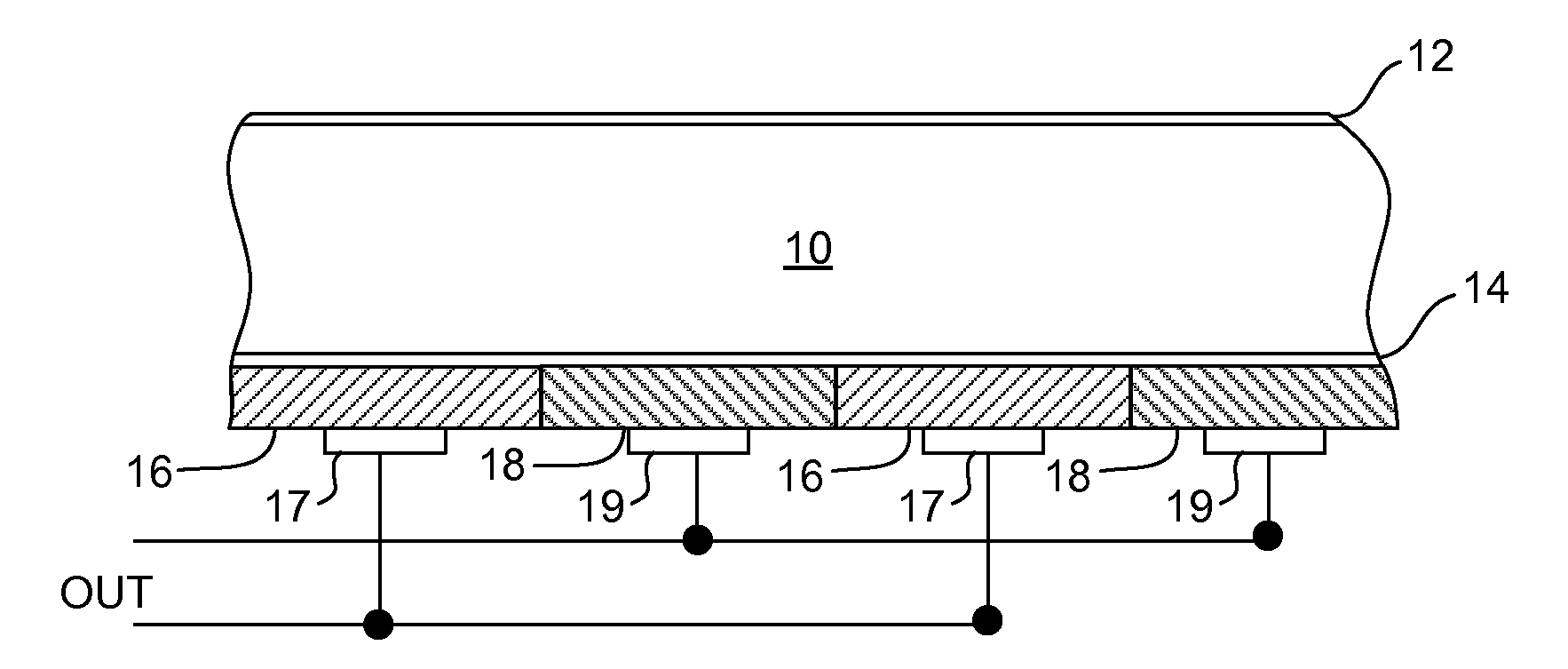
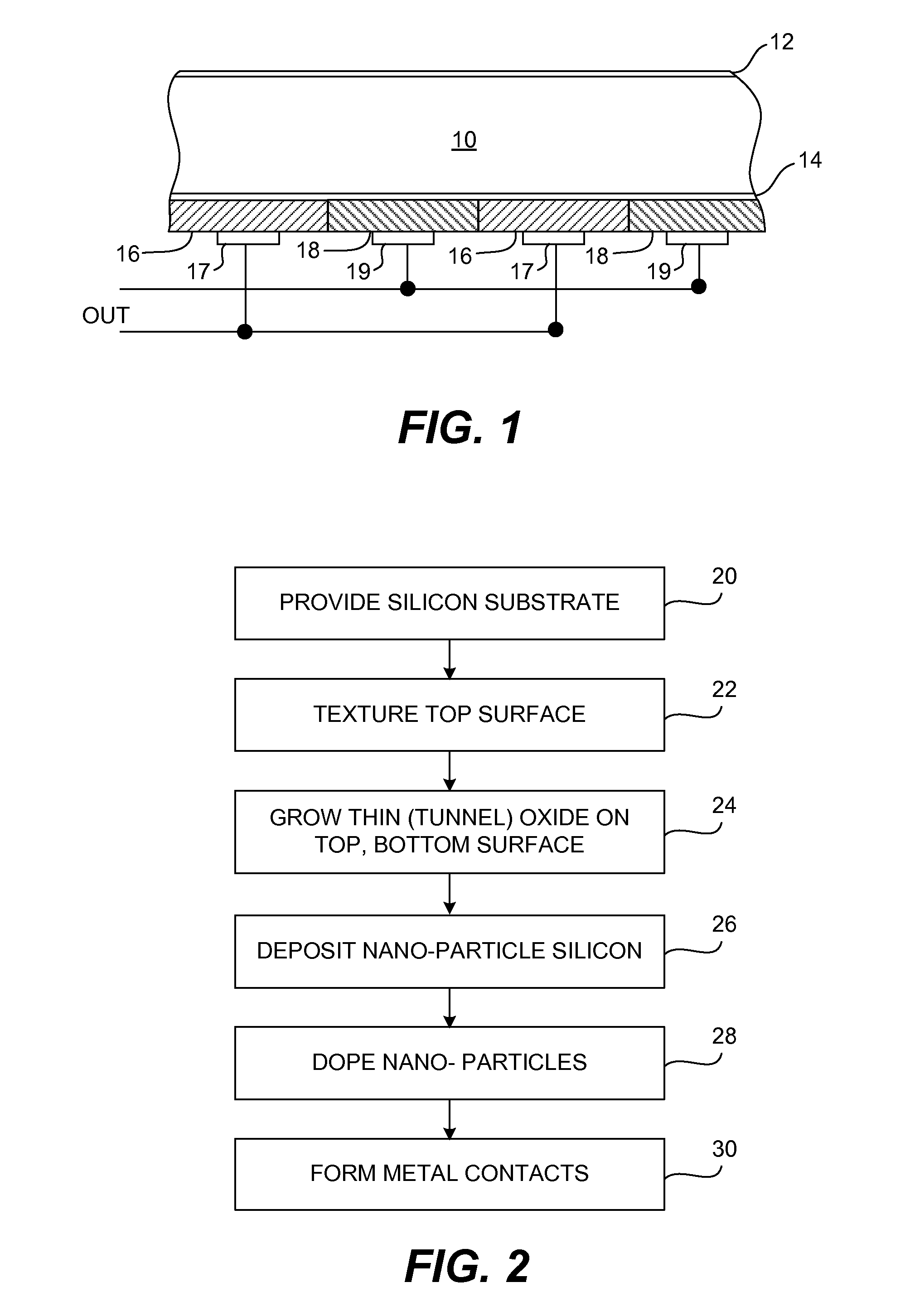
ActiveUS20080121279A1Avoid particle agglomerationReduce interfacePV power plantsSolid-state devicesSilicon solar cellNanometre
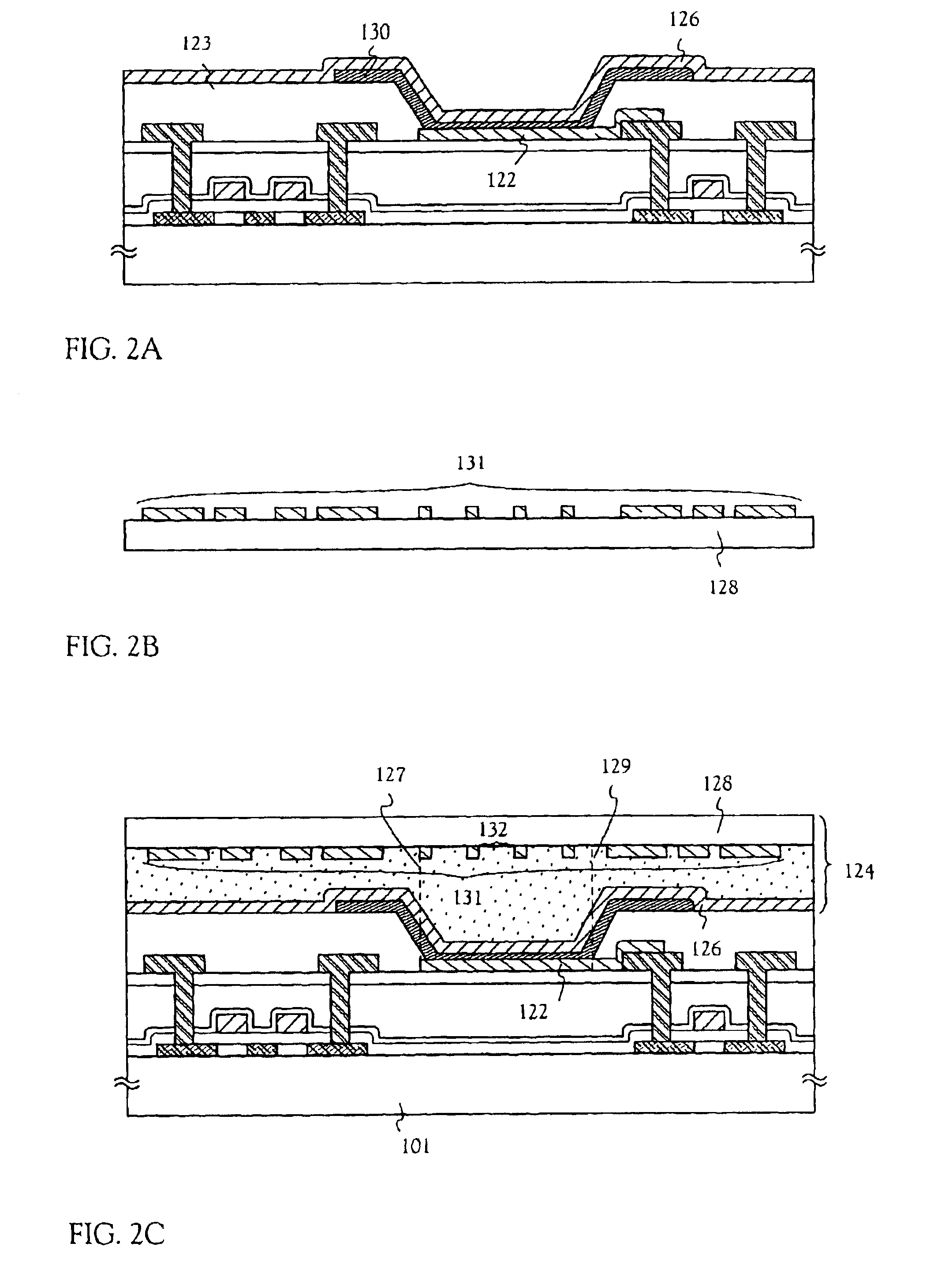
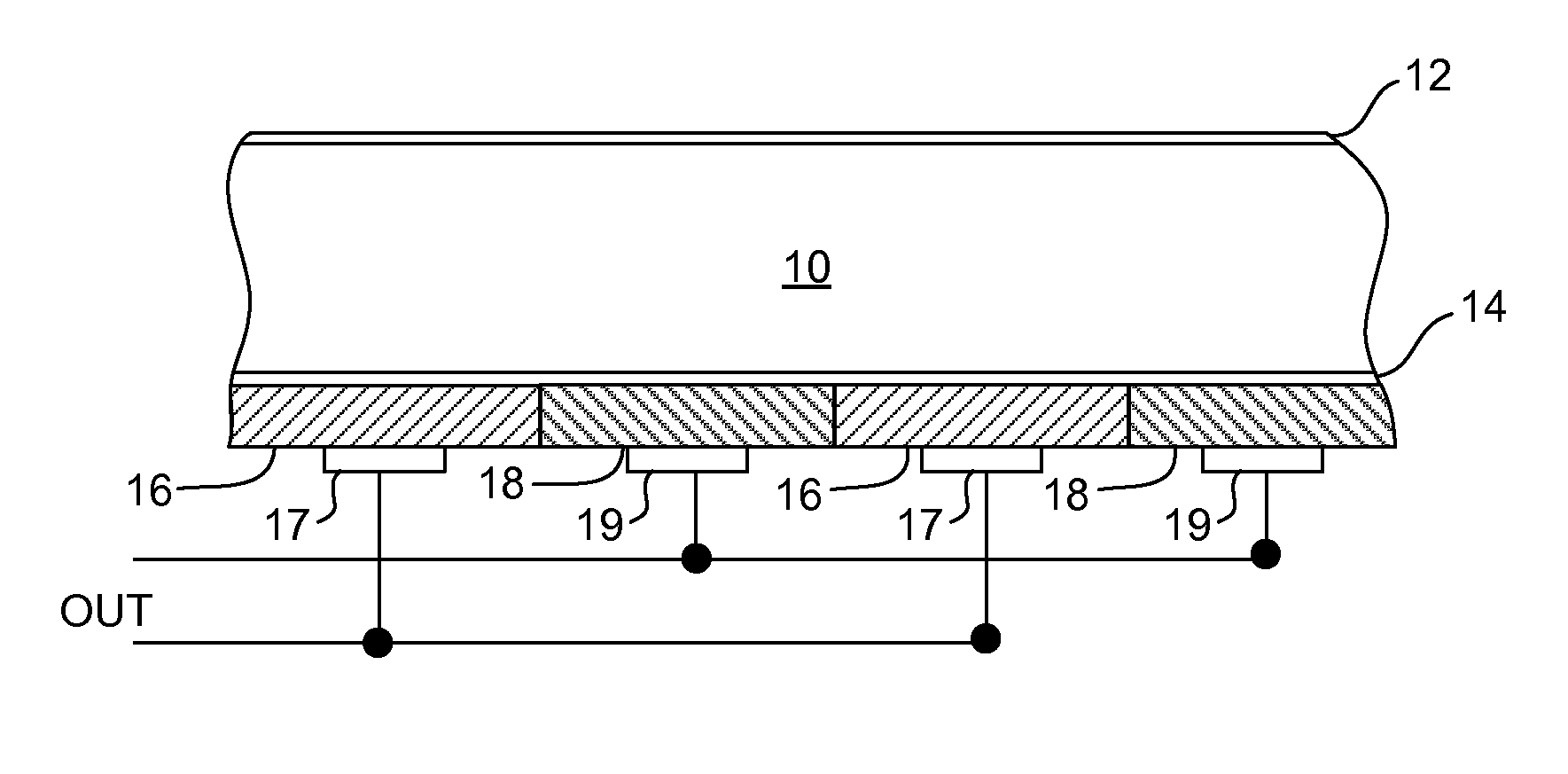
A silicon solar cell having a silicon substrate includes p-type and n-type emitters on a surface of the substrate, the emitters being doped nano-particles of silicon. To reduce high interface recombination at the substrate surface, the nano-particle emitters are preferably formed over a thin interfacial tunnel oxide layer on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:MAXEON SOLAR PTE LTD
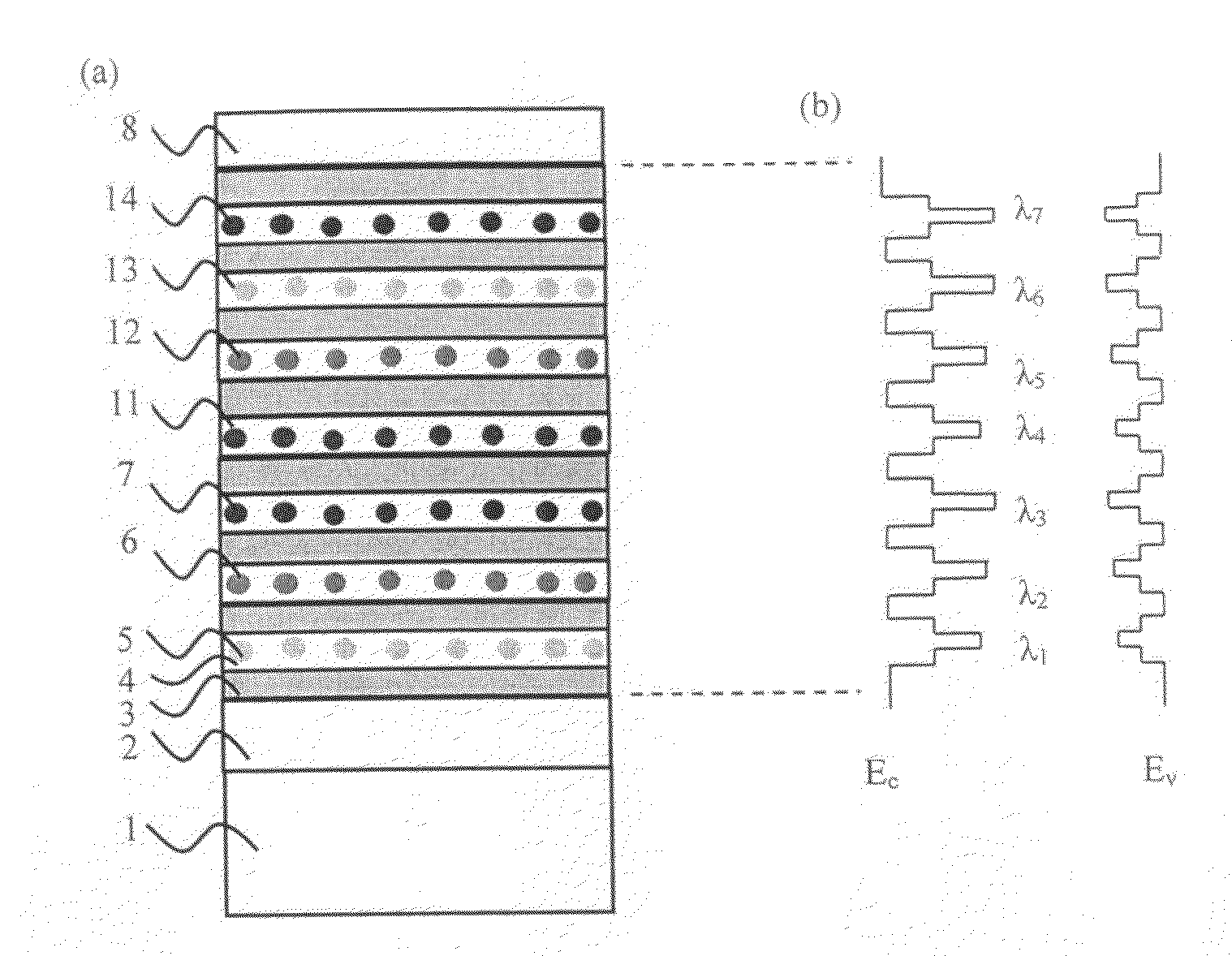
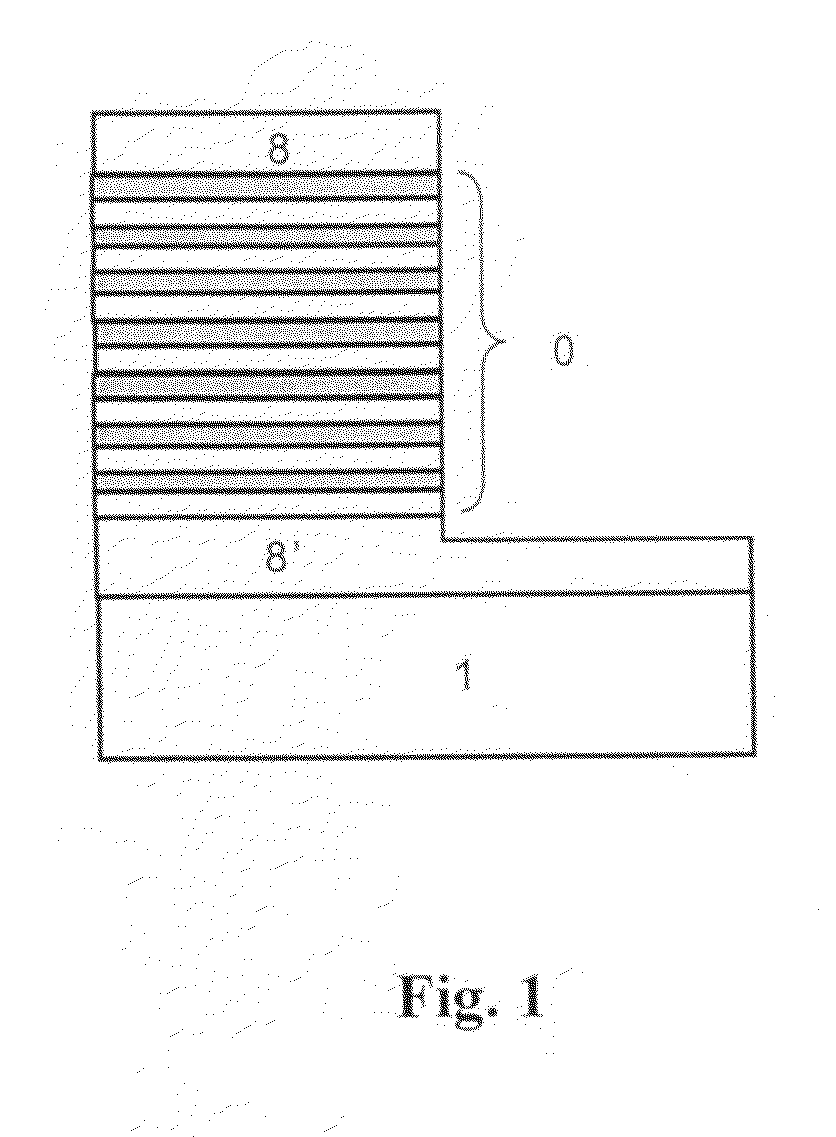
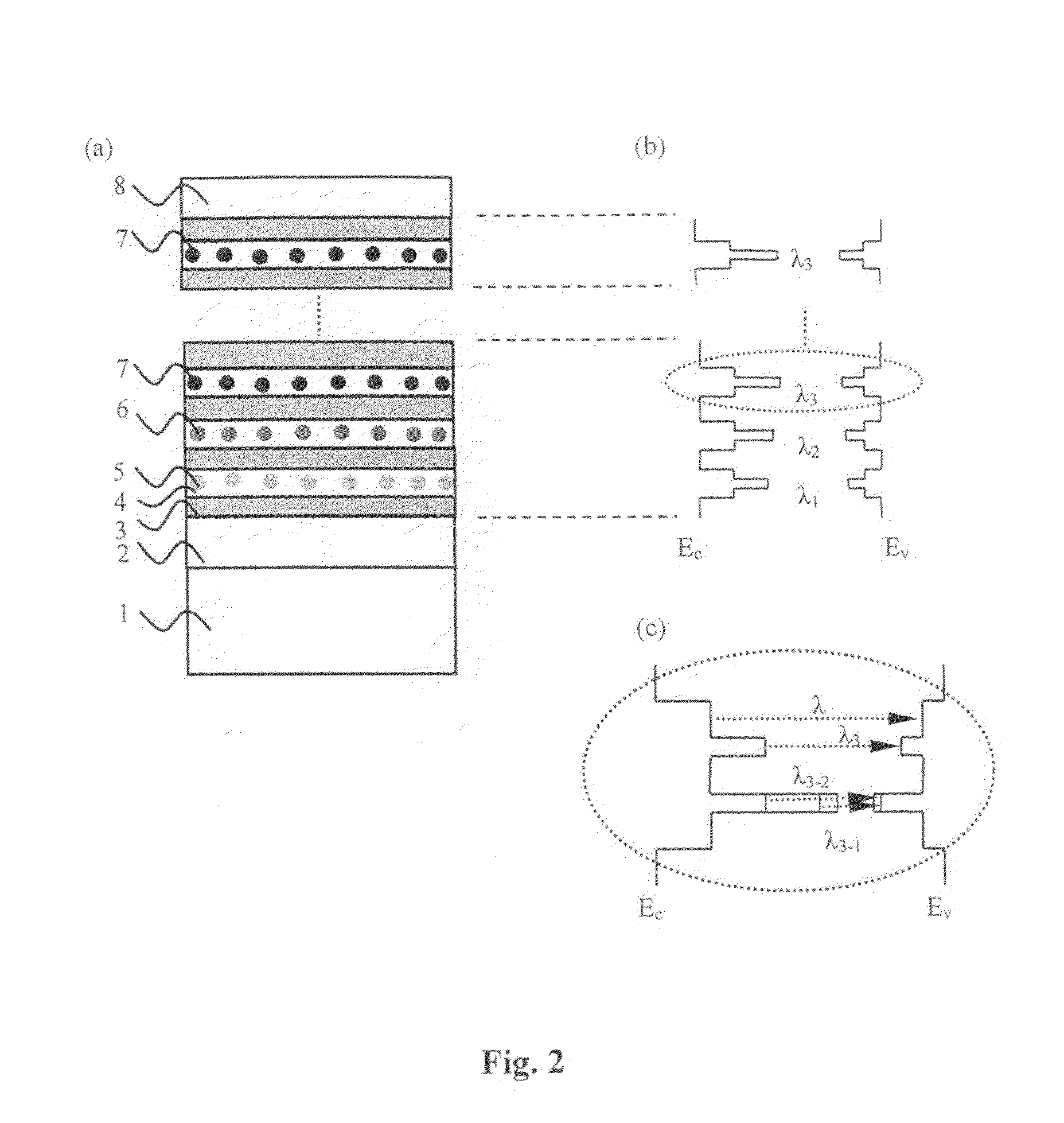
Nanoparticle structure and manufacturing process of multi-wavelength light emitting device
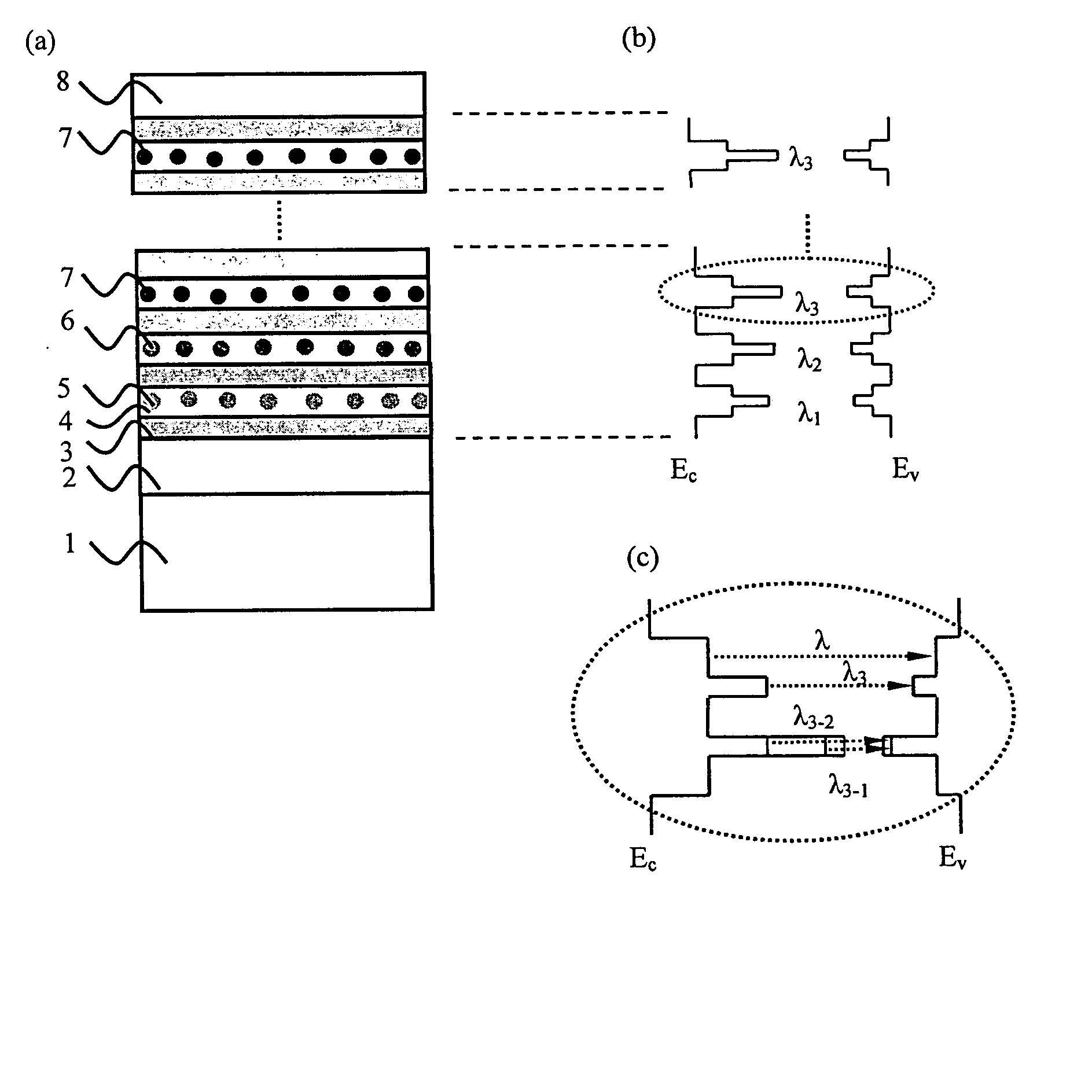
InactiveUS20070108888A1Reduce recombinationImprove luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsManufacturing technologyHigh energy
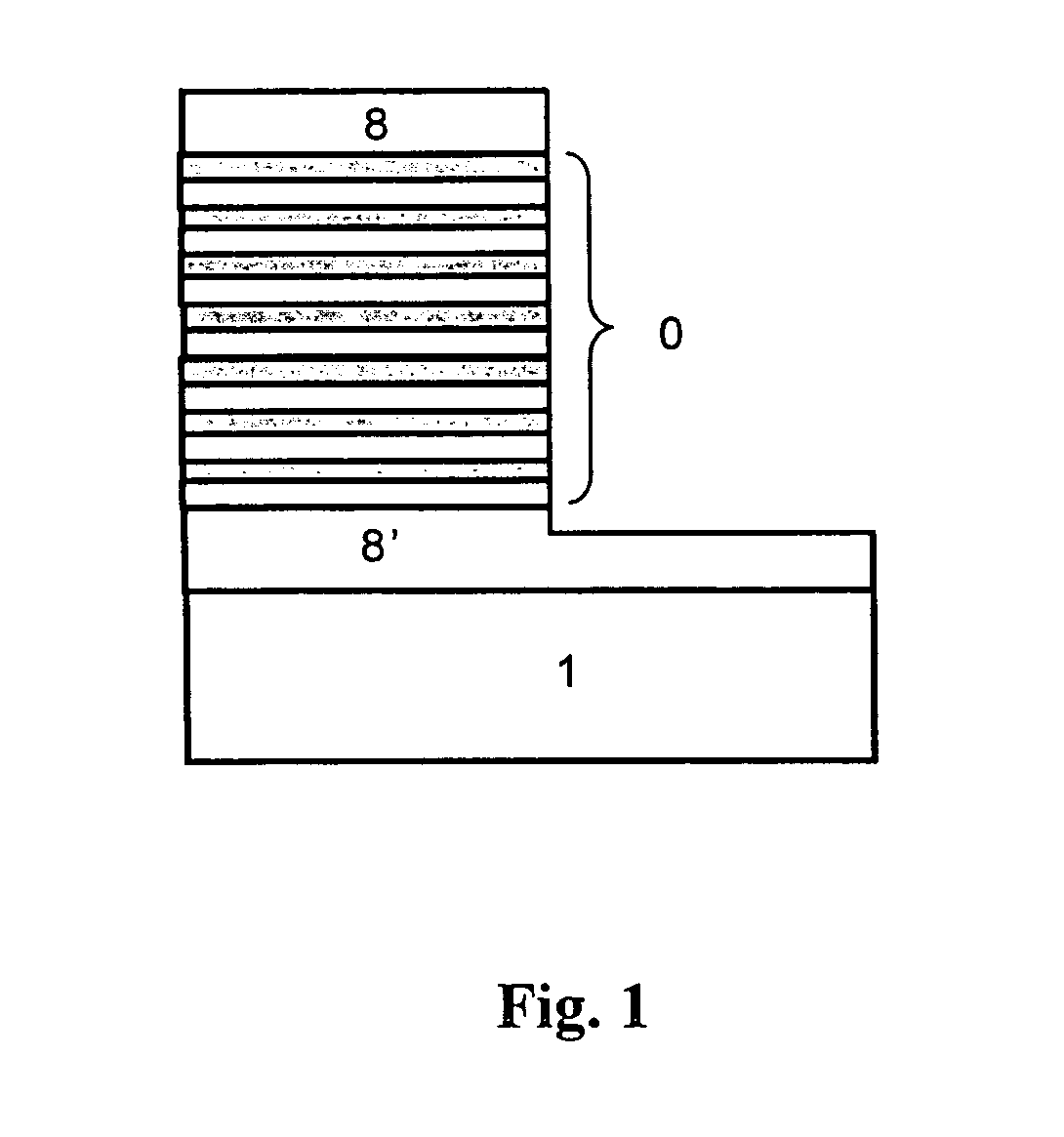
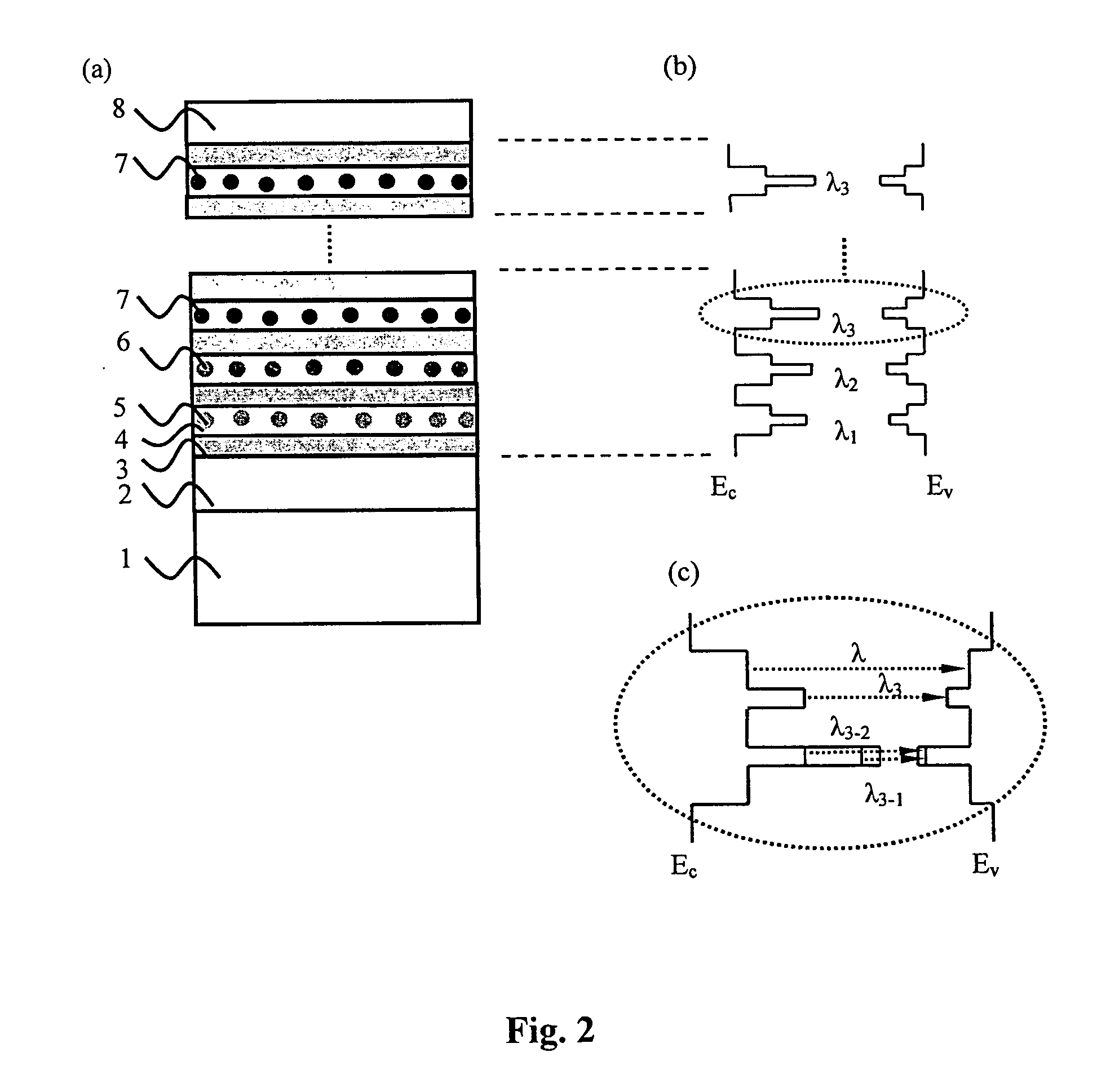
A structure of multi-wavelength light emitting device comprises multi-stacked active layer structure. Each stacked layer comprises lower energy bandgap well 4 and higher energy bandgap barrier layer 3 wherein at least one stacked layer in the device contains nanoparticles. As a result, the emitting wavelengths of the multi-stacked active layer structure consist parts (or all) of the emitting wavelengths come from the stack layers containing nanoparticles, and parts (or all) of the emitting wavelengths come from the stack layers not containing nanoparticles. In another embodiment, parts (or all) of the emitting wavelengths of the multi-stacked active layer structure can be also used to trigger one or more phosphorescences from the phosphors, thus the emitting wavelengths of such a phosphors converted light emitting device may come partially from the multi-stacked active layer itself and partially (or all) from the phosphors.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Light emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6844672B2Reduce light emissionReduce recombinationDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrically conductiveSimple Organic Compounds
A light emitting device is provided in which reduction of recombinations in a light emitting element is prevented by using a low-resistant electrode structure. A light emitting device of the present invention has a light emitting element composed of first and second electrodes and an organic compound layer that is sandwiched between the first and second electrodes, and the device is characterized in that one of the first and second electrodes has a transparent conductive film, a transparent conductive resin formed on the transparent conductive film, and a plurality of conductors formed on the transparent conductive resin.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Solar cell having silicon nano-particle emitter
ActiveUS7705237B2Avoid particle agglomerationReduce interfacePV power plantsSolid-state devicesSilicon solar cellNanometre
Owner:MAXEON SOLAR PTE LTD
Solar cell
ActiveUS20110265870A1Improve featuresImprove efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationBack surface fieldFixed charge
A solar cell includes a substrate of a first conductive type, an emitter layer, of a second conductive type opposite the first conductive type, positioned at one surface of the substrate, a first electrode electrically connected to the emitter layer, a first protective layer positioned on a front surface of the emitter layer where the first electrode is not positioned, a back surface field layer positioned at another surface of the substrate, a second electrode electrically connected to the back surface field layer, and a second protective layer positioned on a back surface of the substrate where the second electrode is not positioned. Each of the first and second protective layers is formed of a material having fixed charges of the first conductive type.
Owner:SHANGRAO JINKO SOLAR TECH DEV CO LTD
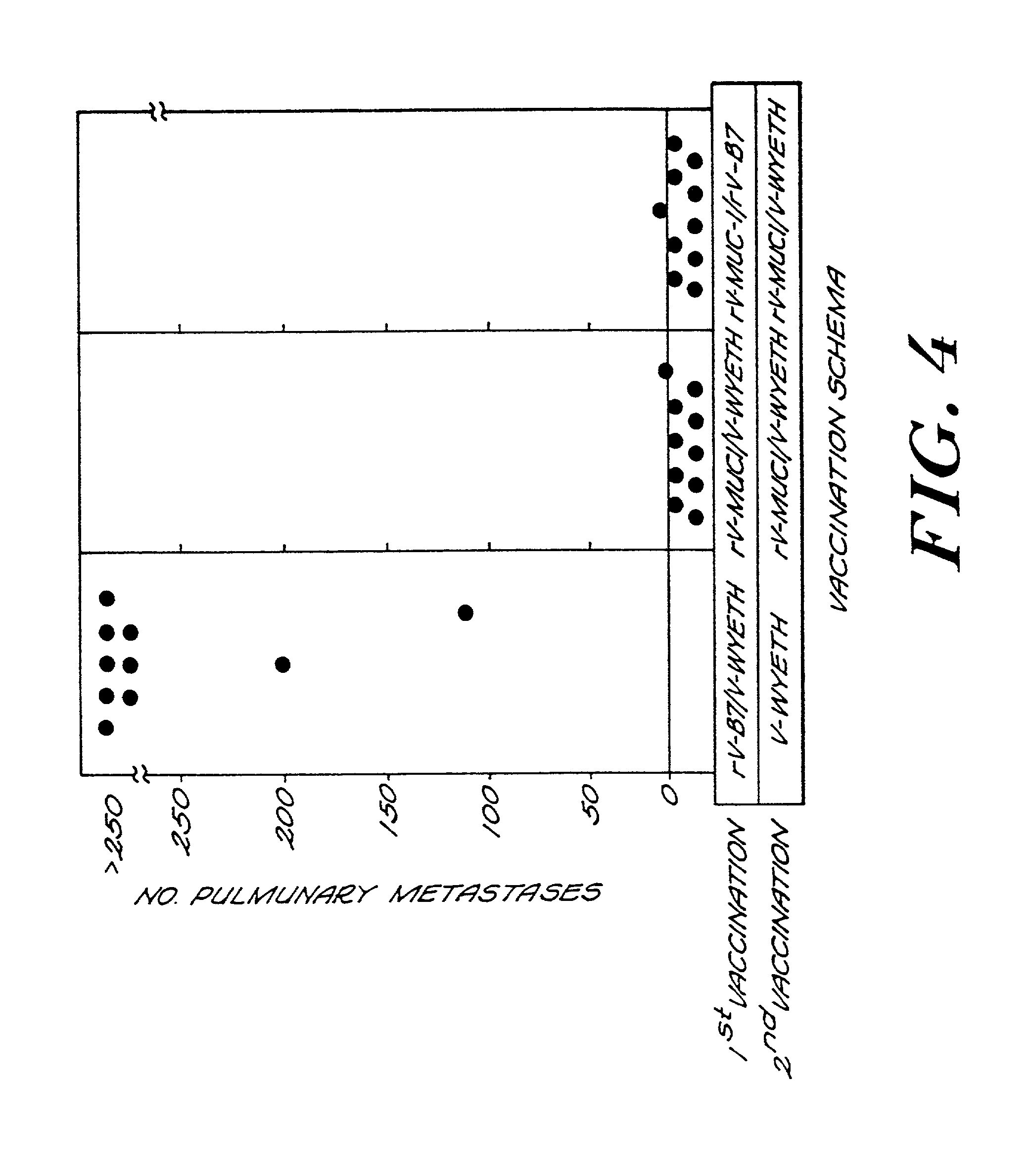
Recombinant pox virus for immunization against MUC1 tumor-associated antigen
Recombinant pox viruses capable of expressing an immunogenic fragment of the MUC1 tumor-associated antigen are disclosed. The recombinant viruses can be used as vaccines to prevent the establishment of or treat tumors or pre-tumorous cells expressing the MUC1 tumor-associated antigen. The vaccines can be provided as an admixture comprising: (1) a recombinant pox virus encoding the immunogenic fragment of the MUC1 tumor-associated antigen, and (2) a recombinant pox virus encoding a T-cell co-stimulatory factor. The vaccine admixture can be used, e.g., to prevent establishment of tumors or pre-tumorous cells expressing the MUC1 tumor-associated antigen. The MUC1 specific cytotoxic T-cells can be isolated and expanded and used in a method for treating a host having a tumor expressing MCU1 positive tumor cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Light emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050118745A1Reduce recombinationReduce resistanceElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesSimple Organic CompoundsTransparent conducting film
A light emitting device is provided in which reduction of recombinations in a light emitting element is prevented by using a low-resistant electrode structure. A light emitting device of the present invention has a light emitting element composed of first and second electrodes and an organic compound layer that is sandwiched between the first and second electrodes, and the device is characterized in that one of the first and second electrodes has a transparent conductive film, a transparent conductive resin formed on the transparent conductive film, and a plurality of conductors formed on the transparent conductive resin.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
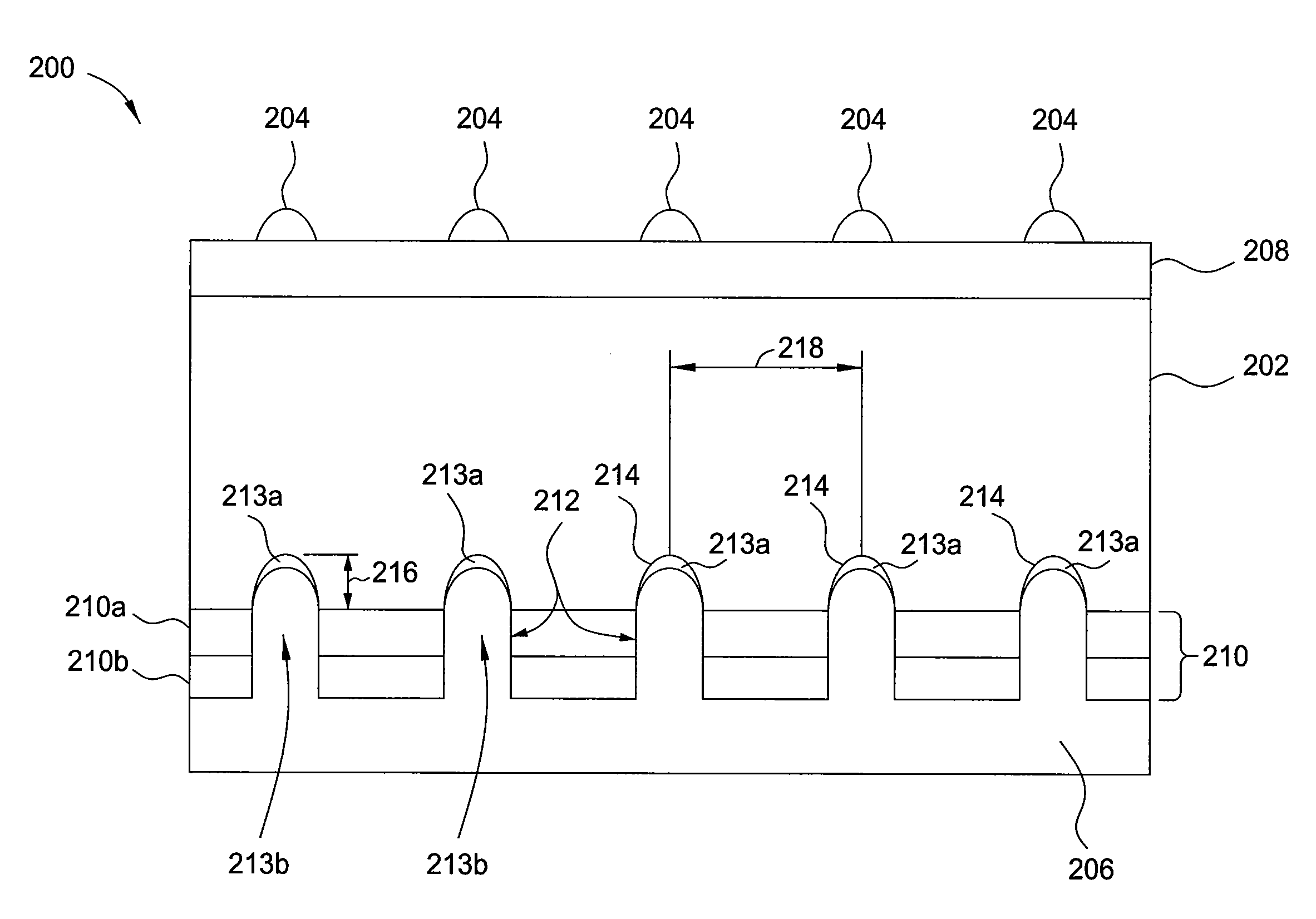
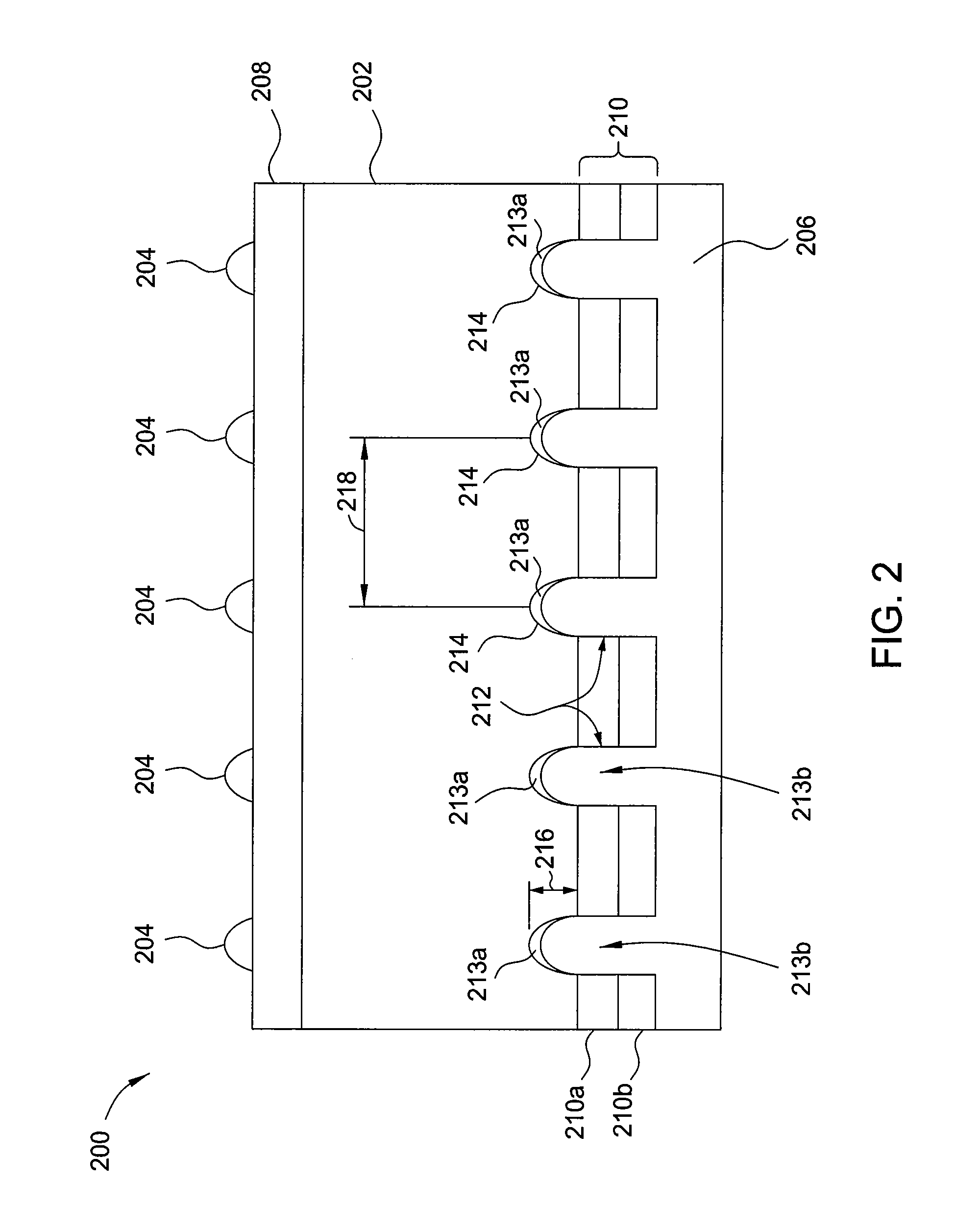
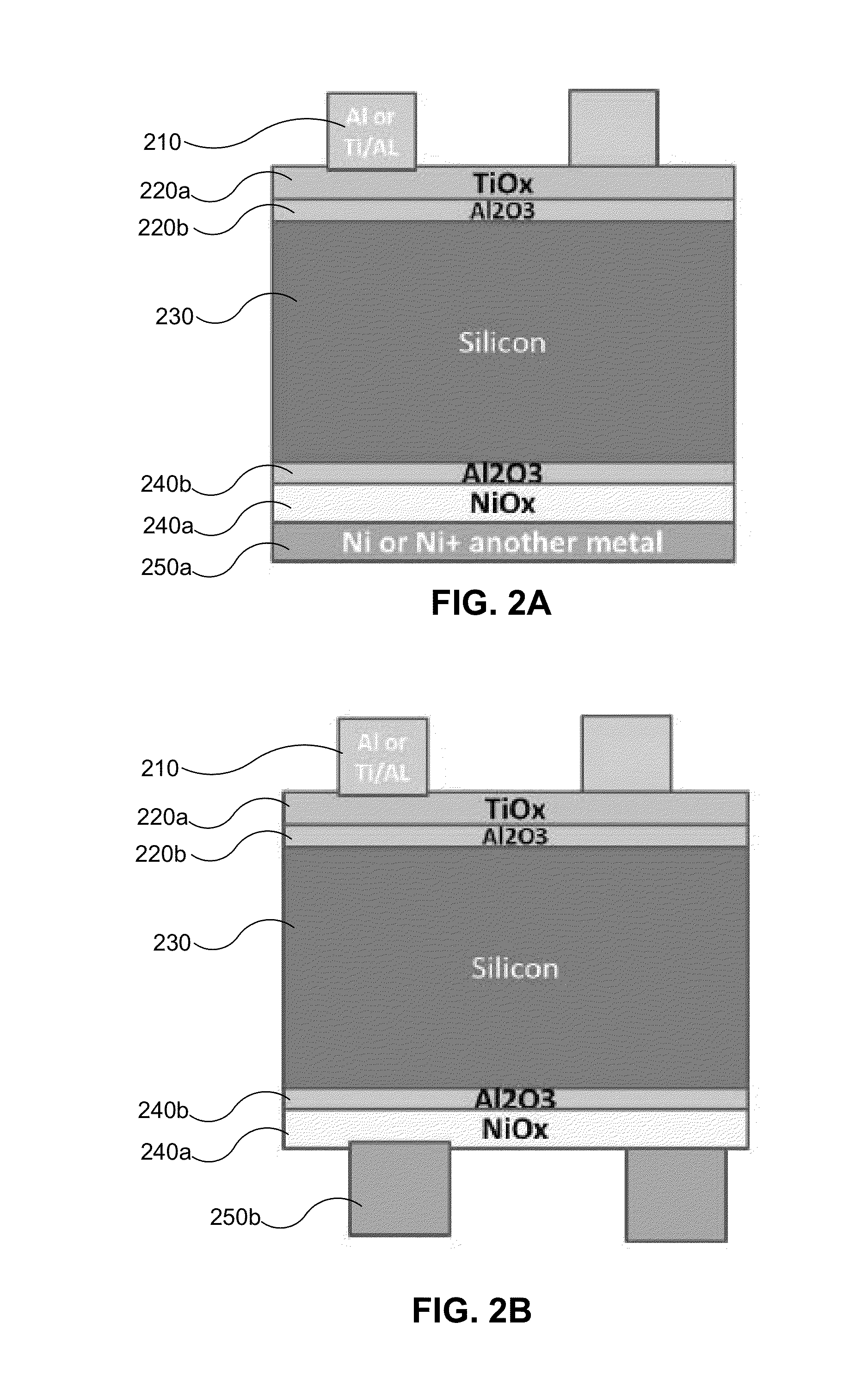
Doped ai paste for local alloyed junction formation with low contact resistance
InactiveUS20130255765A1Reduce carrier recombinationReduces cost-per-wattSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationJunction formationCharge carrier
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to solar cells having reduced carrier recombination and methods of forming the same. The solar cells have eutectic local contacts and passivation layers which reduce recombination by facilitating formation of a back surface field (BSF). A patterned aluminum back contact doped with a Group III element is disposed on the passivation layer for removing current form the solar cell. The methods of forming the solar cells include depositing a passivation layer including aluminum oxide and silicon nitride on a back surface of a solar cell, and then forming openings through the passivation layer. An aluminum back contact doped with a Group III element is disposed on the passivation layer in a pattern covering the holes, and thermally processed to form a silicon-aluminum eutectic within the openings.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor light-emitting element
InactiveUS20020105004A1Easy to exciteEasy to getSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesRare earthSingle crystal
In a semiconductor light-emitting element, an underlayer is made of AlN layer, and a first cladding layer is made of an n-AlGaN layer. A light-emitting layer is composed of a base layer made of i-GaN and plural island-shaped single crystal portions made of i-AlGaInN isolated in the base layer. Then, at least one rare earth metal element is incorporated into the base layer and / or the island-shaped single crystal portions.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Multi-Junction Semiconductor Photovoltaic Apparatus and Methods
InactiveUS20120291859A1Increase long wavelength light efficiencyImprove quantum efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBack surface fieldSemiconductor
A photovoltaic device and methods of manufacturing a photovoltaic device are disclosed. A photovoltaic device includes a first photovoltaic cell, a second photovoltaic cell, a semiconductor layer, and a doped layer. The second photovoltaic cell is in electrical communication with the first photovoltaic cell. The semiconductor layer includes a textured portion. The doped layer is configured to create a back surface field, the doped layer disposed between a proximal layer of the second photovoltaic cell and the semiconductor layer.
Owner:SIONYX
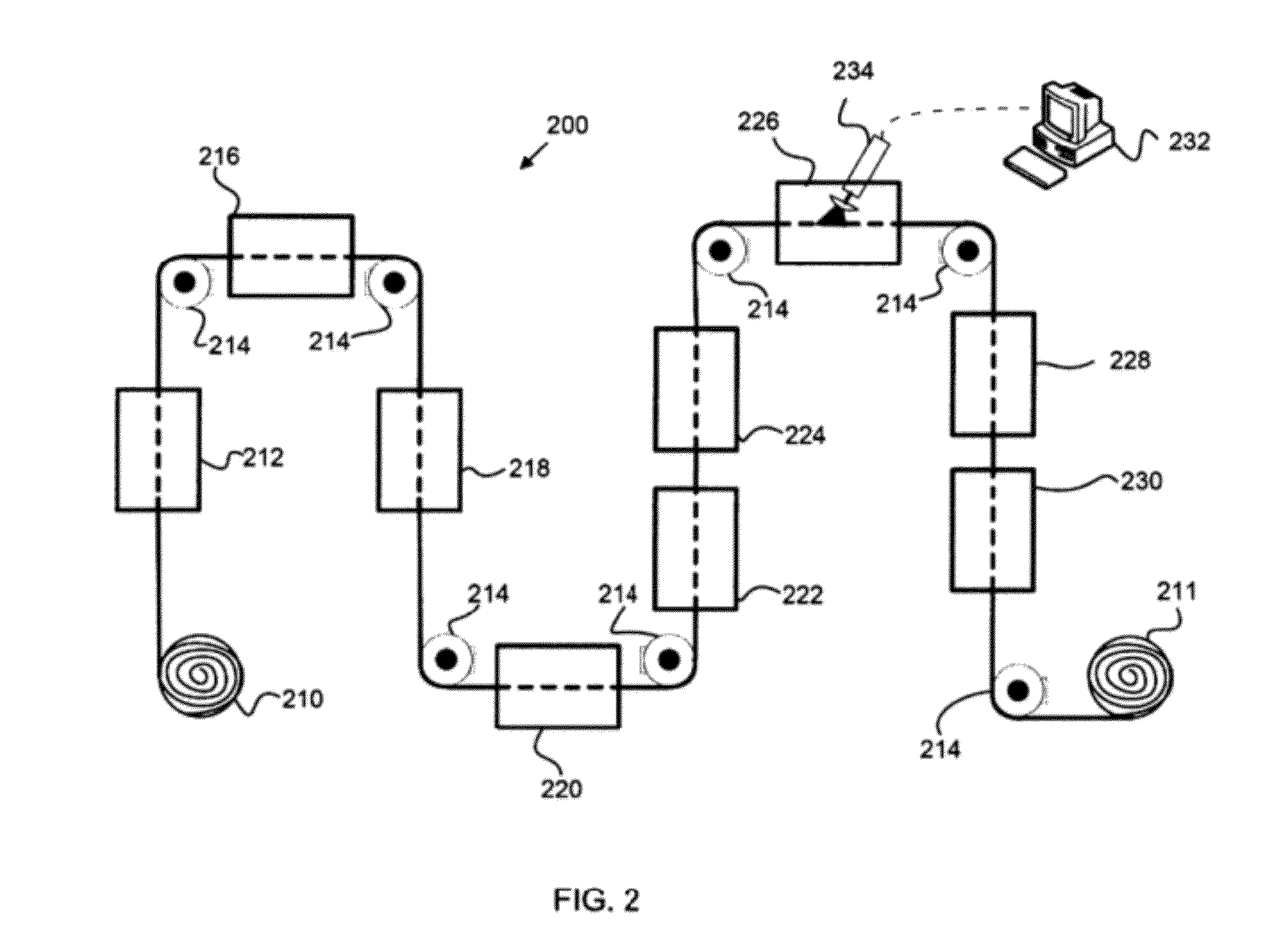
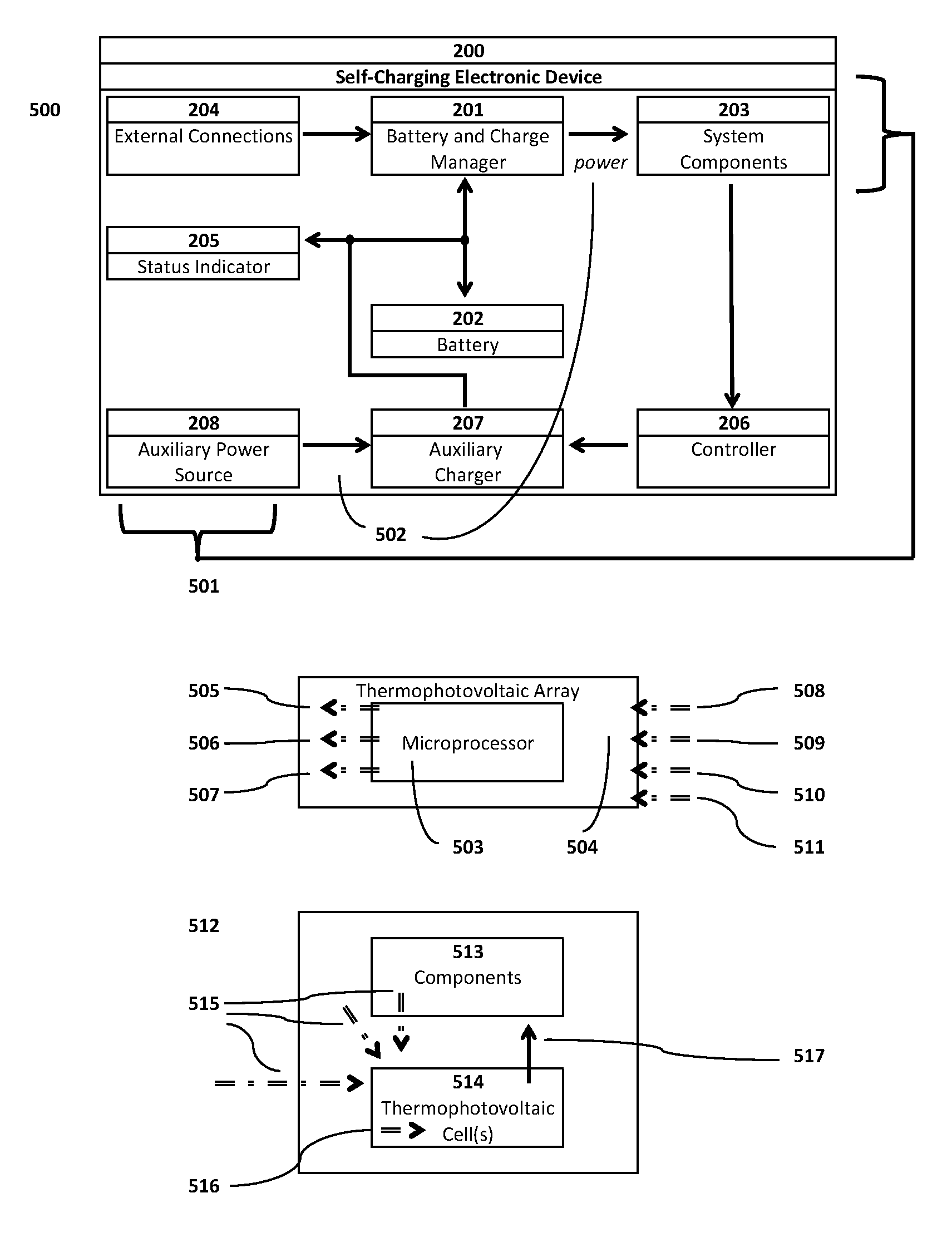
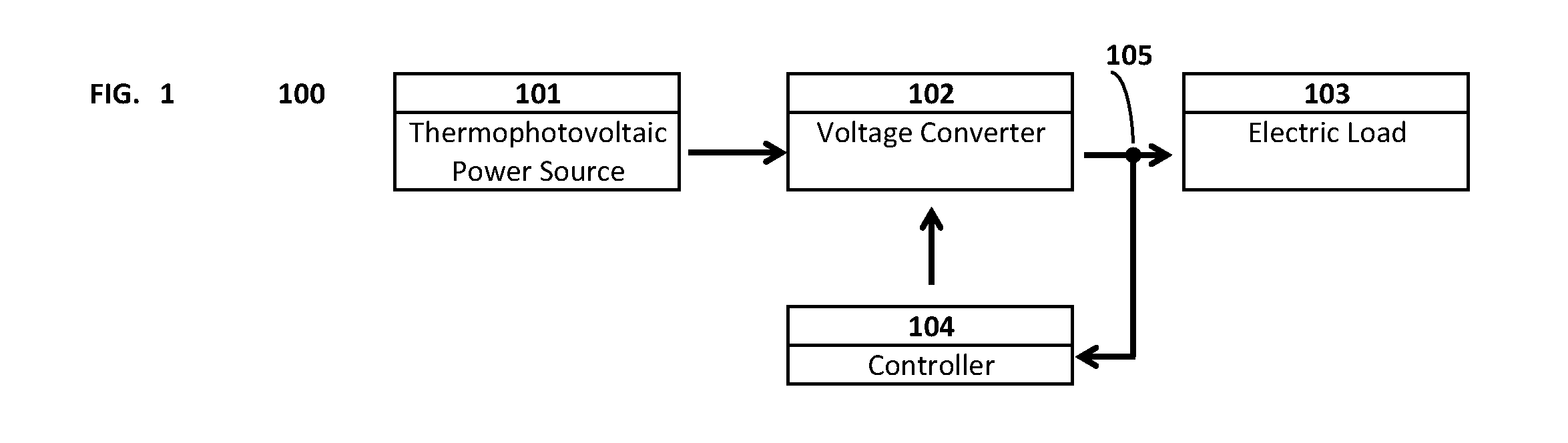
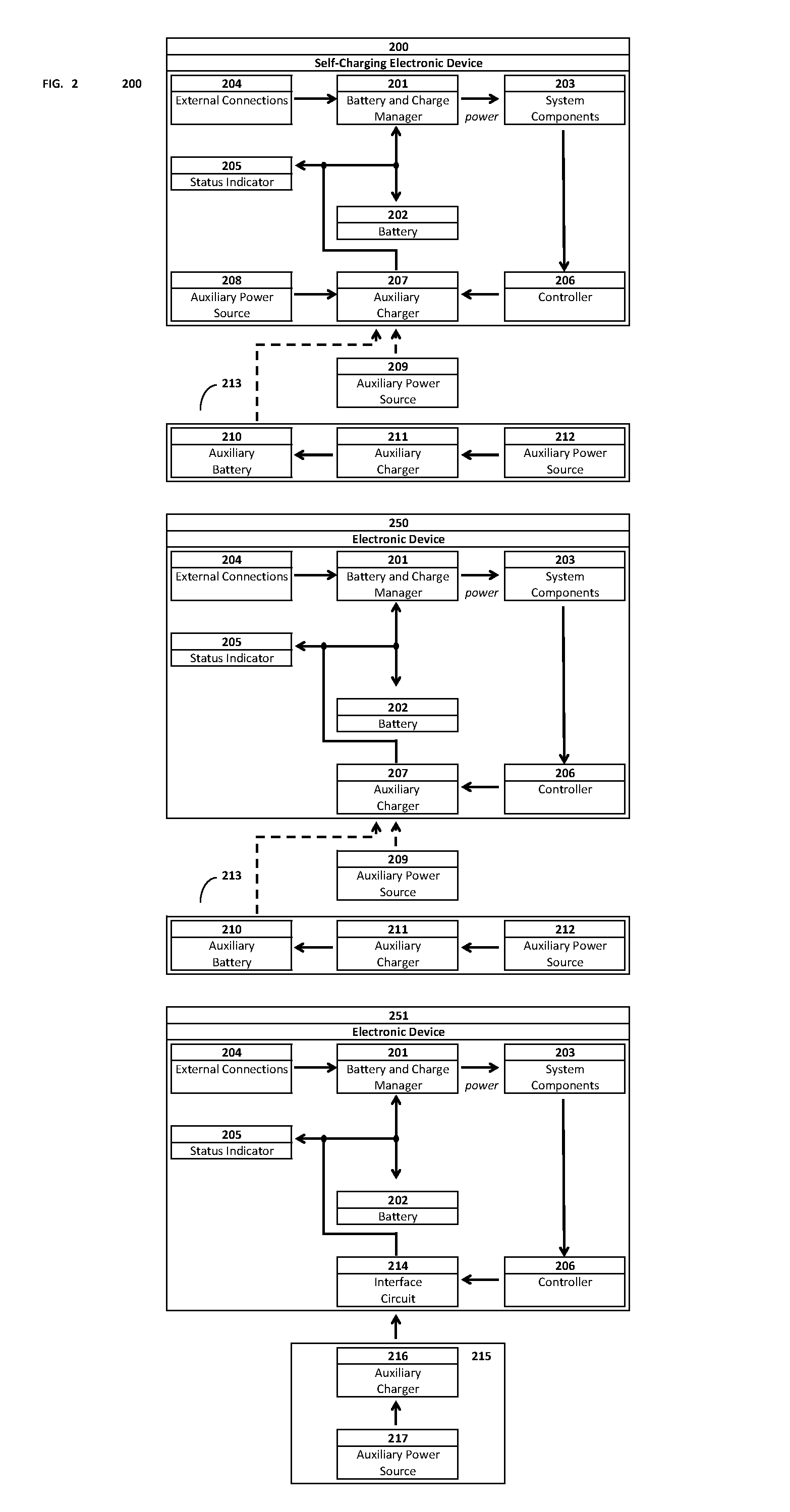
Self-charging electronic devices
ActiveUS20140097786A1Low efficiencyLow mobilityBatteries circuit arrangementsPV power plantsThermal energyElectrical battery
Self-powered portable electronic devices are disclosed that have the capacity to generate their own electrical power, store electrical charge, and distribute electrical power to similarly designed devices in close proximity. Devices generate power in part using one or more non-solar thermal energy sources that have increased stability and efficiency compared to current solar cell powered devices. Devices comprise components including, control processors, data storage, energy storage, dedicated energy and power management processors, and thermophotovoltaic cells that convert thermal energy into electrical power. Devices are capable of transmitting and receiving energy, power, voice and data information using standard frequencies associated with portable devices. Additionally, the invention discloses methods, systems, and apparatuses comprising circuitry that can control power generation from multiple thermophotovoltaic cells and traditional power sources.
Owner:PLAIN SIGHT INNOVATIONS LLC
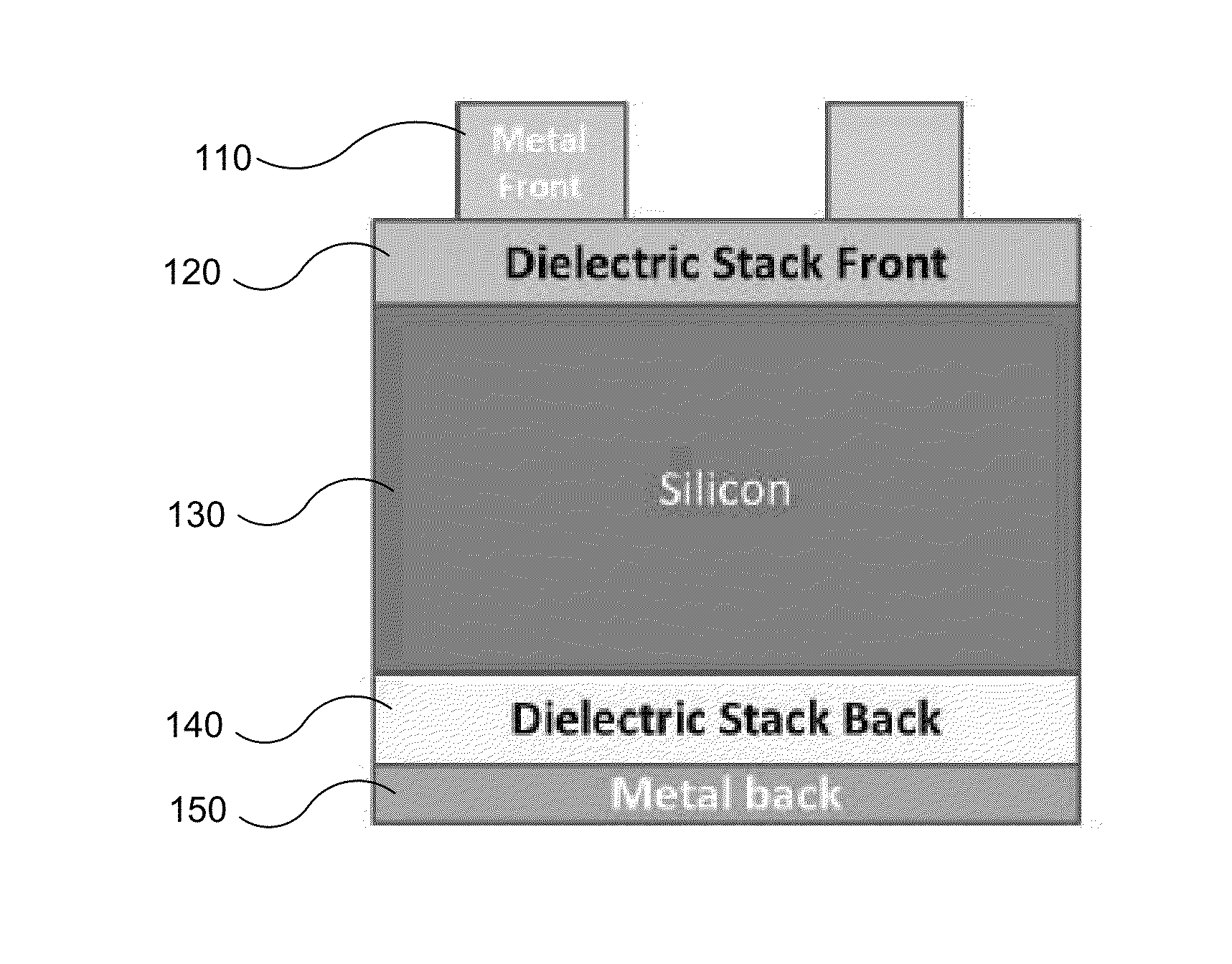
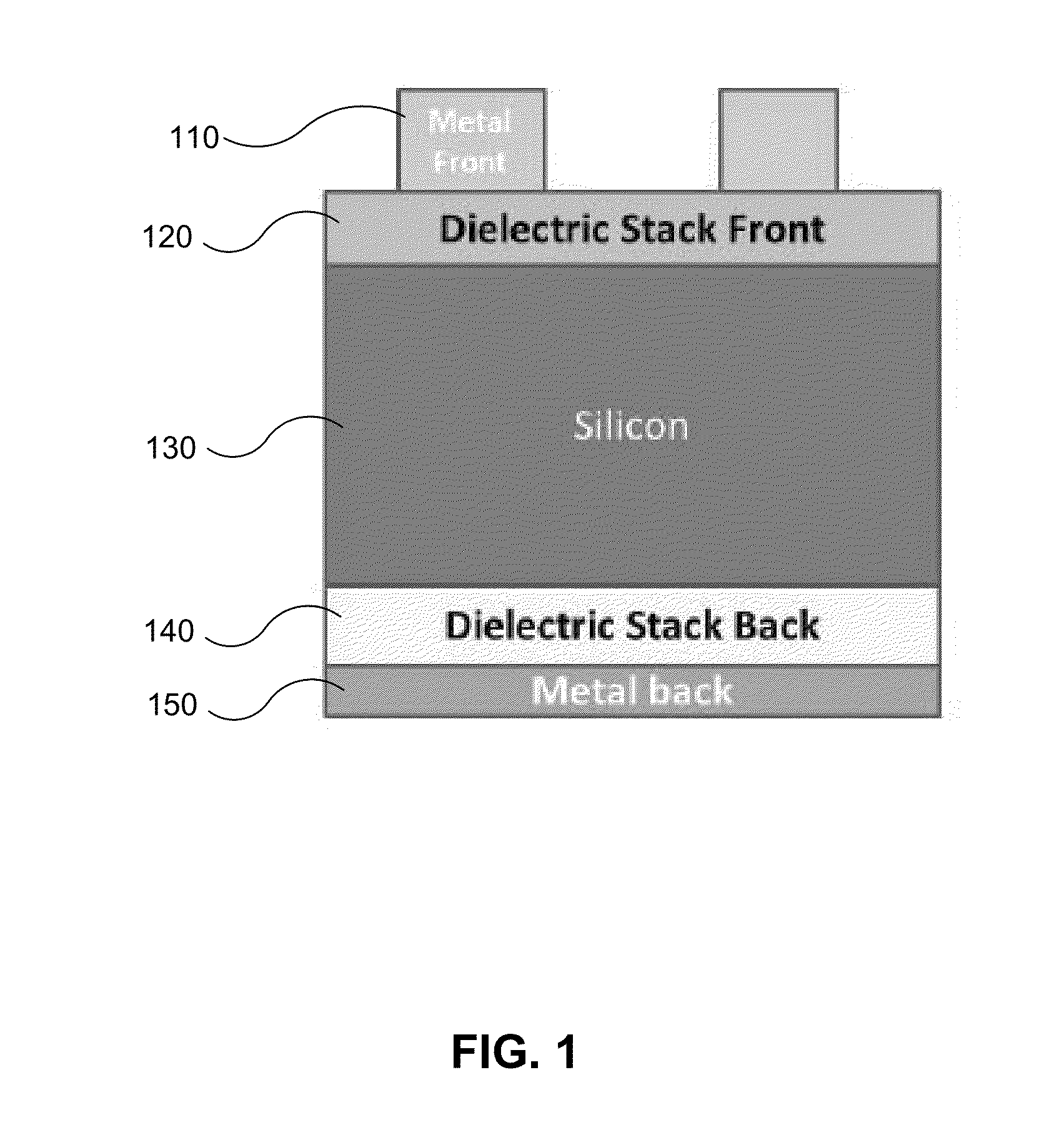
Dielectric-passivated metal insulator photovoltaic solar cells
InactiveUS20150129030A1Sufficient lateral conductionTrap sunlight more efficientlySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationValence bandCharge carrier
A photovoltaic solar cell is described that, according to one example embodiment, includes a semiconductor light absorbing layer and a dielectric stack on at least one of a front side of the light absorbing layer or a back side of the light absorbing layer. The dielectric stack includes a tunneling dielectric layer being sufficiently thin for charge carriers to tunnel across, and an overlaying dielectric layer being a different material than the overlaying dielectric. The solar cell also includes an electrically conductive contact physically contacting the overlaying dielectric. The electrically conductive contact and the overlaying dielectric together have either a work function suitable for selective collection of electrons that closely matches a conduction band of the light absorbing layer, or a work function suitable for selective collection of holes that closely matches a valence band of the light absorbing layer.
Owner:BEAMREACH SOLAR INC
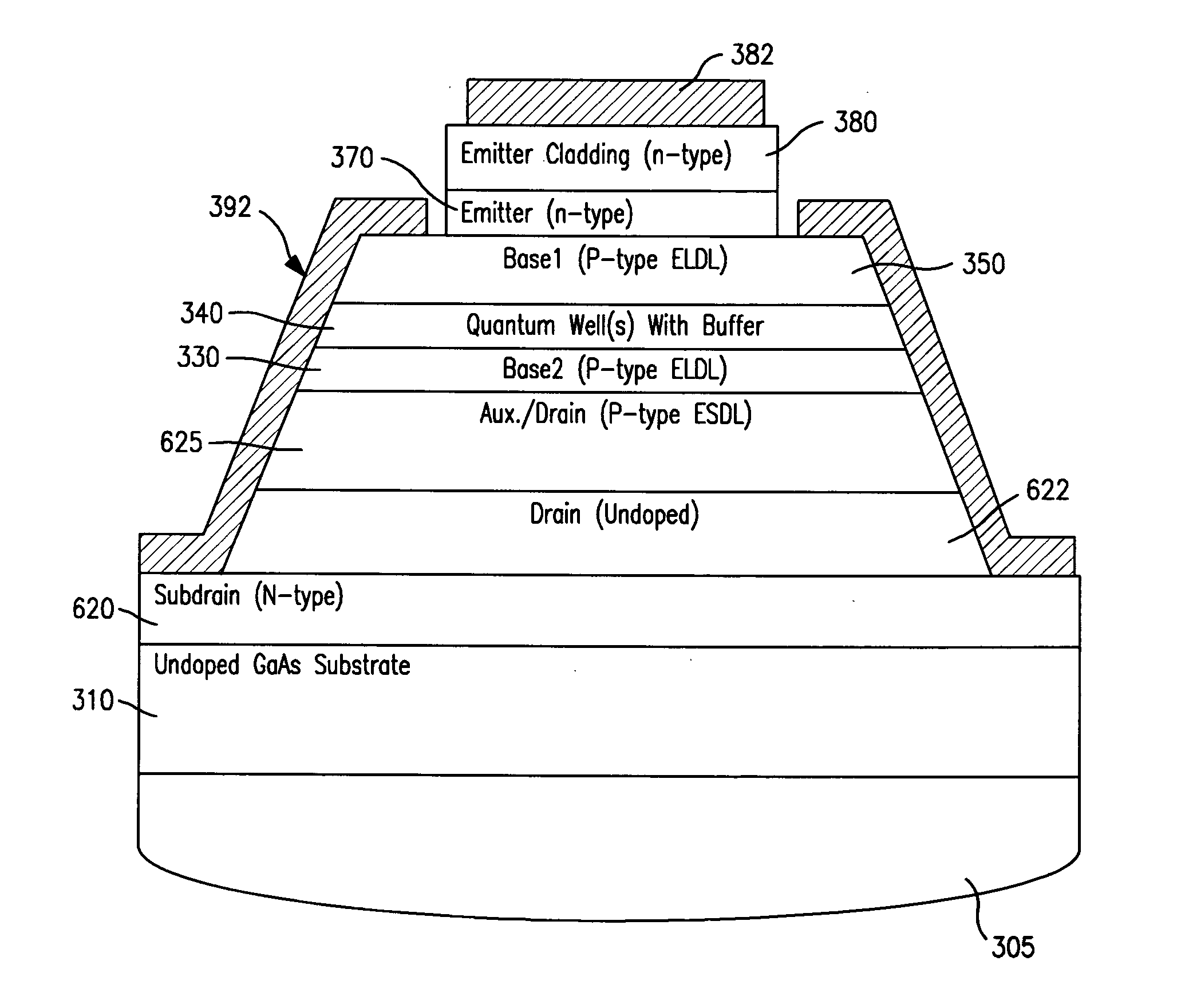
Light emitting and lasing semiconductor methods and devices
InactiveUS20120068151A1Easy to useSmaller (Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor structure
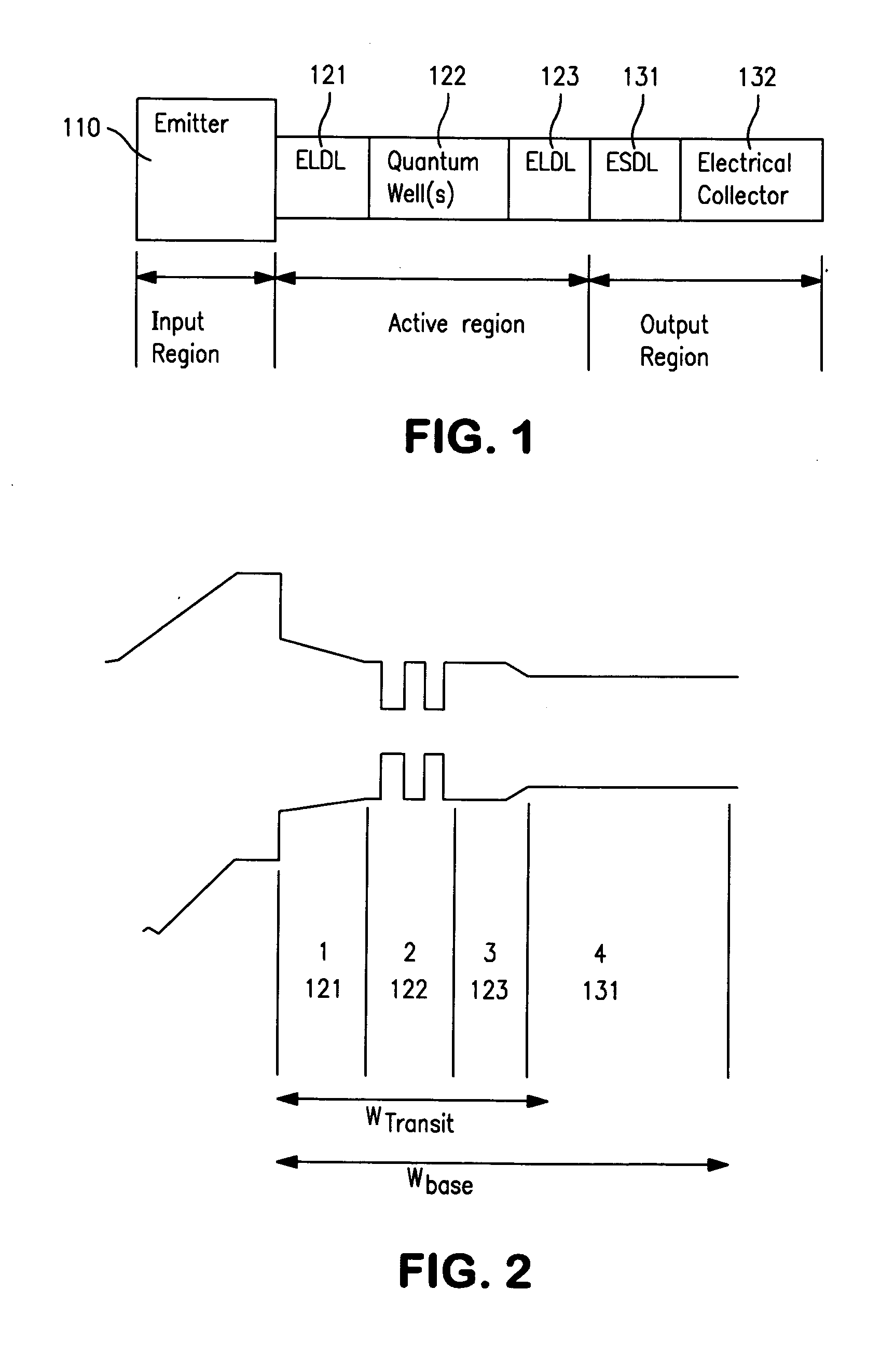
The invention is applicable for use in conjunction with a light-emitting semiconductor structure that includes a semiconductor active region of a first conductivity type containing a quantum size region and having a first surface adjacent a semiconductor input region of a second conductivity type that is operative, upon application of electrical potentials with respect to the active and input regions, to produce light emission from the active region. A method is provided that includes the following steps: providing a semiconductor output region that includes a semiconductor auxiliary layer of the first conductivity type adjacent a second surface, which opposes the first surface of the active region, and providing the auxiliary layer as a semiconductor material having a diffusion length for minority carriers of the first conductivity type material that is substantially shorter than the diffusion length for minority carriers of the semiconductor material of the active region.
Owner:QUANTUM ELECTRO OPTO SYST
Betavoltaic battery with a shallow junction and a method for making same
ActiveUS8017412B2Reduce recombinationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadiation electrical energyBetavoltaicsHigh energy
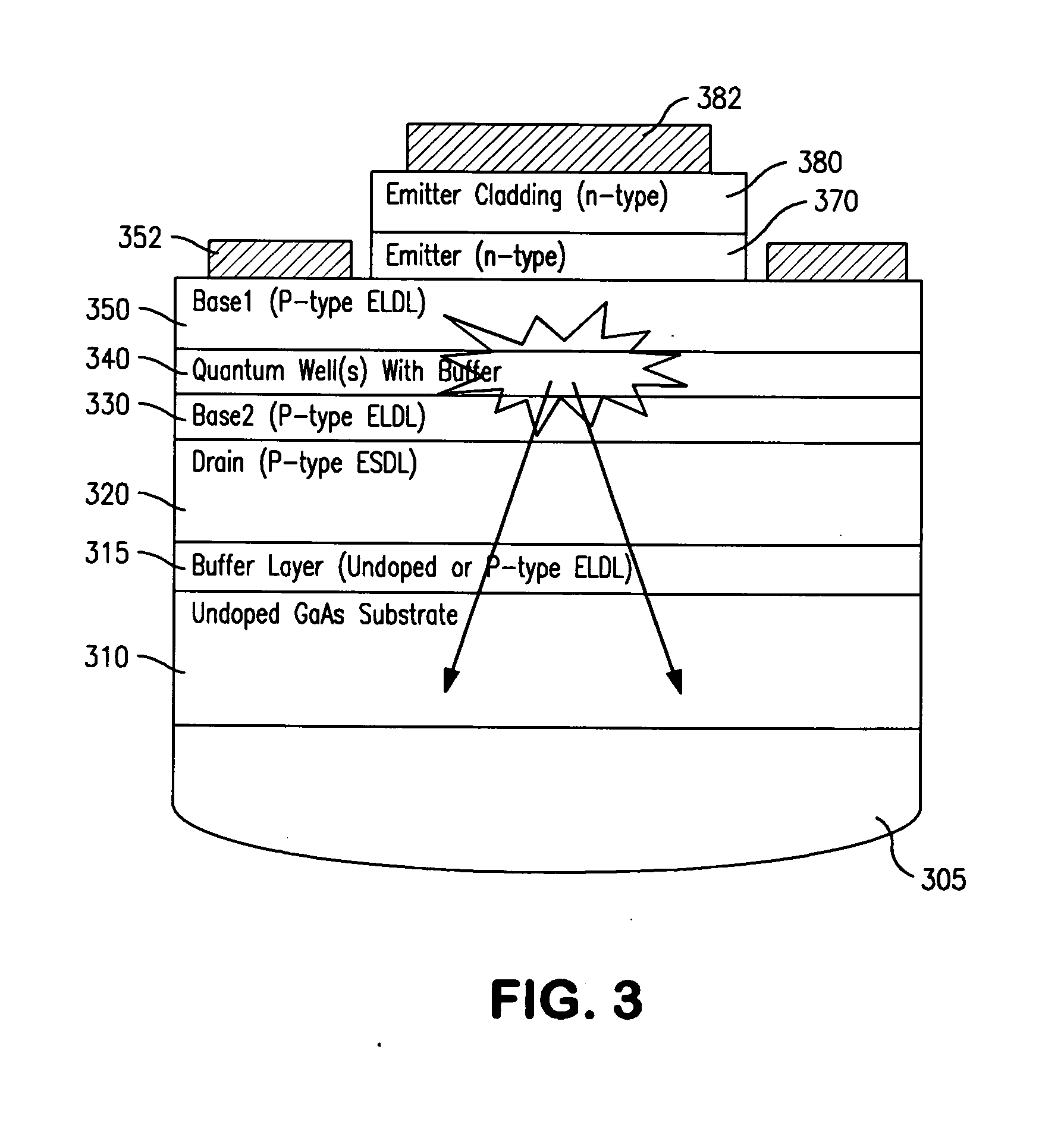
This is a novel SiC betavoltaic device (as an example) which comprises one or more “ultra shallow” P+N− SiC junctions and a pillared or planar device surface (as an example). Junctions are deemed “ultra shallow”, since the thin junction layer (which is proximal to the device's radioactive source) is only 300 nm to 5 nm thick (as an example). In one example, tritium is used as a fuel source. In other embodiments, radioisotopes (such as Nickel-63, promethium or phosphorus-33) may be used. Low energy beta sources, such as tritium, emit low energy beta-electrons that penetrate very shallow distances (as shallow as 5 nm) in semiconductors, including SiC, and can result in electron-hole pair creation near the surface of a semiconductor device rather than pair creation in a device's depletion region. By contrast, as a high energy electron penetrates a semiconductor device surface, such as a diode surface, it produces electron hole-pairs that can be collected at (by drift) and near (by diffusion) the depletion region of the device. This is a betavoltaic device, made of ultra-shallow junctions, which allows such penetration of emitted lower energy electrons, thus, reducing or eliminating losses through electron-hole pair recombination at the surface.
Owner:WIDETRONIX
Solar cell having silicon nano-particle emitter
ActiveUS8716596B1Avoid particle agglomerationReduce interfacePV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon solar cellSilicon nanoparticle
A silicon solar cell having a silicon substrate includes p-type and n-type emitters on a surface of the substrate, the emitters being doped nano-particles of silicon. To reduce high interface recombination at the substrate surface, the nano-particle emitters are preferably formed over a thin interfacial tunnel oxide layer on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:MAXEON SOLAR PTE LTD
Laser annealing for thin film solar cells
InactiveUS20130065355A1High densityLarge particlesFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumSulfide
A method for forming copper indium gallium (sulfide) selenide (CIGS) solar cells, cadmium telluride (CdTe) solar cells, and copper zinc tin (sulfide) selenide (CZTS) solar cells using laser annealing techniques to anneal the absorber and / or the buffer layers. Laser annealing may result in better crystallinity, lower surface roughness, larger grain size, better compositional homogeneity, a decrease in recombination centers, and increased densification. Additionally, laser annealing may result in the formation of non-equilibrium phases with beneficial results.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
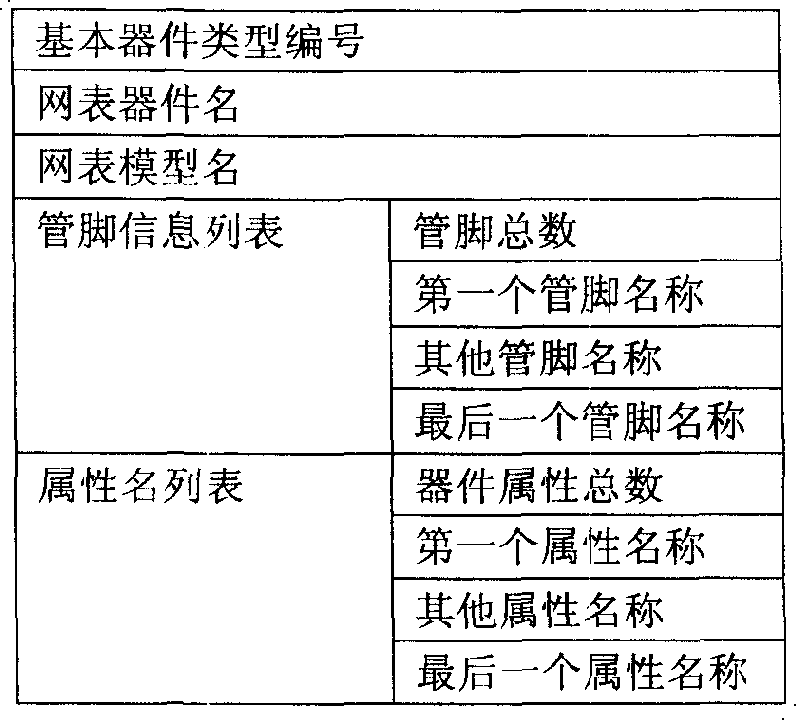
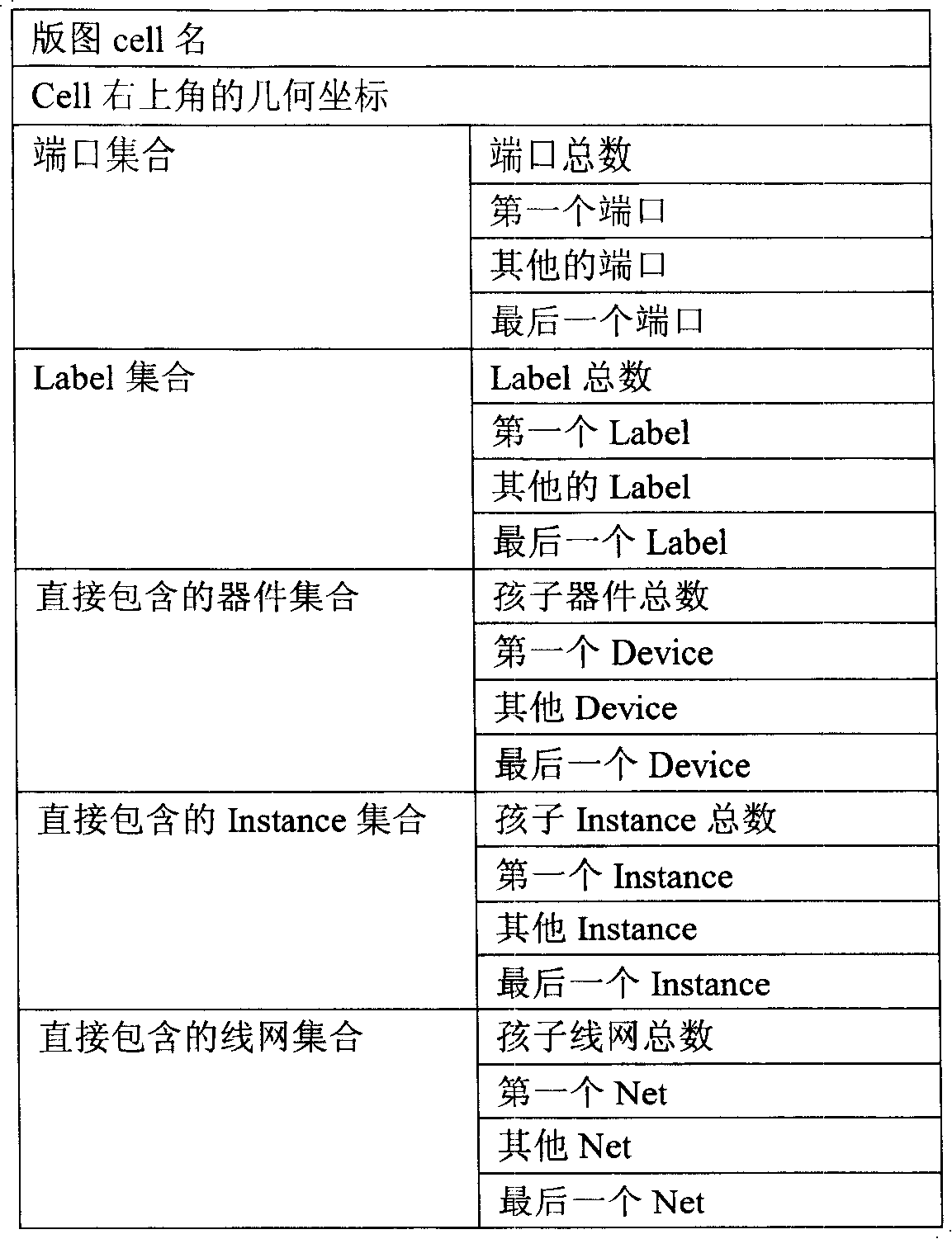
Domain data format dedicated for parasitic parameter extracting tool
InactiveCN101211376AReduce recombinationSave storage spaceSpecial data processing applicationsNetwork connectionData reorganization
A dominion database format that is specially used in parasitic parameter extraction tools belongs to the technical field of IC CAD. When using a regular dominion database to perform parasitic parameter extraction, the efficiency of searching, reading and input data organization with the parasitic parameter extraction tool is not high. The invention provides a ZPD format database, which is a special-purpose dominion database format for the parasitic parameter extraction tools. The special-purpose dominion data format can establish quick indexes for polygon data as well as the bodies of bus network that are distributed inside different layers; define and save the network connection relationship and the element data type of component information, so as to reduce unnecessary data recombination; compress the storage space for the dominion coordinate data; store relevant element data into a continuous space and eliminate redundant information, so as to improve data-reading speed; the invention can considerably improve the capacity of searching, reading and input data organization for parasitic parameter extraction tools.
Owner:北京华大九天科技股份有限公司
Preparation method of core-shell composite material wrapped in titanium dioxide nanoparticle coating
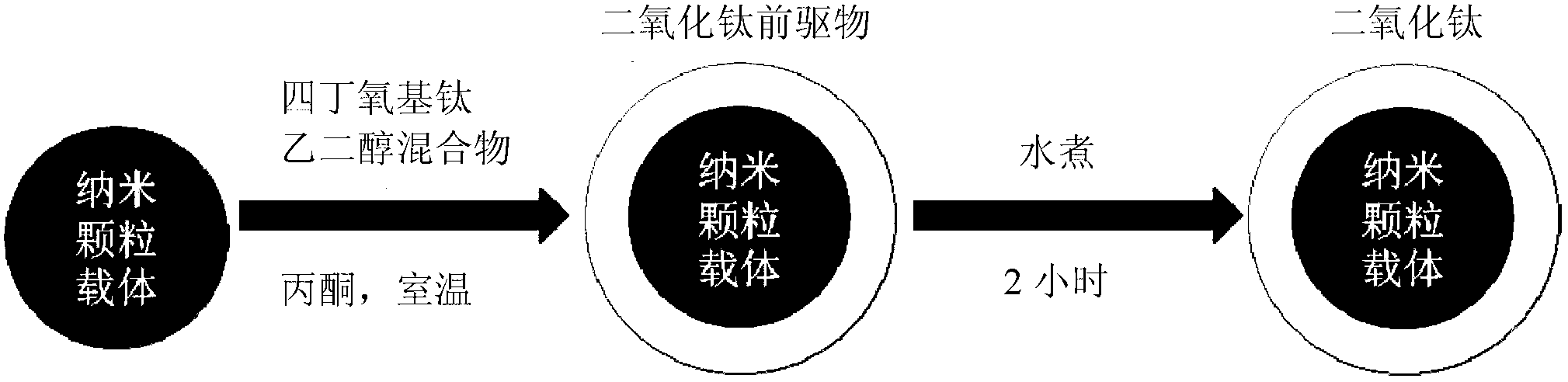
InactiveCN103192075ALarge specific surface areaImprove stabilityNanotechnologyWater bathsMetal oxide nanoparticles
A preparation method of core-shell composite material wrapped in a titanium dioxide nanoparticle coating includes: firstly, acquiring nanoparticle carrier; and secondly, wrapping the surface of the metal or metal oxide nanoparticle carrier with a titanium dioxide nanoparticle coating. The second step includes dissolving titanium isobutoxide in glycol, mixing at room temperature for 4-8 hours to obtain titanium dioxide precursor mixed solution A, dispersing the nanoparticle carrier in acetone, mixing well to obtain even mixed solution B, adding the titanium dioxide precursor mixed solution A into the mixed solution B, allowing for obtained solution to stand at room temperature to form precipitate mixed solution, and subjecting the precipitate mixed solution to centrifugal separation, and heating in water bath at 80-100 DEG C. The preparation method of the core-shell composite material wrapped in the titanium dioxide nanoparticle coating allows for increasing of photocatalysis efficiency and is low in cost.
Owner:杨晓红
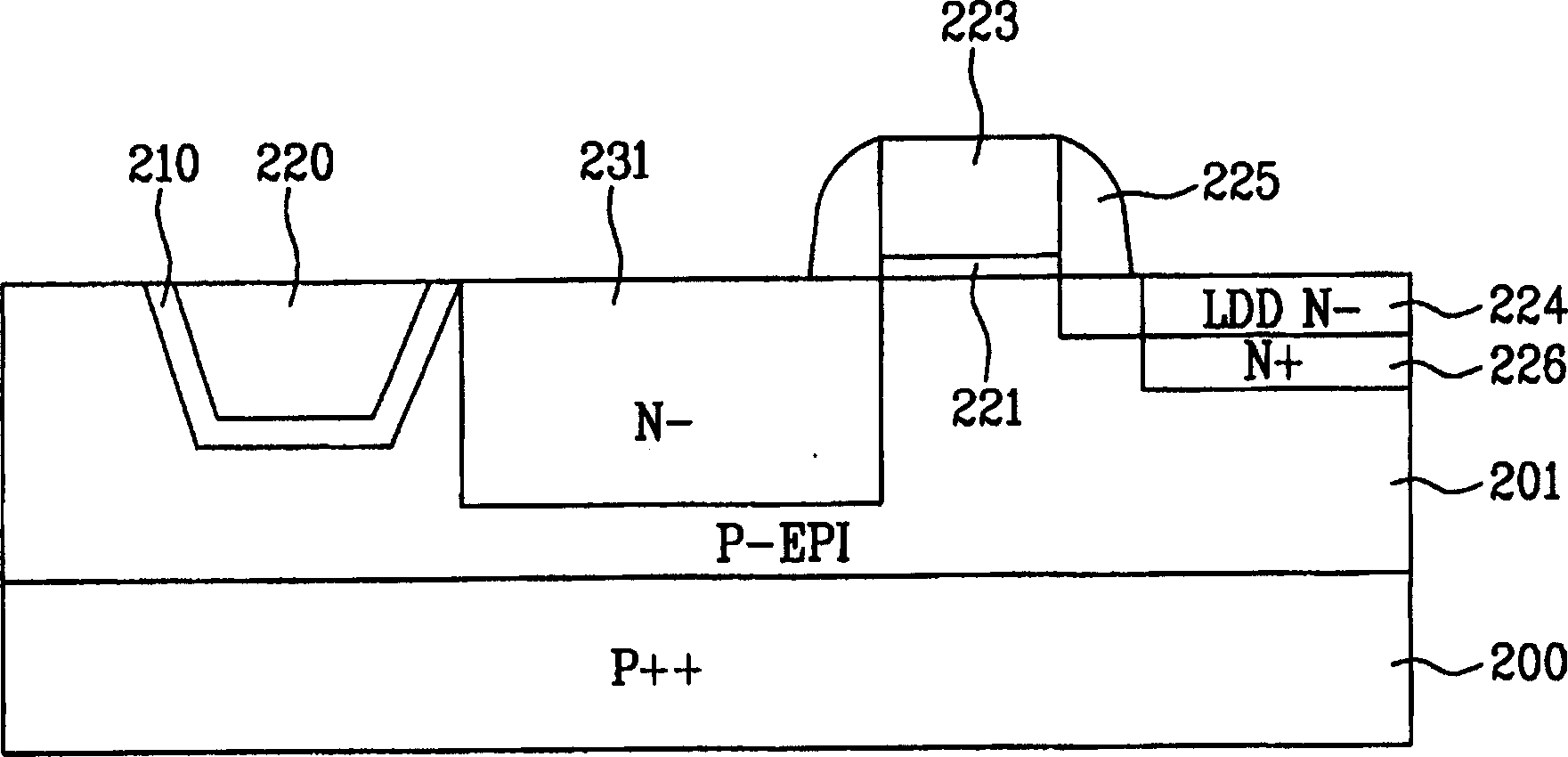
CMOS image sensor and method for fabricating the same
InactiveCN1819225AImprove featuresReduce recombinationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSPhysics
A CMOS image sensor and a method for fabricating the same are disclosed, in which a dark current is prevented from being generated between a device isolation film and a photodiode region to improve characteristics of the image sensor.
Owner:DONGBUANAM SEMICON
Apparatuses and methods for atomic layer deposition
ActiveUS20120000422A1Low densityHigh hole densityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaEngineering
Embodiments of the invention provide apparatuses and methods for atomic layer deposition (ALD), such as plasma-enhanced ALD (PE-ALD). In some embodiments, a PE-ALD chamber is provided which includes a chamber lid assembly coupled with a chamber body having a substrate support therein. In one embodiment, the chamber lid assembly has an inlet manifold assembly containing an annular channel encompassing a centralized channel, wherein the centralized channel extends through the inlet manifold assembly, and the inlet manifold assembly further contains injection holes extending from the annular channel, through a sidewall of the centralized channel, and to the centralized channel. The chamber lid assembly further contains a showerhead assembly disposed below the inlet manifold assembly, a water box disposed between the inlet manifold assembly and the showerhead assembly, and a remote plasma system (RPS) disposed above and coupled with the inlet manifold assembly, and in fluid communication with the centralized channel.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Light receiving element and light receiving device incorporating circuit and optical disc drive
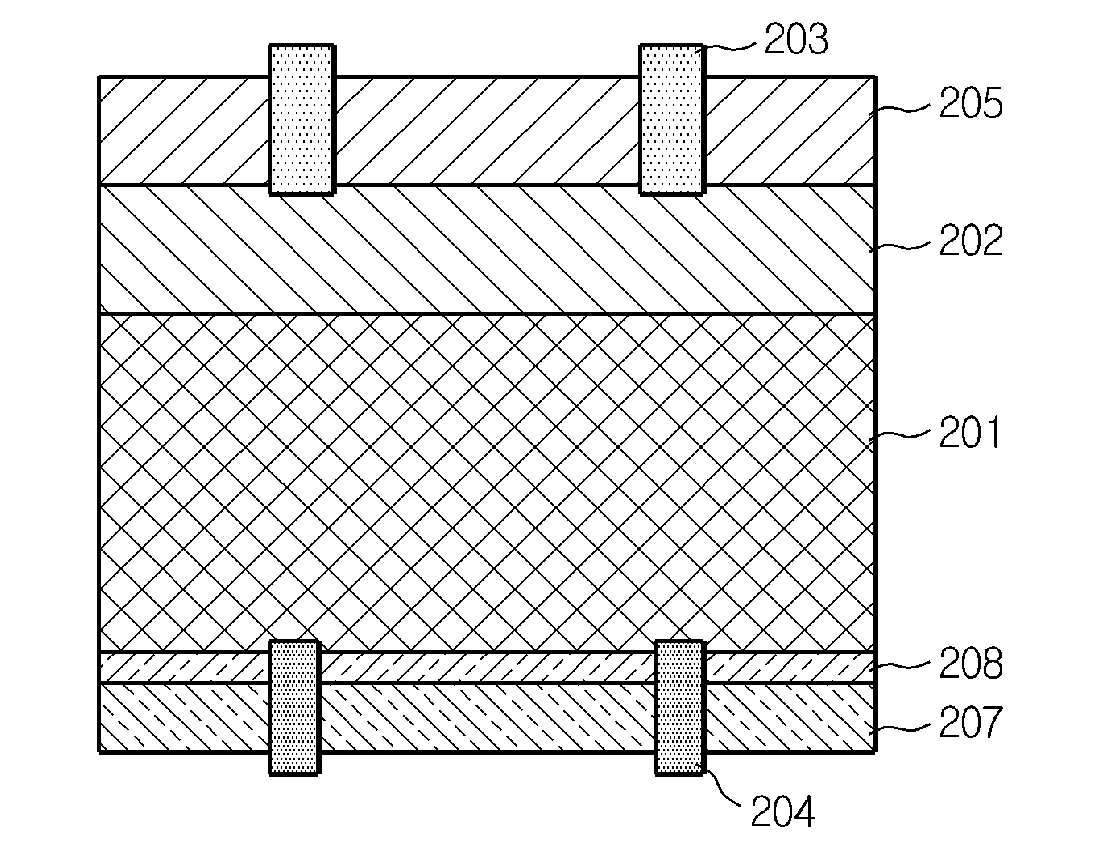
InactiveUS20050001231A1High sensitivityReduce carrier recombinationIntegrated optical head arrangementsSolid-state devicesCharge carrierPeak value
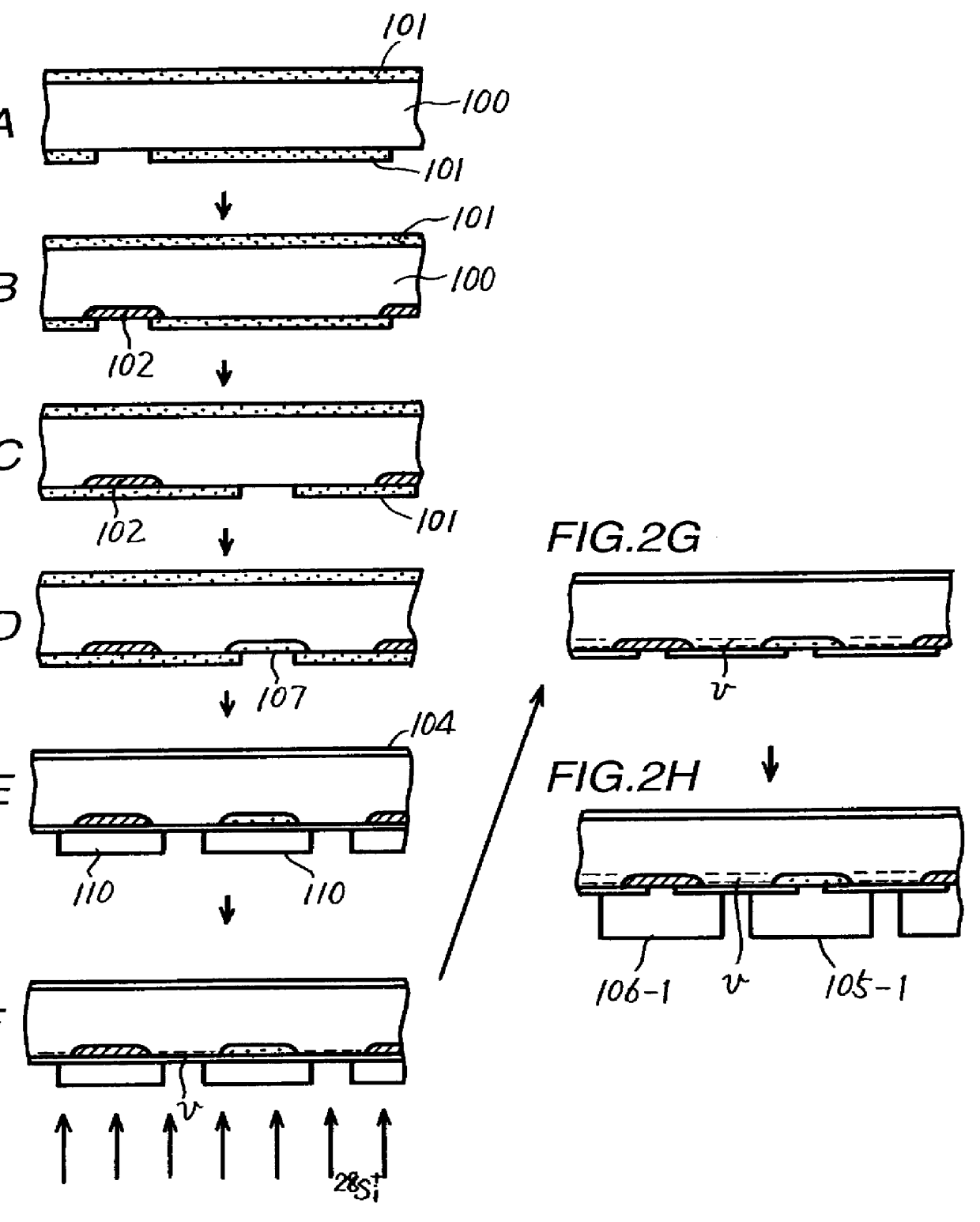
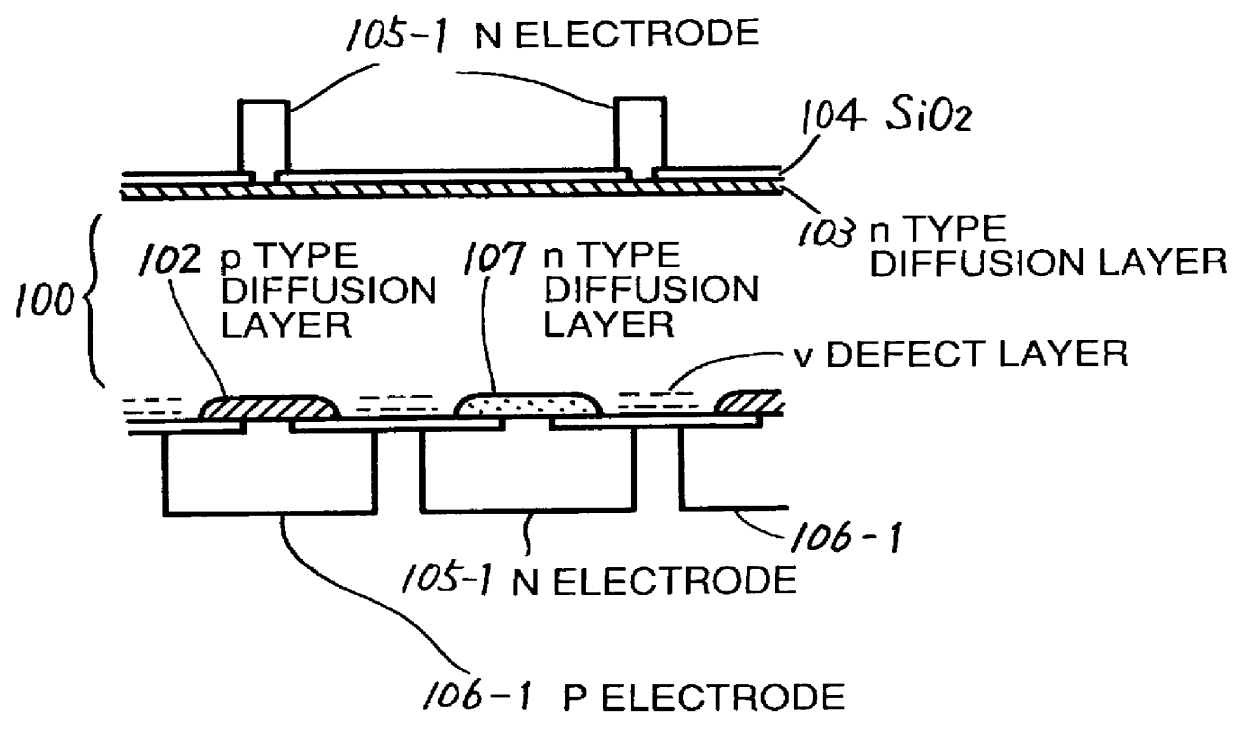
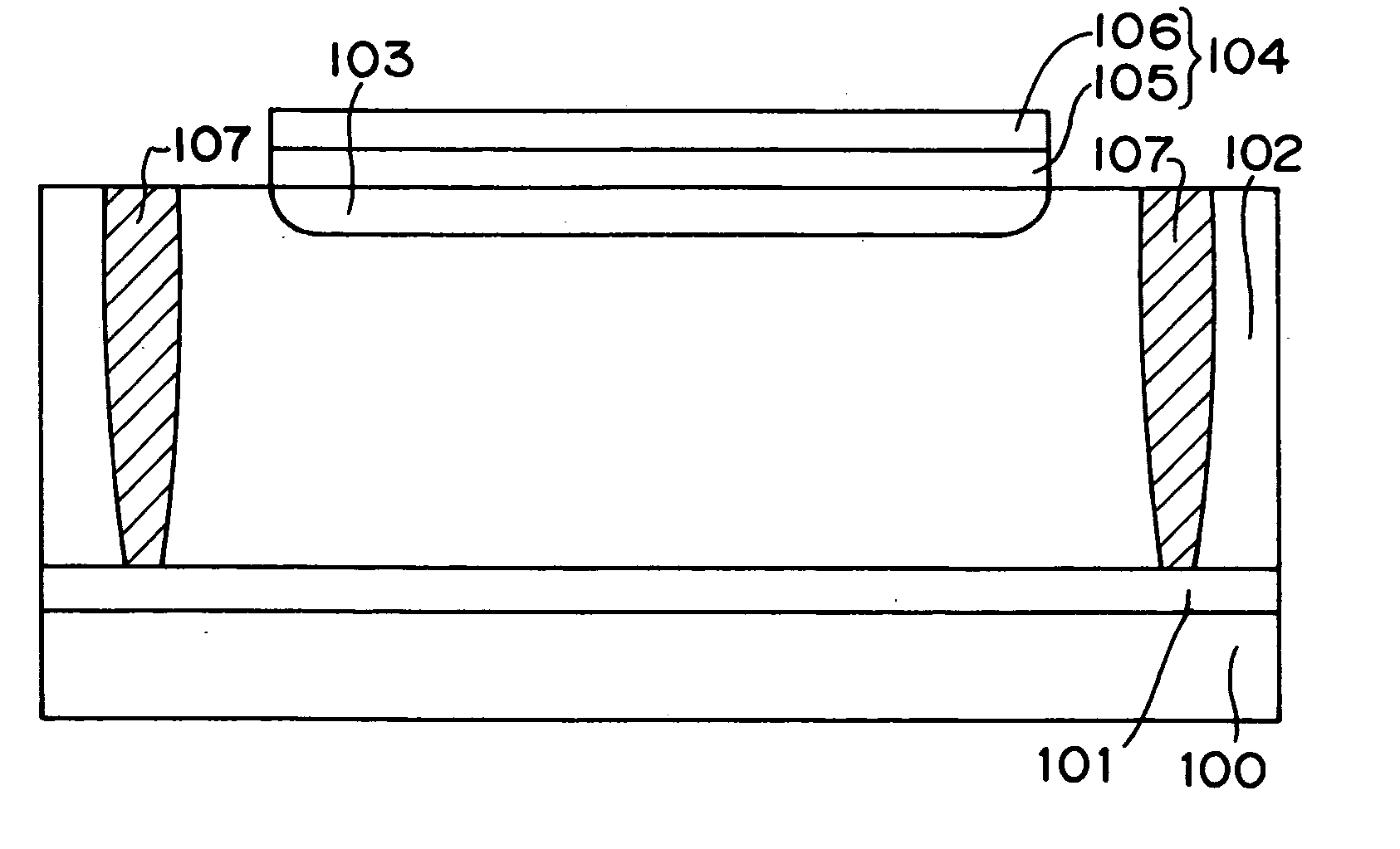
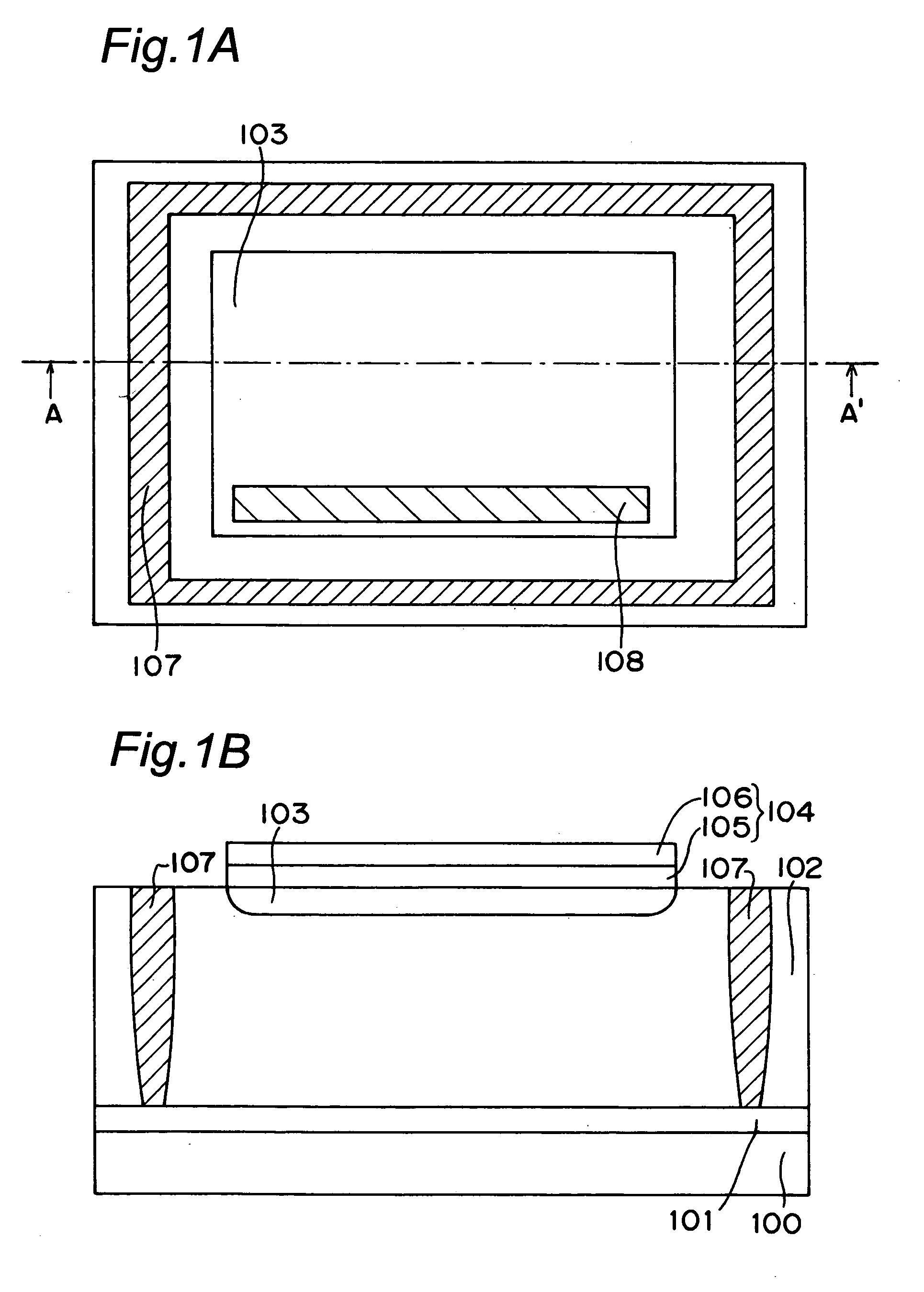
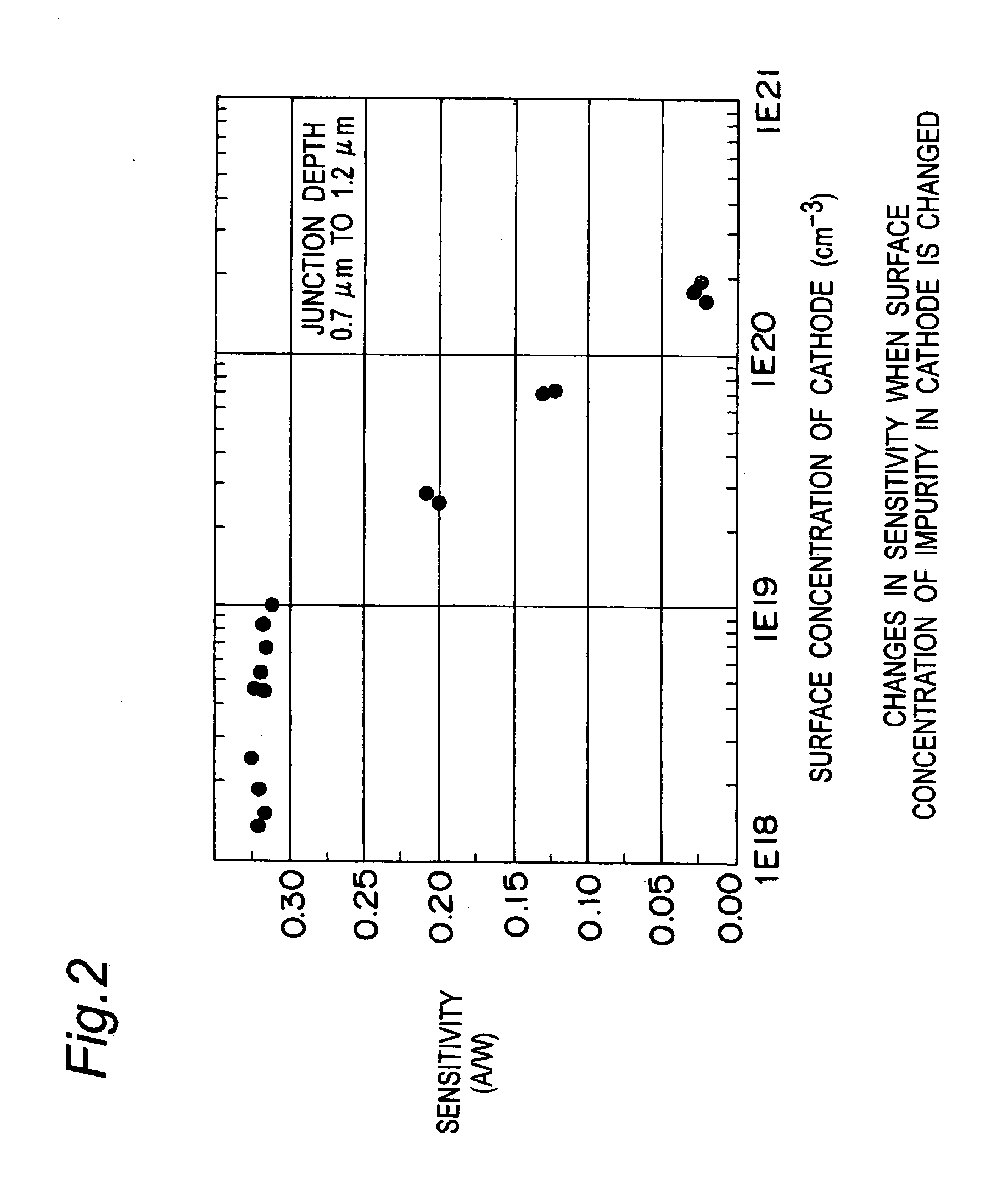
A light receiving device includes a P type diffusion layer (101), a P type semiconductor layer (102), an N type diffusion layer (103) serving as a light receiving part, and a light transmitting film (104), all formed on a p type silicon substrate (100). The N type diffusion layer (103) has a thickness of 0.8 μm to 1.0 μm which is larger than an absorption length of incident light having wavelength of 400 nm, and such a concentration profile that a impurity concentration is not higher than 1E19 cm−3 on a surface and has a peak in a vicinity of the surface. Since recombination of carriers generated by the incident light is prevented in the vicinity of the surface of the N type diffusion layer (103), sensitivity of the light receiving device is enhanced and response speed is increased by the low-resistance N type diffusion layer (103) having a larger junction depth.
Owner:SHARP KK
Solar cell and method for manufacturing solar cell
ActiveUS9252301B2Improve conversion efficiencyReduce recombinationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationElectrical conductorEngineering
A solar cell includes semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type; first semiconductor layer having a first conductivity type; second semiconductor layer having a second conductivity type; first electrode; second electrode; and insulating layer. First semiconductor layer and second semiconductor layer are formed on rear surface. When one end portion of insulating layer which is formed on first semiconductor layer and which is on a side close to first electrode is defined as first insulating-layer end portion and another end portion of insulating layer on a side close to second electrode is defined as second insulating-layer end portion in arrangement direction x, a distance from end point of second-semiconductor-layer end portion in contact with rear surface to second insulating-layer end portion in arrangement direction x is shorter than a distance from end point to first insulating-layer end portion in arrangement direction x.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Solar cell and method for manufacturing solar cell
ActiveUS20130247970A1Improve conversion efficiencyReduce recombinationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorEngineering
A solar cell includes semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type; first semiconductor layer having a first conductivity type; second semiconductor layer having a second conductivity type; first electrode; second electrode; and insulating layer. First semiconductor layer and second semiconductor layer are formed on rear surface. When one end portion of insulating layer which is formed on first semiconductor layer and which is on a side close to first electrode is defined as first insulating-layer end portion and another end portion of insulating layer on a side close to second electrode is defined as second insulating-layer end portion in arrangement direction x, a distance from end point of second-semiconductor-layer end portion in contact with rear surface to second insulating-layer end portion in arrangement direction x is shorter than a distance from end point to first insulating-layer end portion in arrangement direction x.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Photoconversion of light using metal supported atomic quantum clusters
ActiveUS20140318980A1Easy to separateIncrease interface areaMaterial nanotechnologyLight-sensitive devicesTransition metal atomsNanometre
The present invention discloses the use of a metal nanoparticle which comprises at least one semiconductor attached to it, wherein the at least one semiconductor is an atomic quantum cluster (AQC) consisting of between 2 and 55 zero-valent transition metal atoms, as photocatalysts in photocatalytic processes and applications thereof.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SANTIAGO DE COMPOSTELA
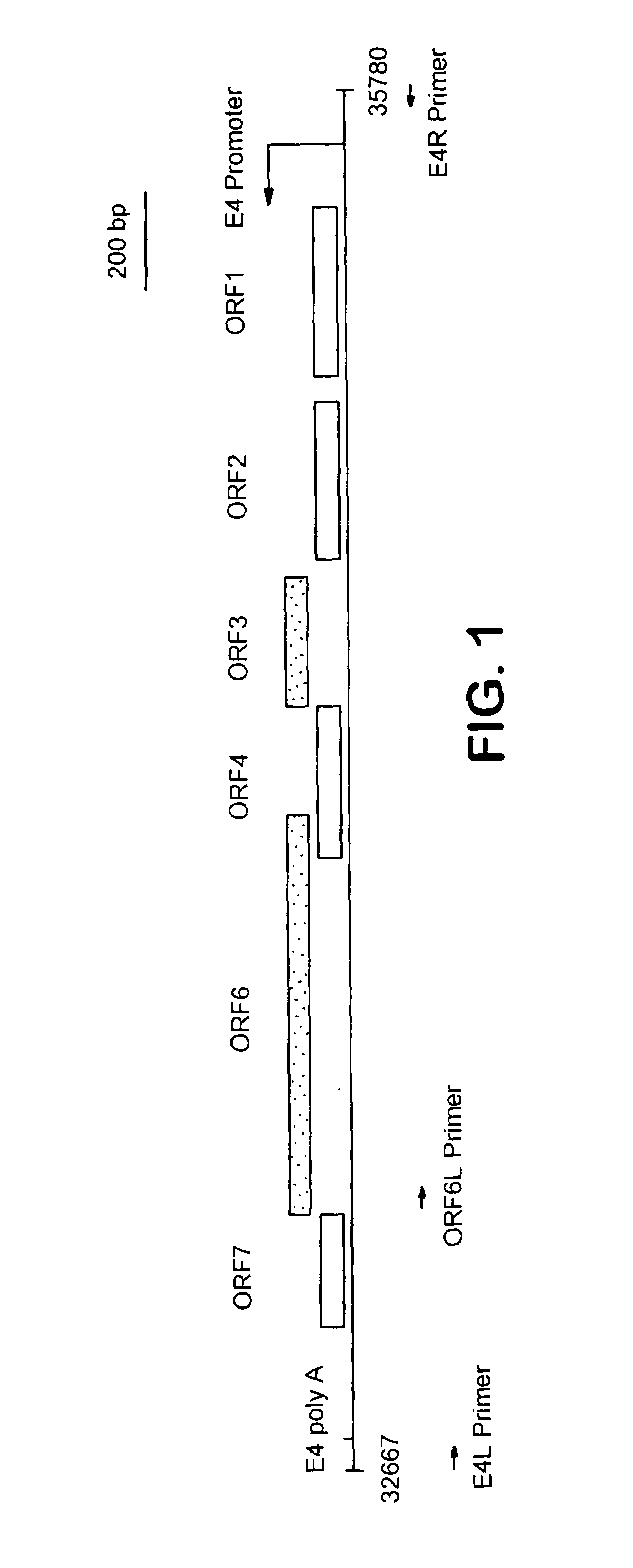
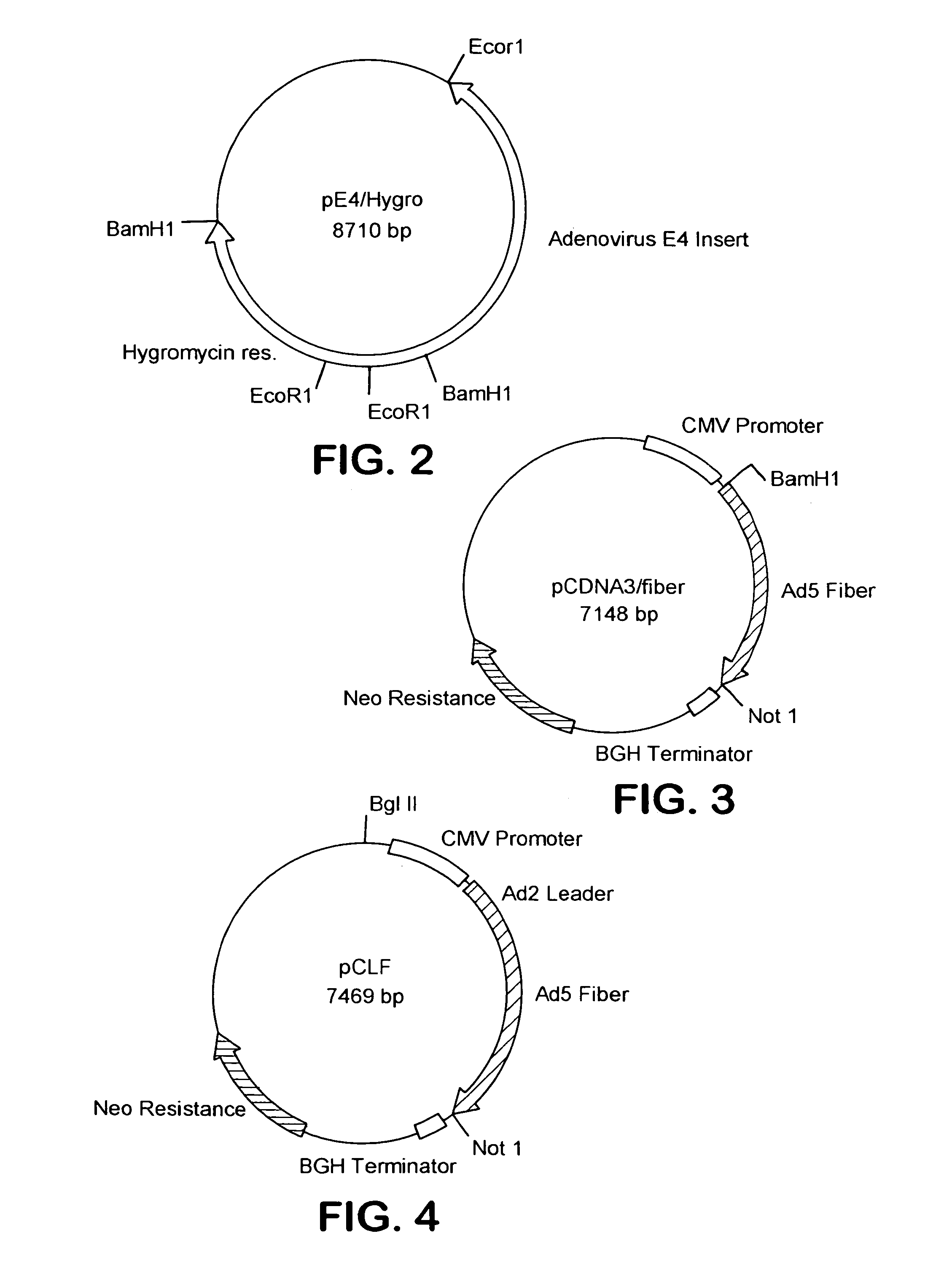
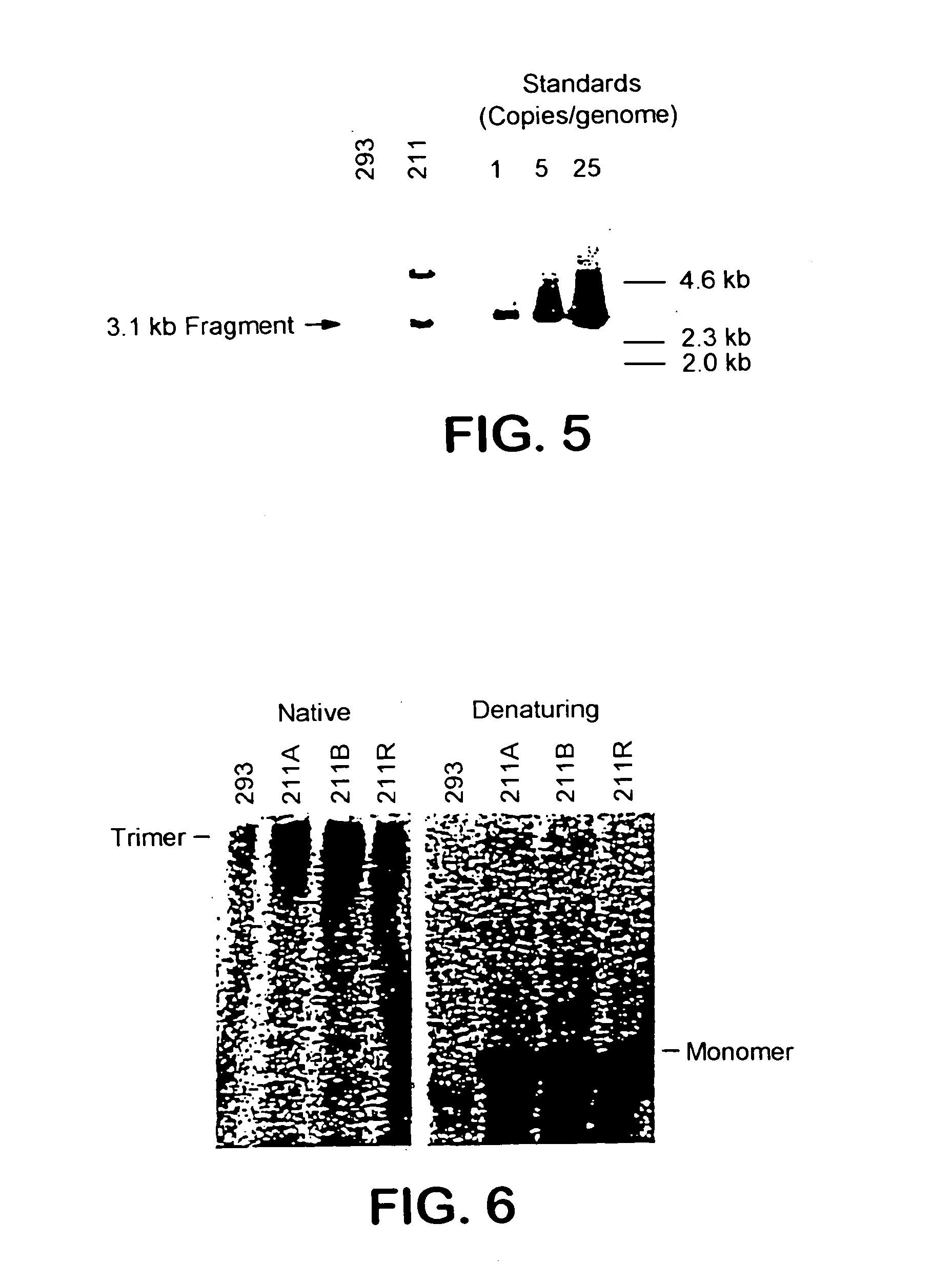
Adenovirus vectors, packaging cell lines, compositions, and methods for preparation and use
InactiveUS7232899B2Little propensityReduce probabilityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGeneLarge capacity
The present invention relates to methods for gene therapy, especially to adenovirus-based gene therapy, and related cell lines and compositions. In particular, novel nucleic acid constructs and packaging cell lines are disclosed, for use in facilitating the development of high-capacity and targeted vectors. The invention also discloses a variety of high-capacity adenovirus vectors and related compositions and kits including the disclosed cell lines and vectors. Finally, the invention discloses methods of preparing and using the disclosed vectors, cell lines and kits.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Solar cell including backside reflection layer composed of high-k dielectrics
InactiveUS20100096013A1Reduce recombinationExcellent optical trappingFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationDielectricTrapping
A solar cell includes a backside reflection layer containing a high-k dielectrics. The backside reflection layer includes a reflection film containing HfO2 or ZrO2 and a backside passivation layer containing of HfSixOy, ZrSixOy or SiO2, which are formed on a rear side of a substrate onto which solar rays are input. Thus, the solar cell exhibits excellent optical trapping for solar rays and low recombination rate of carriers on the rear side. Also, since the reflection film and the backside passivation layer have excellent thermal stability, it is possible to form electrodes by applying various processes such as thermal treatment.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Nanoparticle structure and manufacturing process of multi-wavelength light emitting devices
InactiveUS20090280592A1Improve luminous efficiencyReduce recombinationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsManufacturing technologyHigh energy
A structure of multi-wavelength light emitting device comprises multi-stacked active layer structure. Each stacked layer comprises lower energy bandgap well 4 and higher energy bandgap barrier layer 3 wherein at least one stacked layer in the device contains nanoparticles. As a result, the emitting wavelengths of the multi-stacked active layer structure consist parts (or all) of the emitting wavelengths come from the stack layers containing nanoparticles, and parts (or all) of the emitting wavelengths come from the stack layers not containing nanoparticles. In another embodiment, parts (or all) of the emitting wavelengths of the multi-stacked active layer structure can be also used to trigger one or more phosphorescences from the phosphors, thus the emitting wavelengths of such a phosphors converted light emitting device may come partially from the multi-stacked active layer itself and partially (or all) from the phosphors.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com