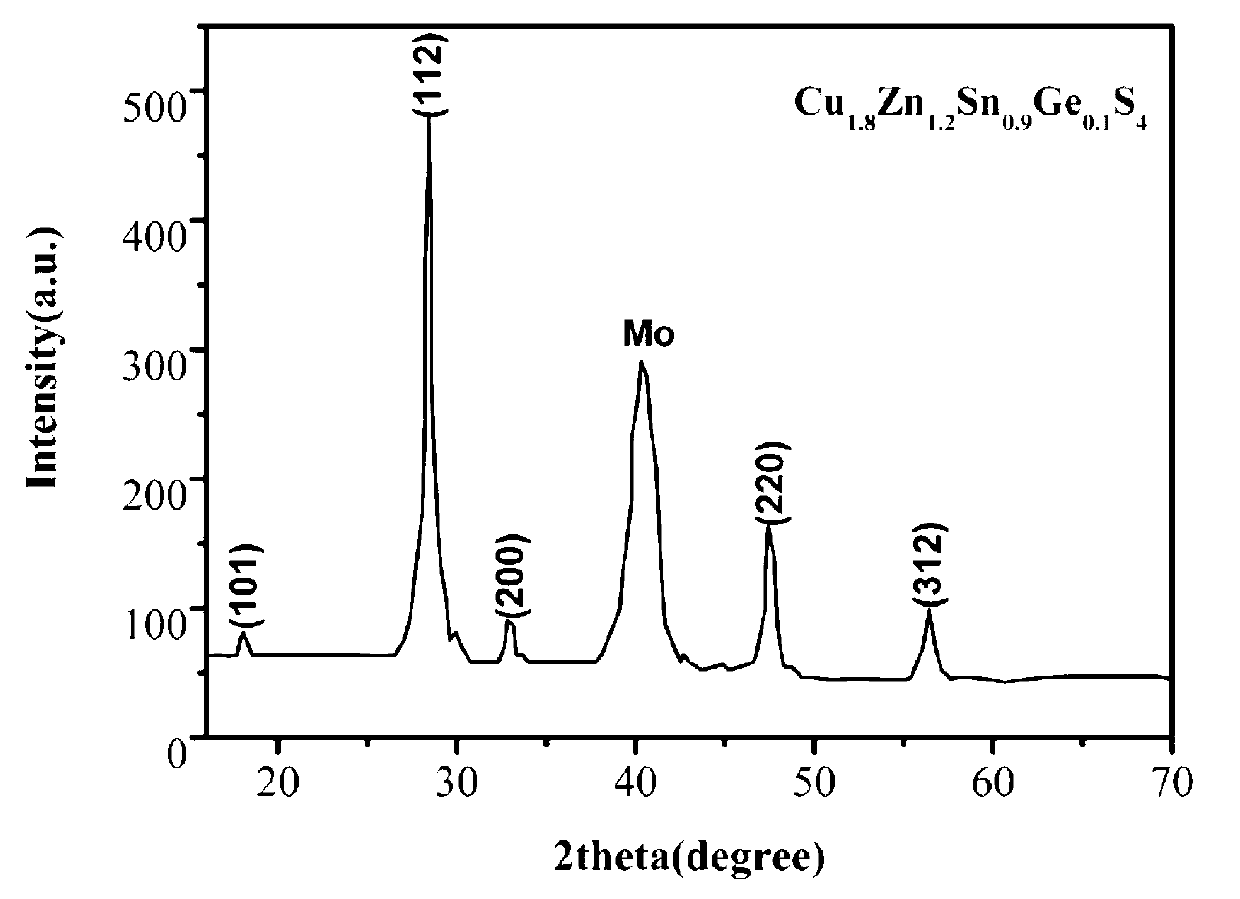
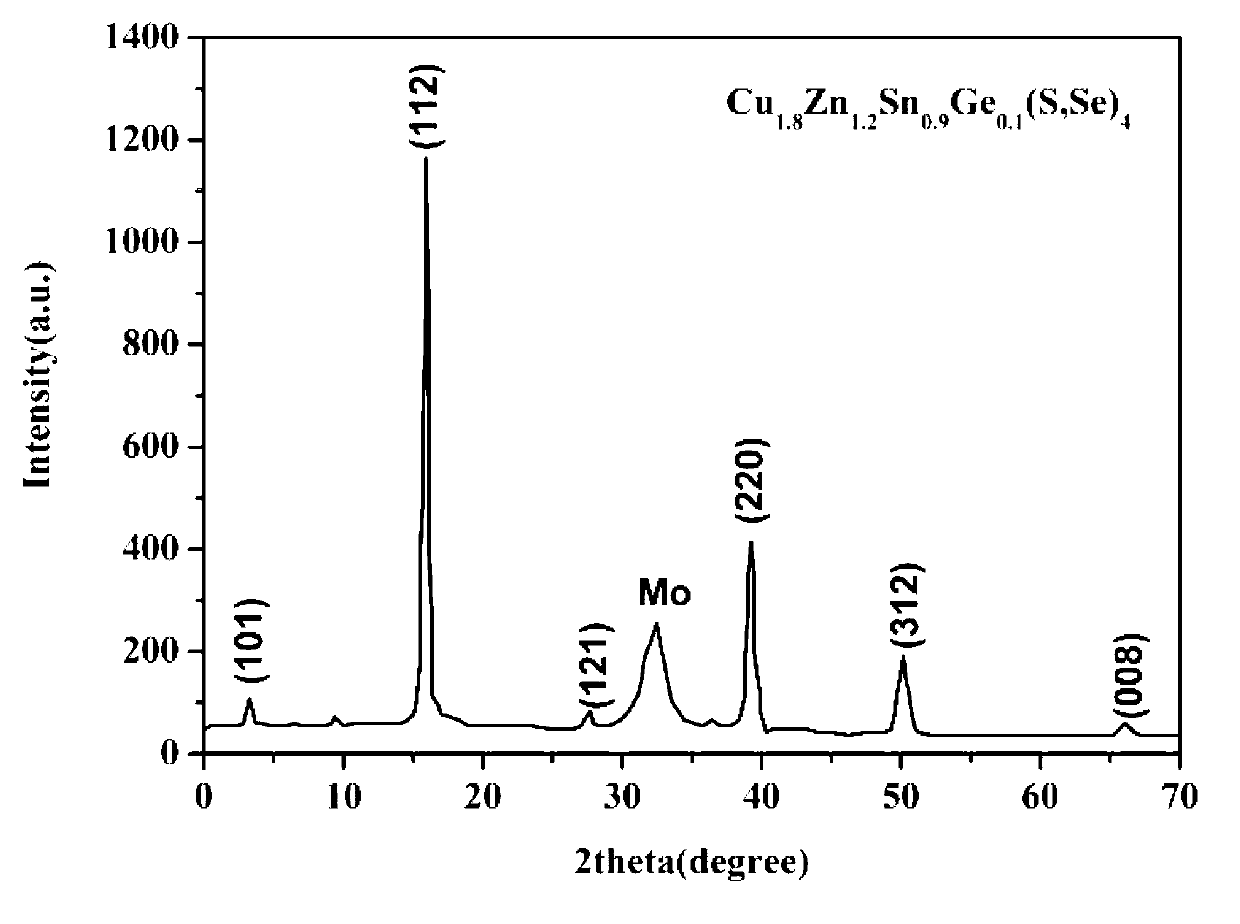
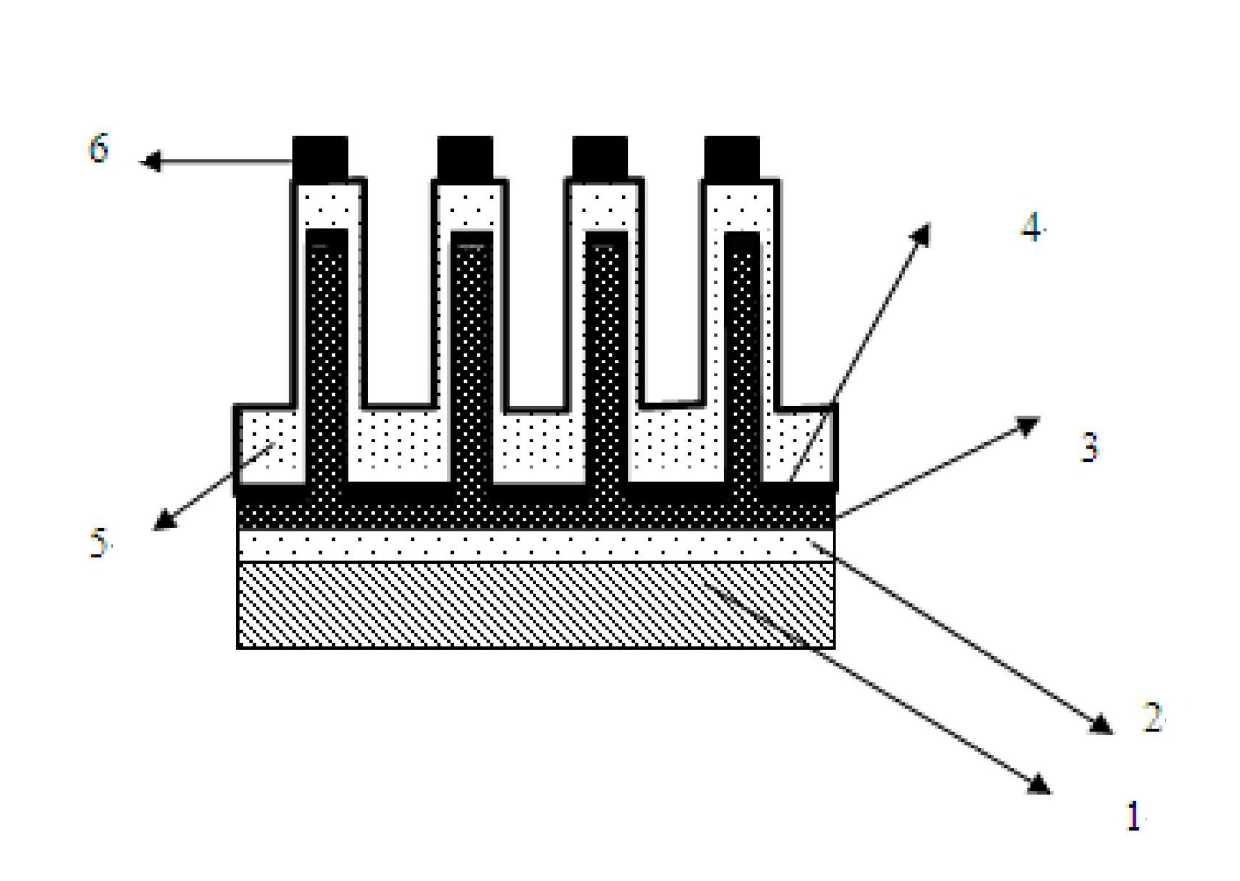
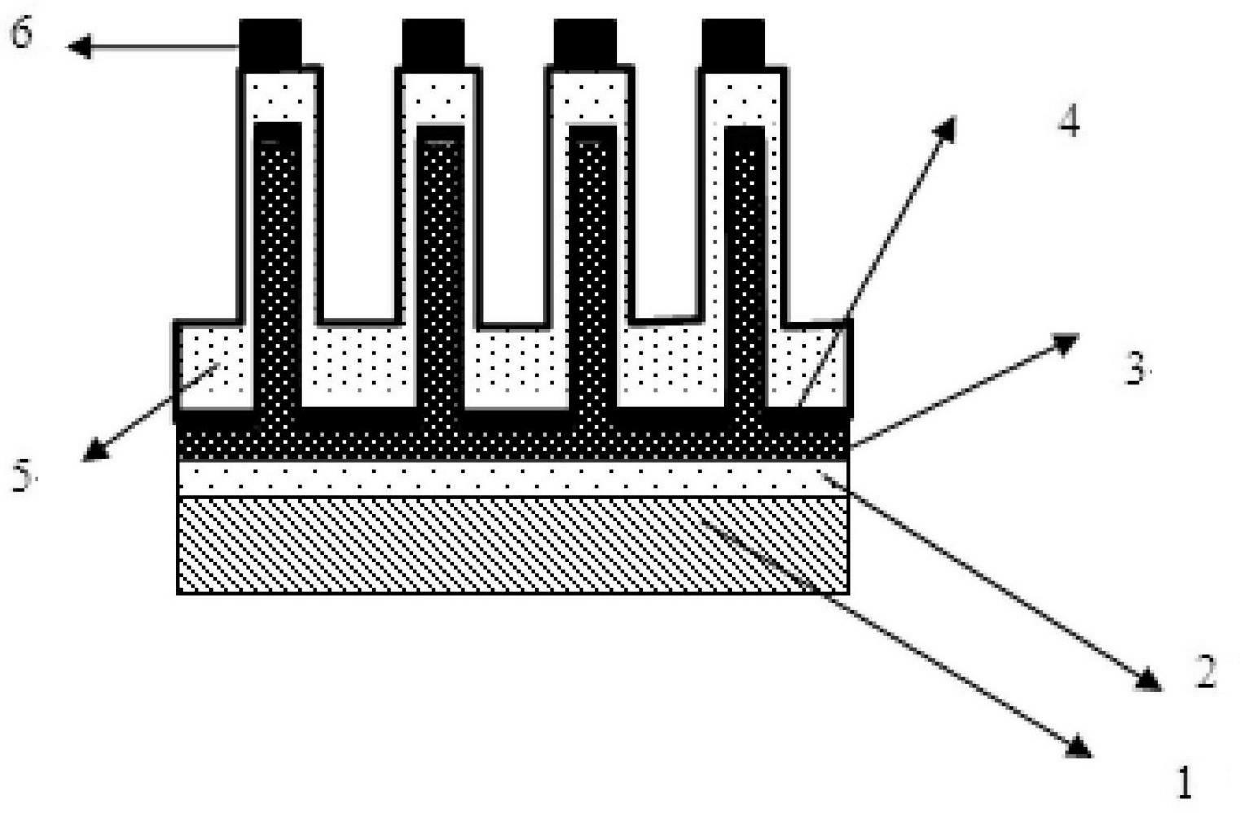
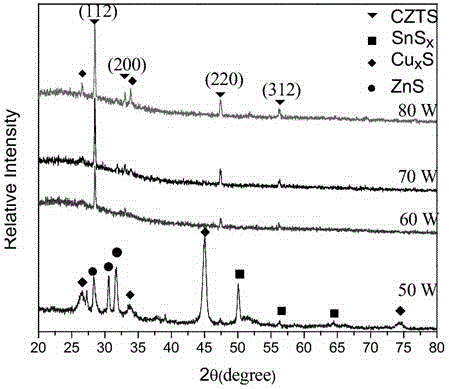
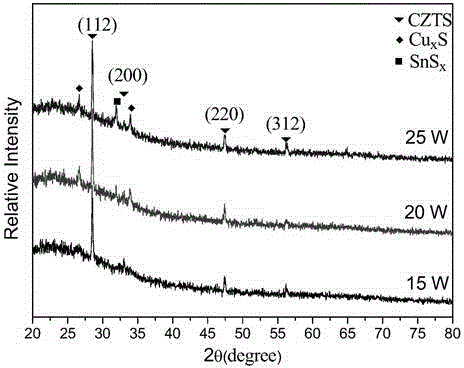
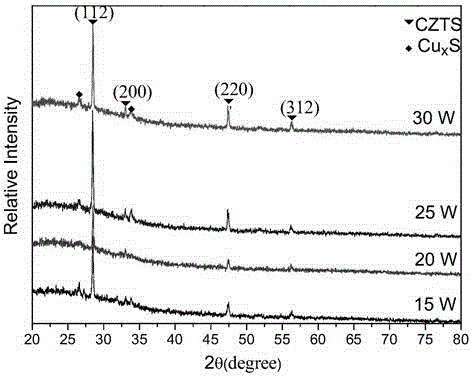
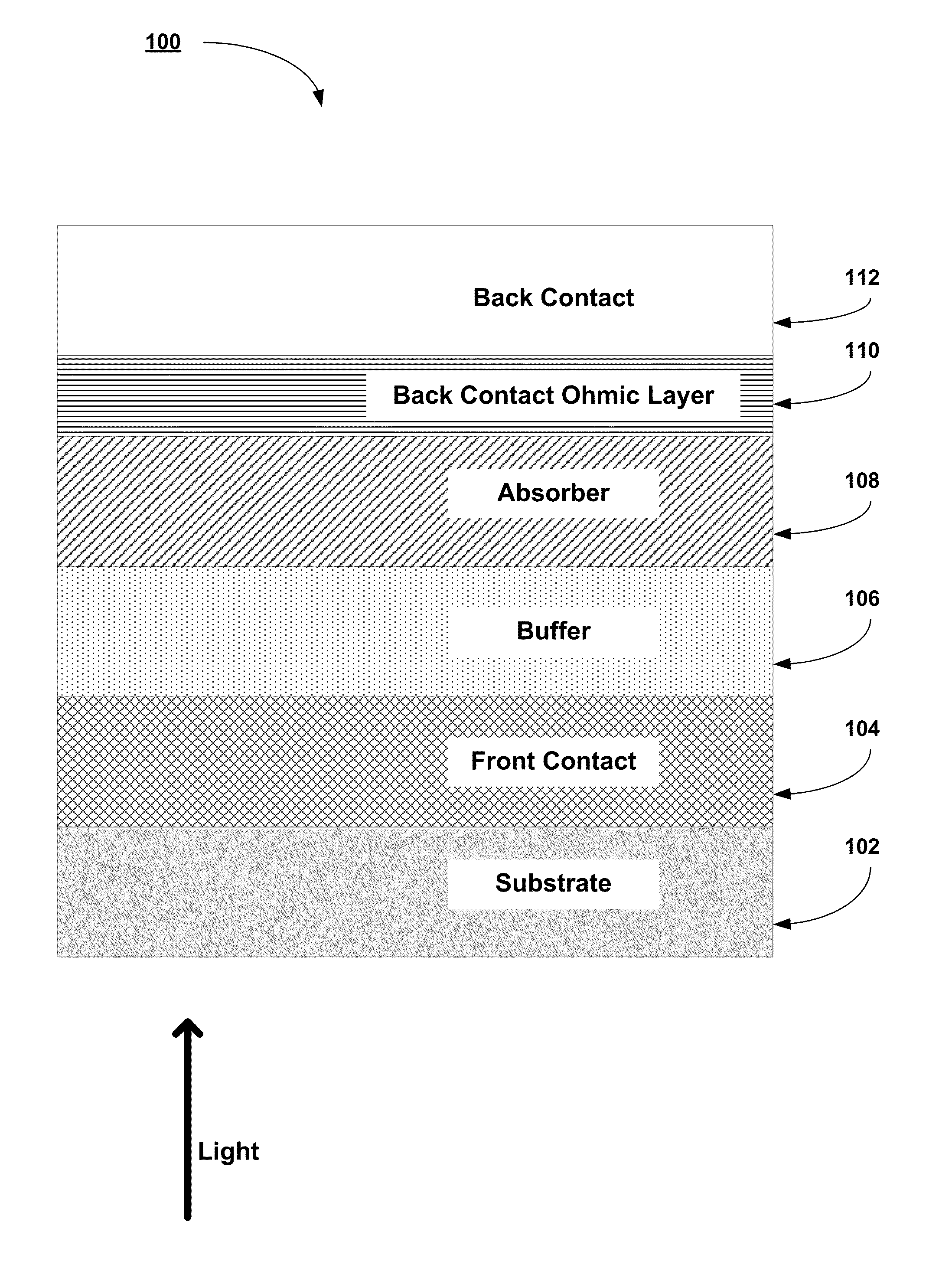
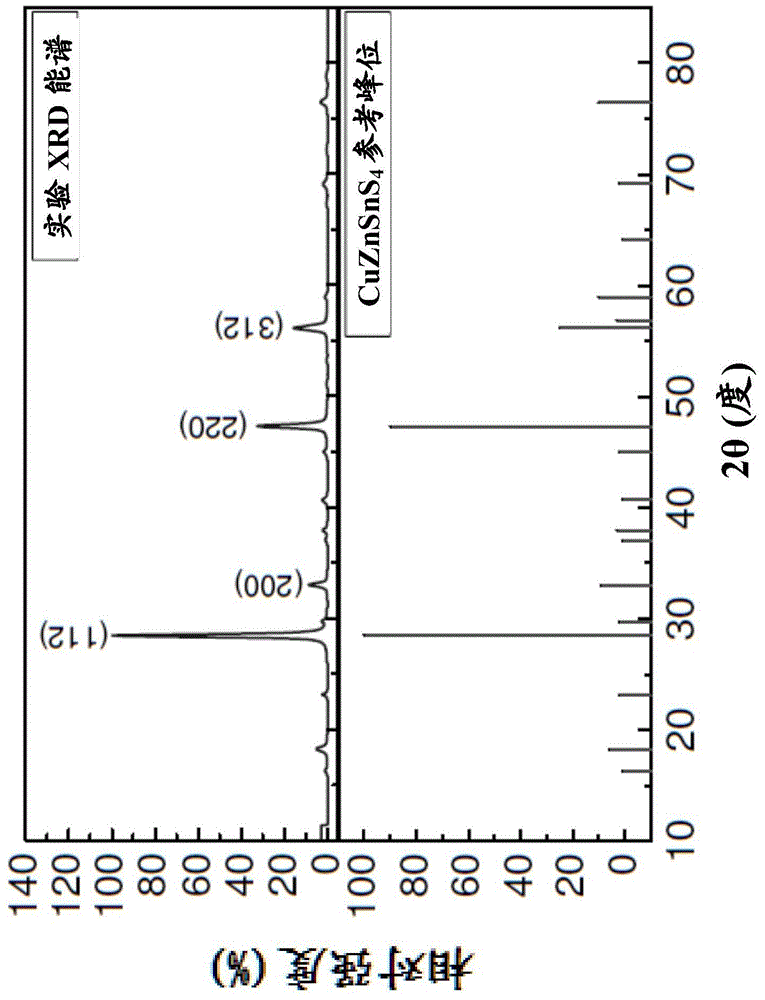
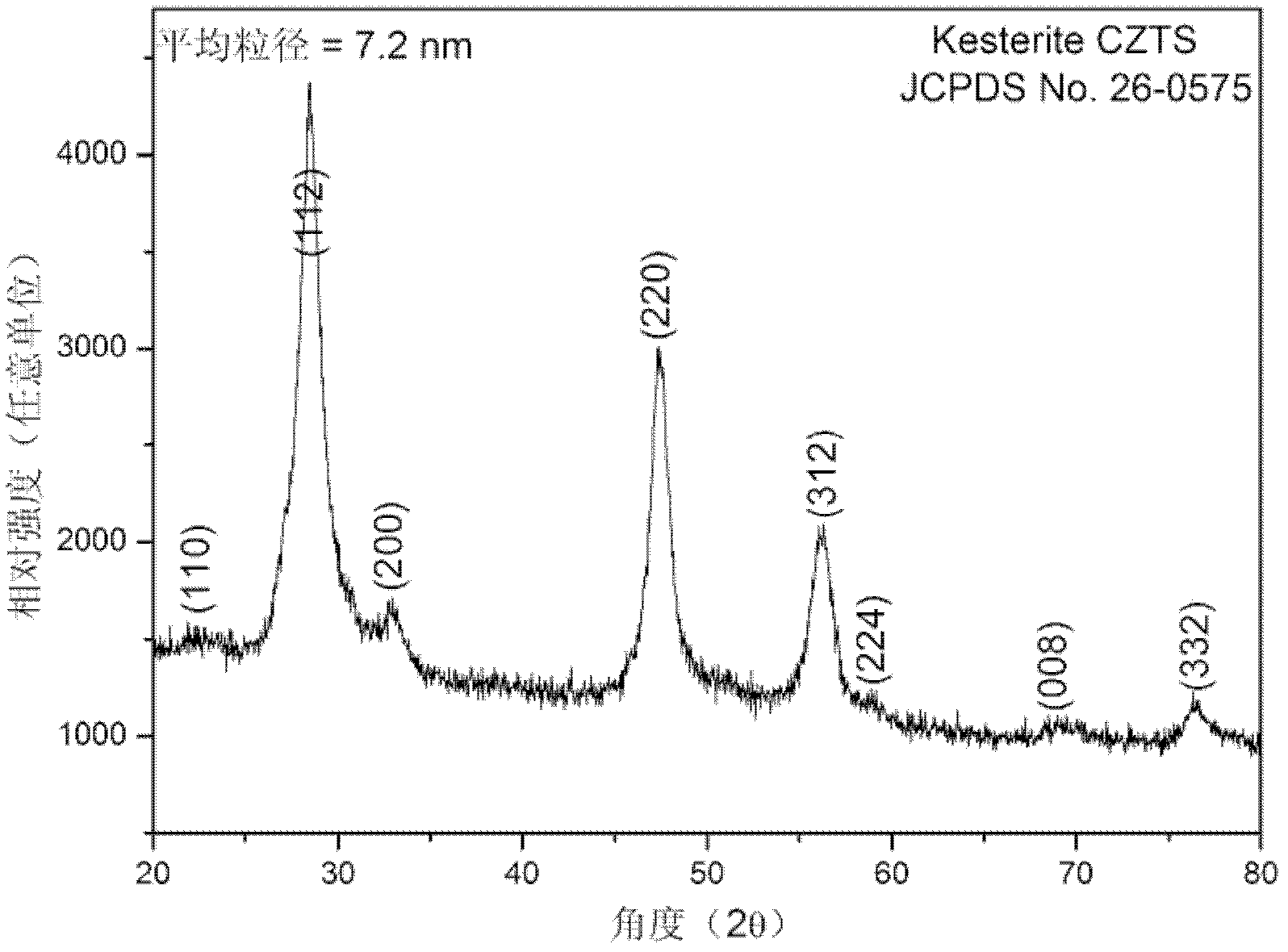
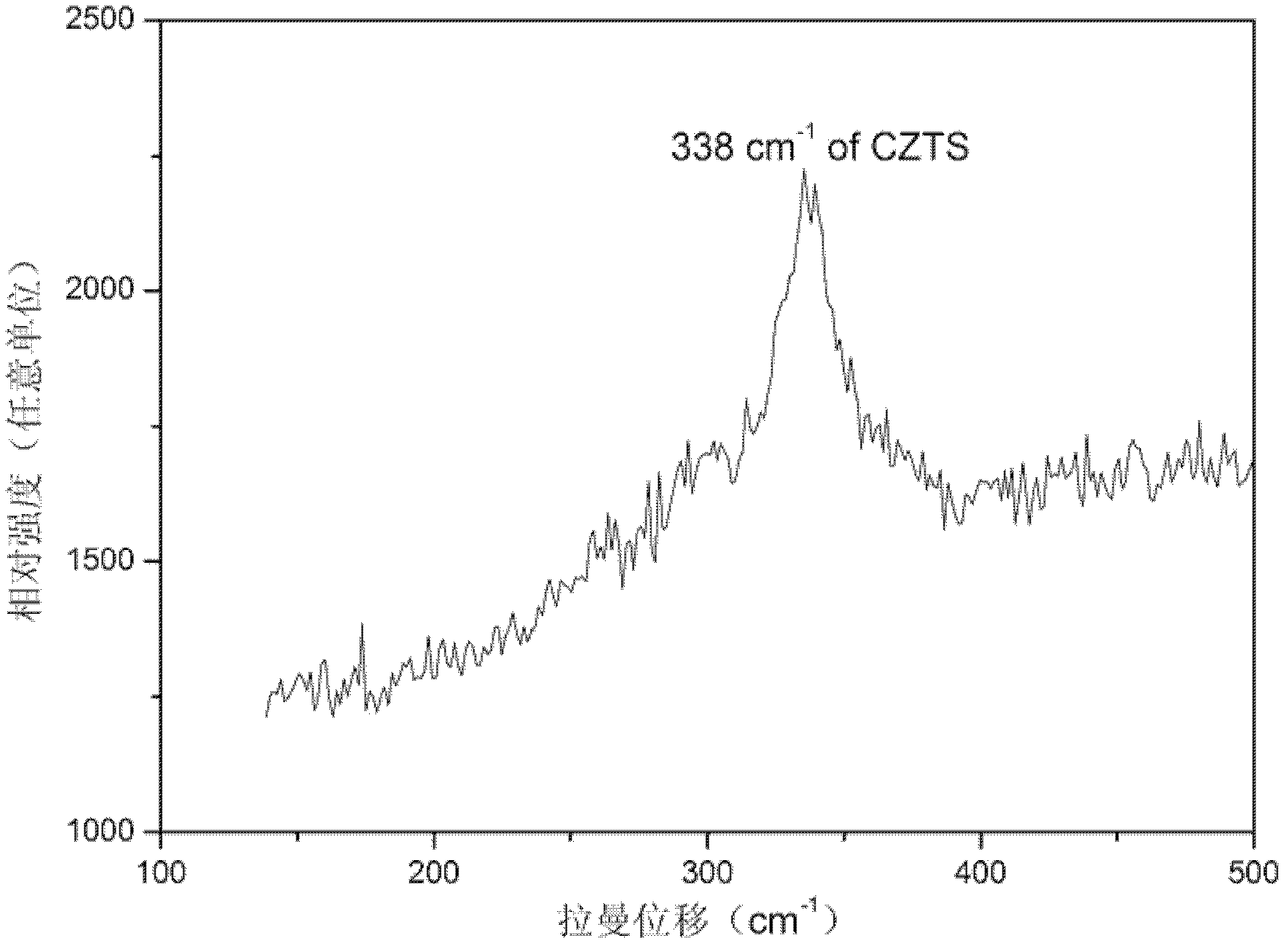
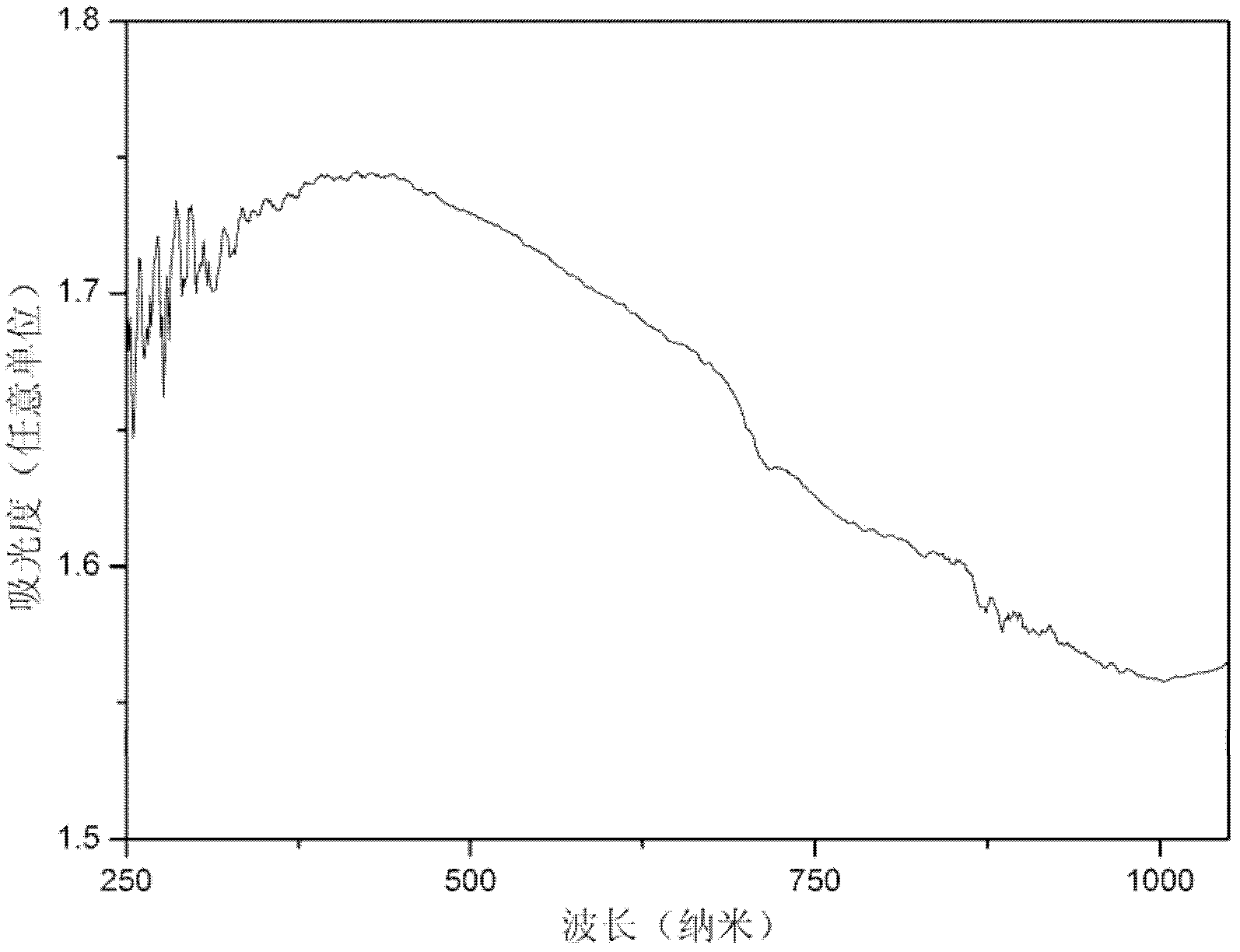
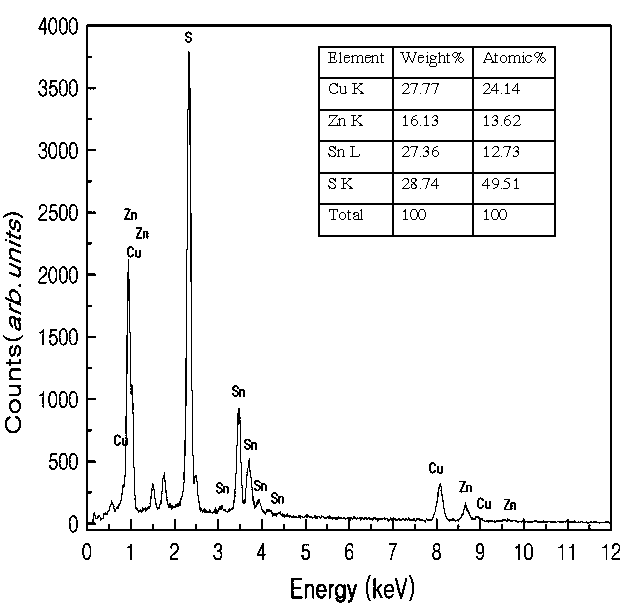
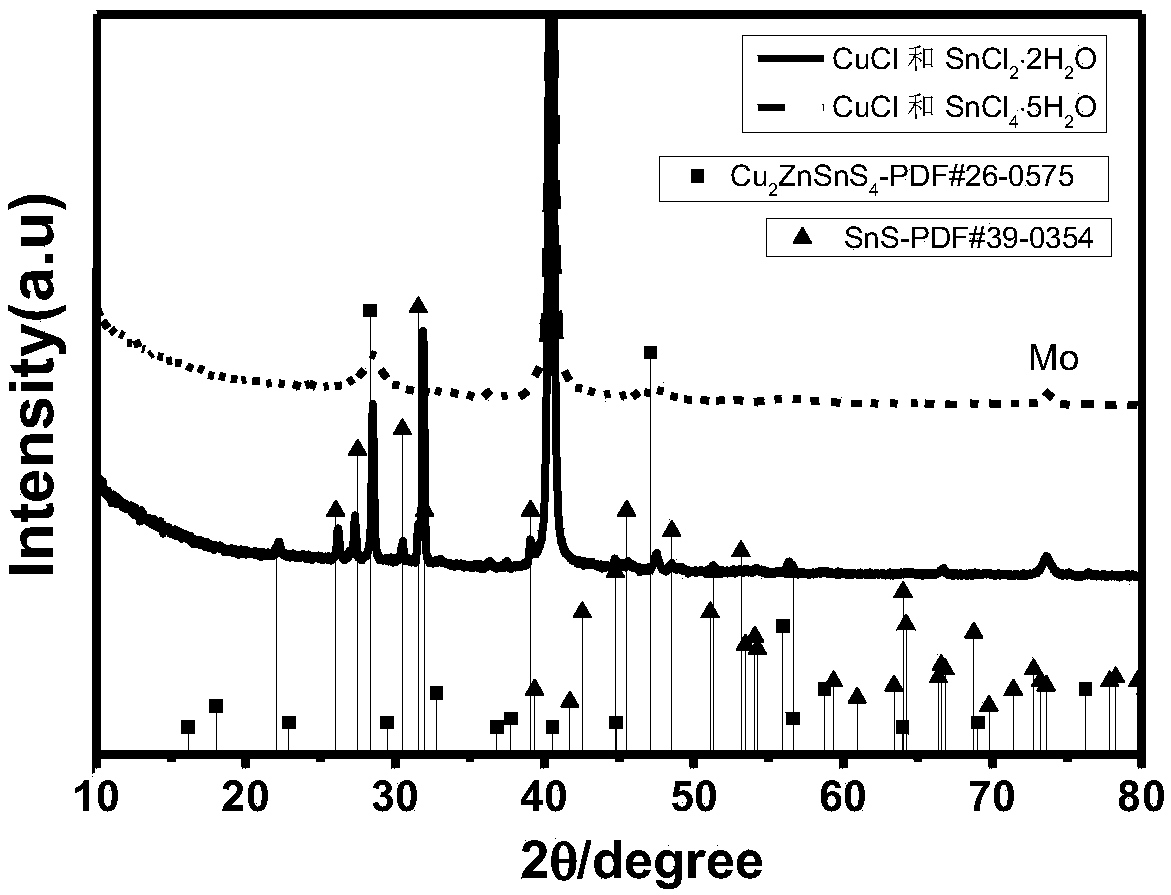
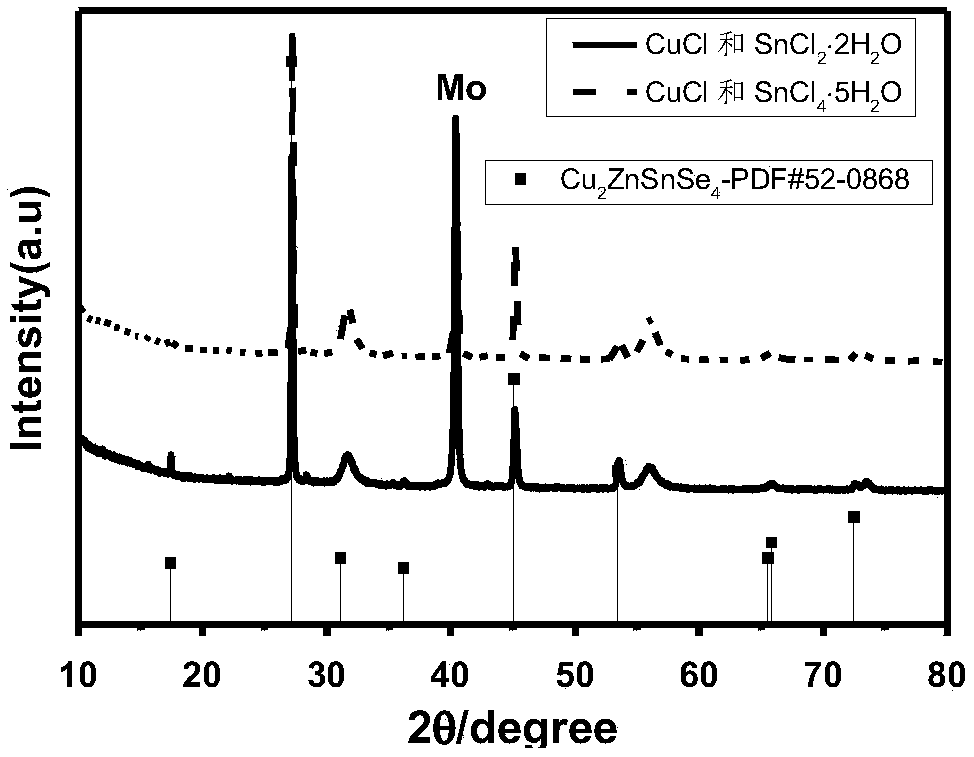
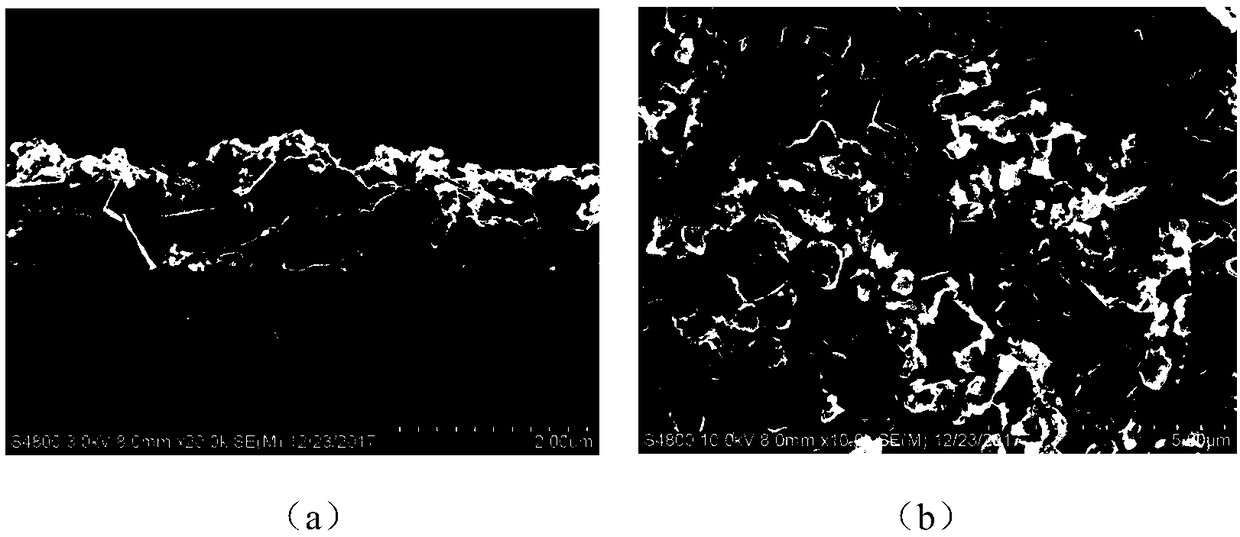
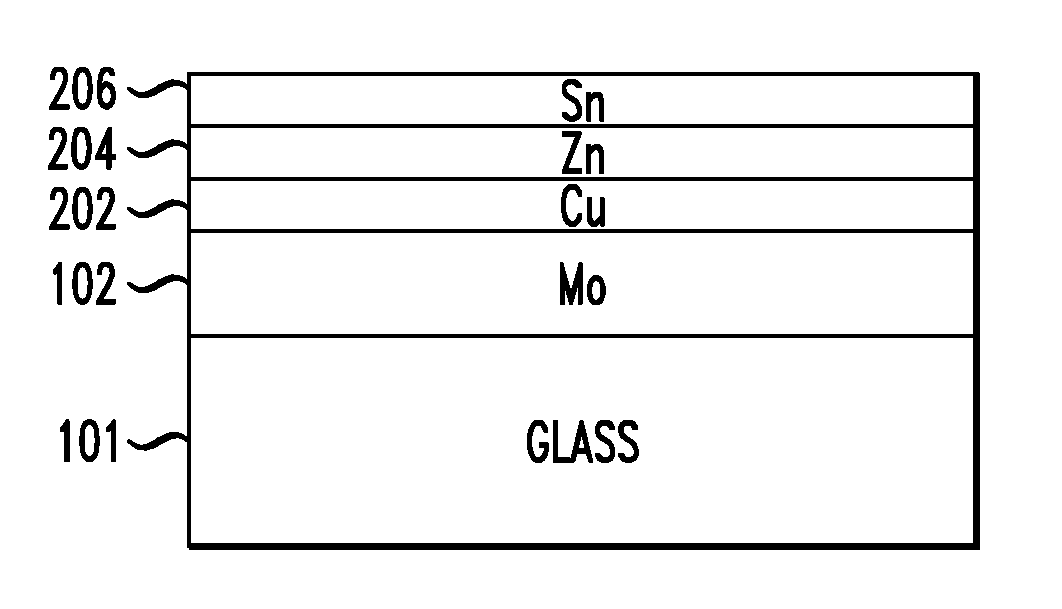Patents
Literature
152 results about "CZTS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
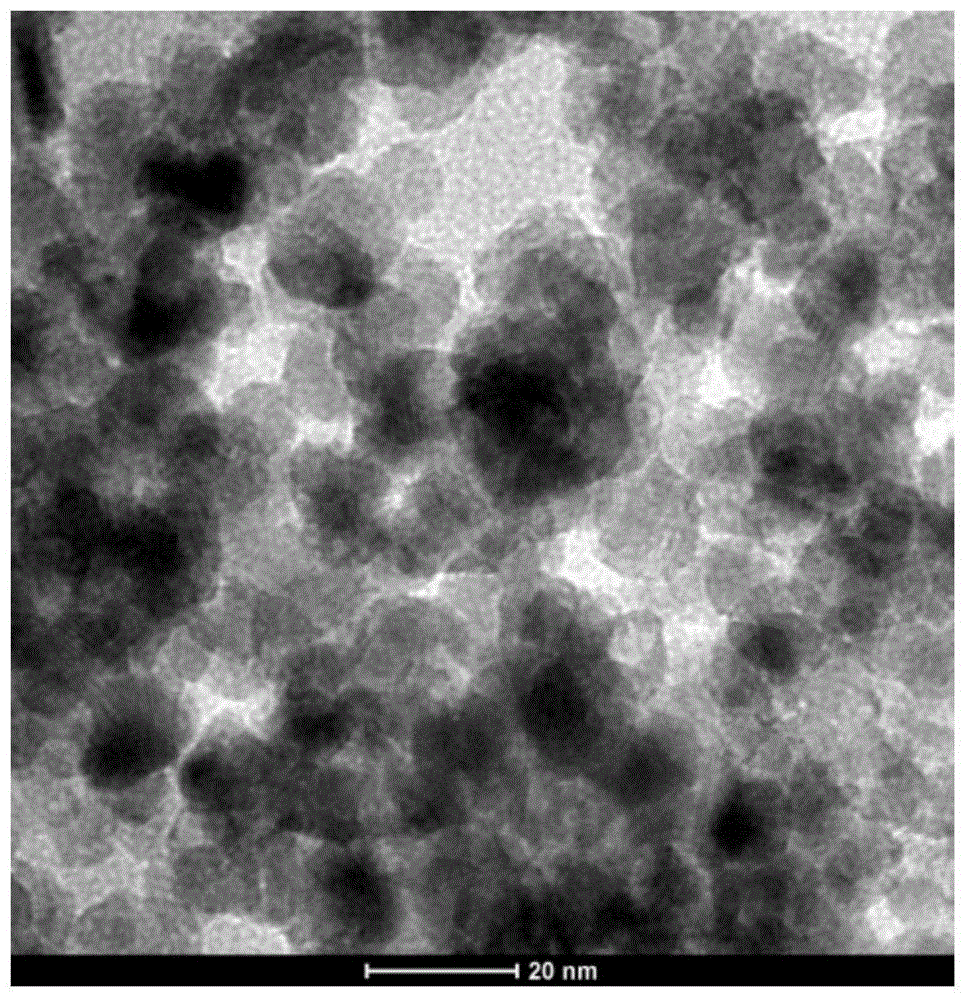
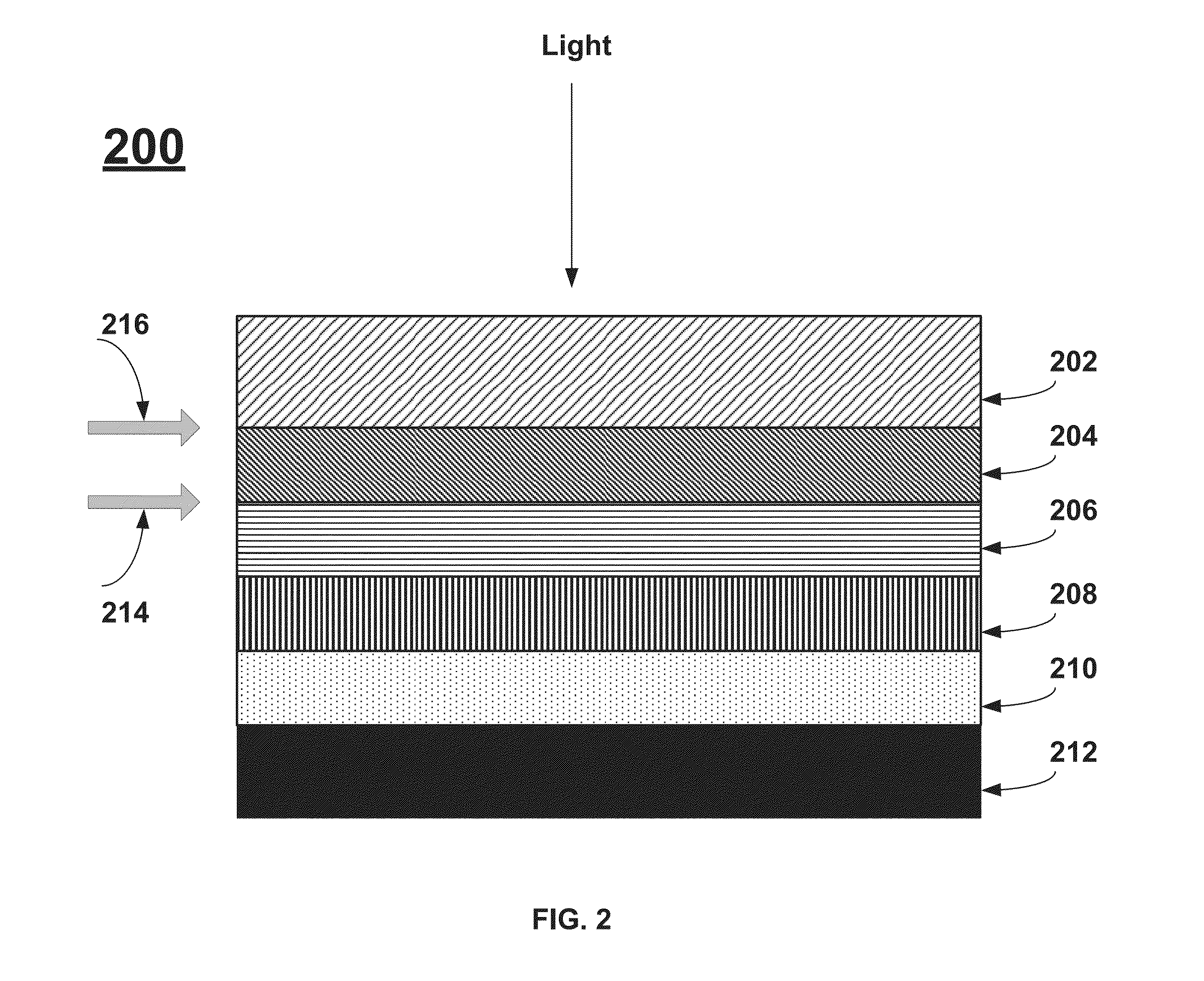
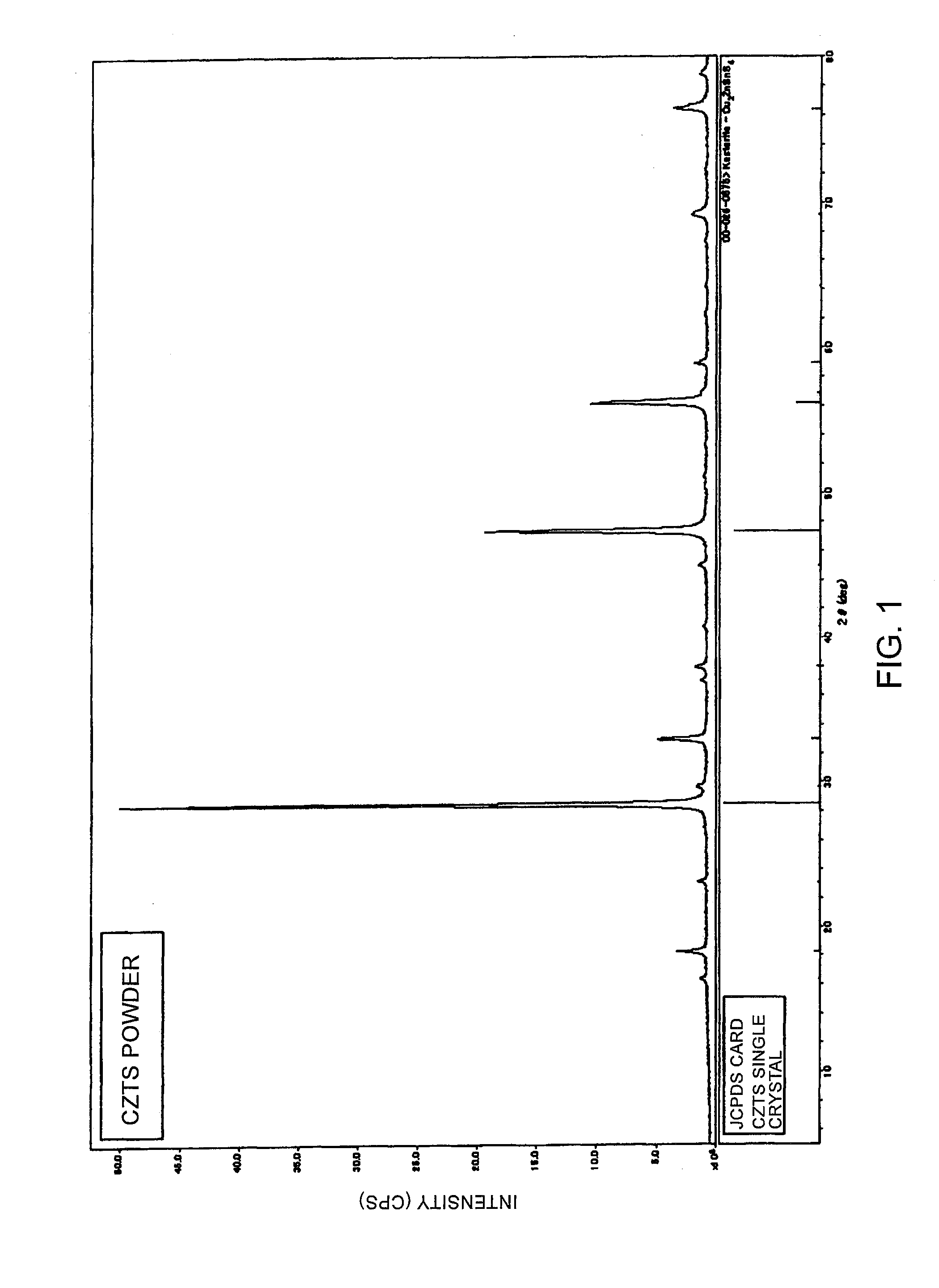
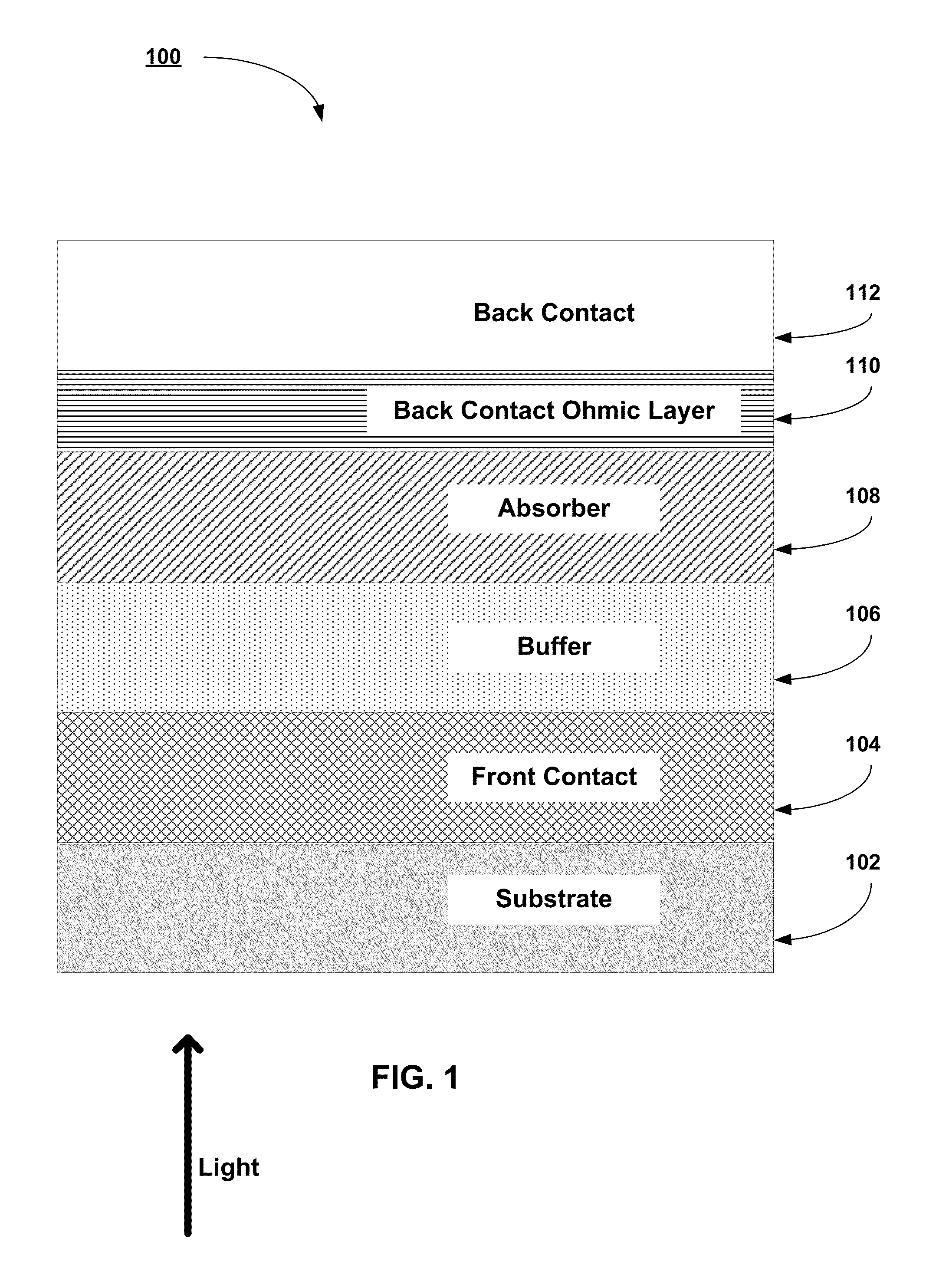
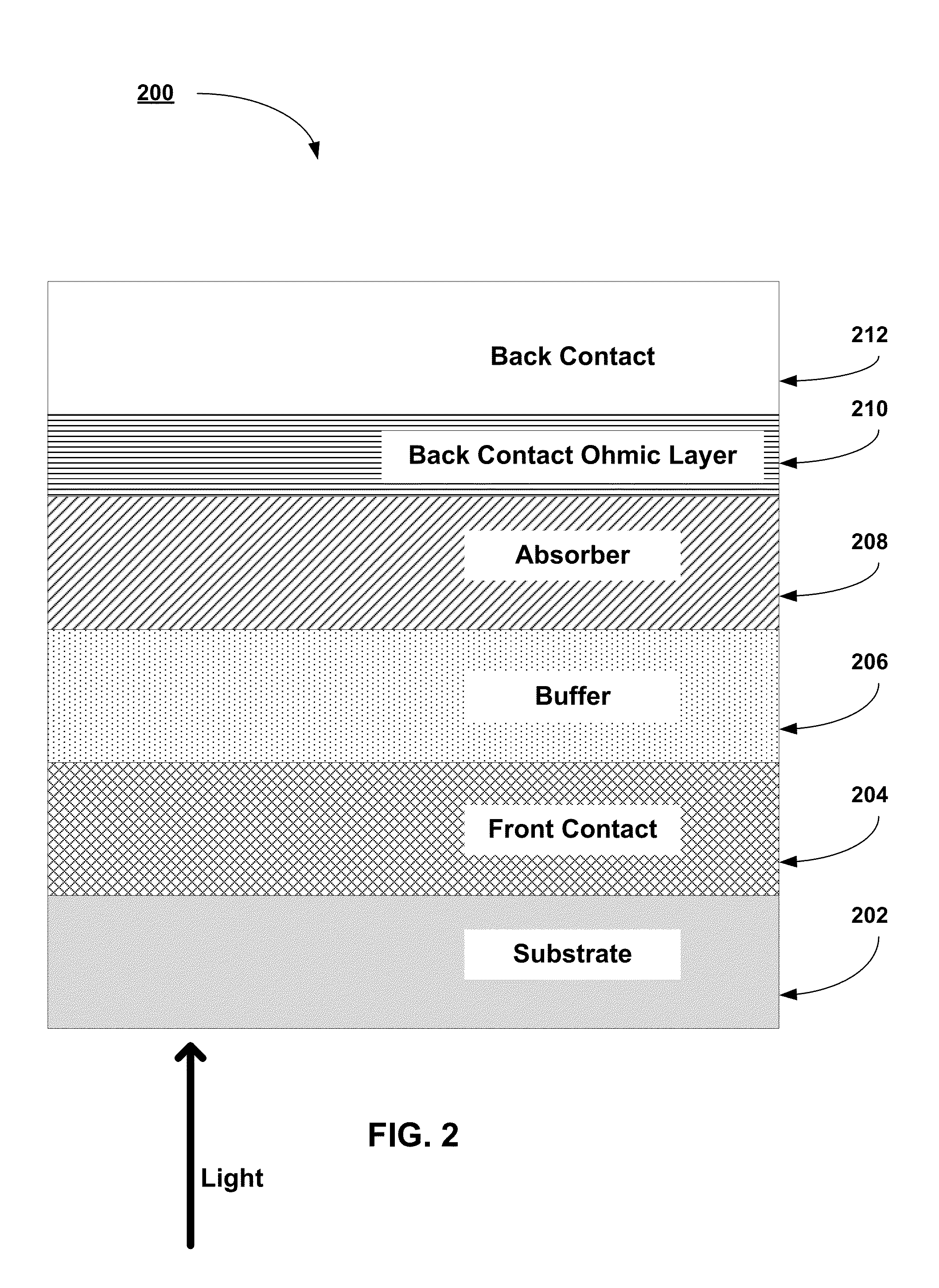
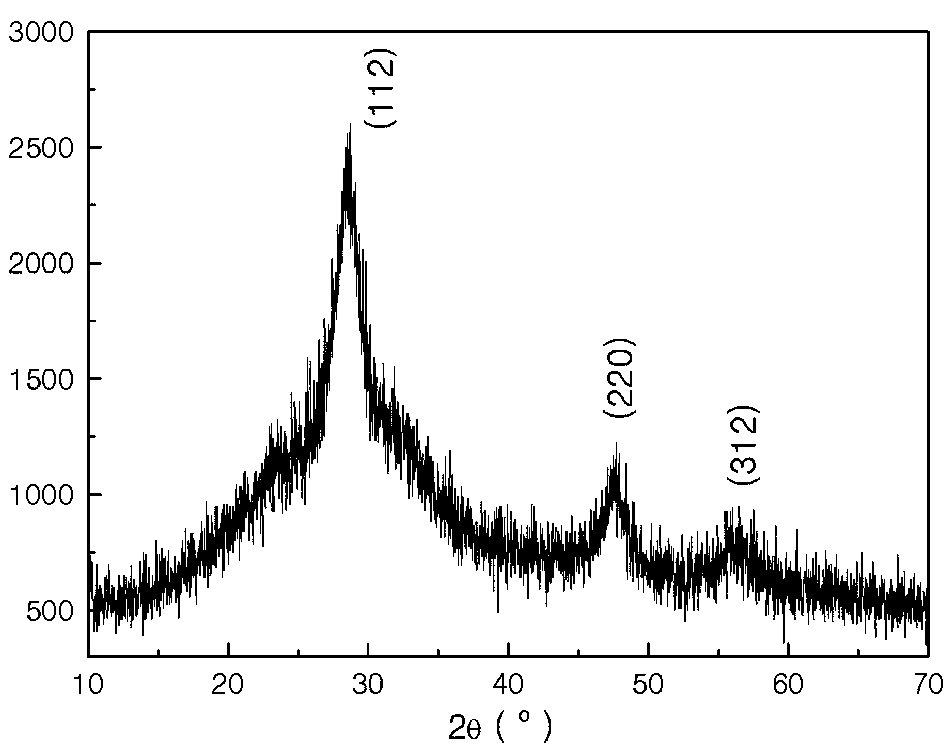
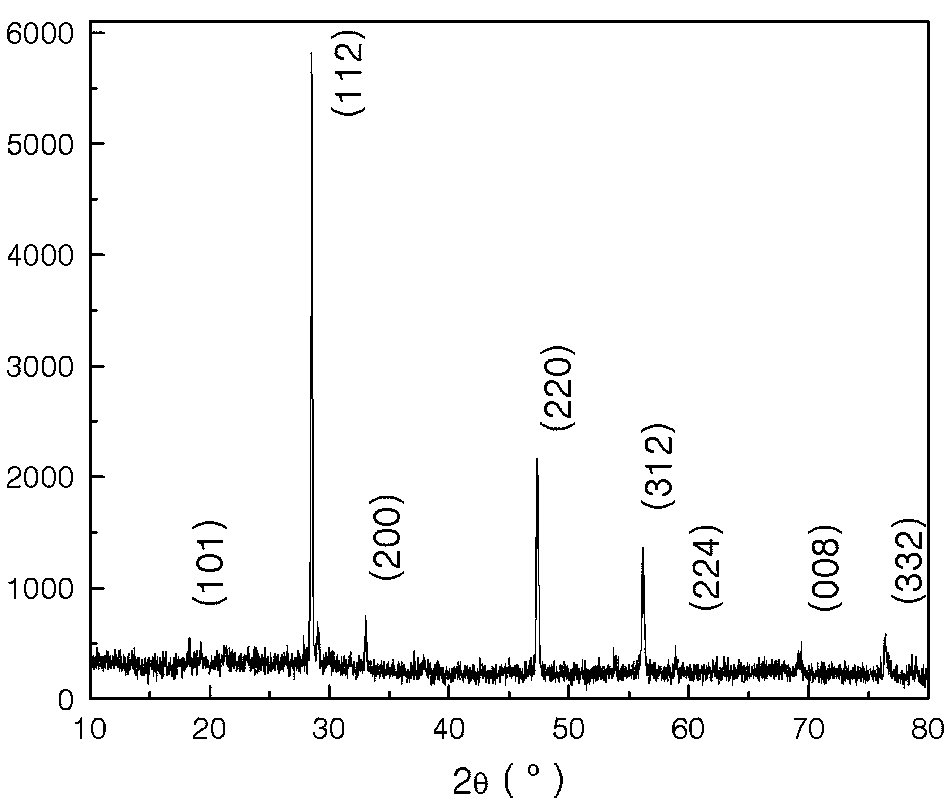
Copper zinc tin sulfide (CZTS) is a quaternary semiconducting compound which has received increasing interest since the late 2000s for applications in thin film solar cells. The class of related materials includes other I₂-II-IV-VI₄ such as copper zinc tin selenide (CZTSe) and the sulfur-selenium alloy CZTSSe. CZTS offers favorable optical and electronic properties similar to CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide) making it well suited for use as a thin-film solar cell absorber layer, but unlike CIGS (or other thin films such as CdTe), CZTS is composed of only abundant and non-toxic elements. Concerns with the price and availability of indium in CIGS and tellurium in CdTe, as well as toxicity of cadmium have been a large motivator to search for alternative thin film solar cell materials. Recent material improvements for CZTS have increased the efficiency to 12.6% in laboratory cells, but more work is needed for their commercialization.
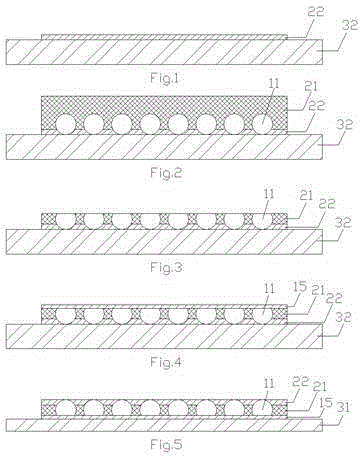
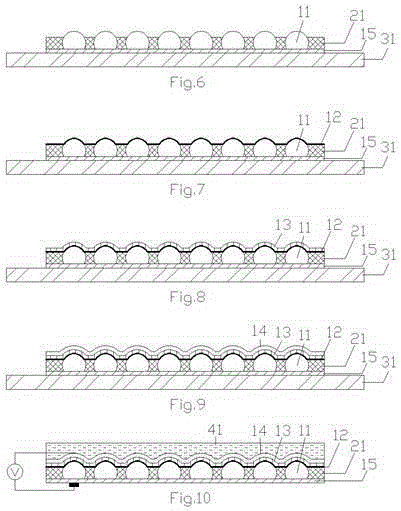
Copper zincium tin sulfur compound semiconductor thin-film solar cell and manufacturing method
InactiveCN101452969ALow costNo pollution in the processFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSolar batteryAbsorption layer
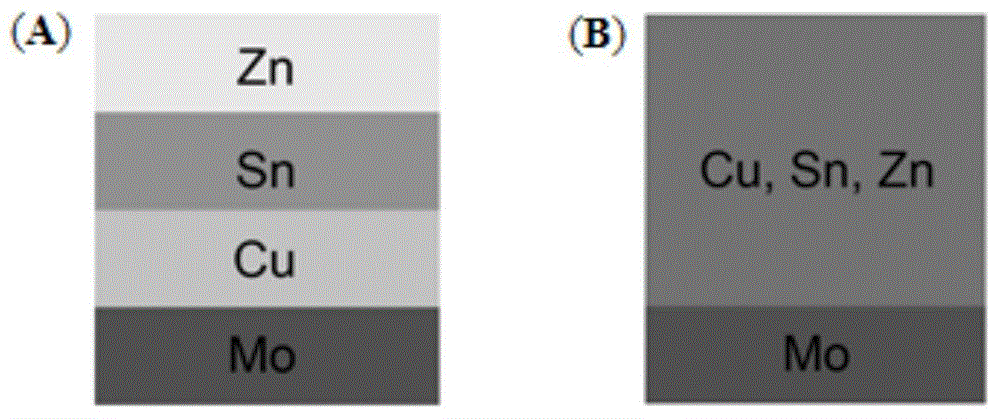
The invention discloses a Cu-Zn-Sn-S compound semiconductor-film solar battery and a preparation method. The battery comprises a glass substrate, wherein a metal back electrode layer, a P-type Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) absorption layer, an n-type CdS buffer layer and a transparent conducting oxide film window layer are sequentially deposited on the glass substrate. The method comprises special aftertreatment for the P-type Cu2ZnSnS4 absorption layer. The preparation method has the advantage of substituting CZTS for CIGS as the novel material of the absorption layer of the film solar battery. As the abundance of Zn and Sn in the CZTS in earth crust is 75 ppm and 2.2 ppm respectively, the solar battery has the advantages of rich resources, no toxic components and environmental friendliness, thereby becoming the novel film solar battery with the highest development potential, low cost and no pollution.
Owner:上海太阳能电池研究与发展中心
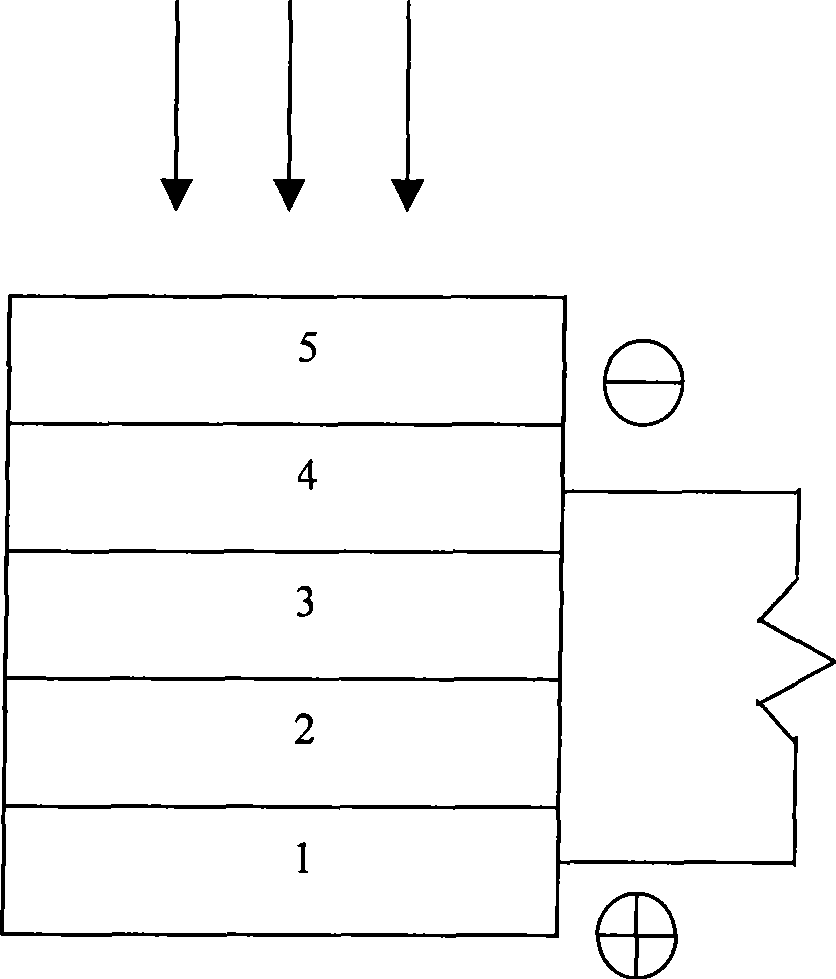
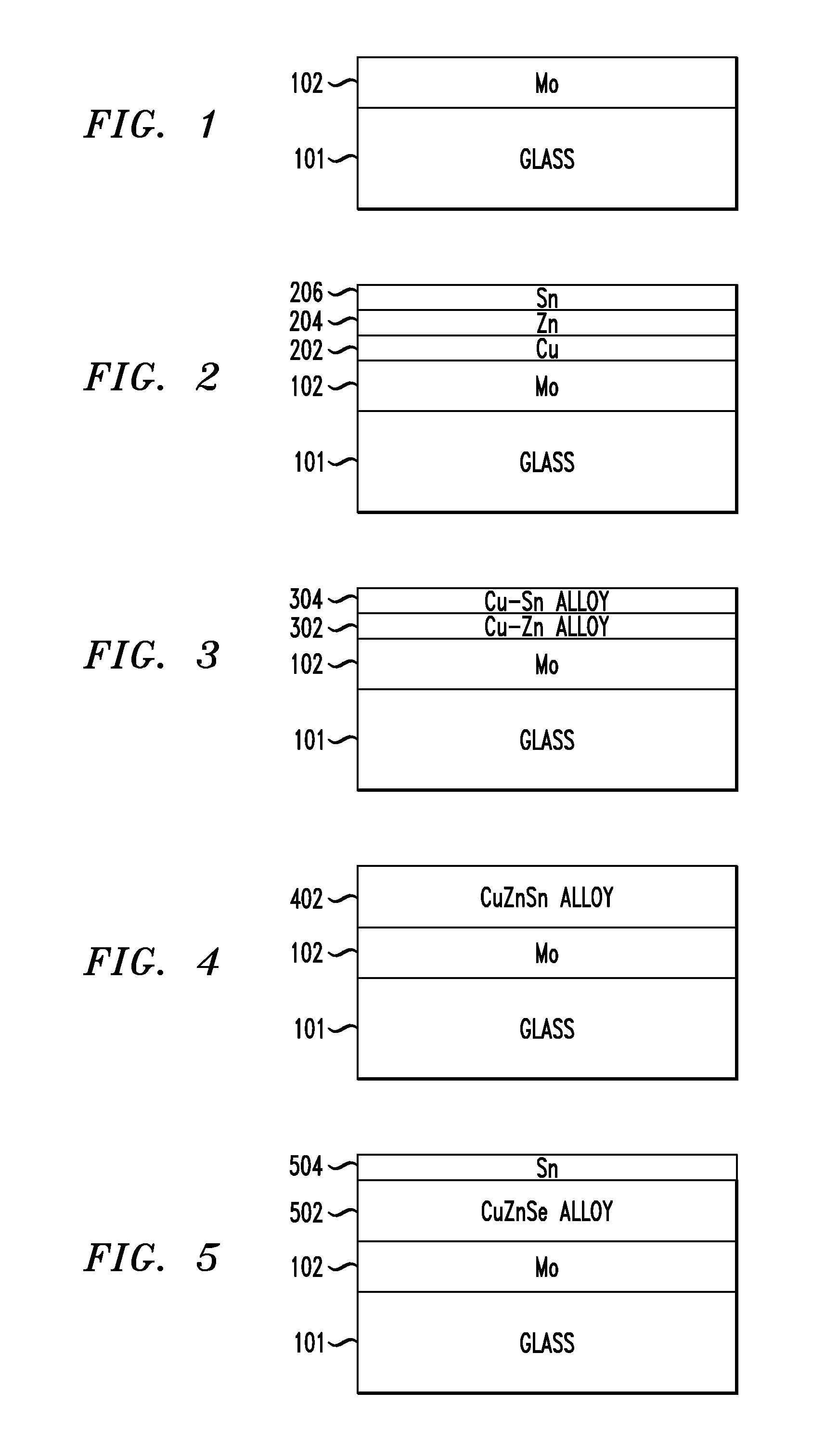
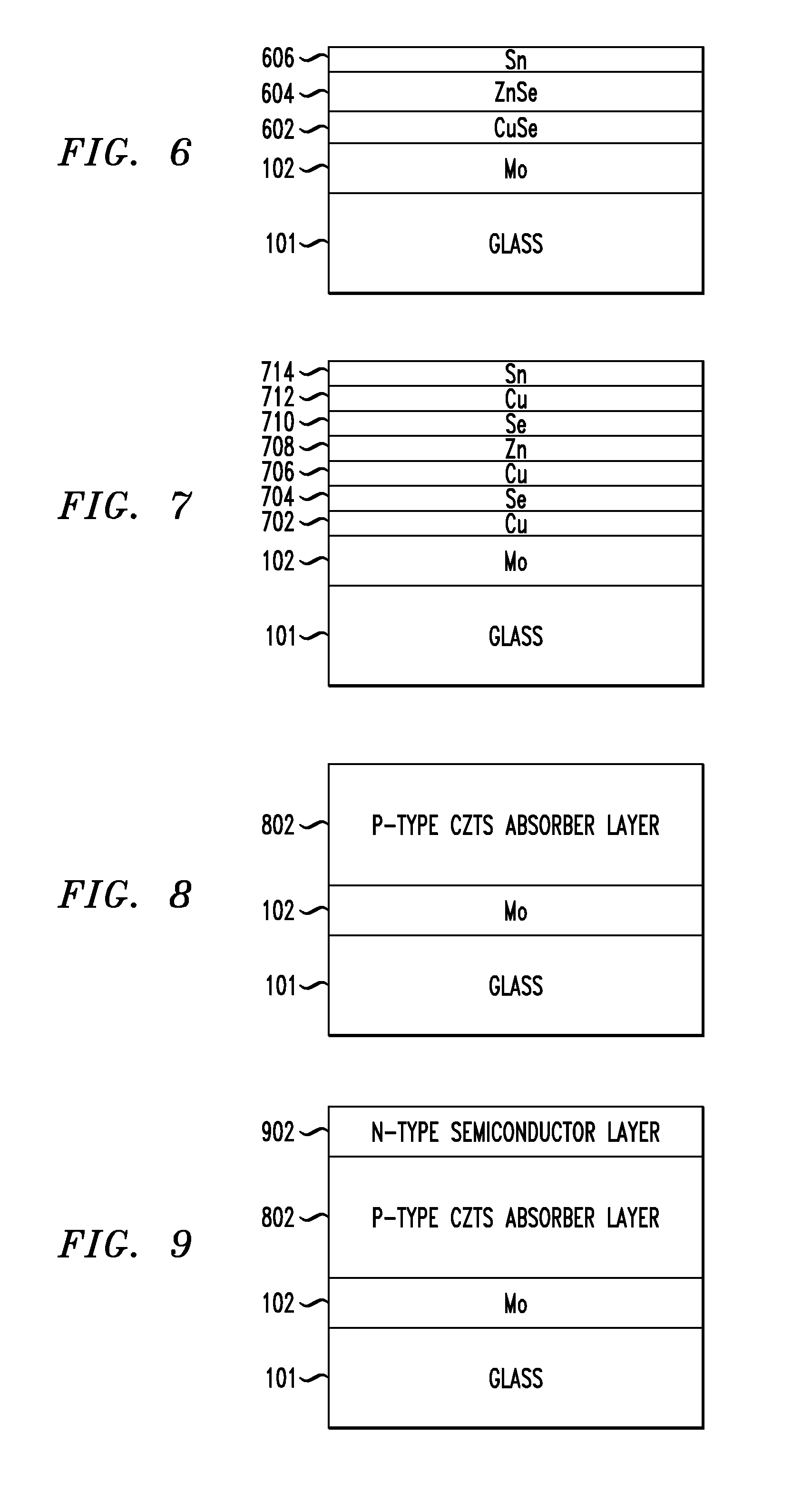
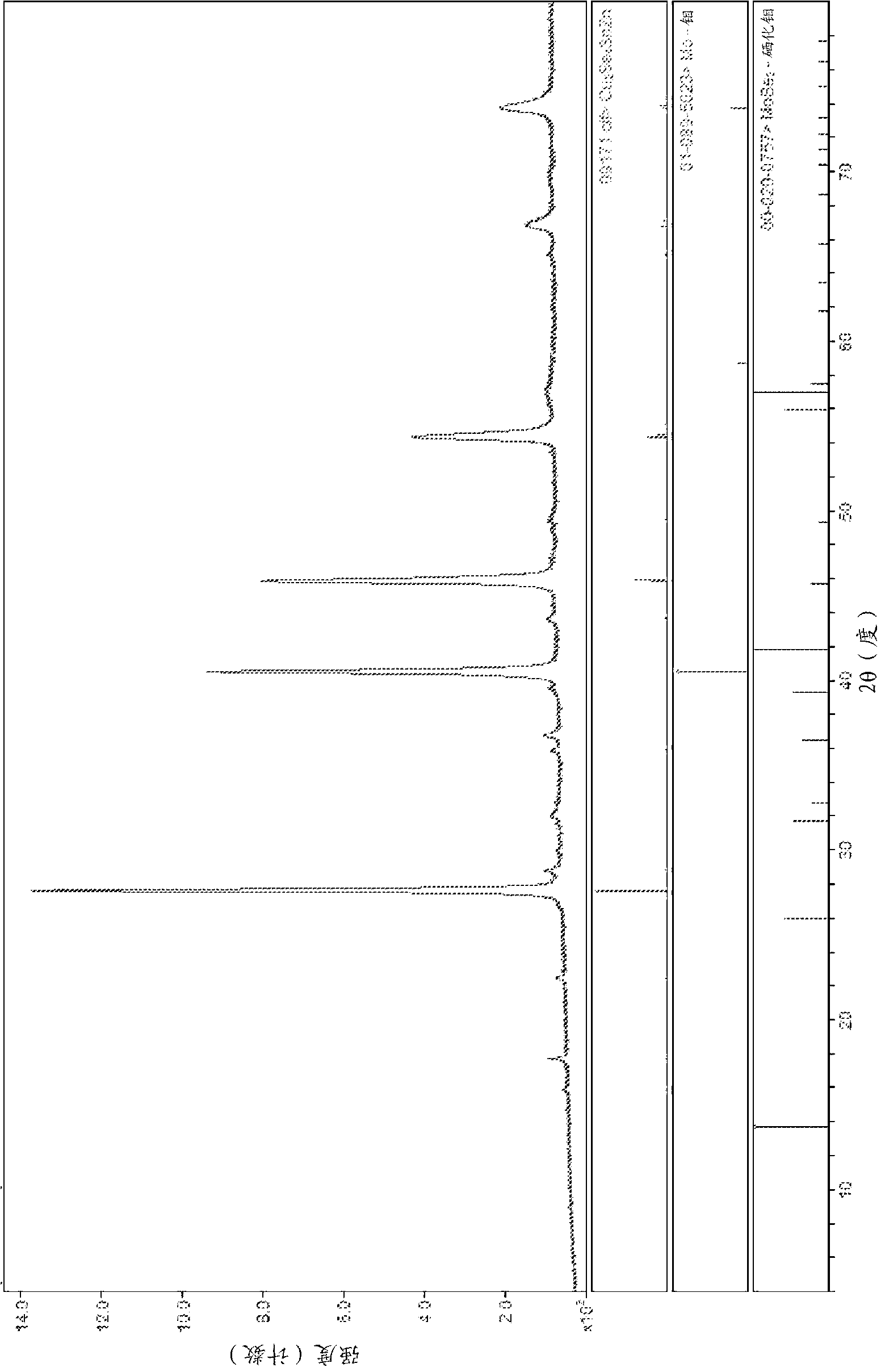
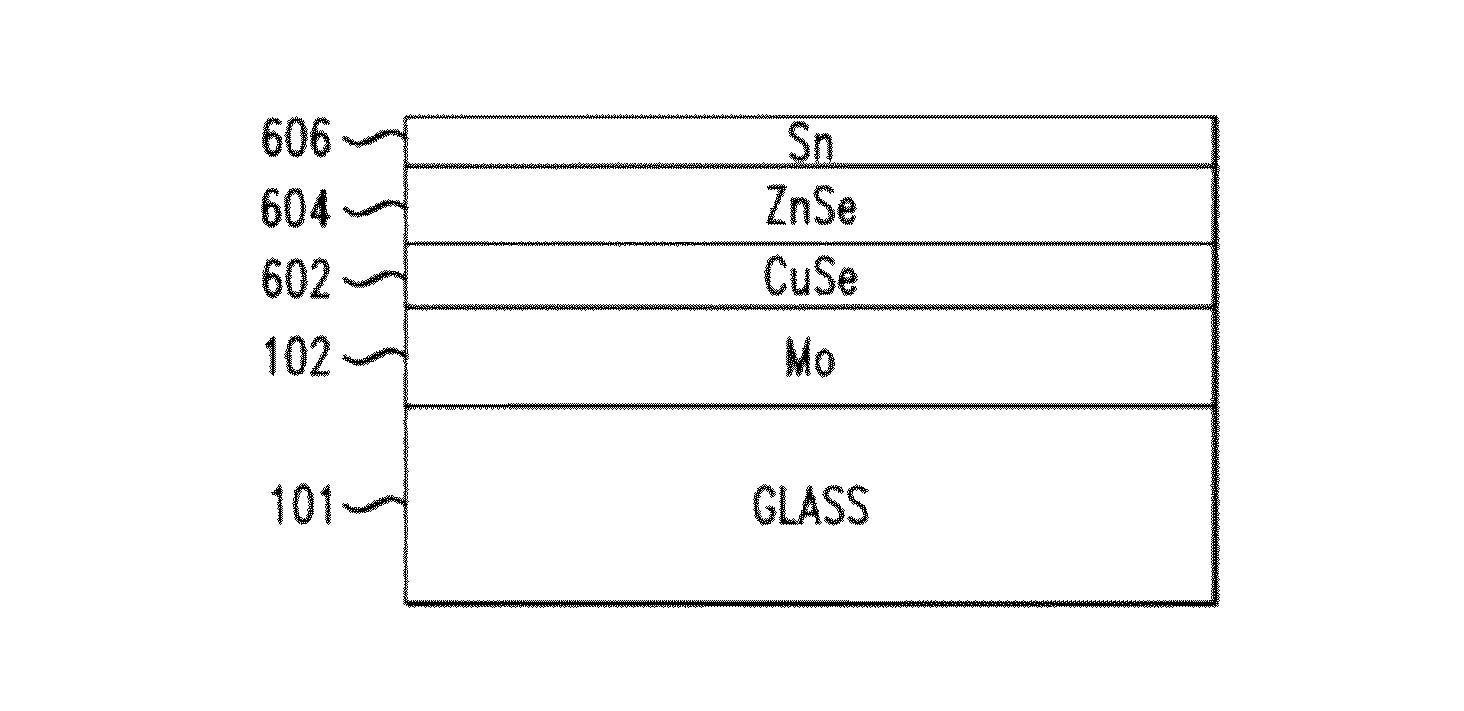
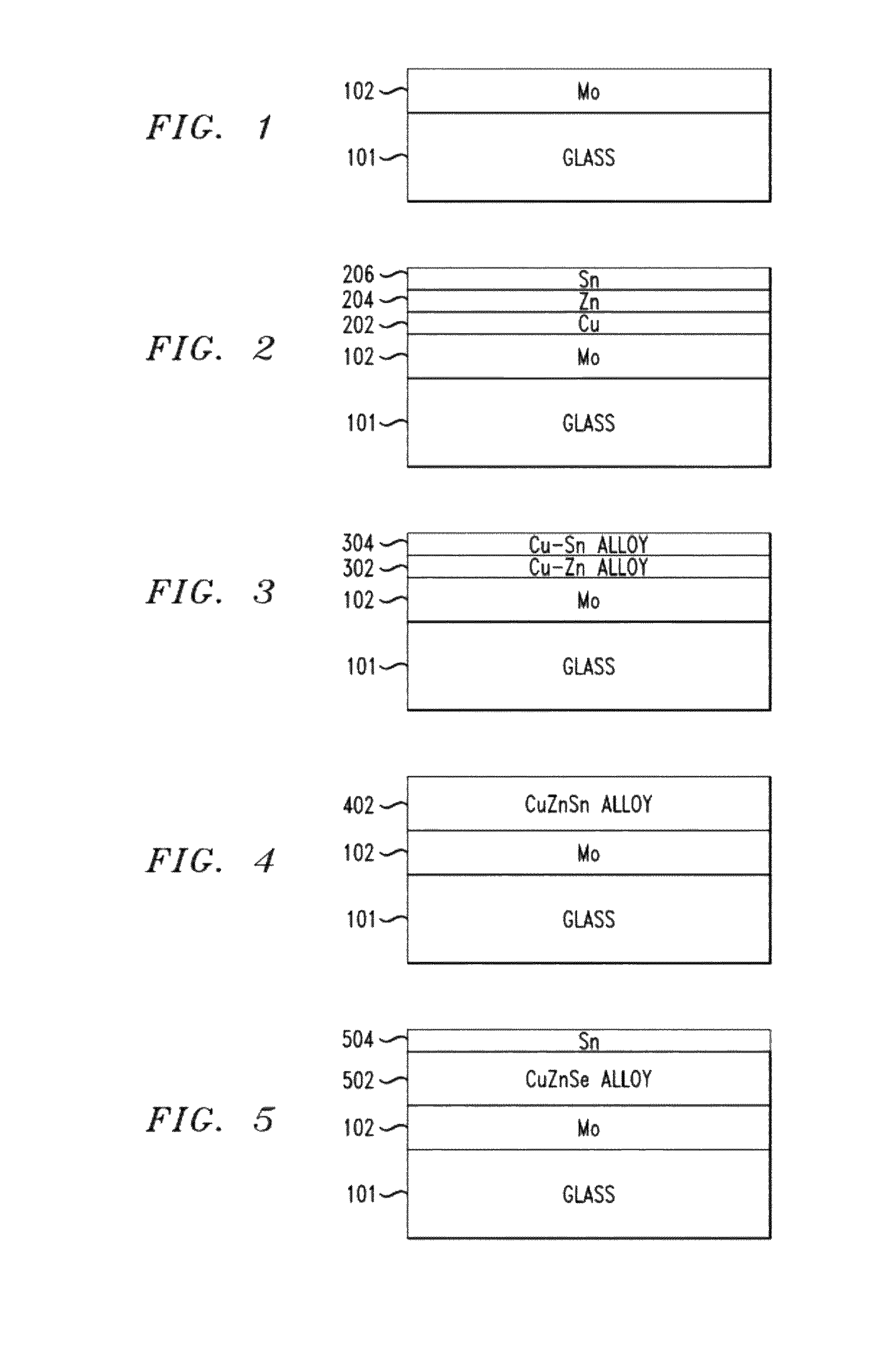
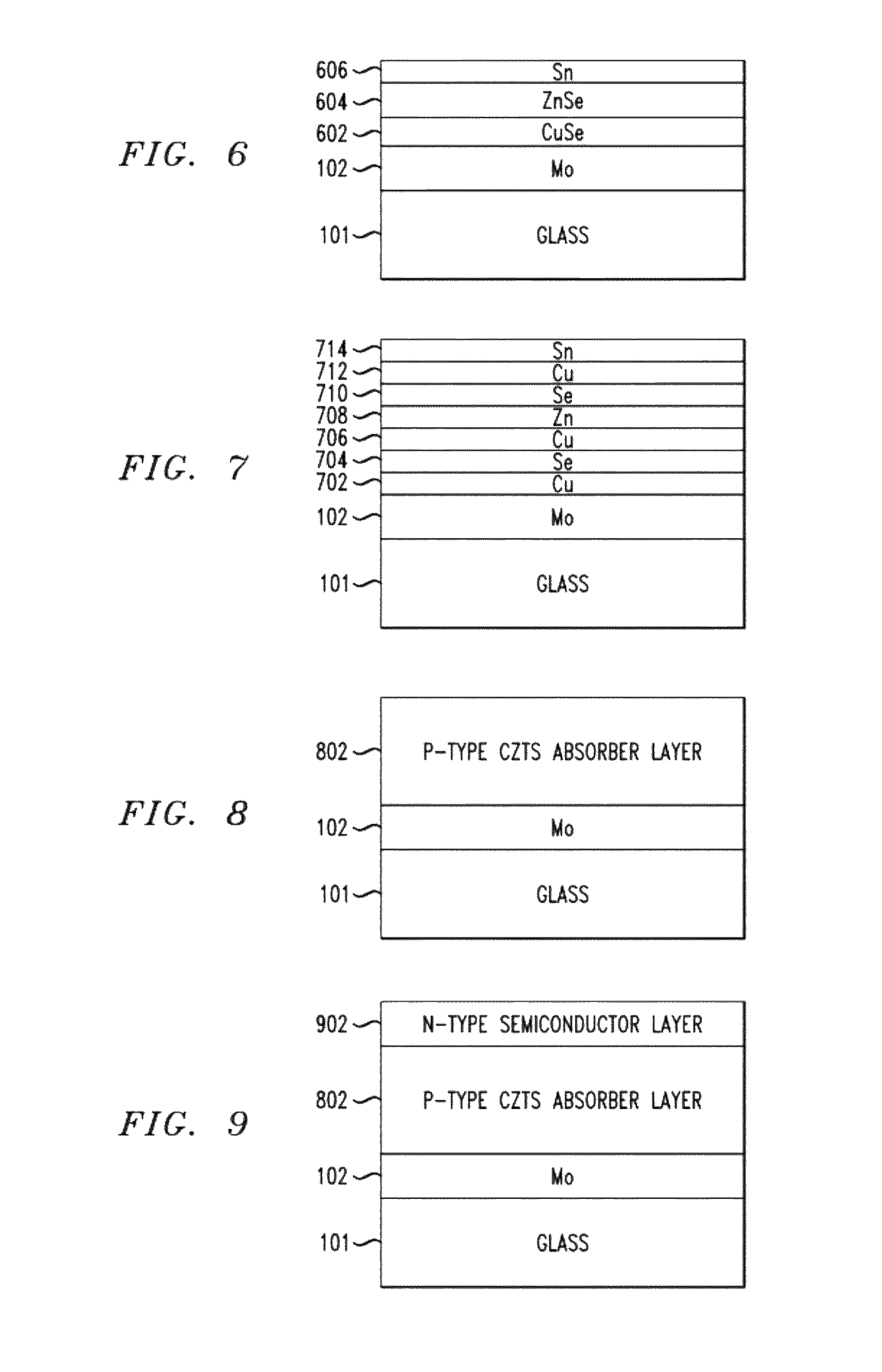
Structure and Method of Fabricating a CZTS Photovoltaic Device by Electrodeposition
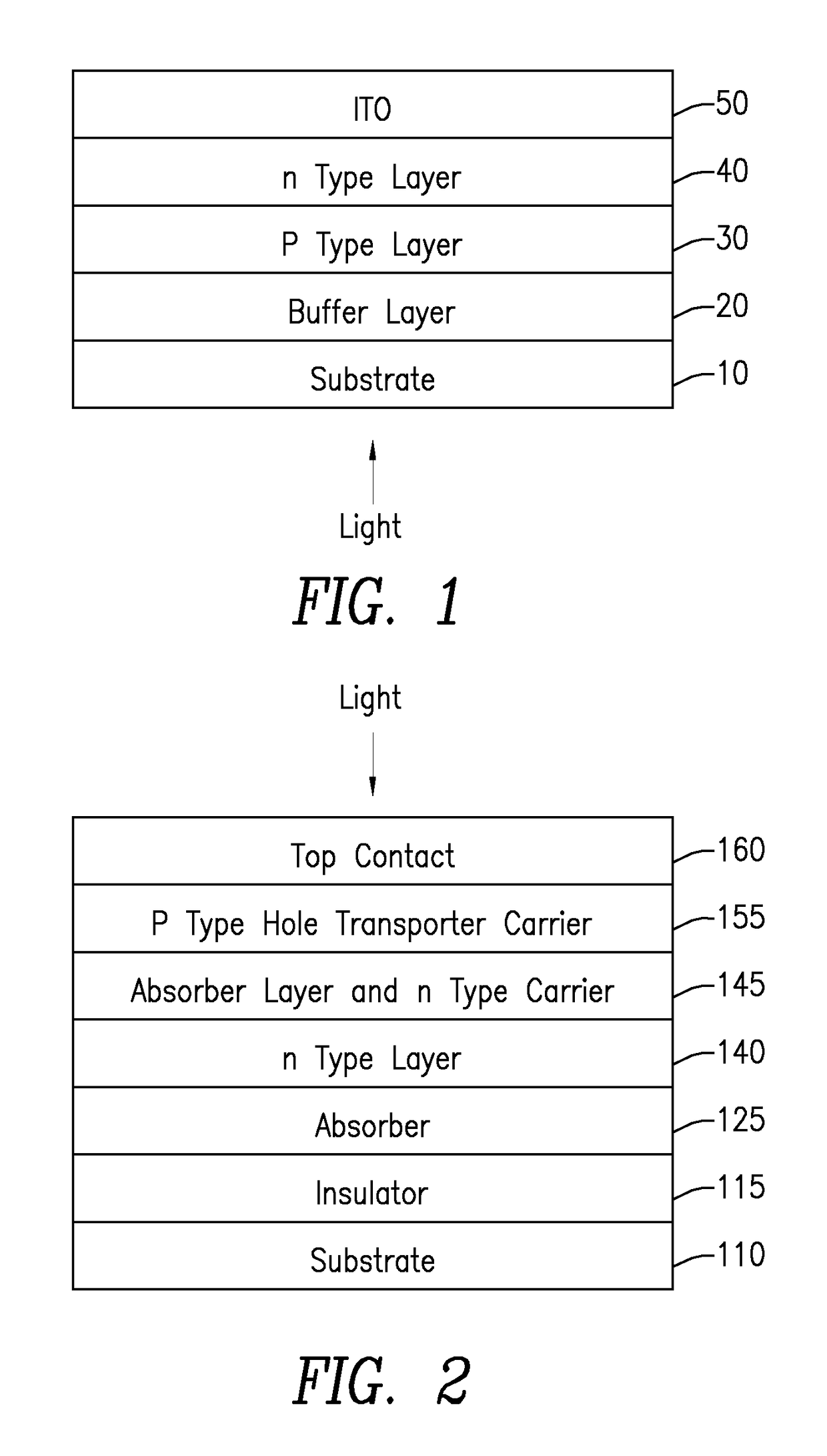
Techniques for using electrodeposition to form absorber layers in diodes (e.g., solar cells) are provided. In one aspect, a method for fabricating a diode is provided. The method includes the following steps. A substrate is provided. A backside electrode is formed on the substrate. One or more layers are electrodeposited on the backside electrode, wherein at least one of the layers comprises copper, at least one of the layers comprises zinc and at least one of the layers comprises tin. The layers are annealed in an environment containing a sulfur source to form a p-type CZTS absorber layer on the backside electrode. An n-type semiconductor layer is formed on the CZTS absorber layer. A transparent conductive layer is formed on the n-type semiconductor layer. A diode is also provided.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method for preparation of metal chalcogenide solar cells on complexly shaped surfaces
InactiveUS20120100660A1Electrolytic coatingsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumMetal chalcogenides
Methods for fabricating a photovoltaic device on complexly shaped fabricated objects, such as car bodies are disclosed. Preferably the photovoltaic device includes absorber layers comprising Copper, Indium, Gallium, Selenide (CIGS) or Copper, Zinc, Tin, Sulfide (CZTS). The method includes the following steps: a colloidal suspension of metal surface-charged nanoparticles is formed; electrophoretic deposition is used to deposit the nanopartieles in a metal thin film onto a complexly shaped surface of the substrate; the metal thin film is heated in the presence of a chalcogen source to convert the metal thin film into a metal chalcogenide thin film layer; a buffer layer is formed on the metal chalcogenide thin film layer using a chemical bath deposition; an intrinsic zinc oxide insulating layer is formed adjacent to a side of the buffer layer, opposite the metal chalcogenide thin film layer, by chemical vapor deposition; and finally, a transparent conducting oxide is formed adjacent to a side of the intrinsic zinc oxide, opposite the buffer layer, by chemical vapor deposition.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method for preparing copper-zinc-tin-sulfur light absorbing layer of film solar batter
InactiveCN102593252ASimple structureEasy to operateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesAir atmosphereCZTS
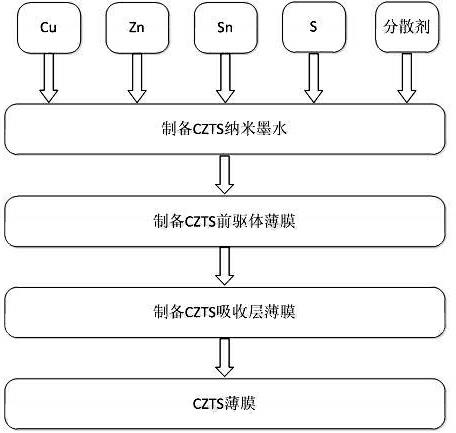
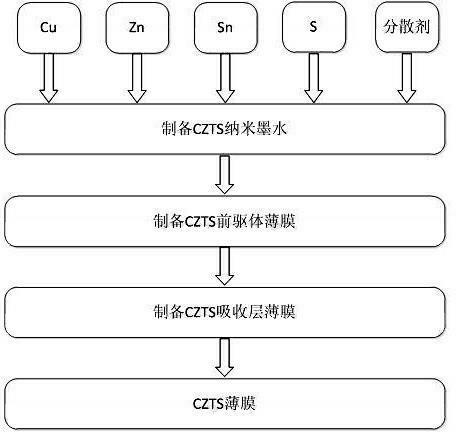
The invention relates to a technology for preparing a film solar battery, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur light absorbing layer. The method for preparing the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur light absorbing layer comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing copper, zinc, tin and sulfur simple substances in a stoichiometric ratio, adding a dispersant into the mixture, fully mixing, and then performing ball milling to obtain a uniformly and stably dispersed copper-zinc-tin-sulfur (CZTS) nano-ink, wherein the mole ratio of Cu atoms to Zn atoms to Sn atoms to S atoms is (1.8-2):(1-1.3):(0.7-1):4, and the mole ratio of the dispersant to the CZTS is (1-1,000):1; (2) coating the CZTS nano-ink on a substrate, and drying in an air atmosphere to remove the dispersant to obtain a CZTS precursor film; and (3) vulcanizing the CZTS precursor film in an inert atmosphere (nitrogen or argon gas atmosphere) to obtain a CZTS light absorbing layer of a solar battery. According to the method for preparing the CZTS light absorbing layer, the equipment structure is simple, the operation is easy, the production efficiency is high, the problems of cost and environmental pollution are fundamentally solved, and a new train of thought for large-scale industrialization of CZTS-based film solar batteries is widened.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High efficiency CZTSe by a two-step approach
InactiveUS20140113403A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationSputteringCZTS
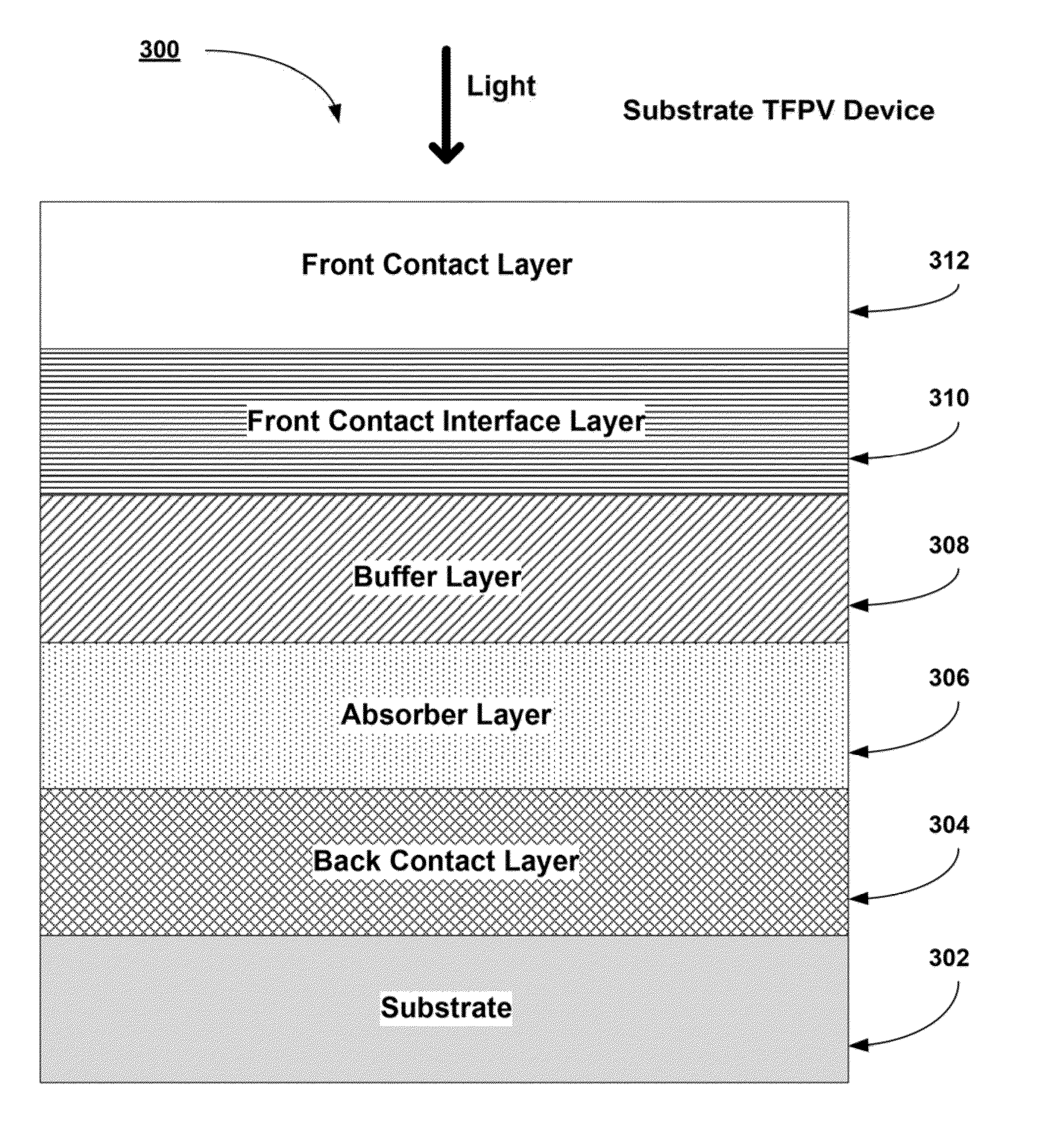
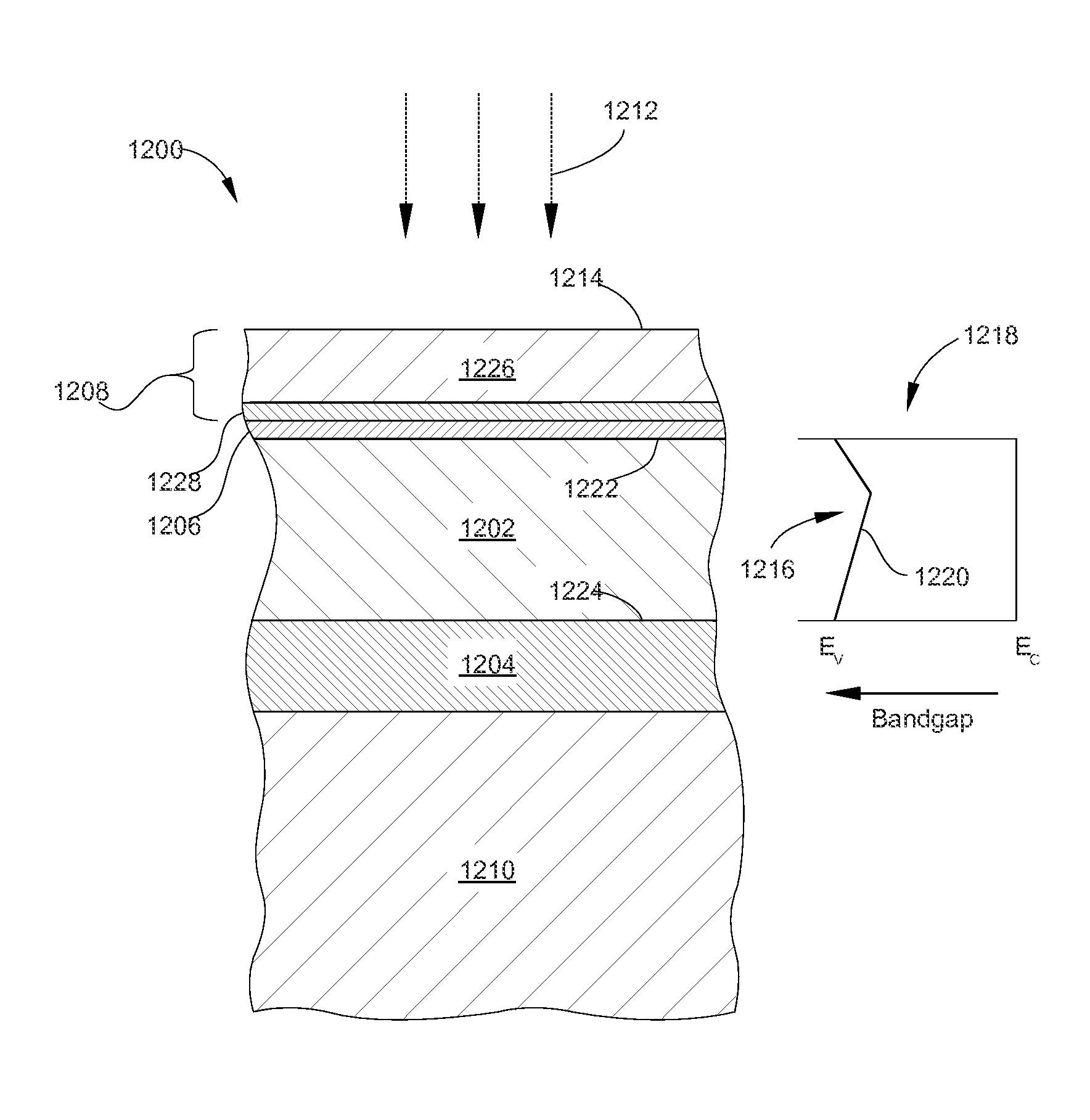
Methods of forming CZTS absorber layers in a TFPV device with a graded bandgap with or without a graded concentration are provided. In general, a Cu—Zn—Sn—(S, Se) precursor film is formed by sputtering. The Cu—Zn—Sn—(S, Se) precursor film can be formed as a single layer or as a multilayer stack. The composition may be uniform or graded throughout the thickness of the film. In some embodiments, the sputtering is performed in a reactive atmosphere including a chalcogen source (e.g. H2S, H2Se, etc.). The films, in conjunction with a subsequent selenization or anneal process, are converted to an absorber layer.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
High efficiency thin film tandem solar cells and other semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20170271622A1Layer is highTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorTandem solar cell
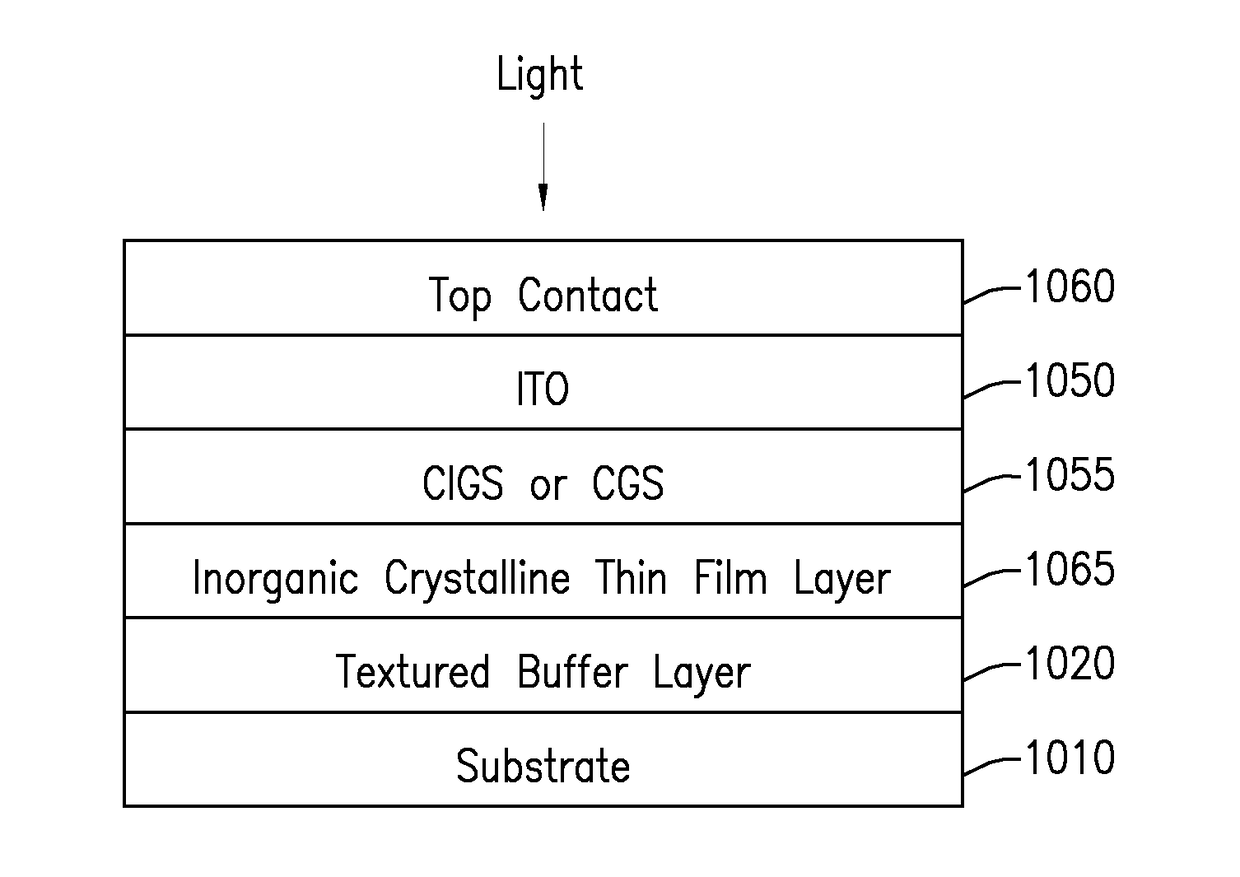
Architectures for tandem solar cell including two thin films forming a top layer and a bottom layer. Such cells can be bi-facial. Exemplary materials used for the top layer are CIGS (CGS), perovskites (Sn and Ge), amorphous silicon (a-Si), copper oxide, tin sulfide, CZTS and III-V materials. For the bottom layer an inorganic film such as either silicon or germanium may be used. In general, the architecture includes of a glass, plastic or metal substrate and a buffer layer, either an oxide insulator or nitride conductor.
Owner:SOLAR TECTIC
Thin-film solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101840942ASimple structureSimple processFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationAbsorption layerTin
The invention discloses a thin-film solar cell and a manufacturing method thereof. The thin-film solar cell sequentially comprises a glass substrate, a molybdenum back electrode, a copper-zinc- tin-sulfur (Cu2ZnSnS4,CZTS) light absorption layer, a zinc sulfide (ZnS) buffer layer, a zinc-aluminum oxide (ZAO) window layer and a nickel-aluminum top electrode from bottom to top. The invention avoids the use of rare and precious metals and toxic elements, also realizes the vacuum deposition of each layer of thin film of the CZTS thin-film solar cell and simultaneously has the advantages of simple structure and manufacturing process, high photoelectric conversion efficiency, good stability and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN DANBANG INVESTMENT GROUP
Absorbers For High-Efficiency Thin-Film PV
InactiveUS20130164918A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationCZTSChemistry
Methods are described for forming CZTS absorber layers in TFPV devices with graded compositions and graded bandgaps. Methods are described for utilizing at least one of Zn, Ge, or Ag to alter the bandgap within the absorber layer. Methods are described for utilizing Te, S, Se, O, Cd, Hg, or Sn to alter the bandgap within the absorber layer. Methods are described for utilizing either a 2-step process or a 4-step process to alter the bandgap within the absorber layer.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Preparation method of ZnS-cladded ZnO nanoarray core-shell structure
InactiveCN102800747AImprove adhesion strengthImprove transmittanceZinc oxides/hydroxidesFinal product manufactureSolar batteryZinc nitrate
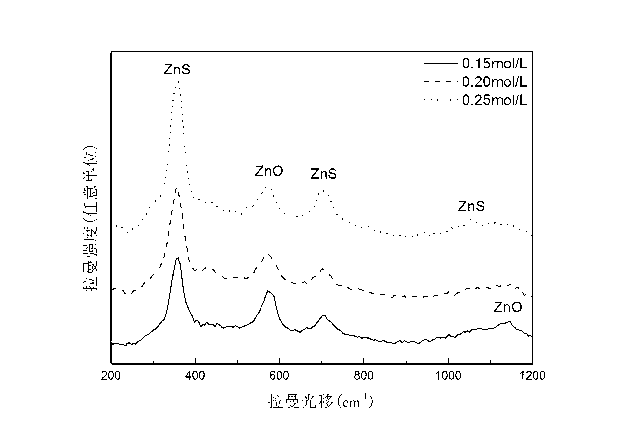
The invention relates to a method for preparing ZnO seed crystal by utilizing a magnetron sputtering method, growing a ZnO nanoarray by utilizing a hydrothermal method and growing a ZnS shell structure by utilizing the hydrothermal method through vulcanization. The grown ZnO @ ZnS nanoarray core-shell structure can be used as a window layer of a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur (CZTS) solar cell. The method belongs to the technical field of preparation process of solar cell thin-film devices. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly adopting the magnetron sputtering method for sputtering ZnO seed crystal on fluorine-doped SnO2 conductive glass (FTO), then using a vacuum tube furnace for thermal treatment on the seed crystal in a N2 atmosphere at the temperature of 400 DEG C for 20 minutes, then growing the ZnO nanoarray through the hydrothermal method with the growth solution of 0.05 mol / L zinc nitrate aqueous solution and 0.05 mol / L methenamine (HMT) aqueous solution, and finally, growing the ZnS shell structure by utilizing the hydrothermal method through vulcanization with the growth solution of 0.05-0.50 mol / L thioacetamide (TAA) aqueous solution, vulcanizing for 1-9 hours in a hydrothermal reaction kettle and taking out, and then putting into a drying oven for drying to obtain the ZnO @ ZnS nanoarray core-shell structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
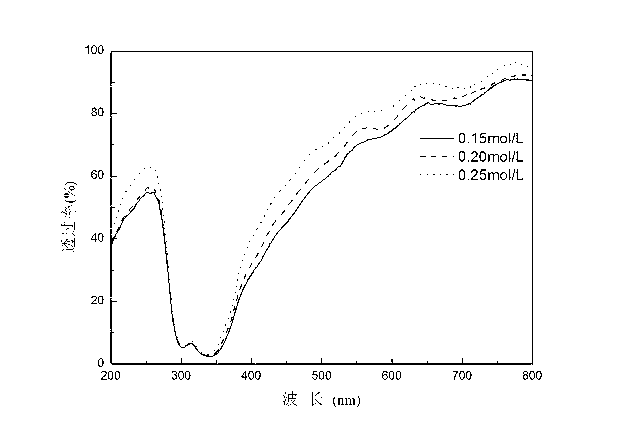
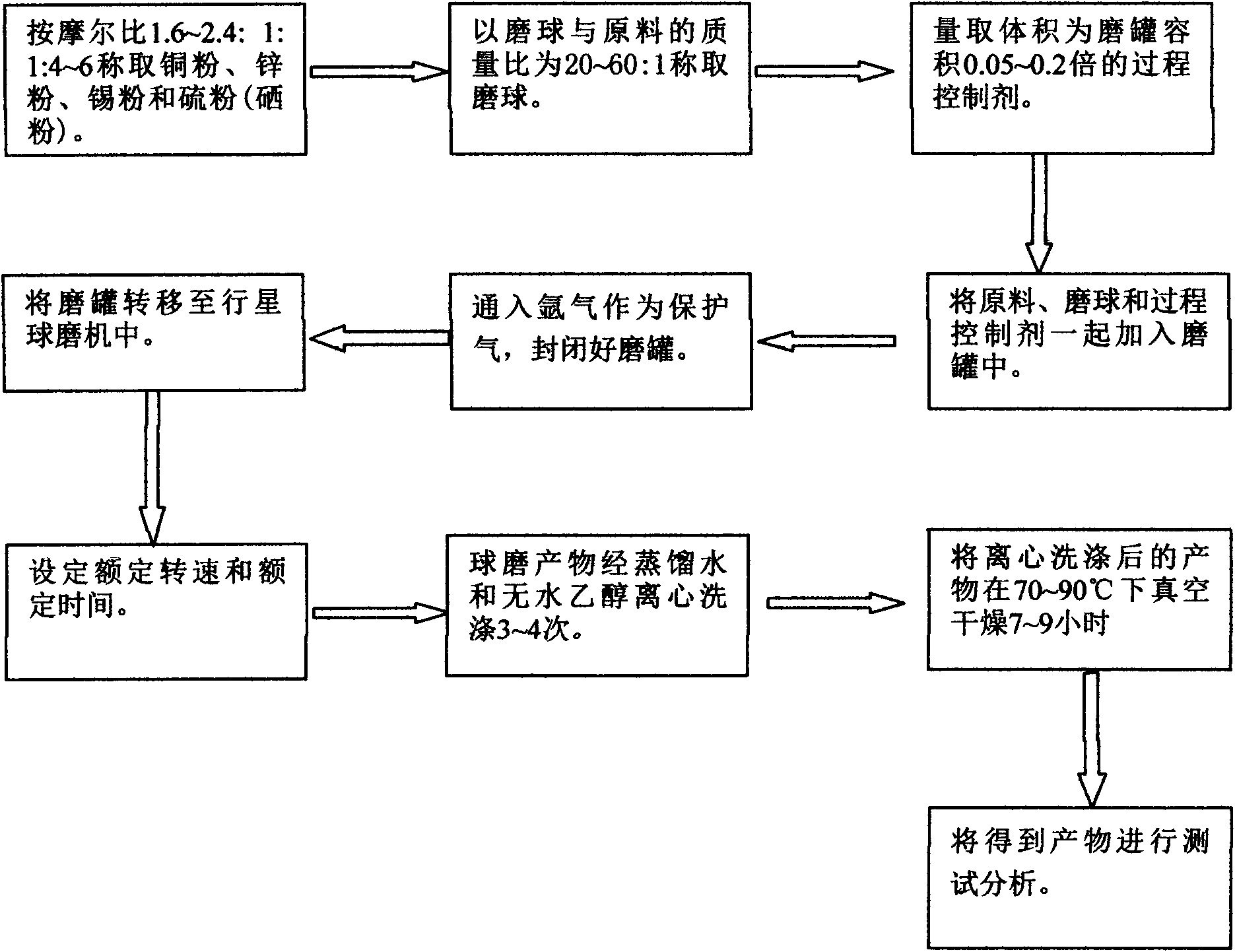
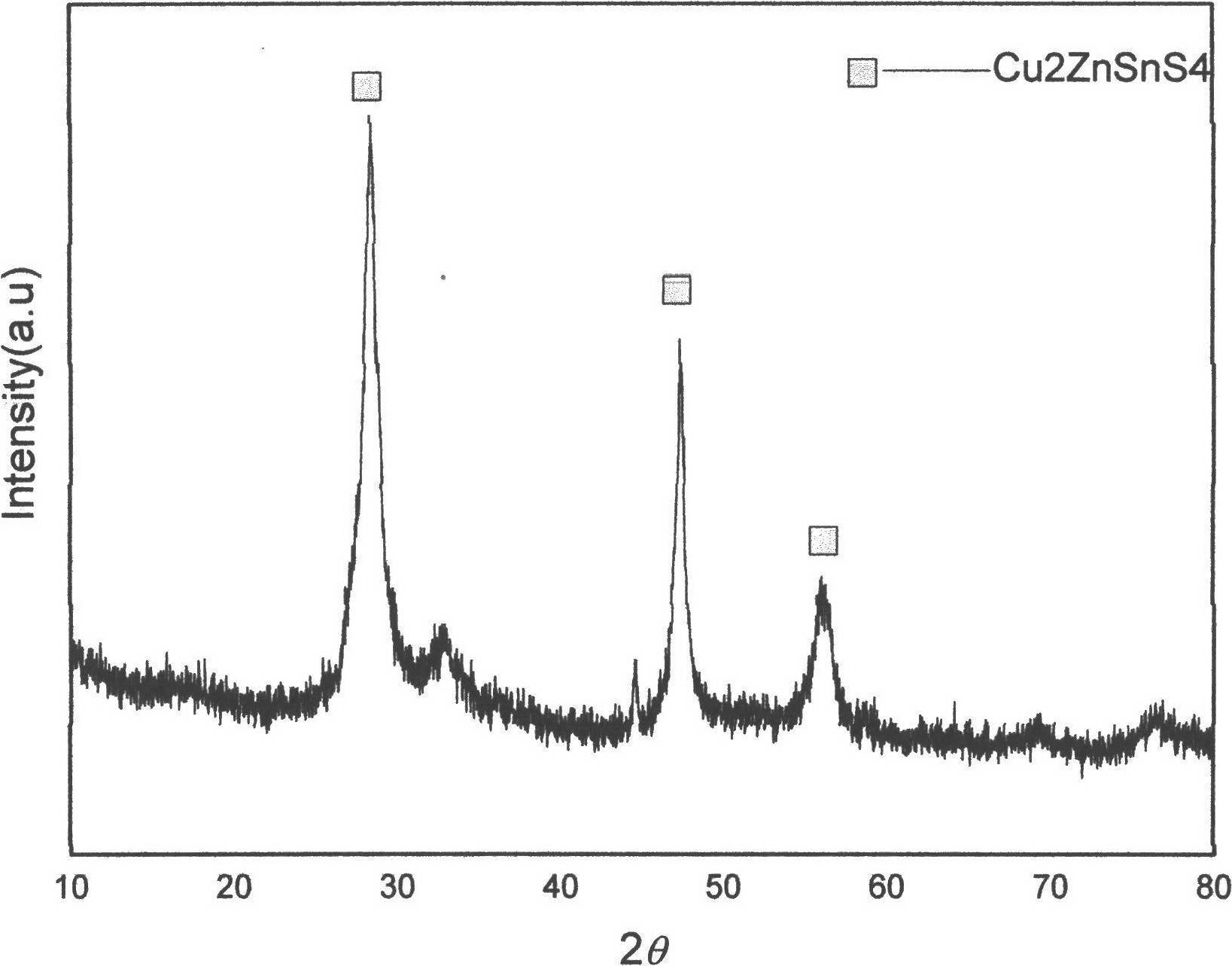
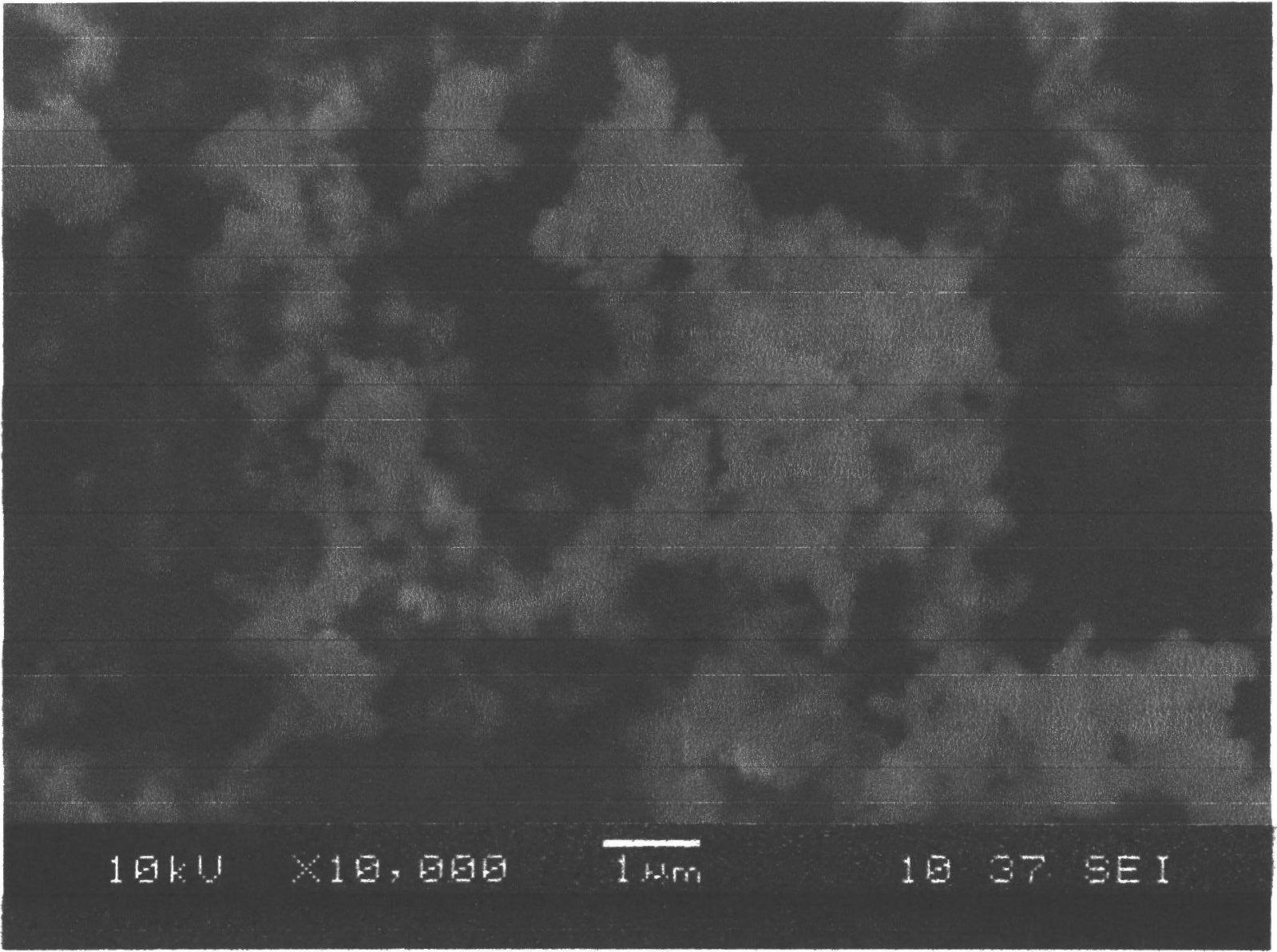
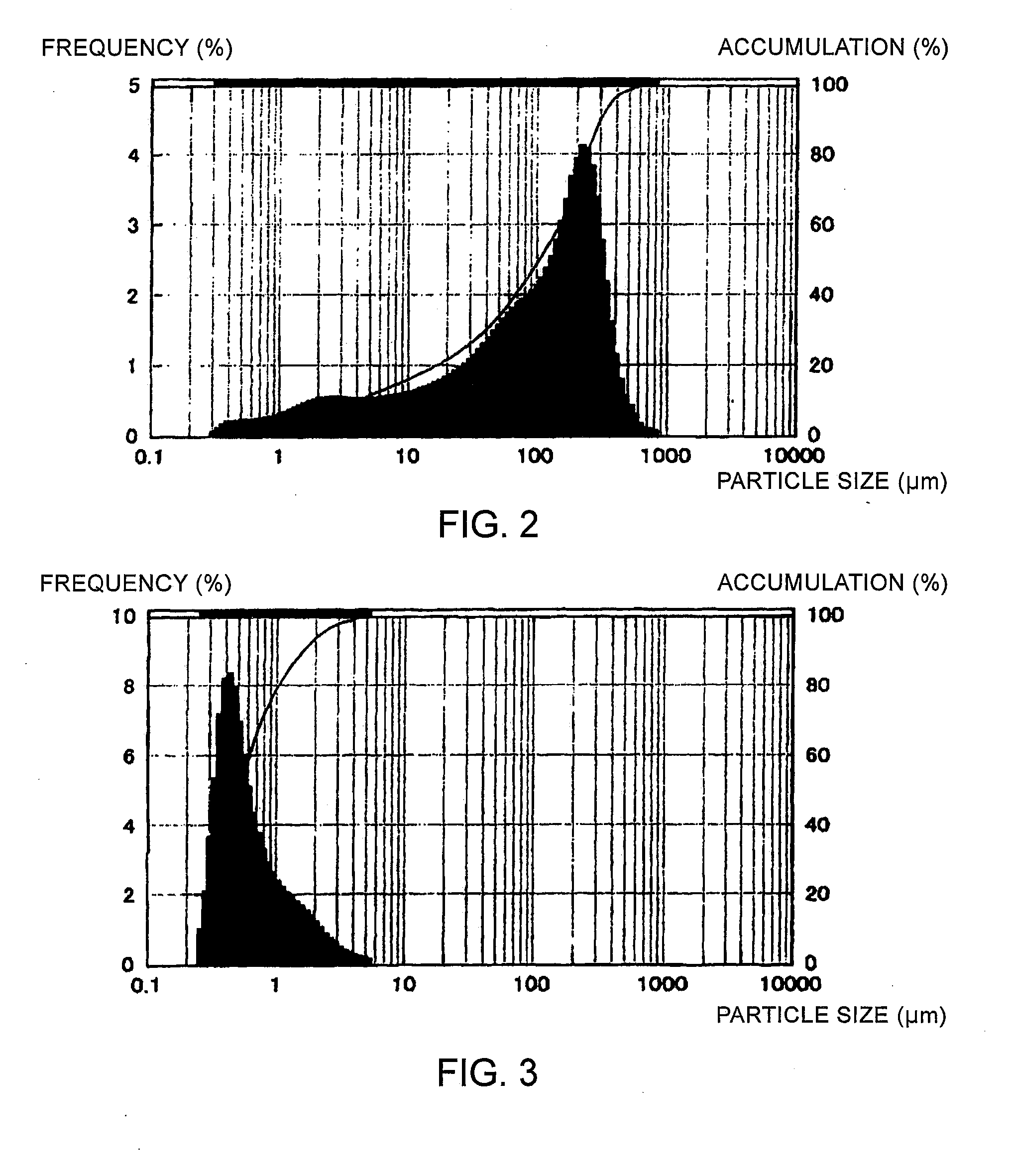
Method for preparing CZTS (Copper Zinc Tin Sulfide) (Se) series nanometer powder by low-temperature mechanical alloying
InactiveCN102642818AAvoid introducingReaction raw materials are readily availableTin compoundsSelenium/tellurium compundsIsobutanolHexamethylenediamine
The invention discloses a method for preparing CZTS (Copper Zinc Tin Sulfide) (Se) series nanometer powder by low-temperature mechanical alloying. Elementary substances Cu powder, Zn powder, Sn powder and S (Se) powder are added into a ball-milling tank according to a certain mole ratio, an alcohol and amine mixed liquor is used as a process control agent, ball milling is carried out according to a rated ratio of grinding media to material, a set rotational speed and ball milling time, and a ball-milled product is centrifugally washed and dried to obtain a target product. In the raw materials, elementary substances sulfur powder and selenium powder can be exchanged in any mole ratio; and the process control agent is the mixed liquor of alcohol and amine with the volume ratio of 1-20:1, the alcohol is one of ethanol, ethylene glycol, normal butanol, isobutanol, isoamylol, tertiary amyl alcohol and glycerol, and the amine is one of ethanediamine, iso-butylamine, diisopropylamine, hexamethylenediamine and triethylamine. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of easy obtainment of raw materials, pure products, low energy consumption, easy control in product shape and appearance, simple process and the like, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Microwave-synthesis method for preparation of copper-zinc-tin-sulphur (CZTS) nanoparticles
The invention relates to a low-cost microwave synthesis method for preparation of a material, namely Cu2ZnSnS4, of an absorbing layer of a solar cell, which belongs to the technical field of solar cell materials and devices. According to the invention, suitable reaction solution is prepared, and then the solution is put into a microwave oven to be heated to obtain Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticles. The microwave synthesis method has the advantages that raw materials are rich in source and low in cost, complicated equipment is not needed, the preparation process is simple, the preparation cost is low, and components of the nanoparticles are controllable. The prepared copper-zinc-tin-sulphur (CZTS) nanoparticles can be dispersed into ethanol or ethylene glycol to form ink, and the ink is coated to form a thin film, so that the CZTS thin film solar cell is manufactured.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Laser annealing for thin film solar cells
InactiveUS20130065355A1High densityLarge particlesFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumSulfide
A method for forming copper indium gallium (sulfide) selenide (CIGS) solar cells, cadmium telluride (CdTe) solar cells, and copper zinc tin (sulfide) selenide (CZTS) solar cells using laser annealing techniques to anneal the absorber and / or the buffer layers. Laser annealing may result in better crystallinity, lower surface roughness, larger grain size, better compositional homogeneity, a decrease in recombination centers, and increased densification. Additionally, laser annealing may result in the formation of non-equilibrium phases with beneficial results.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
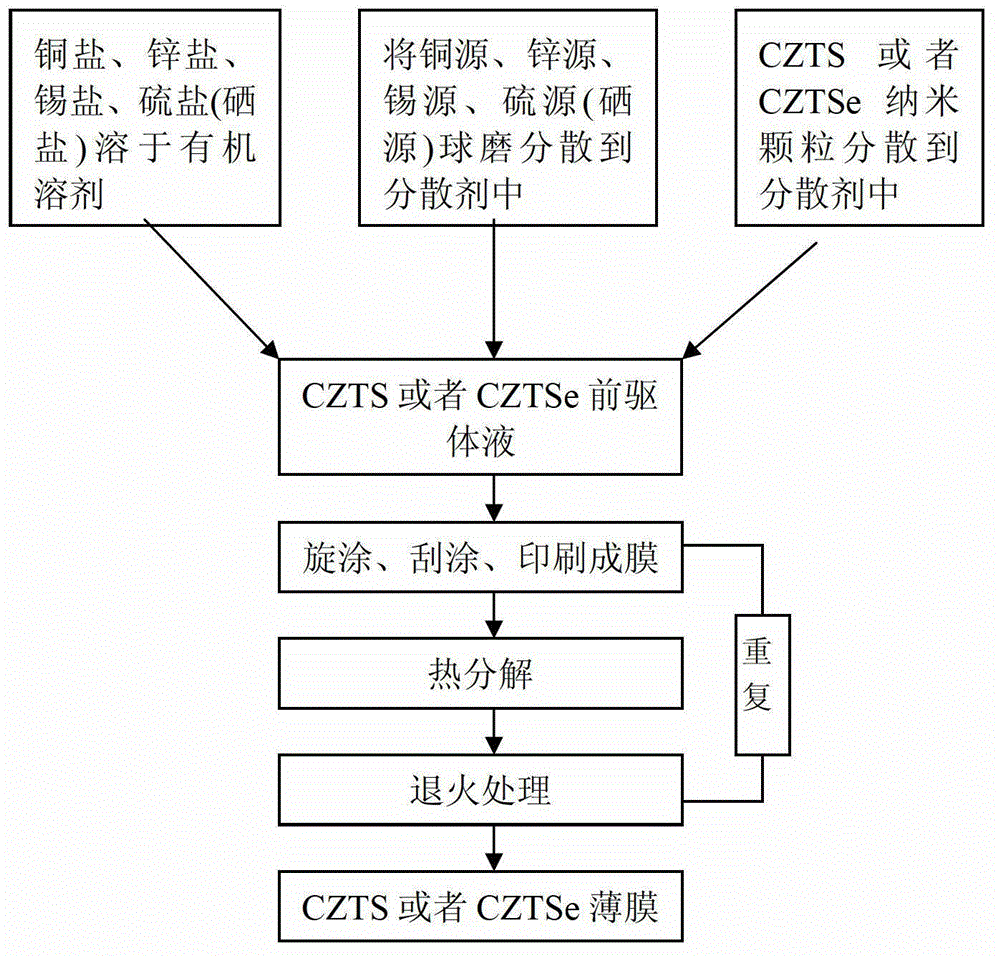
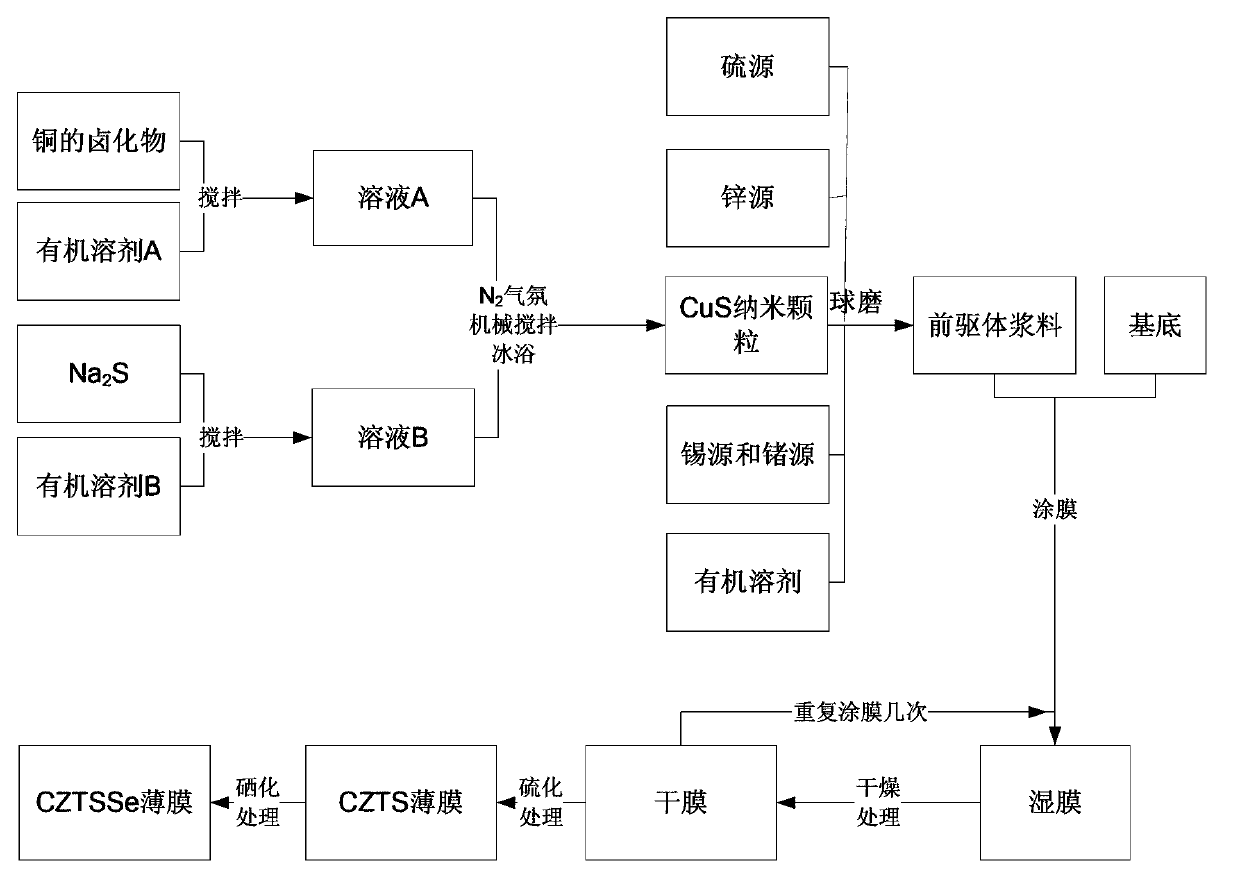
Non-vacuum preparation method of a CZTS or CZTSe thin film not containing carbon layer
InactiveCN103337551AAvoid generatingImprove fill factorFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCarbon layerCZTS
The invention relates to a non-vacuum preparation method of a CZTS or CZTSe thin film not containing a carbon layer and belongs to the technical field of thin-film solar cell preparation. The non-vacuum preparation method has the following implementation steps of coating a CZTS or CZTSe precursor liquid uniformly on a substrate to obtain a wet film; performing thermal decomposition on the wet film under the atmosphere of nitrogen or inertia protection, and after obtaining a non-crystal dry film, performing annealing processing on the non-crystal dry film to obtain a multi-crystal thin film having a non-carbon layer; and continuing coating a wet film on the multi-crystal thin film with the non-carbon layer and repeating the above steps and finally obtaining a finished product. The non-vacuum preparation method is an effective way of improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of CZTS or CZTSe thin-film solar cells. According to the non-vacuum preparation method, the preparation process is simple, the necessary equipment is commonly used equipment, the cost is low, the industrial production is facilitated, the product performance is good, and thus the non-vacuum preparation method has very good market prospects.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Semiconductor Powder and Method for Producing the Same
The present invention provides a semiconductor powder composed of Cu-M-Sn—S in a single phase wherein M is at least one selected from the group consisting of Zn, Co, Ni, Fe and Mn, the powder being obtained by wet synthesis, and a method for producing this semiconductor powder. According to the present invention, it is possible to provide, in a simple way, a high-grade semiconductor powder composed of a single-phase Cu-M-Sn—S such as CZTS.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
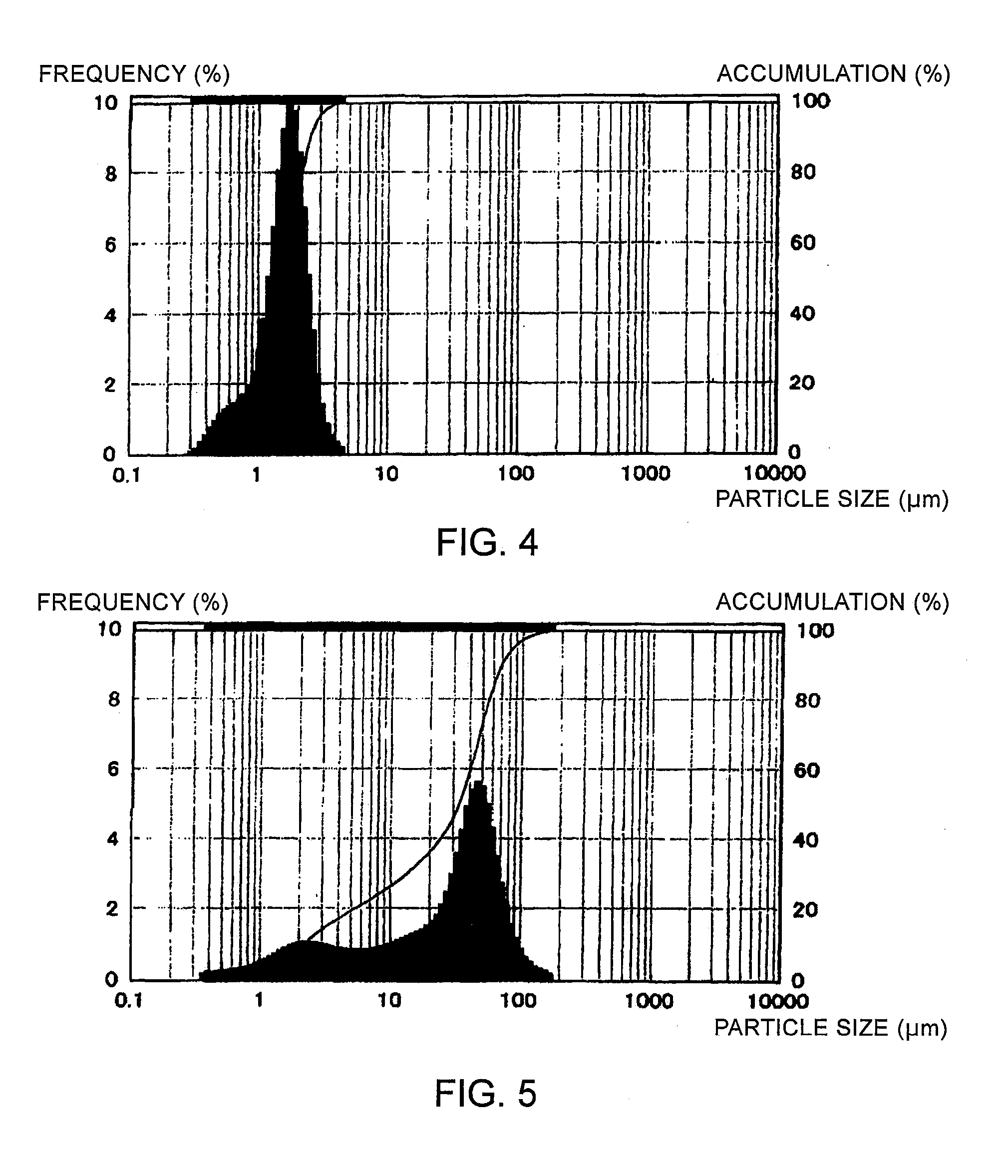
Preparation method of germanium-doped CZTS thin film, thin film and solar cell
ActiveCN103346201APromote growthEasy to dopeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSlurrySe element
The application discloses a preparation method of a germanium-doped CZTS thin film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a CuS nano-particle; preparing a Ge-doped precursor slurry; preparing Ge-doped precursor film; carrying out sulfidizing on the Ge-doped precursor film to obtain a Cu2ZnSn1-xGexS4 film; and carrying out selenylation processing on the Cu2ZnSn1-xGexS4 film to obtain Cu2ZnSn1-xGex(S,Se)4 film. In addition, the application also discloses a germanium-doped CZTS thin film and a solar cell. According to the invention, because the Cus nano-particle is used, grain crystal growing and film densifying can be promoted; the Ge is doped when the precursor slurry is prepared, so that the forbidden band width of the CZTS thin film can be adjusted and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the CZTS cell can be improved; because an organic solvent like methyl alcohol or ethanol and the like is used, the sulfur source used for sulfidizing processing is solid powdered sulfur, and the selenium source used for selenizing processing is solid selenium powder, the whole production process is environmentally friendly; and a volume expansion effect using a Se atom portion to replace an S atom during the selenizing process is used for structural densifying of the film, and the forbidden band width of the CZTS absorption layer is adjusted, so that matching with a solar spectrum is realized well.
Owner:徐东
Nanometer structure copper zinc tin sulfide (CZTS) film photovoltaic cell and preparation method of nanometer structure CZTS film photovoltaic cell
InactiveCN102637755AImprove efficiencyLow costFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationNanowireTe element
The invention discloses a nanometer structure copper zinc tin sulfide (CZTS) film photovoltaic cell, which sequentially consists of a substrate, a back electrode, a p type semiconductor nanometer wire array, an n type semiconductor thin layer, a window layer and a metal grid electrode, wherein the p type semiconductor nanometer wire array consists of semiconductor alloy (CuxB<1-x>)2Cy(DzS<1-z>), wherein x is greater than 0 but is smaller than or equal to 1, y is greater than or equal to 0 but smaller than or equal to 2, z is greater than or equal to 0 but smaller than 1, B is silver and / or gold, C is more than one kind of materials of aluminum, zinc or tin, D is selenium and / or tellurium. Through the subsequent processes of controlling the deposition element types, the deposition element sequence, the heat treatment mode and the like, the ingredients, the phase structure and the energy band structure of the absorption layer nanometer wire array are regulated, so the solar photovoltaic cells with different structures and performance can be prepared. The nanometer structure CZTS film photovoltaic cell provided by the invention has the advantages that the light reflection is reduced, good light capture capability is realized, the band gap regulation is improved, and the great improvement of the photoelectric conversion efficiency is finally realized.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
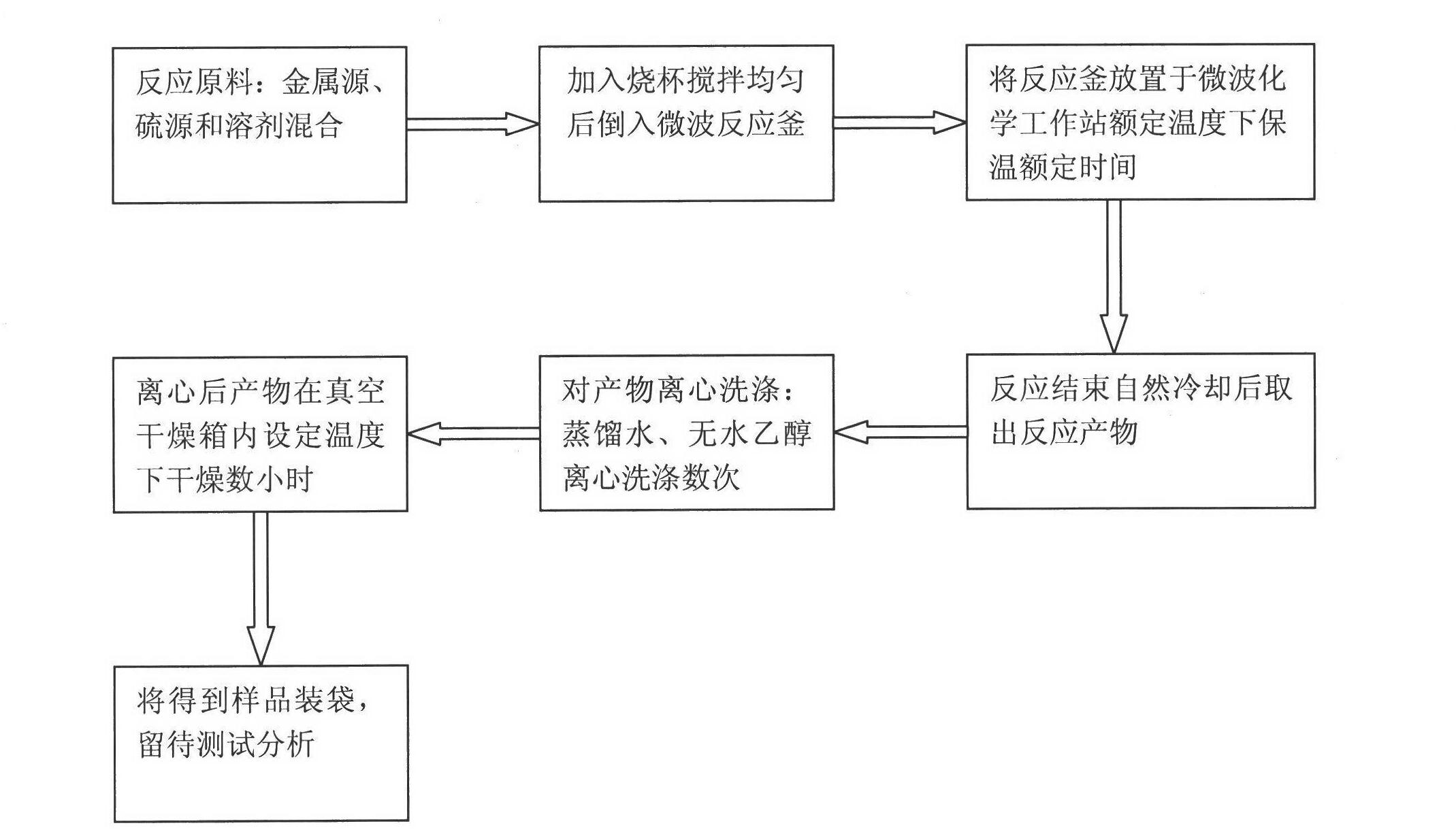
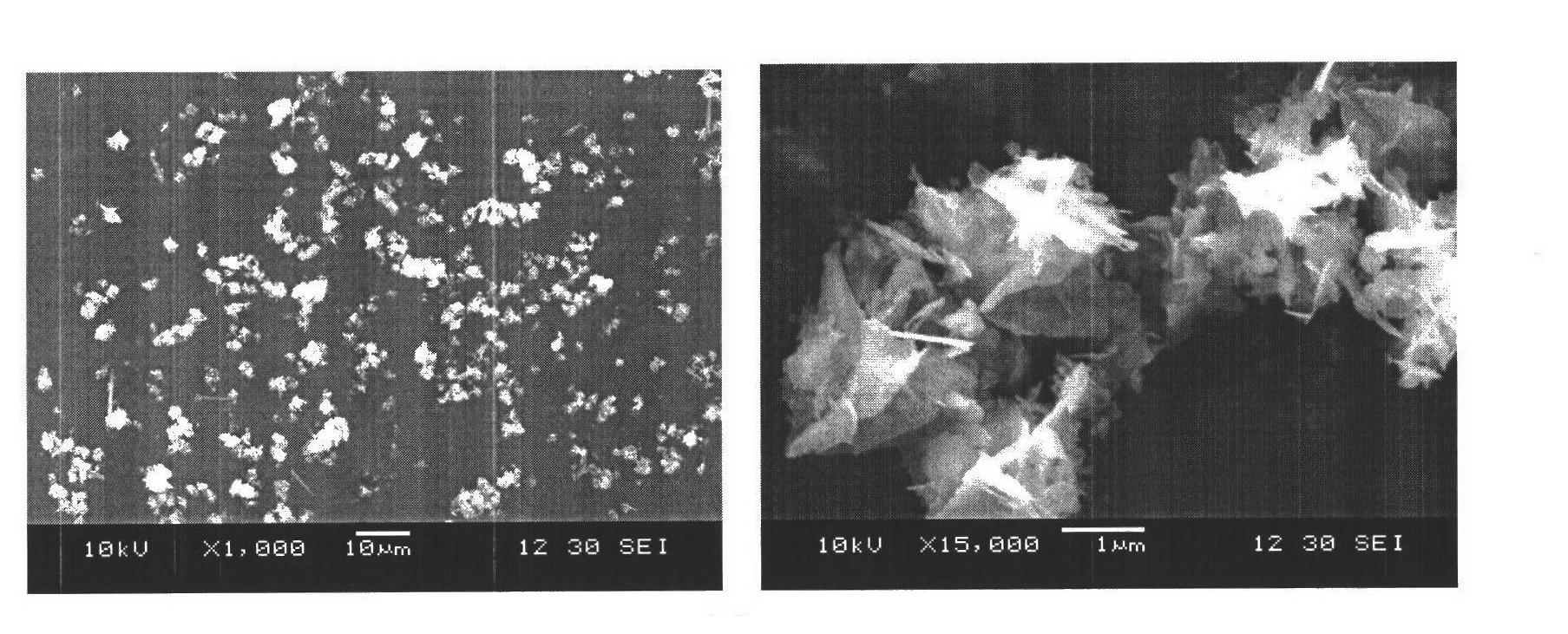
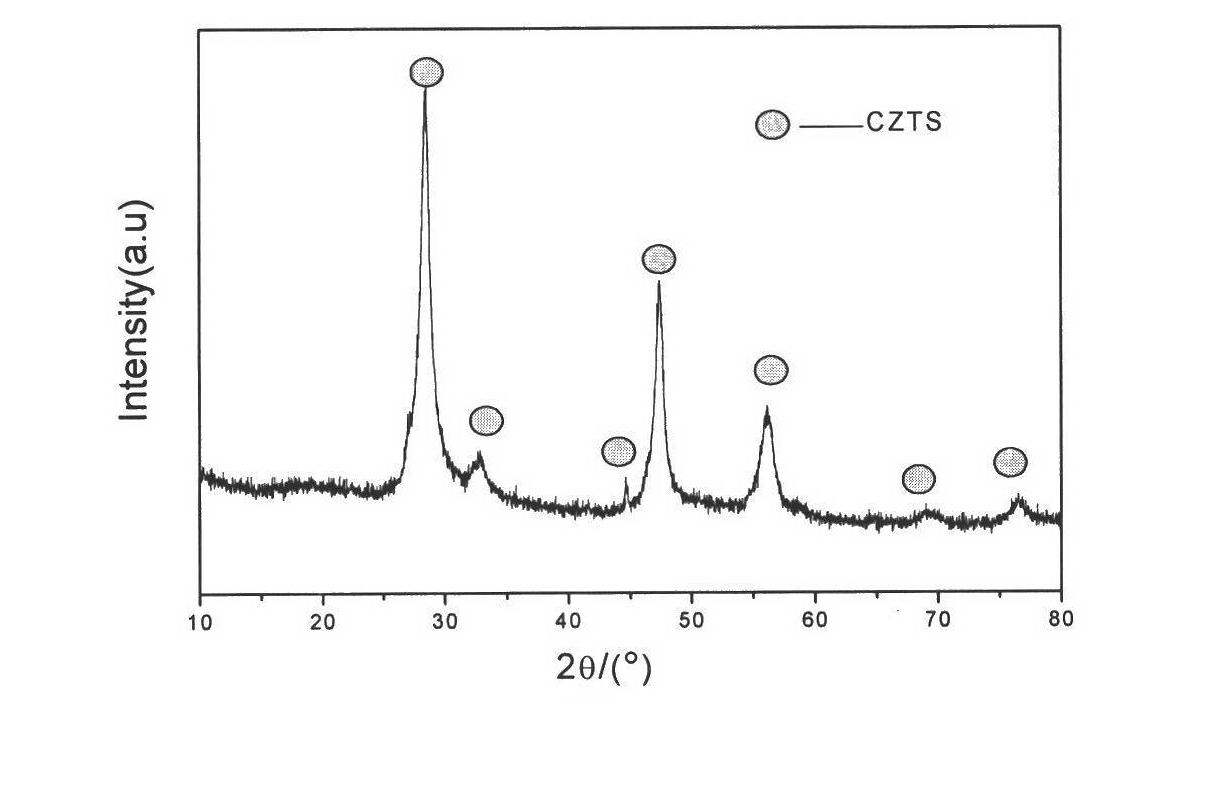
Method for thermally synthesizing Cu2ZnSnS4 semiconductor material by solvent through microwaves
The invention discloses a method for thermally synthesizing a Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) semiconductor material by a solvent through microwaves. The method comprises the following steps of: adding copper salt, zinc salt, tin salt and a sulphur source into a beaker according to a preset molar ratio, adding the solvent, mixing uniformly and pouring the mixture into a reaction kettle, and placing the reaction kettle into a microwave field for heating after being closed, keeping the rated temperature for rated time after the temperature is raised to the rated temperature, and performing centrifugation, washing and vacuum drying on an obtained product to obtain the Cu2ZnSnS4 semiconductor material. The solvent can be one or more of water, glycol, ethanediamine and diamine, and the sulphur source can be sulfourea or sulphur powder. In the method, the Cu2ZnSnS4 semiconductor material prepared by the microwave-assisted solvent thermal synthesis process has high purity, and has the advantages of high synthesis speed, simple reaction device, low cost and easiness in process control.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Preparation method for CZTS nano-particle material
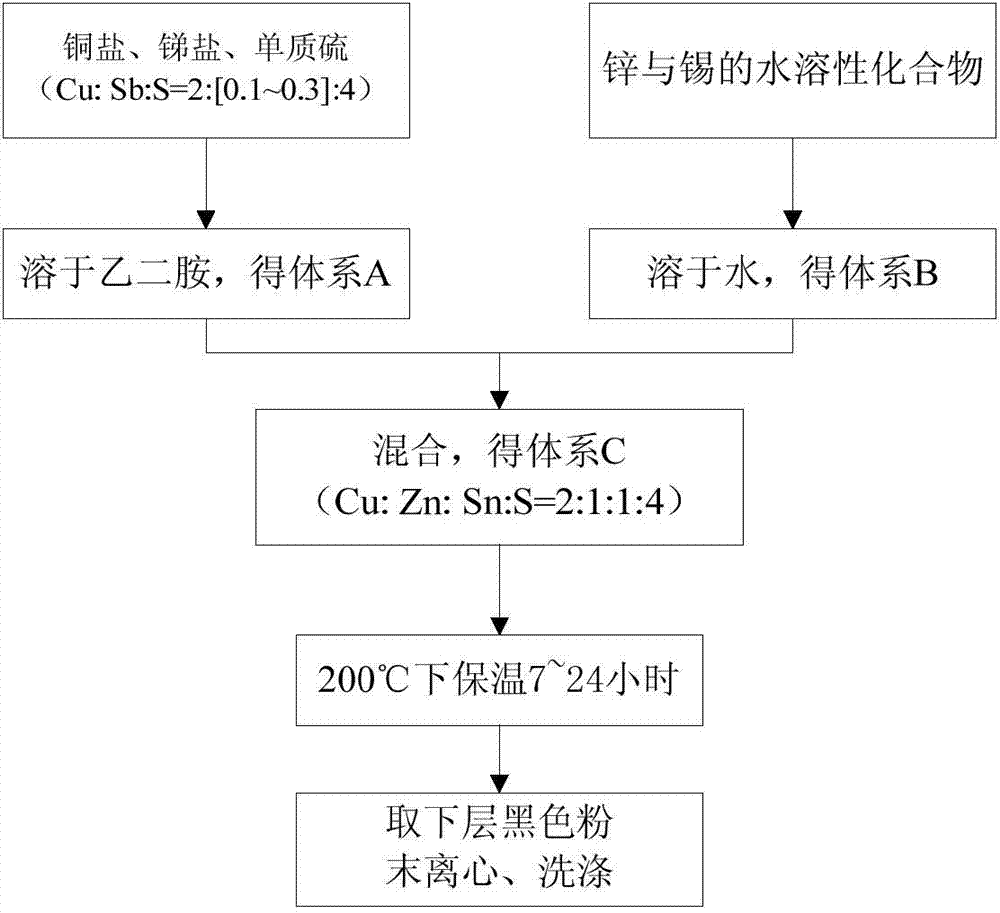
InactiveCN103482687AHigh crystallinityUniform particle size distributionMaterial nanotechnologyTin compoundsEthylenediamineCrystallinity
A preparation method for a CZTS nano-particle material belongs to the technical field of materials. The method comprises the following steps: first, respectively preparing a reaction system A (dissolving copper salt, antimonic salt and elemental sulfur in ethylene diamine in an ultrasonic manner) and a reaction system B (a water solution of zinc salt and tin salt); then, mixing the system A and the system B in an ultrasonic manner, sealing and heating to 200 DEG C; keeping the the temperature for 7-24 hours for reaction; finally, taking black powder at the lower layer, and obtaining a target product through centrifugation and washing. According to the invention, a moderate amount of an antimony compound is added to allow copper ions and Sb ions to react with the sulfur so as to generate a mobile-phase copper-antimony-sulfur compound and to promote the growth of Cu2ZnSnS4; meanwhile, the crystal grain dimensions of the Cu2ZnSnS4 nano particles are more uniform. The prepared CZTS nano-particle is good in crystallinity, has no other impurity phase, and is more uniform in dimension distribution; the reaction time is greatly shortened under the action of the mobile phase; only sealing and heating equipment is required during the preparation process, so that the preparation steps are simple, and mass production is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for manufacturing copper-zinc-tin-sulfide absorbing layer thin film and copper-zinc-tin-sulfide solar cell
InactiveCN103762257AImprove conversion efficiencyStable chemical propertiesFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesVulcanizationSulfur
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a copper-zinc-tin-sulfide absorbing layer thin film. A CZTS solar cell absorbing layer is obtained through vulcanization after a CZTS precursor is co-deposited electrochemically. The invention further discloses a method for manufacturing a copper-zinc-tin-sulfide solar cell. The method can be operated at normal temperature and pressure and easy to adjust and control, H2S pollution is avoided, equipment is simple, cost is saved, the surface of the manufactured copper-zinc-tin-sulfide absorbing layer thin film is smooth and very compact, and the efficiency of the manufactured cell is high. The method can be widely used for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Semiconductor inks, films, coated substrates and methods of preparation
InactiveCN103221471AEasy to manufactureStacked tightlySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInksCZTSMicroparticle
This invention provides compositions useful for preparing films of CZTS and its selenium analogues on a coated substrate. This invention also provides processes for preparing films and coated substrates comprising CZTS / Se microparticles embedded in an inorganic matrix. This invention also provides processes for preparing photovoltaic cells comprising films of CZTS and its selenium analogues.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Structure and method of fabricating a CZTS photovoltaic device by electrodeposition
InactiveUS8426241B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMaterials science
Techniques for using electrodeposition to form absorber layers in diodes (e.g., solar cells) are provided. In one aspect, a method for fabricating a diode is provided. The method includes the following steps. A substrate is provided. A backside electrode is formed on the substrate. One or more layers are electrodeposited on the backside electrode, wherein at least one of the layers comprises copper, at least one of the layers comprises zinc and at least one of the layers comprises tin. The layers are annealed in an environment containing a sulfur source to form a p-type CZTS absorber layer on the backside electrode. An n-type semiconductor layer is formed on the CZTS absorber layer. A transparent conductive layer is formed on the n-type semiconductor layer. A diode is also provided.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Low-cost preparation method of CZTS (Cu2ZnSnS4) thin film solar battery absorption layer
InactiveCN102306685AAvoid emissionsImprove securityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesEvaporationCharge carrier mobility
The invention relates to a low-cost preparation method of a CZTS (Cu2ZnSnS4) thin film solar battery absorption layer, belonging to the technical field of semiconductor photoelectric materials and devices. The method is characterized by preparing a metal precursor of Cu, Zn and Sn by adopting a common evaporation method; and vulcanizing the front precursor in sulfur vapor so as to get a polycrystalline CZTS thin film, wherein the prepared polycrystalline CZTS thin film has a similar stannite structure and a direct band gap width adaptive to the solar spectrum, absorption coefficient for visible light, and the characteristics of electrical resistivity, carrier mobility and the like, and the CZTS thin film is suitable for being taken as the thin film solar battery absorption layer. Raw materials for preparing the CZTS thin film solar battery absorption layer by adopting the method have rich sources and are non-toxic, the preparation technology is simple, the performances of a thin film are easy to control, and the method is suitable for scale chemical engineering production.
Owner:ZHANJIANG NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method for CZTS (Se) nano-crystalline thin film
InactiveCN104701138AHigh crystallinityImprove controllabilityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingToxic materialSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method for a piece of CZTS (Se) nano-crystalline thin film. The preparation method includes that preparing binary nano-crystalline particles of tin, zinc and copper, mixing the binary nano-crystalline particles and dispersing in solvent to prepare reaction precursor solution, and transferring the reaction precursor solution to the surface of a substrate to perform heat treatment to obtain the CZTS (Se) nano-crystalline thin film. The CZTS (Se) nano-crystalline thin film prepared by the method is less in impurity and defect, when the CZTS (Se) nano-crystalline thin film is used as the absorption layer of a solar cell, the conversion efficiency of the solar cell can be obviously improved; the preparation method does not use toxic substances (hydrazine and oleylamine) as solvent, and accordingly the preparation method is friendly to the environment.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
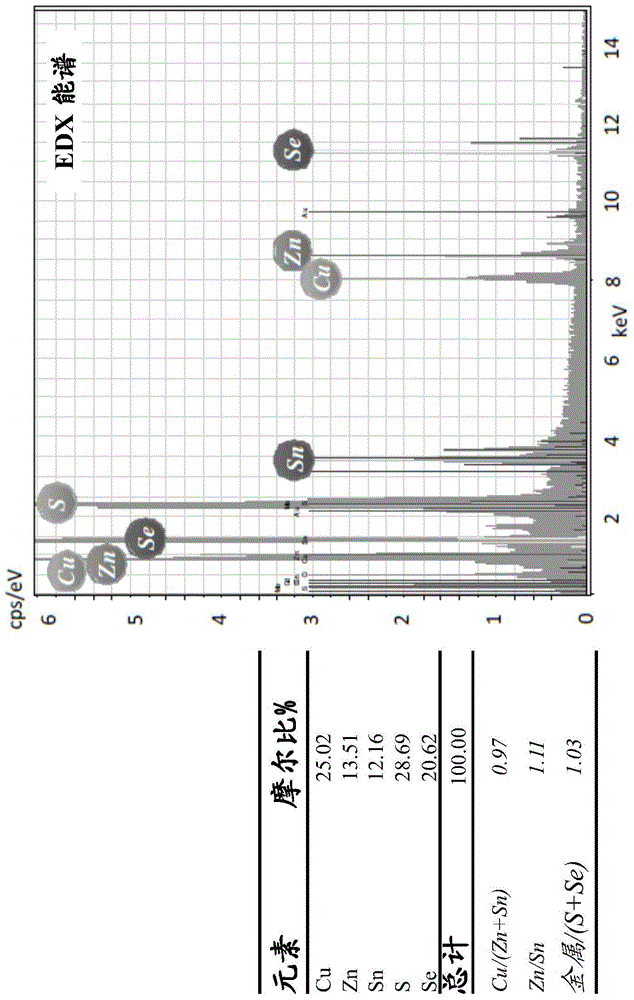
Sulfide target cosputtering preparation method of CZTSSe film and product thereof
InactiveCN104947050AVulcanization step omittedEven distribution of elementsFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingVulcanizationCZTS
The invention relates to a sulfide target cosputtering preparation method of a CZTSSe film and a product thereof. The cosputtering preparation method of a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur-selenium (Cu2ZnSn(SSe)4, CZTSSe for short) film absorption layer comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a Cu-Zn-Sn-S precursor prefabricated film on a soda-lime glass substrate by using a sulfide target by a cosputtering technique; (2) carrying out direct vulcanization-free high-temperature annealing treatment on the Cu-Zn-Sn-S precursor prefabricated film obtained by cosputtering to prepare a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur (Cu2ZnSnS4, CZTS for short) film absorption layer; and (3) preparing the Cu-Zn-Sn-S precursor prefabricated film by using the optimized preparation scheme in the step (2), and preparing the CZTSSe film absorption layer by using a solid selenium source (Se powder) selenizing annealing technique. The product CZTS / CZTSSe film has higher photoabsorption coefficient, and is an ideal film solar cell material.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
High work function low resistivity back contact for thin film solar cells
Back contact materials and processes for use in the manufacturing of CdTe, CIGS, and CZTS TFPV superstrate solar cells are described. High conductivity, high work function materials of ReO3 are used to form the ohmic contact to the absorber layers of the TFPV solar cells. The ReO3 materials may be implemented alone or in combination with other high conductivity materials to for the back contact layer stack.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Non-vacuum method for producing light absorbing material applied in solar battery
ActiveCN104032336AIncreased toxicityImprove flammabilityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCZTSOrganic semiconductor
The present invention describes a method for producing p-type light absorbing semiconducting copper zinc tin selenide / sulfide (Cu2(ZnxSn2-x)(SySel-y)4) (CZTS for short) through utilizing electrochemical deposition. The p-type light absorbing semiconducting copper zinc tin selenide / sulfide can be used in manufacturing solar battery when combined with an n-type inorganic or organic semiconductor layer. The method comprises using one step of electroplating or a series of deposition to produce low-cost large-are CZTS solar battery without using an expensive and complex deposition technology or highly toxic and highly flammable chemicals in the manufacturing process. According to the method of the present invention, the cost and energy requirement in manufacturing the solar battery are reduced.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Method for preparing crystal-phase-controllable monodispersed Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystalline
The invention discloses a method for preparing crystal-phase-controllable monodispersed Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystalline, which belongs to the field of photoelectric material preparation. The method includes: precursor complexation, namely adding metal chloride salt and simple substance sulfur into a container, adding alcohol solvent and oleyl amine, feeding nitrogen or argon as shielding gas, magnetically stirring, heating to a certain temperature and complexing to obtain reaction precursor liquid; solvent thermal preparation, namely stirring while adding the shielding gas nitrogen or argon, heating the reaction precursor liquid to a certain temperature, reacting for a while, cooling and adding ethanol into reaction liquid with liquidity, centrifugally separating for precipitation to obtain Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystalline grains; cleaning, namely using cleaning agent to wash off the oleyl amine on the surfaces of the obtained Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystalline grains to obtain monodispersed CZTS (copper zinc tin sulfide) nanocrystalline colloid; and post-treatment, namely subjecting the obtained monodispersed CZTS nanocrystalline colloid to vacuum drying to obtain monodispersed Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystalline powder. The method is simple and low in cost.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single-crystal particle film and preparation method of substrate-free flexible solar cell employing single-crystal particle film
ActiveCN105161555AEffective controlPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateMicron scaleSingle crystal
The invention discloses a single-crystal particle film and a preparation method of a substrate-free flexible solar cell employing the single-crystal particle film. With an organic polymer material as a binder, micron-sized CZTS and CZTSSe single-crystal particles are mixed into the binder; the single-crystal particle film is prepared by a coating method; the single-crystal particles leaking from the binder on two surfaces are removed through mechanical grinding and plasma etching; and functional layers such as a buffer layer, a window layer and an electrode are prepared, so as to form an entire battery structure. Preparing, screening, cleaning and passivating processes of the single-crystal particles and the preparation process of a single-crystal particle absorption layer are separate, and a harsh high-temperature environment can be used in the preparation and optimization processes of the single-crystal particles, so that effective control on components of CZTS and CZTSSe is achieved; the effects to a substrate, the window layer, the buffer layer and the like caused by preparation conditions of the absorption layer do not need to be considered; and the method has significant advantages in the aspects of material and energy utilization rate and industrial production.
Owner:LINGNAN NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method for improving grain size and density of CZTS film
InactiveCN103400903APrevent volatilizationAvoid pollutionTin compoundsFinal product manufactureNew energyThiourea
The invention provides a preparation method for a CZTS film which has a square structure, high density and large granules, and belongs to the field of semiconductor photoelectric material and new energy material. The preparation method is characterized by adopting four compounds as raw materials, including copper acetate (Cu(CH3OO)2.H2O), zinc acetate (Zn(CH3COO)2), tin chloride (SnCl2) and sulfourea (CN2H4S); after the CZTS film is prepared by adopting a spin coating method, a CZTS film material with high density and good crystallization quality is prepared via high-temperature sulfurization process performed in a sealed quartz tube. The preparation method has the advantages of simple preparation process, short reaction time, controllable component and structure, low cost, no pollution caused during production and the like, can be applicable to production of mass CZTS film photovoltaic cell absorption material.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Precursor solution for preparing the highly-efficient CZTS solar cell, preparation and application of the precursor solution
InactiveCN108461556AQuality improvementImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyTin compoundsFinal product manufactureZinc compoundsThiourea
The invention discloses a precursor solution for preparing the highly-efficient CZTS solar cell as well as preparation and application of the precursor solution. The precursor solution is composed ofdimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), thiourea and a precursor compound, wherein the precursor compound comprises a monovalent copper compound, a tetravalent tin compound and a bivalent zinc compound; with DMSOas a solvent, thiourea, a monovalent copper compound, the tetravalent tin compound and the bivalent zinc compound are dissolved in DMSO to prepare a clear transparent precursor solution. The inventionis advantageous in that a precursor solution is prepared by using a monovalent copper compound and a tetravalent tin compound for CZTS light-absorbing material with high quality and no impurity phase, so that the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the CZTS thin-film solar cell is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com