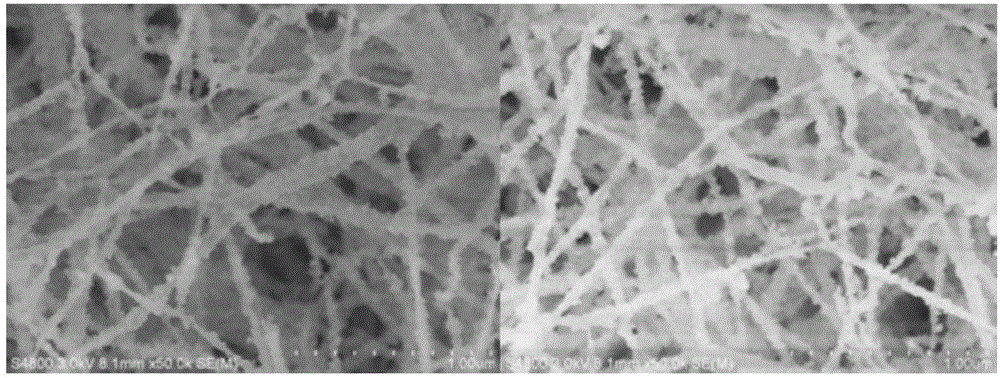
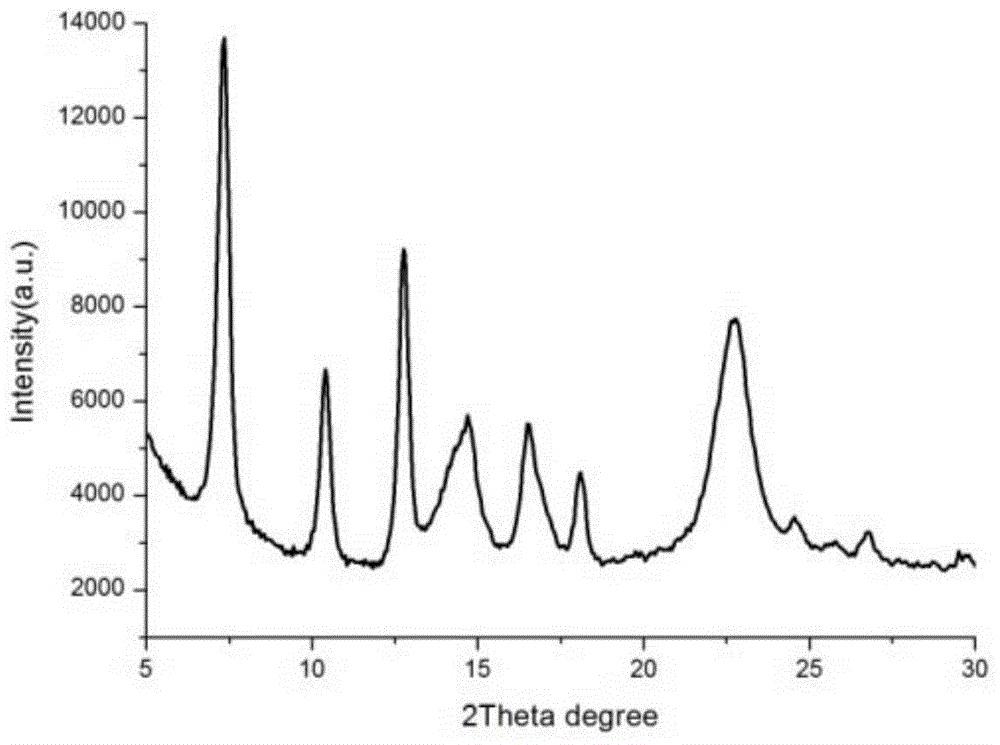
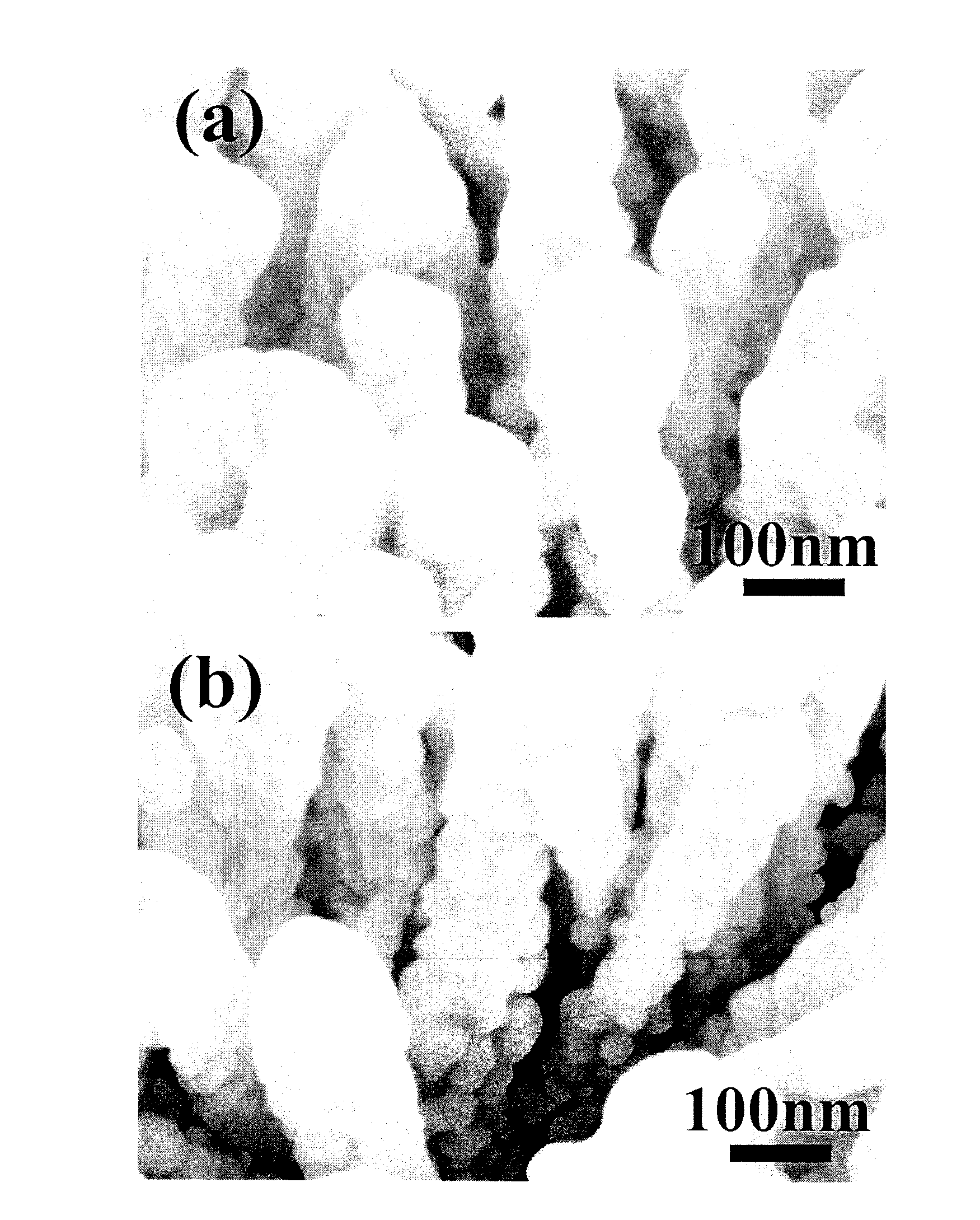
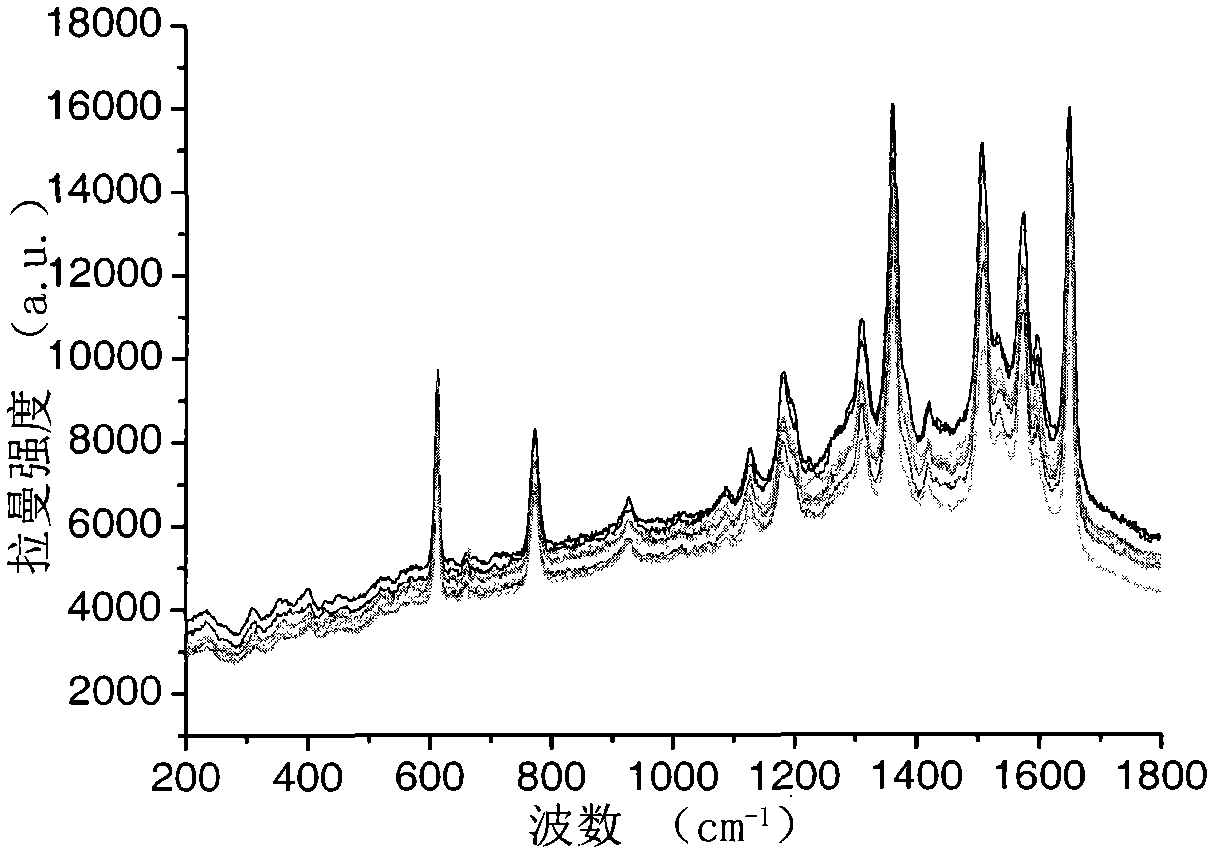
Patents
Literature
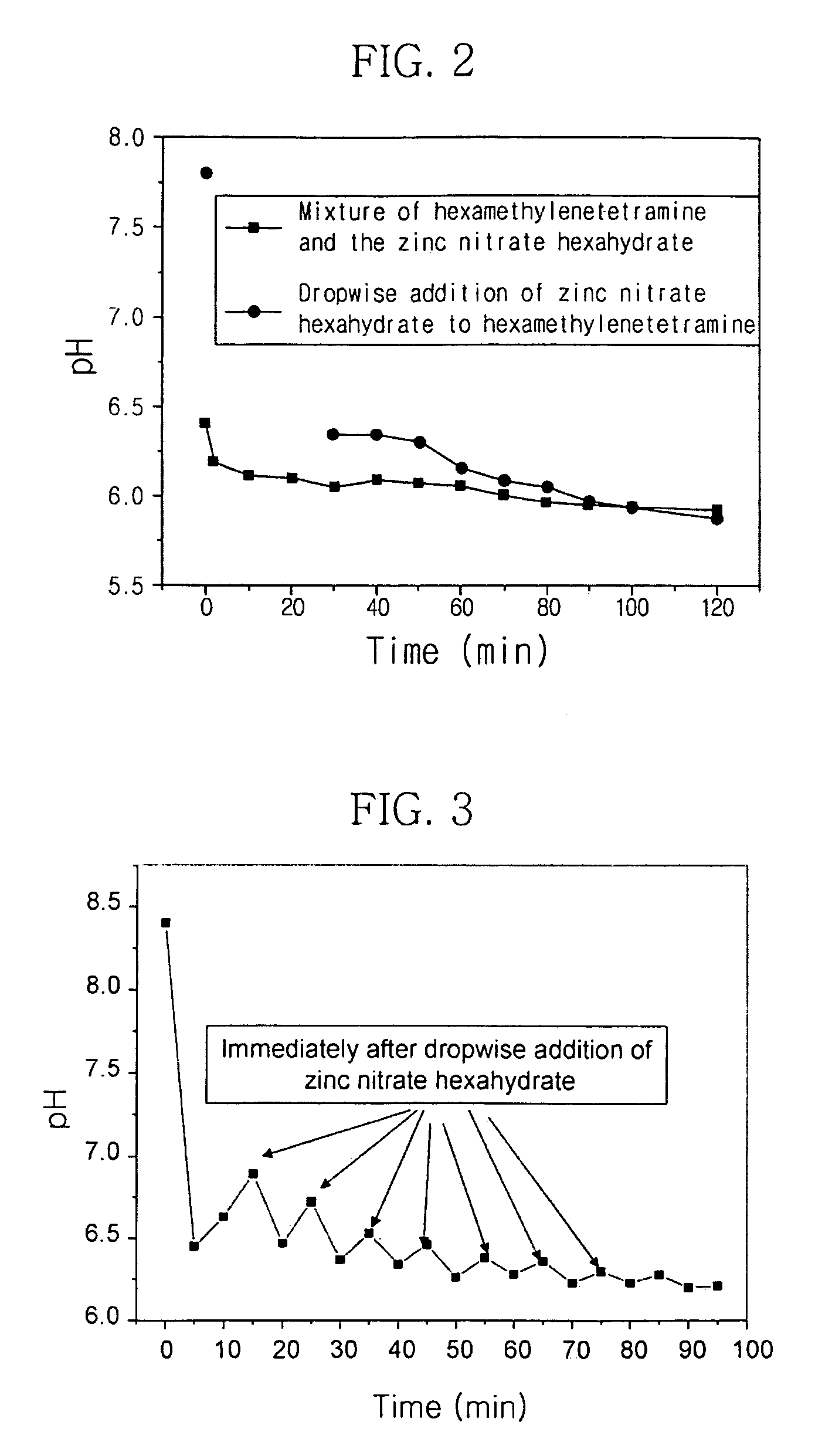
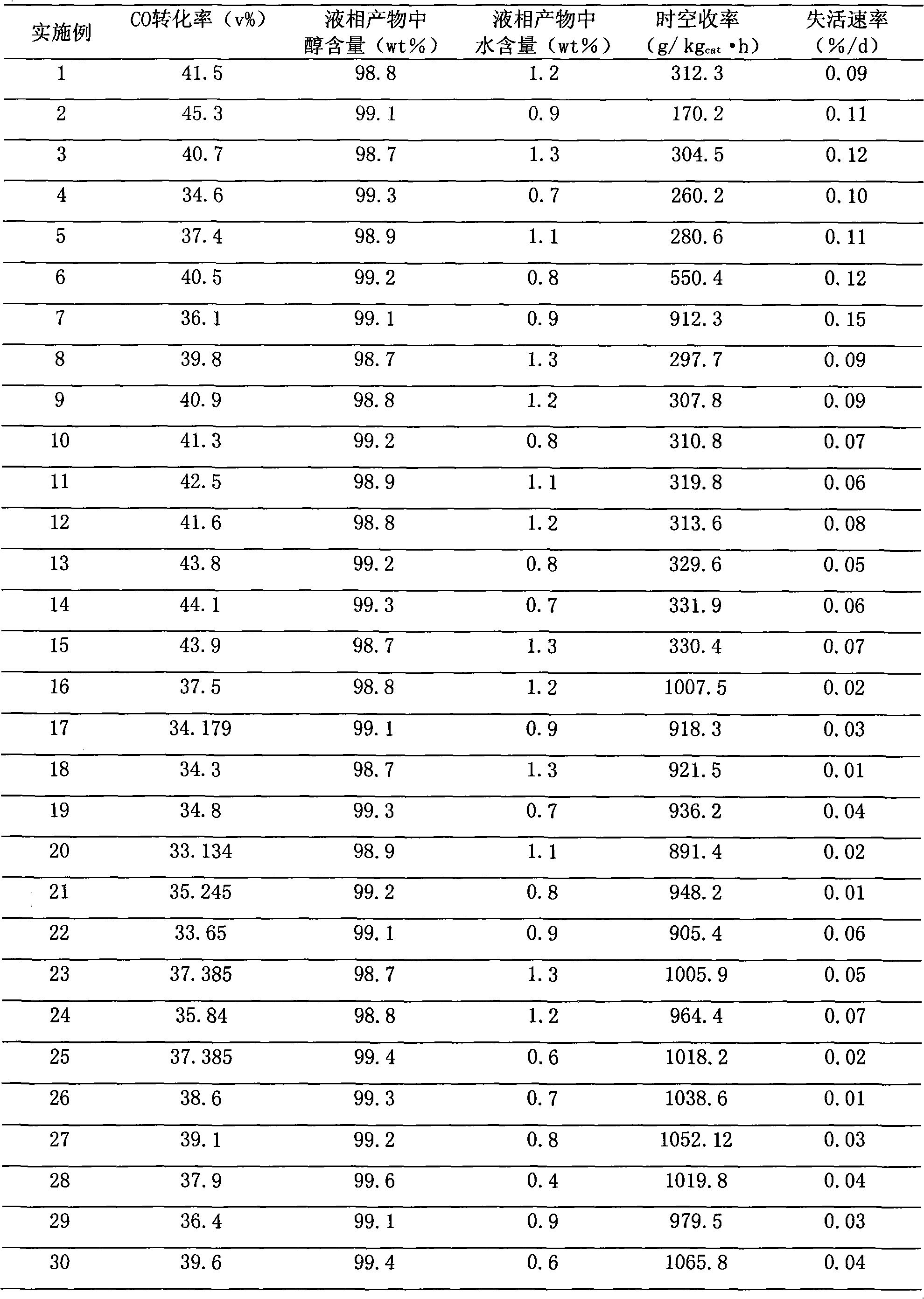
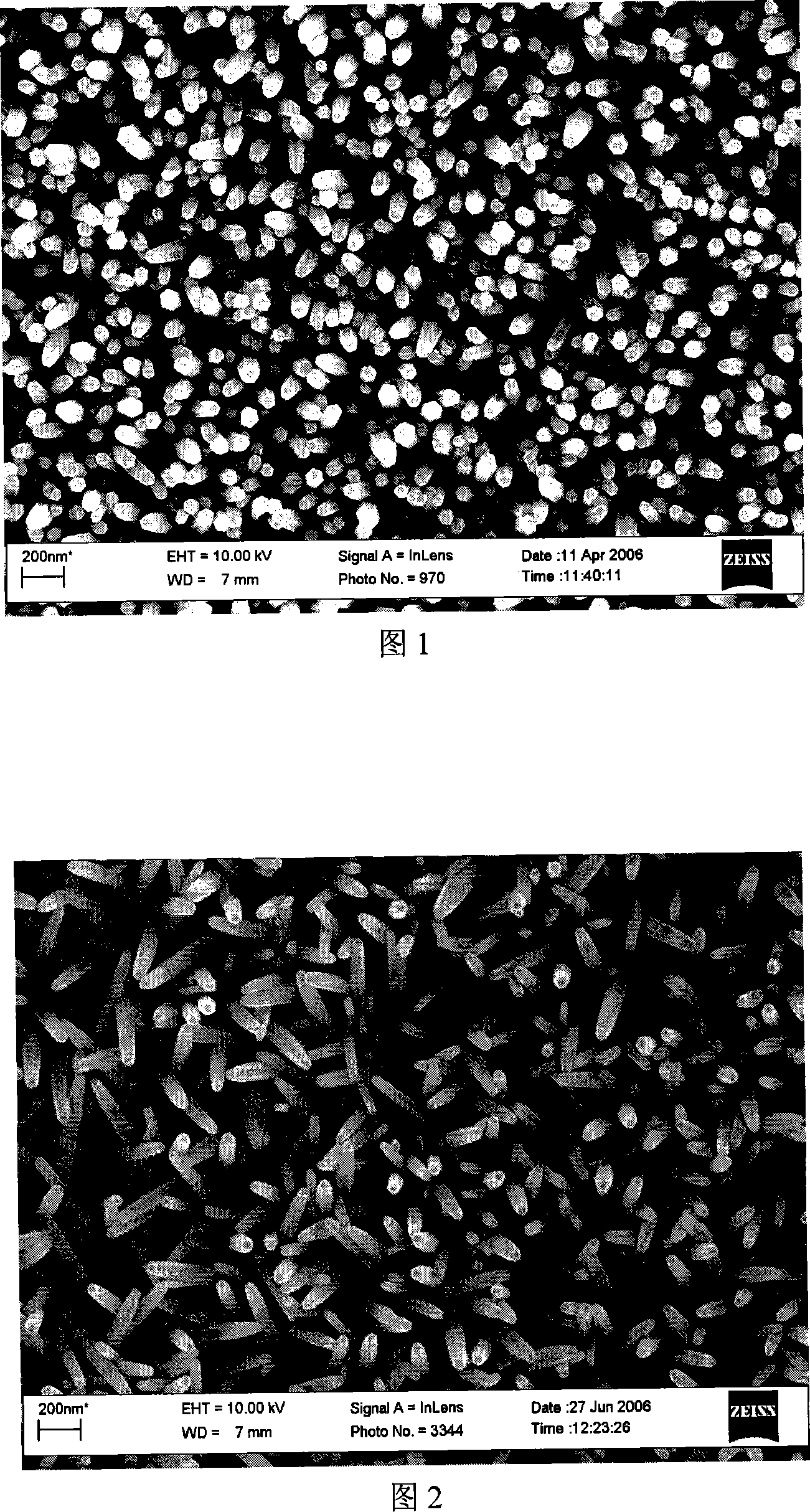
1995 results about "Zinc nitrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zinc nitrate is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula Zn(NO₃)₂ . This white, crystalline solid is highly deliquescent and is typically encountered as a hexahydrate Zn(NO₃)₂•6H₂O. It is soluble in both water and alcohol.
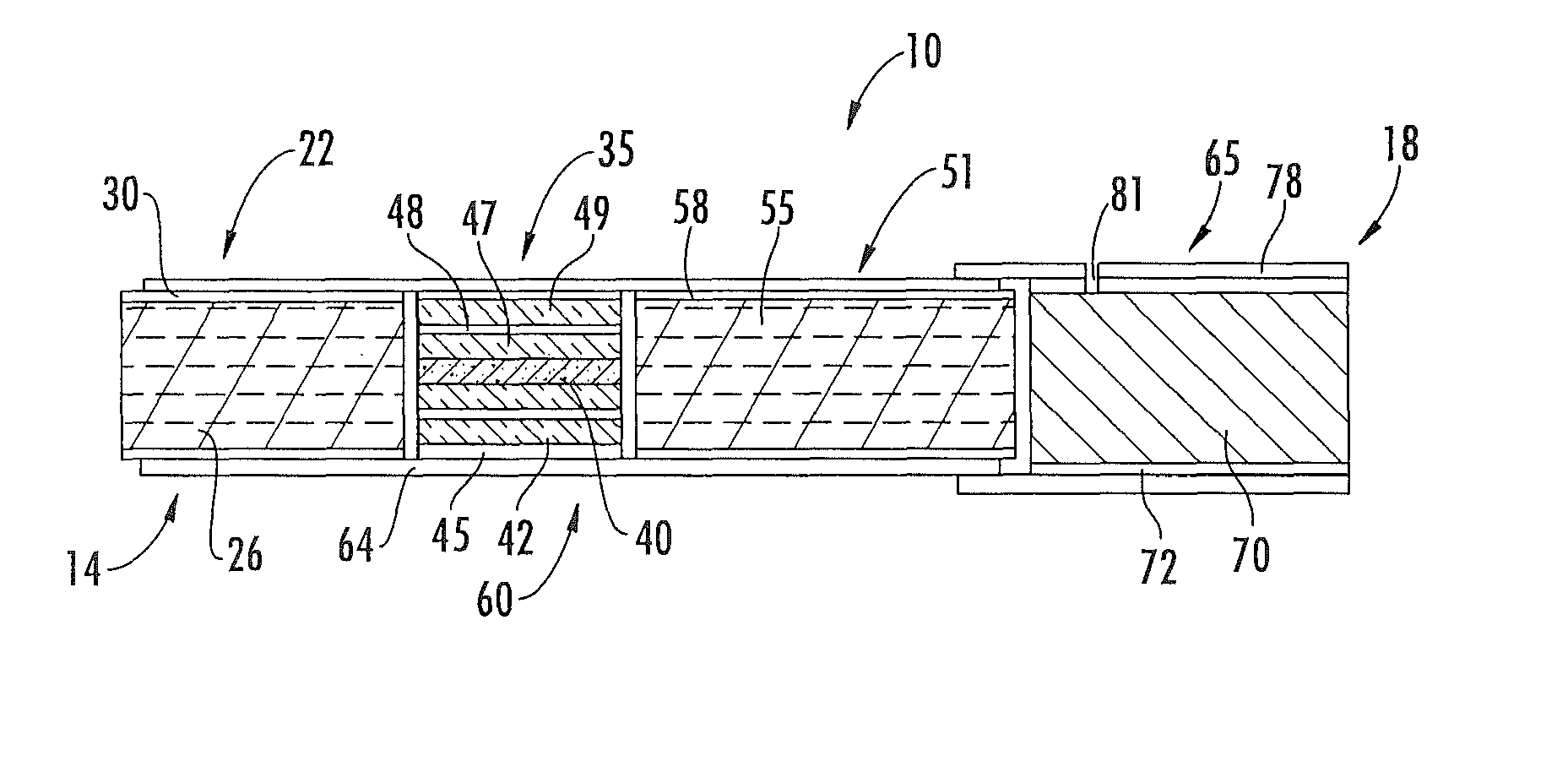
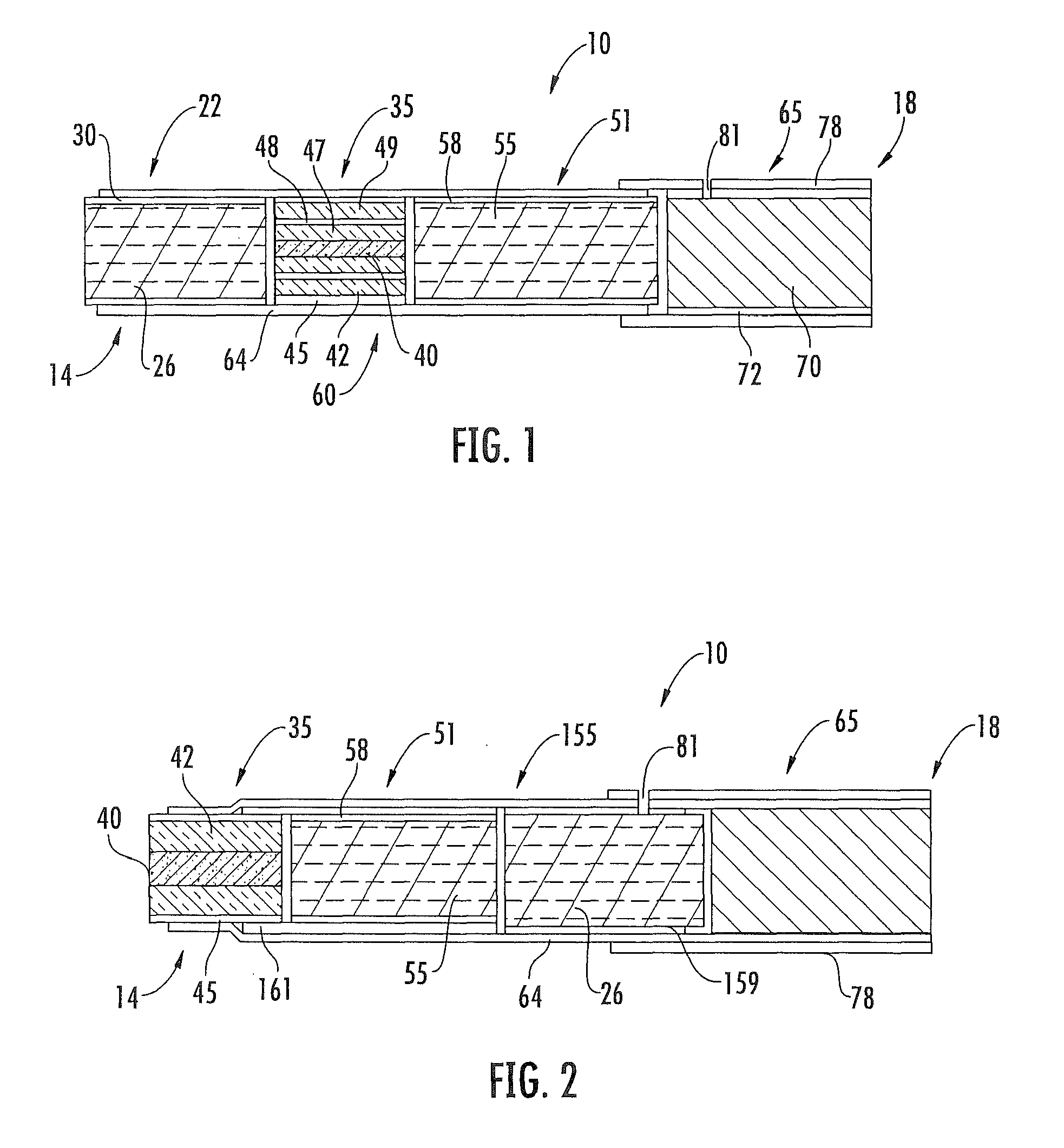
Method for Preparing Fuel Element For Smoking Article
ActiveUS20100065075A1Good water solubilityTobacco treatmentTobacco smoke filtersCerium nitrateCopper nitrate
The invention provides a method for making a fuel element for a smoking article comprising forming a combustible carbonaceous material into a fuel element adapted for use in a smoking article; incorporating a metal-containing catalyst precursor into the fuel element or onto the surface thereof to form a treated fuel element, the incorporating step occurring before, during, or after said forming step; and optionally heating or irradiating the treated fuel element at a temperature and for a time sufficient to convert the catalyst precursor to a catalytic metal compound. Examples of metal-containing catalyst precursors include iron nitrate, copper nitrate, cerium nitrate, cerium ammonium nitrate, manganese nitrate, magnesium nitrate, and zinc nitrate. Fuel elements treated according to the invention, and smoking articles including such fuel elements, are also provided.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Method for preparing fuel element for smoking article
The invention provides a method for making a fuel element for a smoking article including the steps of mixing a metal-containing catalyst precursor with a filler material or graphite or a combination thereof to form a pre-treated fuel element component; optionally calcining the pre-treated fuel element component in order to convert the catalyst precursor to a catalytic metal compound; after the optional calcining step, combining the pre-treated fuel element component with a carbonaceous material and a binder to produce a fuel element composition; and forming the fuel element composition into a fuel element adapted for use in a smoking article. Examples of metal-containing catalyst precursors include iron nitrate, copper nitrate, cerium nitrate, cerium ammonium nitrate, manganese nitrate, magnesium nitrate, and zinc nitrate. Fuel elements treated according to the invention, and smoking articles including such fuel elements, are also provided.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Method for preparing fuel element for smoking article
The invention provides a method for making a fuel element for a smoking article comprising forming a combustible carbonaceous material into a fuel element adapted for use in a smoking article; incorporating a metal-containing catalyst precursor into the fuel element or onto the surface thereof to form a treated fuel element, the incorporating step occurring before, during, or after said forming step; and optionally heating or irradiating the treated fuel element at a temperature and for a time sufficient to convert the catalyst precursor to a catalytic metal compound. Examples of metal-containing catalyst precursors include iron nitrate, copper nitrate, cerium nitrate, cerium ammonium nitrate, manganese nitrate, magnesium nitrate, and zinc nitrate. Fuel elements treated according to the invention, and smoking articles including such fuel elements, are also provided.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Hybrid metal organic scintillator materials system and particle detector
ActiveUS7985868B1Minimized quenching effectMinimize quenching effectPolycrystalline material growthOrganic chemistryOctahedronZinc nitrate
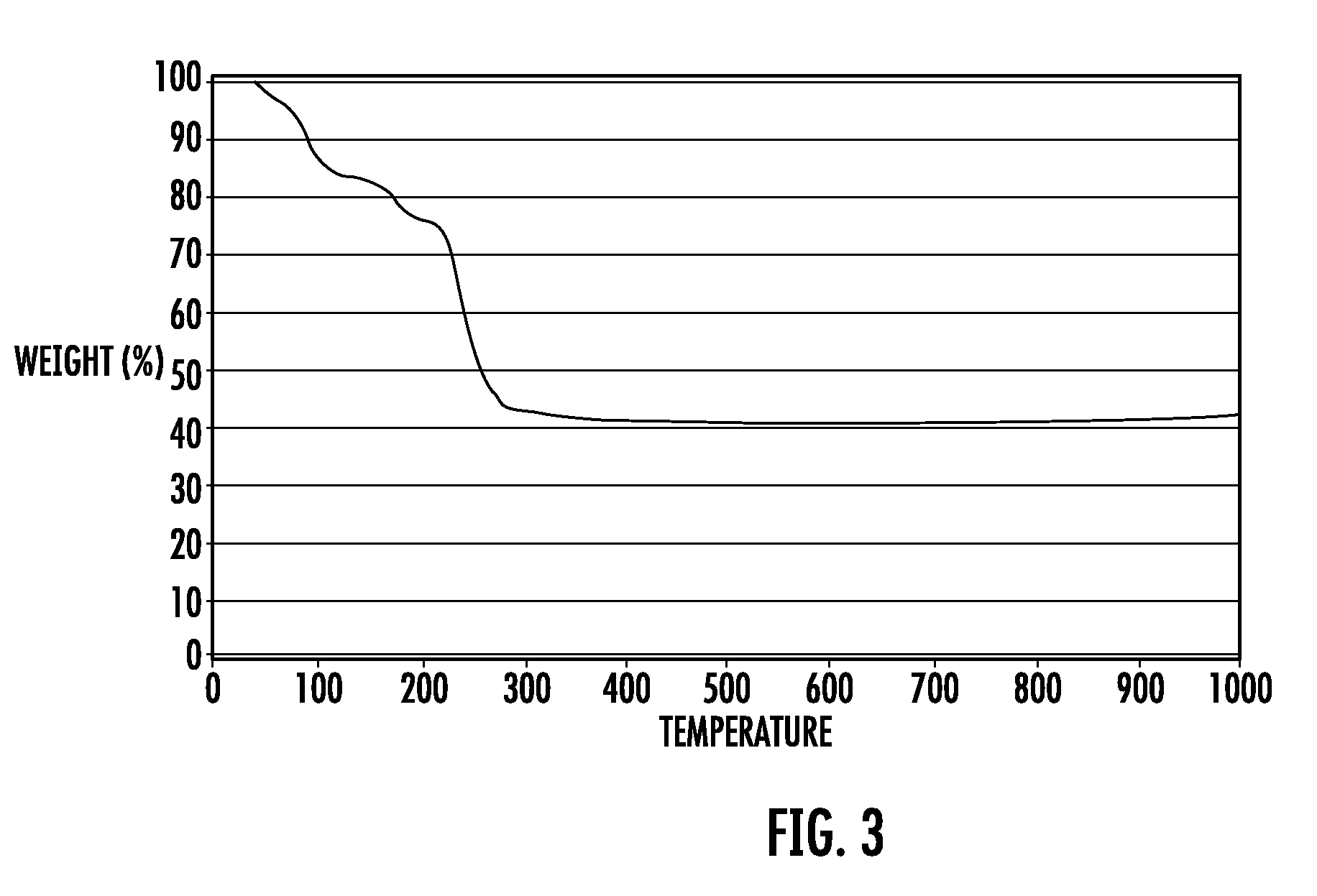
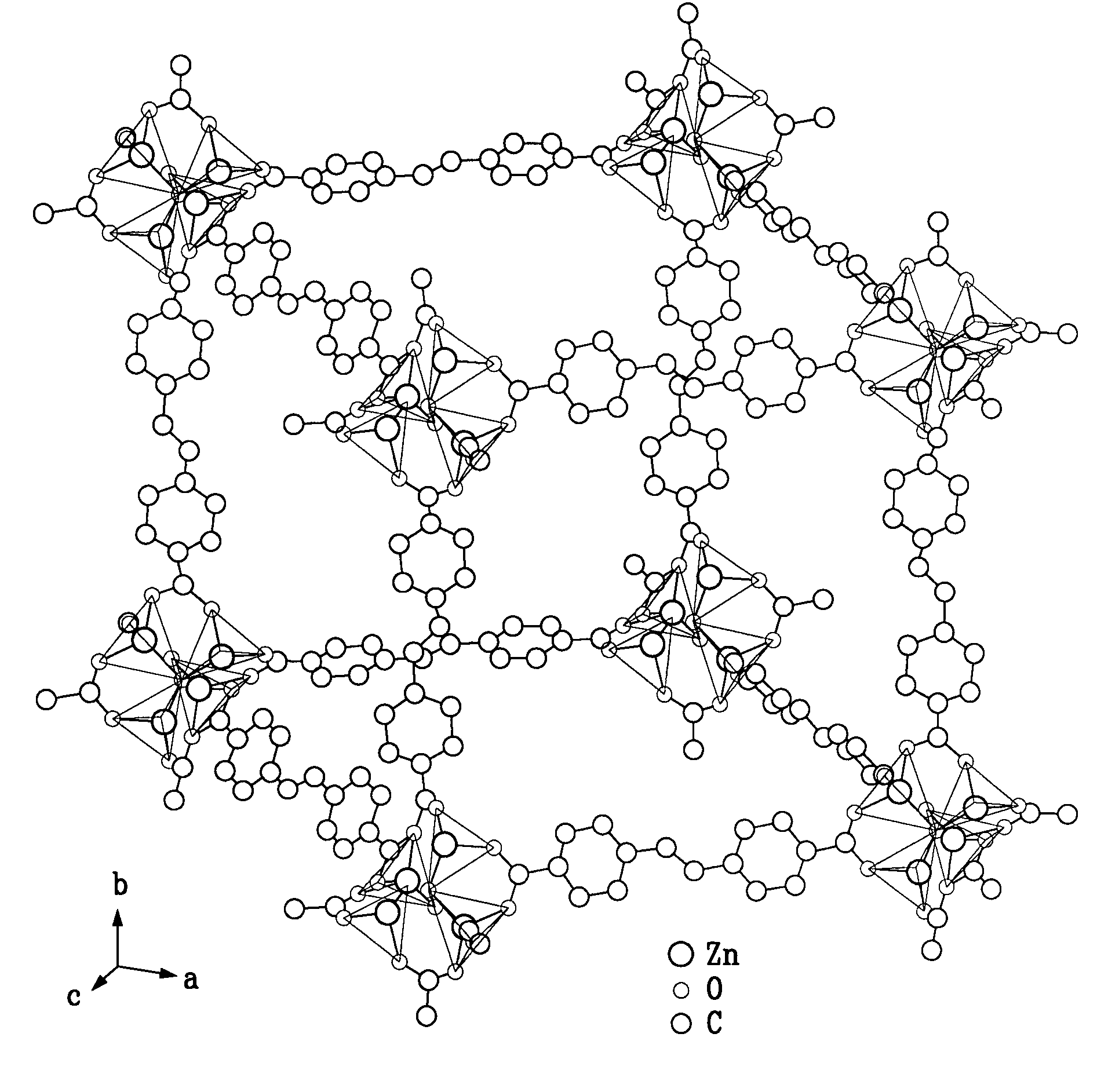
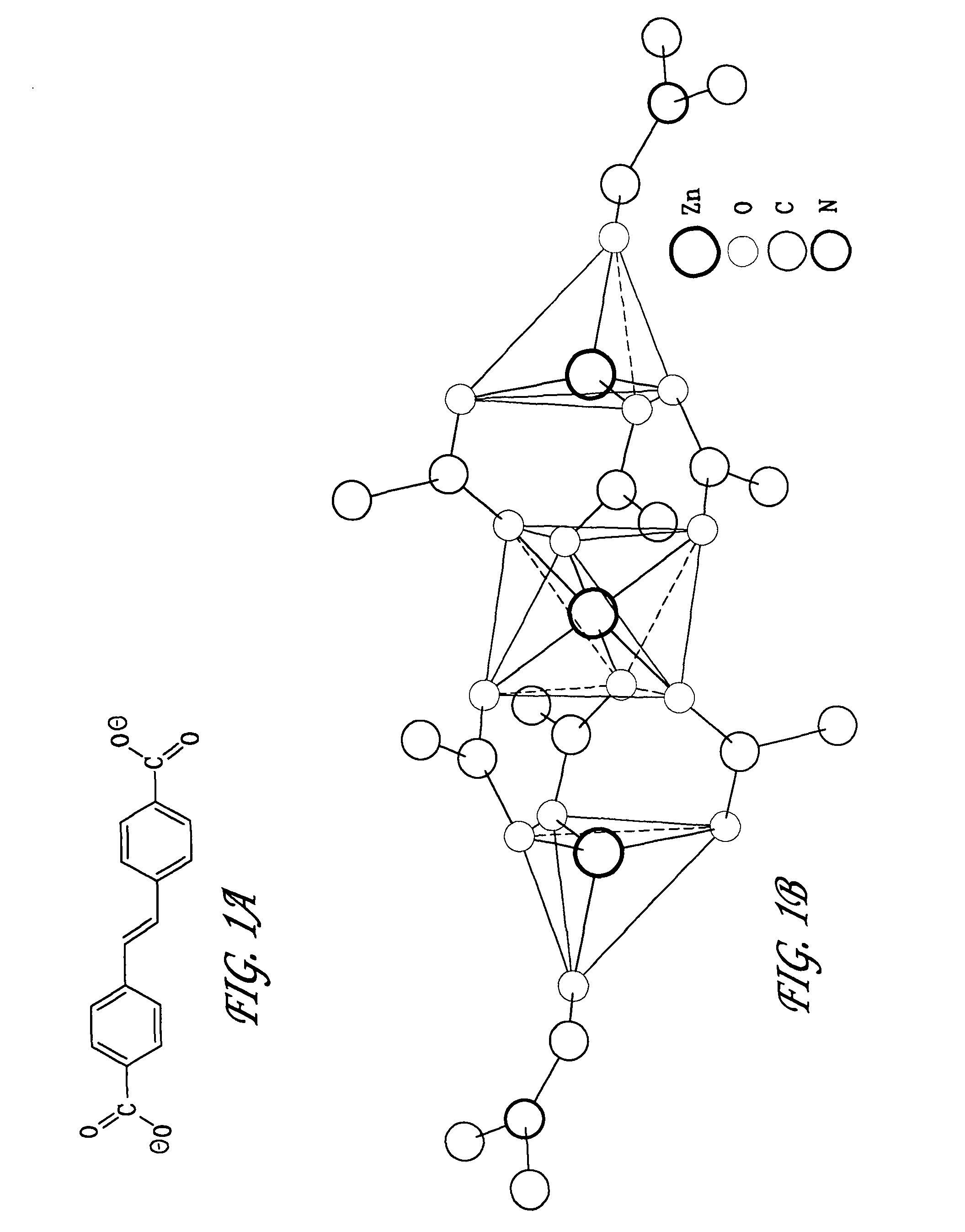
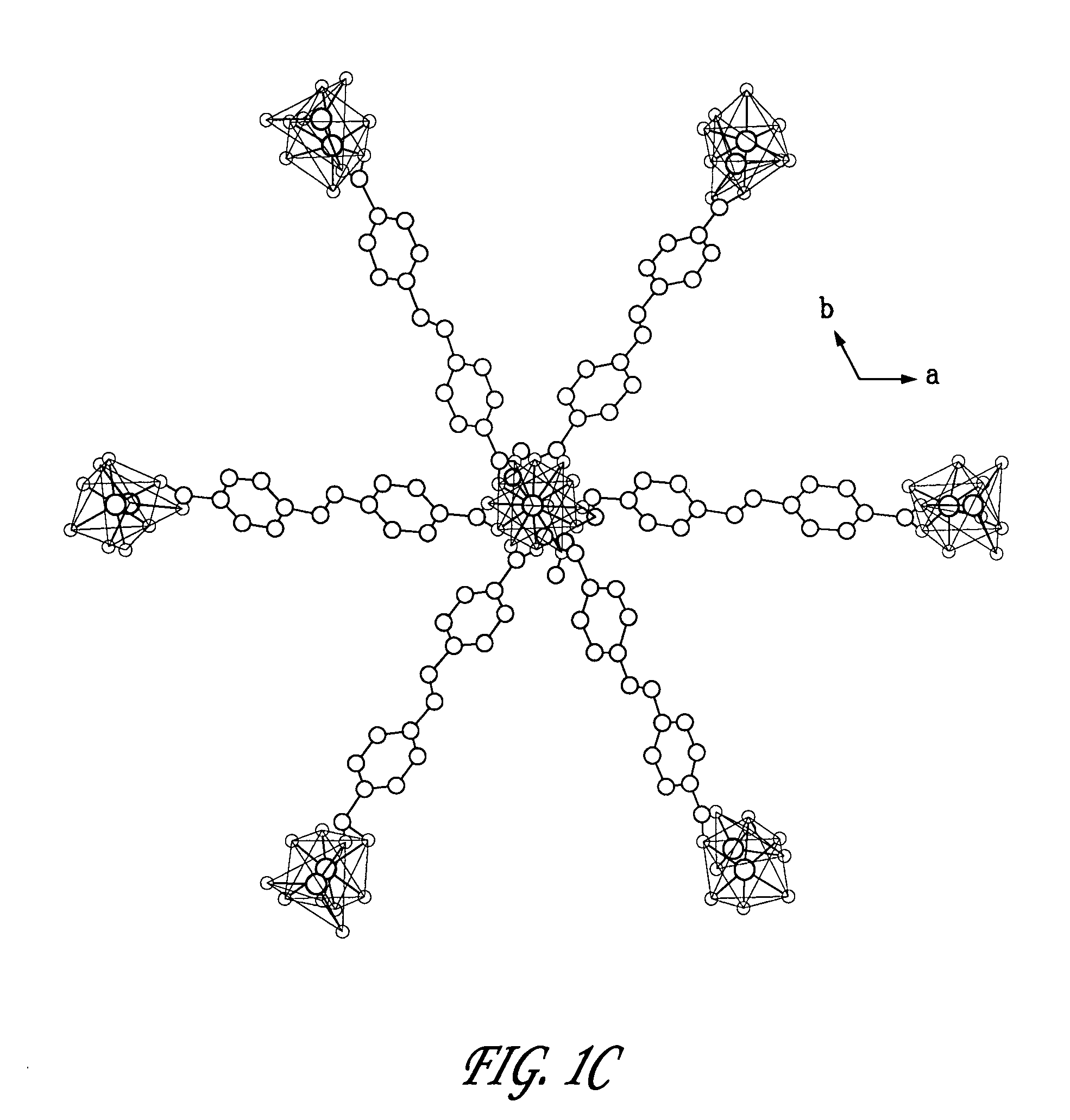
We describe the preparation and characterization of two zinc hybrid luminescent structures based on the flexible and emissive linker molecule, trans-(4-R,4′-R′) stilbene, where R and R′ are mono- or poly-coordinating groups, which retain their luminescence within these solid materials. For example, reaction of trans-4,4′-stilbenedicarboxylic acid and zinc nitrate in the solvent dimethylformamide (DMF) yielded a dense 2-D network featuring zinc in both octahedral and tetrahedral coordination environments connected by trans-stilbene links. Similar reaction in diethylformamide (DEF) at higher temperatures resulted in a porous, 3-D framework structure consisting of two interpenetrating cubic lattices, each featuring basic to zinc carboxylate vertices joined by trans-stilbene, analogous to the isoreticular MOF (IRMOF) series. We demonstrate that the optical properties of both embodiments correlate directly with the local ligand environments observed in the crystal structures. We further demonstrate that these materials produce high luminescent response to proton radiation and high radiation tolerance relative to prior scintillators. These features can be used to create sophisticated scintillating detection sensors.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Method for preparing fuel element for smoking article
The invention provides a method for making a fuel element for a smoking article including the steps of mixing a metal-containing catalyst precursor with a filler material or graphite or a combination thereof to form a pre-treated fuel element component; optionally calcining the pre-treated fuel element component in order to convert the catalyst precursor to a catalytic metal compound; after the optional calcining step, combining the pre-treated fuel element component with a carbonaceous material and a binder to produce a fuel element composition; and forming the fuel element composition into a fuel element adapted for use in a smoking article. Examples of metal-containing catalyst precursors include iron nitrate, copper nitrate, cerium nitrate, cerium ammonium nitrate, manganese nitrate, magnesium nitrate, and zinc nitrate. Fuel elements treated according to the invention, and smoking articles including such fuel elements, are also provided.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Boiler coal combustion-improving desulfurizing and denitrifying agent composition and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a boiler coal combustion-improving desulfurizing and denitrifying agent composition. The composition comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-7 parts of sodium carbonate, 1-3 parts of alumina, 2-8 parts of aluminium hydroxide, 2-5 parts of ferric trichloride, 2-6 parts of ferric oxide, 3-10 parts of potassium permanganate, 3-10 parts of potassium chlorate, 10-35 parts of activated attapulgite clay, 15-30 parts of urea, 2-4 parts of ammonium formate, 2-4 parts of ammonium chloride, 6-23 parts of ammonium acetate, 3-9 parts of manganese oxide, 9-12 parts of copper chloride, 1-3 parts of copper oxide, 2-4 parts of zinc sulfate, 1-3 parts of zinc nitrate, 7-18 parts of potassium dichromate, 1.0-1.5 parts of titanium dioxide, 0.5-1.0 part of barium molybdate, 0.5-1.5 parts of cobalt sulfate, 0.5-1.5 parts of vanadium pentoxide, 0.3-0.7 part of cerium oxide, 0.1-0.2 part of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate and 0.1-0.2 part of alkyl glyceryl ether. The composition is convenient to use, has stable properties, plays roles of combustion improving, desulfurization and denitrification, has coal saving rate of 8-25% and can remove fixed sulfur by 50-70%.
Owner:兰州熙瑞化工科技有限公司
Iron base catalyzer through Fischer-Tropsch synthesis and preparation method
InactiveCN1562471AReduce manufacturing costReduce preparation energy consumptionHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMicrosphereSlurry
A Fe-base catalyst with high antiwear performance, activity and stability for the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis contains Fe, Zn, Cu, K and SiO2. It is prepared through proportionally mixing sodium carbonate solution as precipitant with the mixed solution of iron nitrate, zinc nitrate and copper acetate, depositing to obtain deposit slurry, adding the mixed solution of potassium silicate and silicon sol, spray drying and calcining.
Owner:中科合成油淮南催化剂有限公司
Method for preparing cubic zirconium phosphate silver-carrying antimicrobial powder
The invention relates to a method for preparing a zirconium phosphate silver-carrying antimicrobial powder, particularly a cubic zirconium phosphate silver containing antimicrobial powder. The cubic zirconium phosphate silver-carrying antimicrobial powder is in the microstructure of a cube, the silver is carried by the cube, and the side of the cube has a length of 400-1,000nm. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a cubic zirconium phosphate carrier, mixing the cubic zirconium phosphate carrier with the aqueous solution of zinc nitrate, stirring to generate a zinc-carrying intermediate; preparing the zinc-carrying intermediate into an aqueous dispersion solution, adding the silver nitrate solution so that the carrier contains 1.5-3.5% of silver ions, stirring, washing, filtering, drying and forging to obtain the final product. The carrier is prepared by adopting the atmospheric-pressure hydrothermal synthesis method, and the hydrofluoric acid used as the template agent in the old process is replaced by the sodium oxalate. The process is simple and convenient to operate, and the equipment has high selectivity. The product and the product producing process are truly safe and nontoxic, the enamel equipment can be used as the production equipment, and the production cost can be saved.
Owner:晋大纳米科技(厦门)有限公司
Preparation method for photocatalytic material with strong adsorption and high visible light degradation of performance
The invention discloses a gahnitem, zinc oxide and nickel zinc nano-composite photocatalytic material which has a high specific surface area and a mesoporous structure and is prepared by roasting at high temperature by taking ternary hydrotalcite as a precursor. The material is used for the adsorption and the degradation of organic pollutants. The photocatalytic material is prepared by taking zinc nitrate, nickel nitrate, aluminum nitrate, sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide and the like as raw materials; preparing the raw materials into salt solutions and alkali solutions respectively; mixing the solutions by using a constant-flow pump at the temperature of 80 DEGC with magnetic stirring, transferring the mixed solution into a hydrothermal reaction kettle; performing hydrothermal treatment at 130 to 180 DEG C; performing suction filtration, washing and drying to the precursor; roasting the precursor in Muffle furnace for 2 to 6 hours at the temperature of 400 to 600 DEG C to obtain the product, wherein the specific surface area is greater than 150 m<2>.g<-1>. The photocatalyst disclosed by the invention has regular shape, large specific surface area, and super-high capacity for adsorbing and degrading organics, and can be reused; the raw materials for preparing the composite photocatalyst are abundant, the cost is low, and the process is simple.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for synthesizing vanadium acid zinc micro/nanowire material by adopting hydrothermal method
InactiveCN102140691AEasy to operateExperimental conditions are easy to controlPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsNanowirePhotoluminescence
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a vanadium acid zinc micro / nanowire material by adopting a hydrothermal method. In the method, ammonium metavanadate and zinc nitrate are used as reaction materials, distilled water is used as a solvent, a surfactant is used for controlling a microstructure, and the vanadium acid zinc micro / nanowire material with a regular appearance can be prepared under a hydro-thermal condition. The technology has the advantages of simplicity in operation, feasibility, controllable experimental condition, good repeatability, suitability for mass production and the like; and the synthesized material can play an important and positive role in multiple fields such as electrode material, photoluminescence, gas sensing and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
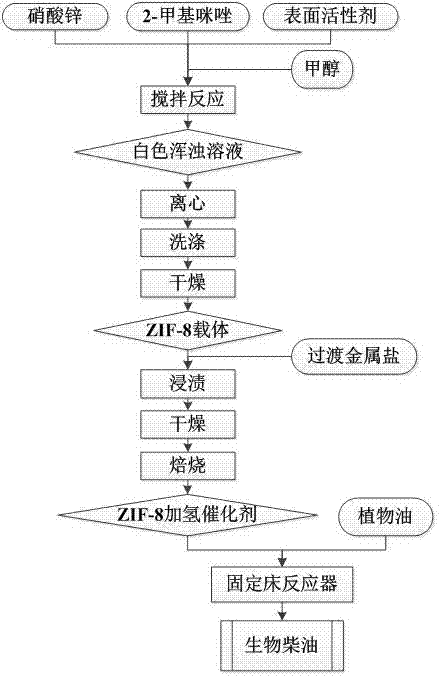
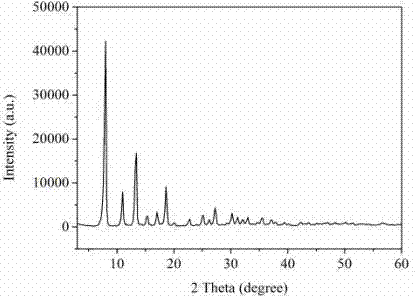
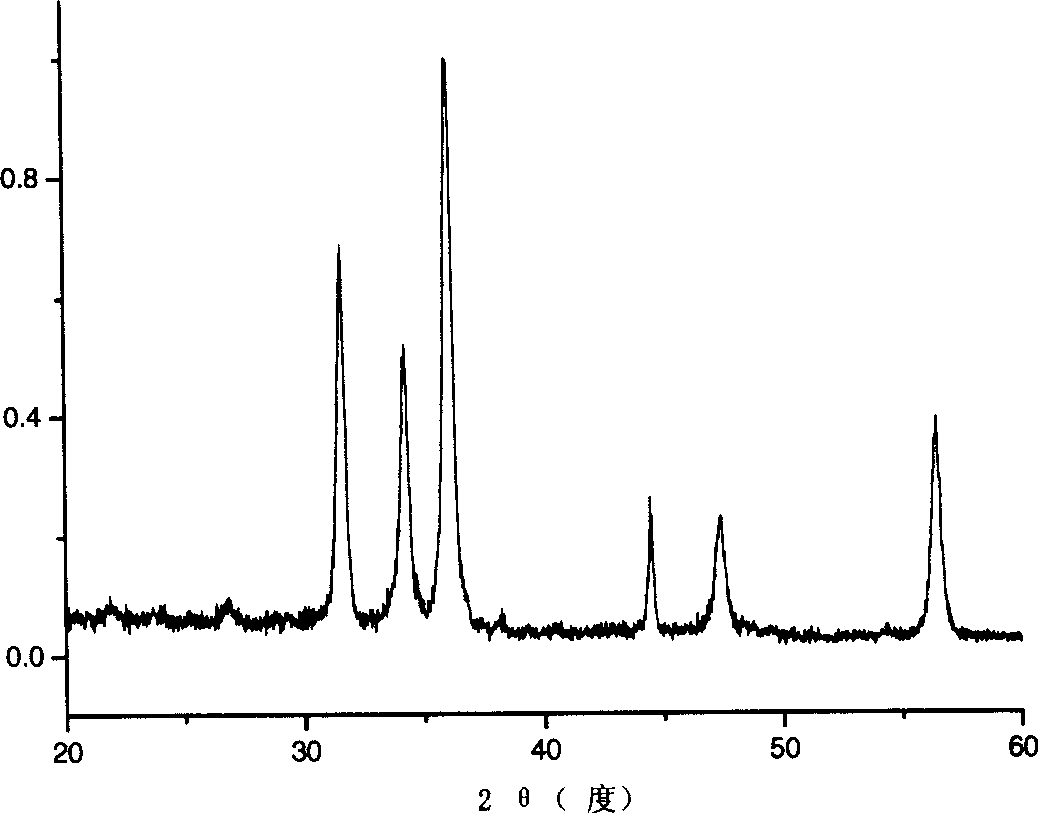
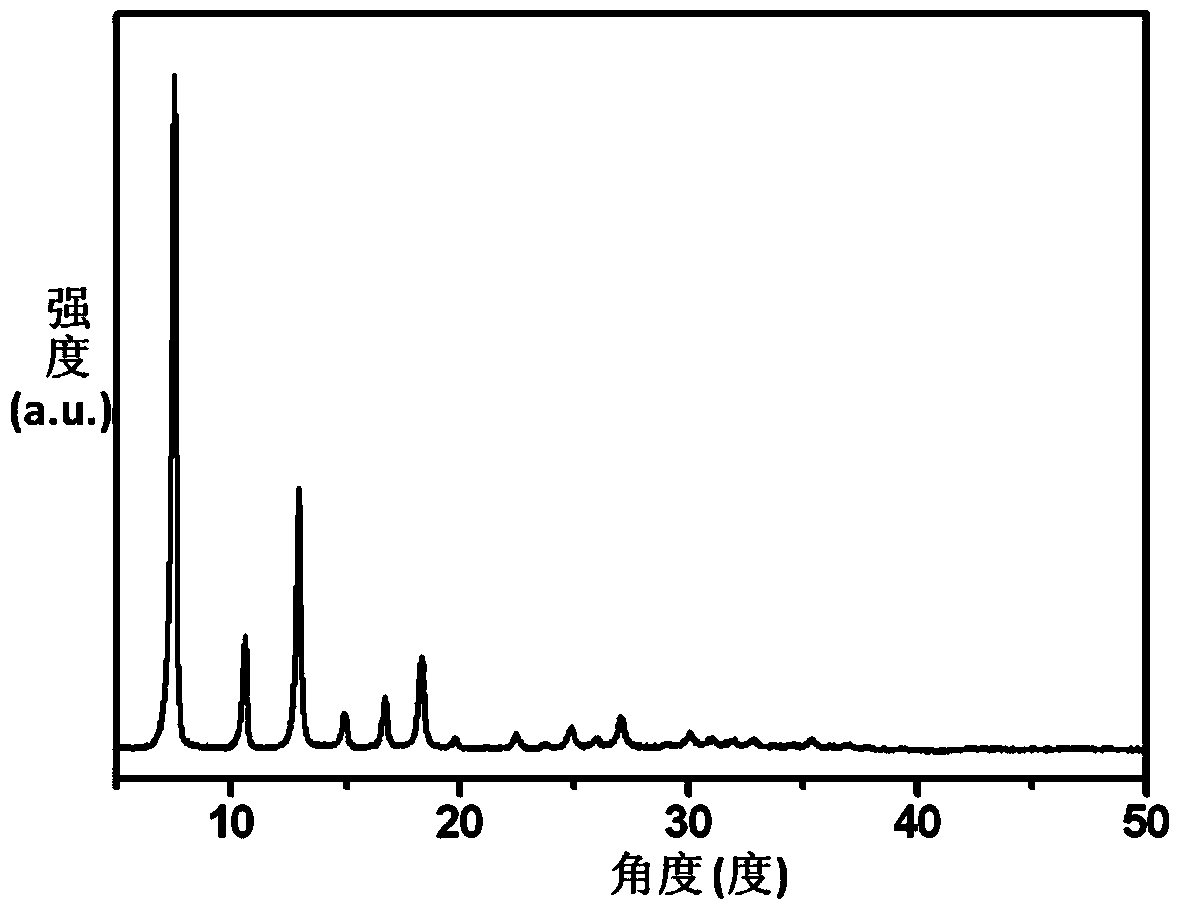
ZIF-8 material-based hydrogenation catalyst and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN104772165ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getEfficient preparation processOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBiodieselPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a ZIF-8 material-based hydrogenation catalyst and a synthetic method thereof. The synthetic method particularly comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving zinc nitrate, 2-methylimidazole and a surface active agent with methanol, carrying out stirring reaction for 1-6h at 20-60 DEG C, and standing for 10-18h to obtain a turbid solution; (2) carrying out centrifugal treatment on the turbid solution, placing sediments in a drying oven to be dried to obtain a ZIF-8 carrier after washing with methanol; and (3) dissolving transition metal salt with water, dipping the ZIF-8 carrier into the dissolved transition metal salt, and roasting in a muffle furnace to obtain the ZIF-8 material based hydrogenation catalyst. The hydrogenation catalyst can be used for preparing biodiesel; the biodiesel preparation method comprises the steps of placing the ZIF-8 material based hydrogenation catalyst into a fixed bed reactor to be reduced, and introducing vegetable oil into the reactor for hydrocracking reaction at 300-400 DEG C under the conditions that the hydrogen partial pressure is 2-4MPa, the air speed is 0.9-3.6h<-1> so as to obtain the biodiesel finally. The catalytic efficiency of the synthesized ZIF-8 material based hydrogenation catalyst is improved by dozens of times compared with the catalytic efficiency of a traditional aluminum oxide catalyst.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
High-adsorptivity modified activated carbon and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103566882ALarge specific surface areaBig gapOther chemical processesHazardous substancePotassium hydroxide
The invention relates to high-adsorptivity modified activated carbon which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-40 parts of grape vine, 40-50 parts of sawdust, 100-120 parts of activated carbon, 30-40 parts of corn cob, 6-9 parts of potassium hydroxide, 7-10 parts of sodium lauryl sulfate or polyethylene glycol, 7-10 parts of urea, 2-5 parts of zinc nitrate, 2-5 parts of nickel nitrate, 10-14 parts of Arabic gum or sodium alginate, 7-10 parts of modified attapulgite and a right amount of water. According to the invention, the grape vine, sawdust and corn cob are subjected to high-temperature heat treatment, and the prepared activated carbon has large specific surface area, realizes new application of wastes and achieves the effects of convenient carbonization activation process and less pollutant discharge; and by using the potassium hydroxide, urea, zinc nitrate and nickel nitrate substances for modification, the activated carbon increases the gap and enhances the adsorption capacity. Besides, the high-adsorptivity modified activated carbon is accessible in raw materials, simple in process, low in cost and suitable for industrial production, causes no generation of harmful substances and has favorable application prospects.
Owner:安徽金叶碳素科技有限公司
Porous carbon adsorbing agent containing nano zinc oxide micropartical and its preparation process and application
InactiveCN1724138AImprove adsorption capacityAvoid breedingOther chemical processesSorbentPorous carbon
A porous charcoal adsorbent for cleaning environment is composed of porous charcoal as carrier and zinc oxide nano-particles as active component. Its preparing process includes such steps as reaction between zinc nitrate micro-emulsion and sodium hydroxide to obtain zinc oxide nano-particles, carrying them by porous charcoal and heat treating. Its advantages are high absorptive power and high photo-catalytic and antibacterial activities.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Preparation method of high-nitrogen-doped graphene nanoparticles and application of high-nitrogen-doped graphene nanoparticles as negative material of lithium ion battery
ActiveCN104201385AEasy to dopeHigh nitrogen contentMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesDoped grapheneZinc nitrate
The invention provides a preparation method of high-nitrogen-doped graphene nanoparticles and application of the high-nitrogen-doped graphene nanoparticles as a negative material of a lithium ion battery. The corresponding method comprises the following steps: slowly dropwise adding a preset quantity of zinc nitrate (Zn(NO3)) methanol solution into a methanol mixed solution which is prepared from a preset amount of 2-methylimidazole (C4H6N2) and a preset amount of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), magnetically stirring and standing for preset time, carrying out centrifugal separation to obtain ZIF-8(a complex formed by zinc and 2-methylimidazole) nanoparticles; and putting the obtained ZIF-8 nanoparticles in a high-temperature furnace and calcining at 600-1,000 DEG C for preset time in the nitrogen atmosphere to obtain the high-nitrogen-doped graphene nanoparticles. The preparation process of the high-nitrogen-doped graphene nanoparticles is simple, and the high-nitrogen-doped graphene nanoparticles are uniform in shape, relatively large in specific surface and high in content of nitrogen, and have great application potentials in aspects of lithium ion batteries, electrochemical energy storage, catalysis and the like. The preparation method of the high-nitrogen-doped graphene nanoparticles is simple and efficient, safe and liable to implement, short in synthesis cycle, is capable of preparing a large quantity of high-nitrogen-doped graphene nanoparticles and is expected to be popularized and industrially applied.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Continuous large-area zinc oxide nano-sheet and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to continuous large-area zinc oxide nano sheets and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of nano material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: building a micro-nano structure on a metal and metal oxide substrate as required; dispersing zinc nitrate and hexamethylenetetramine in deionized water by use of the hydrothermal synthesis method, and softly stirring for dissolution; subsequently, reacting at a constant temperature of 70 to 110 DEG C for 10 minutes to 10 hours, taking out the sample, cleaning and drying to obtain a continuous porous membrane consisting of zinc oxide nano sheets on the substrate. The thickness of the obtained zinc oxide nano sheets is between 1 to 100 nanometers, and the nano sheets are connected with each other on the substrate to form a porous structure, wherein the aperture of the porous structure is between 0.5 to 3 mu m and the total thickness of the porous zinc oxide layer is between 100 nm to 50 mu m. Such continuous zinc oxide porous membrane can form a free independent structure after the substrate is removed, and the application field thereof includes gas sensor, solar battery material, surface coating, nano photoelectric device and so on.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of zinc-oxide nanorod array film
InactiveCN103397382AImprove UV Luminescence PerformanceHigh UV Luminescence PerformancePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsNanogeneratorHexamethylenetetramine
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor film preparation, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a zinc-oxide nanorod array film. The technical scheme adopted by the invention is as follows: the preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) on the basis of adopting height (001)-oriented ZnO as a seed layer, putting the ZnO seed layer into an aqueous solution of zinc nitrate (Zn(NO3)2), polyethyleneimine (PEI) and hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) for epitaxial growth to obtain a (001) preferred-orientation ultralong ZnO nanorod array film; (2) carrying out fast annealing treatment on the film, and improving the photoluminescence performance of the ZnO array film. The technology has the advantages that the continuous growth of the ZnO nanorod at the temperature higher than 100 DEG C can be realized; due to the high-temperature growth condition, the crystallization quality of the nanorod is improved, the internal defects are obviously reduced; the zinc-oxide nanorod array film has excellent photoelectric performance, and is more conductive to being applied in photoelectric devices such as dye-sensitized solar batteries, ultraviolet detectors, field-effect transistors, light-emitting diodes and nanogenerators.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method for preparing zinc oxide nanostructures and zinc oxide nanostructures prepared by the same
InactiveUS20090098043A1Increase probabilityIncrease ratingsMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsZinc ionHexamethylenamine
Example embodiments provide a method for preparing zinc oxide nanostructures. According to the method, zinc oxide nanostructures are prepared by dipping a substrate having a zinc (Zn) seed layer thereon in an aqueous solution of hexamethyleneamine and dropwise adding an aqueous solution of zinc nitrate to the aqueous solution of hexamethyleneamine. In addition, zinc ions can be continuously supplied in a constant amount as the reactions of the reactants proceed to prepare high-quality zinc oxide nanostructures at a high growth rate. Furthermore, zinc oxide nanostructures can be prepared on a large-area substrate at a low processing temperature regardless of the substrate material. Example embodiments also provide zinc oxide nanostructures prepared by the method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for preparing methanol synthesizing catalyst
InactiveCN101584986AEvenly distributedUniform particle size distributionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationCopper nitrateSlurry
According to a method for preparing methanol synthesizing catalyst, a water solution which contains copper nitrate, zinc nitrate, aluminum nitrate and a fourth component with a total concentration of 0.5-2.0mol / L and a water solution that contains the sodium carbonate with a concentration of 0.5-2mol / L are prepared. At a state that the temperature is controlled to 50-80 DEG C with the microwave, the pH value is controlled to 6.5-8.5 for executing coprecipitation reaction. Then the water solution is aged for 0.5-3 hours in the temperature of 60-90 DEG C, which is controlled with the microwave. Then the precipitate is washed and filtered with the de-ionized water. Then the filter cake is dried for 1-11 hours at the condition that the temperature is controlled to 70-150 DEG C with the microwave. Finally the dried precipitate is calcined for 1-5 hours at the condition that the temperature is controlled to 300-400 DEG C with the microwave for obtaining the target catalyst. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple technique, moderate operation condition, smaller and more uniform catalyst particle particularly when the microwave heating is introduced and higher mechanical strength of the catalyst. The test through the static bed and the slurry-bed reactor shows that the activity and the stability of the catalyst are better than those of the catalyst prepared through the conventional heating and the bottleneck of incapability for industrializing of the slurry-bed caused by the easy inactivation is broken through.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing soakage controllable zinc oxide nano-stick array thin film
The invention relates to a method for preparing zinc oxide nano-rods array membrane with controllable wettability, which belongs to a field of nano materials. The invention uses zinc acetate sol to prepare adhesive membrane on a basement through spinning technics; a crystal membrane is generated after annealing; the basement is positioned in mixed precursor solution of zinc nitrate and hexamethylene tetrammine and is hydro-deposited for 3-5 hours under a temperature ranging from 90 DEG C to 100 DEG C; the zinc oxide nano-rods array can be prepared on the basement. At the same time, by controlling concentration of the sol, times of spinning, temperature and time of annealing, controllability of the zinc oxide nano-rods array density and controllability of the array wettability can be realized; problem of unsteady wettability of the array can also be overcome.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
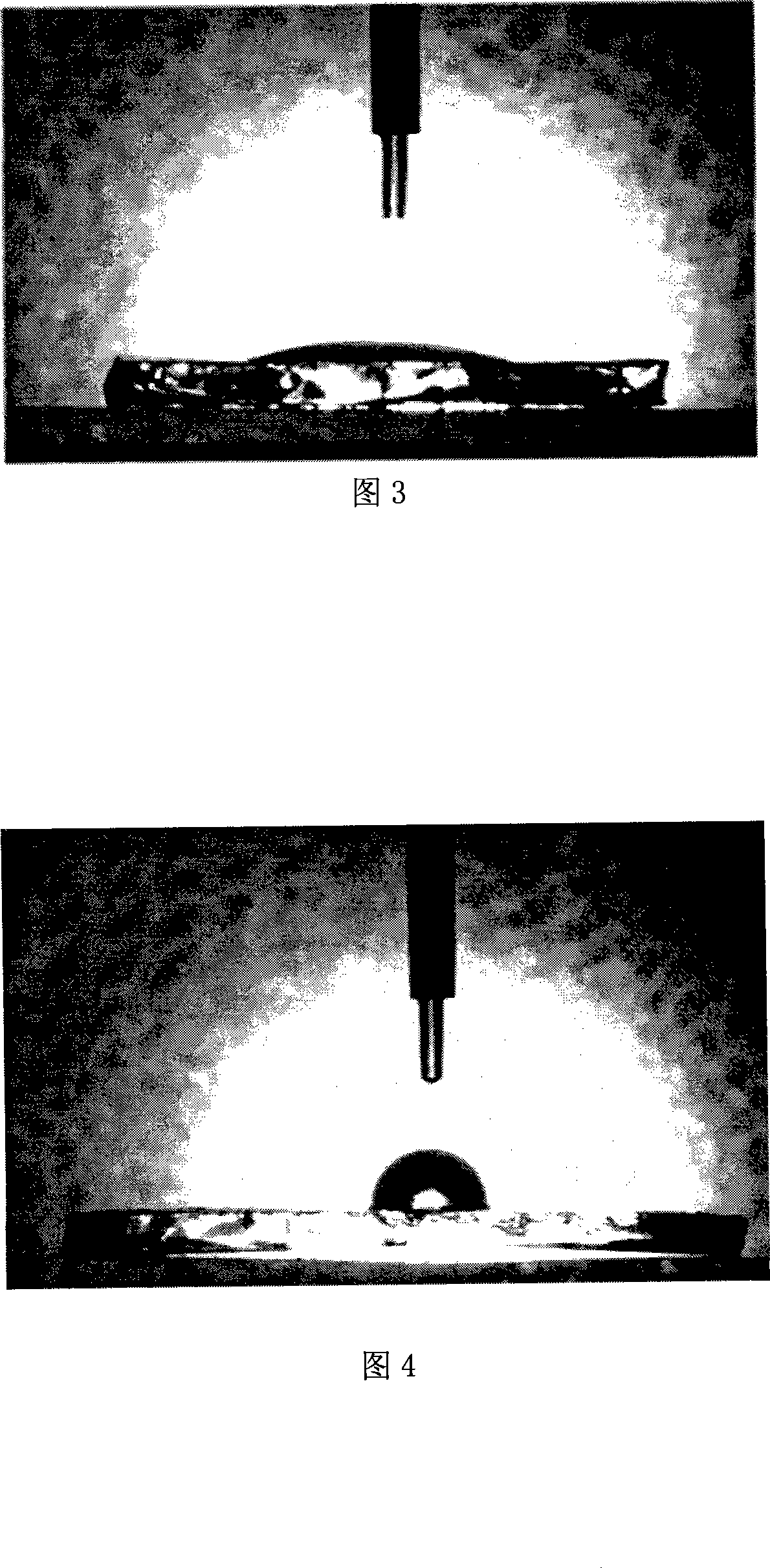
Ordinary temp. parkerizing liquid
InactiveCN1401820AFast phosphatingFast combinationMetallic material coating processesSoftened waterManganese
An ordinary-temp phosphating liquid for the phosphate treatment of surface of iron and steel contains phosphoric acid (2-4 wt.%), zinc oxide (0.4-0.6 wt.%), zinc nitrate (0.5-1.5 wt.%), nickel nitrate (3-5 wt.%), manganese nitrate (2-4 wt.%), sodium borofluorate (0.2-1 wt.%), sodium chlorate (2-3 wt.%), citric acid (0.5-2 wt.%), and softened water (the rest). Its advantages are high stability, long film-forming time, and high film strength and resistance to corrosion.
Owner:CHINA NATIONAL HEAVY DUTY TRUCK GROUP
Zinc oxide/titanium dioxide hybrid electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101702377AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyEasy to industrializeLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesDip-coatingZinc nitrate
The invention discloses a highly ordered zinc oxide nanometer rod electrode compound titanium dioxide electrode belonging to the technology of a dye-sensitized solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The method is as follows: depositing a layer of ZnO nano-crystal particles on a transparent electric conduction glass as a seed crystal surface, using a nonionic surface modifier and a zinc nitrate solution as a precursor, growing a ZnO nano rod array on the seed crystal surface and then calcining the ZnO nano rod array for a period of time in a certain temperature to prepare the highly ordered ZnO nano rod electrode, and finally forming a TiO2 membrane on the ZnO nano rod array electrode by a dip-coating method; the TiO2 membrane is sintered again to form the Zinc oxide / titanium dioxide hybrid electrode.
Owner:IRICO
Zinc-iron metal alramenting liquid capable of being recycled at normal temperature
InactiveCN101935832ALow investment costReduce energy consumptionMetallic material coating processesSlagPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a zinc-iron metal alramenting liquid capable of being recycled at normal temperature. The invention is characterized in that the alramenting liquid is prepared by the following raw materials by weight percent: 14-28% of phosphoric acid, 3.5-7% of zinc oxide, 12.6-17.5% of zinc nitrate, 0.14-0.56% of citric acid, 0.14-0.7% of tartaric acid and 0.14-0.84% of molybdate, and balance of water.In the invention, phosphorization is carried out in one process after oil removing and rust removing are carried out, the processes of neutralizing, surface conditioning, passivating and washing are eliminated, and a compact and uniform phosphorization membrane with strong adhesive force is rapidly formed on the surface of ferrous metal. The process greatly reduces operation procedure, the phosphorization process produces no slag, thus reducing pollution to the environment and greatly improving utilization factor of material; and energy consumption at normal temperature is reduced and water is saved. The invention has the advantages of wide application range, less investment, high efficiency and high safety, and bath solution has good stability, no deterioration or volatilization is caused, and maintenance is easy, thus being beneficial to follow-up spraying processes.
Owner:NANJING YOUWEI CHEM
Method for synthesizing ZIF-8 aerogel on basis of cellulose hard template
ActiveCN104629080AImprove the stability of useGood gas storage performanceCelluloseEnvironmental resistance
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a ZIF-8 aerogel on the basis of a cellulose hard template. The method is based on a cellulose hard template and comprises the following steps: reacting 2-methylimidazole and zinc nitrate to form ZIF-8 carried on the cellulose surface, carrying out solvent washing and repeated carrying so that the ZIF-8 crystal grains uniformly grow on the cellulose surface, and finally, carrying out exchange, freeze-drying and the like to keep the aerogel structure. The ZIF-8 aerogel has larger specific area, and has certain promoting actions on researching application of metal organic frame materials in the field of gas storage. The method has the advantages of simple technique and favorable repetitiveness, uses cheap and accessible industrial raw materials, conforms to the requirements for environmental protection, and can implement mass production.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Silver nanoparticle-modified zinc oxide nanorod array and preparation method and application thereof
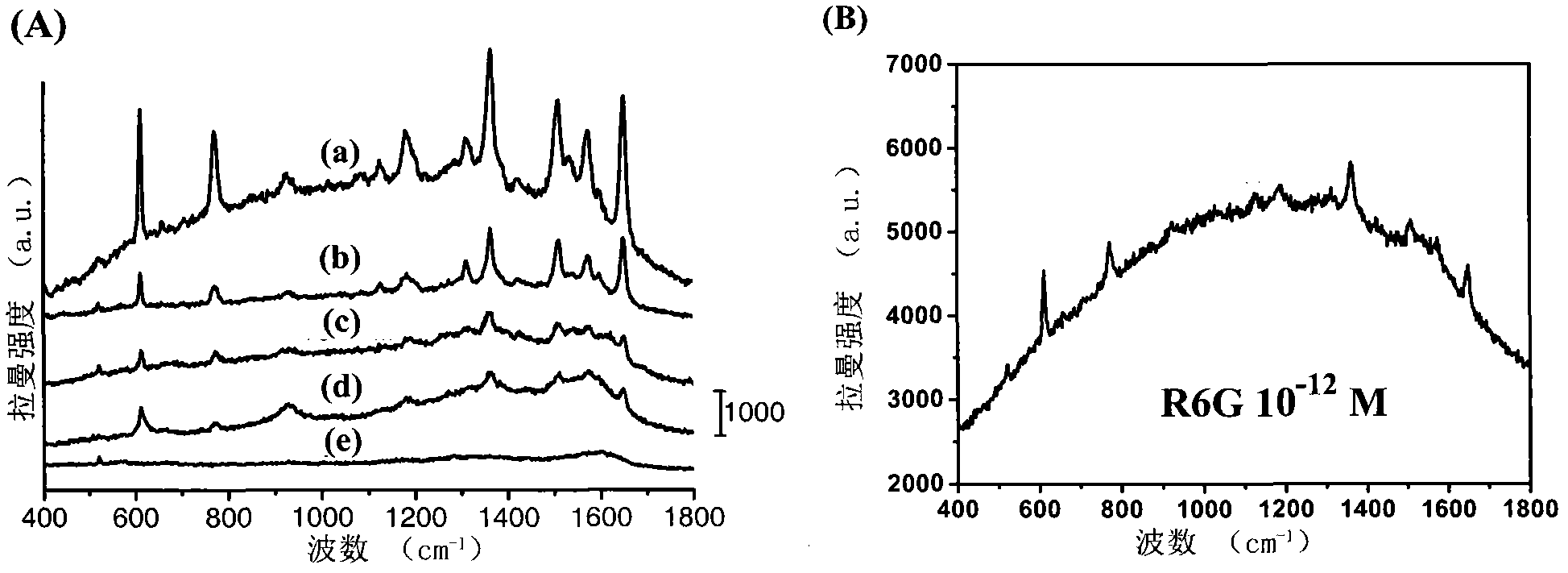
InactiveCN103030095AEliminate the disadvantages of oxidationLow costDecorative surface effectsRaman scatteringPolychlorinated biphenylZinc oxide nanorod sensor
The invention discloses a silver nanoparticle-modified zinc oxide nanorod array, a preparation method thereof and application thereof. An array consisting of zinc oxide nanorods is arranged on a substrate; the length of the zinc oxide nanorods is 1 to 1.4mu.m; the diameter of the rods is 50 to 60nm; the size of silver nanoparticles at the top ends of the rods is 100 to 120nm; the size of the silver nanoparticles on the surfaces of the rods is 25 to 35nm; the distance between the particles is less than or equal to 10nm; the distance between the silver nanoparticles at the top ends of the adjacent rods is 40 to 60nm; and the distance between the silver nanoparticles on the surfaces of the adjacent rods is 25 to 35nm. The method comprises the following steps of coating a zinc acetate ethanol solution on the substrate; after drying the substrate, cleaning, dispersing and thermally decomposing the substrate to obtain a substrate on which a zinc oxide seed layer is coated; performing electro-deposition on the substrate coated with the zinc oxide seed layer in a zinc nitrate ammonia complexation solution to obtain a substrate with the zinc oxide nanorod array; and performing silver ion sputtering on the substrate in an ion sputter to obtain the target product. The silver nanoparticle-modified zinc oxide nanorod array can serve as an active substrate of SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering) and is used for measuring rhodamine 6G or polychlorinated biphenyl 77.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
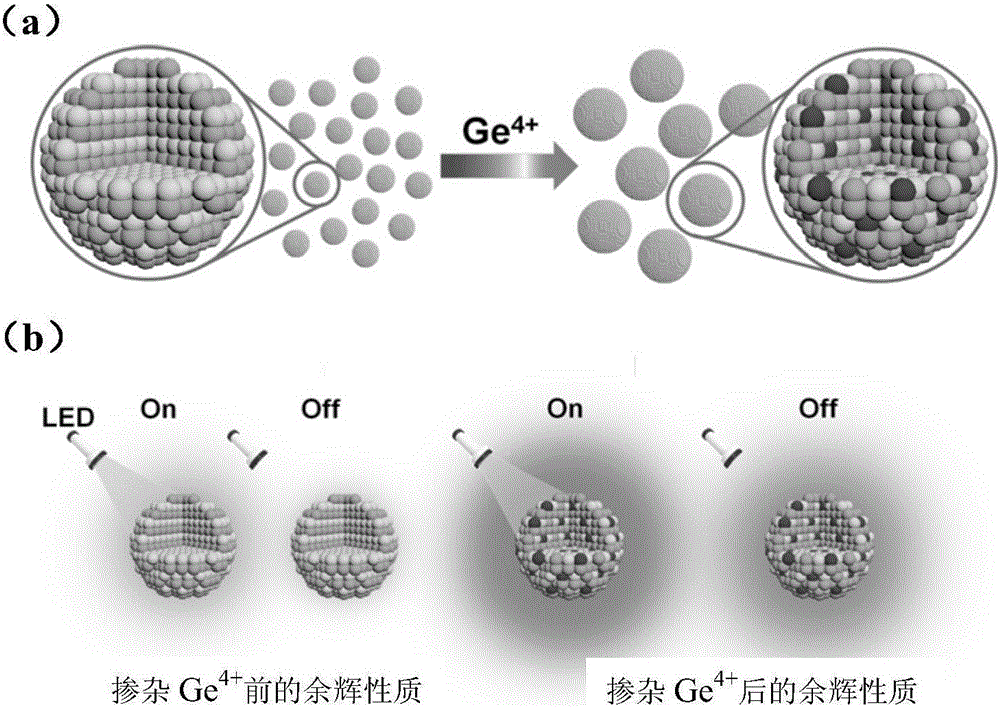
Long-afterglow nanomaterial based on ion doping as well as preparation method and application of long-afterglow nanomaterial
InactiveCN105754595AAbundant and easy to get raw materialsThe synthesis method is simpleIn-vivo testing preparationsLuminescent compositionsZinc nitrateChromium nitrate
The invention discloses an afterglow nanomaterial and a preparation method of a long-afterglow nanomaterial with sizes and spectrum adjusted on basis of ion doping. An expression formula of the nanomaterial is Zn(1+x)Ga(2-2x)GexO4:0.75%Cr, wherein x is larger than or equal to 0 and smaller than or equal to 0.5, and the particle size is 7 nm-80 nm. According to the preparation method, a zinc nitrate solution, a gallium nitrate solution, a sodium germinate solution and a chromium nitrate solution in specific proportions are mixed together, ammonia water is added rapidly while the mixture is stirred, and the pH of the mixed solution is adjusted to 10; then, the mixed solution is transferred to a high-temperature hydrothermal kettle and reacts at the temperature of 120 DEG C, and the afterglow nanomaterial is obtained. The method is simple and easy to implement, severe experiment conditions and complicated large instruments are not required, synthesized nanoparticles are uniform in sizes and have a good water-phase dispersion property and high afterglow strength, the afterglow time can reach 10 h, and accordingly, the synthesized nanoparticles are suitable for improving the physical and chemical properties of the long-afterglow nanomaterial.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Zinc cobaltate nanosheet array/foamed nickel combined electrode, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103440998AAvoid cumbersomeIncrease profitHybrid capacitor electrodesNanotechnologyCapacitanceZinc nitrate
The invention discloses a zinc cobaltate nanosheet array / foamed nickel combined electrode, a preparation method and application of the zinc cobaltate nanosheet array / foamed nickel combined electrode, and belongs to the technical field of energy storage. The preparation method particularly comprises the steps of dissolving zinc nitrate, cobalt nitrate, ammonium fluoride and urea into a mixing solution composed of deionized water and alcohol (one or more kinds of methyl alcohol, ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol), evenly mixing, then immersing foamed nickel into the solution, carrying out hydrothermal reaction, and obtaining the zinc cobaltate nanosheet array / foamed nickel combined electrode after natural cooling, washing drying and calcination. Zinc cobaltate nanosheets obtained through the preparation method perpendicularly or slantly grow on the surface of the foamed nickel and are firmly combined with the foamed nickel, the zinc cobaltate nanosheets and the foamed nickel are mutually connected to form a nanosheet array, therefore, the contact areas between an electrolyte and the nanosheets are increased, and the stability of the nanosheet array and the stability of the whole electrode are further improved. When the zinc cobaltate nanosheet array / foamed nickel combined electrode is tested as the work electrode of a supercapacitor, the high specific capacitance and the cycling stability can still be achieved under the large current density condition.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Precipitating-hydrothermal preparation with high visible light catalytic activity nano CdxZn1-xS photocatalyst
InactiveCN101254467AControl ingredient ratioControl grain sizeCatalyst activation/preparationZinc nitrateVisible light photocatalytic
The invention discloses a deposition-hydrothermal method for preparing a nano-sized CdxZn<1-x>S photocatalyst with high visible-light photocatalytic activity. The method includes the following steps: 1) adding dropwise a mixed solution of cadmium nitrate and zinc nitrate into a sodium sulfide solution, stirring at a medium rate for 0.5-3 hours, maintaining the temperature at 10-40 DEG C to obtain a nano-sized powdery precursor precipitate; 2) placing the nano-sized powdery precursor precipitate in a reaction vessel, raising the temperate at a rate of 1-5 DEG C / min up to 150-240 DEG C, maintaining the temperature, allowing hydrothermal reactions for 12-24 hours, stopping the hydrothermal reactions, naturally cooling down to room temperature, taking out the reaction products, washing with the deionized water and the anhydrous alcohol for 3-4 times, drying at 50-80 DEG C in a vacuum drying oven to obtain a solid solution of nano-sized CdxZn<1-x>S photocatalyst. The production method is carried out in water phase with easy operation and low cost. The product has uniform distribution of particle size, the forbidden band width and optical properties thereof are controlled by changing components, and the product has high visible-light photocatalytic activity and good prospects in industrial application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Shell metal stamping part surface treatment technique
InactiveCN104404491AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove corrosion resistanceMetallic material coating processesWorking fluidPhytic acid
The invention discloses a shell metal stamping part surface treatment technique which comprises the following steps: 1) mixing 65 parts by mass of ethanedioic acid, 7 parts by mass of zinc nitrate, 5 parts by mass of sodium molybdate, 2.3 parts by mass of nickel nitrate, 2 parts by mass of coconut diethanol amide, 3 parts by mass of phytic acid and 2 parts by mass of dodecyl trimethyl ammonium sulfate, and reacting at 115 DEG C for 3 hours to obtain a metal surface treating agent; 2) mixing 17 parts by mass of metal surface treating agent and 136 parts by mass of water to obtain a surface treatment working fluid; and 3) heating the surface treatment working fluid to 54 DEG C, and putting the metal stamping part in the surface treatment working fluid to perform surface treatment for 27 minutes. The surface treatment technique can enhance the oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance of the metal stamping part.
Owner:常熟市宏福塑料金属制品有限公司
Zinc cobaltate nanorod/foam nickel composite electrode, preparation method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN102664103AIncrease contactImprove cycle performanceCapacitor electrodesOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEElectrolytic agent
The invention provides a zinc cobaltate nanorod / foam nickel composite electrode, a preparation method thereof and application thereof. According to the method, a foam nickel plate is immersed in a mixed solution of zinc nitrate and cobalt nitrate, heating and heat preservation are carried out in order, an oxalic acid solution is added dropwise, reaction is carried out until the foam nickel grows a nanostructured precursor, the foam nickel is removed, and cleaning, drying and calcining are carried out in order to obtain the zinc cobaltate nanorod / foam nickel composite electrode. The composite electrode has properties of one-dimensional zinc cobaltate nano material with a large specific surface area and porous foam nickel, a contact area with an electrolyte is effectively increased, the electrode material is more fully involved in an electrochemical reaction, the composite electrode obtained through the reaction has a good electrochemical property and is applied in a super capacitor, the performance of a present capacitor is greatly raised, production process is simple, and the electrode is easy to be applied to the actual mass production.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
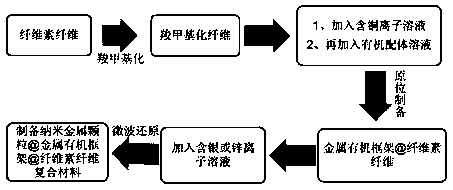
Method for preparing nanometal particle/metal organic frame composite antibacterial cellulose fibers
ActiveCN108589266AImprove antibacterial propertiesGood dispersionBiochemical fibre treatmentVegetal fibresMetal-organic frameworkCellulose fiber
A method for preparing nanometal particle / metal organic frame composite antibacterial cellulose fibers comprises the following steps: carboxymethylating fibers, introducing more carboxyl anion groups,stirring and blending a metal salt solution and the obtained fibers, adding an organic ligand solution, circularly preparing metal organic framework@cellulose fibers, adding a certain concentration of a silver nitrate or zinc nitrate solution, performing uniform stirring, and carrying out microwave-assisted reduction to obtain the novel nanometal particle@metal organic frame composite antibacterial fibers. The large specific surface area and the high surface charge of the metal organic framework@cellulose fiber composite material are fully used to solve the problem of easy agglomeration ofnanometal particles, so the method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, convenience, low cost, and controllable particle size of the metal nanoparticles, the nanometal particle / metal organicframe composite antibacterial cellulose fibers have a good structural stability and an efficient and long-lasting antibacterial property, and the antibacterial rates against Staphylococcus aureus andEscherichia coli respectively are 99% or above.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com