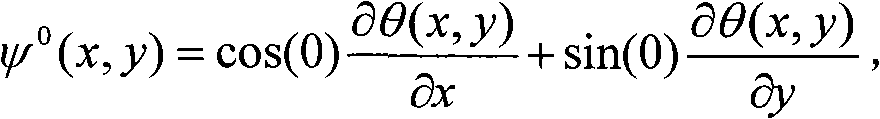Patents
Literature
152 results about "Earth crust" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
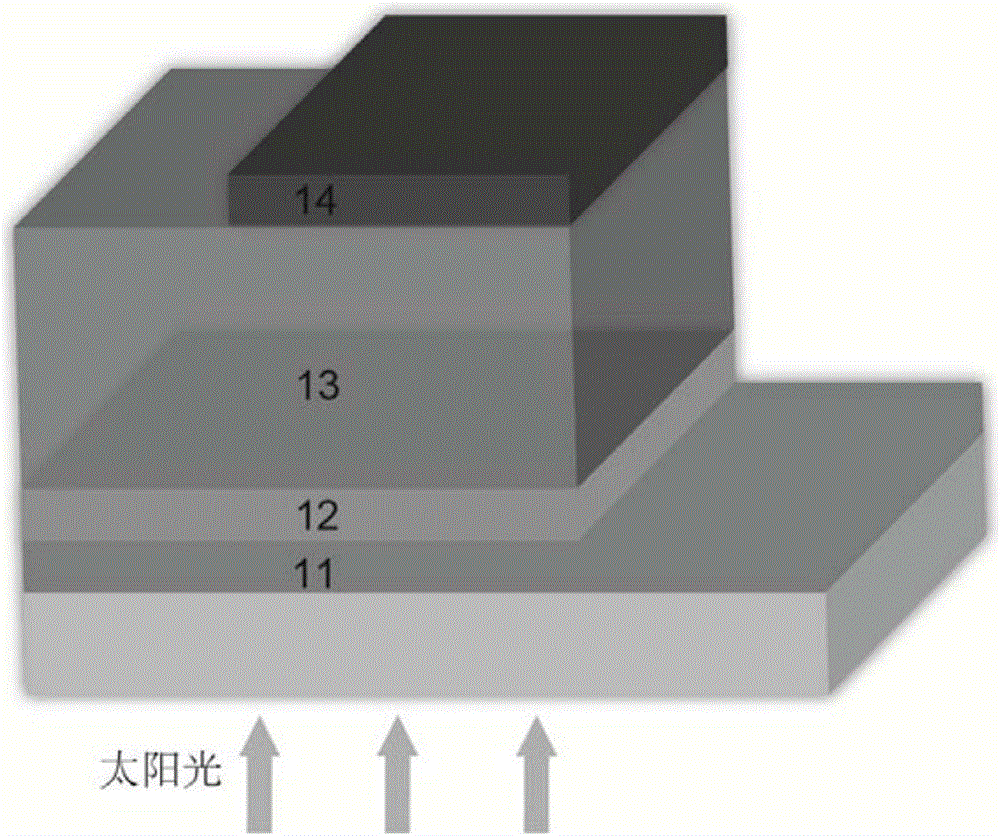
Copper zincium tin sulfur compound semiconductor thin-film solar cell and manufacturing method
InactiveCN101452969ALow costNo pollution in the processFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSolar batteryAbsorption layer
The invention discloses a Cu-Zn-Sn-S compound semiconductor-film solar battery and a preparation method. The battery comprises a glass substrate, wherein a metal back electrode layer, a P-type Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) absorption layer, an n-type CdS buffer layer and a transparent conducting oxide film window layer are sequentially deposited on the glass substrate. The method comprises special aftertreatment for the P-type Cu2ZnSnS4 absorption layer. The preparation method has the advantage of substituting CZTS for CIGS as the novel material of the absorption layer of the film solar battery. As the abundance of Zn and Sn in the CZTS in earth crust is 75 ppm and 2.2 ppm respectively, the solar battery has the advantages of rich resources, no toxic components and environmental friendliness, thereby becoming the novel film solar battery with the highest development potential, low cost and no pollution.
Owner:上海太阳能电池研究与发展中心
Composite thermodynamic engine of power circulation system and refrigerating circulation system
The inventive compound heat engine consists of a power circulation system and a refrigerating circulation system, in which is mounted a control system. It can provide the fields of power engineerings, refrigerating engineerings, communications and transportations, pumping irrigations and the like with mechanical work or electric energy. It not only can convert the high-grade energy, such as the fossil fuel, the nuclear fuel and soon into mechanical work or electric energy, but also can convert the low-grade heat energy stored in the seawater, the air and the earth crust into mechanical work or electric energy. Is also can convert the new energy like the solar energy and the renewable energy into mechanical work or electric energy.
Owner:罗桂荣 +1
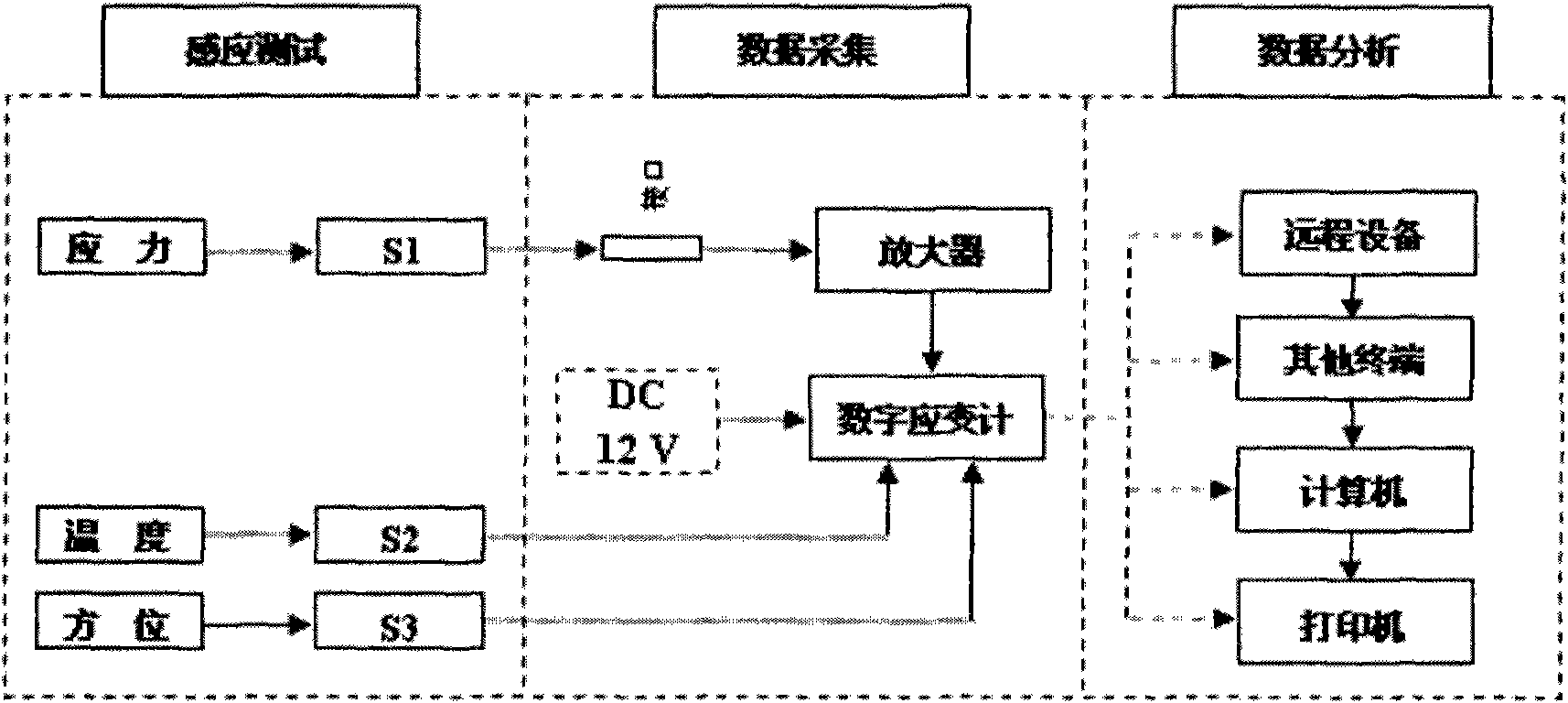
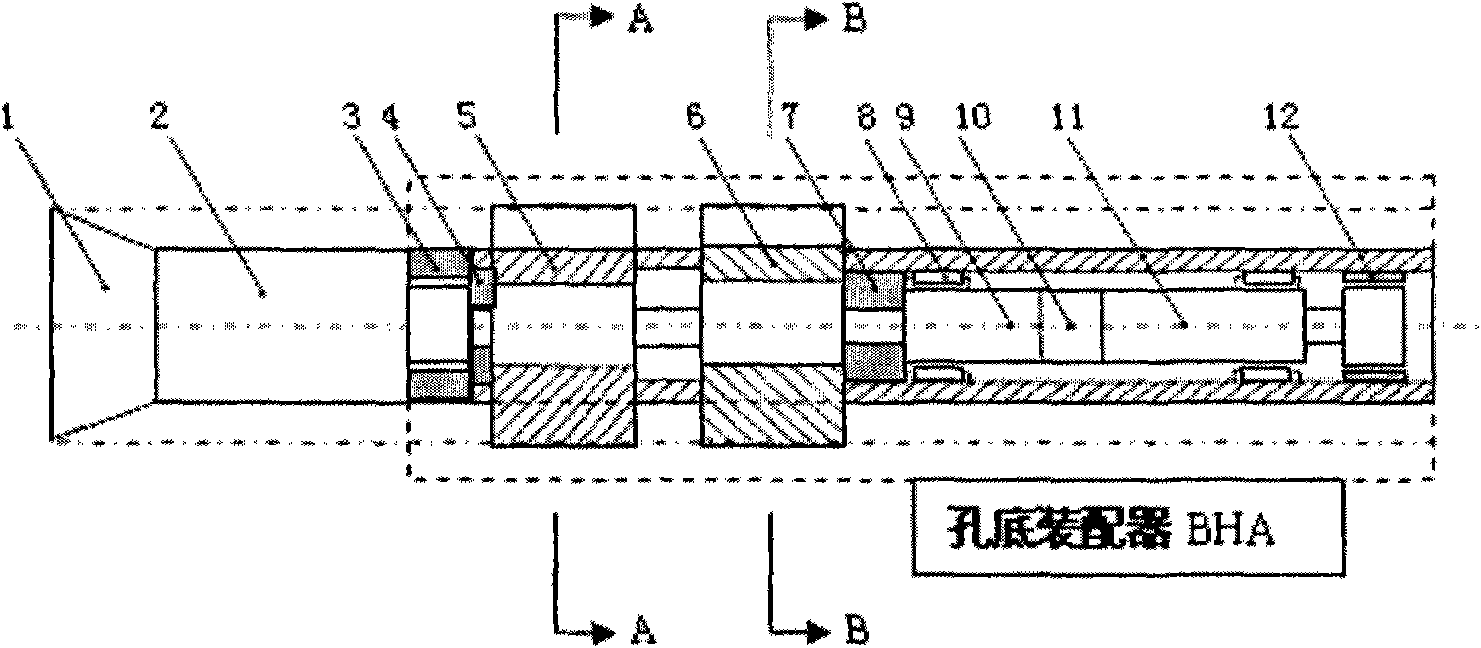
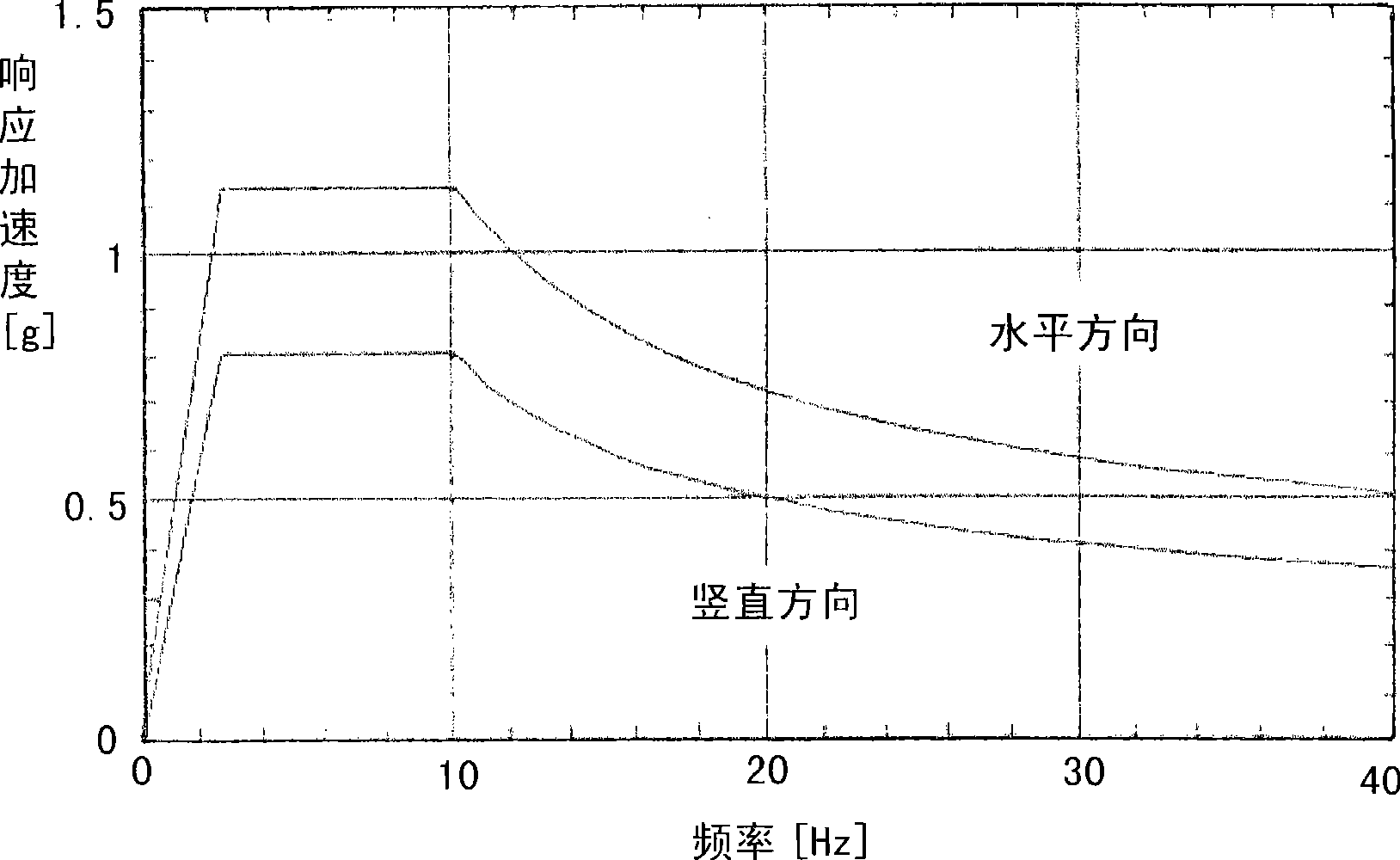
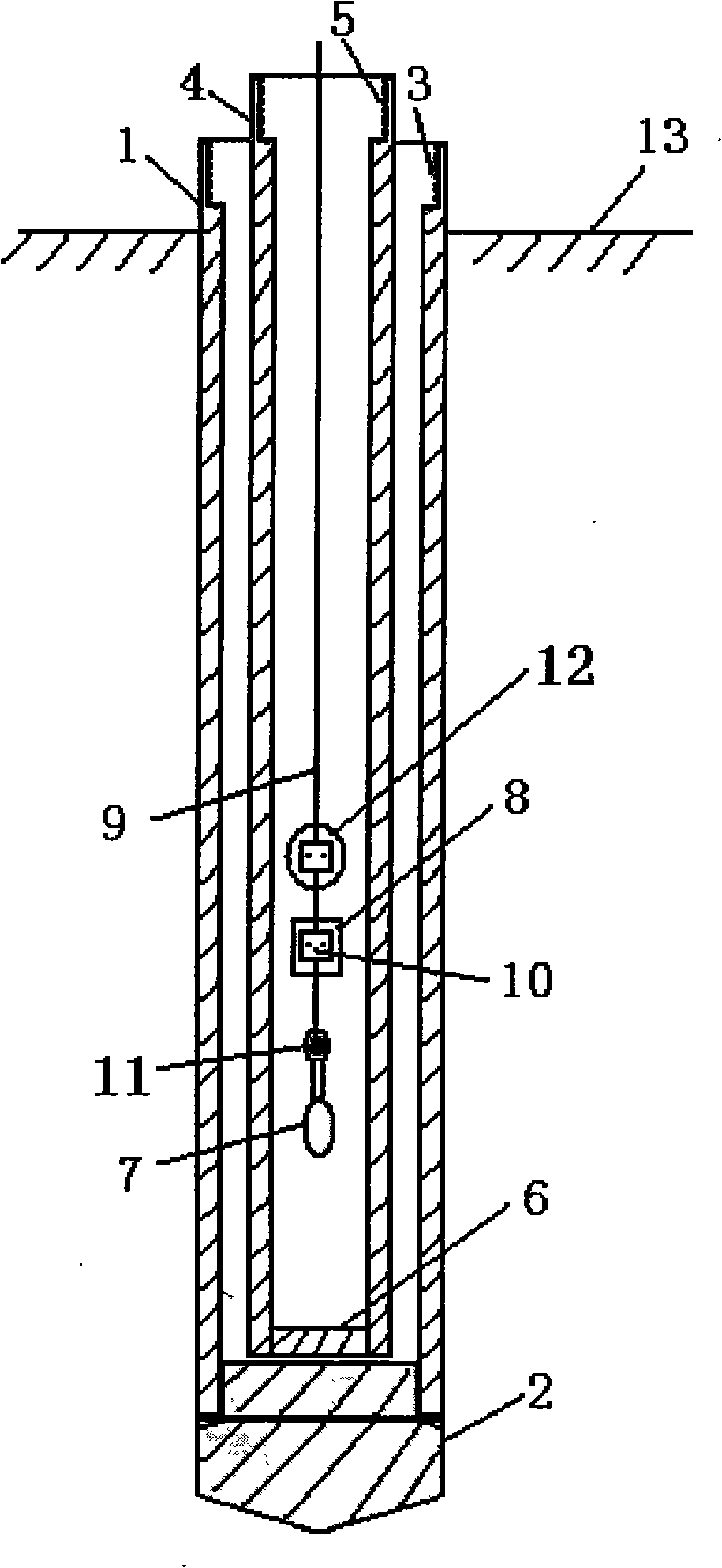
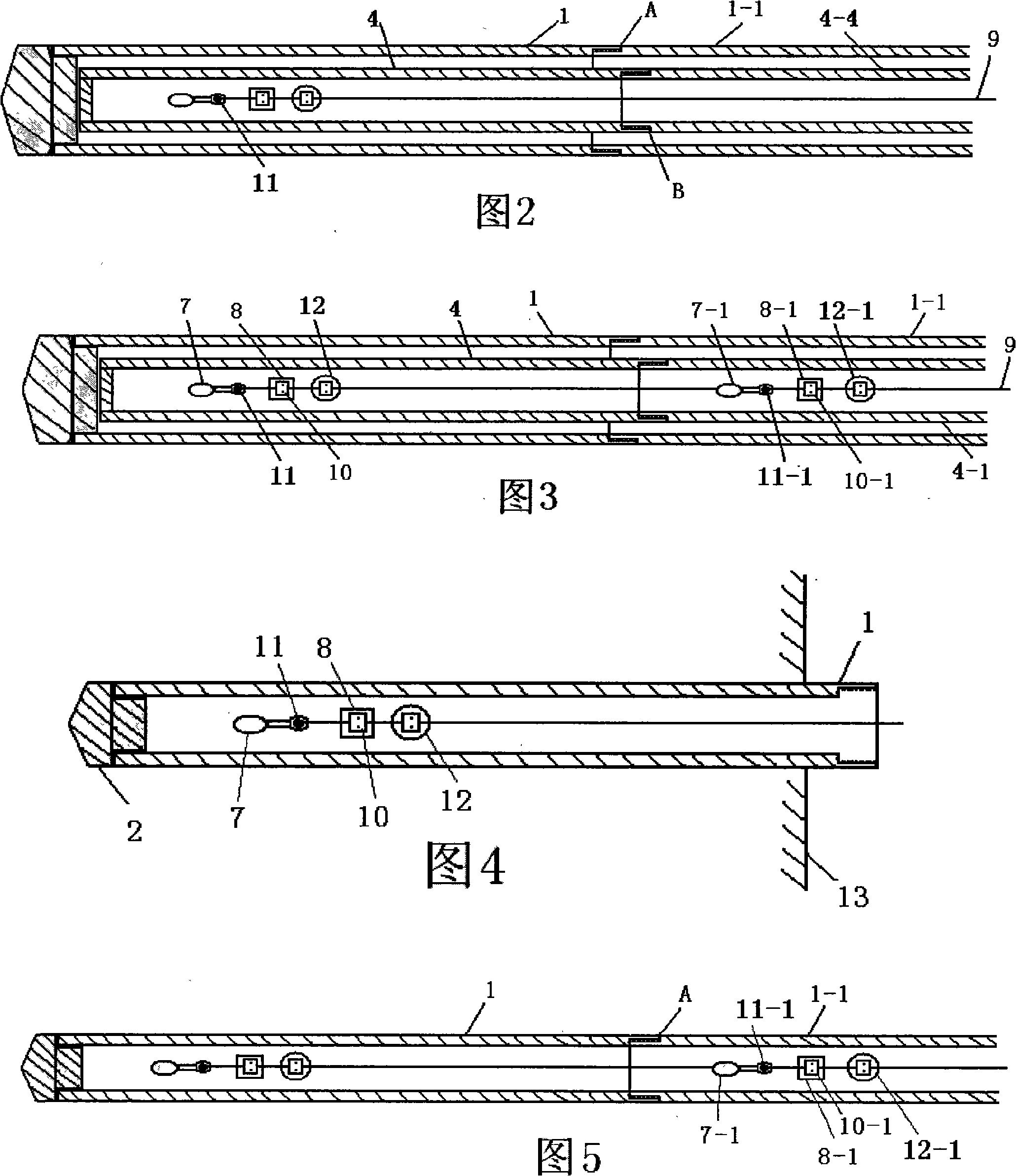
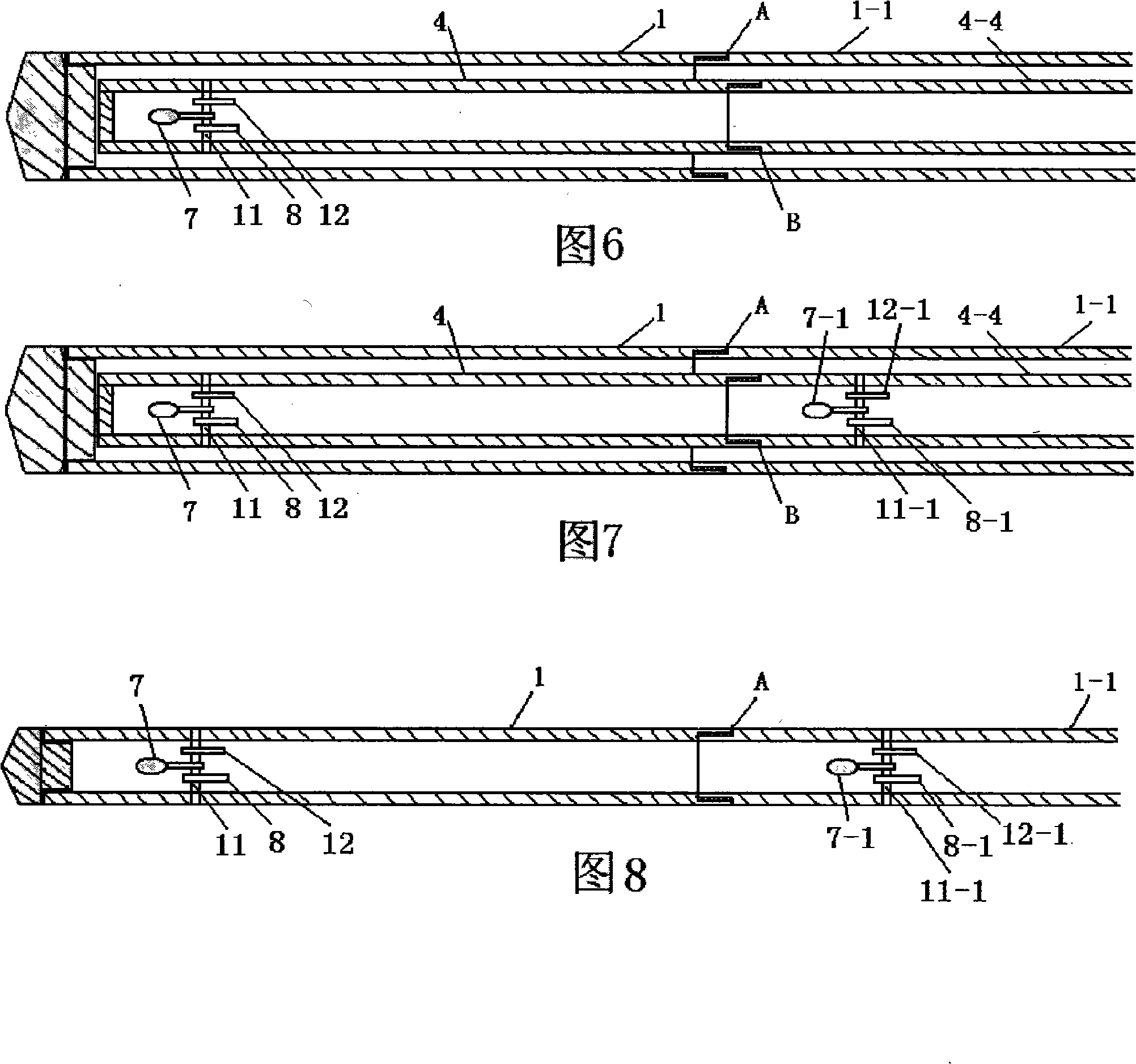
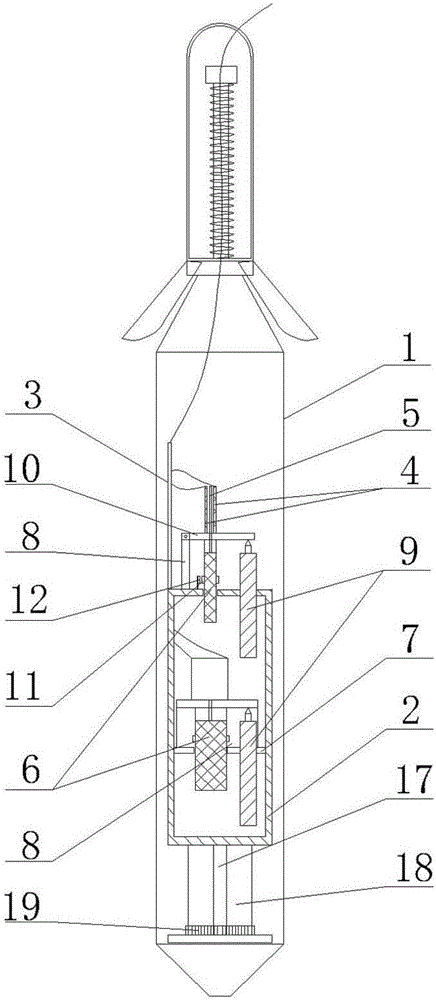
Deep ground stress measurement while drilling (MWD) system
InactiveCN101892830AReal-time measurement while drillingEasy to installSurveyConstructionsEarth crustStress measurement
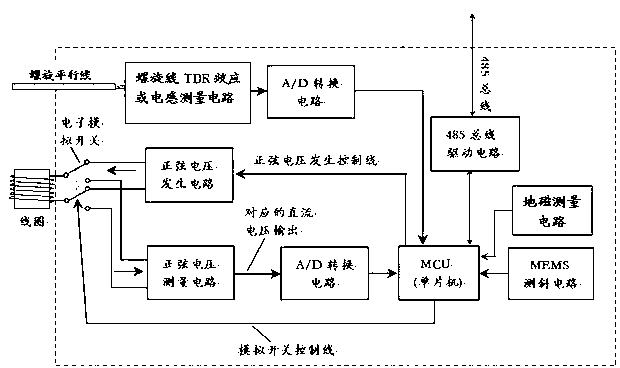
The invention belongs to the technical field of geological energy, minerals and geotechnical engineering investigation, and in particular relates to a deep ground stress measurement while drilling (MWD) technique, which can be used for testing ground stress in the earth crust in real time in geology and geotechnical engineering exploration. A deep ground stress MWD system comprises an induction test unit, a data acquisition unit and a data analysis unit. The system submerges at the bottom of a hole along with a drill, can measure the magnitude and direction of the three-dimensional ground stress, the temperature in the hole and the drilling trace at any sounding position in the drilling process, can overcome the defects of the conventional hydrofracturing method and the deep hole trepanning ground stress measurement technique, can perform measurement along with the drill in drilling production or exploration without specially drilling for measuring the ground stress, and can provide alarge amount of data for the initial ground stress field analysis of a project. The system has the advantages of no influence of ground magnetic field and temperature in the hole and vibration of a drilling tool, easy installation, simple operation, and high testing accuracy.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Real-time accurate monitoring method for earth crust millimeter-level displacement
The invention discloses a real-time precision monitoring method of millimeter crustal displacement, and relates to the seismic survey technology, wherein, the method comprises the following steps: 1) emission points are arranged in a large region grid manner, and a microminiature satellite survey terminal is arranged on nodes of a monitoring network; 2) a national ground information processing central station is divided into a center and a regional center; 3) information acquired by the microminiature satellite survey terminal is transmitted to a synchronous communication satellite, then forwarded to a downlink by a satellite repeater, and received by a large antenna in the ground information processing central station, and the data are acquired and processed in a centralized manner; 4) crustal shock parameters of a position at which the survey terminal is positioned are obtained, in which the survey resolution of the displacement and the amplitude are not greater than 1mm, the survey frequency is not greater than 50HZ, and the survey period is not greater than 20ms; and 5) terminal monitoring points are operated in an unmanned manner. The method can help continuously and exactly monitor the movement and variation of the crust in a real time, provides information for predicting and forecasting earthquakes, and can help survey the shock and the displacement of dams, bridges, high-rise buildings, large facilities and the like.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Two-dimensional Lg wave Q value tomographic imaging method based on single station data, double station data and double event data
ActiveCN104459784AThe effect of attenuation is strongSeismic signal processingEarth crustUltrasound attenuation
The invention discloses a two-dimensional Lg wave Q value tomographic imaging method based on single station data, double station data and double event data. The method comprises the following steps that (a) regional seismic data are collected and preprocessed so that Lg wave true amplitude and a signal to noise ratio can be obtained, the threshold value of the signal to noise ratio is set, and an Lg spectral data body used for Lg wave Q value tomographic imaging is selected; (b) the double station data and the double event data are extracted from the single station data; (c) Lg wave Q value tomographic imaging is performed based on amplitude data. Northeast China adjoins North Korea, and tomographic imaging results for the northeast China can be used for accurately measuring the body wave magnitude of nuclear explosions in North Korea and accurately estimating the yield of nuclear explosions. In addition, northeast China is rich in oil gas, mineral and hydrotherm resources, the resources have a certain corresponding relation with a crustal Q value; the interchange of materials between the earth crust and the upper mantle has intense influence on earth crust attenuation; conversely, lithosphere thinning in east China can be further studied by utilizing a Q value imaging model.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
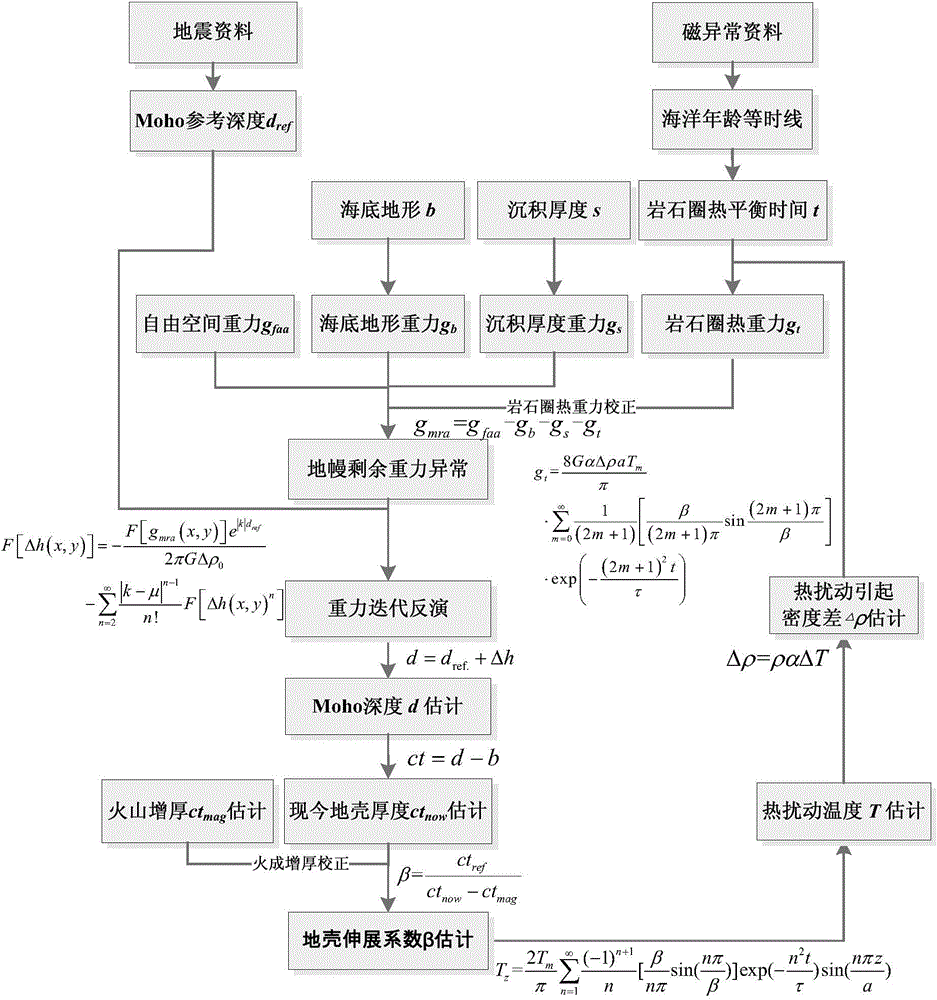
Depth-varying-to-density earth crust extension coefficient thermal calibration gravity anomaly retrieval method
InactiveCN104459795AReduce distortion effectsReduce calculationSeismic signal processingTopographyMagnetic anomaly
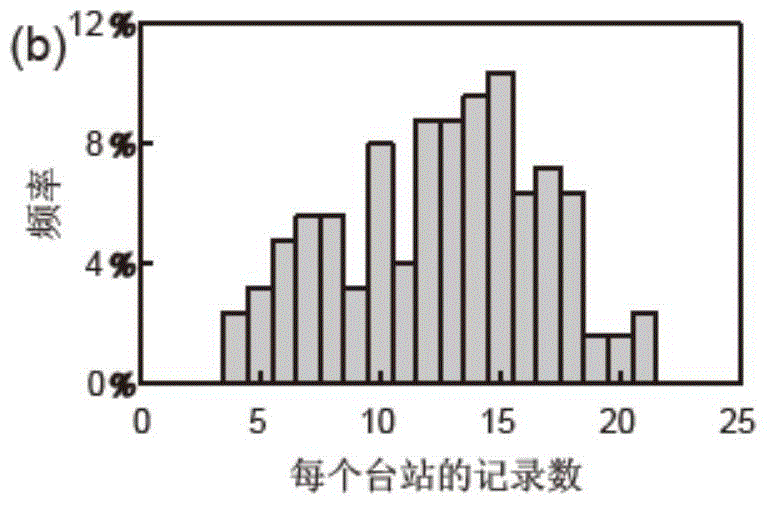
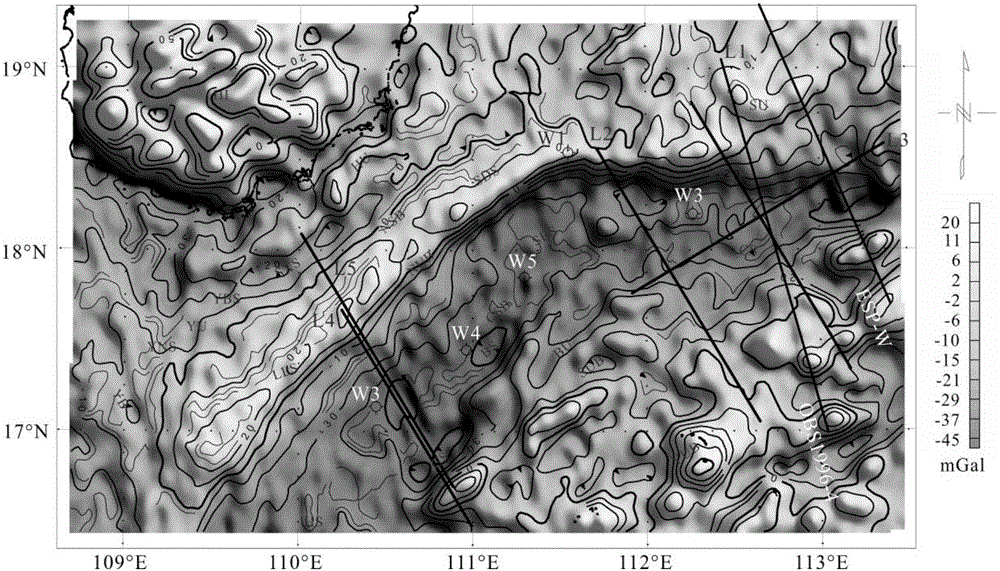
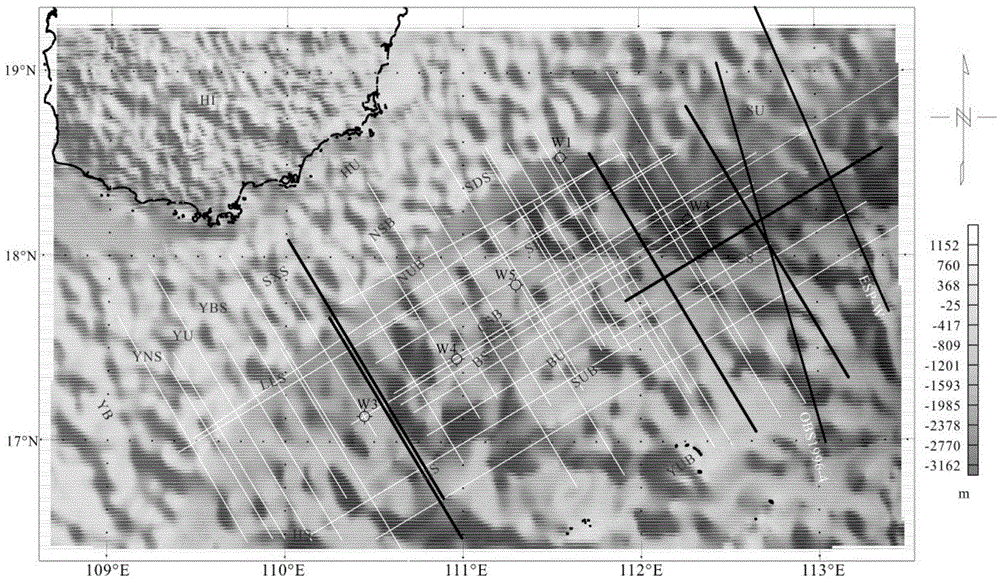
The invention discloses a depth-varying-to-density earth crust expansion coefficient thermal calibration gravity anomaly retrieval method. In the calculation process of a gravity retrieval earth crust expansion coefficient, a lithosphere thermal gravity anomaly calibration and depth constraint strategy is introduced, according to an iterative computation method of multiple parameter constraints such as a submarine topography, a sedimentary thickness, magnetic anomaly, an ocean age isochron and earthquake reflection and refraction, a distortion effect, caused by earth crust density changes resulted from lithosphere thermal disturbance, on gravity interpretation is corrected, and a basis is provided for knowing earth crust expansion and cracking processes.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three-dimensional measuring method and measuring system for underground deformation
ActiveCN103235349AAchieve continuous 3D measurementRealize 3D measurementGeological measurementsMeasuring instrumentObservation data
The invention discloses a three-dimensional measuring method and measuring system for underground deformation. The measuring system comprises an in-site measurement instrument and a remote measurement instrument, which are communicated with each other through wireless sensing communication; the in-site measurement instrument consists of an underground deformation integrated sensor string and an underground deformation measurement centralized processing device; the remote measurement instrument consists of a remote receiving device and a PC (personal computer) upper computer; and one end of the remote receiving device is connected with an antenna, and the other end of the remote receiving device is connected with the PC upper computer. The three-dimensional measuring method and the measuring system can realize the three-dimensional measurement of deformations caused by various below-surface reasons and realize the continuous three-dimensional measurement of the underground deformation, which can not be realized by other existing methods; thus the measuring system can possibly become an instrument used for observing the deformation situation of crust deep parts during plate jamming and provide observation data for the mechanism study of the occurrence of earthquake; and measuring instruments for the observation of geological environments in the research of craton destruction and shale gas development are also realized.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
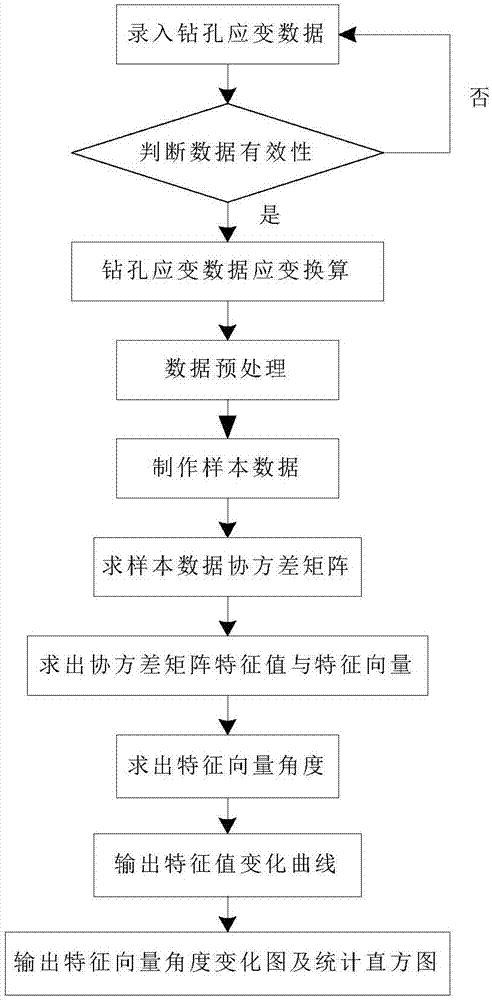
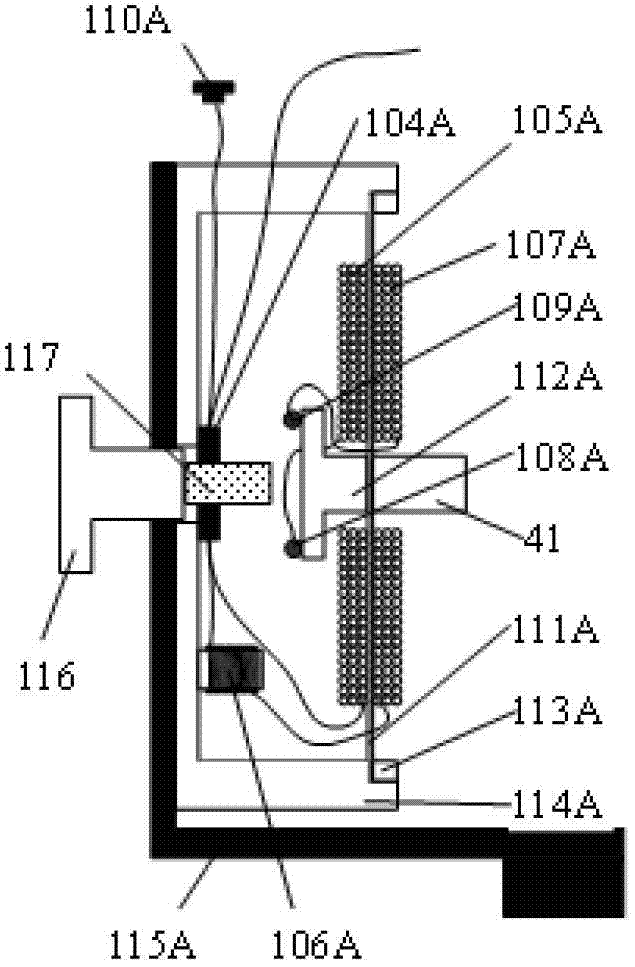
Drilling strain data anomaly extraction method based on principal component analysis
ActiveCN106918836AAccurate extractionEarthquake measurementSeismologyEarth crustKernel principal component analysis
The present invention relates to a drilling strain data anomaly extraction method based on principal component analysis. The method comprises: performing strain conversion of drilling strain data sequence of the same station, and performing preprocessing of the converted data; constructing a matrix through adoption of the drilling strain data after preprocessing; performing principal component analysis of the everyday matrix to obtain the feature value and the feature vector of each matrix; and corresponding the obtained feature value and the calculated feature vector angle and an earthquake event to obtain an abnormal detection result. The drilling strain data anomaly extraction method based on principal component analysis effectively employs the method of the principal component analysis to perform analysis of the drilling strain data, and performs extraction of possible earthquake precursor anomaly according to the correlation of each measurement item of drilling strain. The drilling strain data anomaly extraction method based on principal component analysis employs the feature values in the principal component analysis and the feature vector angle to represent the weak change of an earth crust so as to realize the accurate extraction of the drilling strain data anomaly in the condition having strong background interference.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Planar light waveguide measuring apparatus for micro-displacement
InactiveCN1645040ASimple preparation processEasy to carryUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyEarth crustPhotovoltaic detectors
An optical waveguide microdisplacement transducer setting on optical rotary table comprises photoelectric unit including laser, polarimeter, optical eyelets and photoelectric detector. It is featured as fixing optical eyelets at external of optical rotary table with the same height in coaxis to point optical axis to center of the transducer, setting photoelectric detector and laser in symmetry to center line of the transducer and fixing photoelectric detector on optical rotary table for measuring microdisplacement of dam, building and earth crust.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for improving efficiency of solar cell
ActiveCN101814555AIncrease contentImprove efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEarth crustSolvent
The invention discloses a method for improving the efficiency of a solar cell. The method is realized by attaching silicon quantum dots of which the surfaces are modified to the surface of a work area of the solar cell. The method comprises the following steps: modifying the surfaces of the silicon quantum dots; dispersing the silicon quantum dots into a solvent to prepare silicon ink; and printing the silicon ink on the surface of the work area of the solar cell to attach the silicon quantum dots of which the surface are modified to the surface of the work area of the solar cell. The method has the advantages that: a silicon element in a selected raw material has large content in the earth crust, and is easy to obtain and non-toxic. Simultaneously, due to the utilization of the silicon quantum dots, the efficiency of the solar cell is remarkably improved and environment pollution is avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Porous sealing device for connecting vertical flexible barrier system
ActiveCN102444145BCorrosion resistanceGood chemical stabilityProtective foundationEarth crustGeomembrane
The invention discloses a porous sealing device for connecting a vertical flexible barrier system. The porous sealing device comprises an expansion water stopping gasket and connecting latch fittings which are arranged on both sides of an HDPE (High Density Polyethylene) geomembrane and are sealed with the HDPE geomembrane, wherein when each connecting latch fitting on the HDPE geomembrane is tightly buckled with the other connecting latch fitting on the HDPE geomembrane for forming a sealing device, an expansion water stopping gasket cavity for accommodating the expansion water stopping gasket is formed between the two tightly-buckled connecting latch fittings; and the expansion water stopping gasket is filled into the expansion water stopping gasket cavity. The porous sealing device has extremely high anti-stability chemical performance, is resistant to corrosion of pollutants, and has long service life; and membrane surface wall bodies on both sides have extremely high breaking elongation performance, resistance to foundation precipitation, slight earth crust displacement and the like is realized, and durable sealing of a joint on the vertical flexible barrier system can be ensured by adopting seven-grade sealing.
Owner:BEIJING GEOENVIRON ENG & TECH
Method for checking margin of potential field polydirectionally and multiple dimensions
ActiveCN101256676AOvercome the shortcomings of directional information insensitivityImage enhancement3D modellingPotential fieldMulti field
The invention is a multi-field direction multi-scale edge detection method, which is technique that can carry out quickly inversion for three-dimensional structure of shallow crust based on field data. The invention realizes the calculation of the modulus and angle of wavelet transform after the rotation of coordinate system through directional wavelet transform, thus realizes serving the connection of modulus maximum points of wavelet transform along the vertical direction of gradient vector as the multi-scale edge of the field. The invention overcomes the weak point that the it is insensitive to directional information in the method such as signal analysis method, Euler deconvolution method, level derivative method, field multi-scale edge detection method, etc., can quickly obtains complete and accurate abnormal location of the border of geophysical field in various depths, thus generates a more accurate three-dimensional structure for shallow crust.
Owner:INST OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Efficient earthquake forecasting method
The invention relates to an effective earthquake prediction method, in particular to a method in which a vibration wave / shock wave sensor or an acceleration sensor, or a sonic or ultrasonic sensor, or a sonic frequency sensor which is provided with a sensor chip and / or a microprocessor is arranged into a metal pipe that is deeply embedded in the inner earth crust, and then the received information of the vibration wave or the shock wave or the sonic wave or the ultrasonic wave or the sonic frequency of a crustal movement is fed back to a corresponding apparatus / an instrument / a computer (a central processing unit) / a display / a network system on the ground surface so as to predict the occurrence of the earthquake. The invention comprises a metal pipe, a steel wire or a steel wire rope or a hybrid material rope, a movable metal alarm hammer with a handle, a vibration wave / shock wave sensor or a acceleration sensor or a sonic or ultrasonic sensor or a sonic frequency sensor which is provided with a sensor chip and / or a microprocessor, a corresponding apparatus or an instrument or a computer (a central processing unit) or a display or a network system; the design of the effective earthquake prediction method is capable of obtaining the early movement information of the earth crust from the depth of the earth crust to the location of each layer of the earth crust, thus achieving the best seismic early warning effect.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YIPENG ELECTRICAL TECH +1
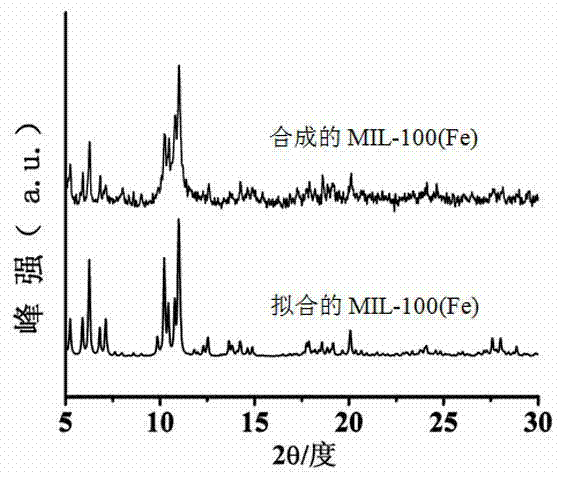
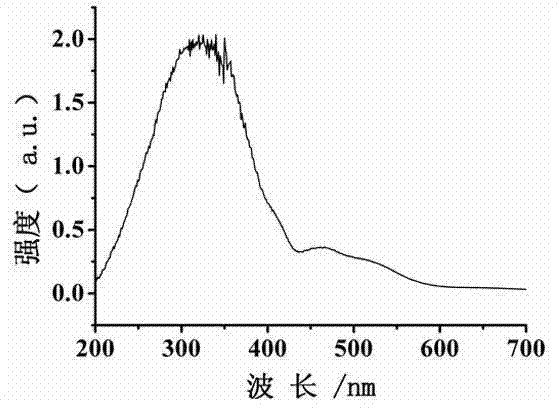
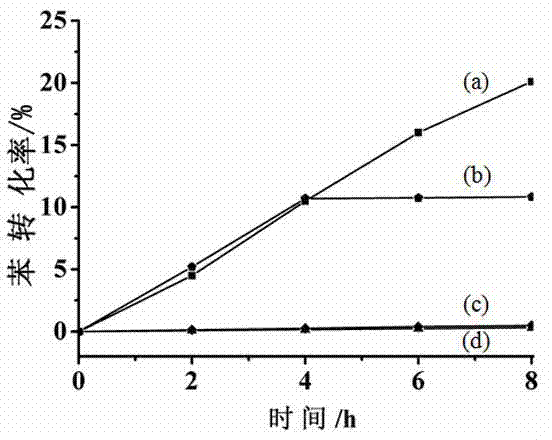
Application of MIL-100 (Fe) in preparation of phenol through photocatalytic hydroxylation of benzene
InactiveCN104844423AReduce energy consumptionReduce pollutionOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationBenzeneEarth crust
The present invention discloses application of MIL-100 (Fe) in preparation of phenol through photocatalytic hydroxylation of benzene, and belongs to the field of photocatalytic technologies. MIL-100 (Fe) is a metal-organic framework material containing the Fe element that is high in abundance in the earth crust. According to the present invention, MIL-100 (Fe) is applied for the first time as a photocatalyst to preparation of phenol through hydroxylation of benzene; and the problems of high energy consumption, low selectivity and production of byproducts same in molar volume with the produced phenol in a three-step-method for phenol synthesization in the prior art are solved. The application of MIL-100 (Fe) in preparation of phenol through photocatalytic hydroxylation of benzene is simple in process, low in cost, and capable of meeting the practical production demands, and has a relatively great potential for application.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
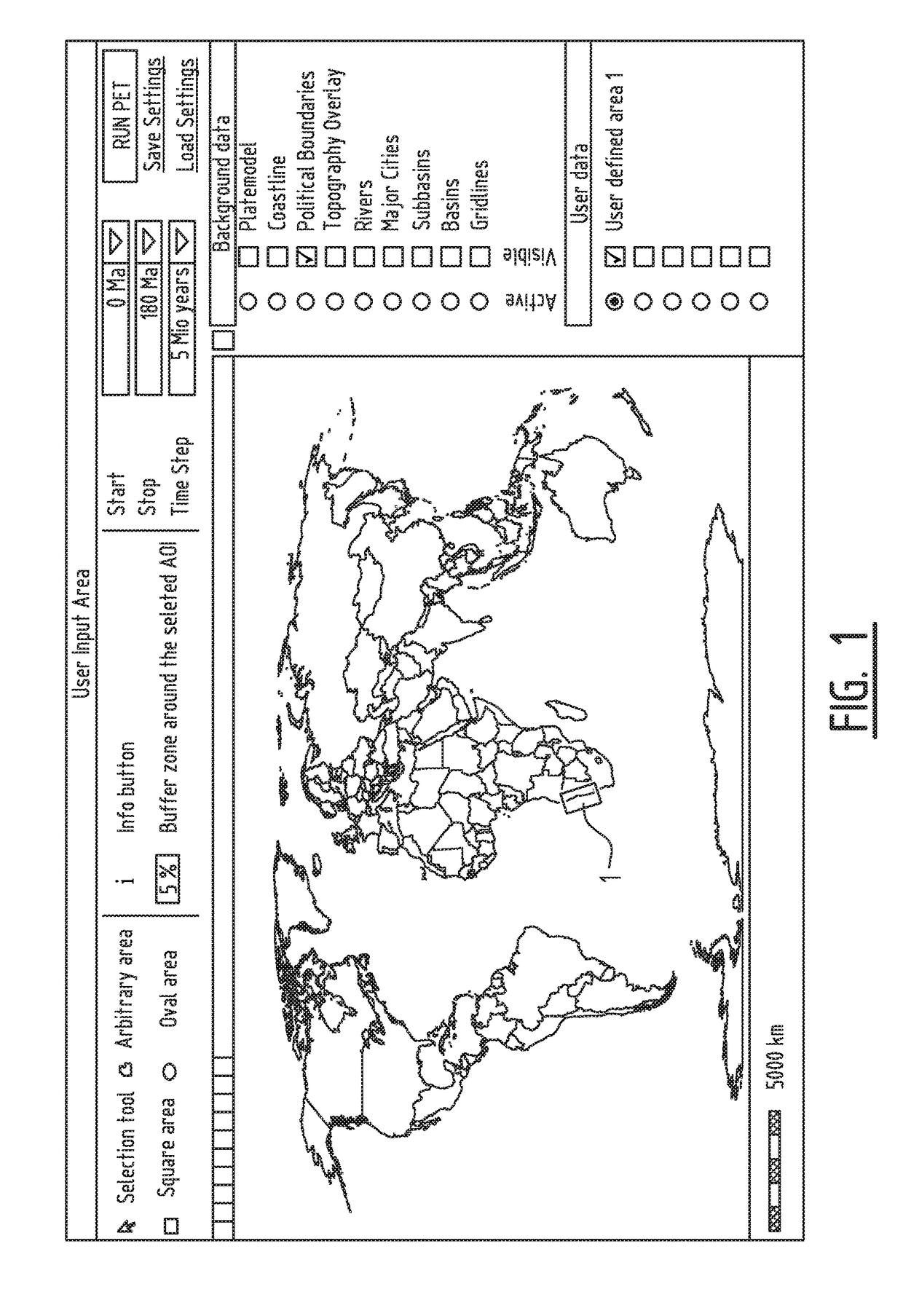
Paleogeographic reconstruction of an area ofthe earth crust
A Paleo Event Table creator tool box is described which is induced and / or allows a user to spatially join a selected area of interest of the earth crust to one selected tectonic plate in a tectonic plate model, which selected tectonic plate has an overlap with the area of interest, and to sample a paleogeographic dataset relevant to the area of interest for a series of paleogeographic time steps. A graphical user interface is induced and / or allows the user to create a Paleo Event Table that displays the sampled paleogeographic dataset. The Paleo Event Table creator tool box is used for paleogeographic reconstruction of the earth crust in the area of interest and identifying information relevant for the area of interest.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Ultra-short base line differential plate type optical fiber displacement sensor and optical fiber strain gauge
The invention provides an ultra-short base line differential plate type optical fiber displacement sensor and an optical fiber strain gauge. The ultra-short base line differential plate type optical fiber displacement sensor comprises an outer frame, wherein an outer ring of a displacement conversion device is tightly pressed on the outer frame by a pressing ring with external threads, a threaded pillar of a central press washer penetrates through a central hole in the displacement conversion device, and a first Faraday rotating mirror and a second Faraday rotating mirror are solidified on the central press washer; and an optical fiber coupler and a phase modulator are fixed on the surface of the inner wall of the outer frame, the outer frame and a fixed base are fixed, a first measurement optical fiber and a second measurement optical fiber are respectively wound into multilayered optical fiber loops with hollow plate type layered structures, the first measurement optical fiber and the second measurement optical fiber are respectively solidified on the upper surface and the lower surface of the displacement conversion device, the coupler is connected with the fist Faraday rotating mirror, the phase modulator and a detector, the fist measurement optical fiber is connected with the first Faraday rotating mirror, the phase modulator is connected with the second measurement optical fiber, and the second measurement optical fiber is connected with the second Faraday rotating mirror. The ultra-short base line differential plate type optical fiber displacement sensor and the optical fiber strain gauge are mainly used for observing earth crust strain and solid tide, and acquiring earthquake precursor information.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
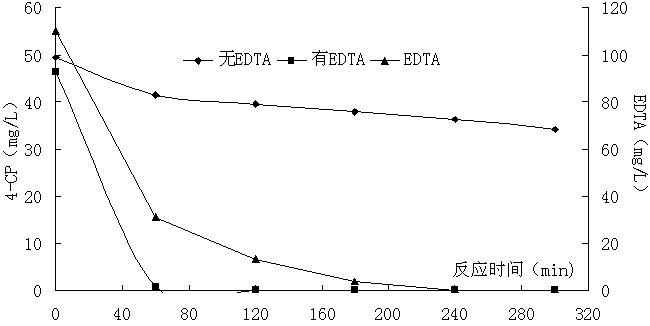
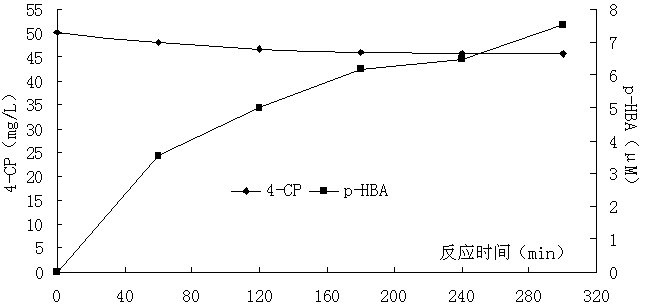
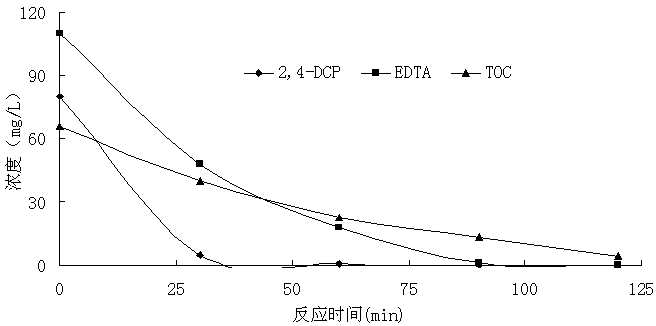
Method for oxidatively degrading chlorophenol substances by using EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid)-reinforced bimetal aluminum-iron system
InactiveCN103011376AQuick breakdownPromote productionWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationDecompositionWater quality
The invention relates to a method for oxidatively degrading chlorophenol substances by using an EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid)-reinforced bimetal aluminum-iron system. Machined metal iron and metal aluminum used as raw materials are filled in a reactor. Before treatment, a certain amount of EDTA is previously added into the reactor, and aeration and stirring are simultaneously carried out after starting introducing water. In the water, the metal aluminum can easily generate hydrogen peroxide after aeration, the EDTA after aeration can promote the metal iron to activate molecular oxygen to generate oxydol and can eliminate the passivation layer on the iron surface to reinforce the leaching of ferrous ions, the ferrous ions immediately produce Fenton advanced oxidation reaction immediately after contacting the hydrogen peroxide, and the generated.OH is subjected to advanced oxidation reaction. Meanwhile, the generated iron and aluminum hydroxides have the capacity for adsorbing and removing pollutants, and thus, are beneficial to further enhancing the quality of effluent water. The invention has the advantages of low operating cost and simplified technical process, implements quick decomposition of the EDTA, and can not bring about combined pollution of the EDTA. The treatment cost is low. The FeO used by the technique is machining waste of metal workpieces, the AlO is the most abundant metal element on the earth crust, and both the FeO and AlO are cheap and accessible and can be used for a long time.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
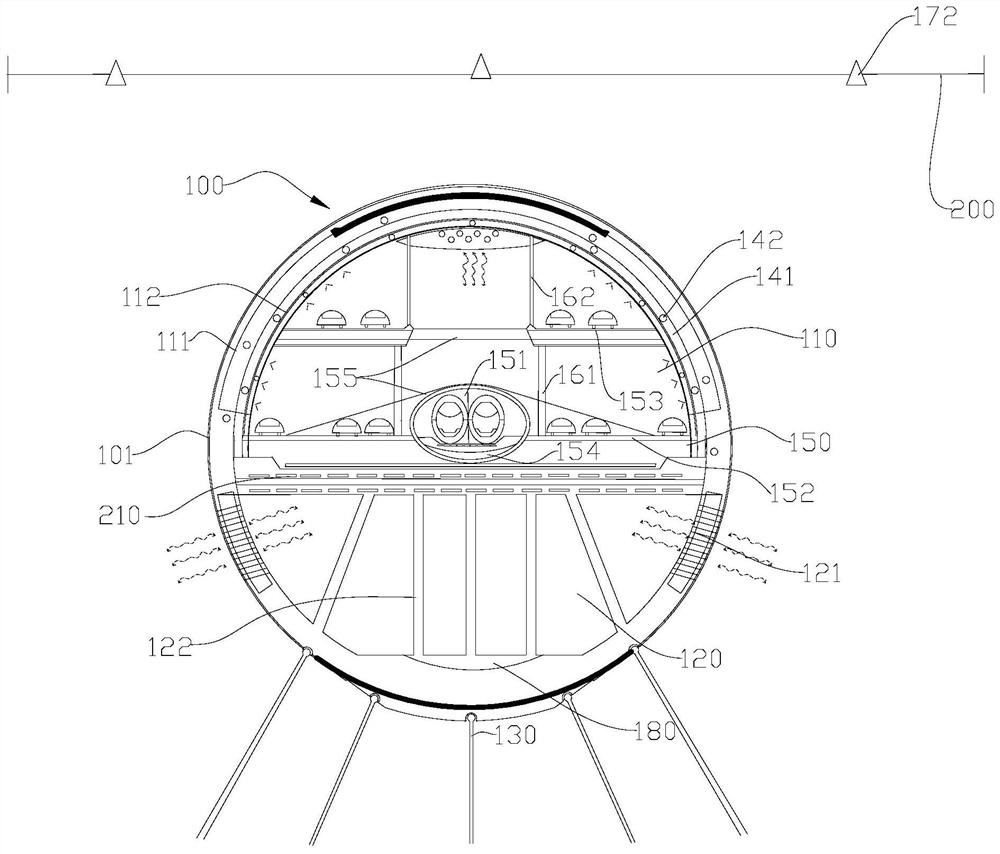
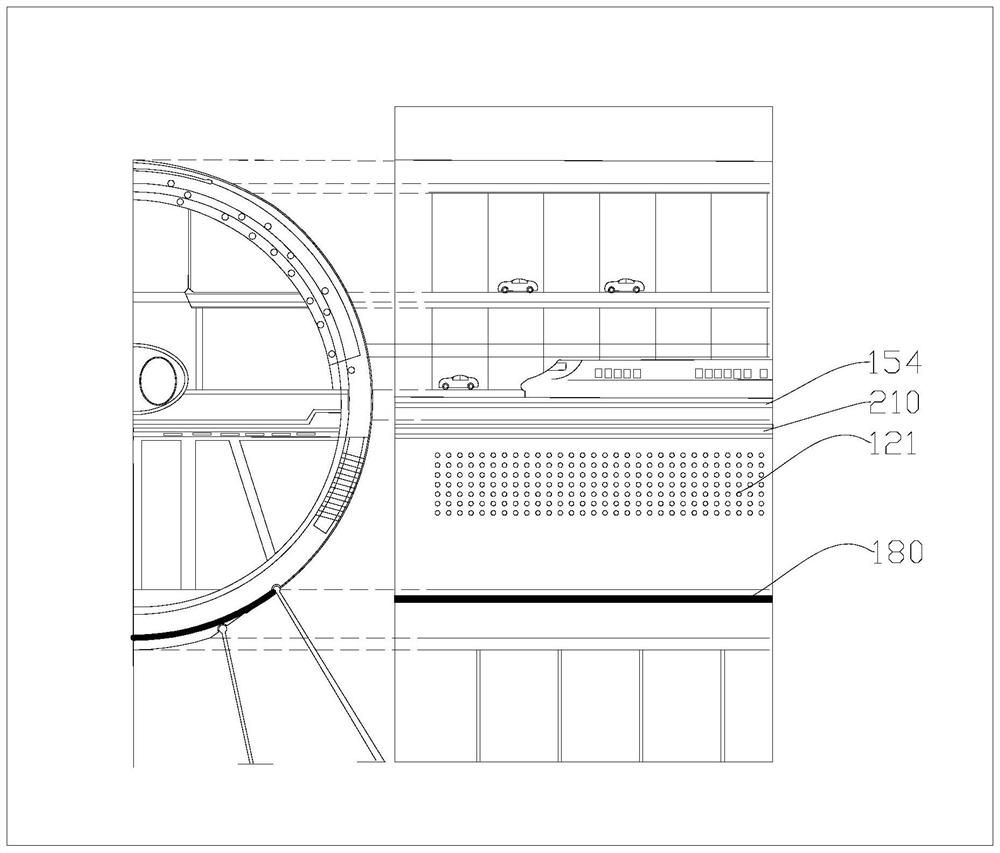
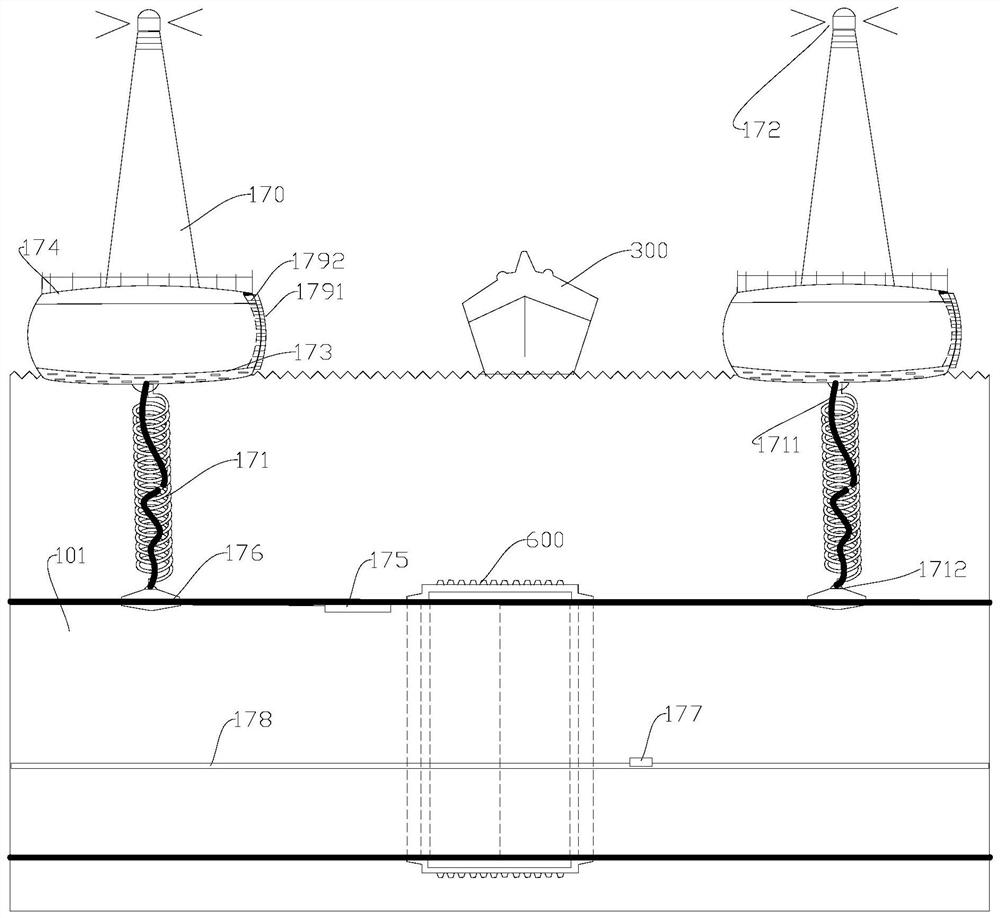
Underwater traffic tunnel
ActiveCN111877401AGood ventilation guaranteeNot easy to overturnArtificial islandsTunnel/mines ventillationEarth crustMarine engineering
The invention provides an underwater traffic tunnel, relates to the field of traffic bridges and tunnels, and solves the problem that offshore, in-water and underwater traffic tunnels are difficult toensure structural stability on the premise of not influencing passing ships. The underwater traffic tunnel comprises a body immersed in water, a connecting piece and a ventilation system, the body comprises a first cavity used for providing a passing space and a second cavity located at the lower portion of the first cavity, and the second cavity is communicated with the water; and the connectingpiece is connected with the body and the water bottom and used for resisting buoyancy, the ventilation system communicates with the first cavity and extends to the position above the water surface, and the ventilation system is arranged in a deformable manner so as to continuously ventilate when impacted. The body is safely immersed in water, and a ship can freely sail above the body; the secondcavity is communicated with water and is not easily overturned by seawater; the connecting piece resists buoyancy; and the ventilation system can be prevented from being damaged by external force through deformation movement, an escape system can be started in emergency, higher safety is achieved, and the influence of earth crust change on the tunnel is reduced.
Owner:杜同
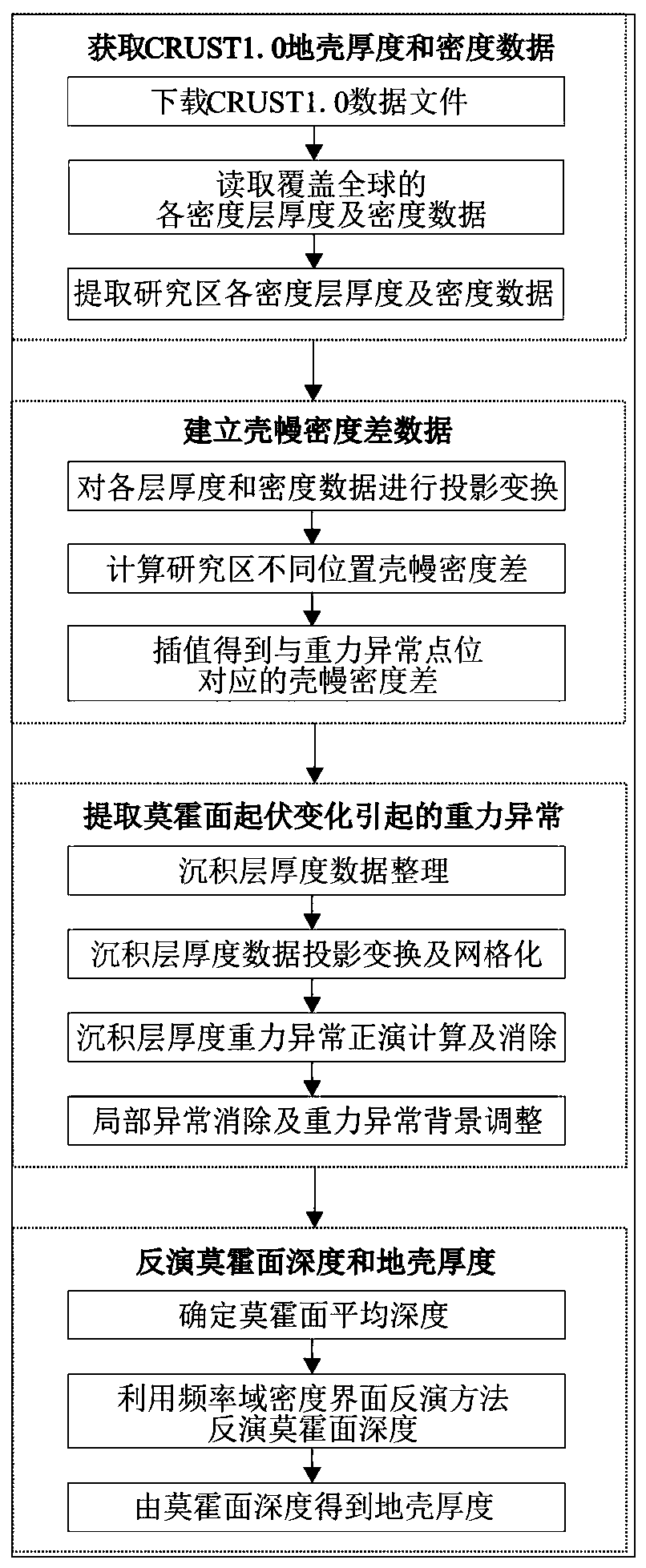
Variable density-based crust thickness gravity inversion method
InactiveCN110244352AThe actual geological characteristics conform toImprove accuracySeismic signal processingUpper crustImage resolution
The invention discloses a variable density-based crust thickness gravity inversion method. The variable density-based crust thickness gravity inversion method comprises the steps of acquiring crust thickness and density data and upper mantle density data of a crust model CRUST 1.0 with global coverage space resolution 1 degree by 1 degree; building crust-mantle density difference changing with a horizontal position according to density and thickness of upper crust, intermediate crust and lower crust and upper mantle density data of the crust model CRUST 1.0; obtaining gravity abnormality caused by fluctuation of a moho surface by bouguer gravity anomaly; and converting depth of the moho surface and obtaining the crust thickness by gravity abnormality caused by the bouguer gravity anomaly. Compared with the prior art, disclosed document is used as a foundation, a practical crust-mantle density model is built, the variable density-based crust thickness gravity inversion method is easily implement from technology, an inversion result more conforms to actual geologic characteristic, and higher accuracy is achieved.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Germanium selenide polycrystal thin film and solar battery comprising thin film, and preparation methods therefor
ActiveCN106783541AFast heating rateQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSolar batteryLight absorption coefficient
The invention discloses a high-quality germanium selenide polycrystal thin film and a preparation method therefor, a solar battery comprising the germanium selenide polycrystal thin film and a preparation method therefor. The germanium selenide polycrystal thin film is 300-500nm in thickness; the preparation method adopts a closed space sublimation method; the preparation method is simple in process, short in reaction period and high in film forming quality; elements included in p type absorption layer material GeSe in the solar battery are all elements with relatively high content in the earth crust, so that the elements are rich in resource, free of toxins and environment friendly; the indirect energy gap is 1.12eV, the absorption edge wavelength is about 1,000nm, response to solar spectrum is in the most ideal solar spectrum band, and the light absorption coefficient is as high as 105cm<-1>; meanwhile, based on the sublimation characteristic of the thin film, the film can be formed rapidly based on the closed space sublimation method; and therefore, the formed compound thin film solar battery has excellent photovoltaic performance, environment protection and is expected to realize low-cost production.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
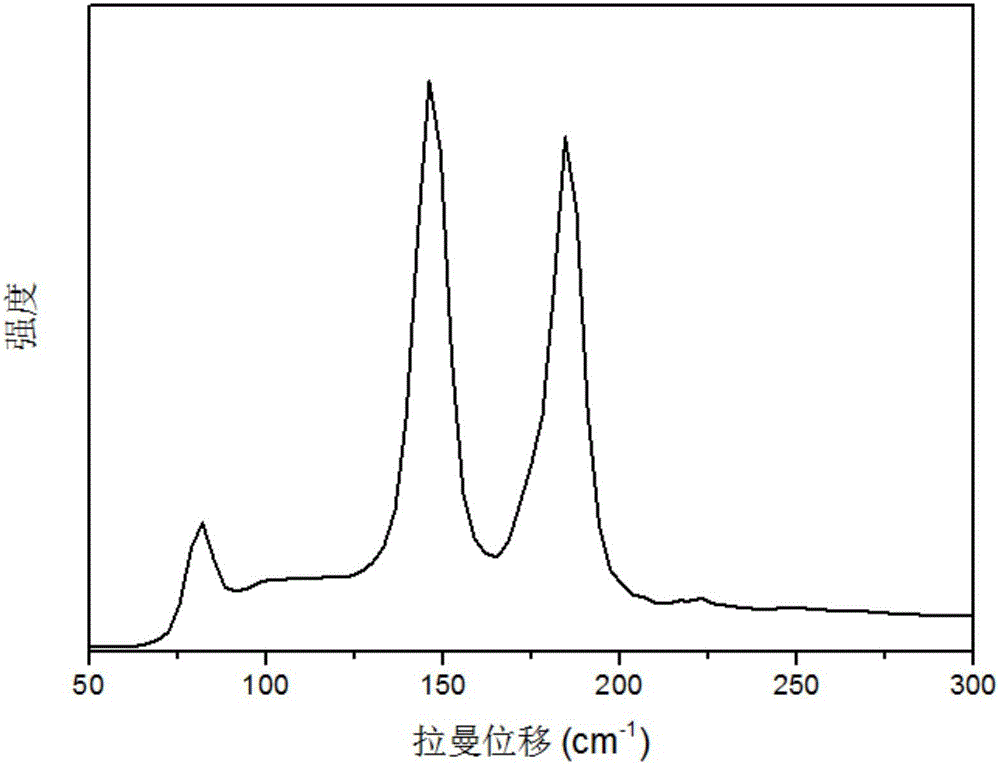
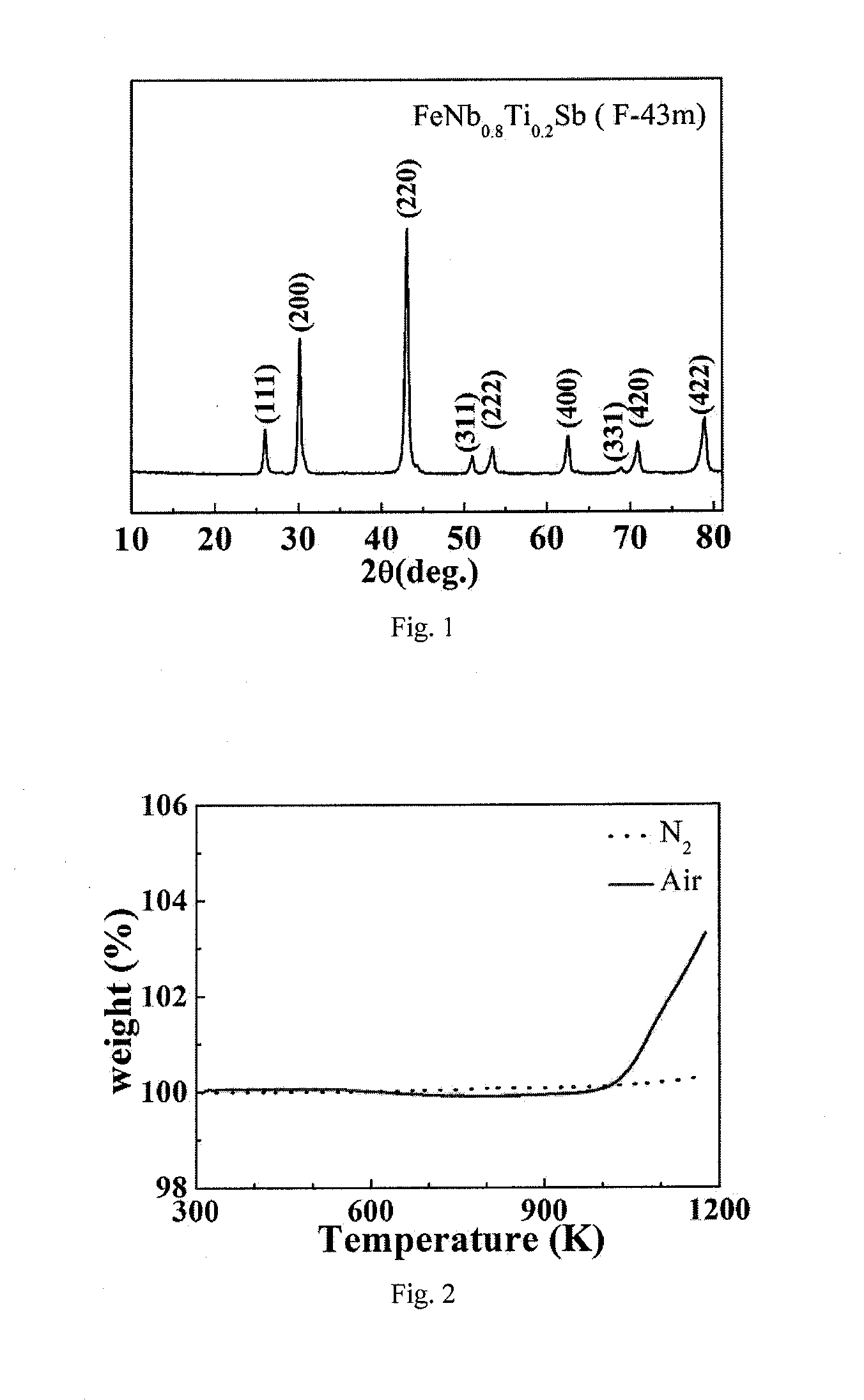
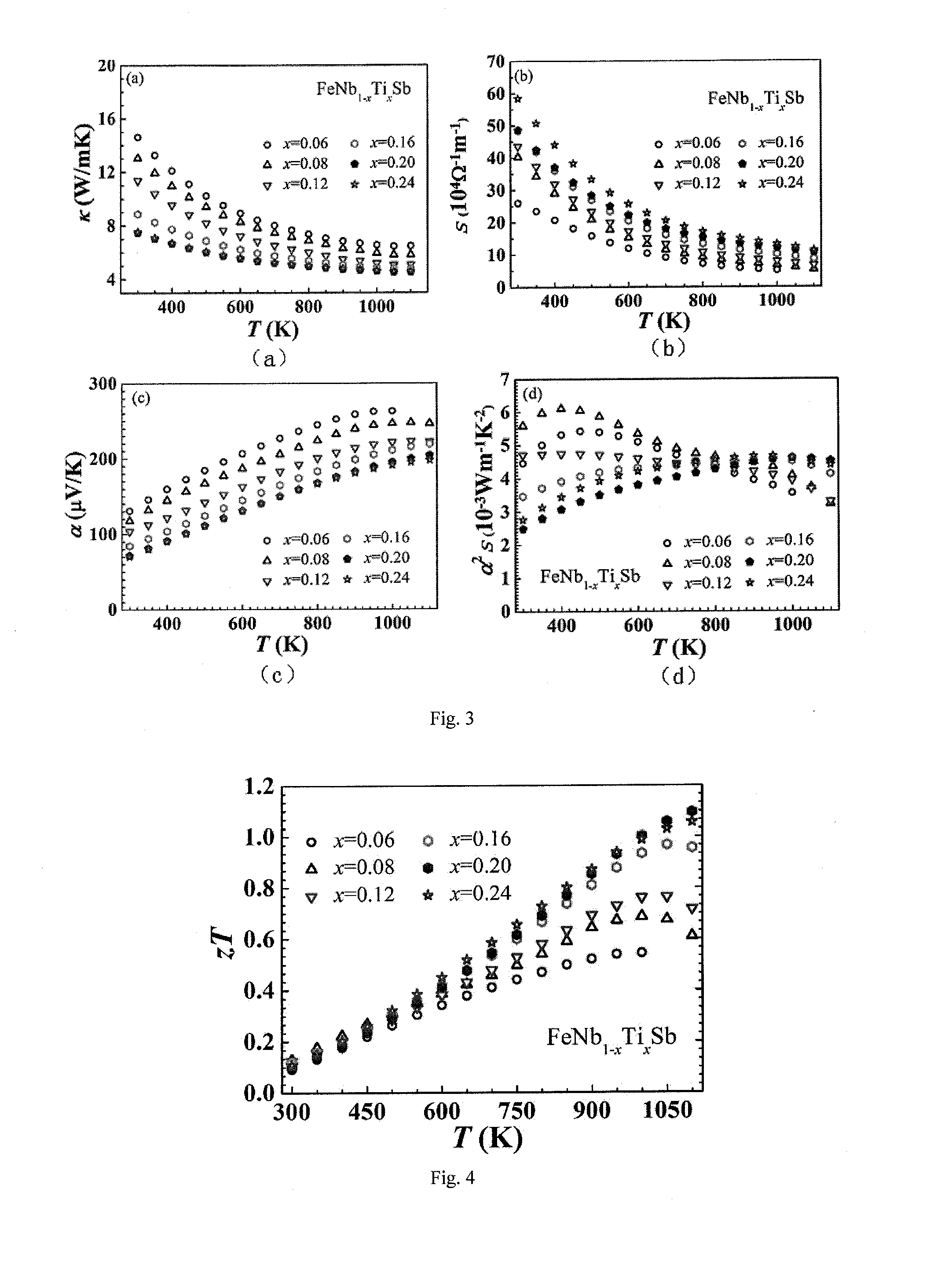
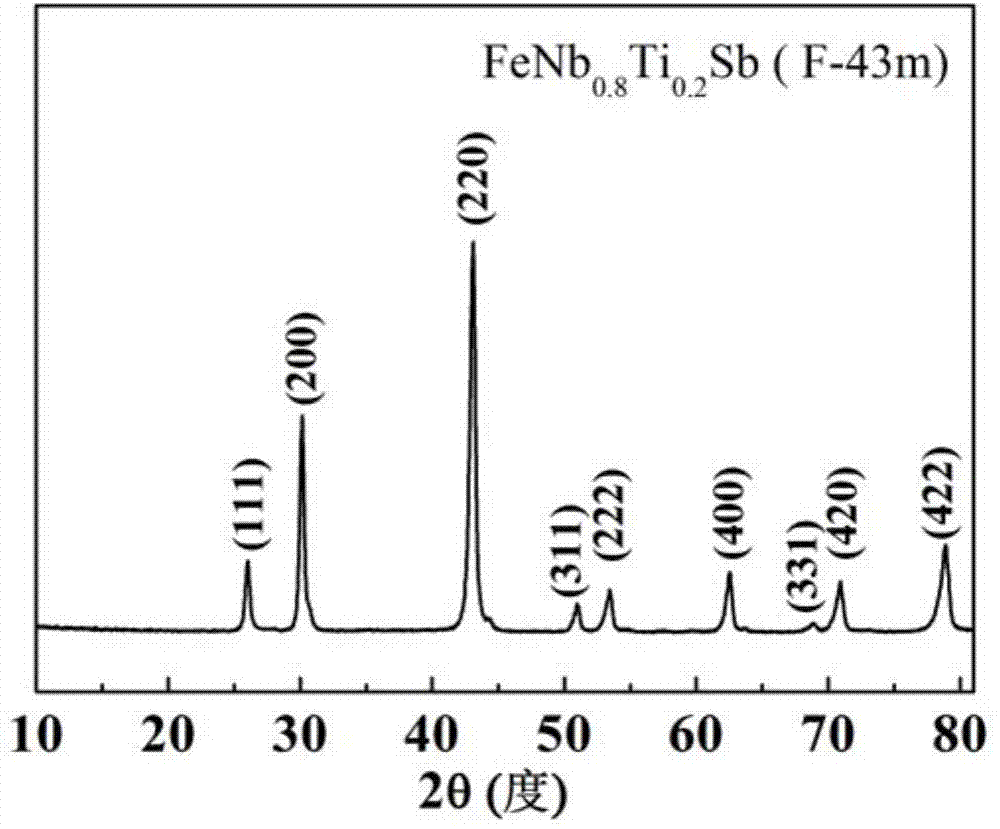
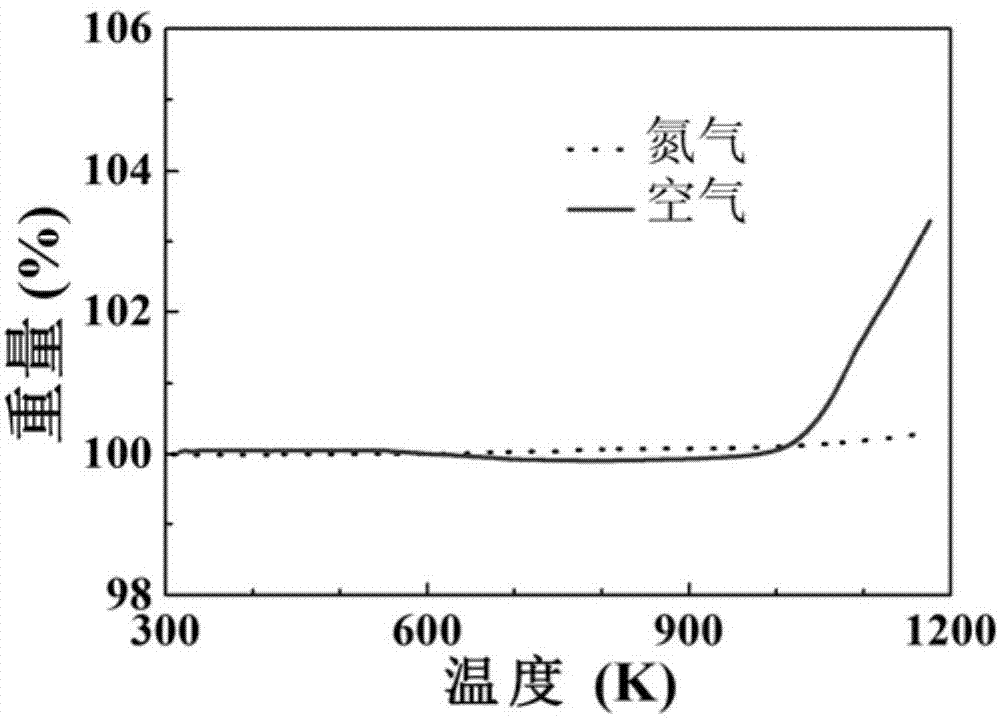
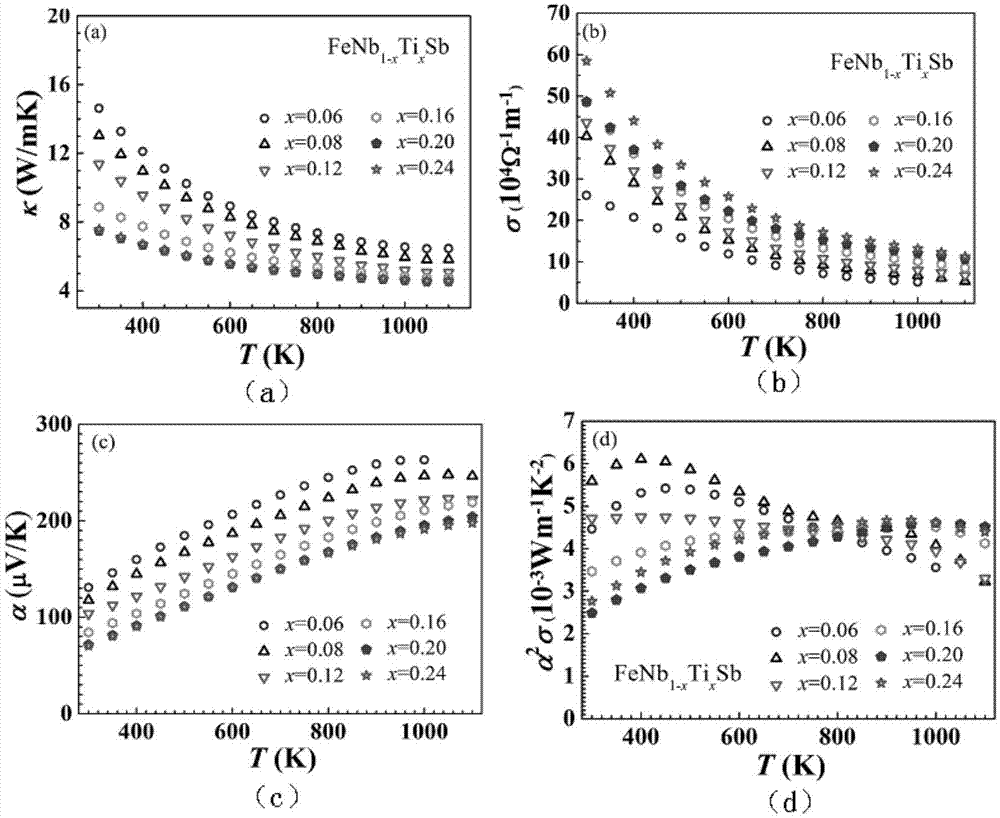
A HIGH FIGURE OF MERIT P-TYPE FeNbTiSb THERMOELECTRIC MATERIAL AND THE PREPARATION METHOD THEREOF
ActiveUS20160141480A1Increase valueThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentConductive materialEarth crustThermoelectric materials
The present invention discloses a type of high figure of merit p-type FeNbTiSb thermoelectric material, whose composition is FeNb1-xTixSb, wherein x=0.06˜0.24. The present invention also discloses the method to prepare these p-type FeNbTiSb thermoelectric materials. The ingots with nominal composition FeNb1-xTixSb are prepared by levitation melting of stoichiometric amounts of Fe, Nb, Ti and Sb under an argon atmosphere. The obtained ingots are mechanically milled to get submicron-scale powders. The obtained powders are compacted by spark plasma sintering to obtain the final bulk p-type FeNbTiSb thermoelectric materials. The compositional elements of these p-type FeNbTiSb thermoelectric materials are abundant in the earth crust. The p-type thermoelectric materials also shows good high temperature stability and the preparation method are simple and high-yield. Therefore, the industrial production cost would be relatively cheap. The maximum zT value of the p-type thermoelectric materials is 1.1 at 1100K, which is the highest value among the p-type Half-Heusler system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
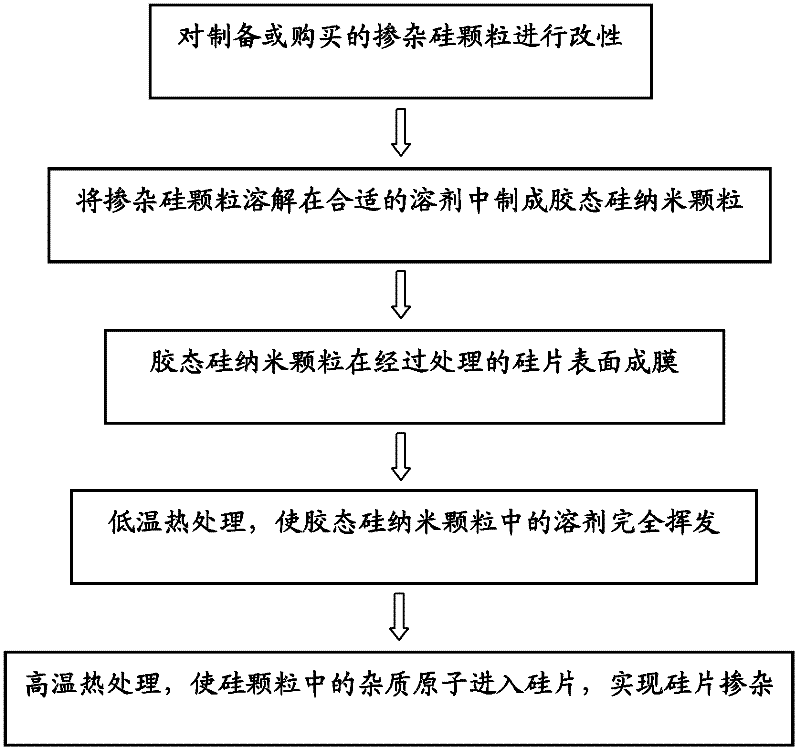
Method for doping silicon wafer with colloidal silicon nano particles
ActiveCN102347223AIncrease contentDoping process simplificationDiffusion/dopingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNano siliconEarth crust
The invention discloses a method for doping a silicon wafer with colloidal silicon nano particles. The method comprises the following steps of: modifying surface of doping nano silicon particles, and dispersing the silicon particles with the modified surface in a solvent to manufacture colloidal silicon nano particles; and forming a film of the colloidal silicon nano particles on a silicon wafer which is subjected to pretreatments of decontamination and removal of an oxidation layer, carrying out heat treatment firstly at a temperature of 200-500 DGE C for 5-60 minutes, carrying out heat treatment in an oxygen atmosphere at a temperature of 750-1100 DEG C for 30-120 minutes again, and forming a doping layer on the near surface of the silicon wafer. Silicon element in raw materials selected in the invention is rich in the earth crust, obtained easily and non-toxic. In addition, by applying the colloidal silicon nano particles, the doping process of the silicon wafer is simplified and the doping in selective regions can be simply and conveniently realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
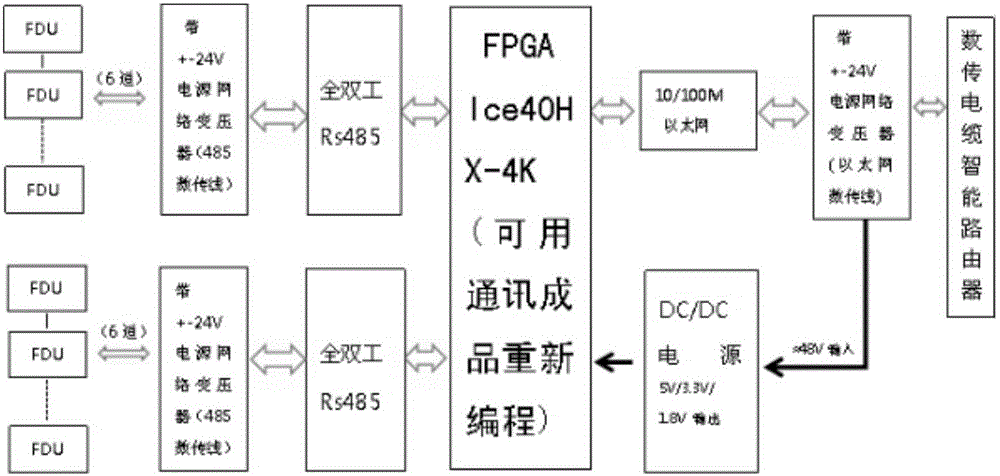
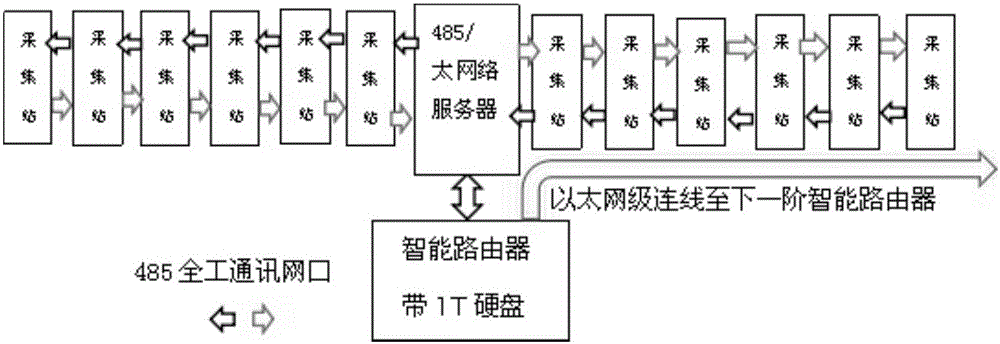
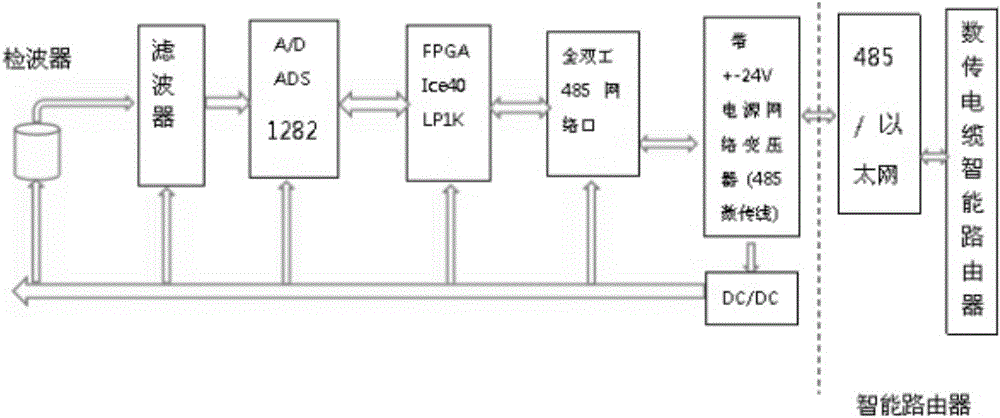
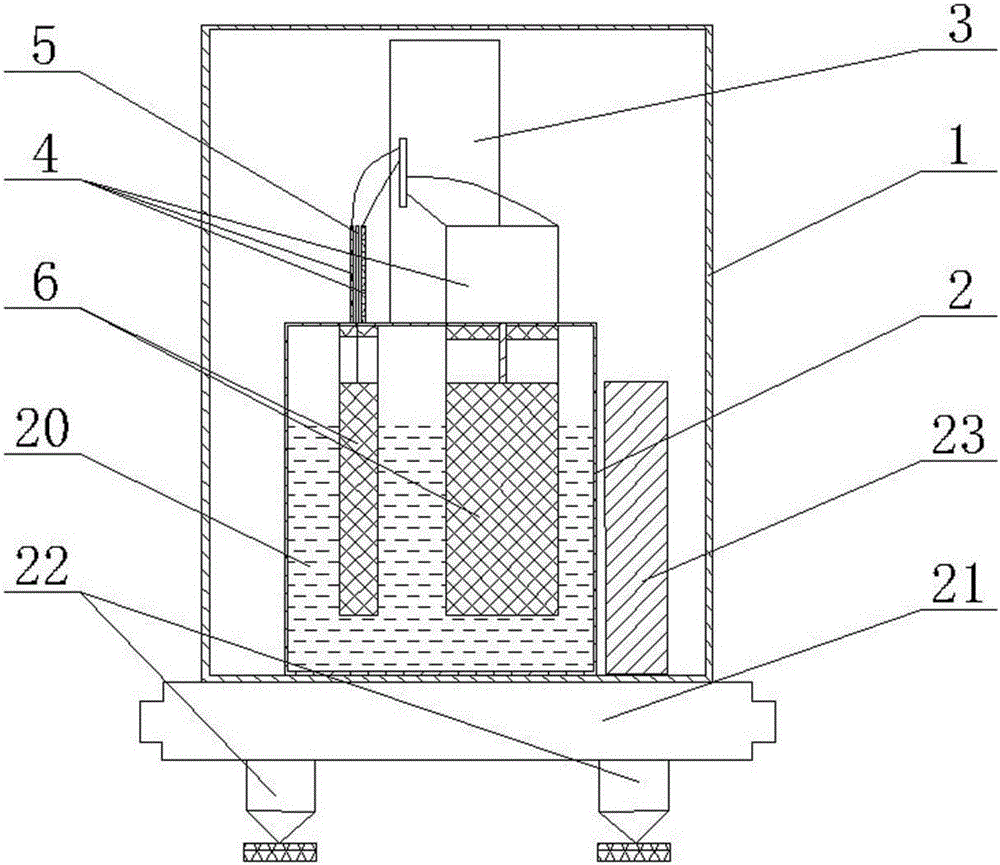
Earth crust shock collection system
InactiveCN106405628AEasy transferSolve problems with a relatively large amount of laborSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal transmissionData centerCollection system
The present invention discloses an earth crust shock collection system. The system comprises: at least one data collection station (FDU is called a data collection station for short), wherein the data collection station performs single-point and single-channel receiving, each point can output earth crust shock information in a digitization mode; a router which enter an intelligent router through passing through a 485 bus and then an Ethernet bus and connects with at least one data collection station to transmit the data collected by at least one data collection station; and an auxiliary data center connected to the intelligent router (a router for short) to receive the information outputted by the at least one data collection station through the router. The auxiliary data center also includes a power module configured to supply power to the at least one data collection station. The problem is solved that the quantity of work is large caused by the data in the wired transmission seismograph in the prior art, and the earth crust shock collection system is convenient for data transmission.
Owner:保定市全正石油物探装备制造有限公司
P type FeNbTiSb thermoelectric material with high optimal value and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104124332ARich reservesReduce manufacturing costThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsEarth crust
The invention discloses a P type FeNbTiSb thermoelectric material with a high optimal value; the P type FeNbTiSb thermoelectric material is made of FeNb(1-x)TixSb, wherein x is equal to 0.06-0.24. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the P type FeNbTiSb thermoelectric material. The preparation method comprises the steps of: weighing raw materials including iron, niobium, titanium and stibium according to chemical dosages of the FeNb(1-x)TixSb, under the protection of argon, smelting to obtain cast ingots; smashing the cast ingots into participles, sintering and thereby obtaining the P type FeNbTiSb thermoelectric material. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple in process, short in production cycle and high in production efficiency; the prepared FeNb(1-x)TixSb thermoelectric material is good in stability at high temperatures, abundant in contents of elements, constituting the material, in the earth crust, and low in industrialized cost; the maximal zT value reaches 1.1 at 1100K, which is the present highest performance in a Half-Heusler system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Underground deep layer seismic monitoring system and working method thereof
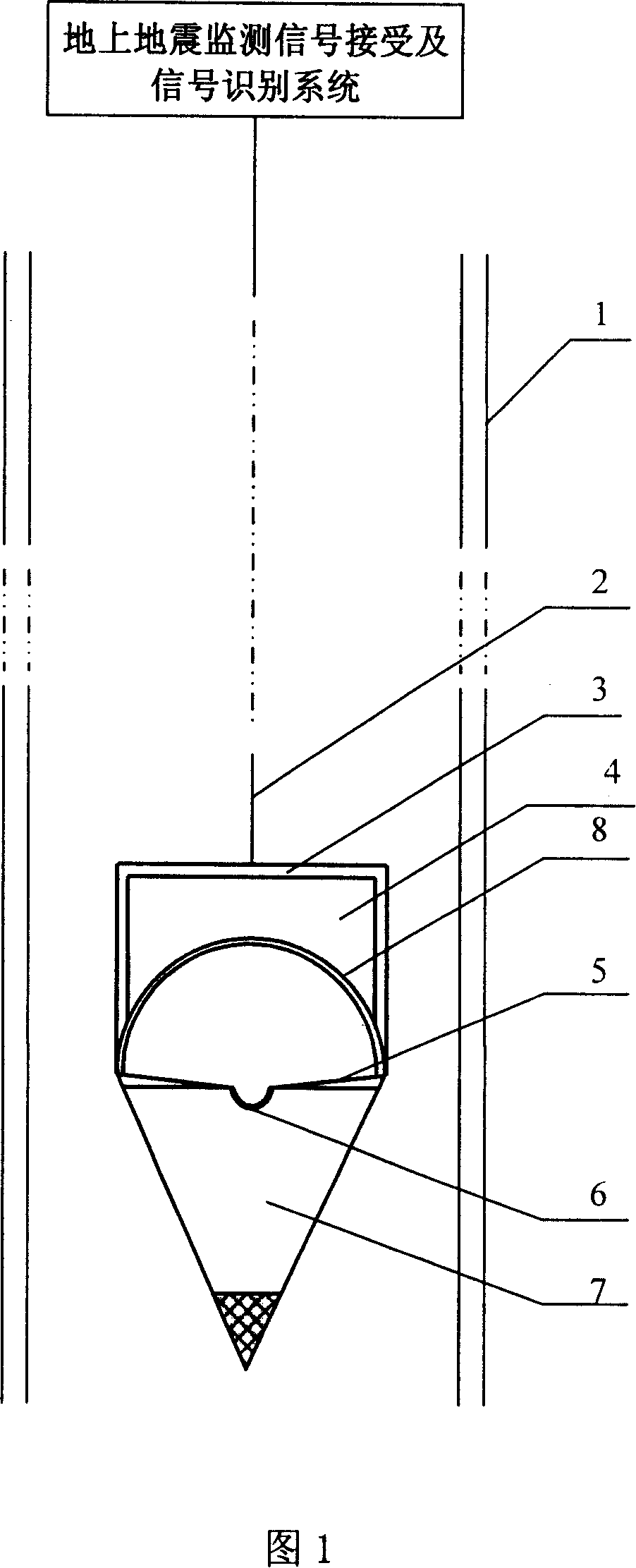
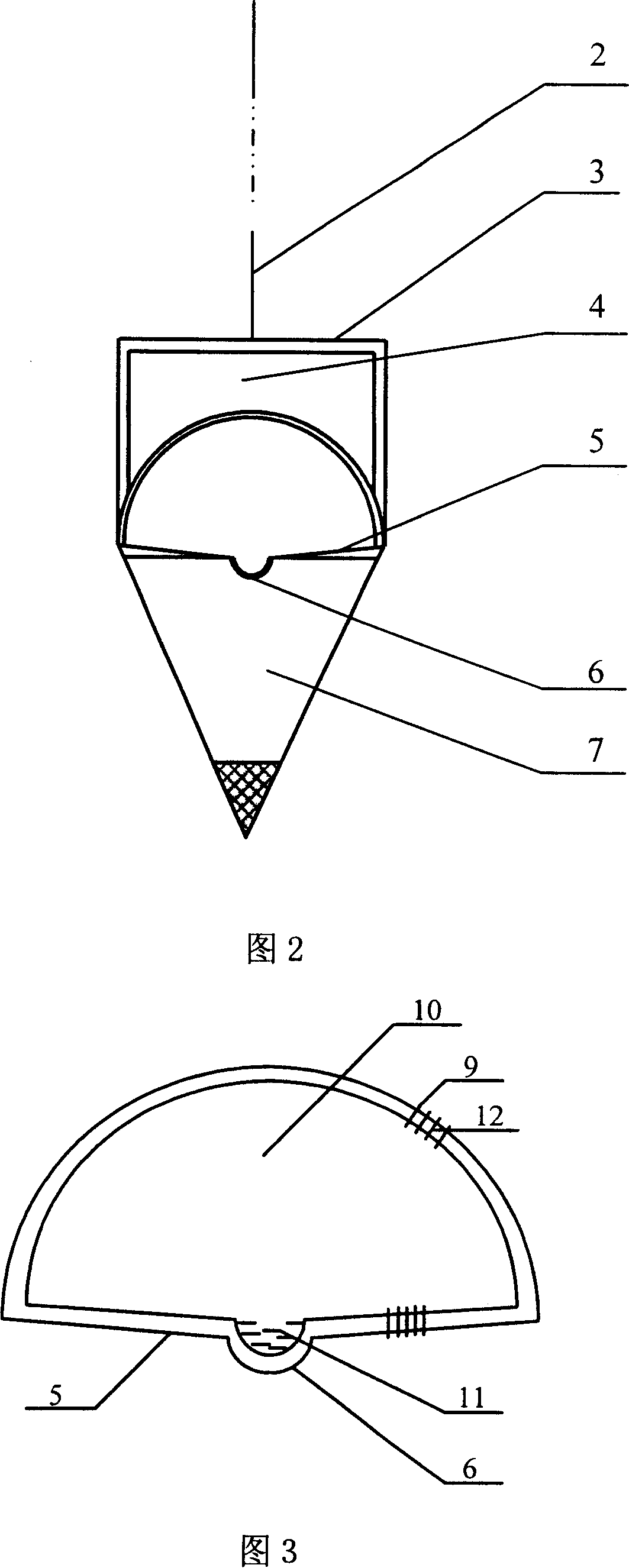
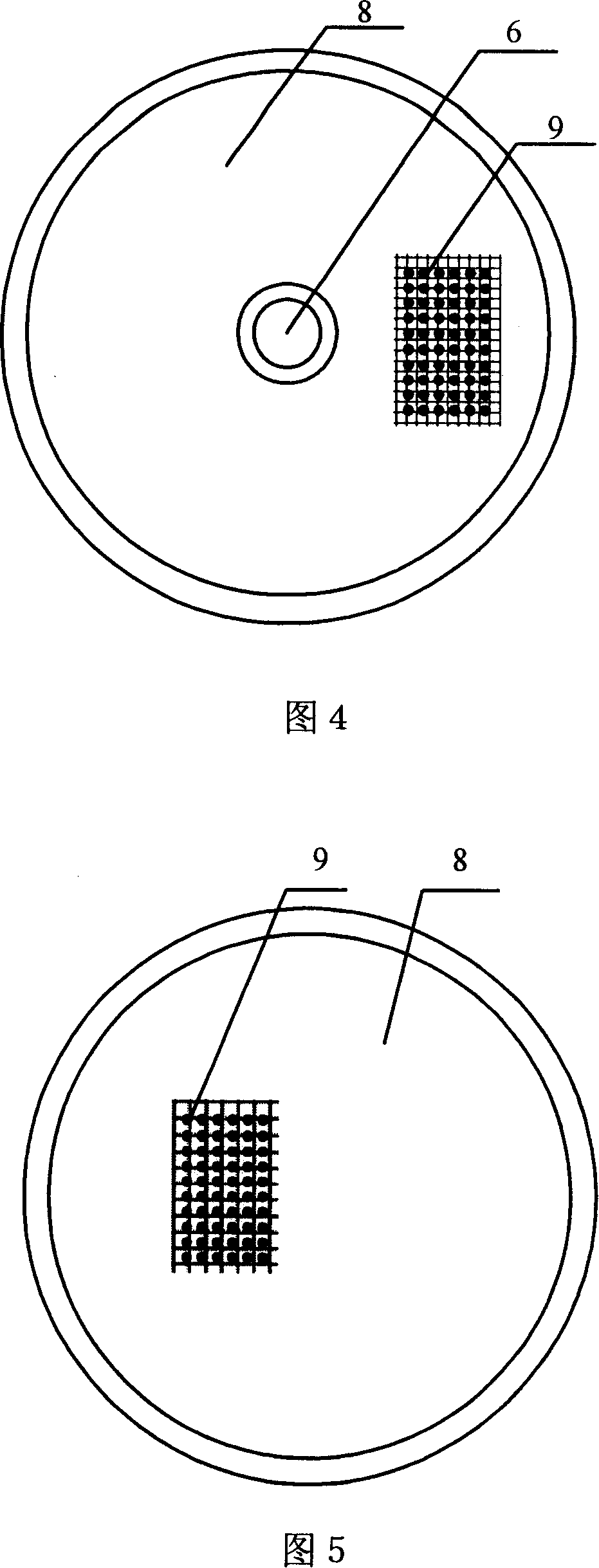
InactiveCN101118286AImprove accuracyLess distracting factorsSeismic signal receiversIntegrative data analysisEarth crust
The present invention provides an underground depth earthquake monitoring system and comprises a deep well wrapper tube. The present invention is characterized in that the present invention consists of an underground vibration monitoring device and an overground earthquake monitoring signal receiving and signal recognition system; the underground vibration monitoring device consists of an underground electric current vibration meter central device, a sensing hemisphere guard shield, a horizontal plumb, and a suspension metal cable of the monitoring device sensor, as well as a signal transmission line. The working method of the present invention is as follows: firstly, the earthquake monitoring point is confirmed; secondly, the underground depth earthquake monitoring system is arranged, and a matrix form multistep earthquake monitoring network is formed; thirdly, the earth crust vibration situation is gathered, processed, analyzed and stored; fourthly, the earth crust vibration situation in the area or the city through the comprehensive data analysis is determined. The present invention has the advantages of high accuracy of the earthquake monitoring; simple method and reliable result; good signal specificity; high measuring accuracy, and high movement sensitivity of the device.
Owner:张维耀
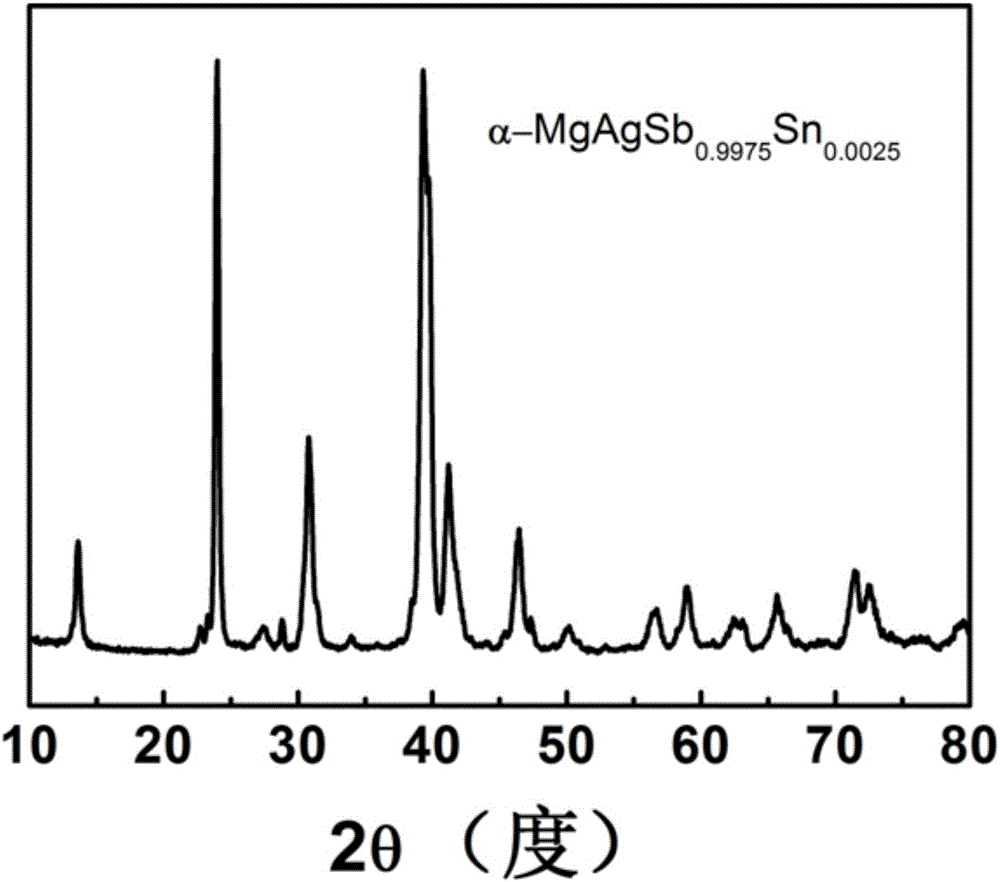
P-type alpha-MgAgSbSn thermoelectric material with high optimum value and preparation method
InactiveCN105970070ARich reservesLow priceThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsEarth crust
The invention discloses a P-type alpha-MgAgSbSn thermoelectric material with a high optimum value. The P-type alpha-MgAgSbSn thermoelectric material comprises raw material compositions of MgAgSb1-xSnx, wherein x=0.001-0.05, x represents atomic percent. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses a preparation method of the P-type alpha-MgAgSbSn thermoelectric material with the high optimum value. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) weighing raw materials which inlcude magnesium, silver, stibonium and stannum according to the stoichiometric ratio of MgAgSb1-xSnx, vacuum-melting to obtain a cast ingot, wherein X=0-0.05; (2) crushing the cast ingot obtained in step (1) into particles, sintering and annealing to obtain the P-type alpha-MgAgSbSn thermoelectric material. A preparation process disclosed by the invention is simple; the prepared P-type alpha-MgAgSbSn thermoelectric material is stable in property and good in repeatability; the contents of elements forming the material are abundant in the earth crust, the industrial cost of the elements is low; a maximum zT value of the P-type alpha-MgAgSbSn thermoelectric material reaches 1.0 at 525K.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Inorganic Ionomers Made From Minerals
ActiveUS20150274927A1Maintain good propertiesLow production costNon-metal conductorsConductive materialIonomerFiber
Inorganic polymers are produced from silicate (—Si—O—) and / or phosphonate (—P—O—) bonds, commonly found in rocks and glass, to create new polymeric materials for rubbers, fibers, and plastics. These inorganic polymers have various advantages over organic counterparts including abundance on the earth's crust, and properties including nonflammability, low toxicity, recyclability, and excellent thermal and chemical resistance.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method for preventing destructive violent earthquakes and volcano eruptions
InactiveCN102767171ARelieve pressureEruption preventionHydraulic engineering apparatusSoil preservationEarth crustInternal pressure
The invention discloses a method of using existing technologies of human beings to prevent destructive violent earthquakes and volcano eruptions. The method is characterized in that existing dormant active volcanoes with no one living around and on the earth are manually detonated when internal pressure of the earth crust is increased according to earthquake period and existing earthquake and volcano monitoring data, high-pressure substances in the earth are erupted and discharged on small scale and in batches to relieve the internal pressure of the earth, and accordingly destructive violent earthquakes and volcano eruptions are prevented.
Owner:张科元
Ground tilt monitoring device
ActiveCN105823465AGuaranteed continuityEliminate static frictionIncline measurementEarth crustElectricity
The invention discloses a ground tilt monitoring device .The ground tilt monitoring device comprises a device shell, a suspension frame and a processing circuit board are arranged in the device shell, two capacitive sensors are orthogonally arranged on the suspension frame, each capacitive sensor comprises capacitor stators, capacitor rotors and pendulum bobs, the capacitor stators are arranged on the two sides of the capacitor rotors at equal intervals, the capacitor stators and the capacitor rotors are horizontally arranged on the same horizontal plane, the capacitor stators are arranged on the suspension frame, the pendulum bobs are arranged on the suspension frame in a hanging mode and arranged on the lower portions of the capacitor rotors to be in rigid connection with the capacitor motors, the capacitive sensors are electrically connected with the processing circuit board respectively, and a zero setting mechanism is further arranged on the suspension frame .According to the ground tilt monitoring device, when zero setting is conducted, the two capacitive sensors do not influence each other, the pendulum bobs drive the capacitor rotors to move to change the space between the capacitor rotors and the capacitor stators so as to produce capacitance variable quantity, and the influence of static friction force of pendulum bobs in the prior art is eliminated; the ground tilt monitoring device is mainly used for monitoring earth tides, earthquake precursors and tilting deformation of an earth crust, and the ground tilt monitoring device is simple in structure, good in stability, high in precision and high in output linearity.
Owner:吴清荣
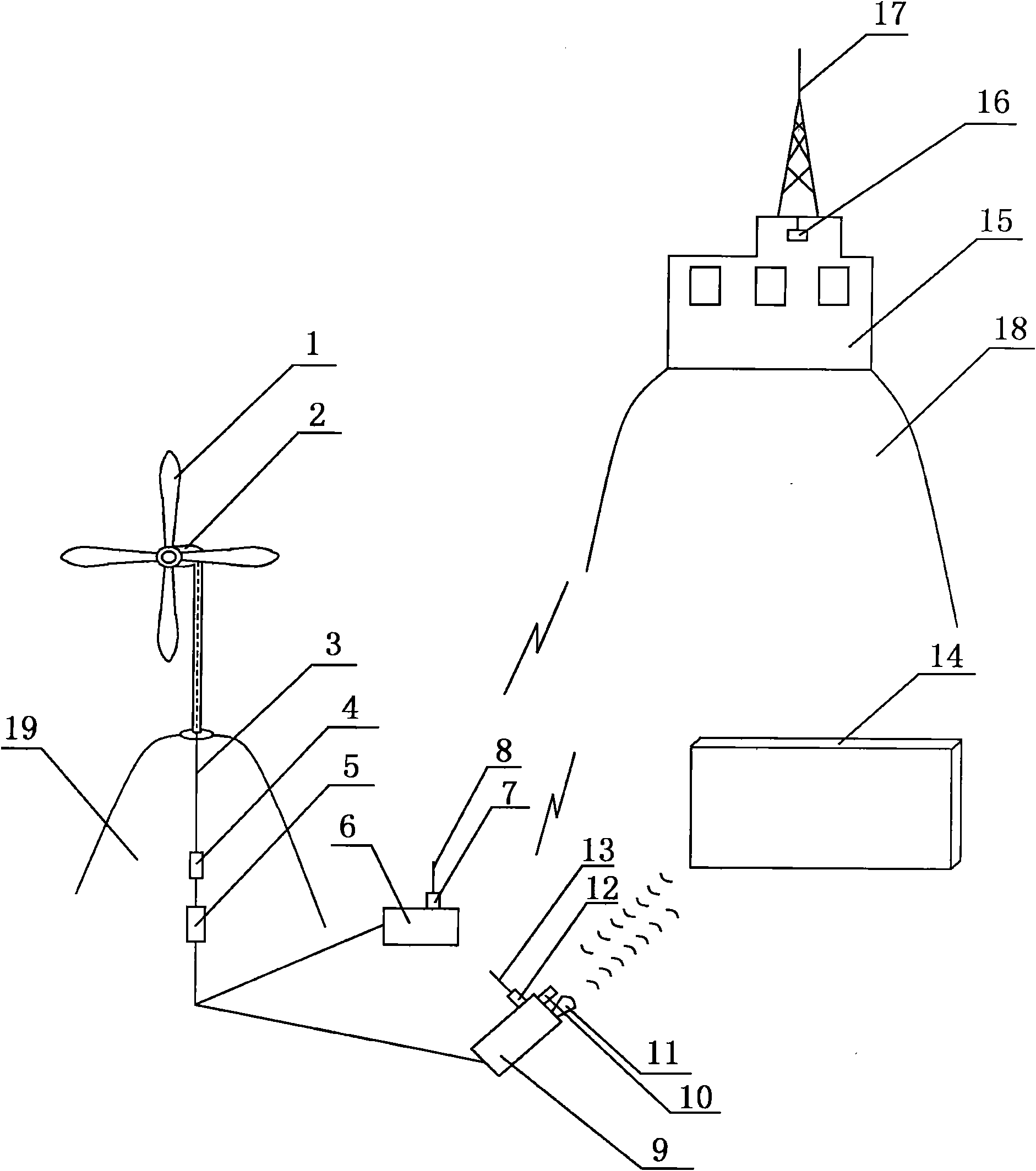
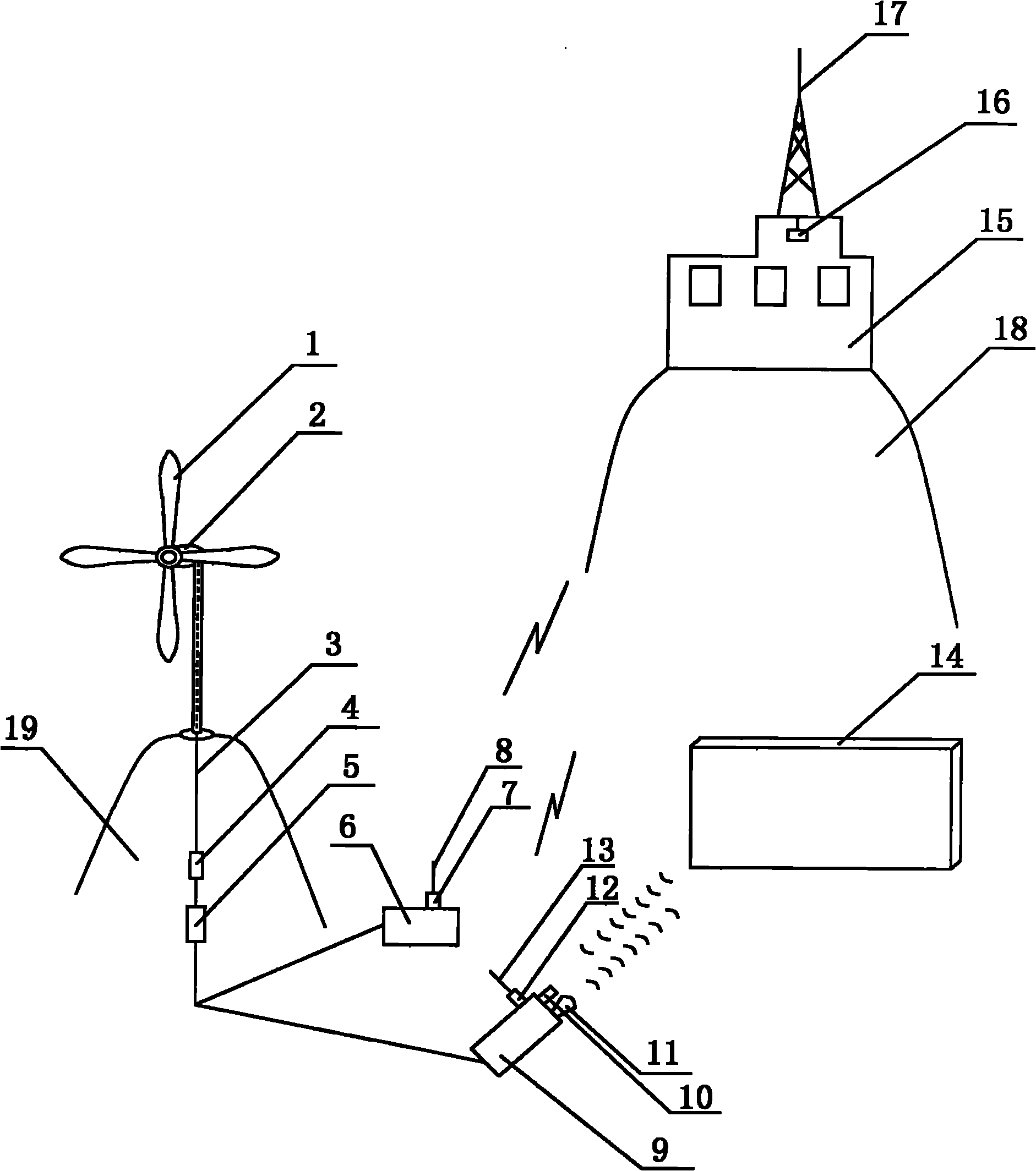
Power supply unit for applying wind generator system to earthquake prediction device
The invention relates to a power supply unit for applying a wind generator system to an earthquake prediction device, which belongs to the technical field of new energy application. Blades of a wind generator installed on a mountain A rotate under the drive of the wind to generate direct current; the direct current is inputted into a controller through a conductor wire for being rectified, and then is inputted into an inverter to be converted into alternating current; the alternating current drives a seismograph to measure change data of the Earth crust moving in a vertical direction; the data is transmitted to a wave receiving antenna on the top of a seismostation arranged on another mountain B and to an information processing system in the seismostation through a sensor A, a transmitting antenna A and radio waves; the alternating current also drives a sound locator to measure change data of the Earth's crust moving in a horizontal direction; and the data is transmitted to the wave receiving antenna and the information processing system through a sensor B and a transmitting antenna B for being analyzed and processed in time. By applying an earthquake prediction network supplied by a wind generator system over a wide area, the level for monitoring earthquakes can be improved.
Owner:NANTONG TONGDA SILICON STEEL STAMPING TECH CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com