Method for oxidatively degrading chlorophenol substances by using EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid)-reinforced bimetal aluminum-iron system
An oxidative degradation, bimetallic technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc. The treatment cost is cheap, the COD and SS are reduced, and the effect of ensuring the emission standard
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
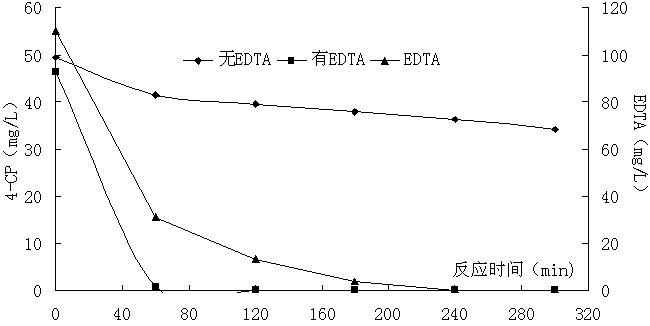
[0048] Example 1: EDTA-enhanced bimetallic aluminum-iron system oxidative degradation of p-chlorophenol (4-CP) wastewater
[0049] Step 1: Weigh iron filings and aluminum filings of 5g / L each, mix them evenly, and put them into two filters respectively. The following implementation steps are the same.
[0050] Step 2: Add EDTA 0.3mmol / L and 50mg / L 4-CP waste water to one of the filters, which is called filter A; the other does not add EDTA, only adds 50mg / L 4-CP CP wastewater, called filter B. Adjust the pH of the wastewater in the filter to 3, aerate at normal temperature and pressure, maintain the dissolved oxygen in the water above 2mg / L, and let the wastewater circulate in the above filter with a reflux ratio of 5:1, and the hydraulic retention time is 5 Hours, make the wastewater fully react in the filter.
[0051] The third step: static precipitation for 30 minutes, and measure the supernatant.
[0052] The result shows that A of the present invention not only realiz...
Embodiment 2
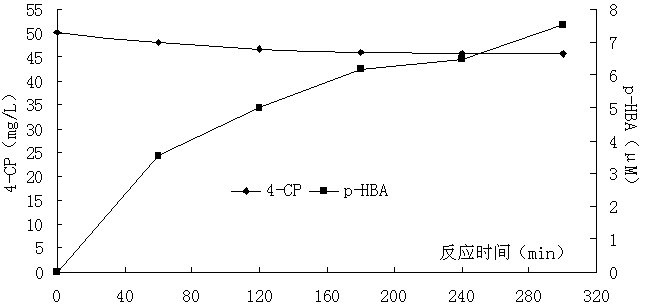
[0056] Example 2: Effect of EDTA concentration on oxidative degradation of p-chlorophenol (4-CP) wastewater by bimetallic aluminum-iron system
[0057] Step 1: Weigh iron scraps and aluminum scraps of 5g / L each, mix them evenly, and put them into four filters respectively. The following implementation steps are the same.
[0058] Step 2: Add 0.2mmol / L, 0.3mmol / L, 0.4mmol / L, and 0.5mmol / L of EDTA to each filter respectively, and call them filters A, B, C, and D in turn. The concentration of 4-CP is 50mg / L. Adjust the pH of the wastewater in the filter to 5, aerate at normal temperature and pressure, maintain the dissolved oxygen in the water above 2mg / L, and let the wastewater circulate in the above filter with a reflux ratio of 10:1, and the hydraulic retention time is 3 Hours, make the wastewater fully react in the filter.
[0059] The third step: static precipitation for 30 minutes, and measure the supernatant.
[0060] The results show that the C of the present inventio...
Embodiment 3
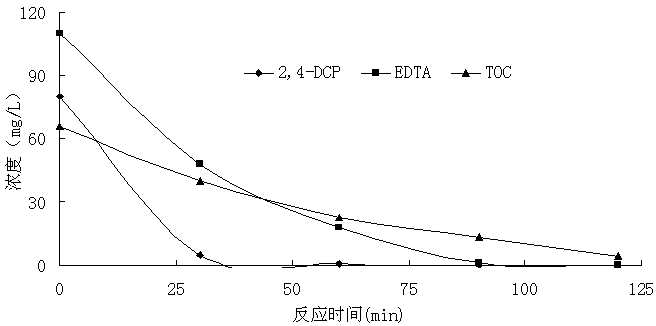
[0063] Example 3: The present invention treats 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) wastewater
[0064] Step 1: Weigh 5g / L iron filings and aluminum filings respectively, mix them evenly and put them into the filter tank. The following implementation steps are the same.
[0065] Step 2: Add EDTA 0.3mmol / L to the filter, adjust the pH of the influent water to 3, aerate at normal temperature and pressure, maintain the dissolved oxygen in the water above 2mg / L, and reflux at a ratio of 5:1 Let the waste water circulate in the above-mentioned filter, and the hydraulic retention time is 2 hours, so that the waste water can fully react in the filter. The initial concentration of EDTA was 0.3mM.
[0066] The third step: static precipitation for 30 minutes, and measure the supernatant.
[0067] The results are attached image 3 As shown, the present invention removes 100% of 2,4-DCP and EDTA within 2 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com