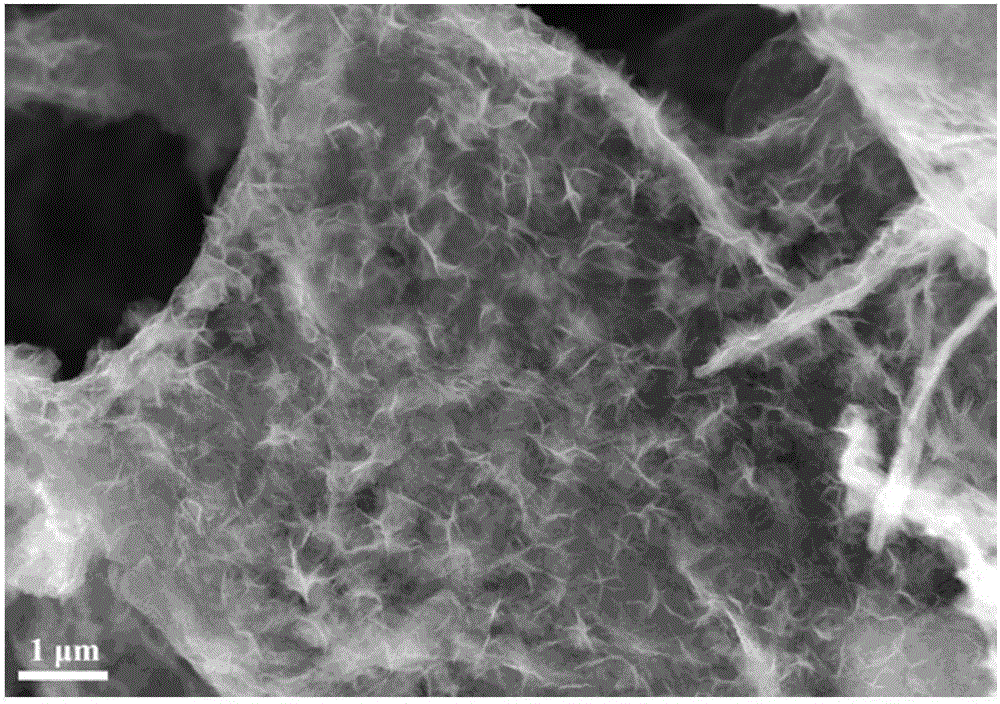
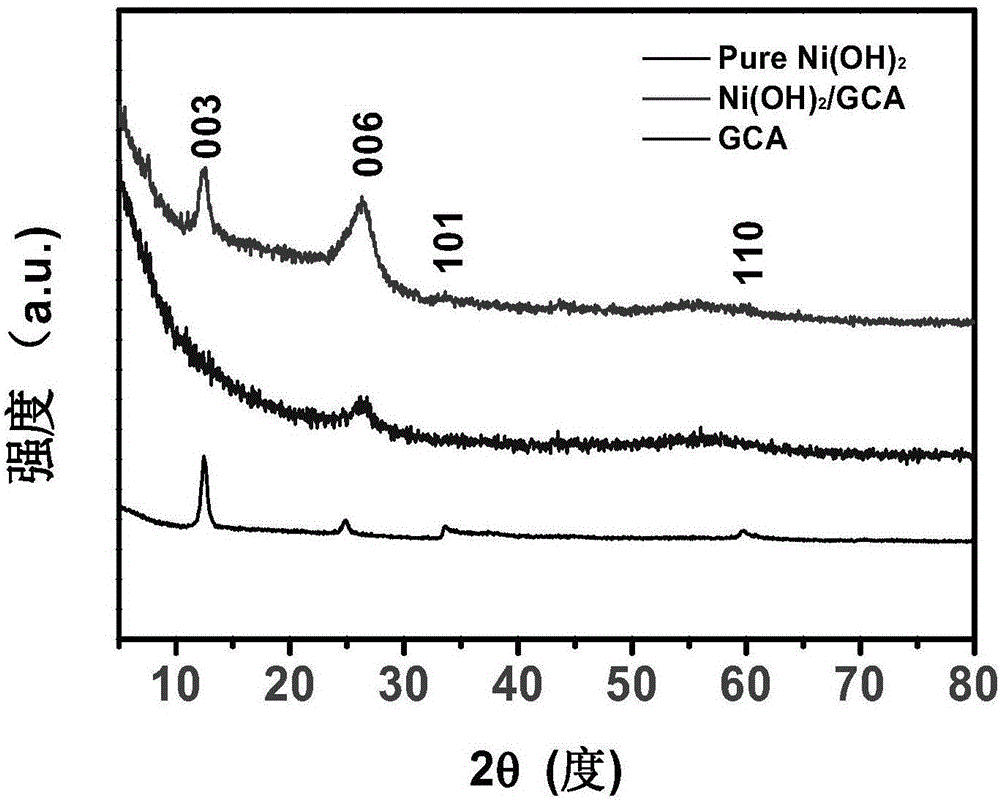
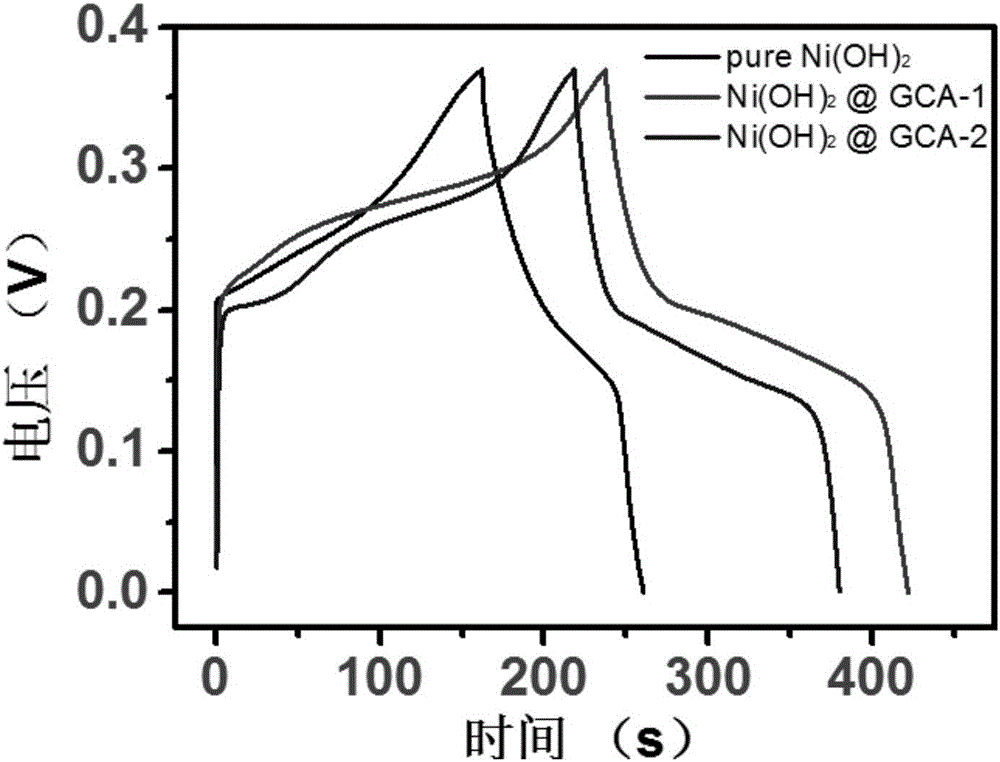
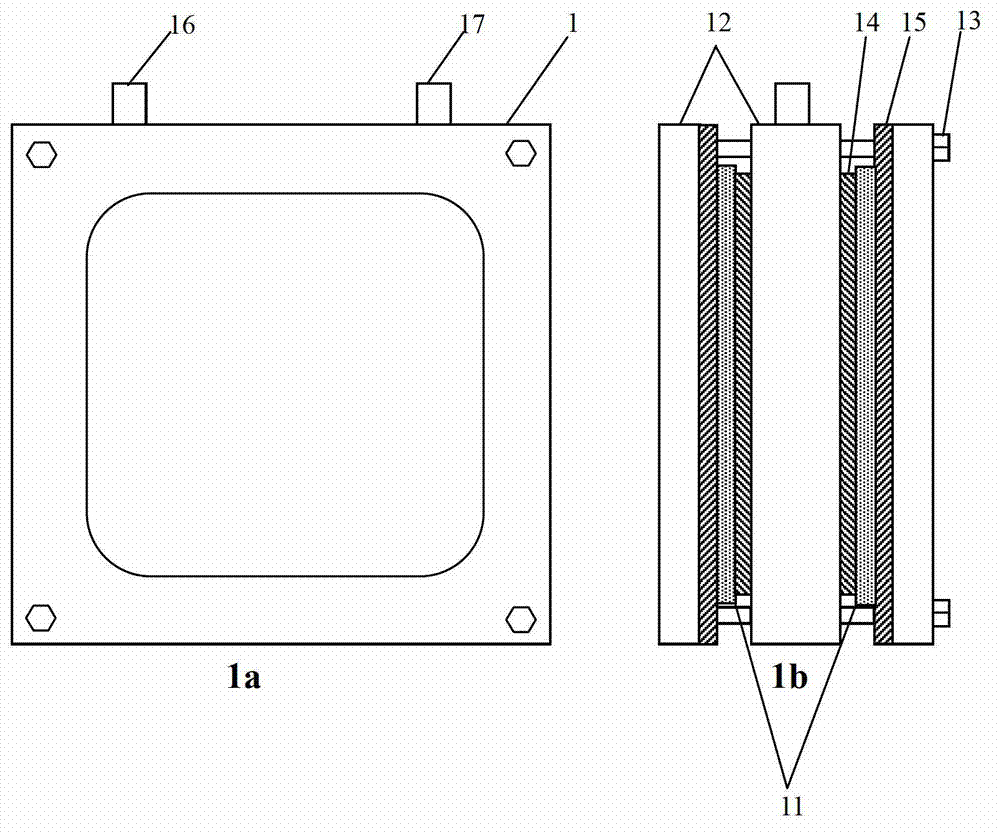
Patents
Literature
219 results about "Chemical bath deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
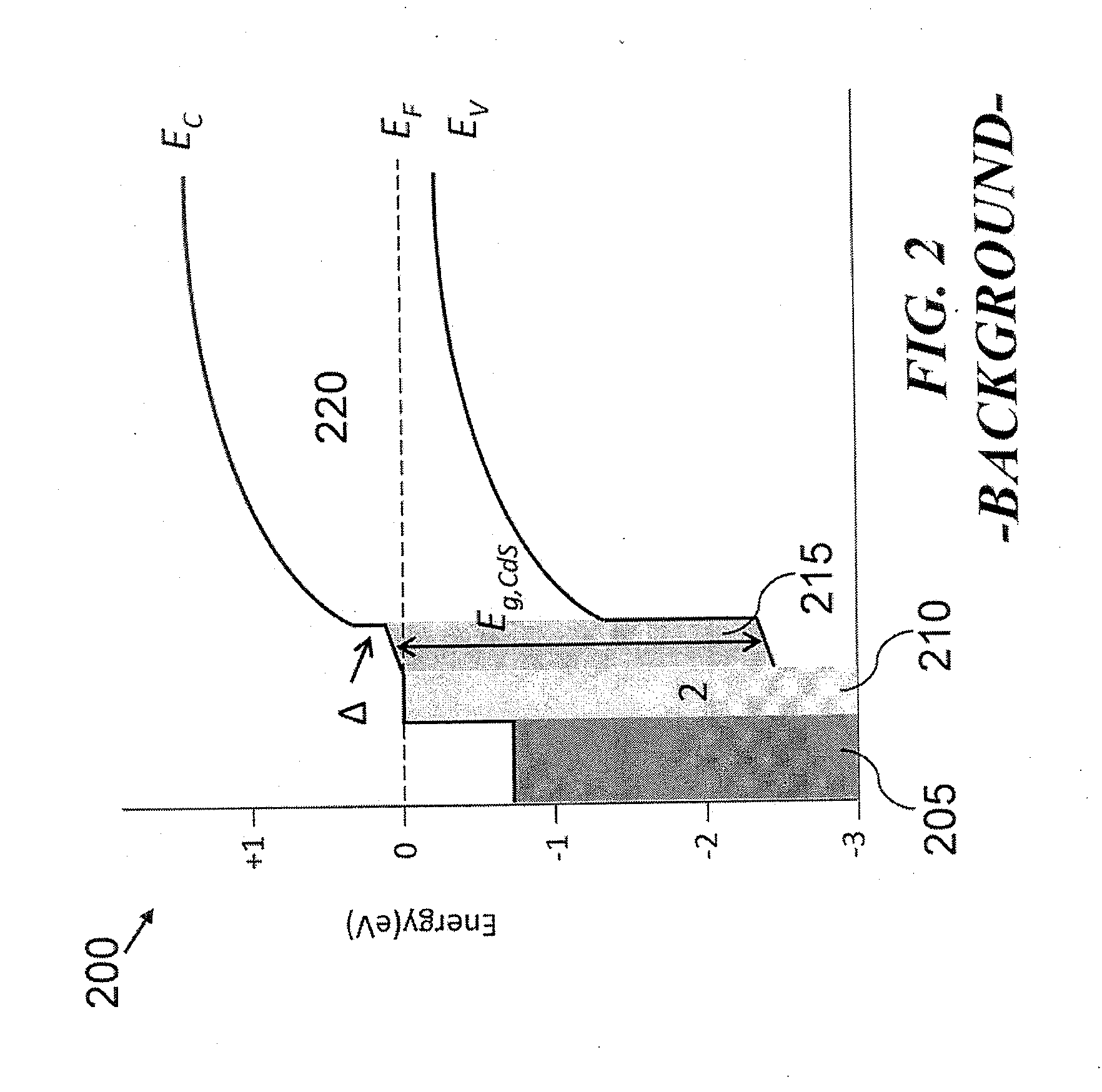
Chemical bath deposition (CBD), or chemical solution deposition (CSD), is a method to deposit thin films and nanomaterials, first described in 1869. It can be employed for large-area batch processing or continuous deposition. In 1933 Bruckman deposited lead(II) sulfide (PbS) thin film by chemical bath deposition, or solution growth method. This technique is extensively used to deposit buffer layers in thin film photovoltaic cells.
Methods to fabricate thin film transistors and circuits
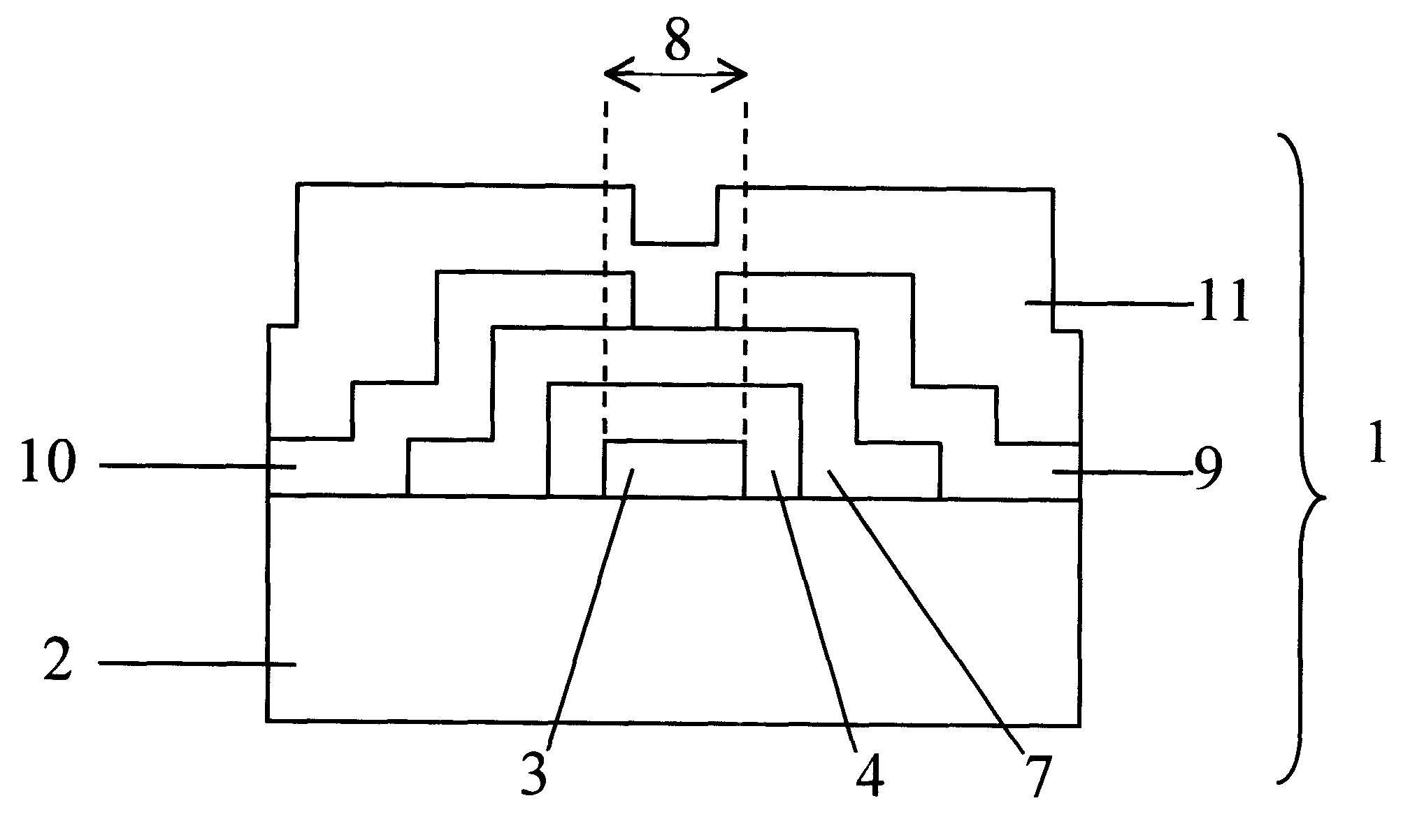
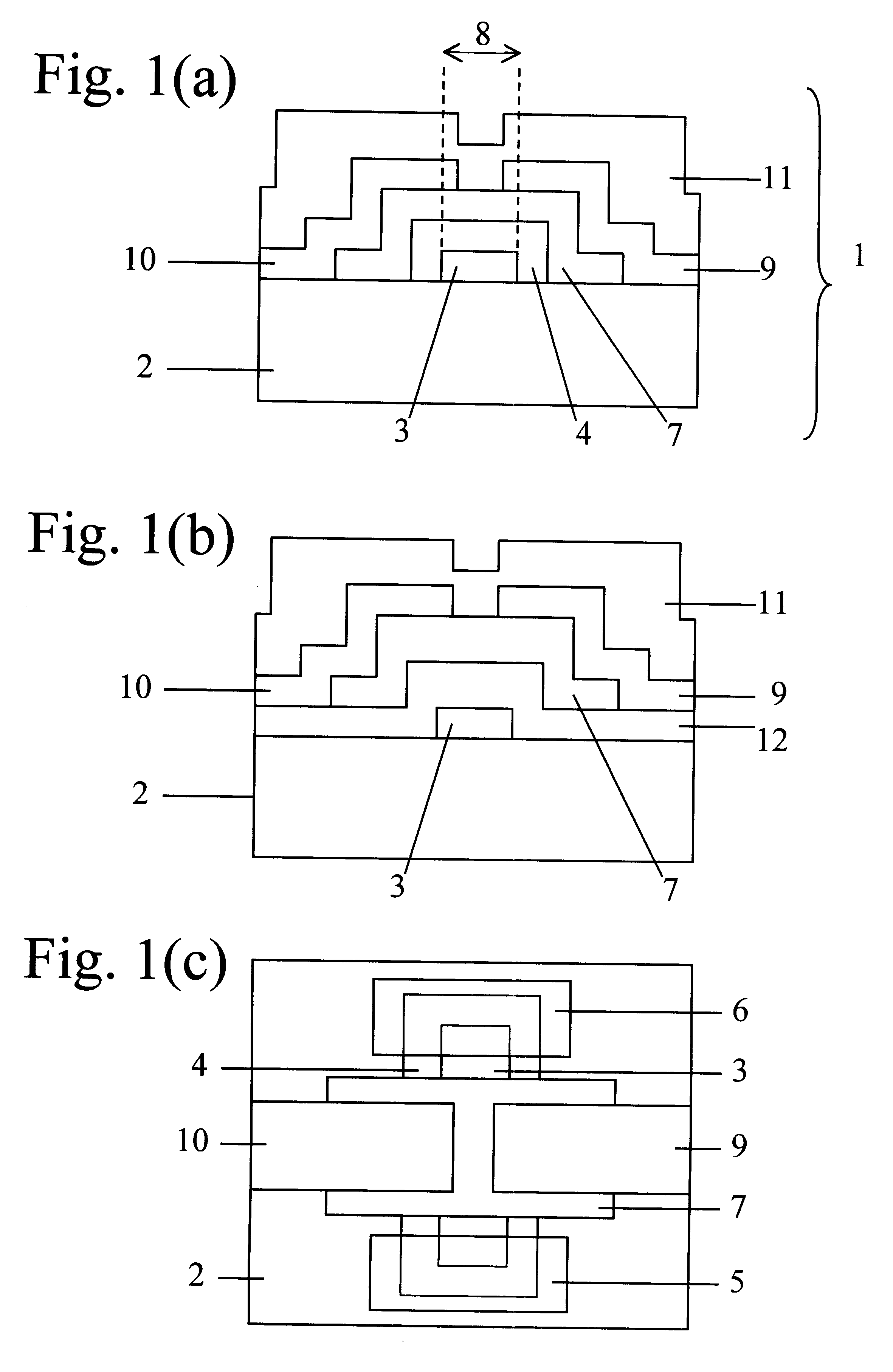
InactiveUS6225149B1Low costLow thermal budgetTransistorLight-sensitive devicesOptoelectronicsField-effect transistor
A method for fabricating a thin film field effect transistor is described in this invention. The active layer of the thin film transistor (TFT) is formed by a low cost chemical bath deposition method. The fabrication procedure includes deposition of a metal layer on an insulating substrate, patterning of the metal layer to form a metal gate, formation of the di-electric layer, deposition of the active layer and formation of source and drain contacts.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV OFFICE OF TECH TRANSFER
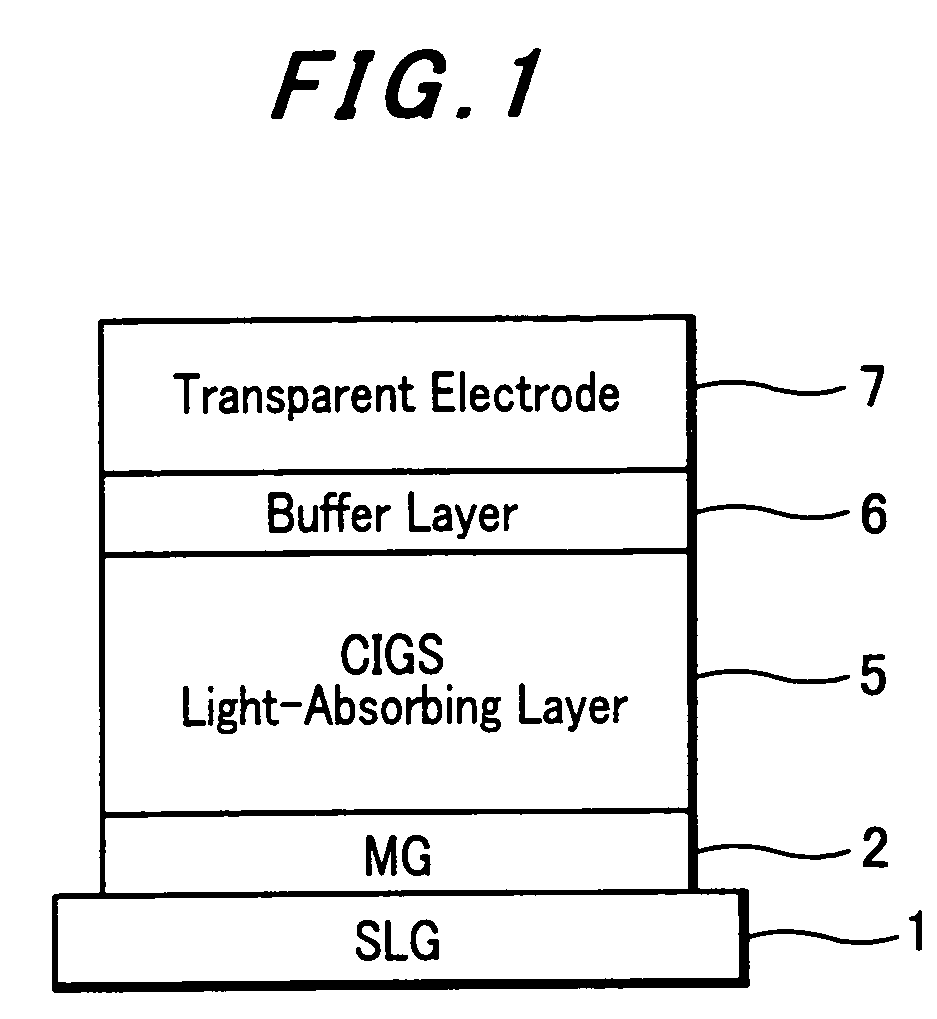
Compound thin-film solar cell and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20050236032A1Increase in sizeSimple structureFinal product manufacturePV power plantsHeterojunctionOptical transmittance
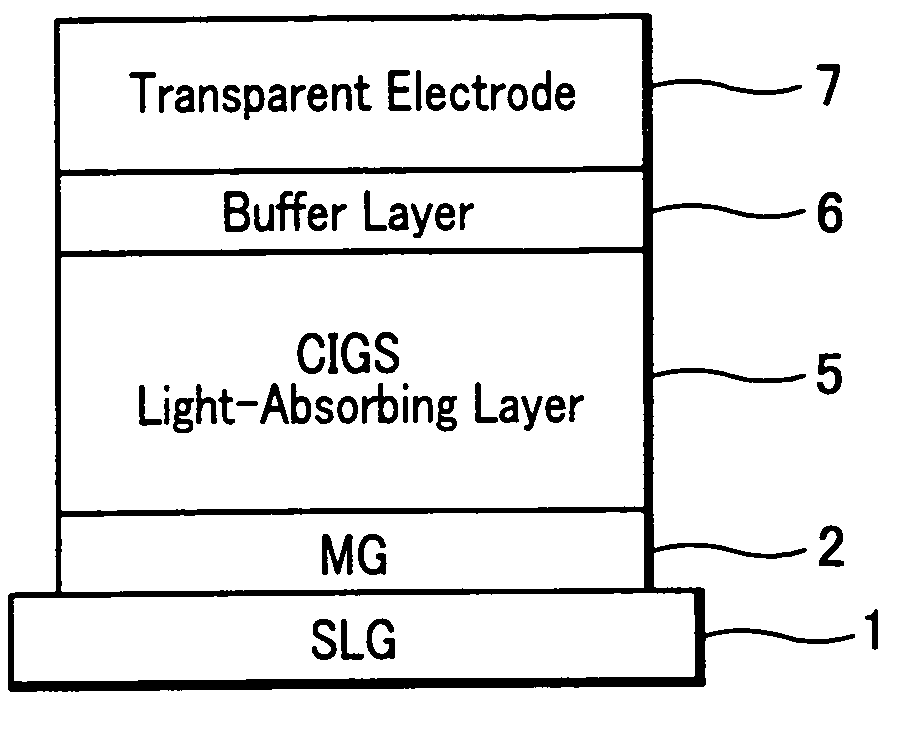
A method of fabricating a thin-film compound solar cell having an n-type buffer layer formed therein for providing a heterojunction with a p-type compound semiconductor light absorbing layer formed on a back electrode by applying a chemical bath deposition (CBD) process using an aqueous solution for dipping the light absorbing layer to deposit particles on the surface thereof. In this process, the temperature of the solution is controlled from low to high to increase sizes of the particles to be deposited on the light absorbing layer so as to form the buffer layer which possesses a high optical transmittance, tight adherence to the light absorbing layer and conformity with the transparent electrode formed thereon even if it would be made of InS material generally possessing a small bandgap and hard to pass light of short wavelengths.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
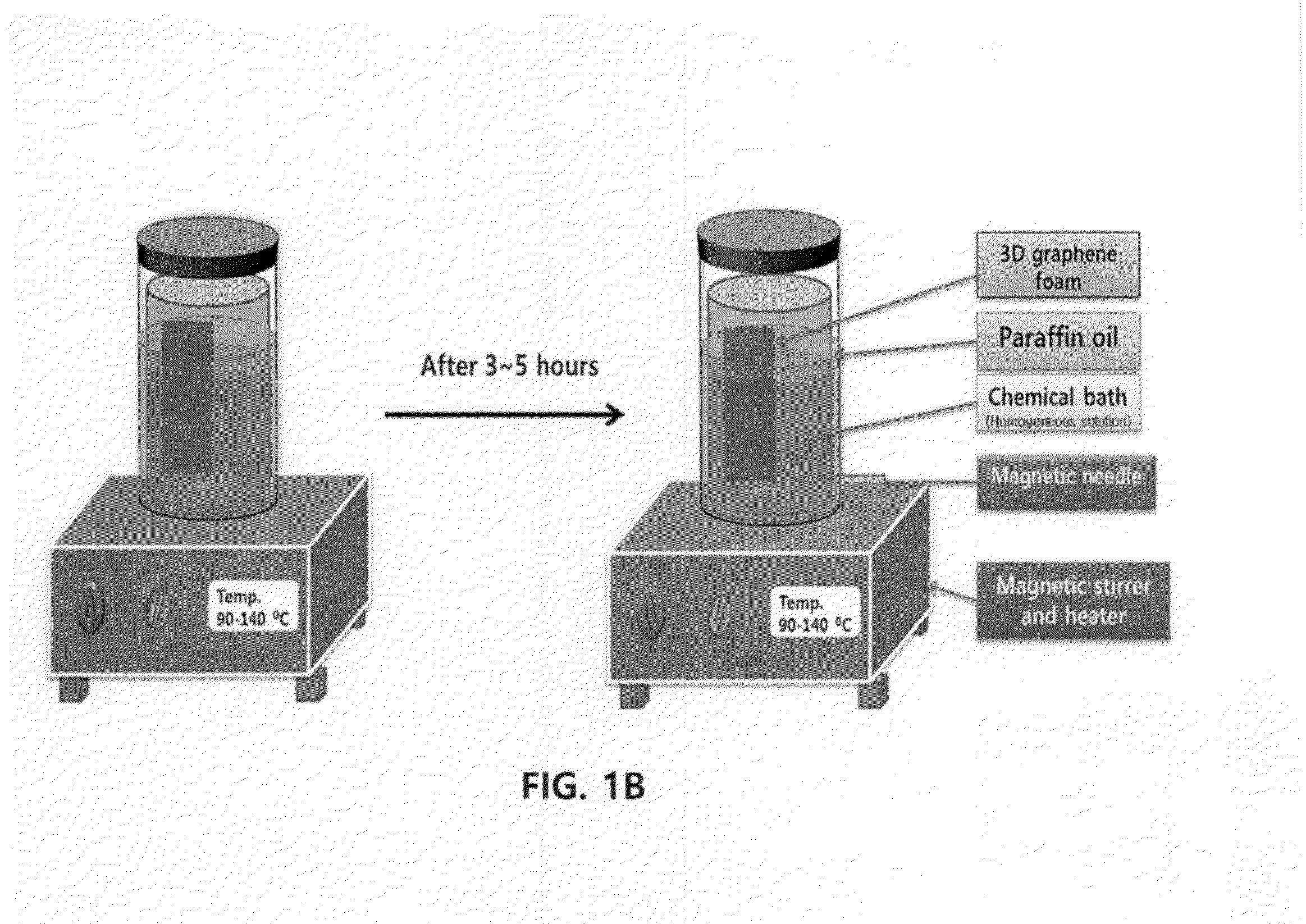
Three-dimensional graphene composite, preparation method for the same, and supercapacitor comprising the same
ActiveUS20150340170A1Improve electrostatic capacityIncrease energy densityHybrid capacitor electrodesElectrolytic capacitorsHigh energyConductive polymer
The present invention relates to a three-dimensional graphene composite, a preparation method for the same, and a supercapacitor including the same, and more particularly to a three-dimensional graphene composite including at least one electrode material nanoparticle selected from a transition metal hydroxide, a transition metal oxide and a conducting polymer as adsorbed onto the surface of a three-dimensional graphene foam, a preparation method for the three-dimensional graphene composite, and a supercapacitor including the three-dimensional graphene composite.The present invention can be used to provide a supercapacitor electrode with greatly enhanced electrostatic capacity and high energy density, by using a foaming resin structure made of a thin graphene frame to achieve lightweightness and also effectively depositing a nanostructure by a relatively simple and economic method such as the chemical bath deposition method or the electrodeposition method, based on an electron collector with high conductivity.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Method for preparation of metal chalcogenide solar cells on complexly shaped surfaces
InactiveUS20120100660A1Electrolytic coatingsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumMetal chalcogenides
Methods for fabricating a photovoltaic device on complexly shaped fabricated objects, such as car bodies are disclosed. Preferably the photovoltaic device includes absorber layers comprising Copper, Indium, Gallium, Selenide (CIGS) or Copper, Zinc, Tin, Sulfide (CZTS). The method includes the following steps: a colloidal suspension of metal surface-charged nanoparticles is formed; electrophoretic deposition is used to deposit the nanopartieles in a metal thin film onto a complexly shaped surface of the substrate; the metal thin film is heated in the presence of a chalcogen source to convert the metal thin film into a metal chalcogenide thin film layer; a buffer layer is formed on the metal chalcogenide thin film layer using a chemical bath deposition; an intrinsic zinc oxide insulating layer is formed adjacent to a side of the buffer layer, opposite the metal chalcogenide thin film layer, by chemical vapor deposition; and finally, a transparent conducting oxide is formed adjacent to a side of the intrinsic zinc oxide, opposite the buffer layer, by chemical vapor deposition.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
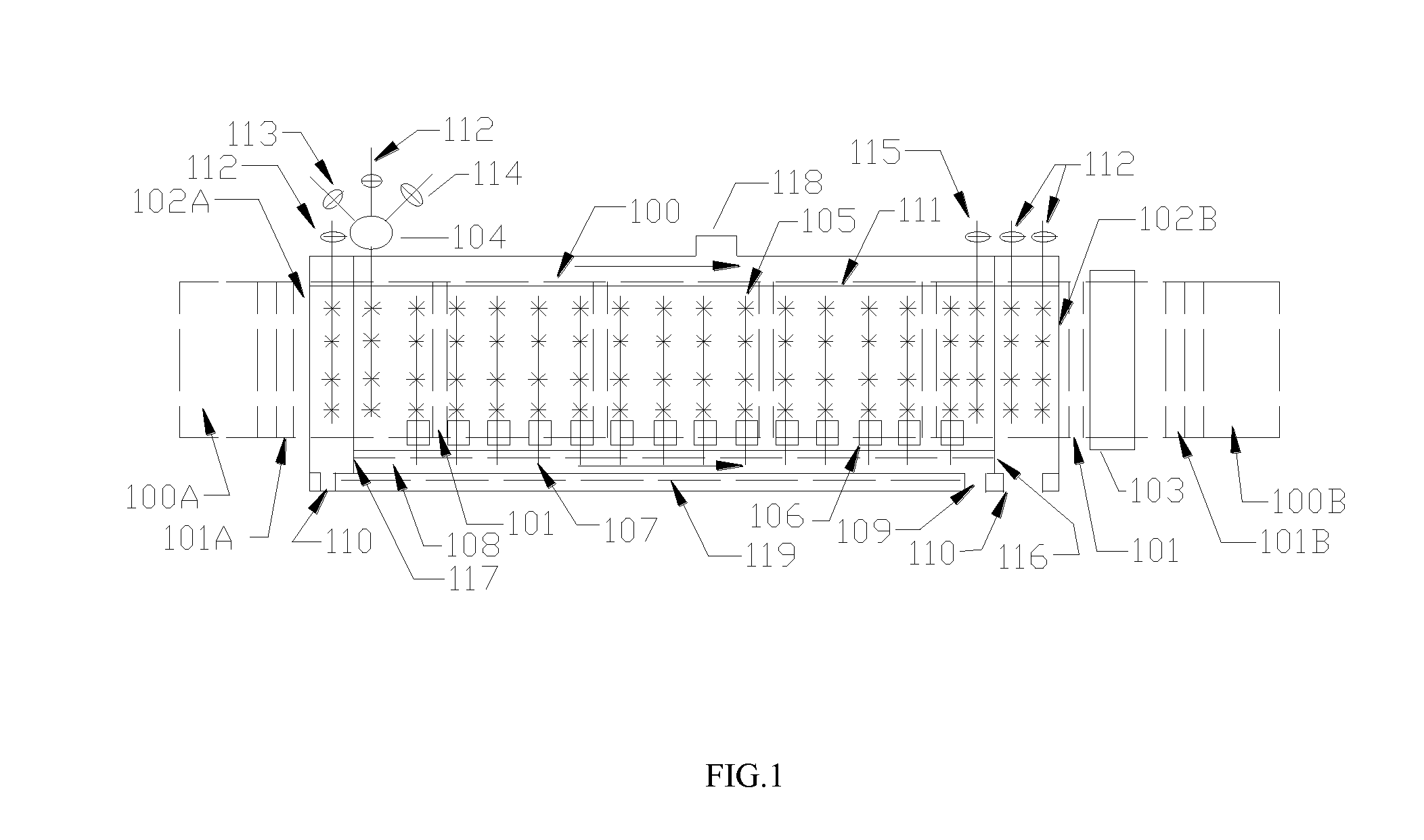
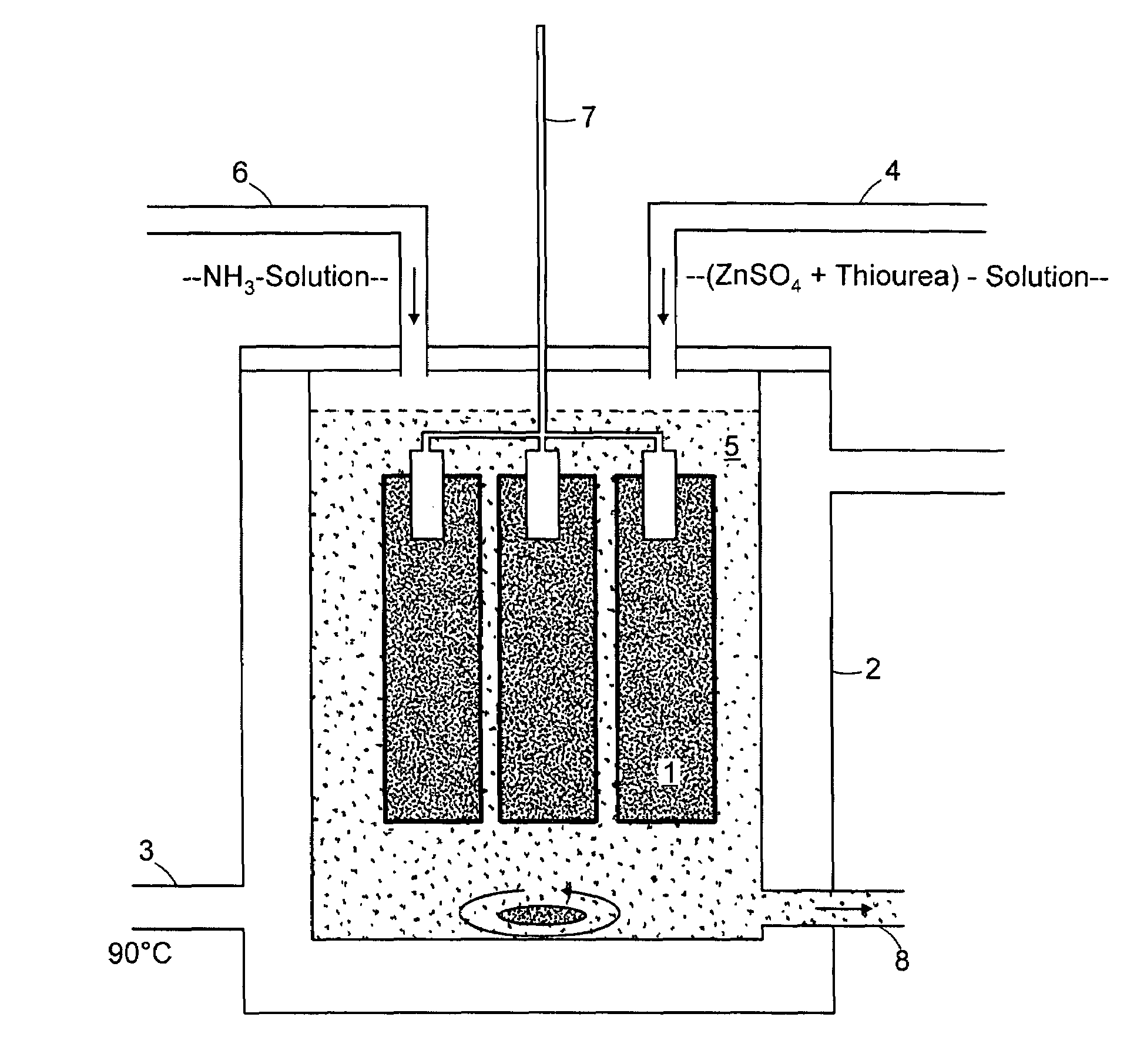
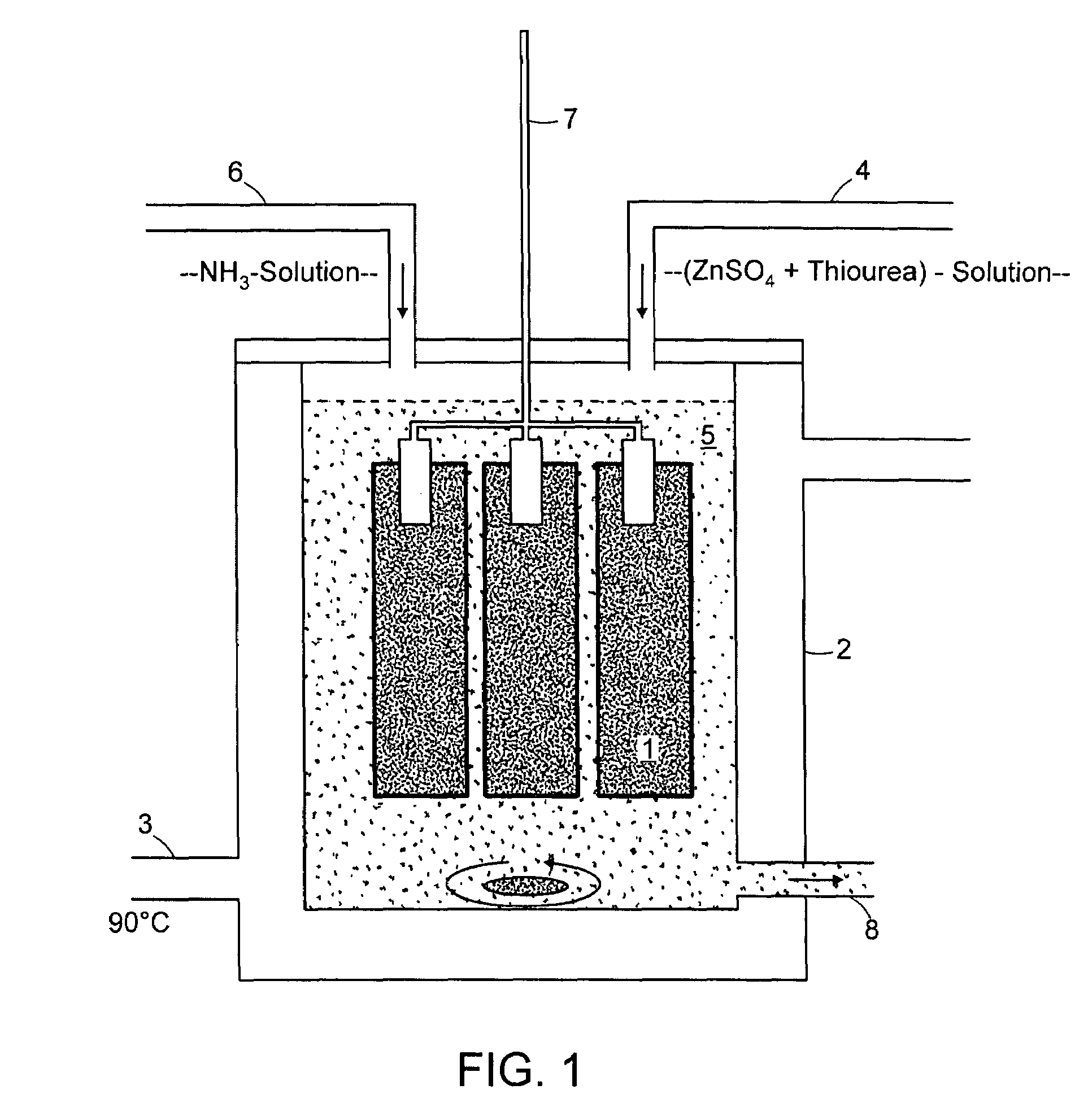
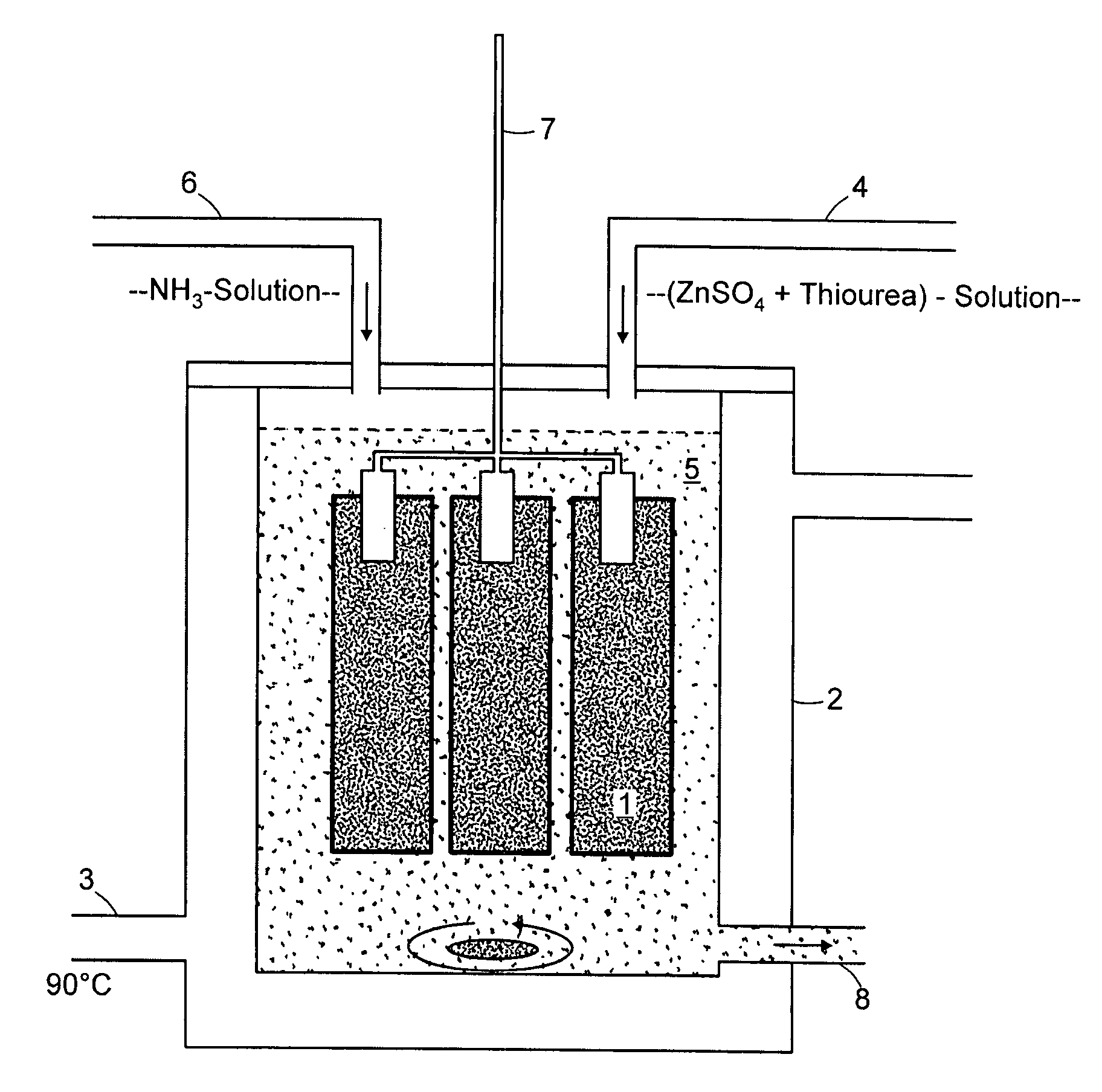
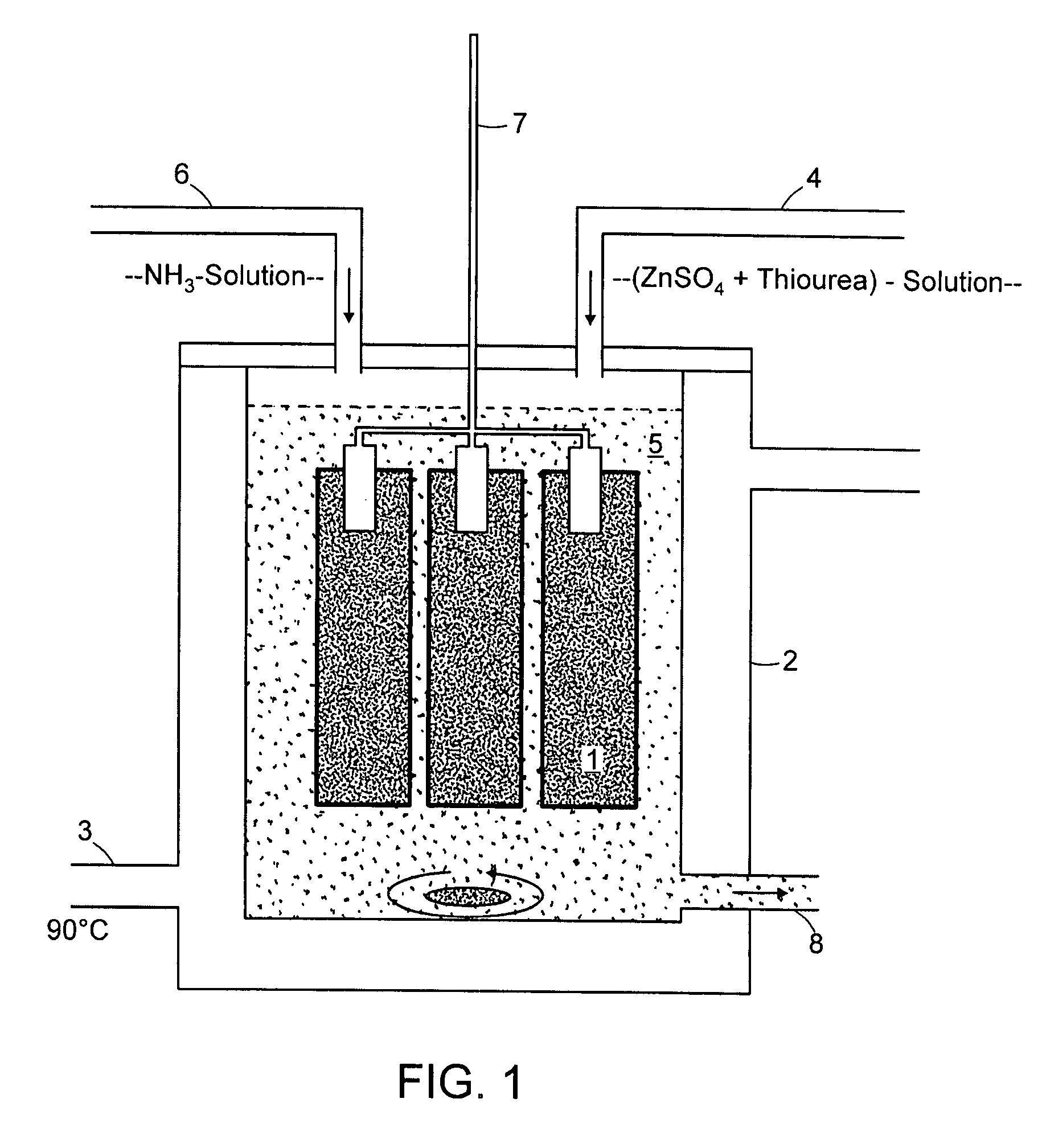
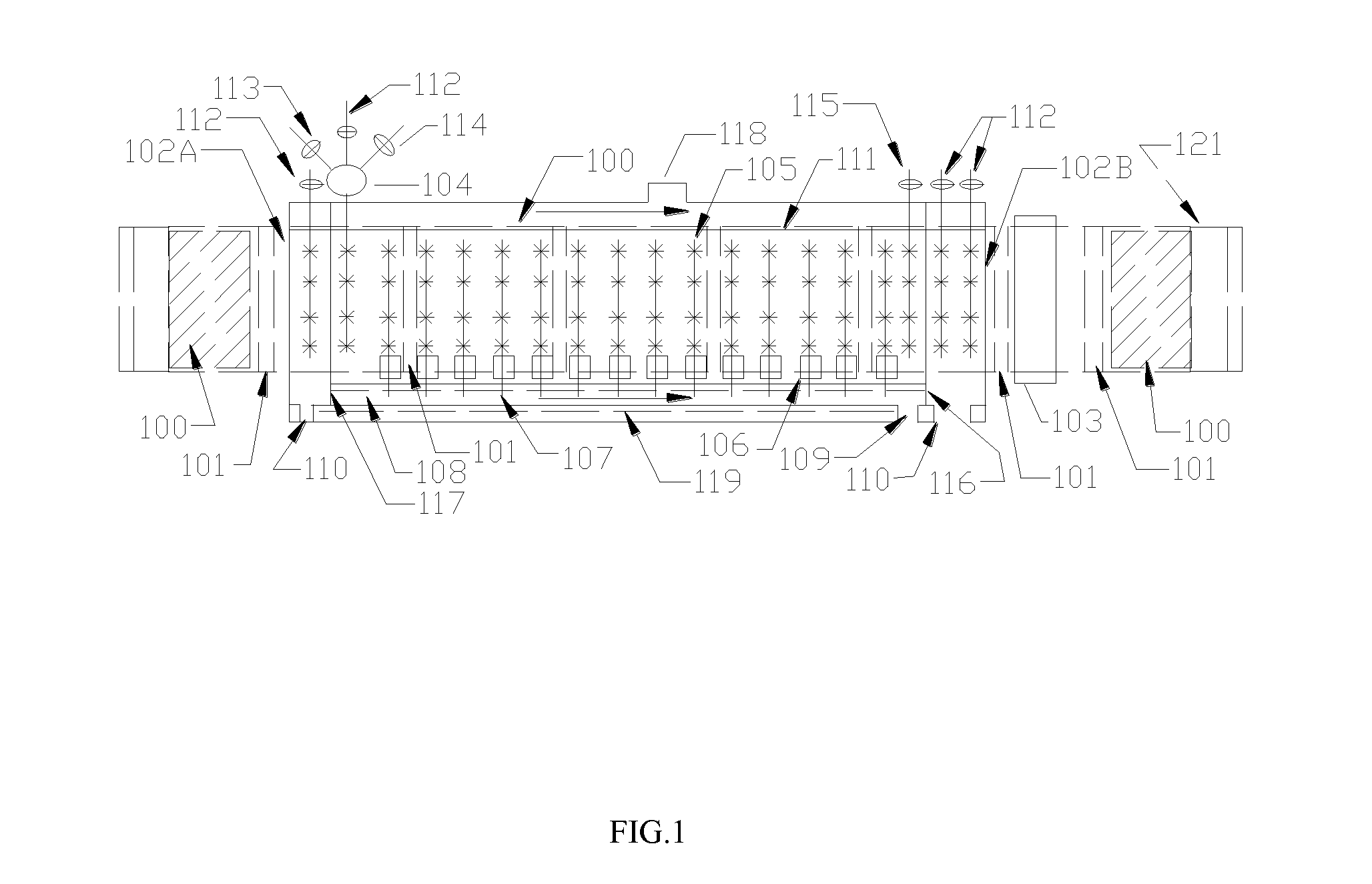
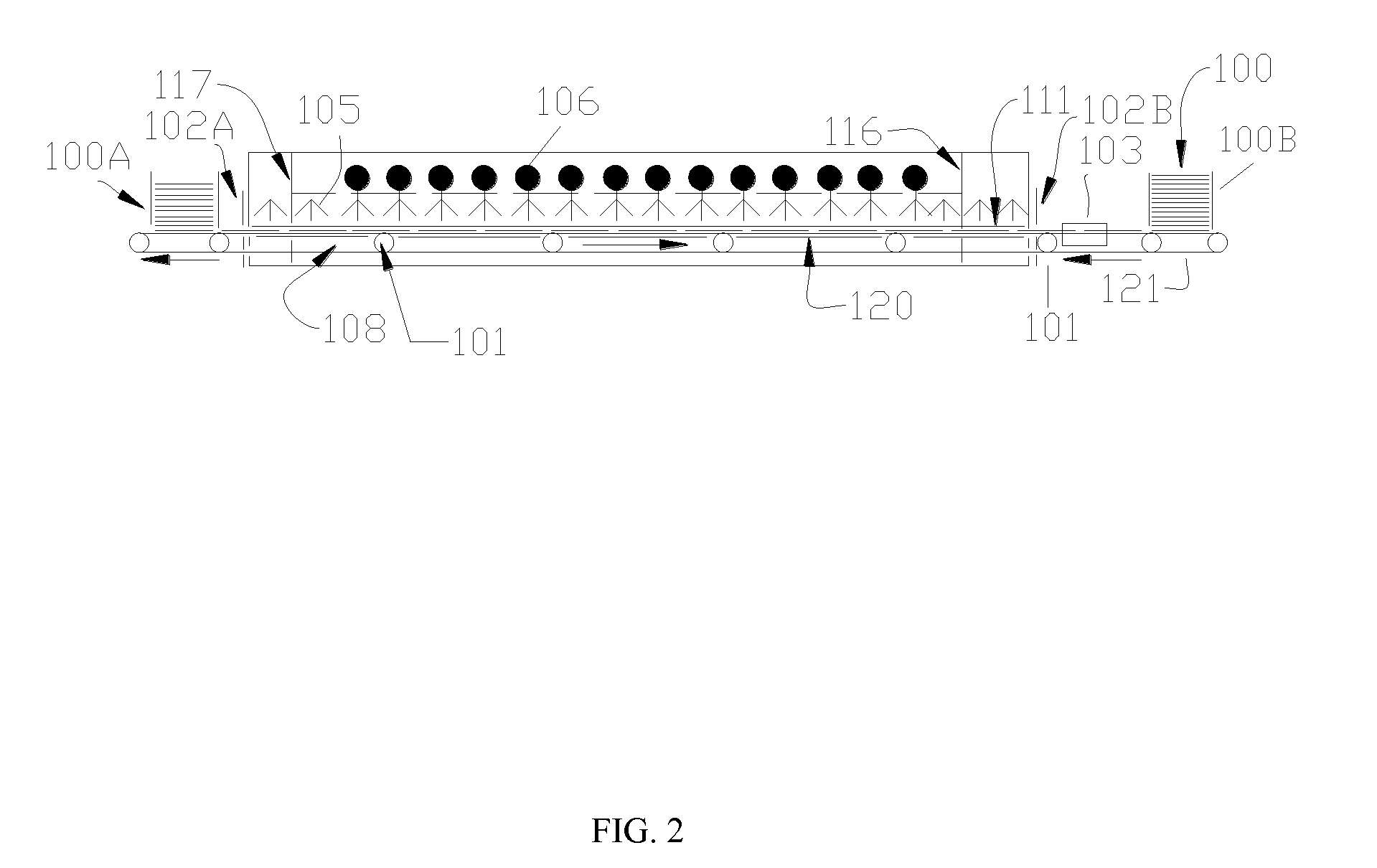
Chemical Bath Deposition Apparatus for Fabrication of Semiconductor Films through Roll-to-Roll Processes
InactiveUS20110256656A1Save volumeReduce expensesLiquid surface applicatorsFinal product manufactureChemical bath depositionDeposition process
A chemical bath deposition method and a system are presented to prepare different thin films on continuous flexible substrates in roll-to-roll processes. In particular, they are useful to deposit CdS or ZnS buffer layers in manufacture of thin film solar cells. This method and the deposition system deposit thin films onto vertically travelling continuous flexible workpieces delivered by a roll-to-roll system. The thin films are deposited with continuously spraying the reaction solutions from their freshly mixed styles to gradually aged forms until the designed thickness is obtained. The substrates and the solutions are heated to a reaction temperature. During the deposition processes, the front surfaces of the flexible substrates are totally covered with the sprayed solutions but the substrate backsides are remained dry. The reaction ambience inside the reactor can be isolated from the outside atmosphere. The apparatus is designed to generate a minimum amount of waste solutions for chemical treatments.
Owner:WANG JIAXIONG
Production Line to Fabricate CIGS Thin Film Solar Cells via Roll-to-Roll Processes
InactiveUS20130224901A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove the quality of workLiquid surface applicatorsFinal product manufactureProduction lineModularity
An industrial production line is presented to fabricate CIGS thin film solar cells on continuous flexible substrates in roll-to-roll processes. It provides an entire solution including procedures and related equipments from starting blank substrates to completed solar cells that can be used to fabricate solar modules. This production line contains some core apparatuses, such as a modular electroplating system to deposit CIGS materials, a modular thermal reactor to annealing the CIGS films, and a chemical bath deposition reactor to coat CdS buffer layer, are recently invented by the present inventor. The present production line can be conveniently used to prepare the CIGS thin film solar cells with high efficiency but low cost.
Owner:WANG JIAXIONG
Photovoltaic Device Including A Back Contact And Method Of Manufacturing
ActiveUS20140284750A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseTe element
A photovoltaic device includes a substrate, a transparent conductive oxide, an n-type window layer, a p-type absorber layer and an electron reflector layer. The electron reflector layer may include zinc telluride doped with copper telluride, zinc telluride alloyed with copper telluride, or a bilayer of multiple layers containing zinc, copper, cadmium and tellurium in various compositions. A process for manufacturing a photovoltaic device includes forming a layer over a substrate by at least one of sputtering, evaporation deposition, CVD, chemical bath deposition process, and vapor transport deposition process. The process includes forming an electron reflector layer over a p-type absorber layer.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
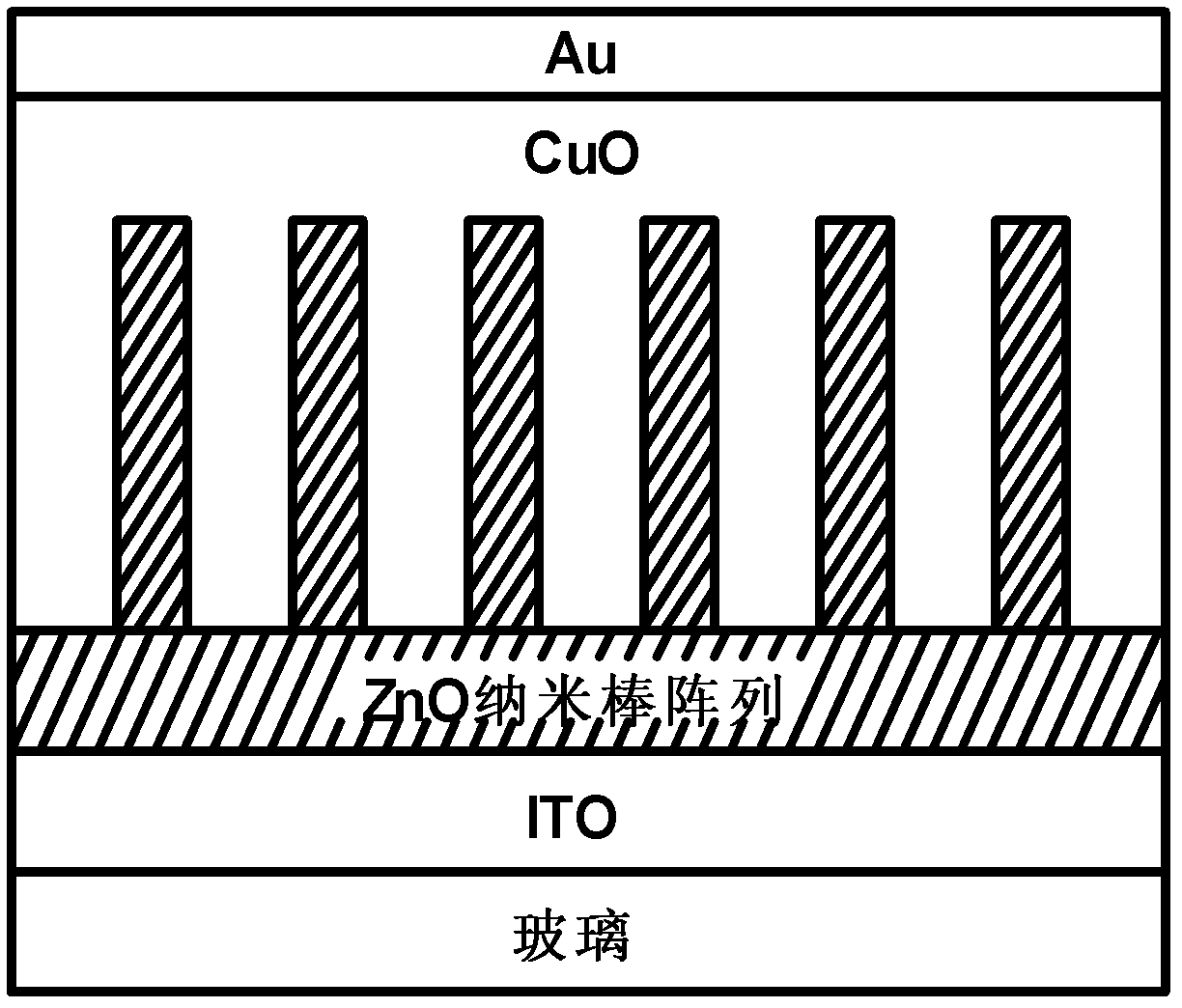
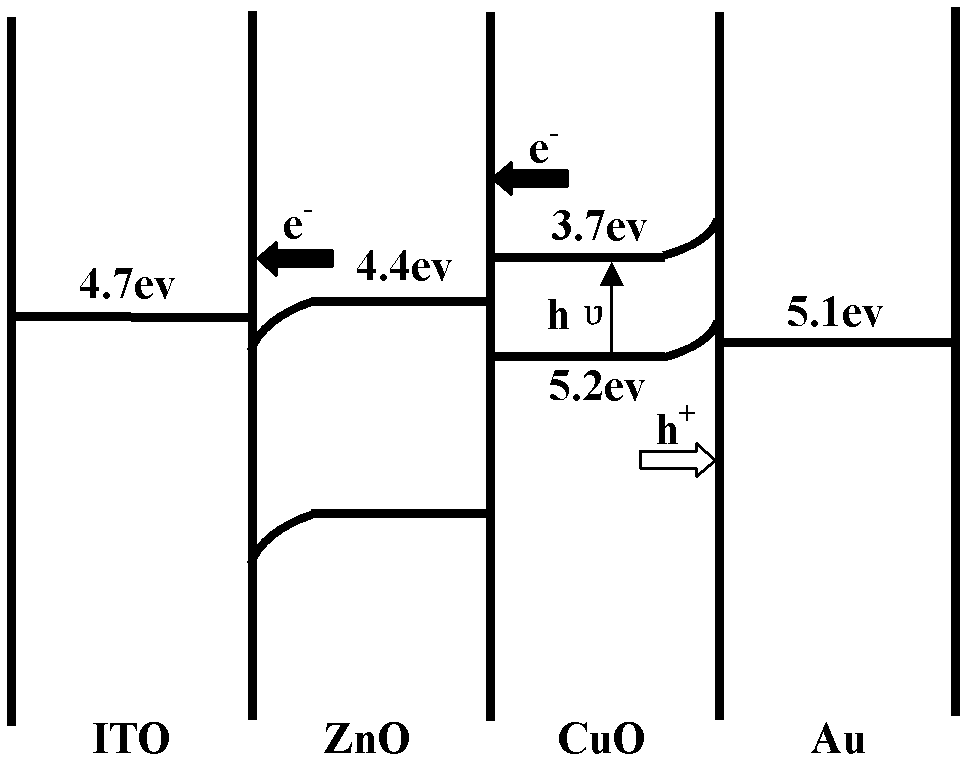
p-CuO-n-ZnO solar cell and preparation method of p-CuO-n-ZnO solar cell
InactiveCN102610687AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyLow costFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHole transport layerZinc oxide nanorod
The invention discloses a p-CuO-n-ZnO solar cell. An indium-tin-oxide (ITO) substrate, a vertically oriented ZnO nanorod array, a CuO film and an Au electrode are superposed in sequence from the bottom layer to the top layer, wherein the vertically oriented ZnO nanorod array is used as an n-type semiconductor absorption layer, and the CuO film is used as a p-type semiconductor light absorption layer and a hole transporting layer. The preparation method of the p-CuO-n-ZnO solar cell comprises the following steps of: preparing a ZnO seed crystal layer on ITO by utilizing a sol-gel method; preparing the vertically oriented ZnO nanorod array by utilizing a chemical bath deposition method; preparing the CuO film on the ZnO nanorod array by utilizing an in-situ growth method; and sputtering the Au electrode by using an ion beam sputtering system. The invention has the advantages that the equipment adopted by the preparation method is simple, and the cost is low; as CuO is adopted to serve as the light absorption layer and the hole transporting layer, compared with organic materials, the CuO has higher electromigration capacity; and by combining with the electrical conduction characteristic of inorganic ZnO with high light absorption and low thermal emittance of the CuO, the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell can be effectively increased.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation process of Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet and magnet prepared by using same
ActiveCN102693828AImprove uniformityFilm thickness controllableInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRemanenceRare earth
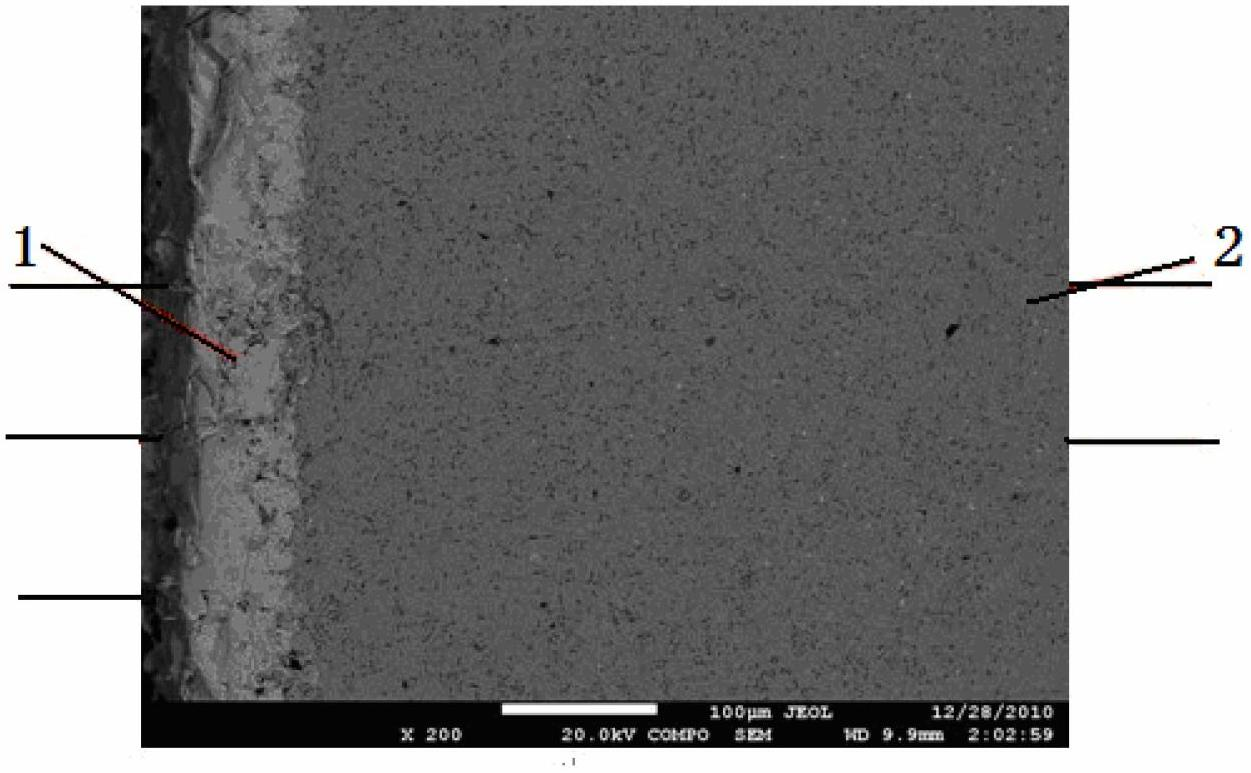
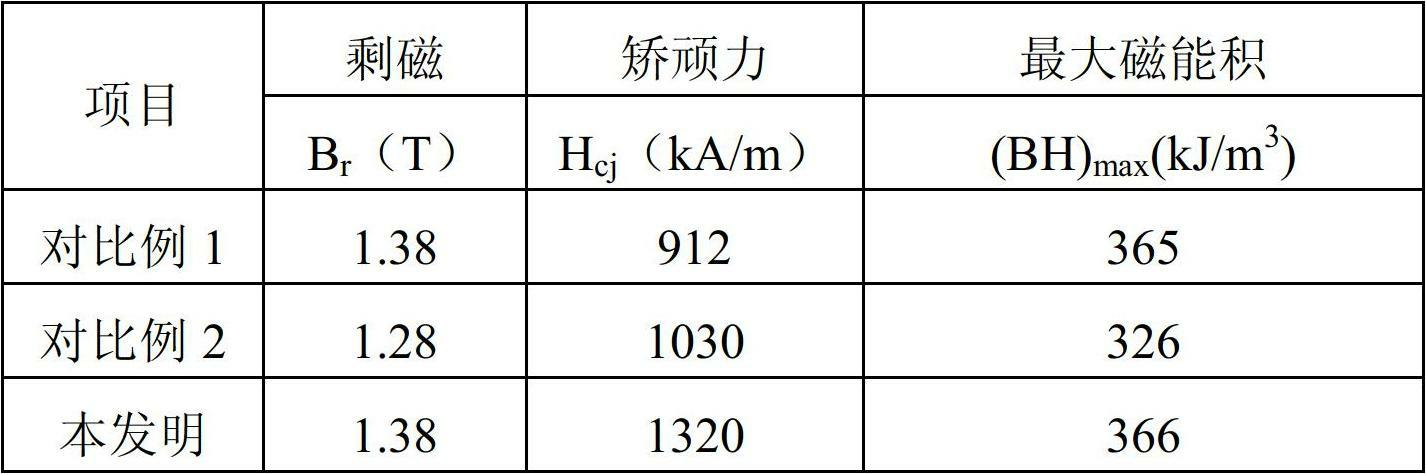
The invention provides a preparation process of an Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet and a magnet prepared by using the preparation process, belonging to the field of a magnetic functional material and a preparation technology. The preparation process comprises the following specific steps of: growing an RbX3 thin film on a surface of the magnet by using a chemical bath deposition method; secondly, diffusing elements in the RbX3 thin film, which is plated on the surface of the magnet, to the inside of the magnet through primary heat treatment; and uniformly distributing an element Rb at a crystal boundary position through secondary heat treatment, and removing an unbalanced structure and an internal stress, which are brought by the primary heat treatment in the magnet, wherein a chemical formula of the prepared magnet is RaRbXFeMB. The preparation process provided by the invention has the advantages that the neodymium-iron-boron magnet is prepared by using the chemical bath method, so that the production efficiency can be improved, and the use amount of heavy rare earth in the preparation process of the magnet is reduced. Meanwhile, a high coercive force is obtained under the premise of not reducing magnet remanence and magnetic energy product.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
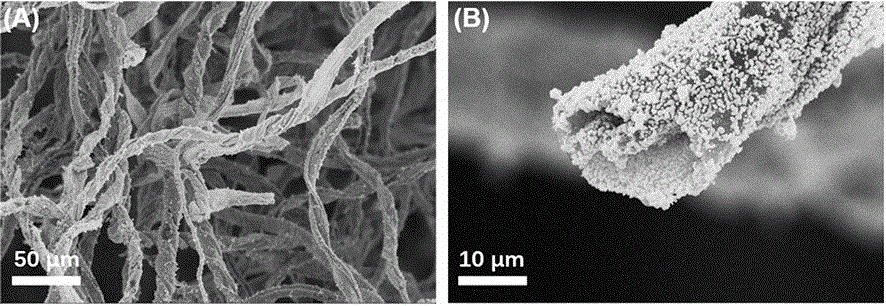
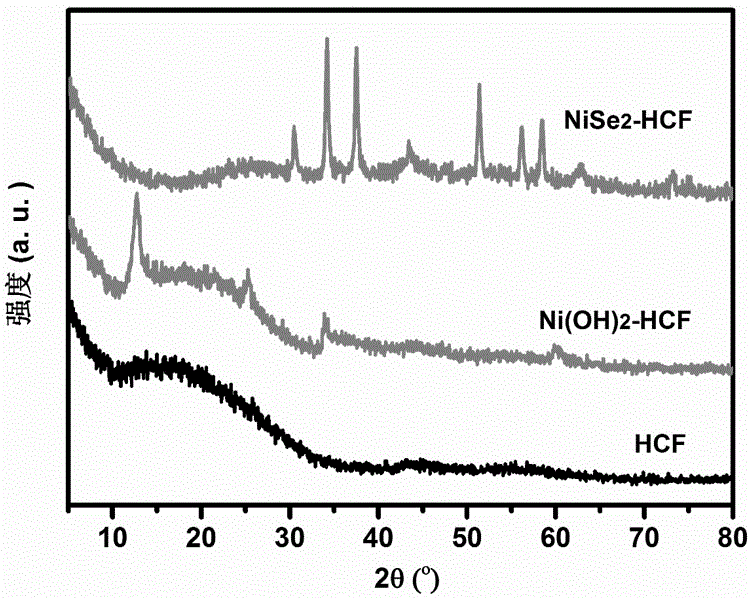
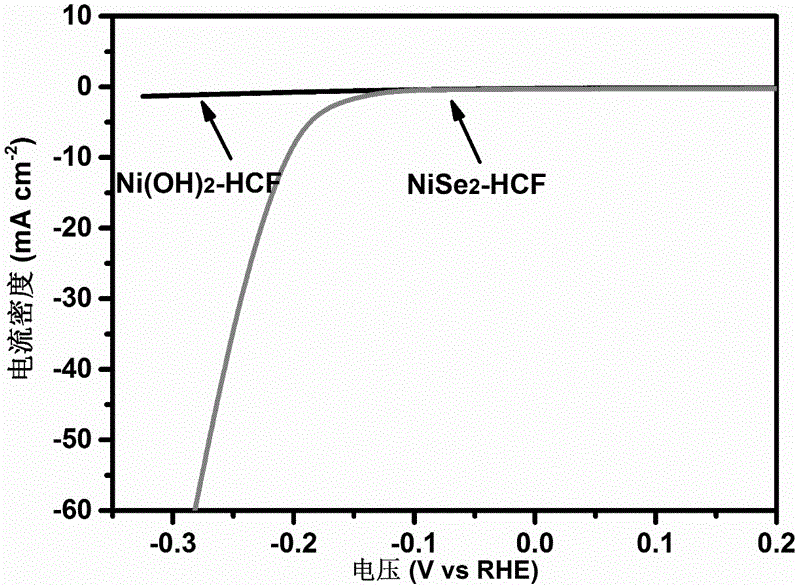
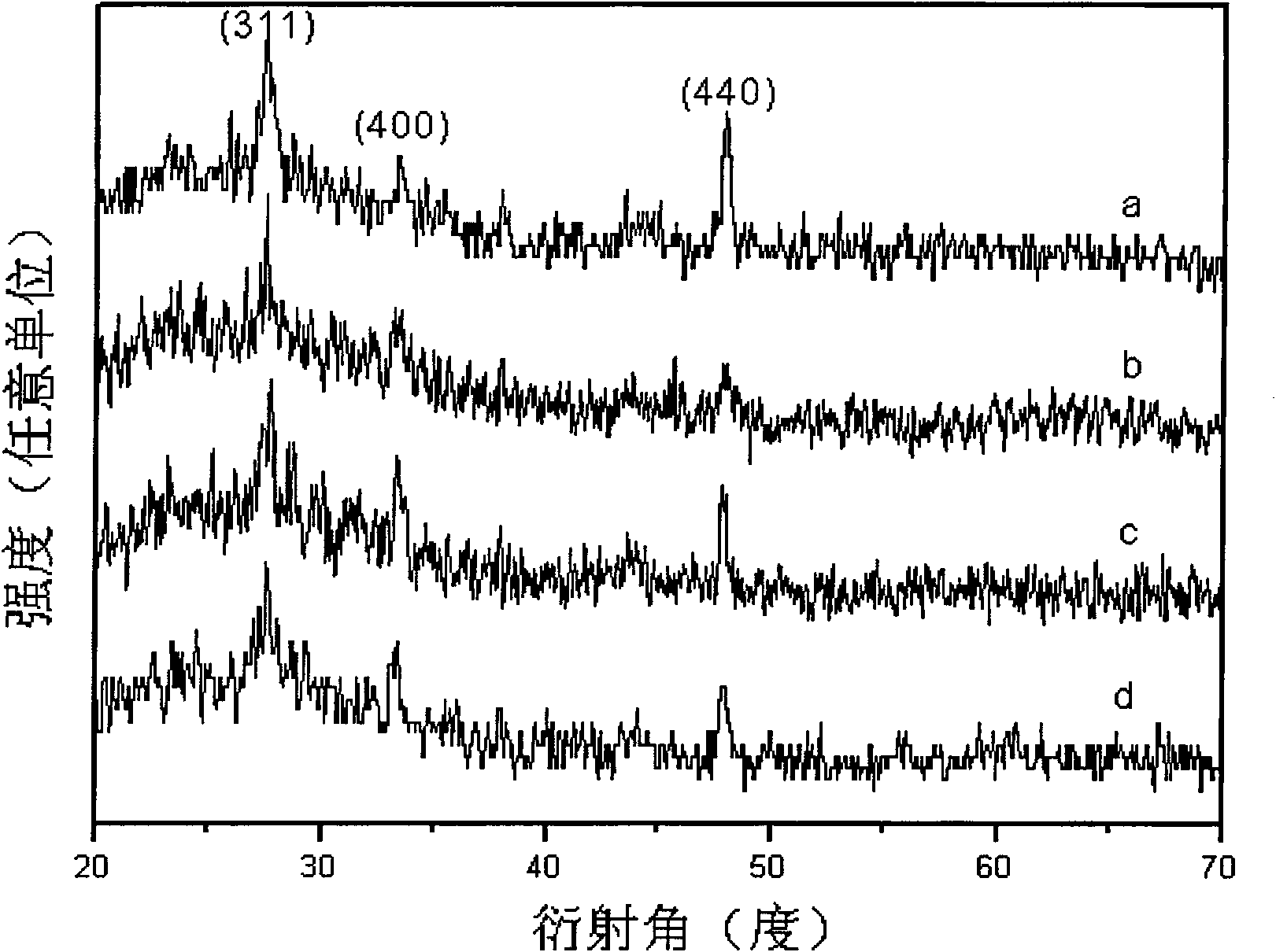
Nickel selenide/hollow carbon-fibre composite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106252616AEasy to makeEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsFiberCarbon nanofiber
The invention belongs to the technical field of transition-metal chalcogenide-carbon material and specifically relates to a nickel selenide / hollow carbon-fibre composite and a preparation method thereof. The preparation process comprises the following steps: preparing hollow carbon fiber by the use of high-temperature carbonized cotton, then growing vertical nickel hydroxide nanosheet in situ on the hollow carbon fiber by a chemical bath deposition method, and finally selenizing the obtained nickel hydroxide / hollow carbon fiber composite so as to prepare the nickel selenide / hollow carbon-fibre composite. The prepared carbon fiber is a hollow structure and has large specific surface area and good conductivity. The preparation process is simple, and cost is low. The morphology of the finally prepared nickel selenide / hollow carbon-fibre composite is controllable. Nickel selenide uniformly grows on the internal and external tube walls of the hollow carbon nanofiber. By full utilization of the unique hollow tube structure and high specific surface area of the hollow carbon fiber, the product can be used as an ideal high-performance electrocatalysis material as well as an electrode material of new energy devices such as a sodium-ion battery and a supercapacitor, etc.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for depositing indium sulfide thin film by chemical bath
InactiveCN101608304AHigh crystallinityAvoid adsorptionGallium/indium/thallium compoundsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingWater bathsIndium
The invention relates to a method for depositing an indium sulfide thin film by a chemical bath, which belongs to the technical field of preparation of functional thin film materials. The prior method for preparing indium sulfide has higher requirements on deposition conditions, needs high-temperature heating and has great limitations in substrate deposition. The method for preparing the indium sulfide adopts citric acid or malonic acid as a complexing agent, and the uniform, dense and high crystalline indium sulfide thin film with a cubic structure can be obtained on modified ordinary glass under a water bath environment which is lower than 100 DEG C. The method has no selectivity to a substrate, is synthesized in low temperature solution and has the advantages of good crystallinity, simple process and low cost, thereby being applicable to large-scale production application.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
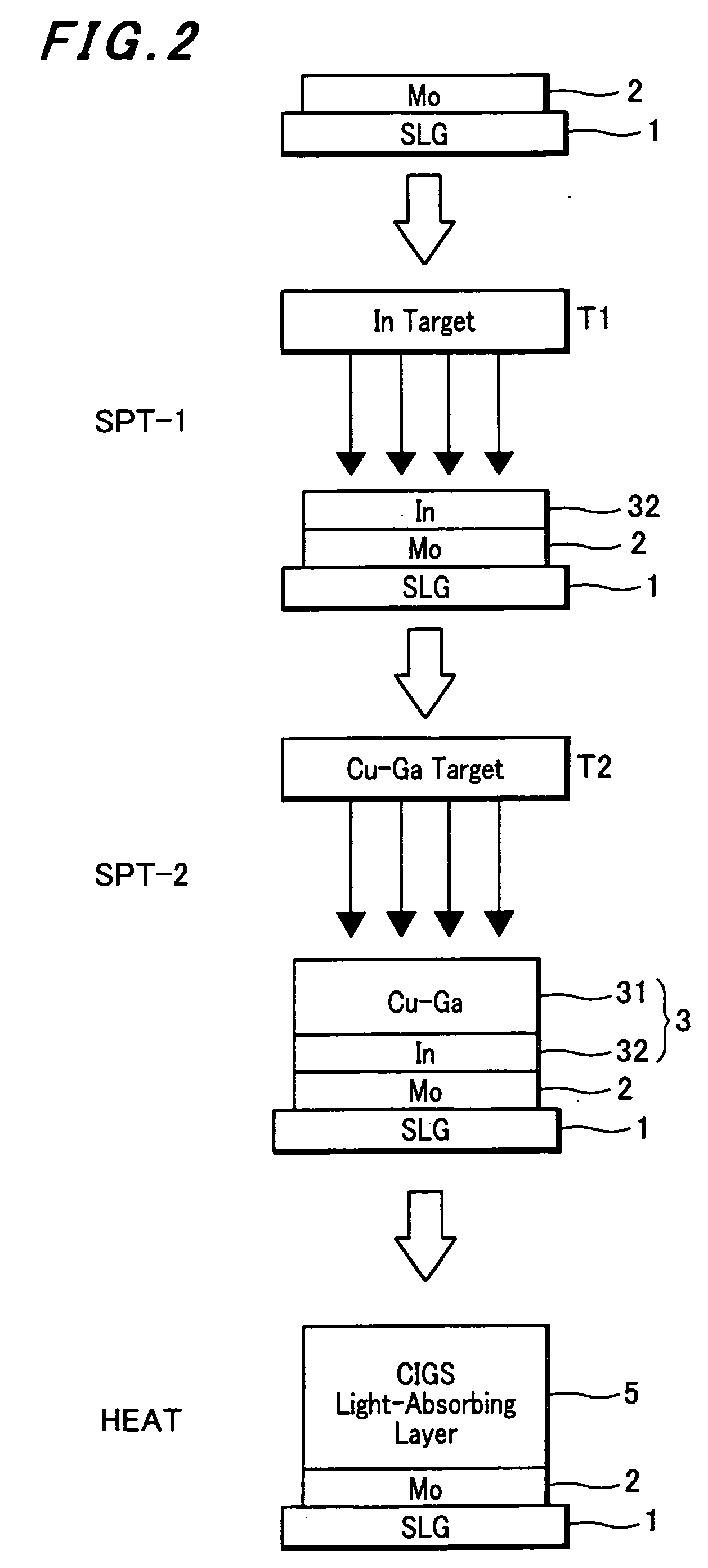
Method for preparing copper-indium-gallium-selenide (CIGS) solar photovoltaic cell
InactiveCN102386283AIncrease profitImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesVulcanizationIndium
The invention discloses a method for preparing a copper-indium-gallium-selenide (CIGS) solar photovoltaic cell. The method for preparing the photovoltaic cell comprises the following steps of: cleaning a glass substrate, sputtering a molybdenum metal, sputtering a copper-indium-gallium alloy, performing selenylation (vulcanization), depositing zinc sulfide in a chemical bath, sputtering zinc oxide and sputtering aluminum-doped zinc oxide. The method is high in utilization rate of raw materials, uniform in components of cell compounds, high in photoelectric conversion efficiency and good in repeatability.
Owner:陈群
Method for preparing Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystalline thin-film solar cell
InactiveCN102201498AReduce weightGood dispersionFinal product manufactureNanotechnologyIntrinsicsNanocrystalline thin films
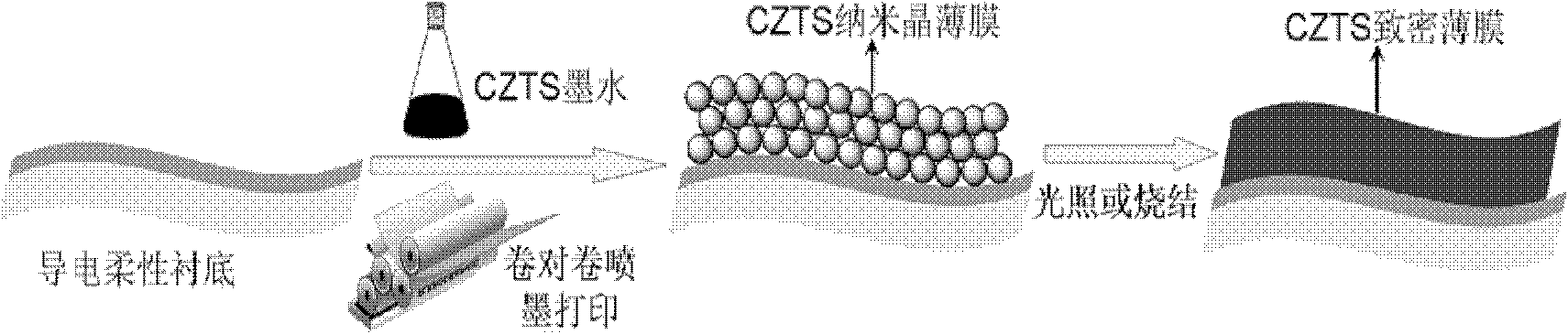
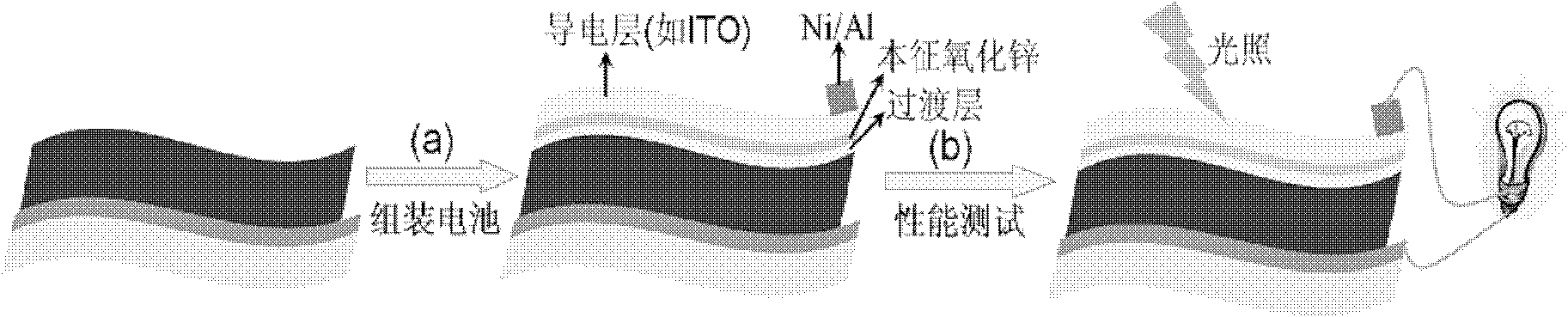
The invention relates to a method for preparing a Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystalline thin-film solar cell, which comprises the following steps of: performing chemical bath deposition on a ZnS film to form a buffer layer by taking molybdenum-plated metal aluminum as a flexible substrate and a film prepared from hydrophilic Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystalline as an absorption layer; and assembling the solar cell by performing magnetron sputtering on intrinsic ZnO, ITO and Ni-Al electrodes. By the method, vacuum equipment is not required, production cost is reduced, and convenience is brought to mass production; raw materials for preparing the Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cell are environment-friendly materials and have low prices, so that the cost of the solar cell is reduced to the great extent; and the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
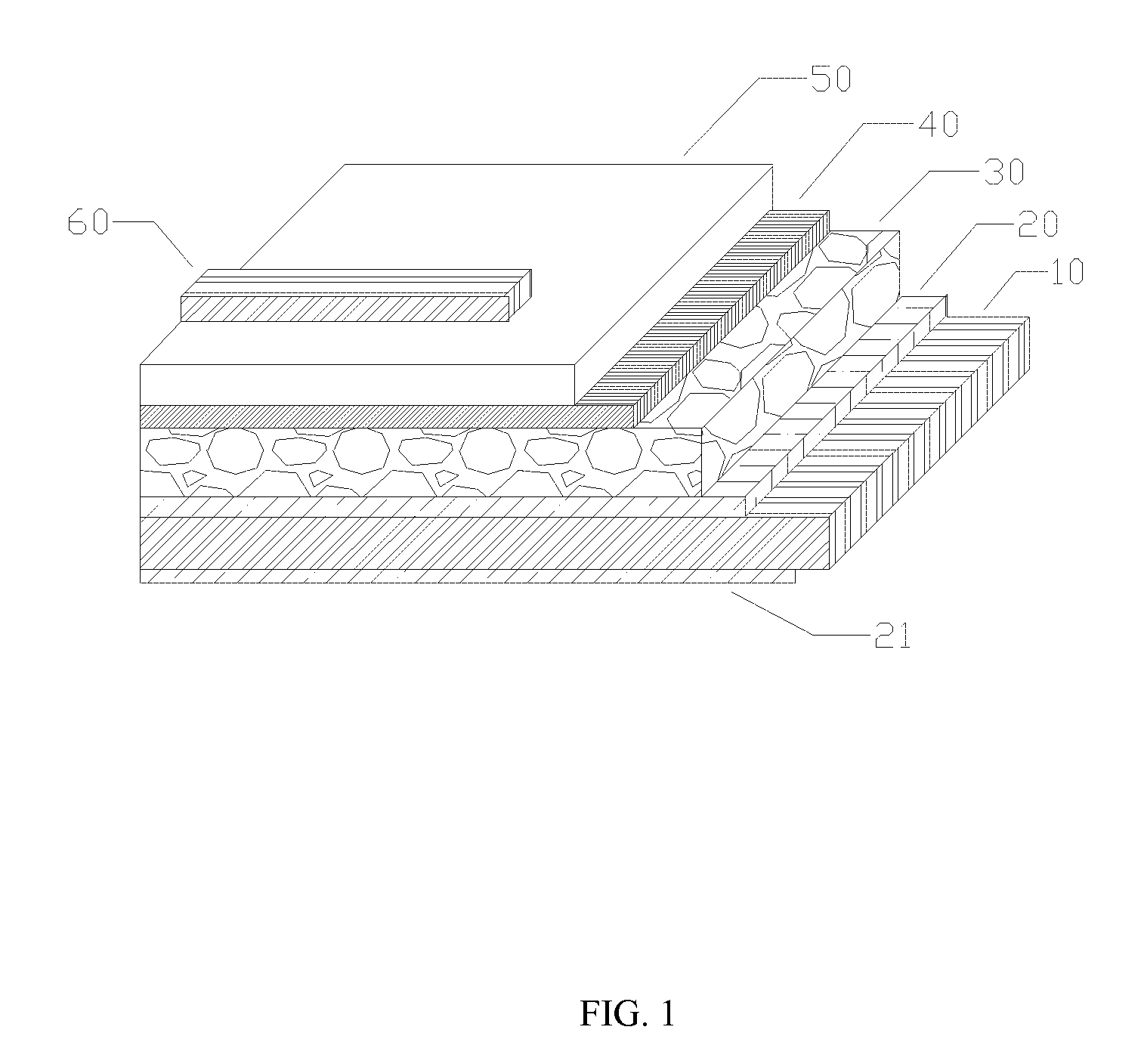
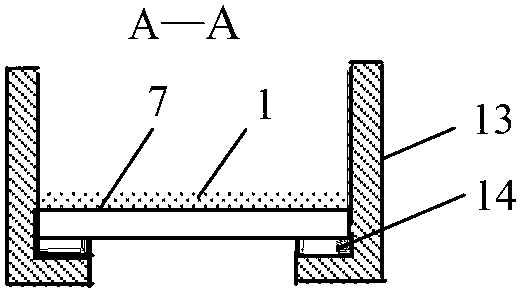
Chemical bath deposition method of cadmium sulfide film and device thereof
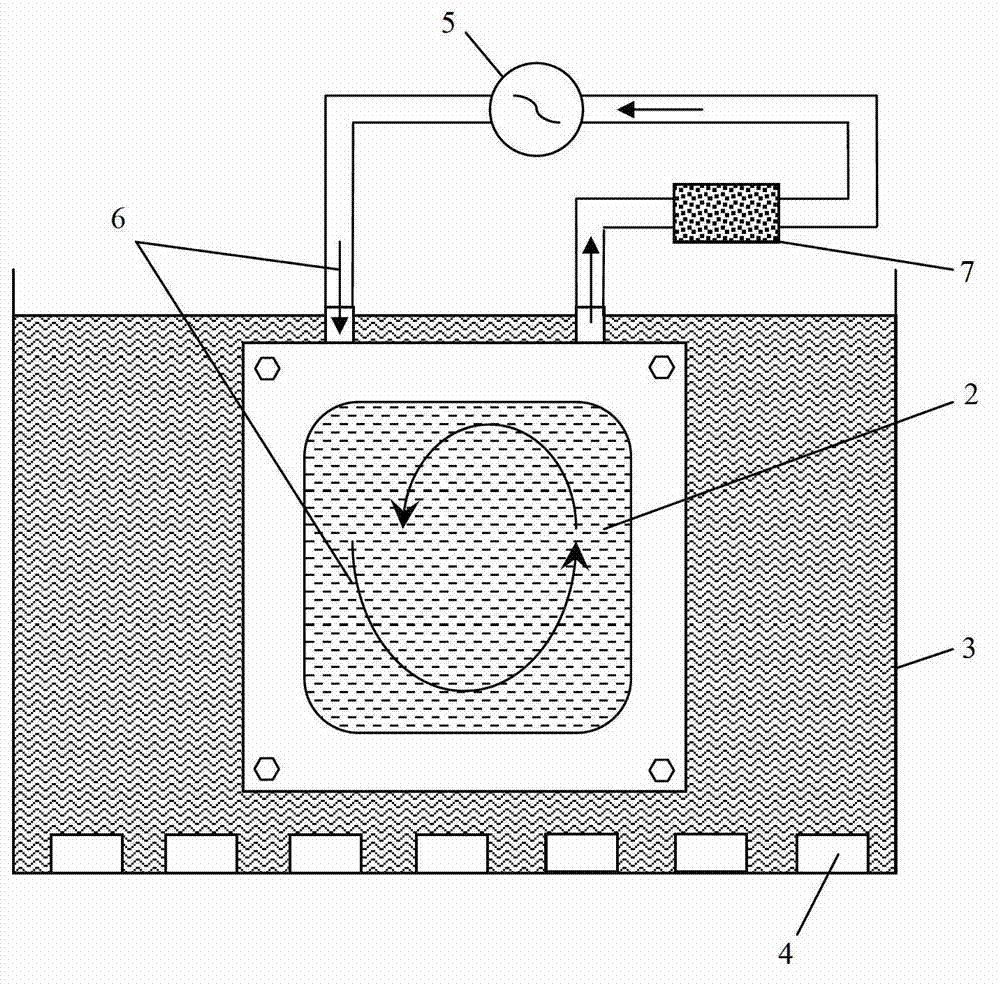
ActiveCN103320774AGuaranteed uniformityGuaranteed compactnessFinal product manufactureLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingWater bathsUltrasonic assisted
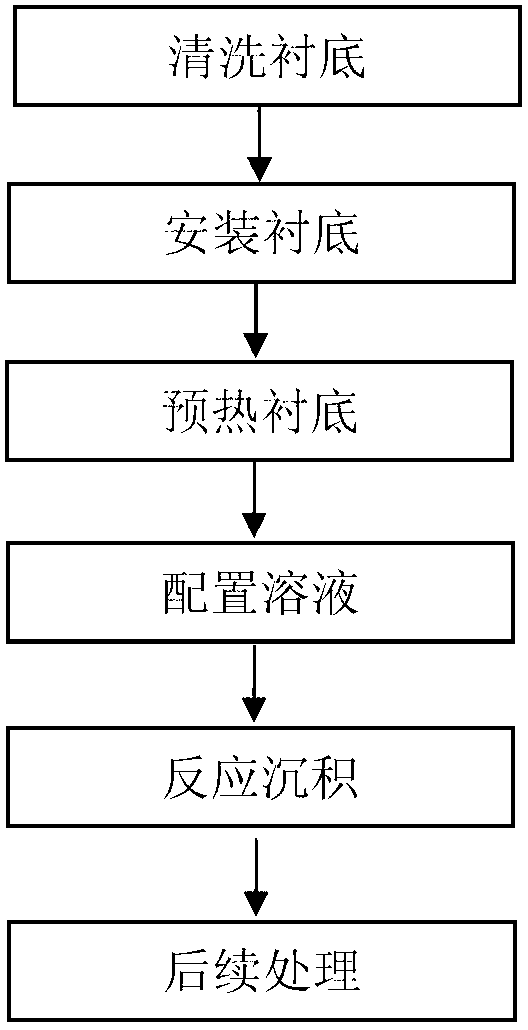
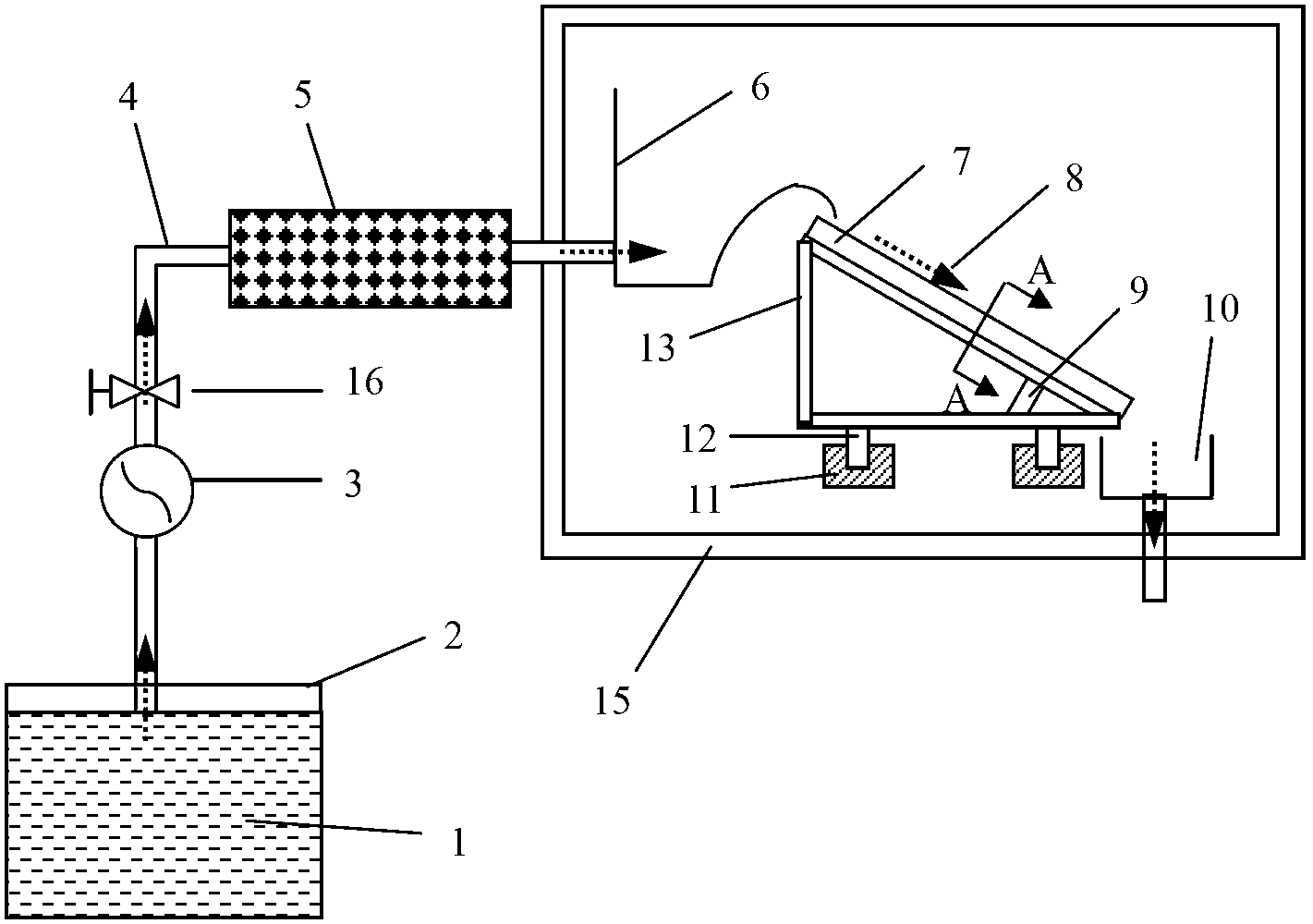
The invention discloses a chemical bath deposition method of a cadmium sulfide film and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cleaning a substrate and blow-drying; (2) installing the substrate; (3) preheating the substrate; (4) preparing a solution; (5) reacting and depositing; and (6) carrying out subsequent processing: washing the coated substrate by the use of deionized water and blow-drying or drying. The device comprises a reaction vessel and a thermotank. A diffuse spray groove, a substrate, a special fixture and a transmission unit are all placed inside the thermotank. A reaction solution flows through a heater and is then injected into the diffuse spray groove. The transmission unit is arranged at the bottom of the special fixture and the substrate. According to the invention, a thermostatic waterbath device, a stirring device and ultrasonic-assisted deposition are not adopted; the method provided by the invention is suitable for continuous production; production efficiency is raised; only one side of the substrate is coated, and aesthetic degree after the substrate is coated is improved; the deposited cadmium sulfide film is uniform and compact; film formation quality is high; and thin-film solar cell buffer layer requirements are met.
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG JIBAO AUTOMATION
Method of the application of a zinc sulfide buffer layer on a semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS7704863B2Improve efficiencyGreat band gapLight-sensitive devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThioureaDissolution
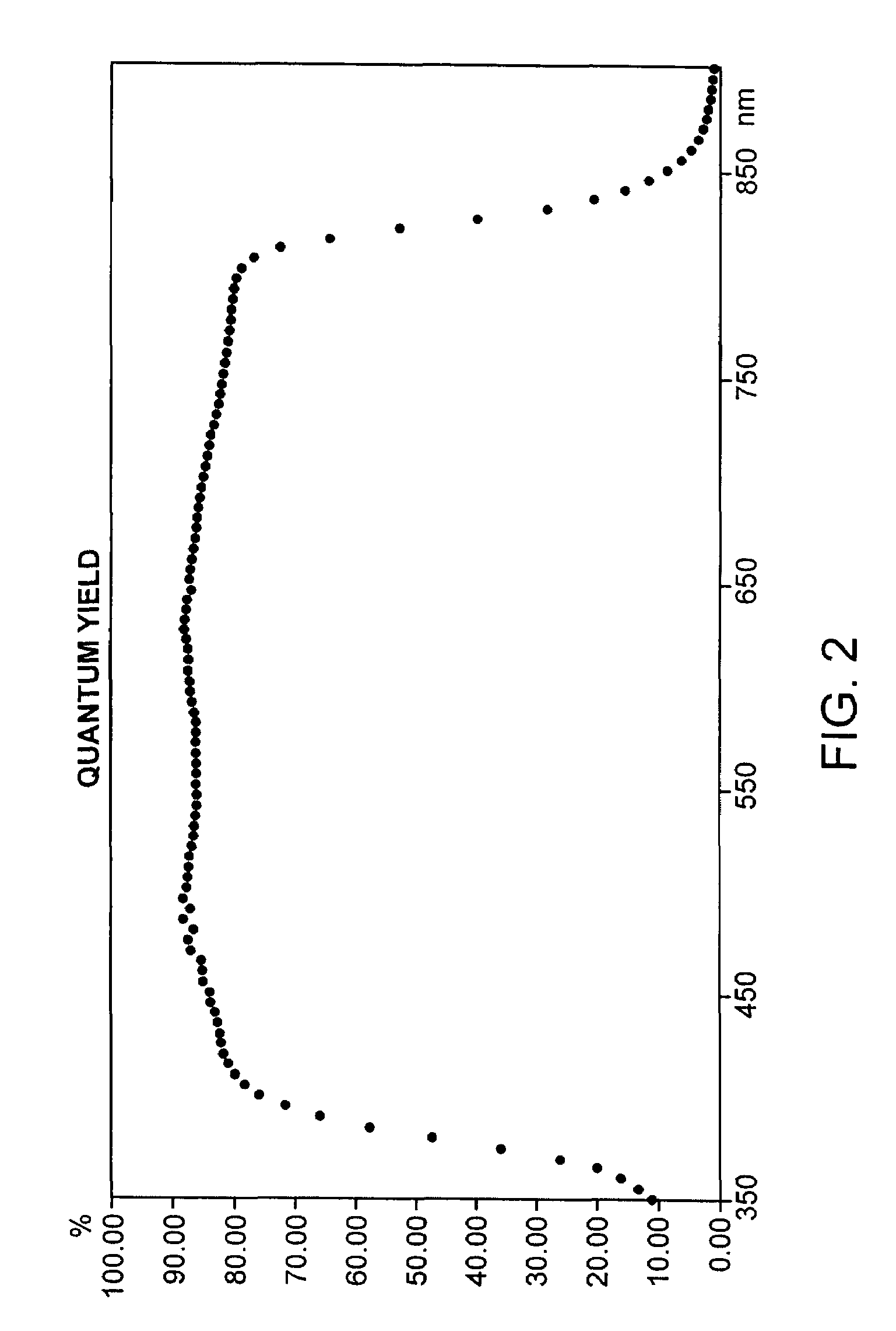
Chemical bath deposition (CBD) has proved top be the most favorable method for application of a buffer layer to semiconductor substrates, for example, chalcopyrite thin-film solar cells, whereby previously cadmium sulphide (CdS) was deposited and as cadmium is a highly toxic heavy metal, alternatives have been required. According to the invention, the semiconductor substrate is dipped in a solution for approximately 10 minutes, produced by the dissolution of zinc sulphate (0.05-0.5 mol / l) and thiourea (0.2 to 1.5 mol / l) in distilled water at a temperature being held essentially constant throughout said period. For the first time, the ZnS layer permits comparable or higher efficiencies than conventionally only achieved with toxic cadmium compounds. The method is hence much more environmentally-friendly with the same result.
Owner:HELMHOLTZ ZENT BERLIN FUER MATERIALIEN & ENERGIE GMBH
Method for preparing super-hydrophilic and hydrophobic composite nano array interface material
ActiveCN104846369AEfficient condensation nucleation is goodGood fast growth effectPretreated surfacesNanotechnologyPolyvinyl alcoholUltrasonic atomization
The invention relates to a method for preparing a super-hydrophilic and hydrophobic composite nano array interface material, which comprises the following steps: 1)taking a copper sheet as a base material, preparing a zinc oxide nano conical fascia by a chemical bath sedimentation method in hot bath; 2)using seventeen perfluorinated silane for modifying the oxidative nano conical fascia at 120 DEG C by a vapour deposition method; 3)preparing a polyvinyl alcohol low-solid content aqueous solution; 4)establishing an ultrasonic atomization and condensation platform, atomizing the polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution with concentration being 0.1-0.2%, reducing the temperature of the surface of the copper-based zinc oxide nano conical fascia to 1-5 DEG C through the condensation platform, uniformly condensing the surface of the super-hydrophobic zinc oxide nano conical fascia by the polyvinyl alcohol dispersion liquid dispersed in air, performing spray deposition under observation of a high power CCD imaging system; and 5)rapidly transferring to a constant temperature heating stage, solidifying at constant temperature, after solvent moisture is completely volatilized, solidifying polyvinyl alcohol and absorbing on the surface of the zinc oxide nano conical fascia to form a hydrophilic and hydrophobic composite nano array interface. The method has the advantages of simple process and low cost, and the material has high anti-condensation frosting performance.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
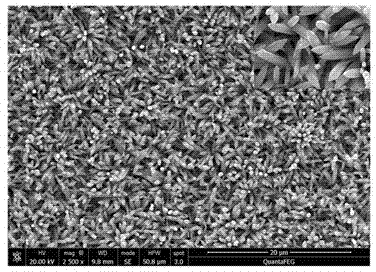
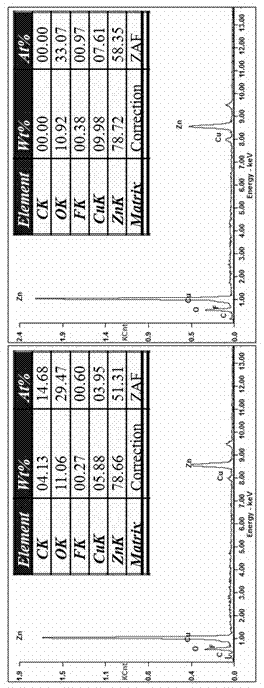
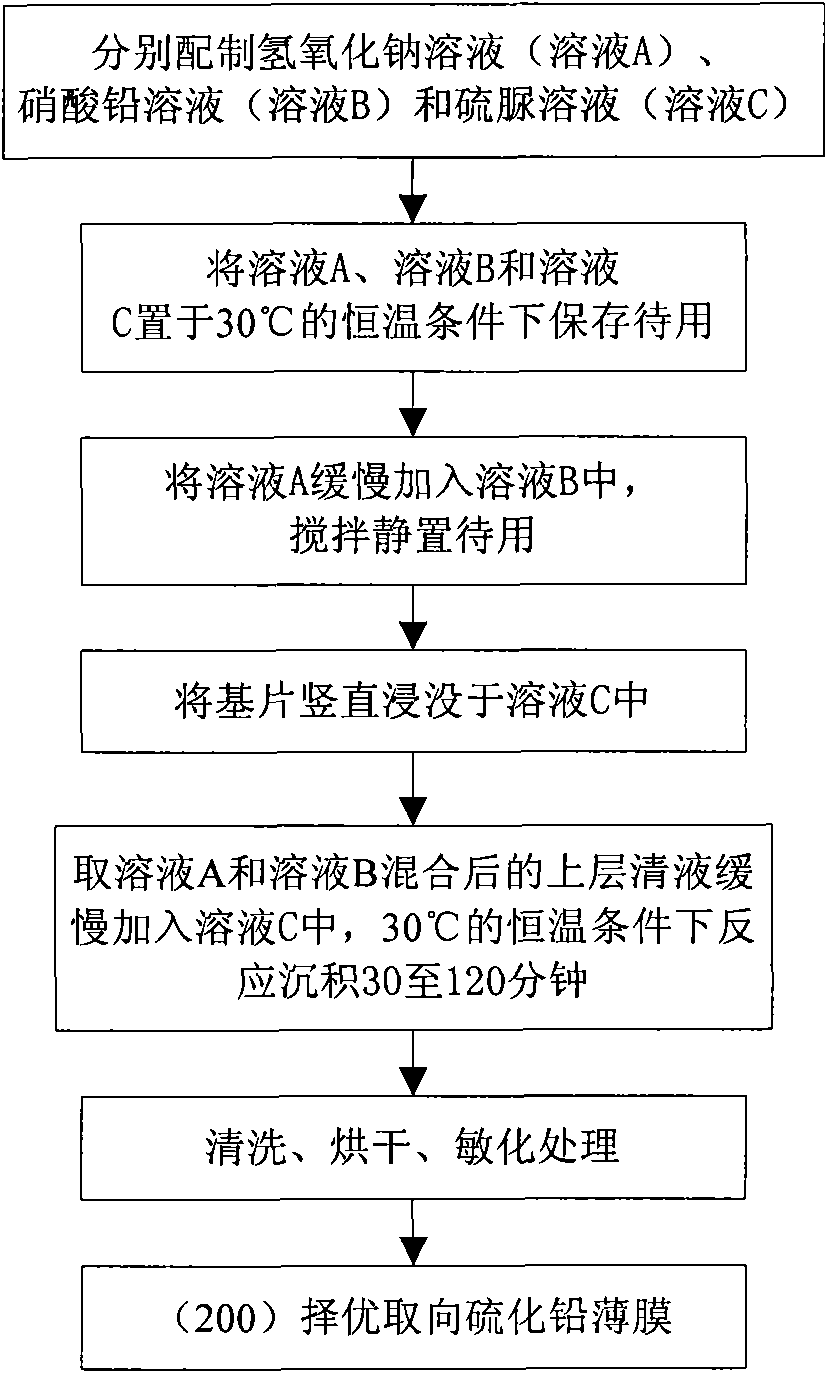
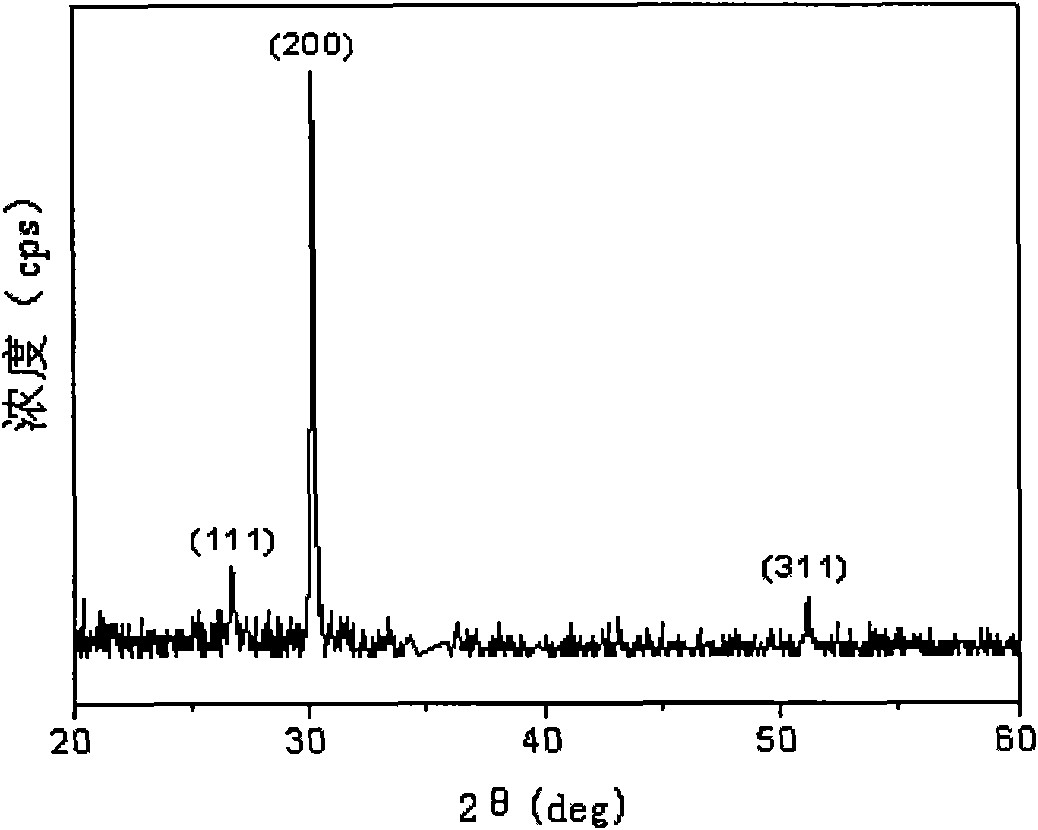
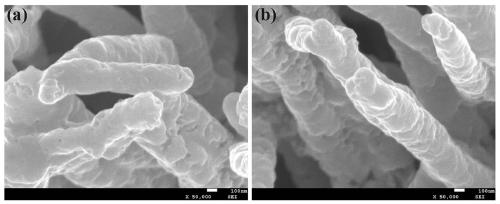
Method for preparing lead sulfide thin films with (200) preferred orientation
InactiveCN101792930AImprove uniformityImprove featuresPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPhotovoltaic detectorsLead sulfide
The invention provides a method for preparing lead sulfide thin films with (200) preferred orientation, which belongs to the technical field of electronic materials and relates to semiconductor optoelectronic thin films and infrared photoelectric detectors, in particular to a method for preparing the lead sulfide thin films with (200) preferred orientation of near-infrared photoelectric detectors by using chemical bath deposition. In the invention, the bicontinuous cubic phase lead sulfide thin films with (200) preferred orientation are obtained by using the chemical bath deposition, designing a preparation flow of solution of a reaction precursor, strictly controlling the initial nucleating process of the thin films and performing a subsequent high-temperature sensitizing process. The lead sulfide thin films prepared by the method have high uniformity and a light sensitive characteristic and can be used in the near-infrared photoelectric detectors. The invention has the advantages that: the whole preparation technical process is simple and easy to control; and the preparation device is simple and low in cost.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
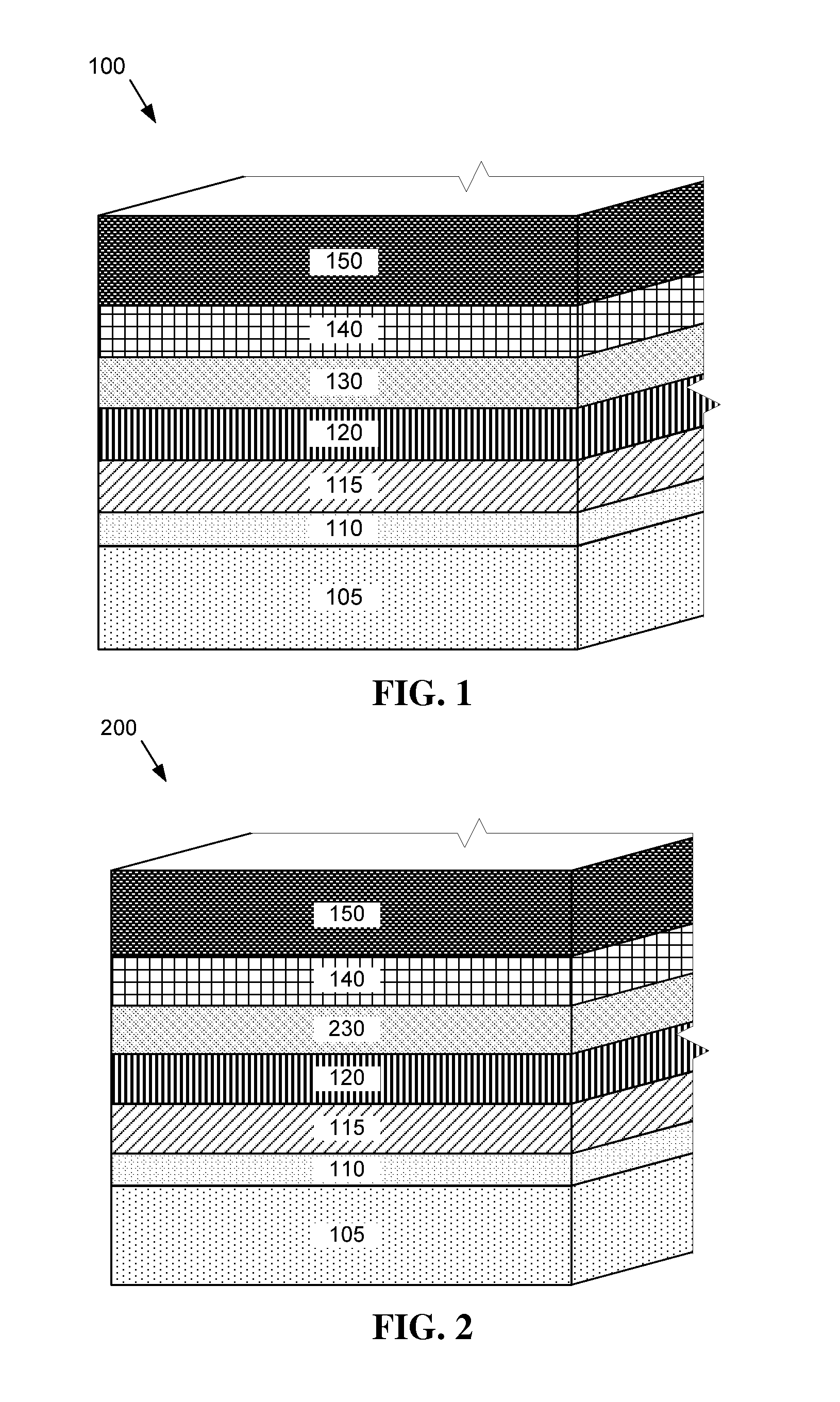
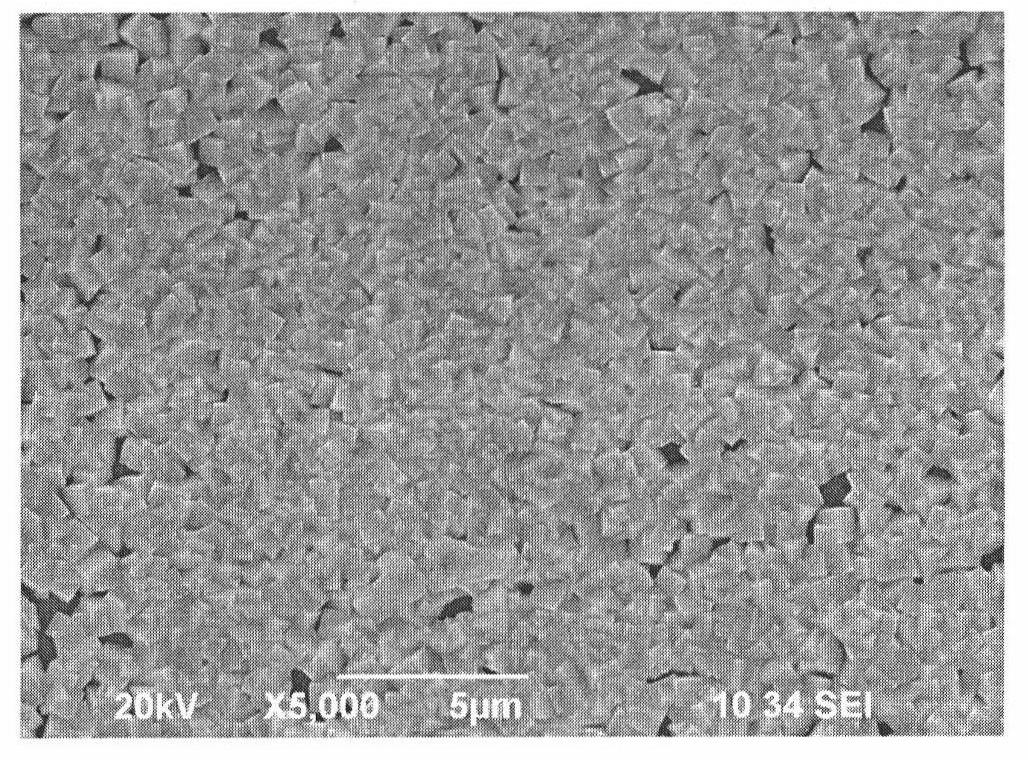
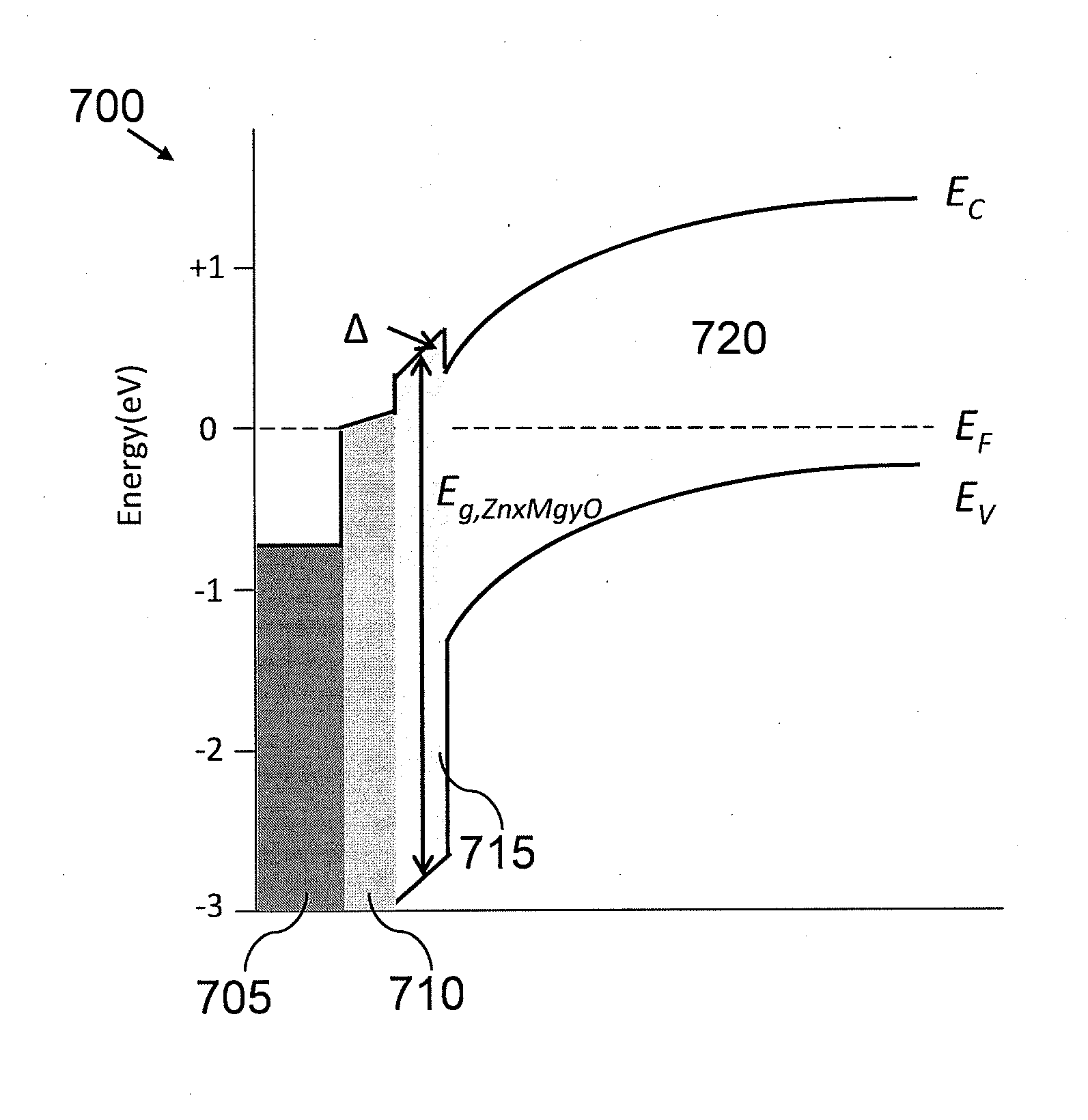
Photovoltaic device with a zinc magnesium oxide window layer
ActiveUS20120067421A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSputteringGas phase
Methods and devices are described for a photovoltaic device and substrate structure. In one embodiment, a photovoltaic device includes a substrate structure and a CdTe absorber layer, the substrate structure including a Zn1−xMgxO window layer and a low conductivity buffer layer. Another embodiment is directed to a process for manufacturing a photovoltaic device including forming a Zn1−xMgxO window layer over a substrate by at least one of sputtering, evaporation deposition, CVD, chemical bath deposition process and vapor transport deposition process. The process including forming a CdTe absorber layer above the Zn1−xMgxO window layer.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Method of the Application of a Zinc Sulfide Buffer Layer on a Semiconductor Substrate
InactiveUS20080274577A1Less complexityLess timeLight-sensitive devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemistryChemical bath deposition
A chemical bath deposition method of depositing on a semiconductor substrate a layer of zinc sulfide by dipping the semiconductor substrate into an aqueous solution of zinc sulfate and thiourea and ammonia.
Owner:HELMHOLTZ ZENT BERLIN FUER MATERIALIEN & ENERGIE GMBH
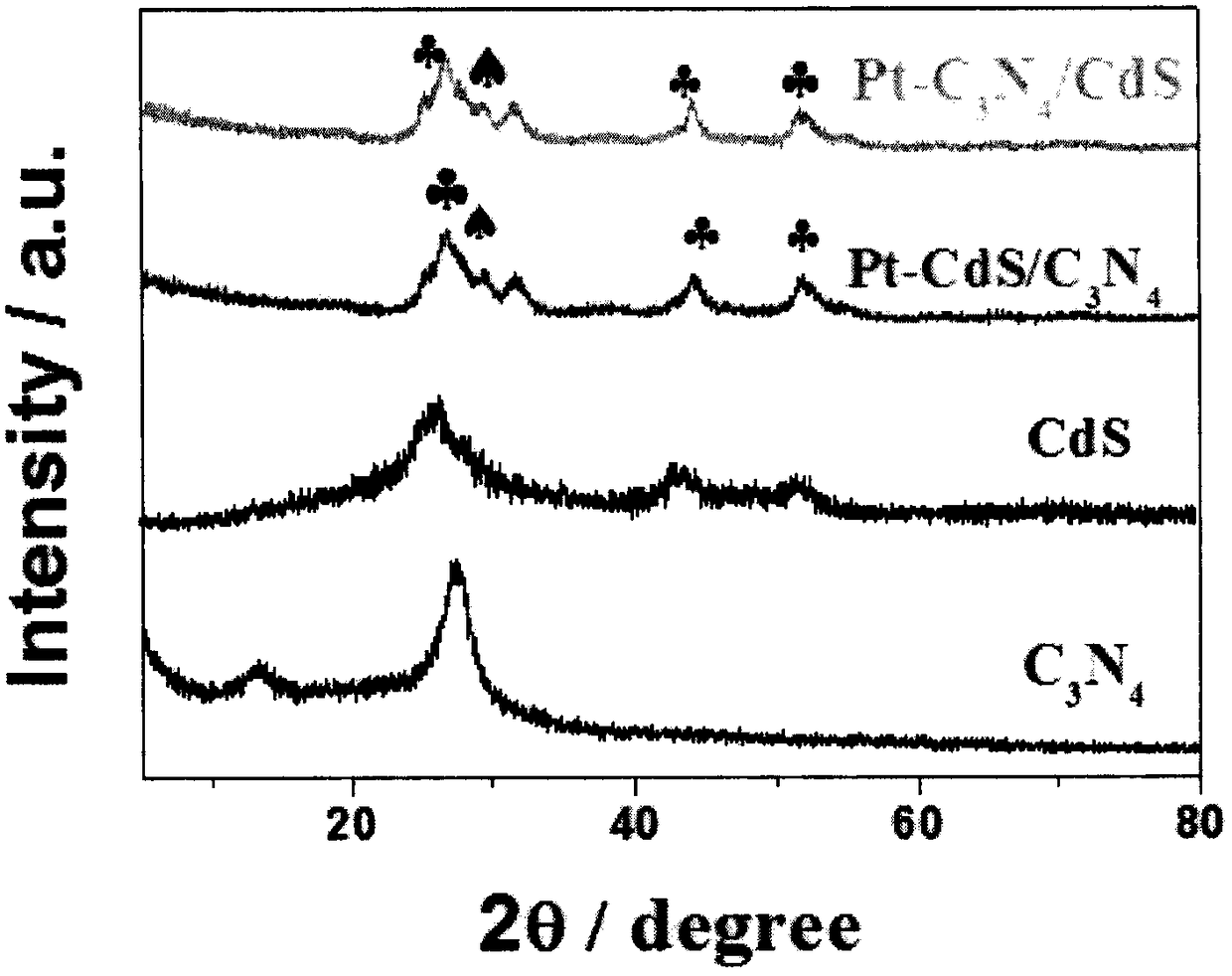
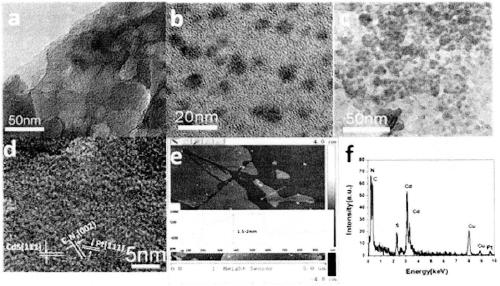
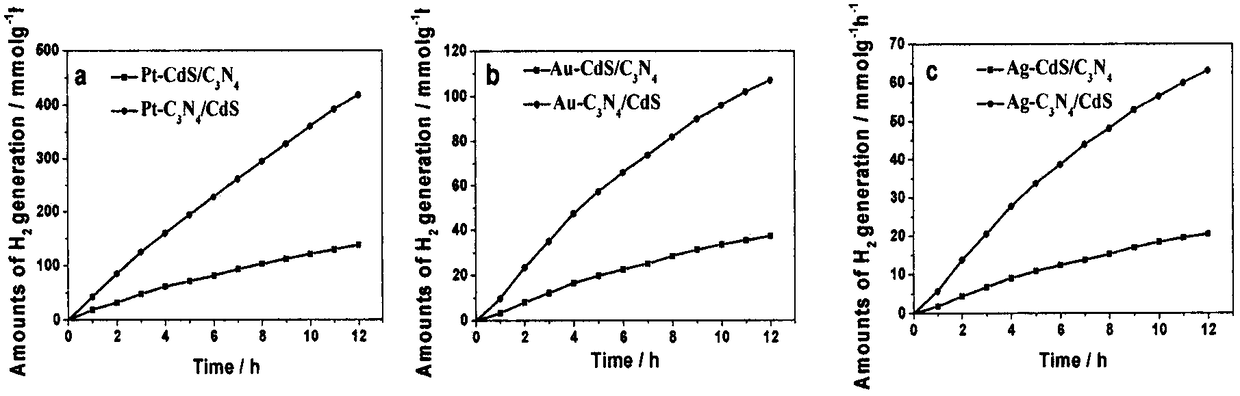
Preparation method of Z type heterojunction M-C3N4/CdS composite photocatalyst
ActiveCN109201102AImprove photocatalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionChemical synthesisHeterojunction
The invention provides a preparation method of a Z type heterojunction M-C3N4 / CdS composite photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises following steps: at first, synthesizing a porous g-C3N4 nanosheet through a urea thermal polymerization method; then pre-depositing a metal co-catalyst (M) such as Pt, Au, Ag, and the like, on the surface of g-C3N4 to synthesize M (Pt, Au, Ag)-g-C3N4 througha photo deposition method; and finally growing CdS quantum dots on the surface in-situ through a chemical bath deposition method to synthesize M-C3N4 / CdS. The chemical synthesis method comprises several steps, the metal co-catalyst is deposited selectively, and the process of converting a TypeII catalyst to a Z type heterojunction composite catalyst can be effectively controlled and regulated. Compared with a traditional type II composite photocatalyst (M-CdS / C3N4), the prepared M-C3N4 / CdS has a better performance on photo-catalyzing hydrolysis to produce hydrogen.
Owner:SHANGQIU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
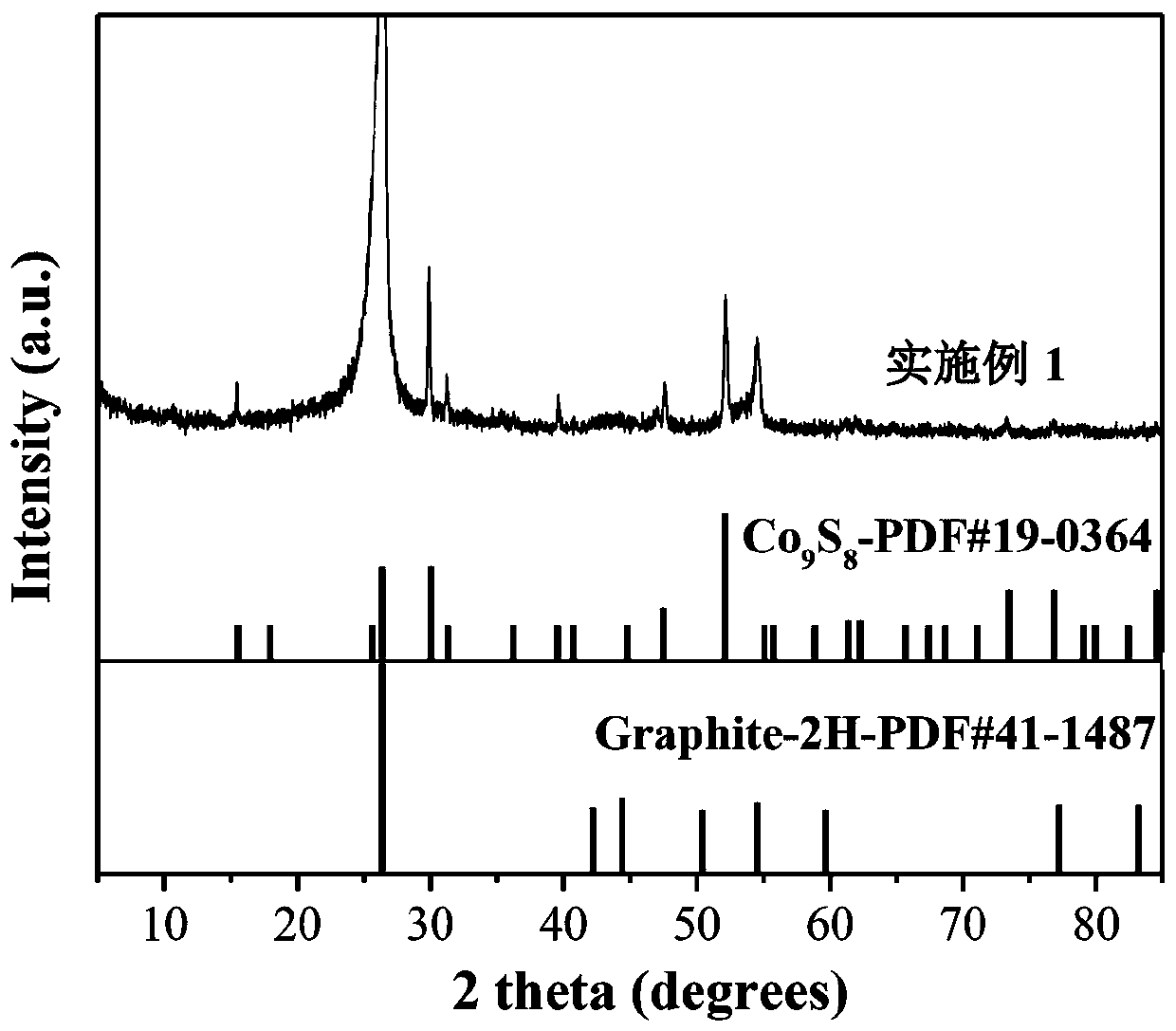
Method for preparing Co9S8 and nitrogen doped carbon composite array electrode
ActiveCN109852994AImprove inner motivationLower potentialPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesCarbon compositesHeterojunction
The invention provides a method for preparing a bifunctional Co9S8 and nitrogen doped carbon composite array electrode. The method comprises the steps of preparing an alkali type cobalt salt needle-shaped array in-situ electrode by a chemical bath deposition method, then, growing polydopamine on the surface of an alkali type cobalt salt array by using dopamine, then, adding thiourea in a protective atmosphere, and carrying out a vulcanization reaction by a CVD method, wherein during the reaction, the polydopamine is converted into a nitrogen doped carbon material, and an alkali type cobalt salt is converted into Co9S8 in a thiourea atmosphere. The product obtained by the method provided by the invention has a variety of high-electrocatalytic-activity loci, including nitrogen doped active sites in the carbon material and other crystal lattice defects resulting from the nitrogen doped active sites, thereby having excellent electrocatalytic oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) performance; theCo9S8 has a relatively good electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction (OER) performance; and furthermore, a heterojunction formed by the Co9S8 and the carbon material also has excellent electrocatalytic OER and OER performance.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
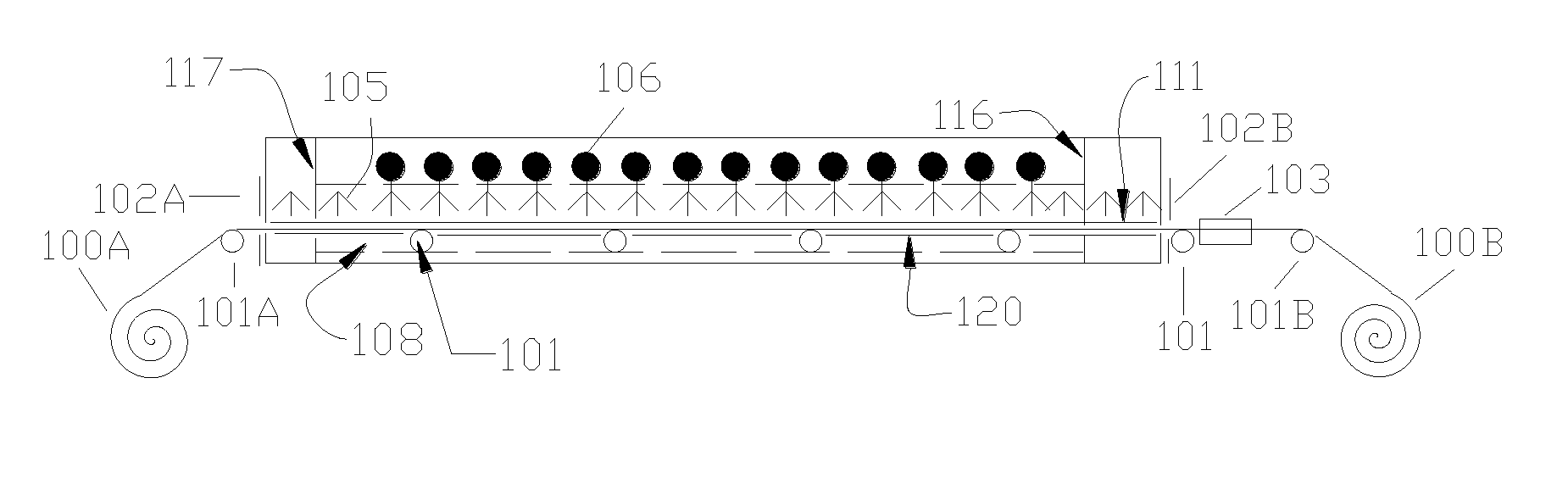
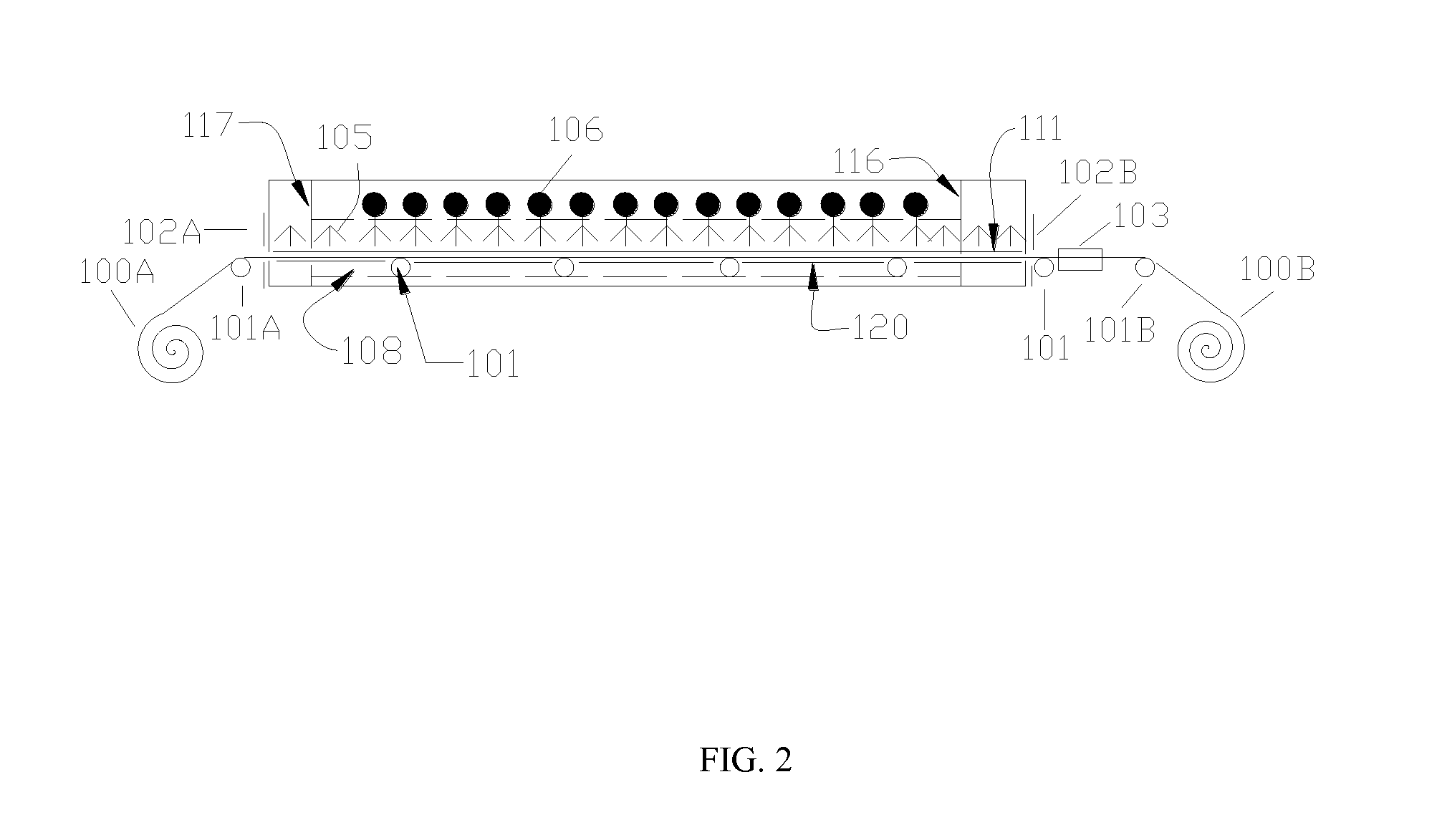
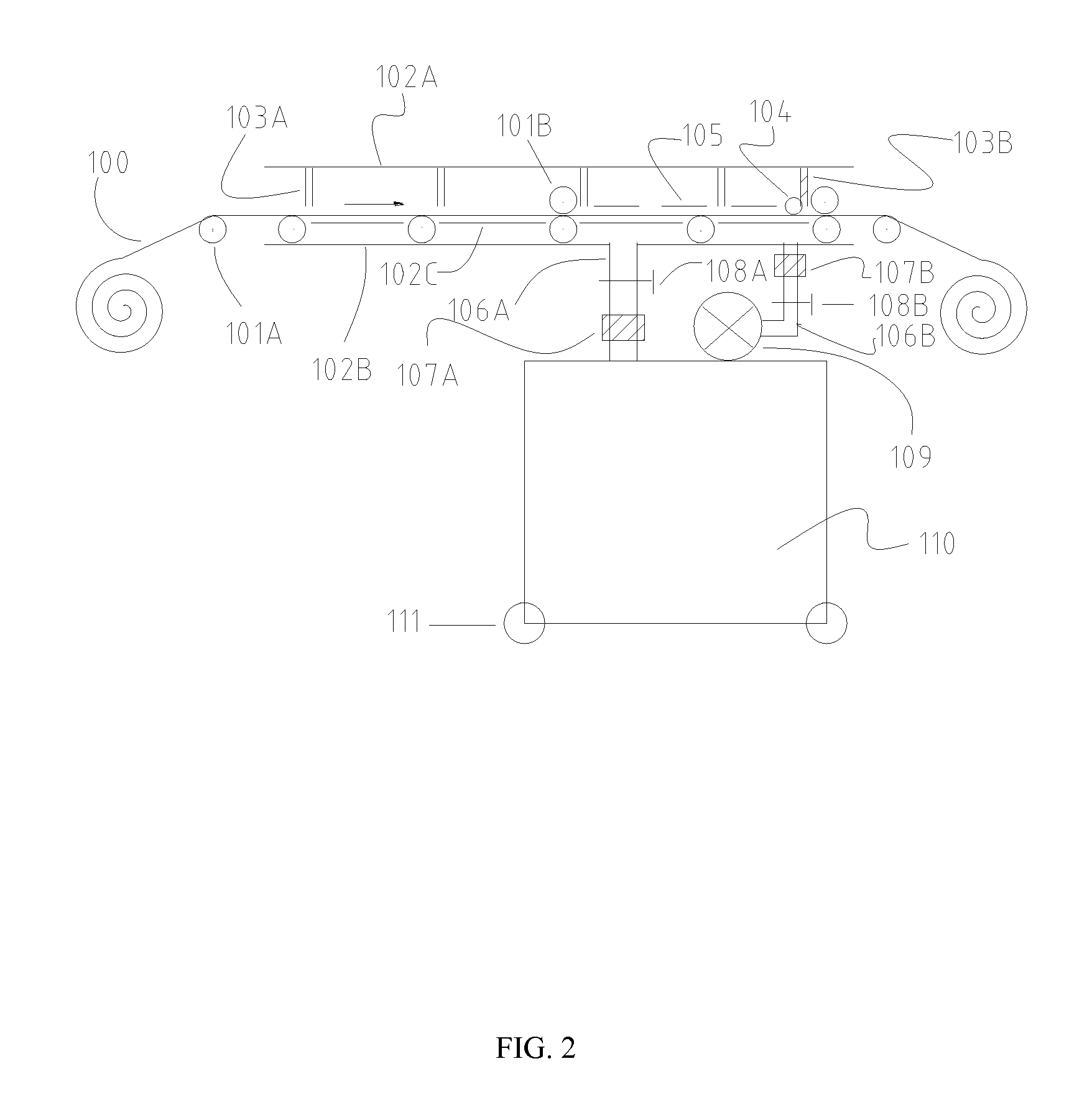
Chemical Bath Deposition Apparatus for Fabrication of Semiconductor Films
InactiveUS20130005073A1Save volumeReduce expensesLiquid surface applicatorsFinal product manufactureChemical treatmentReaction temperature
A chemical bath deposition method and a system are presented to prepare different thin films on plane substrates. In particular, they are useful to deposit CdS or ZnS buffer layers in manufacture of thin film solar cells. This method and the deposition system deposit thin films onto vertically travelling plane workpieces delivered by a conveyor belt. The thin films are deposited with continuously spraying the reaction solutions from their freshly mixed styles to gradually aged forms until the designed thickness is obtained. The substrates and the solutions are heated to a reaction temperature. During the deposition processes, the front surfaces of the substrates are totally covered with the sprayed solutions but the substrate backsides are remained dry. The reaction ambience inside the reactor can be isolated from the outside atmosphere. The apparatus is designed to generate a minimum amount of waste solutions for chemical treatments.
Owner:WANG JIAXIONG
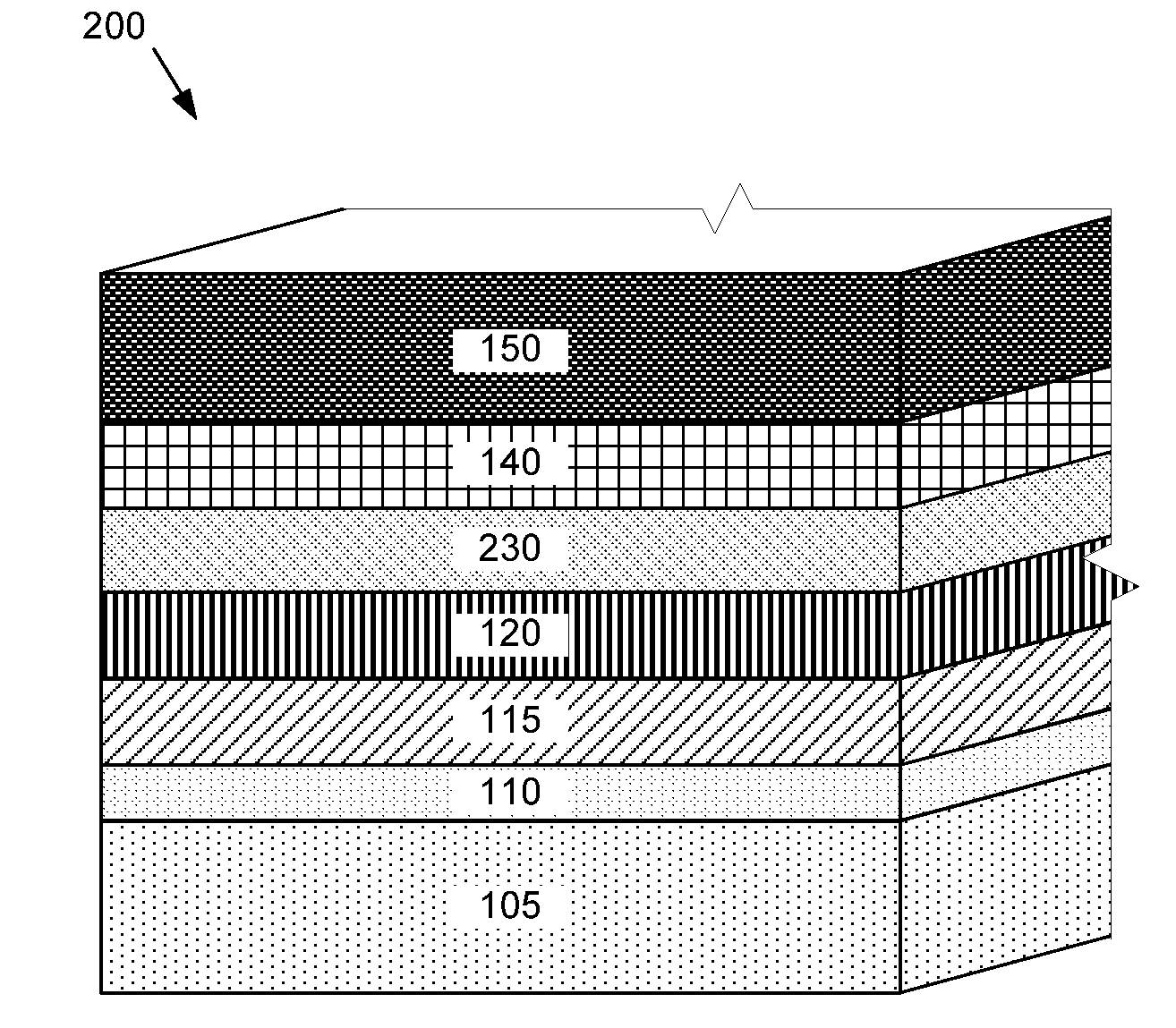
Process for producing photoelectric conversion devices
ActiveUS20110189814A1Improve device characteristicsQuality improvementPV power plantsSolid-state devicesChemical bath depositionSemiconductor
In a process for producing a photoelectric conversion device comprising a bottom electrode layer, a photoelectric conversion semiconductor layer, a buffer layer, and a transparent conductive layer, which are stacked in this order on a substrate, all film forming stages ranging from a stage of forming the buffer layer to a stage of forming the transparent conductive layer are performed with a liquid phase technique. The buffer layer is formed with a chemical bath deposition technique, and the transparent conductive layer is formed with an electrolytic deposition technique.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
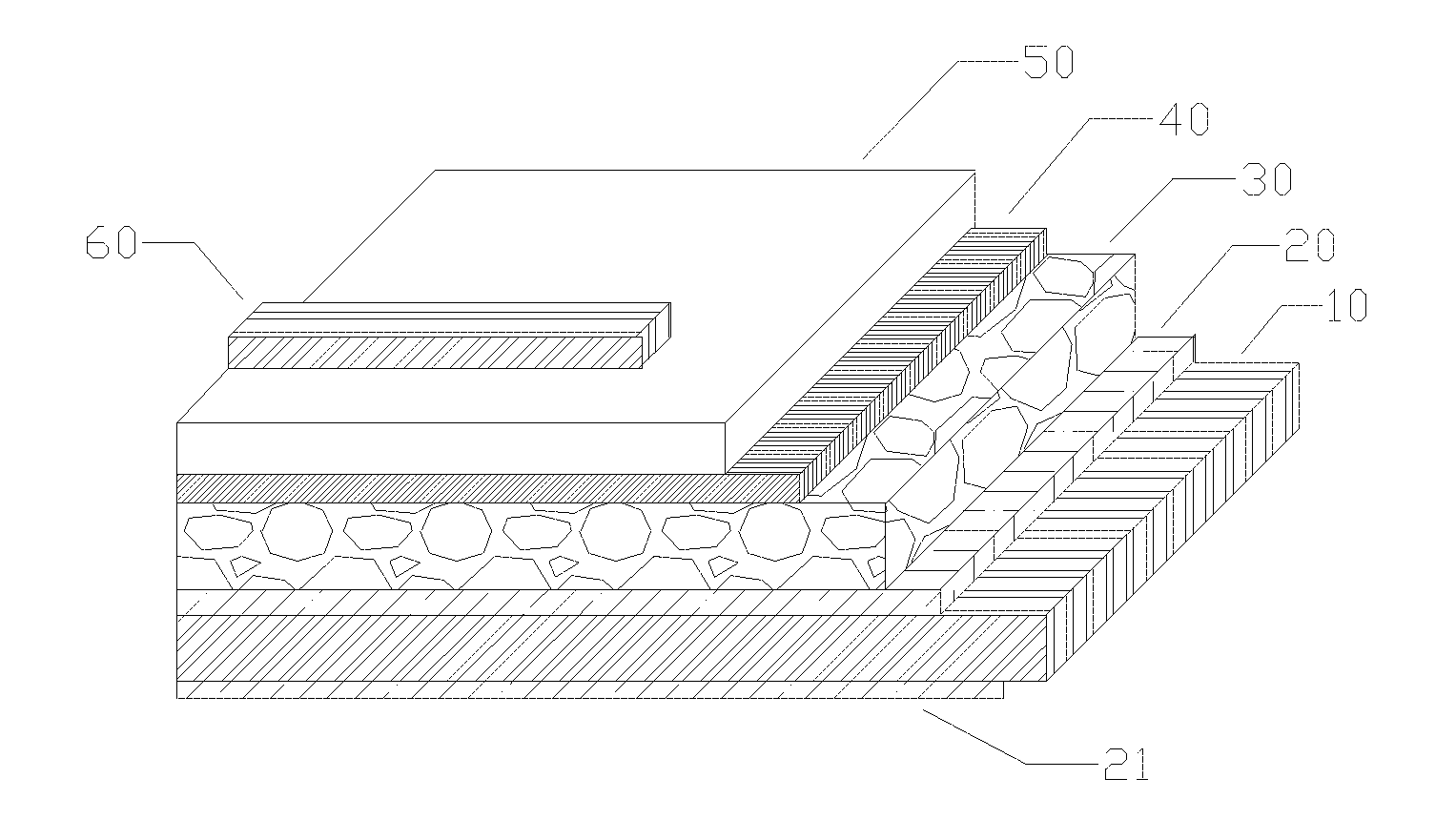
Hot water non-stick surface structure and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a hot water non-stick surface structure and a preparation method thereof. The super-hydrophobic interface structure comprises a nano cone array structure formed on the surface of a substrate, wherein the nano array structure comprises a plurality of nano protrusions arranged in an array manner; at least the top of the nano protrusion is provided with a conical structure; the distance between two adjacent nano protrusions is 50-500nm; the top diameter of the nano protrusions is 1-200nm; and the surface of the nano array structure is modified with low surface energy substances. The preparation method is mainly implemented by virtue of a chemical bath deposition method. The super-hydrophobic surface structure disclosed by the invention has good hot water non-stick properties, non-stick impact and instantaneous rebound of hot water drops or hot water flow can be realized, the preparation process is easy to operate and control, any expensive equipment is not needed, and the super-hydrophobic surface structure is low in consumption, environment-friendly, high in reproducibility and short in period, can be prepared in large area and has excellent industrial application prospects.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of H-TiO2/CdS/Cu(2-x)S nanoribbon
ActiveCN106622293AImprove catalytic performanceHigh reusabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsEnergy inputIon exchangeLight response
The invention discloses a preparation method of an H-TiO2 / CdS / Cu(2-x)S nanoribbon, relates to a preparation method of a semiconductor composite and aims to solve the technical problems that existing catalysts have lower solar energy conversion rate and higher cost. The method comprises steps as follows: firstly, a TiO2 nanoribbon is subjected to acid corrosion and reducing atmosphere treatment, and an H-TiO2 nanoribbon with a rough surface is obtained; CdS nanoparticles are modified on the surface of the H-TiO2 nanoribbon with a chemical deposition method, and an H-TiO2 / CdS nanocomposite is obtained; finally, part of Cd<2+> is reduced with Cu<+> with an ion exchange method, and an H-TiO2 / CdS / Cu(2-x)S nanoribbon catalyst is obtained. The catalyst has good light response to visible light and near infrared areas and can be used in a reaction for producing hydrogen from water through photolysis.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
In-doped zinc sulfide thin film and preparation method and application thereof
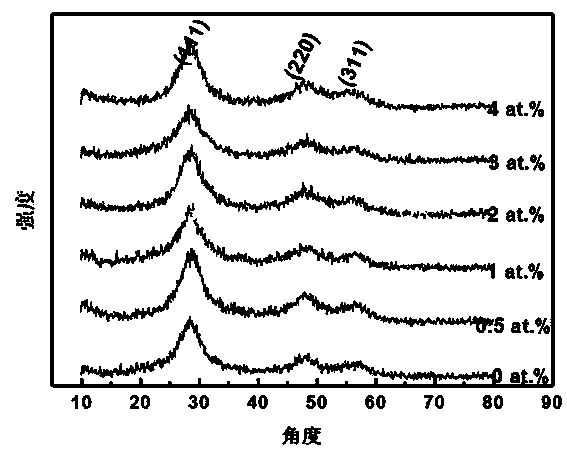
ActiveCN103531660AEasy to controlReduce manufacturing costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImpurity dopingPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses an In-doped zinc sulfide thin film and a preparation method and application thereof. A chemical bath deposition method is adopted to prepare the thin film. The invention belongs to non-vacuum chemical vapor deposition. The method is easy in control on ingredients of the thin film, is low in preparation cost and is suitable for large-scale production. According to the invention, an impurity doping method is utilized to reduce resistivity of the zinc sulfide thin film; tests show that when 2at. percent of In is doped in ZnS, the thin film comprises a small quantity of impurity phases and has high optical transmittance (the optical transmittance in a visible region is about 85 percent) and low resistivity (26*105ohmcm). The prepared ZnS thin film is suitable to be used as a buffer layer material of a solar cell.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing AgInS2 quantum dot sensitized TiO2 photoelectrode with In2S3 used as buffer layer
InactiveCN104377036ASimple processLow costLight-sensitive devicesCapacitor electrodesOrganic solventPorous membrane
The invention relates to a method for preparing an AgInS2 quantum dot sensitized TiO2 photoelectrode with In2S3 used as a buffer layer. The method comprises the steps that (1) a TiO2 porous membrane is prepared on an FTO conducting glass matrix; (2) an Ag2S quantum dot sensitized TiO2 electrode is obtained through the continuous ionic adsorption reaction method; (3) on the Ag2S quantum dot / TiO2 electrode, the chemical bath deposition and reaction of In2S3 is used for synthesizing the AgInS2 quantum dot sensitized TiO2 photoelectrode with In2S3 used as the buffer layer in a one-step in-situ mode. The method is simple in preparing process and low in requirement for equipment, and common organic solvents used for semiconductor quantum dot synthesis are not involved; the photoelectrode is composed of AgInS2, In2S3 and TiO2 which are low in toxicity, has high photoelectric response performance when being applied to solar cells, and has potential application prospects.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Apparatus and method for rotating drum chemical bath deposition
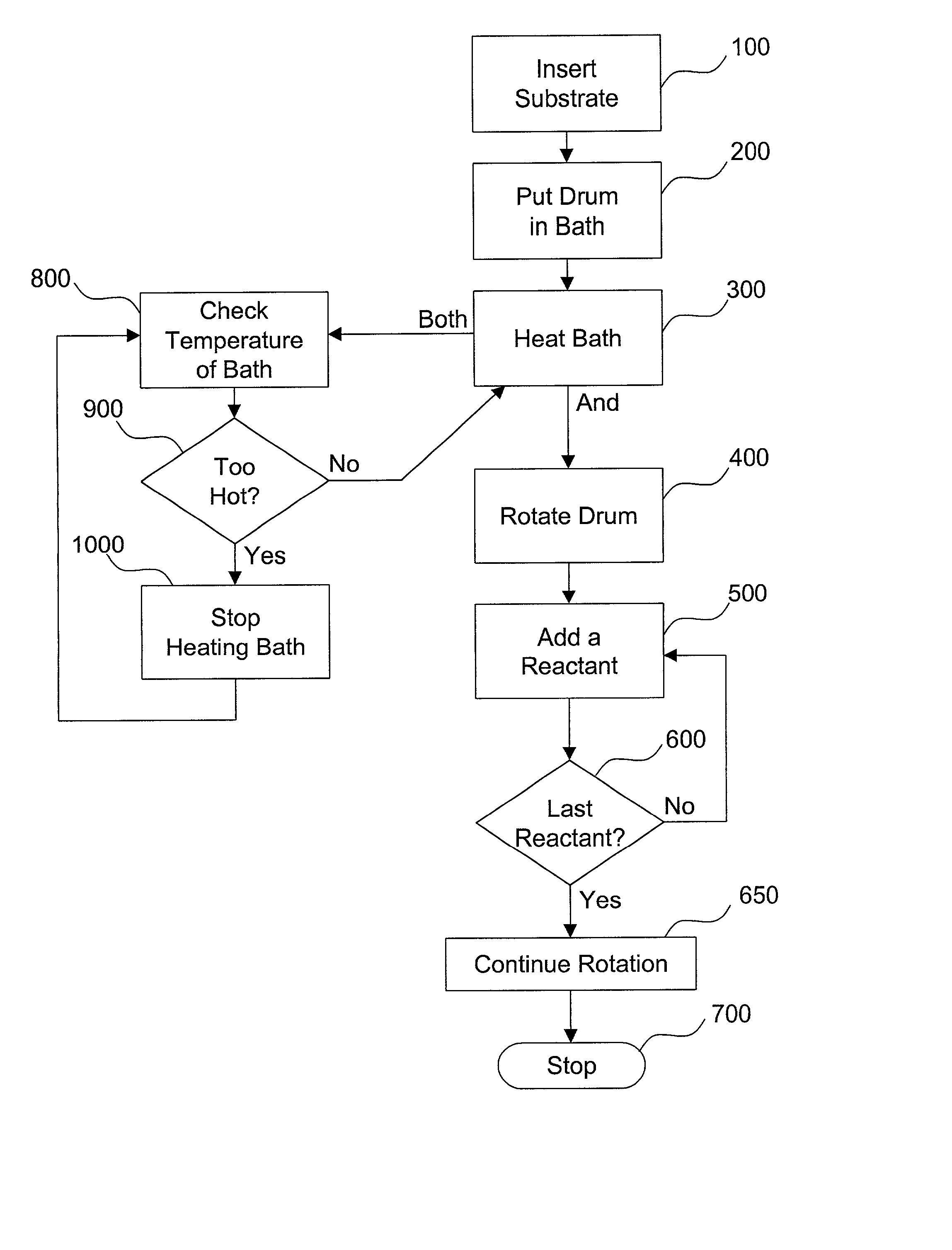
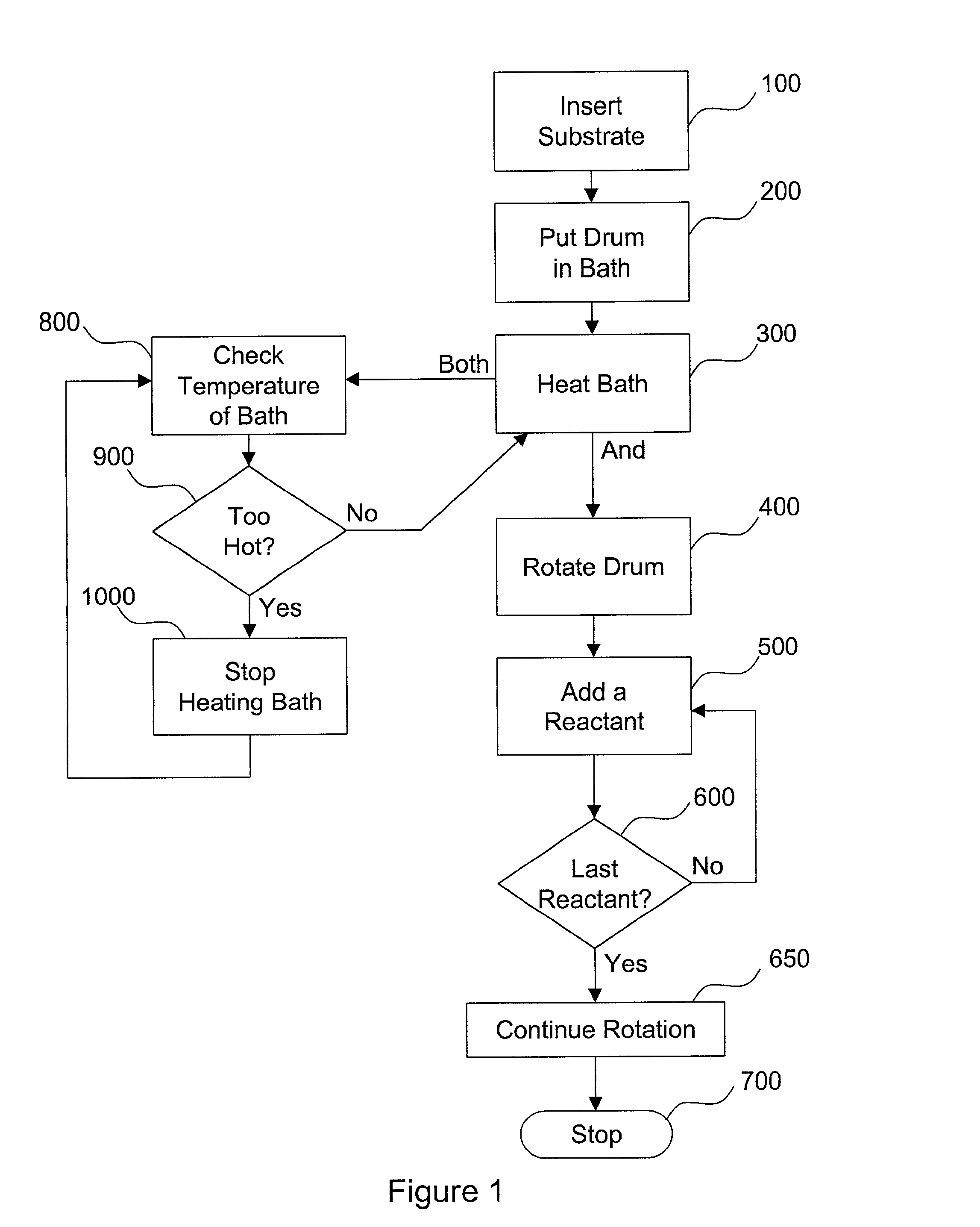
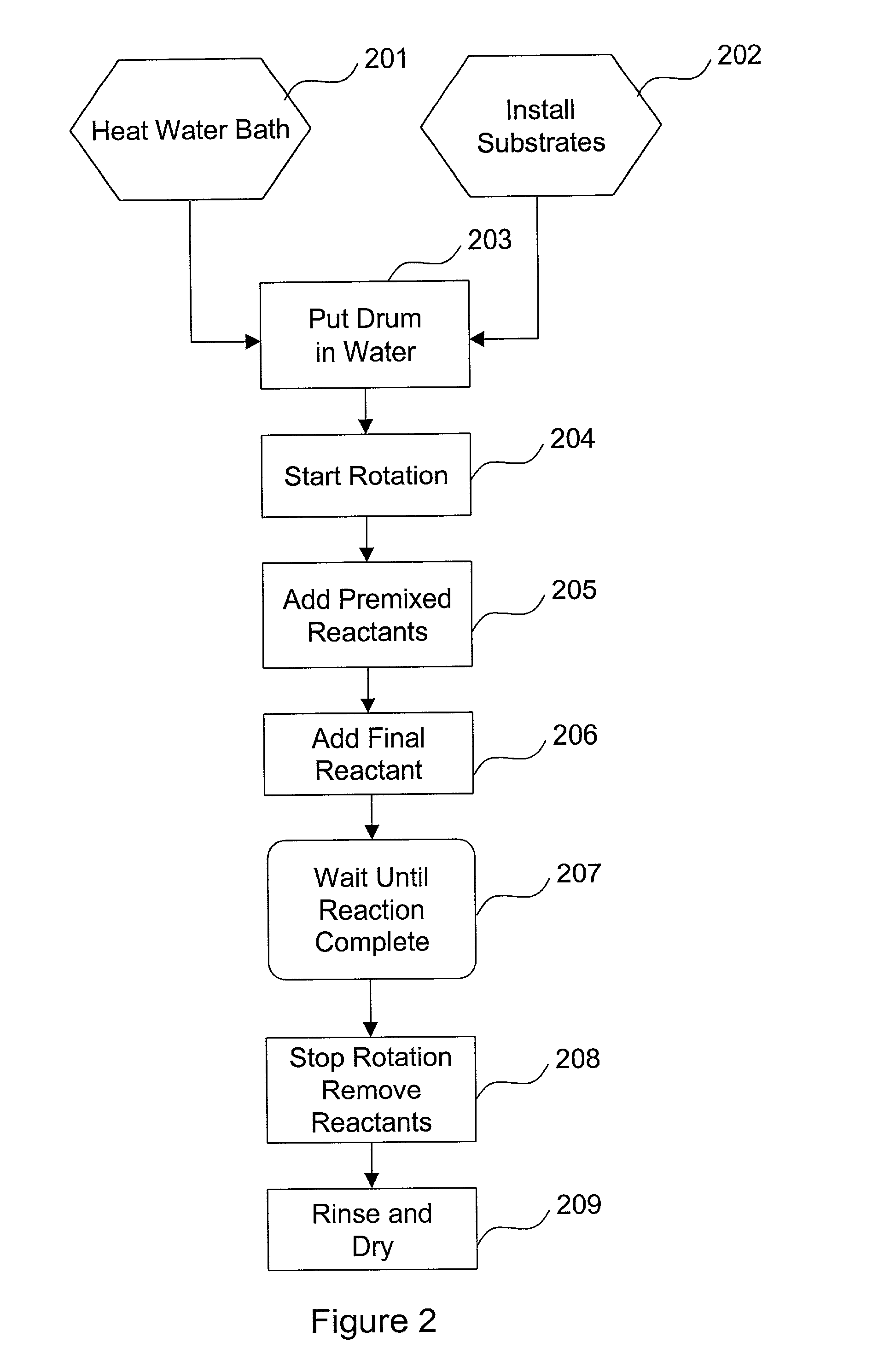
InactiveUS20020182338A1Reduce depositionLower energy requirementsPretreated surfacesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingEngineeringElectroplating
The present invention relates to a novel method and apparatus for chemical bath deposition or other plating or similar processes. The deposition may be performed in a rotating drum that has been provided with a mechanism for temperature elevation. A substrate or other suitable recipient bed upon which deposition is sought may be removably attached to the interior of the drum. Reactants or other materials may be added to the drum to deposit a film, layer, or uniform particles on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:ITN ENERGY SYST INC
Nickel hydroxide/graphene roll-carbon nano-tube composite carbon aerogel, preparation thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN106024424AImprove Capacitive PerformanceImprove electrochemical performanceHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesCapacitanceNickel oxide hydroxide
The present invention relates to a nickel hydroxide / graphene roll-carbon nano-tube composite carbon aerogel, a preparation thereof and an application thereof. The composite carbon aerogel is composed of a composite carbon aerogel skeleton and a nickel hydroxide nano sheet formed on the surface of the composite carbon aerogel skeleton through the in-situ growth process. The preparation of the composite carbon aerogel comprises the steps of adding a graphene roll-carbon nano-tube composite carbon aerogel into a nickel nitrate solution, subjecting the above materials to deposition reaction in a chemical bath, washing and drying to obtain the composite carbon aerogel. According to the technical scheme of the invention, in the simple chemical and deposition means, the nickel hydroxide having pseudo-capacitive properties is compounded with the graphene roll-carbon nano-tube aerogel having double-electrode-layer capacitance properties, so that the advantages of the nickel hydroxide and the graphene roll-carbon nano-tube aerogel are given full play to. Therefore, the obtained material is excellent in electrochemical performance and high in capacitive character.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing cadmium sulfide film by using chemical bath deposition method
ActiveCN102766900AImprove aestheticsImprove uniformityPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsWater bathsUltrasonic assisted
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cadmium sulfide film by using a chemical bath deposition method. The method comprises the steps: cleaning a substrate; mounting the substrate, forming a reactor by the substrate and a fixture; preparing a solution, mixing cadmium salt, ammonia water, buffering agents, thiourea and deionized water according to a certain ratio to form a reaction solution, and then adding the solution into the reactor; reacting and depositing the reaction solution, placing the reactor with the reaction solution in a constant temperature bath container, heating the reaction solution to 50 DEG C to 90 DEG C, exerting 20 to 50 KHz ultrasonic waves to assist the depositing simultaneously, or adding a water pump so that the reaction solution circulates constantly in the reactor through a water inlet and a water outlet of the fixture and the total reaction time is about 5 minutes to 60 minutes; and subjecting the reaction solution to further treatment, taking down the substrate deposited with the cadmium sulfide film, and cleaning, drying or stoving the substrate. According to the method for preparing the cadmium sulfide film by the chemical bath deposition method, reaction materials are saved, only single side coating happens on the substrate, the attractiveness is improved, the deposited cadmium sulfide film is continuous, uniform and compact, and the film-forming quality is improved.
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG JIBAO AUTOMATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com