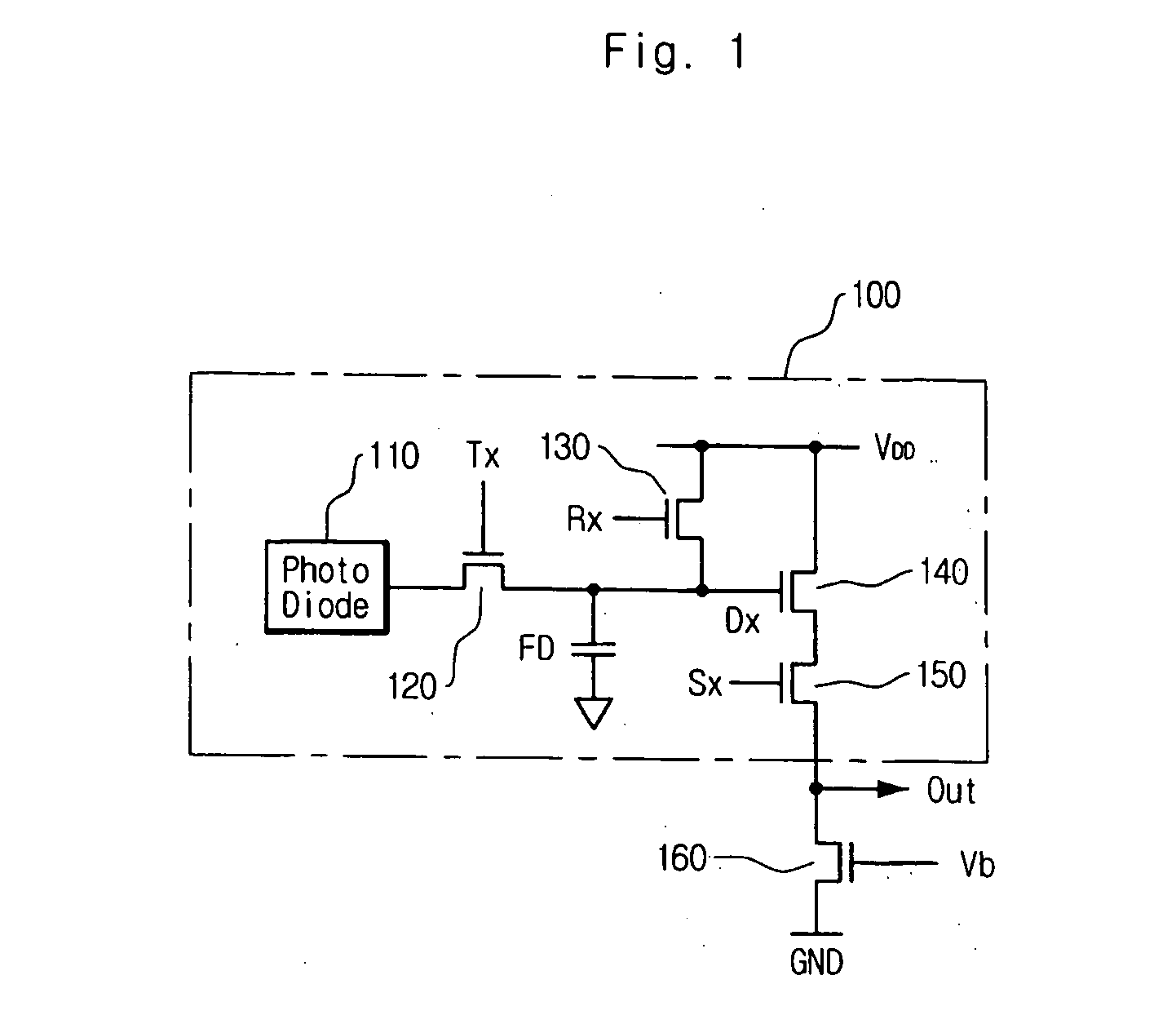
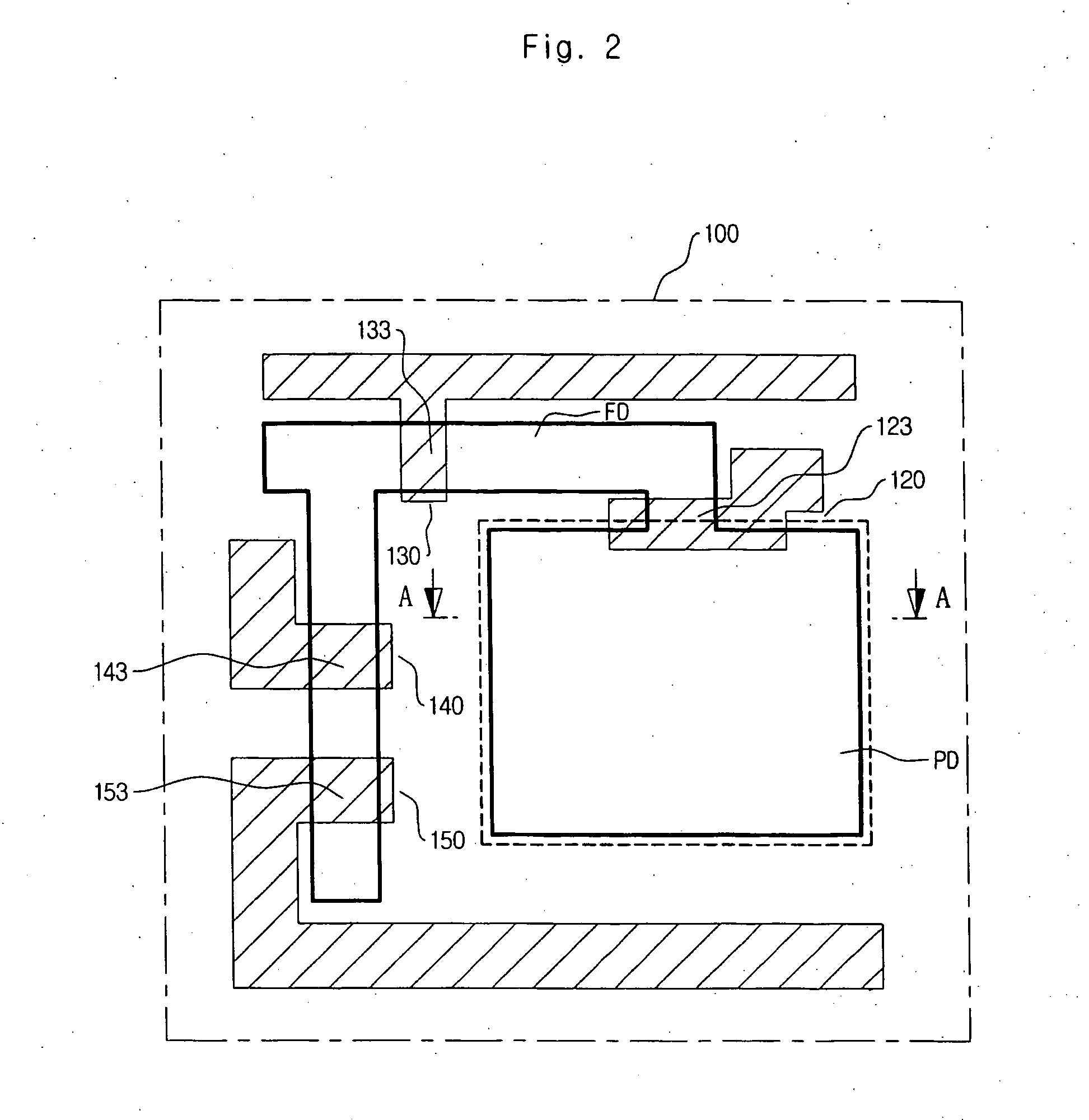
Patents
Literature
91results about How to "Improve device characteristics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
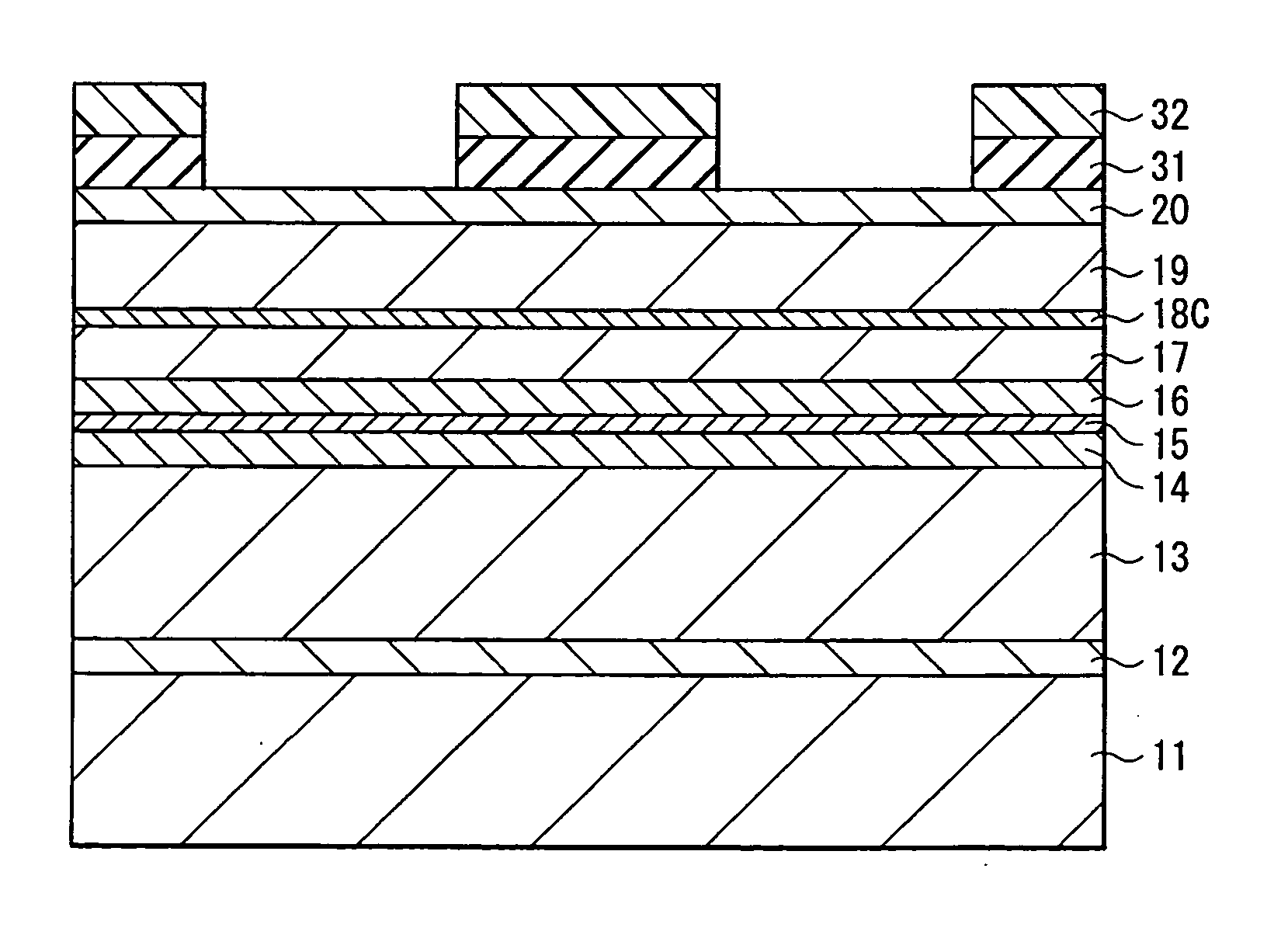
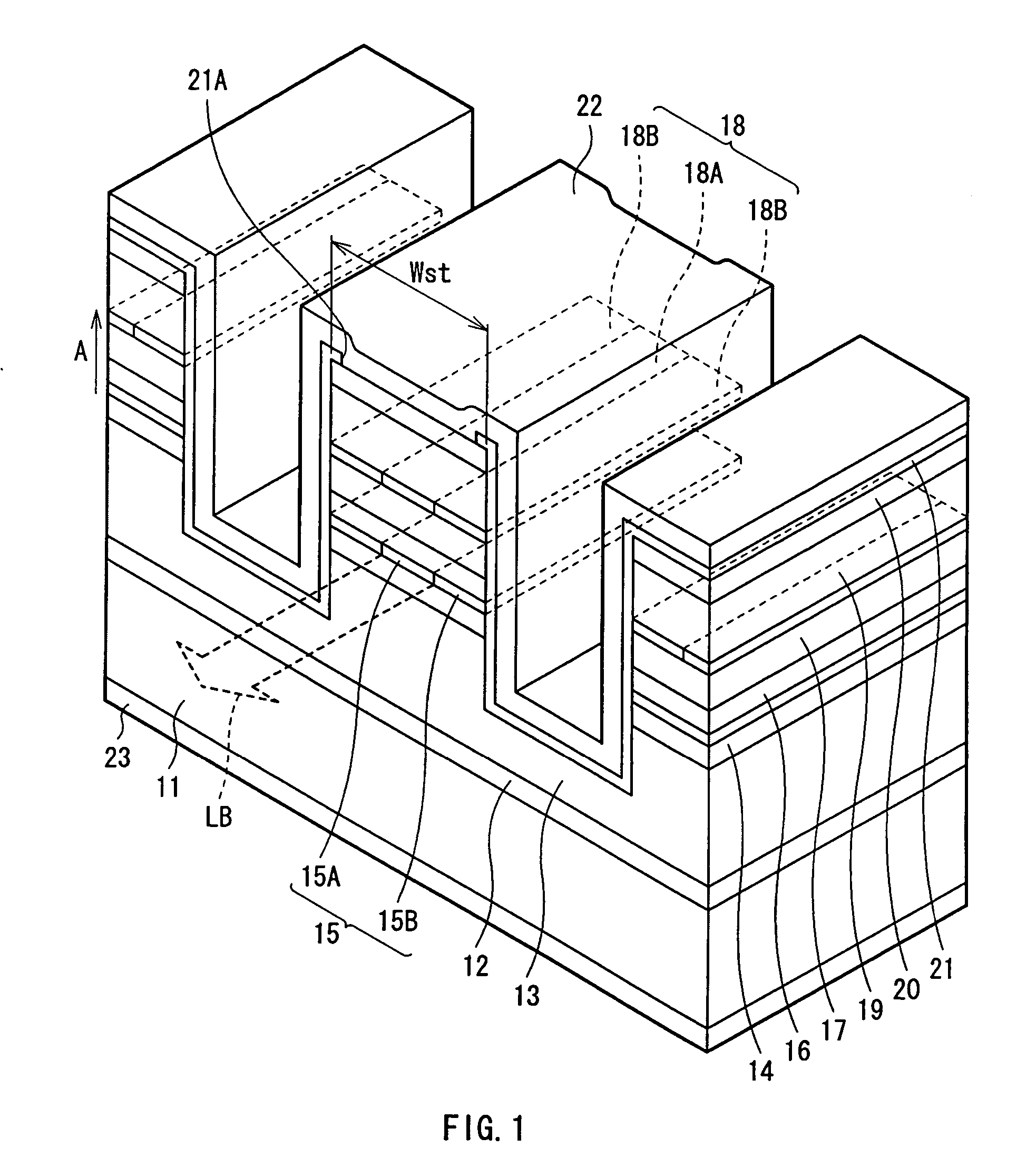
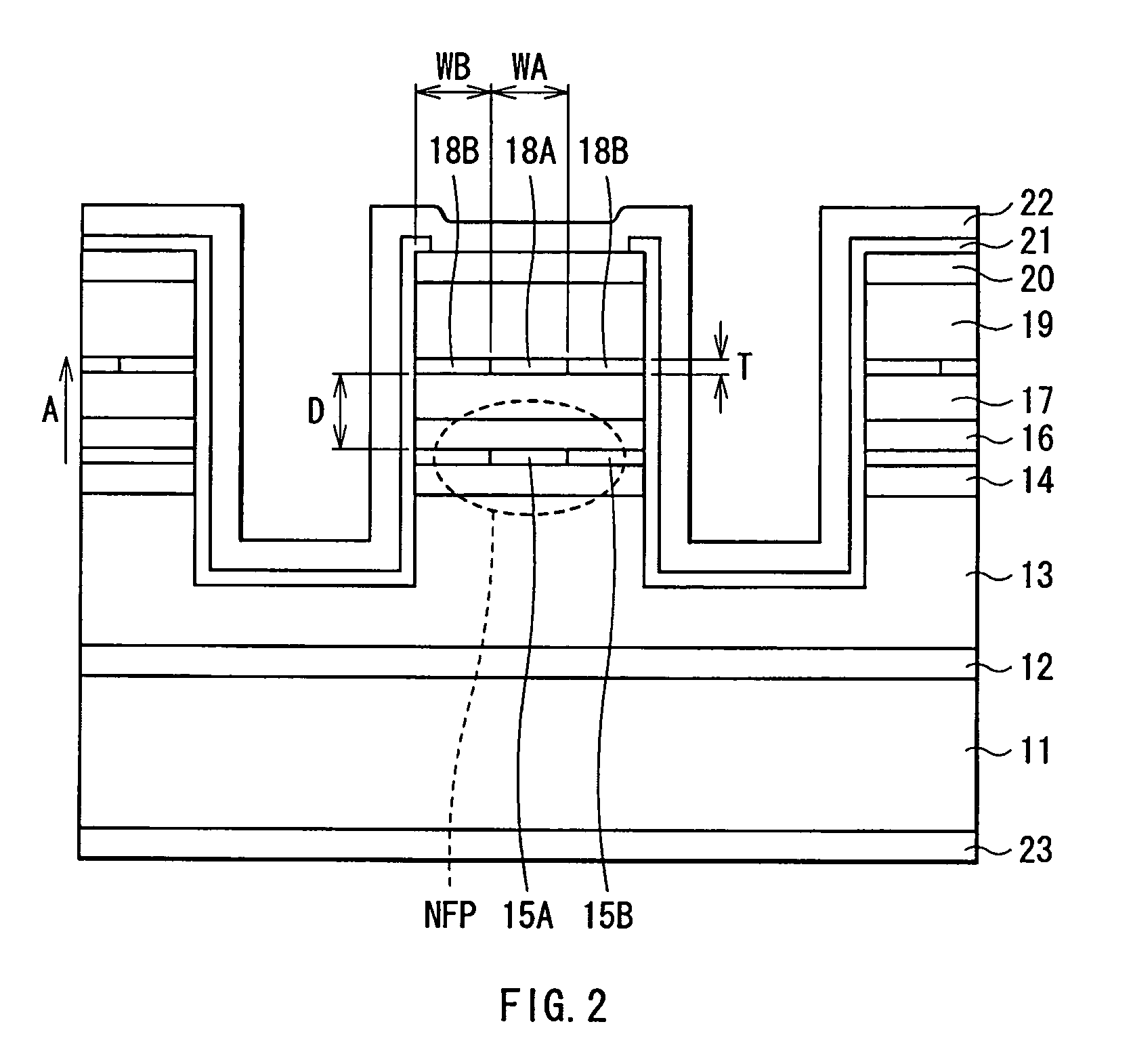
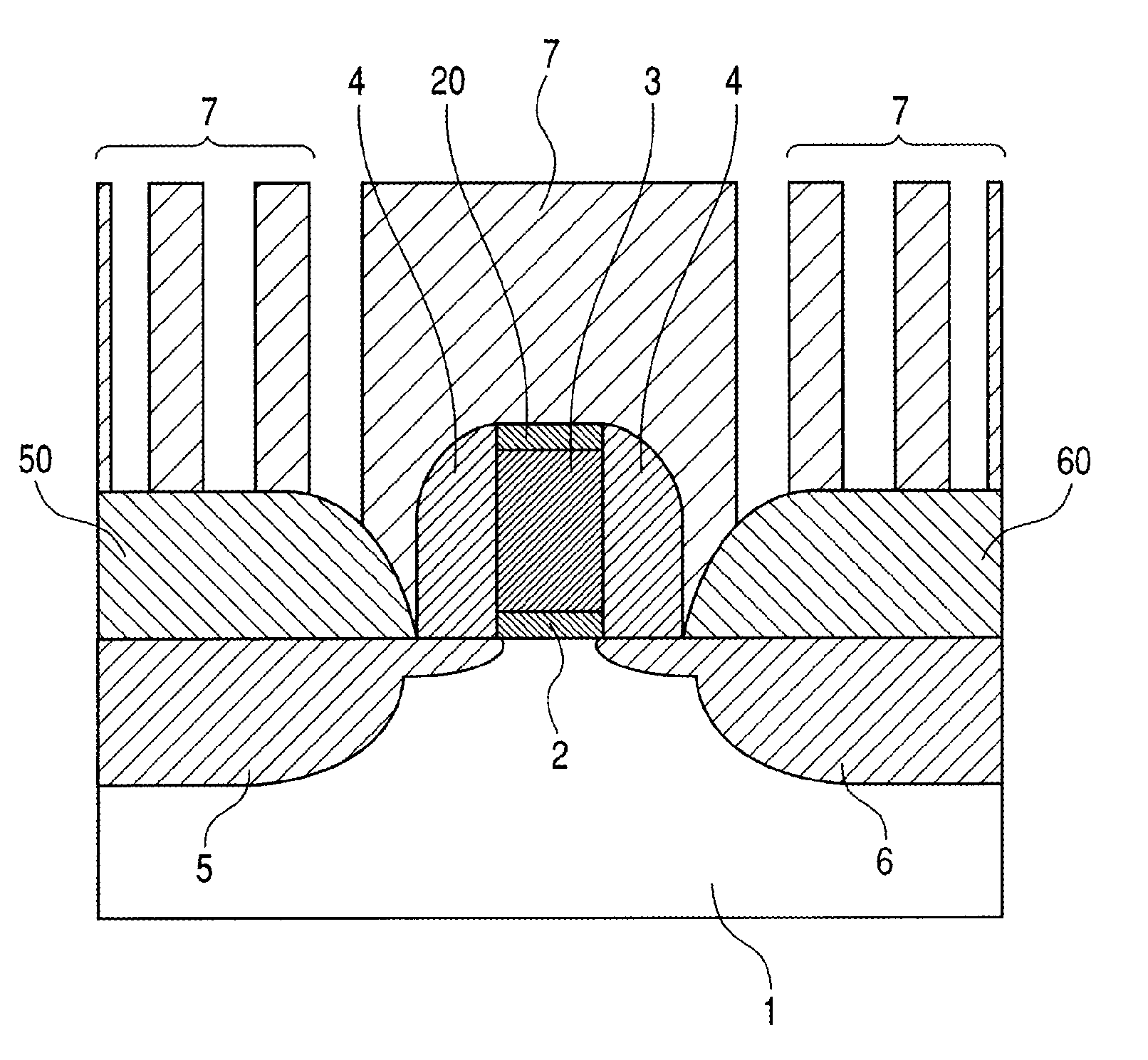
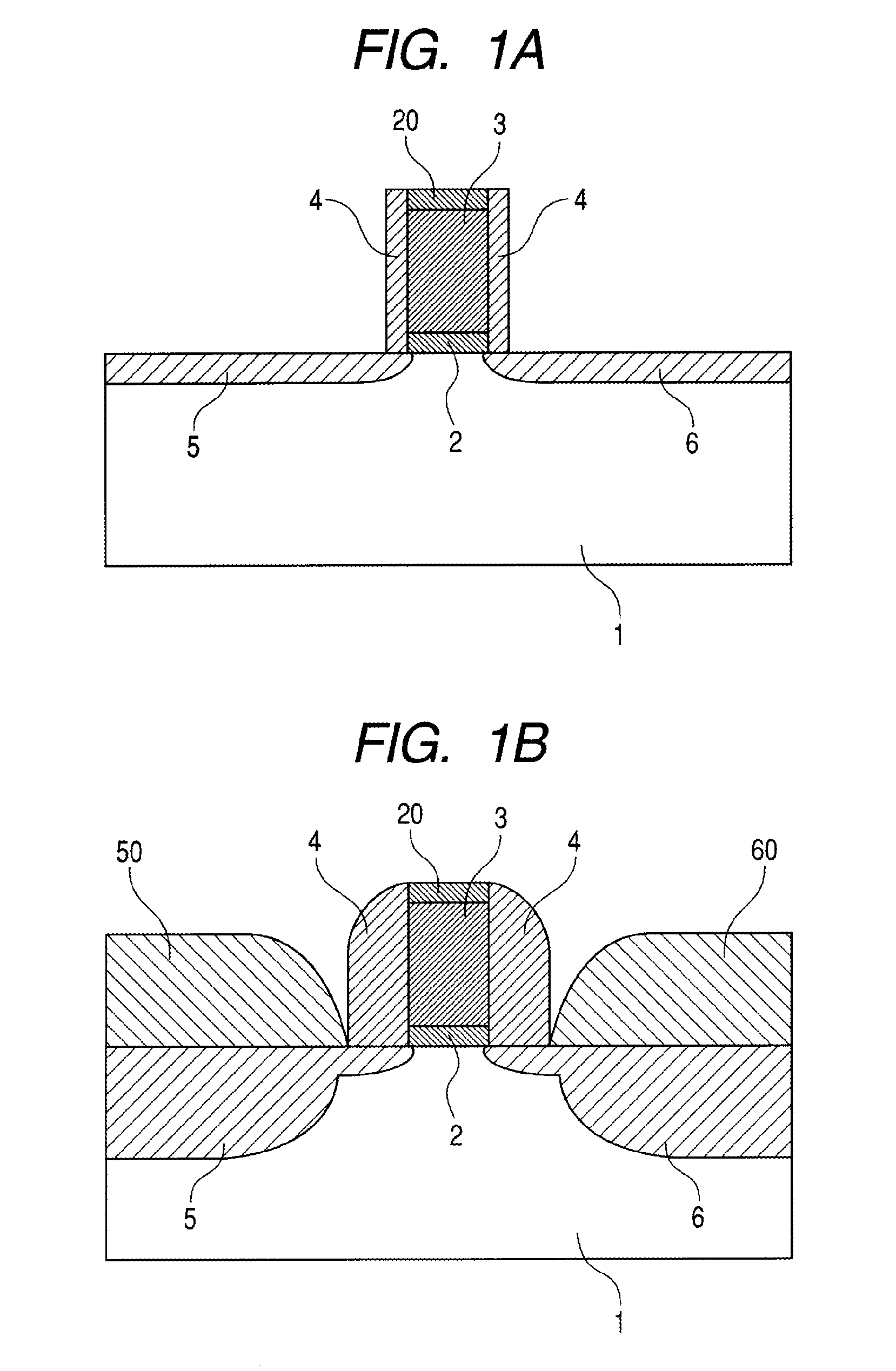
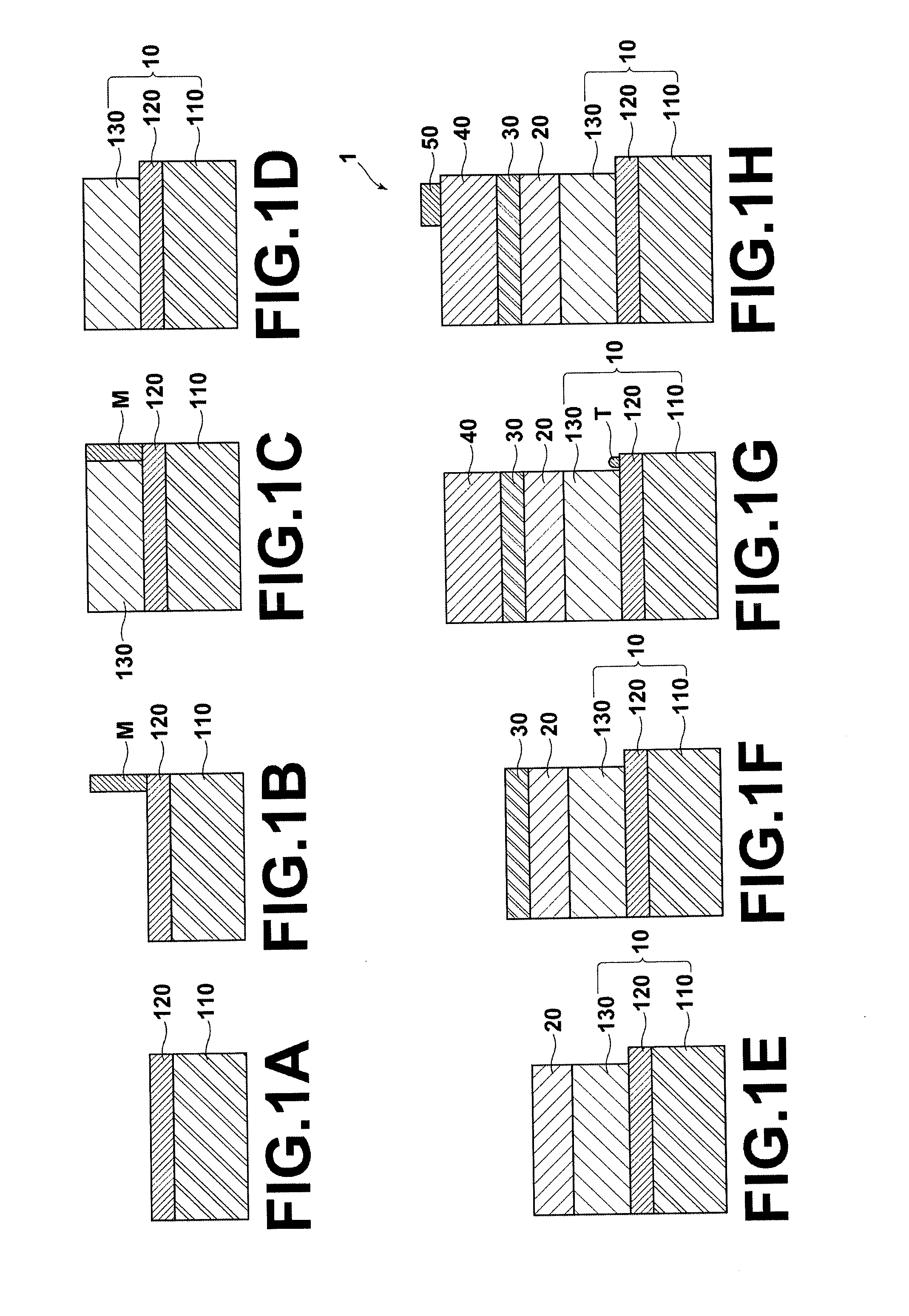
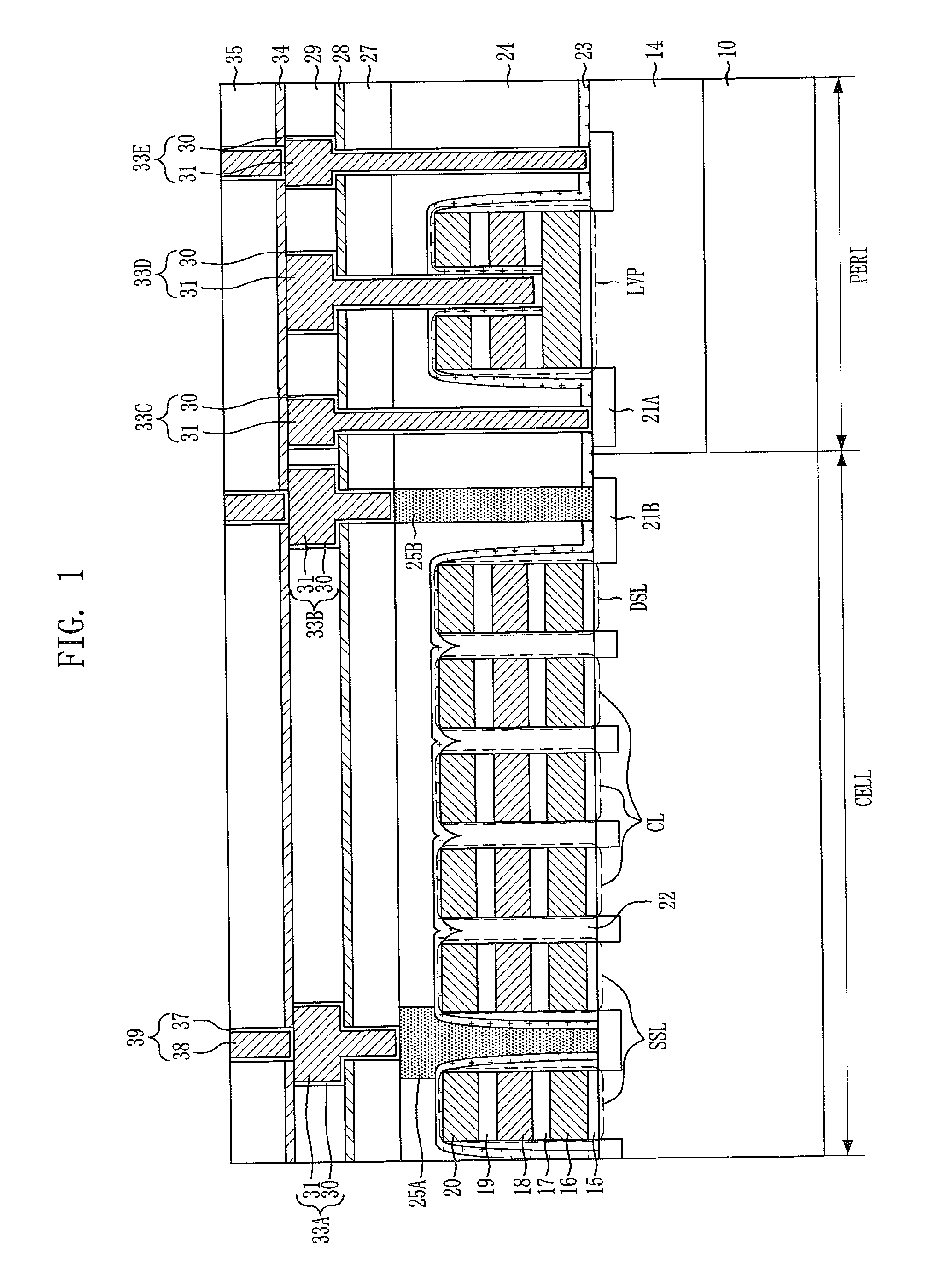
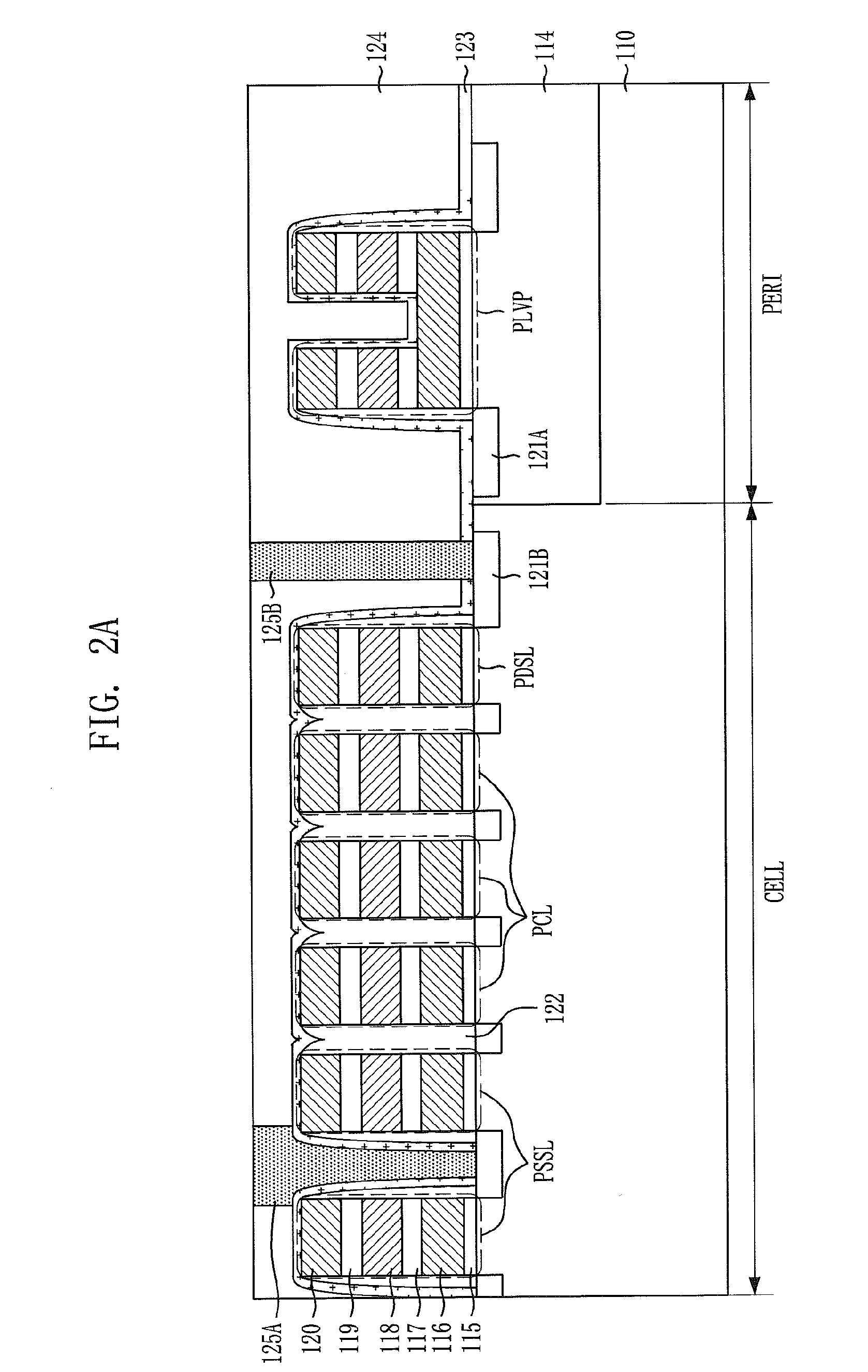
Field effect transistor and method for fabricating the same
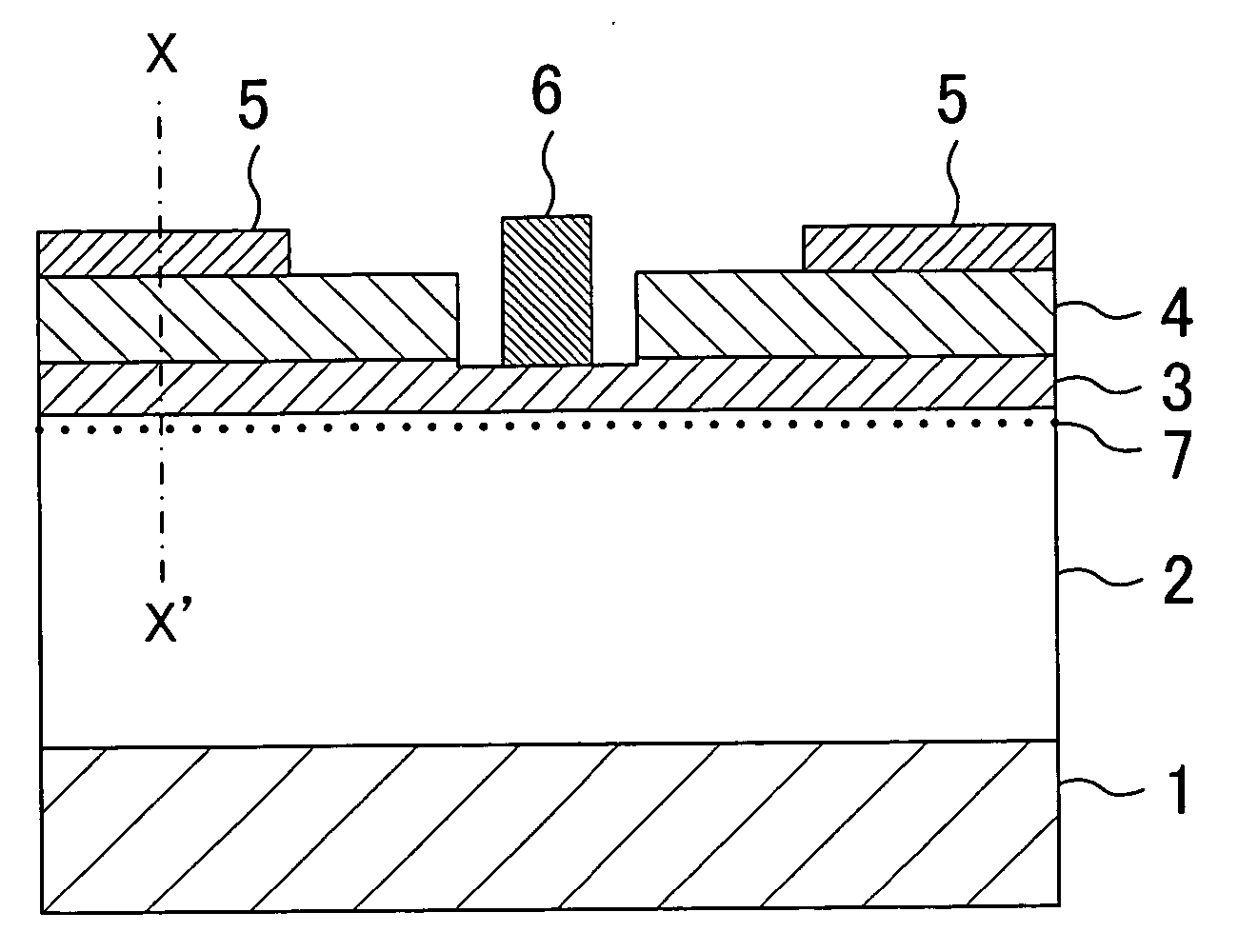
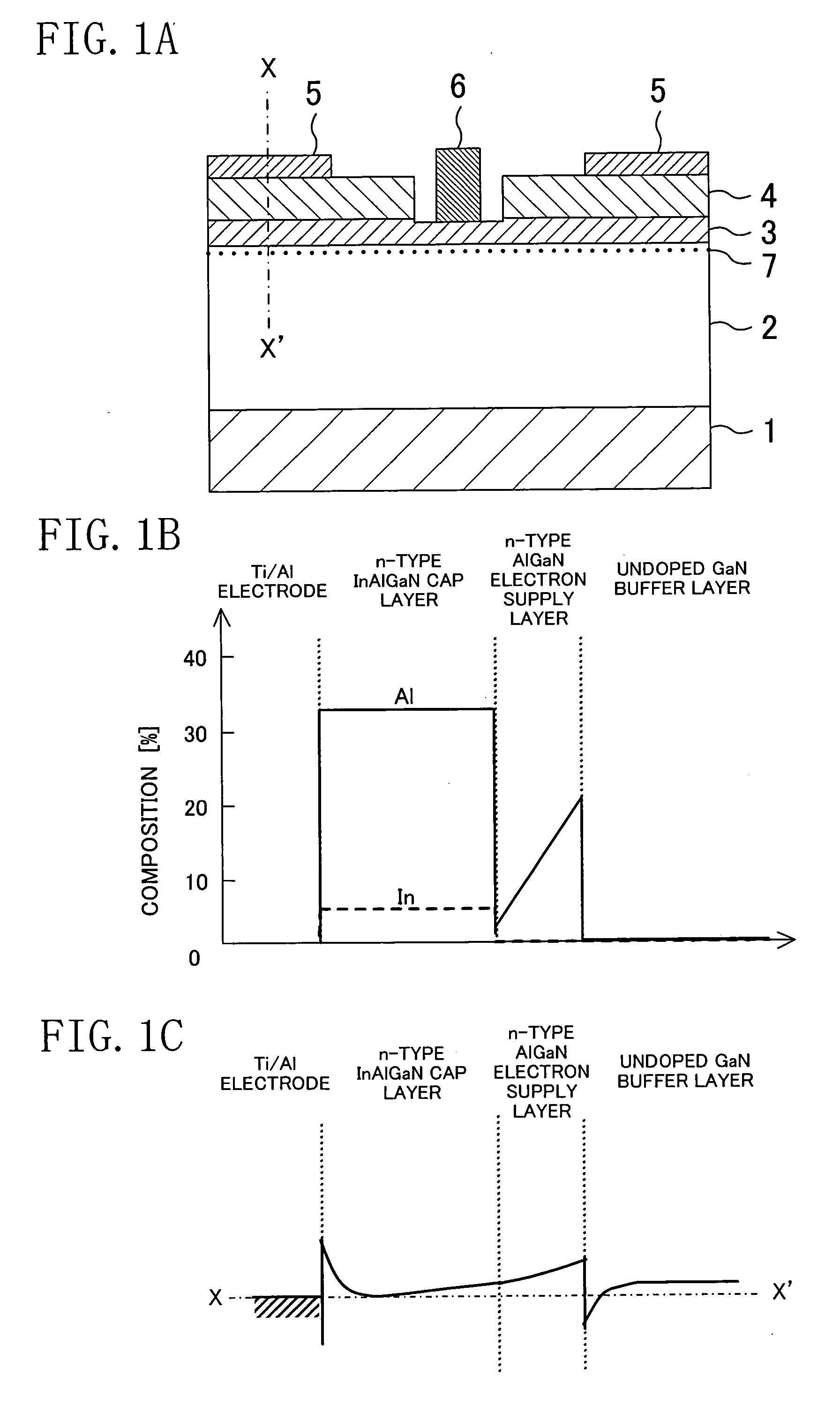
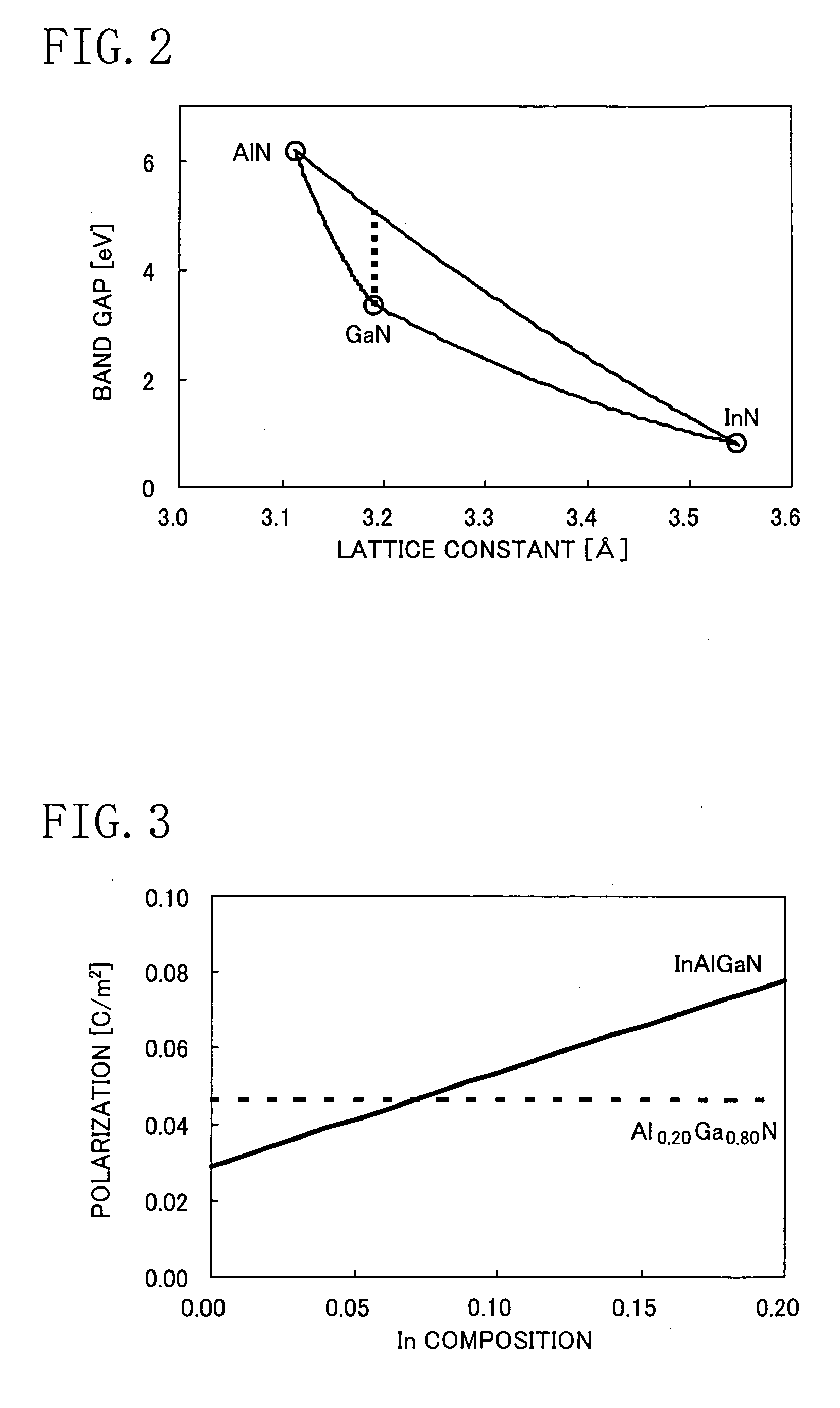
ActiveUS20060180831A1High crystallinityIncrease parasitic resistanceSemiconductor devicesConduction bandField-effect transistor
A field effect transistor includes a nitride semiconductor layer; an InxAlyGa1-x-yN layer (wherein 0<x<1, 0<y<1 and 0<x+y<1) formed on the nitride semiconductor layer; and a source electrode and a drain electrode formed on and in contact with the InxAlyGa1-x-yN layer. The lower ends of the conduction bands of the nitride semiconductor layer and the InxAlyGa1-x-yN layer are substantially continuous on the interface therebetween.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090283895A1Improve device characteristicsImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor chip
A semiconductor device including a metal frame having a penetrating opening; a semiconductor chip provided in the opening; an insulating layer provided on the upper surface of the metal frame such that the insulating layer covers the upper surface, which is the circuit-formed surface of the semiconductor chip; an interconnect layer provided only on the upper-surface side of the metal frame with intervention of the insulating material and electrically connected to a circuit of the semiconductor chip; a via conductor provided on the upper surface of said semiconductor chip to electrically connect the circuit of the semiconductor chip and the interconnect layer; and a resin layer provided on the lower surface of the metal frame.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Organic thin film transistor, production method thereof, and electronic device
InactiveUS20100032660A1Improve device characteristicsLow costFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesOhmic contactMetallic materials
An organic thin film transistor is disclosed, including a substrate formed of an organic insulating layer, a first layer deposited on the substrate using a plating technique to be used for forming a source electrode and a drain electrode, a second layer of a metal material deposited covering the first layer using a further plating technique to be used for forming the source electrode and the drain electrode with the metal material capable of forming an ohmic contact with an organic semiconductor material lower than the first layer, and an organic semiconductor layer over a region between the source electrode and the drain electrode, which are each formed with the first layer and the second layer. Also disclosed is an electric device provided with the organic thin film transistor.
Owner:SONY CORP
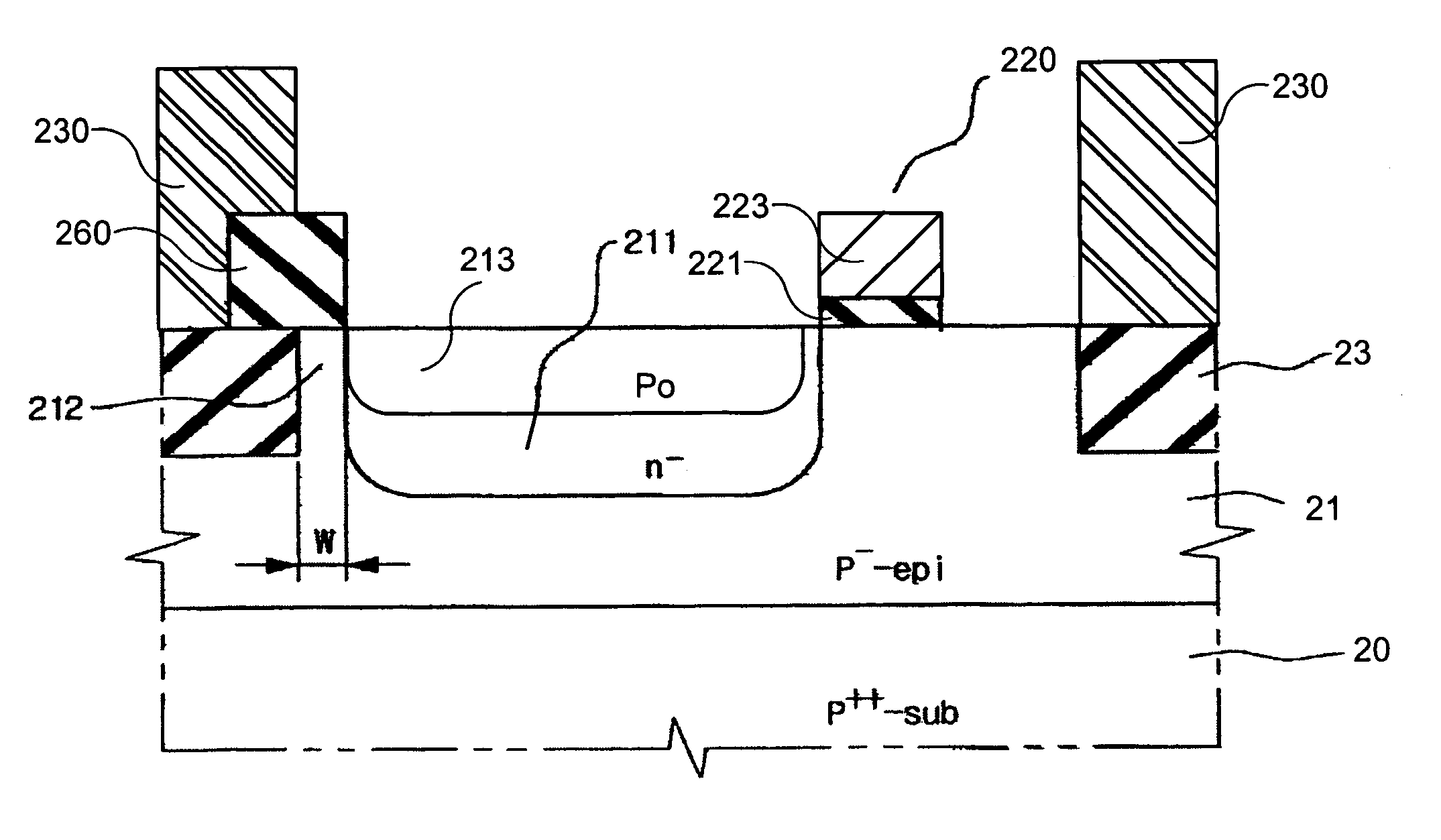
Method and device for forming an STI type isolation in a semiconductor device
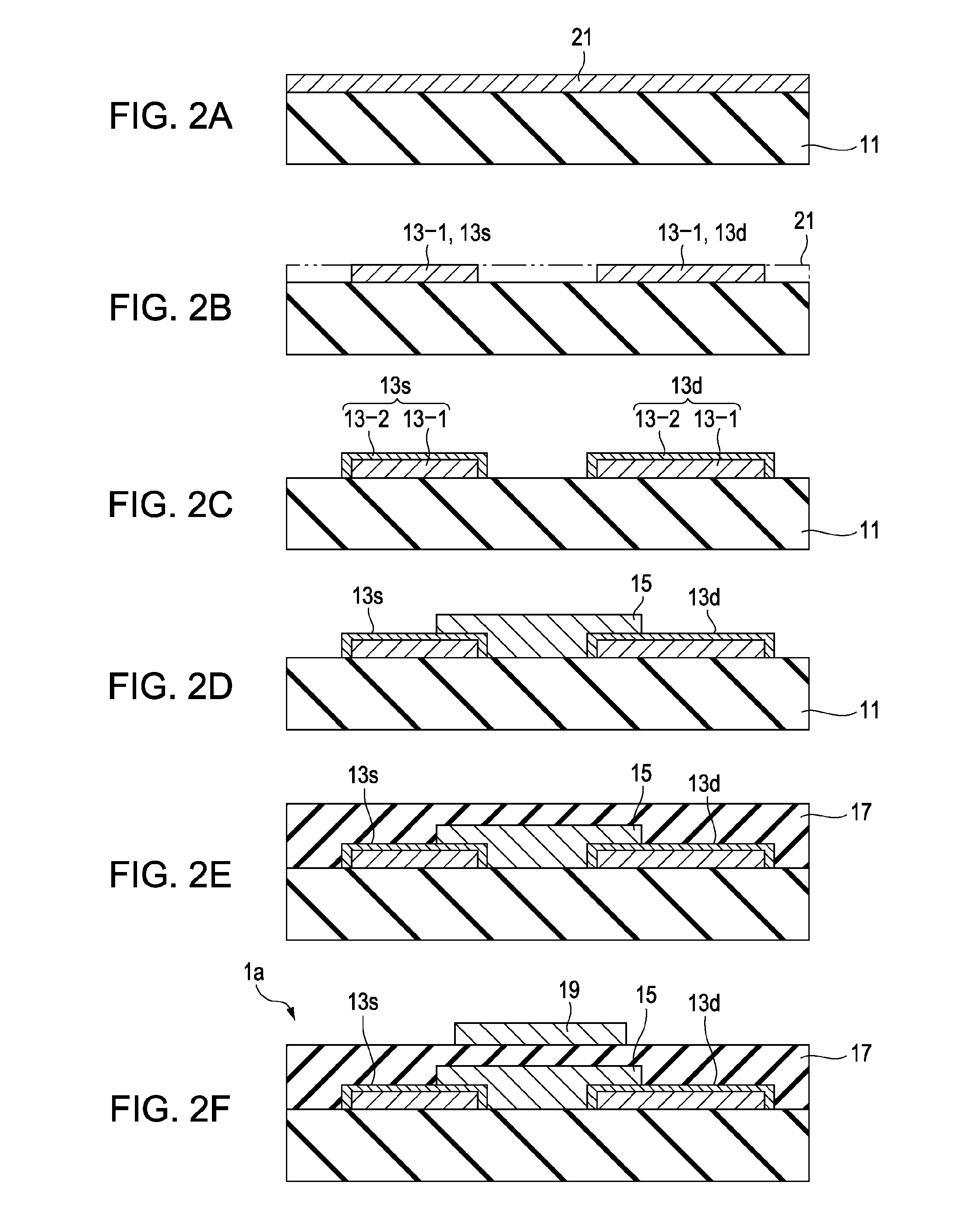
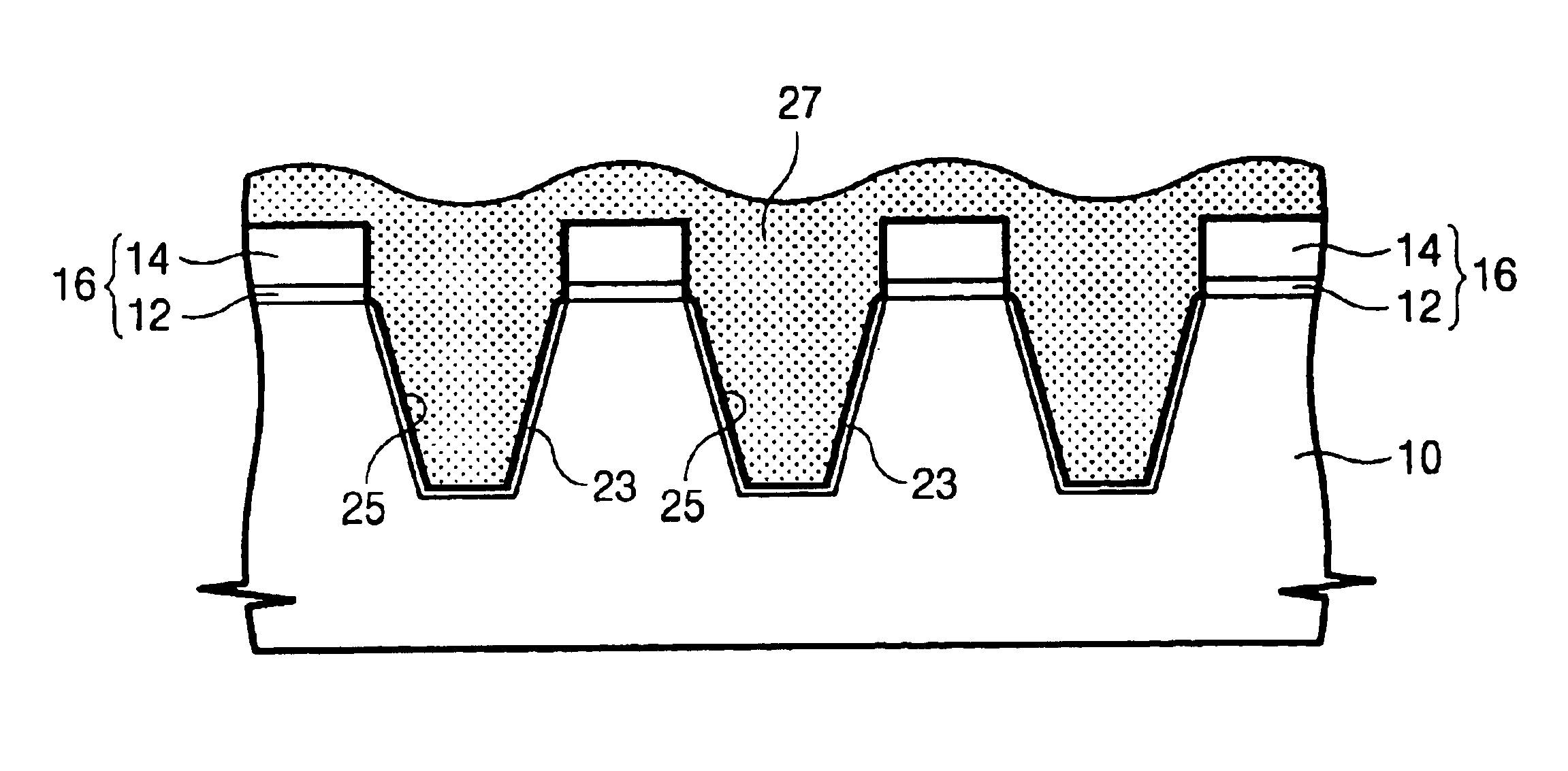
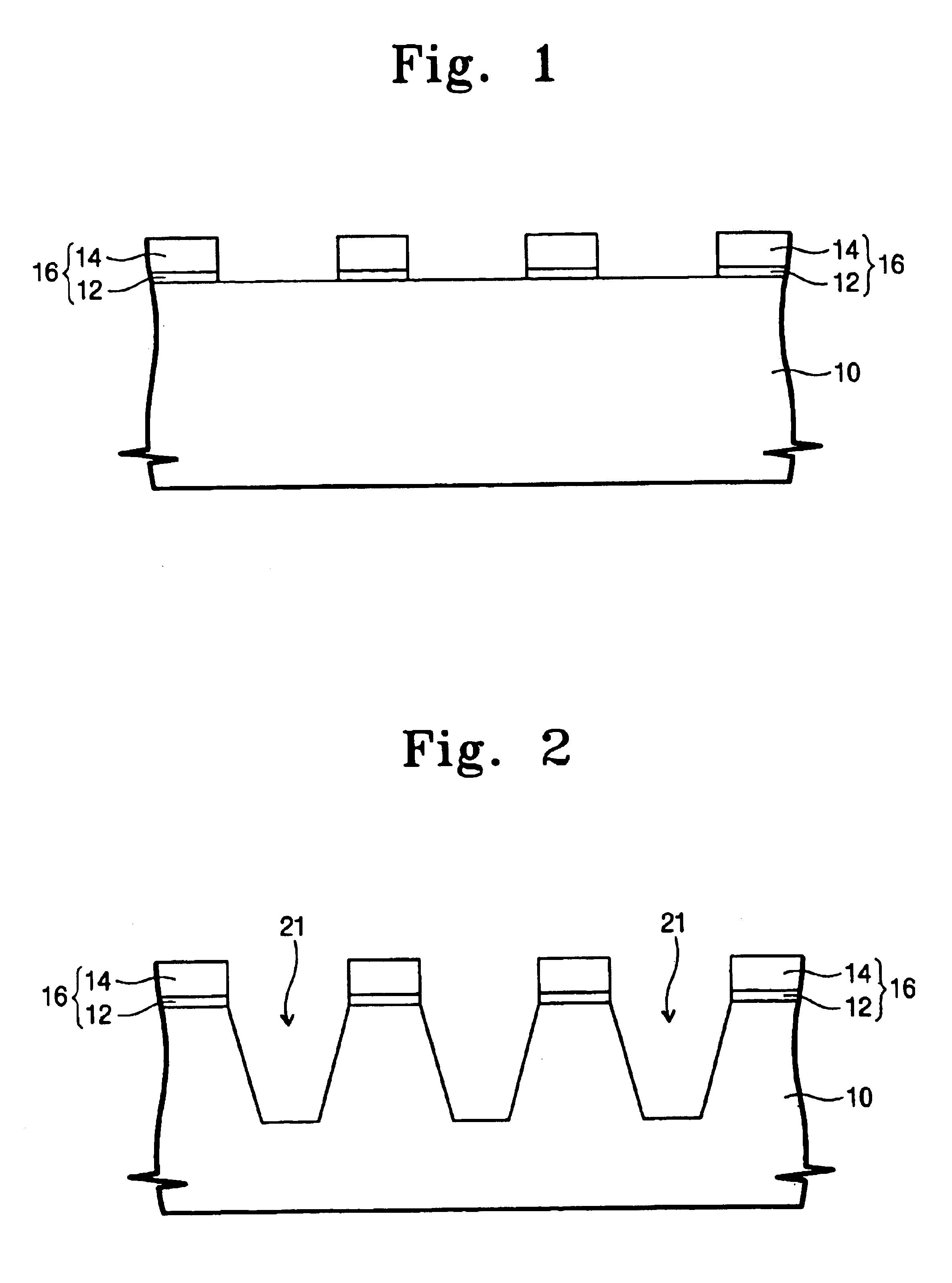
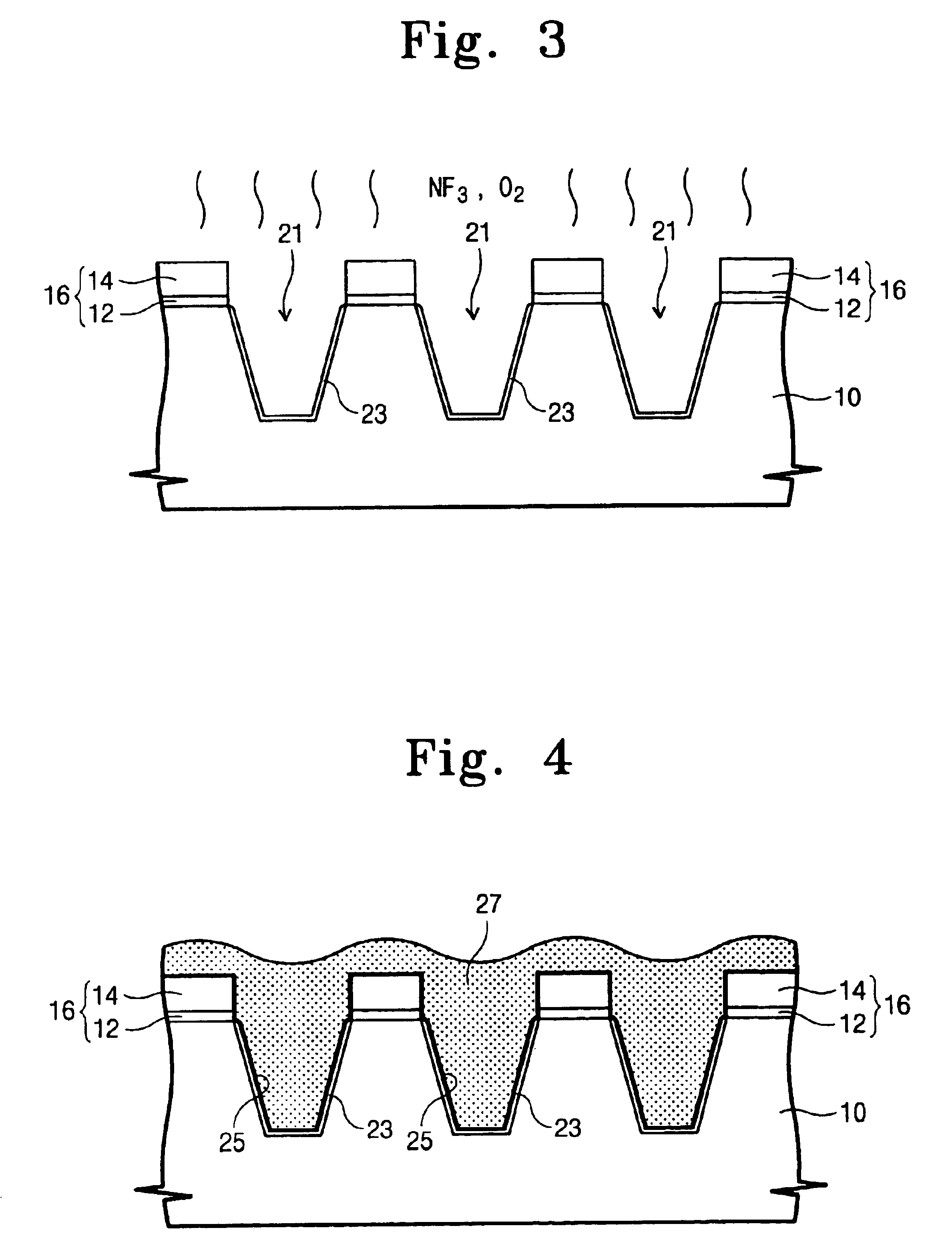
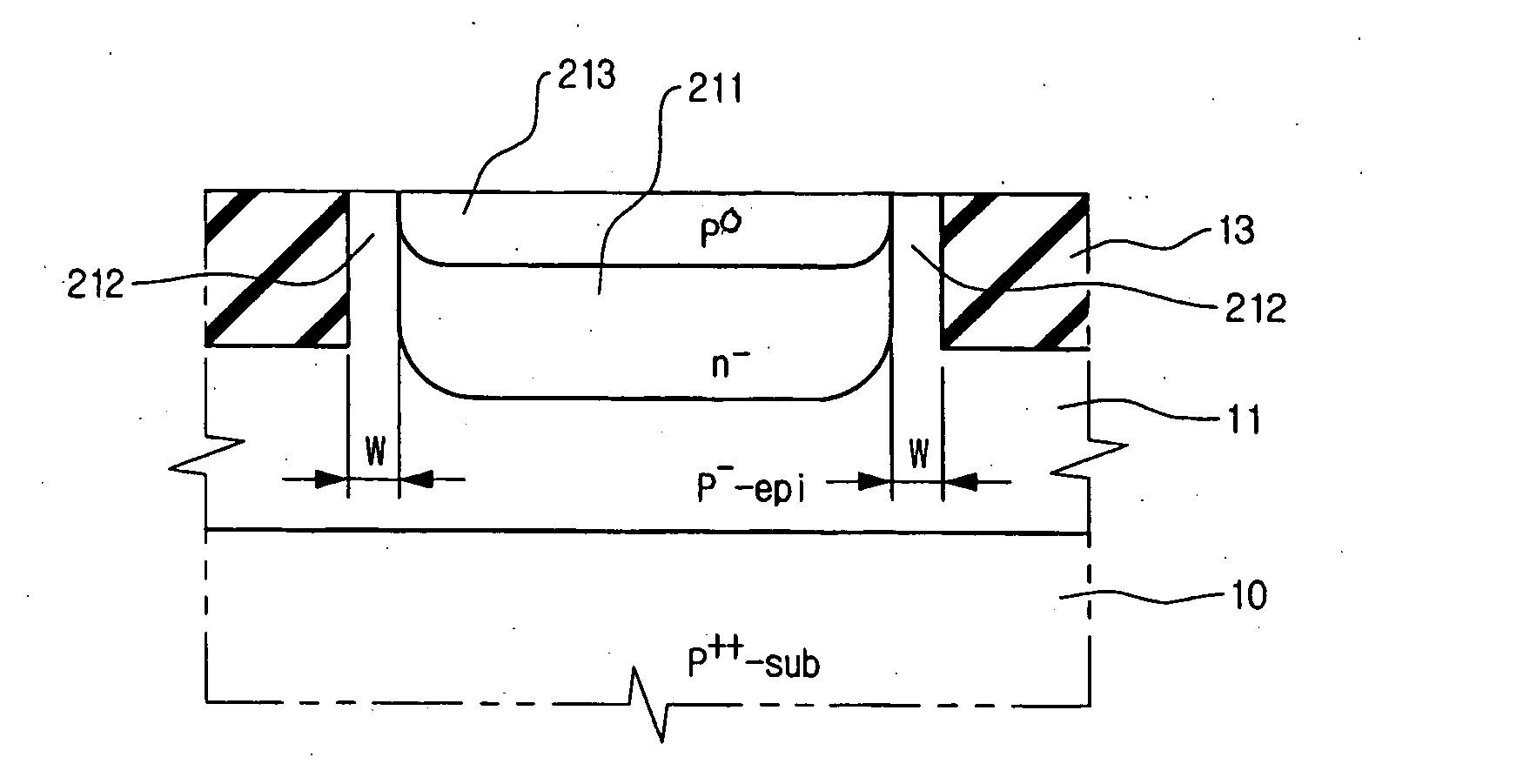
InactiveUS6849520B2Improve device characteristicsReduce charge leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialIsolation layer
A trench isolation in a semiconductor device, and a method for fabricating the same, includes: forming a trench having inner sidewalls for device isolation in a silicon substrate; forming an oxide layer on a surface of the silicon substrate that forms the inner sidewalls of the trench; supplying healing elements to the silicon substrate to remove dangling bonds; and filling the trench with a device isolation layer, thereby forming the trench isolation without dangling bonds causing electrical charge traps.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
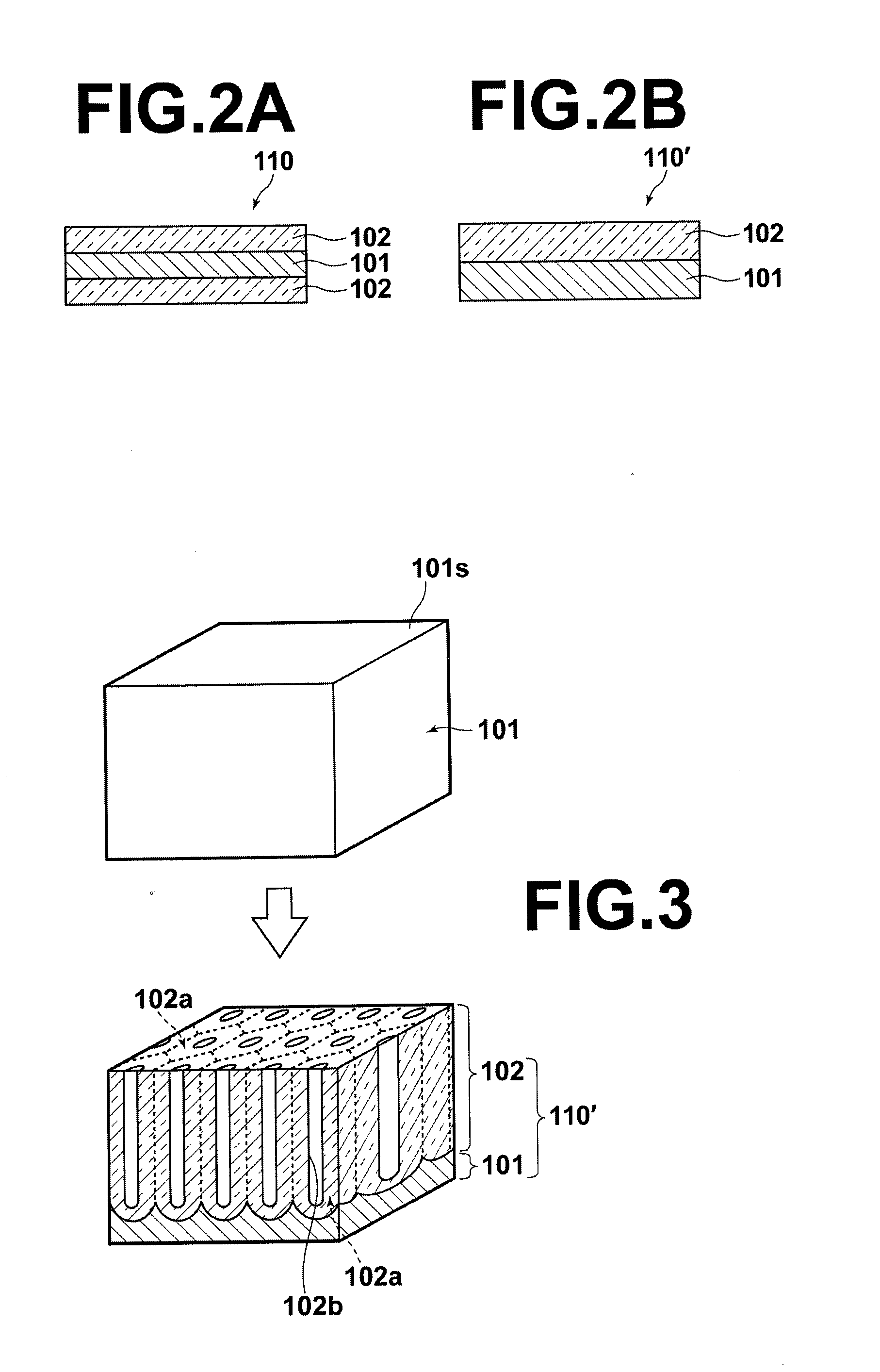
III-V group nitride system semiconductor self-standing substrate, method of making the same and III-V group nitride system semiconductor wafer
ActiveUS20060033119A1Improve crystal qualityLess distortionPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingDensity distribution
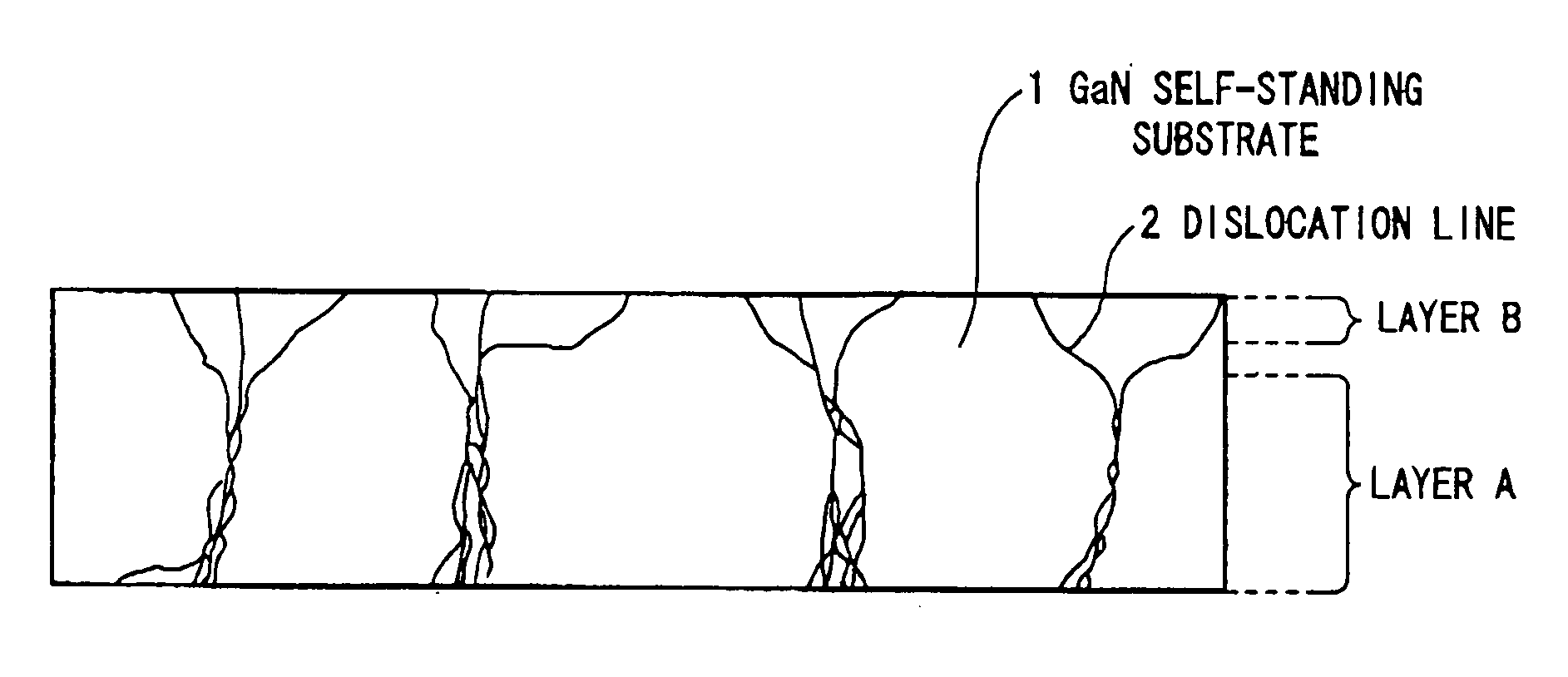
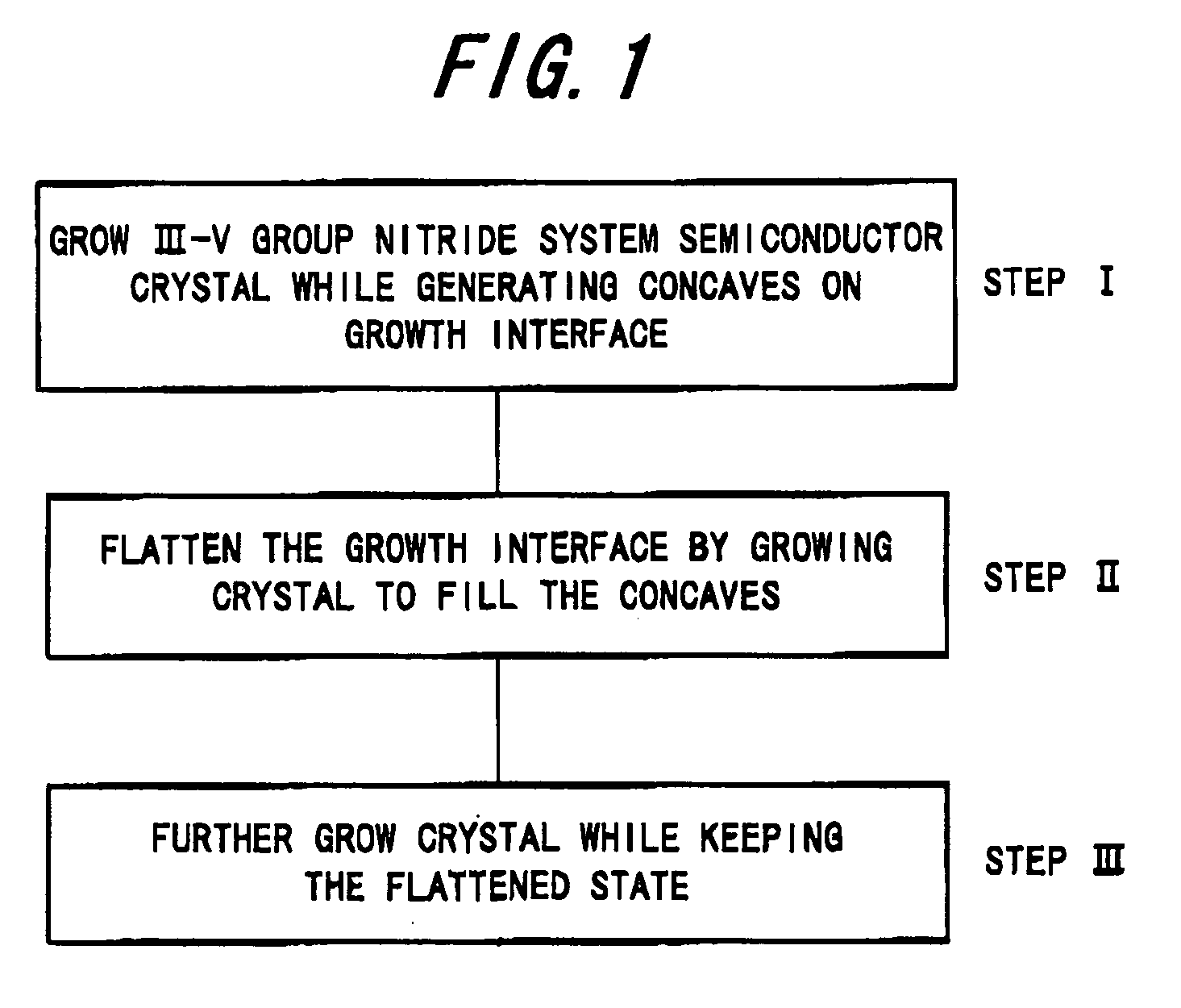
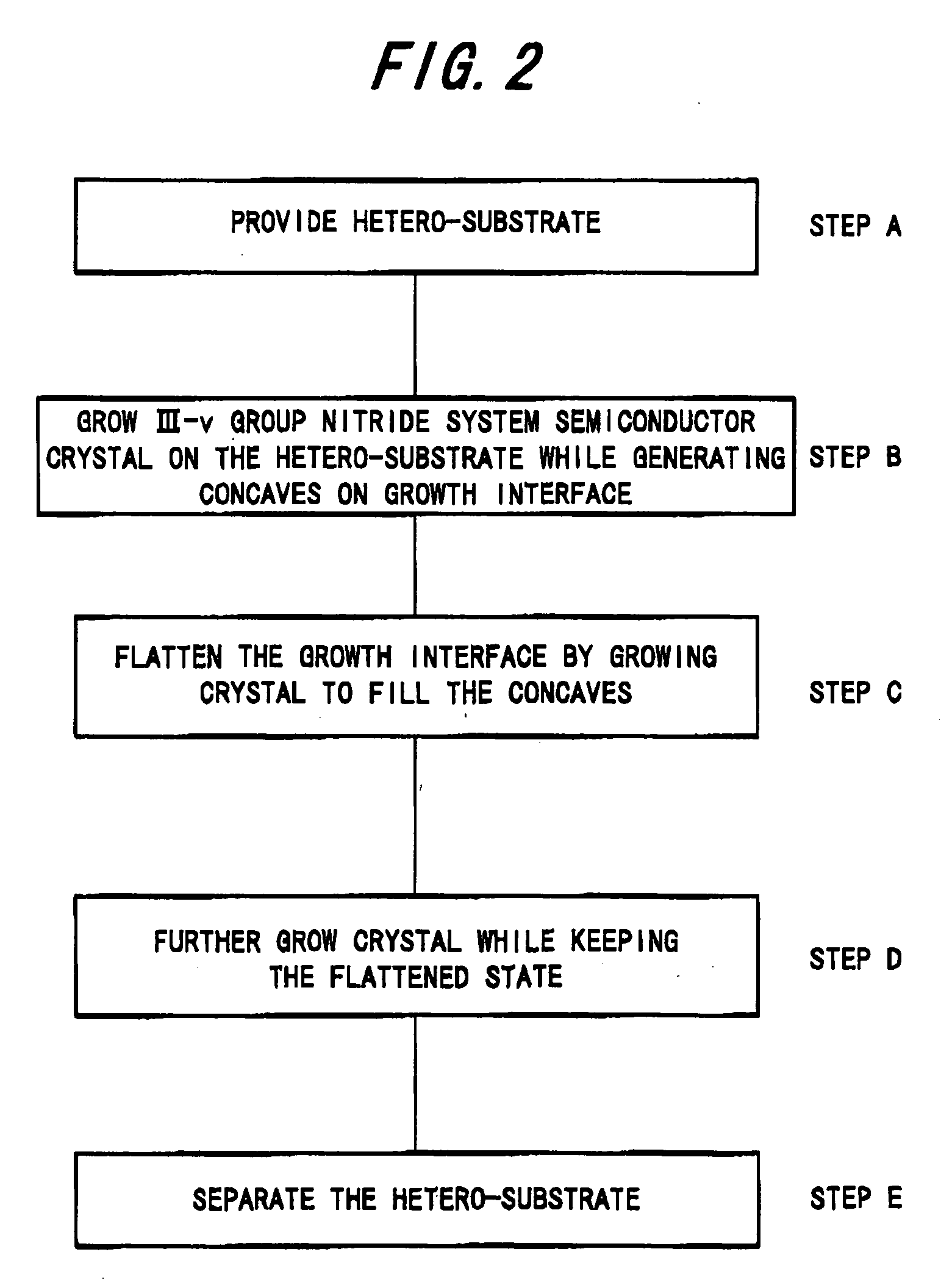
A III-V group nitride system semiconductor self-standing substrate has: a first III-V group nitride system semiconductor crystal layer that has a region with dislocation lines gathered densely, the dislocation lines being gathered substantially perpendicular to a surface of the substrate, and a region with dislocation lines gathered thinly; and a second III-V group nitride system semiconductor crystal layer that is formed up to 10 μm from the surface of the substrate on the first III-V group nitride system semiconductor crystal layer and that has a dislocation density distribution that is substantially uniform.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20130134478A1Lower resistanceImprove breakdown voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
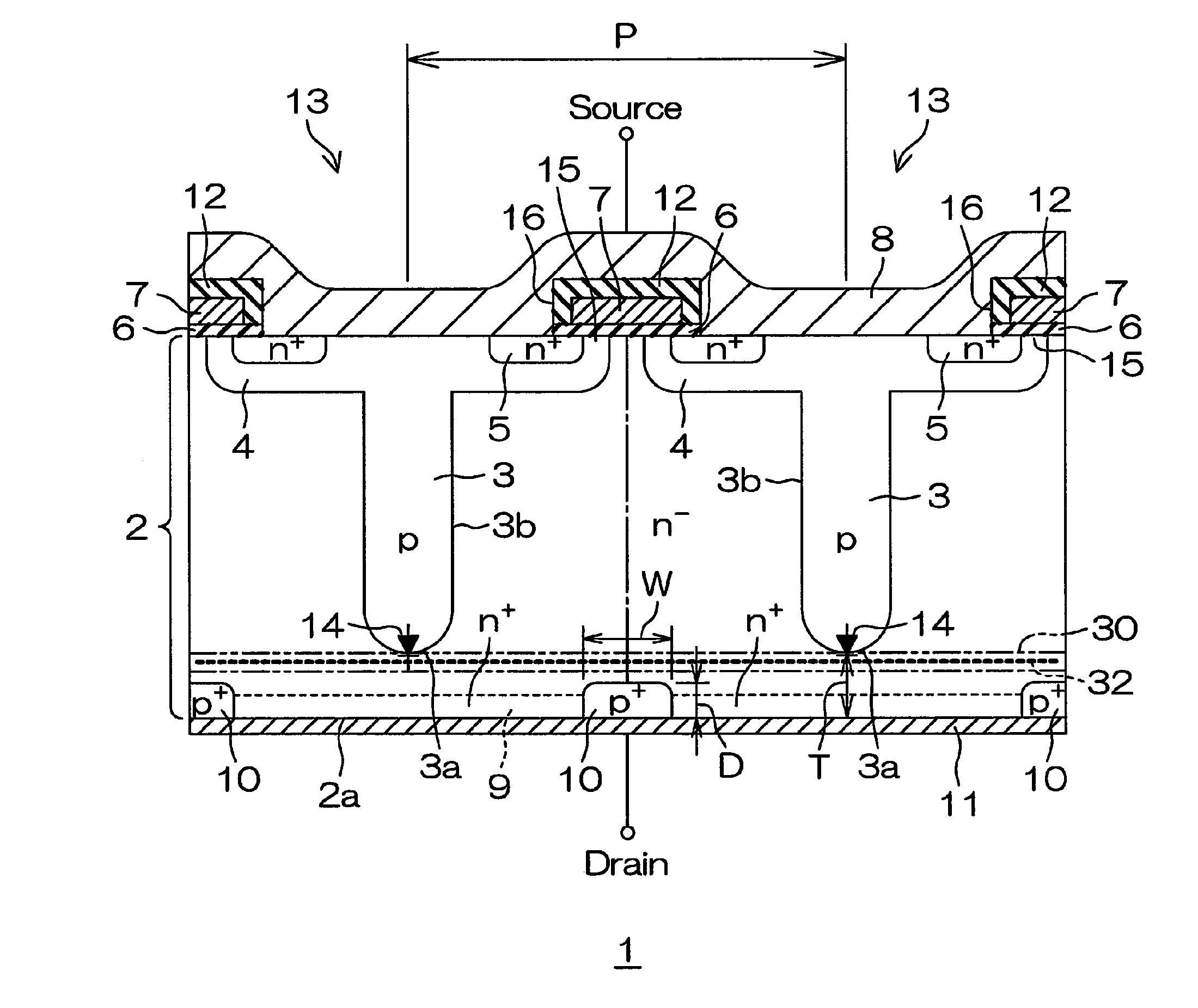
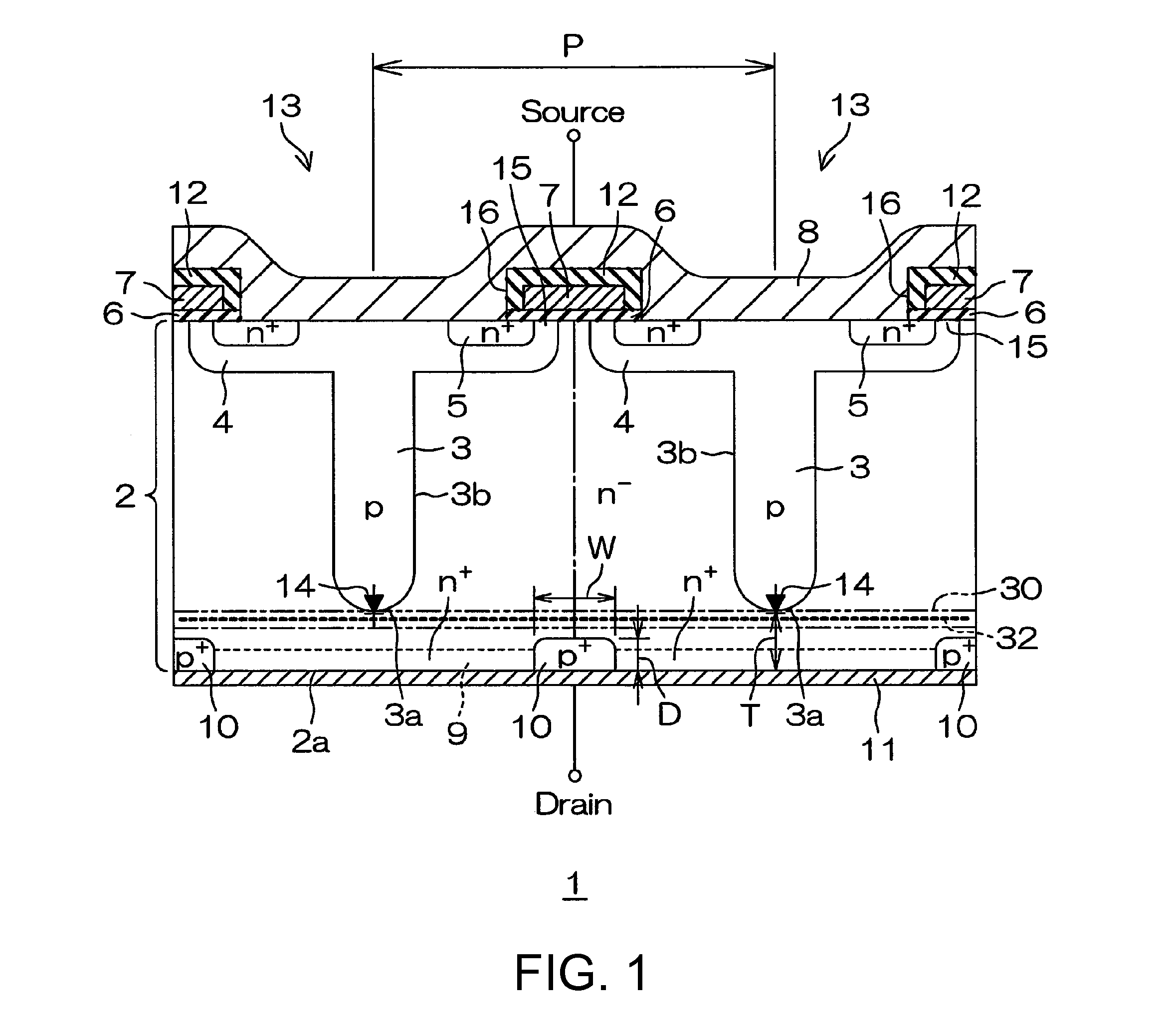
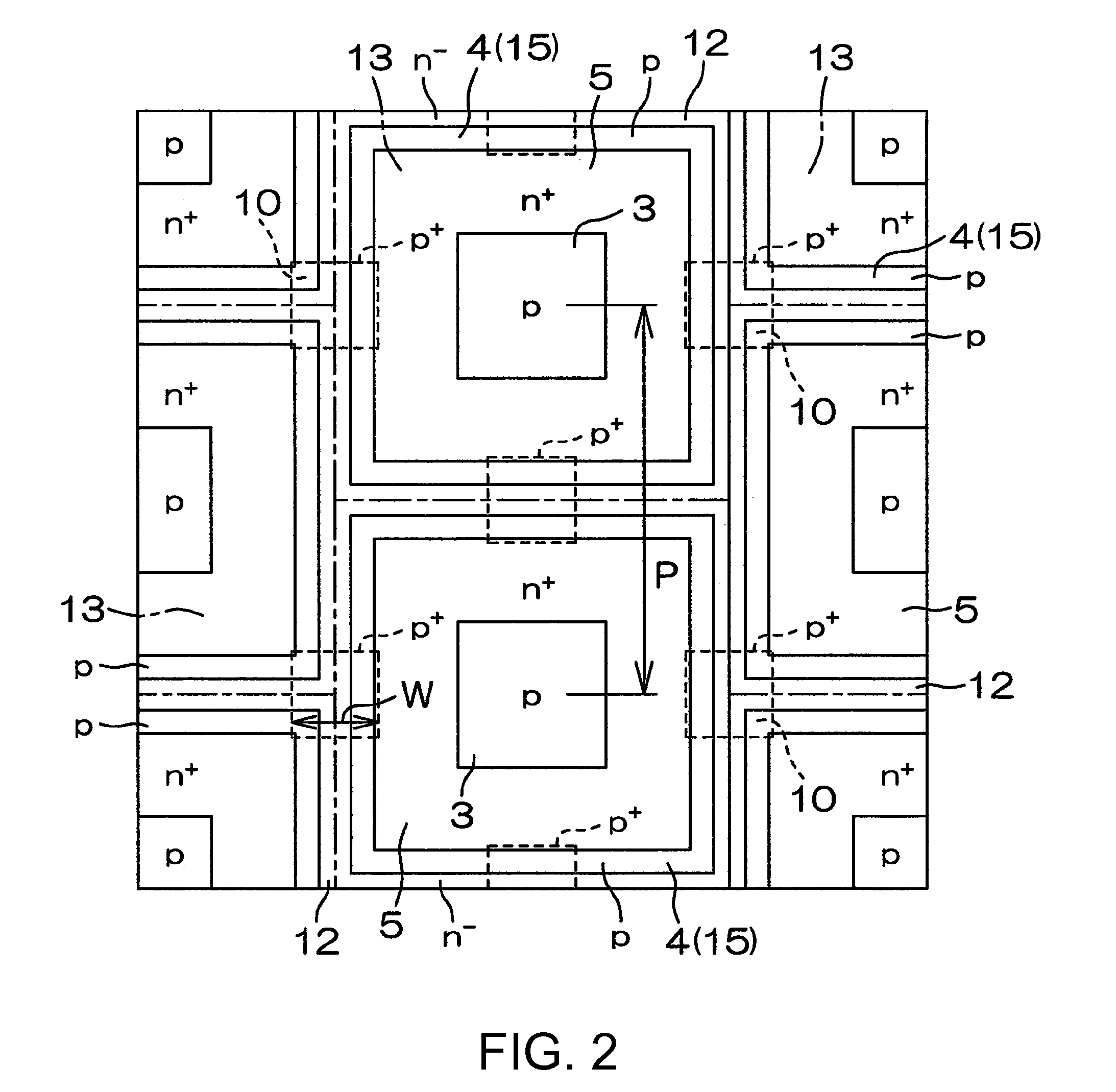
A semiconductor device includes: an n−-type base layer; a p-type base layer formed in a part of a front surface portion of the n−-type base layer; an n+-type source layer formed in a part of a front surface portion of the p-type base layer; a gate insulating film formed on the front surface of the p-type base layer between the n+-type source layer and the n−-type base layer; a gate electrode that faces the p-type base layer through the gate insulating film; a p-type column layer formed continuously from the p-type base layer in the n−-type base layer; a p+-type collector layer formed in a part of a rear surface portion of the n−-type base layer; a source electrode electrically connected to the n+-type source layer; and a drain electrode electrically connected to the n−-type base layer and to the p+-type collector layer.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
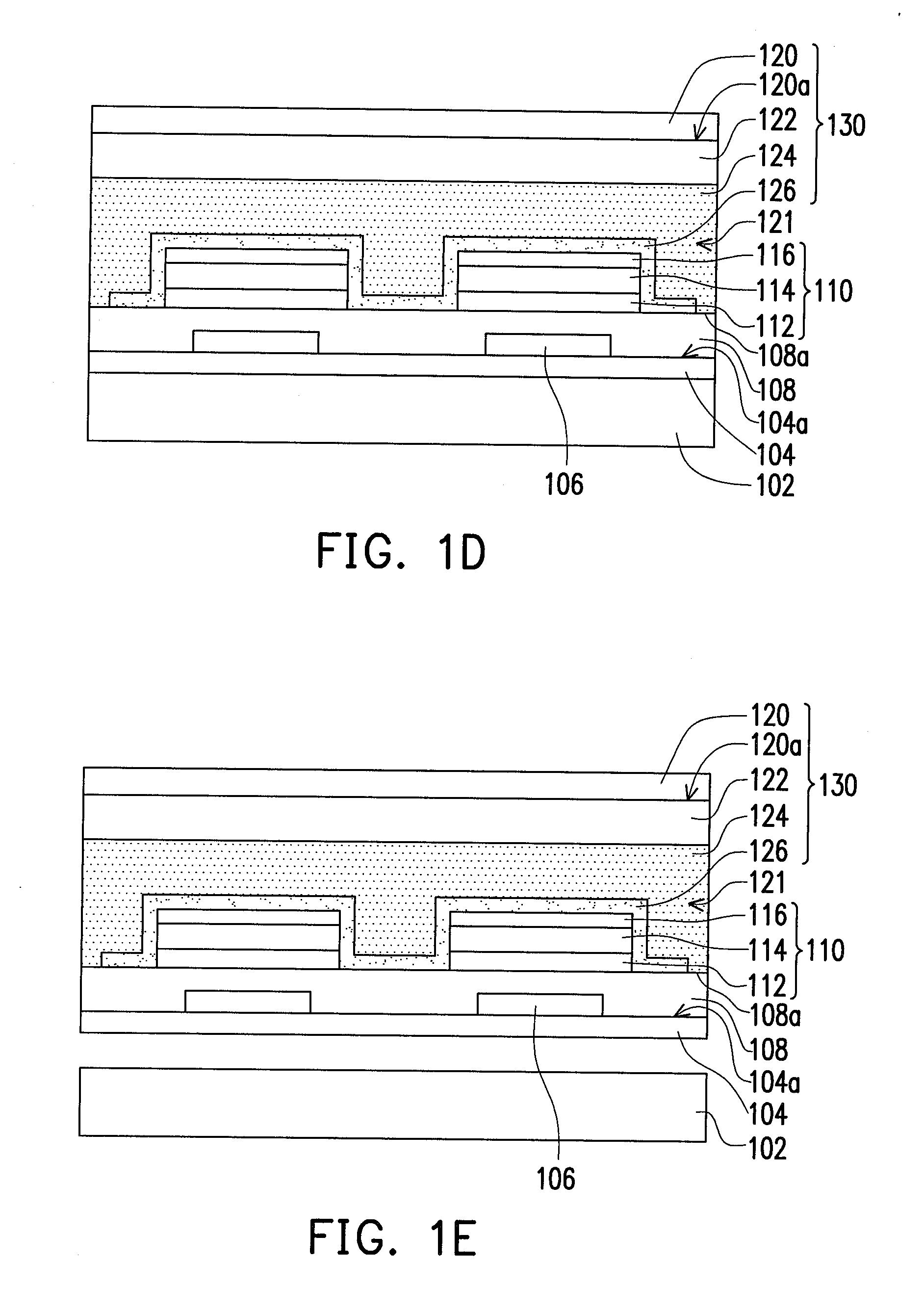
InactiveUS20060145293A1Simplify the manufacturing processImprove device characteristicsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetal interconnectInsulation layer
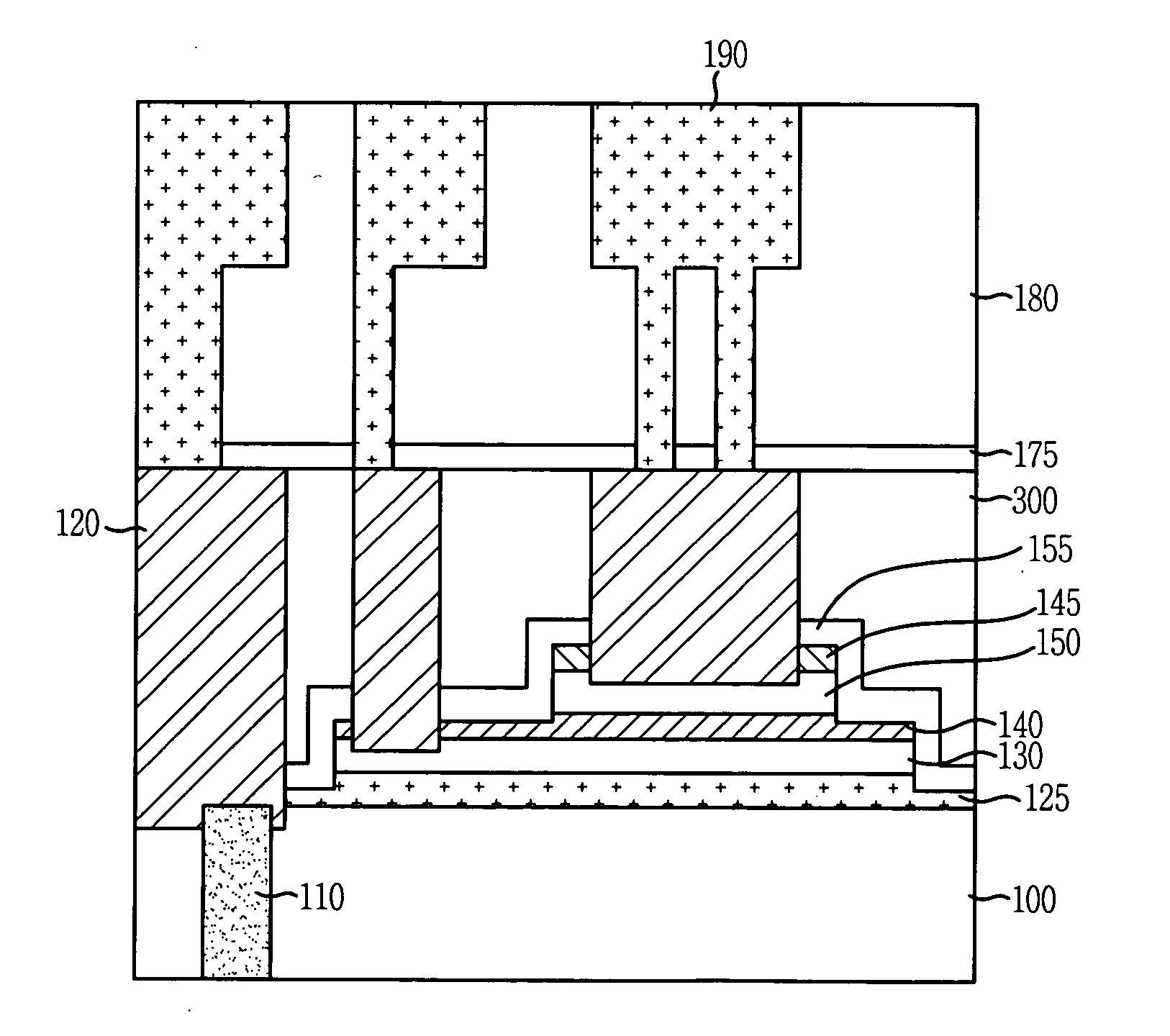
A semiconductor device and a method for fabricating the same are provided. The method includes: forming a contact plug passing through an inter-layer insulation layer; sequentially forming a lower electrode layer, a dielectric layer and an upper electrode layer on the inter-layer insulation layer; patterning the upper electrode layer; patterning the dielectric layer and the lower electrode layer, thereby obtaining a capacitor including an upper electrode, a patterned dielectric layer and a lower electrode; and sequentially forming a first metal interconnection line connected with the contact plug and second metal interconnection lines connected with the capacitor.
Owner:ATRIA TECH INC
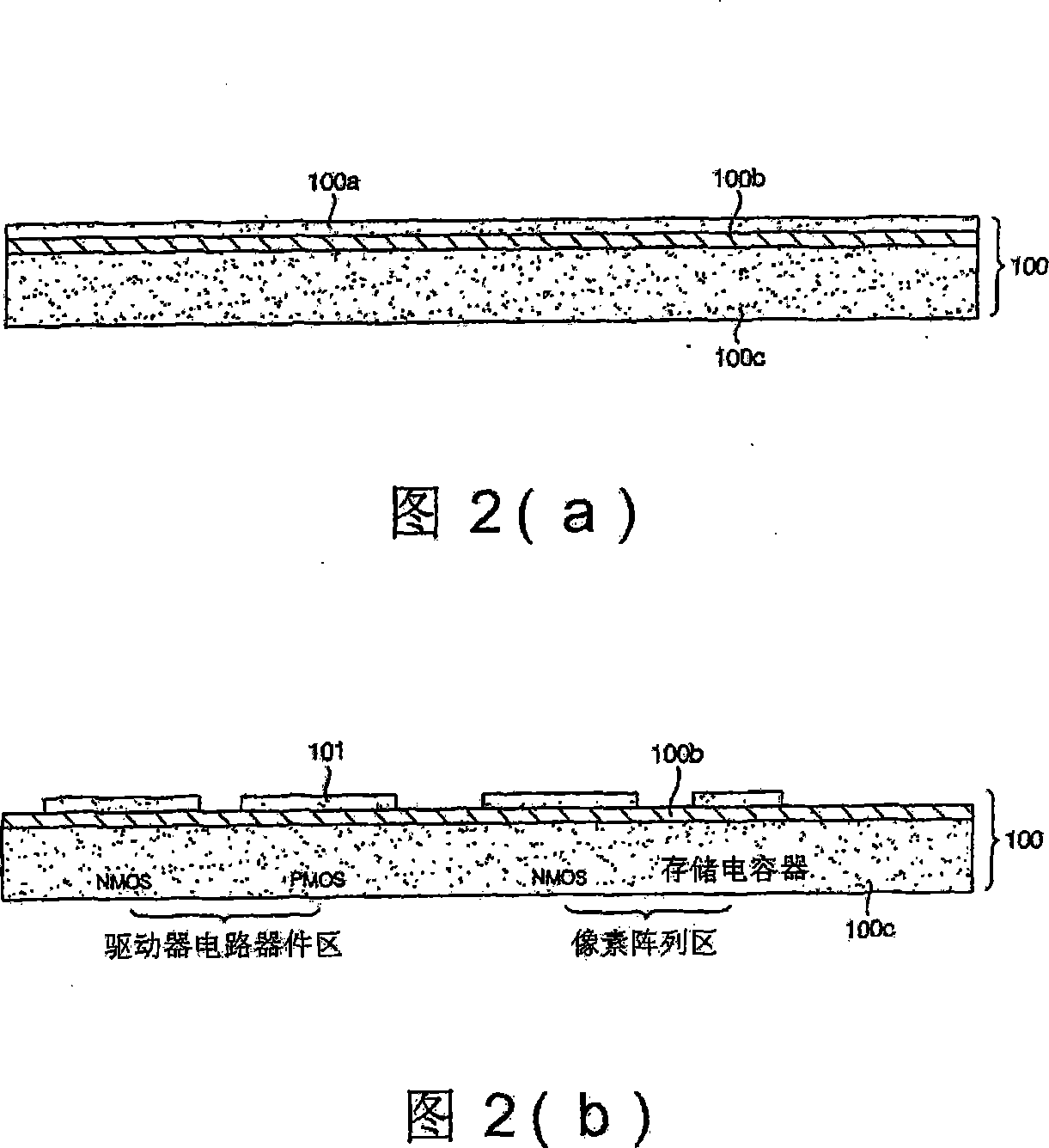
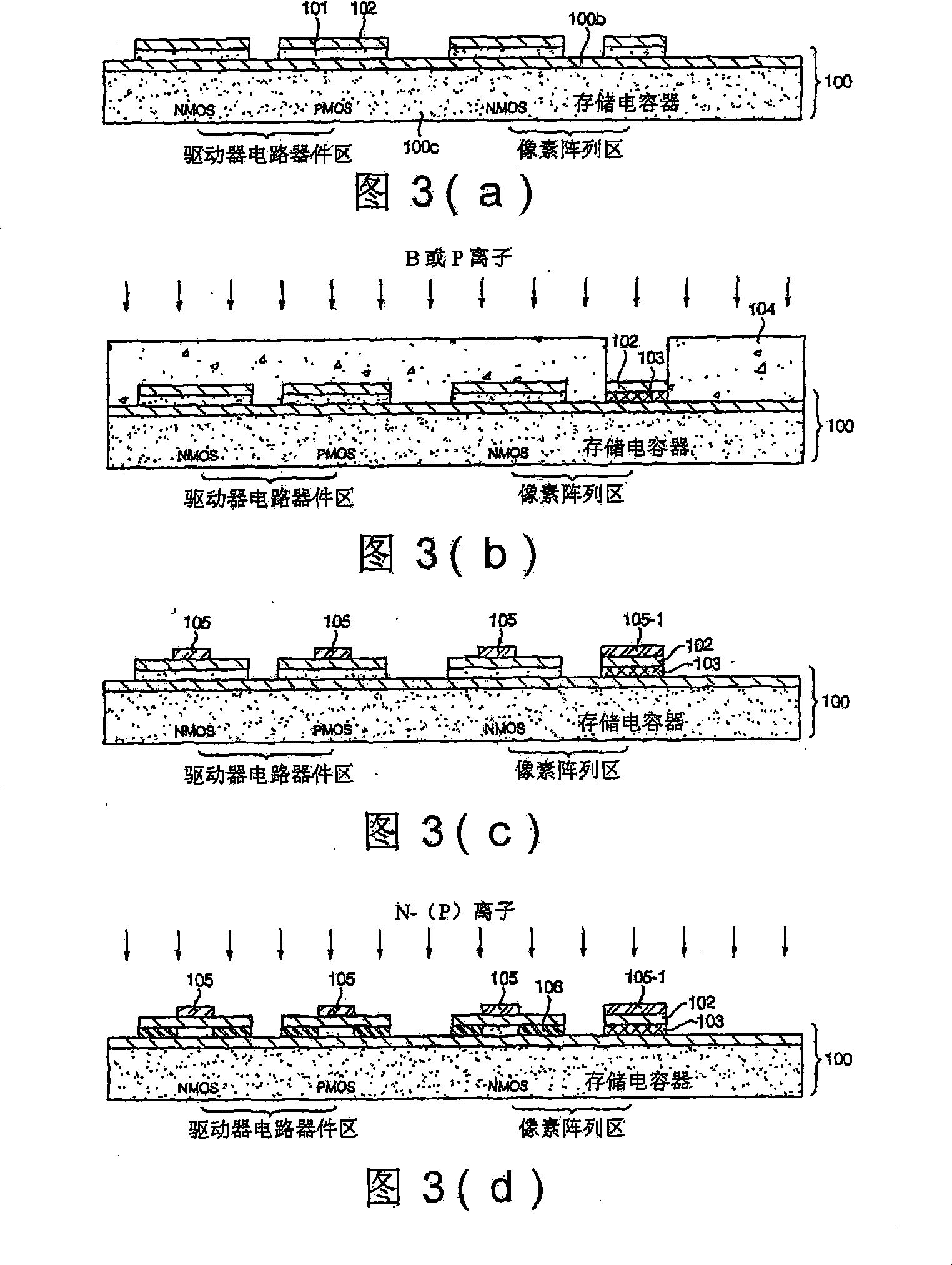
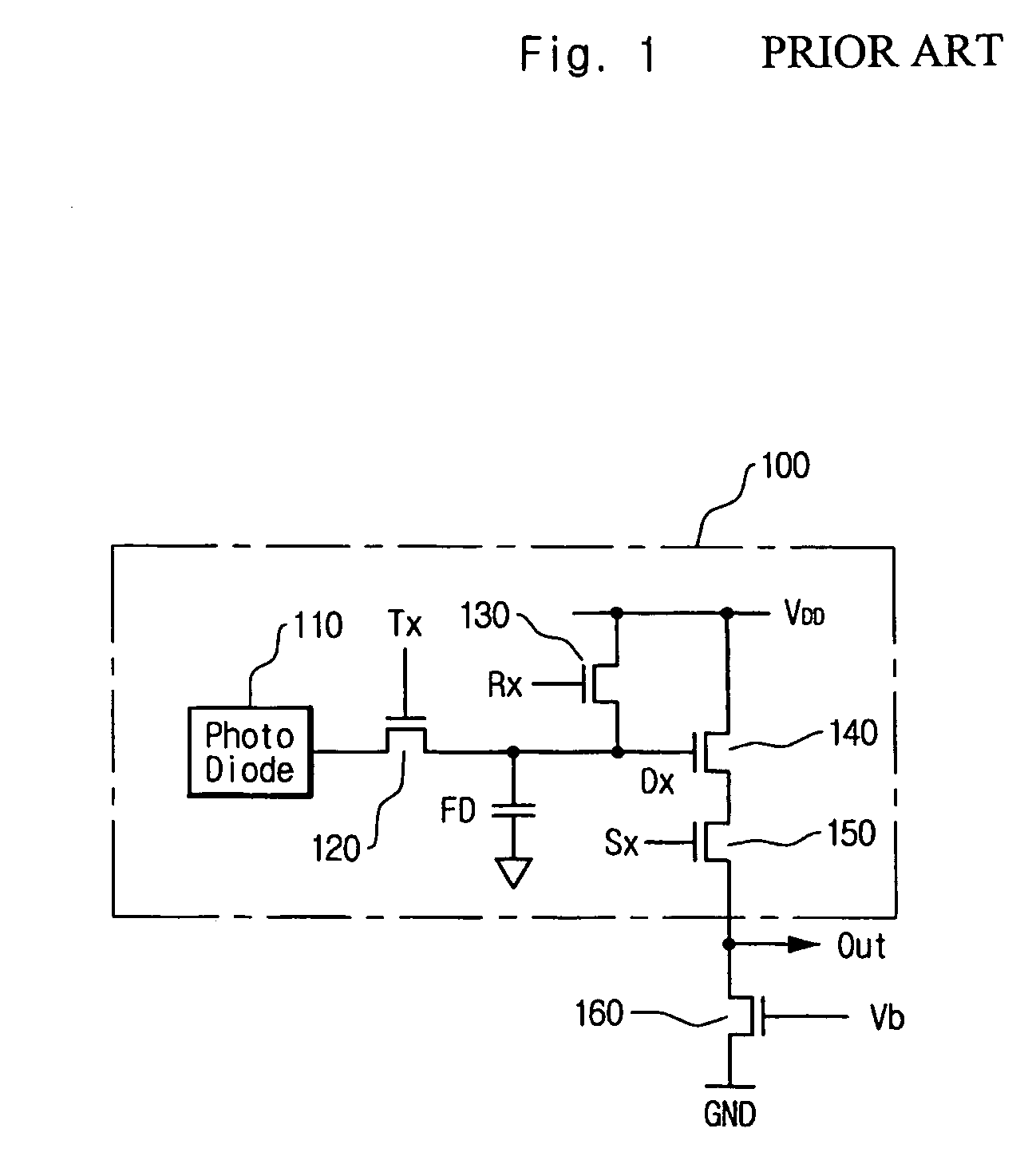
CMOS image sensor and method for manufacturing the same
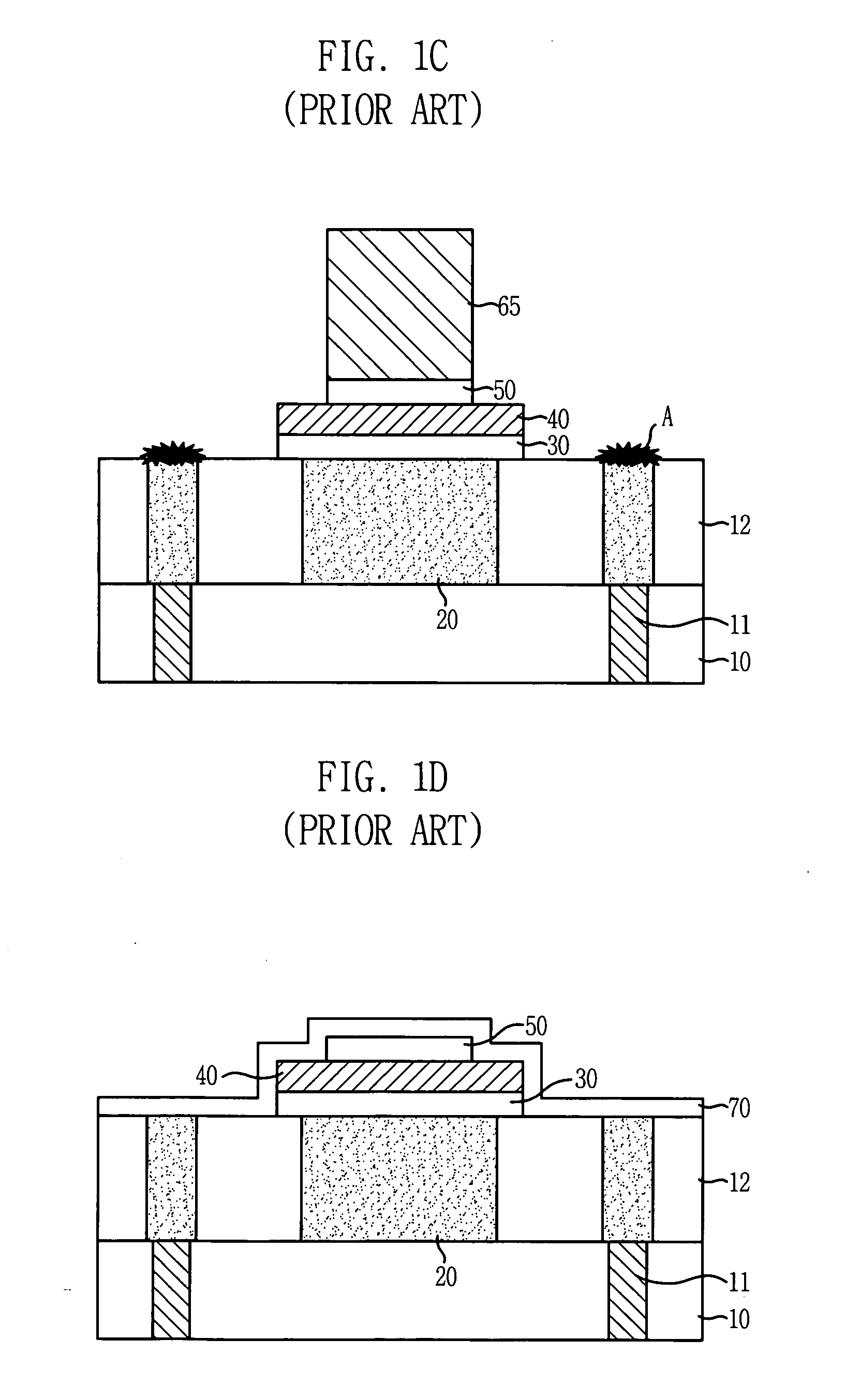
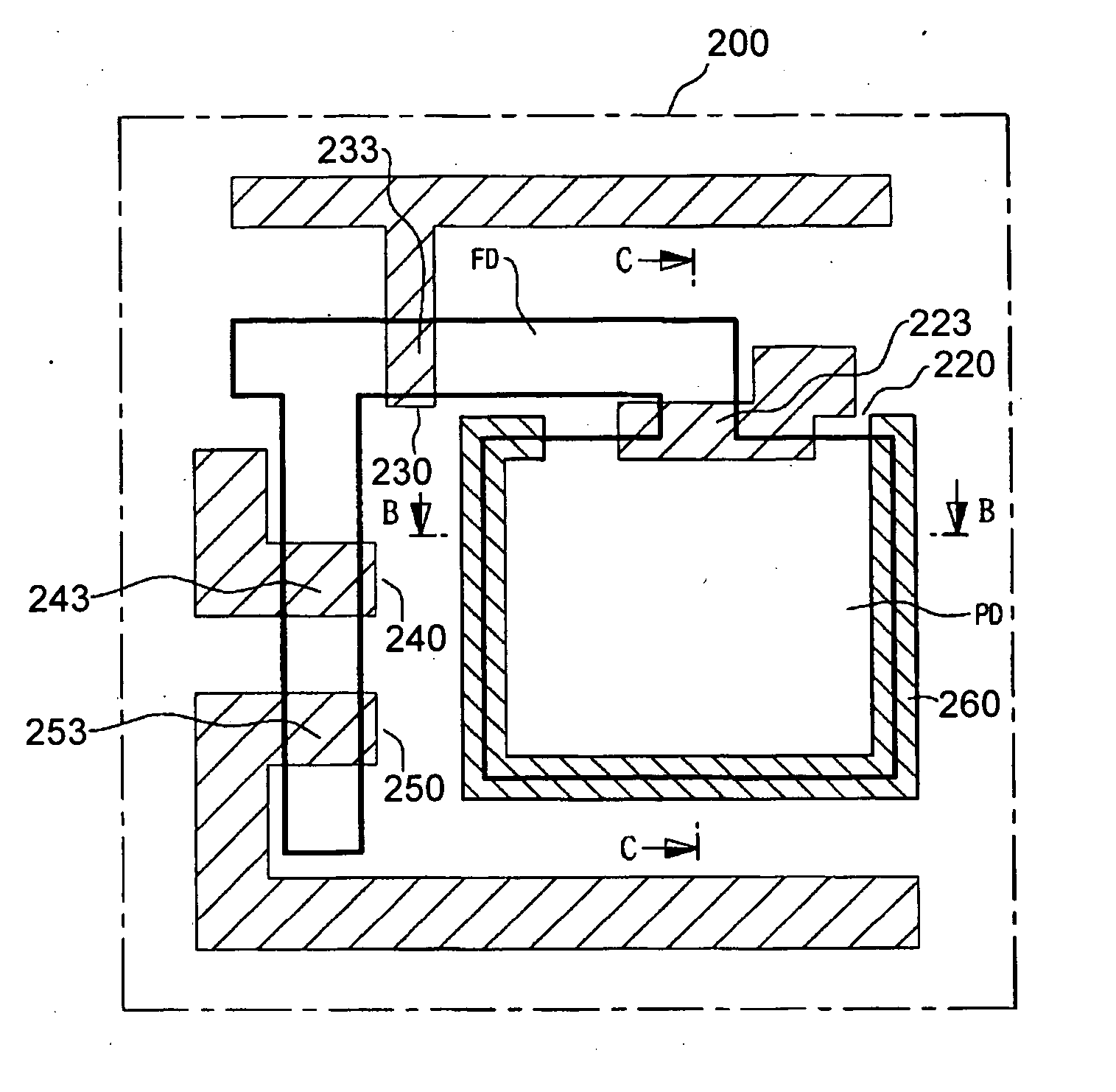
InactiveUS20050062084A1Reduce dark currentImprove device characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSEngineering
A CMOS image sensor and a manufacturing method thereof, wherein the gates of several transistors of the CMOS image sensor are formed in an active region defined by an isolation region for a unit pixel of the CMOS image sensor, and a passivation layer composed of insulating layer is formed on the semiconductor substrate. Impurities are ion-implanted into the active region to form one or more diffusion regions of a photo diode of the CMOS image sensor, wherein the passivation layer prevents a boundary portion of the active region from being ion-implanted. Thus, damages by ion implantation at the boundary portion between the diffusion region for the photo diode and the isolation region are prevented, and the dark current of the CMOS image sensor is reduced.
Owner:DONGBUANAM SEMICON
Semiconductor light-emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050139856A1Improve device characteristicsImproving device characteristicOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsCurrent limitingEngineering
A semiconductor light-emitting device capable of improving device characteristics such as life and reliability is provided. A current confinement layer includes a non-oxidized region made of AlAs or the like corresponding to a current injection region in an active layer, and an oxidized region made of aluminum oxide corresponding to a non-current injection region. The oxidized region is formed by forming a non-oxidized layer made of AlAs or the like and then oxidizing part of the non-oxidized layer at a temperature from 240° C. to less than 375° C. The thickness of the oxidized region is preferably from 10 nm to 1000 nm. The width of the one side of the oxidized region is one time or more of the width of the non-oxidized region or seven times or less thereof The distance between current confinement layer and the active layer is preferably 50 nm or more, or 500 nm or less, and more preferably 180 nm or more.
Owner:SONY CORP
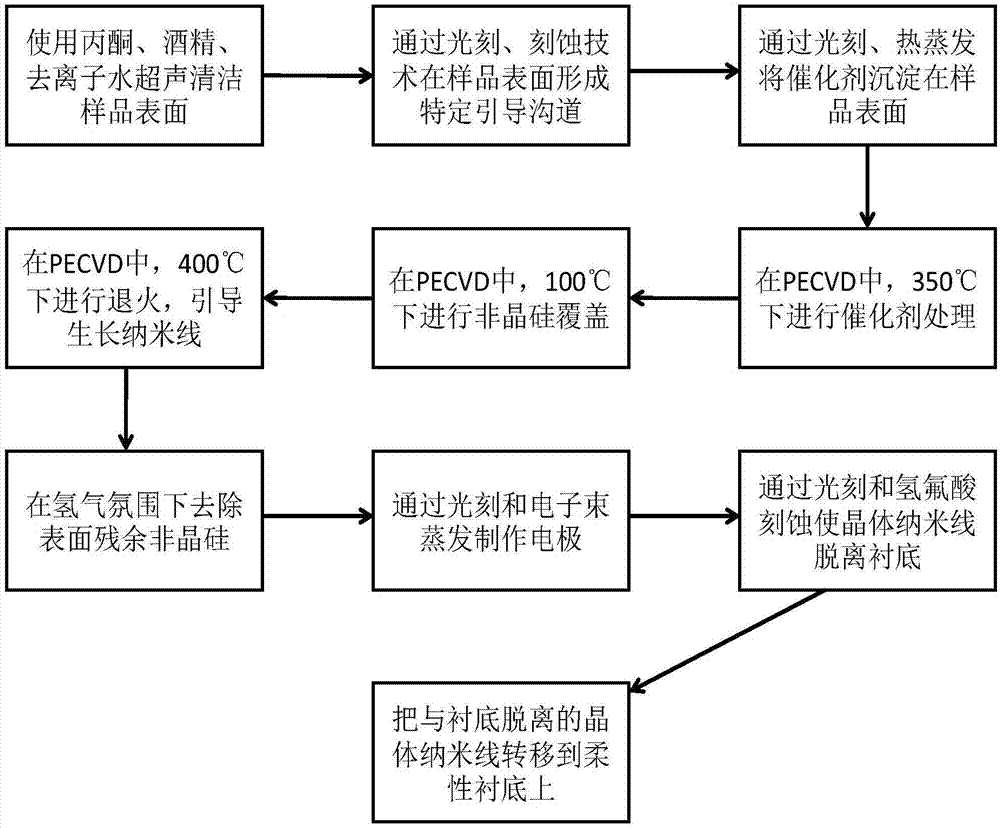
Preparation method of stretchable crystalline semiconductor nanowire based on linear design and guidance of planar nanowire
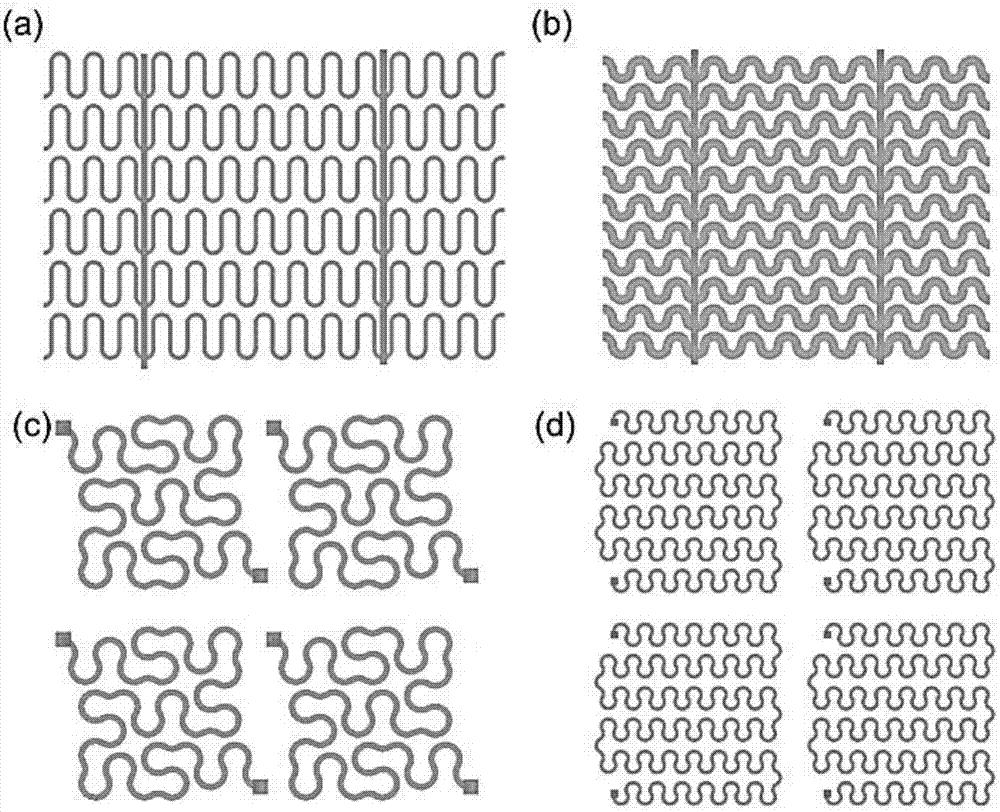
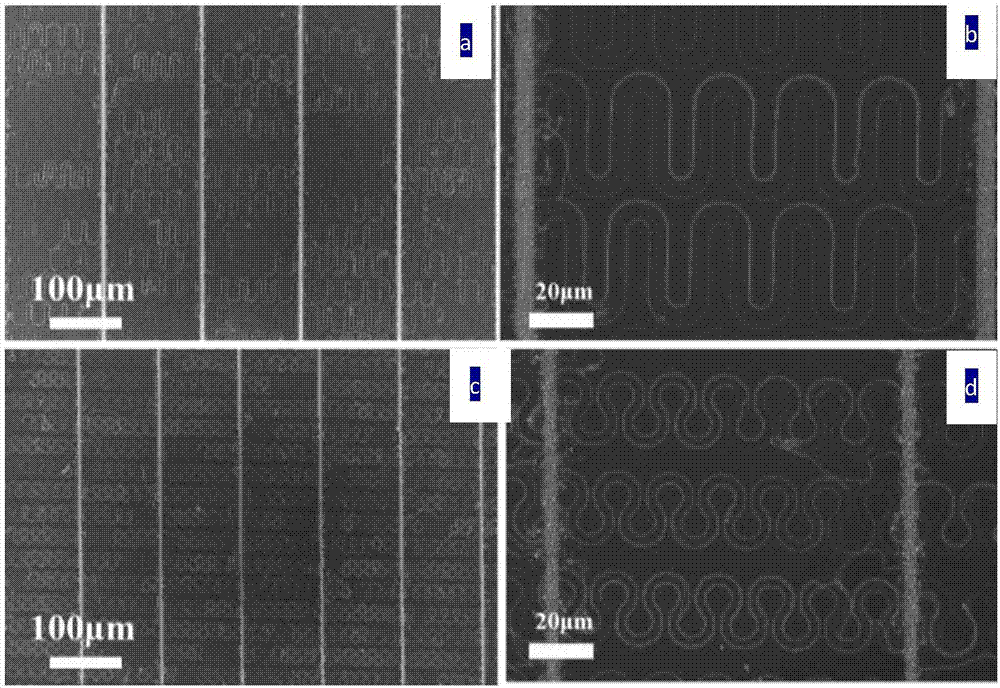
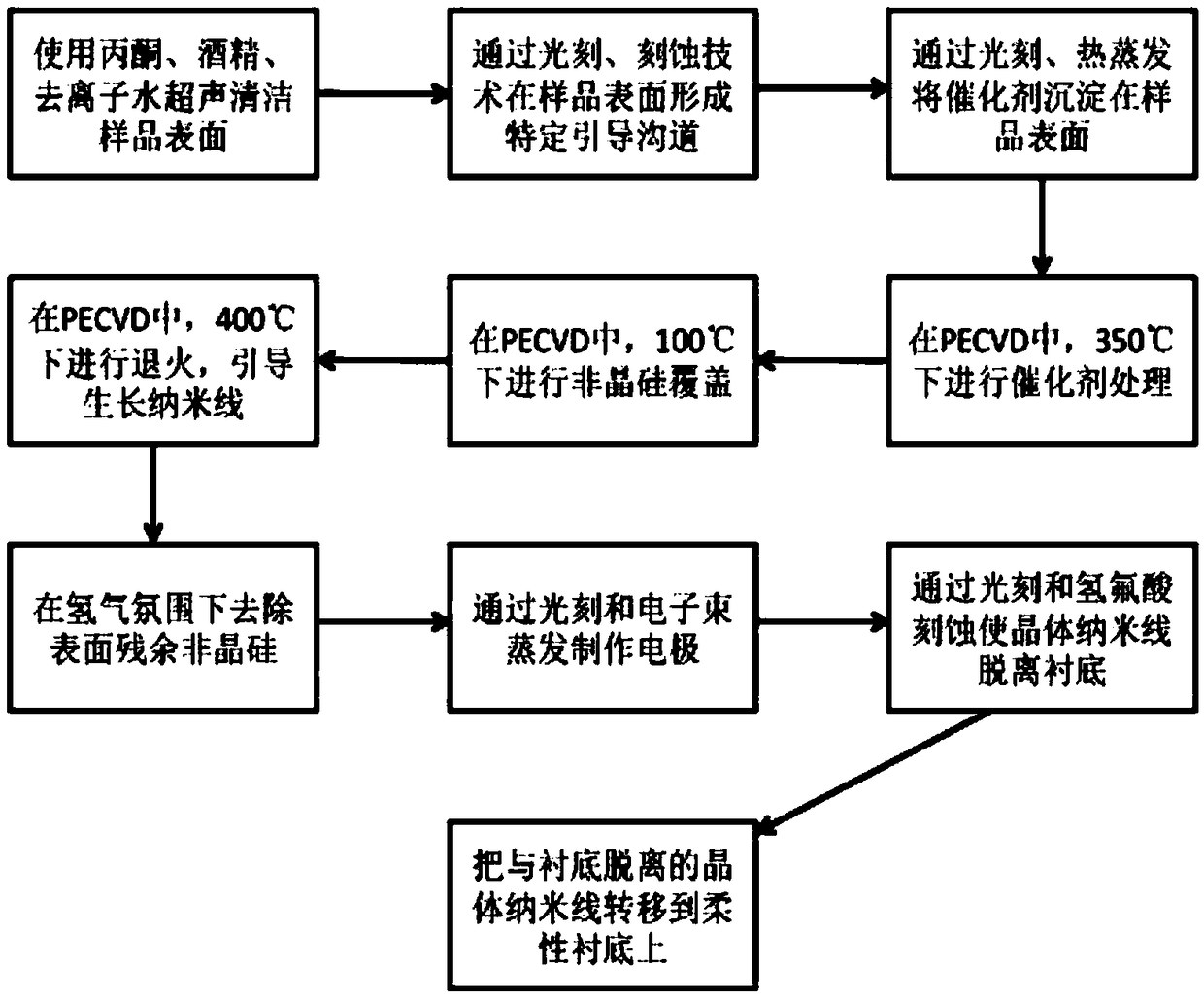
InactiveCN107460542ARealize self-positioningAchieve self-orientationPolycrystalline material growthNanoinformaticsSurface patternNanowire
A preparation method of a stretchable crystalline semiconductor nanowire based on linear design and guidance of a planar nanowire comprises the steps that 1, standardized cleaning is conducted on glass, silicon dioxide sheet or a silicon wafer substrate; 2, a photoetching or surface pattern etching technology is utilized to etch a step having a certain depth on the surface of the substrate; 3, the crystal nanowire with the diameter of about 130 + / - 20 nm accurately grows along a guiding channel through a planar nanowire guidance growth method to form a nanowire spring array; 4, a metal film is treatment in a PECVD system by utilizing reductive plasmas including hydrogen and the like to form nano metal catalysis particles in the range from dozens of nanometers to one micrometer; 5, an amorphous semiconductor layer having appropriate thickness deposits in a covering mode to serve as a precursor medium; 6, annealing growth is performed in a vacuum or nonoxidative atmosphere, and an amorphous layer is absorbed and a crystalline nanowire structure deposits in the way at the temperature of 250 DEG C or above.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Semiconductor device and production method thereof
ActiveUS20110147815A1Improve device characteristicsStrong strainSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
Disclosed is a semiconductor device wherein device characteristics are improved by applying a strong stress to a channel region. The semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate, a gate insulating film formed over a first plane of the semiconductor substrate, a gate electrode formed over the gate insulating film, a gate sidewall insulating film formed over the sidewall of the gate electrode, source / drain diffusion layer regions into which impurities are implanted, the source / drain diffusion layer regions being adjacent to a channel region formed in the semiconductor substrate below the gate electrode, and a stress applying film formed over the source / drain diffusion layer regions except over the upper part of the gate electrode; and recesses or protrusions are formed in the region where the source / drain diffusion layer regions are formed over the first plane of the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
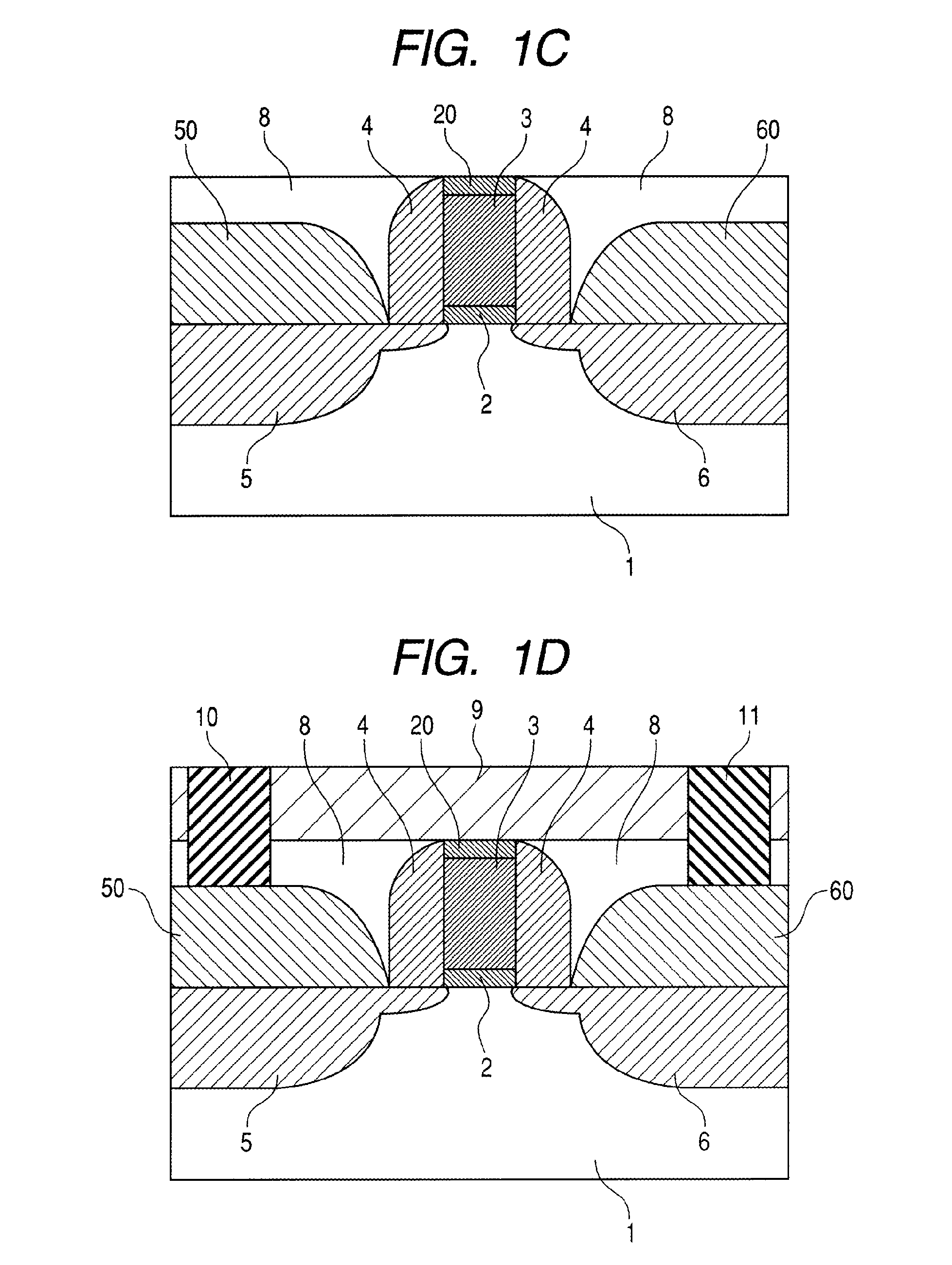
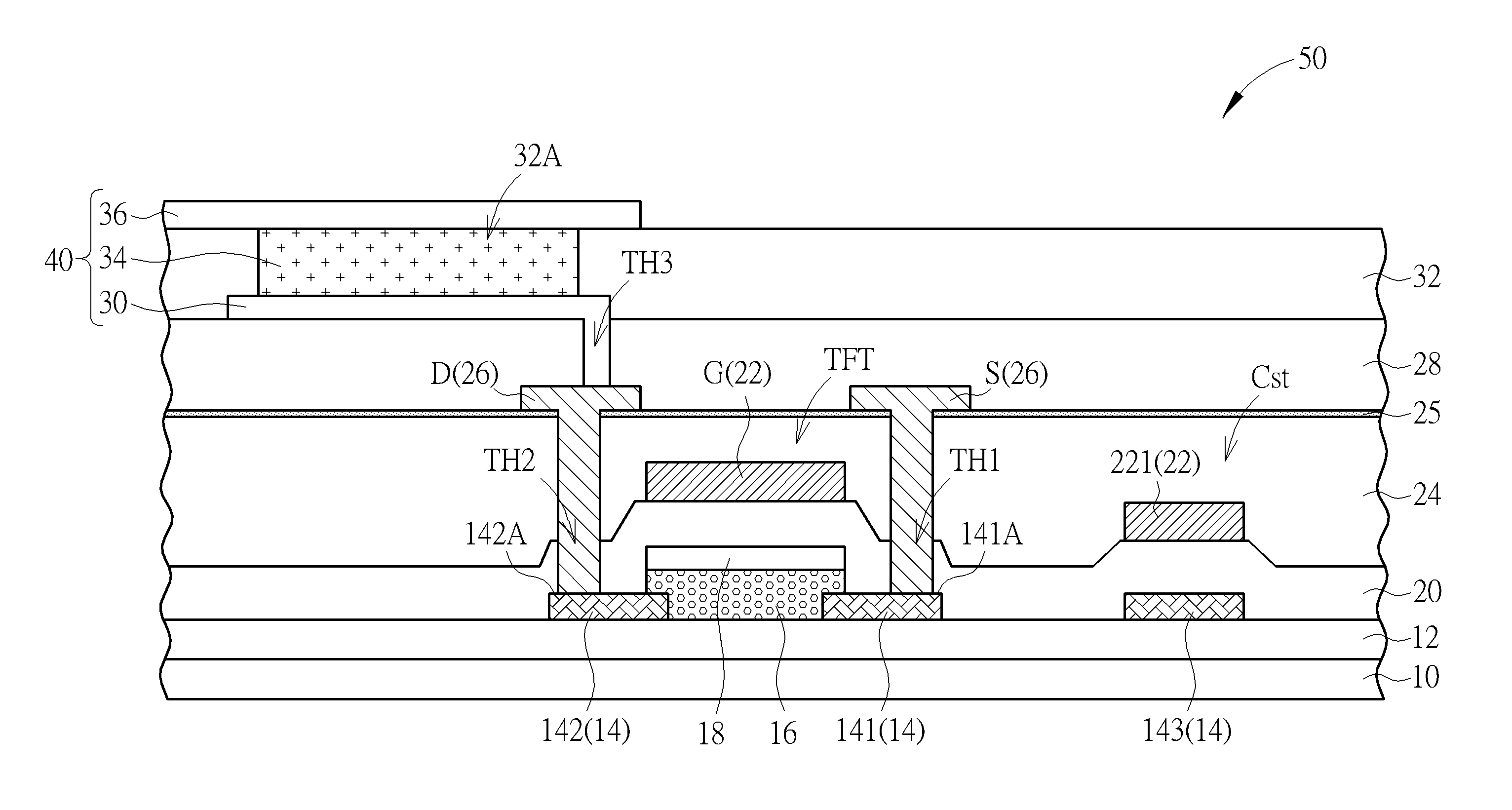
Pixel structure and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20150214248A1Avoid defectsImprove featuresSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerEngineering
A pixel structure includes a thin film transistor device. The thin film transistor device includes a first connection electrode, a second connection electrode, an oxide semiconductor channel layer, a gate insulation layer, a gate electrode, a dielectric layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode. The oxide semiconductor channel layer at least partially covers a top surface of the first connection electrode and a top surface of the second connection electrode. The gate electrode is disposed on the gate insulation layer. The dielectric layer is disposed on the gate electrode and the gate insulation layer. The gate insulation layer and the dielectric layer have a first contact hole at least partially exposing the top surface of the first connection electrode and a second contact hole at least partially exposing the top surface of the second connection electrode. The source electrode is electrically connected to the first connection electrode via the first contact hole, and the drain electrode is electrically connected to the second connection electrode via the second contact hole.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
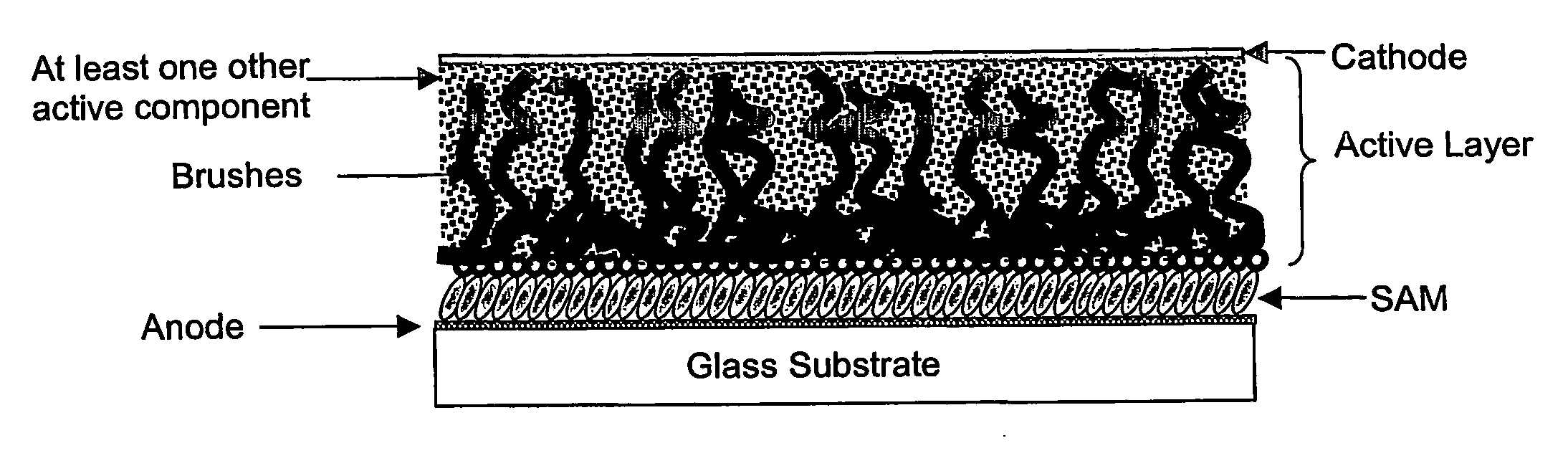
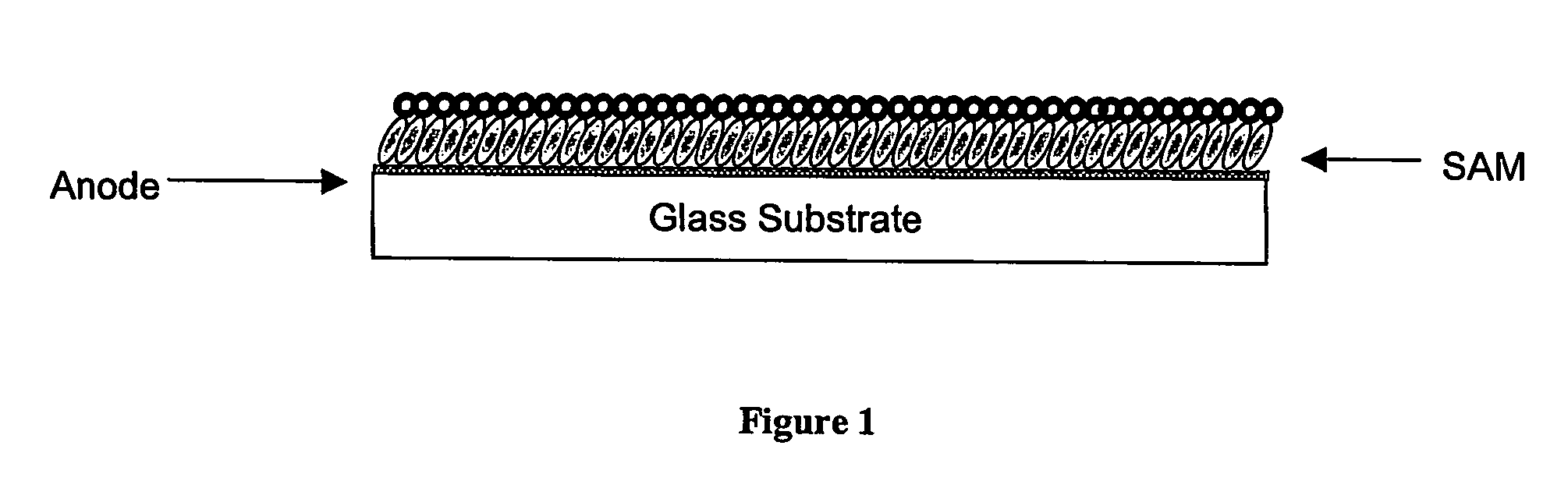
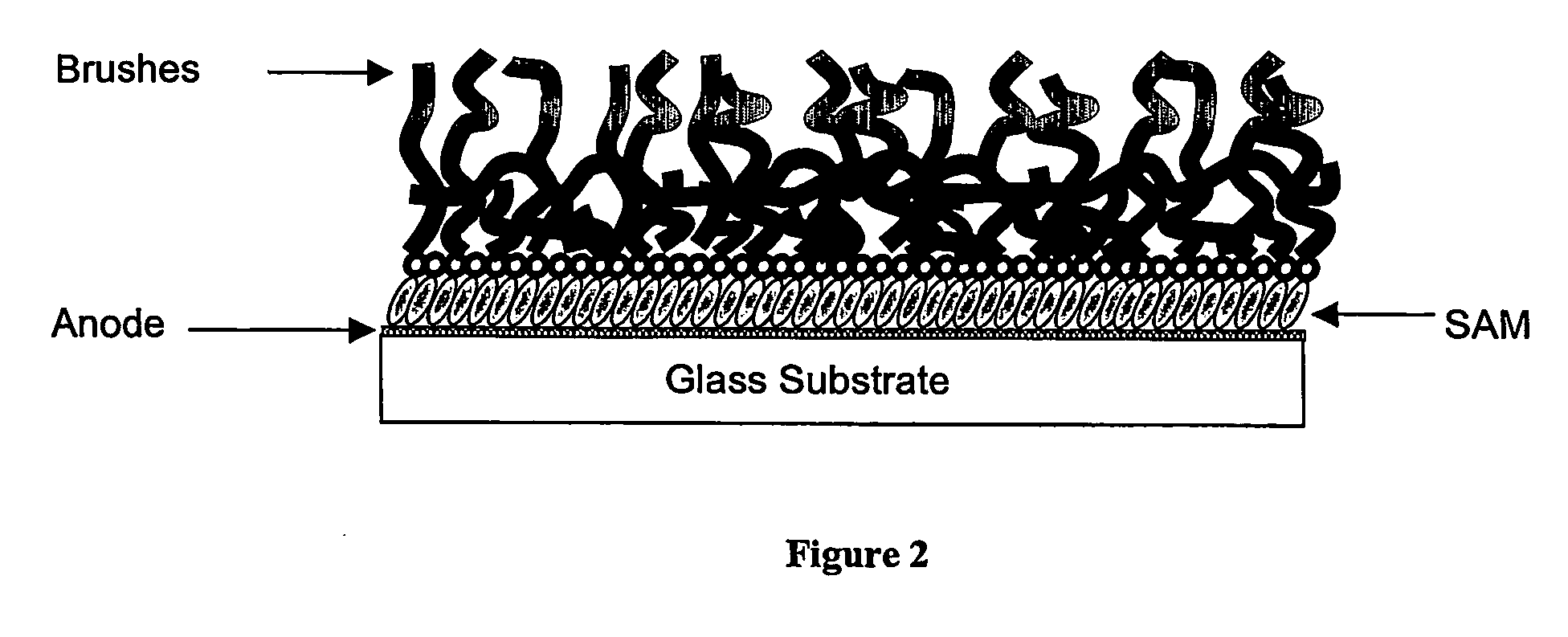
Organic electronic devices incorporating semiconducting polymer brushes
InactiveUS20070169814A1Improve device characteristicsHigh charge transport performanceMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor materialsPolymer chemistry
An organic electronic device comprises at least two electrodes and a semiconducting layer comprising a mixture of at least one hole-transporting semiconducting material and at least one electron-transporting semiconducting material, wherein at least one of said semiconducting materials is in the form of semiconducting polymer brushes which are attached to the surface of at least one of said electrodes and are in contact with at least one of said other semiconducting materials. Also provided is an organic electronic device comprising at least two electrodes and a semiconducting layer comprising at least one hole-transporting or electron-transporting semiconducting material, wherein said at least one semiconducting material is in the form of semiconducting polymer brushes which are attached to the surface of at least one of said electrodes. Processes for the manufacture of said devices are also provided.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE UNIV TECH SERVICES LTD
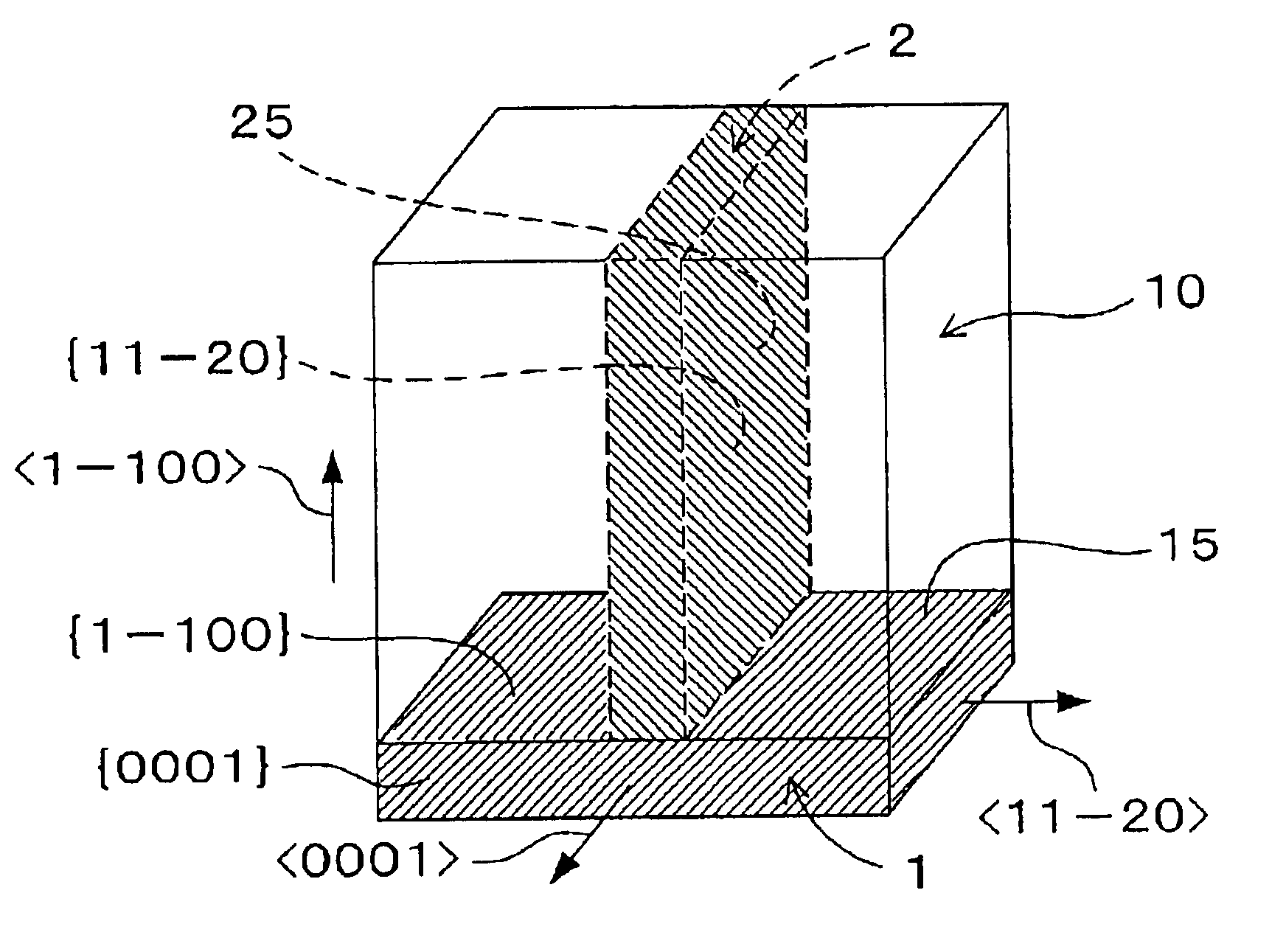
SiC single crystal, method for manufacturing SiC single crystal, SiC wafer having an epitaxial film, method for manufacturing SiC wafer having an epitaxial film, and SiC electronic device
InactiveUS6890600B2Improve device characteristicsLower resistancePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSeed crystalEngineering
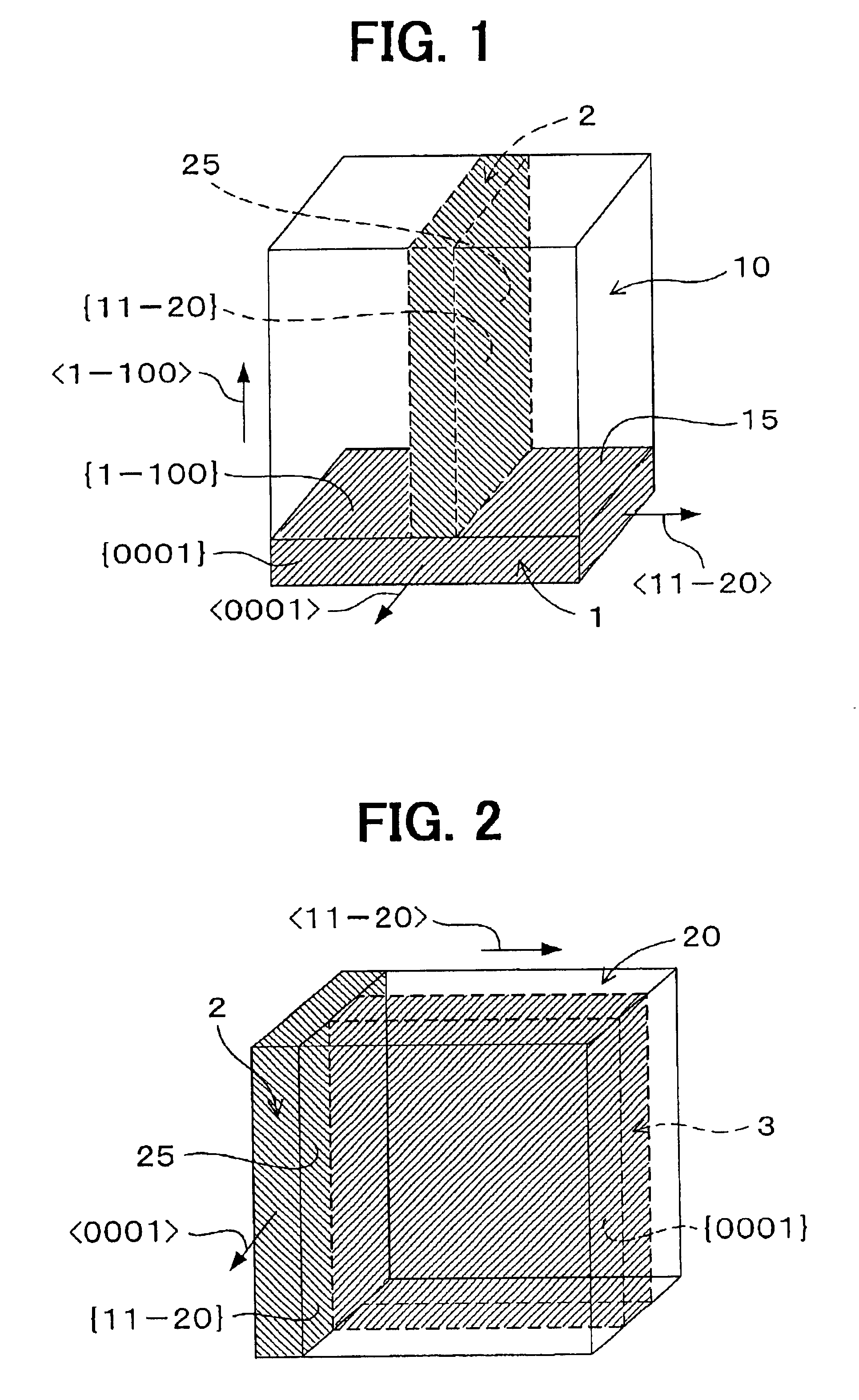
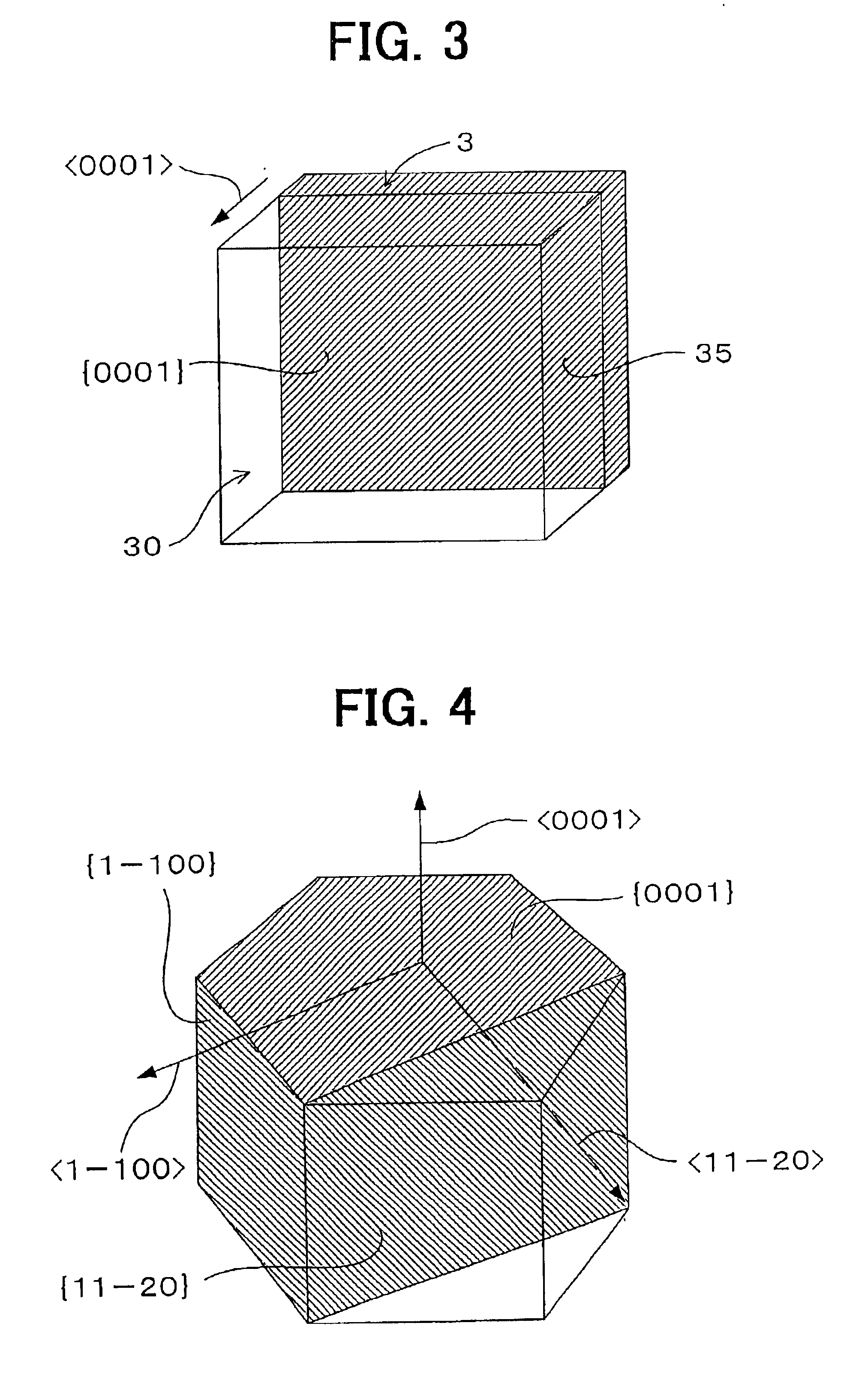
A refined SiC single crystal that includes a small number of defects is provided as follows. At a first growth step, a first seed crystal is formed from a crude SiC single crystal, and a first grown crystal is formed on a first growth surface, which is a plane having an inclination of 20 degrees or smaller from a {1-100} plane or an inclination of 20 degrees or smaller from a {11-20} plane. At an intermediate growth step, an n growth crystal is formed on an n growth surface, which is a plane having an inclination of 45 to 90 degrees from an (n−1) growth surface and an inclination of 60 to 90 degrees from a {0001} plane. At a final growth step, a final SiC single crystal is formed on a final growth surface, which has an inclination of 20 degrees or smaller from a {0001} plane.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Flexible organic light emitting device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20130099658A1High yieldImprove device characteristicsDischarge tube luminescnet screensFinal product manufactureInsulation layerOrganic light emitting device
A flexible organic light emitting device includes a flexible substrate, an organic light emitting unit and a covering substrate. The organic light emitting unit includes a first electrode layer, a second electrode layer opposing the first electrode, and a light emitting layer, which is disposed between the first and second electrode layers. The covering substrate includes a base film, an insulation layer and an adhesion layer. An inner surface of the base film is facing an inner surface of the flexible substrate, and space is formed there-between. The insulation layer is disposed on the inner surface of the base film, and an adhesive force between the insulation layer and the organic light emitting unit is less than 0.1 N / cm. The adhesion layer is disposed between the insulation layer and the inner surface of the base film, covers the insulation layer and the organic light emitting unit, and fills the space.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
CMOS image sensor and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050062078A1Reduce dark currentImprove dark currentSolid-state devicesDiodeCMOSIsolation layer
A CMOS image sensor and a manufacturing method are disclosed. The gates of the transistors are formed in the active region of the unit pixel, and a diffusion region for the photo diode is defined by an ion implantation of impurities to the semiconductor substrate. The patterns of the photoresist that are the masking layer against ion implantation are formed on the semiconductor substrate in such a manner that they have the boundary portion of the isolation layer so as not to make the boundary of the defined photo diode contact with the boundary of the isolation layer. Damages by an ion implantation of impurities at the boundary portion between the diffusion region for the photo diode and the isolation layer are prevented, which reduces dark current of the COMS image sensor.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
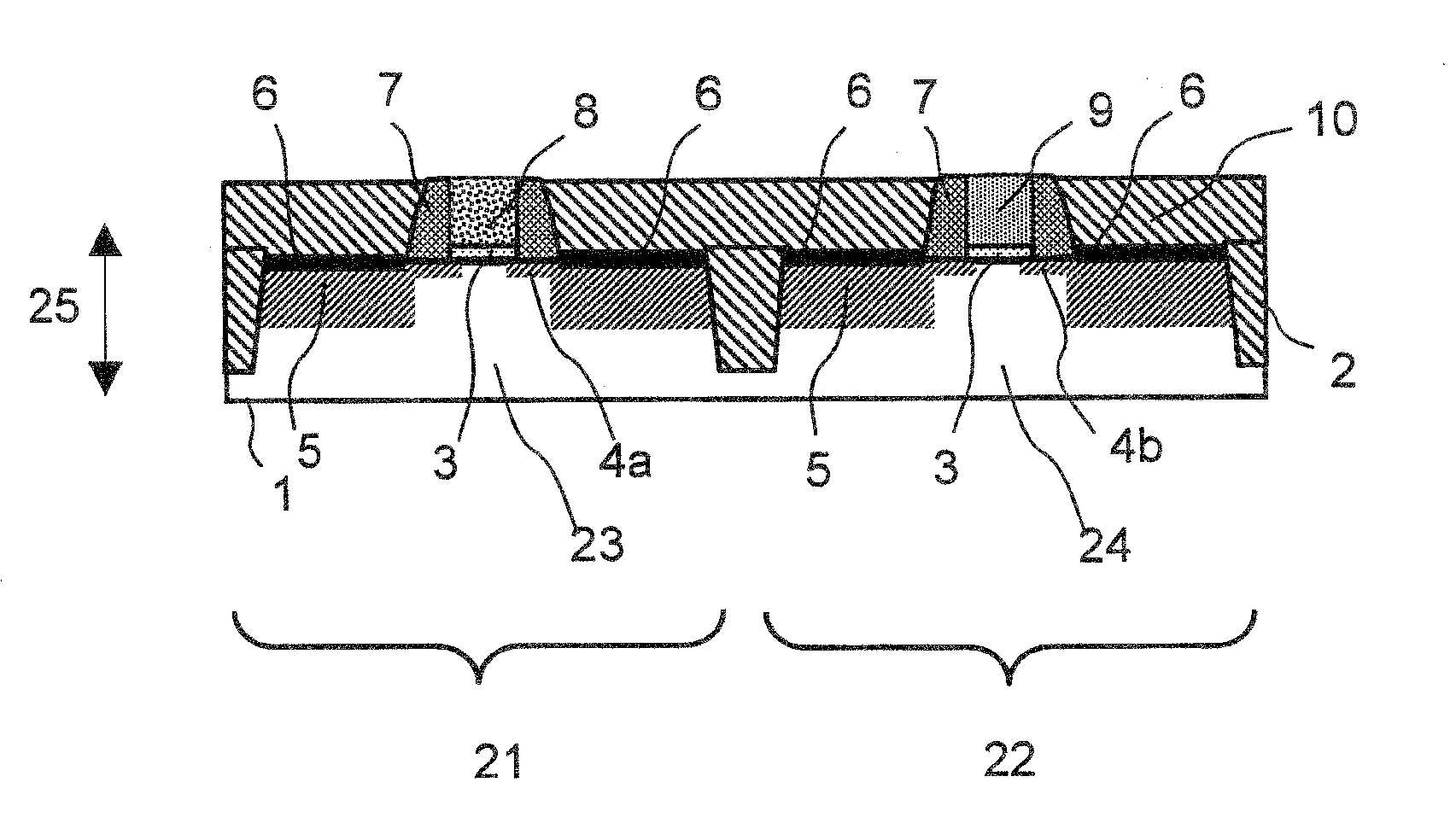
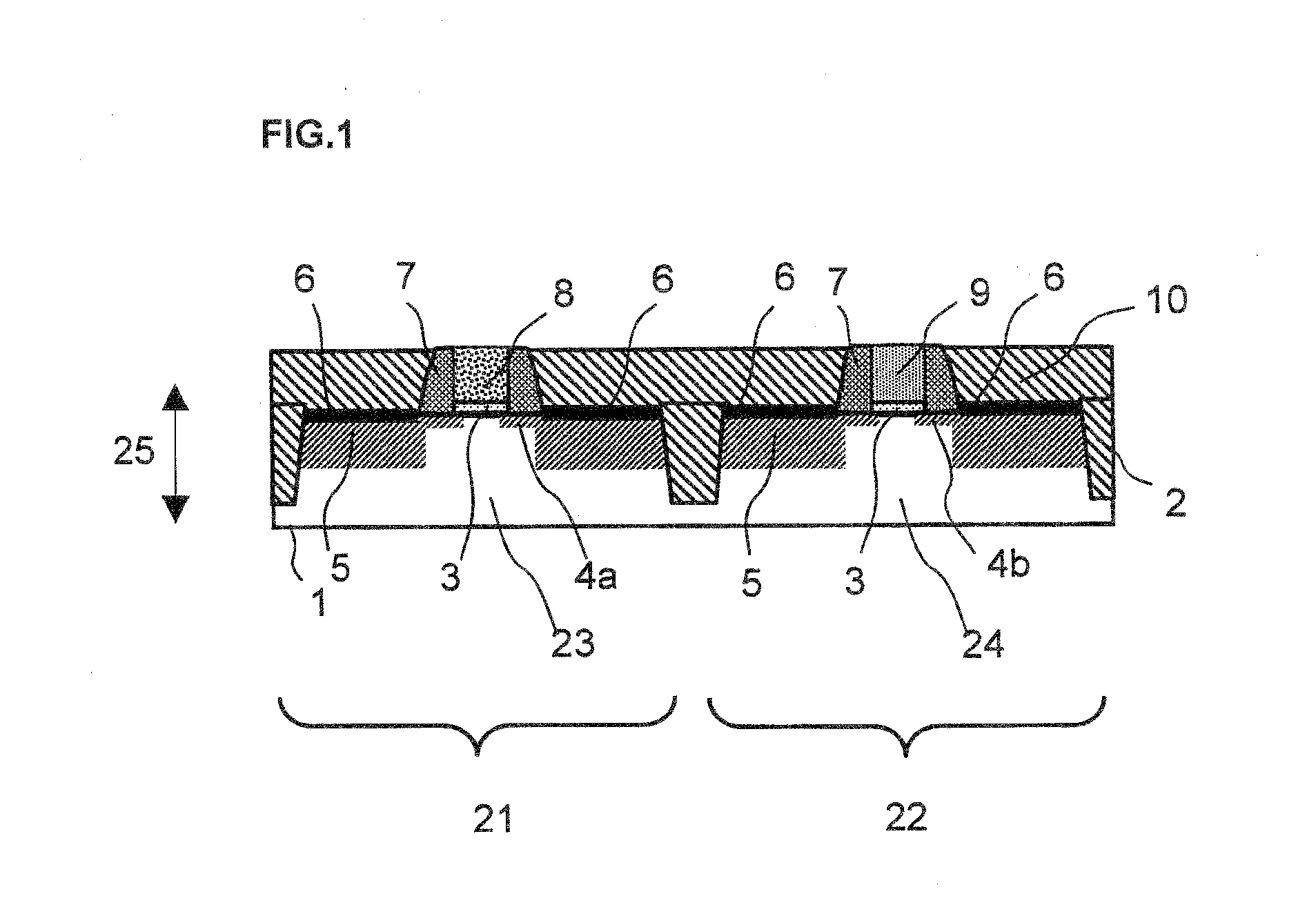
Semiconductor device having device characteristics improved by straining surface of active region and its manufacture method
InactiveUS20070228488A1Improve device characteristicsImproved filling characteristicTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsTensile strain
A trench is formed in the surface layer of a semiconductor substrate, surrounding an active region. A lower insulating film made of insulating material fills a lower region of the trench. An upper insulating film fills a region of the trench above the lower insulating film. The upper insulating film has therein a stress generating tensile strain in a surface layer of the active region.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Flexible electro-optical apparatus and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveCN101027753AImprove device characteristicsIncrease the aperture ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesDriver circuitLiquid-crystal display
The present invention relates to a flexible electro-optical apparatus such as a flexible high-resolution liquid crystal display wherein single-crystal silicon semiconductor is used in manufacturing driver circuits and pixel arrays, and a method for manufacturing the same. The flexible electro-optical apparatus according to the present invention comprises a flexible lower substrate portion including device layers where electronic devices are formed on a flexible single-crystal layer; a flexible upper substrate portion to be bonded to said lower substrate portion; and an electro-optical layer between said lower substrate portion and said upper substrate portion.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUNDATION HANYANG UNIV)
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
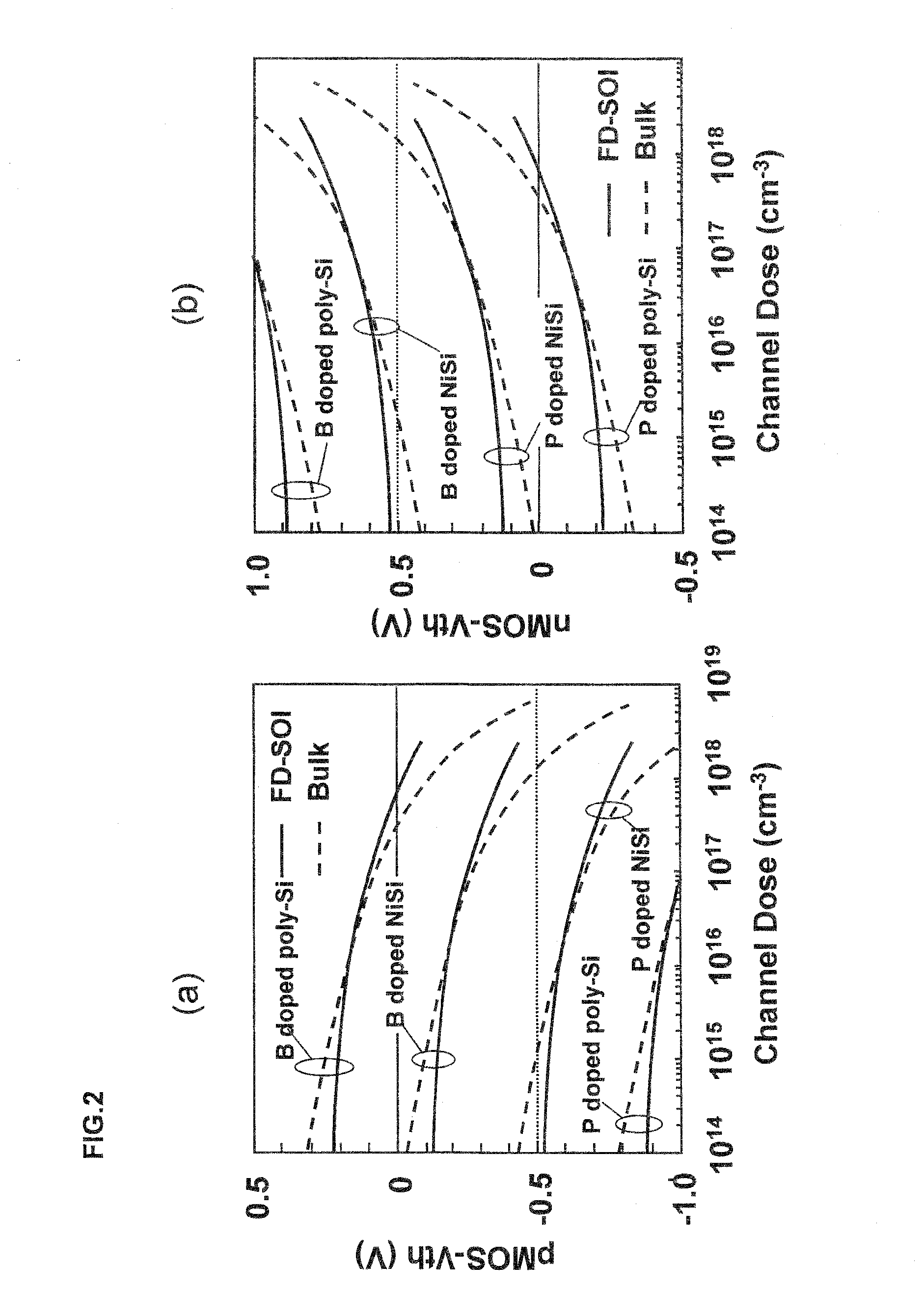
InactiveUS20100155844A1Reduce power levelImprove mobilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialSoi substrate
There is provided a semiconductor device having excellent device characteristics in which Vth values of an nMOS transistor and a pMOS transistor are controlled to be desired values. The semiconductor device includes a pMOS transistor and an nMOS transistor formed by using an SOI substrate. The pMOS transistor is a fully depleted transistor including an n-type region, a first gate electrode, a first gate insulating film, and a source / drain region, and the nMOS transistor is a fully depleted transistor including a p-type region, a second gate electrode, a second gate insulating film, and a source / drain region. The first gate electrode includes silicide region comprising an NiSi crystalline phase containing an n-type impurity, the silicide region being in contact with the first gate insulating film, and the second gate electrode includes silicide region comprising an NiSi crystalline phase containing a p-type impurity, the silicide region being in contact with the second gate insulating film.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Photoelectric transducer, photoelectric transducer apparatus, and iron silicide film
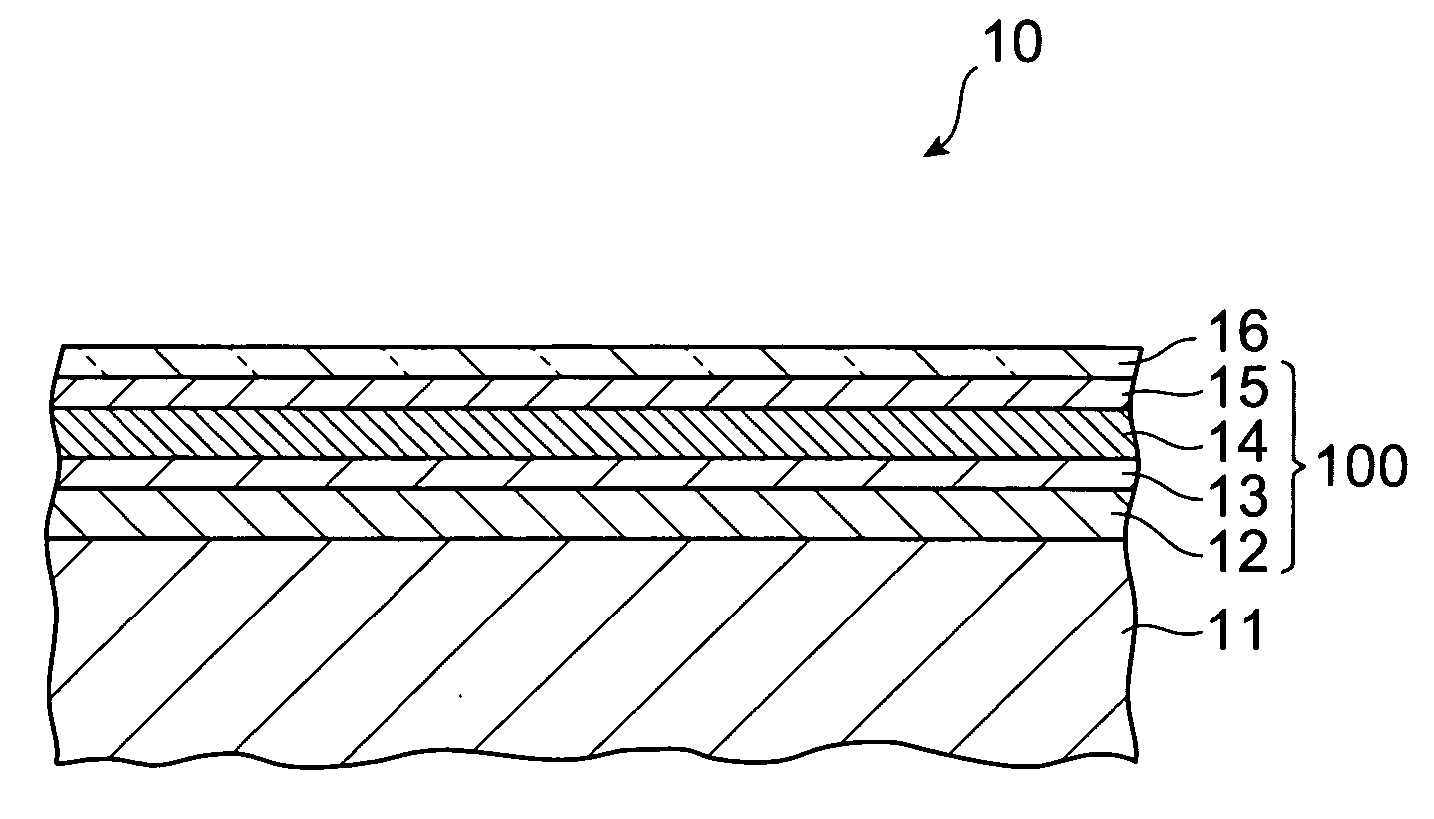
InactiveUS7352044B2Strengthen restrictionsIncrease volumePV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationHydrogen atomTransducer
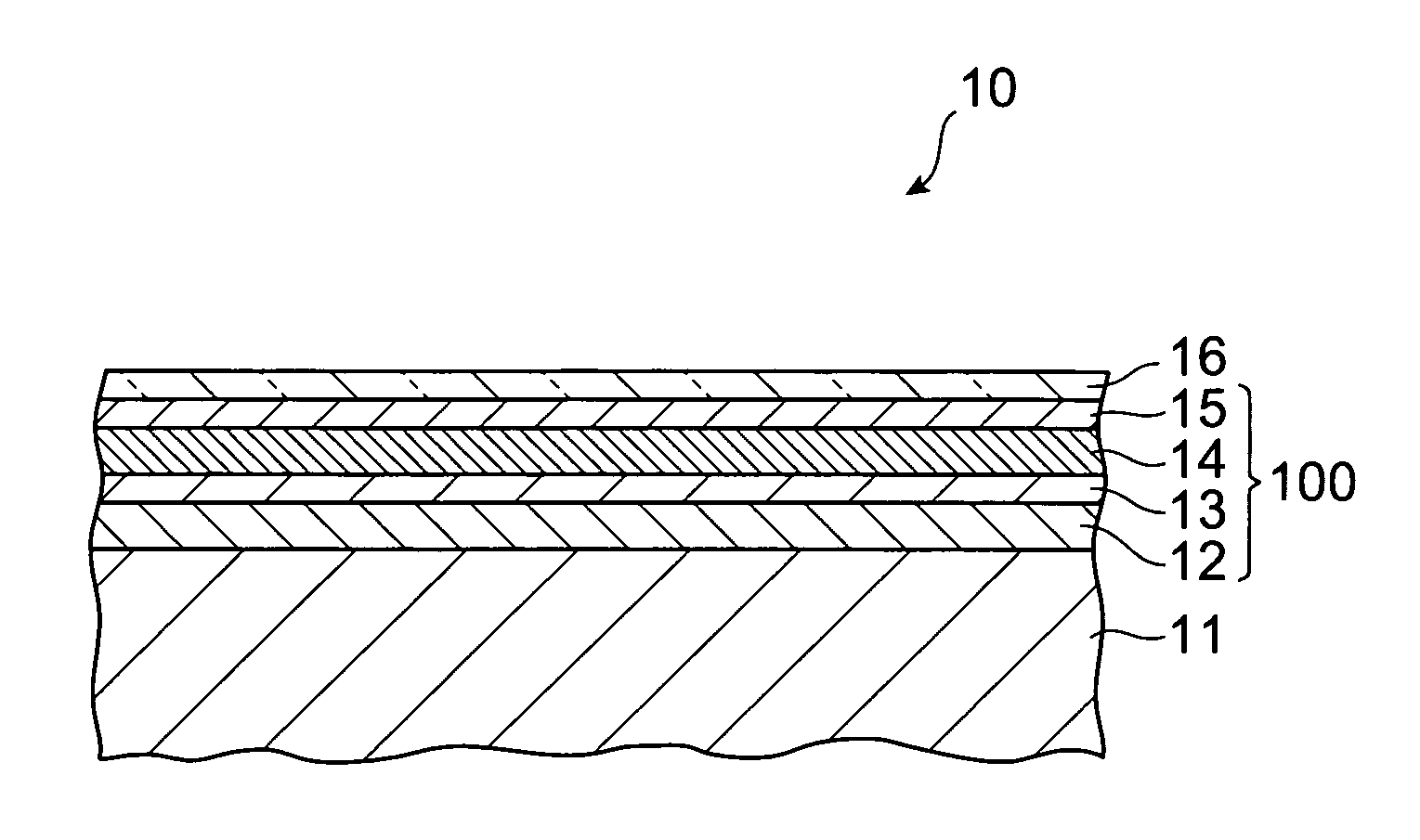
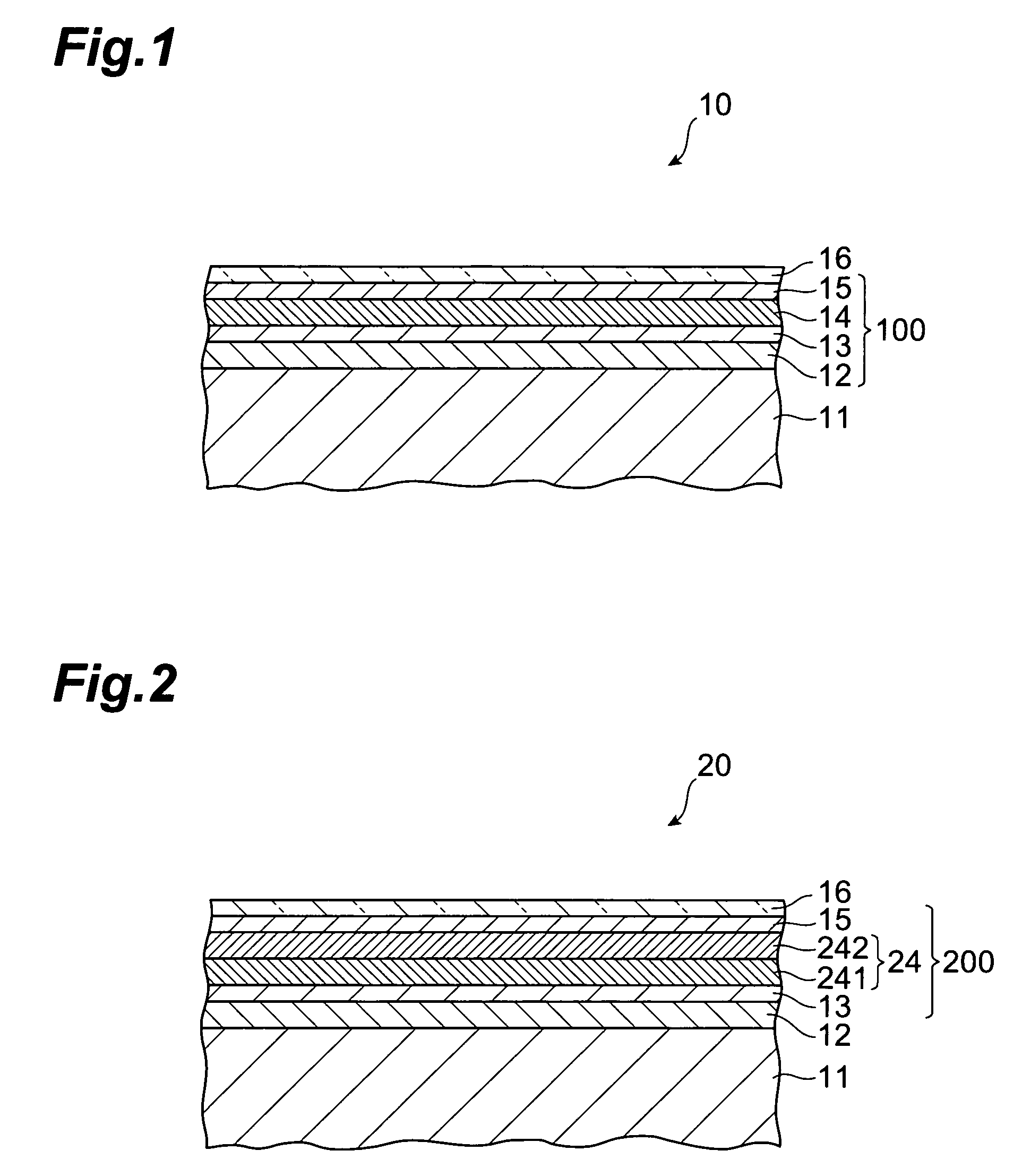
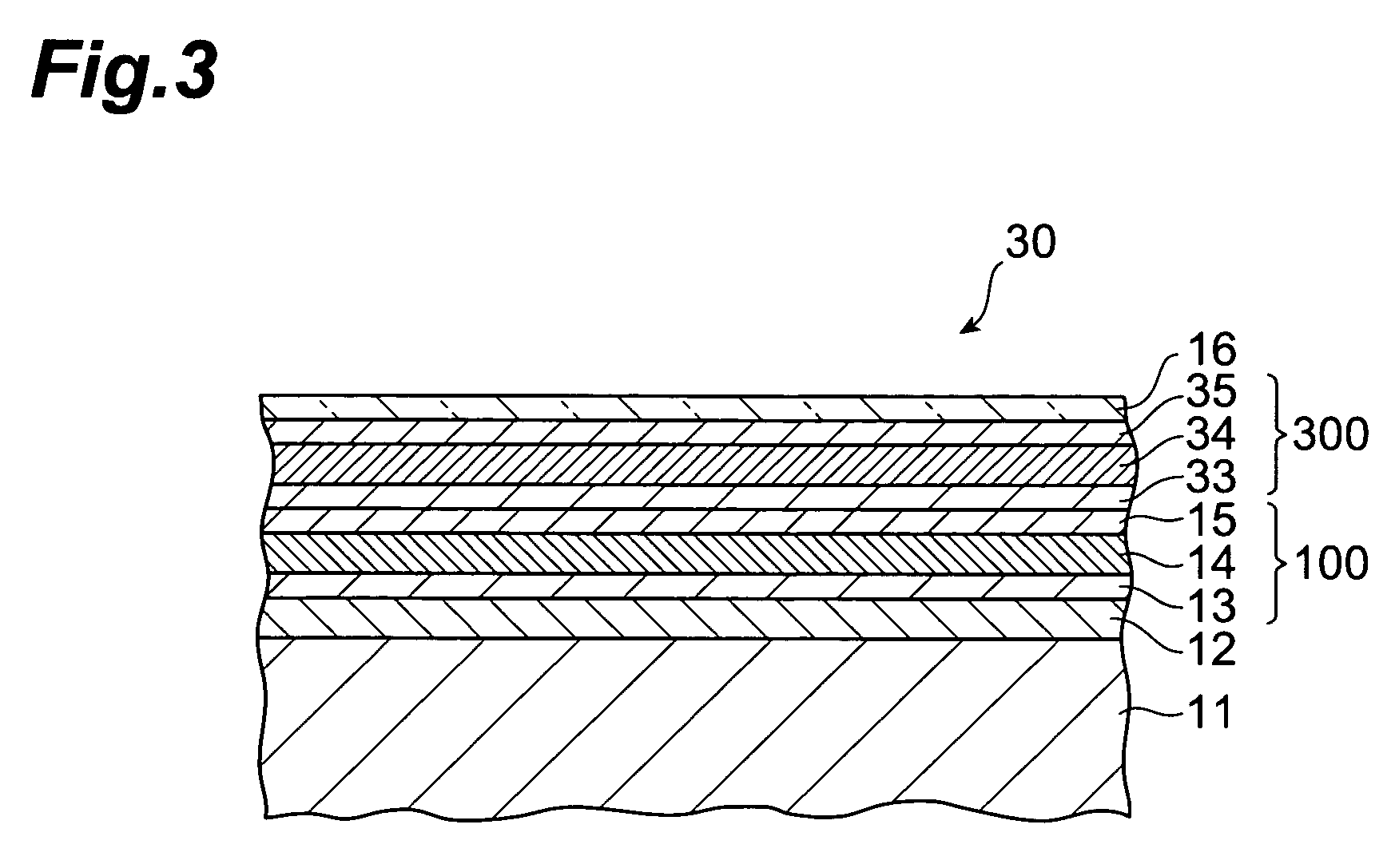
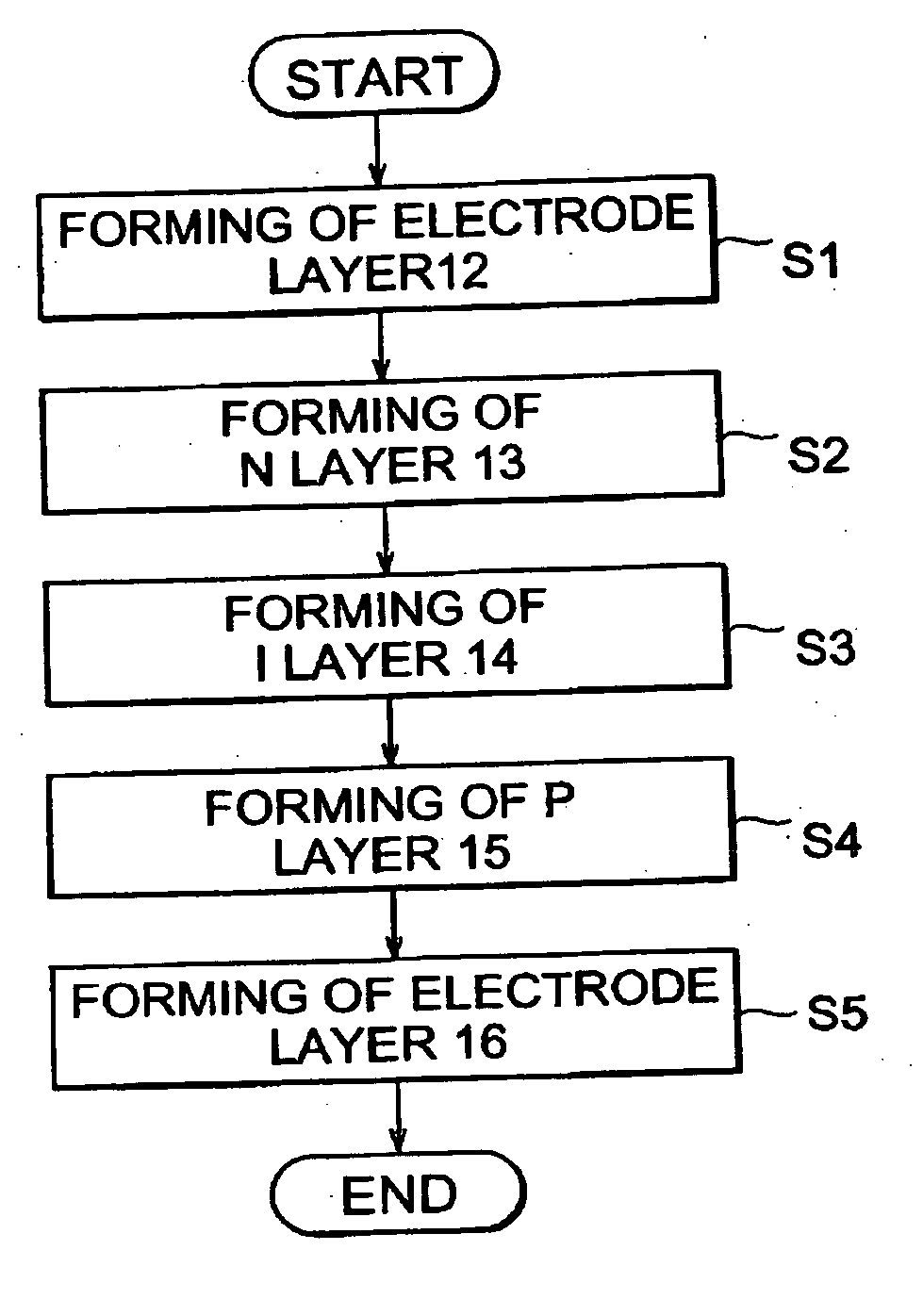
A solar battery 10 comprises a metal electrode layer 12, a pin junction 100, and a transparent electrode layer 16 which are successively laminated on a substrate 11 such as a silicon substrate. The pin junction 100 comprises an n-layer 13, an i-layer 14, and a p-layer 15 which are laminated in succession. The i-layer 14 is formed by amorphous iron silicide (FexSiy:H) containing hydrogen atoms. In the i-layer 14, at least a part of the hydrogen atoms contained therein terminate dangling bonds of silicon atoms and / or iron atoms, so that a number of trap levels which may occur in an amorphous iron silicide film can be eliminated, whereby the i-layer 14 exhibits a characteristic as an intrinsic semiconductor layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
Method for grid connecting with SOI dynamic threshold transistor through anti-off schottky
InactiveCN101090122AImprove device characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSoi substrateEngineering
This invention relates to a method that a grid is connected to a SOI dynamic threshold transistor by a pull-down Schottky joint including: a SOI substrate, a transistor formed in the SOI top layer silicom film and including a grid, a grid oxidation layer, a drain, a source and a transistor region and a pull-down Schottky joint connected between the grid and the transistor region, in which, a metal is used to connect the grid with a leading-out part of the transistor and necessary electric isolation should be done among appliances.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving the quality of an SiC crystal and an SiC semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080026544A1Improve device characteristicsCarrier trapping centers can be effectively reduced or eliminatedPolycrystalline material growthDiffusion/dopingTrappingHelium atom
It is an object to provide a method for improving the quality of an SiC layer by effectively reducing or eliminating the carrier trapping centers by high temperature annealing and an SiC semiconductor device fabricated by the method.A method for improving the quality of an SiC layer by eliminating or reducing some carrier trapping centers comprising the steps of:(a) carrying out ion implantation of carbon atoms (C), silicon atoms, hydrogen atoms, or helium atoms into a shallow surface layer (A) of the starting SiC crystal layer (E) to introduce excess carbon interstitials into the implanted surface layer, and(b) heating the layer for making the carbon interstitials (C) to diffuse out from the implanted surface layer (A) into a bulk layer (E) and for making the electrically active point defects in the bulk layer inactive. After the above steps, the surface layer (A) can be etched or mechanically removed. A semiconductor device according to the invention is fabricated by the method.
Owner:CENTRAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF ELECTRIC POWER INDUSTRY
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100224884A1LiquidityLower resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20090250757A1Increase speedSuppression of short channel effectsTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialPhysical chemistry
There is provided a semiconductor device having excellent device characteristics and reliability in which Vth values of an nMOS transistor and a pMOS transistor are controlled to be values necessary for a low-power device. The semiconductor device includes a pMOS transistor and an nMOS transistor formed by using an SOI substrate. The pMOS transistor is a fully depleted MOS transistor including a first gate electrode comprising at least one type of crystalline phase selected from the group consisting of a WSi2 crystalline phase, an MoSi2 crystalline phase, an NiSi crystalline phase, and an NiSi2 crystalline phase as silicide region (1). The nMOS transistor is a fully depleted MOS transistor comprising at least one type of crystalline phase selected from the group consisting of a PtSi crystalline phase, a Pt2Si crystalline phase, an IrSi crystalline phase, an Ni2Si crystalline phase, and an Ni3Si crystalline phase as silicide region (2).
Owner:NEC CORP
Method of making iron silicide and method of making photoelectric transducer
InactiveUS20060003585A1Strengthen restrictionsIncrease volumeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilanesTransducer
A solar cell comprises a substrate, and a metal electrode layer, a p-i-n junction, and a transparent electrode layer which are successively laminated on the substrate. The p-i-n junction comprises an n layer, an i layer, and a p layer which are laminated in this order. The i layer is made of an amorphous iron silicide film containing hydrogen in accordance with the present invention, and is formed on the n layer by supplying an iron vapor into a plasma of a material gas in which a silane type gas and a hydrogen gas are mixed. In the i layer, dangling bonds of silicon atoms and / or iron atoms are terminated with hydrogen, whereby a number of trap levels which may occur in the amorphous iron silicide film are eliminated.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
Process for producing photoelectric conversion devices
ActiveUS20110189814A1Improve device characteristicsQuality improvementPV power plantsSolid-state devicesChemical bath depositionSemiconductor
In a process for producing a photoelectric conversion device comprising a bottom electrode layer, a photoelectric conversion semiconductor layer, a buffer layer, and a transparent conductive layer, which are stacked in this order on a substrate, all film forming stages ranging from a stage of forming the buffer layer to a stage of forming the transparent conductive layer are performed with a liquid phase technique. The buffer layer is formed with a chemical bath deposition technique, and the transparent conductive layer is formed with an electrolytic deposition technique.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
CMOS image sensor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7037748B2Improve device characteristicsTotal current dropSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSEngineering
A CMOS image sensor and a manufacturing method thereof, wherein the gates of several transistors of the CMOS image sensor are formed in an active region defined by an isolation region for a unit pixel of the CMOS image sensor, and a passivation layer composed of insulating layer is formed on the semiconductor substrate. Impurities are ion-implanted into the active region to form one or more diffusion regions of a photo diode of the CMOS image sensor, wherein the passivation layer prevents a boundary portion of the active region from being ion-implanted. Thus, damages by ion implantation at the boundary portion between the diffusion region for the photo diode and the isolation region are prevented, and the dark current of the CMOS image sensor is reduced.
Owner:DONGBUANAM SEMICON
Photoelectric converter, photoelectric conversion device and iron silicide film
InactiveUS20060049478A1Strengthen restrictionsIncrease volumePV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationHydrogen atomAmorphous silicon
A solar battery 10 comprises a metal electrode layer 12, a pin junction 100, and a transparent electrode layer 16 which are successively laminated on a substrate 11 such as a silicon substrate. The pin junction 100 comprises an n-layer 13, an i-layer 14, and a p-layer 15 which are laminated in succession. The i-layer 14 is formed by amorphous iron silicide (FexSiy:H) containing hydrogen atoms. In the i-layer 14, at least a part of the hydrogen atoms contained therein terminate dangling bonds of silicon atoms and / or iron atoms, so that a number of trap levels which may occur in an amorphous iron silicide film can be eliminated, whereby the i-layer 14 exhibits a characteristic as an intrinsic semiconductor layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
Stretchable crystalline semiconductor nanowire and preparation method thereof
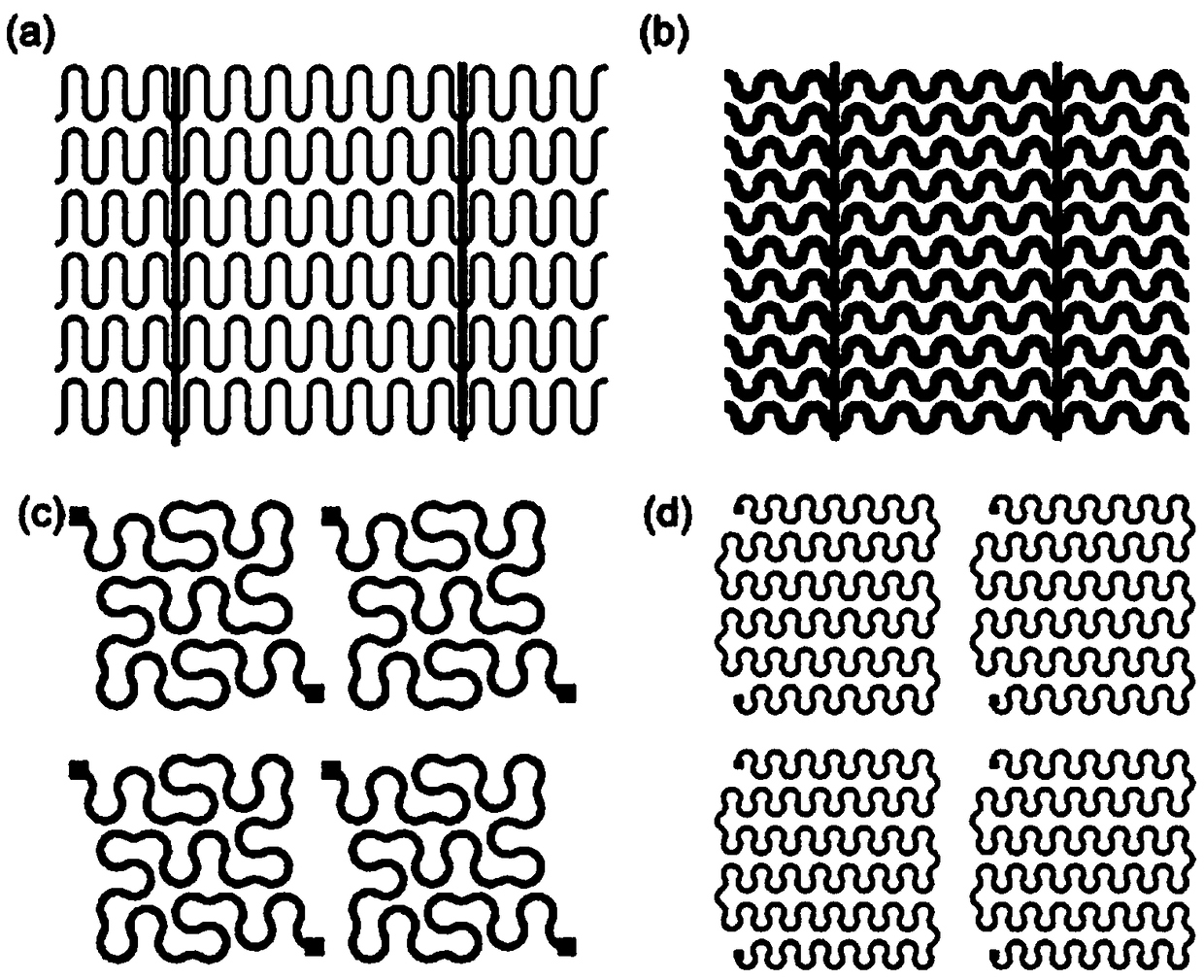
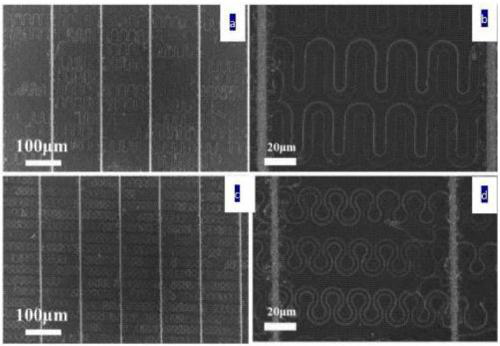
ActiveCN109234807ARealize self-positioningAchieve self-orientationPolycrystalline material growthNanoinformaticsSemiconductor structureFlexible electronics
The invention relates to a stretchable crystalline semiconductor nanowire and a preparation method thereof. The stretchable crystalline semiconductor nanowire comprises a long and thin main body, thediameter of the nanowire is 20-200 nm, and the nanowire is of a crystalline inorganic semiconductor structure. The stretchable crystalline semiconductor nanowire is of a bending structure and is provided with multiple stretchable units in the axial direction, the multiple stretchable units are connected in sequence, and therefore, the stretchable crystalline semiconductor nanowire is formed. Withthe adoption of IP-SLS and other methods, the channel step guided nanowire grows in PECVD, and a spring-structured crystalline nanowire array is manufactured with a modern micro-machining technology.The nanowire and guide channel sections can be effectively adjusted, so that the nanowire can be further peeled and transferred to other flexible substrates. The method for preparing the spring-structured crystalline nanowire has broad prospects in the fields of flexible electronics and sensors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for fabricating semiconductor device
InactiveUS20080081462A1Improve device characteristicsPreventing decrease in charge mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerEngineering
A method for fabricating a semiconductor device includes forming a plurality of memory cells and transistors over a substrate, forming a first stopping layer having tensile stress over the plurality of memory cells and transistors, forming a first insulation layer over the substrate and the first stopping layer, and forming a second stopping layer having compression stress over the first insulation layer.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com